
ADVANCED COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY SATELLITE - ACTS - VISITOR CENTER
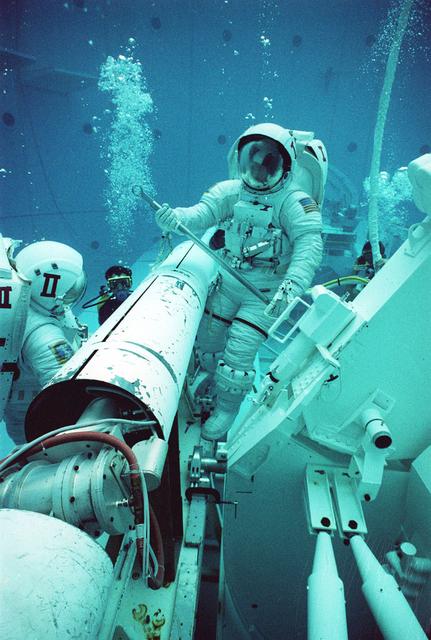

Two years prior to being used during a shuttle mission, the Transfer to Orbit System (TOS) is being demonstrated at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). TOS is an upper stage launch system used to place satellites into higher orbits. TOS was used only once, on September 12, 1993 when the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS51) deployed ACTS (Advanced Communications Technology Satellite). The test pictured was to provide an evaluation of the extravehicular activity (EVA) tools that were to be used by future shuttle crews.
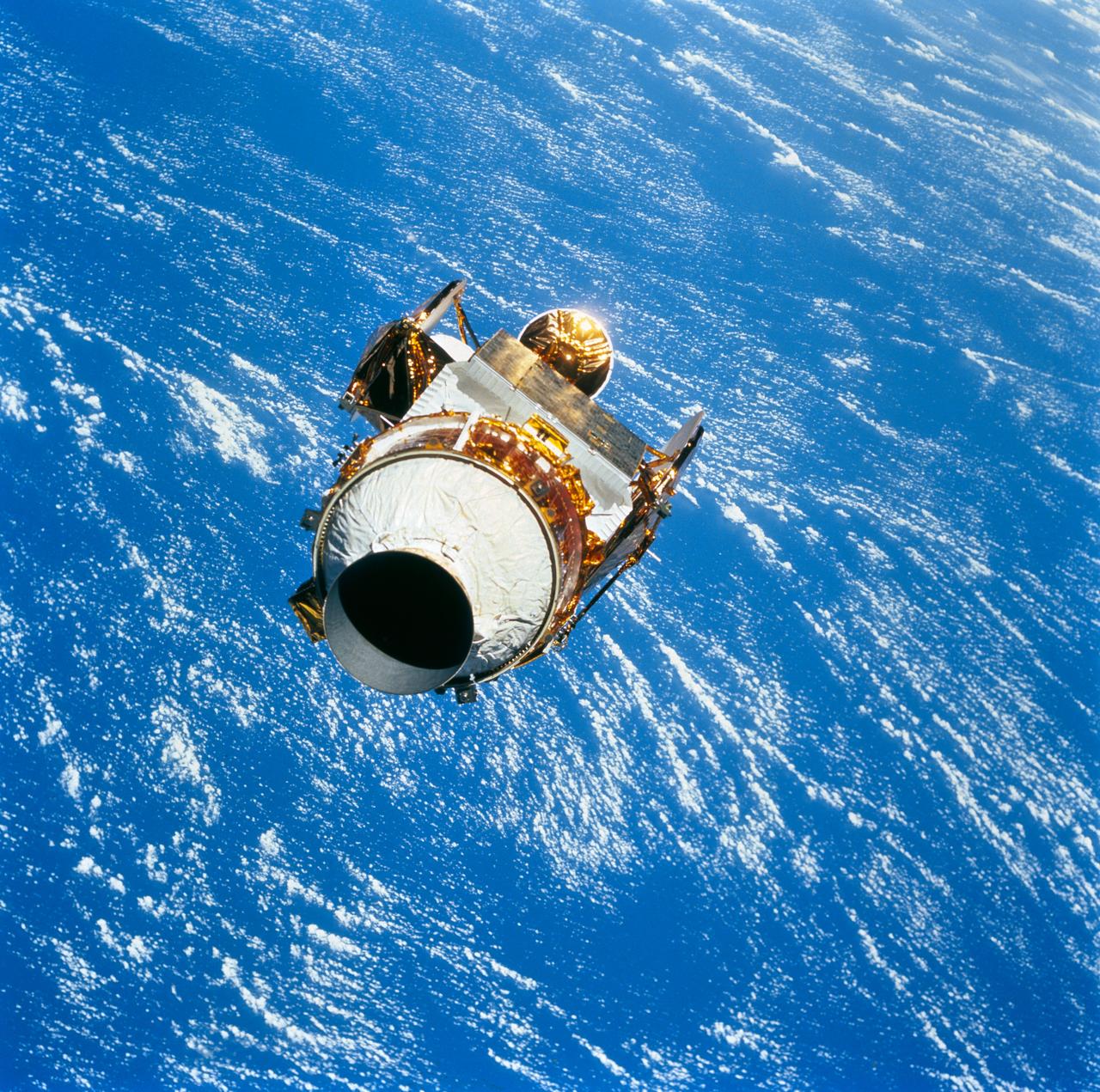

STS051-71-054 (12 Sept 1993) --- The Advanced Communications Technology Satellite (ACTS) with its Transfer Orbit Stage (TOS) is backdropped over the blue ocean following its release from the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery. ACTS/TOS deploy was the first major task performed on the almost ten-day mission. The frame was exposed with a 70mm handheld Hasselblad camera from Discovery's flight deck.
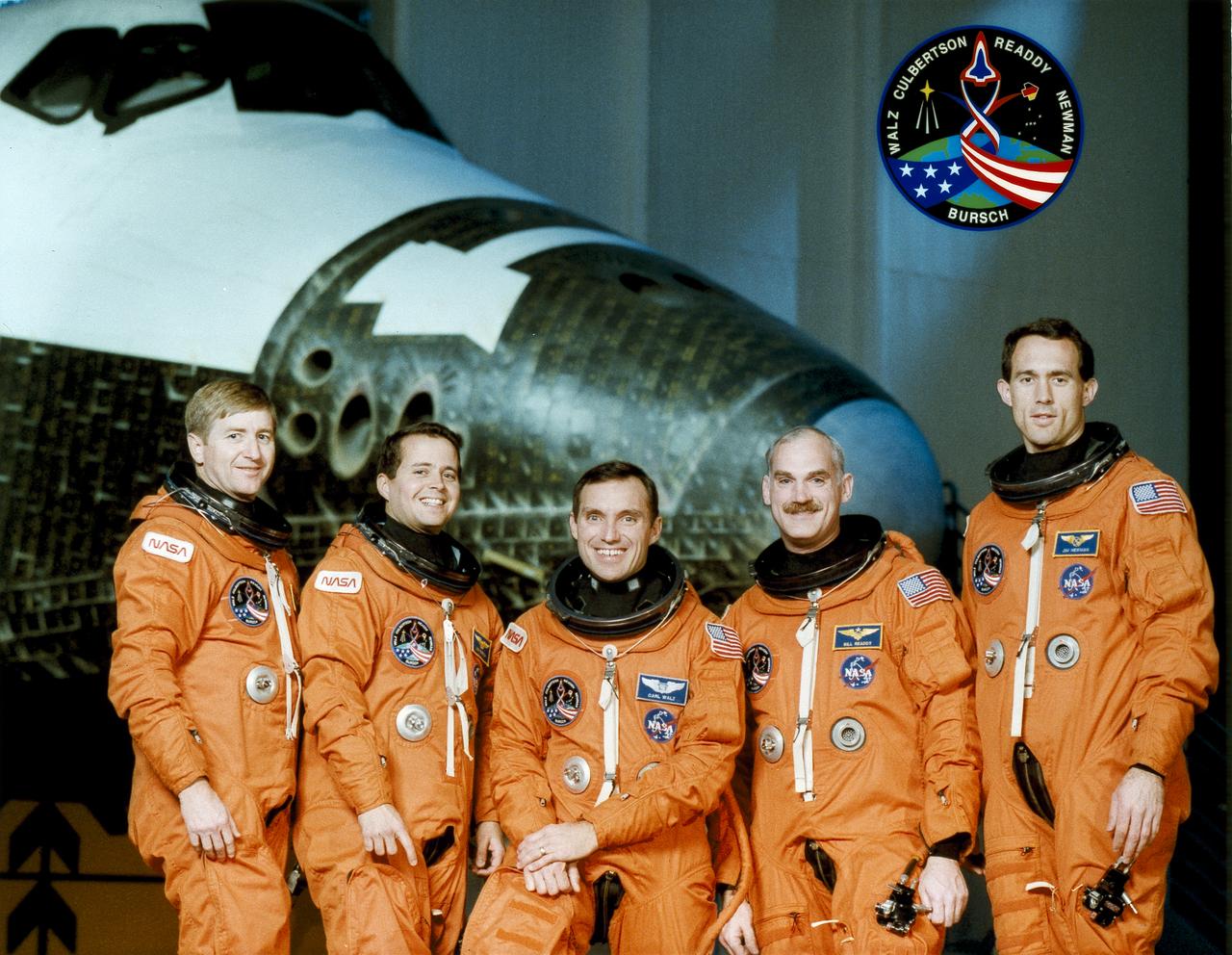

The STS-51 crew portrait features (left to right): Frank L. Culbertson, commander; Daniel W. Bursch, mission specialist; Carl E. Walz, mission specialist; William F. Readdy, pilot; and James H. Newman, mission specialist. The crew of five launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on September 12, 1993 at 7:45:00 am (EDT). Two primary payloads included the Advanced Communications Technology Satellite (ACTS), and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrograph Shuttle Pallet Satellite (OERFEUS-SPAS).
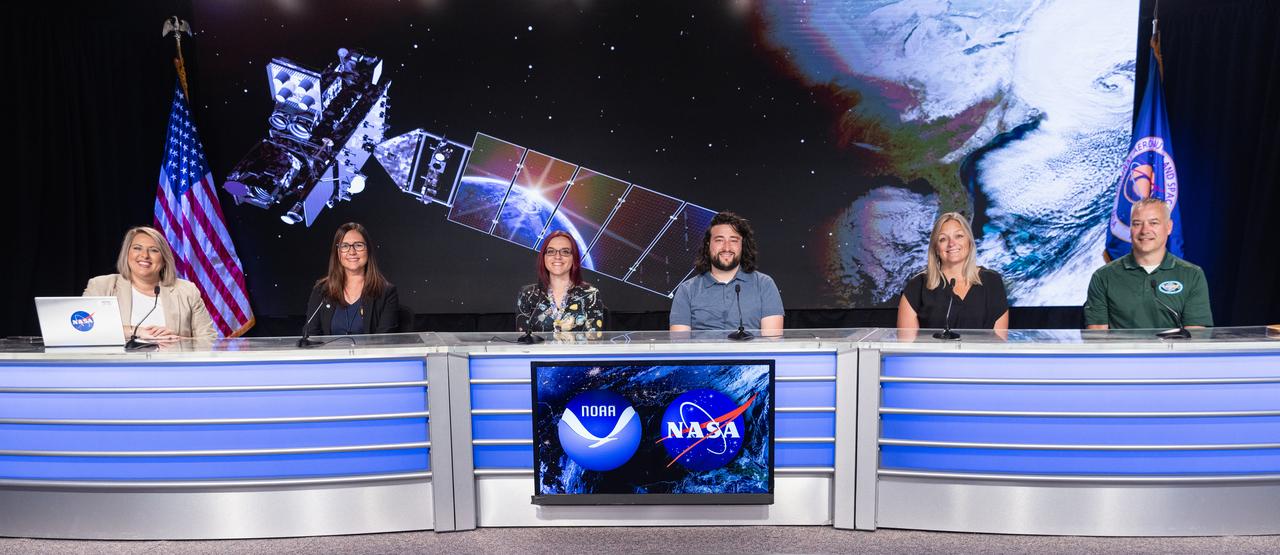

Officials from NASA, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and other mission managers participate in a social panel on Monday, June 24, 2024, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the launch of GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) mission. From left to right, Leah Martin, NASA Communications; Ellen Ramirez, deputy division chief, Mission Operations Division, National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service Office of Satellite and Product Operations, NOAA; Jade Zsiros, telemetry engineer, NASA’s Launch Services Program; Dakota Smith, satellite analyst and communicator, NOAA’s Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere; Allana Nepomuceno, senior manager, GOES-U Assembly, Test, and Launch Operations, Lockheed Martin; Chris Reith, program manager, Advanced Baseline Imager, L3Harris Technologies. The two-hour launch window opens at 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, for the satellite’s launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
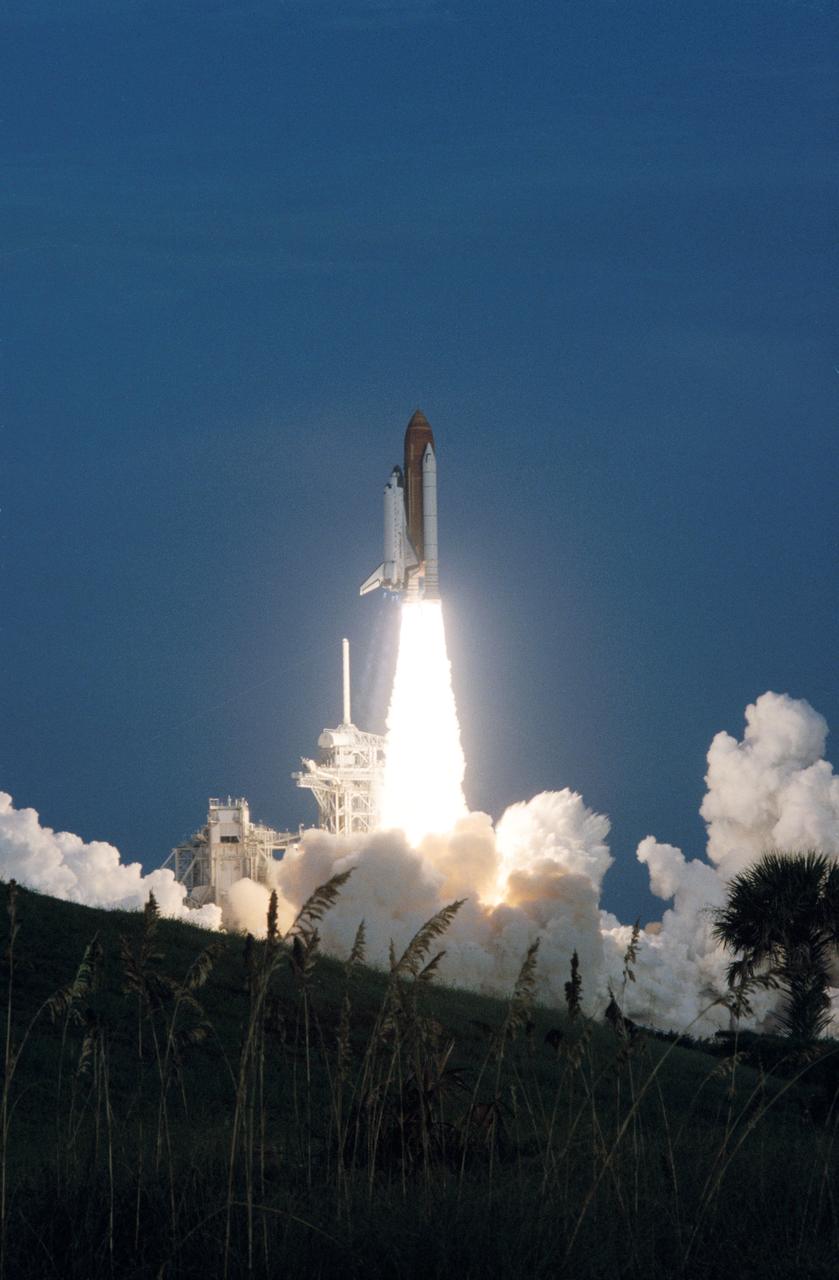

STS051-S-108 (12 Sept. 1993) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery soars toward a nine-day stay in Earth-orbit to support the mission. Launch occurred at 7:45 a.m. (EDT) September 12, 1993. Note the diamond shock effect coming from the thrust of the three main engines. Onboard the shuttle were astronauts Frank L. Culbertson, Jr., William F. Readdy, Daniel W. Bursch, James H. Newman and Carl E. Walz, along with a number of payloads. The payloads included the Advanced Communications Technology Satellite (ACTS) with its Transfer Orbit Stage (TOS), the Orbiting Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer (ORFEUS) and its Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS) carrier. This photograph was taken with a 35mm camera.

S85-31266 (May 1985) --- The STS-51G insignia illustrates the advances in aviation technology in the United States within a relatively short span of the twentieth century. The surnames of the crew members for the Discovery's mission appear near the center edge of the circular design. They are astronauts Daniel C. Brandenstein, mission commander; John O. Creighton, pilot; John M. Fabian, Steven R. Nagel and Shannon W. Lucid, mission specialists; Sultan Salman Abdelazize Al-Saud and Patrick Baudry, payload specialists. Al-Saud is flying as part of the reimbursable agreement with the Arab Satellite Communications Organization covering the launch of the Arabsat 1B communications satellite and Baudry represents France's Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA

CRAY AND SP-2 COMPUTERS

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California finish attaching the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
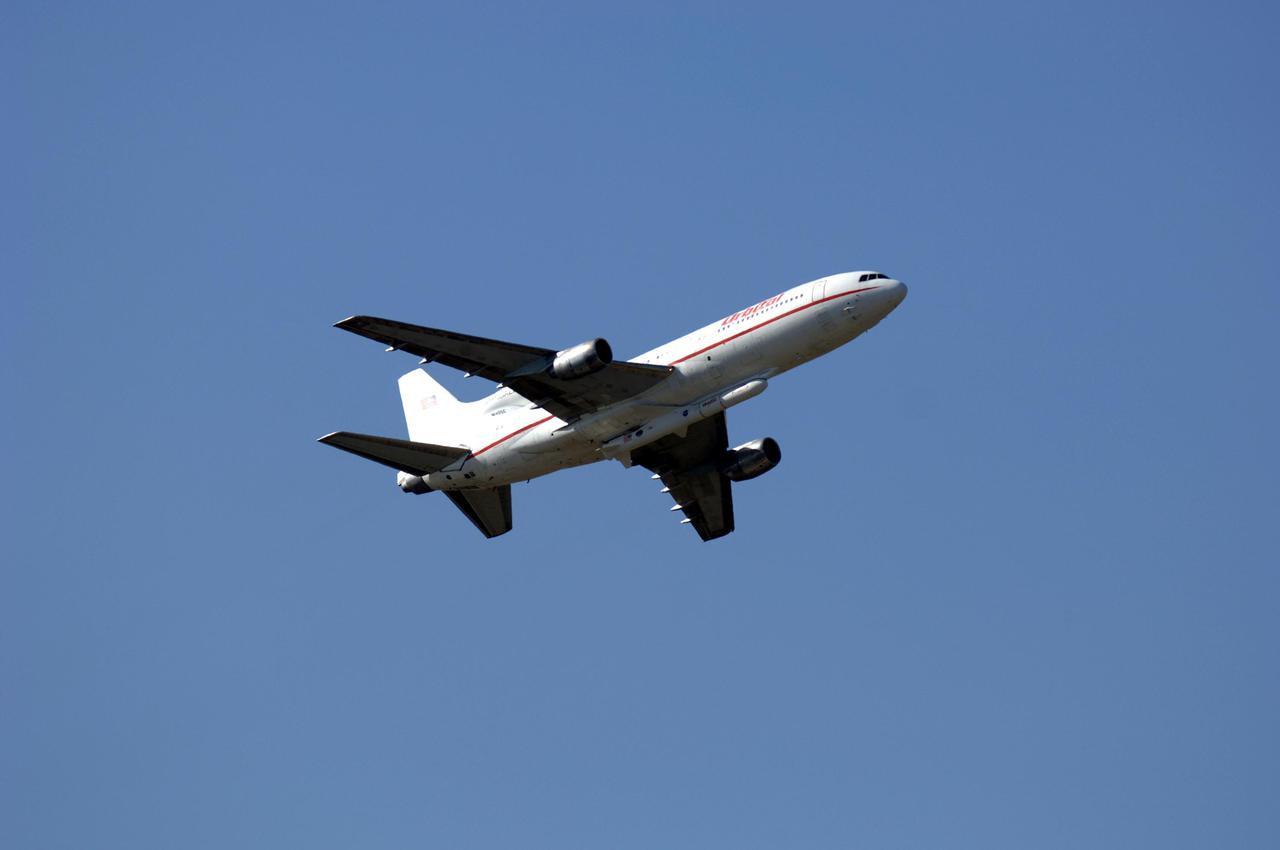

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, FLA. - The Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft soars through the sky to launch the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft attached to its underbelly. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
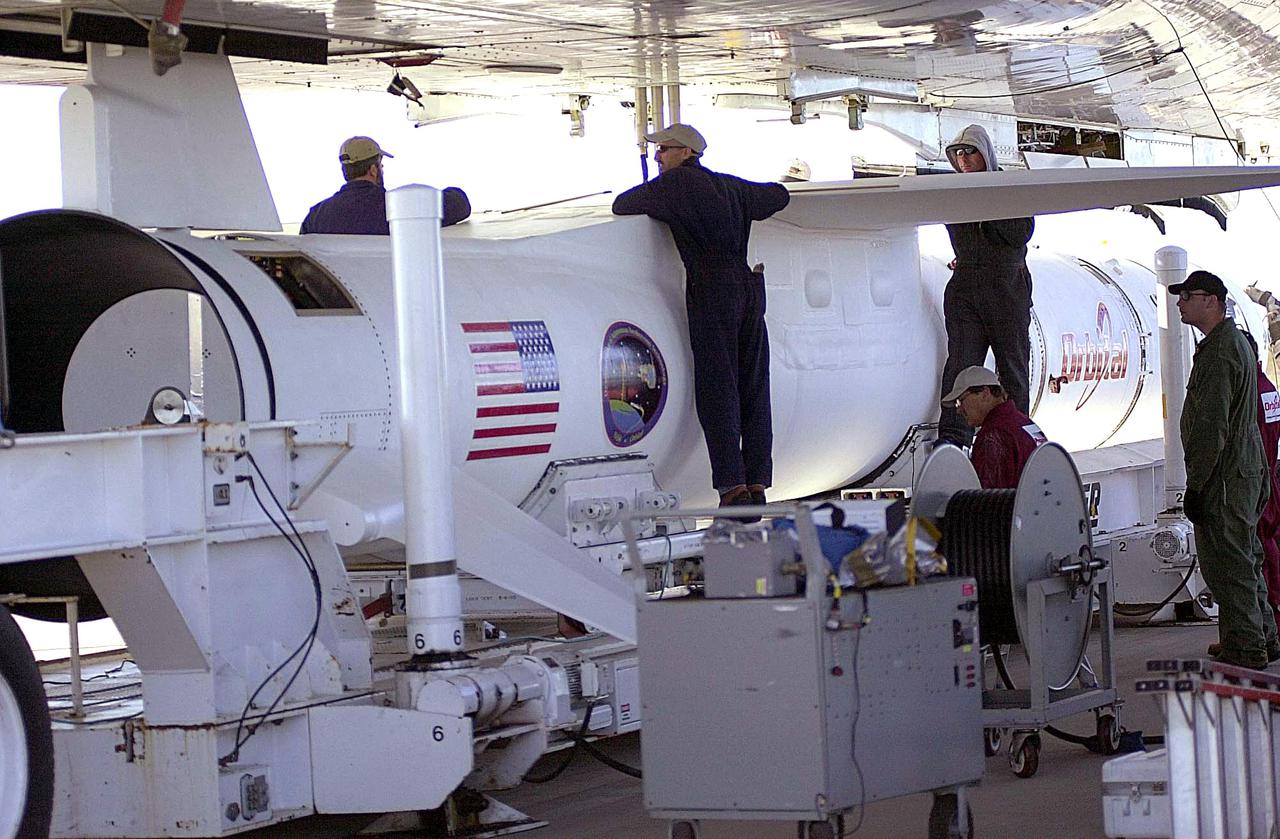

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft, which are mated, are being attached to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
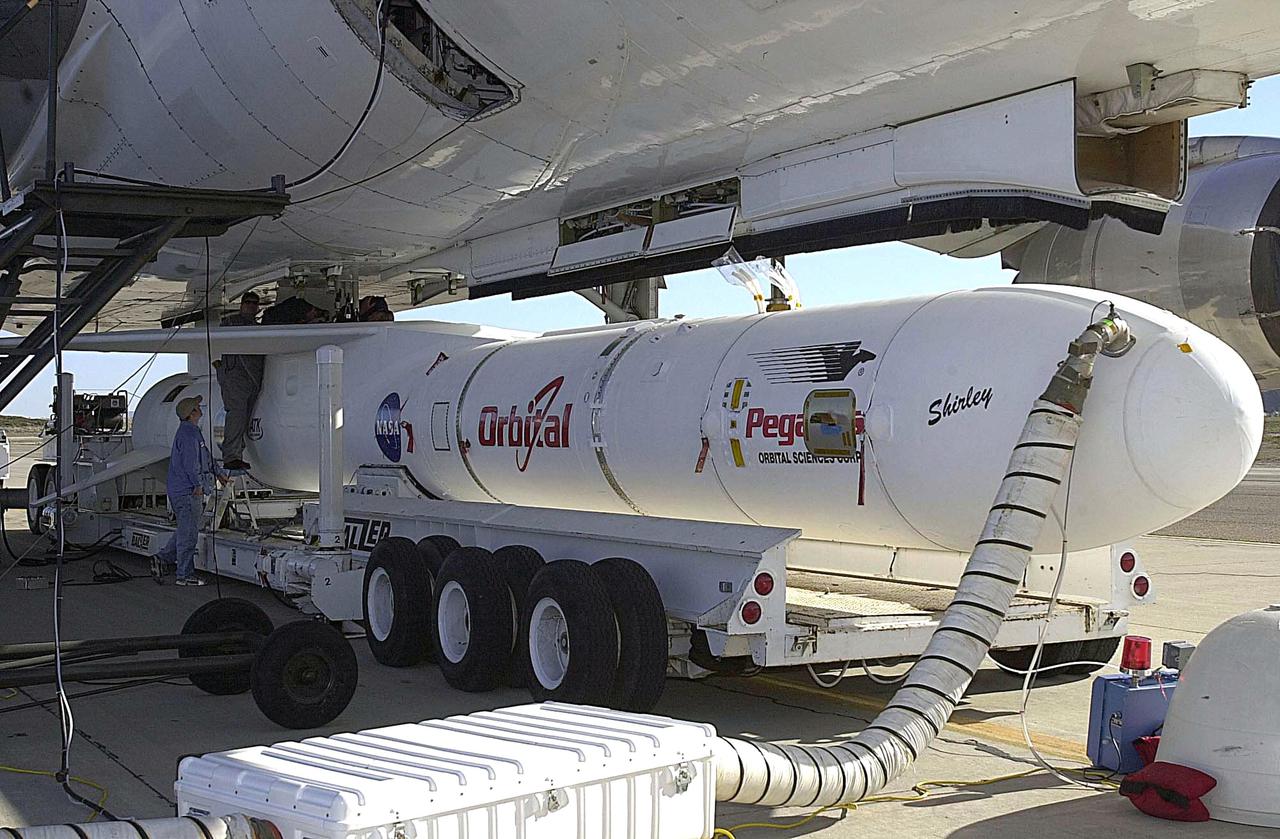

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft, which are mated, are being attached to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
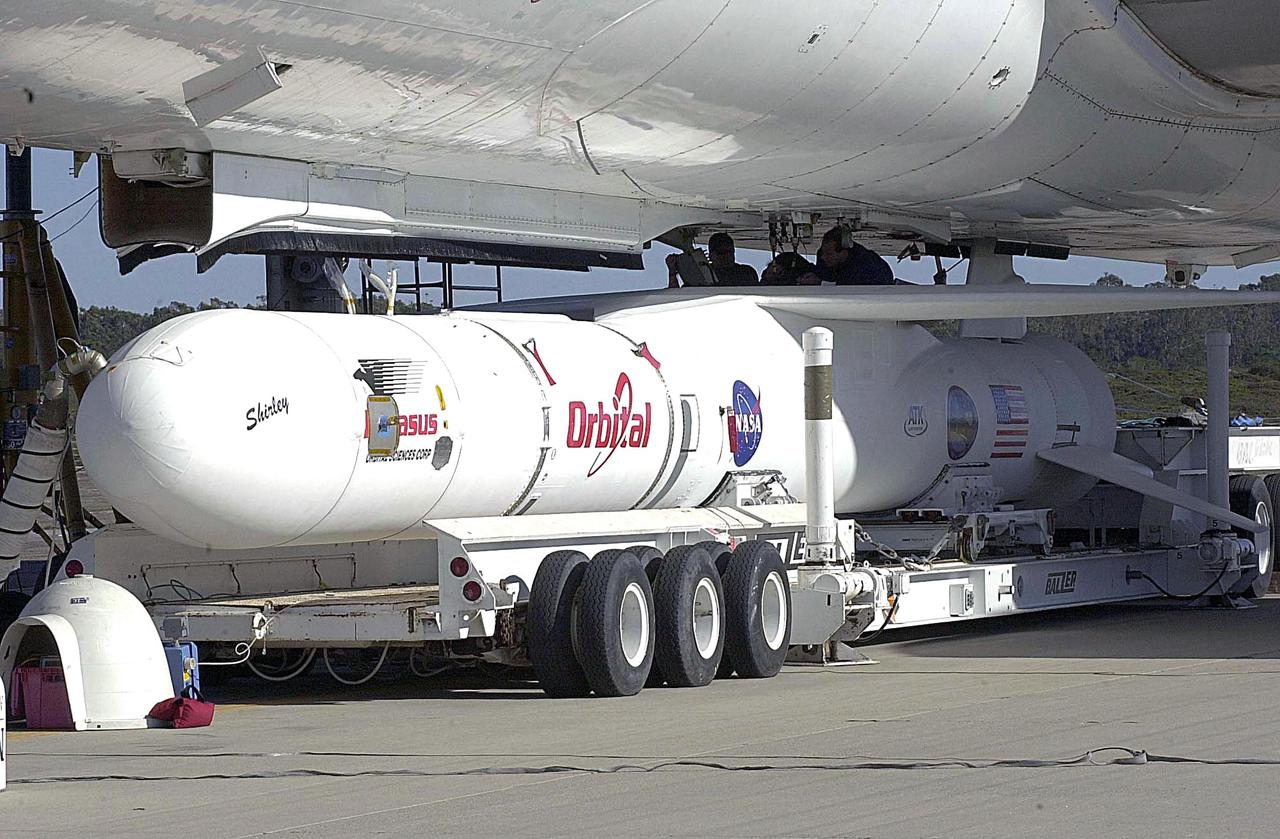

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft, which are mated, are being attached to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
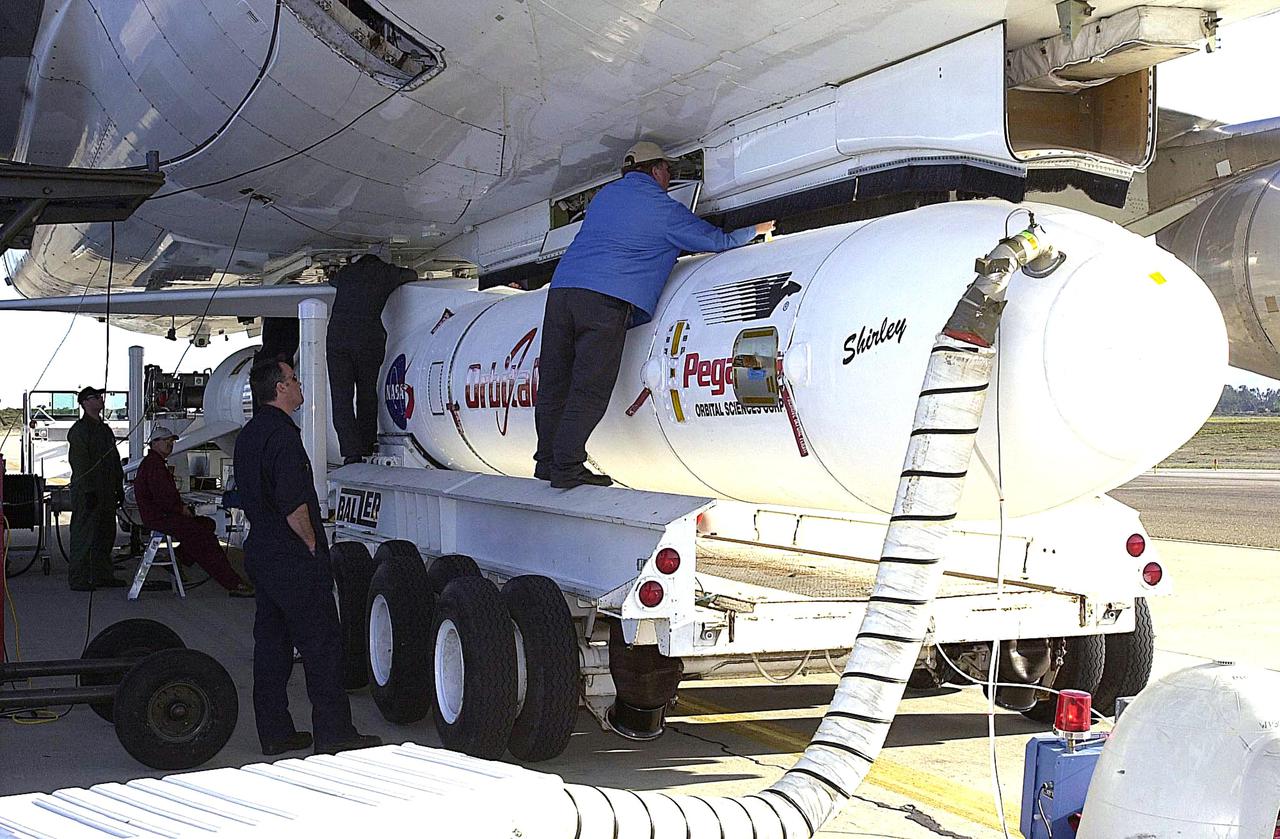

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker stands on the transporter to attach the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, FLA. - The Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft soars through the sky to launch the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft attached to its underbelly. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
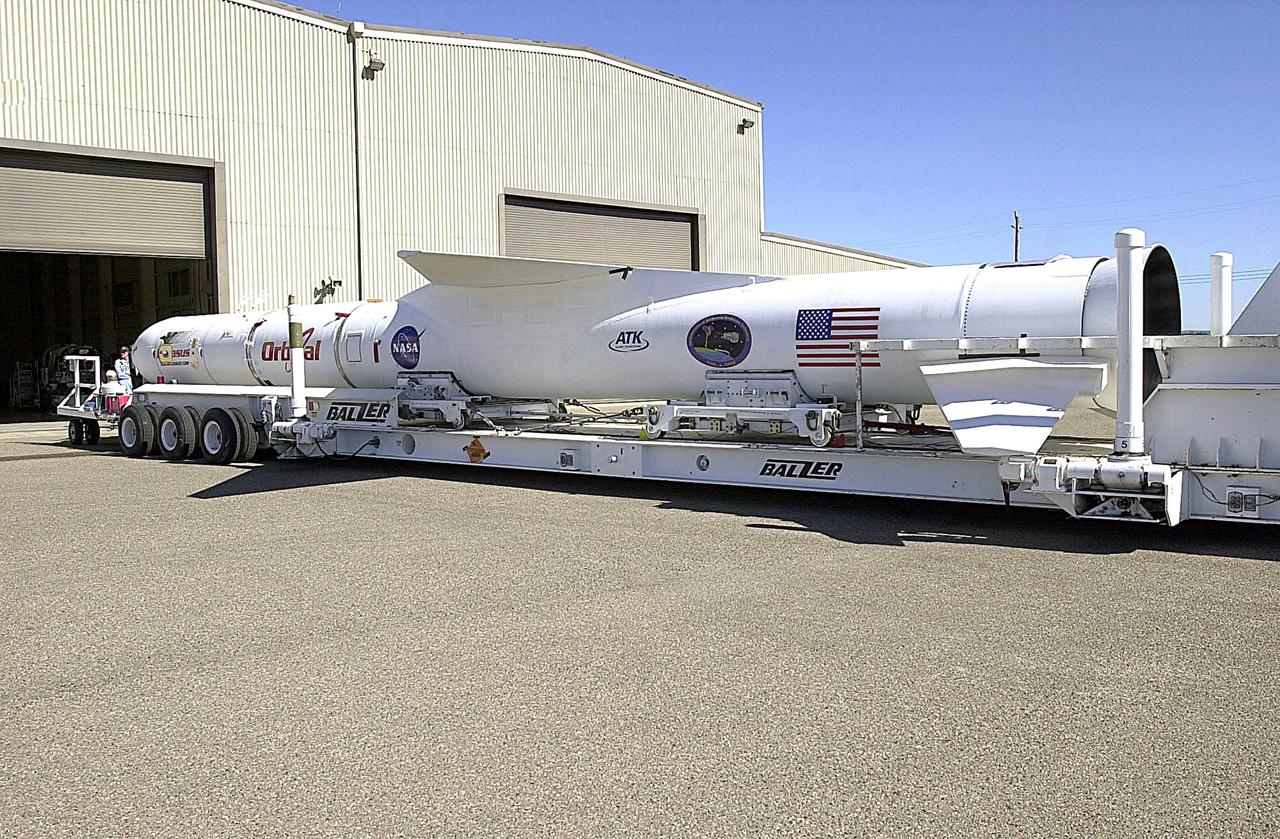

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft roll out of the hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. They will head to the runway and be attached to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
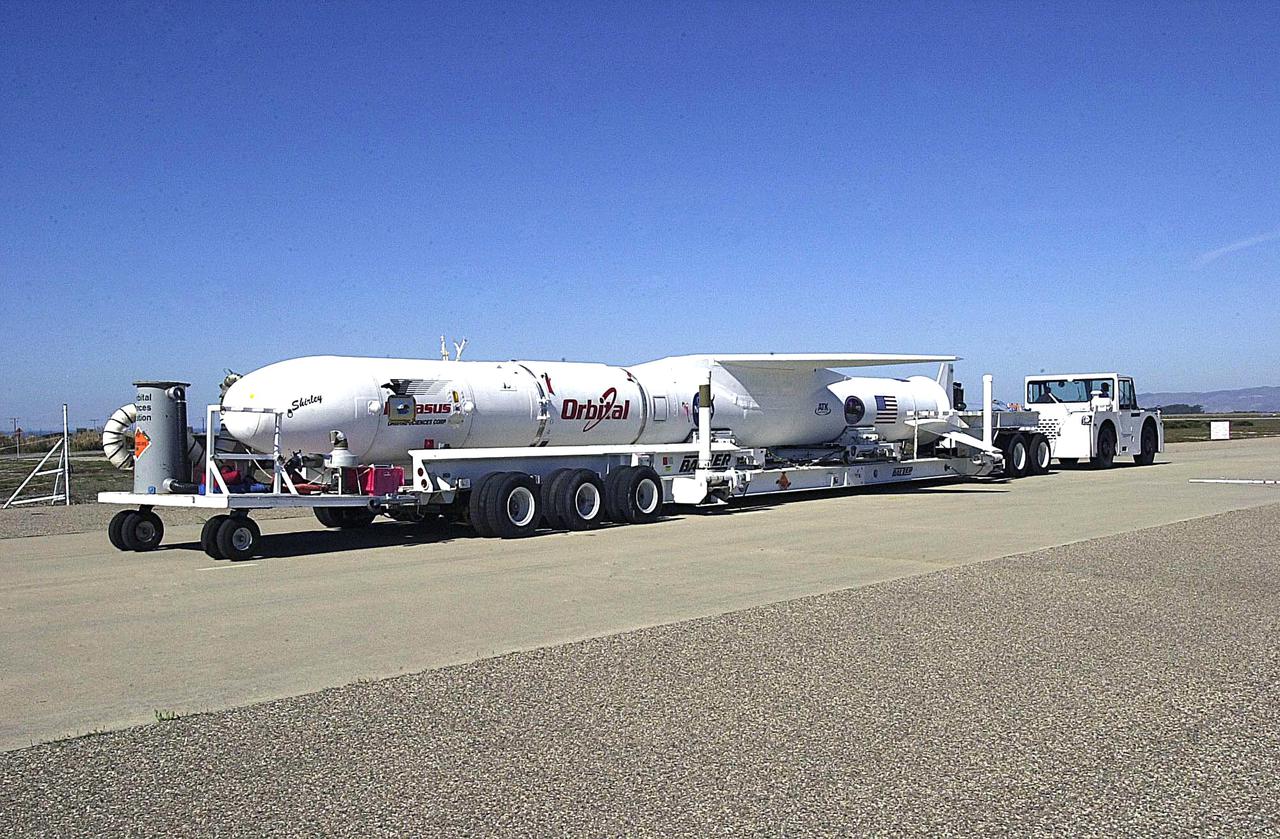

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft head for the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California and the waiting Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft. The Pegasus_DART will be attached to the underbelly of the L-1011 for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
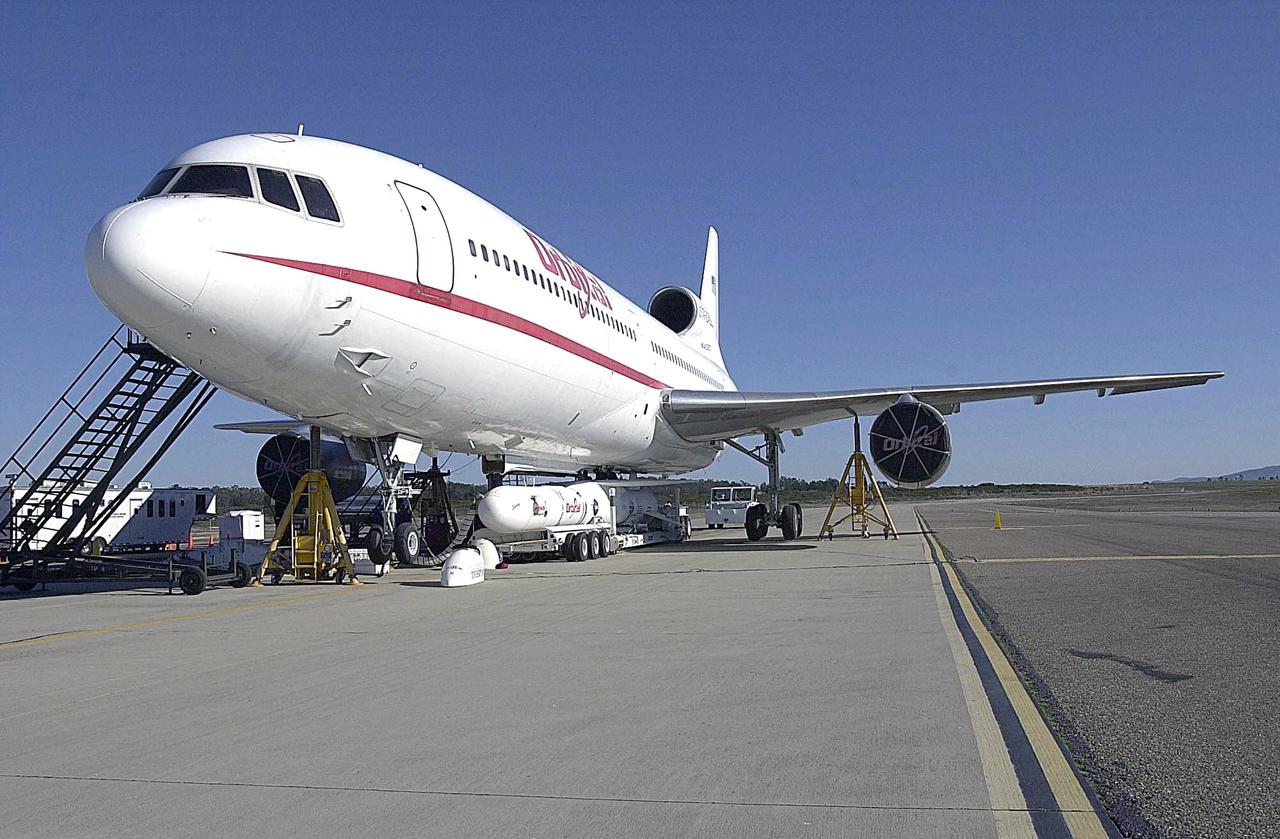

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft, which are mated, are being attached to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.

A science briefing for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is held on Feb. 25, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Participants from left, are Tylar Greene, briefing moderator, NASA Communications; Dr. Dan Lindsey, GOES-R program scientist, NOAA; Candace Carlisle, GOES-R flight project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center; Tewa Kpulun, Geostationary Lightning Mapper science lead, Lockheed Martin; and Daniel Gall, Advanced Baseline Imager chief systems engineer, Space and Airborne Systems, L3 Harris Technologies, participates in the briefing. GOES-T is scheduled to lift off on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
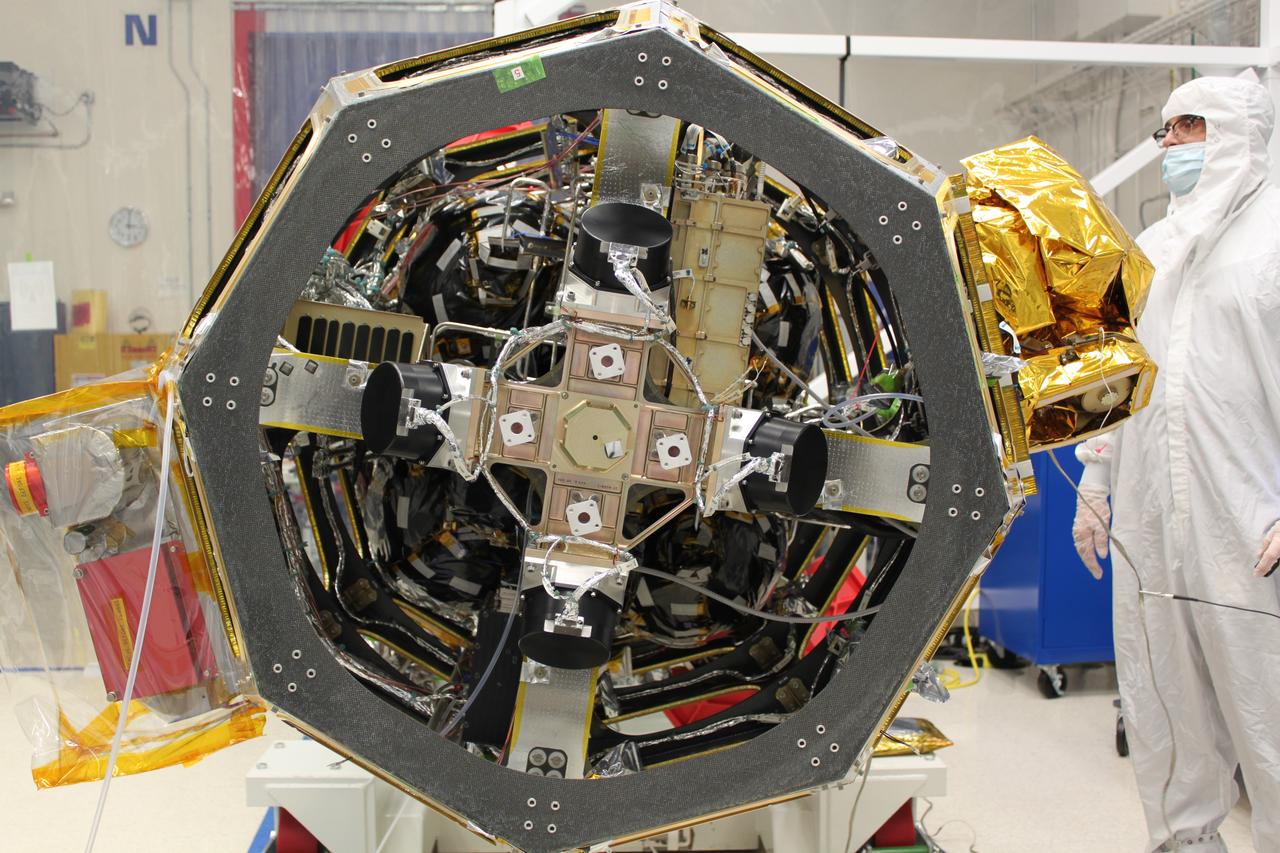
A new NASA-developed, laser-based space communication system will enable higher rates of satellite communications similar in capability to high-speed fiber optic networks on Earth. The space terminal for the Lunar Laser Communication Demonstration (LLCD), NASA's first high-data-rate laser communication system, was recently integrated onto the Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) spacecraft. LLCD will demonstrate laser communications from lunar orbit to Earth at six times the rate of the best modern-day advanced radio communication systems. Credit: NASA ----- What is LADEE? The Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) is designed to study the Moon's thin exosphere and the lunar dust environment. An "exosphere" is an atmosphere that is so thin and tenuous that molecules don't collide with each other. Studying the Moon's exosphere will help scientists understand other planetary bodies with exospheres too, like Mercury and some of Jupiter's bigger moons. The orbiter will determine the density, composition and temporal and spatial variability of the Moon's exosphere to help us understand where the species in the exosphere come from and the role of the solar wind, lunar surface and interior, and meteoric infall as sources. The mission will also examine the density and temporal and spatial variability of dust particles that may get lofted into the atmosphere. The mission also will test several new technologies, including a modular spacecraft bus that may reduce the cost of future deep space missions and demonstrate two-way high rate laser communication for the first time from the Moon. LADEE now is ready to launch when the window opens on Sept. 6, 2013. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/ladee" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/ladee</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

STS051-S-001 (January 1993) --- Designed by the crew members, the crew patch honors all who have contributed to mission success. It symbolizes NASA's continuing quest to increase mankind's knowledge and use of space through this multi-faceted mission. The gold star represents the United States Advanced Communications Technology Satellite (ACTS) boosted by the Transfer Orbit Stage (TOS). The rays below the ACT\TOS represent the innovative communication technologies to be tested by this experiment. The stylized Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS) represents the German-sponsored ASTRO\SPAS mission. The constellation Orion below SPAS is representative of the types of stellar objects to be studied by its experimenters. The stars in Orion also commemorate the astronauts who have sacrificed their lives for the space program. The ascending spiral, symbolizing America's continuing commitment to leadership in space exploration and development, originates with the thousands of persons who ensure the success of each space shuttle flight. The five large white stars, representing the five crew members, along with the single gold star, form the mission's numerical designation. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
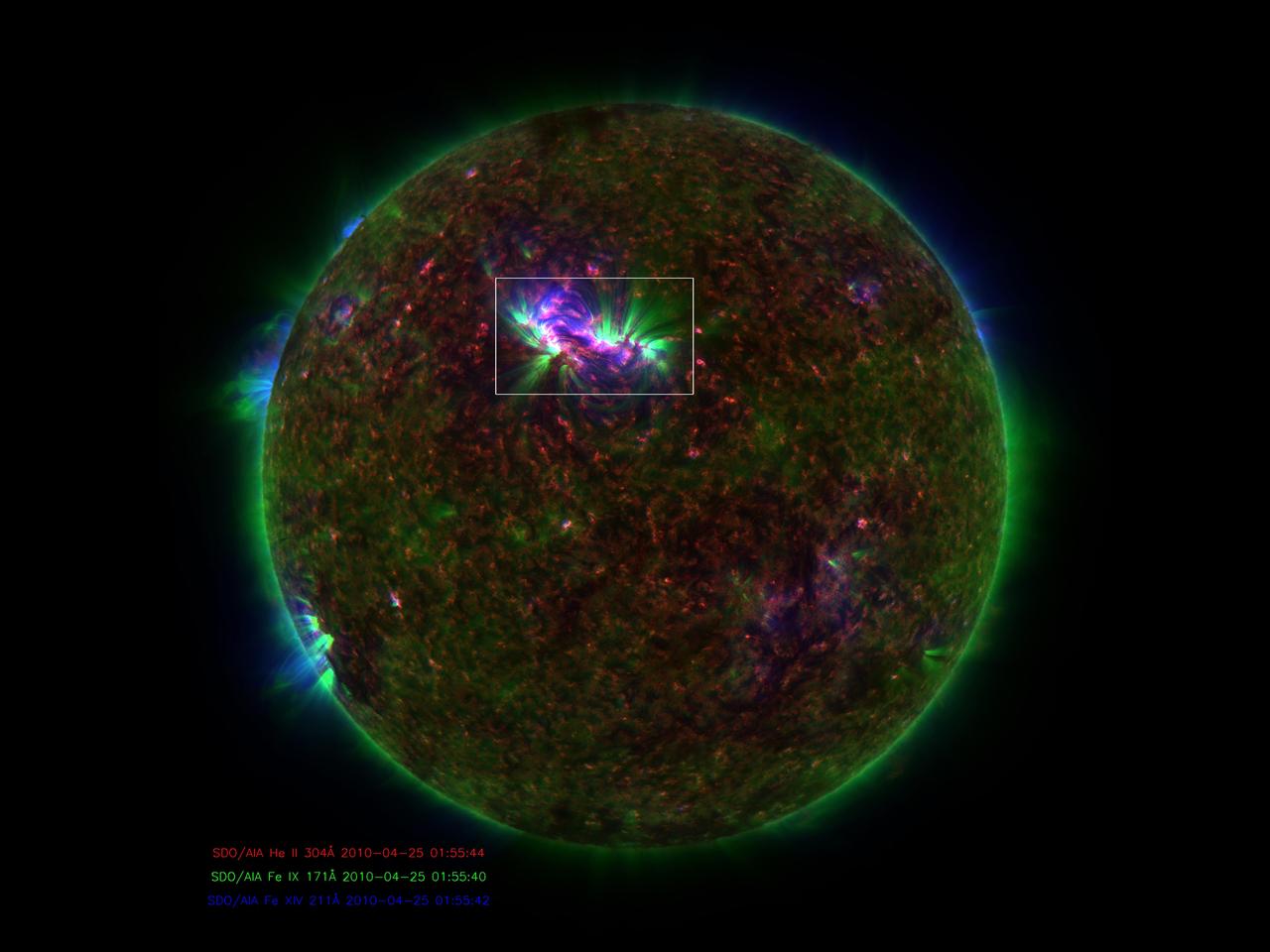
NASA image release January 6, 2010 Caption: Spicules on the sun, as observed by the Solar Dynamics Observatory. These bursts of gas jet off the surface of the sun at 150,000 miles per hour and contain gas that reaches temperatures over a million degrees. GREENBELT, Md. -- Observations from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the Japanese satellite Hinode show that some gas in the giant, fountain-like jets in the sun's atmosphere known as spicules can reach temperatures of millions of degrees. The finding offers a possible new framework for how the sun's high atmosphere gets so much hotter than the surface of the sun. What makes the high atmosphere, or corona, so hot – over a million degrees, compared to the sun surface's 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit -- remains a poorly understood aspect of the sun's complicated space weather system. That weather system can reach Earth, causing auroral lights and, if strong enough, disrupting Earth's communications and power systems. Understanding such phenomena, therefore, is an important step towards better protecting our satellites and power grids. "The traditional view is that all the heating happens higher up in the corona," says Dean Pesnell, who is SDO's project scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "The suggestion in this paper is that cool gas is being ejected from the sun's surface in spicules and getting heated on its way to the corona." Spicules were first named in the 1940s, but were hard to study in detail until recently, says Bart De Pontieu of Lockheed Martin's Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory, Palo Alto, Calif. who is the lead author on a paper on this subject in the January 7, 2011 issue of Science magazine. In visible light, spicules can be seen to send large masses of so-called plasma – the electromagnetic gas that surrounds the sun – up through the lower solar atmosphere or photosphere. The amount of material sent up is stunning, some 100 times as much as streams away from the sun in the solar wind towards the edges of the solar system. But nobody knew if they contained hot gas. "Heating of spicules to the necessary hot temperatures has never been observed, so their role in coronal heating had been dismissed as unlikely," says De Pontieu. Now, De Pontieu's team -- which included researchers at Lockheed Martin, the High Altitude Observatory of the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Colorado and the University of Oslo, Norway -- was able to combine images from SDO and Hinode to produce a more complete picture of the gas inside these gigantic fountains. The scientists found that a large fraction of the gas is heated to a hundred thousand degrees, while a small fraction is heated to millions of degrees. Time-lapsed images show that this material spews up into the corona, with most falling back down towards the surface of the sun. However, the small fraction of the gas that is heated to millions of degrees does not immediately return to the surface. Given the large number of spicules on the Sun, and the amount of material in the spicules, the scientists believe that if even some of that super hot plasma stays aloft it would make a contribution to coronal heating. Astrophysicist Jonathan Cirtain, who is the U.S. project scientist for Hinode at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala., says that incorporating such new information helps address an important question that reaches far beyond the sun. "This breakthrough in our understanding of the mechanisms which transfer energy from the solar photosphere to the corona addresses one of the most compelling questions in stellar astrophysics: How is the atmosphere of a star heated?" he says. "This is a fantastic discovery, and demonstrates the muscle of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, comprised of numerous instruments on multiple observatories." Hinode is the second mission in NASA's Solar Terrestrial Probes program, the goal of which is to improve understanding of fundamental solar and space physics processes. The mission is led by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ). The collaborative mission includes the U.S., the United Kingdom, Norway and Europe. NASA Marshall manages Hinode U.S. science operations and oversaw development of the scientific instrumentation provided for the mission by NASA, academia and industry. The Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center is the lead U.S. investigator for the Solar Optical Telescope on Hinode. SDO is the first mission in a NASA science program called Living With a Star, the goal of which is to develop the scientific understanding necessary to address those aspects of the sun-Earth system that directly affect our lives and society. NASA Goddard built, operates, and manages the SDO spacecraft for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules...</a> Credit: NASA Goddard/SDO/AIA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

NASA image acquired August 4, 2010 Though many areas in northwest Pakistan were bracing for heavy rain and additional flash flooding on August 4, 2010, the city of Kheshgi, in northwest Pakistan, had clear skies. This image, taken by the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA’s Terra satellite reveals a city awash in flood water. Thick with mud, the Kabul River is pale green in this false color image. Clearer water is dark blue. The river flows through its usual channel, but in places, water seeps over the channel and across the landscape. The buildings and roads of Kheshgi are silver. Spots of turquoise blue—shallow, muddy water or water-logged ground—covers several sections of the city. On the south side of the Kabul River, water flows down the hills, washing over neighborhoods. The bare ground in the hills is brown and tan. Plant-covered land, red in this image, is divided into long, narrow rectangles, pointing to agriculture. Geometric shapes under the water near the river are probably submerged fields of crops. Thousands of acres of crops had been lost in floods throughout Pakistan, said the United Nations. Kheshgi is in the Nowshera district in the Khyber Pakhutnkhwa province. As of August 2, Khyber Pakhutnkhwa was the hardest hit province in Pakistan, said the United Nations, and Nowshera was the most impacted district in the province. Nowshera reported 500,000 people displaced with 161 dead, said the Government of Khuber Pakhtunkhwa. The floods affected communities throughout Pakistan. More than 1,100 people had died, 15,000 homes were damaged or destroyed, and at least one million people were in need of emergency assistance throughout Pakistan, said the United Nations on August 2. The floods occurred as unusually heavy monsoon rains fell over Pakistan. NASA image courtesy NASA/GSFC/MITI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team. Caption by Holli Riebeek. Instrument: Terra - ASTER Credit: <b><a href="#//earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA’s Earth Observatory</a></b> To learn more about this image go here: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=45050" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=45050</a> Or here: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=45343" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=45343</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>