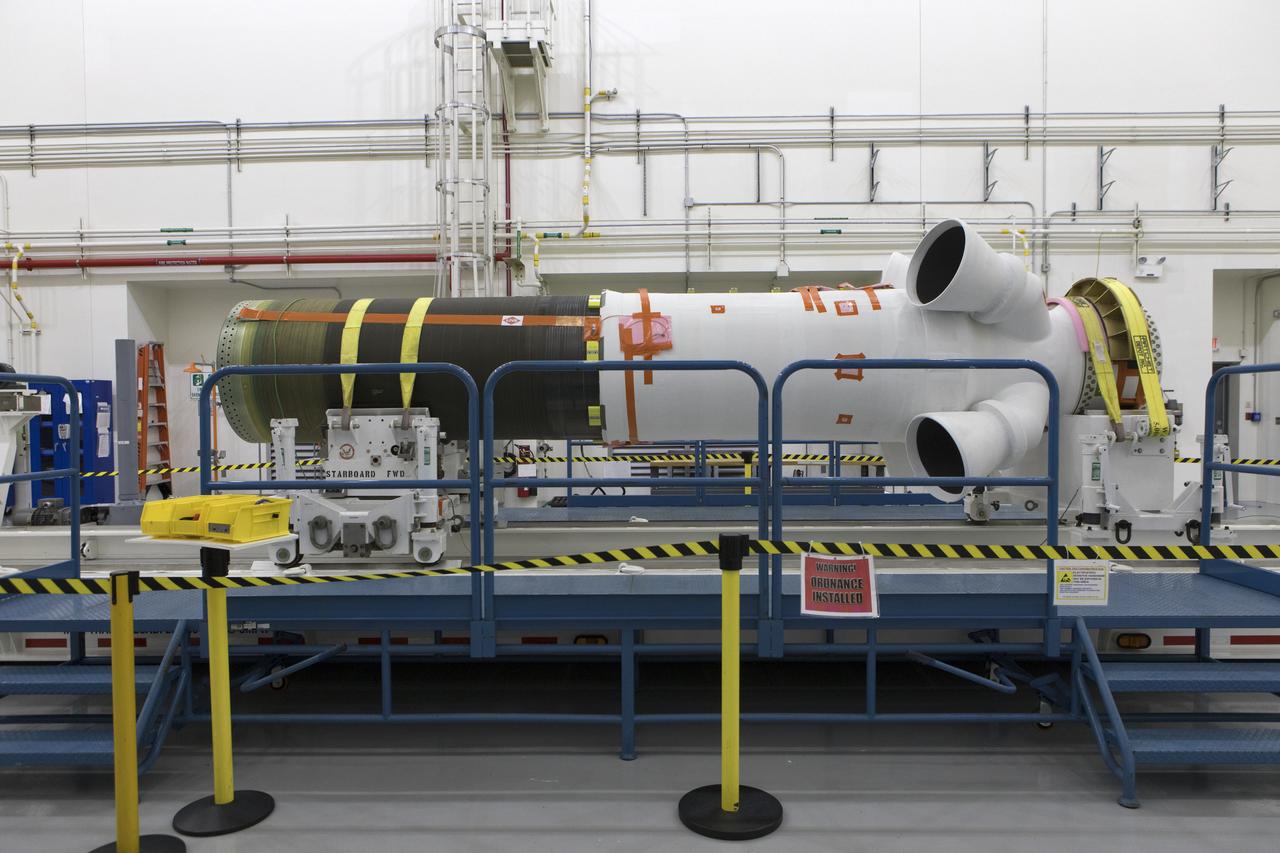

The abort motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility on Aug. 28, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This motor will be used for flight during a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. The abort motor is what will activate to pull the Orion crew module away during the event of an emergency during ascent. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
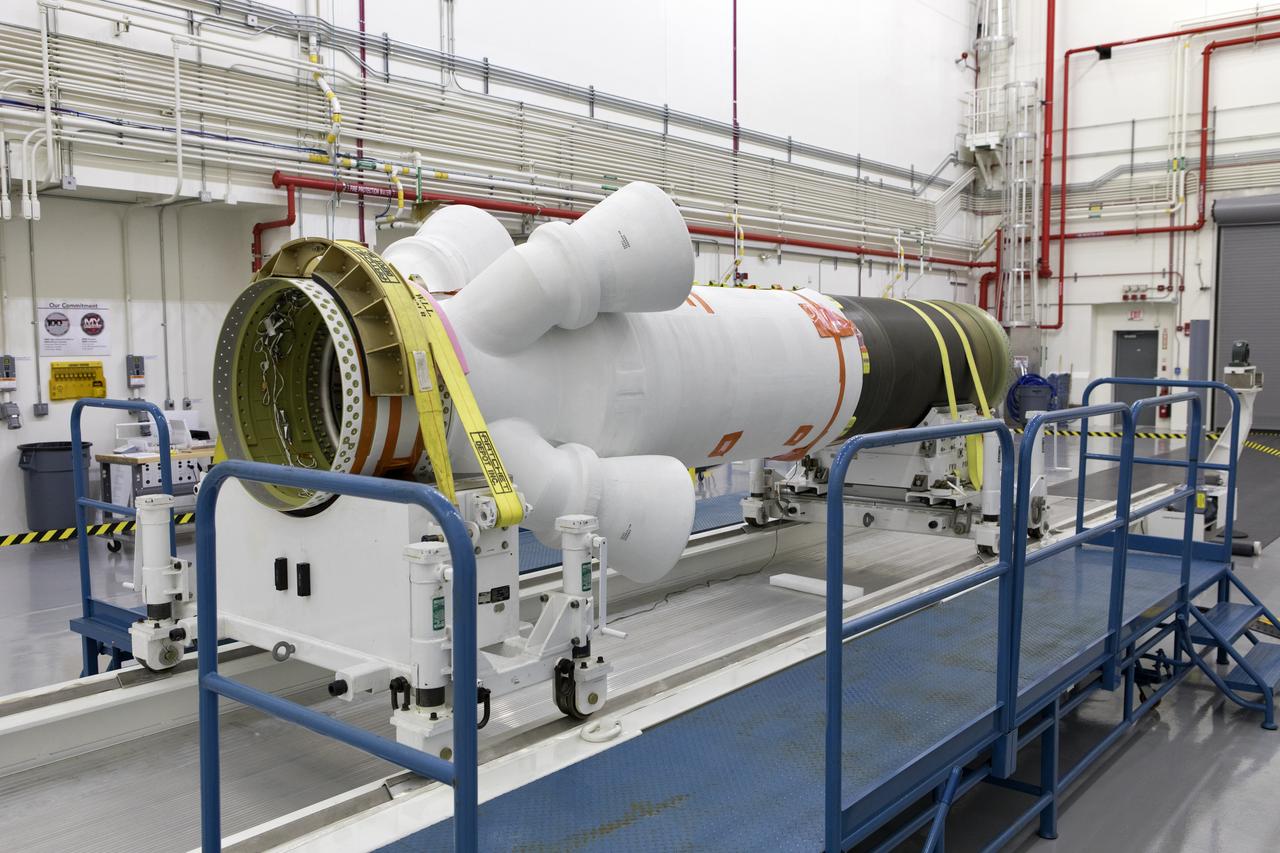

The abort motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility on Aug. 28, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This motor will be used for flight during a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. The abort motor is what will activate to pull the Orion crew module away during the event of an emergency during ascent. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
The abort motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility on Aug. 28, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This motor will be used for flight during a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. The abort motor is what will activate to pull the Orion crew module away during the event of an emergency during ascent. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
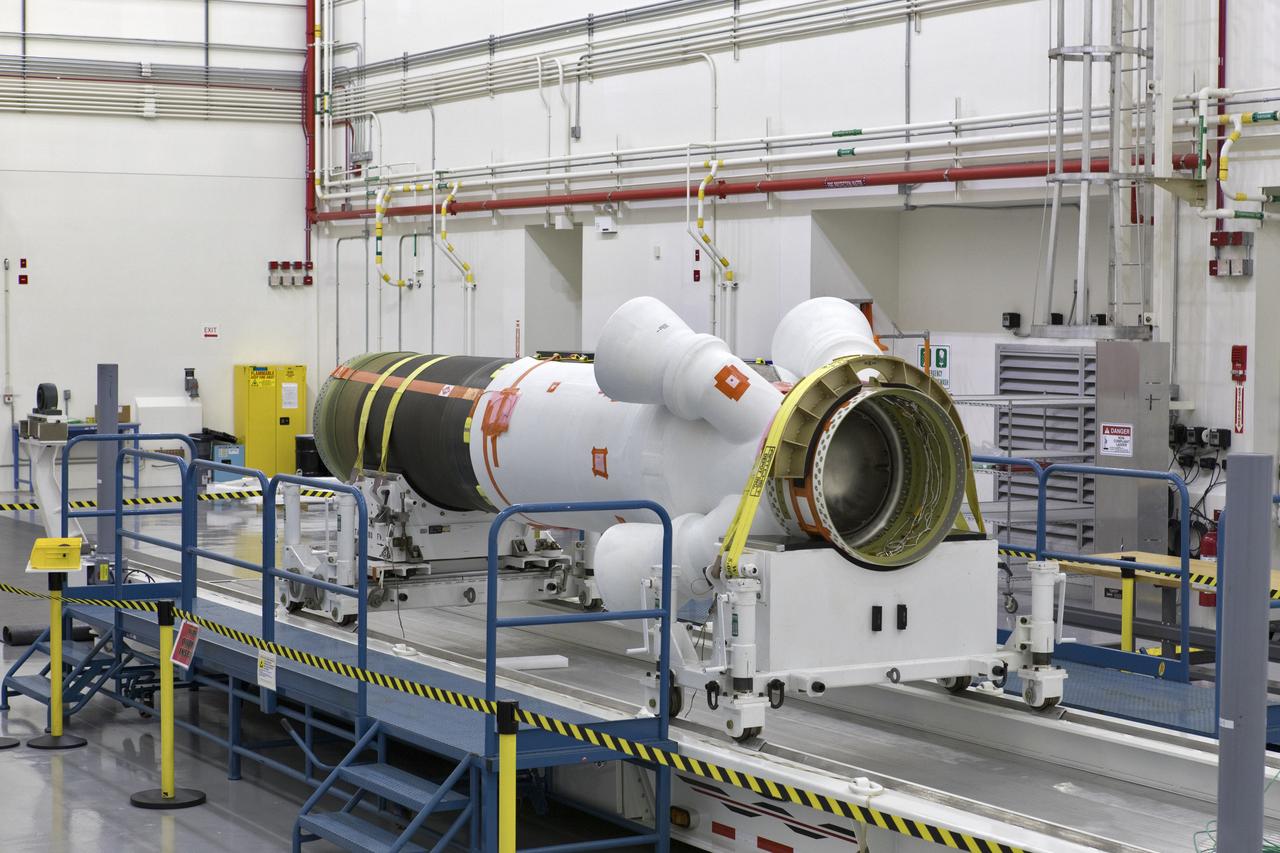

The abort motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility on Aug. 28, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This motor will be used for flight during a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. The abort motor is what will activate to pull the Orion crew module away during the event of an emergency during ascent. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
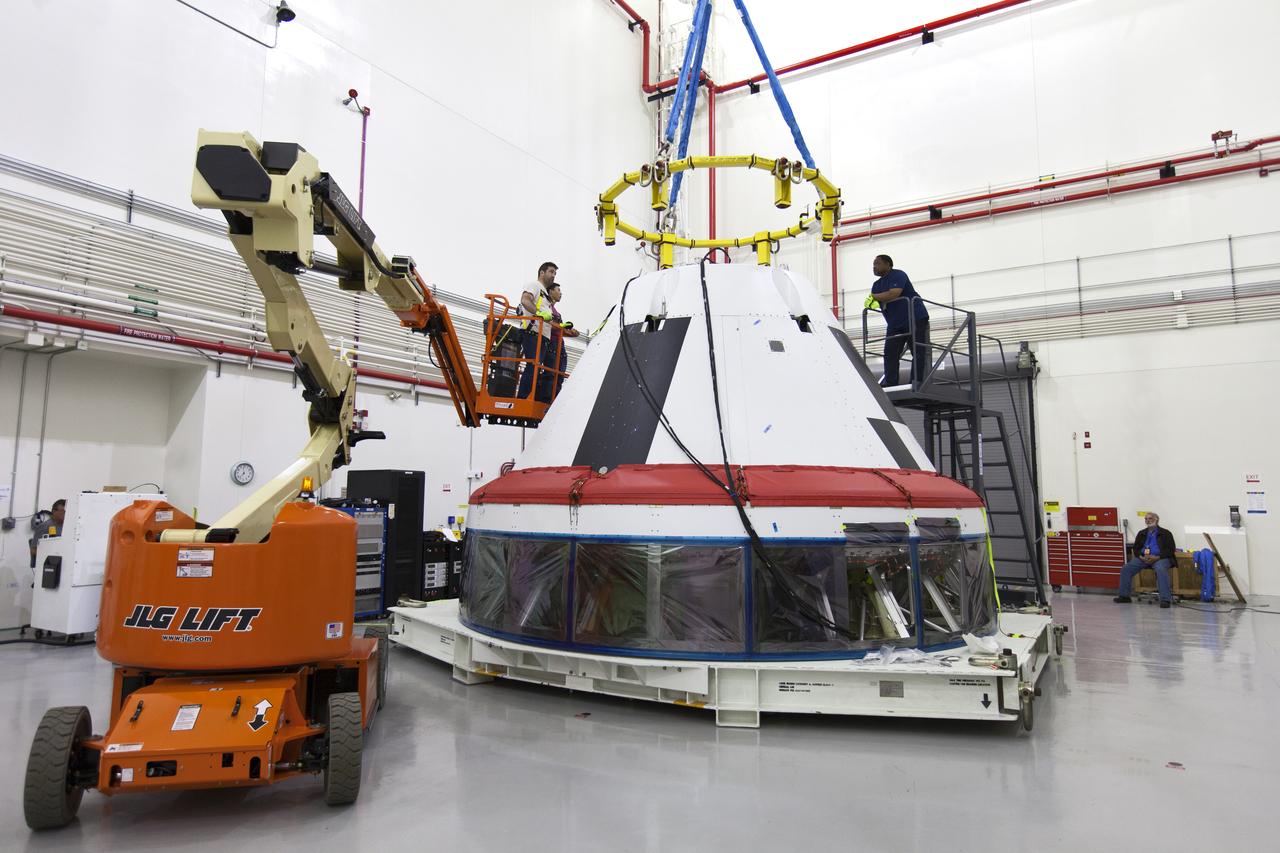

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers attach a crane to a test version of the Orion crew module to integrate it with the Launch Abort System on March 13, 2019. The Orion test module and the Launch Abort System will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test, a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
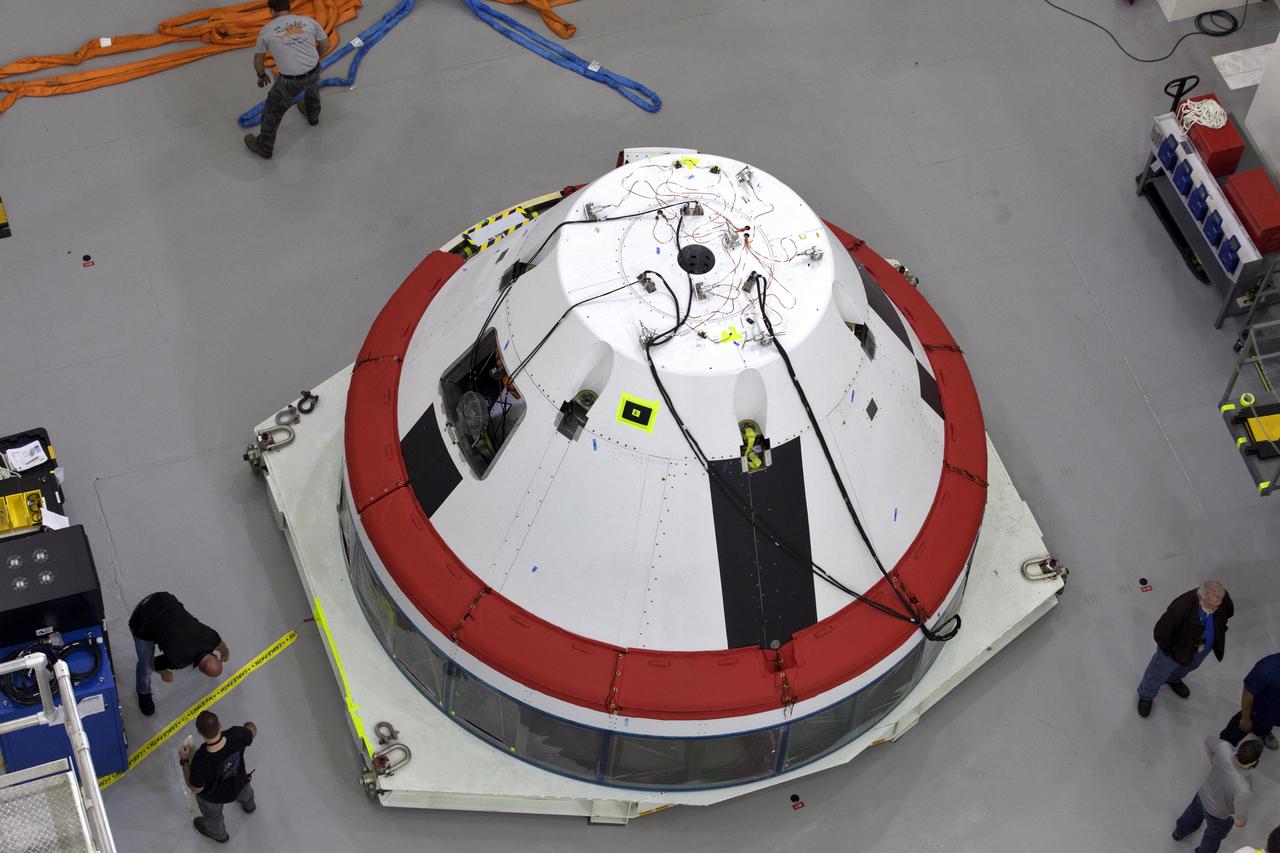

A test version of the Orion crew module is inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 13, 2019, where they will be integrated. A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test, a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying the LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers prepare to attach a crane to a test version of the Orion crew module on March 13, 2019. The Orion test module and the Launch Abort System will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test, a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.

A test version of the Orion crew module is integrated with the Launch Abort System (LAS) in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 13, 2019. Workers will use a crane to practice lifting the test vehicle. The LAS, in view, will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
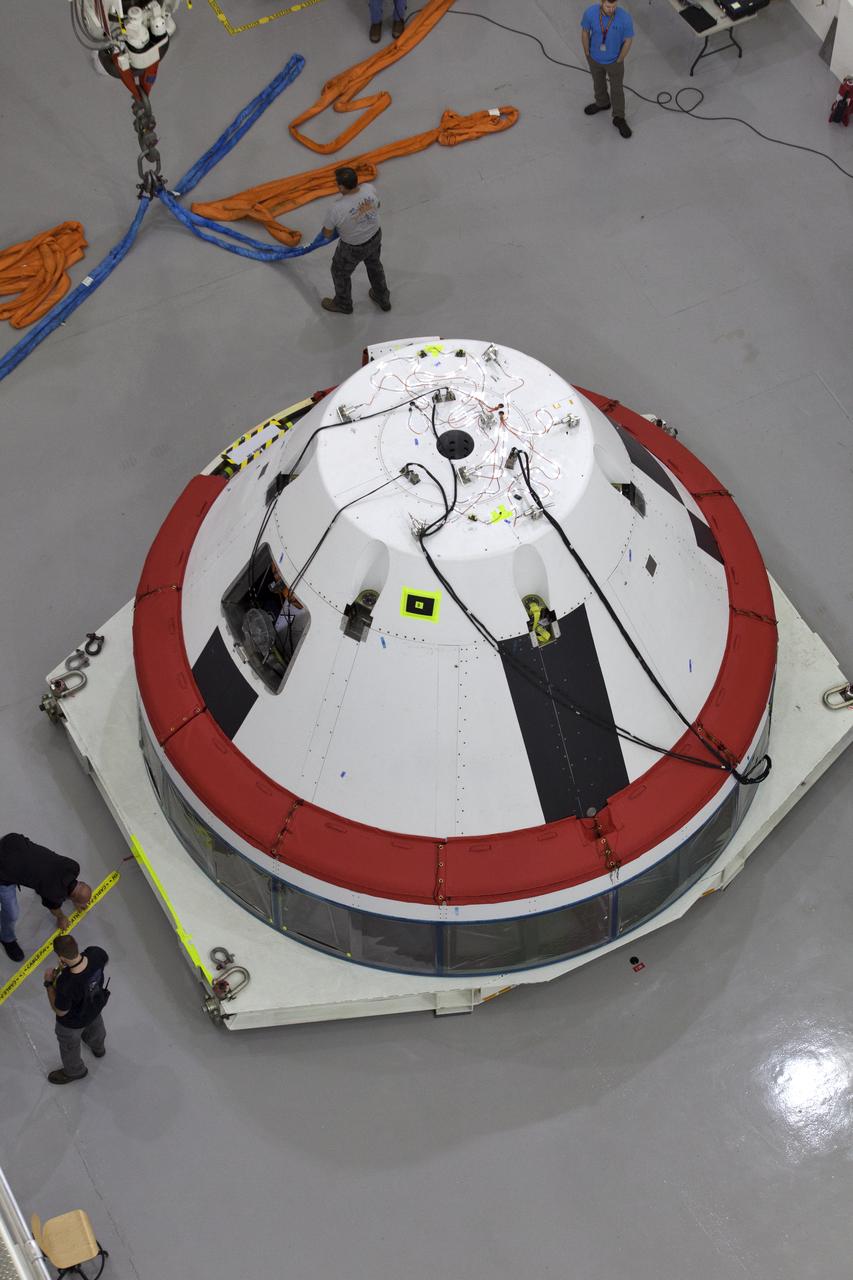

A test version of the Orion crew module is inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 13, 2019, where they will be integrated. A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test, a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying the LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
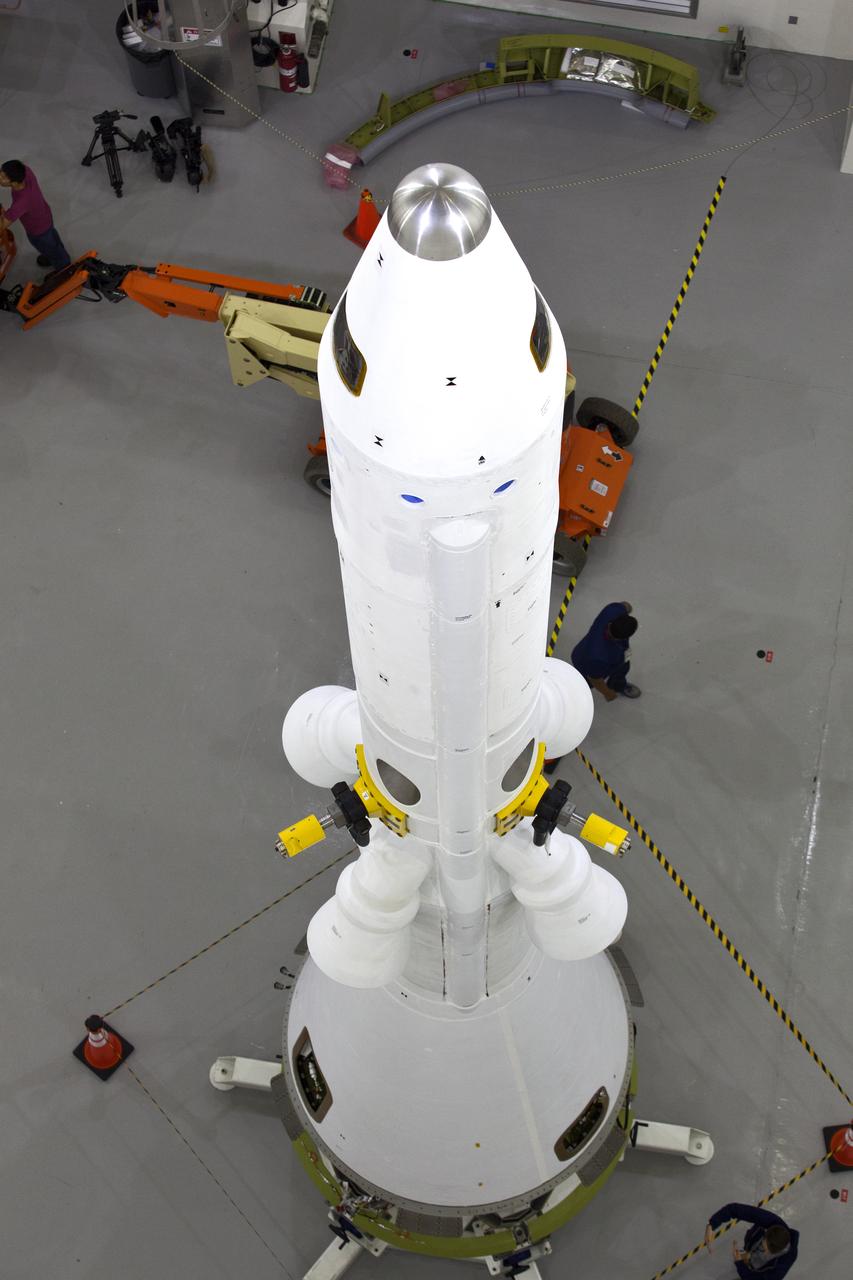

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) is inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 13, 2019. The LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test, a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying the LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
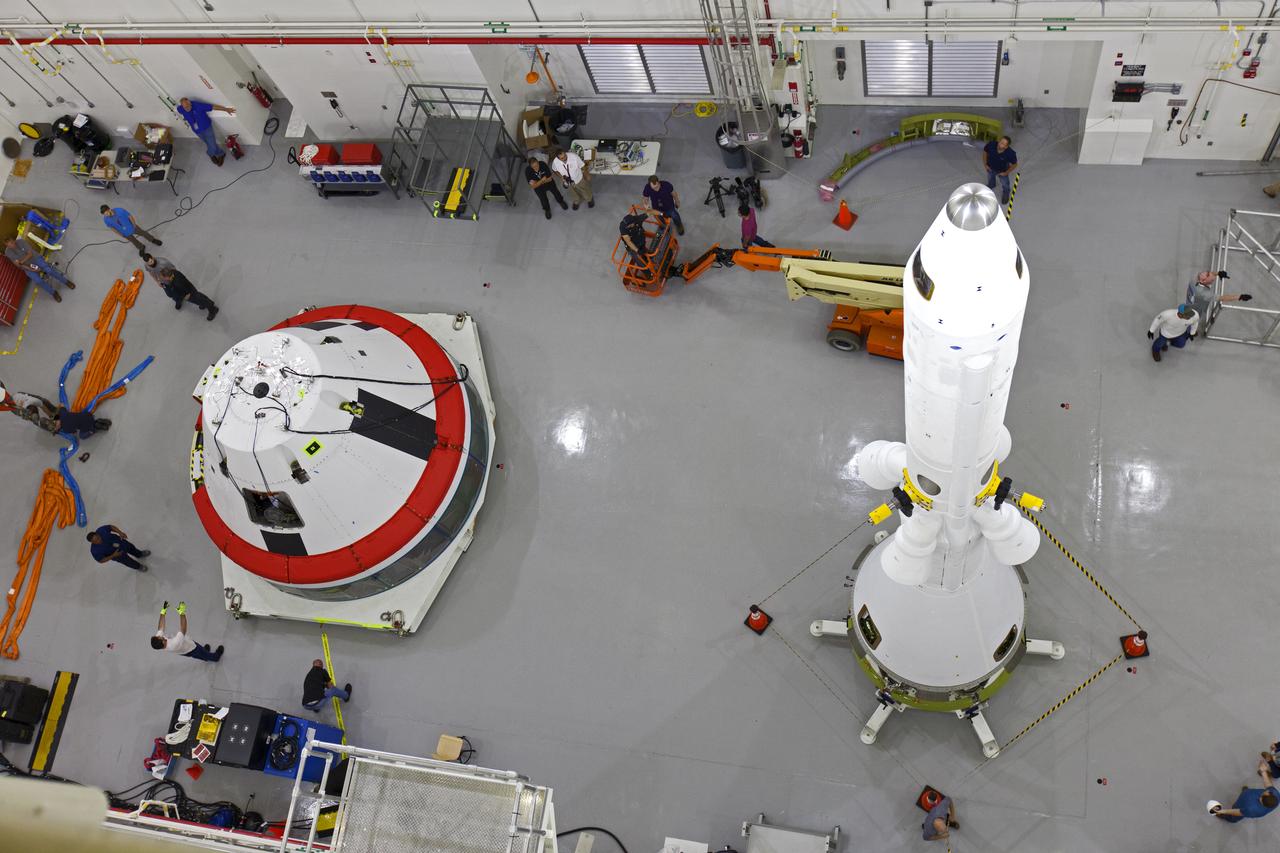

A test version of the Orion crew module, at left, and the Launch Abort System (LAS) are inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 13, 2019, where they will be integrated. The fully functional LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test, a full-stress test of the LAS that will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
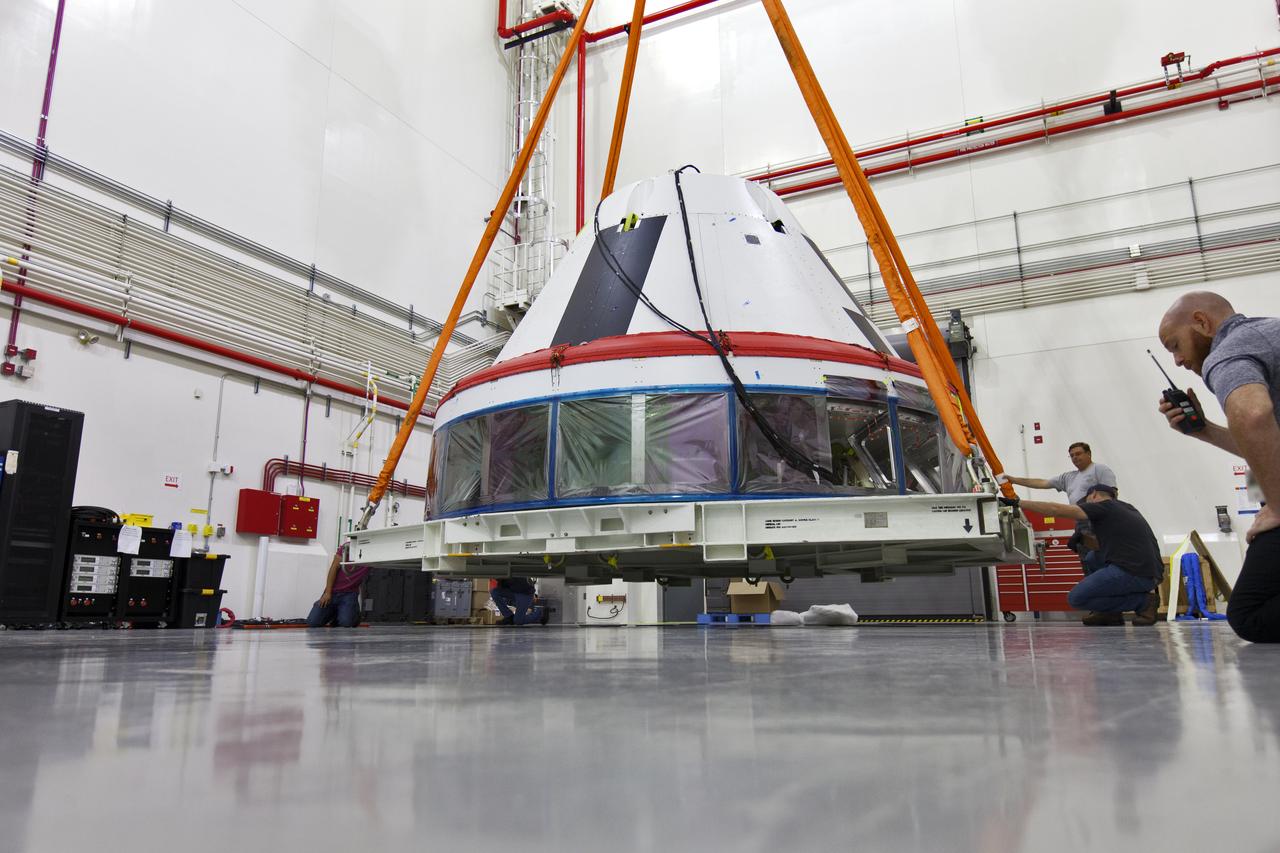

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers attach a crane to a test version of the Orion crew module on March 13, 2019. The Orion test module and the Launch Abort System will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test, a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
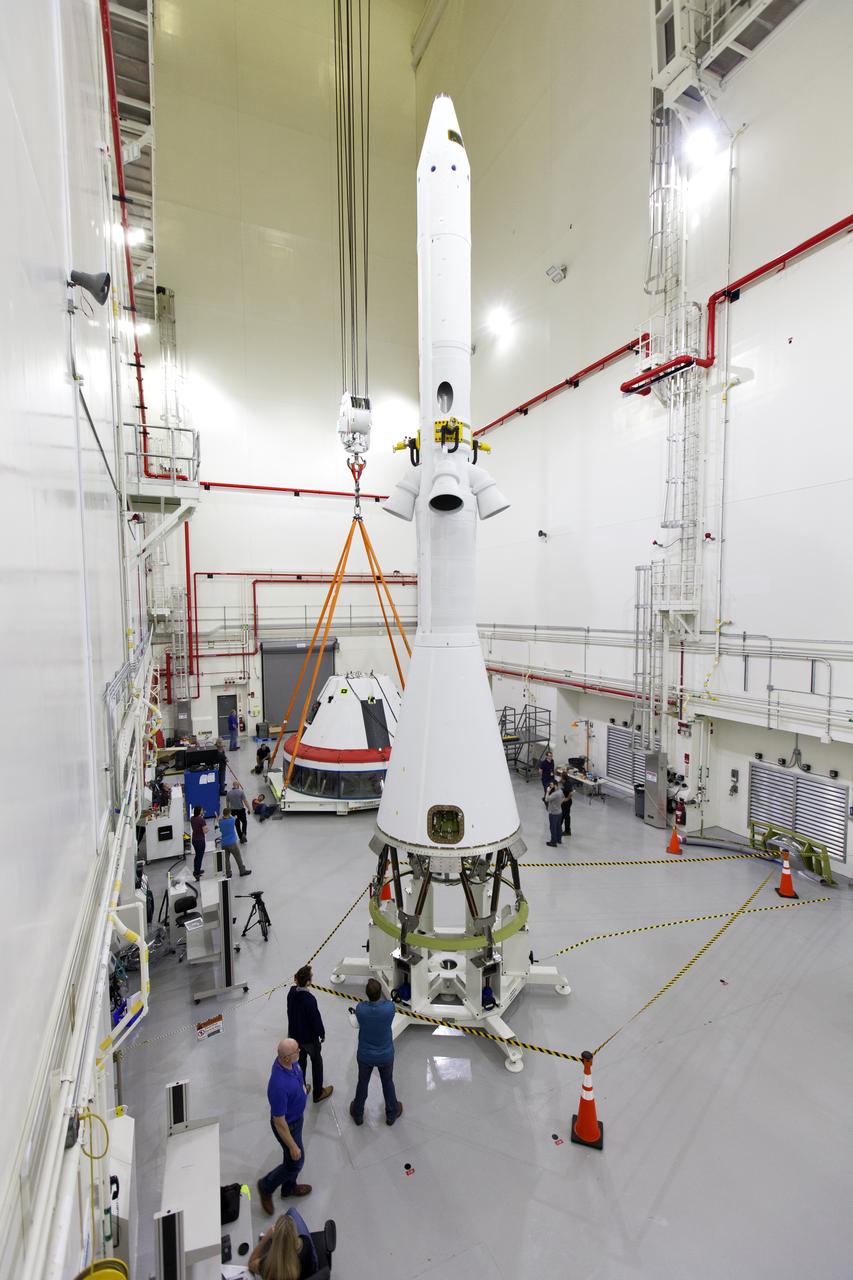

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Launch Abort System (LAS) that will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is in view in the foreground on March 13, 2019. In the background, workers are attaching a crane to a test version of the Orion crew module. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
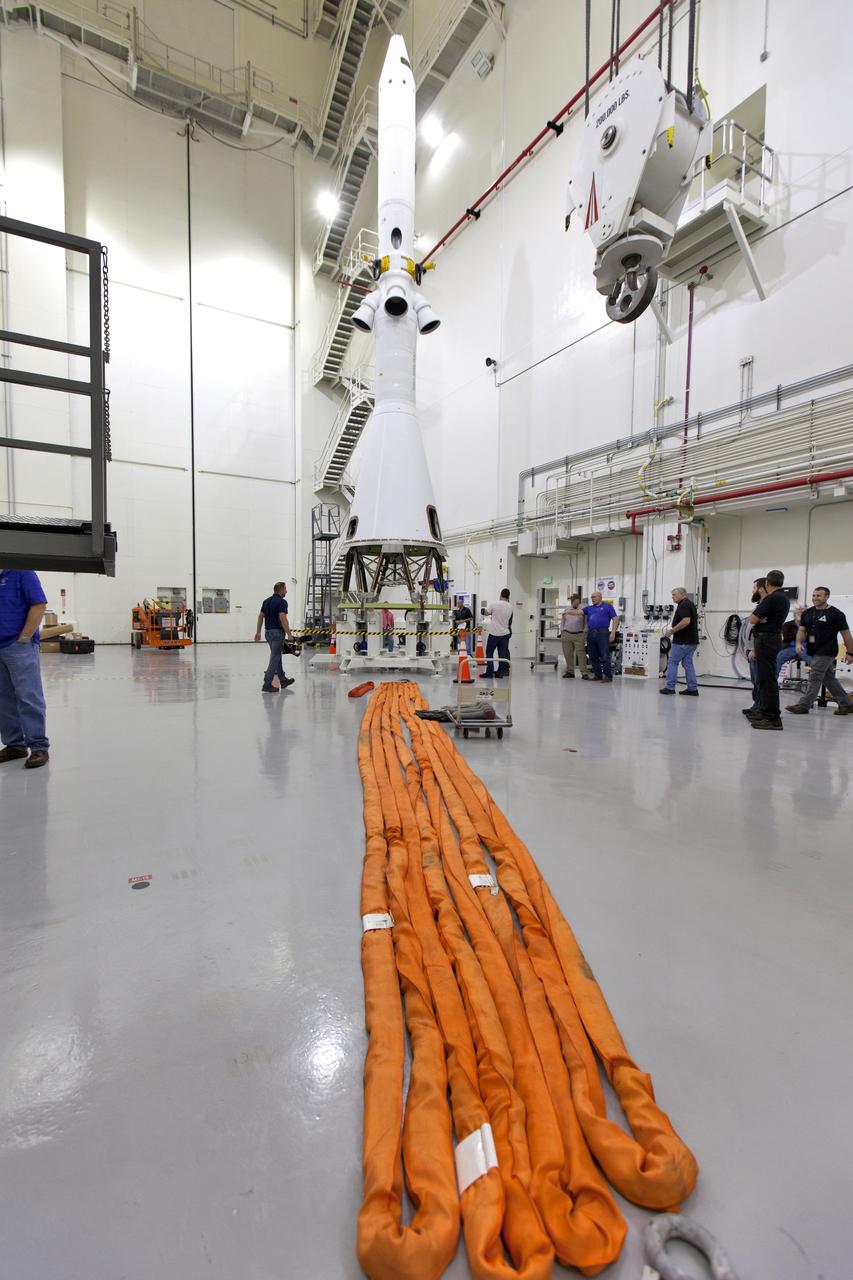

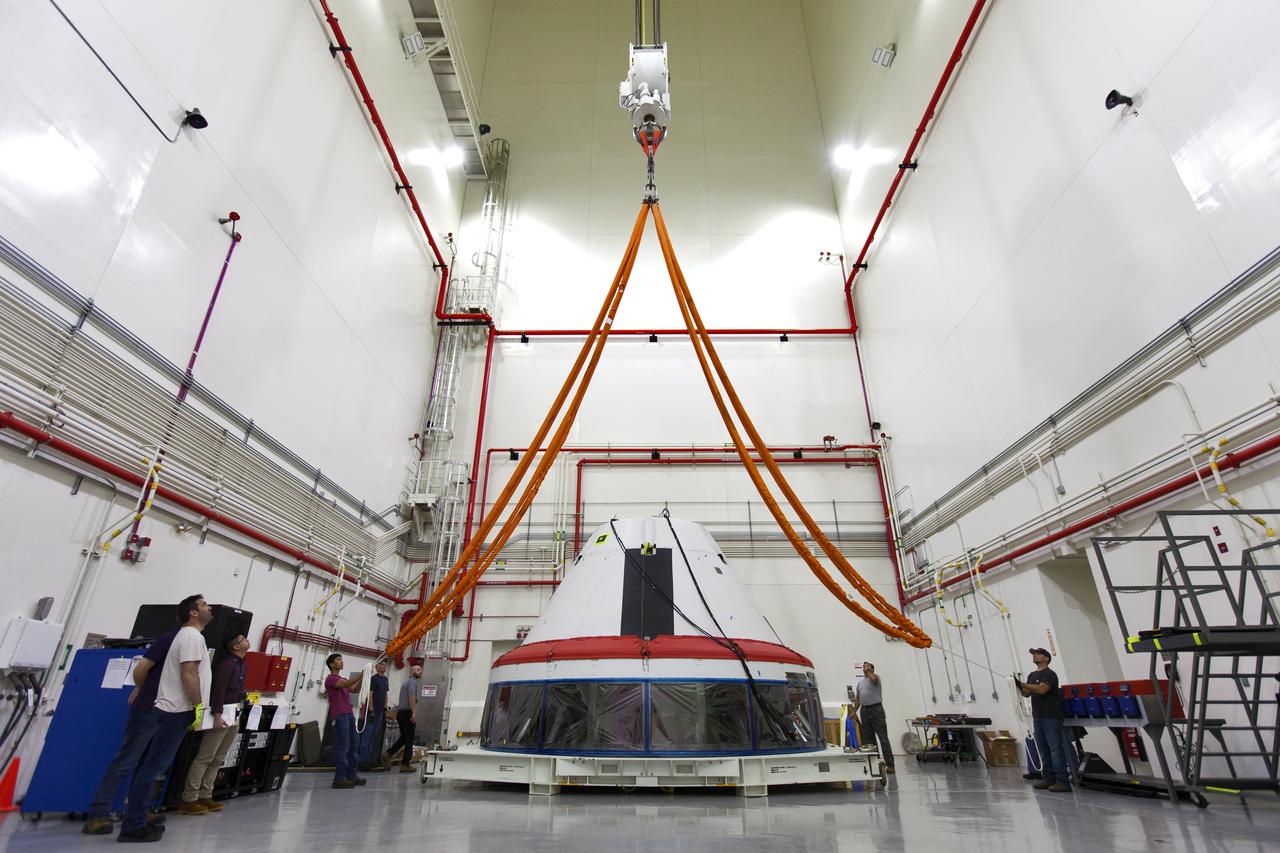
Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are preparing to integrate a test version of the Orion crew module with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on March 13, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
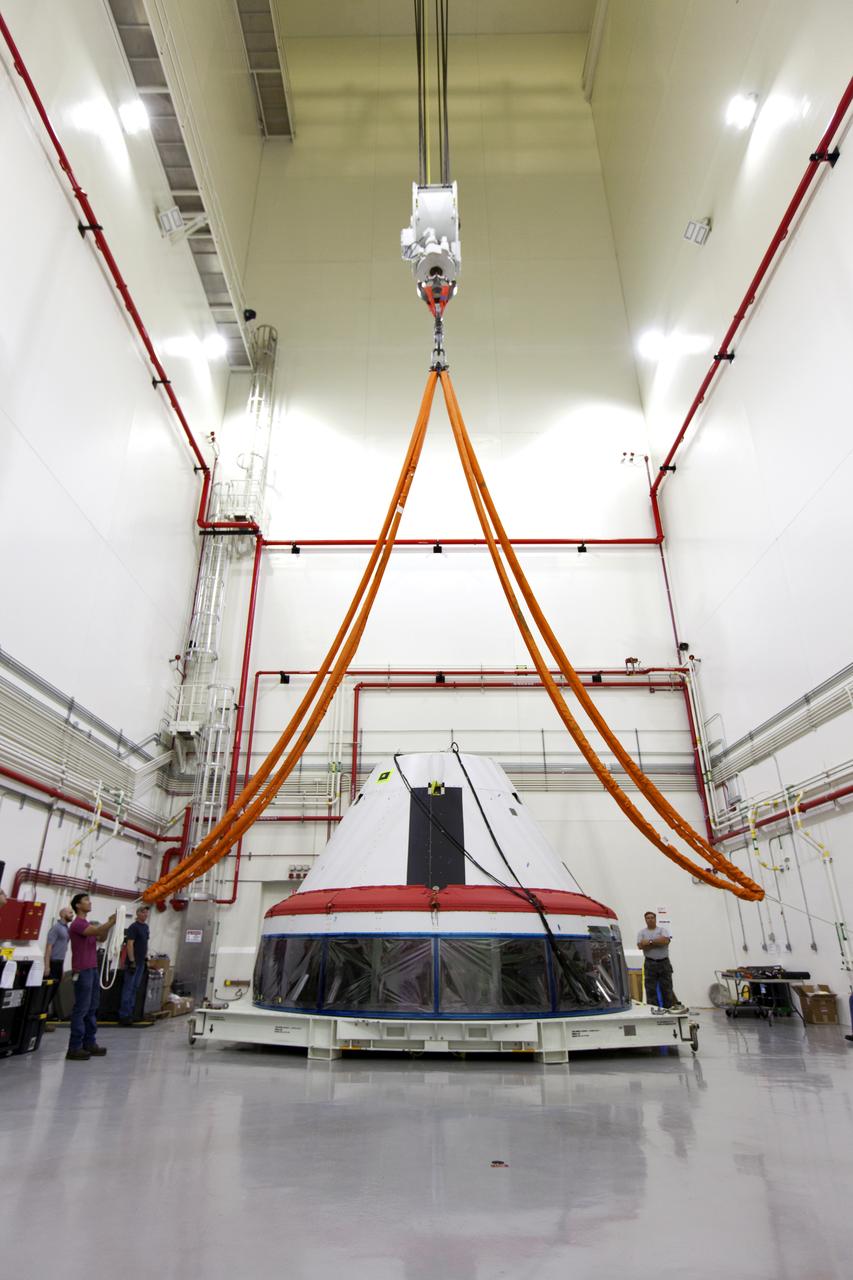

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers prepare to attach a crane to a test version of the Orion crew module on March 13, 2019. The Orion test module and the Launch Abort System will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test, a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.

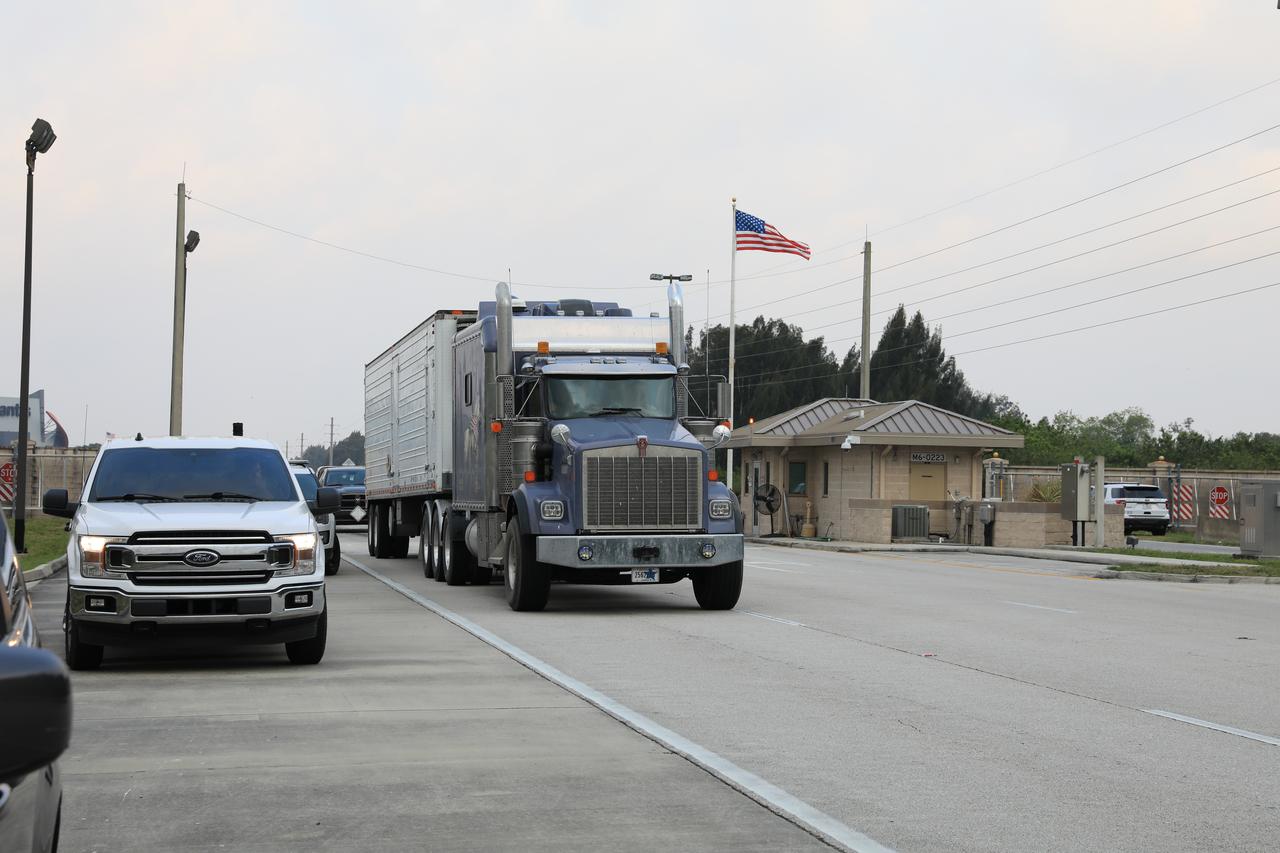
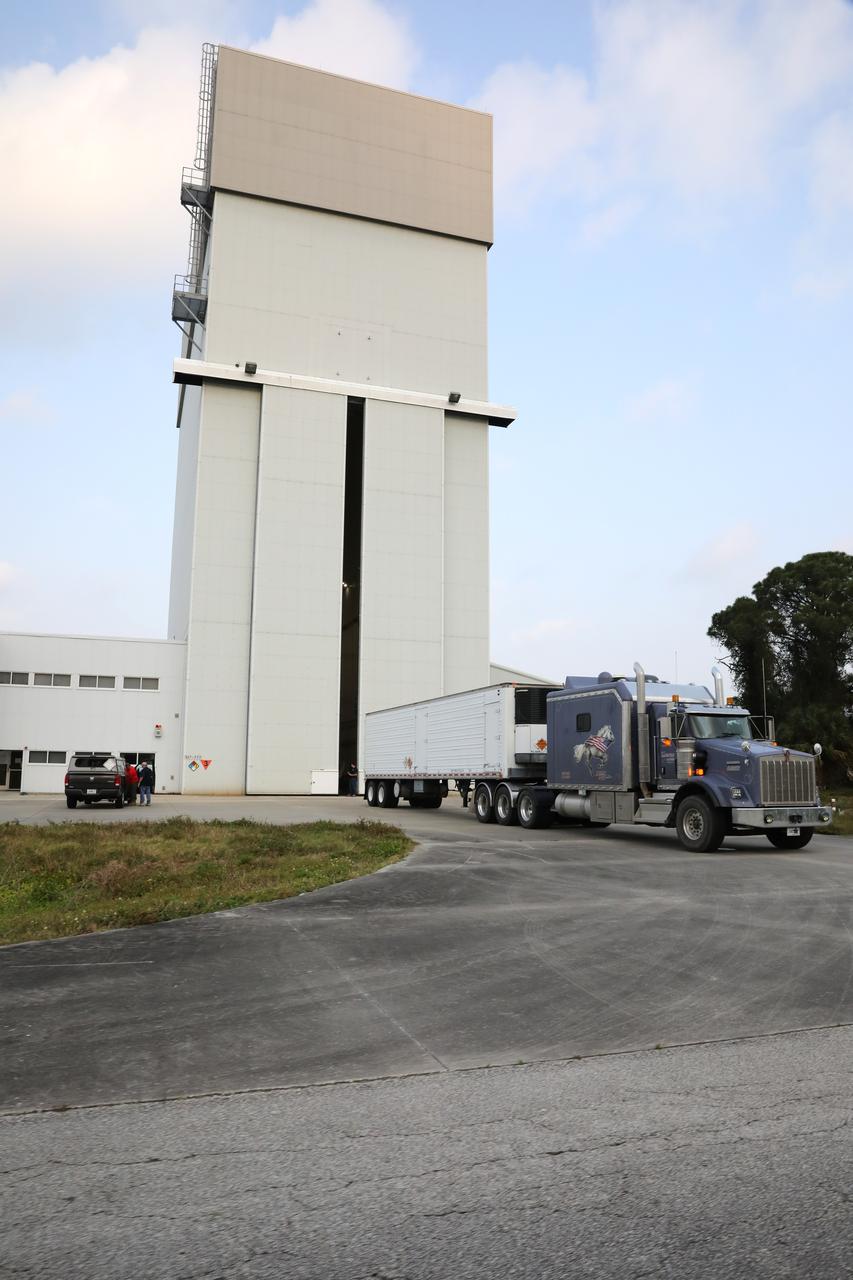
The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Abort System facility on July 10, 2021, after being transported from the Florida spaceport’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility earlier in the day. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
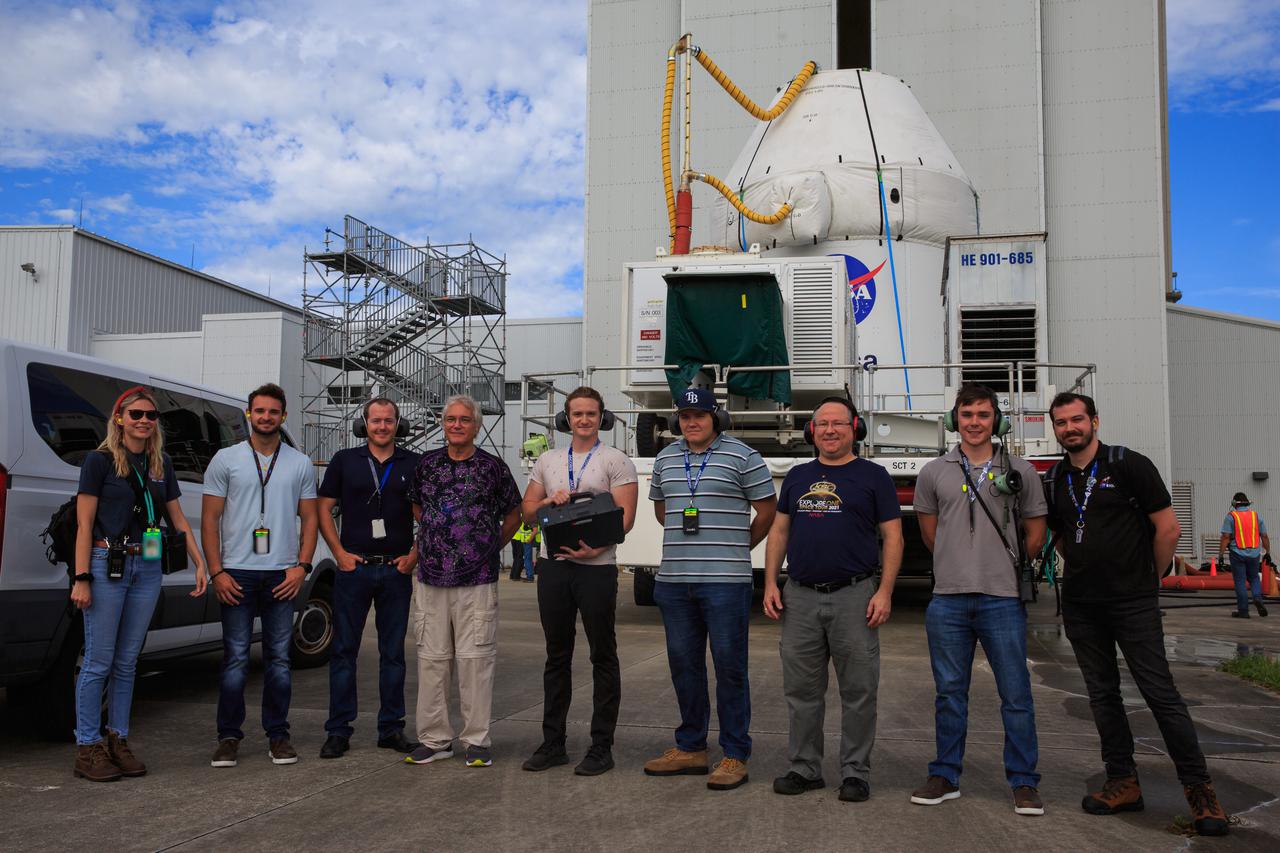

Teams from Kennedy’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs pose as the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. They will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
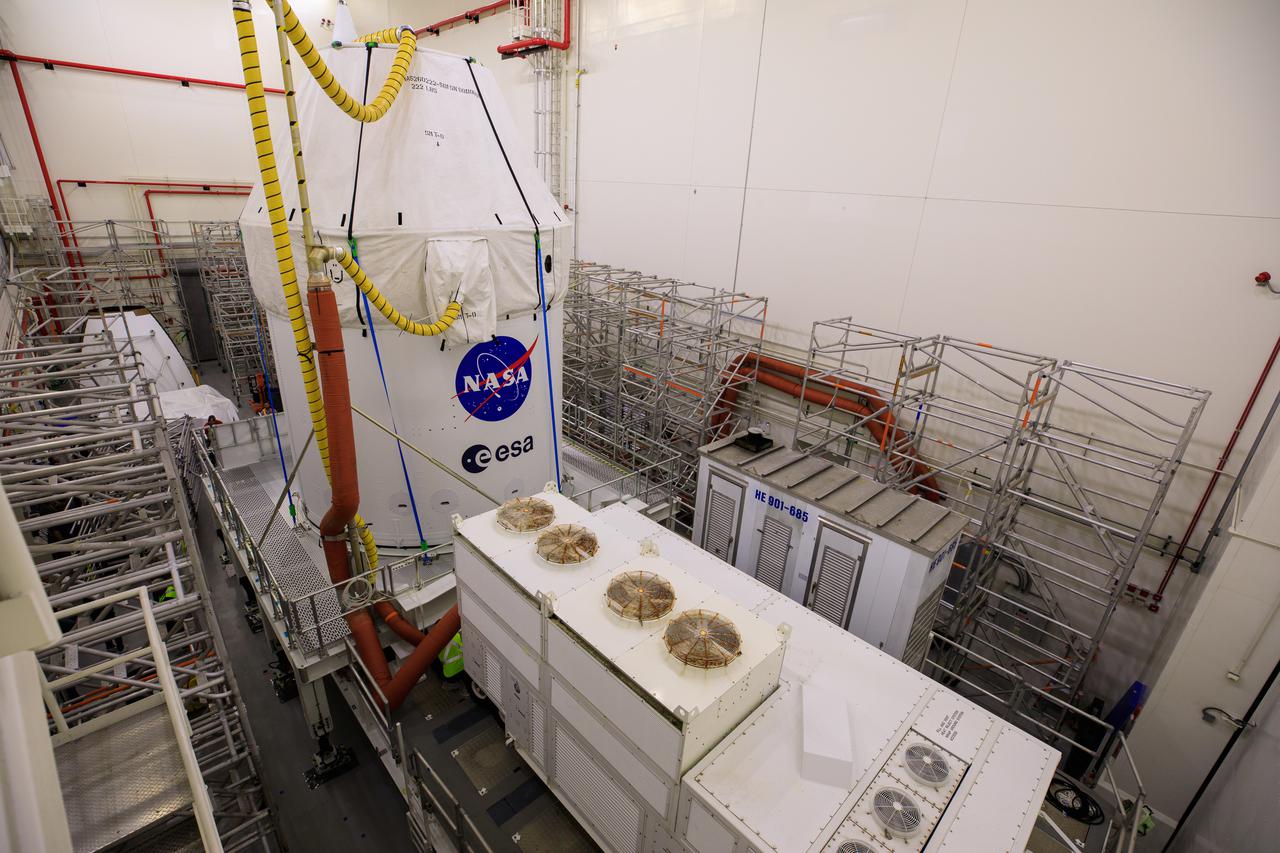

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Abort System facility on July 10, 2021, after being transported from the Florida spaceport’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility earlier in the day. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
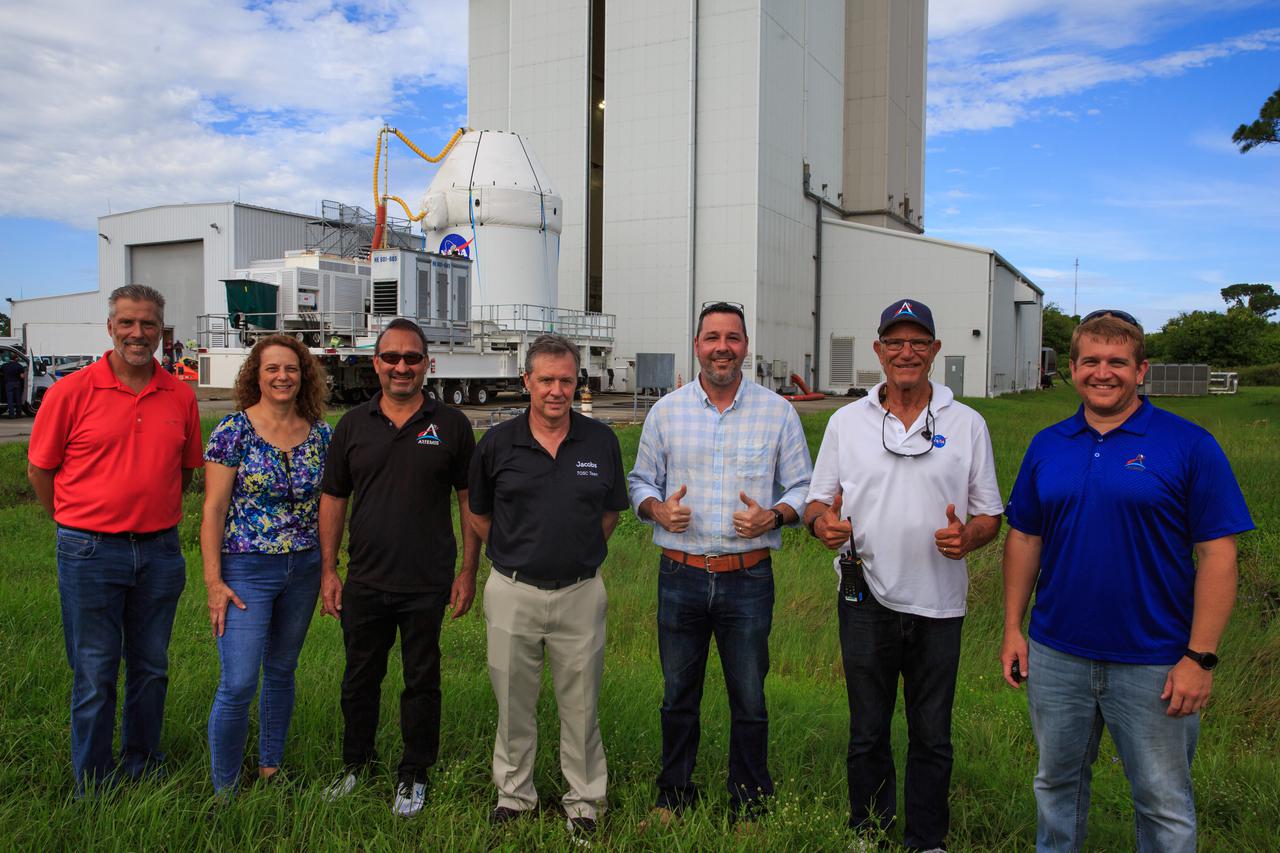

Teams from Kennedy’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs pose as the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. They will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
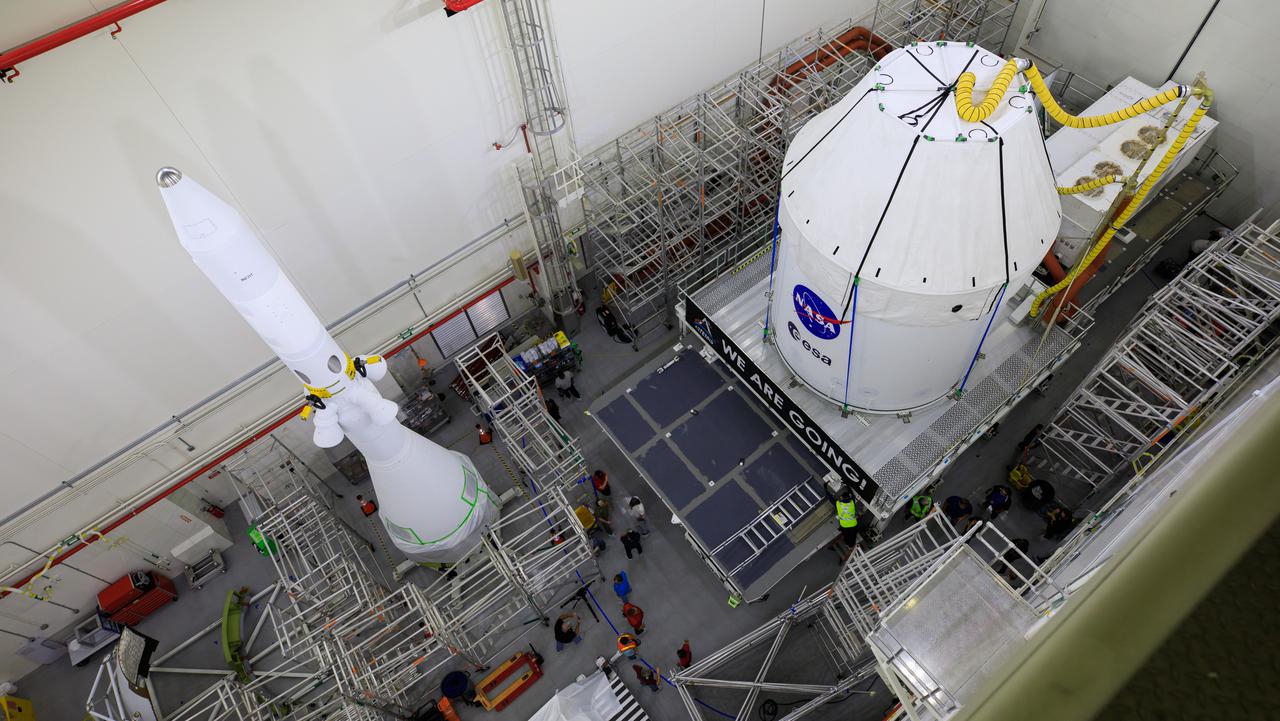

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Abort System facility on July 10, 2021, after being transported from the Florida spaceport’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility earlier in the day. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
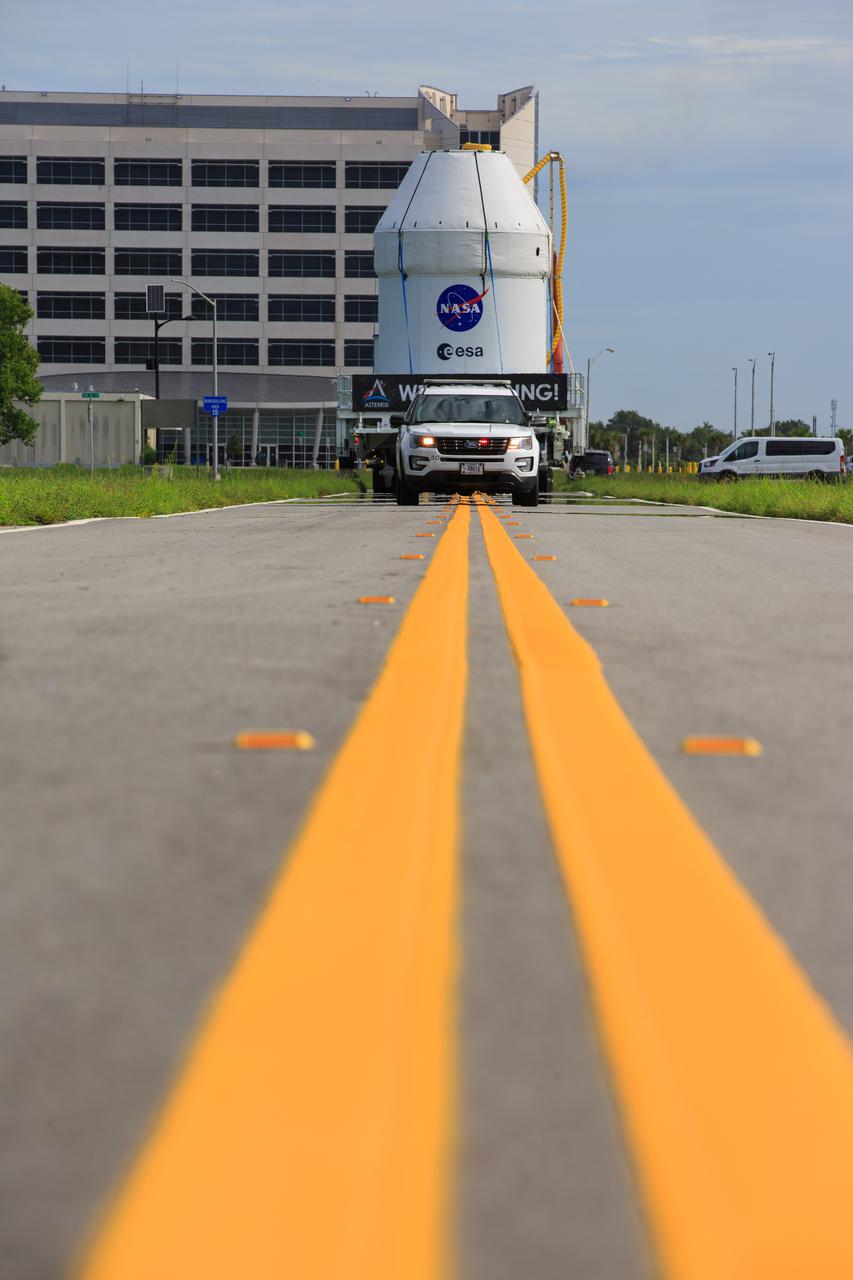

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
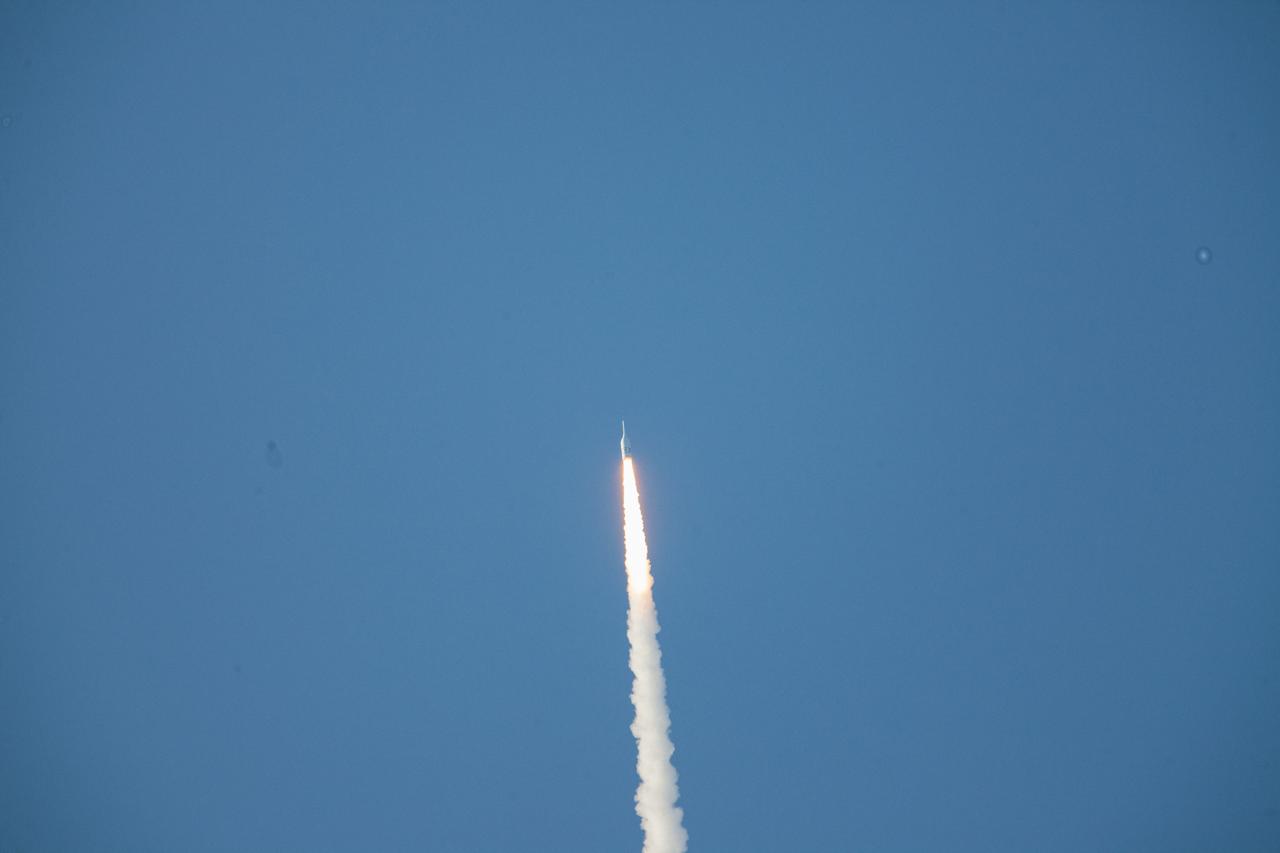

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, soars upward on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, after launching at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
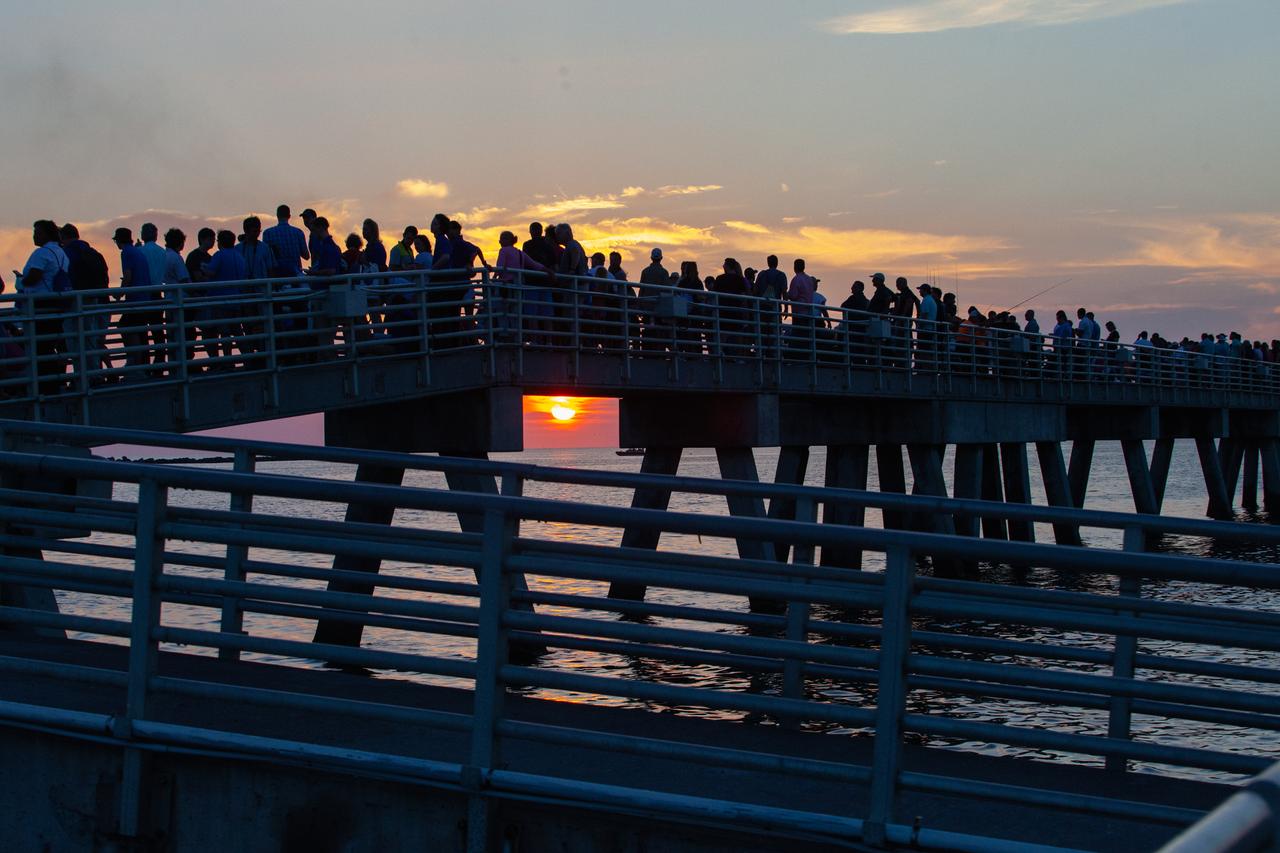

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
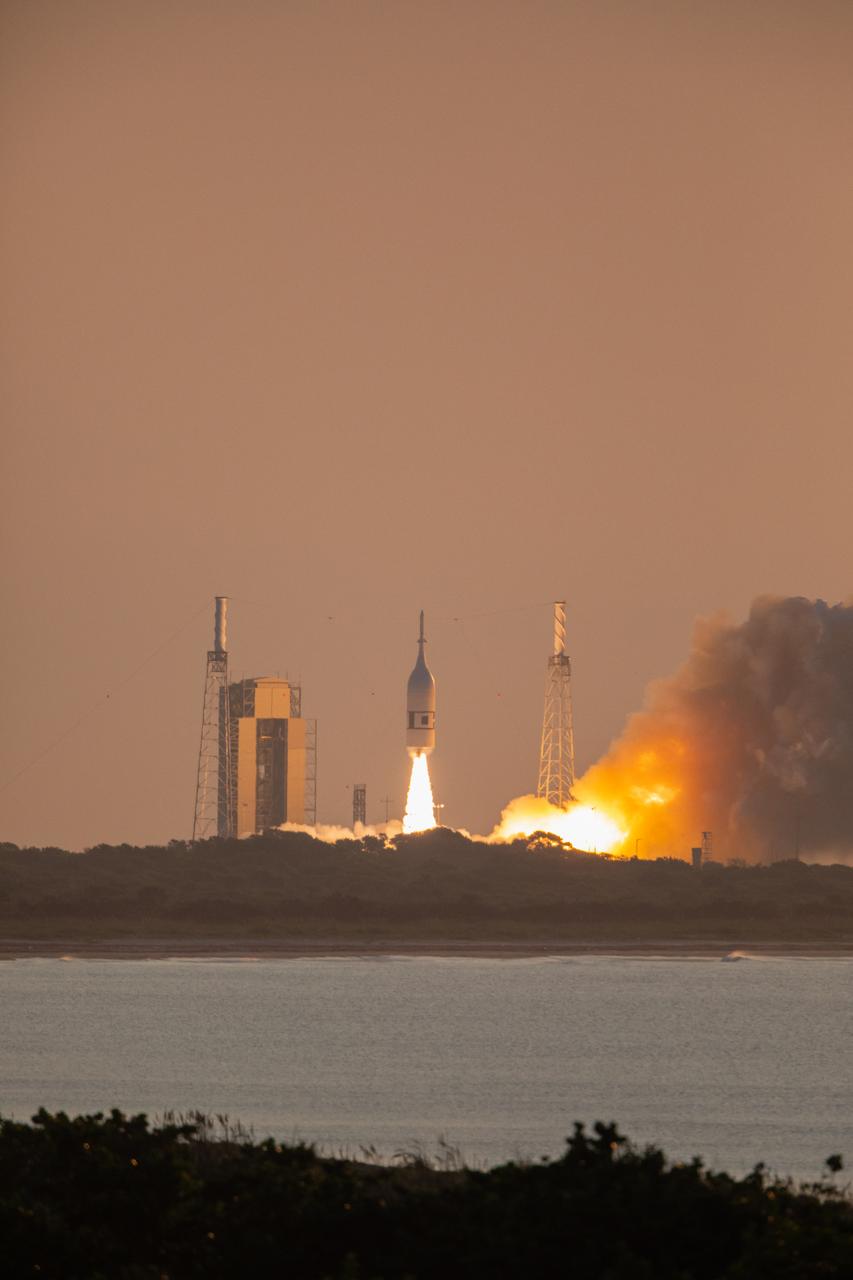

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
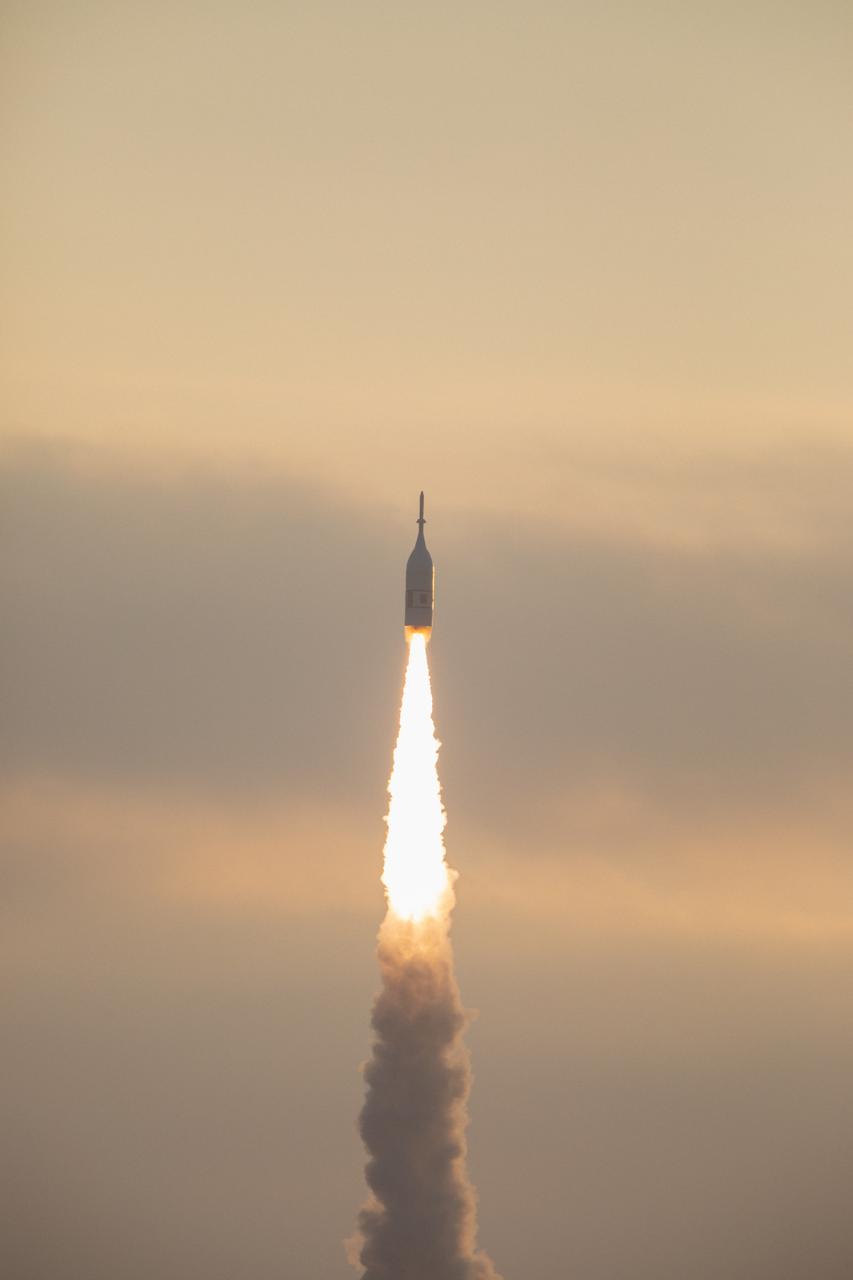

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
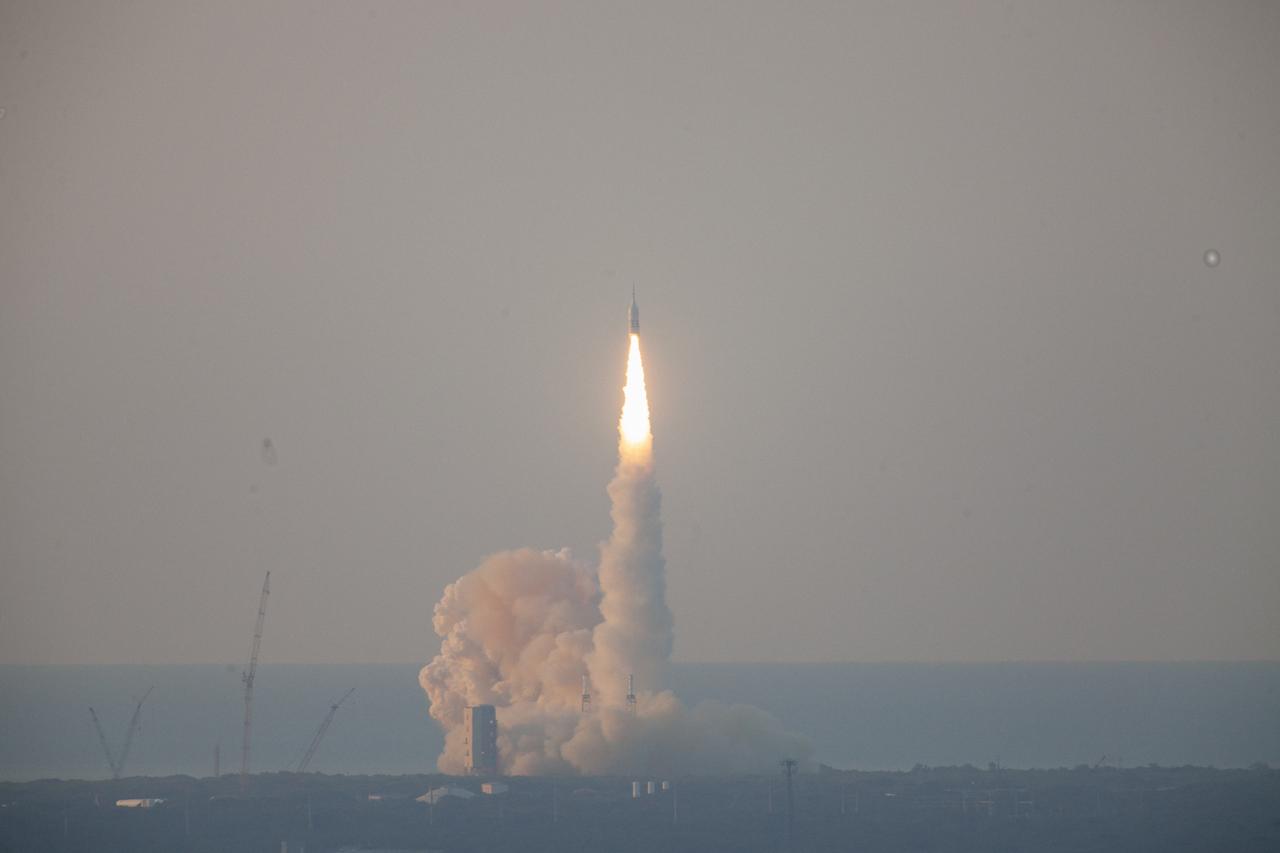

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
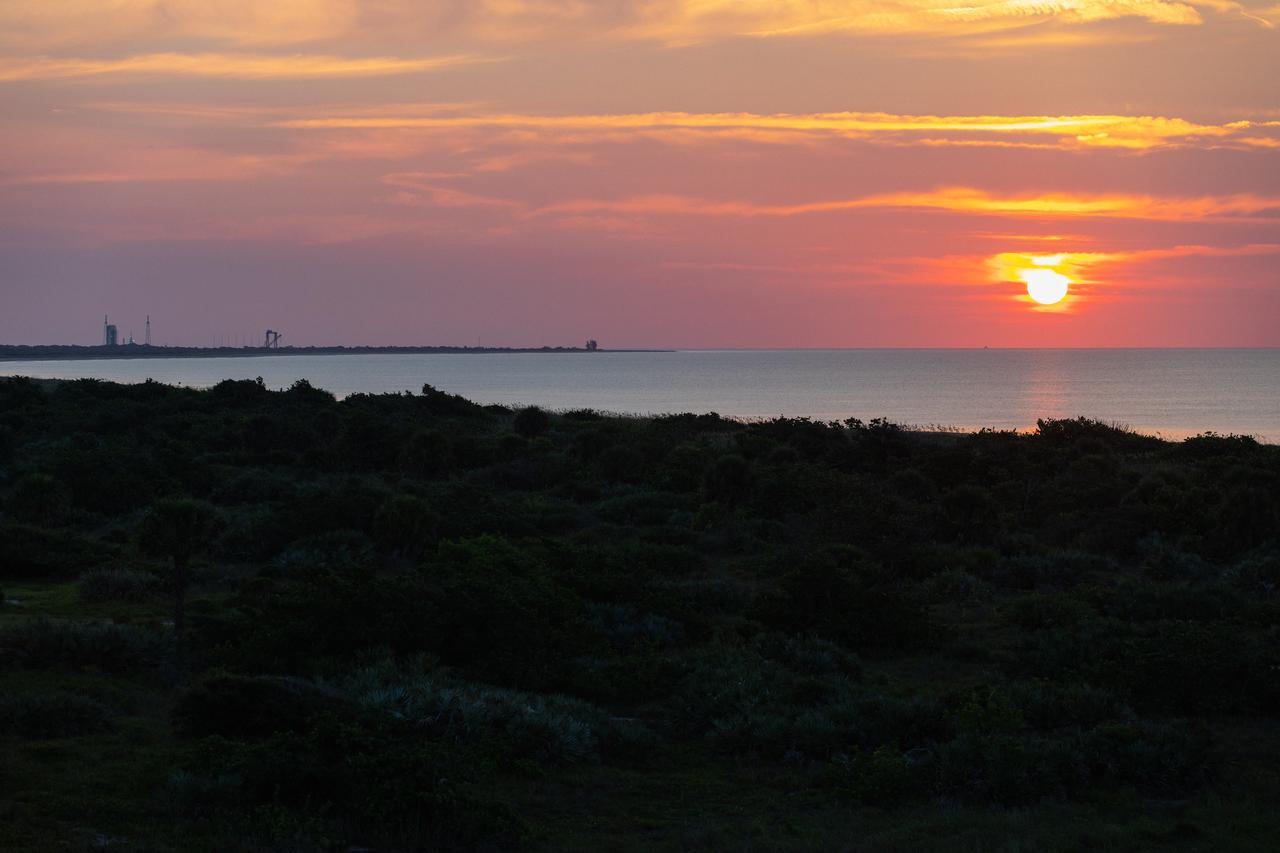

A brilliant sunrise fills the sky before a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
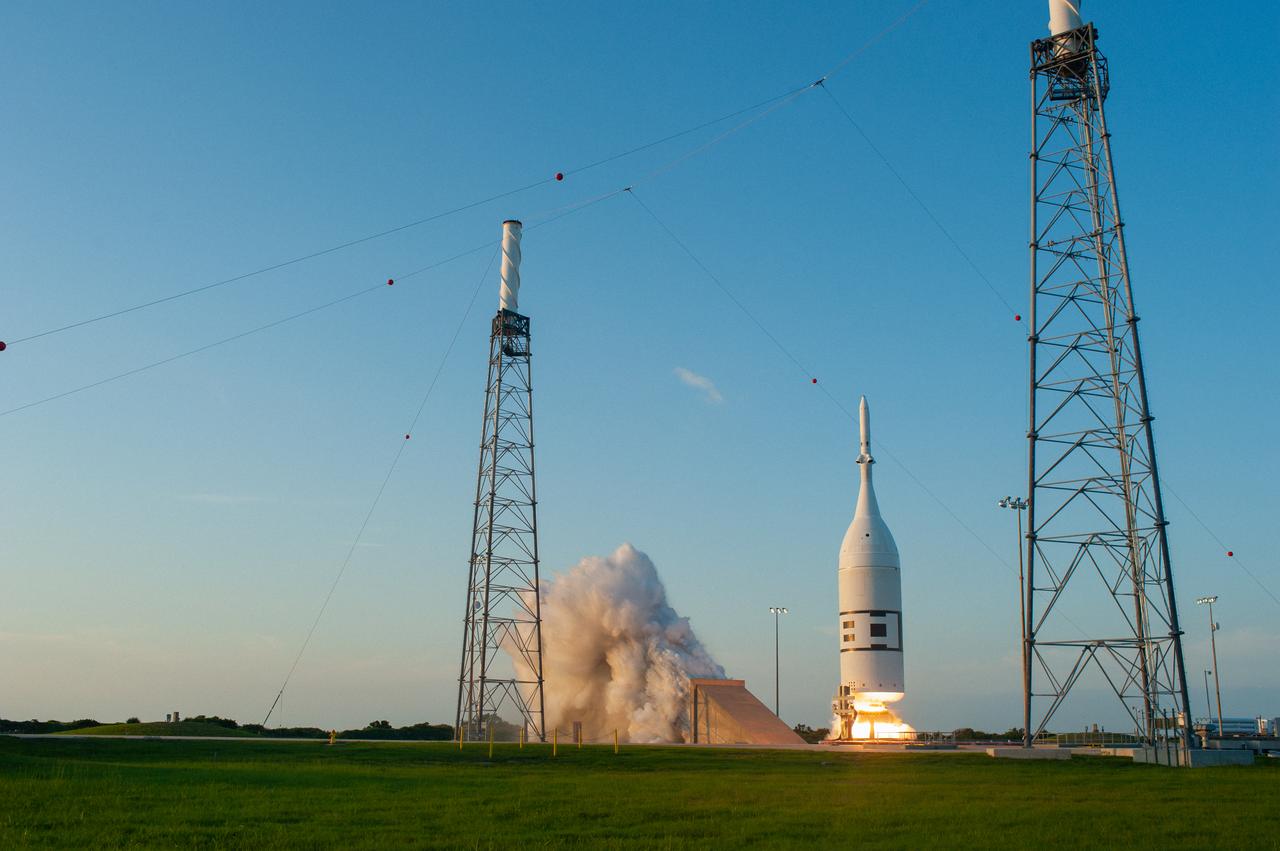

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
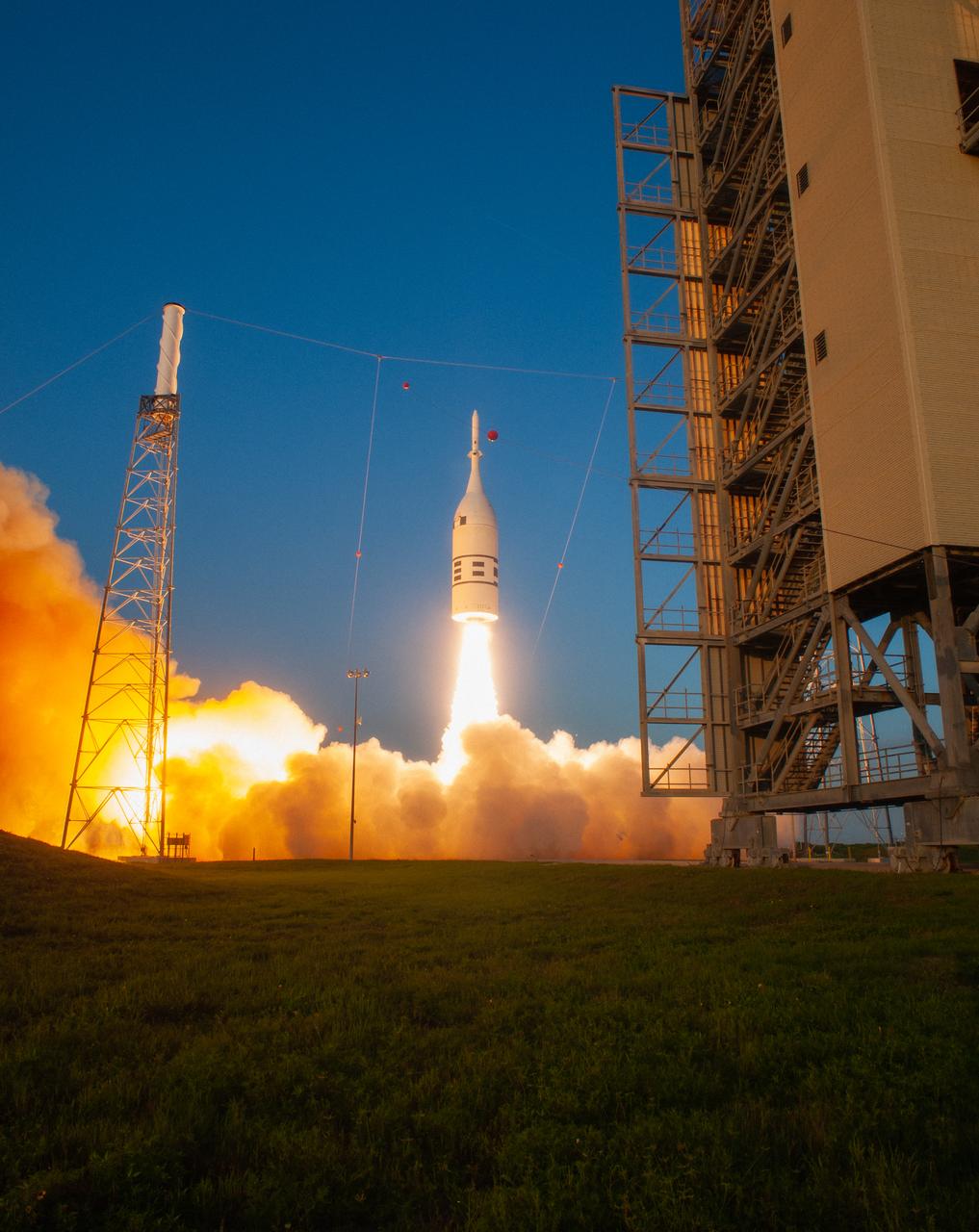

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
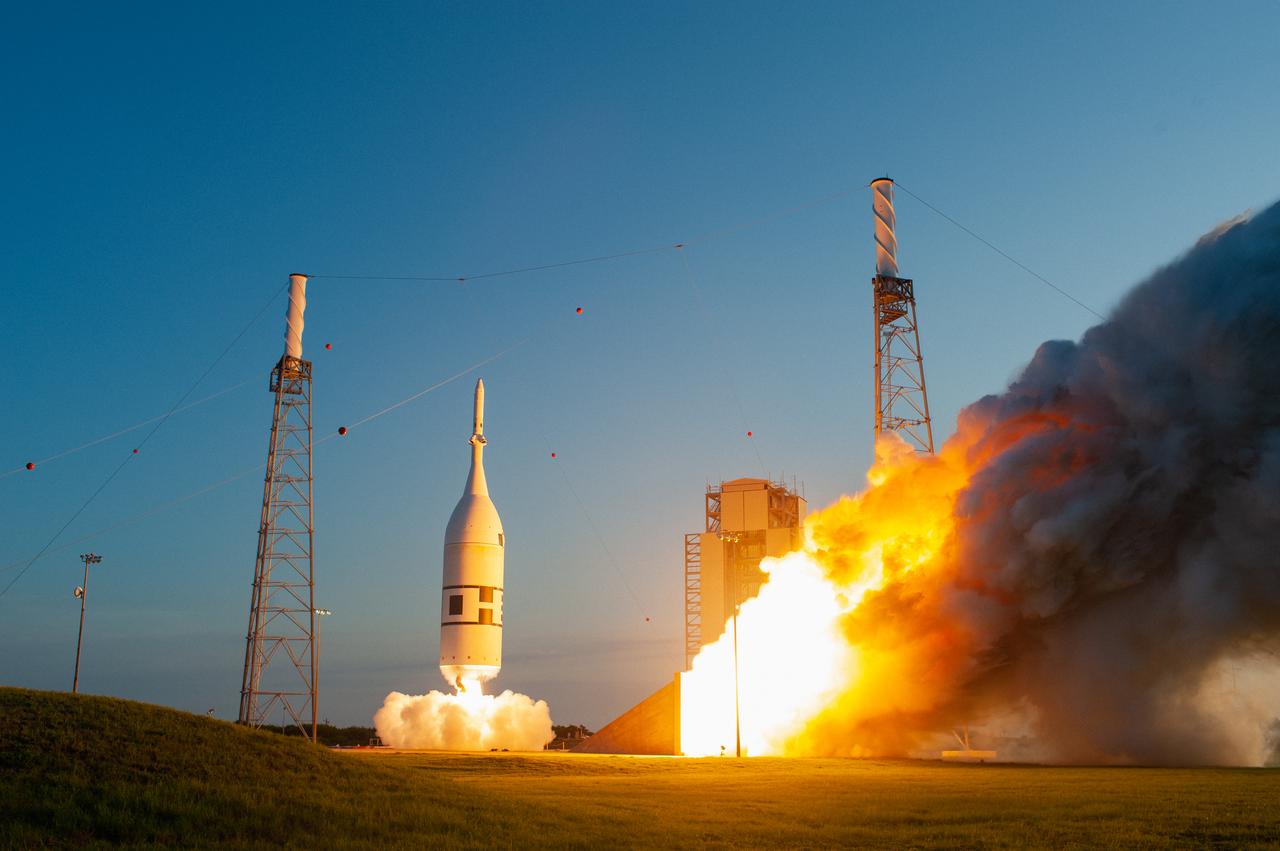

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
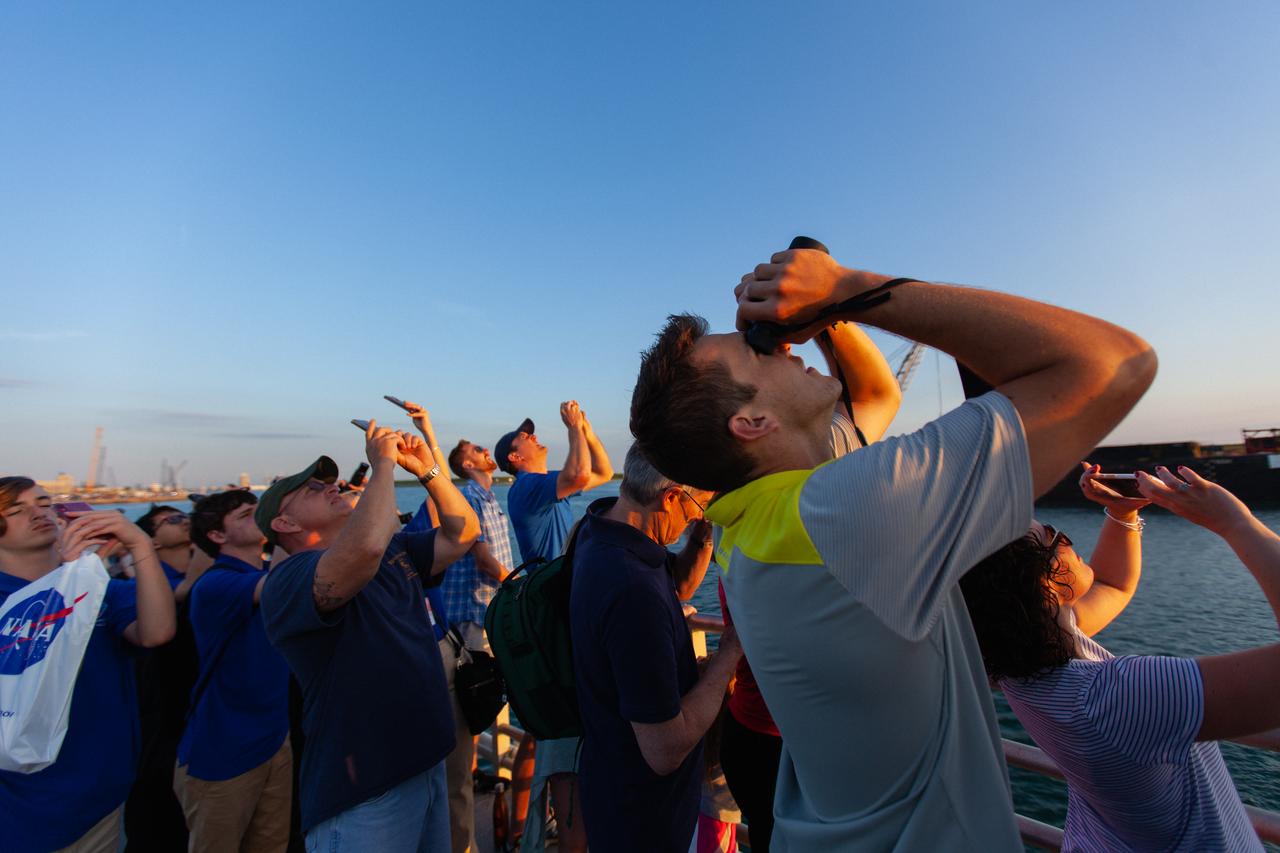

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
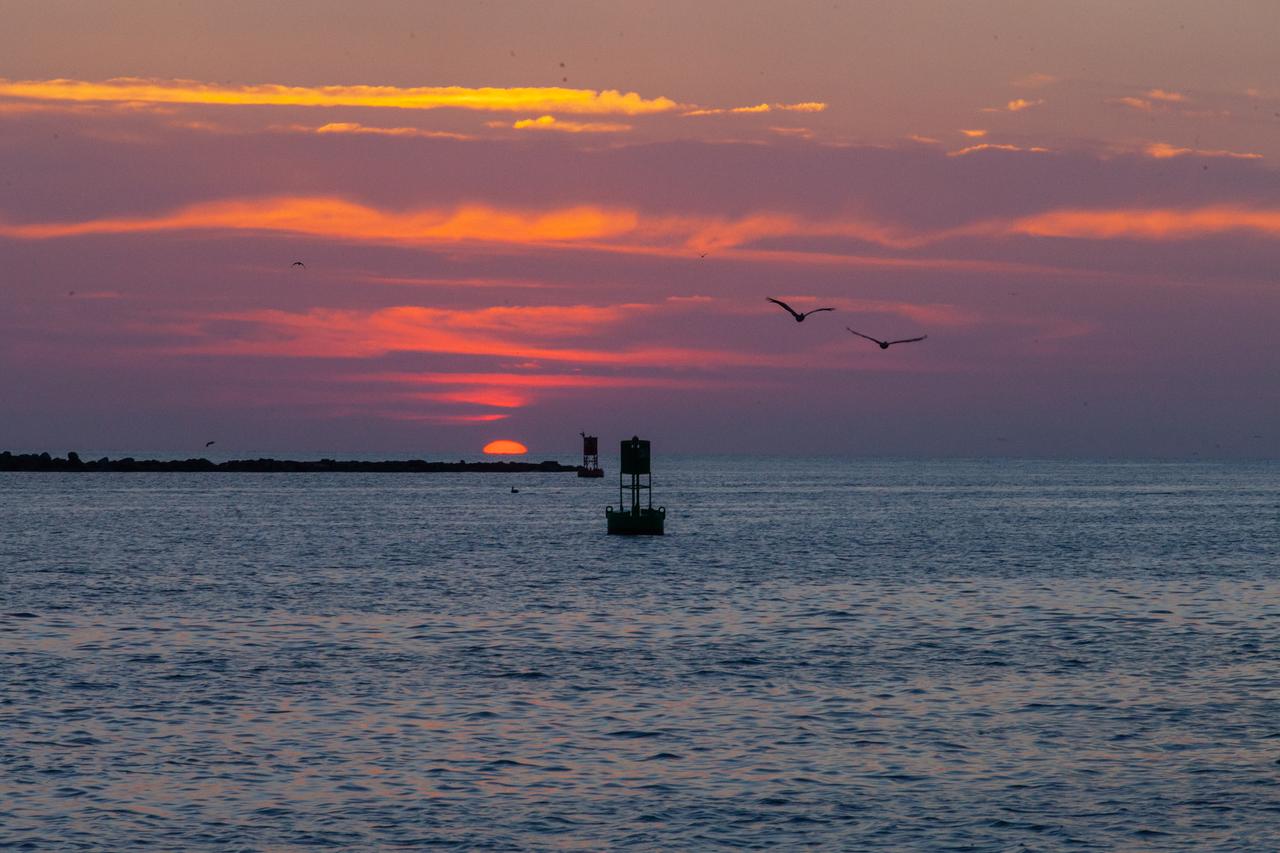

A view of the sunrise at Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as crowds gather to watch a Northrop Grumman provided booster launch from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
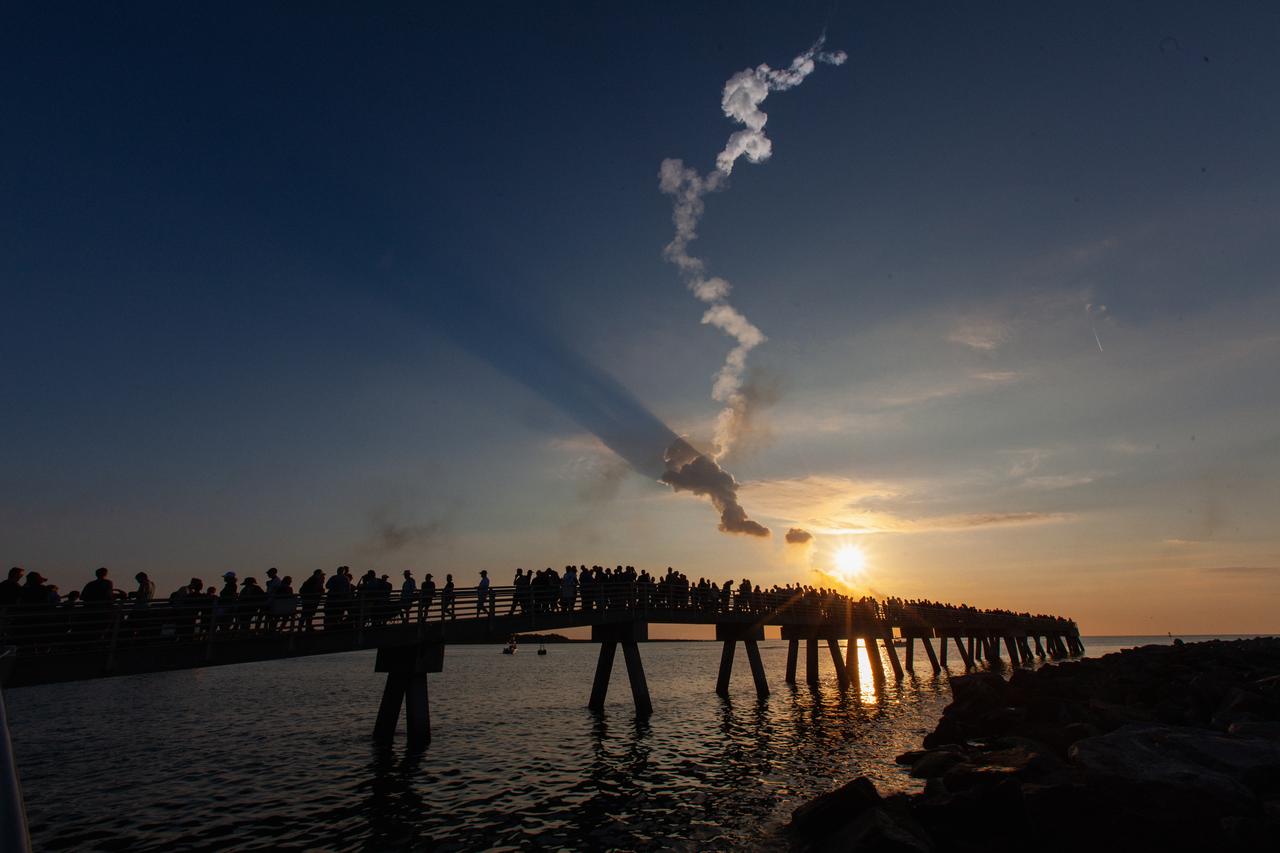

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
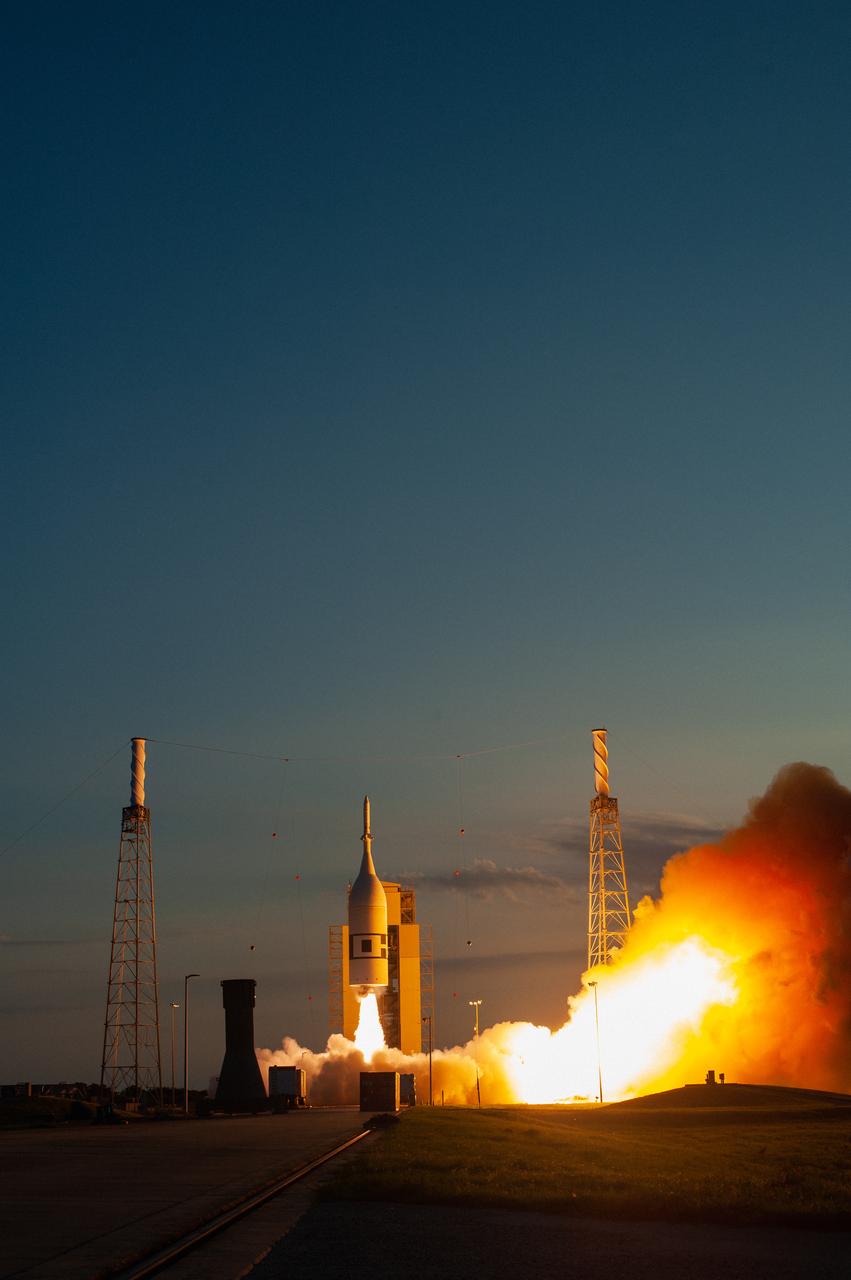

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
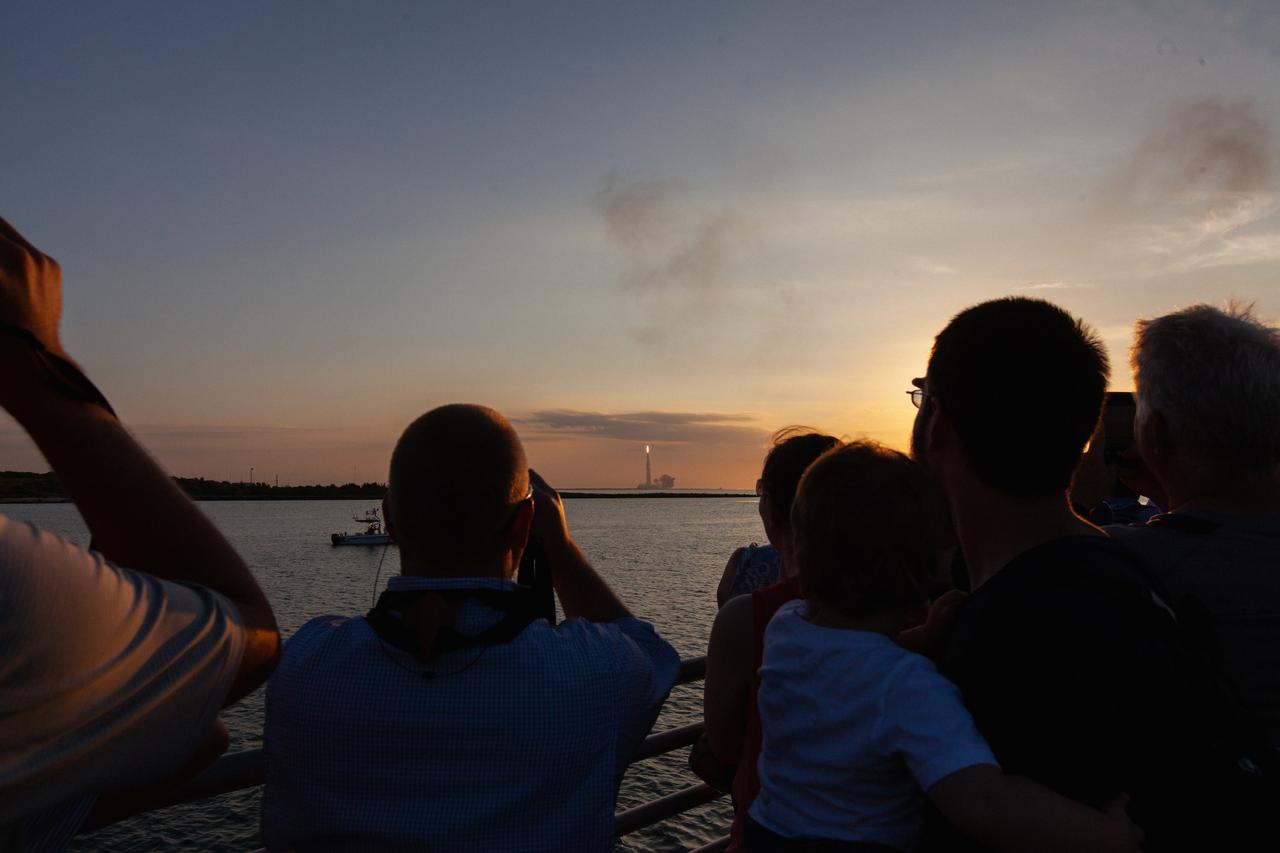

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
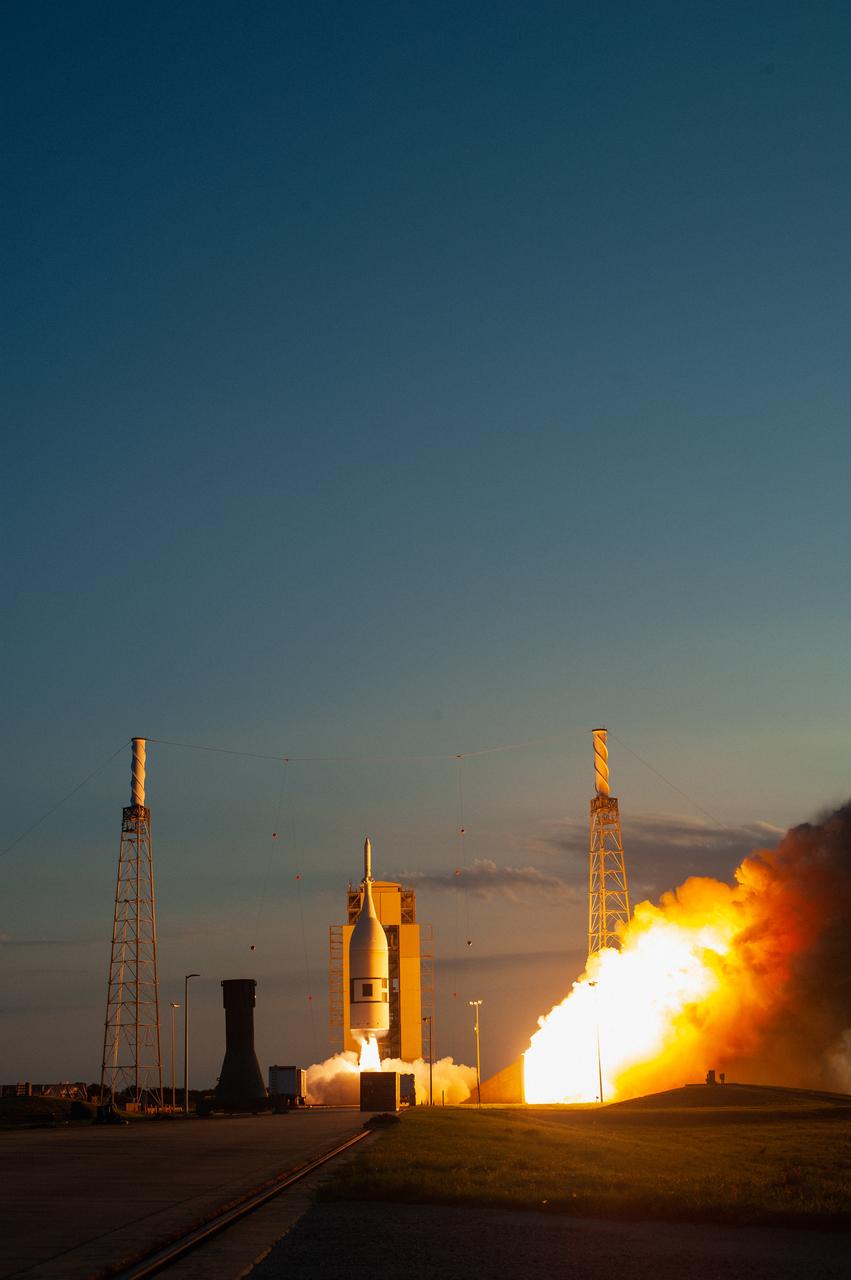

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
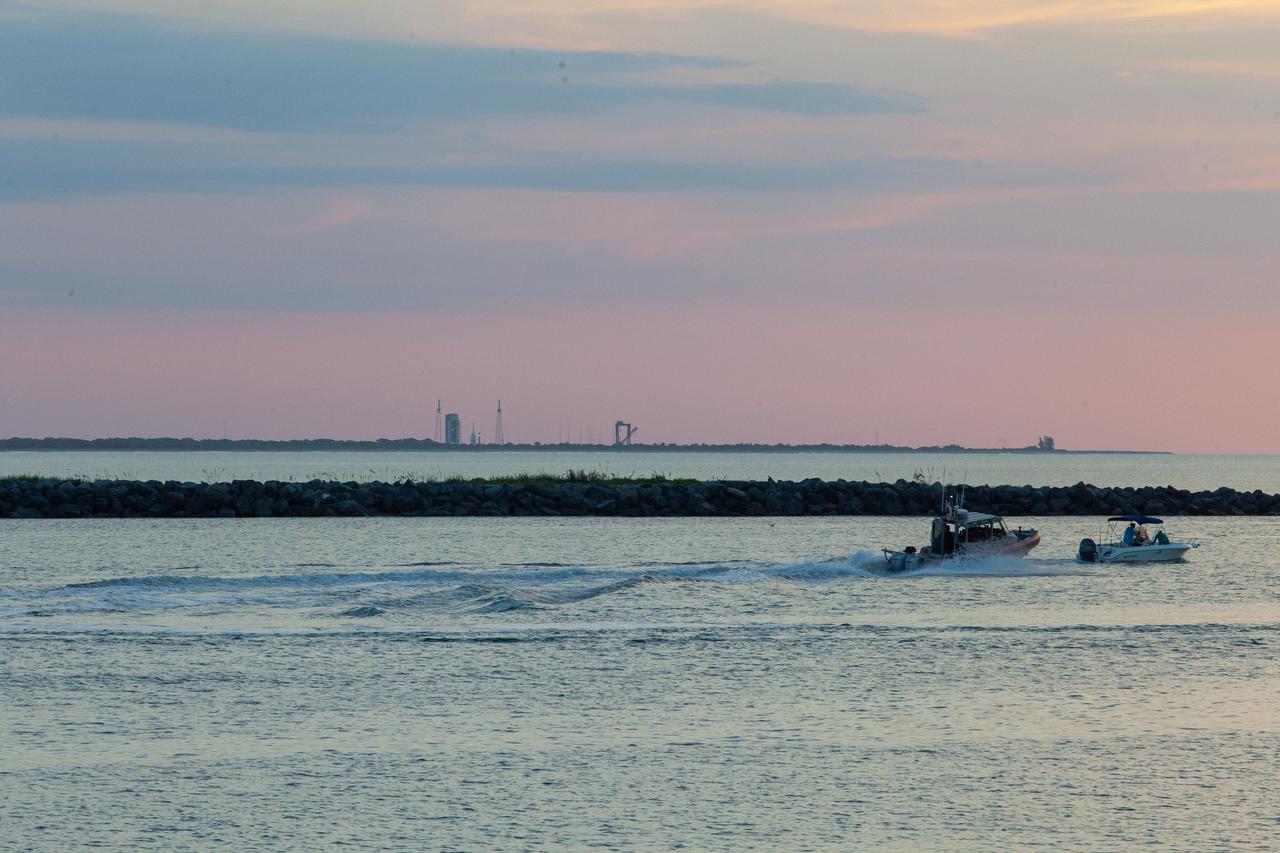

A view of Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, during sunrise on July 2, 2019. Crowds will soon gather to watch as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46, carrying a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
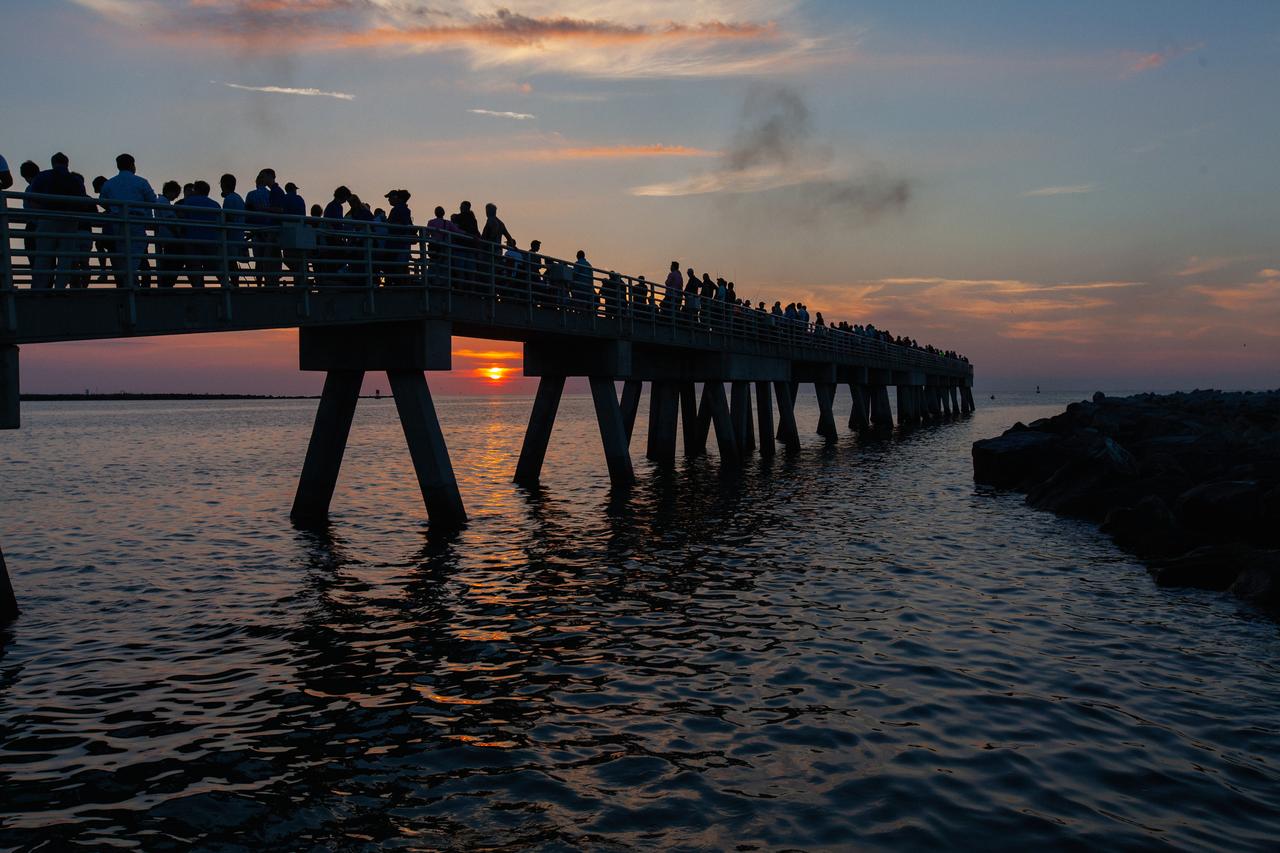

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
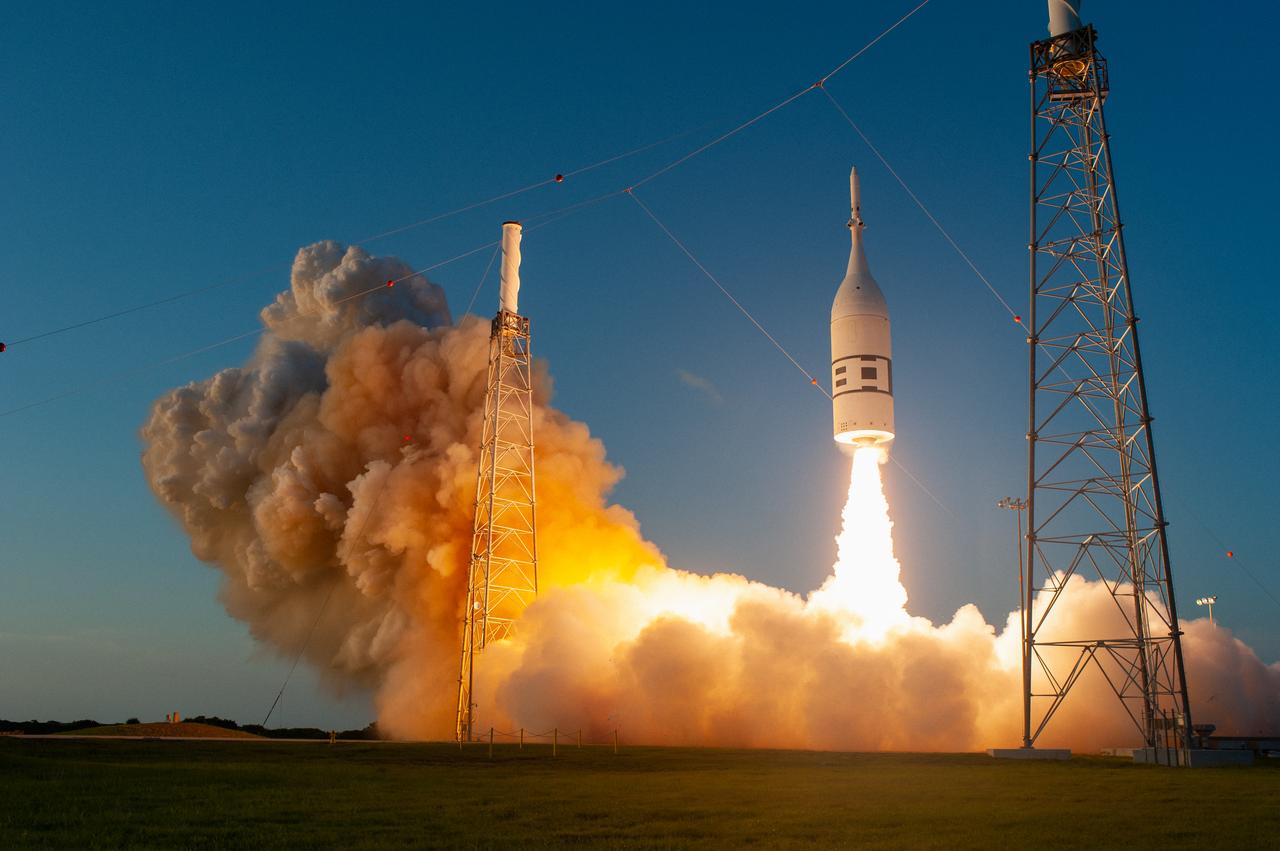

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
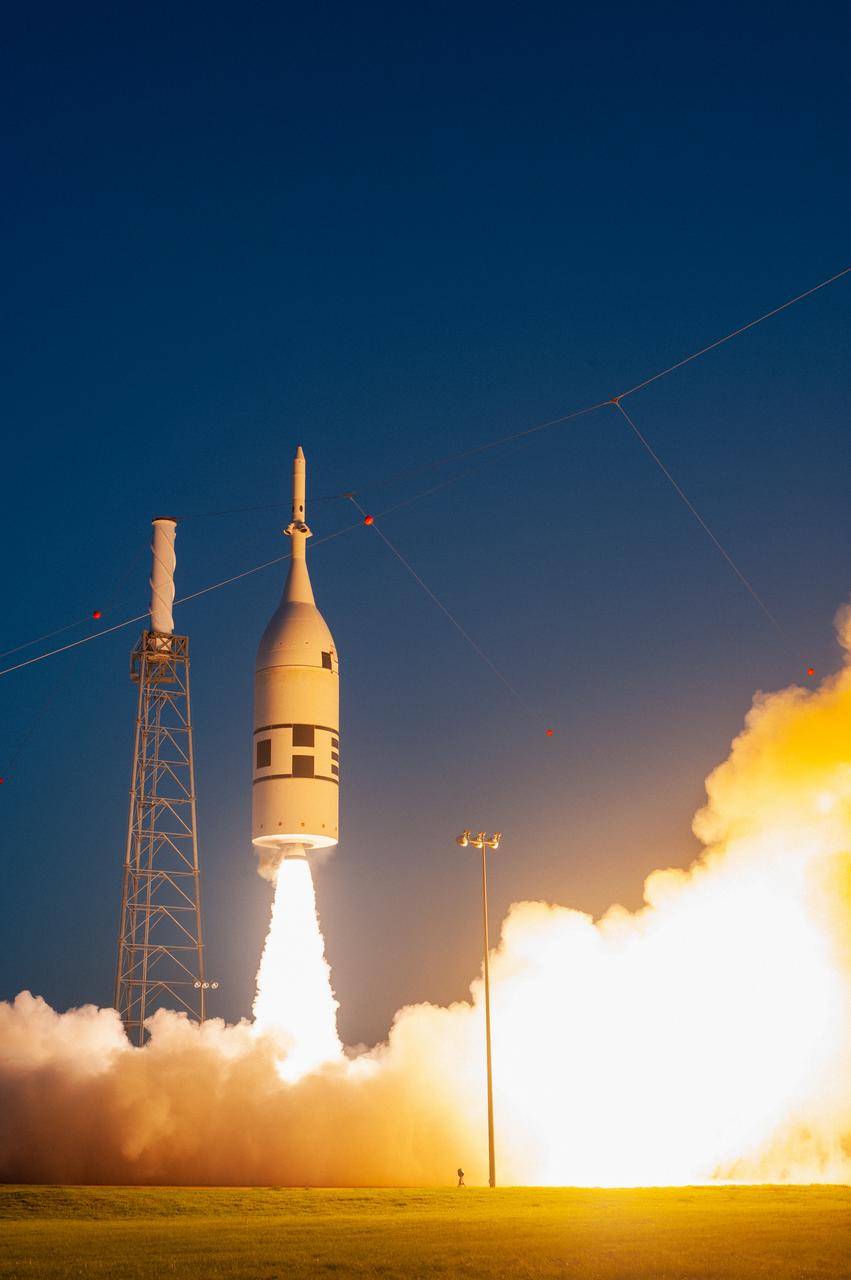

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
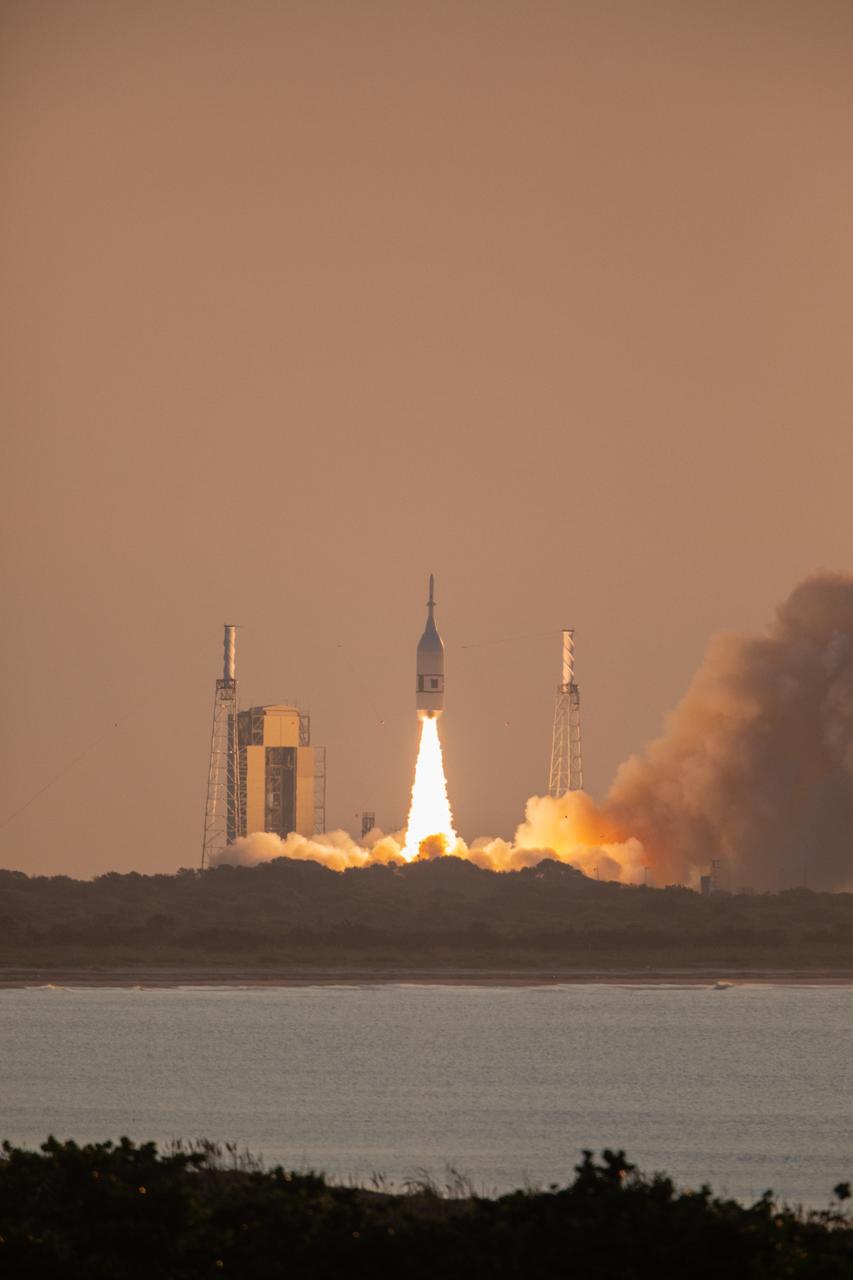

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
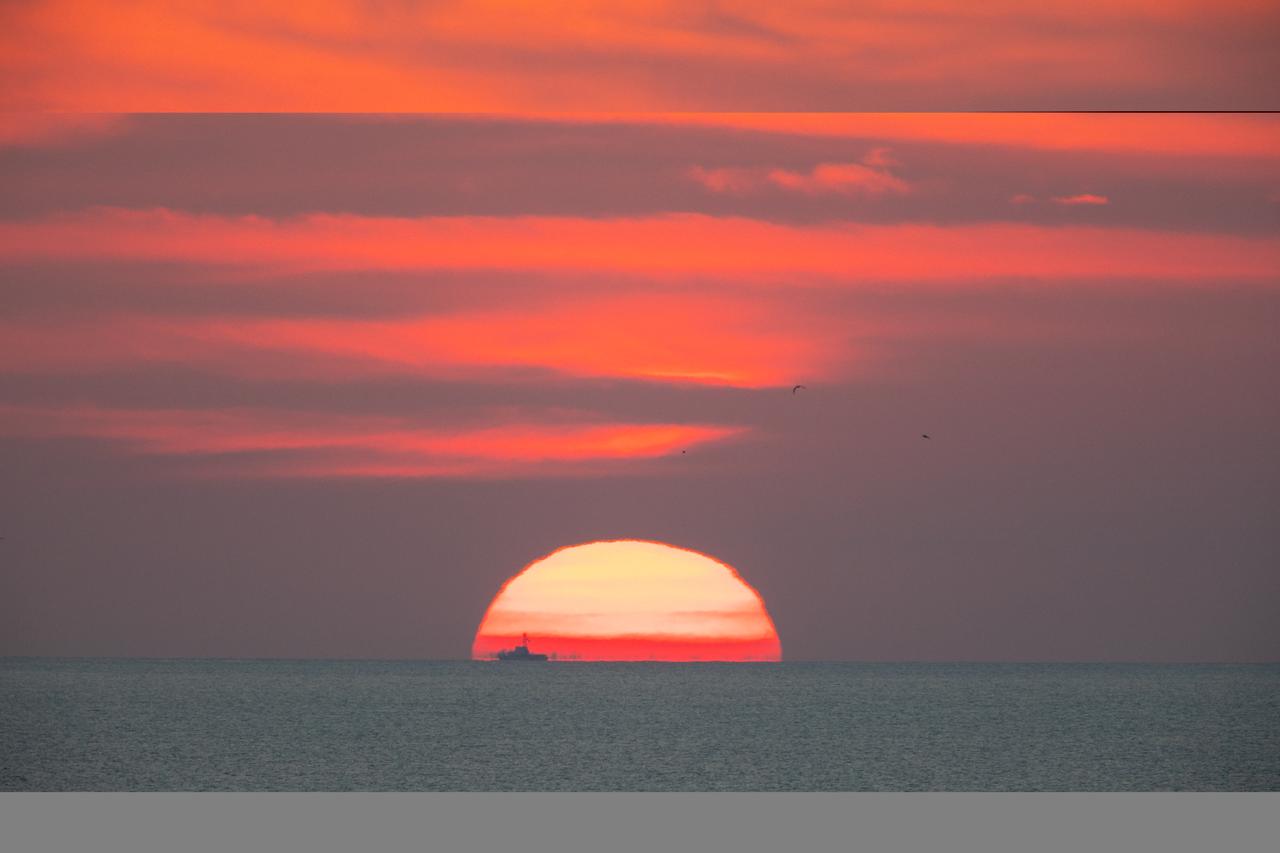

A brilliant sunrise fills the sky before a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
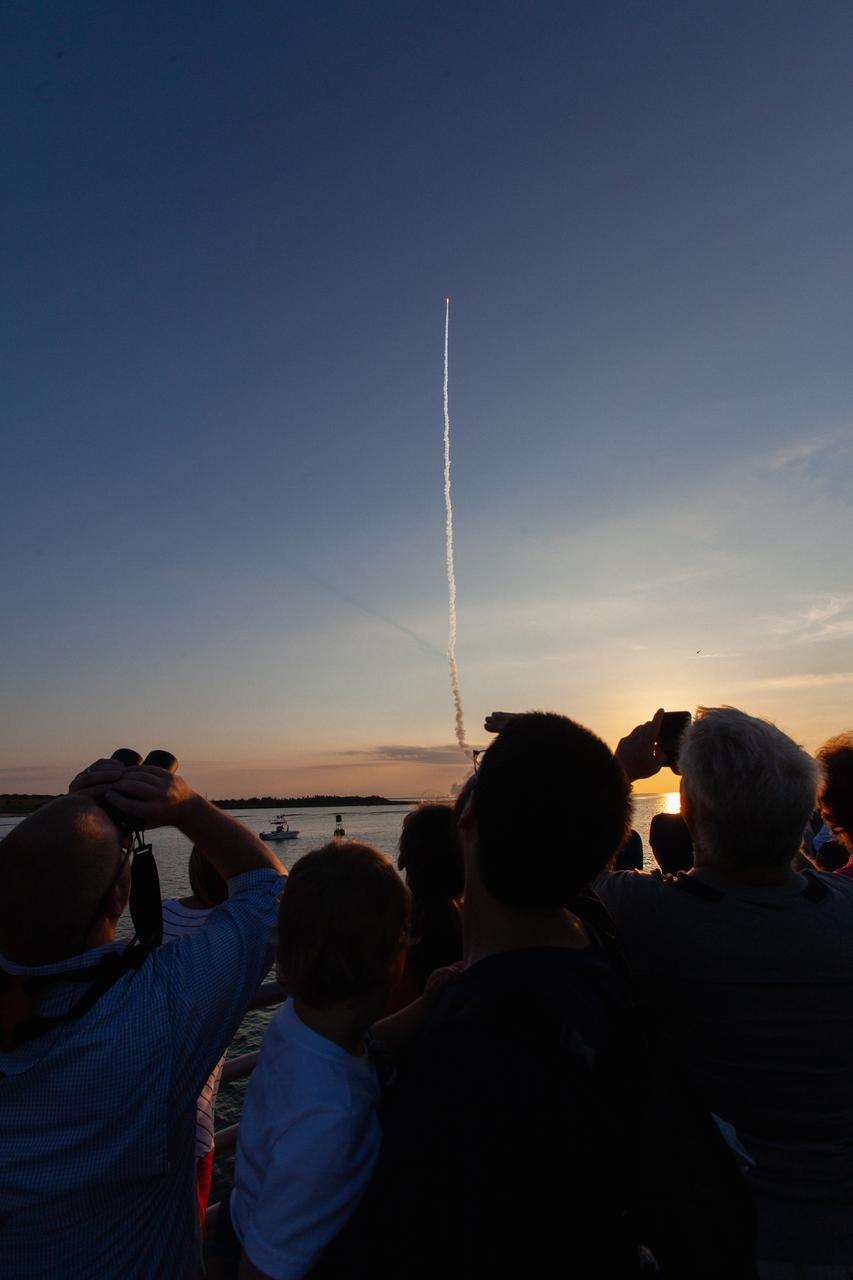

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
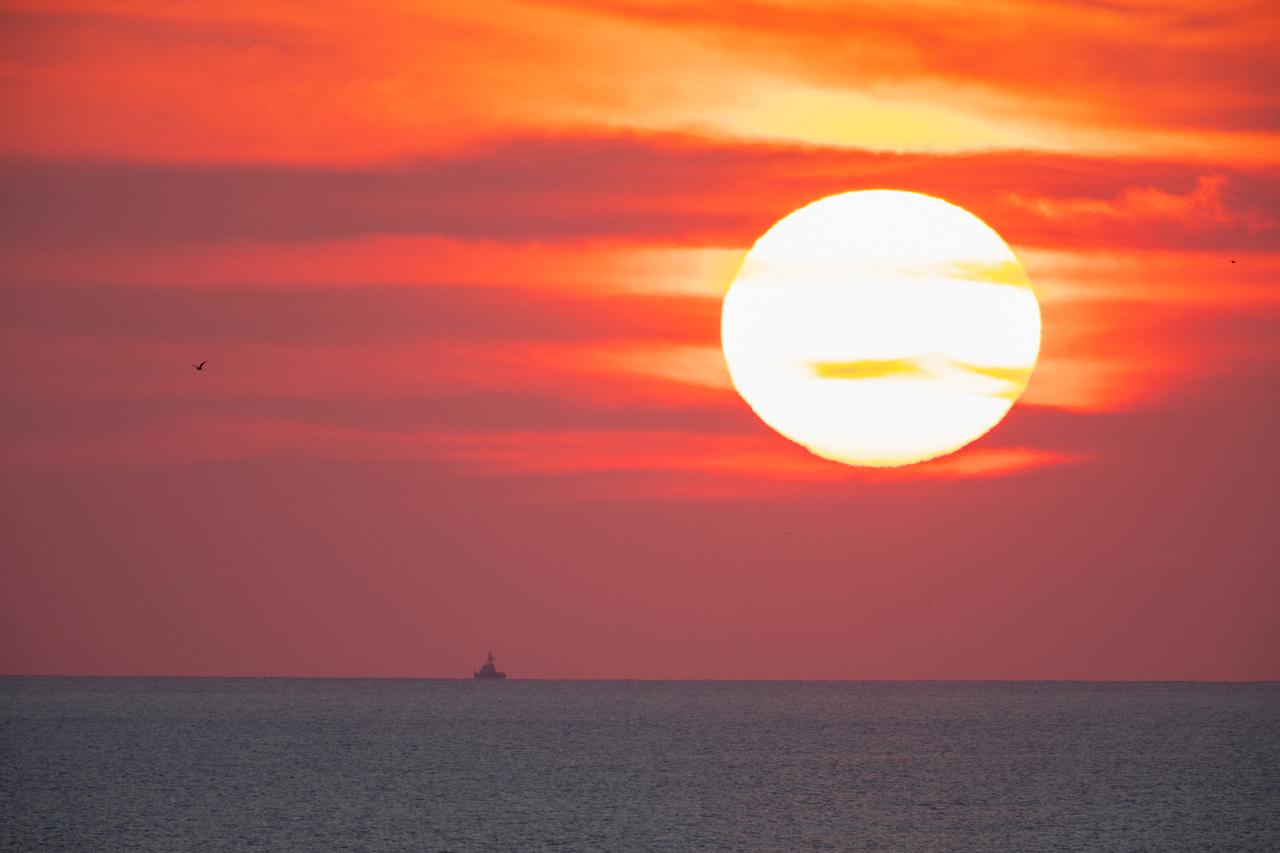

A brilliant sunrise fills the sky before a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
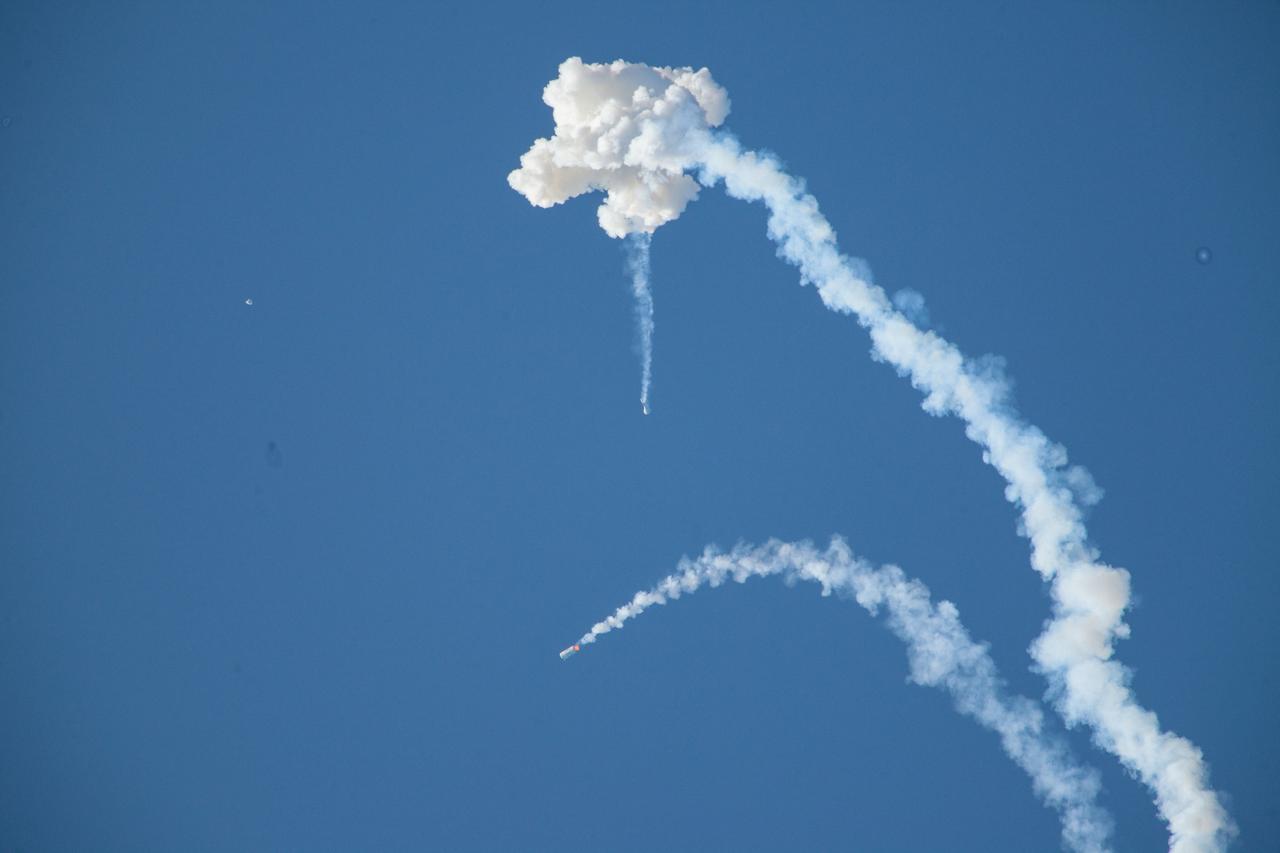

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, soars upward on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, after launching at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
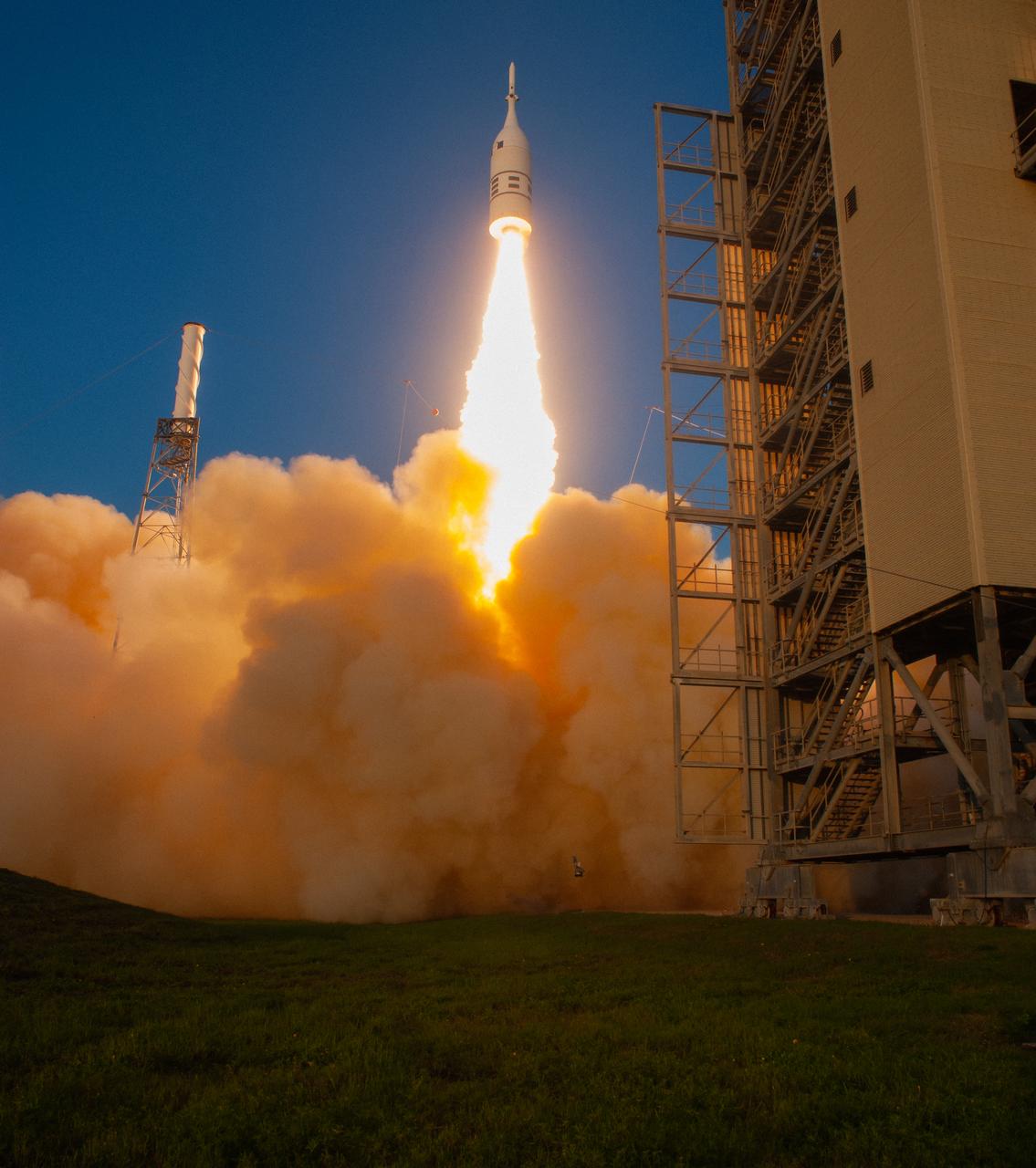

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
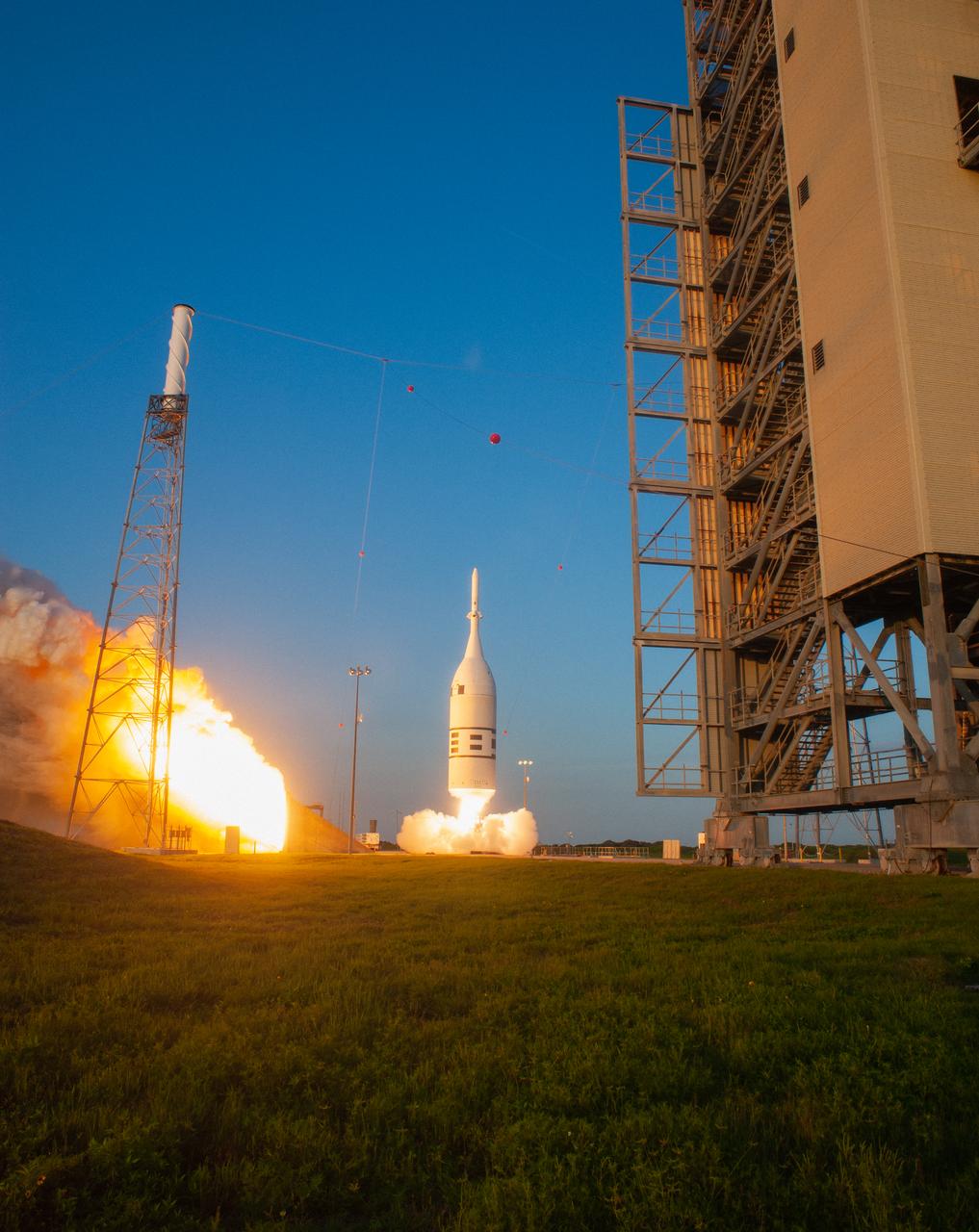

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
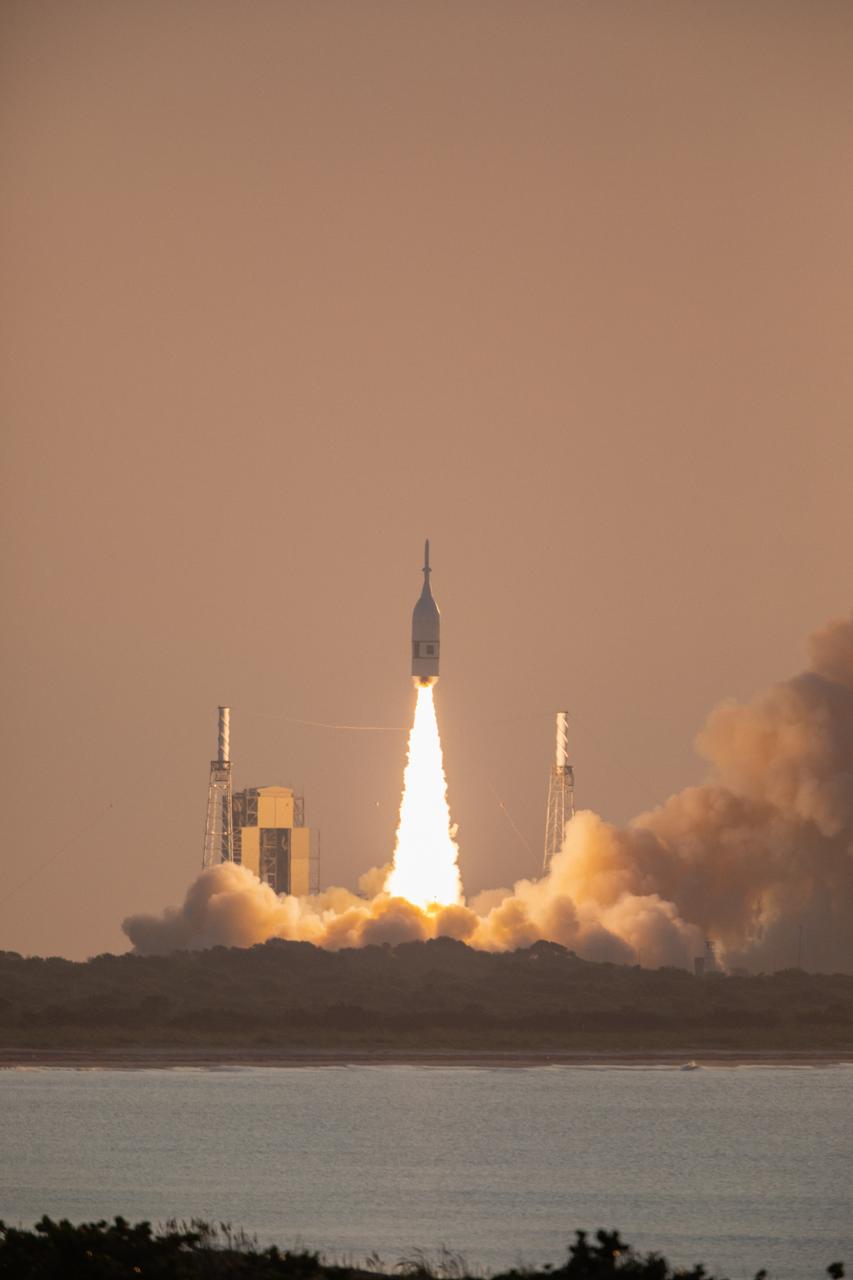

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
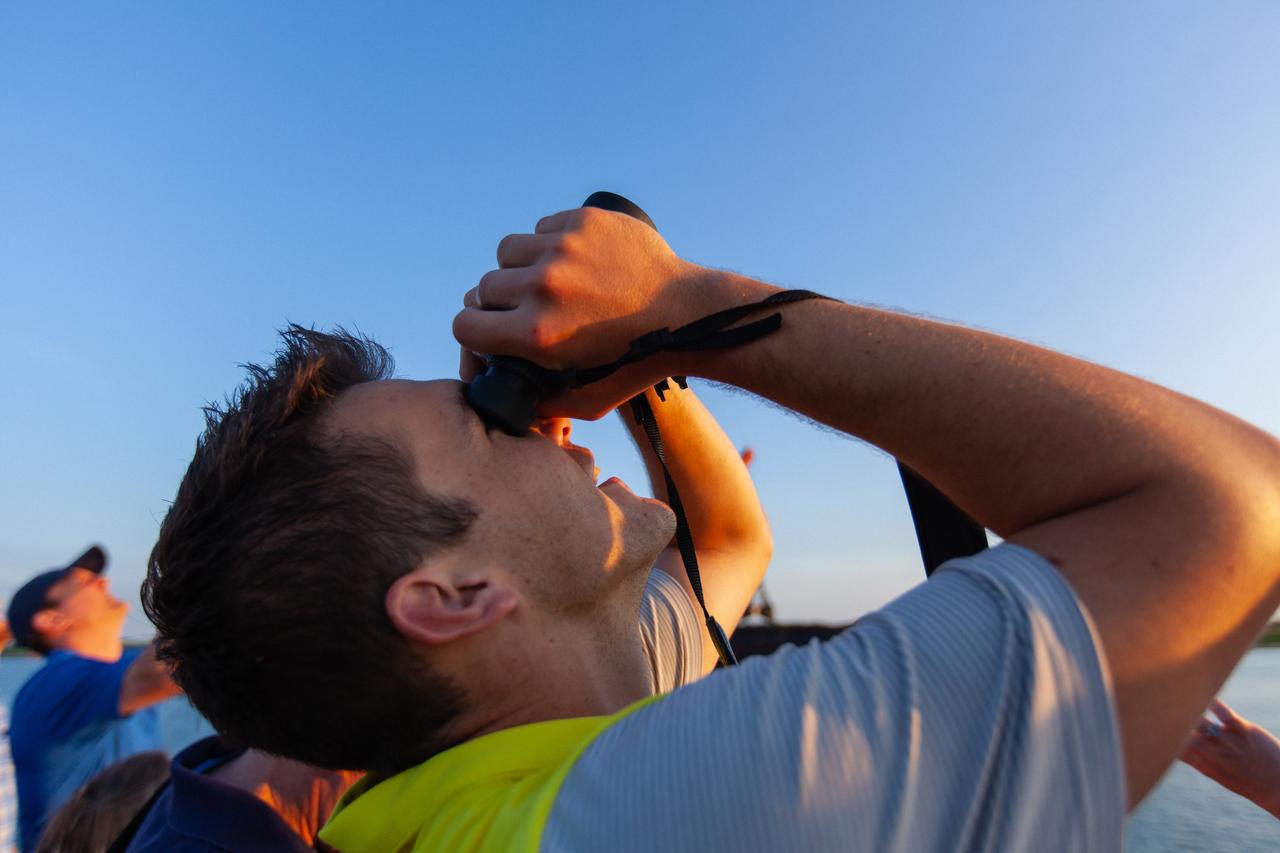

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
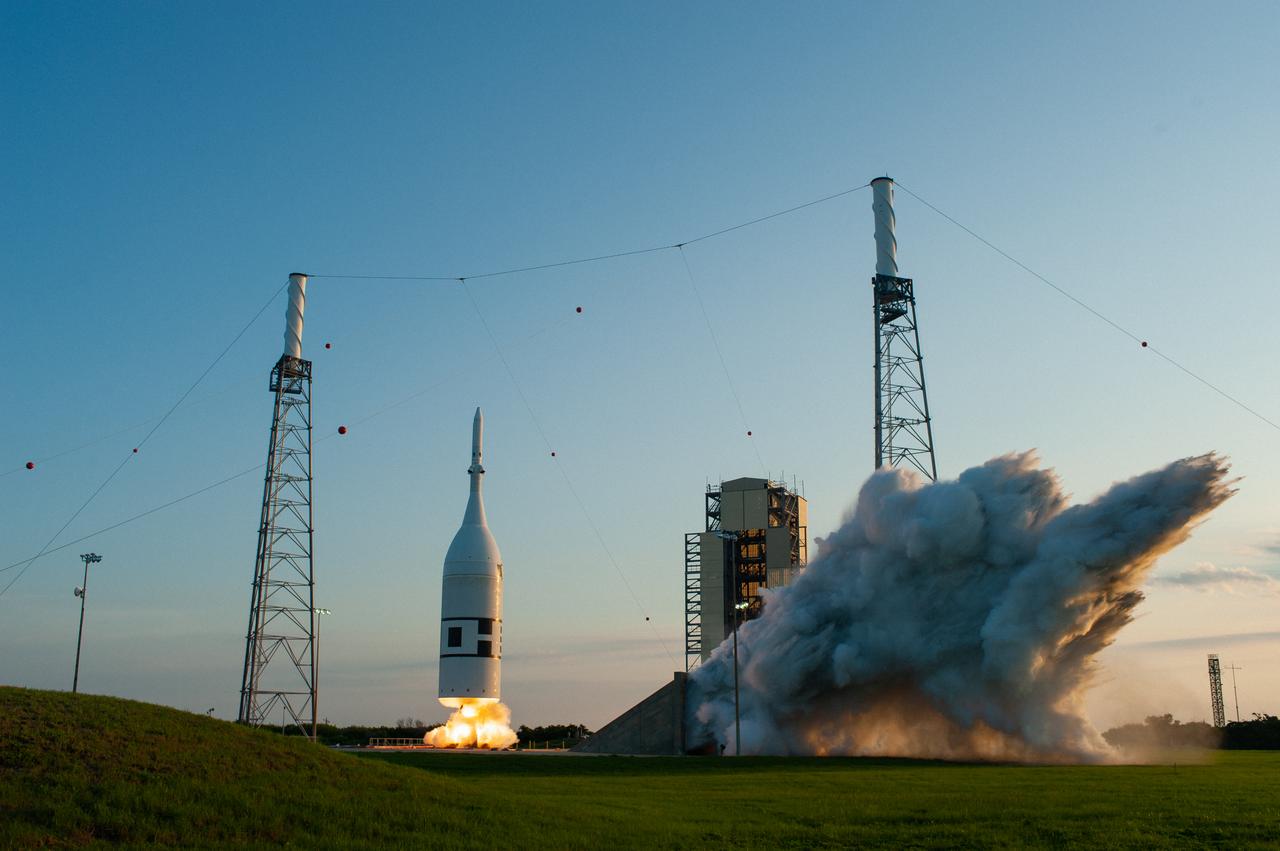

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
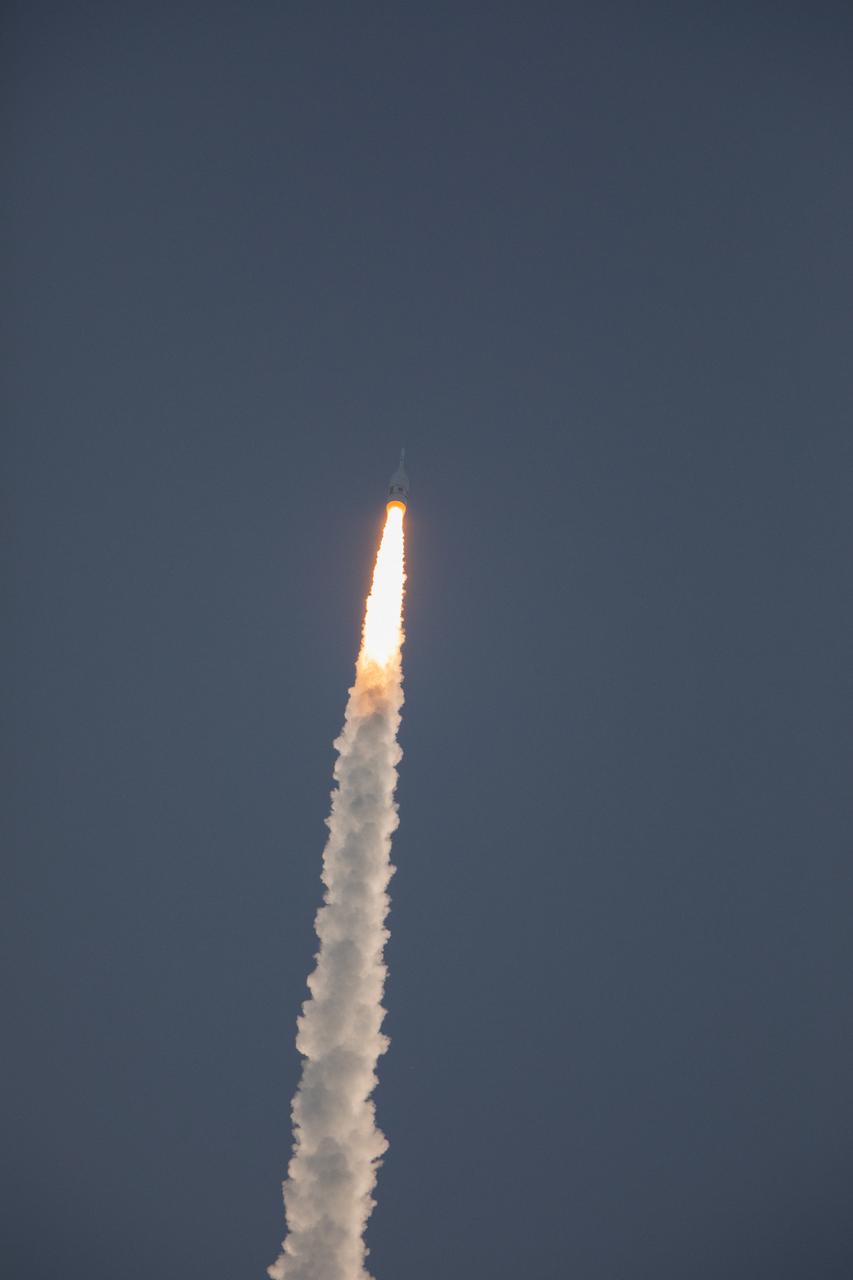

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, soars upward on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, after launching at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
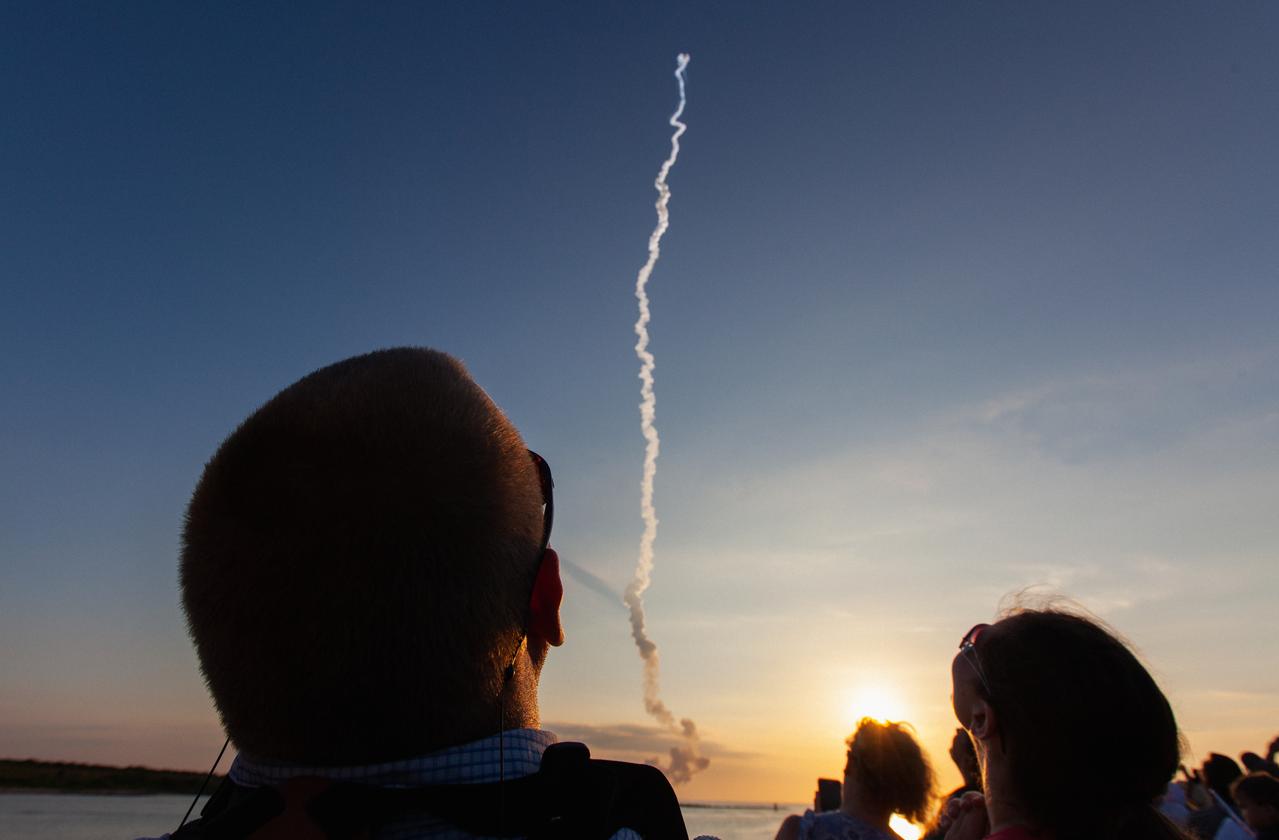

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
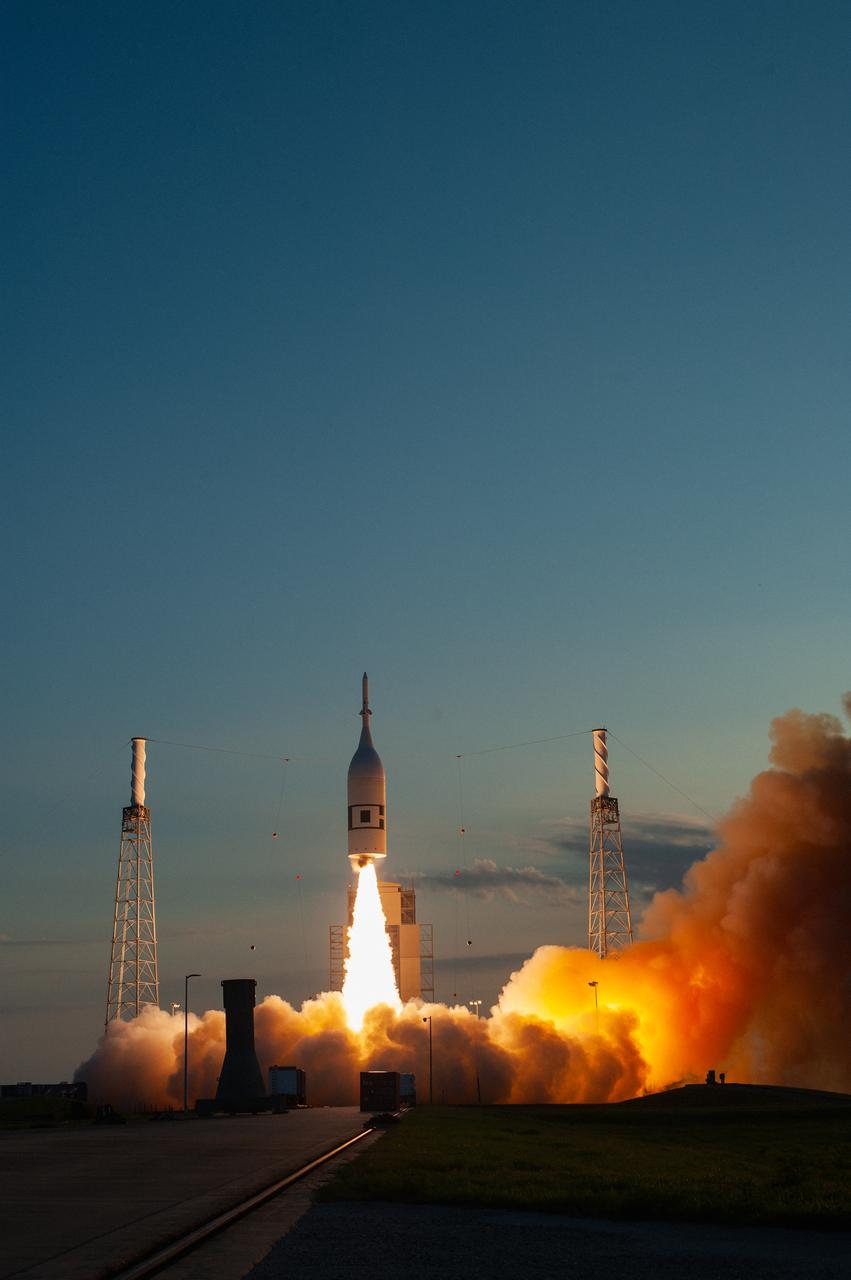

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
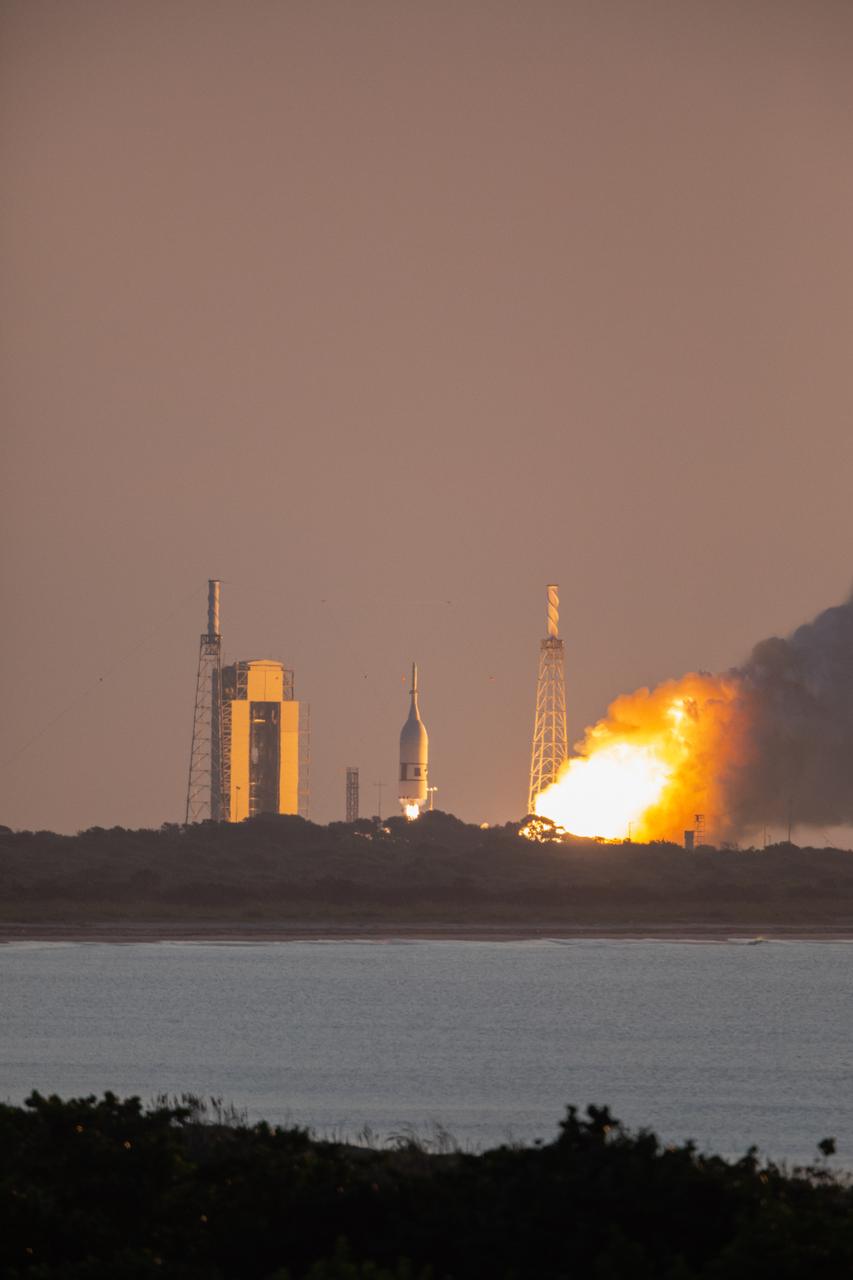

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
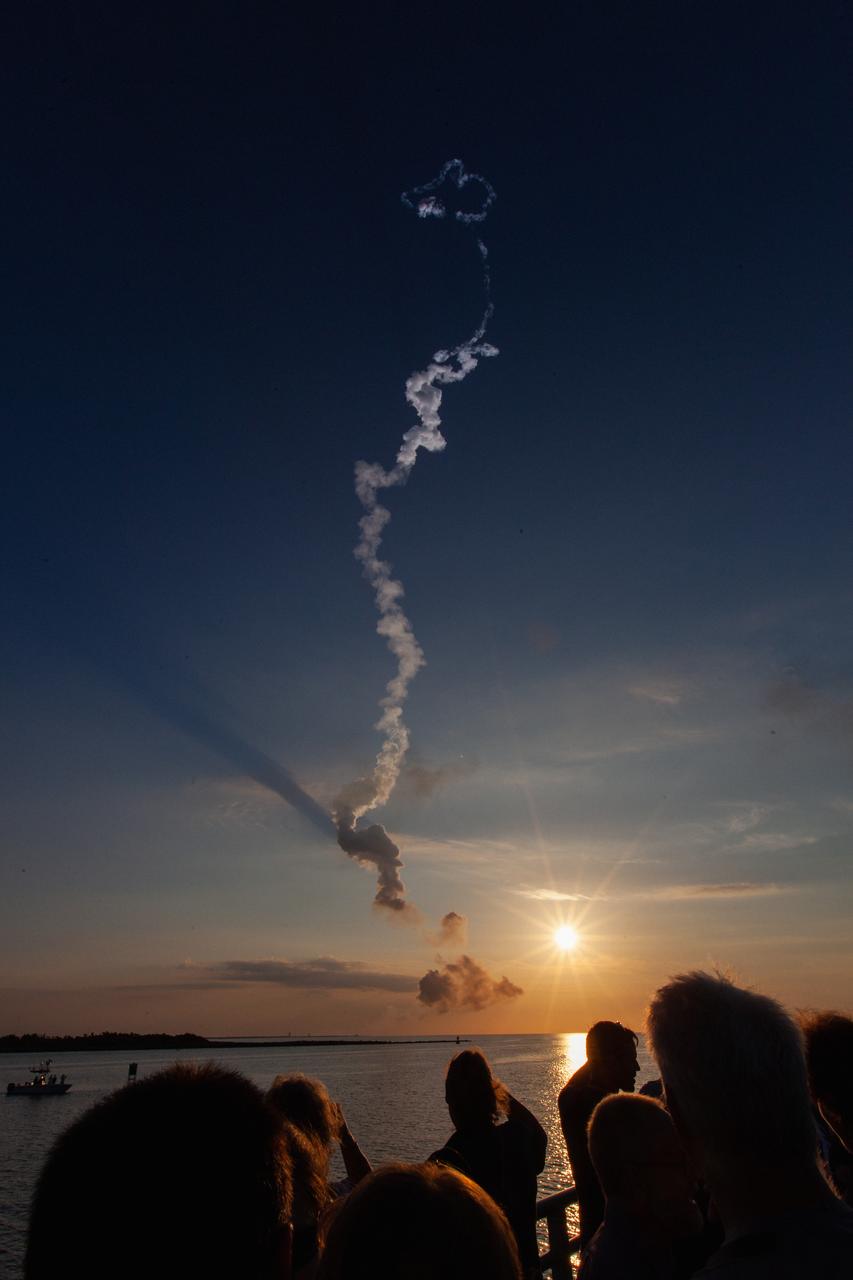

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
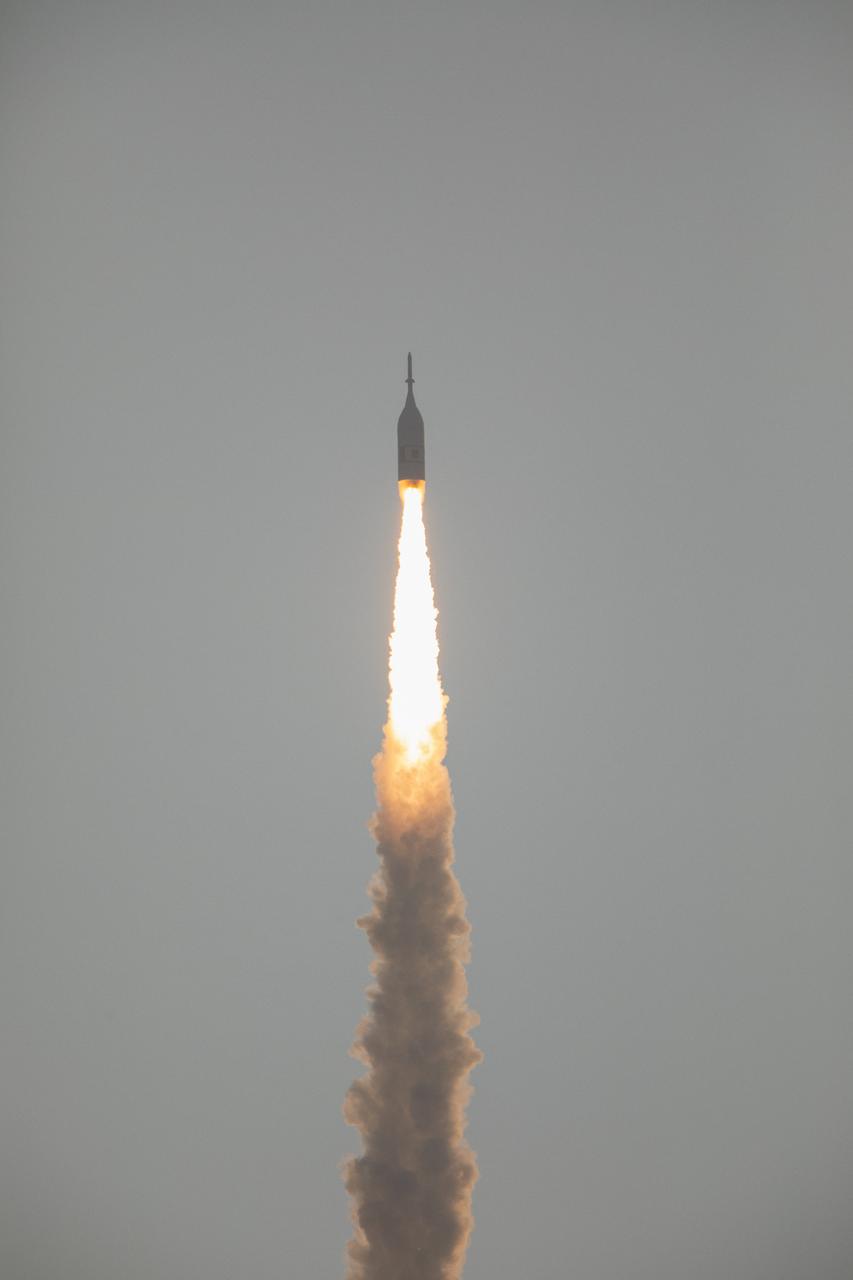

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
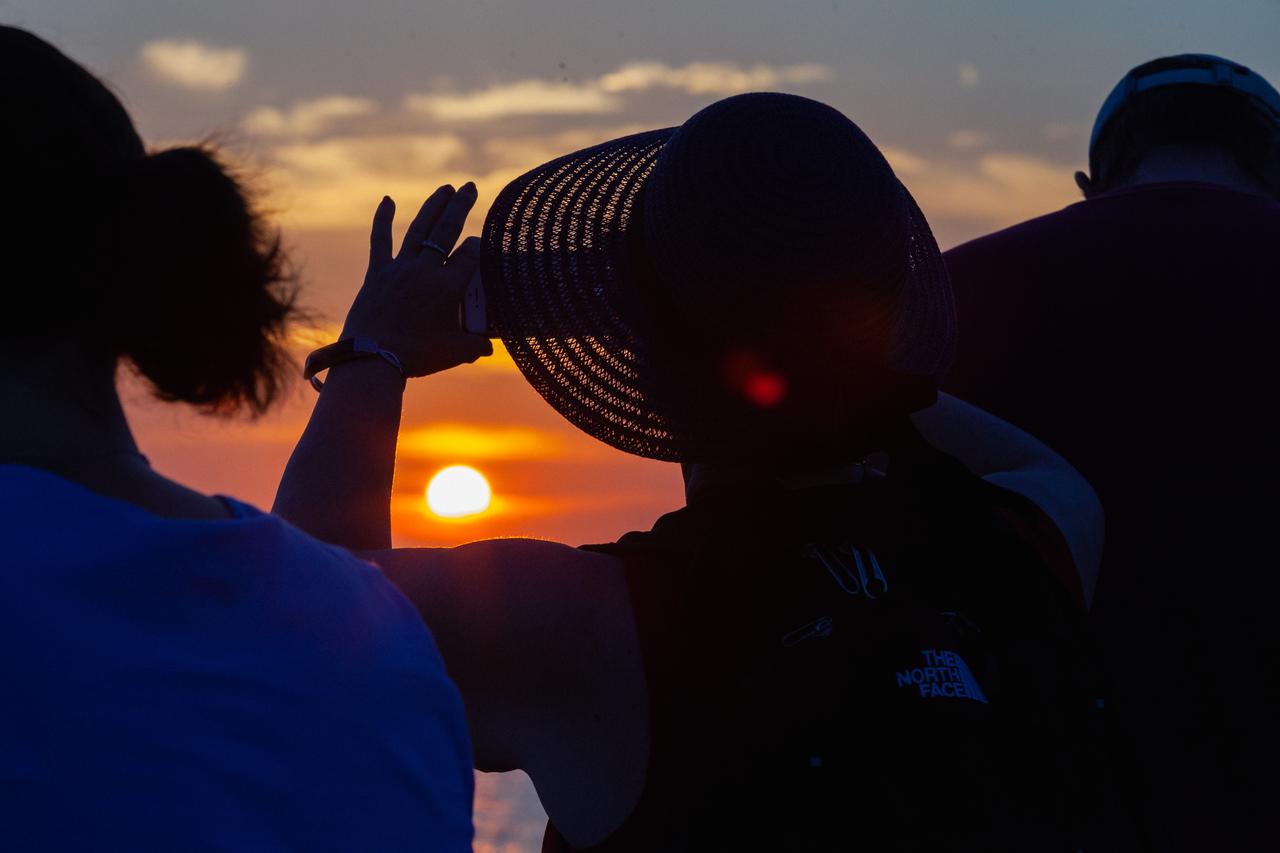

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
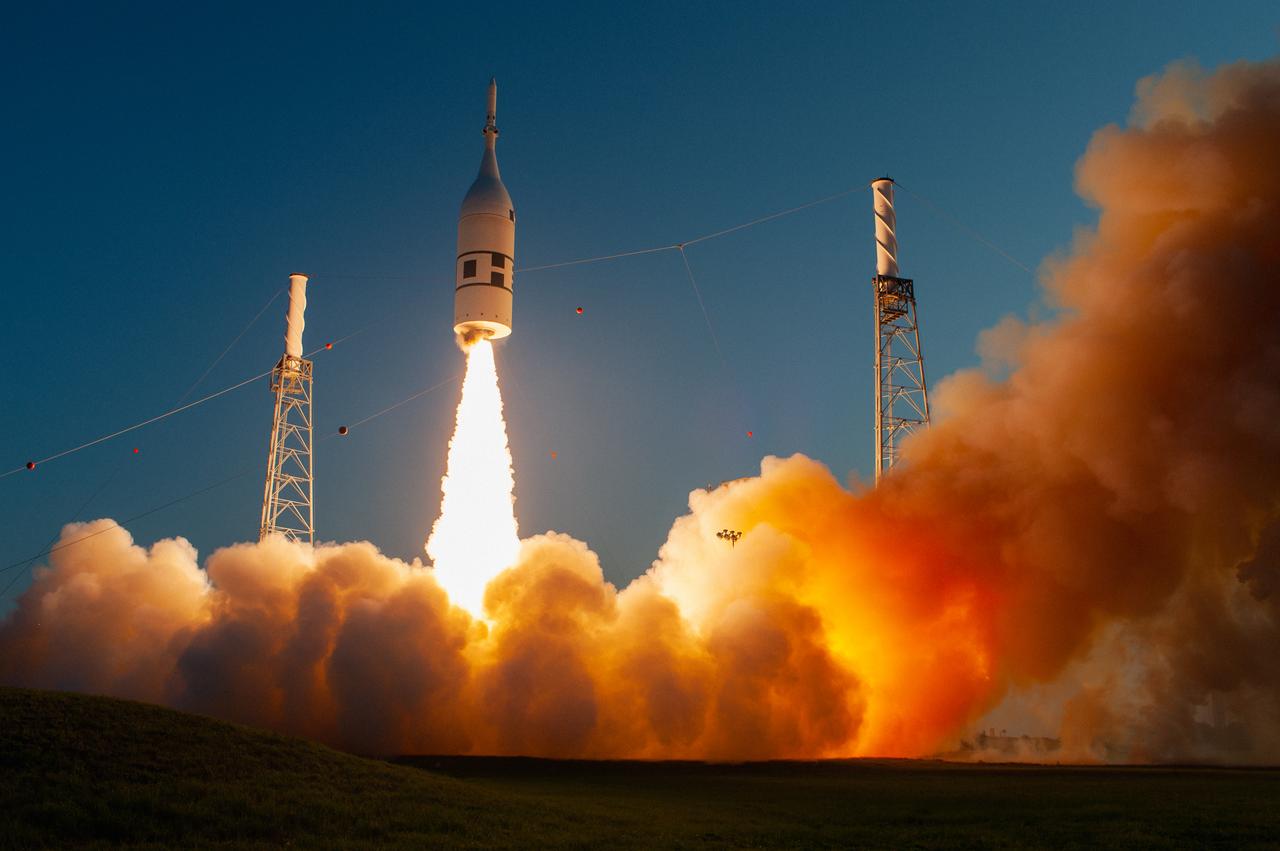

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, soars upward on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, after launching at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
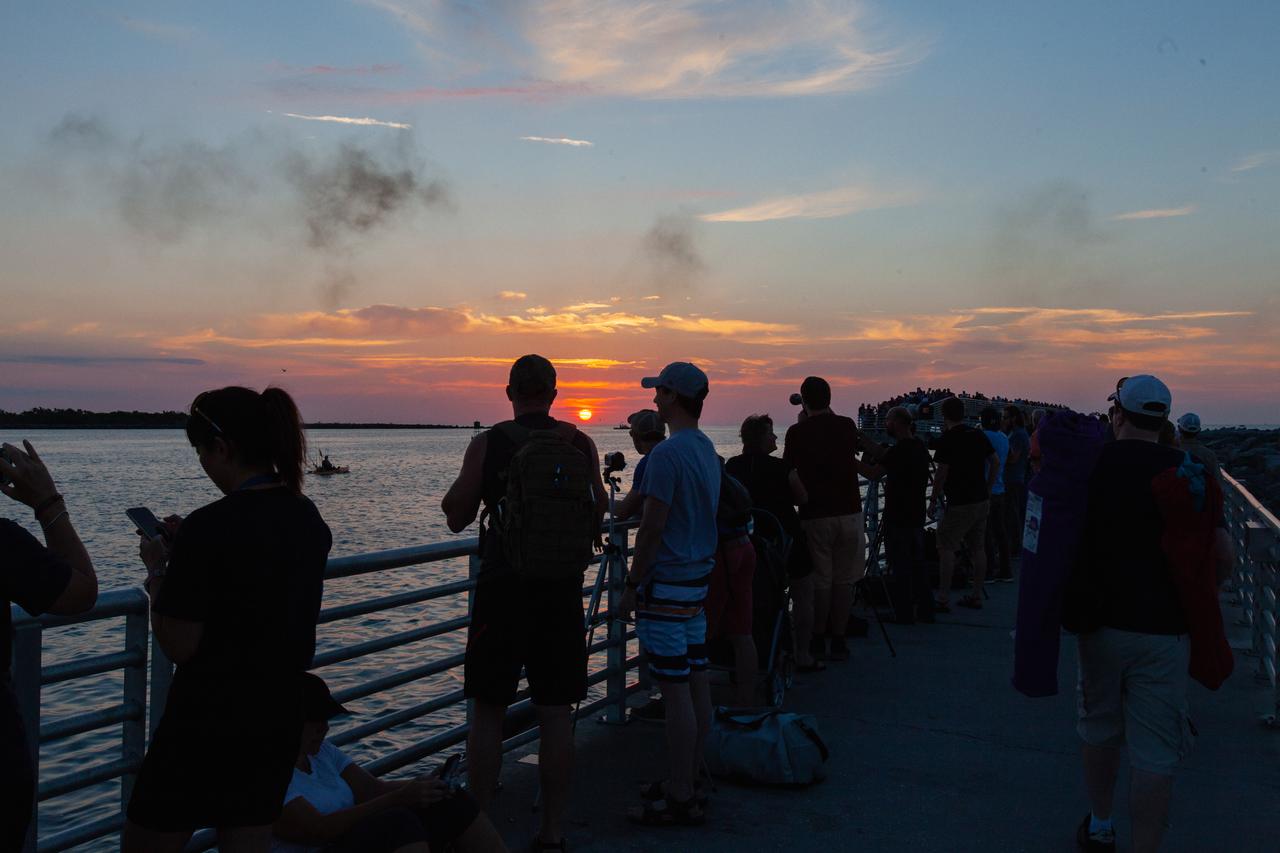

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, soars upward on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, after launching at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
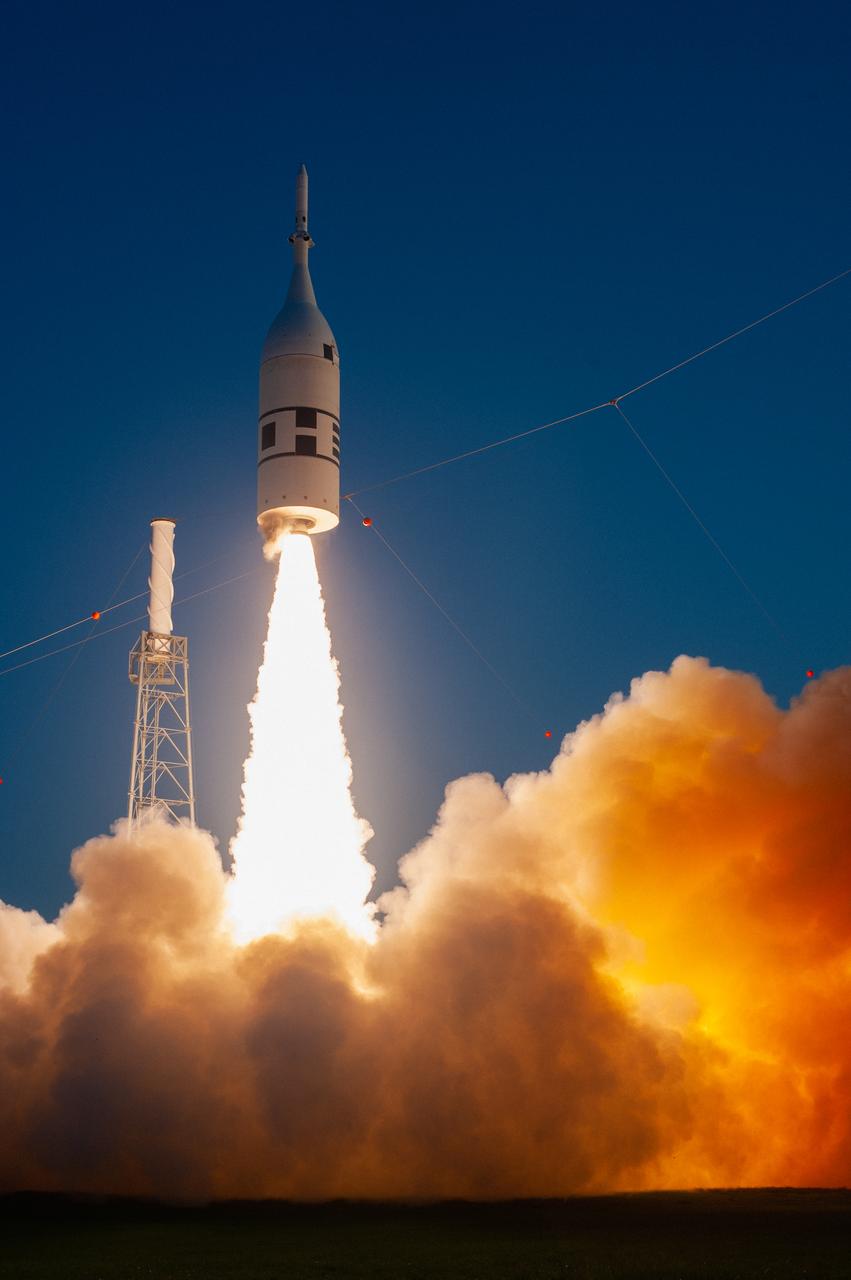

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
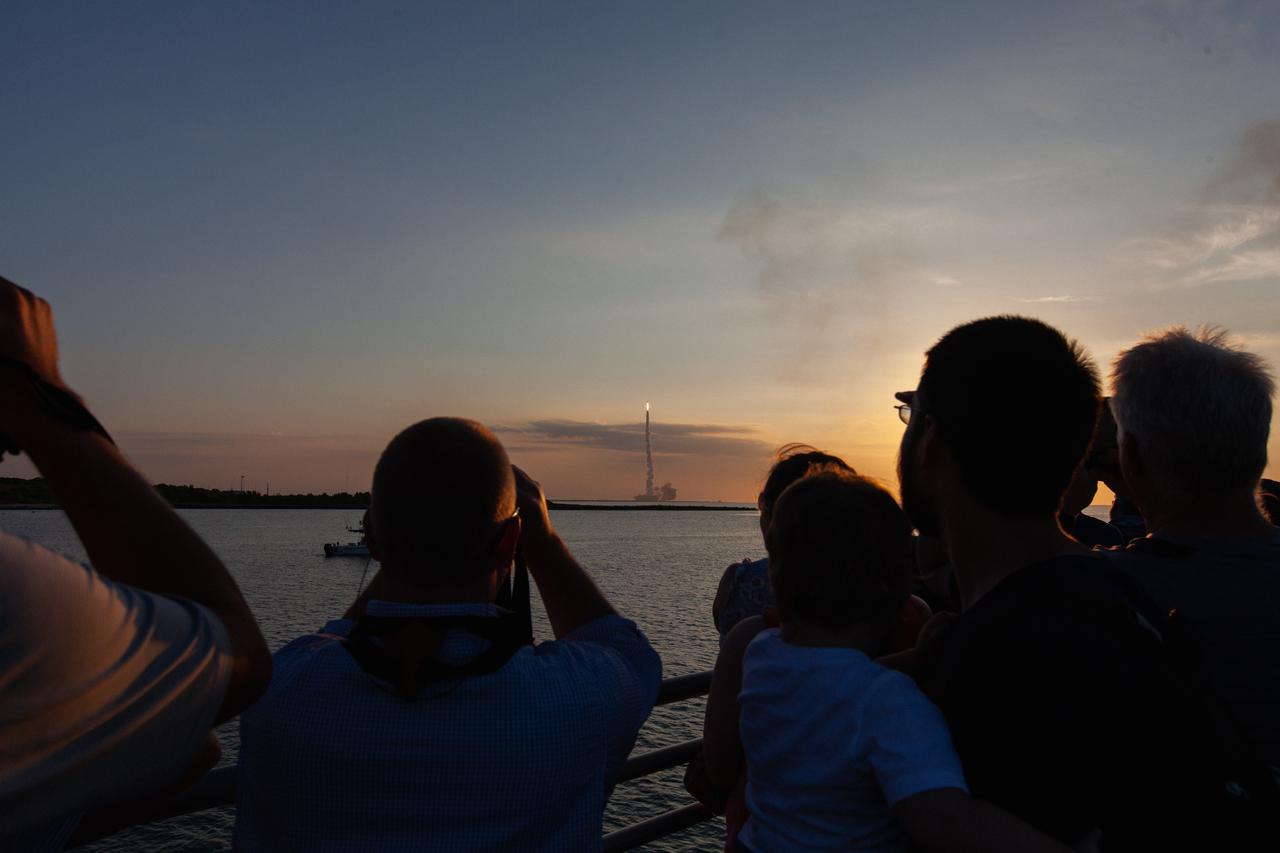

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
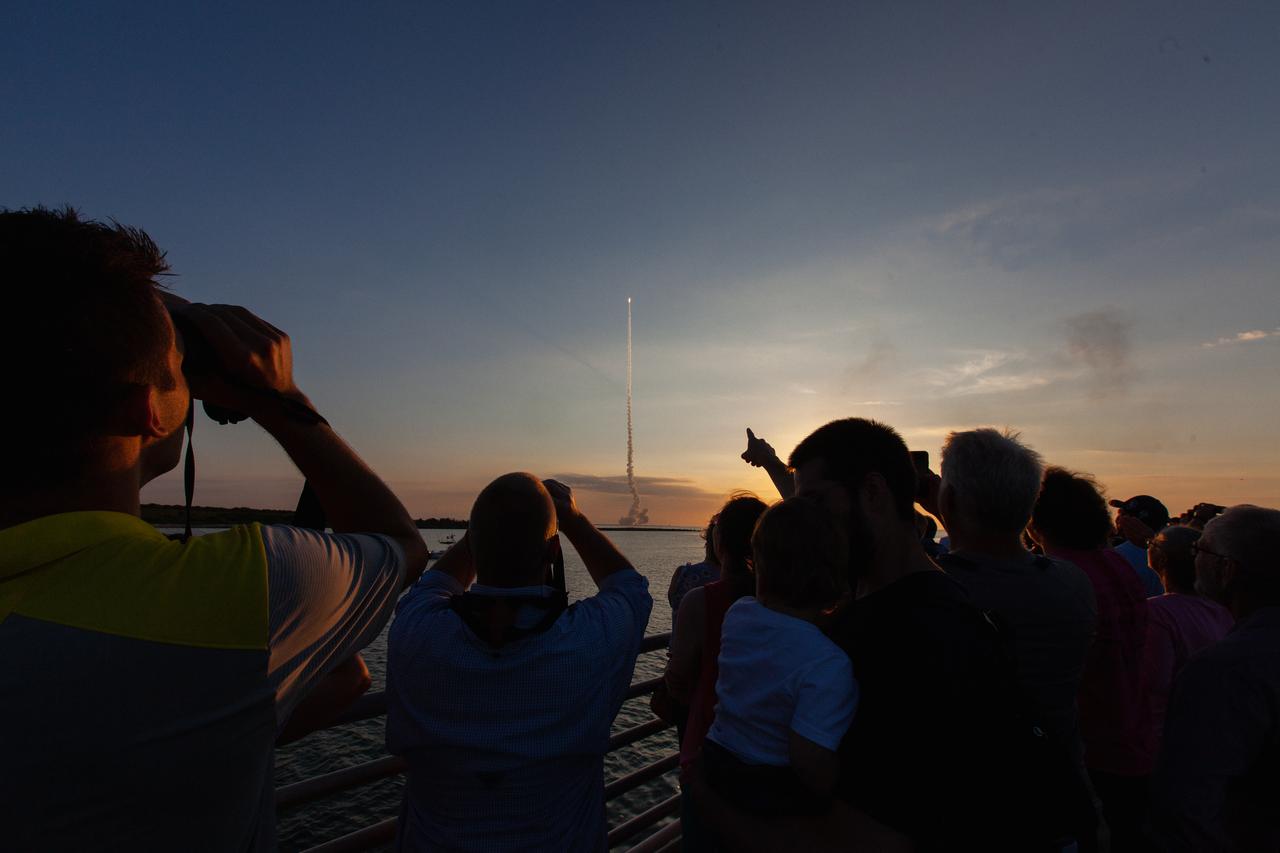

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
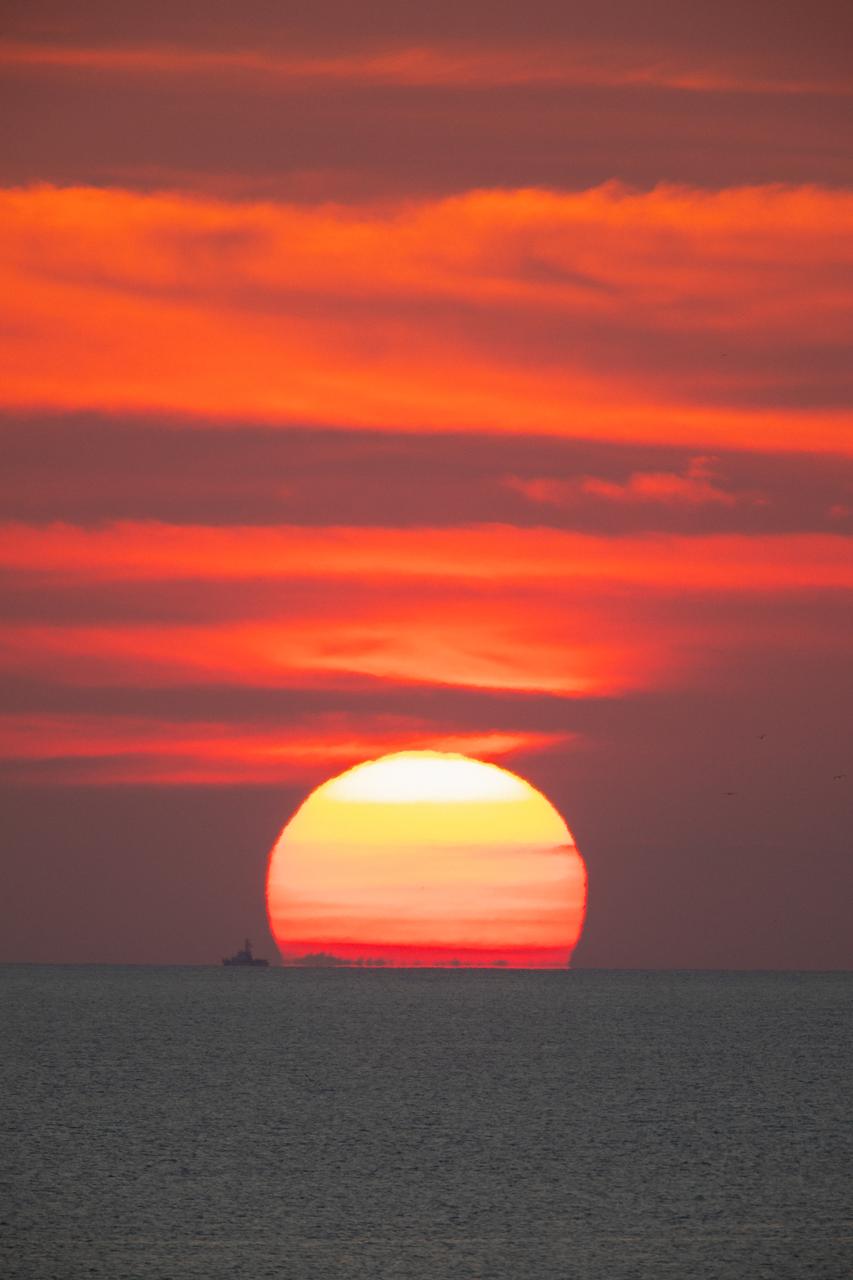

A brilliant sunrise fills the sky before a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
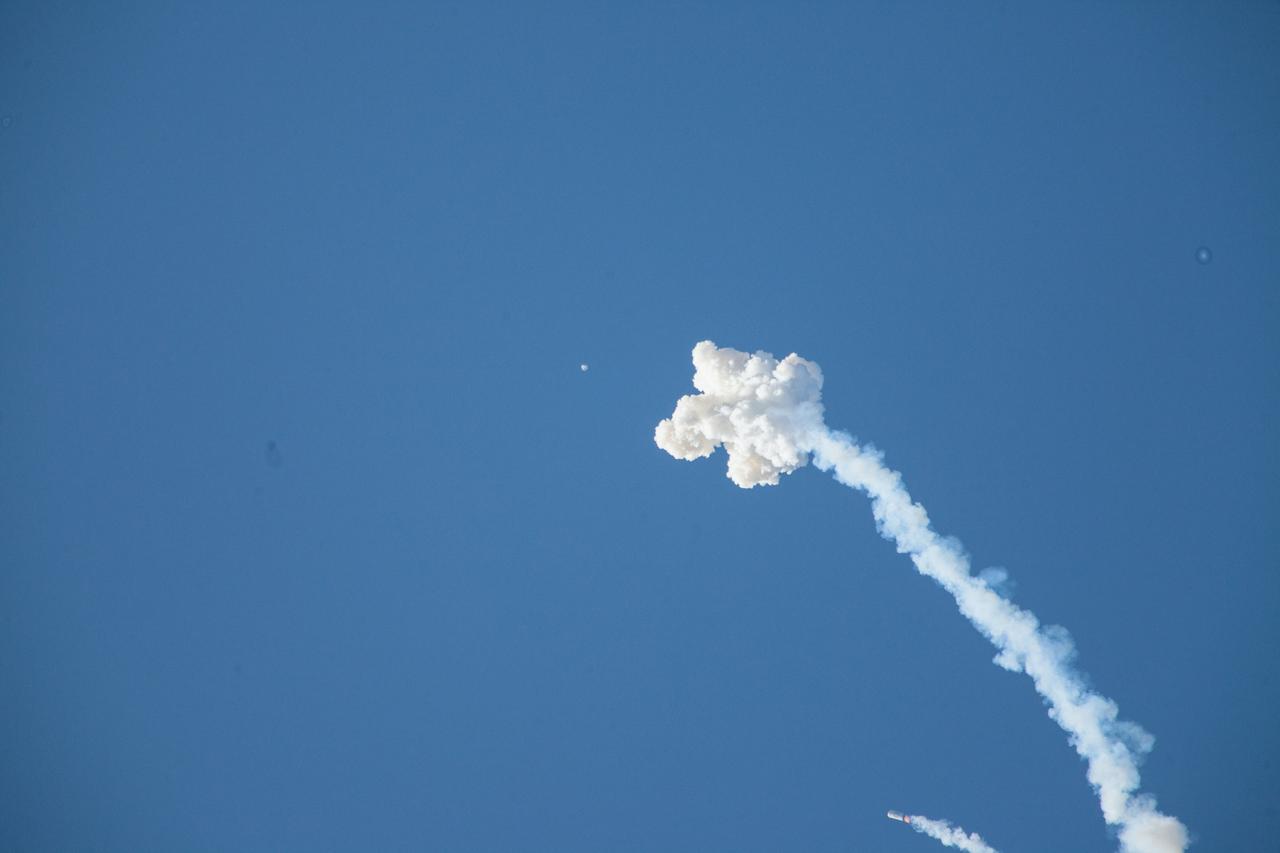

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, soars upward on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, after launching at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, soars upward on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, after launching at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
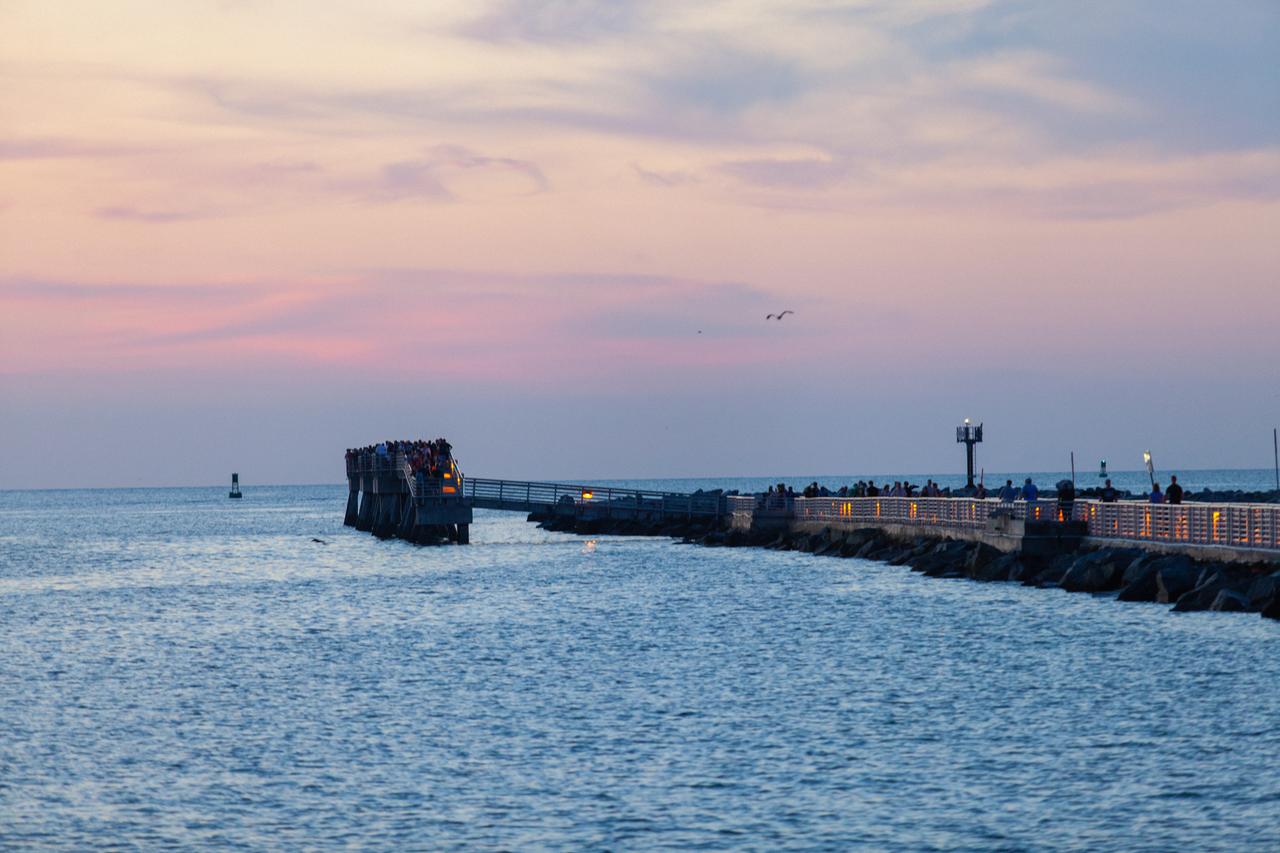

A view of Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as crowds gather to watch a Northrop Grumman provided booster launch from Launch Pad 46 carrying a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
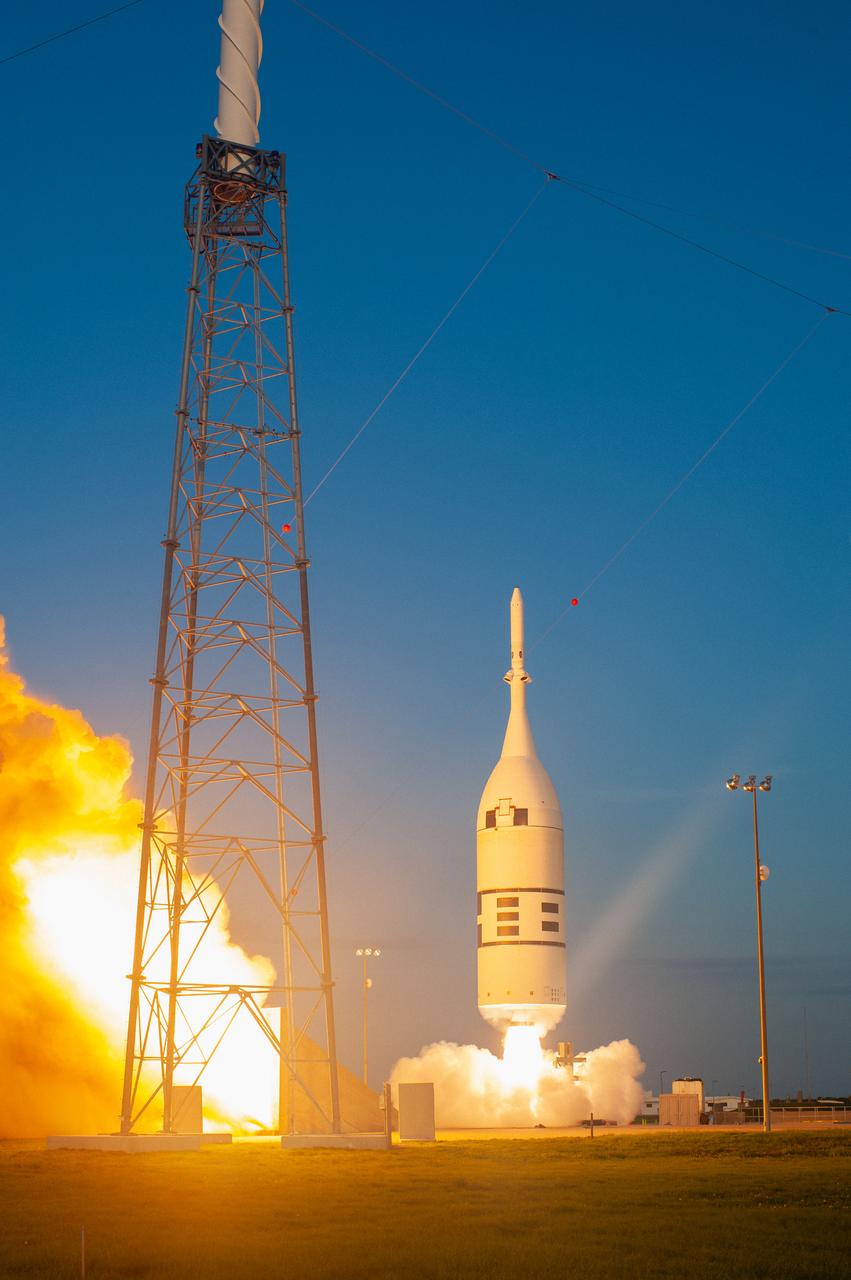

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
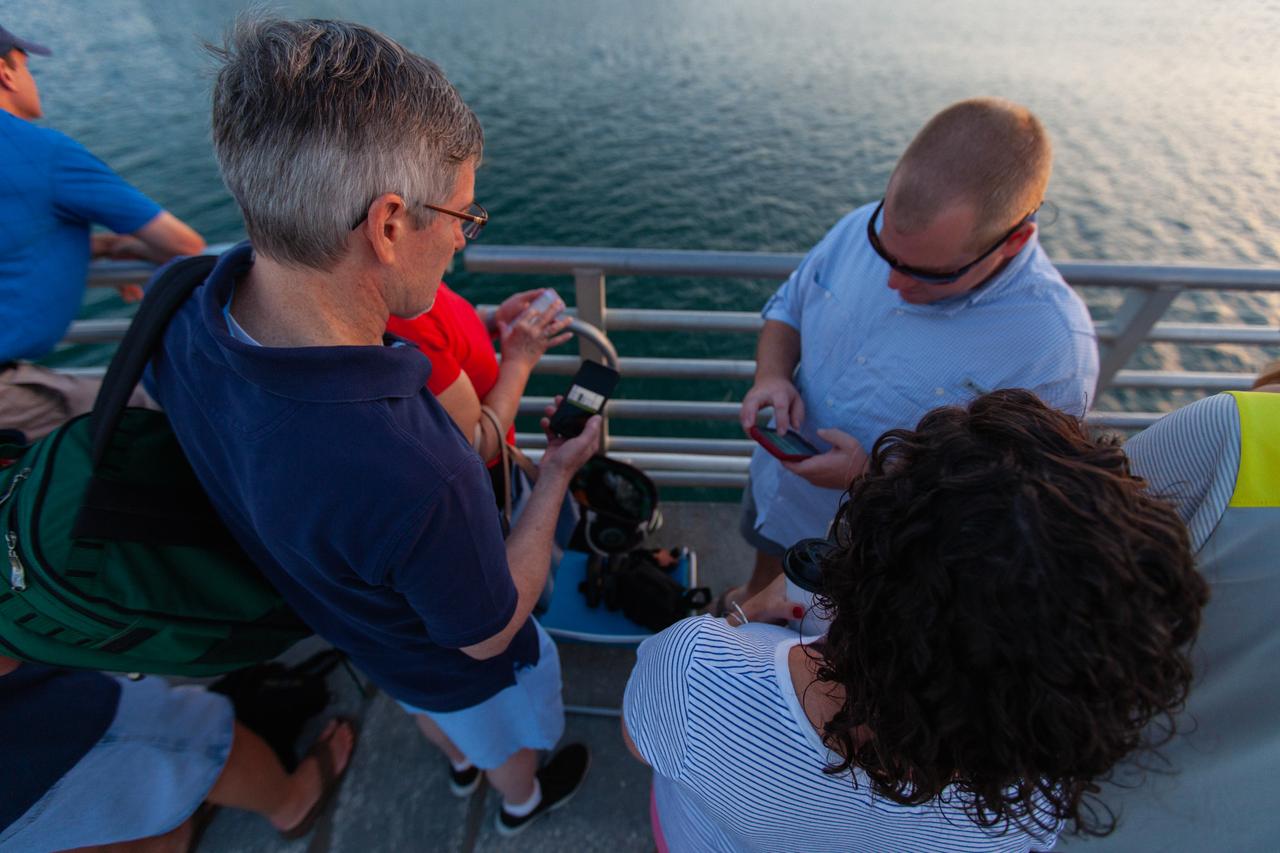

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
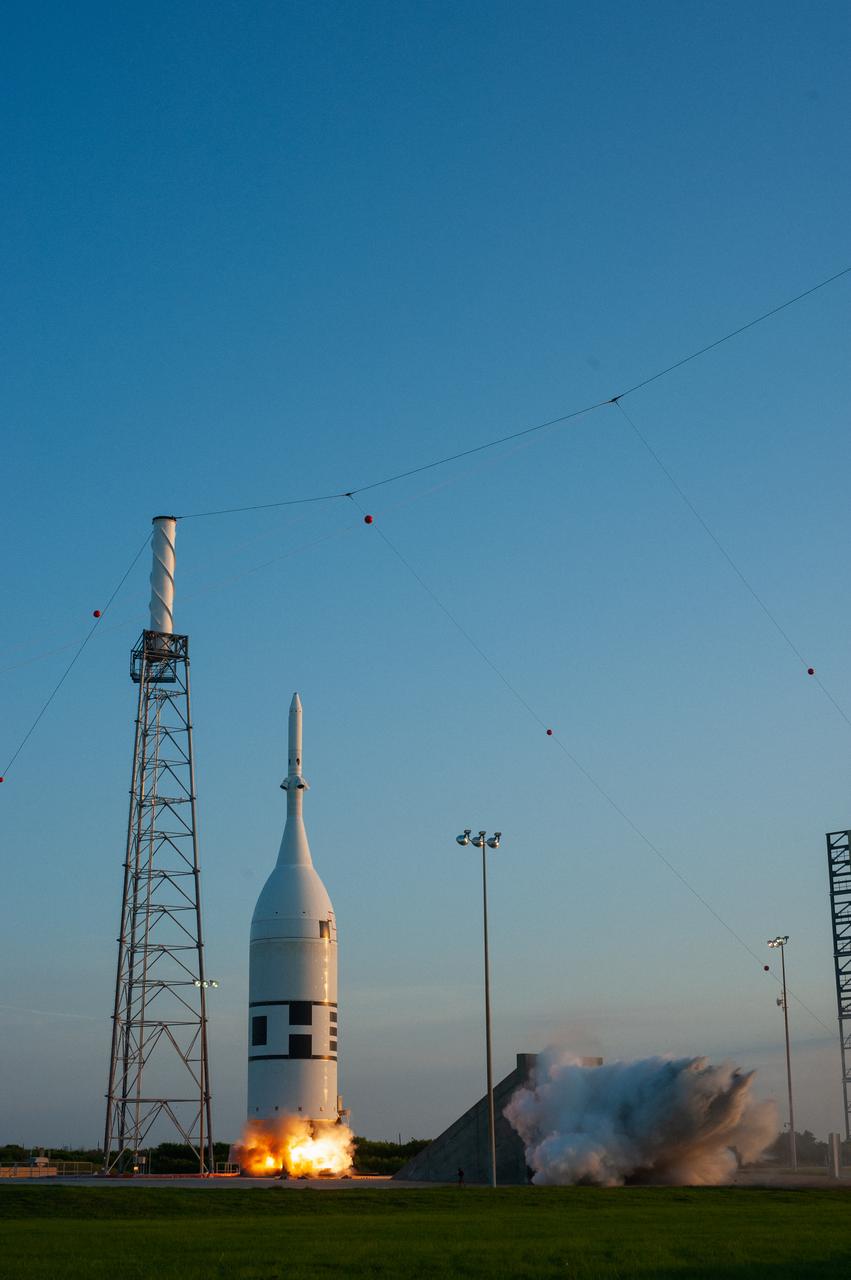

A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launches on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster on July 2, 2019, at 7 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
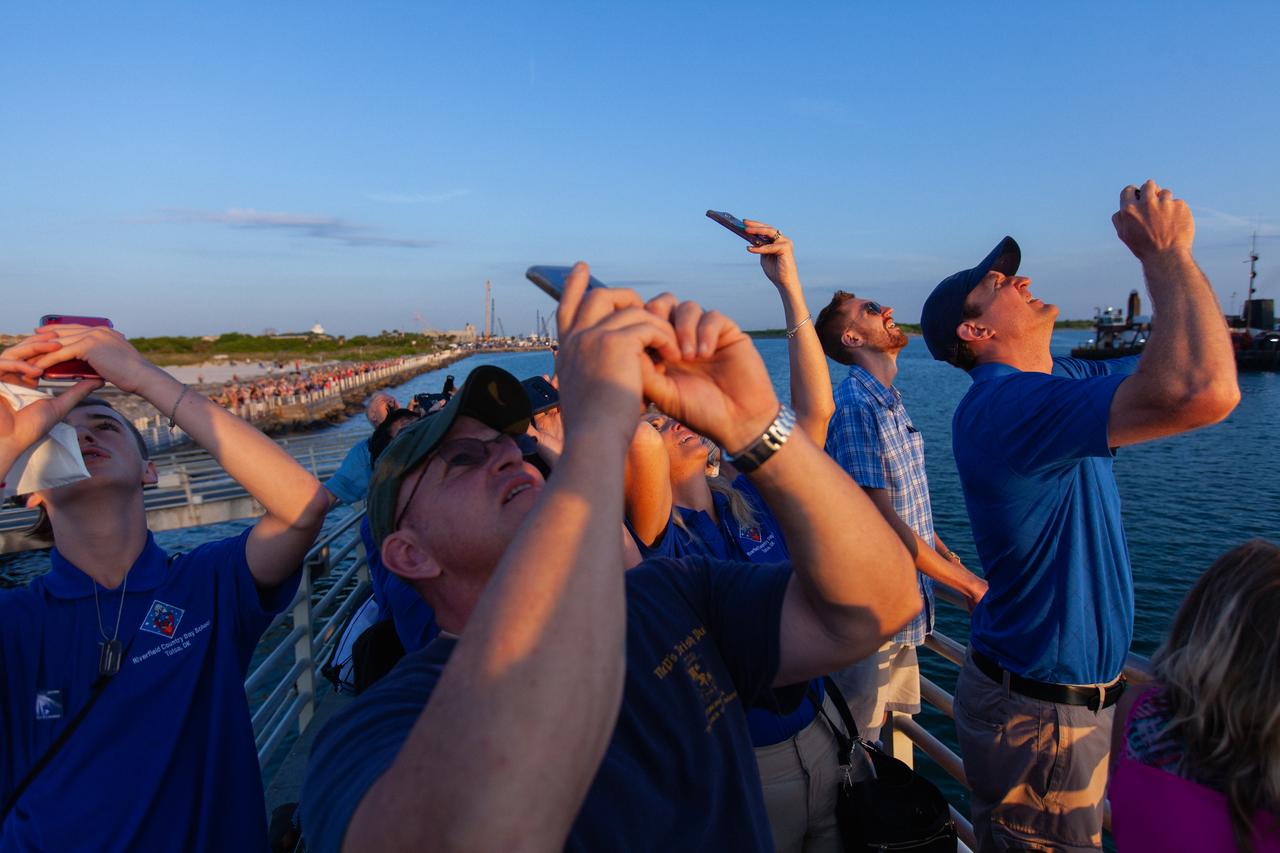

Crowds of spectators watch from Jetty Park in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 2, 2019, as a Northrop Grumman provided booster launches from Launch Pad 46 carrying, a fully functional Launch Abort System with a test version of Orion attached for NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2). Launch time was 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
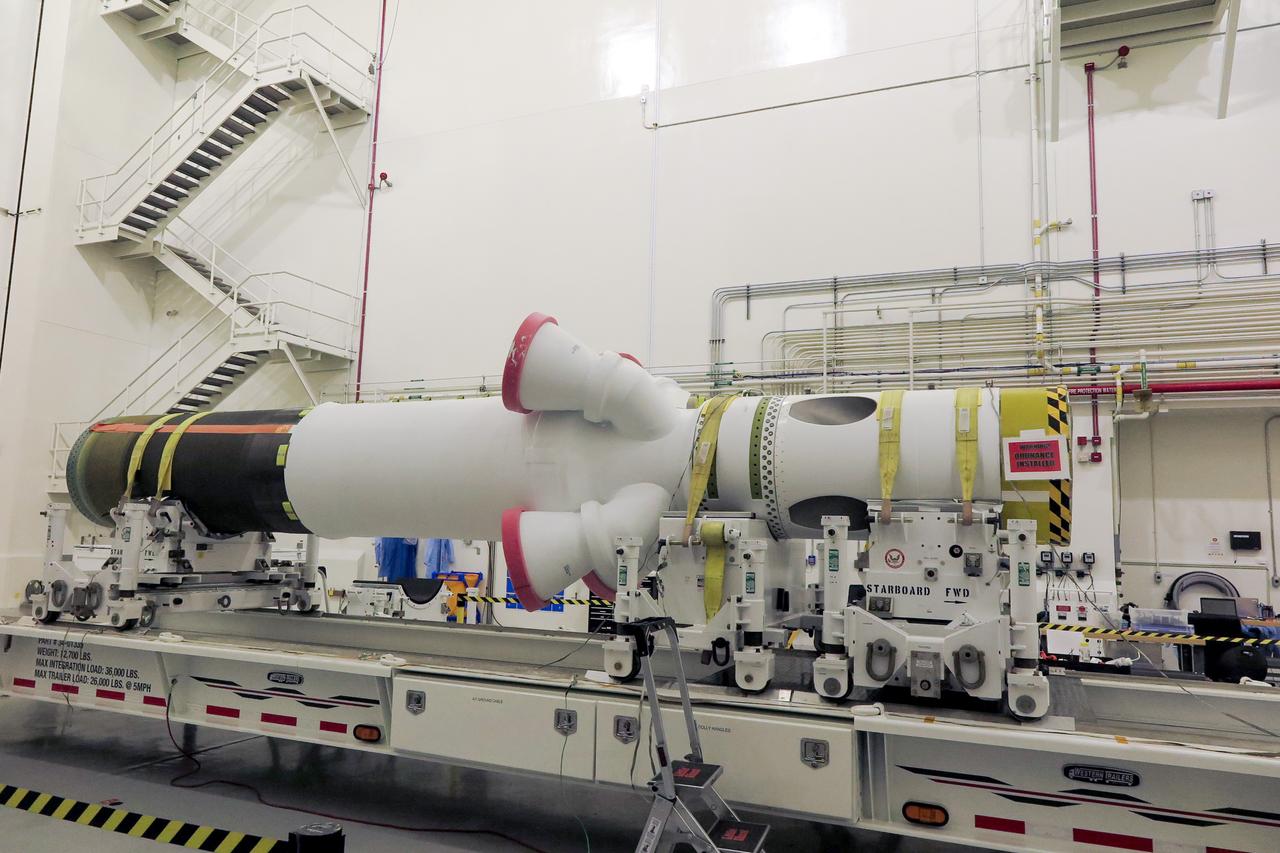

The launch abort motor is integrated with the jettison motor for Orion’s launch abort system (LAS) for Artemis II, inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 15, 2020. The launch abort and jettison motors are two of three motors on the LAS. The LAS will be positioned atop the Orion crew module and is designed to protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. Artemis II will take the first humans in orbit around the Moon in the 21st century.
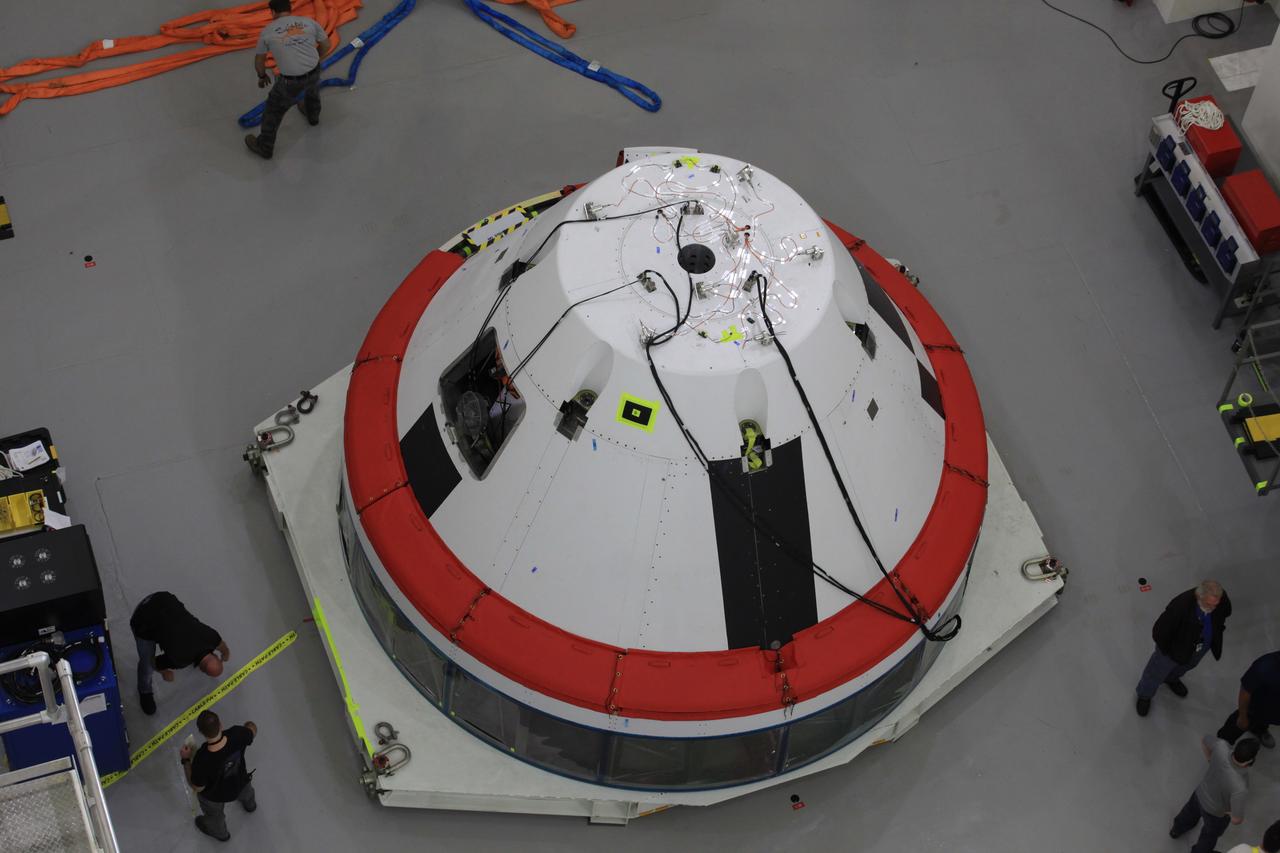

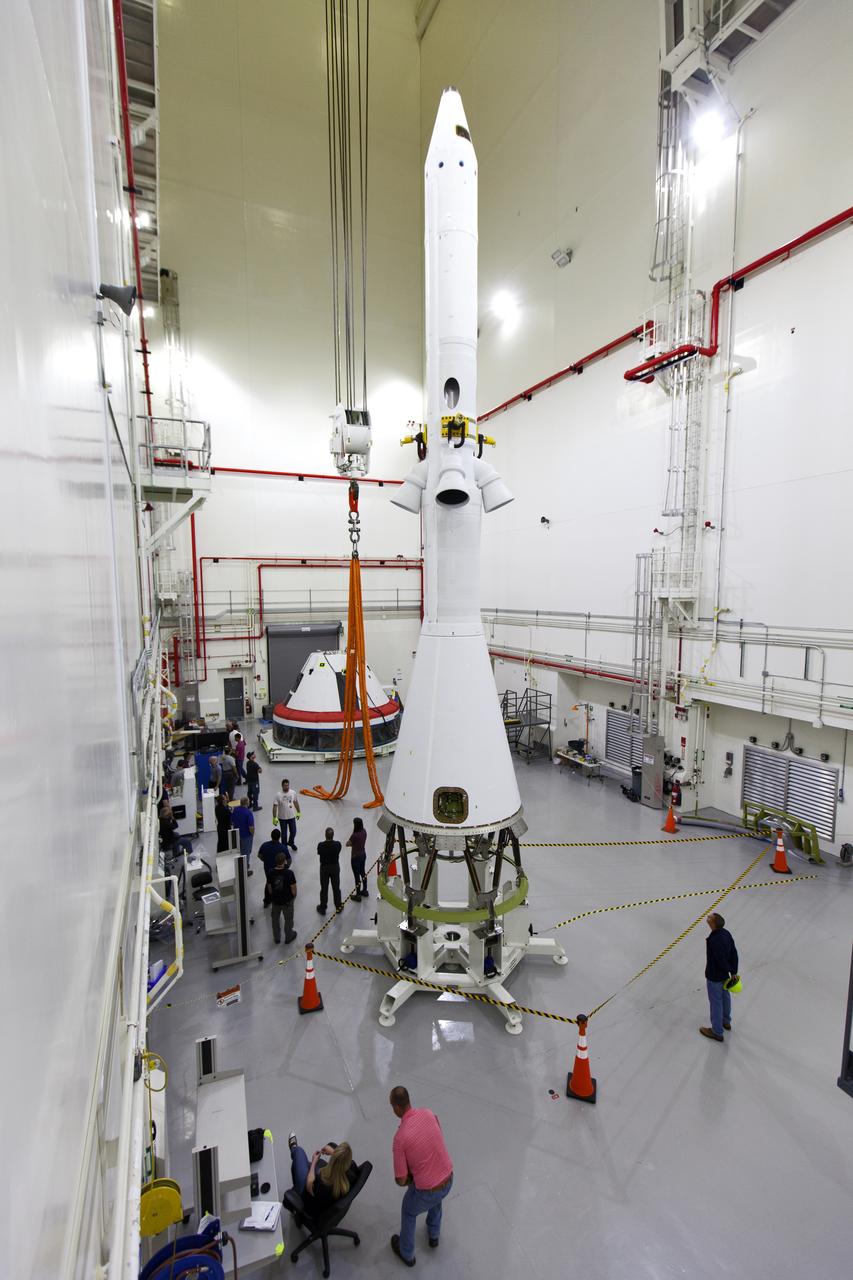
The Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is vertical and integrated with the crew module test article at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 13, 2019.
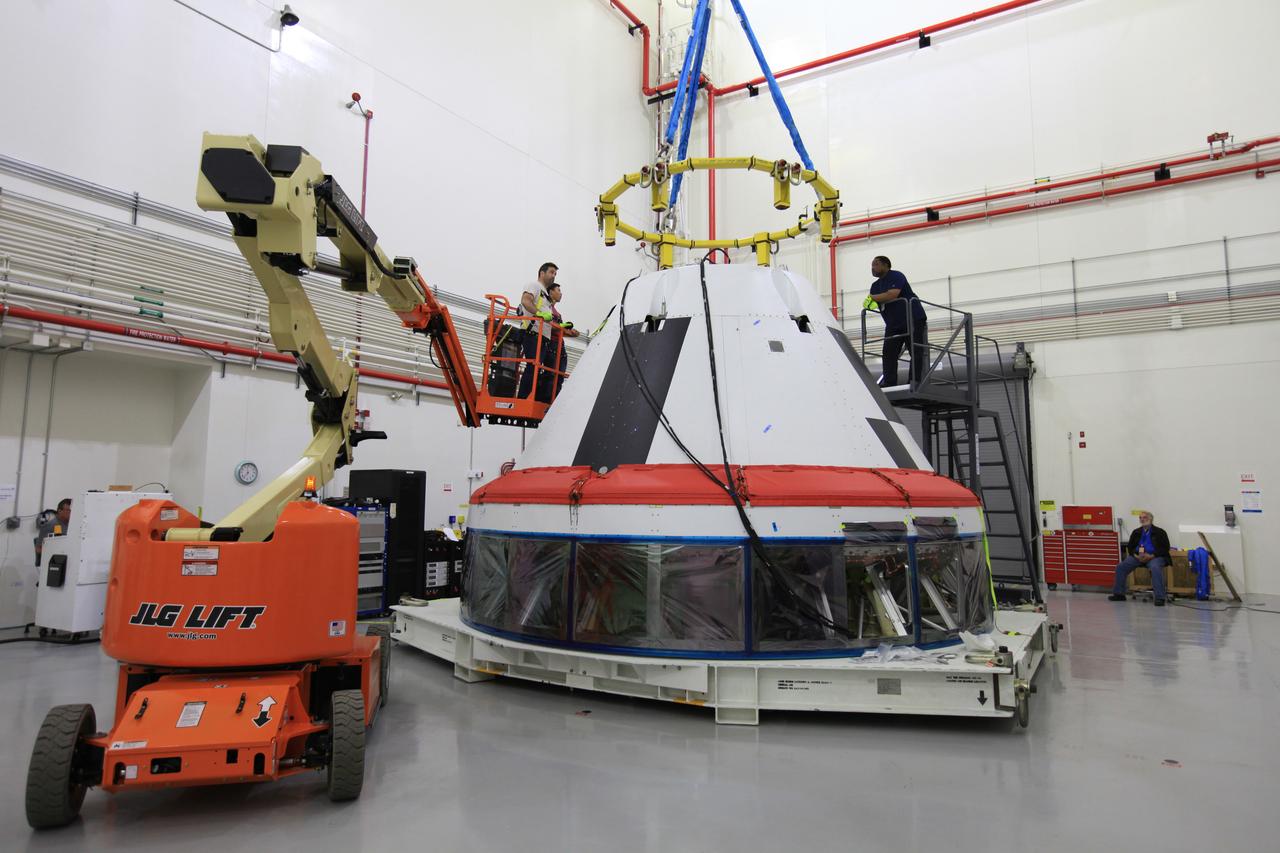

The Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is vertical and integrated with the crew module test article at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 13, 2019.
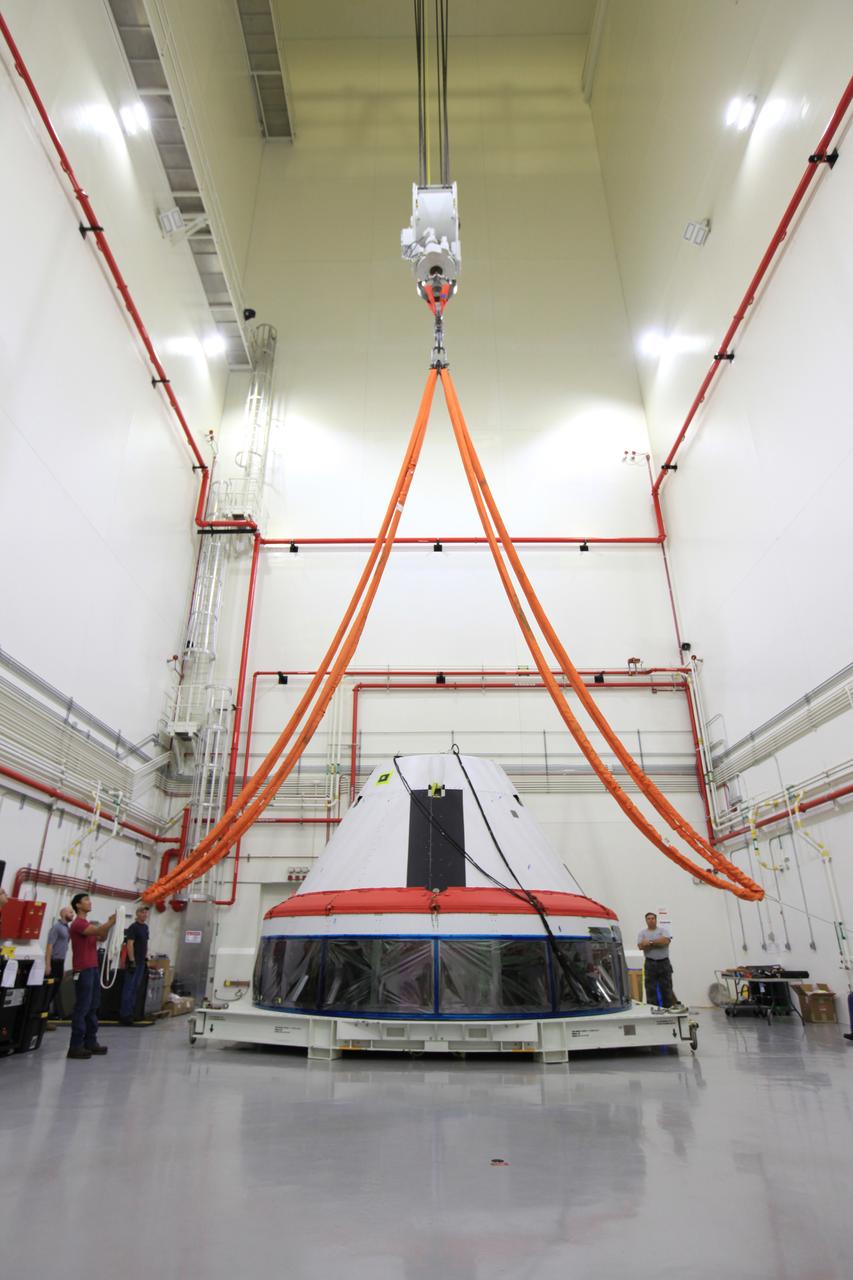

The Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is vertical and integrated with the crew module test article at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 13, 2019.
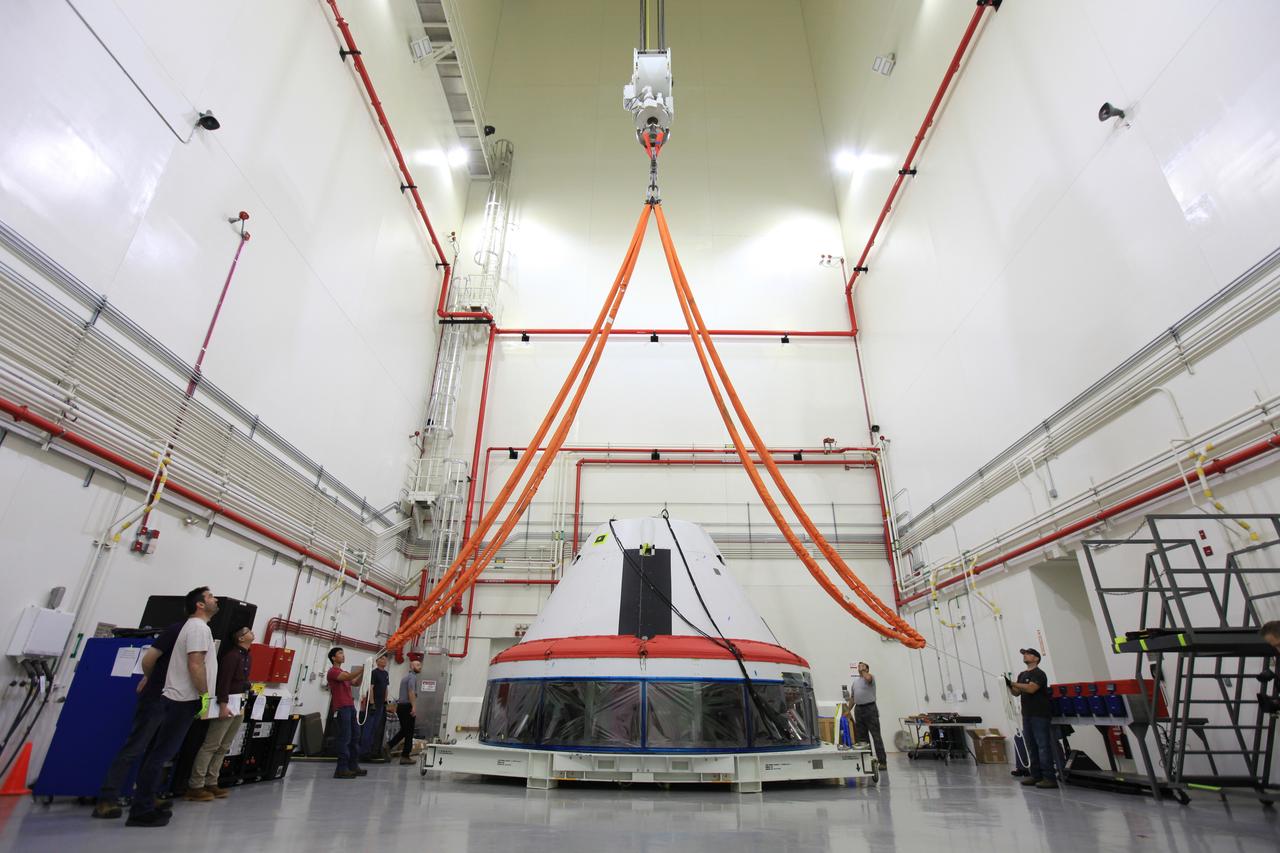

The Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is vertical and integrated with the crew module test article at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 13, 2019.
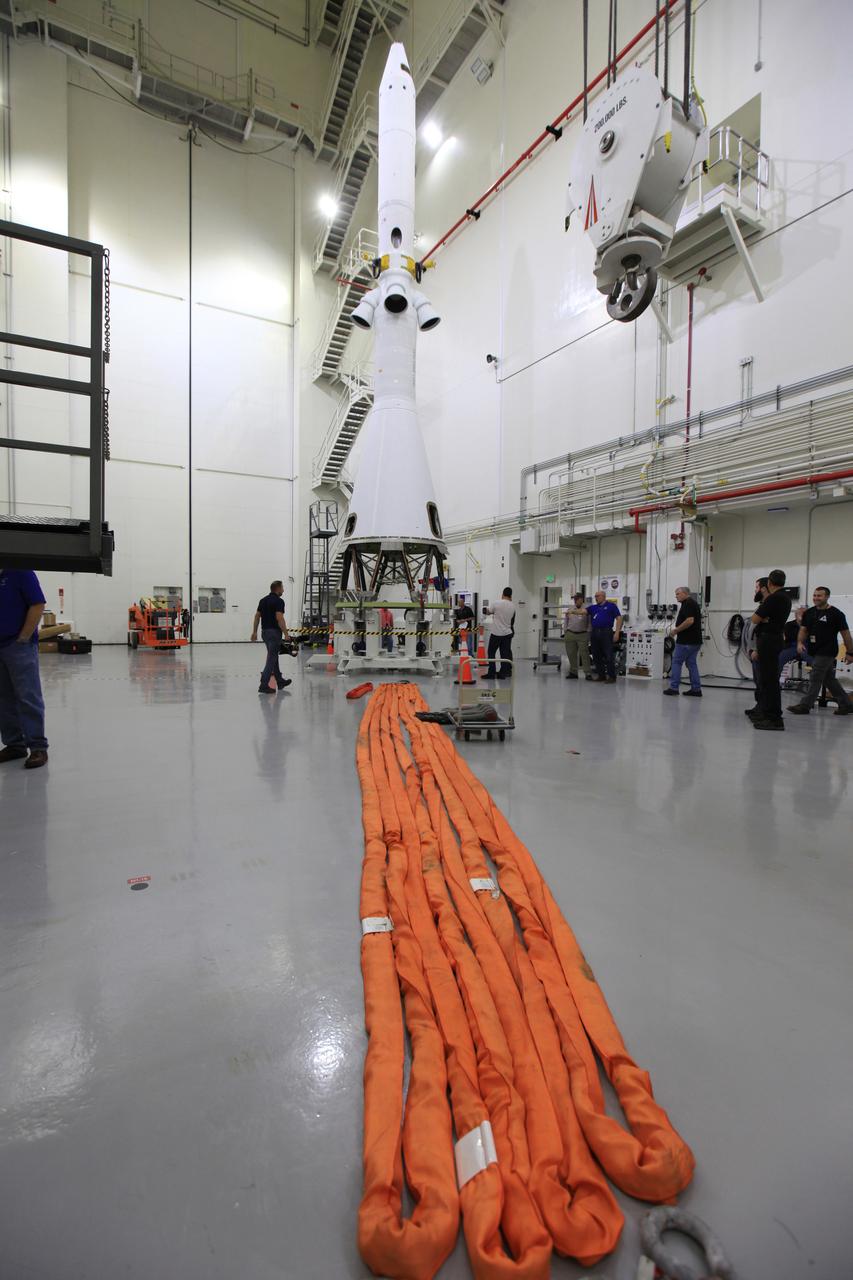

The Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is vertical and integrated with the crew module test article at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 13, 2019.
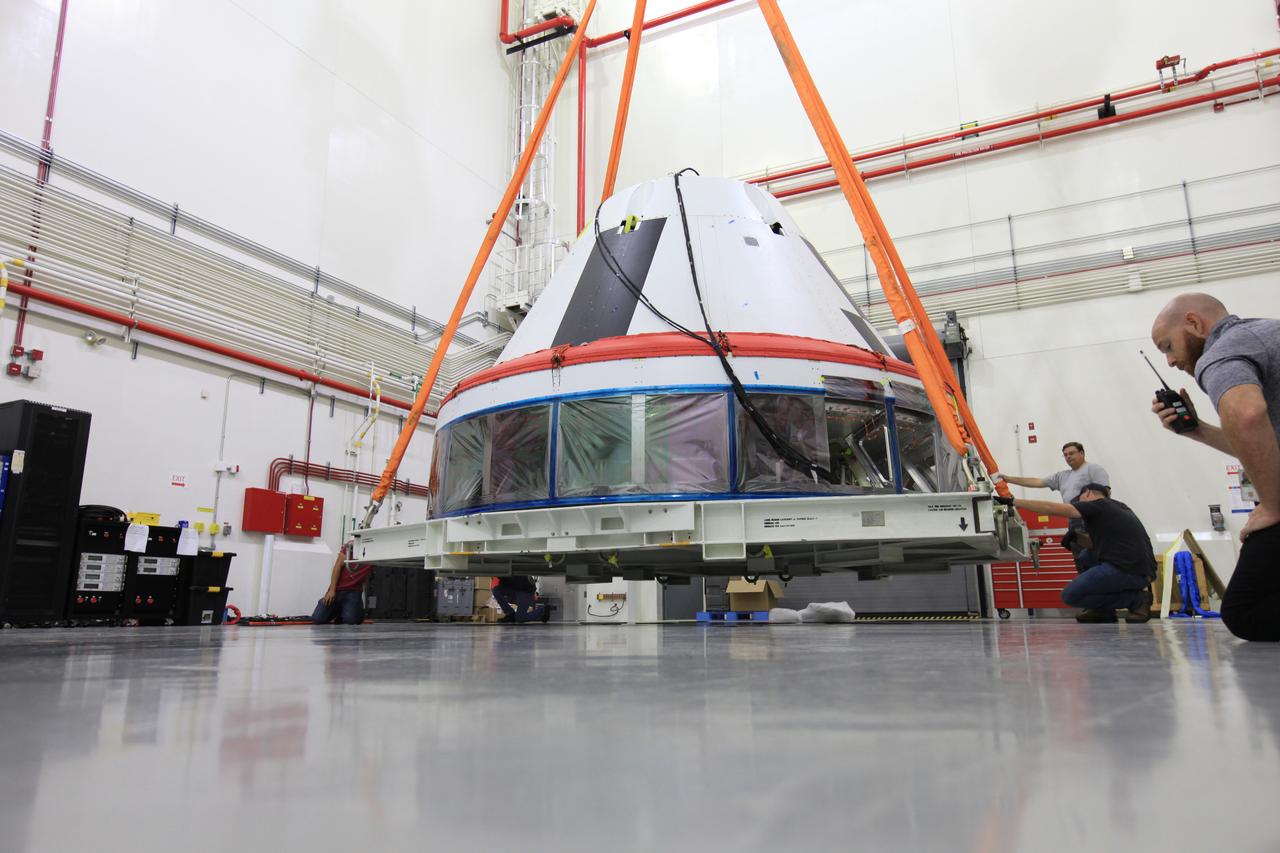

The Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is vertical and integrated with the crew module test article at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 13, 2019.

The Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is vertical and integrated with the crew module test article at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 13, 2019.
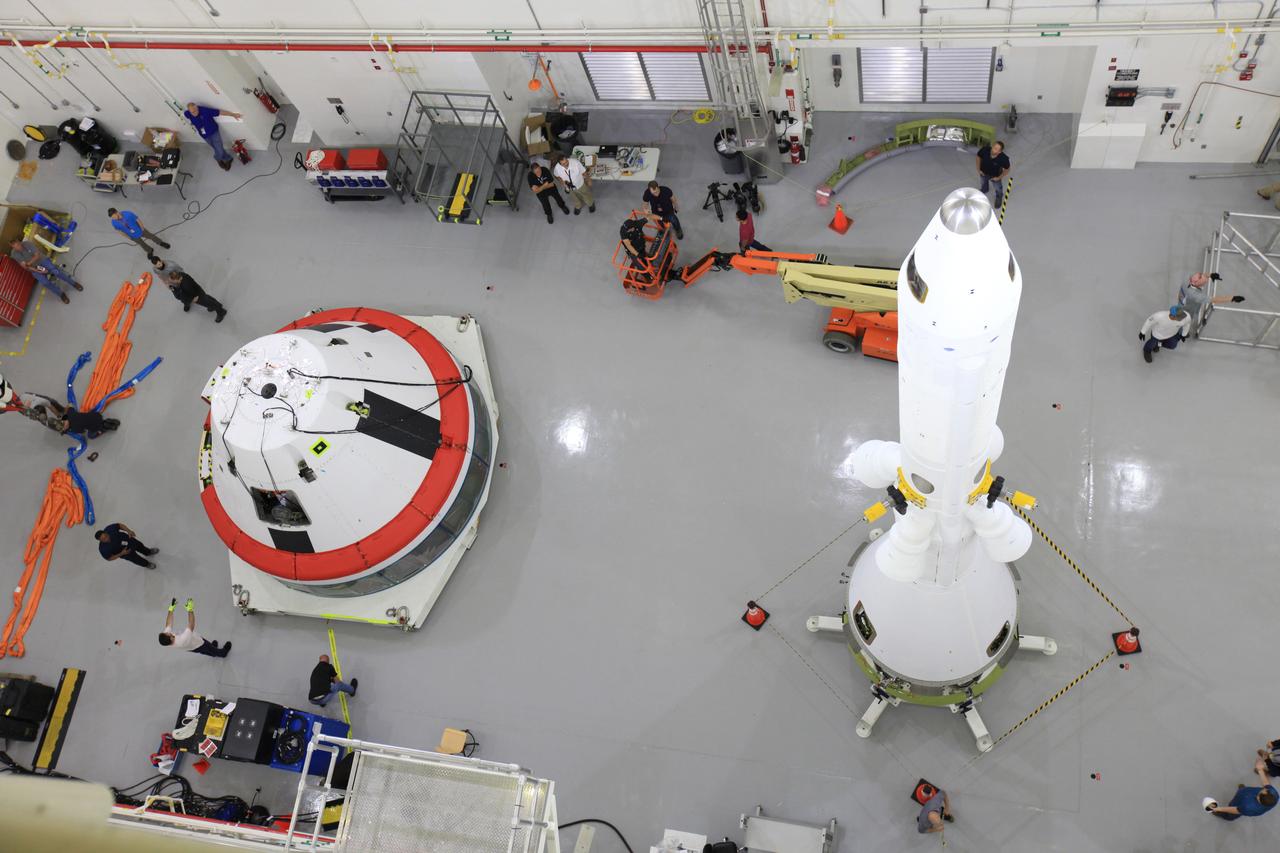

The Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is vertical and integrated with the crew module test article at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 13, 2019.
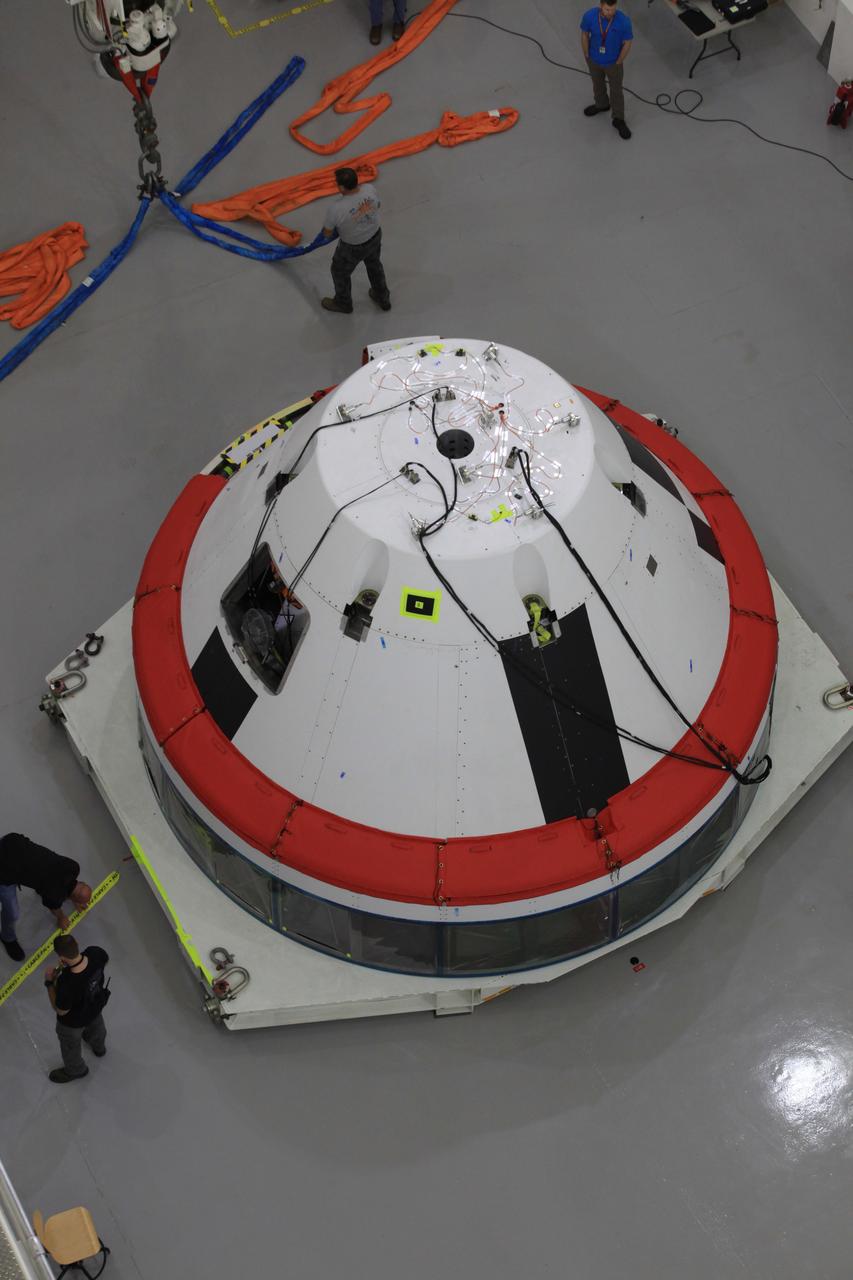

The Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is vertical and integrated with the crew module test article at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 13, 2019.
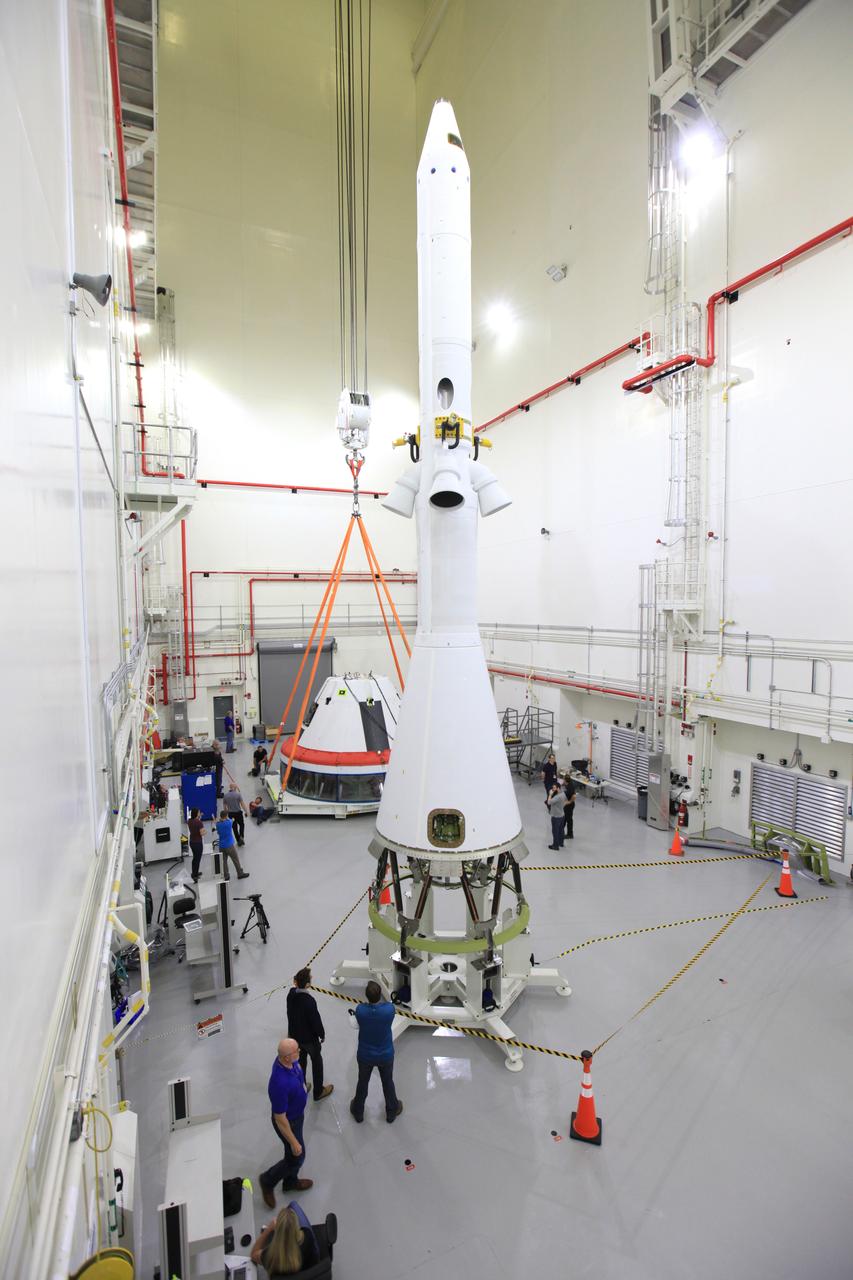

The Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is vertical and integrated with the crew module test article at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 13, 2019.
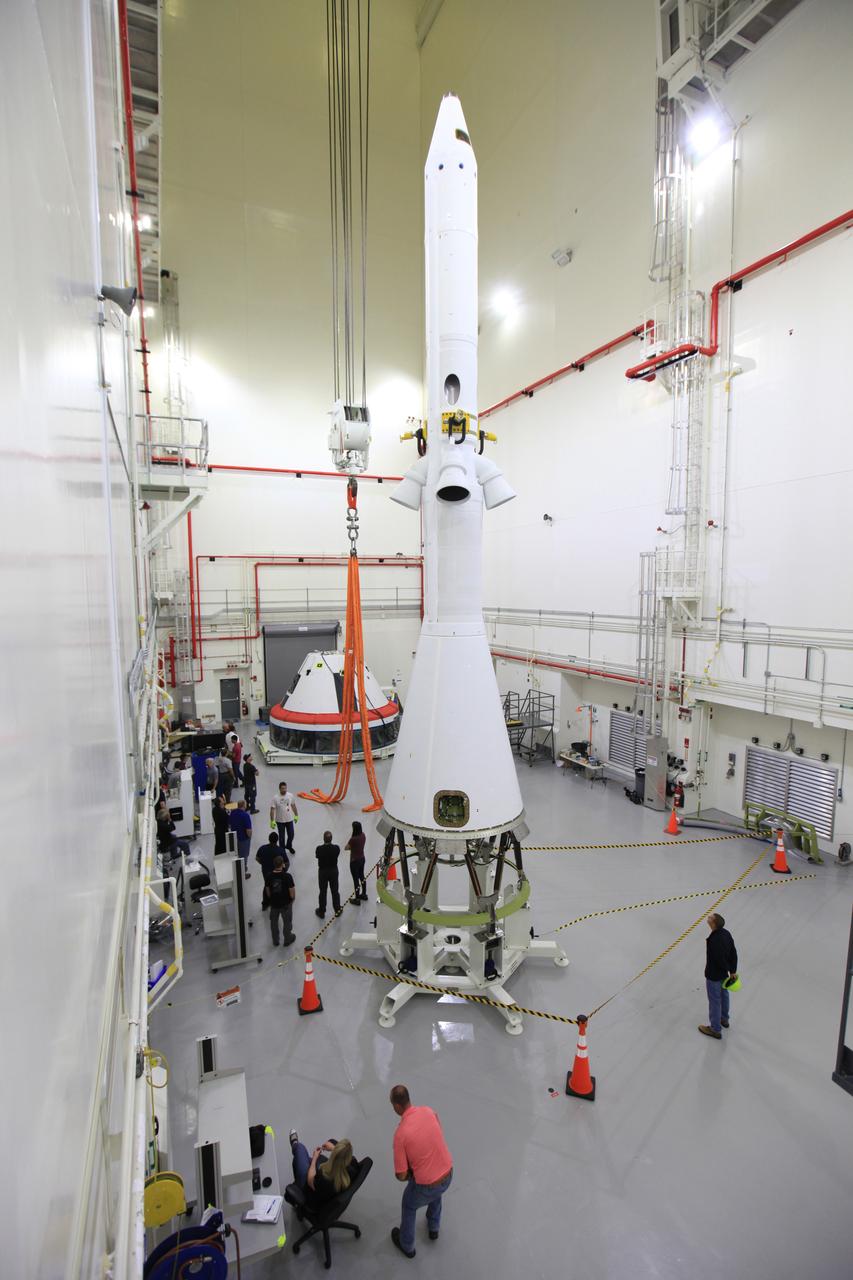

The Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is vertical and integrated with the crew module test article at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 13, 2019.

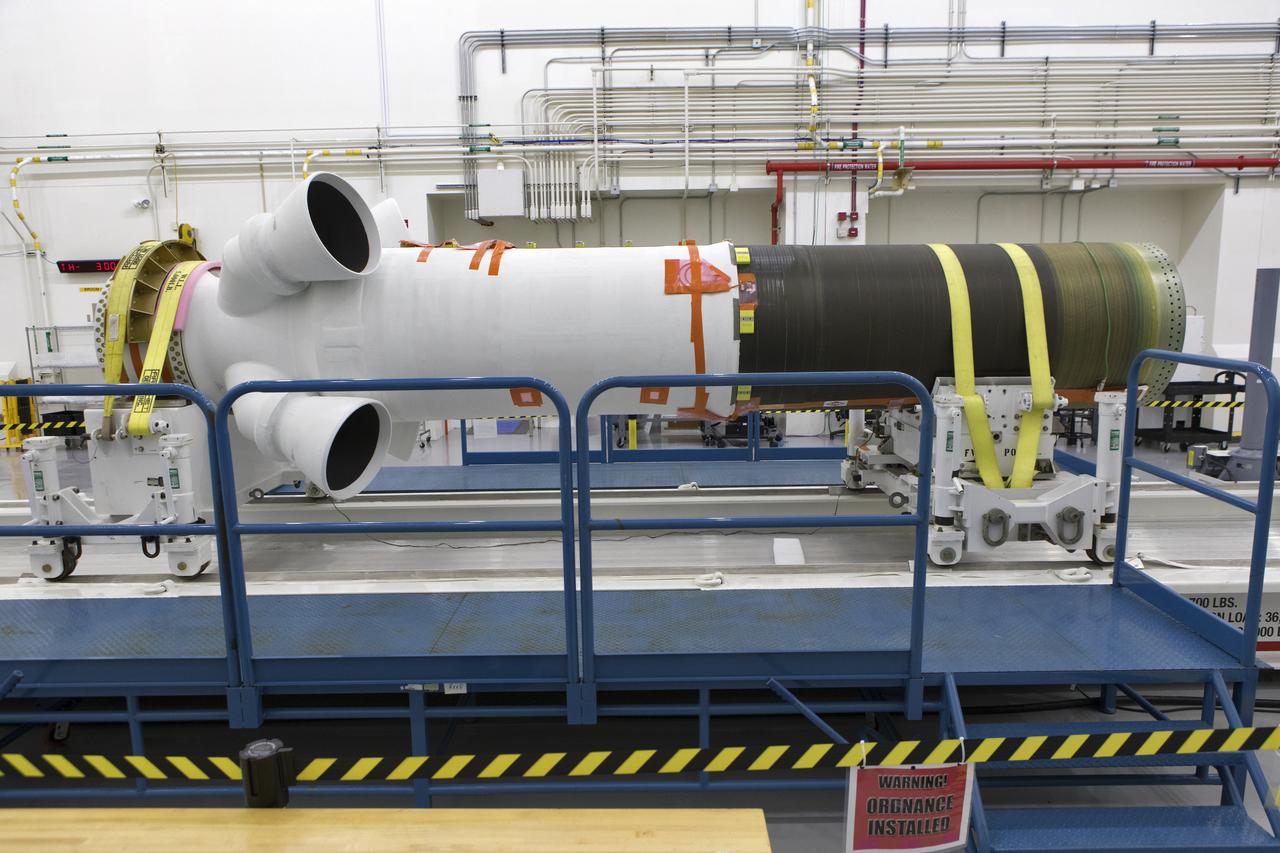
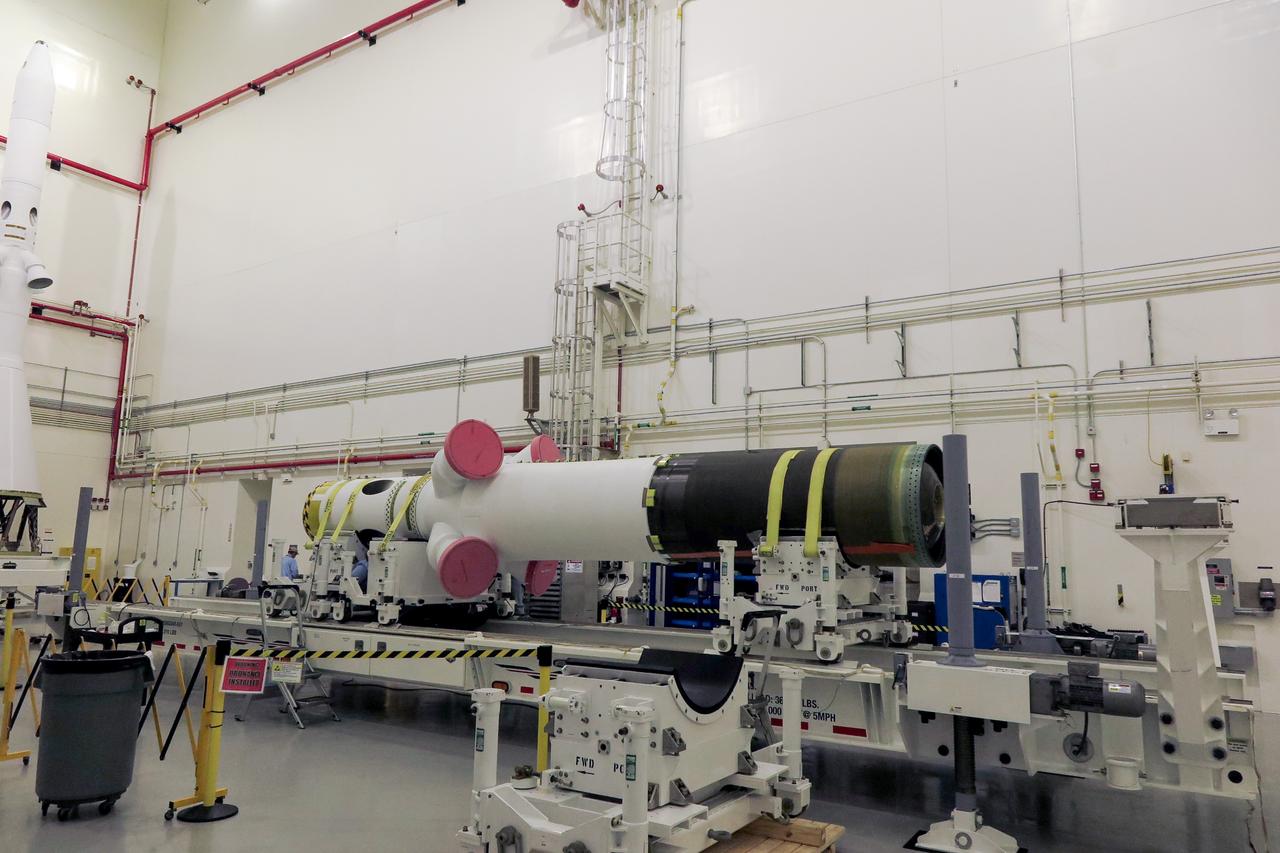
The launch abort motor for Orion’s launch abort system (LAS) for Artemis II, enclosed in its shipping container, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 13, 2020. The motor arrived from Northrop Grumman in Promontory, Utah, and was transported to the Launch Abort System Facility where it will undergo testing in preparation for the second Artemis mission. The launch abort motor is one of three motors on the LAS. The LAS will be positioned atop the Orion crew module and is designed to protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. Artemis II will take the first humans in orbit around the Moon in the 21st century.

The launch abort motor for Orion’s launch abort system (LAS) for Artemis II, enclosed in its shipping container, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 13, 2020. The motor arrived from Northrop Grumman in Promontory, Utah, and was transported to the Launch Abort System Facility where it will undergo testing in preparation for the second Artemis mission. The launch abort motor is one of three motors on the LAS. The LAS will be positioned atop the Orion crew module and is designed to protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. Artemis II will take the first humans in orbit around the Moon in the 21st century.

The launch abort motor is integrated with the jettison motor for Orion’s launch abort system (LAS) for Artemis II, inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 15, 2020. The launch abort and jettison motors are two of three motors on the LAS. The LAS will be positioned atop the Orion crew module and is designed to protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. Artemis II will take the first humans in orbit around the Moon in the 21st century. In view, at far left, is the Launch Abort System for Artemis I, the first uncrewed mission of Orion atop the Space Launch System rocket.
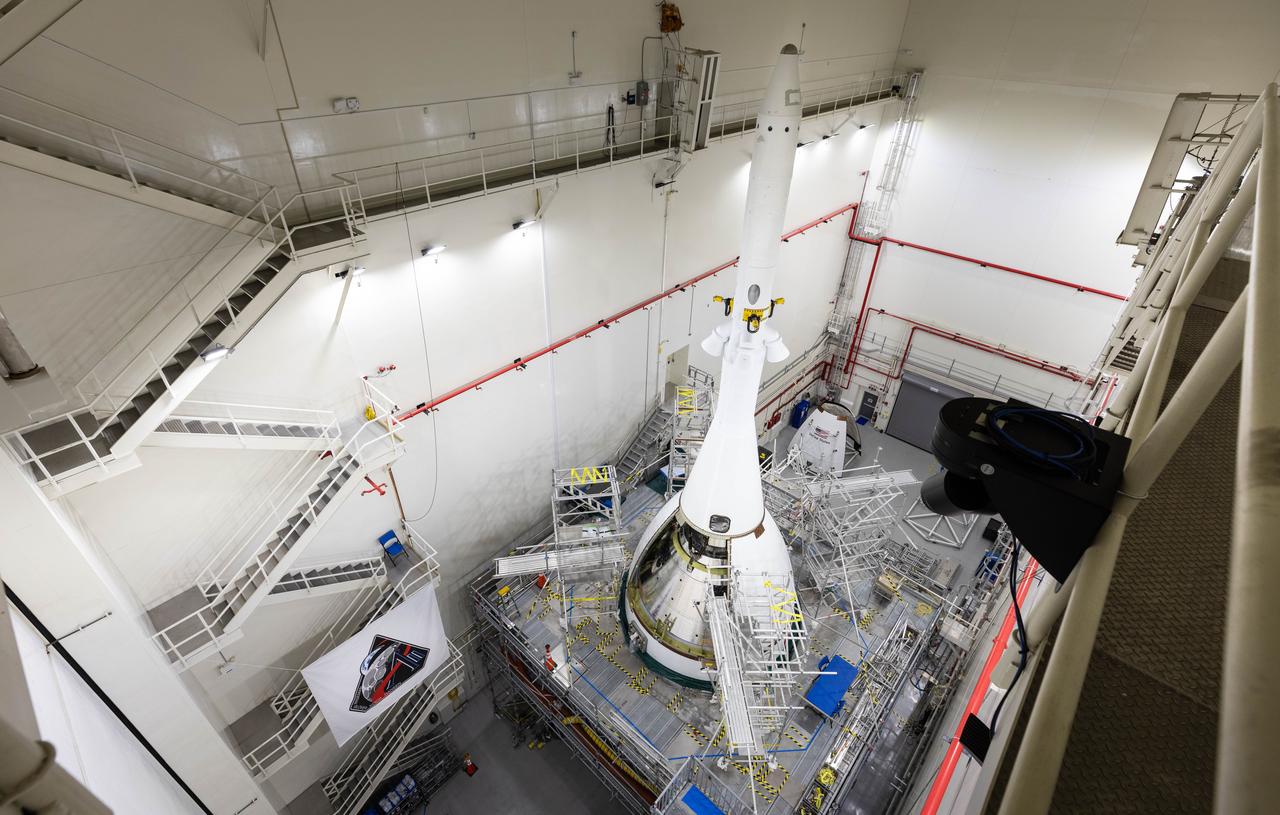

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems completed installation of two ogive fairings onto the launch abort system inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Sept. 10, 2025. The ogives consist of four protective panels that will shield the crew module from the severe vibrations and sounds it will experience during launch. Positioned at the top of Orion, the 44-foot-tall launch abort system is designed to carry the crew to safety in the event of an emergency during launch or ascent, with its three solid rocket motors working together to propel Orion – and astronauts inside – away from the rocket for a safe landing in the ocean, or detach from the spacecraft when it is no longer needed.
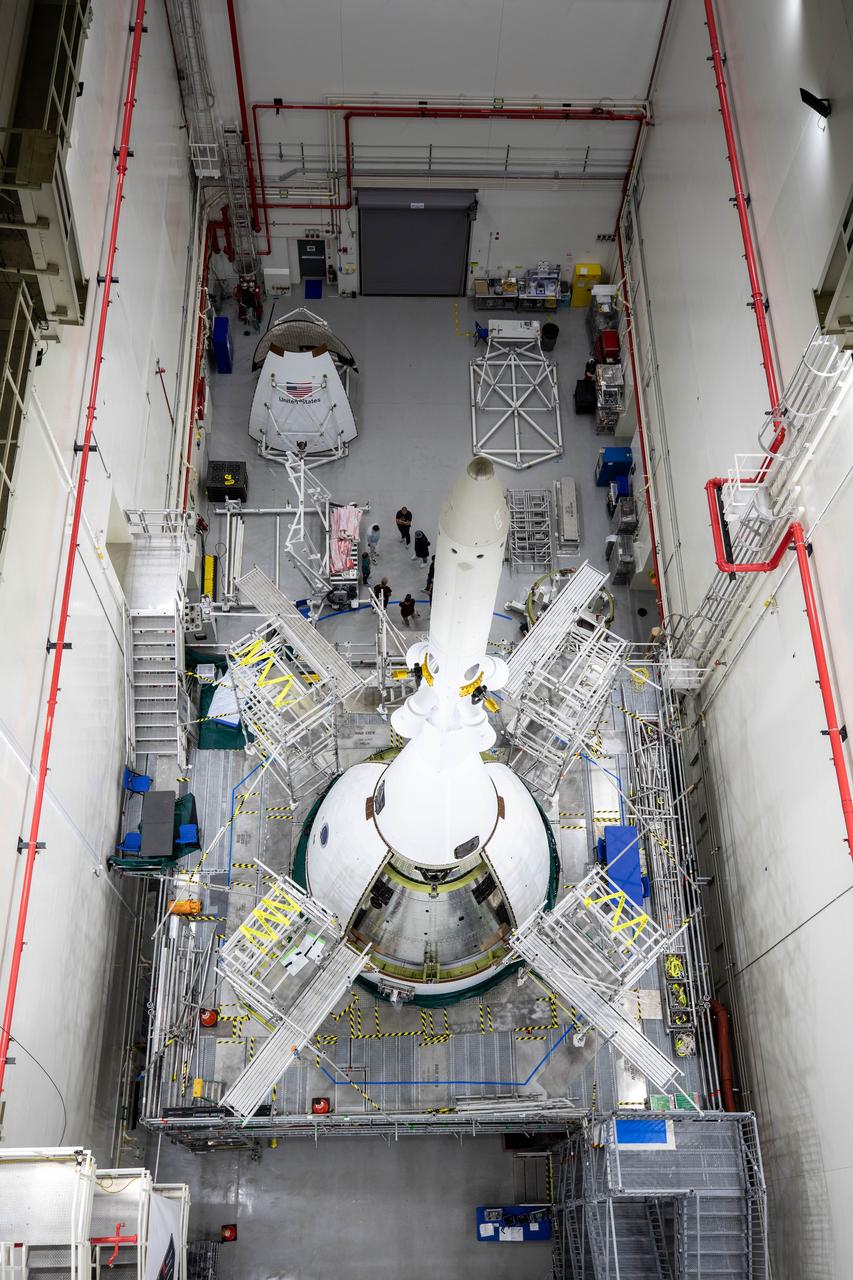

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems completed installation of two ogive fairings onto the launch abort system inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Sept. 10, 2025. The ogives consist of four protective panels that will shield the crew module from the severe vibrations and sounds it will experience during launch. Positioned at the top of Orion, the 44-foot-tall launch abort system is designed to carry the crew to safety in the event of an emergency during launch or ascent, with its three solid rocket motors working together to propel Orion – and astronauts inside – away from the rocket for a safe landing in the ocean, or detach from the spacecraft when it is no longer needed.
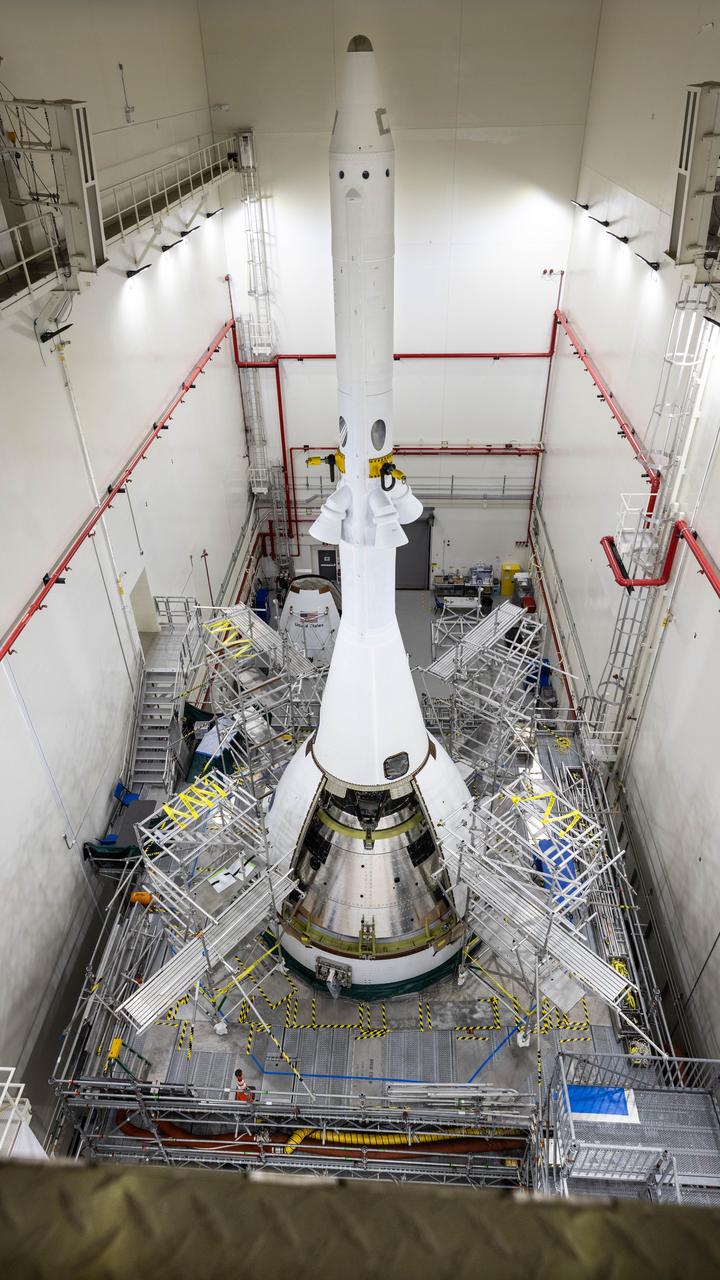

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems completed installation of two ogive fairings onto the launch abort system inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Sept. 10, 2025. The ogives consist of four protective panels that will shield the crew module from the severe vibrations and sounds it will experience during launch. Positioned at the top of Orion, the 44-foot-tall launch abort system is designed to carry the crew to safety in the event of an emergency during launch or ascent, with its three solid rocket motors working together to propel Orion – and astronauts inside – away from the rocket for a safe landing in the ocean, or detach from the spacecraft when it is no longer needed.
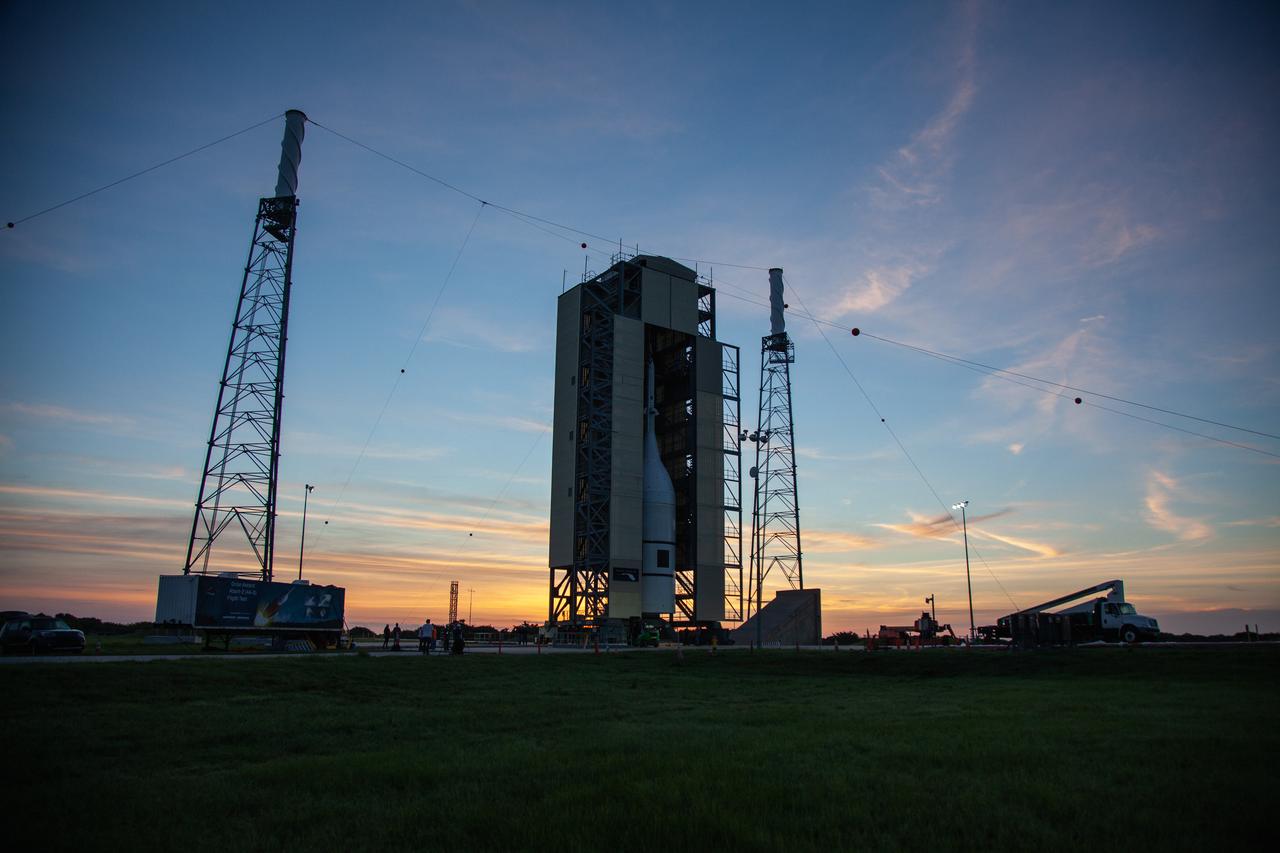

In the early morning on July 1, 2019, the vertical integration facility surrounding the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) test vehicle begins to rollback at Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) mated to a test version of the Orion spacecraft are on a Northrop Grumman provided booster on the pad for launch on NASA’s AA-2 flight test on July 2, 2019. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at more than 1,000 mph. The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
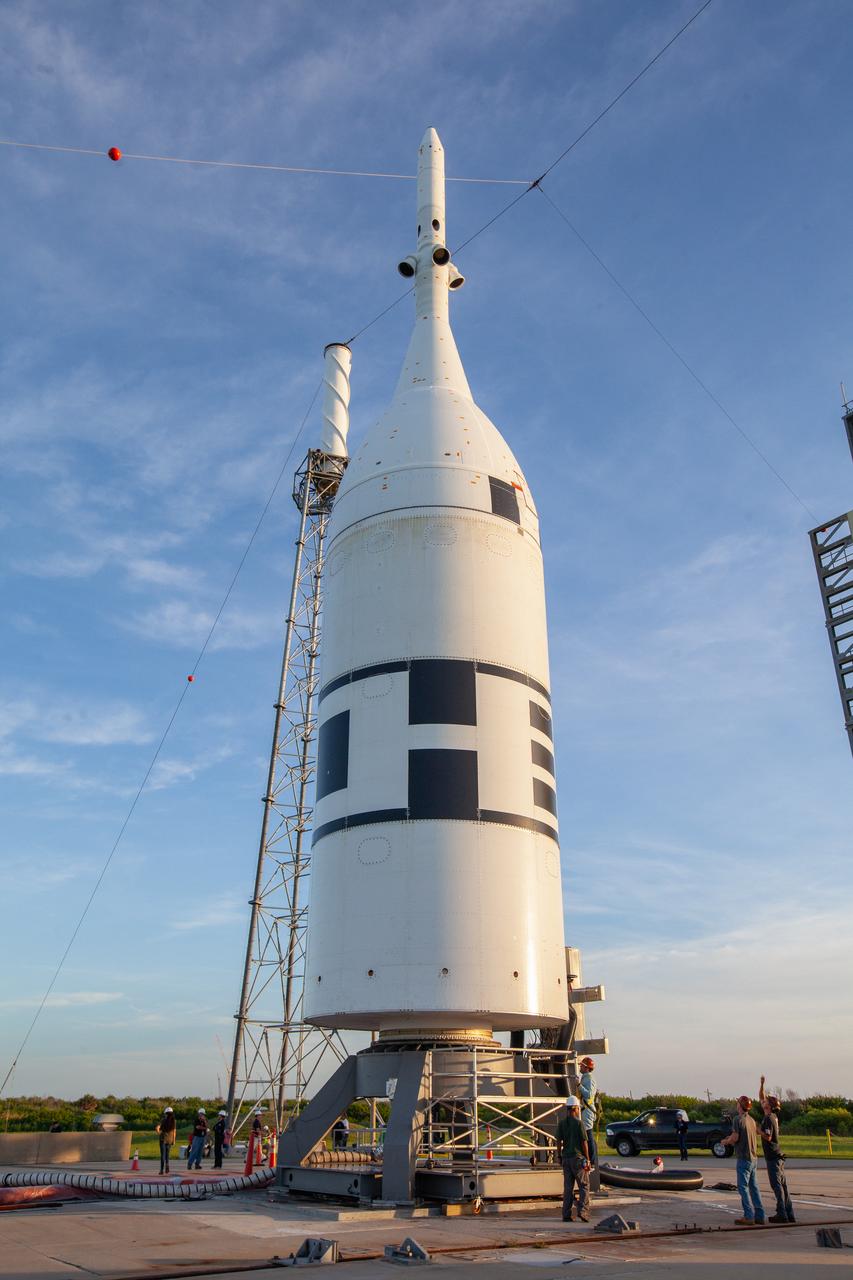

The Ascent Abort-2 test vehicle is secured on the pad at Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida after rollback of the vertical integration facility on July 1, 2019. A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) mated to a test version of the Orion spacecraft are on a Northrop Grumman provided booster on the pad for launch on NASA’s AA-2 flight test on July 2, 2019. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at more than 1,000 mph. The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
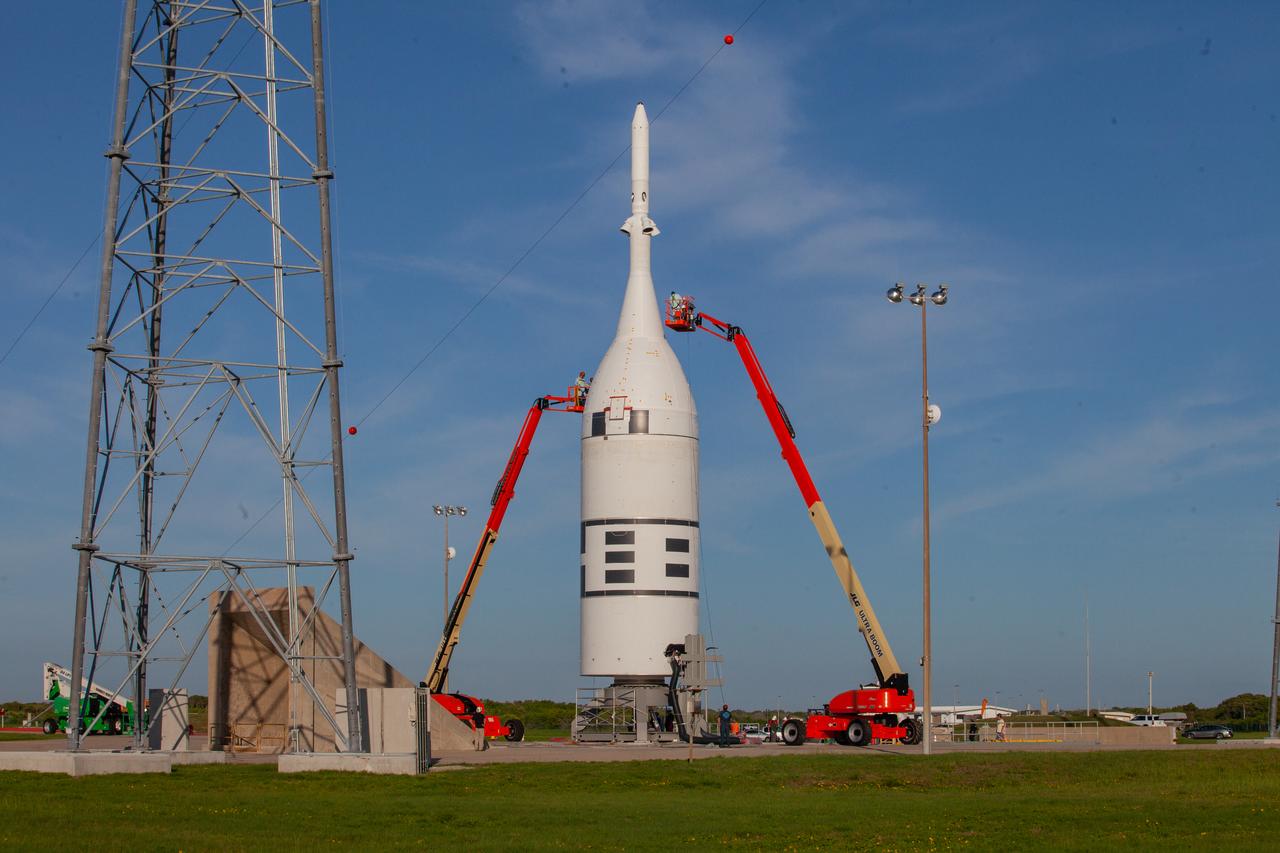

On July 1, 2019, workers prepare the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) test vehicle for launch at Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida after rollback of the integration facility. A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) mated to a test version of the Orion spacecraft are on a Northrop Grumman provided booster on the pad for launch on NASA’s AA-2 flight test on July 2, 2019. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at more than 1,000 mph. The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
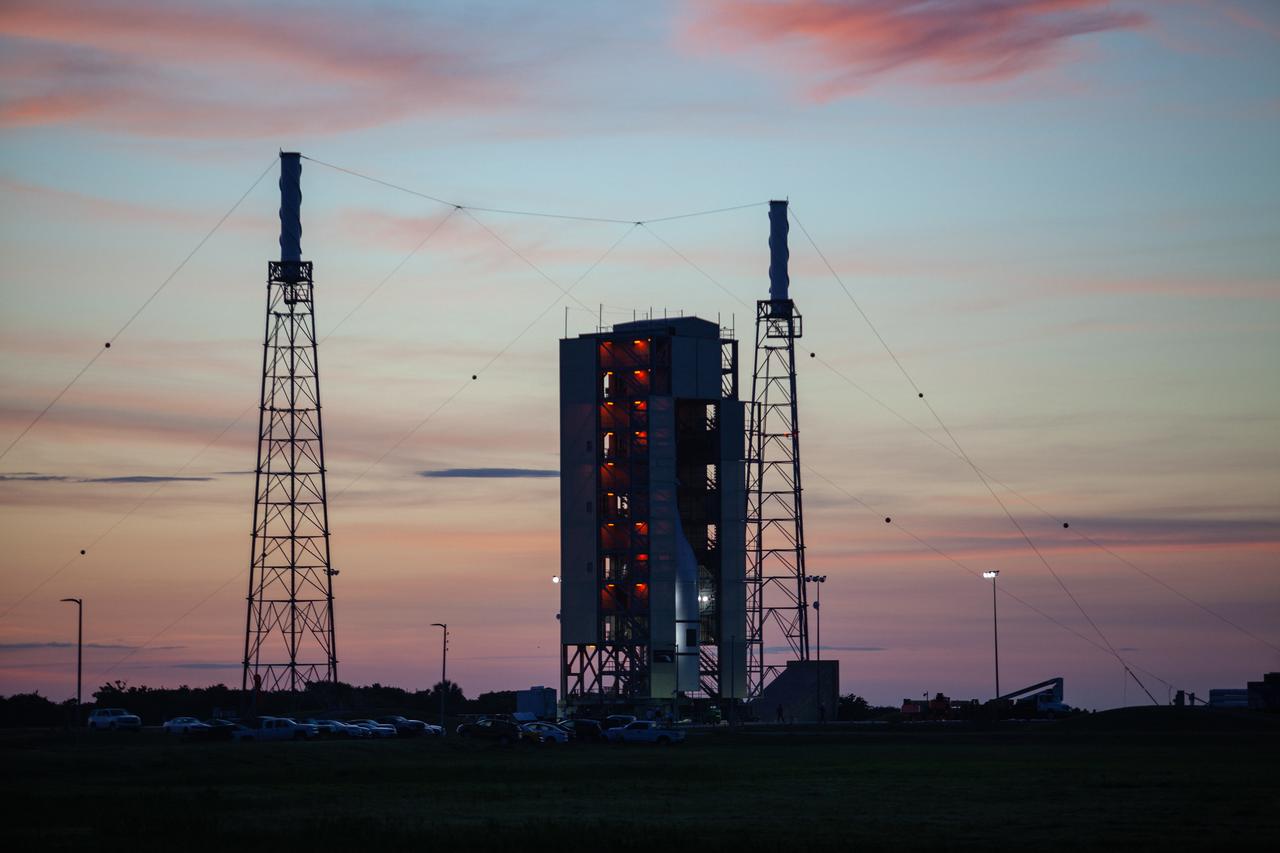

A sunrise view of Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 1, 2019. A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) mated to a test version of the Orion spacecraft are on a Northrop Grumman provided booster on the pad for launch on NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test on July 2, 2019. The vertical integration facility surrounding the test vehicle begins to roll back from the pad. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at more than 1,000 mph. The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
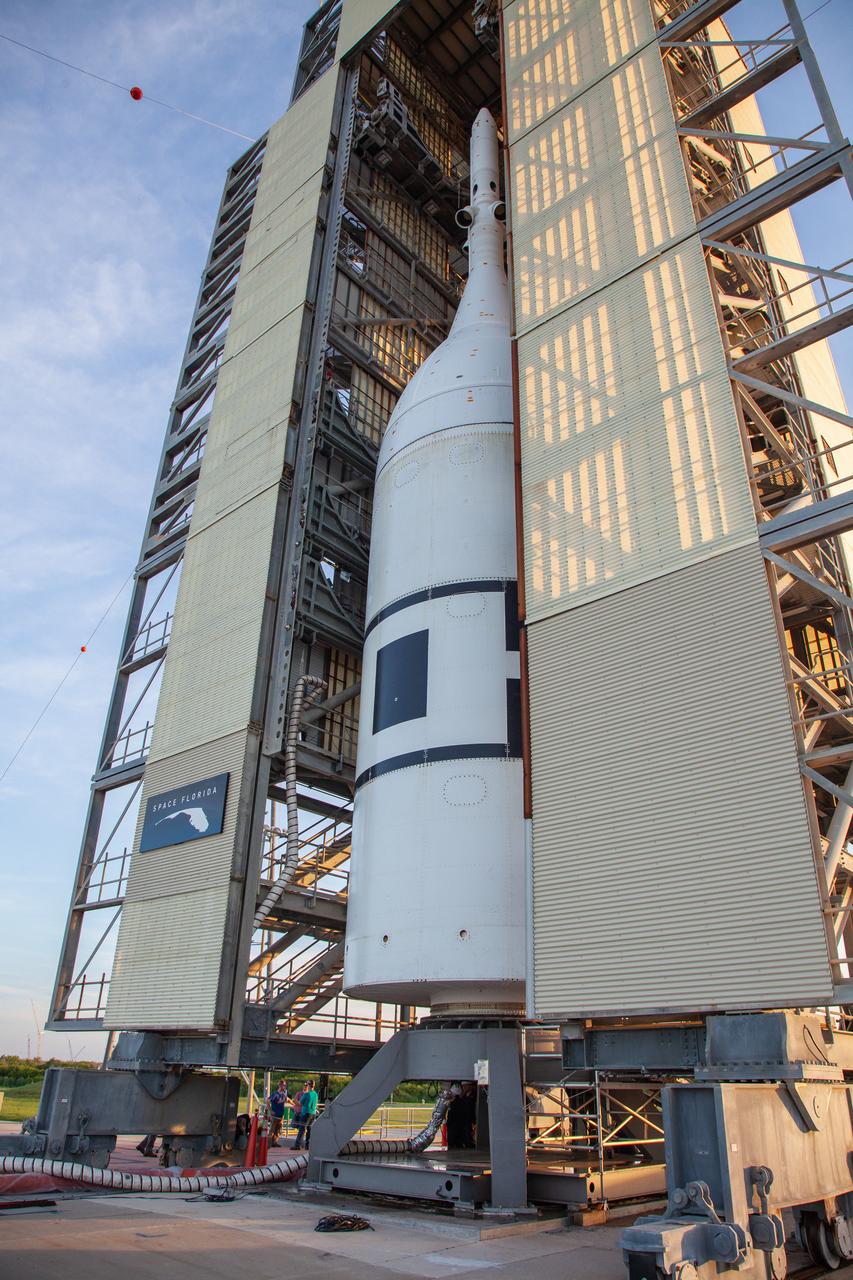

In the early morning on July 1, 2019, the vertical integration facility surrounding the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) test vehicle begins to rollback at Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) mated to a test version of the Orion spacecraft are on a Northrop Grumman provided booster on the pad for launch on NASA’s AA-2 flight test on July 2, 2019. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at more than 1,000 mph. The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.
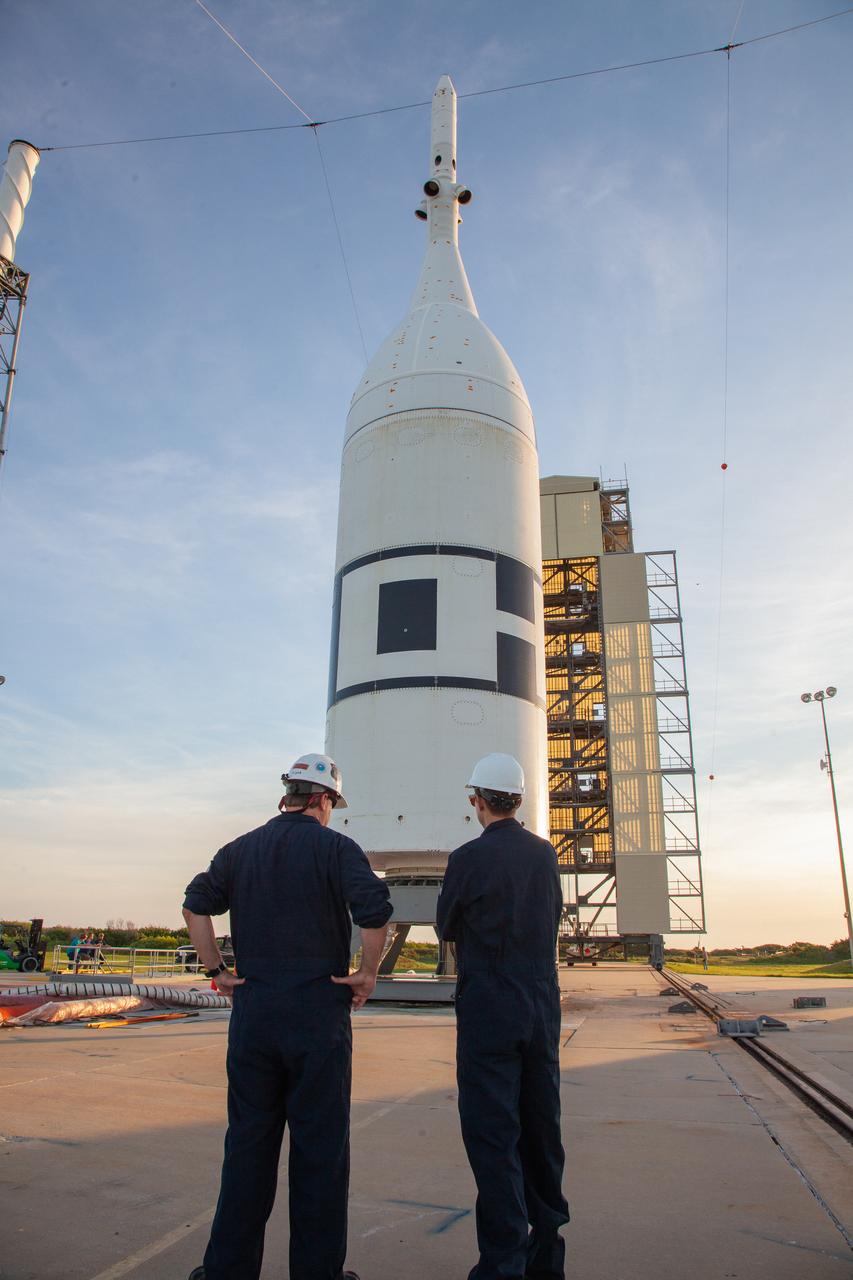

The Ascent Abort-2 test vehicle is secured on the pad at Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida after rollback of the vertical integration facility on July 1, 2019. A fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) mated to a test version of the Orion spacecraft are on a Northrop Grumman provided booster on the pad for launch on NASA’s AA-2 flight test on July 2, 2019. During AA-2, the booster will send the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at more than 1,000 mph. The LAS’ three motors will work together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test will prove that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent.