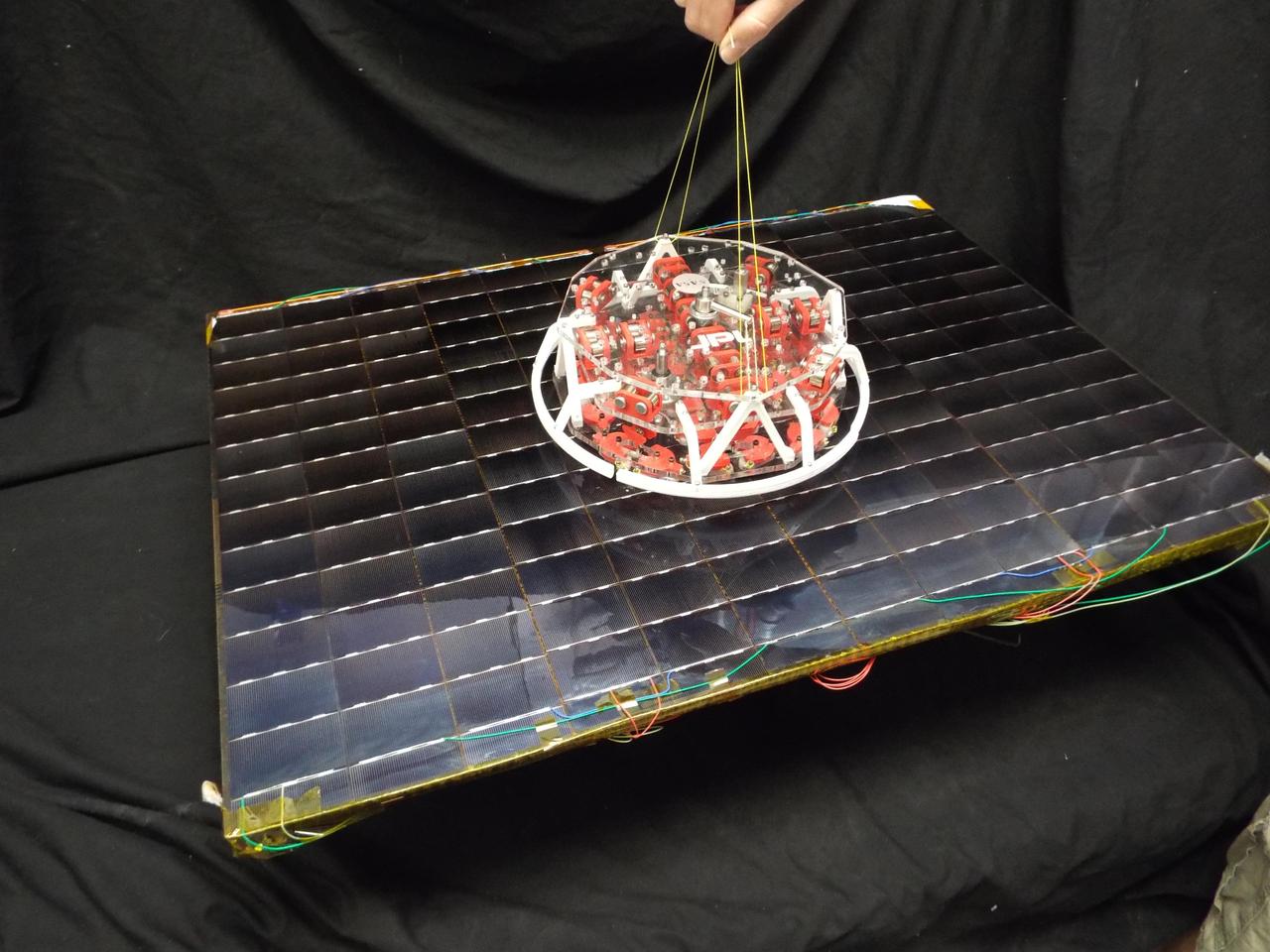
Scientists at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory have developed a tool for grappling non-cooperative objects that incorporates gecko-like adhesives. The adhesives are reusable and can be turned on and off.
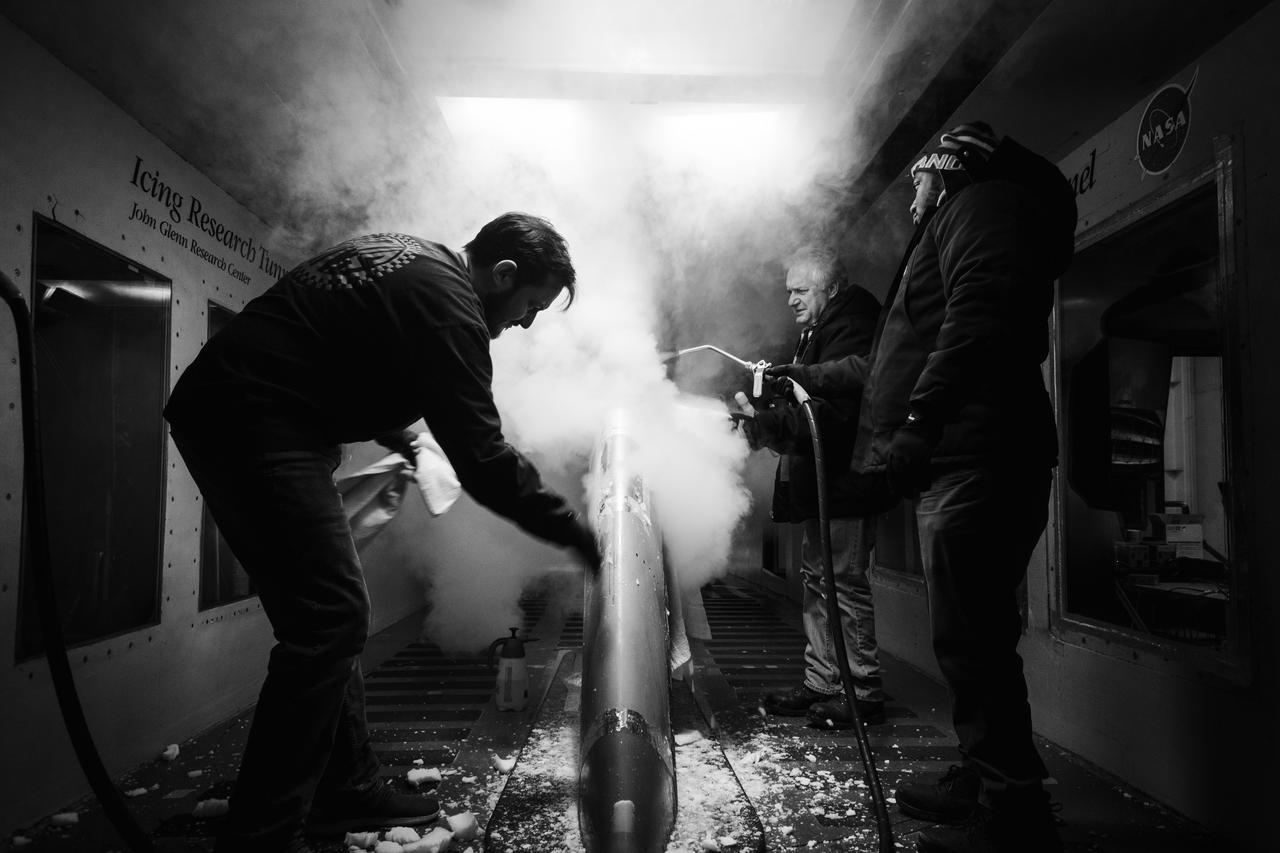

Technicians spray steam to help scrape off ice at the Icing Research Tunnel. The technicians need all the help they can get in sub-zero temperatures. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)

NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Victor Glover works with the Astrobee robot aboard the space station to test an adhesive for robotic grasping and manipulating as part of the Astrobee/Gecko-2 experiment. Assistive Free-Flyers with Gecko-Inspired Adhesive Appendages for Automated Logistics in Space uses the Astrobee robot aboard the space station to test an adhesive for robotic grasping and manipulating.
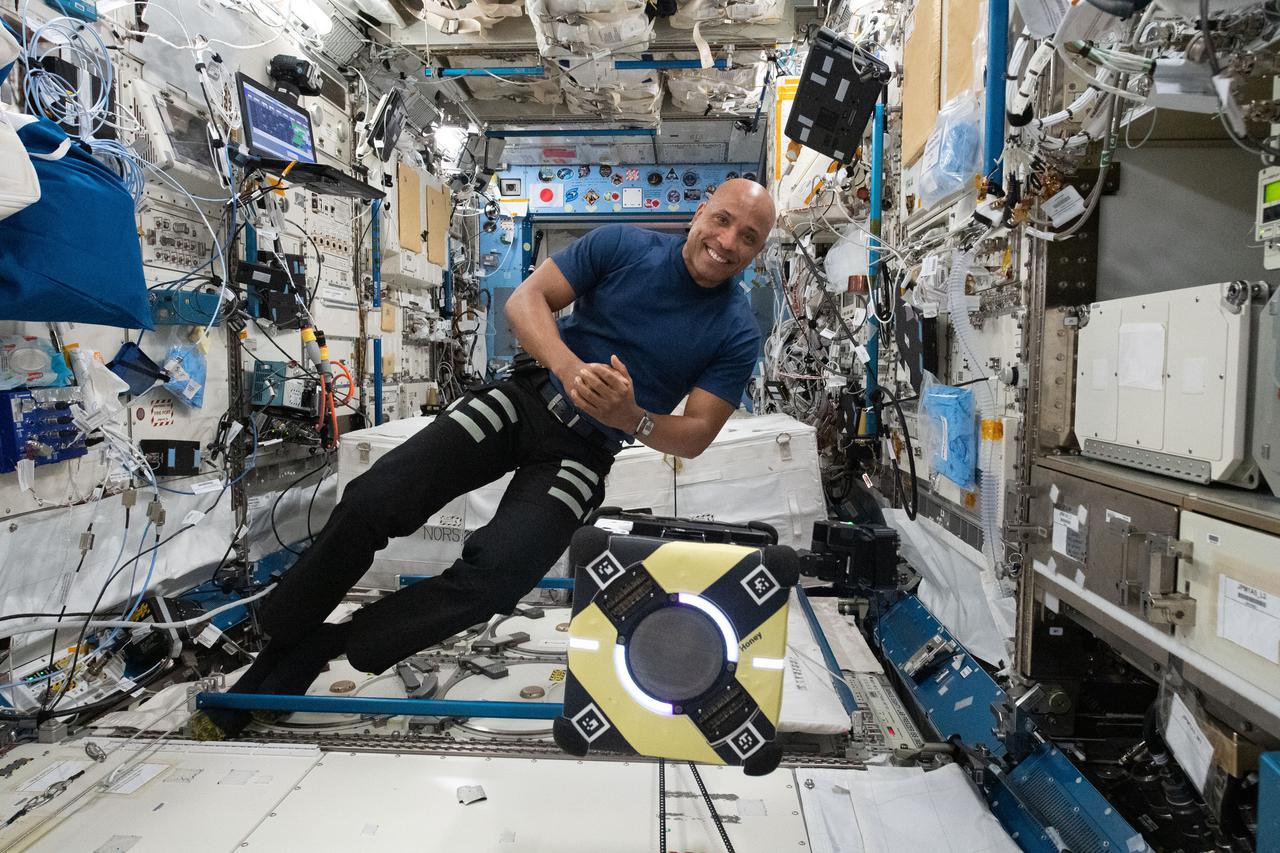

NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Victor Glover works with the Astrobee robot aboard the space station to test an adhesive for robotic grasping and manipulating as part of the Astrobee/Gecko-2 experiment. Assistive Free-Flyers with Gecko-Inspired Adhesive Appendages for Automated Logistics in Space uses the Astrobee robot aboard the space station to test an adhesive for robotic grasping and manipulating.
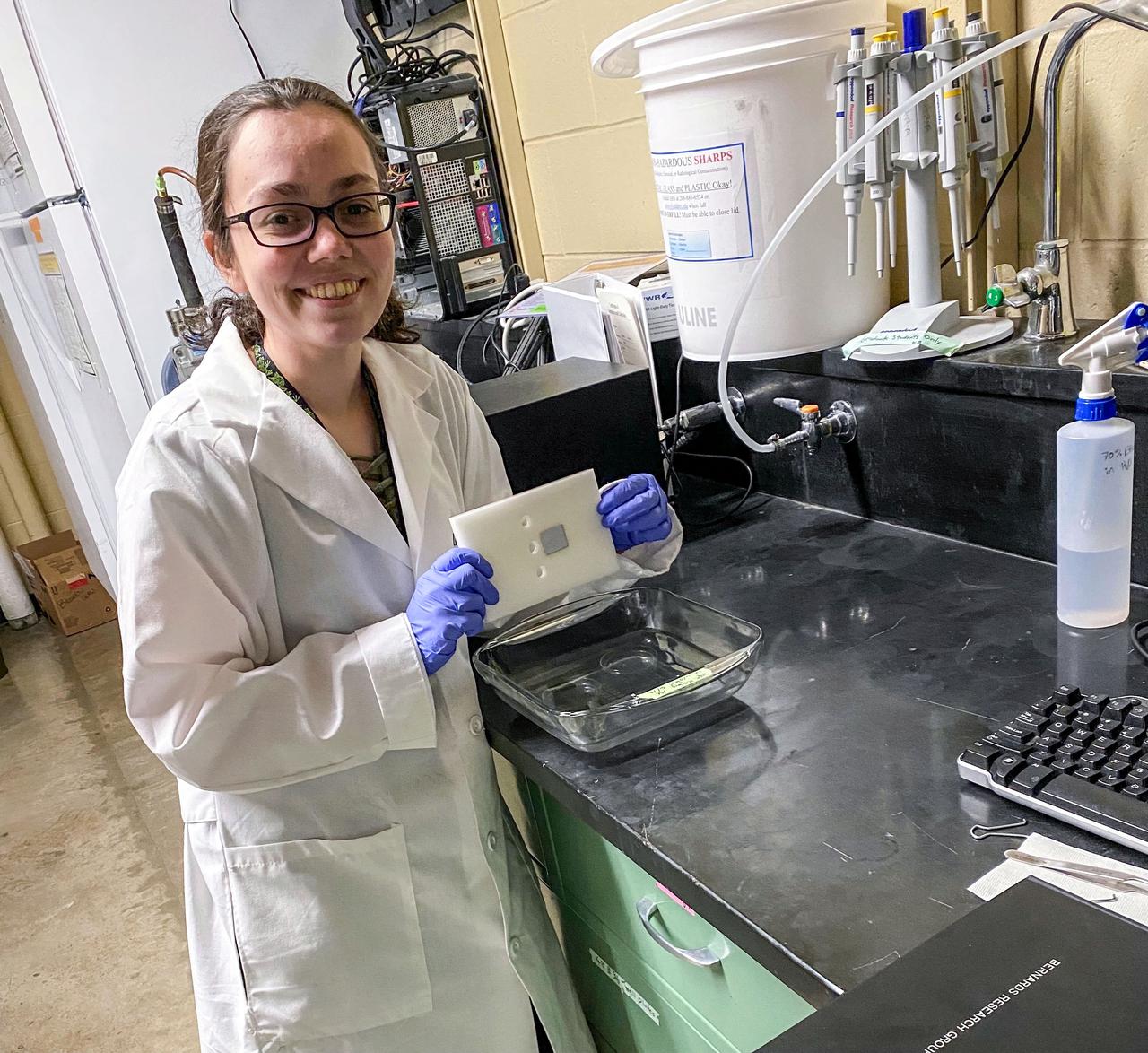

jsc2021e064550 (12/14/2021) --- Ashley Keeley tests the long-term performance of the adhesive binding the aluminum substrates to the housing material under wet conditions for the Determining the Efficacy of Bacteria Resistant Polymers in Microgravity (Bacteria Resistant Polymers in Space) investigation. Image courtesy of University of Idaho SPOCS Team.
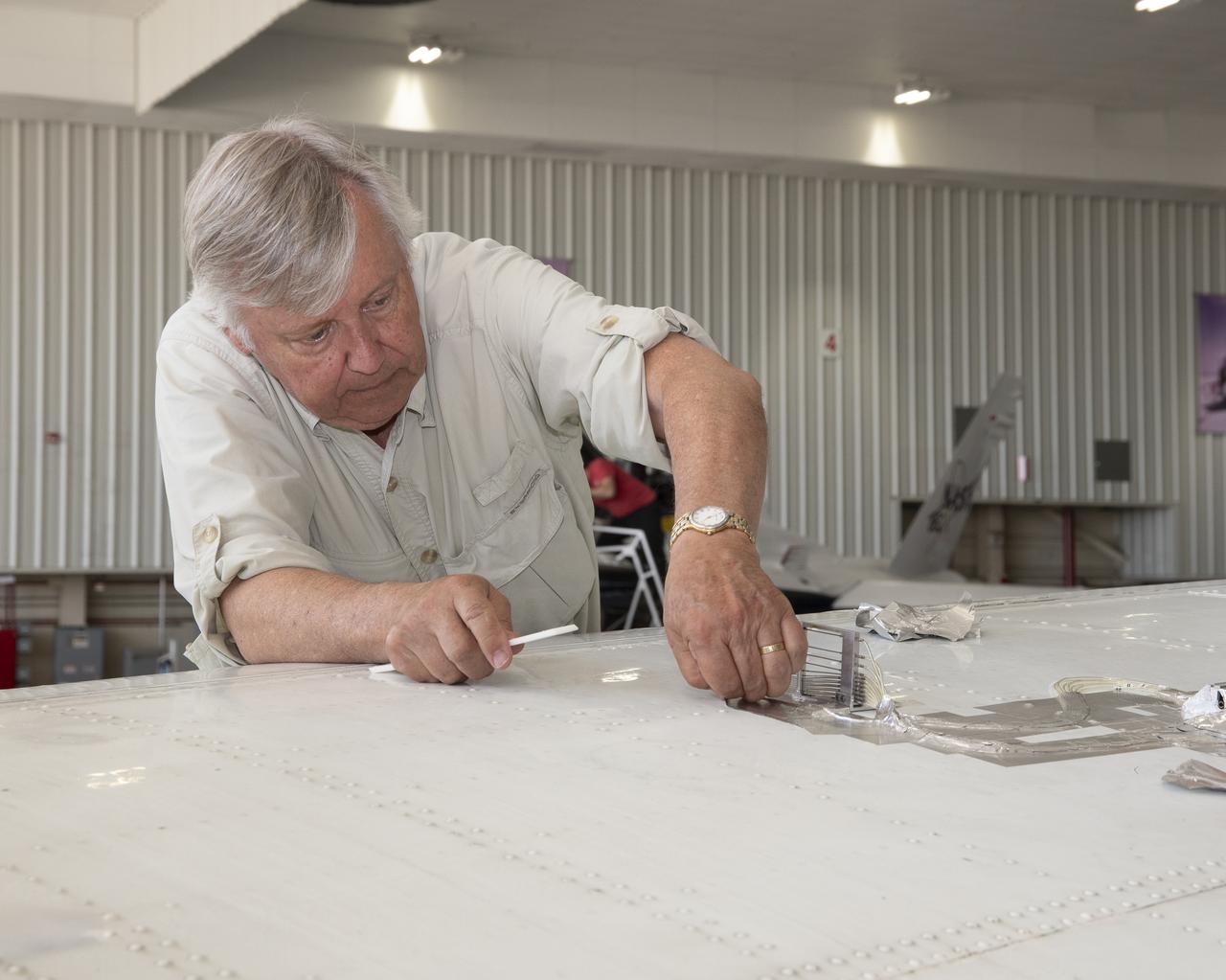

Cal Poly San Luis Obispo Professor Russ Westphal works on the Boundary Layer Data System (BLDS) attached to the wing of a Beechcraft Beech 200 Super King Air aircraft. The BLDS was attached to the aircraft with removable adhesives for a flight test at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center.
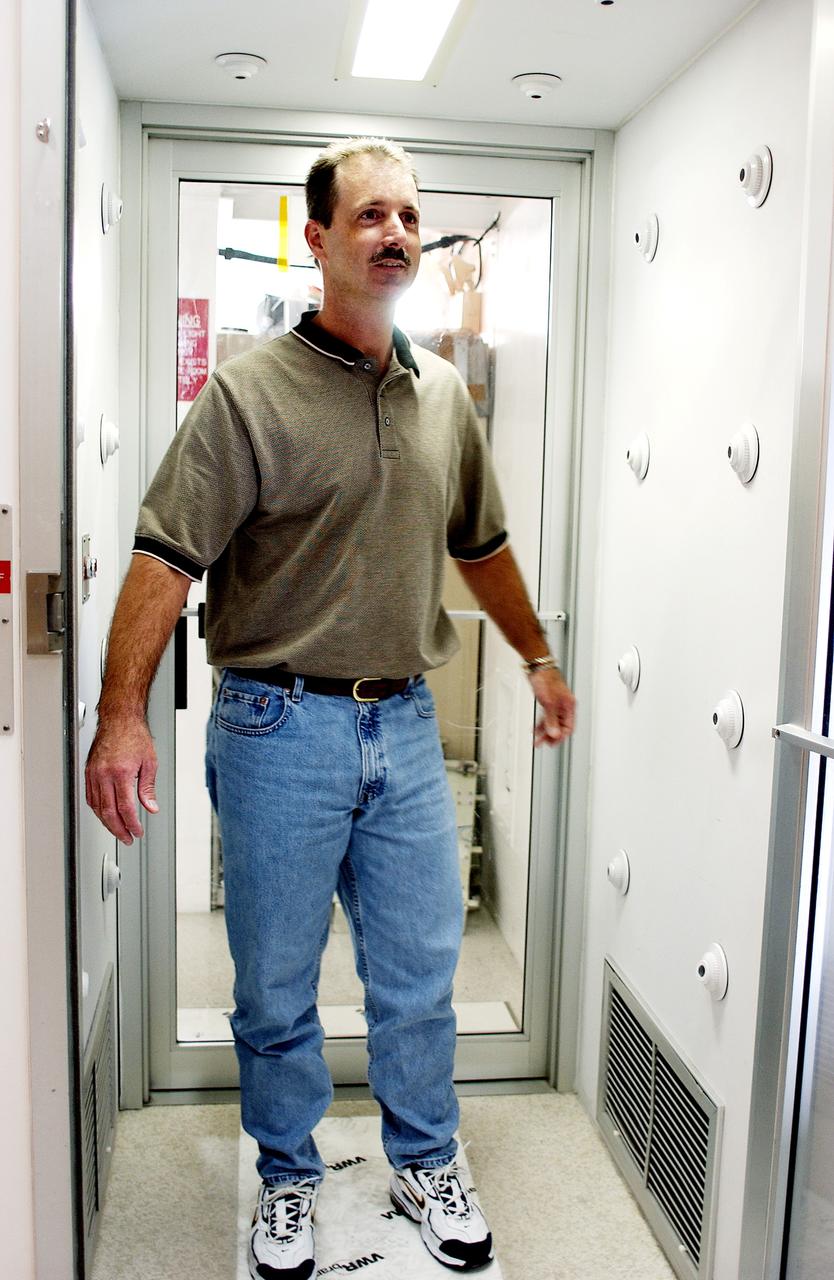

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A KSC employee uses a clean-air shower before entering a clean room. Streams of pressurized air directed at the occupant from nozzles in the chamber's ceiling and walls are designed to dislodge particulate matter from hair, clothing and shoes. The adhesive mat on the floor captures soil from shoe soles, as well as particles that fall on its surface. Particulate matter has the potential to contaminate the space flight hardware being stored or processed in the clean room. The shower is part of KSC's Foreign Object Debris (FOD) control program, an important safety initiative.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A KSC employee uses a clean-air shower before entering a clean room. Streams of pressurized air directed at the occupant from nozzles in the chamber's ceiling and walls are designed to dislodge particulate matter from hair, clothing and shoes. The adhesive mat on the floor captures soil from shoe soles, as well as particles that fall on its surface. Particulate matter has the potential to contaminate the space flight hardware being stored or processed in the clean room. The shower is part of KSC's Foreign Object Debris (FOD) control program, an important safety initiative.
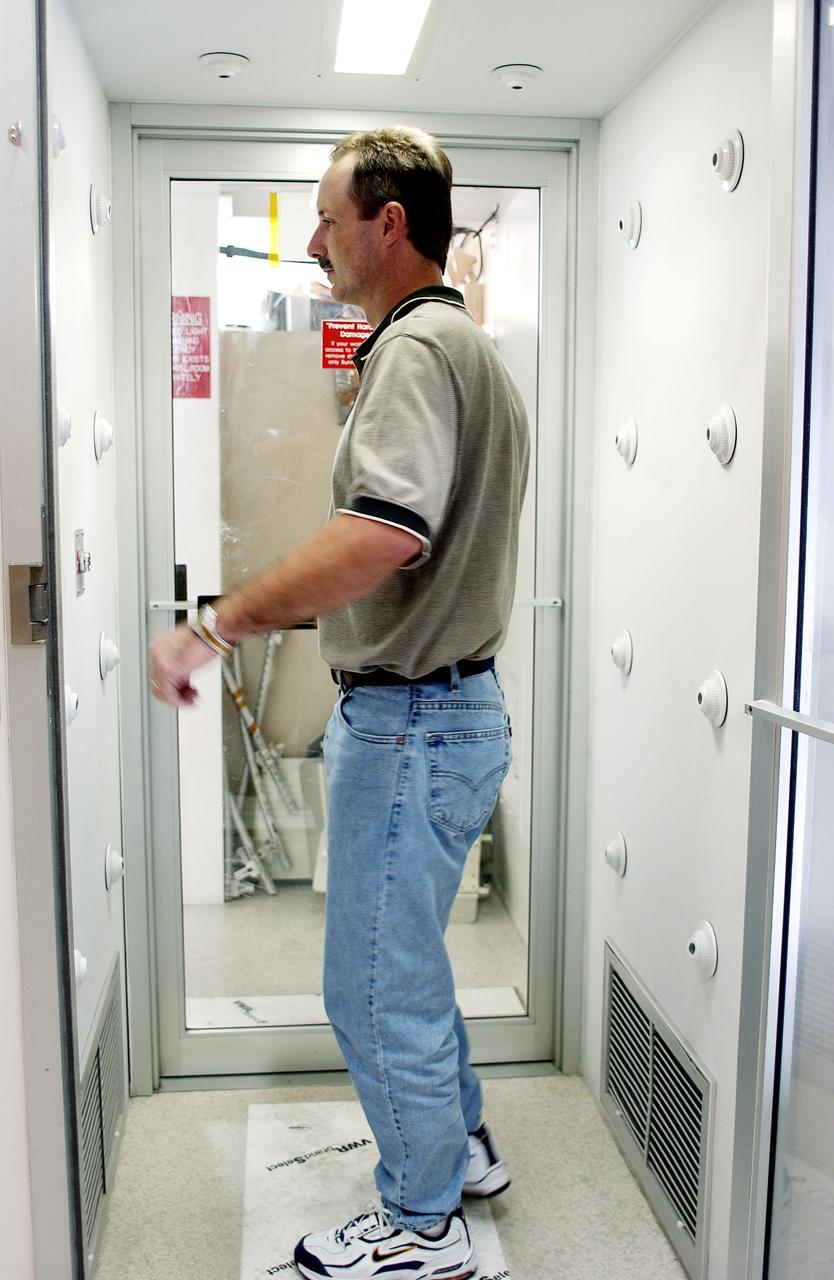

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A KSC employee uses a clean-air shower before entering a clean room. Streams of pressurized air directed at the occupant from nozzles in the chamber's ceiling and walls are designed to dislodge particulate matter from hair, clothing and shoes. The adhesive mat on the floor captures soil from shoe soles, as well as particles that fall on its surface. Particulate matter has the potential to contaminate the space flight hardware being stored or processed in the clean room. The shower is part of KSC's Foreign Object Debris (FOD) control program, an important safety initiative.

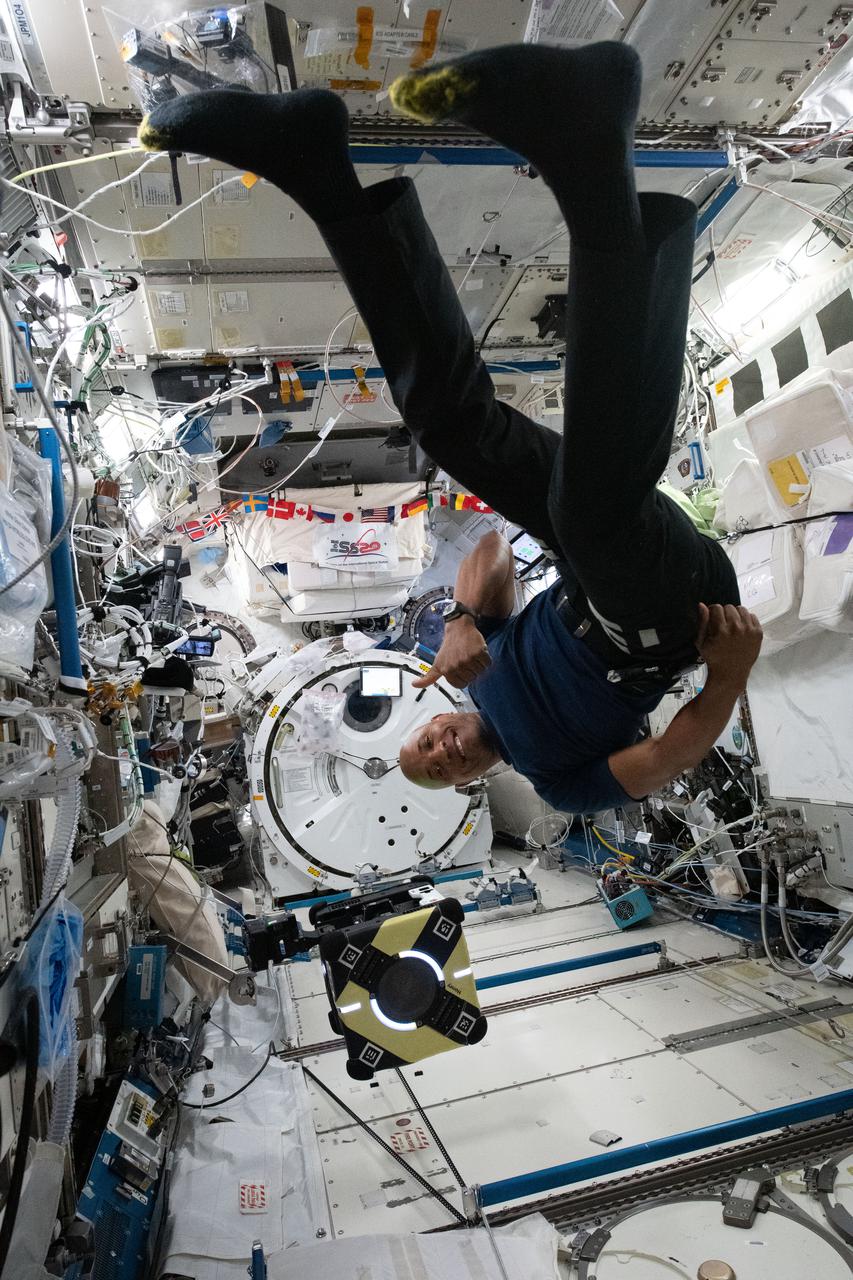
iss072e593598 (Feb. 4, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams monitors an Astrobee robotic free-flyer outfitted with tentacle-like arms containing gecko-like adhesive pads preparing to grapple a "capture cube." The toaster sized Astrobee, with the experimental grippers attached, demonstrated autonomous detection and capture techniques that may be used to remove space debris and service satellites in low Earth orbit.
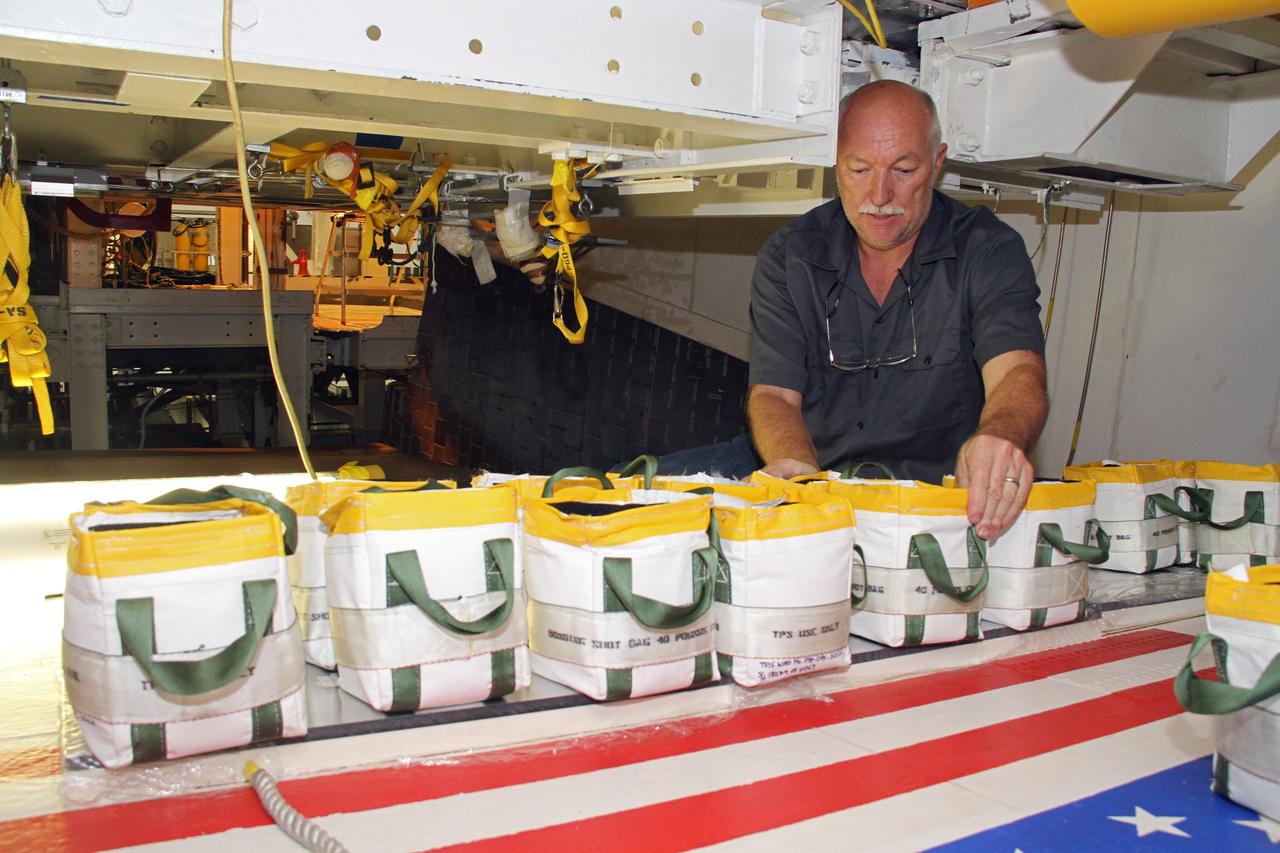

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mike Williams, a thermal protection system technician with United Space Alliance, arranges weights atop a freshly installed section of tile on the right wing of space shuttle Endeavour at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The weights will hold the section in place while the adhesive hardens beneath. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
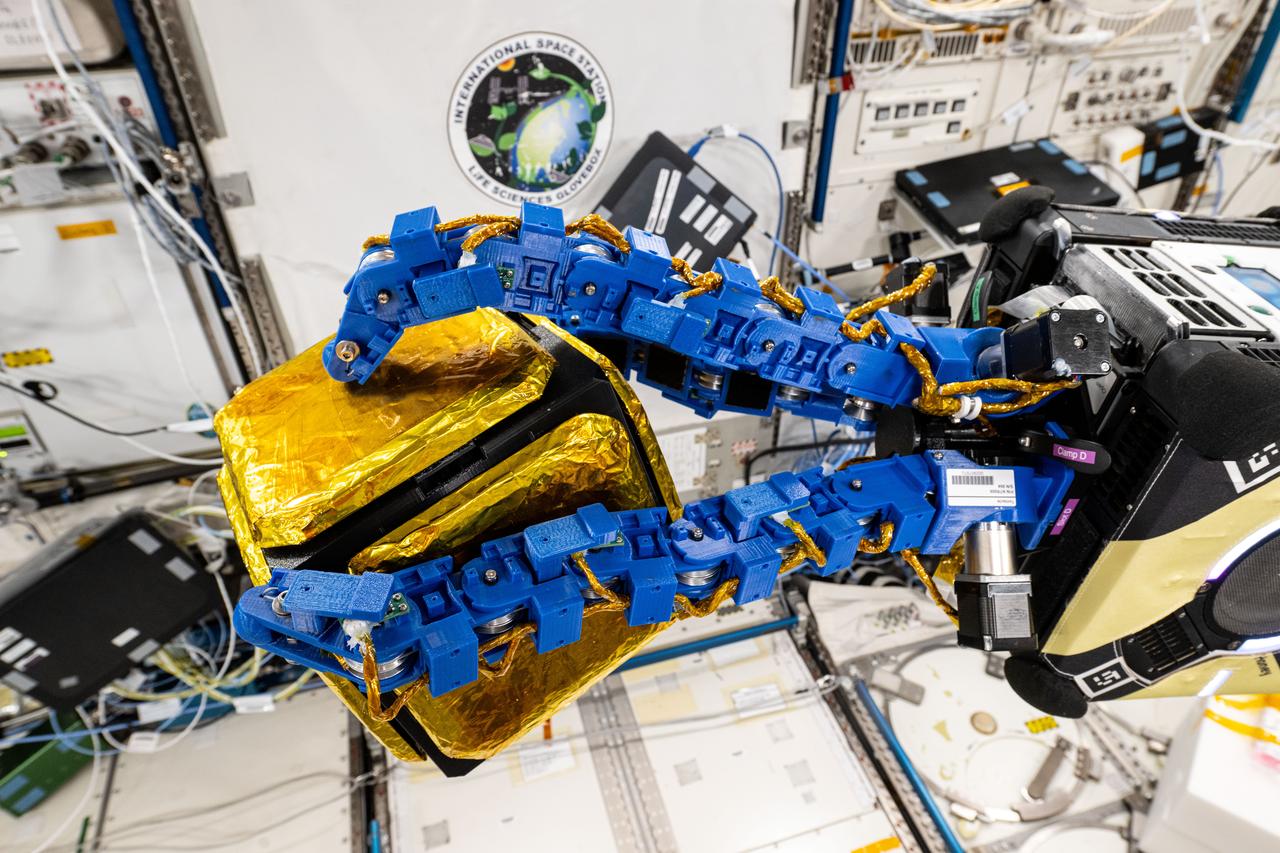
iss072e593717 (Feb. 4, 2025) --- The blue tentacle-like arms containing gecko-like adhesive pads, attached to an Astrobee robotic free-flyer, reach out and grapple a "capture cube" inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. The experimental grippers, outfitted on the toaster-sized Astrobee, demonstrated autonomous detection and capture techniques that may be used to remove space debris and service satellites in low Earth orbit.
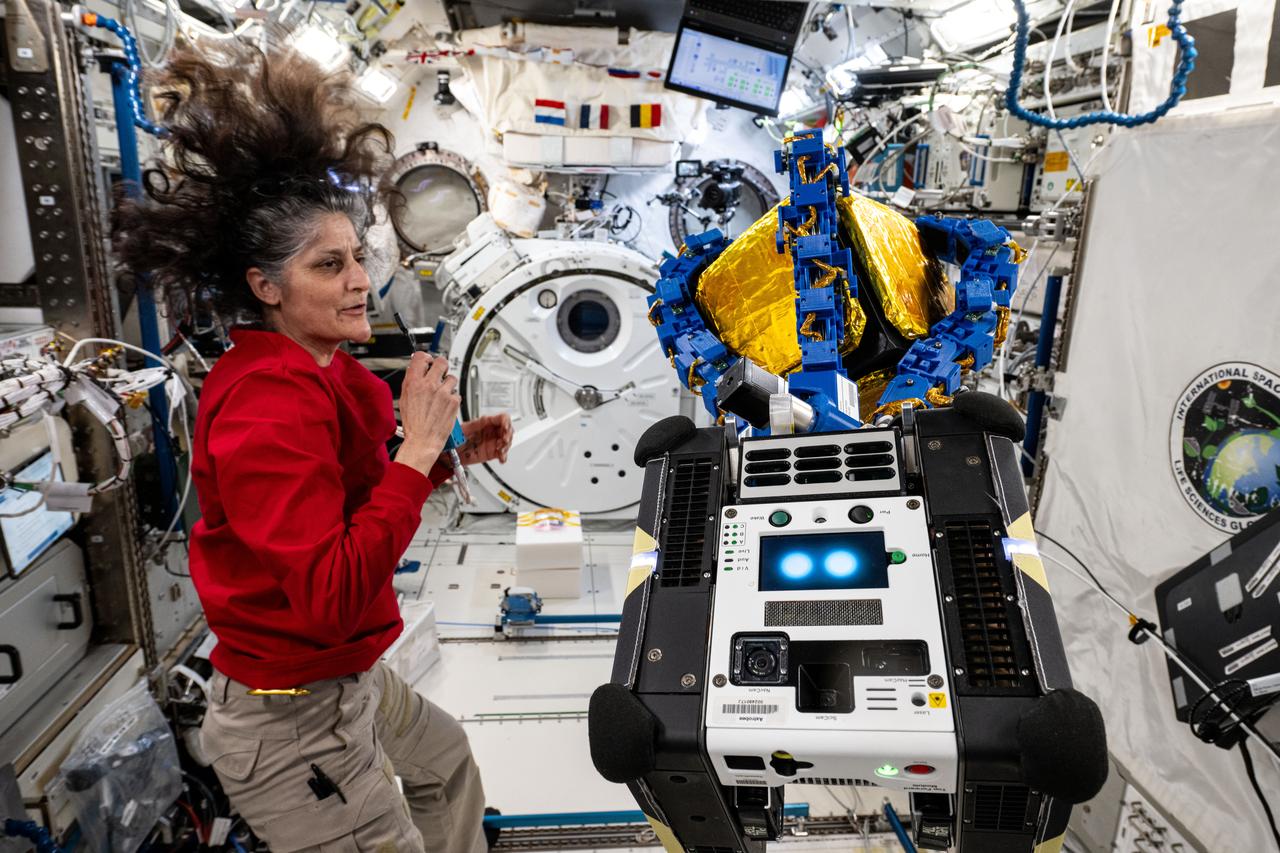

iss072e593606 (Feb. 4, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams monitors an Astrobee robotic free-flyer outfitted with tentacle-like arms containing gecko-like adhesive pads as it grapples a "capture cube." The toaster sized Astrobee, with the experimental grippers attached, demonstrated autonomous detection and capture techniques that may be used to remove space debris and service satellites in low Earth orbit.
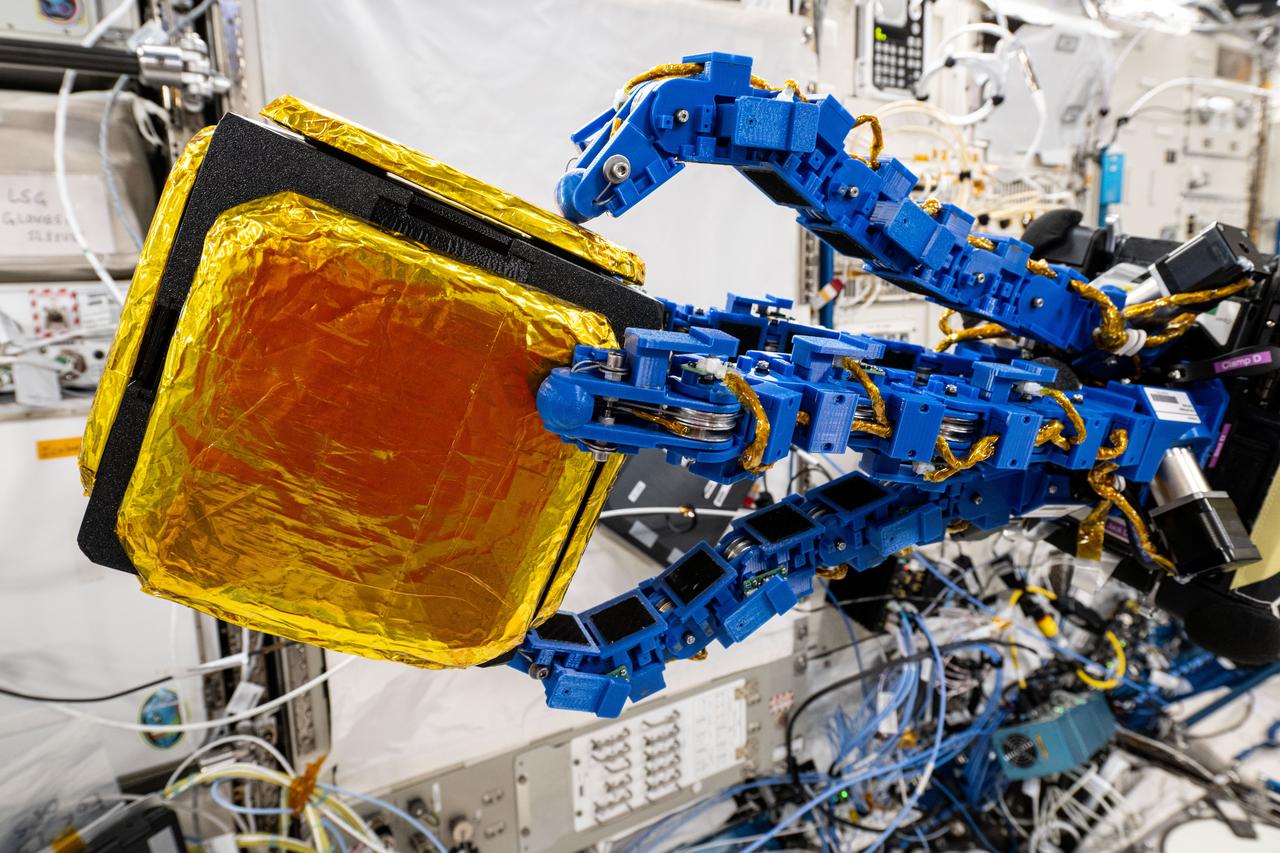
iss072e593737 (Feb. 4, 2025) --- The blue tentacle-like arms containing gecko-like adhesive pads, attached to an Astrobee robotic free-flyer, reach out and grapple a "capture cube" inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. The experimental grippers, outfitted on the toaster-sized Astrobee, demonstrated autonomous detection and capture techniques that may be used to remove space debris and service satellites in low Earth orbit.
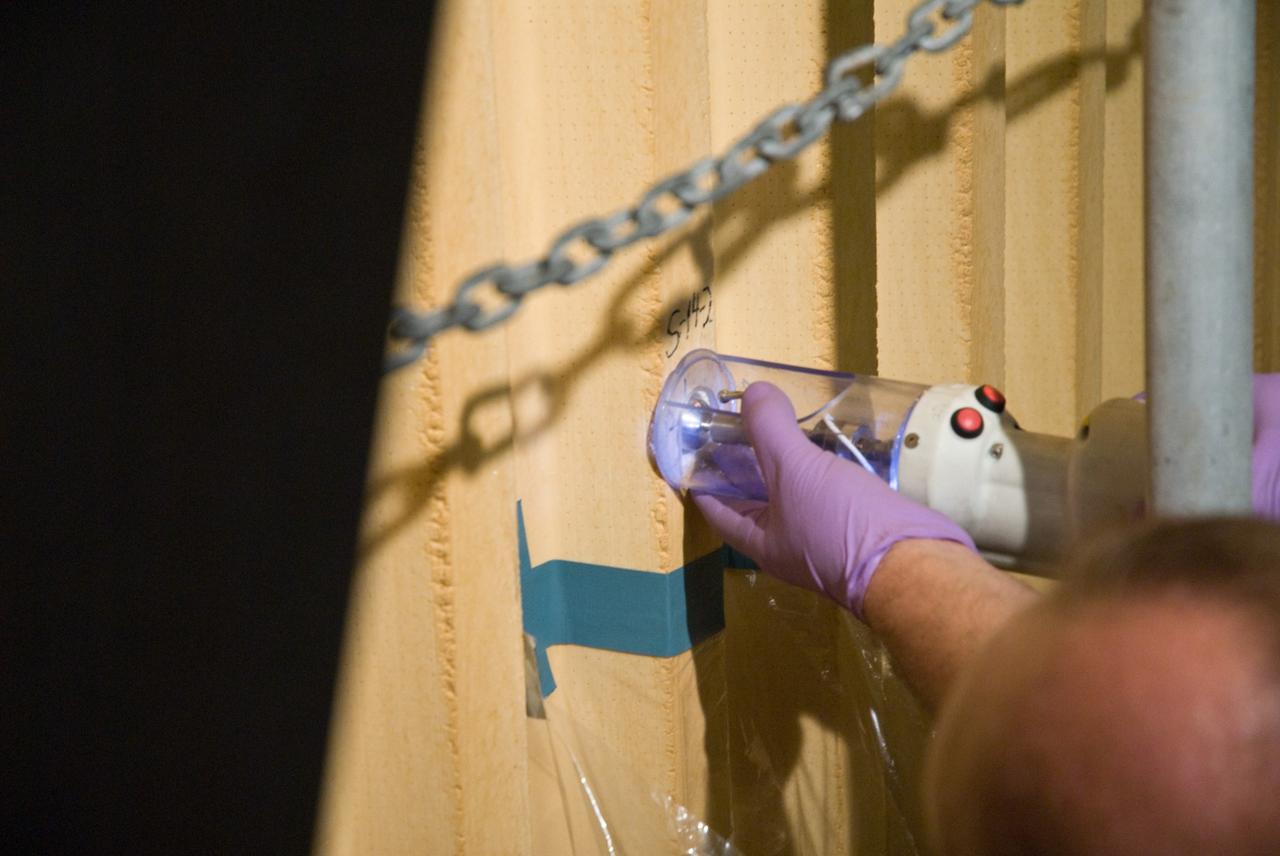

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, foam adhesion is being tested on the intertank of space shuttle Discovery's external tank. Foam samples an inch-and-half in diameter are being collected for analysis to confirm the foam is bonded well to the metal primer underneath. The testing was prompted by the foam loss during launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission July 15. Samples are being sent to Michoud for study. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
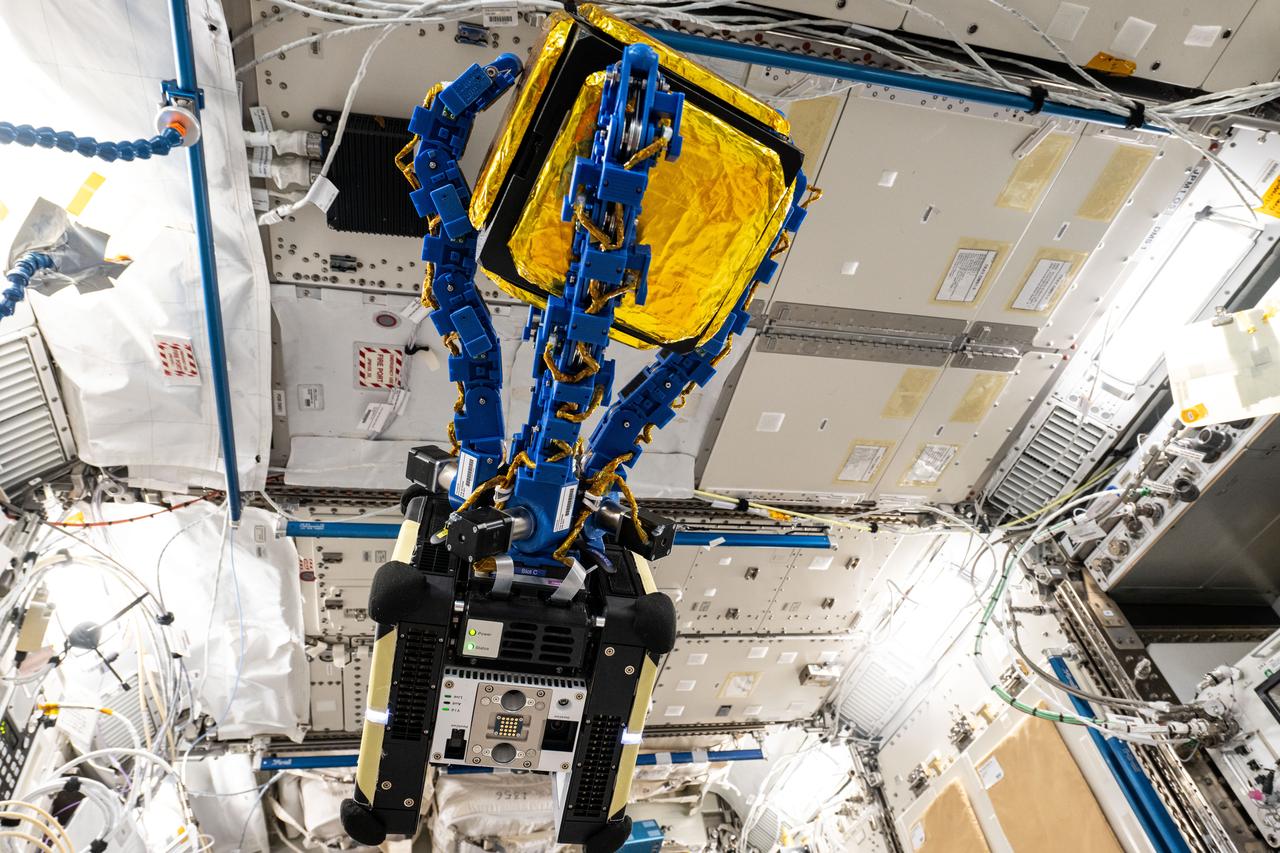

iss072e593734 (Feb. 4, 2025) --- The blue tentacle-like arms containing gecko-like adhesive pads, attached to an Astrobee robotic free-flyer, reach out and grapple a "capture cube" inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. The experimental grippers, outfitted on the toaster-sized Astrobee, demonstrated autonomous detection and capture techniques that may be used to remove space debris and service satellites in low Earth orbit.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mike Williams, a thermal protection system technician with United Space Alliance, applies adhesive to the right wing of space shuttle Endeavour in preparation for tile bonding. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
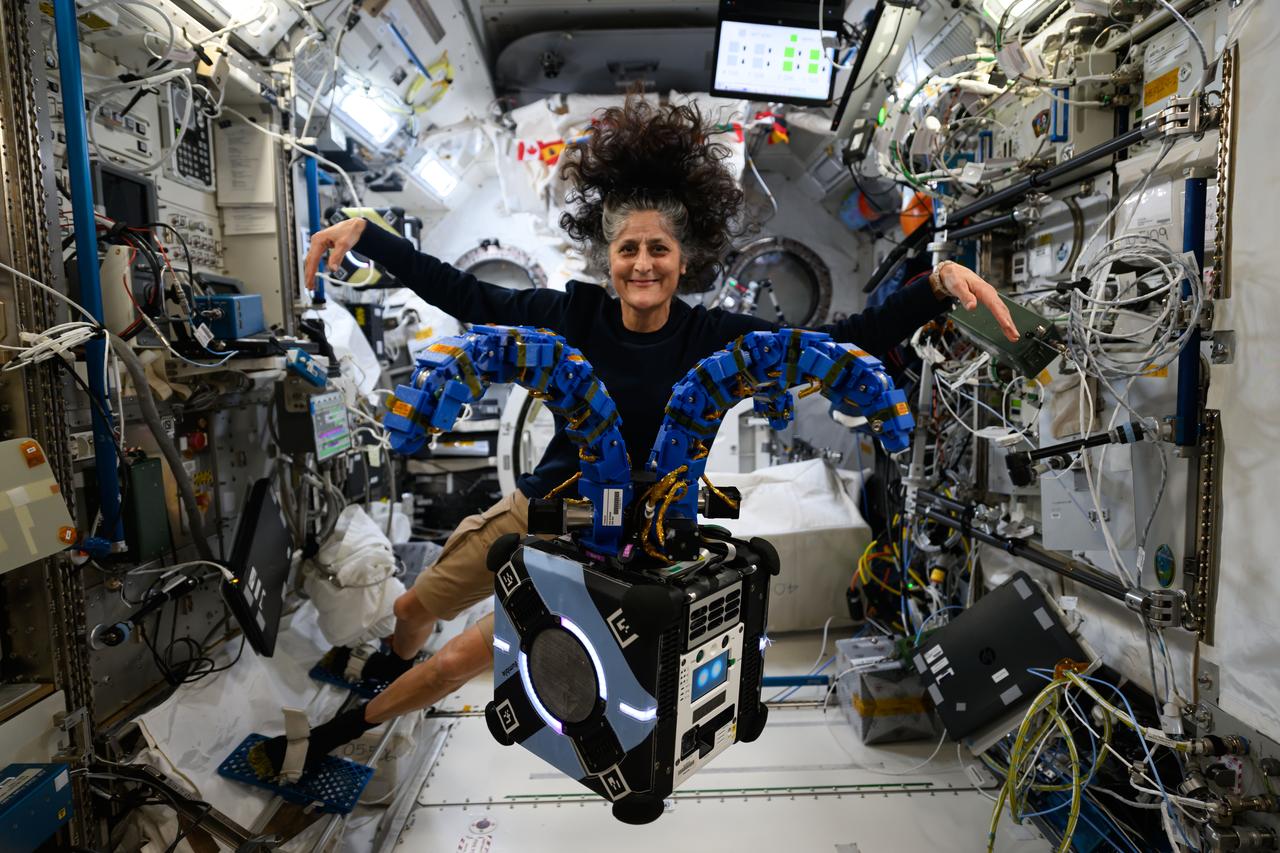

iss072e189028 (Nov. 15, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams checks out the Astrobee robotic free-flyer in the Kibo laboratory module outfitted with tentacle-like arms containing gecko-like adhesive pads to demonstrate satellite capture techniques. Development of this robotic technology may increase the life span of satellites and enable the removal of space debris.
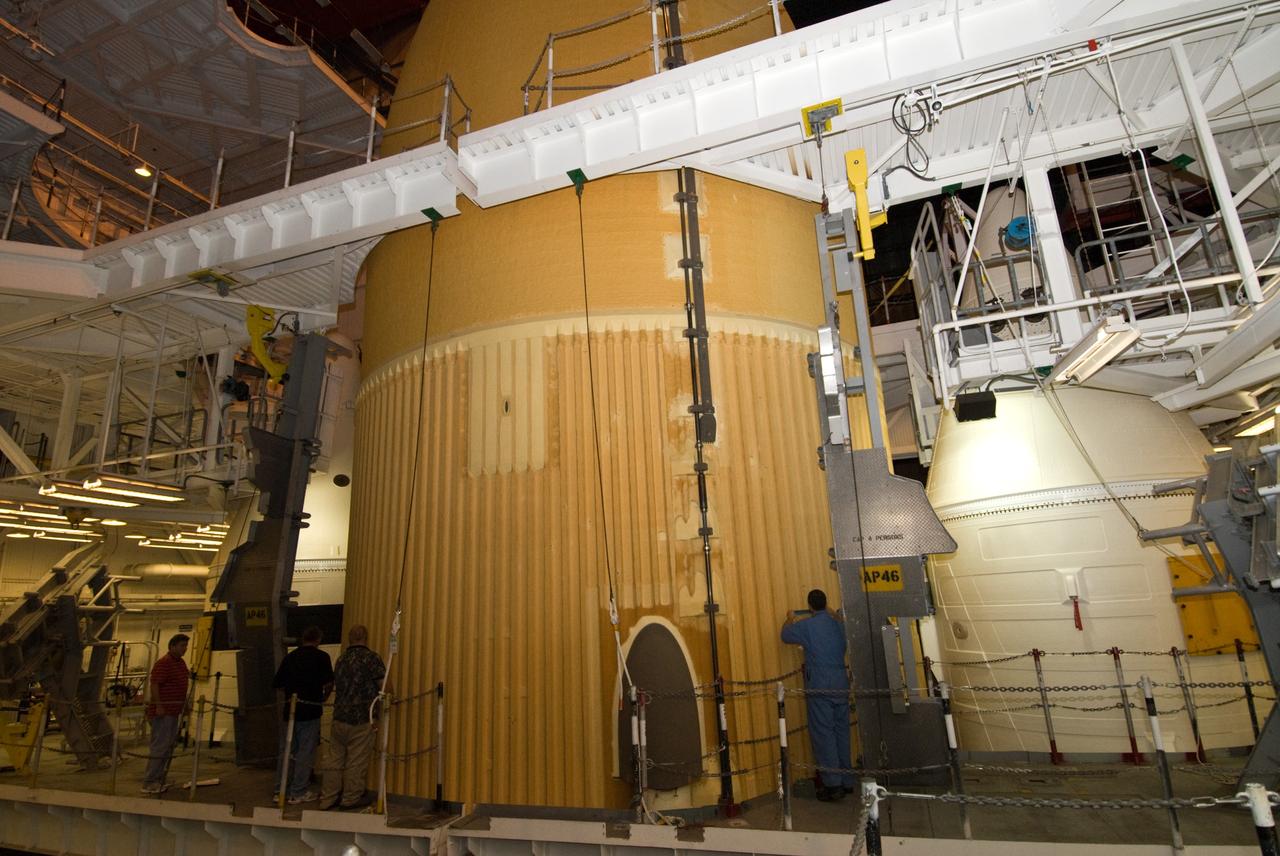

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers begin "pull plug testing" on foam adhesion from the intertank of space shuttle Discovery's external tank. They are collecting 26 foam samples an inch-and-half in diameter for analysis to confirm the foam is bonded well to the metal primer underneath. The testing was prompted by the foam loss during launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission July 15. Samples are being sent to Michoud for study. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
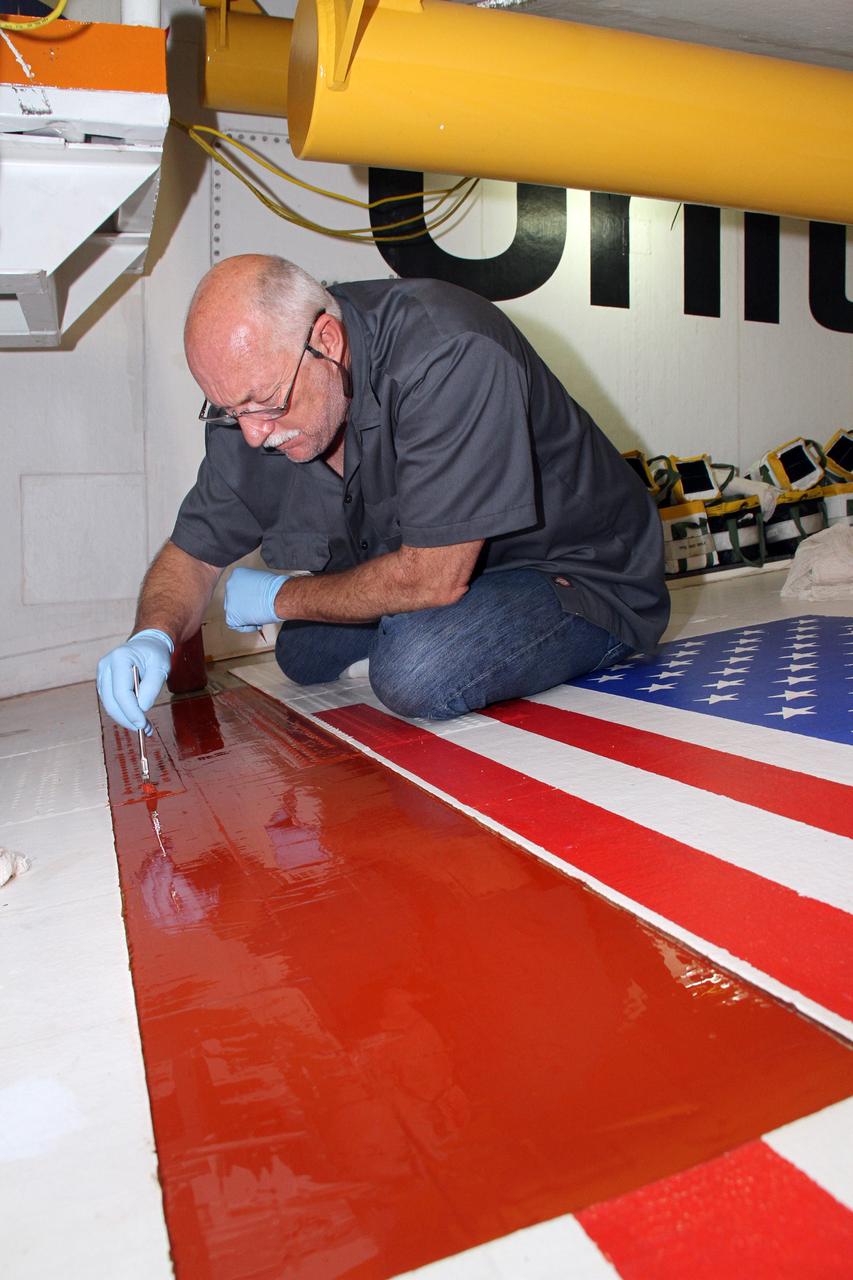

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mike Williams, a thermal protection system technician with United Space Alliance, puts the finishing touches on a layer of adhesive applied to the right wing of space shuttle Endeavour. The work is being done in preparation for tile bonding. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
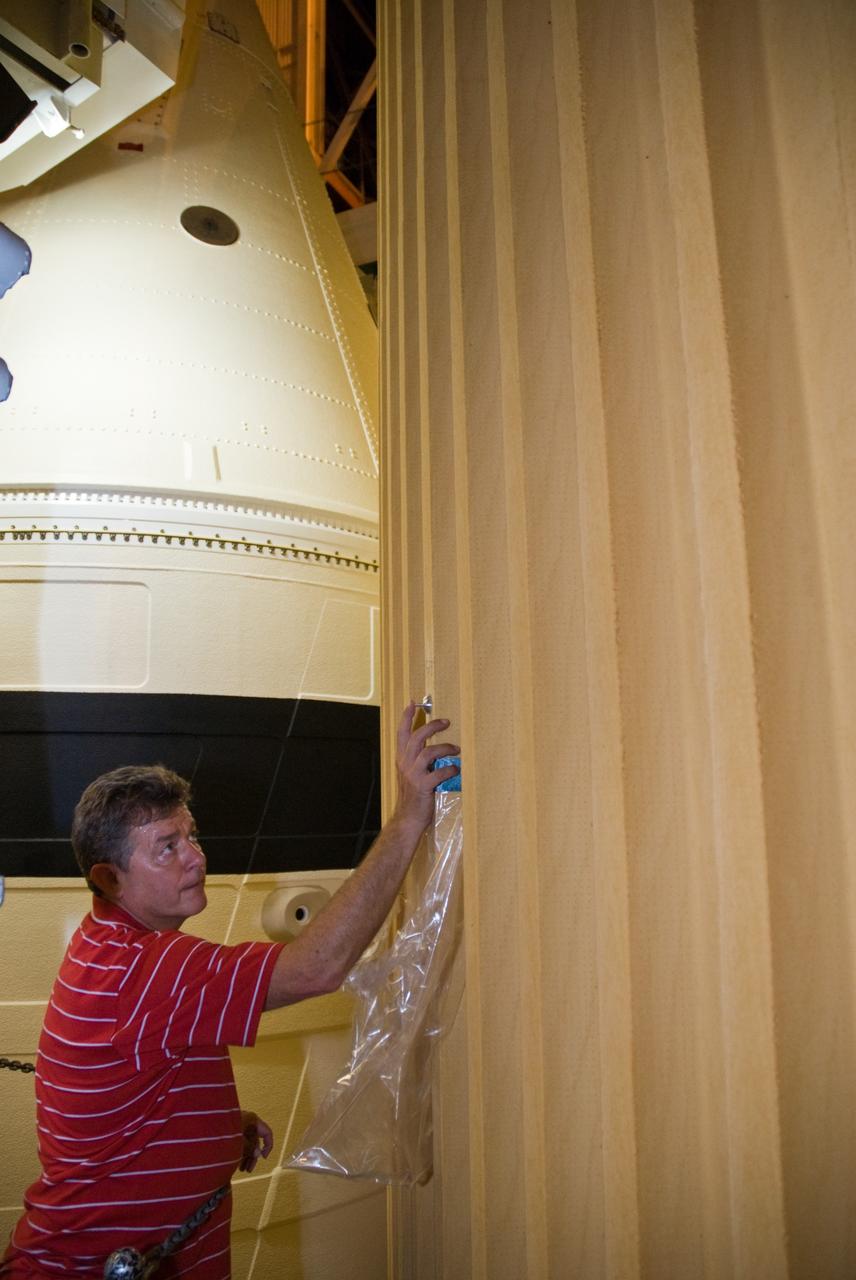

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Eugene Sweet, a principal liaison engineer from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans where the external fuel tanks are built, is testing foam adhesion on the intertank of space shuttle Discovery's external tank. He is collecting foam samples an inch-and-half in diameter for analysis to confirm the foam is bonded well to the metal primer underneath. The testing was prompted by the foam loss during launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission July 15. Samples are being sent to Michoud for study. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
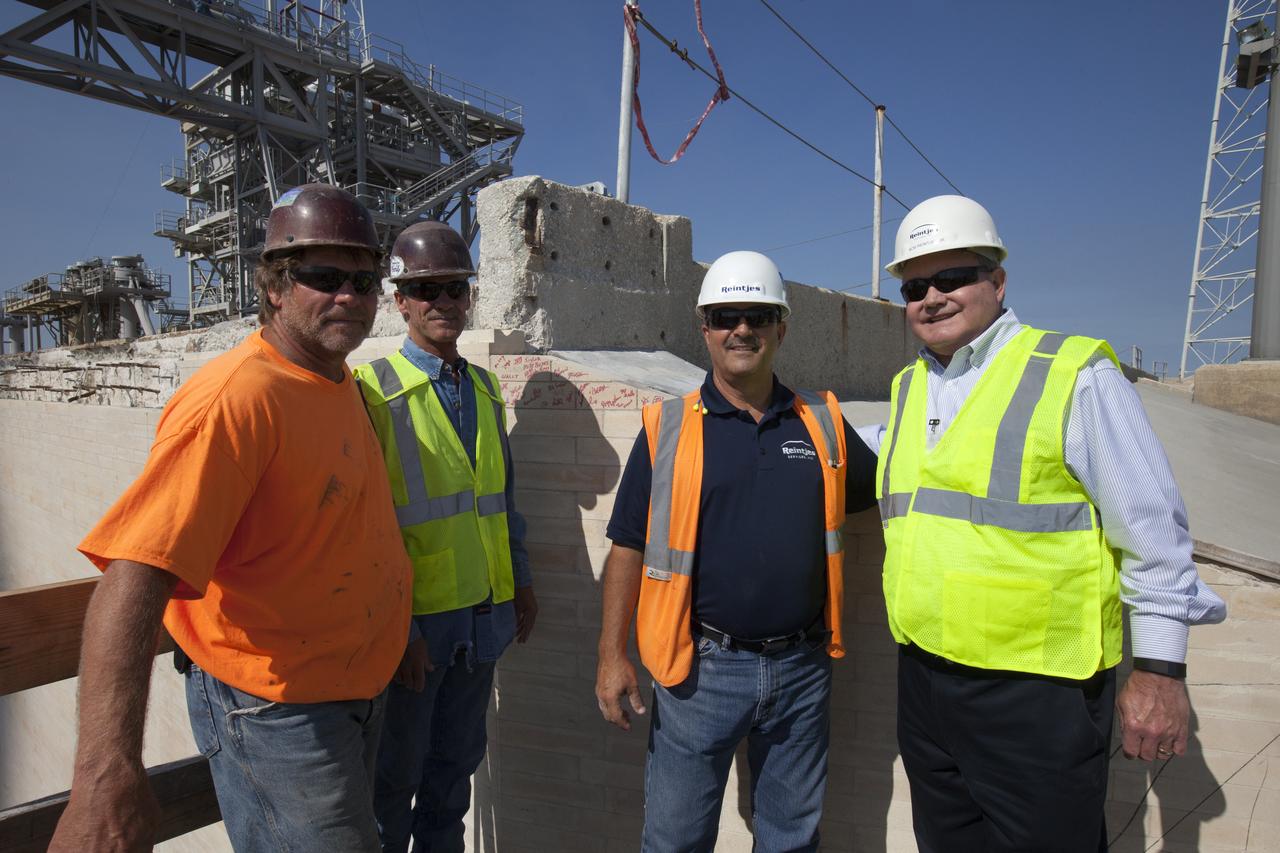

Construction workers sign the final bricks after they were installed on the north side of the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The walls of the flame trench are being upgraded to withstand the intense heat and fire at launch of NASA's Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop. About 96,000 heat-resistant bricks, in three different sizes, were secured to the walls using bonding mortar in combination with adhesive anchors. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and NASA’s journey to Mars.
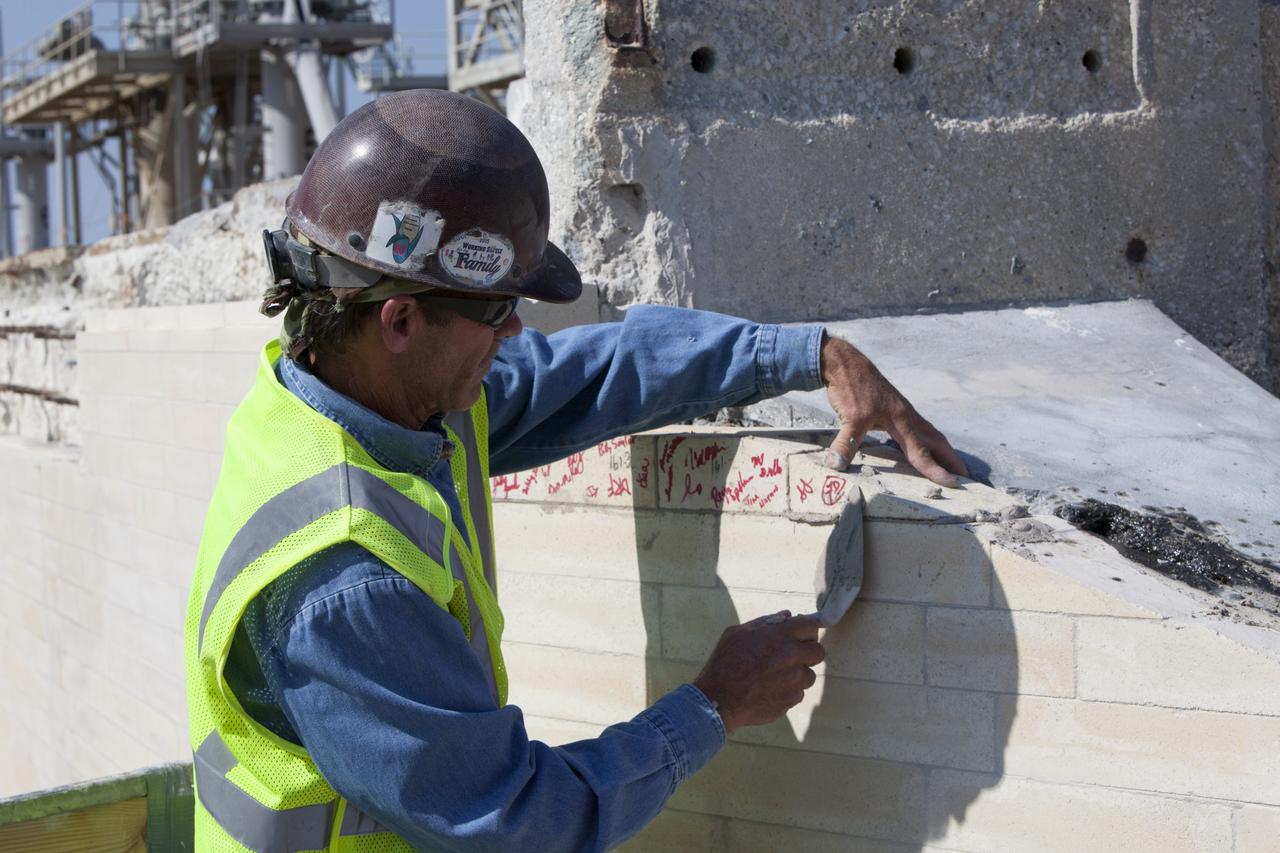

A construction worker installs the final brick on the north side of the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The walls of the flame trench are being upgraded to withstand the intense heat and fire at launch of NASA's Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop. About 96,000 heat-resistant bricks, in three different sizes, were secured to the walls using bonding mortar in combination with adhesive anchors. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and NASA’s journey to Mars.

The final brick was installed on the north side of the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The walls of the flame trench are being upgraded to withstand the intense heat and fire at launch of NASA's Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop. About 96,000 heat-resistant bricks, in three different sizes, were secured to the walls using bonding mortar in combination with adhesive anchors. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and NASA’s journey to Mars.
/jsc2024e063104 (2)~medium.jpg)
Josh Litofsky leads a Gateway lunar dust adhesion testing campaign at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. His team studies how lunar dust interacts with materials chosen for Gateway's construction. Here, Litofsky carefully positions a sample holder inside a vacuum chamber. Litofksy’s work seeks to validate the Gateway On-orbit Lunar Dust Modeling and Analysis Program (GOLDMAP), developed by Ronald Lee, also of Johnson Space Center. By considering factors such as the design and configuration of the space station, the materials used, and the unique conditions in lunar orbit, GOLDMAP helps predict how dust may move and settle on Gateway’s external surfaces.
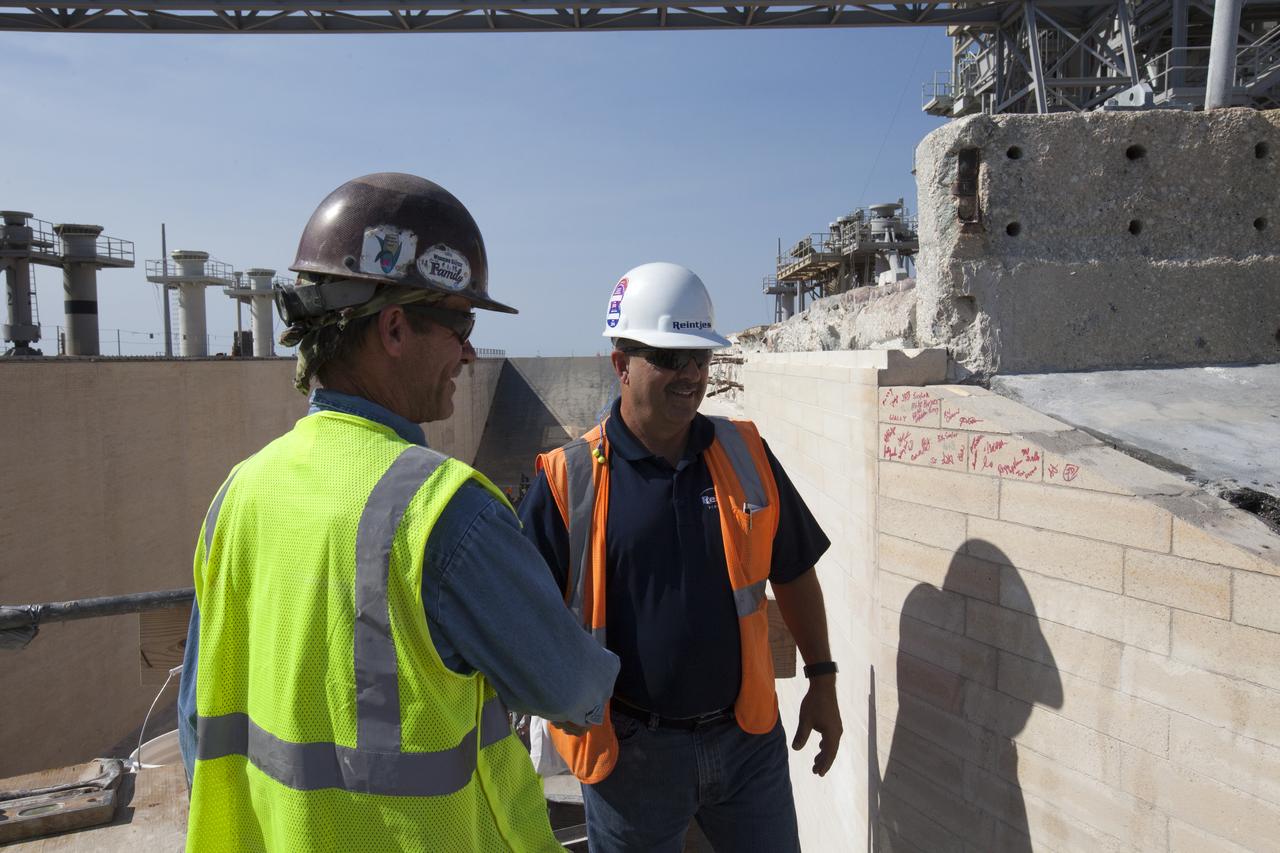

Construction workers sign the final bricks after they were installed on the north side of the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The walls of the flame trench are being upgraded to withstand the intense heat and fire at launch of NASA's Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop. About 96,000 heat-resistant bricks, in three different sizes, were secured to the walls using bonding mortar in combination with adhesive anchors. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and NASA’s journey to Mars.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, David Buras, a Material and Process engineer from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans where the fuel tanks are built, is testing foam adhesion on the intertank of space shuttle Discovery's external tank . He is collecting foam samples an inch-and-half in diameter for analysis to confirm the foam is bonded well to the metal primer underneath. The testing was prompted by the foam loss during launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission July 15. Samples are being sent to Michoud for study. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
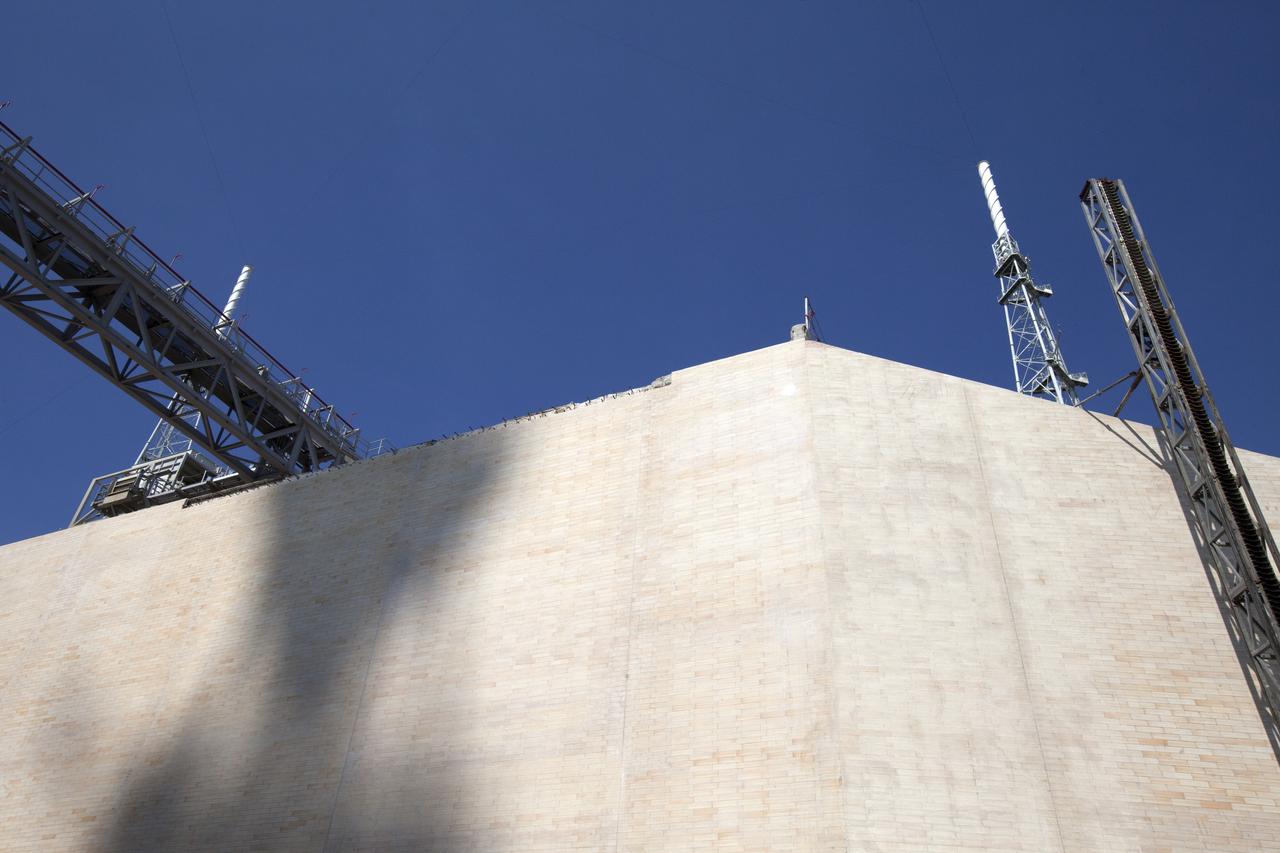

A view looking up from the north side of the flame trench beneath the pad at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The walls of the flame trench are being upgraded to withstand the intense heat and fire at launch of NASA's Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop. About 96,000 heat-resistant bricks, in three different sizes, were secured to the walls using bonding mortar in combination with adhesive anchors. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and NASA’s journey to Mars.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Jeremy Schwarz, left, quality assurance technician, and Mike Williams, right, a thermal protection system technician, both with United Space Alliance, apply adhesive to space shuttle Endeavour's right wing. The work is being done in preparation for tile bonding. Endeavour is inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
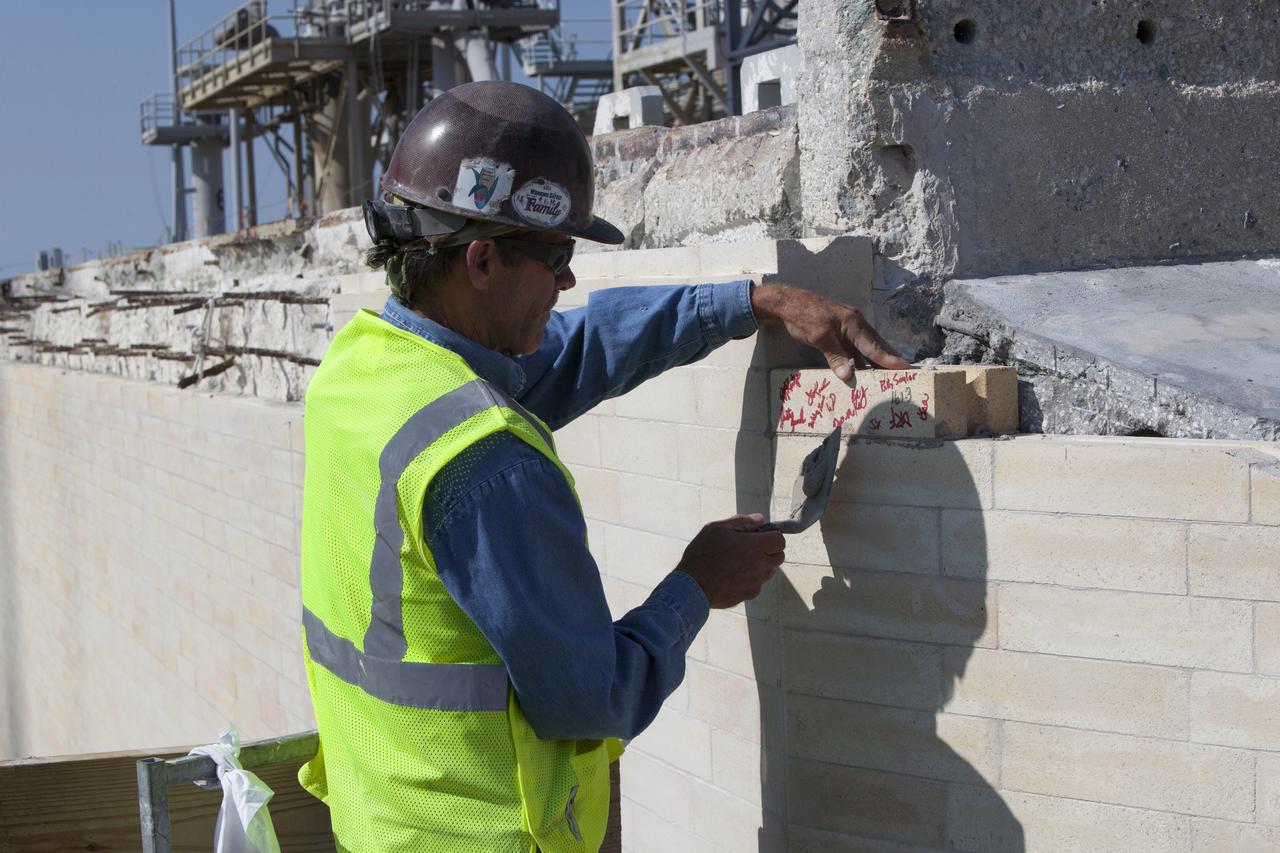

A construction worker installs one of the final bricks on the north side of the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The walls of the flame trench are being upgraded to withstand the intense heat and fire at launch of NASA's Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop. About 96,000 heat-resistant bricks, in three different sizes, were secured to the walls using bonding mortar in combination with adhesive anchors. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and NASA’s journey to Mars.
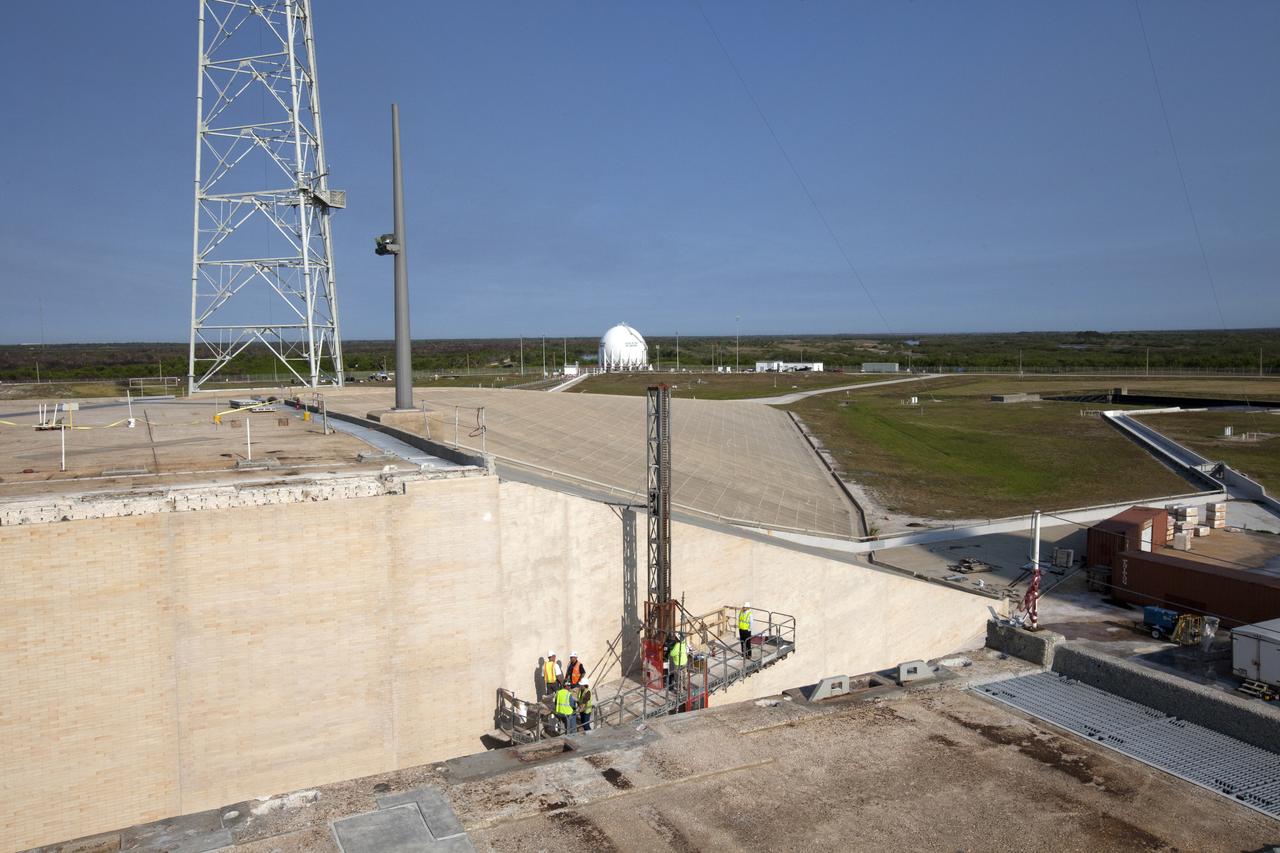

Preparations are underway to install the final brick on the north side of the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The walls of the flame trench are being upgraded to withstand the intense heat and fire at launch of NASA's Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop. About 96,000 heat-resistant bricks, in three different sizes, were secured to the walls using bonding mortar in combination with adhesive anchors. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and NASA’s journey to Mars.
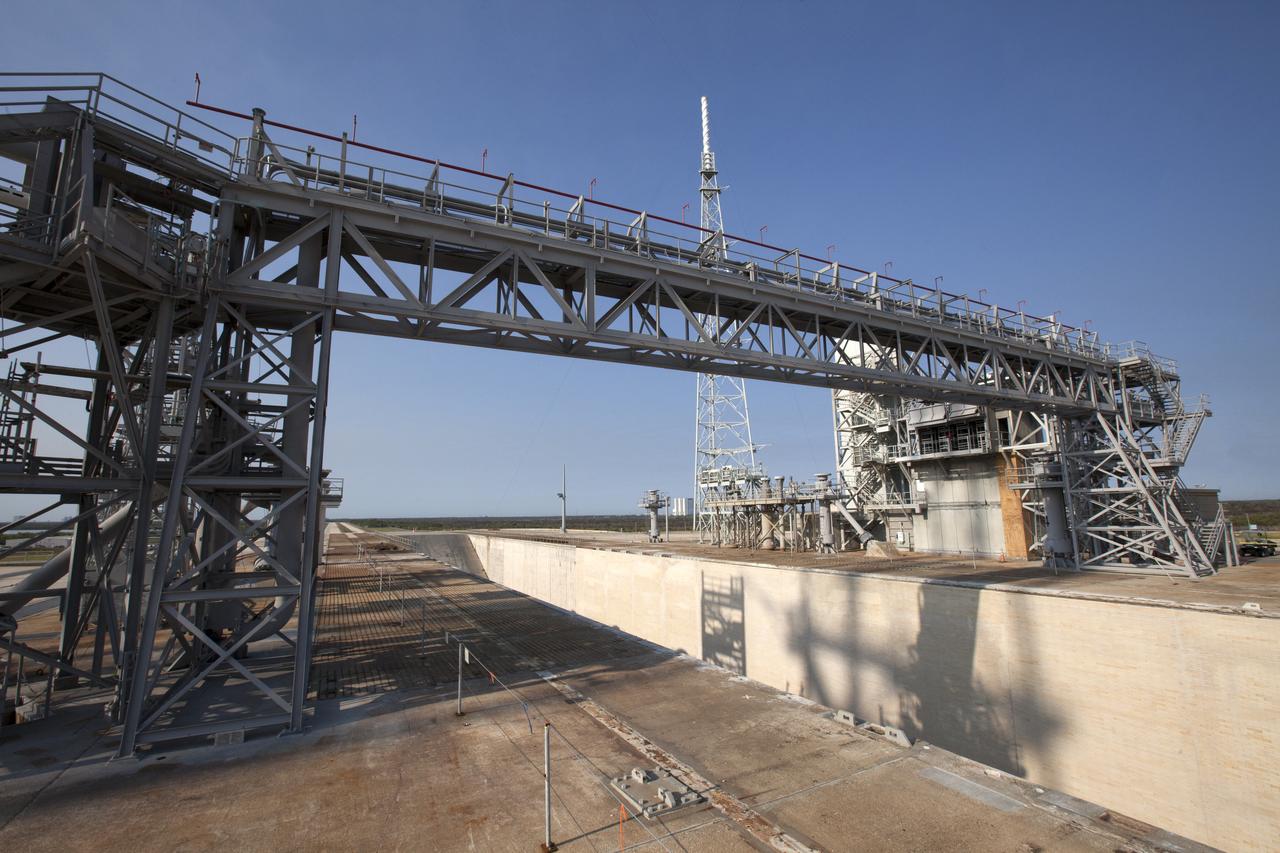

A view of the north side of the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The final brick was installed in the flame trench, completing about a year's worth of work to upgrade the walls to withstand the intense heat and fire at launch of NASA's Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop. About 96,000 heat-resistant bricks, in three different sizes, were secured to the walls using bonding mortar in combination with adhesive anchors. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and NASA’s journey to Mars.
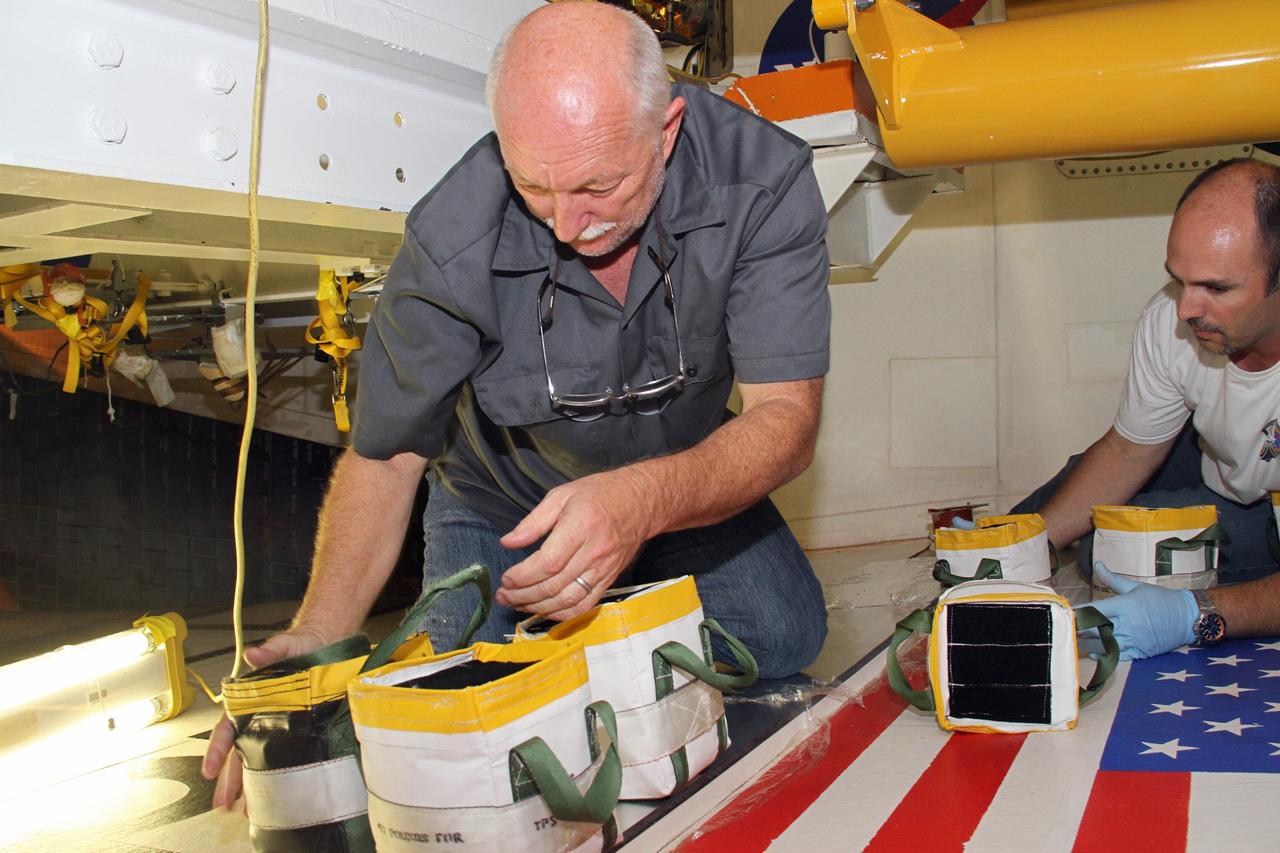

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mike Williams, left, a thermal protection system technician, and Jeremy Schwarz, right, quality assurance technician, both with United Space Alliance, set weights atop a newly installed section of tile on the right wing of space shuttle Endeavour at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The weights will hold the section in place while the adhesive hardens beneath. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
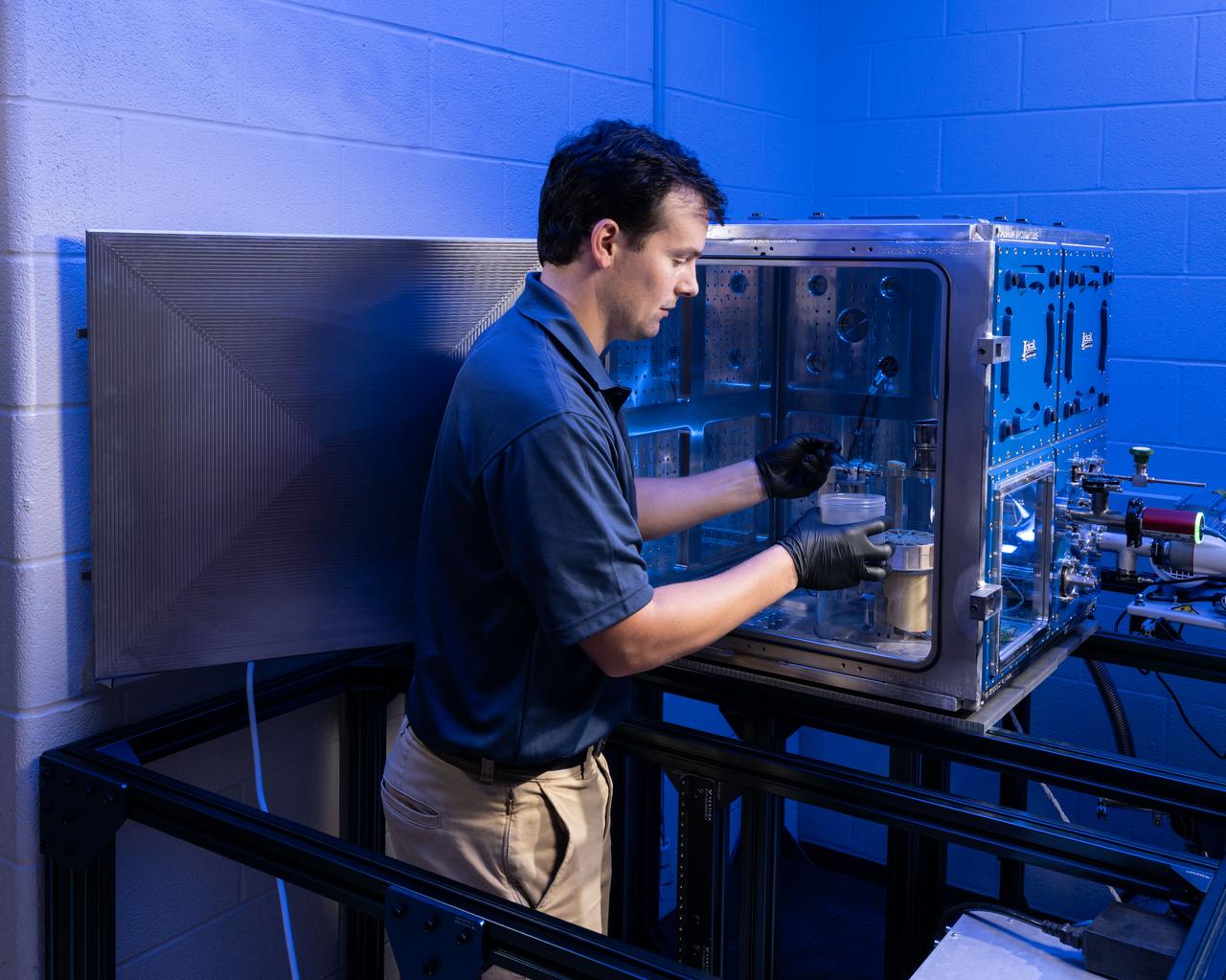

Josh Litofsky leads a Gateway lunar dust adhesion testing campaign at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. His team studies how lunar dust interacts with materials chosen for Gateway's construction. Here, Litofsky scoops lunar stimulant into a sample holder. Litofksy’s work seeks to validate the Gateway On-orbit Lunar Dust Modeling and Analysis Program (GOLDMAP), developed by Ronald Lee, also of Johnson Space Center. By considering factors such as the design and configuration of the space station, the materials used, and the unique conditions in lunar orbit, GOLDMAP helps predict how dust may move and settle on Gateway’s external surfaces.
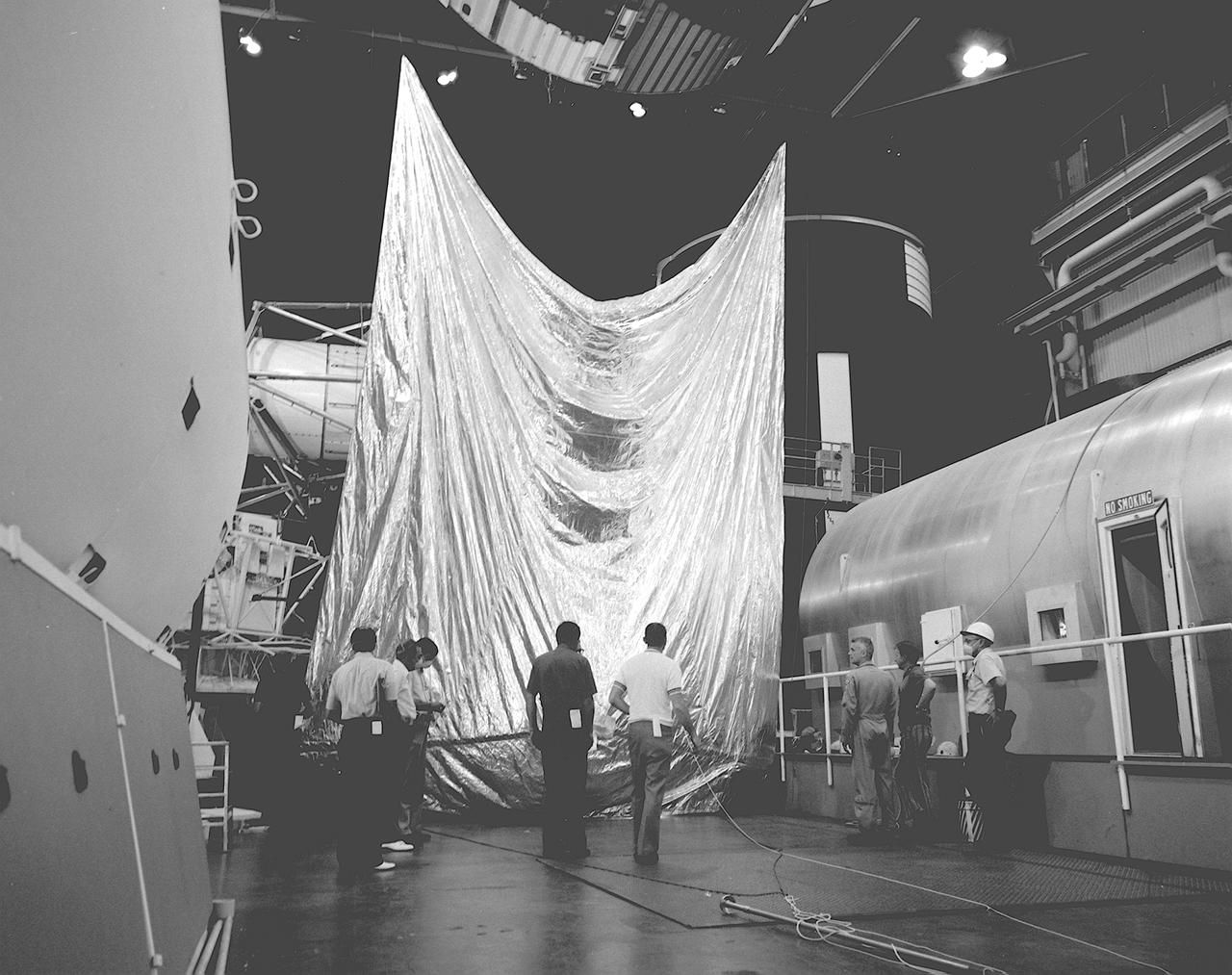

Engineers from the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and its contractors were testing the twin-pole sunshade at the Skylab mockup in the MSFC Building 4619. The Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) lost its thermal protection shield during launch on May 14, 1963. Without the heat shield, the temperature inside the OWS became dangerously high, rendering the workshop uninhabitable and threatened deterioration of the interior insulation and adhesive. Engineers from the MSFC, its contractors, and NASA persornel at other centers worked day and night for several days to develop the way to save the Skylab OWS. Eventually, they developed, tested, rehearsed, and approved three repair options. These options included a parasol sunshade and a twin-pole sunshade to restore the temperature inside the workshop, and a set of metal cutting tools to free the jammed solar panel.
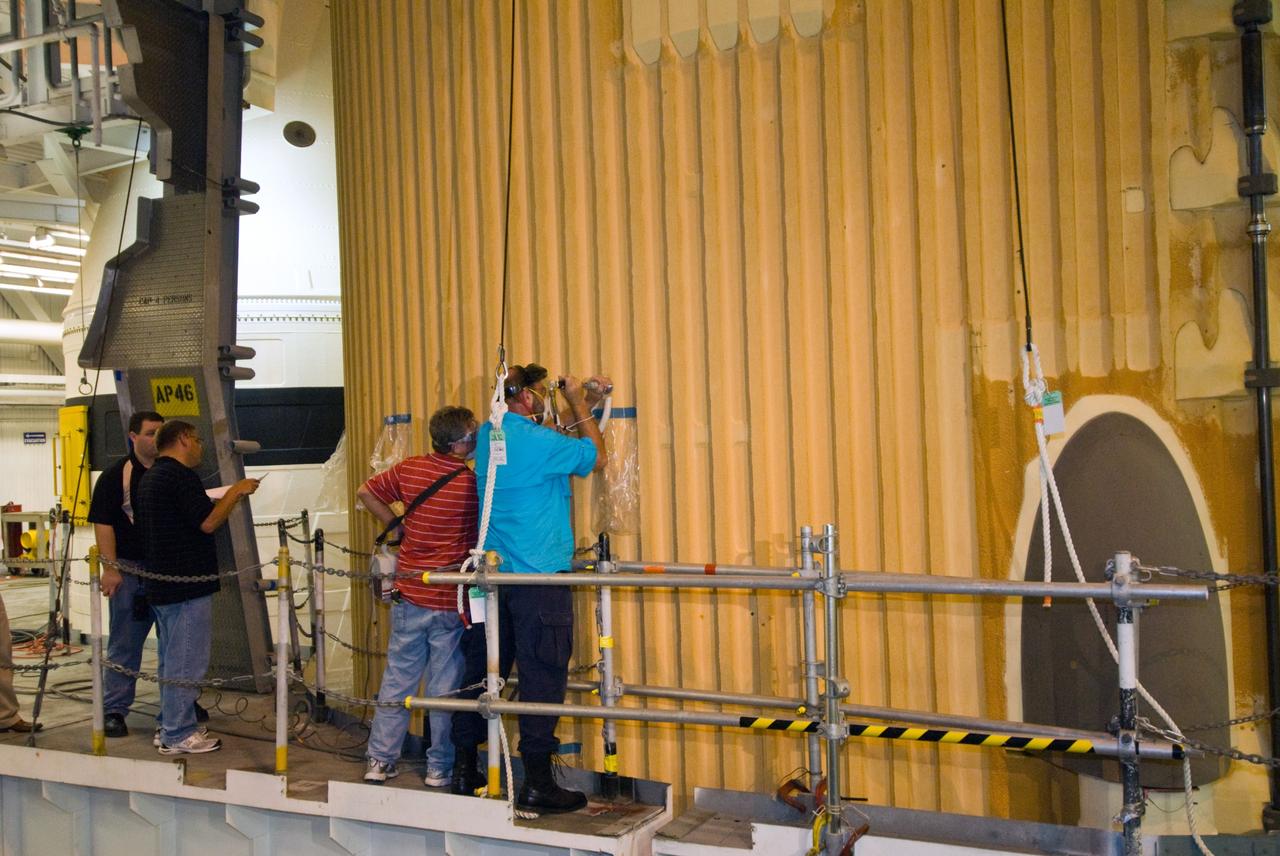

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are testing foam adhesion on the intertank of space shuttle Discovery's external tank. At right are Eugene Sweet (red shirt), principal liaison engineer, and David Buras, a Material and Process engineer from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans where the fuel tanks are built. They are collecting 26 foam samples an inch-and-half in diameter for analysis to confirm the foam is bonded well to the metal primer underneath. The testing was prompted by the foam loss during launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission July 15. Samples are being sent to Michoud for study. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
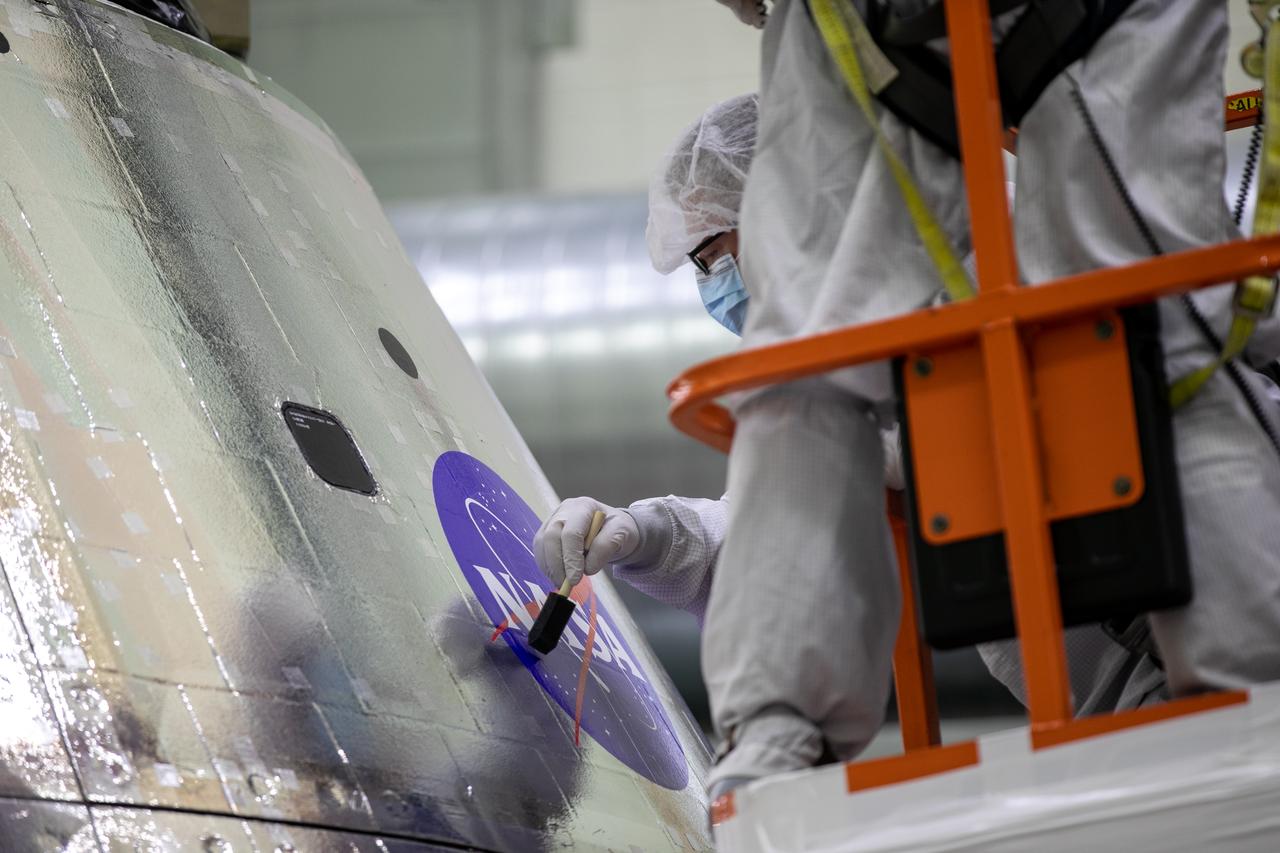

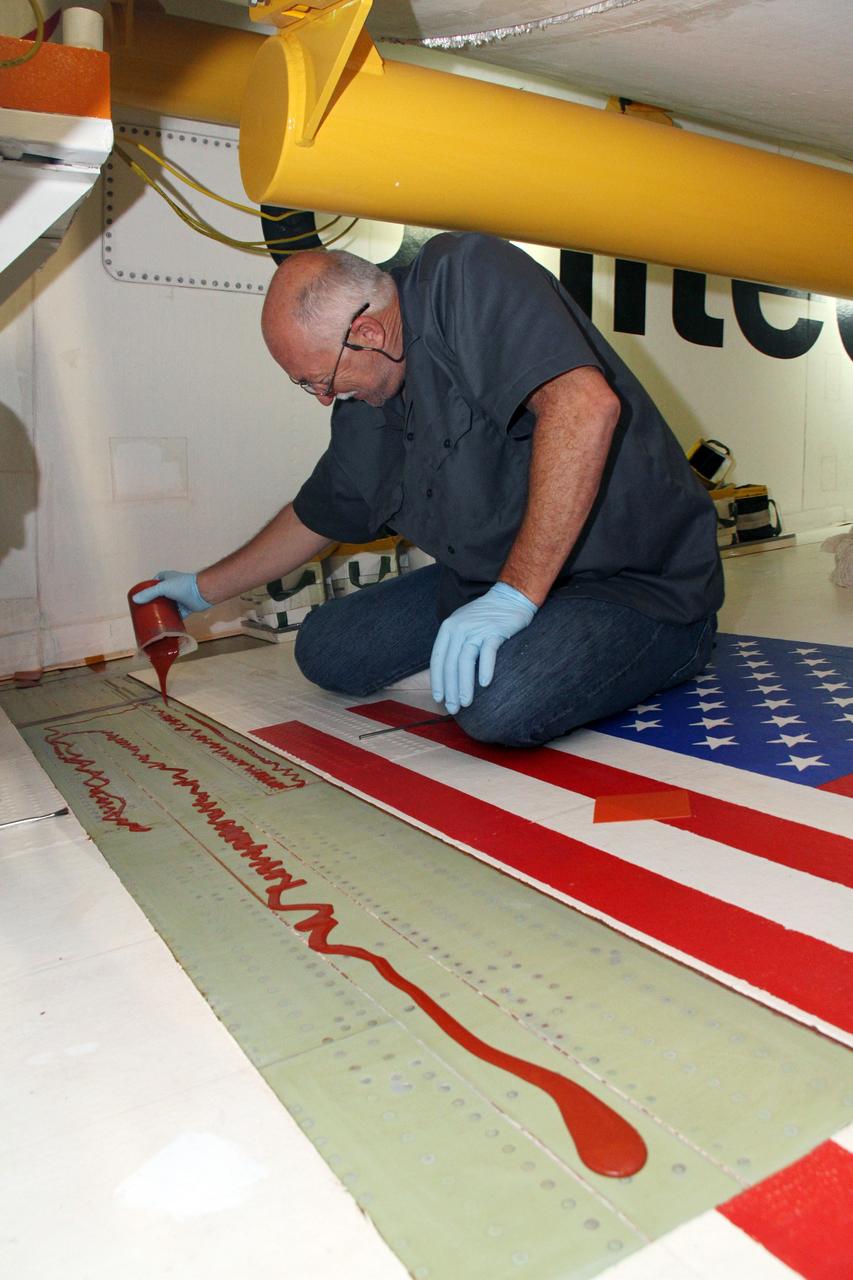
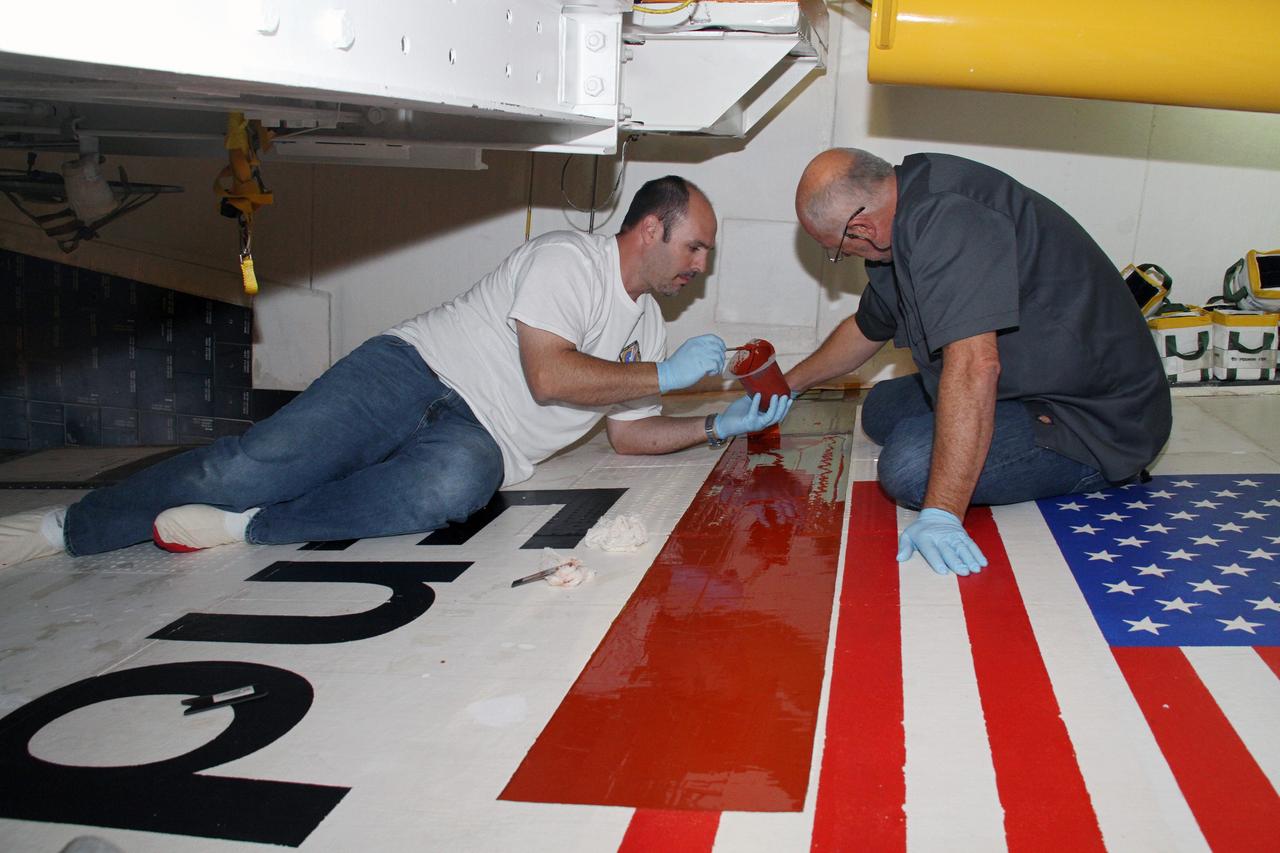
Frank Pelkey, ASRC technician, paints a clear adhesive over the NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” on the Orion crew module back shell for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The American Flag also has been added. Attached below Orion (not in view) are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
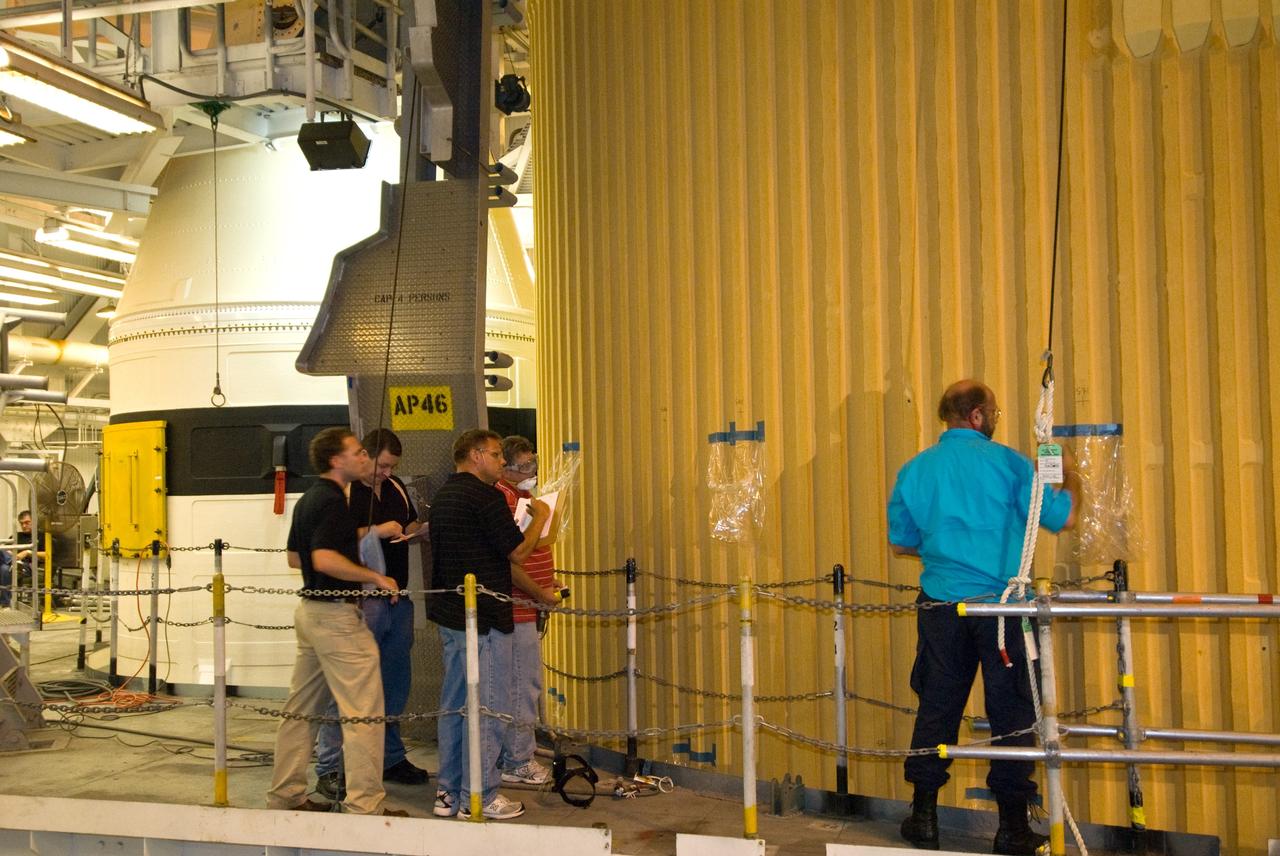

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are doing "pull plug testing" on foam adhesion from the intertank of space shuttle Discovery's external tank. At right is David Buras, a Material and Process engineer from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans where the fuel tanks are built. They are collecting 26 foam samples an inch-and-half in diameter for analysis to confirm the foam is bonded well to the metal primer underneath. The testing was prompted by the foam loss during launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission July 15. Samples are being sent to Michoud for study. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
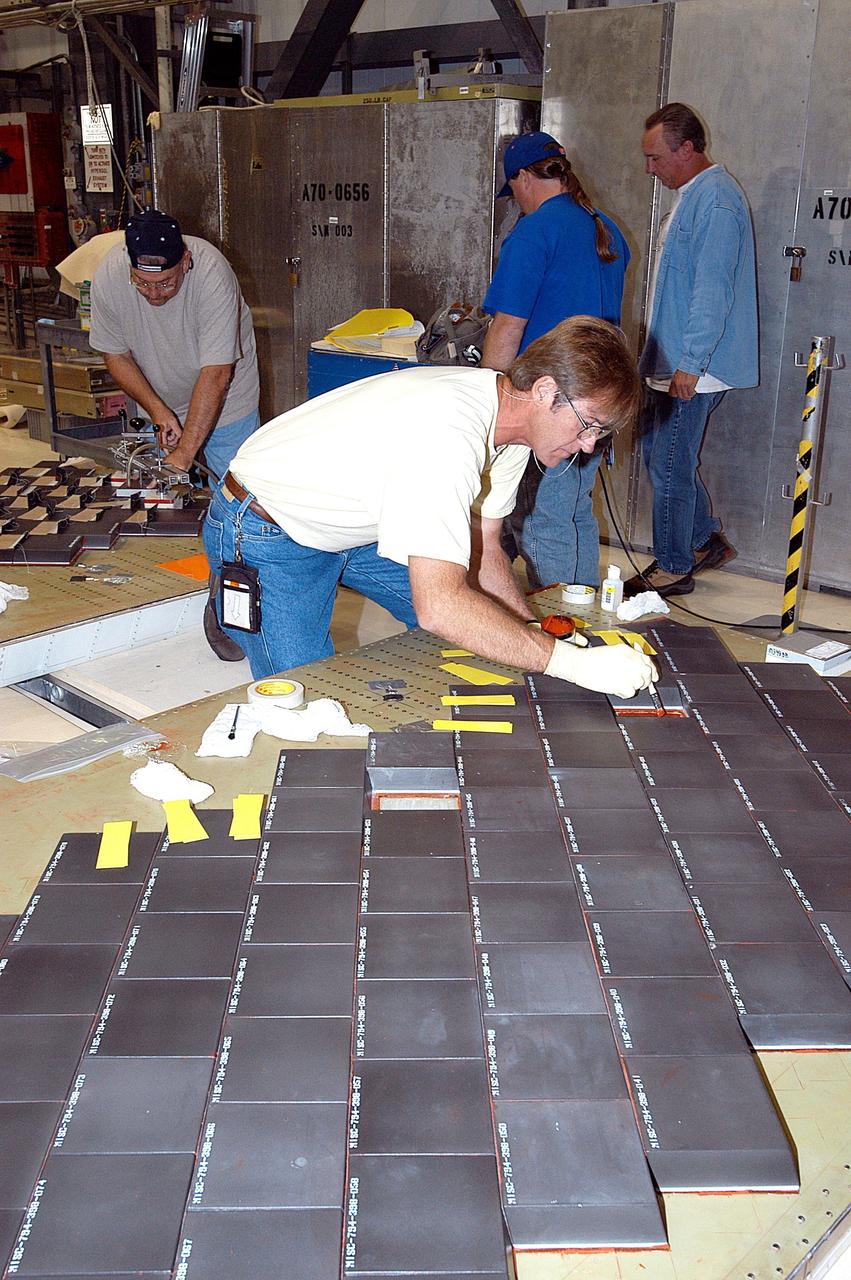

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Harrell Watts applies RTV, a room-temperature vulcanizing silicone adhesive, to a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) on which Thermal Protection System tiles are being installed. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
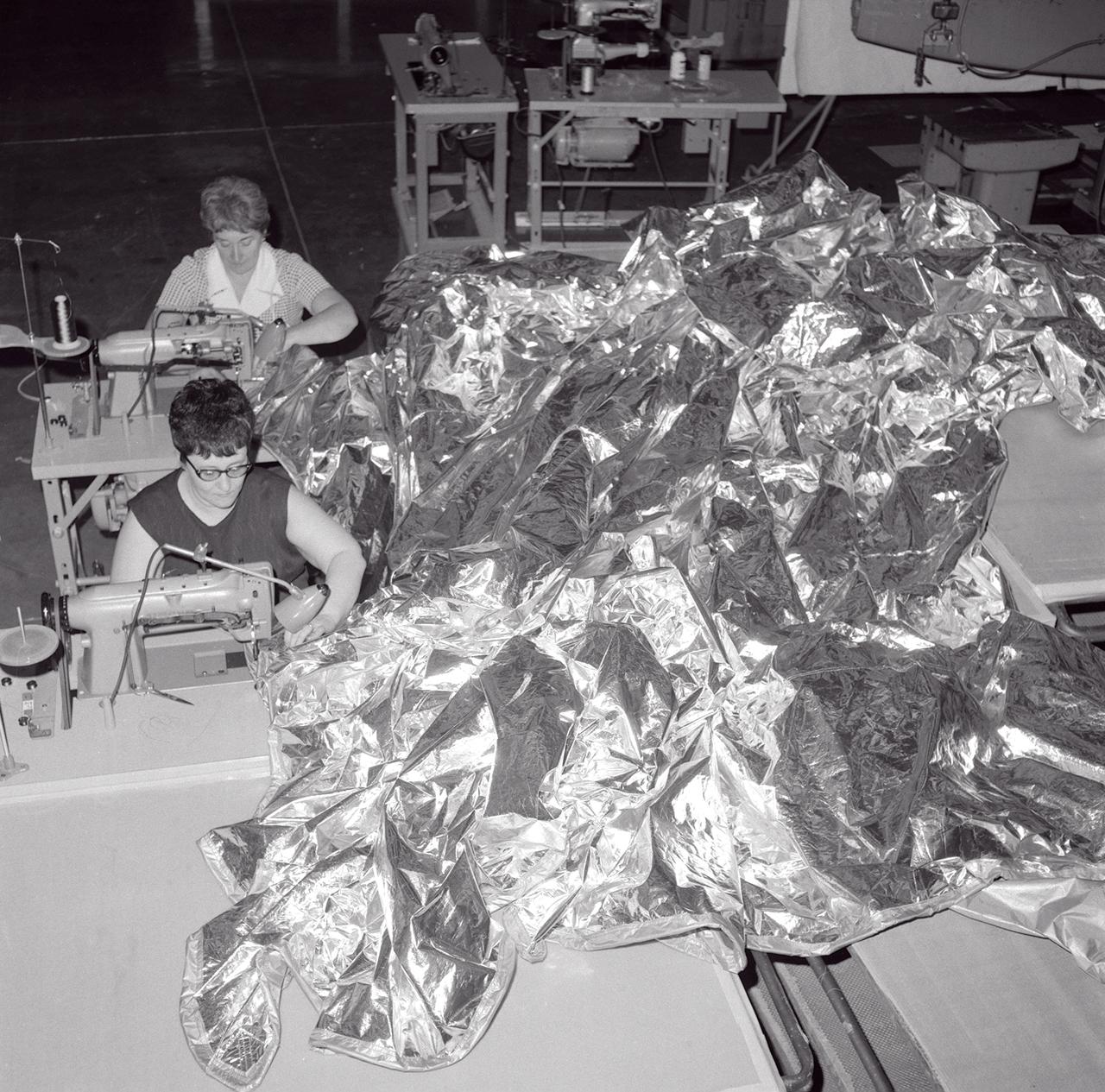

Two seamstresses stitch together a sun-shade for Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS), the first U.S. experimental space station in orbit, which lost its thermal protection shield during the launch on May 14, 1973. Without the heat shield, the temperature inside the Orbital Workshop became dangerously high, rendering the workshop uninhabitable and threatened deterioration of the interior insulation and adhesive. Engineers and scientists at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) worked tirelessly around the clock on the emergency repair procedure. The Skylab crew and the repair kits were launched just 11 days after the incident. The crew successfully deployed the twin-pole sail parasol sun-shade during their EVA (Extravehicular Activity) the next day.
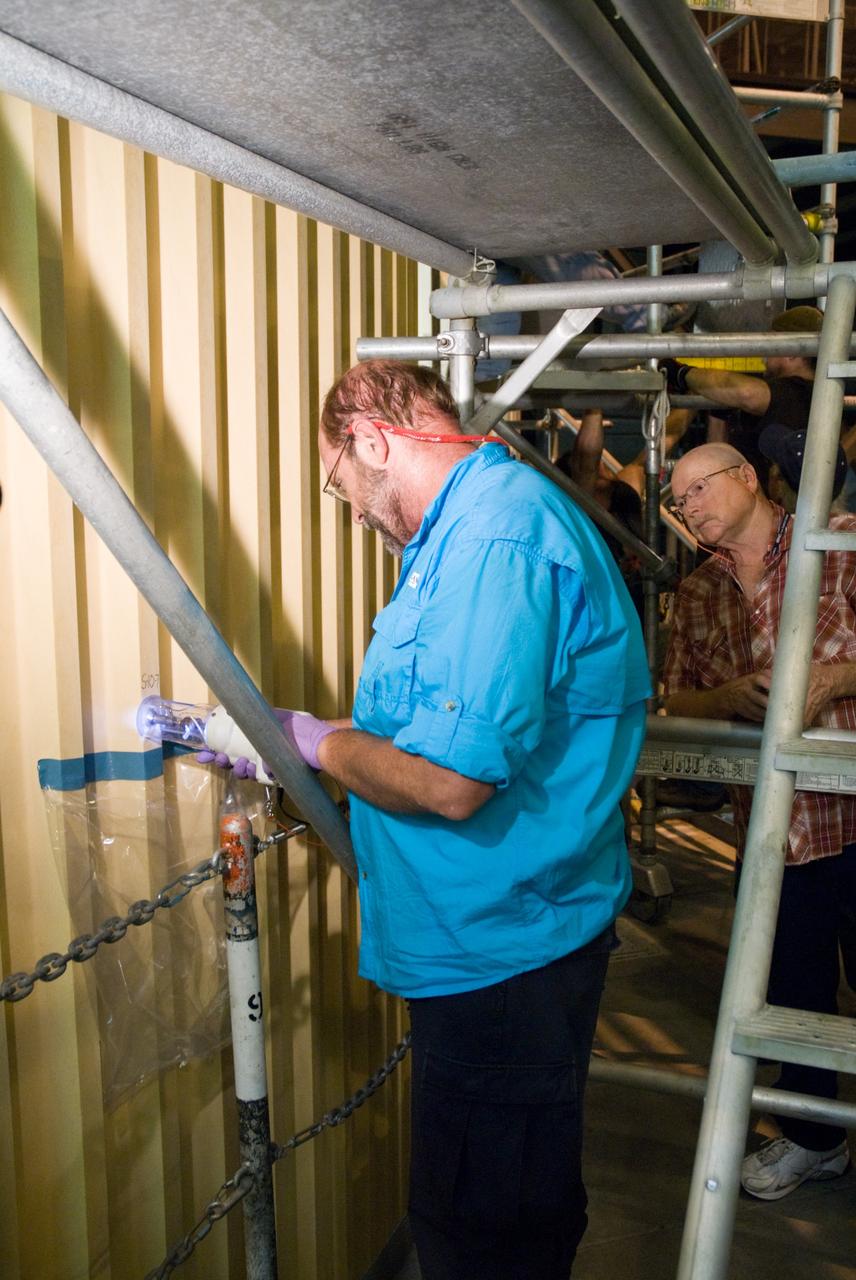

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, David Buras, a Material and Process engineer from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans where external fuel tanks are built, is testing foam adhesion on the intertank of space shuttle Discovery's external tank. He is collecting foam samples an inch-and-half in diameter for analysis to confirm the foam is bonded well to the metal primer underneath. At right is Jerrol Kinsey, a NASA quality inspector. The testing was prompted by the foam loss during launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission July 15. Samples are being sent to Michoud for study. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Eugene Sweet (left), a principal liaison engineer, and David Buras, a Material and Process engineer from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans where the fuel tanks are built, are testing foam samples taken from the intertank of space shuttle Discovery's external tank. They are collecting foam samples an inch-and-half in diameter for analysis to confirm the foam is bonded well to the metal primer underneath. The testing of foam adhesion was prompted by the foam loss during launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission July 15. Samples are being sent to Michoud for study. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
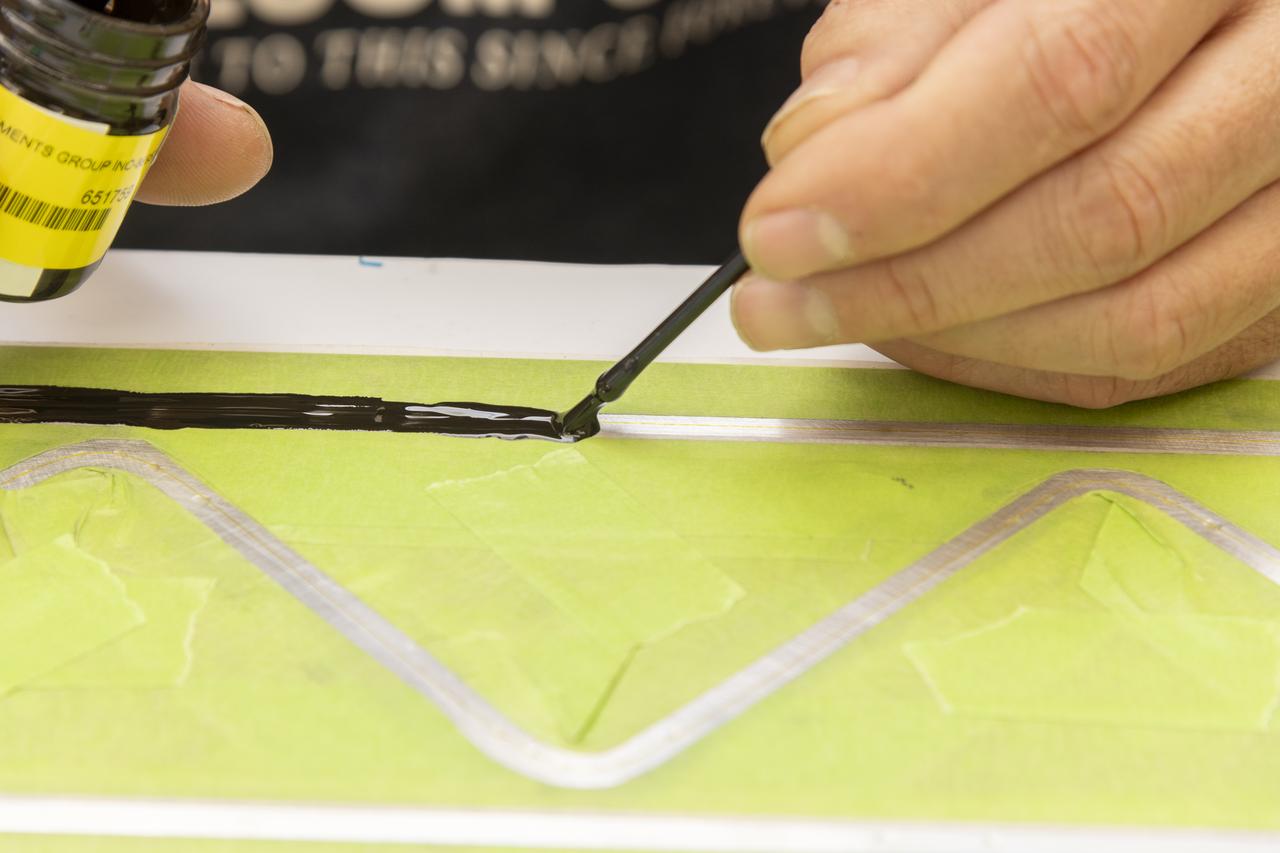
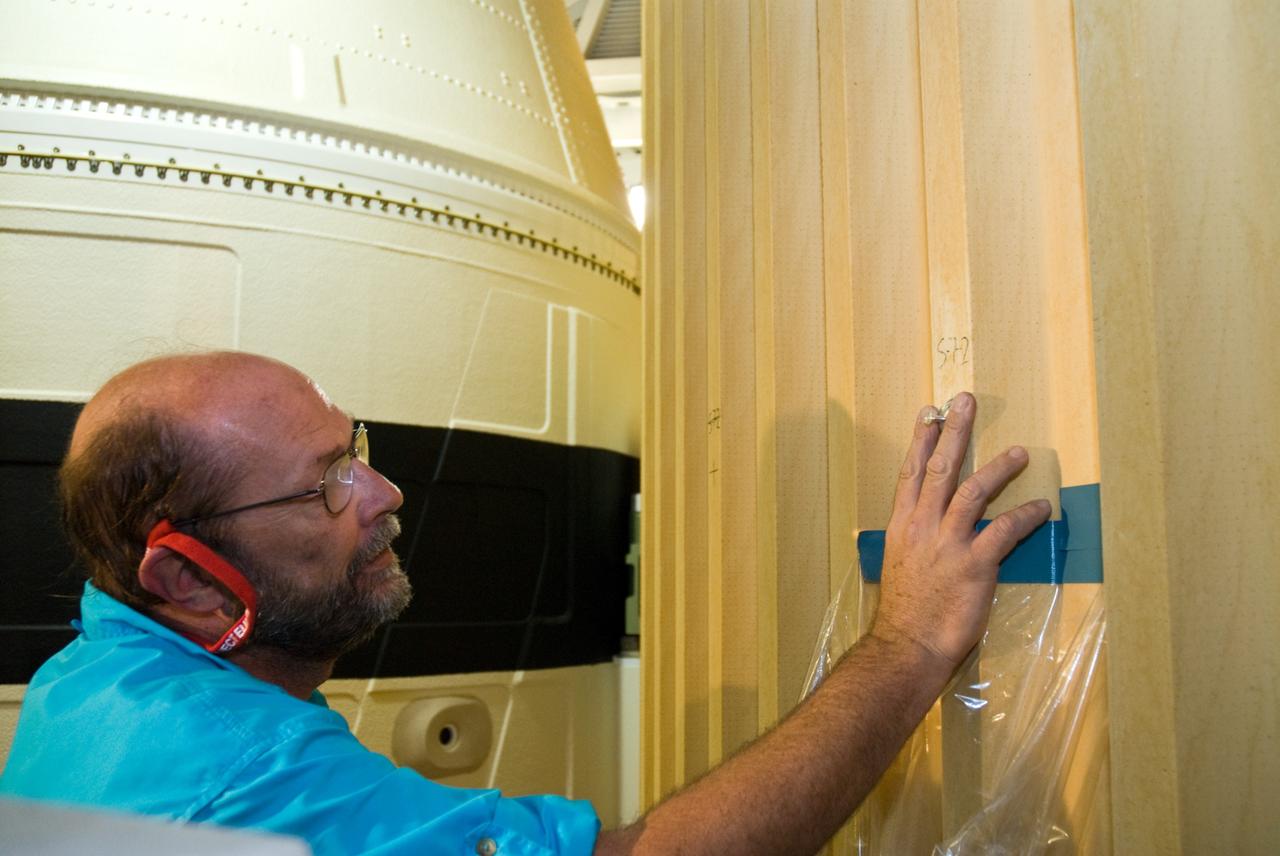
An epoxy is applied to adhere the fiber optic sensor installation on the Mock Truss-Braced Wing 10-foot model at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.

This image, received today, shows the trench excavated by NASA's Viking 1 surface sampler. The trench was dug by extending the surface sampler collection head in a direction from lower right toward the upper left and then withdrawing the surface sampler collector head. Lumpy piles of material at end of trench at lower right was pulled by plowing from trench by the backhoe which will be used to dig trenches later in the mission. Area around trench has ripple marks produced by Martian wind. The trench which was dug early on Sol 8, is about 3 inches wide, 2 inches deep and 6 inches long. Steep dark crater walls show the grains of the Martian surface material stick together (have adhesion). The doming of the surface at far end of the trench show the granular material is dense. The Martian surface material behaves somewhat like moist sand on Earth. Evidence from the trench indicate a sample was collected and delivered to the experiments after repeated tries. The biology experiment level full indicator indicates a sample was received for analysis. The X-Ray fluorescence experiment has no indication to show it received a sample. The GCMS experiment level full indicator suggests no sample was received but this matter is being investigated. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00389
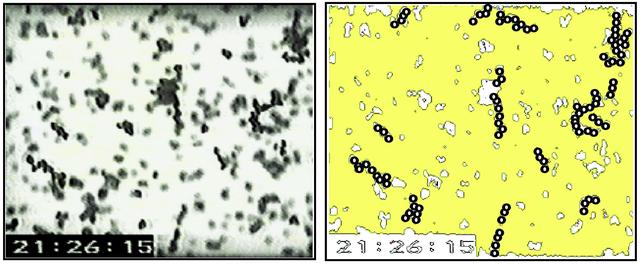
John Marshall, an investigator at Ames Research Center and a principal investigator in the microgravity fluid physics program, is studying the adhesion and cohesion of particles in order to shed light on how granular systems behave. These systems include everything from giant dust clouds that form planets to tiny compressed pellets, such as the ones you swallow as tablets. This knowledge should help us control the grains, dust, and powders that we encounter or use on a daily basis. Marshall investigated electrostatic charge in microgravity on the first and second U.S. Microgravity Laboratory shuttle missions to see how grains aggregate, or stick together. With gravity's effects eliminated on orbit, Marshall found that the grains of sand that behaved ever so freely on Earth now behaved like flour. They would just glom together in clumps and were quite difficult to disperse. That led to an understanding of the prevalence of the electrostatic forces. The granules wanted to aggregate as little chains, like little hairs, and stack end to end. Some of the chains had 20 or 30 grains. This phenomenon indicated that another force, what Marshall believes to be an electrostatic dipole, was at work.(The diagram on the right emphasizes the aggregating particles in the photo on the left, taken during the USML-2 mission in 1995.)

W. Brian Dunlap of Youngstown, Ohio, proposed Skylab student experiment ED-78, Liquid Motion in Zero-G, a study of wave motion in a liquid. He was particularly interested in comparing surface waves over a liquid in zero-gravity with those occurring on Earth. In space, with the absence of gravity, a liquid does not necessarily take the shape of its container as it does on Earth. Adhesion forces may hold the liquid in contact with its container, but the liquid can also assume a free-floating condition. It was in this latter state that Dunlap wished to examine the behavior of surface waves. Data were recorded on videotape and subsequently converted to 16-mm film. Dunlap analyzed these data to determine periods of oscillation of free-floating globules and found agreement with the theory to be much better than expected. In March 1972, NASA and the National Science Teachers Association selected 25 experiment proposals for flight on Skylab. Science advisors from the Marshall Space Flight Center aided and assisted the students in developing the proposals for flight on Skylab.

Technicians set up test hardware inside the test section of the Icing Research Tunnel at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The Icing Research Tunnel was built in the early 1940s to study the formation of ice on aircraft surfaces and develop methods of preventing or eradicating that ice. Ice buildup is dangerous because it adds extra weight, effects aerodynamics, and sometimes blocks air flow through engines. The Icing Research Tunnel is a closed-loop atmospheric wind tunnel with a 6- by 9-foot test section. The tunnel can produce speeds up to 300 miles per hour and temperatures from 30 to -45 °F. NACA engineers struggled initially to perfect a spray bar system to introduce moisture into the airstream. The tunnel was shut down in the late 1950s as the center focused its energy exclusively on space. Industrial customers began using the tunnel sporadically, then steadily, in the 1960s. Boeing, Aerojet, Lockheed, Sikorsky, Beech and others ran tests during the 1960s. Boeing analyzed engine inlets for the CH-47 Chinook, CH-46 (Sea Knight) and CH-113. This photograph was taken during a series of 100 ice-phobic coatings for the Federal Aviation Administration. They found that many of the coatings reduced ice adhesion to the test sample, but they could not be used for aircraft applications.

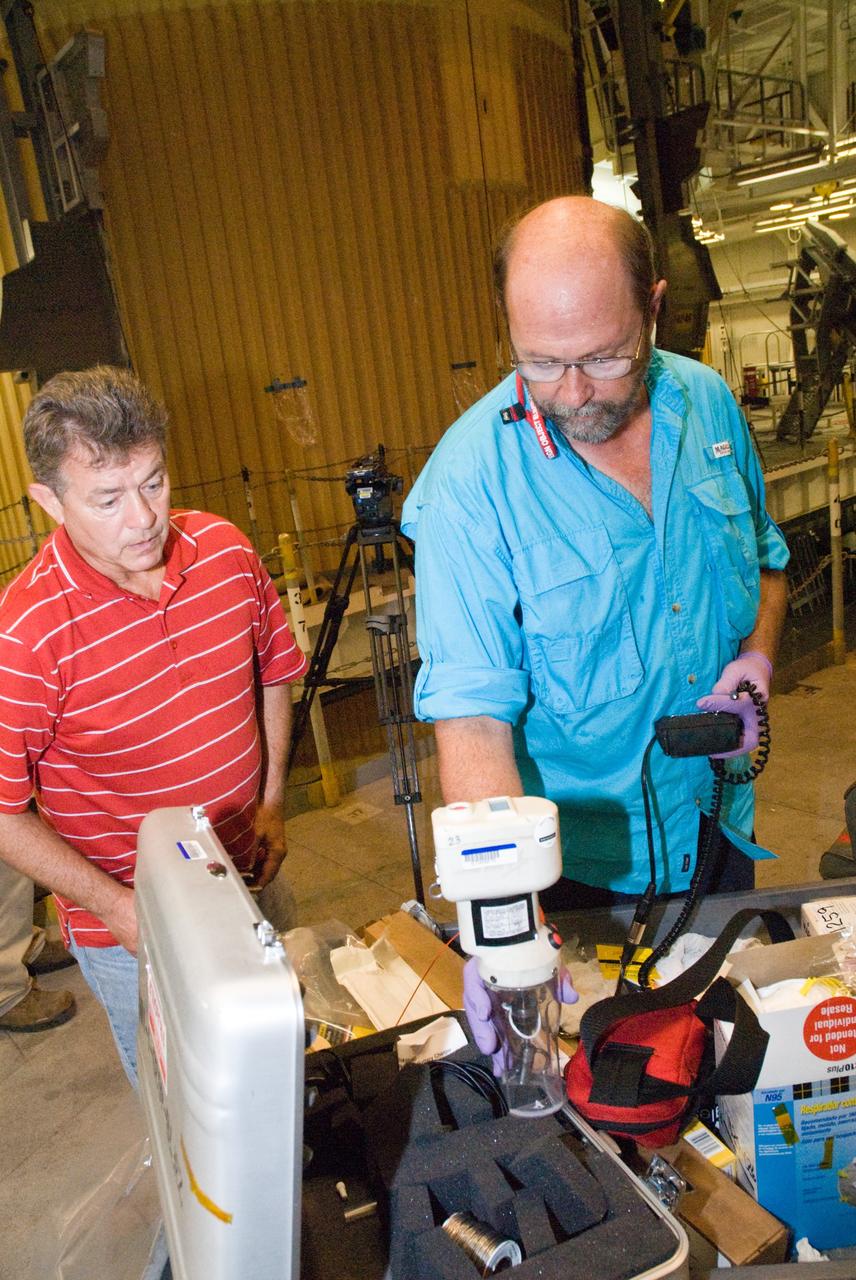
Sylvie Crowell who works in the Environmental Effects and Coatings Branch at NASA Glenn Research Center performs ball milling and particle size analysis on some lunar dust simulant on January 29, 2025.

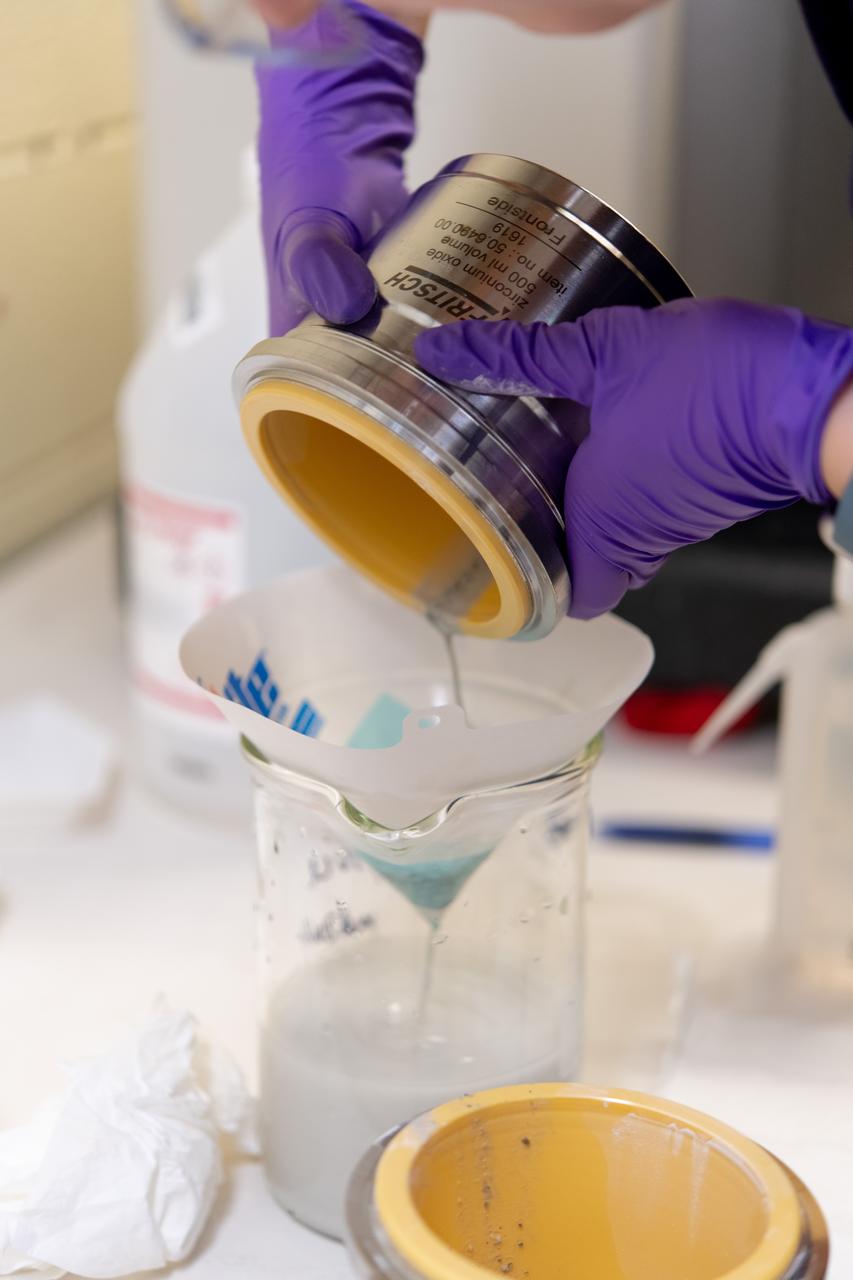
Sylvie Crowell who works in the Environmental Effects and Coatings Branch at NASA Glenn Research Center performs ball milling and particle size analysis on some lunar dust simulant on January 29, 2025.

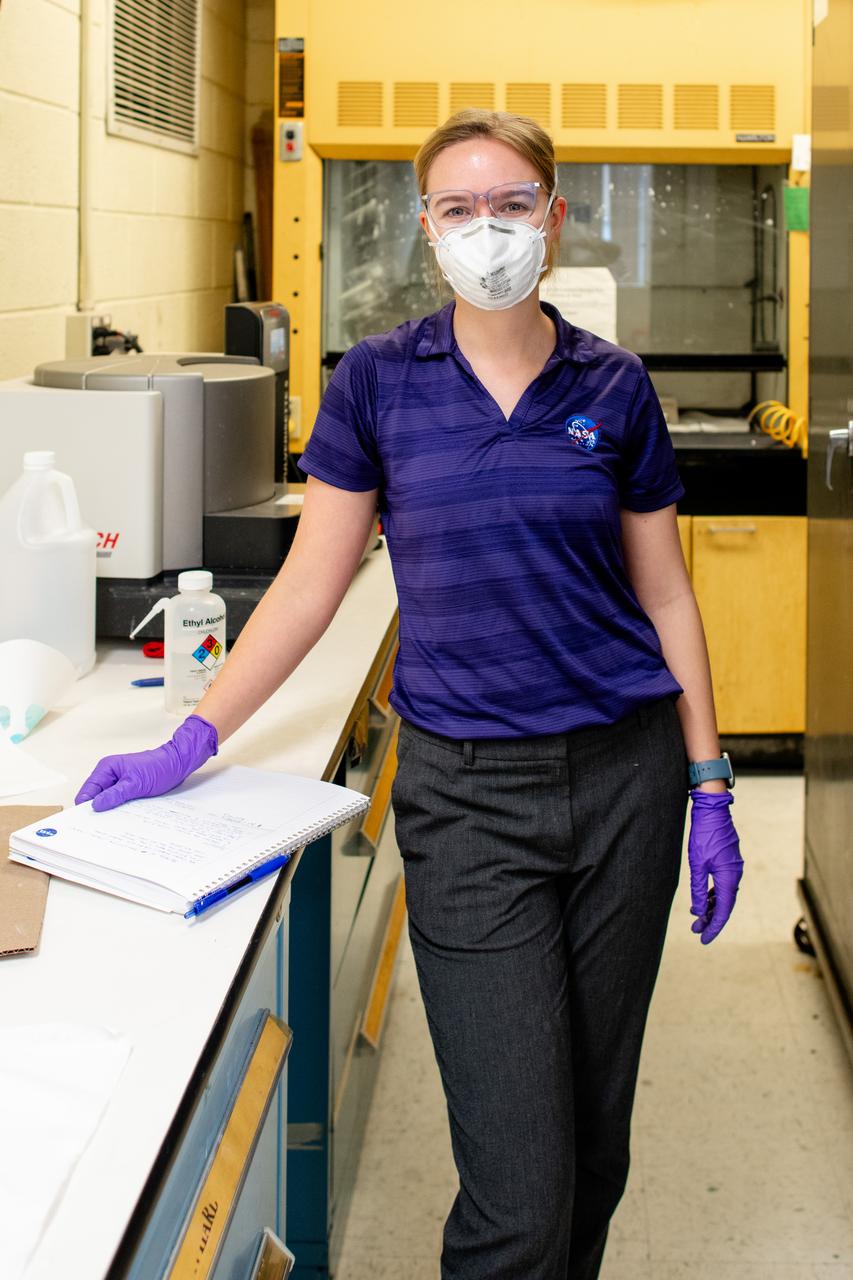
Sylvie Crowell who works in the Environmental Effects and Coatings Branch at NASA Glenn Research Center performs ball milling and particle size analysis on some lunar dust simulant on January 29, 2025.
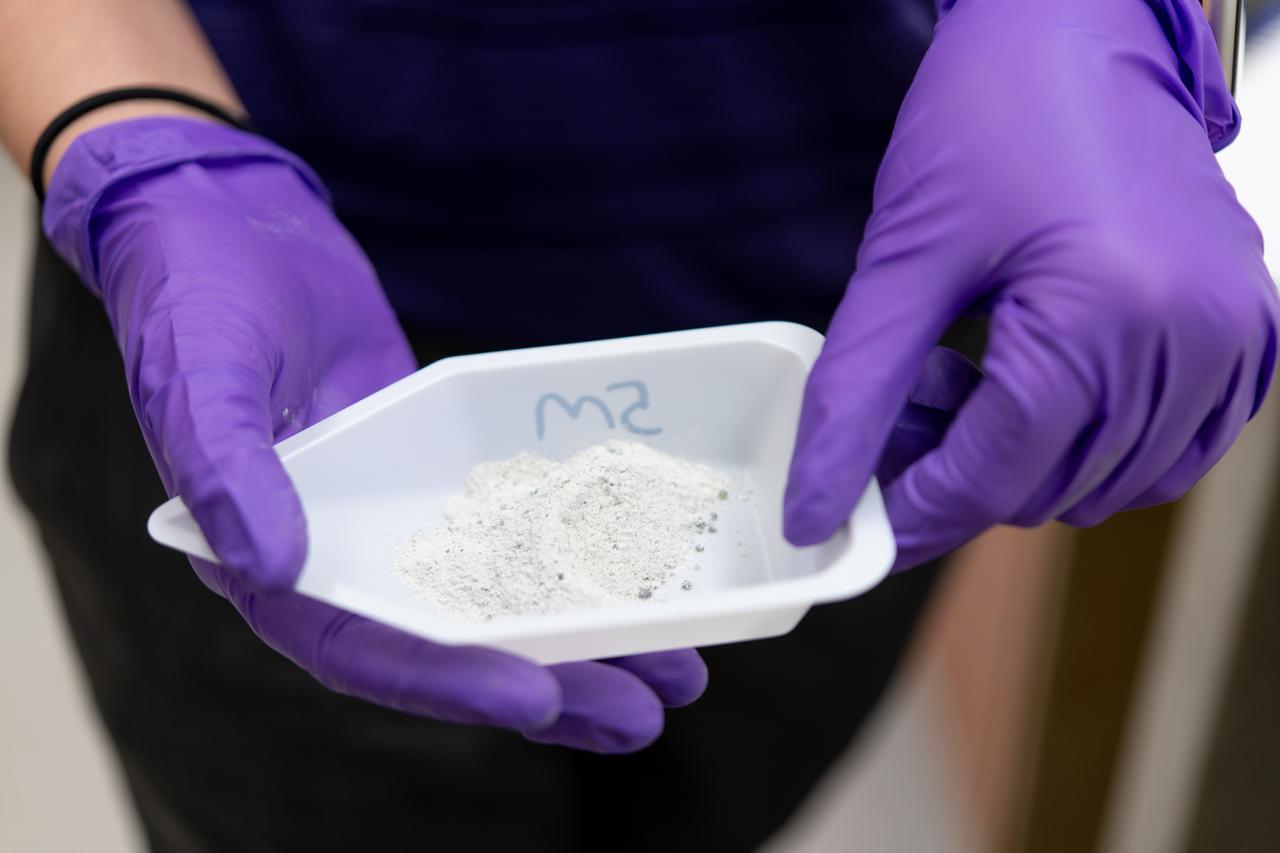

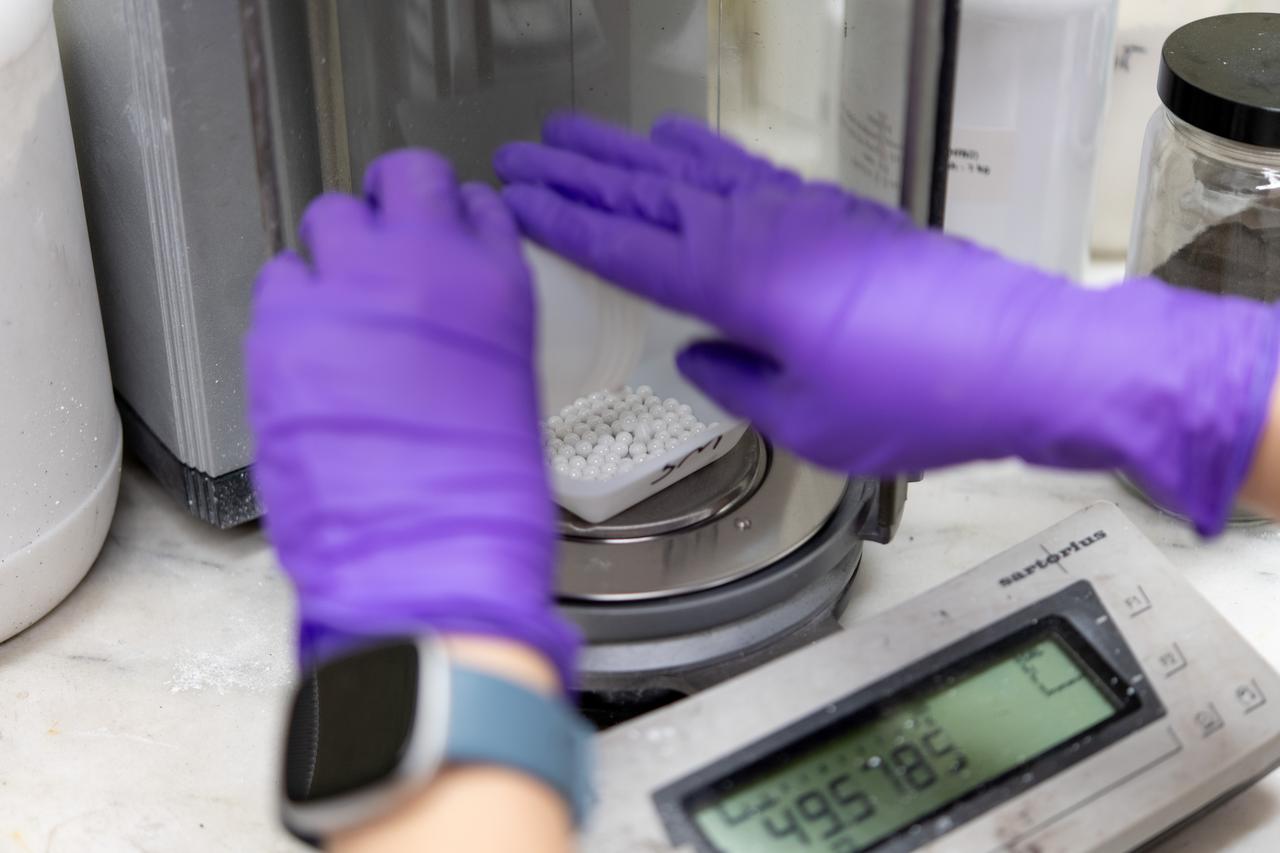
Sylvie Crowell who works in the Environmental Effects and Coatings Branch at NASA Glenn Research Center performs ball milling and particle size analysis on some lunar dust simulant on January 29, 2025.
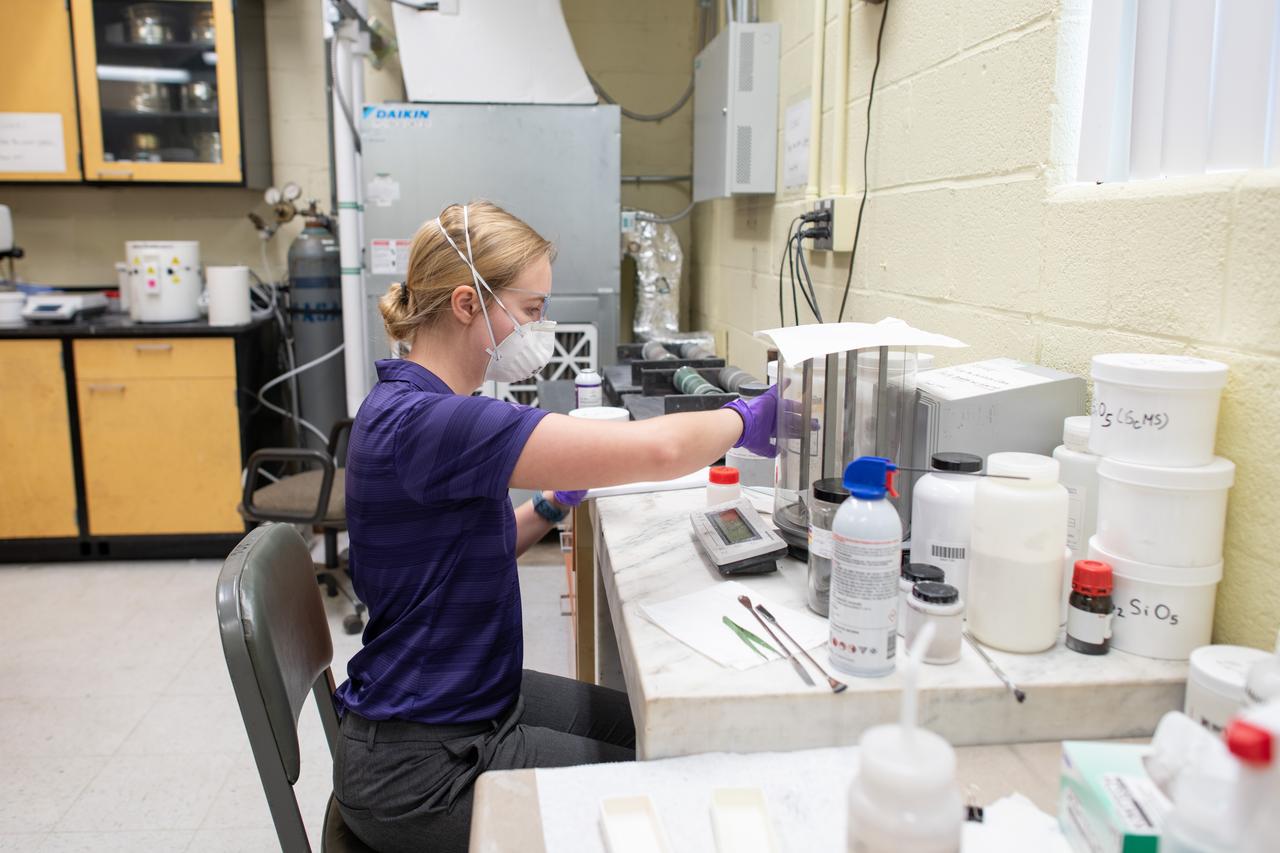

Sylvie Crowell who works in the Environmental Effects and Coatings Branch at NASA Glenn Research Center performs ball milling and particle size analysis on some lunar dust simulant on January 29, 2025.
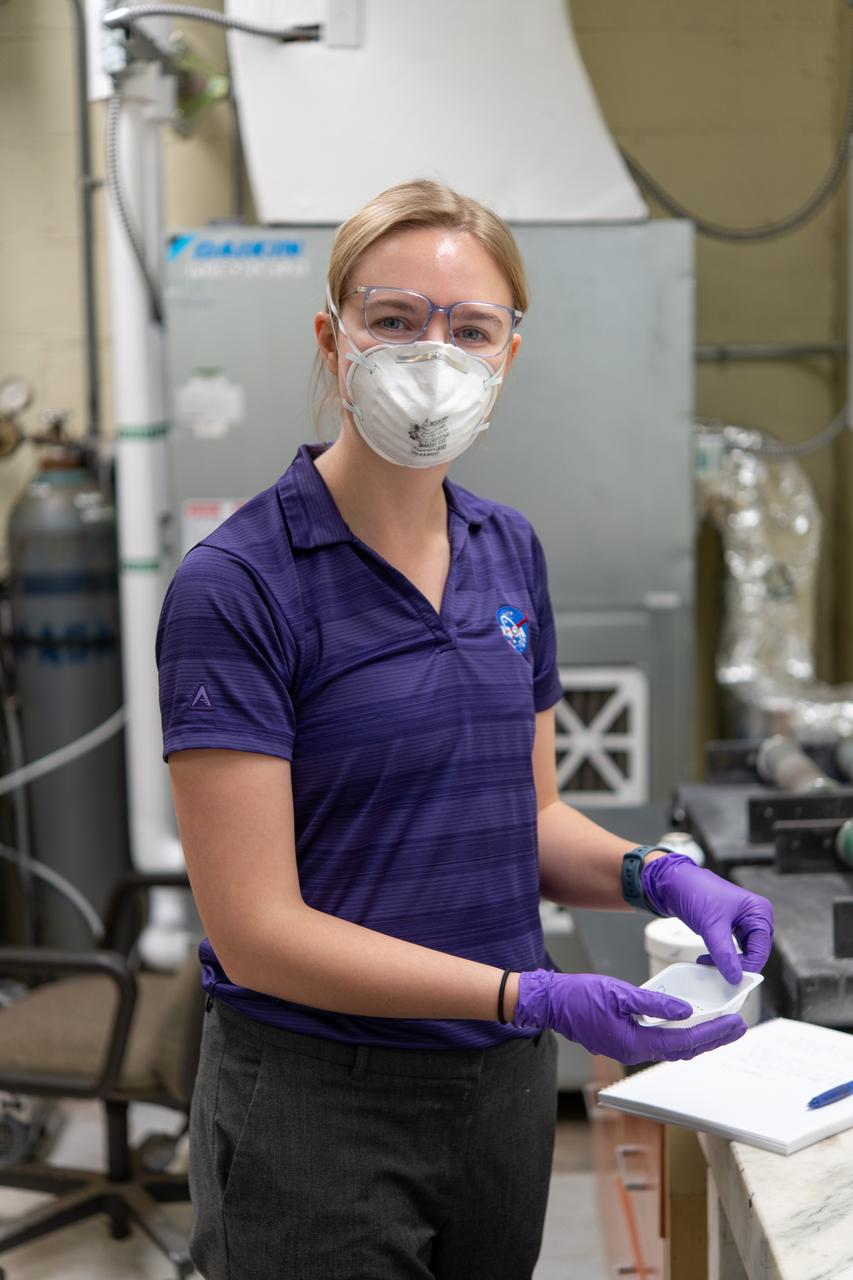

Sylvie Crowell who works in the Environmental Effects and Coatings Branch at NASA Glenn Research Center performs ball milling and particle size analysis on some lunar dust simulant on January 29, 2025.
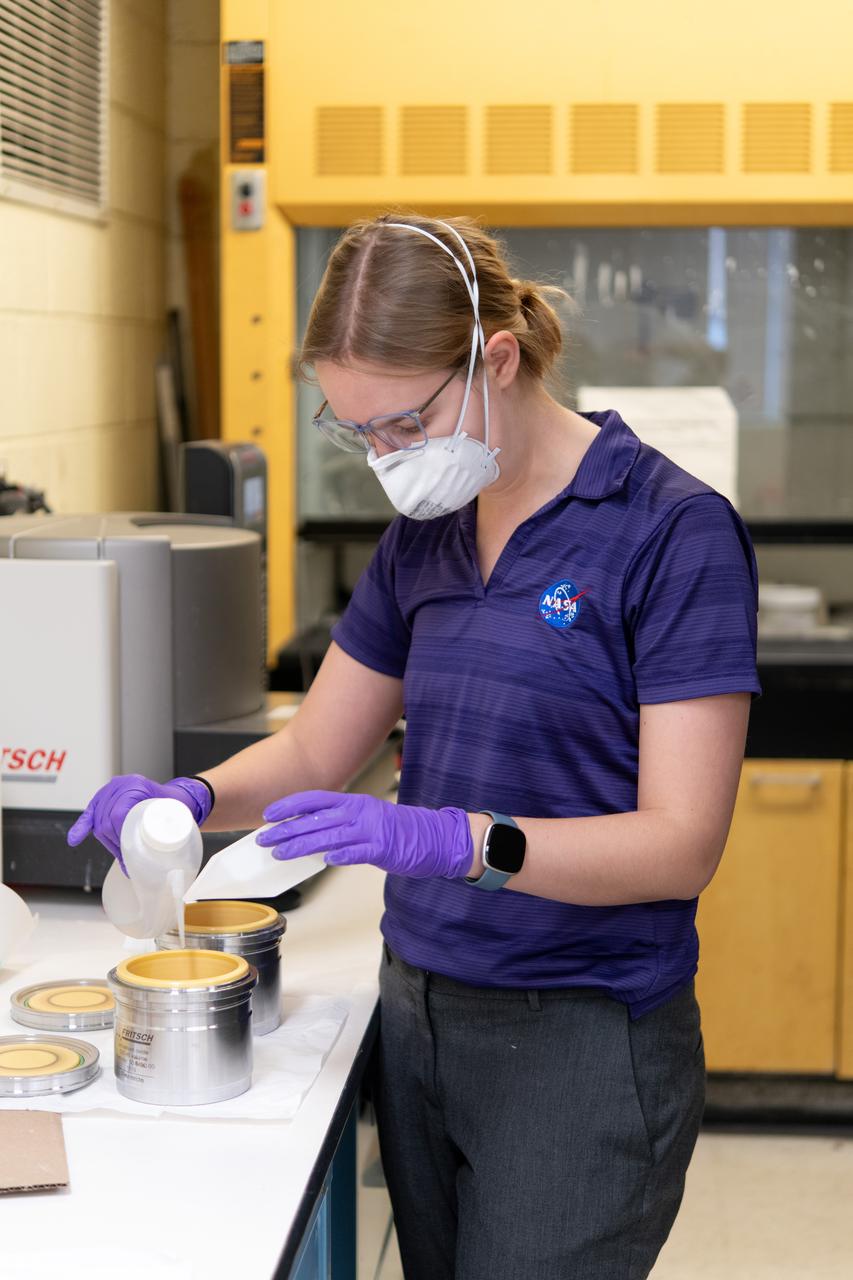

Sylvie Crowell who works in the Environmental Effects and Coatings Branch at NASA Glenn Research Center performs ball milling and particle size analysis on some lunar dust simulant on January 29, 2025.