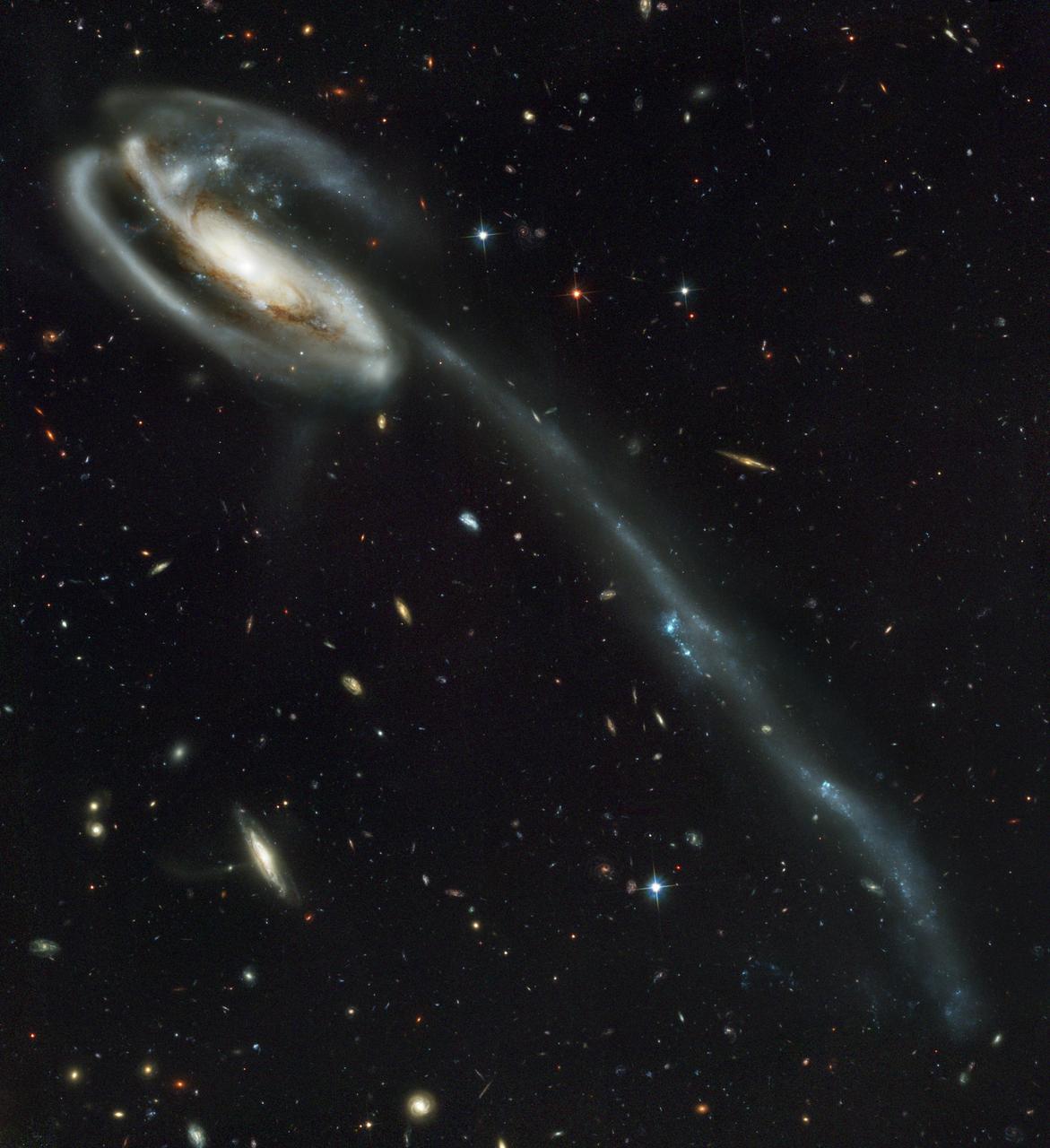

This picture of the galaxy UGC 10214 was was taken by the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), which was installed aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in March 2002 during HST Servicing Mission 3B (STS-109 mission). Dubbed the "Tadpole," this spiral galaxy is unlike the textbook images of stately galaxies. Its distorted shape was caused by a small interloper, a very blue, compact galaxy visible in the upper left corner of the more massive Tadpole. The Tadpole resides about 420 million light-years away in the constellation Draco. Seen shining through the Tadpole's disk, the tiny intruder is likely a hit-and-run galaxy that is now leaving the scene of the accident. Strong gravitational forces from the interaction created the long tail of debris, consisting of stars and gas that stretch our more than 280,000 light-years. The galactic carnage and torrent of star birth are playing out against a spectacular backdrop: a "wallpaper pattern" of 6,000 galaxies. These galaxies represent twice the number of those discovered in the legendary Hubble Deep Field, the orbiting observatory's "deepest" view of the heavens, taken in 1995 by the Wide Field and planetary camera 2. The ACS picture, however, was taken in one-twelfth of the time it took to observe the original HST Deep Field. In blue light, ACS sees even fainter objects than were seen in the "deep field." The galaxies in the ACS picture, like those in the deep field, stretch back to nearly the begirning of time. Credit: NASA, H. Ford (JHU), G. Illingworth (USCS/LO), M. Clampin (STScI), G. Hartig (STScI), the ACS Science Team, and ESA.
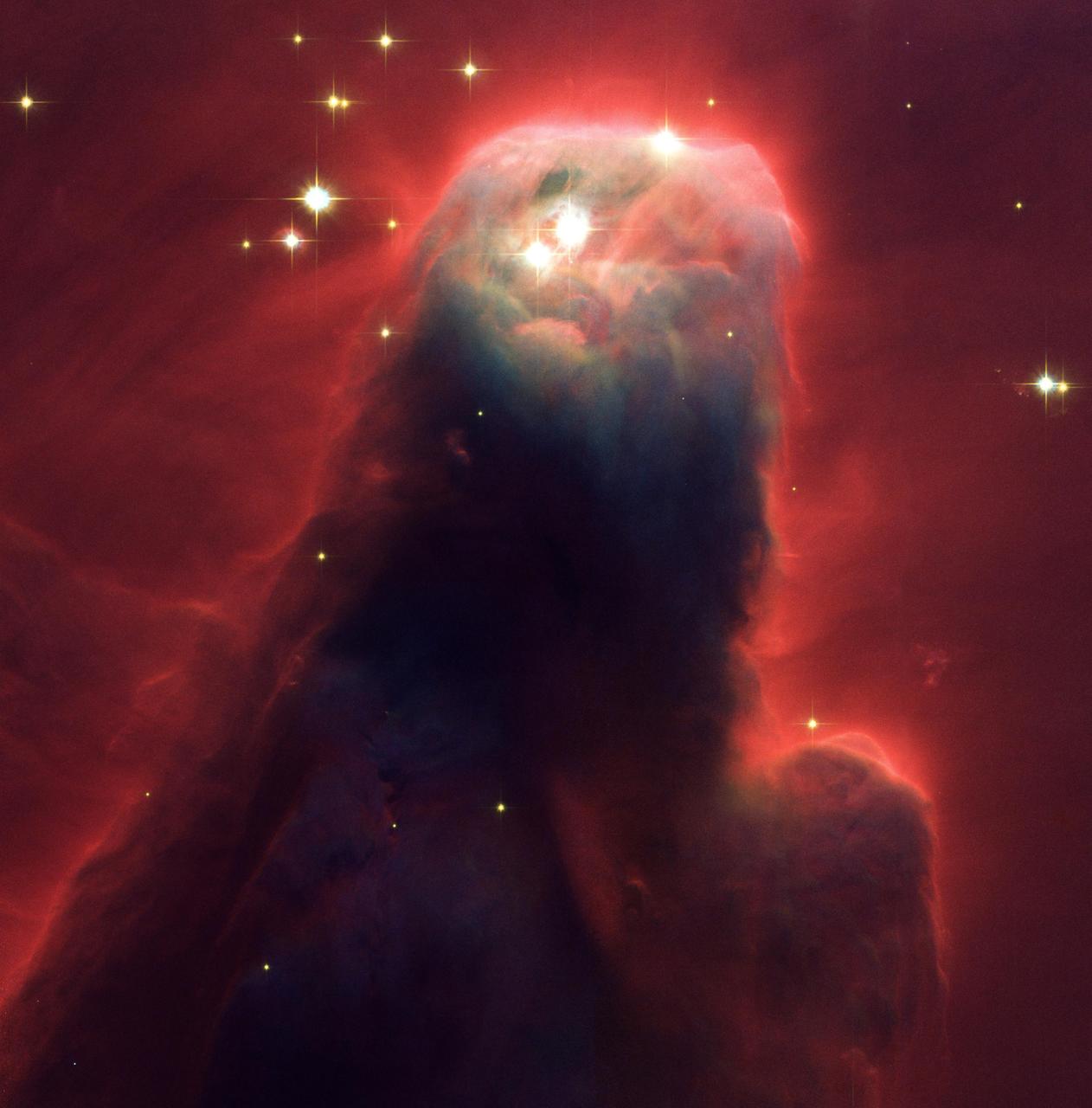

Resembling a nightmarish beast rearing its head from a crimson sea, this monstrous object is actually an irnocuous pillar of gas and dust. Called the Cone Nebula (NGC 2264), this giant pillar resides in a turbulent star-forming region. This picture, taken by the newly installed Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) aboard Hubble Space Telescope (HST) during Space Shuttle STS-109 mission in March 2002, shows the upper 2.5 light-years of the nebula, a height that equals 23 million roundtrips to the Moon. The entire nebula is 7 light-years long. The Cone Nebula resides 2,500 light-years away in the constellation Monoceros. Radiation from hot, young stars (located beyond the top of the image) has slowly eroded the nebula over millions of years. Ultraviolet light heats the edges of the dark cloud, releasing gas into the relatively empty region of surrounding space. There, additional ultraviolet radiation causes the hydrogen gas to glow, which produces the red halo of light seen around the pillar. A similar process occurs on a much smaller scale to gas surrounding a single star, forming the bow-shaped arc seen near the upper left side of the Cone. This arc, seen previously with the HST, is 65 times larger than the diameter of our solar system. The blue-white light from surrounding stars is reflected by dust. Background stars can be seen peeking through the evaporating tendrils of gas, while the turbulent base is pockmarked with stars reddened by dust. Credit: NASA, H. Ford (JHU), G. Illingworth (USCS/LO), M. Clampin (STScI), G. Hartig (STScI), the ACS Science Team, and ESA.
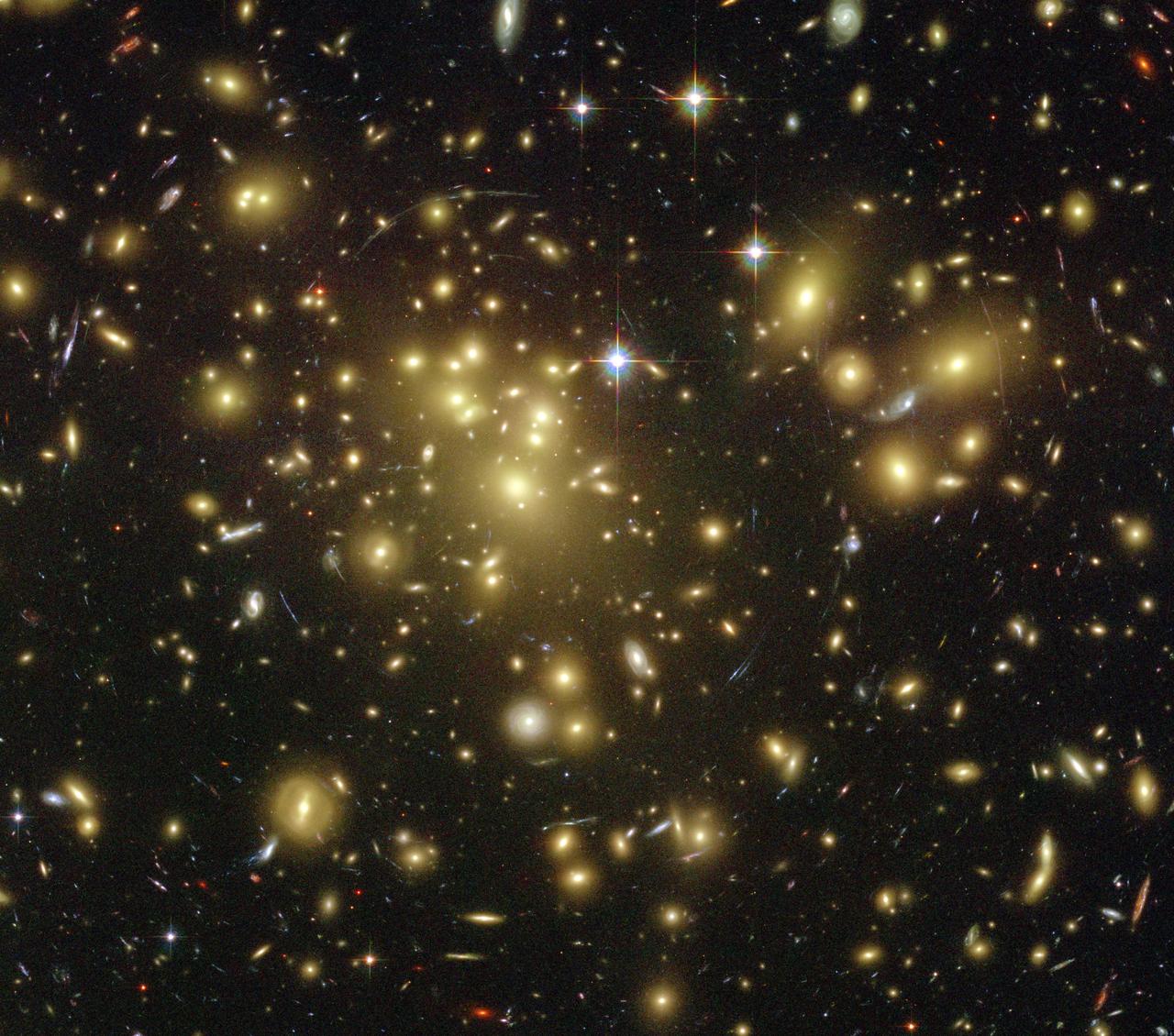

A massive cluster of yellowish galaxies is seemingly caught in a spider web of eerily distorted background galaxies in the left-hand image, taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys ACS aboard NASA Hubble Space Telescope.

This sturning image, taken by the newly installed Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), is an image of the center of the Omega Nebula. It is a hotbed of newly born stars wrapped in colorful blankets of glowing gas and cradled in an enormous cold, dark hydrogen cloud. The region of nebula shown in this photograph is about 3,500 times wider than our solar system. The nebula, also called M17 and the Swan Nebula, resides 5,500 light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius. The Swan Nebula is illuminated by ultraviolet radiation from young, massive stars, located just beyond the upper-right corner of the image. The powerful radiation from these stars evaporates and erodes the dense cloud of cold gas within which the stars formed. The blistered walls of the hollow cloud shine primarily in the blue, green, and red light emitted by excited atoms of hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur. Particularly striking is the rose-like feature, seen to the right of center, which glows in the red light emitted by hydrogen and sulfur. As the infant stars evaporate the surrounding cloud, they expose dense pockets of gas that may contain developing stars. One isolated pocket is seen at the center of the brightest region of the nebula. Other dense pockets of gas have formed the remarkable feature jutting inward from the left edge of the image. The color image is constructed from four separate images taken in these filters: blue, near infrared, hydrogen alpha, and doubly ionized oxygen. Credit: NASA, H. Ford (JHU), G. Illingworth (USCS/LO), M. Clampin (STScI), G. Hartig (STScI), the ACS Science Team, and ESA.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- A large truck delivers part of the equipment to be used on mission STS-109, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope, to KSC. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
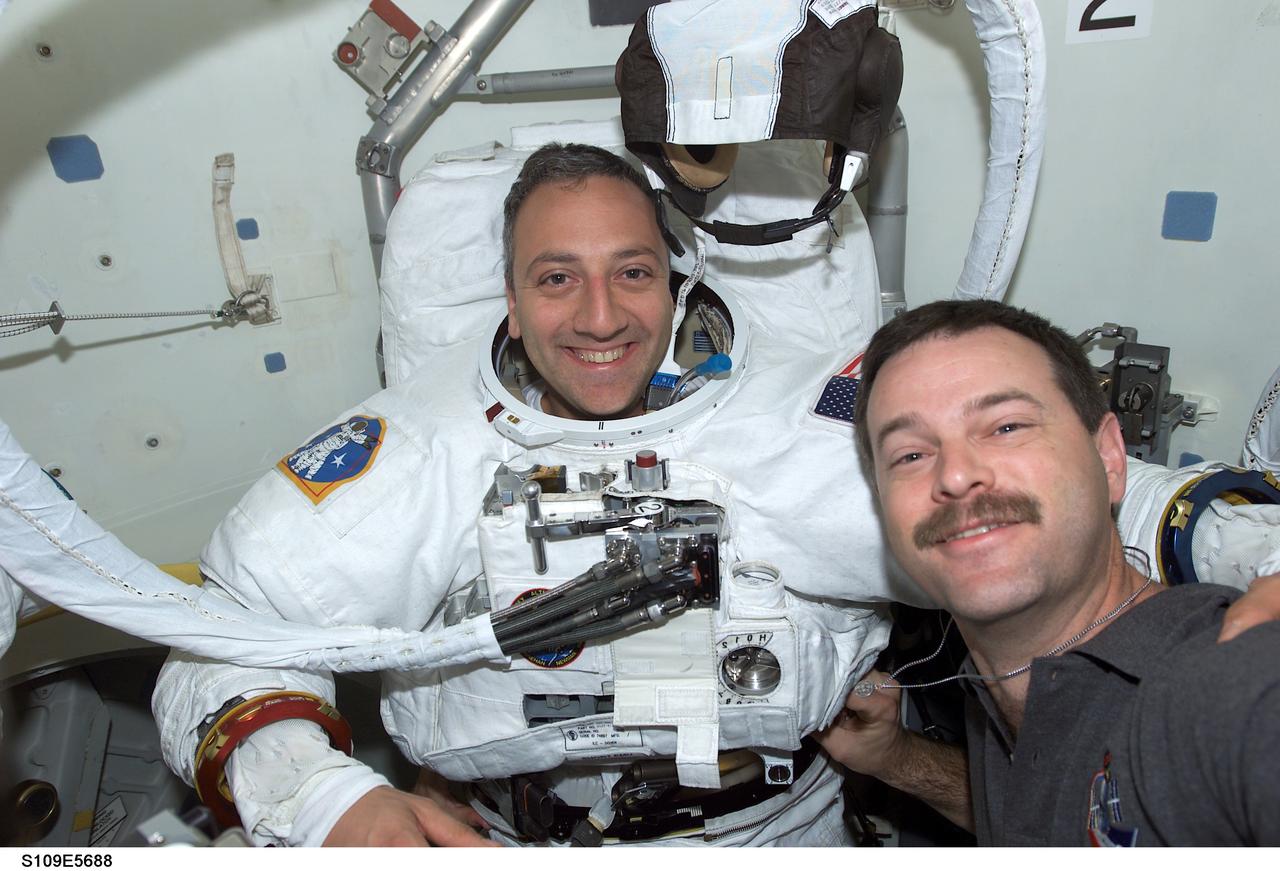

STS109-E-5688 (7 March 2002) --- Astronaut Scott D. Altman, mission commander, assists astronaut Michael J. Massimino, mission specialist, with suit-donning tasks prior to the STS-109 mission's fourth space walk (EVA-4). Astronauts Massimino and James H. Newman went on to install the new Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
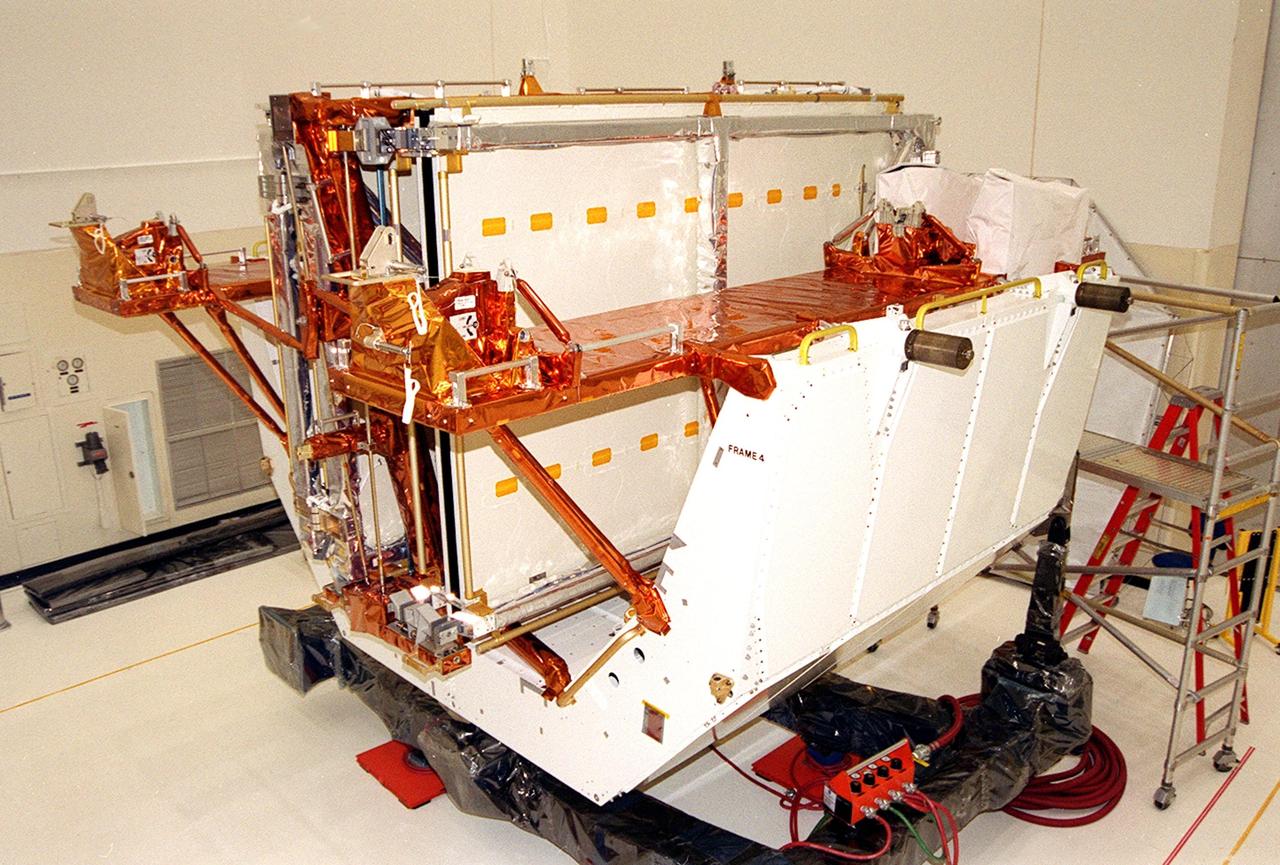
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Solar arrays part of the payload for the Hubble Servicing Mission, STS-109, await processing in the Vertical Processing Facility. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility check over part of the payload for the Hubble Servicing Mission, STS-109. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Part of the equipment to be used on mission STS-109, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope, is moved into a facility at KSC. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
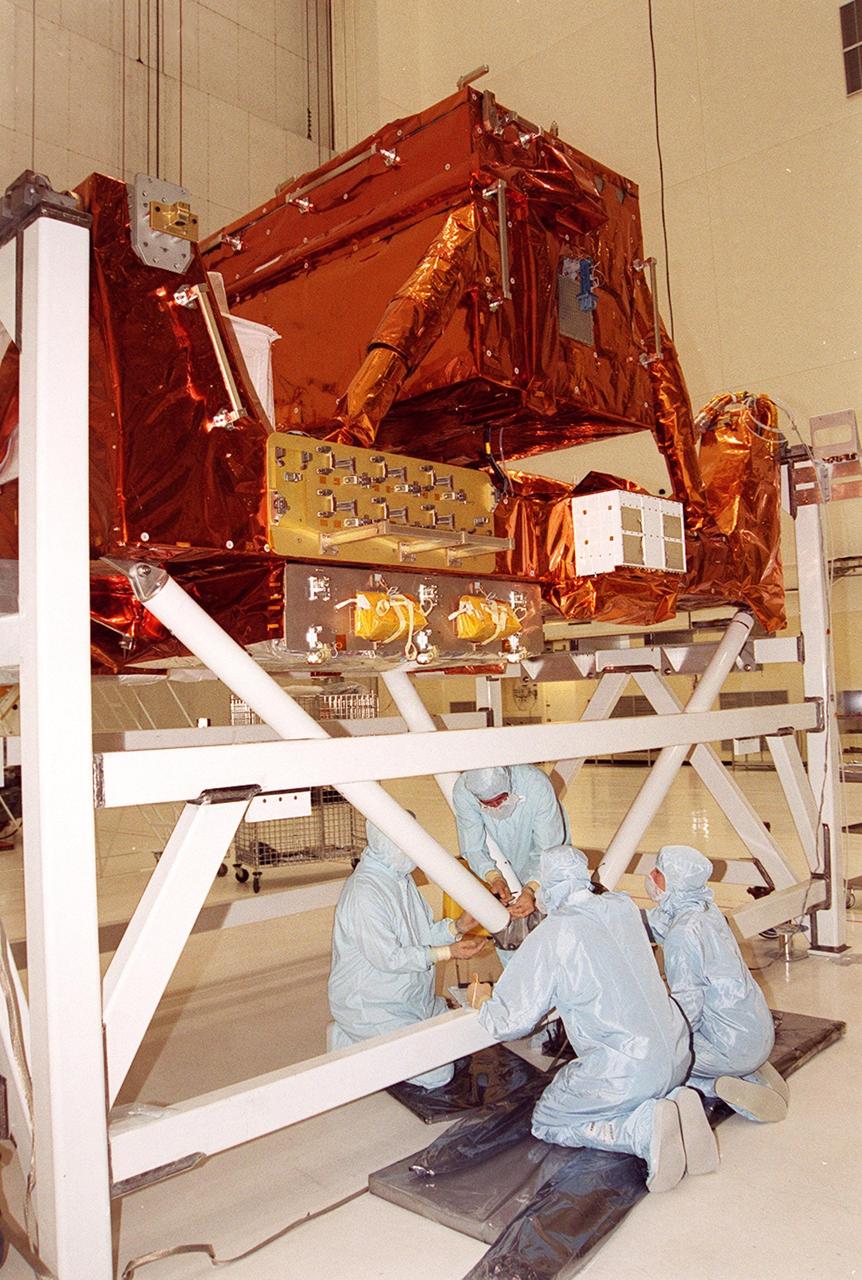
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Workers begin preparations for testing part of the payload (behind them) for the Hubble Servicing Mission, STS-109. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
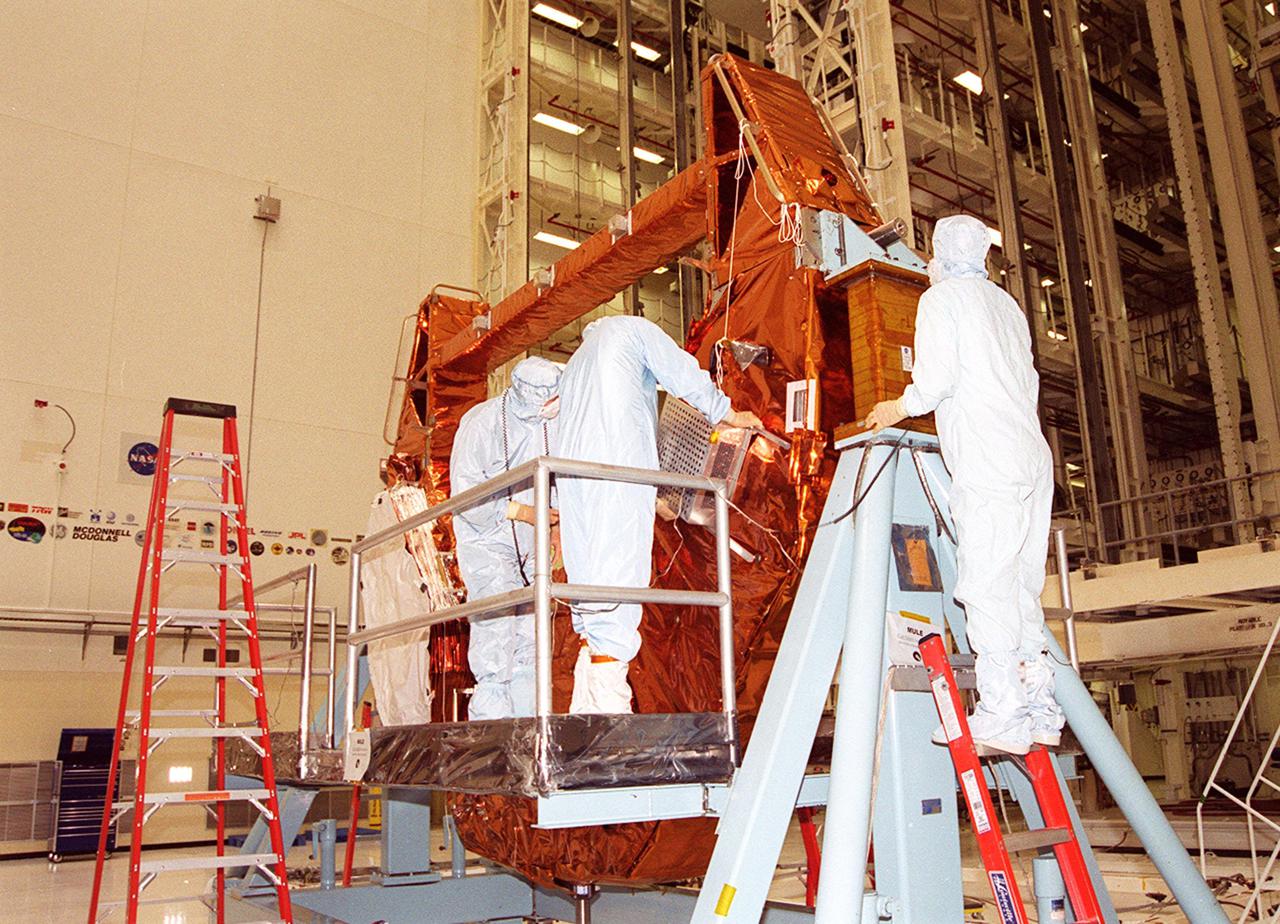

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility check out equipment that is part of the payload for the Hubble Servicing Mission, STS-109. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
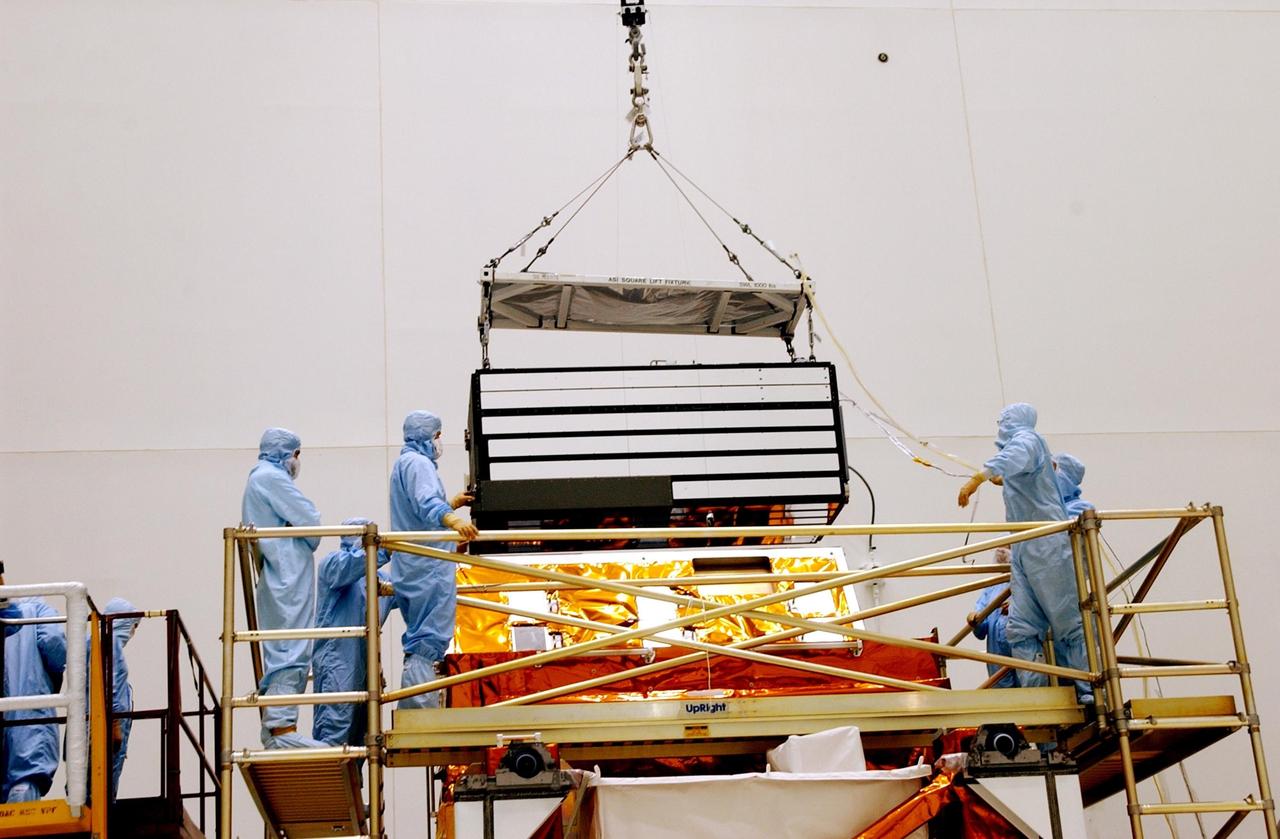

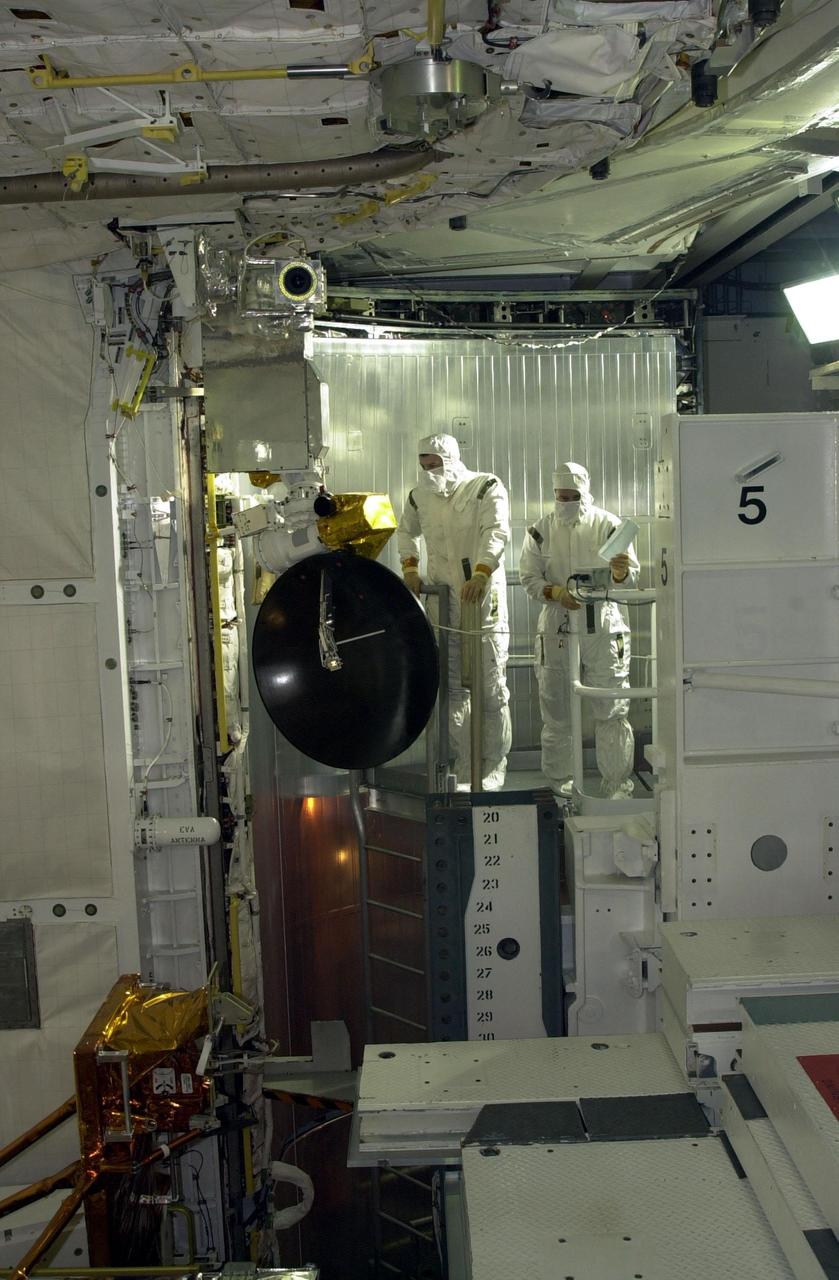
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, workers watch while an overhead crane lowers the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) toward the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE). The ACS is part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch no earlier than Feb. 21, 2002
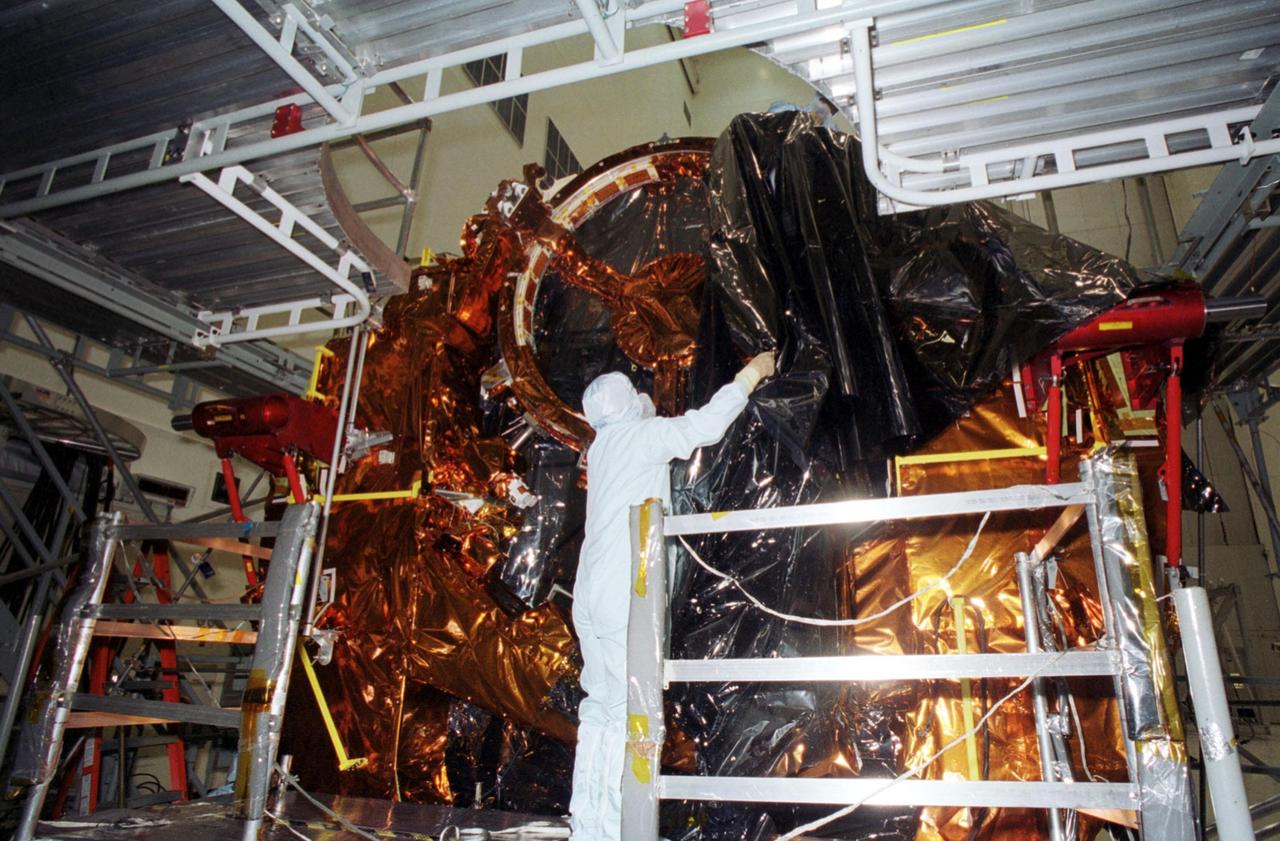

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility a worker removes the protective covering from the equipment to be used on mission STS-109. The mission is to service the Hubble Space Telescope, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
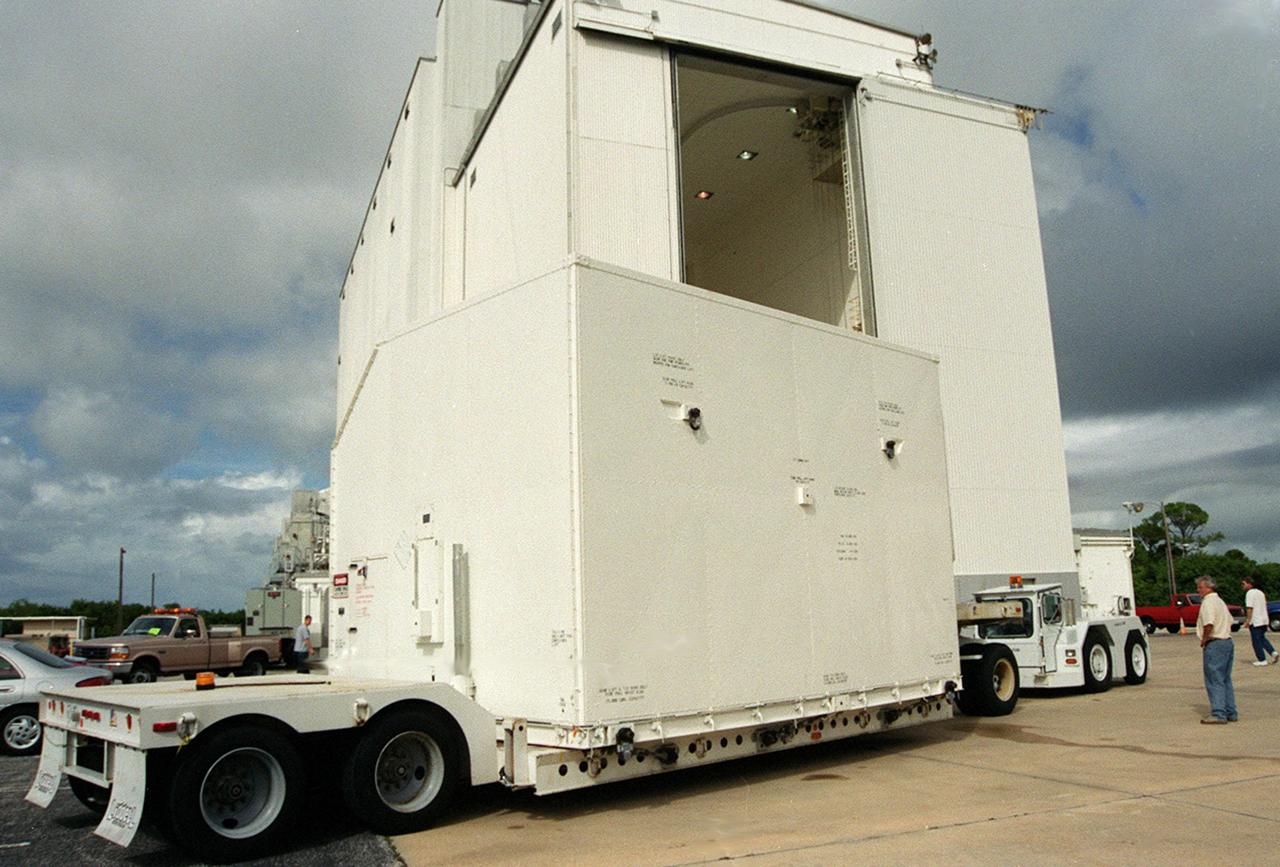

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Part of the equipment to be used on mission STS-109, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope, arrives at a facility at KSC. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
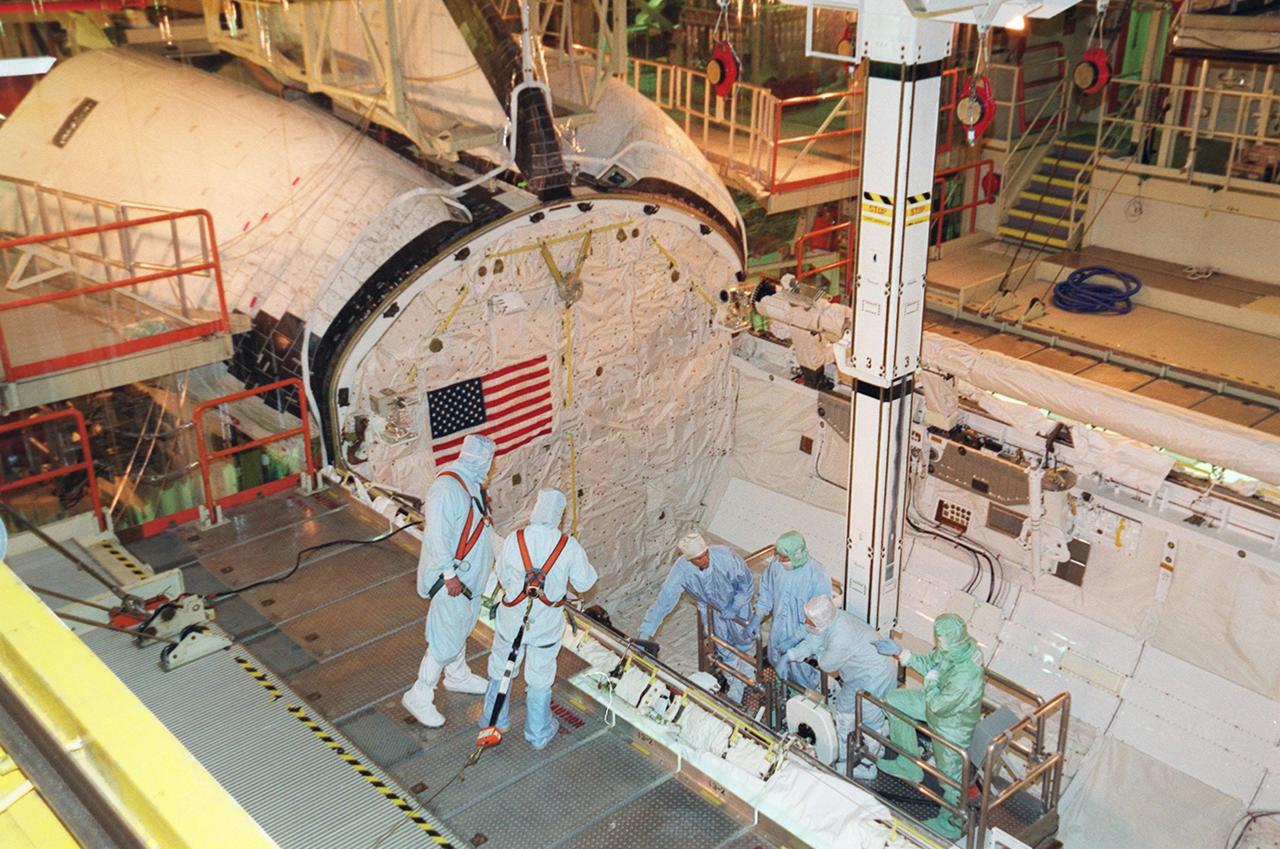
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Members of the STS-109 crew are lowered into the payload bay of orbiter Columbia to check out some of the equipment. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities that include familiarization with the orbiter and equipment. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
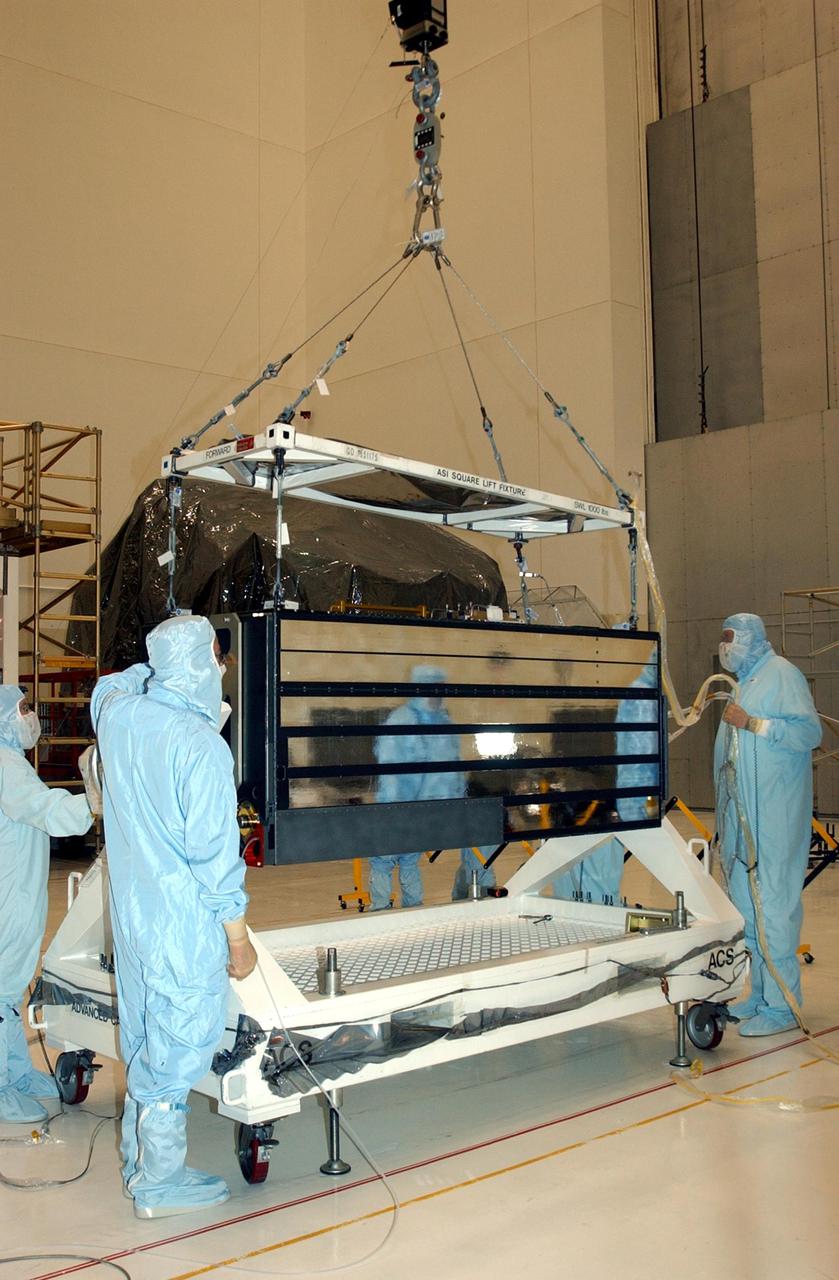

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, workers watch while an overhead crane lifts the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) off the stand. The ACS is part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch no earlier than Feb. 21, 2002
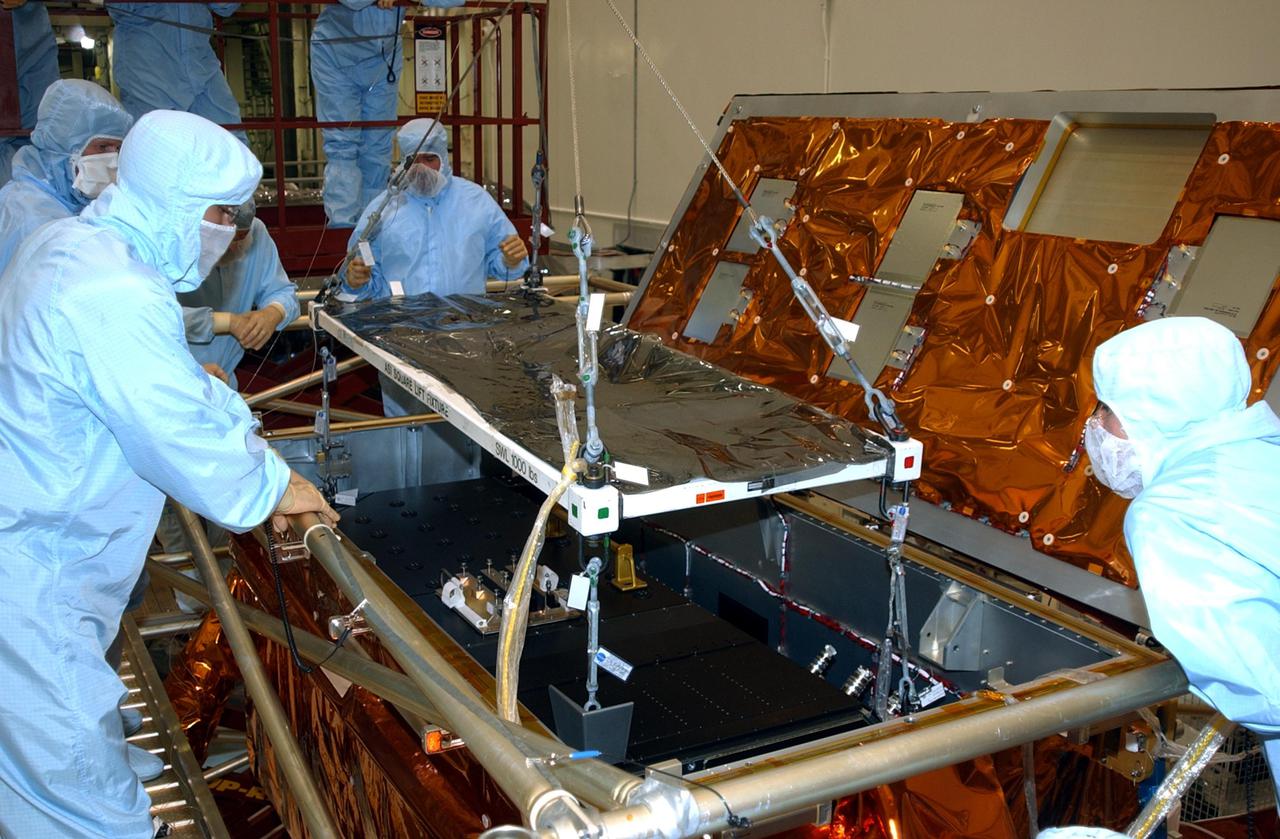

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, workers watch while the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) is lowered into the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE). The ACS is part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch no earlier than Feb. 21, 2002
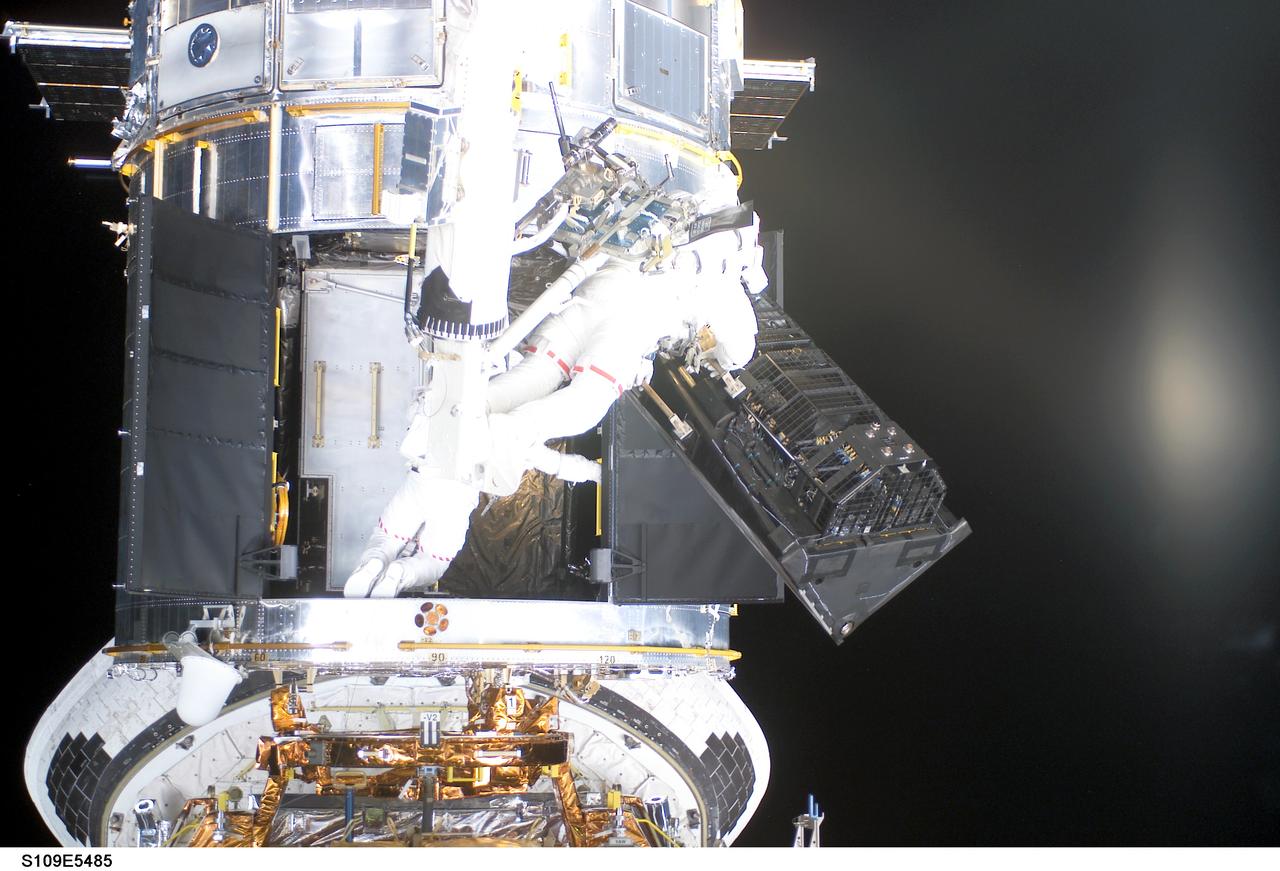

STS109-E-5485 (7 March 2002) --- Two of Columbia's four spacewalkers--astronauts James H. Newman and Michael J. Massimino--participate in the first science instrument upgrade of the fourth Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission during the flight's fourth day of extravehicular activity (EVA). The two, with Newman on Columbia's remote manipulator system (RMS) robotic arm, remove the Faint Object Camera to make room for the new Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). This image was recorded with a digital still camera by one of the duo's crewmates on the aft flight deck.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, workers watch while an overhead crane lowers the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) into the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE). The ACS is part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch no earlier than Feb. 21, 2002
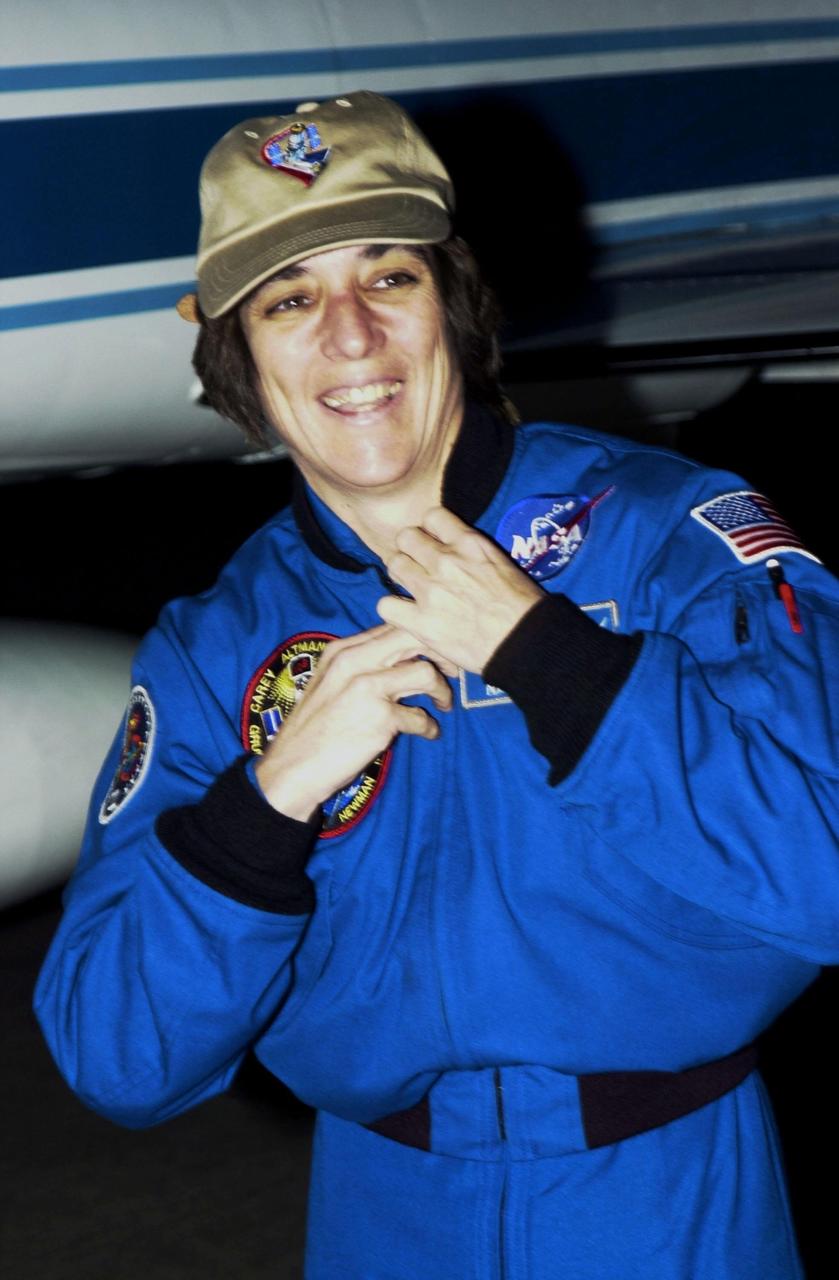

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - STS-109 Mission Specialist Nancy Currie arrives at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft to begin launch preparations. This is Currie's fourth Shuttle flight. The goal of the 11-day mission is repair and maintenance on the Hubble Space Telescope. Five spacewalks are planned to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 28 at 6:48 a.m. EST
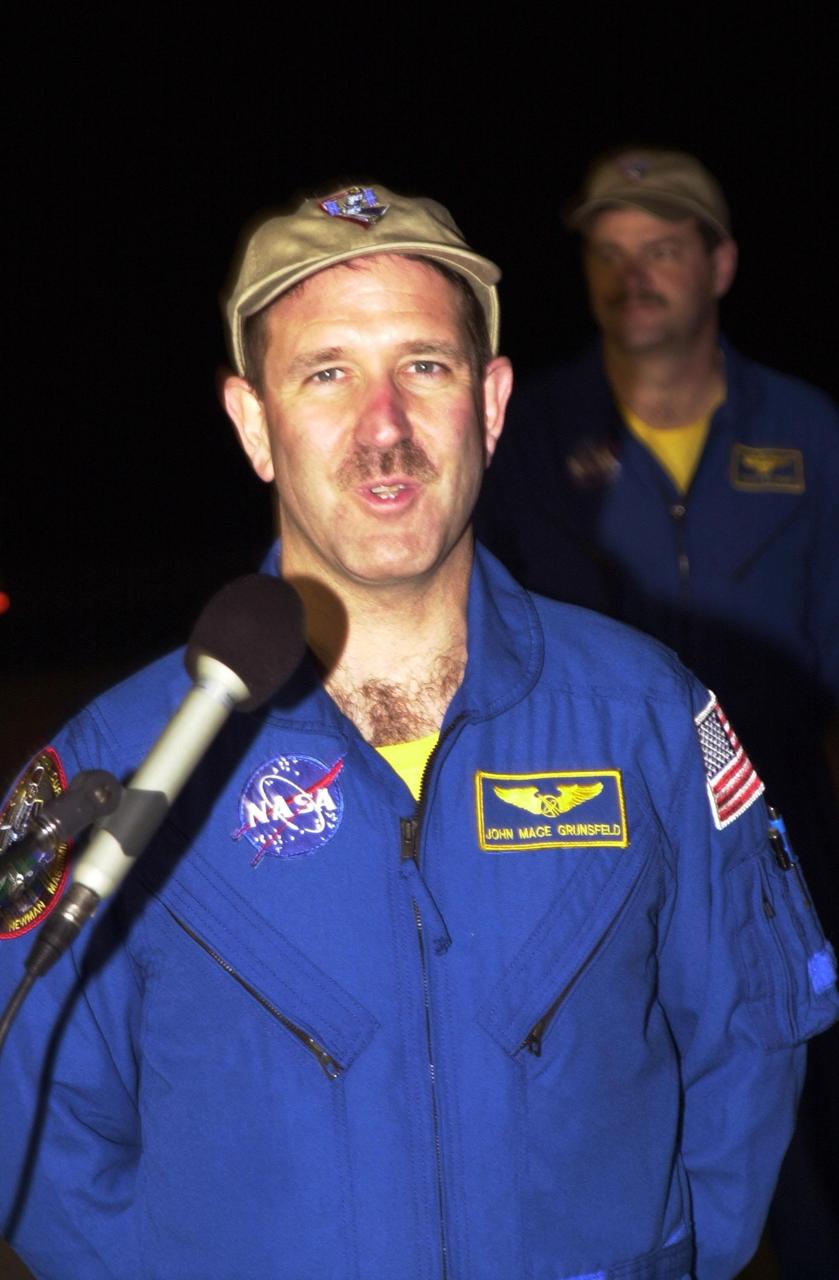

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - STS-109 Payload Commander John Grunsfeld arrives at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft to begin launch preparations. This is Grunsfeld's fourth Shuttle flight. The goal of the 11-day mission is repair and maintenance on the Hubble Space Telescope. Five spacewalks are planned to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 28 at 6:48 a.m. EST
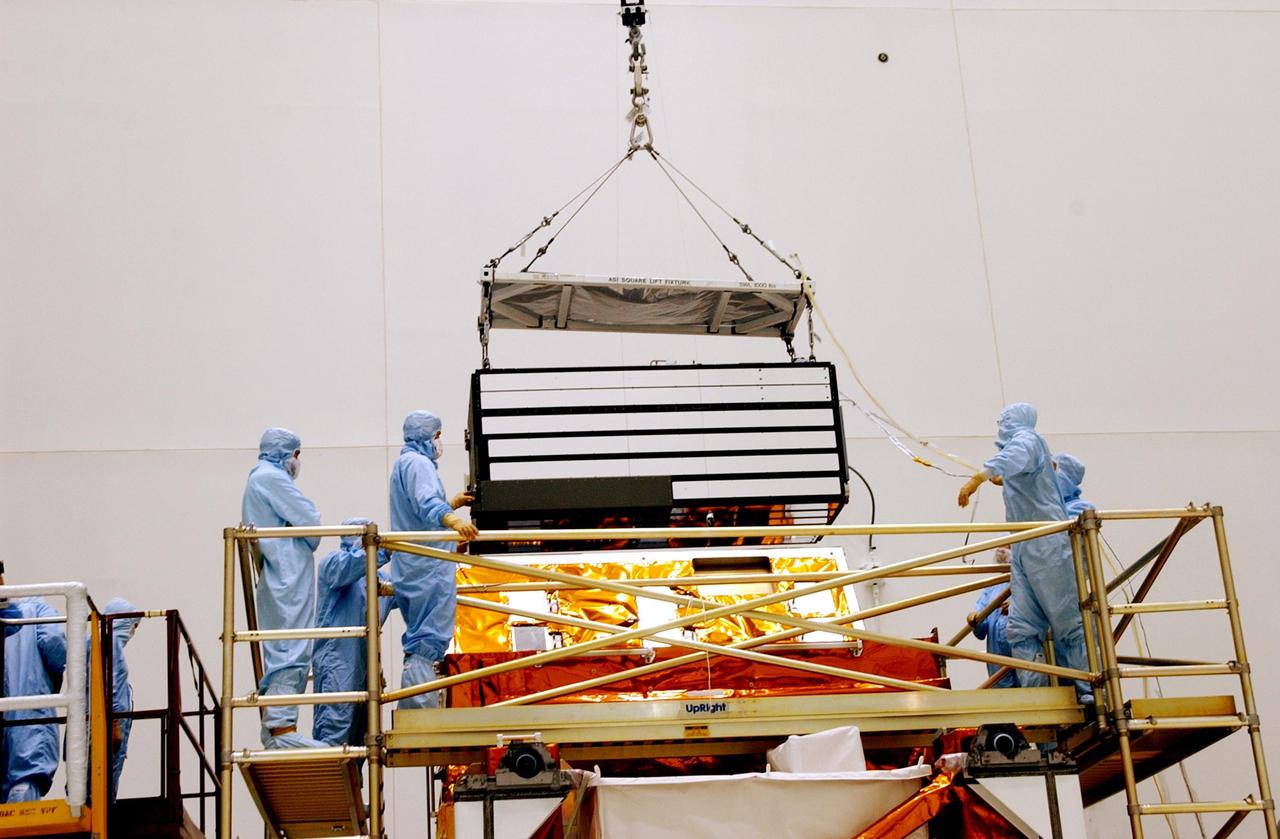

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, workers watch while an overhead crane lowers the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) toward the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE). The ACS is part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch no earlier than Feb. 21, 2002
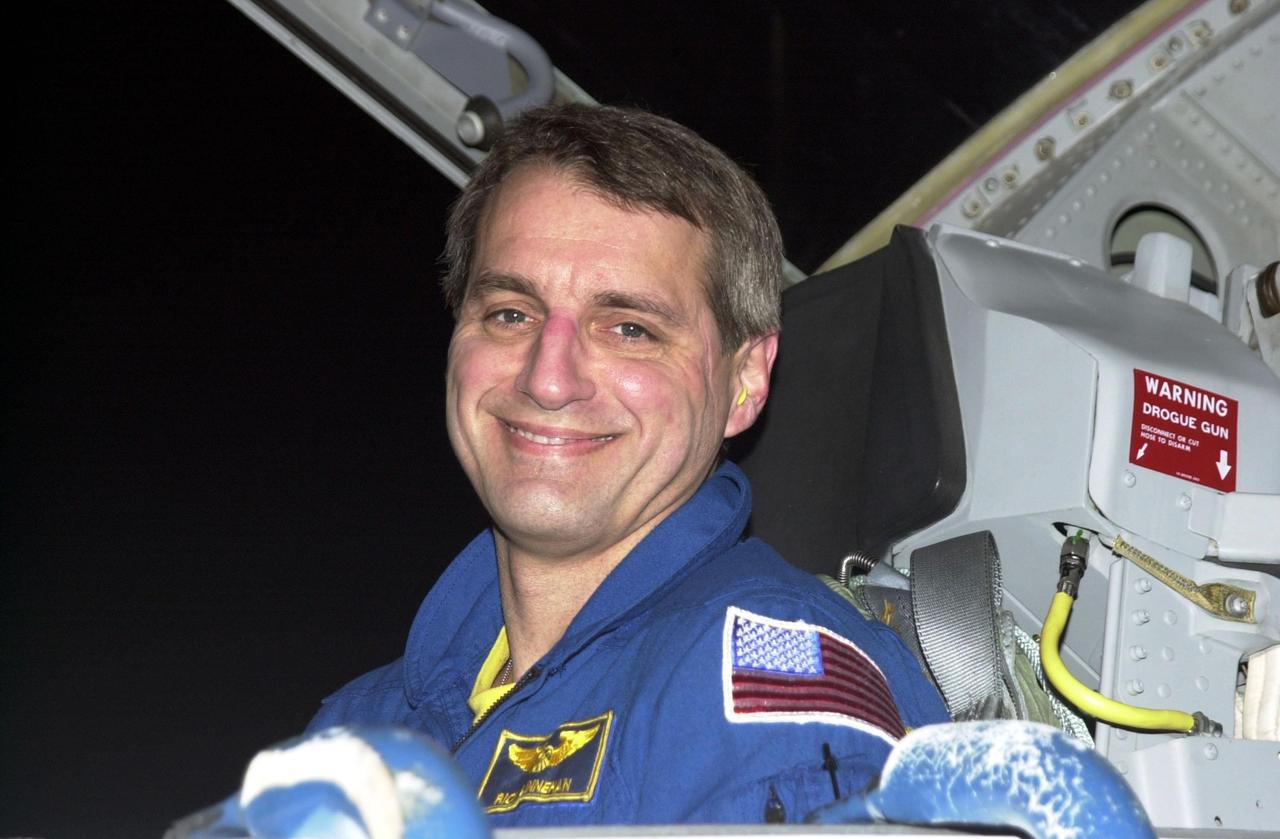

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-109 Mission Specialist Richard Linnehan arrives at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft to begin launch preparations. This is Linnehan's third Shuttle flight. The goal of the 11-day mission is repair and maintenance on the Hubble Space Telescope. Five spacewalks are planned to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 28 at 6:48 a.m. EST
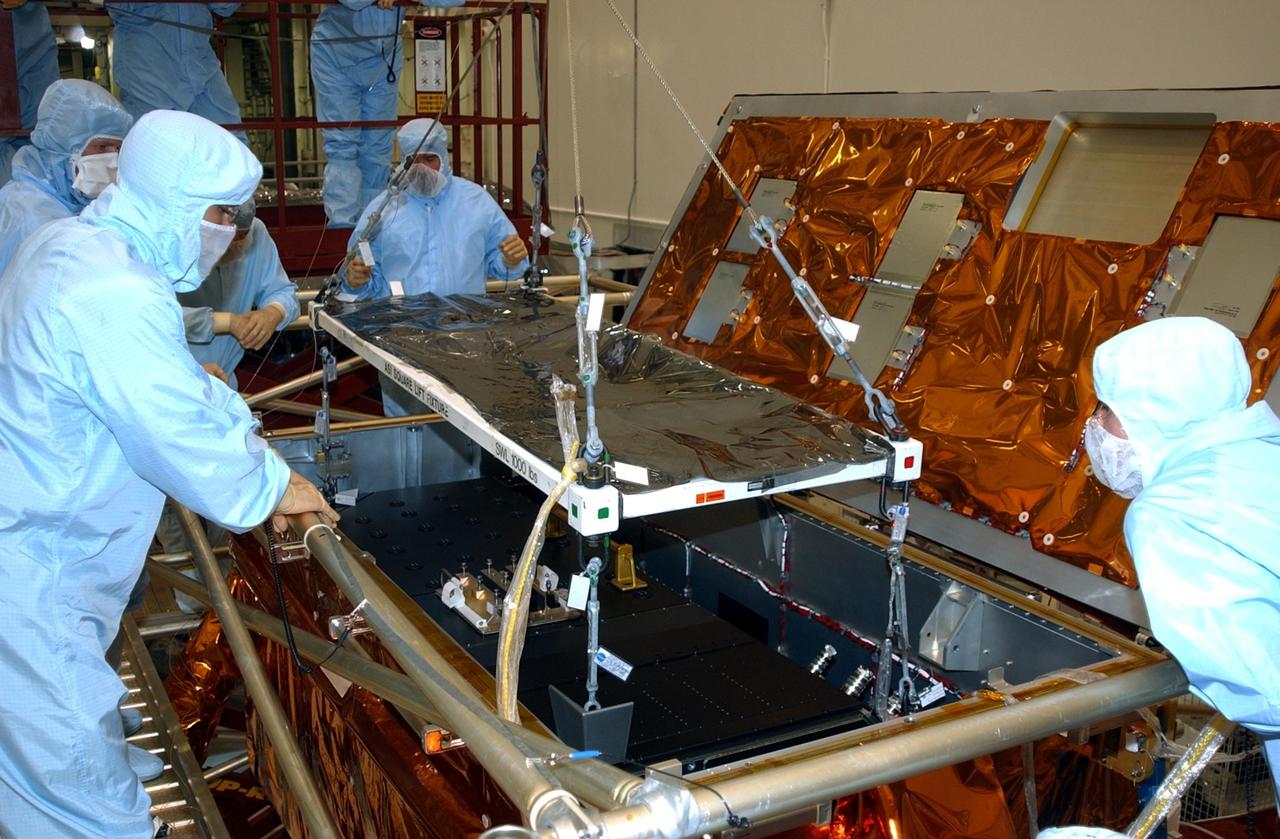

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, workers watch while the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) is lowered into the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE). The ACS is part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch no earlier than Feb. 21, 2002
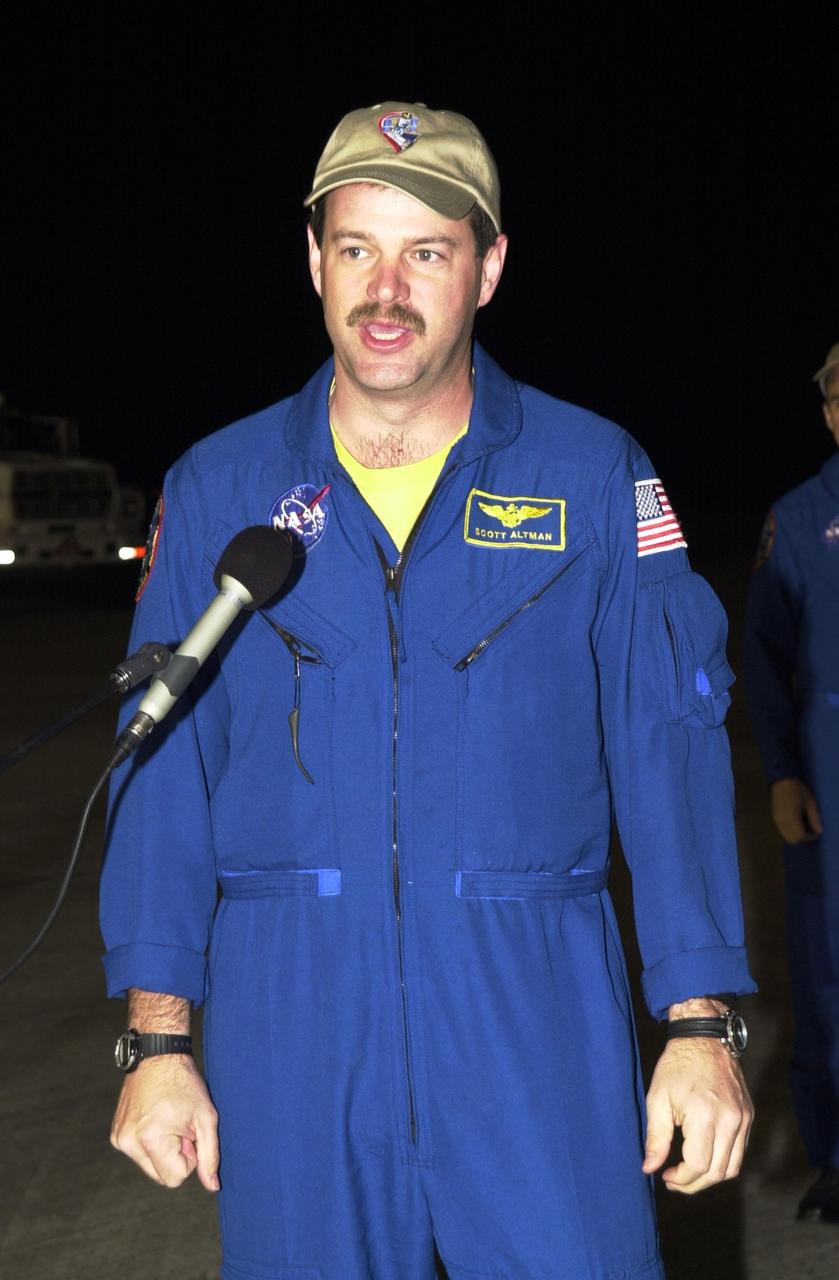

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - STS-109 Shuttle Commander Scott Altman arrives at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft to begin launch preparations. This is Altman's third Shuttle flight. The goal of the 11-day mission is repair and maintenance on the Hubble Space Telescope. Five spacewalks are planned to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 28 at 6:48 a.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, part of the equipment to be used on mission STS-109 is revealed after removal of the protective cover. The mission is to service the Hubble Space Telescope, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
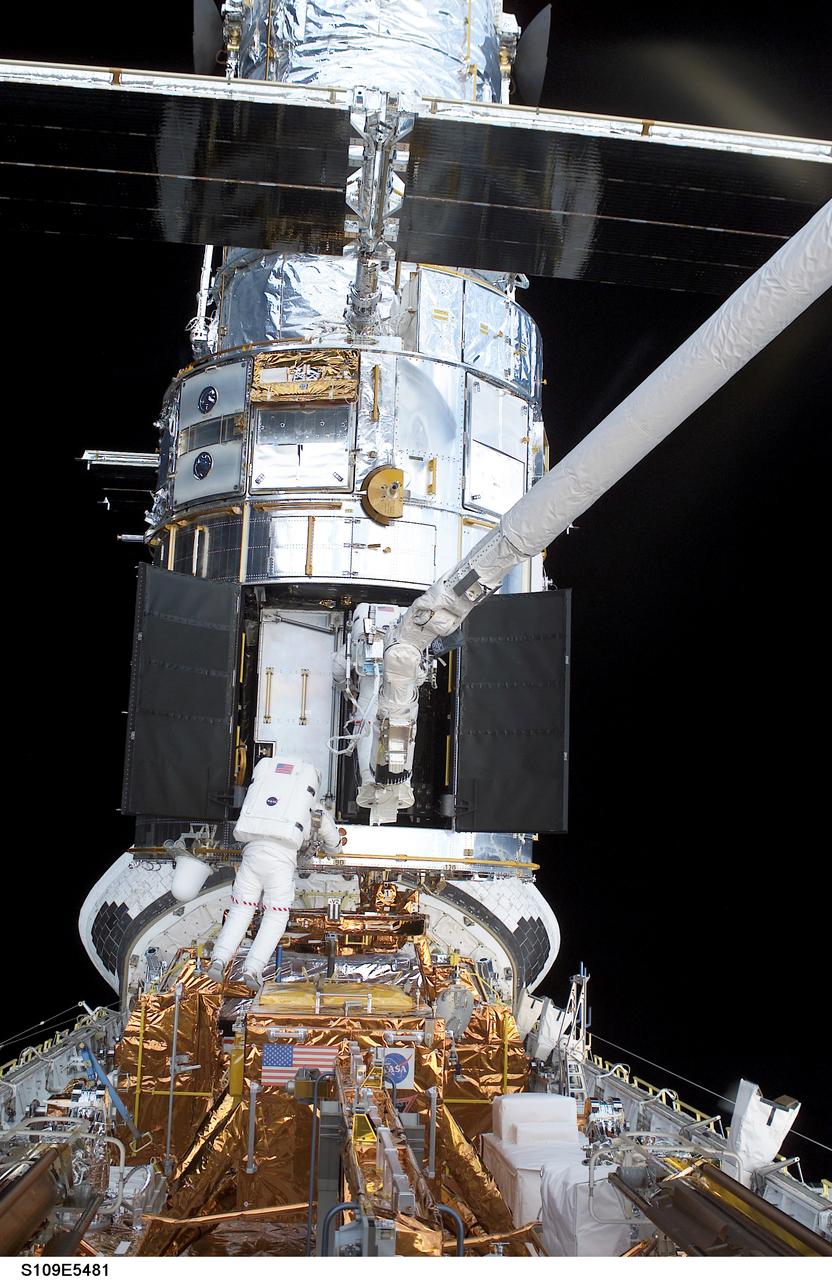

STS109-E-5481 (7 March 2002) --- Two of Columbia's four spacewalkers--astronauts James H. Newman and Michael J. Massimino--participate in the first science instrument upgrade of the fourth Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission during the flight's fourth day of extravehicular activity (EVA). The two, with Newman on Columbia's remote manipulator system (RMS) robotic arm, removed the Faint Object Camera to make room for the new Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). This image was recorded with a digital still camera by one of the duo's crewmates on the aft flight deck.
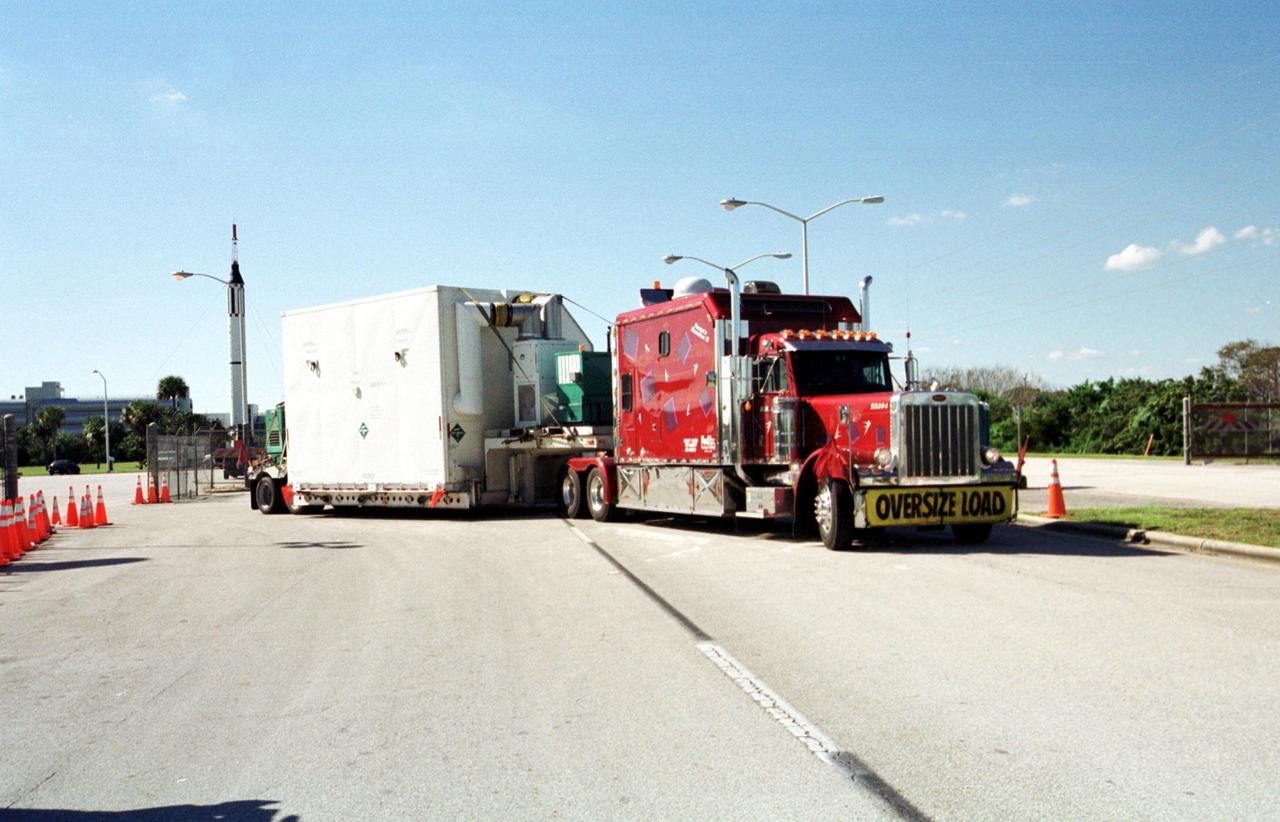

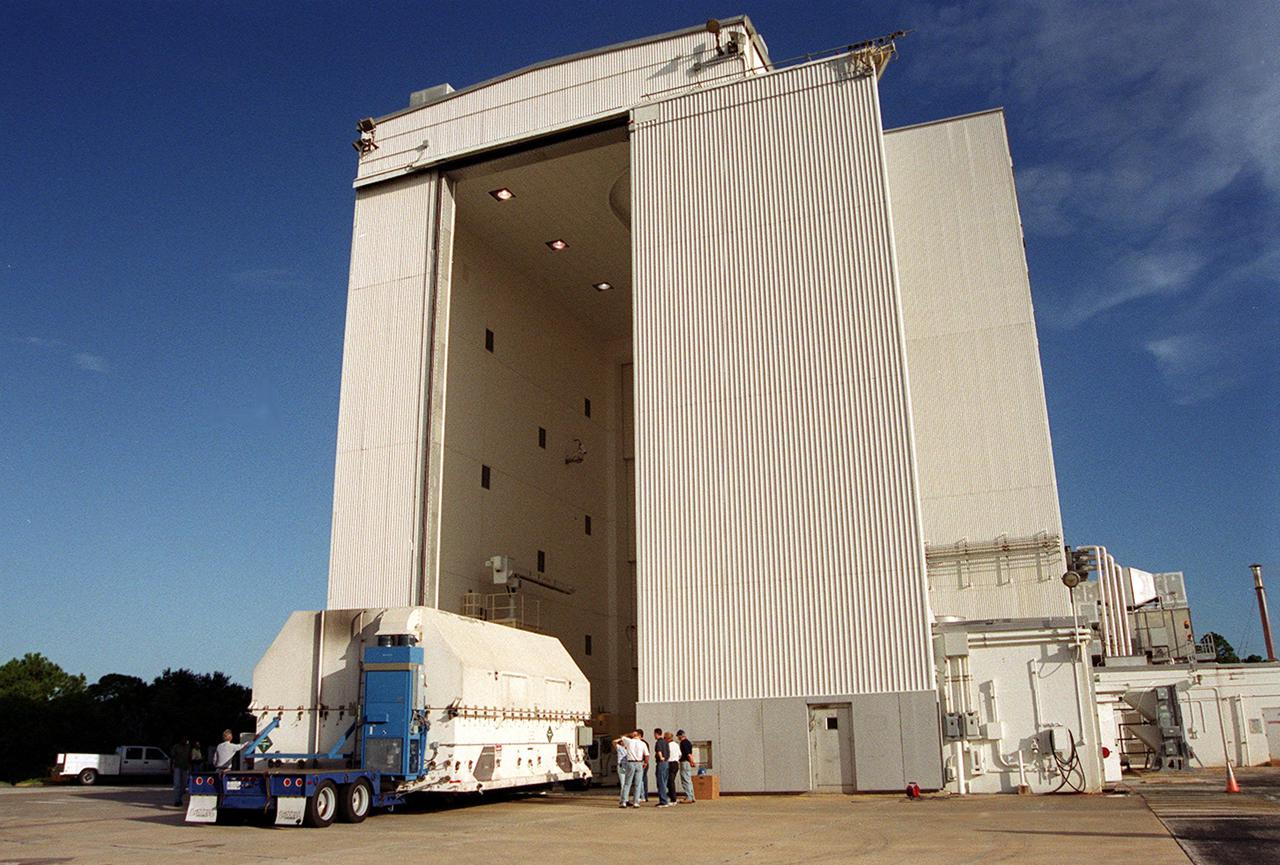
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- A large truck arrives at the gate to KSC, delivering part of the equipment to be used on mission STS-109, the Hubble Servicing mission. The primary tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
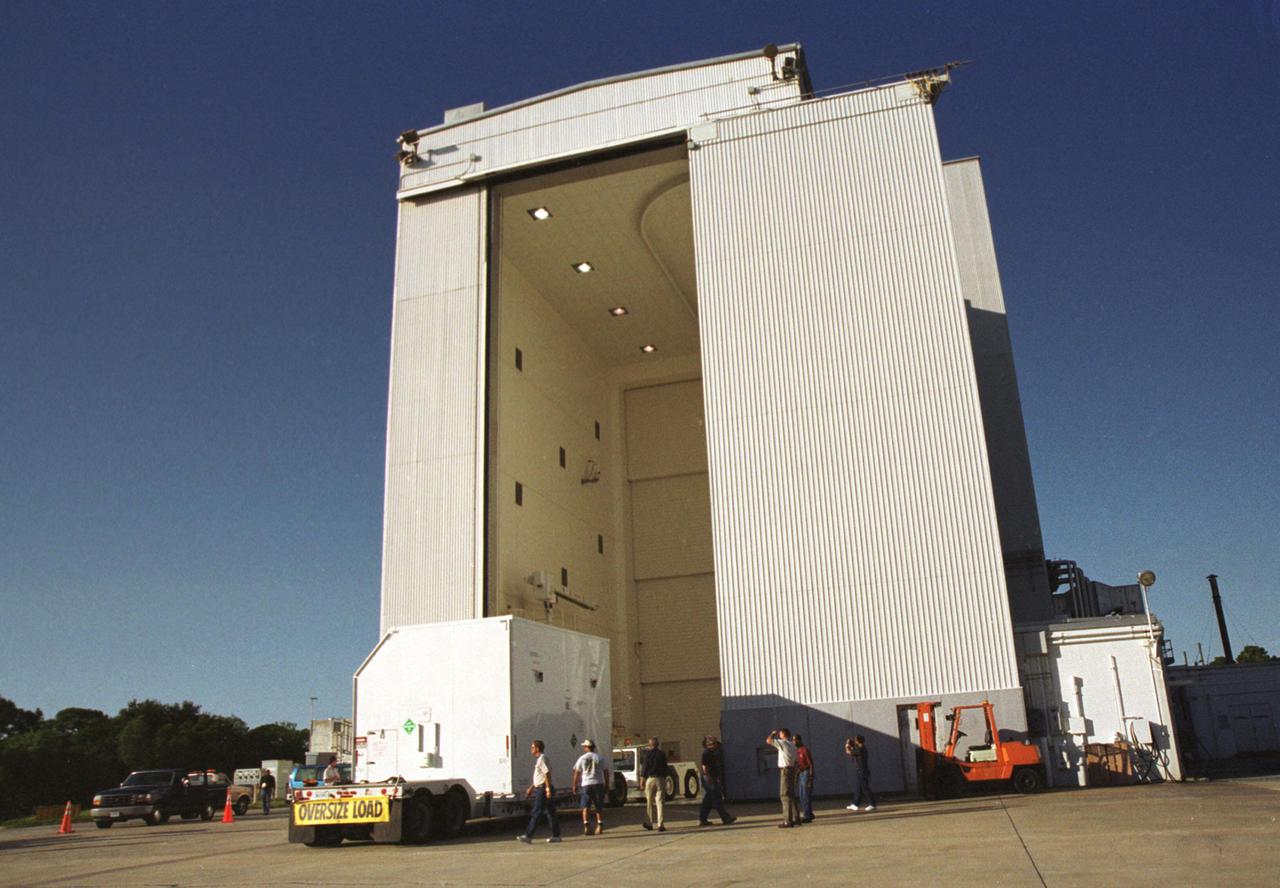

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The truck delivering part of the equipment to be used on mission STS-109 moves into the Vertical Processing Facility at KSC. The mission is to service the Hubble Space Telescope, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002.
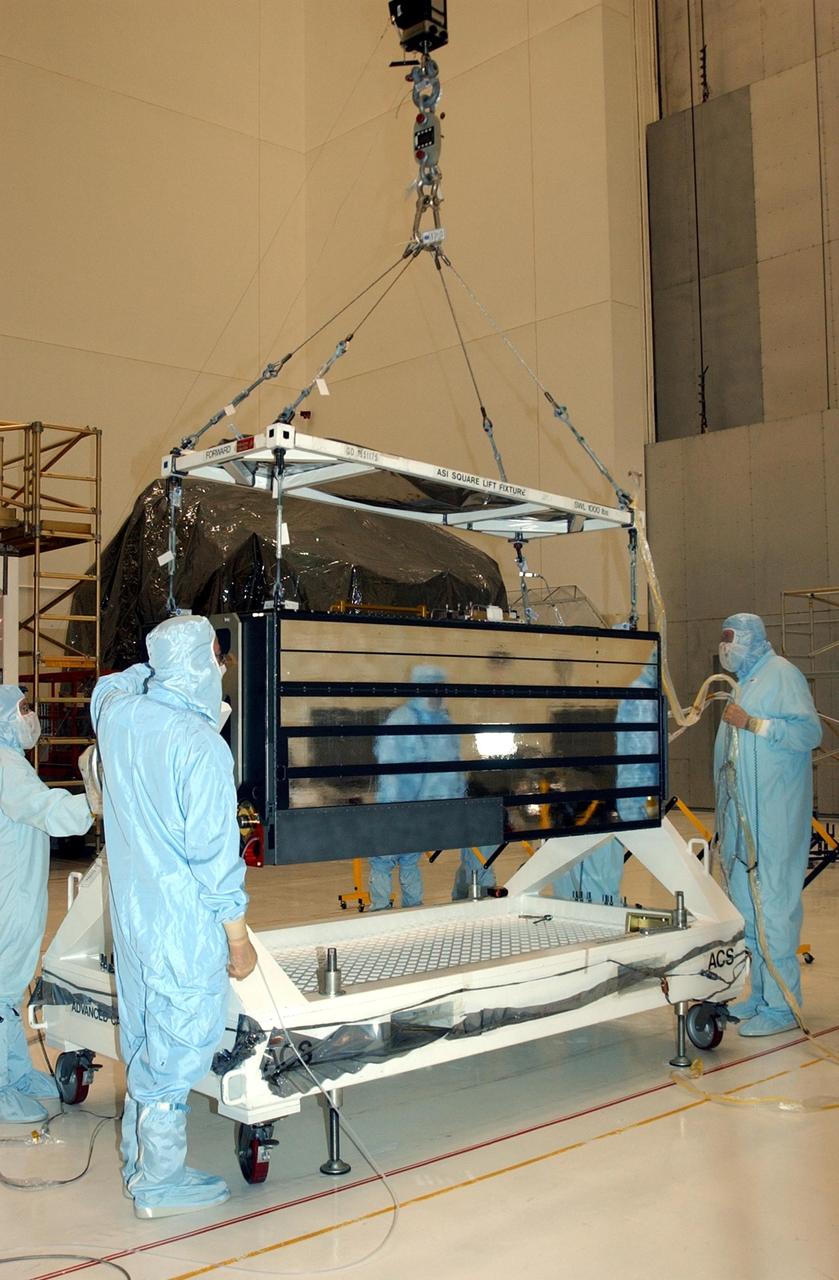

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, workers watch while an overhead crane lifts the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) off the stand. The ACS is part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch no earlier than Feb. 21, 2002
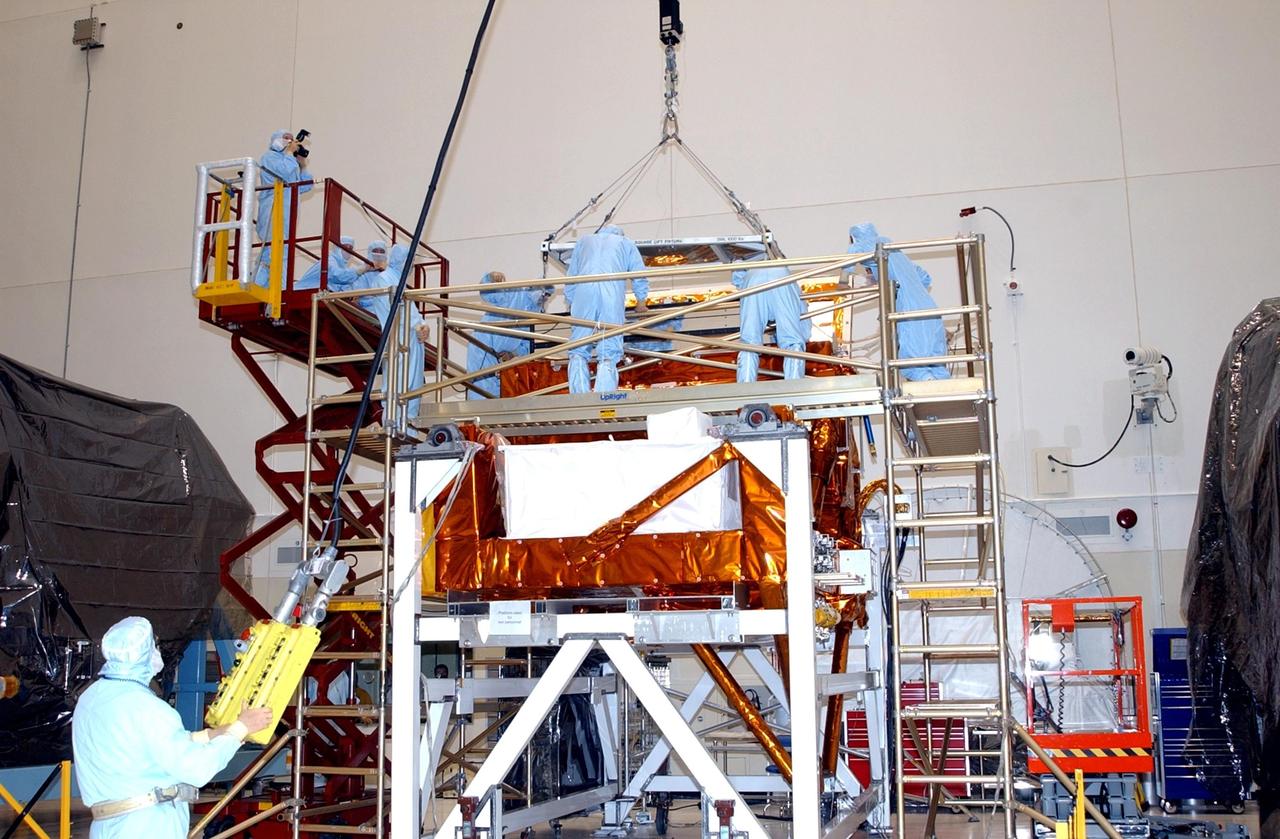

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, workers watch while an overhead crane lowers the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) into the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE). The ACS is part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch no earlier than Feb. 21, 2002

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, part of the equipment to be used on mission STS-109 sits on a workstand after removal of the protective cover. The mission is to service the Hubble Space Telescope, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
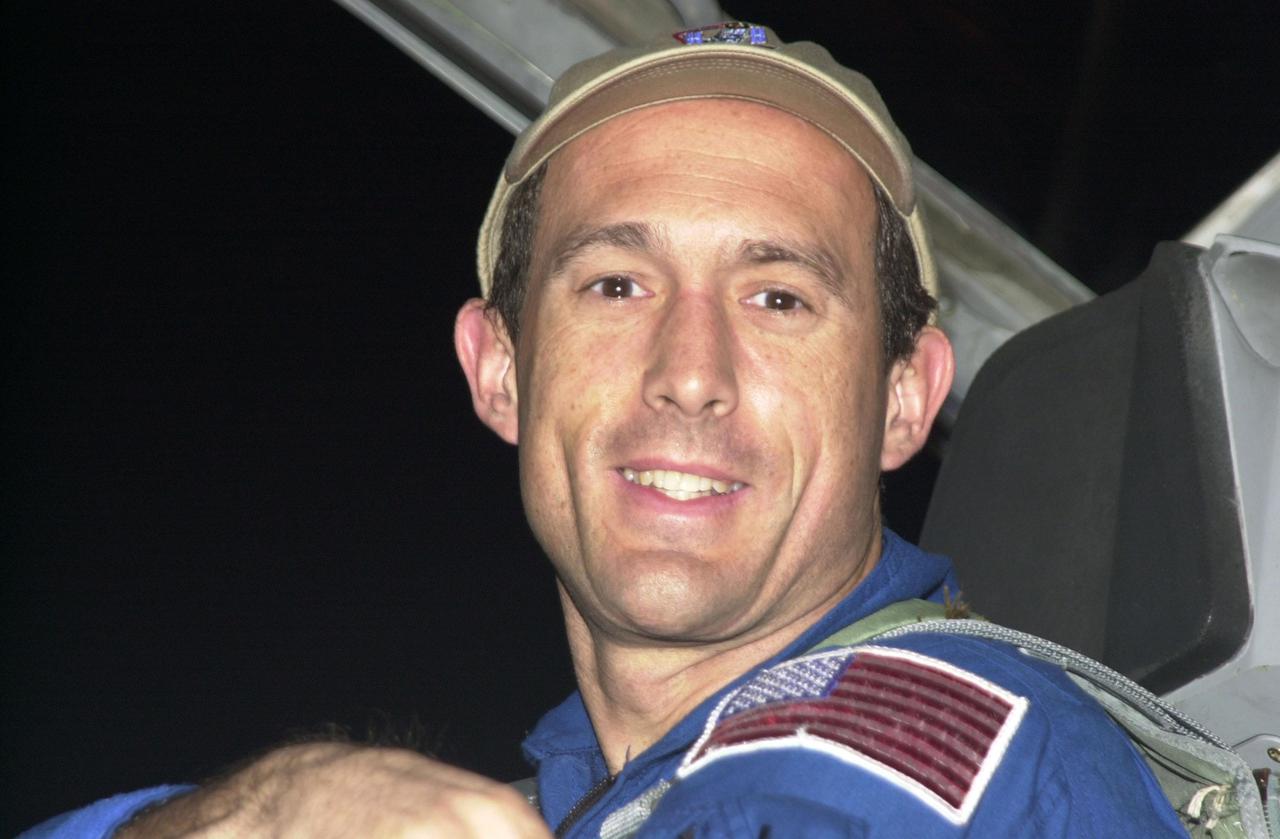

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - STS-109 Mission Specialist James Newman arrives at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft to begin launch preparations. This is Newman's fourth Shuttle flight. The goal of the 11-day mission is repair and maintenance on the Hubble Space Telescope. Five spacewalks are planned to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 28 at 6:48 a.m. EST
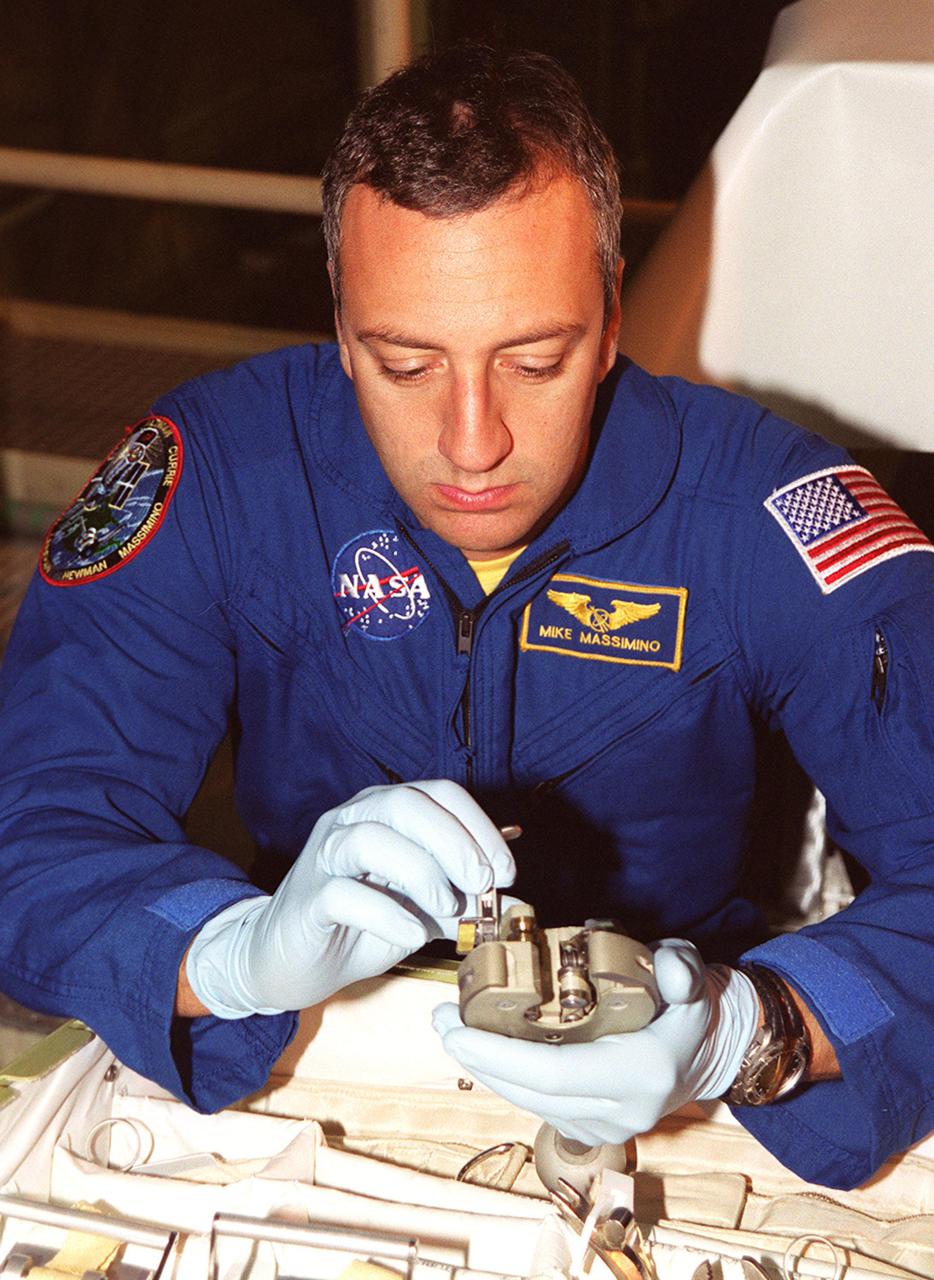

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-109 Mission Specialist Michael Massimino practices on equipment that will be used on the mission. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities that include familiarization with the orbiter and equipment. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
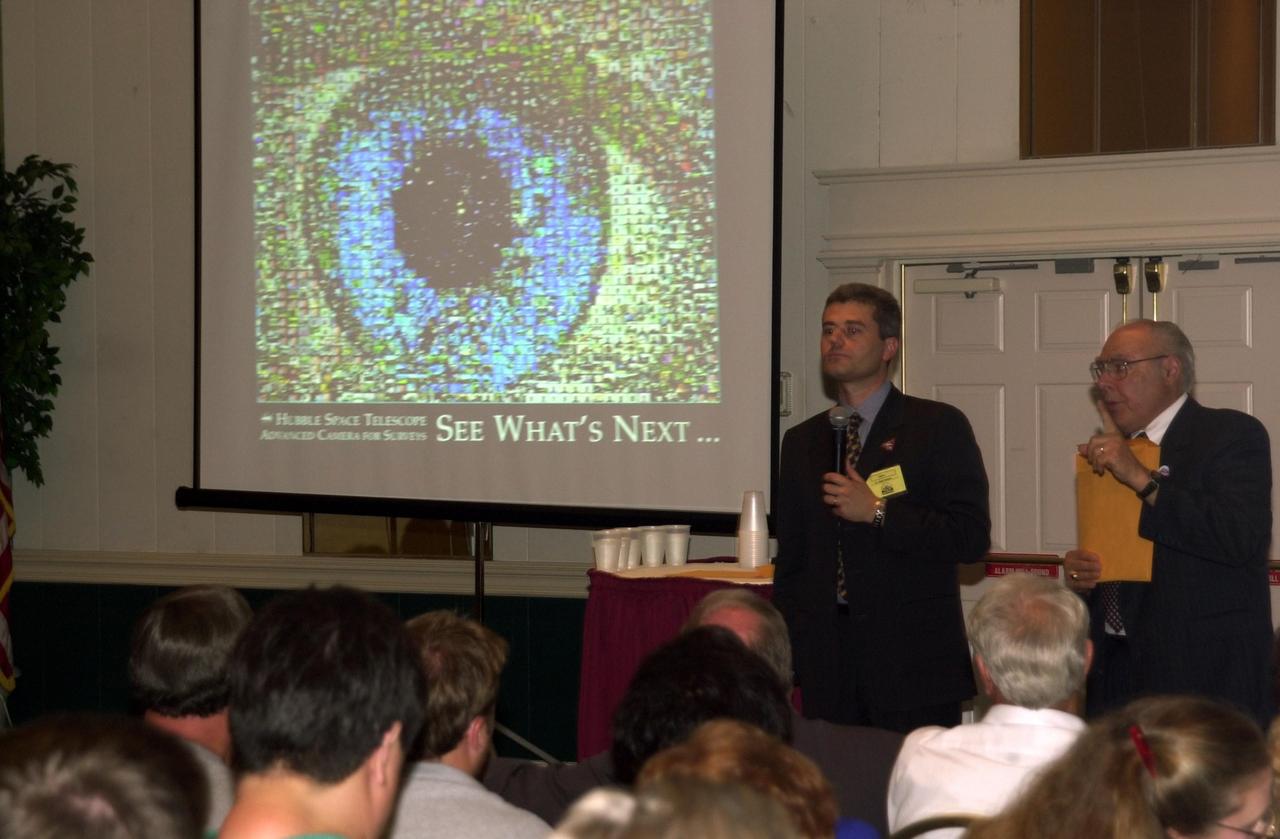

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the 2002 Space Congress, Cape Canaveral, Fla., a presentation on "Hubble Discoveries" by Dr. Mark Clampin (with microphone), Advanced Camera for Surveys team, included an image of an eye (seen on the screen) comprising hundreds of photos of all the people who worked on Hubble. On the right is Frank Ceppolina, project manager, Hubble Space Telescope Development Project. The Space Congress is held annually to highlight military and space initiatives, new technologies, and Florida's role in programs and research. This year's theme is Beginning a New Era - Initiatives in Space. NASA presented several paper sessions, including Advancements in Technology. Space Congress is sponsored by the Canaveral Council of Technical Societies
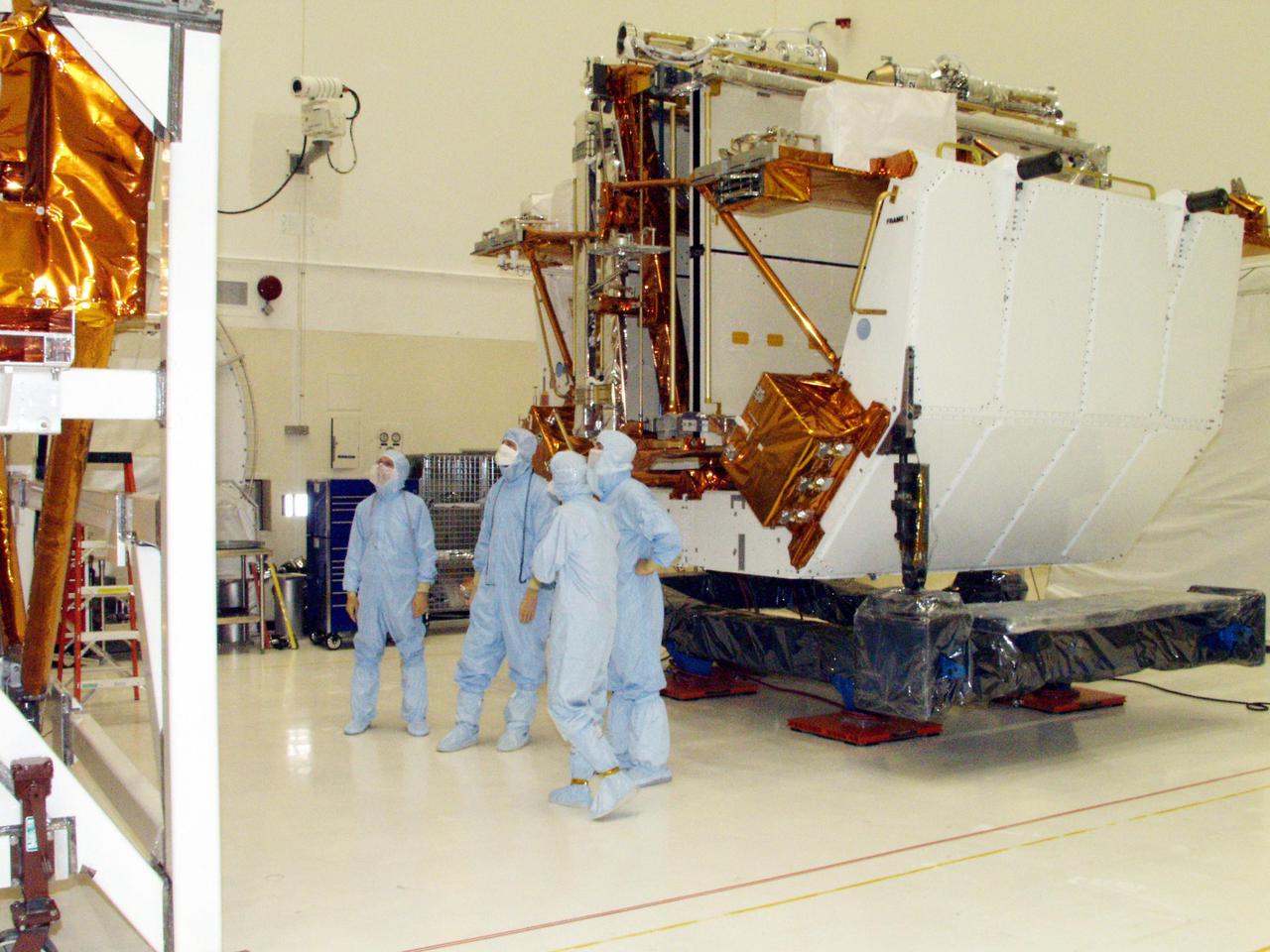

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility look over the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Solar Array 3 panels behind them, and other HST hardware, are installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
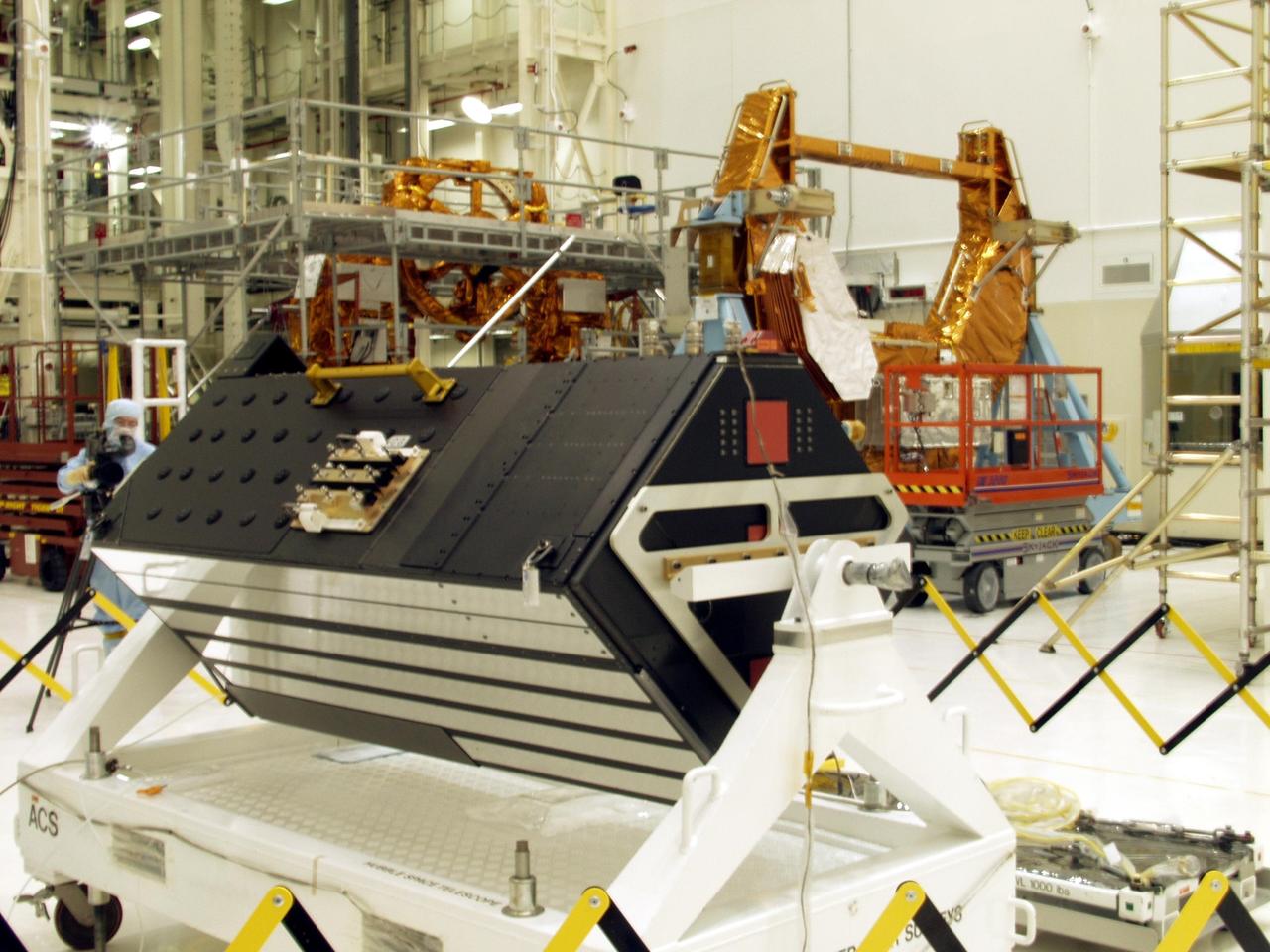

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), foreground, is part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The ACS and other hardware, installed on four principle payload carriers, are being processed inside the clean room at the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF). The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
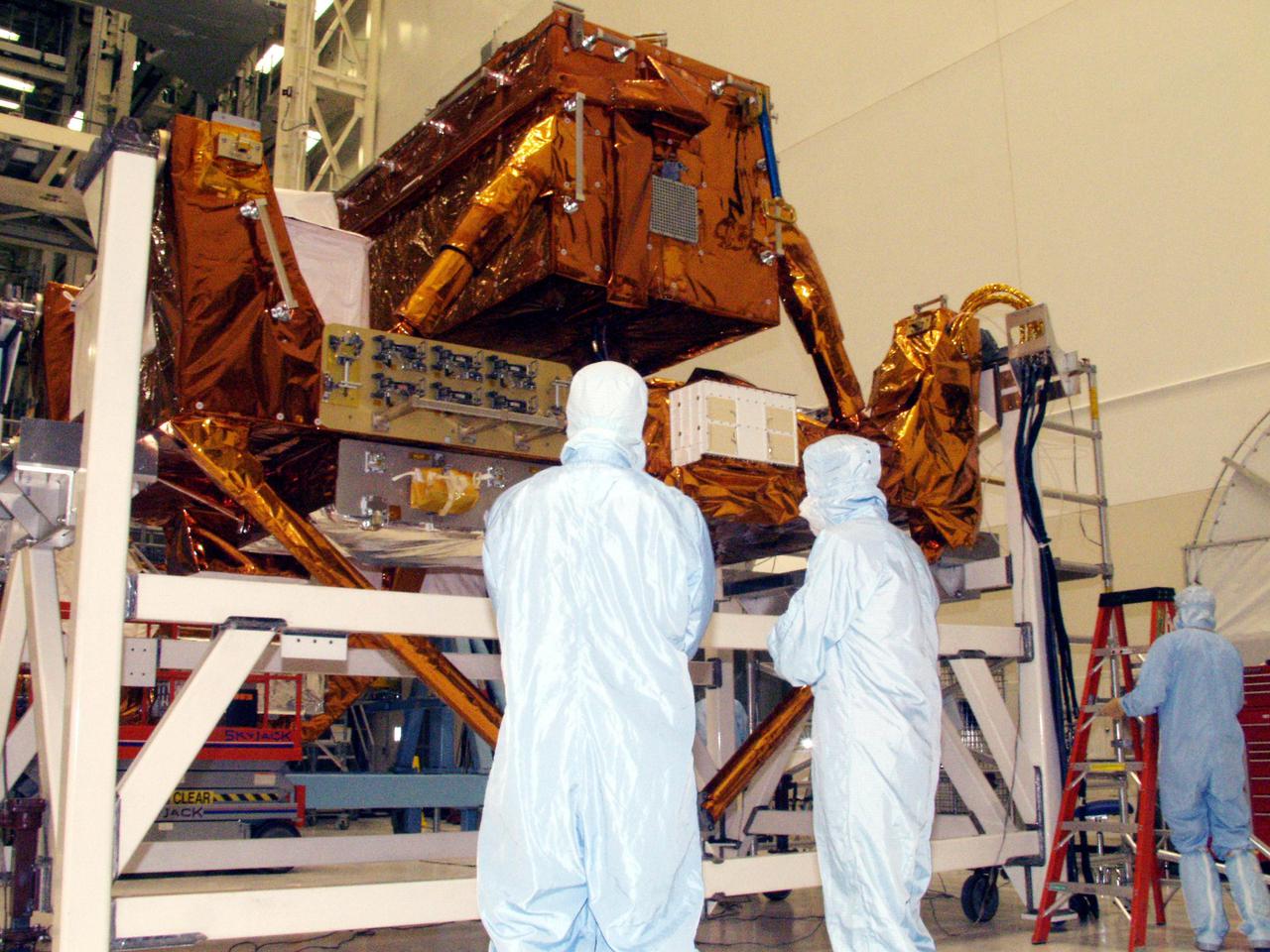

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility take a close look at the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The hardware is installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
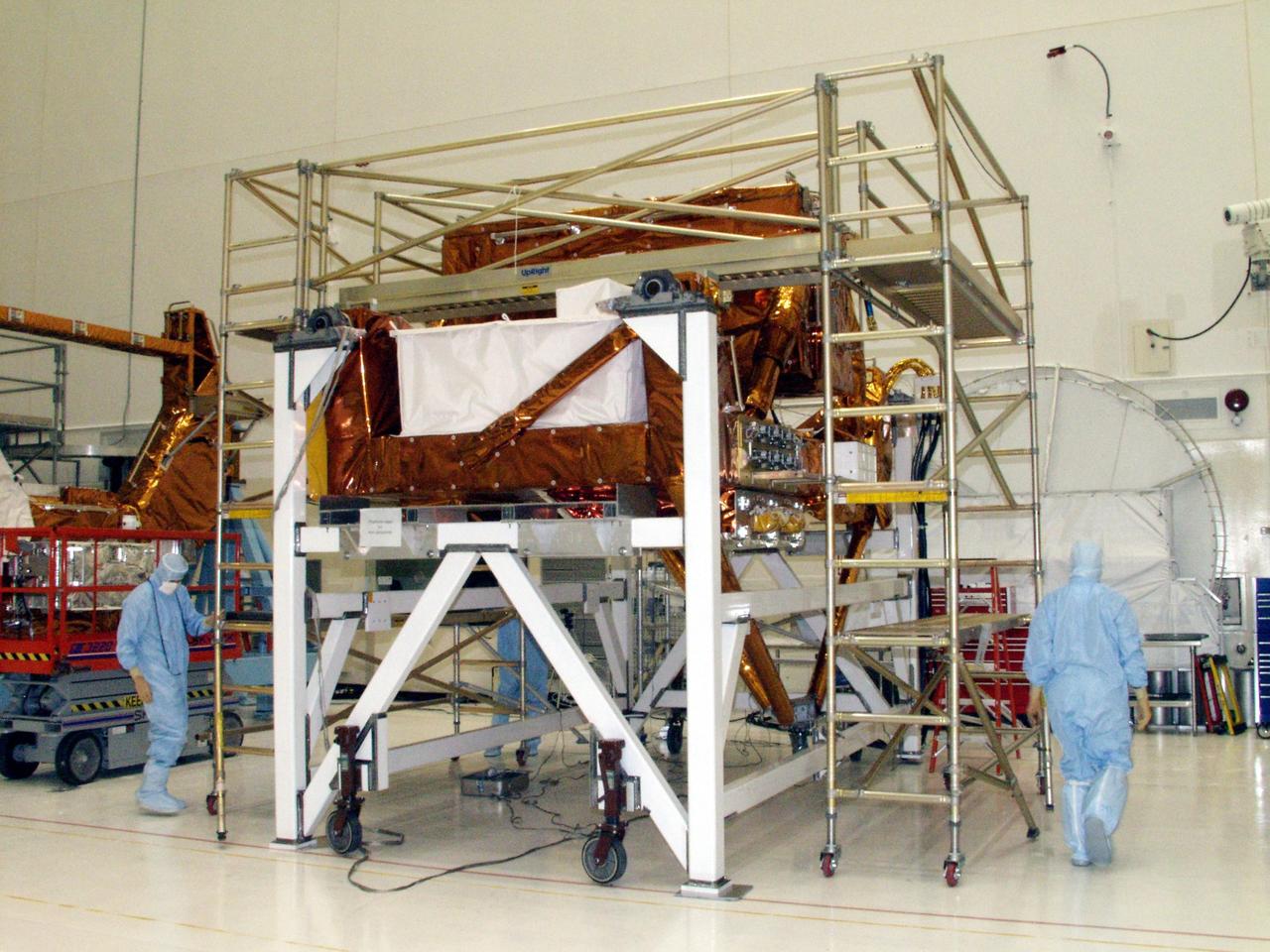

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. --The STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is being processed inside the clean room at the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF). Seen here is the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). The hardware will be installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
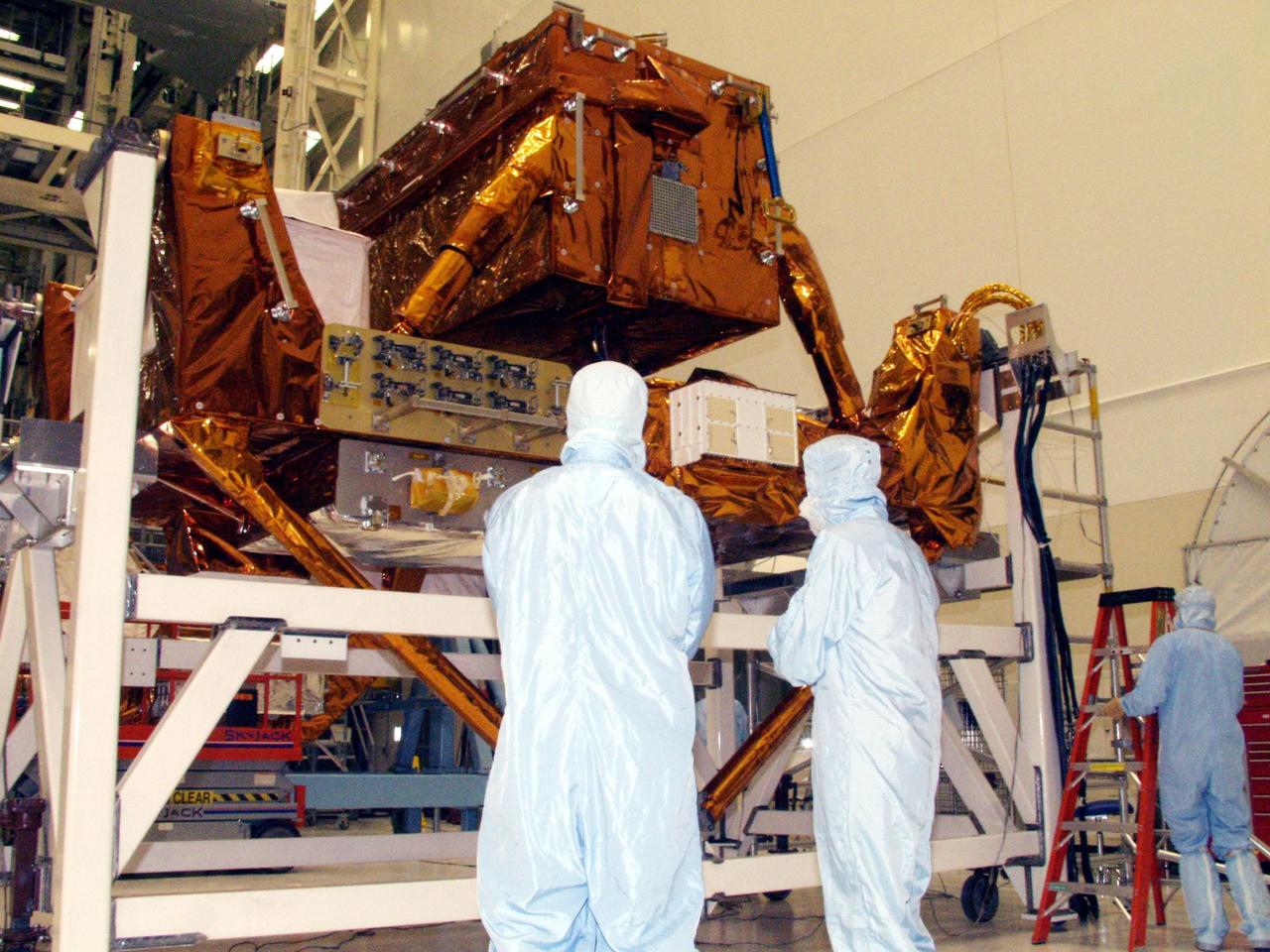

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility take a close look at the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The hardware is installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
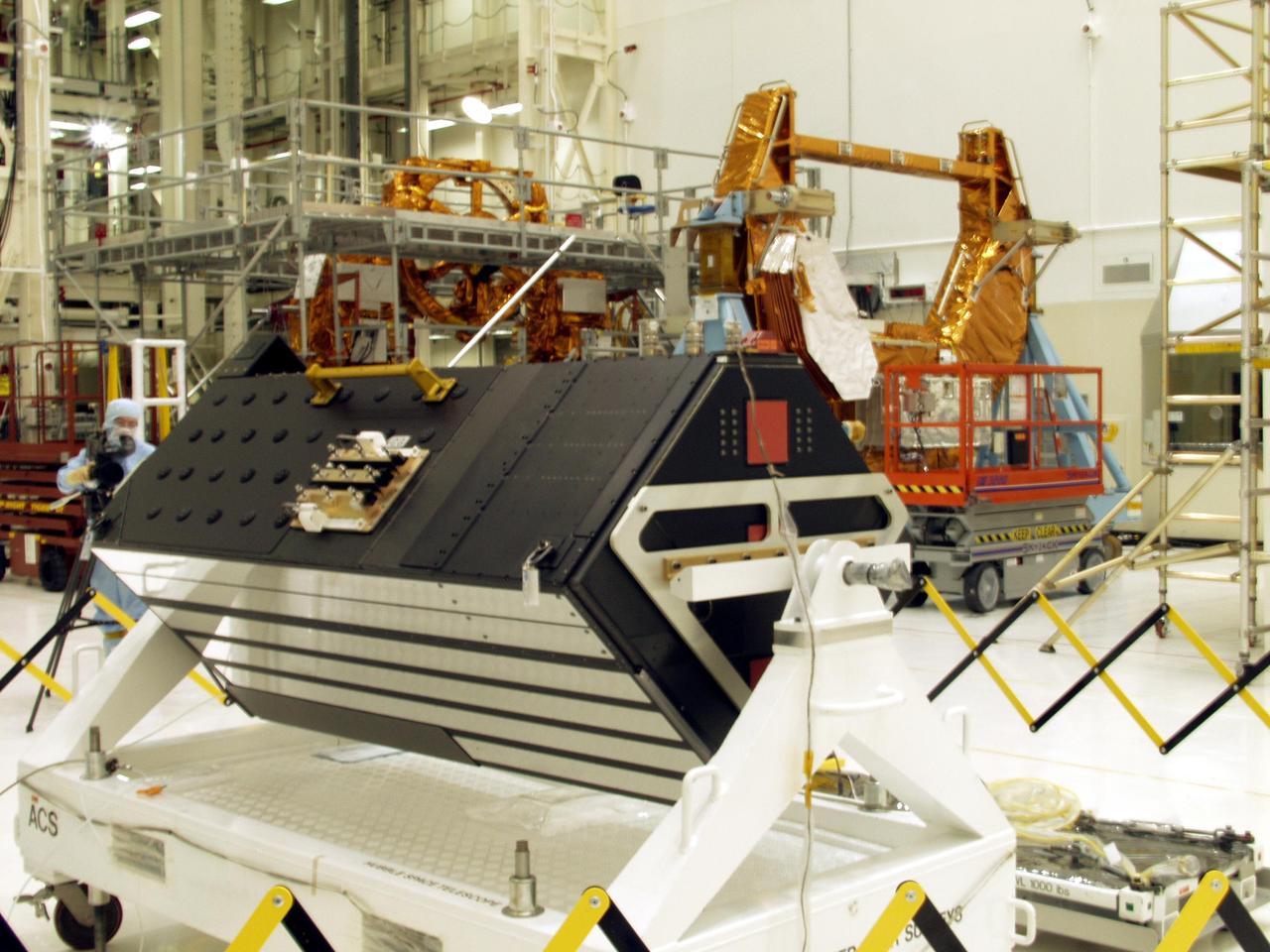

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), foreground, is part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The ACS and other hardware, installed on four principle payload carriers, are being processed inside the clean room at the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF). The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
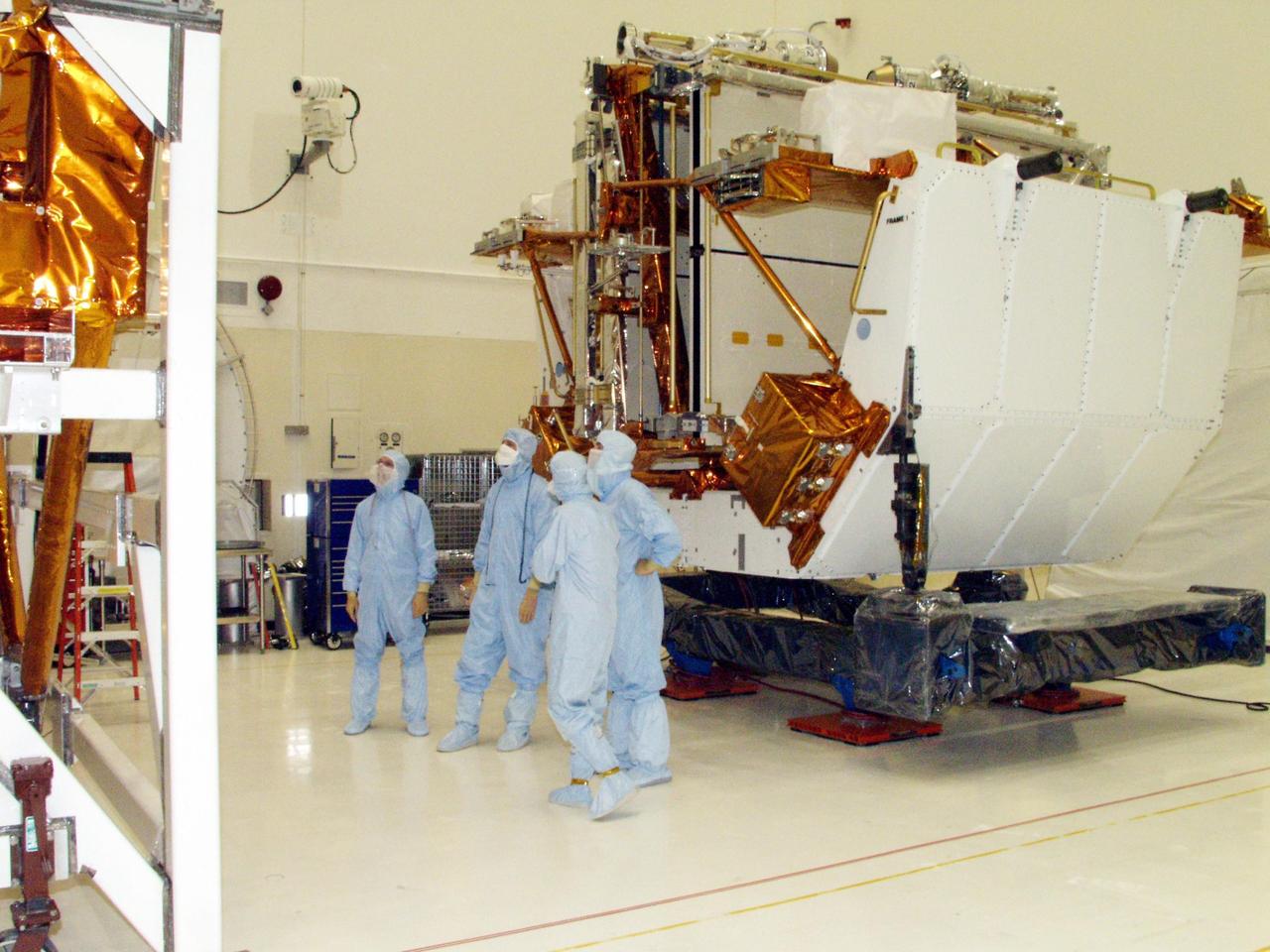

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility look over the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Solar Array 3 panels behind them, and other HST hardware, are installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
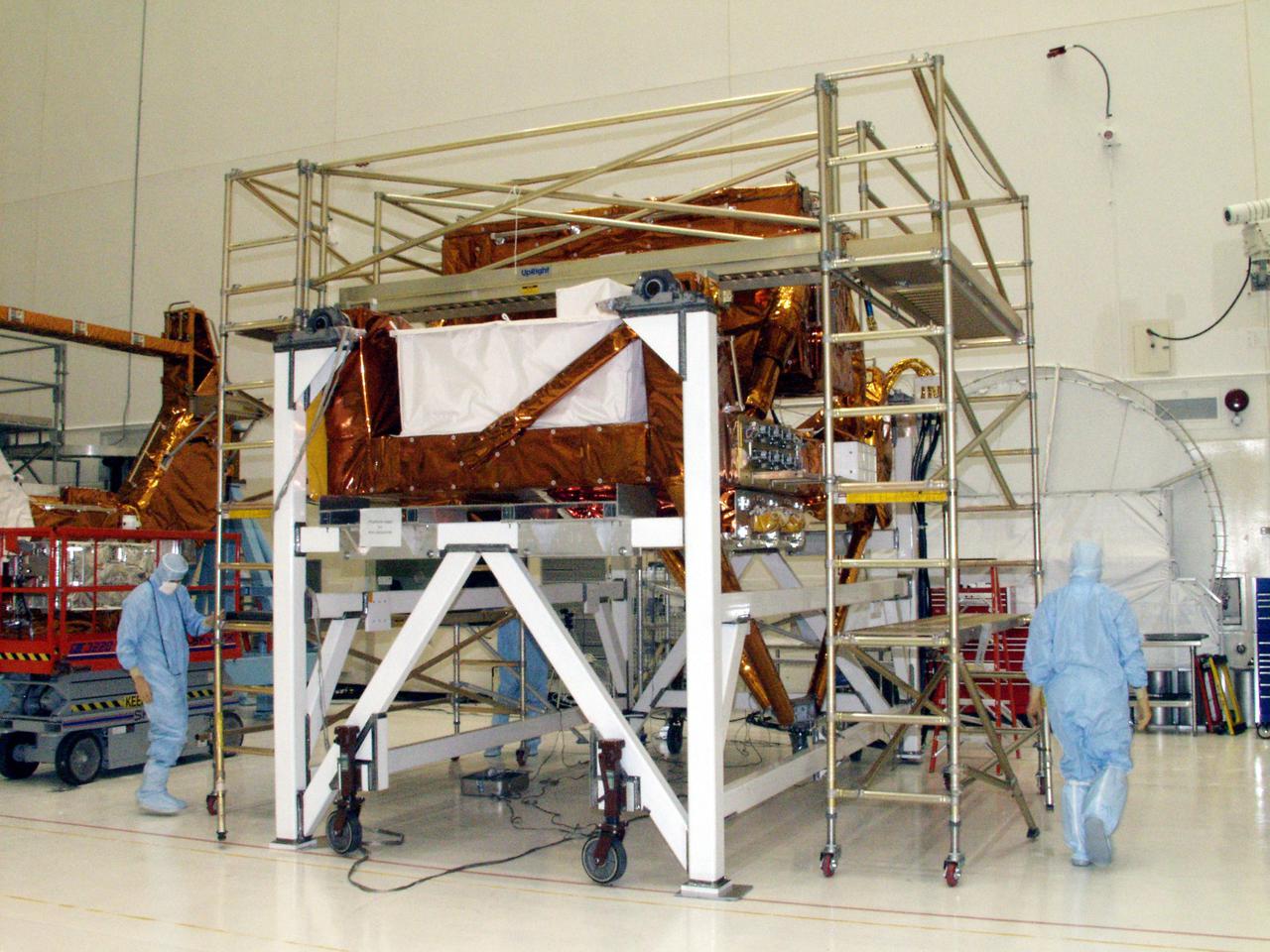

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. --The STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is being processed inside the clean room at the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF). Seen here is the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). The hardware will be installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
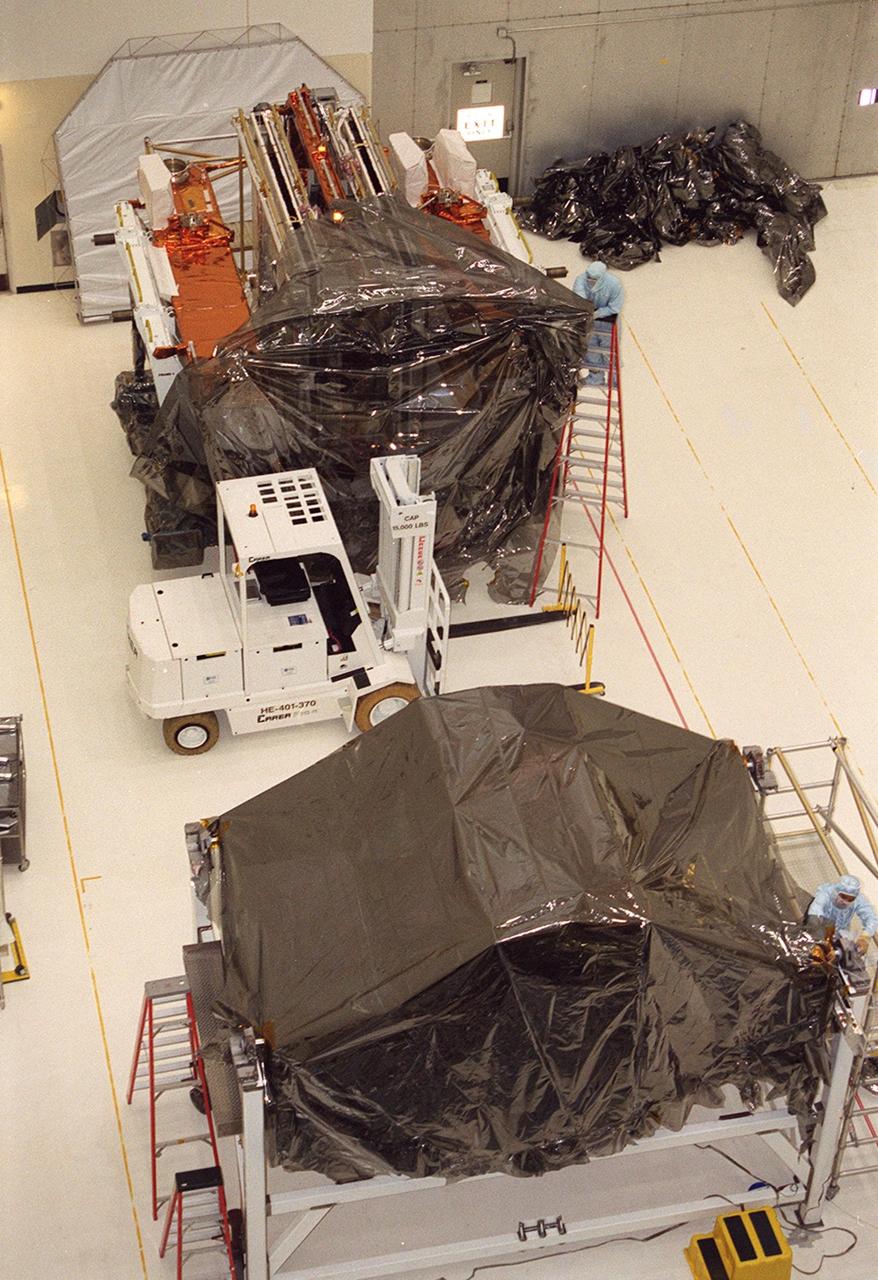

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, workers remove the wrapping from several components of the STS-109 payload. The purpose of the mission is servicing the Hubble Space Telescope. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
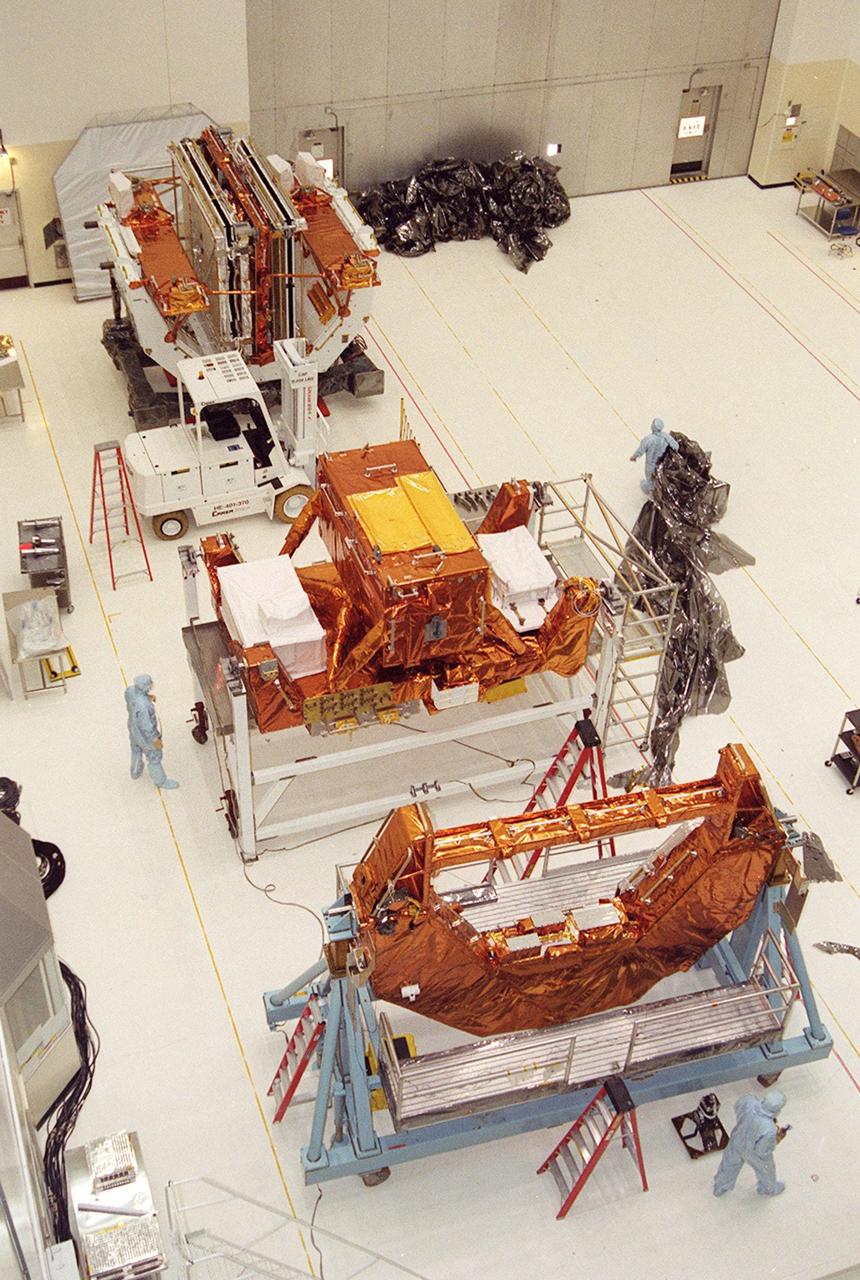
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, various components of the payload on mission STS-109 rest on workstands after being unwrapped. The purpose of the STS-109 mission is servicing the Hubble Space Telescope. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
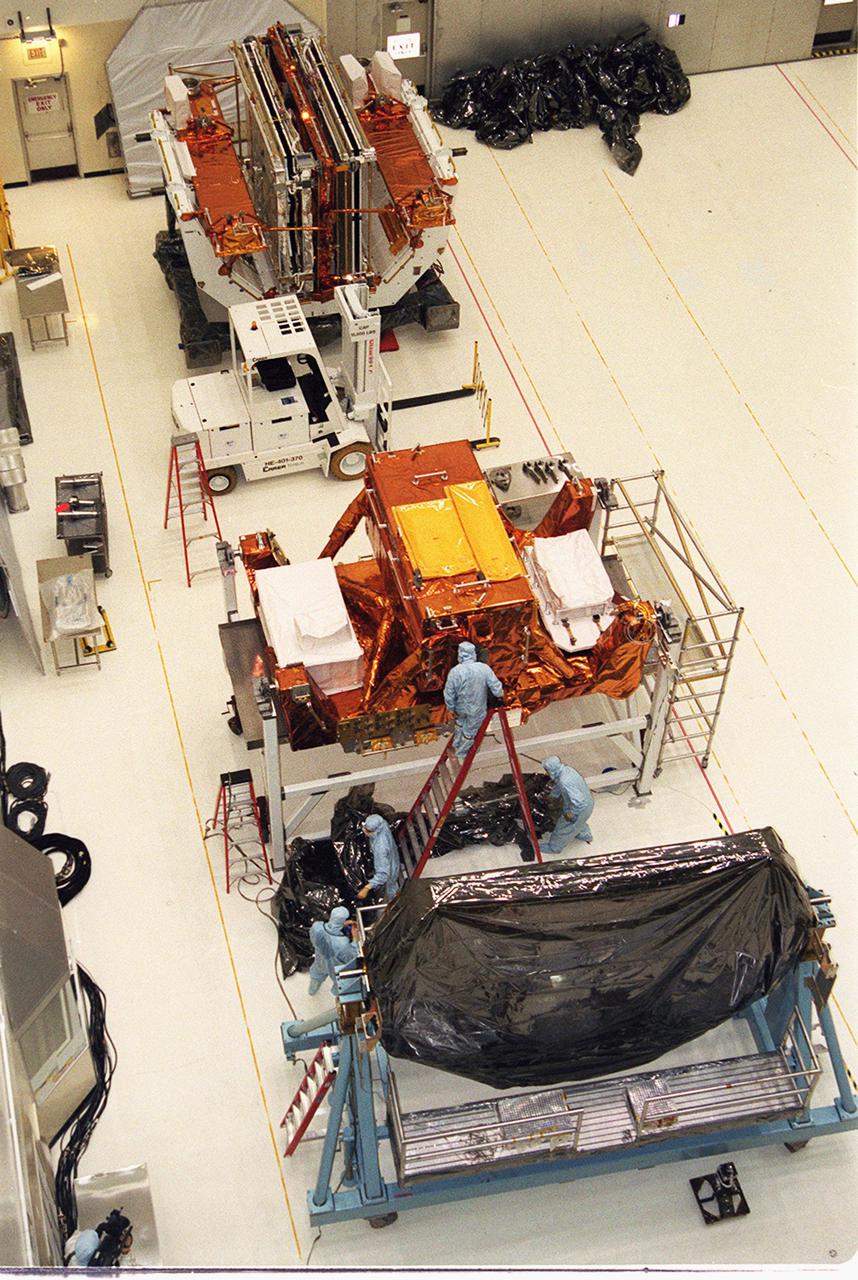
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, two components of the STS-109 payload are revealed while a third is being unwrapped. The purpose of the STS-109 mission is servicing the Hubble Space Telescope. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
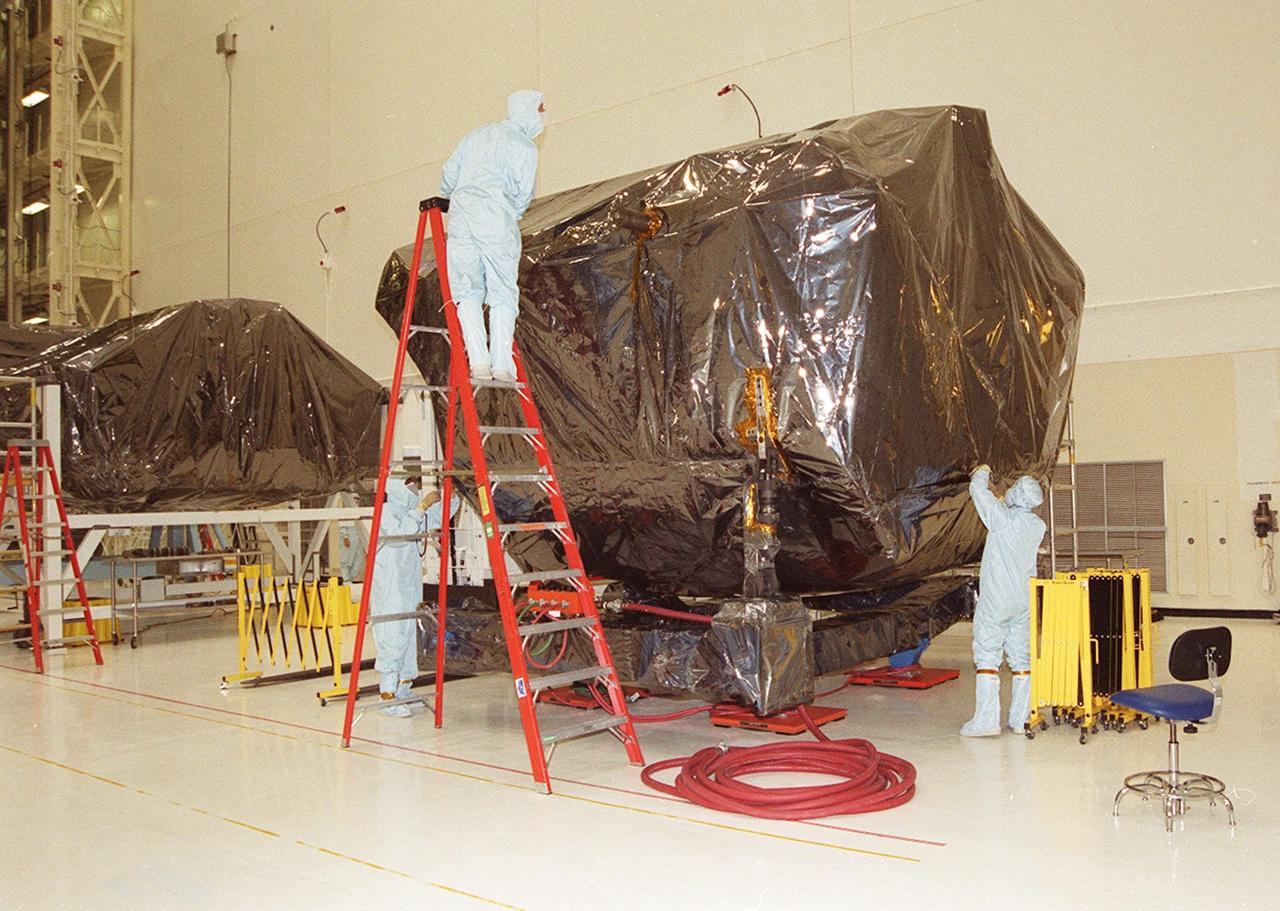

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility begin to unwrap the payload that recently arrived for STS-109, whose mission is servicing the Hubble Space Telescope. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
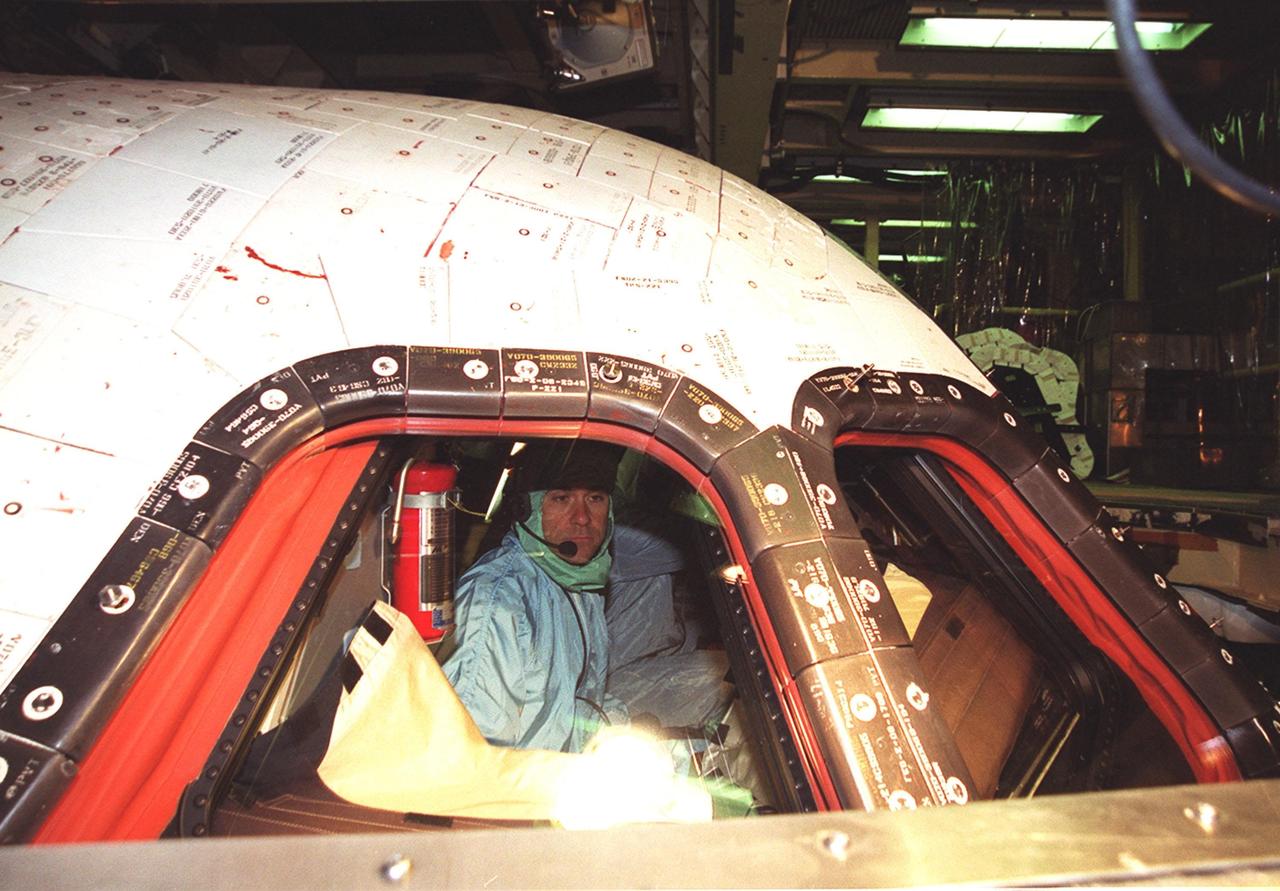

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - STS-109 Pilot Duane Carey checks the windshield and windows from inside Columbia. This is Carey's first Shuttle flight. He and the crew are at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities that include familiarization with the orbiter and equipment. STS-109 is the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing mission. The crew also comprises Commander Scott Altman, Payload Commander John Grunsfeld and Mission Specialists Nancy Currie, James Newman, Richard Linnehan and Michael Massimino. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
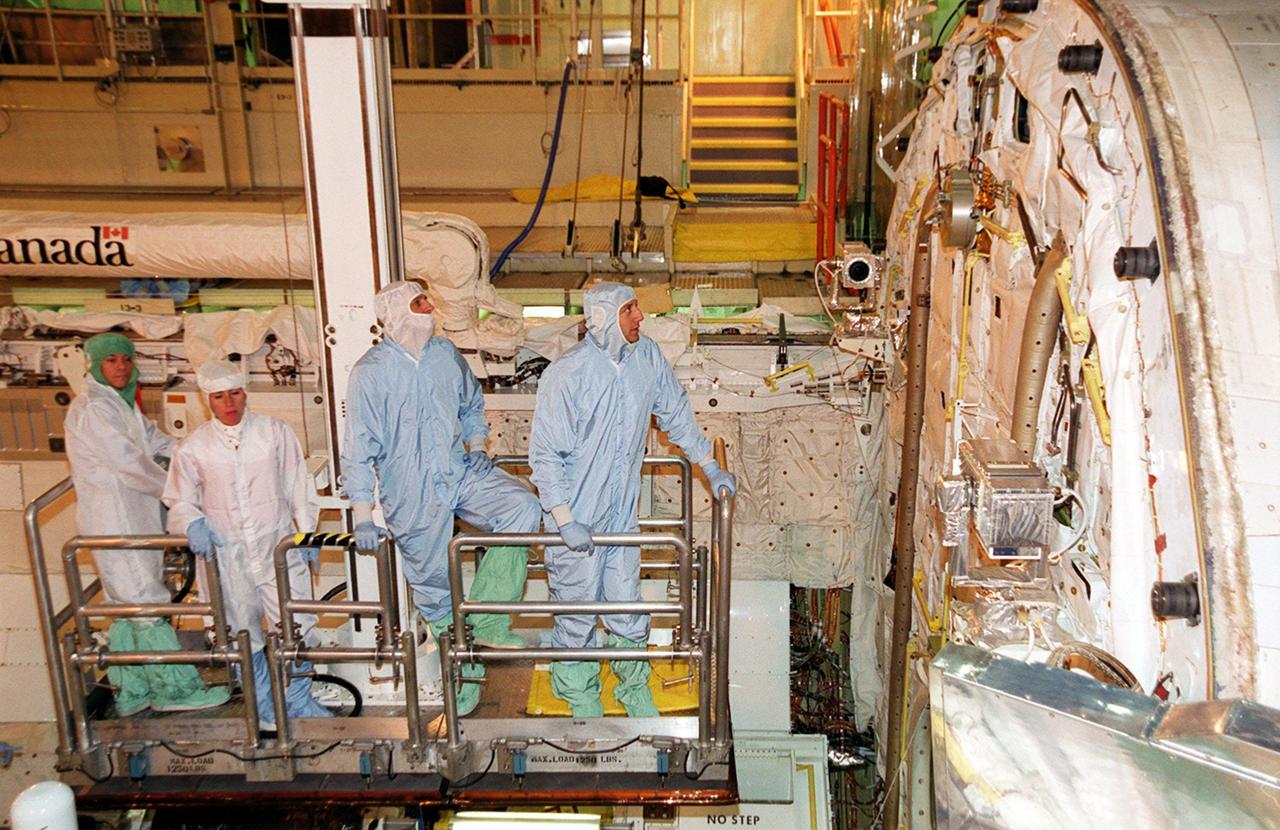

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Members of the STS-109 crew look over the interior of orbiter Columbia's payload bay. At right is Mission Specialist Michael Massimino; next to him is Commander Scott Altman. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities that include familiarization with the orbiter and equipment. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
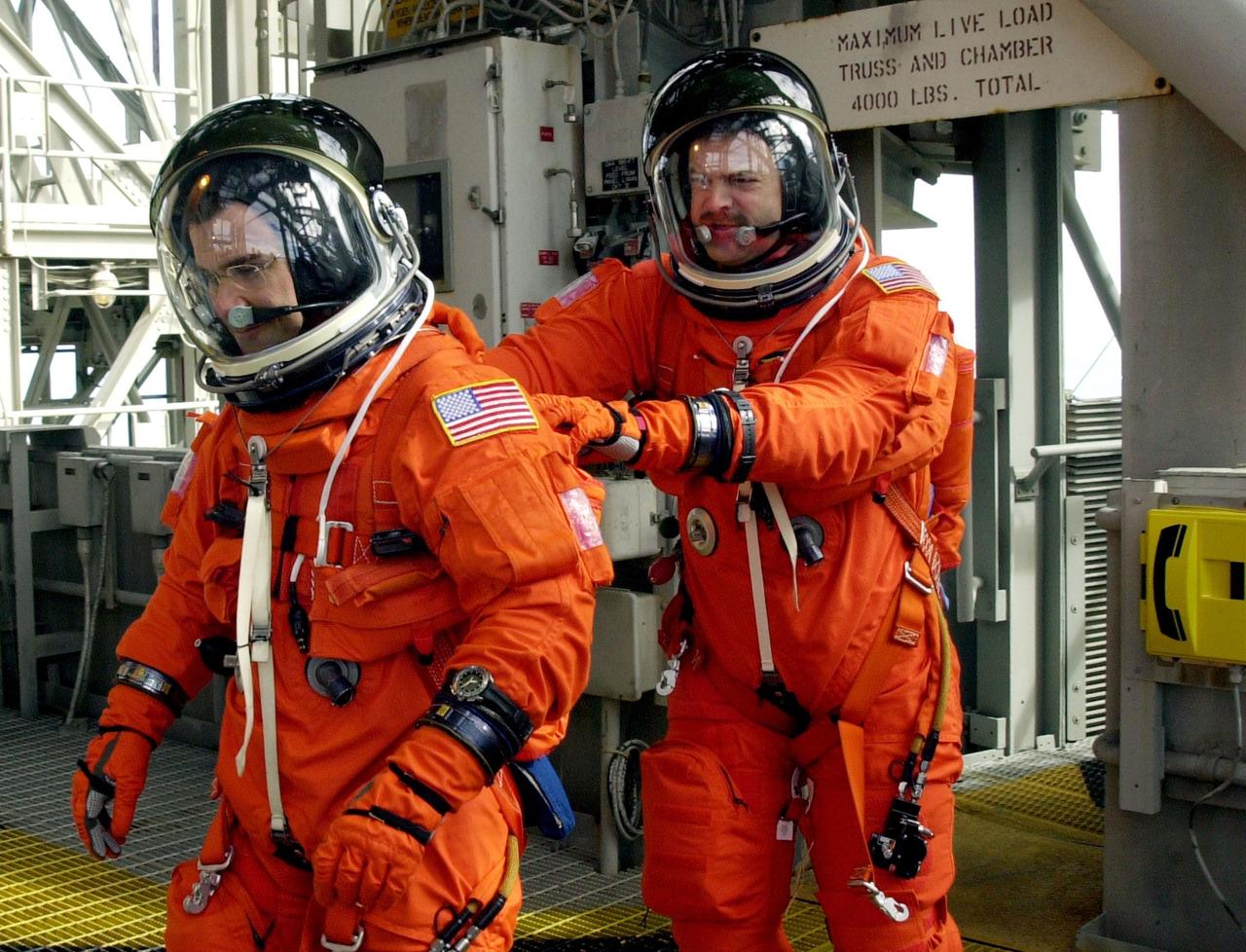

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- As part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, the STS-109 crew practices emergency exit from the Shuttle. Leading the way to the slidewire basket on the 195-foot level is Pilot Duane Carey, followed by Commander Scott Altman. The TCDT also includes a simulated launch countdown. STS-109 is a Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, with goals to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. The 11-day mission will require five spacewalks to perform the tasks. Launch of STS-109 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002
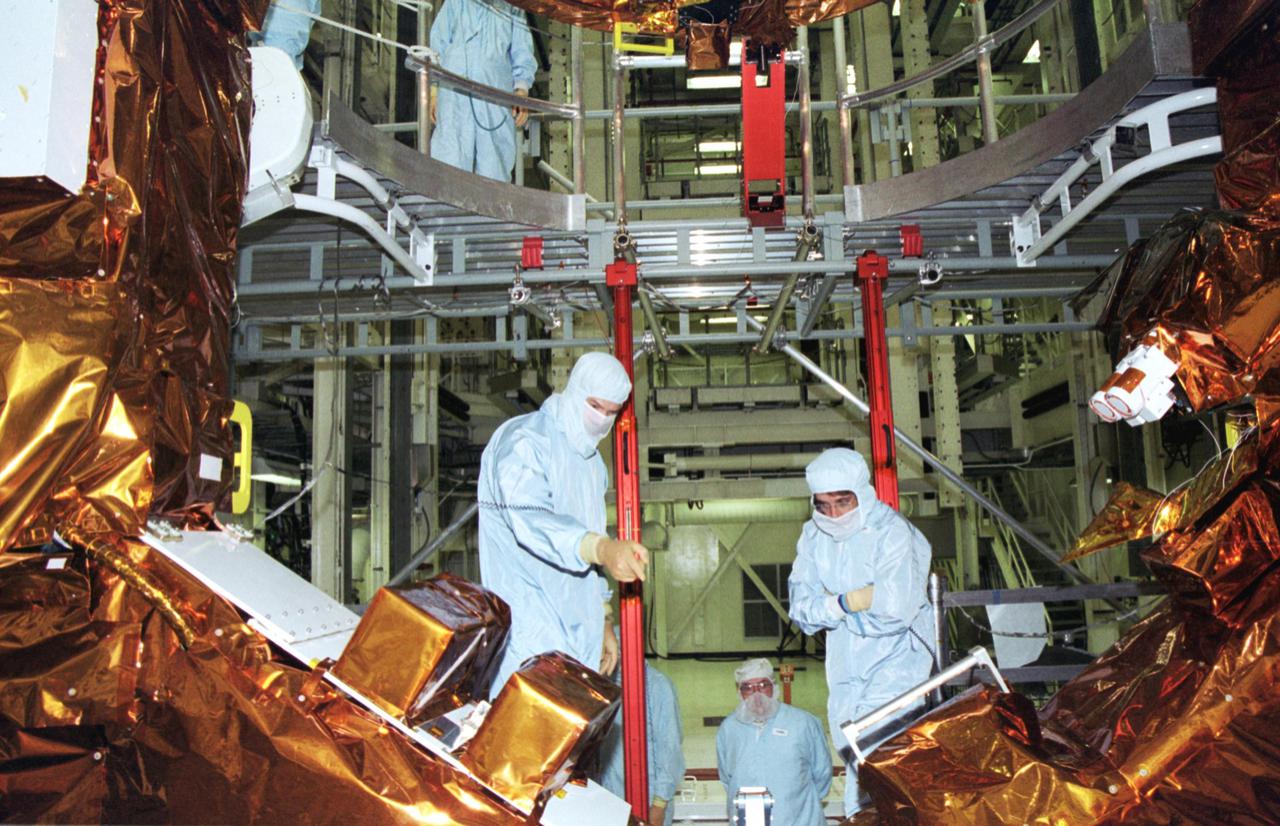

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Inside the Vertical Processing Facility, members of the STS-109 crew looks over equipment for their Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing mission. Seen in the foreground are Commander Scott Altman and Mission Specialist Nancy Currie. Other crew members are Pilot Duane Carey, Payload Commander John Grunsfeld and Mission Specialists James Newman, Richard Linnehan and Michael Massimino. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
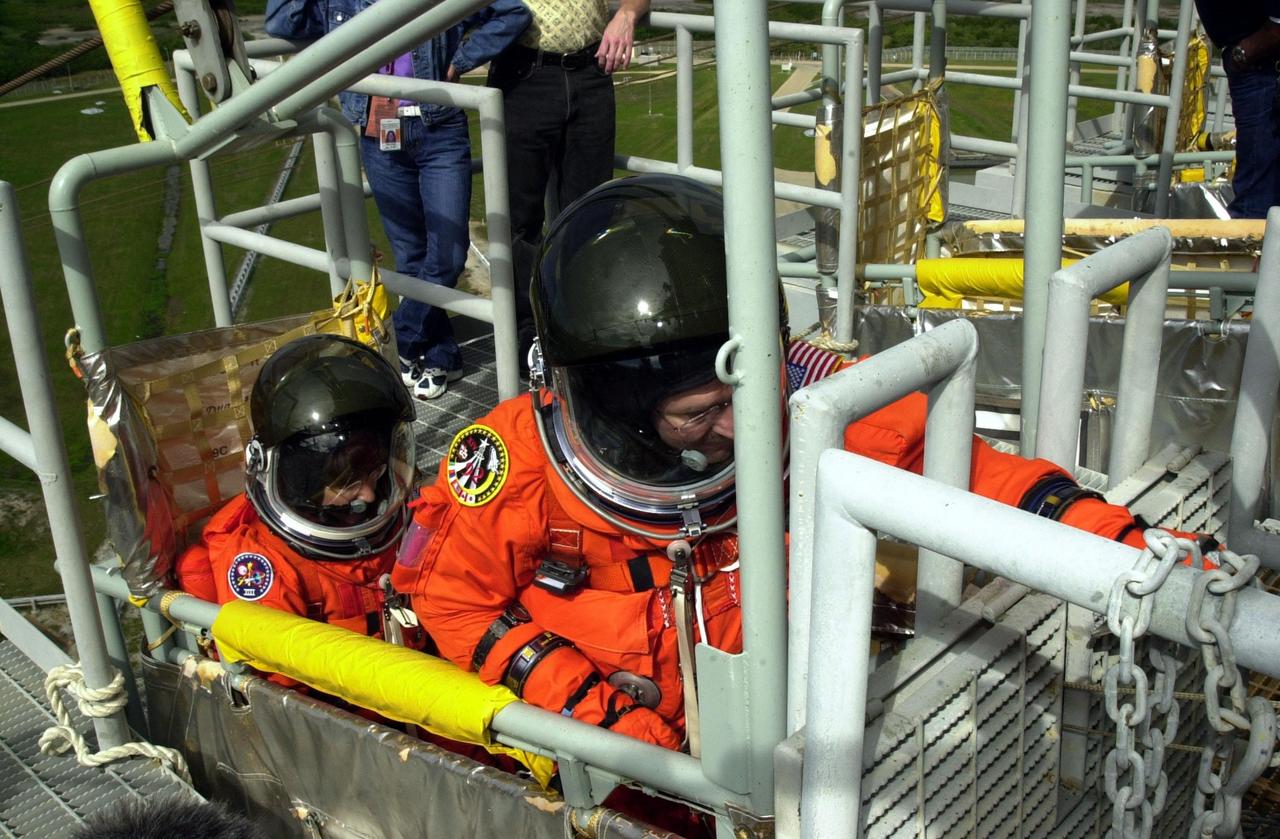

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- As part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, the STS-109 crew practices emergency exit from the Shuttle. Seated in the slidewire basket at the 195-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure are Mission Specialists Nancy Currie (left) and John Grunsfeld (reaching for the release lever). The TCDT also includes a simulated launch countdown. STS-109 is a Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, with goals to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. The 11-day mission will require five spacewalks to perform the tasks. Launch of STS-109 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-109 Mission Specialist Nancy Currie is ready to practice driving the M-113 armored personnel carrier, part of emergency egress training at the launch pad. Crew members are taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which also include a simulated launch countdown. STS-109 is a Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, with goals to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. The 11-day mission will require grasping the satellite with a robotic arm in order for the crew to perform the tasks during five spacewalks. Launch of STS-109 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002
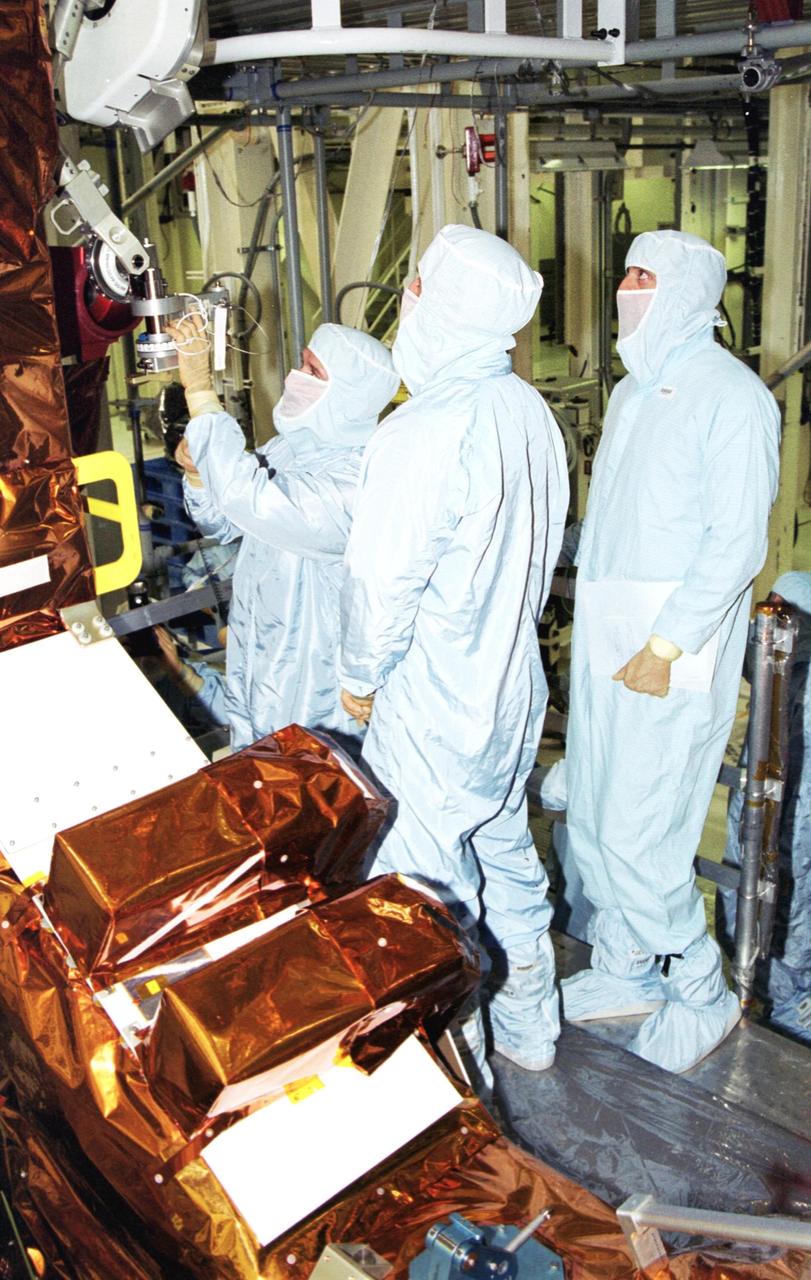

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - In the Vertical Processing Facility, members of the STS-109 crew look over a piece of the equipment for their Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing mission. Seen are Payload Commander John Grunsfeld and Mission Specialists Richard Linnehan and Michael Massimino. Other crew members are Commander Scott Altman, Pilot Duane Carey and Mission Specialists Nancy Currie and James Newman. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
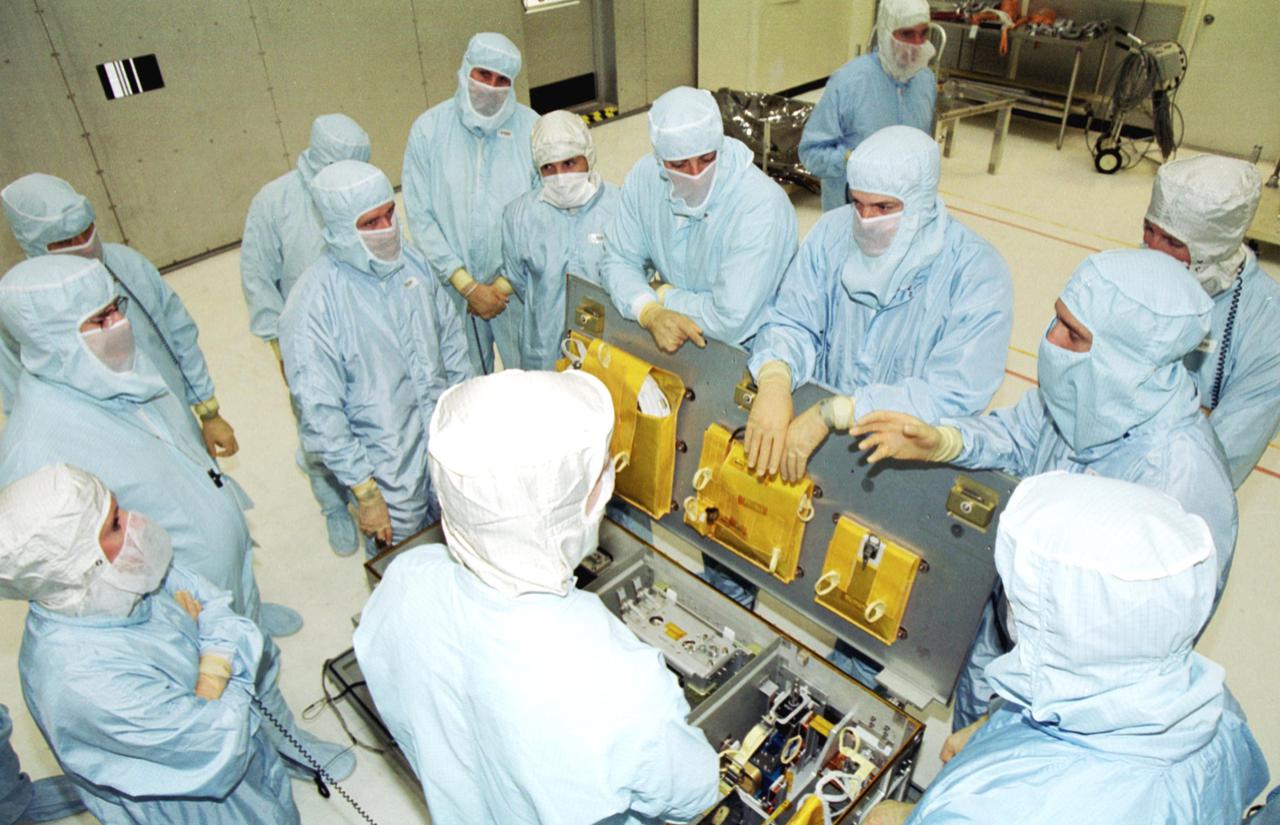

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - In the Vertical Processing Facility, members of the STS-109 crew listen to instructions about using some of the equipment for their Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing mission. At left are three trainers. The crew, whose faces can be seen, are (left to right) Payload Commander John Grunsfeld, Pilot Duane Carey, Mission Specialists Nancy Currie and Richard Linnehan, Commander Scott Altman, and Mission Specialists James Newman and Michael Massimino (behind Newman). The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
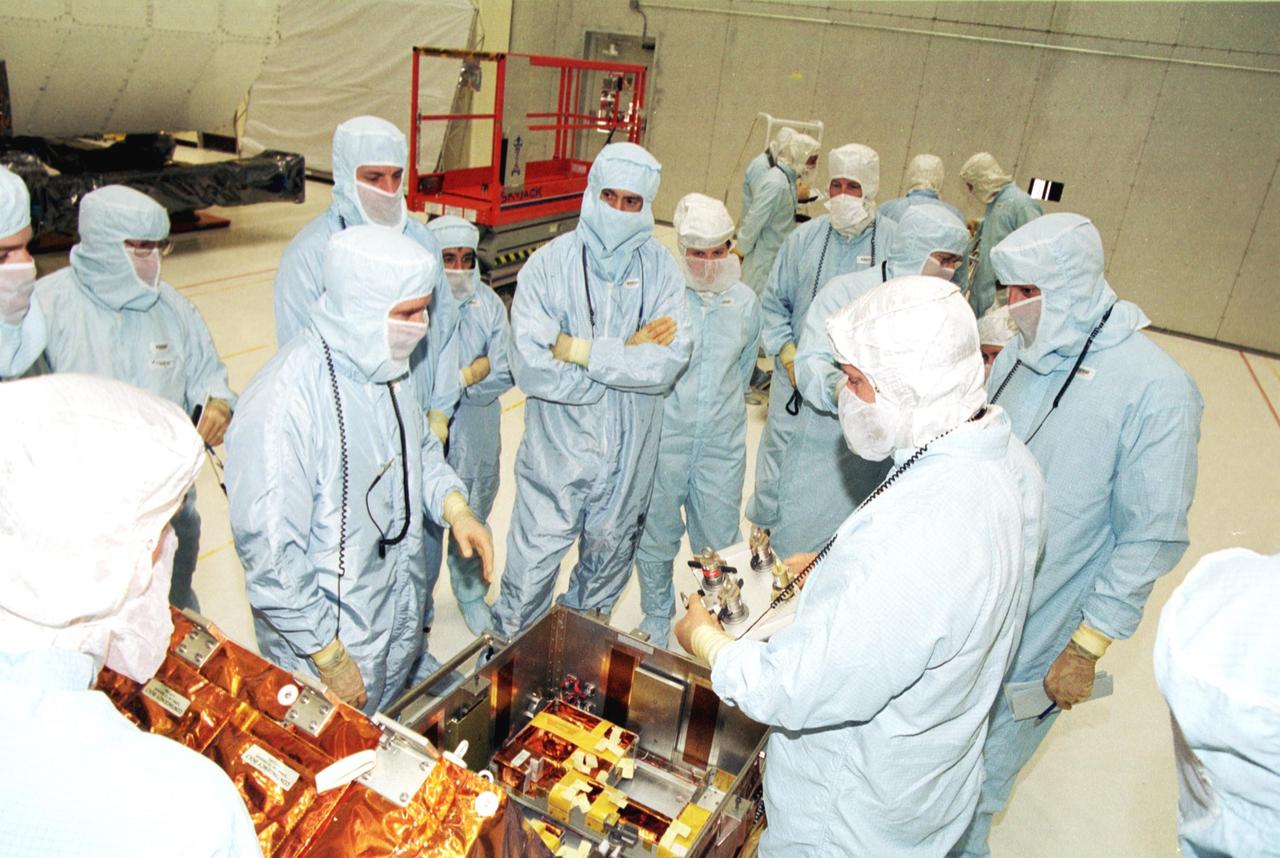

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - The STS-109 crew is in the Vertical Processing Facility to look over equipment for their Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing mission. The crew comprises Commander Scott Altman, Pilot Duane Carey, Payload Commander John Grunsfeld and Mission Specialists Nancy Currie, James Newman, Richard Linnehan and Michael Massimino. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
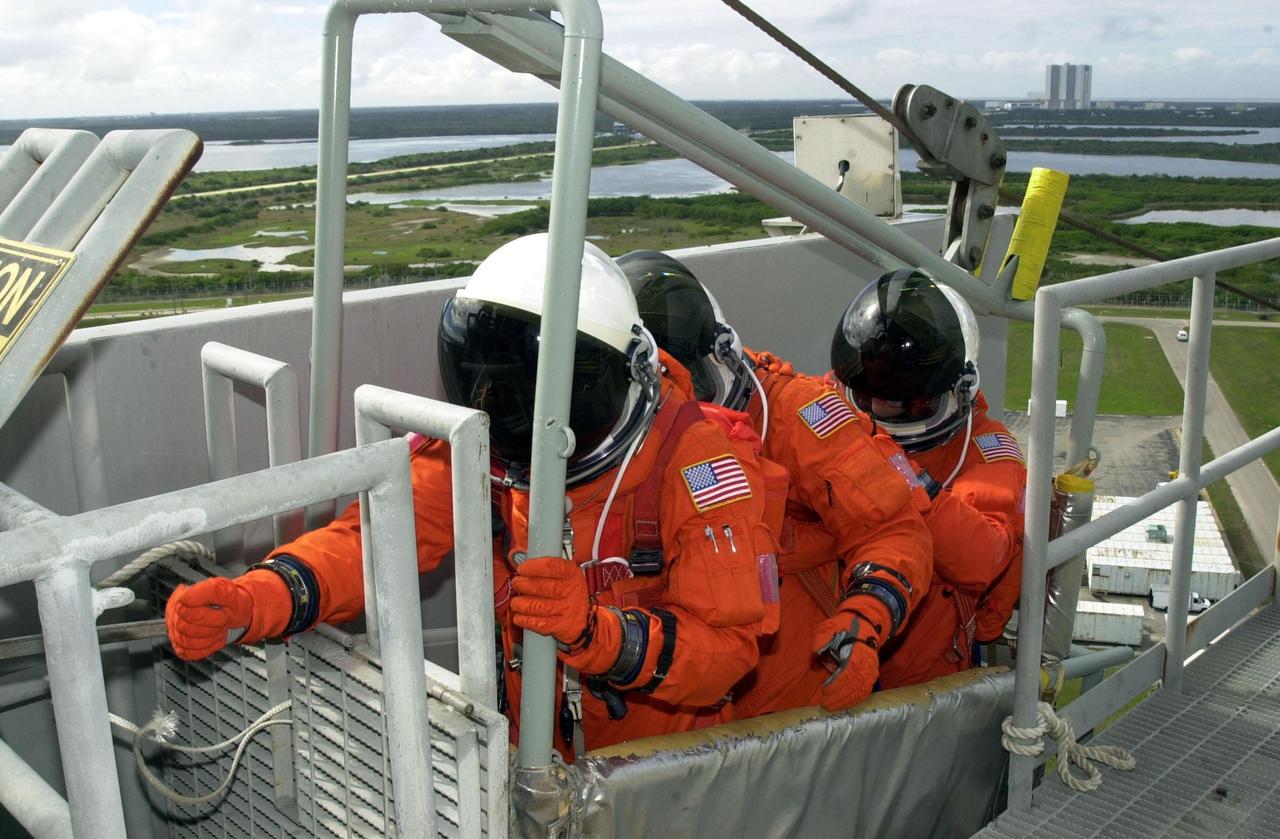

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- As part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, the STS-109 crew practices emergency exit from the Shuttle. Seated in the slidewire basket at the 195-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure are Mission Specialists Richard Linnehan (reaching for the release lever), Michael Massimino and James Newman. The TCDT also includes a simulated launch countdown. STS-109 is a Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, with goals to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. The 11-day mission will require five spacewalks to perform the tasks. Launch of STS-109 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002
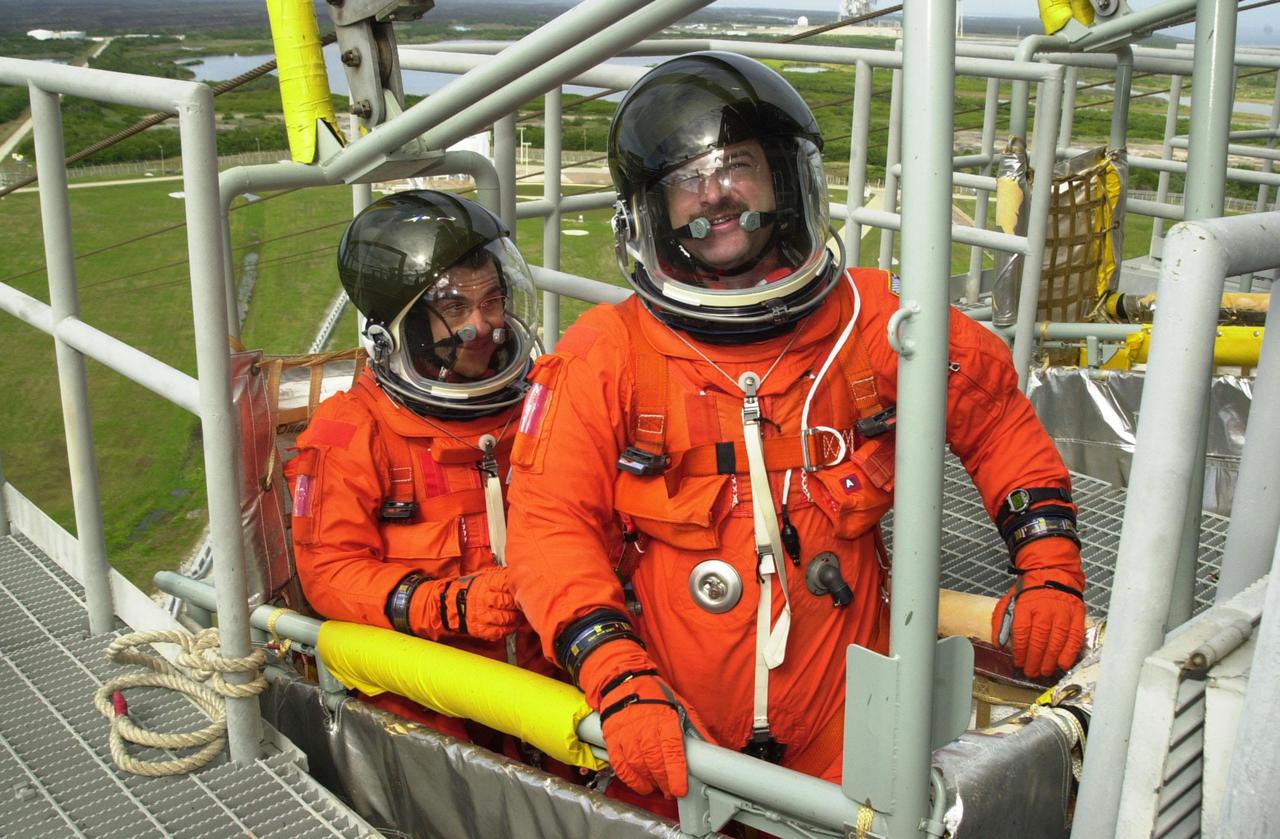

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- As part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, the STS-109 crew practices emergency exit from the Shuttle. Seated in the slidewire basket at the 195-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure are Pilot Duane Carey (left) and Commander Scott Altman (right). The TCDT also includes a simulated launch countdown. STS-109 is a Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, with goals to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. The 11-day mission will require five spacewalks to perform the tasks. Launch of STS-109 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002
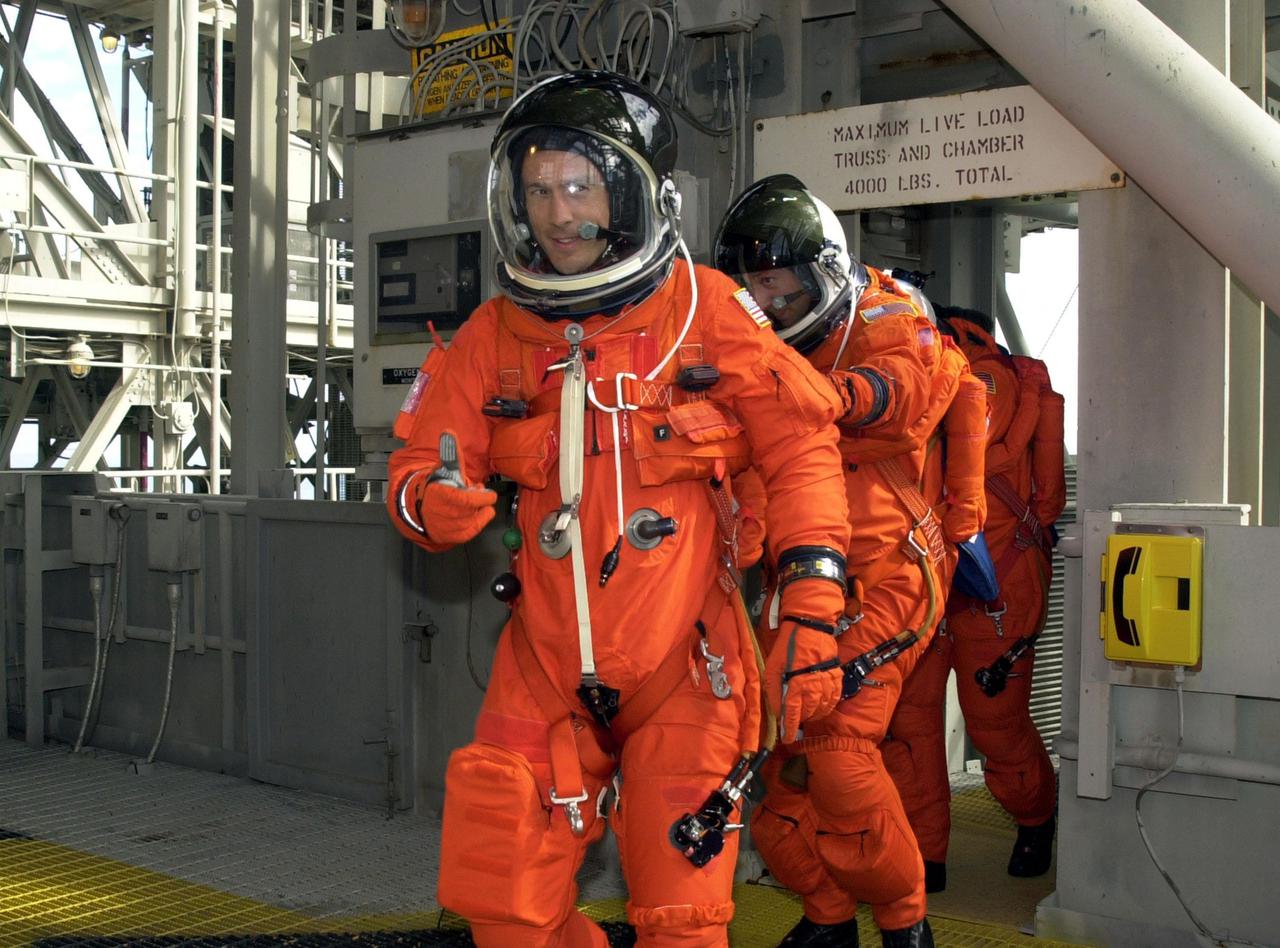

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- As part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, the STS-109 crew practices emergency exit from the Shuttle. Leading the way to the slidewire basket is Mission Specialist James Newman, followed by Michael Massimino and Richard Linnehan. The TCDT also includes a simulated launch countdown. STS-109 is a Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, with goals to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. The 11-day mission will require five spacewalks to perform the tasks. Launch of STS-109 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - On Launch Pad 39A, members of the STS-109 crew perform a final inspection of the Hubble payload they will deploy on orbit during five spacewalks. The crew comprises Commander Scott Altman, Pilot Duane Carey, Payload Commander John Grunsfeld, and Mission Specialists Nancy Currie, James Newman, Richrd Linnehan and Michael Massimino. The goal of the mission is to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Launch of Shuttle Columbia on mission STS-109 is scheduled for Feb. 28 at 6:48 a.m. EST
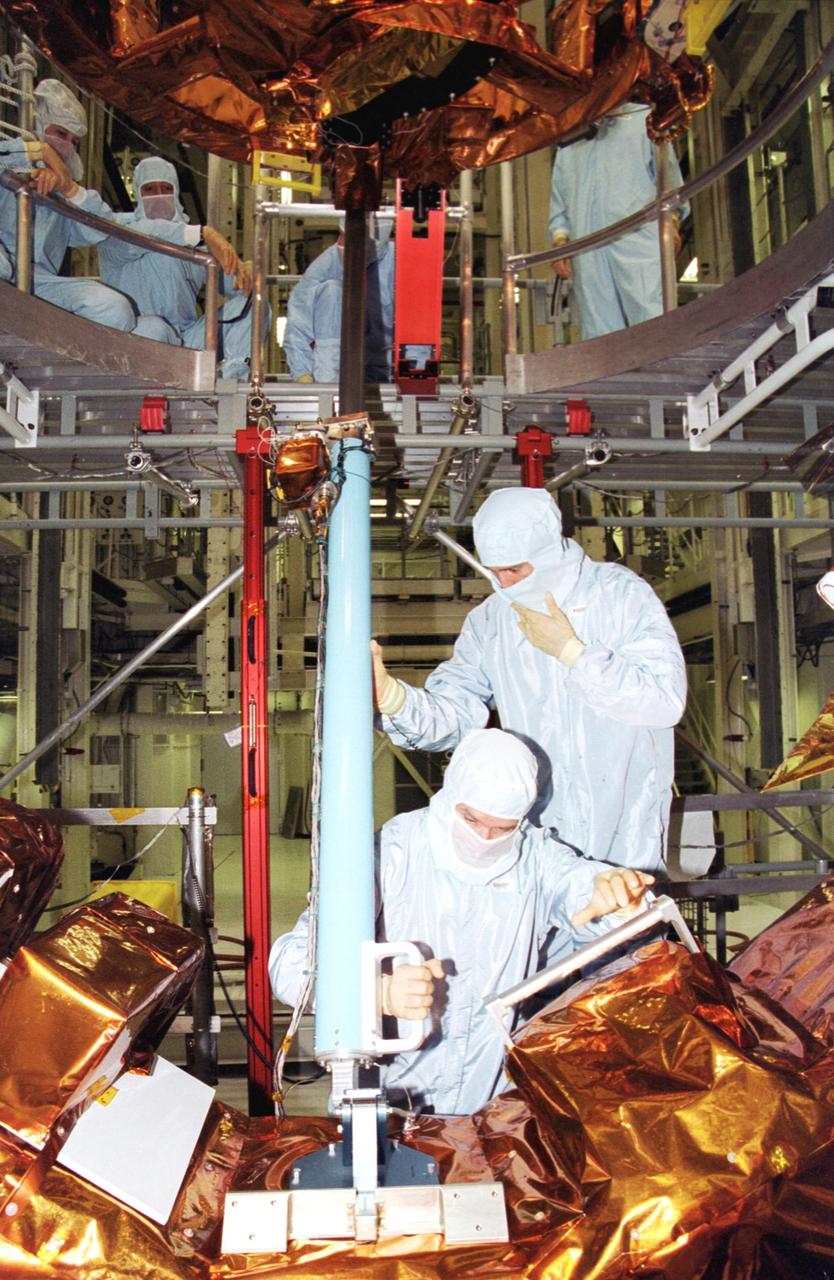

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - In the Vertical Processing Facility, members of the STS-109 crew practice on some of the equipment for their Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing mission. Seen in the foreground are (left) Payload Commander John Grunsfeld and (right) Mission Specialist James Newman. The rest of the crew are Commander Scott Altman, Pilot Duane Carey, and Mission Specialists Nancy Currie, Richard Linnehan and Michael Massimino. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
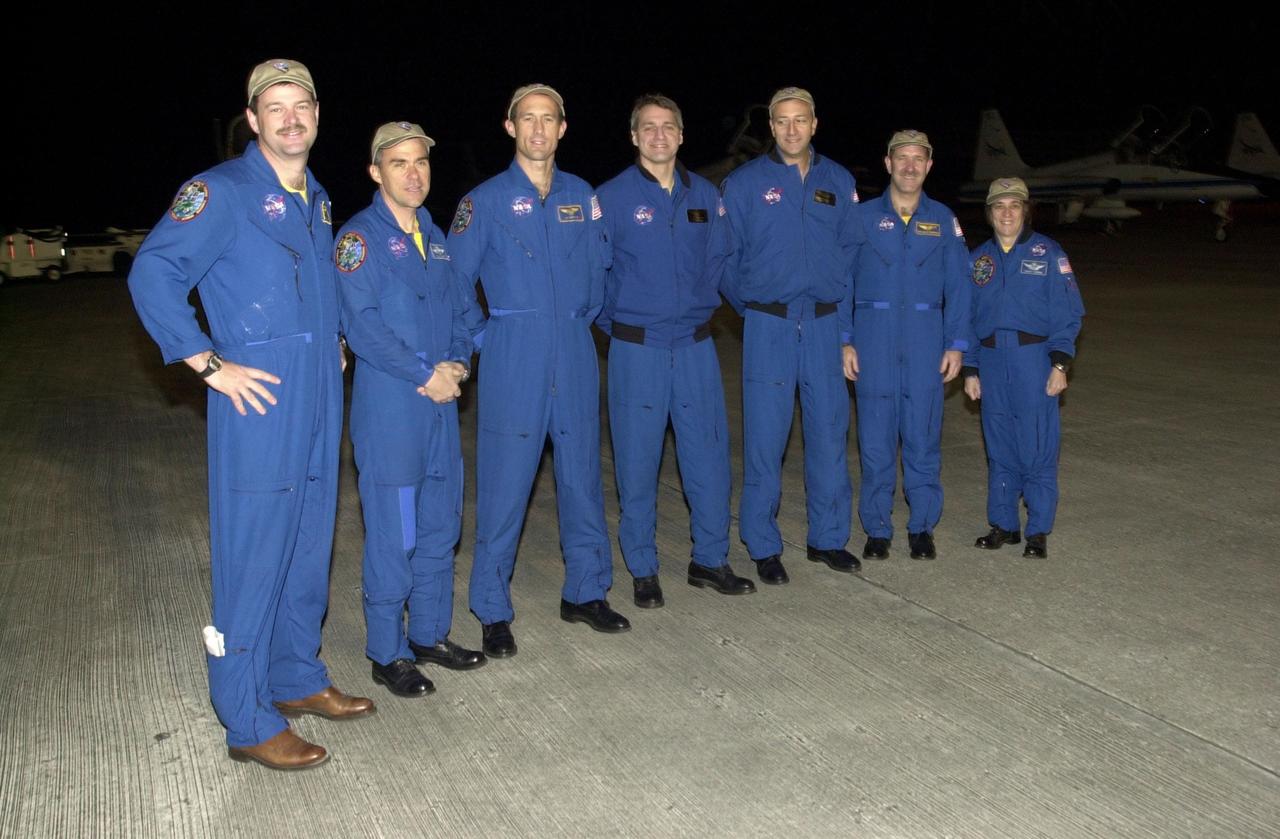

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - The STS-109 crew stops for a photograph after arriving at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft to begin launch preparations. Standing left to right are Commander Scott Altman, Pilot Duane Carey, and Mission Specialists James Newman, Richard Linnehan and Michael Massimino, Payload Commander John Grunsfeld, and Mission Specialist Nancy Currie. The goal of the 11-day mission is repair and maintenance on the Hubble Space Telescope. Five spacewalks are planned to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 28 at 6:48 a.m. EST
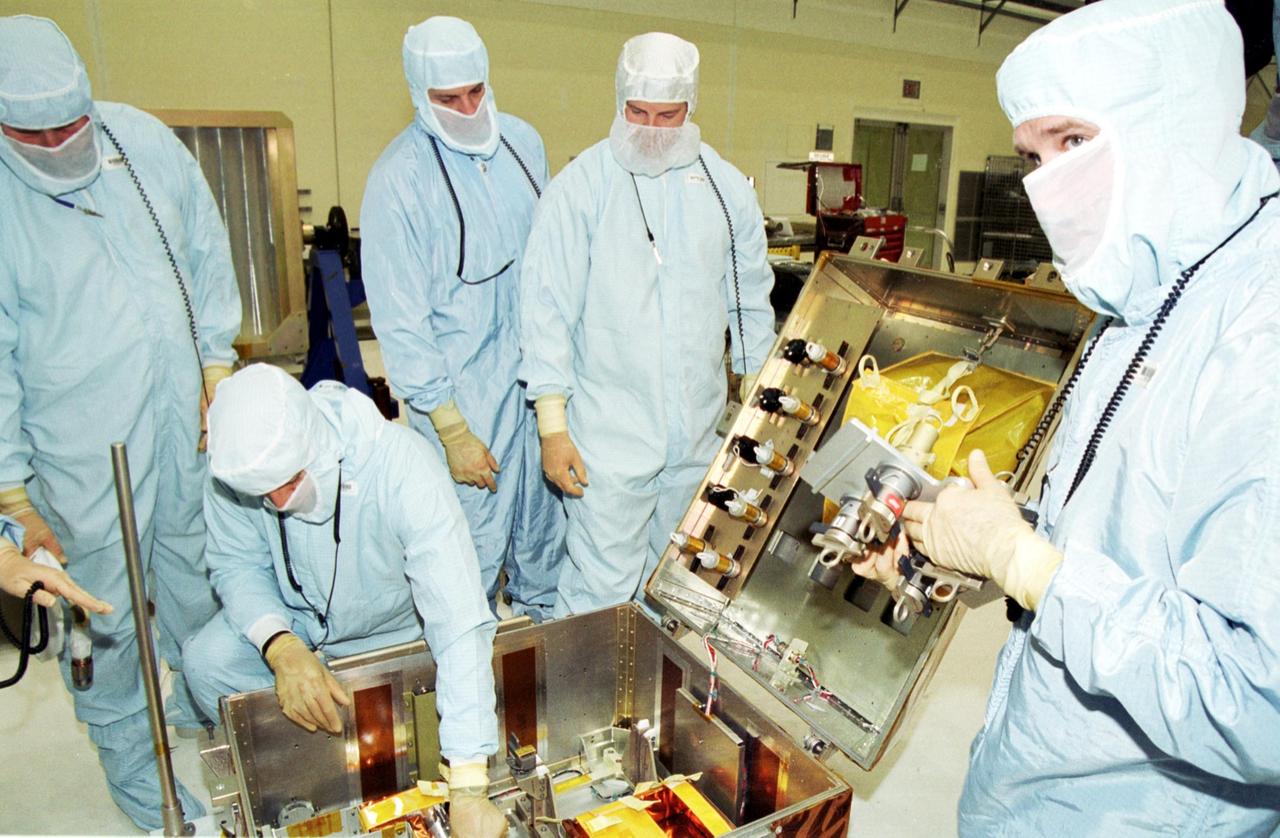

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Inside the Vertical Processing Facility, the STS-109 crew looks over equipment for their Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing mission. Seen are (starting second from left), Mission Specialists Michael Massimino and Richard Linnehan, Commander Scott Altman and Payload Commander John Grunsfeld. Other crew members are Pilot Duane Carey and Mission Spcialists Nancy Currie and James Newman. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
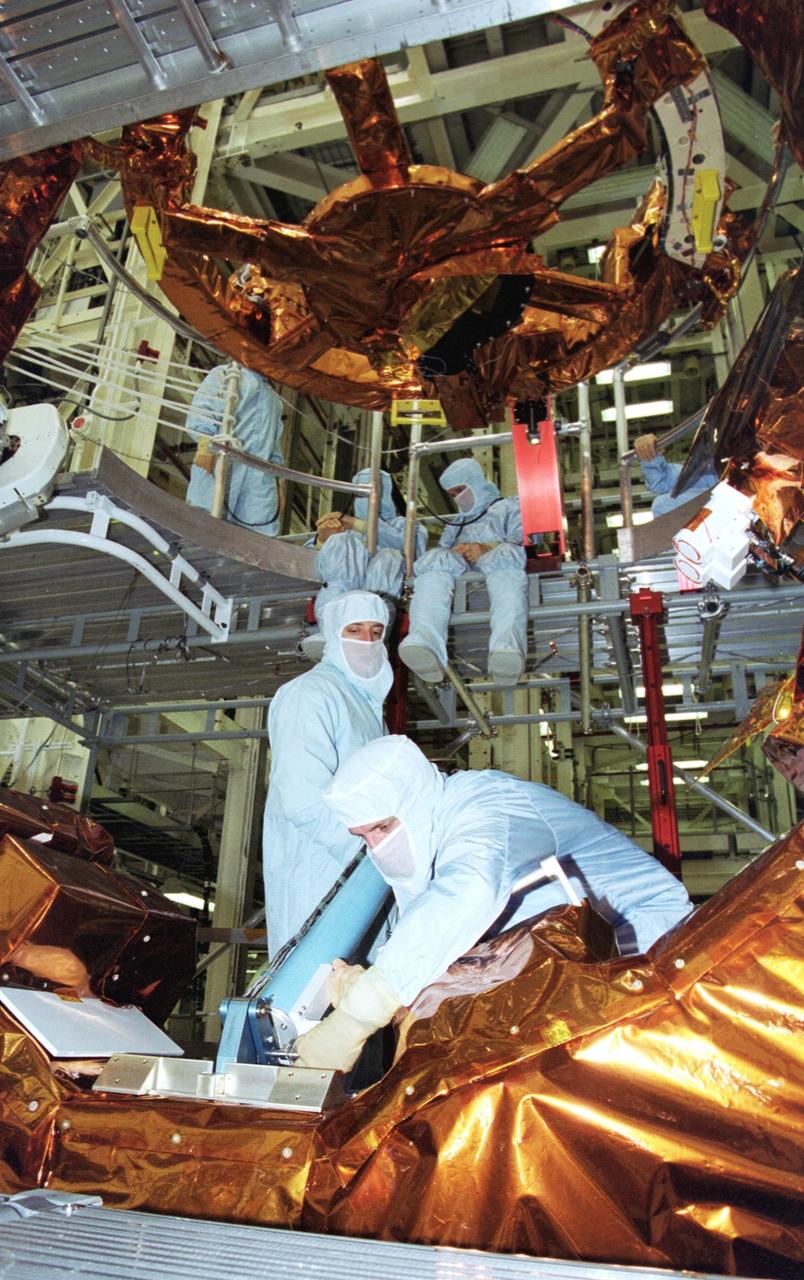

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - In the Vertical Processing Facility, members of the STS-109 crew practice using some of the equipment for their Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing mission. Seen in the foreground are Mission Specialists Michael Massimino (standing) and Richard Linnehan (bending over). The rest of the crew members are Commander Scott Altman, Pilot Duane Carey, Payload Commander John Grunsfeld and Mission Specialists Nancy Currie and James Newman. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
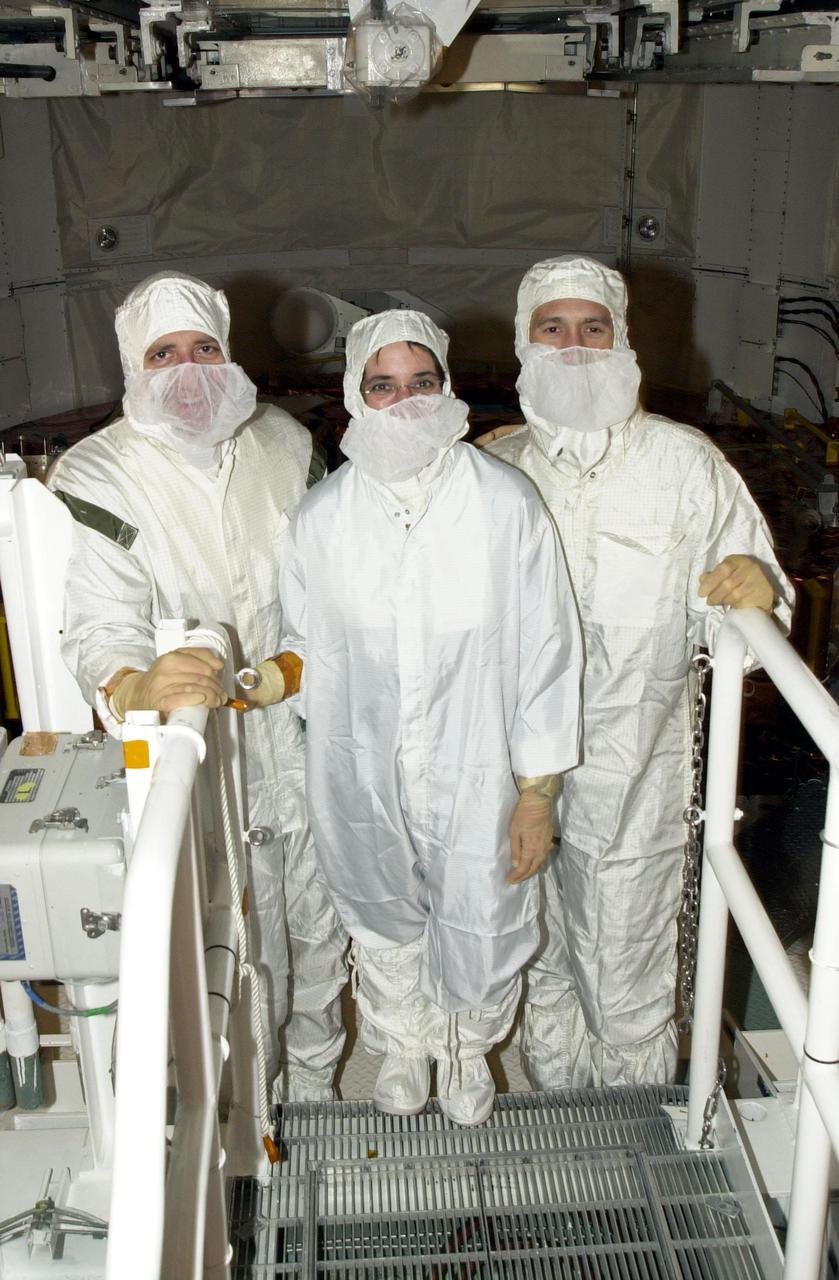

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - On Launch Pad 39A, members of the STS-109 crew pause during their final inspection of the Hubble payload they will deploy on orbit during five spacewalks. Seen here (left to right) are Mission Specialists Michael Massimino, Nancy Currie and James Newman. The crew also comprises Commander Scott Altman, Pilot Duane Carey, Payload Commander John Grunsfeld, and Mission Specialist Richard Linnehan. The goal of the mission is to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Launch of Shuttle Columbia on mission STS-109 is scheduled for Feb. 28 at 6:48 a.m. EST
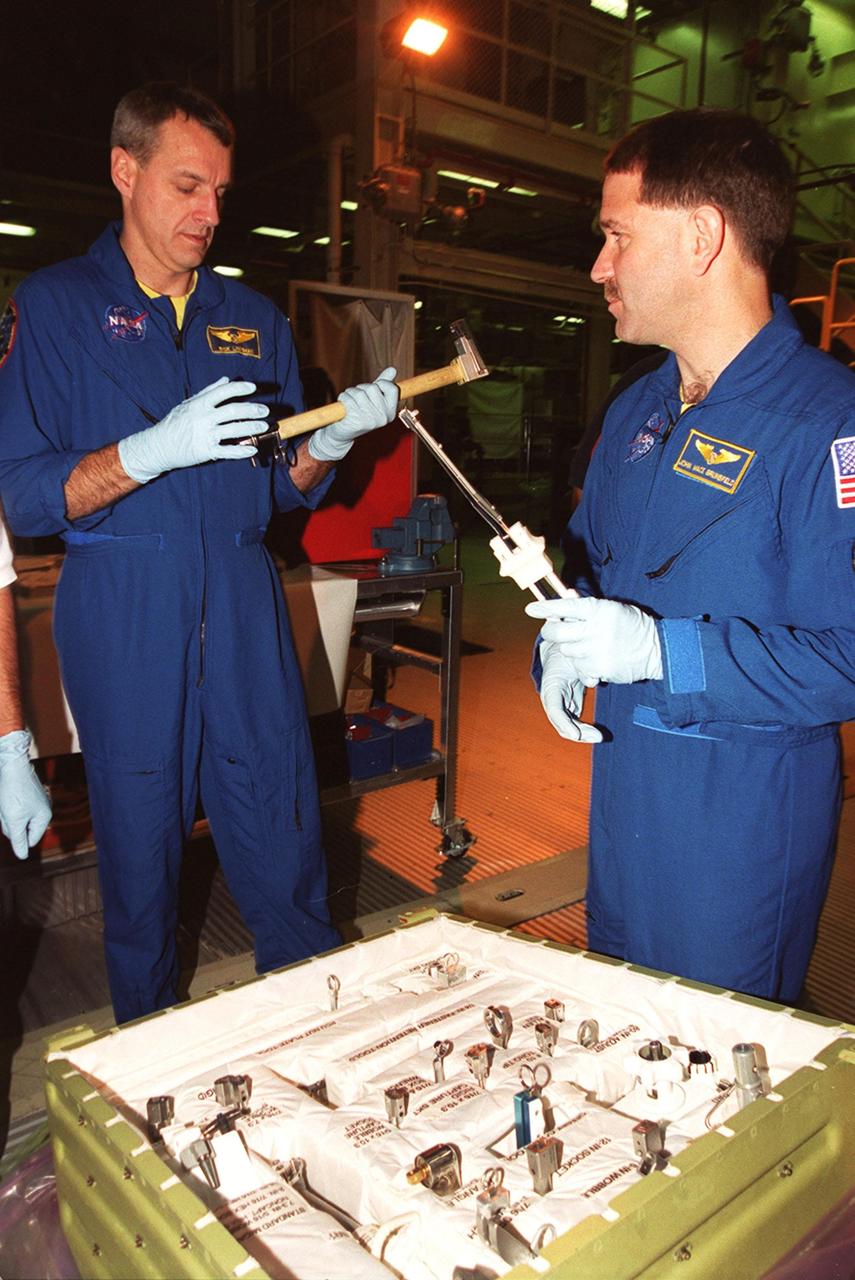

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - STS-109 Mission Specialist Richard Lennehan (left) and Payload Commander John Grunsfeld get a feel for tools and equipment that will be used on the mission. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities that include familiarization with the orbiter and equipment. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
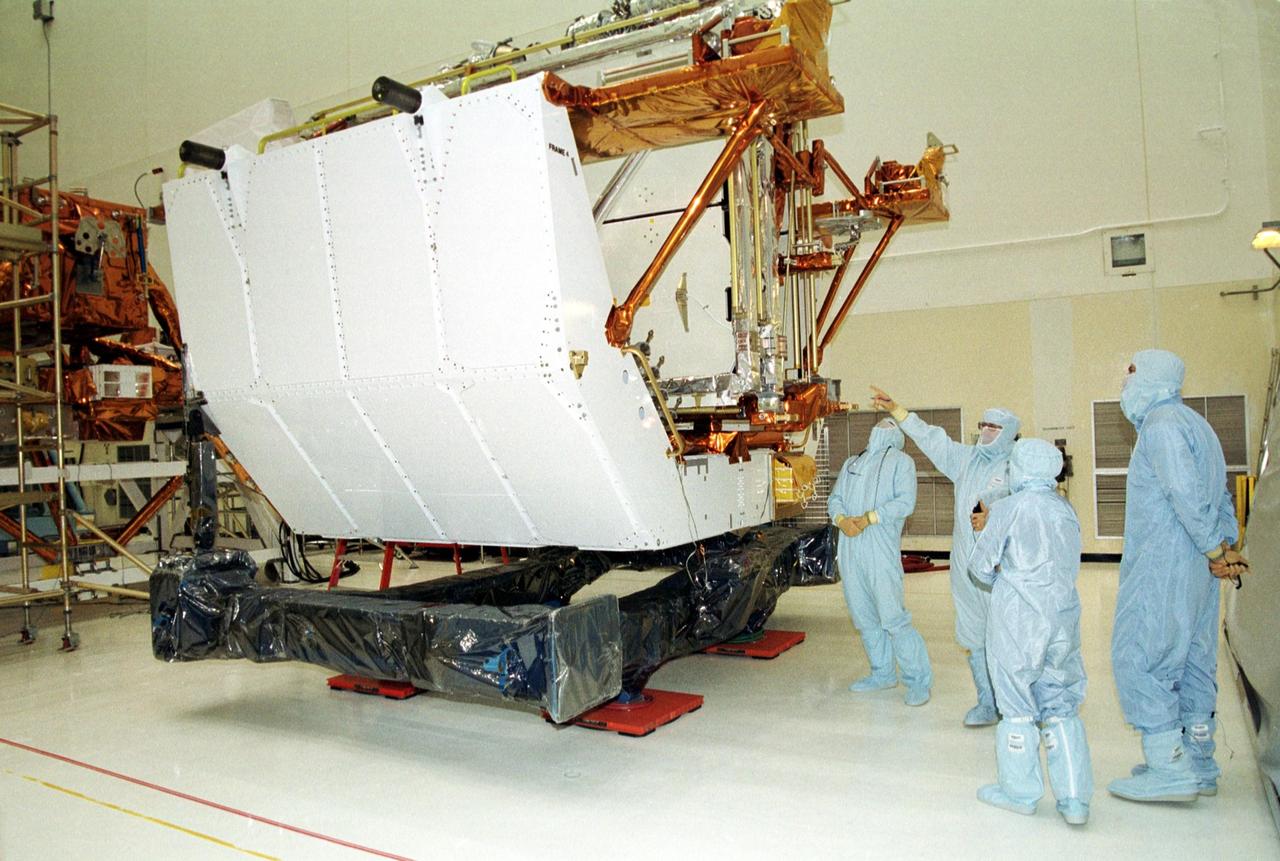

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, members of the STS-109 crew look over the Solar Array 3 panels that will be replacing Solar Array 2 panels on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Trainers, at left, point to the panels while Mission Specialist Nancy Currie (second from right) and Commander Scott Altman (far right) look on. Other crew members are Pilot Duane Carey, Payload Commander John Grunsfeld and Mission Specialists James Newman, Richard Linnehan and Michael Massimino. The other goals of the mission are replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
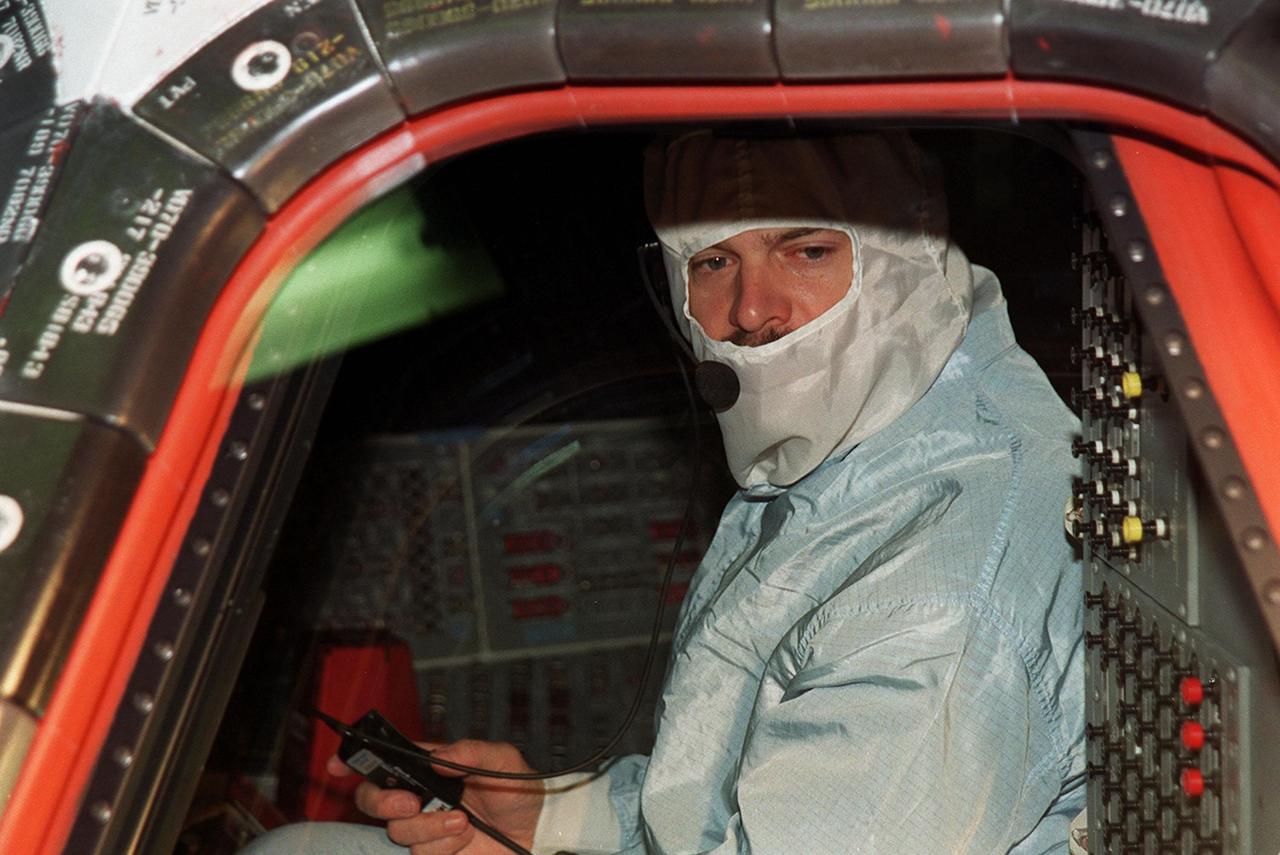

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-109 Commander Scott Altman checks the windshield and windows from inside Columbia. He and the crew are at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities that include familiarization with the orbiter and equipment. STS-109 is the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing mission. The crew also comprises Pilot Duane Carey, Payload Commander John Grunsfeld and Mission Specialists Nancy Currie, James Newman, Richard Linnehan and Michael Massimino. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
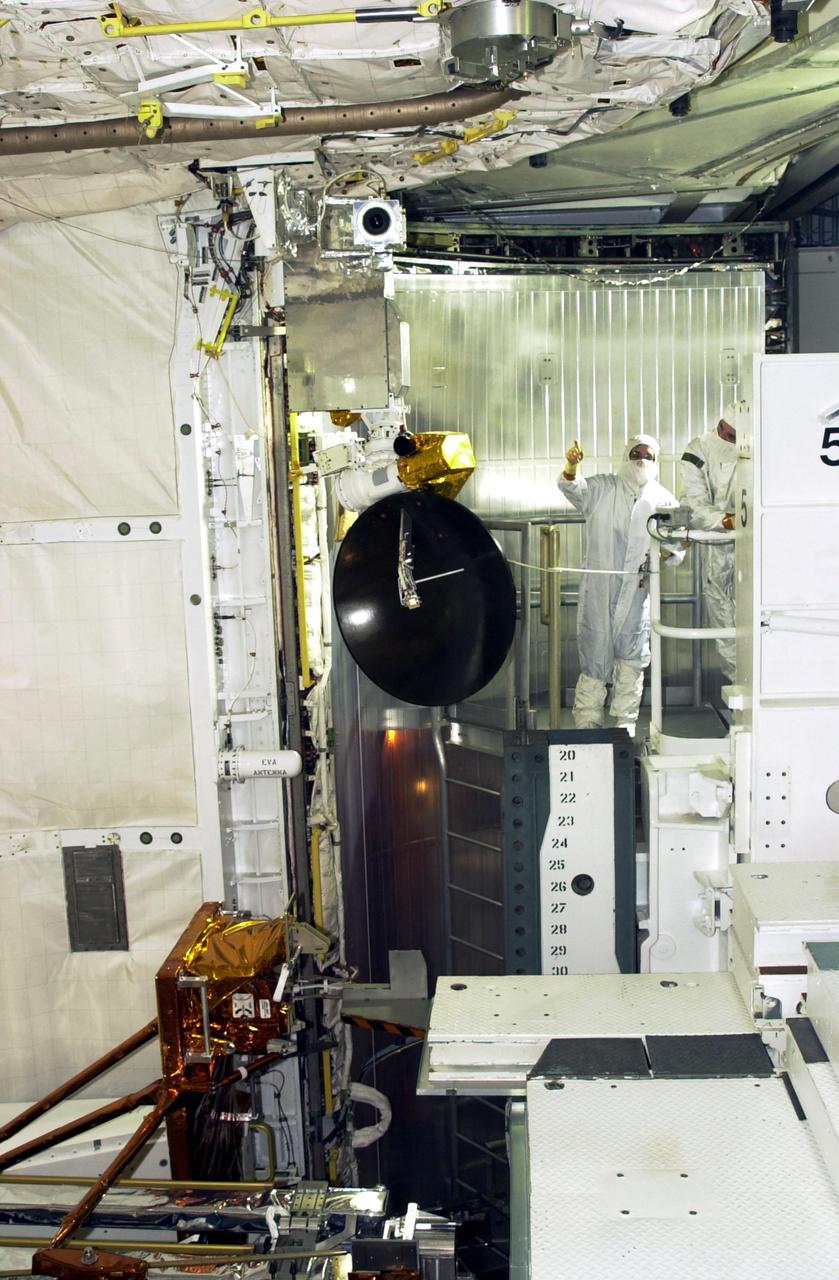

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39A, members of the STS-109 crew perform a final inspection of the Hubble payload they will deploy on orbit during five spacewalks. Mission Specialist Nancy Currie is seen pointing at a piece of the equipment. Other crew members are Commander Scott Altman, Pilot Duane Carey, Payload Commander John Grunsfeld, and Mission Specialists James Newman, Richrd Linnehan and Michael Massimino. The goal of the mission is to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Launch of Shuttle Columbia on mission STS-109 is scheduled for Feb. 28 at 6:48 a.m. EST
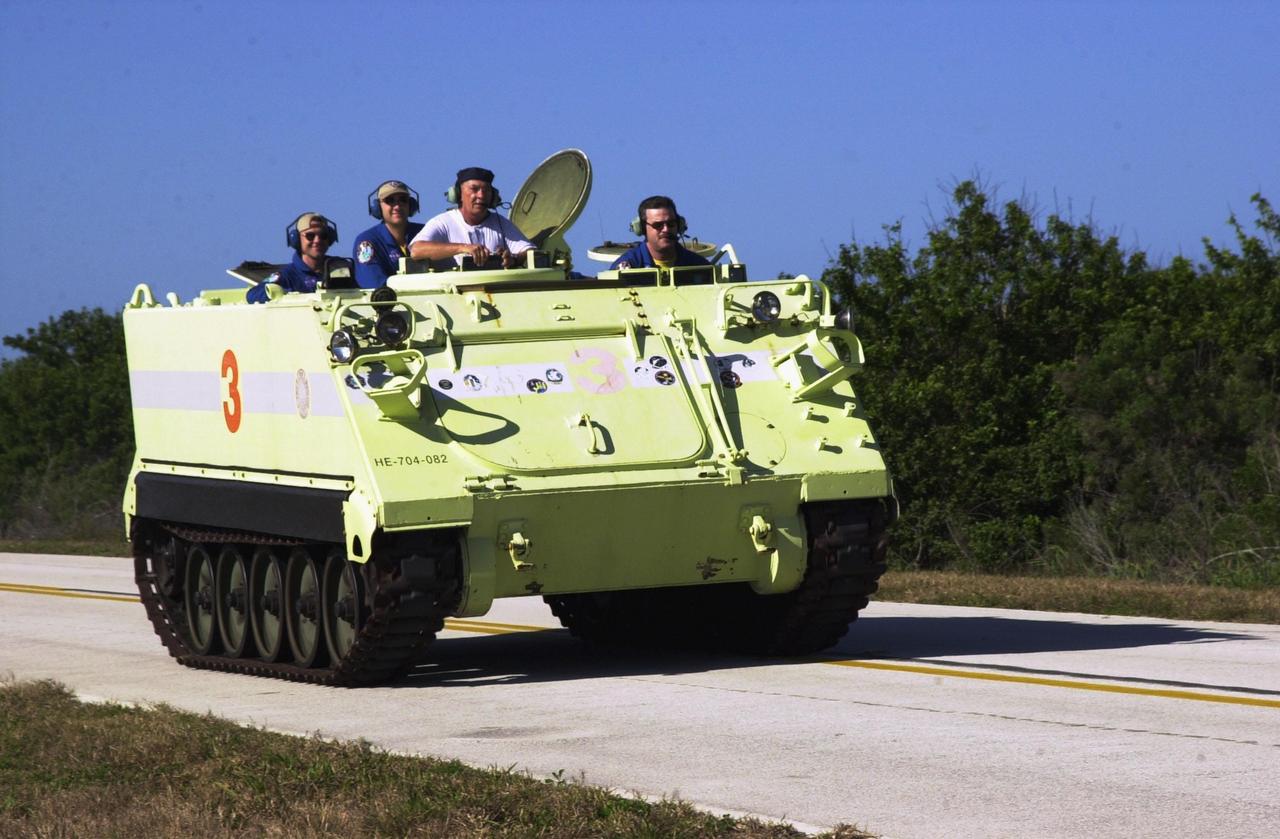

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-109 Commander Scott Altman drives the M-113 armored personnel carrier during emergency egress training at the launch pad. He and other crew members are taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which also include a simulated launch countdown. STS-109 is a Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, with goals to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. The 11-day mission will require grasping the satellite with a robotic arm in order for the crew to perform the tasks during five spacewalks. Launch of STS-109 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002
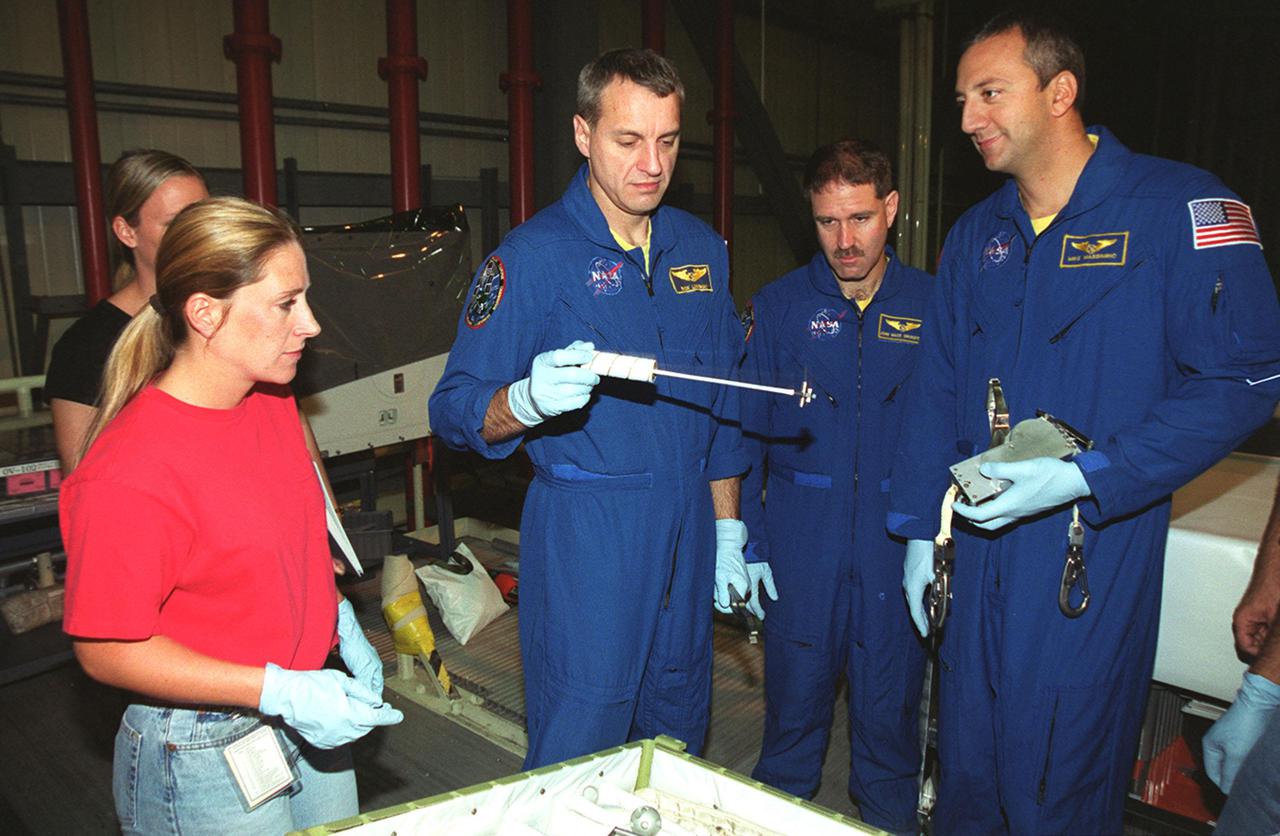

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - In the company of two technicians (left), STS-109 crew members look over equipment related to their mission. Holding the equipment is Mission Specialist Richard Linnehan (left); at center is Payload Commander John Grunsfeld; at right is Mission Specialist Michael Massimino. STS-109, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing mission, is Massimino's first Shuttle flight. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities that include familiarization with the orbiter and equipment. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
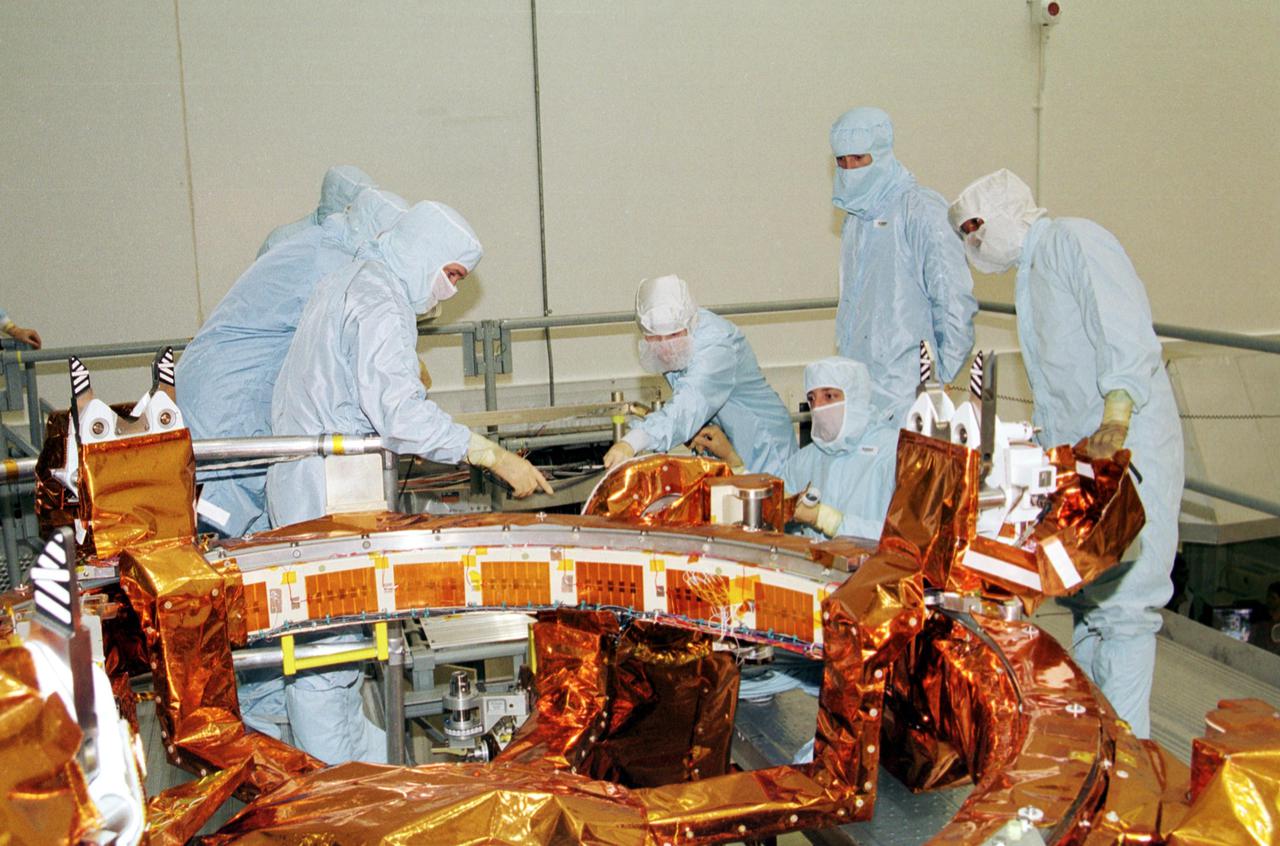

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Inside the Vertical Processing Facility, the STS-109 crew checks out part of the equipment for their Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing mission. The crew comprises Commander Scott altman, Pilot Duane Carey, Payload Commander John Grunsfeld and Mission Specialists Nancy Currie, James Newman, Richard Linnehan and Michael Massimino. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
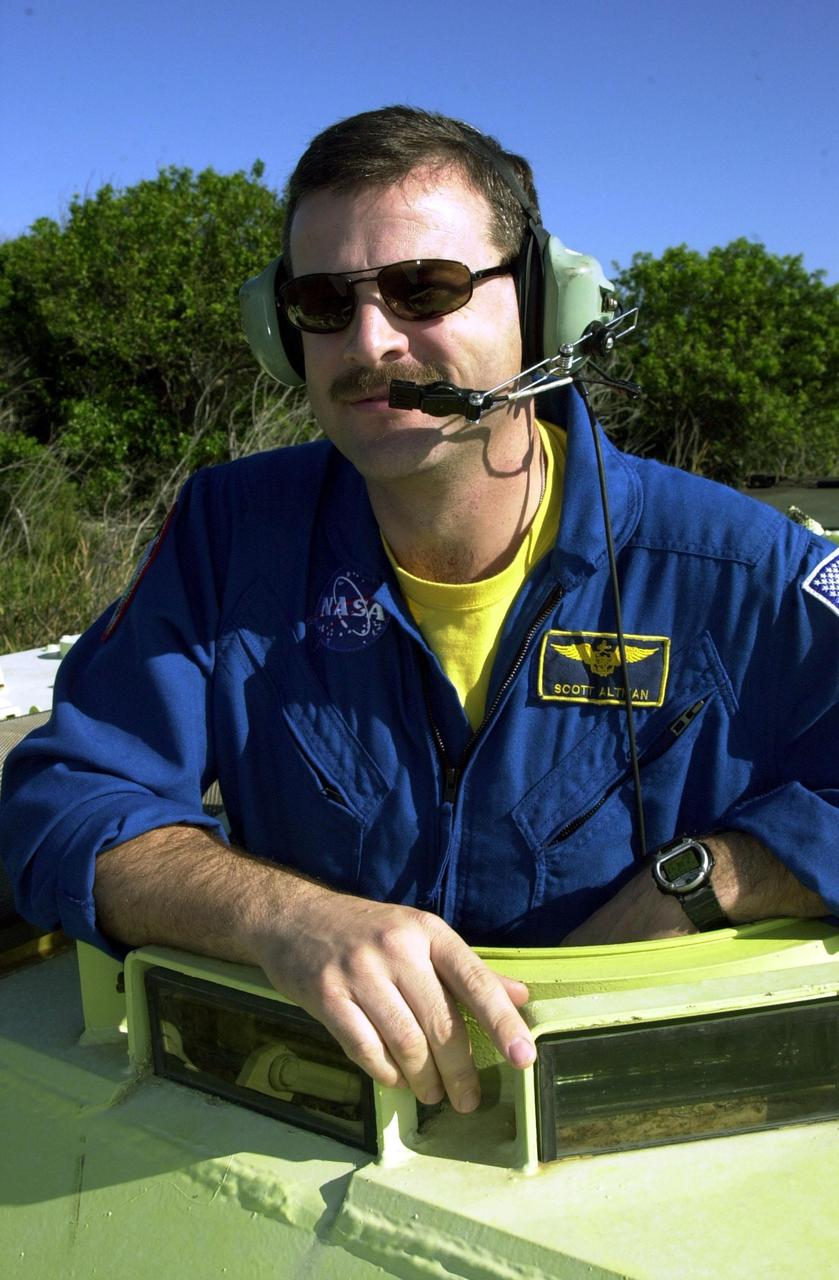

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-109 Commander Scott Altman is ready to practice driving the M-113 armored personnel carrier, part of emergency egress training at the launch pad. He and other crew members are taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which also include a simulated launch countdown. STS-109 is a Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, with goals to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. The 11-day mission will require grasping the satellite with a robotic arm in order for the crew to perform the tasks during five spacewalks. Launch of STS-109 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002
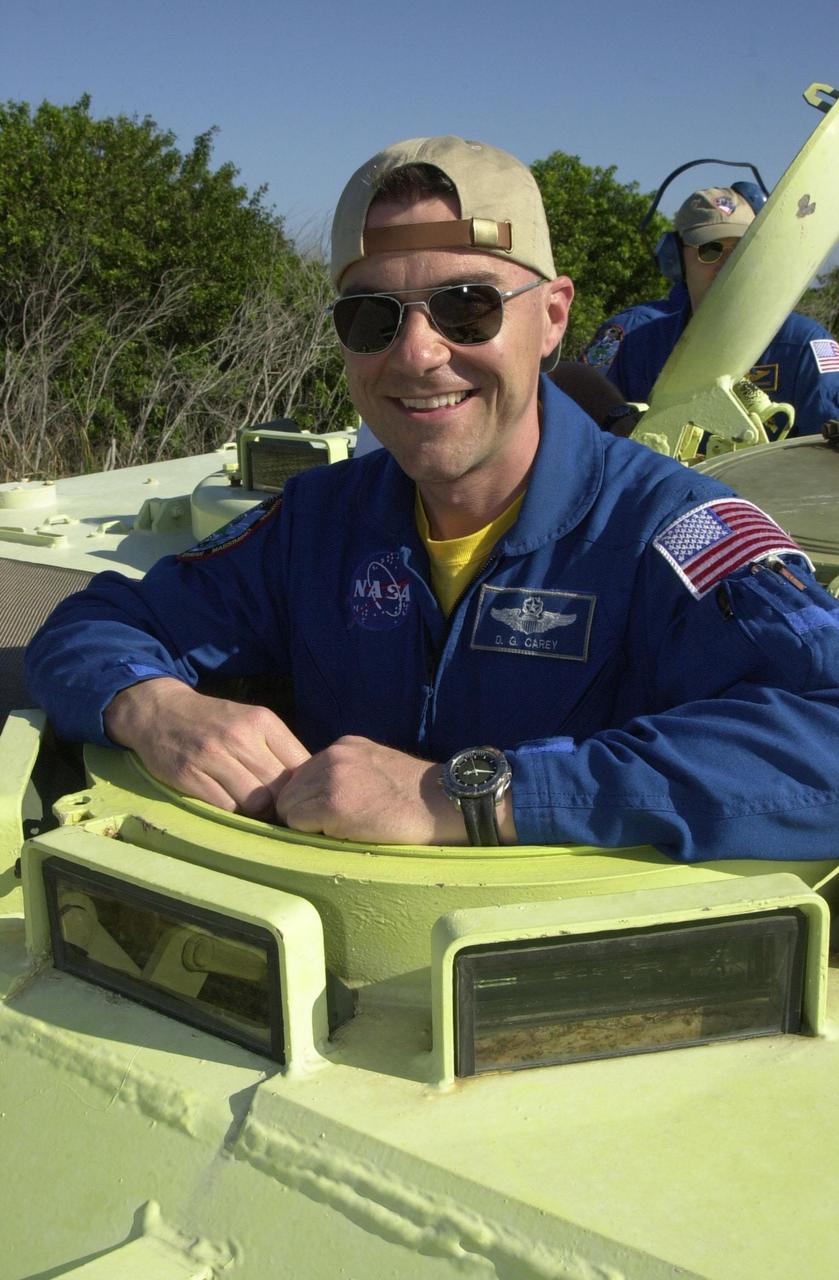

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-109 Pilot Duane Carey is ready to practice driving the M-113 armored personnel carrier, part of emergency egress training at the launch pad. He and other crew members are taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which also include a simulated launch countdown. STS-109 is a Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, with goals to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. The 11-day mission will require grasping the satellite with a robotic arm in order for the crew to perform the tasks during five spacewalks. Launch of STS-109 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002
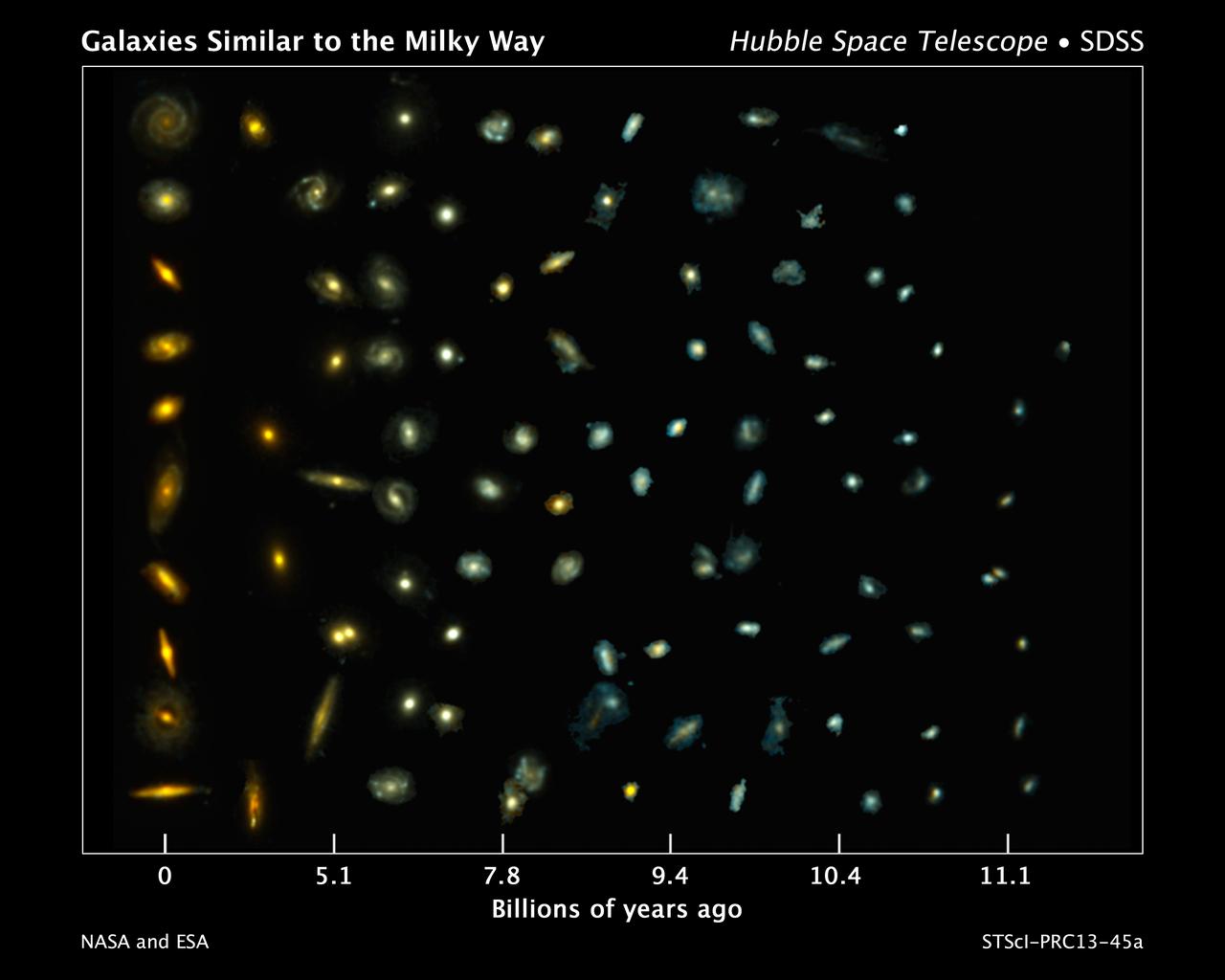
This composite image shows examples of galaxies similar to our Milky Way at various stages of construction over a time span of 11 billion years. The galaxies are arranged according to time. Those on the left reside nearby; those at far right existed when the cosmos was about 2 billion years old. The bluish glow from young stars dominates the color of the galaxies on the right. The galaxies at left are redder from the glow of older stellar populations. Astronomers found the distant galaxies in two Hubble Space Telescope surveys: 3D-HST and the Cosmic Assembly Near-infrared Deep Extragalactic Legacy Survey, or CANDELS. The observations were made in visible and near-infrared light by Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 and Advanced Camera for Surveys. The nearby galaxies were taken from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. This image traces Milky Way-like galaxies over most of cosmic history, revealing how they evolve over time. Hubble's sharp vision resolved the galaxies' shapes, showing that their bulges and disks grew simultaneously. Credit: NASA, ESA, P. van Dokkum (Yale University), S. Patel (Leiden University), and the 3D-HST Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
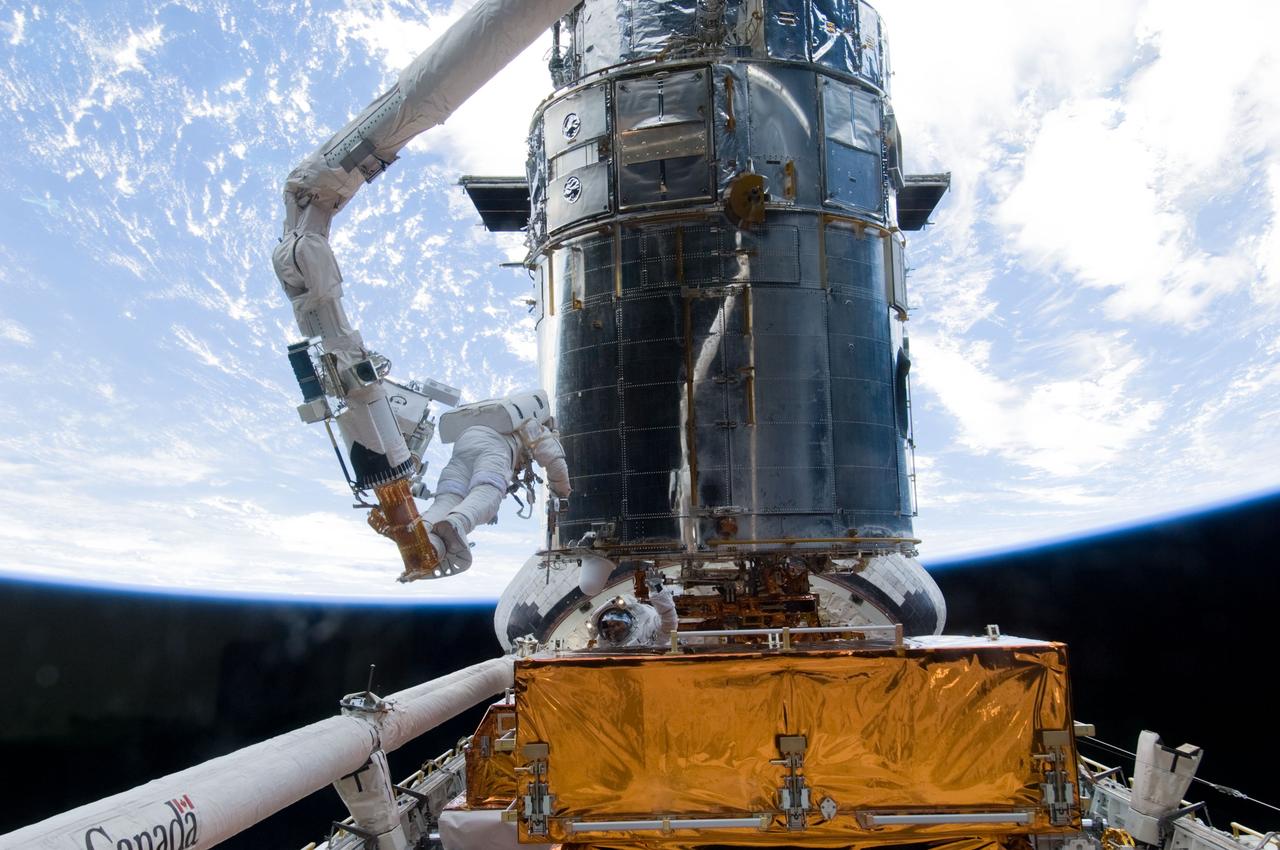

S125-E-008007 (16 May 2009) --- Astronauts Andrew Feustel and John Grunsfeld (partially obscured at bottom), both STS-125 mission specialists, participate in the mission?s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as work continues to refurbish and upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope. During the six-hour, 36-minute spacewalk, Grunsfeld and Feustel removed the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement and installed in its place the new Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. They also completed the Advanced Camera for Surveys electronic card replacement work, and completed part 2 of the ACS repair, installing a new electronics box and cable.
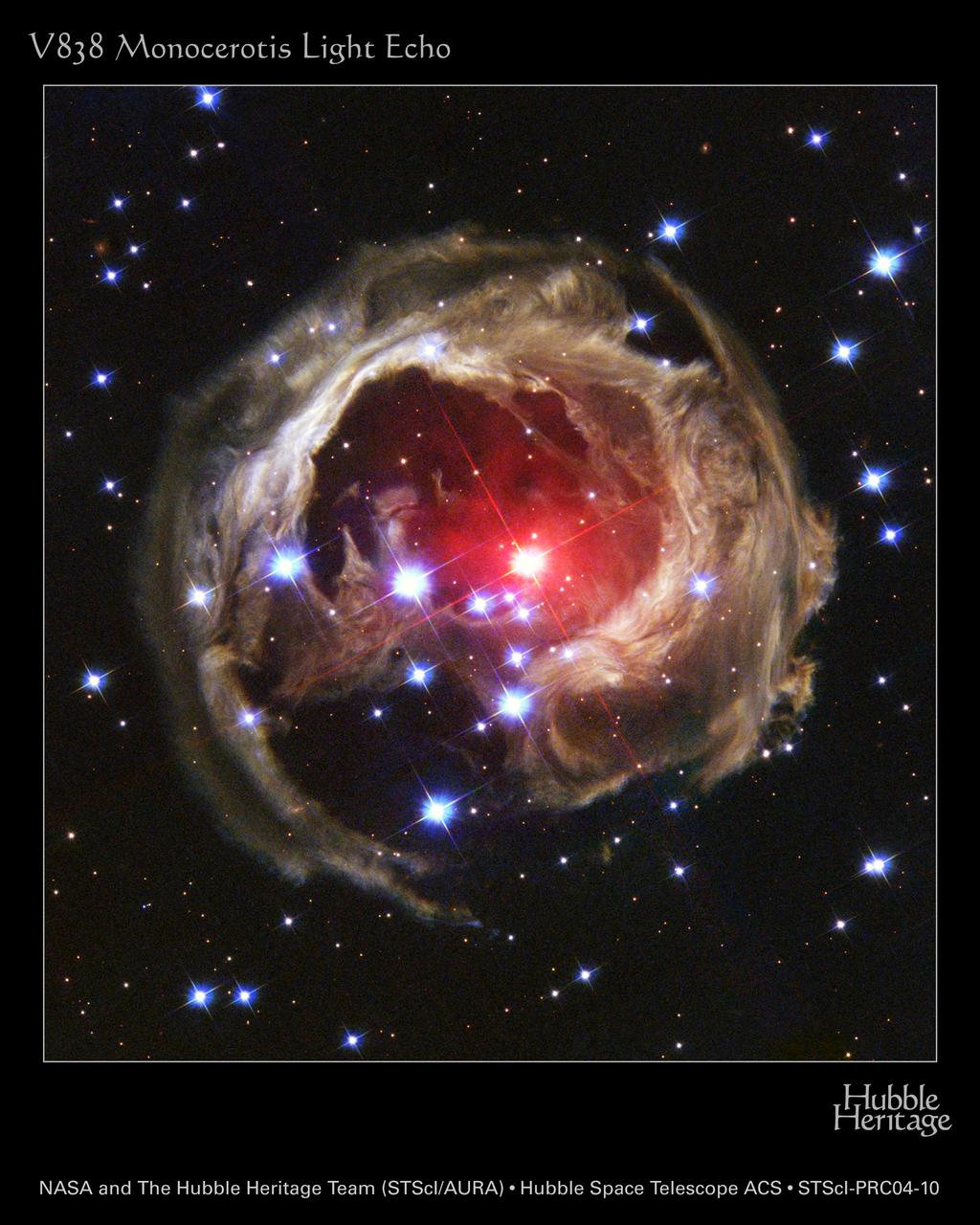

This photo, captured by the NASA Hubble Space Telescope's (HST) Advanced Camera for Surveys, is Hubble's latest view of an expanding halo of light around the distant star V838 Monocerotis, or V Mon, caused by an unusual stellar outburst that occurred back in January 2002. A burst of light from the bizarre star is spreading into space and reflecting off of surrounding circumstellar dust. As different parts are sequentially illuminated, the appearance of the dust changes. This effect is referred to as a "light echo". Located about 20,000 light-years away in the winter constellation Monoceros (the Unicorn), the star brightened to more than 600,000 times our Sun's luminosity. The light echo gives the illusion of contracting, until it finally disappears by the end of the decade.
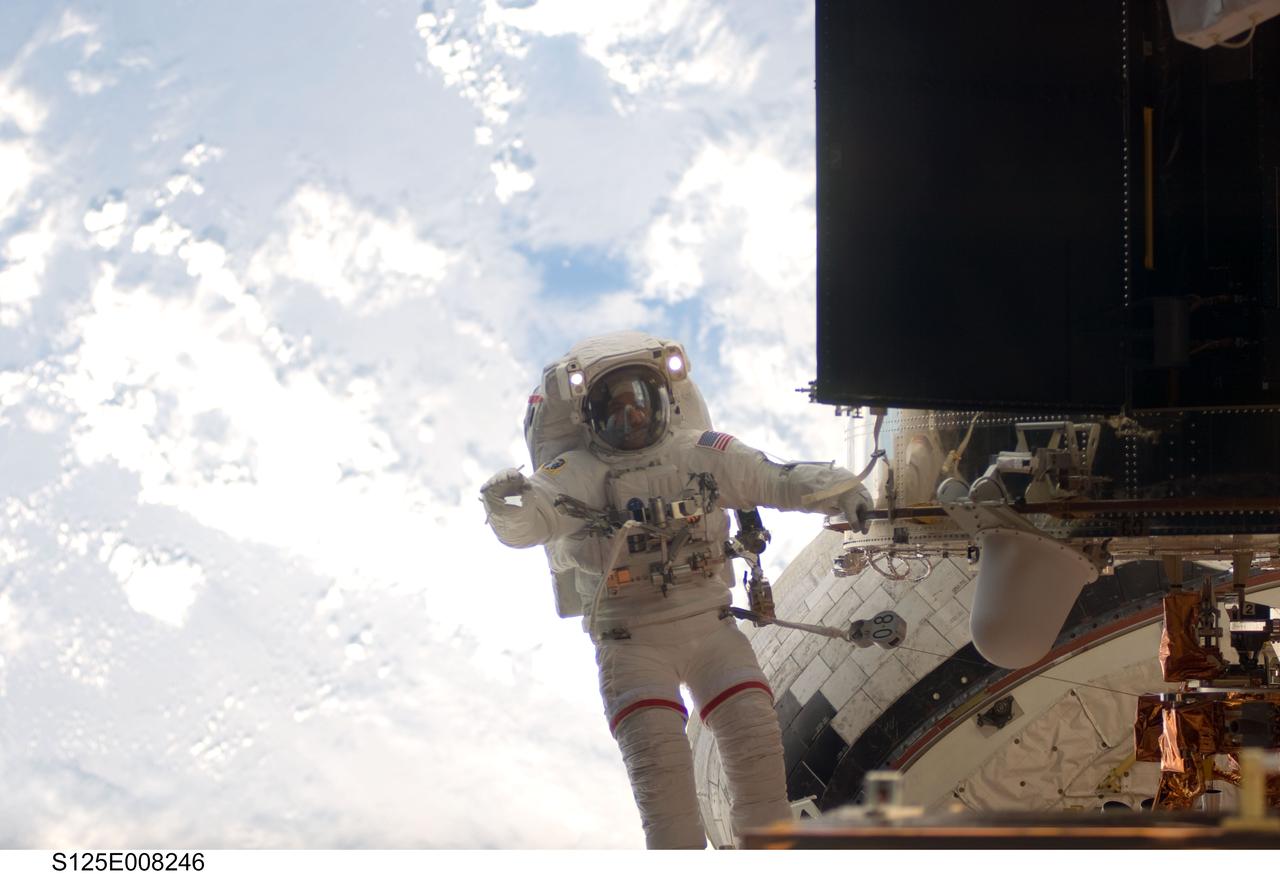

S125-E-008246 (16 May 2009) --- Astronaut John Grunsfeld, STS-125 mission specialist, participates in the mission?s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as work continues to refurbish and upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope. During the six-hour, 36-minute spacewalk, Grunsfeld and astronaut Andrew Feustel (out of frame), mission specialist, removed the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement and installed in its place the new Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. They also completed the Advanced Camera for Surveys electronic card replacement work, and completed part 2 of the ACS repair, installing a new electronics box and cable.
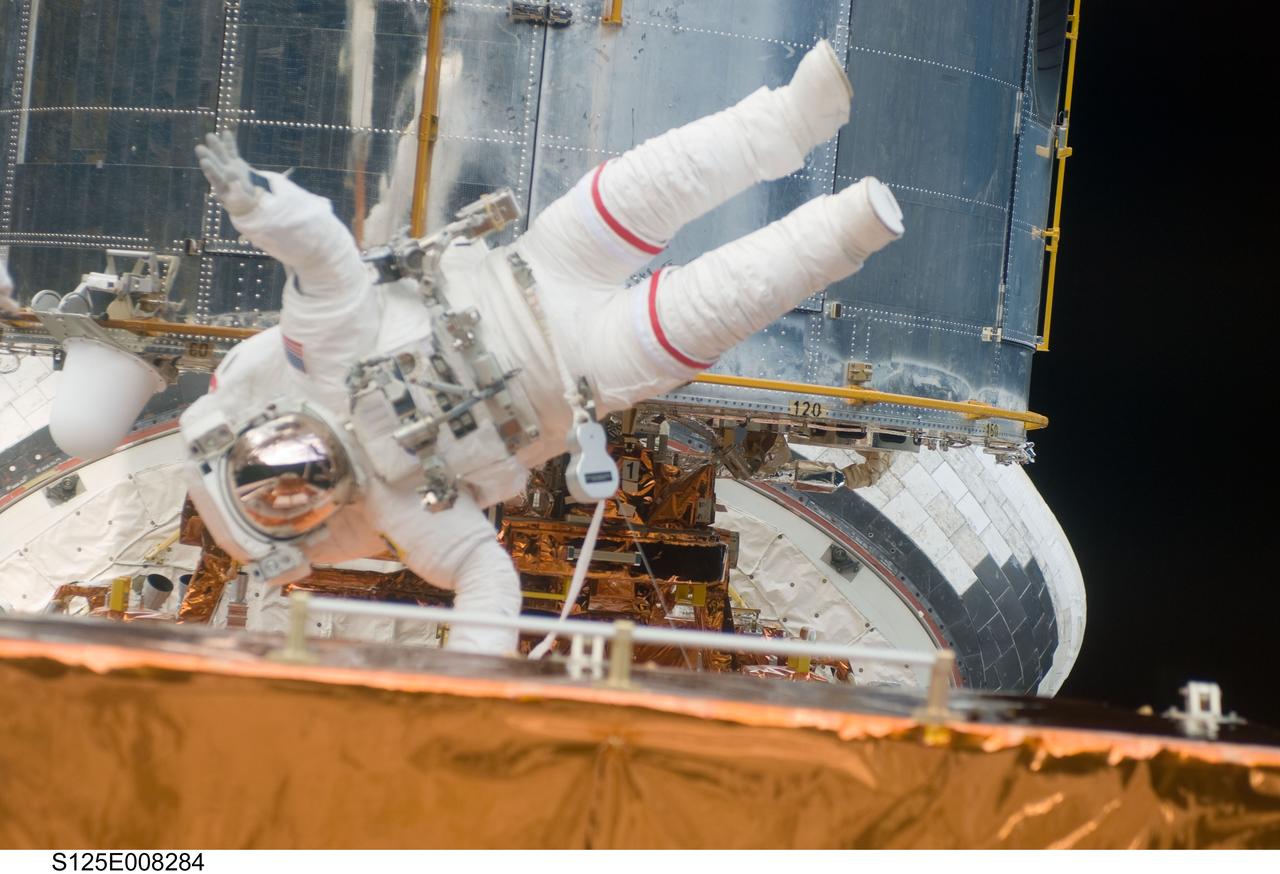

S125-E-008284 (16 May 2009) --- Astronaut John Grunsfeld, STS-125 mission specialist, participates in the mission?s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as work continues to refurbish and upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope. During the six-hour, 36-minute spacewalk, Grunsfeld and astronaut Andrew Feustel (out of frame), mission specialist, removed the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement and installed in its place the new Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. They also completed the Advanced Camera for Surveys electronic card replacement work, and completed part 2 of the ACS repair, installing a new electronics box and cable.
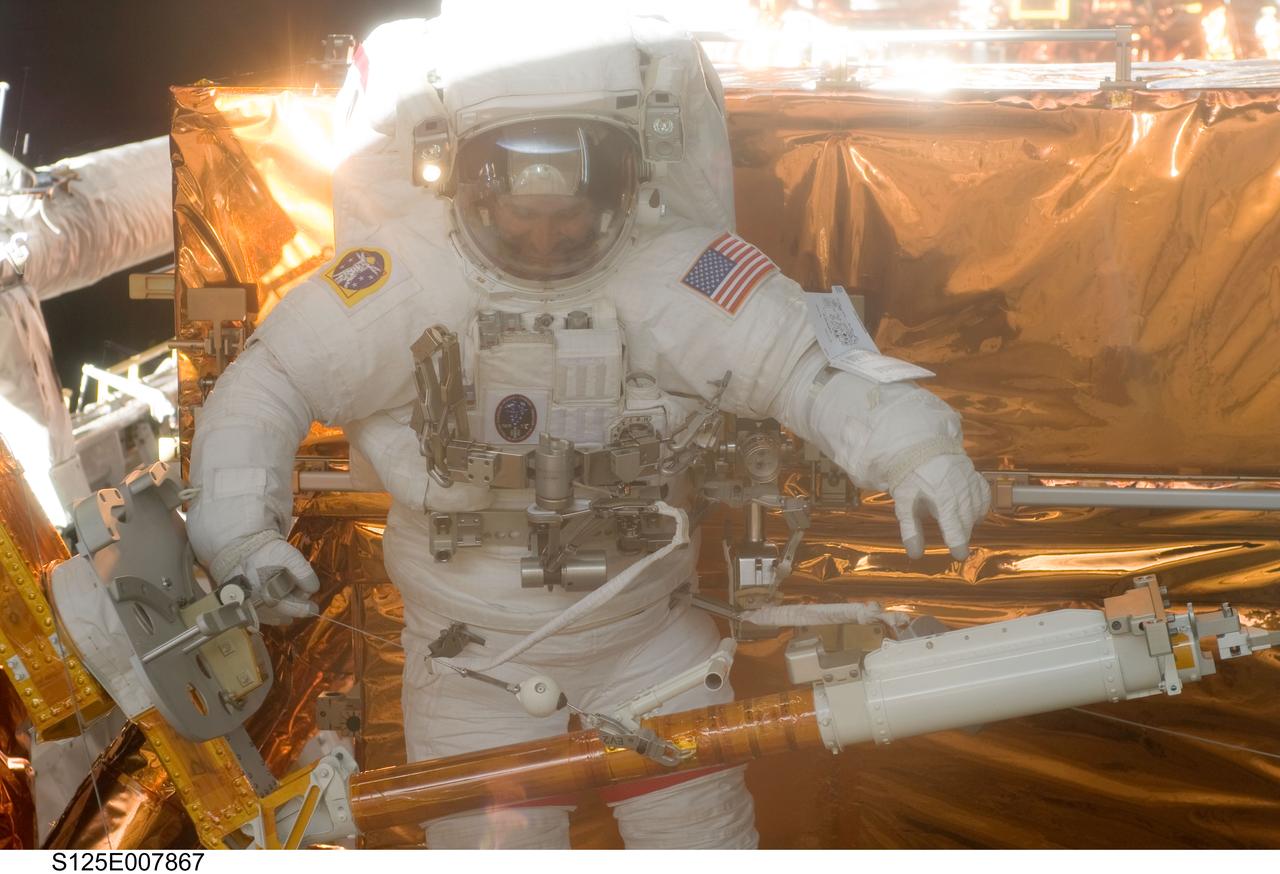

S125-E-007867 (16 May 2009) --- Astronaut John Grunsfeld, STS-125 mission specialist, participates in the mission?s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as work continues to refurbish and upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope. During the six-hour, 36-minute spacewalk, Grunsfeld and astronaut Andrew Feustel (out of frame), mission specialist, removed the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement and installed in its place the new Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. They also completed the Advanced Camera for Surveys electronic card replacement work, and completed part 2 of the ACS repair, installing a new electronics box and cable.
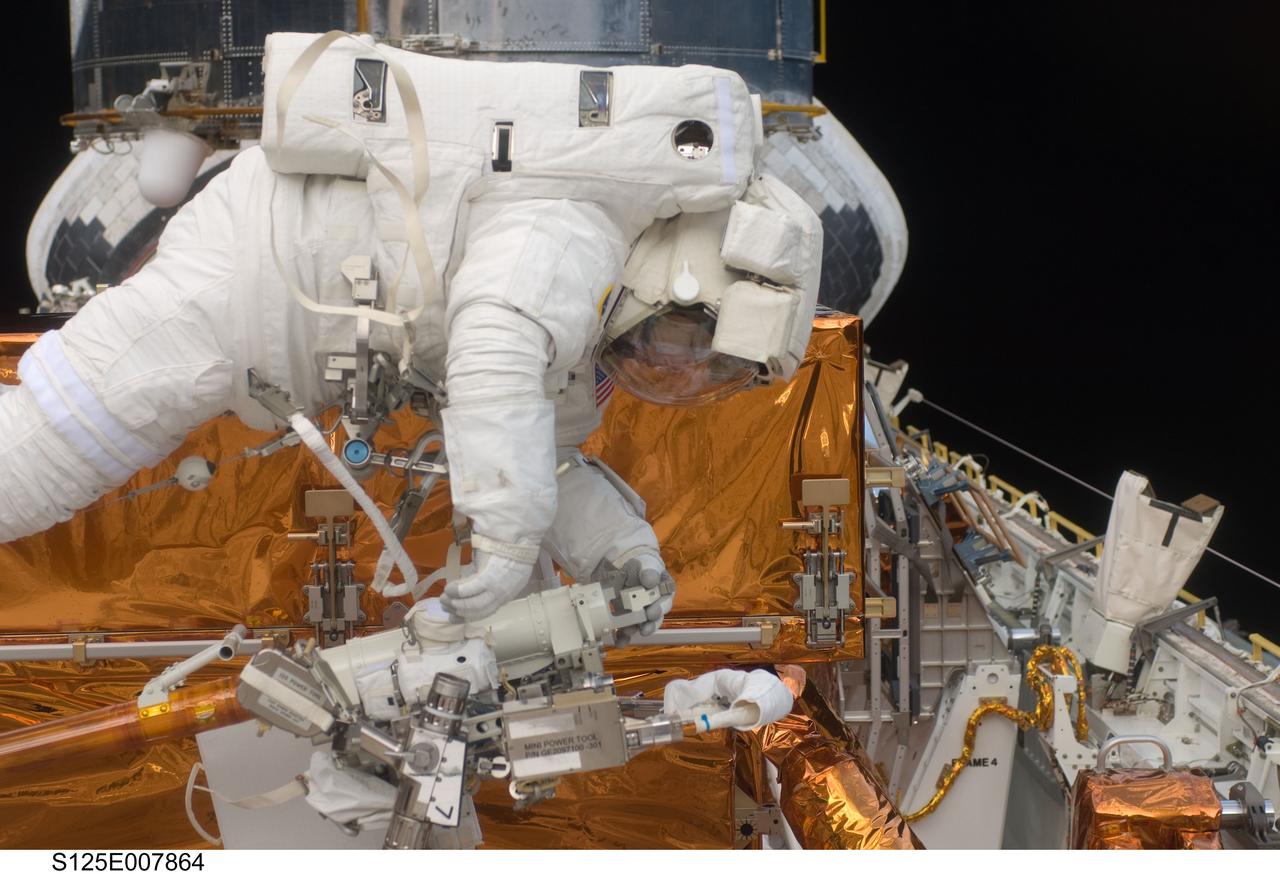

S125-E-007864 (16 May 2009) --- With the Hubble Space Telescope in the background, astronaut Andrew Feustel, STS-125 mission specialist, is seen here working during the mission?s third extravehicular activity (EVA). Feustel and astronaut John Grunsfeld (out of frame), mission specialist, removed the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement and installed in its place the new Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. They also completed the Advanced Camera for Surveys electronic card replacement work, and completed part 2 of the ACS repair, installing a new electronics box and cable.
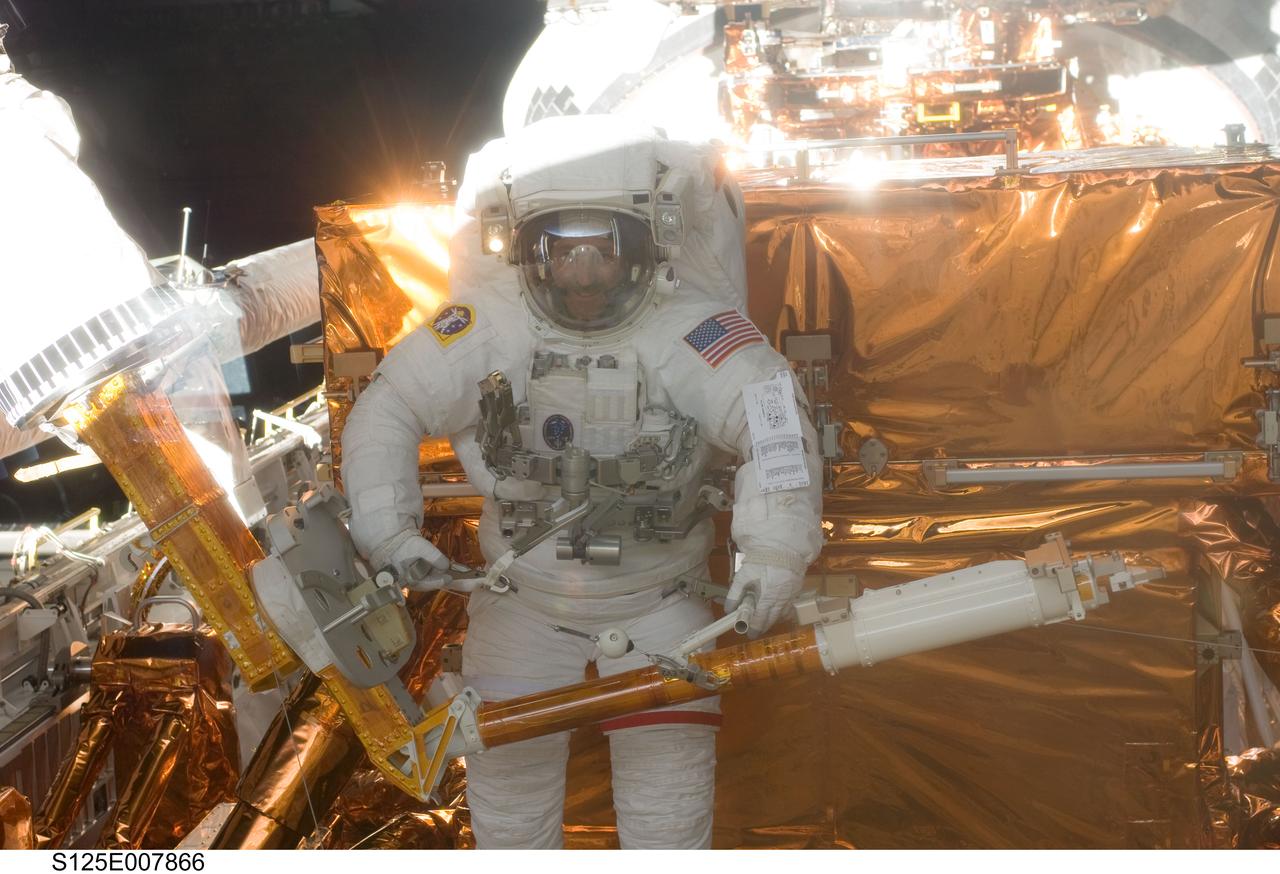

S125-E-007866 (16 May 2009) --- Astronaut John Grunsfeld, STS-125 mission specialist, participates in the mission?s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as work continues to refurbish and upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope. During the six-hour, 36-minute spacewalk, Grunsfeld and astronaut Andrew Feustel (out of frame), mission specialist, removed the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement and installed in its place the new Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. They also completed the Advanced Camera for Surveys electronic card replacement work, and completed part 2 of the ACS repair, installing a new electronics box and cable.
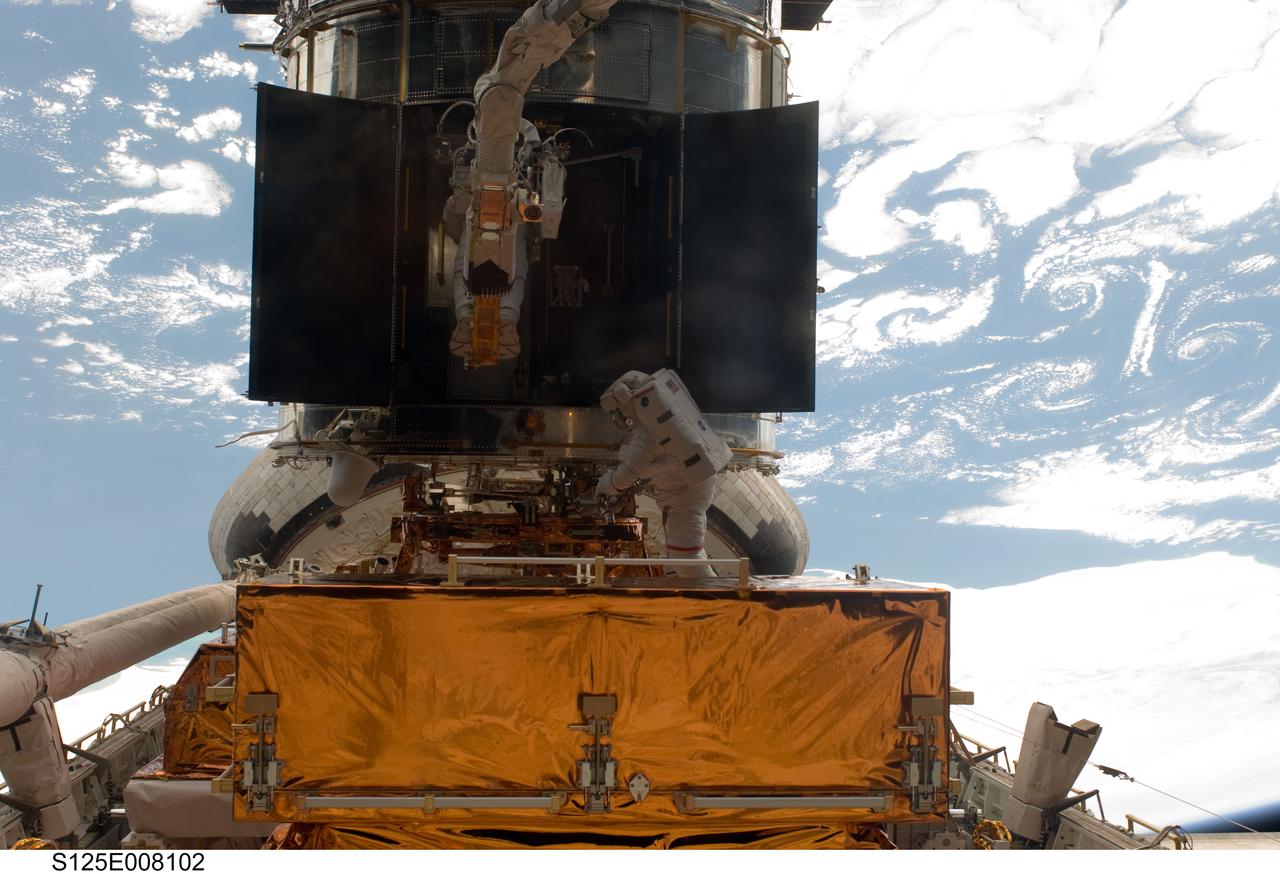

S125-E-008102 (16 May 2009) --- Astronauts Andrew Feustel (partially obscured at top) and John Grunsfeld, both STS-125 mission specialists, participate in the mission?s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as work continues to refurbish and upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope. During the six-hour, 36-minute spacewalk, Grunsfeld and Feustel removed the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement and installed in its place the new Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. They also completed the Advanced Camera for Surveys electronic card replacement work, and completed part 2 of the ACS repair, installing a new electronics box and cable.
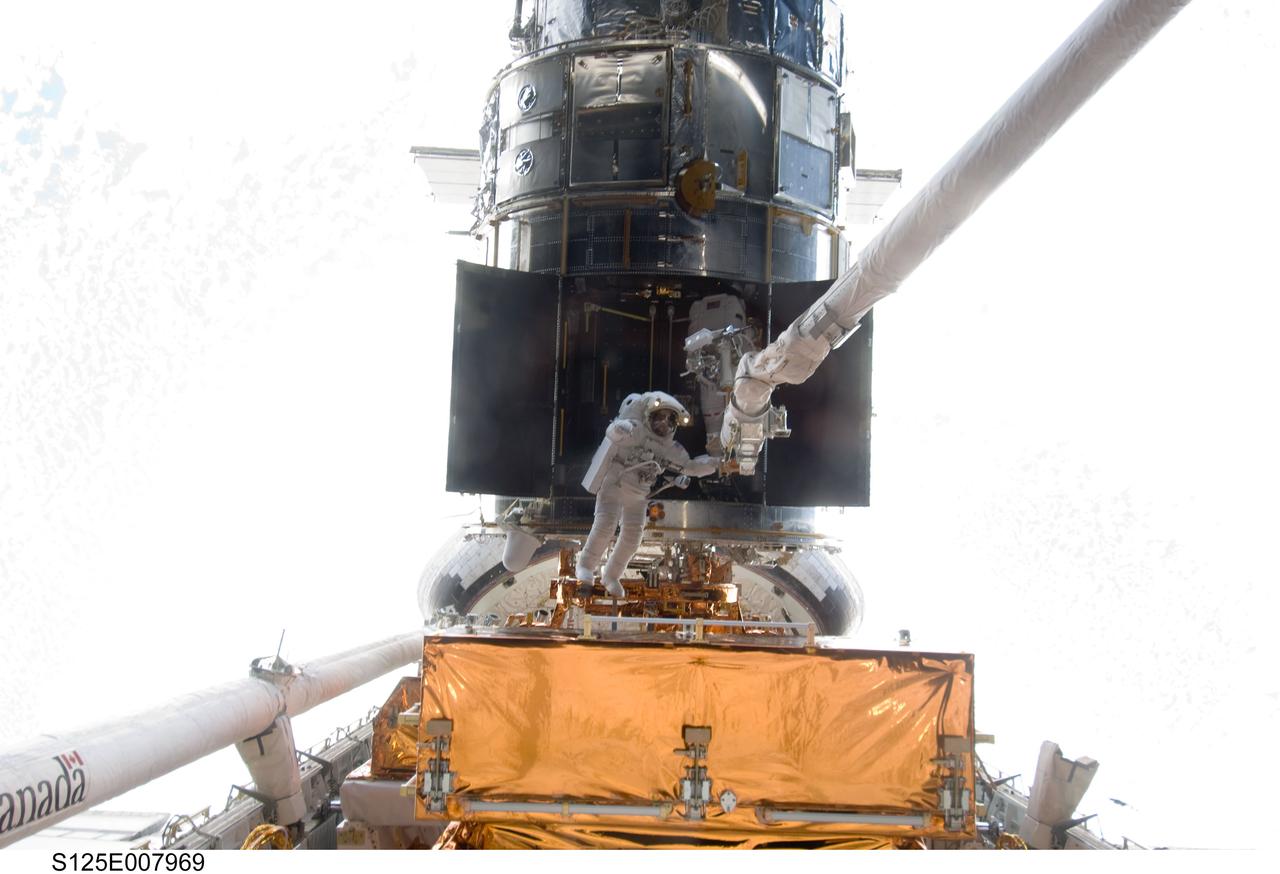

S125-E-007969 (16 May 2009) --- Astronauts Andrew Feustel (left) and John Grunsfeld, both STS-125 mission specialists, participate in the mission?s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as work continues to refurbish and upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope. During the six-hour, 36-minute spacewalk, Grunsfeld and Feustel removed the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement and installed in its place the new Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. They also completed the Advanced Camera for Surveys electronic card replacement work, and completed part 2 of the ACS repair, installing a new electronics box and cable.
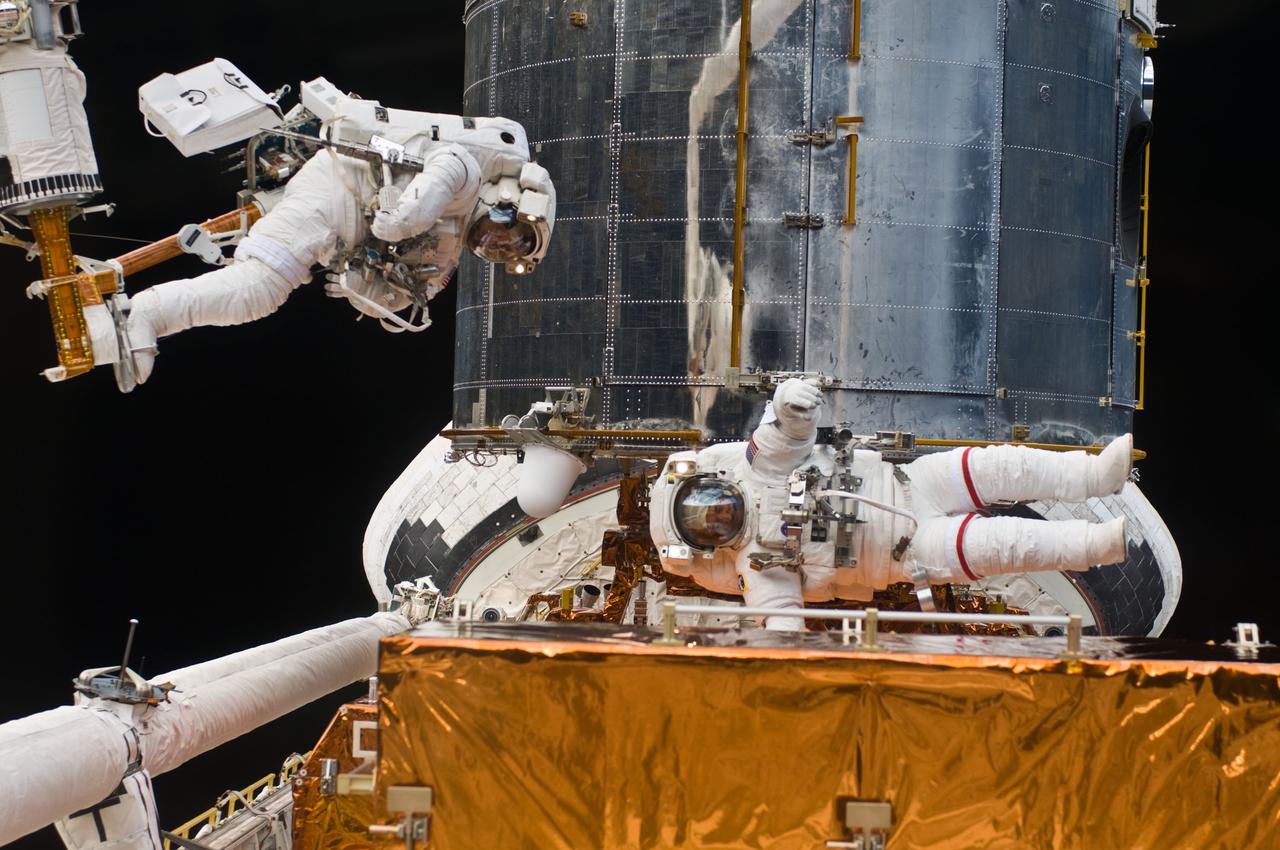

S125-E-008276 (16 May 2009) --- Astronauts Andrew Feustel (left) and John Grunsfeld, both STS-125 mission specialists, participate in the mission?s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as work continues to refurbish and upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope. During the six-hour, 36-minute spacewalk, Grunsfeld and Feustel removed the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement and installed in its place the new Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. They also completed the Advanced Camera for Surveys electronic card replacement work, and completed part 2 of the ACS repair, installing a new electronics box and cable.
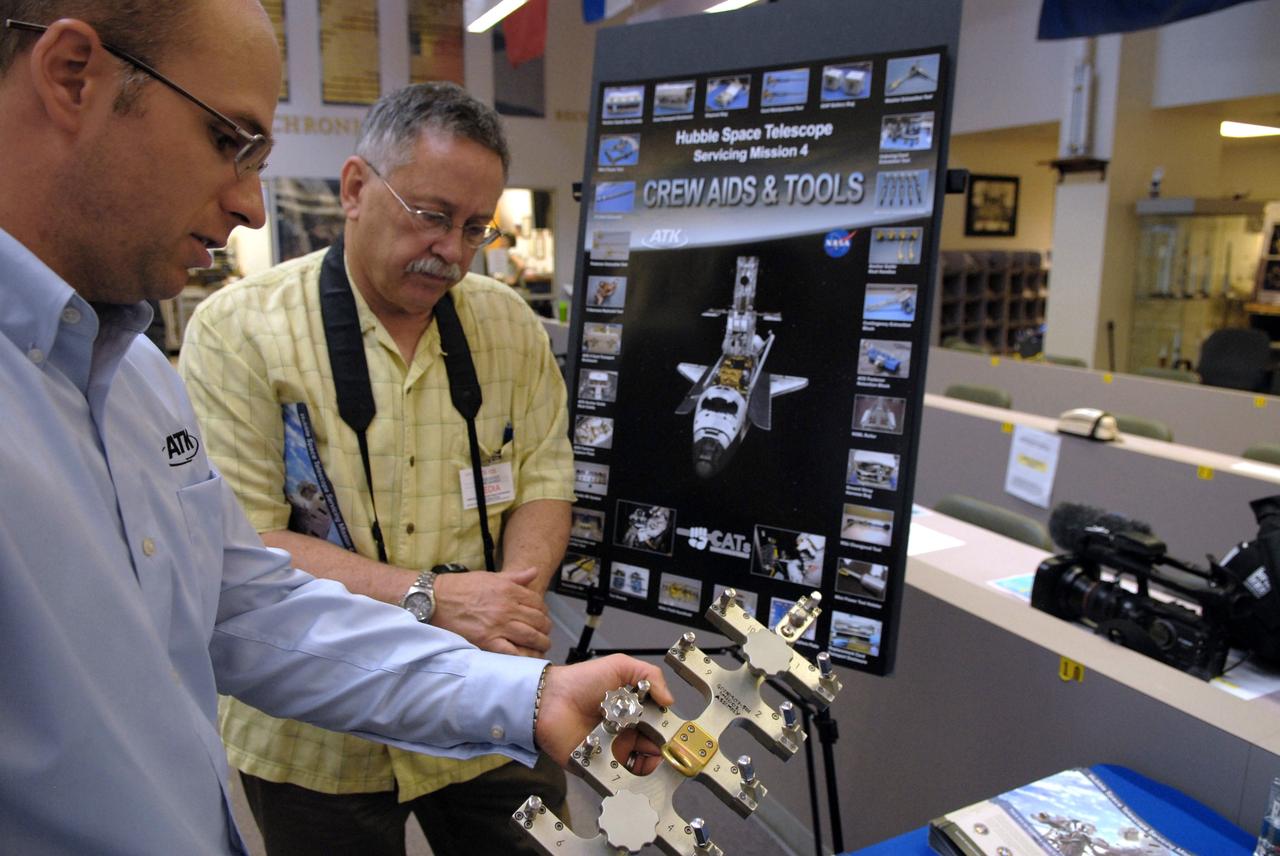

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The tools that will be used to service NASA's Hubble Space Telescope on the STS-125 mission are displayed in the NASA News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Being held in the foreground is the grid cutter tool, which will enable removal of the Electromagnetic Interference Grid from the Advanced Camera for Surveys access cover. On space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission, Hubble will be serviced for the fifth and final time. The flight will include five spacewalks during which astronauts will refurbish and upgrade the telescope with these state-of-the-art science instruments. As a result, Hubble's capabilities will be expanded and its operational lifespan extended through at least 2014. The payload includes a Wide Field Camera 3, fine guidance sensor and the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. Launch is scheduled for 2:01 p.m. EDT May 11. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
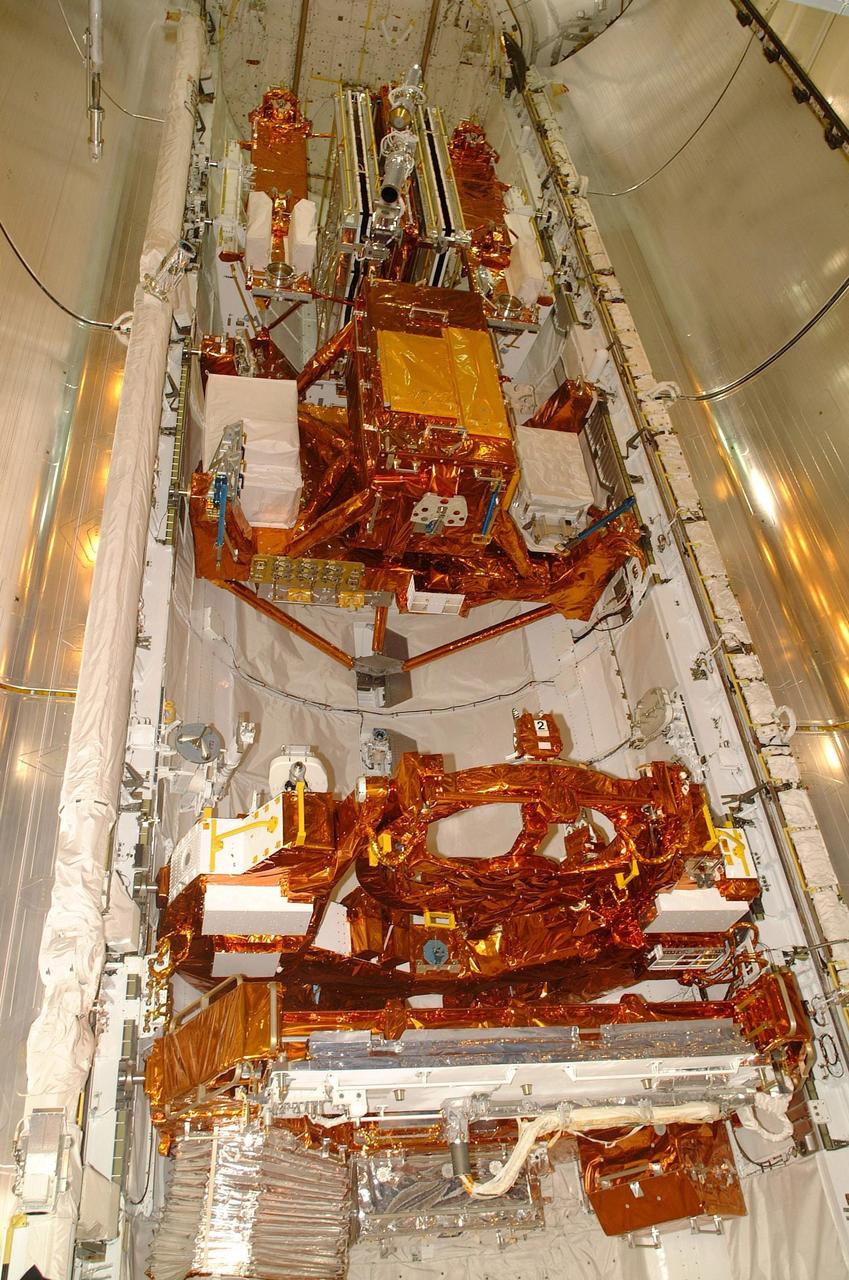
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- All of the payload elements on mission STS-109 are installed in Columbia's payload bay: Solar Array 3, a new Power Control Unit, the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), Near Infrared Camera, Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Four mission specialists will perform five scheduled spacewalks to complete system upgrades to the telescope with these components. The STS-109 crew includes Commander Scott D. Altman, Pilot Duane G. Carey, and Mission Specialists John M. Grunsfeld, Nancy J. Currie, James H. Newman, Richard M. Linnehan and Michael J. Massimino. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002, at 6:48 a.m. EST (11:48 GMT). Photo by Carl Winebarger
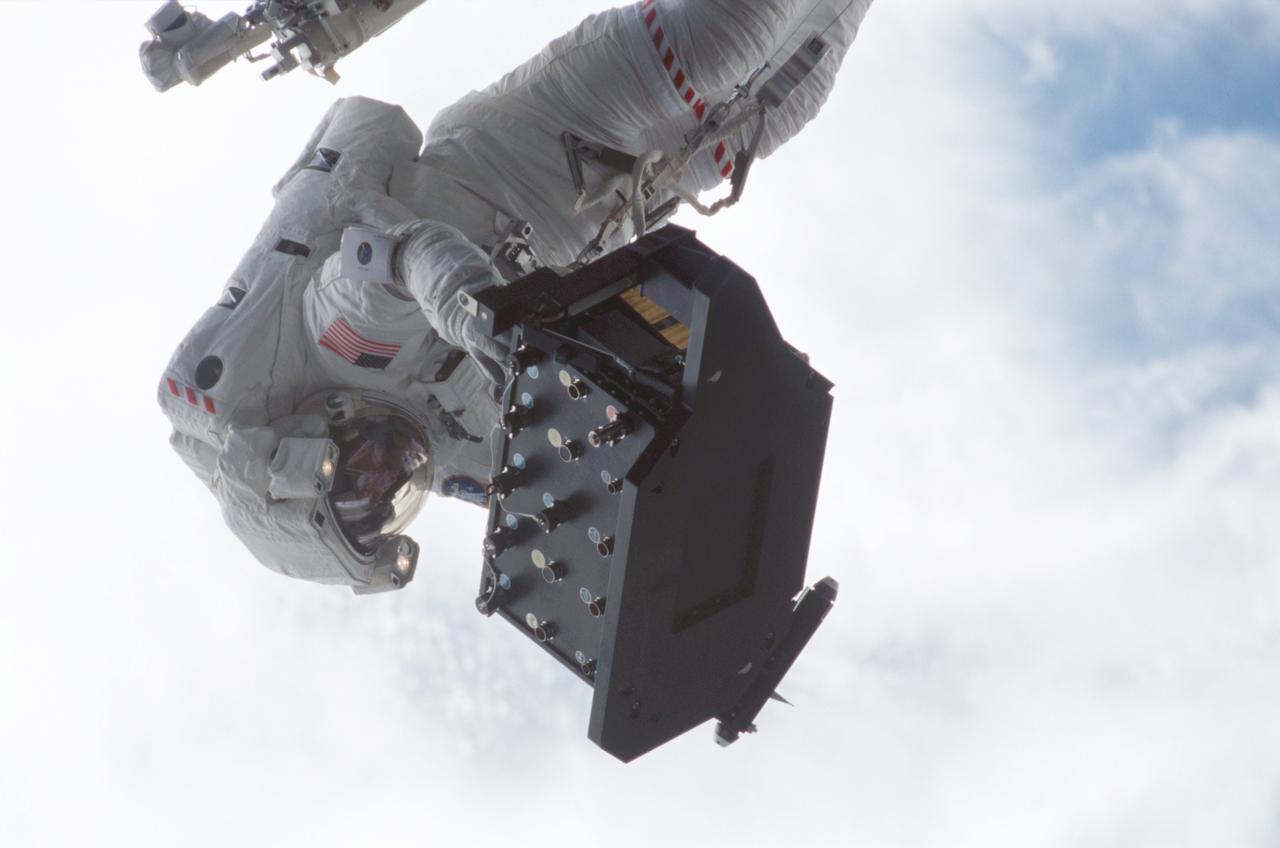

STS-109 Astronaut Michael J. Massimino, mission specialist, perched on the Shuttle's robotic arm, is preparing to install the Electronic Support Module (ESM) in the aft shroud of the Hubble Space telescope (HST), with the assistance of astronaut James H. Newman (out of frame). The module will support a new experimental cooling system to be installed during the next day's fifth and final space walk of the mission. That cooling system is designed to bring the telescope's Near-Infrared Camera and Multi Spectrometer (NICMOS) back to life the which had been dormant since January 1999 when its original coolant ran out. The Space Shuttle Columbia STS-109 mission lifted off March 1, 2002 with goals of repairing and upgrading the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama had the responsibility for the design, development, and construction of the HST, which is the most powerful and sophisticated telescope ever built. In addition to the installation of the experimental cooling system for the Hubble's Near-Infrared Camera and NICMOS, STS-109 upgrades to the HST included replacement of the solar array panels, replacement of the power control unit (PCU), and replacement of the Faint Object Camera (FOC) with a new advanced camera for Surveys (ACS). Lasting 10 days, 22 hours, and 11 minutes, the STS-109 mission was the 108th flight overall in NASA's Space Shuttle Program.
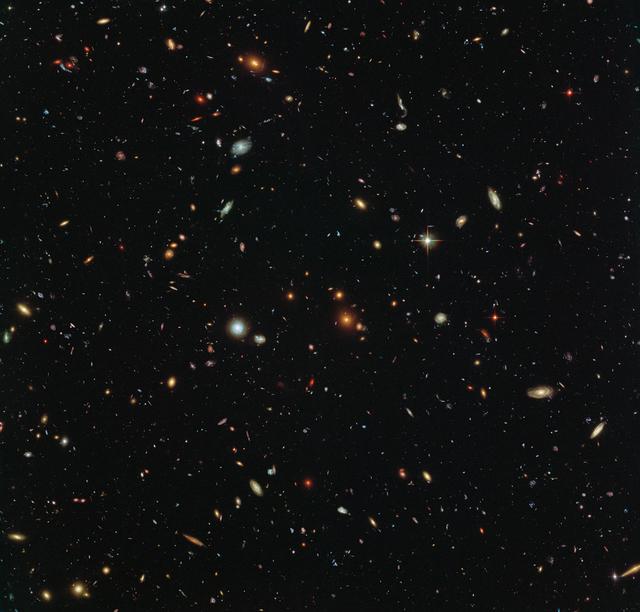

Peering deep into the early Universe, this picturesque parallel field observation from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope reveals thousands of colourful galaxies swimming in the inky blackness of space. A few foreground stars from our own galaxy, the Milky Way, are also visible. In October 2013 Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) and Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) began observing this portion of sky as part of the Frontier Fields programme. This spectacular skyscape was captured during the study of the giant galaxy cluster Abell 2744, otherwise known as Pandora’s Box. While one of Hubble’s cameras concentrated on Abell 2744, the other camera viewed this adjacent patch of sky near to the cluster. Containing countless galaxies of various ages, shapes and sizes, this parallel field observation is nearly as deep as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field. In addition to showcasing the stunning beauty of the deep Universe in incredible detail, this parallel field — when compared to other deep fields — will help astronomers understand how similar the Universe looks in different directions
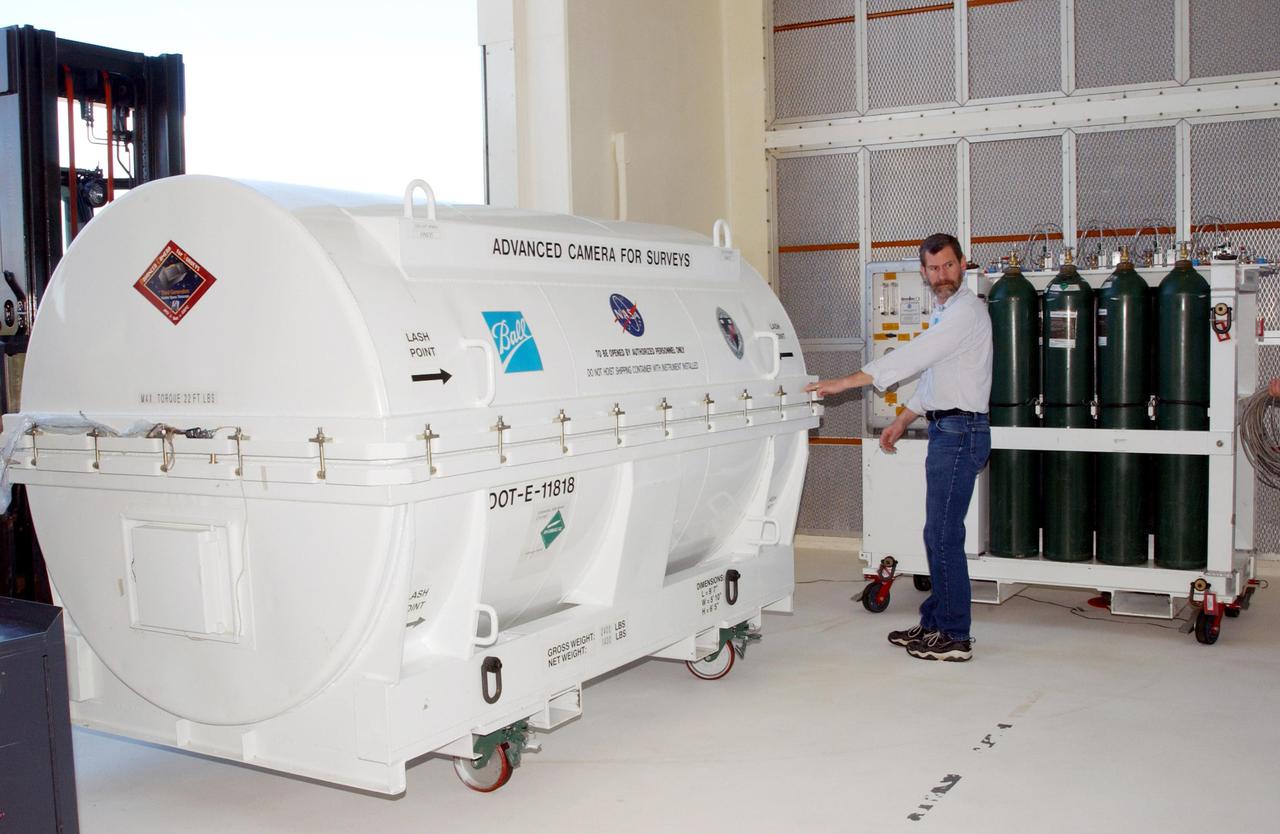

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- A piece of equipment for Hubble Space Telescope Servicing mission is moved inside Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral. In the canister is the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). The ACS will increase the discovery efficiency of the HST by a factor of ten. It consists of three electronic cameras and a complement of filters and dispersers that detect light from the ultraviolet to the near infrared (1200 - 10,000 angstroms). The ACS was built through a collaborative effort between Johns Hopkins University, Goddard Space Flight Center, Ball Aerospace Corporation and Space Telescope Science Institute. The goal of the mission, STS-109, is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
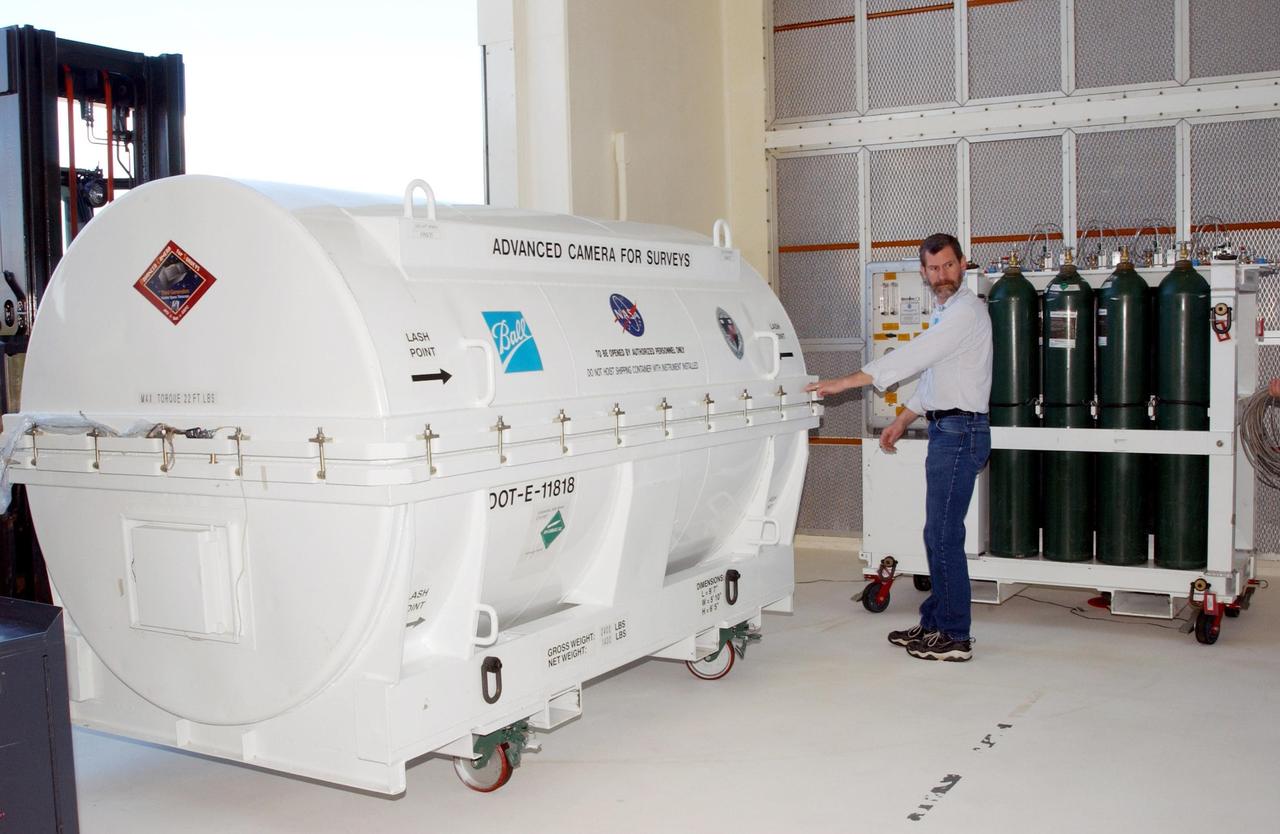

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- A piece of equipment for Hubble Space Telescope Servicing mission is moved inside Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral. In the canister is the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). The ACS will increase the discovery efficiency of the HST by a factor of ten. It consists of three electronic cameras and a complement of filters and dispersers that detect light from the ultraviolet to the near infrared (1200 - 10,000 angstroms). The ACS was built through a collaborative effort between Johns Hopkins University, Goddard Space Flight Center, Ball Aerospace Corporation and Space Telescope Science Institute. The goal of the mission, STS-109, is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
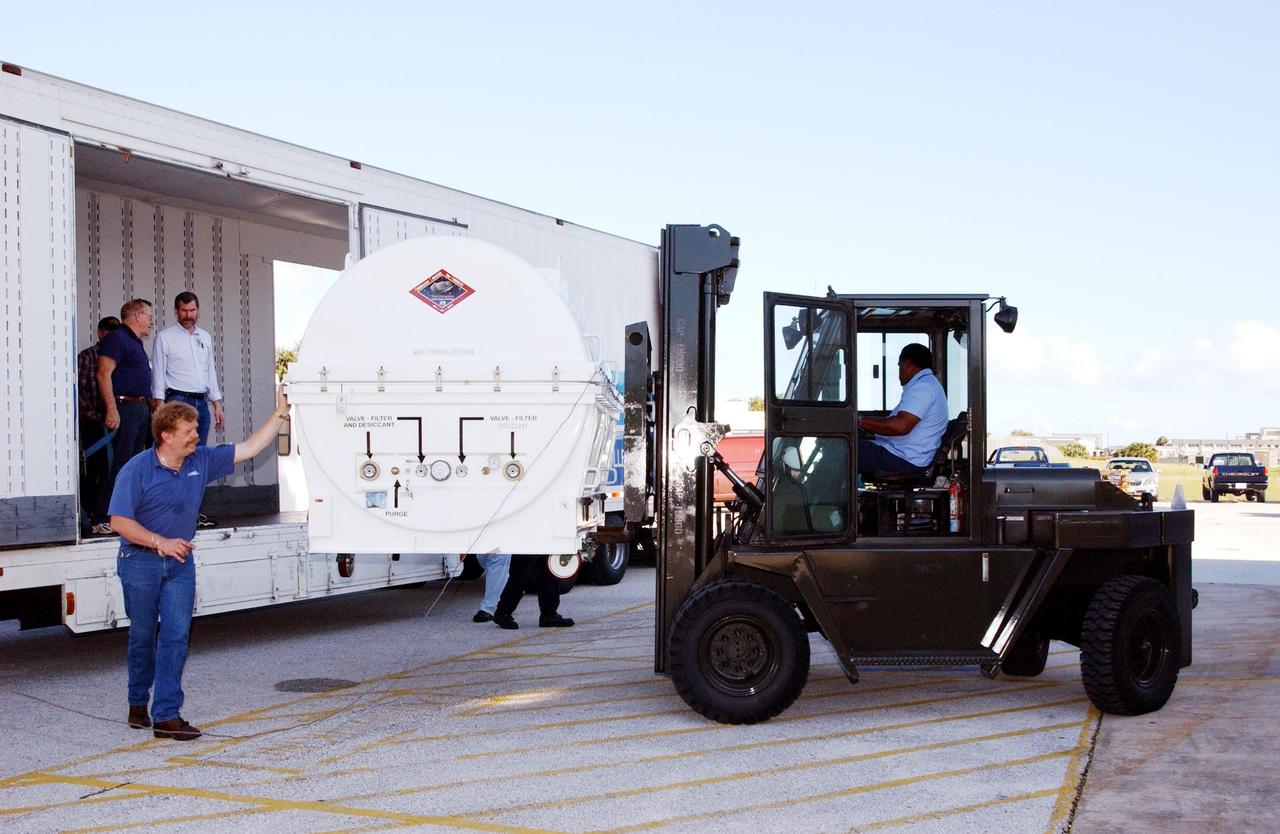

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - A piece of equipment for Hubble Space Telescope Servicing mission arrives at Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral. Inside the canister is the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). The ACS will increase the discovery efficiency of the HST by a factor of ten. It consists of three electronic cameras and a complement of filters and dispersers that detect light from the ultraviolet to the near infrared (1200 - 10,000 angstroms). The ACS was built through a collaborative effort between Johns Hopkins University, Goddard Space Flight Center, Ball Aerospace Corporation and Space Telescope Science Institute. The goal of the mission, STS-109, is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002

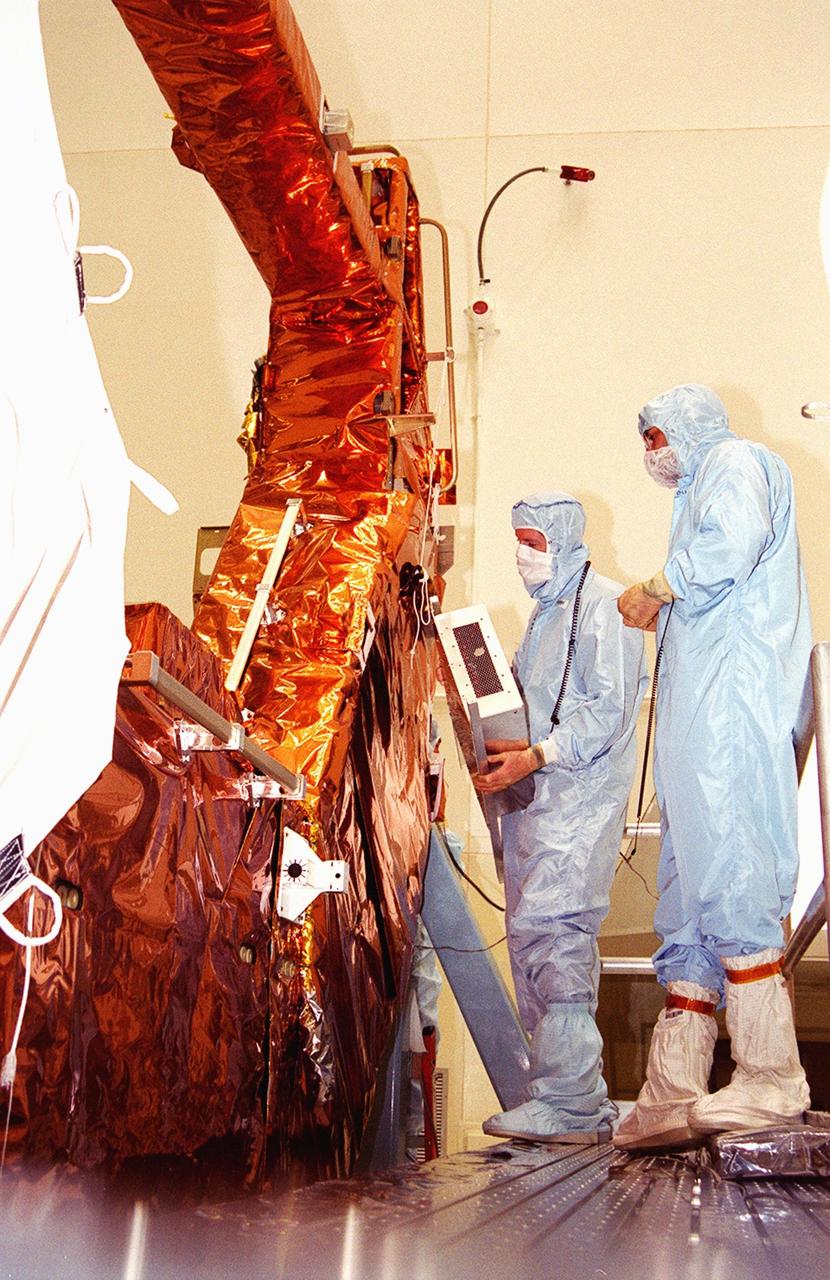
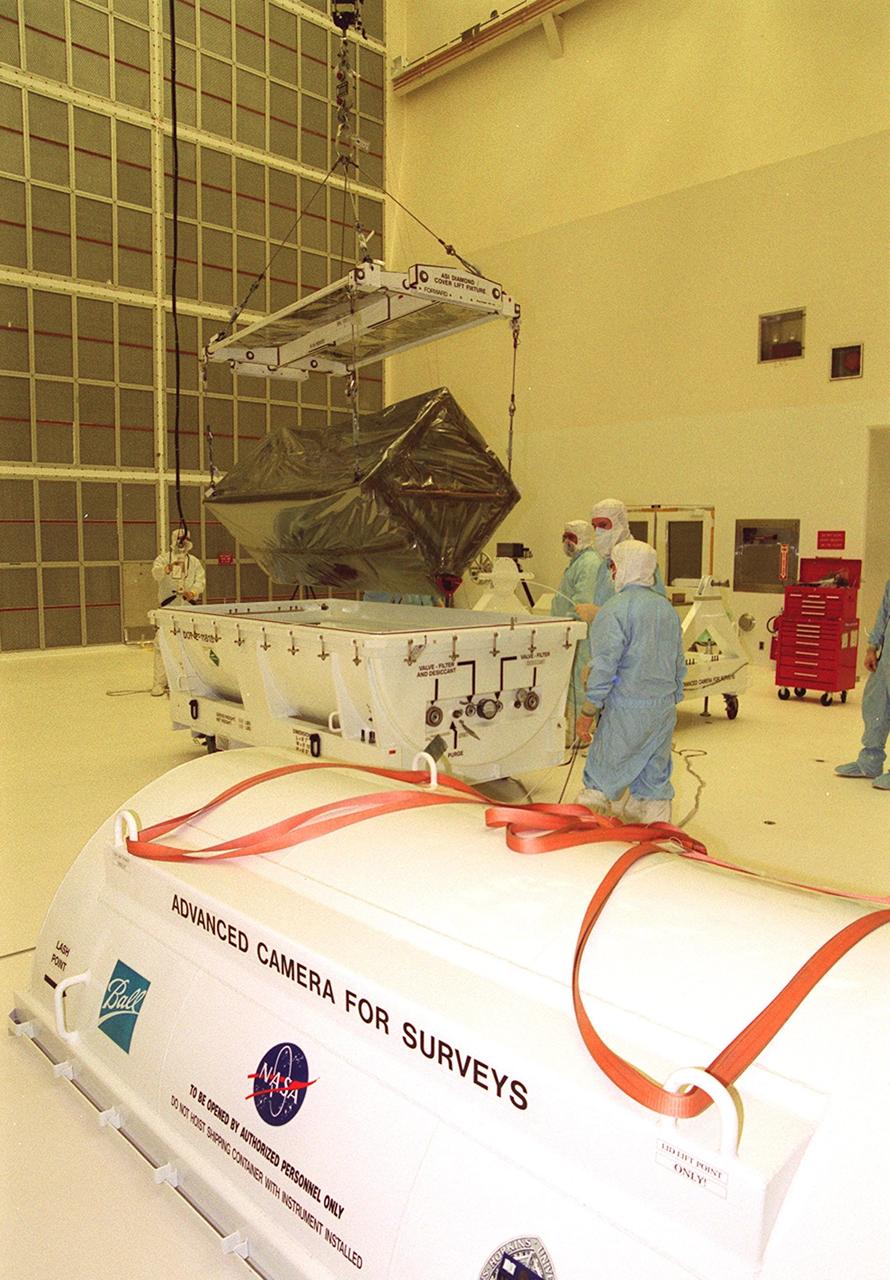
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Workers in Hangar AandE remove the wrapping from around the Advanced Camera for Surveys, which is suspended by an overhead crane. Part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109, the ACS will increase the discovery efficiency of the HST by a factor of ten. It consists of three electronic cameras and a complement of filters and dispersers that detect light from the ultraviolet to the near infrared (1200 - 10,000 angstroms). The ACS was built through a collaborative effort between Johns Hopkins University, Goddard Space Flight Center, Ball Aerospace Corporation and Space Telescope Science Institute. Tasks for the mission include replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002

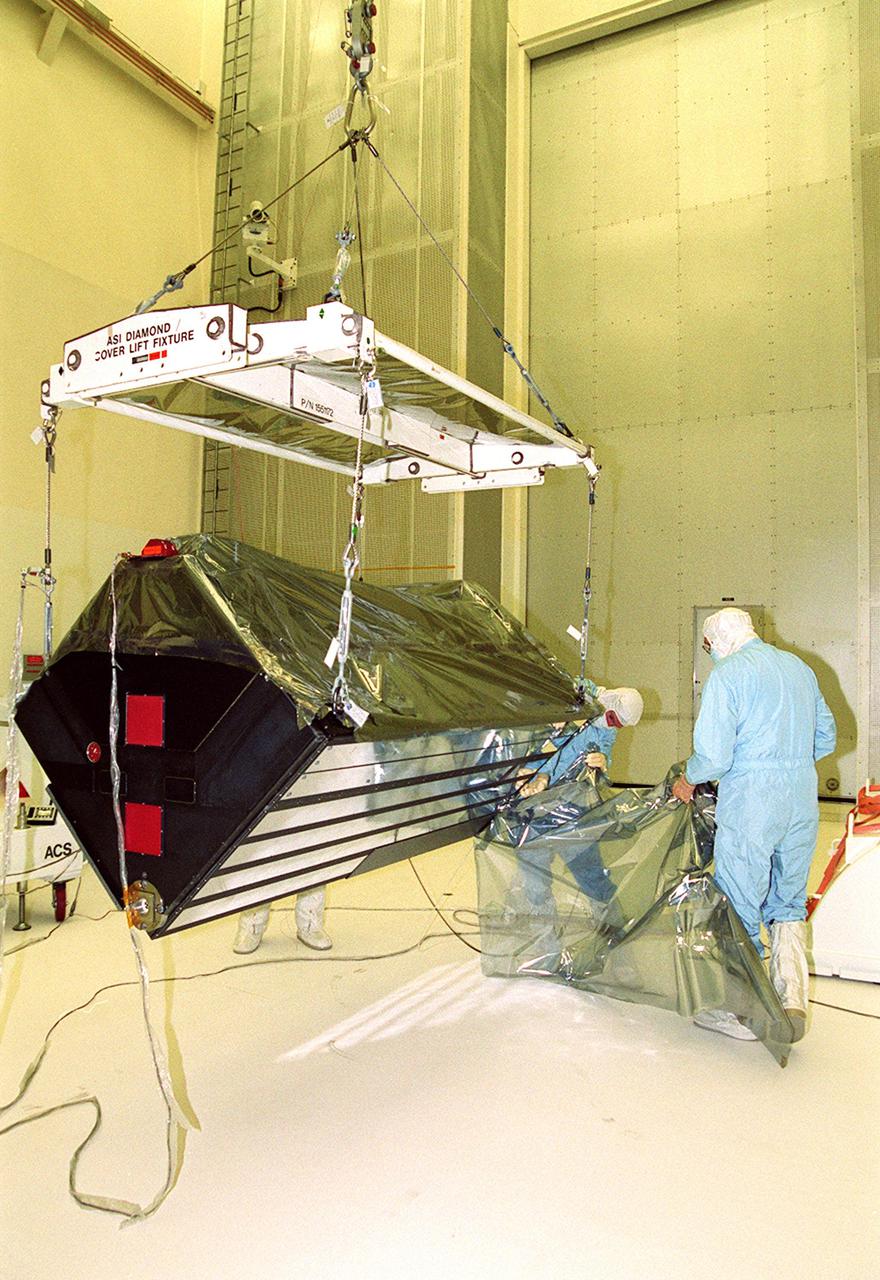
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In Hangar A&E, workers watch as an overhead crane lifts the Advanced Camera for Surveys out of its transportation container. Part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109, the ACS will increase the discovery efficiency of the HST by a factor of ten. It consists of three electronic cameras and a complement of filters and dispersers that detect light from the ultraviolet to the near infrared (1200 - 10,000 angstroms). The ACS was built through a collaborative effort between Johns Hopkins University, Goddard Space Flight Center, Ball Aerospace Corporation and Space Telescope Science Institute. Tasks for the mission include replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Fully unwrapped, the Advanced Camera for Surveys, which is suspended by an overhead crane, is checked over by workers. Part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109, the ACS will increase the discovery efficiency of the HST by a factor of ten. It consists of three electronic cameras and a complement of filters and dispersers that detect light from the ultraviolet to the near infrared (1200 - 10,000 angstroms). The ACS was built through a collaborative effort between Johns Hopkins University, Goddard Space Flight Center, Ball Aerospace Corporation and Space Telescope Science Institute. Tasks for the mission include replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
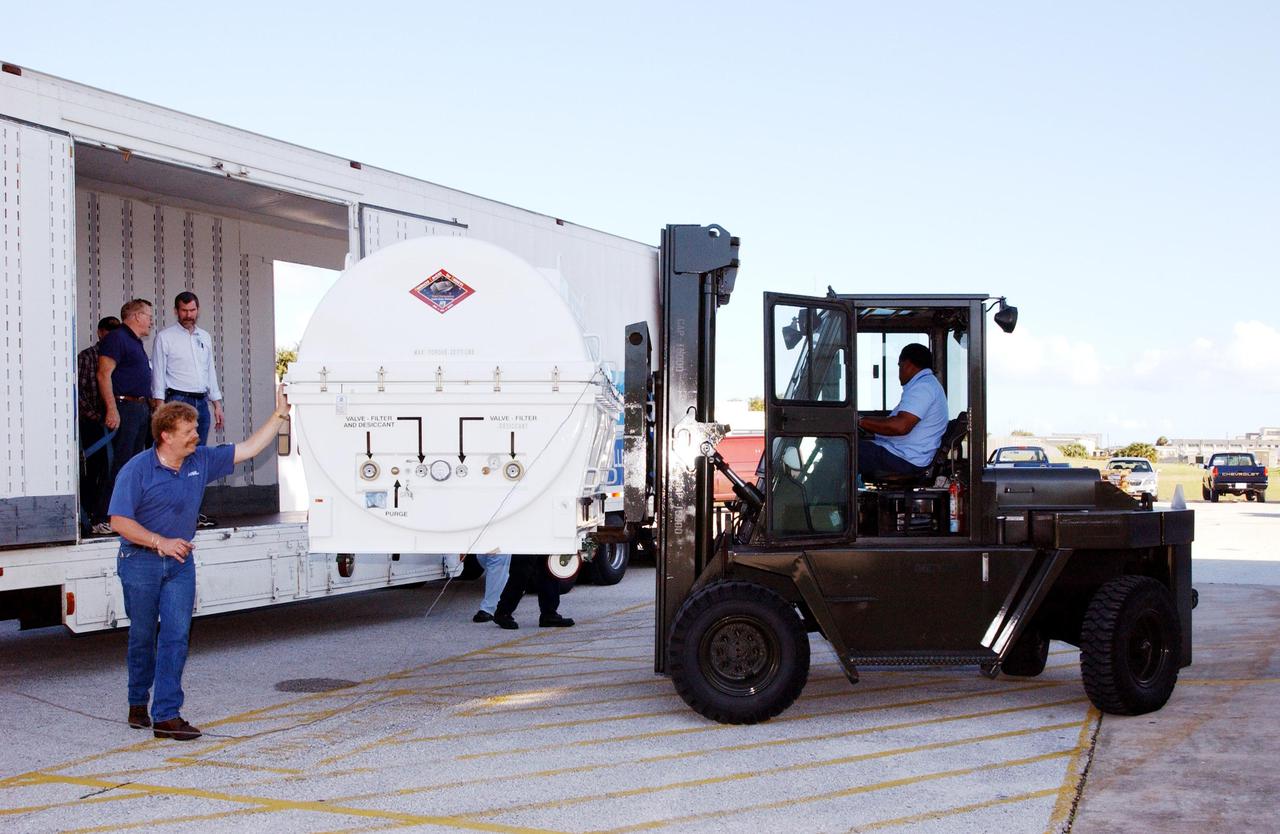

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - A piece of equipment for Hubble Space Telescope Servicing mission arrives at Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral. Inside the canister is the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). The ACS will increase the discovery efficiency of the HST by a factor of ten. It consists of three electronic cameras and a complement of filters and dispersers that detect light from the ultraviolet to the near infrared (1200 - 10,000 angstroms). The ACS was built through a collaborative effort between Johns Hopkins University, Goddard Space Flight Center, Ball Aerospace Corporation and Space Telescope Science Institute. The goal of the mission, STS-109, is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
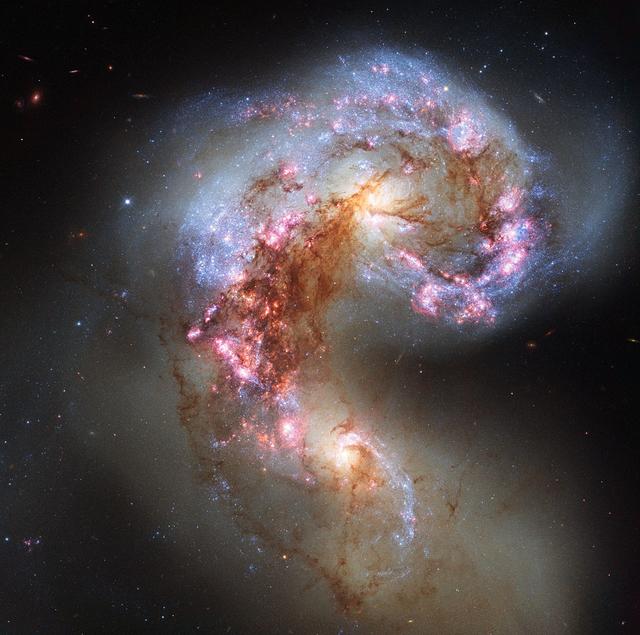

The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has snapped the best ever image of the Antennae Galaxies. Hubble has released images of these stunning galaxies twice before, once using observations from its Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) in 1997, and again in 2006 from the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). Each of Hubble’s images of the Antennae Galaxies has been better than the last, due to upgrades made during the famous servicing missions, the last of which took place in 2009. The galaxies — also known as NGC 4038 and NGC 4039 — are locked in a deadly embrace. Once normal, sedate spiral galaxies like the Milky Way, the pair have spent the past few hundred million years sparring with one another. This clash is so violent that stars have been ripped from their host galaxies to form a streaming arc between the two. In wide-field images of the pair the reason for their name becomes clear — far-flung stars and streamers of gas stretch out into space, creating long tidal tails reminiscent of antennae. This new image of the Antennae Galaxies shows obvious signs of chaos. Clouds of gas are seen in bright pink and red, surrounding the bright flashes of blue star-forming regions — some of which are partially obscured by dark patches of dust. The rate of star formation is so high that the Antennae Galaxies are said to be in a state of starburst, a period in which all of the gas within the galaxies is being used to form stars. This cannot last forever and neither can the separate galaxies; eventually the nuclei will coalesce, and the galaxies will begin their retirement together as one large elliptical galaxy. This image uses visible and near-infrared observations from Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3), along with some of the previously-released observations from Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). Credit: NASA/European Space Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
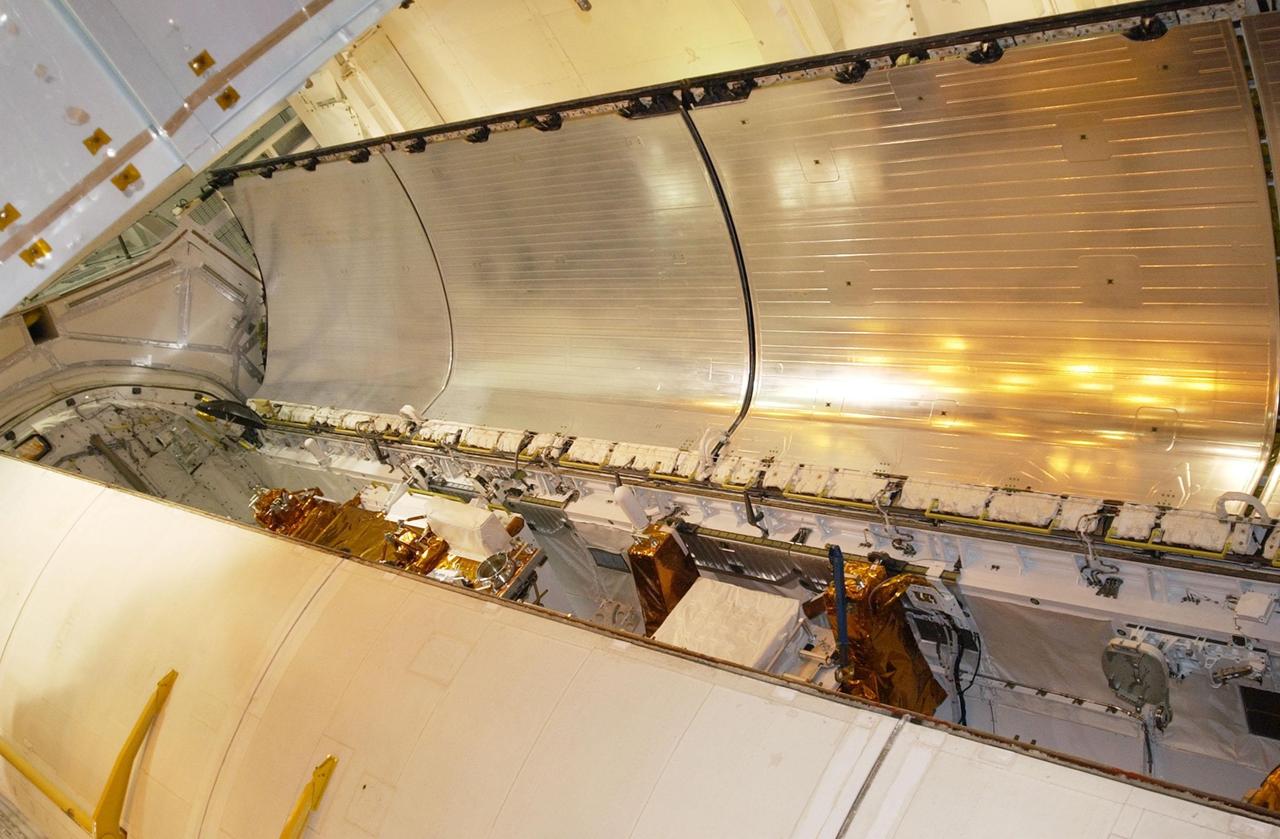

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Columbia’s payload bay doors begin closing over the equipment inside to be used on mission STS-109. During their 11 days in space, the seven-member crew will capture the Hubble Space Telescope using the Shuttle's robotic arm and secure it on a workstand in Columbia’s payload bay. Four mission specialists will perform five scheduled spacewalks to complete system upgrades to the telescope. More durable solar arrays, a large gyroscopic assembly to help point the telescope properly, a new telescope power control unit, and a cooling system to restore the use of a key infrared camera and spectrometer unit, which has been dormant since 1999, will all be installed. In addition, the telescope's view of the Universe will be improved with the addition of the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), which replaces the Faint Object Camera, the last of Hubble's original instruments. The STS-109 crew includes Commander Scott D. Altman, Pilot Duane G. Carey, and Mission Specialists John M. Grunsfeld, Nancy J. Currie, James H. Newman, Richard M. Linnehan and Michael J. Massimino. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002, at 6:48 a.m. EST (11:48 GMT).

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - During suitup, STS-109 Mission Specialist Richard M. Linnehan shows he is ready for launch. Liftoff of Space Shuttle Columbia is scheduled for 6:22 a.m. EST March 1. On mission STS-109, the crew will capture the Hubble Space Telescope using the Shuttle's robotic arm and secure it on a workstand in Columbia's payload bay. Four mission specialists will perform five scheduled spacewalks to complete system upgrades to the telescope. More durable solar arrays, a large gyroscopic assembly to help point the telescope properly, a new telescope power control unit, and a cooling system to restore the use of a key infrared camera and spectrometer unit, which has been dormant since 1999, will all be installed. In addition, the telescope's view of the Universe will be improved with the addition of the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), which replaces the Faint Object Camera, the last of Hubble's original instruments. Mission STS-109 is the 27th flight of the orbiter Columbia and the 108th flight overall in NASA's Space Shuttle program. After the 11-day mission, Columbia is scheduled to land about 4:35 a.m. EST March 12
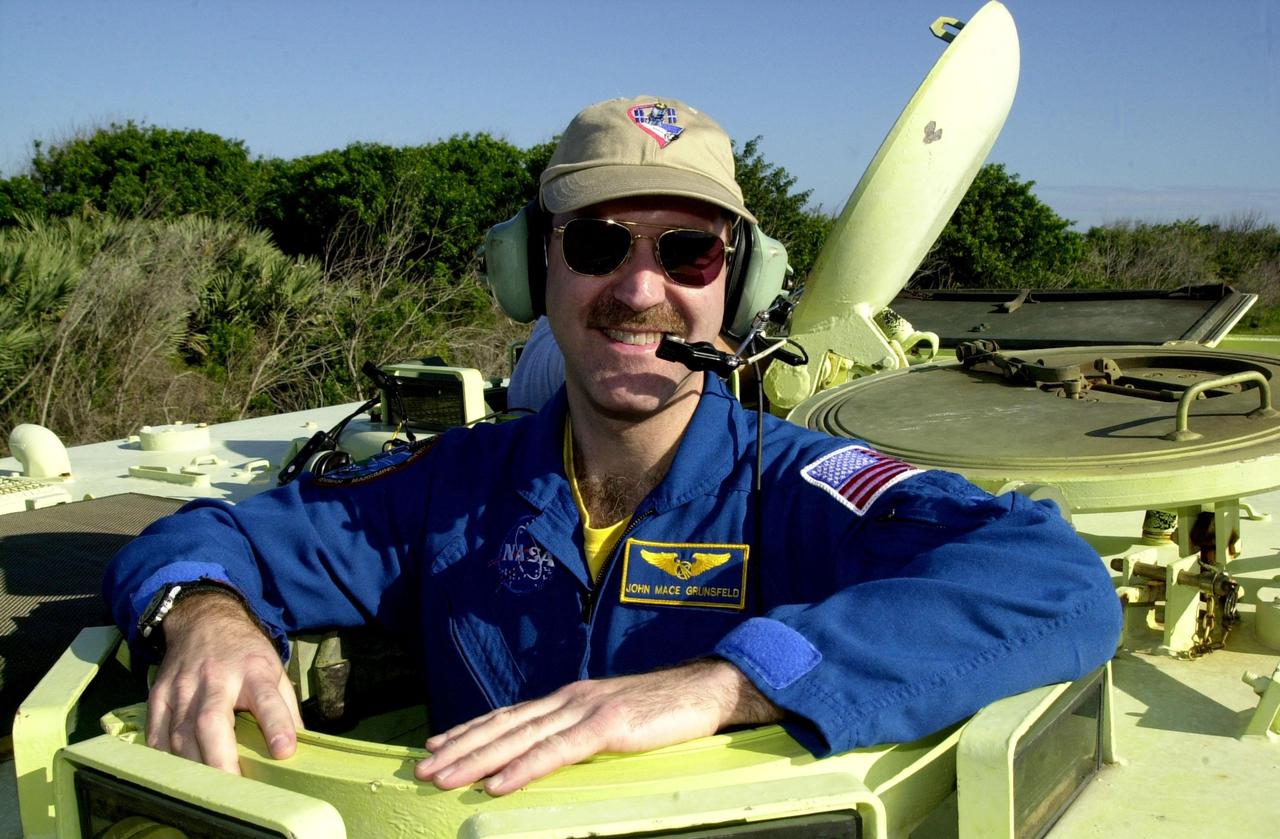

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-109 Payload Commander John Grunsfeld is ready to practice driving the M-113 armored personnel carrier, part of emergency egress training at the launch pad. Behind him is Mission Specialist Michael Massimino. Crew members are taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which also include a simulated launch countdown. STS-109 is a Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, with goals to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. The 11-day mission will require grasping the satellite with a robotic arm in order for the crew to perform the tasks during five spacewalks. Launch of STS-109 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia is scheduled for Feb. 28, 2002