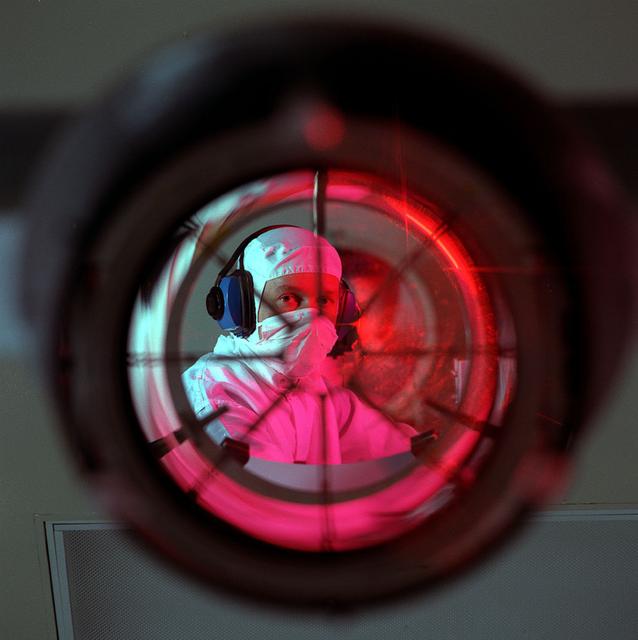

Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility-S (AXAF-S) nickel prototype mirror optical test setup.
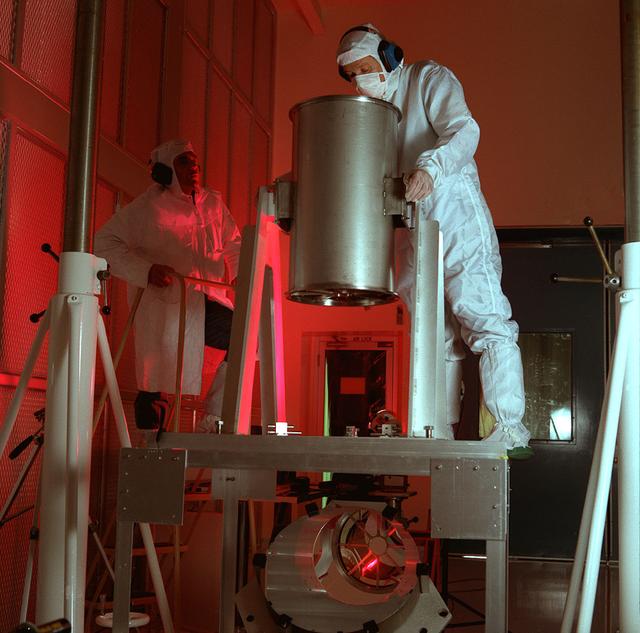

Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility-S (AXAF-S) nickel prototype mirror optical test setup.

STS093-S-001 (September 1998) --- This is the STS-93 mission insignia designed by the crew members. Space shuttle Columbia will carry the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF) into low Earth orbit initiating its planned five-year astronomy mission. AXAF is the third of NASA's great observatories, following the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO). AXAF will provide scientists and order-of magnitude improvement over current capabilities at X-ray wavelengths. In the words of the crew, "Observations of X-ray emissions from energetic galaxies and clusters, as well as black holes, promise to greatly expand current understanding of the origin and evolution of our universe." The patch depicts AXAF separating from the space shuttle Columbia after a successful deployment. A spiral galaxy is shown in the background as a possible target for AXAF observations. The two flags represent the international crew, consisting of astronauts from both the United States and France. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
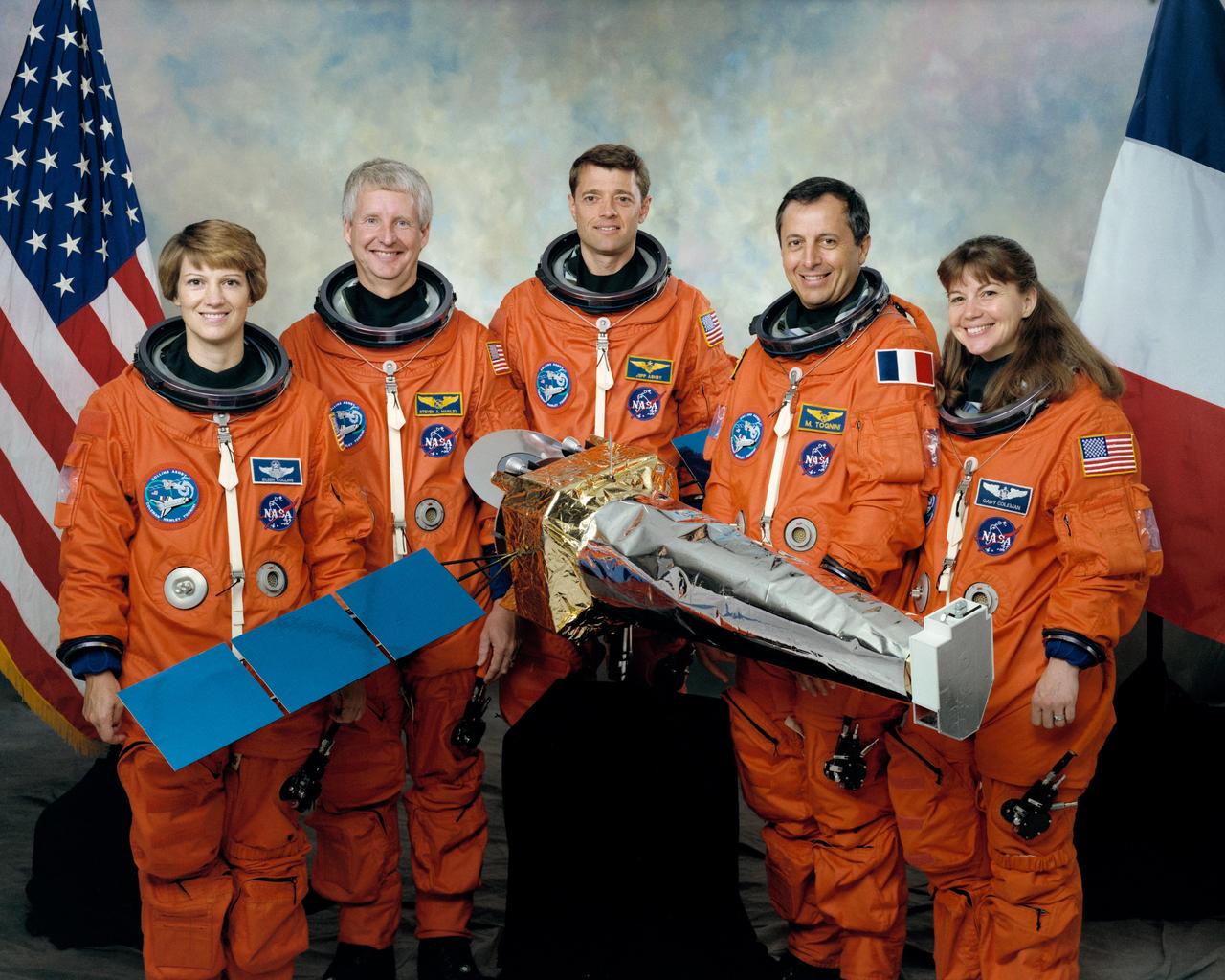

STS093-S-002 (September 1998) --- The five astronauts assigned to fly aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia early next year for the STS-93 mission pose with a small model of their primary payload-the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF). From the left are astronauts Eileen M. Collins, mission commander; Steven A. Hawley, mission specialist; Jeffrey S. Ashby, pilot; Michel Tognini and Catherine G. Coleman, both mission specialists. Tognini represents France's Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). The scheduled five-day mission will feature the deployment of AXAF, which will enable scientists to conduct comprehensive studies of exotic phenomena in the universe. Among bodies studied will be exploding stars, quasars and black holes.
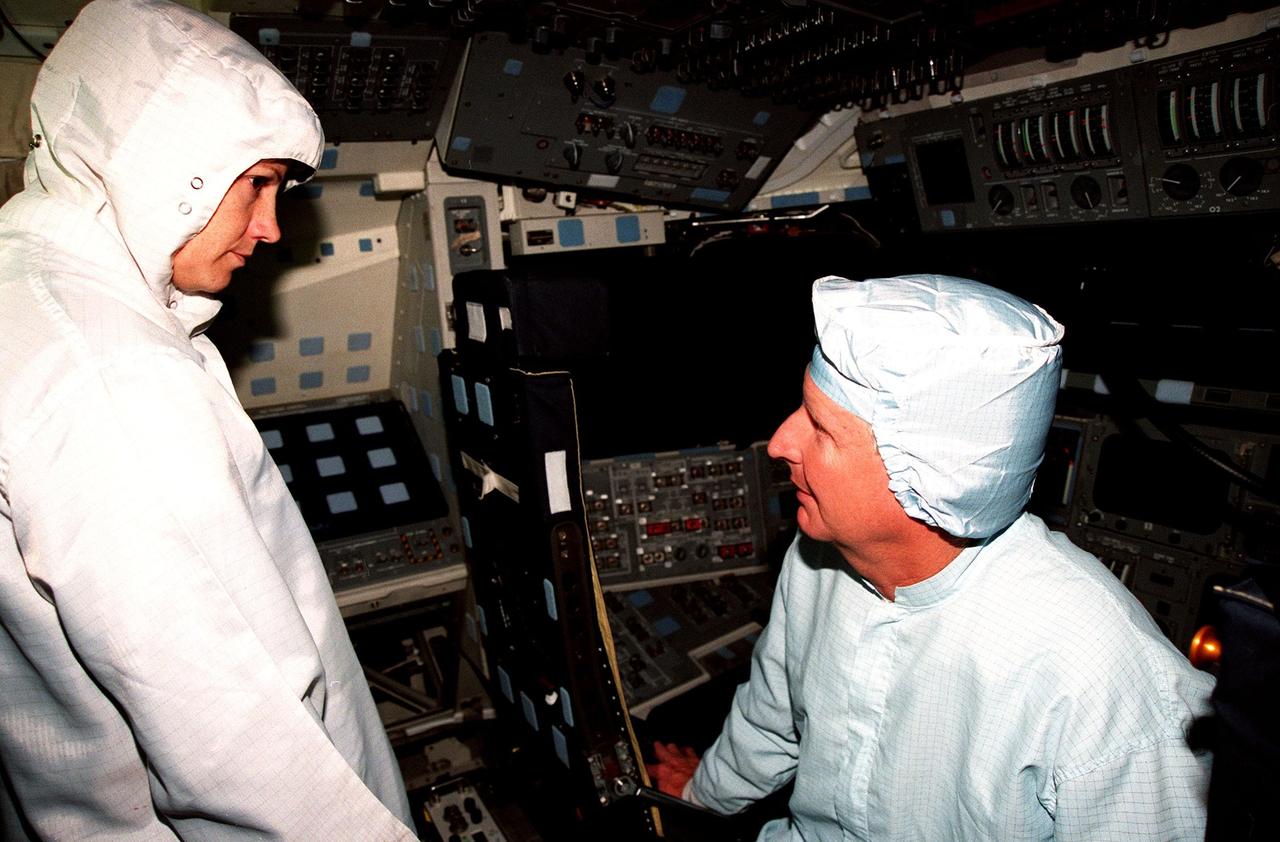

In the Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3, aboard the orbiter Columbia, STS-93 Mission Commander Eileen M. Collins listens to Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley during the Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT). Collins is the first woman to serve as a mission commander on a shuttle flight. The CEIT provides an opportunity for crew members to check equipment and facilities that will be aboard the orbiter during their mission. The rest of the crew members are Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman, and Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France. The STS-93 mission will deploy the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), which comprises three major elements: the spacecraft, the telescope, and the science instrument module (SIM). AXAF will allow scientists from around the world to obtain unprecedented X-ray images of a variety of high-energy objects to help understand the structure and evolution of the universe. Targeted date for the launch of STS-93 is March 18, 1999
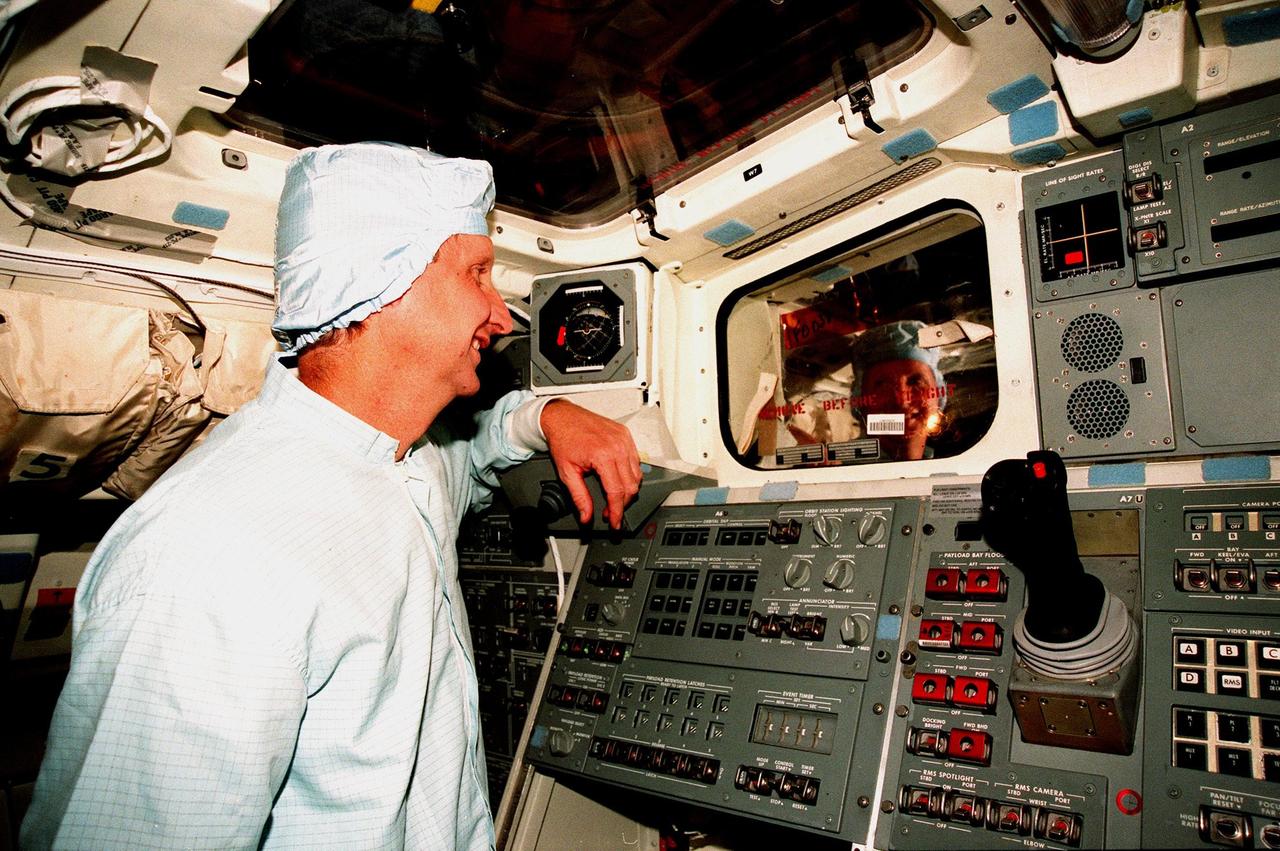
In the Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3, during the Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) for mission STS-93, Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley checks out equipment in the orbiter Columbia. The CEIT provides an opportunity for crew members to check equipment and facilities that will be aboard the orbiter during their mission. The STS-93 mission will deploy the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), which comprises three major elements: the spacecraft, the telescope, and the science instrument module (SIM). AXAF will allow scientists from around the world to obtain unprecedented X-ray images of a variety of high-energy objects to help understand the structure and evolution of the universe. The other STS-93 crew members are Mission Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman and Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France. Targeted date for the launch of STS-93 is March 18, 1999
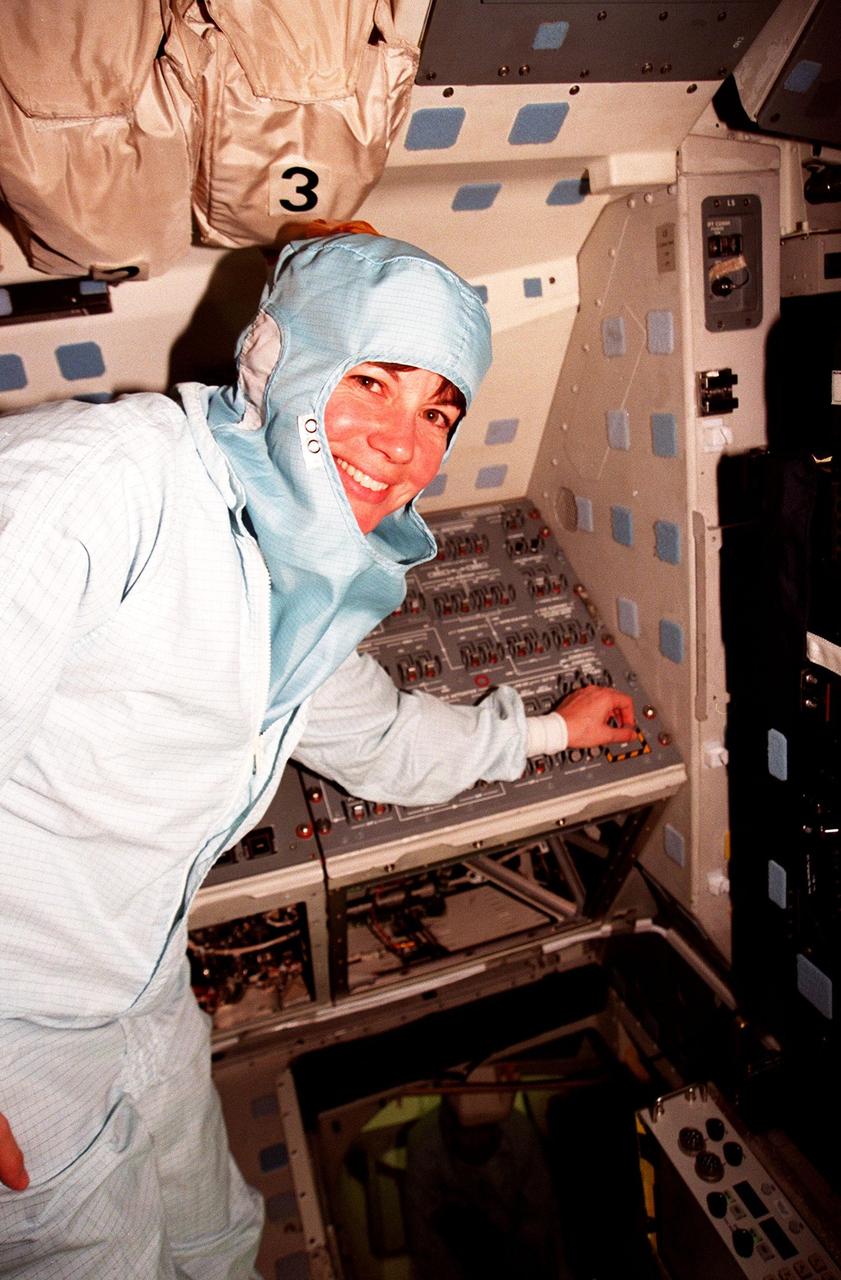

In the Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3, during the Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT), Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman checks equipment that will fly on mission STS-93. The STS-93 mission will deploy the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF) which comprises three major elements: the spacecraft, the telescope, and the science instrument module (SIM). AXAF will allow scientists from around the world to obtain unprecedented X-ray images of a variety of high-energy objects to help understand the structure and evolution of the universe. The other STS-93 crew members are Mission Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley and Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France. Targeted date for the launch of STS-93 is March 18, 1999
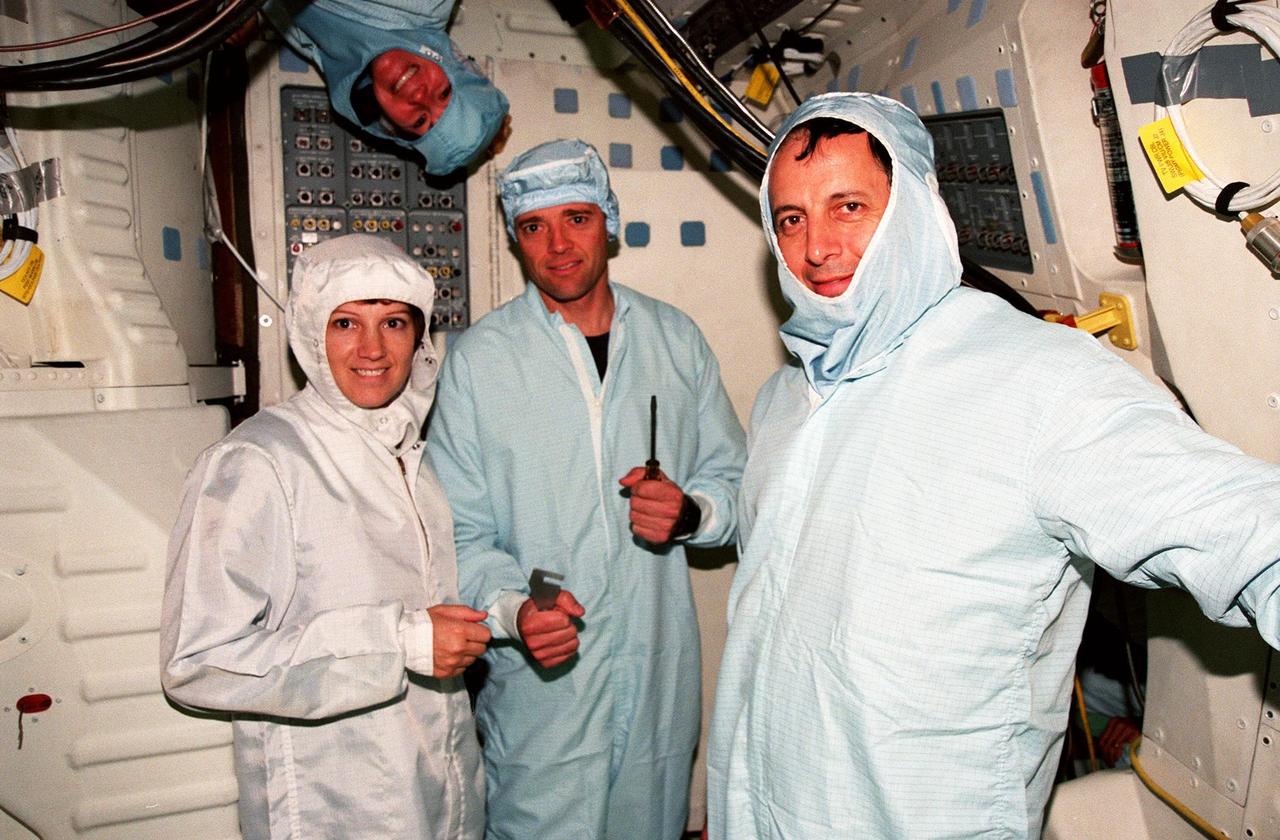

In the Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3, during the Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) for mission STS-93, crew members pose for a photograph . From left they are Mission Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France. Above Ashby's head is Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman. Not shown is Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley. Collins is the first woman to serve as a mission commander on a shuttle flight. The CEIT provides an opportunity for crew members to check equipment and facilities that will be aboard the orbiter during their mission. The STS-93 mission will deploy the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), which comprises three major elements: the spacecraft, the telescope, and the science instrument module (SIM). AXAF will allow scientists from around the world to obtain unprecedented X-ray images of a variety of high-energy objects to help understand the structure and evolution of the universe. Targeted date for the launch of STS-93 is March 18, 1999
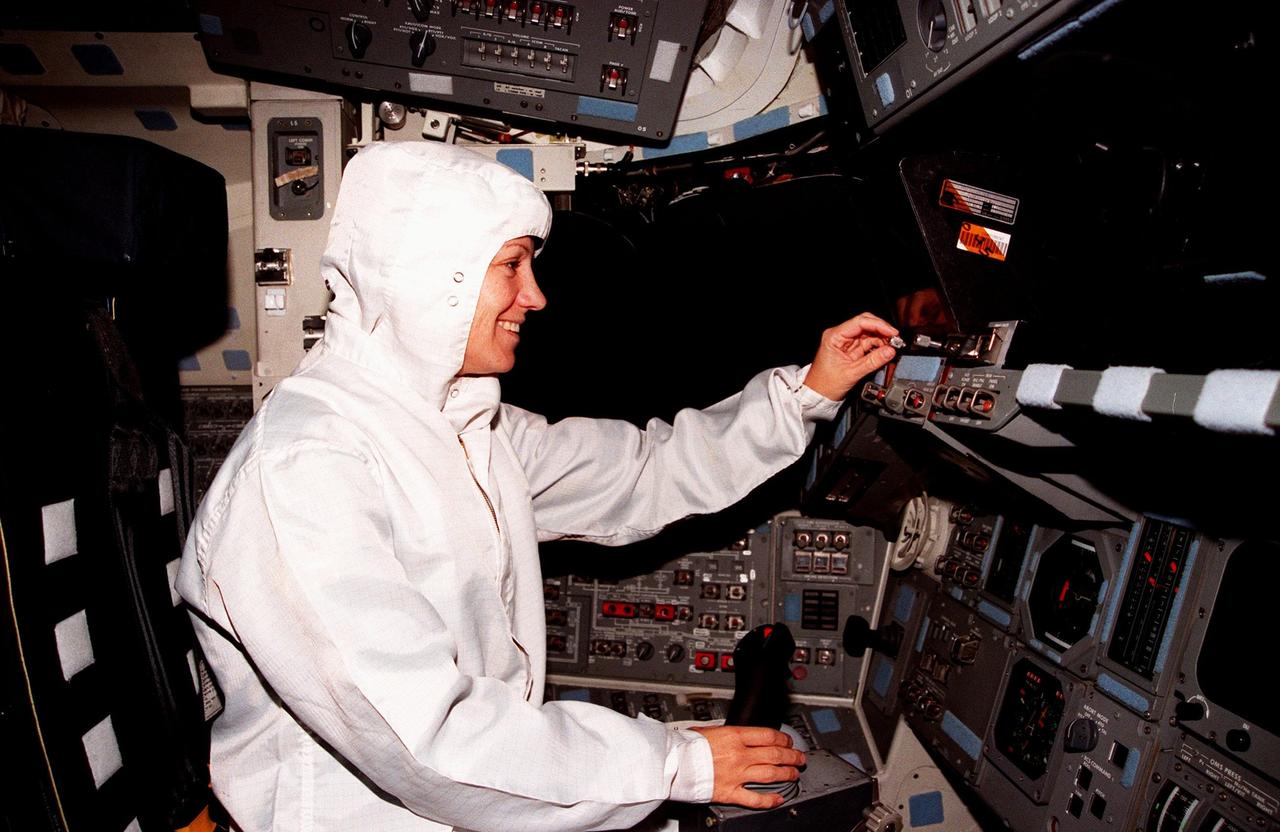

During the Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) for mission STS-93, Mission Commander Eileen M. Collins checks out the flight deck on the orbiter Columbia, in the Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3. The CEIT provides an opportunity for crew members to check equipment and facilities that will be aboard the orbiter during their mission. The STS-93 mission will deploy the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF) which comprises three major elements: the spacecraft, the telescope, and the science instrument module (SIM). AXAF will allow scientists from around the world to obtain unprecedented X-ray images of a variety of high-energy objects to help understand the structure and evolution of the universe. Collins is the first woman to serve as a shuttle mission commander. The other STS-93 crew members are Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley and Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France. Targeted date for the launch of STS-93 is March 18, 1999
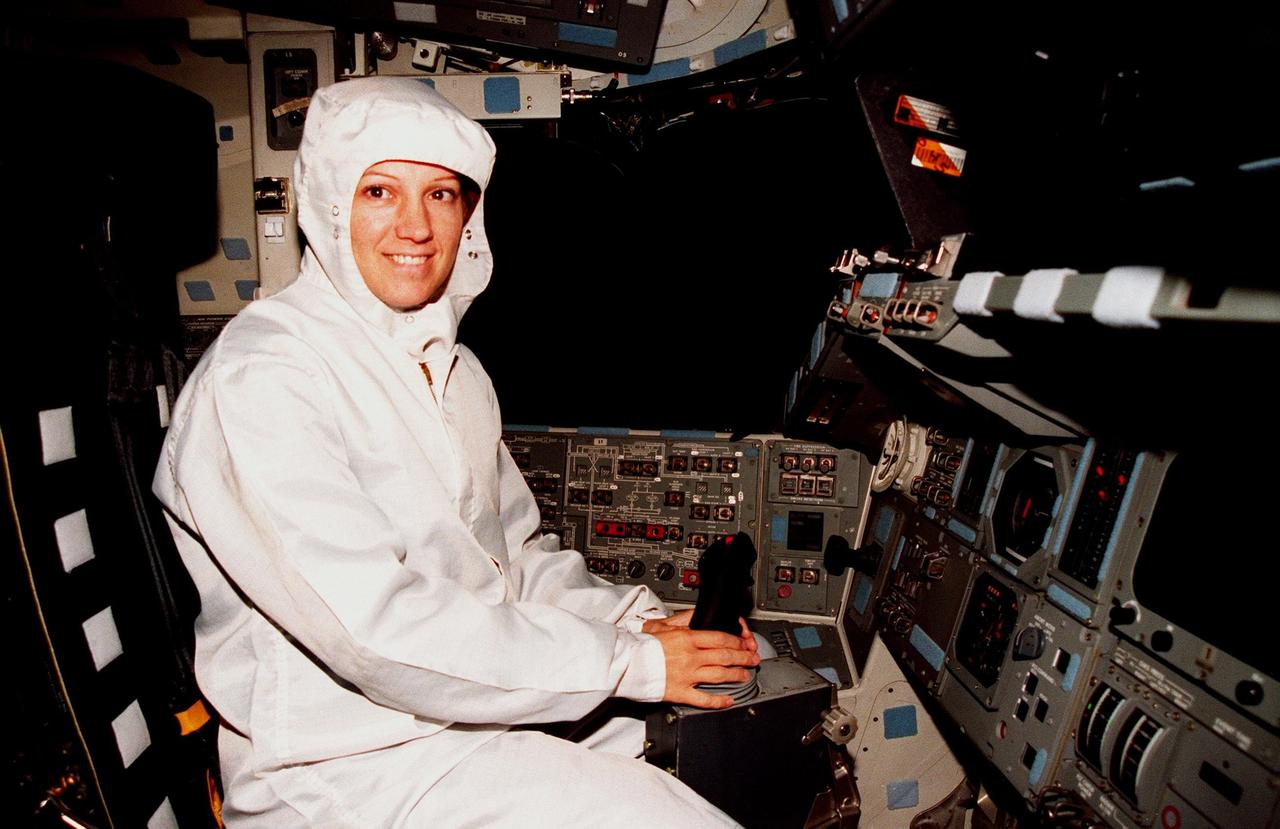

In the Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3, during the Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) for mission STS-93, Mission Commander Eileen M. Collins checks out her seat in the orbiter Columbia. Collins is the first woman to serve as a mission commander on a shuttle flight. The CEIT provides an opportunity for crew members to check equipment and facilities that will be aboard the orbiter during their mission. The STS-93 mission will deploy the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), which comprises three major elements: the spacecraft, the telescope, and the science instrument module (SIM). AXAF will allow scientists from around the world to obtain unprecedented X-ray images of a variety of high-energy objects to help understand the structure and evolution of the universe. The other STS-93 crew members are Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman, Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley and Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France. Targeted date for the launch of STS-93 is March 18, 1999