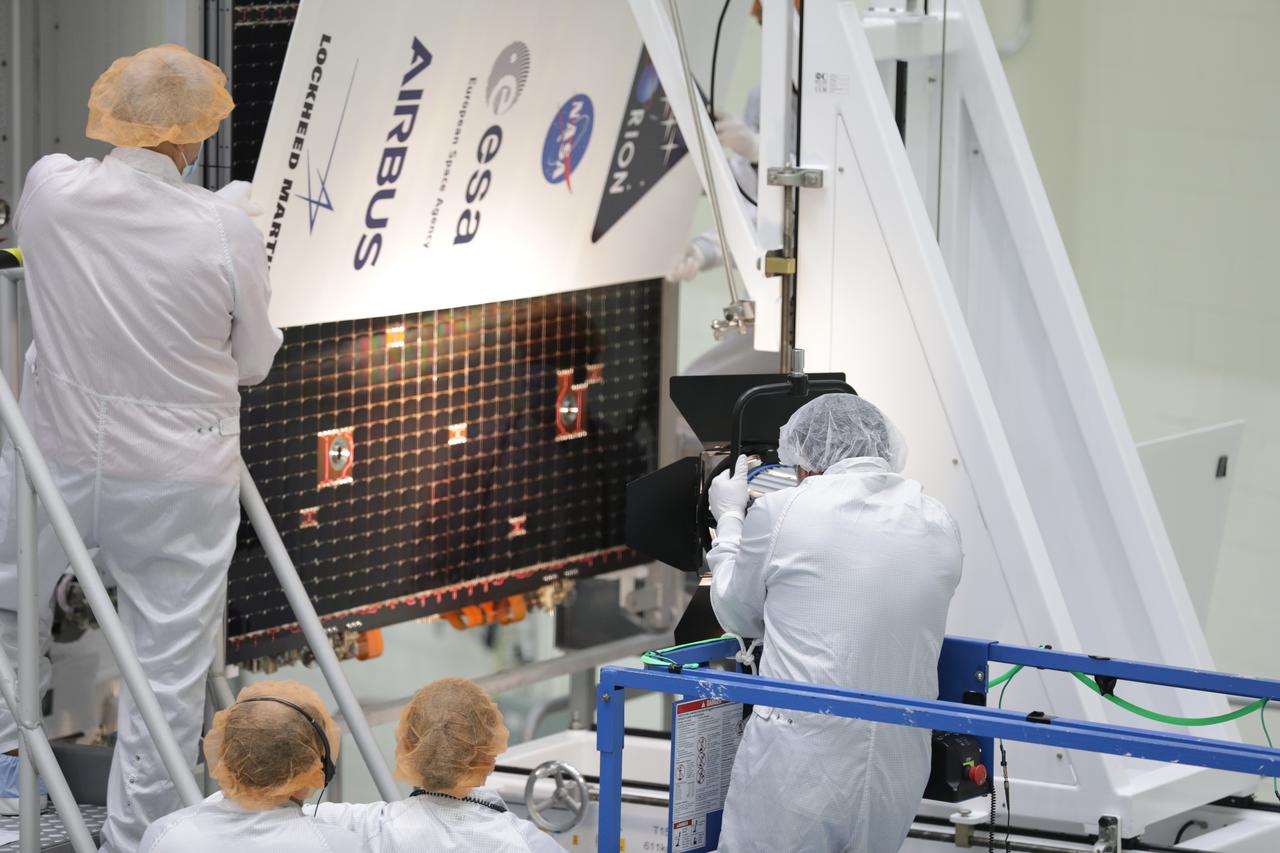

Technicians with the European Space Agency and Airbus/Airbus Netherlands are shown performing an illumination test on one of the solar array wing panels during installation on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
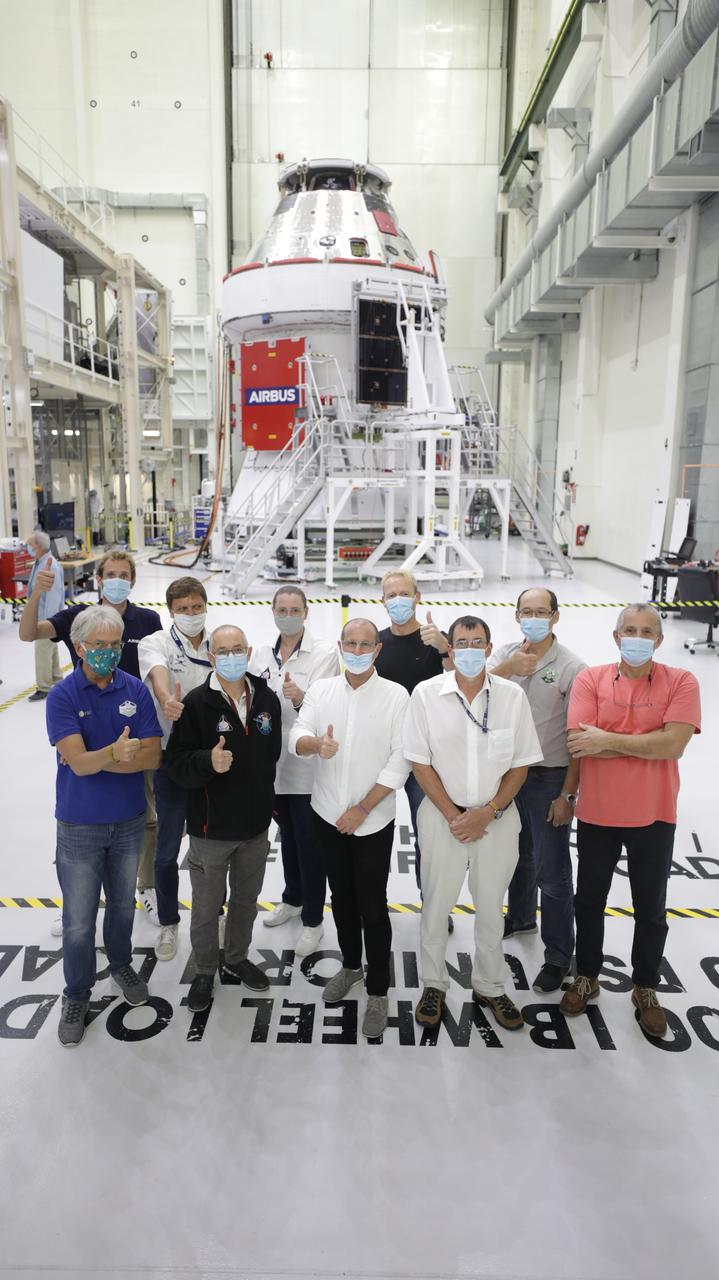

Members of the European Service Module processing team from the European Space Agency, Airbus, and Airbus Netherlands are shown with Orion’s solar array wings installed on the spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
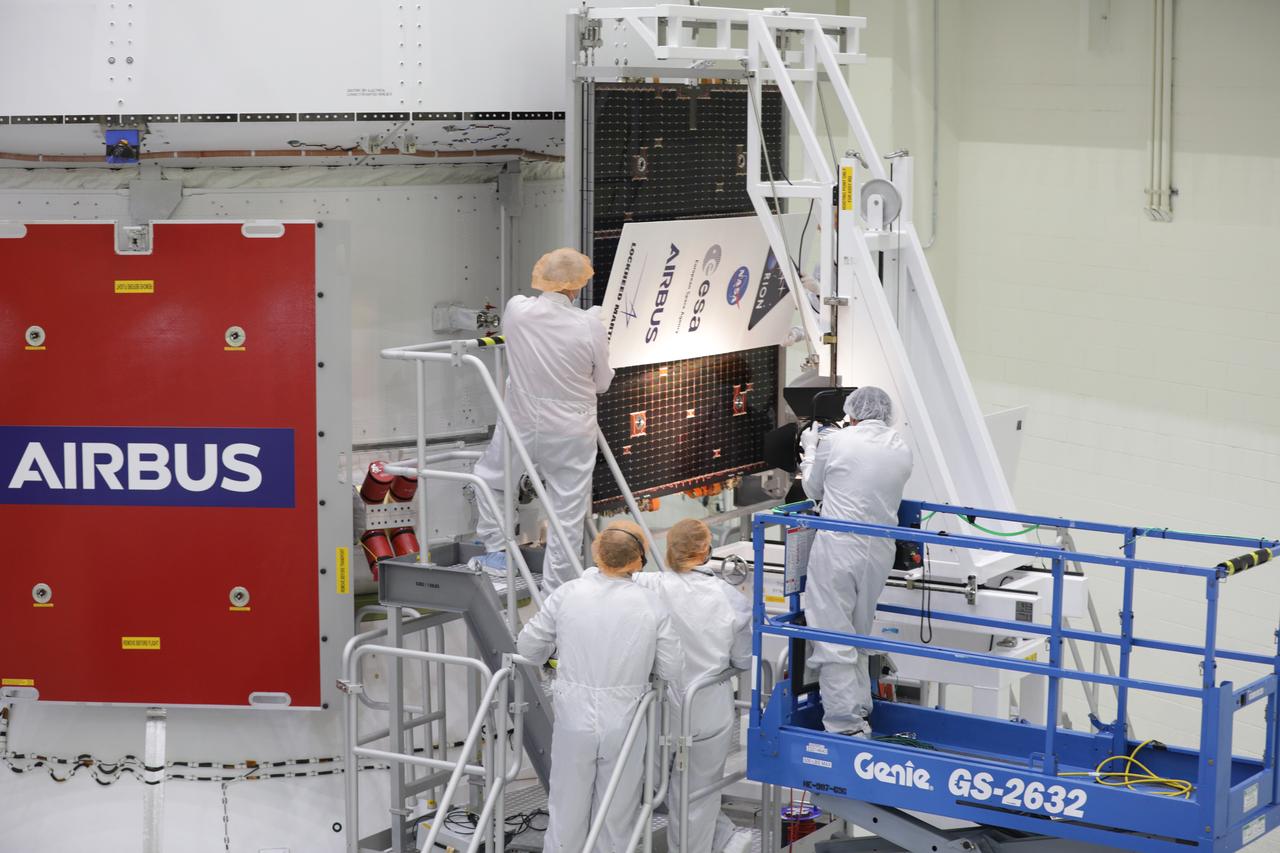

Technicians with the European Space Agency and Airbus/Airbus Netherlands are shown performing an illumination test on one of the solar array wing panels during installation on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
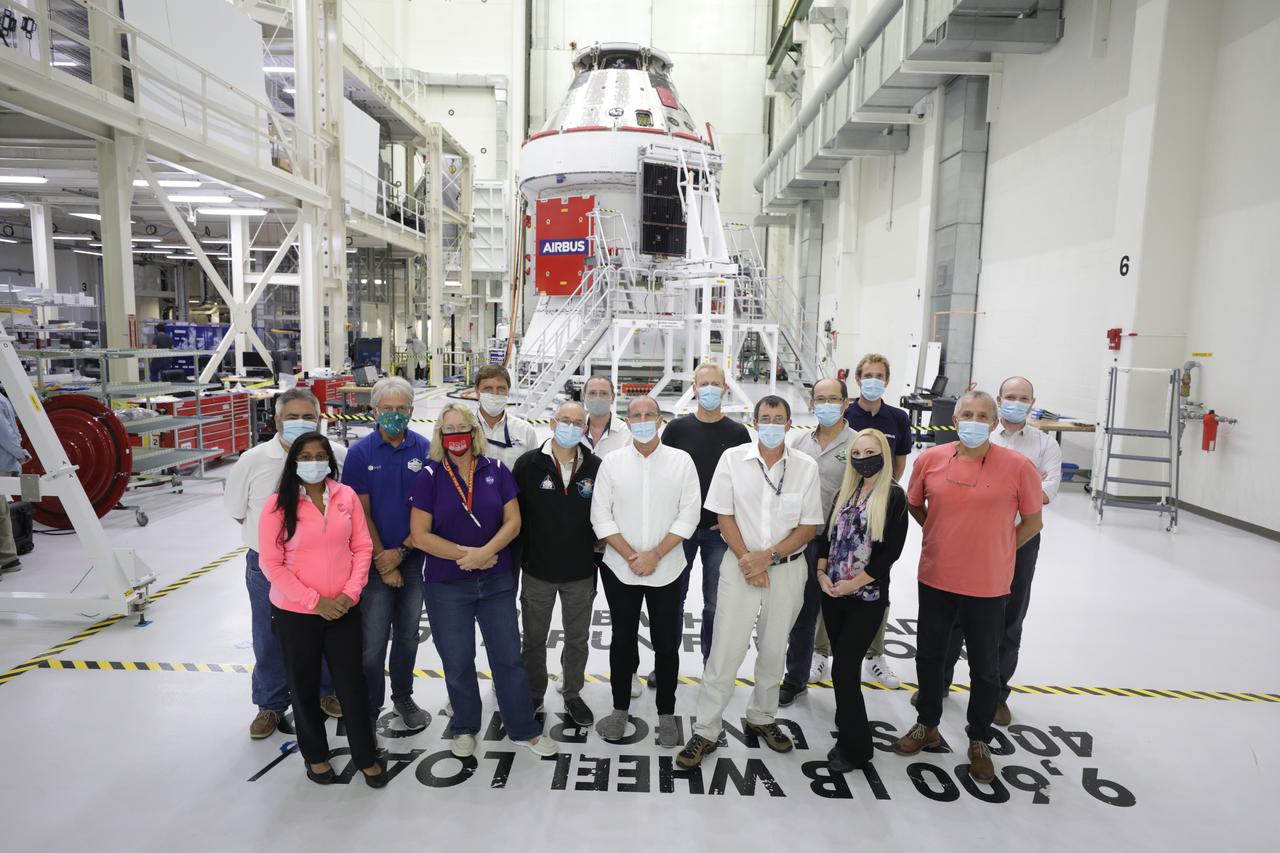

Members of the European Service Module processing team from NASA, the European Space Agency, Airbus, Airbus Netherlands, and Lockheed Martin are shown with Orion’s solar array wings installed on the spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
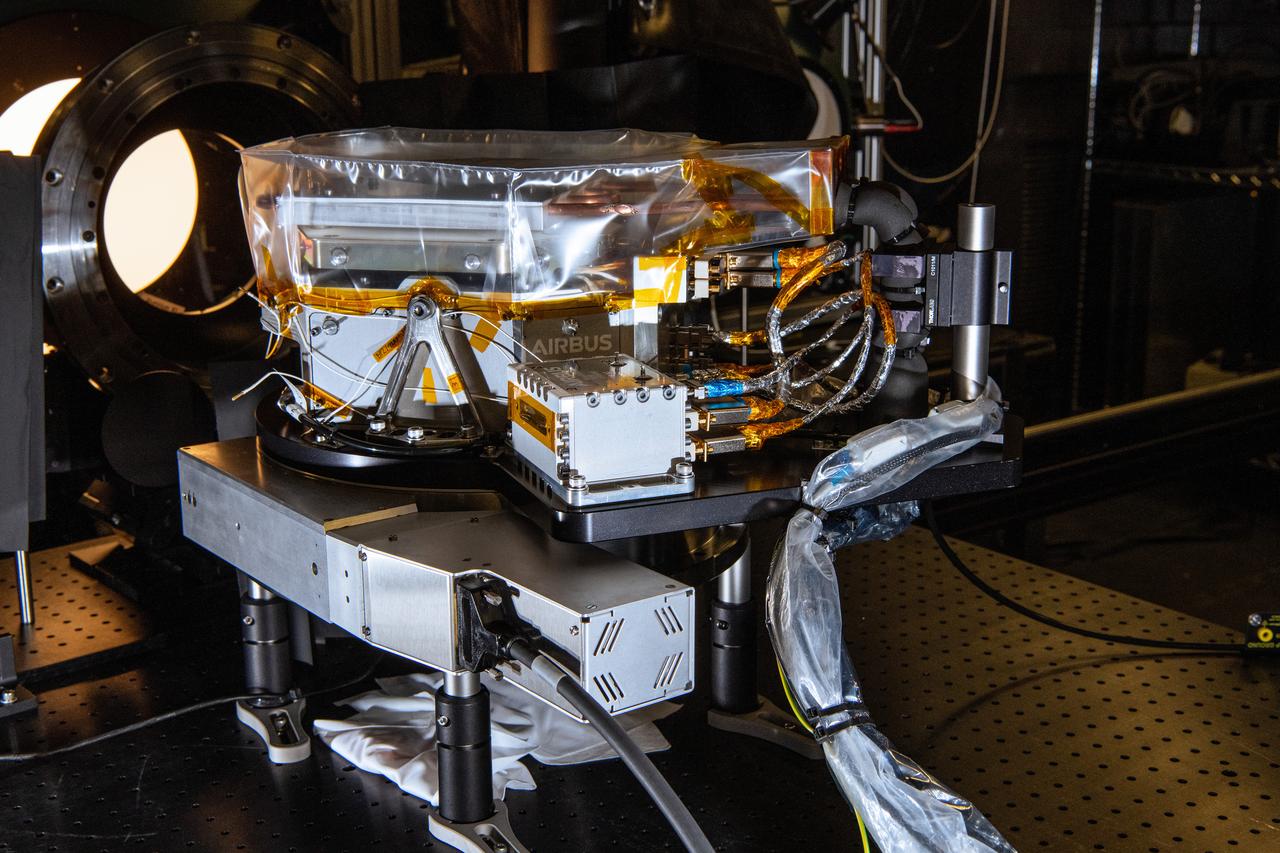
The SPEXone instrument undergoes Polarimetric Calibration at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt,Maryland on April 8th, 2021. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
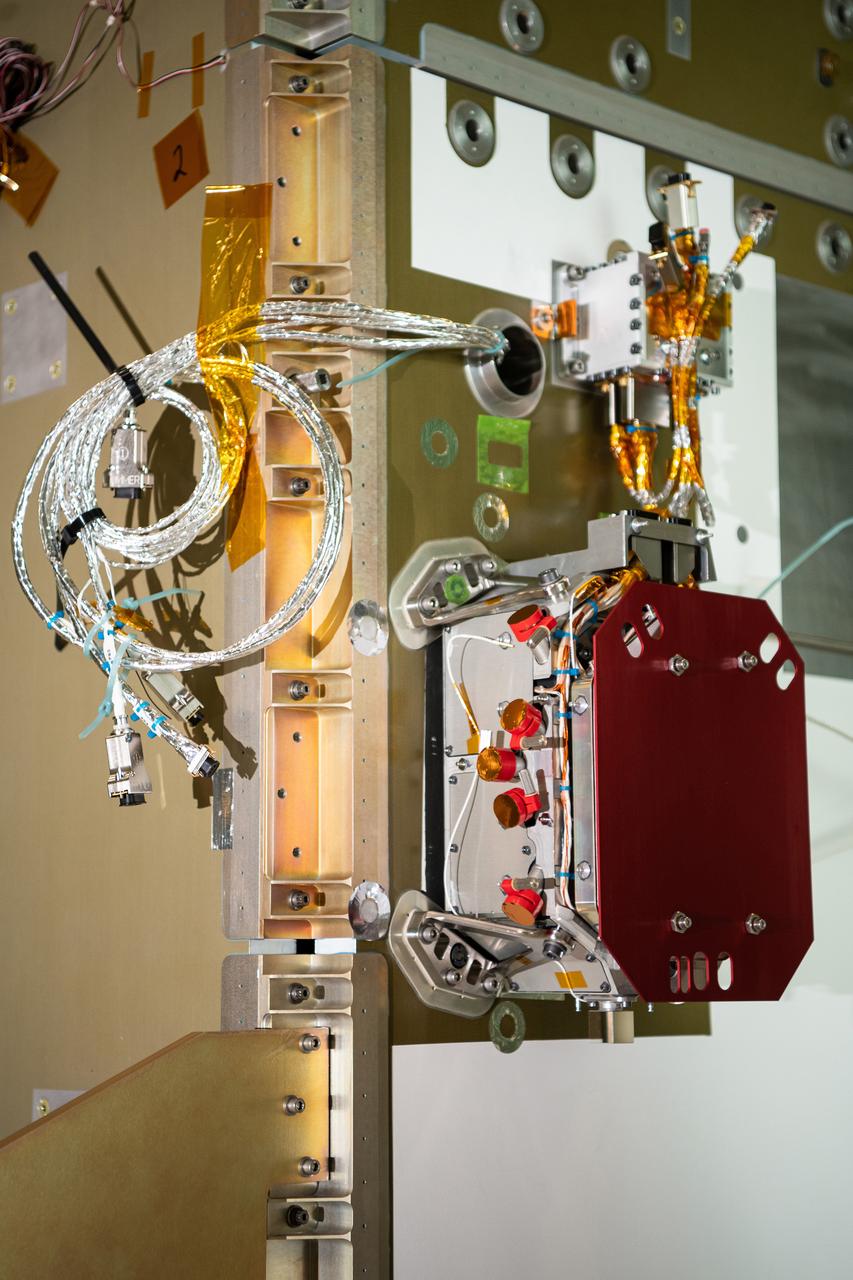
The SPEXone instrument after integration to the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Observatory. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
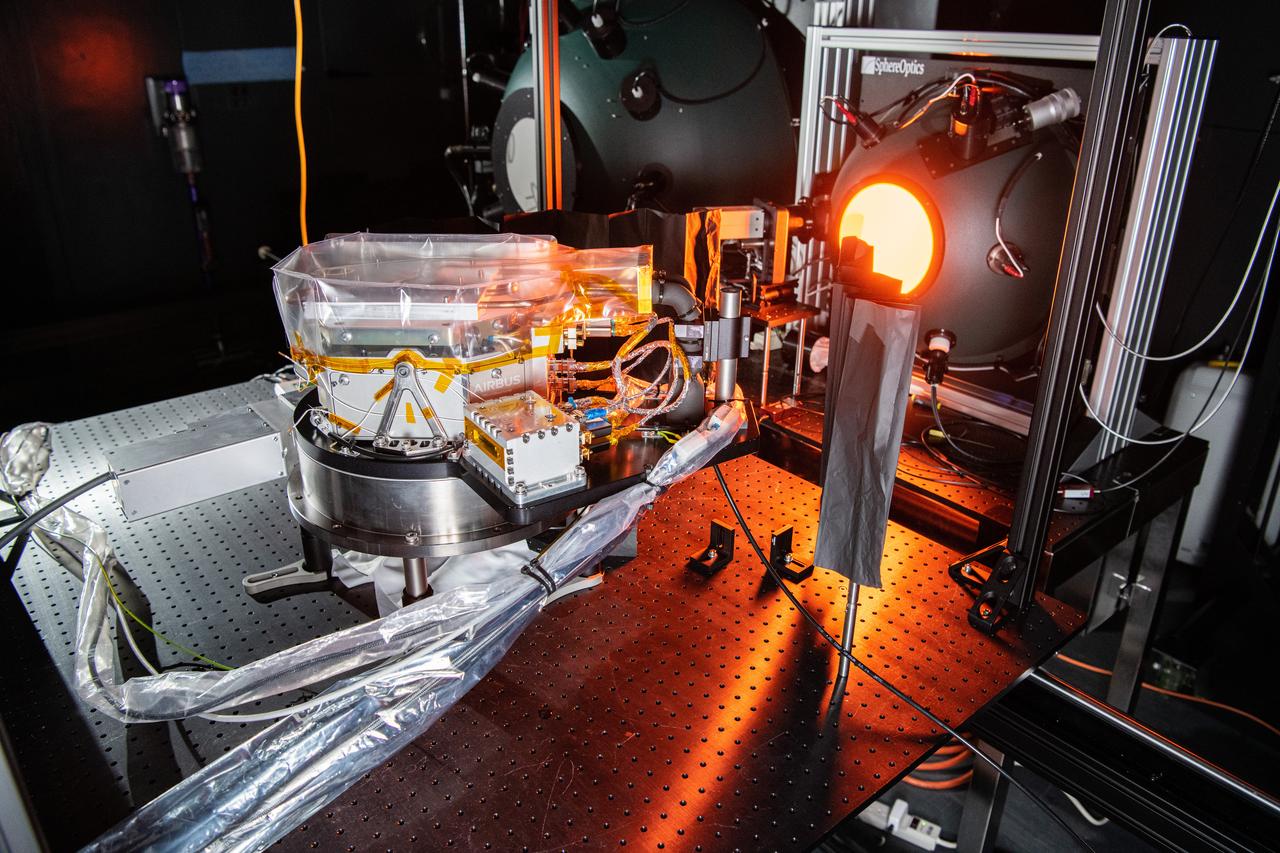
The SPEXone instrument undergoes cross calibration at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt,Maryland on April 20th, 2021. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
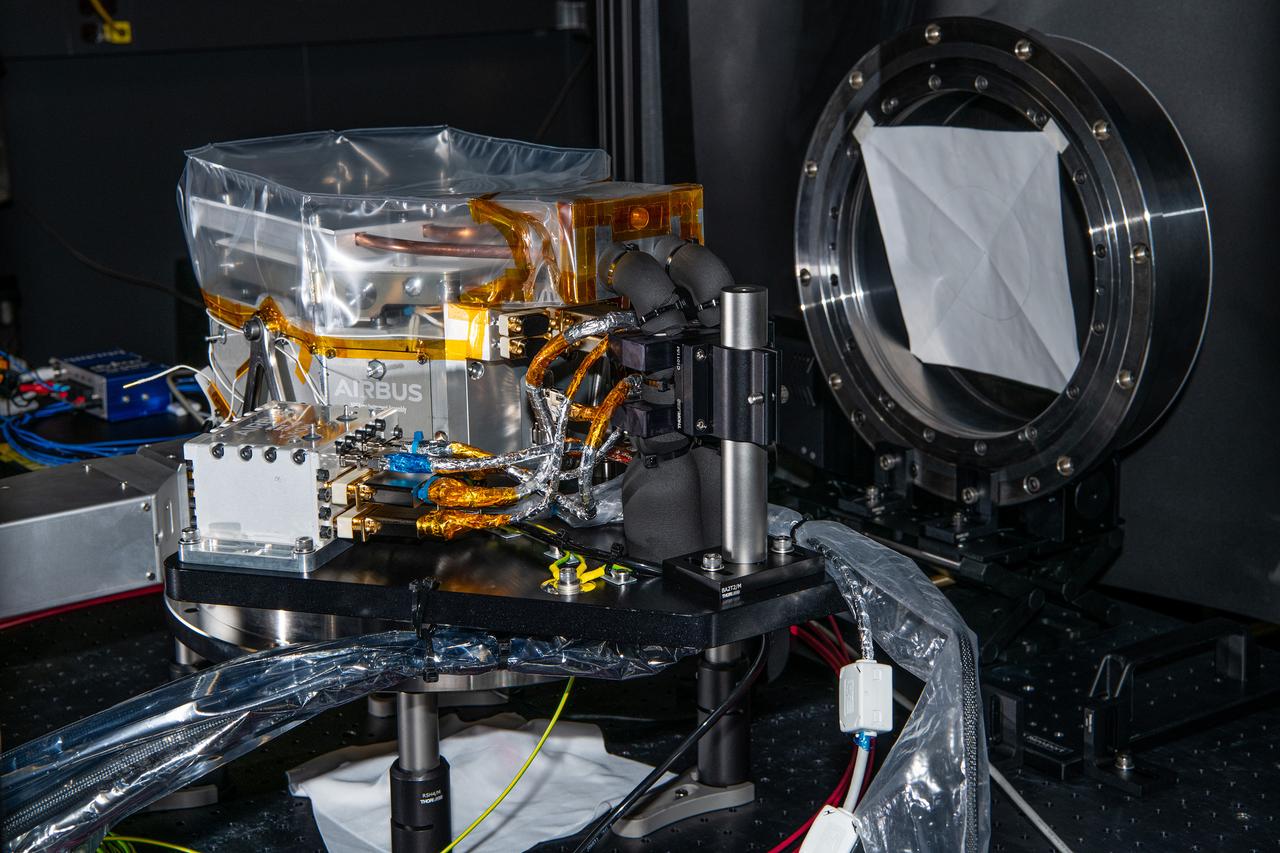
The SPEXone instrument undergoes comprehensive performace and calibration testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt,Maryland on April 8th, 2021. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
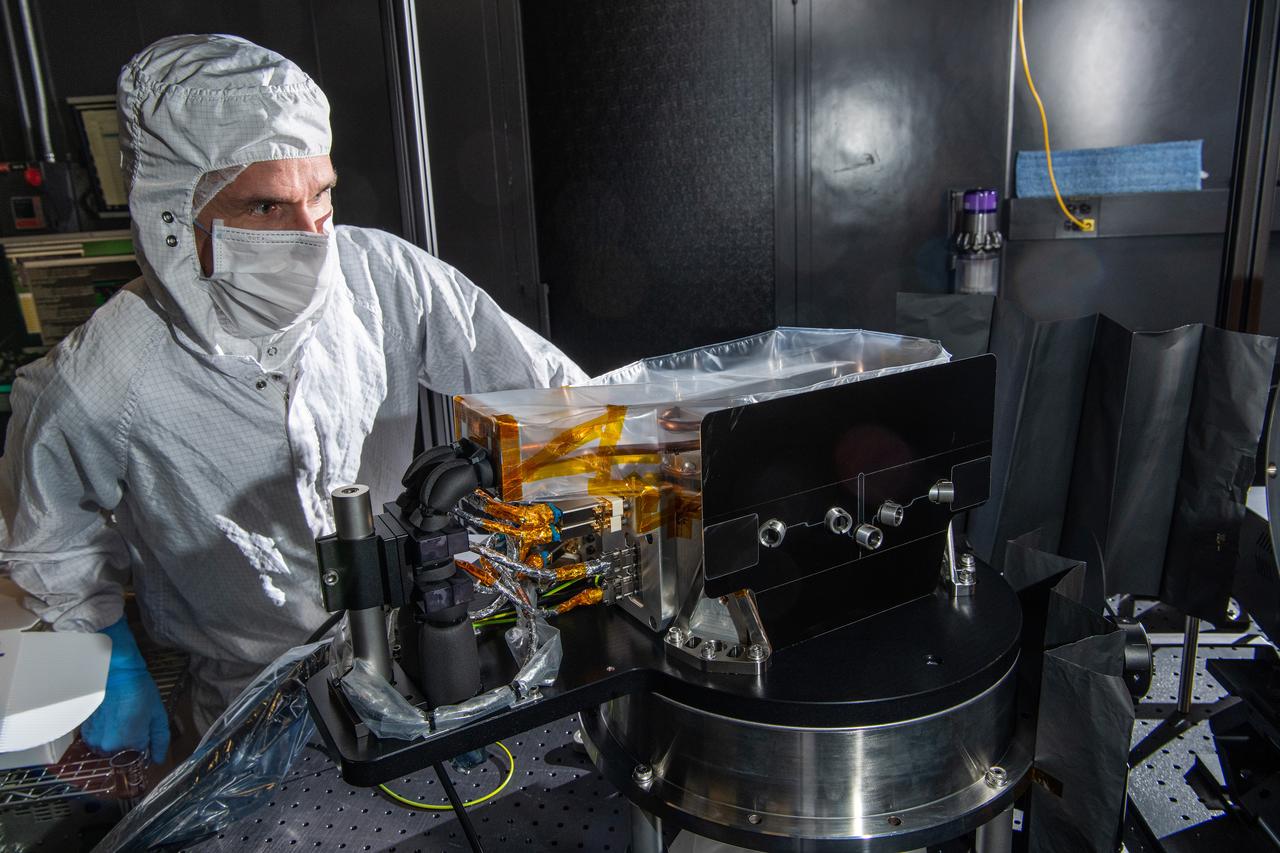

Jochen Campo from SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research with the The SPEXone Polarimetric Calibration at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt,Maryland on April 8th, 2021. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
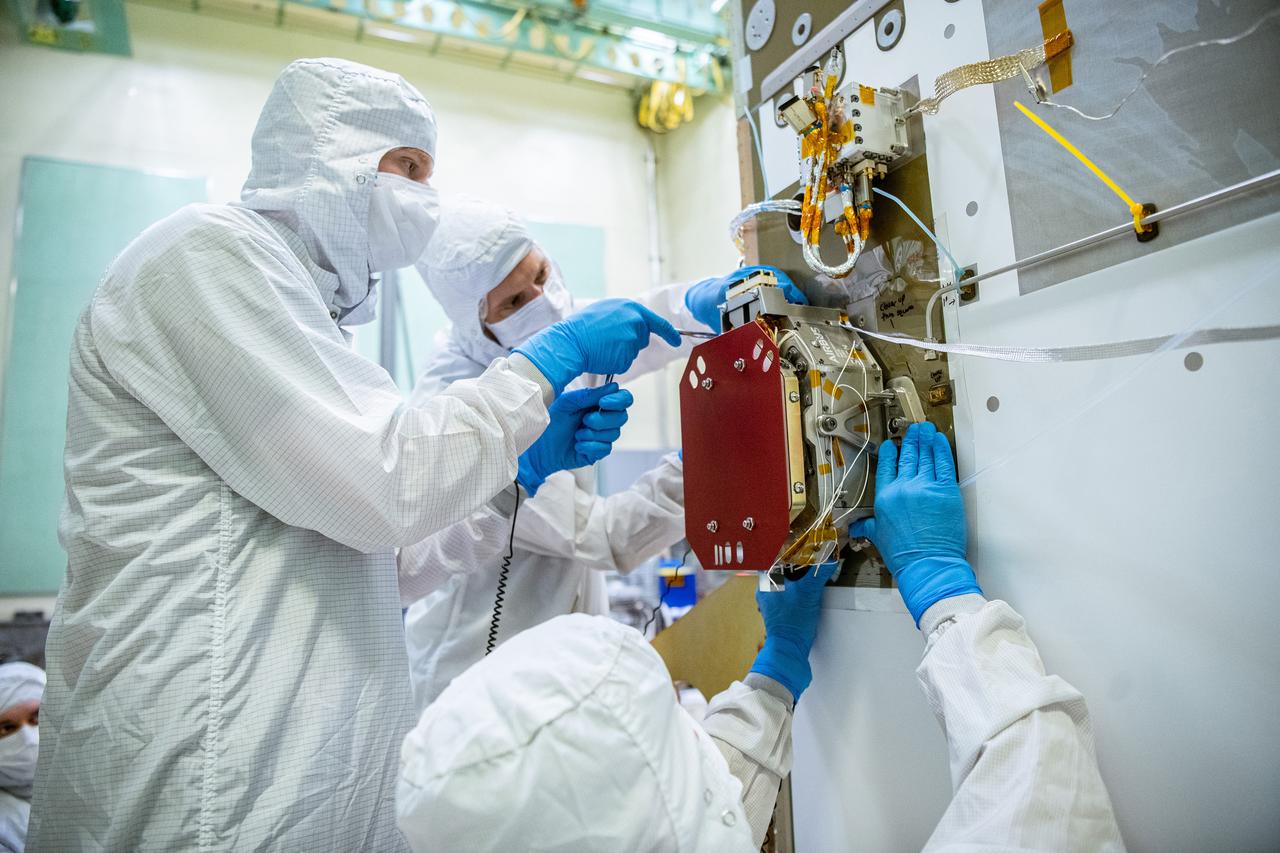

NASA technicians and Engineers from SRON, the Netherlands Institute for Space Research, integrate the SPEXone instrument to the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Spacecraft at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 13th, 2022. SPEXone is a compact, optical satellite instrument that will characterize aerosols from low Earth orbit as part of the NASA PACE mission. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
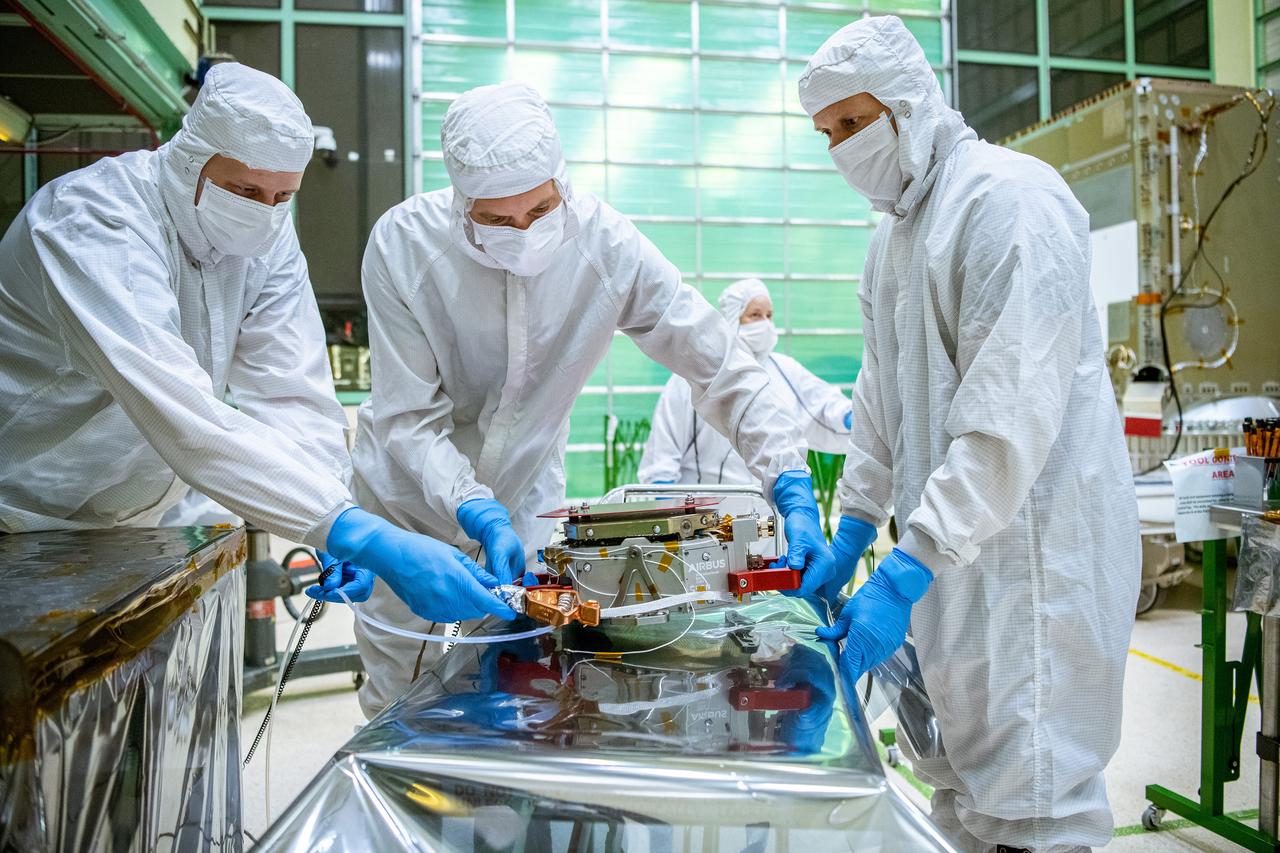

Engineers from SRON, the Netherlands Institute for Space Research, move the SPEXone instrument before it is integrated onto the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Spacecraft at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 13th, 2022. SPEXone is a compact, optical satellite instrument that will characterize aerosols from low Earth orbit as part of the NASA PACE mission. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
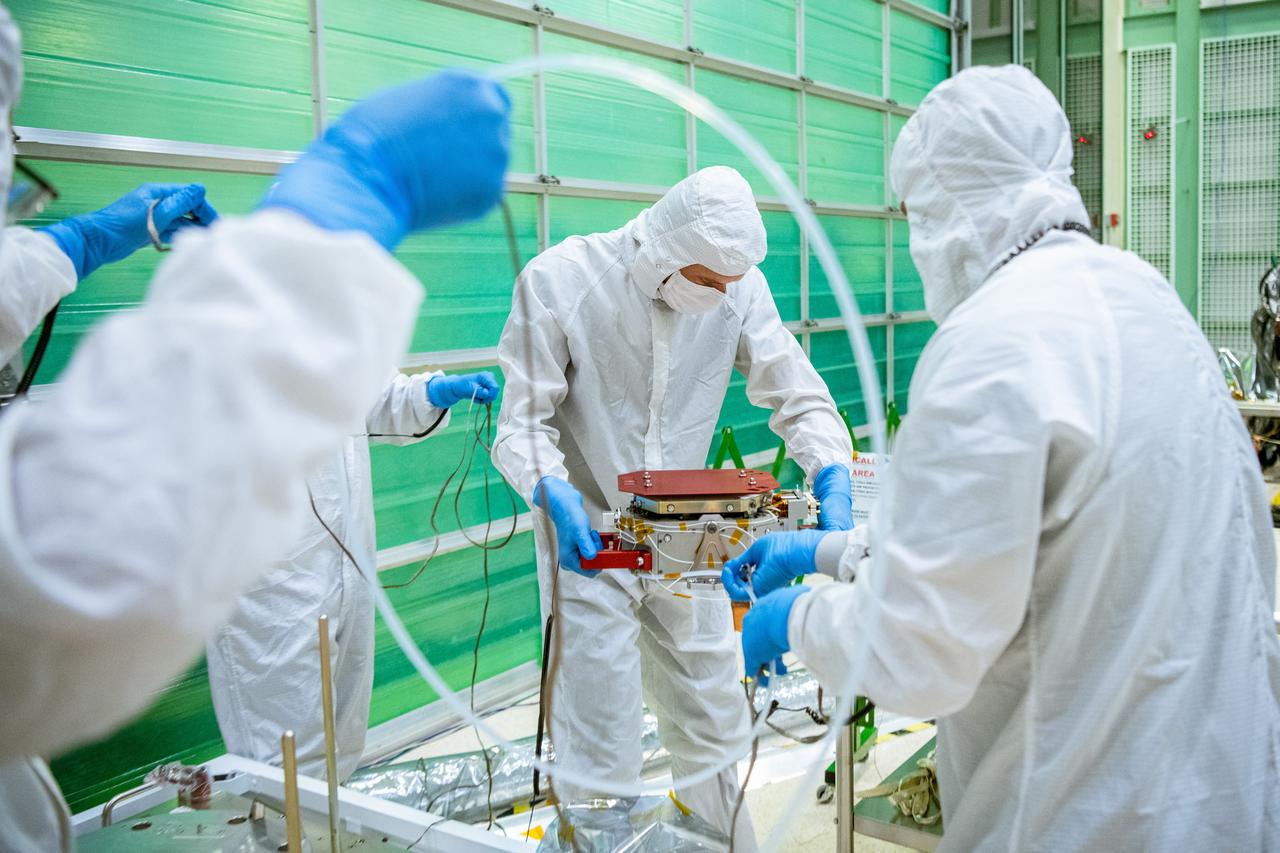

Senior Mechanical Design Engineer Alexander Eigenraam from SRON, the Netherlands Institute for Space Research, moves the SPEXone instrument before it is integrated onto the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Spacecraft at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 13th, 2022. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
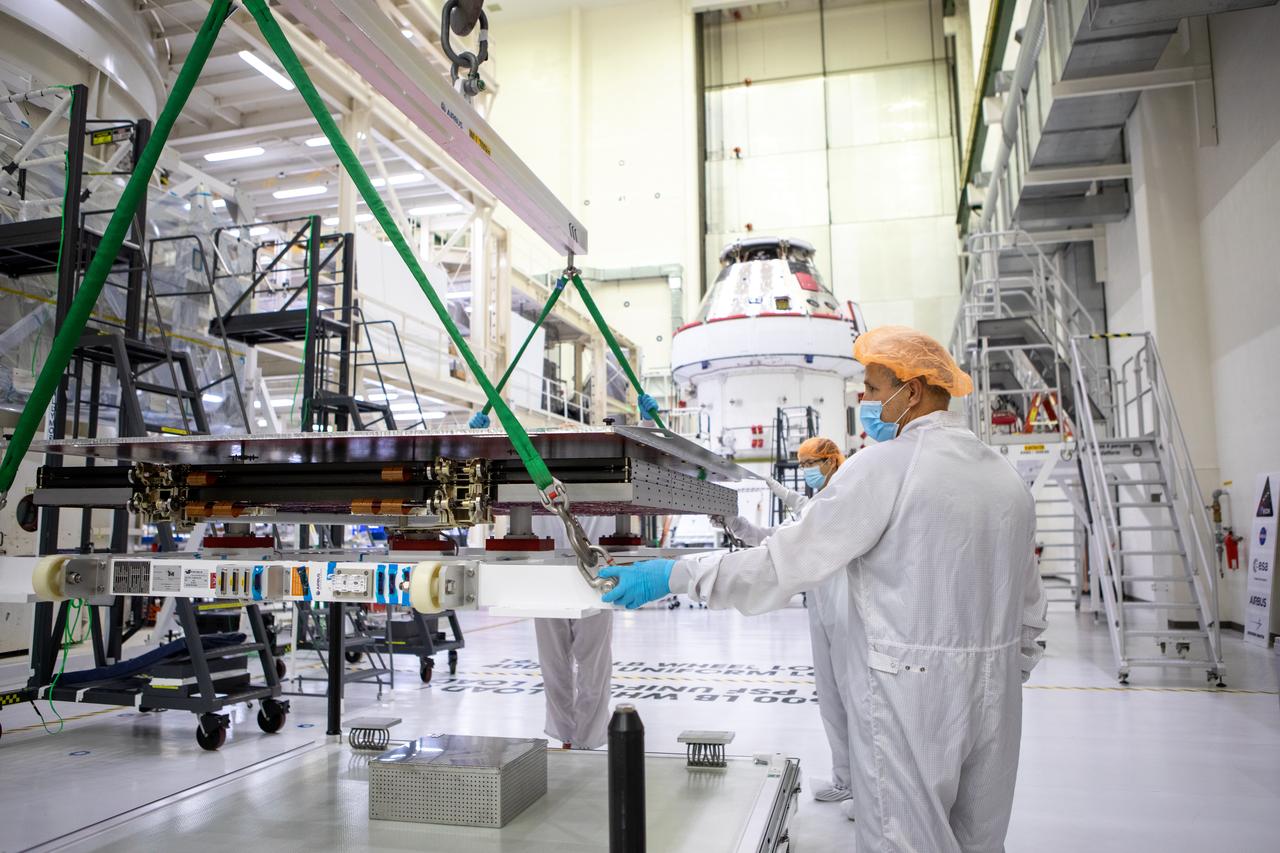

Technicians with European Service Module processing teams from the European Space Agency, Airbus, and Airbus Netherlands assist with securing a protective cover as a crane prepares to lift the panel during installation of one of four solar array wings inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The Orion spacecraft for Artemis I is shown in the background. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
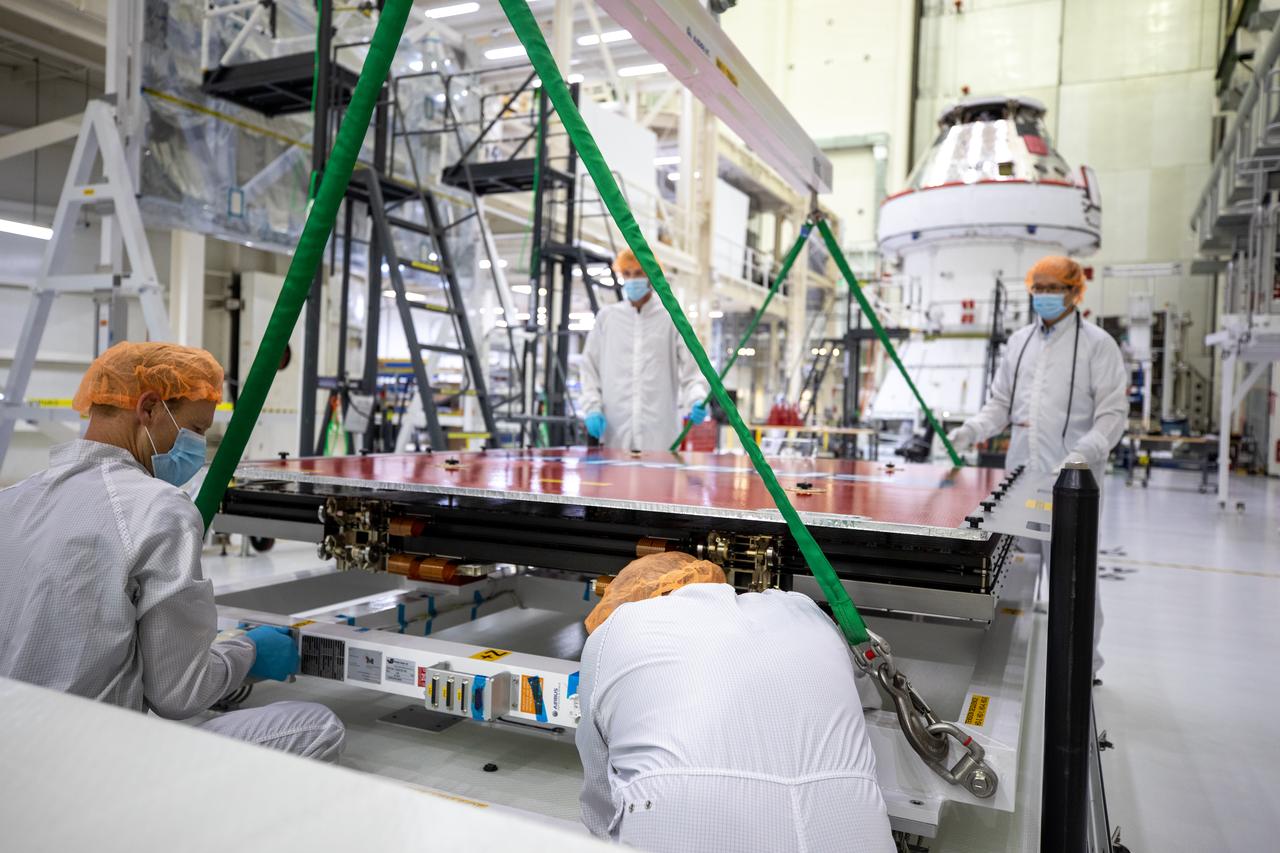

Technicians with European Service Module processing teams from the European Space Agency, Airbus, and Airbus Netherlands assist with securing a protective cover as a crane prepares to lift the panel during installation of one of four solar array wings inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The Orion spacecraft for Artemis I is shown in the background. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
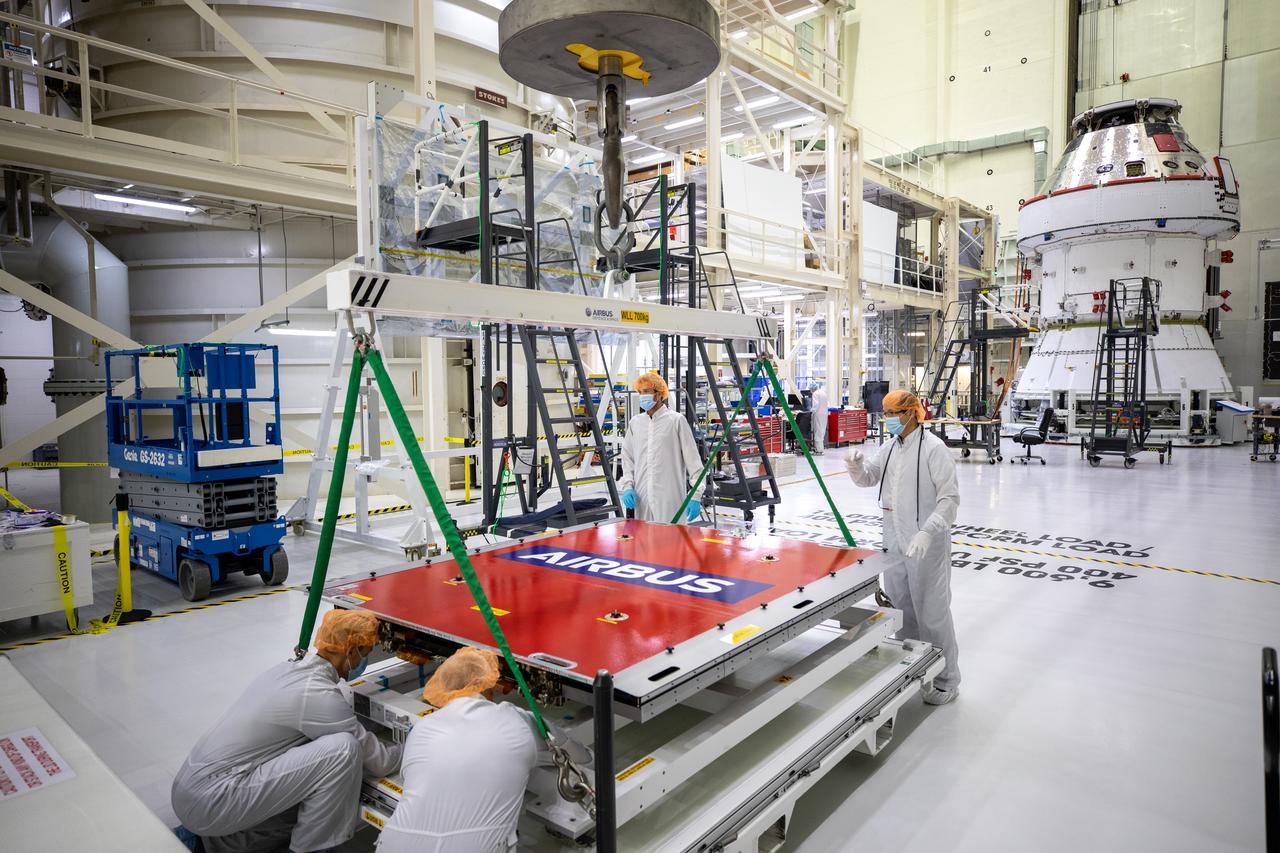

Technicians with European Service Module processing teams from the European Space Agency, Airbus, and Airbus Netherlands assist with securing a protective cover as a crane prepares to lift the panel during installation of one of four solar array wings inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The Orion spacecraft for Artemis I is shown in the background. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

The SPEXone instrument on The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 31st, 2023. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.

The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument (top) and the SPEXone instrument on The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 31st, 2023. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's PACE observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute. SPEXone has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.

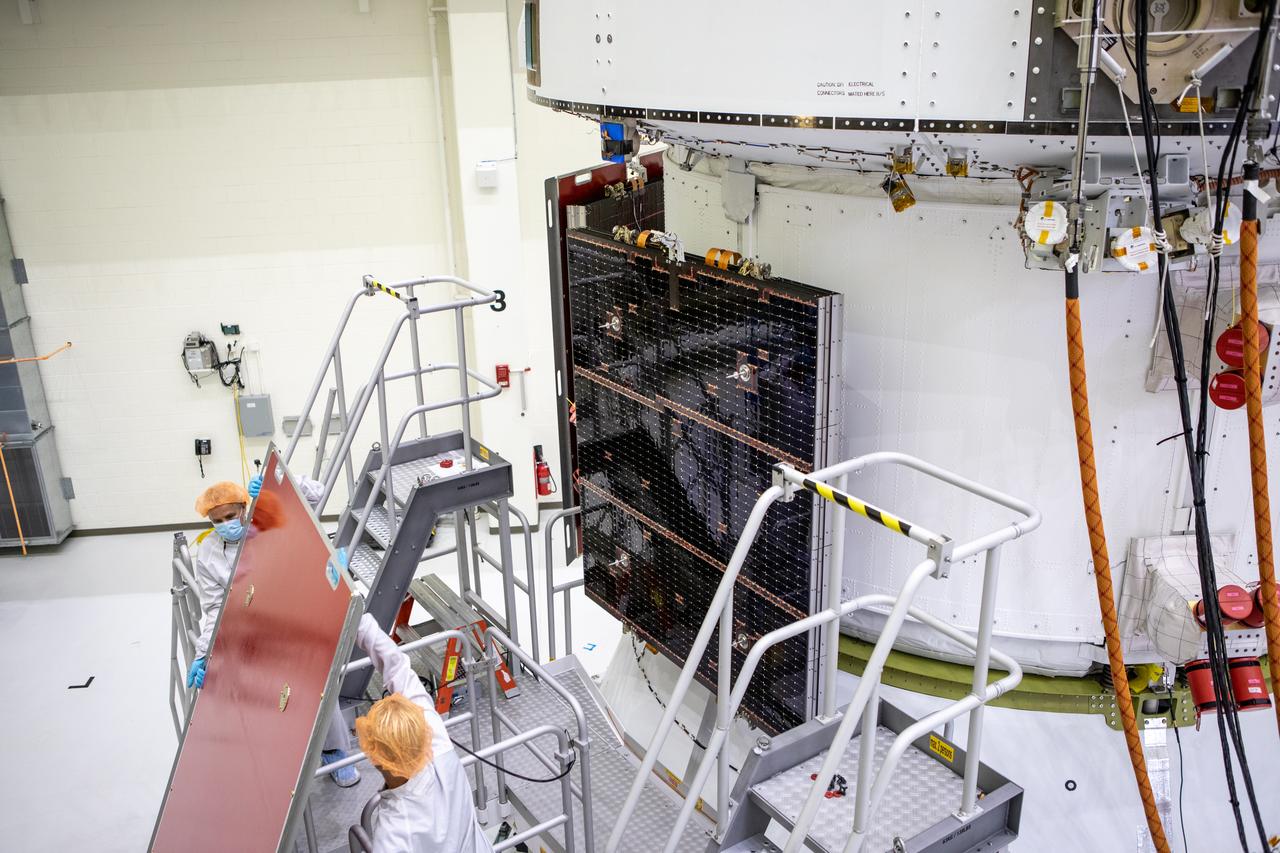
Members of the European Service Module processing team from the European Space Agency (ESA), Airbus, and Airbus Netherlands install the four solar array wings on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by ESA and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air, and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
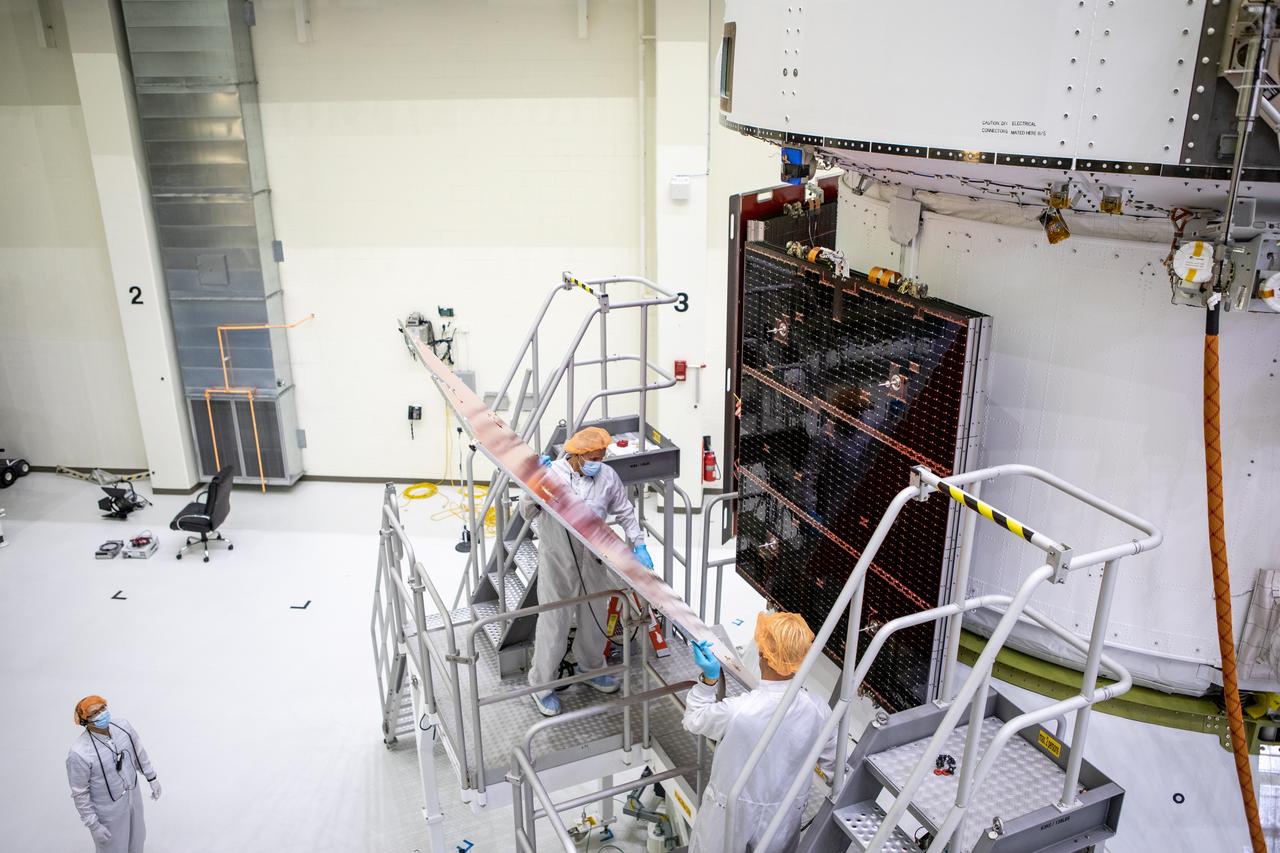
Members of the European Service Module processing team from the European Space Agency (ESA), Airbus, and Airbus Netherlands fit a protective cover over the solar array wings on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by ESA and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air, and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

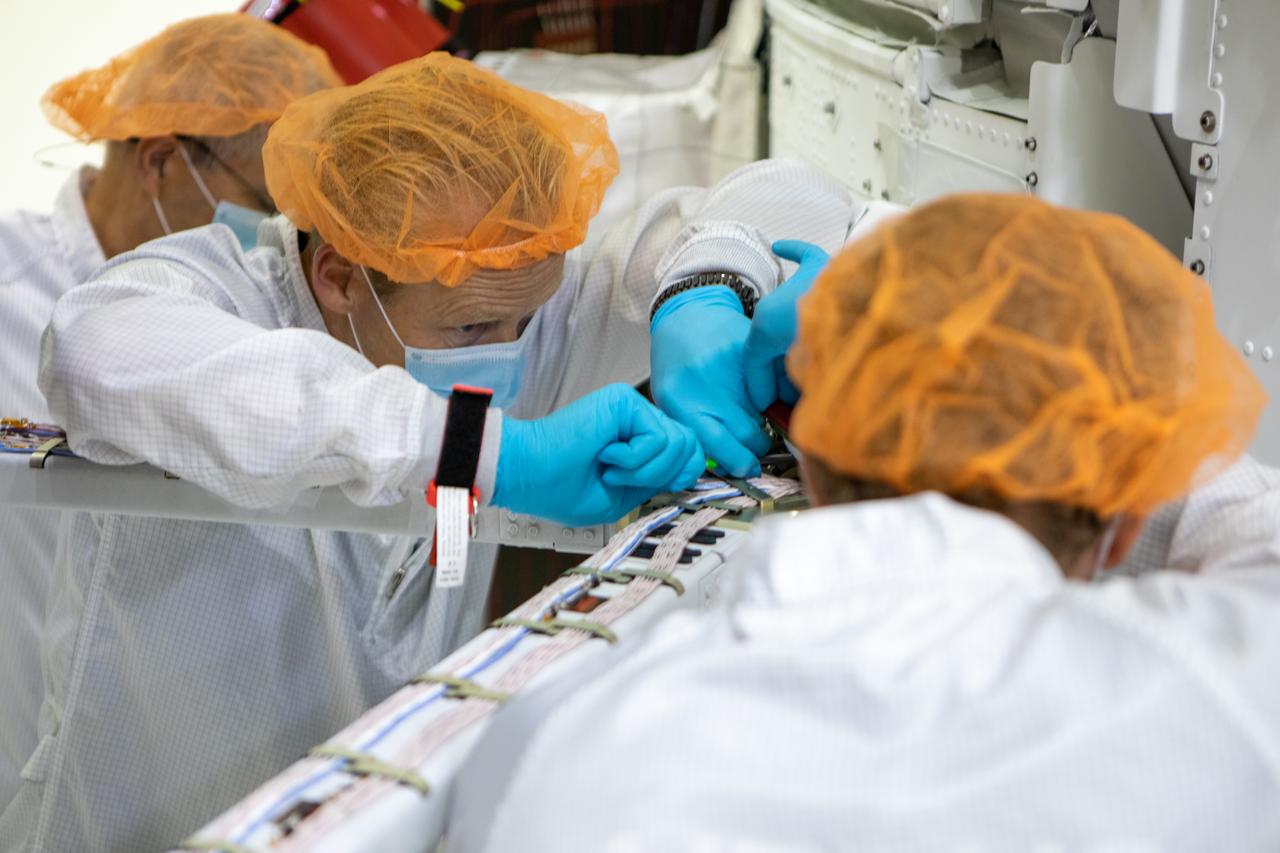
Members of the European Service Module processing team from the European Space Agency (ESA), Airbus, and Airbus Netherlands fit a protective cover over the solar arrays on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted before installation on the spacecraft. Each of the four solar array panels will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air, and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Members of the European Service Module processing team from the European Space Agency (ESA), Airbus, and Airbus Netherlands install the four solar array wings on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by ESA and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air, and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
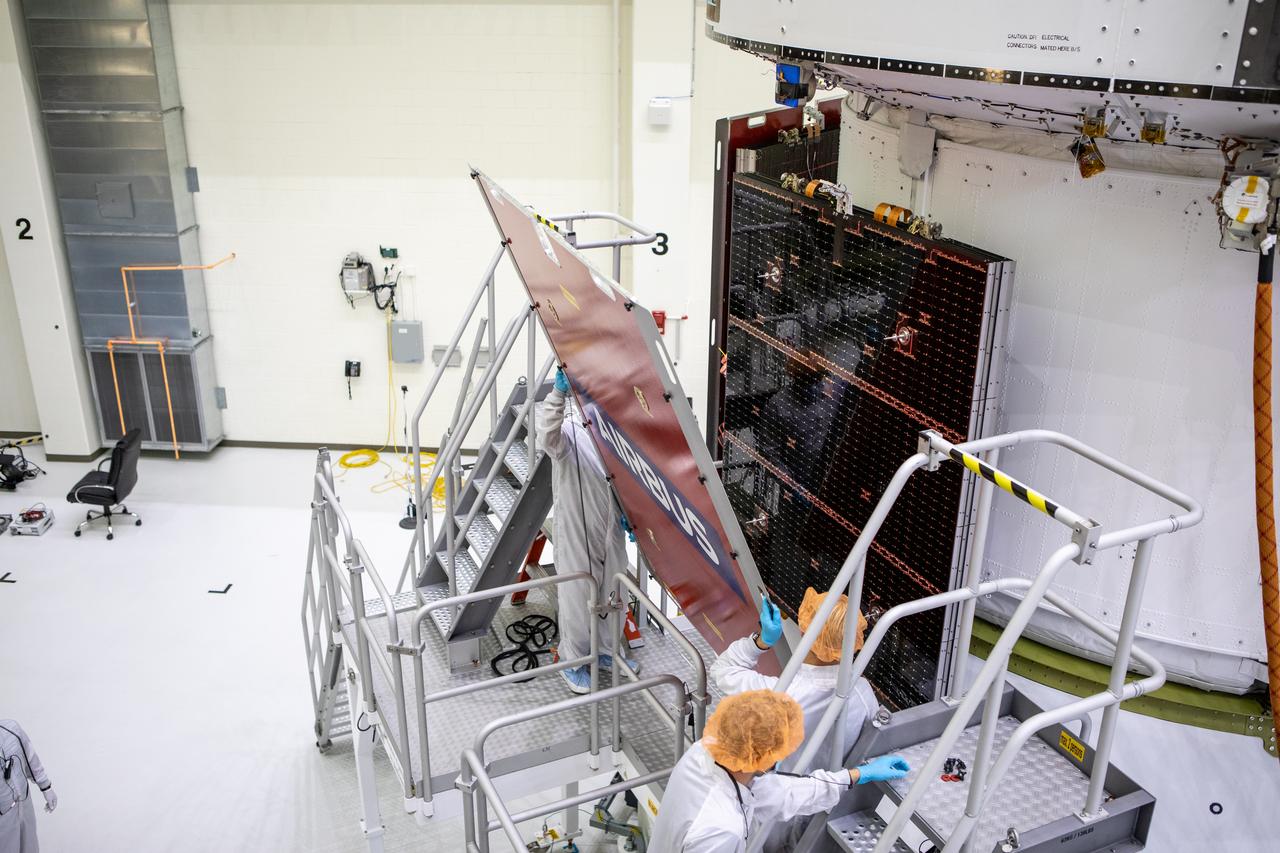
Technicians with the European Space Agency (ESA) and Airbus/Airbus Netherlands install a protective cover over one of the solar array wing panels installed on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted before installation on the spacecraft. Each of the four solar array panels will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by ESA and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air, and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
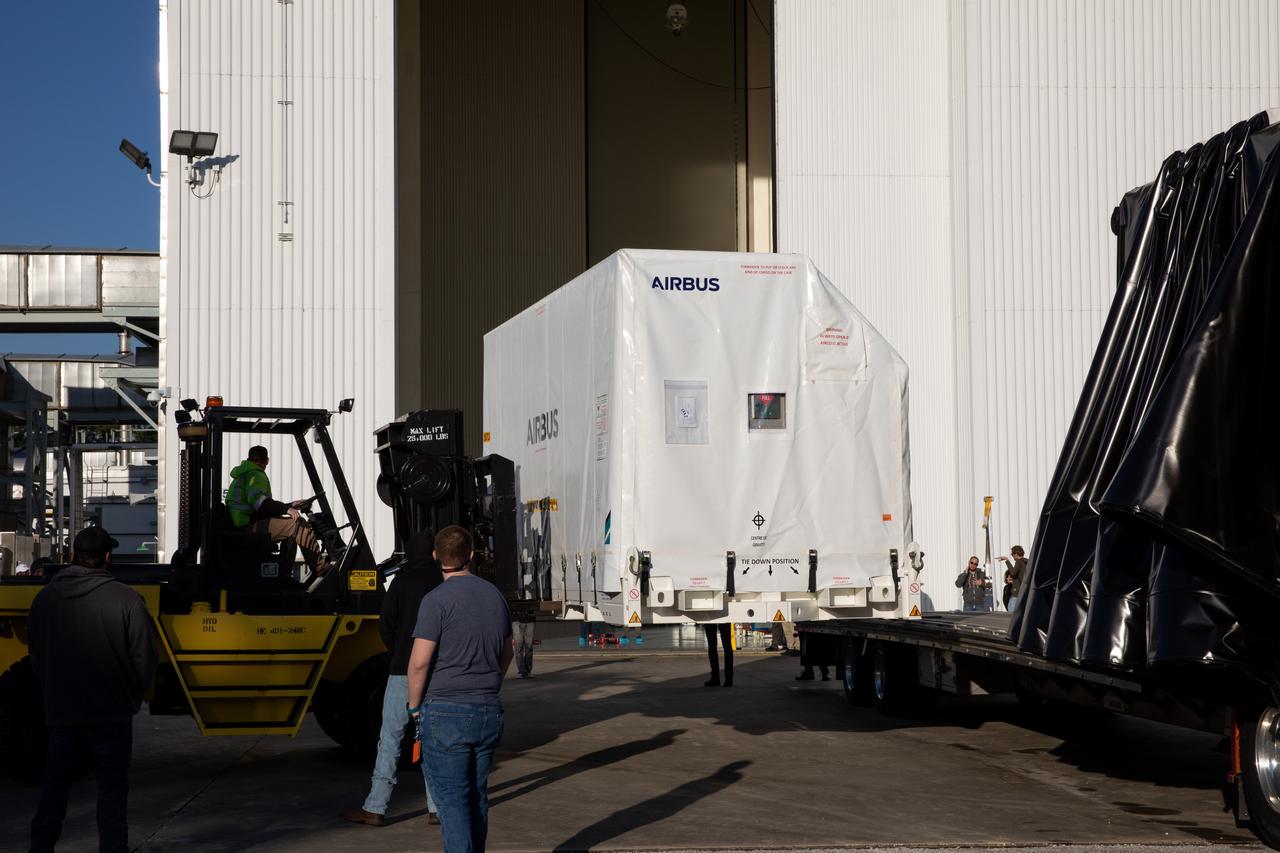

The transport carrier containing the five-panel solar arrays for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 21, 2024. The arrival completes the solar array journey which began in Leiden, Netherlands, where Airbus workers assembled them before shipping them by barge to Port of Miami in Florida and transporting them by truck to Kennedy. The solar arrays will attach to the spacecraft to power it on the 1.8-billion-mile journey to study Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. Launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket is no earlier than October 2024.
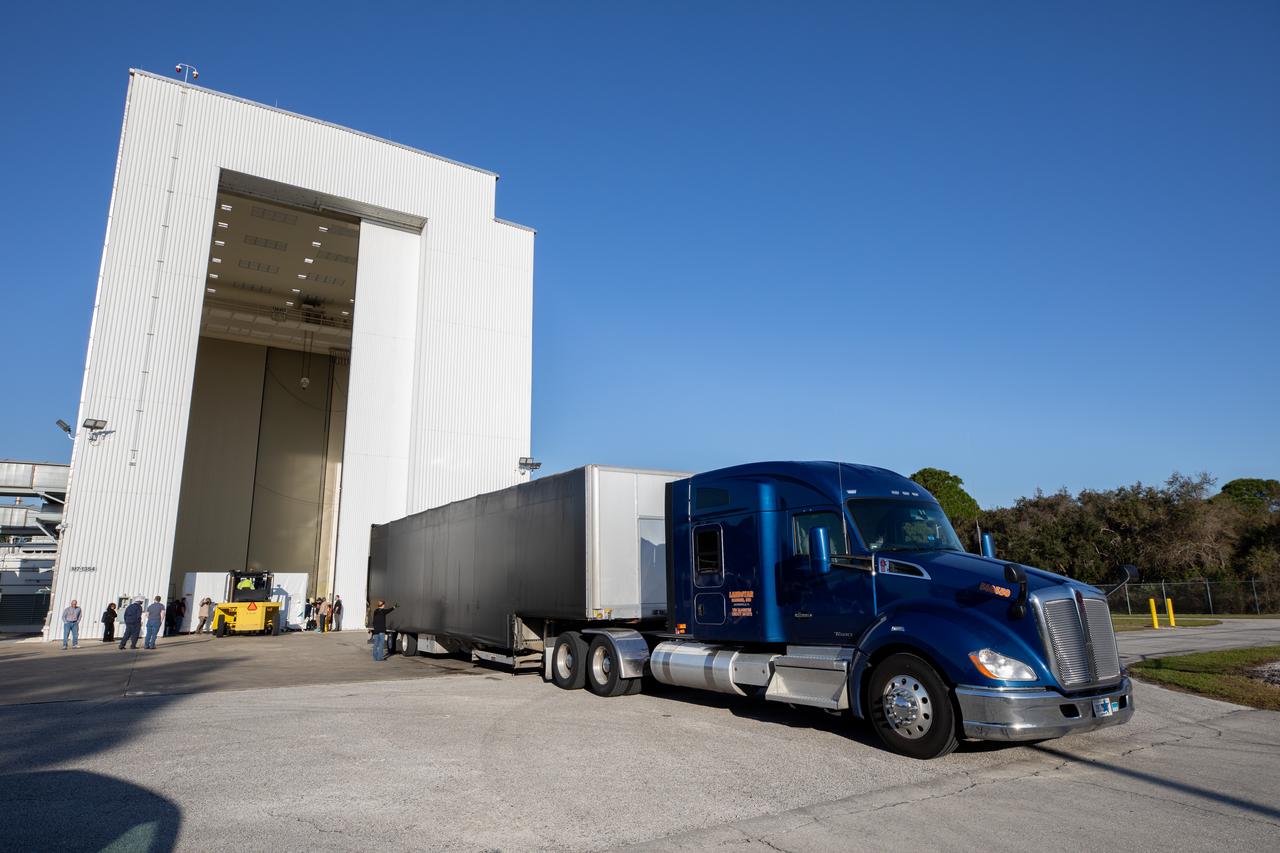

The transport carrier containing the five-panel solar arrays for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 21, 2024. The arrival completes the solar array journey which began in Leiden, Netherlands, where Airbus workers assembled them before shipping them by barge to Port of Miami in Florida and transporting them by truck to Kennedy. The solar arrays will attach to the spacecraft to power it on the 1.8-billion-mile journey to study Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. Launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket is no earlier than October 2024.
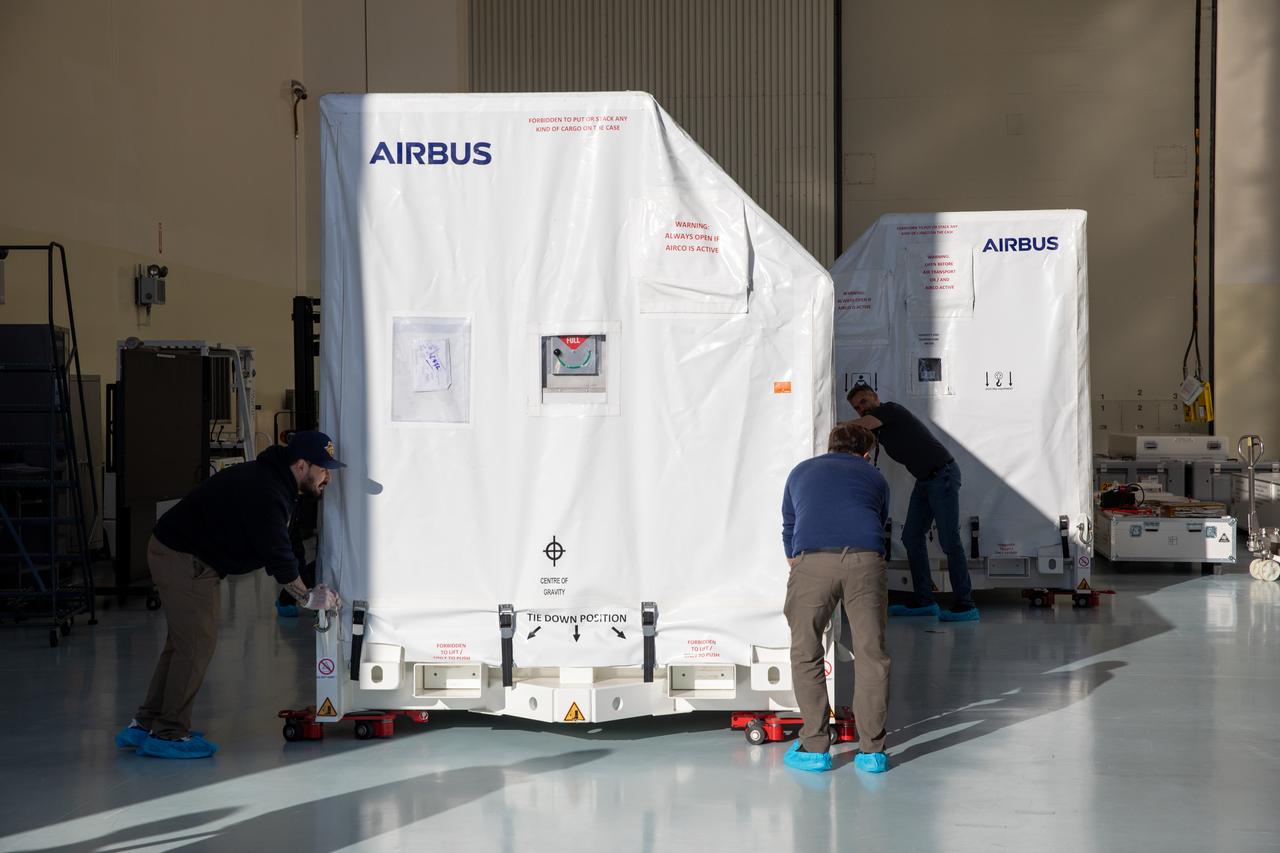

The transport carrier containing the five-panel solar arrays for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 21, 2024. The solar array travelled by air from Leiden, Netherlands, where Airbus workers assembled them over the last year, and then put on a barge to travel to the Port of Miami in Florida and loaded onto a semi-truck to be driven to Kennedy. The solar arrays will attach to the spacecraft to power it for the 1.8-billion-mile journey to study Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. Launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket is no earlier than October 2024.
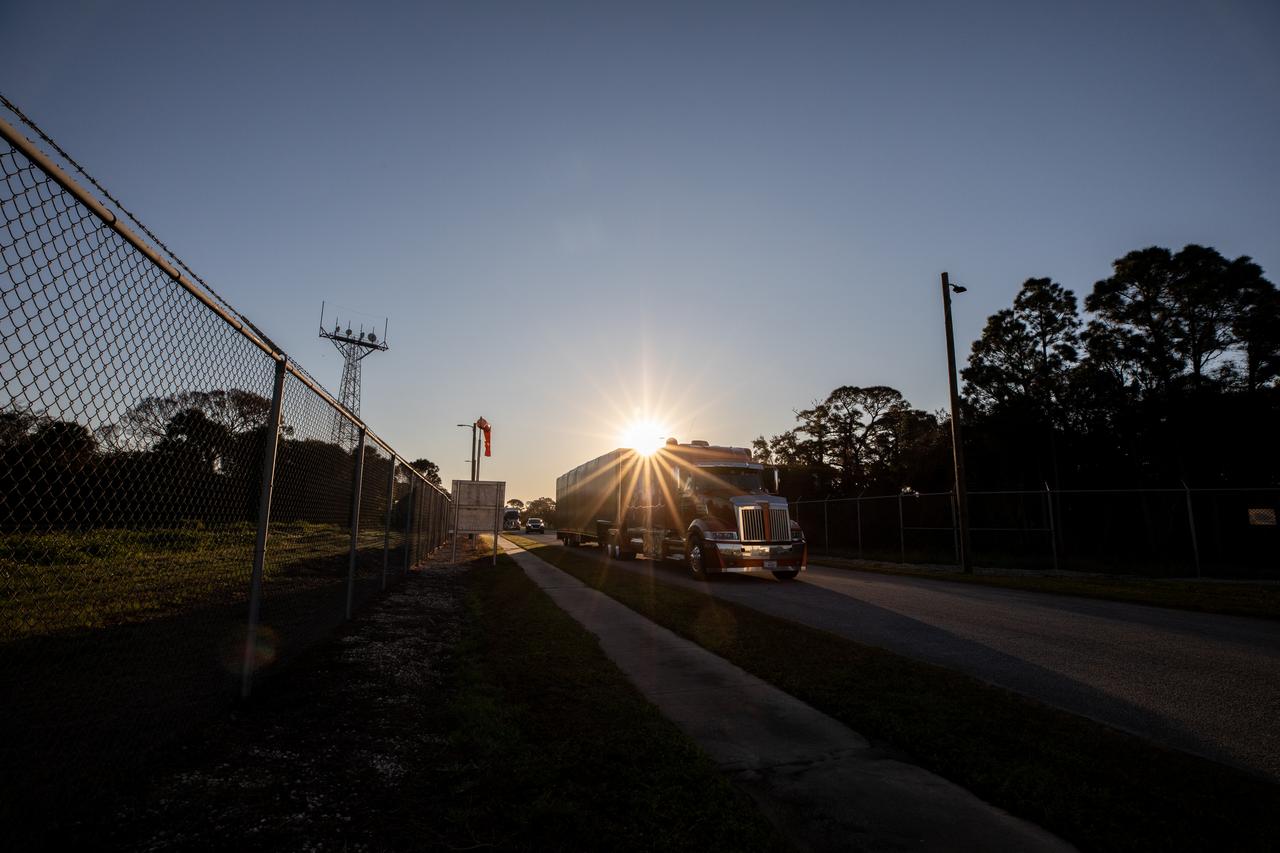

The transport carrier containing the five-panel solar arrays for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 21, 2024. The arrival completes the solar array journey which began in Leiden, Netherlands, where Airbus workers assembled them before shipping them by barge to Port of Miami in Florida and transporting them by truck to Kennedy. The solar arrays will attach to the spacecraft to power it on the 1.8-billion-mile journey to study Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. Launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket is no earlier than October 2024.
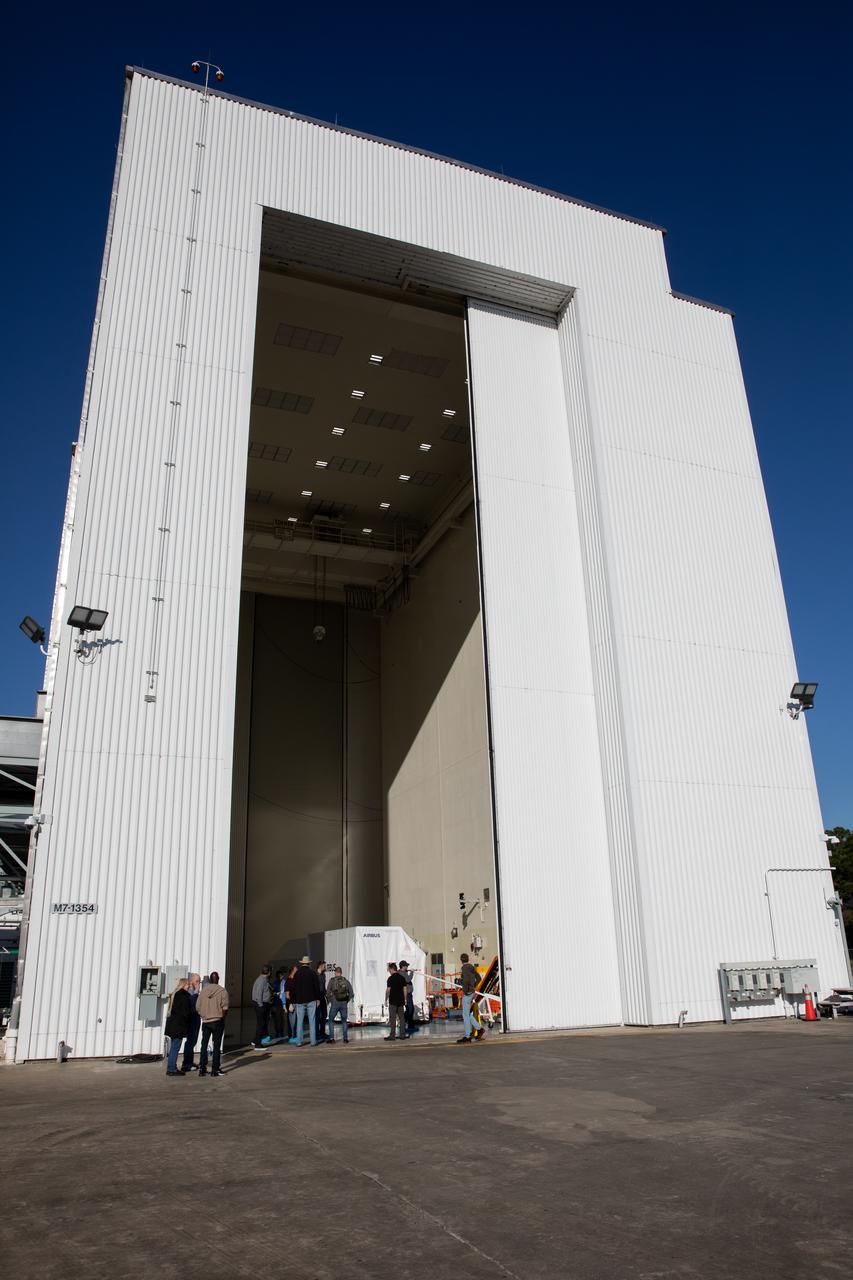

The transport carrier containing the five-panel solar arrays for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 21, 2024. The solar array travelled by air from Leiden, Netherlands, where Airbus workers assembled them over the last year, and then put on a barge to travel to the Port of Miami in Florida and loaded onto a semi-truck to be driven to Kennedy. The solar arrays will attach to the spacecraft to power it for the 1.8-billion-mile journey to study Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. Launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket is no earlier than October 2024.
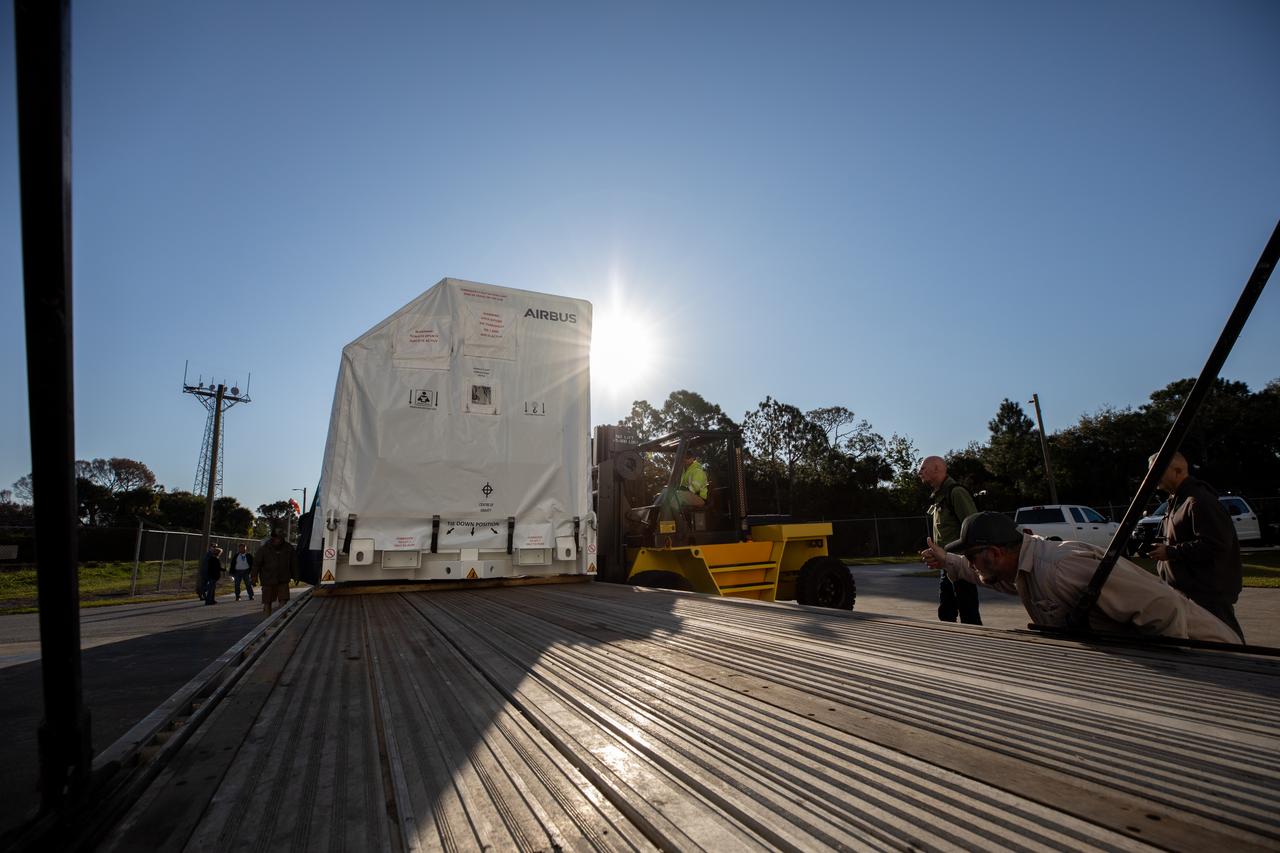

The transport carrier containing the five-panel solar arrays for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 21, 2024. The arrival completes the solar array journey which began in Leiden, Netherlands, where Airbus workers assembled them before shipping them by barge to Port of Miami in Florida and transporting them by truck to Kennedy. The solar arrays will attach to the spacecraft to power it on the 1.8-billion-mile journey to study Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. Launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket is no earlier than October 2024.
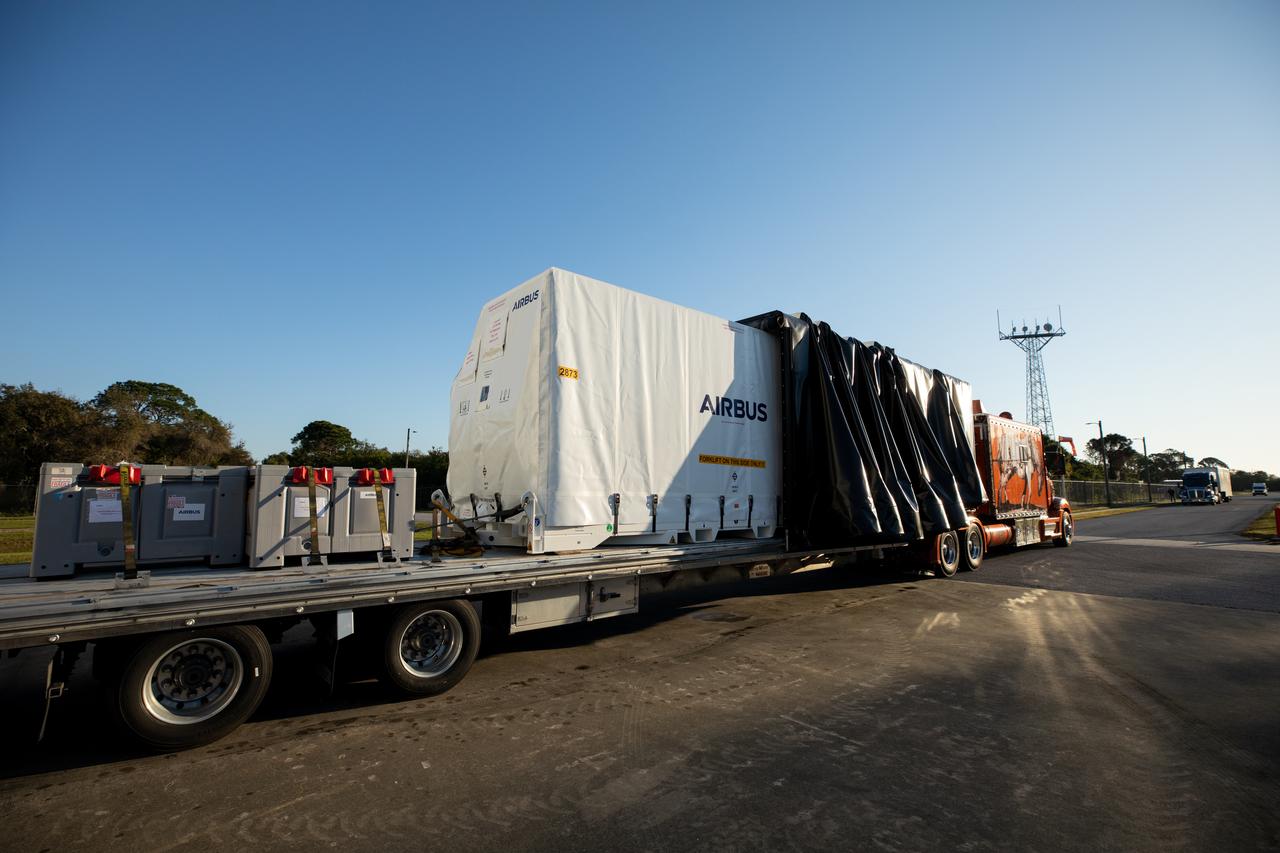

The transport carrier containing the five-panel solar arrays for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 21, 2024. The arrival completes the solar array journey which began in Leiden, Netherlands, where Airbus workers assembled them before shipping them by barge to Port of Miami in Florida and transporting them by truck to Kennedy. The solar arrays will attach to the spacecraft to power it on the 1.8-billion-mile journey to study Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. Launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket is no earlier than October 2024.
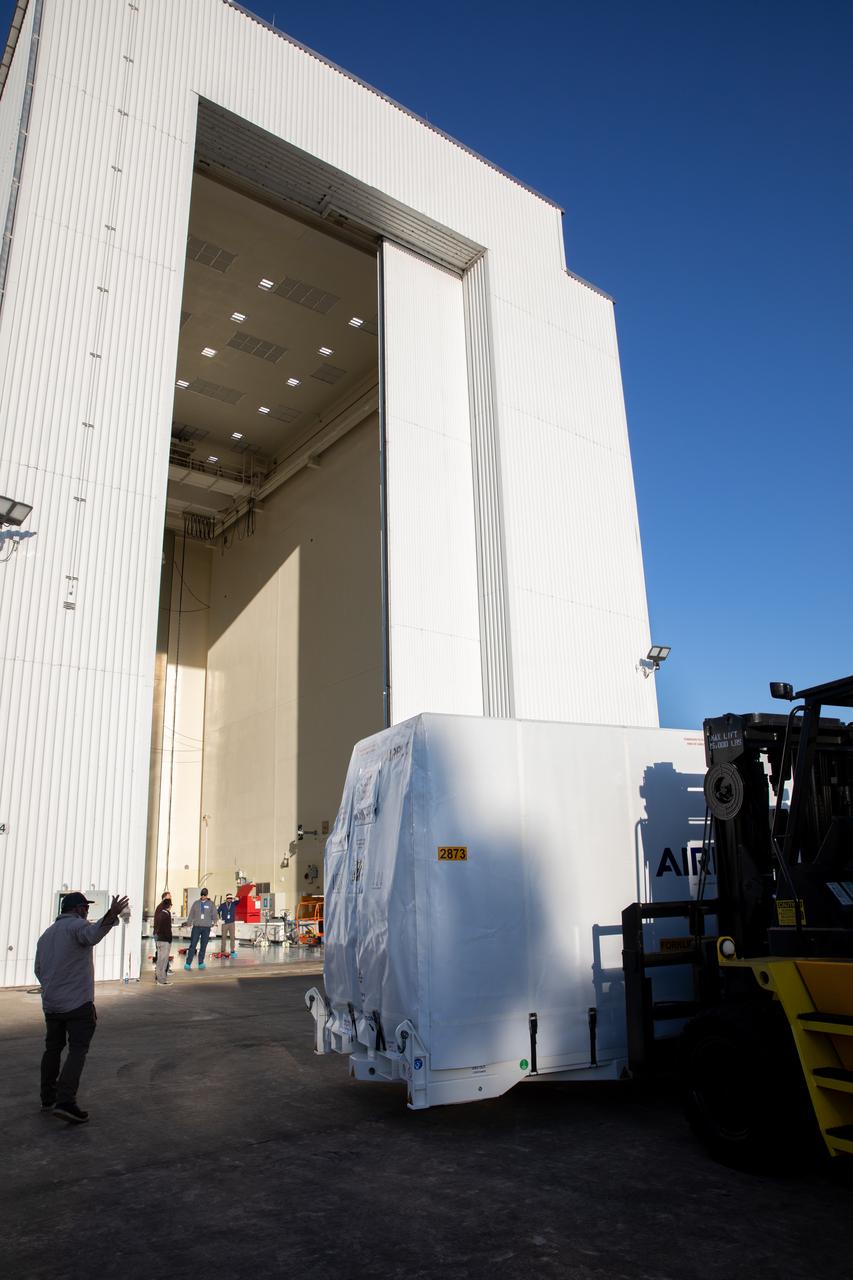

The transport carrier containing the five-panel solar arrays for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 21, 2024. The arrival completes the solar array journey which began in Leiden, Netherlands, where Airbus workers assembled them before shipping them by barge to Port of Miami in Florida and transporting them by truck to Kennedy. The solar arrays will attach to the spacecraft to power it on the 1.8-billion-mile journey to study Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. Launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket is no earlier than October 2024.
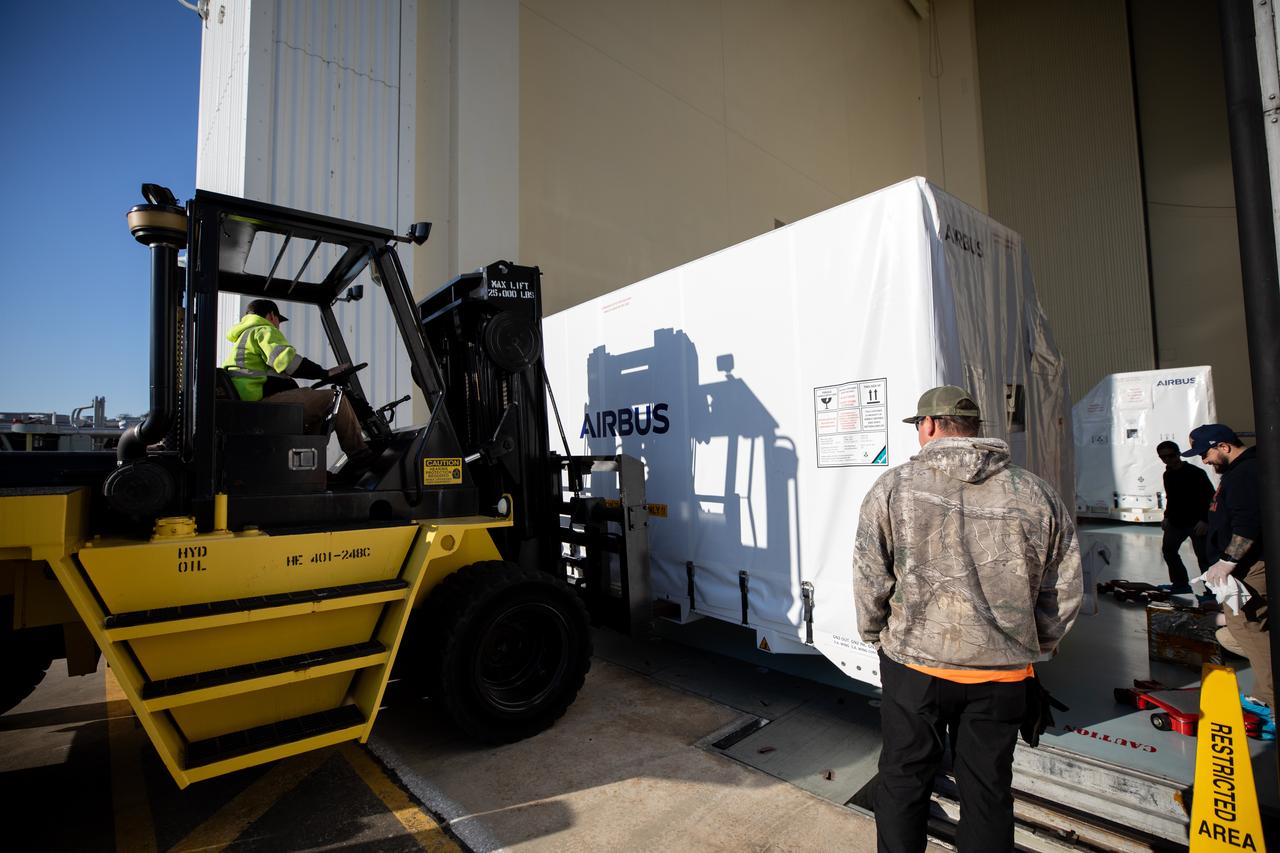

The transport carrier containing the five-panel solar arrays for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 21, 2024. The solar array travelled by air from Leiden, Netherlands, where Airbus workers assembled them over the last year, and then put on a barge to travel to the Port of Miami in Florida and loaded onto a semi-truck to be driven to Kennedy. The solar arrays will attach to the spacecraft to power it for the 1.8-billion-mile journey to study Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. Launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket is no earlier than October 2024.
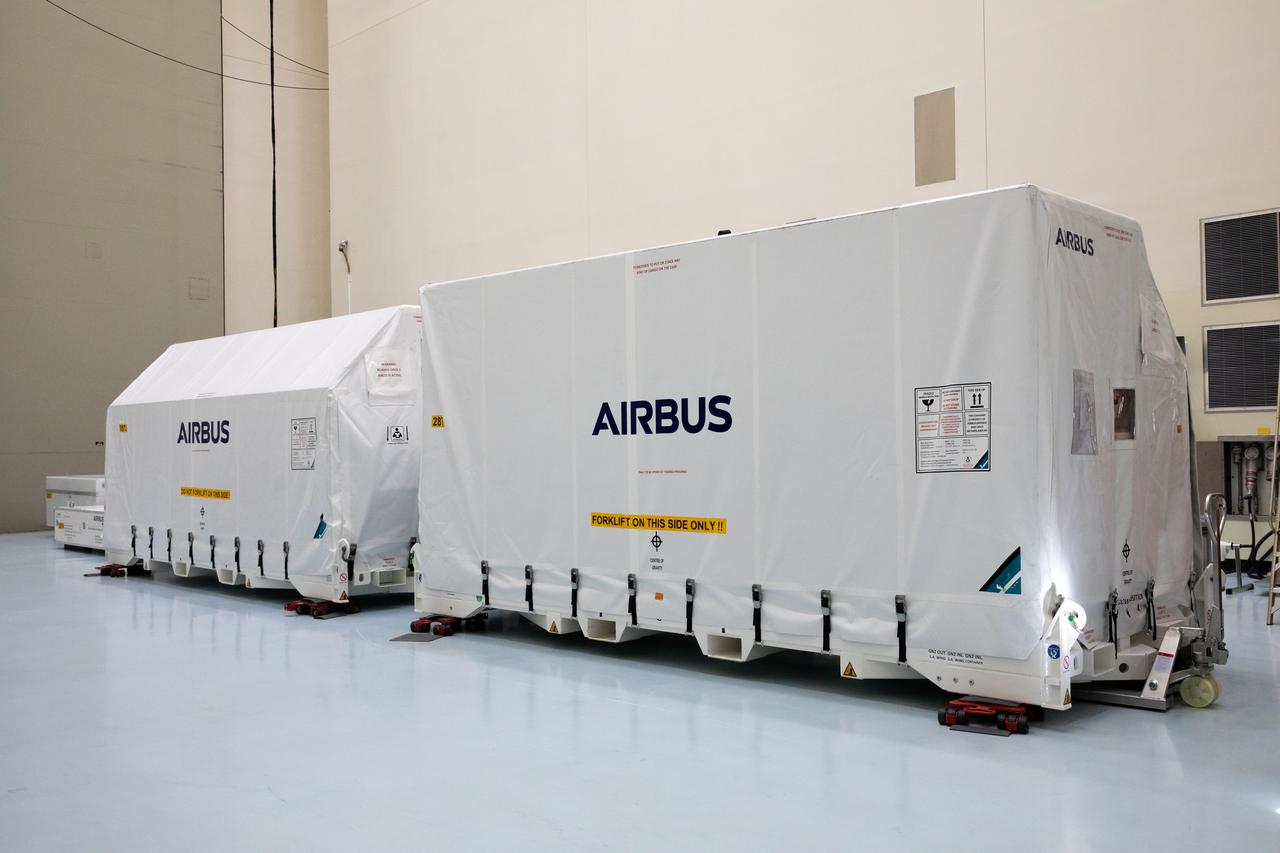

The transport carrier containing the five-panel solar arrays for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 21, 2024. The solar array travelled by air from Leiden, Netherlands, where Airbus workers assembled them over the last year, and then put on a barge to travel to the Port of Miami in Florida and loaded onto a semi-truck to be driven to Kennedy. The solar arrays will attach to the spacecraft to power it for the 1.8-billion-mile journey to study Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. Launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket is no earlier than October 2024.
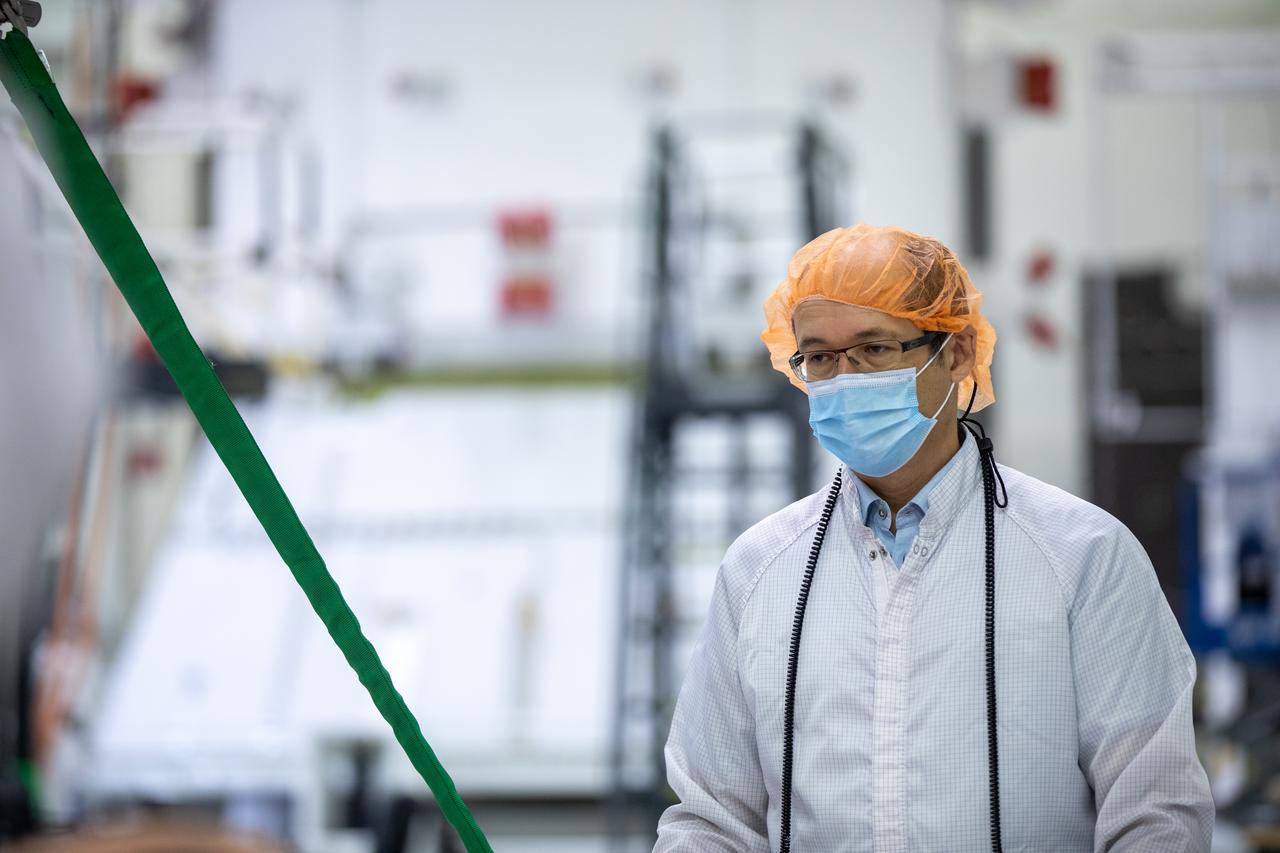

Rachid Amekrane, Airbus Defence and Space Integration test director, assists with securing a protective cover as a crane prepares to lift the panel during installation of one of four solar array wings inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The Orion spacecraft for Artemis I is shown in the background. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
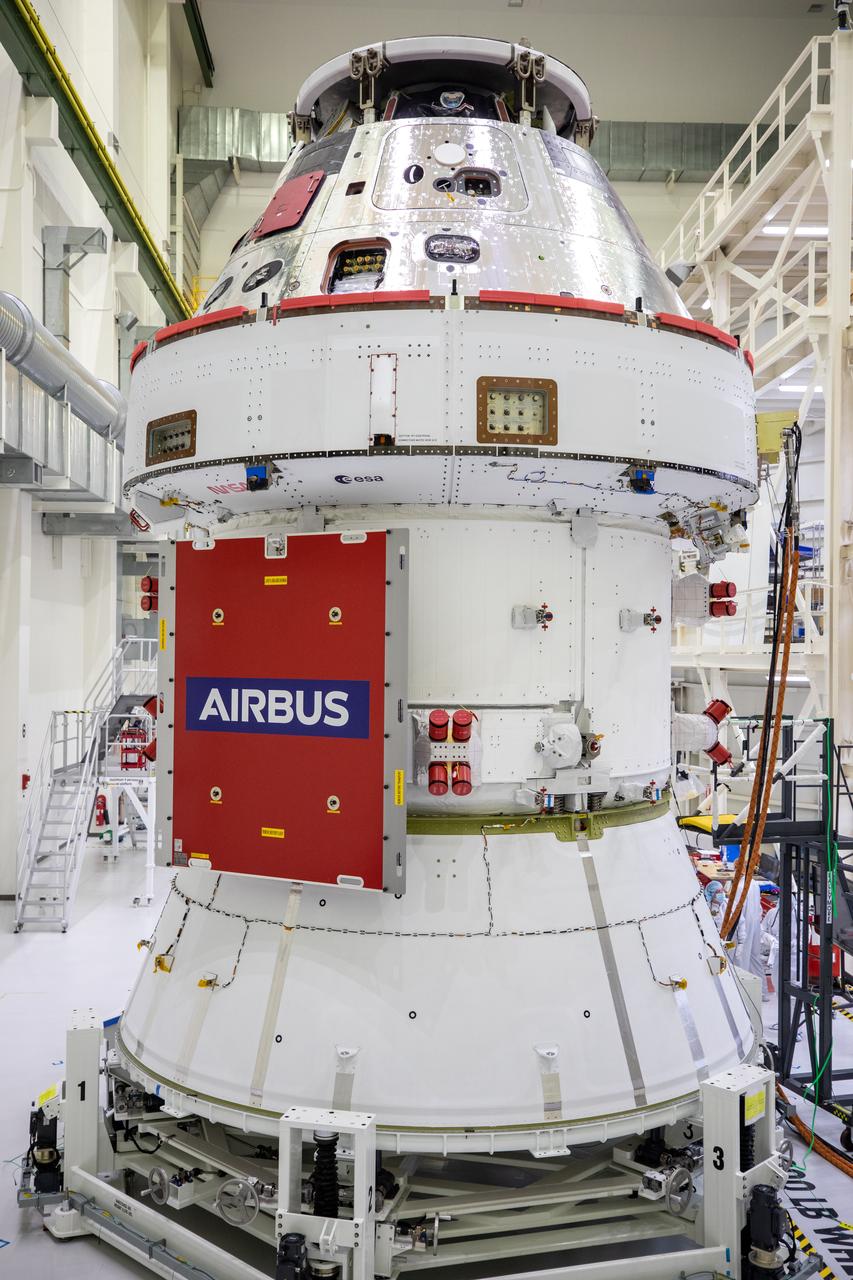

A protective cover panel has been installed over one of the solar arrays shown on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The iconic NASA worm and European Space Agency insignias on the Crew Module Adapter outer wall can be seen just above the panel. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each of the four solar array panels will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
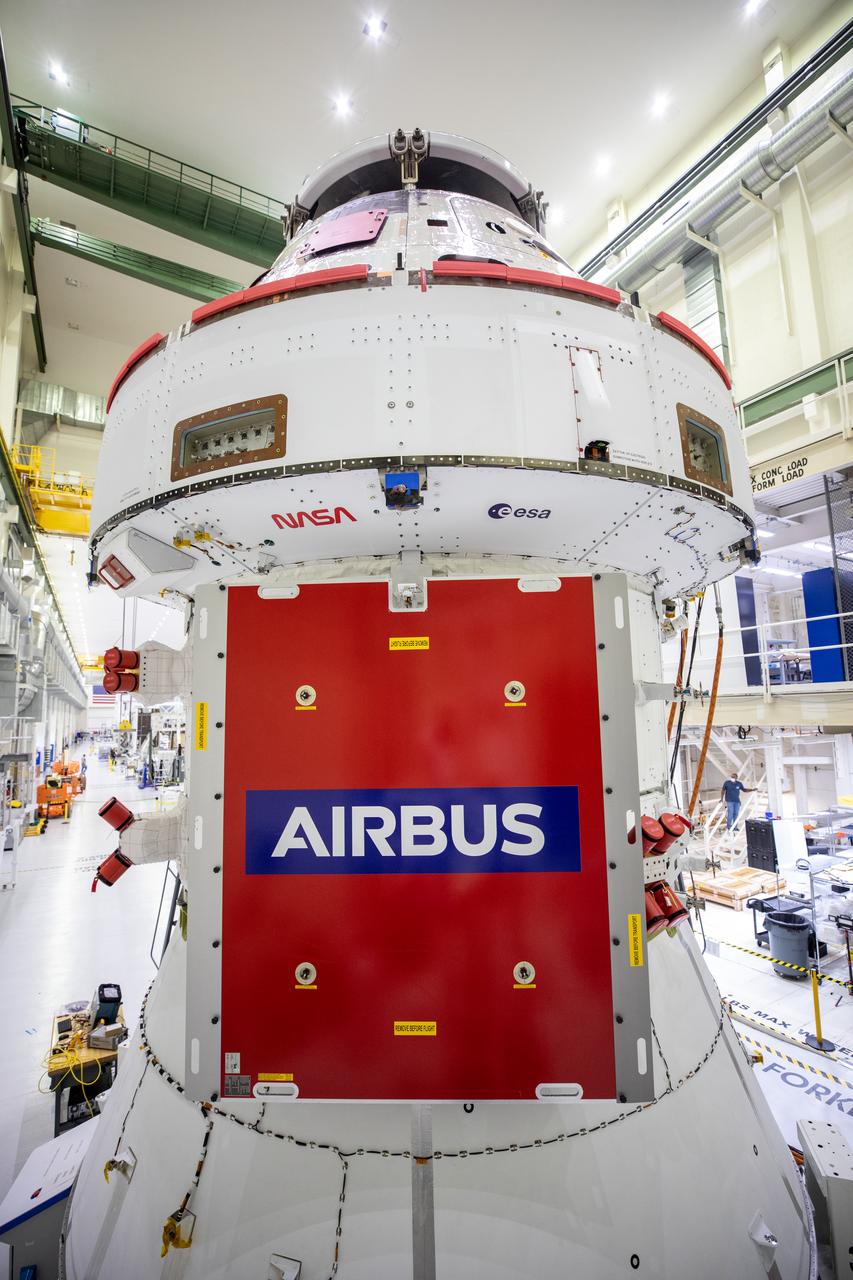

A protective cover panel has been installed over one of the solar arrays on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The iconic NASA worm and European Space Agency insignias on the Crew Module Adapter outer wall can be seen just above the panel. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each of the four solar array panels will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
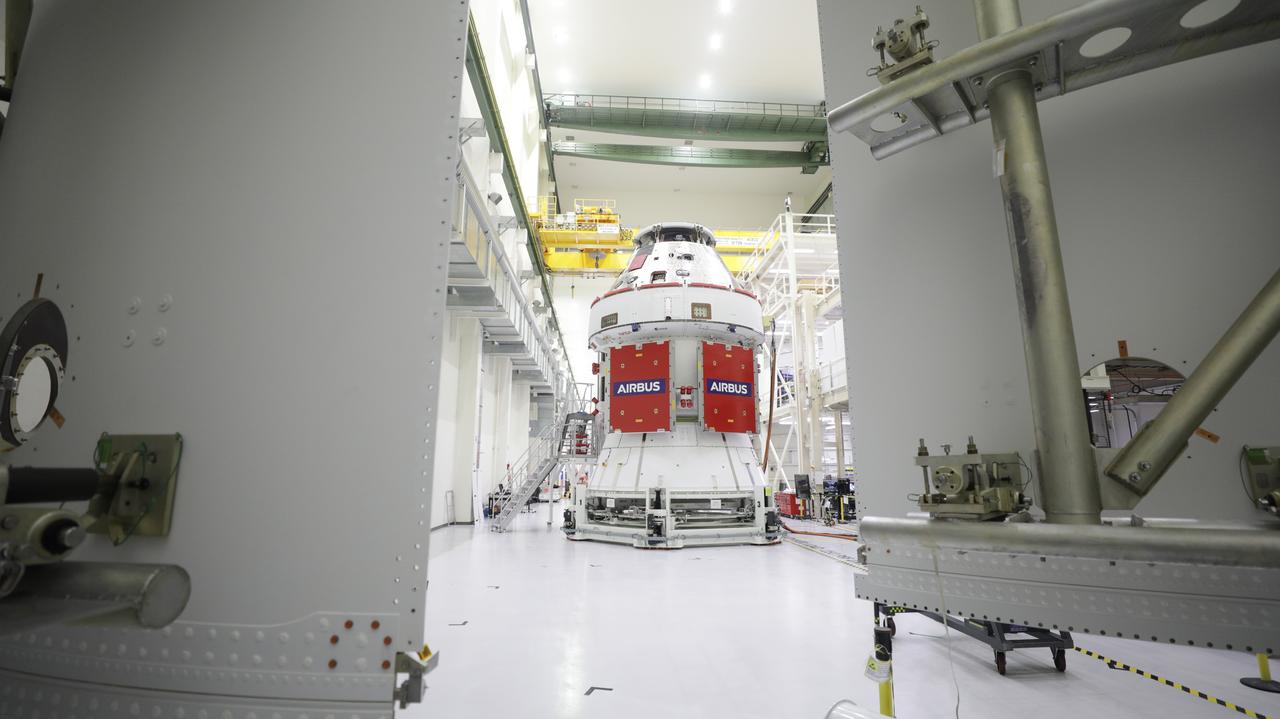

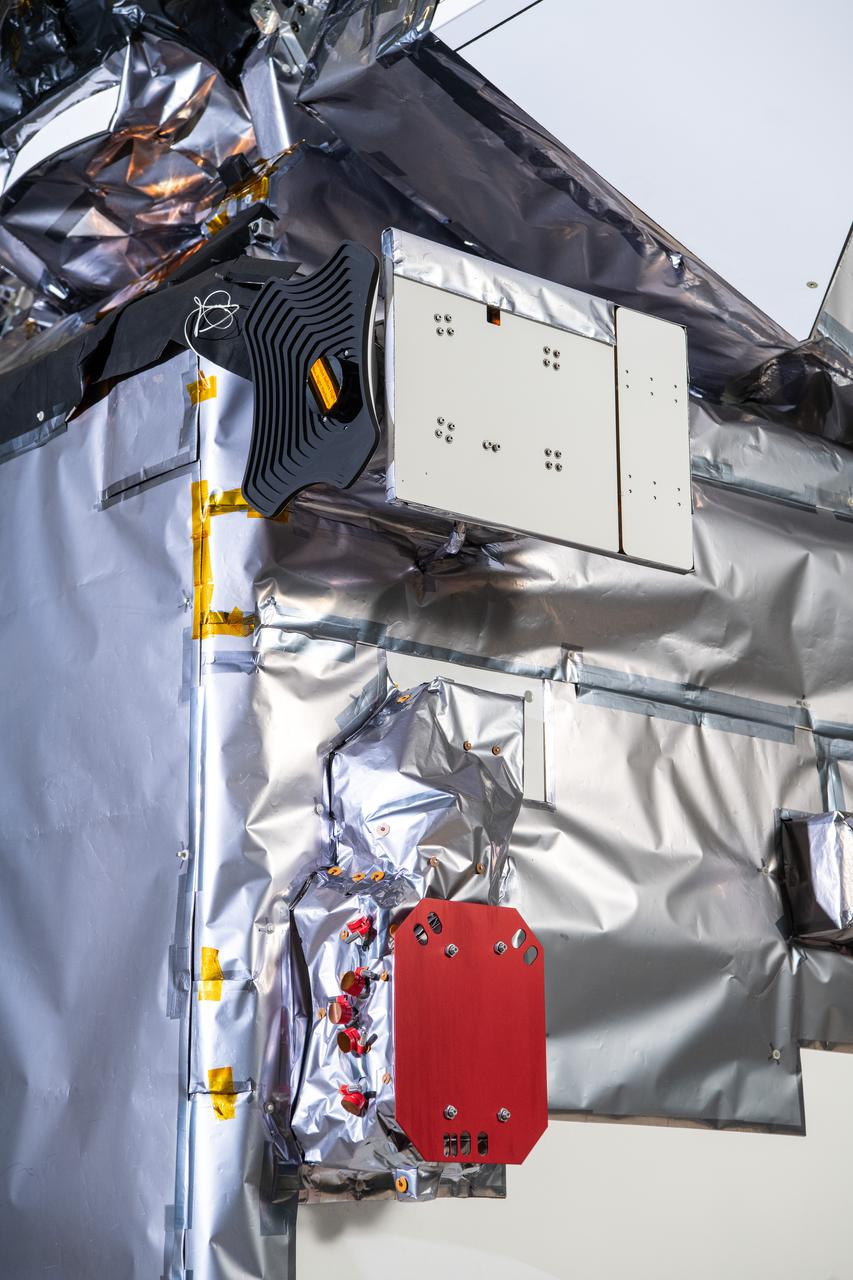
Two of the four solar array wings are shown from behind the spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels after being installed on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020. Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020, work begins to install four solar array wings on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
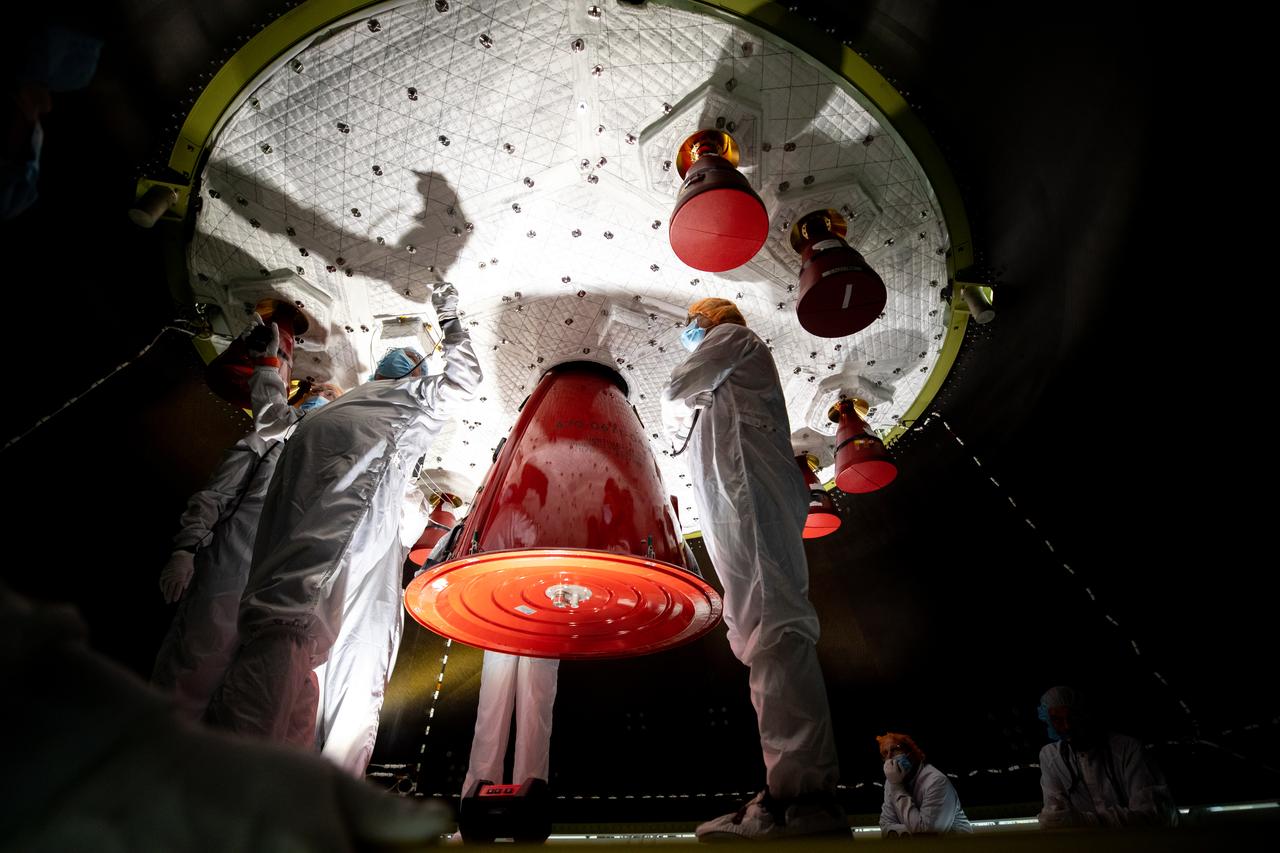

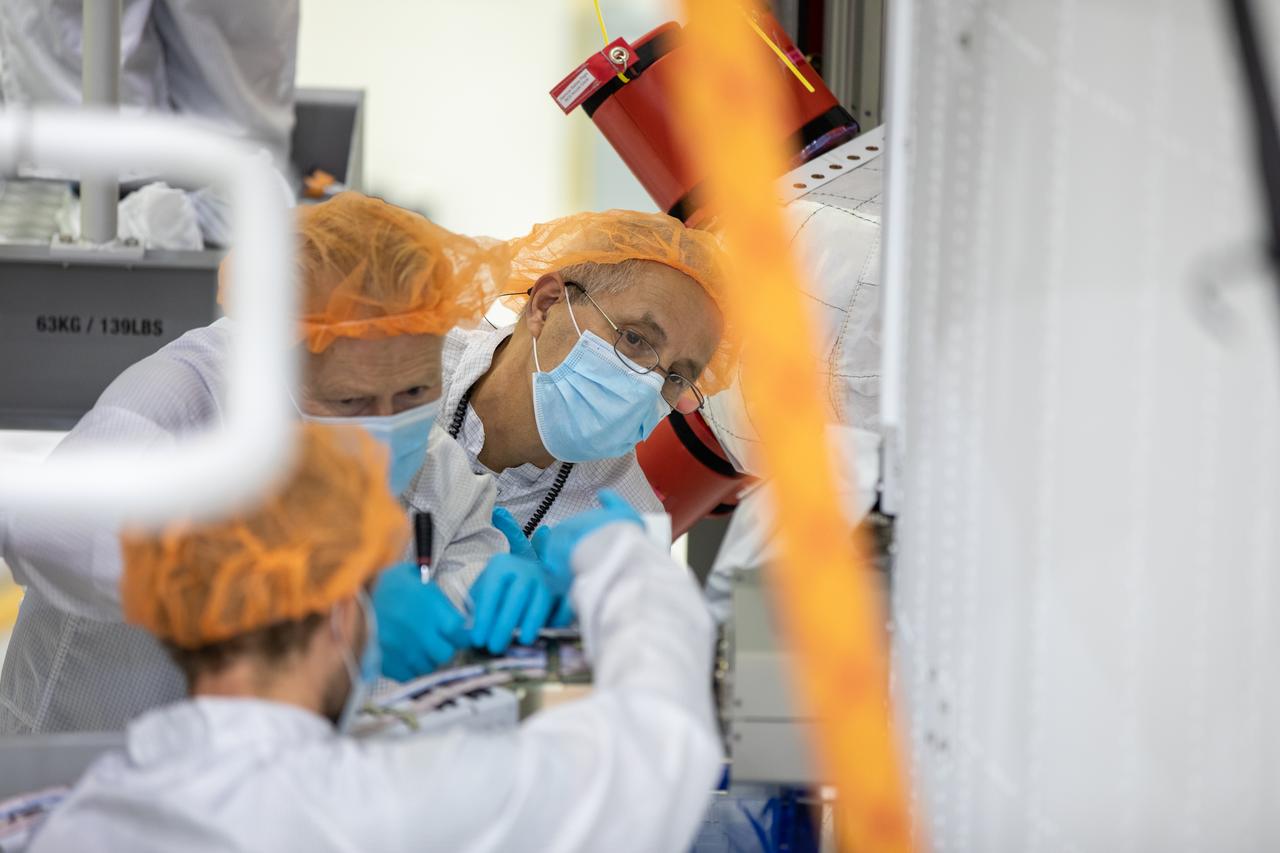
Members of the European Service Module processing team from the European Space Agency and Airbus inspect the insulation on the underside of the Orion service module for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. Work is also underway to attach protective covers over the solar arrays wings that were installed on the service module. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
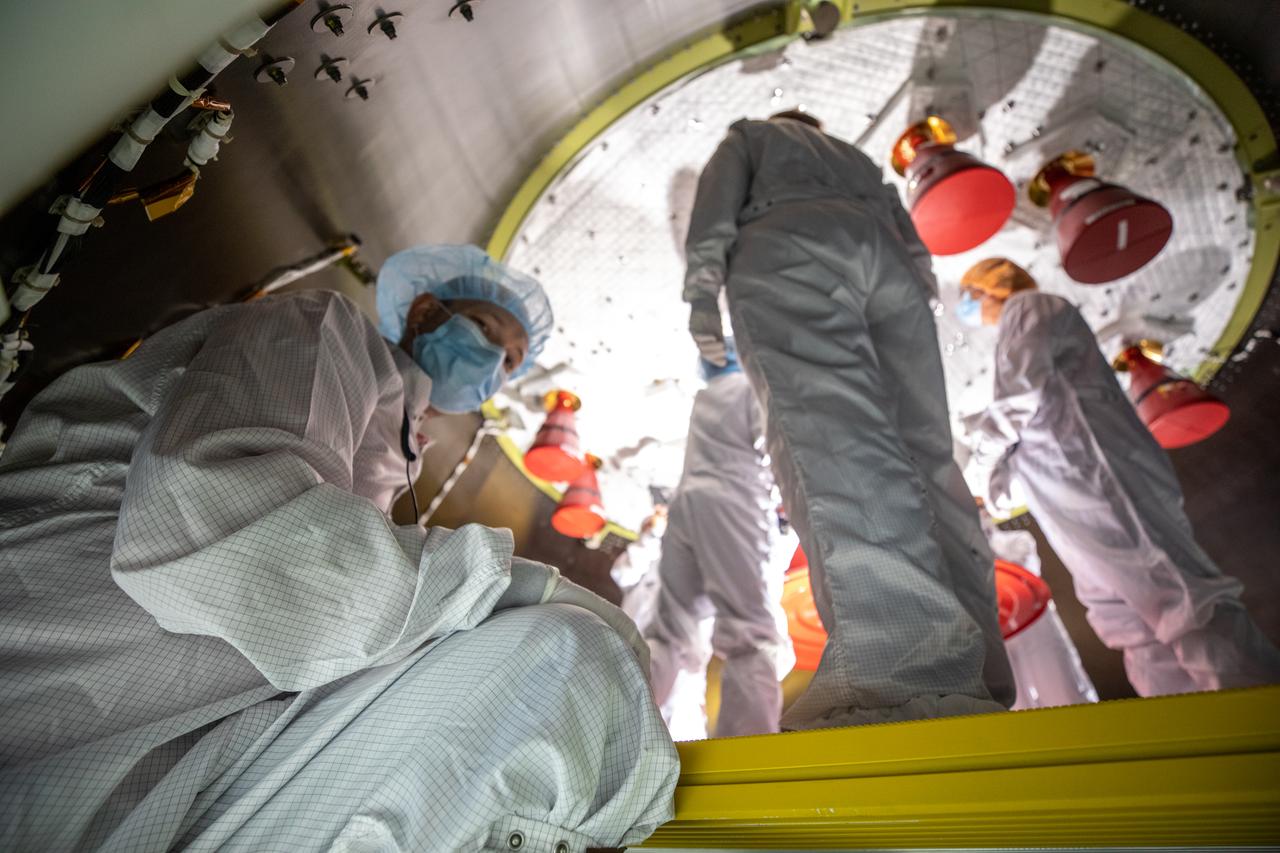

Members of the European Service Module processing team from the European Space Agency and Airbus inspect the insulation on the underside of the Orion service module for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. Work is also underway to attach protective covers over the solar arrays wings that were installed on the service module. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

A protective cover panel has been installed over one of the solar arrays on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The iconic NASA worm and European Space Agency insignias on the Crew Module Adapter outer wall can be seen just above the panel. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each of the four solar array panels will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

The final of four solar array wings is shown being installed prior to receiving its protective covering on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
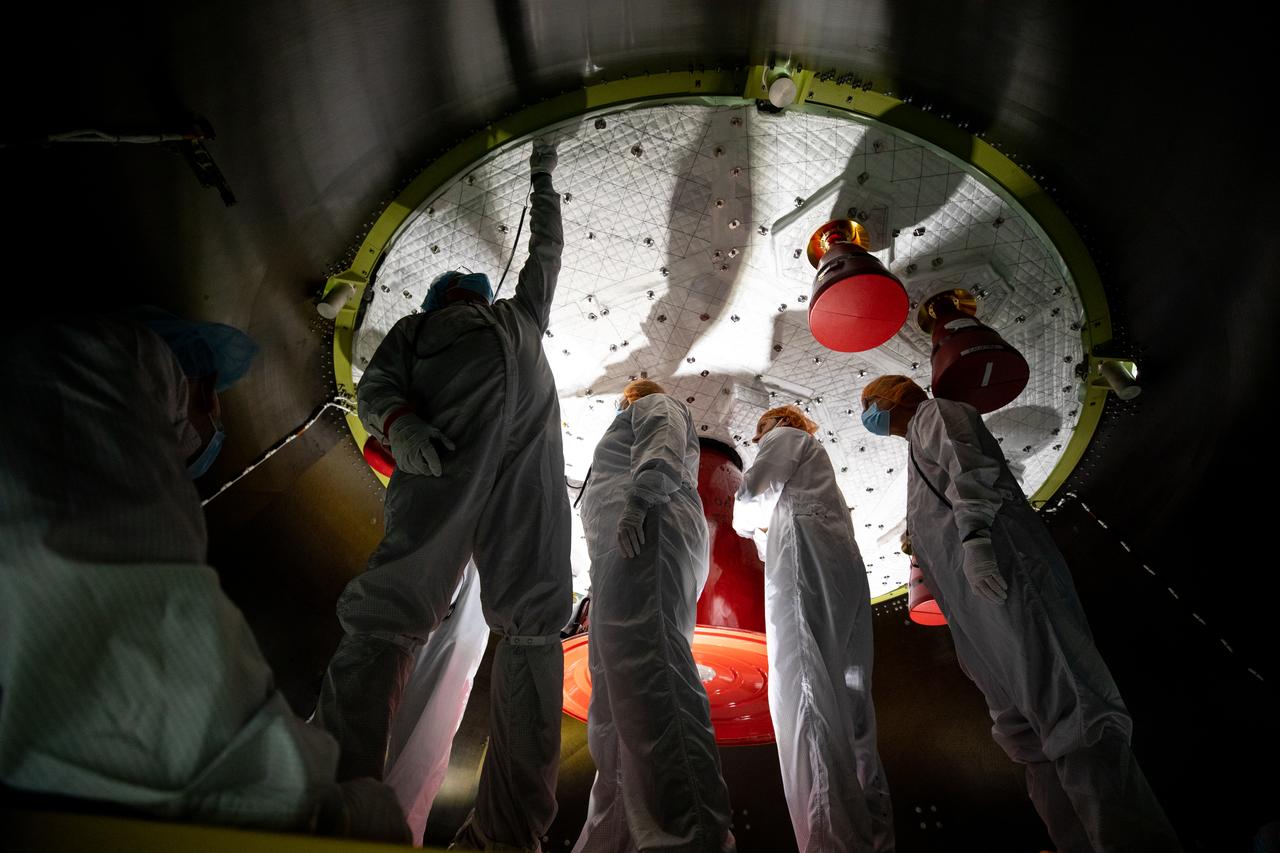

Members of the European Service Module processing team from the European Space Agency and Airbus inspect the insulation on the underside of the Orion service module for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. Work is also underway to attach protective covers over the solar arrays wings that were installed on the service module. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
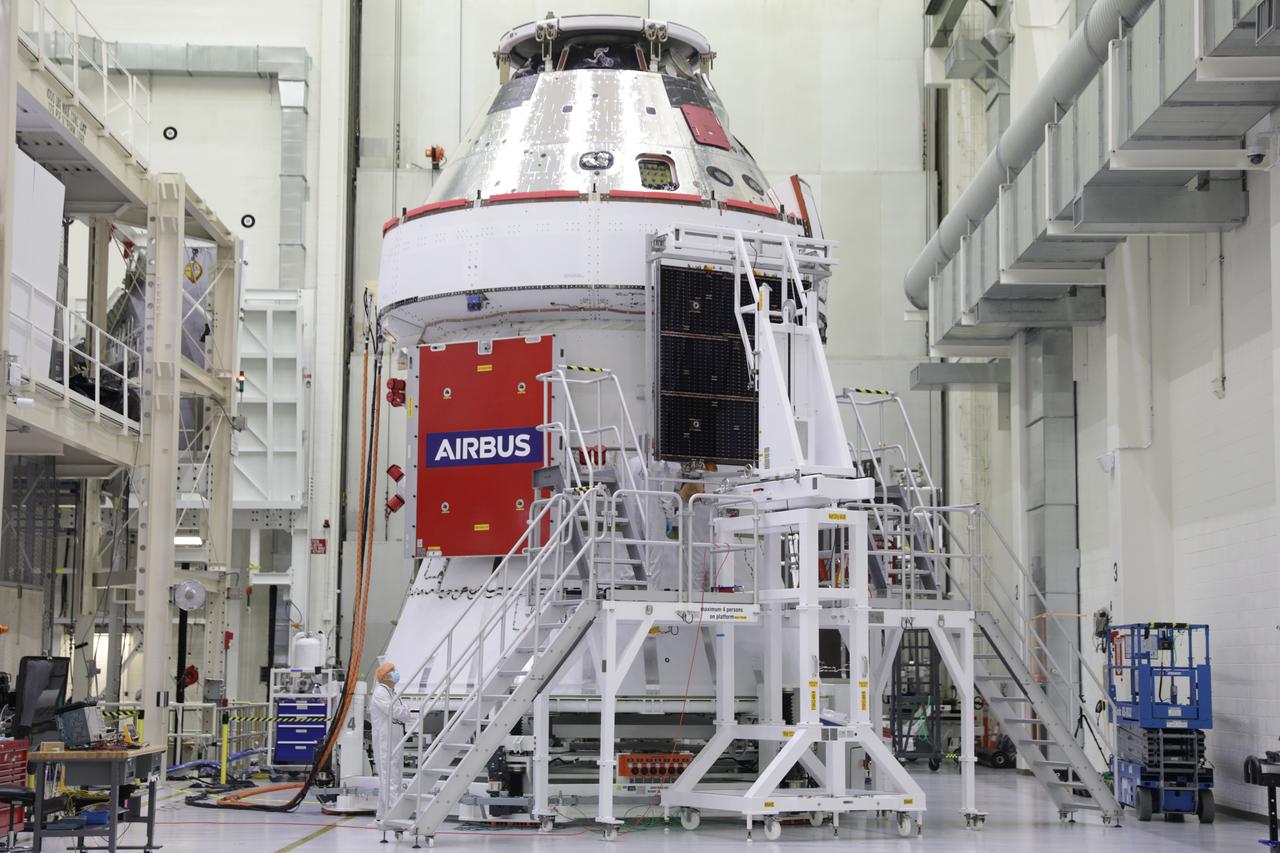

The final of four solar array wings is shown being installed prior to receiving its protective covering on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
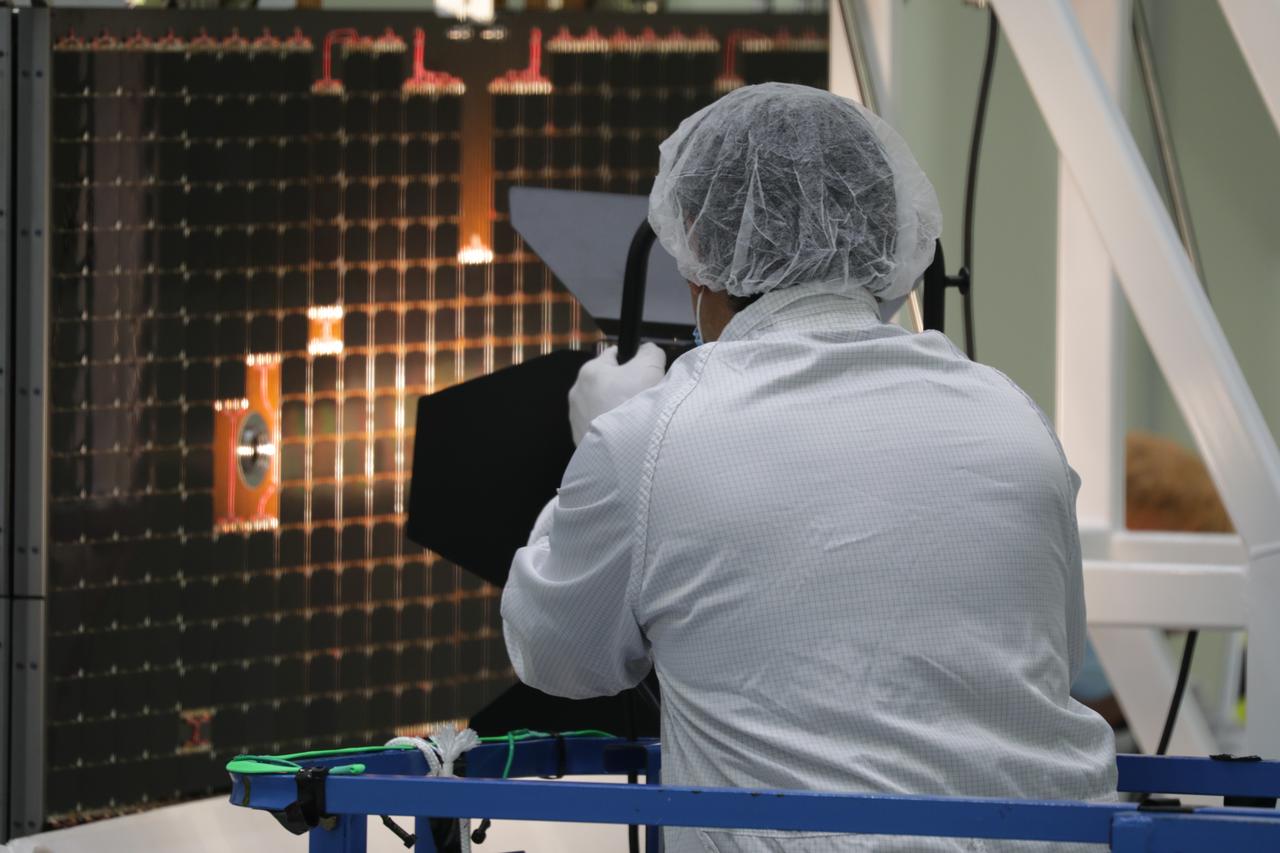

A Lockheed Martin technician is shown assisting with lighting one of the solar array wing panels as part of an illumination test during installation on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
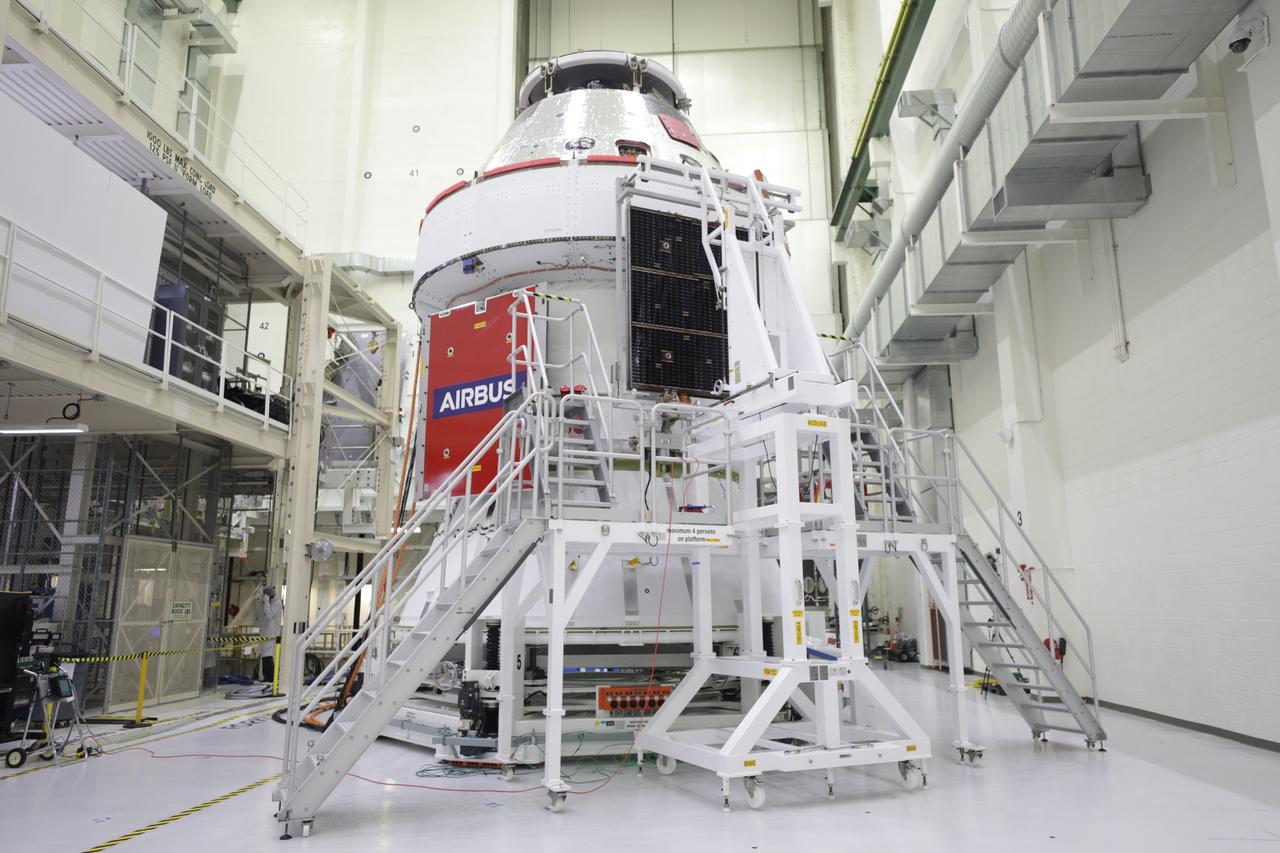

The final of four solar array wings is shown being installed prior to receiving its protective covering on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.