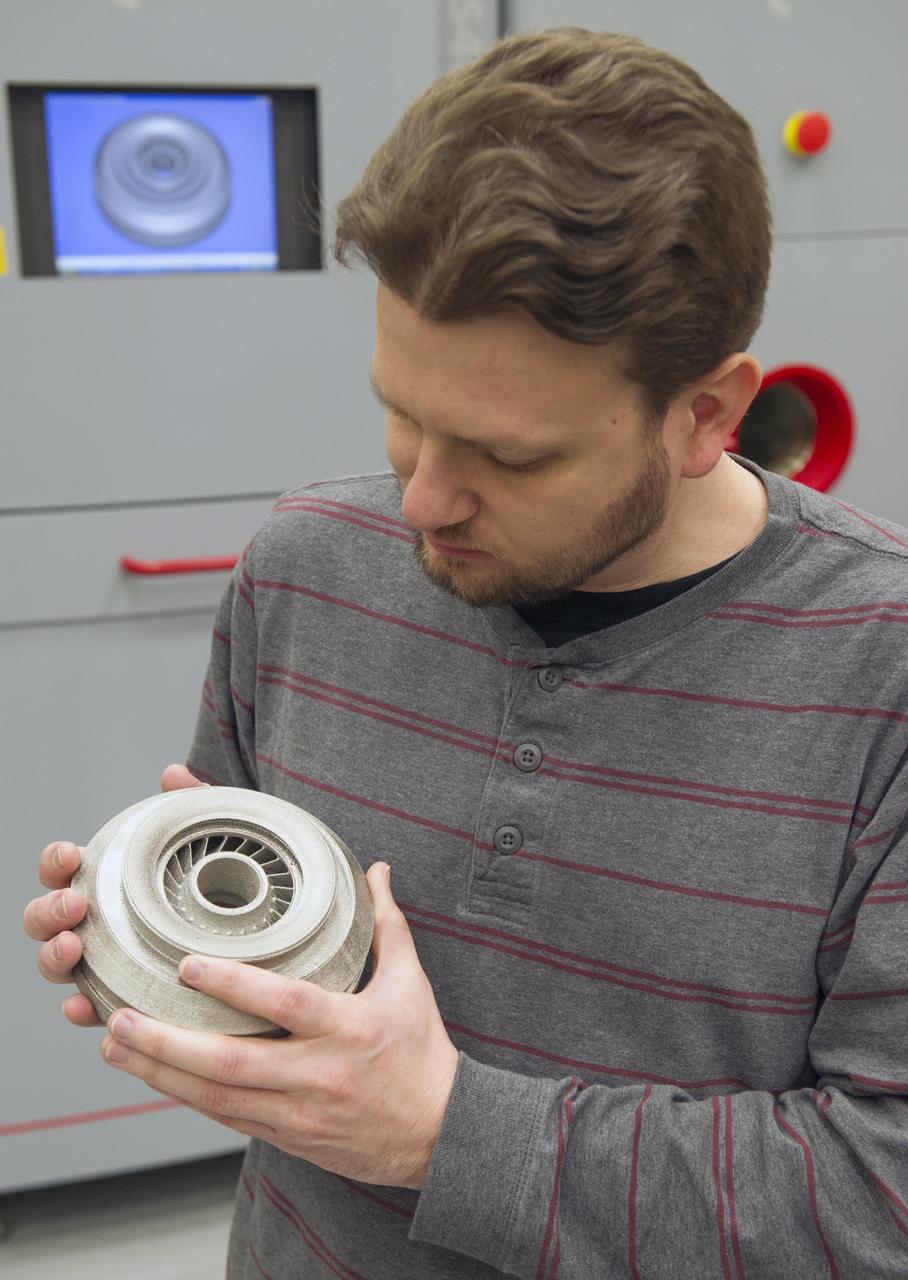

QUINCY BEAN OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH TITANIUM ALLOY TURBOPUMP COMPONENT FABRICATED WITH MSFC’S ELECTRON BEAM MELTING SYSTEM (BACKGROUND).

ZACK JONES AND JIM LYDON OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH MSFC’S M2 SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. THE M2 IS CURRENTLY DEDICATED TO ADVANCED COPPER MATERIAL DEVELOPMENT FOR THE LOW COST UPPER STAGE PROGRAM.

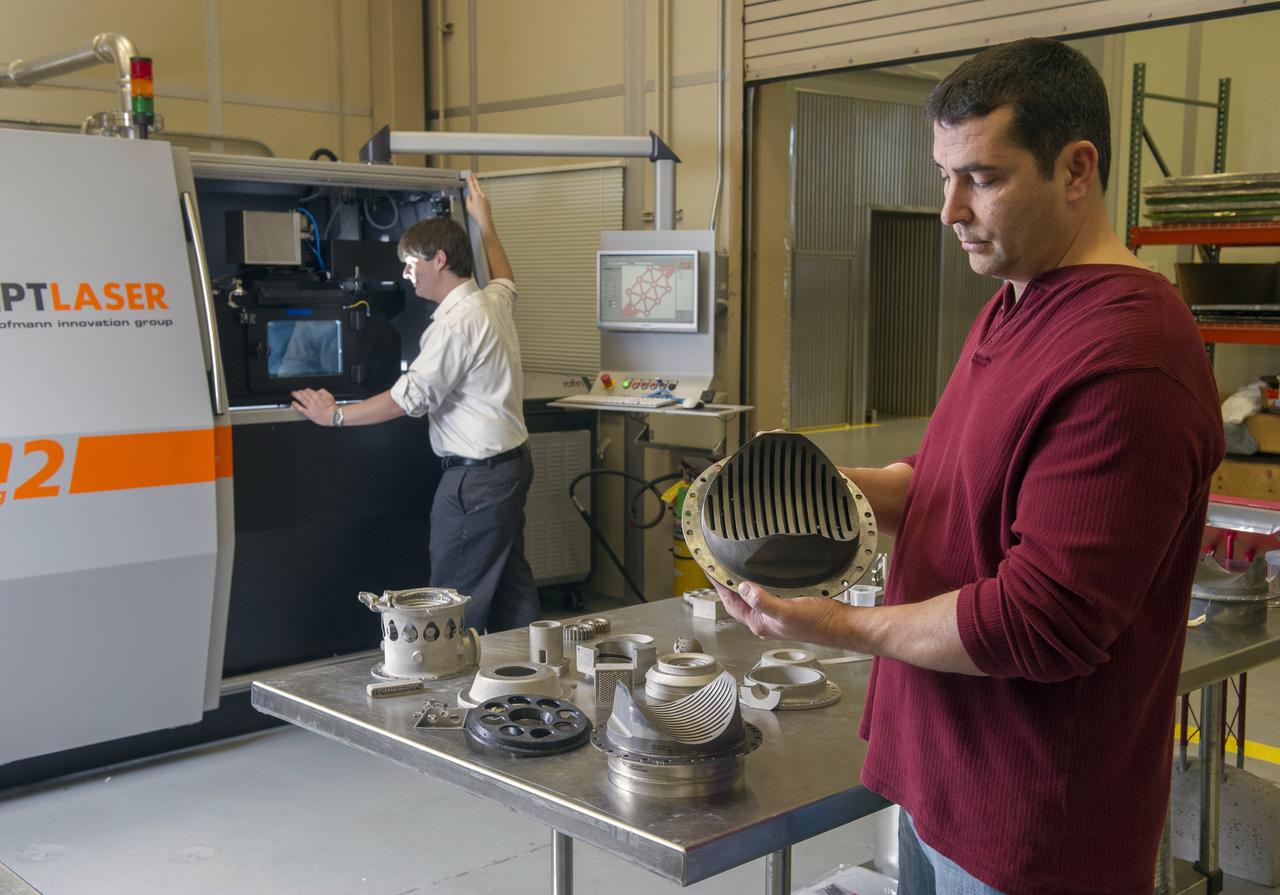
QUINCY BEAN, JIM LYDON, AND ZACK JONES OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH MSFC’S M2 SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. THE M2 IS CURRENTLY DEDICATED TO ADVANCED COPPER MATERIAL DEVELOPMENT FOR THE LOW COST UPPER STAGE PROGRAM.

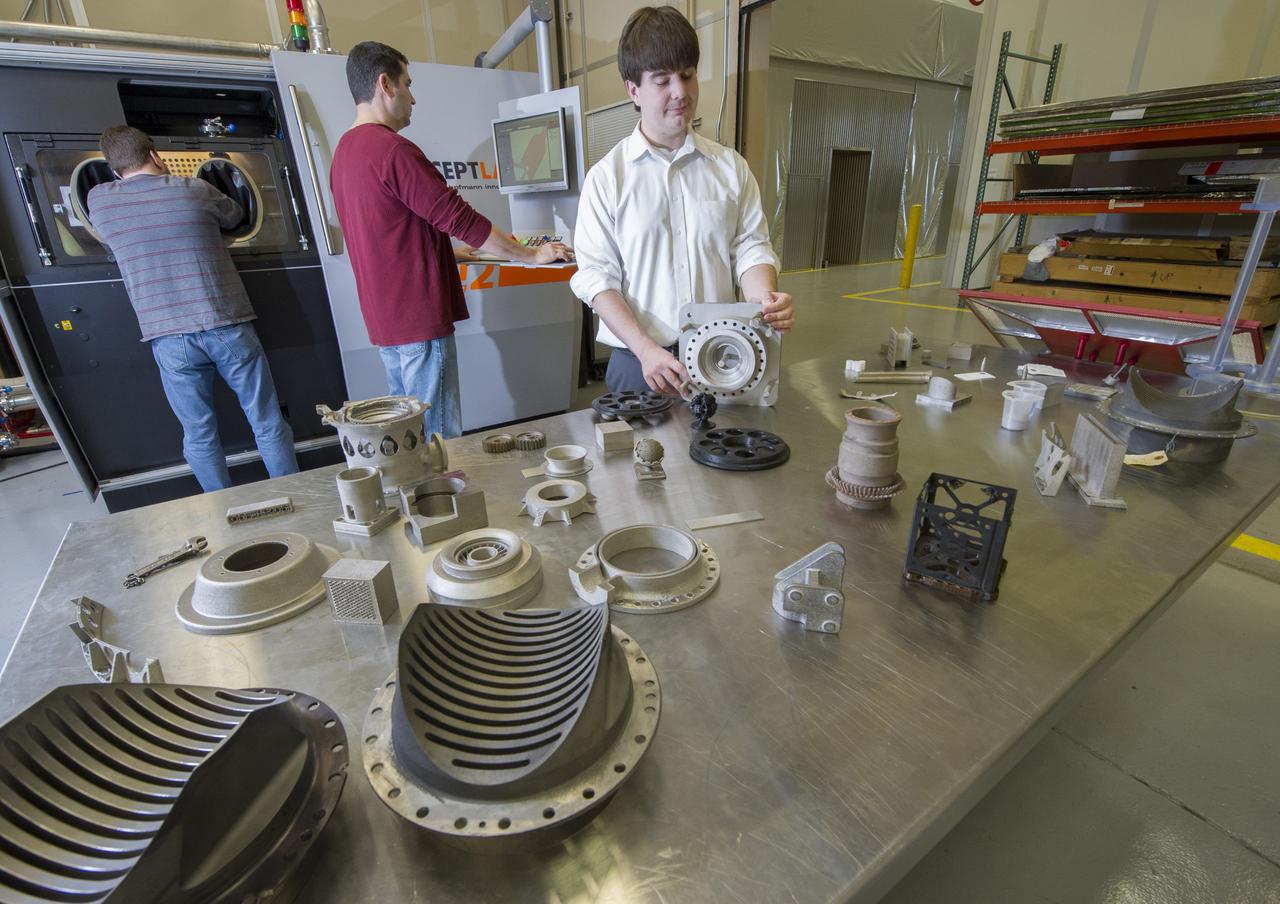
JOHNNIE CLARK, BRIAN WEST, AND ZACK JONES OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH MSFC’S XLINE SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. CURRENTLY ONE OF THE LARGEST METAL 3D PRINTERS, THE XLINE AT MARSHALL IS BEING USED TO DEVELOP AND CERTIFY NICKEL ALLOY 718 MATERIAL PROPERTIES AND LARGE MANUFACTURING TECH DEMOS FOR THE RS25 ENGINE AND THE COMMERCIAL CREWED VEHICLE PROJECTS.
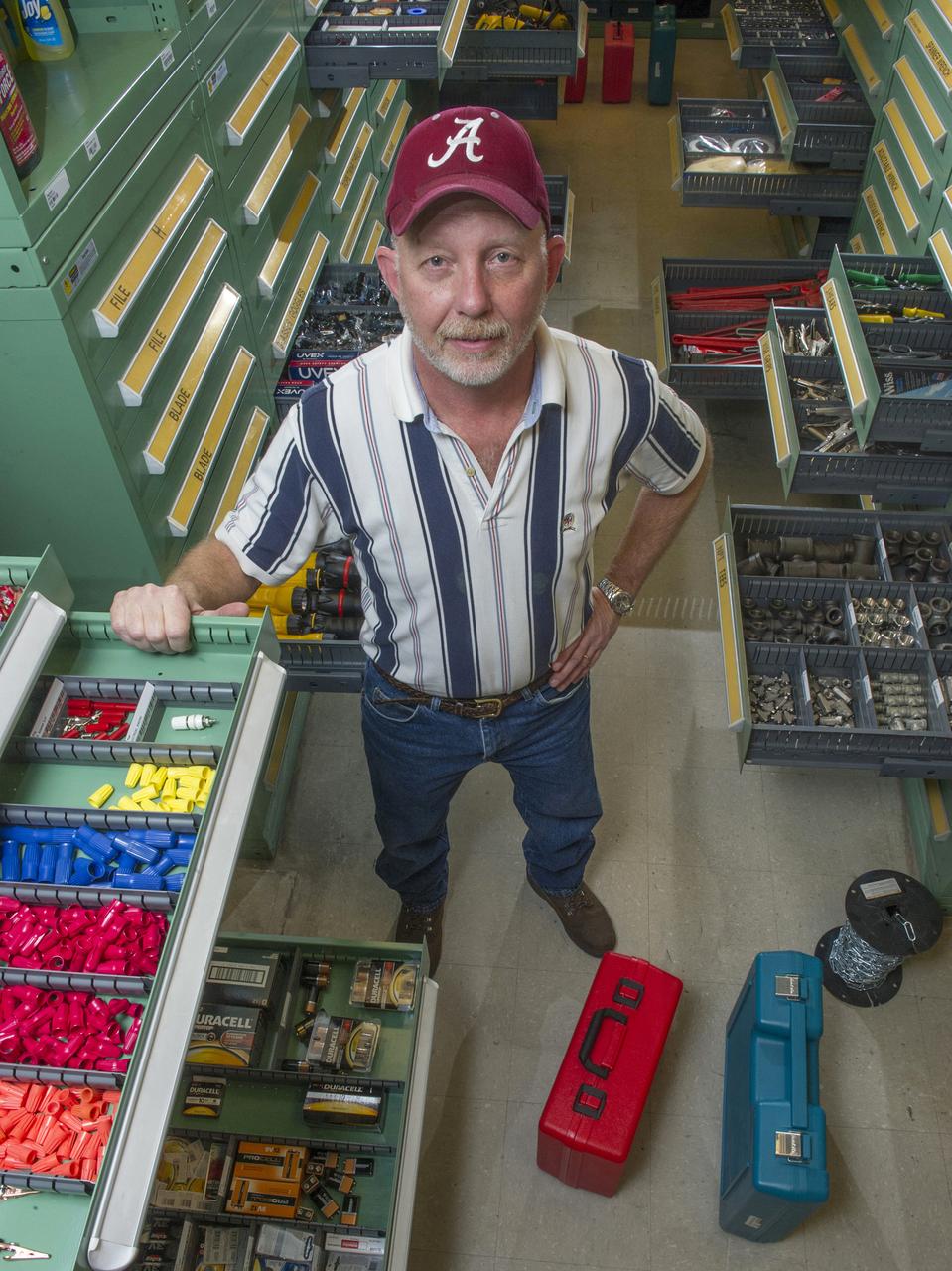

RON LEE MANAGES THE 900 SQUARE FOOT TOOL CRIB IN BLDG. 4707
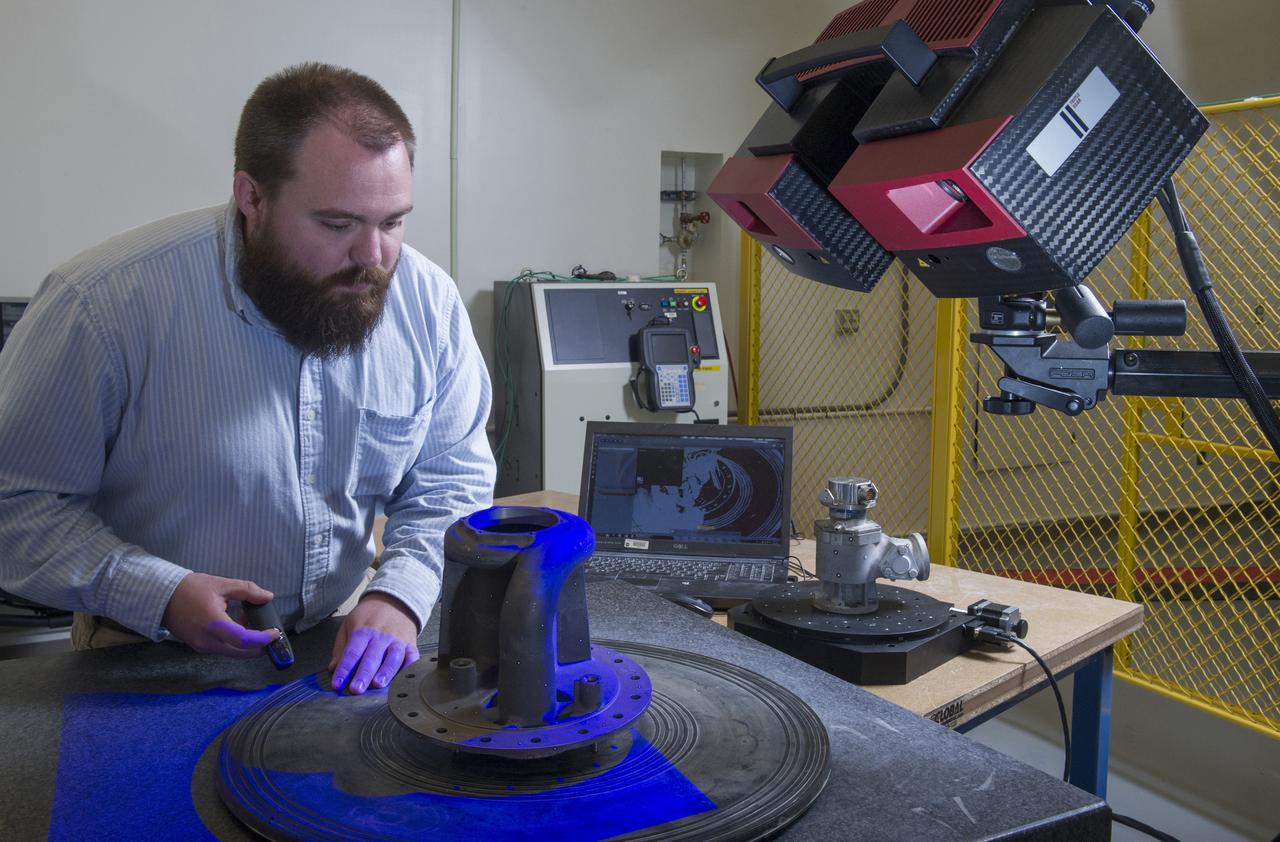

JOHN IVESTER PERFORMING STRUCTURED LIGHT SCANNING OF HERITAGE HARDWARE TO CAPTURE THE AS-BUILT GEOMETRY.
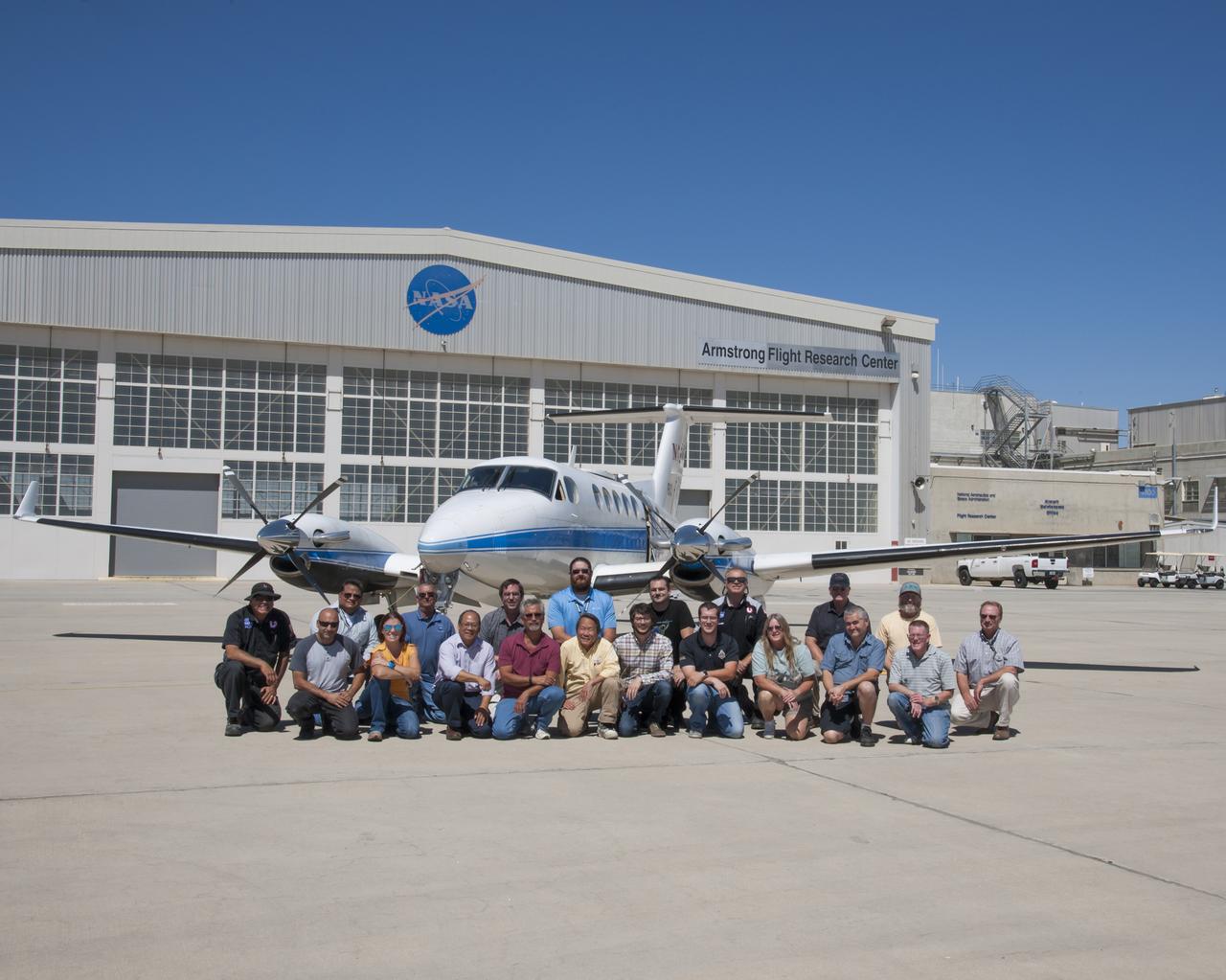

The Advanced Data Acquisition and Telemetry System team includes front row from left Mario Soto, Sam Habbal, Tiffany Titas, RIchard Hang, Randy Torres, Thang Quach, Otto Schnarr, Matthew Waldersen, Karen Estes, Andy Olvera, Stanley Wertenberger and Rick Cordes. In the second row from left are John Atherly, Doug Boston, Tom Horn, Brady Rennie, Chris Birkinbine, Jim McNally, Martin Munday and Tony Lorek.
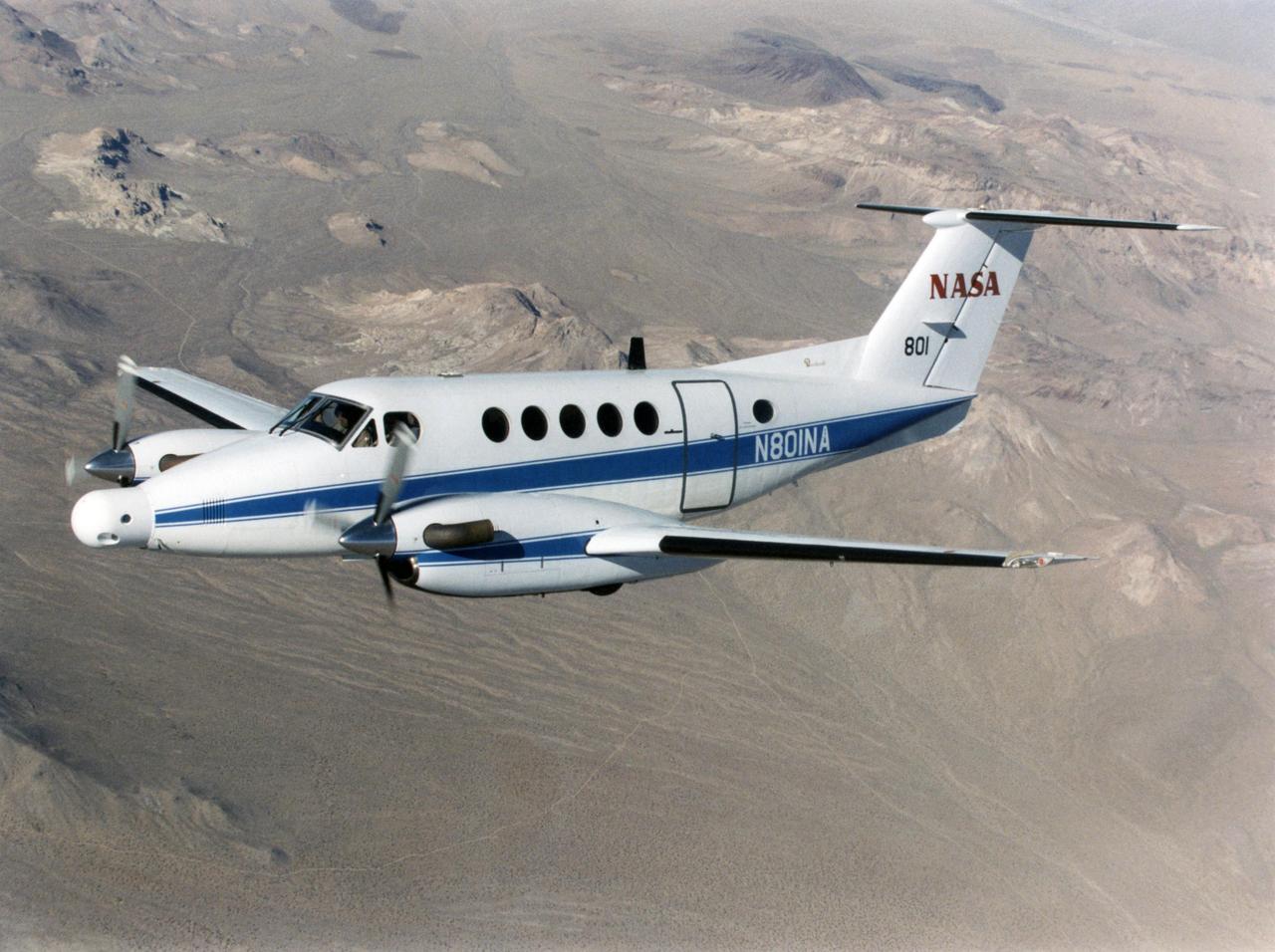

A NASA King Air successfully tested the Advanced Data Acquisition and Telemetry System during a recent series of three research flights.
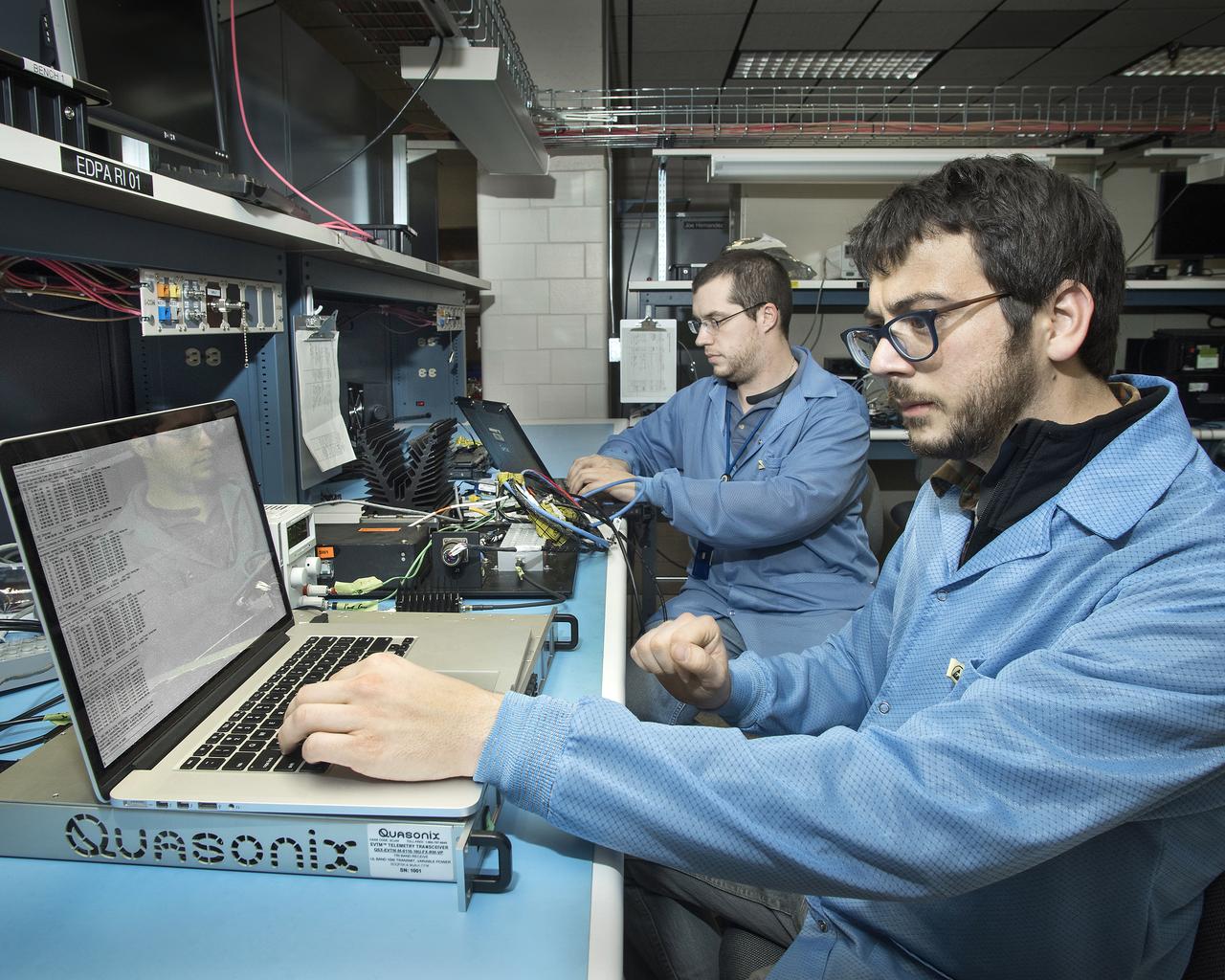

Otto Schnarr, front, and Matthew Waldersen check out the Advanced Data Acquisition and Telemetry System in an Armstrong laboratory.

Otto Schnarr and Matthew Waldersen check out the Advanced Data Acquisition and Telemetry System in an Armstrong laboratory.
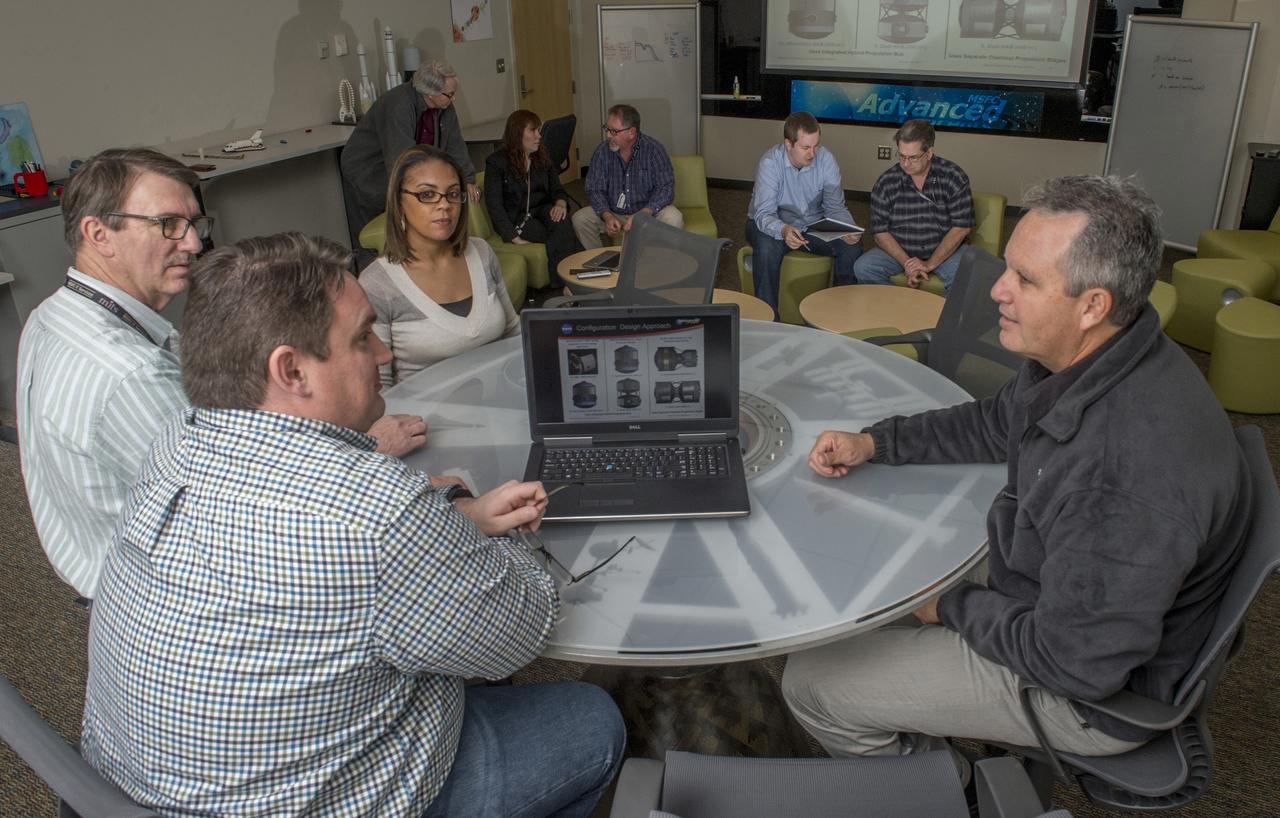

Advance Concept Office Space Transportation Team Assess the Latest Vehicle Studies
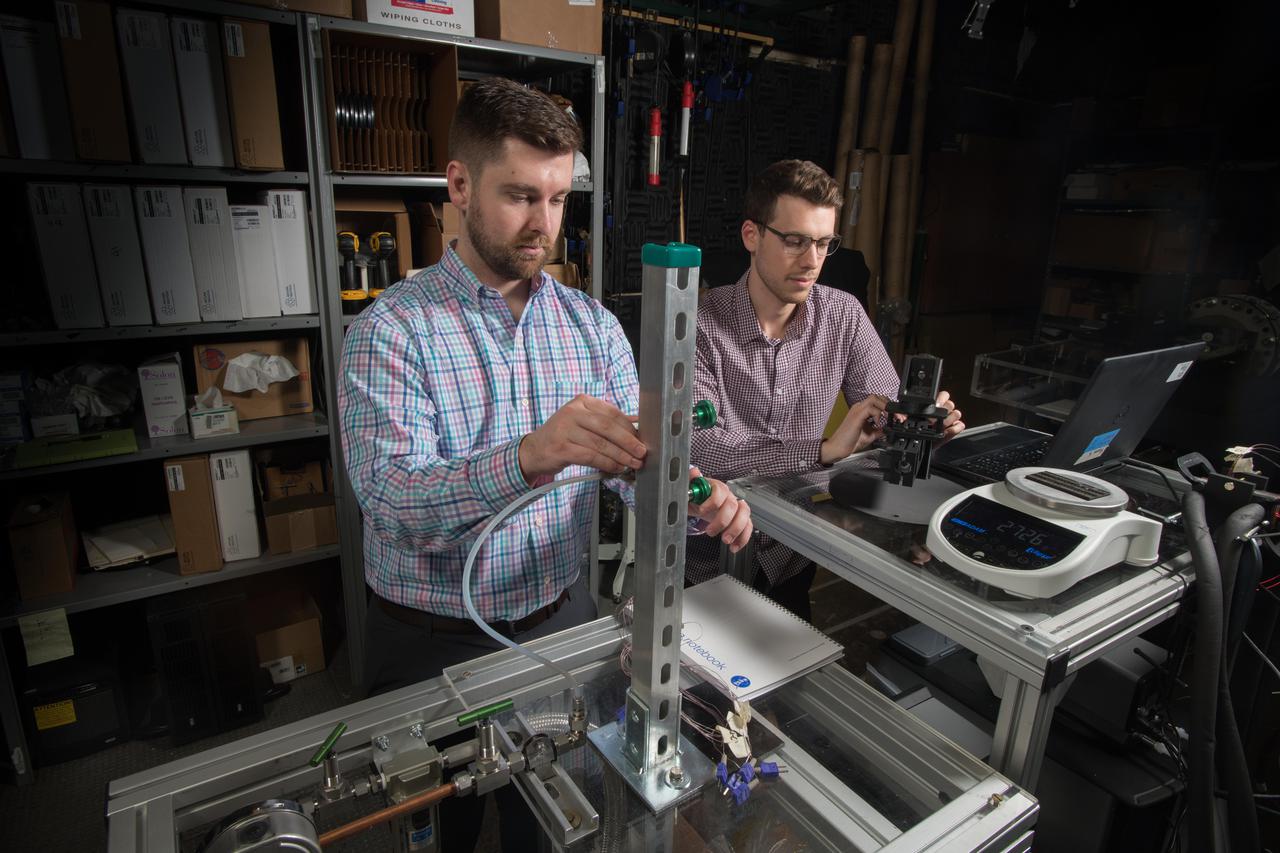
Advanced Thermal Management, High Power Density Core, Advanced Air Transport Technology,
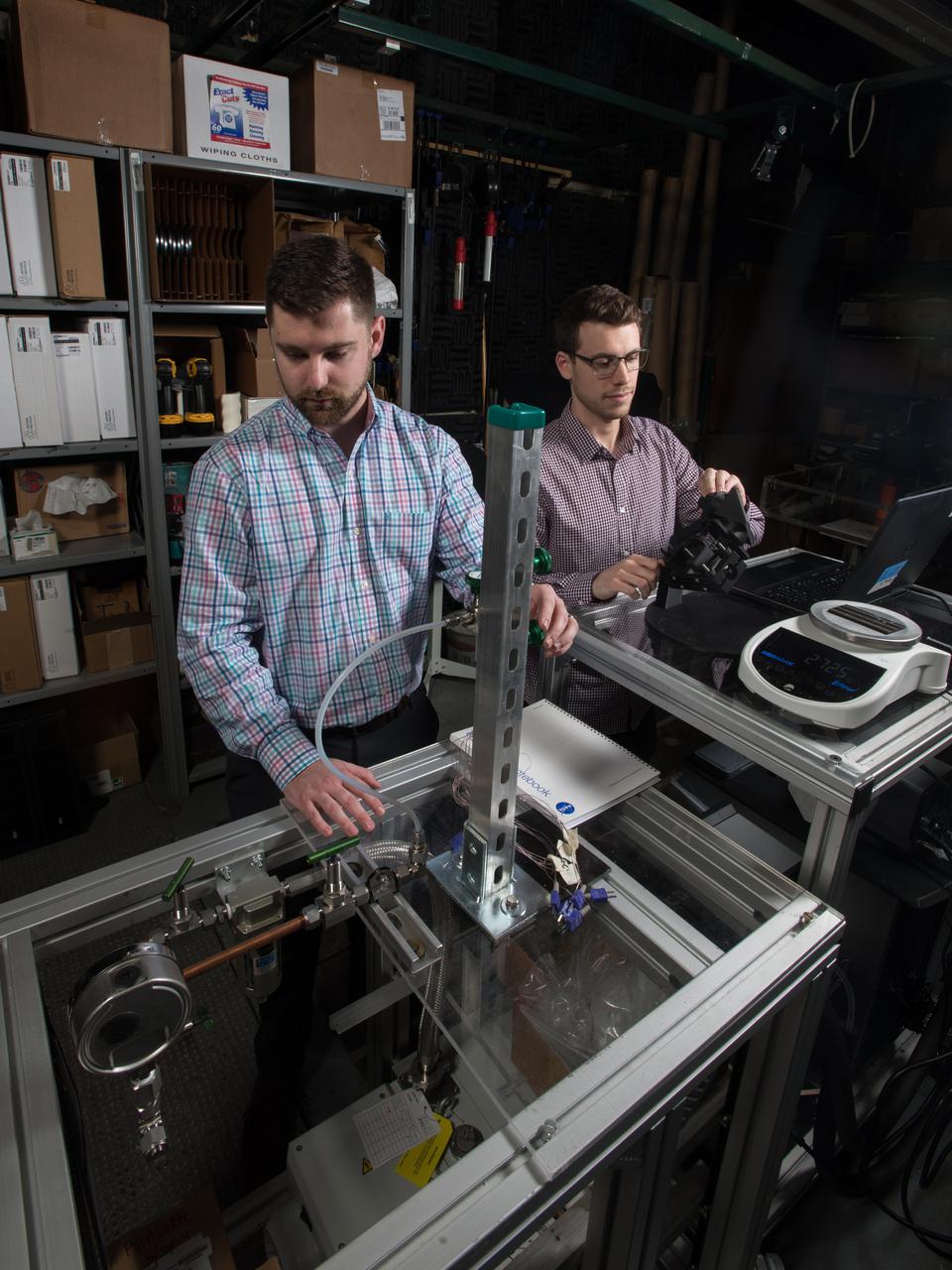
Advanced Thermal Management, High Power Density Core, Advanced Air Transport Technology,
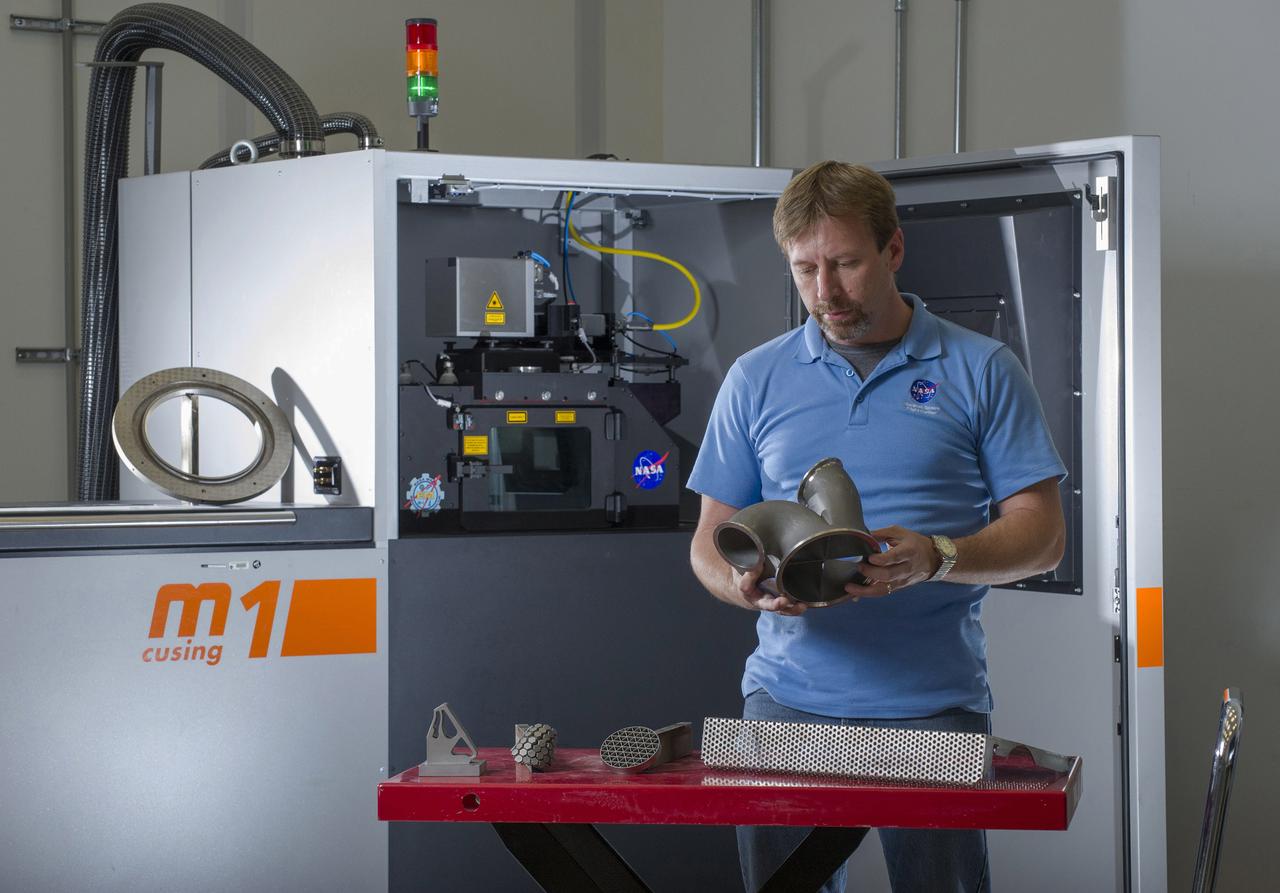

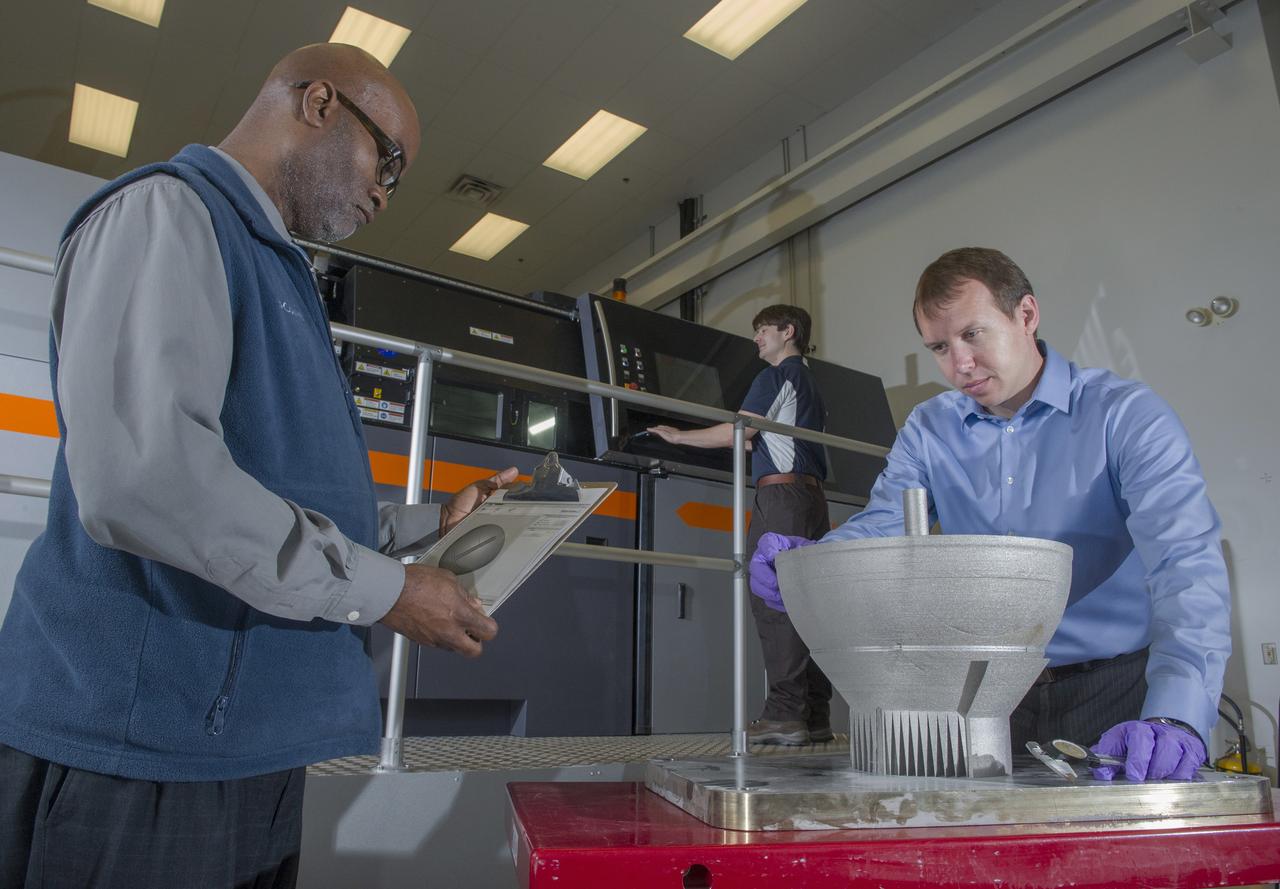
KEN COOPER, TEAM LEAD OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH NICKEL ALLOY 718 PARTS FABRICATED USING THE M1 SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. THE M1 MACHINE IS DEDICATED TO BUILDING QUALIFICATION SAMPLES AND HARDWARE DEMONSTRATORS FOR THE RS25 ENGINE PROJECT.
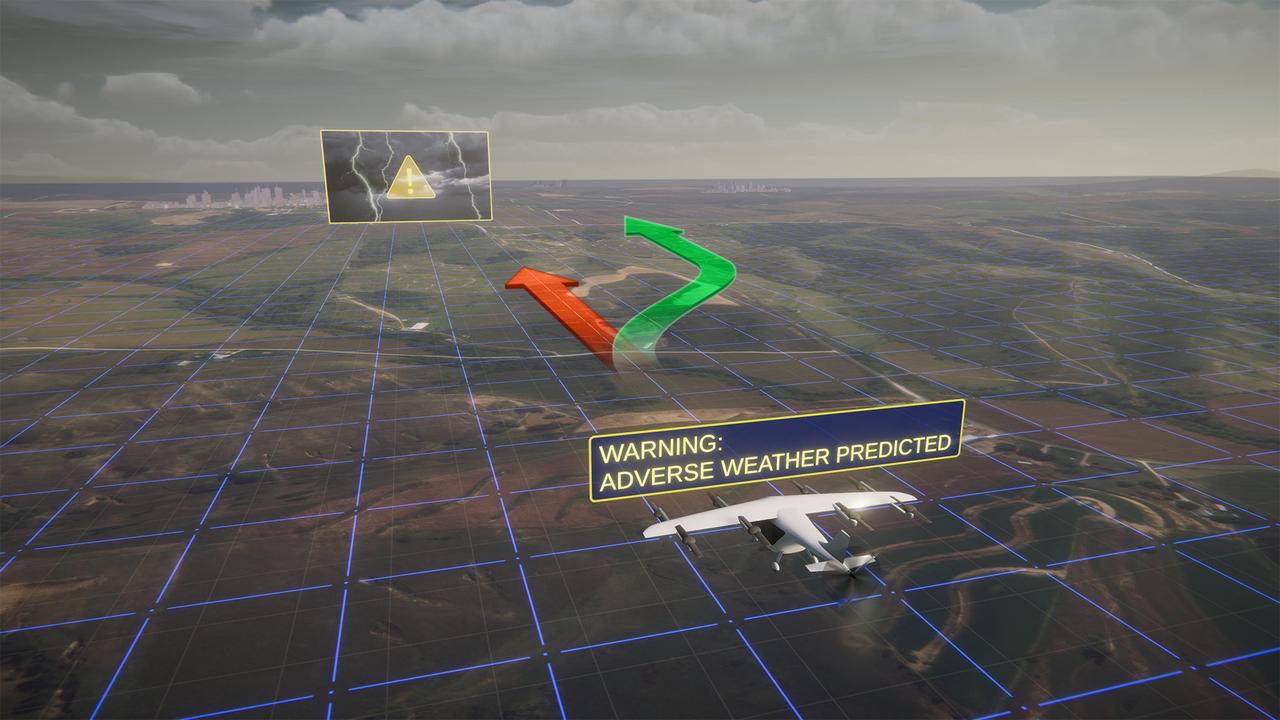
NASA's Advanced Air Mobility mission is helping to ensure this new class of aircraft that industry is developing is safe to operate. This concept art represents how the addition of automated technologies on the aircraft like hazard avoidance could help.
Advanced Stirling Radioisotope Lab
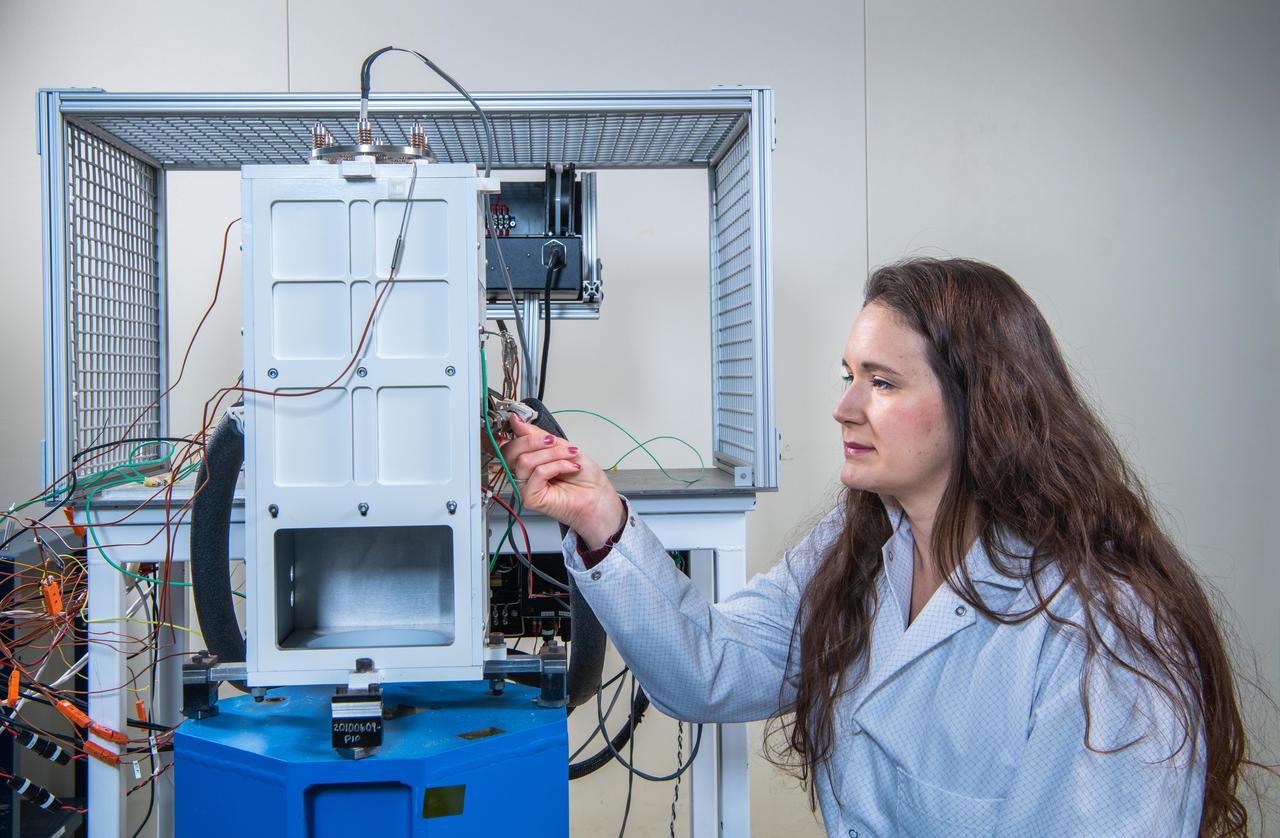
Advanced Stirling Radioisotope Lab
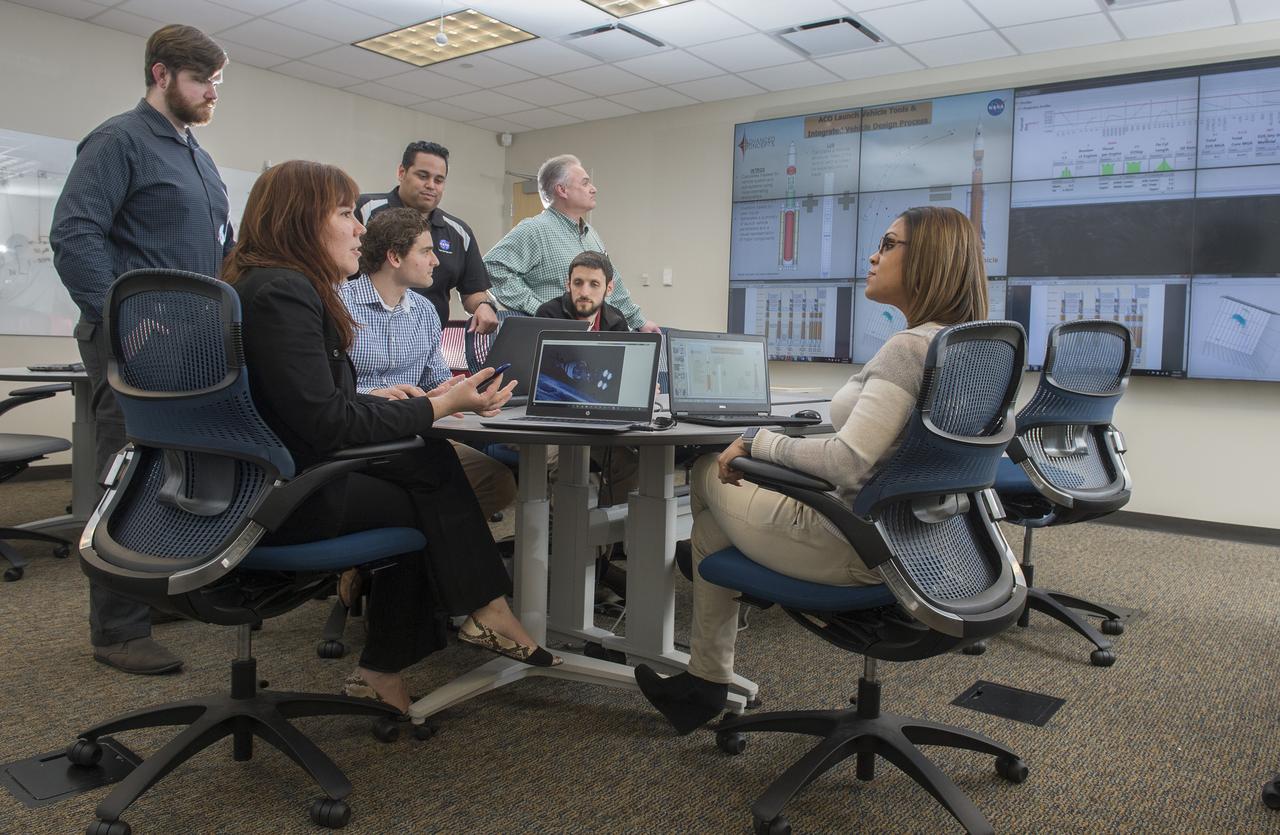

Advance Concept Office Space Transportation Team Assess the Latest Vehicle Studies
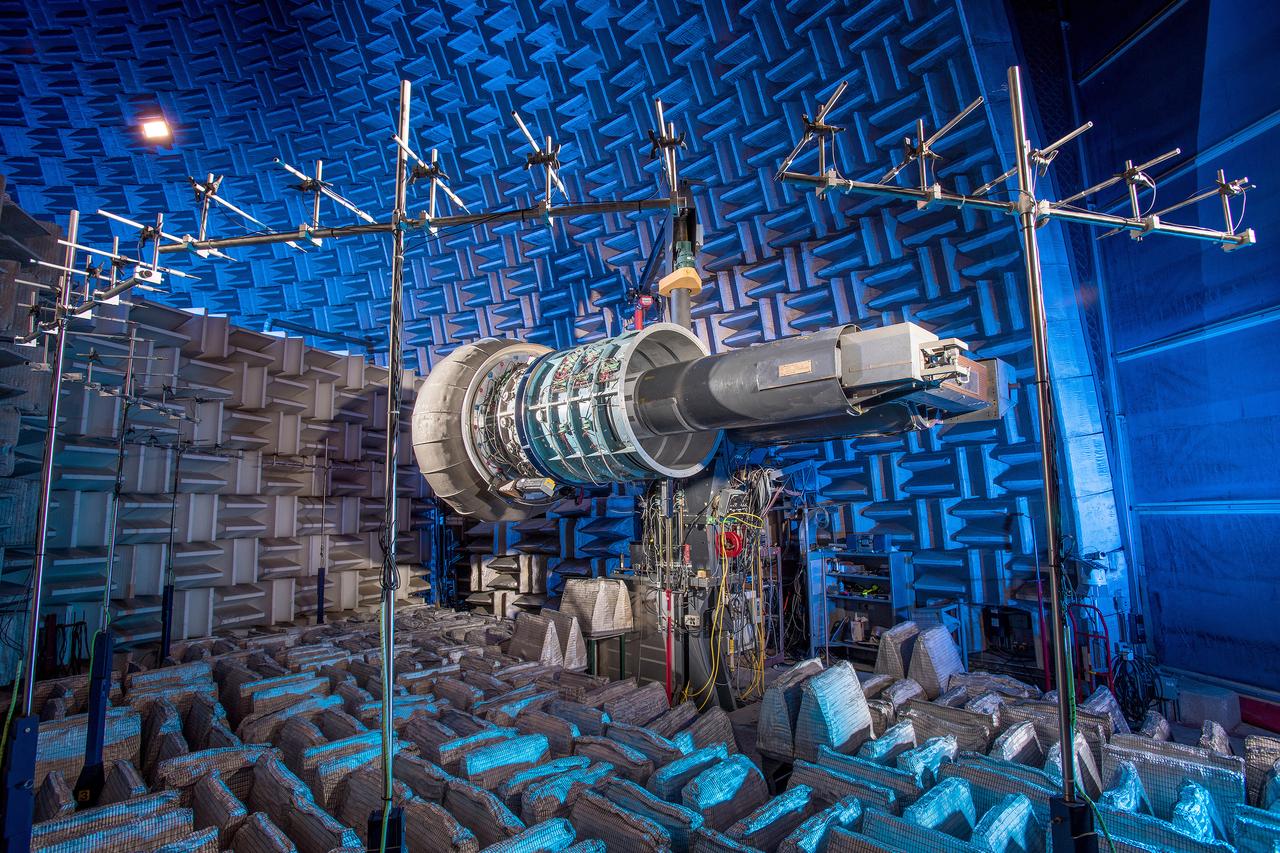
The Advanced Noise Control Fan shown here is located in NASA Glenn’s Aero-Acoustic Propulsion Laboratory. The 4-foot diameter fan is used to evaluate innovate aircraft engine noise reduction concepts less expensively and more quickly.

A test unit, or prototype, of NASA's Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) with its first initial grow test in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The taller plants pictured are dwarf wheat and the smaller plants are Arabidopsis. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

NASA is uniquely qualified to help revolutionize the Advanced Air Mobility cargo transportation industry by finding solutions for faster and cleaner modes of moving packages, using both large cargo delivery aircraft and small package delivery drones like seen in this concept image.
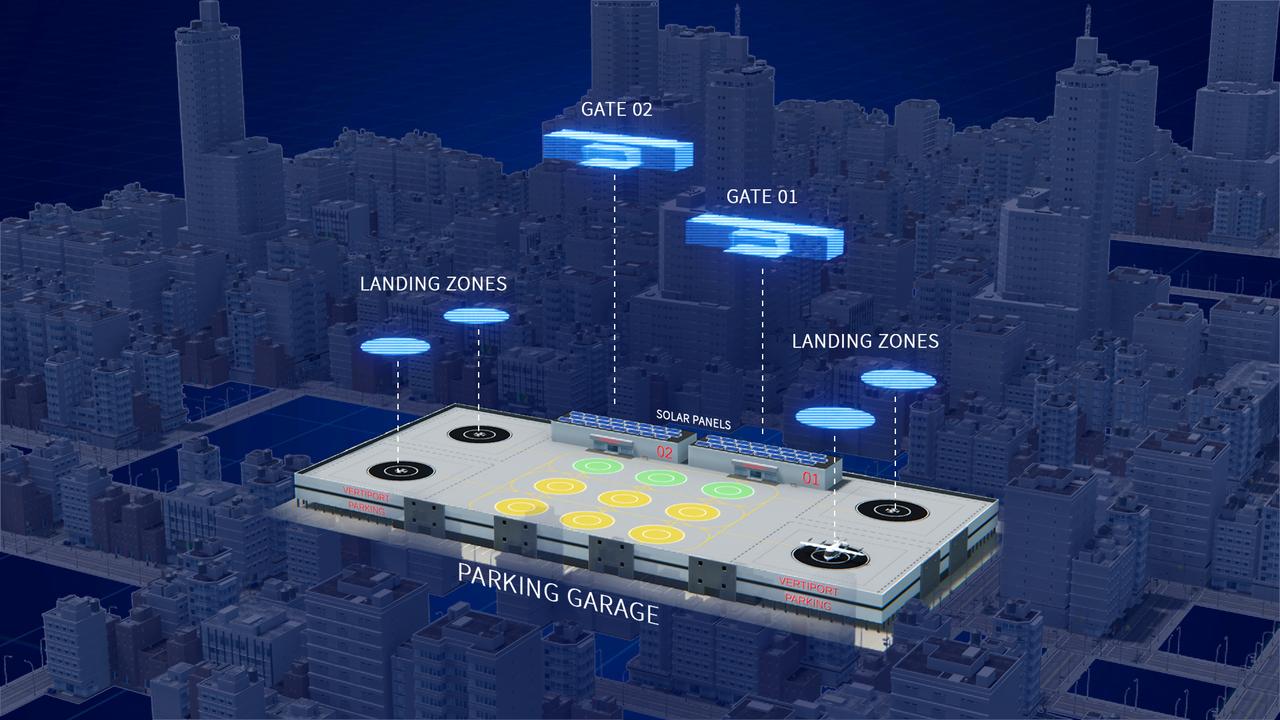
Several projects supporting NASA's Advanced Air Mobility, or AAM mission, are working on different elements to help make AAM a reality. In order for these new AAM aircraft to safely operate, new infrastructure and changes to current infrastructure will need to be developed in cities, suburbs, and rural areas.
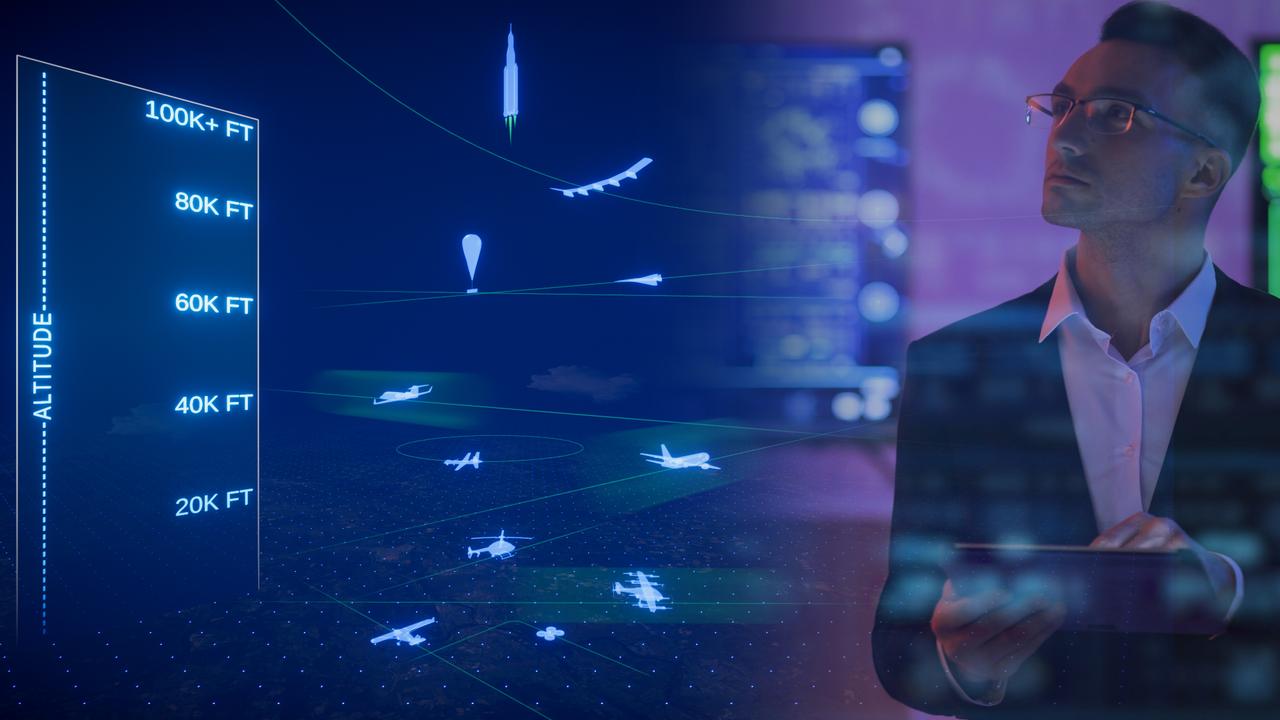

For NASA’s Advanced Air Mobility mission's vision to be successful, partners in industry and government must develop new air traffic management technologies. This concept art represents how different types of aircraft could fly safely and efficiently in a busy airspace with the help of new air traffic management technologies.
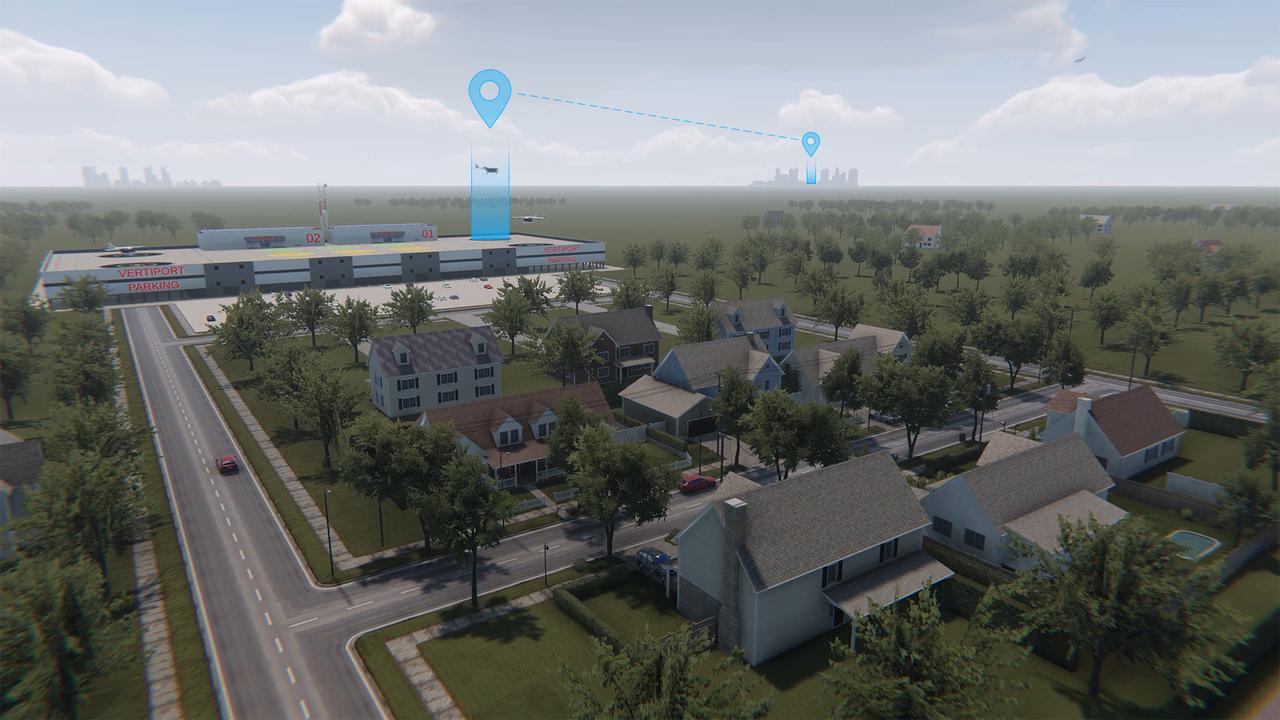
Advanced Air Mobility will connect both urban dwellers and rural residents by adding a new way to travel by air. As shown in this concept art, passengers could travel from rural areas into the city quicker than by car to board a commercial airliner, access medical care or to purchase goods.

Advanced Plant Experiment, APEX-4, support in the Telescience Support Center at NASA Glenn. APEX-4 continues a highly successful investigation into the effects of microgravity on the development of roots and cells on plant seedlings. After four days of growth, the petri plate will be inserted into the Fluids Integrated Rack (FIR) Light Microscopy Module (LMM) facility for detailed imaging.
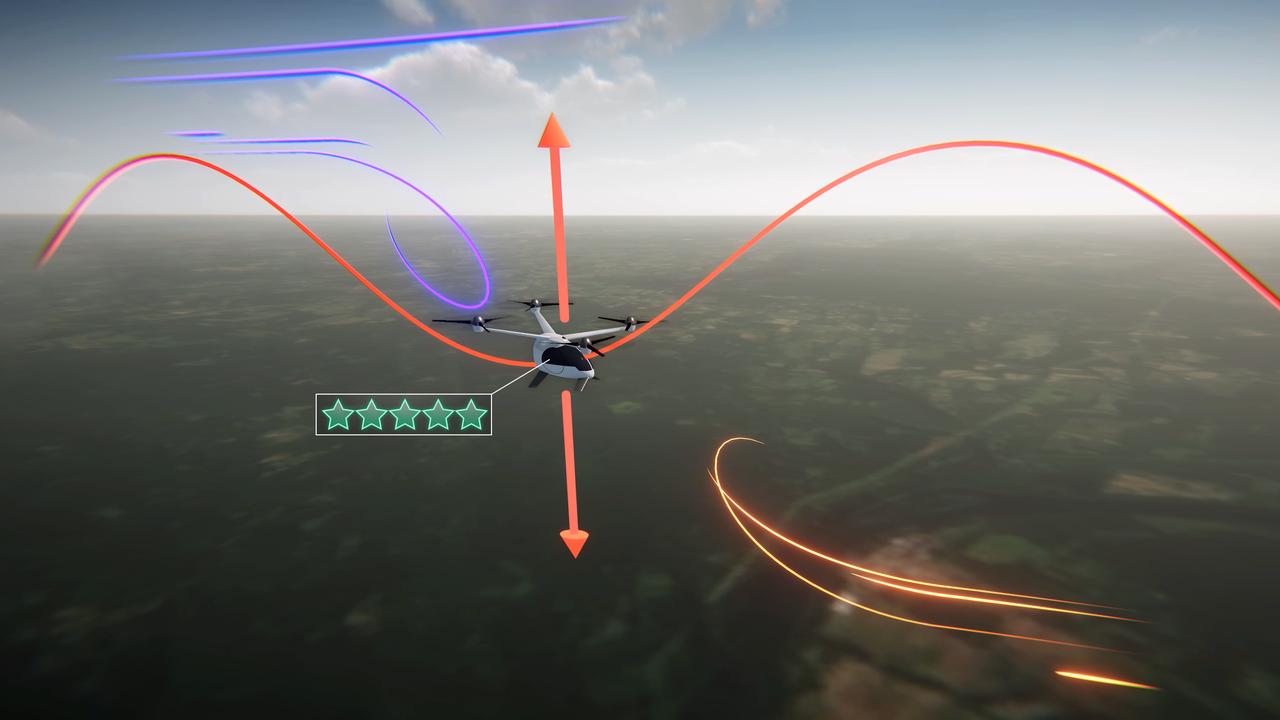
Electrical vertical takeoff and landing aircraft (eVTOLs), like the one shown in this concept art, could be a crucial part of the next generation of air transportation. In order to create a viable market, designers will have to create a comfortable passenger experience. NASA's Advanced Air Mobility mission is researching ride quality to better understand how these aircraft should be designed.

A test unit, or prototype, of NASA's Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) was delivered to the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. The base of the APH is being prepared for engineering development tests to see how the science will integrate with the various systems of the plant habitat. It will have 180 sensors and four times the light output of Veggie. The APH will be delivered to the International Space Station in March 2017.

A test unit, or prototype, of NASA's Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) was delivered to the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. Oscar Monje, a scientist on the Engineering Services Contract, prepares the base of the APH for engineering development tests to see how the science will integrate with the various systems of the plant habitat. The APH will have about 180 sensors and fourt times the light output of Veggie. The APH will be delivered to the International Space Station in March 2017.

A test unit, or prototype, of NASA's Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) was delivered to the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. The unit is being prepared for engineering development tests to see how the science will integrate with the various systems of the plant habitat. It will have 180 sensors and four times the light output of Veggie. The APH will be delivered to the International Space Station in March 2017.

A test unit, or prototype, of NASA's Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) was delivered to the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. The unit is being prepared for engineering development tests to see how the science will integrate with the various systems of the plant habitat. It will have 180 sensors and four times the light output of Veggie. The APH will be delivered to the International Space Station in March 2017.

Arabidopsis thaliana plants are seen inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1 prior to harvest of half the plants. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, harvests half the Arabidopsis thaliana plants inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.
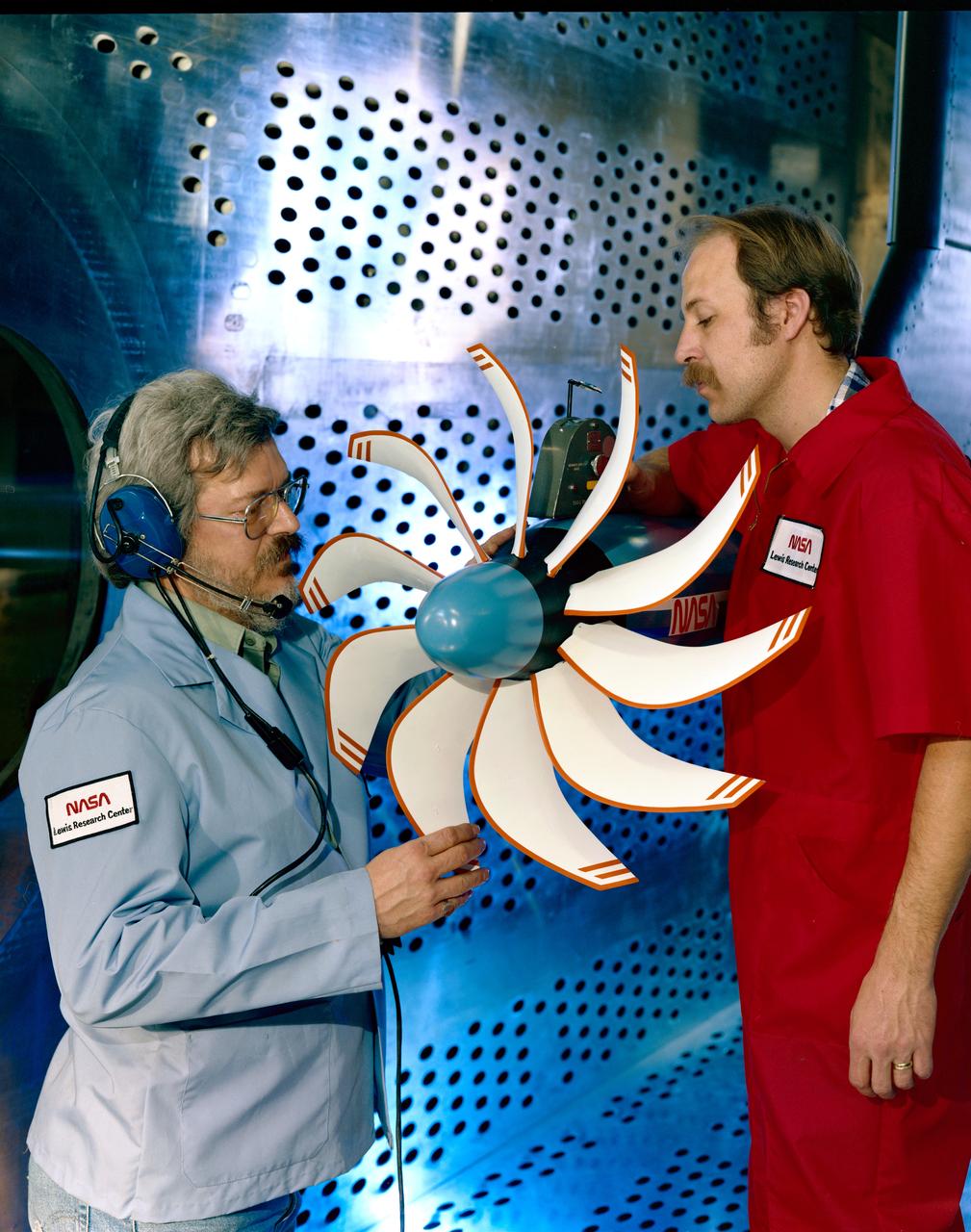

SR-3 Advanced Turboprop (Propfan) in 8x6 foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel

A test unit, or prototype, of NASA's Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) was delivered to the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside a laboratory, Engineering Services Contract engineers set up test parameters on computers. From left, are Glenn Washington, ESC quality engineer; Claton Grosse, ESC mechanical engineer; and Jeff Richards, ESC project scientist. The APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It will have 180 sensors and four times the light output of Veggie. The APH will be delivered to the International Space Station in March 2017.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, uses a FluorPen to measure the chlorophyll fluorescence of Arabidopsis thaliana plants inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1. Half the plants were then harvested. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

Team members pause for a photo after the successful harvest of half the Arabidopsis thaliana plants inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1. From right to left are Jeff Richards with Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies; David Hanson, part of the principal investigator's team; Oscar Monje with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Engineering Services Contract; and John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with Kennedy's Test and Operations Support Contract. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, places Arabidopsis thaliana plants harvested from the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1 into an Ultra-low Freezer chilled to -150 degrees Celsius. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, places Arabidopsis thaliana plants harvested from the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1 into a Mini ColdBag that quickly freezes the plants. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, opens the door to the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1 for a test harvest of half of the Arabidopsis thaliana plants growing within. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, uses a FluorPen to measure the chlorophyll fluorescence of Arabidopsis thaliana plants inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1. Half the plants were then harvested. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, opens the door to the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1 for a test harvest of half of the Arabidopsis thaliana plants growing within. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

Dr. Oscar Monje, a research scientist, packs a growing substrate called arcillite in the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

Dr. Oscar Monje, a research scientist, pours a growing substrate called arcillite in the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

Dr. Oscar Monje, a research scientist, pours a growing substrate called arcillite in the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.
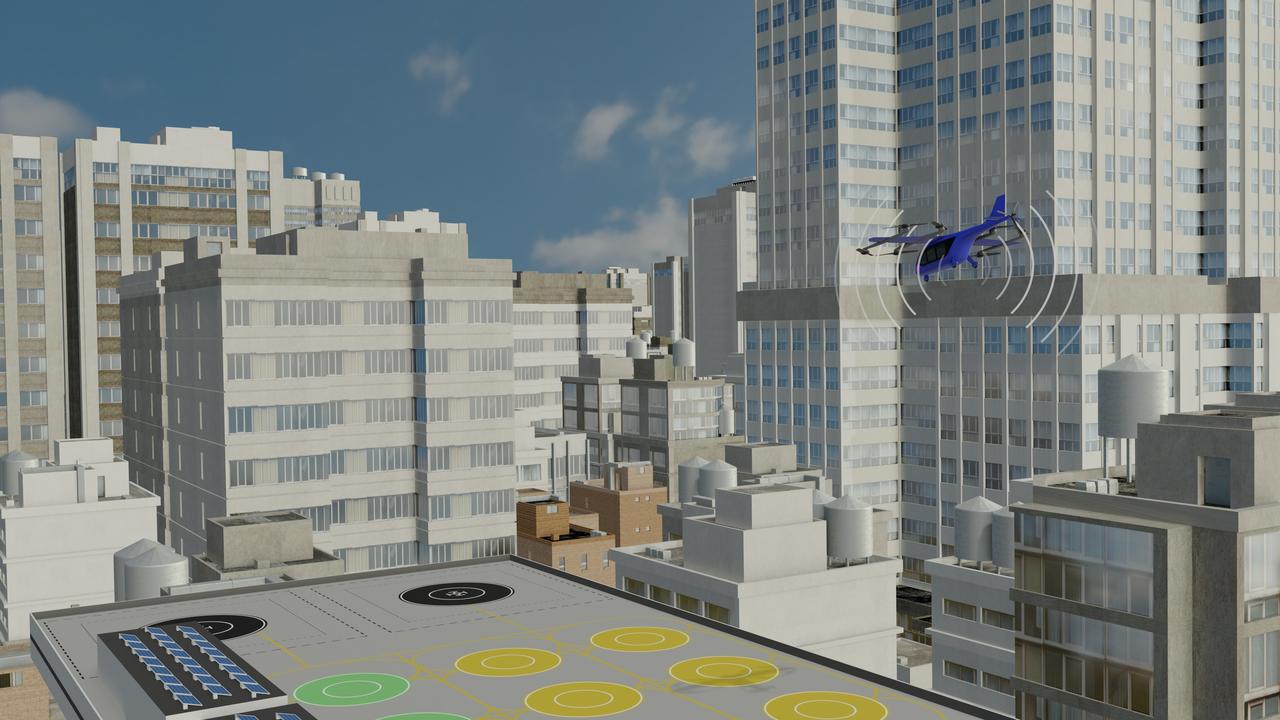

Several projects supporting NASA's Advanced Air Mobility, or AAM mission, are working on different elements to help make AAM a reality. One focus area is developing design tools manufacturers can use to reduce noise impacts.
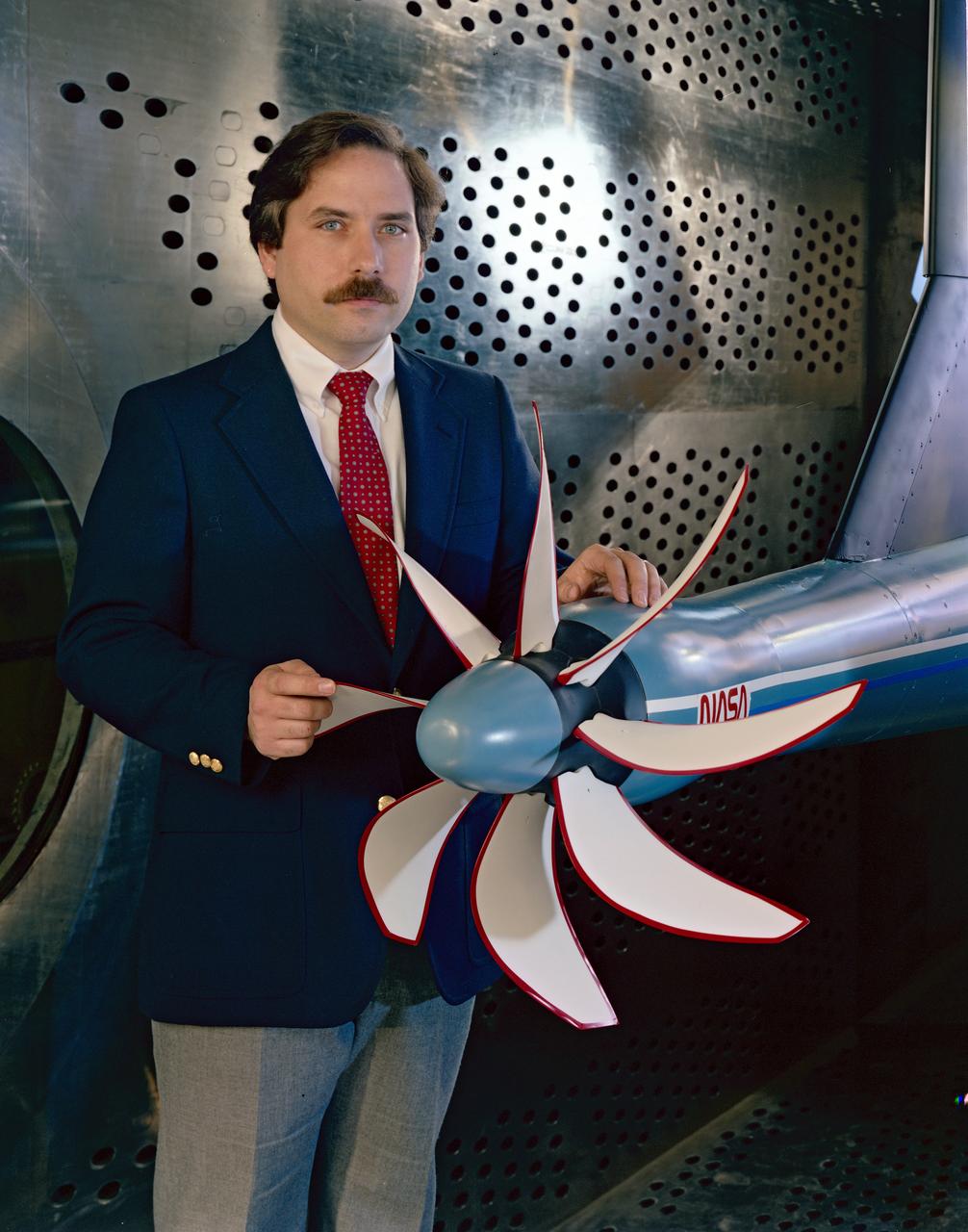

SR-3 Advanced Turboprop (Propfan) in 8x6 foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel (SWT)
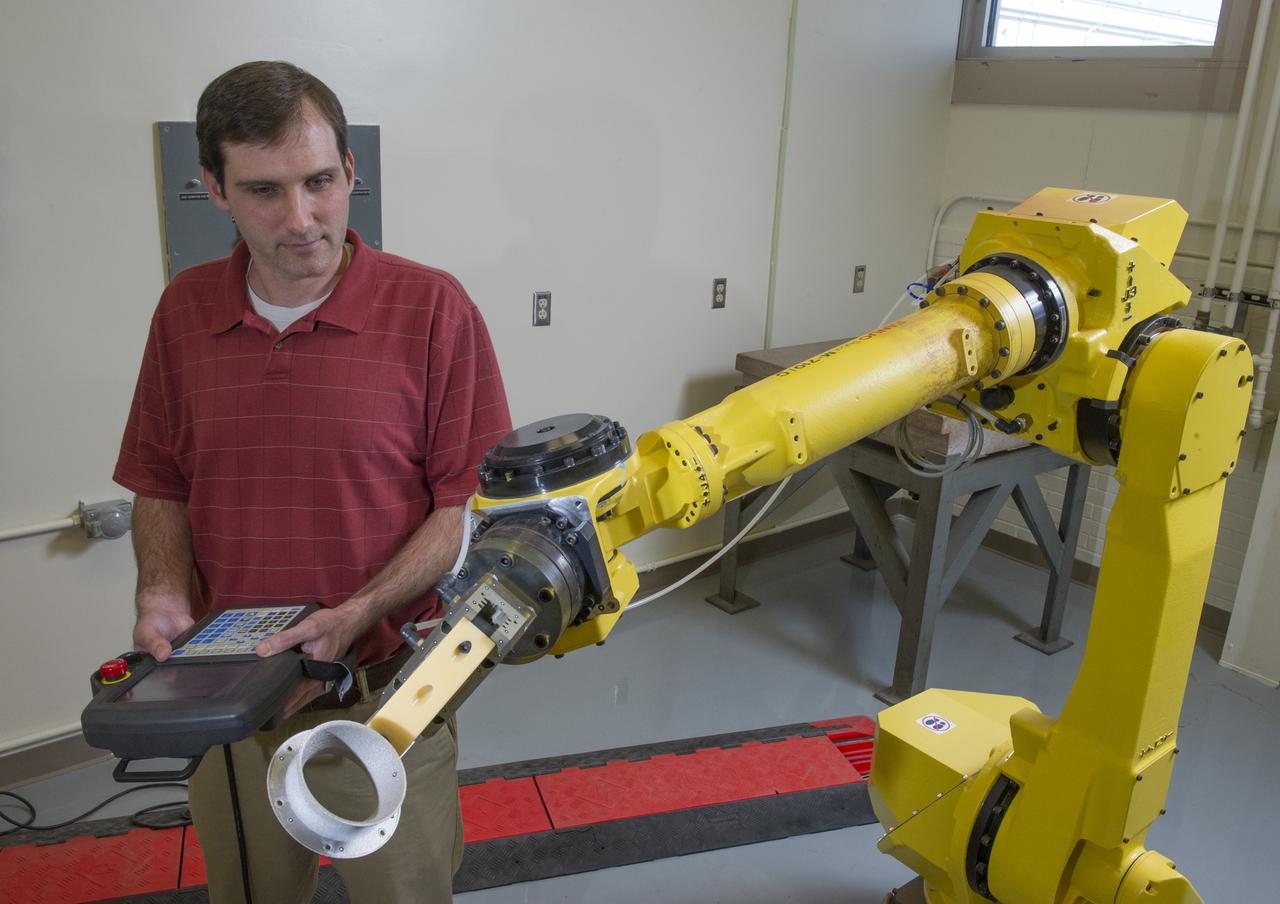

JOSH WHITE DEMONSTRATING THE CAPABILITIES OF THE SYSTEM TO AUTONOMOUSLY INSPECT AND MACHINE ADDITIVELY MANUFACTURED PARTS (SAIMAP).
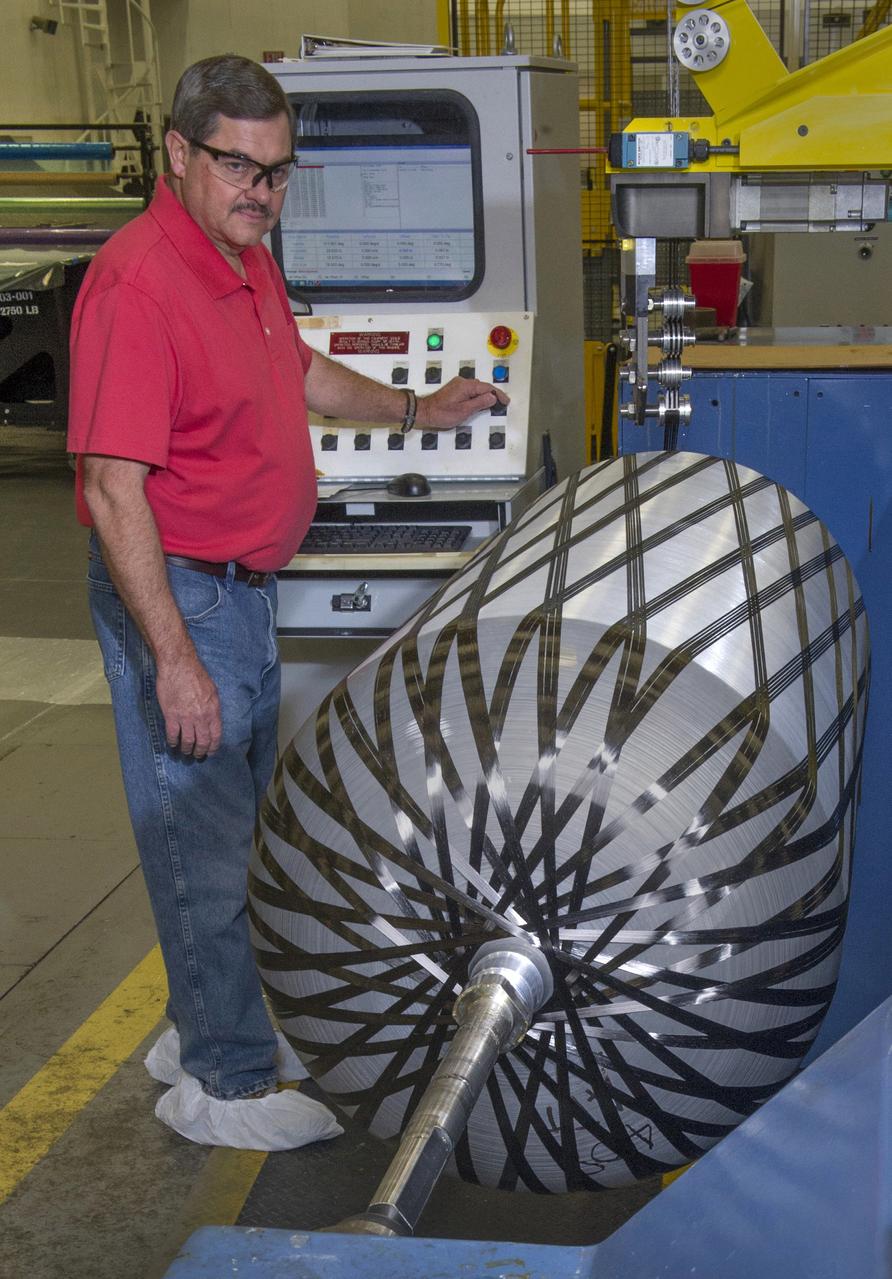

PHILLIP THOMPSON WRAPS PRESSURE VESSEL WITH COMPOSITE MATERIAL
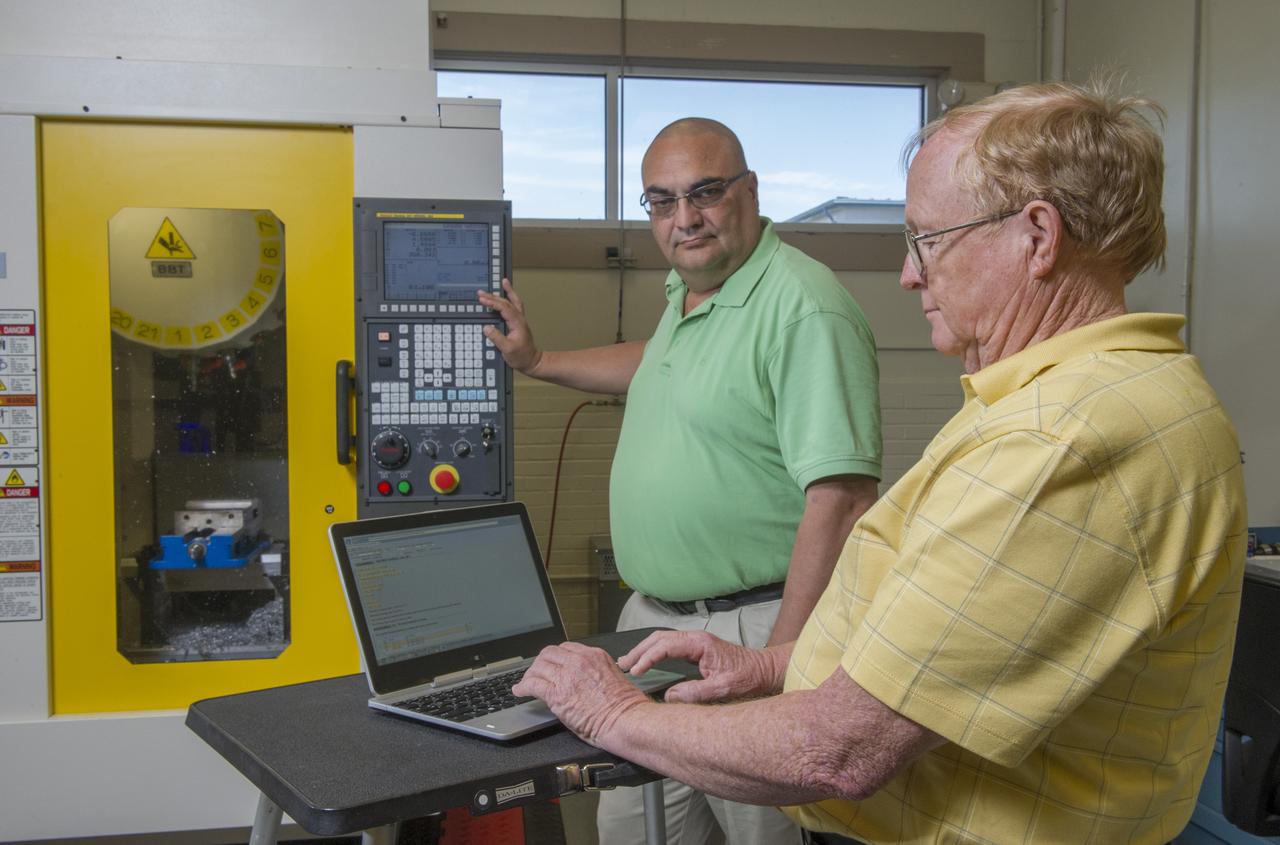

RON BROOKS (FOREGROUND) AND DON JAMES (BACKGROUND) USING THE SOLUMINA MANUFACTURING EXECUTION SYSTEM TO DELIVER AND EXECUTE WORK INSTRUCTIONS ON THE SHOP FLOOR.
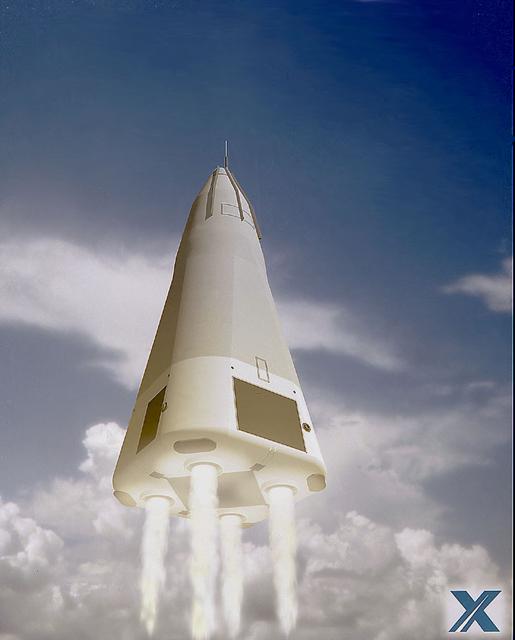

Pictured here is a DC-XA Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) prototype concept with an RLV logo. The Delta Clipper-Experimental (DC-X) was originally developed by McDornell Douglas for the Department of Defense (DOD). The DC-XA is a single-stage-to-orbit, vertical takeoff/vertical landing, launch vehicle concept, whose development is geared to significantly reduce launch costs and will provide a test bed for NASA Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) technology as the Delta Clipper-Experimental Advanced (DC-XA).

Inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, scientists are preparing the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH). A growing substrate called arcillite has been packed down in the base and coverings are being secured to seal the base. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

Inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, scientists prepared the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH). A growing substrate called arcillite was packed down in the base and coverings were secured on top of the base. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

Inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, scientists are preparing the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH). A growing substrate called arcillite has been packed down in the base and coverings are being secured to seal the base. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a quality technician checks the hardware for the Advanced Plant Habitat flight unit. The flight unit is an exact replica of the APH that was delivered to the International Space Station. Validation tests and post-delivery checkout was performed to prepare for space station in-orbit APH activities. The flight unit will be moved to the International Space Station Environmental Simulator to begin an experiment verification test for the science that will fly on the first mission, PH-01. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the space station.

Inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a scientist inserts Apogee wheat seeds into the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH). A growing substrate called arcillite was packed down in the base and coverings were secured on top of the base. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, quality technicians check the hardware for the Advanced Plant Habitat flight unit. The flight unit is an exact replica of the APH that was delivered to the International Space Station. Validation tests and post-delivery checkout was performed to prepare for space station in-orbit APH activities. The flight unit will be moved to the International Space Station Environment Simulator to begin an experiment verification test for the science that will fly on the first mission, PH-01. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the space station.

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, quality technicians check components of the hardware for the Advanced Plant Habitat flight unit. The flight unit is an exact replica of the APH that was delivered to the International Space Station. Validation tests and post-delivery checkout was performed to prepare for space station in-orbit APH activities. The flight unit will be moved to the International Space Station Environmental Simulator to begin an experiment verification test for the science that will fly on the first mission, PH-01. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the space station.

Inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, scientists prepare Apogee wheat seeds for the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH). A growing substrate called arcillite was packed down in the base and coverings were secured on top of the base. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

Inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, scientists prepare Apogee wheat seeds for the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH). A growing substrate called arcillite was packed down in the base and coverings were secured on top of the base. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, quality technicians check the hardware for the Advanced Plant Habitat flight unit. The flight unit is an exact replica of the APH that was delivered to the International Space Station. Validation tests and post-delivery checkout was performed to prepare for space station in-orbit APH activities. The flight unit will be moved to the International Space Station Environmental Simulator to begin an experiment verification test for the science that will fly on the first mission, PH-01. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the space station.

Inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, scientists prepare Apogee wheat seeds for the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH). A growing substrate called arcillite was packed down in the base and coverings were secured on top of the base. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

Dr. Oscar Monje, a research scientist, packs a growing substrate called arcillite in the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Seated at right is Susan Manning-Roach, a quality assurance specialist on the Engineering Services Contract. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System is seen orbiting Earth in this 13-second exposure photograph, Monday, Sept. 2, 2024, from Arlington, Virginia. The mission team confirmed the spacecraft’s unique composite boom system unfurled its reflective sail on Thursday, accomplishing a critical milestone in the agency’s demonstration of next-generation solar sail technology that will allow small spacecraft to “sail on sunlight.” Just as a sailboat is powered by wind in a sail, a spacecraft can use the pressure of sunlight on a solar sail for propulsion. This technology demonstration serves as a pathfinder for future missions powered by solar sail technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a quality technician checks the hardware for the Advanced Plant Habitat flight unit. The flight unit is an exact replica of the APH that was delivered to the International Space Station. Validation tests and post-delivery checkout was performed to prepare for space station in-orbit APH activities. The flight unit will be moved to the International Space Station Environmental Simulator to begin an experiment verification test for the science that will fly on the first mission, PH-01. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the space station.

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a quality technician checks the control panel on hardware for the Advanced Plant Habitat flight unit. The flight unit is an exact replica of the APH that was delivered to the International Space Station. Validation tests and post-delivery checkout was performed to prepare for space station in-orbit APH activities. The flight unit will be moved to the International Space Station Environmental Simulator to begin an experiment verification test for the science that will fly on the first mission, PH-01. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the space station.
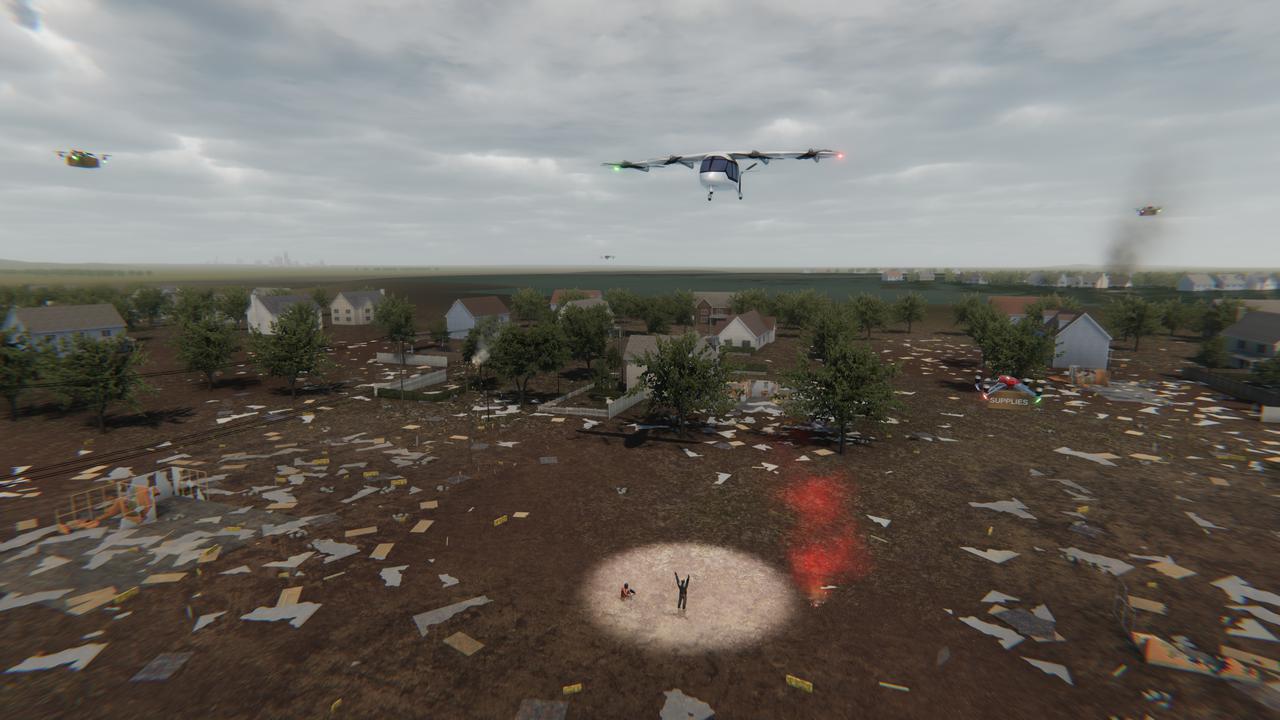

Several projects under NASA's Advanced Air Mobility or AAM mission are working on different elements to help make AAM a reality in emergency operations. This concept graphic shows how a future AAM vehicle could aid in disaster response.
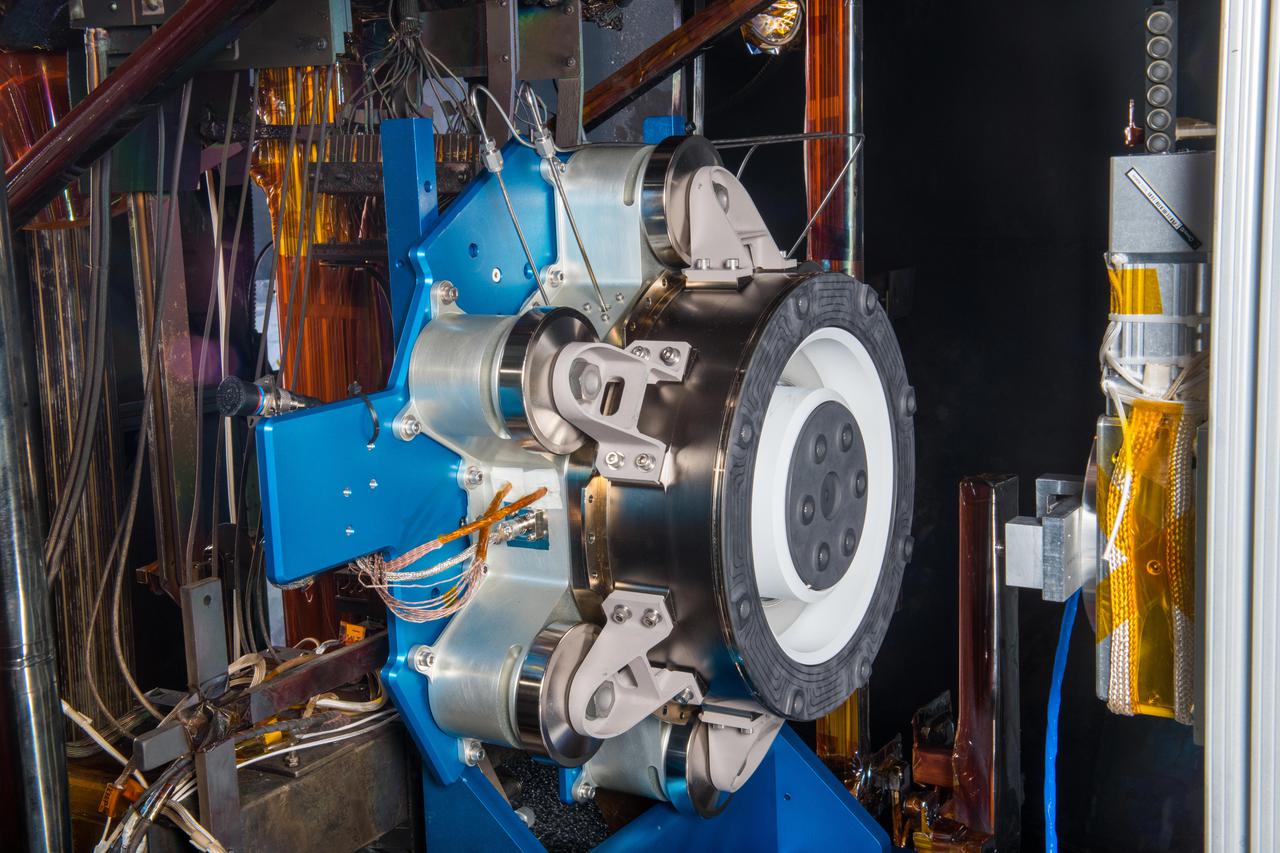
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
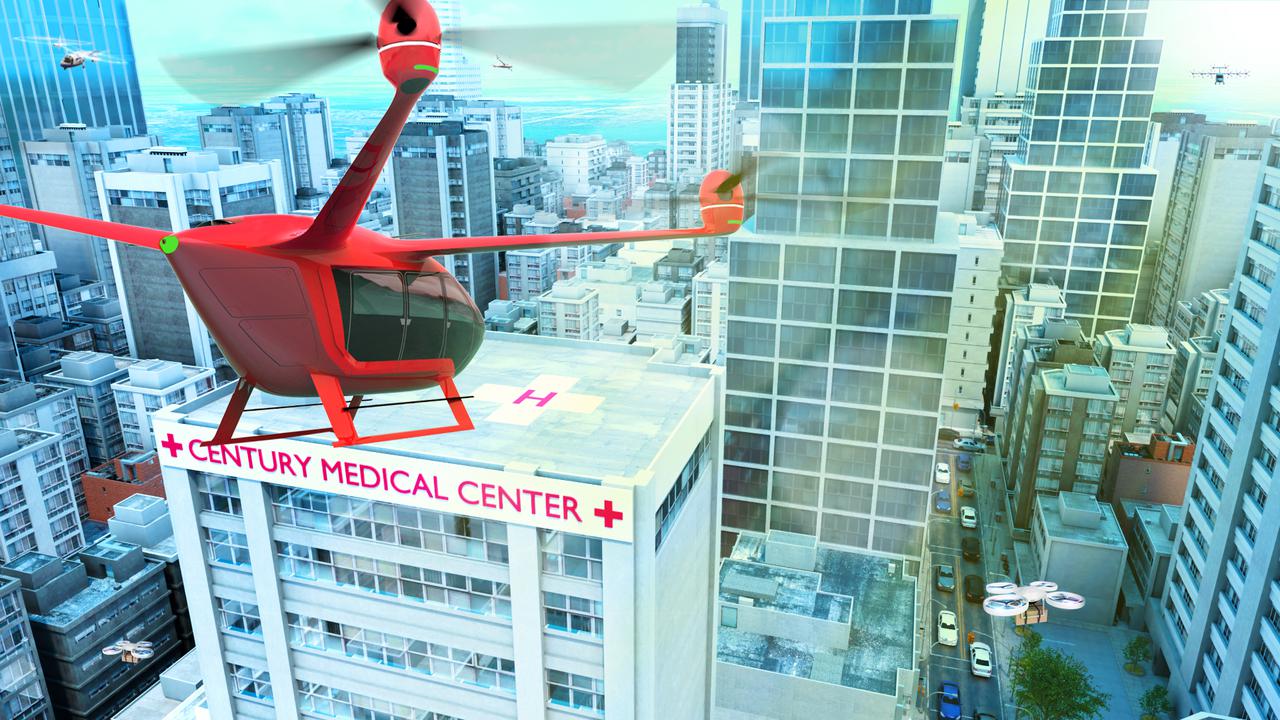

Several projects supporting NASA's Advanced Air Mobility or AAM mission are working on different research initiatives to help make AAM a reality. AAM could be used in healthcare operations in the form of air taxi ambulances or medical supply delivery in the future. This concept graphic shows how a future AAM vehicle could aid in healthcare by carrying passengers to a hospital.

Dr. Oscar Monje, (far right) a research scientist, packs a growing substrate called arcillite in the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assisting him is Jeffrey Richards, project science coordinator with SGT on the Engineering Services Contract (ESC). Seated in the foreground is Susan Manning-Roach, a quality assurance specialist, also with ESC. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, LED plant growth lights are being checked out on the hardware for the Advanced Plant Habitat flight unit. The flight unit is an exact replica of the APH that was delivered to the International Space Station. Validation tests and post-delivery checkout was performed to prepare for space station in-orbit APH activities. The flight unit will be moved to the International Space Station Environmental Simulator to begin an experiment verification test for the science that will fly on the first mission, PH-01. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the space station.

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, LED plant growth lights are being checked out on the hardware for the Advanced Plant Habitat flight unit. The flight unit is an exact replica of the APH that was delivered to the International Space Station. Validation tests and post-delivery checkout was performed to prepare for space station in-orbit APH activities. The flight unit will be moved to the International Space Station Environmental Simulator to begin an experiment verification test for the science that will fly on the first mission, PH-01. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the space station.
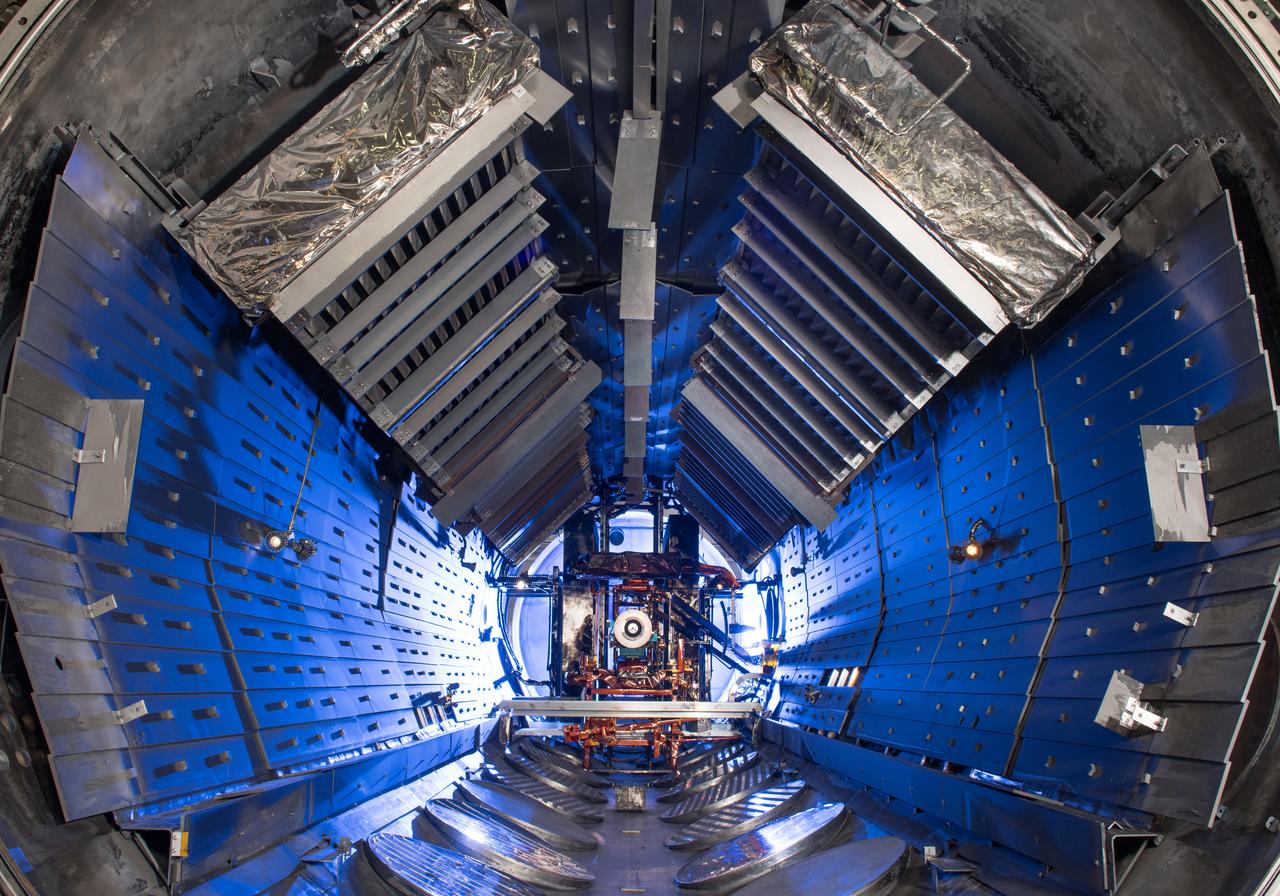

Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
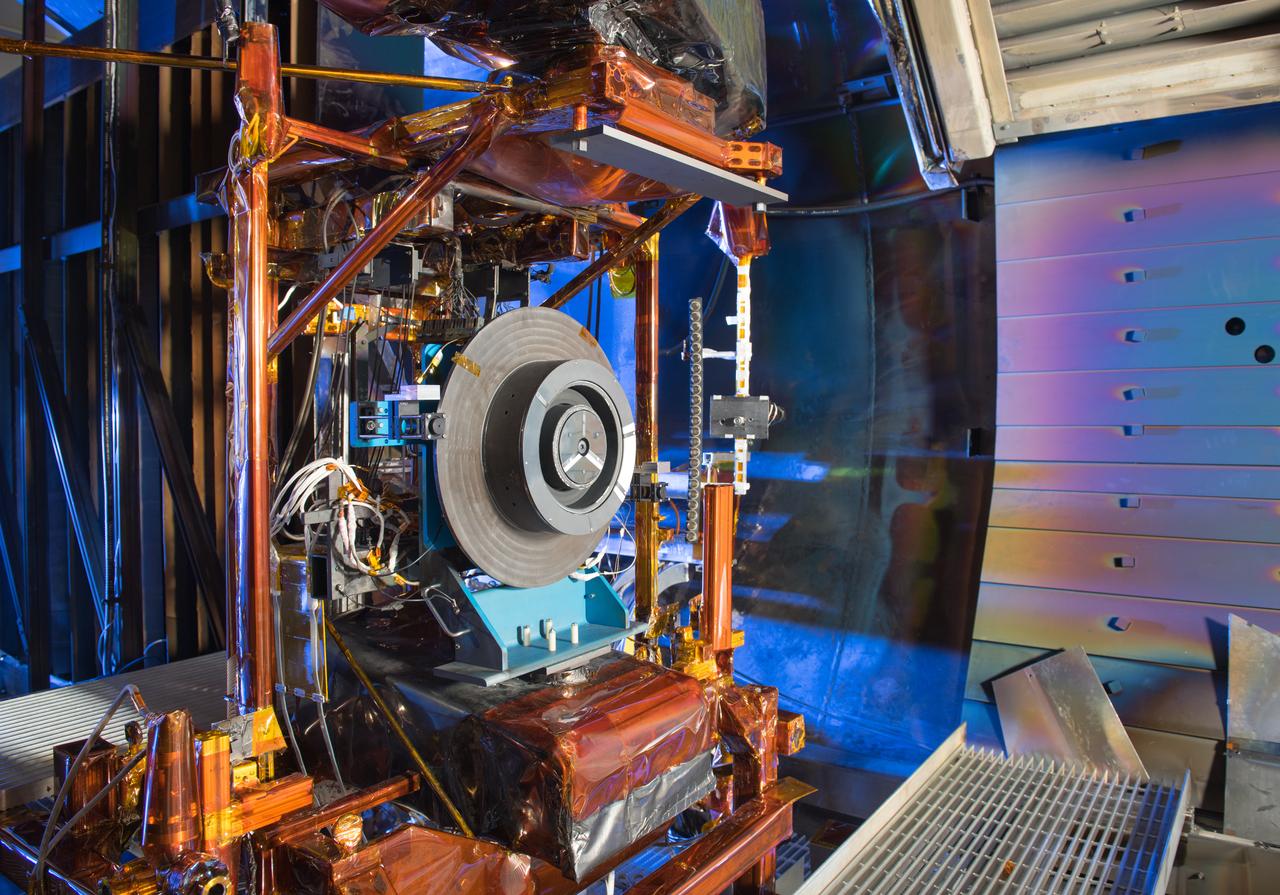
Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
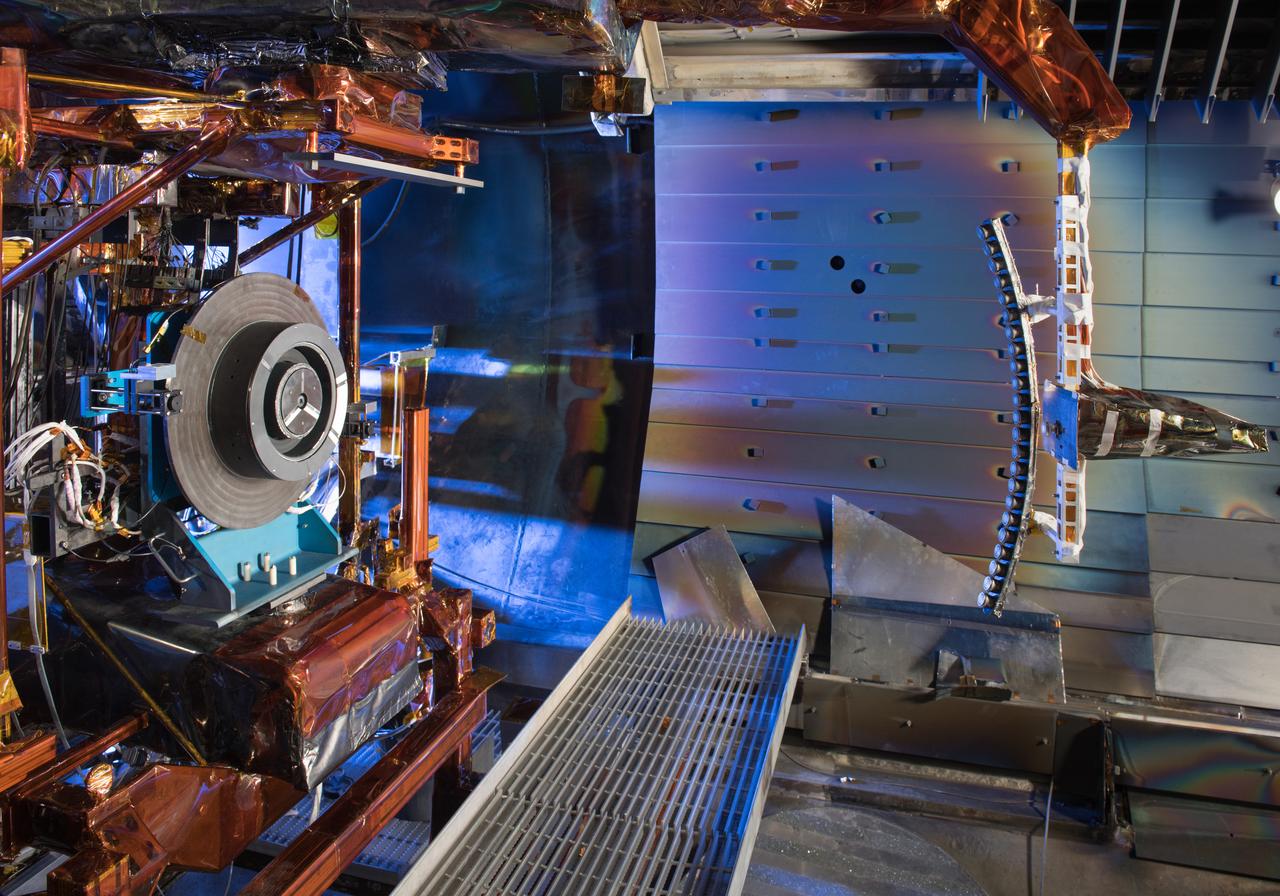
Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
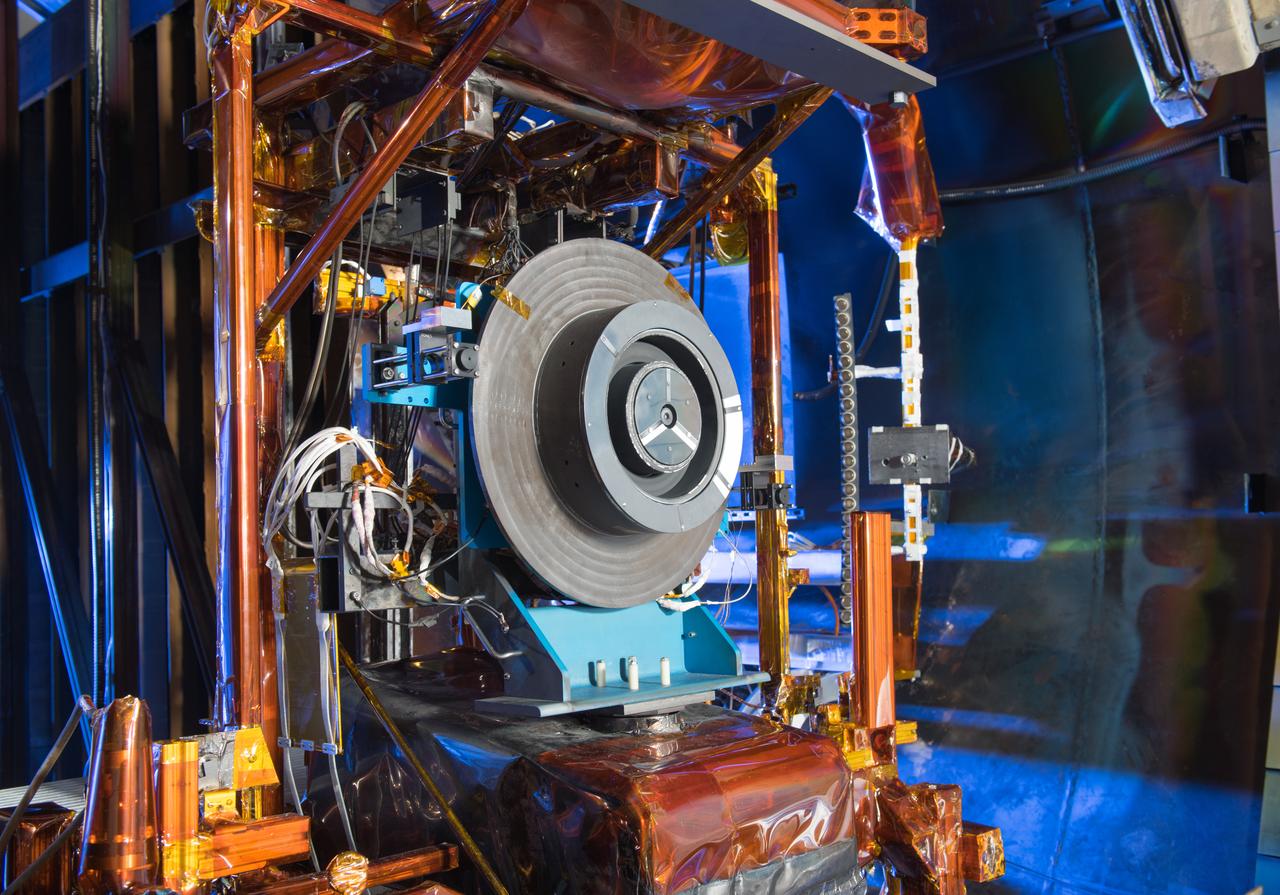
Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
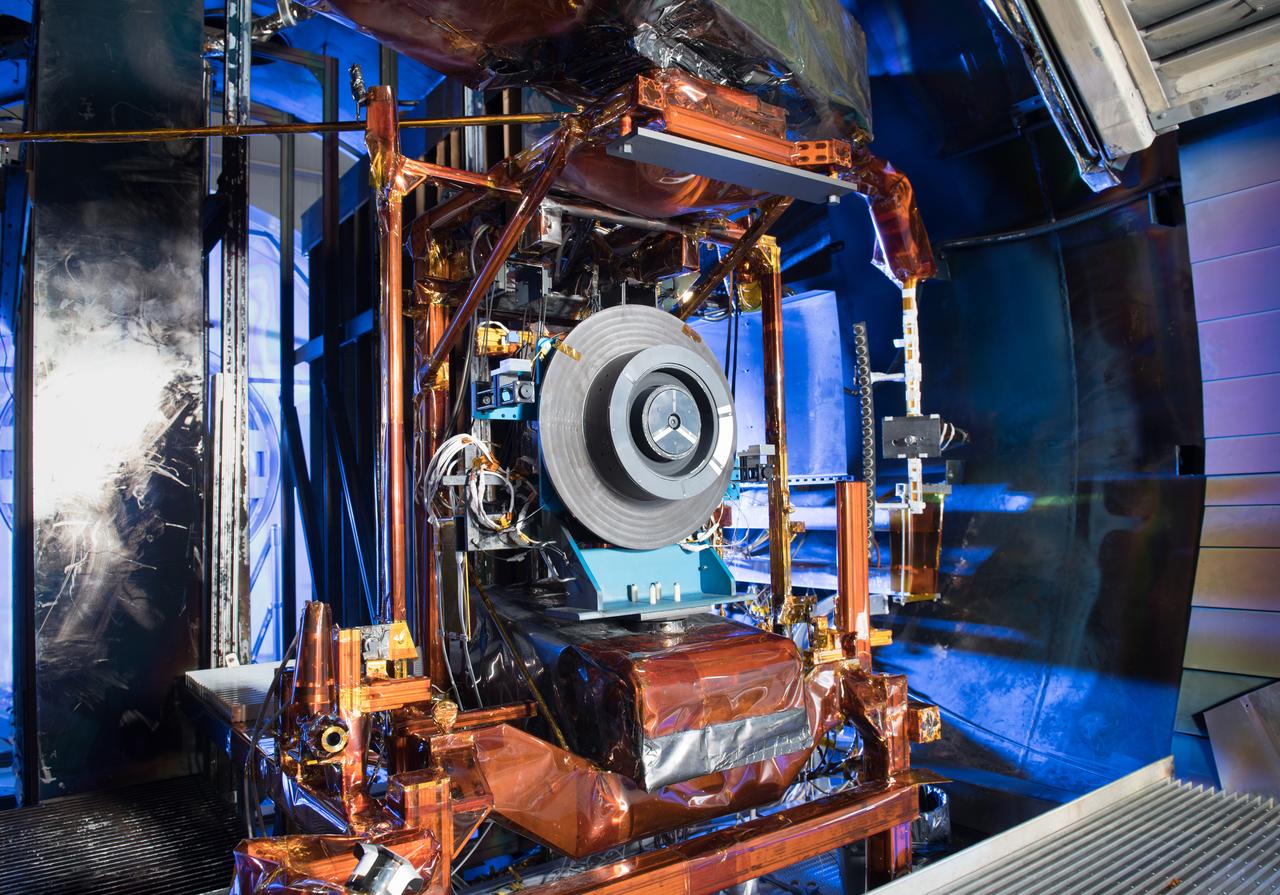
Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
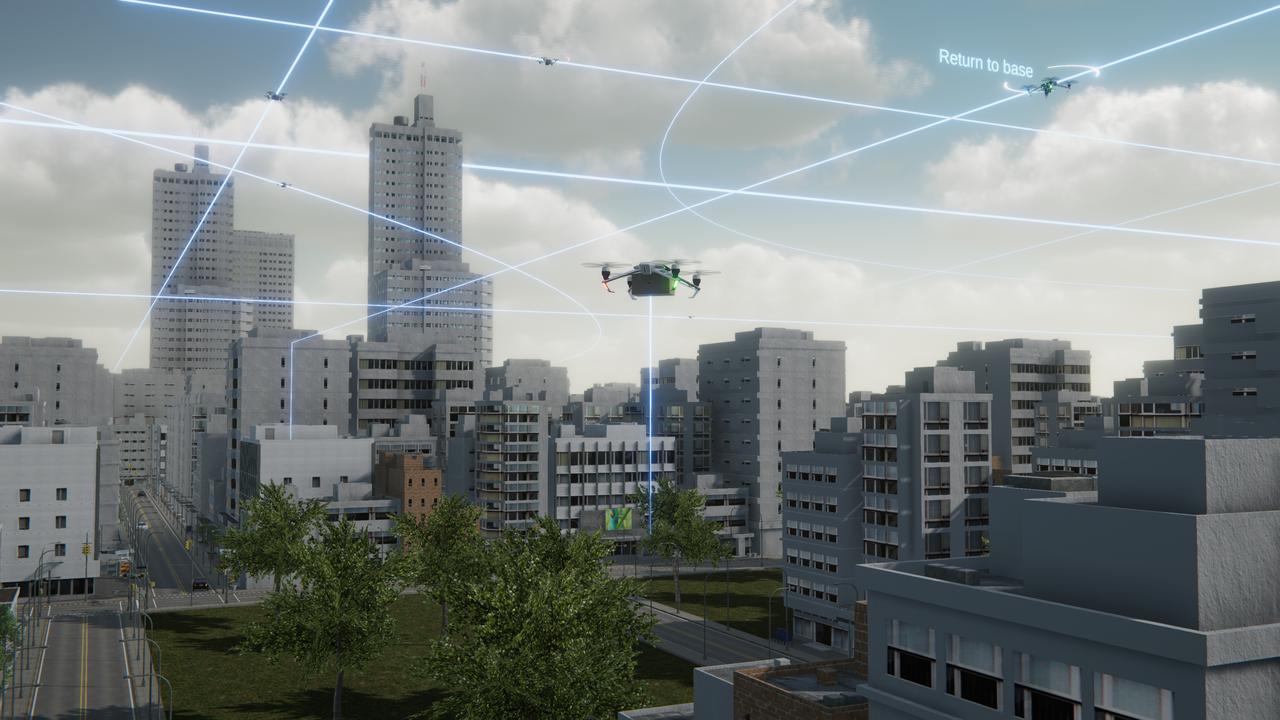

Several projects supporting NASA's Advanced Air Mobility or AAM mission are working on different elements to help make AAM a reality and one of these research areas is automation. This concept graphic shows how elements of automation could be integrated into a future airspace. Technology like this could enable vehicles to operate without a pilot, or if a pilot is in the loop, increase the safety.

Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
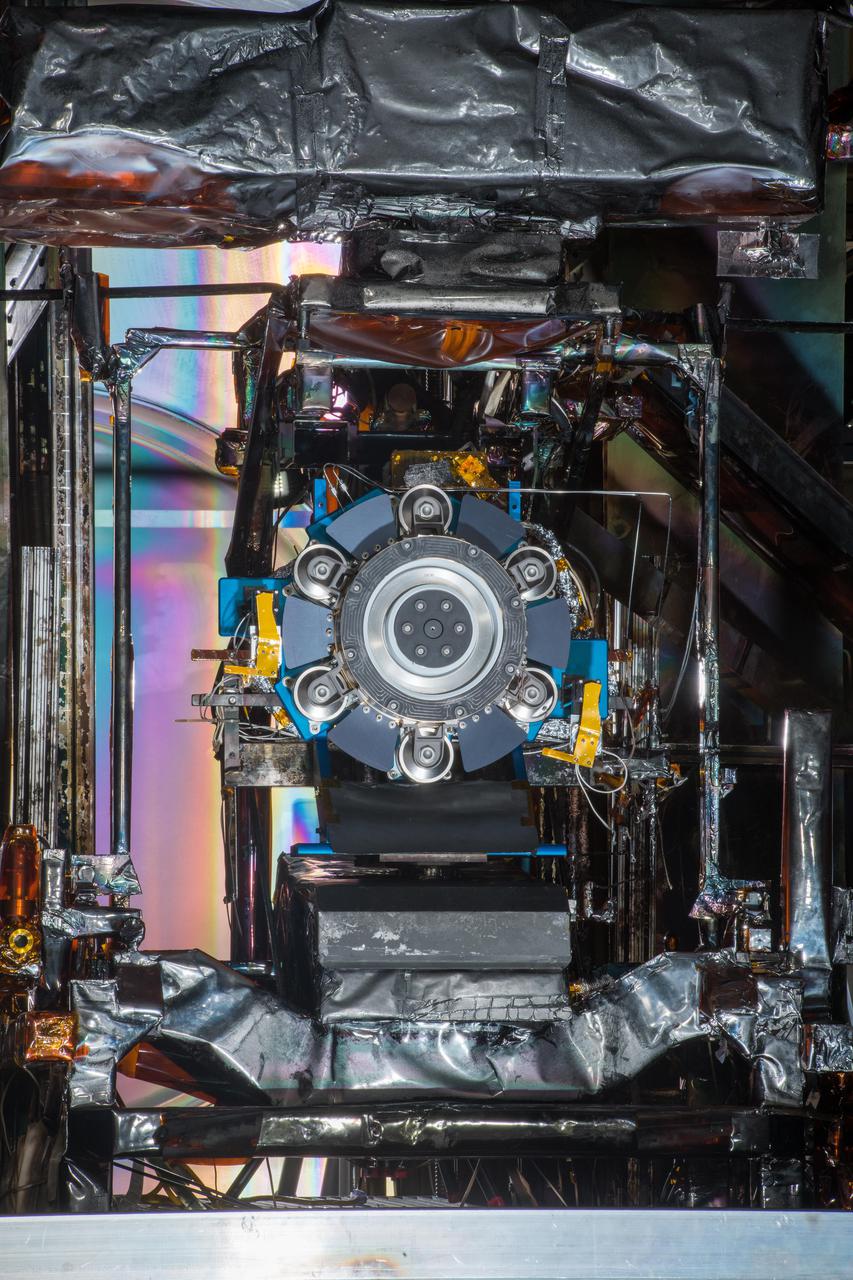
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
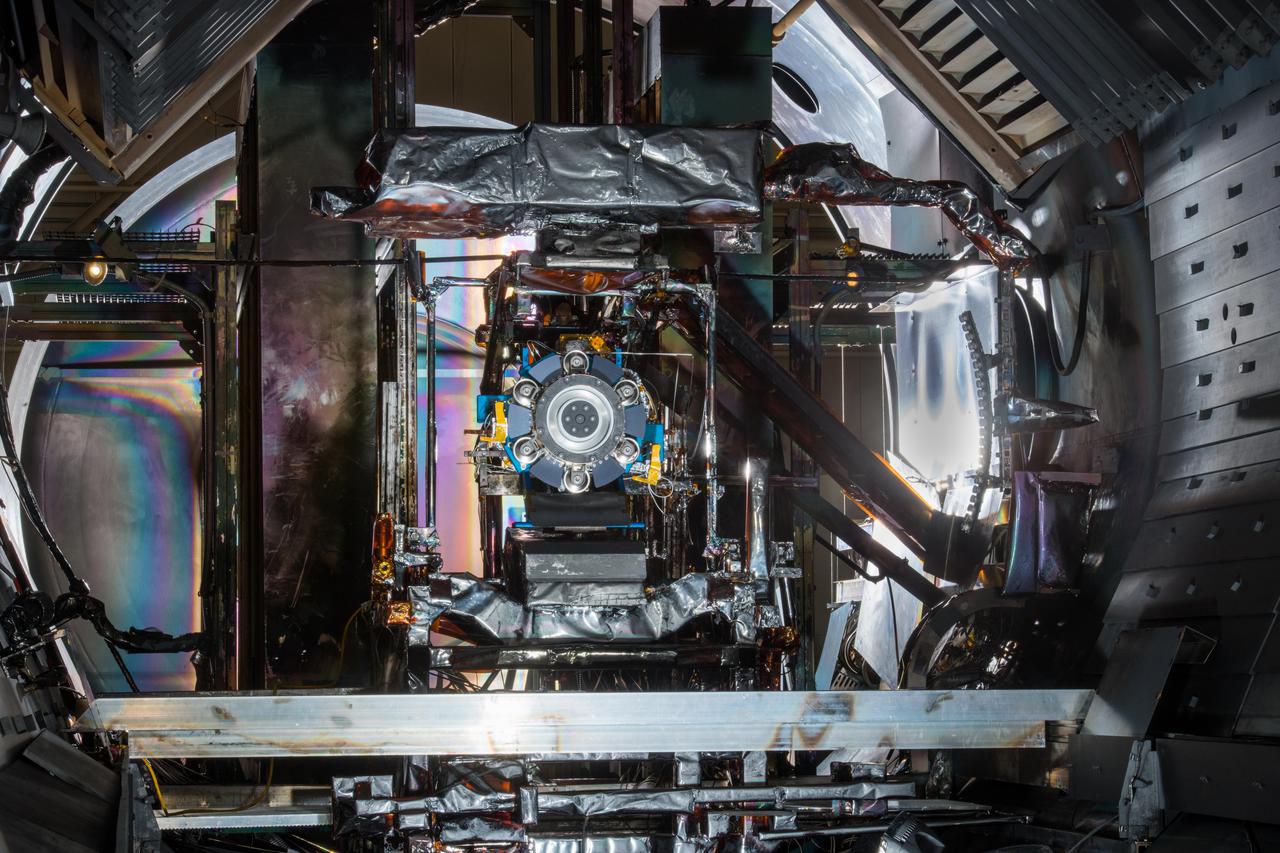
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
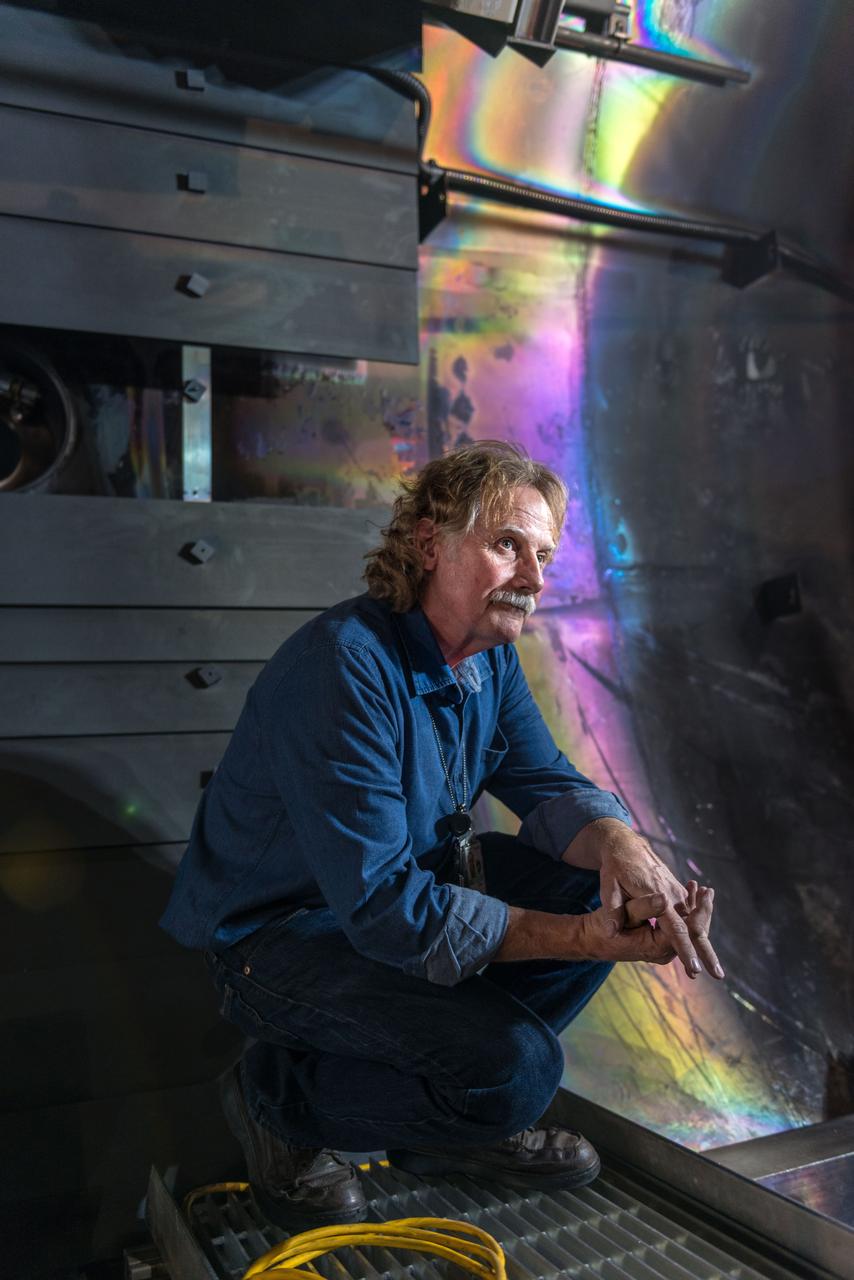

Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
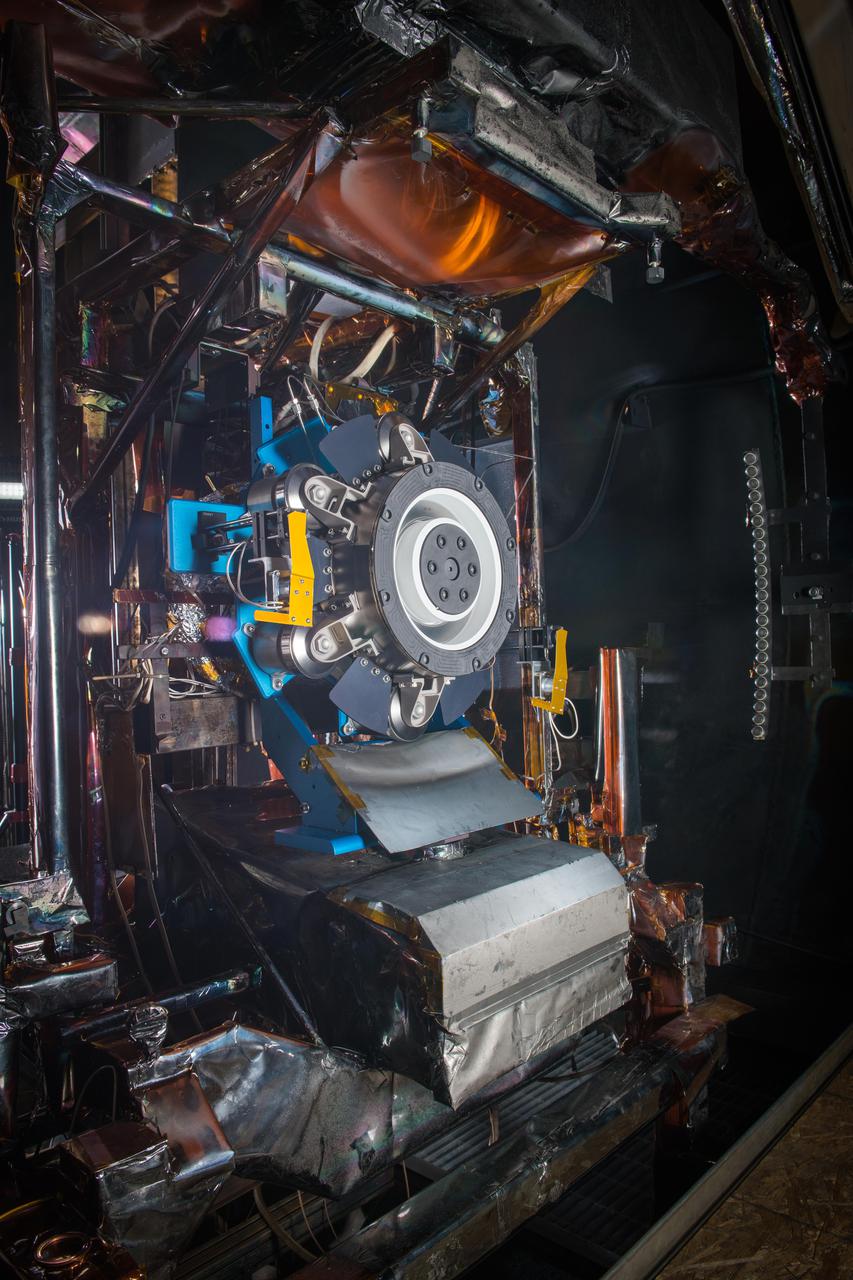
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware

Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
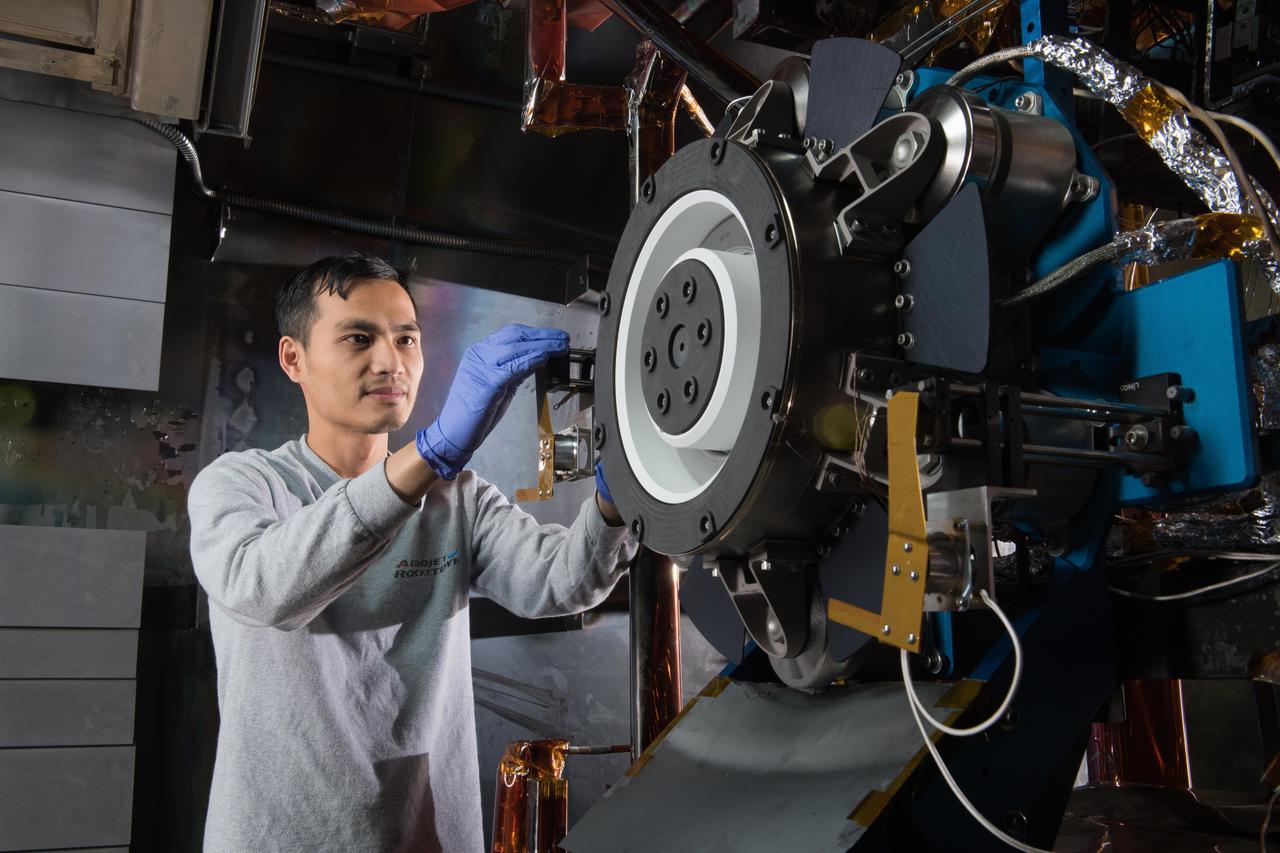
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
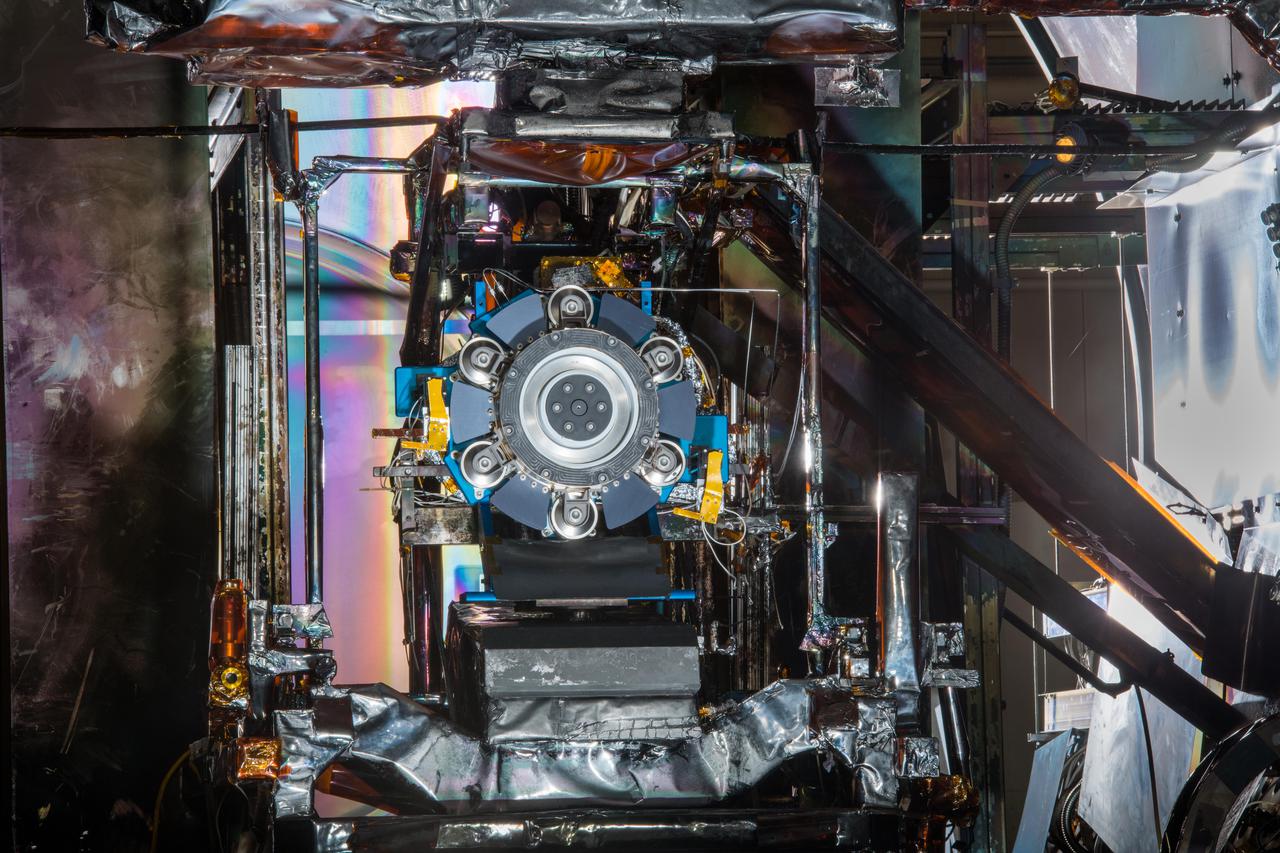
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
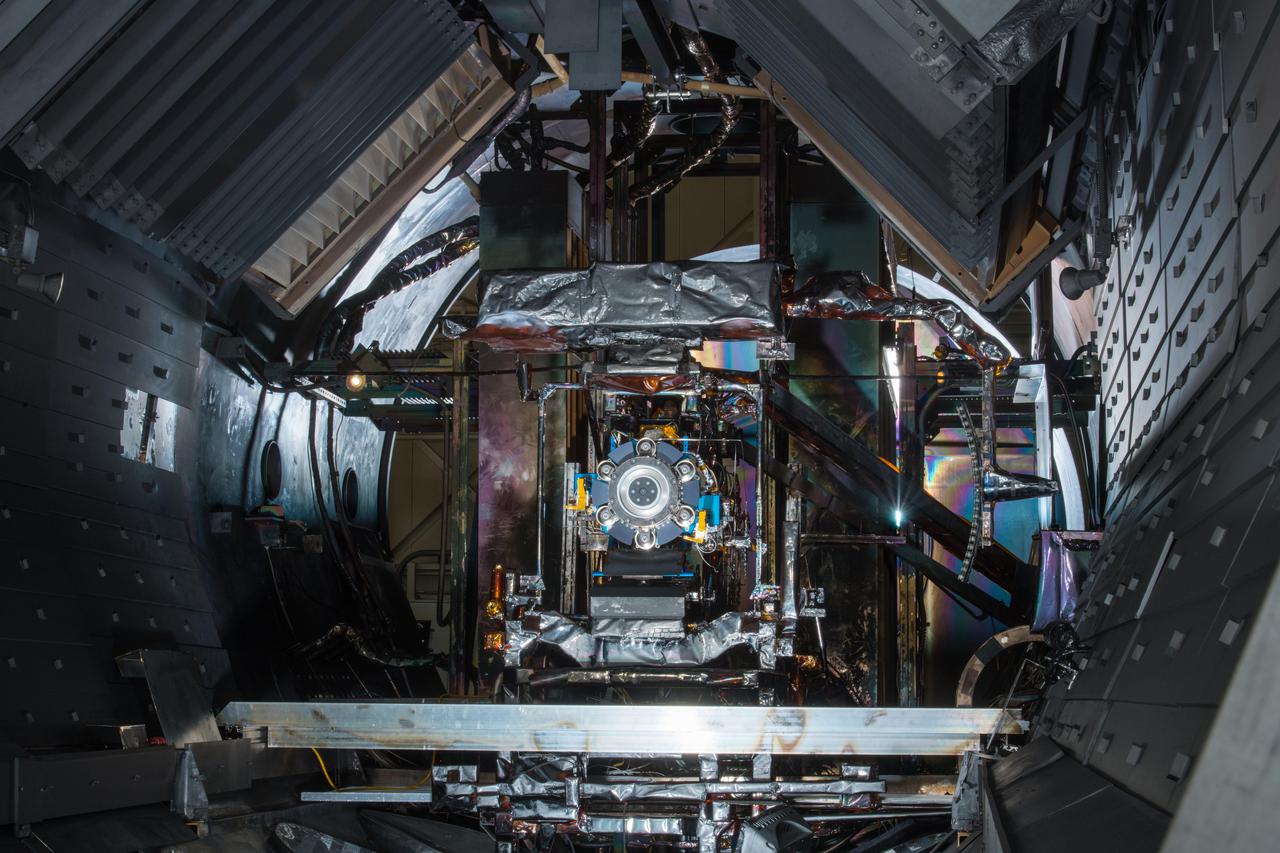
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
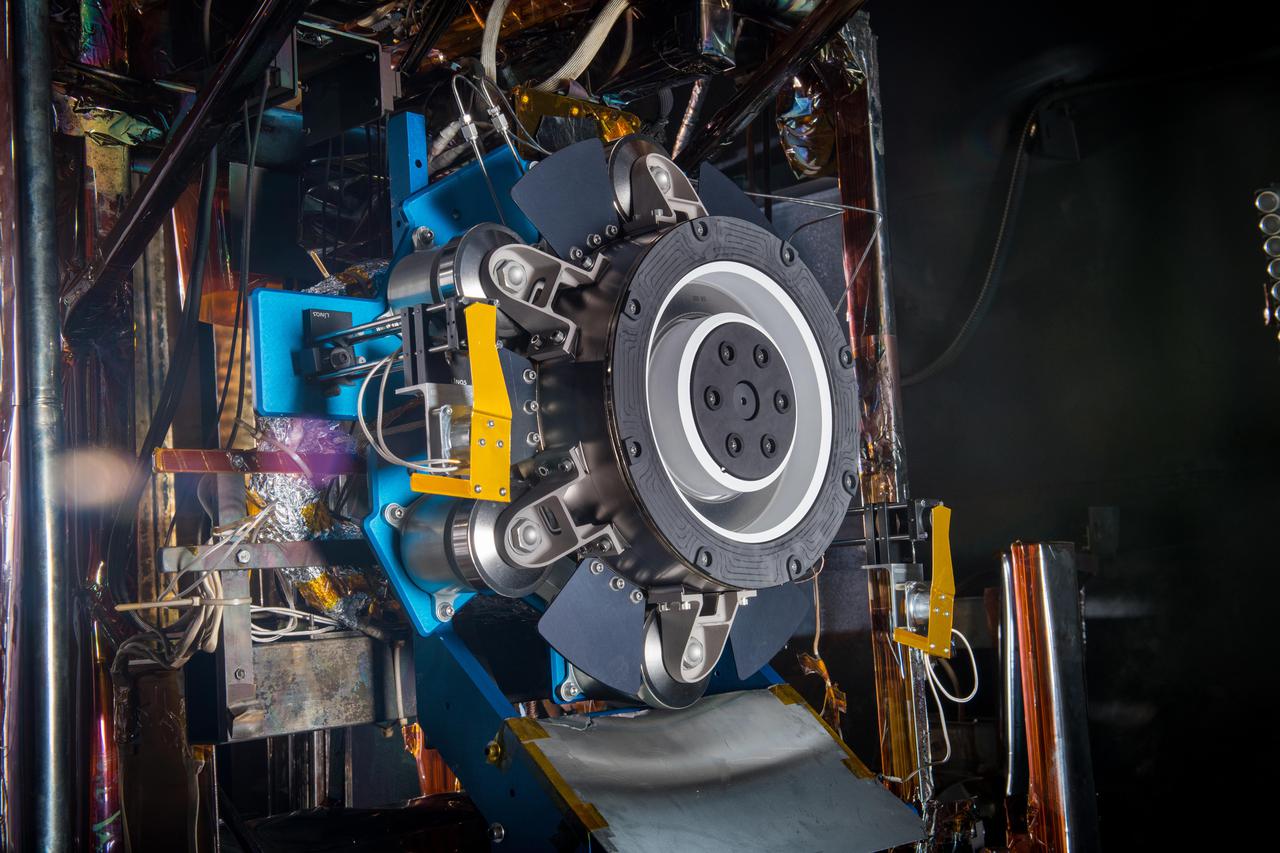
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
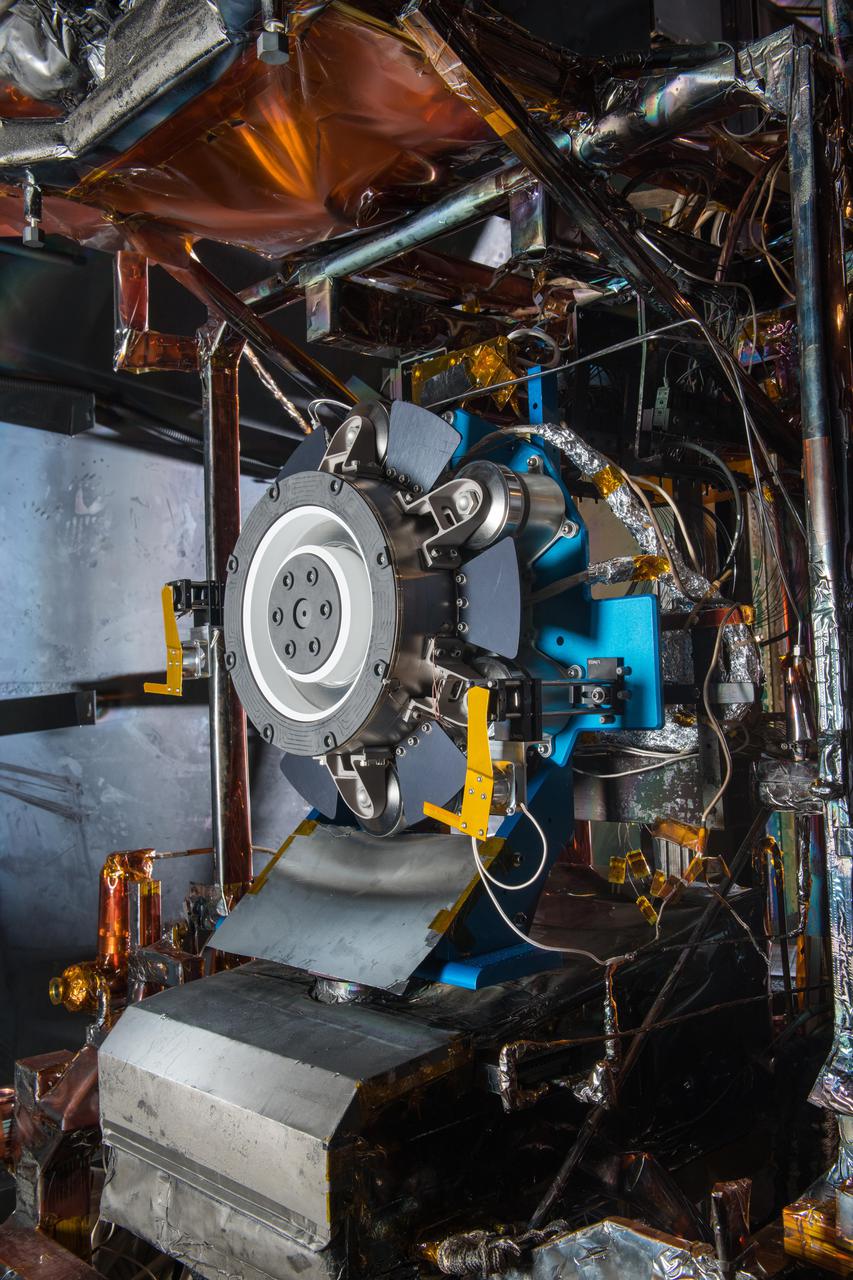
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
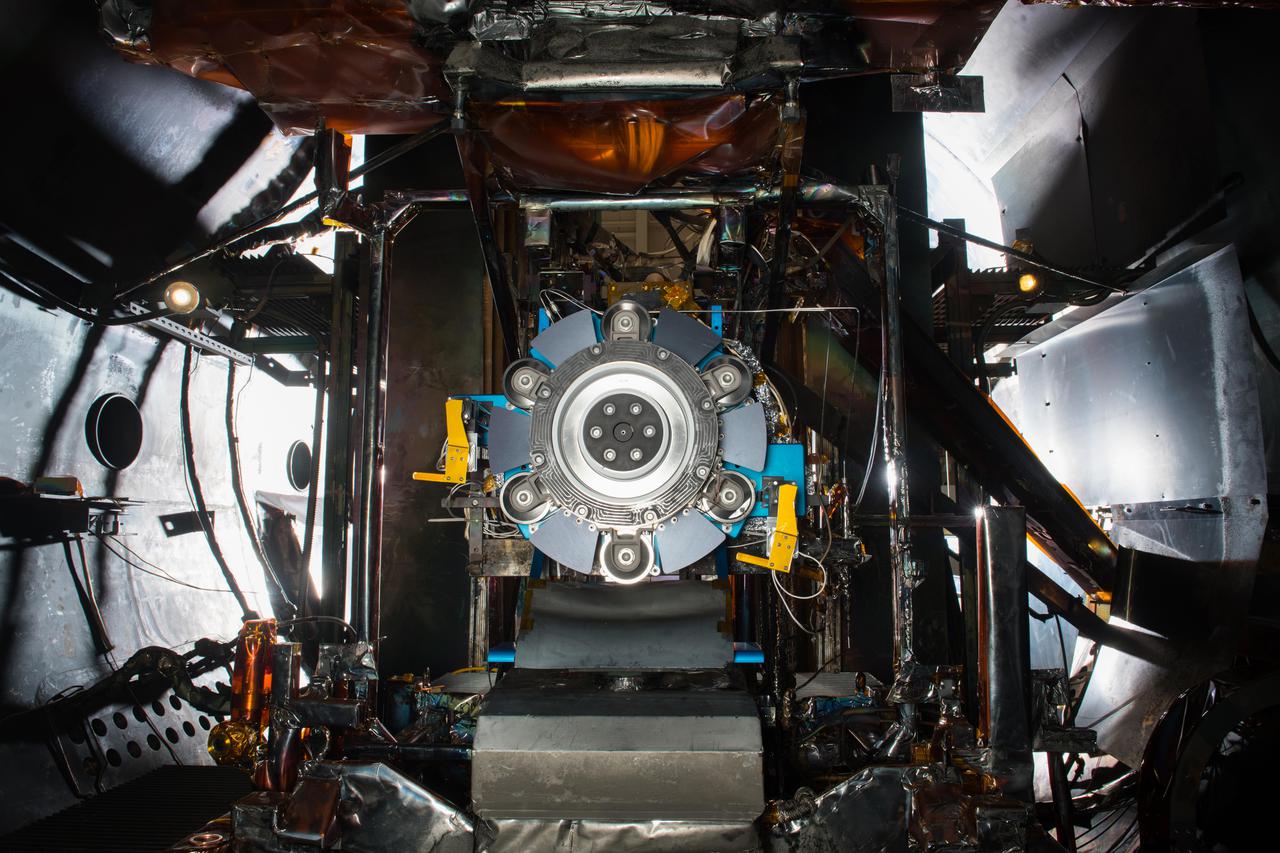
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
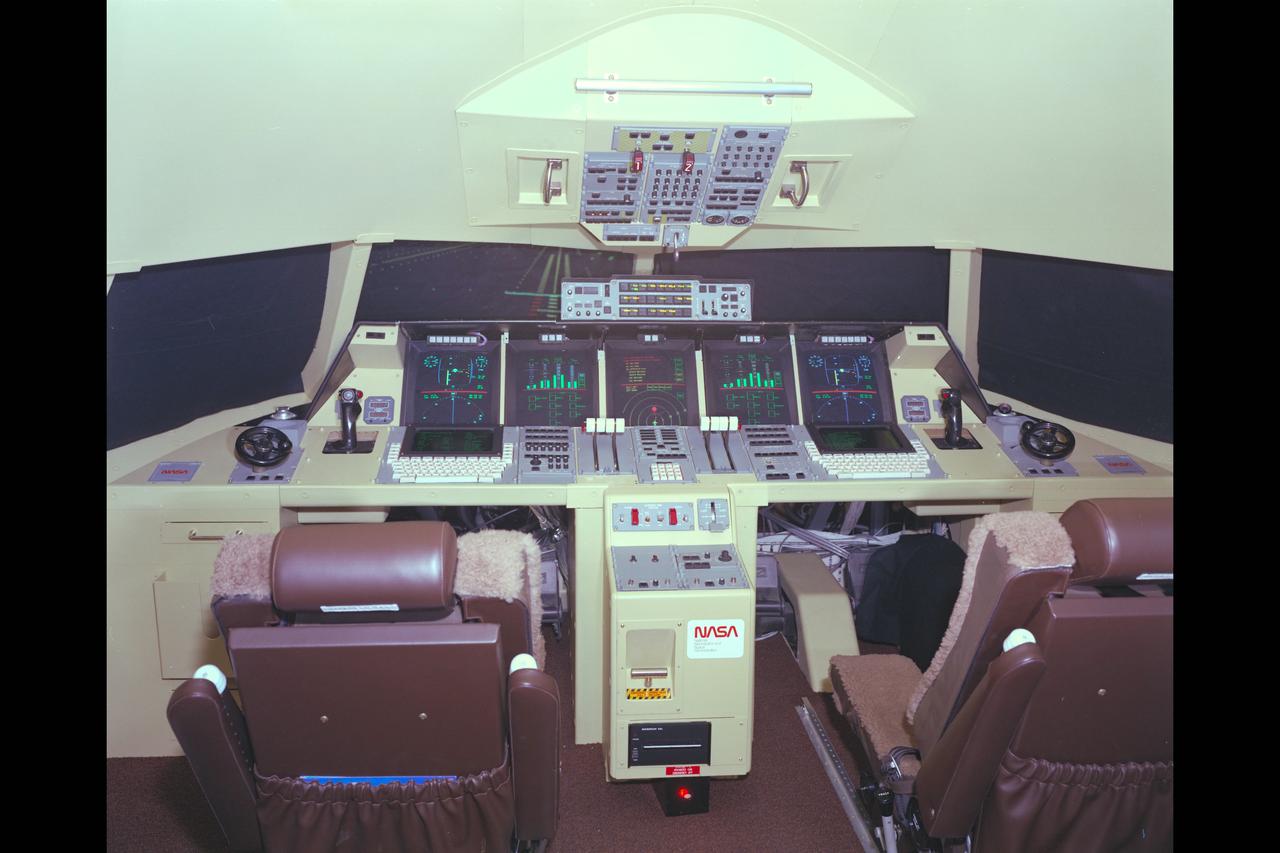

MVSRF Advanced Cockpit
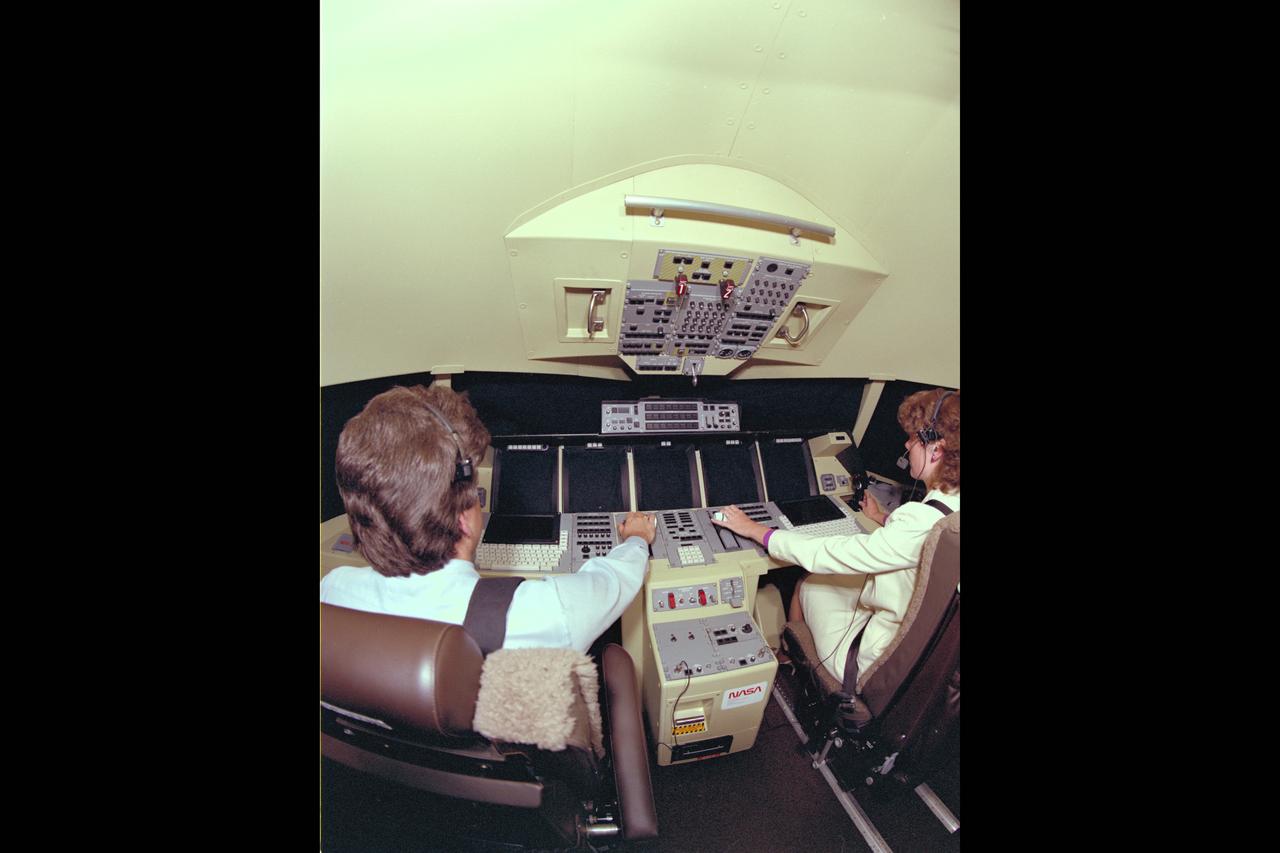

MVSRF Advanced Cockpit
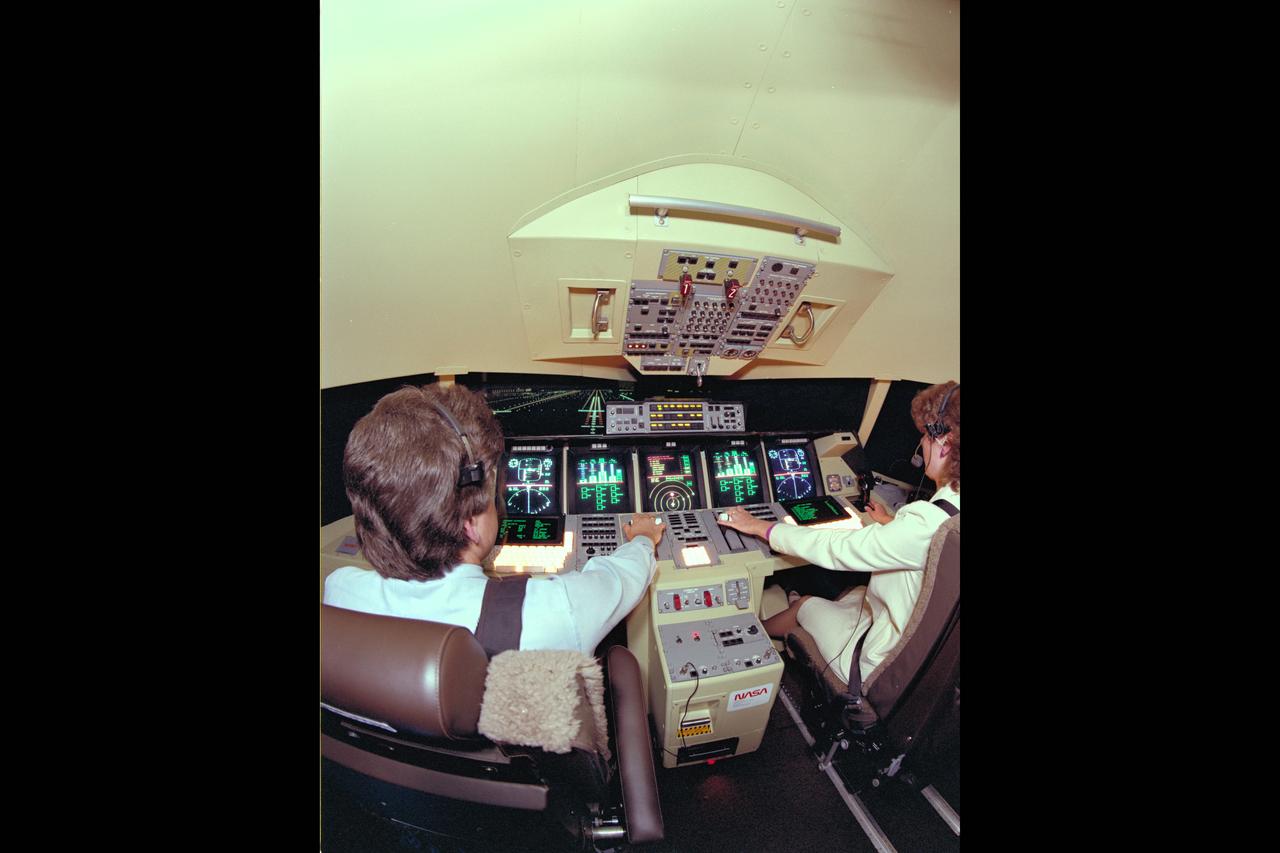

MVSRF Advanced Cockpit
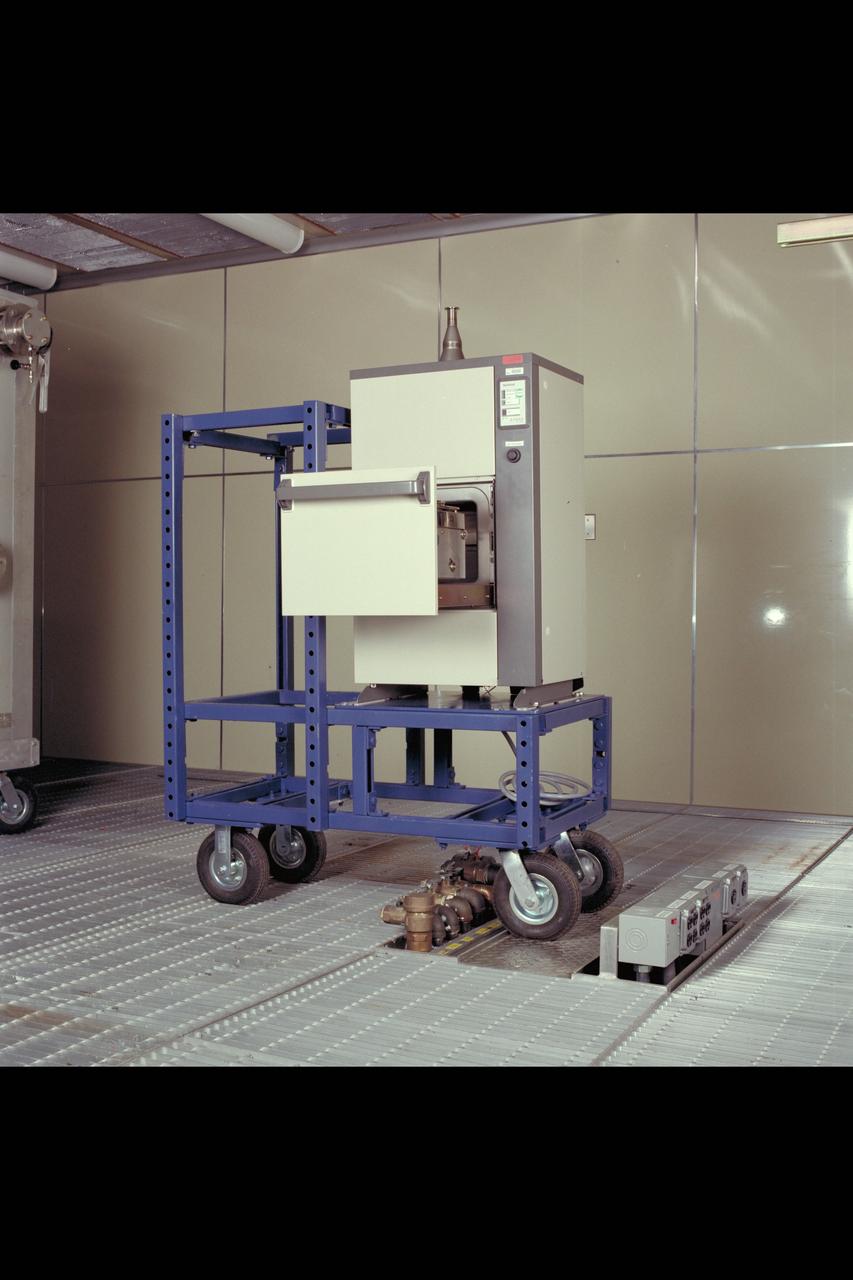

Advanced Life Support Division Equipment
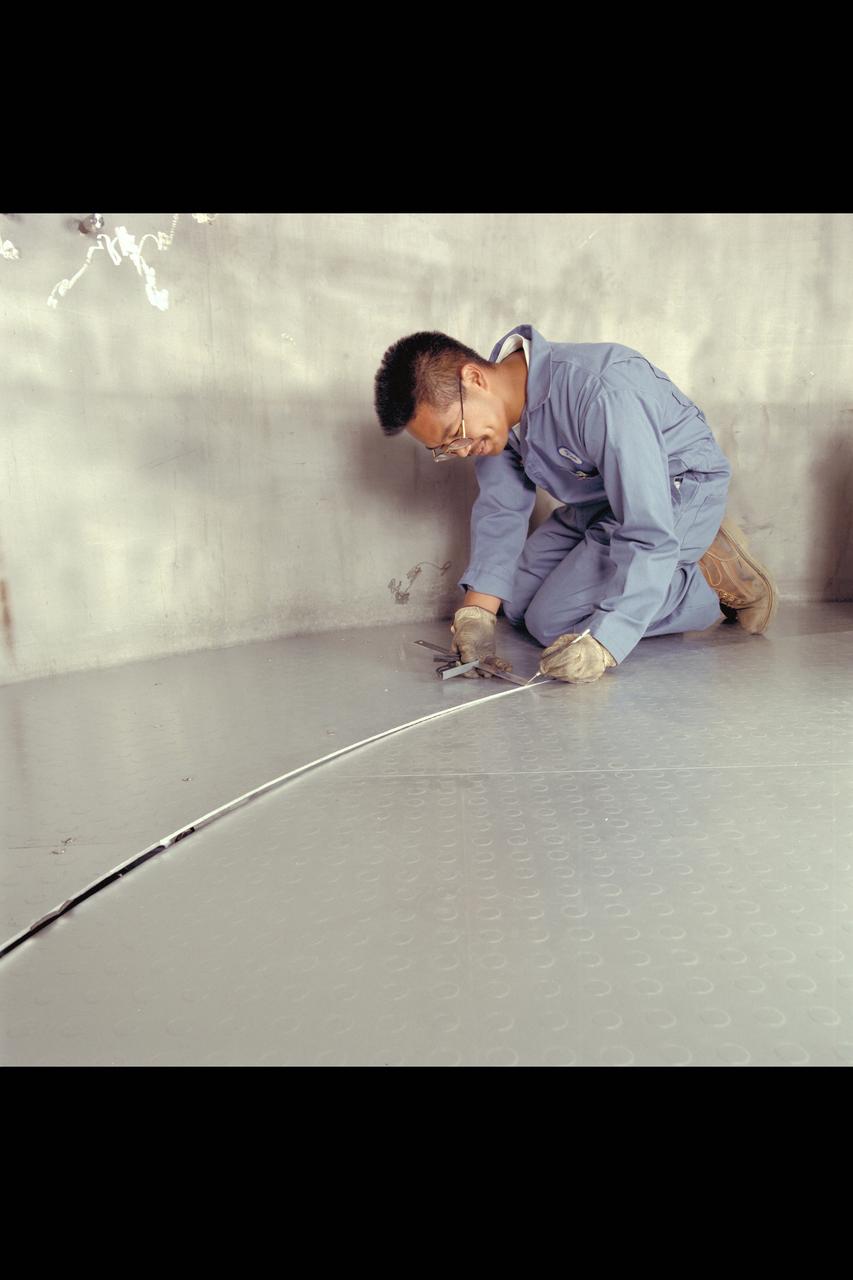

Advanced Life Support Division Equipment
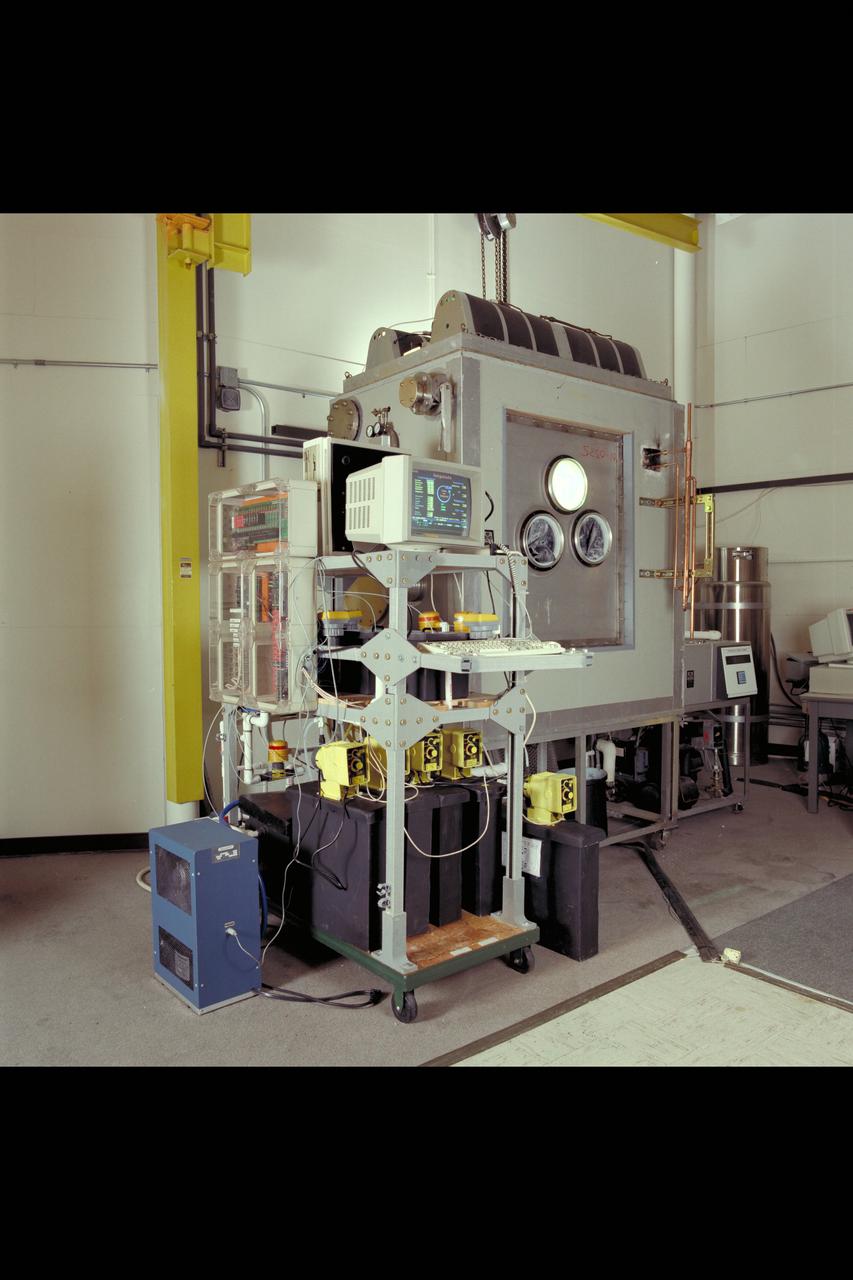

Advanced Life Support Division Equipment
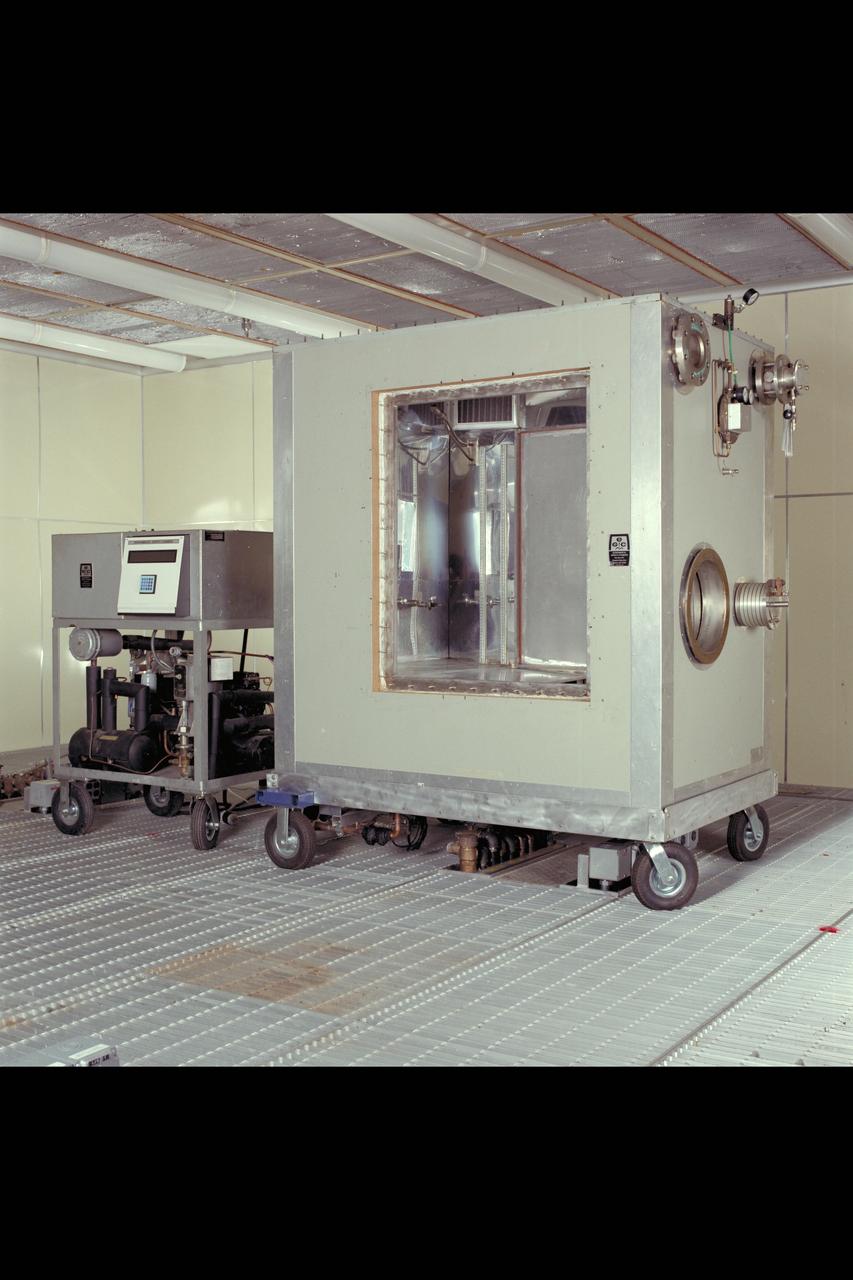

Advanced Life Support Division Equipment
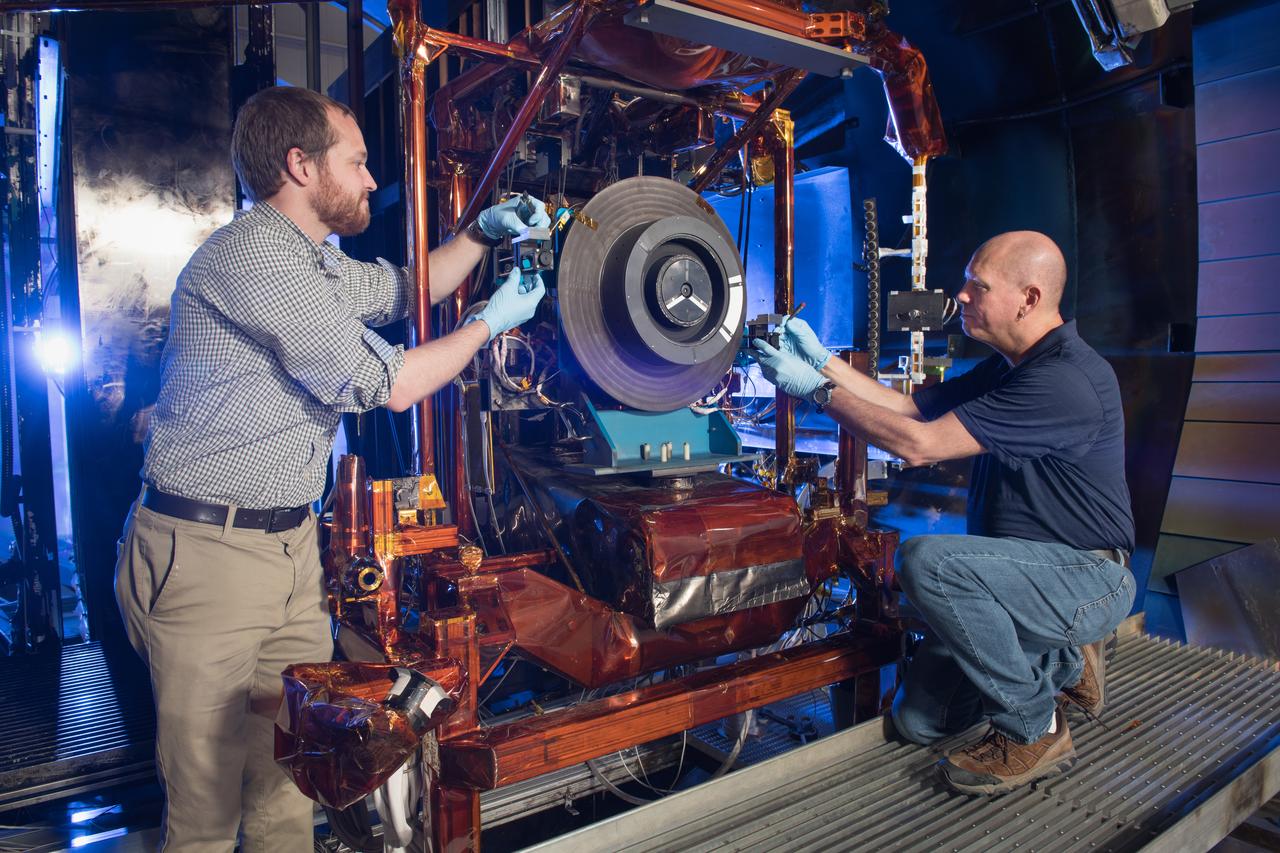

Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
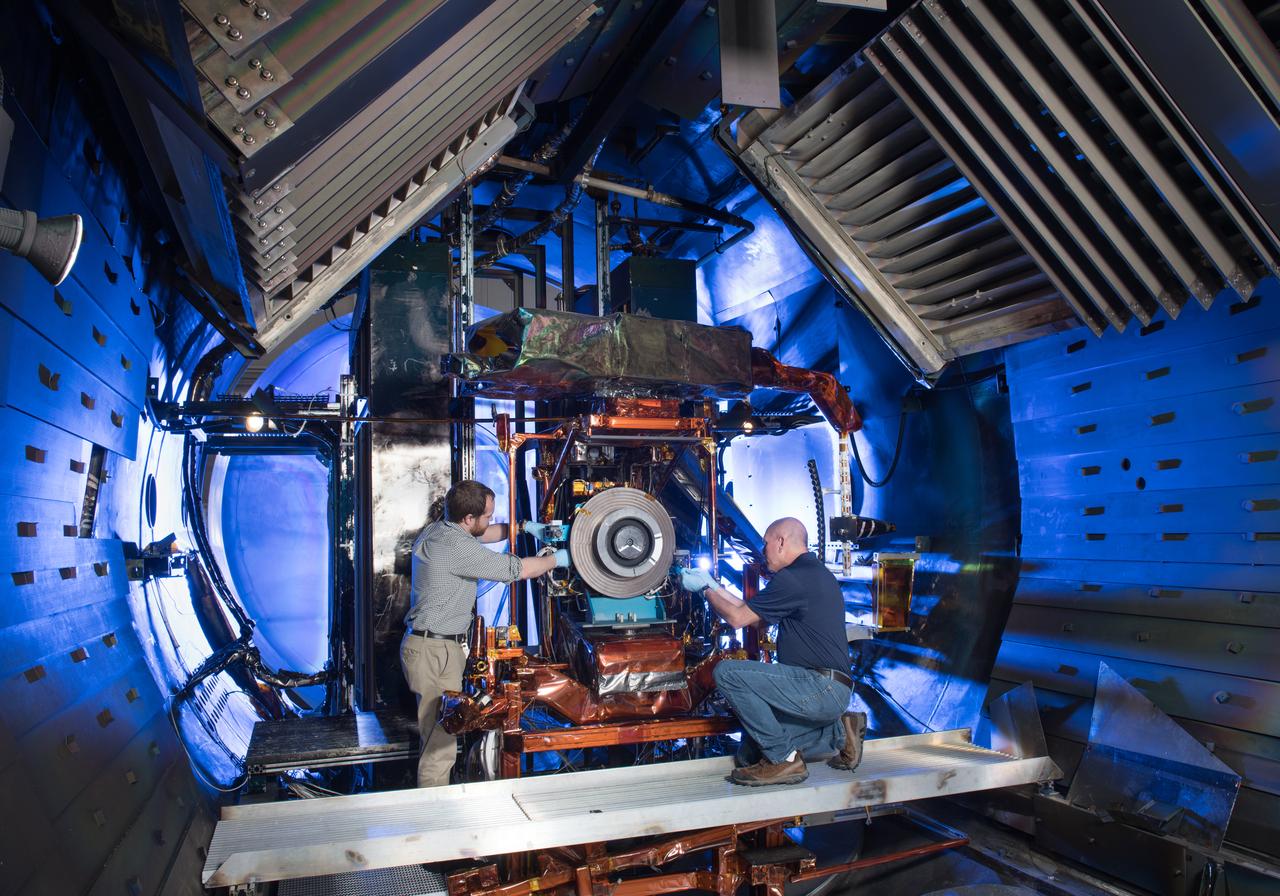
Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
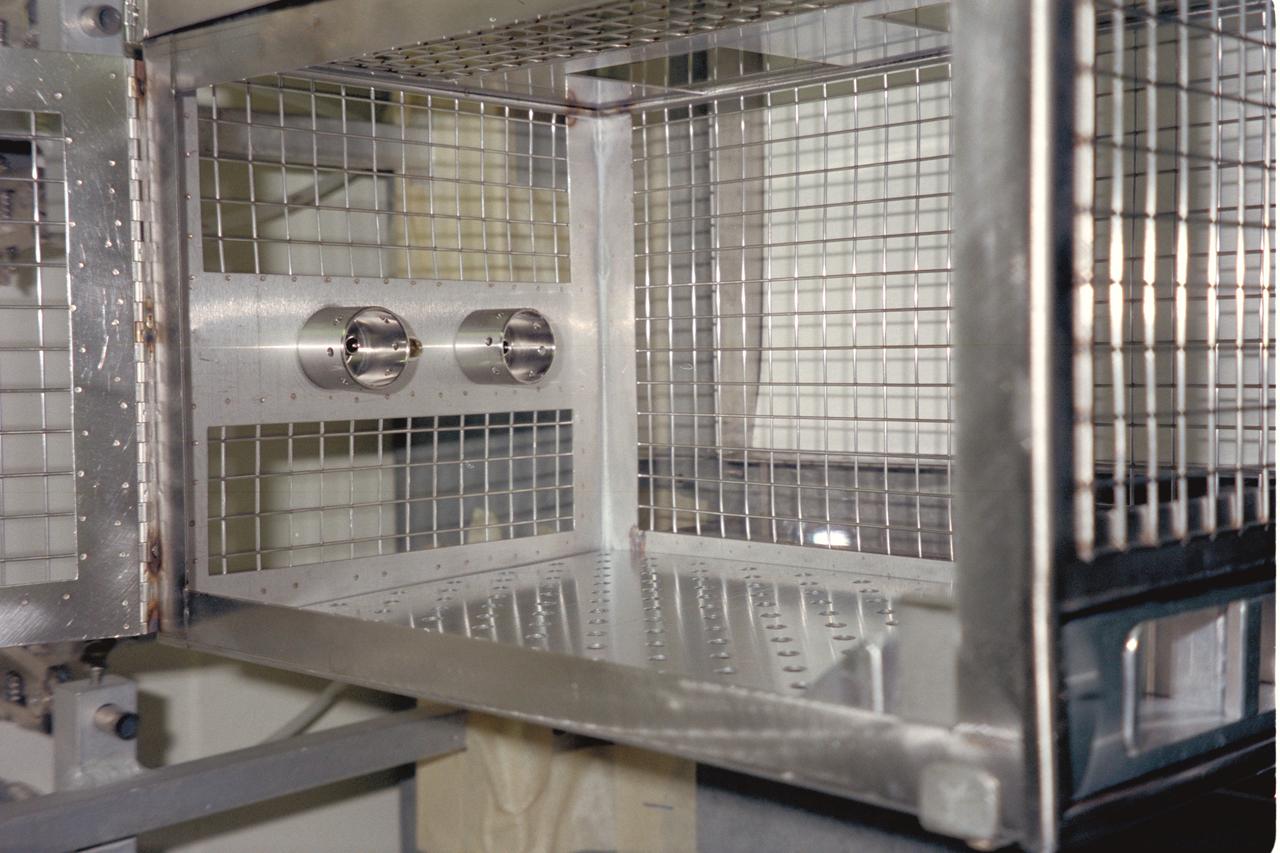

N-213 Advanced Animal Habitat (AAH)
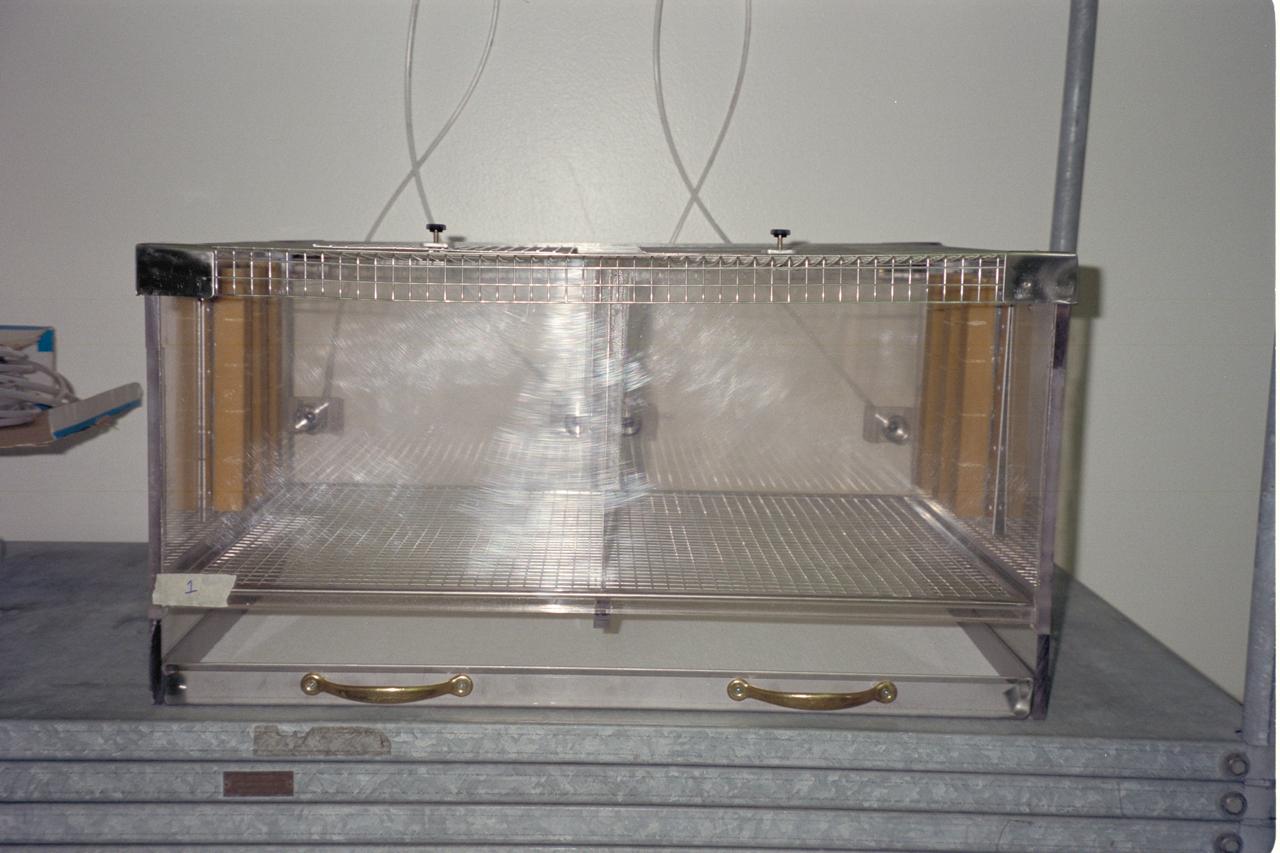
N-213 Advanced Animal Habitat (AAH)