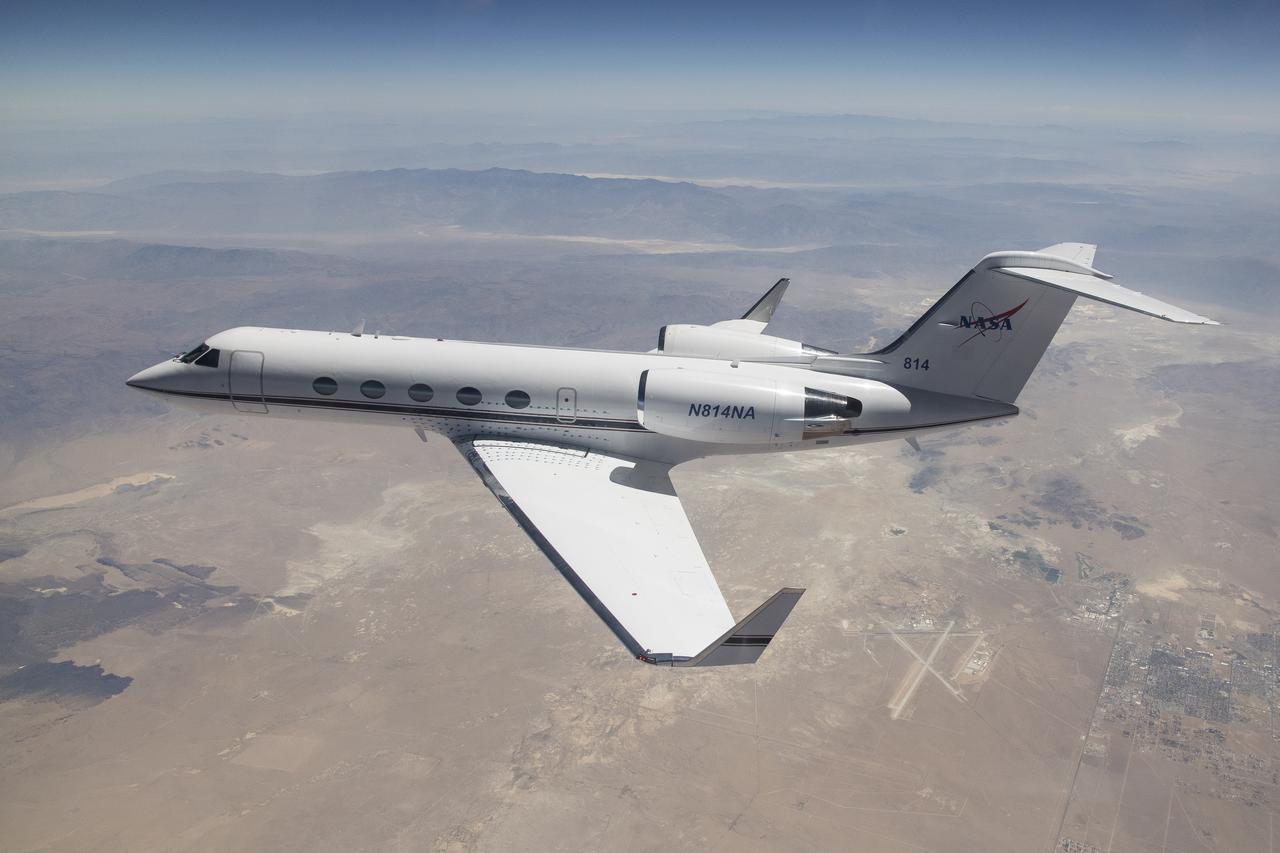

In a series of baseline flights beginning on June 24, 2024, the G-IV aircraft flew over the Antelope Valley to analyze aircraft performance. To accommodate a new radar instrument developed by JPL, NASA’s Airborne Science Program has selected the Gulfstream-IV aircraft to be modified and operated by Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California and will accommodate new instrumentation on board in support of the agency’s science mission directorate. Baseline flights began at NASA Armstrong in June 2024
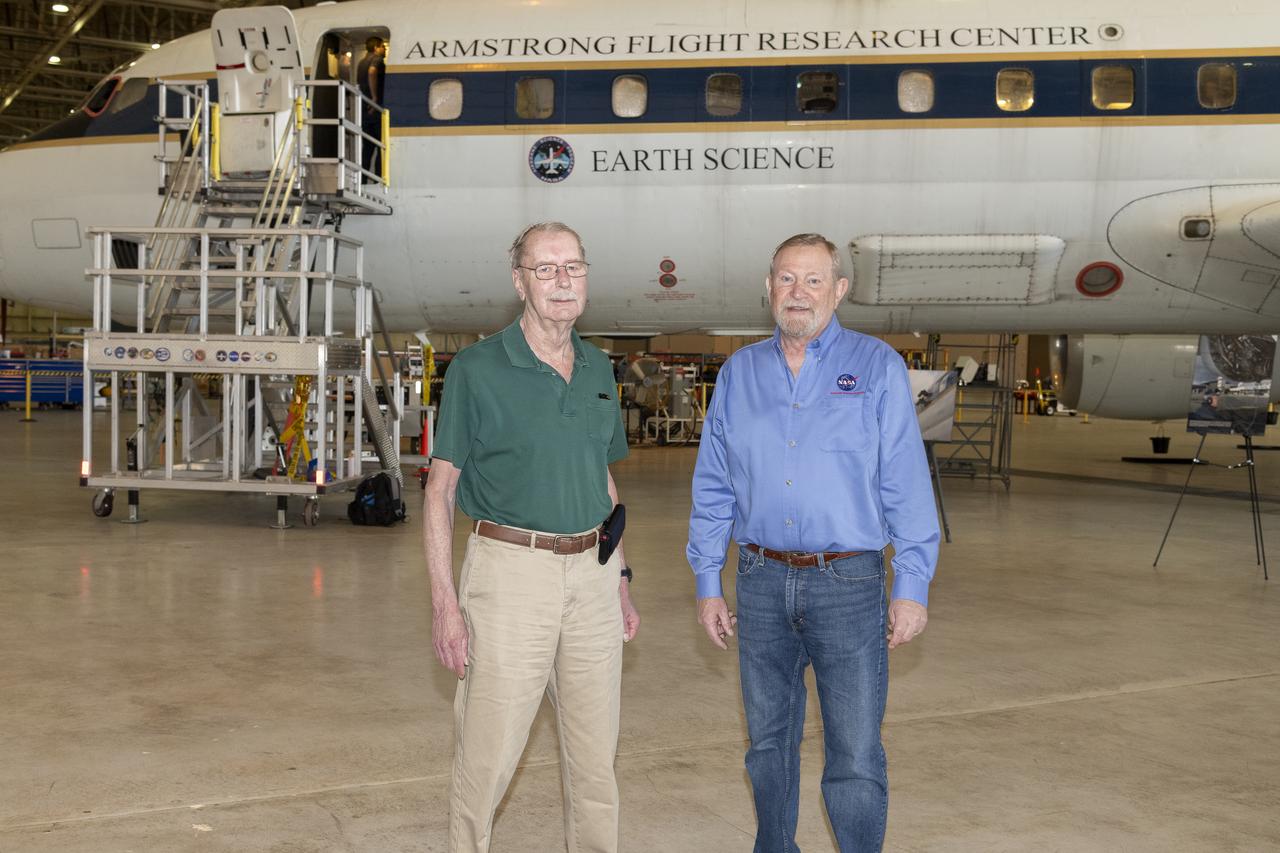

Retired NASA mission manager Chris Jennison and Randy Albertson, right, who retired in 2019 as NASA’s Airborne Science Program deputy director, stand in front of the DC-8 aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.
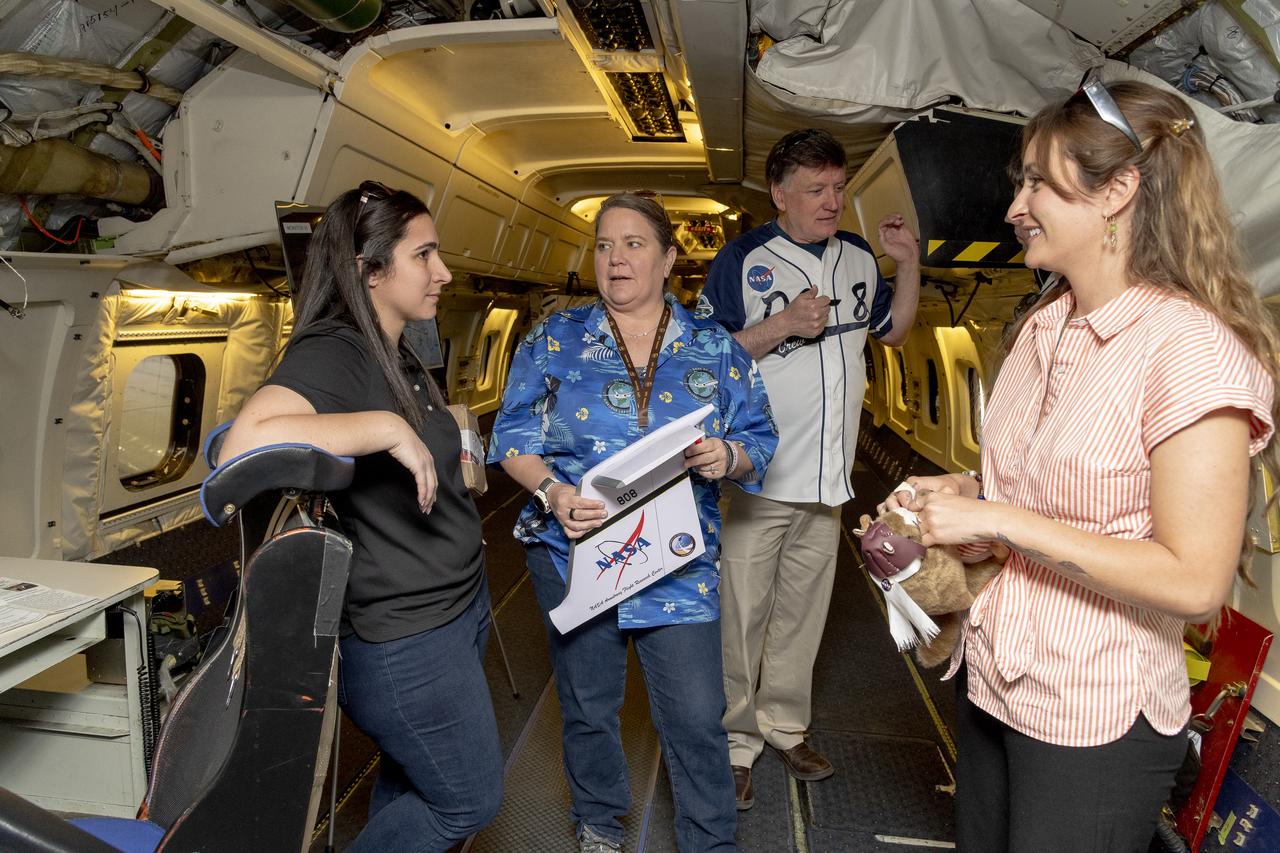

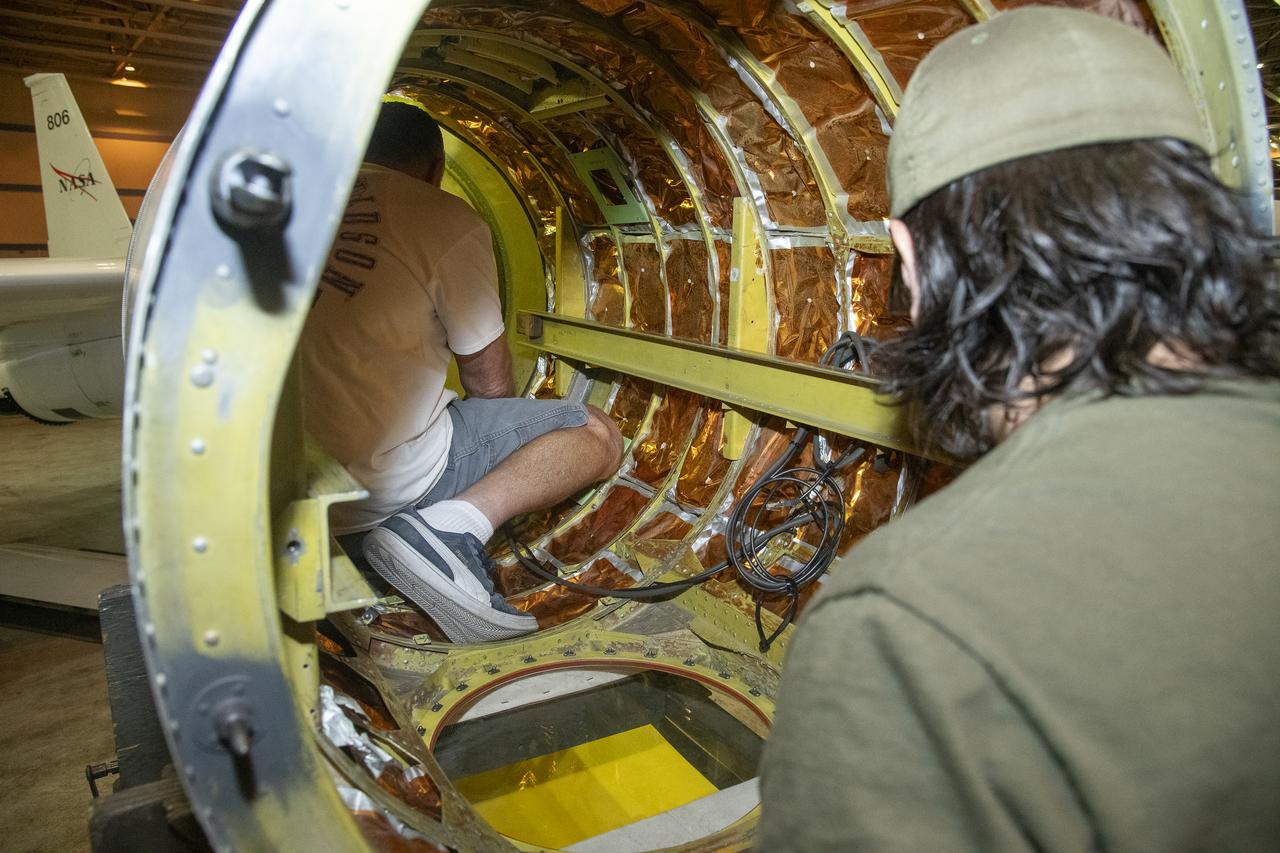
Members of the DC-8 program team tour an empty aircraft and recall past missions. Usually the DC-8 has between 15 and 30 instrument racks installed for a given science mission. The aircraft was spacious by comparison on May 2, 2024, when NASA personnel, friends, and family gathered at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California to celebrate the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns. Conversing here are DC-8 aircraft deputy manager Kirsten Boogaard, left, with NASA Armstrong pilot Carrie Worth, Mike Zimmerman, and NASA Armstrong public affairs specialist for airborne science, Erica Heim.
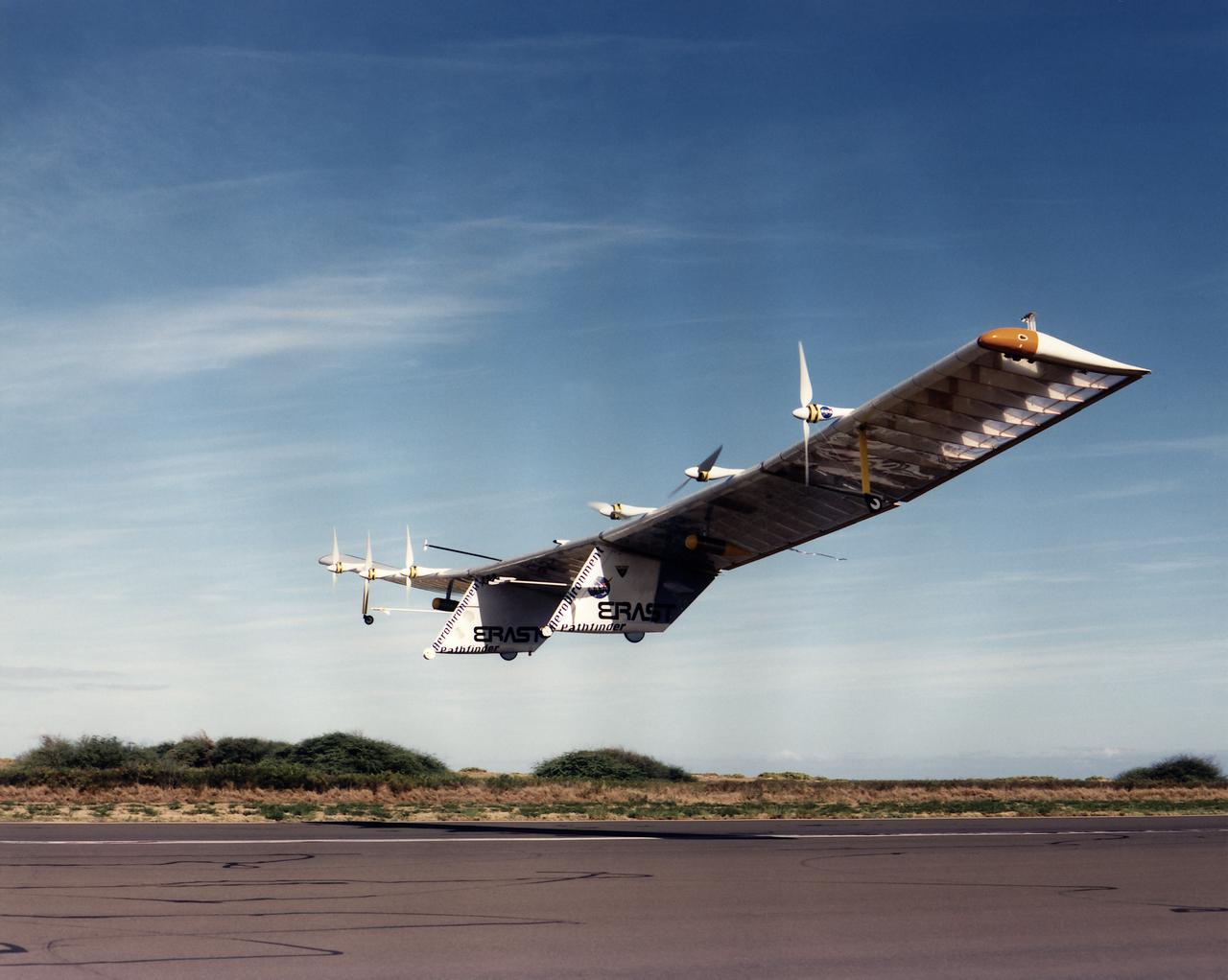

Pathfinder, NASA's solar-powered, remotely-piloted aircraft is shown while it was conducting a series of science flights to highlight the aircraft's science capabilities while collecting imagery of forest and coastal zone ecosystems on Kauai, Hawaii. The flights also tested two new scientific instruments, a high-spectral-resolution Digital Array Scanned Interferometer (DASI) and a high-spatial-resolution Airborne Real-Time Imaging System (ARTIS). The remote sensor payloads were designed by NASA's Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, to support NASA's Mission to Planet Earth science programs.
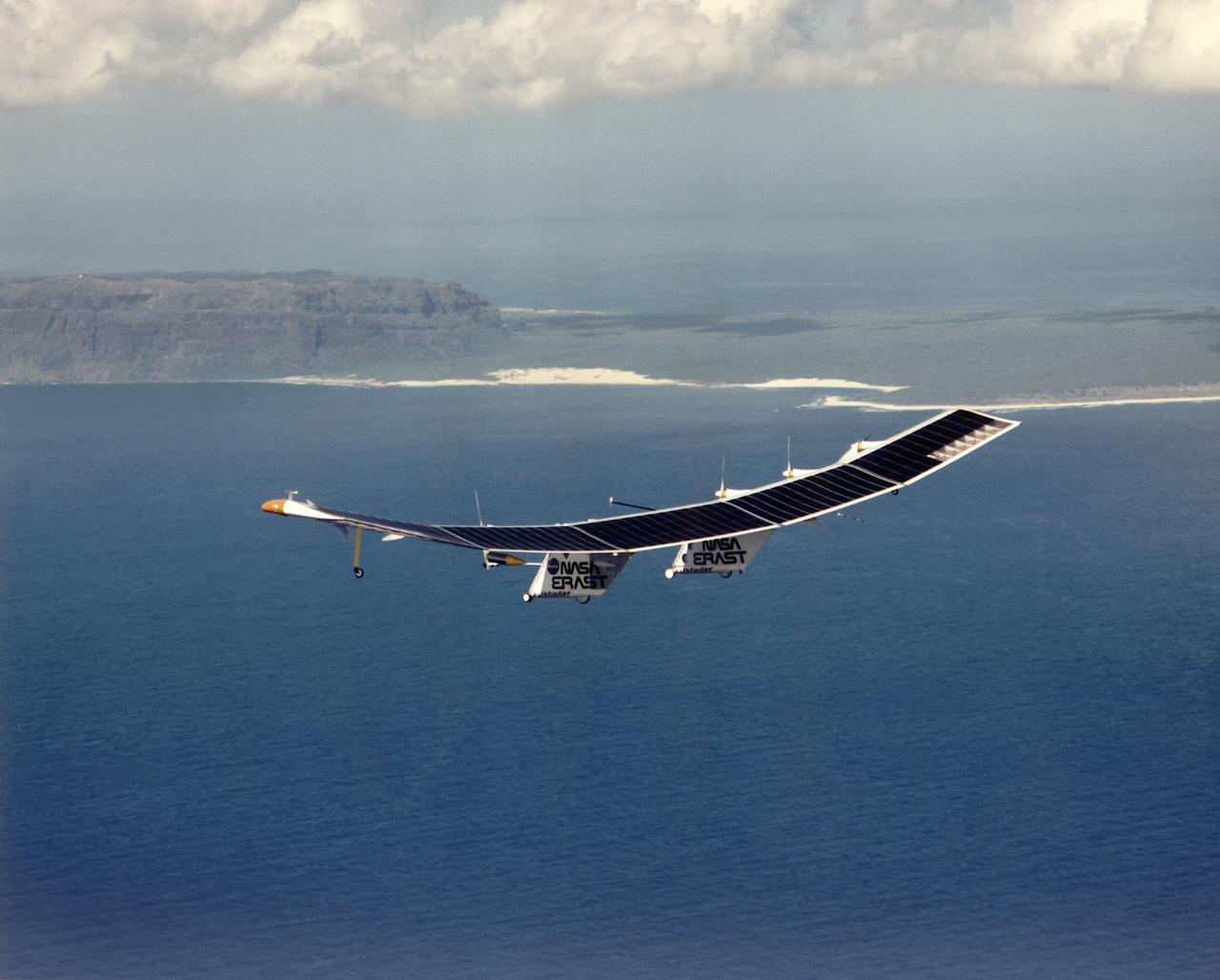

Pathfinder, NASA's solar-powered, remotely-piloted aircraft is shown while it was conducting a series of science flights to highlight the aircraft's science capabilities while collecting imagery of forest and coastal zone ecosystems on Kauai, Hawaii. The flights also tested two new scientific instruments, a high spectral resolution Digital Array Scanned Interferometer (DASI) and a high spatial resolution Airborne Real-Time Imaging System (ARTIS). The remote sensor payloads were designed by NASA's Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, to support NASA's Mission to Planet Earth science programs.
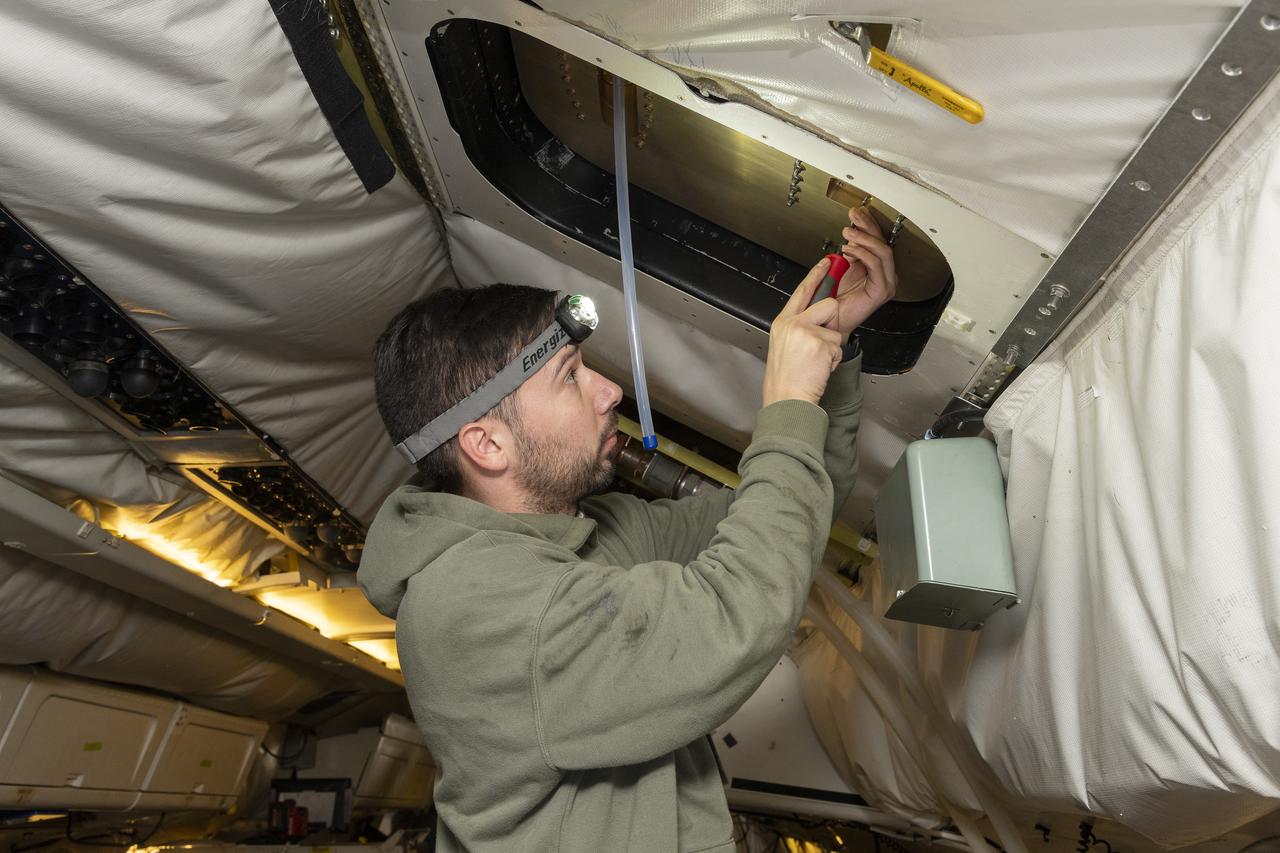

Isac Mata, engineering technician at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center, attends to the interior of the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
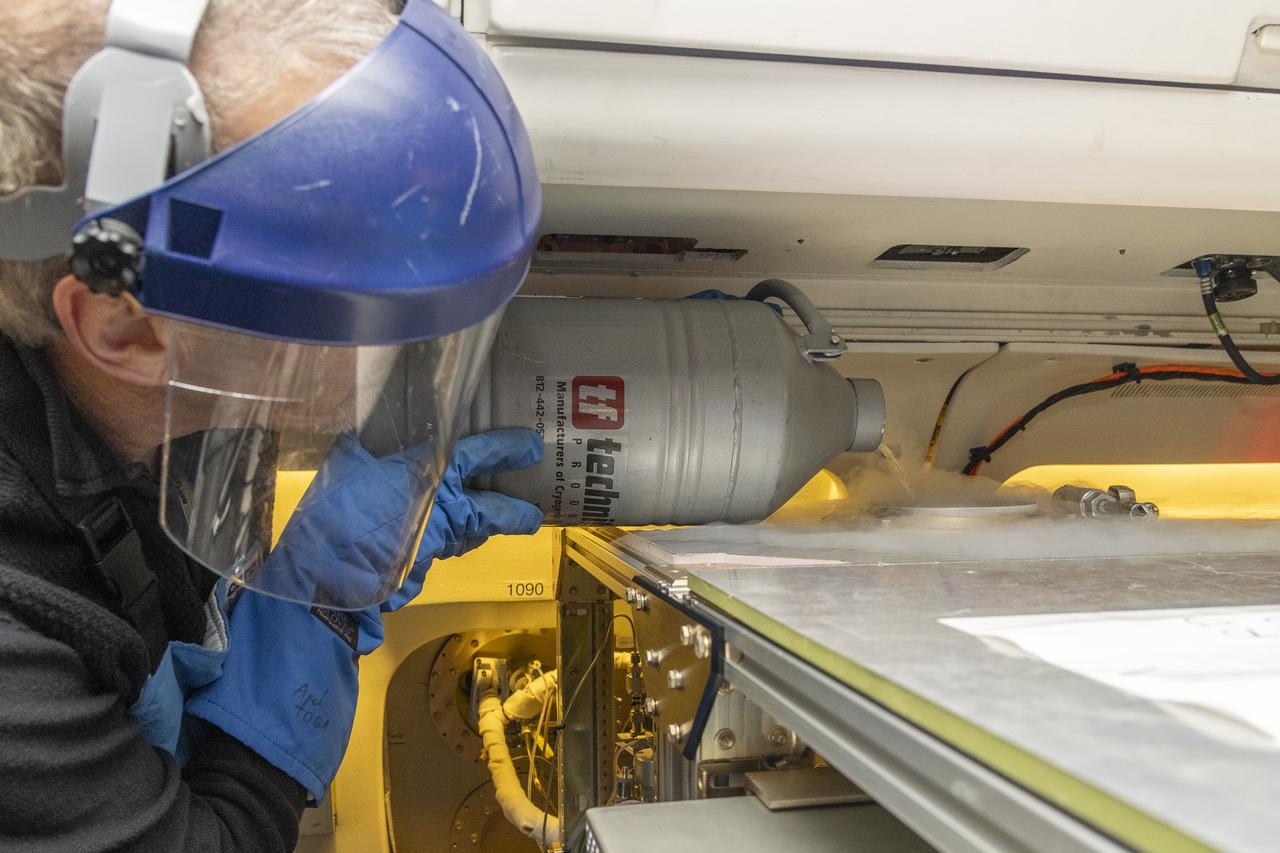

Alan Hills fills liquid nitrogen in the Trace Organic Gas Analyzer (TOGA) instrument onboard the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. This instrument measures volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
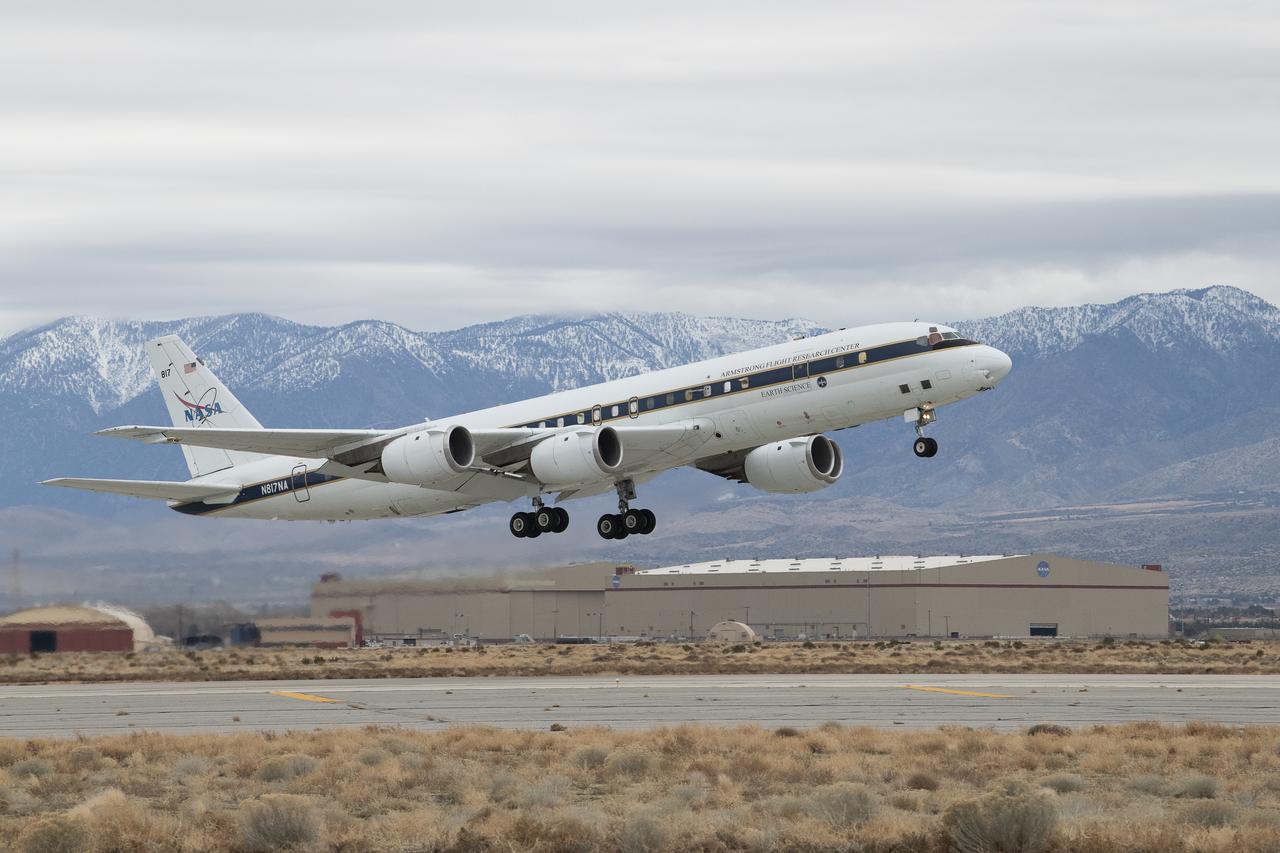

DC-8 aircraft conducts test flights at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
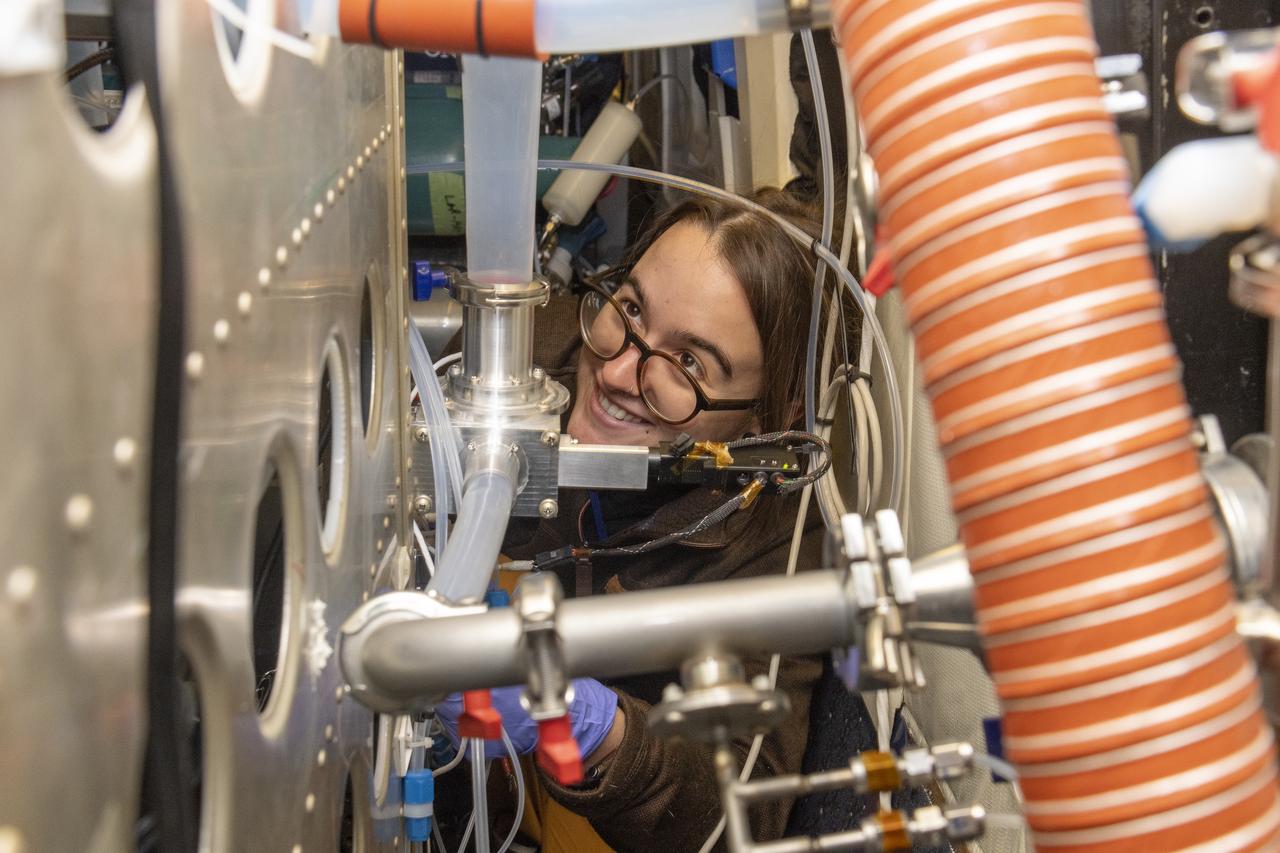
Kat Ball, Chemical Engineering Ph.D candidate at Caltech, attends to the Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometer (CIMS) rack onboard the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
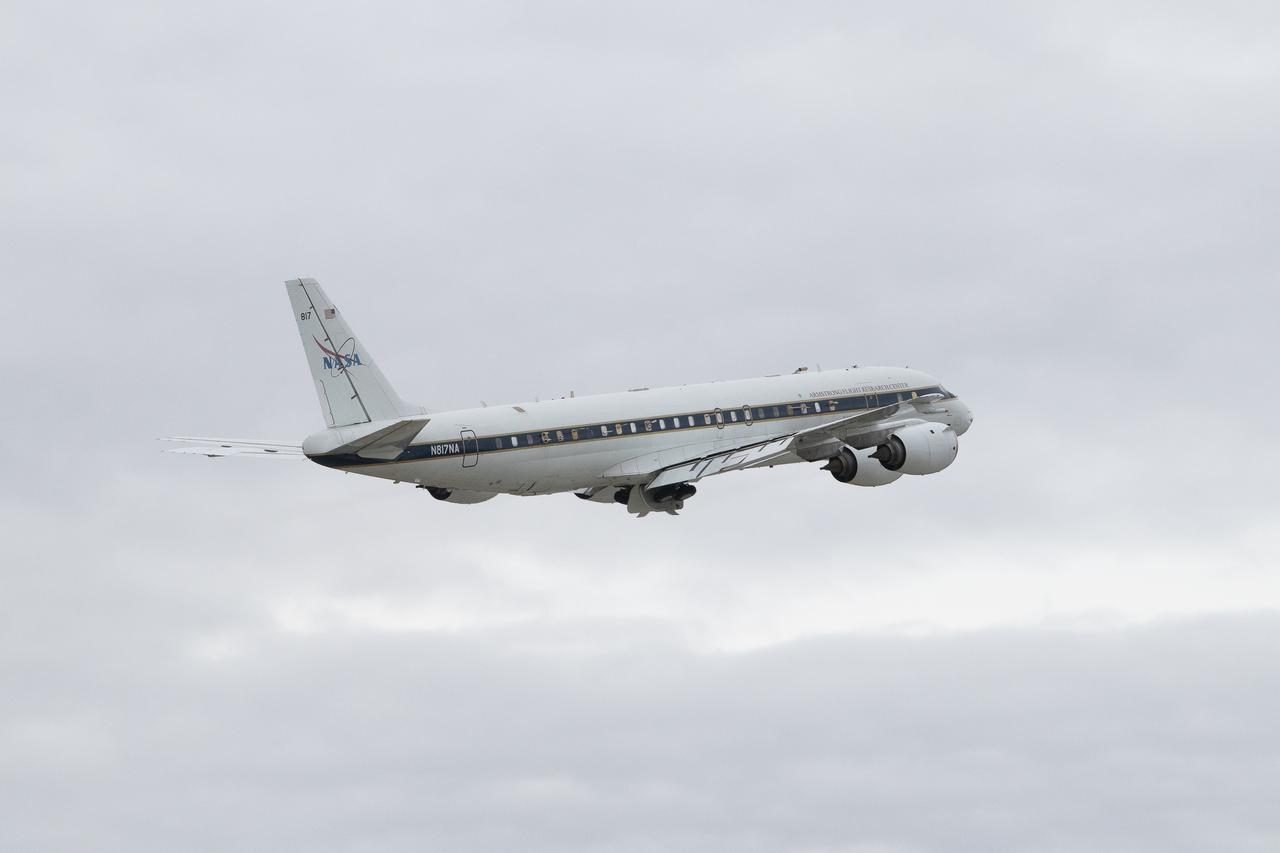

DC-8 aircraft conducts test flights at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
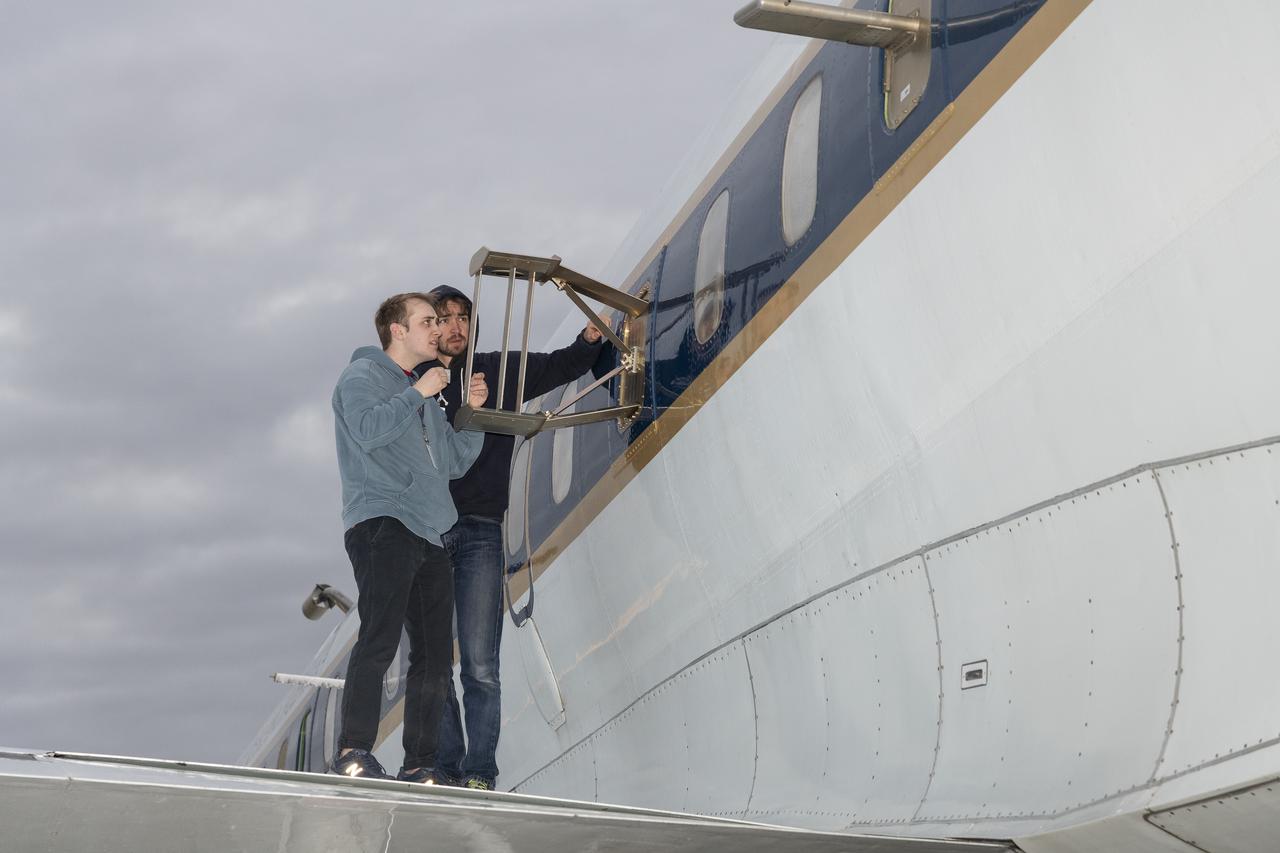

Scientists Ryan Boyd (left) and Vladislav Sevostianov (right) attend to the Optical Payload for Lasercomm Science (OPALS) instrument on the exterior the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
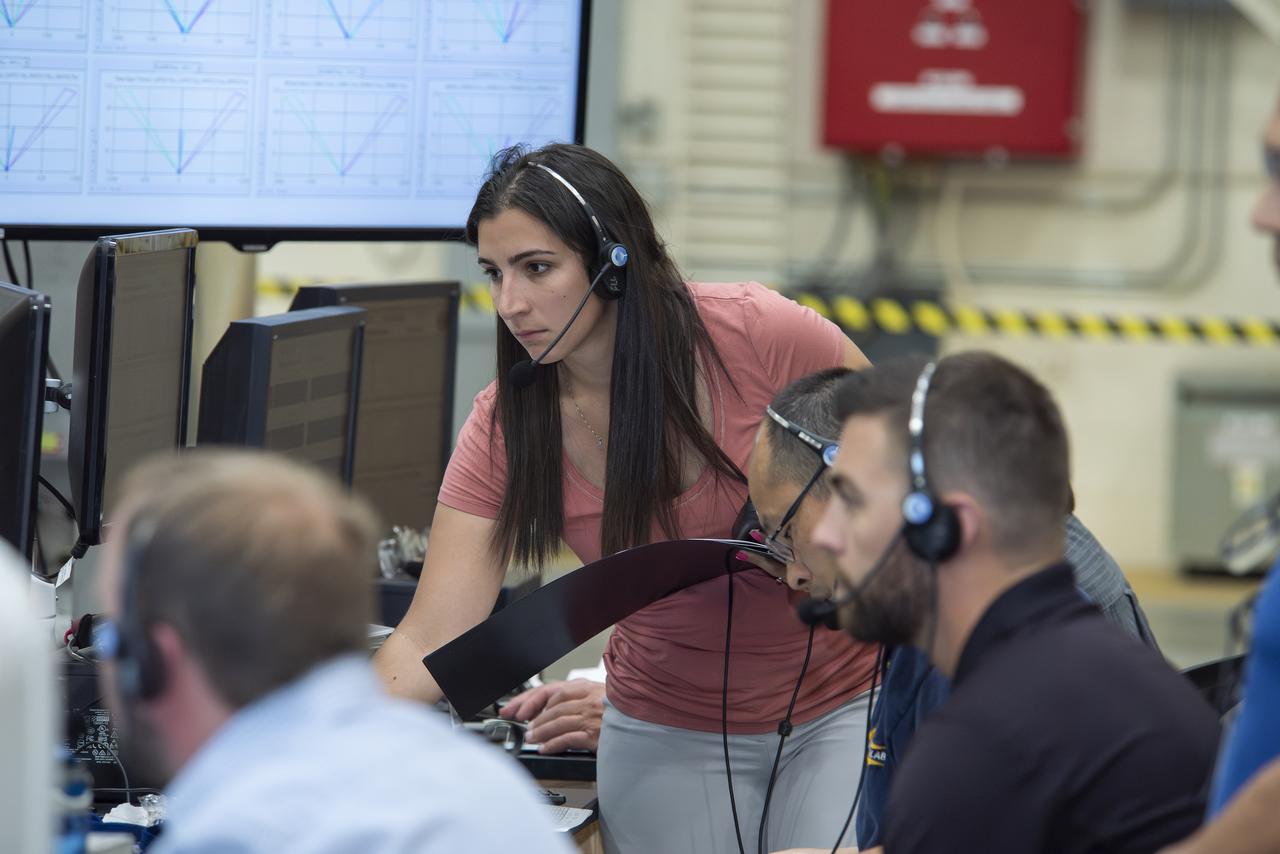

Kirsten Boogaard, Deputy Project Manager for the DC-8 aircraft, leads and manages project planning, integration and resources for airborne science missions since 2020
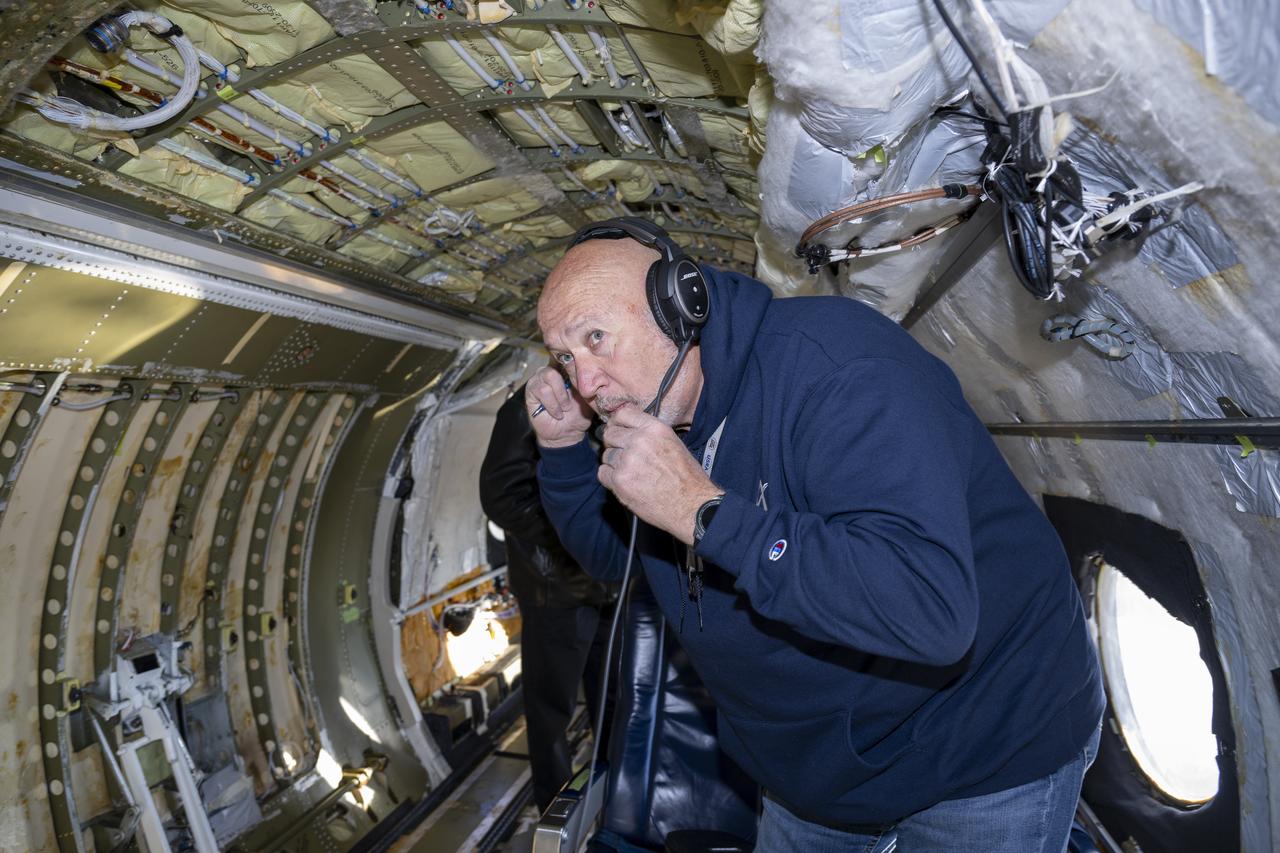

Martin Hench, flight systems engineer, checks the communications system onboard the G-IV aircraft as it prepares to depart NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, on March 18, 2025. As the newest member of NASA Armstrong’s airborne science fleet, the G-IV was sent to Avenger Aerospace Solutions in Cartersville, Georgia, for modifications that will optimize the G-IV’s performance as a research aircraft.
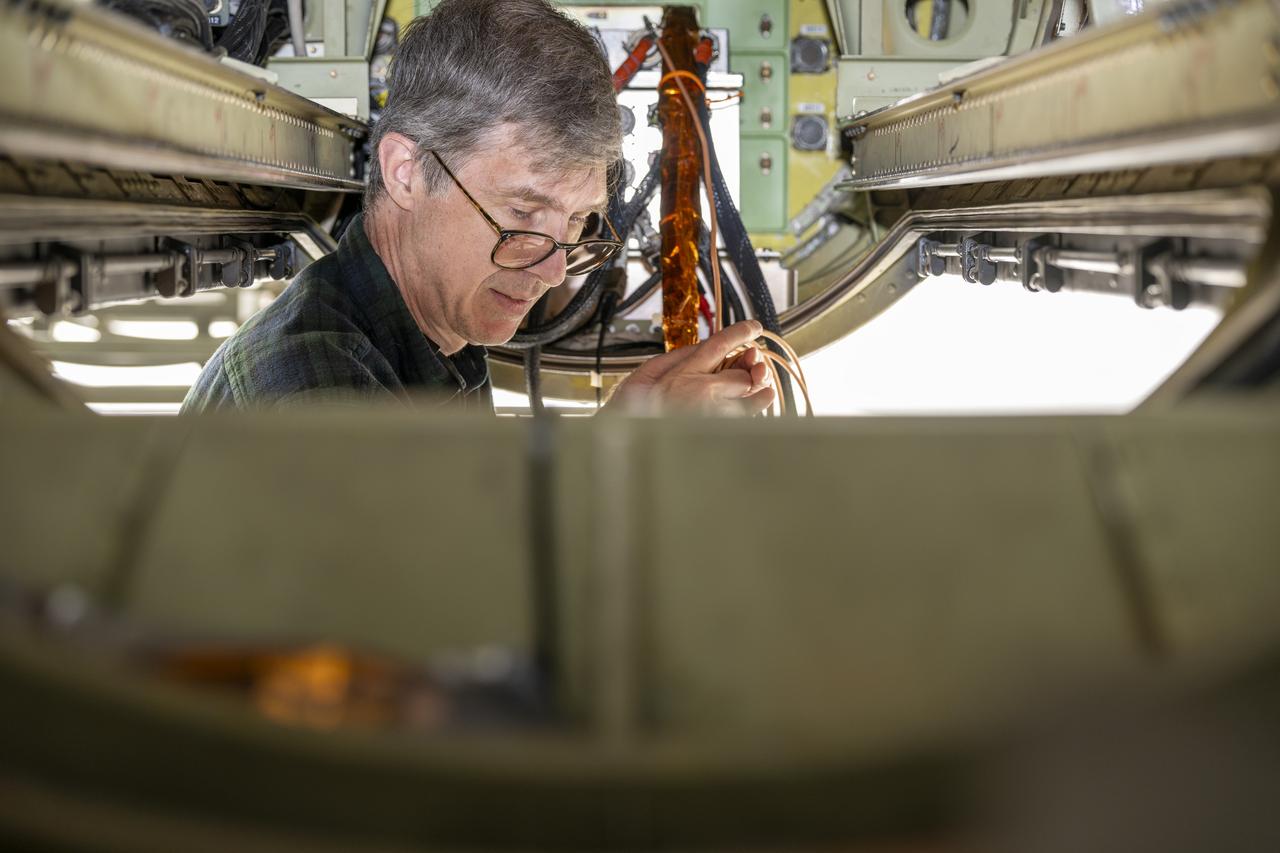

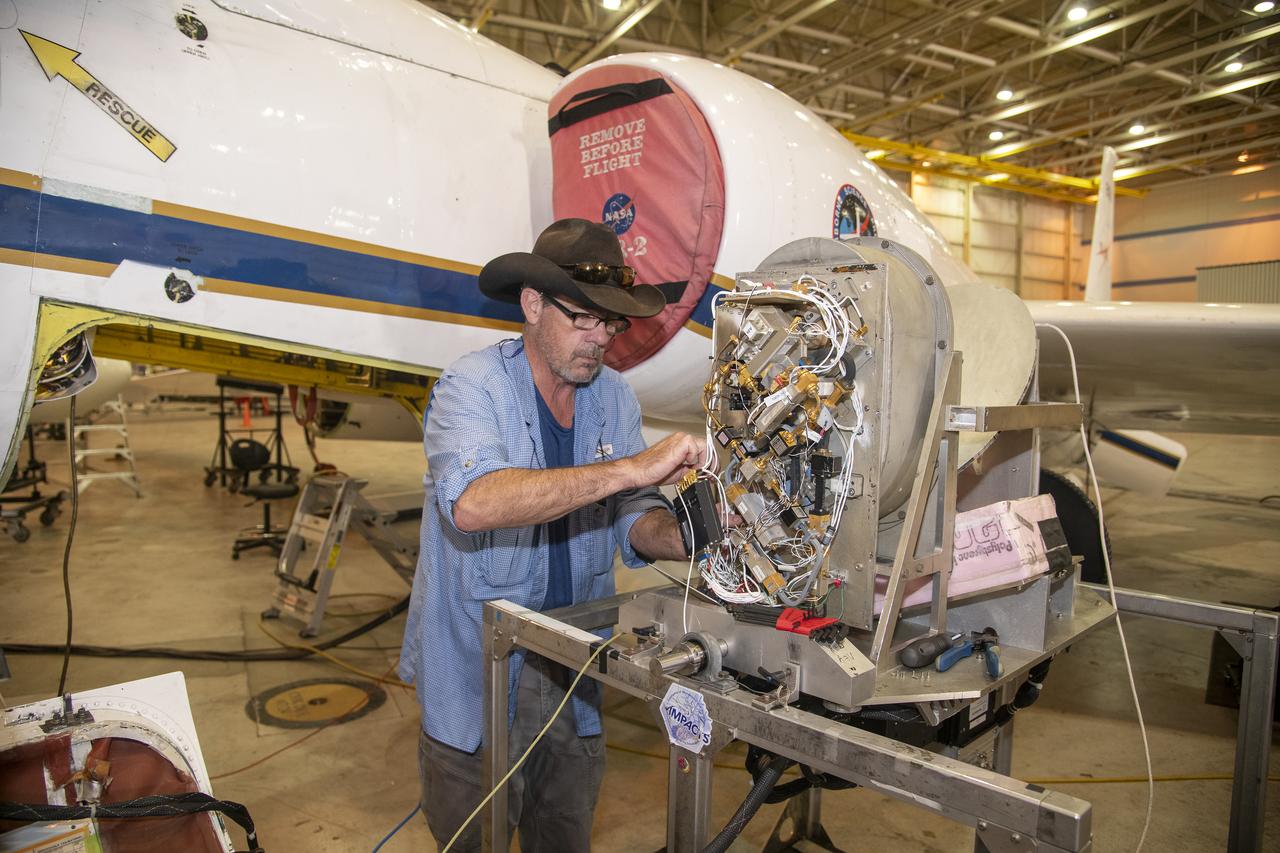
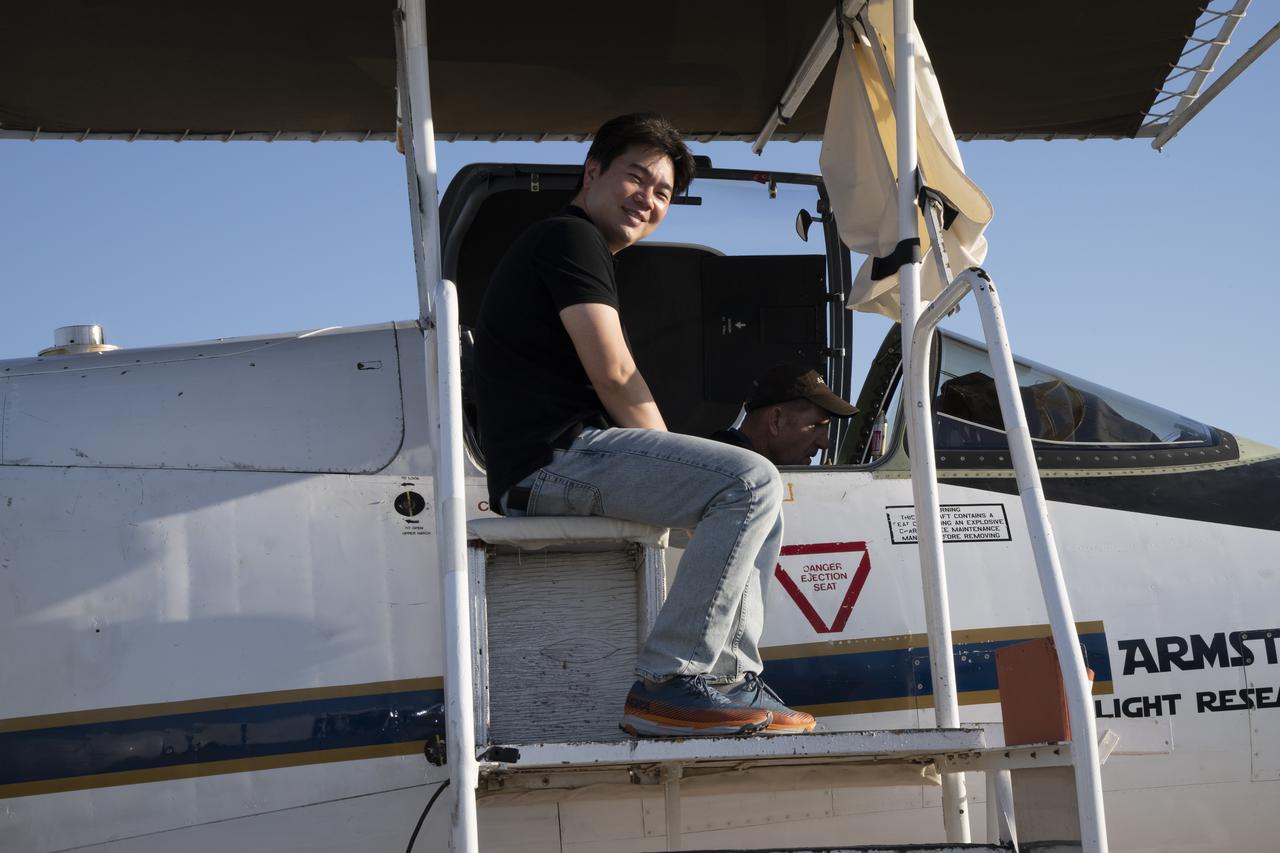
Dr. John Woodward, of the National Institute of Standards and Technology and co-investigator on the airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance (air-LUSI) mission, prepares the instrument for upload onto the ER-2 aircraft in March 2025 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
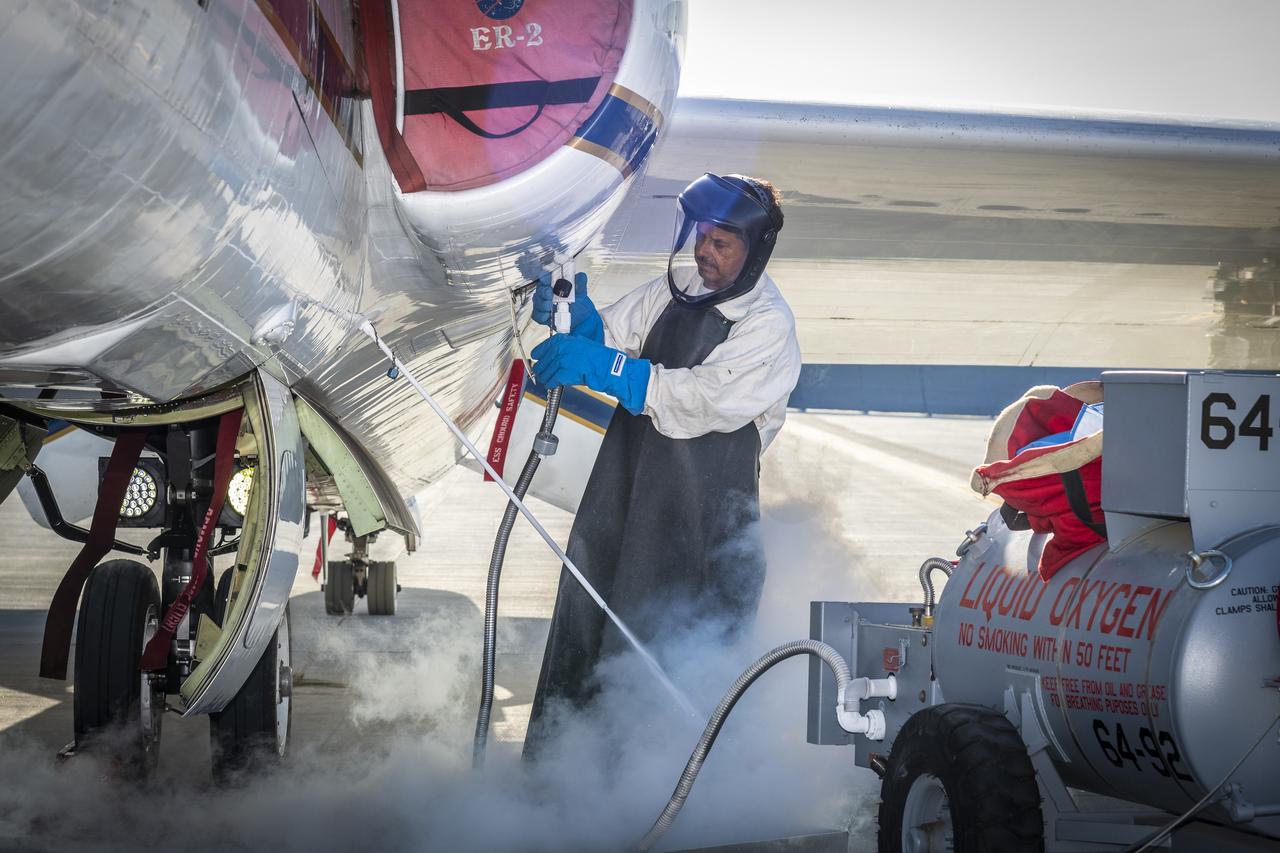

Francisco Rodriguez (aircraft mechanic) services liquid oxygen or LOX on the ER-2 during the Geological Earth Mapping Experiment (GEMx) research project. Experts like Rodriguez sustain a high standard of safety on airborne science aircraft like the ER-2 and science missions like GEMx. The ER-2 is based out of NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
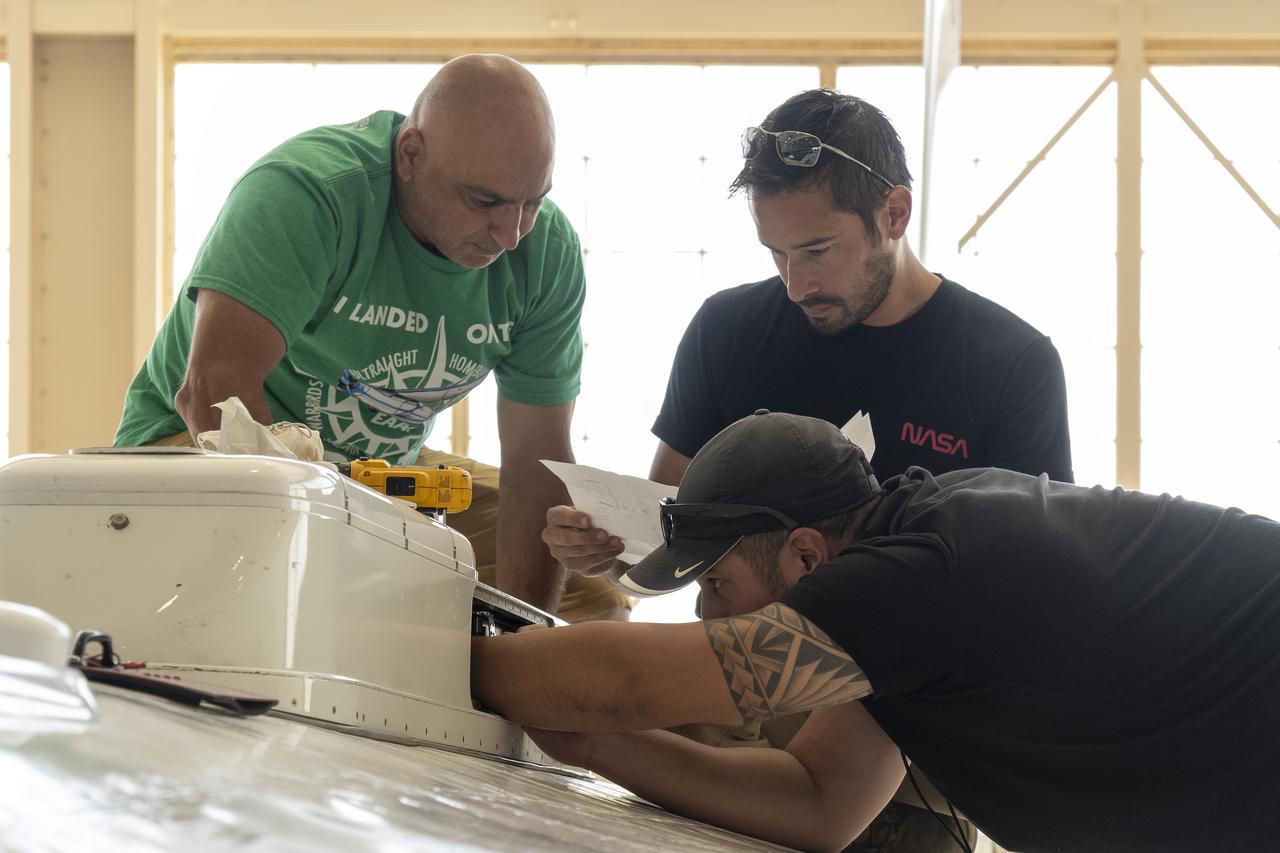

Sam Habbal (quality inspector), Darick Alvarez (aircraft mechanic), and Juan Alvarez (crew chief) work on the network “canoe” on top of the ER-2 aircraft, which provides network communication with the pilot onboard. Experts like these sustain a high standard of safety while outfitting instruments onboard science aircraft like the ER-2 and science missions like the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem Postlaunch Airborne eXperiment (PACE-PAX) mission. The ER-2 is based out of NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
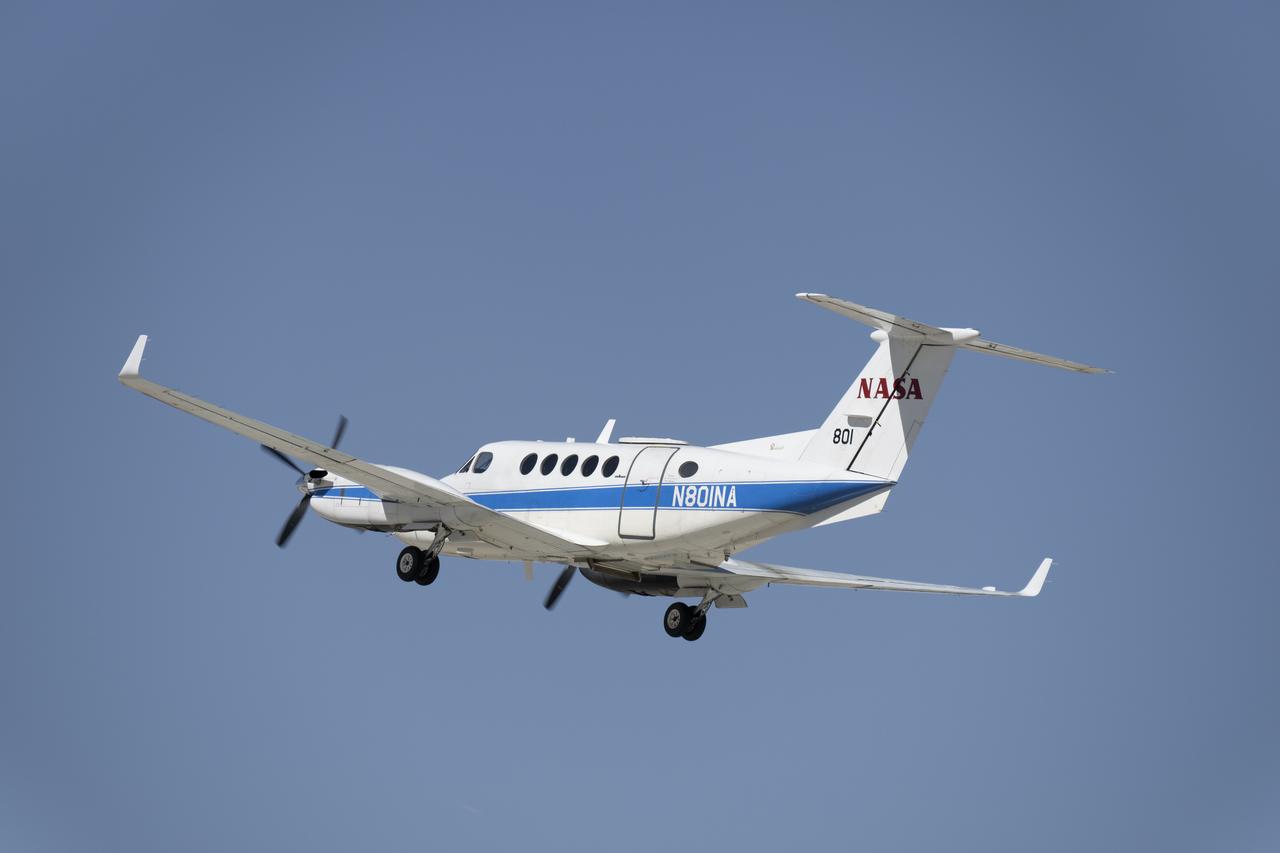

NASA’s B200 King Air aircraft – based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California – ascends to support a prescribed burn in Geneva State Forest, about 100 miles south of Montgomery, Alabama, on March 17, 2025. The effort is part of NASA’s multi-year FireSense project, which aims to test technology that predicts fire and smoke behavior. This data could eventually benefit the U.S. Forest Service as well as local, state, and other federal wildland fire agencies.
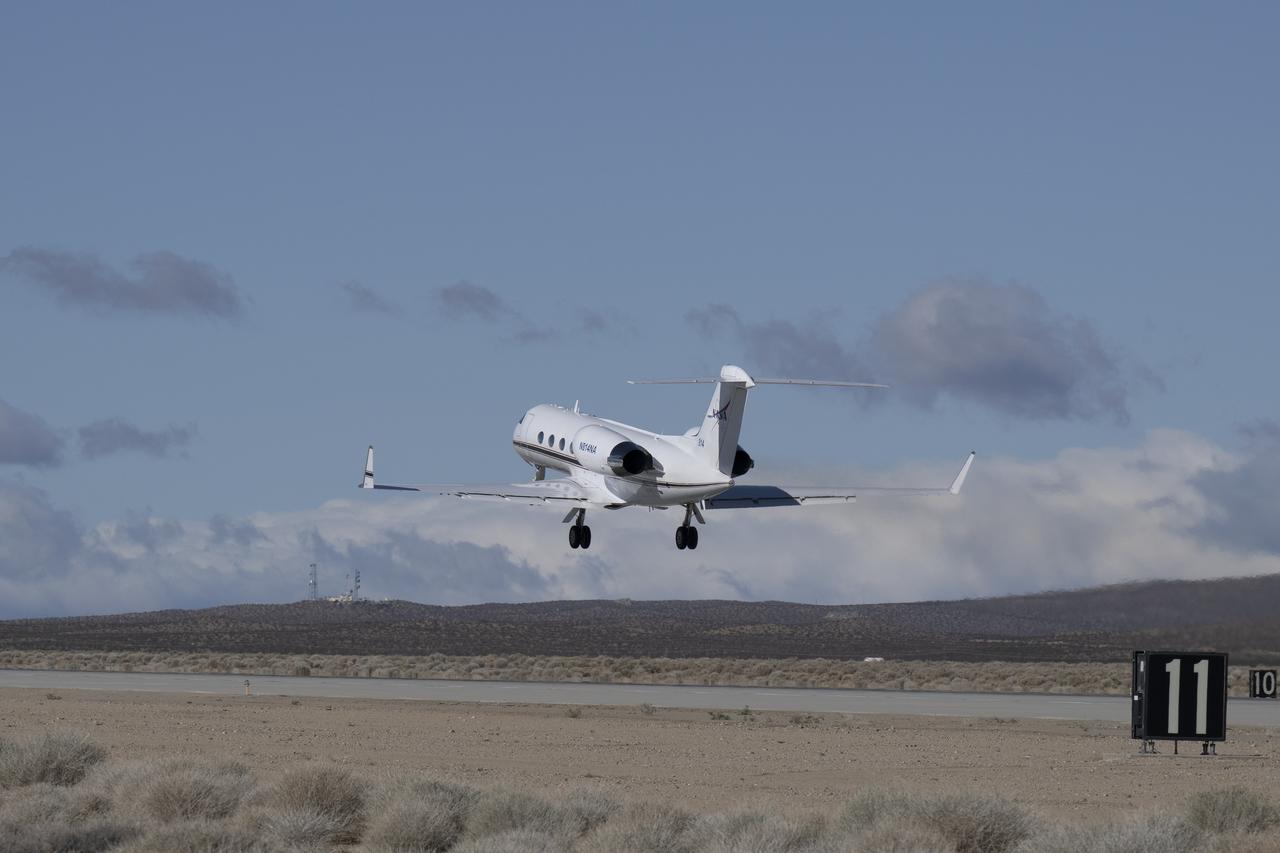

The G-IV aircraft lifts off from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, on March 18, 2025. As the newest member of NASA Armstrong’s airborne science fleet, the G-IV was sent to Avenger Aerospace Solutions in Cartersville, Georgia, for modifications that will optimize the G-IV’s performance as a research aircraft.
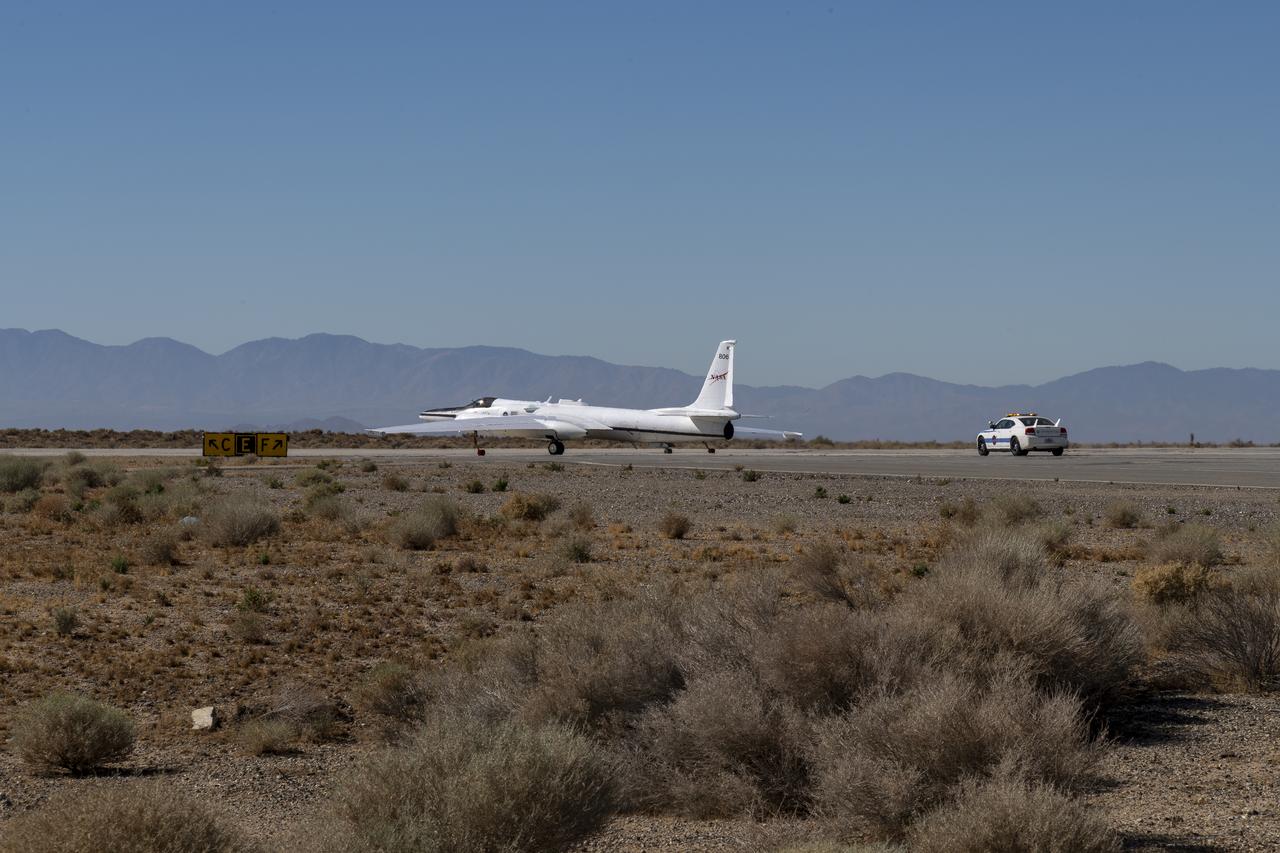

The ER-2 conducted over 80 flight hours in service of the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem Postlaunch Airborne eXperiment (PACE-PAX) mission. The ER-2 is uniquely qualified to conduct the high-altitude scientific flights that this project required, and is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
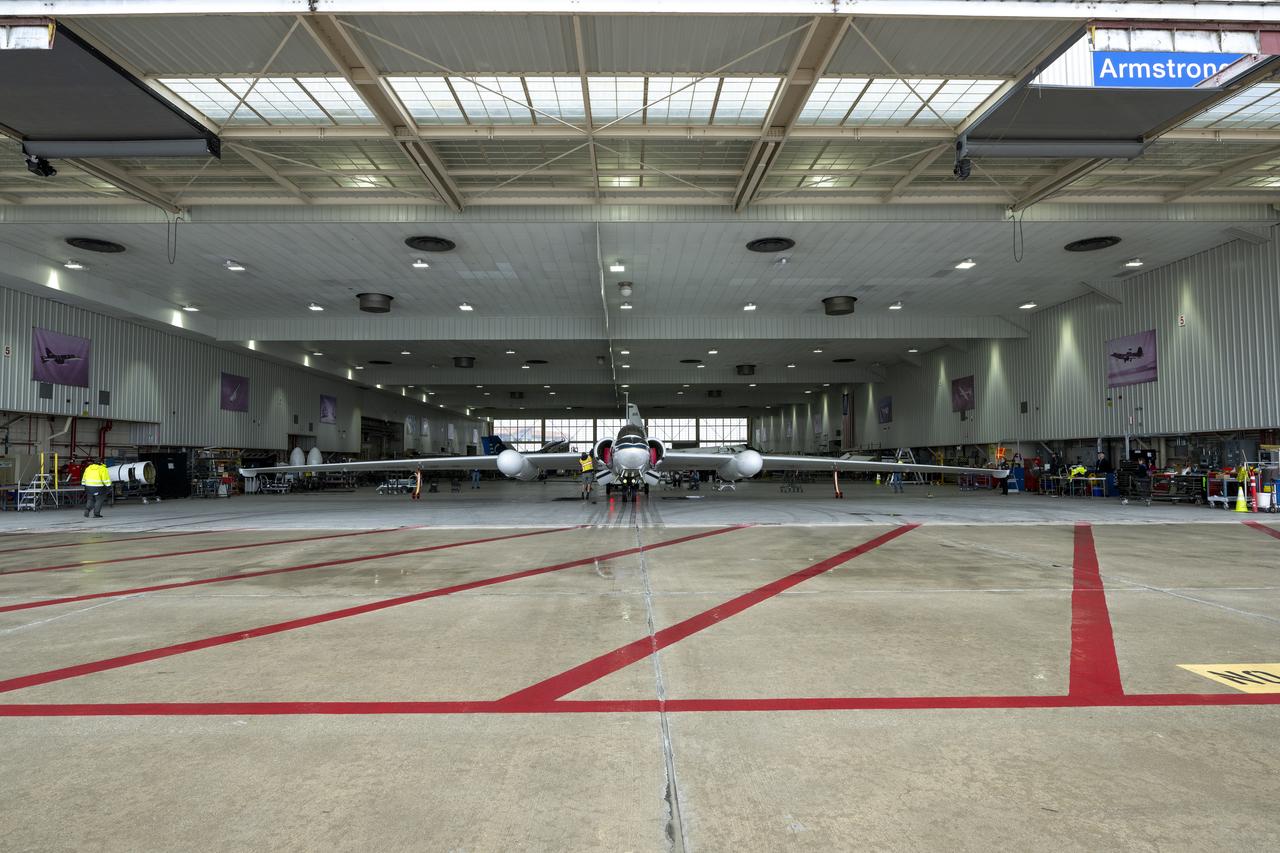

The ER-2 aircraft is parked in a hangar at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, in March 2025. The plane is prepared for takeoff to support the airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance, or air-LUSI, mission.
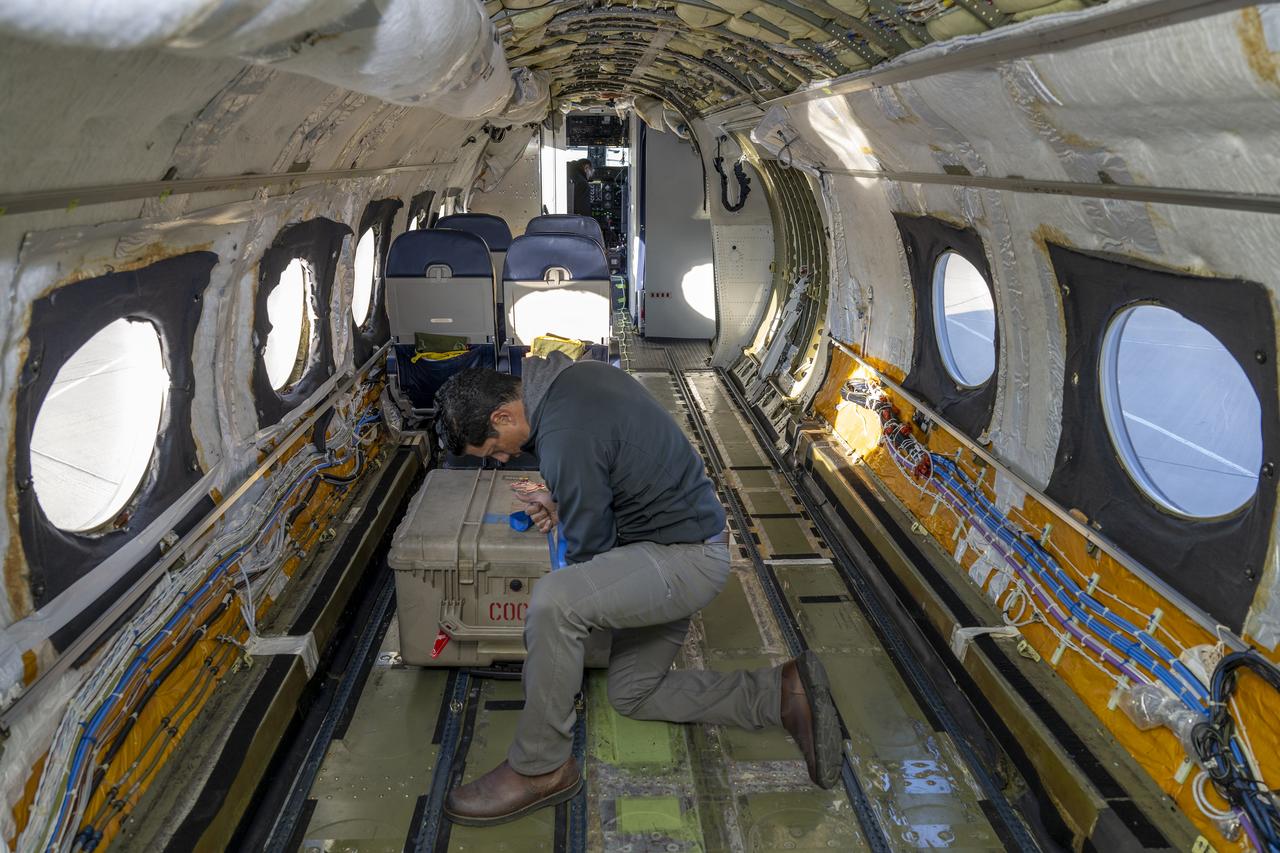

Jose “Manny” Rodriguez, technical engineer at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, secures a trunk onboard the G-IV aircraft on March 18, 2025. As the newest member of NASA Armstrong’s airborne science fleet, the G-IV was sent to Avenger Aerospace Solutions in Cartersville, Georgia, for modifications that will optimize the G-IV’s performance as a research aircraft.
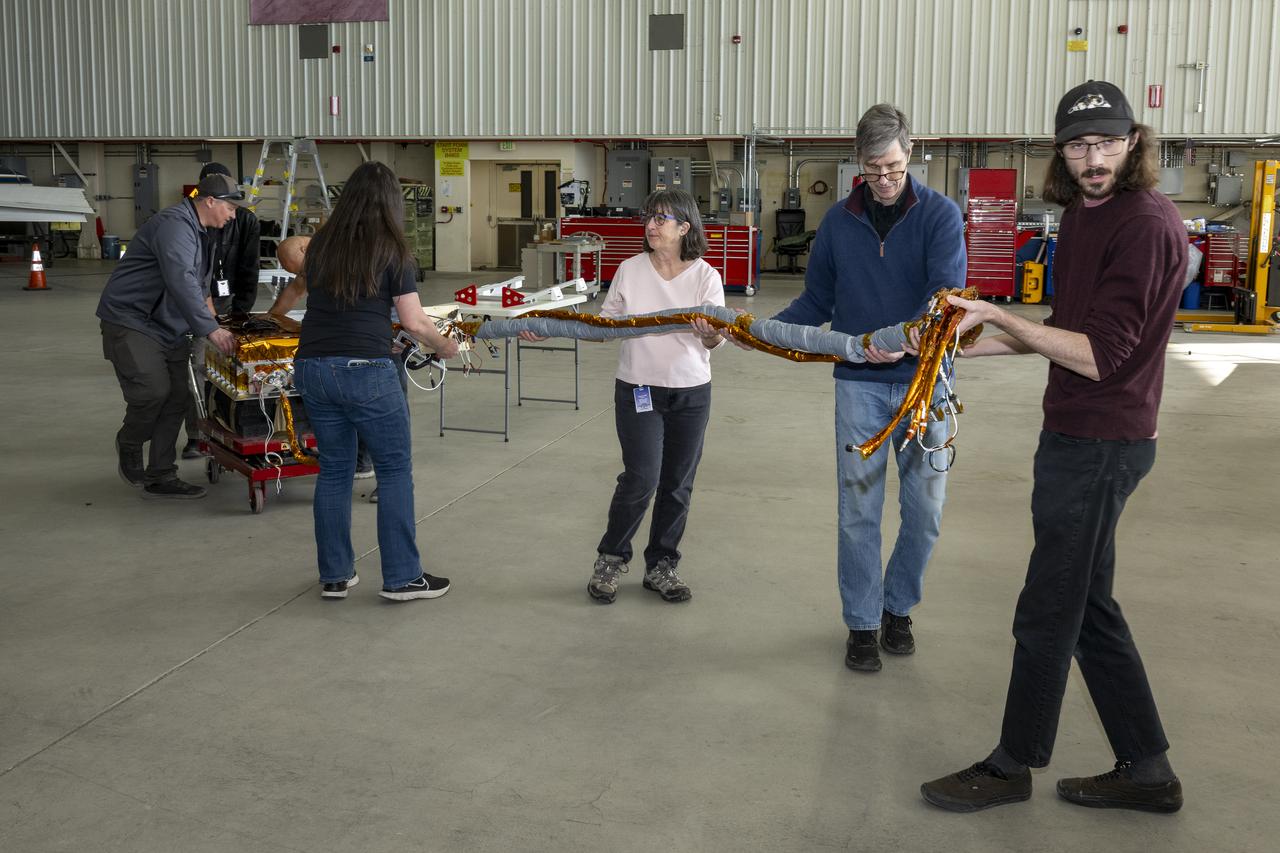

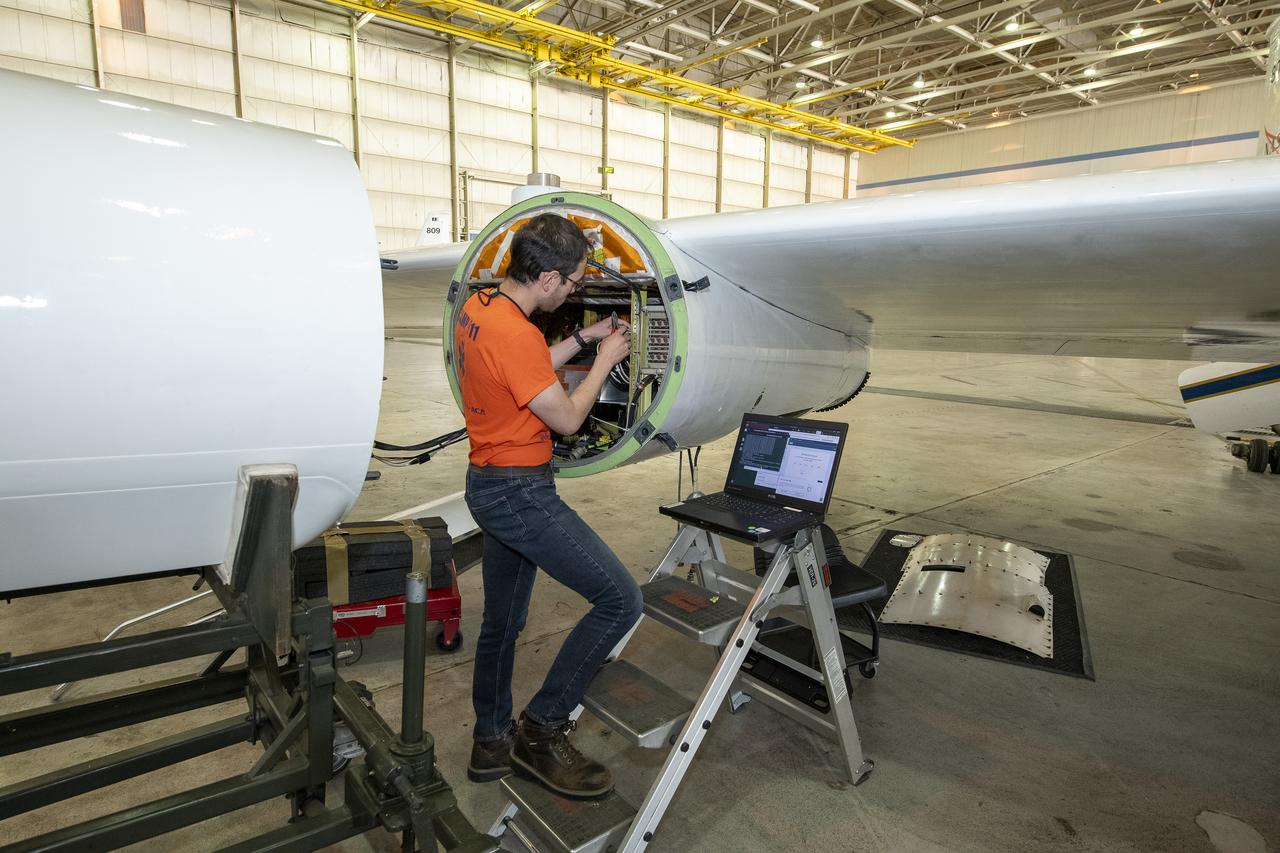
The airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance (air-LUSI) instrument is moved across the hangar floor by robotic engineer Alexander McCafferty-Leroux ,from right to left, co-investigator Dr. John Woodward, NIST astronomer Dr. Susana Deustua, air-LUSI chief system engineer Dr. Kathleen “Kat” Scanlon, and members of the ER-2 ground crew at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, in March 2025.

The ER-2 ground crew Wissam Habbal, left, and Dr. Kevin Turpie, airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance (air-LUSI) principal investigator, guide delicate fiber optic and electric cabling into place while uploading the air-LUSI instrument onto the ER-2 aircraft in March 2025 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
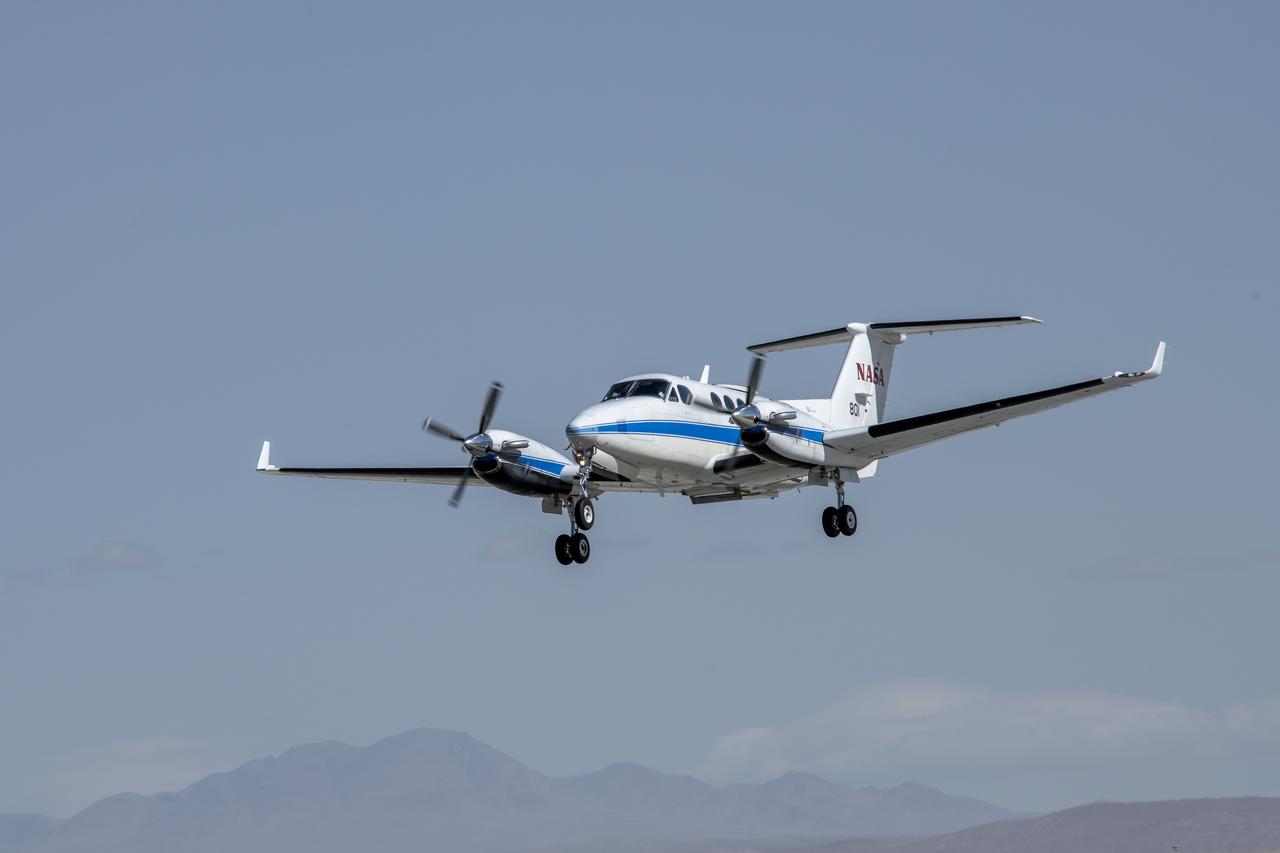

NASA’s B200 King Air aircraft – based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California – ascends to support a prescribed burn in Geneva State Forest, about 100 miles south of Montgomery, Alabama, on March 17, 2025. The effort is part of NASA’s multi-year FireSense project, which aims to test technology that predicts fire and smoke behavior. This data could eventually benefit the U.S. Forest Service as well as local, state, and other federal wildland fire agencies.

The DC-8 flies low for the last time over NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, before it retires to Idaho State University in Pocatello, Idaho. The DC-8 will provide real-world experience to train future aircraft technicians at the college’s Aircraft Maintenance Technology Program.
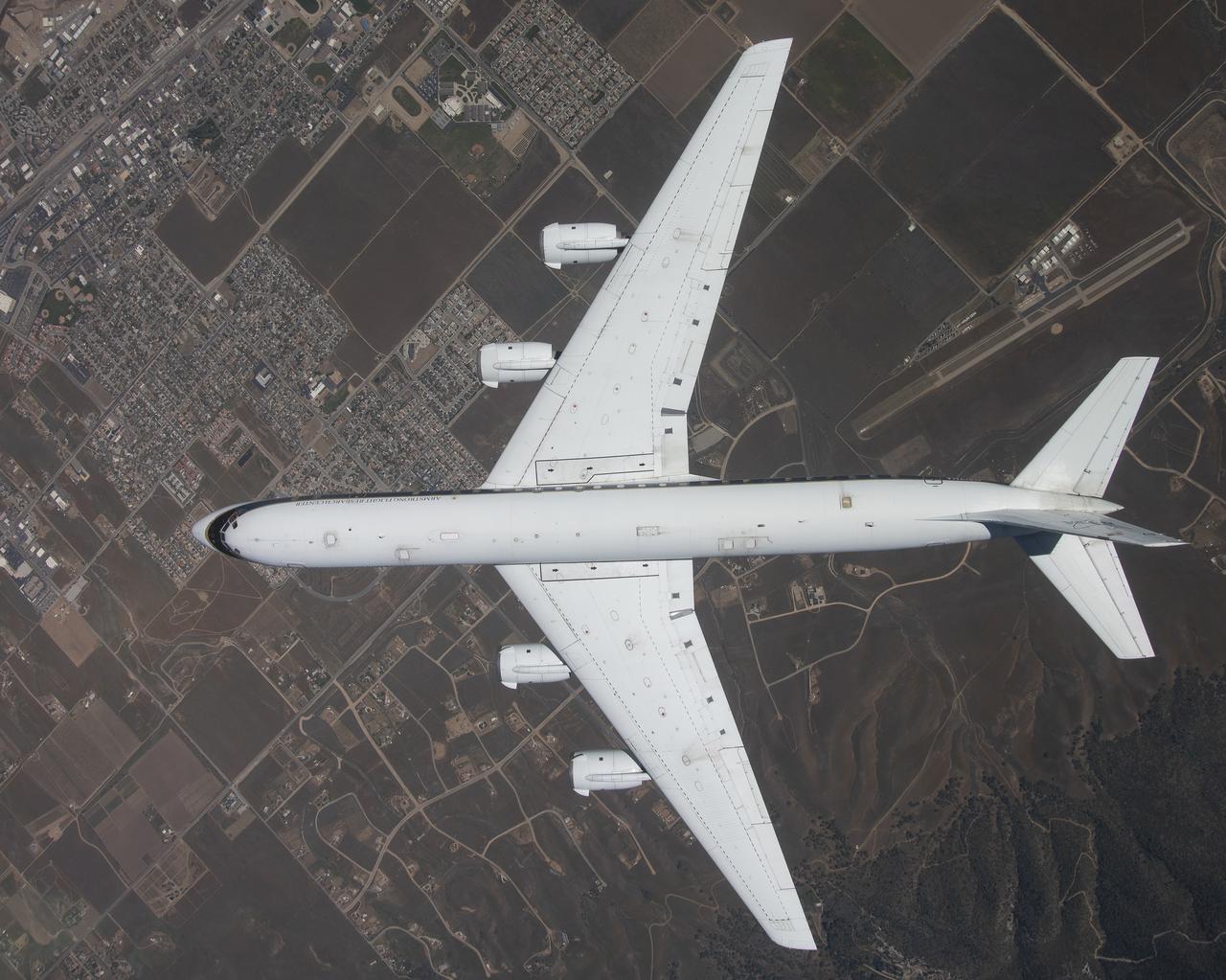

The DC-8 is shown overhead during its final flight from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, before it retires to Idaho State University in Pocatello, Idaho. The DC-8 will provide real-world experience to train future aircraft technicians at the college’s Aircraft Maintenance Technology Program.
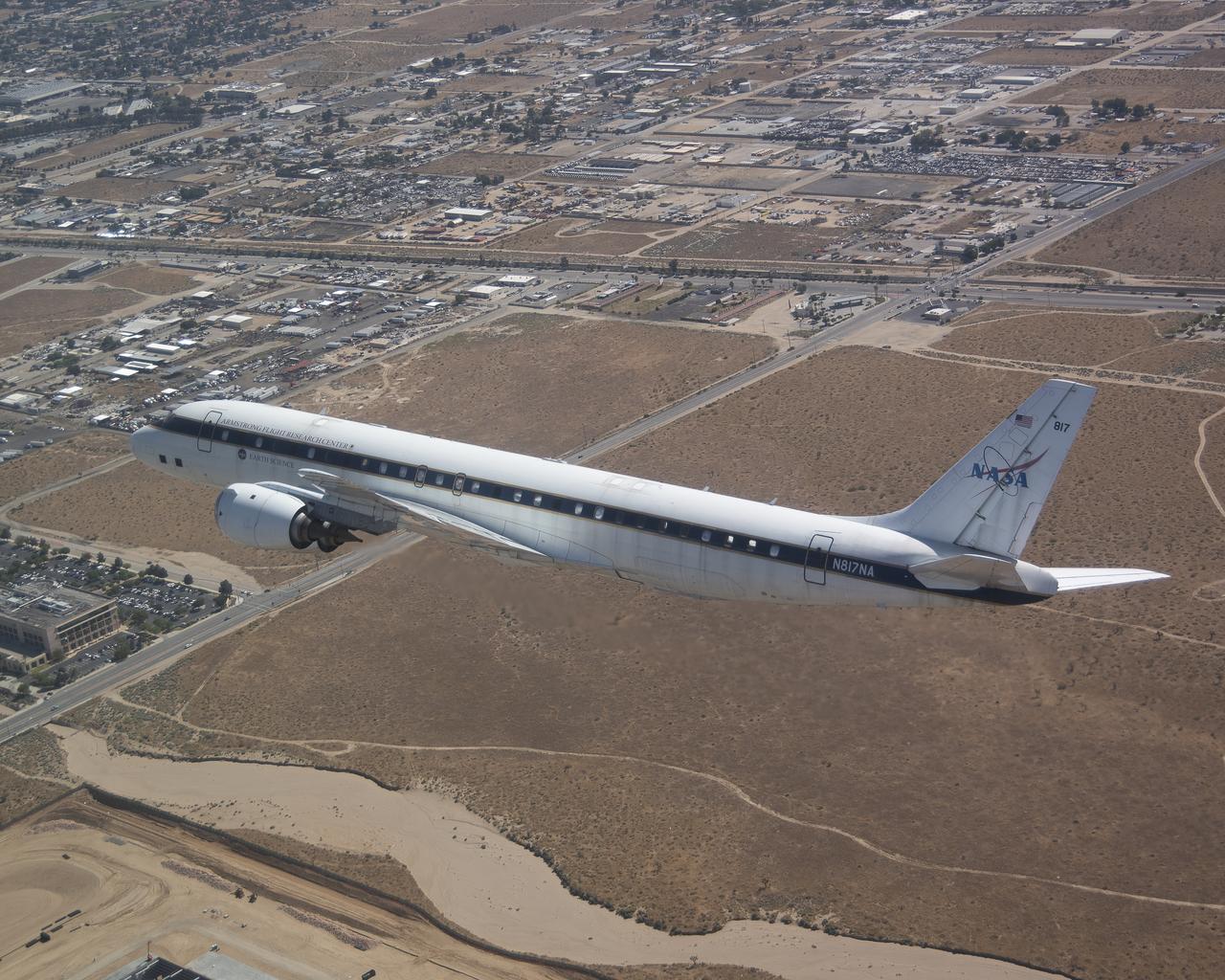

The DC-8 flies low over the Antelope Valley during its final flight before it is retired from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, to Idaho State University in Pocatello, Idaho. The DC-8 will provide real-world experience to train future aircraft technicians at the college’s Aircraft Maintenance Technology Program.
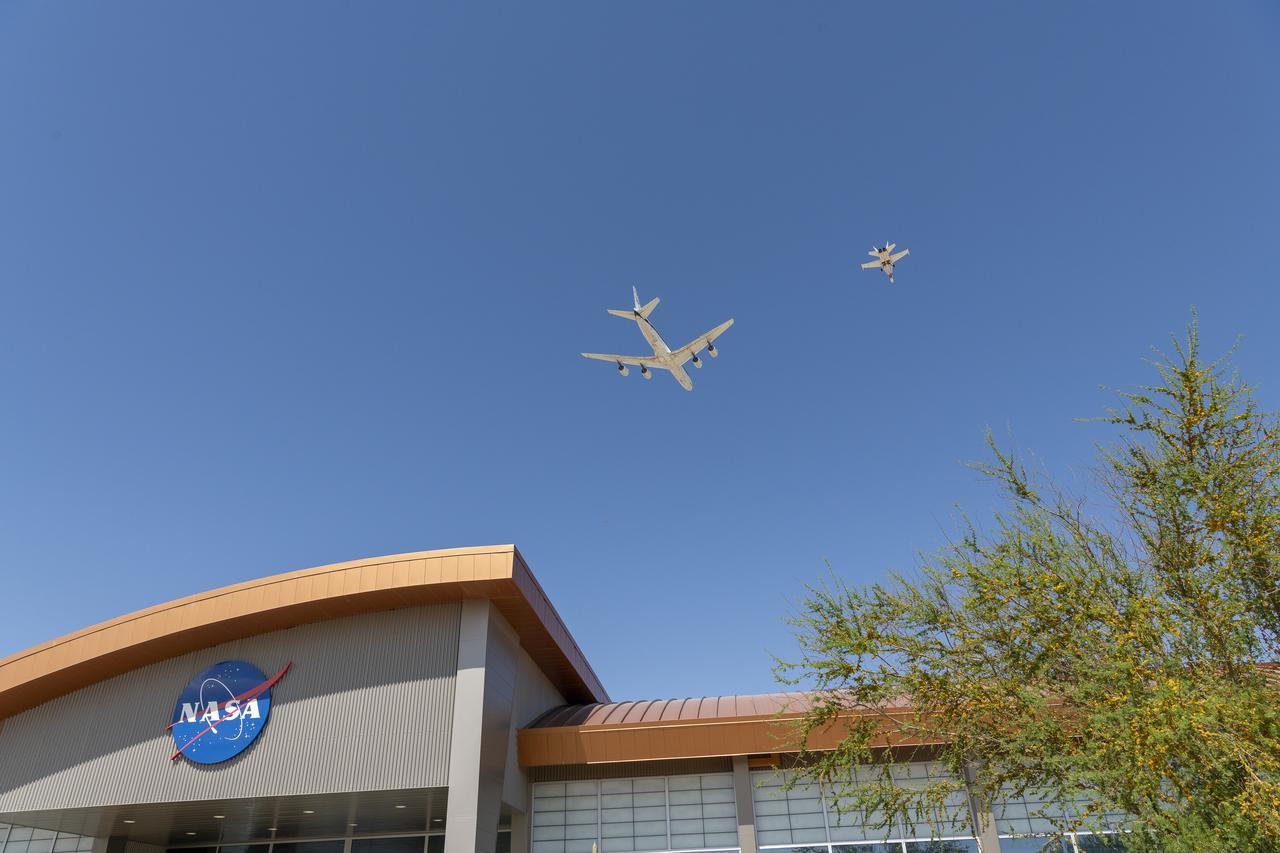

The DC-8 flies low for the last time over NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, before it retires to Idaho State University in Pocatello, Idaho. The DC-8 will provide real-world experience to train future aircraft technicians at the college’s Aircraft Maintenance Technology Program.
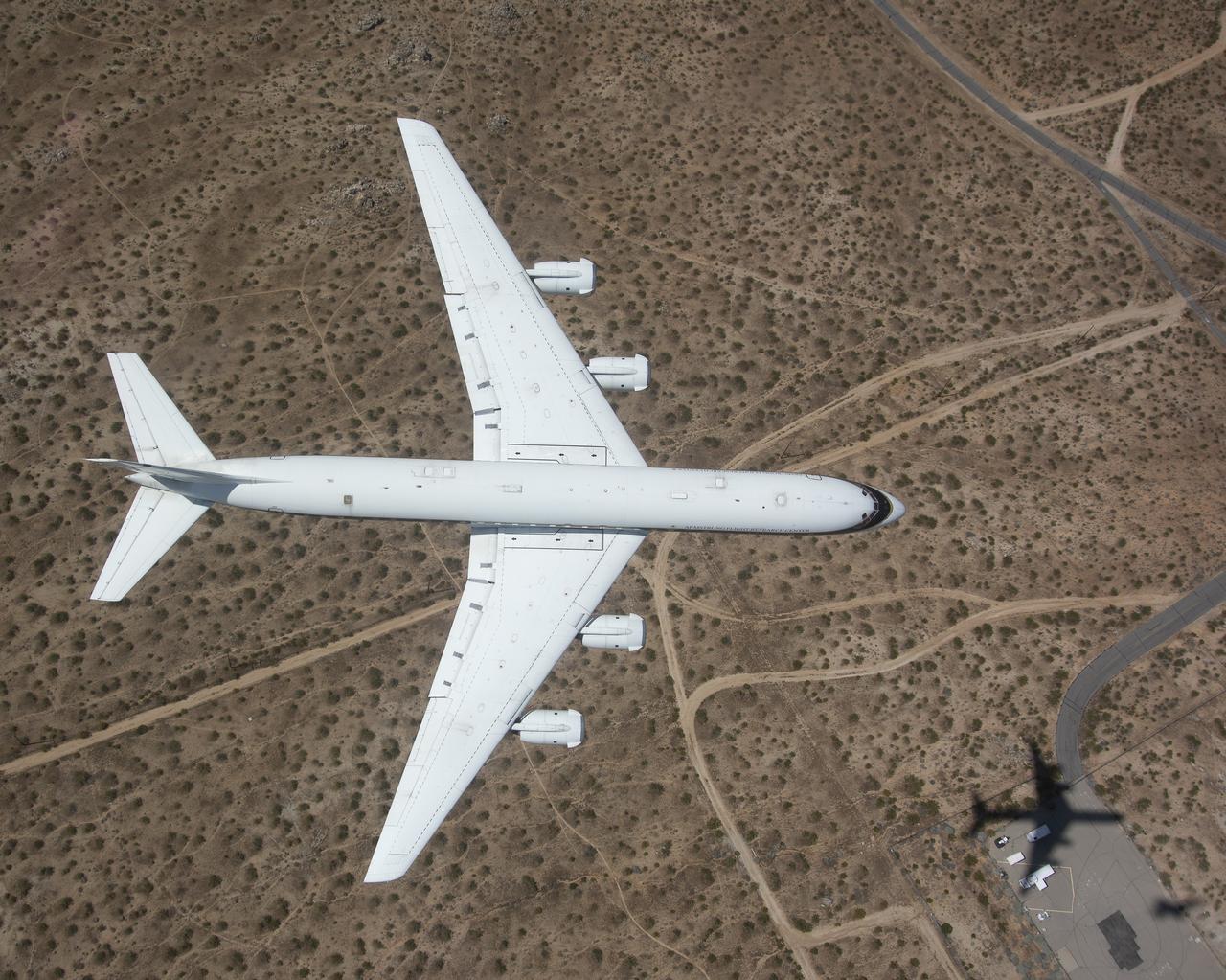

The DC-8 flies for the last time from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, to Idaho State University in Pocatello, Idaho. The DC-8 will provide real-world experience to train future aircraft technicians at the college’s Aircraft Maintenance Technology Program.
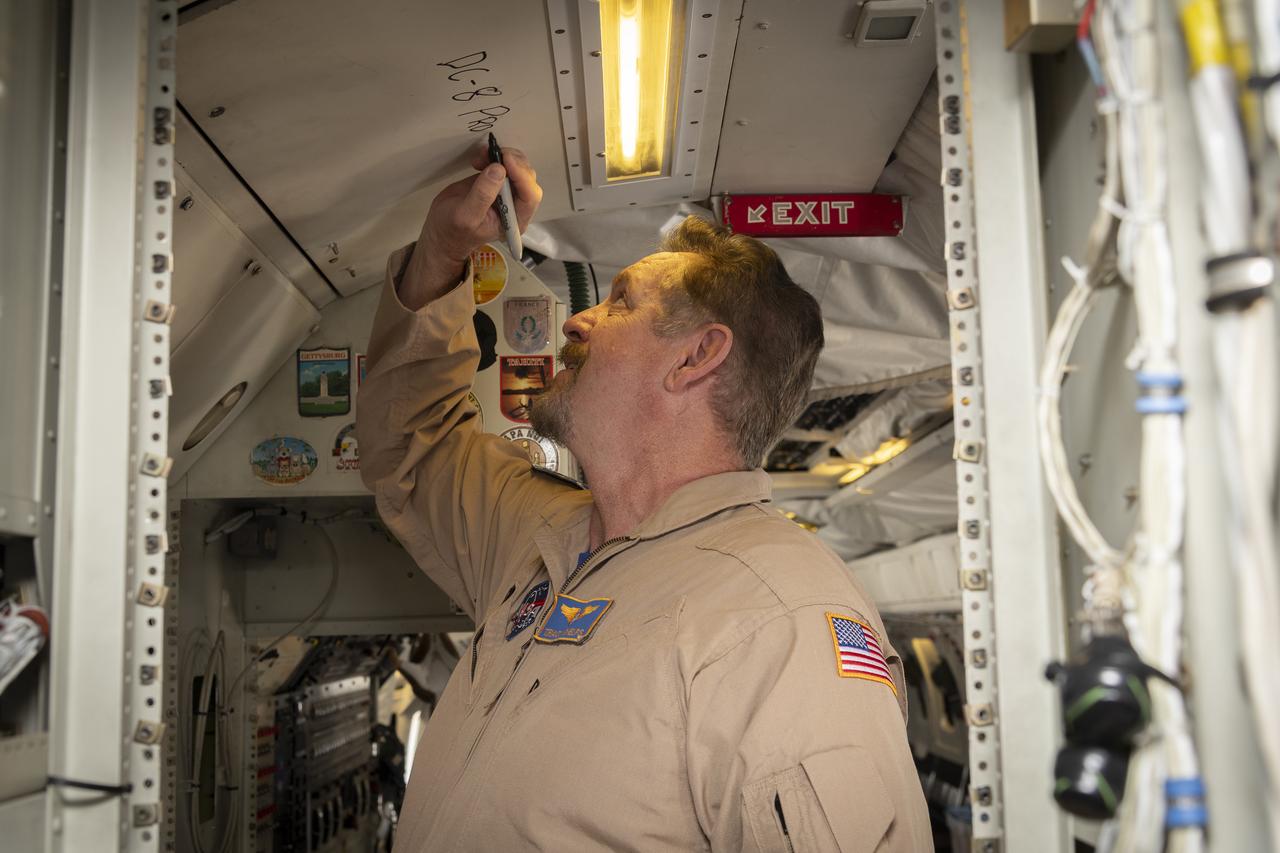

Aerospace engineer and research pilot Tracy Phelps signs the ceiling inside the DC-8 aircraft. Phelps piloted the aircraft’s final flight before it is retired from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, to Idaho State University in Pocatello, Idaho. The DC-8 will provide real-world experience to train future aircraft technicians at the college’s Aircraft Maintenance Technology Program.
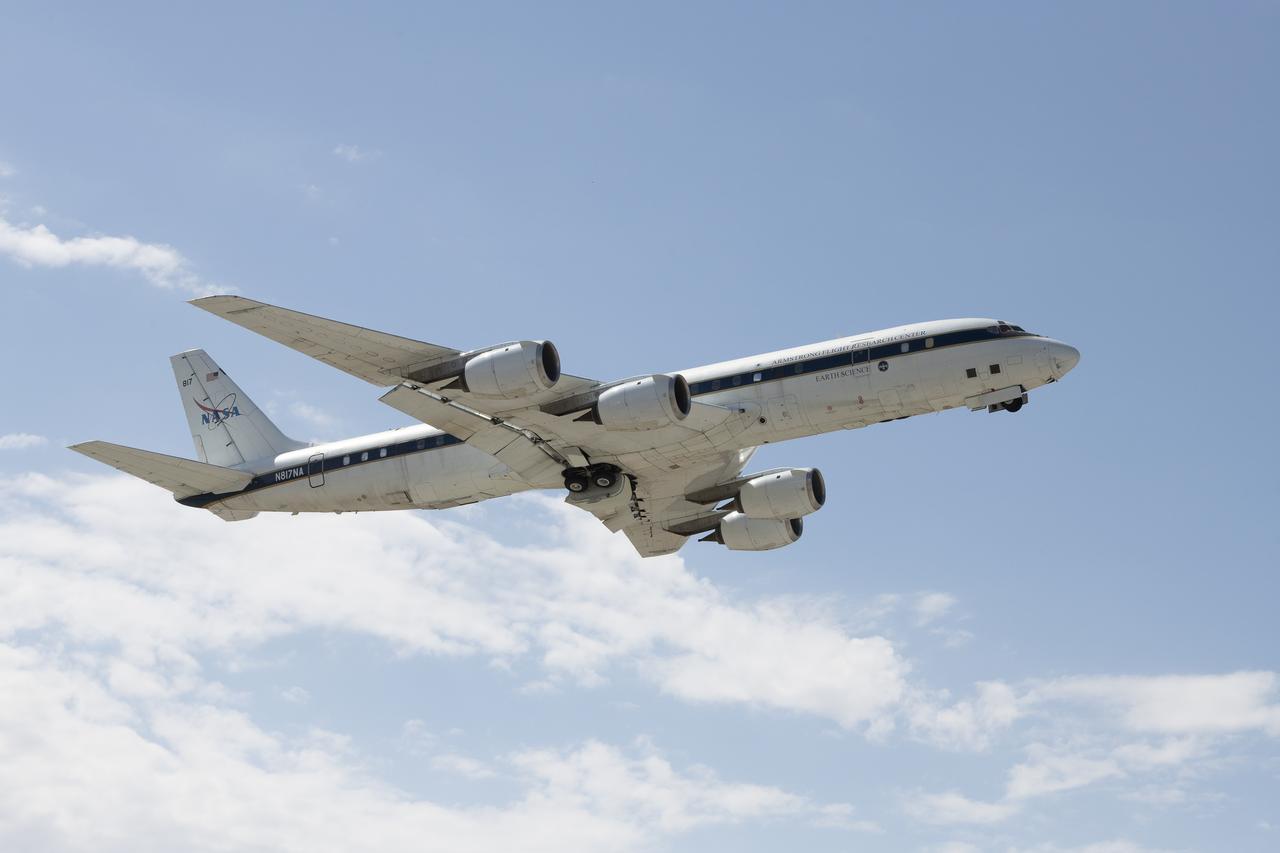

The DC-8 ascents during its final flight before it is retired from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, to Idaho State University in Pocatello, Idaho. The DC-8 will provide real-world experience to train future aircraft technicians at the college’s Aircraft Maintenance Technology Program.
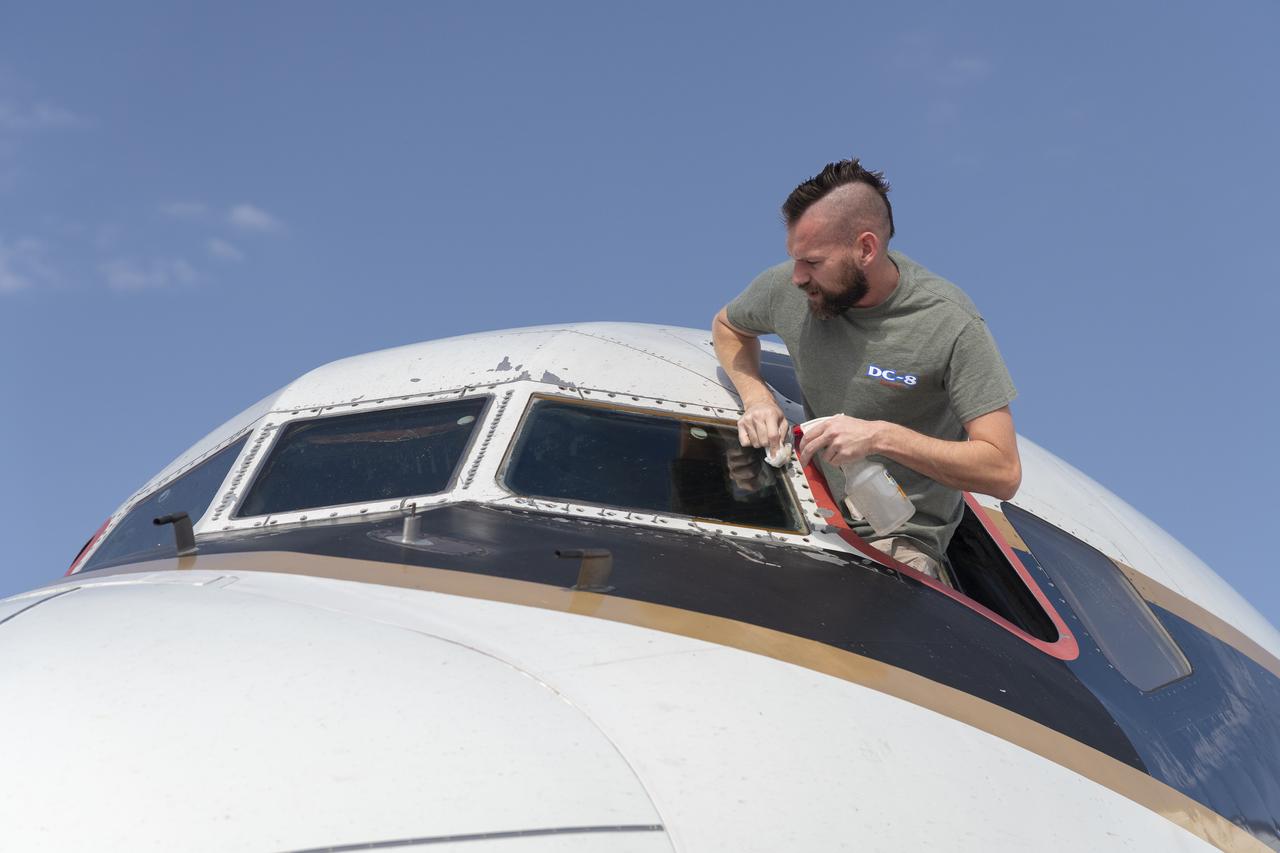

Avionics lead Kelly Jellison wipes the windshield of the DC-8 aircraft prior to its final flight before it is retired from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, to Idaho State University in Pocatello, Idaho. The DC-8 will provide real-world experience to train future aircraft technicians at the college’s Aircraft Maintenance Technology Program.
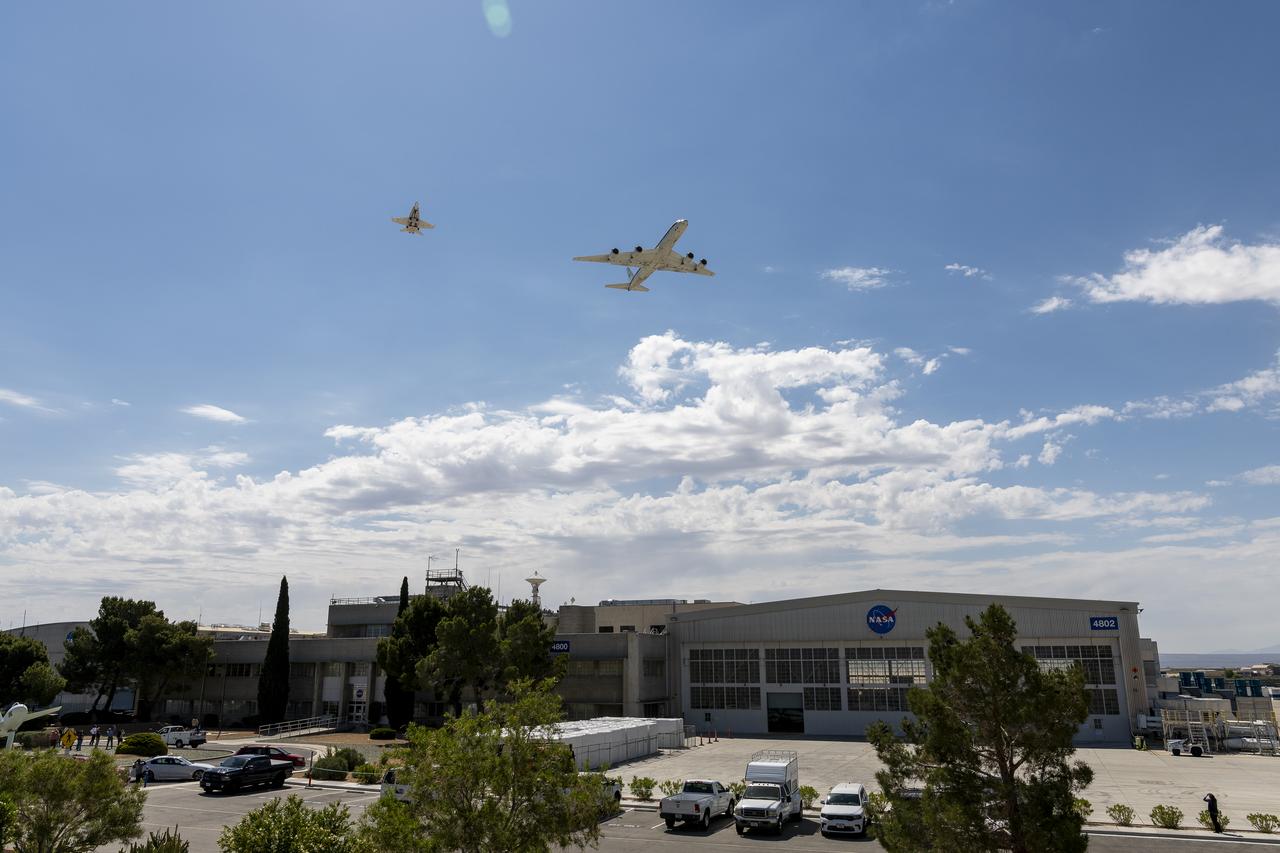

The DC-8 flies for the last time from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, before it retires to Idaho State University in Pocatello, Idaho. The DC-8 will provide real-world experience to train future aircraft technicians at the college’s Aircraft Maintenance Technology Program.
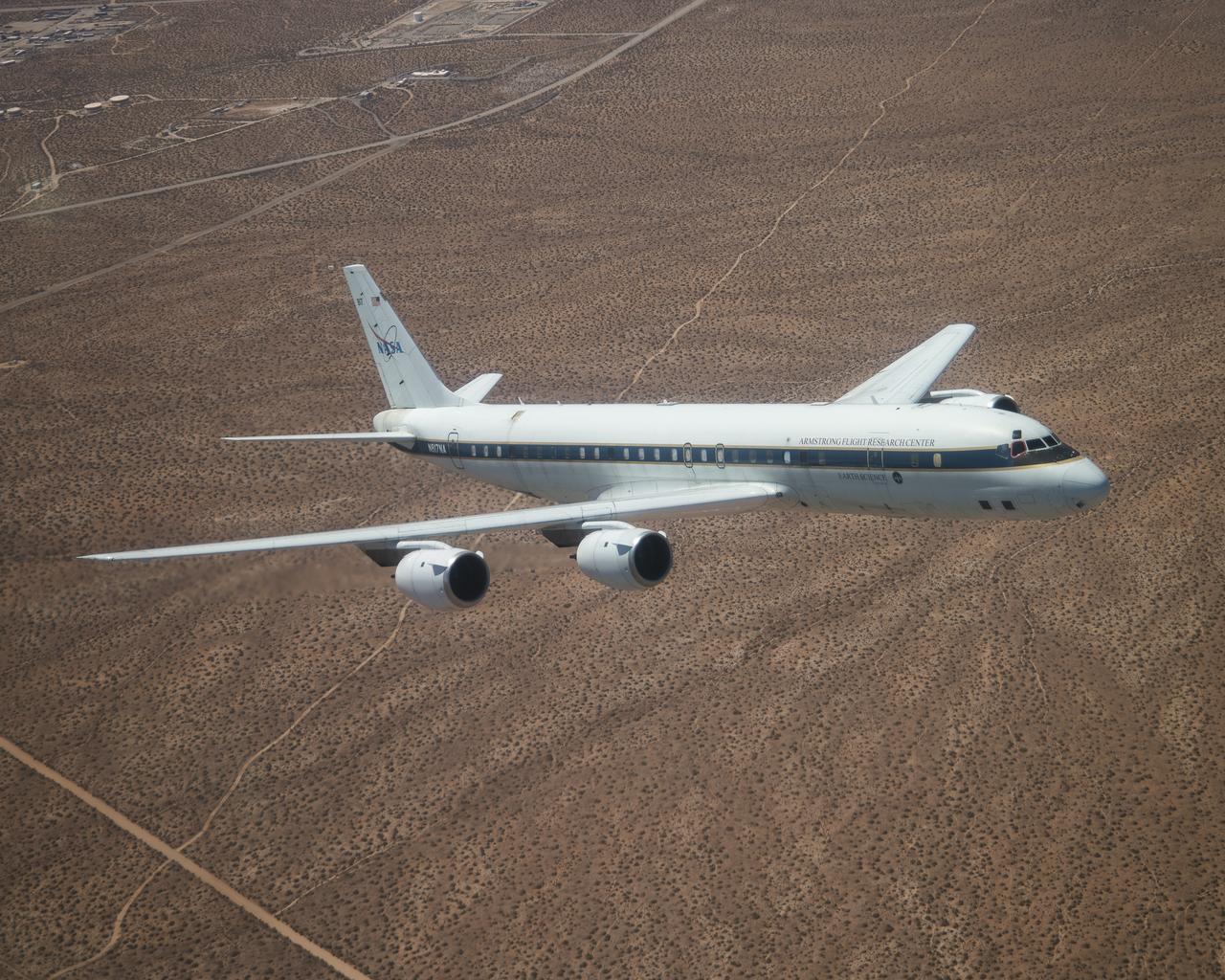

The DC-8 flies for the last time from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, before it retires to Idaho State University in Pocatello, Idaho. The DC-8 will provide real-world experience to train future aircraft technicians at the college’s Aircraft Maintenance Technology Program.
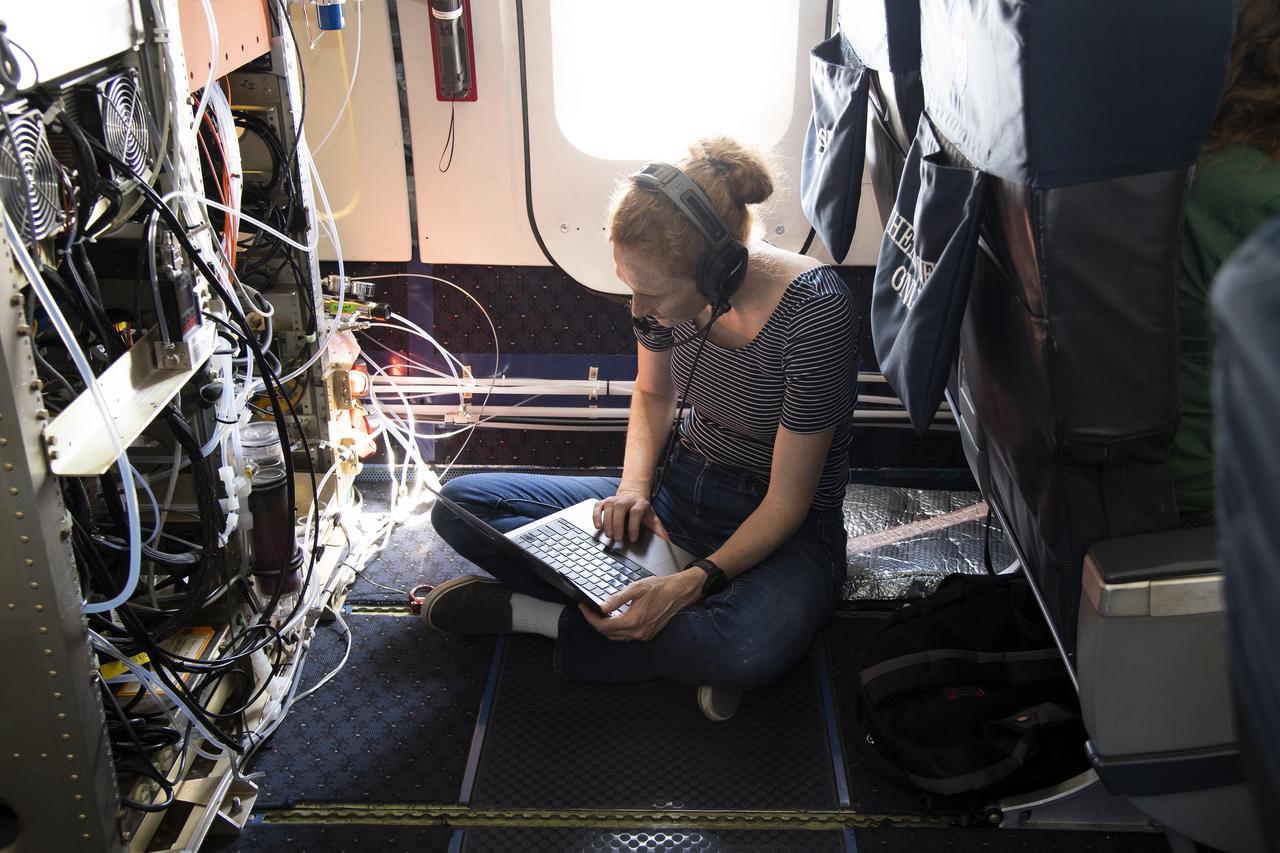

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
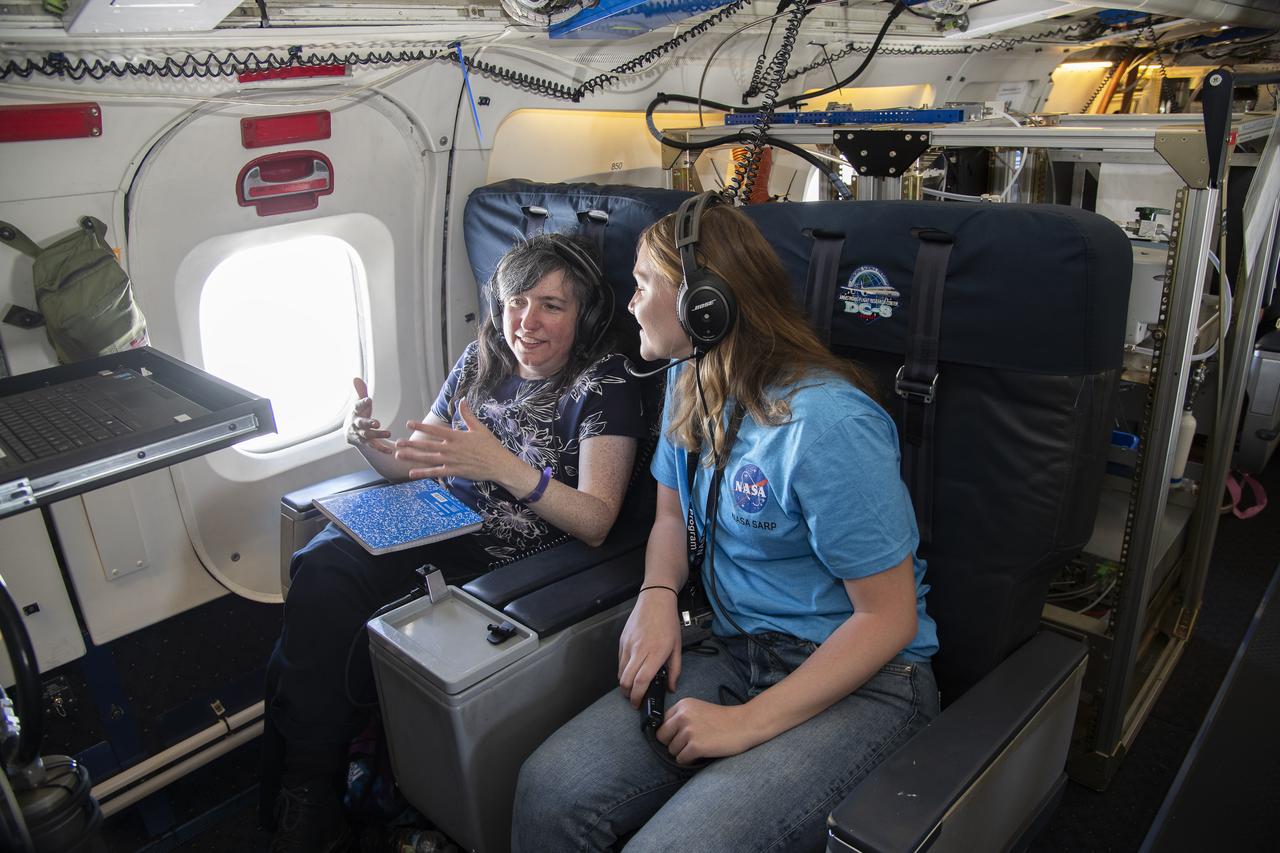

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
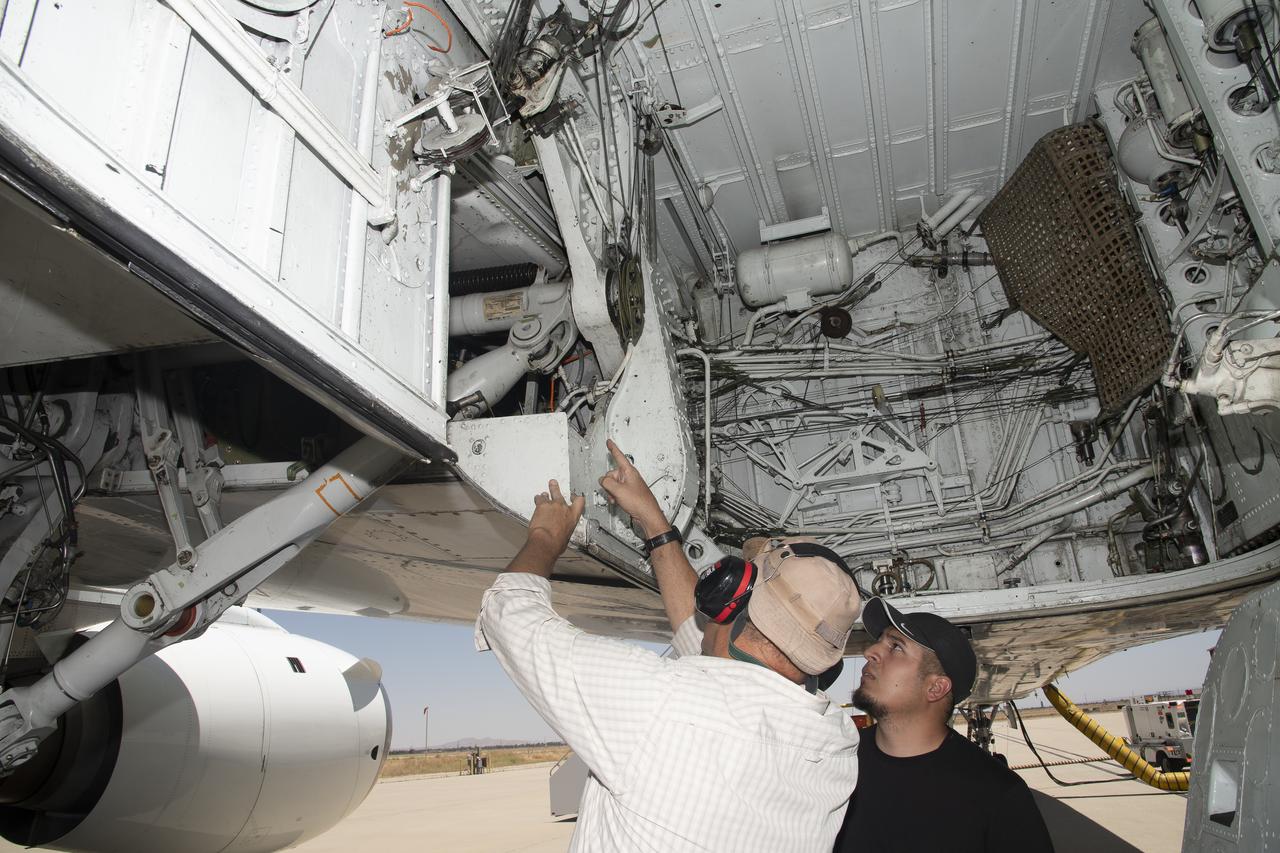

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
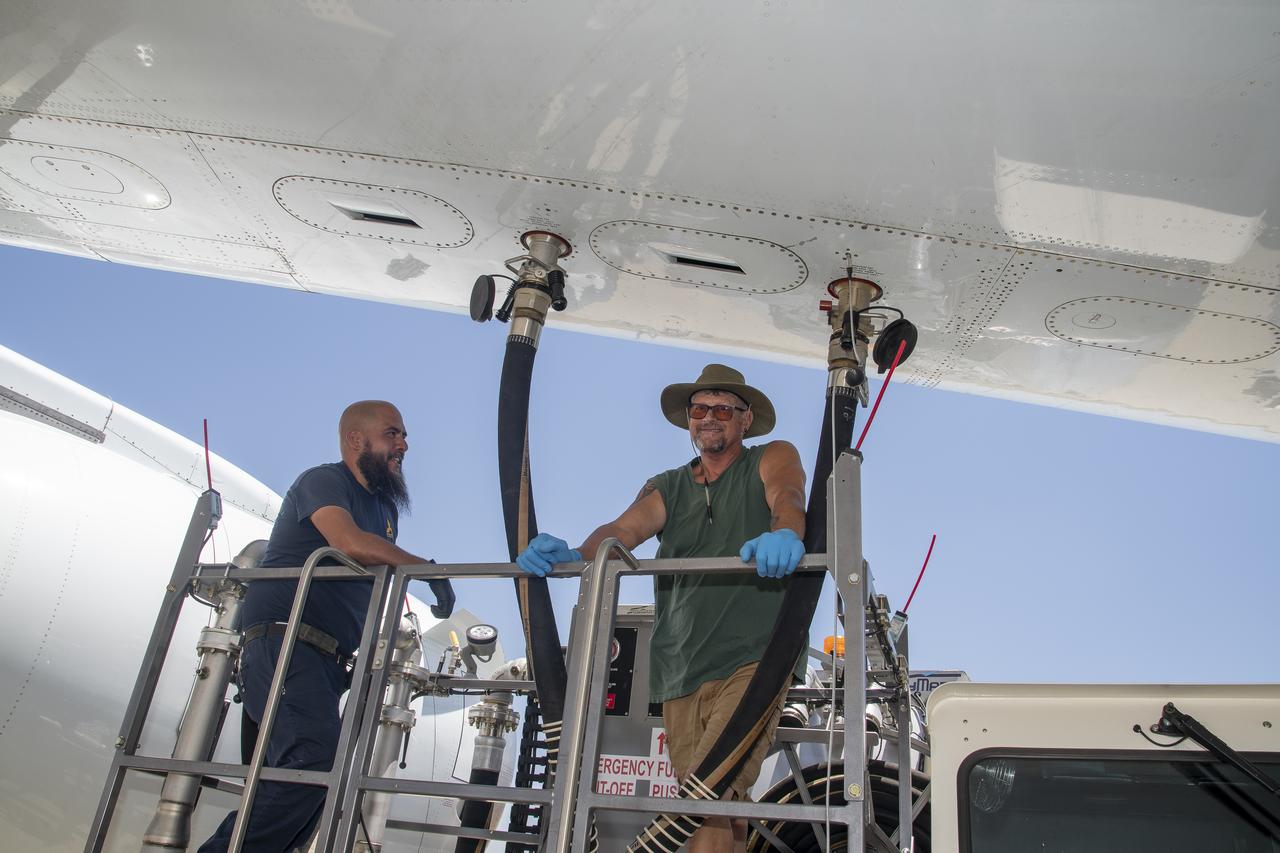

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
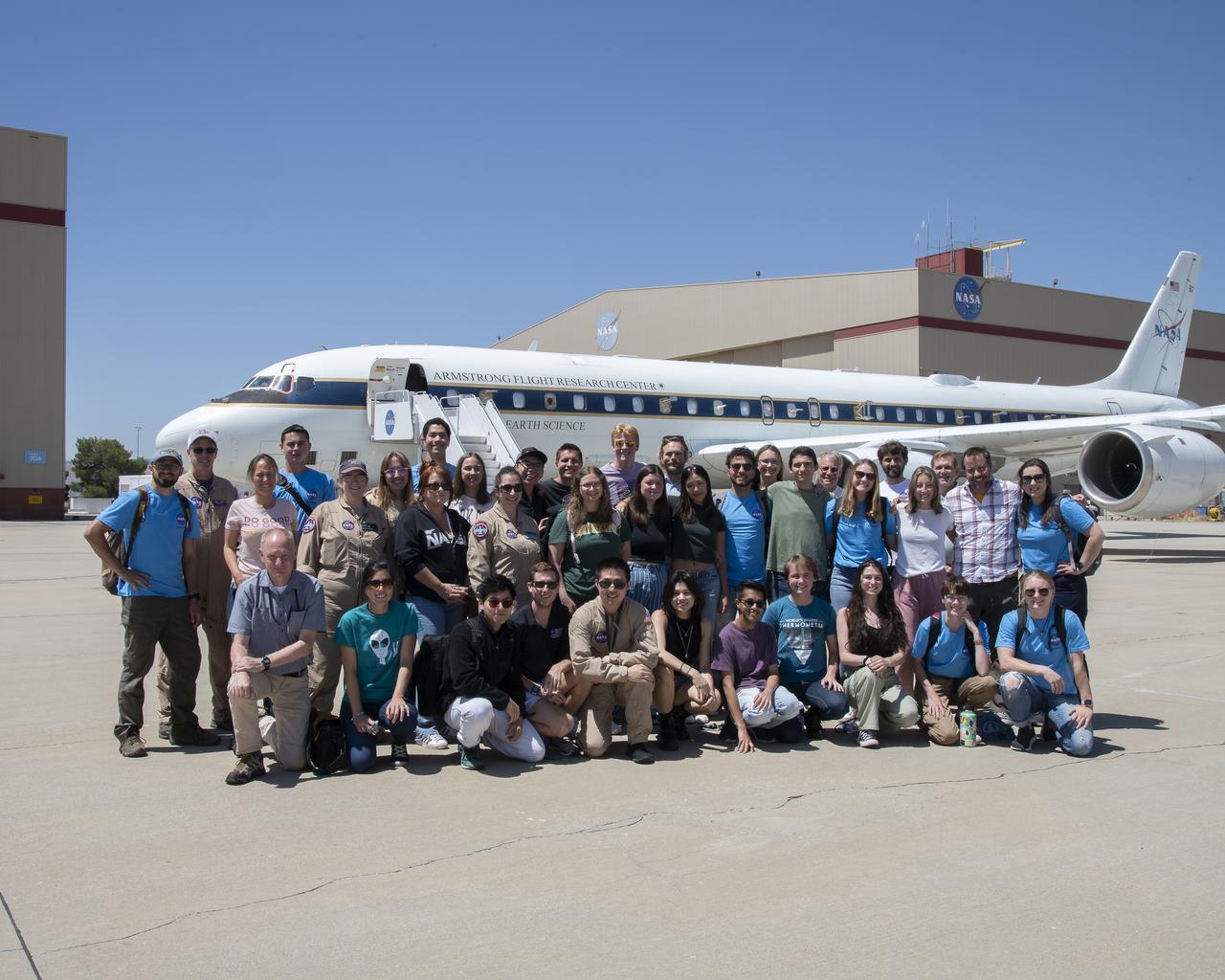

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
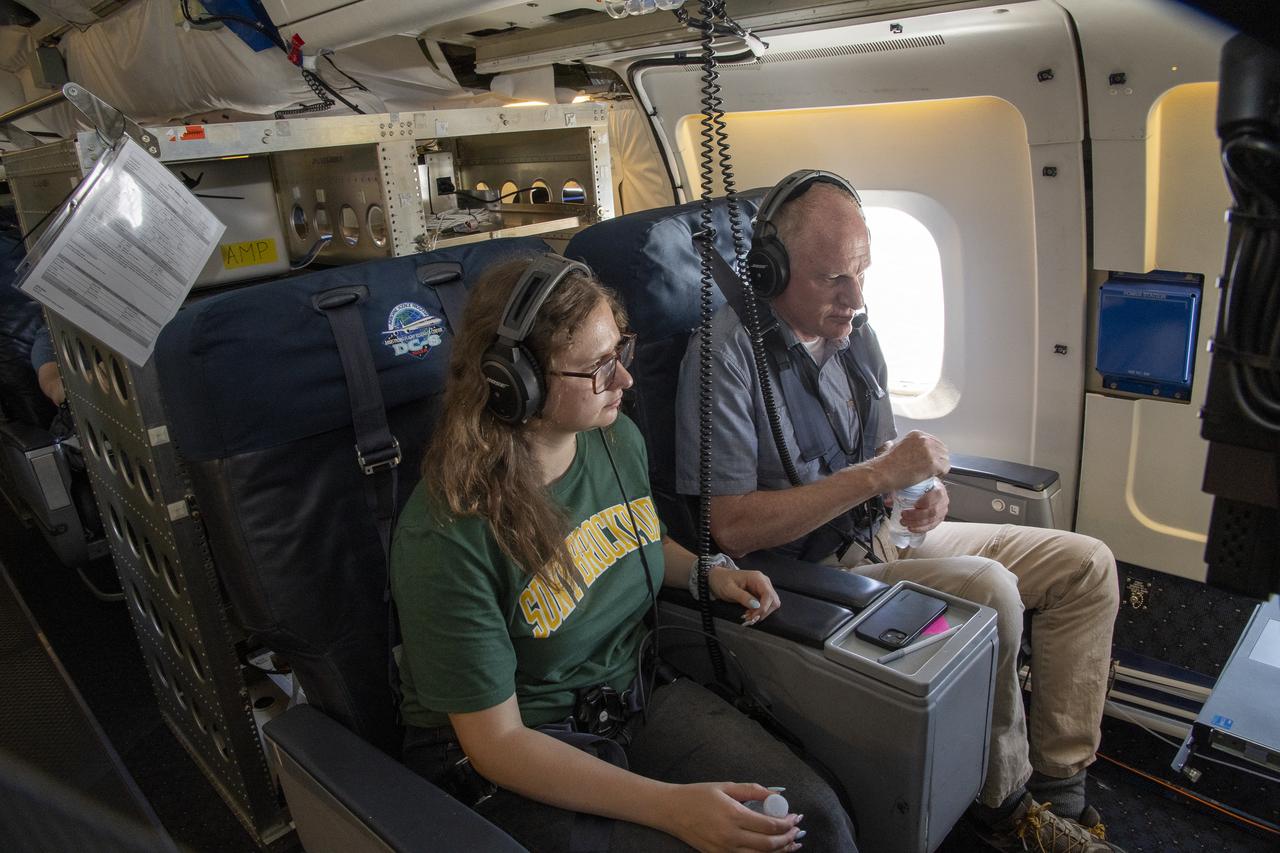

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
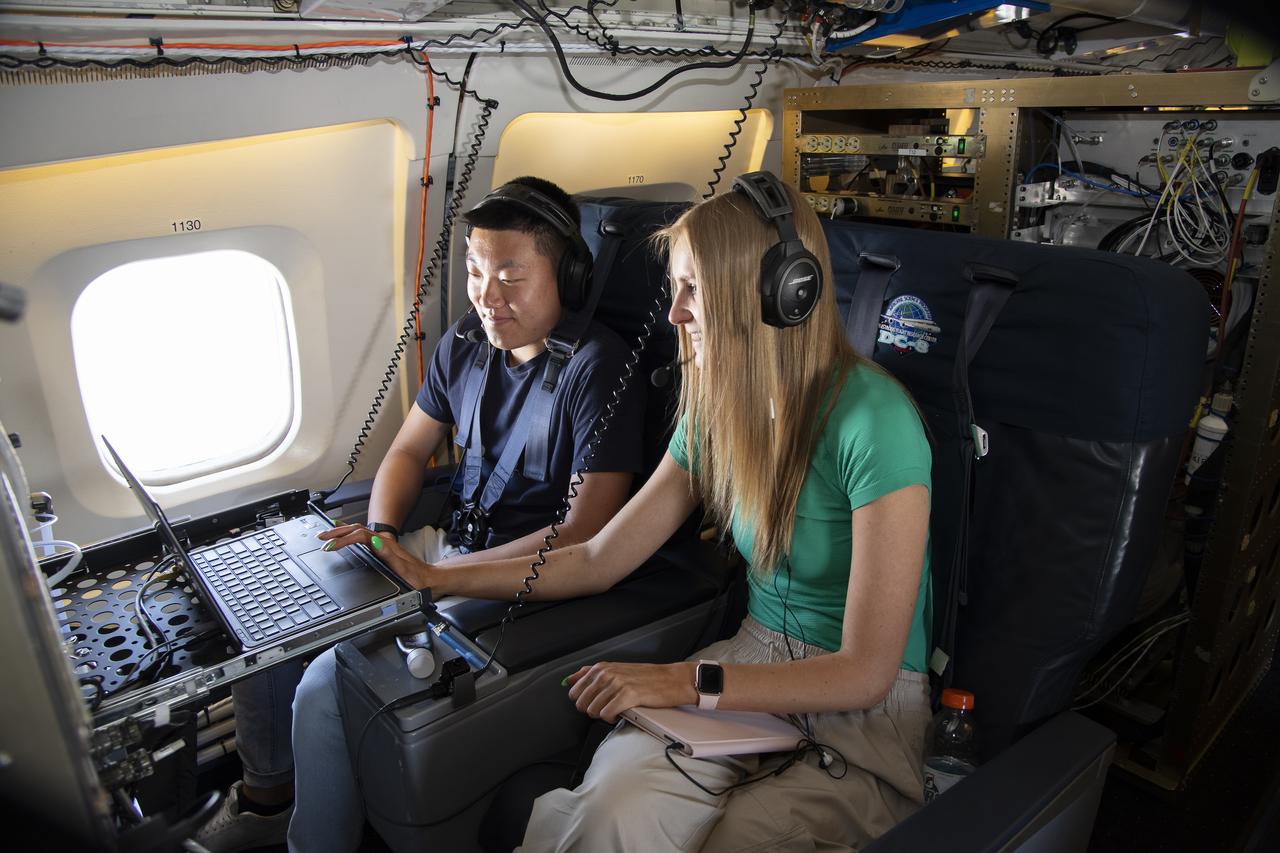

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.

James Barrilleaux is the assistant chief pilot for ER-2s in the Flight Crew Branch of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The ER-2s--civilian variants of the military U-2S reconnaissance aircraft--are part of NASA's Airborne Science program. The ER-2s can carry airborne scientific payloads of up to 2,600 pounds to altitudes of about 70,000 feet to investigate such matters as earth resources, celestial phenomena, atmospheric chemistry and dynamics, and oceanic processes. Barrilleaux has held his current position since February 1998. Barrilleaux joined NASA in 1986 as a U-2/ER-2 pilot with NASA's Airborne Science program at Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California. He flew both the U-2C (until 1989) and the ER-2 on a wide variety of missions both domestic and international. Barrilleaux flew high-altitude operations over Antarctica in which scientific instruments aboard the ER-2 defined the cause of ozone depletion over the continent, known as the ozone hole. He has also flown the ER-2 over the North Pole. Barrilleaux served for 20 years in the U.S. Air Force before he joined NASA. He completed pilot training at Reese Air Force Base, Lubbock, Texas, in 1966. He flew 120 combat missions as a F-4 fighter pilot over Laos and North Vietnam in 1970 and 1971. He joined the U-2 program in 1974, becoming the commander of an overseas U-2 operation in 1982. In 1983, he became commander of the squadron responsible for training all U-2 pilots and SR-71 crews located at Beale Air Force Base, Marysville, California. He retired from the Air Force as a lieutenant colonel in 1986. On active duty, he flew the U-2, F-4 Phantom, the T-38, T-37, and the T-33. His decorations included two Distinguished Flying Crosses, 12 Air Medals, two Meritorious Service Medals, and other Air Force and South Vietnamese awards. Barrilleaux earned a bachelor of science degree in chemical engineering from Texas A&M University, College Station, in 1964 and a master of science
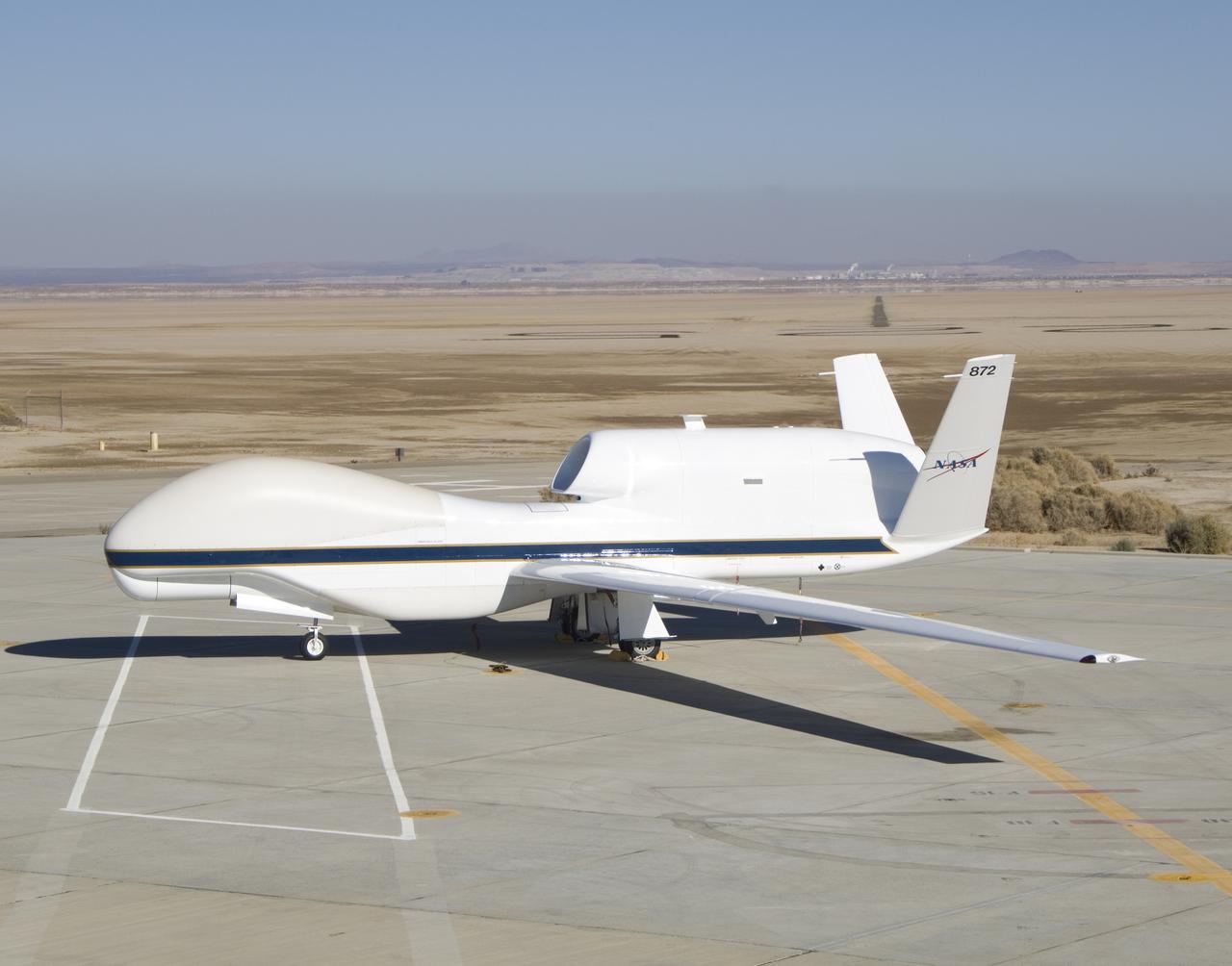

In its new white-and-blue NASA livery, an early development model of the Global Hawk unmanned aircraft rests on the ramp at the Dryden Flight Research Center.
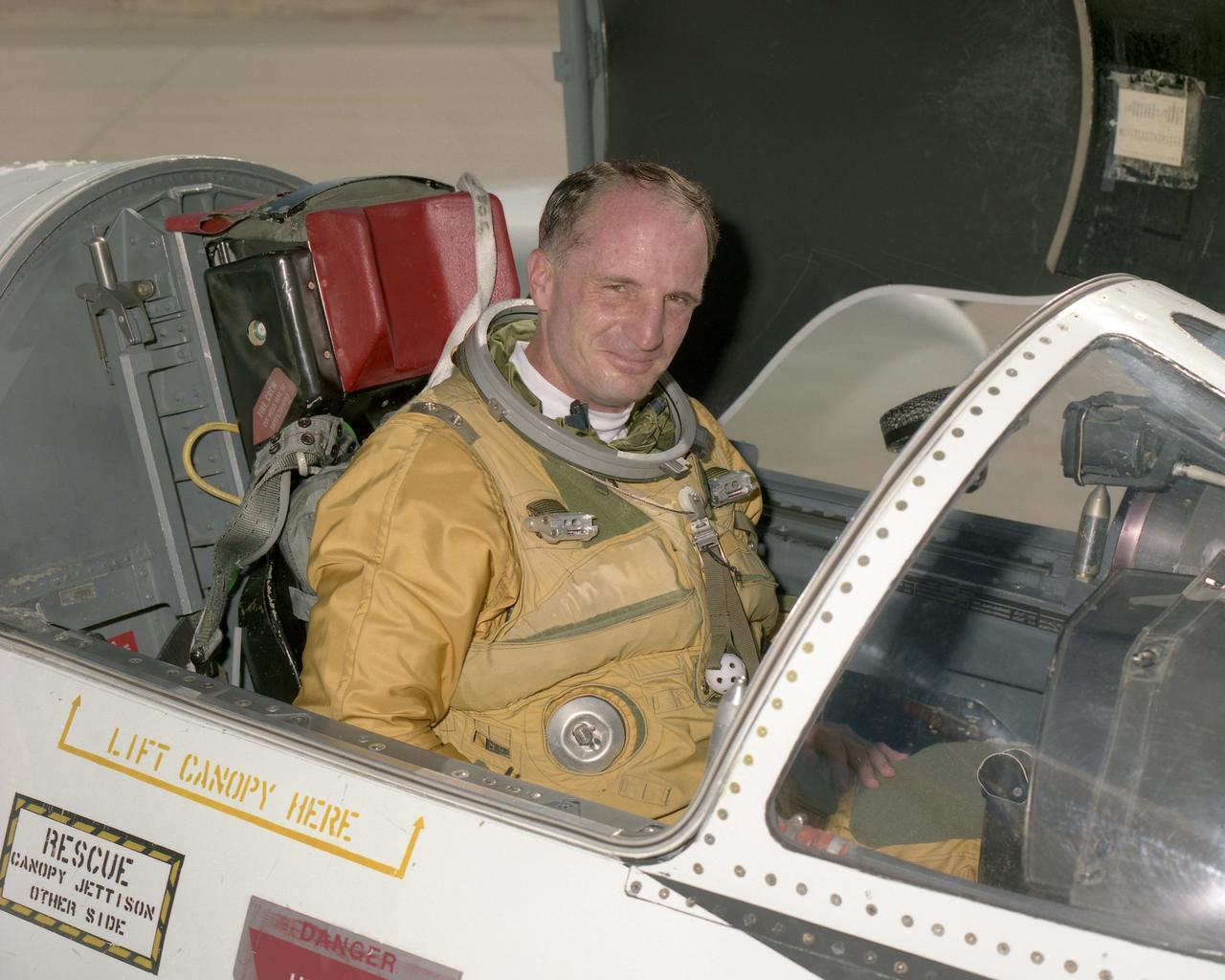

David A. Wright is associate director for Center Operations at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif. He was formerly director of Flight Operations. He is also a research pilot, flying NASA's ER-2 and T-38. The ER-2s are civilian variants of the military U-2S reconnaissance aircraft and carry scientific instruments to study the Earth during worldwide deployments. Wright has more than 4,500 hours in six different aircraft. He held the position of deputy director of the Airborne Science Program at Dryden from 2002 until 2004. Wright came to Dryden after retiring from the U.S. Air Force as a lieutenant colonel. His final assignment was to the Joint Staff J3, Directorate of Operations at the Pentagon from November 1996 until August 1999. Prior to the Pentagon assignment, he served as commander of the 1st Reconnaissance Squadron at Beale Air Force Base near Marysville, Calif., the unit responsible for training all U-2 pilots. He was the operations officer for one the largest U-2 operations in history, flying combat missions against Iraq and managing an unprecedented U-2 flying schedule during the 1991 Desert Storm conflict. He was selected for the Air Force U-2 program in 1987 following duty as an aircraft commander in the E-3A AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System) aircraft. Wright was a T-38 instructor for three years at Reese Air Force Base, Lubbock, Texas, following completion of pilot training in 1978. He graduated from the U.S. Air Force Academy in 1977 with a Bachelor of Science in mathematics and computer science. Wright earned a Master of Arts in Adult Education from Troy State University, Montgomery, Ala., in 1987, and a Master of Science in National Security and Strategic Studies from the Naval War College, Newport, R.I., in 1995.
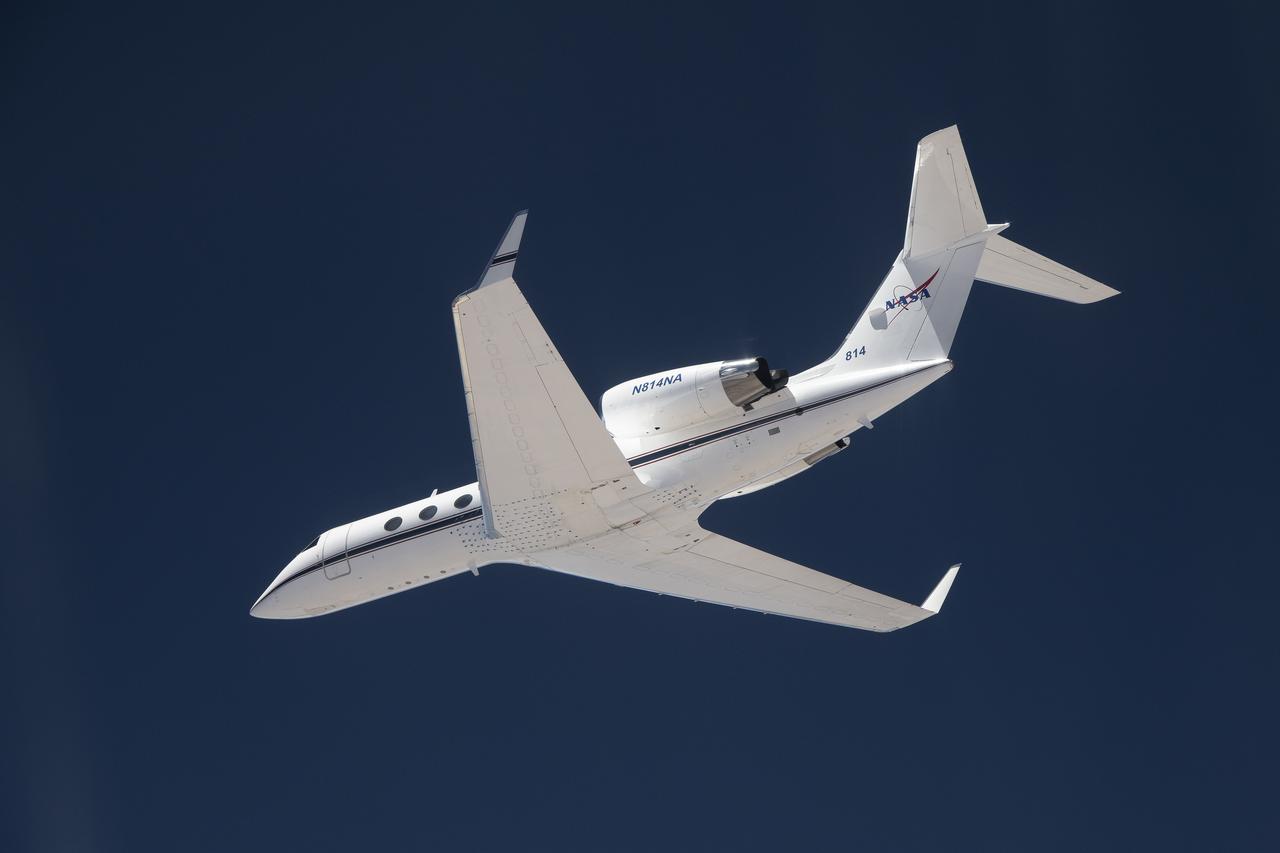

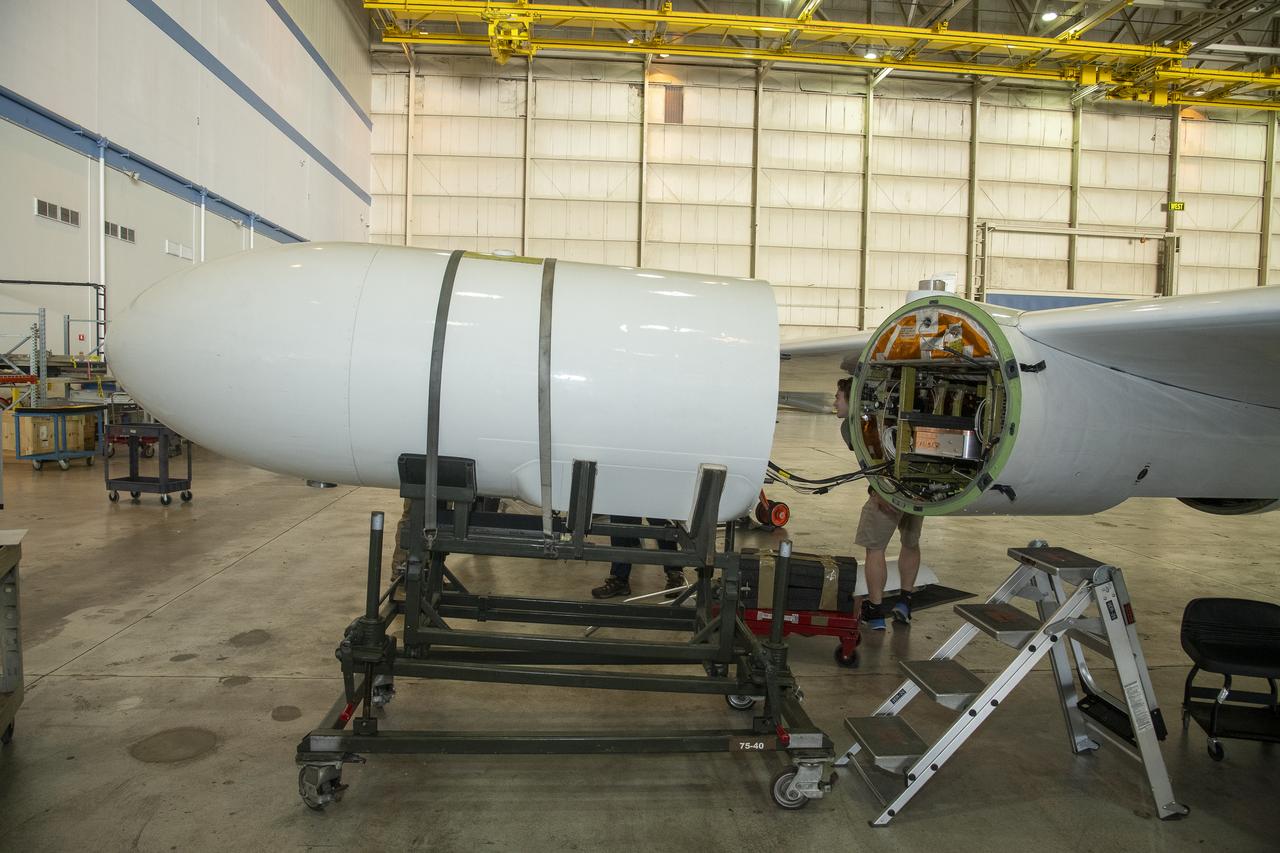
The G-IV aircraft flies overhead in the Mojave Desert near NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Baseline flights like this one occurred in June 2024, and future flights in service of science research will benefit from the installment of the Soxnav navigational system, developed in collaboration with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and the Bay Area Environmental Research Institute in California’s Silicon Valley. This navigational system provides precise, economical aircraft guidance for a variety of aircraft types moving at high speeds.
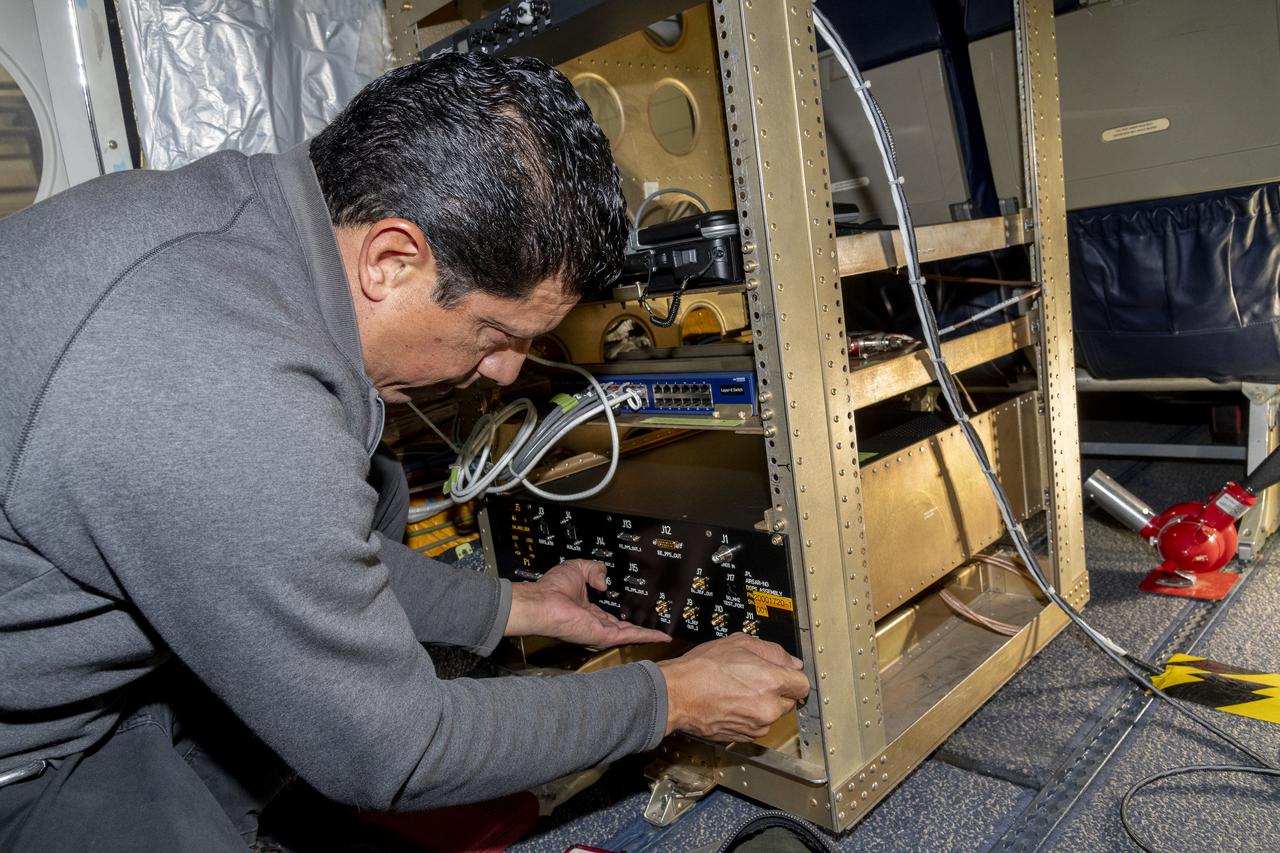

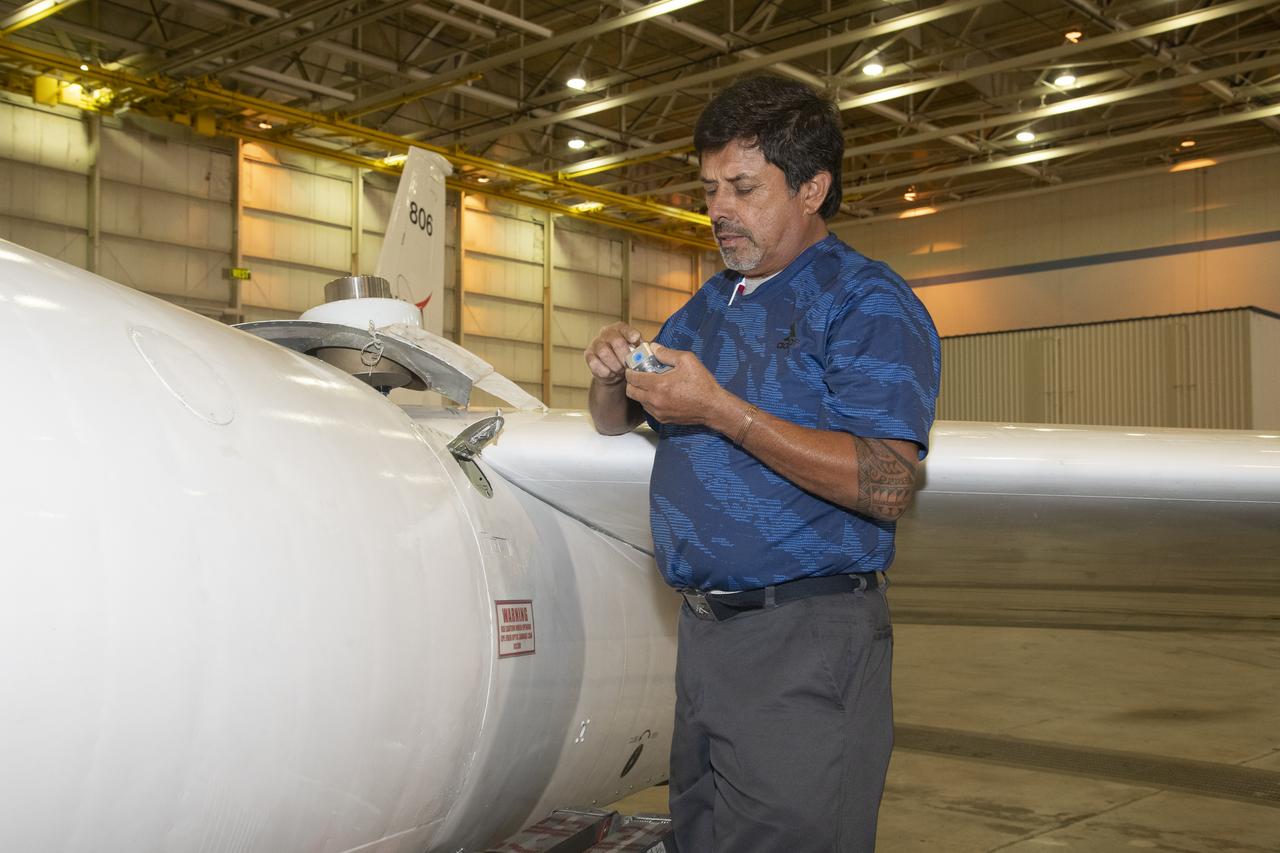
Jose “Manny” Rodriguez adjusts the Soxnav instrument onboard the G-IV aircraft in December 2024. As part of the team of experts, Rodriguez ensures that the electronic components of this instrument are installed efficiently. His expertise will help bring the innovative navigational guidance of the Soxnav system to the G-IV and the wider airborne science fleet at NASA. Precision guidance provided by the Soxnav enables research aircraft like the G-IV to collect more accurate, more reliable Earth science data to scientists on the ground.

NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center marked its 60th anniversary as the aerospace agency's lead center for atmospheric flight research and operations in 2006. In connection with that milestone, hundreds of the center's staff and retirees gathered in nearby Lancaster, Calif., in November 2006 to reflect on the center's challenges and celebrate its accomplishments over its six decades of advancing the state-of-the-art in aerospace technology. The center had its beginning in 1946 when a few engineers from the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics' Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory were detailed to Muroc Army Air Base (now Edwards Air Force Base) in Southern California's high desert to support the joint Army Air Force / NACA / Bell Aircraft XS-1 research airplane program. Since that inauspicious beginning, the center has been at the forefront of many of the advances in aerospace technology by validating advanced concepts through actual in-flight research and testing. Dryden is uniquely situated to take advantage of the excellent year-round flying weather, remote area, and visibility to test some of the nation�s most exciting aerospace vehicles. Today, NASA Dryden is NASA's premier flight research and test organization, continuing to push the envelope in the validation of high-risk aerospace technology and space exploration concepts, and in conducting airborne environmental and space science missions in the 21st century.

NASA’s B200 King Air team includes, from left, principal engineer Cory Hill, operations engineer KC Sujan, pilot Tracy Phelps, crew chief Mario Soto, aircraft technician Ruben Saiza, quality assurance technician Scott Silver, and senior engineer Alexander Soibel. The compact Fire Infrared Radiance Spectral Tracker (c-FIRST) instrument was tested on the B200 aircraft – based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California – over the wildfires in the Pacific Palisades and Altadena, California, on November 21, 2024.
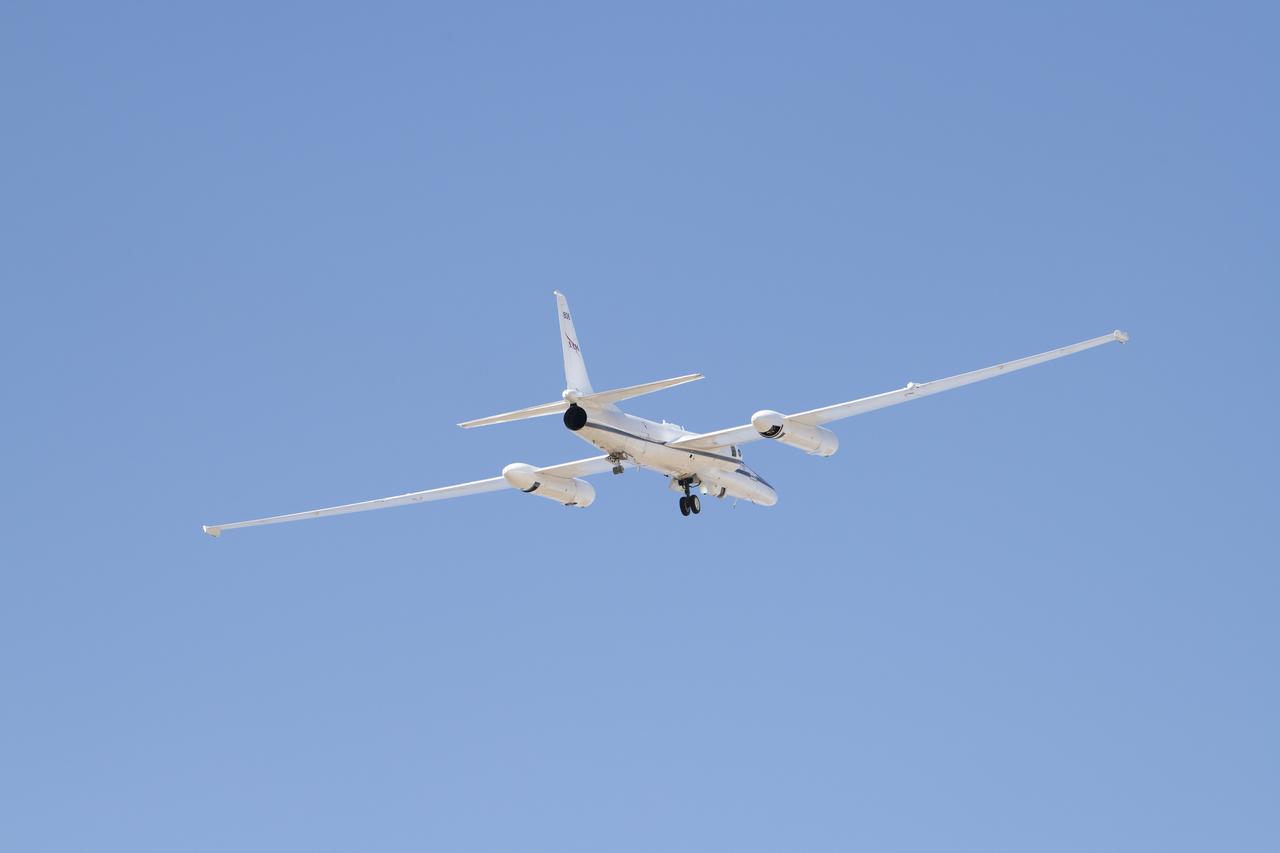

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
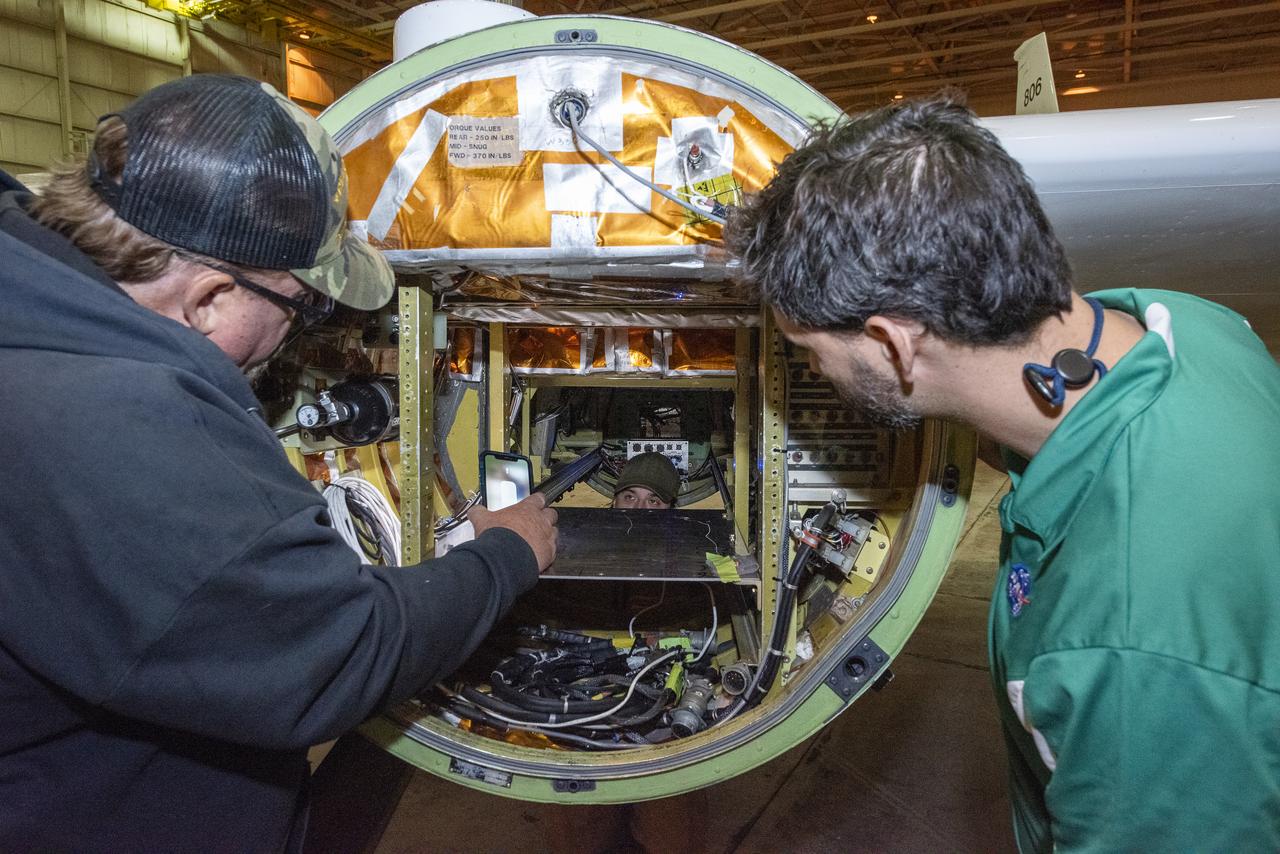

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
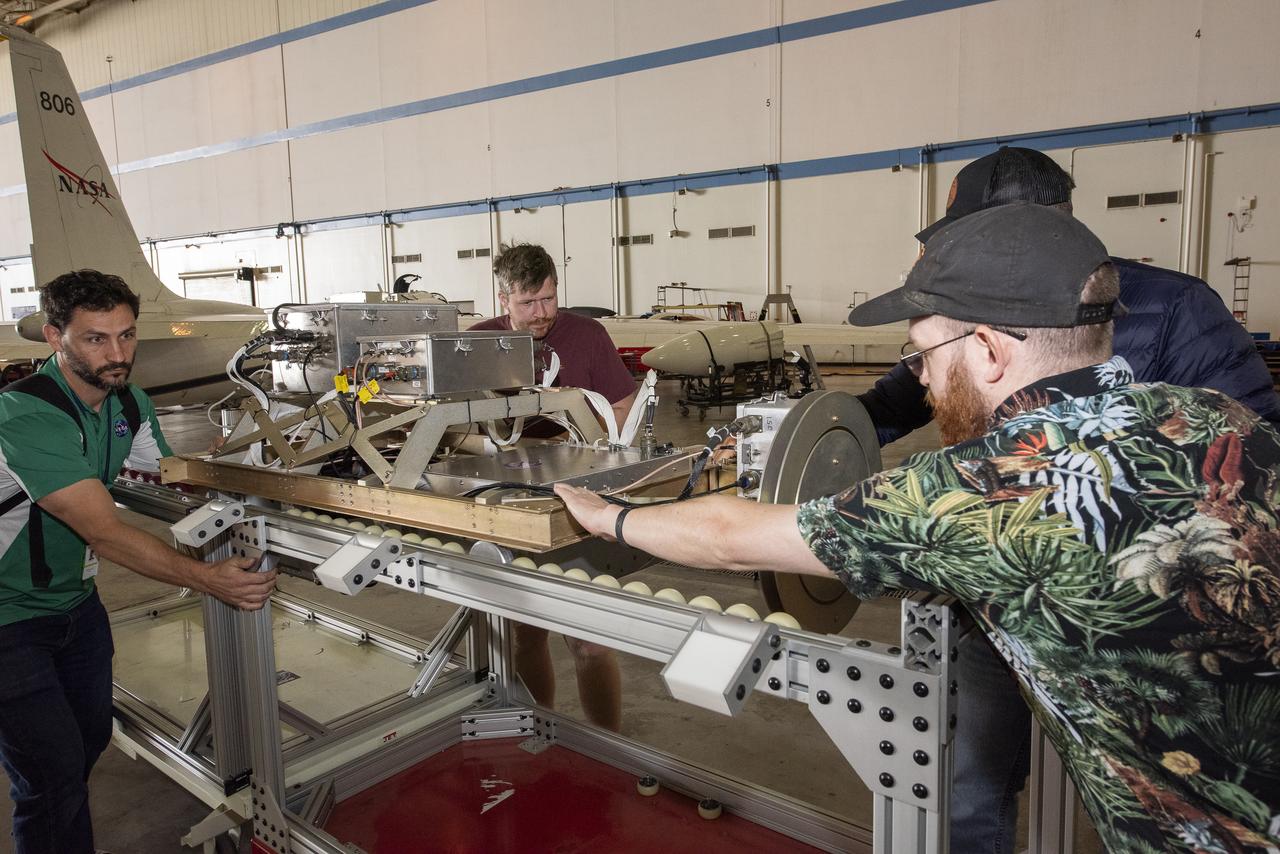

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.

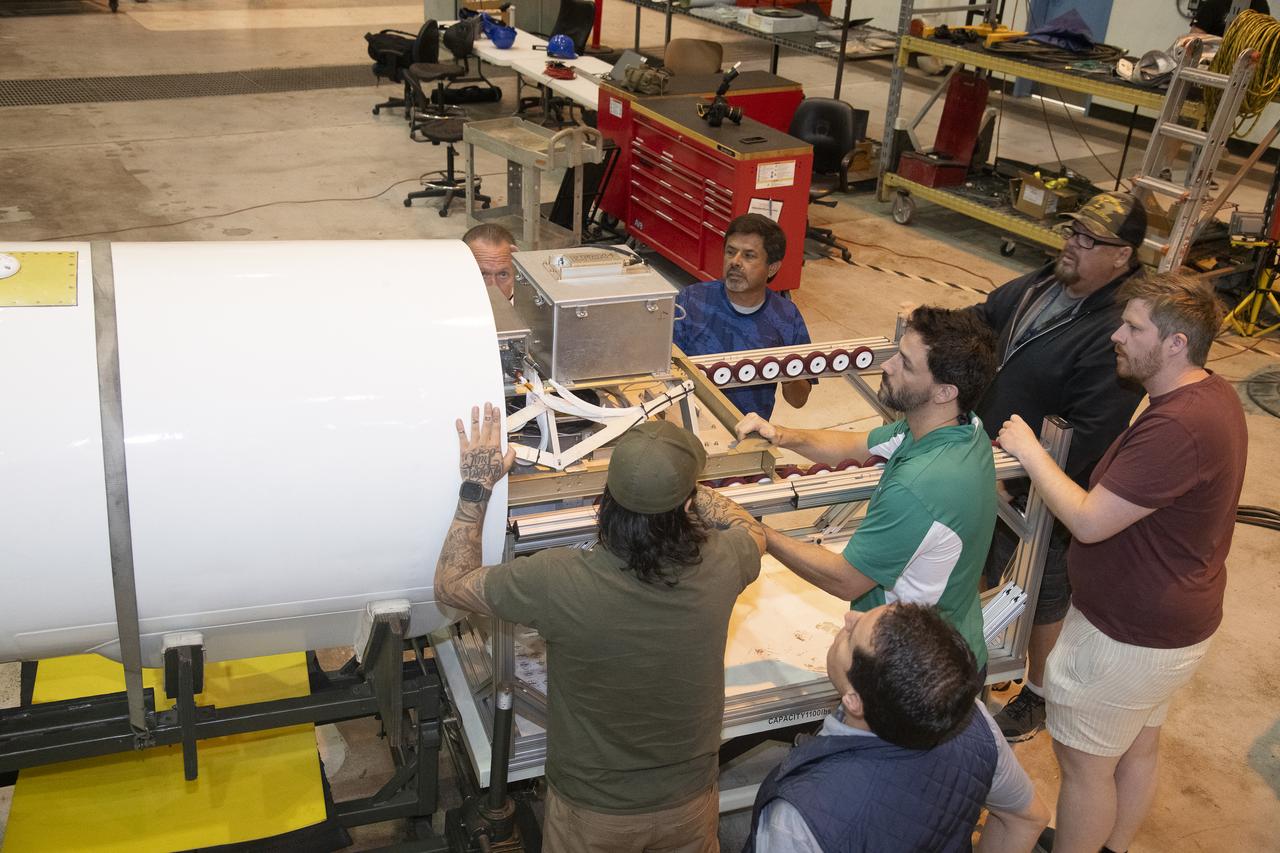
NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
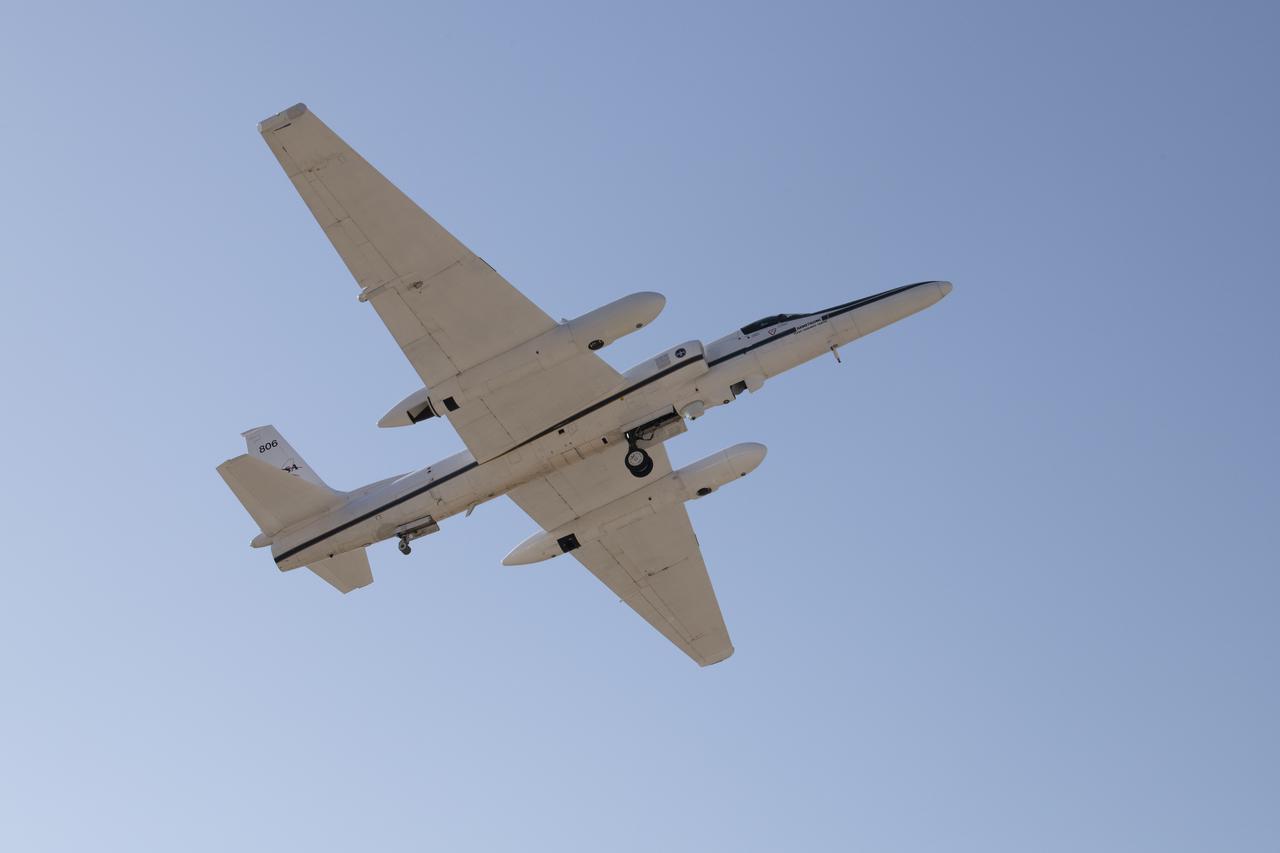

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
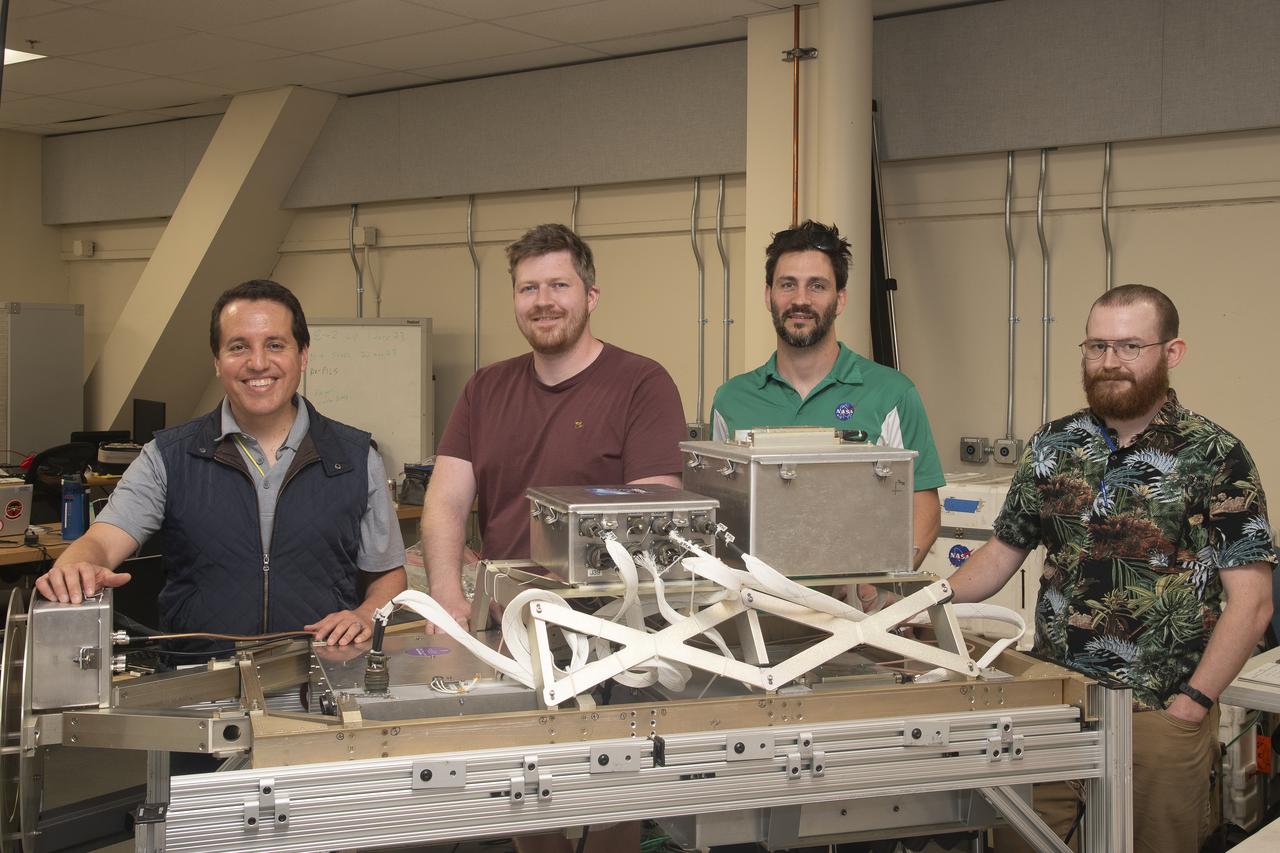
NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
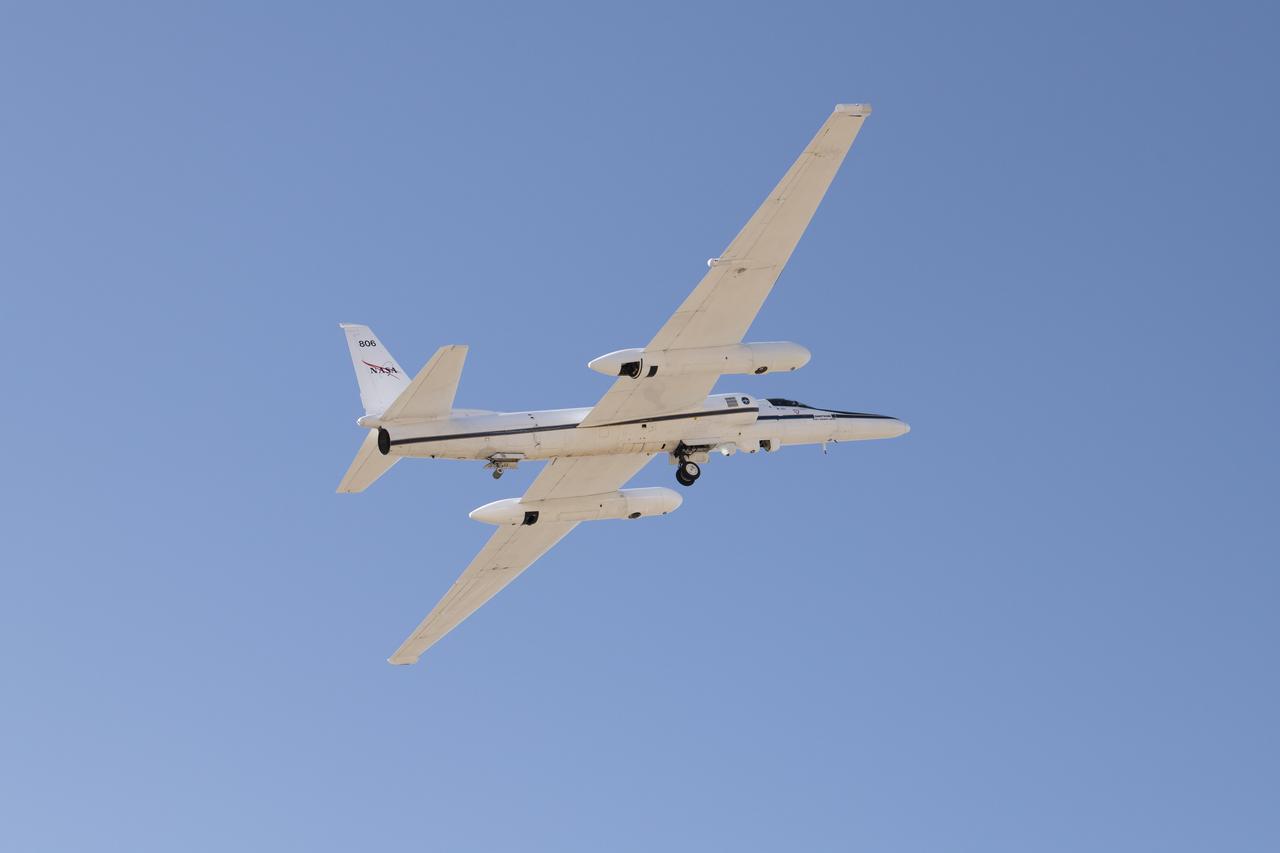

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
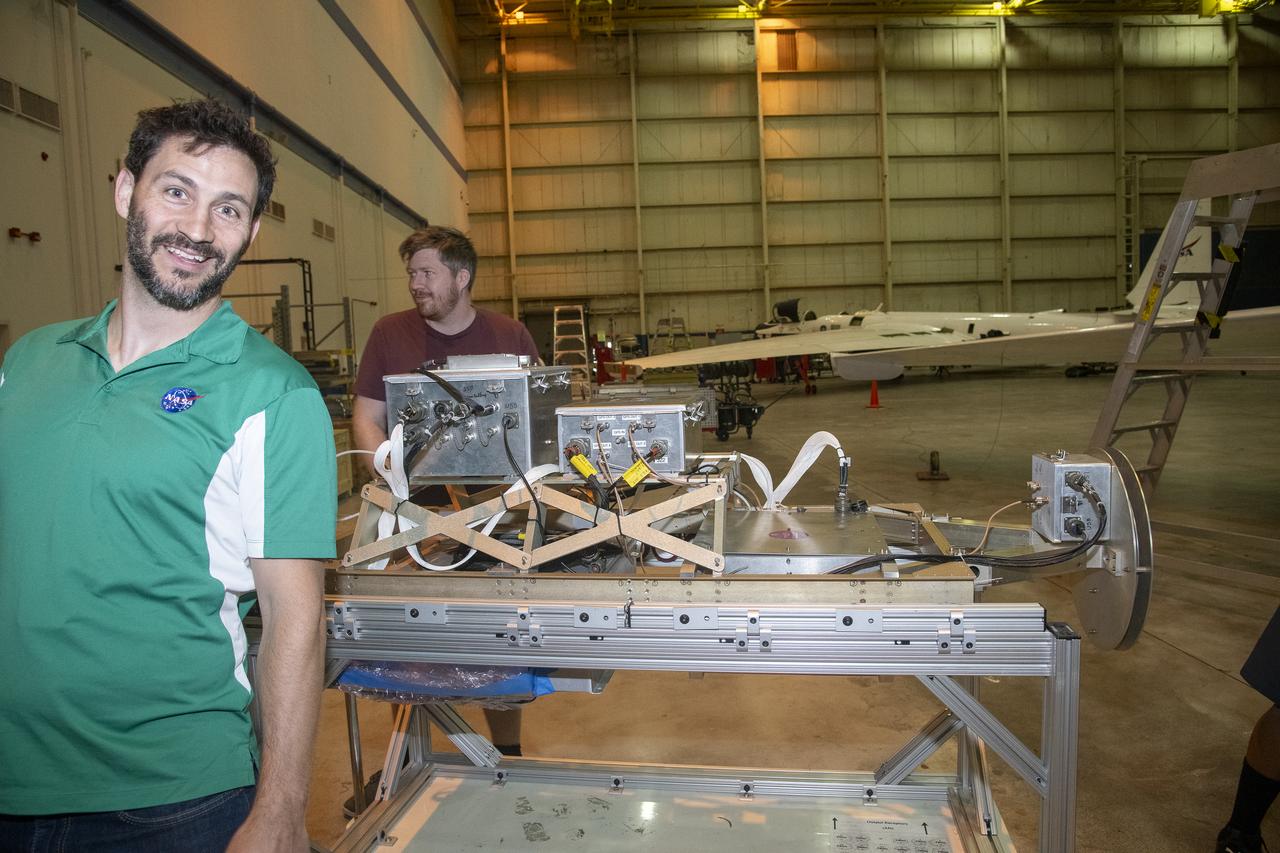

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
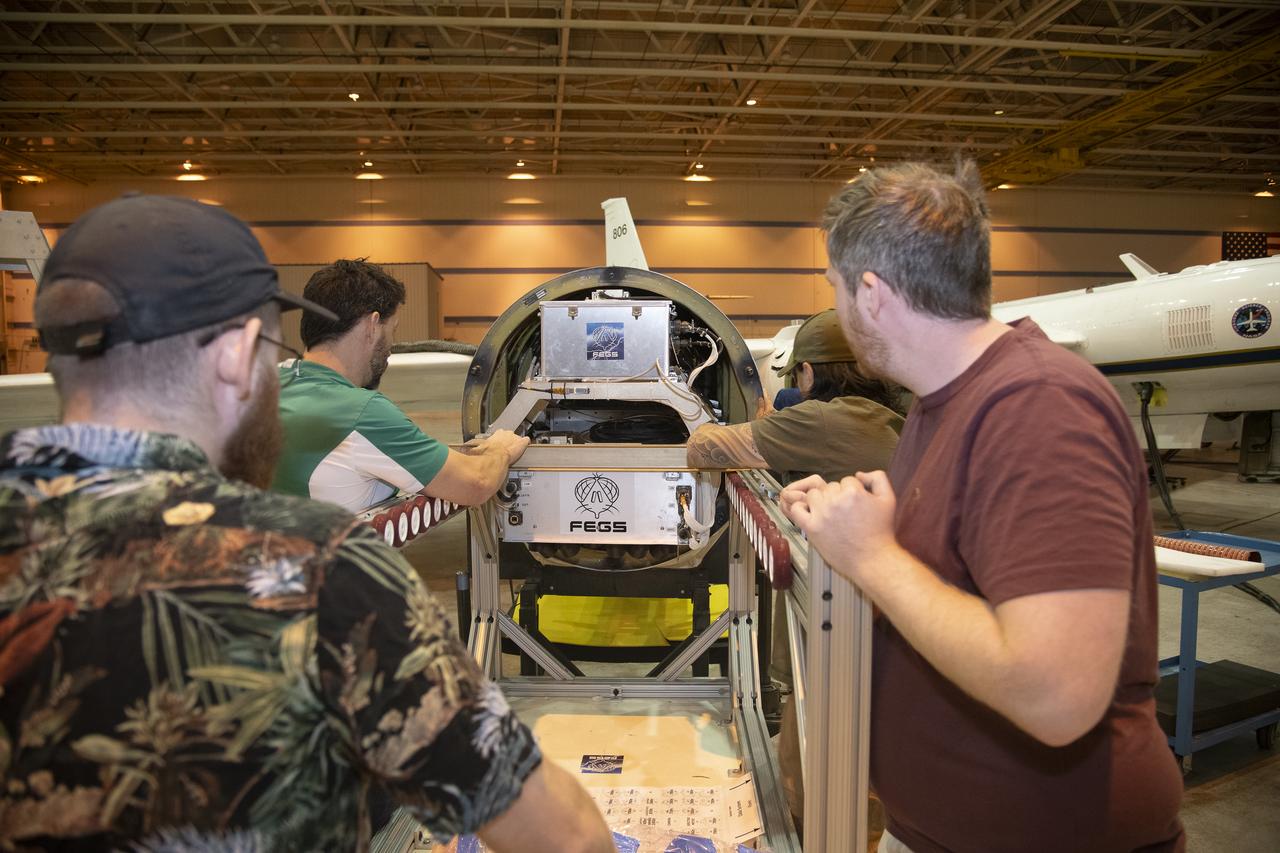

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
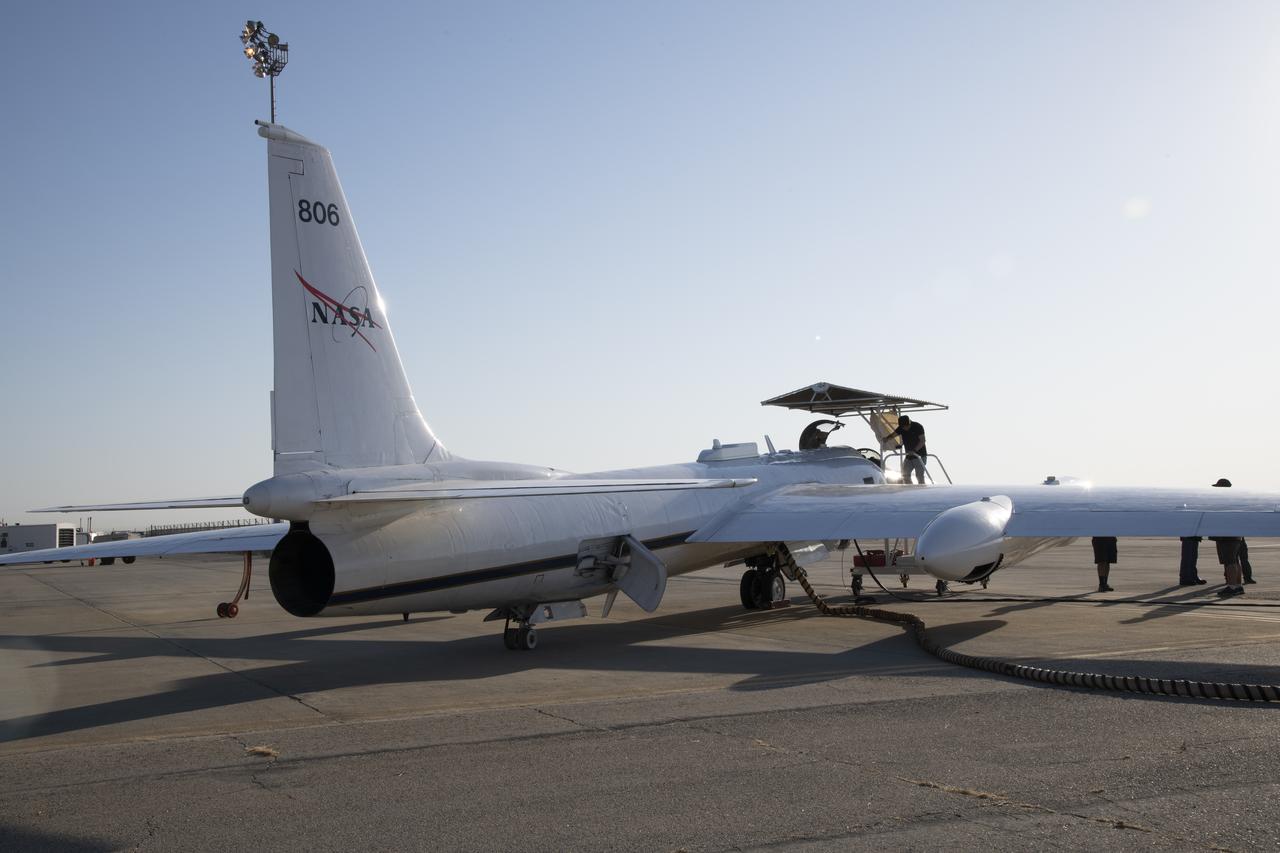

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
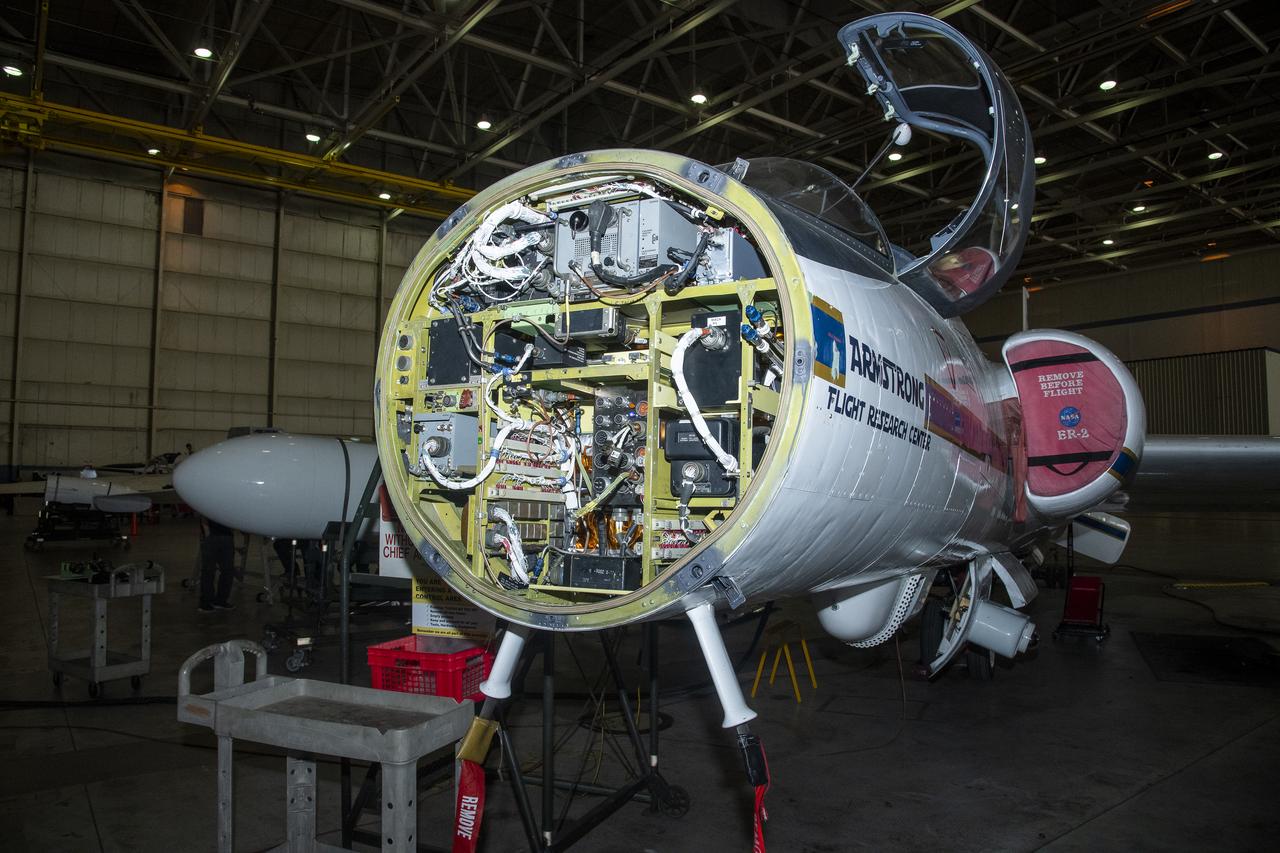

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
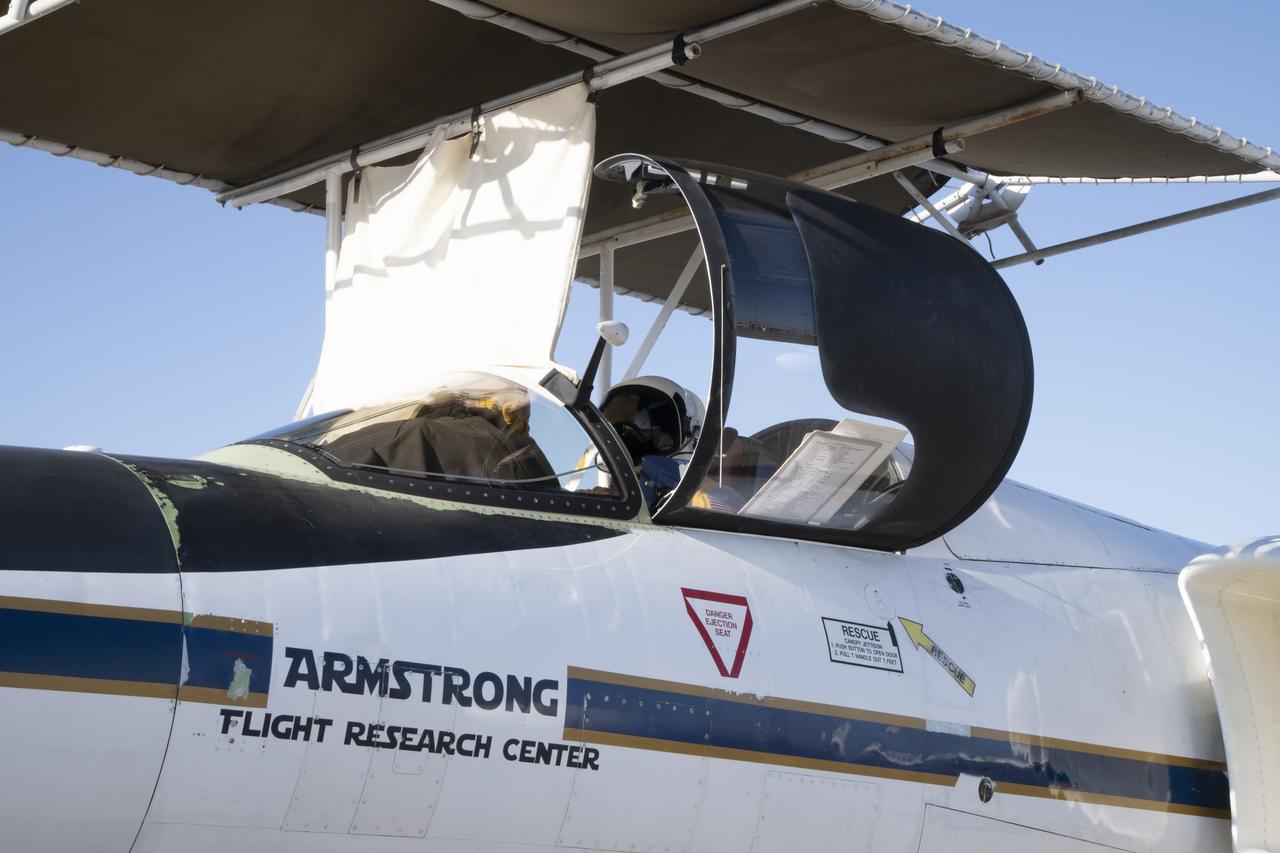

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
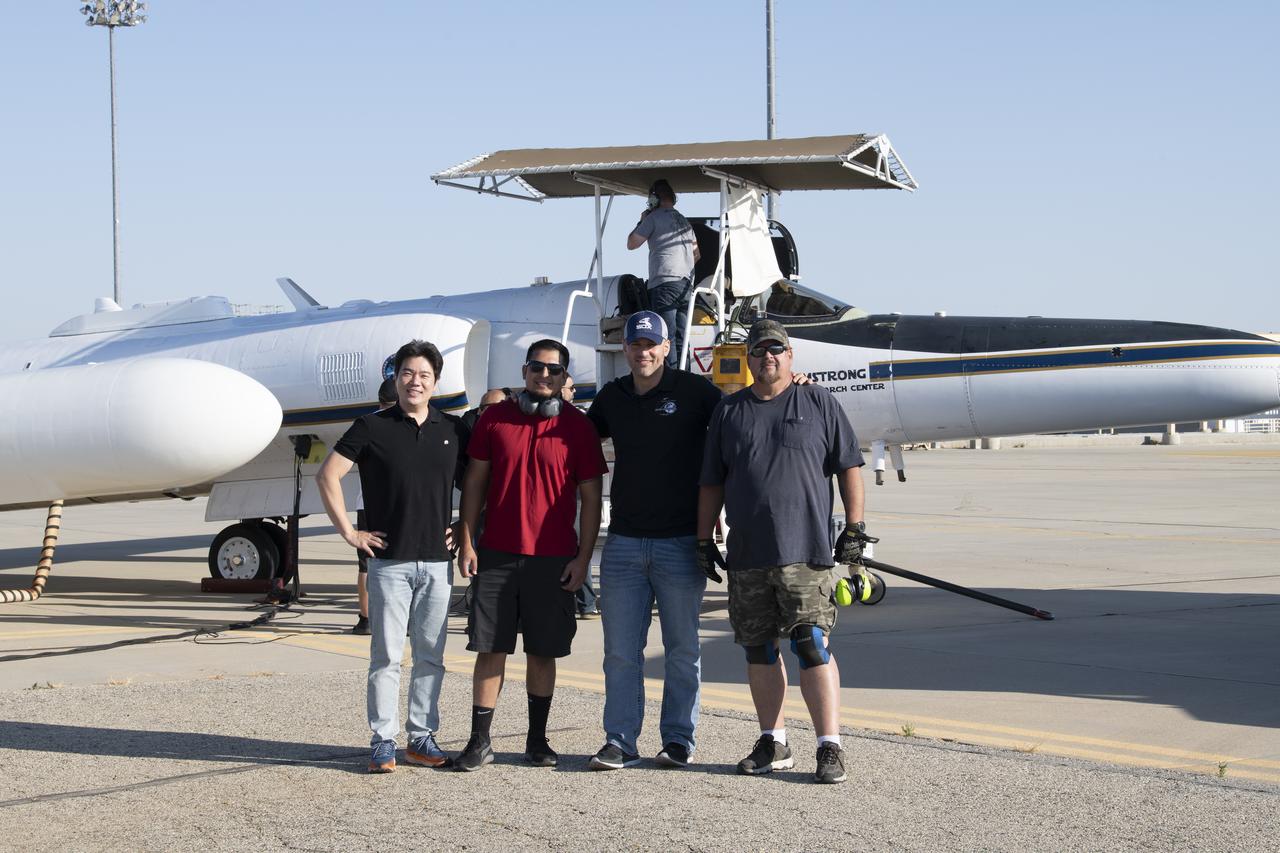

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
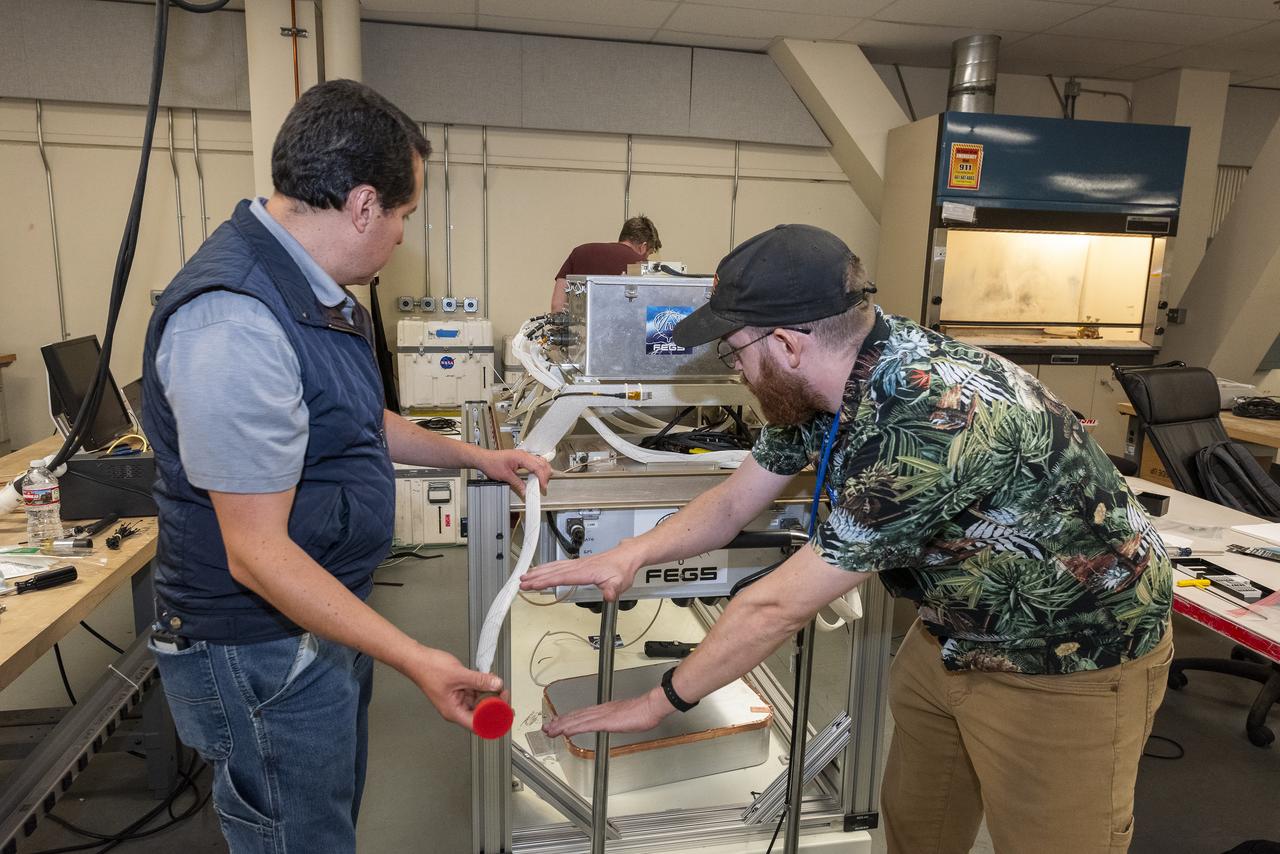

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
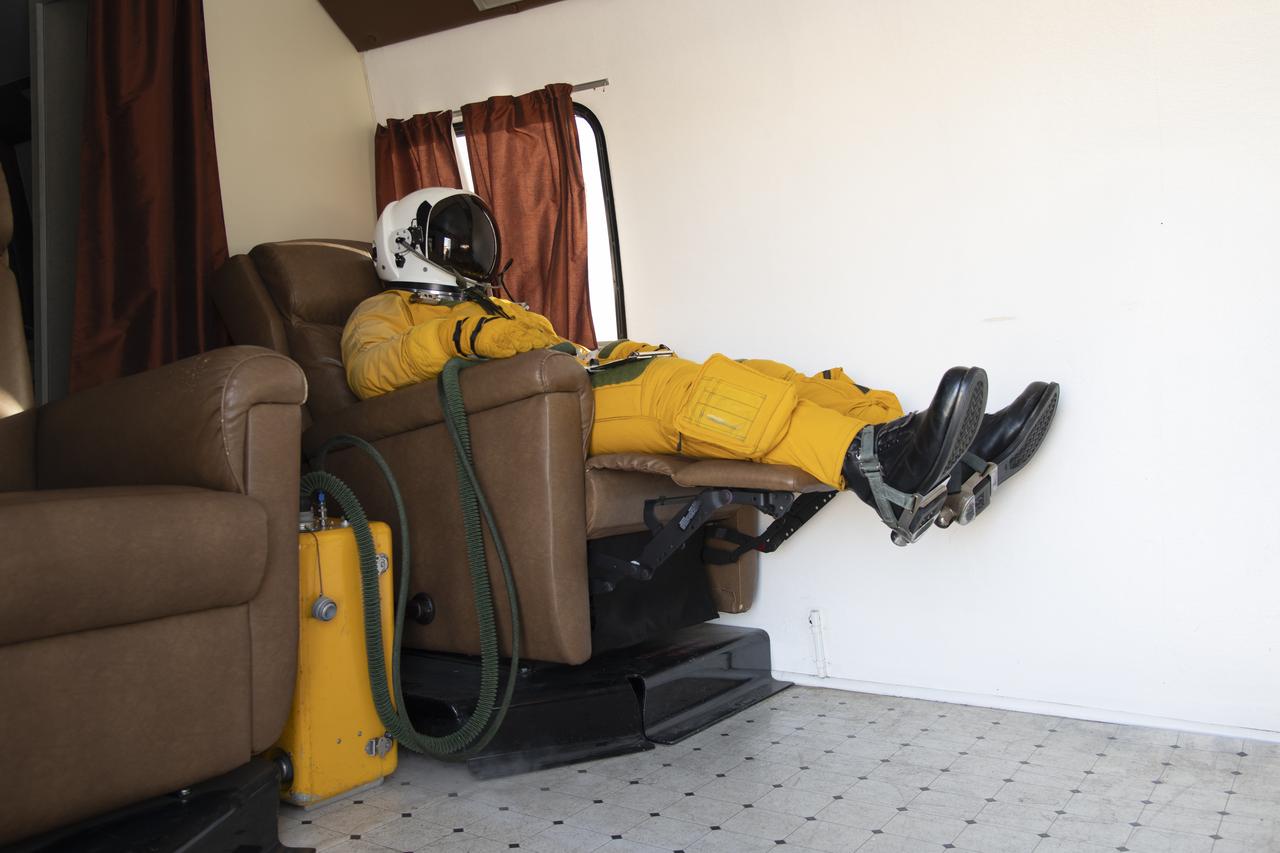

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
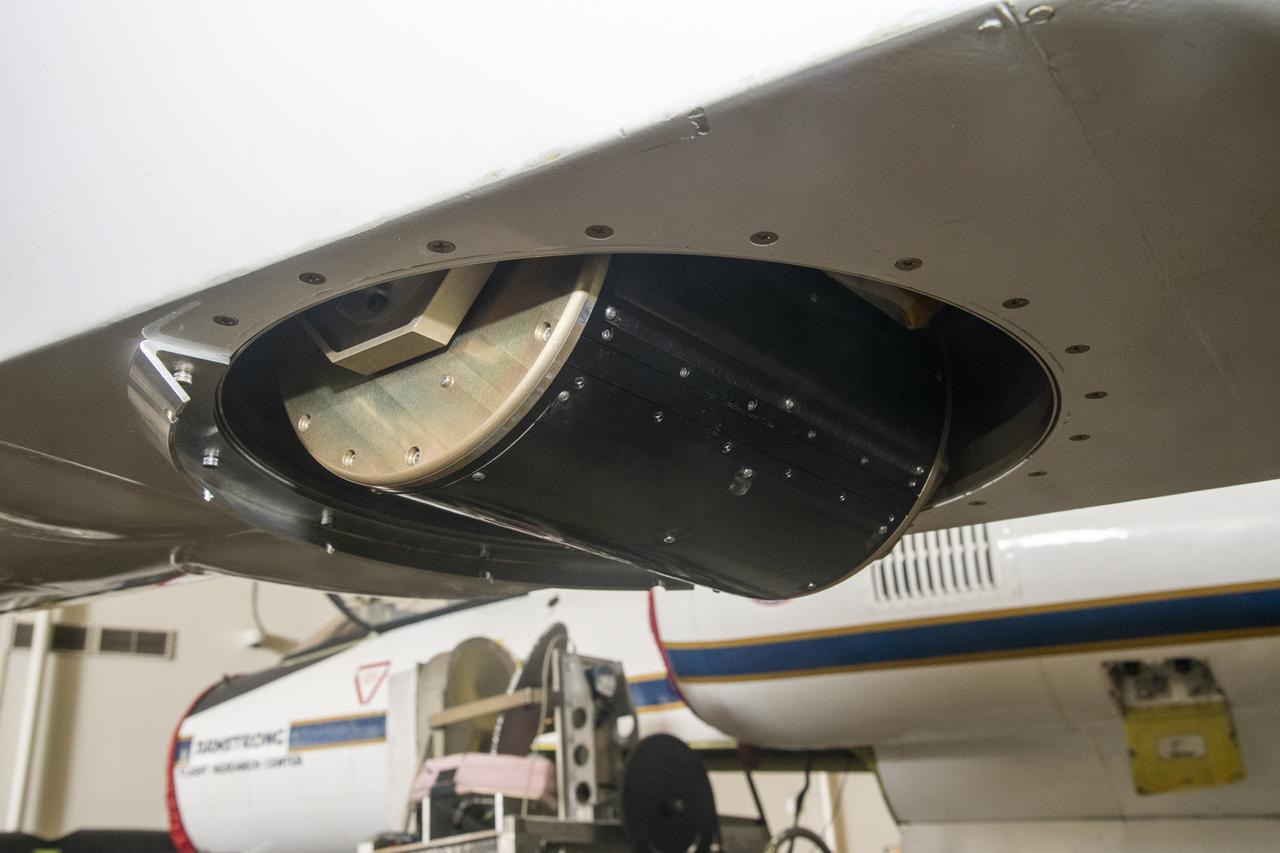

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
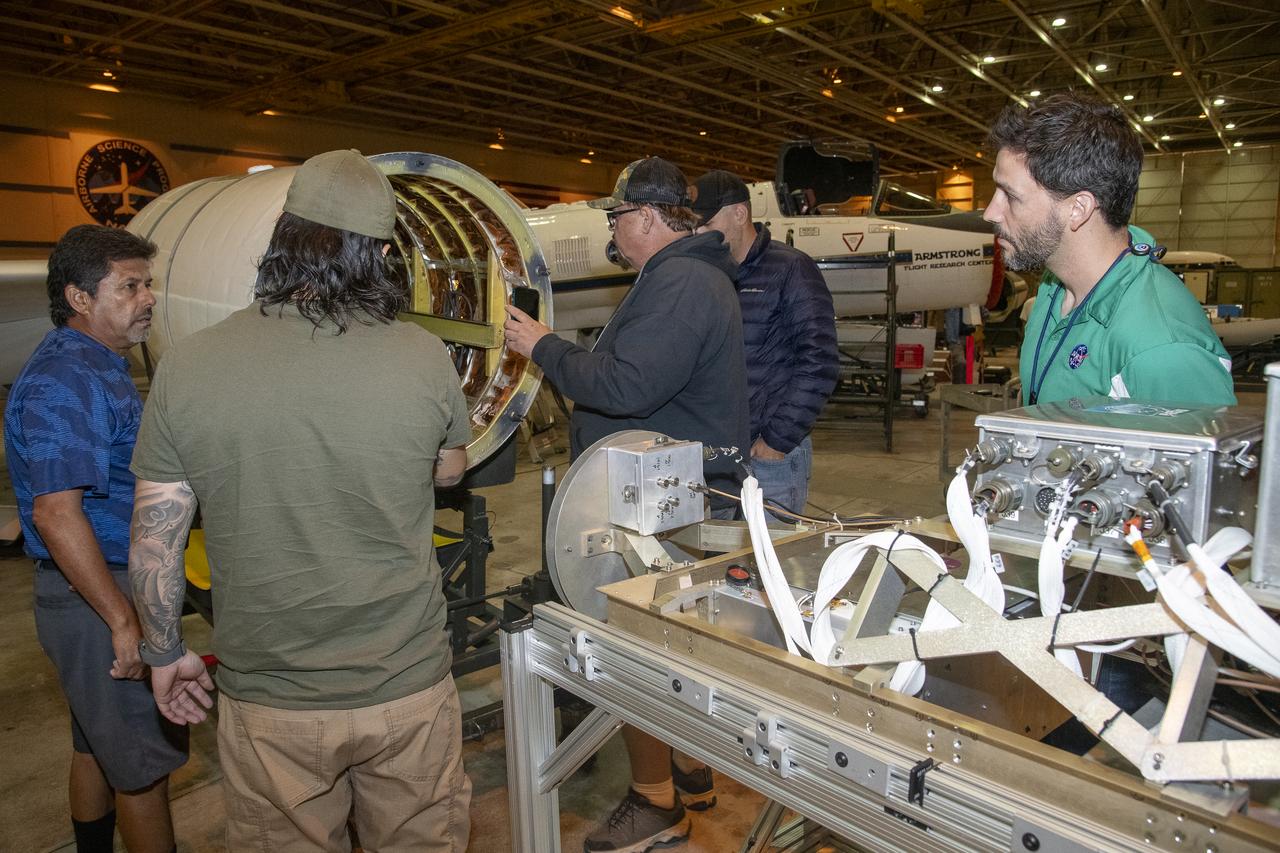

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
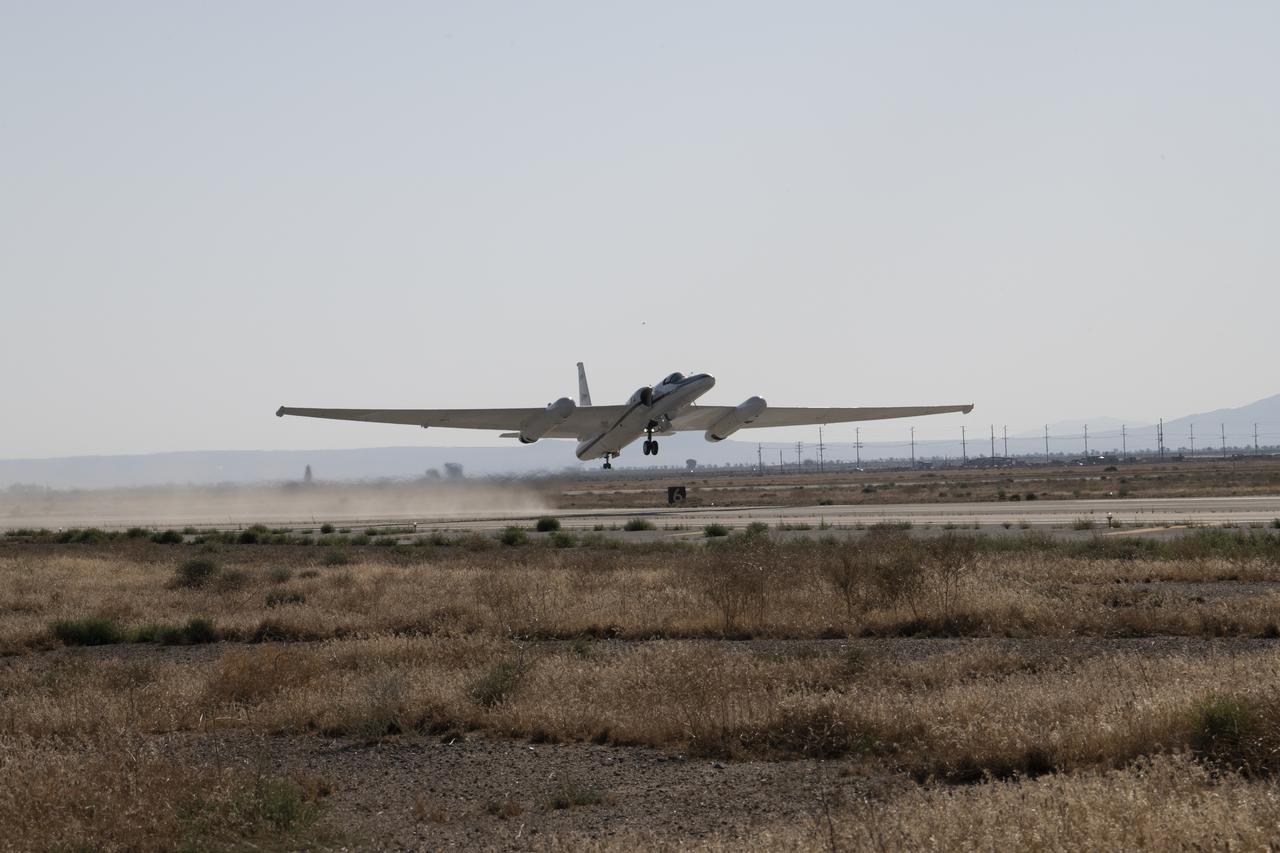

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
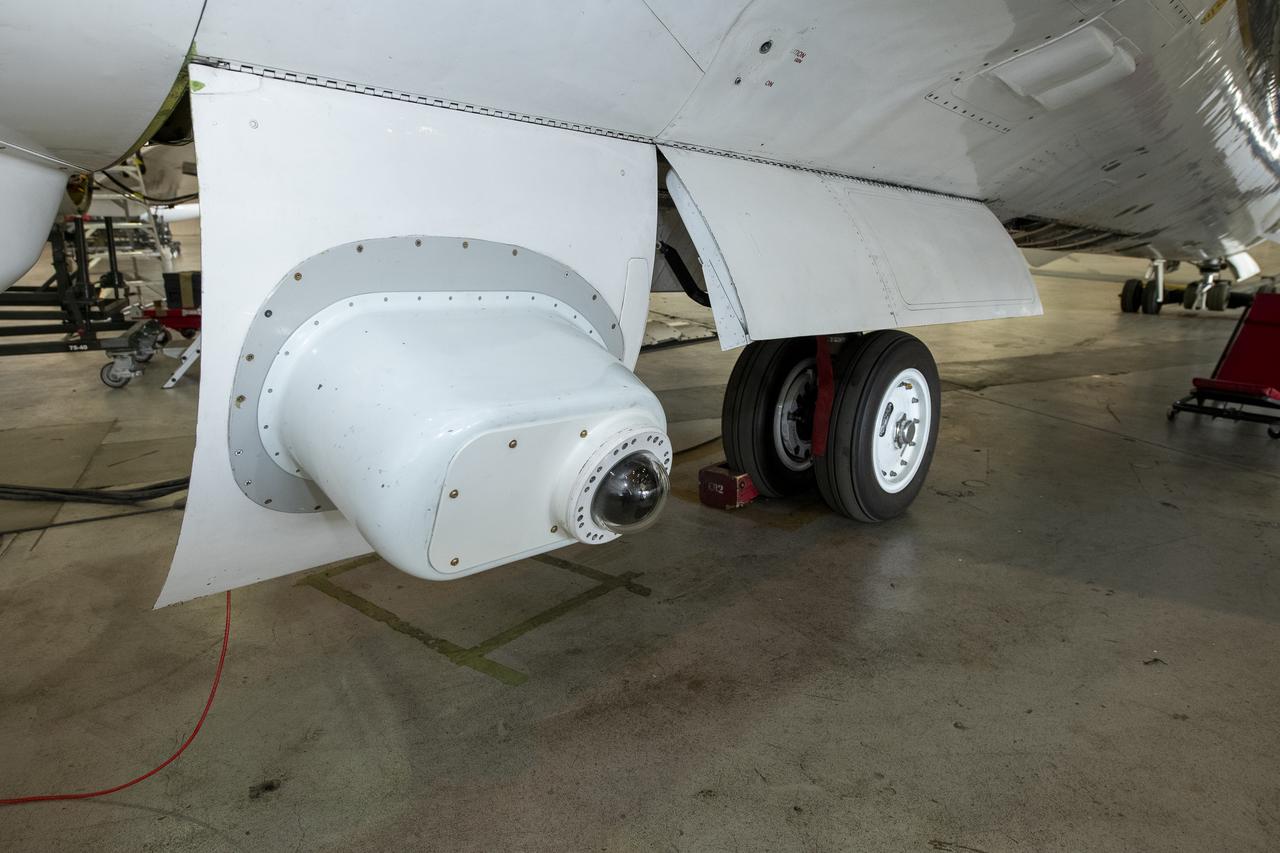

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
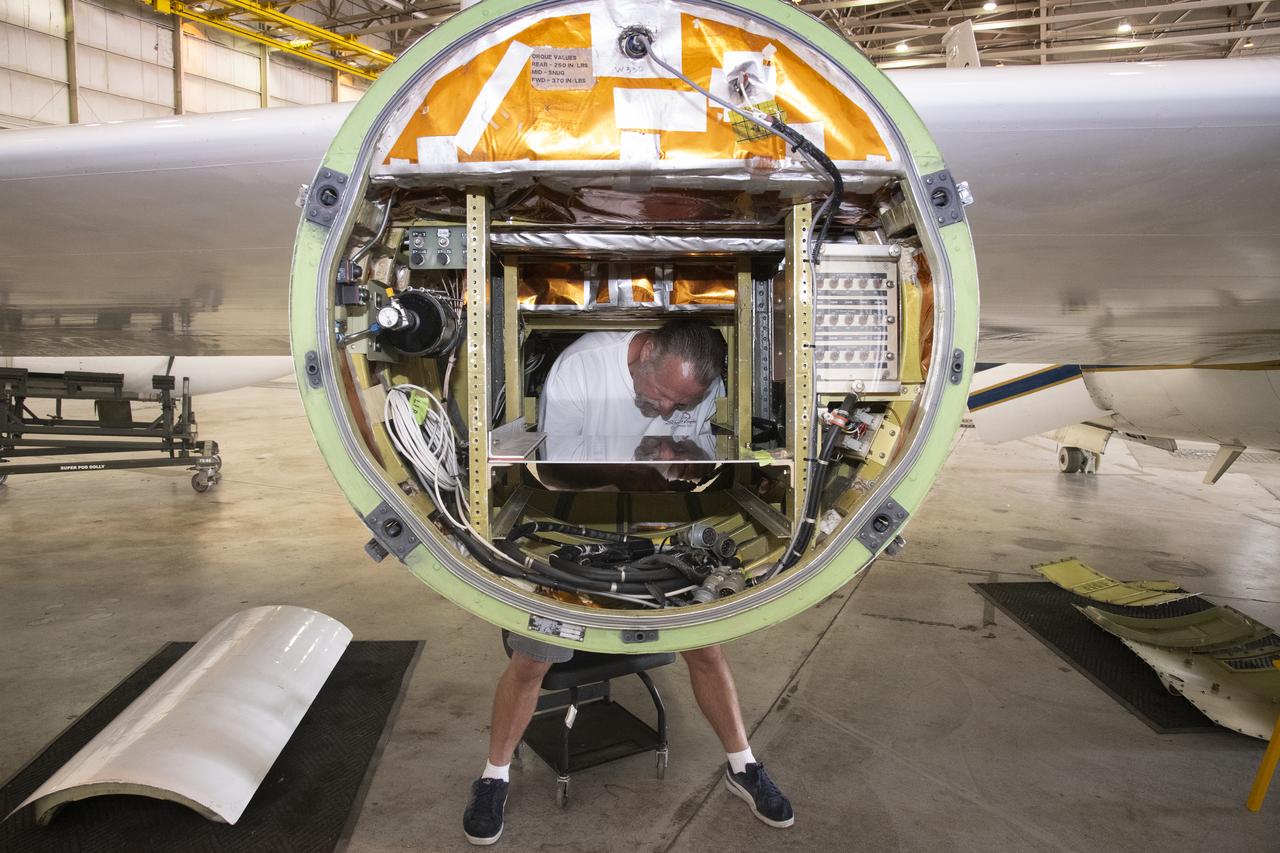

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
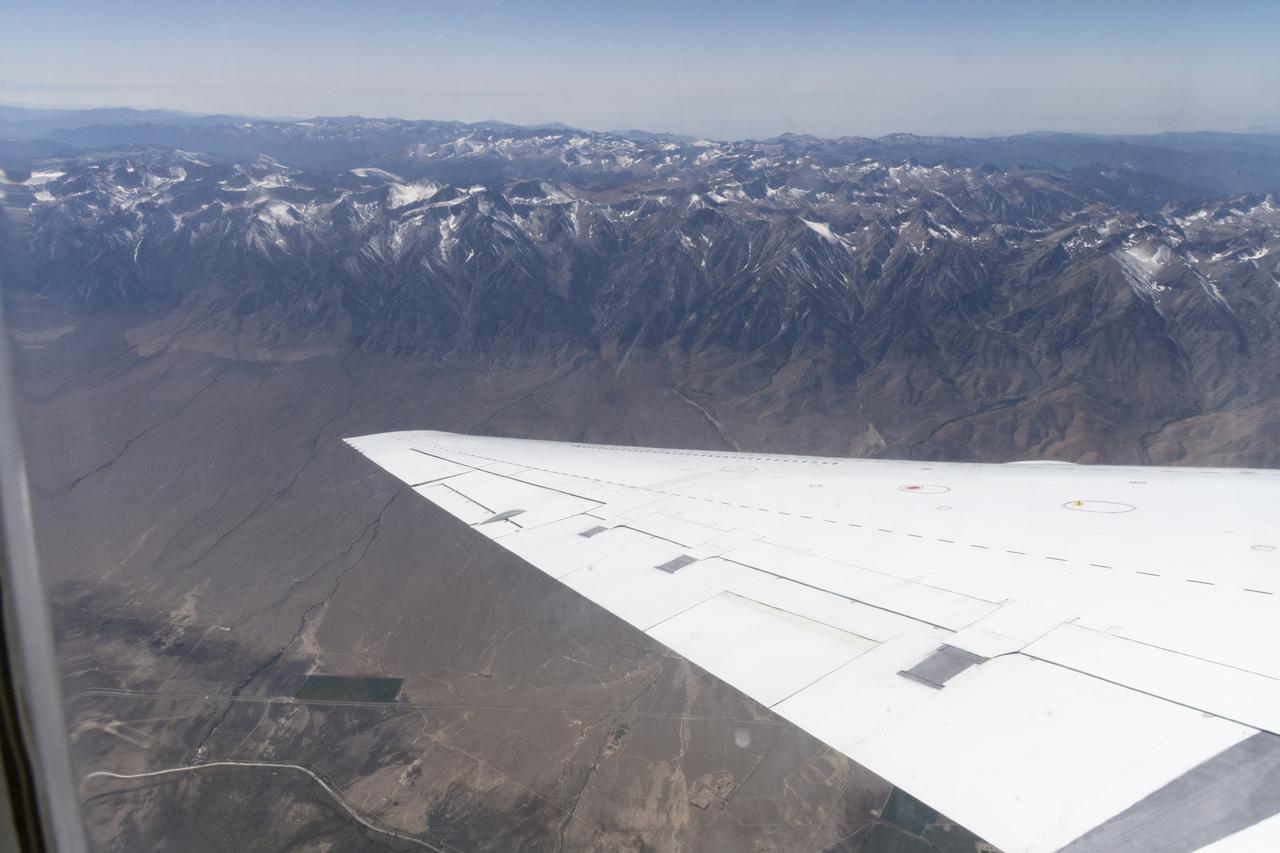

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
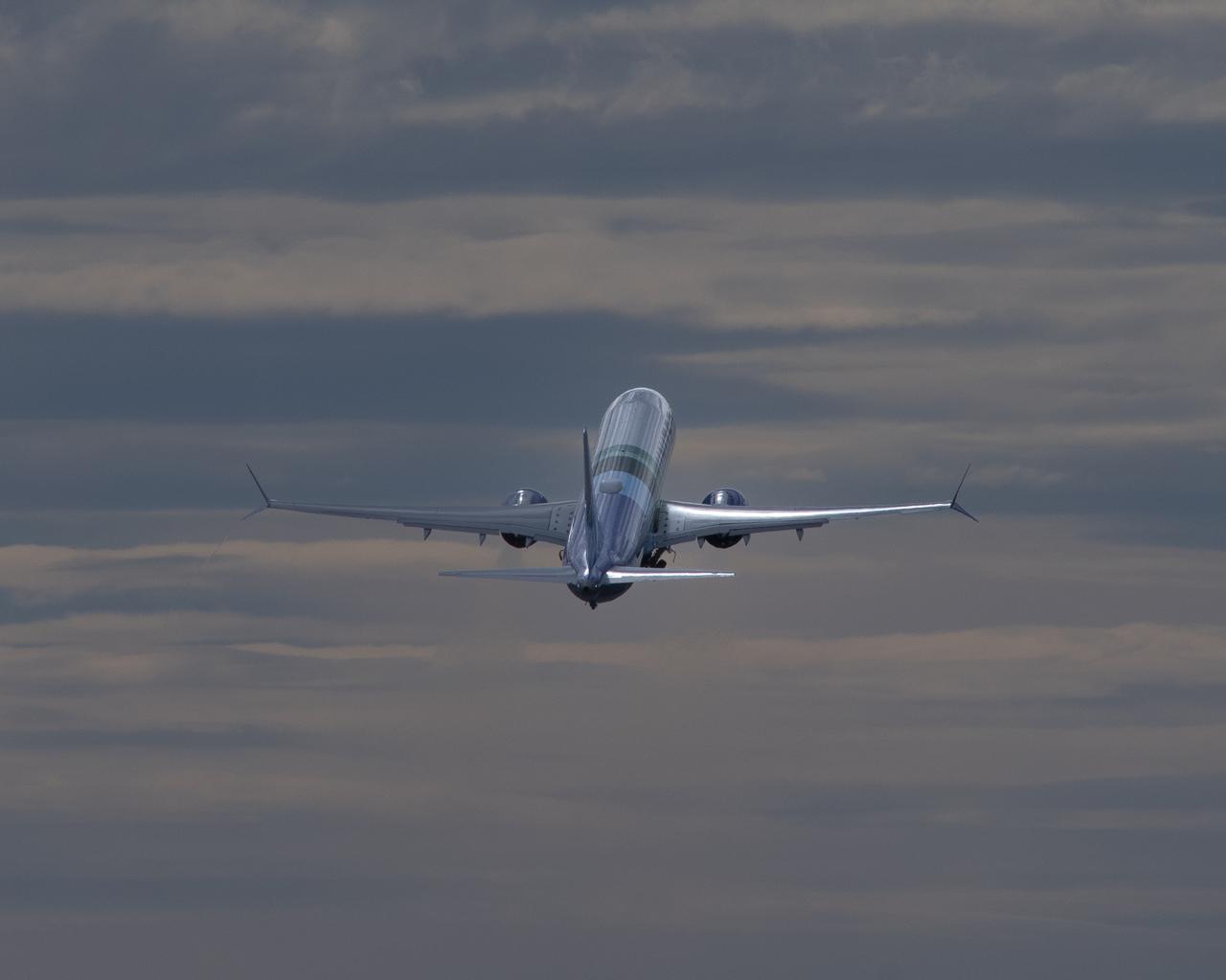

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
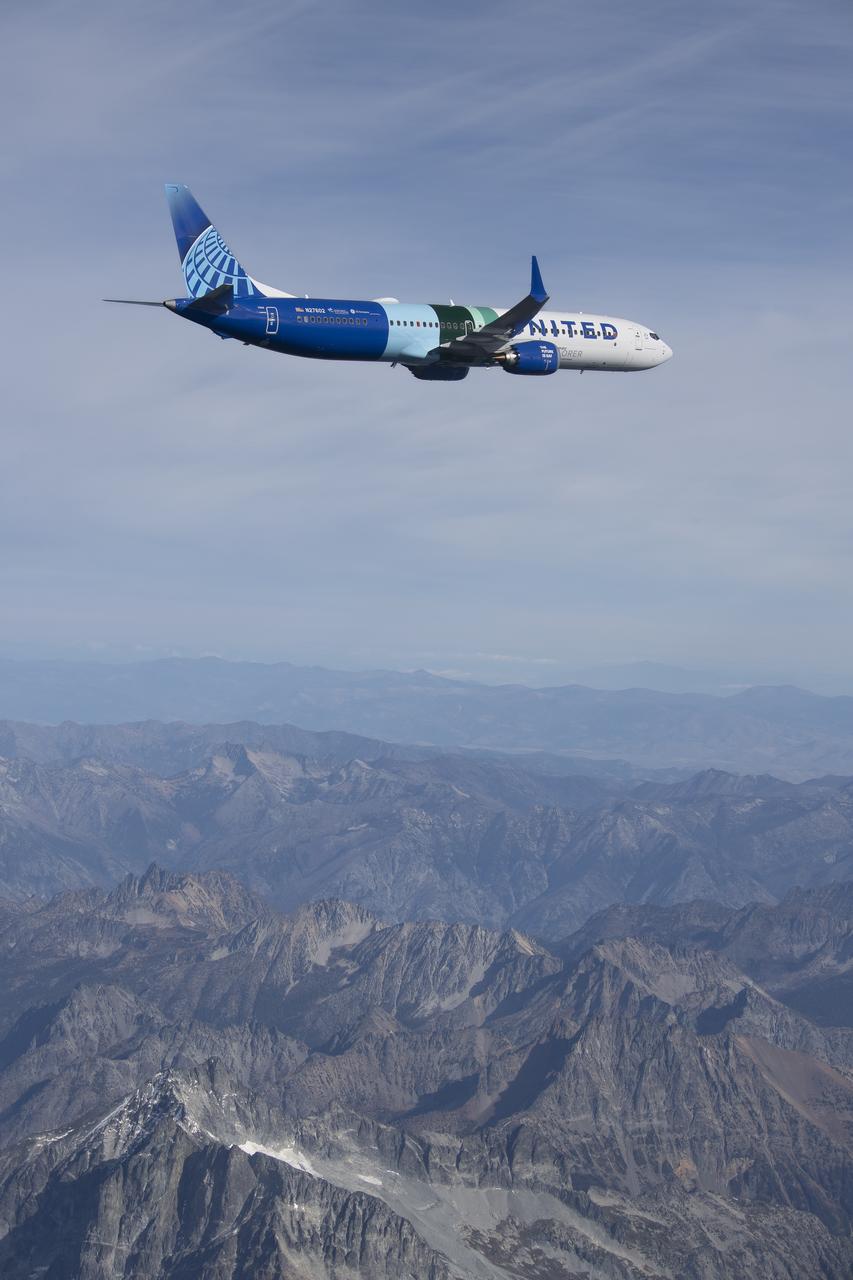

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
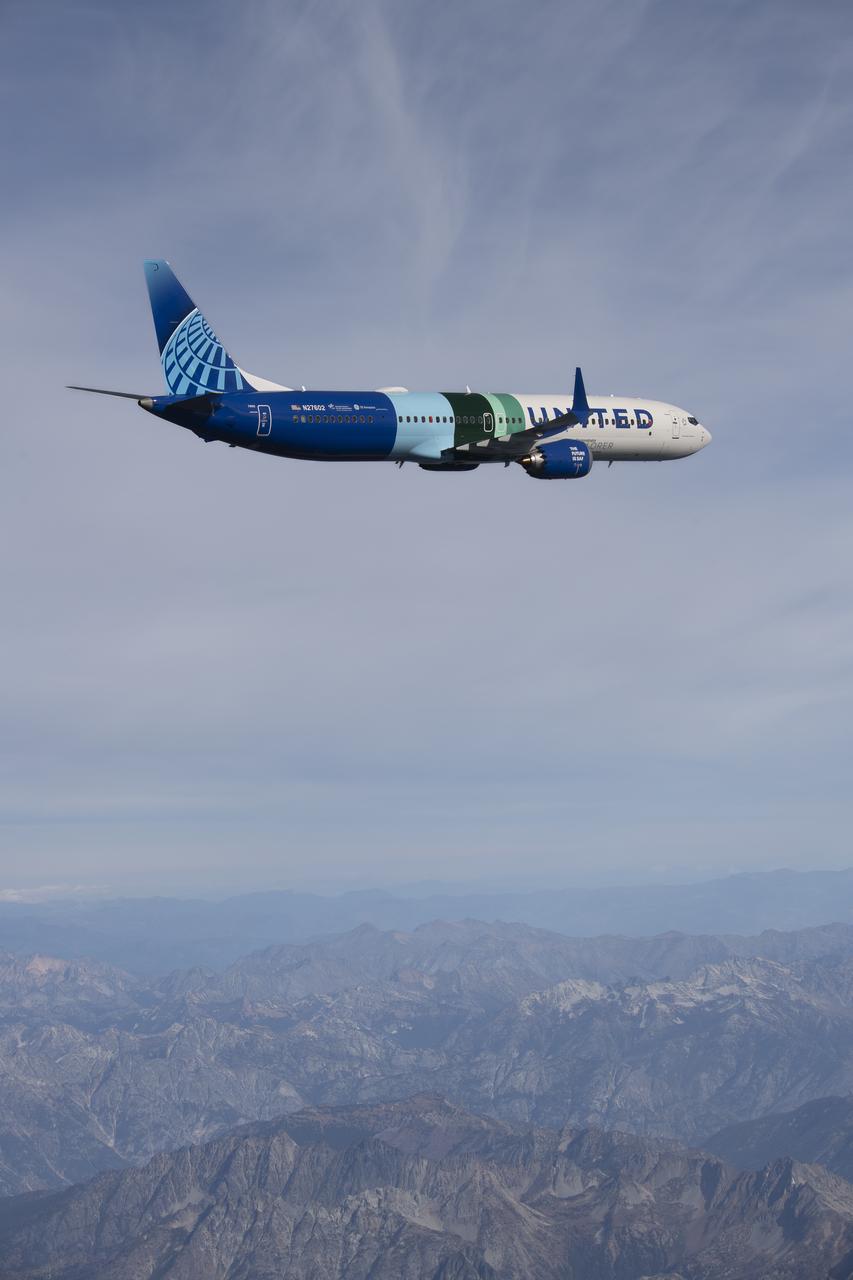

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
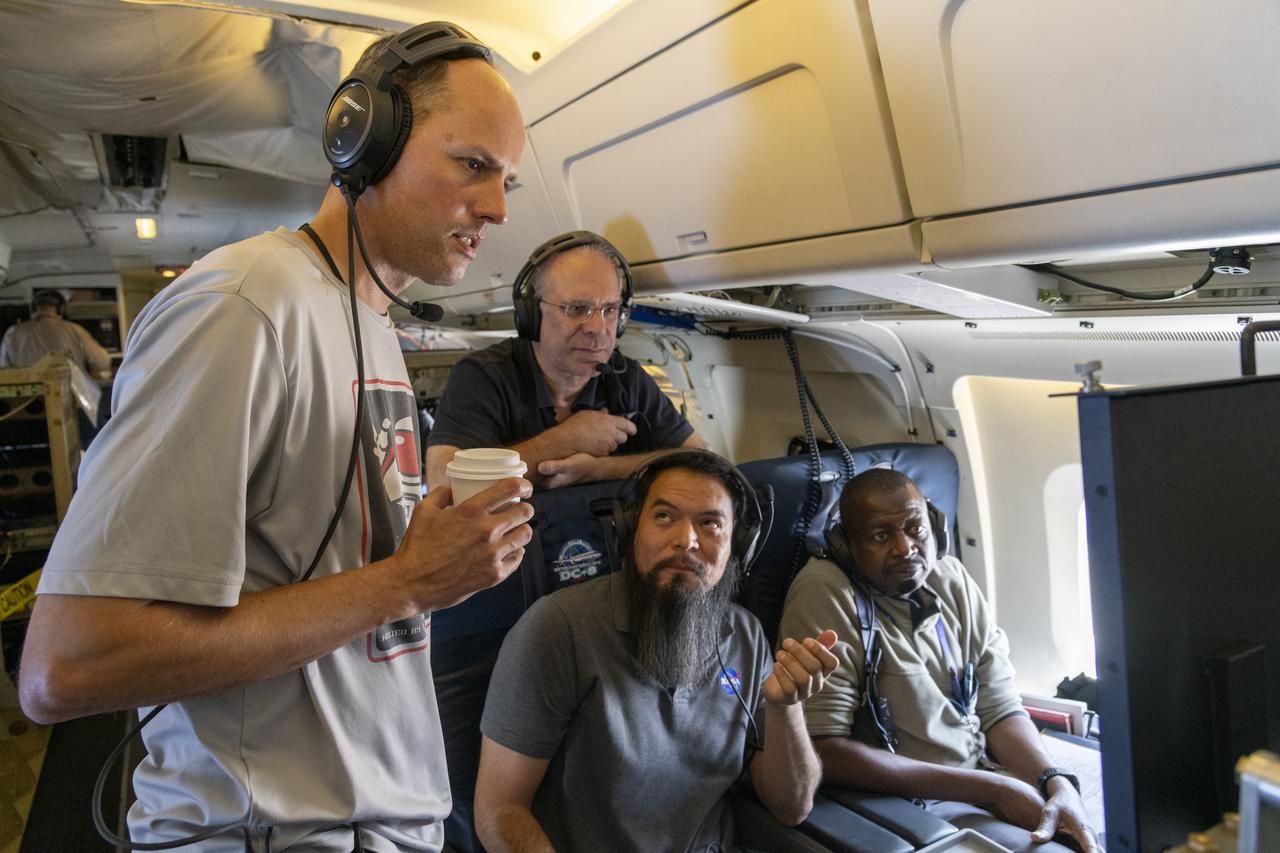

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
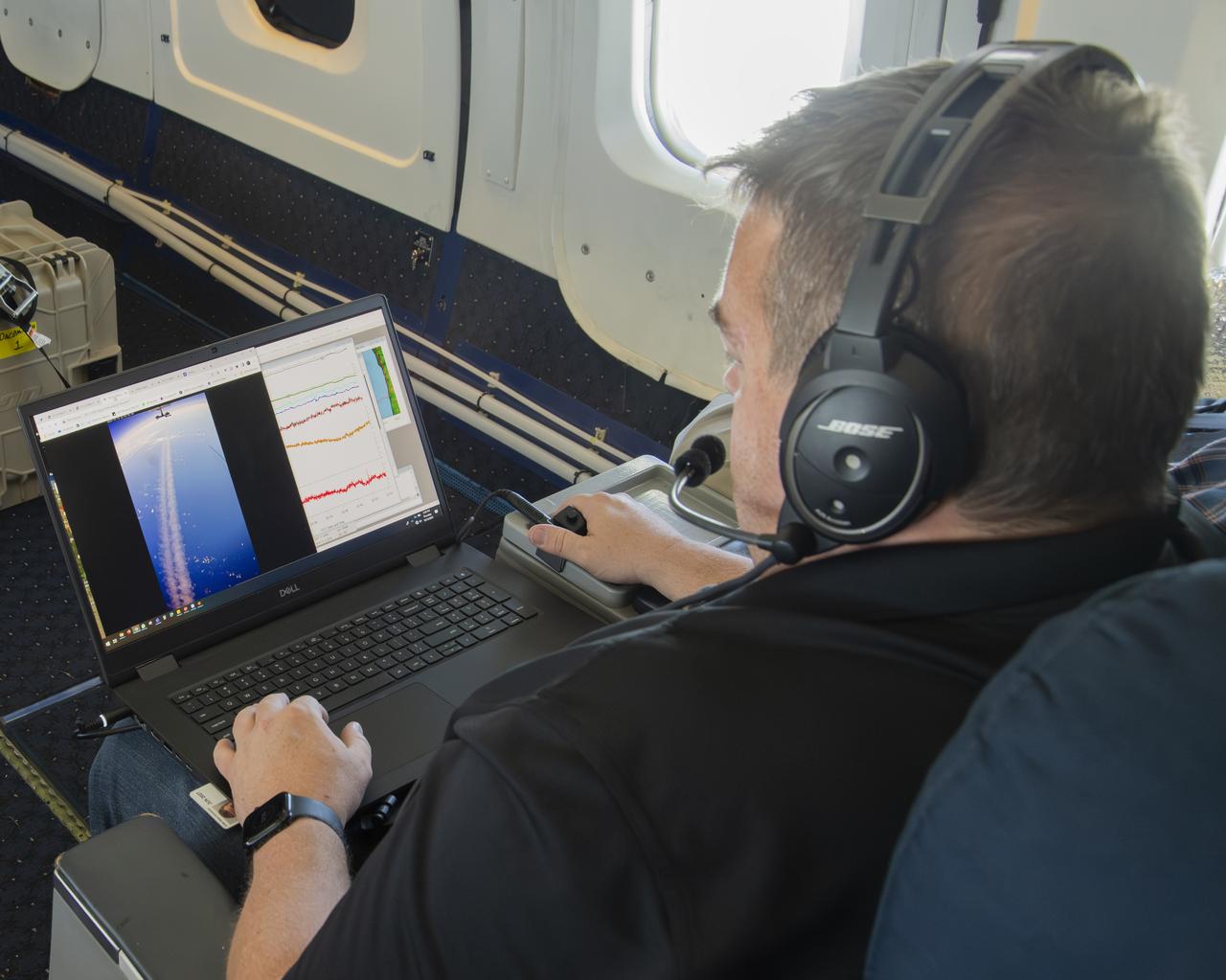

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
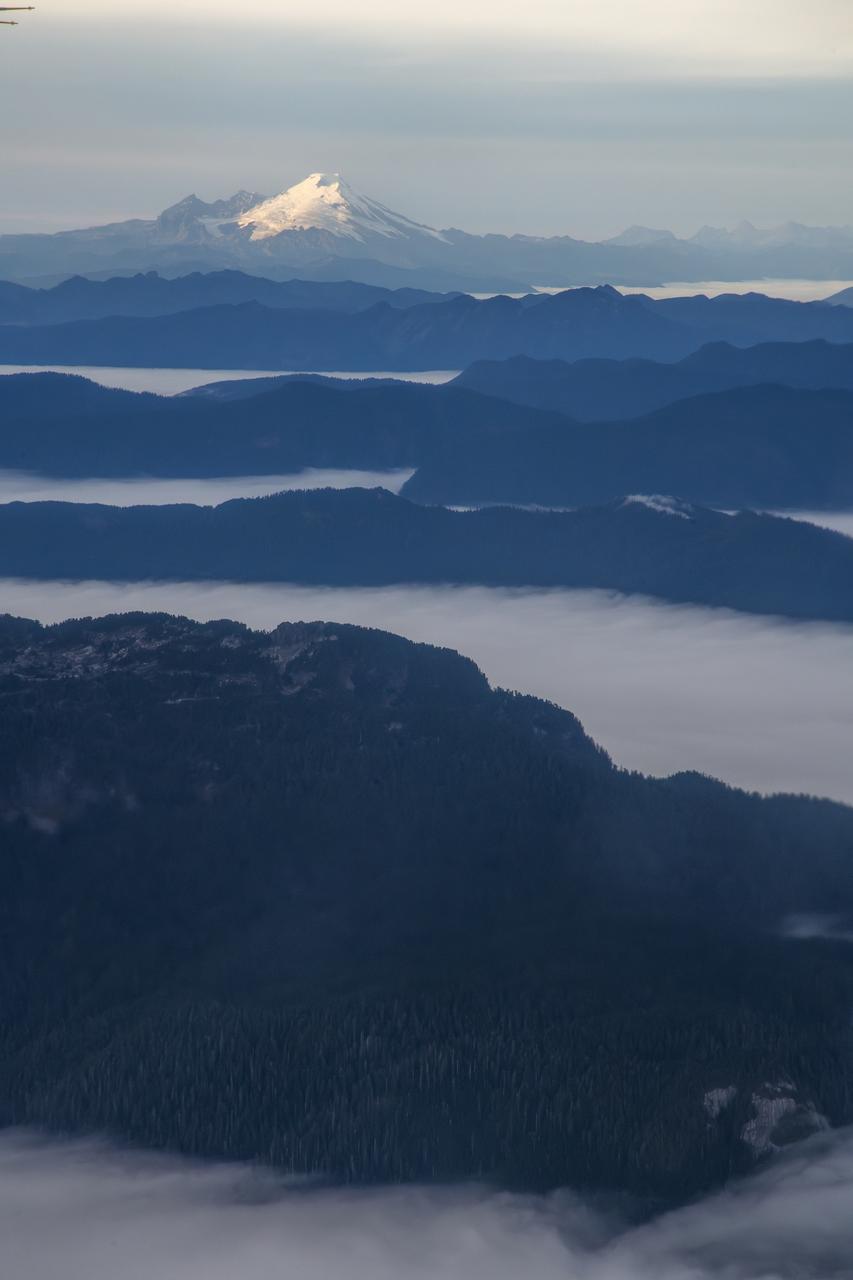

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
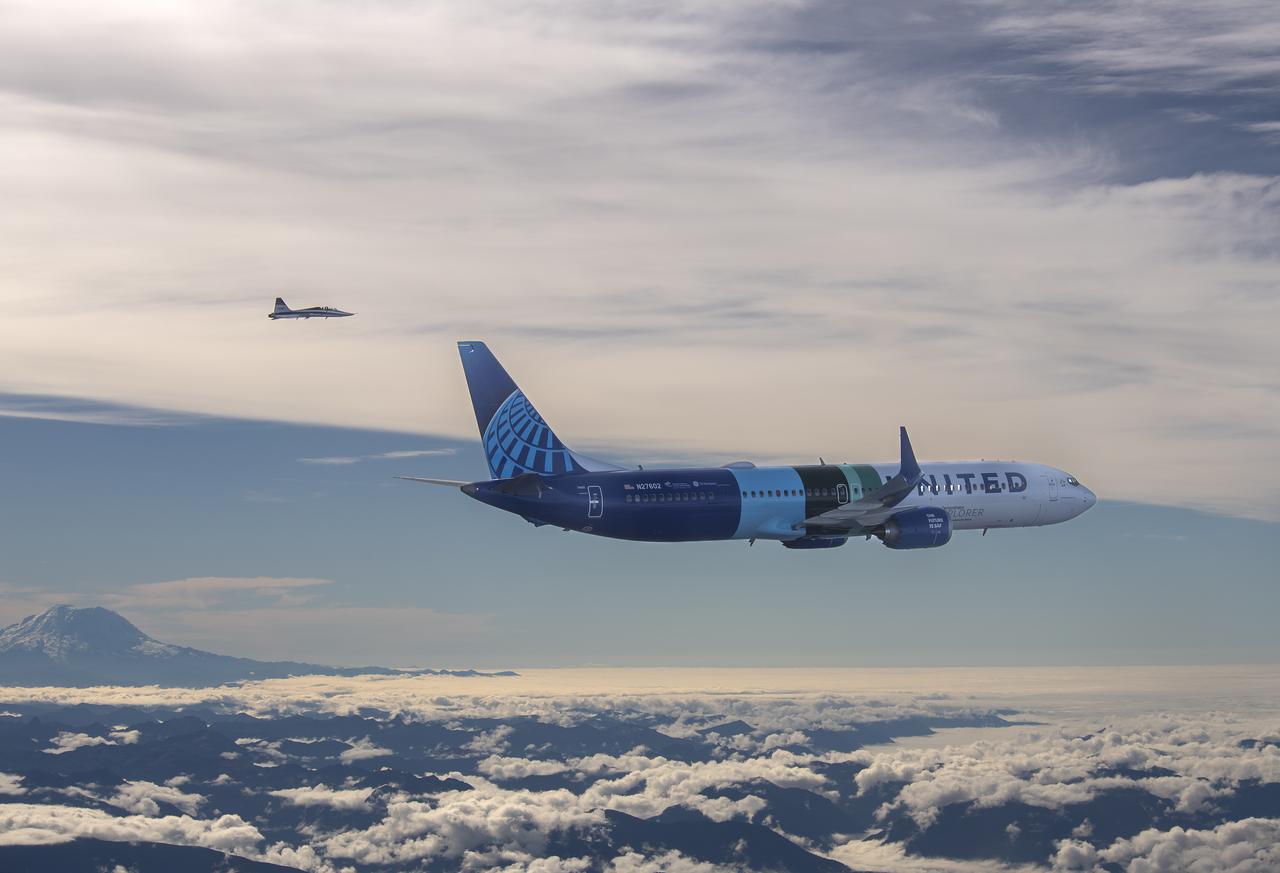

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
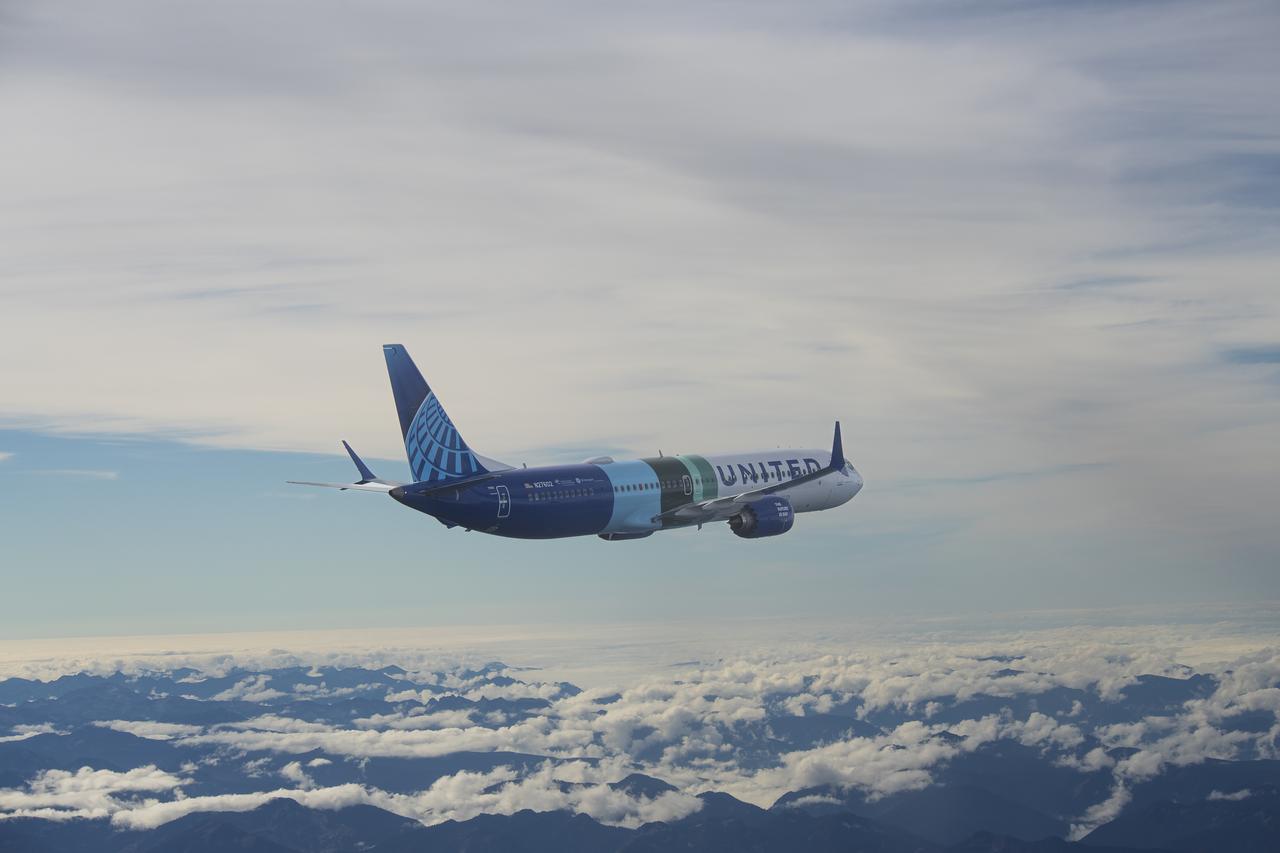

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
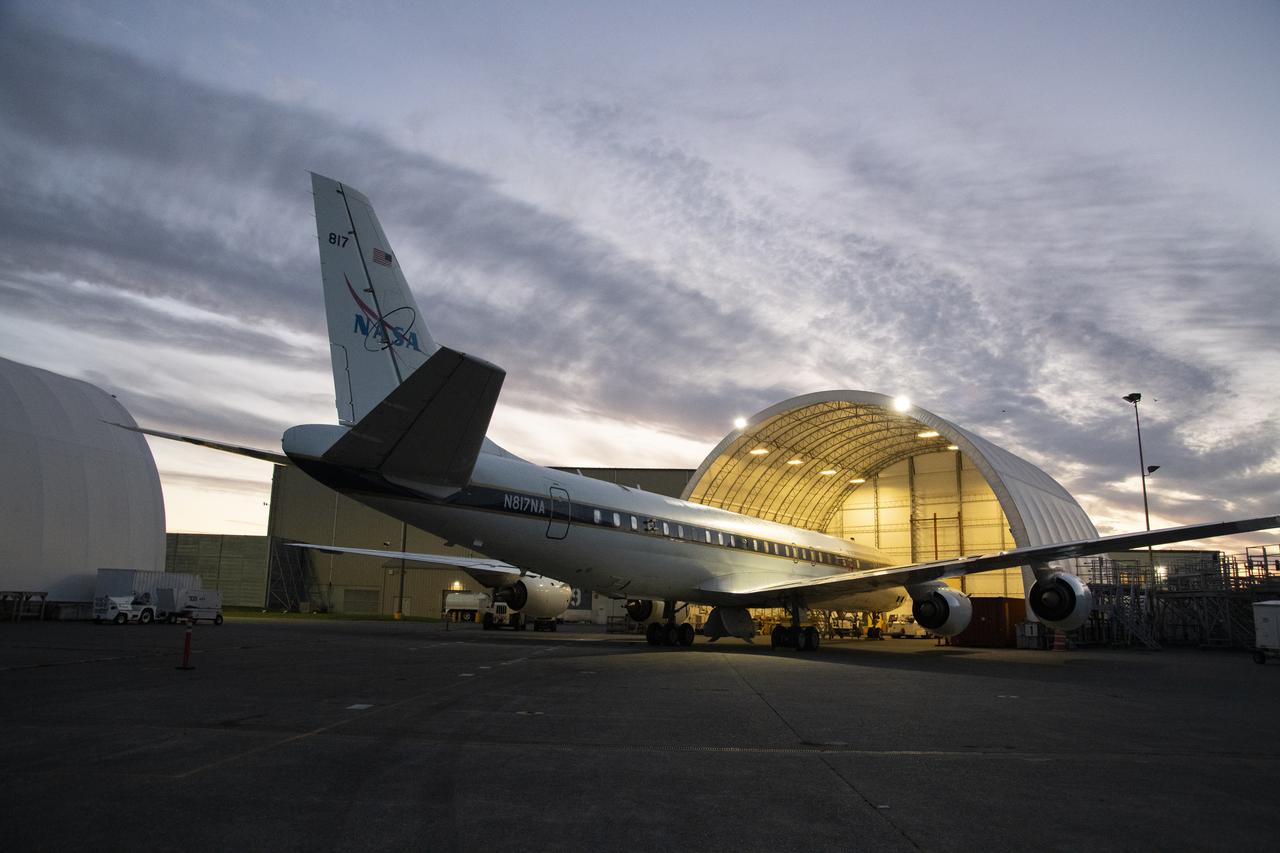

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
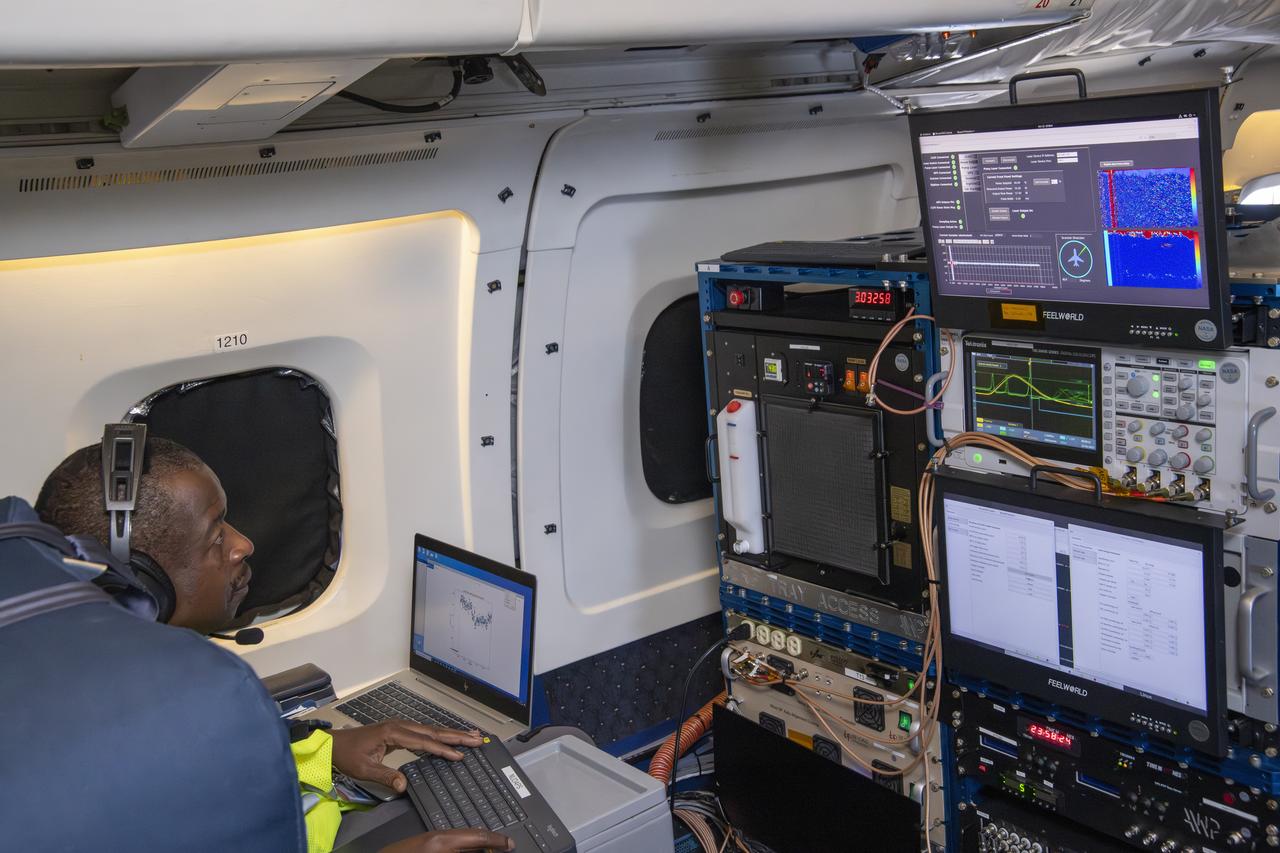

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
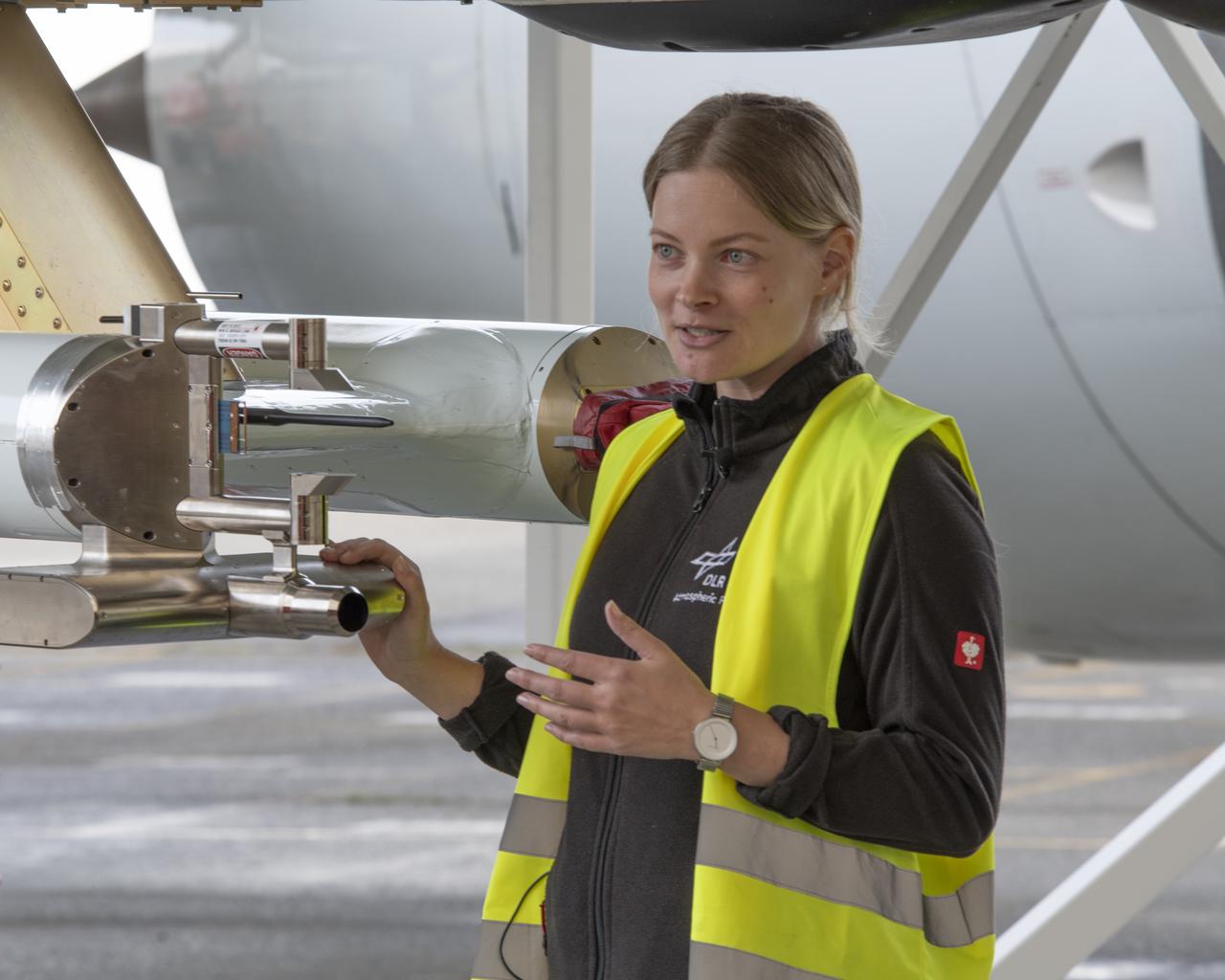

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
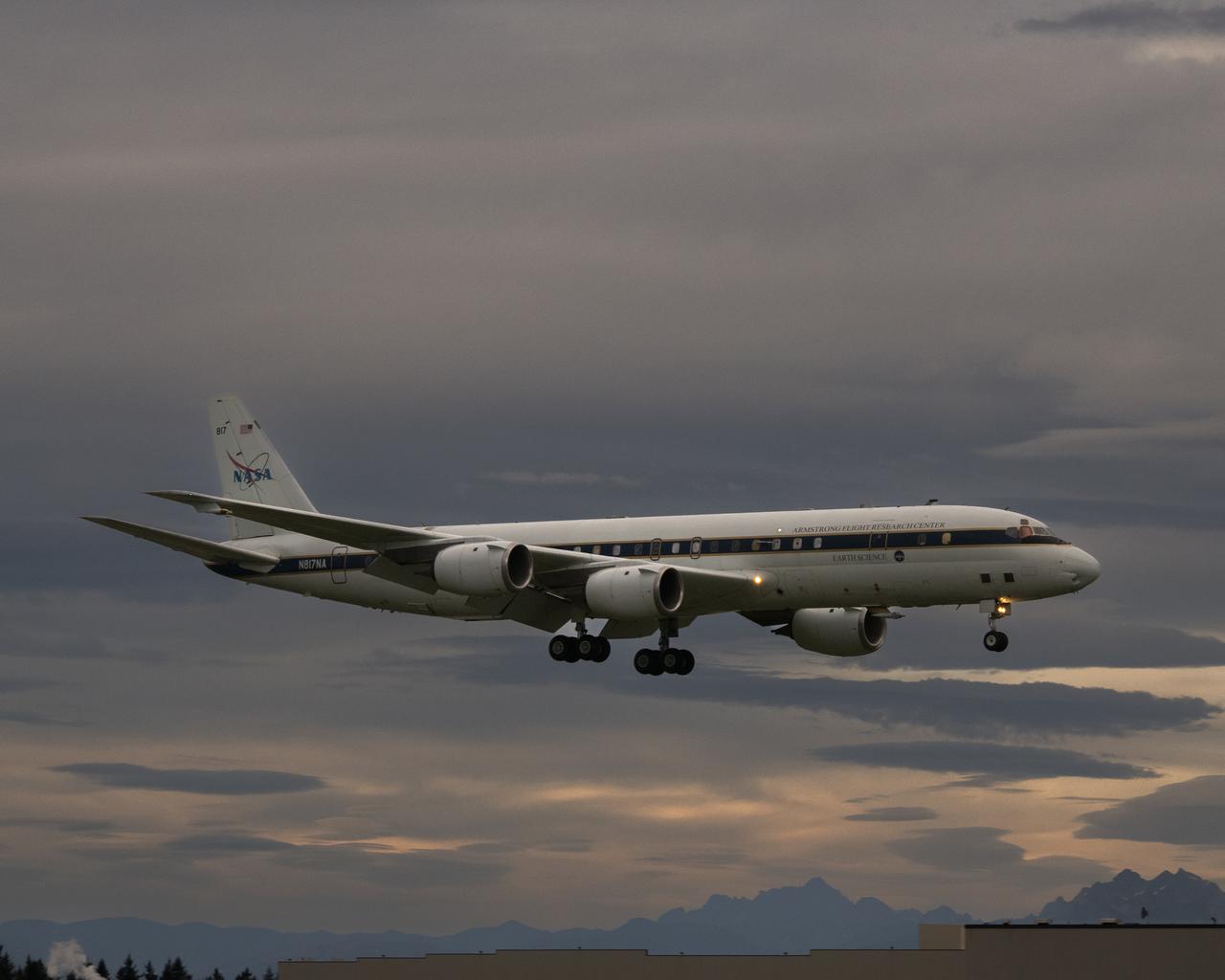

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
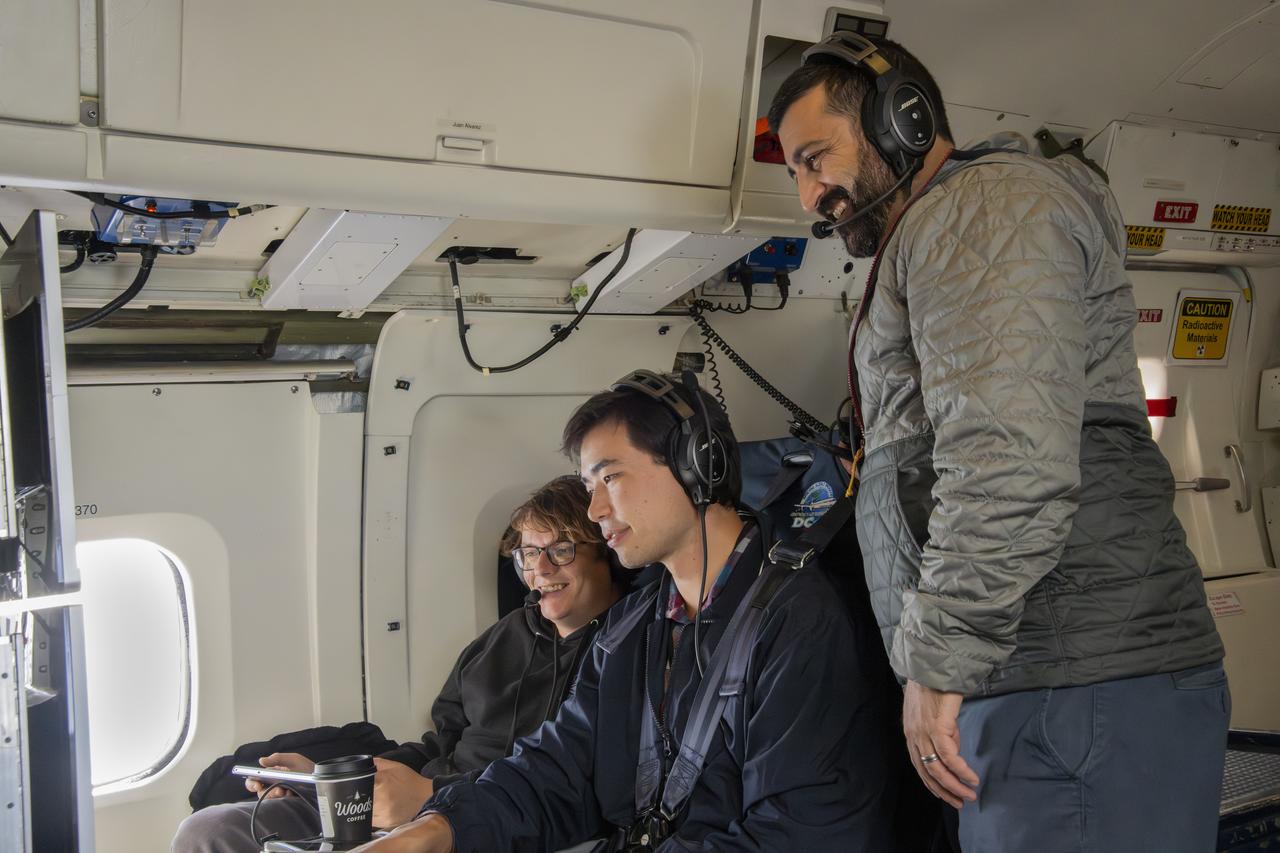

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
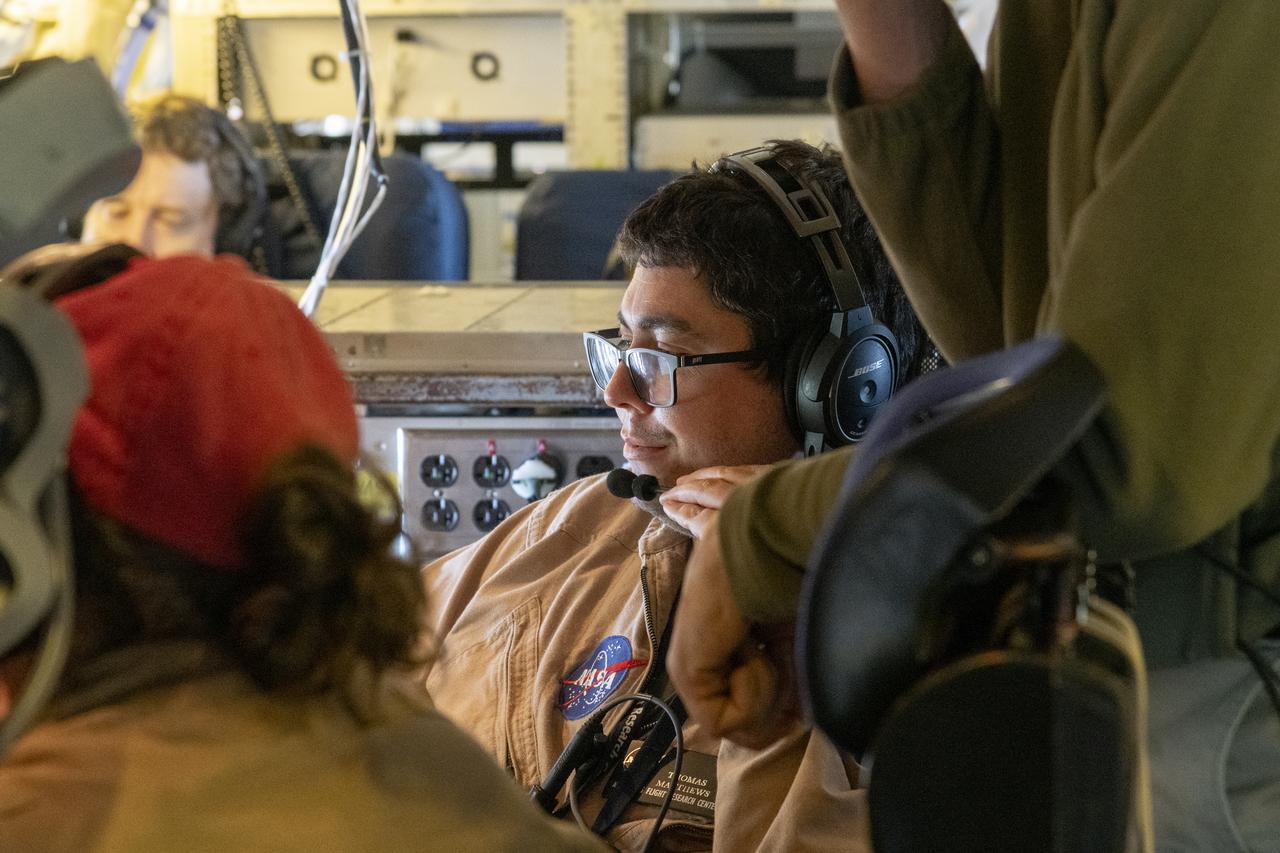

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
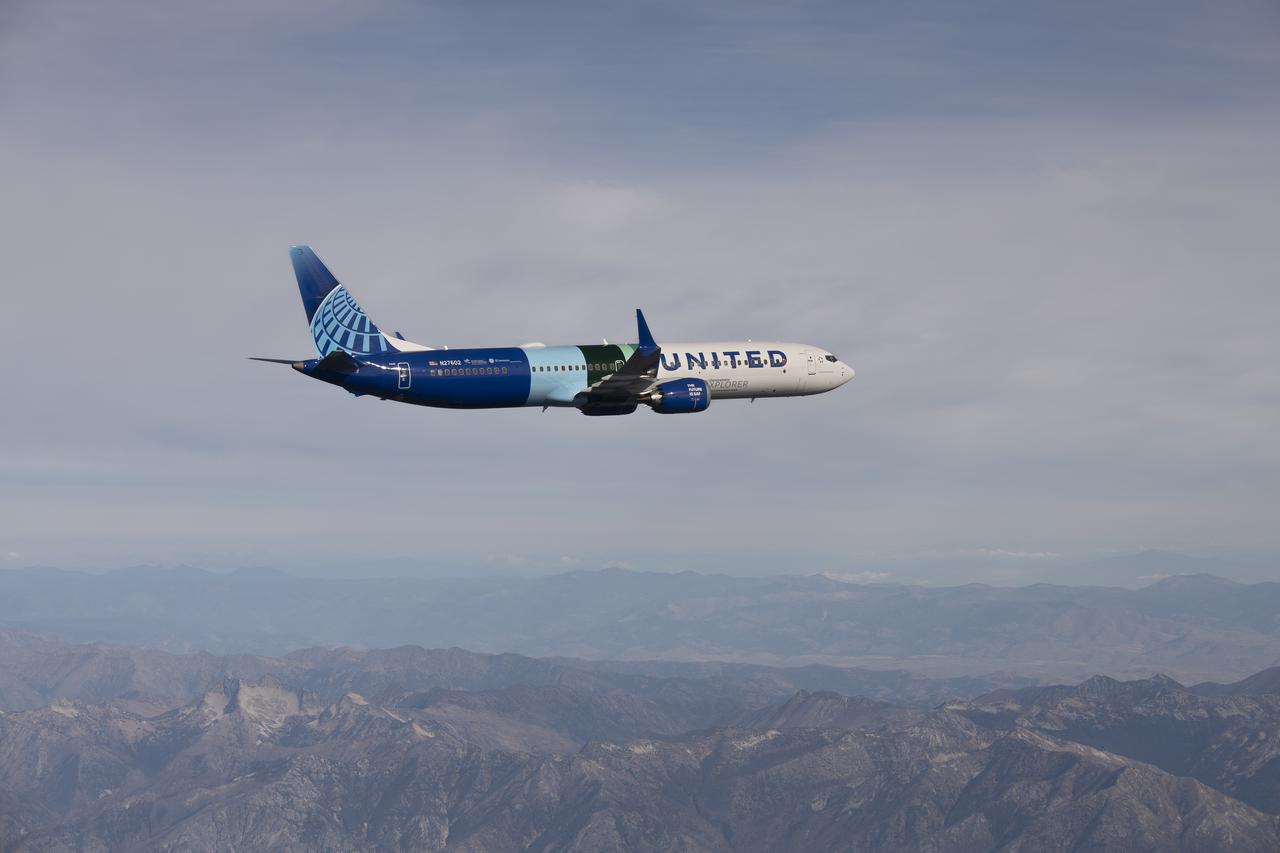

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
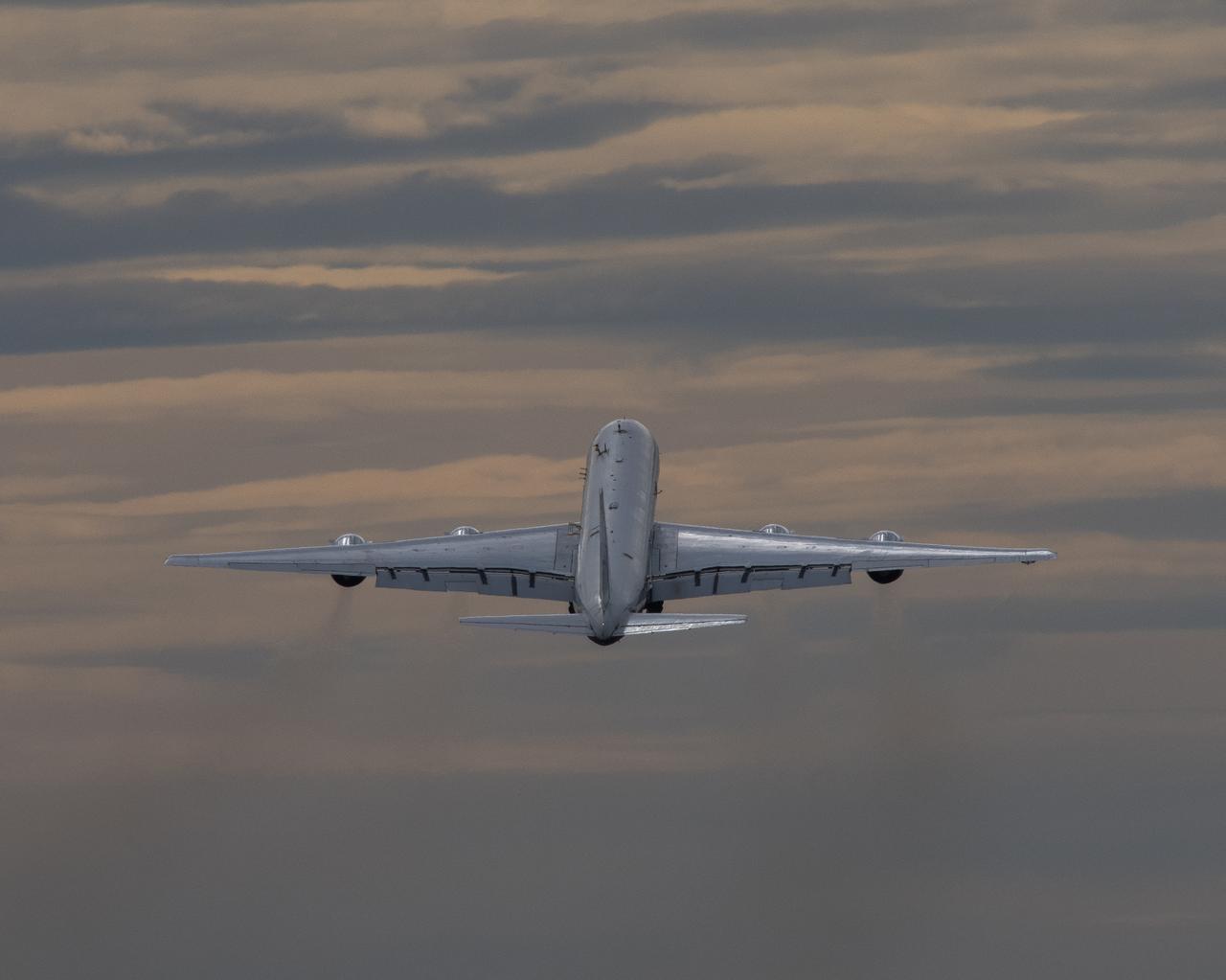

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
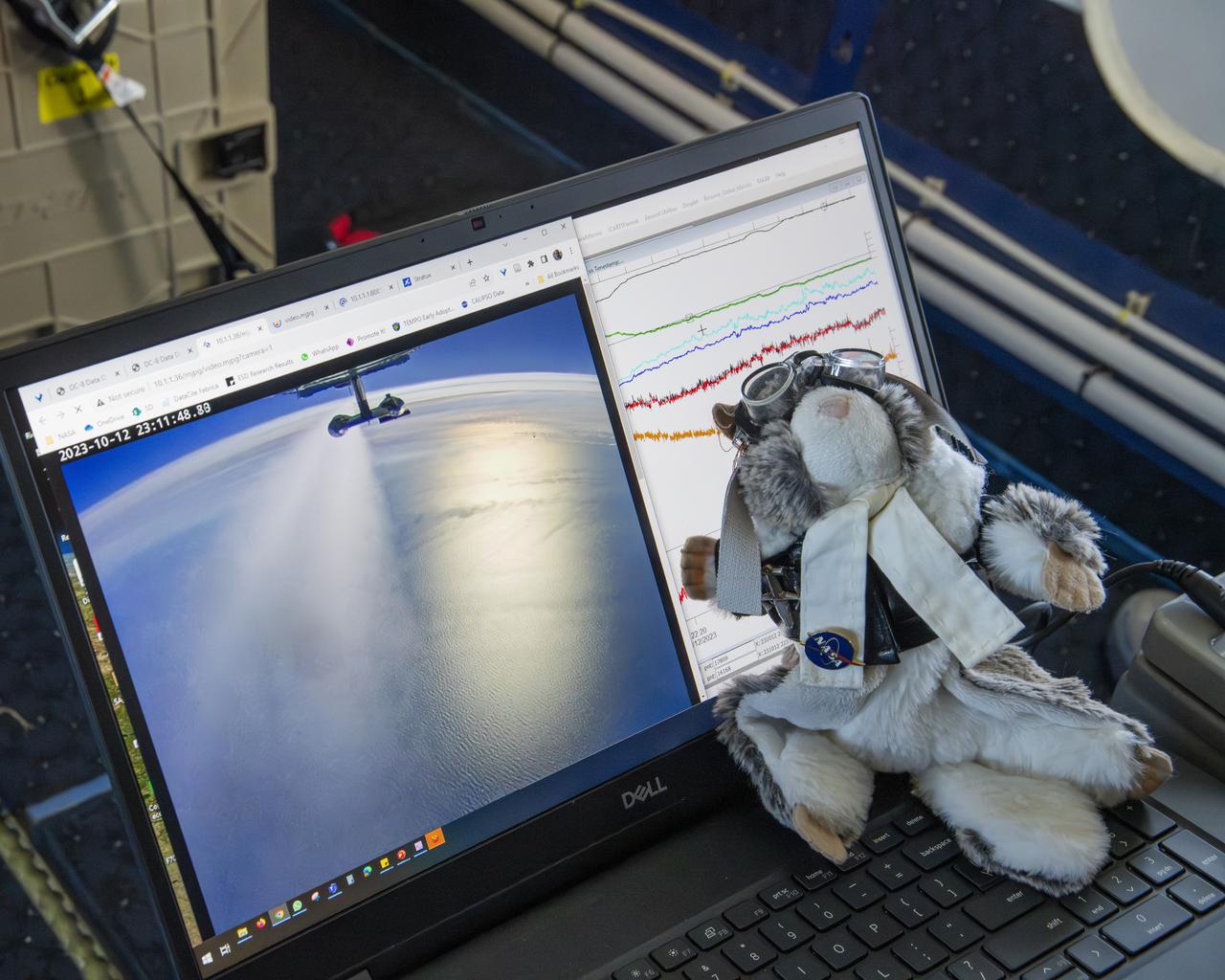

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
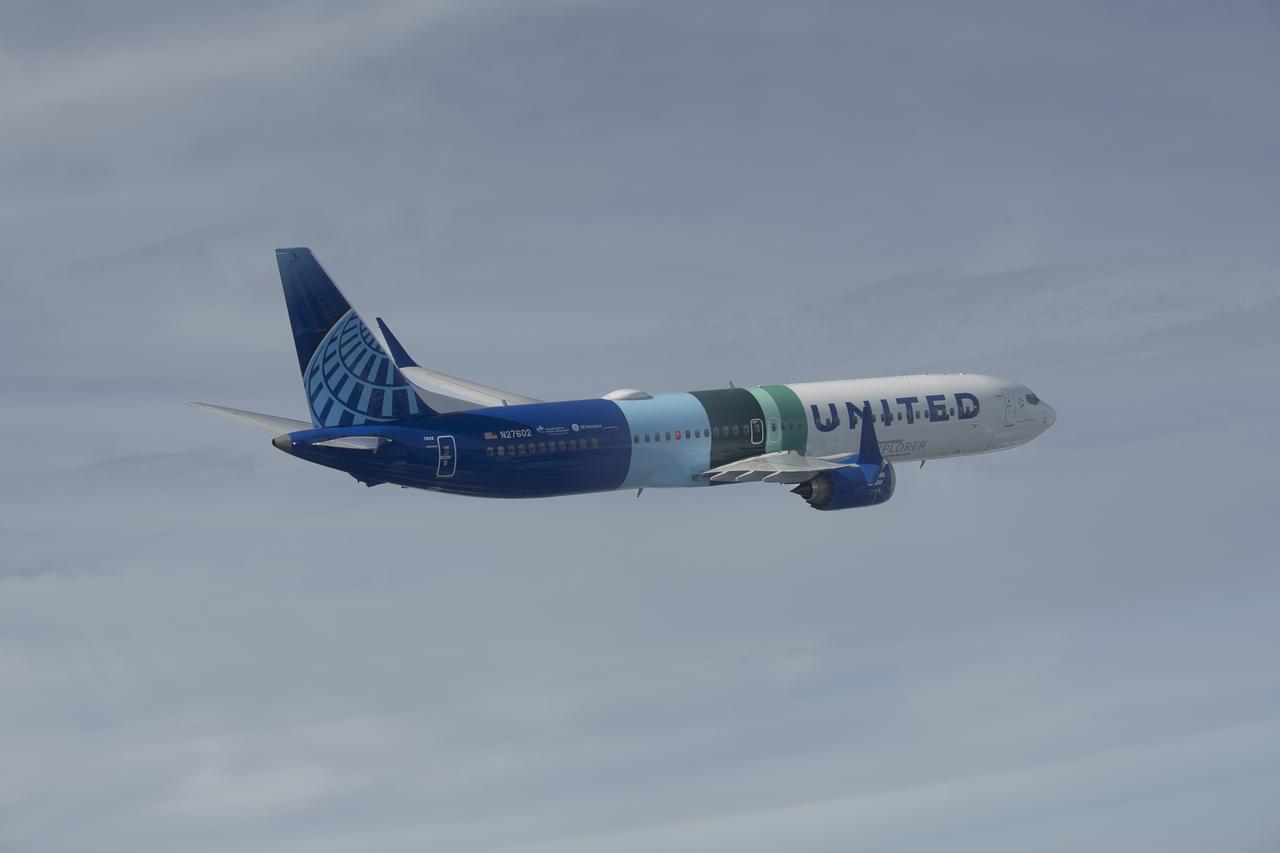

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.