
N-257 Air Traffic Control simulator

An Air Traffic Control radar is being constructed at Shiloh for the NASA control tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility. It will be used by NASA and the Eastern Range for surveillance of controlled air space in Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station restricted areas. Shiloh is on the northern end of Merritt Island.
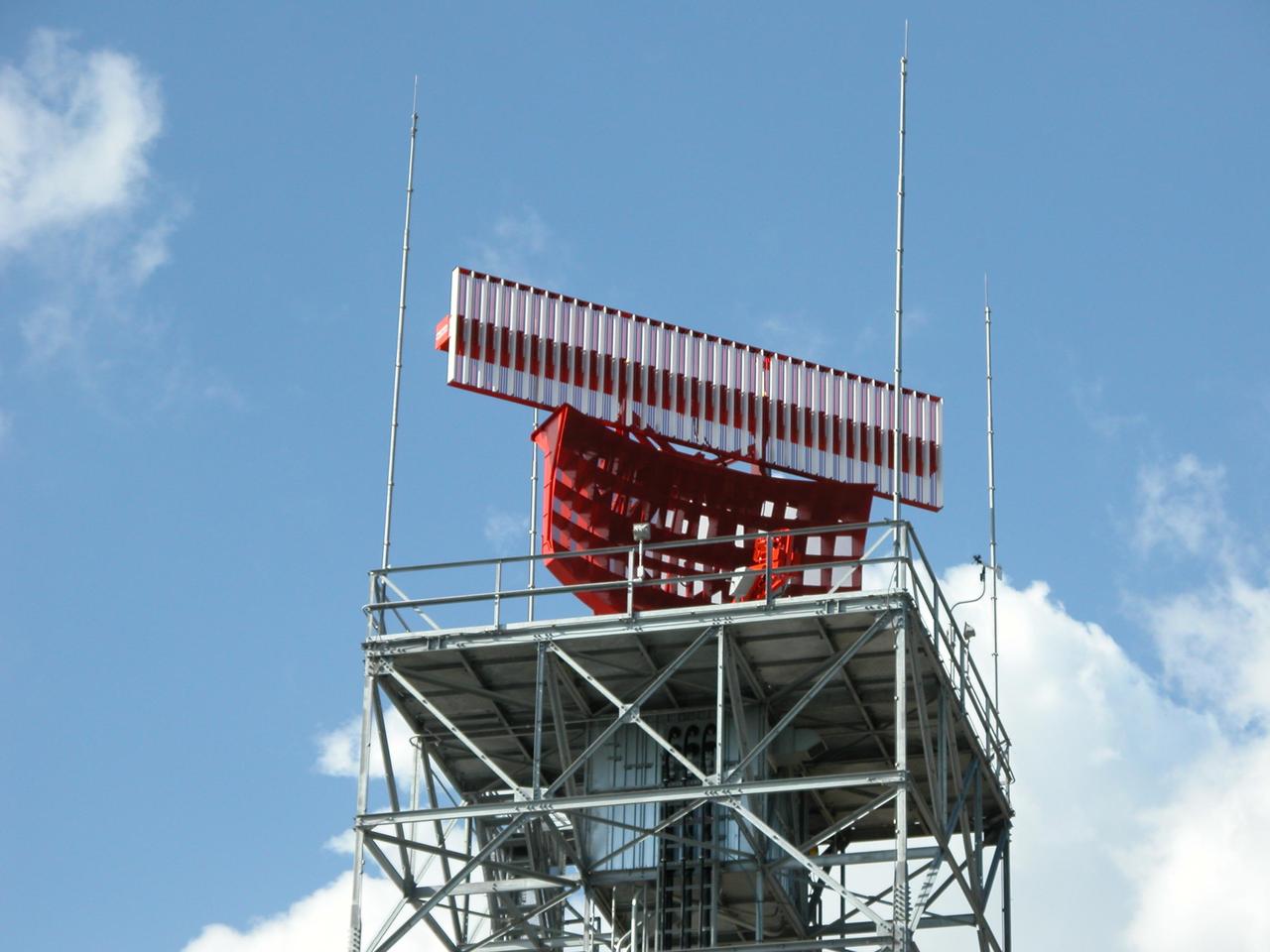

An Air Traffic Control radar has been constructed at Shiloh for the NASA control tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility. It will be used by NASA and the Eastern Range for surveillance of controlled air space in Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station restricted areas. Shiloh is on the northern end of Merritt Island.

An Air Traffic Control radar is being constructed at Shiloh for the NASA control tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility. It will be used by NASA and the Eastern Range for surveillance of controlled air space in Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station restricted areas. Shiloh is on the northern end of Merritt Island.

An Air Traffic Control radar has been constructed at Shiloh for the NASA control tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility. It will be used by NASA and the Eastern Range for surveillance of controlled air space in Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station restricted areas. Shiloh is on the northern end of Merritt Island.

An Air Traffic Control radar has been constructed at Shiloh for the NASA control tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility. It will be used by NASA and the Eastern Range for surveillance of controlled air space in Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station restricted areas. Shiloh is on the northern end of Merritt Island.

An Air Traffic Control radar is being constructed at Shiloh for the NASA control tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility. It will be used by NASA and the Eastern Range for surveillance of controlled air space in Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station restricted areas. Shiloh is on the northern end of Merritt Island.

An Air Traffic Control radar has been constructed at Shiloh for the NASA control tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility. It will be used by NASA and the Eastern Range for surveillance of controlled air space in Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station restricted areas. Shiloh is on the northern end of Merritt Island.
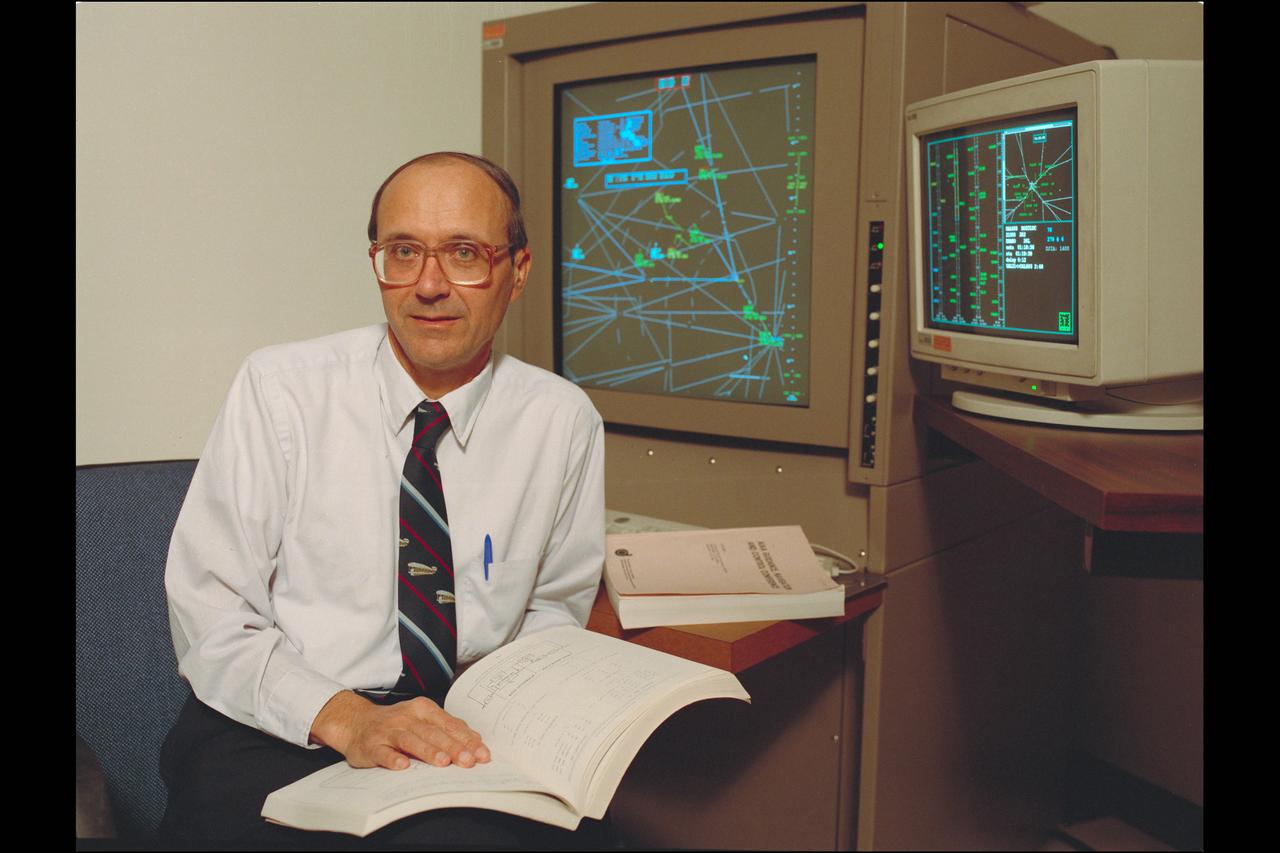

Dr Heinz Erzberger, Ames Fellow (1999) in the Air Traffic Control (ATC). Dr Erzberger displays the complicated algorithms he devised as part of Ames' work to improve air traffic safety.
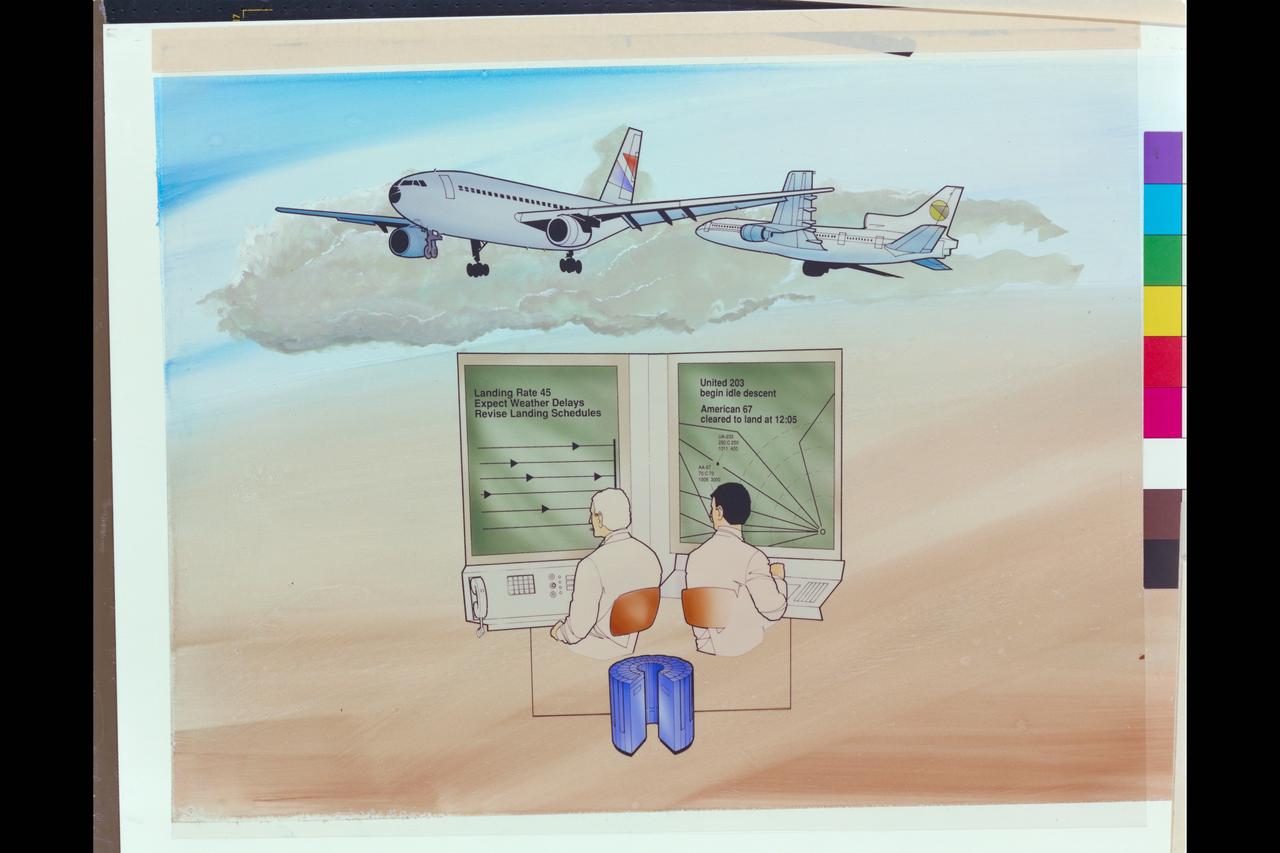

Date: Feb 11, 1988 Artist: unknown ATC (Air Traffic Control) SIGMA Lab Artwork
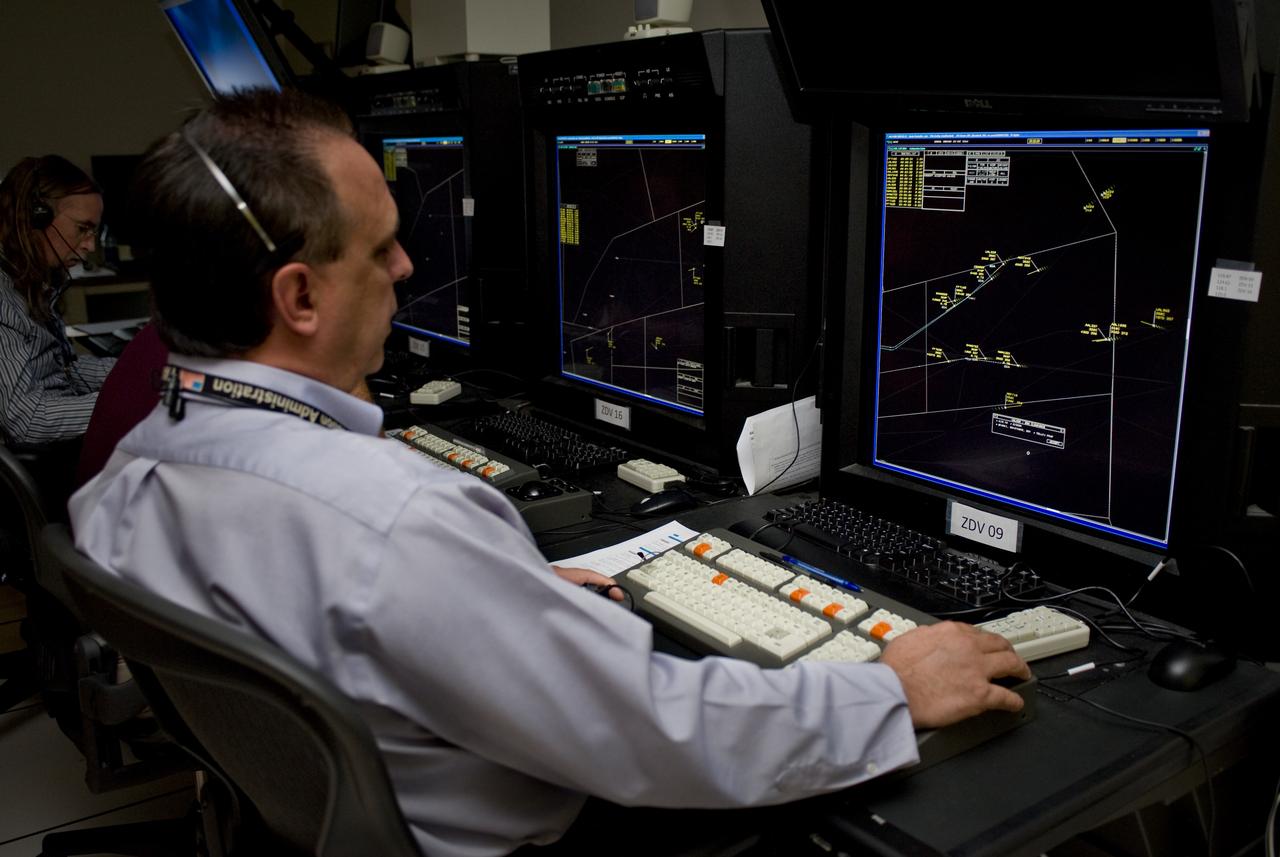

Efficient Descent Advisor, Simulaiton Number 2, ATC Lab N-257; ATC lab with Denver Air Traffic Controler Glen Hilgedick
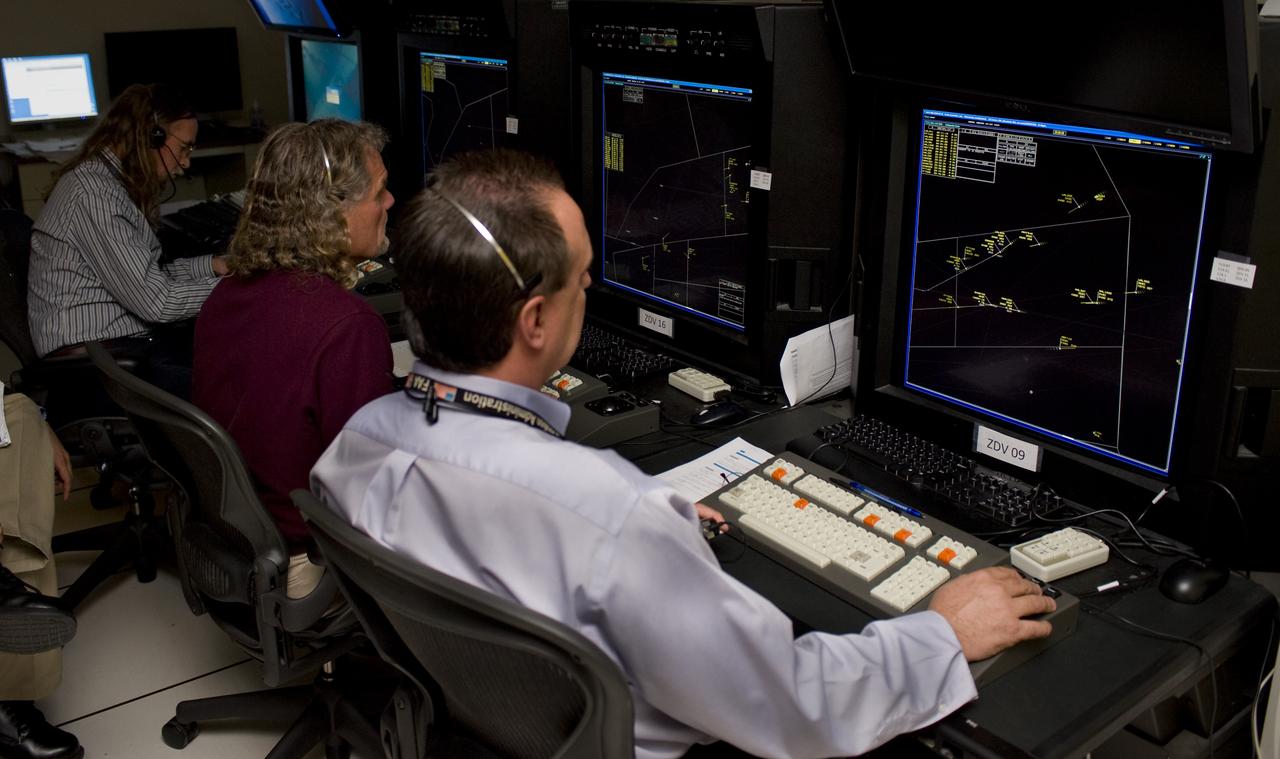

Efficient Descent Advisor, Simulaiton Number 2, ATC Lab N-257; ATC lab with Denver Air Traffic Controlers Glen Hilgedick and Roger Bruce (on left)
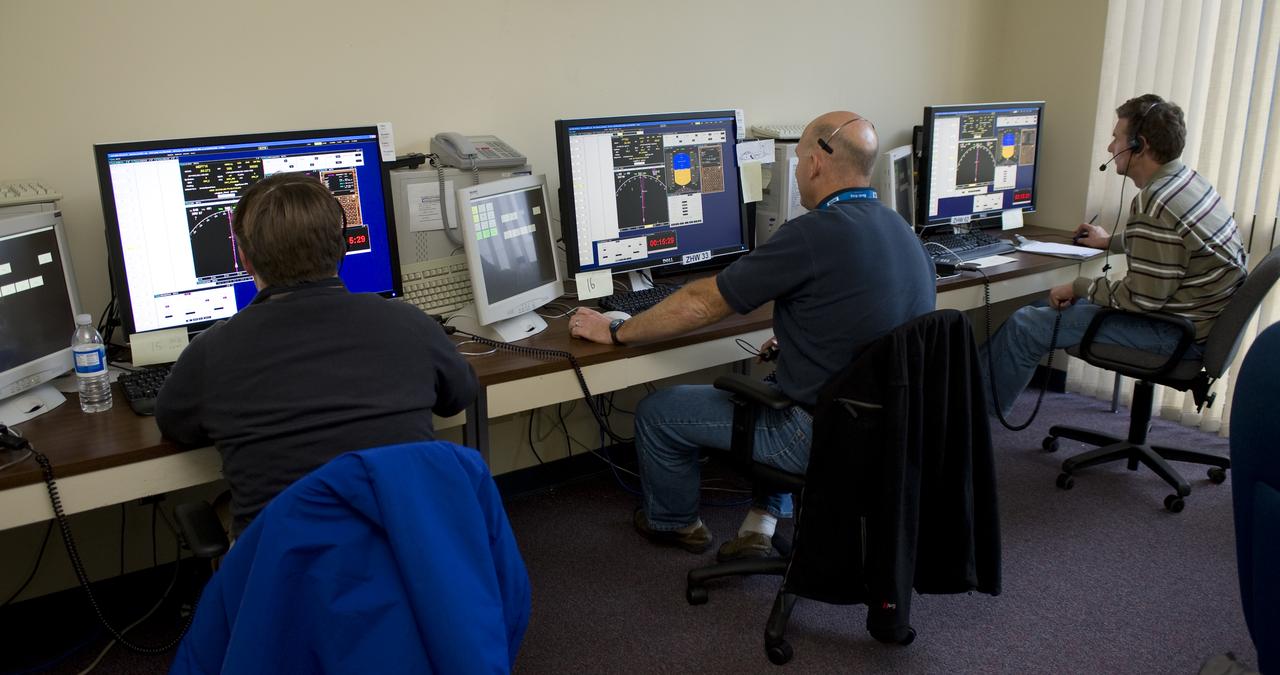

Efficient Descent Advisor, Simulaiton Number 2, ATC Lab N-257; with left to right Andrew Robertson, Lawrence Henderson, Ron Thompson
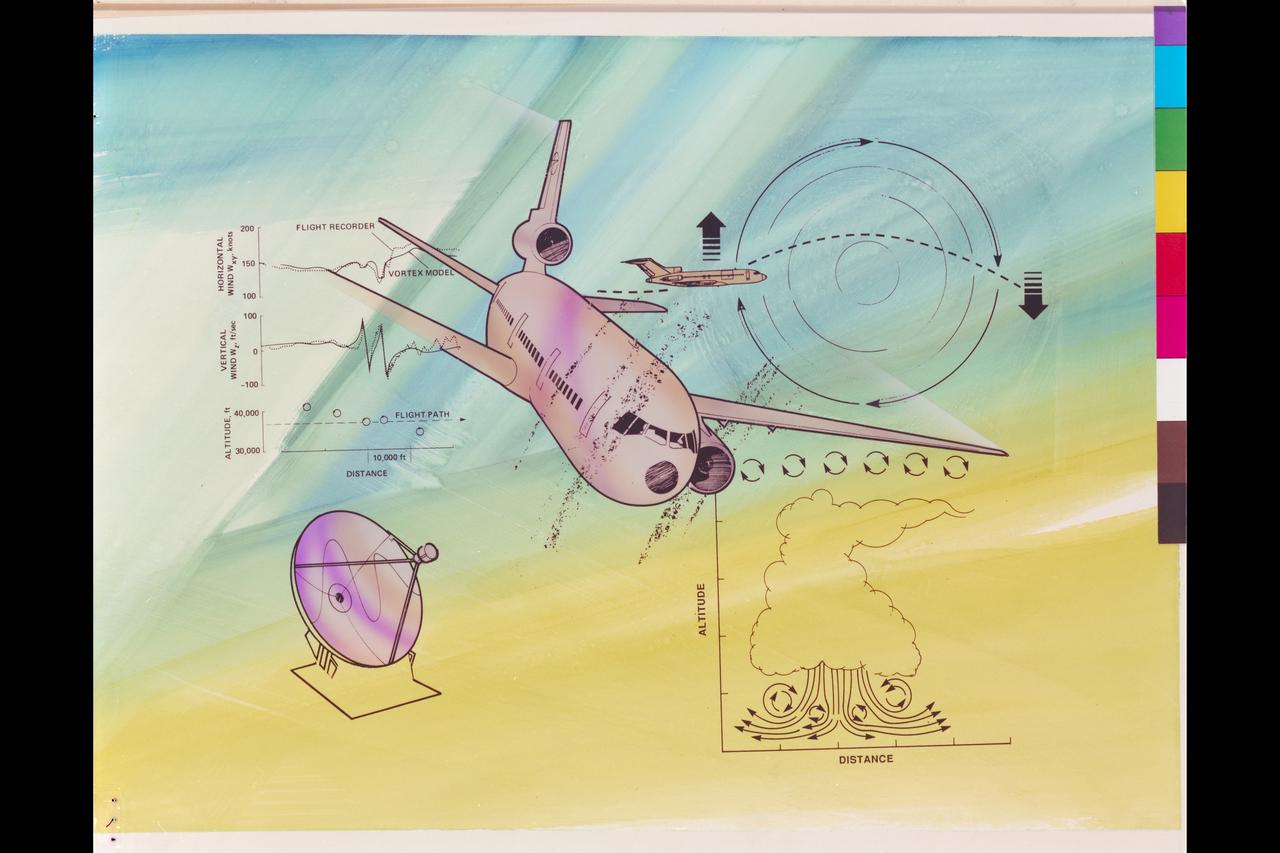
Research Automation - ATC (Air Traffic Control) Sever weather flight (Artwork)

Airspace Operations Lab (AOL); on route air traffic control room

Airspace Operations Lab (AOL); on route air traffic control room
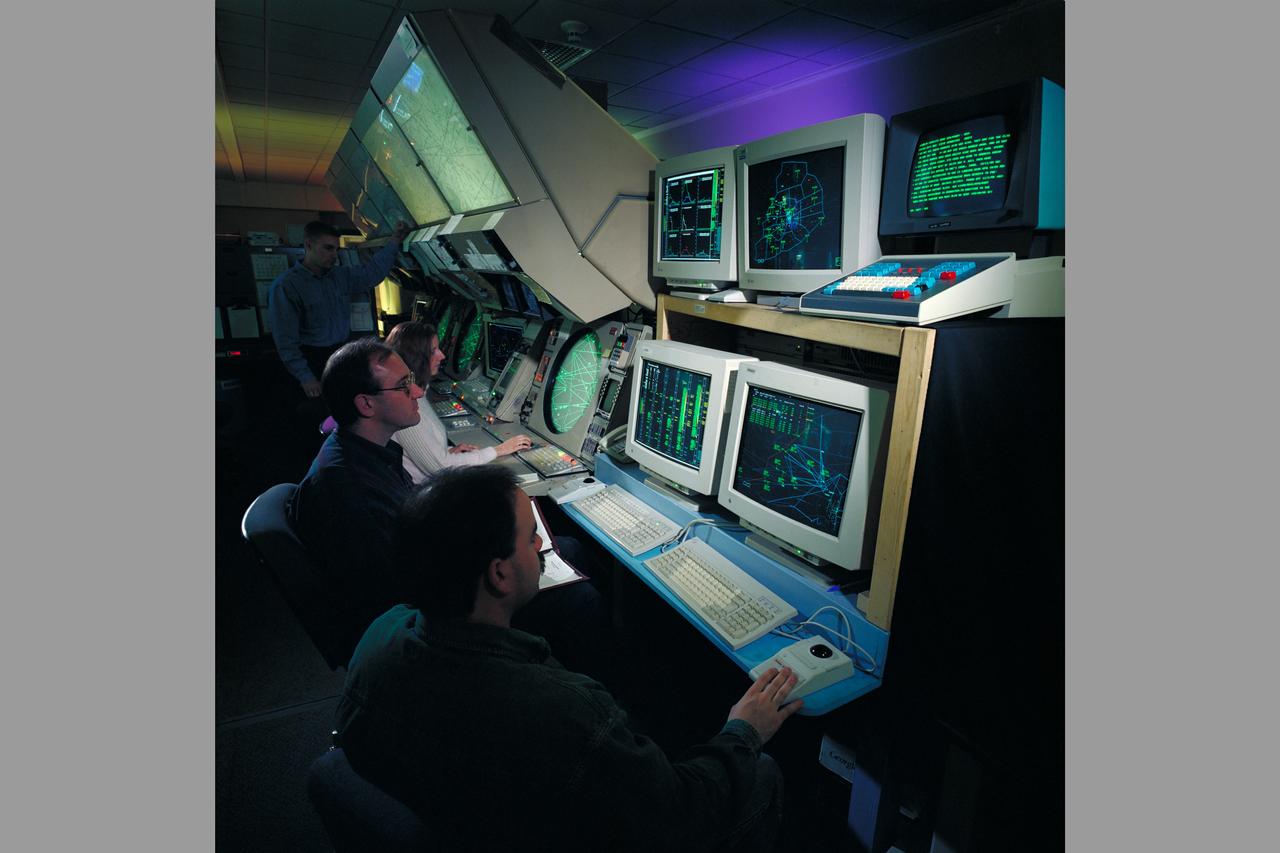

Air Traffic Control Center, Longmont, Colorado showing evaluation demonistrations of Ames CTAS System
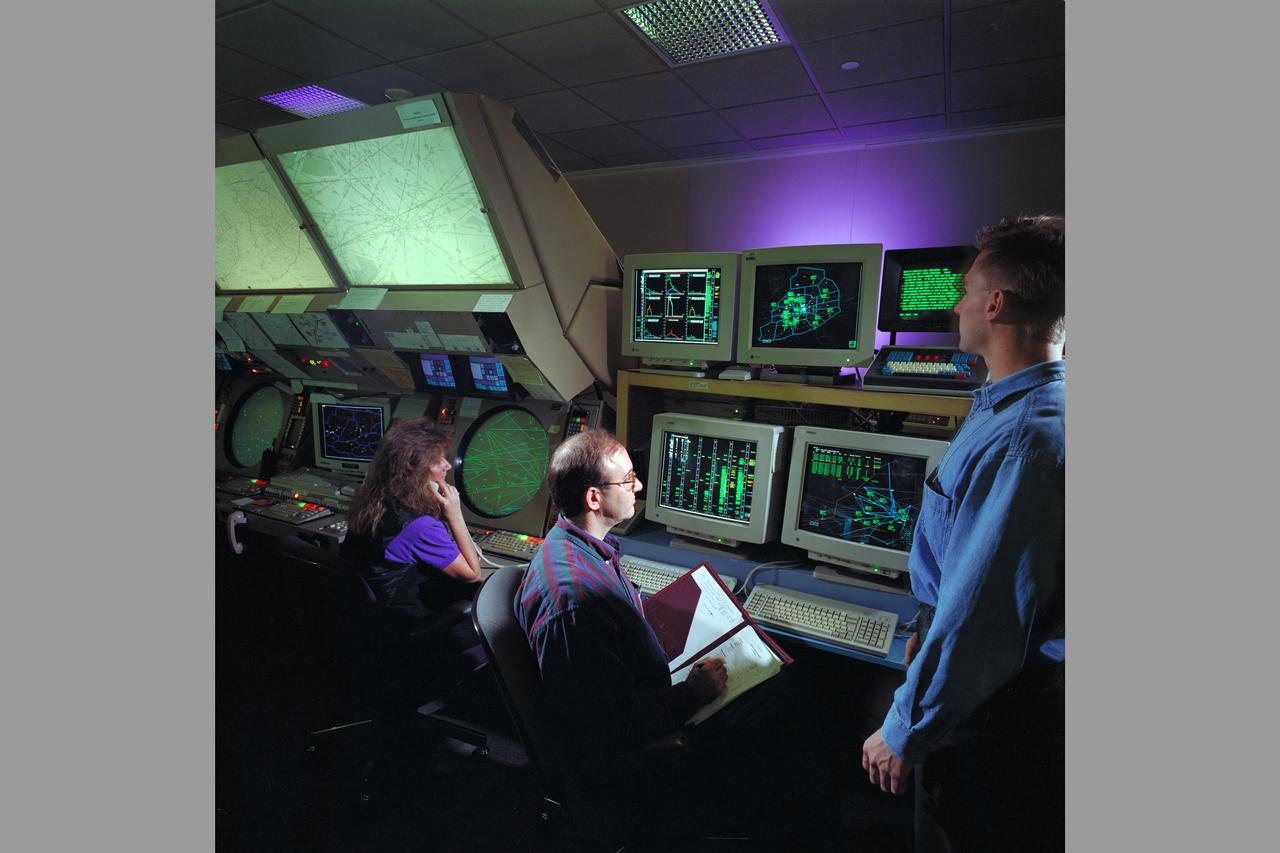

Air Traffic Control Center, Longmont, Colorado showing evaluation demonistrations of Ames CTAS System
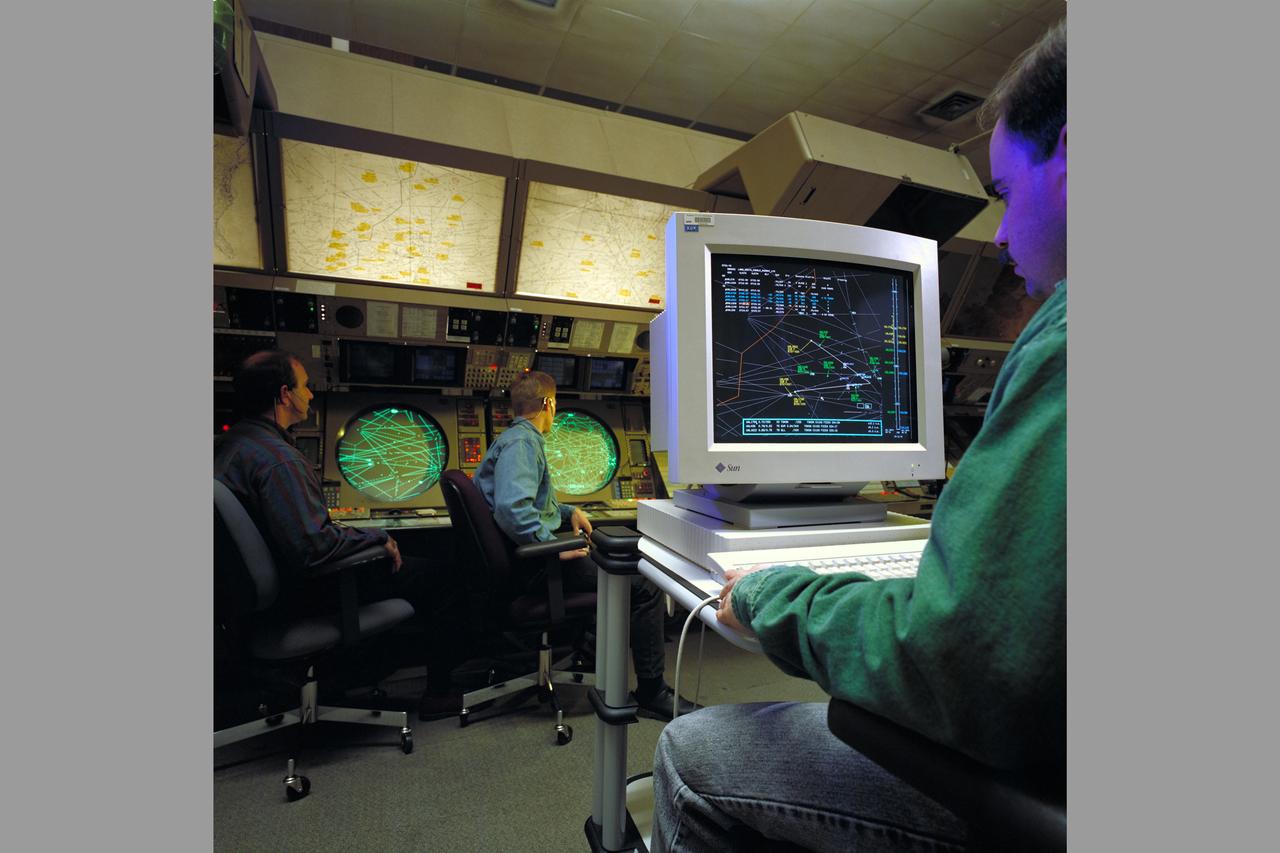

Air Traffic Control Center, Longmont, Colorado showing evaluation demonistrations of Ames CTAS System
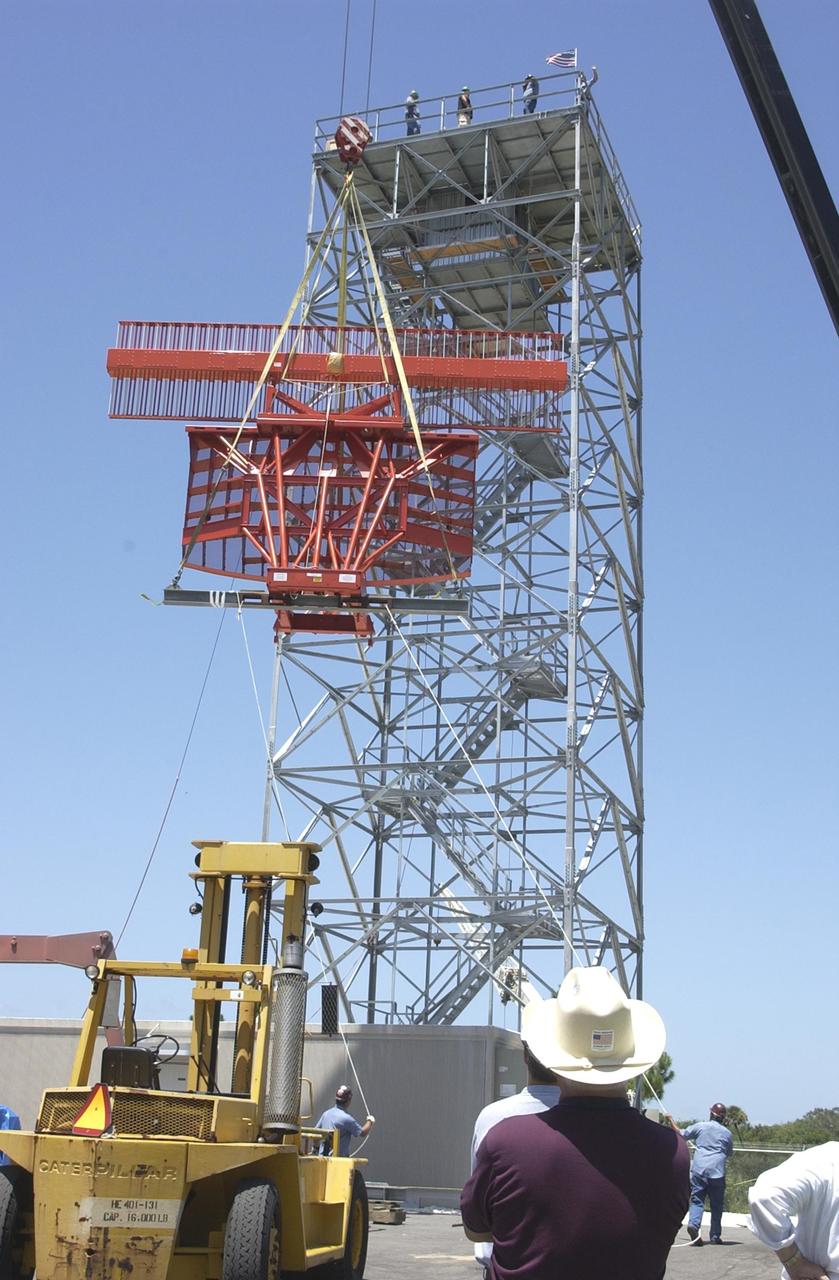

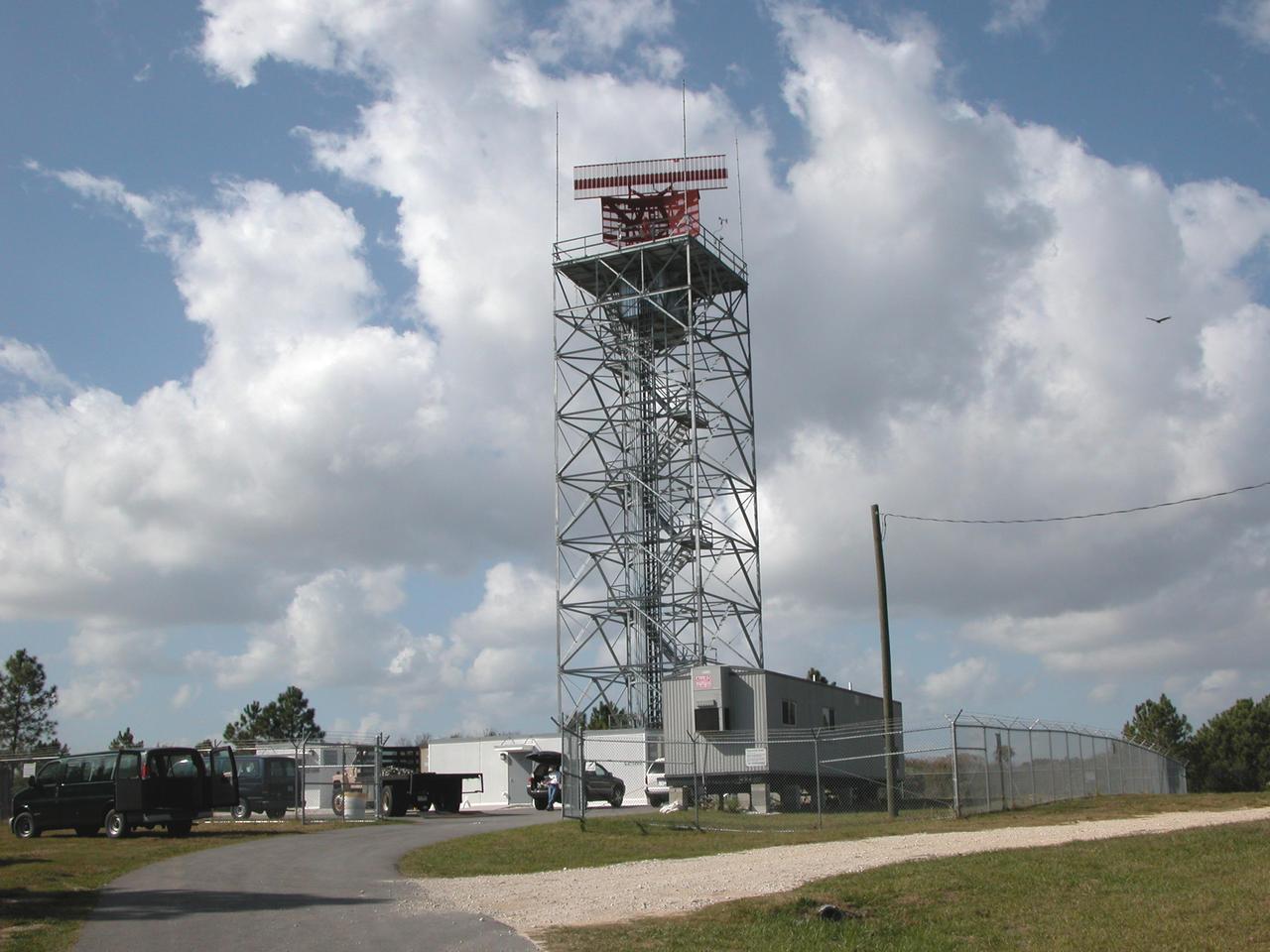
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An Air Traffic Control radar is being constructed at Shiloh for the NASA control tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility. It will be used by NASA and the Eastern Range for surveillance of controlled air space in Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station restricted areas. Shiloh is on the northern end of Merritt Island.

The test subject of Airspace Technology Demonstration 2 is “Integrated Arrivals Departures Scheduling,” a software tool that coordinates schedules between the ramp, tower, terminal and center control facilities, allowing air traffic controllers to better predict where and when to send aircraft in order to reduce congestion.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This aerial view shows the air traffic control radar at Shiloh for the NASA control tower at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility. It is used by NASA and the Eastern Range for surveillance of controlled air space in Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station restricted areas. Shiloh is on the northern end of Merritt Island. Photo credit: Cory Huston

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This aerial view shows the air traffic control radar at Shiloh for the NASA control tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility. It is used by NASA and the Eastern Range for surveillance of controlled air space in Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station restricted areas and for aircraft landings and departures. Shiloh is on the northern end of Merritt Island. Photo credit: Cory Huston
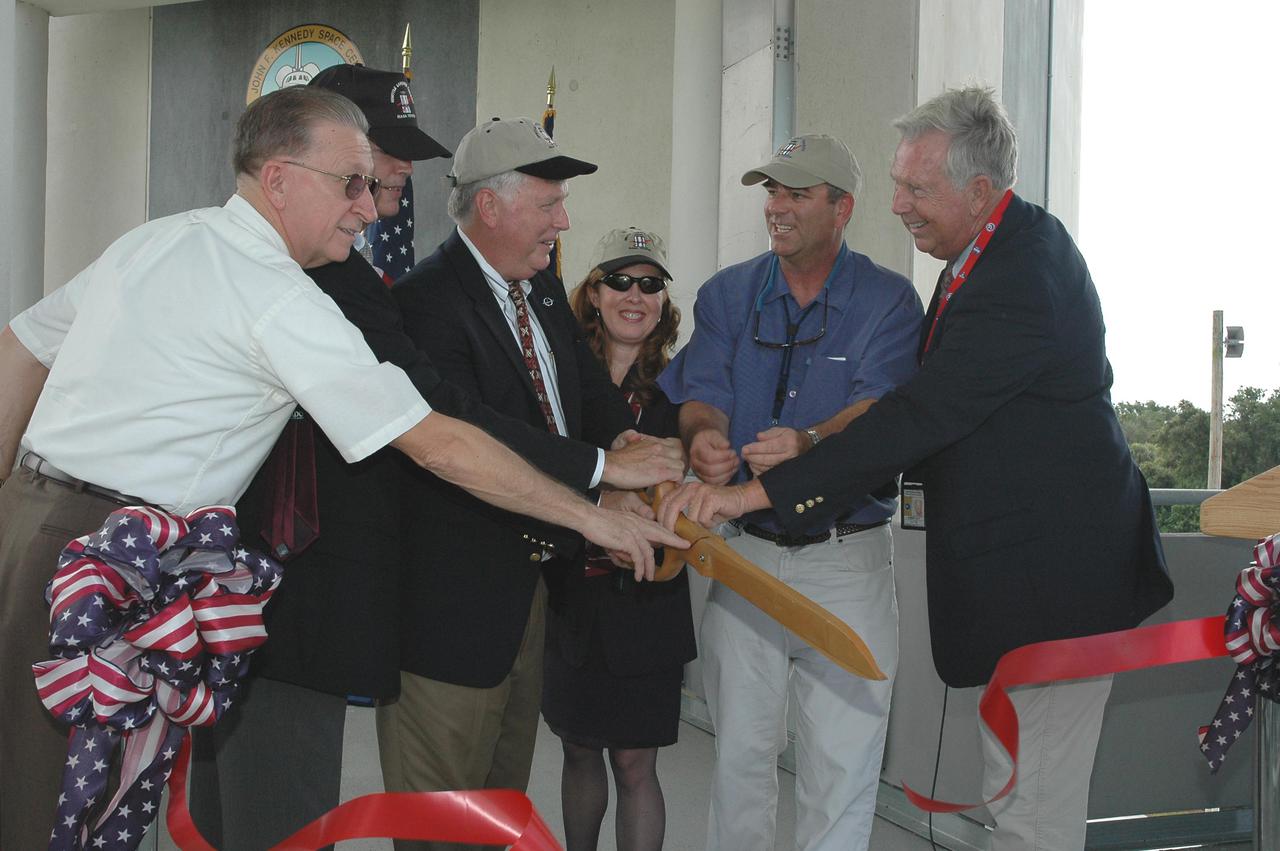

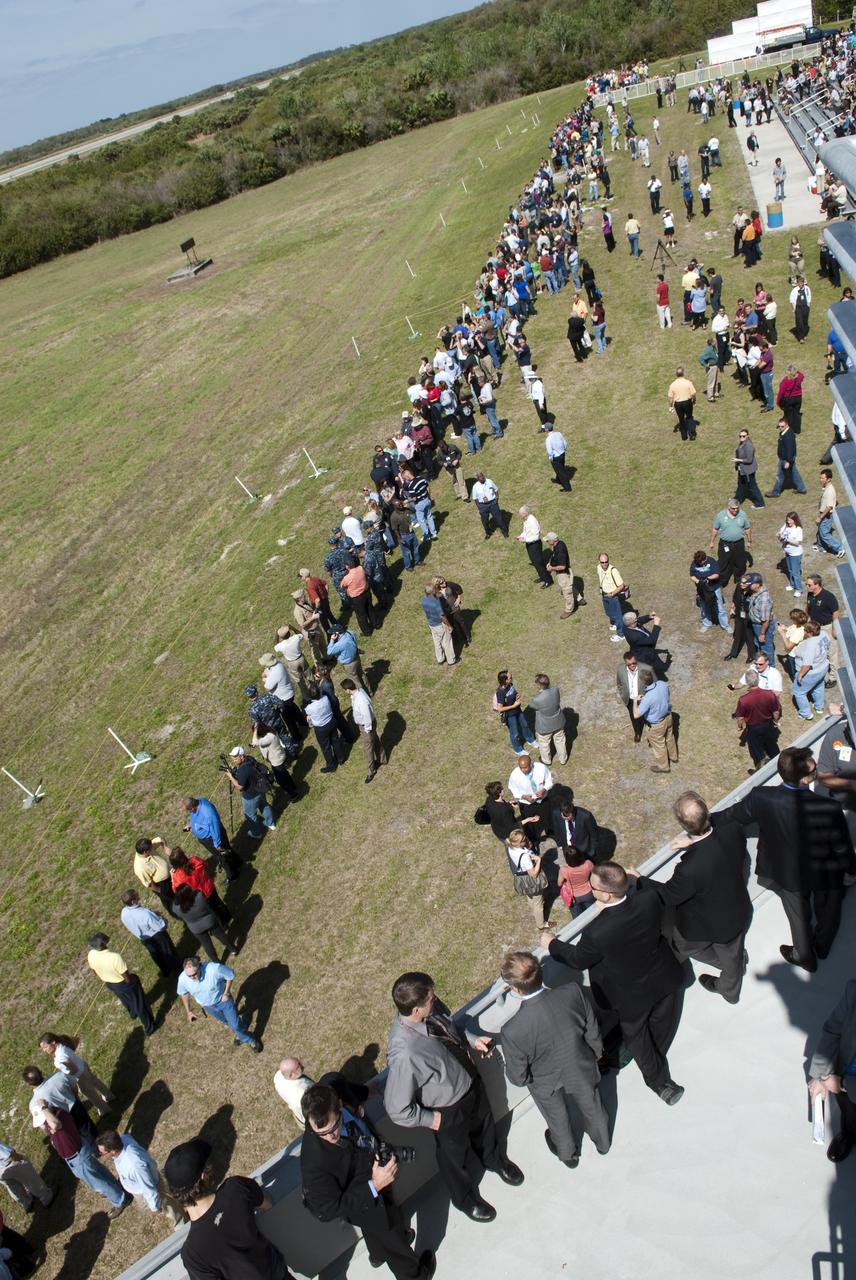
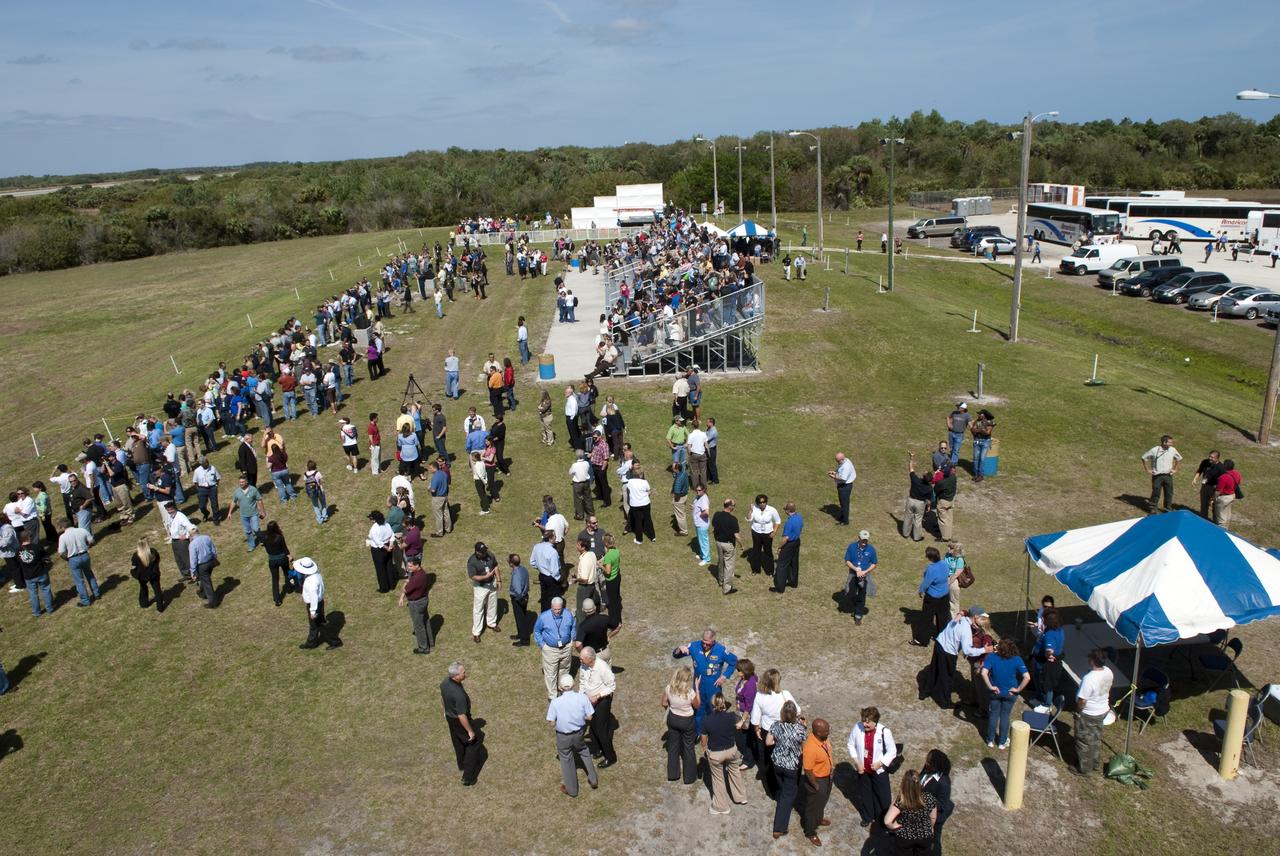
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility on NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, a ribbon-cutting dedicated the new NASA Air Traffic Control Tower. From left are James H. Jones, Space Gateway Support President William A. Sample, Center Director Jim Kennedy, External Relations Director Lisa Malone, Center Operations Director Scott D. Kerr, and KSC Safety Aviation Officer Albert E. Taff. The structure rises 110 feet over the midpoint of the runway and offers air traffic controllers a magnificent 360-degree view of Kennedy Space Center, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and north Brevard County. It replaces the small, portable tower installed at the edge of the runway in 1986. The new control tower will manage all landings and departures from the SLF, including air traffic within the Kennedy Space Center-Cape Canaveral restricted airspace. The facility provides a 24-hour weather-observing facility providing official hourly weather observations for the SLF and the Cape Canaveral vicinity, including special observations for all launches and landings. State-of-the-art, weather-observing equipment has been installed for Space Shuttle landings and for serving conventional aircraft landing at the SLF. At this location, weather observers will have a multi-directional view of the weather conditions at the runway and Launch Complex 39.
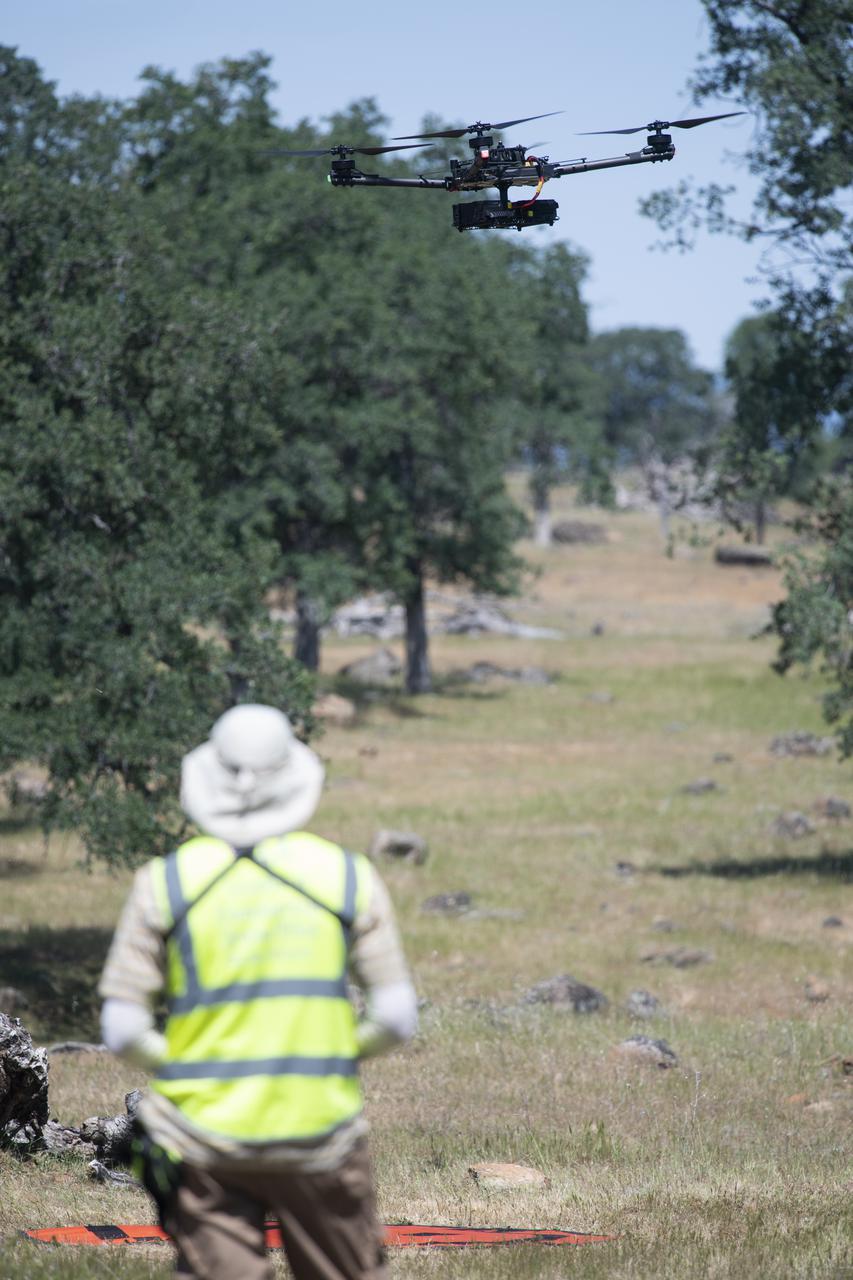

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
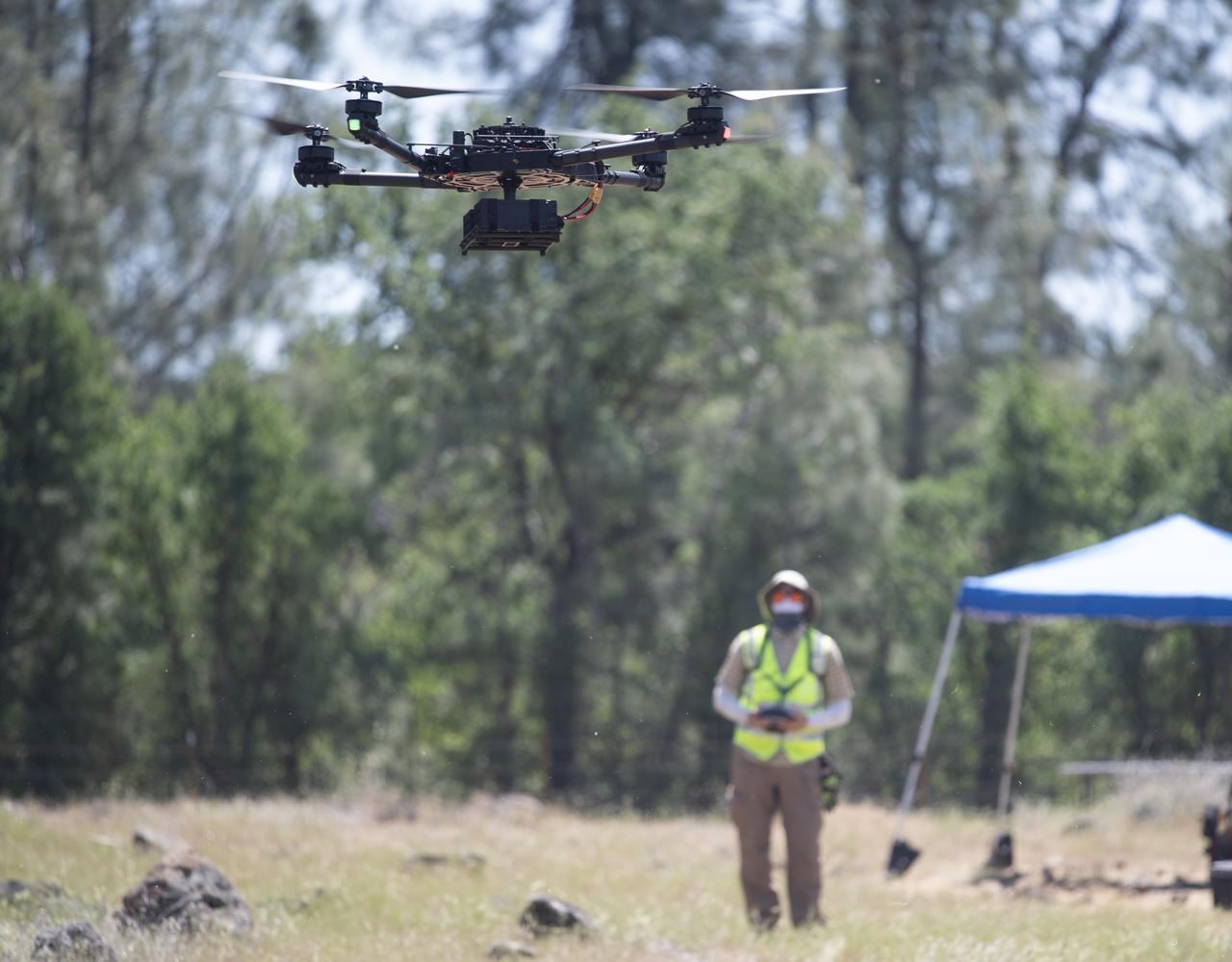

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
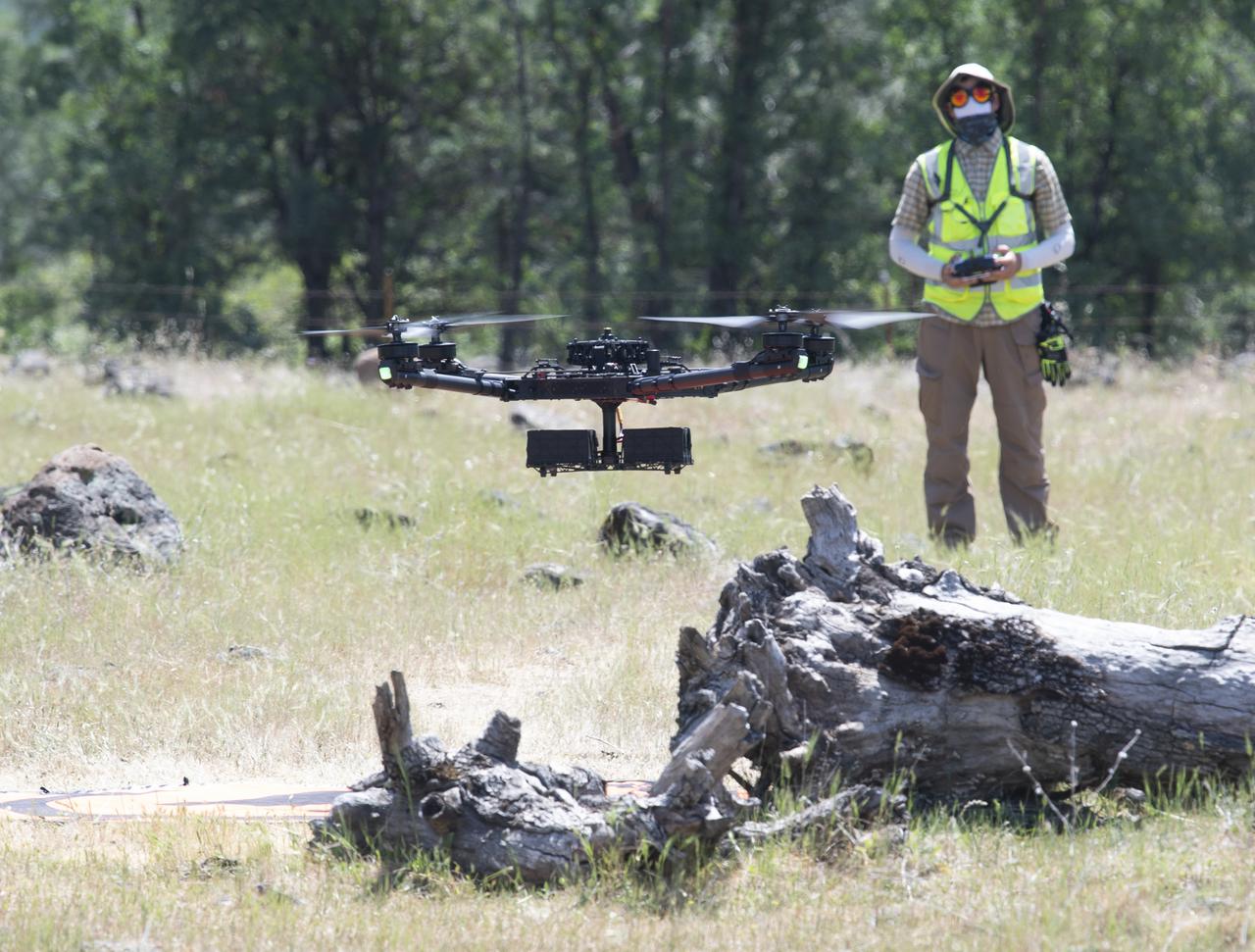

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
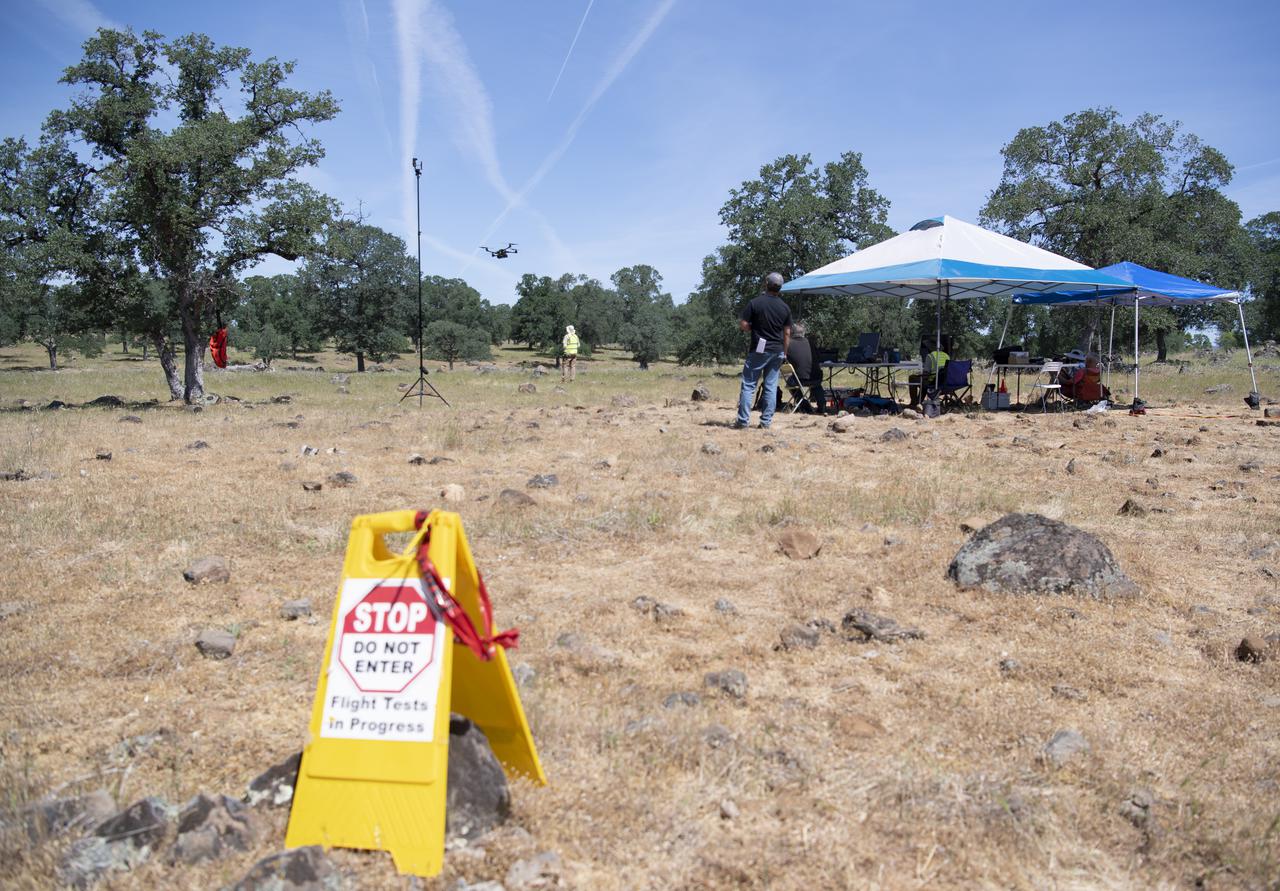

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
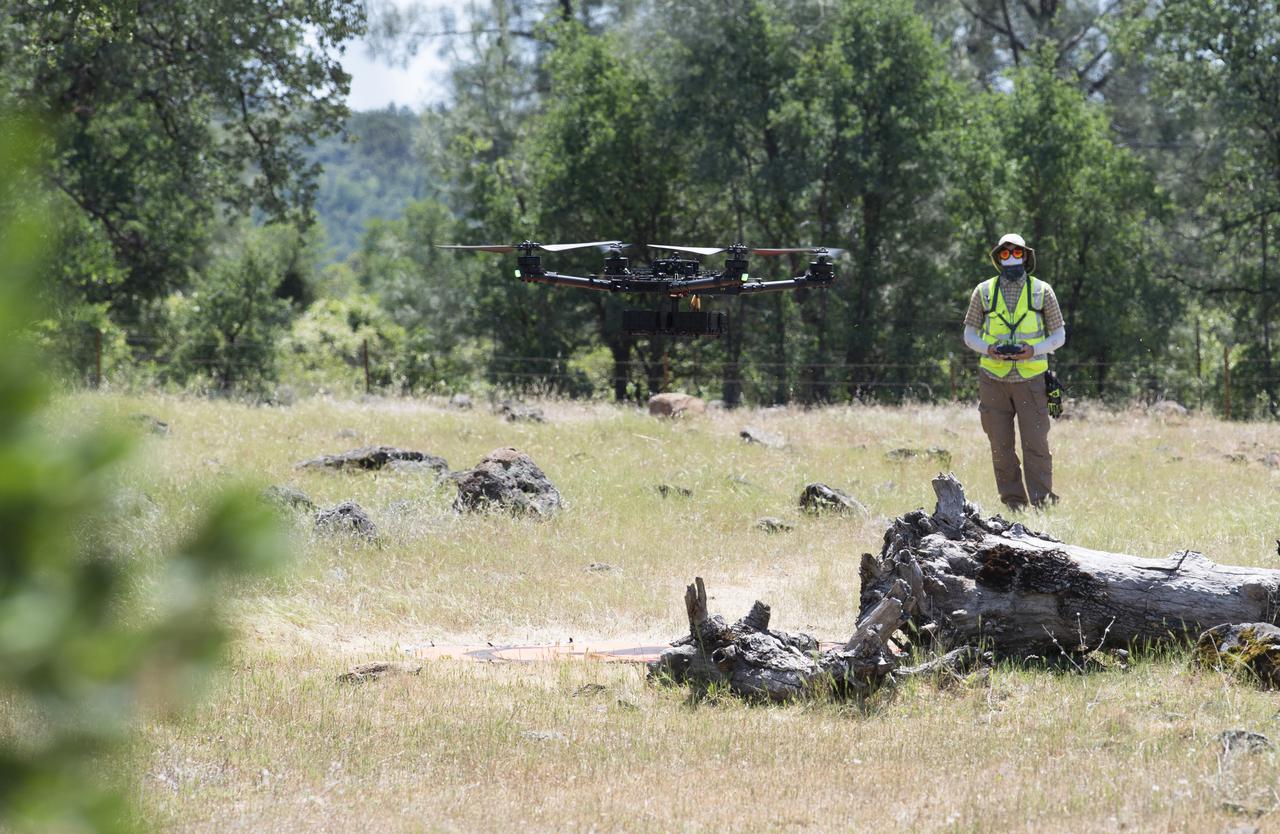

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
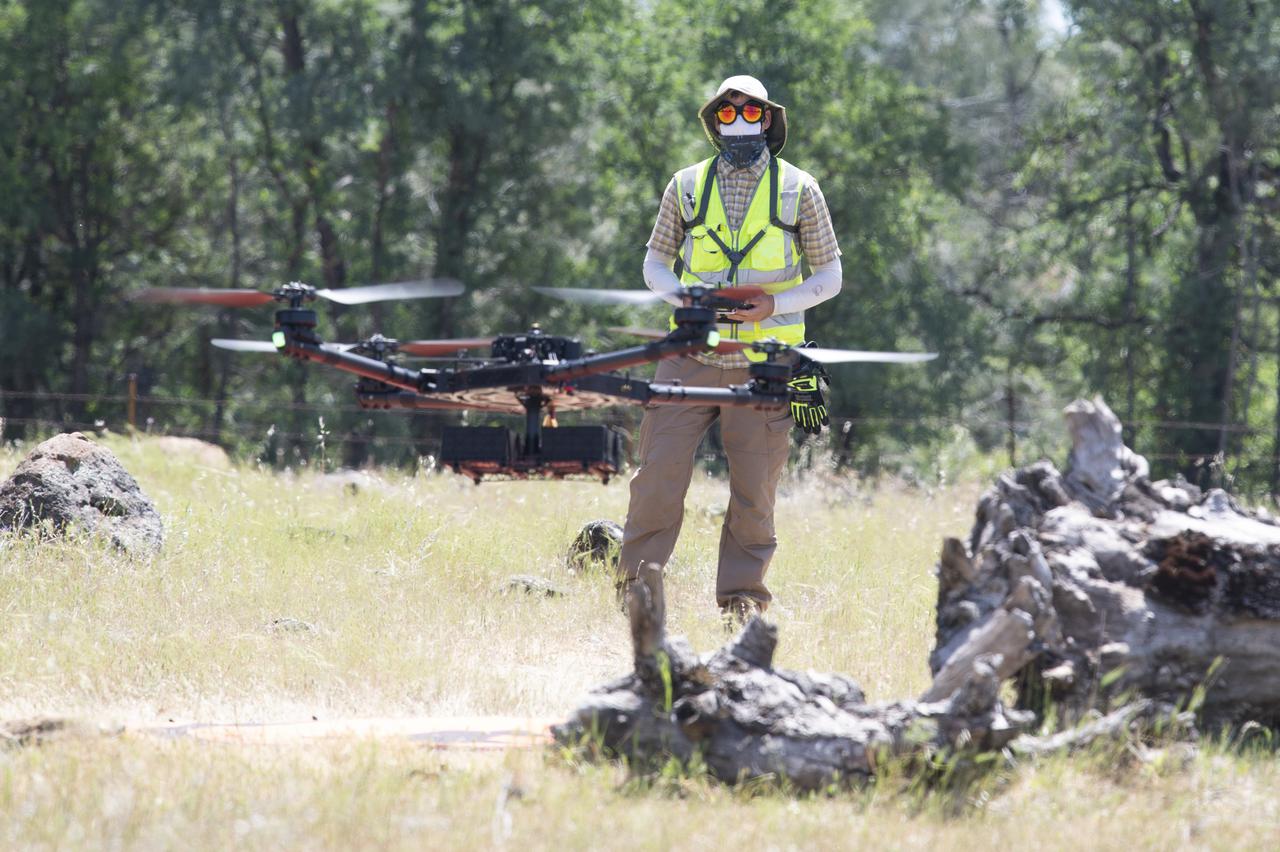

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
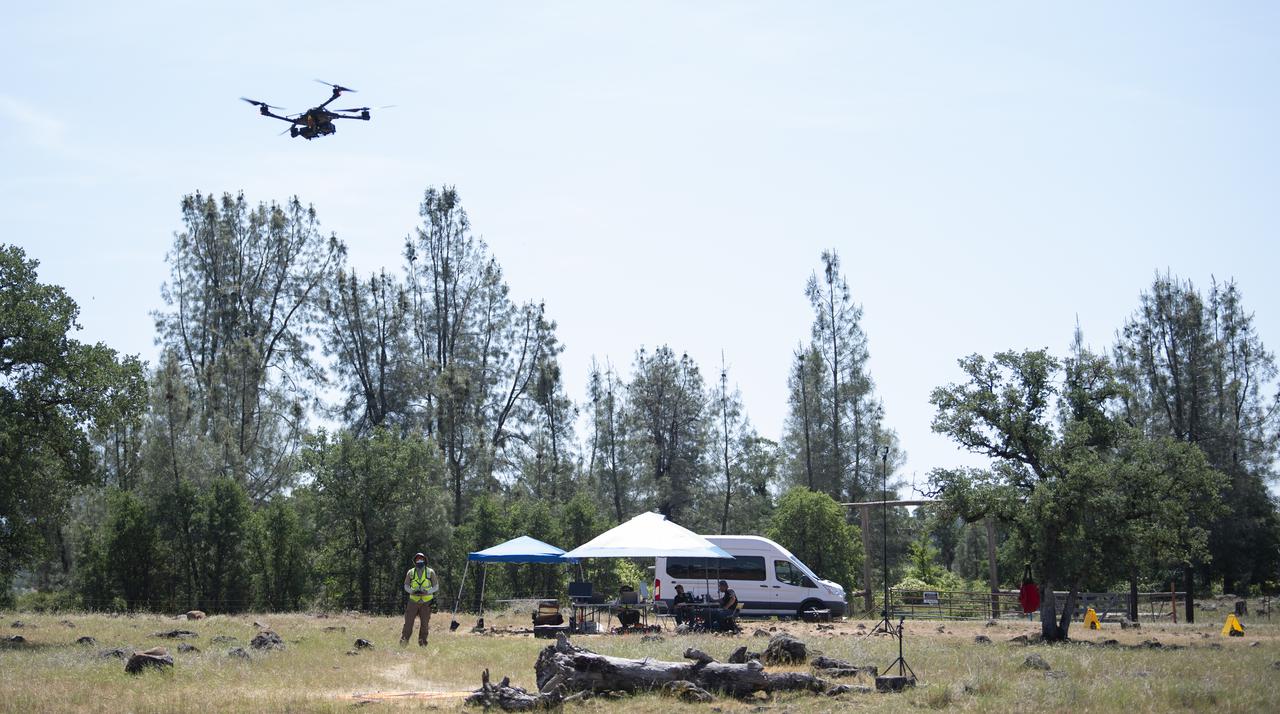

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
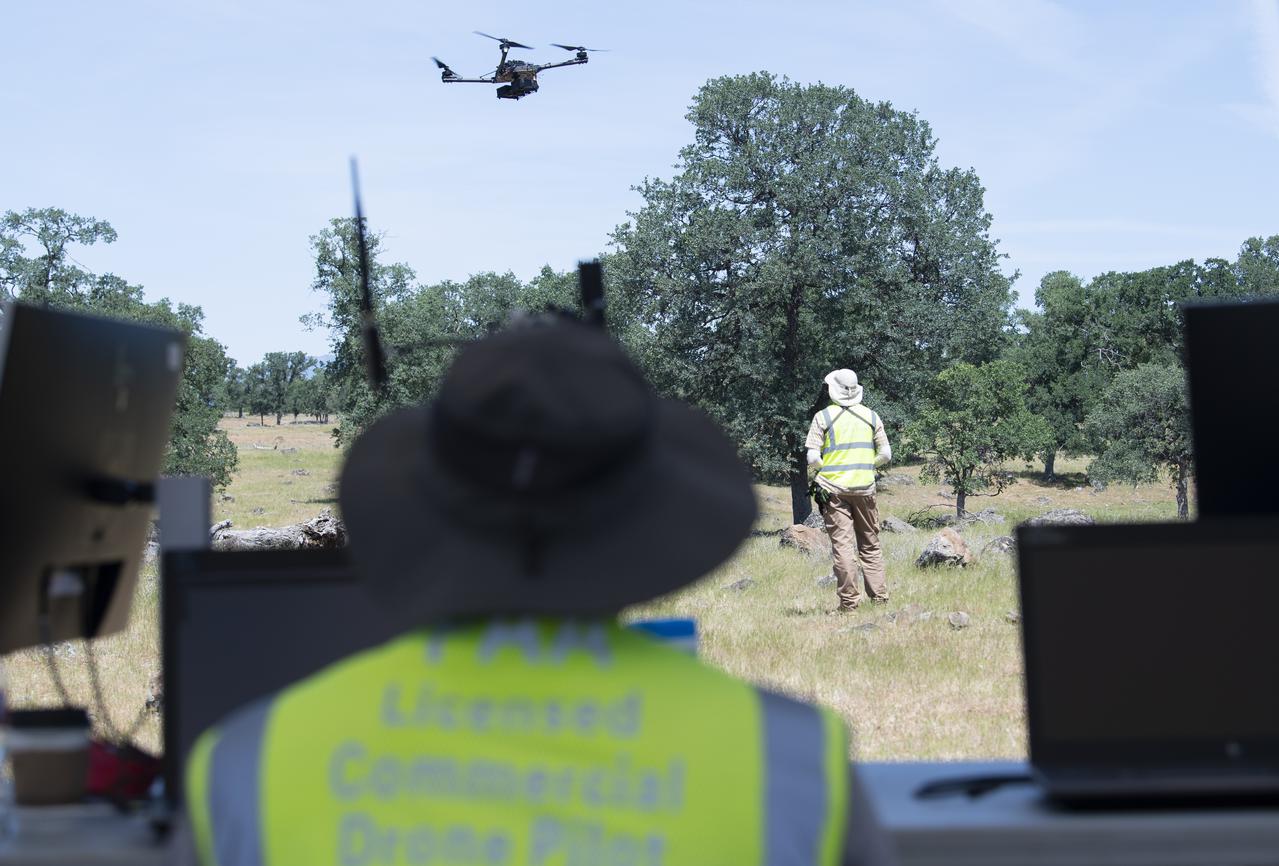

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
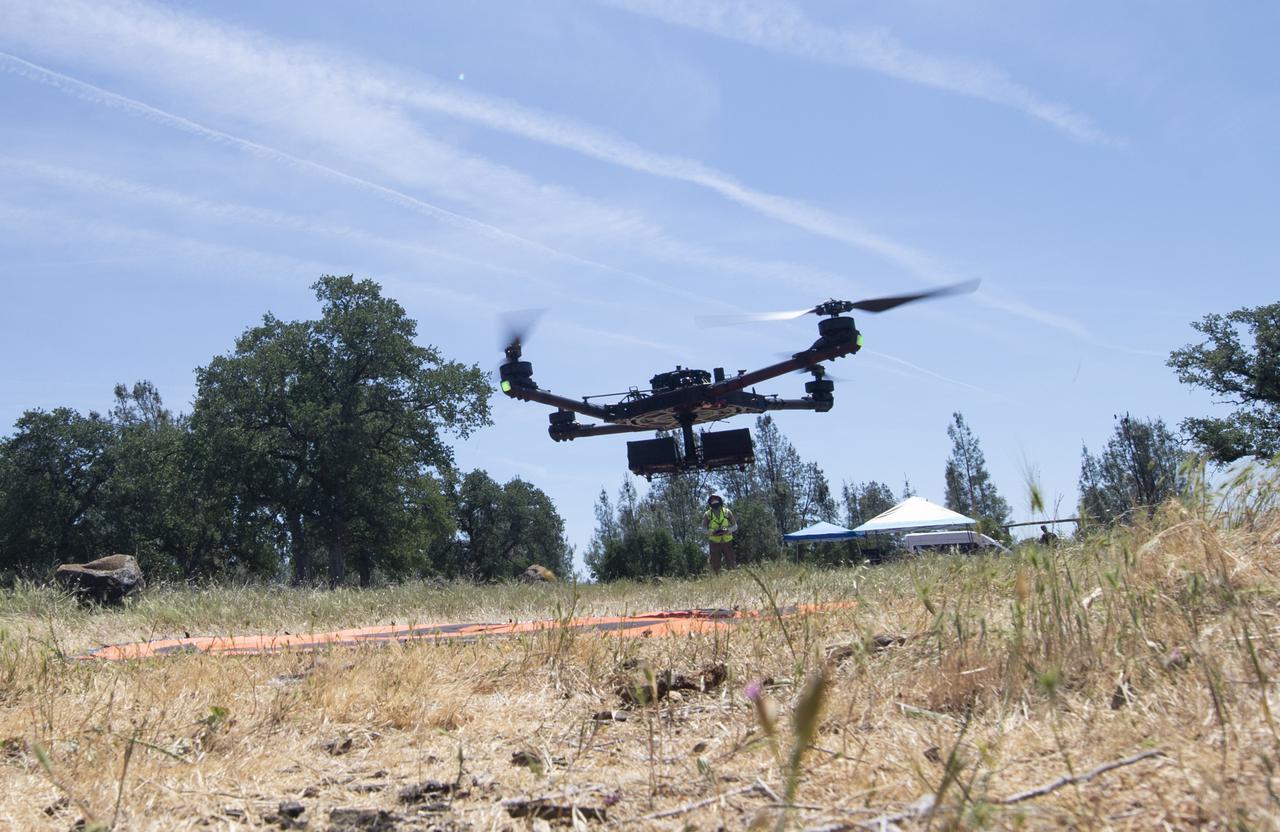

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
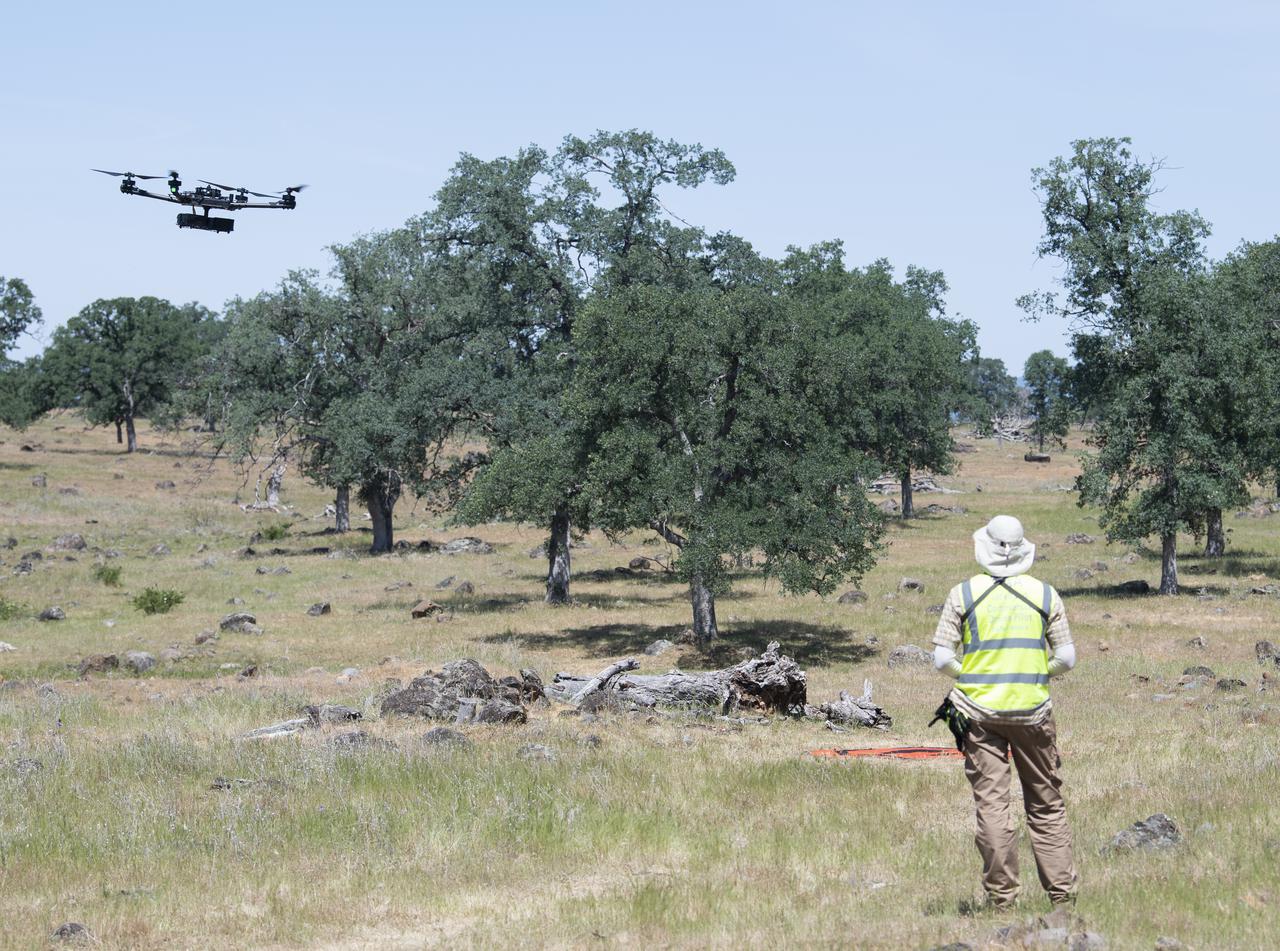

A FreeFly Systems Alta X drone is seen in flight under the control of Jonas Jonsson, pilot in command for STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, at NASA's Ames Research Center, as part of STEReO test activities, Wednesday, May 5, 2021 as Cal Fire conducts aerial fire fighting training exercises near Redding, California. STEReO, the Scalable Traffic Management for Emergency Response Operations project, led by NASA’s Ames Research Center, builds on NASA’s expertise in air traffic management, human factors research, and autonomous technology development to apply the agency’s work in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management, or UTM, to public safety uses. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
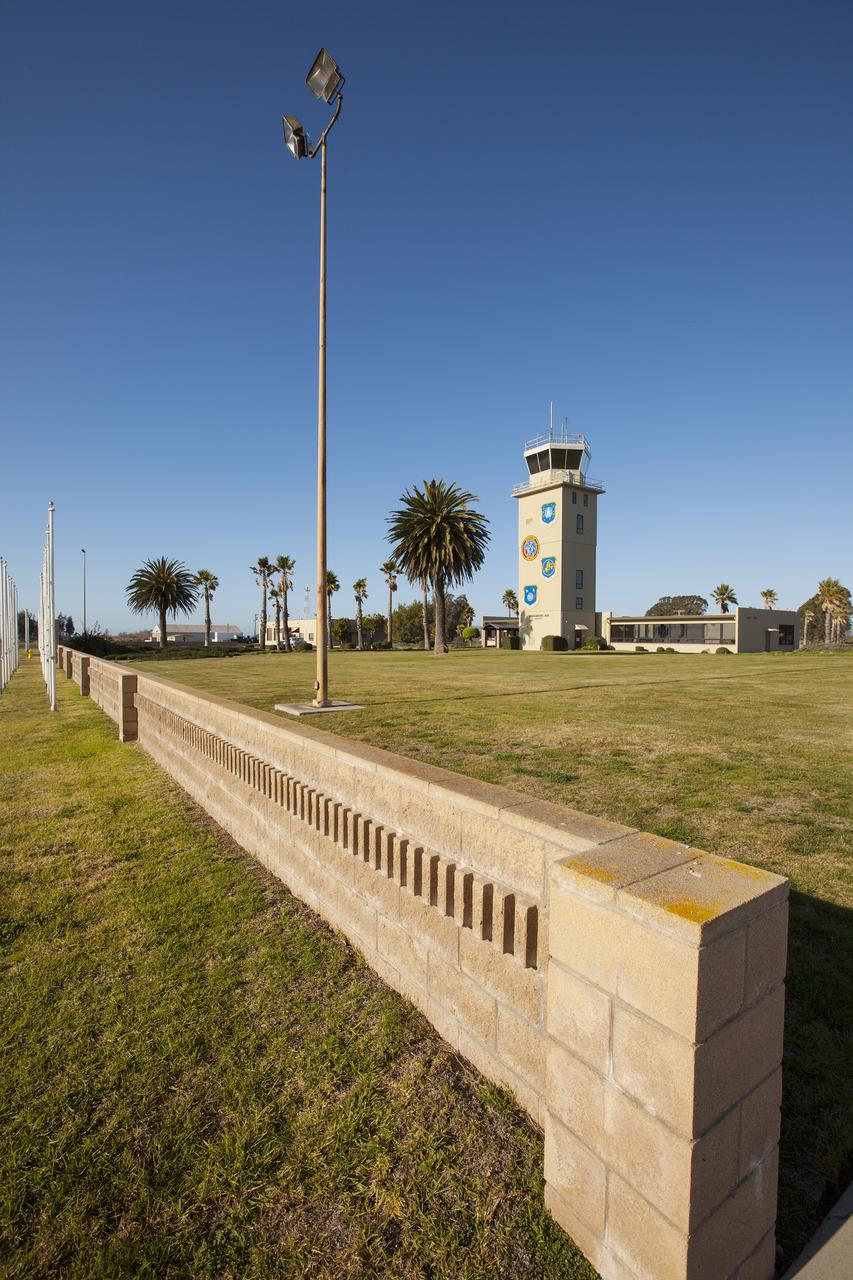

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. -- The air traffic control tower for the 30th Space Wing air field at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Vandenberg Air Force Base has a mission of placing satellites into polar orbit from the West Coast, using expendable boosters such as the Pegasus, Taurus, Minotaur, Atlas V and Delta IV. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston
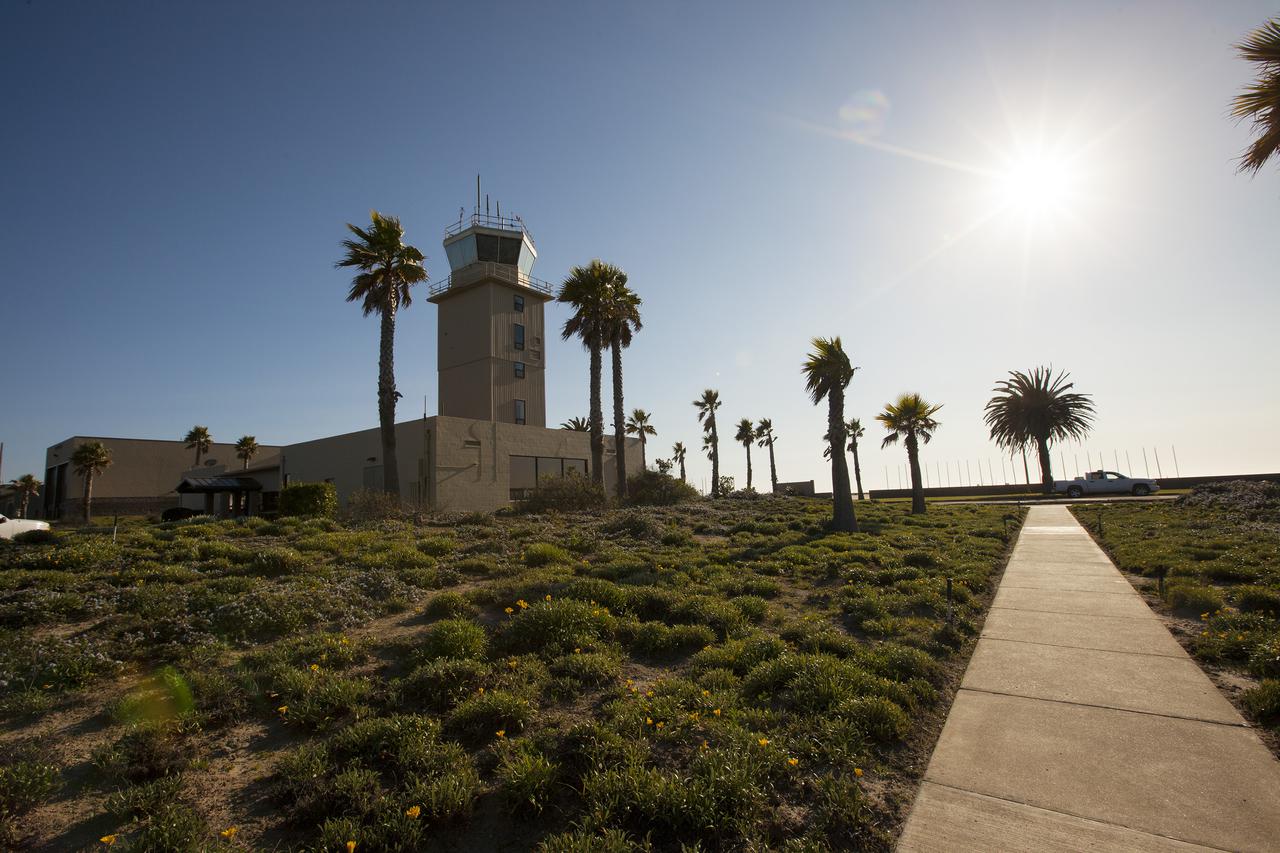

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. -- The air traffic control tower for the 30th Space Wing air field at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Vandenberg Air Force Base has a mission of placing satellites into polar orbit from the West Coast, using expendable boosters such as the Pegasus, Taurus, Minotaur, Atlas V and Delta IV. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston
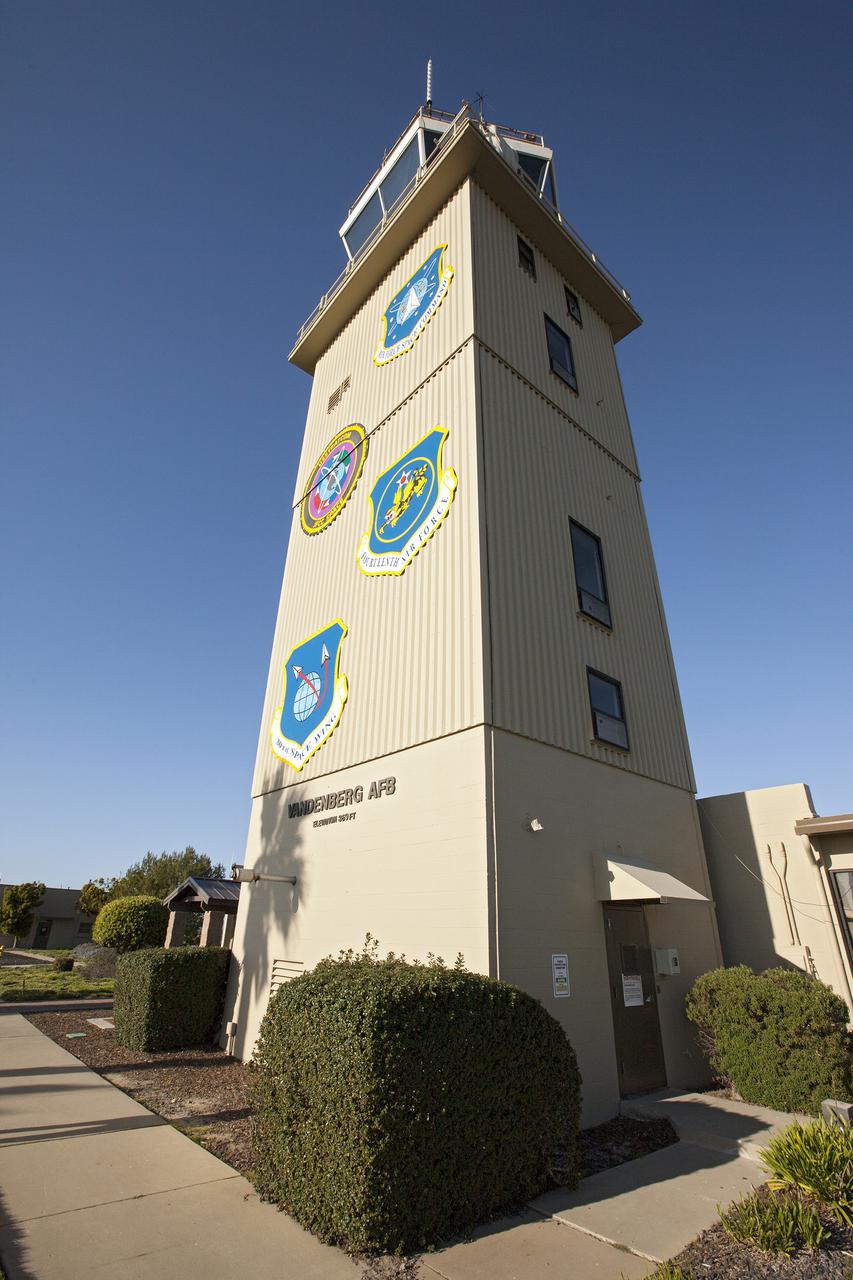

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. -- The air traffic control tower for the 30th Space Wing air field at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Vandenberg Air Force Base has a mission of placing satellites into polar orbit from the West Coast, using expendable boosters such as the Pegasus, Taurus, Minotaur, Atlas V and Delta IV. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston
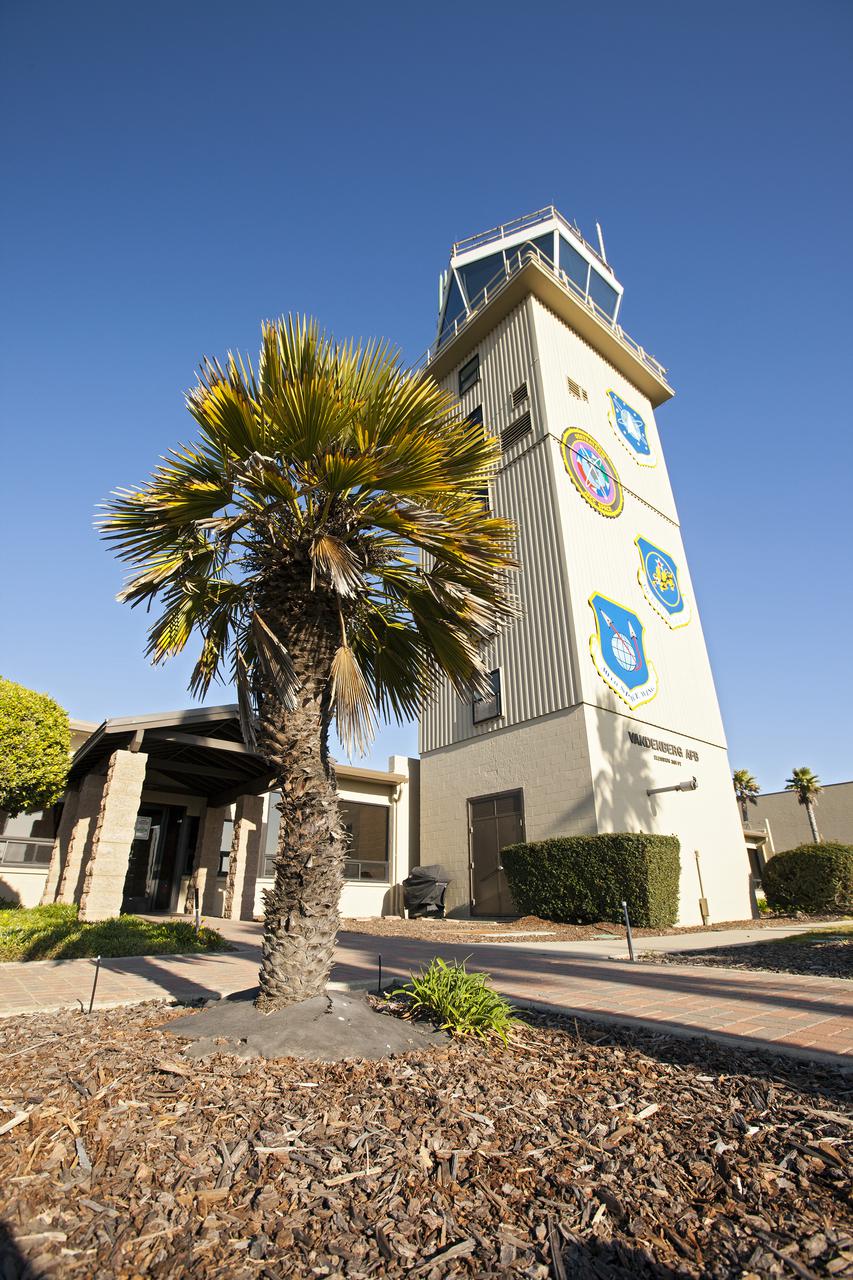

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. -- The air traffic control tower for the 30th Space Wing air field at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Vandenberg Air Force Base has a mission of placing satellites into polar orbit from the West Coast, using expendable boosters such as the Pegasus, Taurus, Minotaur, Atlas V and Delta IV. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston
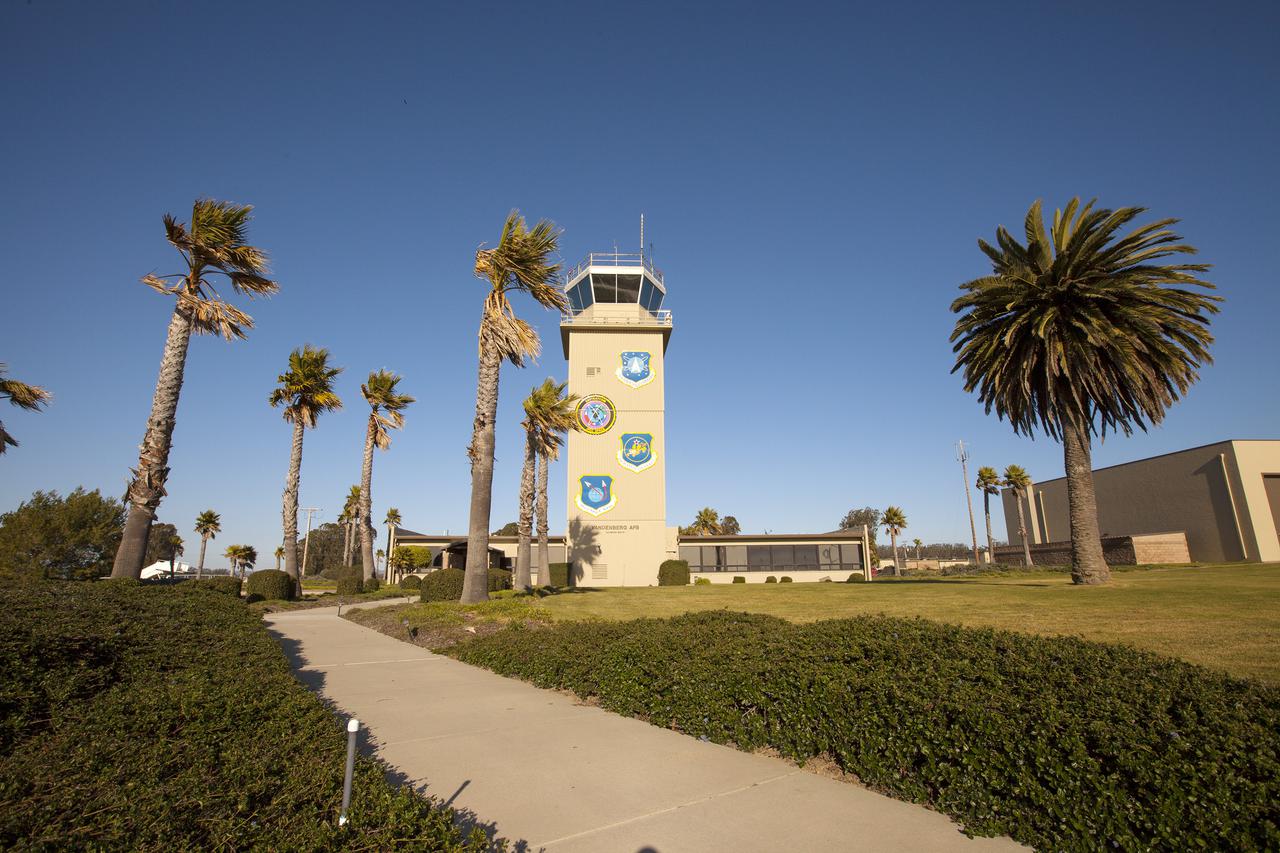

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. -- The air traffic control tower for the 30th Space Wing air field at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Vandenberg Air Force Base has a mission of placing satellites into polar orbit from the West Coast, using expendable boosters such as the Pegasus, Taurus, Minotaur, Atlas V and Delta IV. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston
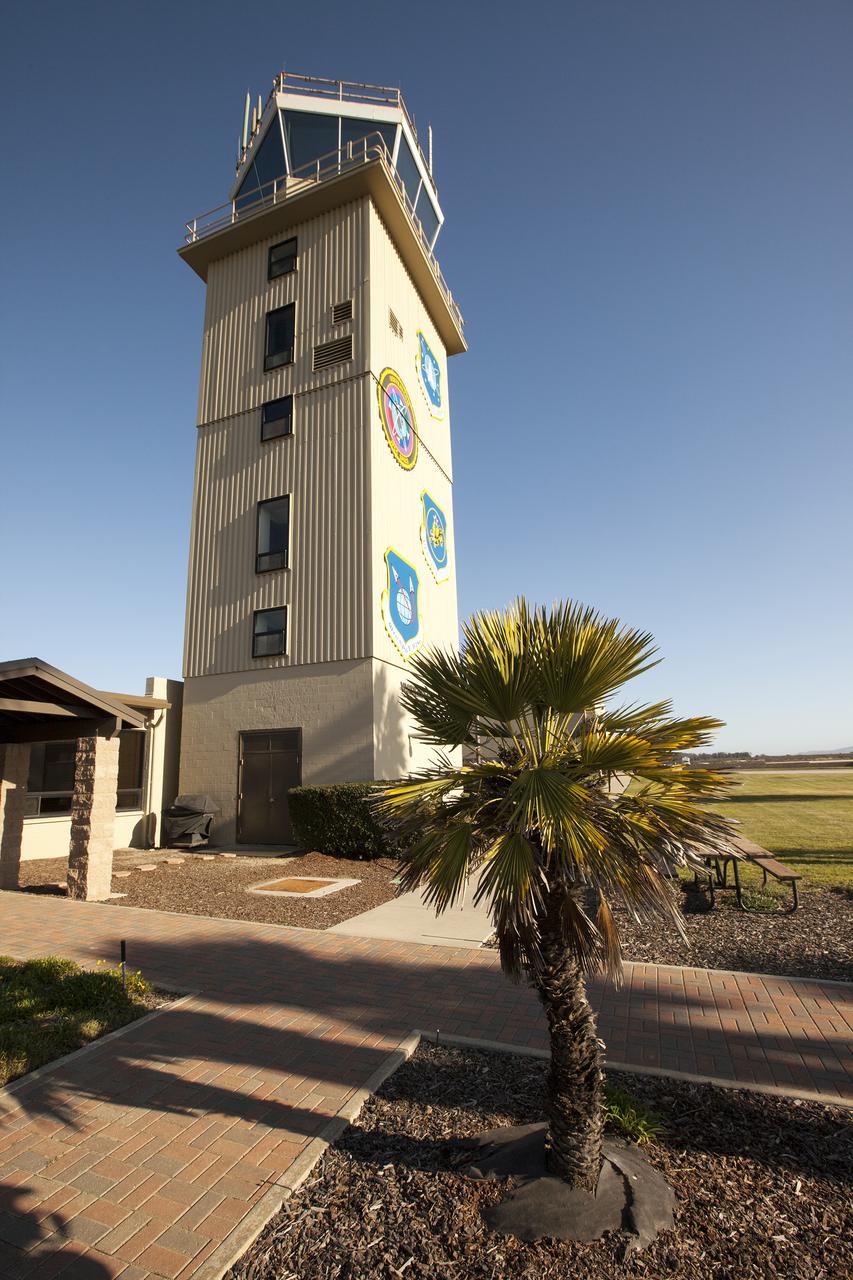

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. -- The air traffic control tower for the 30th Space Wing air field at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Vandenberg Air Force Base has a mission of placing satellites into polar orbit from the West Coast, using expendable boosters such as the Pegasus, Taurus, Minotaur, Atlas V and Delta IV. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston
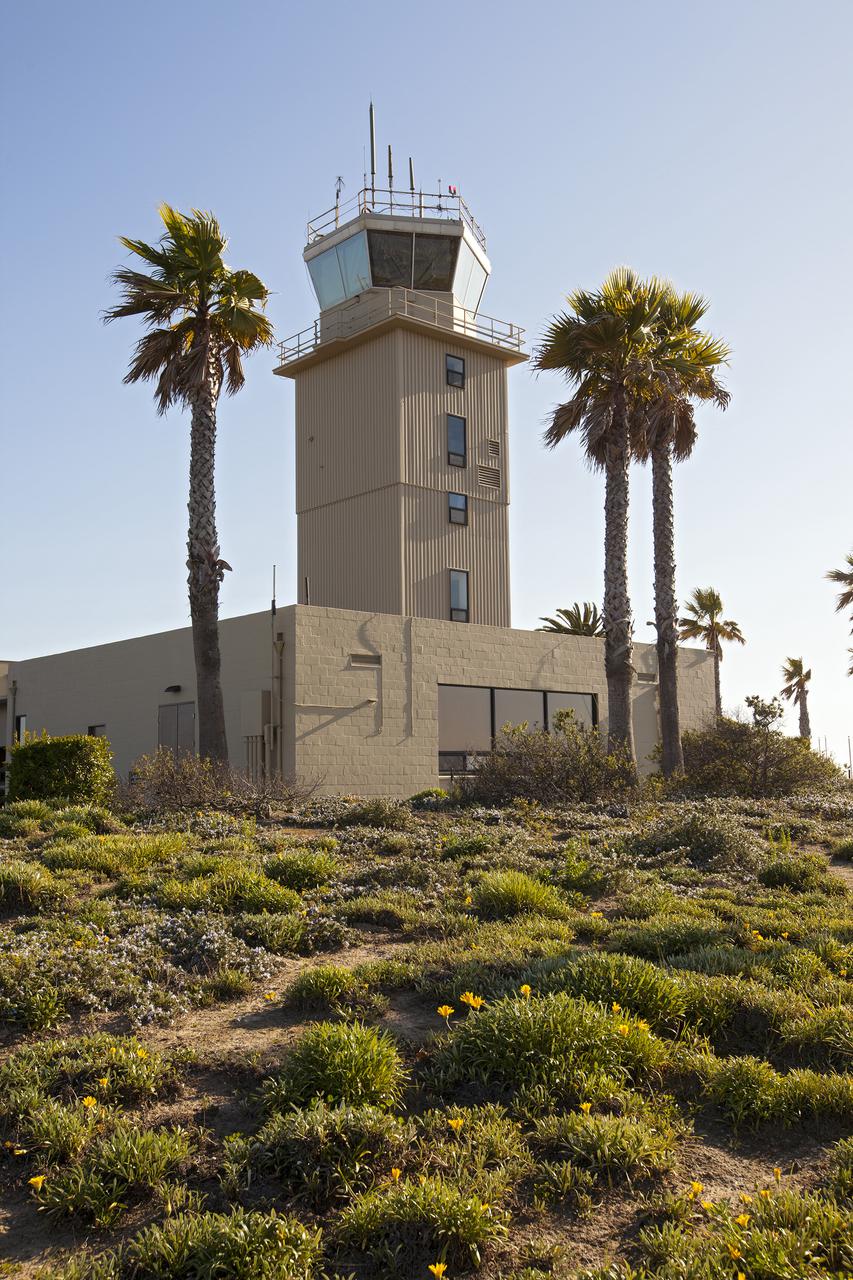

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. -- The air traffic control tower for the 30th Space Wing air field at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Vandenberg Air Force Base has a mission of placing satellites into polar orbit from the West Coast, using expendable boosters such as the Pegasus, Taurus, Minotaur, Atlas V and Delta IV. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston
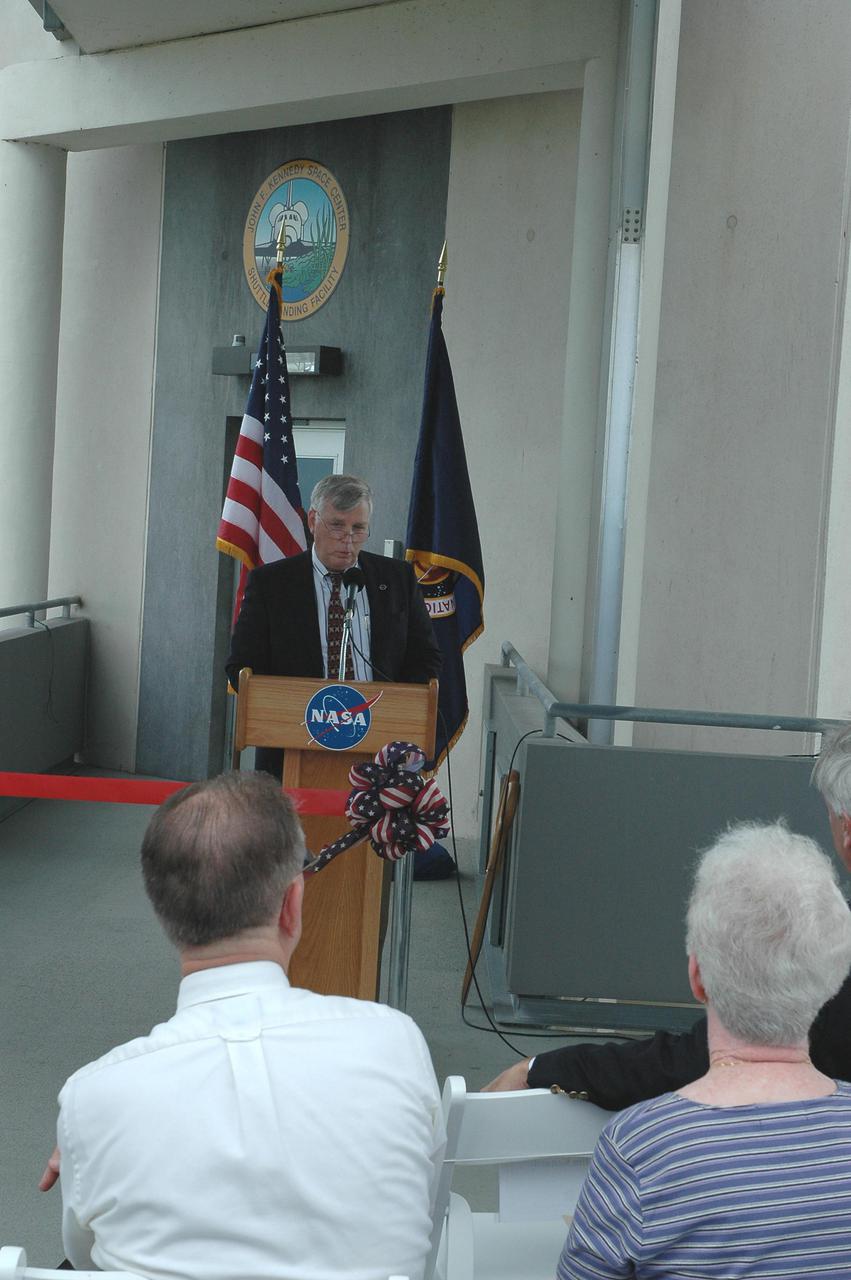

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility on NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, KSC Director Jim Kennedy talks to attendees at the ribbon-cutting ceremony for the new NASA Air Traffic Control Tower. The dedication took place in the SLF’s new media facilities, which were built for the Return to Flight mission STS-114 and the landing of Shuttle Discovery. The facilities are co-located with the new control tower. The dedication and ribbon cutting were held at the base of the tower and included Center Director Jim Kennedy, Space Gateway Support President William A. Sample, External Relations Director Lisa Malone, Center Operations Director Scott D. Kerr, and KSC Safety Aviation Officer Albert E. Taff. The structure rises 110 feet over the midpoint of the runway and offers air traffic controllers a magnificent 360-degree view of Kennedy Space Center, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and north Brevard County. It replaces the small, portable tower installed at the edge of the runway in 1986. The new control tower will manage all landings and departures from the SLF, including air traffic within the Kennedy Space Center-Cape Canaveral restricted airspace. The facility provides a 24-hour weather-observing facility providing official hourly weather observations for the SLF and the Cape Canaveral vicinity, including special observations for all launches and landings. State-of-the-art, weather-observing equipment has been installed for Space Shuttle landings and for serving conventional aircraft landing at the SLF. At this location, weather observers will have a multi-directional view of the weather conditions at the runway and Launch Complex 39.
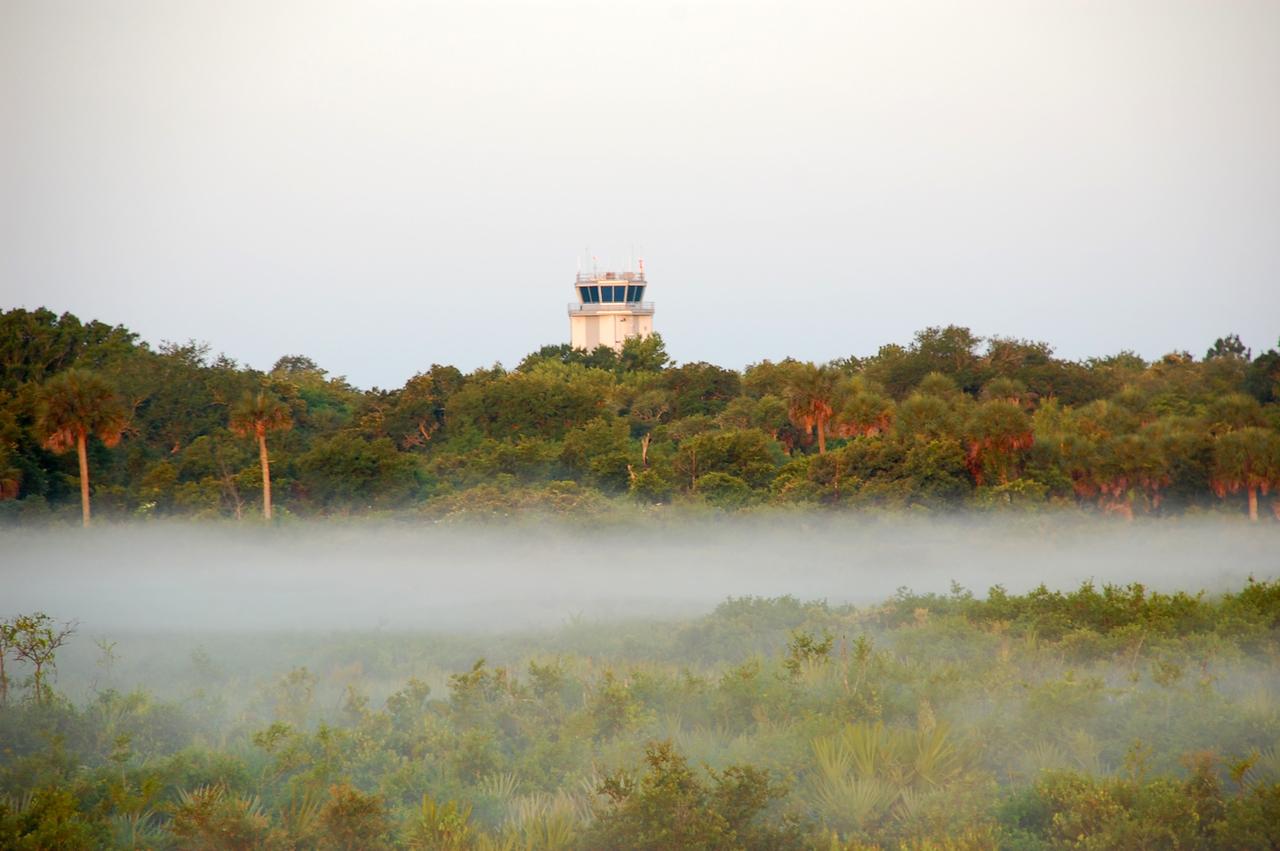

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Fog near the traffic control tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility begins to burn off as the sun rises over NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. On this particular morning, preparations are underway for a launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a part of the spaceport which neighbors Kennedy Space Center. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
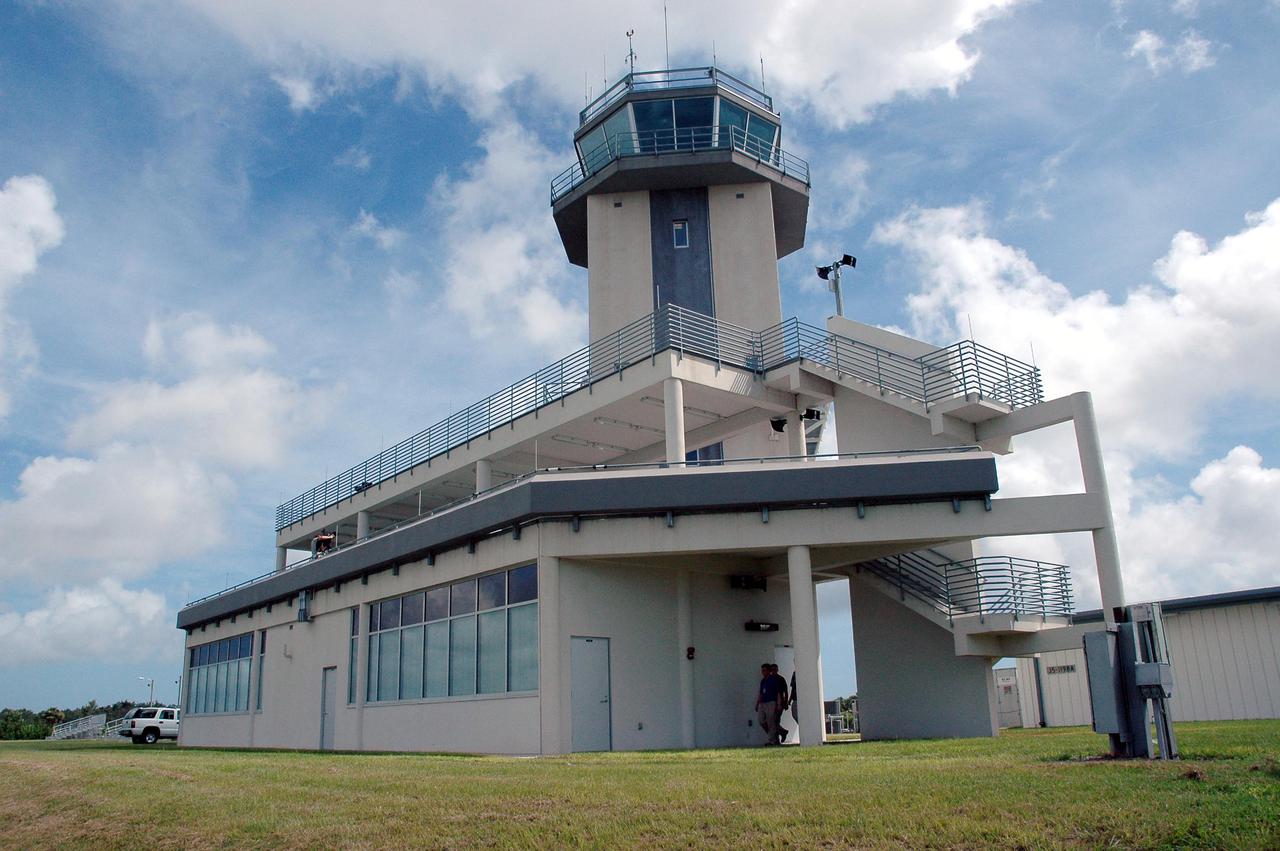

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility on NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, this new media building features a new Air Traffic Control Tower. The facility was dedicated in a ribbon-cutting ceremony July 8 that included Center Director Jim Kennedy, Space Gateway Support President William A. Sample, External Relations Director Lisa Malone, Center Operations Director Scott D. Kerr, and KSC Safety Aviation Officer Albert E. Taff. The facility was built for the Return to Flight mission STS-114 and the landing of Shuttle Discovery. The structure rises 110 feet over the midpoint of the runway and offers air traffic controllers a magnificent 360-degree view of Kennedy Space Center, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and north Brevard County. It replaces the small, portable tower installed at the edge of the runway in 1986. The new control tower will manage all landings and departures from the SLF, including air traffic within the Kennedy Space Center-Cape Canaveral restricted airspace. The facility provides a 24-hour weather-observing facility providing official hourly weather observations for the SLF and the Cape Canaveral vicinity, including special observations for all launches and landings. State-of-the-art, weather-observing equipment has been installed for Space Shuttle landings and for serving conventional aircraft landing at the SLF. At this location, weather observers will have a multi-directional view of the weather conditions at the runway and Launch Complex 39.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Day in the Life, page 3. Coming in for landing. Inside the control building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, air traffic controller Donny Linton, left, and SGS air facility manager Bob Bryen survey the SLF runway. This photograph was taken for a special color edition of Spaceport News designed to portray in photographs a single day at KSC, July 26, 2000. The special edition, published Aug. 25, 2000, was created to give readers a look at KSC’s diverse workforce and the critical roles workers play in the nation’s space program. Spaceport News is an official publication of the Kennedy Space Center and is published on alternate Fridays by the Public Affairs Office in the interest of KSC civil service and contractor employees
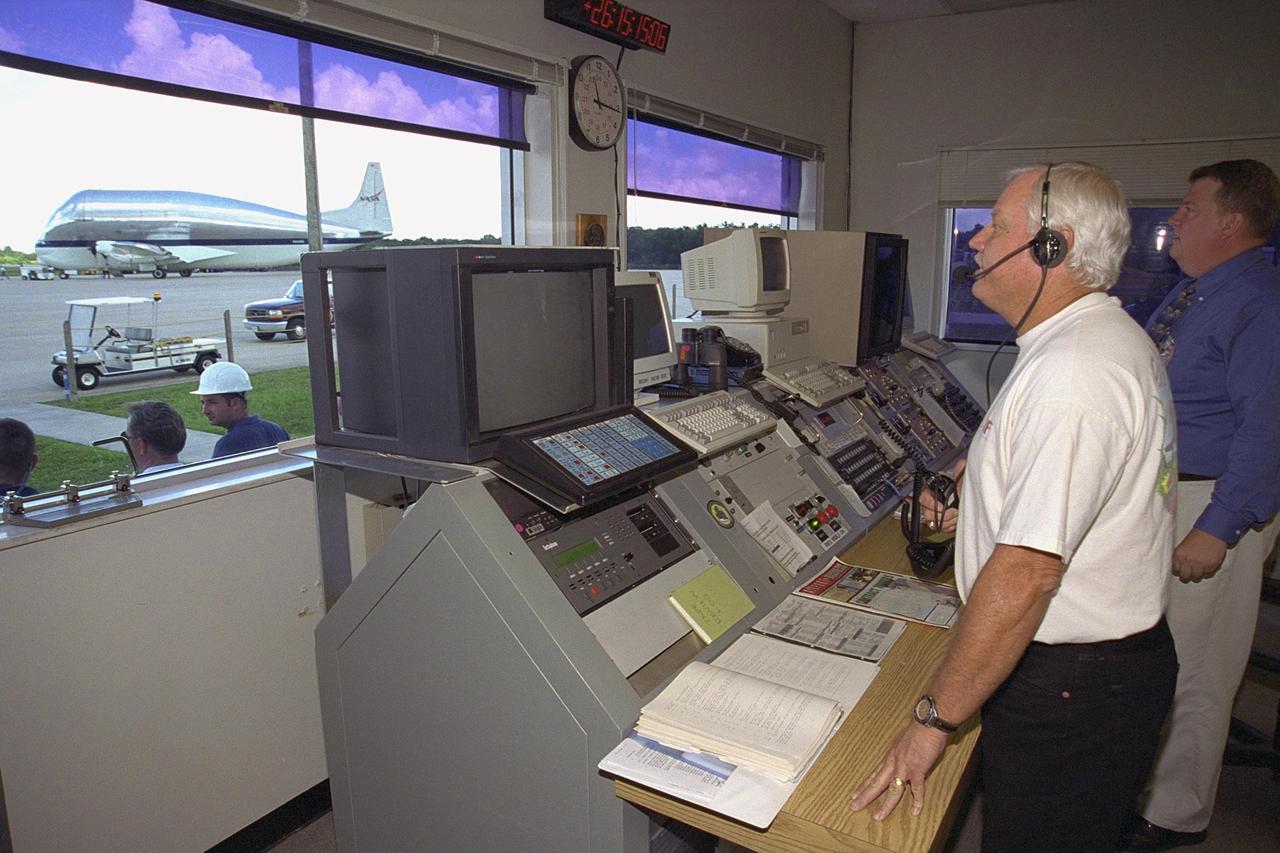

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Day in the Life, page 3. Coming in for landing. Inside the control building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, air traffic controller Donny Linton, left, and SGS air facility manager Bob Bryen survey the SLF runway. This photograph was taken for a special color edition of Spaceport News designed to portray in photographs a single day at KSC, July 26, 2000. The special edition, published Aug. 25, 2000, was created to give readers a look at KSC’s diverse workforce and the critical roles workers play in the nation’s space program. Spaceport News is an official publication of the Kennedy Space Center and is published on alternate Fridays by the Public Affairs Office in the interest of KSC civil service and contractor employees
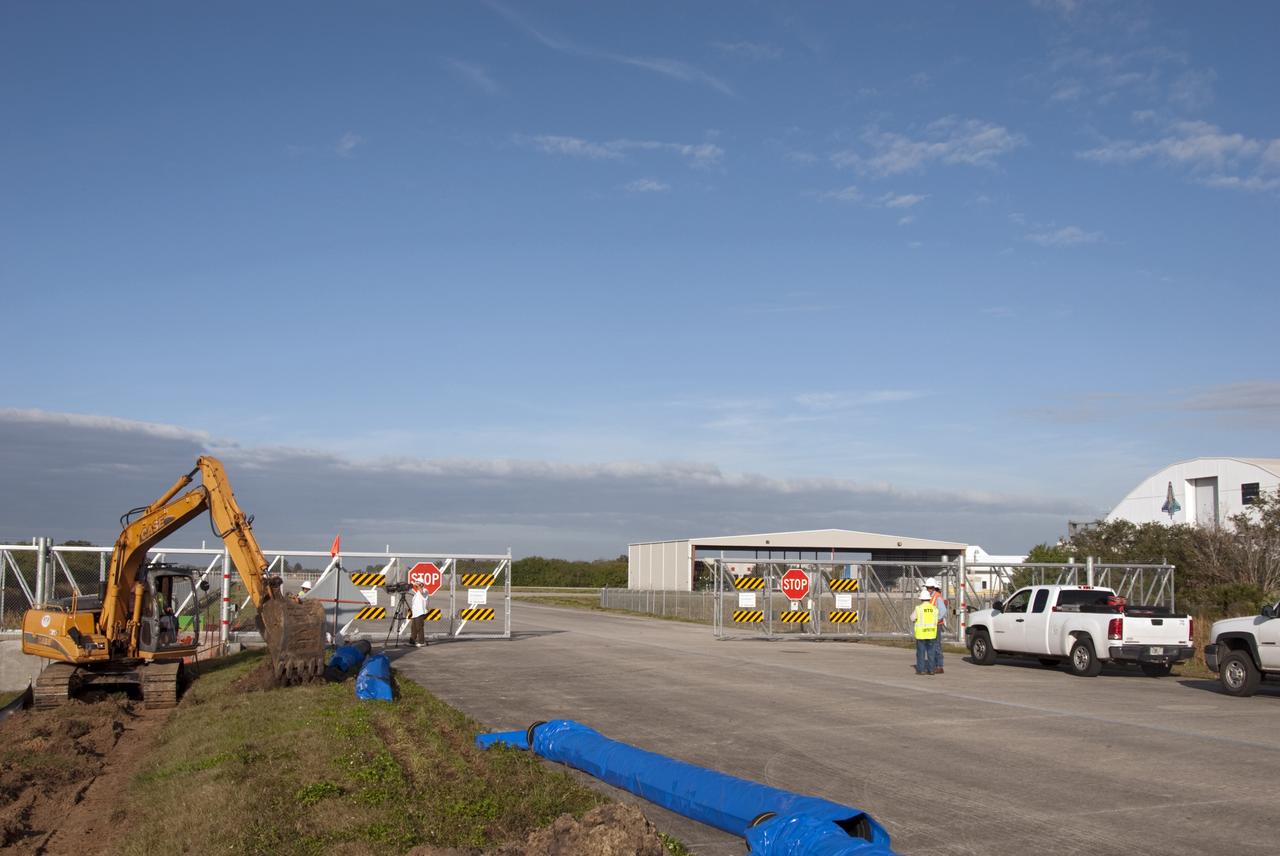

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a new 12-inch water main is being installed as part of a water/wastewater revitalizing plan. The main will provide water to the area around the shuttle landing facility's Landing Aids Control Building and fire station. NASA’s space shuttle runway is a unique national asset designed to enable the recovery of the agency’s fleet of space shuttle orbiters. The shuttle landing facility is a single, 15,000-foot long concrete runway oriented to the southeast and northwest. Air traffic control is provided from a control tower built to FAA standards. Fire and emergency response services are also available from an onsite facility. For more information, visit http://kscpartnerships.ksc.nasa.gov/slf.htm Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
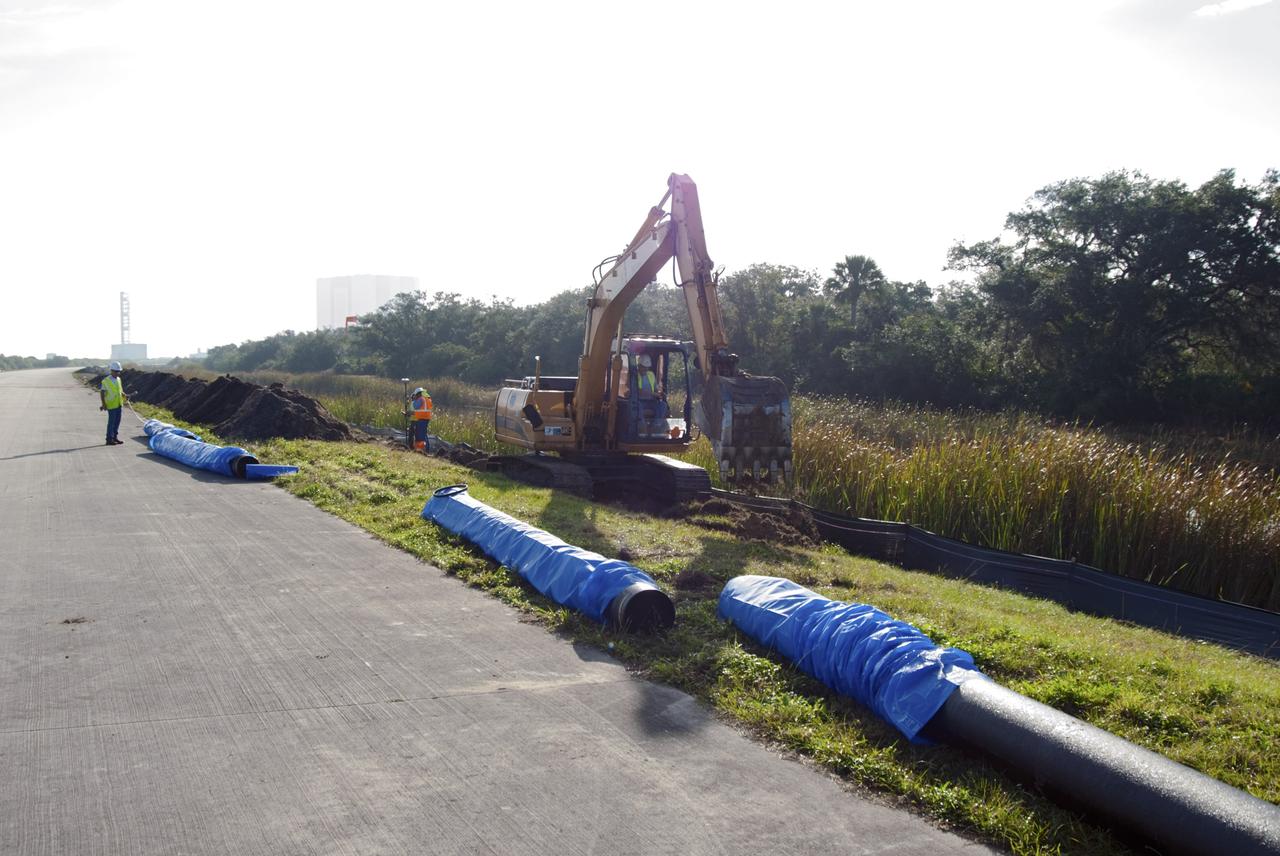

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a new 12-inch water main is being installed as part of a water/wastewater revitalizing plan. The main will provide water to the area around the shuttle landing facility's Landing Aids Control Building and fire station. NASA’s space shuttle runway is a unique national asset designed to enable the recovery of the agency’s fleet of space shuttle orbiters. The shuttle landing facility is a single, 15,000-foot long concrete runway oriented to the southeast and northwest. Air traffic control is provided from a control tower built to FAA standards. Fire and emergency response services are also available from an onsite facility. For more information, visit http://kscpartnerships.ksc.nasa.gov/slf.htm Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
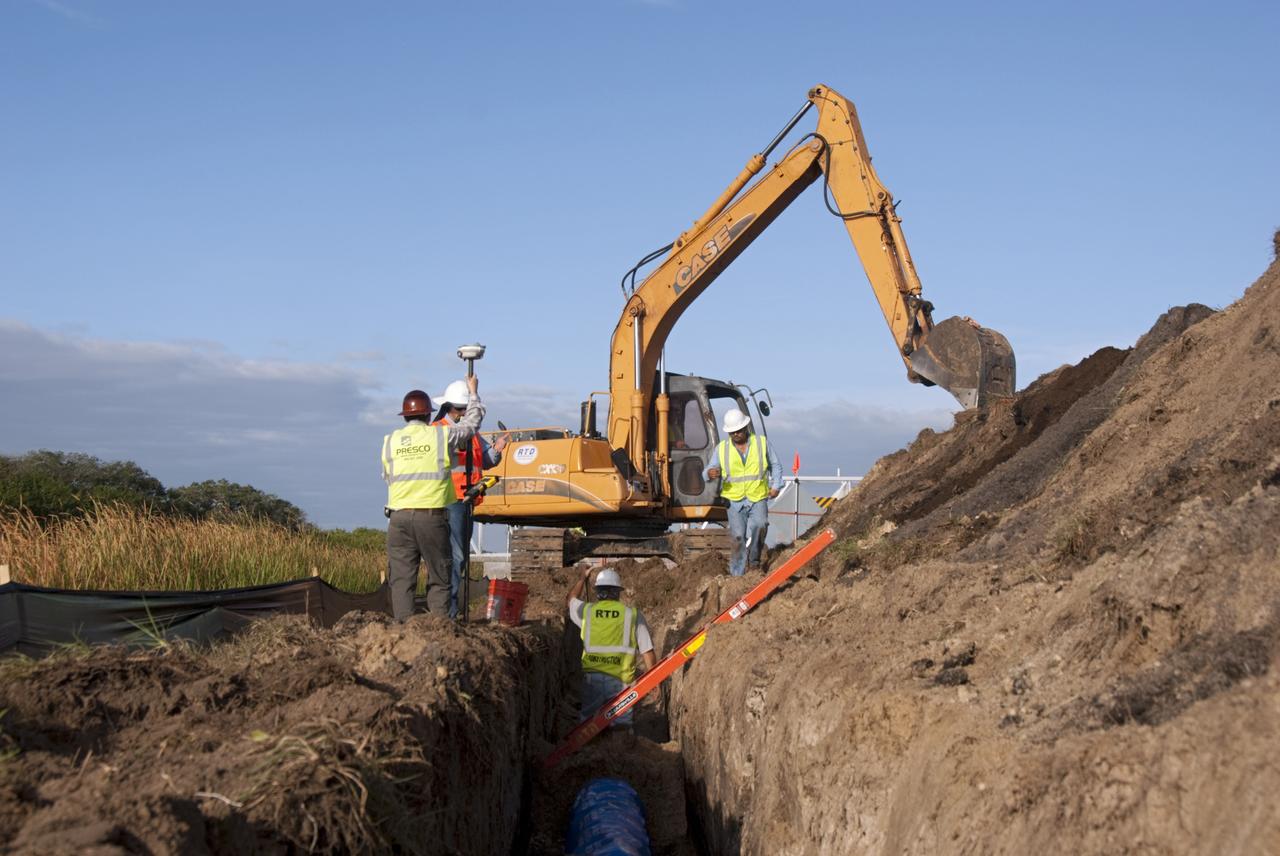

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a new 12-inch water main is being installed as part of a water/wastewater revitalizing plan. The main will provide water to the area around the shuttle landing facility's Landing Aids Control Building and fire station. NASA’s space shuttle runway is a unique national asset designed to enable the recovery of the agency’s fleet of space shuttle orbiters. The shuttle landing facility is a single, 15,000-foot long concrete runway oriented to the southeast and northwest. Air traffic control is provided from a control tower built to FAA standards. Fire and emergency response services are also available from an onsite facility. For more information, visit http://kscpartnerships.ksc.nasa.gov/slf.htm Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a new 12-inch water main is being installed as part of a water/wastewater revitalizing plan. The main will provide water to the area around the shuttle landing facility's Landing Aids Control Building and fire station. NASA’s space shuttle runway is a unique national asset designed to enable the recovery of the agency’s fleet of space shuttle orbiters. The shuttle landing facility is a single, 15,000-foot long concrete runway oriented to the southeast and northwest. Air traffic control is provided from a control tower built to FAA standards. Fire and emergency response services are also available from an onsite facility. For more information, visit http://kscpartnerships.ksc.nasa.gov/slf.htm Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a new 12-inch water main is being installed as part of a water/wastewater revitalizing plan. The main will provide water to the area around the shuttle landing facility's Landing Aids Control Building and fire station. NASA’s space shuttle runway is a unique national asset designed to enable the recovery of the agency’s fleet of space shuttle orbiters. The shuttle landing facility is a single, 15,000-foot long concrete runway oriented to the southeast and northwest. Air traffic control is provided from a control tower built to FAA standards. Fire and emergency response services are also available from an onsite facility. For more information, visit http://kscpartnerships.ksc.nasa.gov/slf.htm Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a new 12-inch water main is being installed as part of a water/wastewater revitalizing plan. The main will provide water to the area around the shuttle landing facility's Landing Aids Control Building and fire station. NASA’s space shuttle runway is a unique national asset designed to enable the recovery of the agency’s fleet of space shuttle orbiters. The shuttle landing facility is a single, 15,000-foot long concrete runway oriented to the southeast and northwest. Air traffic control is provided from a control tower built to FAA standards. Fire and emergency response services are also available from an onsite facility. For more information, visit http://kscpartnerships.ksc.nasa.gov/slf.htm Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
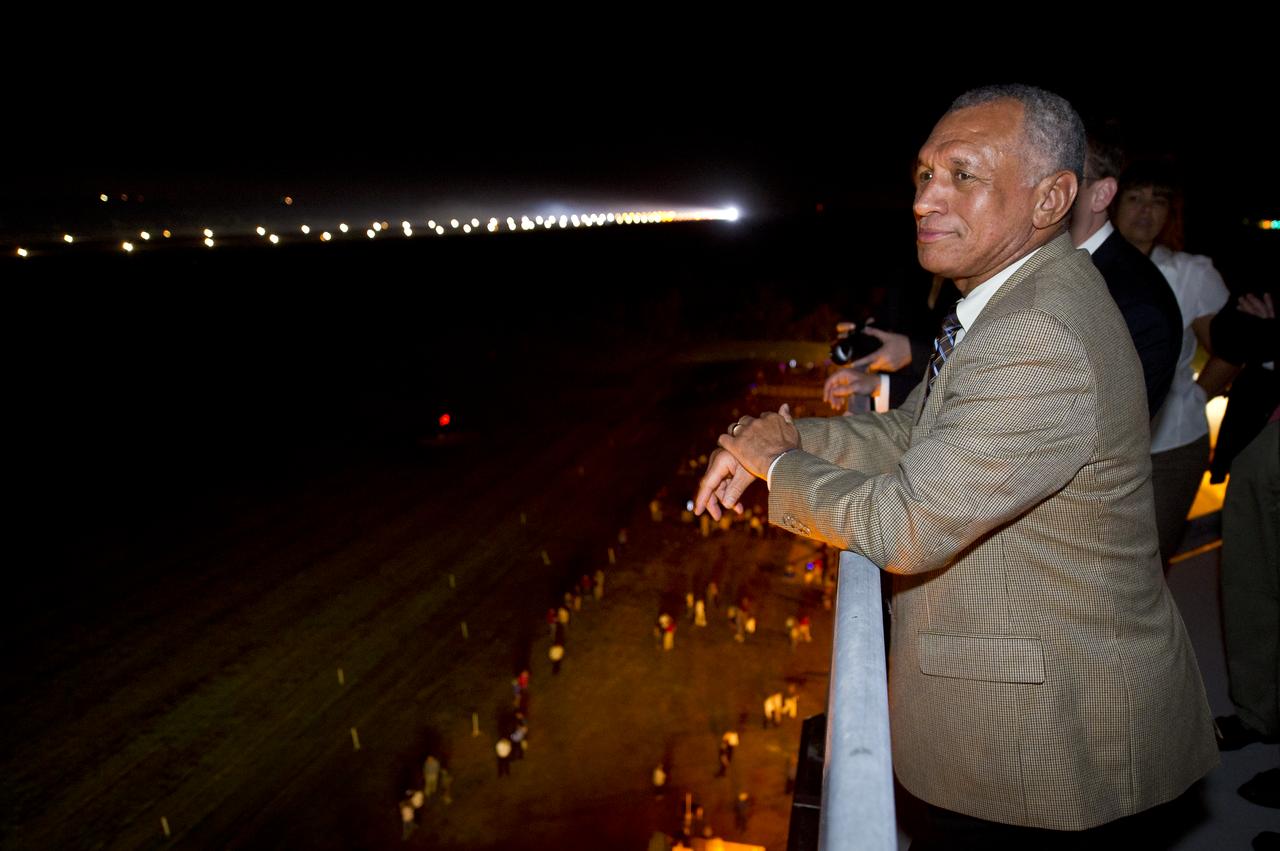

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden looks at the Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-134) from the air traffic control tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) shortly after Endeavour made its final landing at the Kennedy Space Center, Wednesday, June 1, 2011, in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Endeavour, after completing a 16-day mission to outfit the International Space Station, spent 299 days in space and traveled more than 122.8 million miles during its 25 flights. It launched on its first mission on May 7, 1992. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
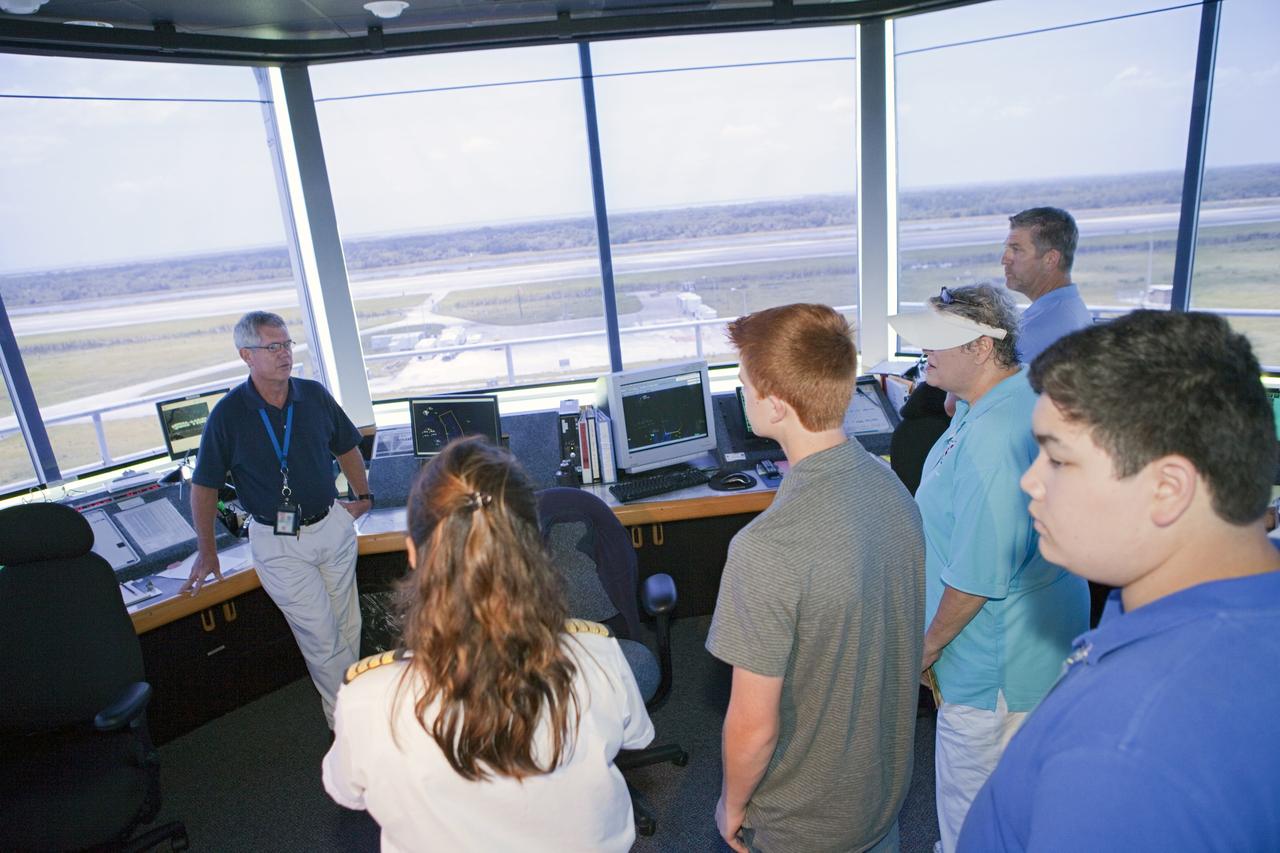

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, students and their flight instructors from Florida Tech, or FIT, in Melbourne, tour the midfield Air Traffic Control Tower. The instructors and their students arrived at the SLF in Cherokee Warrior and Cessna 172S lightweight aircraft. The middle and high school students are participating in FIT’s Av/Aero summer camp experience. They and their flight instructors toured the SLF midfield control tower, viewed F104 Starfighters and NASA Huey helicopters in the RLV Hangar, viewed the runway plaques marking wheels stop for each of the three space shuttles, and toured the Vehicle Assembly Building where space shuttle Atlantis currently is stored. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
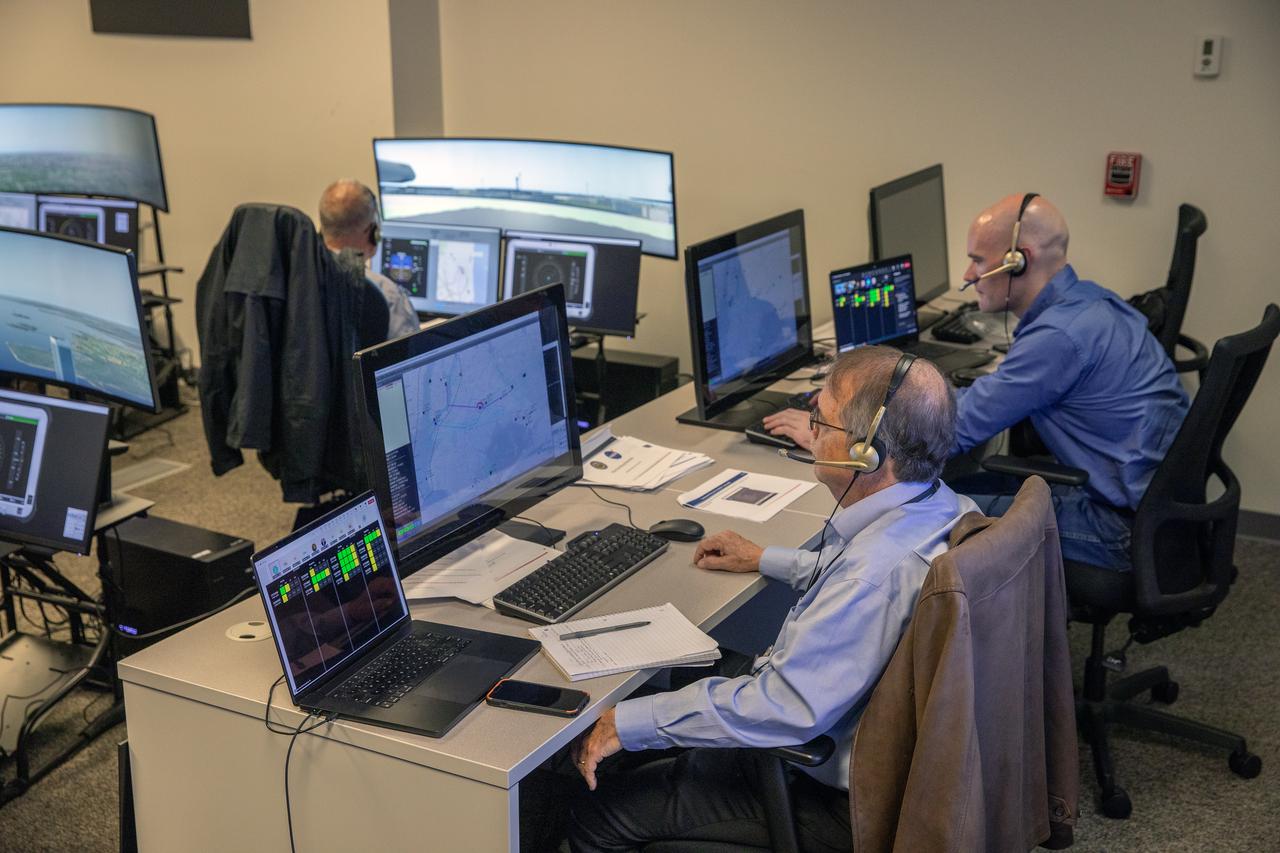

Focus on active photos –Class B Simulation Evaluation in the ATOL Lab at Langley (Also at FAA Tech Center) where team is working with one another in the lab, reviewing data on the monitors. Working the software, adjusting the software systems. Going over the shoulder to show the displays and screens as the software is running. John Foster (left) in the role of an air taxi pilot in the simulator chair with Jim Chamberlain and Terence McClain at the flight manager stations running virtual air taxi integration simulations focusing on urban air space at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia on Sept. 25, 2024.

Focus on active photos –Class B Simulation Evaluation in the ATOL Lab at Langley (Also at FAA Tech Center) where team is working with one another in the lab, reviewing data on the monitors. Working the software, adjusting the software systems. Going over the shoulder to show the displays and screens as the software is running. A pilot’s point of view from the controls of the air taxi simulator. An out-the-window simulation appears on the top screen, the primary flight display on the lower left, the virtual moving map in the middle, and the detect and avoid display on the lower right at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia on Sept. 25, 2024.
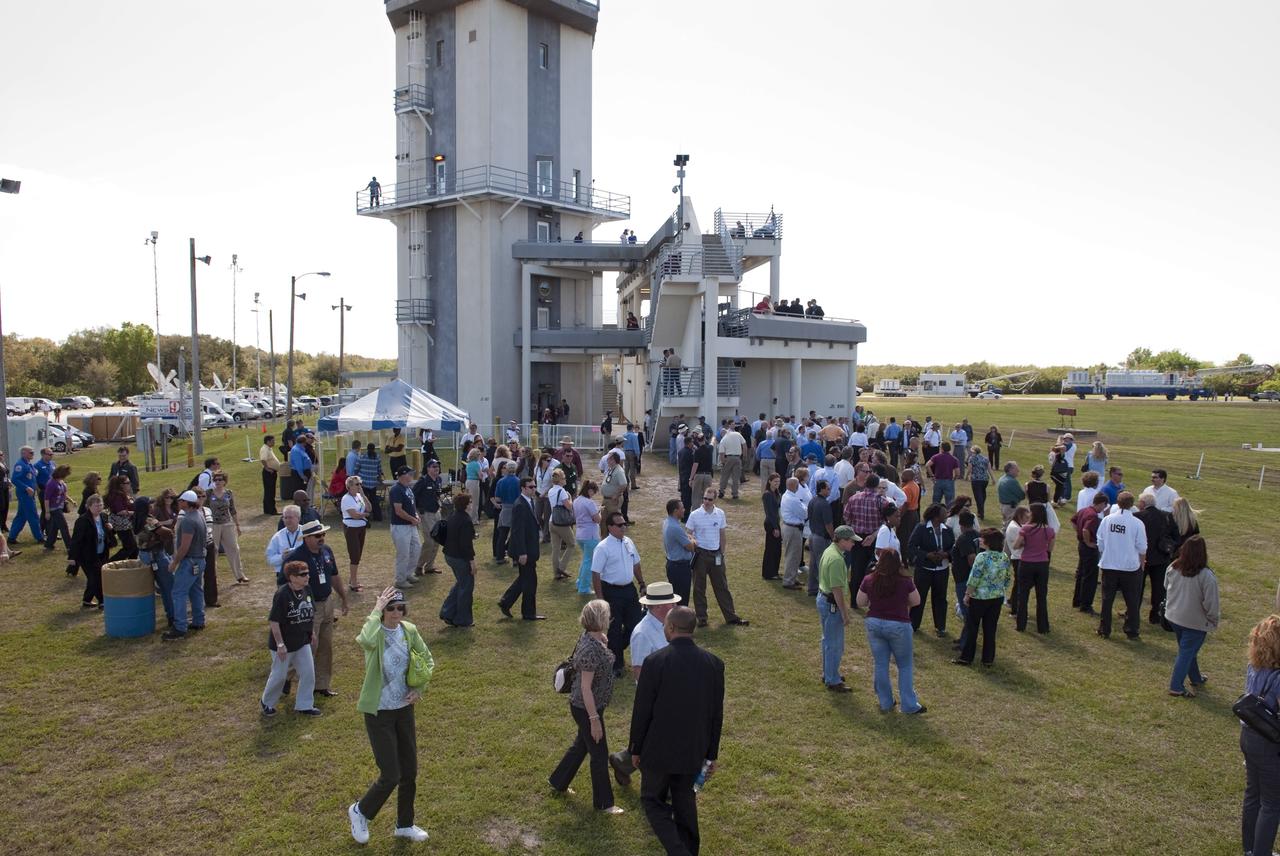

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, invited guests, managers and employees gather near the Air Traffic Control Tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) to watch shuttle Discovery return from space for the last time. Discovery touched down on Runway 15 at 11:57 a.m. EST, completing the 13-day STS-133 mission to the International Space Station. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
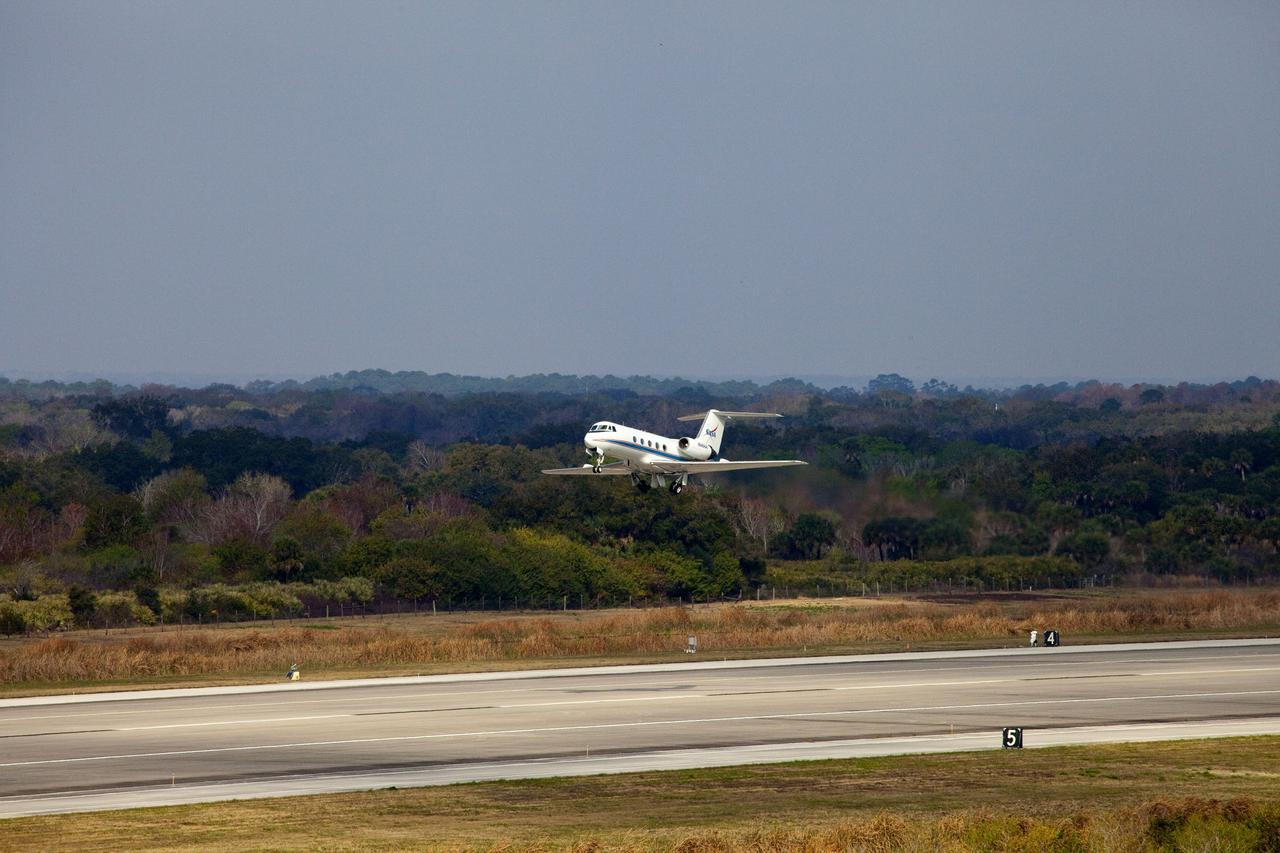

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This image was taken from the Shuttle Landing Facility's air traffic control tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and provides a birds-eye view of STS-133 Pilot Eric Boe performing touch-and-go landings aboard one of two Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA). STAs are Gulfstream II business jets that are modified to mimic the shuttle's handling during the final phase of landing. Practice landings are part of standard training before space shuttle Discovery's launch to the International Space Station. Scheduled to lift off Feb. 24 at 4:50 p.m. EST, Discovery and its six-member crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. For more information on the STS-133 mission, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
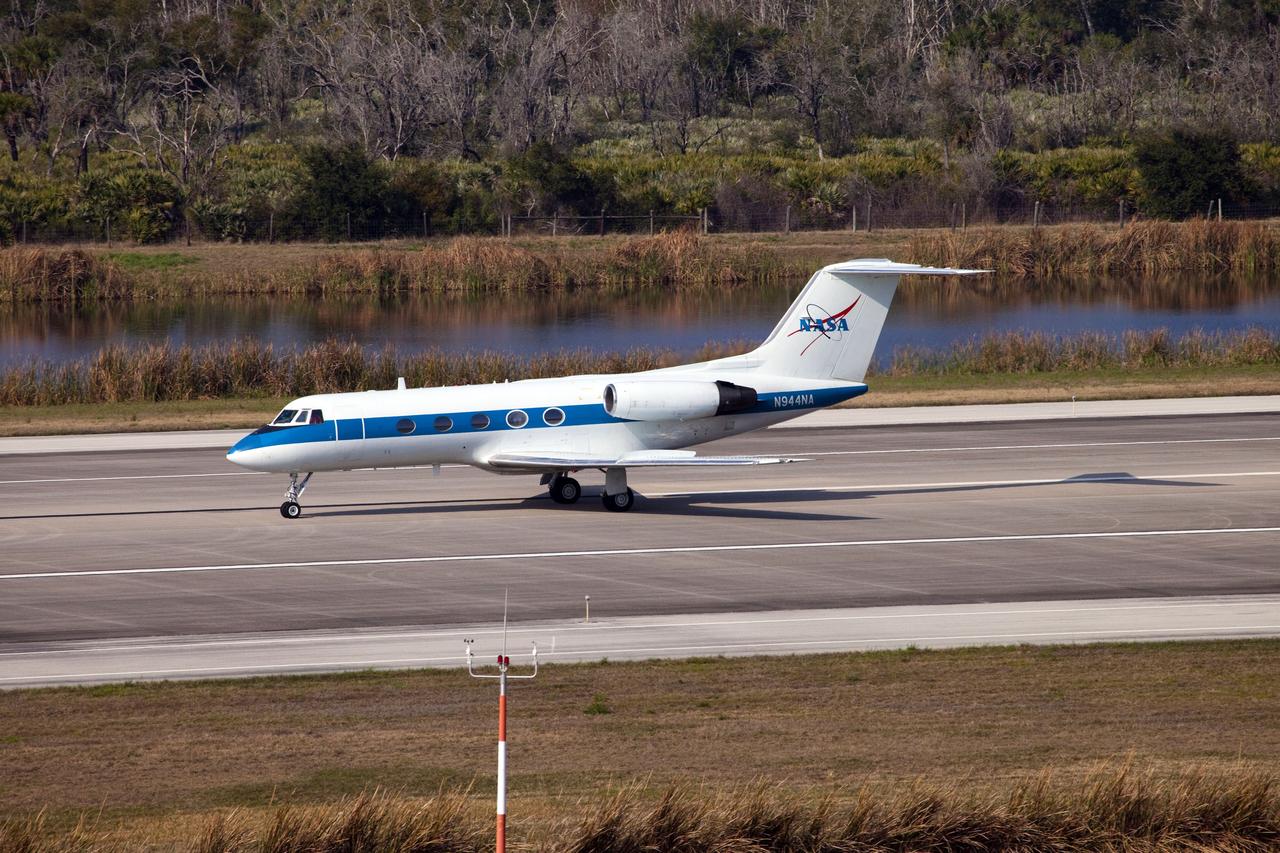

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This image was taken from the Shuttle Landing Facility's air traffic control tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and provides a birds-eye view of STS-133 Commander Steve Lindsey performing touch-and-go landings aboard one of two Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA). STAs are Gulfstream II business jets that are modified to mimic the shuttle's handling during the final phase of landing. Practice landings are part of standard training before space shuttle Discovery's launch to the International Space Station. Scheduled to lift off Feb. 24 at 4:50 p.m. EST, Discovery and its six-member crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. For more information on the STS-133 mission, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This image was taken from the Shuttle Landing Facility's air traffic control tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and provides a birds-eye view of STS-133 Commander Steve Lindsey performing touch-and-go landings aboard one of two Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA). STAs are Gulfstream II business jets that are modified to mimic the shuttle's handling during the final phase of landing. Practice landings are part of standard training before space shuttle Discovery's launch to the International Space Station. Scheduled to lift off Feb. 24 at 4:50 p.m. EST, Discovery and its six-member crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. For more information on the STS-133 mission, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
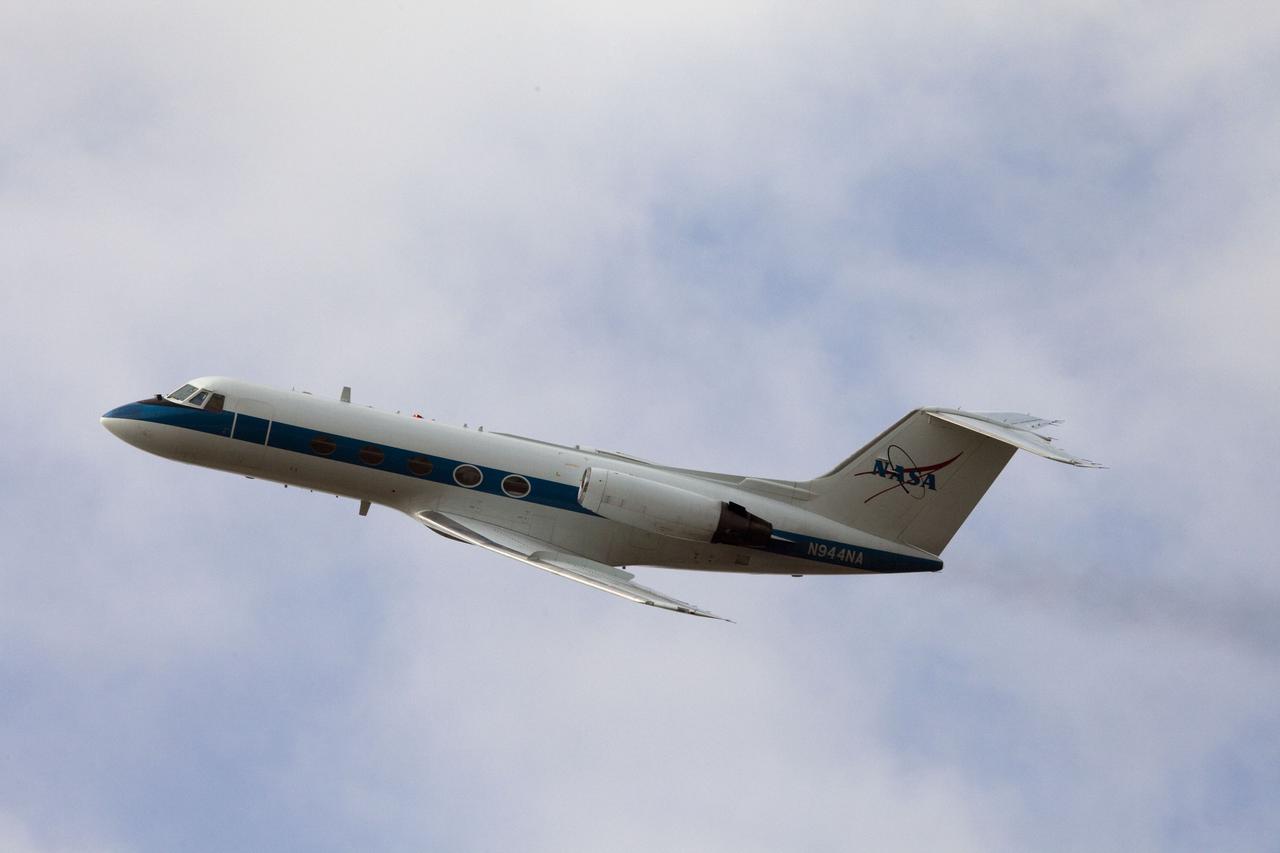

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This image was taken from the Shuttle Landing Facility's air traffic control tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and provides a birds-eye view of STS-133 Commander Steve Lindsey performing touch-and-go landings aboard one of two Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA). STAs are Gulfstream II business jets that are modified to mimic the shuttle's handling during the final phase of landing. Practice landings are part of standard training before space shuttle Discovery's launch to the International Space Station. Scheduled to lift off Feb. 24 at 4:50 p.m. EST, Discovery and its six-member crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. For more information on the STS-133 mission, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
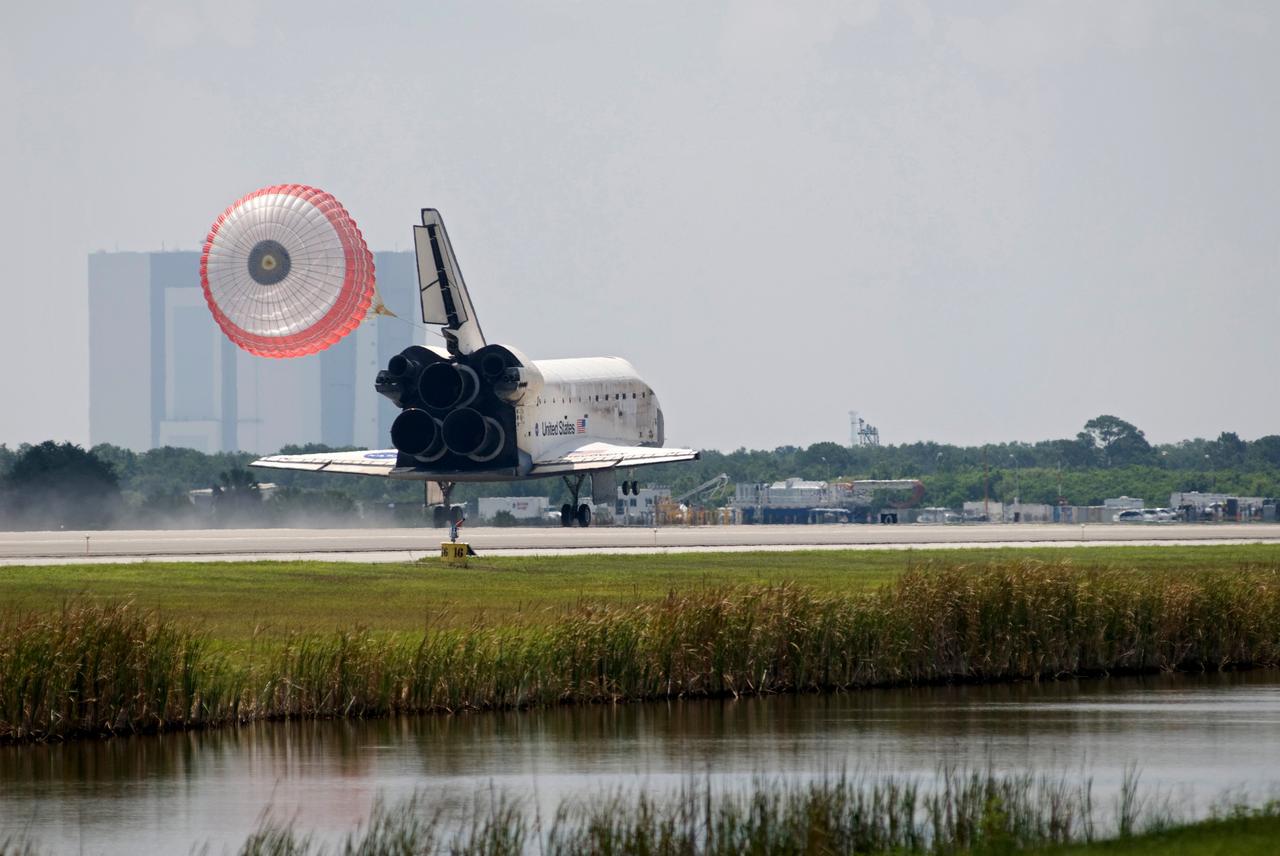

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Release of the drag chute helps slow space shuttle Discovery's landing as it touches down on Runway 15 to end the STS-124 mission, a 14-day flight to the International Space Station. This landing was the 69th at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. At right is the air traffic control tower next to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The main landing gear touched down at 11:15:19 a.m. EDT. The nose landing gear touched down at 11:15:30 a.m. and wheel stop was at 11:16:19 a.m. The mission completed 5.7 million miles. The STS-124 mission delivered the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Tom Joseph

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, invited guests, managers and employees gather near the Air Traffic Control Tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) to watch shuttle Discovery return from space for the last time. Discovery touched down on Runway 15 at 11:57 a.m. EST, completing the 13-day STS-133 mission to the International Space Station. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, invited guests, managers and employees gather near the Air Traffic Control Tower at the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) to watch shuttle Discovery return from space for the last time. Discovery touched down on Runway 15 at 11:57 a.m. EST, completing the 13-day STS-133 mission to the International Space Station. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This image was taken from the Shuttle Landing Facility's air traffic control tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and provides a birds-eye view of STS-133 Pilot Eric Boe performing touch-and-go landings aboard one of two Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA). STAs are Gulfstream II business jets that are modified to mimic the shuttle's handling during the final phase of landing. Practice landings are part of standard training before space shuttle Discovery's launch to the International Space Station. Scheduled to lift off Feb. 24 at 4:50 p.m. EST, Discovery and its six-member crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. For more information on the STS-133 mission, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
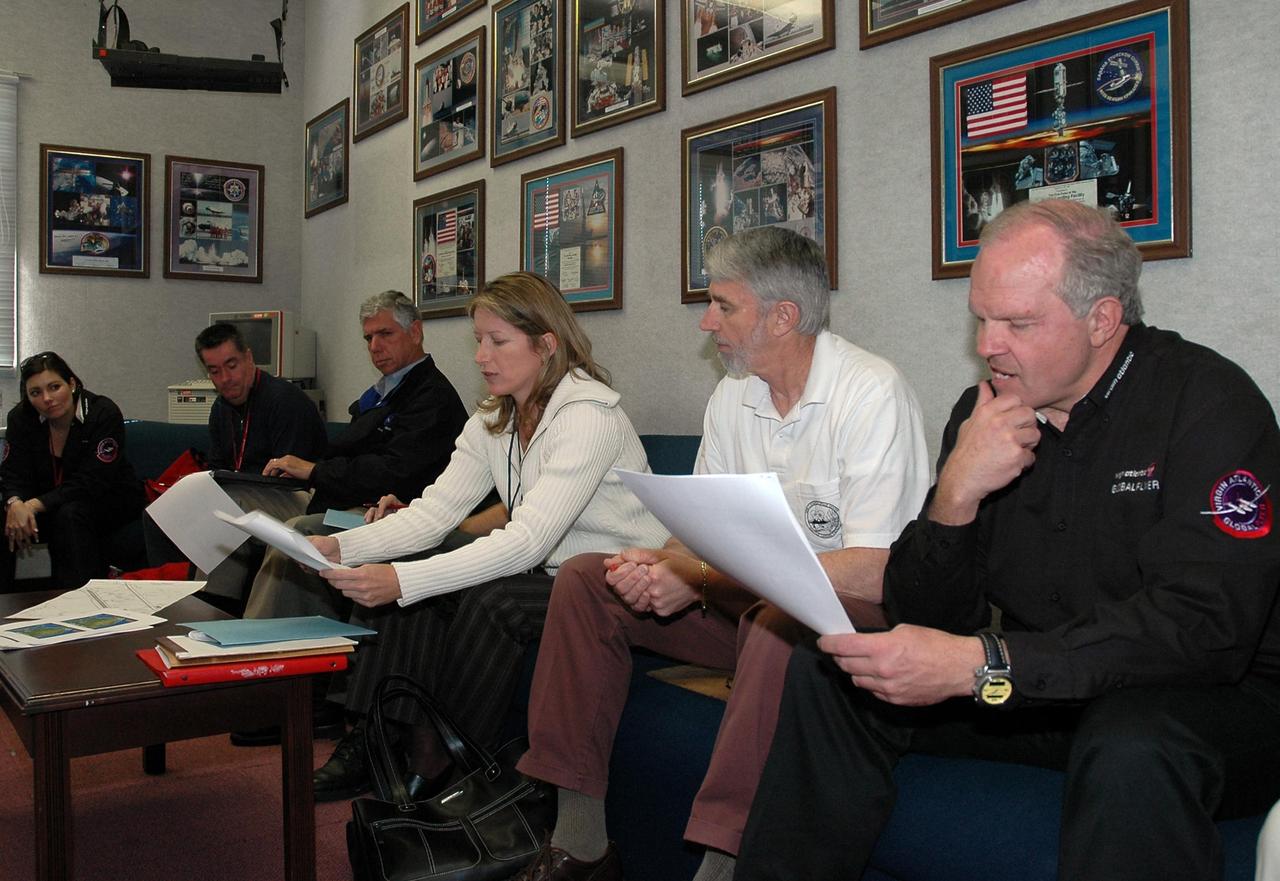

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer team gets a weather briefing. Seated from right are Steve Fossett, the pilot; Ron Feile, lead air traffic controller at the Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility that will serve as the launch site; Kathy Winters, 45th Space Wing weather officer; Jim Ball, manager of KSC Spaceport Development; and other GlobalFlyer team members. Fossett will pilot the aircraft on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility early Tuesday morning. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
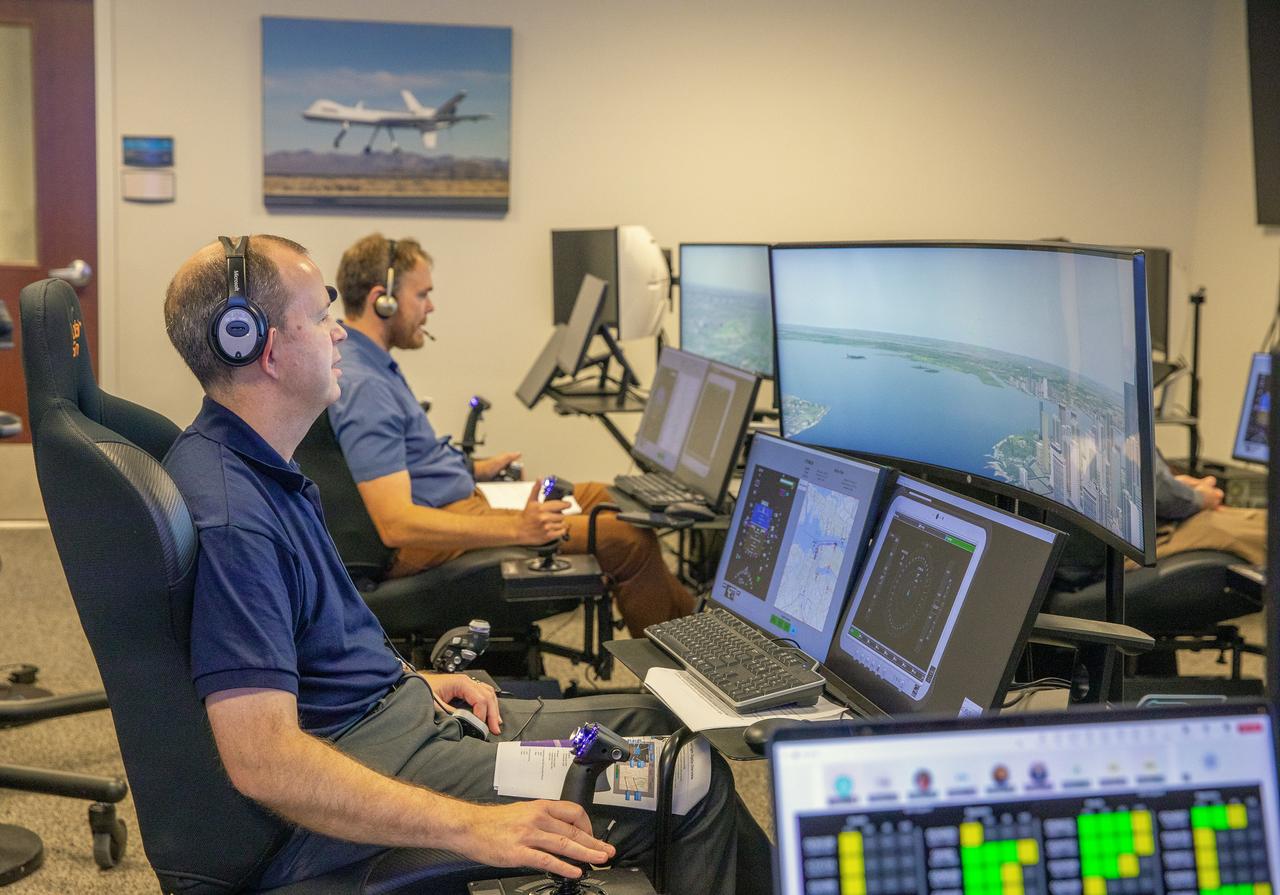

Focus on active photos –Class B Simulation Evaluation in the ATOL Lab at Langley (Also at FAA Tech Center) where team is working with one another in the lab, reviewing data on the monitors. Working the software, adjusting the software systems. Going over the shoulder to show the displays and screens as the software is running. Andy Burroughs (left) and Paul Friz in the roles of air taxi pilots running through air taxi integration simulations focusing on urban air space at NASA’s Langley Research in Hampton, Virginia on Sept. 25, 2024.
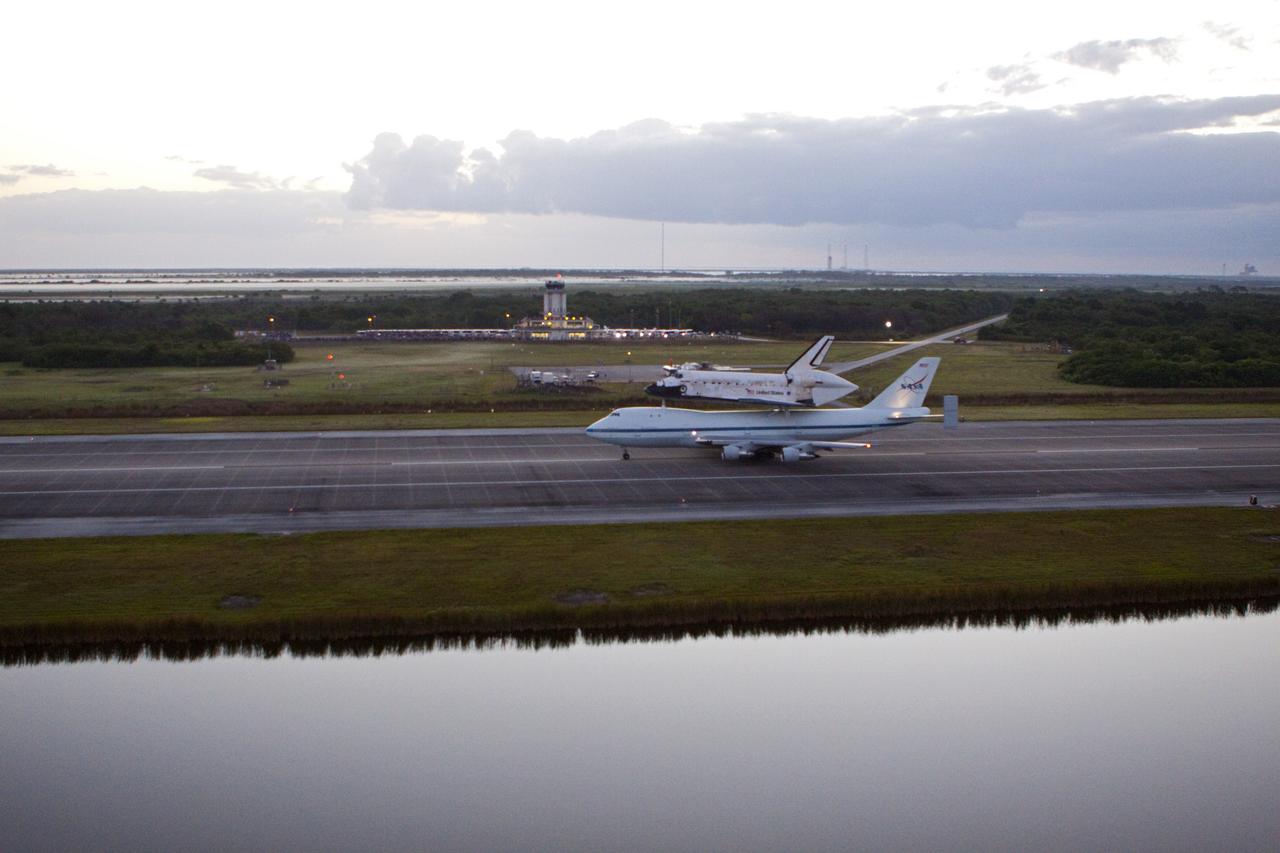

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the early morning hours at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility in Florida, the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, with space shuttle Discovery secured atop, taxies down the runway for a takeoff at 7 a.m. EDT. In the background is the midfield air traffic control tower. The aircraft, known as an SCA, is a Boeing 747 jet, originally manufactured for commercial use, which was modified by NASA to transport the shuttles between destinations on Earth. This SCA, designated NASA 905, is assigned to the remaining ferry missions, delivering the shuttles to their permanent public display sites. NASA 905 is scheduled to ferry Discovery to the Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia on April 17, after which the shuttle will be placed on display in the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information on the SCA, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/news/FactSheets/FS-013-DFRC.html. For more information on shuttle transition and retirement activities, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
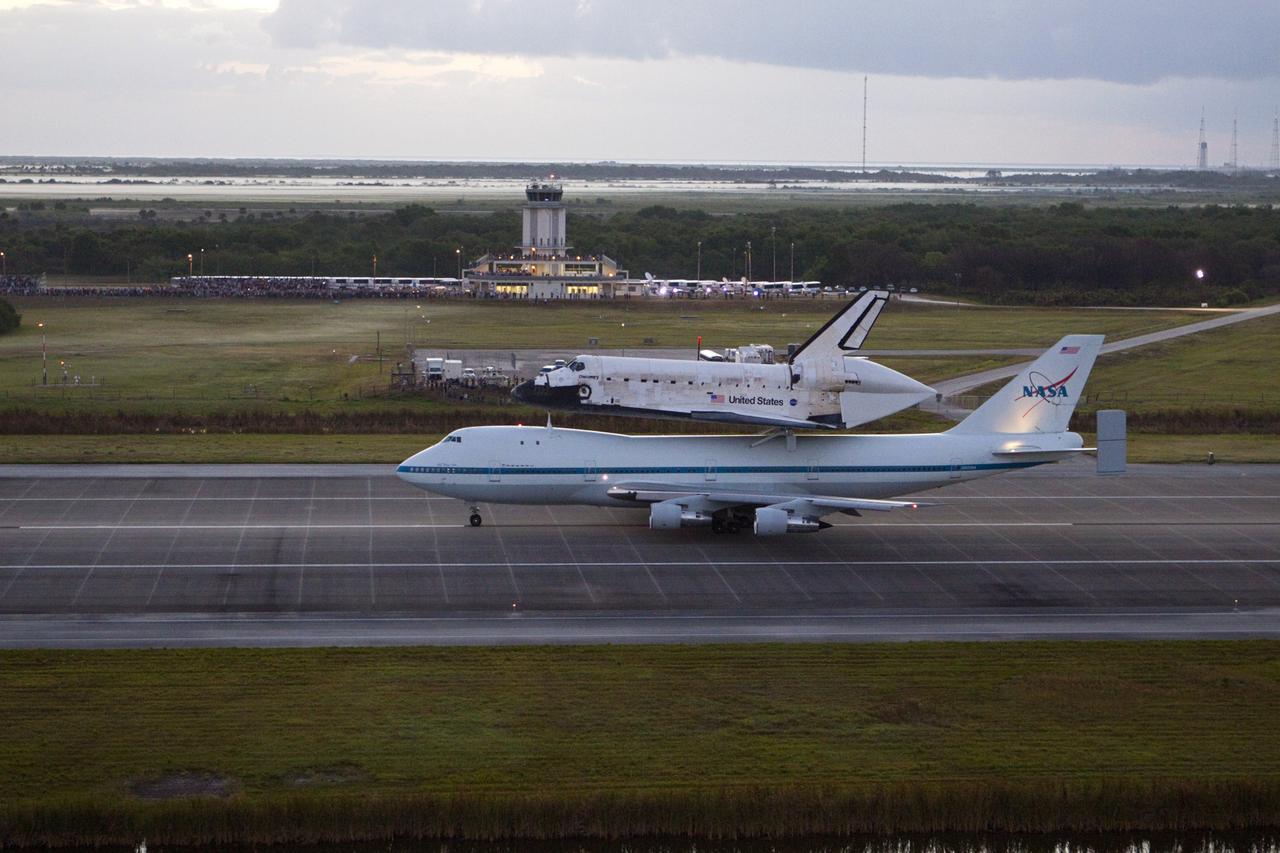

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the early morning hours at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility in Florida, the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, with space shuttle Discovery secured atop, taxies down the runway for a takeoff at 7 a.m. EDT. In the background is the midfield air traffic control tower. The aircraft, known as an SCA, is a Boeing 747 jet, originally manufactured for commercial use, which was modified by NASA to transport the shuttles between destinations on Earth. This SCA, designated NASA 905, is assigned to the remaining ferry missions, delivering the shuttles to their permanent public display sites. NASA 905 is scheduled to ferry Discovery to the Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia on April 17, after which the shuttle will be placed on display in the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information on the SCA, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/news/FactSheets/FS-013-DFRC.html. For more information on shuttle transition and retirement activities, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the early morning hours at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility in Florida, the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, with space shuttle Discovery secured atop, taxies down the runway for a takeoff at 7 a.m. EDT. In the background is the midfield air traffic control tower. The aircraft, known as an SCA, is a Boeing 747 jet, originally manufactured for commercial use, which was modified by NASA to transport the shuttles between destinations on Earth. This SCA, designated NASA 905, is assigned to the remaining ferry missions, delivering the shuttles to their permanent public display sites. NASA 905 is scheduled to ferry Discovery to the Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia on April 17, after which the shuttle will be placed on display in the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information on the SCA, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/news/FactSheets/FS-013-DFRC.html. For more information on shuttle transition and retirement activities, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
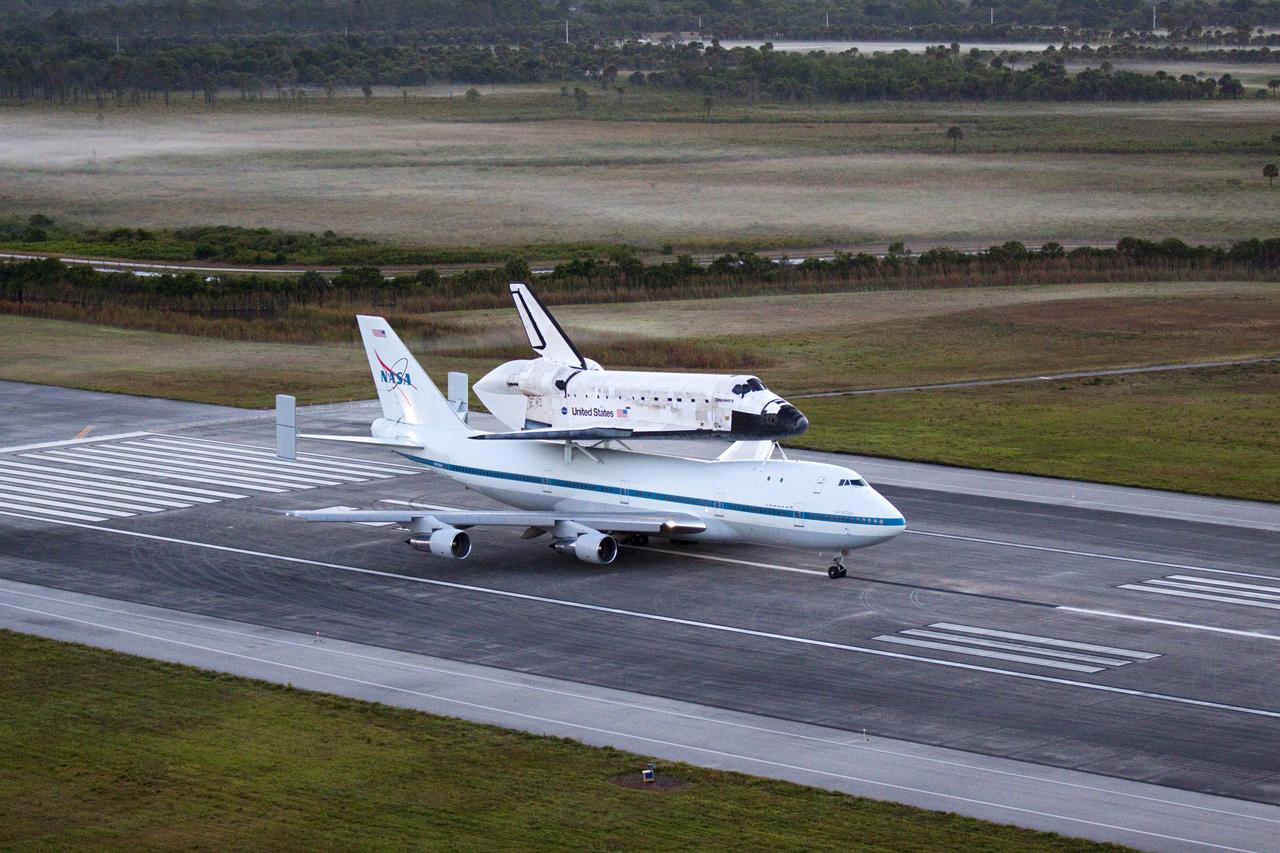

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the early morning hours at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility in Florida, the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, with space shuttle Discovery secured atop, waits on runway 15 for clearance from Kennedy’s air traffic control tower to begin takeoff at 7 a.m. EDT. The SCA will deliver Discovery to its new home. The aircraft, known as an SCA, is a Boeing 747 jet, originally manufactured for commercial use, which was modified by NASA to transport the shuttles between destinations on Earth. This SCA, designated NASA 905, is assigned to the remaining ferry missions, delivering the shuttles to their permanent public display sites. NASA 905 is scheduled to ferry Discovery to the Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia on April 17, after which the shuttle will be placed on display in the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information on the SCA, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/news/FactSheets/FS-013-DFRC.html. For more information on shuttle transition and retirement activities, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the early morning hours at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility in Florida, the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, with space shuttle Discovery secured atop, taxies down the runway for a takeoff at 7 a.m. EDT. In the background are the midfield air traffic control tower and the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building. The aircraft, known as an SCA, is a Boeing 747 jet, originally manufactured for commercial use, which was modified by NASA to transport the shuttles between destinations on Earth. This SCA, designated NASA 905, is assigned to the remaining ferry missions, delivering the shuttles to their permanent public display sites. NASA 905 is scheduled to ferry Discovery to the Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia on April 17, after which the shuttle will be placed on display in the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information on the SCA, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/news/FactSheets/FS-013-DFRC.html. For more information on shuttle transition and retirement activities, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
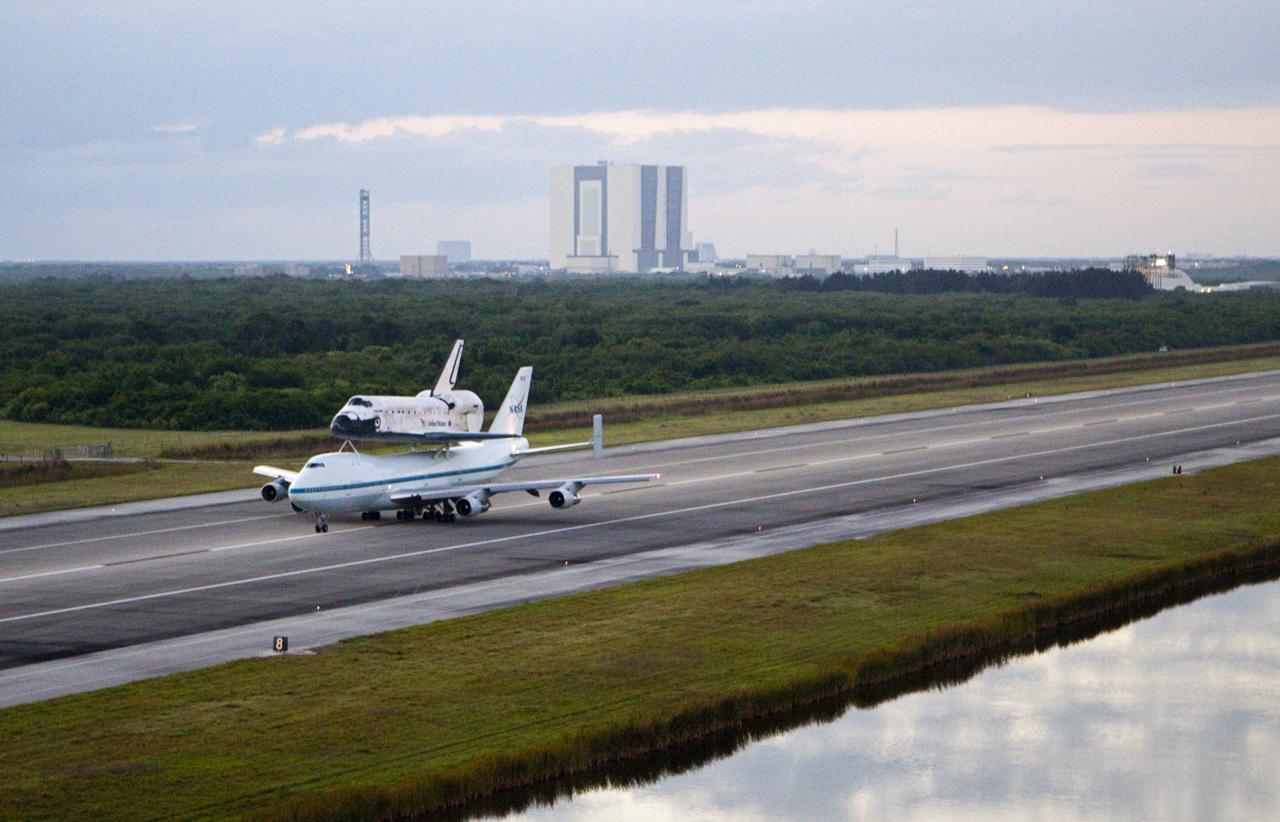

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the early morning hours at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility in Florida, the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, with space shuttle Discovery secured atop, taxies down the runway for a takeoff at 7 a.m. EDT. In the background is the midfield air traffic control tower. The aircraft, known as an SCA, is a Boeing 747 jet, originally manufactured for commercial use, which was modified by NASA to transport the shuttles between destinations on Earth. This SCA, designated NASA 905, is assigned to the remaining ferry missions, delivering the shuttles to their permanent public display sites. NASA 905 is scheduled to ferry Discovery to the Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia on April 17, after which the shuttle will be placed on display in the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information on the SCA, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/news/FactSheets/FS-013-DFRC.html. For more information on shuttle transition and retirement activities, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility in Florida, A T-38 chase aircraft sits on runway 15 waiting for clearance from Kennedy’s air traffic control tower to begin takeoff prior to the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, with space shuttle Discovery attached atop. The aircraft, known as an SCA, is a Boeing 747 jet, originally manufactured for commercial use, which was modified by NASA to transport the shuttles between destinations on Earth. This SCA, designated NASA 905, is assigned to the remaining ferry missions, delivering the shuttles to their permanent public display sites. NASA 905 is scheduled to ferry Discovery to the Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia on April 17, after which the shuttle will be placed on display in the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information on the SCA, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/news/FactSheets/FS-013-DFRC.html. For more information on shuttle transition and retirement activities, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
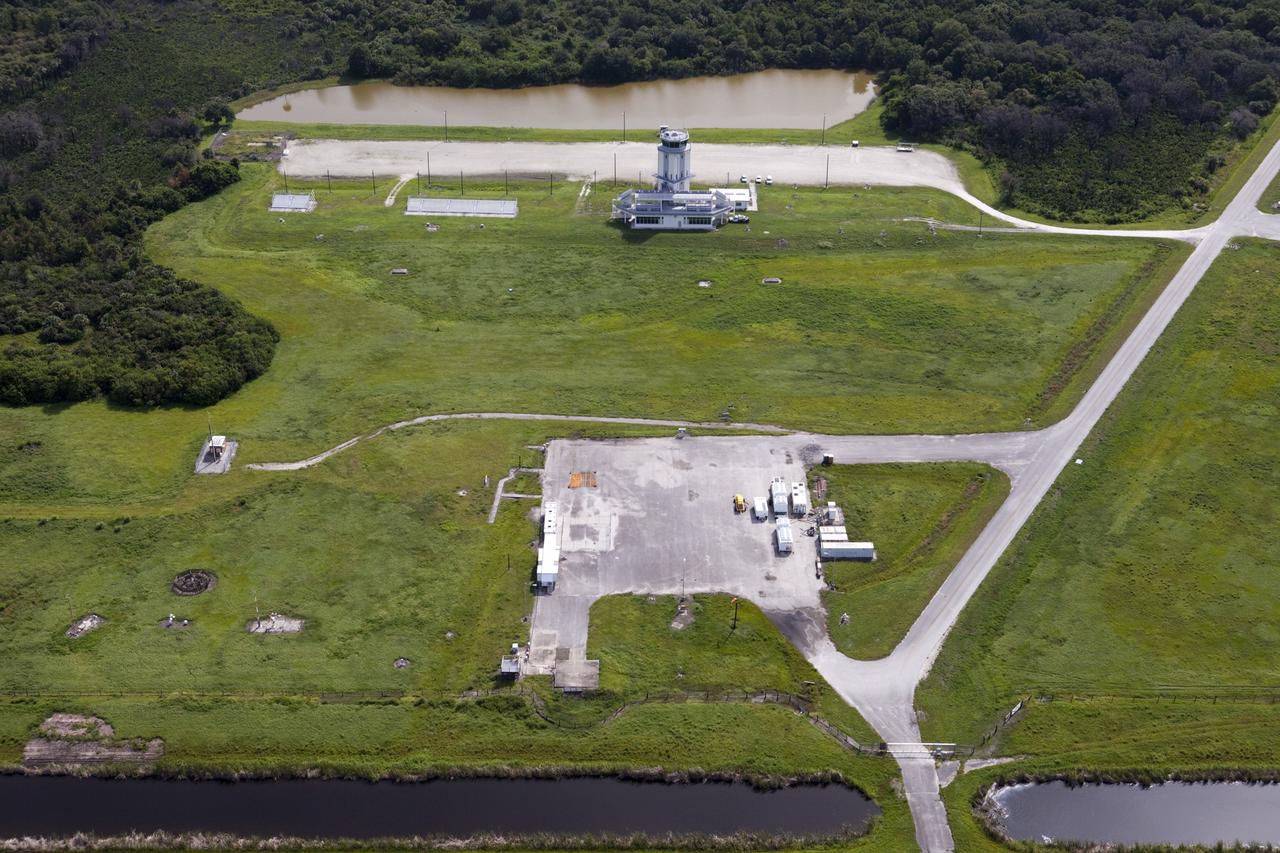

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This aerial view shows the Shuttle Landing Facility’s air traffic control tower at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Just below the tower is the mid-field park site used for runway support vehicles. At the north end of the runway, a rock and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT system on the Project Morpheus lander. Testing will demonstrate ALHAT’s ability to provide required navigation data negotiating the Morpheus lander away from risks during descent. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
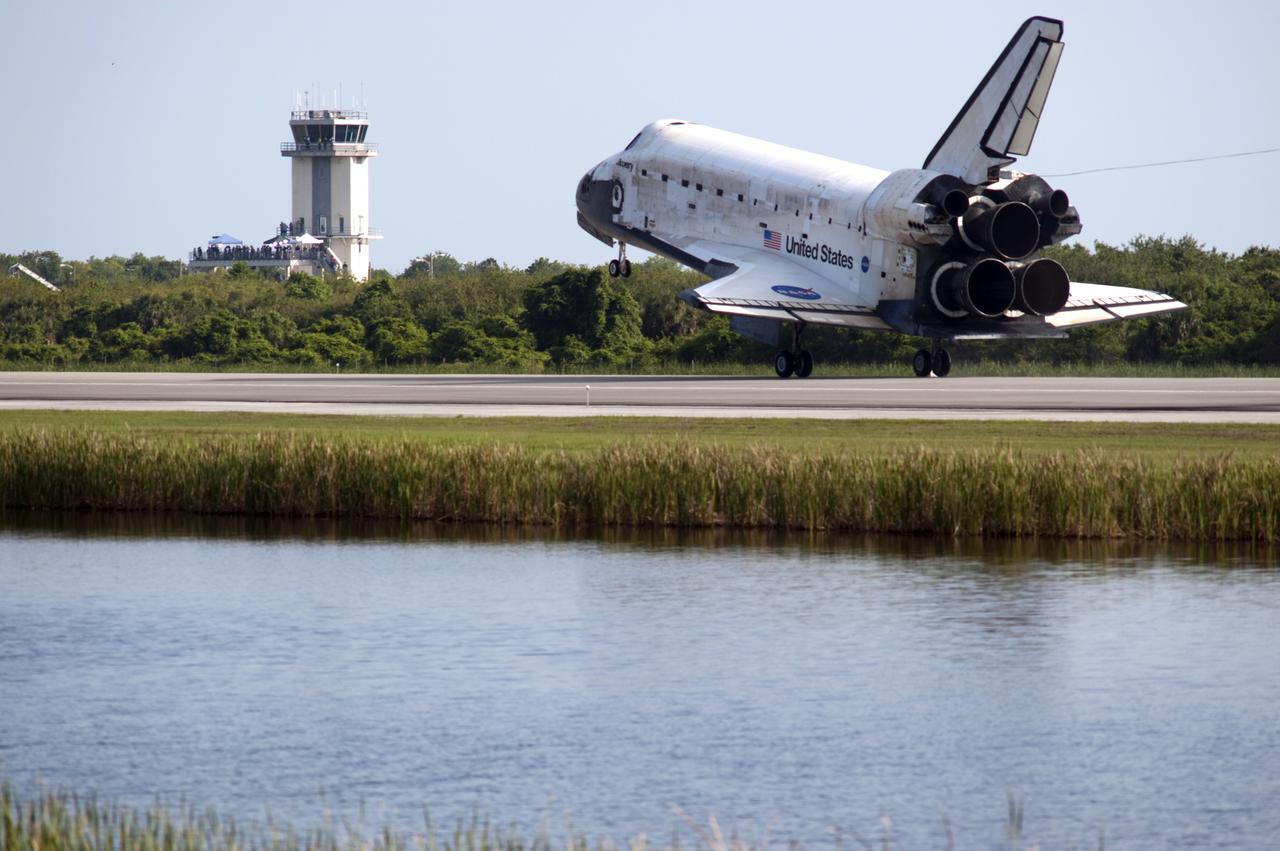

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle Discovery lands on Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 9:08 a.m. EDT, completing the 15-day STS-131 mission to the International Space Station. The air traffic control tower can be seen in the background. Main gear touchdown was at 9:08:35 a.m. EDT followed by nose gear touchdown at 9:08:47 a.m. and wheelstop at 9:09:33 a.m. Aboard are Commander Alan Poindexter; Pilot James P. Dutton Jr.; and Mission Specialists Rick Mastracchio, Clayton Anderson, Dorothy Metcalf-Lindenburger, Stephanie Wilson and Naoko Yamazaki of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. The seven-member STS-131 crew carried the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo, filled with supplies, a new crew sleeping quarters and science racks that were transferred to the International Space Station's laboratories. The crew also switched out a gyroscope on the station’s truss, installed a spare ammonia storage tank and retrieved a Japanese experiment from the station’s exterior. STS-131 is the 33rd shuttle mission to the station and the 131st shuttle mission overall. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts131_index.html. Photo Credit: NASA_Rusty Backer
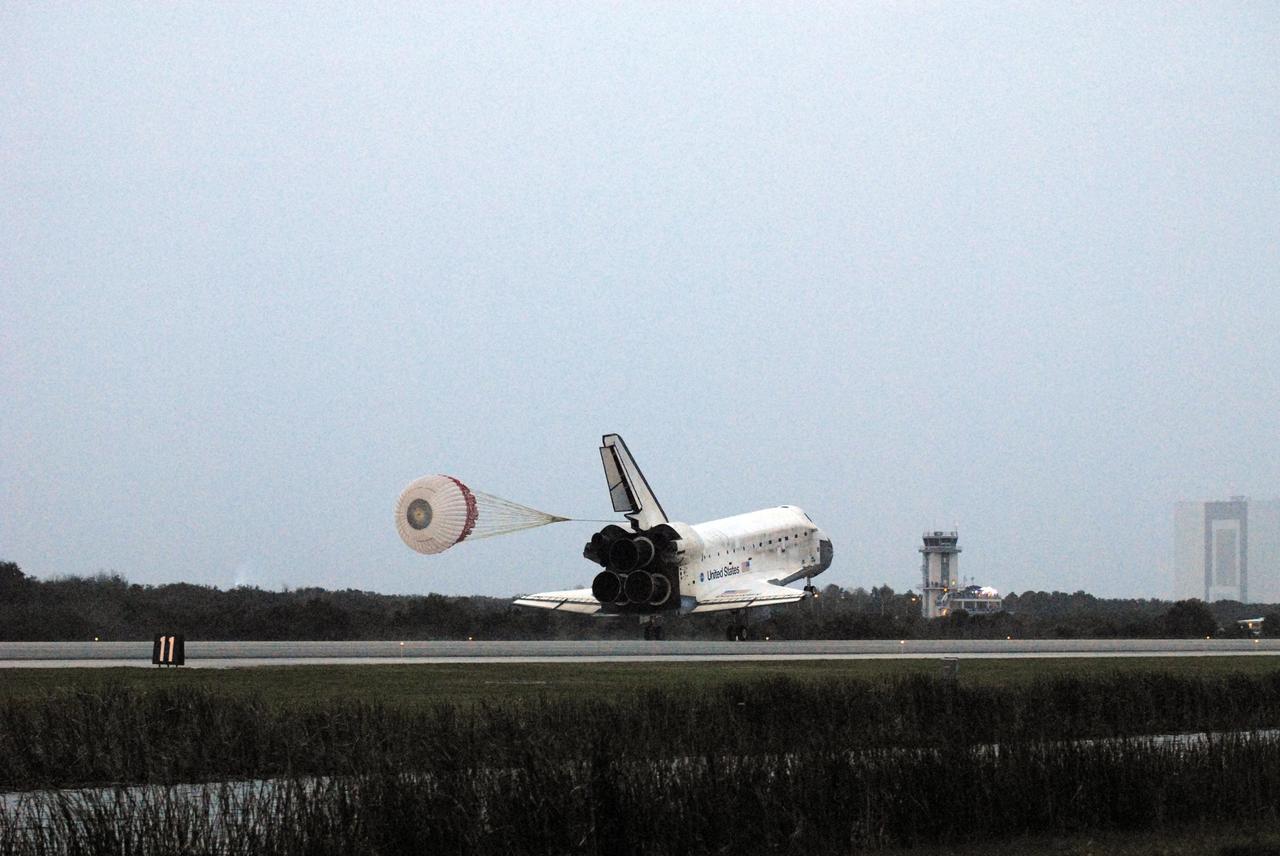

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Discovery's drag chute unfurls upon landing on Runway 15 at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility as the sun sets on the shortest day of the year, concluding mission STS-116. In the background are the runway's Air Traffic Control Tower and the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building (far right). Aboard are Commander Mark Polansky, Pilot William Oefelein, and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam, Joan Higginbotham, Nicholas Patrick and Christer Fuglesang, who represents the European Space Agency, as well as Thomas Reiter, who is returning from a 6-month stay on the International Space Station. During the mission, three spacewalks attached the P5 integrated truss structure to the station, and completed the rewiring of the orbiting laboratory's power system. A fourth spacewalk retracted a stubborn solar array. Main gear touchdown was at 5:32 p.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 5:32:12 p.m. and wheel stop was at 5:32:52 p.m. At touchdown -- nominally about 2,500 ft. beyond the runway threshold -- the orbiter is traveling at a speed ranging from 213 to 226 mph. Discovery traveled 5,330,000 miles, landing on orbit 204. Mission elapsed time was 12 days, 20 hours, 44 minutes and 16 seconds. This is the 64th landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Tom Joseph

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Endeavour passes the air traffic control tower (left) next to the Shuttle Landing Facility as it touches down on runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center after traveling nearly 5.3 million miles on mission STS-118. Behind Endeavour is the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Space Shuttle Endeavour crew, led by Commander Scott Kelly, completes a 13-day mission to the International Space Station. The STS-118 mission began Aug. 8 and installed a new gyroscope, an external spare parts platform and another truss segment to the expanding station. Endeavour's main gear touched down at 12:32:16 p.m. EDT. Nose gear touchdown was at 12:32:29 p.m. and wheel stop was at 12:33:20 p.m. Endeavour landed on orbit 201. STS-118 was the 119th space shuttle flight, the 22nd flight to the station, the 20th flight for Endeavour and the second of four missions planned for 2007. This was the 65th landing of an orbiter at Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Rafael Hernandez
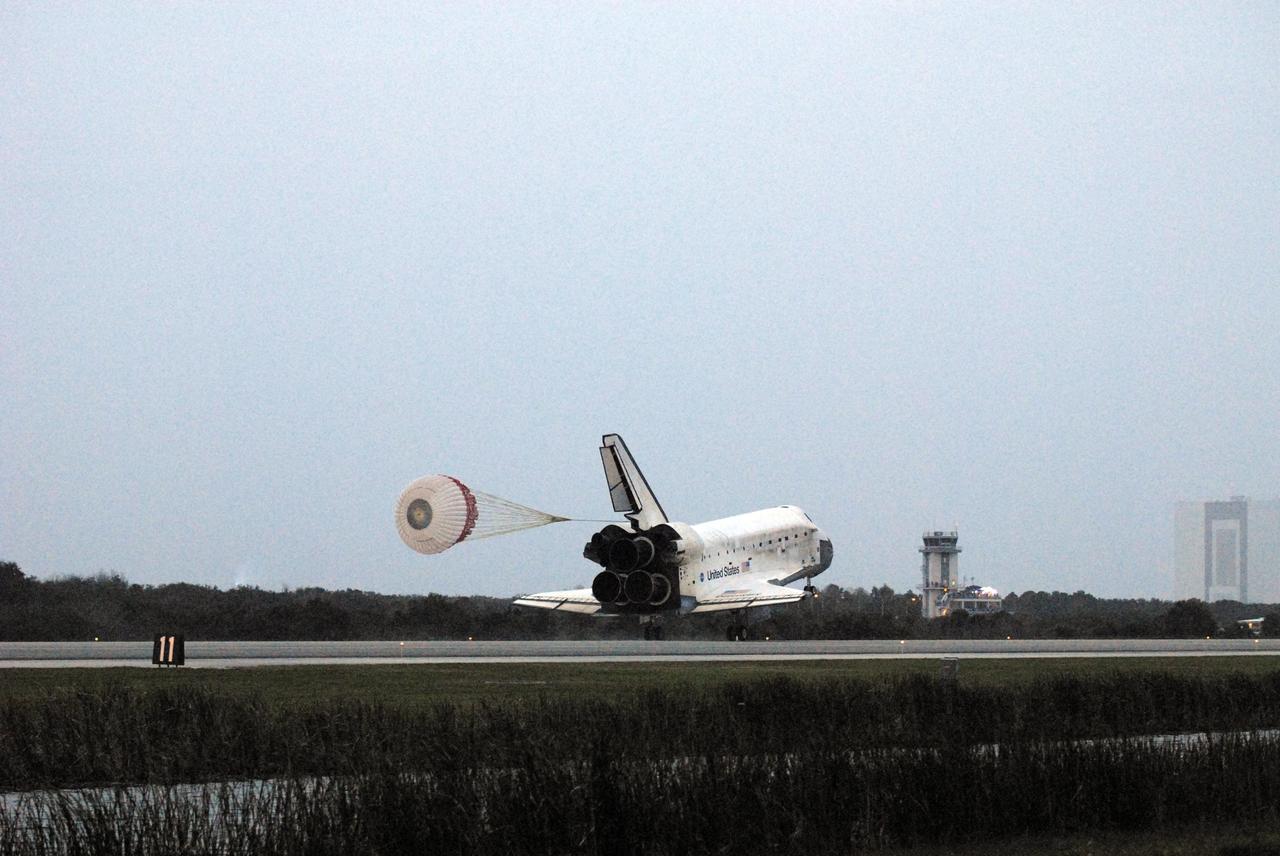

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Discovery's drag chute unfurls upon landing on Runway 15 at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility as the sun sets on the shortest day of the year, concluding mission STS-116. In the background are the runway's Air Traffic Control Tower and the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building (far right). Aboard are Commander Mark Polansky, Pilot William Oefelein, and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam, Joan Higginbotham, Nicholas Patrick and Christer Fuglesang, who represents the European Space Agency, as well as Thomas Reiter, who is returning from a 6-month stay on the International Space Station. During the mission, three spacewalks attached the P5 integrated truss structure to the station, and completed the rewiring of the orbiting laboratory's power system. A fourth spacewalk retracted a stubborn solar array. Main gear touchdown was at 5:32 p.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 5:32:12 p.m. and wheel stop was at 5:32:52 p.m. At touchdown -- nominally about 2,500 ft. beyond the runway threshold -- the orbiter is traveling at a speed ranging from 213 to 226 mph. Discovery traveled 5,330,000 miles, landing on orbit 204. Mission elapsed time was 12 days, 20 hours, 44 minutes and 16 seconds. This is the 64th landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Tom Joseph
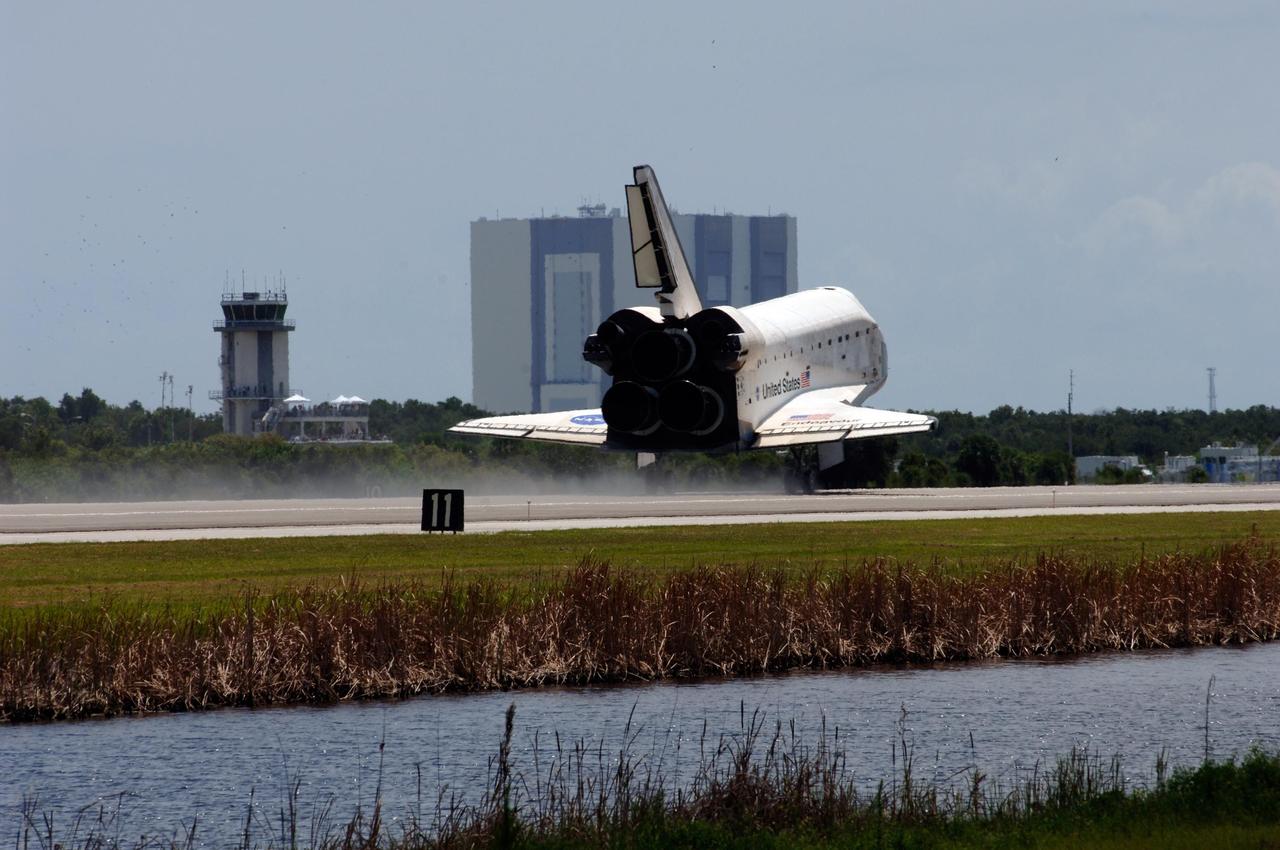

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Endeavour passes the air traffic control tower (left) next to the Shuttle Landing Facility as it touches down on runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center after traveling nearly 5.3 million miles on mission STS-118. Behind Endeavour is the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Space Shuttle Endeavour crew, led by Commander Scott Kelly, completes a 13-day mission to the International Space Station. The STS-118 mission began Aug. 8 and installed a new gyroscope, an external spare parts platform and another truss segment to the expanding station. Endeavour's main gear touched down at 12:32:16 p.m. EDT. Nose gear touchdown was at 12:32:29 p.m. and wheel stop was at 12:33:20 p.m. Endeavour landed on orbit 201. STS-118 was the 119th space shuttle flight, the 22nd flight to the station, the 20th flight for Endeavour and the second of four missions planned for 2007. This was the 65th landing of an orbiter at Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Rafael Hernandez
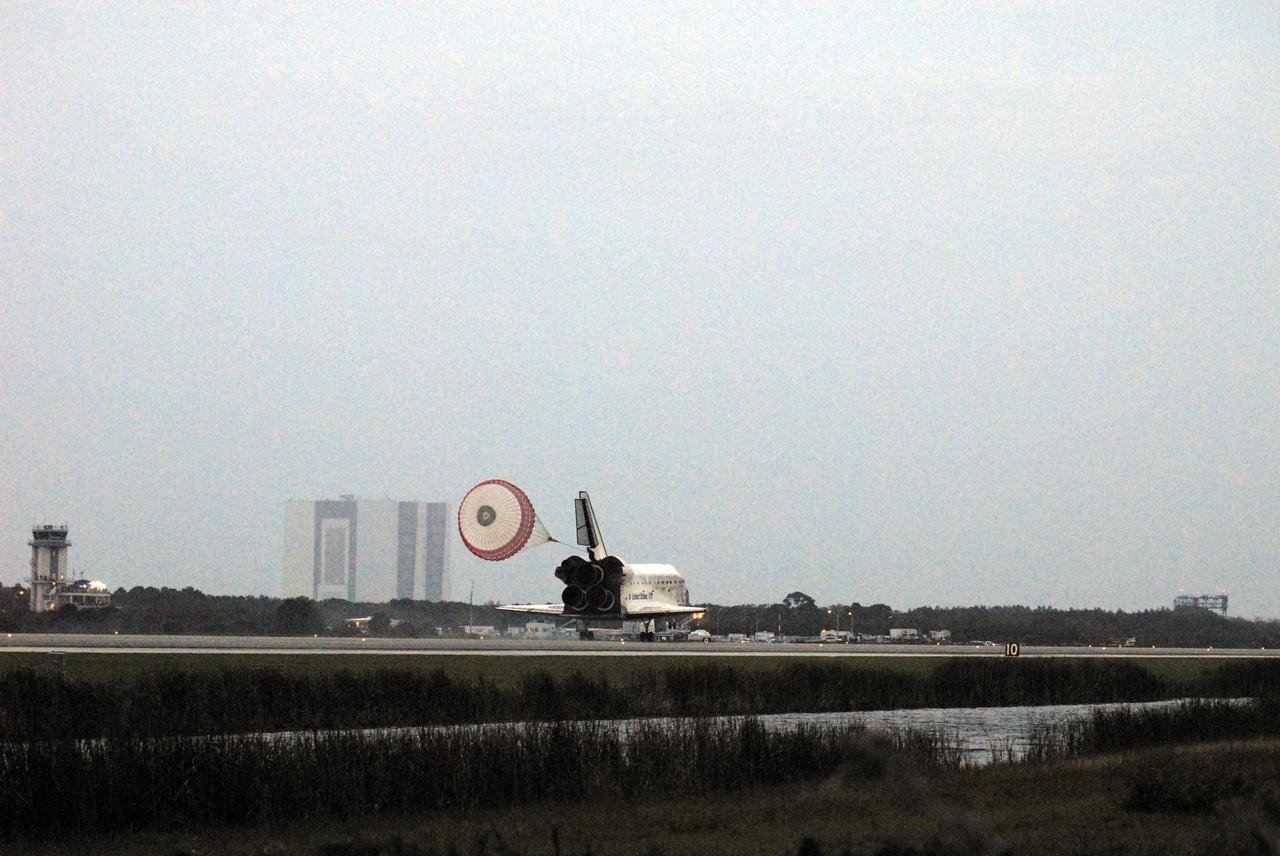

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Discovery's drag chute unfurls upon landing on Runway 15 at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility as the sun sets on the shortest day of the year, concluding mission STS-116. In the background are the runway's Air Traffic Control Tower (far right) and the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building. Aboard are Commander Mark Polansky, Pilot William Oefelein, and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam, Joan Higginbotham, Nicholas Patrick and Christer Fuglesang, who represents the European Space Agency, as well as Thomas Reiter, who is returning from a 6-month stay on the International Space Station. During the mission, three spacewalks attached the P5 integrated truss structure to the station, and completed the rewiring of the orbiting laboratory's power system. A fourth spacewalk retracted a stubborn solar array. Main gear touchdown was at 5:32 p.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 5:32:12 p.m. and wheel stop was at 5:32:52 p.m. At touchdown -- nominally about 2,500 ft. beyond the runway threshold -- the orbiter is traveling at a speed ranging from 213 to 226 mph. Discovery traveled 5,330,000 miles, landing on orbit 204. Mission elapsed time was 12 days, 20 hours, 44 minutes and 16 seconds. This is the 64th landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Tom Joseph

Tropical Cyclone Mahasen is moving north through the Indian Ocean along a track that places landfall along the Bangladesh coast on May 16th around 1200Z. On May 13, 2013 the Suomi NPP satellite caught an interesting glimpse of the storm as it moved off the eastern coast of India. The VIIRS Day-Night Band was able to resolve lightning flashes towards the center of the storm, along with mesopheric gravity waves emanating outwards like ripples in a pond. These gravity waves are of particular interest to air traffic controllers so assist in identifying areas of turbulence. Since the moon was in a new phase, the lights and other surface features of India and Sri Lanka are clearly visible, though the clouds of TC Mahasen are not - a tradeoff that occurs as the amount of moonlight cycles throughout the month. Credit: NASA/NOAA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>