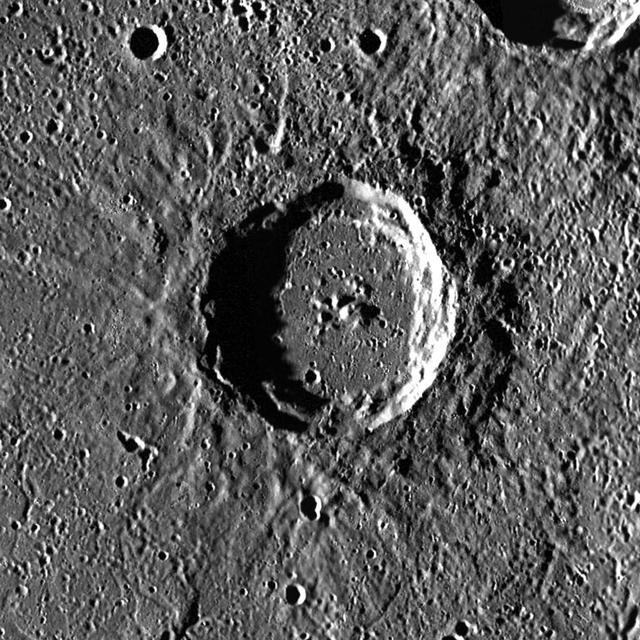
20 Million Buys an Awful Lot of Crater

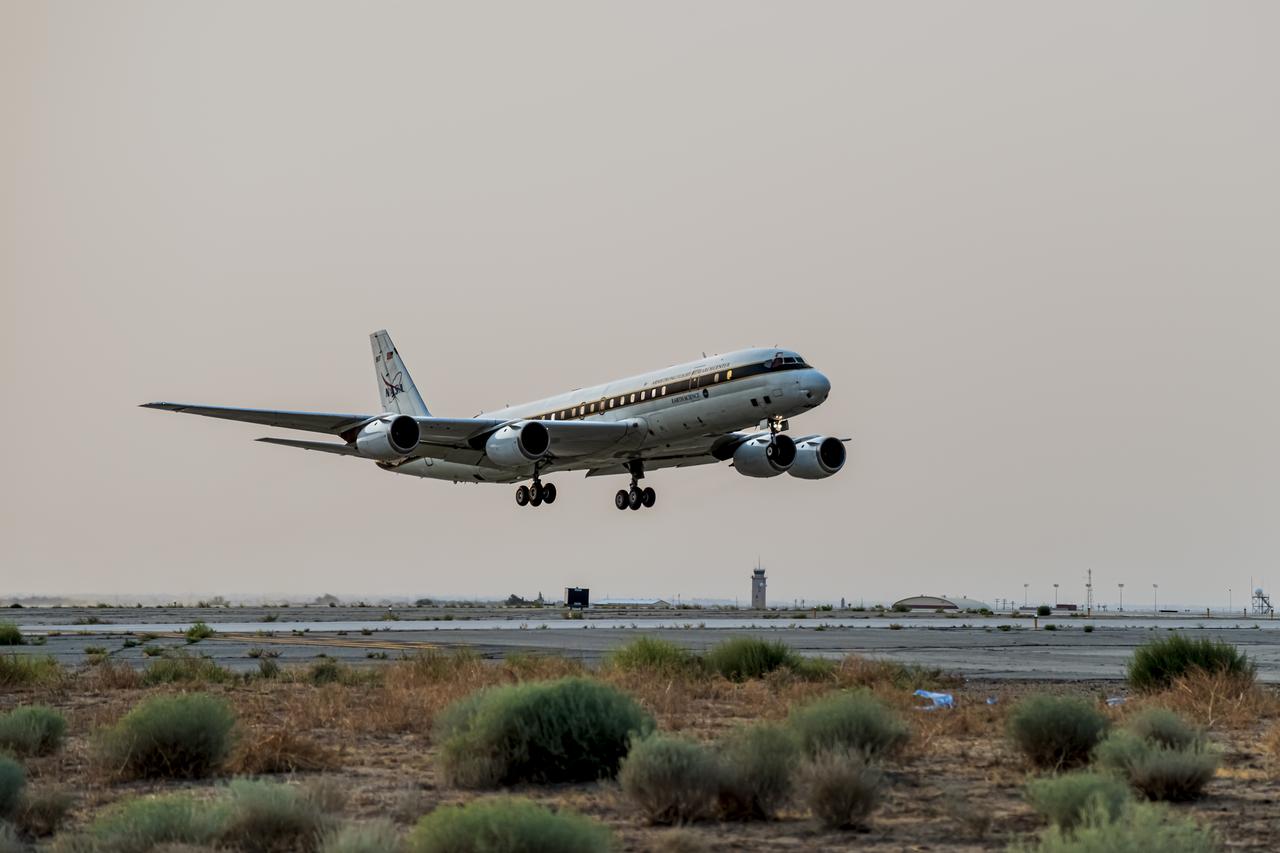
NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center flies the DC-8 airborne science laboratory in support of the Convective Processes Experiment - Aerosols and Winds campaign, CPEX-AW, on Aug 6, 2021.
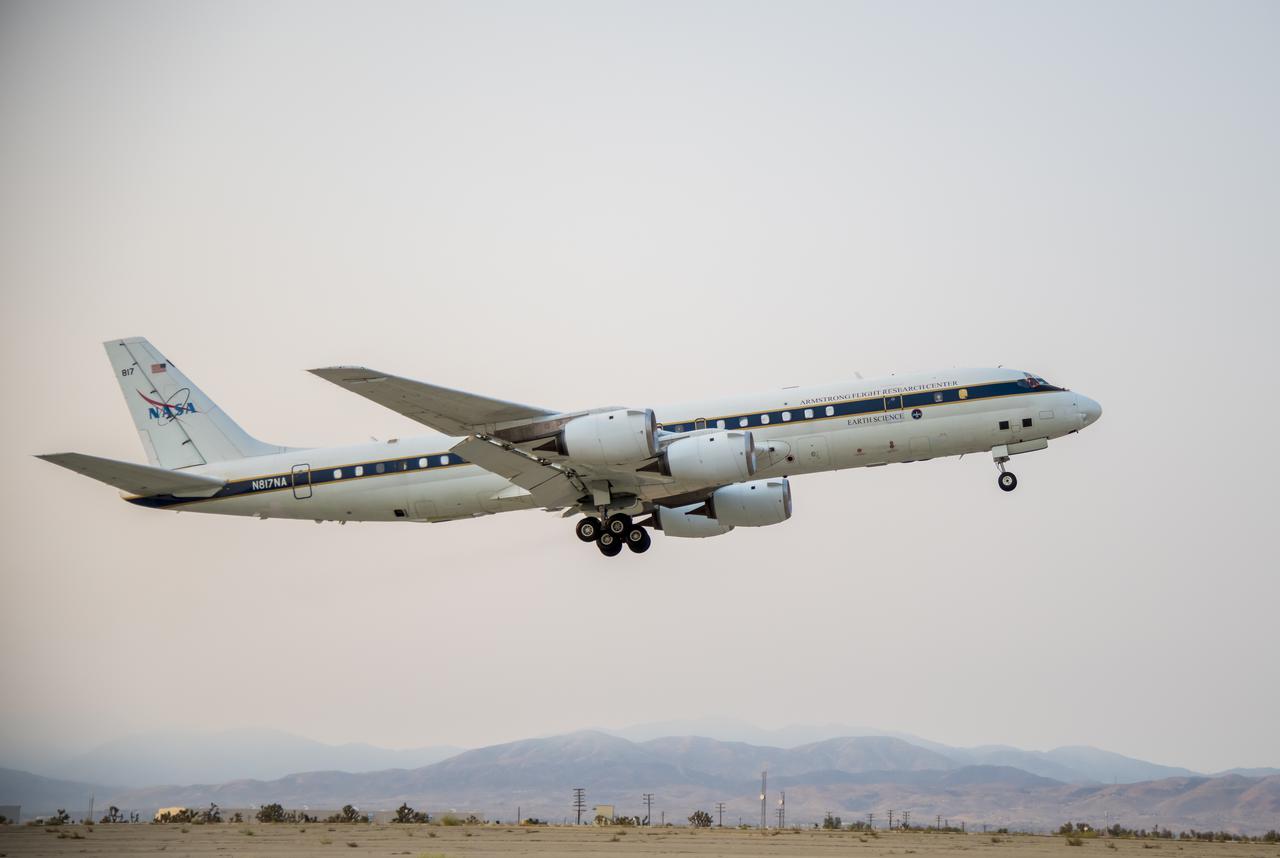

NASA's DC-8 taking off to St. Croix in support of the Convective Processes Experiment - Aerosols and Winds campaign (CPEX-AW) on Aug 17, 2021.
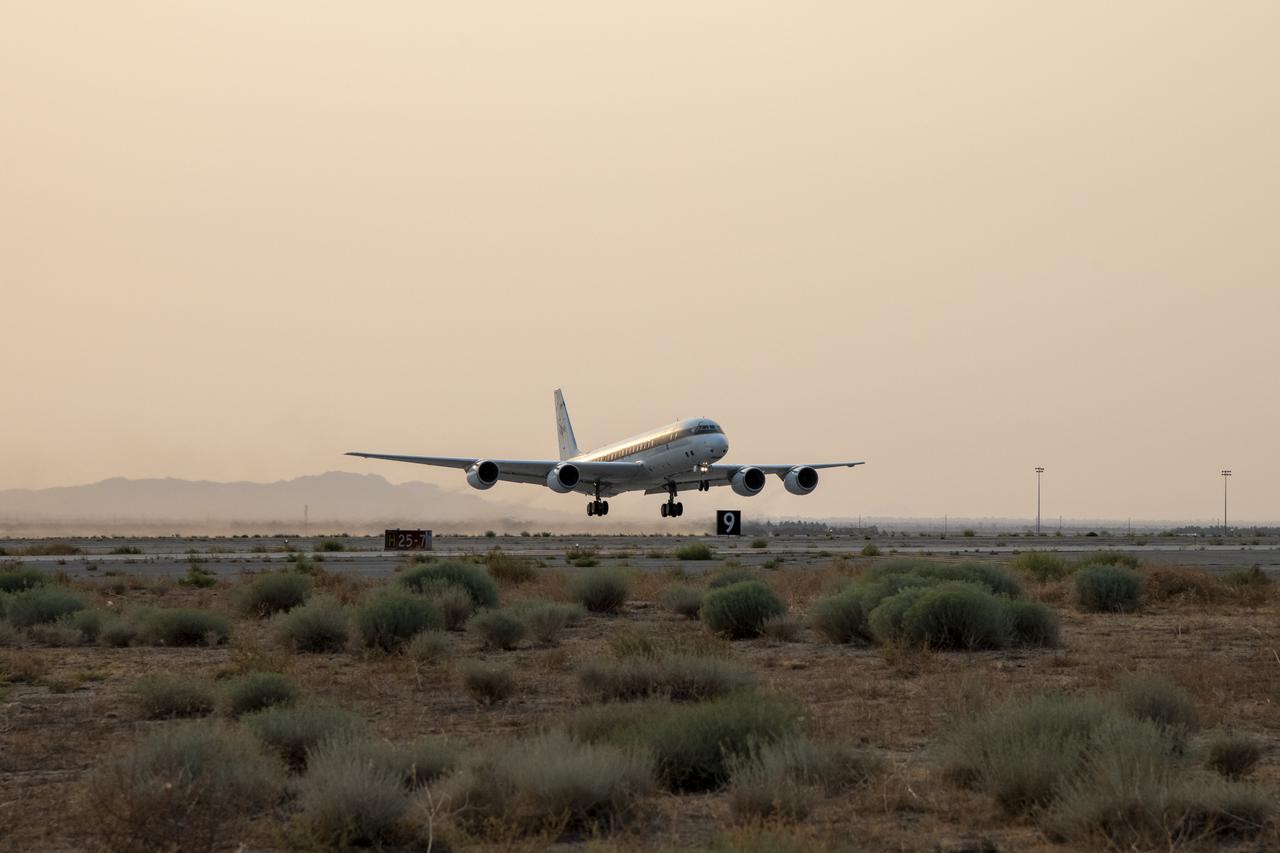

NASA's DC-8 taking off to St. Croix in support of the Convective Processes Experiment - Aerosols and Winds campaign (CPEX-AW) on Aug 17, 2021.
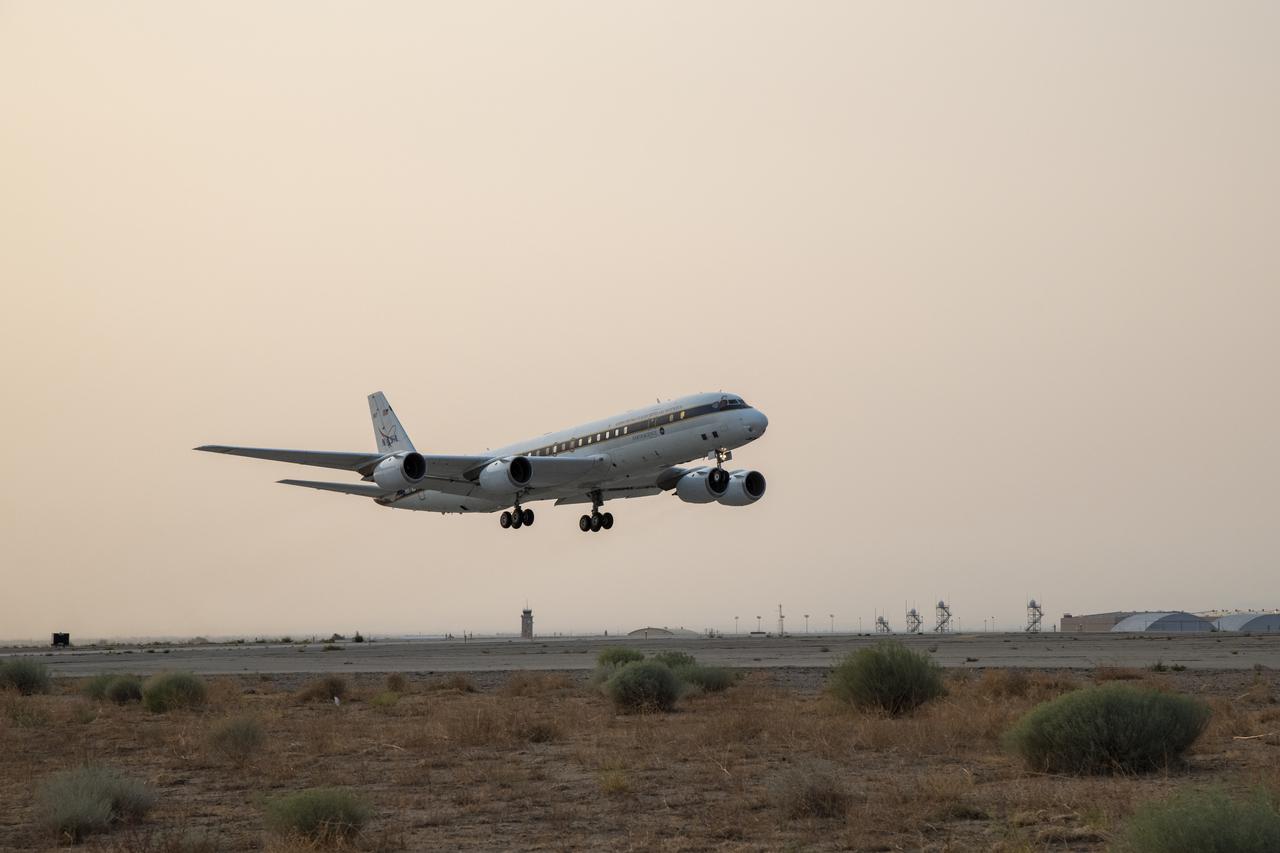

NASA’s DC-8 taking off to St. Croix in support of the Convective Processes Experiment – Aerosols and Winds campaign (CPEX-AW) on Aug 17, 2021.
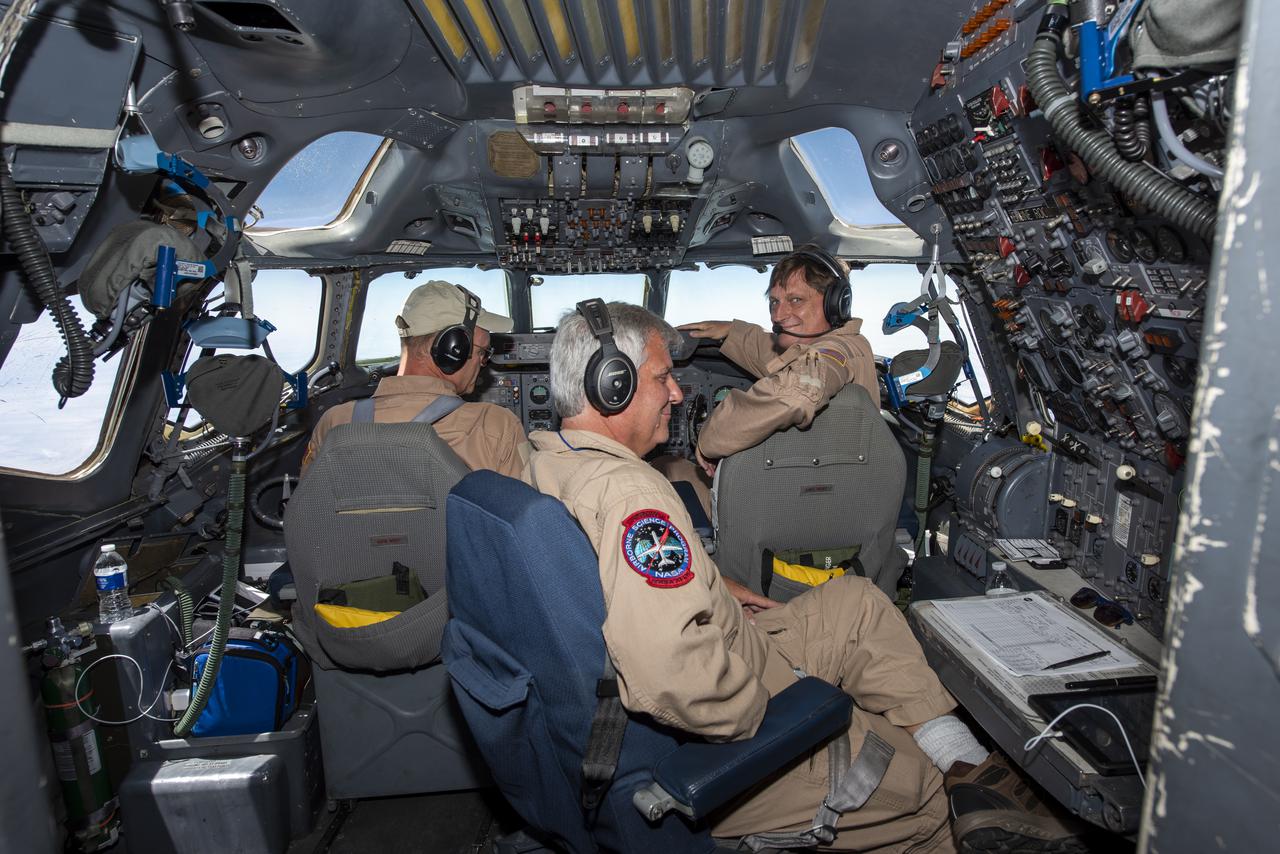

NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center flies the DC-8 airborne science laboratory in support of the Convective Processes Experiment - Aerosols and Winds campaign, CPEX-AW, on Aug 6, 2021. From left to right: Nils Larson, David Fedors and Mark Crane

NASA image release April 22, 2010 This brand new Hubble photo is of a small portion of one of the largest seen star-birth regions in the galaxy, the Carina Nebula. Towers of cool hydrogen laced with dust rise from the wall of the nebula. The scene is reminiscent of Hubble's classic "Pillars of Creation" photo from 1995, but is even more striking in appearance. The image captures the top of a three-light-year-tall pillar of gas and dust that is being eaten away by the brilliant light from nearby bright stars. The pillar is also being pushed apart from within, as infant stars buried inside it fire off jets of gas that can be seen streaming from towering peaks like arrows sailing through the air. Credit: NASA, ESA, and M. Livio and the Hubble 20th Anniversary Team (STScI) To read learn more about this image go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/hubble20th-img.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/hubble20th-img....</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
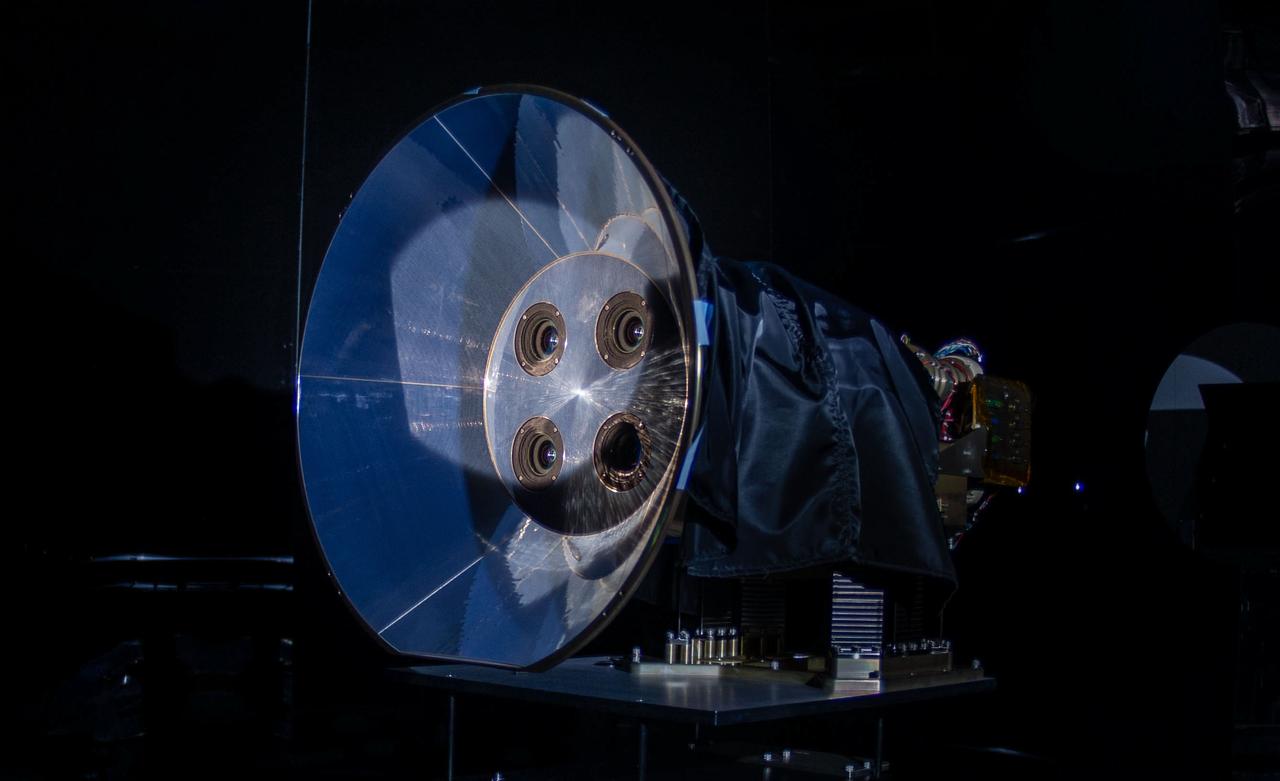
jsc2023e055877 (3/31/2022) --- The Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE) Optical Mechanical Assembly in a clean room at Space Dynamics Laboratory (SDL) facilities on Utah State University’s Innovation Campus. Image courtesy of SDL/Allison Bills.
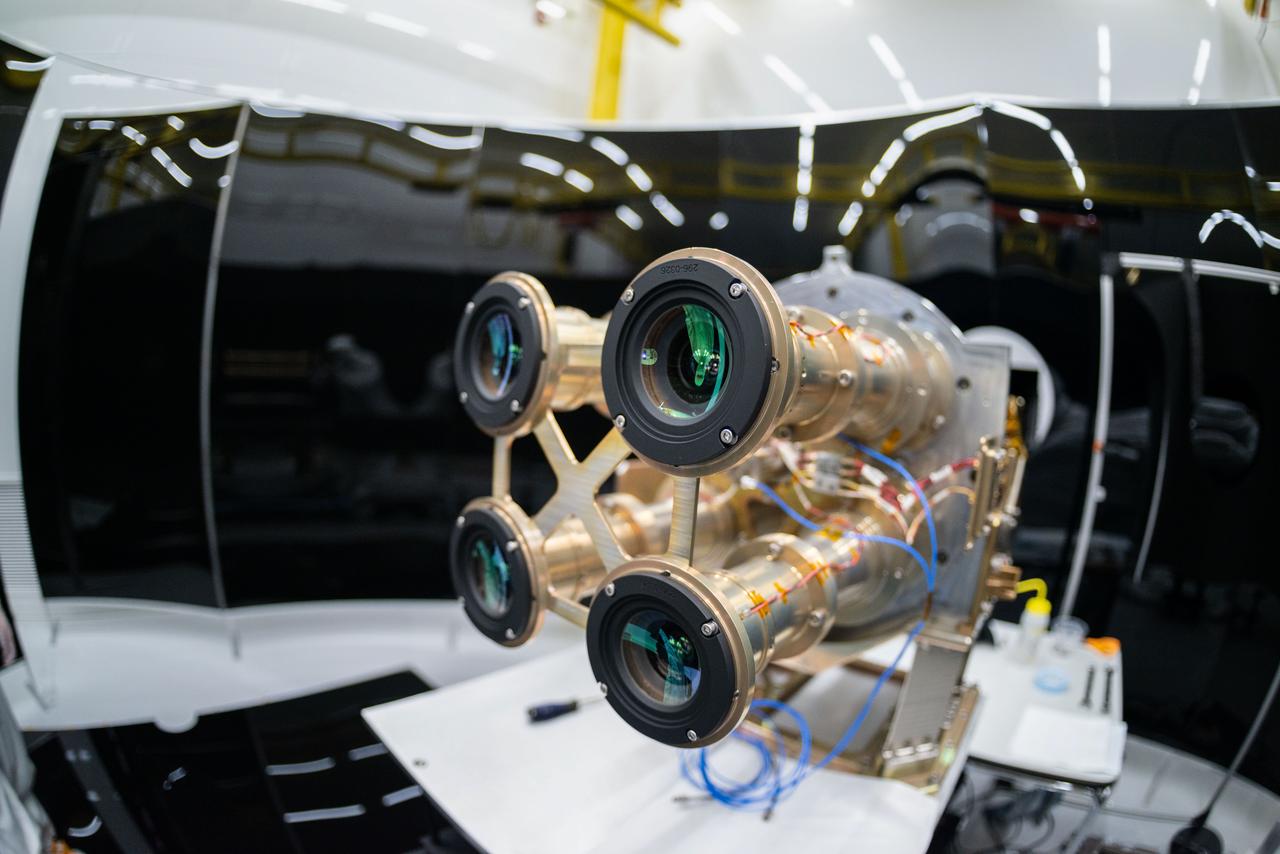

jsc2023e055878 (3/31/2022) --- Preflight image of the four Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE) telescopes at Space Dynamics Laboratory (SDL) facilities on Utah State University’s Innovation Campus. Image courtesy of SDL/Allison Bills.
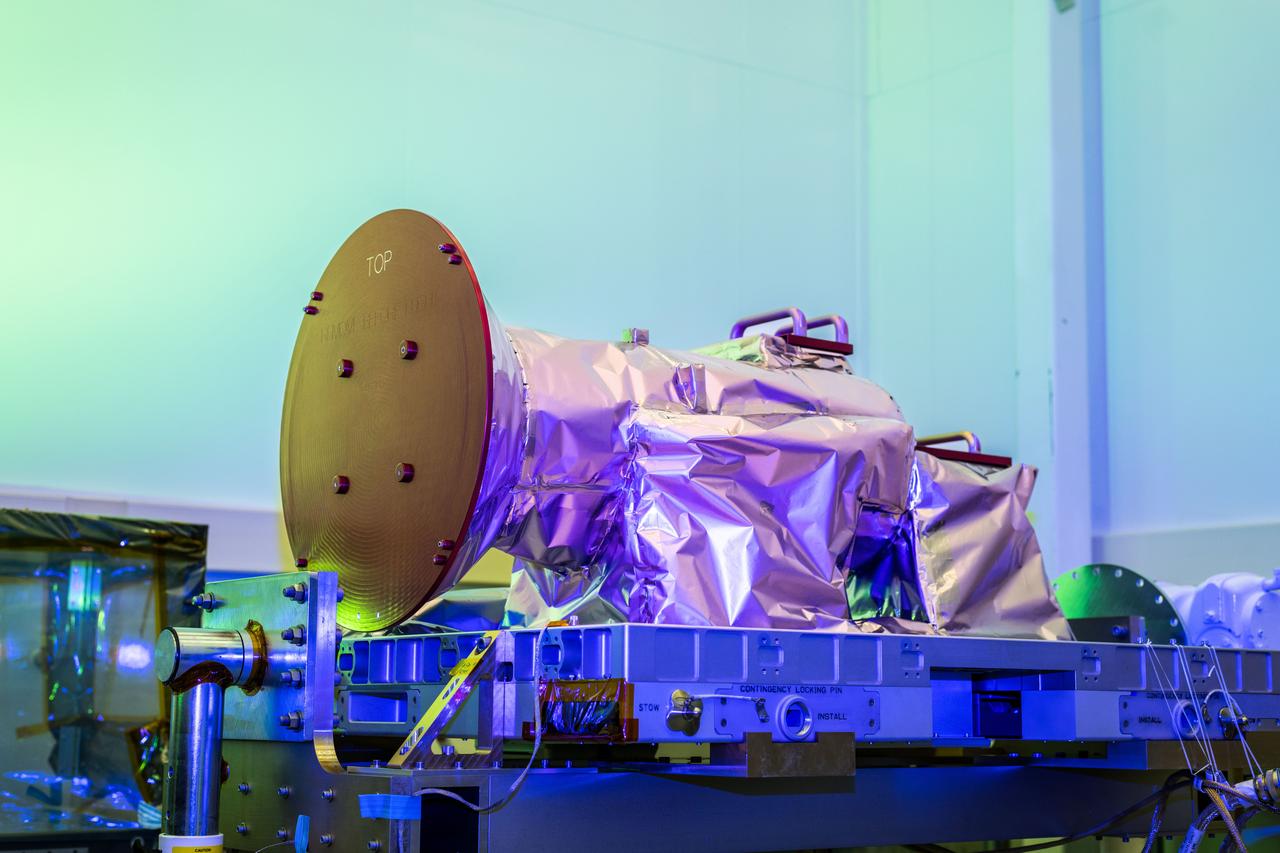
jsc2023e055881 (5/26/2023) --- NASA’s Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE) payload is shown in this May 26, 2023, photo at Space Dynamics Laboratory (SDL) facilities on Utah State University’s Innovation Campus with its red remove-before-flight covers installed. Image courtesy of SDL/Allison Bills.
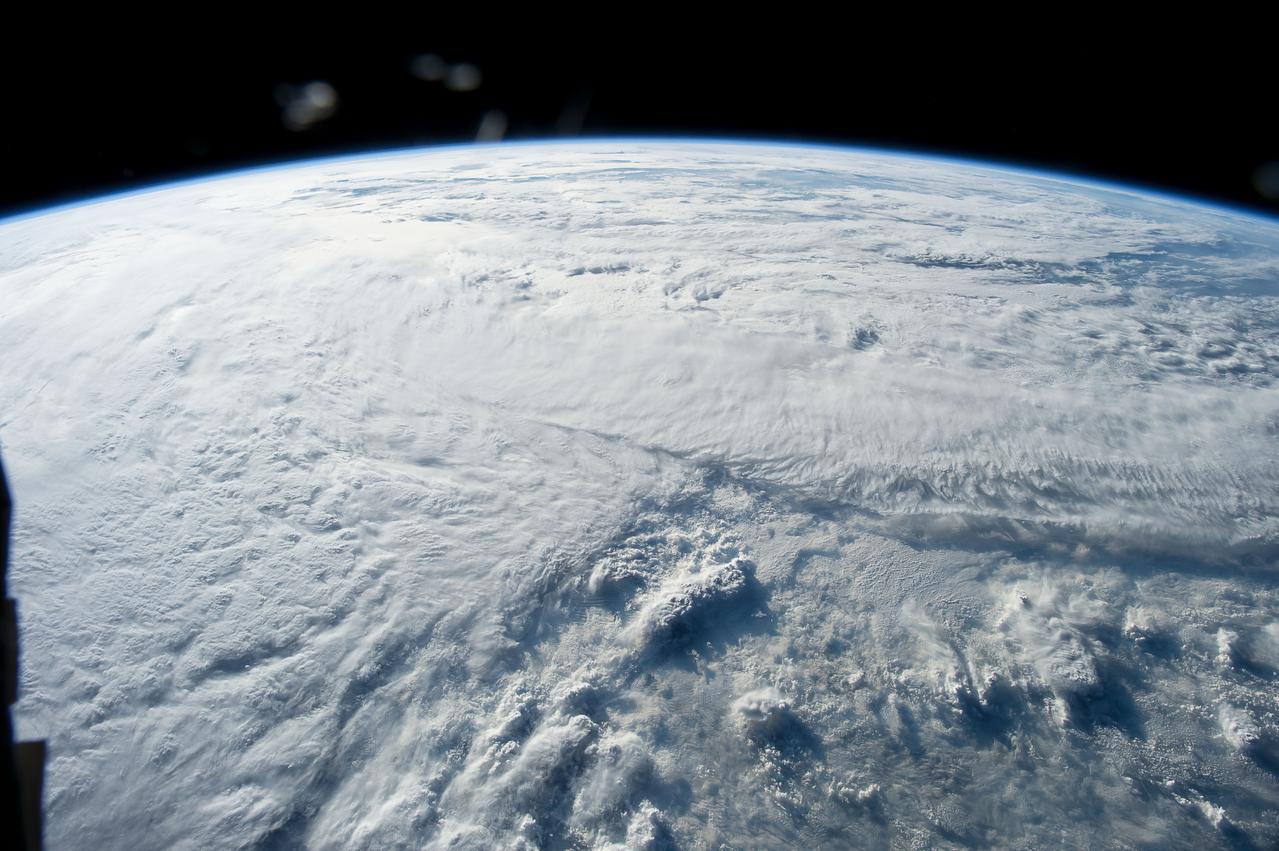

ISS043E044527 (03/23/2015) --- This Earth observation of the Patagonia Ice Fields in South America was taken during a day pass of the International Space Station by the crew of Expedition 43. The Commander of 43, NASA astronaut Terry Virts tweeted this comment on the Earth image: "Awe-inspiring Earth"!
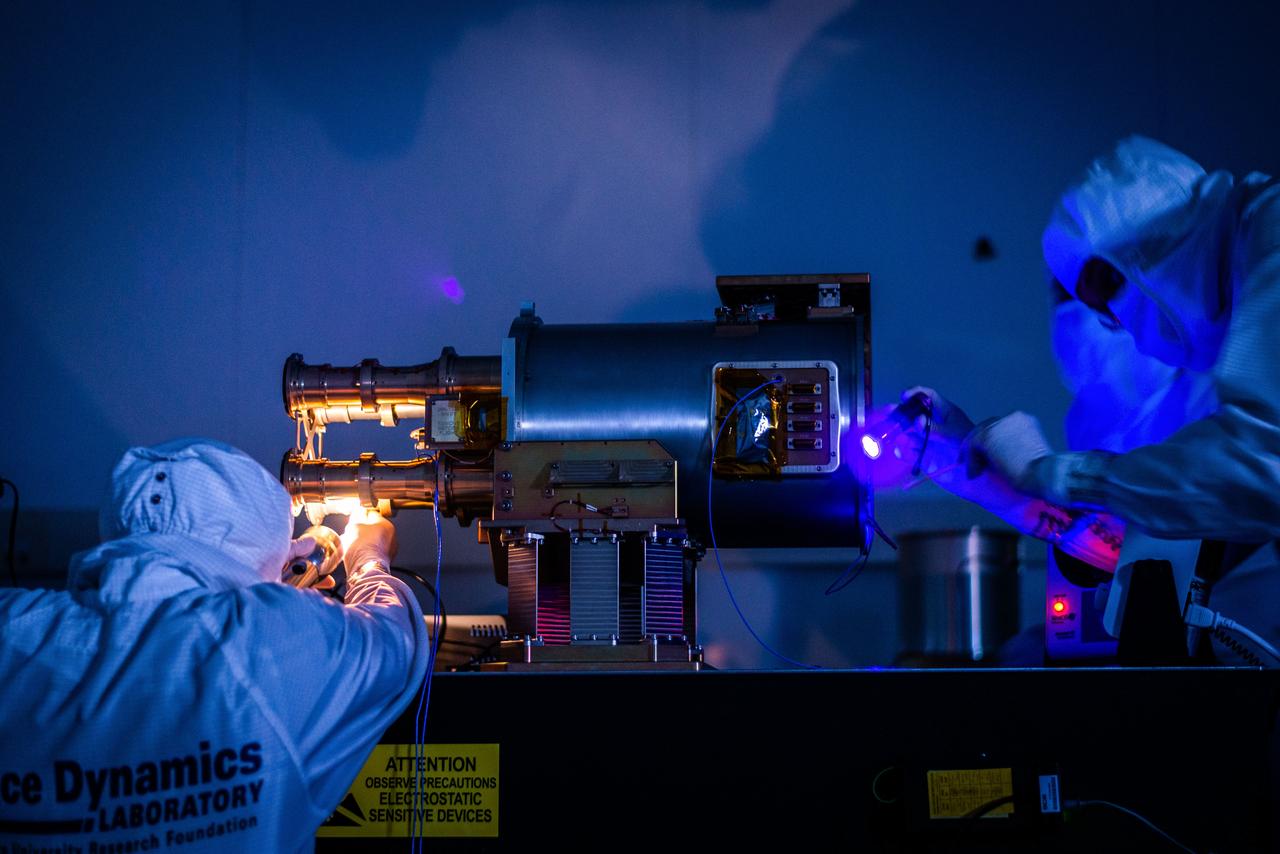

jsc2023e055876 (6/3/2021) --- Space Dynamics Laboratory (SDL) engineering and safety mission assurance personnel perform a cleanliness check with a black light on the The Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE) engineering model at SDL facilities on Utah State University’s Innovation Campus. Image courtesy of SDL/Allison Bills.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after its liftoff from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th Commercial Resupply Services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. The Dragon spacecraft will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
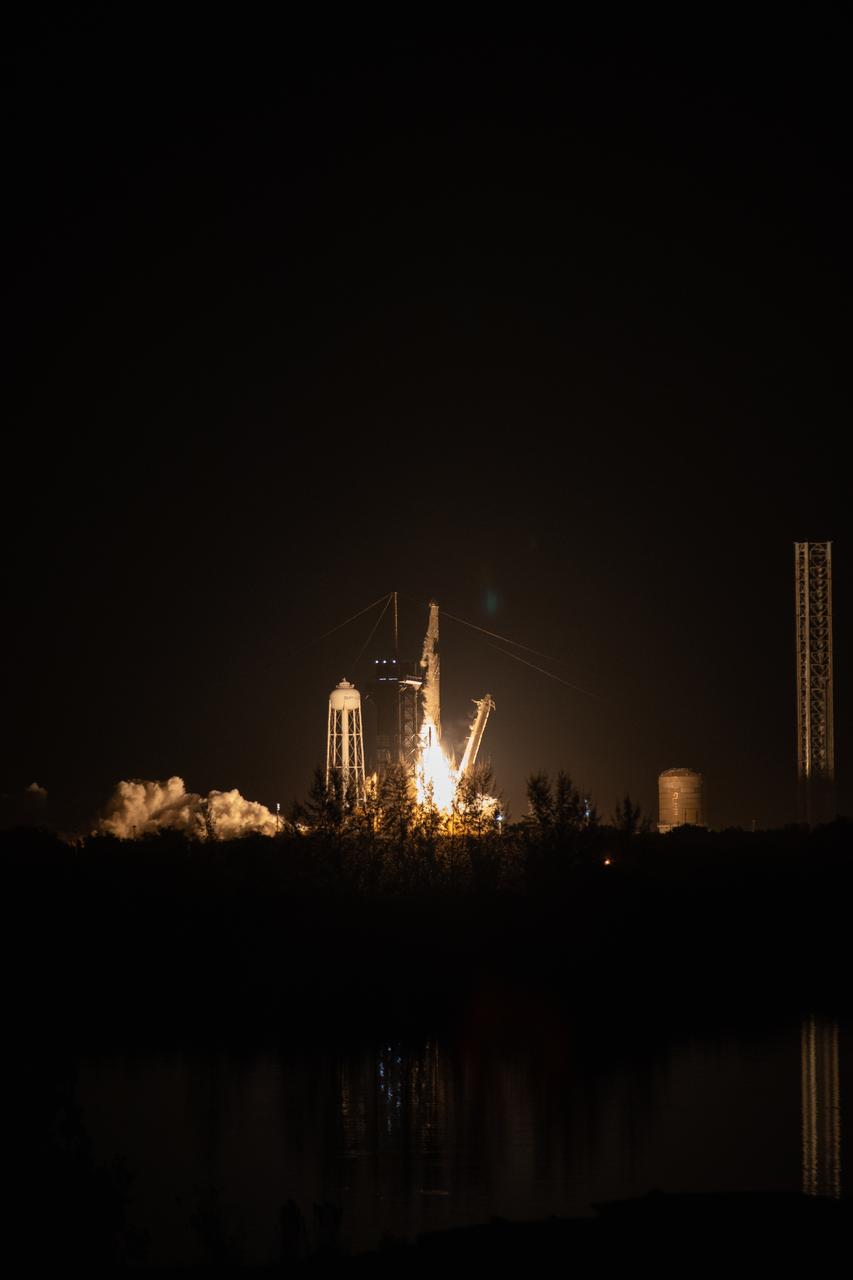

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
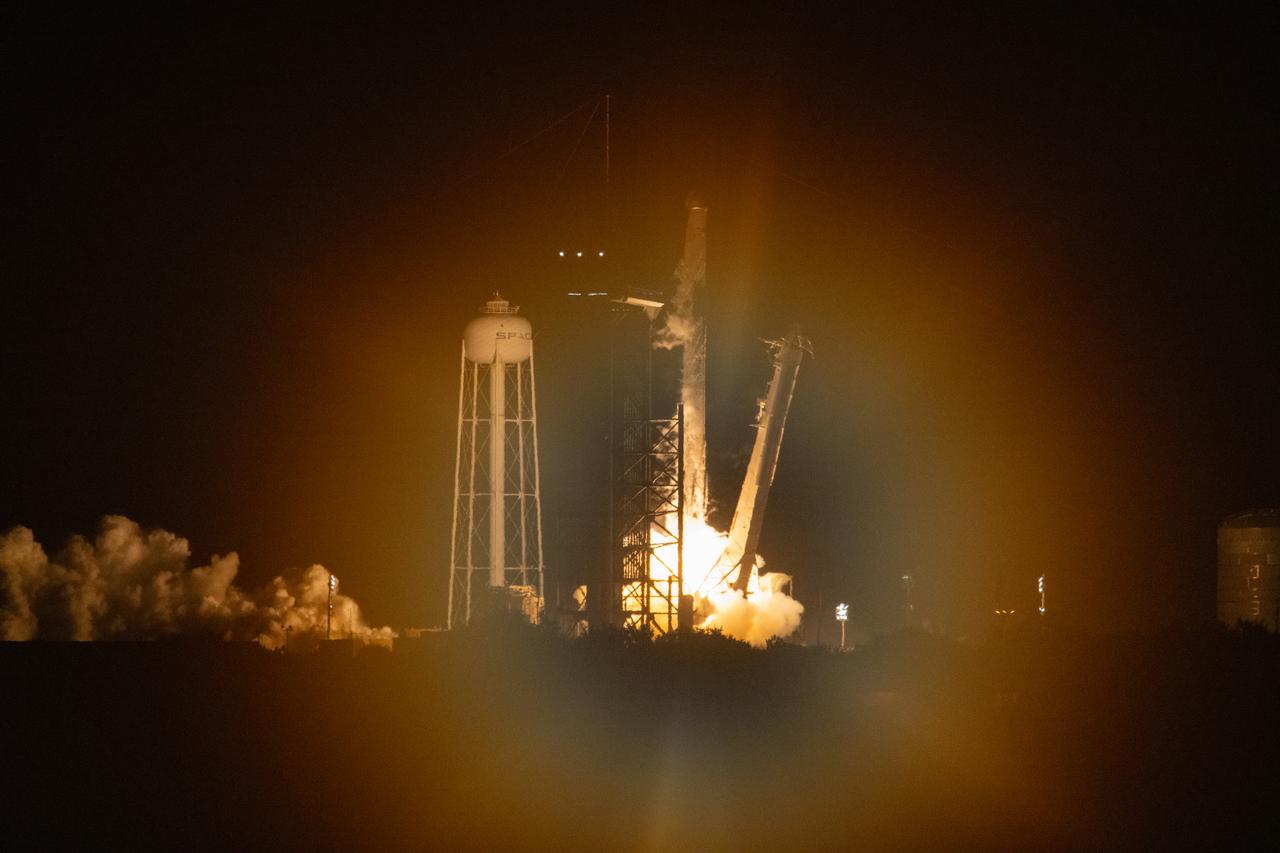

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
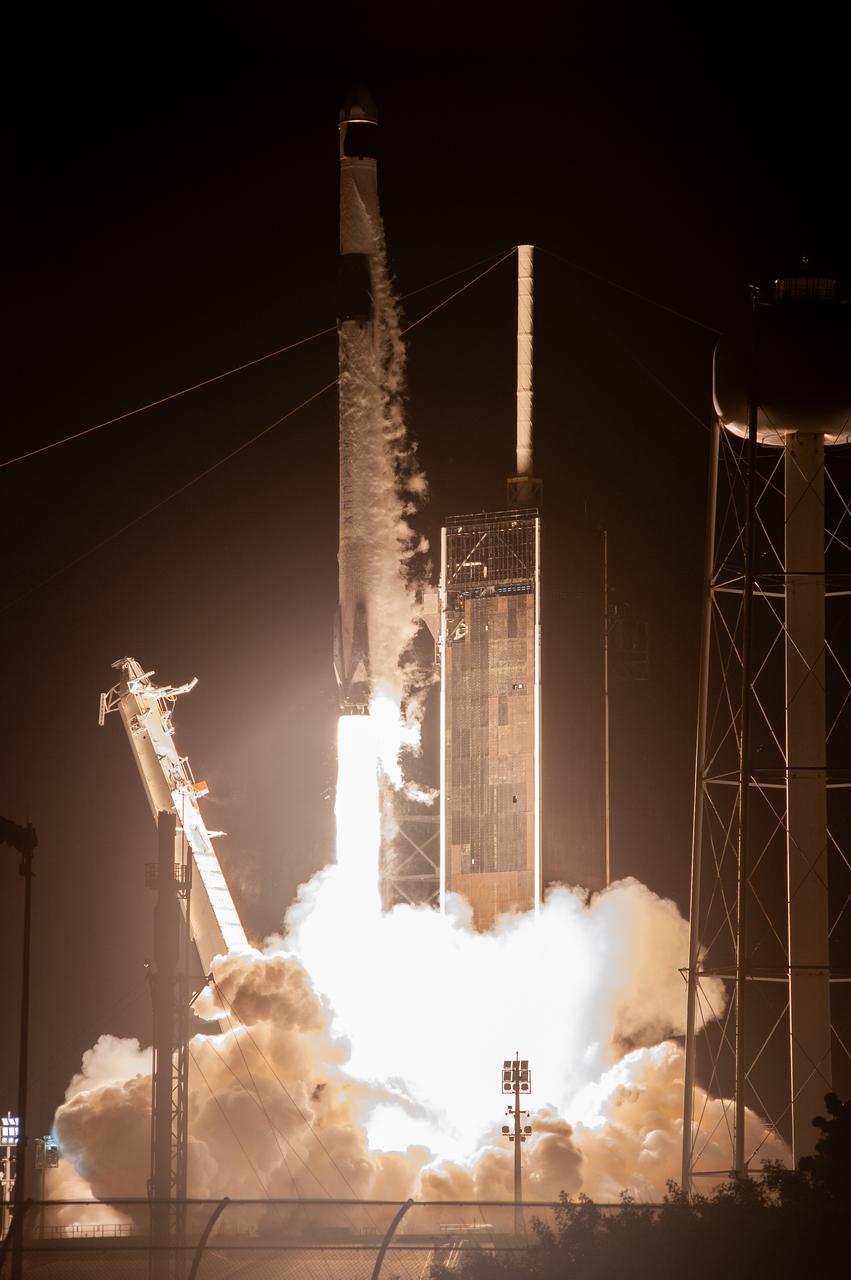

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
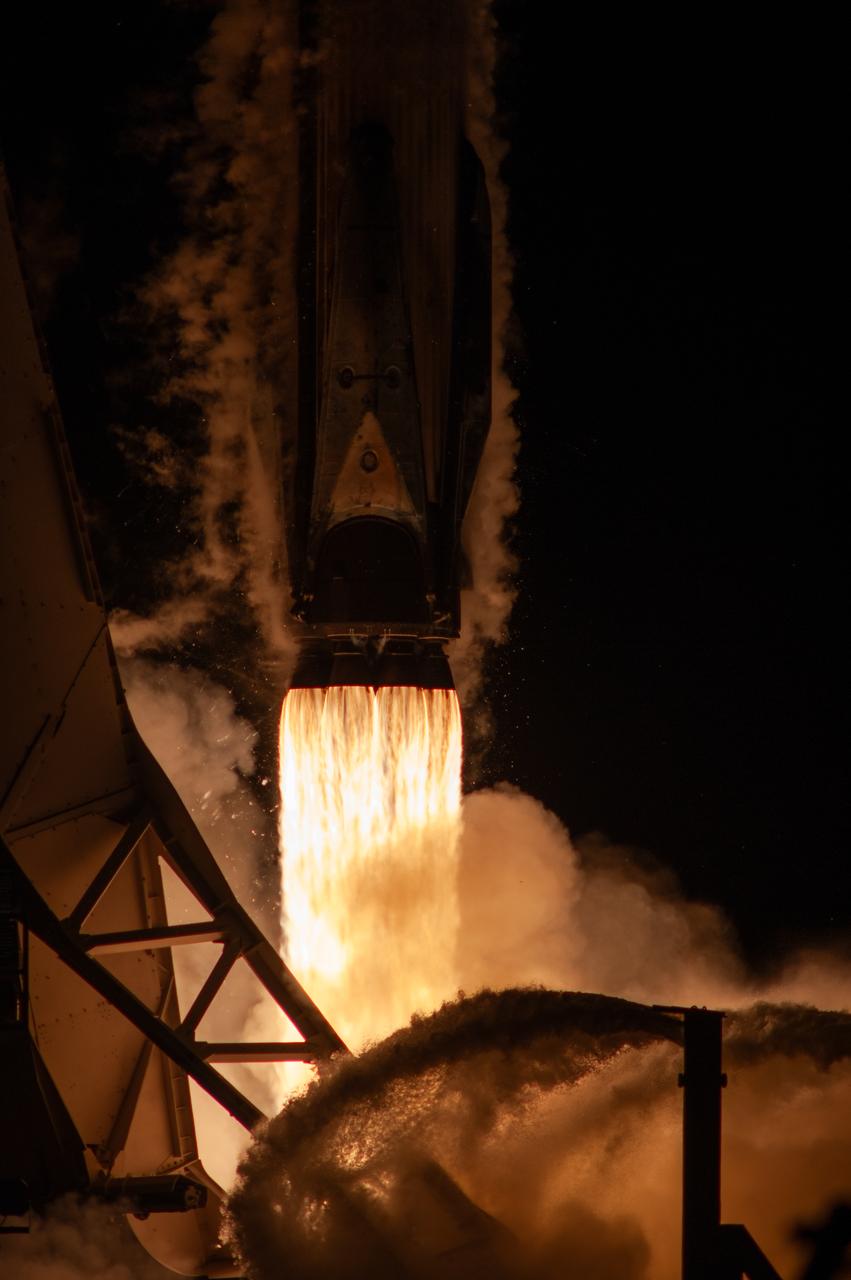

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
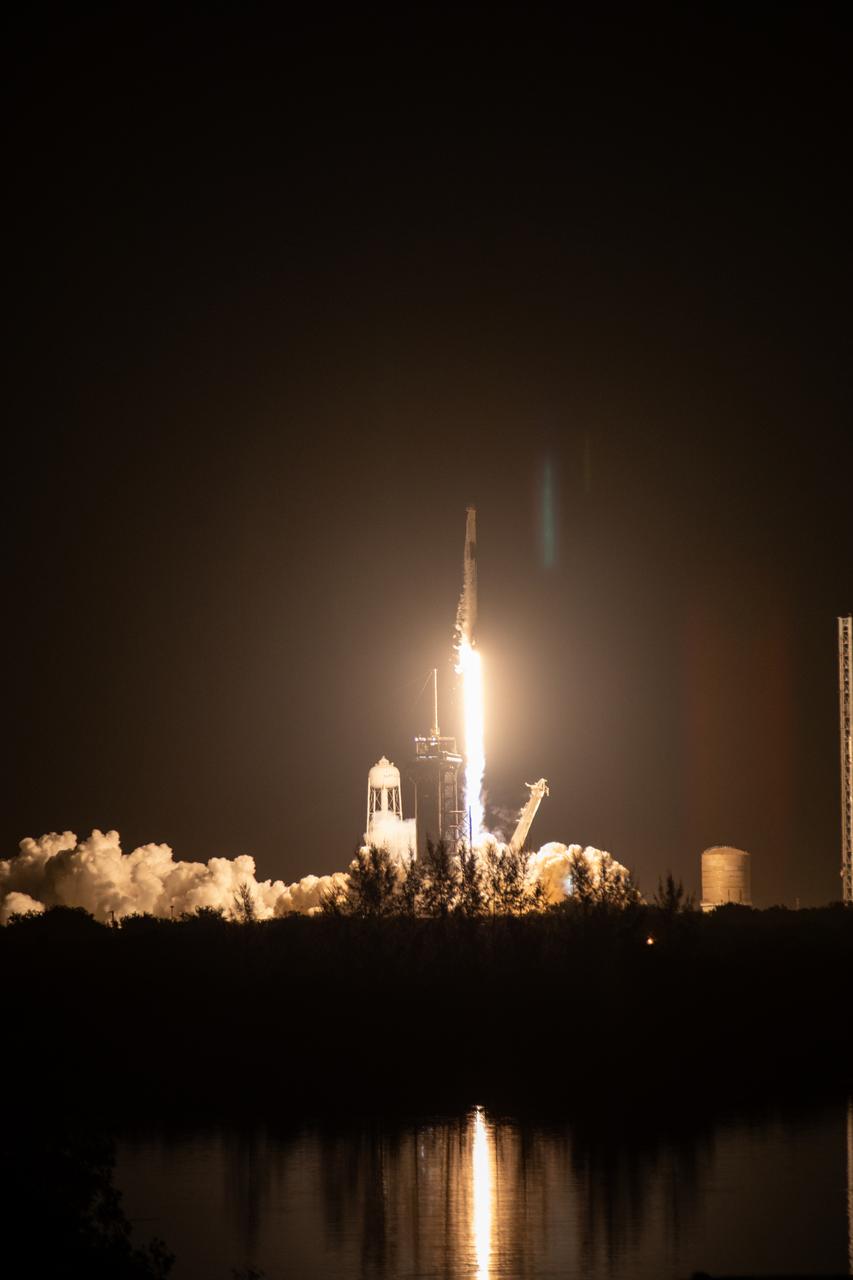

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
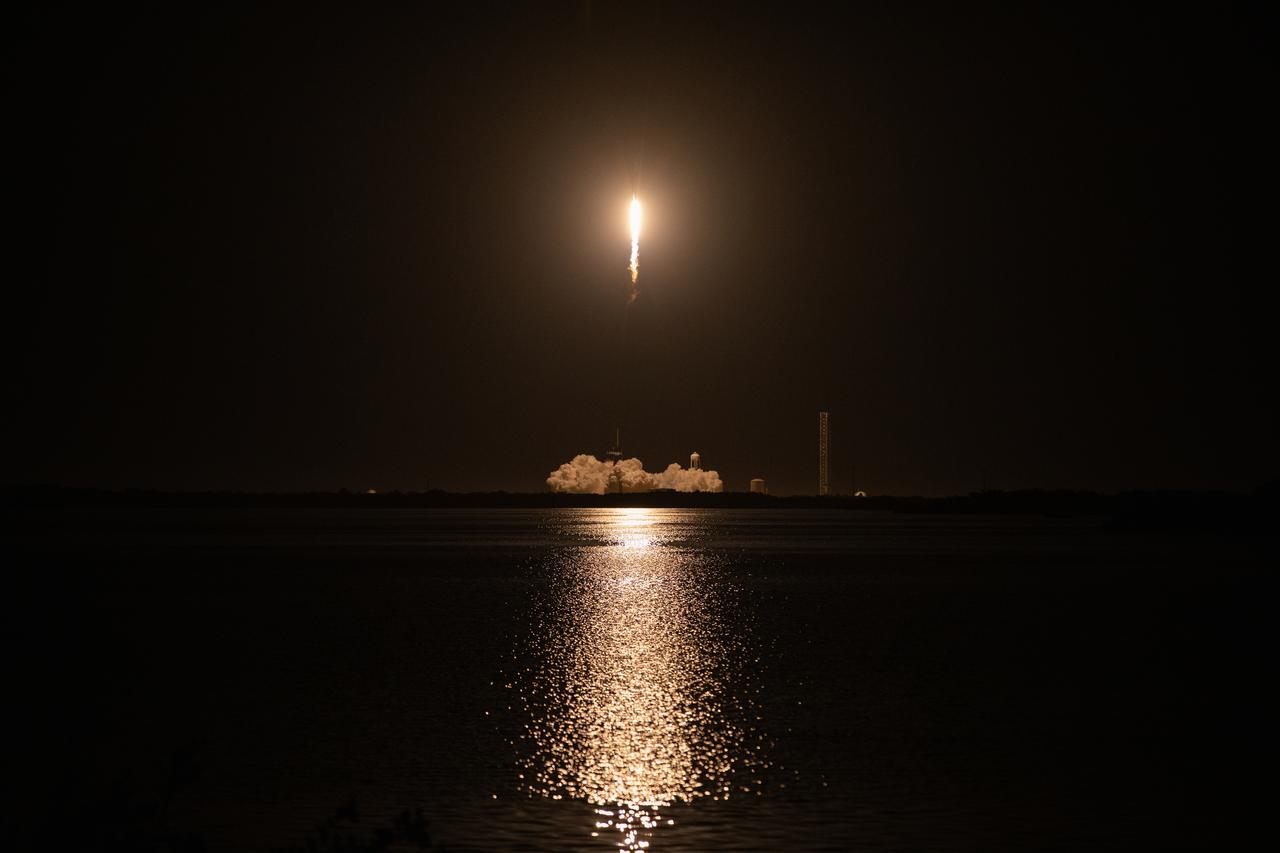

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
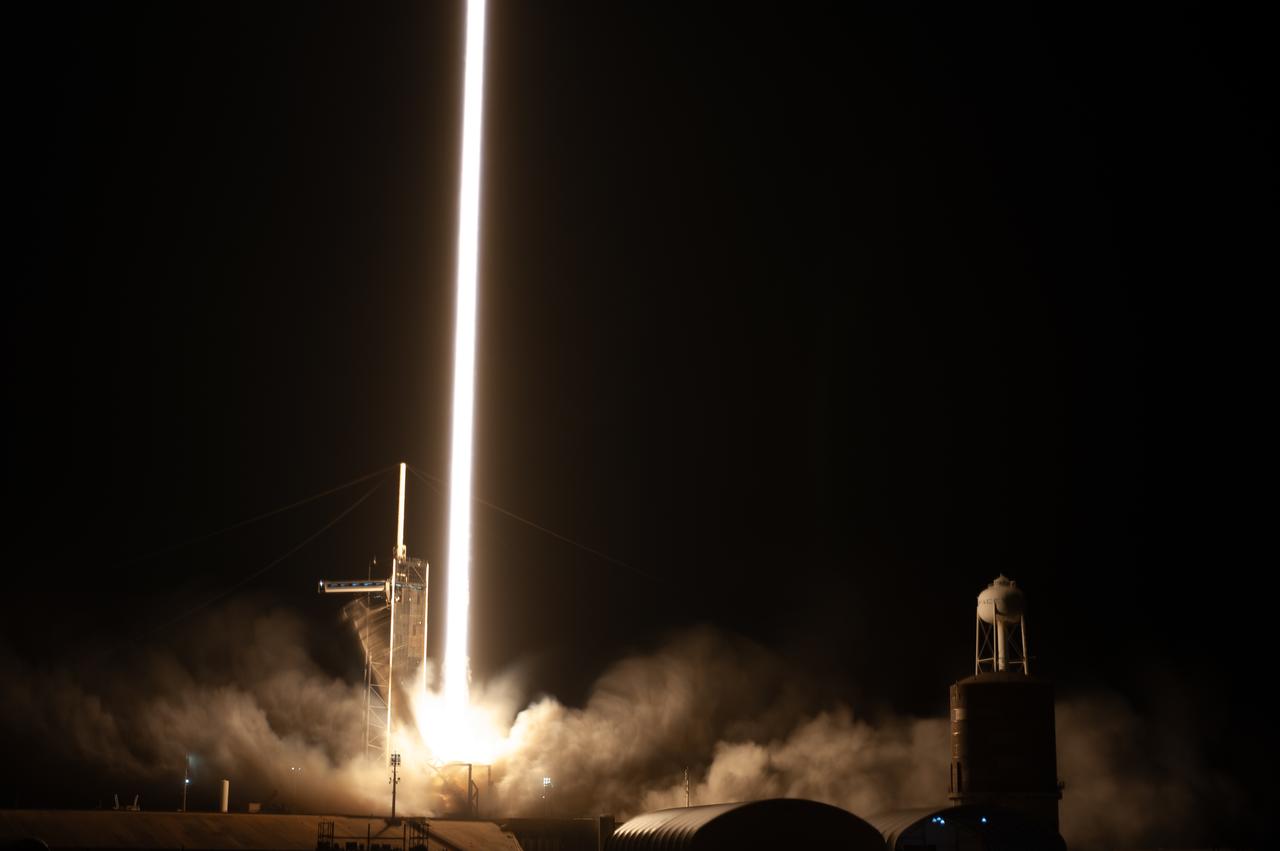

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
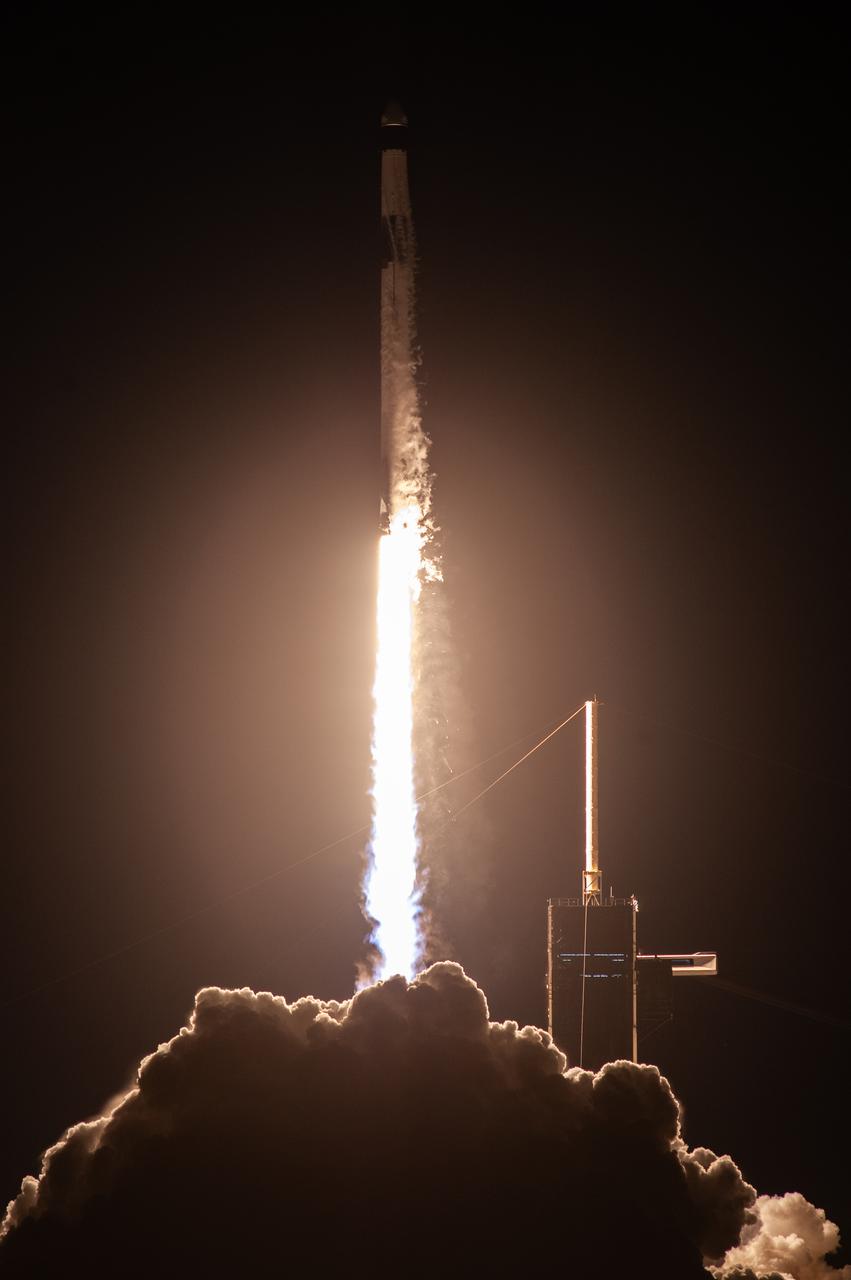

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
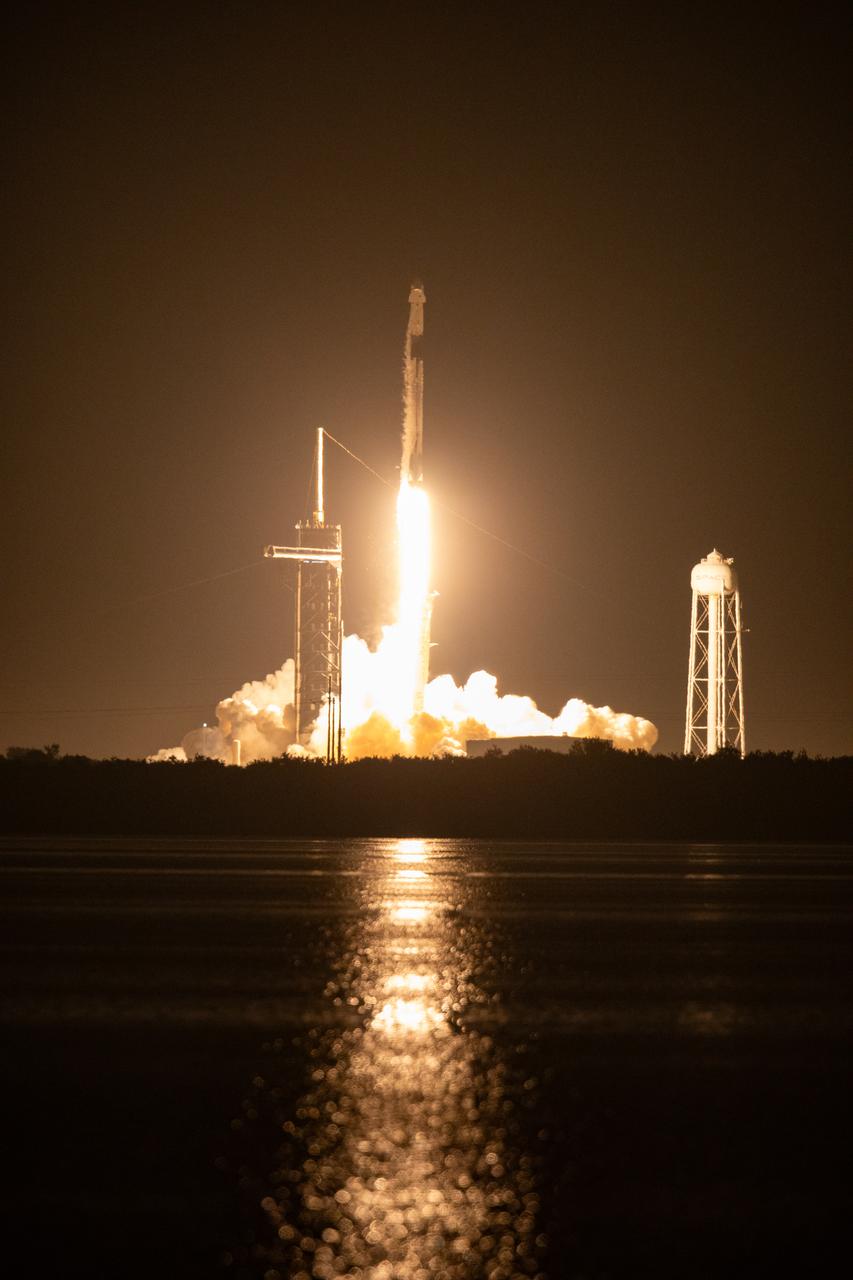

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
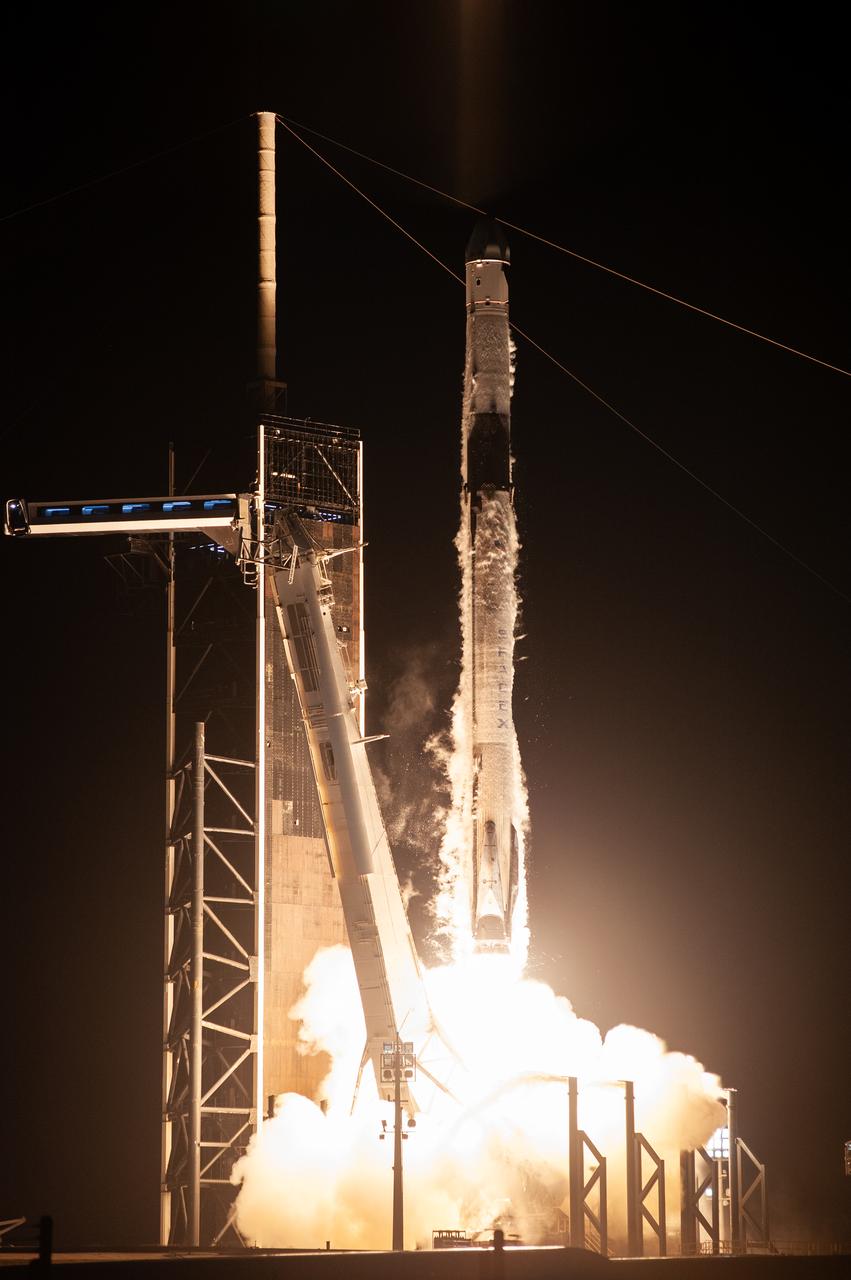

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company’s 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
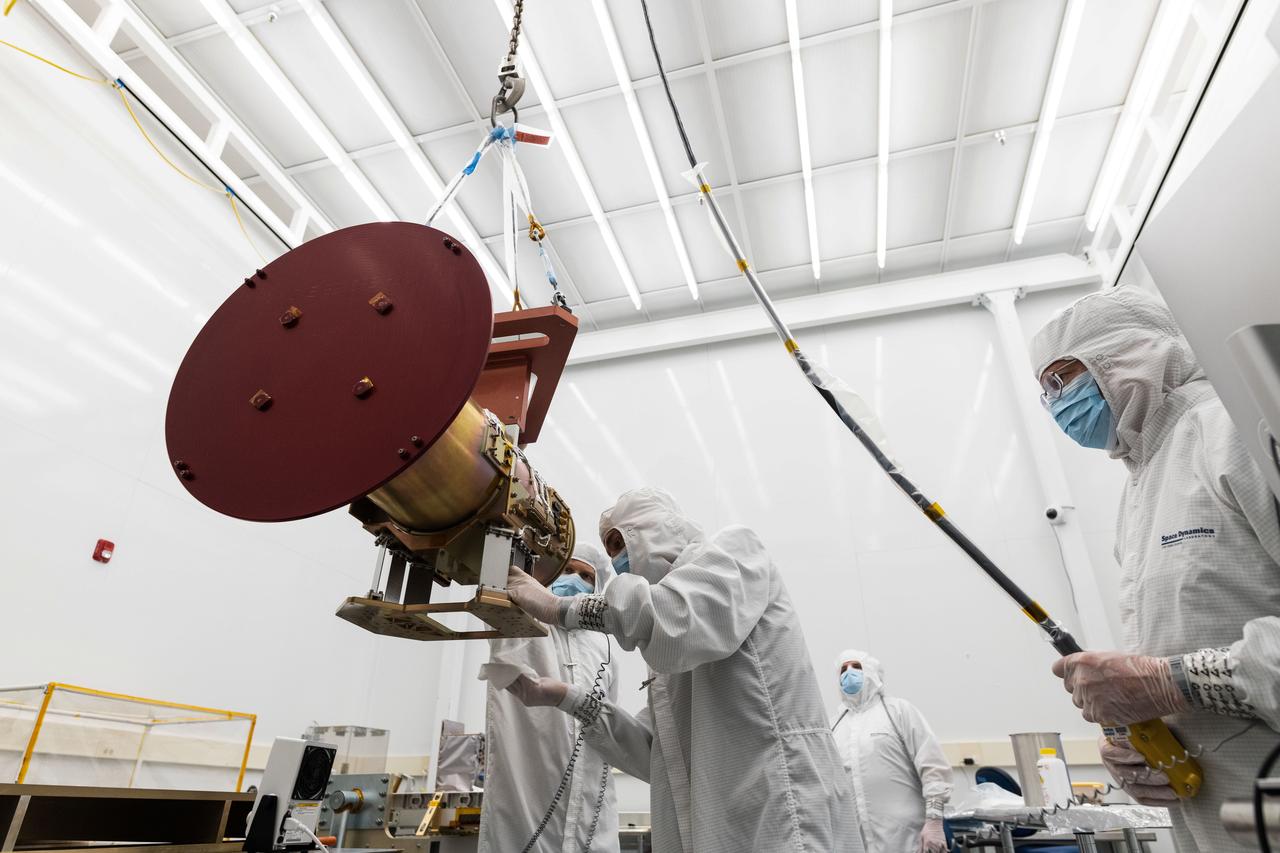

jsc2023e055879 (11/9/2022) --- Space Dynamics Laboratory (SDL) employees ensure the Opto-Mechanical Assembly interface to the flight EXPRESS Payload Adapter is clean before mounting. The Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE) examines the global distribution of small-scale atmospheric gravity waves (AGWs) and how they move through the upper atmosphere, vary with season and geographic location, and contribute to space weather. Image courtesy of SDL/Allison Bills.
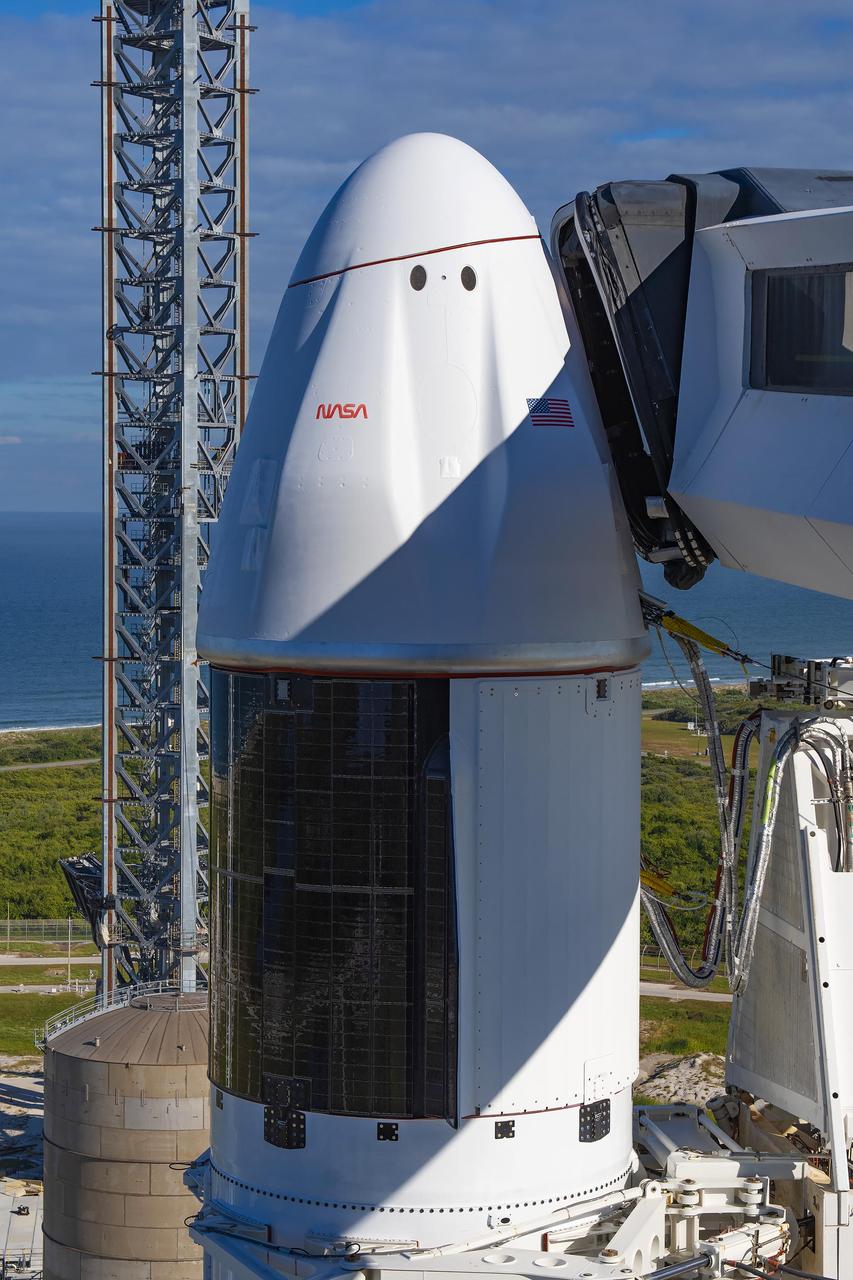

In preparation for SpaceX’s 29th commercial resupply services launch to the International Space Station for NASA, the company’s Falcon 9 rocket, with the Dragon spacecraft atop, is raised to a vertical position at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 8, 2023. The mission will carry scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). Liftoff is scheduled for 8:28 p.m. EST Thursday, Nov. 9, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
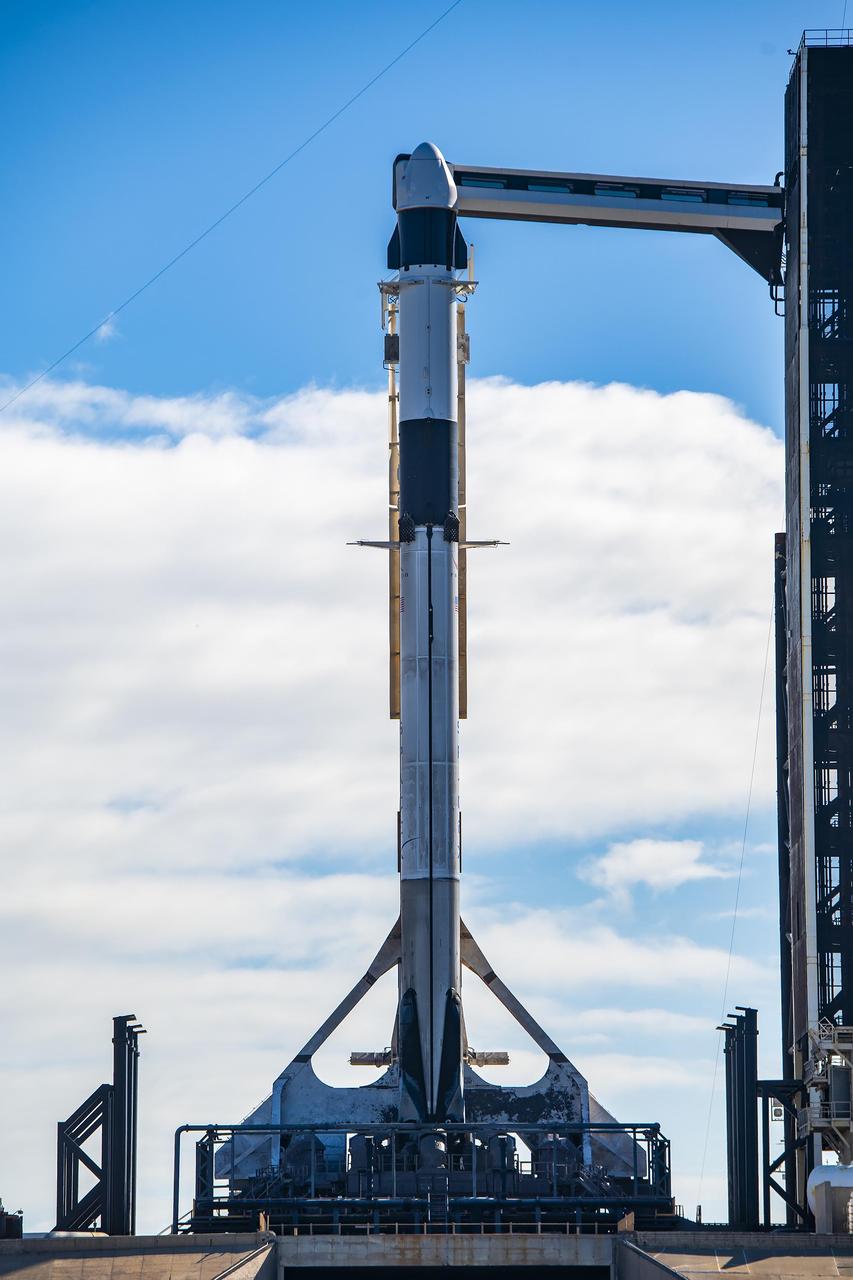

In preparation for SpaceX’s 29th commercial resupply services launch to the International Space Station for NASA, the company’s Falcon 9 rocket, with the Dragon spacecraft atop, is raised to a vertical position at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 8, 2023. The mission will carry scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). Liftoff is scheduled for 8:28 p.m. EST Thursday, Nov. 9, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.

In preparation for SpaceX’s 29th commercial resupply services launch to the International Space Station for NASA, the company’s Falcon 9 rocket, with the Dragon spacecraft atop, is raised to a vertical position at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 8, 2023. The mission will carry scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). Liftoff is scheduled for 8:28 p.m. EST Thursday, Nov. 9, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
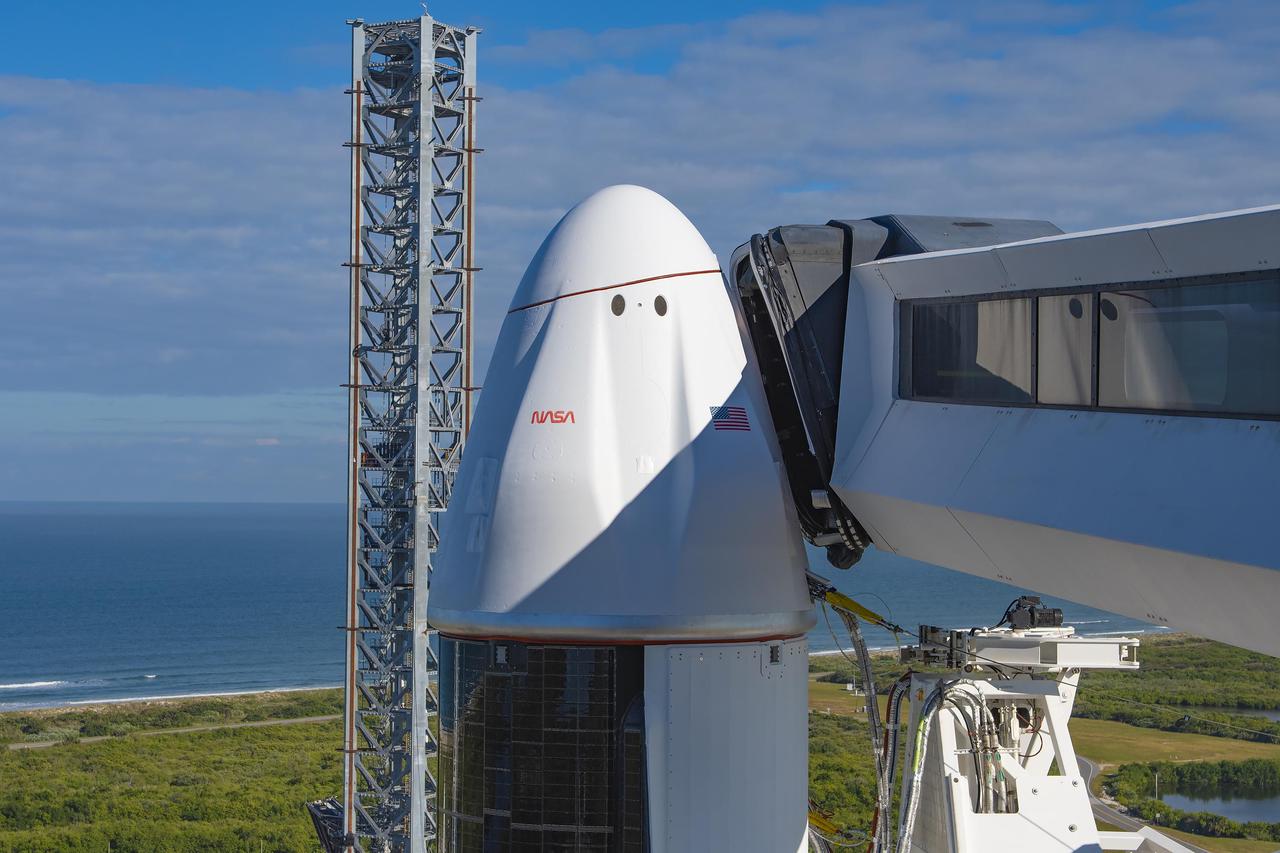

In preparation for SpaceX’s 29th commercial resupply services launch to the International Space Station for NASA, the company’s Falcon 9 rocket, with the Dragon spacecraft atop, is raised to a vertical position at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 8, 2023. The mission will carry scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). Liftoff is scheduled for 8:28 p.m. EST Thursday, Nov. 9, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.

jsc2021e037879 (8/24/2021) --- A preflight view of the Touching Surfaces investigation hardware. The Touch Array (136 mm x 45 mm x 8 mm). Housing : Aluminum (EN-AW 7075 T7351). (Panel A) Nine metallic test surfaces: 3 x steel, copper, brass (from left to right) – with no greater than 3 ?m and less than 3 ?m laser structure (from top to bottom); (Panel B) in each Touch Array two 3 printed humidity detectors are mounted. Image Courtesy DLR
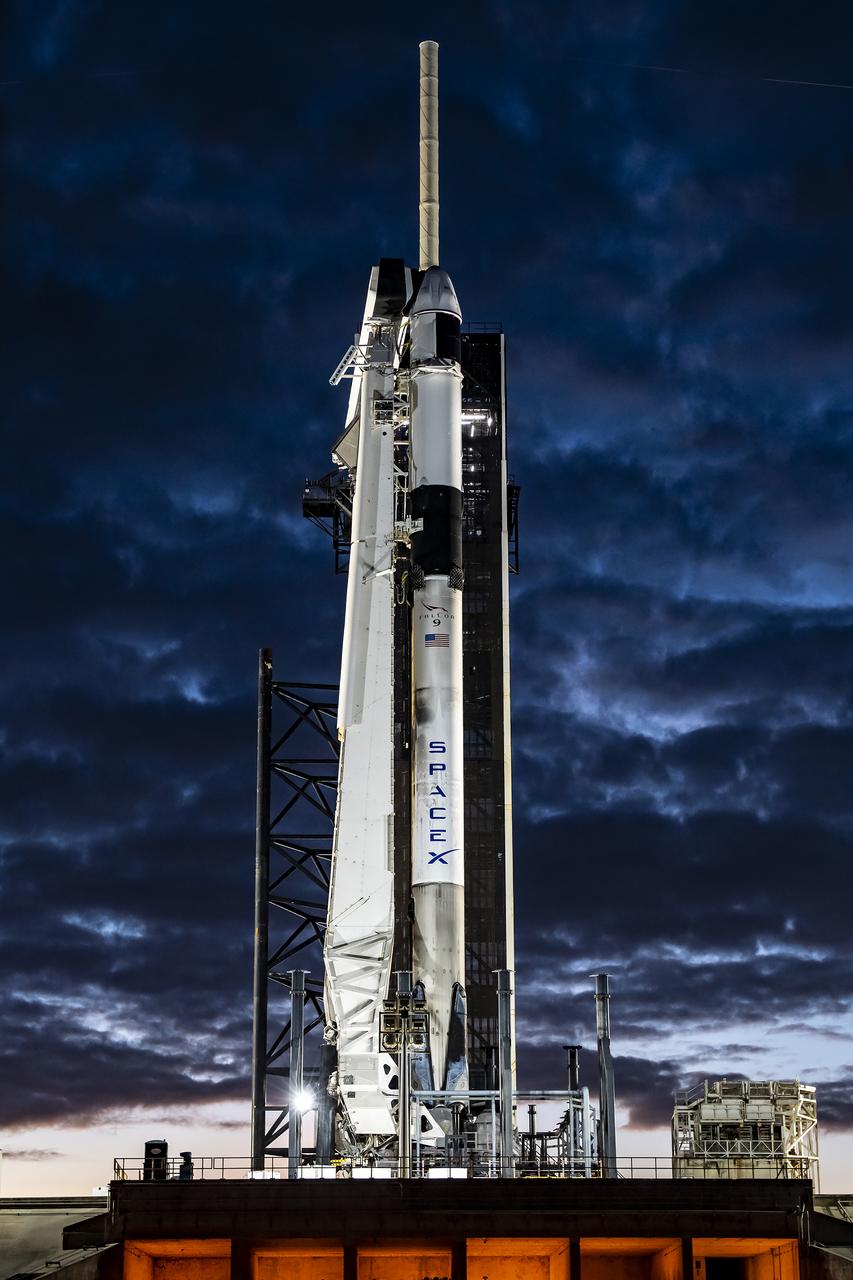

In preparation for SpaceX’s 29th commercial resupply services launch to the International Space Station for NASA, the company’s Falcon 9 rocket, with the Dragon spacecraft atop, is raised to a vertical position at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 8, 2023. The mission will carry scientific research, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, and hardware to the space station to support its Expedition 70 crew, including NASA’s Integrated Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). Liftoff is scheduled for 8:28 p.m. EST Thursday, Nov. 9, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
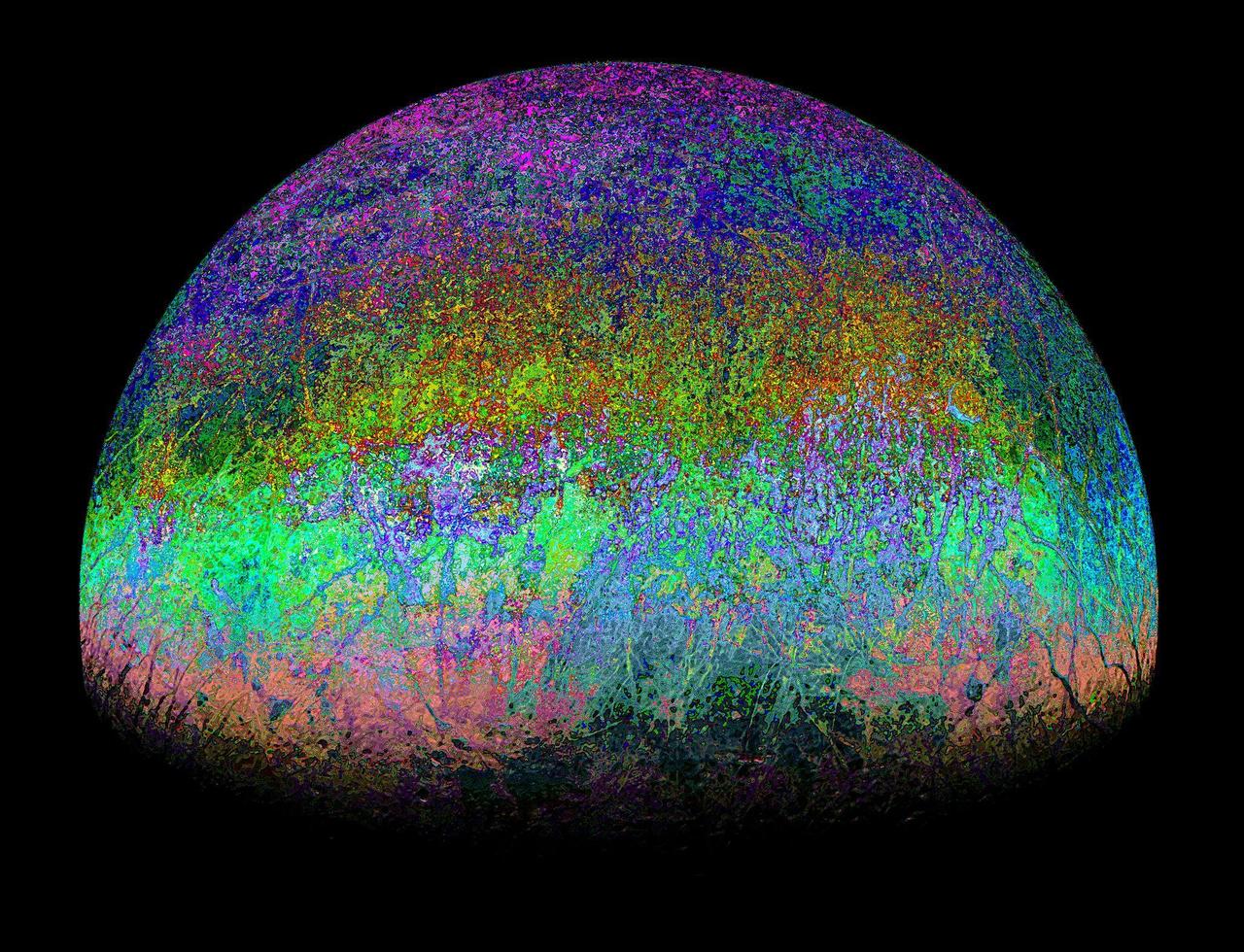
This highly stylized view of Jupiter's icy moon Europa is based on an image captured by JunoCam, the public engagement camera aboard NASA's Juno spacecraft, during the mission's close flyby on Sept. 29, 2022. Citizen scientist Fernando Garcia Navarro created the image by processing a JunoCam previously worked on by fellow citizen scientist Kevin M. Gill. Navarro calls his rendering "Fall Colors of Europa." In processing raw images taken by JunoCam, members of the public create deep-space portraits of the Jovian moon that aren't only awe-inspiring but also worthy of further scientific scrutiny. Juno citizen scientists have played an invaluable role in processing the numerous JunoCam images obtained during science operations at Jupiter. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25335
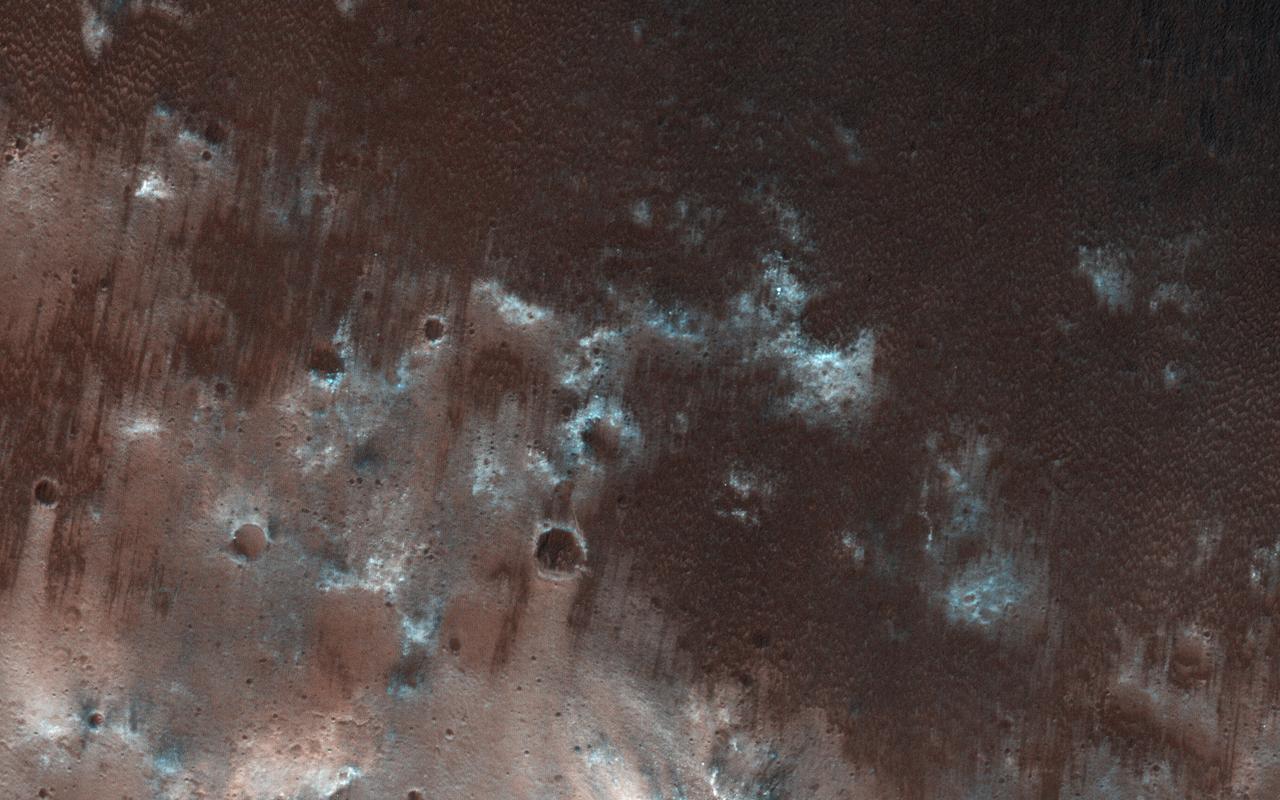

This view from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows the downwind stretches of a sand sheet in central part of the much larger Herschel Crater. This sandy province began kilometers upwind in a string of barchan sand dunes. As the north-to-south blowing wind weakened downwind, it could no longer fashion the sand into dunes but rather into amorphously-shaped sand sheets. While perhaps not awe-inspiringly beautiful, sand sheets can tell us about Mars' current and past environmental conditions as a piece of the puzzle for understanding habitability. Having dunes upwind of sheets is the opposite situation Earth has, where upwind sand sheets evolve downwind into sand dunes. This mystery is receiving ongoing research to to understand these sandy differences between Earth and Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21933

Portrait of Author W. Vogeley

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Children and adults at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida snap photos and stare in awe as space shuttle Atlantis lifts off Launch Pad 39A. Launch of the STS-132 mission to the International Space Station occurred right on time at 2:20 p.m. on May 14. The Russian-built Mini Research Module-1 known as Rassvet, or 'dawn,' is inside the shuttle's cargo bay. It will provide additional storage space and a new docking port for Russian Soyuz and Progress spacecraft. The laboratory will be attached to the bottom port of the station's Zarya module. The mission's three spacewalks will focus on storing spare components outside the station, including six batteries, a communications antenna and parts for the Canadian Dextre robotic arm. STS-132 is the 132nd shuttle flight, the 32nd for Atlantis and the 34th shuttle mission dedicated to station assembly and maintenance. For more information on the STS-132 mission objectives, payload and crew, visit www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts132_index.html. Photo Credit: NASA_Ben Cooper
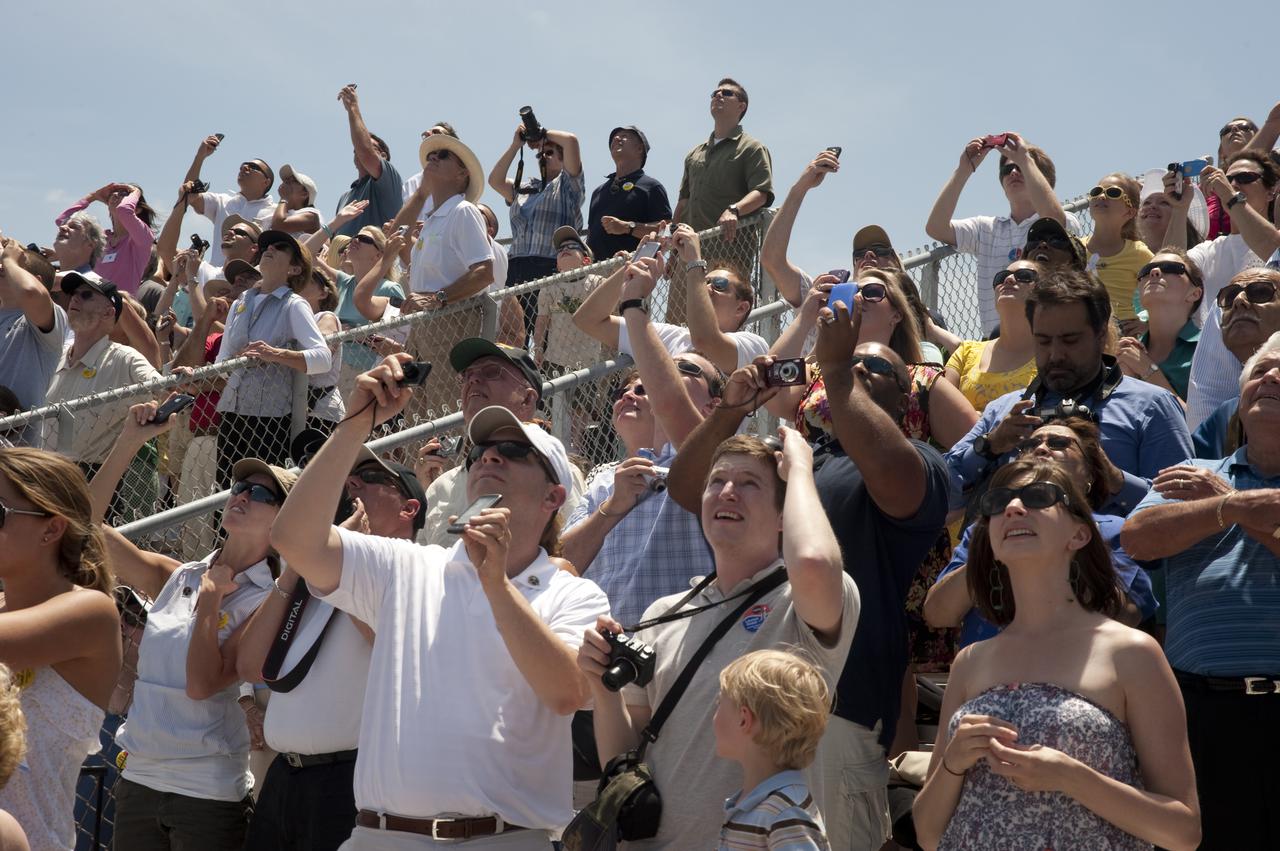

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida snap photos and stare in awe as space shuttle Atlantis lifts off Launch Pad 39A. Launch of the STS-132 mission to the International Space Station occurred right on time at 2:20 p.m. on May 14. The Russian-built Mini Research Module-1 known as Rassvet, or 'dawn,' is inside the shuttle's cargo bay. It will provide additional storage space and a new docking port for Russian Soyuz and Progress spacecraft. The laboratory will be attached to the bottom port of the station's Zarya module. The mission's three spacewalks will focus on storing spare components outside the station, including six batteries, a communications antenna and parts for the Canadian Dextre robotic arm. STS-132 is the 132nd shuttle flight, the 32nd for Atlantis and the 34th shuttle mission dedicated to station assembly and maintenance. For more information on the STS-132 mission objectives, payload and crew, visit www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts132_index.html. Photo Credit: NASA_Ben Cooper
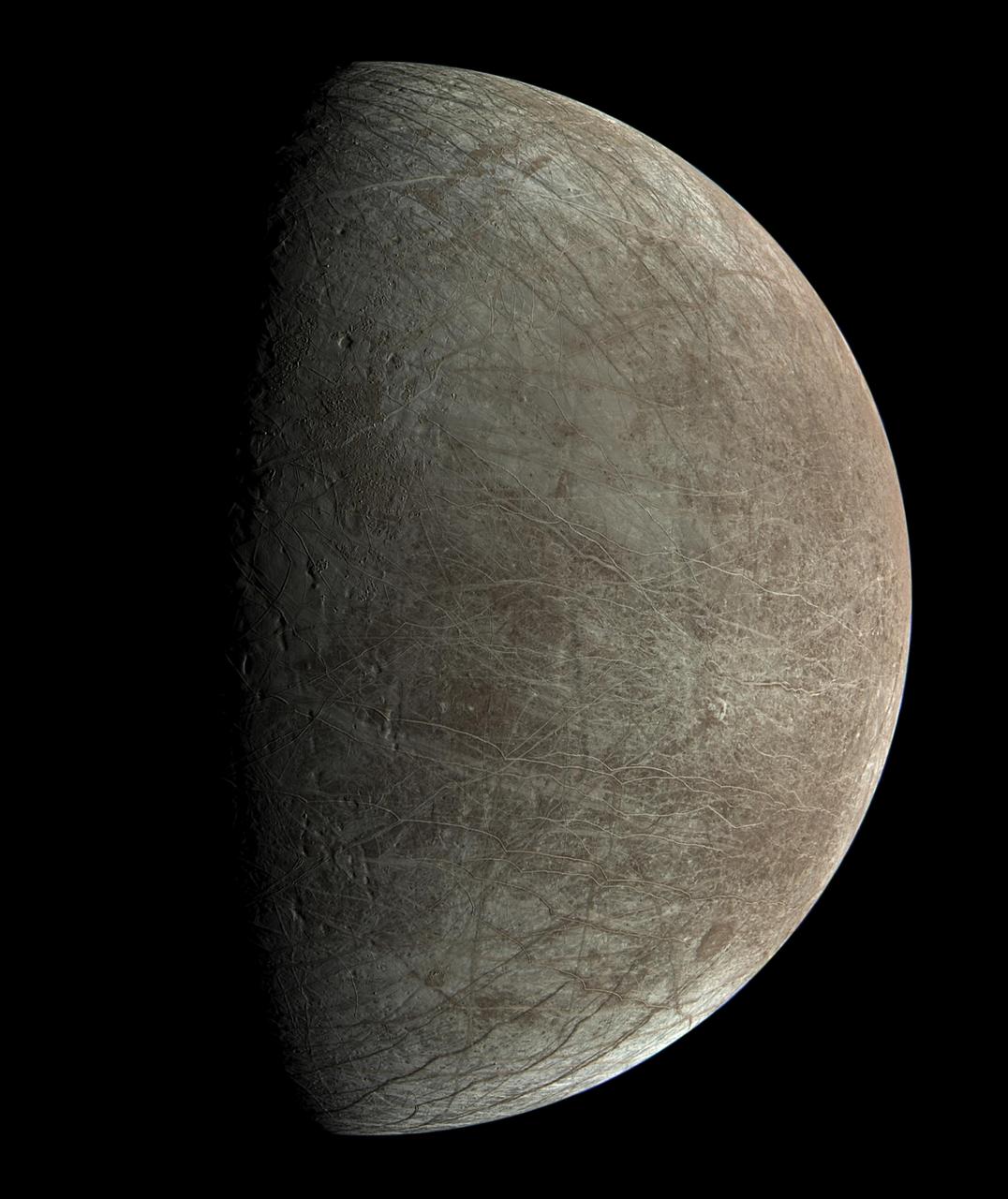

This view of Jupiter's icy moon Europa was captured by JunoCam, the public engagement camera aboard NASA's Juno spacecraft, during the mission's close flyby on Sept. 29, 2022. Citizen scientist Björn Jónsson processed the view to create this image. Jónsson processed the image to enhance the color and contrast. The resolution is about 0.6 miles (1 kilometer) per pixel. JunoCam took the image at an altitude of 945 miles (1,521 kilometers) above a region of the moon called Annwn Regio. In the image, terrain beside the day-night boundary is revealed to be rugged, with pits and troughs. Numerous bright and dark ridges and bands stretch across a fractured surface, revealing the tectonic stresses that the moon has endured over millennia. The circular dark feature at the lower right is Callanish Crater. JunoCam images of Europa help fill in gaps in the maps from images obtained during by NASA's Voyager and Galileo missions. In processing raw images taken by JunoCam, members of the public create deep-space portraits of the Jovian moon that aren't only awe-inspiring but also worthy of further scientific scrutiny. Juno citizen scientists have played an invaluable role in processing the numerous JunoCam images obtained during science operations at Jupiter. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25334

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Children and adults at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida snap photos and stare in awe as space shuttle Atlantis lifts off Launch Pad 39A. Launch of the STS-132 mission to the International Space Station occurred right on time at 2:20 p.m. on May 14. The Russian-built Mini Research Module-1 known as Rassvet, or 'dawn,' is inside the shuttle's cargo bay. It will provide additional storage space and a new docking port for Russian Soyuz and Progress spacecraft. The laboratory will be attached to the bottom port of the station's Zarya module. The mission's three spacewalks will focus on storing spare components outside the station, including six batteries, a communications antenna and parts for the Canadian Dextre robotic arm. STS-132 is the 132nd shuttle flight, the 32nd for Atlantis and the 34th shuttle mission dedicated to station assembly and maintenance. For more information on the STS-132 mission objectives, payload and crew, visit www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts132_index.html. Photo Credit: NASA_Ben Cooper

Some 5,000 light years (2,900 trillion miles) from Earth, in the constellation Puppis, is the 1.4 light years (more than 8 trillion miles) long Calabash Nebula, referred to as the Rotten Egg Nebula because of its sulfur content which would produce an awful odor if one could smell in space. This image of the nebula captured by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (HST) depicts violent gas collisions that produced supersonic shock fronts in a dying star. Stars, like our sun, will eventually die and expel most of their material outward into shells of gas and dust These shells eventually form some of the most beautiful objects in the universe, called planetary nebulae. The yellow in the image depicts the material ejected from the central star zooming away at speeds up to one and a half million kilometers per hour (one million miles per hour). Due to the high speeds of the gas, shock-fronts are formed on impact and heat the surrounding gas. Although computer calculations have predicted the existence and structure of such shocks for some time, previous observations have not been able to prove the theory.
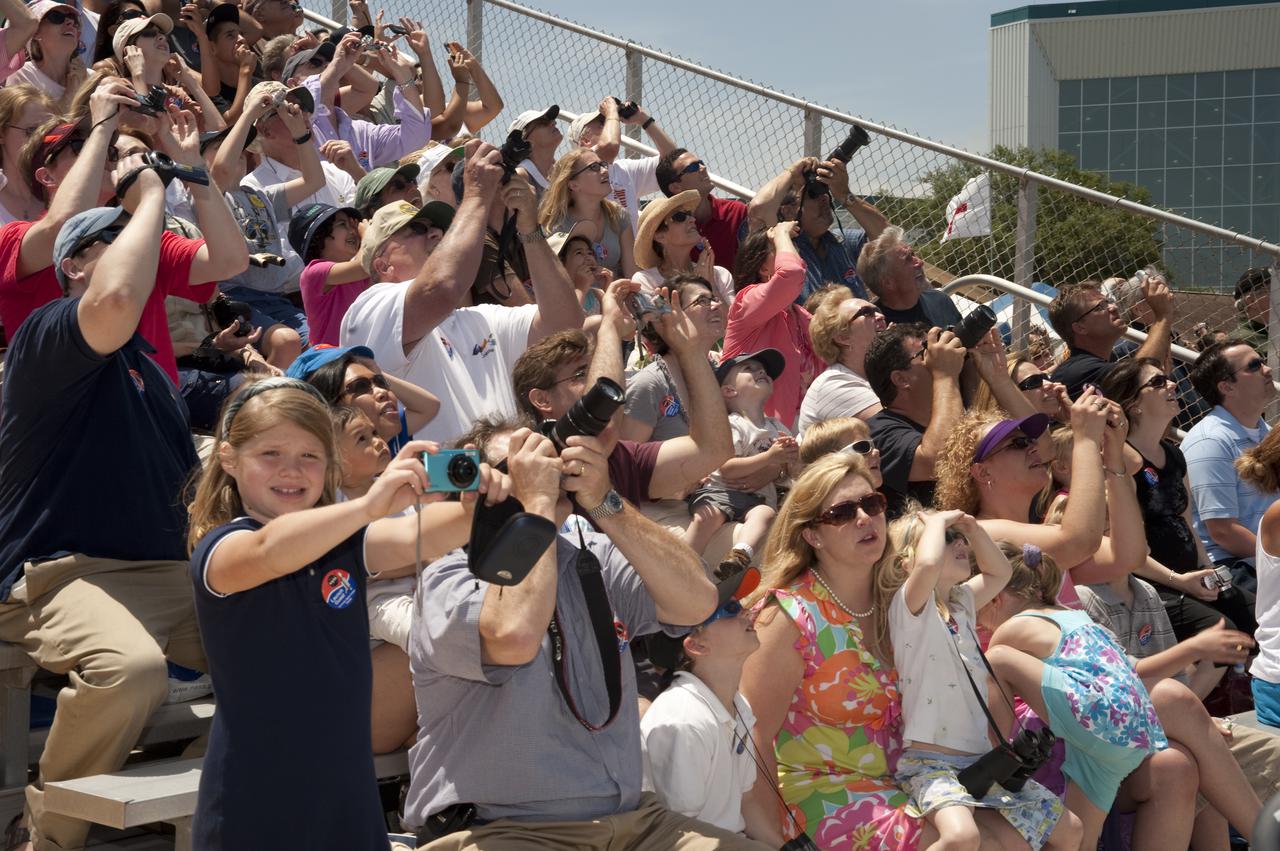

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Children and adults at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida snap photos and stare in awe as space shuttle Atlantis lifts off Launch Pad 39A. Launch of the STS-132 mission to the International Space Station occurred right on time at 2:20 p.m. on May 14. The Russian-built Mini Research Module-1 known as Rassvet, or 'dawn,' is inside the shuttle's cargo bay. It will provide additional storage space and a new docking port for Russian Soyuz and Progress spacecraft. The laboratory will be attached to the bottom port of the station's Zarya module. The mission's three spacewalks will focus on storing spare components outside the station, including six batteries, a communications antenna and parts for the Canadian Dextre robotic arm. STS-132 is the 132nd shuttle flight, the 32nd for Atlantis and the 34th shuttle mission dedicated to station assembly and maintenance. For more information on the STS-132 mission objectives, payload and crew, visit www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts132_index.html. Photo Credit: NASA_Ben Cooper
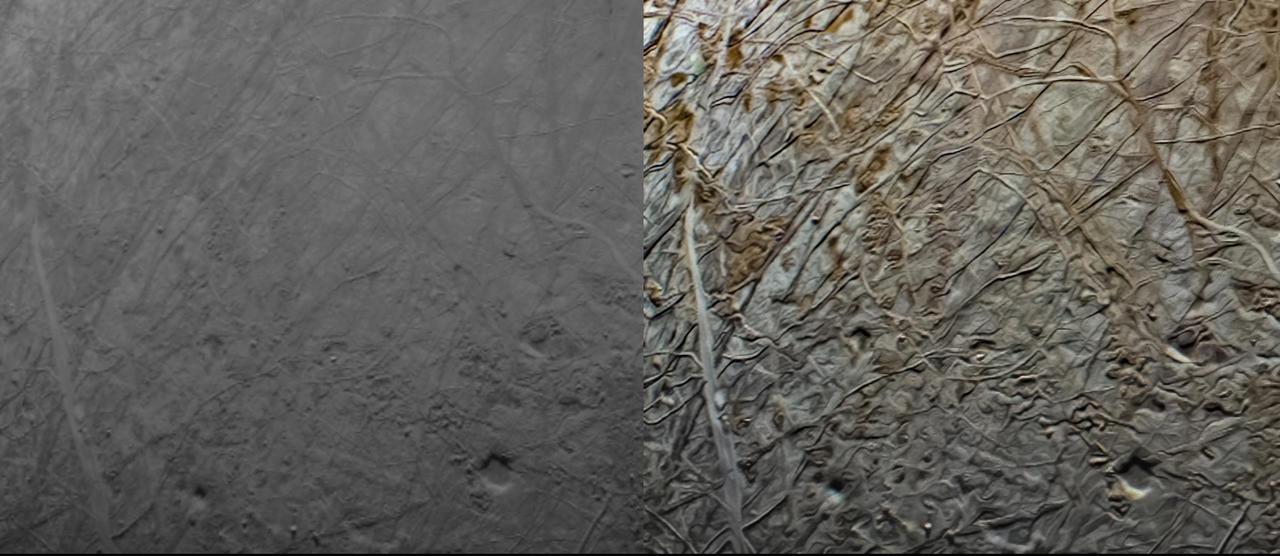

This pair of images shows the same portion of Jupiter's moon Europa before and after it was processed. The original (minimally processed) image, left, was captured by JunoCam, the public engagement camera aboard NASA's Juno spacecraft, during the mission's close flyby on Sept. 29, 2022. Captured at an altitude of 945 miles (1,521 kilometers) above a region of the moon called Annwn Regio, it was minimally processed. Citizen scientist Navaneeth Krishnan reprocessed the image to produce the version on the right. The enhanced color contrast causes larger surface features to stand out more. An example of the results can be seen in the lower right of this image, where the pits and a small rectangular block (reflecting more light than surrounding features) cast notable shadows. Small-scale texturing of the surface in the image needs to be carefully studied to distinguish between features and artifacts from processing, but the image serves both art and science by drawing us deeper into Europa's alien landscape. In processing raw images taken by JunoCam, members of the public create deep-space portraits of the Jovian moon that aren't only awe-inspiring but also worthy of further scientific scrutiny. Juno citizen scientists have played an invaluable role in processing the numerous JunoCam images obtained during science operations at Jupiter. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25333
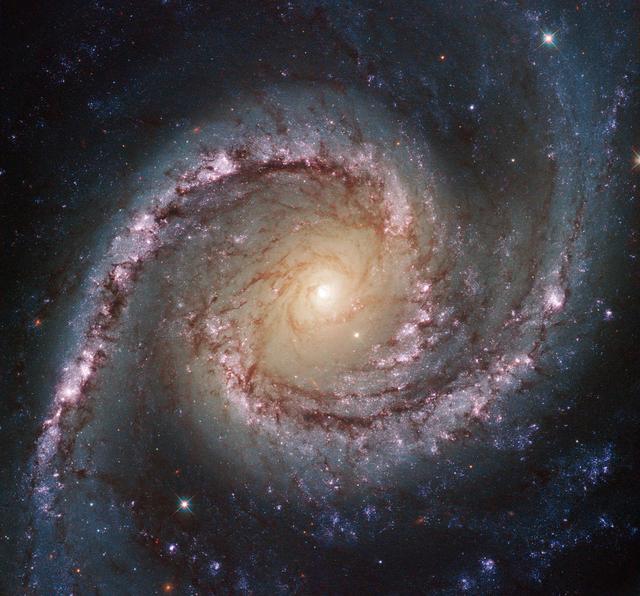

This new Hubble image shows NGC 1566, a beautiful galaxy located approximately 40 million light-years away in the constellation of Dorado (The Dolphinfish). NGC 1566 is an intermediate spiral galaxy, meaning that while it does not have a well-defined bar-shaped region of stars at its center — like barred spirals — it is not quite an unbarred spiral either. The small but extremely bright nucleus of NGC 1566 is clearly visible in this image, a telltale sign of its membership of the Seyfert class of galaxies. The centers of such galaxies are very active and luminous, emitting strong bursts of radiation and potentially harboring supermassive black holes that are many millions of times the mass of the sun. NGC 1566 is not just any Seyfert galaxy; it is the second brightest Seyfert galaxy known. It is also the brightest and most dominant member of the Dorado Group, a loose concentration of galaxies that together comprise one of the richest galaxy groups of the southern hemisphere. This image highlights the beauty and awe-inspiring nature of this unique galaxy group, with NGC 1566 glittering and glowing, its bright nucleus framed by swirling and symmetrical lavender arms. This image was taken by Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) in the near-infrared part of the spectrum. European Space Agency Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Flickr user Det58 <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
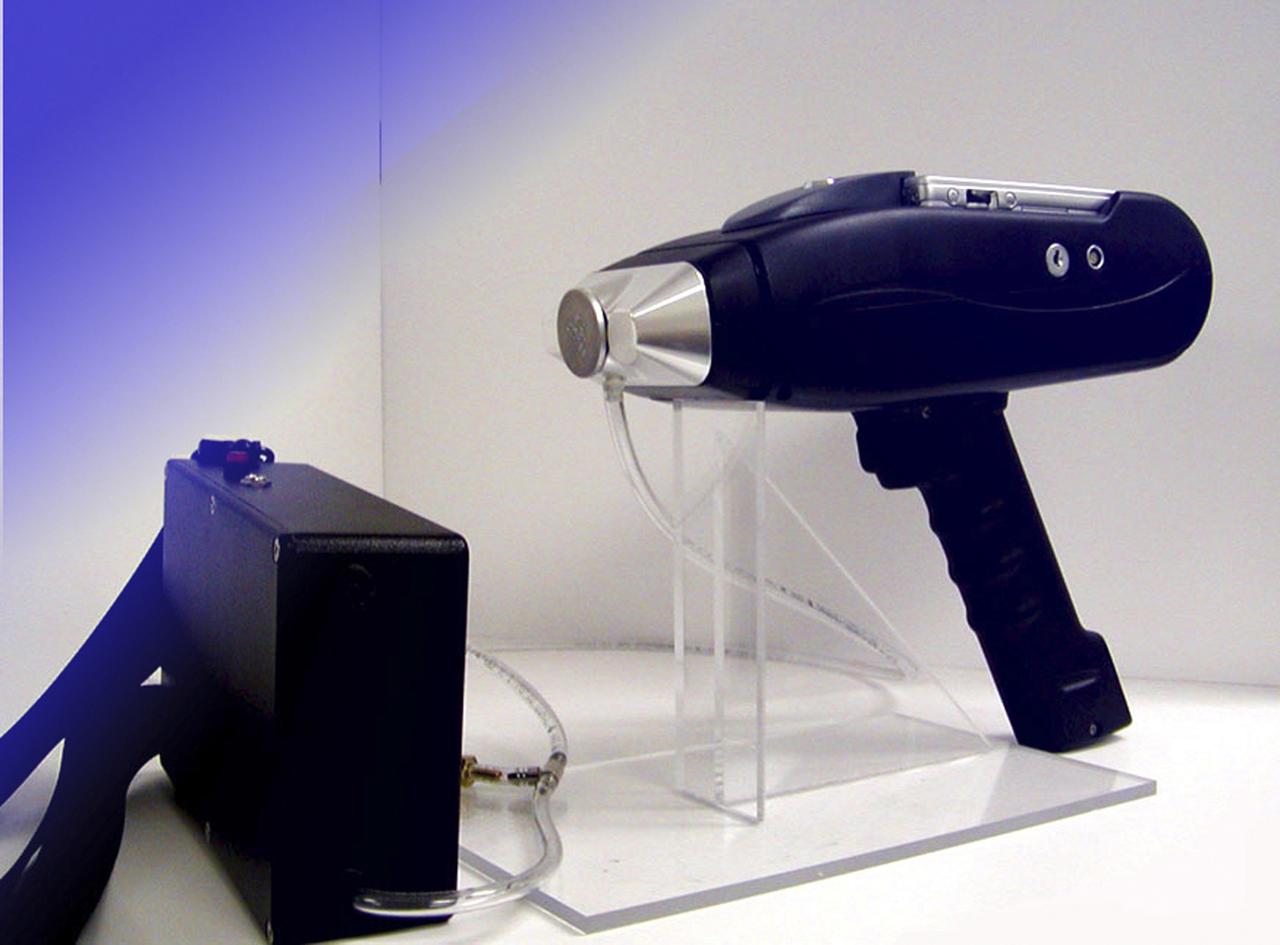

Marshall Space Flight Center engineers have teamed with KeyMaster Technologies, Kennewick, Washington, to develop a portable vacuum analyzer that performs on-the-spot chemical analyses under field conditions, a task previously only possible in a chemical laboratory. The new capability is important not only to the aerospace industry, but holds potential for broad applications in any industry that depends on materials analysis, such as the automotive and pharmaceutical industries. Weighing in at a mere 4 pounds, the newly developed handheld vacuum X-ray fluorescent analyzer can identify and characterize a wide range of elements, and is capable of detecting chemical elements with low atomic numbers, such as sodium, aluminum and silicon. It is the only handheld product on the market with that capability. Aluminum alloy verification is of particular interest to NASA because vast amounts of high-strength aluminum alloys are used in the Space Shuttle propulsion system such as the External Tank, Main Engine, and Solid Rocket Boosters. This capability promises to be a boom to the aerospace community because of unique requirements, for instance, the need to analyze Space Shuttle propulsion systems on the launch pad. Those systems provide the awe-inspiring rocket power that propels the Space Shuttle from Earth into orbit in mere minutes. The scanner development also marks a major improvement in the quality assurance field, because screws, nuts, bolts, fasteners, and other items can now be evaluated upon receipt and rejected if found to be substandard. The same holds true for aluminum weld rods. The ability to validate the integrity of raw materials and partially finished products before adding value to them in the manufacturing process will be of benefit not only to businesses, but also to the consumer, who will have access to a higher value product at a cheaper price. Three vacuum X-ray scanners are already being used in the Space Shuttle Program. The External Tank Project Office is using one for aluminum alloy analysis, while a Marshall contractor is evaluating alloys with another unit purchased for the Space Shuttle Main Engine Office. The Reusable Solid Rocket Motor Project Office has obtained a scanner that is being used to test hardware and analyze materials.

<b>Join NASA's Google+ Hangout on Friday, December 20th 2:00 - 3:00 PM (EST) at <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/18S2TbC" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/18S2TbC</a> </b> It was 45 years ago, on December 24, 1968 when Apollo 8 astronauts captured 'Earthrise' – the first color photograph of Earth taken by a person in lunar orbit. NASA announces a new simulation of the events leading to the creation of 'Earthrise,' one of the iconic photographs of the 20th Century – Earth seen from the moon captured by the crew of Apollo 8. This new simulation allows anyone to virtually ride with the astronauts and experience the awe they felt at the vista in front of them. Apollo 8 Commander Frank Borman and crew members William A. Anders and James A. Lovell photographed the stunning scene as their spacecraft orbited the moon on December 24, 1968. The new computer simulation was created using data from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, spacecraft and includes details not seen in the previous visualization released last year. Participants in this Hangout include: * John Keller, project scientist for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter project * Ernie Wright, project lead with the Scientific Visualization Studio at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center * Andrew Chaikin, space historian, author of the book A Man on the Moon "This will also be the first time we've released a video that's synchronized with the onboard audio recording of the astronauts,", says Ernie Wright. "The new visualization tells us not only what time the photos were taken, but also exactly which way the spacecraft was pointing and therefore which window each photo was taken from." Earthrise is the cover photo of TIME's Great Images of the 20th Century and is among photos on the cover of LIFE's 100 Photographs That Changed the World. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
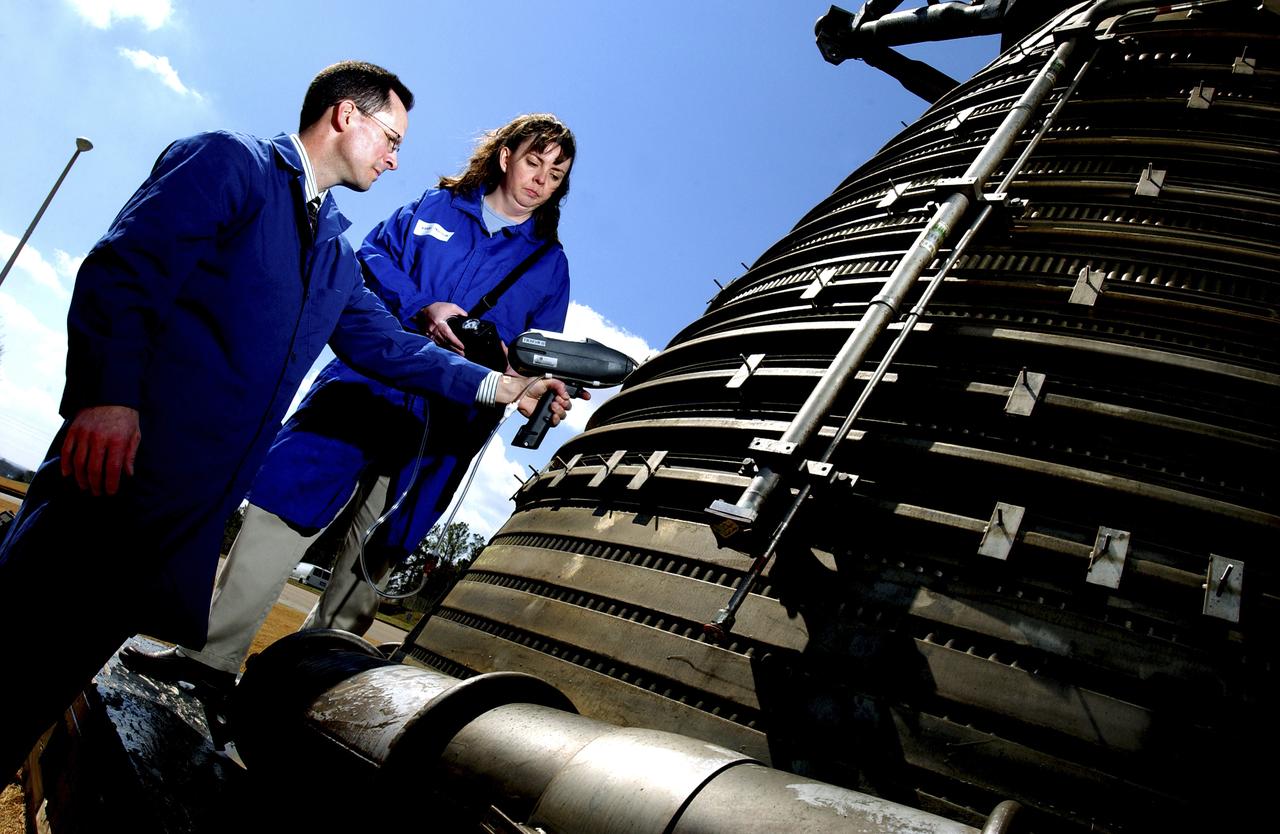

Teamed with KeyMaster Technologies, Kennewick, Washington, the Marshall Space Flight Center engineers have developed a portable vacuum analyzer that performs on-the-spot chemical analyses under field conditions— a task previously only possible in a chemical laboratory. The new capability is important not only to the aerospace industry, but holds potential for broad applications in any industry that depends on materials analysis, such as the automotive and pharmaceutical industries. Weighing in at a mere 4 pounds, the newly developed handheld vacuum X-ray fluorescent analyzer can identify and characterize a wide range of elements, and is capable of detecting chemical elements with low atomic numbers, such as sodium, aluminum and silicon. It is the only handheld product on the market with that capability. Aluminum alloy verification is of particular interest to NASA because vast amounts of high-strength aluminum alloys are used in the Space Shuttle propulsion system such as the External Tank, Main Engine, and Solid Rocket Boosters. This capability promises to be a boom to the aerospace community because of unique requirements, for instance, the need to analyze Space Shuttle propulsion systems on the launch pad. Those systems provide the awe-inspiring rocket power that propels the Space Shuttle from Earth into orbit in mere minutes. The scanner development also marks a major improvement in the quality assurance field, because screws, nuts, bolts, fasteners, and other items can now be evaluated upon receipt and rejected if found to be substandard. The same holds true for aluminum weld rods. The ability to validate the integrity of raw materials and partially finished products before adding value to them in the manufacturing process will be of benefit not only to businesses, but also to the consumer, who will have access to a higher value product at a cheaper price. Three vacuum X-ray scanners are already being used in the Space Shuttle Program. The External Tank Project Office is using one for aluminum alloy analysis, while a Marshall contractor is evaluating alloys with another unit purchased for the Space Shuttle Main Engine Office. The Reusable Solid Rocket Motor Project Office has obtained a scanner that is being used to test hardware and analyze materials. In this photograph, Richard Booth, Marshall Engineering Directorate, and Wanda Hudson, ATK Thiokol, use an enhanced vacuum X-ray fluorescent scanner to analyze materials in an F-1 engine, which was used to boost the Saturn V rocket from Earth’s orbit that carried astronauts to the moon in the 1960s.
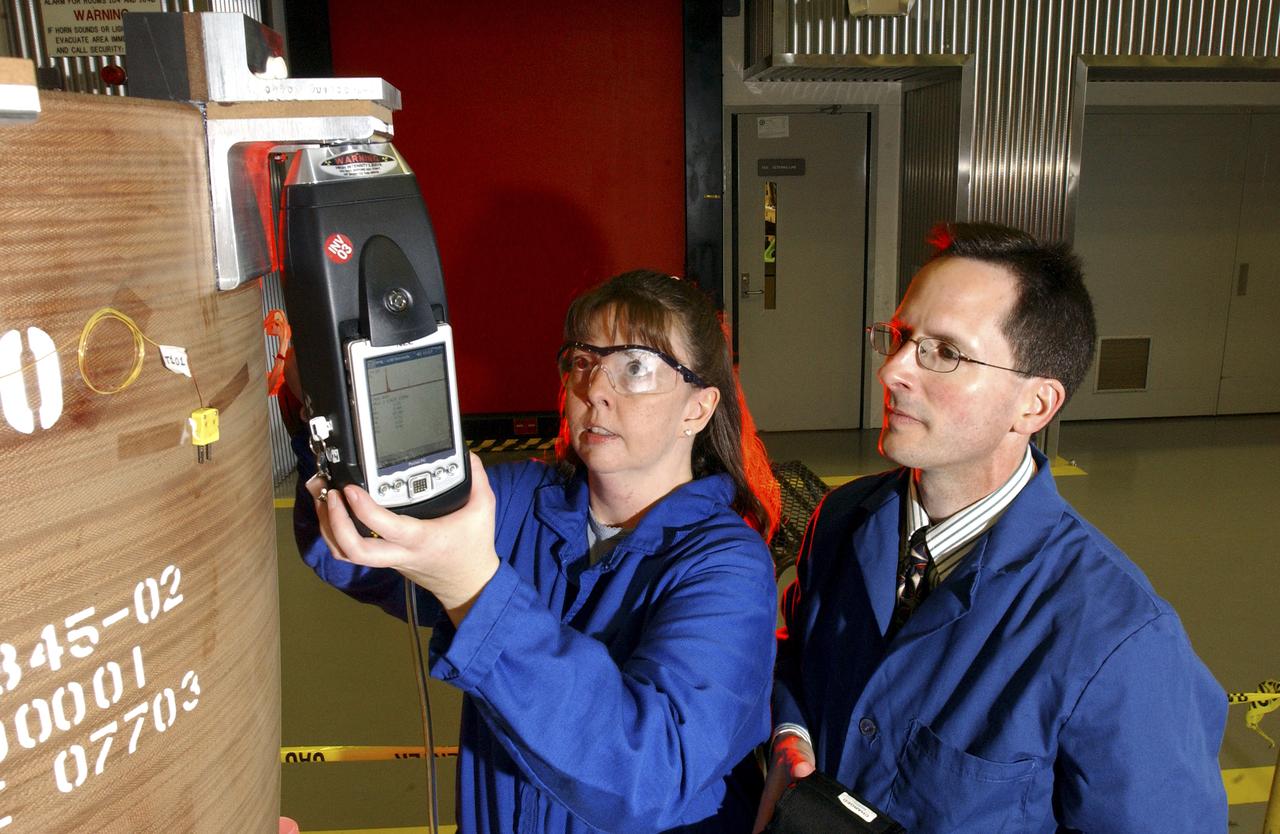

Teamed with KeyMaster Technologies, Kennewick, Washington, the Marshall Space Flight Center engineers have developed a portable vacuum analyzer that performs on-the-spot chemical analyses under field conditions— a task previously only possible in a chemical laboratory. The new capability is important not only to the aerospace industry, but holds potential for broad applications in any industry that depends on materials analysis, such as the automotive and pharmaceutical industries. Weighing in at a mere 4 pounds, the newly developed handheld vacuum X-ray fluorescent analyzer can identify and characterize a wide range of elements, and is capable of detecting chemical elements with low atomic numbers, such as sodium, aluminum and silicon. It is the only handheld product on the market with that capability. Aluminum alloy verification is of particular interest to NASA because vast amounts of high-strength aluminum alloys are used in the Space Shuttle propulsion system such as the External Tank, Main Engine, and Solid Rocket Boosters. This capability promises to be a boom to the aerospace community because of unique requirements, for instance, the need to analyze Space Shuttle propulsion systems on the launch pad. Those systems provide the awe-inspiring rocket power that propels the Space Shuttle from Earth into orbit in mere minutes. The scanner development also marks a major improvement in the quality assurance field, because screws, nuts, bolts, fasteners, and other items can now be evaluated upon receipt and rejected if found to be substandard. The same holds true for aluminum weld rods. The ability to validate the integrity of raw materials and partially finished products before adding value to them in the manufacturing process will be of benefit not only to businesses, but also to the consumer, who will have access to a higher value product at a cheaper price. Three vacuum X-ray scanners are already being used in the Space Shuttle Program. The External Tank Project Office is using one for aluminum alloy analysis, while a Marshall contractor is evaluating alloys with another unit purchased for the Space Shuttle Main Engine Office. The Reusable Solid Rocket Motor Project Office has obtained a scanner that is being used to test hardware and analyze materials. In this photograph, Wanda Hudson, left, ATK Thiokol, and Richard Booth, Marshall Engineering Directorate, use an enhanced vacuum X-ray fluorescent scanner to evaluate Reusable Solid Rocket Motor hardware.

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) recently captured a unique view of Earth from the spacecraft's vantage point in orbit around the moon. "The image is simply stunning," said Noah Petro, Deputy Project Scientist for LRO at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. "The image of the Earth evokes the famous 'Blue Marble' image taken by Astronaut Harrison Schmitt during Apollo 17, 43 years ago, which also showed Africa prominently in the picture." In this composite image we see Earth appear to rise over the lunar horizon from the viewpoint of the spacecraft, with the center of the Earth just off the coast of Liberia (at 4.04 degrees North, 12.44 degrees West). The large tan area in the upper right is the Sahara Desert, and just beyond is Saudi Arabia. The Atlantic and Pacific coasts of South America are visible to the left. On the moon, we get a glimpse of the crater Compton, which is located just beyond the eastern limb of the moon, on the lunar farside. LRO was launched on June 18, 2009, and has collected a treasure trove of data with its seven powerful instruments, making an invaluable contribution to our knowledge about the moon. LRO experiences 12 earthrises every day; however the spacecraft is almost always busy imaging the lunar surface so only rarely does an opportunity arise such that its camera instrument can capture a view of Earth. Occasionally LRO points off into space to acquire observations of the extremely thin lunar atmosphere and perform instrument calibration measurements. During these movements sometimes Earth (and other planets) pass through the camera's field of view and dramatic images such as the one shown here are acquired. This image was composed from a series of images taken Oct. 12, when LRO was about 83 miles (134 kilometers) above the moon's farside crater Compton. Capturing an image of the Earth and moon with LRO's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) instrument is a complicated task. First the spacecraft must be rolled to the side (in this case 67 degrees), then the spacecraft slews with the direction of travel to maximize the width of the lunar horizon in LROC's Narrow Angle Camera image. All this takes place while LRO is traveling faster than 3,580 miles per hour (over 1,600 meters per second) relative to the lunar surface below the spacecraft! The high-resolution Narrow Angle Camera (NAC) on LRO takes black-and-white images, while the lower resolution Wide Angle Camera (WAC) takes color images, so you might wonder how we got a high-resolution picture of the Earth in color. Since the spacecraft, Earth, and moon are all in motion, we had to do some special processing to create an image that represents the view of the Earth and moon at one particular time. The final Earth image contains both WAC and NAC information. WAC provides the color, and the NAC provides high-resolution detail. "From the Earth, the daily moonrise and moonset are always inspiring moments," said Mark Robinson of Arizona State University in Tempe, principal investigator for LROC. "However, lunar astronauts will see something very different: viewed from the lunar surface, the Earth never rises or sets. Since the moon is tidally locked, Earth is always in the same spot above the horizon, varying only a small amount with the slight wobble of the moon. The Earth may not move across the 'sky', but the view is not static. Future astronauts will see the continents rotate in and out of view and the ever-changing pattern of clouds will always catch one's eye, at least on the nearside. The Earth is never visible from the farside; imagine a sky with no Earth or moon - what will farside explorers think with no Earth overhead?" NASA's first Earthrise image was taken with the Lunar Orbiter 1 spacecraft in 1966. Perhaps NASA's most iconic Earthrise photo was taken by the crew of the Apollo 8 mission as the spacecraft entered lunar orbit on Christmas Eve Dec. 24, 1968. That evening, the astronauts -- Commander Frank Borman, Command Module Pilot Jim Lovell, and Lunar Module Pilot William Anders -- held a live broadcast from lunar orbit, in which they showed pictures of the Earth and moon as seen from their spacecraft. Said Lovell, "The vast loneliness is awe-inspiring and it makes you realize just what you have back there on Earth." Credit: NASA/Goddard/Arizona State University <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This image depicts a vast canyon of dust and gas in the Orion Nebula from a 3-D computer model based on observations by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and created by science visualization specialists at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md. A 3-D visualization of this model takes viewers on an amazing four-minute voyage through the 15-light-year-wide canyon. Credit: NASA, G. Bacon, L. Frattare, Z. Levay, and F. Summers (STScI/AURA) Go here to learn more about Hubble 3D: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/hubble_imax_premiere.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/hubble_imax_premier...</a> or <a href="http://www.imax.com/hubble/" rel="nofollow">www.imax.com/hubble/</a> Take an exhilarating ride through the Orion Nebula, a vast star-making factory 1,500 light-years away. Swoop through Orion's giant canyon of gas and dust. Fly past behemoth stars whose brilliant light illuminates and energizes the entire cloudy region. Zoom by dusty tadpole-shaped objects that are fledgling solar systems. This virtual space journey isn't the latest video game but one of several groundbreaking astronomy visualizations created by specialists at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, the science operations center for NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The cinematic space odysseys are part of the new Imax film "Hubble 3D," which opens today at select Imax theaters worldwide. The 43-minute movie chronicles the 20-year life of Hubble and includes highlights from the May 2009 servicing mission to the Earth-orbiting observatory, with footage taken by the astronauts. The giant-screen film showcases some of Hubble's breathtaking iconic pictures, such as the Eagle Nebula's "Pillars of Creation," as well as stunning views taken by the newly installed Wide Field Camera 3. While Hubble pictures of celestial objects are awe-inspiring, they are flat 2-D photographs. For this film, those 2-D images have been converted into 3-D environments, giving the audience the impression they are space travelers taking a tour of Hubble's most popular targets. "A large-format movie is a truly immersive experience," says Frank Summers, an STScI astronomer and science visualization specialist who led the team that developed the movie visualizations. The team labored for nine months, working on four visualization sequences that comprise about 12 minutes of the movie. "Seeing these Hubble images in 3-D, you feel like you are flying through space and not just looking at picture postcards," Summers continued. "The spacescapes are all based on Hubble images and data, though some artistic license is necessary to produce the full depth of field needed for 3-D." The most ambitious sequence is a four-minute voyage through the Orion Nebula's gas-and-dust canyon, about 15 light-years across. During the ride, viewers will see bright and dark, gaseous clouds; thousands of stars, including a grouping of bright, hefty stars called the Trapezium; and embryonic planetary systems. The tour ends with a detailed look at a young circumstellar disk, which is much like the structure from which our solar system formed 4.5 billion years ago. Based on a Hubble image of Orion released in 2006, the visualization was a collaborative effort between science visualization specialists at STScI, including Greg Bacon, who sculpted the Orion Nebula digital model, with input from STScI astronomer Massimo Roberto; the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign; and the Spitzer Science Center at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. For some of the sequences, STScI imaging specialists developed new techniques for transforming the 2-D Hubble images into 3-D. STScI image processing specialists Lisa Frattare and Zolt Levay, for example, created methods of splitting a giant gaseous pillar in the Carina Nebula into multiple layers to produce a 3-D effect, giving the structure depth. The Carina Nebula is a nursery for baby stars. Frattare painstakingly removed the thousands of stars in the image so that Levay could separate the gaseous layers on the isolated Carina pillar. Frattare then replaced the stars into both foreground and background layers to complete the 3-D model. For added effect, the same separation was done for both visible and infrared Hubble images, allowing the film to cross-fade between wavelength views in 3-D. In another sequence viewers fly into a field of 170,000 stars in the giant star cluster Omega Centauri. STScI astronomer Jay Anderson used his stellar database to create a synthetic star field in 3-D that matches recent razor-sharp Hubble photos. The film's final four-minute sequence takes viewers on a voyage from our Milky Way Galaxy past many of Hubble's best galaxy shots and deep into space. Some 15,000 galaxies from Hubble's deepest surveys stretch billions of light-years across the universe in a 3-D sequence created by STScI astronomers and visualizers. The view dissolves into a cobweb that traces the universe's large-scale structure, the backbone from which galaxies were born. In addition to creating visualizations, STScI's education group also provided guidance on the "Hubble 3D" Educator Guide, which includes standards-based lesson plans and activities about Hubble and its mission. Students will use the guide before or after seeing the movie. "The guide will enhance the movie experience for students and extend the movie into classrooms," says Bonnie Eisenhamer, STScI's Hubble Formal Education manager. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) and is managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in Greenbelt, Md. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. The institute is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., Washington, D.C.
