
Stefanie Tompkins, director of the Defense Advance Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is seen during a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
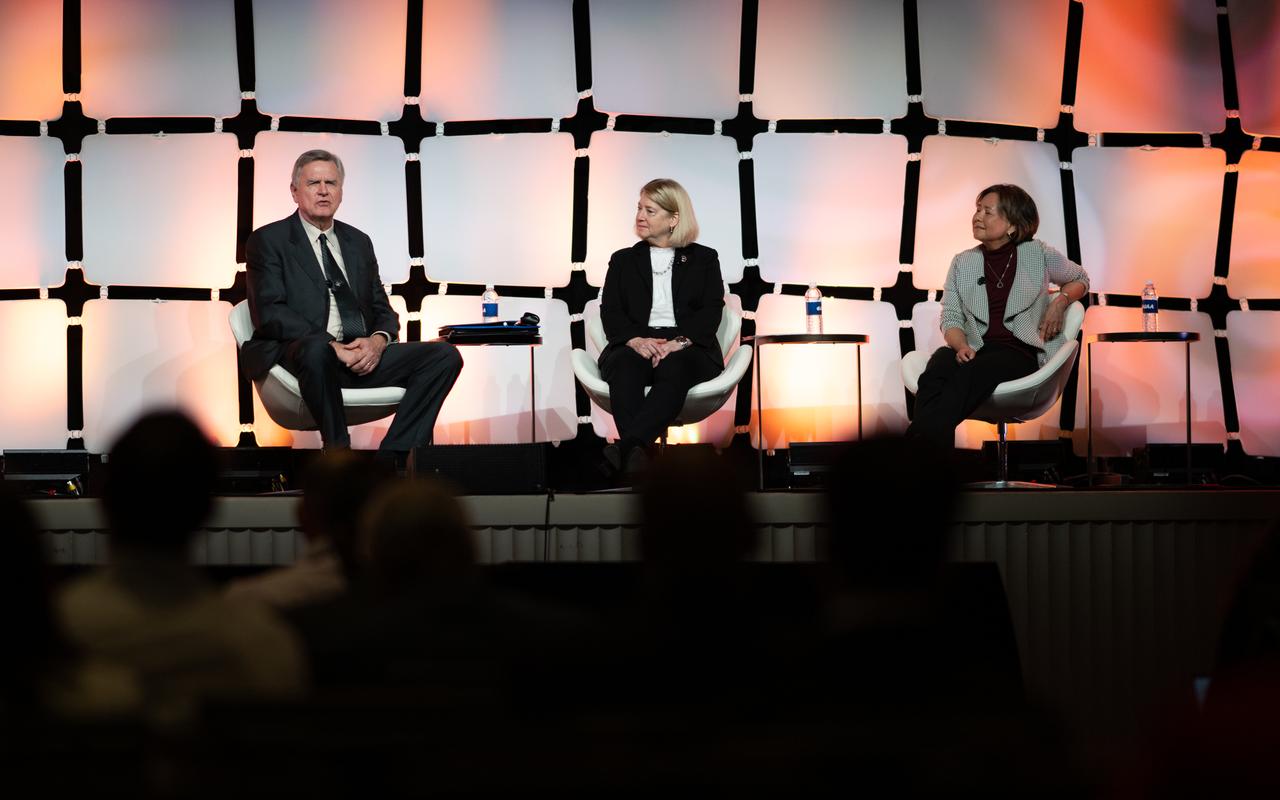

Steve Howe, former director of the Center for Space Nuclear Research at the Idaho National Laboratory, left, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, center, and Stefanie Tompkins, director of the Defense Advance Research Projects Agency (DARPA), right, are seen during a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Steve Howe, former director of the Center for Space Nuclear Research at the Idaho National Laboratory, left, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, center, and Stefanie Tompkins, director of the Defense Advance Research Projects Agency (DARPA), right, are seen during a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Steve Howe, former director of the Center for Space Nuclear Research at the Idaho National Laboratory, left, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, center, and Stefanie Tompkins, director of the Defense Advance Research Projects Agency (DARPA), right, are seen during a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
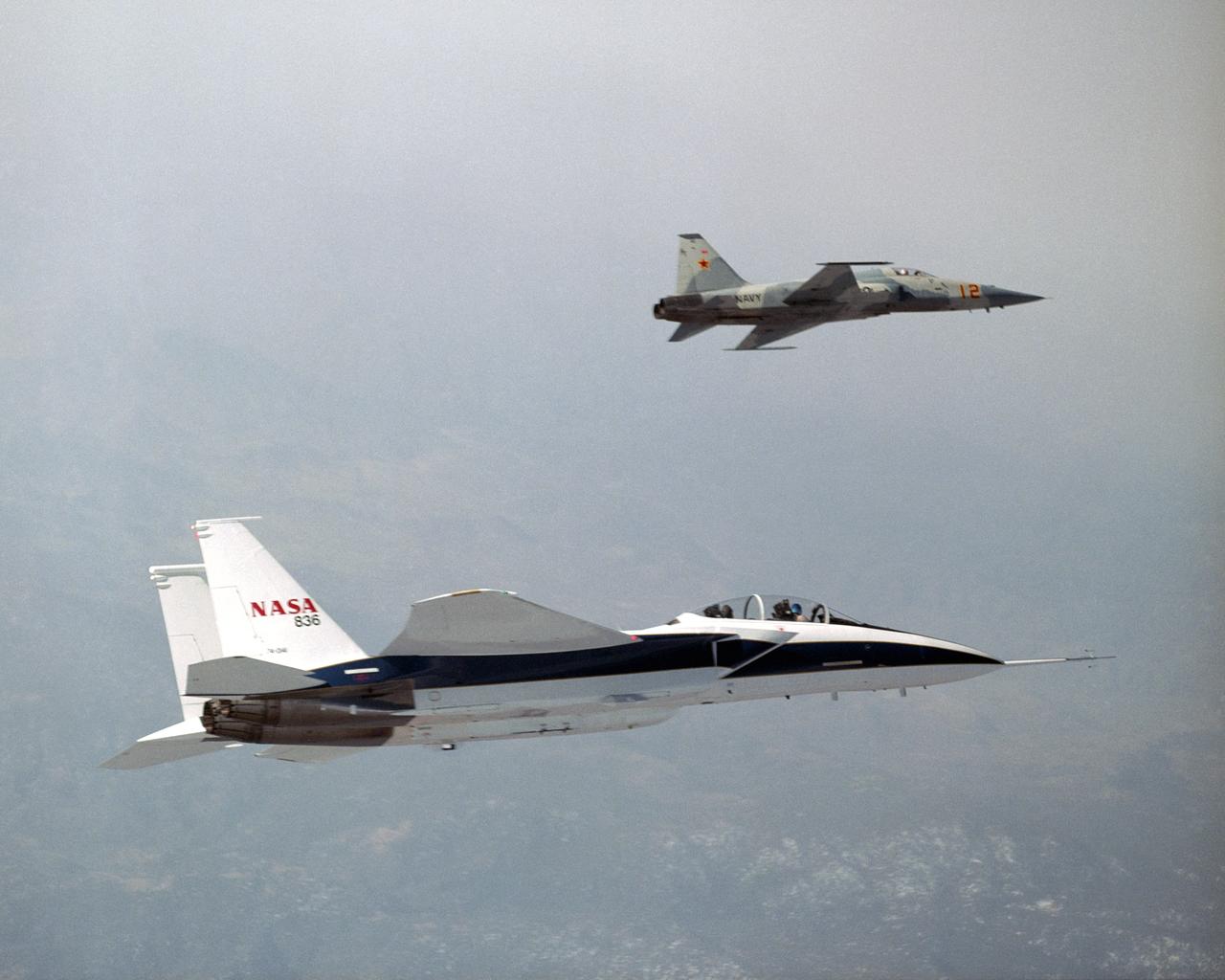

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.
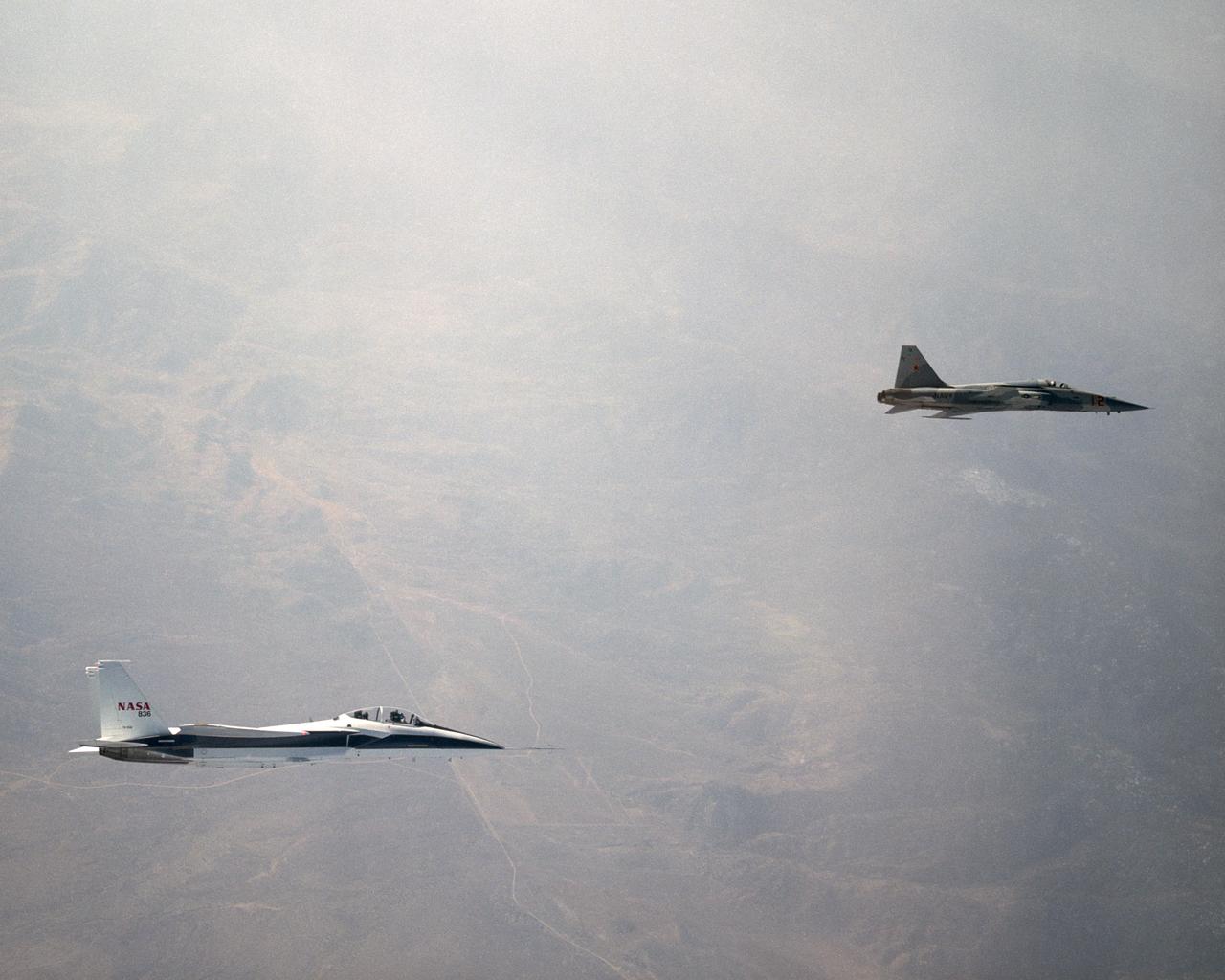

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.
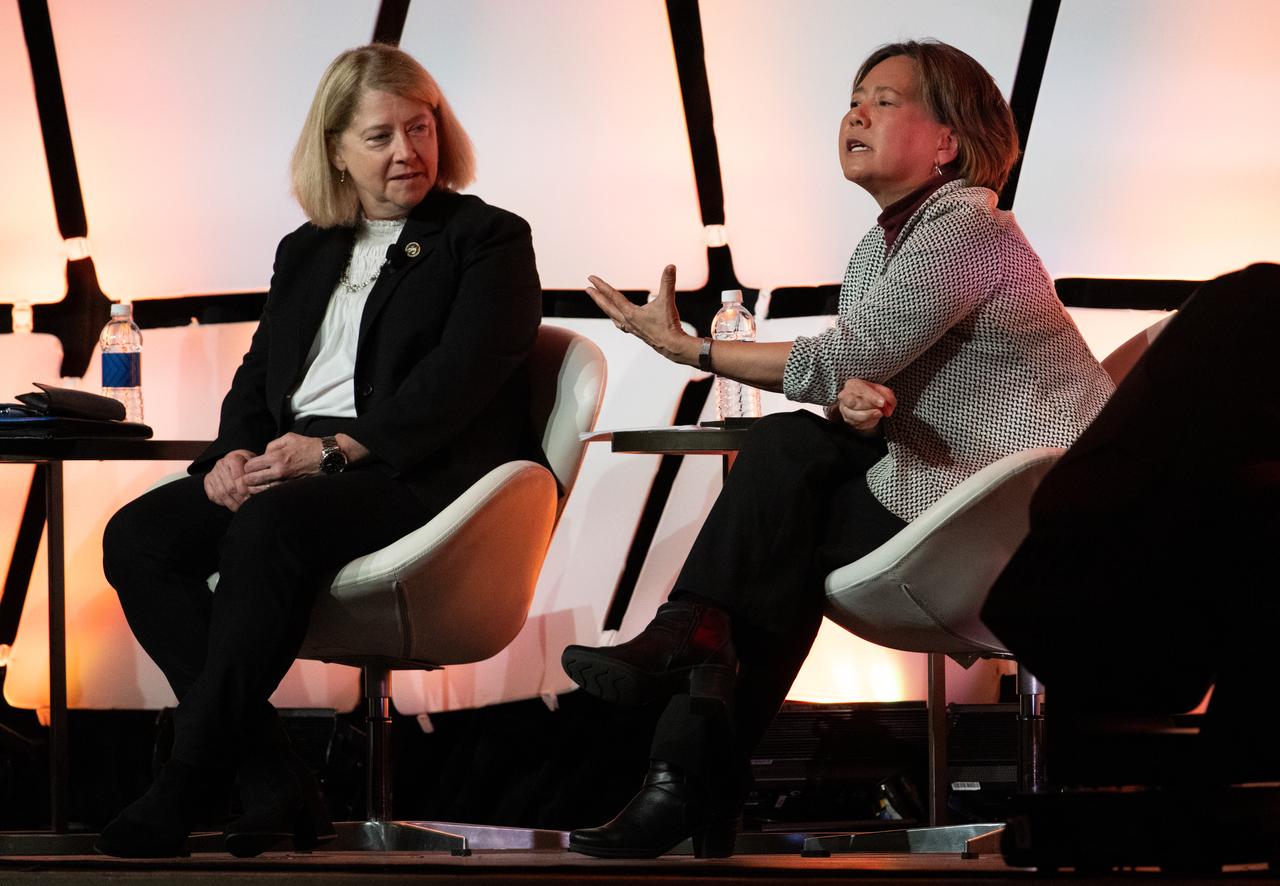

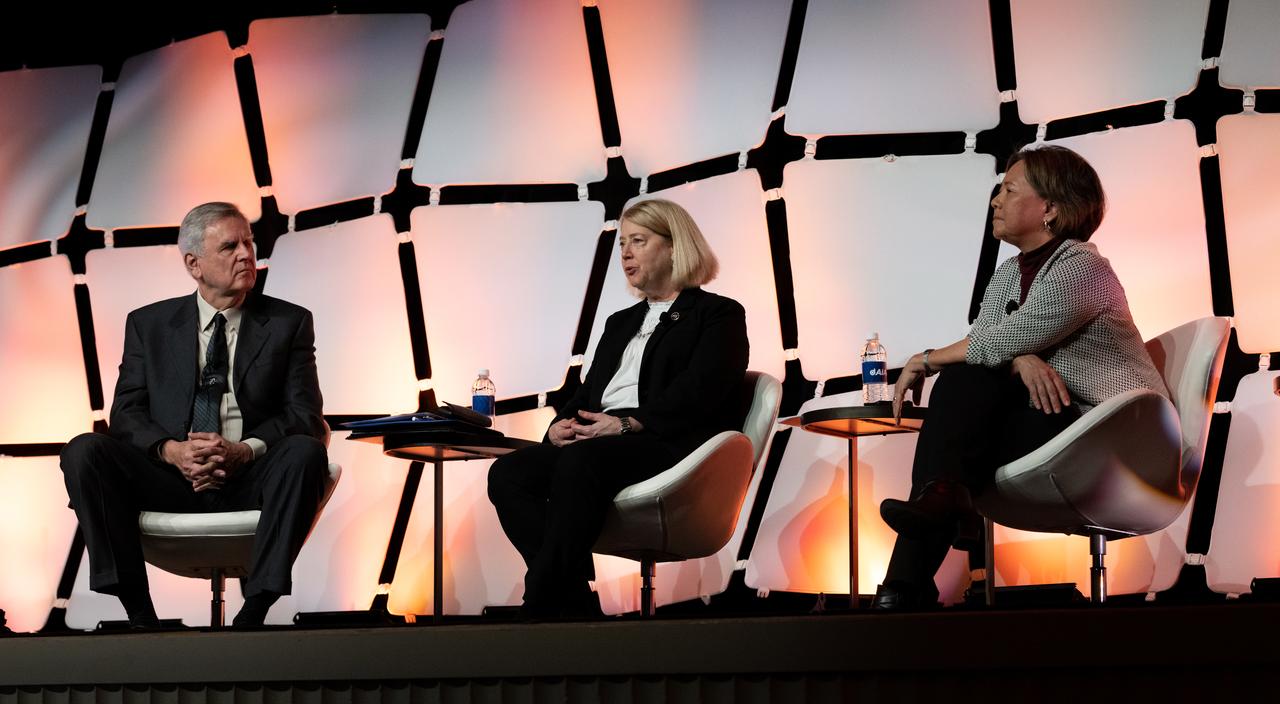
NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, left, and Stefanie Tompkins, director of the Defense Advance Research Projects Agency (DARPA), right, are seen during a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, left, and Stefanie Tompkins, director of the Defense Advance Research Projects Agency (DARPA), right, are seen during a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
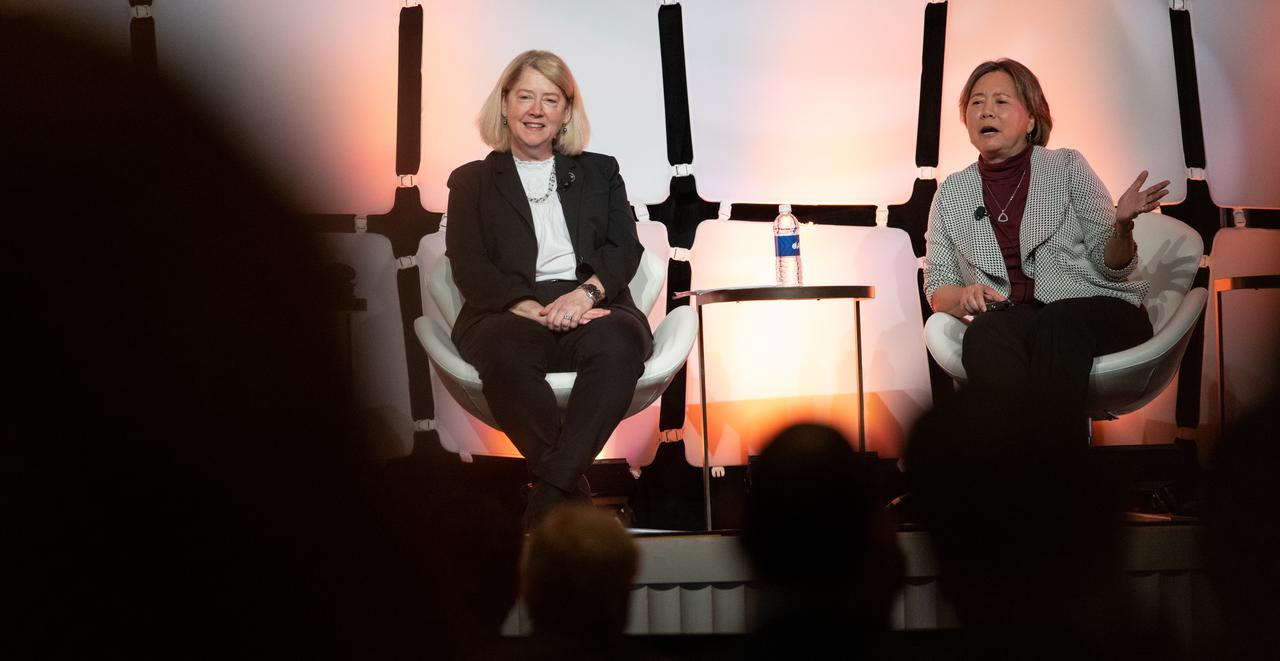

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, left, and Stefanie Tompkins, director of the Defense Advance Research Projects Agency (DARPA), right, are seen during a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
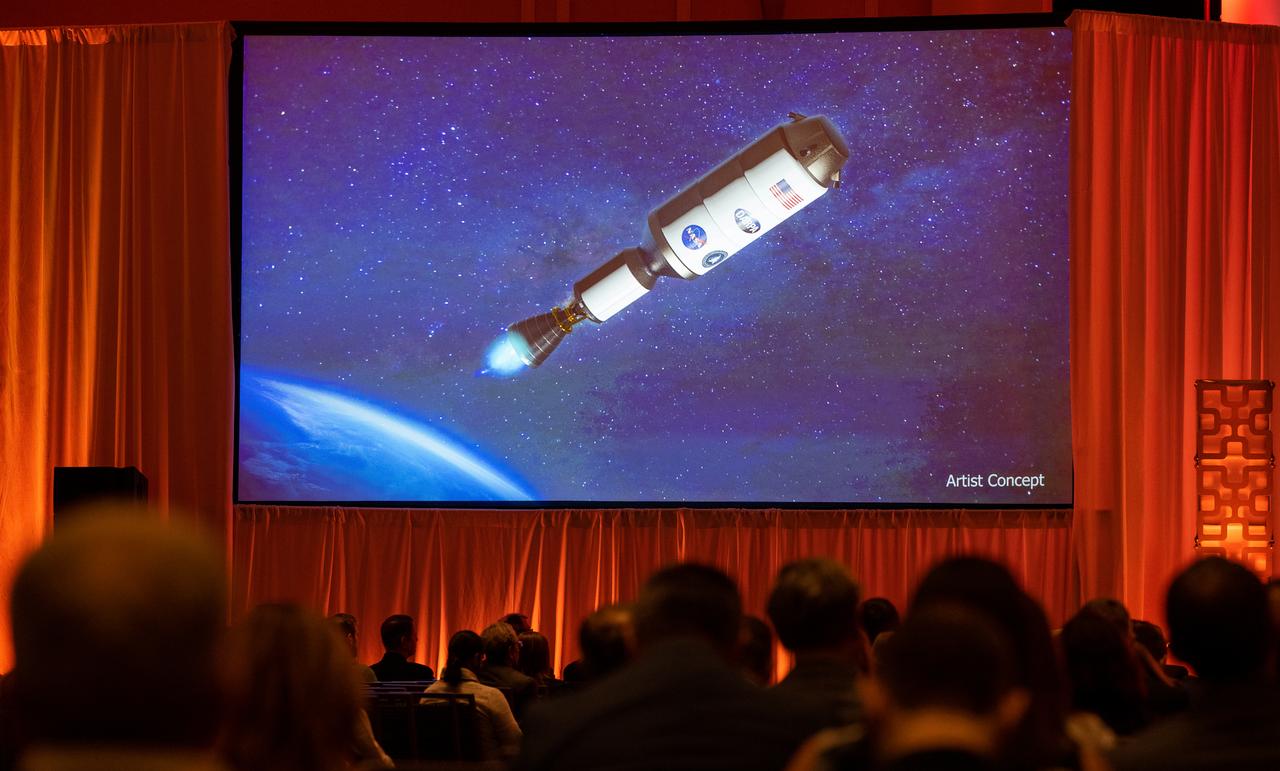

An artists concept of the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, spacecraft is seen on a screen during a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
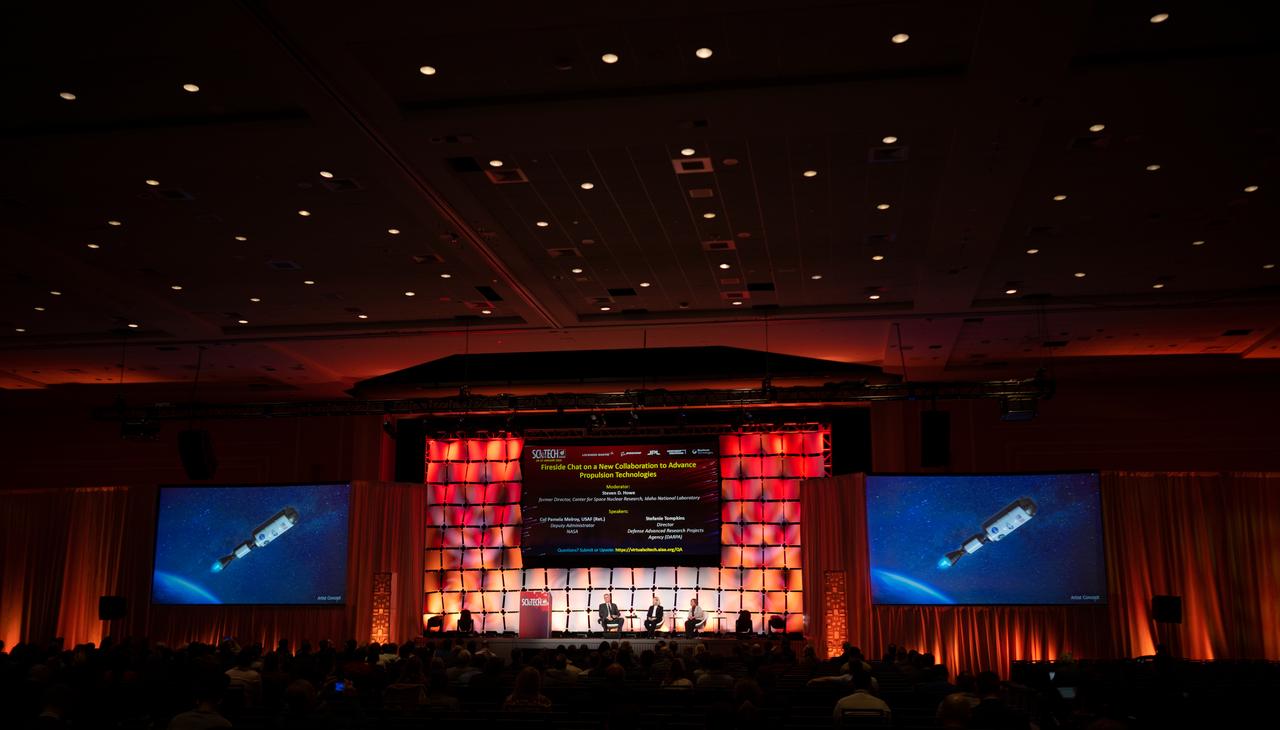

An artists concept of the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, spacecraft is seen on a screen as Steve Howe, former director of the Center for Space Nuclear Research at the Idaho National Laboratory, left, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, center, and Stefanie Tompkins, director of the Defense Advance Research Projects Agency (DARPA), right, participate in a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
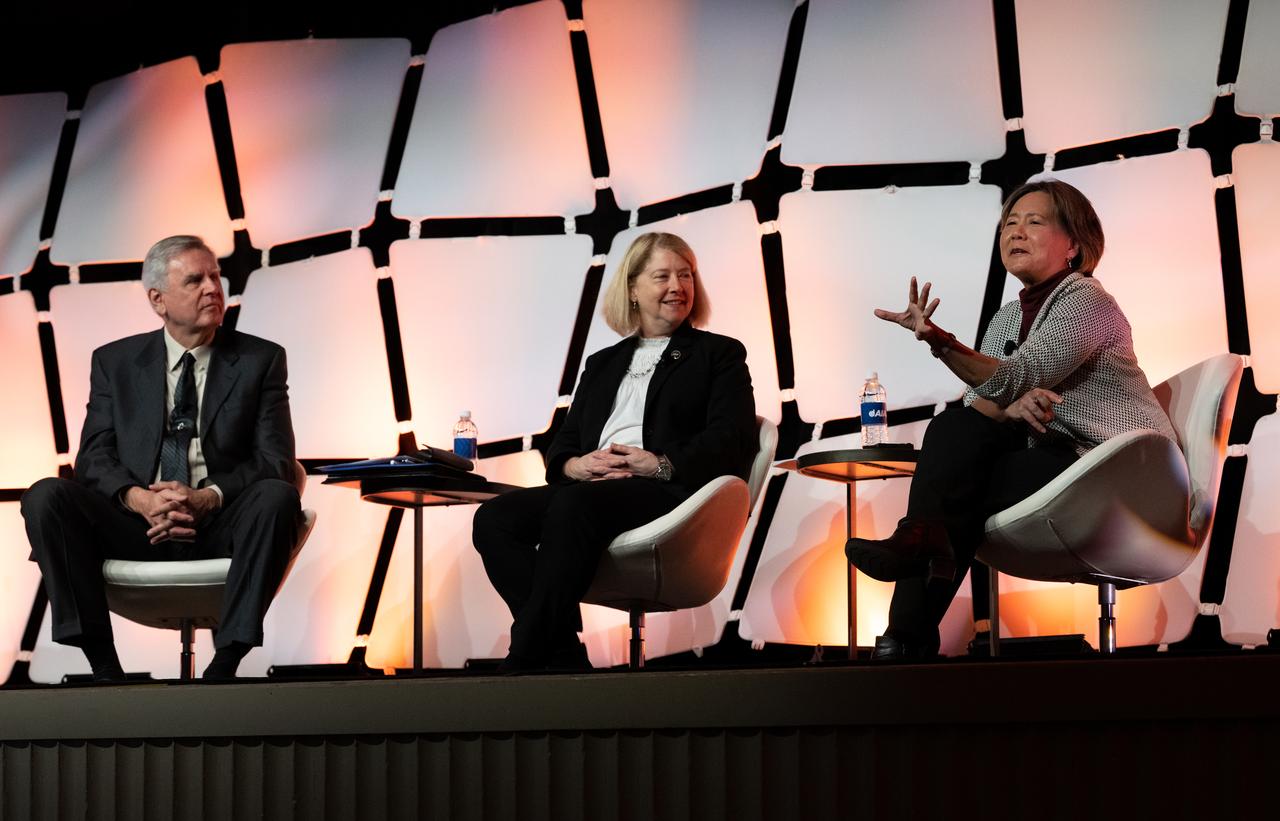

Stefanie Tompkins, director of the Defense Advance Research Projects Agency (DARPA), right, answers a question alongside Steve Howe, former director of the Center for Space Nuclear Research at the Idaho National Laboratory, left, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, center, during a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
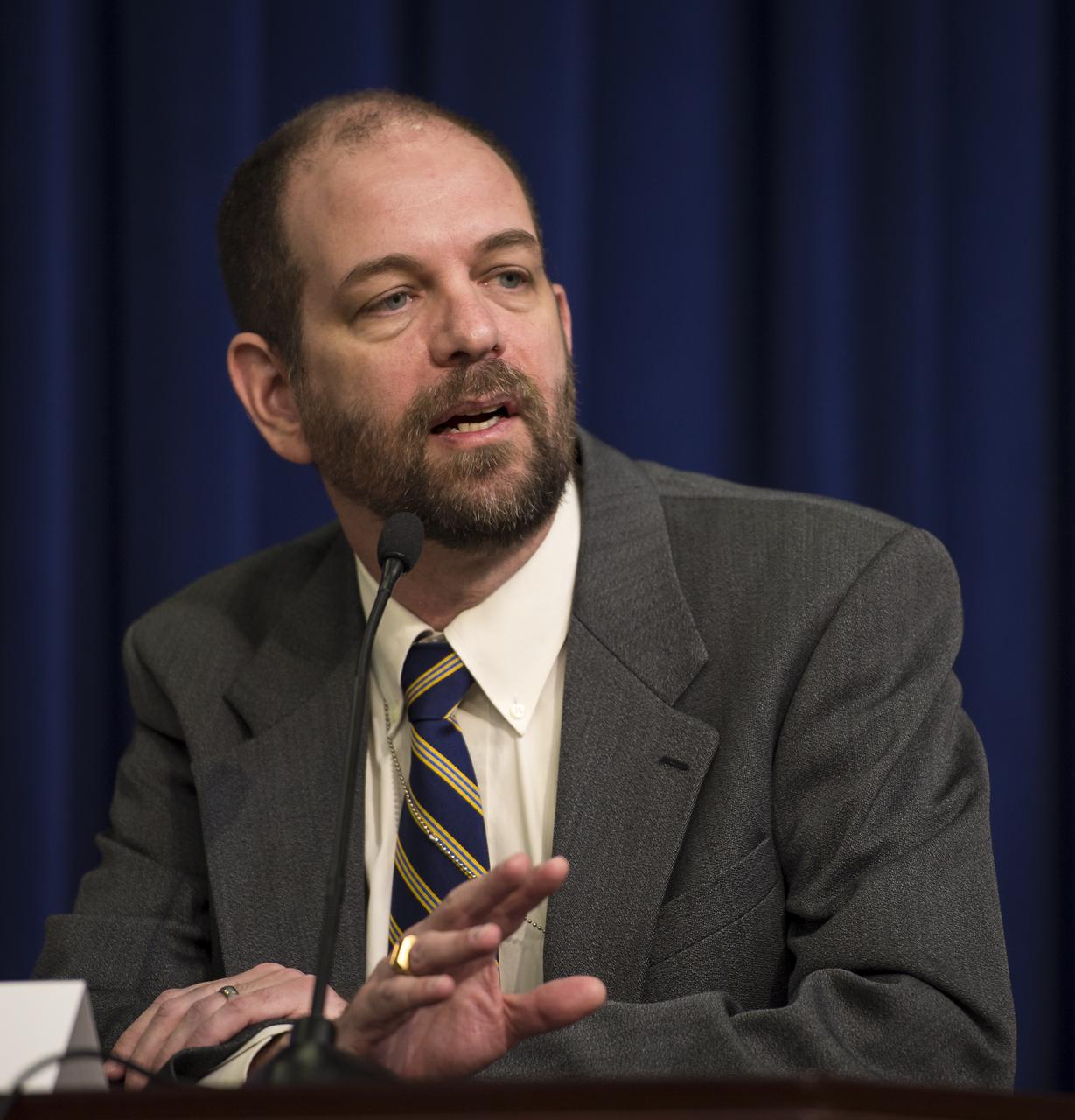

Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Gill Pratt speaks at the annual White House State of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (SoSTEM) address, Wednesday, Jan. 29, 2014, in the South Court Auditorium in the Eisenhower Executive Office Building on the White House complex in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
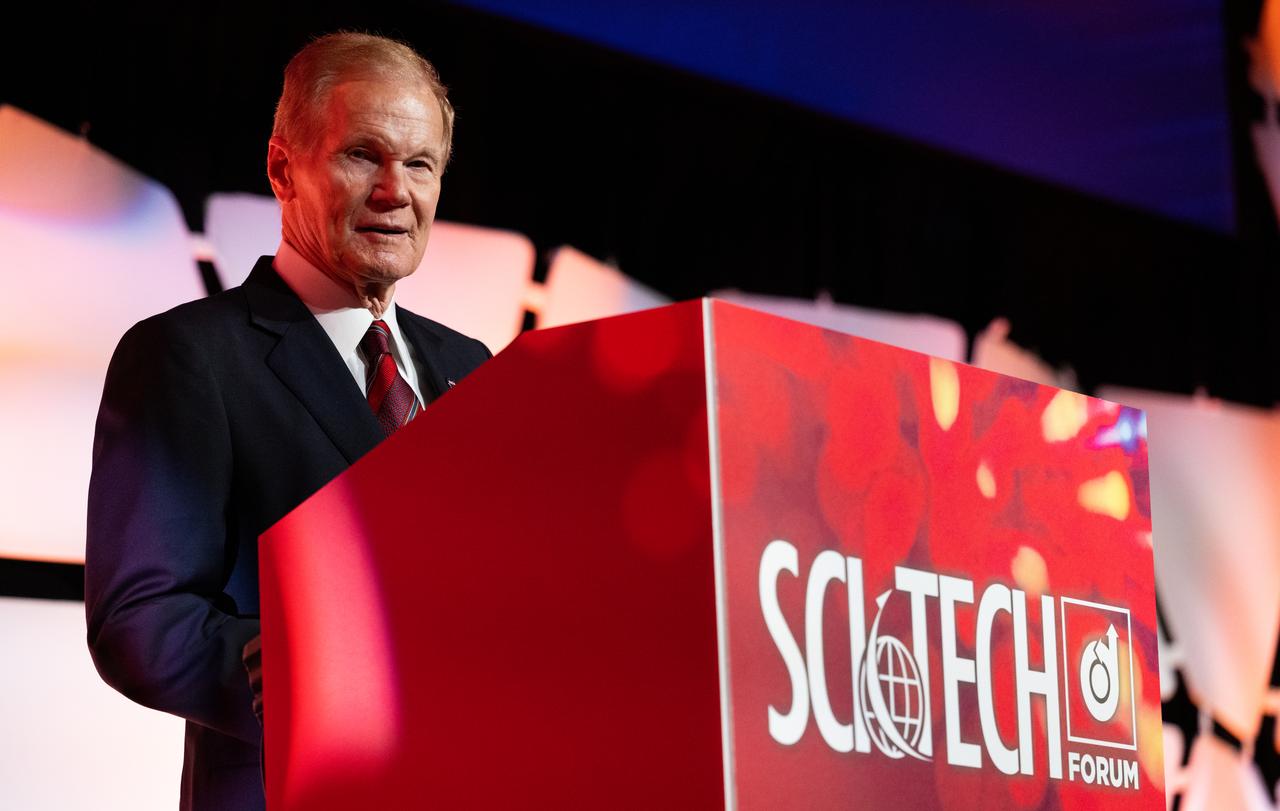

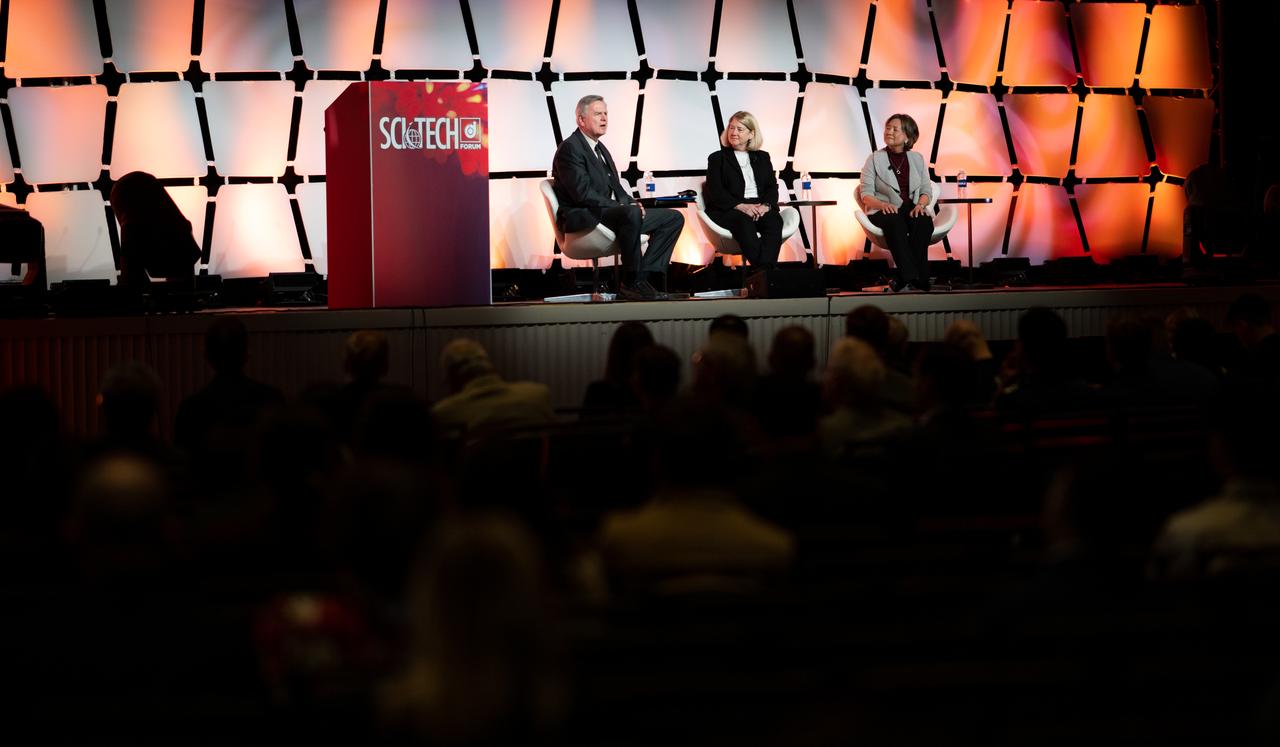
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson delivers opening remarks during a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
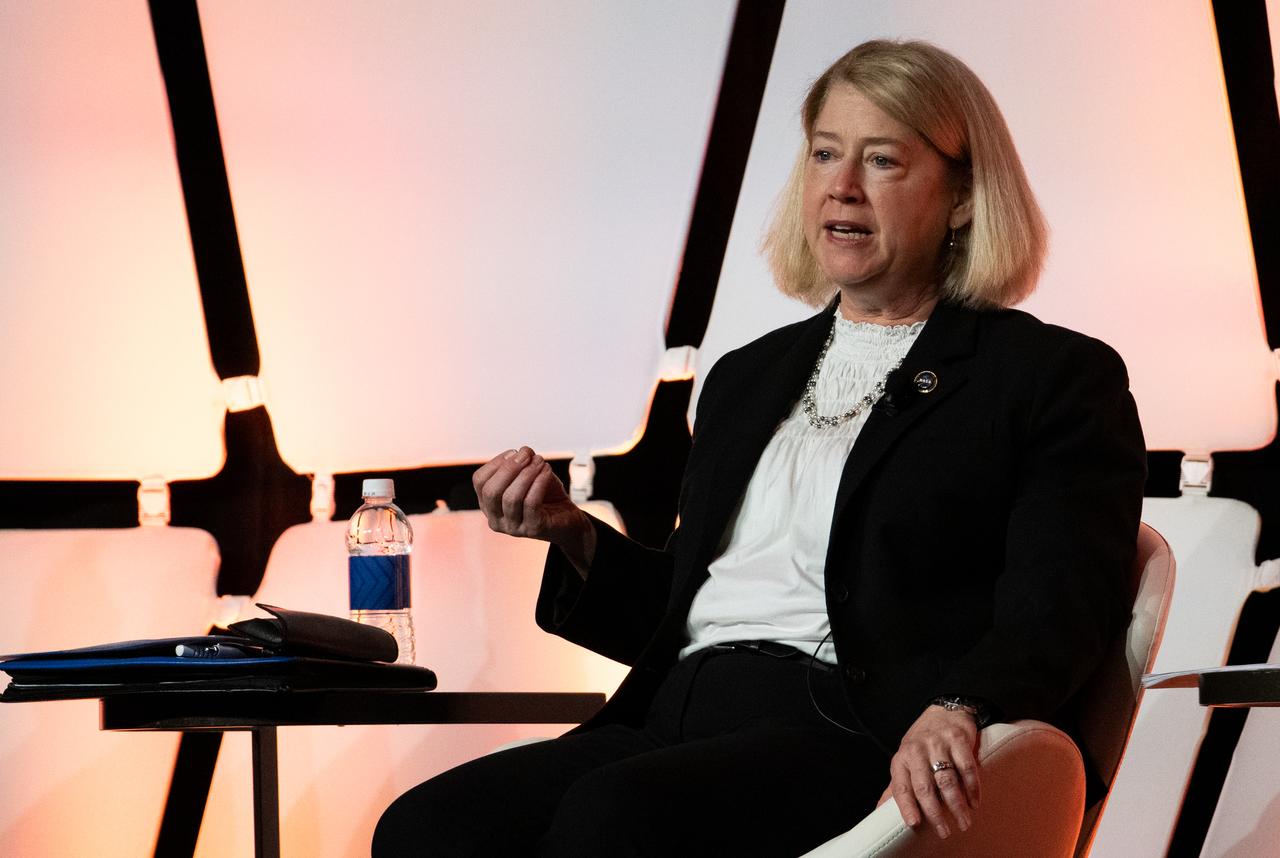

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy answers a question during a fireside chat announcing a new collaboration on nuclear thermal propulsion at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum, Tuesday, Jan. 24, 2023, at the Gaylord National Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, project to develop and demonstrate in-space a nuclear thermal engine. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
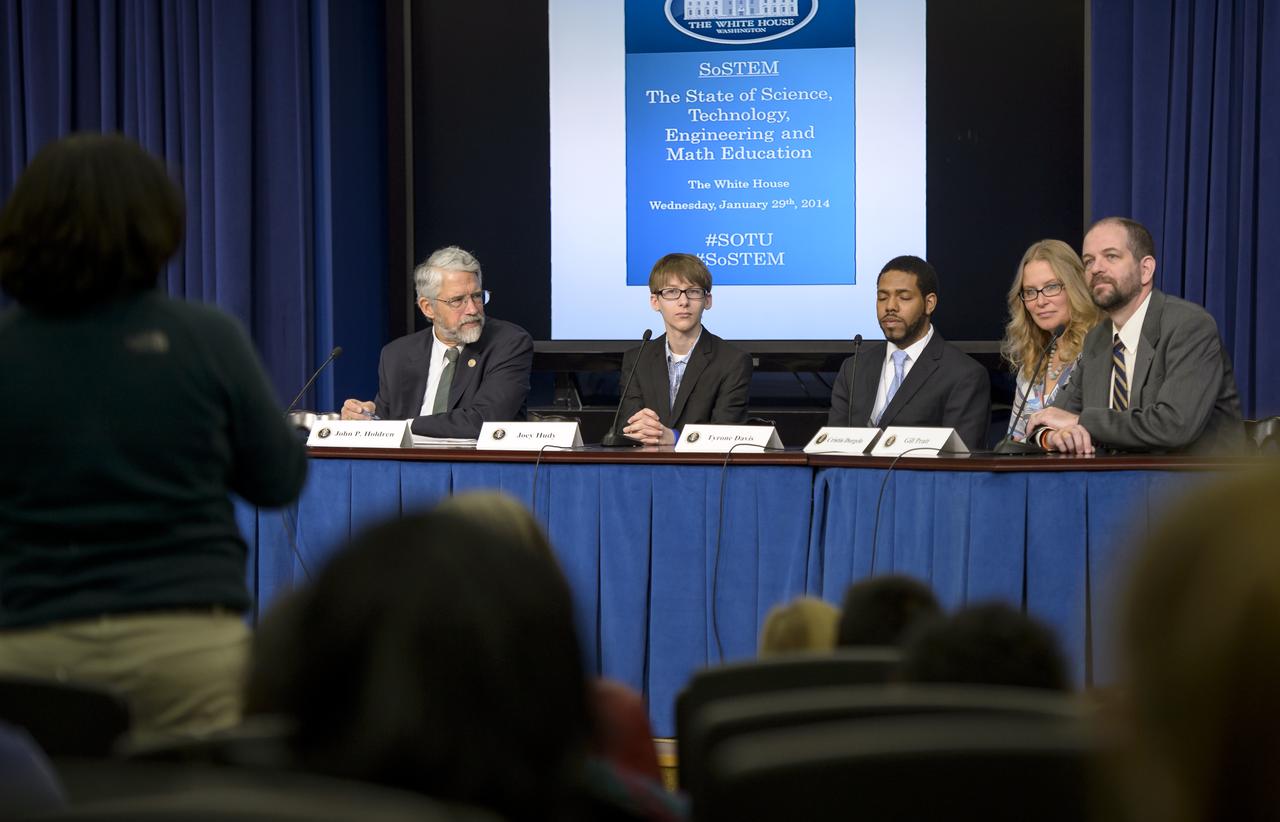

Panels participants, from left, Dr. John P. Holdren, Assistant to the President for Science and Technology and Director of the White House Office of Science & Technology Policy, former White House Science Fair participant Joey Hudy, Environmentalist and third-year law student at Elon University School of Law Tyrone Davis, White House innovation expert Cristin Dorgelo, and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Gill Pratt, take a question from the audience during the annual White House State of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (SoSTEM) address, Wednesday, Jan. 29, 2014, in the South Court Auditorium in the Eisenhower Executive Office Building on the White House complex in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Panels participants, from left, Dr. John P. Holdren, Assistant to the President for Science and Technology and Director of the White House Office of Science & Technology Policy, former White House Science Fair participant Joey Hudy, Environmentalist and third-year law student at Elon University School of Law Tyrone Davis, White House innovation expert Cristin Dorgelo, and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Gill Pratt, take a question from the audience during the annual White House State of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (SoSTEM) address, Wednesday, Jan. 29, 2014, in the South Court Auditorium in the Eisenhower Executive Office Building on the White House complex in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
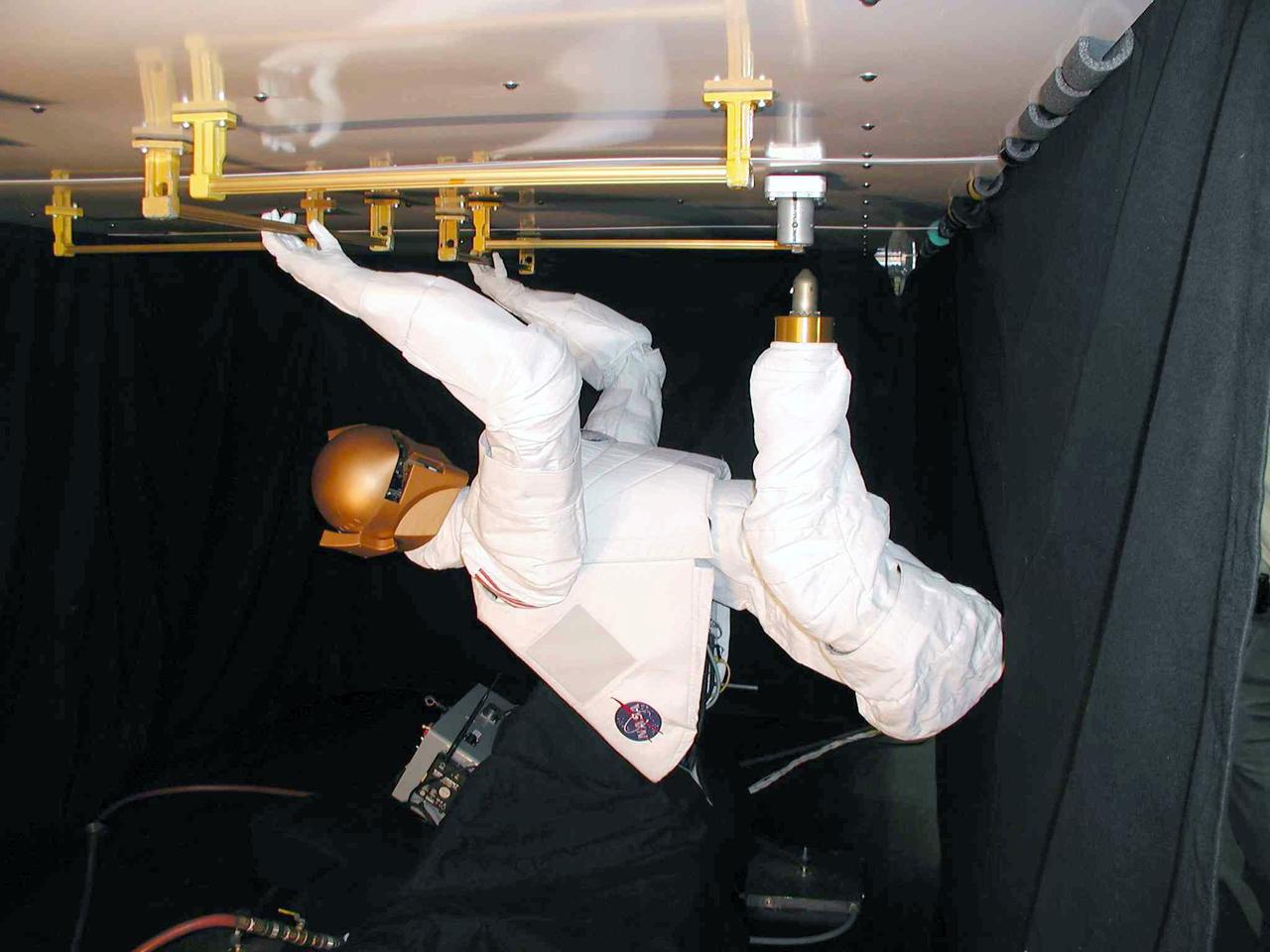

JSC2004-E-16343 (March 2004) --- Robonaut – which uses a head, torso, arms and dexterous hands to perform tasks using the same tools used by human spacewalkers – was fitted with a movable leg that ended in a “foot” that was a common interface for the standard Work Interface Facility (WIF) anchors on the International Space Station (ISS). The Robonaut Project is a collaborative effort with the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), and has been under development at Johnson Space Center (JSC) for several years.
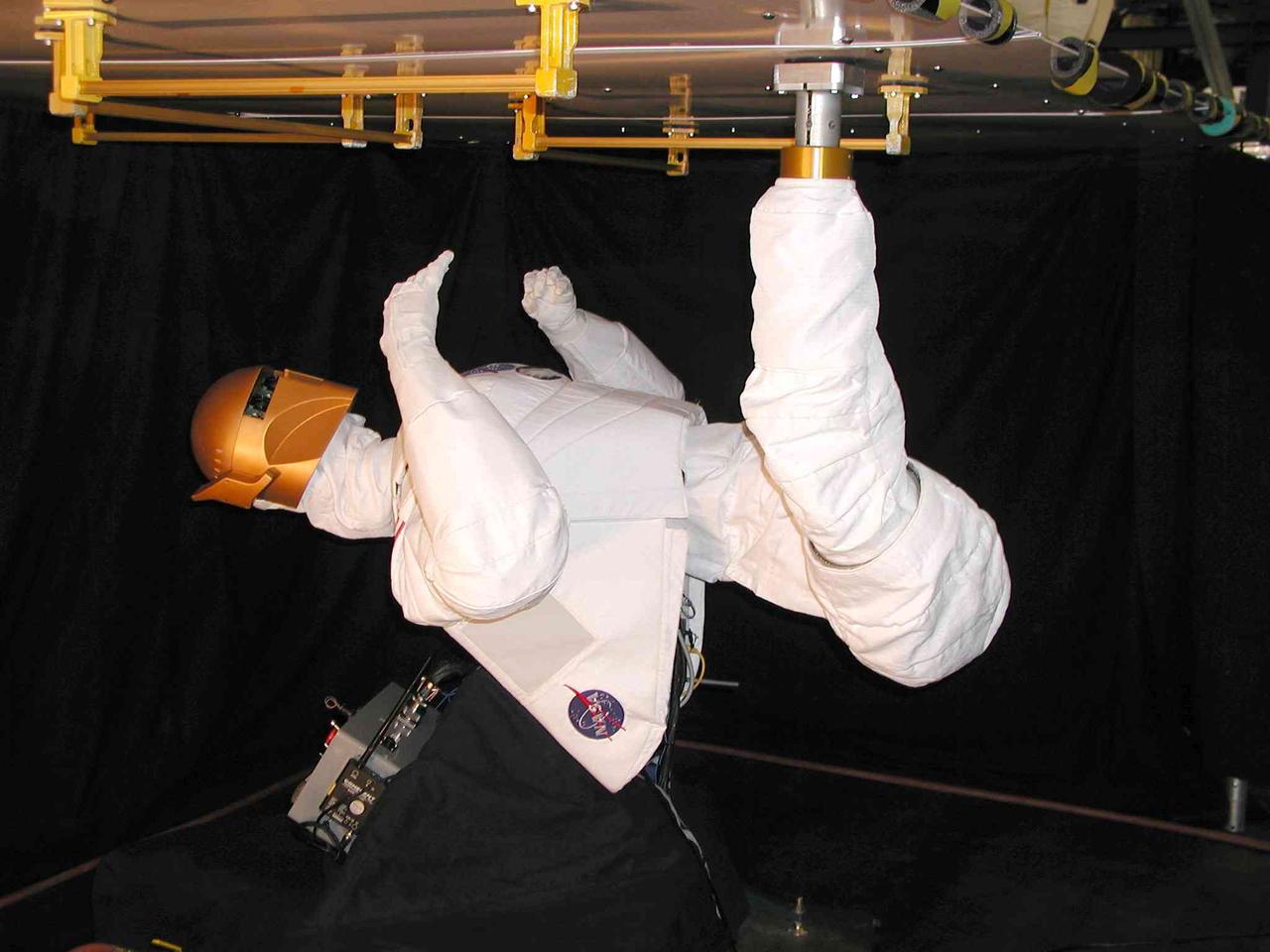

JSC2004-E-16339 (March 2004) --- Robonaut - which uses a head, torso, arms and dexterous hands to perform tasks using the same tools used by human spacewalkers – has both hands free once its leg is anchored in a standard Work Interface Facility (WIF) attached to the test panel. The Robonaut Project is a collaborative effort with the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), and has been under development at Johnson Space Center (JSC) for several years.
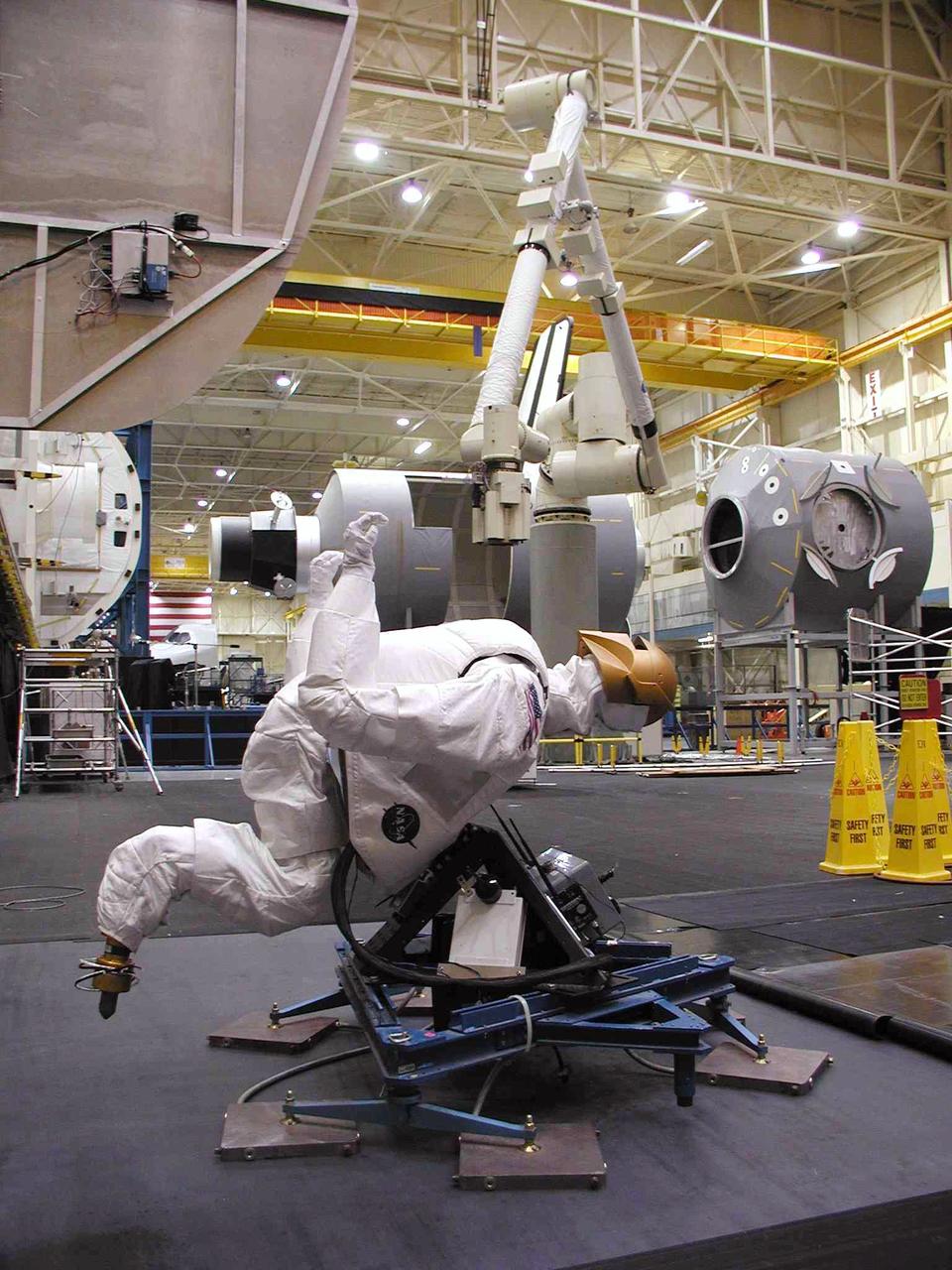
JSC2004-E-16342 (March 2004) --- Tests of Robonaut’s ability were conducted on the Precision Air-Bearing Floor in Johnson Space Center’s (JSC) Space Vehicle Mockup Facility. Robonaut was mounted to a pressurized air sled, which allowed teleoperators to emulate some of the conditions of weightlessness. The Robonaut Project is a collaborative effort with the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), and has been under development at JSC for several years.
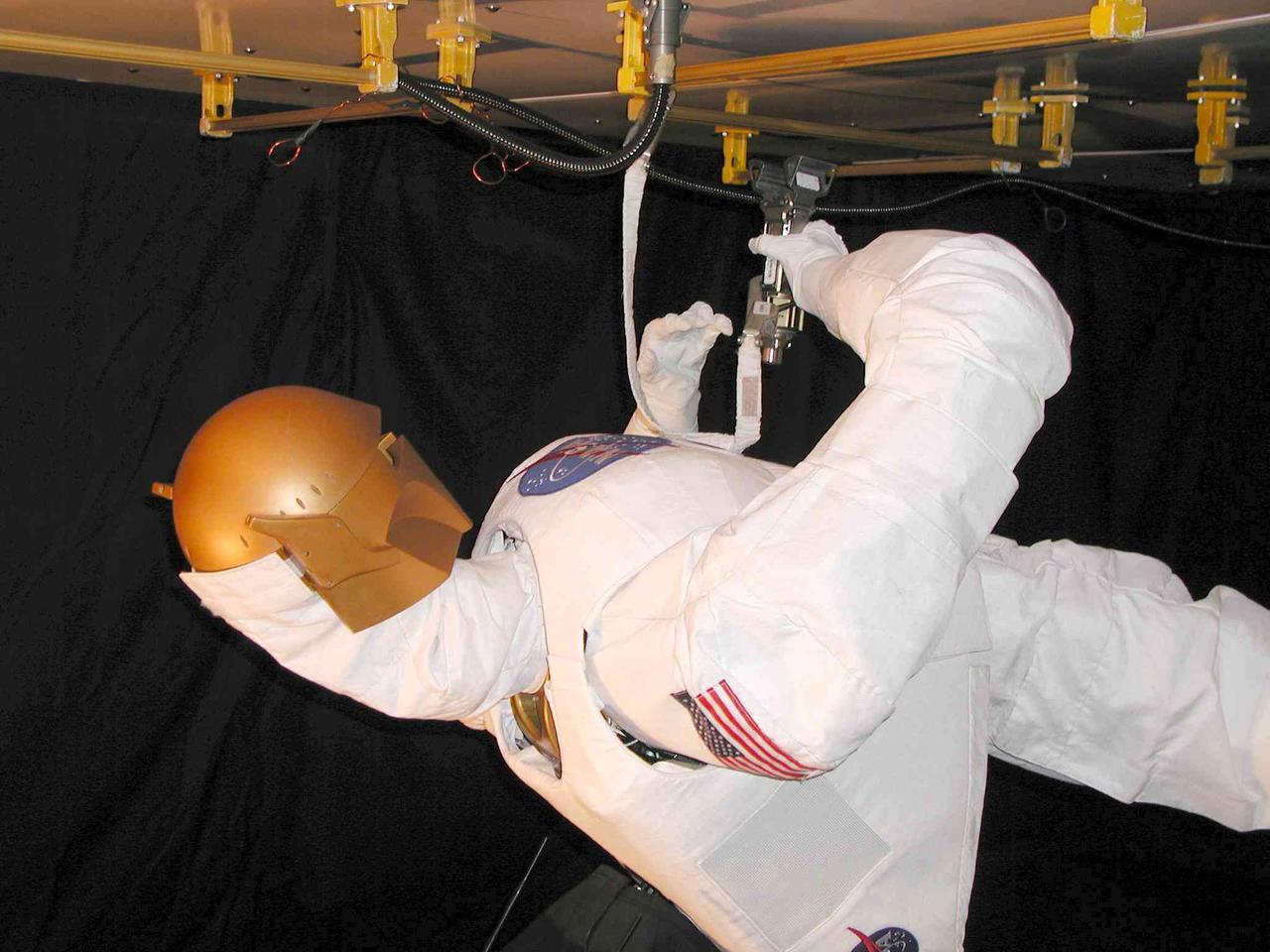

JSC2004-E-16341 (March 2004) --- Robonaut uses a standard human spacewalk tether to connect itself to an International Space Station (ISS) exterior handrail on the test panel. The Robonaut Project is a collaborative effort with the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), and has been under development at Johnson Space Center (JSC) for several years.
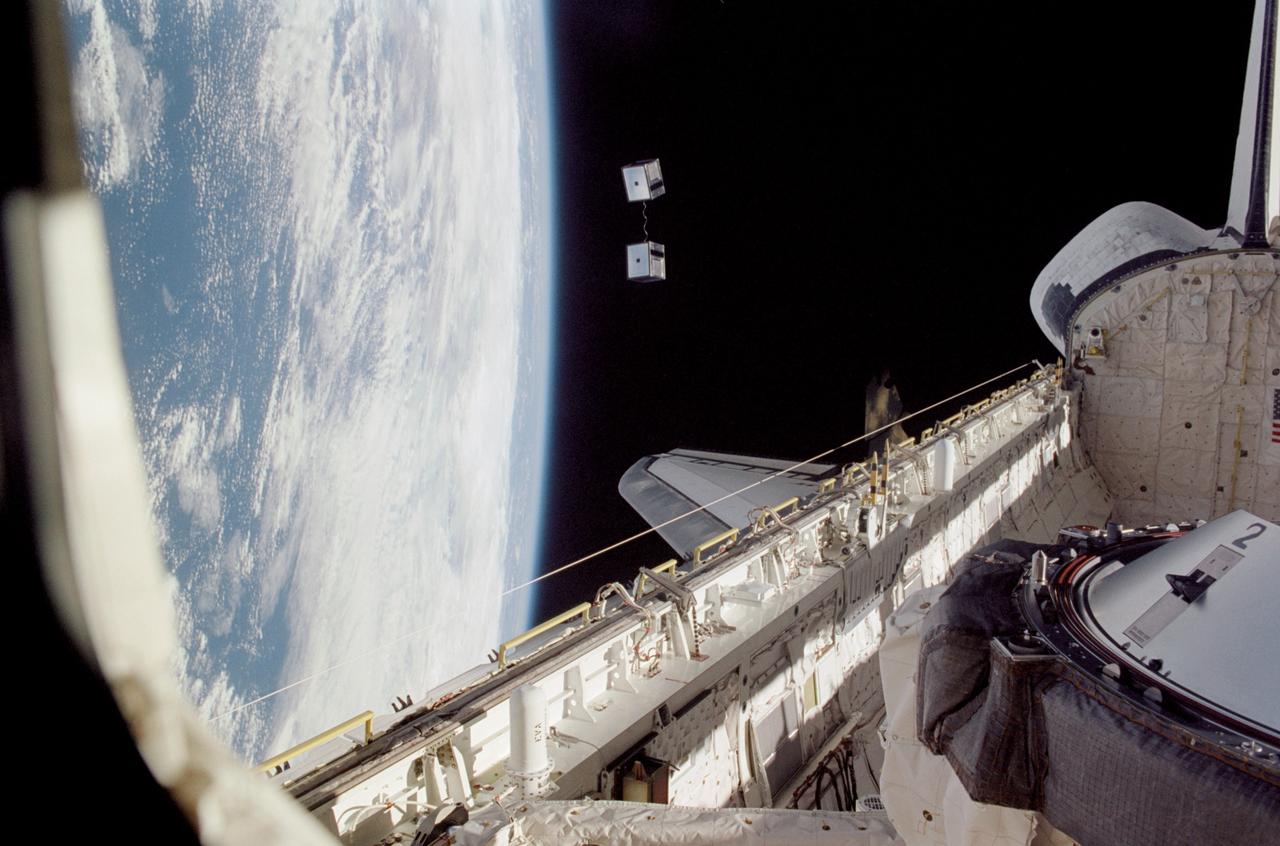

STS113-370-012 (2 December 2002) --- The horizon of a blue and white Earth and the blackness of space form the backdrop for this view, as two miniature satellites are released from the Space Shuttle Endeavour as part of an experiment referred to as MEPSI. Funded by the Defense Advance Research Projects Agency (DARPA), the two small satellites, which are tethered together, were released from Endeavour’s payload bay (visible in foreground) to fly free for three days as a technology demonstration of the launcher and use of micro- and nano-technologies in space systems.
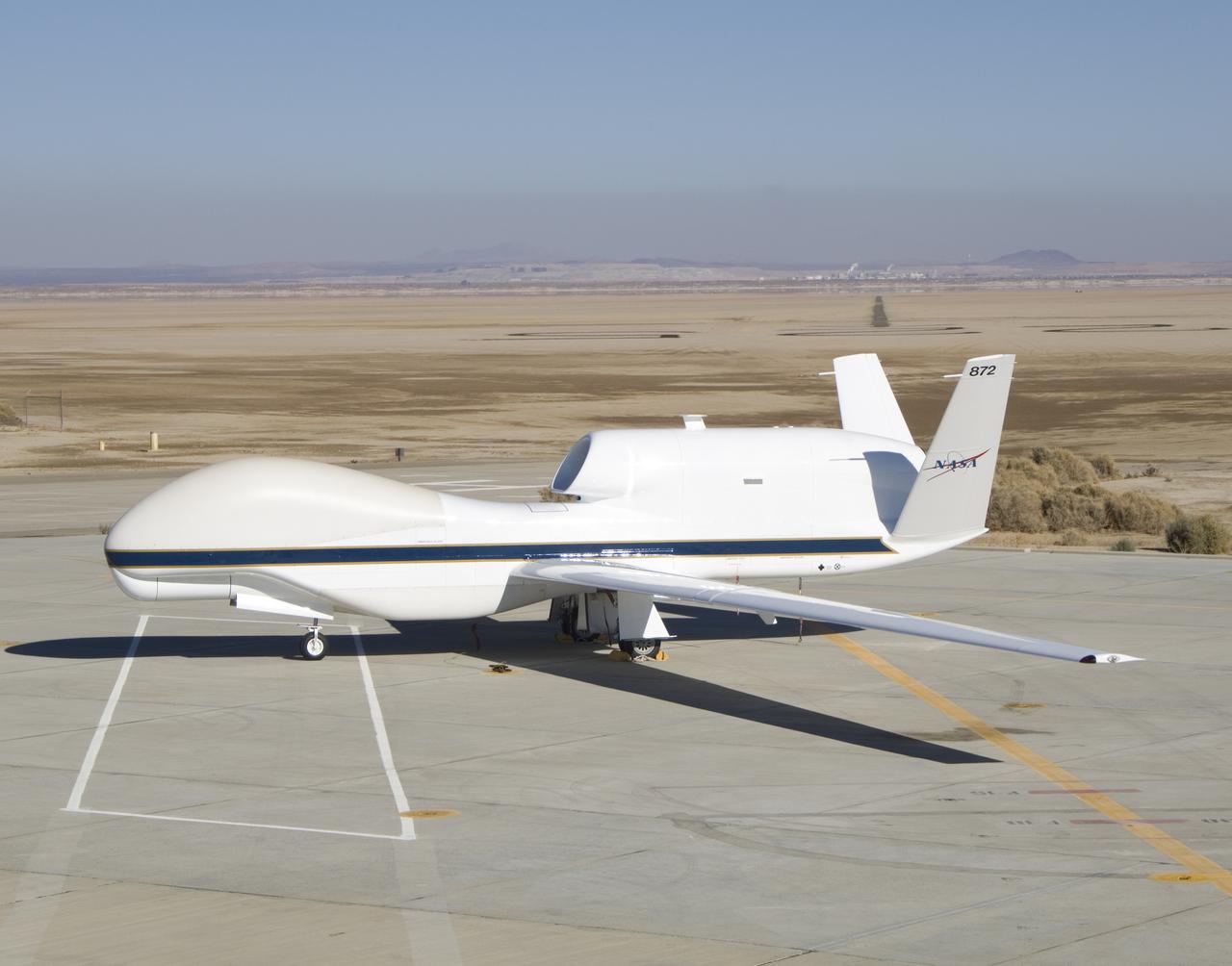

In its new white-and-blue NASA livery, an early development model of the Global Hawk unmanned aircraft rests on the ramp at the Dryden Flight Research Center.
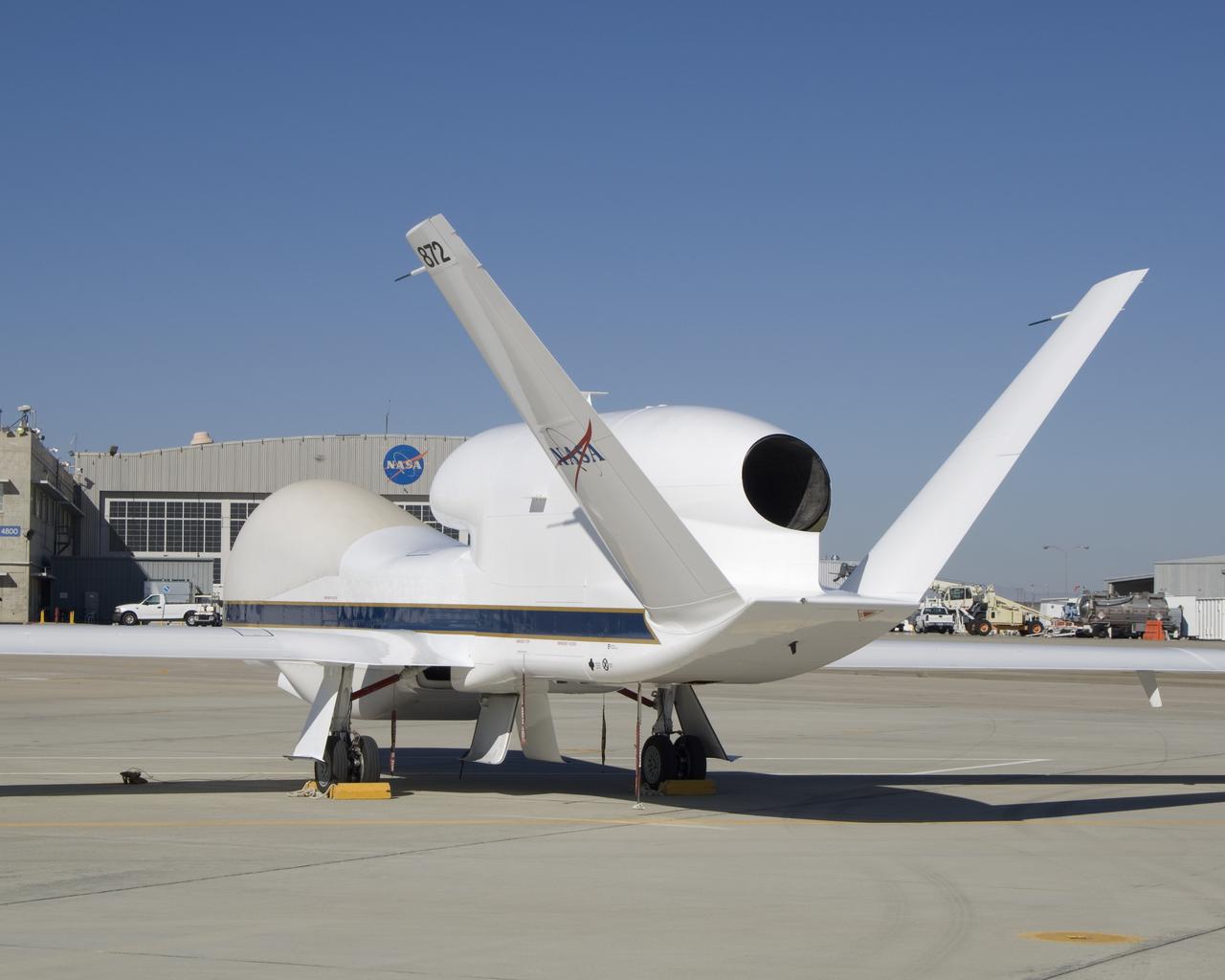

The above-the-fuselage engine and V-tail distinguish one of NASA's two Global Hawk unmanned aircraft parked on the ramp at the Dryden Flight Research Center.
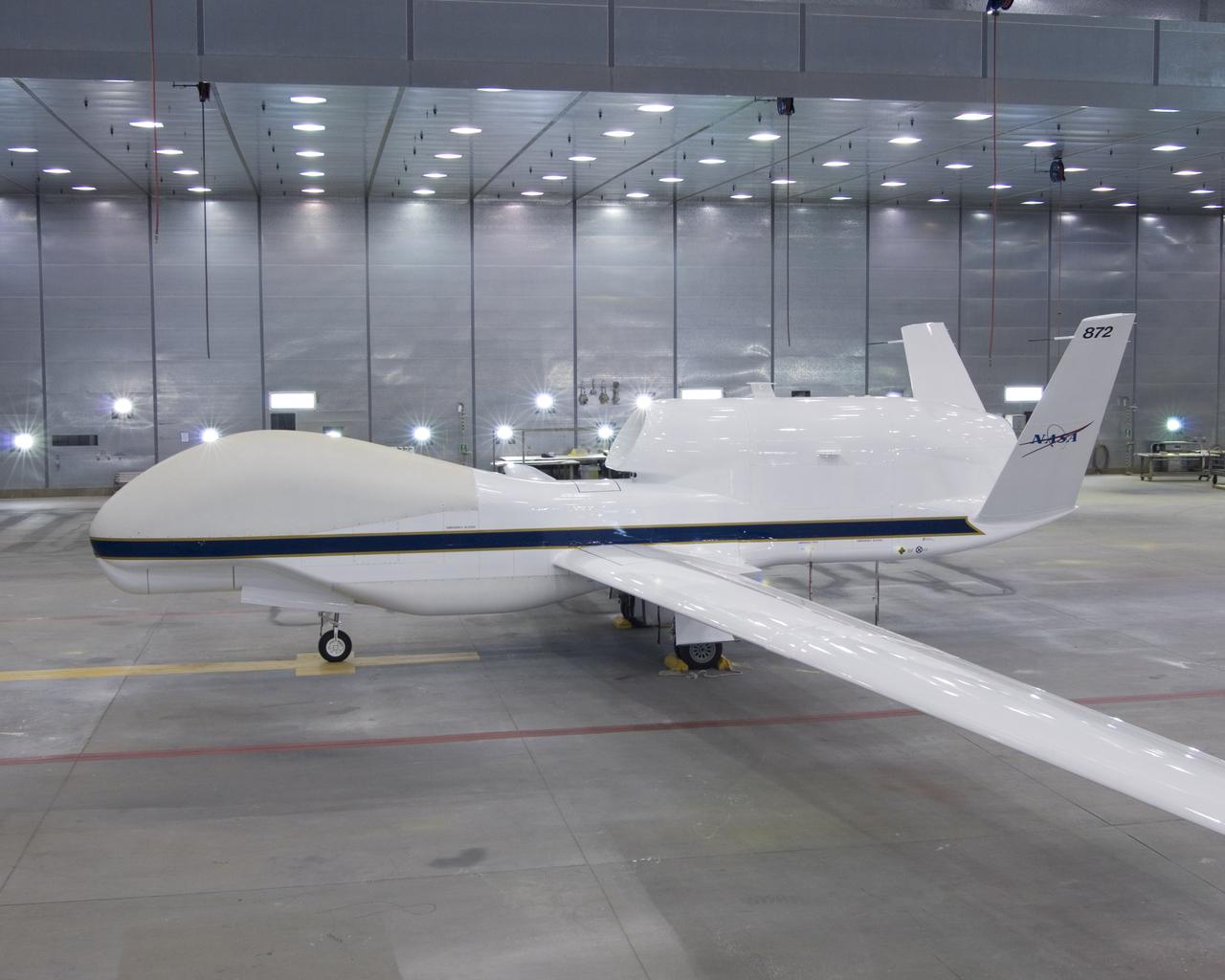

One of NASA's two Global Hawk unmanned aircraft shows off its new blue-and-white livery shortly after being repainted in the Edwards Air Force Base paint hangar.
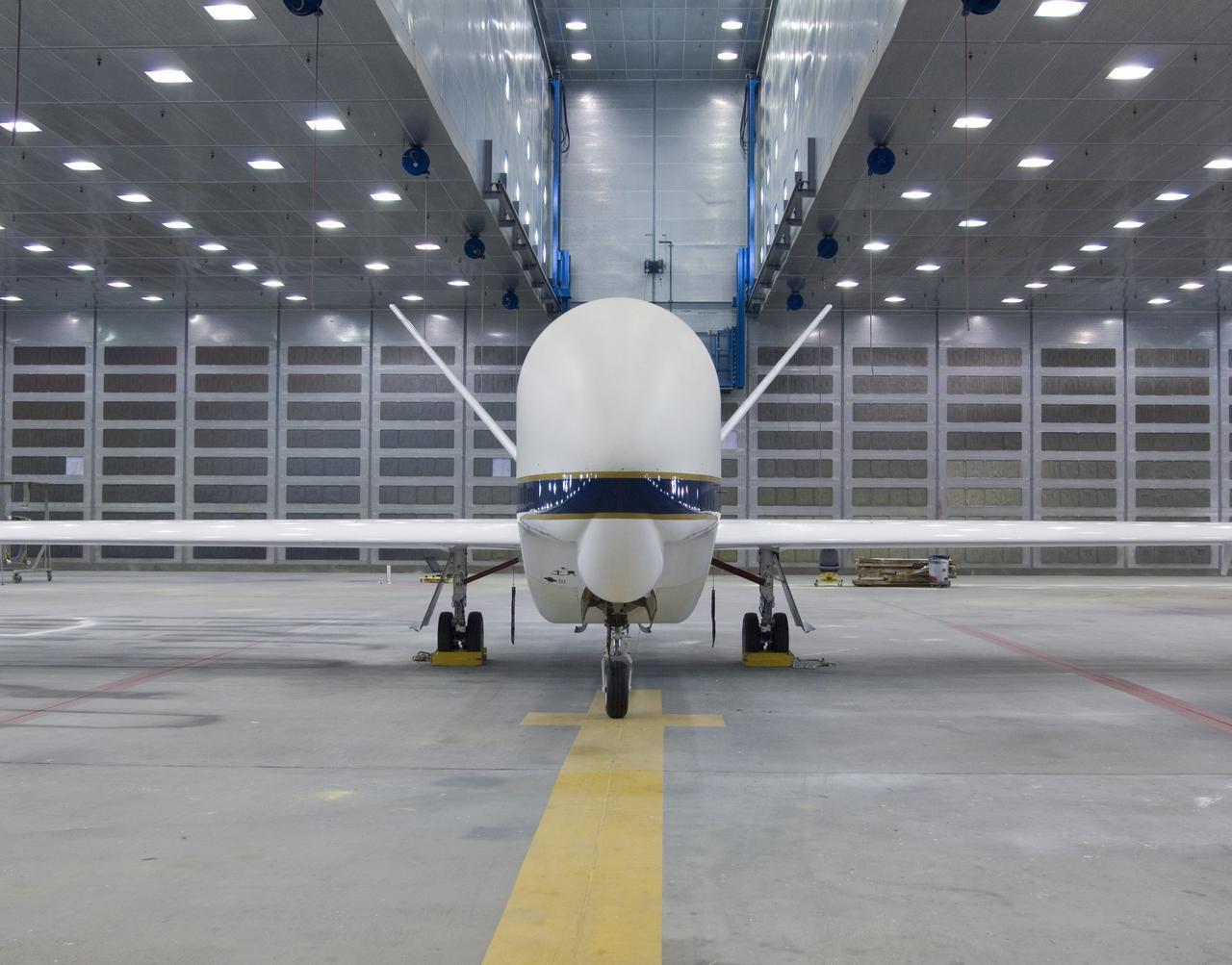

The bulbous nose of one of NASA's Global Hawk unmanned aircraft sports a blue-and-white paint scheme after repainting in the Edwards Air Force Base paint shop.
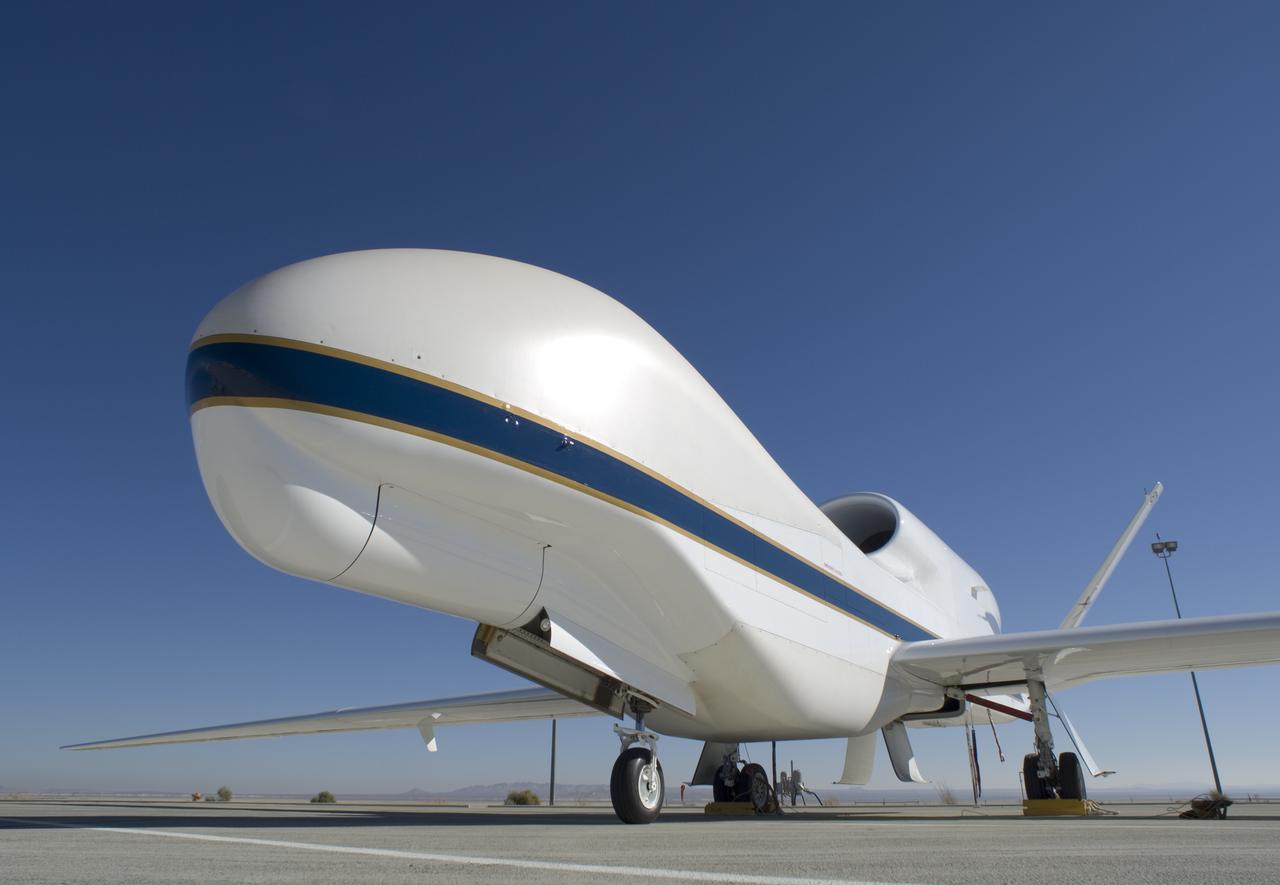

One of NASA's Global Hawk unmanned science aircraft displays its bulbous nose while parked on the ramp at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif.
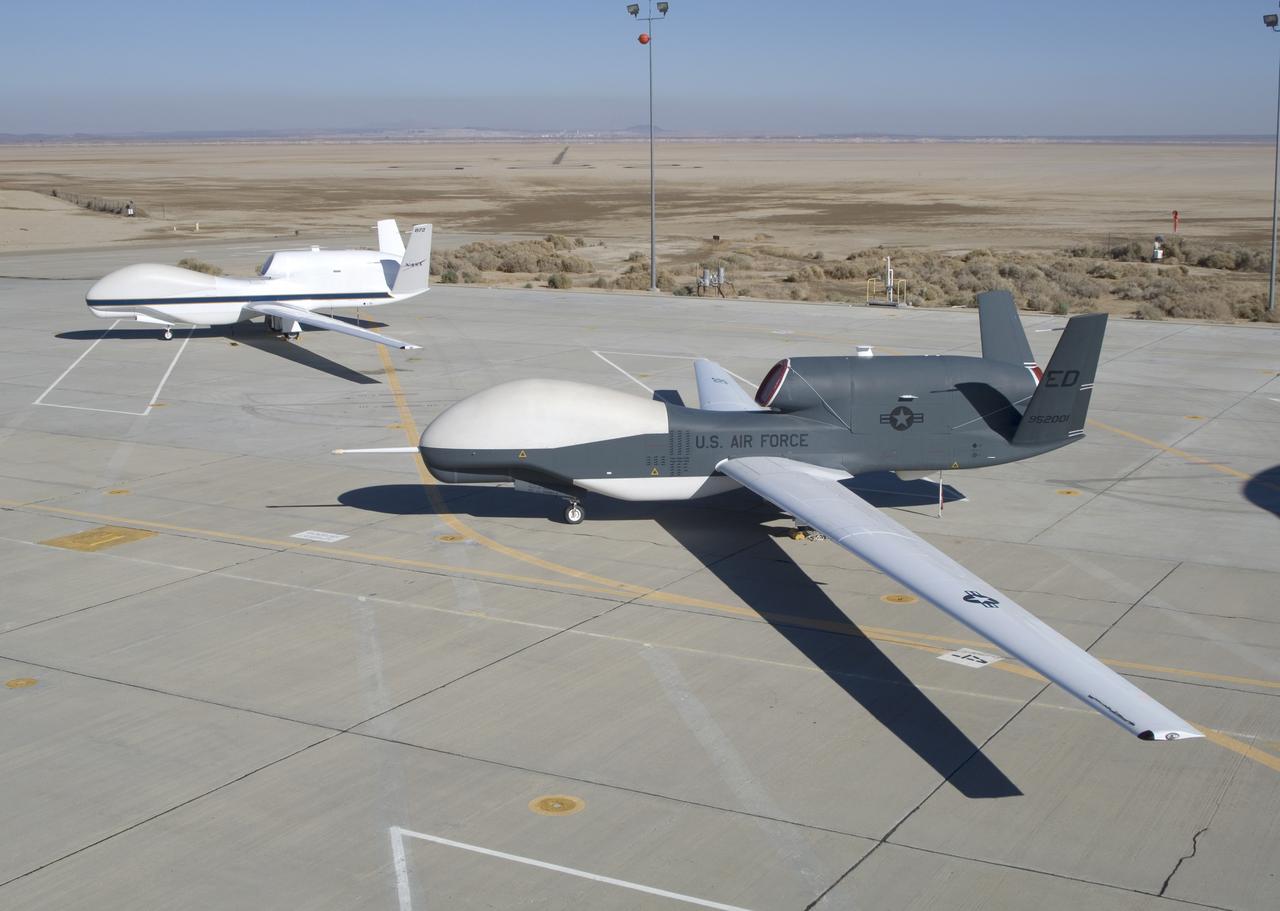

NASA's two Global Hawks, one sporting a NASA paint scheme, the other in its prior Air Force livery, are shown on the ramp at the Dryden Flight Research Center.
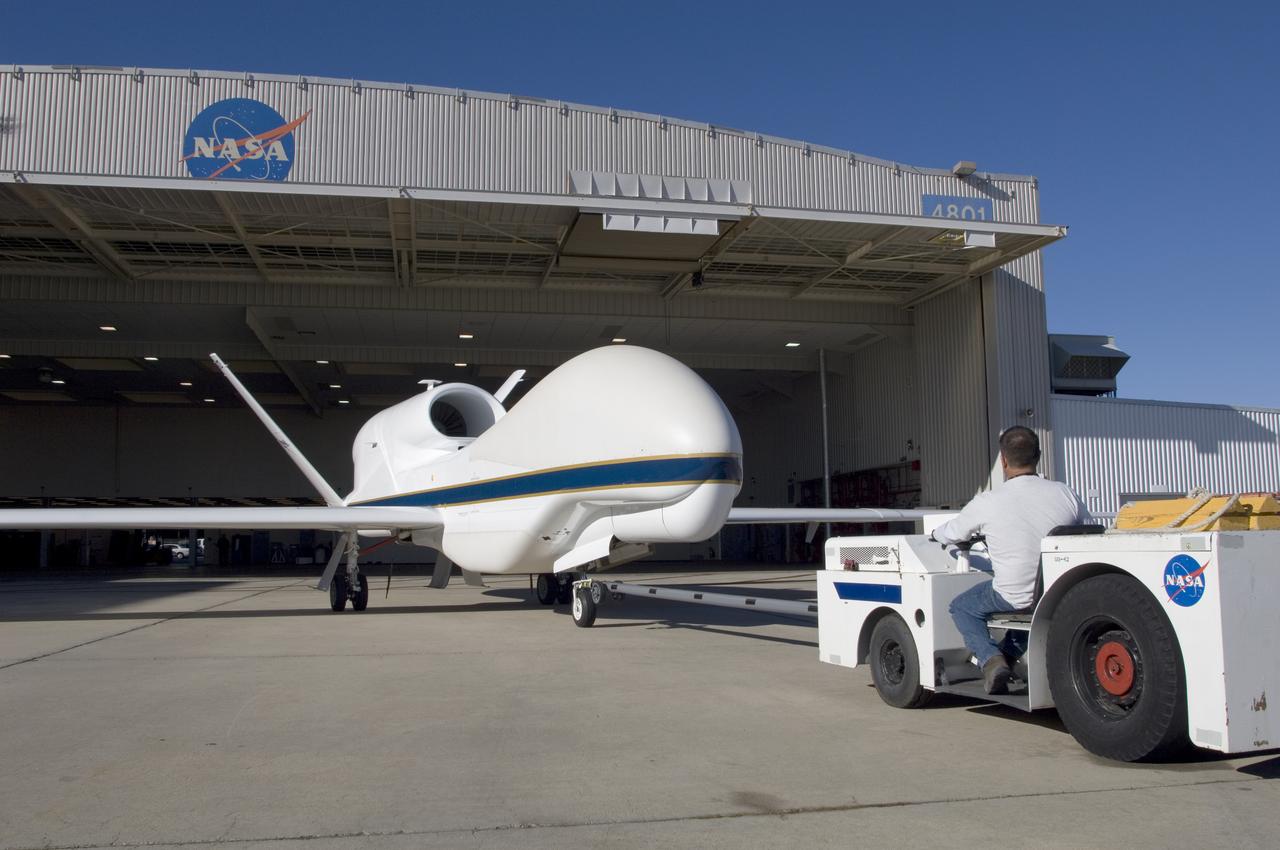

A ground crewman maneuvers one of NASA's Global Hawk unmanned science aircraft into Hangar 4801 at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif.
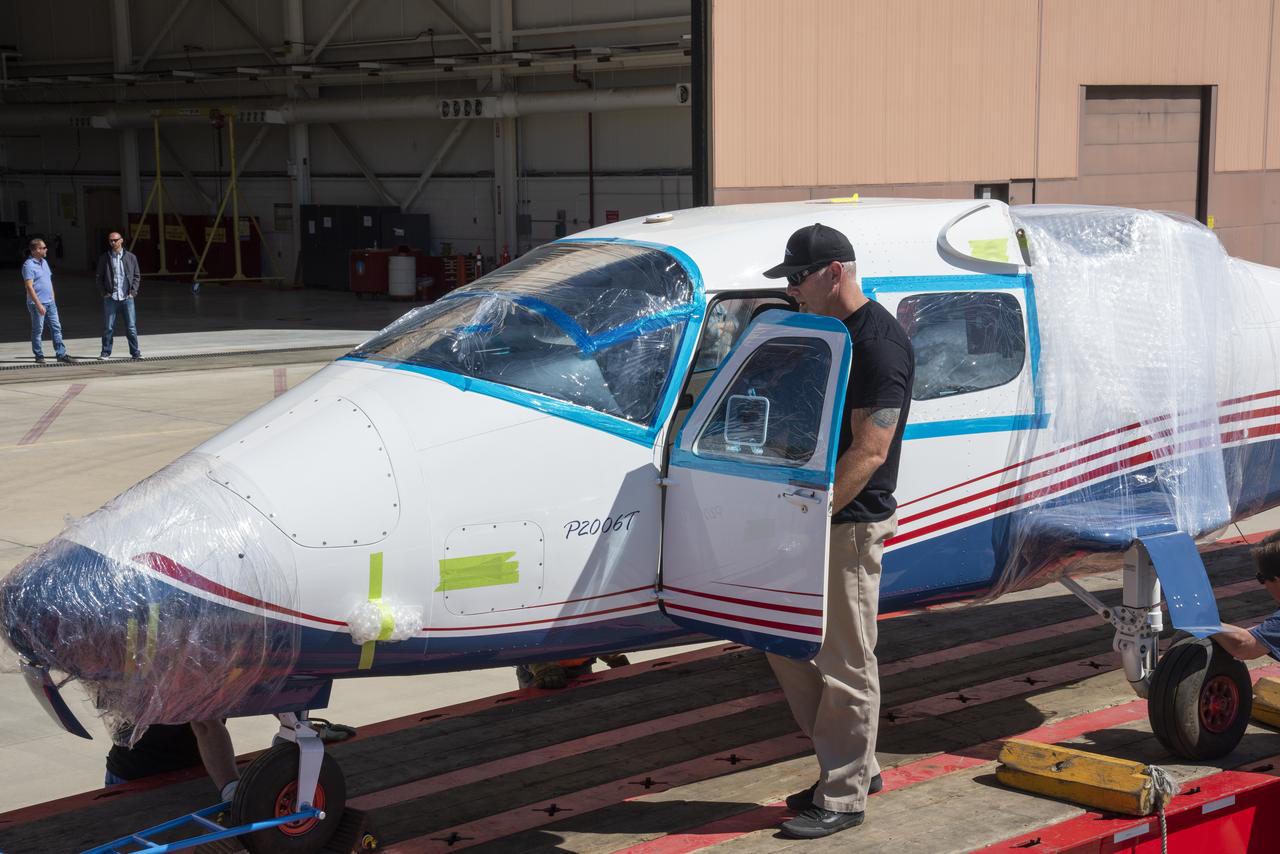

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
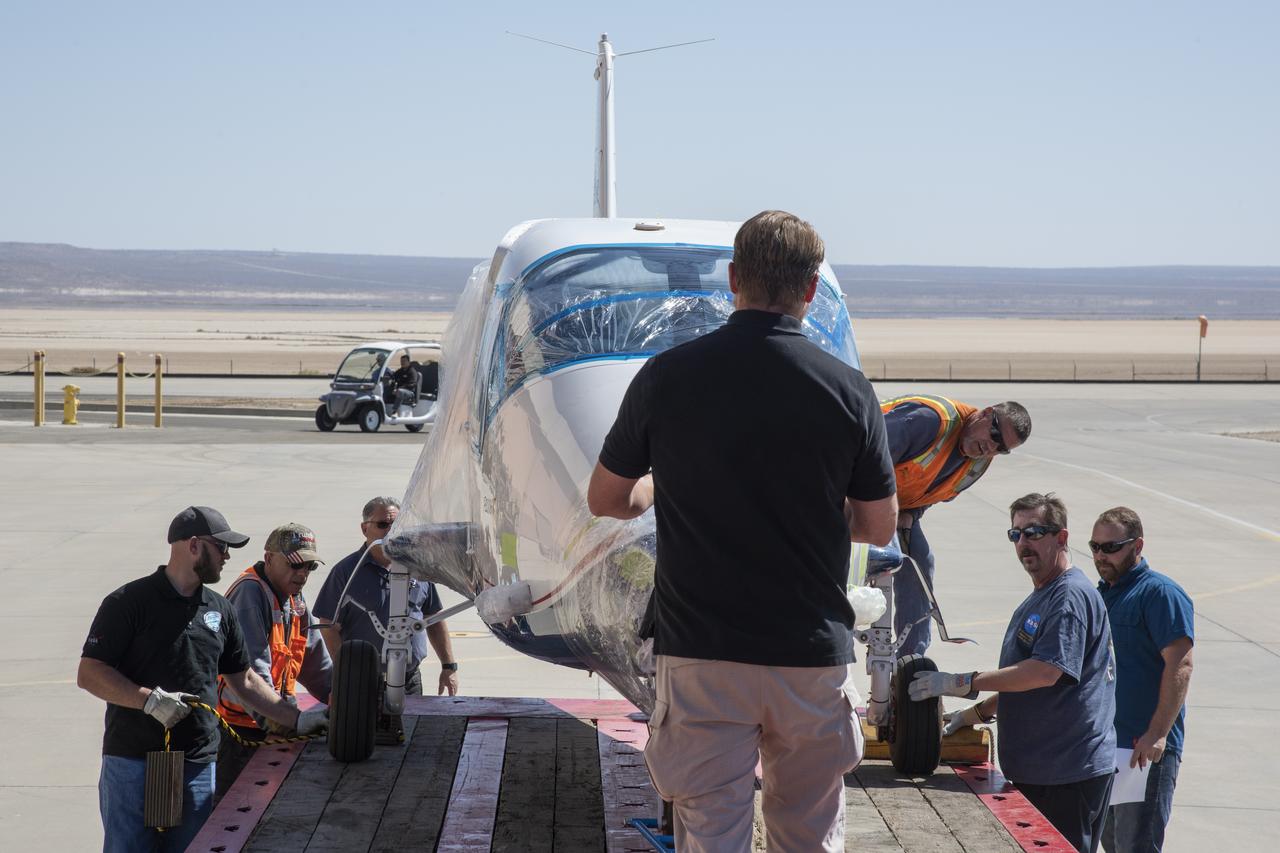

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
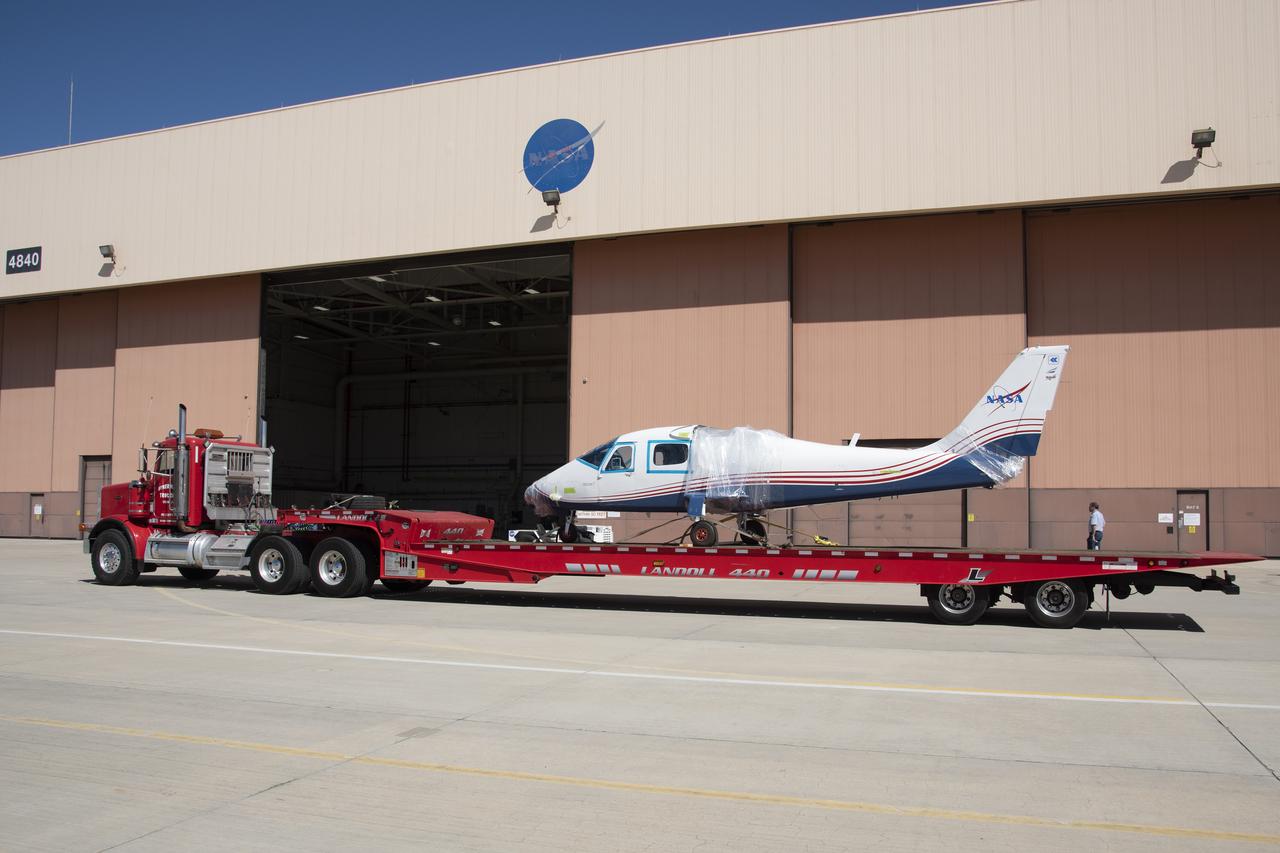

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
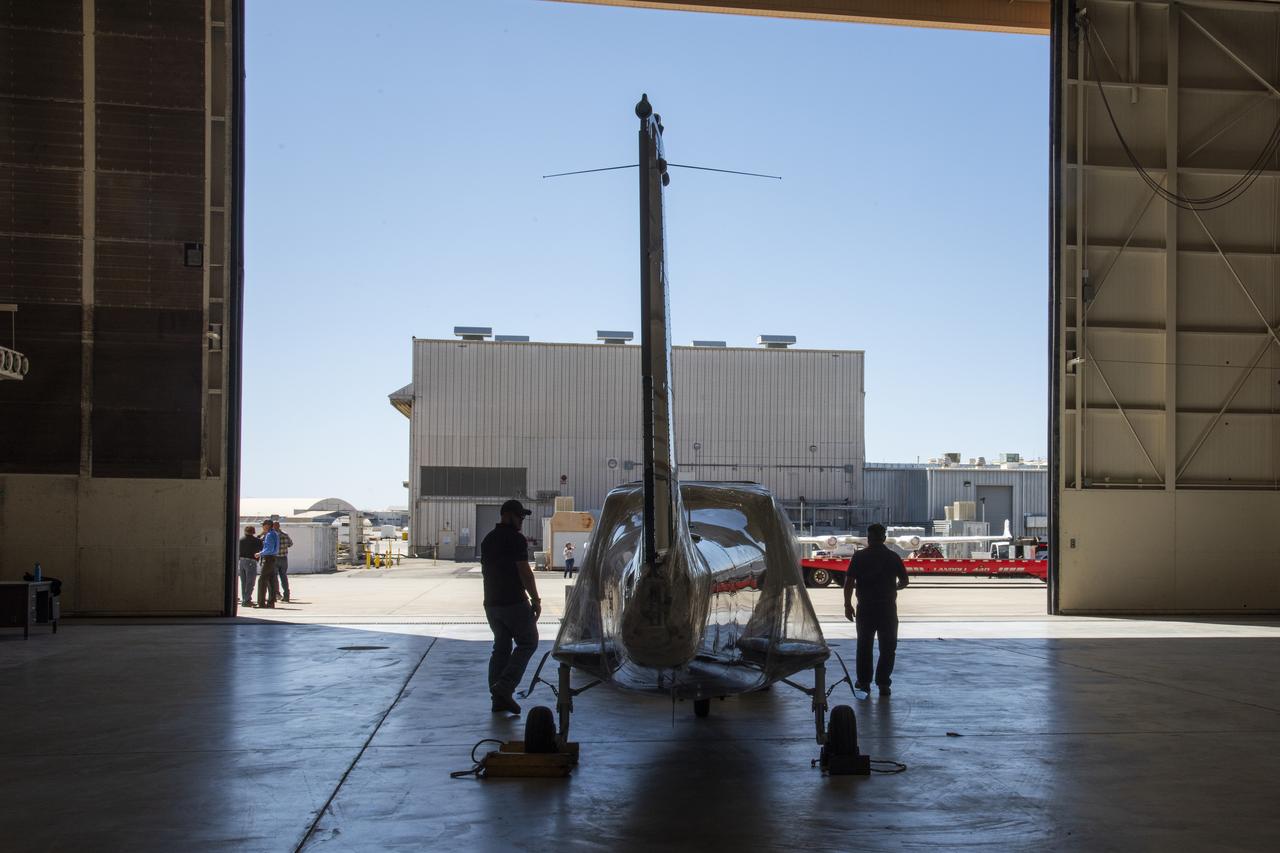

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
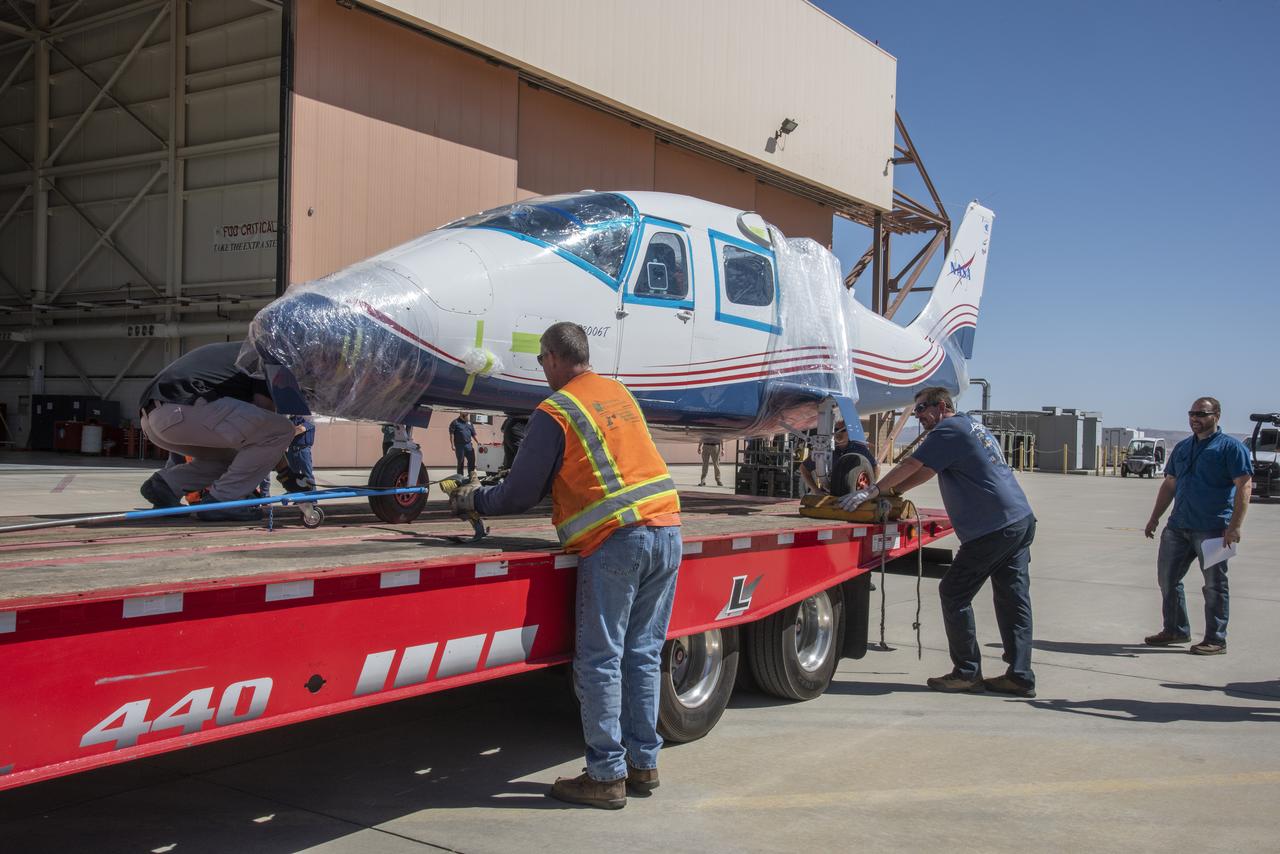

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
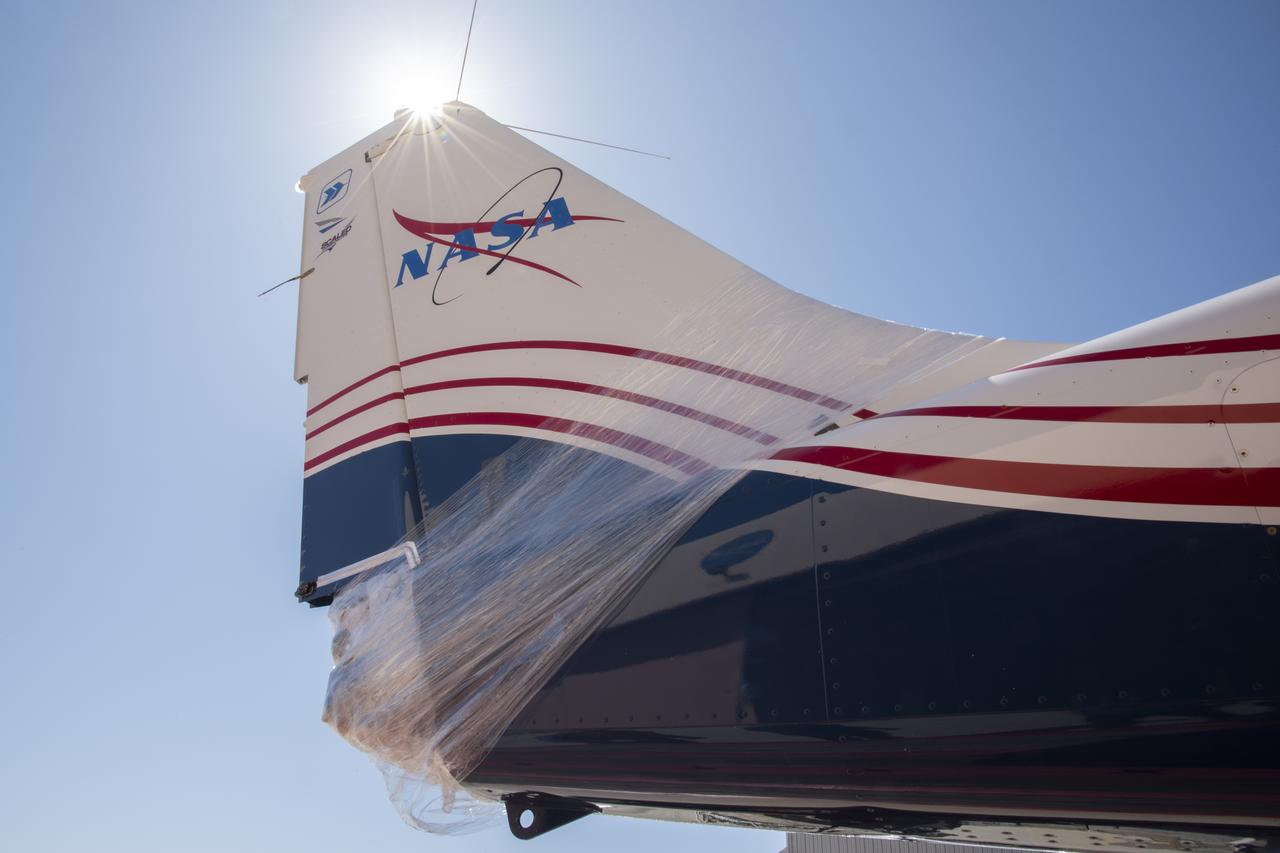

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
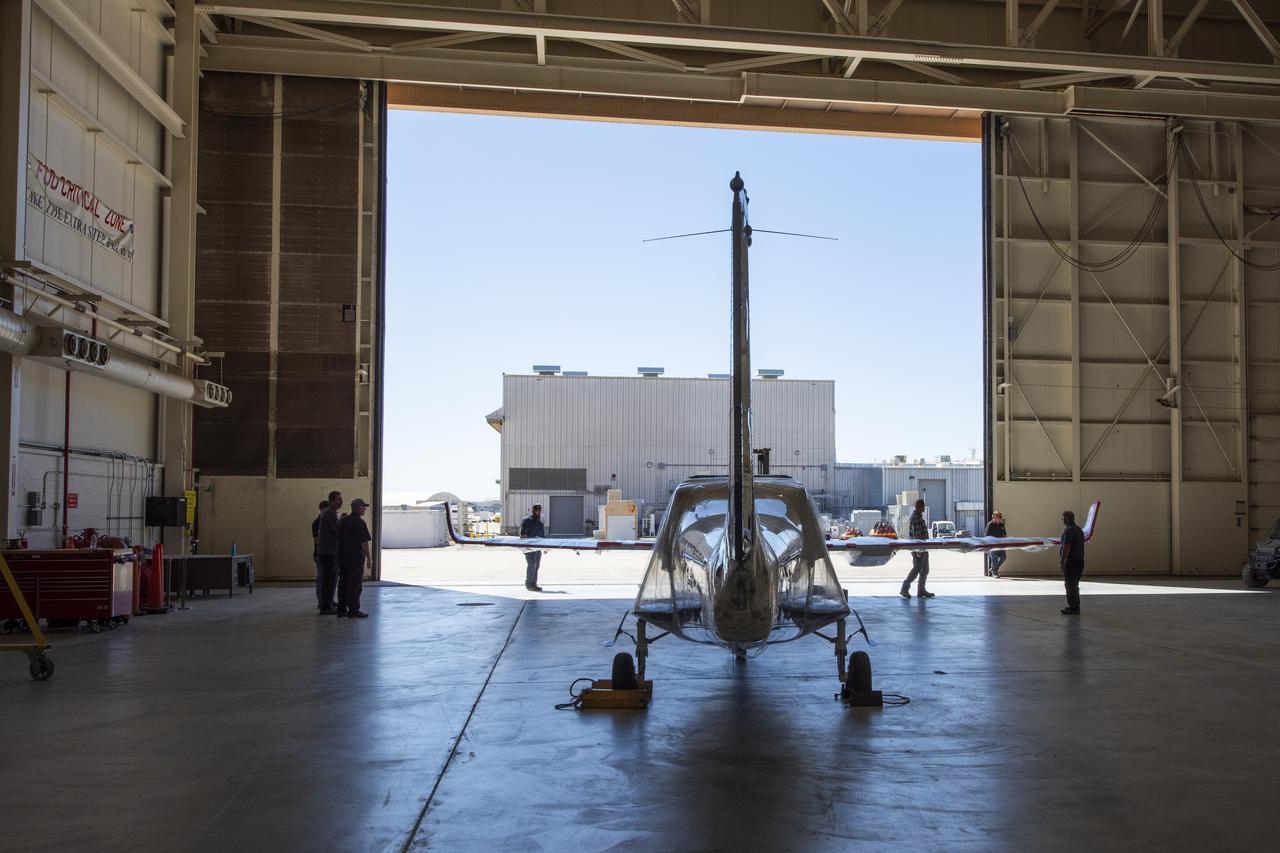

NASA’s X-57 Maxwell, the agency’s first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft’s cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57’s goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
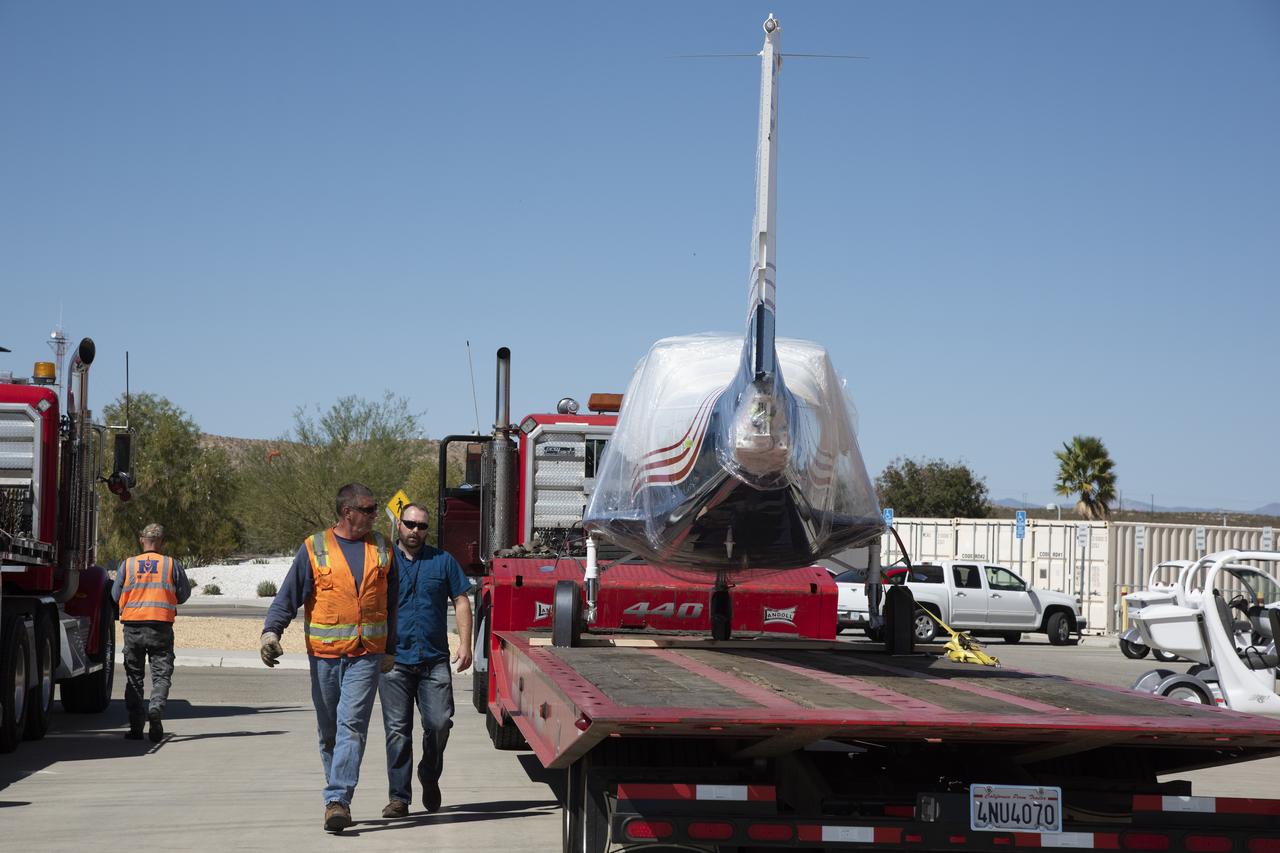

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
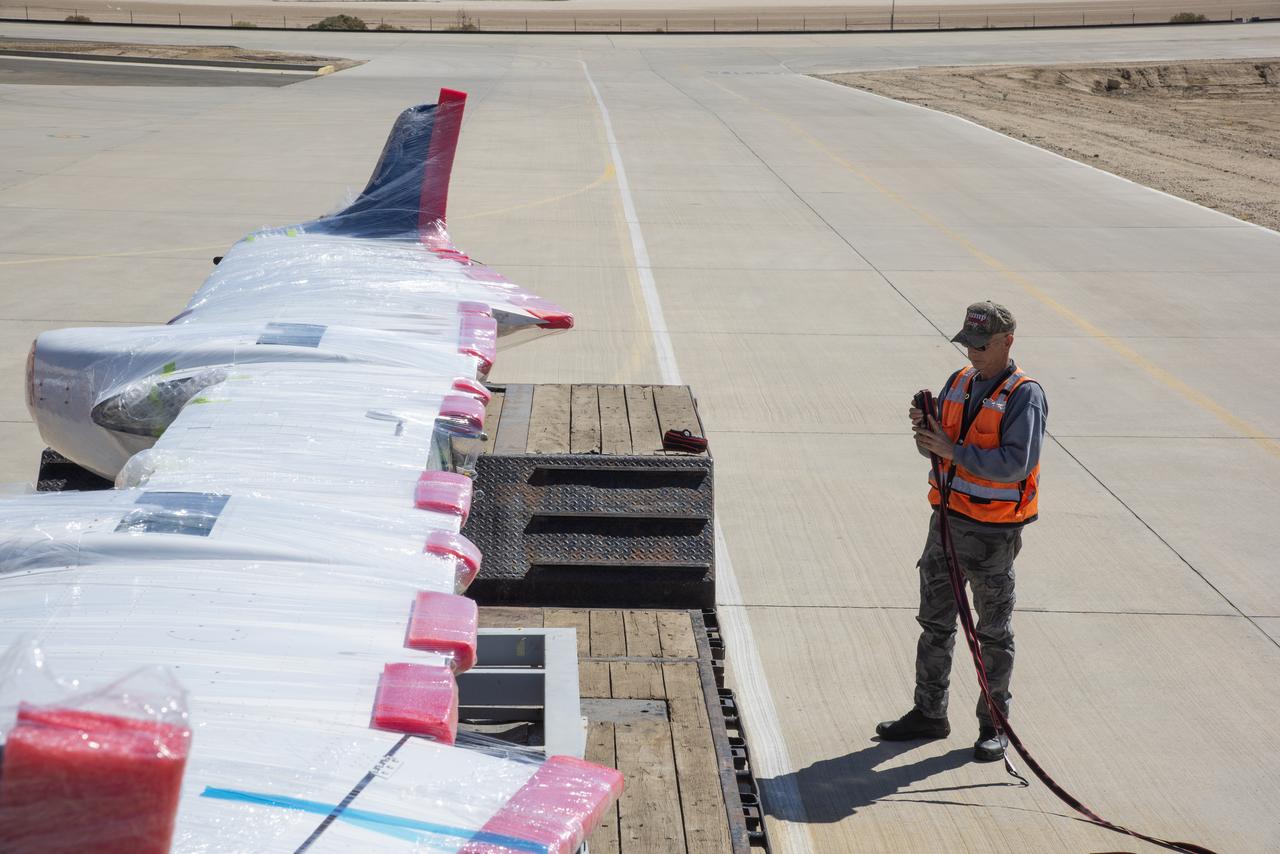

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
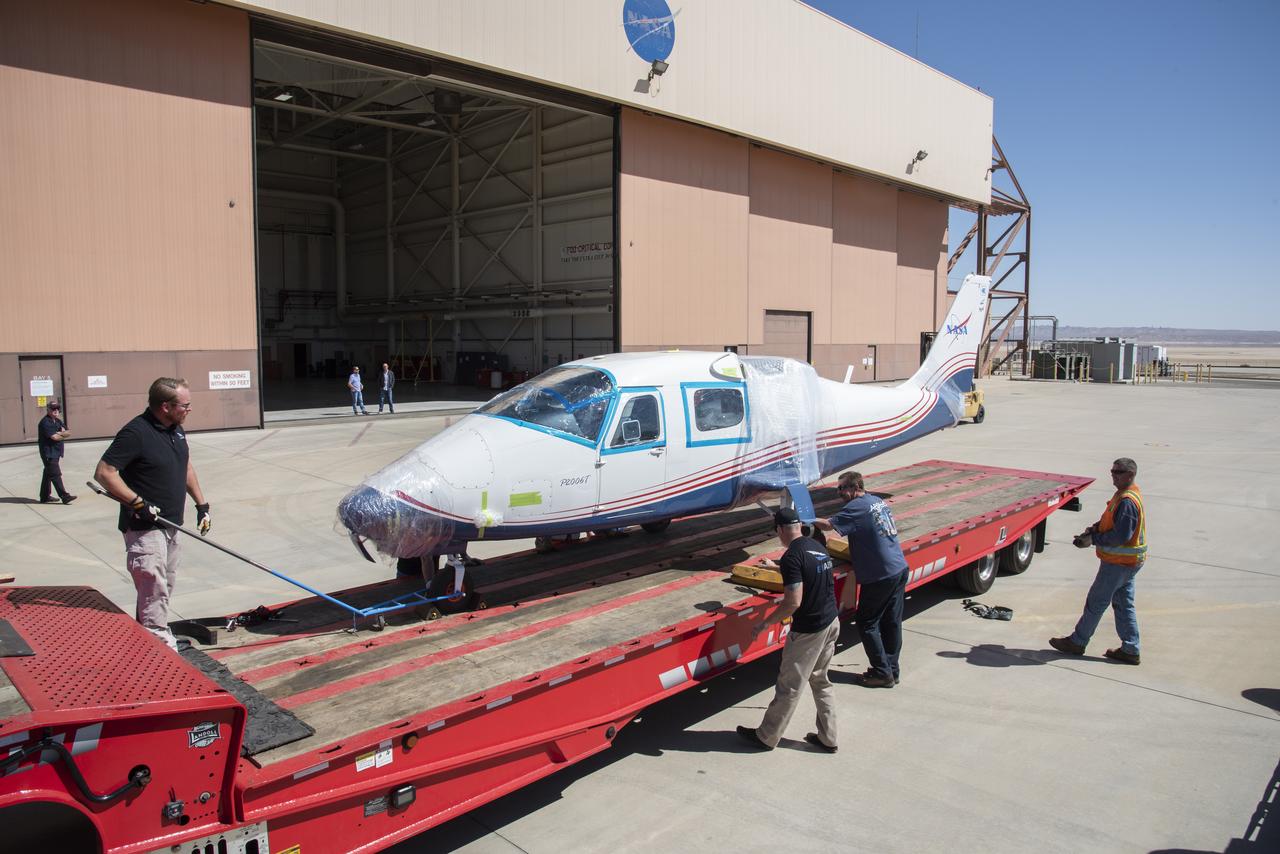

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
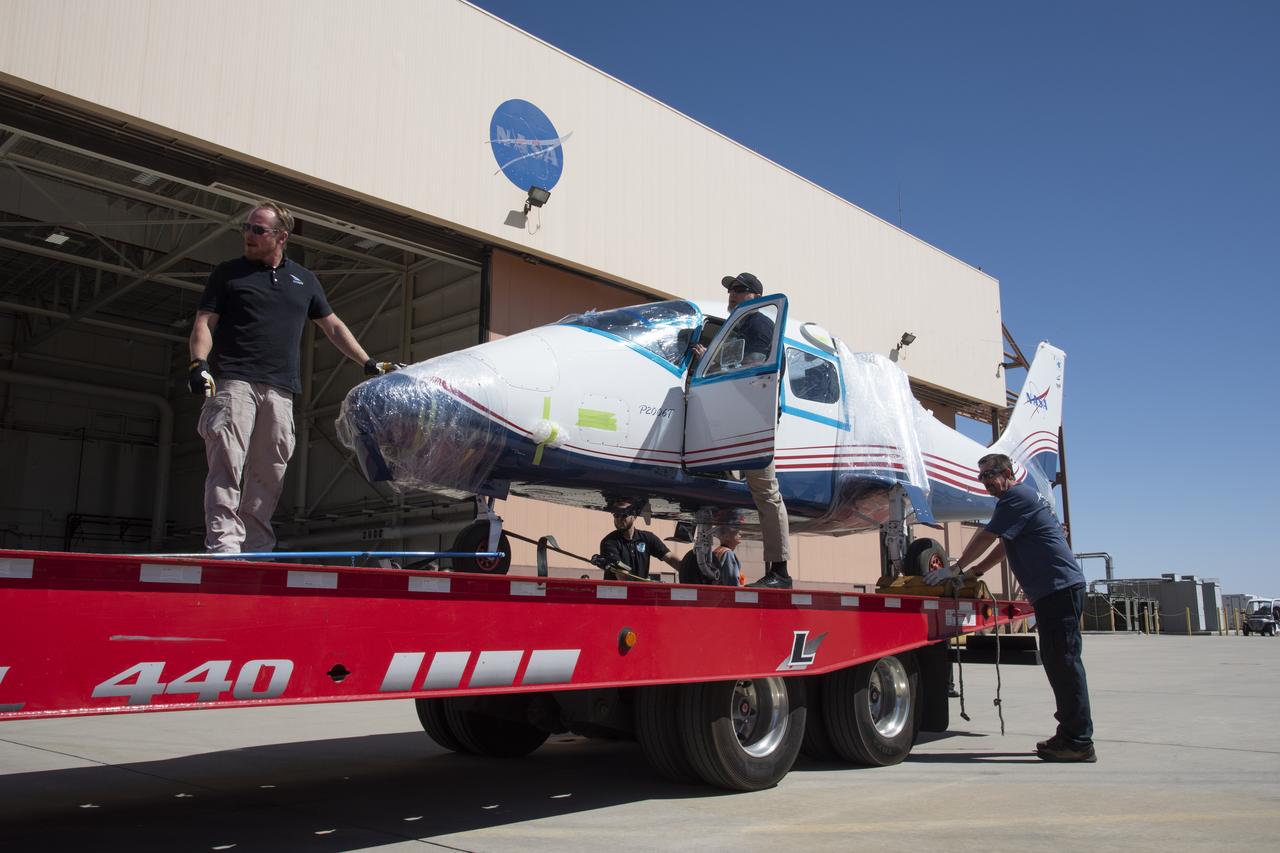

NASA’s X-57 Maxwell, the agency’s first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft’s cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57’s goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
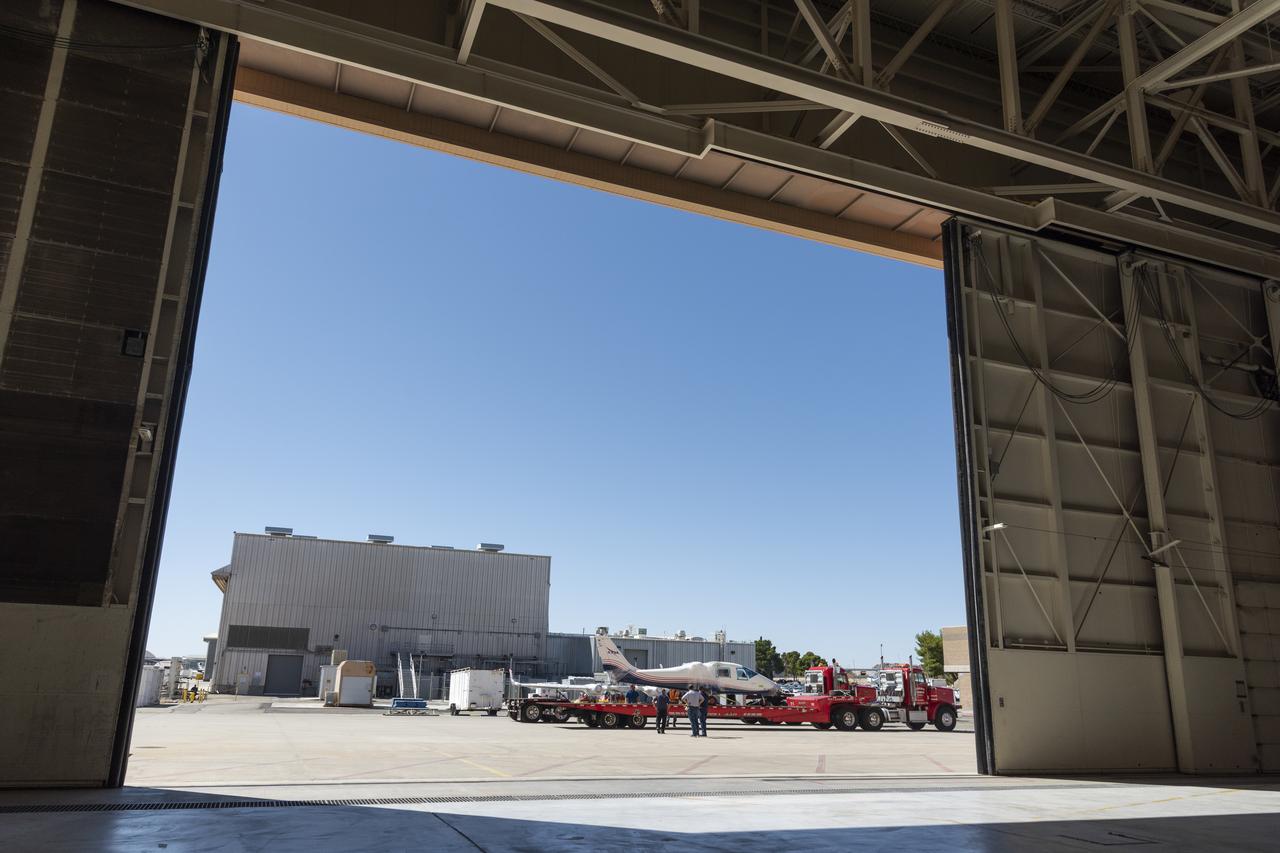

NASA’s X-57 Maxwell, the agency’s first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft’s cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57’s goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
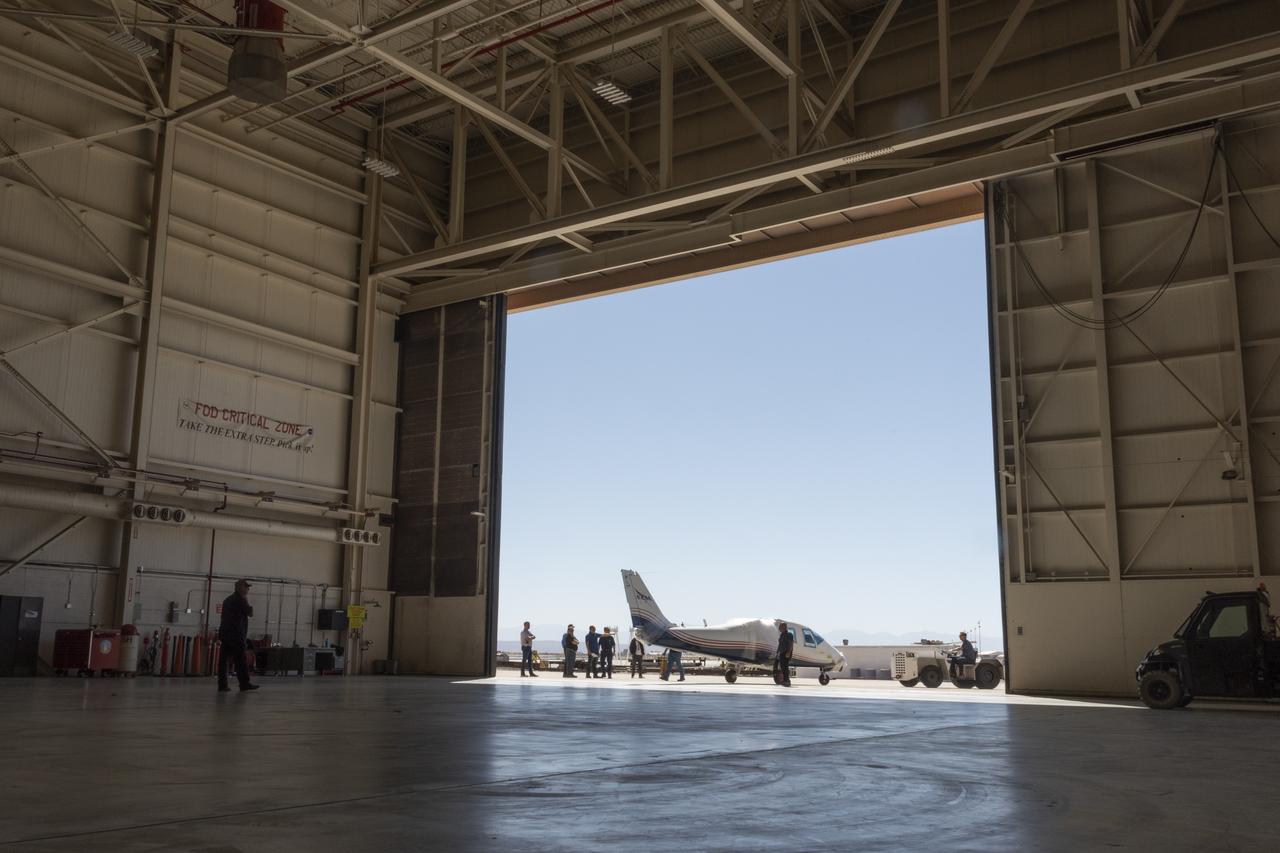

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
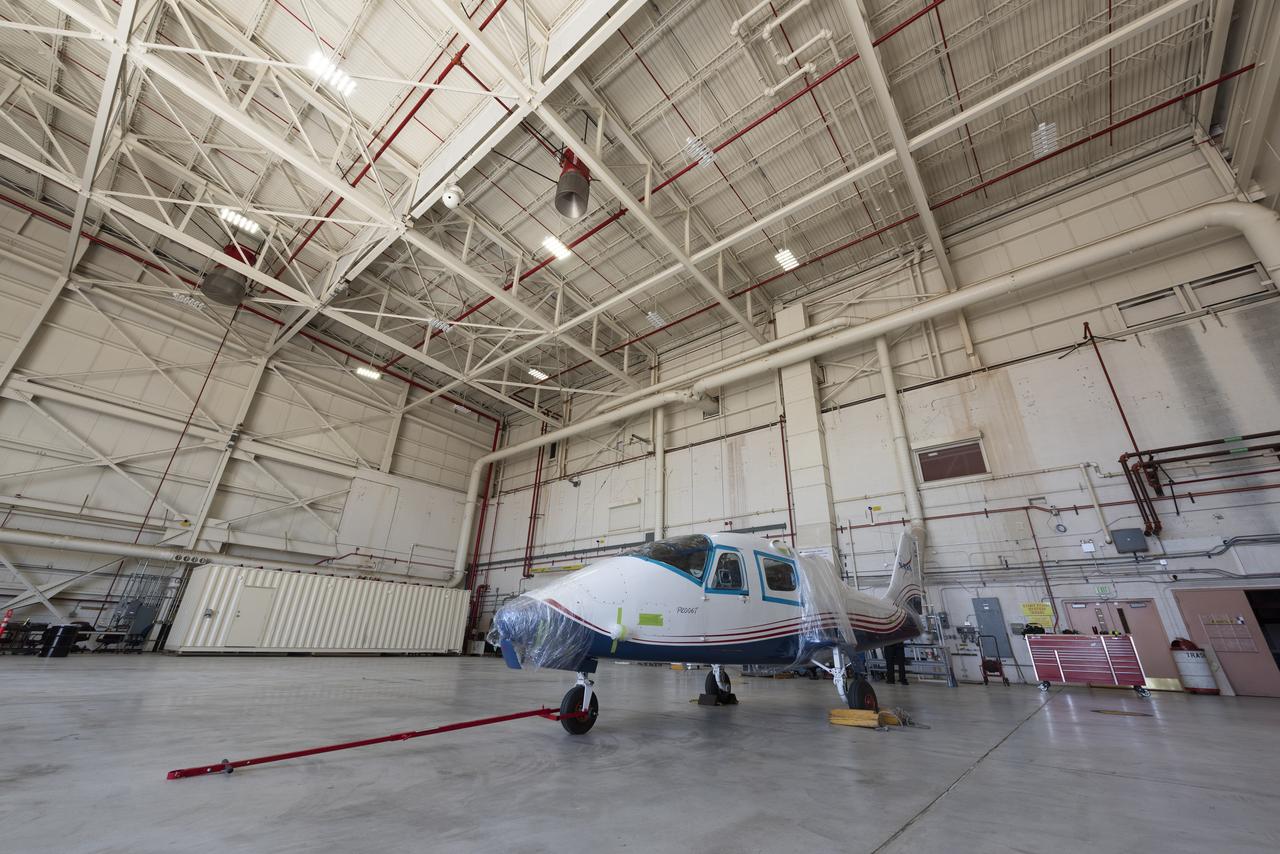

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
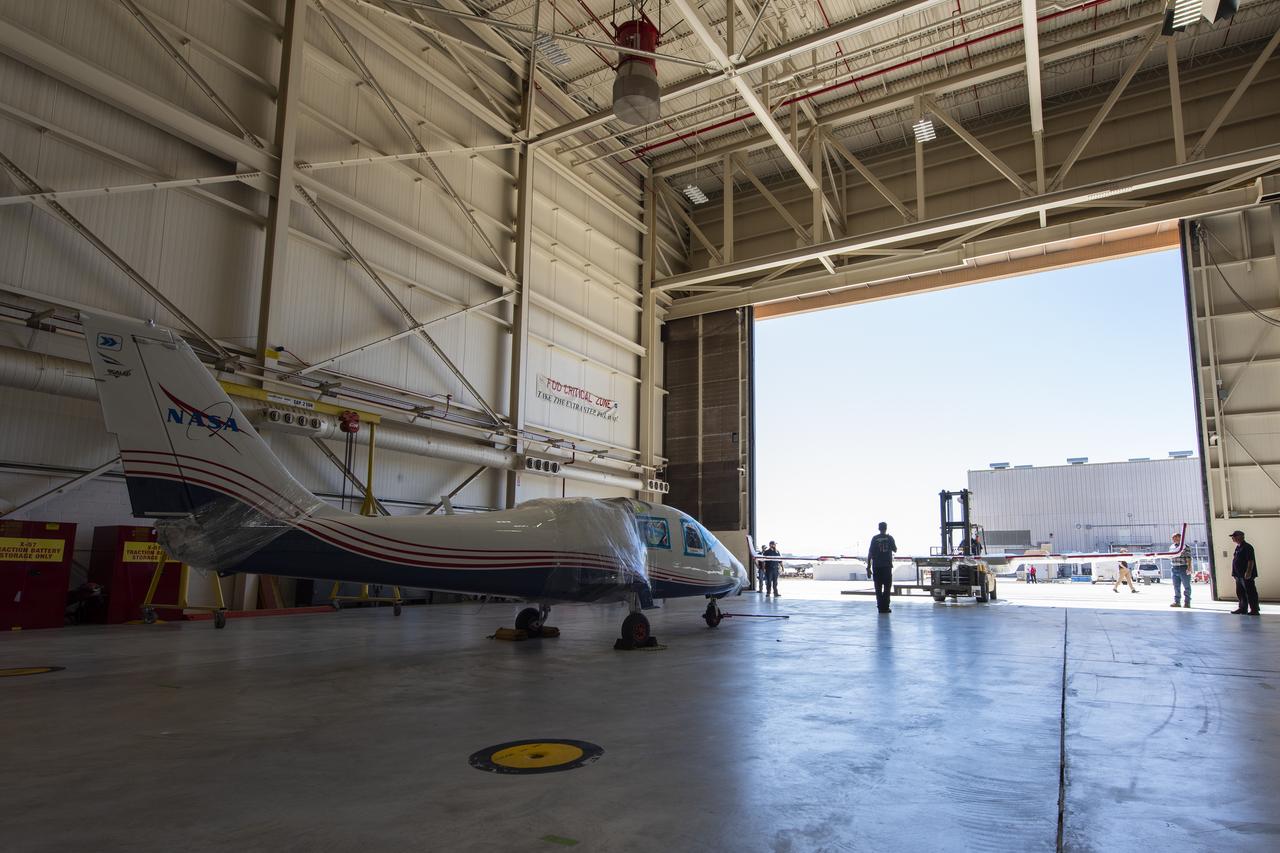

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
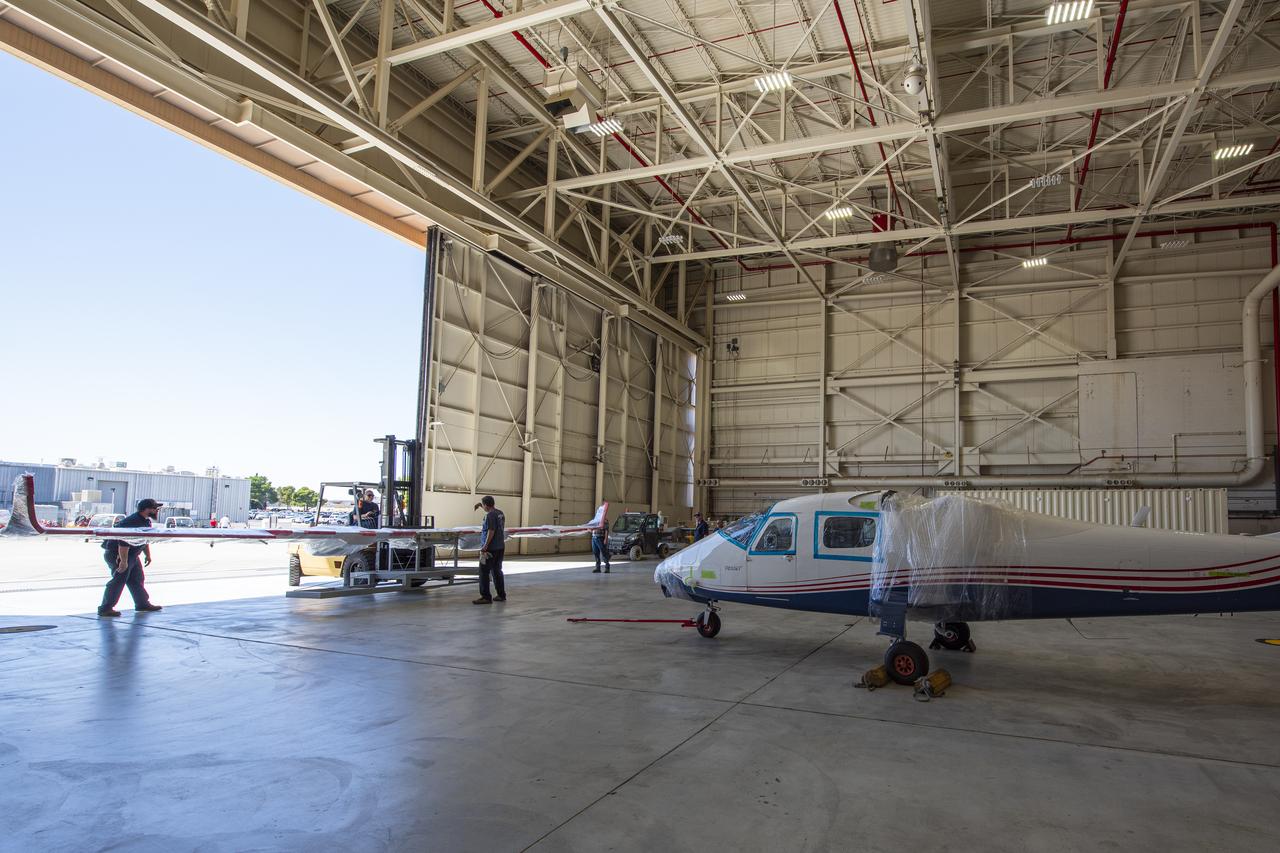

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
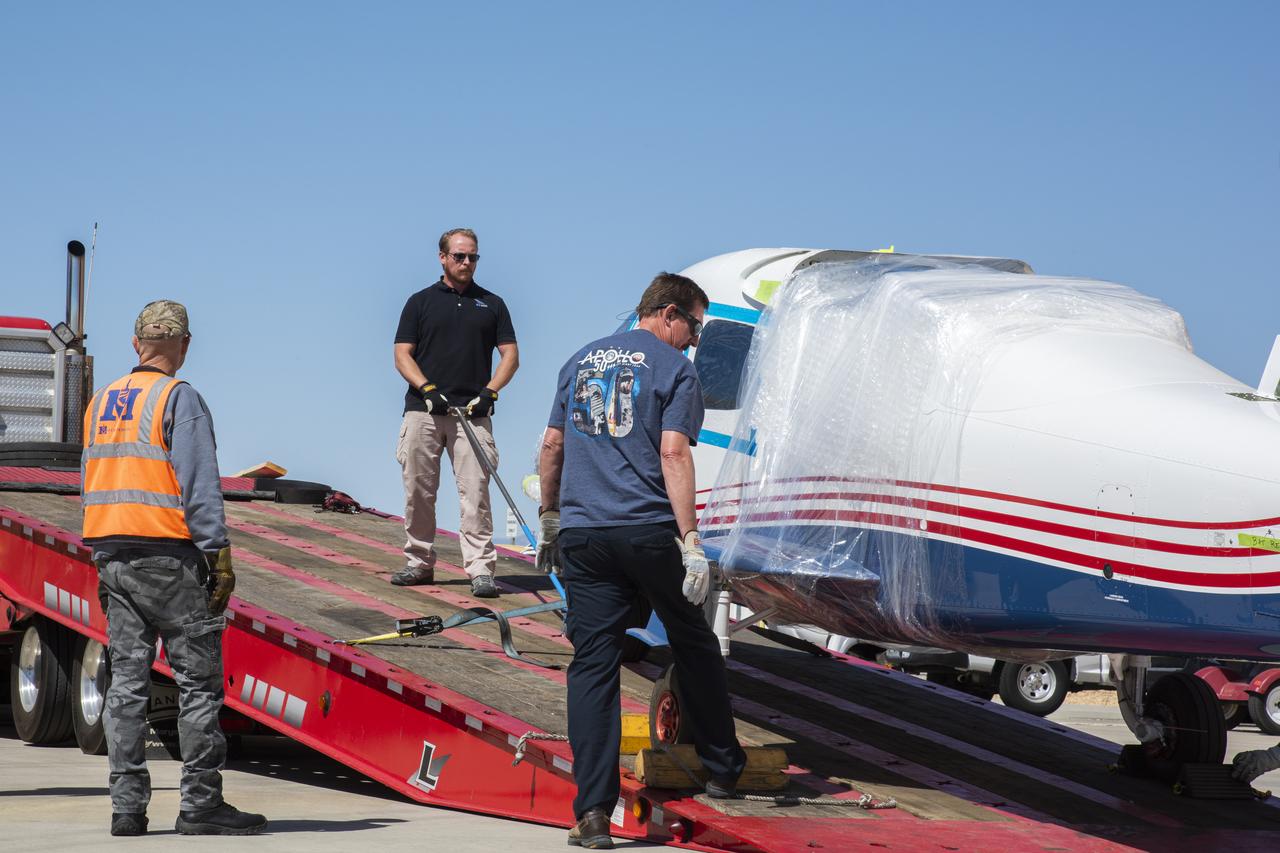

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
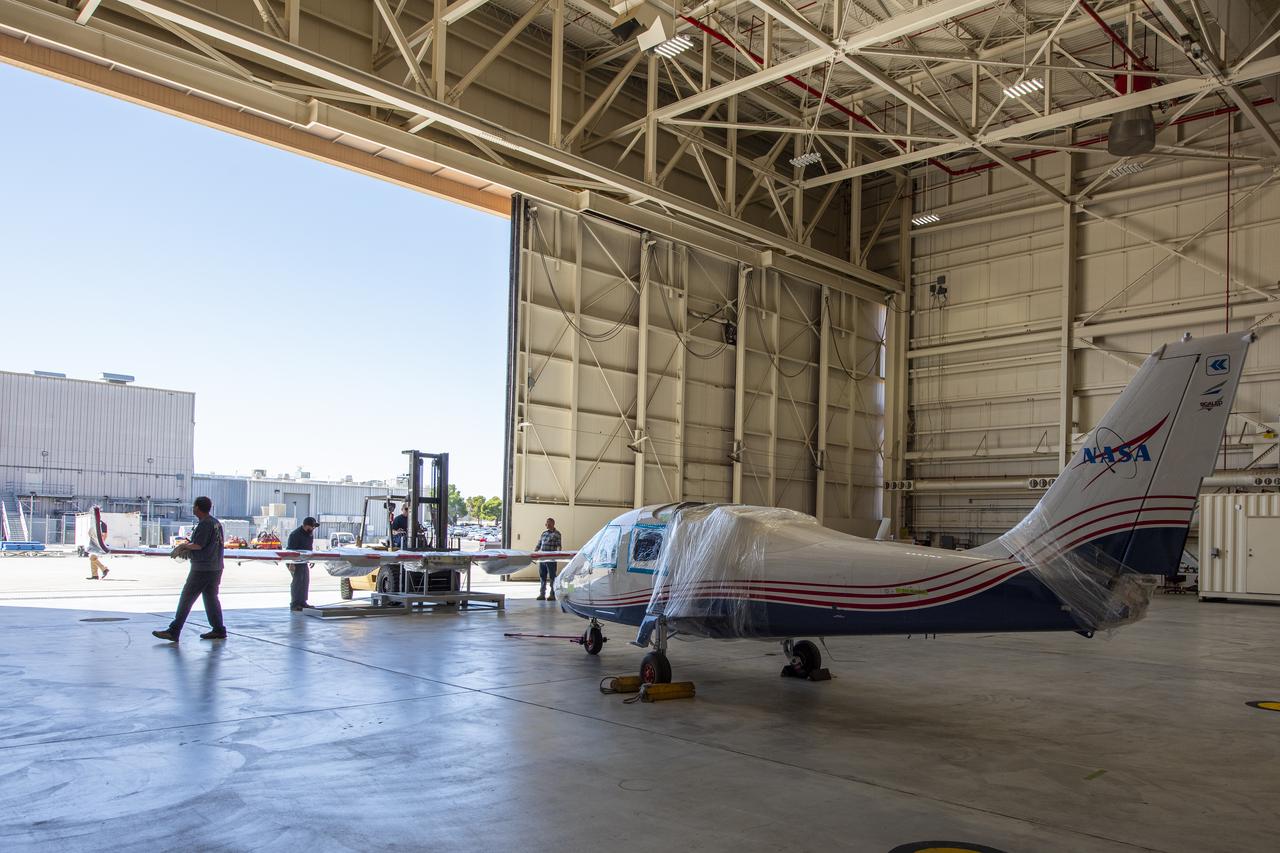

NASA’s X-57 Maxwell, the agency’s first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft’s cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57’s goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
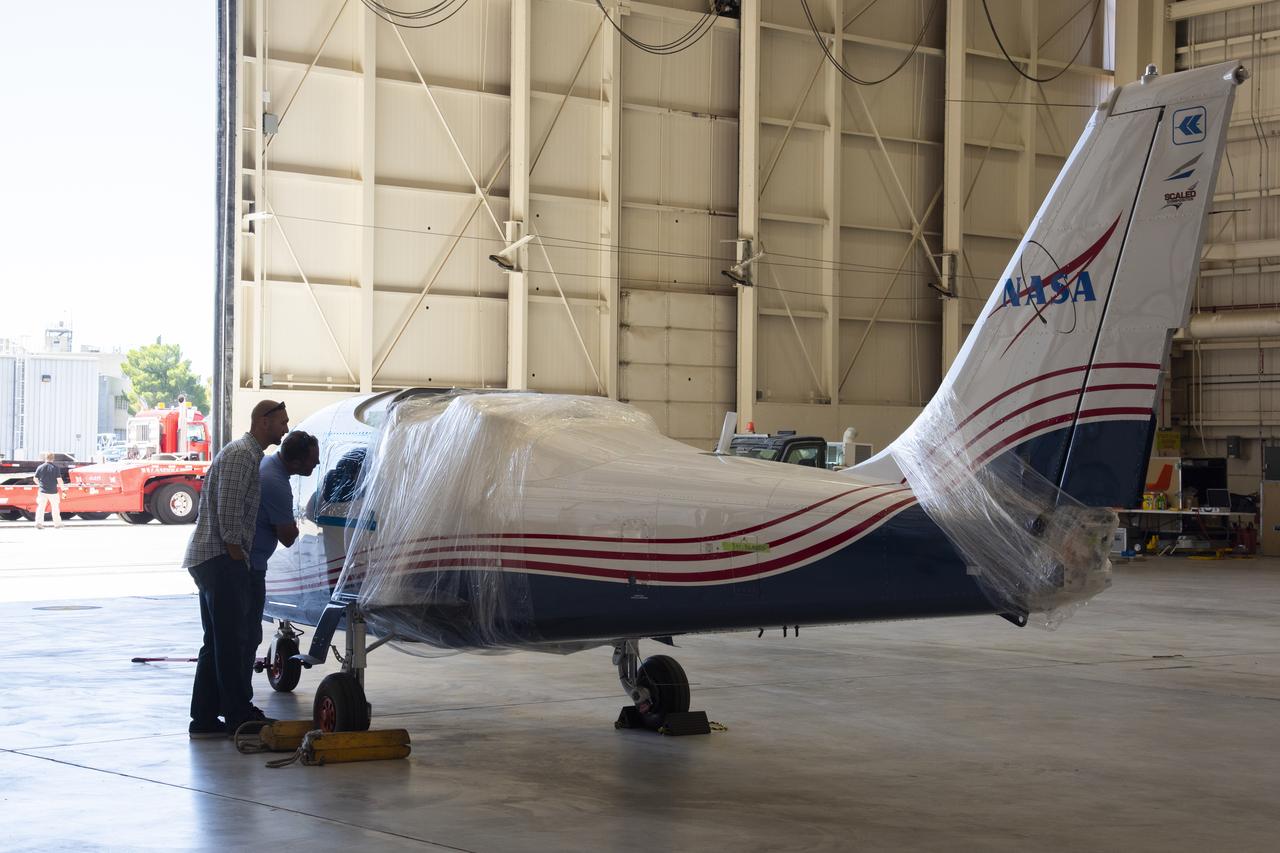

NASA's X-57 Maxwell, the agency's first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft's cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57's goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.
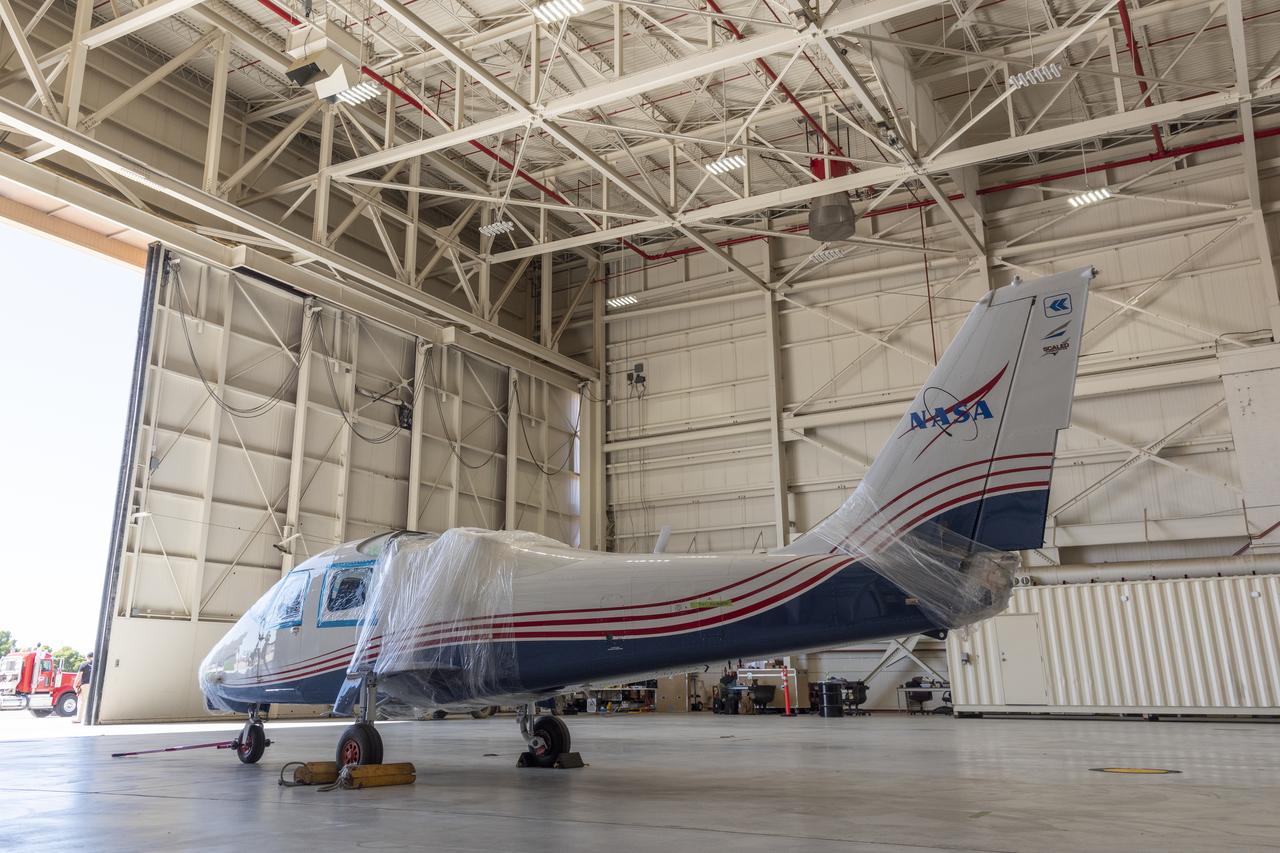

NASA’s X-57 Maxwell, the agency’s first all-electric X-plane and first crewed X-planed in two decades, is delivered to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in its Mod II configuration. The first of three primary modifications for the project, Mod II involves testing of the aircraft’s cruise electric propulsion system. Delivery to NASA from prime contractor Empirical Systems Aerospace of San Luis Obispo, California, marks a major milestone for the project, at which point the vehicle is reintegrated for ground tests, to be followed by taxi tests, and eventually, flight tests. X-57’s goal is to further advance the design and airworthiness process for distributed electric propulsion technology for general aviation aircraft, which can provide multiple benefits to efficiency, emissions, and noise.

Dr. Oscar Monje, (far right) a research scientist, packs a growing substrate called arcillite in the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assisting him is Jeffrey Richards, project science coordinator with SGT on the Engineering Services Contract (ESC). Seated in the foreground is Susan Manning-Roach, a quality assurance specialist, also with ESC. Developed by NASA and ORBITEC of Madison, Wisconsin, the APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that will be used to conduct bioscience research on the International Space Station. The APH will be delivered to the space station aboard future Commercial Resupply Services missions.
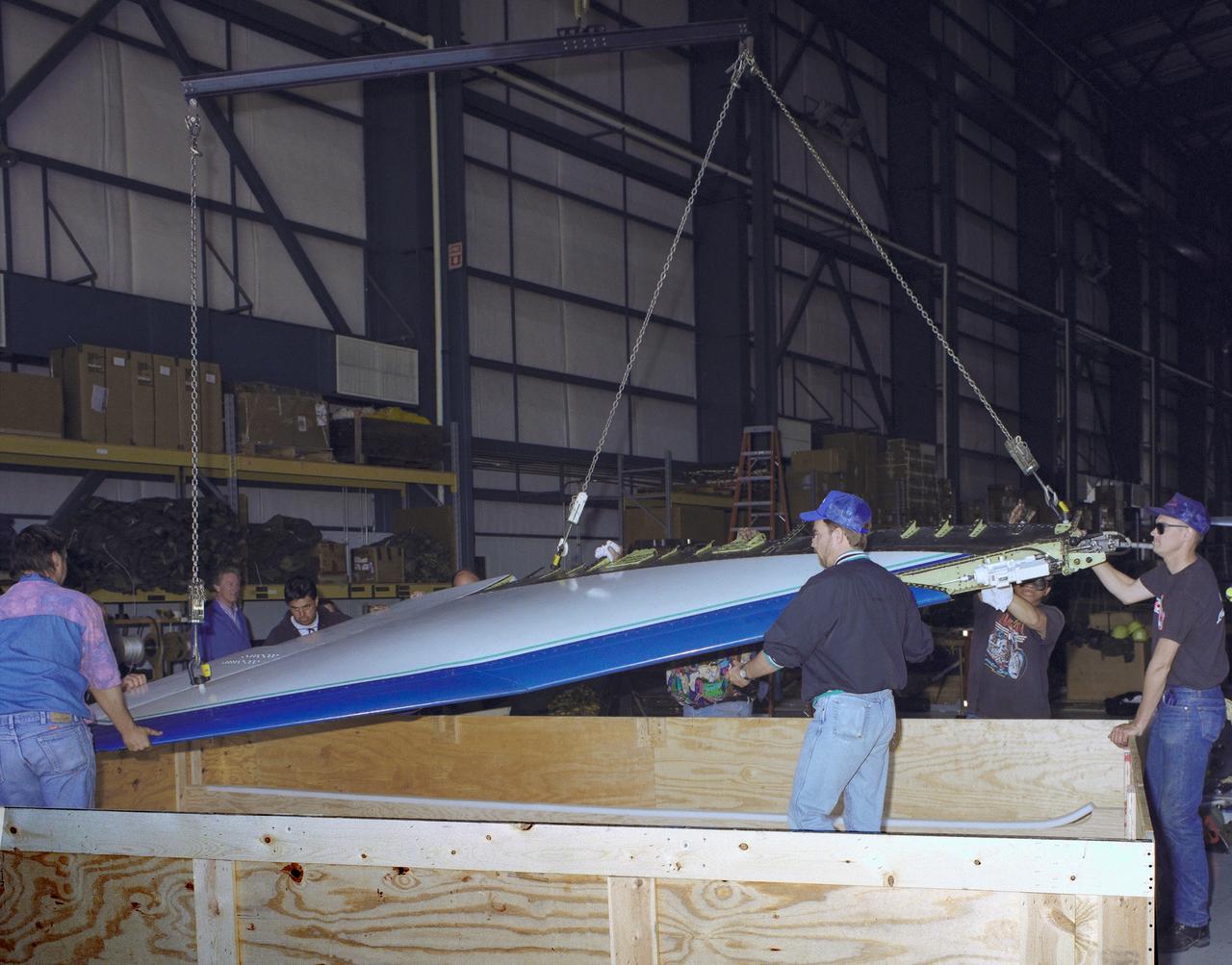

The right wing of the X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability Technology Demonstrator Aircraft is seen here being put into a shipping container May 18, 1995, at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, by U.S. and German members of the program. To fit inside an Air Force Reserve C-5 transport, which was used to ferry the X-31 to Europe on May 22, 1995, the right wing had to be removed. Manching, Germany, was used as a staging base to prepare the aircraft for participation in the Paris Air Show. At the air show on June 11 through the 18th, the X-31 demonstrated the value of using thrust vectoring (directing engine exhaust flow) coupled with advanced flight control systems to provide controlled flight at very high angles of attack. The aircraft arrived back at Edwards in an Air Force Reserve C-5 on June 25, 1995, and off loaded at Dryden the 27th. The X-31 aircraft was developed jointly by Rockwell International's North American Aircraft Division (now part of Boeing) and Daimler-Benz Aerospace (formerly Messerschmitt-Bolkow-Blohm), under sponsorship by the U.S. Department of Defense and the German Federal Ministry of Defense.
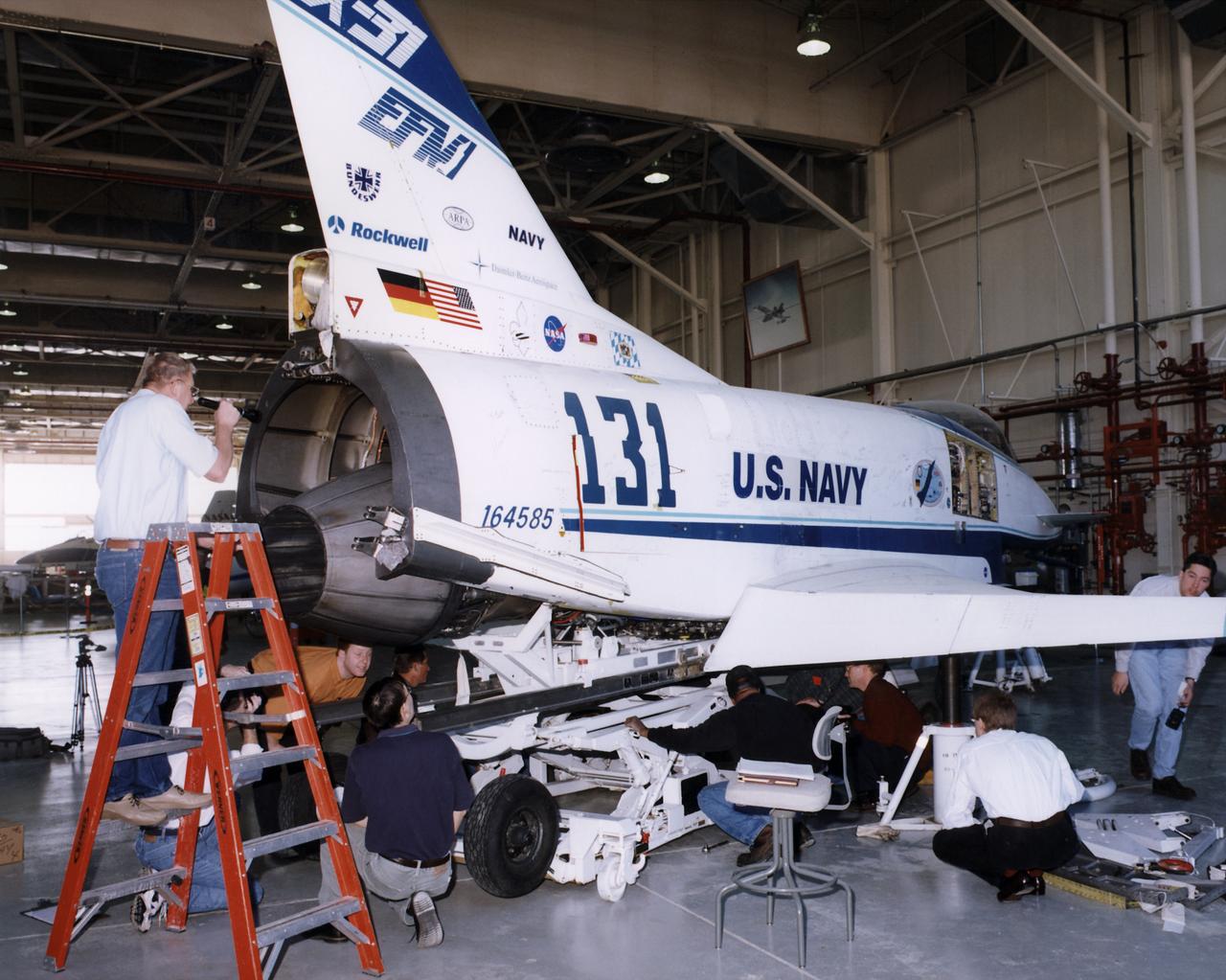

X-31 team members perform an engine fit check on the X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability demonstrator aircraft in a hangar at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
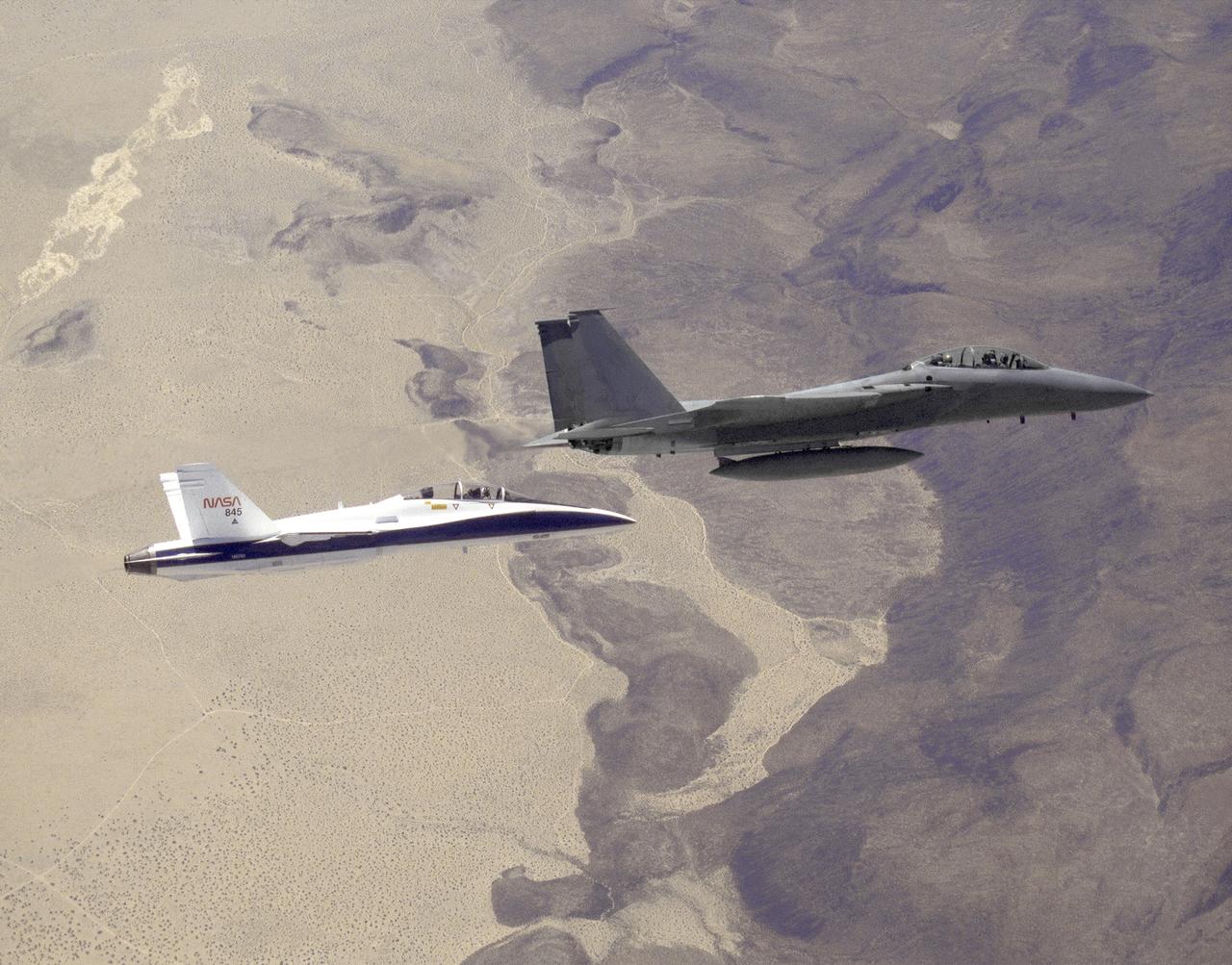

The three thrust-vectoring aircraft at Edwards, California, each capable of flying at extreme angles of attack, cruise over the California desert in formation during flight in March 1994. They are, from left, NASA's F-18 High Alpha Research Vehicle (HARV), flown by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center; the X-31, flown by the X-31 International Test Organization (ITO) at Dryden; and the Air Force F-16 Multi-Axis Thrust Vectoring (MATV) aircraft.
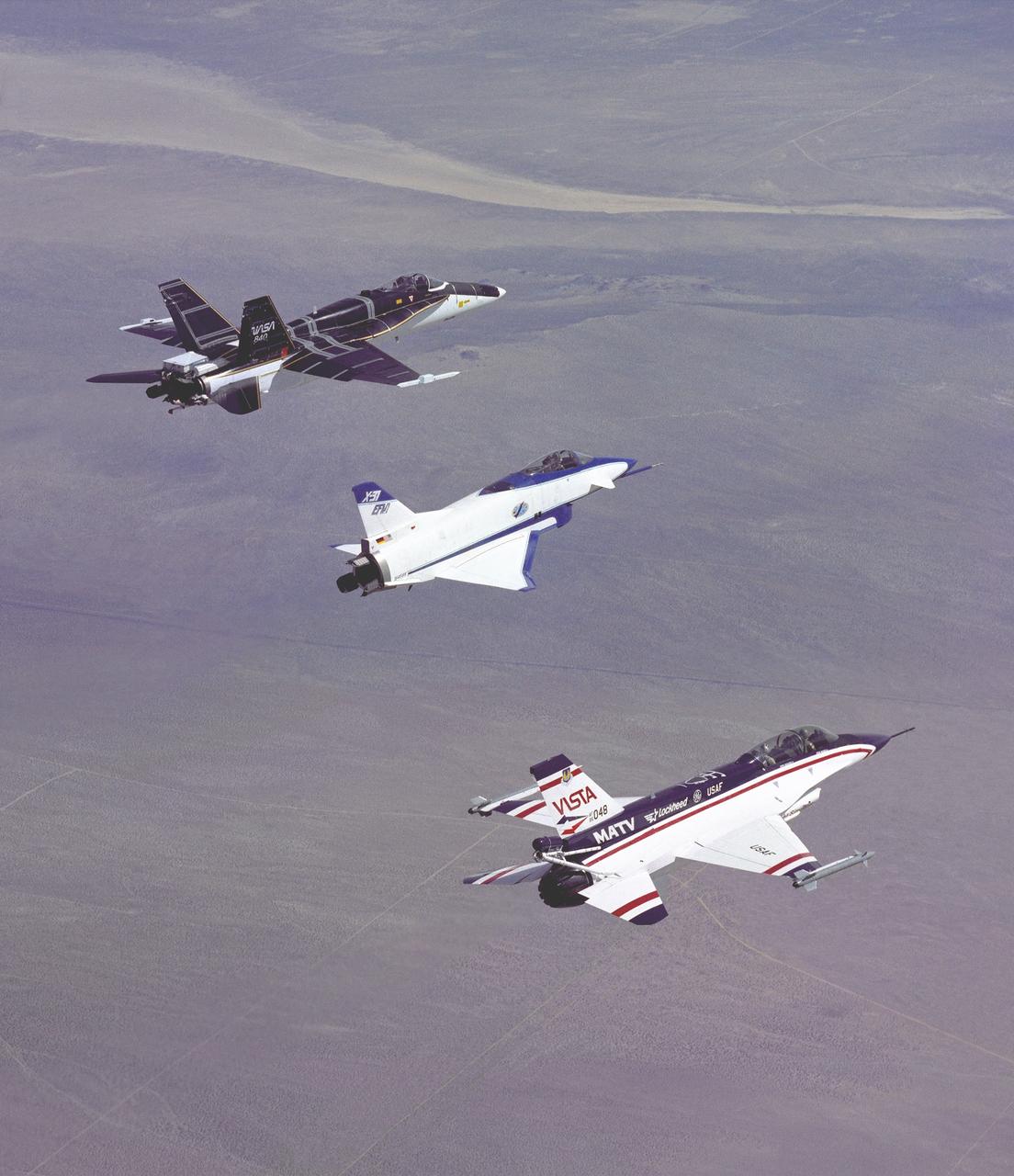

The three thrust-vectoring aircraft at Edwards, California, each capable of flying at extreme angles of attack, cruise over the California desert in formation during flight in March 1994. They are, from left, NASA's F-18 High Alpha Research Vehicle (HARV), flown by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center; the X-31, flown by the X-31 International Test Organization (ITO) at Dryden; and the Air Force F-16 Multi-Axis Thrust Vectoring (MATV) aircraft.
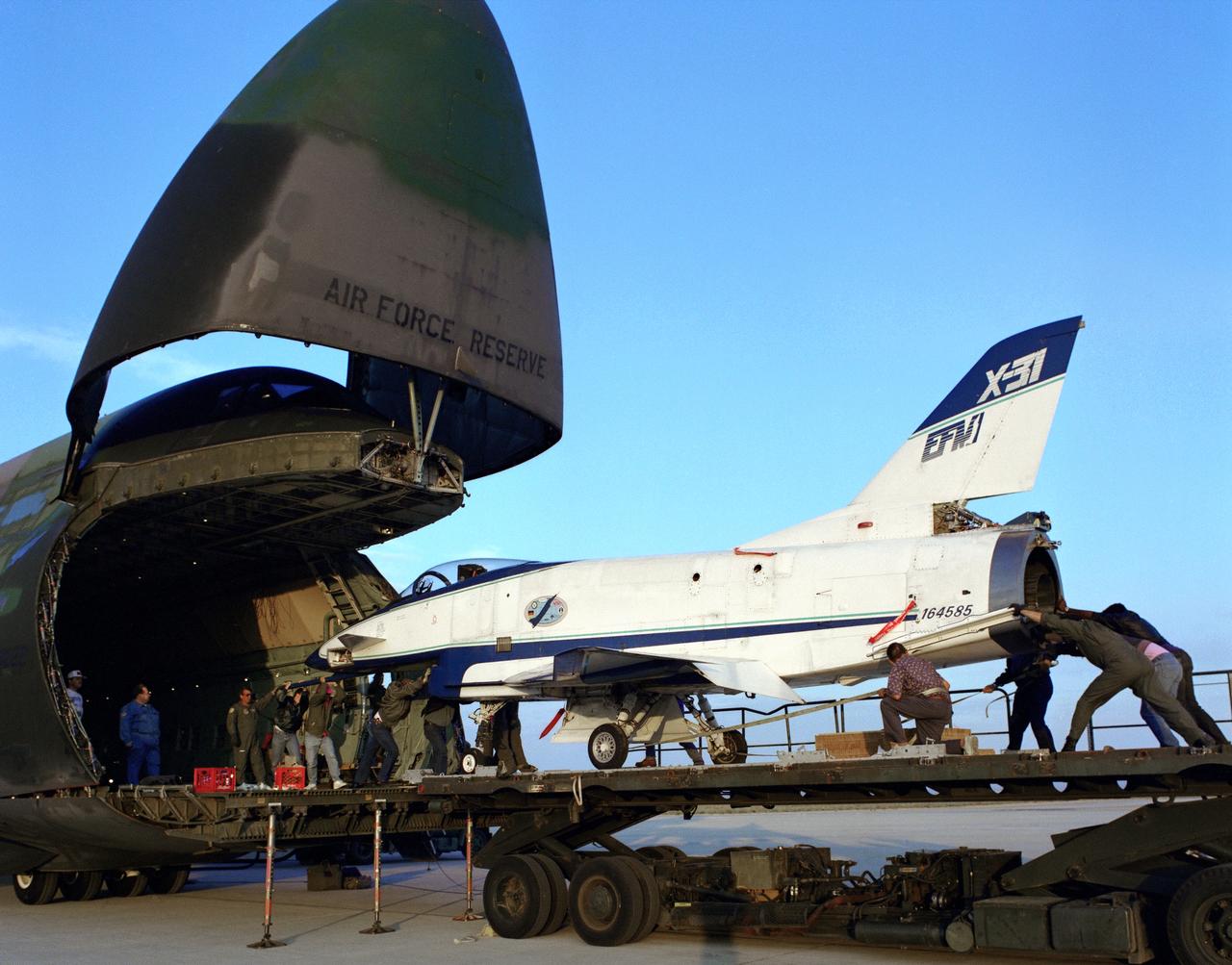

The X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability Technology Demonstrator Aircraft, based at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, begins rolling aboard an Air Force Reserve C-5 transport which ferried it on May 22, 1995 to Europe where it was flown in the Paris Air Show in June 1995. To fit in the C-5 the right wing of the X-31 had to be removed. At the air show, the X-31 demonstrated the value of using thrust vectoring (directing engine exhaust flow) coupled with advanced flight control systems to provide controlled flight at very high angles of attack.
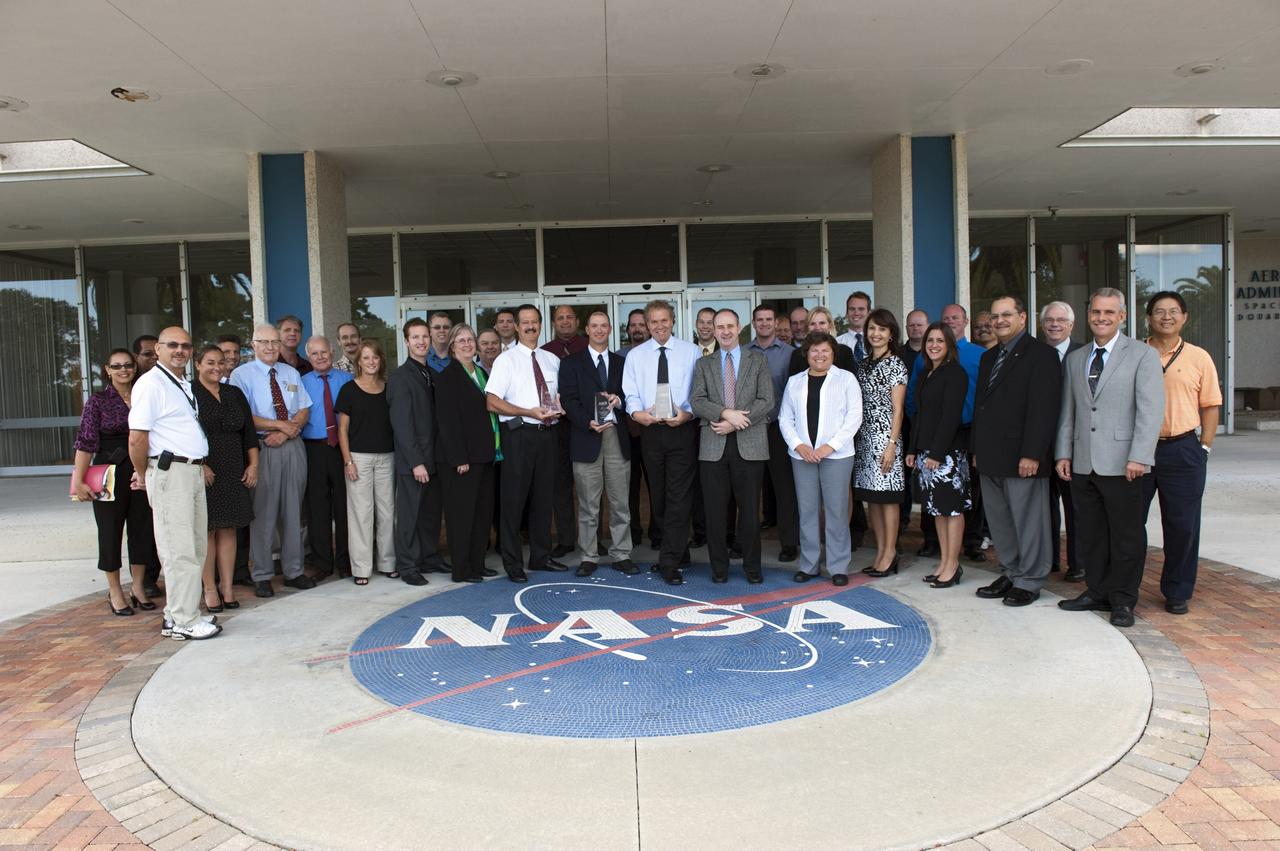

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Members of the crawlerway system evaluation team pose for a group portrait in front of the Headquarters Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The team received the Florida Project of the Year award from the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE). The Cape Canaveral branch of the ASCE nominated the team for its project, the Crawlerway Evaluation to Support a Heavy-Lift Program. The crawlerway is a 130-foot-wide, specialty-built roadway between Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), where rockets and spacecraft are prepared for flight, and Launch Pad 39A and 39B. The team's more than two-year evaluation confirmed the crawlerway system would be able to support the weight of moving the agency's future heavy-lift rockets and potential commercial vehicles from the VAB to the launch pads. The award honors the team's outstanding engineering efforts in research, design, construction and management, recognizing the complexity of multi-agency coordination and cost-effective engineering advances. For more information on the American Society of Civil Engineers, visit: http://www.asce.org. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA managers at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida show off the Florida Project of the Year trophies that the crawlerway system evaluation team received from the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE). From left are Michael Benik, director of Center Operations; Pepper Phillips, manager of the 21st Century Ground Systems Program Office; and Russell Romanella, associate director for Engineering and Technical Operations. The Cape Canaveral branch of the ASCE nominated the team for its project, the Crawlerway Evaluation to Support a Heavy-Lift Program. The crawlerway is a 130-foot-wide, specialty-built roadway between Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), where rockets and spacecraft are prepared for flight, and Launch Pad 39A and 39B. The team's more than two-year evaluation confirmed the crawlerway system would be able to support the weight of moving the agency's future heavy-lift rockets and potential commercial vehicles from the VAB to the launch pads. The award honors the team's outstanding engineering efforts in research, design, construction and management, recognizing the complexity of multi-agency coordination and cost-effective engineering advances. For more information on the American Society of Civil Engineers, visit: http://www.asce.org. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
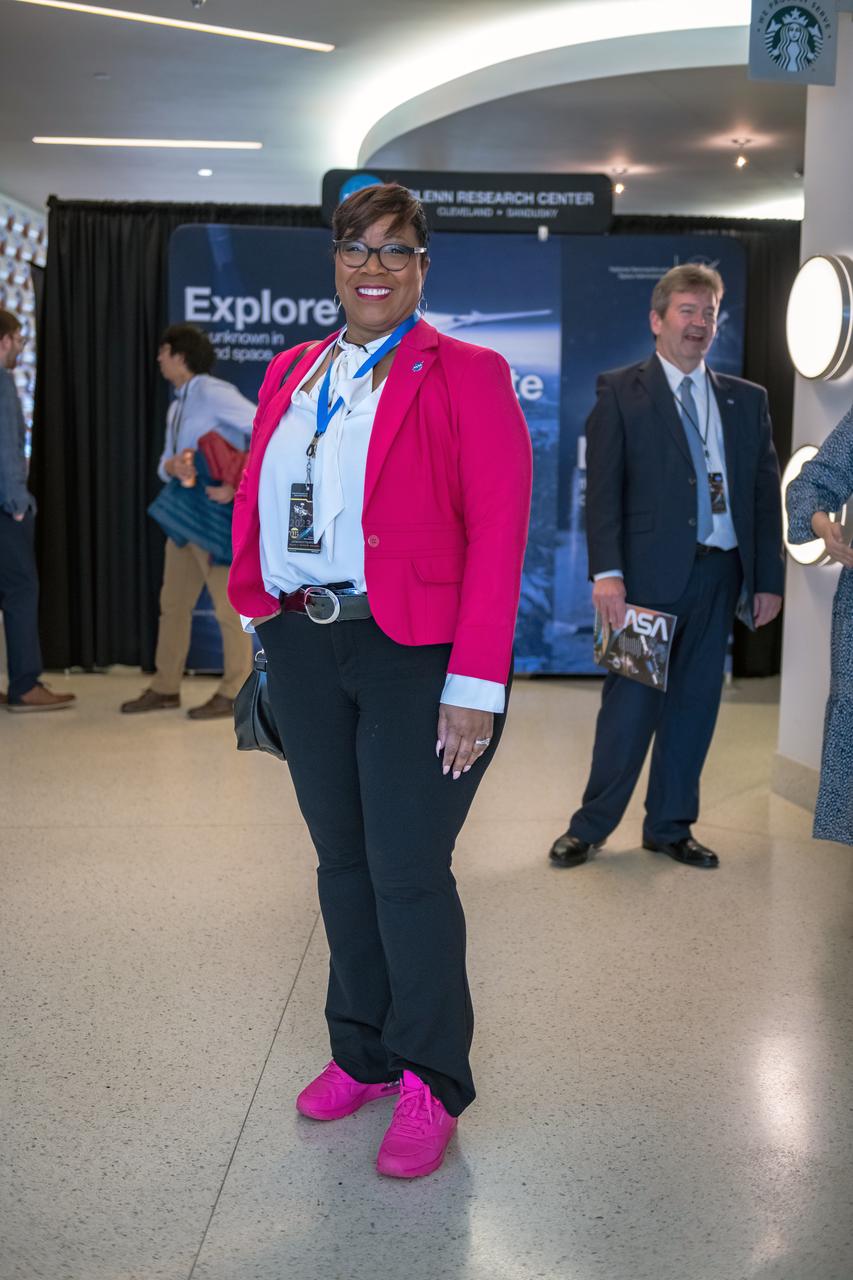

On March 28, 2024 NASA held its 2023 Administrator’s Agency Honor Awards at the Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, OH. Donya Douglas-Bradshaw from Goddard Space Flight Center was recognized for exceptional leadership, engineering and programmatic expertise, and project execution for several of NASA's highest profile missions and organizations. She received the Distinguished Service Medal. This celebratory event recognized the invaluable contributions of civil servants and contractors alike, each one instrumental in propelling humanity further into the realms of space exploration, understanding, and discoverThis is NASA's highest form of recognition that is awarded to any Government employee who, by distinguished service, ability, or vision has personally contributed to NASA's advancement of United States' interests.

Jeffrey Richards, a project science coordinator with URS Federal Services, secures Arabidopsis seeds, commonly known as thale cress, in the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, May 9. The APH base will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard Orbital ATK's Cygnus spacecraft on the company's ninth Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA. The APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that is being used to conduct bioscience research on the space station. Cygnus will launch on Orbital ATK's Antares rocket from Wallops Flight Facility in Wallops Island, Virginia. Launch is targeted for May 20, 2018.

Jeffrey Richards, a project science coordinator with URS Federal Services, secures Arabidopsis seeds, commonly known as thale cress, in the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, May 9. The APH base will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard Orbital ATK's Cygnus spacecraft on the company's ninth Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA. The APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that is being used to conduct bioscience research on the space station. Cygnus will launch on Orbital ATK's Antares rocket from Wallops Flight Facility in Wallops Island, Virginia. Launch is targeted for May 20, 2018.

Jeffrey Richards, at left, a project science coordinator with URS Federal Services, secures Arabidopsis seeds, commonly known as thale cress, in the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, May 9. The APH base will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard Orbital ATK's Cygnus spacecraft on the company's ninth Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA. The APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that is being used to conduct bioscience research on the space station. Cygnus will launch on Orbital ATK's Antares rocket from Wallops Flight Facility in Wallops Island, Virginia. Launch is targeted for May 20, 2018.
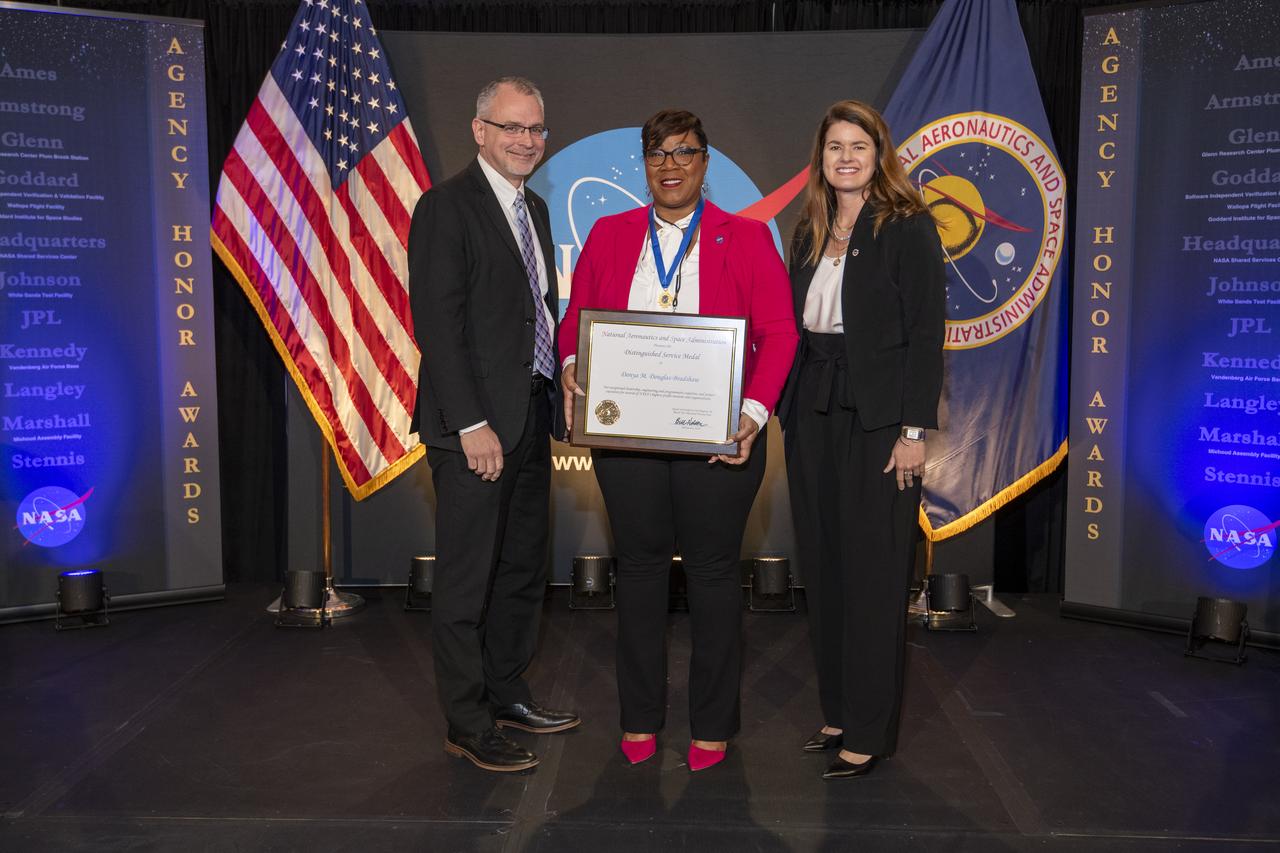

On March 28, 2024 NASA held its 2023 Administrator’s Agency Honor Awards at the Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, OH. Donya Douglas-Bradshaw from Goddard Space Flight Center was recognized for exceptional leadership, engineering and programmatic expertise, and project execution for several of NASA's highest profile missions and organizations. She received the Distinguished Service Medal. Associate Administrator, James Free and Deputy Associate Administrator Casey Swails present the award to Mrs. Douglas-Bradshaw. This celebratory event recognized the invaluable contributions of civil servants and contractors alike, each one instrumental in propelling humanity further into the realms of space exploration, understanding, and discoverThis is NASA's highest form of recognition that is awarded to any Government employee who, by distinguished service, ability, or vision has personally contributed to NASA's advancement of United States' interests.

Jeffrey Richards, a project science coordinator with URS Federal Services, uses a fixative to secure Arabidopsis seeds, commonly known as thale cress, in the science carrier, or base, of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, May 9. The APH base will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard Orbital ATK's Cygnus spacecraft on the company's ninth Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA. The APH is the largest plant chamber built for the agency. It is a fully automated plant growth facility that is being used to conduct bioscience research on the space station. Cygnus will launch on Orbital ATK's Antares rocket from Wallops Flight Facility in Wallops Island, Virginia. Launch is targeted for May 20, 2018.

On March 28, 2024 NASA held its 2023 Administrator’s Agency Honor Awards at the Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, OH. Donya Douglas-Bradshaw from Goddard Space Flight Center was recognized for exceptional leadership, engineering and programmatic expertise, and project execution for several of NASA's highest profile missions and organizations. She received the Distinguished Service Medal. This celebratory event recognized the invaluable contributions of civil servants and contractors alike, each one instrumental in propelling humanity further into the realms of space exploration, understanding, and discoverThis is NASA's highest form of recognition that is awarded to any Government employee who, by distinguished service, ability, or vision has personally contributed to NASA's advancement of United States' interests. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
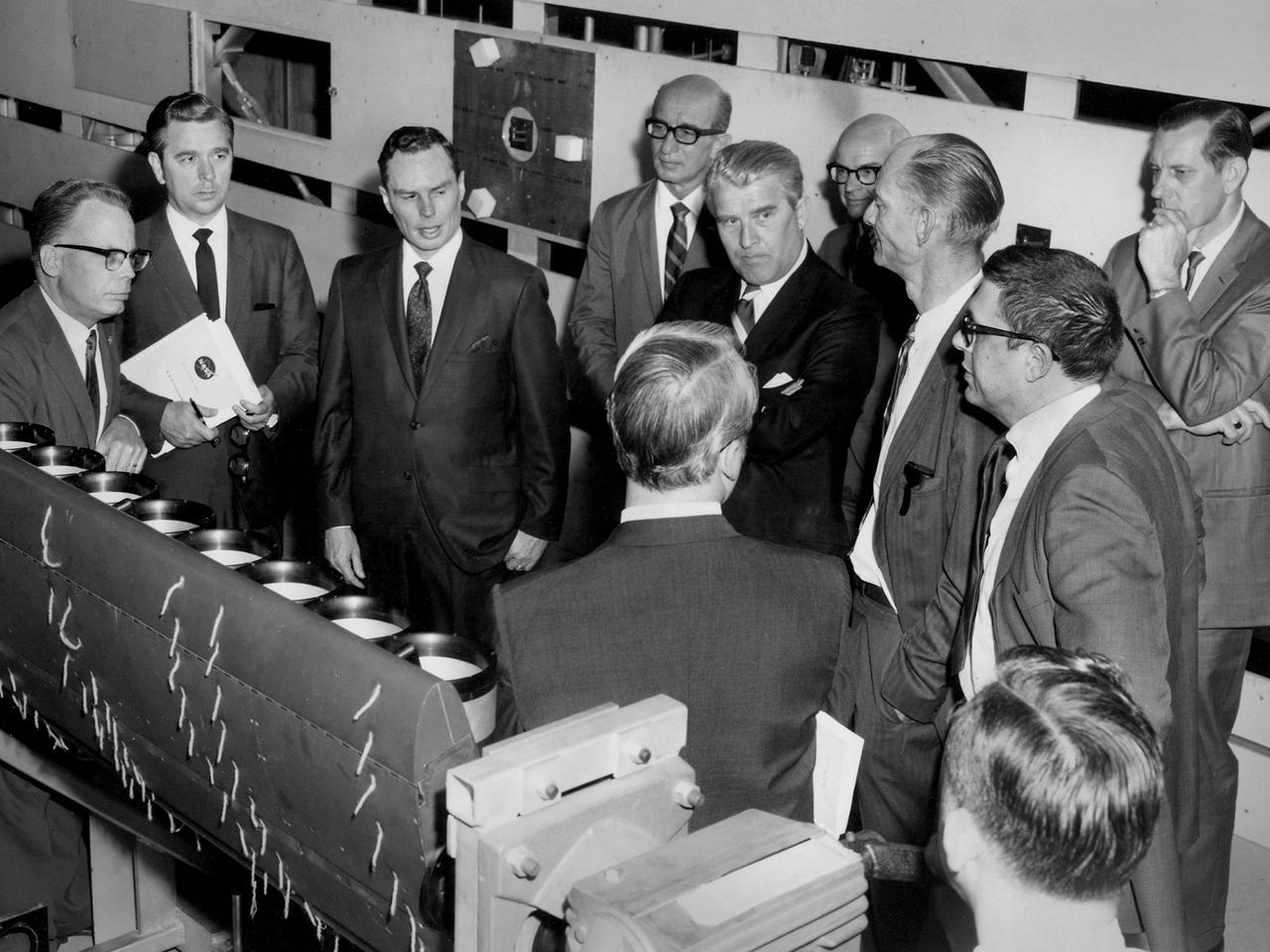

Werner von Braun, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Deputy Associate Administrator for Planning, among a group from Headquarters touring the Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. Lewis Special Projects Chief Newell Sanders, left, describes a Short Takeoff and Landing wing-propulsion model. Lewis had recently converted the return leg of its 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel into the 9- by 15-Foot Low Speed Wind Tunnel to investigate Vertical and Short Takeoff and Landing propulsion systems. Gathered from the left near Sanders are James Daniels, Headquarters Executive Secretary; Oran Hicks, Acting Associate Administrator for the Headquarters Office of Advanced Research and Technology; Eugene Manganiello, Lewis Deputy Director; von Braun; Dr. Walter Olson, Lewis Assistant Director; Bruce Lundin, Lewis Director and Dr. Bernard Lubarsky, Lewis Assistant Director. Just months before this photograph, NASA asked von Braun to give up his post as Director of the Marshall Space Flight Center after nearly ten years in order to head up the strategic planning effort for the agency from Washington DC. Von Braun retired from NASA two years later.
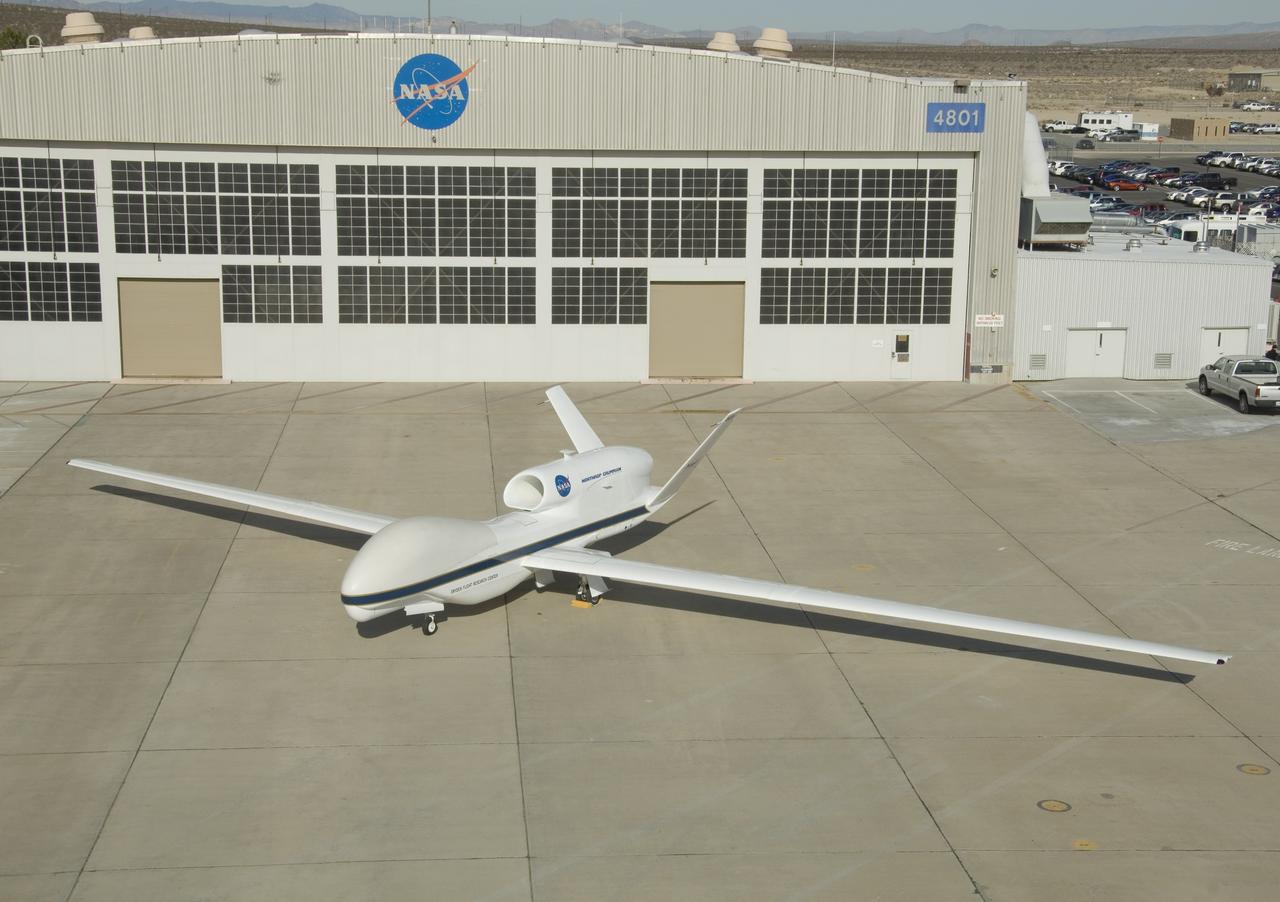

One of NASA's two Global Hawk high-altitude unmanned science aircraft displays its contours outside its hangar at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center.
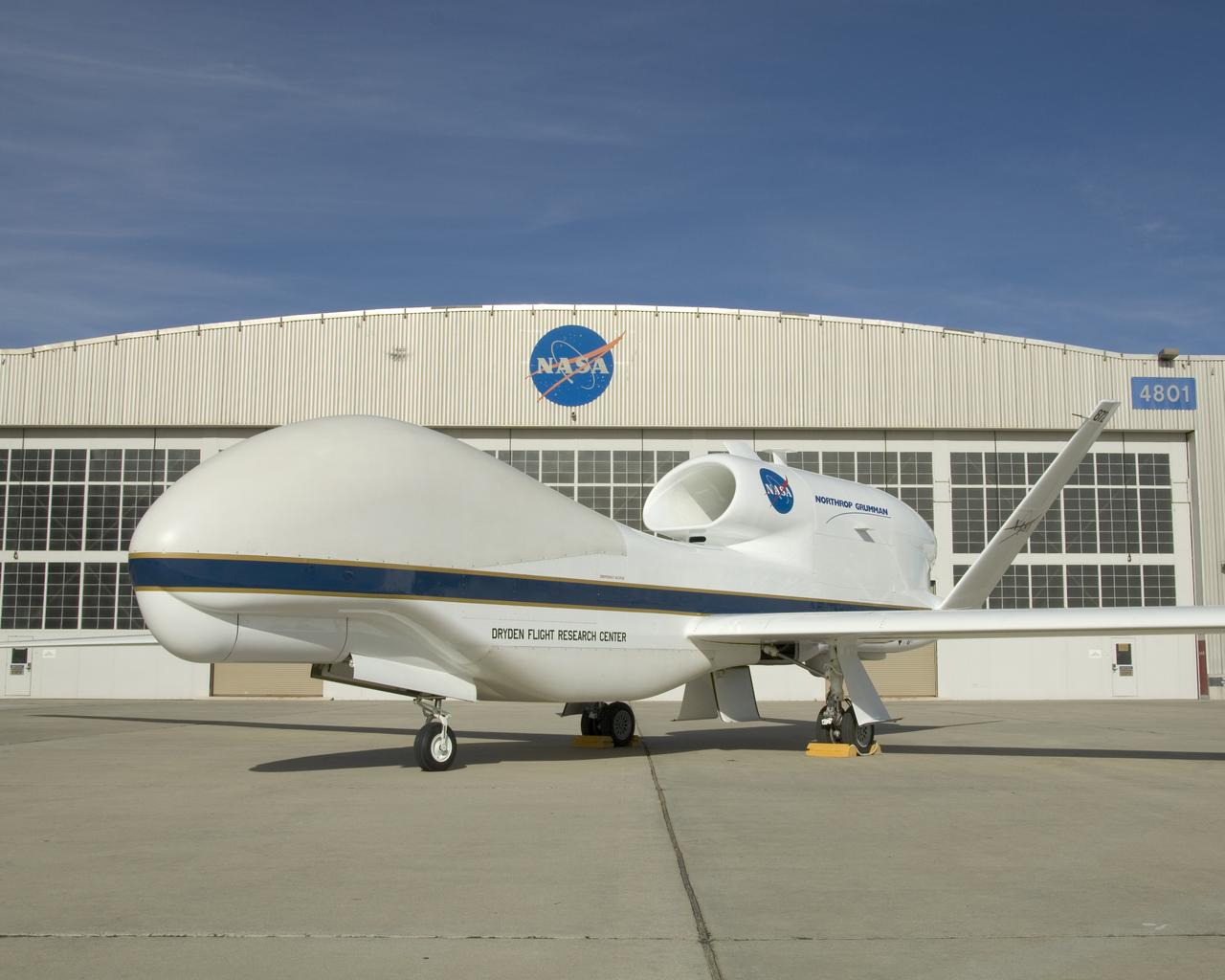

One of NASA's two Global Hawk unmanned high-altitude aircraft shows off its blue-and-white livery in front of its hangar at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center.
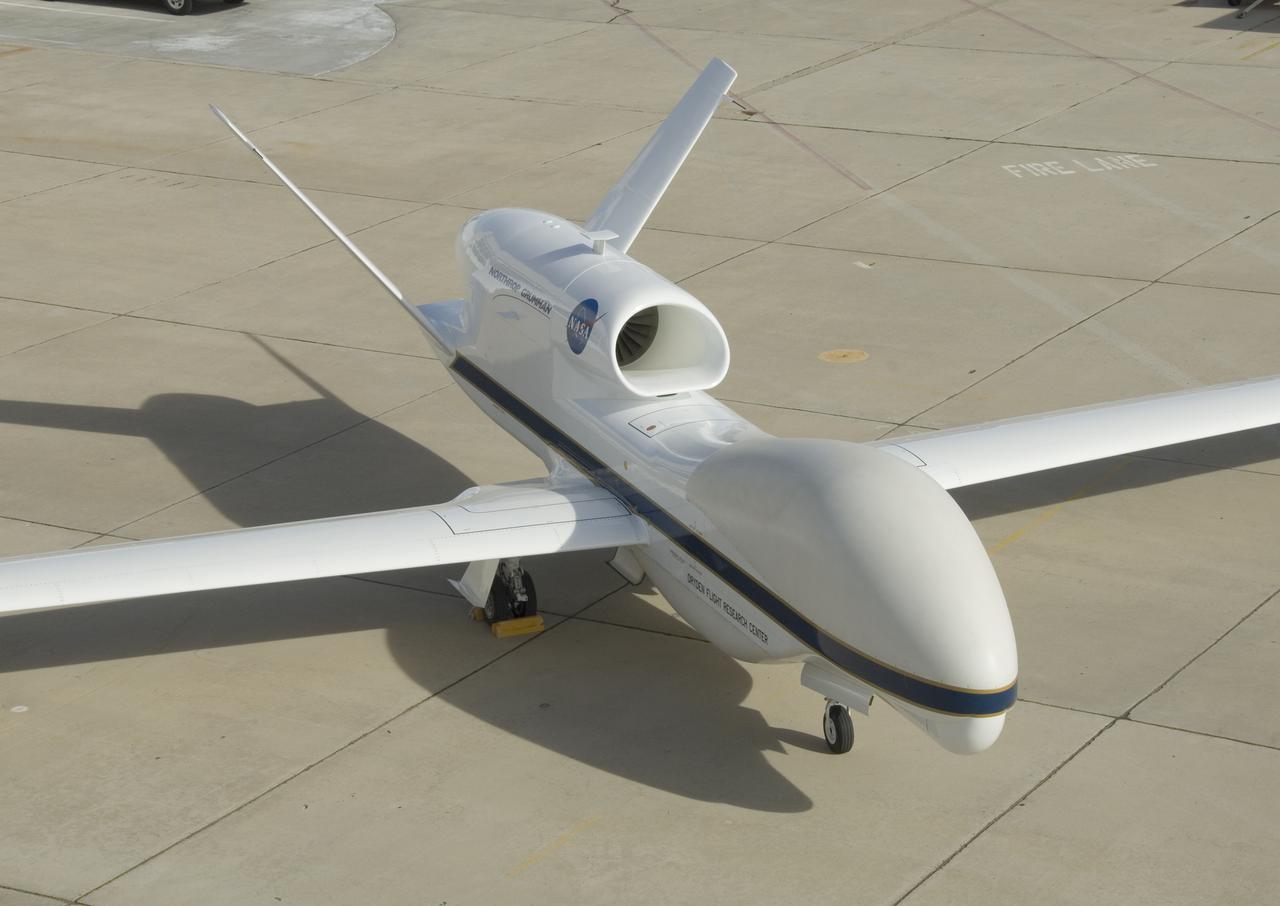

This Global Hawk unmanned aircraft is one of two that are used by NASA for Earth science missions and by Northrop Grumman for follow-on developmental testing.
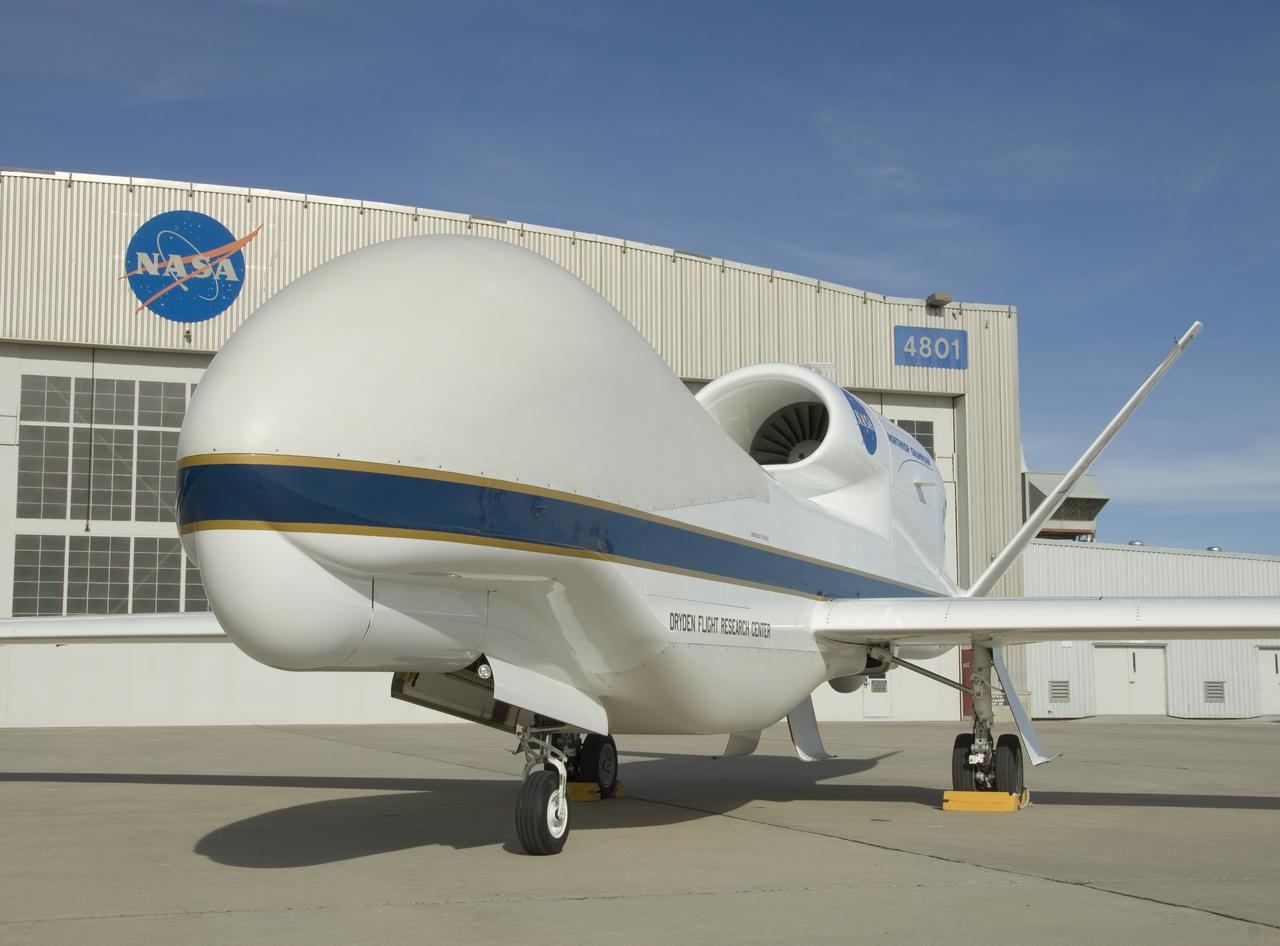

The bulbous nose of one of NASA's two Global Hawk unmanned high-altitude aircraft houses communications and sensor payloads on Earth science missions.
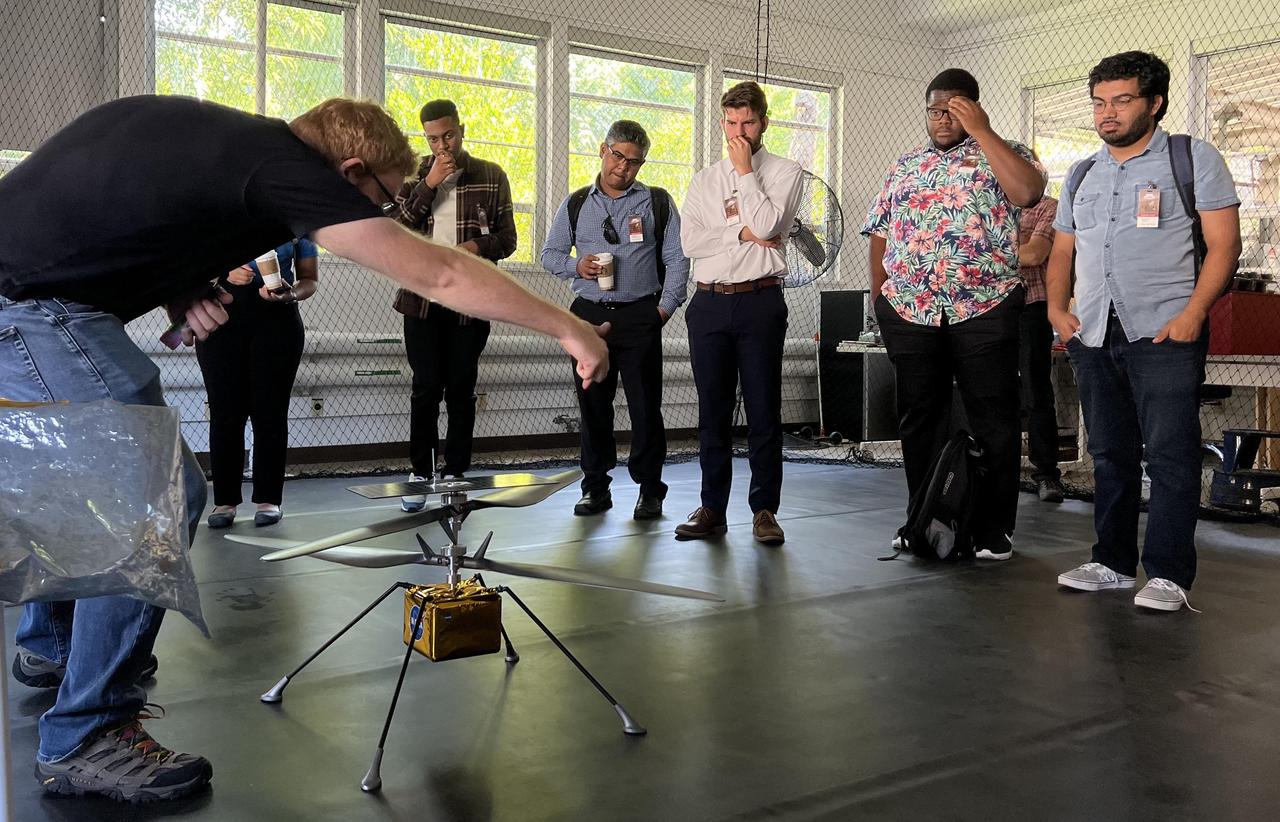

Participants in NASA's Minority Serving Institutions Space Accelerator program surround a full-scale model of NASA's Mars Ingenuity Helicopter as engineer Michael Starch discusses the mission. The group was visiting NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Aug. 18, 2022. These participants were members of three teams named as awardees in the first-of-its-kind accelerator program, a competition to advance the NASA's goals and meet its needs in the areas of machine learning, artificial intelligence, and development of autonomous systems while also engaging underrepresented academic institutions and reducing barriers for them to submit ideas to the agency. The program provides funding, business training through a 10-week accelerator course, and mentorship to help the teams develop ideas for systems that can operate without human oversight for future science missions in space and on Earth. The teams were made up of professors and students from Fayetteville State University in North Carolina, University of Massachusetts Boston, and California State University, Northridge. At the conclusion of the accelerator, participants arrived in Southern California for a variety of events, including two days at JPL. The program is a partnership between NASA's Science Mission Directorate, its Earth Science Technology Office, the Minority University Research Education Project within the agency's Office of STEM Engagement, JPL, and Starburst, a global aerospace accelerator company based in Los Angeles. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25315
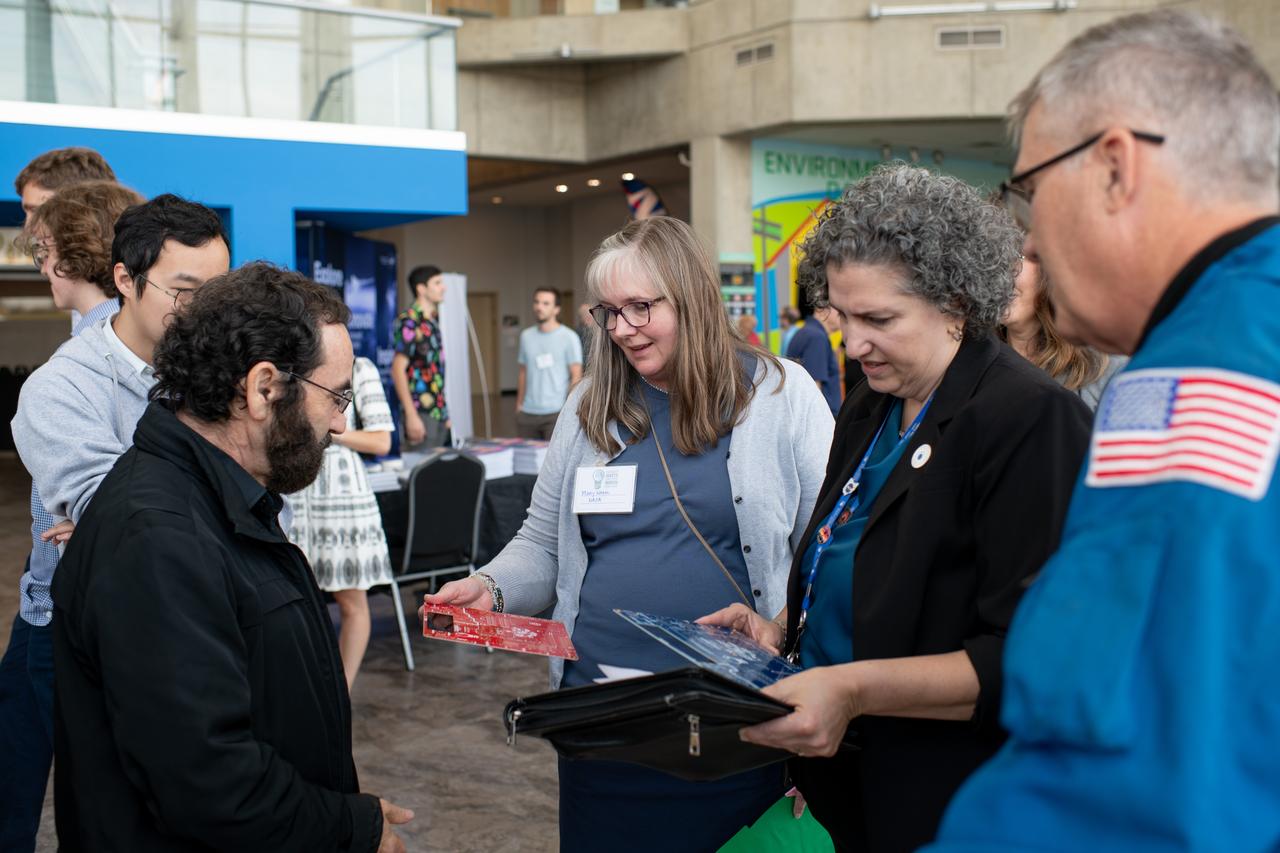

Philip Lubin from Team H.E.L.P.S. (High Efficiency Long-Range Power Solution) explains his project to Mary Wadel, Kirsten Ellenbogen and Stephen Bowen. NASA has awarded a total of $1.5 million to two U.S. teams for their novel technology solutions addressing energy distribution, management, and storage as part of the agency’s Watts on the Moon Challenge. The innovations from this challenge aim to support NASA’s Artemis missions, which will establish long-term human presence on the Moon. This two-phase competition has challenged U.S. innovators to develop breakthrough power transmission and energy storage technologies that could enable long-duration Moon missions to advance the nation’s lunar exploration goals. The final phase of the challenge concluded with a technology showcase and winners’ announcement ceremony Friday at Great Lakes Science Center, home of the visitor center for NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. Team H.E.L.P.S. (High Efficiency Long-Range Power Solution) from The University of California, Santa Barbara won the $1 million grand prize in NASA’s Watts on the Moon Challenge. Their team developed a low-mass, high efficiency cable and featured energy storage batteries on both ends of their power transmission and energy storage system. Second prize ($500,000): Orbital Mining Corporation of Golden, Colorado Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
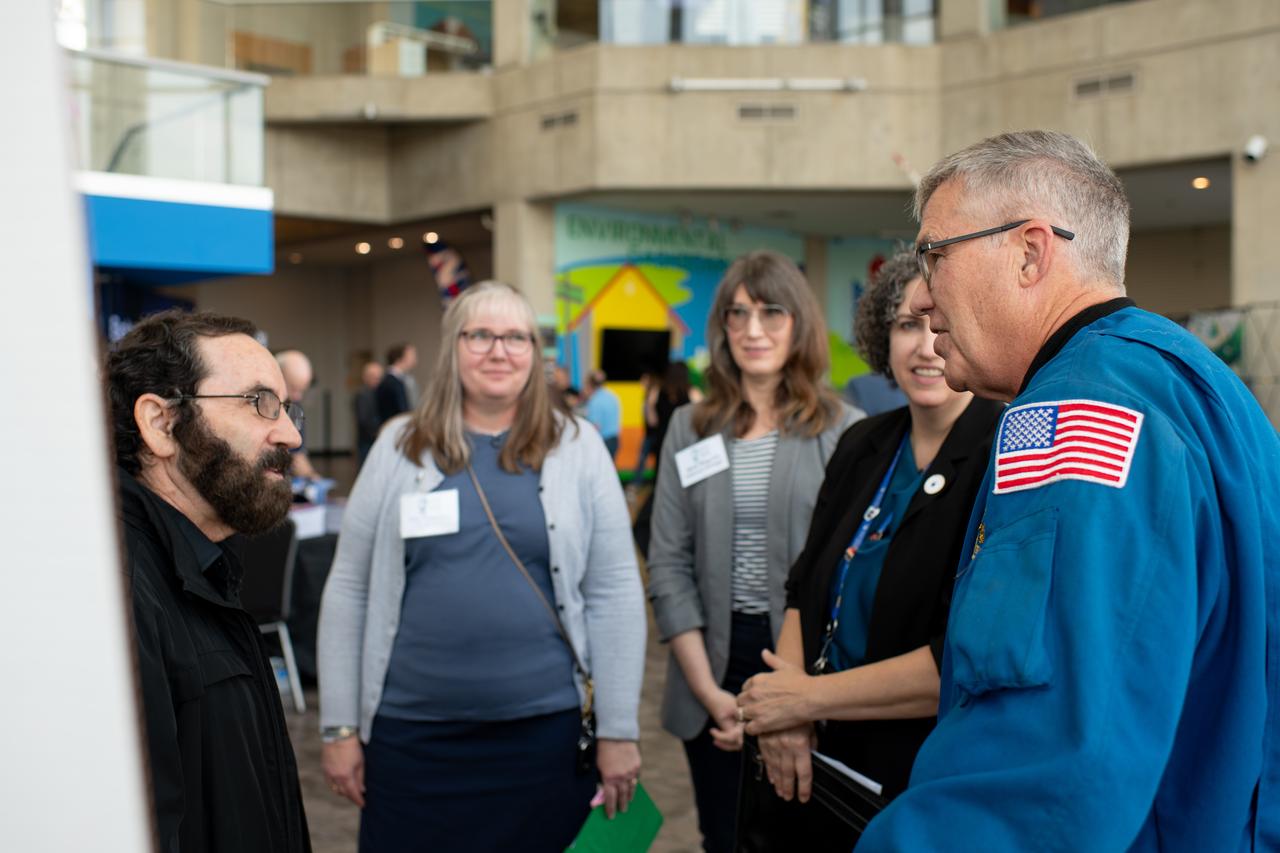

Philip Lubin from Team H.E.L.P.S. (High Efficiency Long-Range Power Solution) explains his project to Mary Wadel, Lisa Ferguson, Kirsten Ellenbogen and Stephen Bowen. NASA has awarded a total of $1.5 million to two U.S. teams for their novel technology solutions addressing energy distribution, management, and storage as part of the agency’s Watts on the Moon Challenge. The innovations from this challenge aim to support NASA’s Artemis missions, which will establish long-term human presence on the Moon. This two-phase competition has challenged U.S. innovators to develop breakthrough power transmission and energy storage technologies that could enable long-duration Moon missions to advance the nation’s lunar exploration goals. The final phase of the challenge concluded with a technology showcase and winners’ announcement ceremony on September 20, 2024 at Great Lakes Science Center, home of the visitor center for NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. Team H.E.L.P.S. (High Efficiency Long-Range Power Solution) from The University of California, Santa Barbara won the $1 million grand prize in NASA’s Watts on the Moon Challenge. Their team developed a low-mass, high efficiency cable and featured energy storage batteries on both ends of their power transmission and energy storage system. Second prize ($500,000): Orbital Mining Corporation of Golden, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
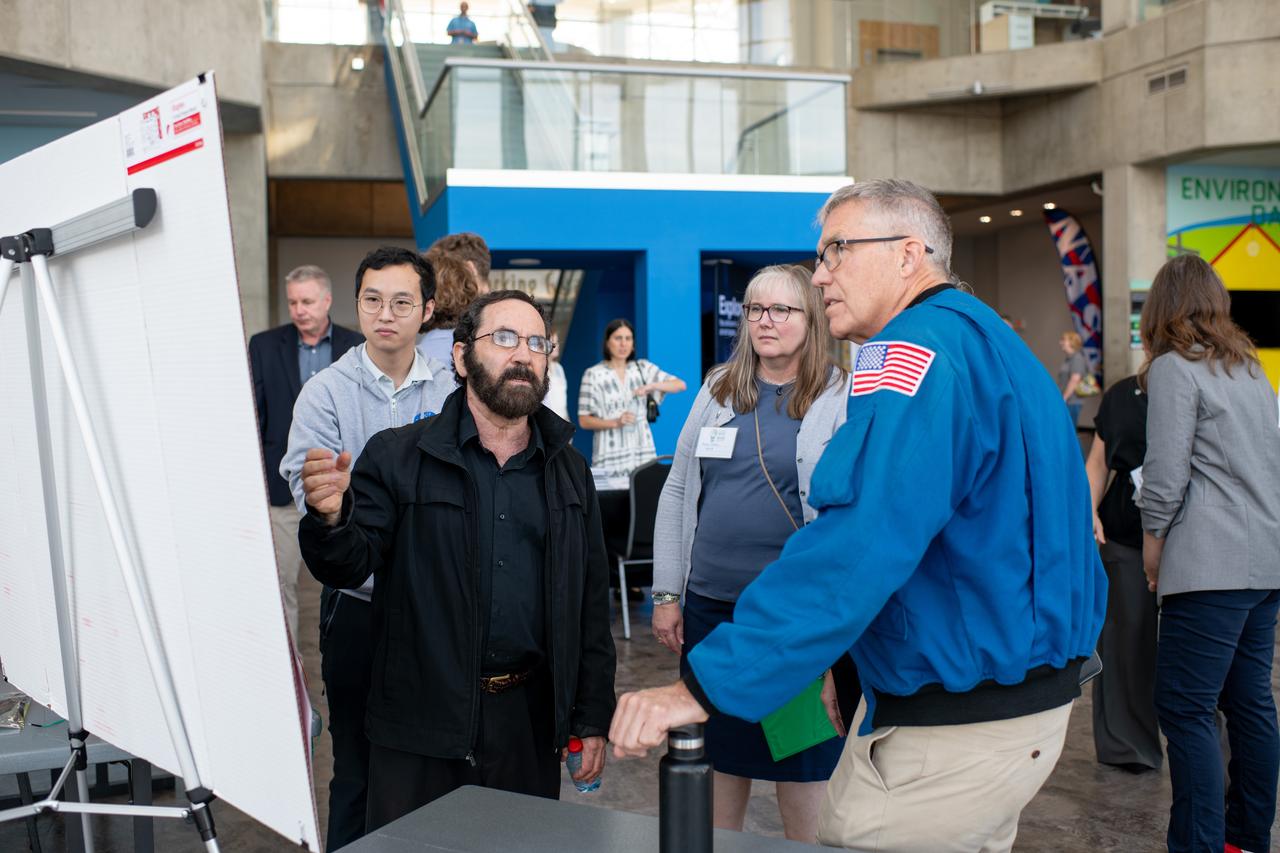

Philip Lubin from Team H.E.L.P.S. (High Efficiency Long-Range Power Solution) explains his project to Mary Wadel and Stephen Bowen. NASA has awarded a total of $1.5 million to two U.S. teams for their novel technology solutions addressing energy distribution, management, and storage as part of the agency’s Watts on the Moon Challenge. The innovations from this challenge aim to support NASA’s Artemis missions, which will establish long-term human presence on the Moon. This two-phase competition has challenged U.S. innovators to develop breakthrough power transmission and energy storage technologies that could enable long-duration Moon missions to advance the nation’s lunar exploration goals. The final phase of the challenge concluded with a technology showcase and winners’ announcement ceremony on September 20, 2024 at Great Lakes Science Center, home of the visitor center for NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. Team H.E.L.P.S. (High Efficiency Long-Range Power Solution) from The University of California, Santa Barbara won the $1 million grand prize in NASA’s Watts on the Moon Challenge. Their team developed a low-mass, high efficiency cable and featured energy storage batteries on both ends of their power transmission and energy storage system. Second prize ($500,000): Orbital Mining Corporation of Golden, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
Droughts in the U.S. Southwest and Central Plains at the end of this century could be drier and longer compared to drought conditions seen in those regions in the last 1,000 years, according to a new NASA study. The study, published Feb 12 in the journal Science Advances, is based on projections from several climate models, including one sponsored by NASA. The research found the risk of severe droughts in those regions would increase if human-produced greenhouse gas emissions continue to increase. "Natural droughts like the 1930s Dust Bowl and the current drought in the Southwest have historically lasted maybe a decade or a little less," said Ben Cook, climate scientist at NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies and the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory at Columbia University in New York City, and lead author of the study. "What these results are saying is we're going to get a drought similar to those events, but it is probably going to last at least 30 to 35 years." Read more:http://bit.ly/nasa-megadroughts Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
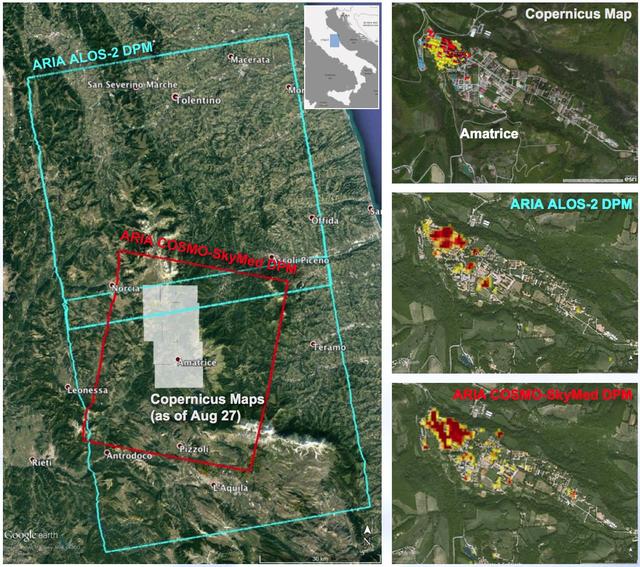
A NASA-funded program provided valuable information for responders and groups supporting the recovery efforts for the Aug. 24, 2016, magnitude 6.2 earthquake that struck central Italy. The earthquake caused significant loss of life and property damage in the town of Amatrice. To assist in the disaster response efforts, scientists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Caltech, both in Pasadena, California, obtained and used radar imagery of the earthquake's hardest-hit region to discriminate areas of damage from that event. The views indicate the extent of damage caused by the earthquake and subsequent aftershocks in and around Amatrice, based on changes to the ground surface detected by radar. The color variations from yellow to red indicate increasingly more significant ground surface change. The damage maps were created from data obtained before and after the earthquake by satellites belonging to the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The radar-derived damage maps compare well with a damage map produced by the European Commission Copernicus Emergency Management Service based upon visual inspection of high-resolution pre-earthquake aerial photographs and post-earthquake satellite optical imagery, and provide broader geographic coverage of the earthquake's impact in the region. The X-band COSMO-SkyMed (CSK) data were provided through a research collaboration with ASI and were acquired on July 3, August 20, and August 28, 2016. The L-band ALOS/PALSAR-2 data were provided by JAXA through its science research program and were acquired on September 9, 2015, January 27, 2016, and August 24, 2016. The radar data were processed by the Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis (ARIA) team at JPL and Caltech. ARIA is a NASA-funded project that is building an automated system for demonstrating the ability to rapidly and reliably provide GPS and satellite data to support the local, national and international hazard monitoring and response communities. Using space-based imagery of disasters, ARIA data products can provide rapid assessments of the geographic region impacted by a disaster, as well as detailed imaging of the locations where damage occurred. Radar can "see" through clouds day and night and measure centimeter-level ground movements. NASA is partnering with the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) to develop the NASA ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission that will routinely provide systematic SAR observations of Earth's land and ice-covered surfaces at least twice every 12 days, enabling greater scientific understanding of the dynamic processes that drive the Earth system and natural hazards, as well as providing actionable support for disaster response and recovery. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21091
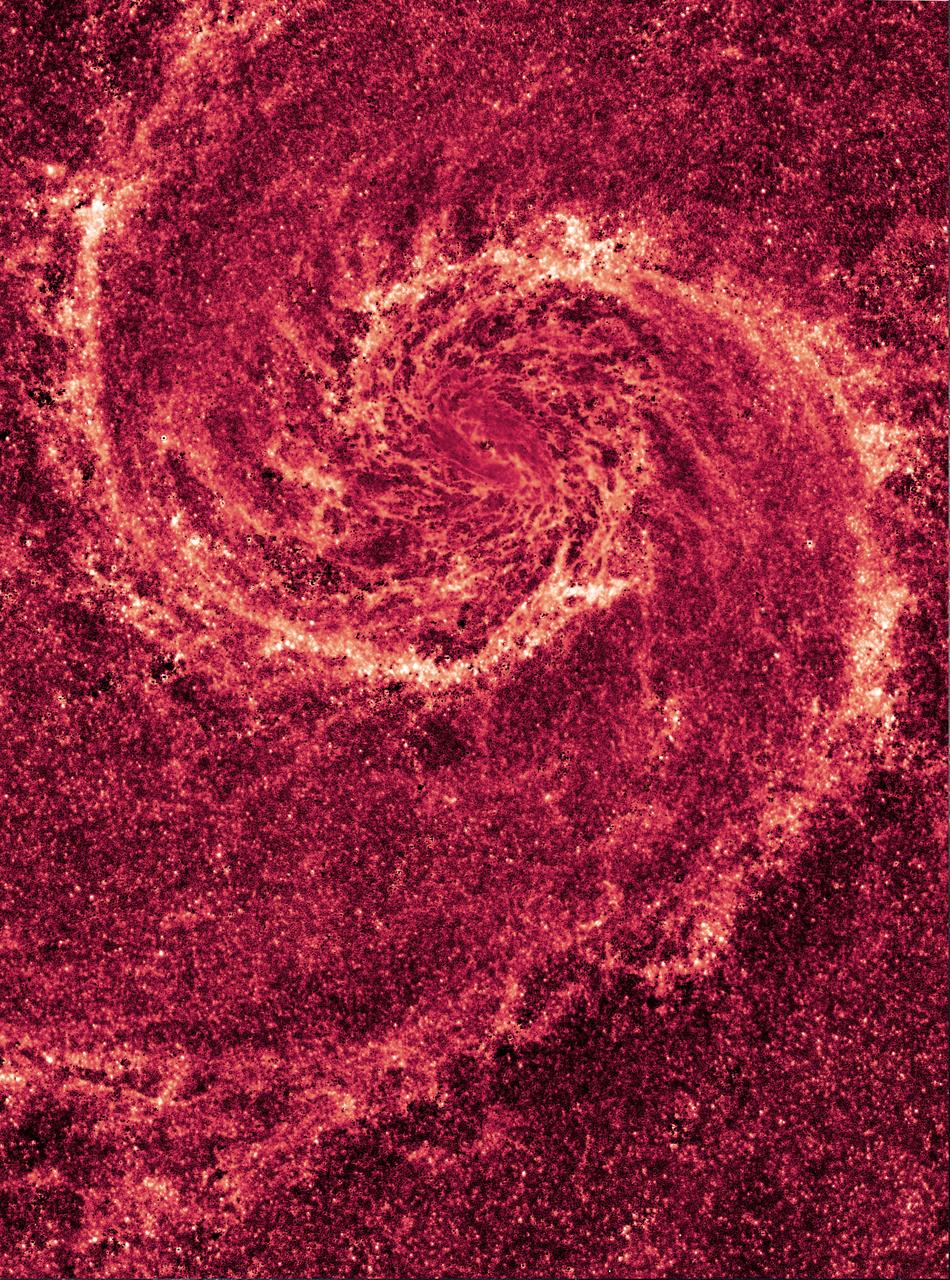
NASA image release January 13, 2011 <b><a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5352962836">These images</a></b> by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope show off two dramatically different face-on views of the spiral galaxy M51, dubbed the Whirlpool Galaxy. <b><a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5352955200/">The image here,</a></b> taken in visible light, highlights the attributes of a typical spiral galaxy, including graceful, curving arms, pink star-forming regions, and brilliant blue strands of star clusters. <b>In the image above,</b> most of the starlight has been removed, revealing the Whirlpool's skeletal dust structure, as seen in near-infrared light. This new image is the sharpest view of the dense dust in M51. The narrow lanes of dust revealed by Hubble reflect the galaxy's moniker, the Whirlpool Galaxy, as if they were swirling toward the galaxy's core. To map the galaxy's dust structure, researchers collected the galaxy's starlight by combining images taken in visible and near-infrared light. The visible-light image captured only some of the light; the rest was obscured by dust. The near-infrared view, however, revealed more starlight because near-infrared light penetrates dust. The researchers then subtracted the total amount of starlight from both images to see the galaxy's dust structure. The red color in the near-infrared image traces the dust, which is punctuated by hundreds of tiny clumps of stars, each about 65 light-years wide. These stars have never been seen before. The star clusters cannot be seen in visible light because dense dust enshrouds them. The image reveals details as small as 35 light-years across. Astronomers expected to see large dust clouds, ranging from about 100 light-years to more than 300 light-years wide. Instead, most of the dust is tied up in smooth and diffuse dust lanes. An encounter with another galaxy may have prevented giant clouds from forming. Probing a galaxy's dust structure serves as an important diagnostic tool for astronomers, providing invaluable information on how the gas and dust collapse to form stars. Although Hubble is providing incisive views of the internal structure of galaxies such as M51, the planned James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is expected to produce even crisper images. Researchers constructed the image by combining visible-light exposures from Jan. 18 to 22, 2005, with the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), and near-infrared light pictures taken in December 2005 with the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS). The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> Credit: NASA, ESA, M. Regan and B. Whitmore (STScI), and R. Chandar (University of Toledo)

NASA image release January 13, 2011 <b><a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5352962836">These images</a></b> by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope show off two dramatically different face-on views of the spiral galaxy M51, dubbed the Whirlpool Galaxy. <b>The image above,</b> taken in visible light, highlights the attributes of a typical spiral galaxy, including graceful, curving arms, pink star-forming regions, and brilliant blue strands of star clusters. <b><a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5352344517">In the image here,</a></b> most of the starlight has been removed, revealing the Whirlpool's skeletal dust structure, as seen in near-infrared light. This new image is the sharpest view of the dense dust in M51. The narrow lanes of dust revealed by Hubble reflect the galaxy's moniker, the Whirlpool Galaxy, as if they were swirling toward the galaxy's core. To map the galaxy's dust structure, researchers collected the galaxy's starlight by combining images taken in visible and near-infrared light. The visible-light image captured only some of the light; the rest was obscured by dust. The near-infrared view, however, revealed more starlight because near-infrared light penetrates dust. The researchers then subtracted the total amount of starlight from both images to see the galaxy's dust structure. The red color in the near-infrared image traces the dust, which is punctuated by hundreds of tiny clumps of stars, each about 65 light-years wide. These stars have never been seen before. The star clusters cannot be seen in visible light because dense dust enshrouds them. The image reveals details as small as 35 light-years across. Astronomers expected to see large dust clouds, ranging from about 100 light-years to more than 300 light-years wide. Instead, most of the dust is tied up in smooth and diffuse dust lanes. An encounter with another galaxy may have prevented giant clouds from forming. Probing a galaxy's dust structure serves as an important diagnostic tool for astronomers, providing invaluable information on how the gas and dust collapse to form stars. Although Hubble is providing incisive views of the internal structure of galaxies such as M51, the planned James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is expected to produce even crisper images. Researchers constructed the image by combining visible-light exposures from Jan. 18 to 22, 2005, with the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), and near-infrared light pictures taken in December 2005 with the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS). Credit: NASA, ESA, S. Beckwith (STScI), and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
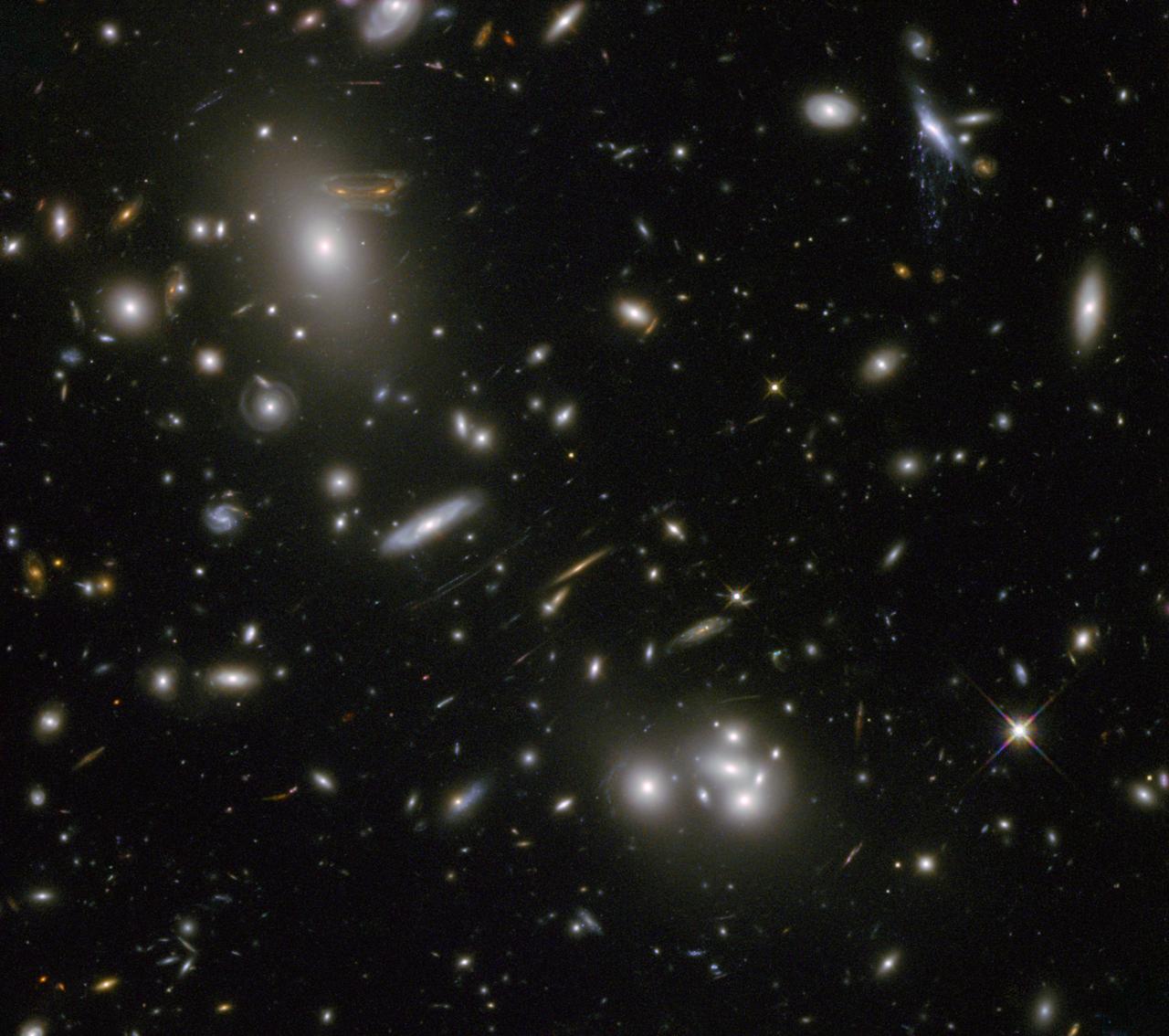

The gravitational field surrounding this massive cluster of galaxies, Abell 68, acts as a natural lens in space to brighten and magnify the light coming from very distant background galaxies. Like a fun house mirror, lensing creates a fantasy landscape of arc-like images and mirror images of background galaxies. The foreground cluster is 2 billion light-years away, and the lensed images come from galaxies far behind it. In this photo, the image of a spiral galaxy at upper left has been stretched and mirrored into a shape similar to that of a simulated alien from the classic 1970s computer game "Space Invaders!" A second, less distorted image of the same galaxy appears to the left of the large, bright elliptical galaxy. In the upper right of the photo is another striking feature of the image that is unrelated to gravitational lensing. What appears to be purple liquid dripping from a galaxy is a phenomenon called ram-pressure stripping. The gas clouds within the galaxy are being stripped out and heated up as the galaxy passes through a region of denser intergalactic gas. This image was taken in infrared light by Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3, and combined with near-infrared observations from Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. The image is based in part on data spotted by Nick Rose in the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures image processing competition. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md., conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington. Credit: NASA and ESA Acknowledgement: N. Rose For image files and more information about Abell 68, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2013/09" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2013/09</a> <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic04" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic04</a> <a href="http://heritage.stsci.edu/2013/09" rel="nofollow">heritage.stsci.edu/2013/09</a> <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/projects/hiddentreasures/" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/projects/hiddentreasures/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
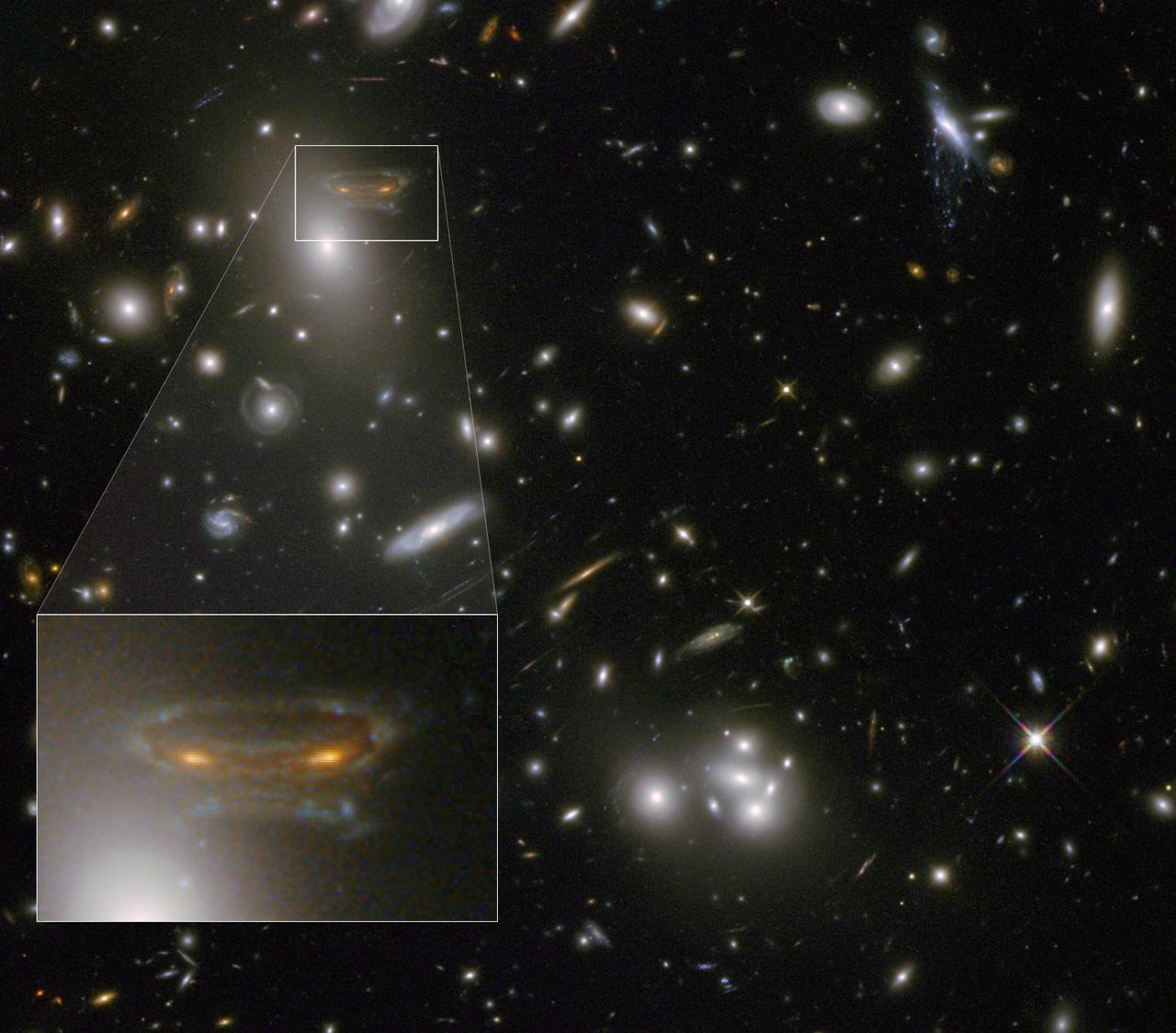

The gravitational field surrounding this massive cluster of galaxies, Abell 68, acts as a natural lens in space to brighten and magnify the light coming from very distant background galaxies. Like a fun house mirror, lensing creates a fantasy landscape of arc-like images and mirror images of background galaxies. The foreground cluster is 2 billion light-years away, and the lensed images come from galaxies far behind it. In this photo, the image of a spiral galaxy at upper left has been stretched and mirrored into a shape similar to that of a simulated alien from the classic 1970s computer game "Space Invaders!" A second, less distorted image of the same galaxy appears to the left of the large, bright elliptical galaxy. In the upper right of the photo is another striking feature of the image that is unrelated to gravitational lensing. What appears to be purple liquid dripping from a galaxy is a phenomenon called ram-pressure stripping. The gas clouds within the galaxy are being stripped out and heated up as the galaxy passes through a region of denser intergalactic gas. This image was taken in infrared light by Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3, and combined with near-infrared observations from Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. The image is based in part on data spotted by Nick Rose in the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures image processing competition. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md., conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/Z6uDUp" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/Z6uDUp</a> Credit: NASA and ESA Acknowledgement: N. Rose For image files and more information about Abell 68, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2013/09" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2013/09</a> <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic04" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic04</a> <a href="http://heritage.stsci.edu/2013/09" rel="nofollow">heritage.stsci.edu/2013/09</a> <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/projects/hiddentreasures/" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/projects/hiddentreasures/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
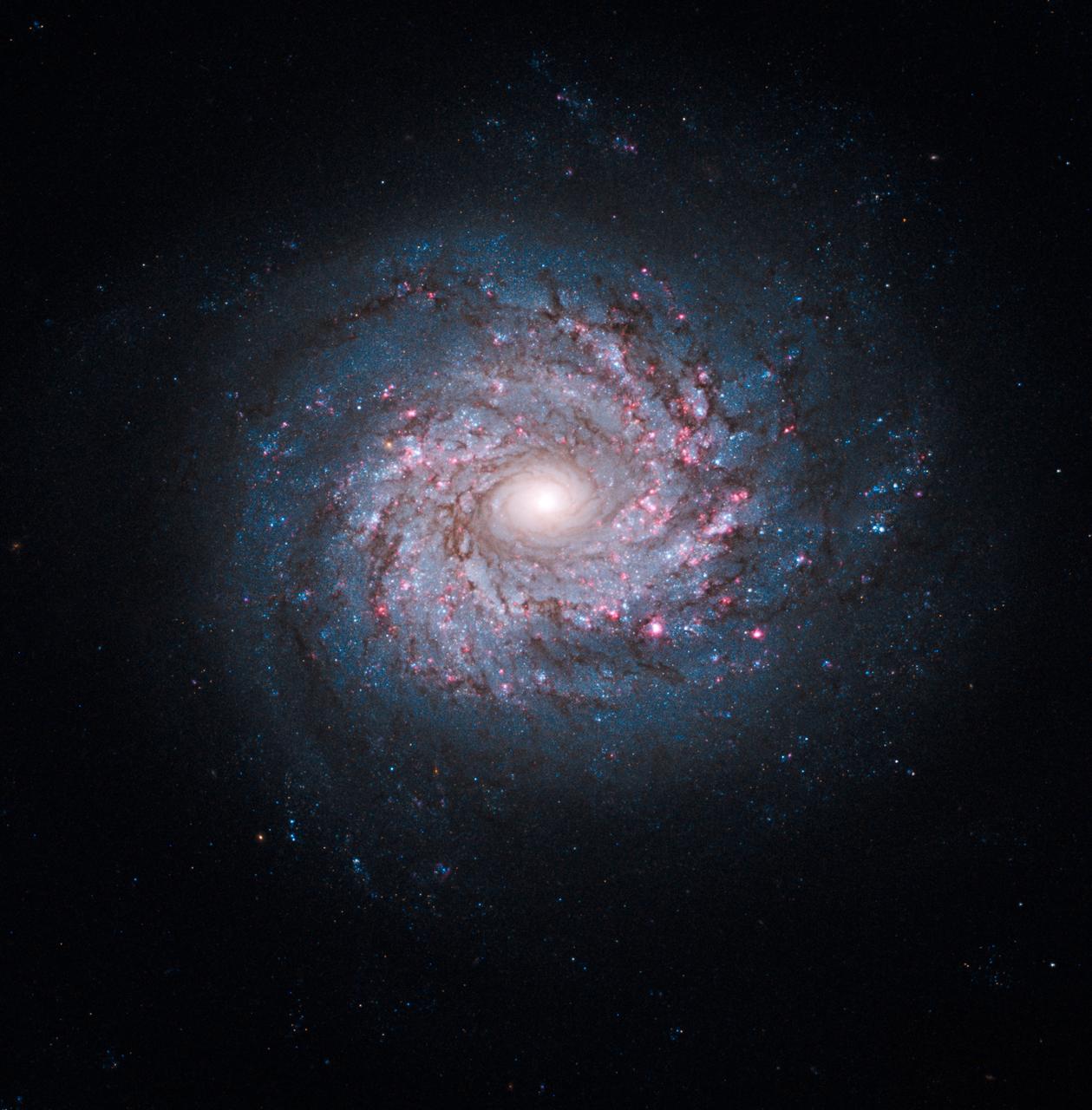

NASA image release October 19, 2010 Though the universe is chock full of spiral-shaped galaxies, no two look exactly the same. This face-on spiral galaxy, called NGC 3982, is striking for its rich tapestry of star birth, along with its winding arms. The arms are lined with pink star-forming regions of glowing hydrogen, newborn blue star clusters, and obscuring dust lanes that provide the raw material for future generations of stars. The bright nucleus is home to an older population of stars, which grow ever more densely packed toward the center. NGC 3982 is located about 68 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major. The galaxy spans about 30,000 light-years, one-third of the size of our Milky Way galaxy. This color image is composed of exposures taken by the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2), the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), and the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3). The observations were taken between March 2000 and August 2009. The rich color range comes from the fact that the galaxy was photographed invisible and near-infrared light. Also used was a filter that isolates hydrogen emission that emanates from bright star-forming regions dotting the spiral arms. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: A. Riess (STScI) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
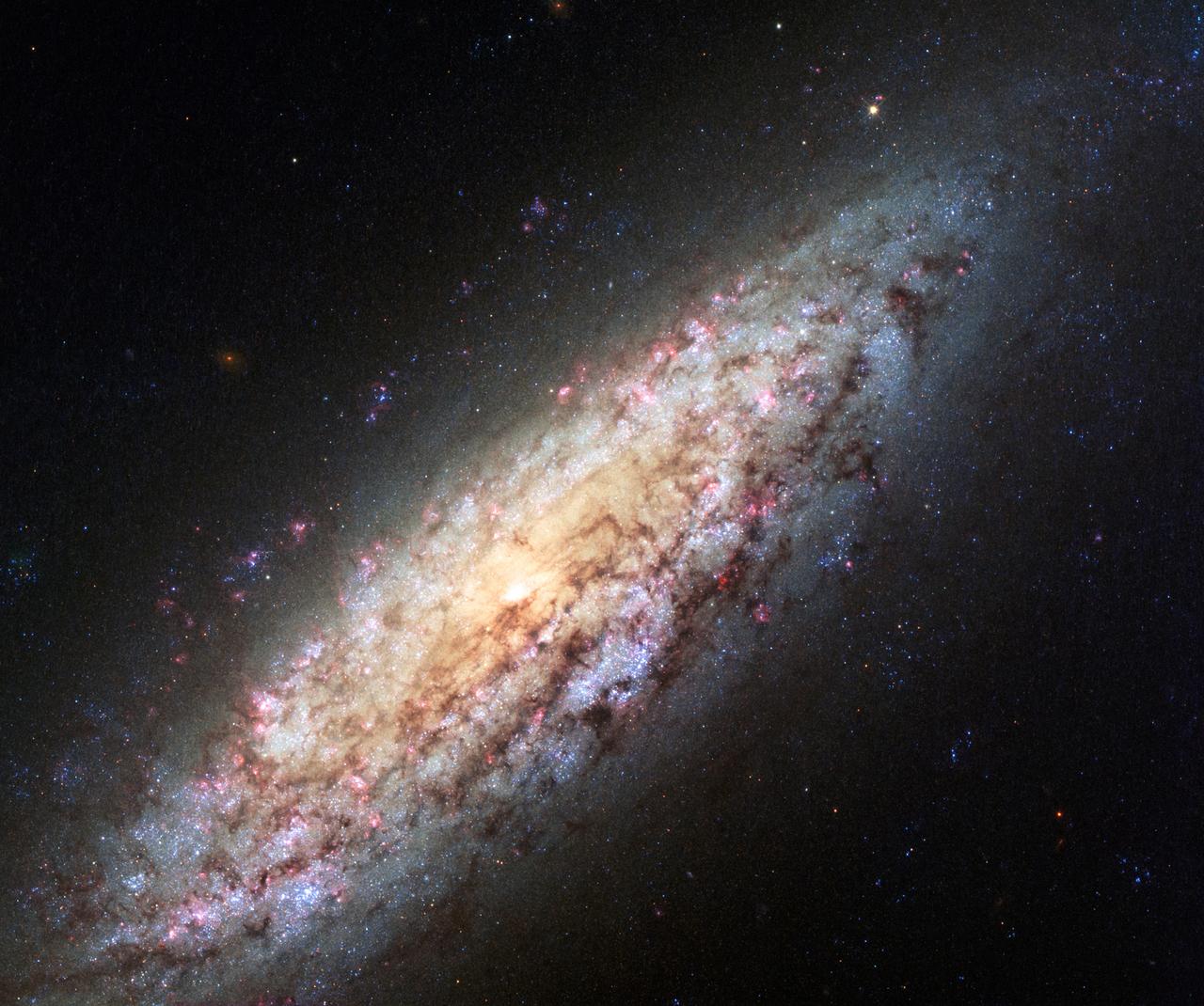

Most galaxies are clumped together in groups or clusters. A neighboring galaxy is never far away. But this galaxy, known as NGC 6503, has found itself in a lonely position, at the edge of a strangely empty patch of space called the Local Void. The Local Void is a huge stretch of space that is at least 150 million light-years across. It seems completely empty of stars or galaxies. The galaxy’s odd location on the edge of this never-land led stargazer Stephen James O’Meara to dub it the “Lost-In-Space galaxy” in his 2007 book, Hidden Treasures. NGC 6503 is 18 million light-years away from us in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco. NGC 6503 spans some 30,000 light-years, about a third of the size of the Milky Way. This Hubble Space Telescope image shows NGC 6503 in striking detail and with a rich set of colors. Bright red patches of gas can be seen scattered through its swirling spiral arms, mixed with bright blue regions that contain newly forming stars. Dark brown dust lanes snake across the galaxy’s bright arms and center, giving it a mottled appearance. The Hubble Advanced Camera for Surveys data for NGC 6503 were taken in April 2003, and the Wide Field Camera 3 data were taken in August 2013. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. Photo Credit: NASA, ESA, D. Calzetti (University of Massachusetts), H. Ford (Johns Hopkins University), and the Hubble Heritage Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Because the number two X-29 at NASA's Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later the Dryden Flight Research Center) flew at higher angles of attack than the number one aircraft, it required a spin chute system for safety. The system deployed a parachute for recovery of the aircraft if it inadvertently entered an uncontrolled spin. Most of the components of the spin chute system were located on a truss at the aft end of the aircraft. In addition, there were several cockpit modifications to facilitate use of the chute. The parachute was made of nylon and was of the conical ribbon type.

This photo shows the X-29 during a 1991 research flight. Smoke generators in the nose of the aircraft were used to help researchers see the behavior of the air flowing over the aircraft. The smoke here is demonstrating forebody vortex flow. This mission was flown September 10, 1991, by NASA research pilot Rogers Smith.

Daily weather analysis at the airfield in St. John’s Canada were essential for planning the day’s flight operations. The airborne side of the NAAMES project travels with two full-time meteorologists. --- The <b><a href="http://naames.larc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">North Atlantic Aerosols and Marine Ecosystems Study </a></b> (NAAMES) is a five year investigation to resolve key processes controlling ocean system function, their influences on atmospheric aerosols and clouds and their implications for climate. Michael Starobin joined the NAAMES field campaign on behalf of Earth Expeditions and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center’s Office of Communications. He presented stories about the important, multi-disciplinary research being conducted by the NAAMES team, with an eye towards future missions on the NASA drawing board. This is a NAAMES photo essay put together by Starobin, a collection of 49 photographs and captions. Photo and Caption Credit: Michael Starobin <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="https://www.instagram.com/nasagoddard/?hl=en" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Piers Sellers is currently Deputy Director of the Sciences and Exploration Directorate and Acting Director of the Earth Sciences Division at NASA/GSFC. He was born and educated in the United Kingdom and moved to the U.S. in 1982 to carry out climate research at NASA/GSFC. From 1982 to 1996, he worked on global climate problems, particularly those involving interactions between the biosphere and the atmosphere, and was involved in constructing computer models of the global climate system, satellite data interpretation and conducting large-scale field experiments in the USA, Canada, Africa, and Brazil. He served as project scientist for the first large Earth Observing System platform, Terra, launched in 1998. He joined the NASA astronaut corps in 1996 and flew to the International Space Station (ISS) in 2002, 2006, and 2010, carrying out six spacewalks and working on ISS assembly tasks. He returned to Goddard Space Flight Center in June, 2011. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

A model of a tiny, wedge-shaped robot designed to explore subsurface oceans of icy moons, right, sits beside a large waterproof capsule containing electronics and sensors for testing below glacial ice at the Juneau Icefield in Alaska in July 2023. The model, about 5 inches (12 centimeters) long, was 3D-printed to show the final envisioned size of a futuristic NASA mission concept called SWIM, short for Sensing With Independent Micro-swimmers. Led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory from spring 2021 to fall 2024, SWIM envisions a swarm of dozens of self-propelled, cellphone-size robots exploring the waters of icy moons like Jupiter's Europa and Saturn's Enceladus. Delivered to the subsurface ocean by an ice-melting cryobot, the tiny robots would zoom away to look for chemical and temperature signals that could point to life. The capsule shown here contains the first generation of an ocean composition sensor built for the SWIM robots by a team at Georgia Tech. The final version of the sensor would enable each robot to simultaneously measure temperature, pressure, acidity or alkalinity, conductivity, and chemical makeup. During the Alaska field test, the team lowered the capsule through a borehole in the ice and measured pressure and conductivity down to a depth of 164 feet (50 meters). This field test was conducted as part of a JPL-managed project called ORCAA (Ocean Worlds Reconnaissance and Characterization of Astrobiological Analogs). Known as an analog mission, ORCAA is working to answer science questions and test technology in preparation for a potential future mission to explore the surface or subsurface of icy moons. ORCAA is funded by NASA's Planetary Science and Technology from Analog Research program. SWIM was supported by Phase I and II funding from NASA's Innovative Advanced Concepts program under the agency's Space Technology Mission Directorate. JPL is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26424

Deputy Project Scientist Rich Moore considers weather and technical details for the next day’s flight. --- The <b><a href="http://naames.larc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">North Atlantic Aerosols and Marine Ecosystems Study </a></b> (NAAMES) is a five year investigation to resolve key processes controlling ocean system function, their influences on atmospheric aerosols and clouds and their implications for climate. Michael Starobin joined the NAAMES field campaign on behalf of Earth Expeditions and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center’s Office of Communications. He presented stories about the important, multi-disciplinary research being conducted by the NAAMES team, with an eye towards future missions on the NASA drawing board. This is a NAAMES photo essay put together by Starobin, a collection of 49 photographs and captions. Photo and Caption Credit: Michael Starobin <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="https://www.instagram.com/nasagoddard/?hl=en" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
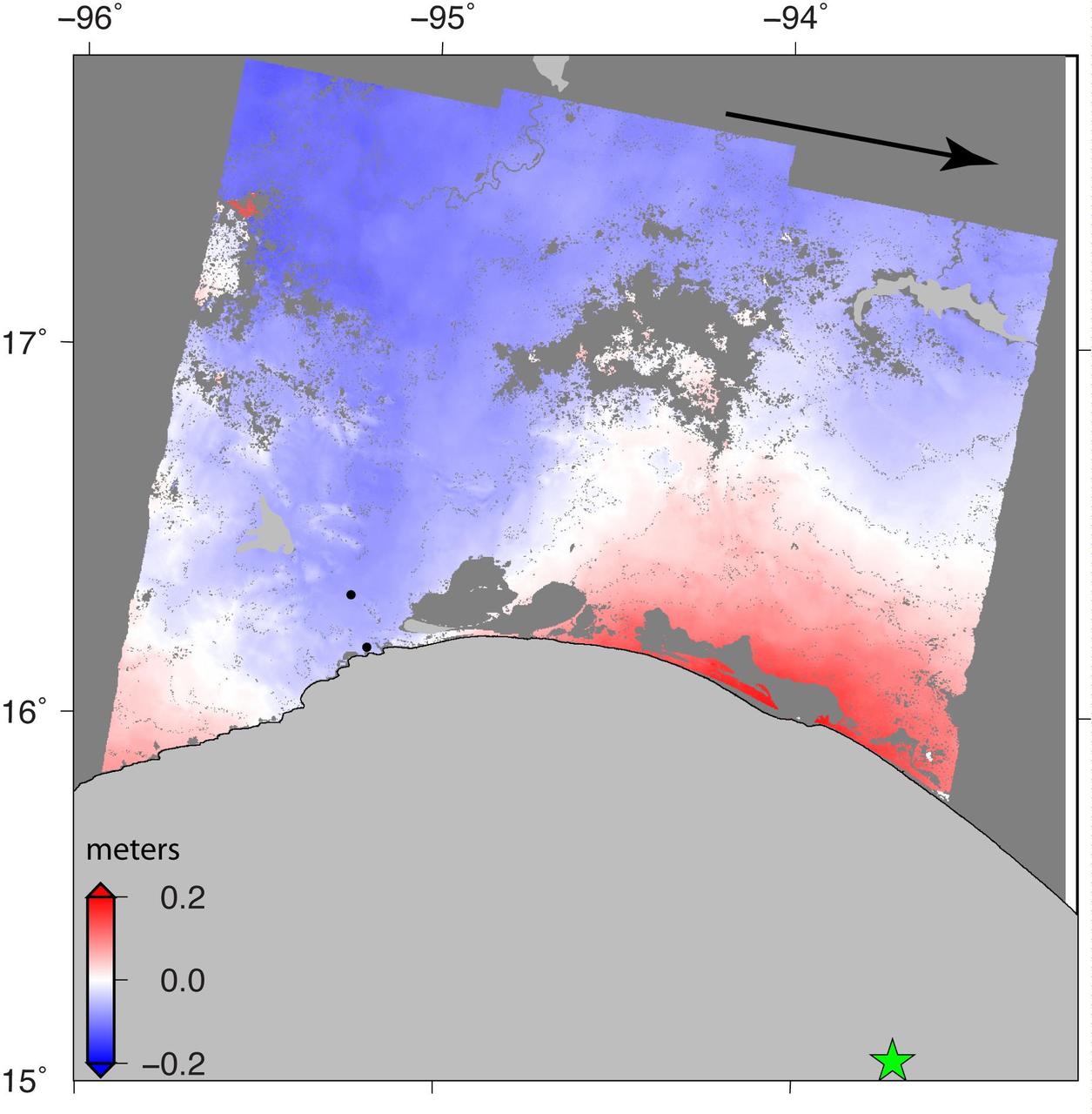
NASA and its partners are contributing important observations and expertise to the ongoing response to the Sept. 7, 2017 (local time), magnitude 8.1 Oaxaca-Chiapas earthquake in Mexico. This earthquake was the strongest in more than a century in Mexico. It has caused a significant humanitarian crisis, with widespread building damage and triggered landslides throughout the region. Scientists with the Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis project (ARIA), a collaboration between NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California; and Caltech, also in Pasadena, analyzed interferometric synthetic aperture radar images from the radar instrument on the Copernicus Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-1B satellites operated by the European Space Agency (ESA) to calculate a map of the deformation of Earth's surface caused by the quake. This false-color map shows the amount of permanent surface movement caused almost entirely by the earthquake, as viewed by the satellite, during a six-day interval between radar images acquired by the two Sentinel-1 satellites on Sept. 7 and Sept. 13, 2017. In this map, the colors of the surface displacements are proportional to the surface motion. The red tones show the areas along the coast of Chiapas and Oaxaca have moved toward the satellite by as much as 9 inches (22 centimeters) in a combination of up and eastward motion. The area in between and farther north with various shades of blue moved away from the satellite, mostly downward or westward, by as much as 6 inches (15 centimeters). Areas without color are open water or heavy vegetation, which prevent the radar from measuring change between the satellite images. Scientists use these maps to build detailed models of the fault slip at depth and associated land movements to better understand the impact on future earthquake activity. The green star shows the location of the earthquake epicenter estimated by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) National Earthquake Information Center. Map contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data 2017, processed by ESA and analyzed by the NASA-JPL/Caltech ARIA team. This research was carried out at JPL under a contract with NASA. Sentinel-1 data were accessed through the Copernicus Open Access Hub. An annotated figures is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21962

Daily science team meetings are an integral part of NAAMES field work. Chris Hostetler (pointing) is the project scientist. --- The <b><a href="http://naames.larc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">North Atlantic Aerosols and Marine Ecosystems Study </a></b> (NAAMES) is a five year investigation to resolve key processes controlling ocean system function, their influences on atmospheric aerosols and clouds and their implications for climate. Michael Starobin joined the NAAMES field campaign on behalf of Earth Expeditions and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center’s Office of Communications. He presented stories about the important, multi-disciplinary research being conducted by the NAAMES team, with an eye towards future missions on the NASA drawing board. This is a NAAMES photo essay put together by Starobin, a collection of 49 photographs and captions. Photo and Caption Credit: Michael Starobin <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="https://www.instagram.com/nasagoddard/?hl=en" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release September 16, 2010 Enjoying a frozen treat on a hot summer day can leave a sticky mess as it melts in the Sun and deforms. In the cold vacuum of space, there is no edible ice cream, but there is radiation from massive stars that is carving away at cold molecular clouds, creating bizarre, fantasy-like structures. These one-light-year-tall pillars of cold hydrogen and dust, imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope, are located in the Carina Nebula. Violent stellar winds and powerful radiation from massive stars are sculpting the surrounding nebula. Inside the dense structures, new stars may be born. This image of dust pillars in the Carina Nebula is a composite of 2005 observations taken of the region in hydrogen light (light emitted by hydrogen atoms) along with 2010 observations taken in oxygen light (light emitted by oxygen atoms), both times with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys. The immense Carina Nebula is an estimated 7,500 light-years away in the southern constellation Carina. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. in Washington, D.C. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
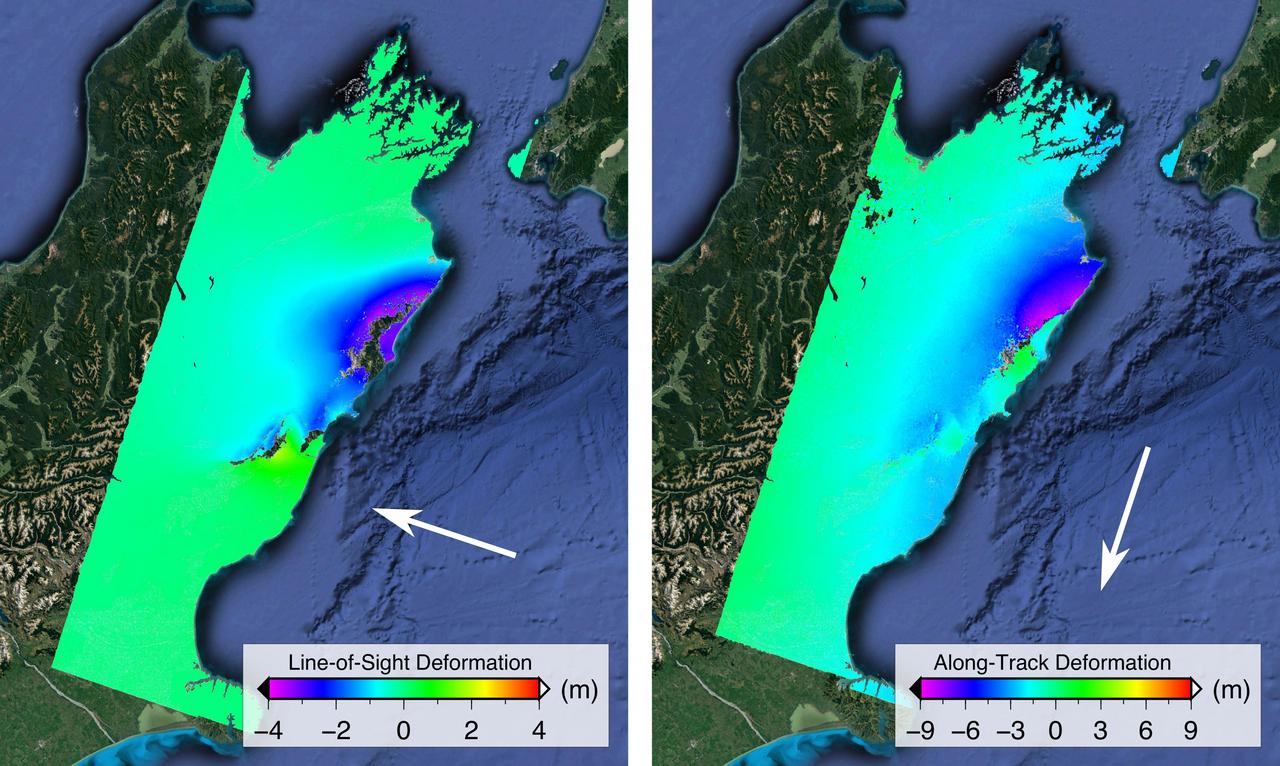
NASA and its partners are contributing important observations and expertise to the ongoing response to the Nov. 14, 2016, magnitude 7.8 Kaikoura earthquake in New Zealand. This shallow earthquake was so complex and unusual, it is likely to change how scientists think about earthquake hazards in plate boundary zones around the world. Scientists with the Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis project (ARIA), a collaboration between NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, and Caltech in Pasadena, analyzed interferometric synthetic aperture radar images from the PALSAR-2 instrument on the ALOS-2 satellite operated by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to calculate maps of the deformation of Earth's surface caused by the quake. Two maps show motion of the surface in two different directions. Each false-color map shows the amount of permanent surface movement caused almost entirely by the earthquake, as viewed by the satellite, during a 28-day interval between two ALOS-2 wide-swath images acquired on Oct. 18 and Nov. 15, 2016. In these two new maps made from the wide-swath images, the colors of the surface displacements are proportional to the surface motion. The wide-swath images cover the entire 106-mile (170-kilometer) length of the complex set of earthquake ruptures. The arrows show the direction of the radar motion measurement. In the left image, the blue and purple tones show the areas where the land around the Kaikoura peninsula in the Marlborough region of New Zealand's South Island has moved toward the satellite by up to 13.2 feet (4 meters), both eastward and upward. In the right image, the blue and purple tones show the areas that moved to the north by up to 30 feet (9 meters) and green tones show the area that moved to the south. The sharp line of color change is across the Kekerengu Fault, which had the largest amount of motion in the earthquake. Field studies found maximum rupture at the surface was measured at 39 feet (12 meters) of horizontal displacement. Several other faults have sharp color changes due to smaller amounts of motion, with a total of at least 12 faults rupturing in this single large earthquake. Areas without color have snow, heavy vegetation or open water that prevents the radar measurements from being coherent between satellite images – a required condition to measure ground displacement. Scientists use these maps to build detailed models of the fault slip at depth and associated land movements to better understand the impact on future earthquake activity. The PALSAR-2 data were provided by JAXA through the Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (CEOS) and through scientific research projects. The background image is from Google Earth. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21210

A group picture of all the researchers – from various science projects -- at the South African research station, SANAE IV, Antarctica, in the (Southern) summer 2013-2014. Credit: NASA/Goddard/BARREL/Brett Anderson Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/nasas-barrel-returns-successful-from-antarctica/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/nasas-barrel-returns-successful-from...</a> -- Three months, 20 balloons, and one very successful campaign. The team for NASA's BARREL – short for Balloon Array for Radiation belt Relativistic Electron Losses -- mission returned from Antarctica in March 2014. BARREL's job is to help unravel the mysterious Van Allen belts, two gigantic donuts of radiation that surround Earth, which can shrink and swell in response to incoming energy and particles from the sun and sometimes expose satellites to harsh radiation. While in Antarctica, the team launched 20 balloons carrying instruments that sense charged particles that are scattered into the atmosphere from the belts, spiraling down the magnetic fields near the South Pole. Each balloon traveled around the pole for up to three weeks. The team will coordinate the BARREL data with observations from NASA's two Van Allen Probes to better understand how occurrences in the belts relate to bursts of particles funneling down toward Earth. BARREL team members will be on hand at the USA Science and Engineering Festival in DC on April 26 and 27, 2014 for the exhibit Space Balloons: Exploring the Extremes of Space Weather. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
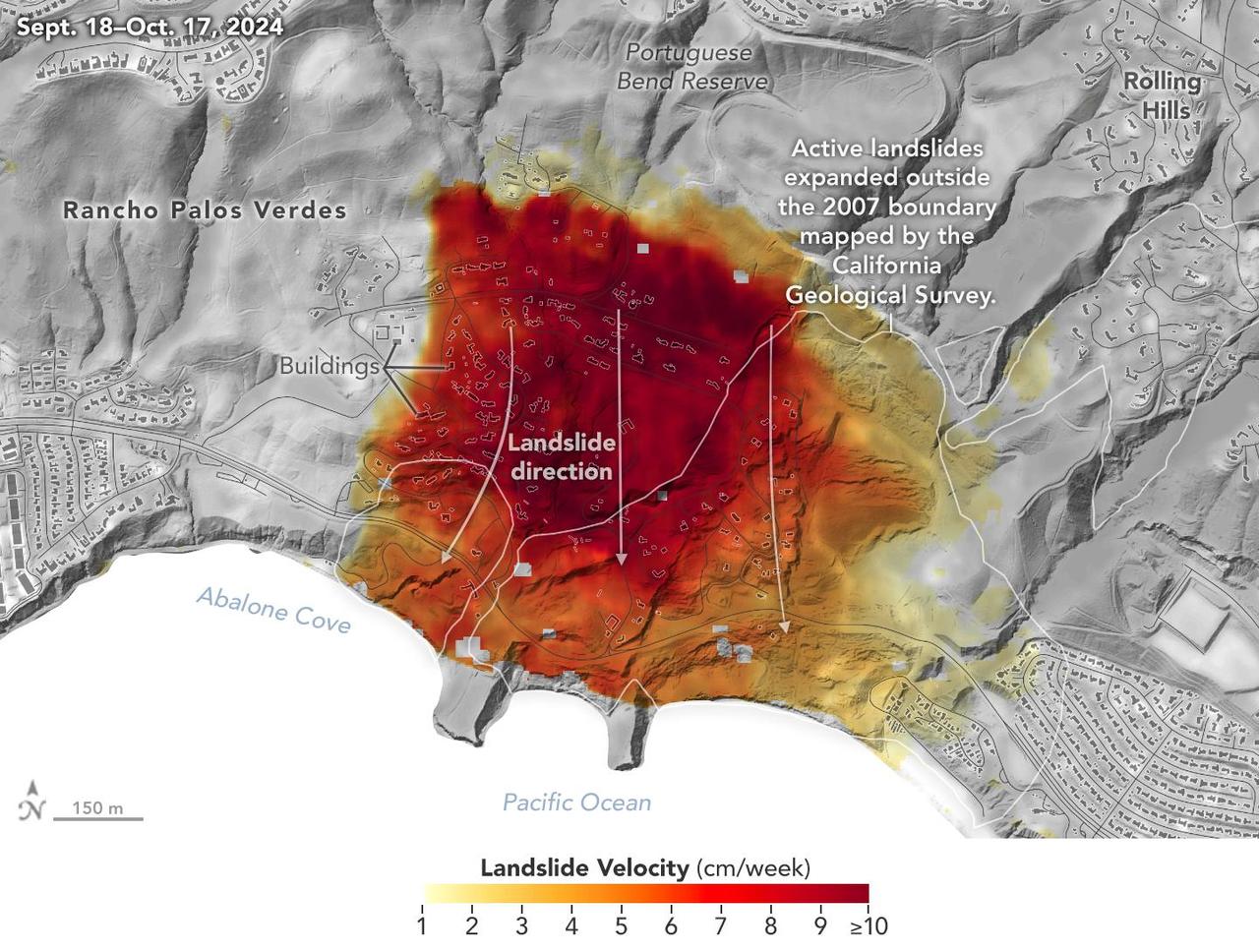
Researchers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California used data from an airborne radar to measure the movement of the slow-moving landslides on the Palos Verdes Peninsula in Los Angeles County. The analysis determined that, during a period of four weeks in the fall of 2024, land in the residential area slid toward the ocean by as much as 4 inches (10 centimeters) per week. Portions of the peninsula, which juts into the Pacific Ocean just south of the city of Los Angeles, is part of an ancient complex of landslides and has been moving for at least the past six decades, affecting hundreds of buildings in local communities. The motion accelerated and the active area expanded following record-breaking rainfall in Southern California in 2023 and another heavy-precipitation winter in 2024. To create this visualization, the Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis (ARIA) team used data from four flights of NASA's Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar (UAVSAR) that took place between Sept. 18 and Oct. 17. The UAVSAR instrument was mounted to a Gulfstream III jet flown out of NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, and the four flights were planned to estimate the speed and direction of the landslides in three dimensions. In the image, colors indicate how fast parts of the landslide complex were moving in late September and October, with the darkest reds indicating the highest speeds. The arrows represent the direction of horizontal motion. The white solid lines are the boundaries of active landslide areas as defined in 2007 by the California Geological Survey. The insights from the UAVSAR flights were part of a package of analyses by the ARIA team that also used data from ESA's (the European Space Agency's) Copernicus Sentinel-1A/B satellites. The analyses were provided to California officials to support the state's response to the landslides and made available to the public at NASA's Disaster Mapping Portal. The ARIA mission is a collaboration between JPL and Caltech, which manages JPL for NASA, to leverage radar and optical remote-sensing, GPS, and seismic observations for science as well as to aid in disaster response. The project investigates the processes and impacts of earthquakes, volcanoes, landslides, fires, subsurface fluid movement, and other natural hazards. UAVSAR has flown thousands of radar missions around the world since 2007 studying phenomena such as glaciers and ice sheets, vegetation in ecosystems, and natural hazards like earthquakes, volcanoes, and landslides. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26495
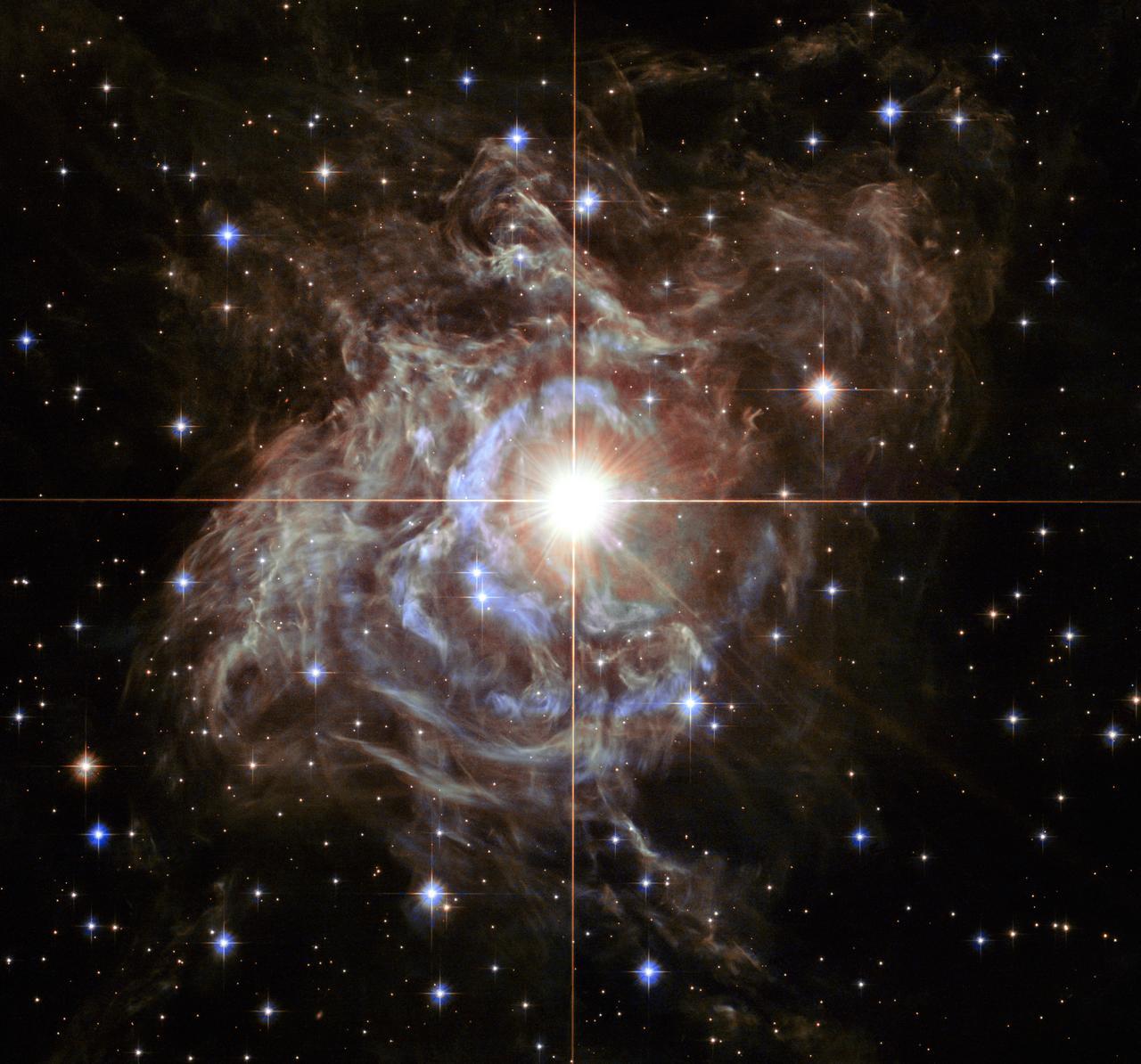

This festive NASA Hubble Space Telescope image resembles a holiday wreath made of sparkling lights. The bright southern hemisphere star RS Puppis, at the center of the image, is swaddled in a gossamer cocoon of reflective dust illuminated by the glittering star. The super star is ten times more massive than our sun and 200 times larger. RS Puppis rhythmically brightens and dims over a six-week cycle. It is one of the most luminous in the class of so-called Cepheid variable stars. Its average intrinsic brightness is 15,000 times greater than our sun’s luminosity. The nebula flickers in brightness as pulses of light from the Cepheid propagate outwards. Hubble took a series of photos of light flashes rippling across the nebula in a phenomenon known as a "light echo." Even though light travels through space fast enough to span the gap between Earth and the moon in a little over a second, the nebula is so large that reflected light can actually be photographed traversing the nebula. By observing the fluctuation of light in RS Puppis itself, as well as recording the faint reflections of light pulses moving across the nebula, astronomers are able to measure these light echoes and pin down a very accurate distance. The distance to RS Puppis has been narrowed down to 6,500 light-years (with a margin of error of only one percent). The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md., conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. Acknowledgment: H. Bond (STScI and Pennsylvania State University) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
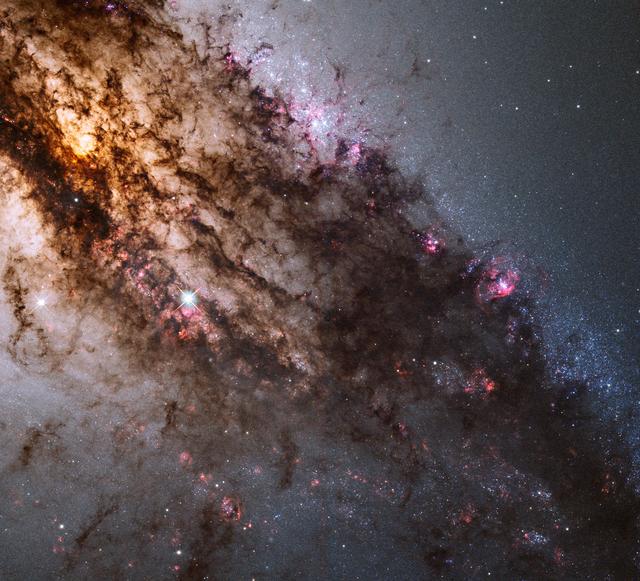

NASA image release June 16, 2011 Resembling looming rain clouds on a stormy day, dark lanes of dust crisscross the giant elliptical galaxy Centaurus A. Hubble's panchromatic vision, stretching from ultraviolet through near-infrared wavelengths, reveals the vibrant glow of young, blue star clusters and a glimpse into regions normally obscured by the dust. The warped shape of Centaurus A's disk of gas and dust is evidence for a past collision and merger with another galaxy. The resulting shockwaves cause hydrogen gas clouds to compress, triggering a firestorm of new star formation. These are visible in the red patches in this Hubble close-up. At a distance of just over 11 million light-years, Centaurus A contains the closest active galactic nucleus to Earth. The center is home for a supermassive black hole that ejects jets of high-speed gas into space, but neither the supermassive or the jets are visible in this image. This image was taken in July 2010 with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. For images and more information about the findings, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> and <a href="http://www.hubblesite.org/news/2011/18" rel="nofollow">www.hubblesite.org/news/2011/18</a> Cheryl Gundy, STSCI <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
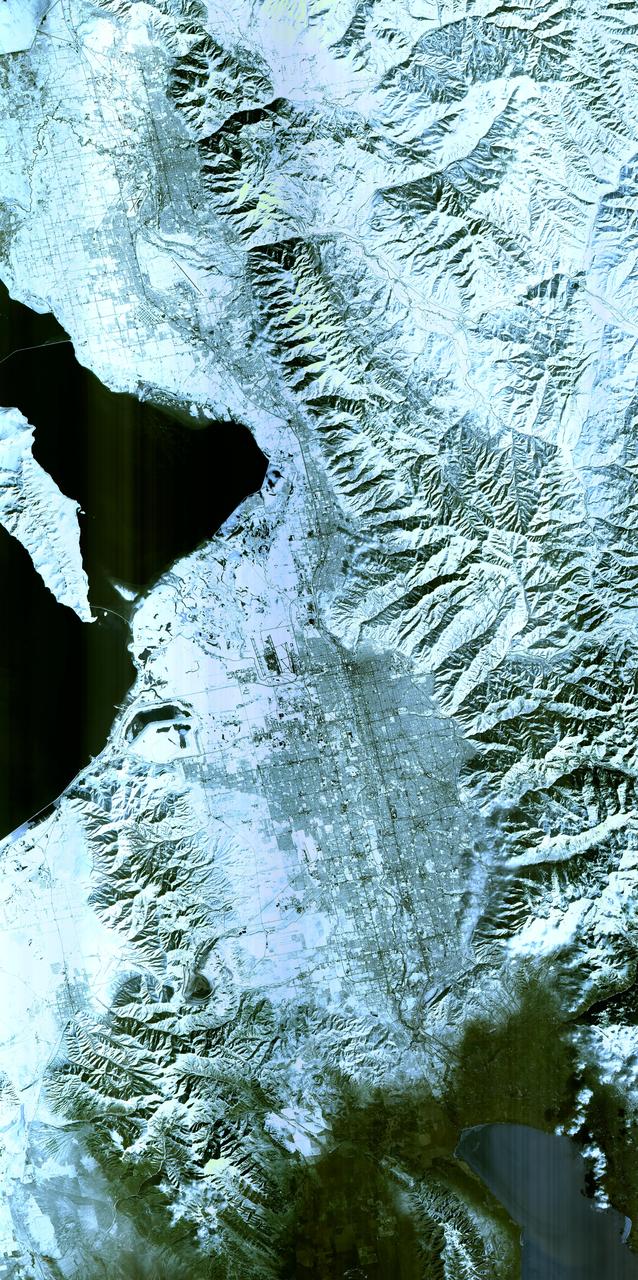

Salt Lake City, Utah, Winter 2001 The 2002 Winter Olympics are hosted by Salt Lake City at several venues within the city, in nearby cities, and within the adjacent Wasatch Mountains. This simulated natural color image presents a snowy, winter view of north central Utah that includes all of the Olympic sites. The image extends from Ogden in the north, to Provo in the south; and includes the snow-capped Wasatch Mountains and the eastern part of the Great Salt Lake. This image was acquired on February 8, 2001 by the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA's Terra satellite. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region, and its high spatial resolution of 15 to 90 meters (about 50 to 300 feet), ASTER will image Earth for the next 6 years to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. ASTER is one of five Earth-observing instruments launched December 18,1999, on NASA's Terra satellite. The instrument was built by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. A joint U.S./Japan science team is responsible for validation and calibration of the instrument and the data products. Dr. Anne Kahle at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, is the U.S. Science team leader; Bjorn Eng of JPL is the project manager. ASTER is the only high resolution imaging sensor on Terra. The Terra mission is part of NASA's Earth Science Enterprise, along-term research and technology program designed to examine Earth's land, oceans, atmosphere, ice and life as a total integrated system. The broad spectral coverage and high spectral resolution of ASTER will provide scientists in numerous disciplines with critical information for surface mapping, and monitoring dynamic conditions and temporal change. Example applications are: monitoring glacial advances and retreats; monitoring potentially active volcanoes; identifying crop stress; determining cloud morphology and physical properties; wetlands evaluation; thermal pollution monitoring; coral reef degradation; surface temperature mapping of soils and geology; and measuring surface heat balance. Image credit: NASA/GSFC/METI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release December 14, 2010 A delicate sphere of gas, photographed by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, floats serenely in the depths of space. The pristine shell, or bubble, is the result of gas that is being shocked by the expanding blast wave from a supernova. Called SNR 0509-67.5 (or SNR 0509 for short), the bubble is the visible remnant of a powerful stellar explosion in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a small galaxy about 160,000 light-years from Earth. Ripples in the shell's surface may be caused by either subtle variations in the density of the ambient interstellar gas, or possibly driven from the interior by pieces of the ejecta. The bubble-shaped shroud of gas is 23 light-years across and is expanding at more than 11 million miles per hour (5,000 kilometers per second). Astronomers have concluded that the explosion was one of an especially energetic and bright variety of supernovae. Known as Type Ia, such supernova events are thought to result from a white dwarf star in a binary system that robs its partner of material, takes on much more mass than it is able to handle, and eventually explodes. Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys observed the supernova remnant on Oct. 28, 2006 with a filter that isolates light from glowing hydrogen seen in the expanding shell. These observations were then combined with visible-light images of the surrounding star field that were imaged with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 on Nov. 4, 2010. With an age of about 400 years as seen from Earth, the supernova might have been visible to southern hemisphere observers around the year 1600, however, there are no known records of a "new star" in the direction of the LMC near that time. A more recent supernova in the LMC, SN 1987A, did catch the eye of Earth viewers and continues to be studied with ground- and space-based telescopes, including Hubble. For images and more information about SNR 0509, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2010/27" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2010/27</a> <a href="http://heritage.stsci.edu/2010/27" rel="nofollow">heritage.stsci.edu/2010/27</a> <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. <b>Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: J. Hughes (Rutgers University)</b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
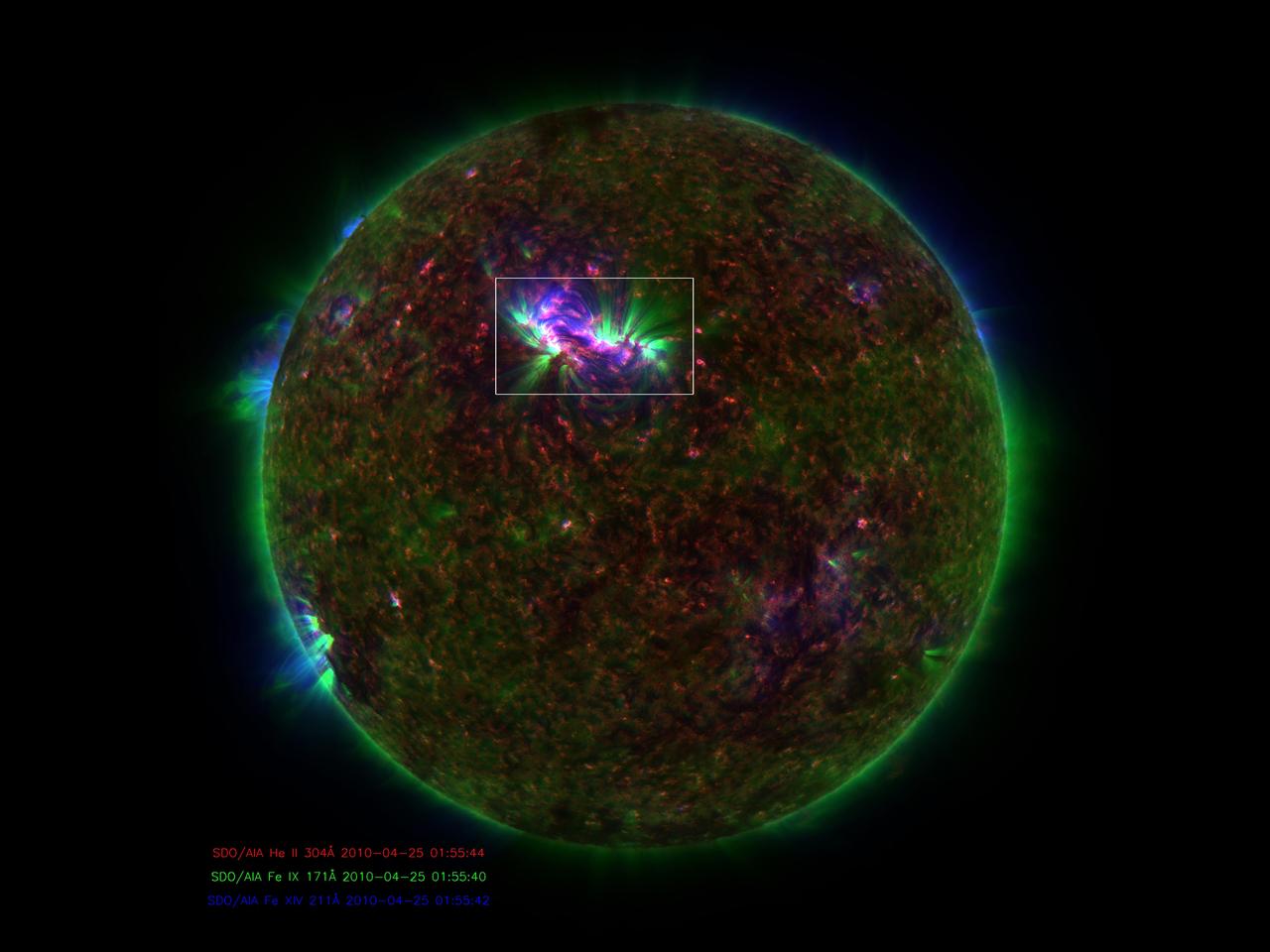
NASA image release January 6, 2010 Caption: Spicules on the sun, as observed by the Solar Dynamics Observatory. These bursts of gas jet off the surface of the sun at 150,000 miles per hour and contain gas that reaches temperatures over a million degrees. GREENBELT, Md. -- Observations from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the Japanese satellite Hinode show that some gas in the giant, fountain-like jets in the sun's atmosphere known as spicules can reach temperatures of millions of degrees. The finding offers a possible new framework for how the sun's high atmosphere gets so much hotter than the surface of the sun. What makes the high atmosphere, or corona, so hot – over a million degrees, compared to the sun surface's 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit -- remains a poorly understood aspect of the sun's complicated space weather system. That weather system can reach Earth, causing auroral lights and, if strong enough, disrupting Earth's communications and power systems. Understanding such phenomena, therefore, is an important step towards better protecting our satellites and power grids. "The traditional view is that all the heating happens higher up in the corona," says Dean Pesnell, who is SDO's project scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "The suggestion in this paper is that cool gas is being ejected from the sun's surface in spicules and getting heated on its way to the corona." Spicules were first named in the 1940s, but were hard to study in detail until recently, says Bart De Pontieu of Lockheed Martin's Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory, Palo Alto, Calif. who is the lead author on a paper on this subject in the January 7, 2011 issue of Science magazine. In visible light, spicules can be seen to send large masses of so-called plasma – the electromagnetic gas that surrounds the sun – up through the lower solar atmosphere or photosphere. The amount of material sent up is stunning, some 100 times as much as streams away from the sun in the solar wind towards the edges of the solar system. But nobody knew if they contained hot gas. "Heating of spicules to the necessary hot temperatures has never been observed, so their role in coronal heating had been dismissed as unlikely," says De Pontieu. Now, De Pontieu's team -- which included researchers at Lockheed Martin, the High Altitude Observatory of the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Colorado and the University of Oslo, Norway -- was able to combine images from SDO and Hinode to produce a more complete picture of the gas inside these gigantic fountains. The scientists found that a large fraction of the gas is heated to a hundred thousand degrees, while a small fraction is heated to millions of degrees. Time-lapsed images show that this material spews up into the corona, with most falling back down towards the surface of the sun. However, the small fraction of the gas that is heated to millions of degrees does not immediately return to the surface. Given the large number of spicules on the Sun, and the amount of material in the spicules, the scientists believe that if even some of that super hot plasma stays aloft it would make a contribution to coronal heating. Astrophysicist Jonathan Cirtain, who is the U.S. project scientist for Hinode at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala., says that incorporating such new information helps address an important question that reaches far beyond the sun. "This breakthrough in our understanding of the mechanisms which transfer energy from the solar photosphere to the corona addresses one of the most compelling questions in stellar astrophysics: How is the atmosphere of a star heated?" he says. "This is a fantastic discovery, and demonstrates the muscle of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, comprised of numerous instruments on multiple observatories." Hinode is the second mission in NASA's Solar Terrestrial Probes program, the goal of which is to improve understanding of fundamental solar and space physics processes. The mission is led by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ). The collaborative mission includes the U.S., the United Kingdom, Norway and Europe. NASA Marshall manages Hinode U.S. science operations and oversaw development of the scientific instrumentation provided for the mission by NASA, academia and industry. The Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center is the lead U.S. investigator for the Solar Optical Telescope on Hinode. SDO is the first mission in a NASA science program called Living With a Star, the goal of which is to develop the scientific understanding necessary to address those aspects of the sun-Earth system that directly affect our lives and society. NASA Goddard built, operates, and manages the SDO spacecraft for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules...</a> Credit: NASA Goddard/SDO/AIA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

Just in time for the release of the movie “Star Wars Episode VII: The Force Awakens,” NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has photographed what looks like a cosmic, double-bladed lightsaber. In the center of the image, partially obscured by a dark, Jedi-like cloak of dust, a newborn star shoots twin jets out into space as a sort of birth announcement to the universe. “Science fiction has been an inspiration to generations of scientists and engineers, and the film series Star Wars is no exception,” said John Grunsfeld, astronaut and associate administrator for the NASA Science Mission directorate. “There is no stronger case for the motivational power of real science than the discoveries that come from the Hubble Space Telescope as it unravels the mysteries of the universe." This celestial lightsaber does not lie in a galaxy far, far away, but rather inside our home galaxy, the Milky Way. It’s inside a turbulent birthing ground for new stars known as the Orion B molecular cloud complex, located 1,350 light-years away. When stars form within giant clouds of cool molecular hydrogen, some of the surrounding material collapses under gravity to form a rotating, flattened disk encircling the newborn star. Though planets will later congeal in the disk, at this early stage the protostar is feeding on the disk with a Jabba-like appetite. Gas from the disk rains down onto the protostar and engorges it. Superheated material spills away and is shot outward from the star in opposite directions along an uncluttered escape route — the star’s rotation axis. Shock fronts develop along the jets and heat the surrounding gas to thousands of degrees Fahrenheit. The jets collide with the surrounding gas and dust and clear vast spaces, like a stream of water plowing into a hill of sand. The shock fronts form tangled, knotted clumps of nebulosity and are collectively known as Herbig-Haro (HH) objects. The prominent HH object shown in this image is HH 24. Just to the right of the cloaked star, a couple of bright points are young stars peeking through and showing off their own faint lightsabers — including one that has bored a tunnel through the cloud towards the upper-right side of the picture. Overall, just a handful of HH jets have been spotted in this region in visible light, and about the same number in the infrared. Hubble’s observations for this image were performed in infrared light, which enabled the telescope to peer through the gas and dust cocooning the newly forming stars and capture a clear view of the HH objects. These young stellar jets are ideal targets for NASA’s upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, which will have even greater infrared wavelength vision to see deeper into the dust surrounding newly forming stars. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, in Washington, D.C. Credits: NASA/ESA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release October 5, 2010 Hubble Space Telescope observations of comet 103P/Hartley 2, taken on September 25, are helping in the planning for a November 4 flyby of the comet by NASA's Deep Impact eXtended Investigation (DIXI) spacecraft. Analysis of the new Hubble data shows that the nucleus has a diameter of approximately 0.93 miles (1.5 km), which is consistent with previous estimates. The comet is in a highly active state, as it approaches the Sun. The Hubble data show that the coma is remarkably uniform, with no evidence for the types of outgassing jets seen from most "Jupiter Family" comets, of which Hartley 2 is a member. Jets can be produced when the dust emanates from a few specific icy regions, while most of the surface is covered with relatively inert, meteoritic-like material. In stark contrast, the activity from Hartley 2's nucleus appears to be more uniformly distributed over its entire surface, perhaps indicating a relatively "young" surface that hasn't yet been crusted over. Hubble's spectrographs - the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS) and the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) -- are expected to provide unique information about the comet's chemical composition that might not be obtainable any other way, including measurements by DIXI. The Hubble team is specifically searching for emissions from carbon monoxide (CO) and diatomic sulfur (S2). These molecules have been seen in other comets but have not yet been detected in 103P/Hartley 2. 103P/Hartley has an orbital period of 6.46 years. It was discovered by Malcolm Hartley in 1986 at the Schmidt Telescope Unit in Siding Spring, Australia. The comet will pass within 11 million miles of Earth (about 45 times the distance to the Moon) on October 20. During that time the comet may be visible to the naked eye as a 5th magnitude "fuzzy star" in the constellation Auriga. Credit: NASA, ESA, and H. Weaver (The Johns Hopkins University/Applied Physics Lab) The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>