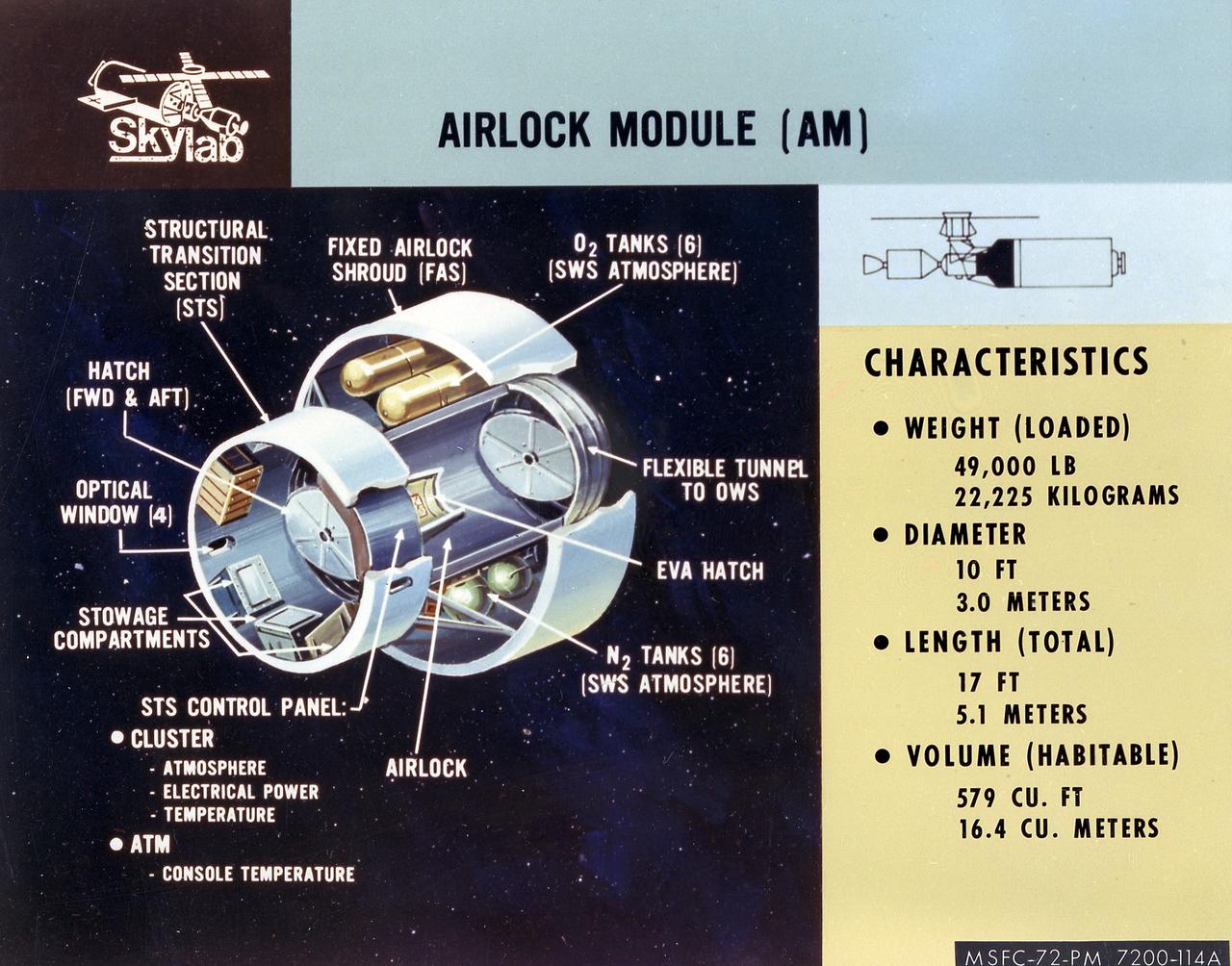
This artist's concept is a cutaway illustration of the Skylab Airlock Module and its characteristics. The aft end of the Docking Adapter mated to the Airlock Module (AM), and served as the environmental, electrical, and communications control center. The docking adapter also contained the port through which the astronauts exited to perform extravehicular activity. The AM contained a turnel section through which Skylab crewmen could move between the workshop and the forward end of the airlock. It was encircled, for part of its length, at its aft end by the fixed Airlock Shroud (FAS), that had the same diameter as the workshop (22 feet) and was attached to the workshop's forward end. High pressure containers for oxygen and nitrogen providing Skylab's atmosphere, were mounted in the annular space between the outside of the tunnel and the inside of the shroud. The forward end of the FAS was the base on which the tubular structure supporting the solar observatory was mounted. Many of the supplies, and most of the control systems for Skylab were located in the AM; this module could well be the "utility center" of the Skylab cluster. McDonnell Douglas fabricated the module with close Marshall Space Flight Center's involvement in design, development, and test activities.
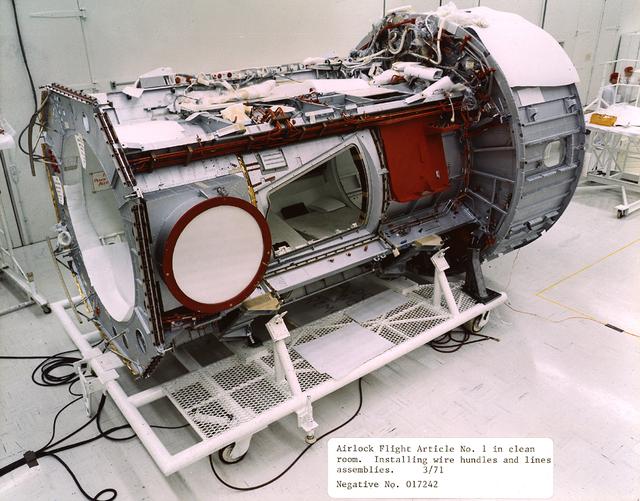
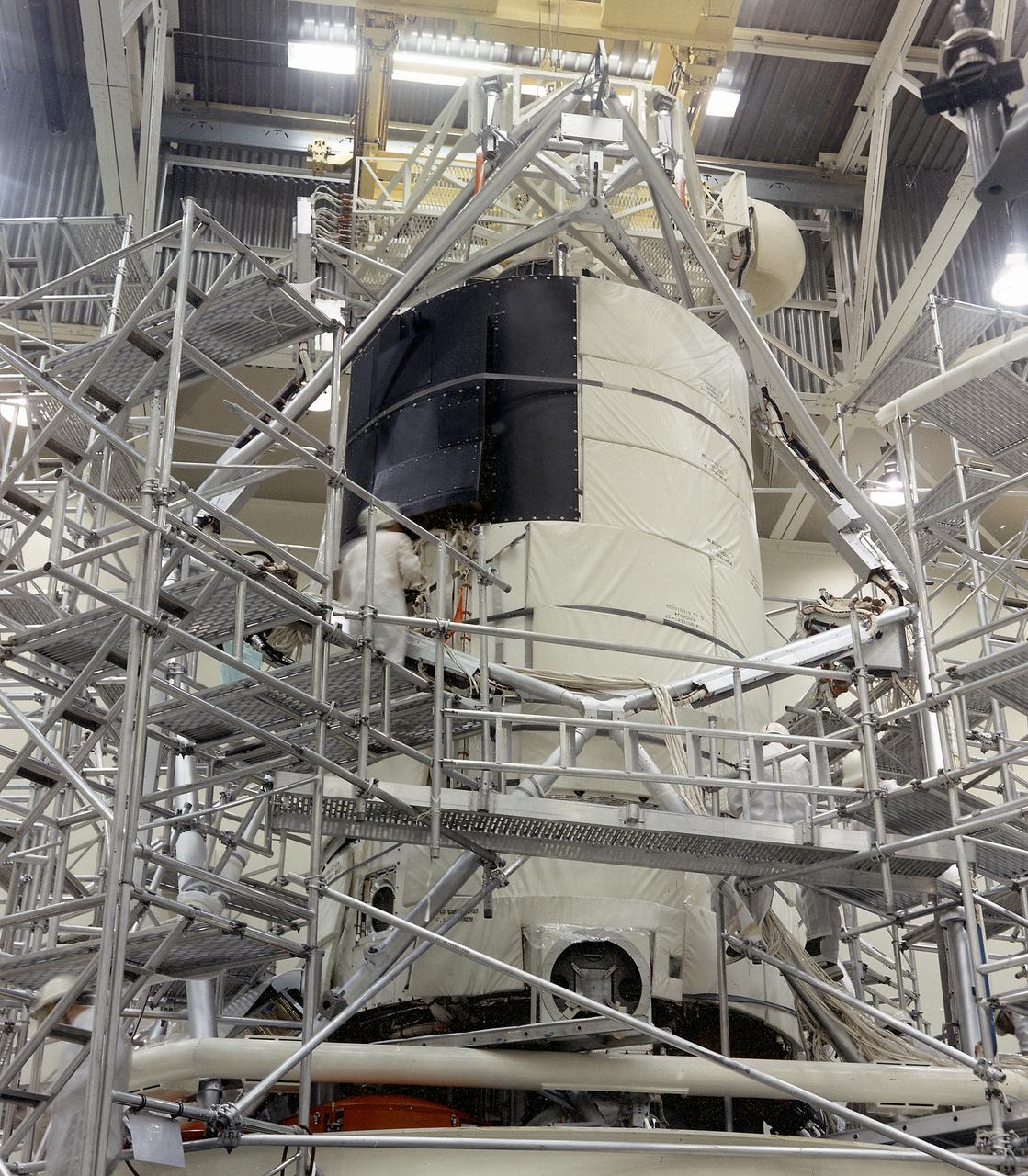
This 1971 photograph was taken during the assembly of the Flight Article of the Skylab Airlock Module (AM). The Am, fabricated by McDornell Douglas under the direction of the Marshall Flight Center, allowed Skylab crew members an exit to perform extravehicular activities. The Module also contained many of the supplies and control panels for electrical power distribution and internal environment.
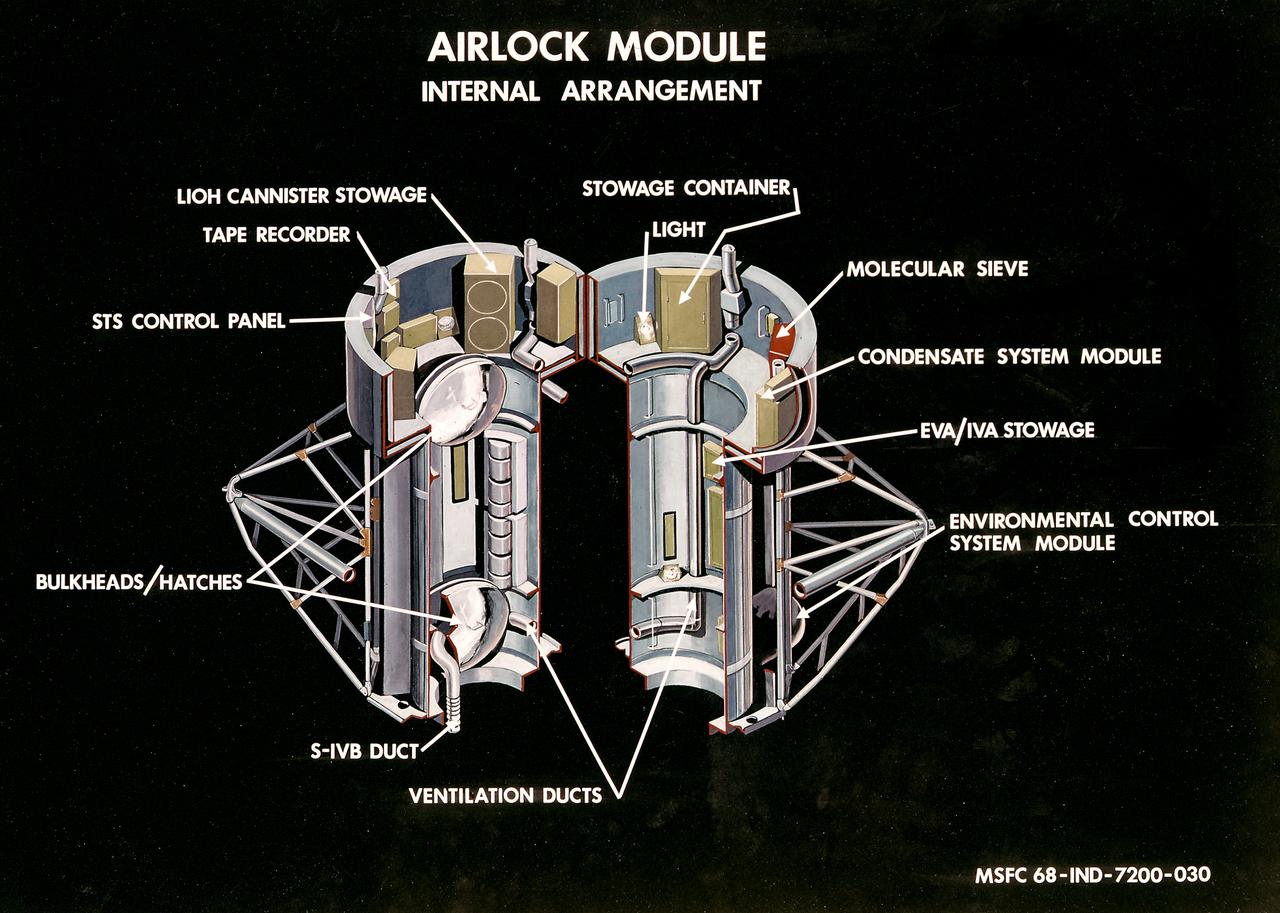
This illustration is a cutaway view of the internal arrangement of the Airlock Module (AM). The aft end of the Docking Adapter mated to the AM, and served as the environmental, electrical, and communications control center. The docking adapter also contained the port through which the astronauts exited to perform extravehicular activity. The AM contained a turnel section through which Skylab crewmen could move between the workshop and the forward end of the airlock. It was encircled, for part of its length, at its aft end by the fixed Airlock Shroud (FAS), that had the same diameter as the workshop (22 feet) and was attached to the workshop's forward end. High pressure containers for oxygen and nitrogen providing Skylab's atmosphere, were mounted in the annular space between the outside of the tunnel and the inside of the shroud. The forward end of the FAS was the base on which the tubular structure supporting the solar observatory was mounted. Many of the supplies, and most of the control systems for Skylab were located in the AM; this module could well be the "utility center" of the Skylab cluster. McDonnell Douglas fabricated the module with close Marshall Space Flight Center's involvement in design, development, and test activities.
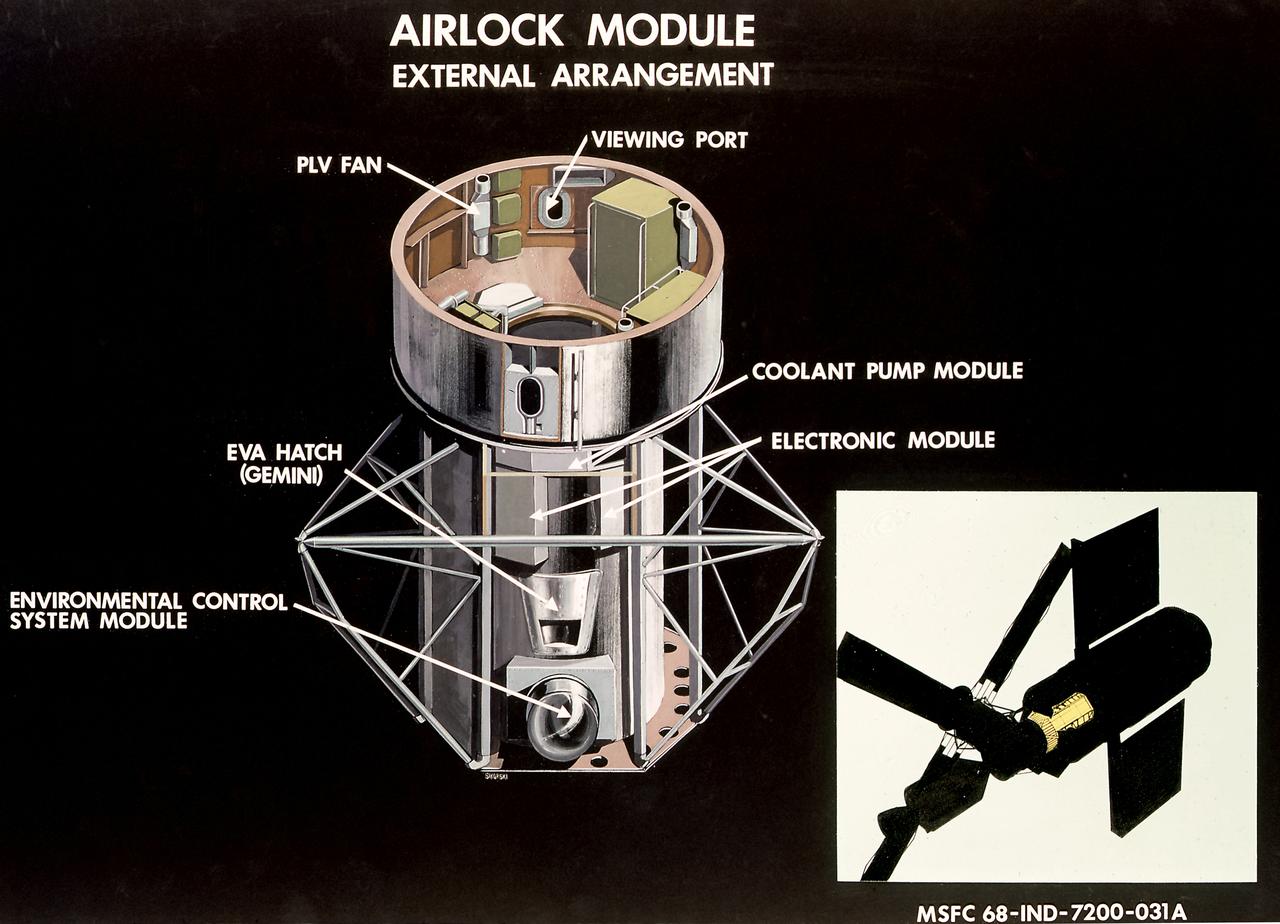
This illustration is a cutaway view of the external arrangement of the Airlock Module (AM). The aft end of the Docking Adapter mated to the AM, and served as the environmental, electrical, and communications control center. The docking adapter also contained the port through which the astronauts exited to perform extravehicular activity. The AM contained a turnel section through which Skylab crewmen could move between the workshop and the forward end of the airlock. It was encircled, for part of its length, at its aft end by the fixed Airlock Shroud (FAS), that had the same diameter as the workshop (22 feet) and was attached to the workshop's forward end. High pressure containers for oxygen and nitrogen providing Skylab's atmosphere, were mounted in the annular space between the outside of the tunnel and the inside of the shroud. The forward end of the FAS was the base on which the tubular structure supporting the solar observatory was mounted. Many of the supplies, and most of the control systems for Skylab were located in the AM; this module could well be the "utility center" of the Skylab cluster. McDonnell Douglas fabricated the module with close Marshall Space Flight Center's involvement in design, development, and test activities.

This photograph depicts the flight article of the Airlock Module (AM) Flight Article being mated to the Fixed Airlock Shroud and aligned in a clean room of the McDornell Douglas Plant in St. Louis, Missouri. The AM enabled crew members to conduct extravehicular activities outside Skylab as required for experiment support. Separated from the Workshop and the Multiple Docking Adapter by doors, the AM could be evacuated for egress or ingress of a space-suited astronaut through a side hatch. Oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks needed for Skylab's life support system were mounted on the external truss work of the AM. Major components in the AM included Skylab's electric power control and distribution station, environmental control system, communication system, and data handling and recording systems. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for the design and development of the Skylab hardware and experiment management.
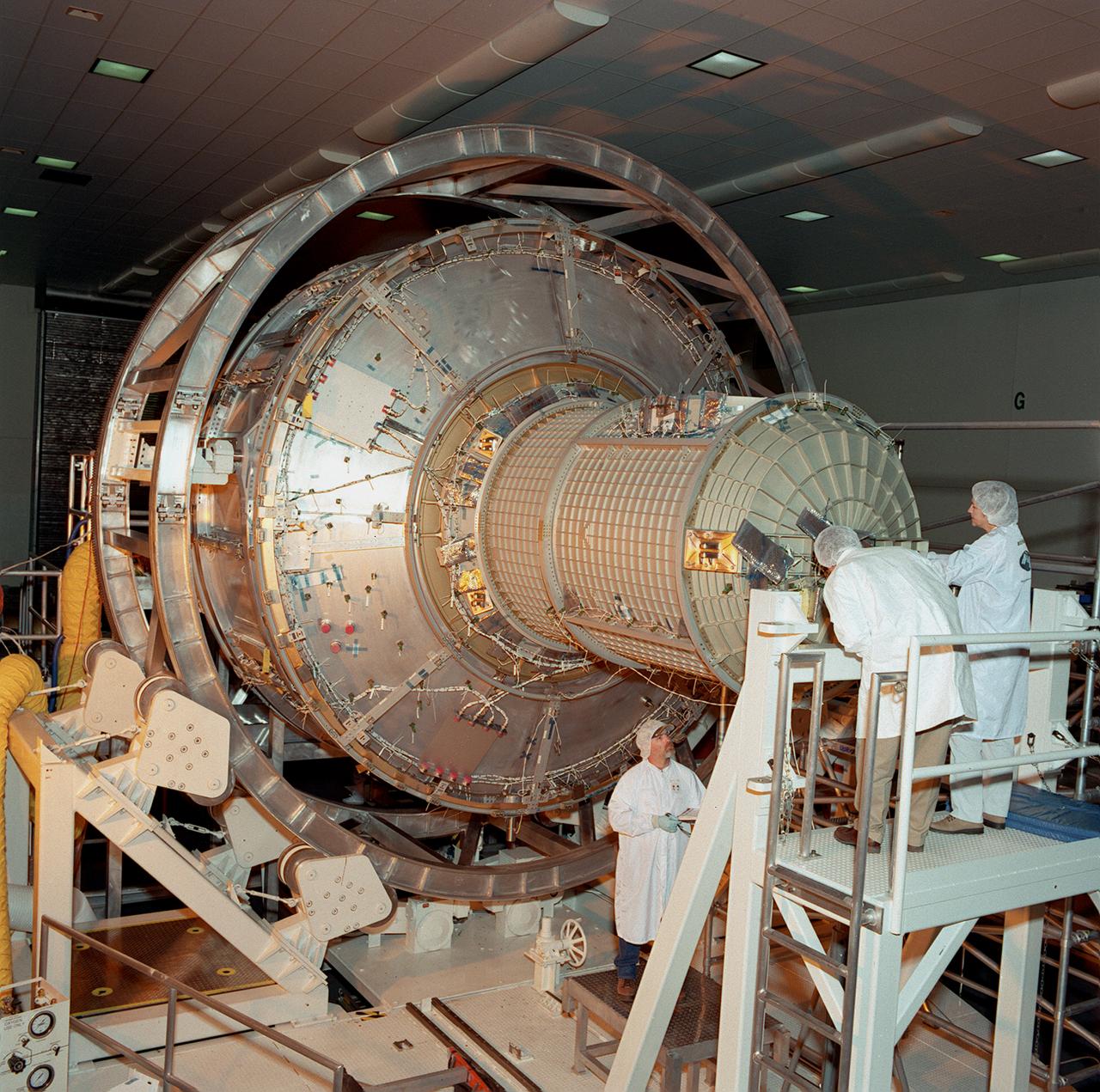

This photograph depicts the International Space Station's (ISS) Joint Airlock Module undergoing exhaustive structural and systems testing in the Space Station manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) prior to shipment to the Kennedy Space Center. The Airlock includes two sections. The larger equipment lock, on the left, will store spacesuits and associated gear and the narrower crewlock is on the right, from which the astronauts will exit into space for extravehicular activity. The airlock is 18 feet long and has a mass of about 13,500 pounds. It was launched to the station aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis (STS-104 mission) on July 12, 2001. The MSFC is playing a primary role in NASA's development, manufacturing, and operations of the ISS.
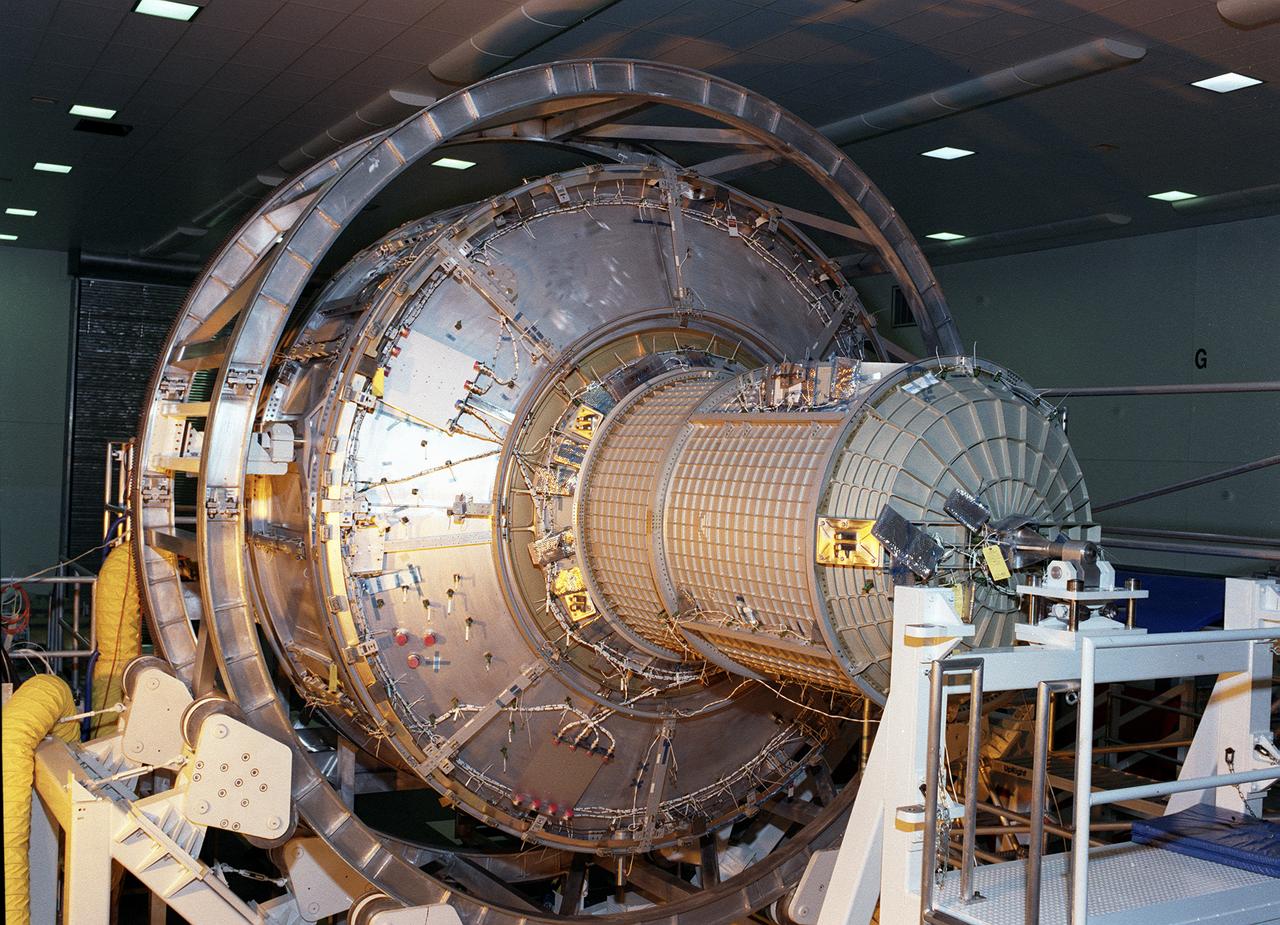
The Joint Airlock Module for the International Space Station (ISS) awaits shipment to the Kennedy Space Center in the Space Station manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The Airlock includes two sections. The larger equipment lock on the left is where crews will change into and out of their spacesuits for extravehicular activities, and store spacesuits, batteries, power tools, and other supplies. The narrower crewlock from which the astronauts will exit into space for extravehicular activities, is on the right. The airlock is 18 feet long and has a mass of about 13,500 pounds. It was launched to the station aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis (STS-104 mission) on July 12, 2001. The MSFC is playing a primary role in NASA's development, manufacturing, and operations of the ISS.
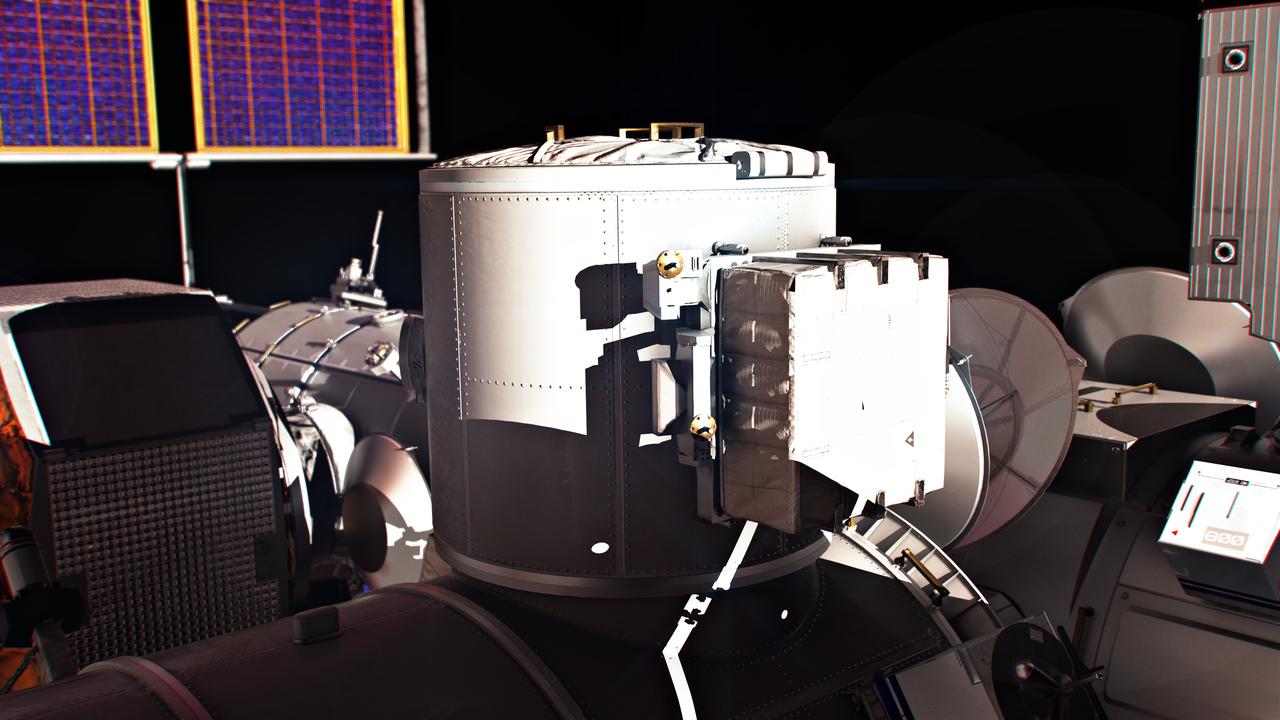
A close-up of a government-reference airlock module for the Gateway Space Station. Mission planning calls for an airlock to be delivered and integrated to Gateway by the crewed Orion spacecraft on the Artemis VI mission after launching on a Space Launch System (SLS) Block 1B rocket.
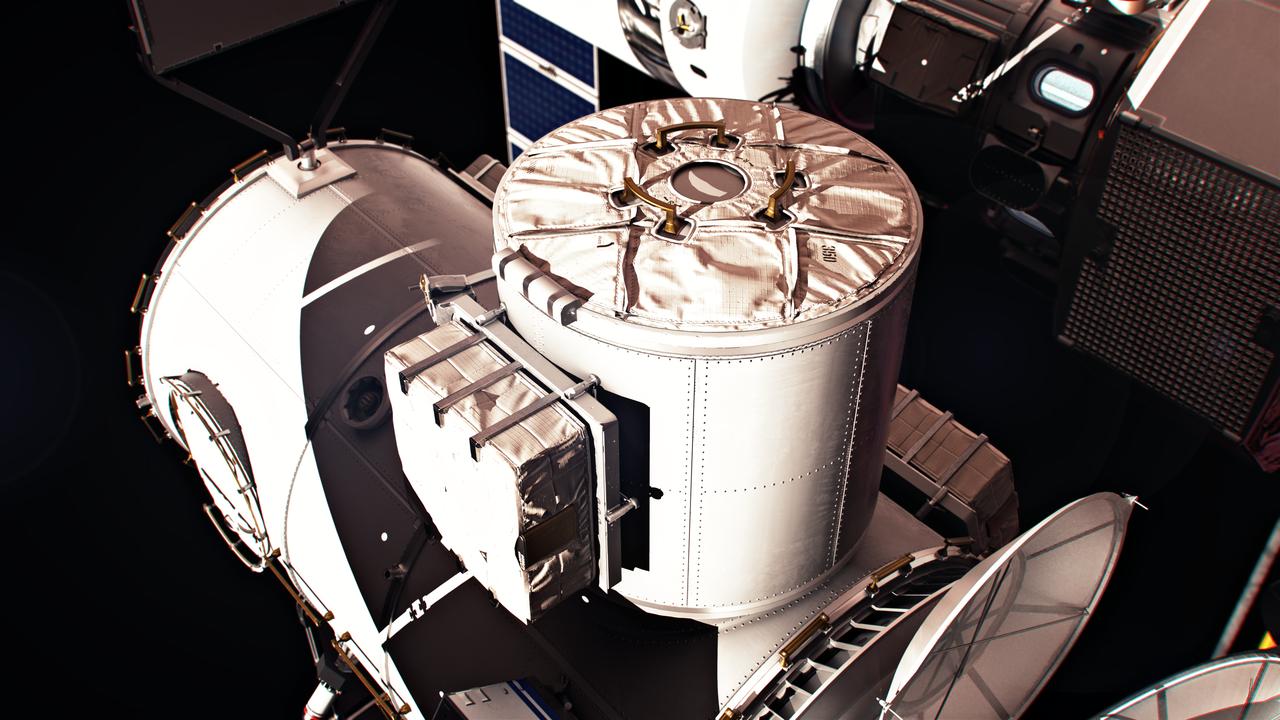

A close-up of a government-reference airlock module for the Gateway Space Station. Mission planning calls for an airlock to be delivered and integrated to Gateway by the crewed Orion spacecraft on the Artemis VI mission after launching on a Space Launch System (SLS) Block 1B rocket.

This photograph shows the flight article of the mated Airlock Module (AM) and Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) being lowering into horizontal position on a transporter. Although the AM and the MDA were separate entities, they were in many respects simply two components of a single module. The AM enabled crew members to conduct extravehicular activities outside Skylab as required for experiment support. Oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks needed for Skylab's life support system were mounted on the external truss work of the AM. Major components in the AM included Skylab's electric power control and distribution station, environmental control system, communication system, and data handling and recording systems. The MDA, forward of the AM, provided docking facilities for the Command and Service Module. It also accommodated several experiment systems, among them the Earth Resource Experiment Package, the materials processing facility, and the control and display console needed for the Apollo Telescope Mount solar astronomy studies. The AM was built by McDornell Douglas and the MDA was built by Martin Marietta. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for the design and development of the Skylab hardware and experiment management.
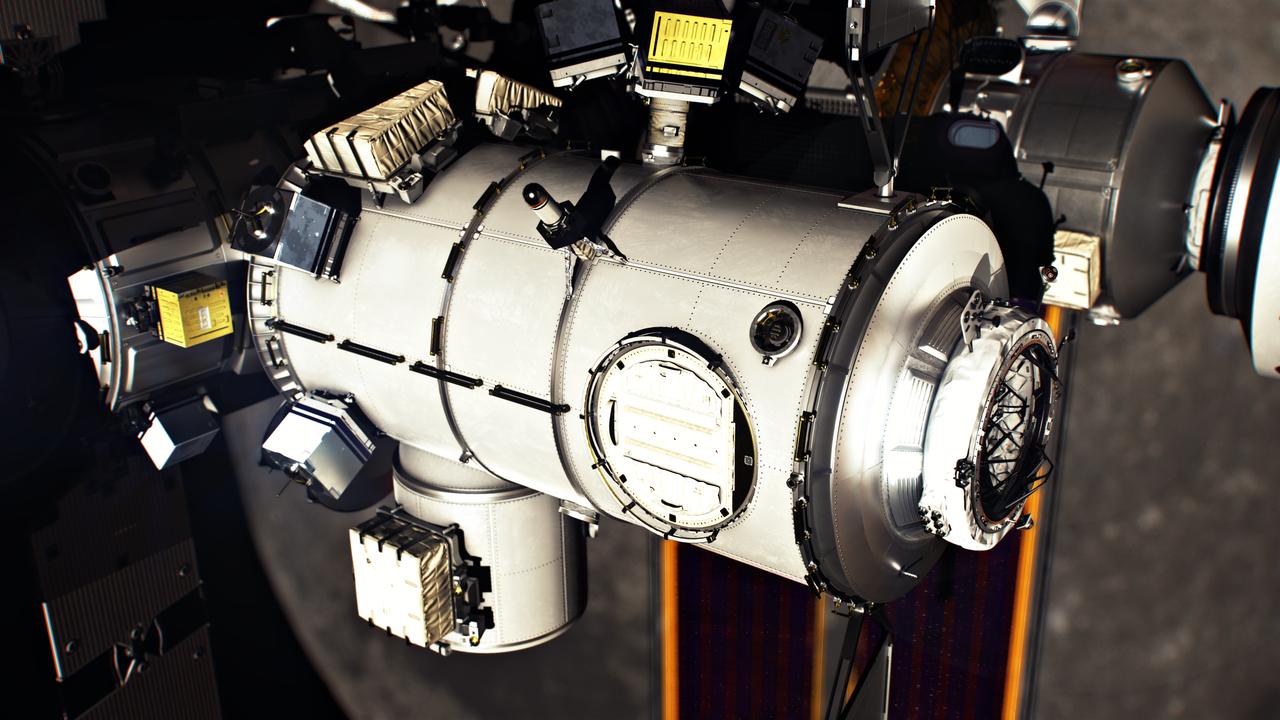
A close-up of a government-reference airlock module for the Gateway Space Station. Mission planning calls for an airlock to be delivered and integrated to Gateway by the crewed Orion spacecraft on the Artemis VI mission after launching on a Space Launch System (SLS) Block 1B rocket.
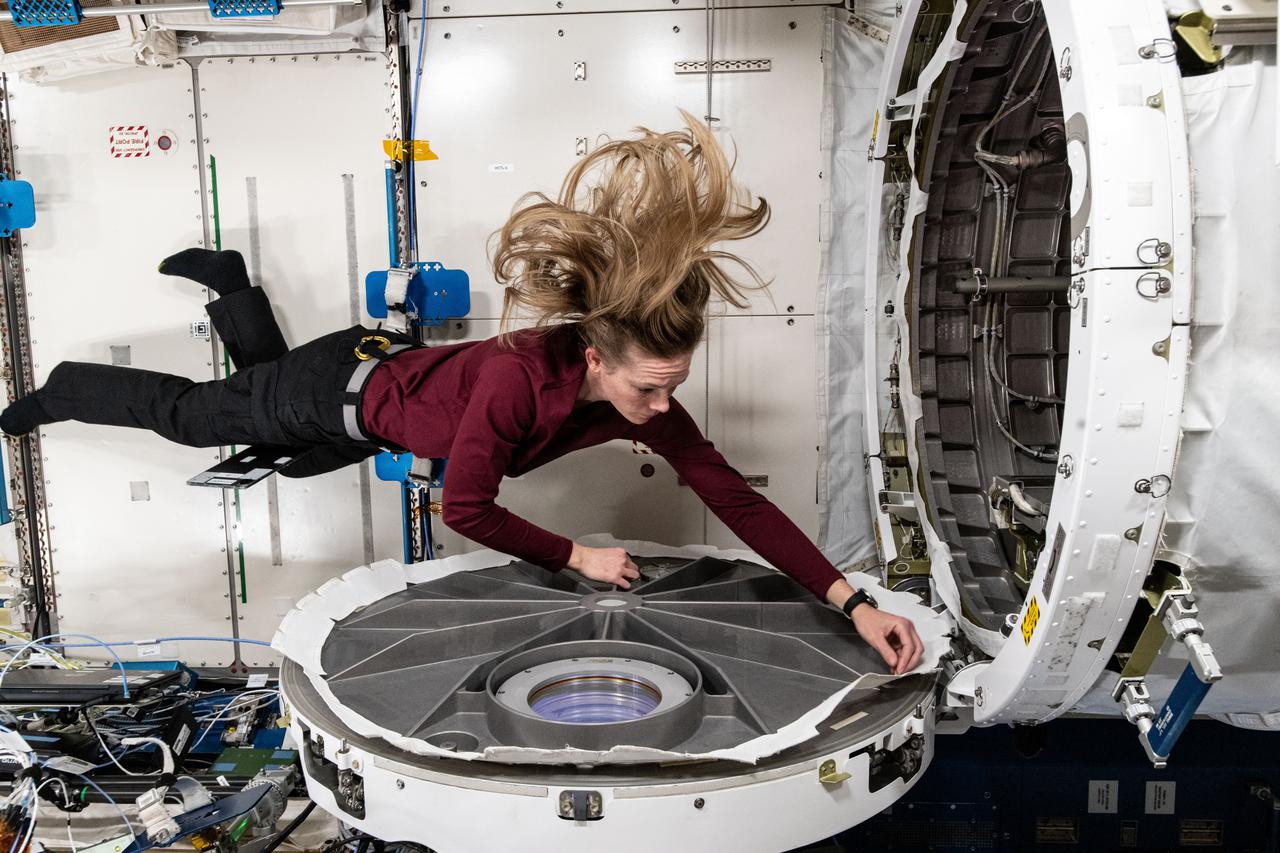

iss072e861697 (March 28, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers opens the hatch to the Kibo laboratory module's airlock aboard the International Space Station.

SL4-150-5074 (February 1974) --- Scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot for the Skylab 4 mission, demonstrates the effects of zero-gravity as he sails through airlock module hatch. Photo credit: NASA

This photograph shows the flight article of the Airlock Module (AM)/Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) assembly being readied for testing in a clean room at the McDornell Douglas Plant in St. Louis, Missouri. Although the AM and the MDA were separate entities, they were in many respects simply two components of a single module. The AM enabled crew members to conduct extravehicular activities outside Skylab as required for experiment support. Oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks needed for Skylab's life support system were mounted on the external truss work of the AM. Major components in the AM included Skylab's electric power control and distribution station, environmental control system, communication system, and data handling and recording systems. The MDA, forward of the AM, provided docking facilities for the Command and Service Module. It also accommodated several experiment systems, among them the Earth Resource Experiment Package, the materials processing facility, and the control and display console needed for the Apollo Telescope Mount solar astronomy studies. The AM was built by McDonnell Douglas and the MDA was built by Martin Marietta. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for the design and development of the Skylab hardware and experiment management.
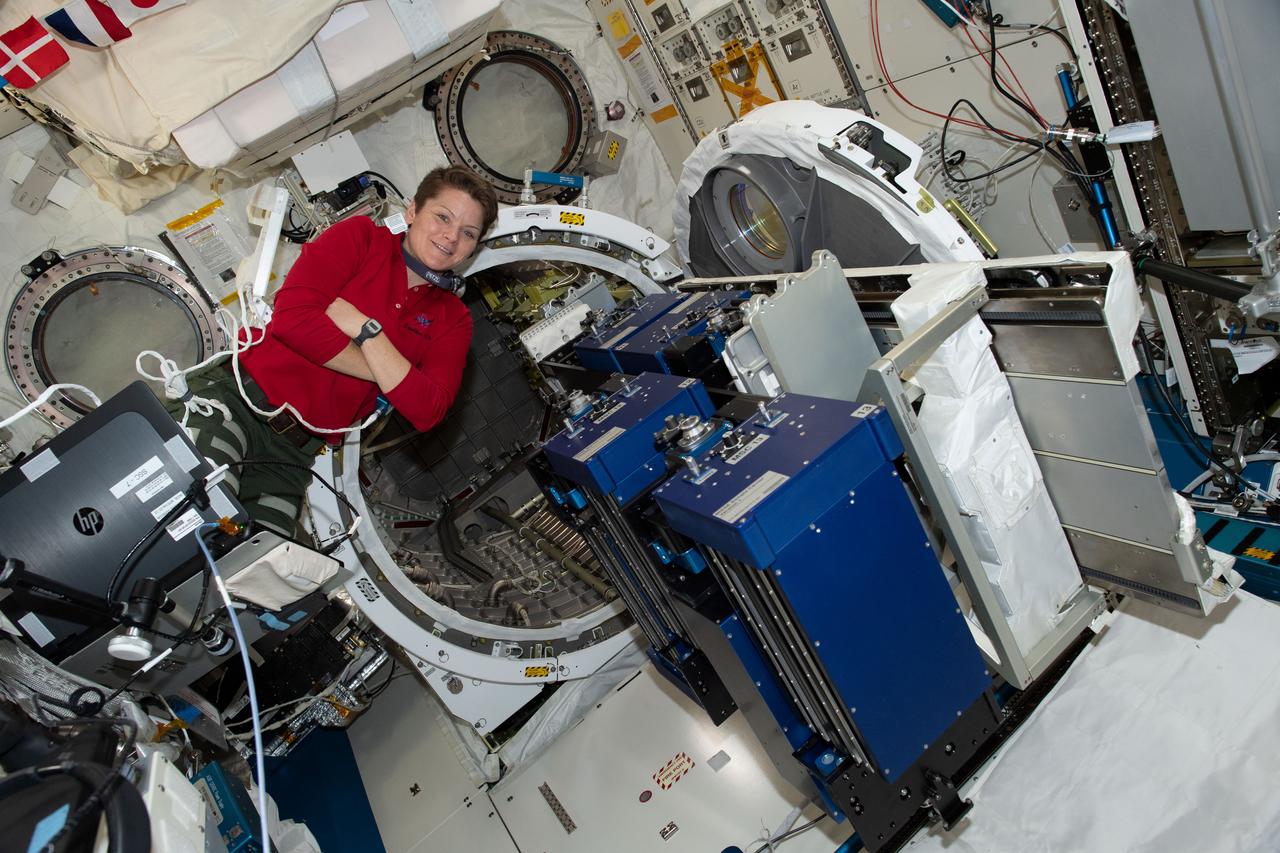

iss058e001000 (Dec. 26, 2018) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 58 Flight Engineer Anne McClain works inside Japan's Kibo laboratory module installing the Material Transfer Tray before inserting it into the module's airlock.
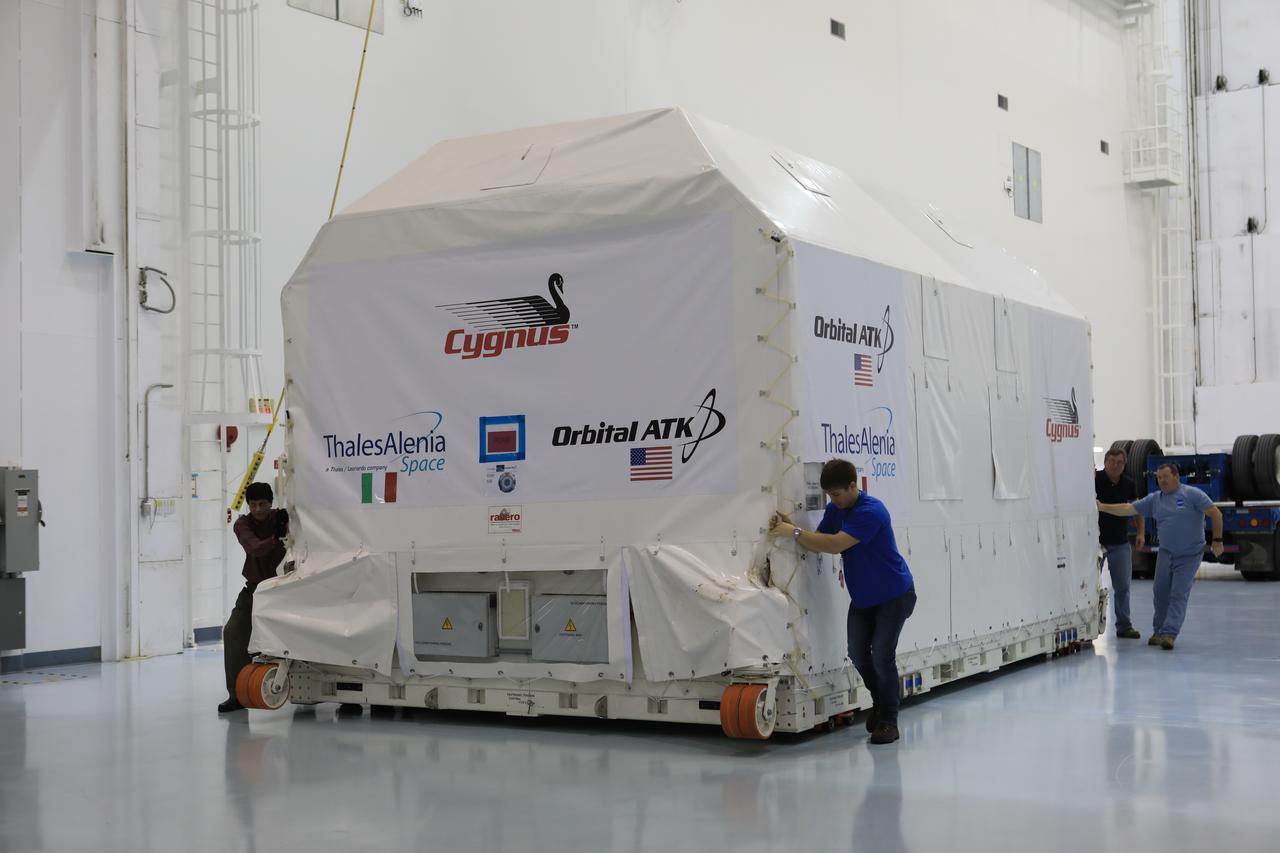

Inside an environmentally controlled shipping container the Orbital ATK OA-7 Cygnus spacecraft's pressurized cargo module (PCM) moves from an airlock to the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Scheduled to launch on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK OA-7 mission will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
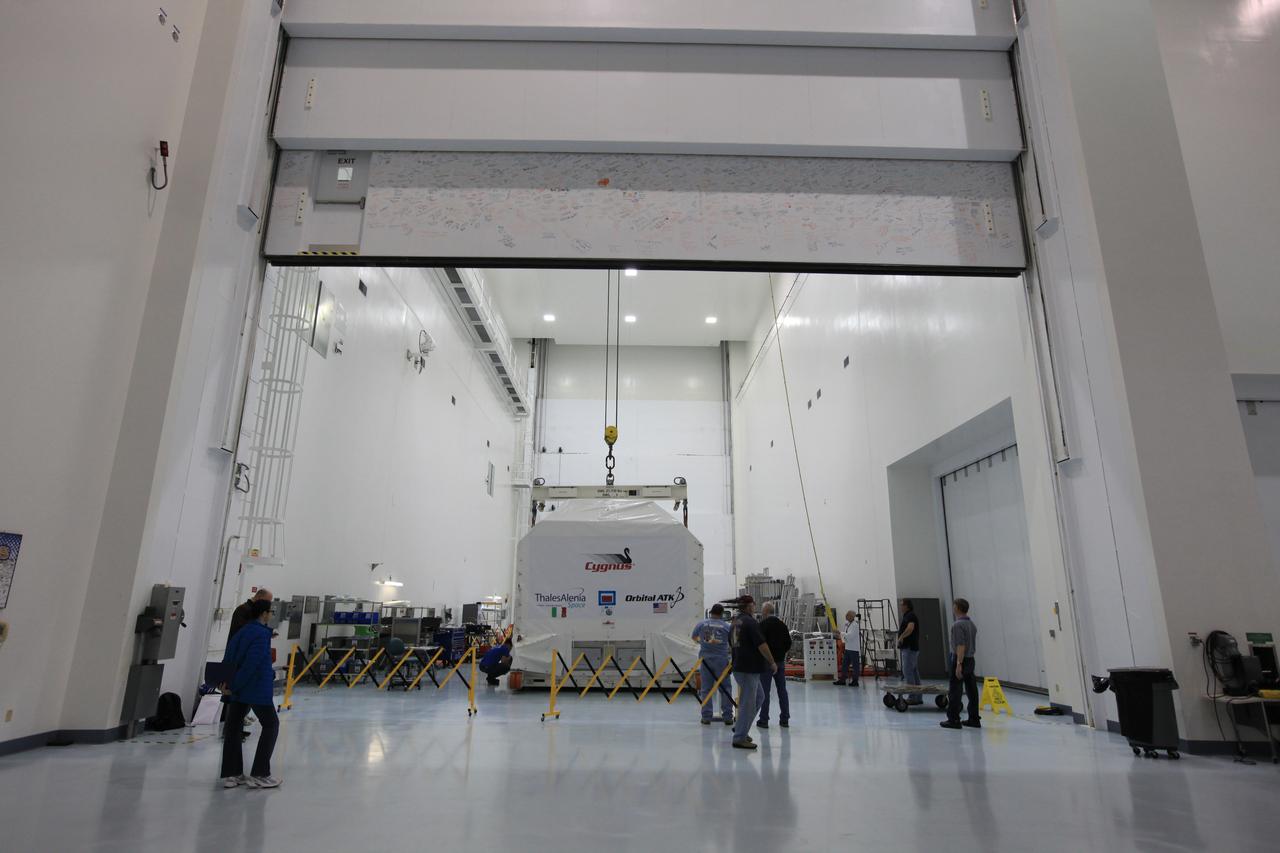

Inside an environmentally controlled shipping container the Orbital ATK OA-7 Cygnus spacecraft's pressurized cargo module (PCM) moves from an airlock to the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Scheduled to launch on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK OA-7 mission will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
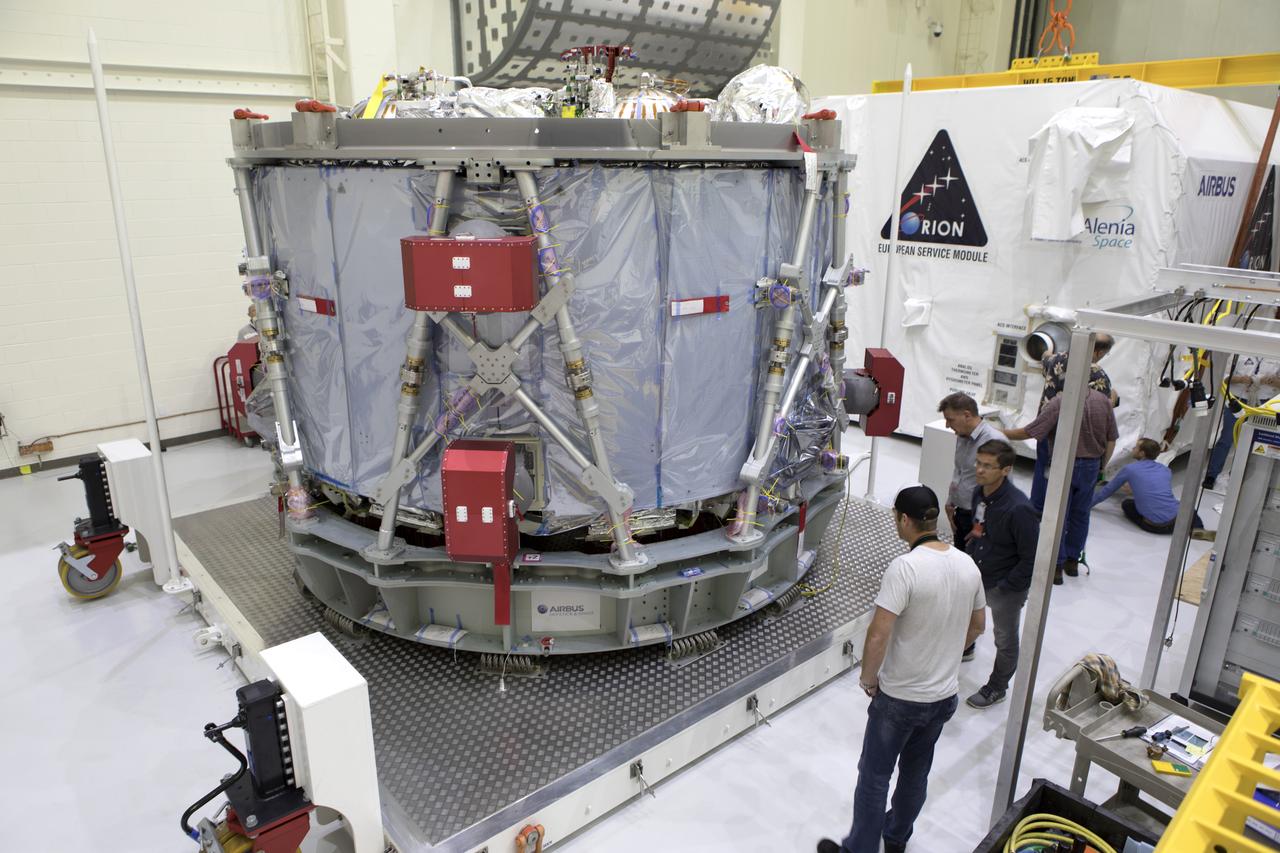

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) is uncrated at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) is uncrated at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

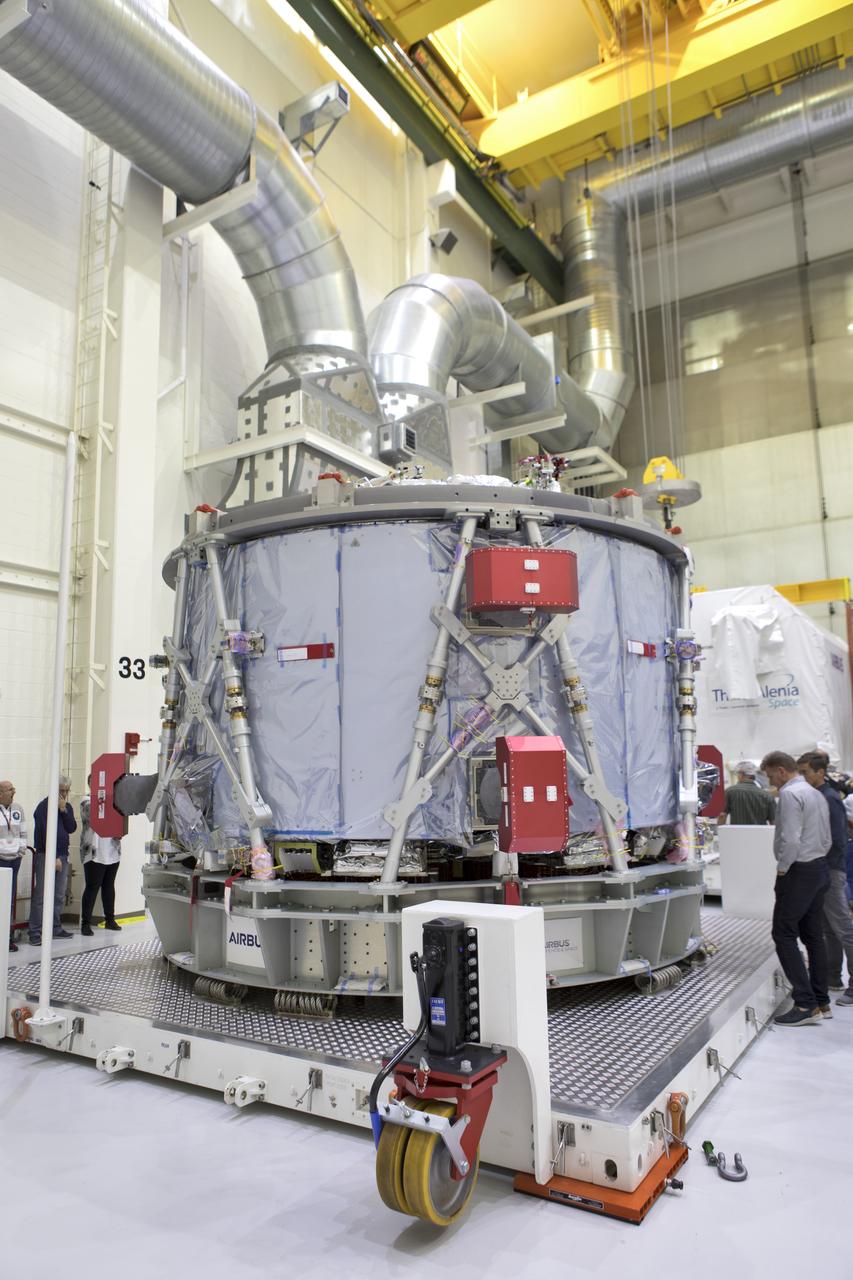
Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay On Nov. 6, 2018, a crane is used to uncrate the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
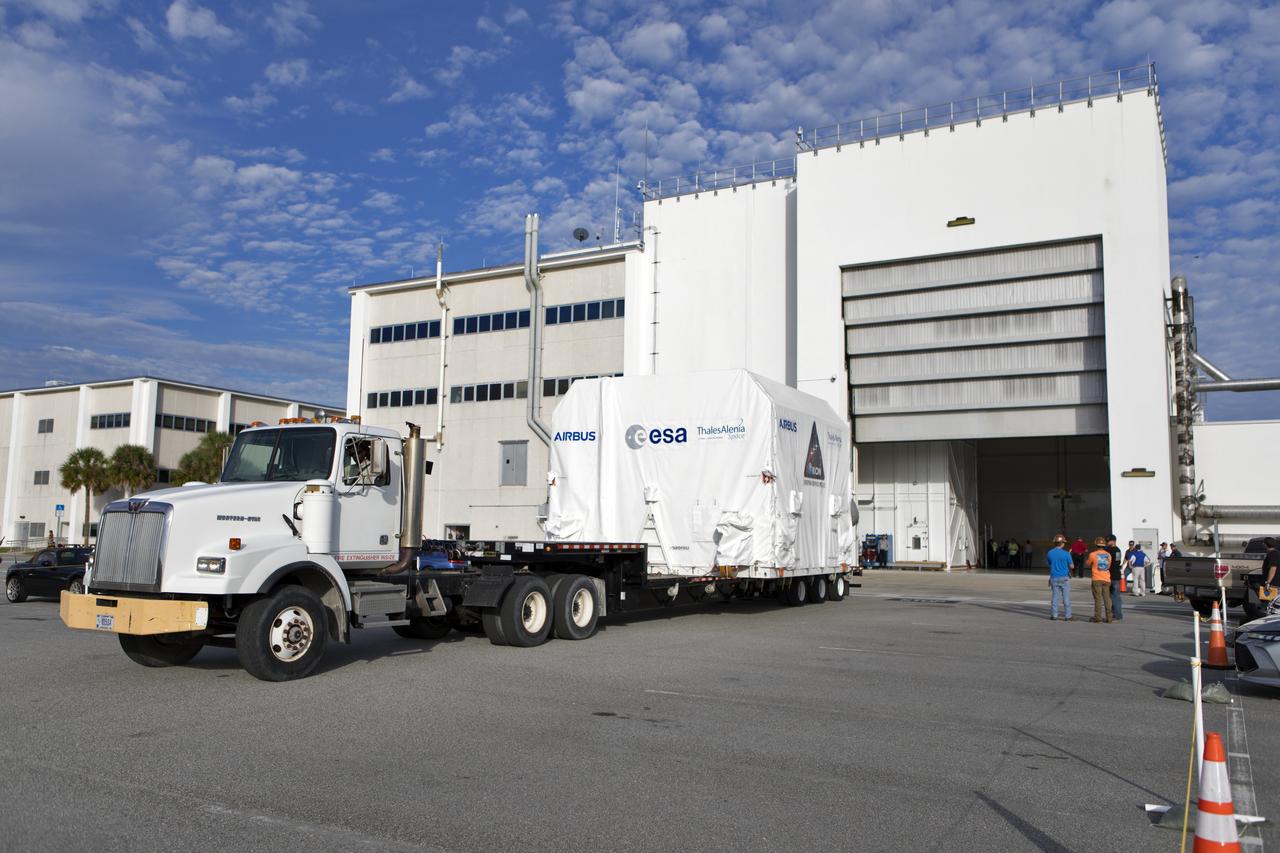

A flatbed truck carrying the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) in its shipping container begins to back into the airlock of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Nov. 6, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
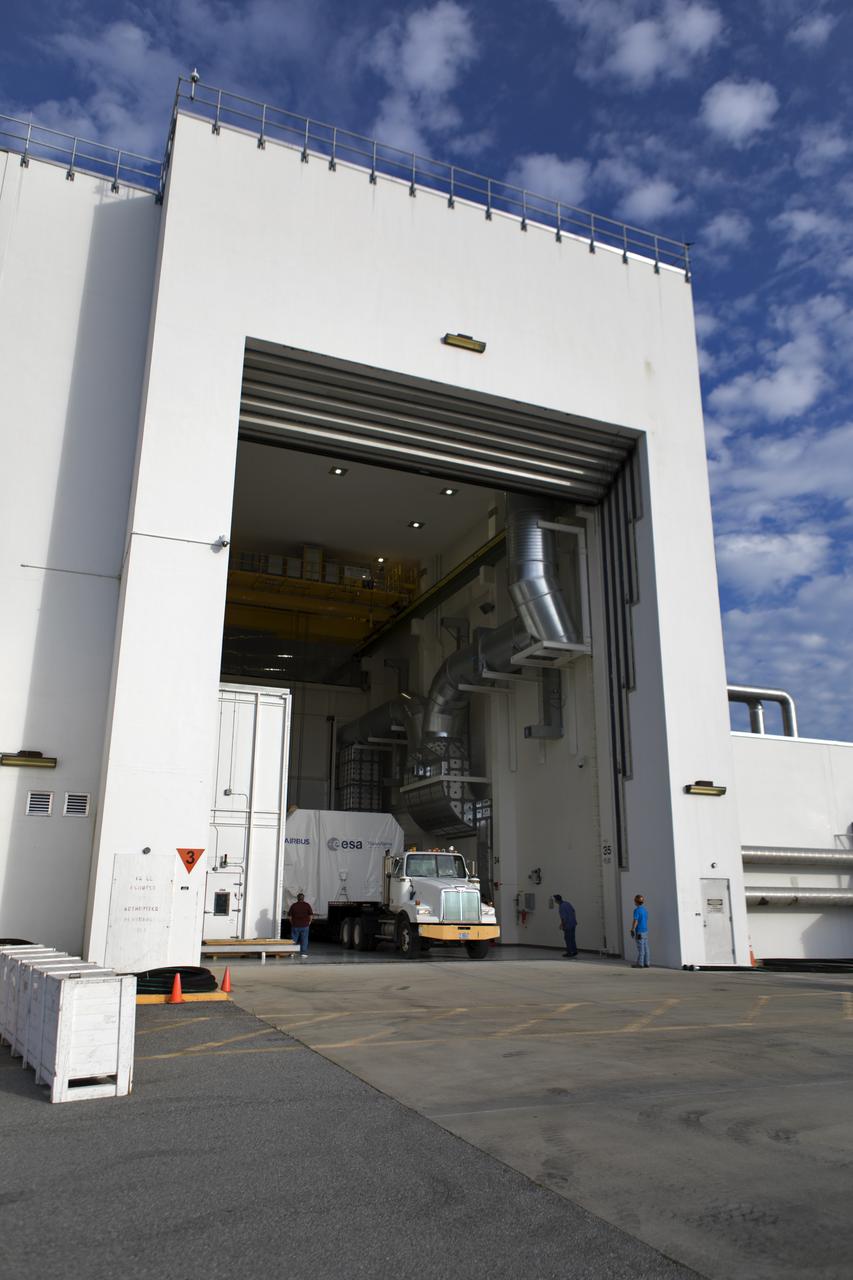

A flatbed truck carrying the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) in its shipping container backs into the airlock of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Nov. 6, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
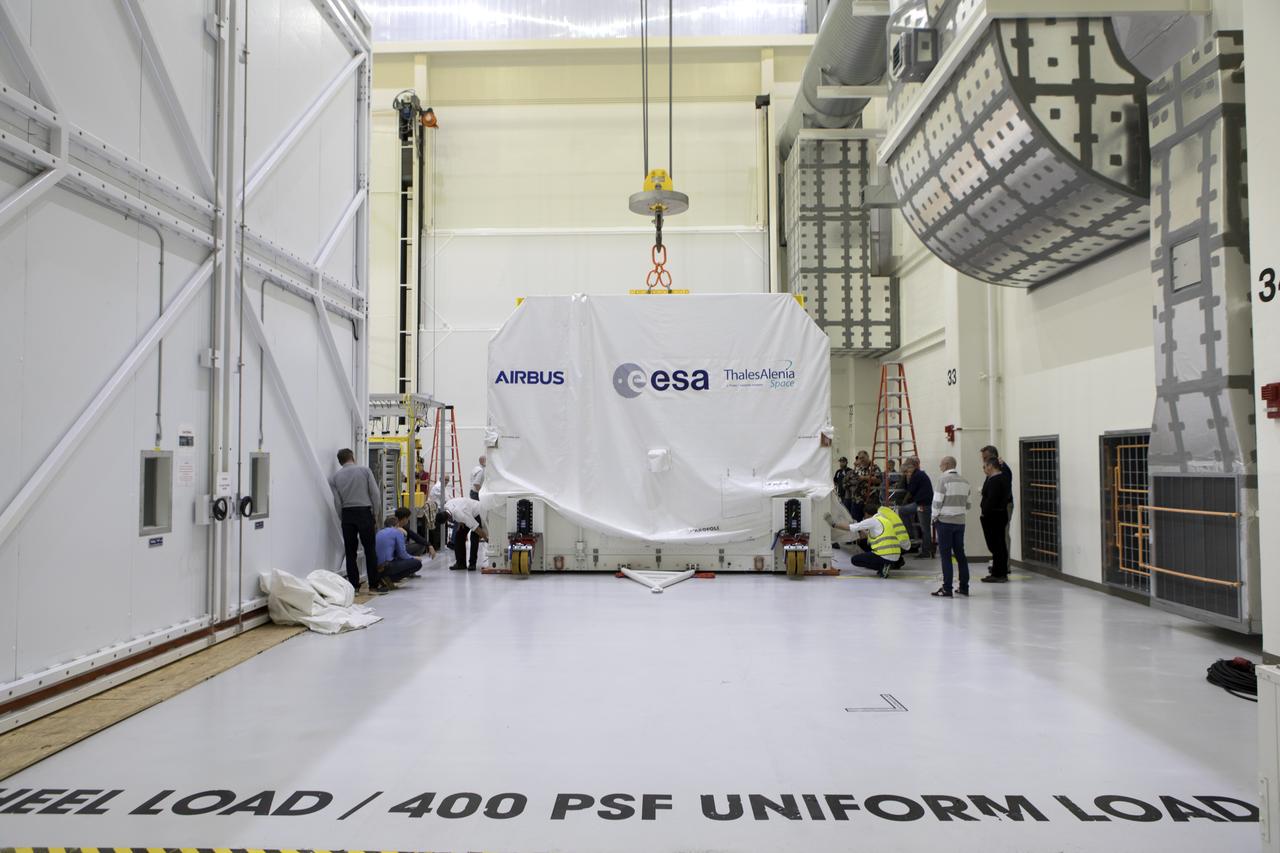

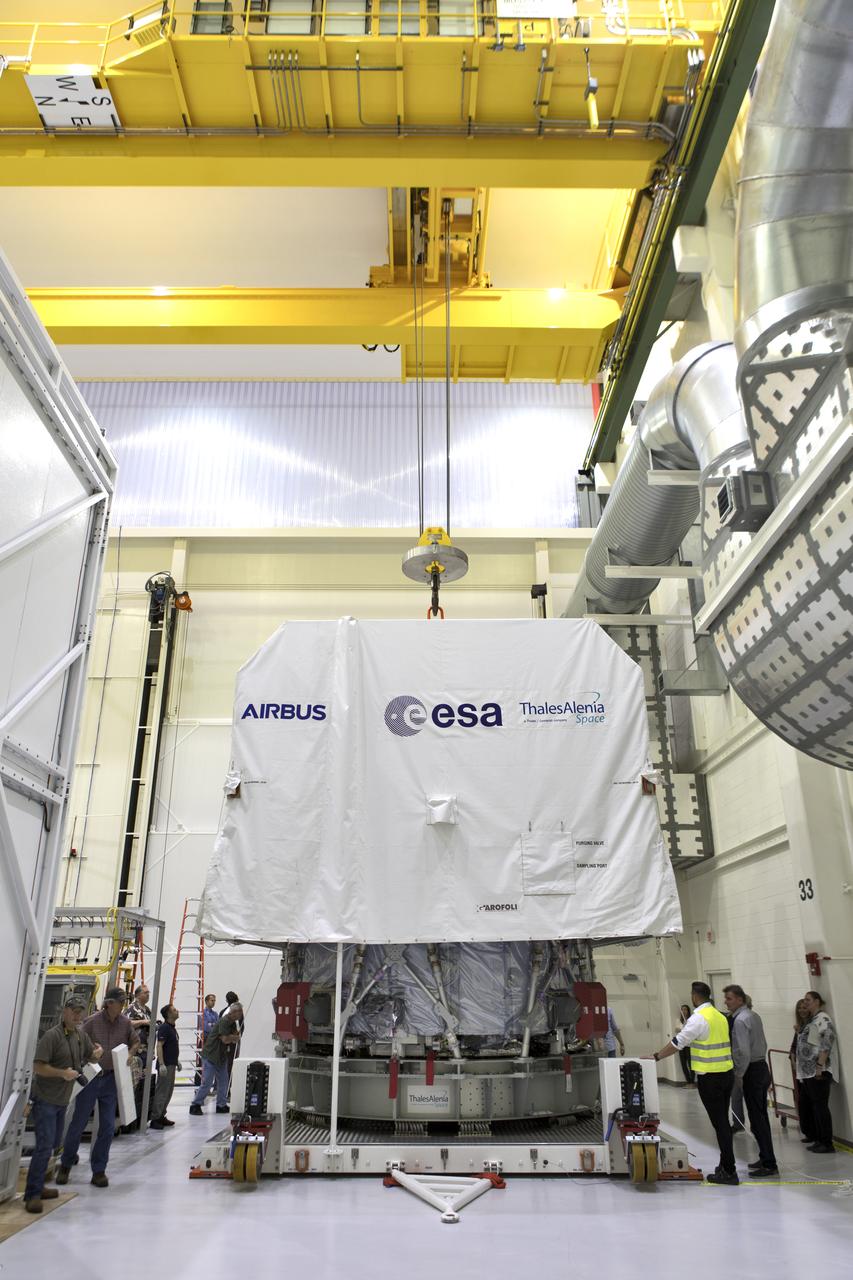
The European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM), in its shipping container, is inside the airlock at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
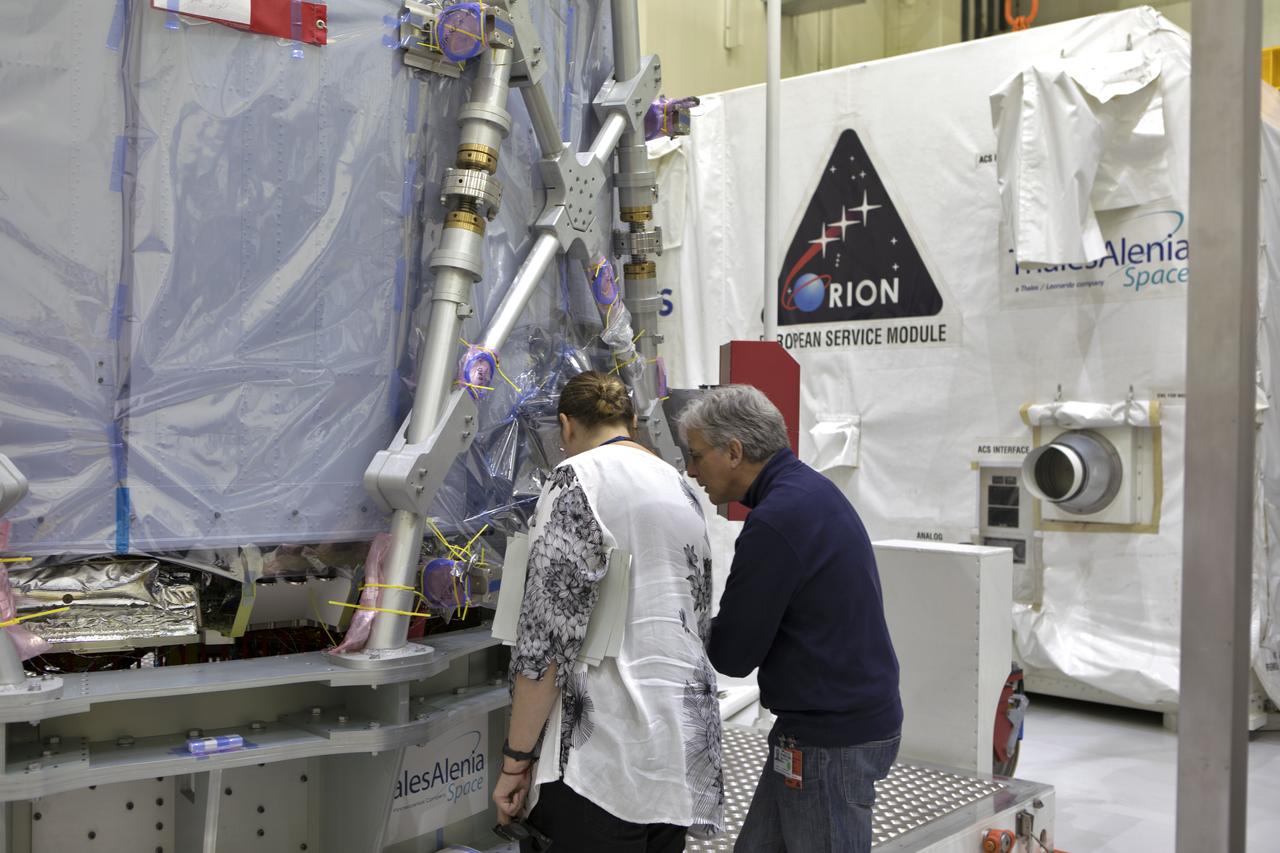

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, European Space Agency (ESA) and Airbus engineers check the ESA European Service Module (ESM) after it is uncrated at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
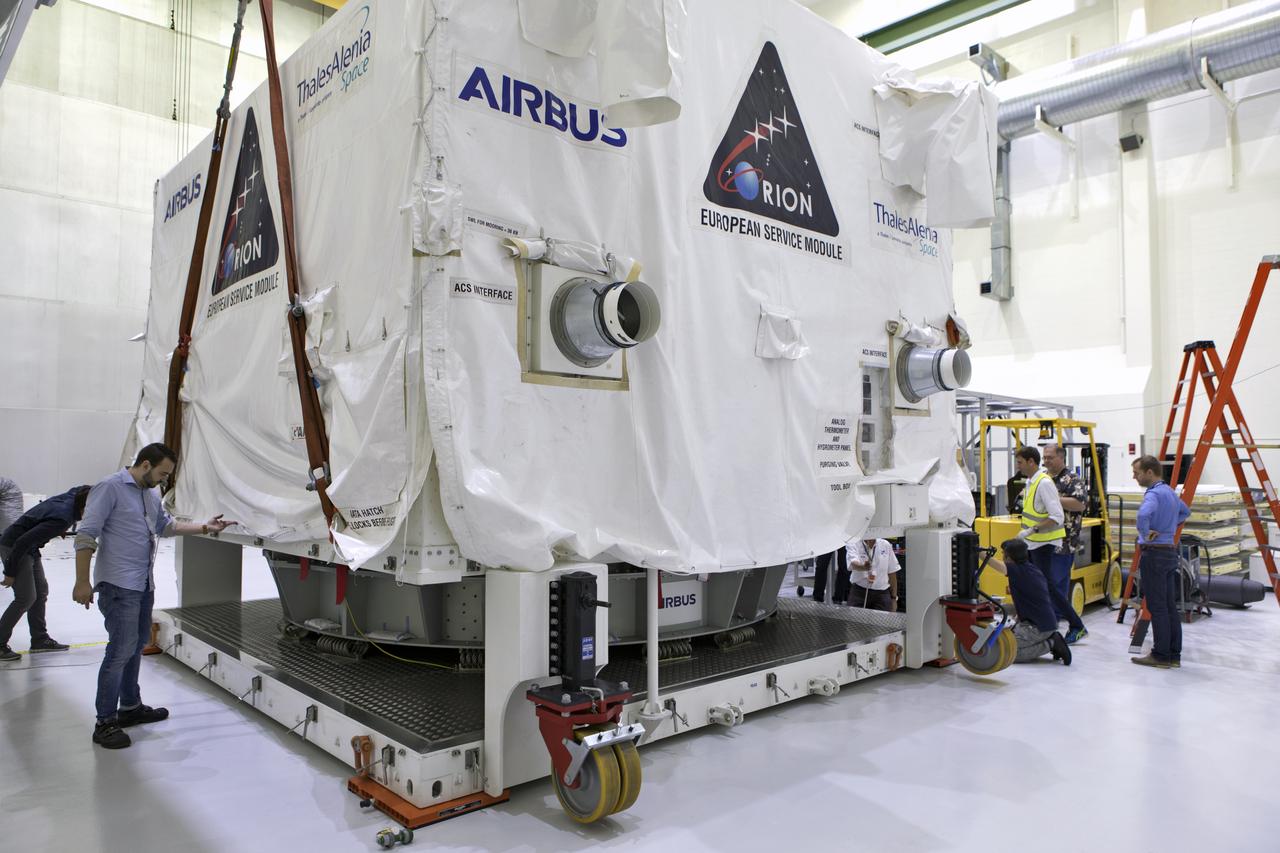

The European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM), in its shipping container, is inside the airlock at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
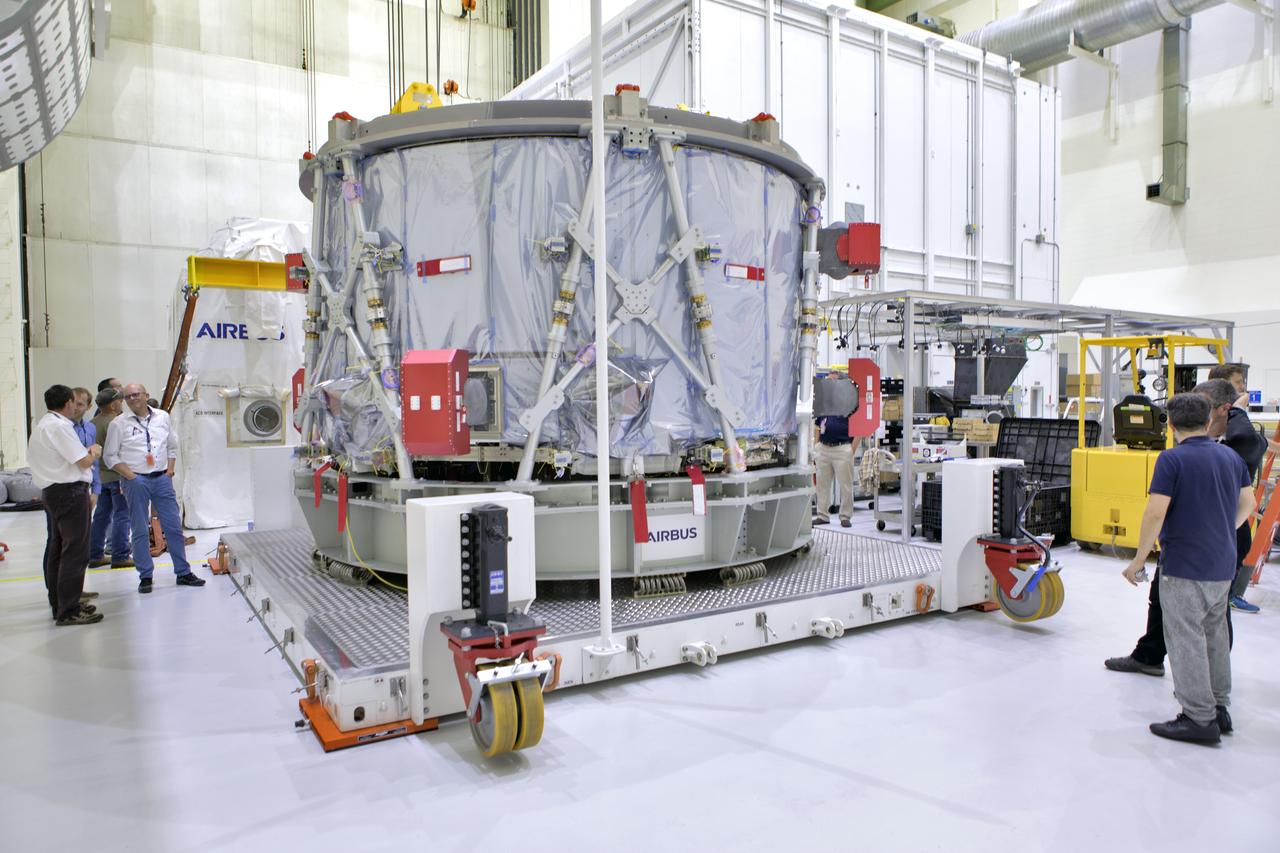

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) is uncrated and ready for its move to the high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
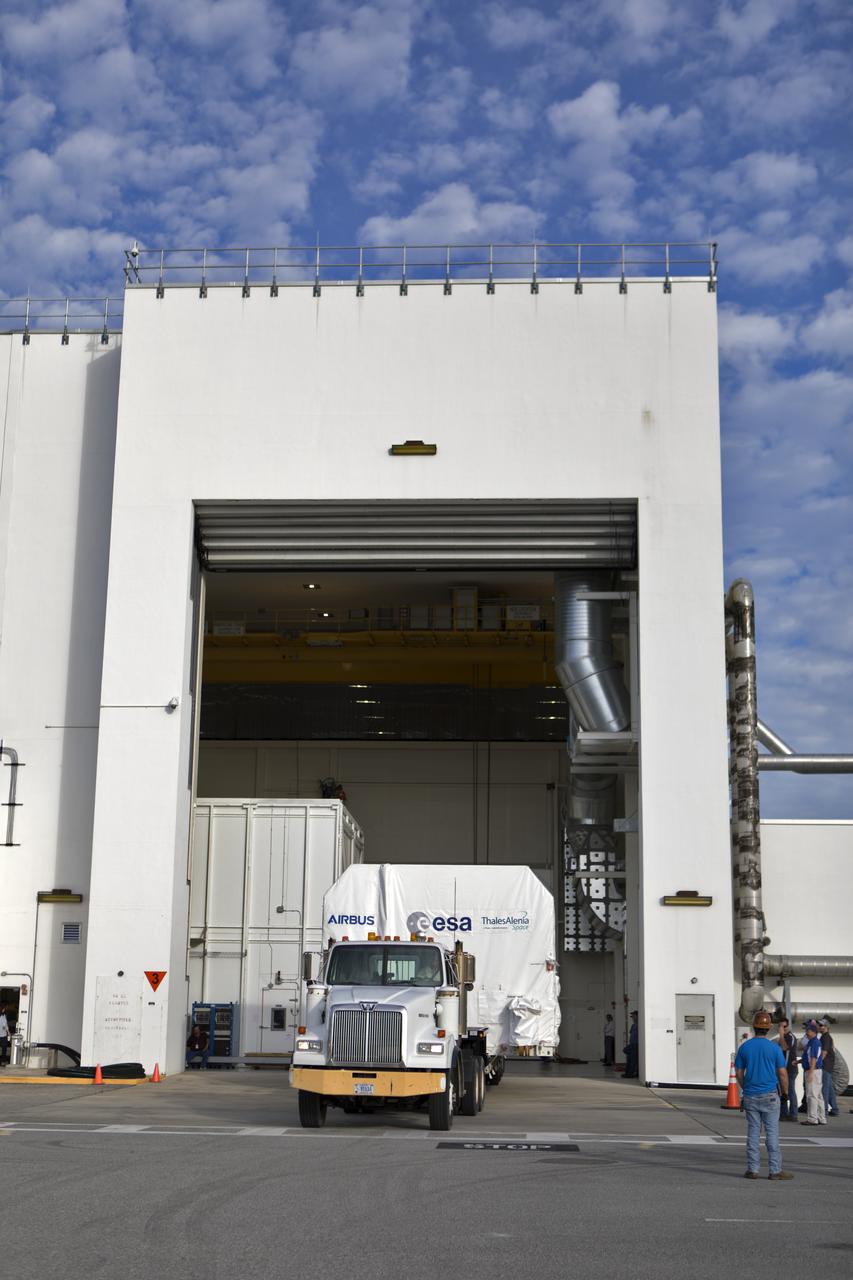

A flatbed truck carrying the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) in its shipping container backs into the airlock of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Nov. 6, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, European Space Agency (ESA) and Airbus technicians begin to uncrate the ESA's European Service Module (ESM) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
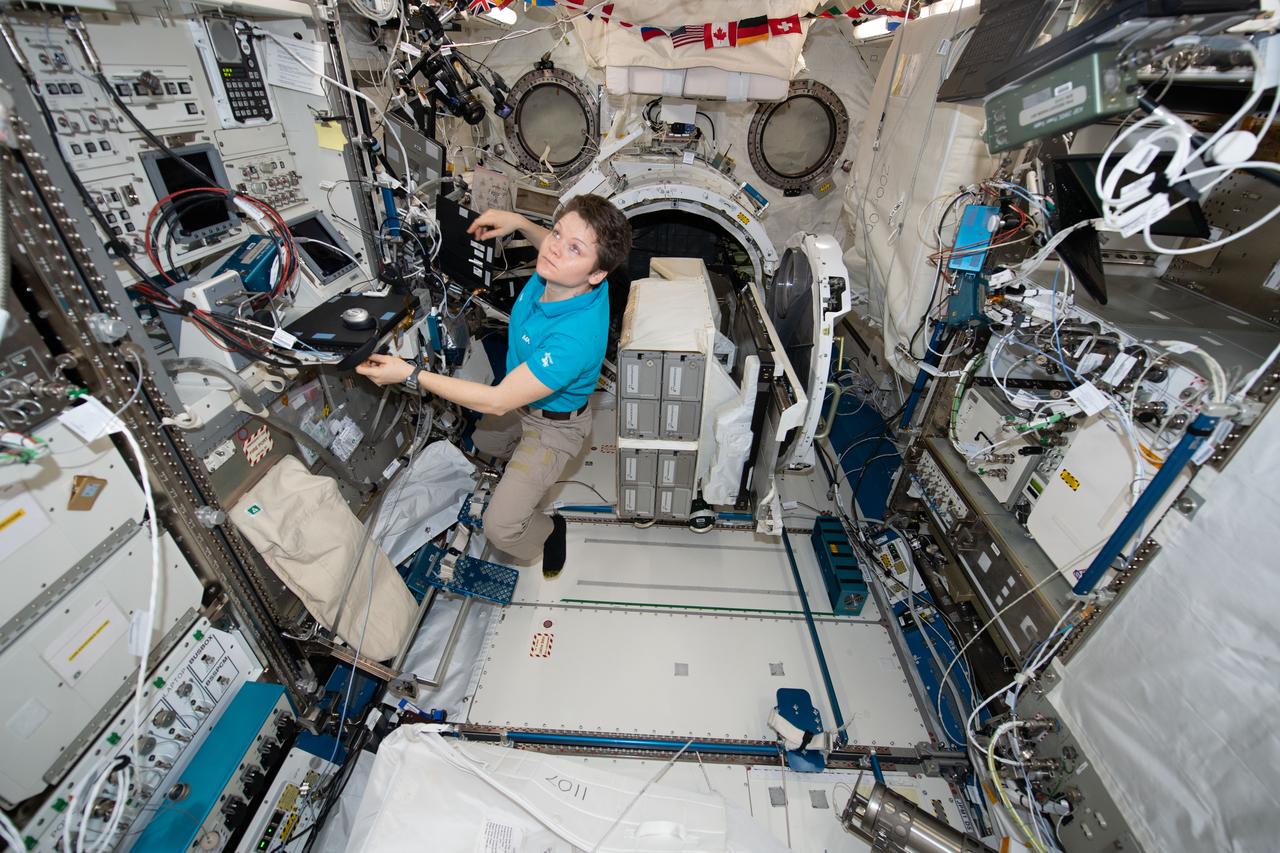

iss058e007642 (Jan. 30, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Anne McClain works inside the Kibo laboratory module designed and built by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. McClain is working to install the NanoRacks CubeSat Deployer in Kibo's airlock.
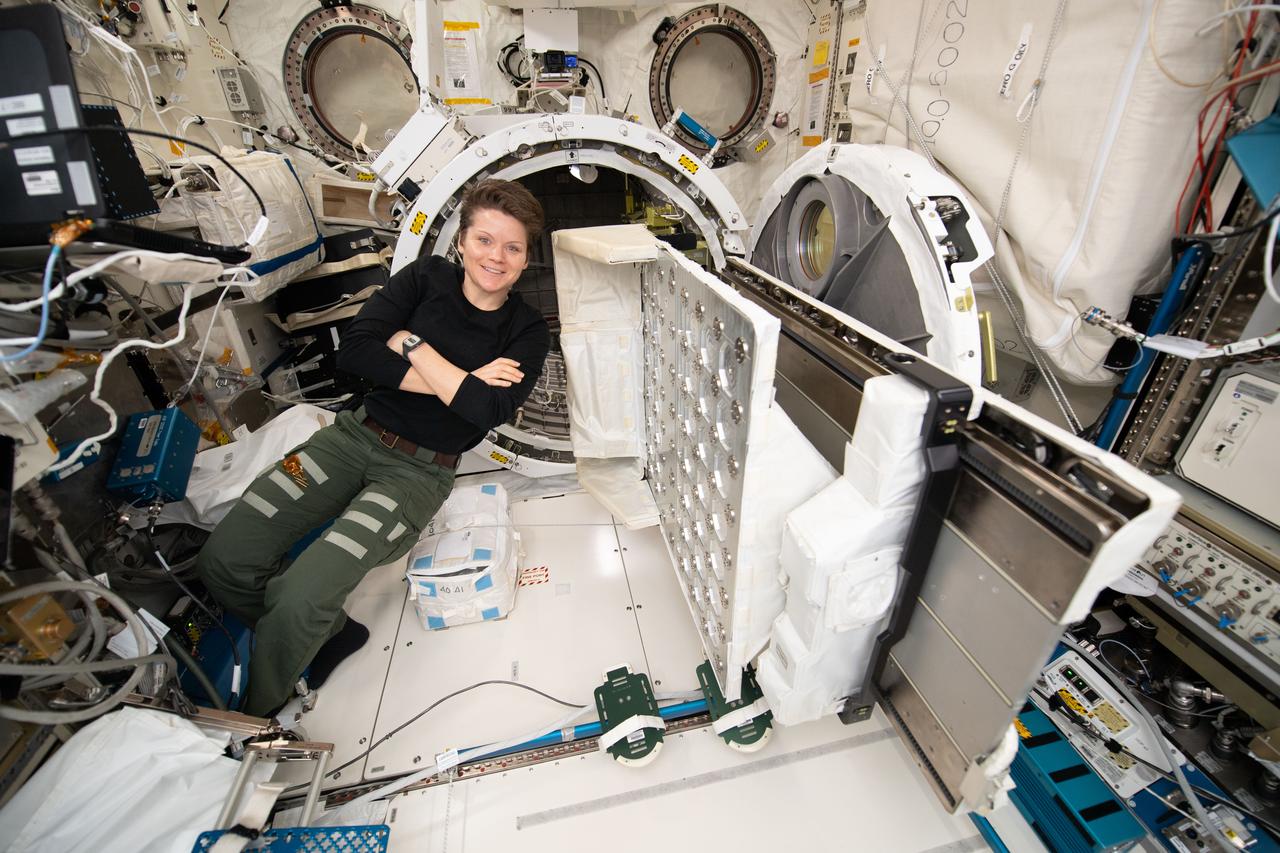

iss058e007370 (Jan. 29, 2019) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 58 Flight Engineer Anne McClain works inside Japan's Kibo laboratory module. She was setting up and installing small satellite deployment hardware inside Kibo's airlock to eject a set of CubeSats outside the Japanese module.
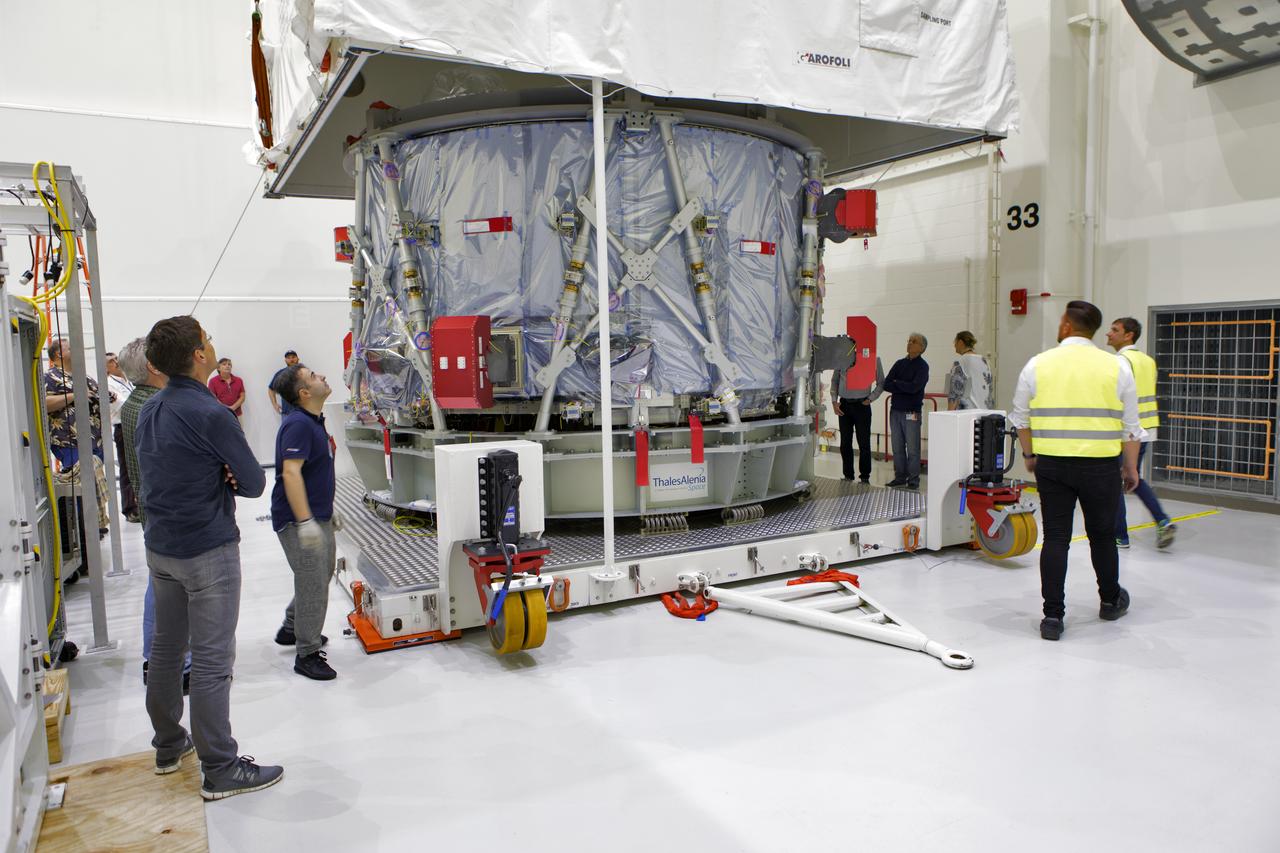

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay On Nov. 6, 2018, European Space Agency (ESA) and Airbus engineers and technicians watch as a crane is used to uncrate the ESA's European Service Module (ESM) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
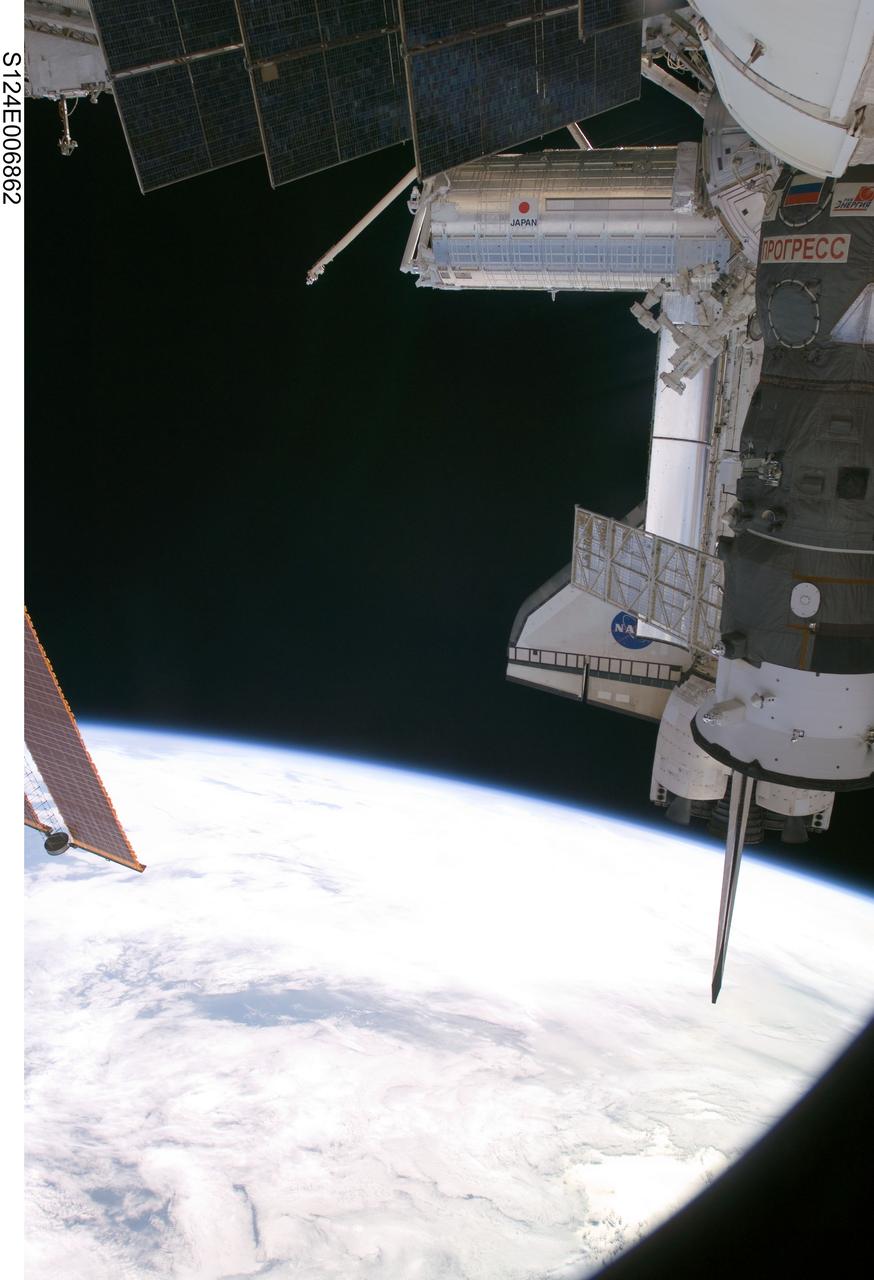

S124-E-006862 (6 June 2008) --- One of a series of digital still images documenting the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, also called Kibo, in its new home on the International Space Station, this view depicts Kibo's exterior in the distance, joined in the frame by some not so permanent hardware. The pictured components include the visiting Space Shuttle Discovery and a Russian Progress resupply vehicle.
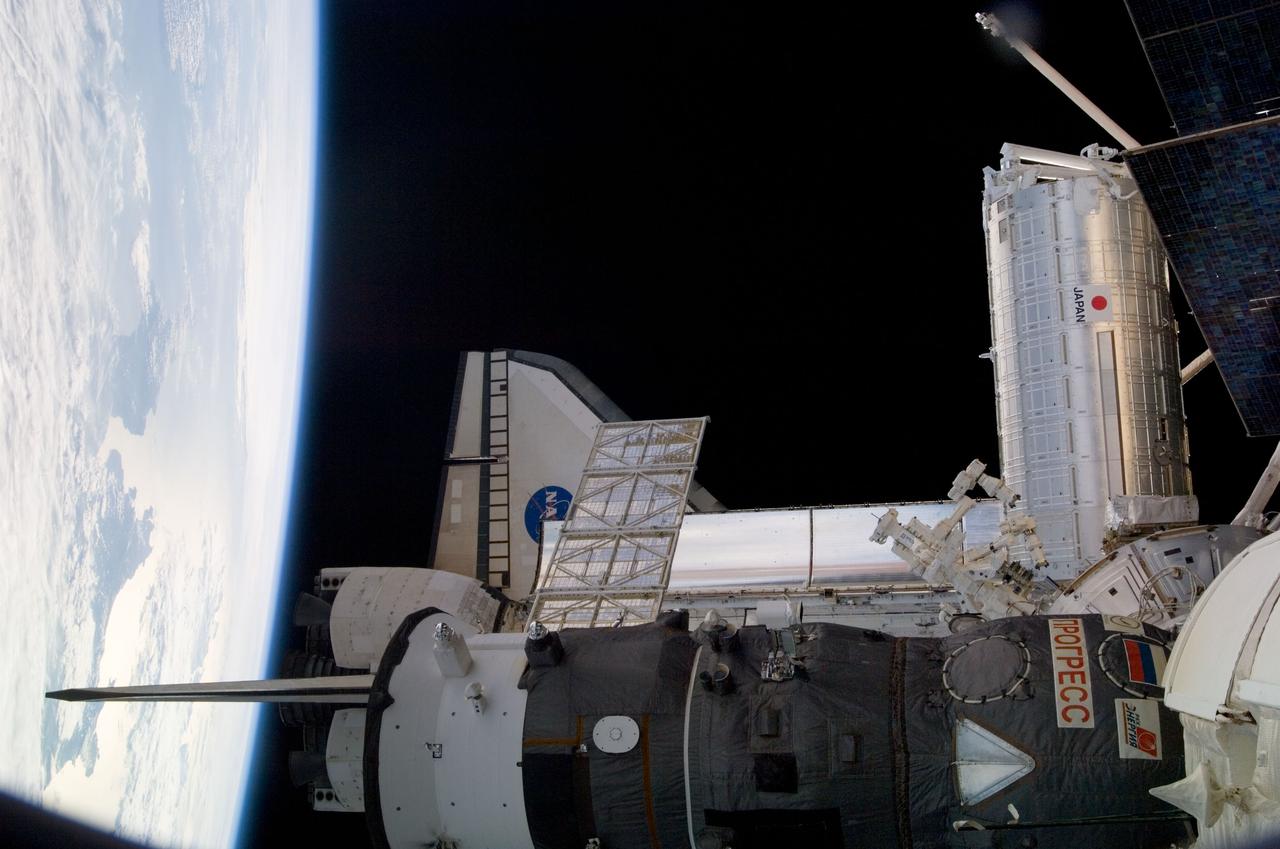

S124-E-006865 (6 June 2008) --- One of a series of digital still images documenting the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, also called Kibo, in its new home on the International Space Station, this view features Kibo's exterior, Earth's horizon and a couple of "visiting" spacecraft. The Space Shuttle Discovery and a Russian Progress resupply craft are seen near foreground.
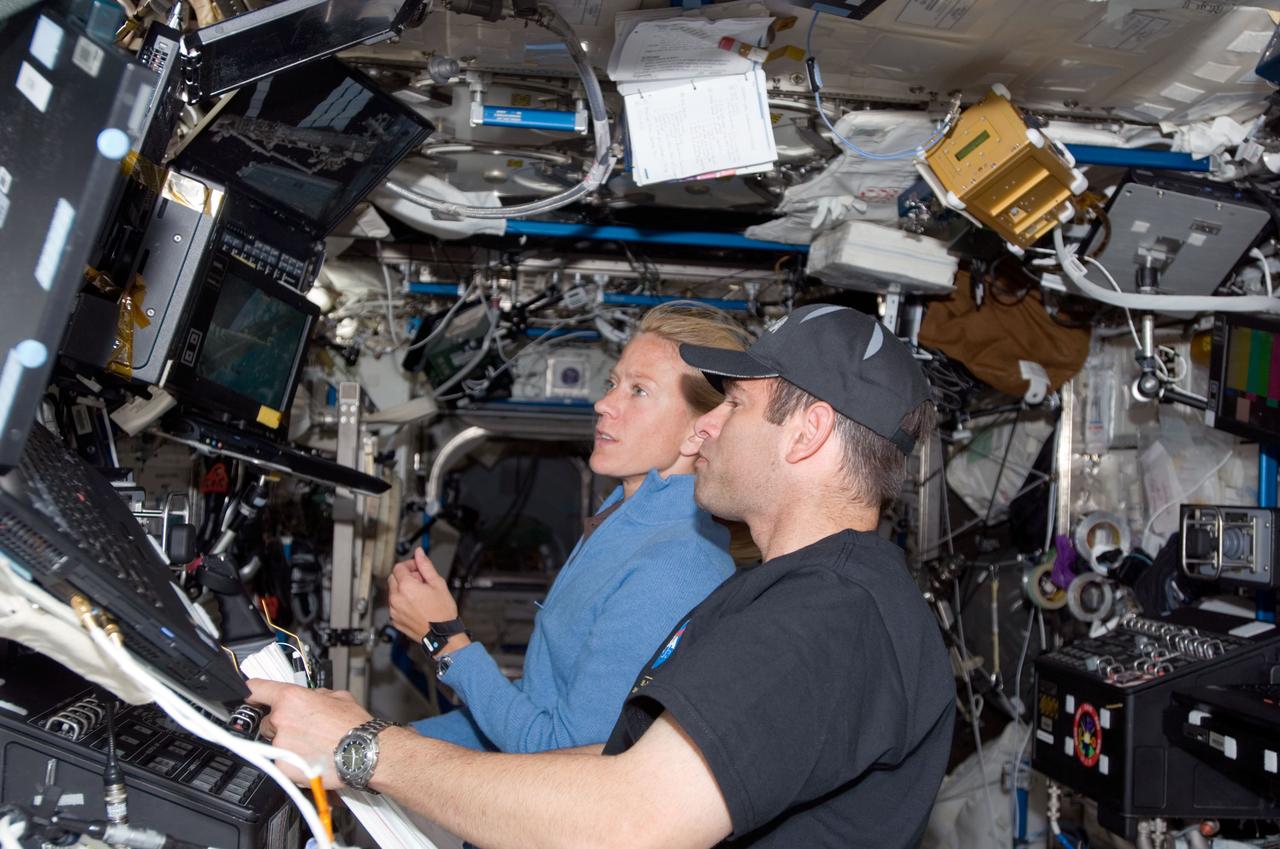

S124-E-006858 (6 June 2008) --- Astronauts Greg Chamitoff, Expedition 17 flight engineer, and Karen Nyberg, STS-124 mission specialist, use the controls of the International Space Station's robotic Canadarm2 in the Destiny laboratory to maneuver the Kibo Japanese logistics module from atop the Harmony node to the top of the Kibo Japanese Pressurized Module.
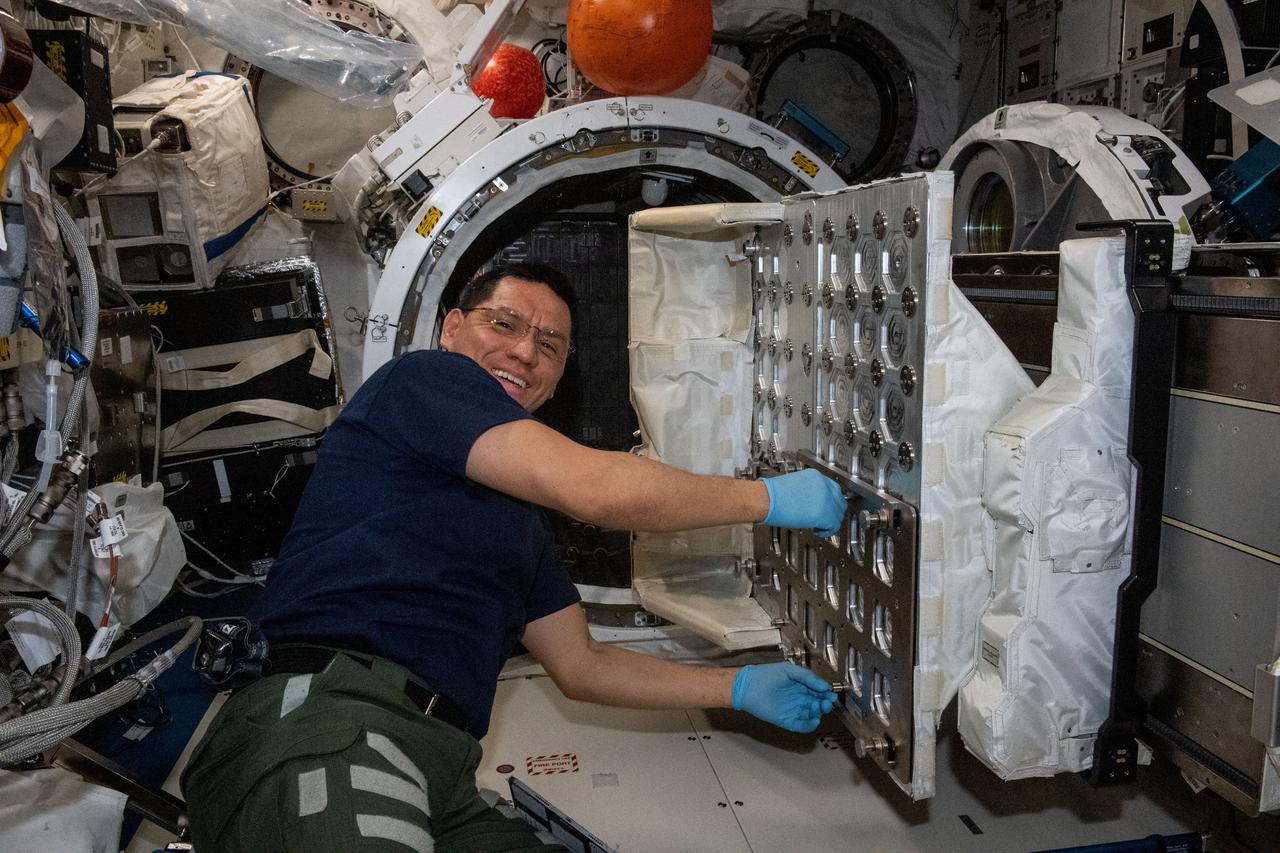

iss069e004389 (April 20, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Frank Rubio works to install the NanoRacks CubeSat Deployer inside the Kibo laboratory module's airlock. After the airlock is depressurized, the Japanese robotic arm grapples the deployer and places it outside in the vacuum of microgravity pointing it away from the International Space Station. CubeSats from private, governmental, and academic organizations are then deployed into Earth orbit for a variety of research objectives.
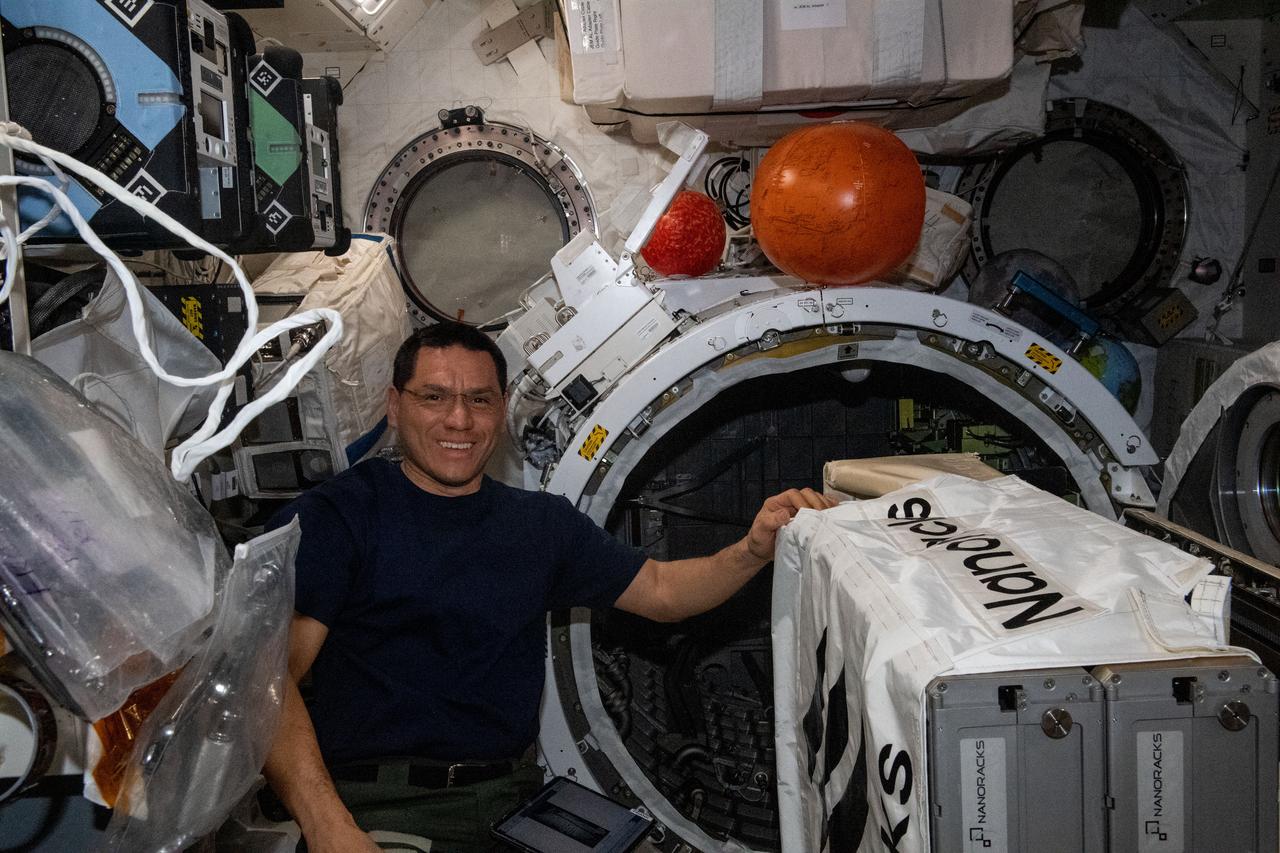

iss069e004397 (April 20, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Frank Rubio works to install the NanoRacks CubeSat Deployer inside the Kibo laboratory module's airlock. After the airlock is depressurized, the Japanese robotic arm grapples the deployer and places it outside in the vacuum of microgravity pointing it away from the International Space Station. CubeSats from private, governmental, and academic organizations are then deployed into Earth orbit for a variety of research objectives.
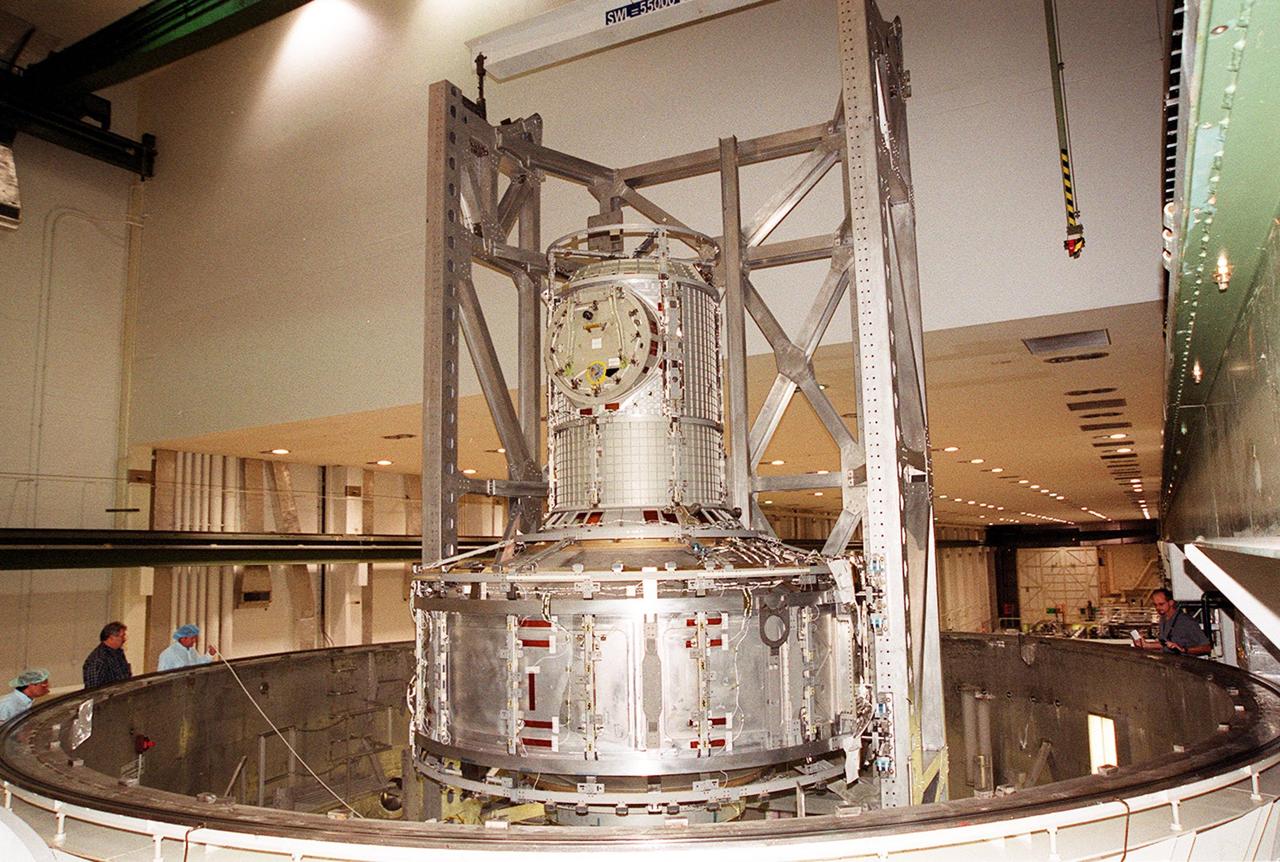

The overhead crane lowers the Joint Airlock Module inside the vacuum chamber in the Operations and Checkout Building. The airlock is being tested for leaks. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module provides a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
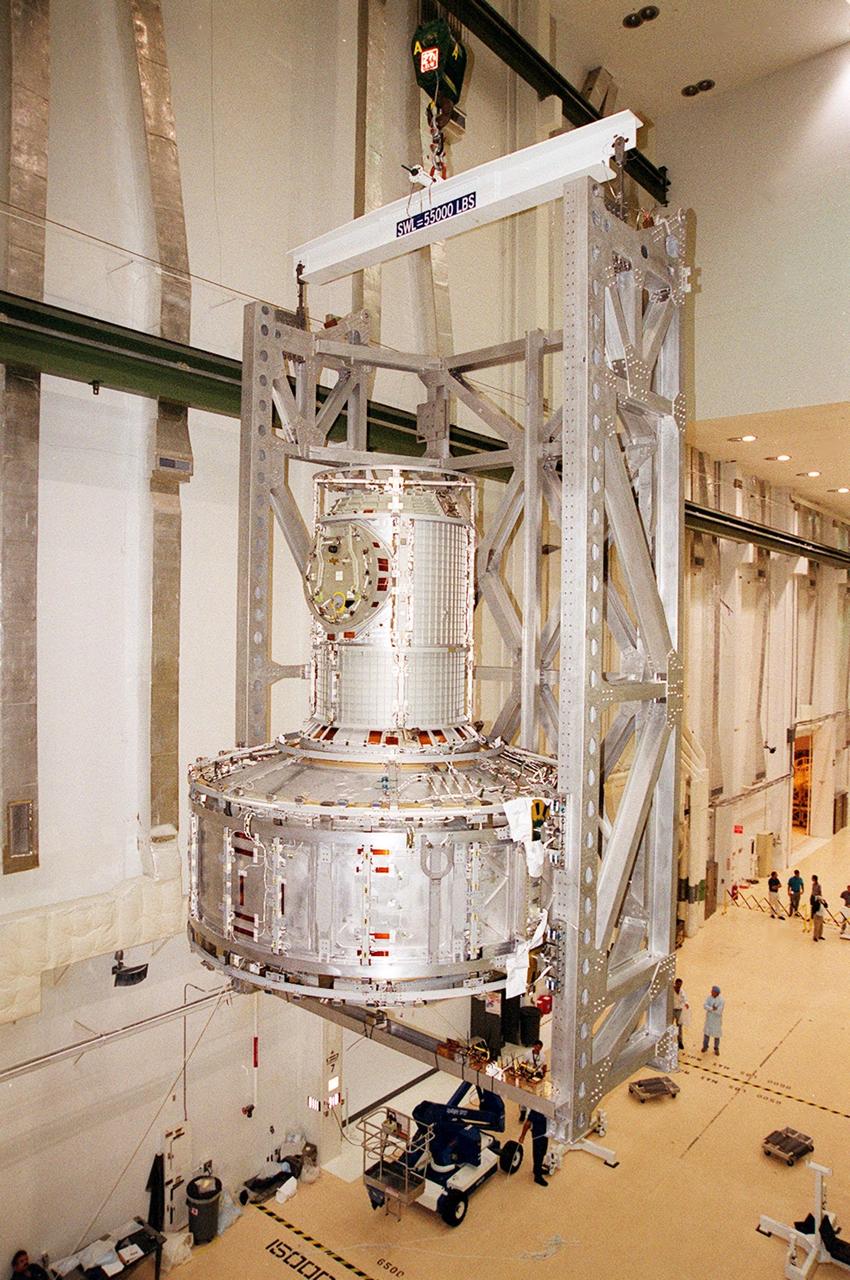
In the Operations and Checkout Building, an overhead crane lifts the Joint Airlock Module to move it to a vacuum chamber for testing. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module is specially designed to accommodate both suits, providing a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
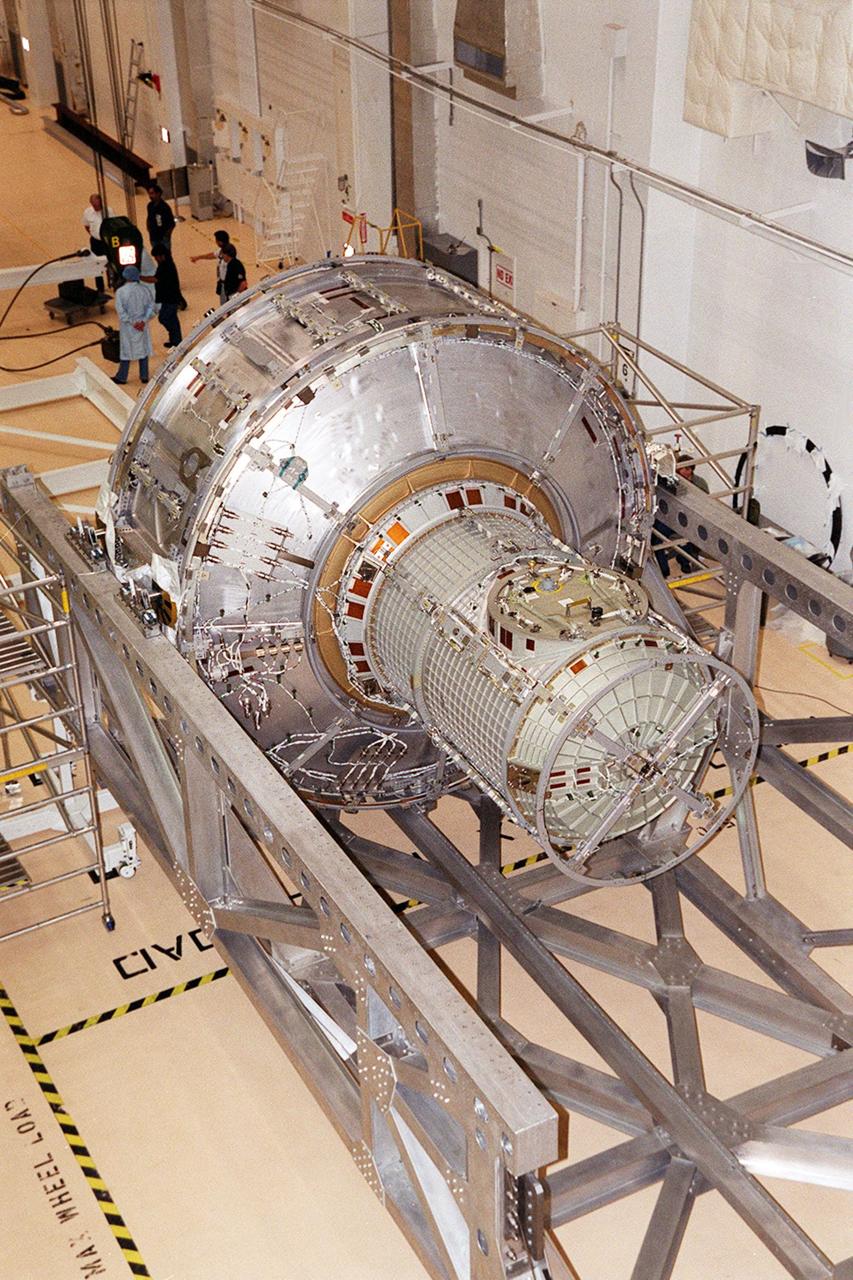
The Joint Airlock Module waits on a stand in the Operations and Checkout Building to be lifted and moved into a vacuum chamber for testing. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module is specially designed to accommodate both suits, providing a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
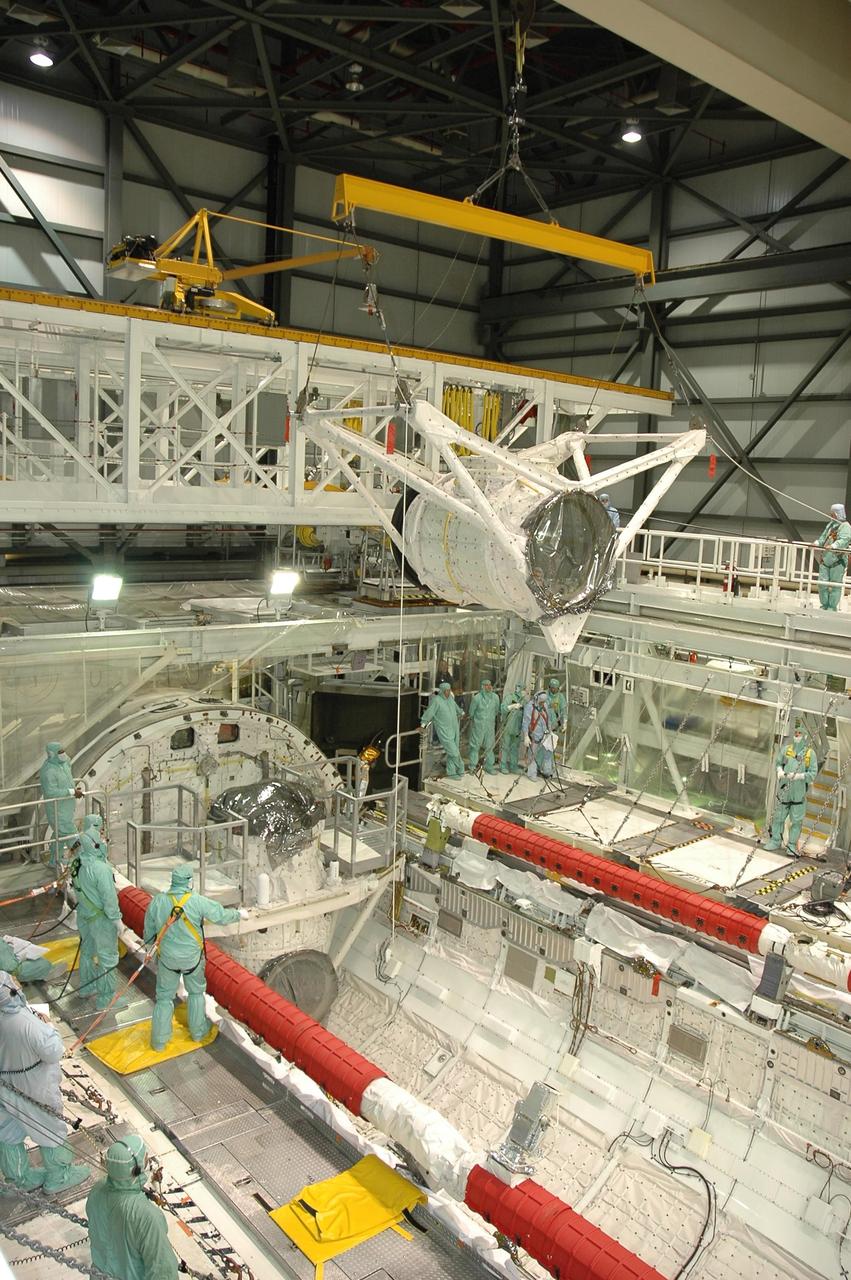

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the crew airlock module is suspended above Endeavour's payload bay. The module will be lowered into the payload bay and installed. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
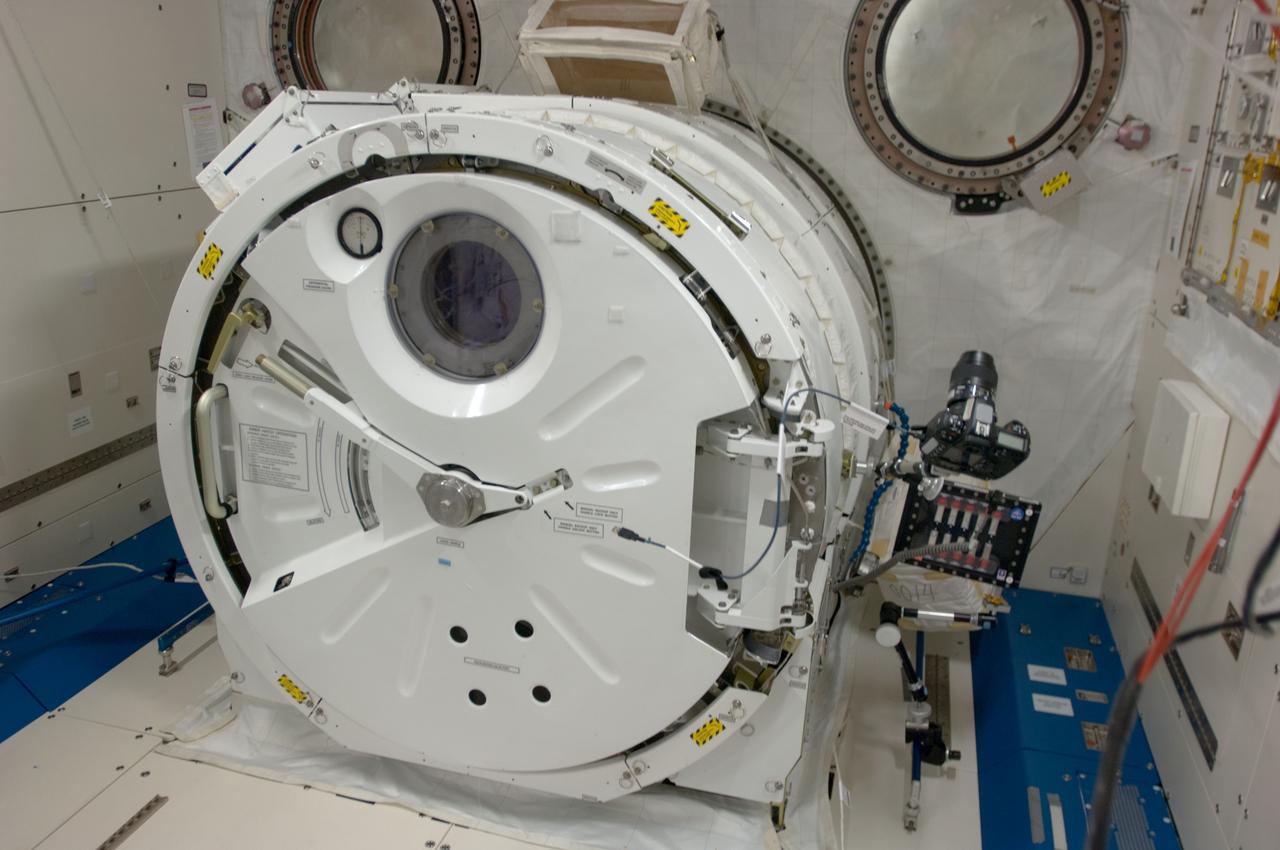

View of internal airlock (A/L) in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Pressurized Module (JPM). Photo was taken during Expedition 34.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-120 Mission Specialist Michael Foreman looks over the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Pressurized Module. Known as Kibo, the JEM consists of six components: two research facilities -- the Pressurized Module and Exposed Facility; a Logistics Module attached to each of them; a Remote Manipulator System; and an Inter-Orbit Communication System unit. Kibo also has a scientific airlock through which experiments are transferred and exposed to the external environment of space. The various components of JEM will be assembled in space over the course of three Space Shuttle missions. The STS-120 mission will deliver the second of three Station connecting modules, Node 2, which attaches to the end of U.S. Lab. It will provide attach locations for the Japanese laboratory, European laboratory, the Centrifuge Accommodation Module and later Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules. The addition of Node 2 will complete the U.S. core of the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-120 Mission Specialist Piers Sellers looks over the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Pressurized Module. Known as Kibo, the JEM consists of six components: two research facilities -- the Pressurized Module and Exposed Facility; a Logistics Module attached to each of them; a Remote Manipulator System; and an Inter-Orbit Communication System unit. Kibo also has a scientific airlock through which experiments are transferred and exposed to the external environment of space. The various components of JEM will be assembled in space over the course of three Space Shuttle missions. The STS-120 mission will deliver the second of three Station connecting modules, Node 2, which attaches to the end of U.S. Lab. It will provide attach locations for the Japanese laboratory, European laboratory, the Centrifuge Accommodation Module and later Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules. The addition of Node 2 will complete the U.S. core of the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-120 Mission Specialists Piers Sellers and Michael Foreman look at the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Pressurized Module located in the Space Station Processing Facility. Known as Kibo, the JEM consists of six components: two research facilities -- the Pressurized Module and Exposed Facility; a Logistics Module attached to each of them; a Remote Manipulator System; and an Inter-Orbit Communication System unit. Kibo also has a scientific airlock through which experiments are transferred and exposed to the external environment of space. The various components of JEM will be assembled in space over the course of three Space Shuttle missions. The STS-120 mission will deliver the second of three Station connecting modules, Node 2, which attaches to the end of U.S. Lab. It will provide attach locations for the JEM, European laboratory, the Centrifuge Accommodation Module and later Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules. The addition of Node 2 will complete the U.S. core of the International Space Station.
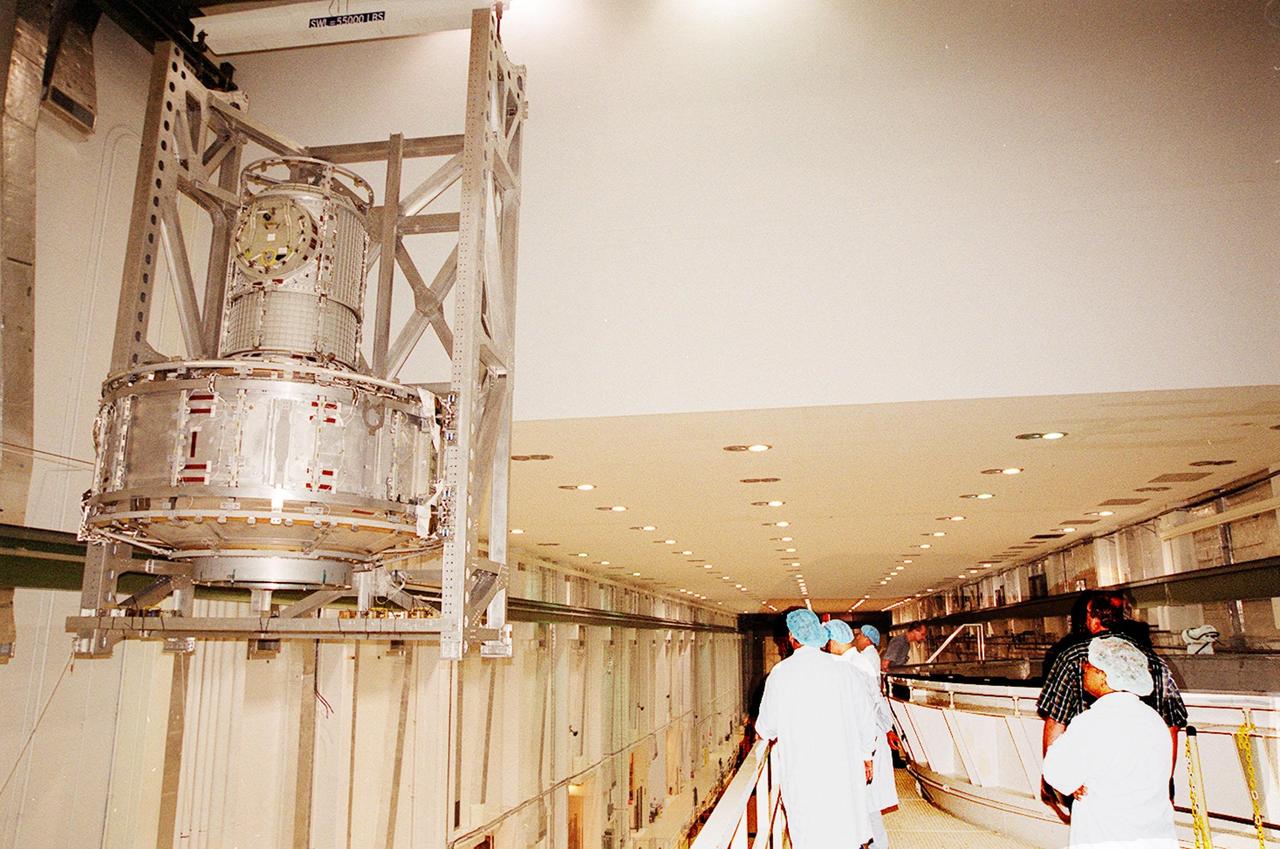

The Joint Airlock Module swings into position near the top of the Operations and Checkout Building to move toward the vacuum chamber at right. Workers alongside the chamber watch the airlock’s progress. The airlock is being tested for leaks. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module provides a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
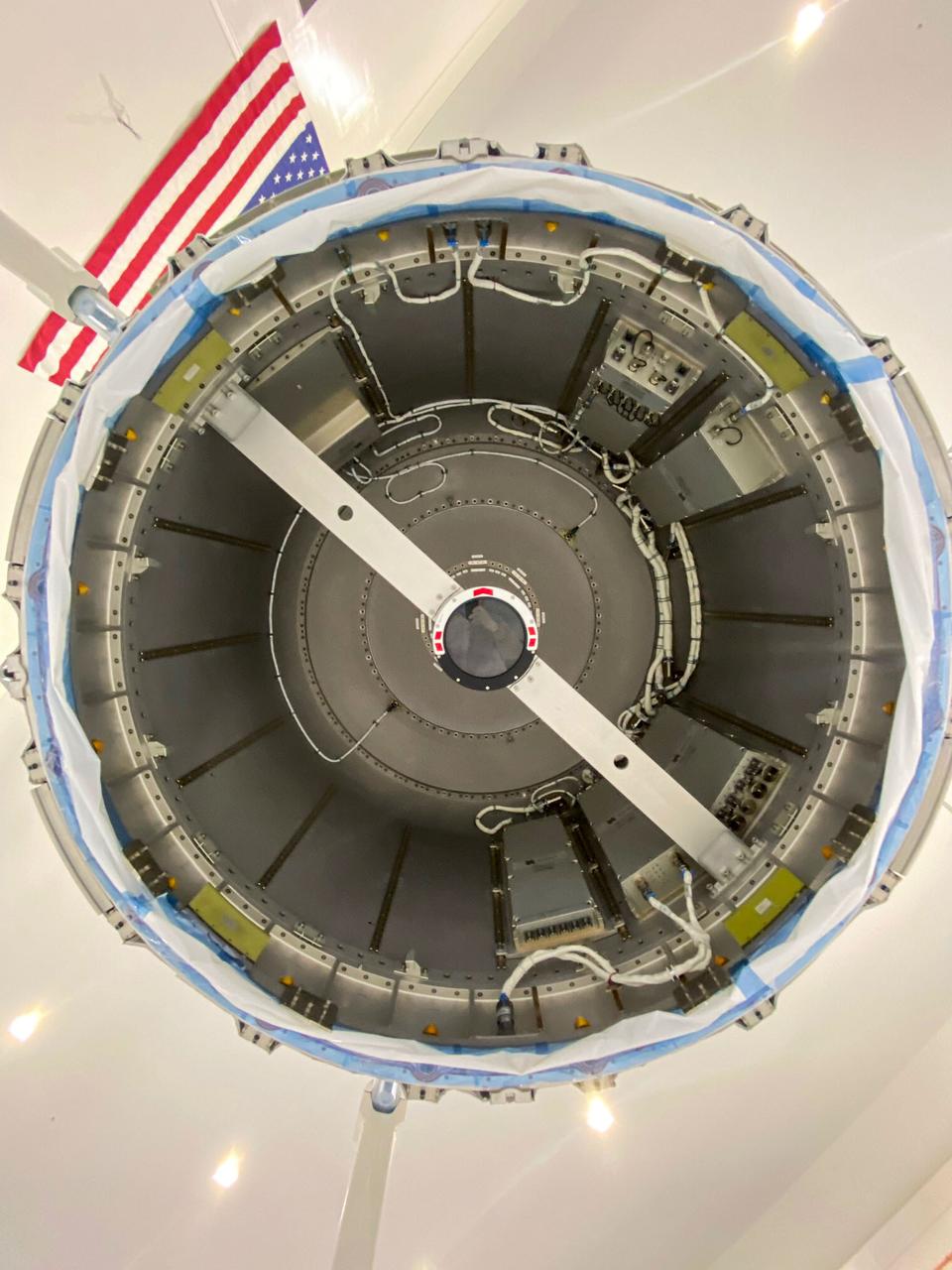

jsc2020e044492 (10/6/2020) —- A preflight view of the Nanoracks Airlock. The Nanoracks Bishop Airlock (Nanoracks Airlock) is the first-ever commercially owned and operated airlock on the International Space Station. It provides a variety of capabilities including jettisoning of payloads such as Cubesats, deployment of external payloads, support for small exterior payloads and locker-sized internal payloads, recovery of external on-orbit replaceable units (ORUs), and the ability to move hardware outside in support of extravehicular activities (EVAs). It is approximately five times larger than the Japanense Experiment Module (JEM) Airlock so it can accommodate more and larger payloads. The Airlock’s capabilities support many different types of scientific investigations.
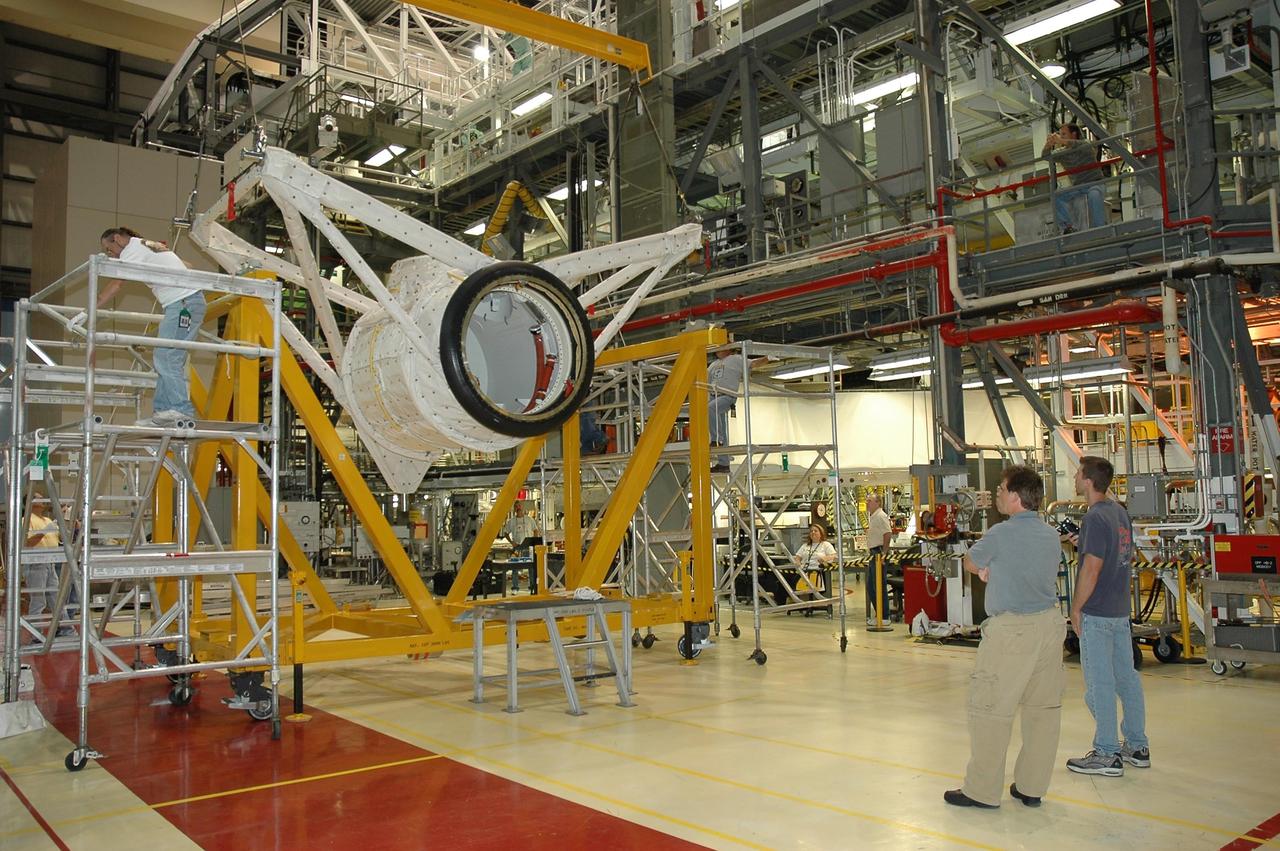

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the crew airlock module off its stand. The airlock is being moved to install it in Endeavour's payload bay. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
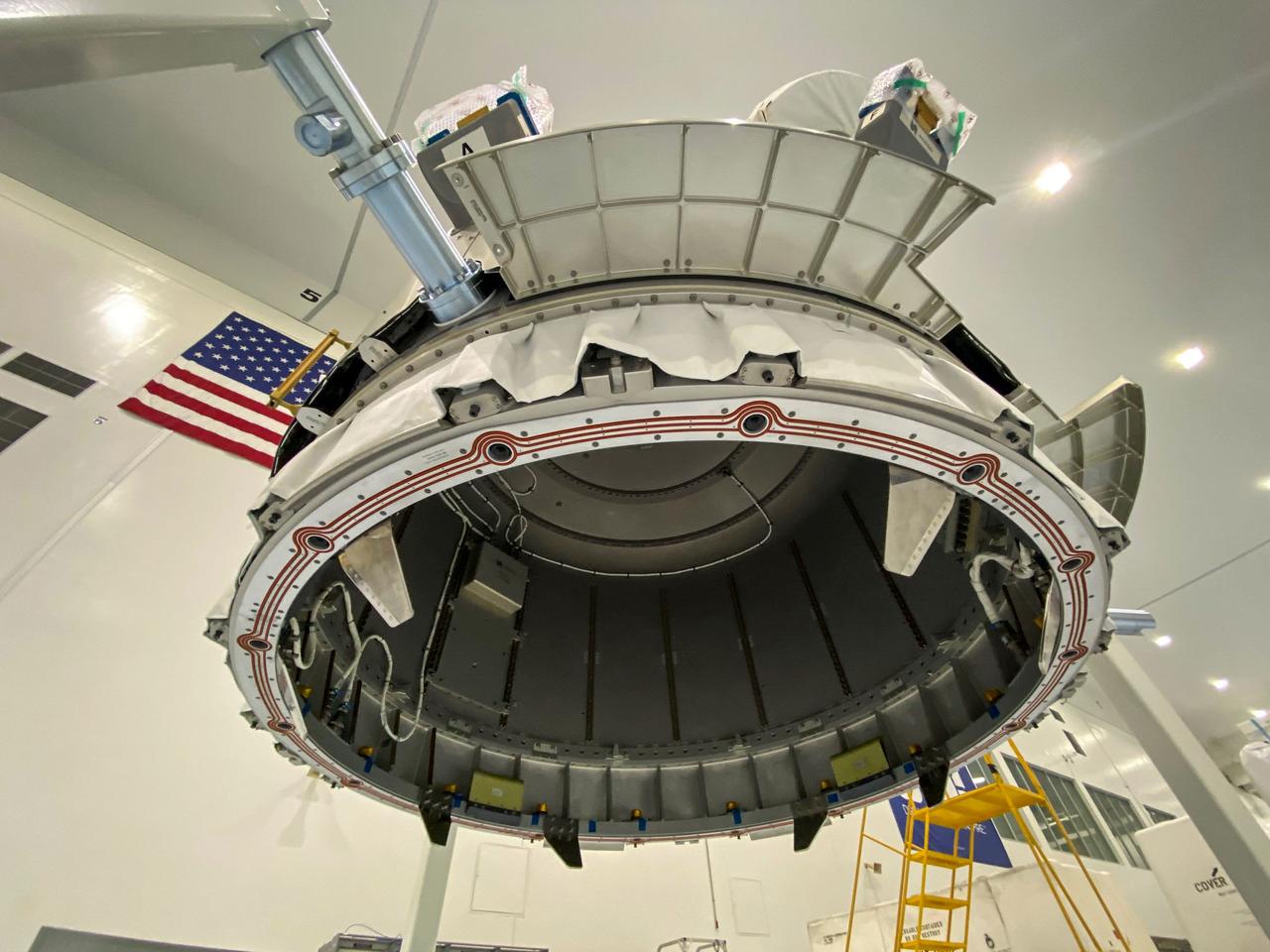

jsc2020e044494 (10/1/2020) --- A preflight view of the Nanoracks Airlock. The Nanoracks Bishop Airlock (Nanoracks Airlock) is the first-ever commercially owned and operated airlock on the International Space Station. It provides a variety of capabilities including jettisoning of payloads such as Cubesats, deployment of external payloads, support for small exterior payloads and locker-sized internal payloads, recovery of external on-orbit replaceable units (ORUs), and the ability to move hardware outside in support of extravehicular activities (EVAs). It is approximately five times larger than the Japanense Experiment Module (JEM) Airlock so it can accommodate more and larger payloads. The Airlock’s capabilities support many different types of scientific investigations.
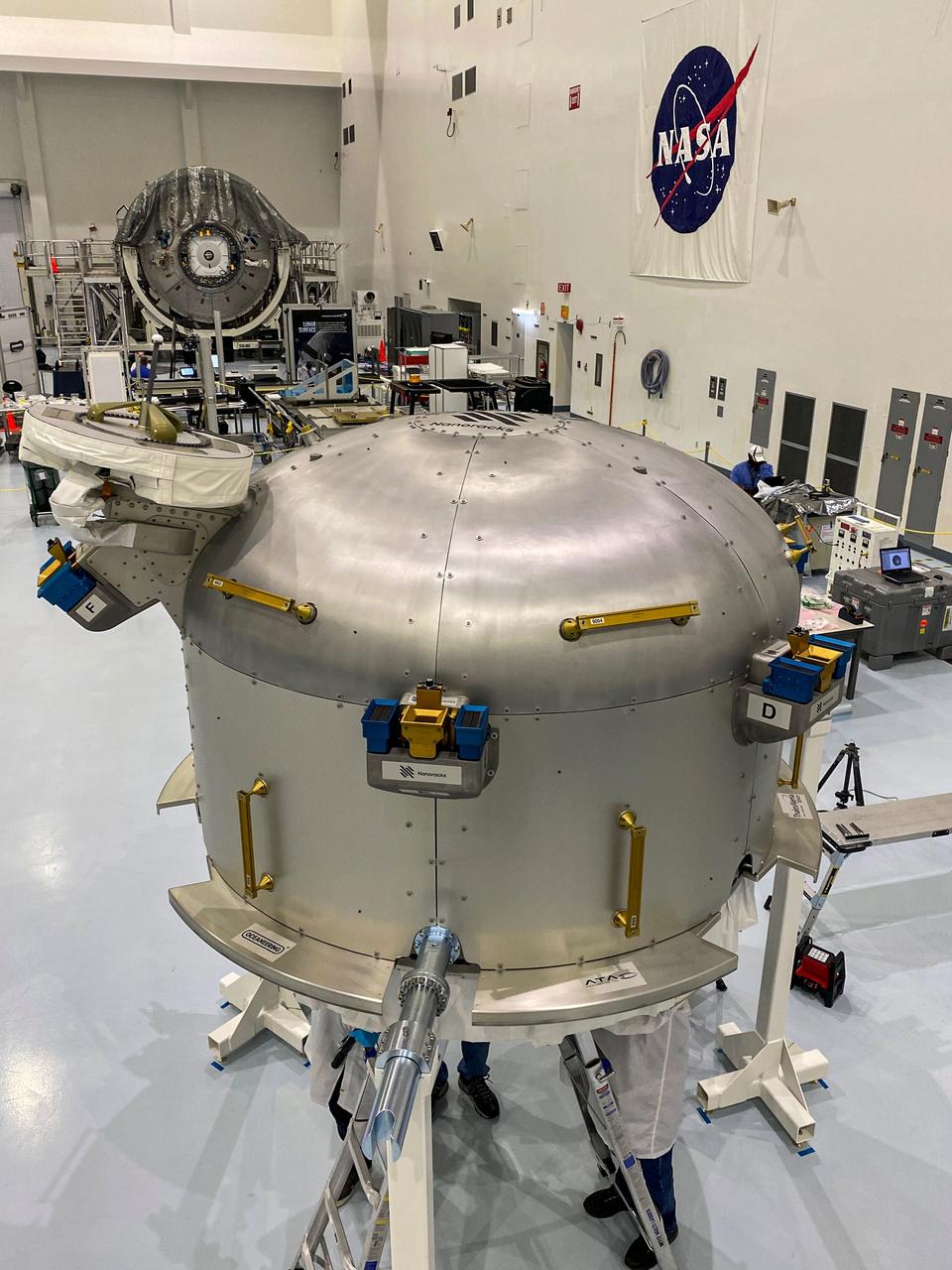

jsc2020e044491 (10/5/2020) —- A preflight view of the Nanoracks Airlock. The Nanoracks Bishop Airlock (Nanoracks Airlock) is the first-ever commercially owned and operated airlock on the International Space Station. It provides a variety of capabilities including jettisoning of payloads such as Cubesats, deployment of external payloads, support for small exterior payloads and locker-sized internal payloads, recovery of external on-orbit replaceable units (ORUs), and the ability to move hardware outside in support of extravehicular activities (EVAs). It is approximately five times larger than the Japanense Experiment Module (JEM) Airlock so it can accommodate more and larger payloads. The Airlock’s capabilities support many different types of scientific investigations.
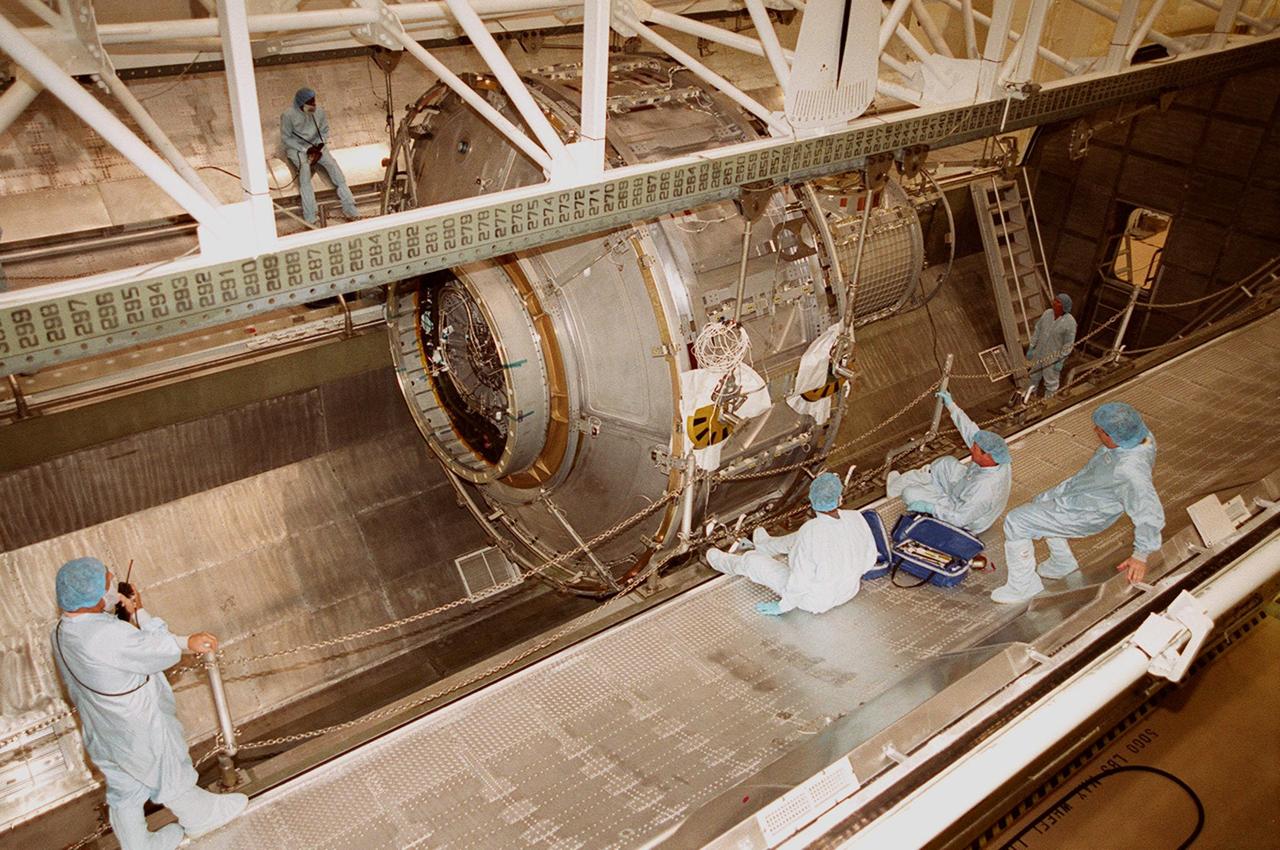
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers at right maneuver to their feet as the Joint Airlock Module is lowered into the payload canister. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
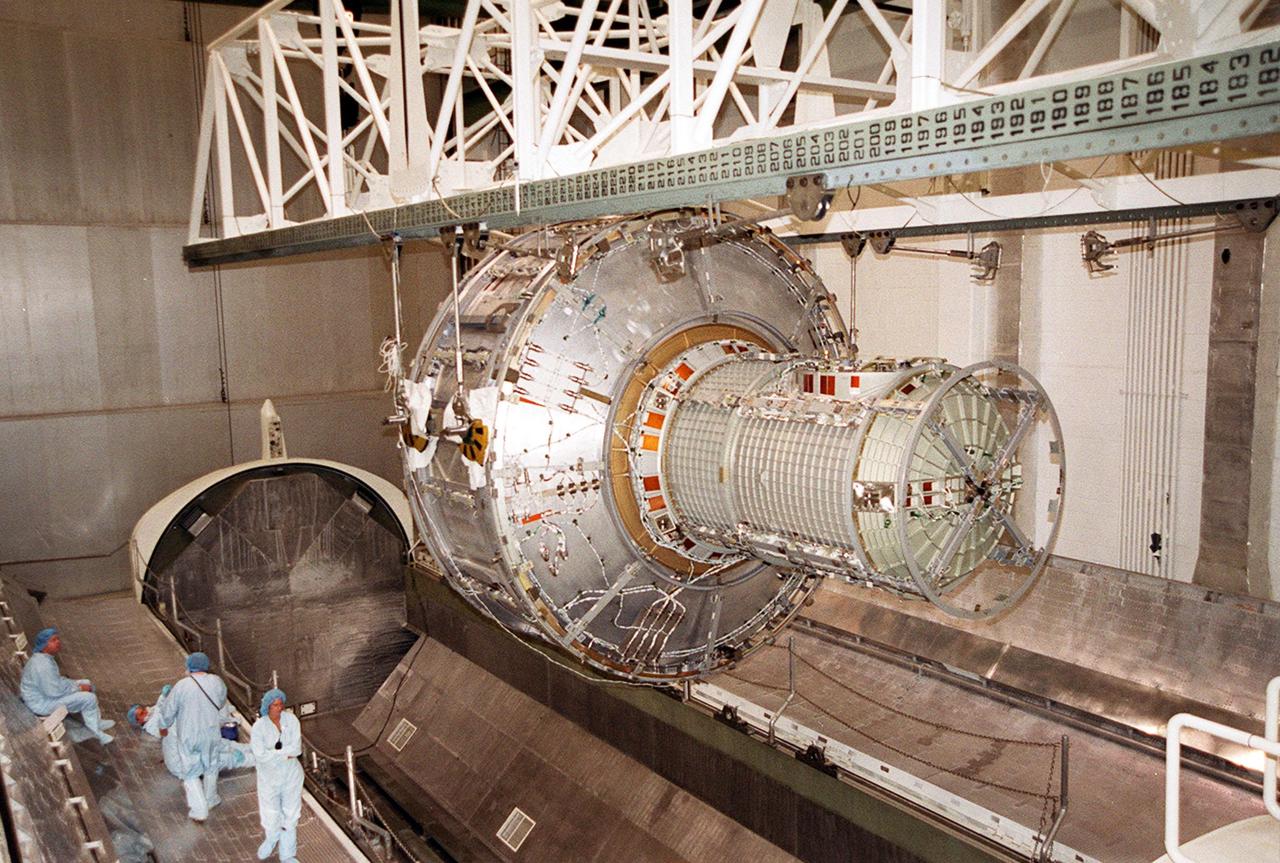
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Joint Airlock Module, suspended from an overhead crane, moves toward the payload canister below. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
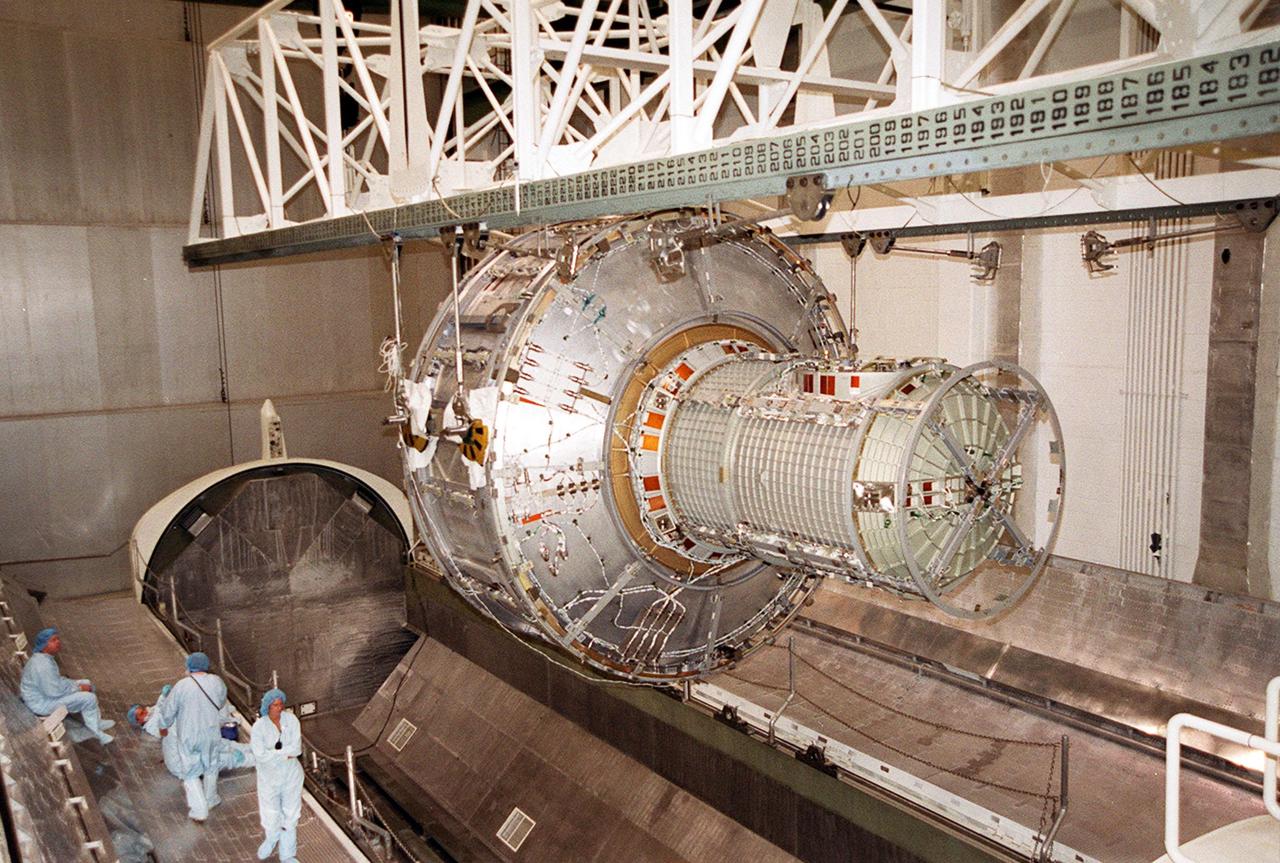
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Joint Airlock Module, suspended from an overhead crane, moves toward the payload canister below. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
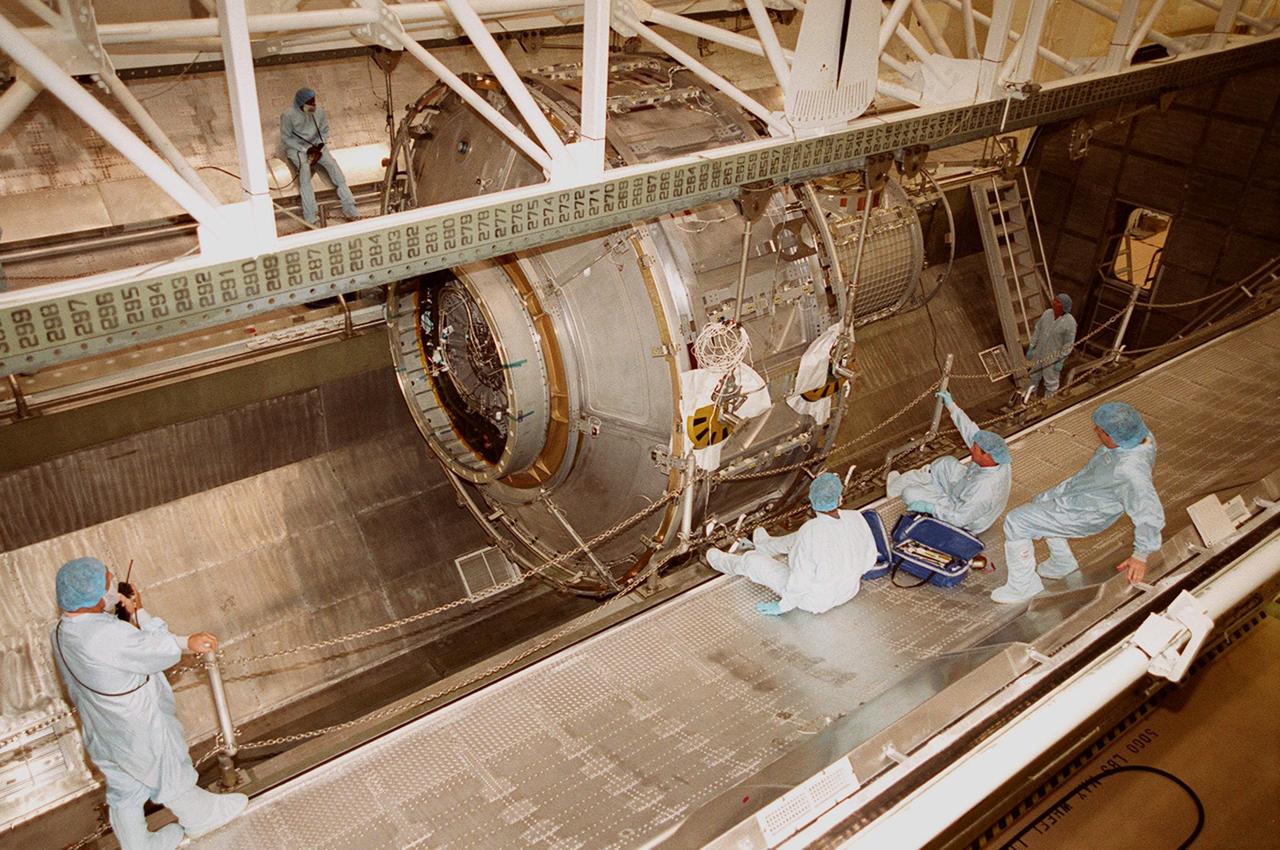
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers at right maneuver to their feet as the Joint Airlock Module is lowered into the payload canister. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
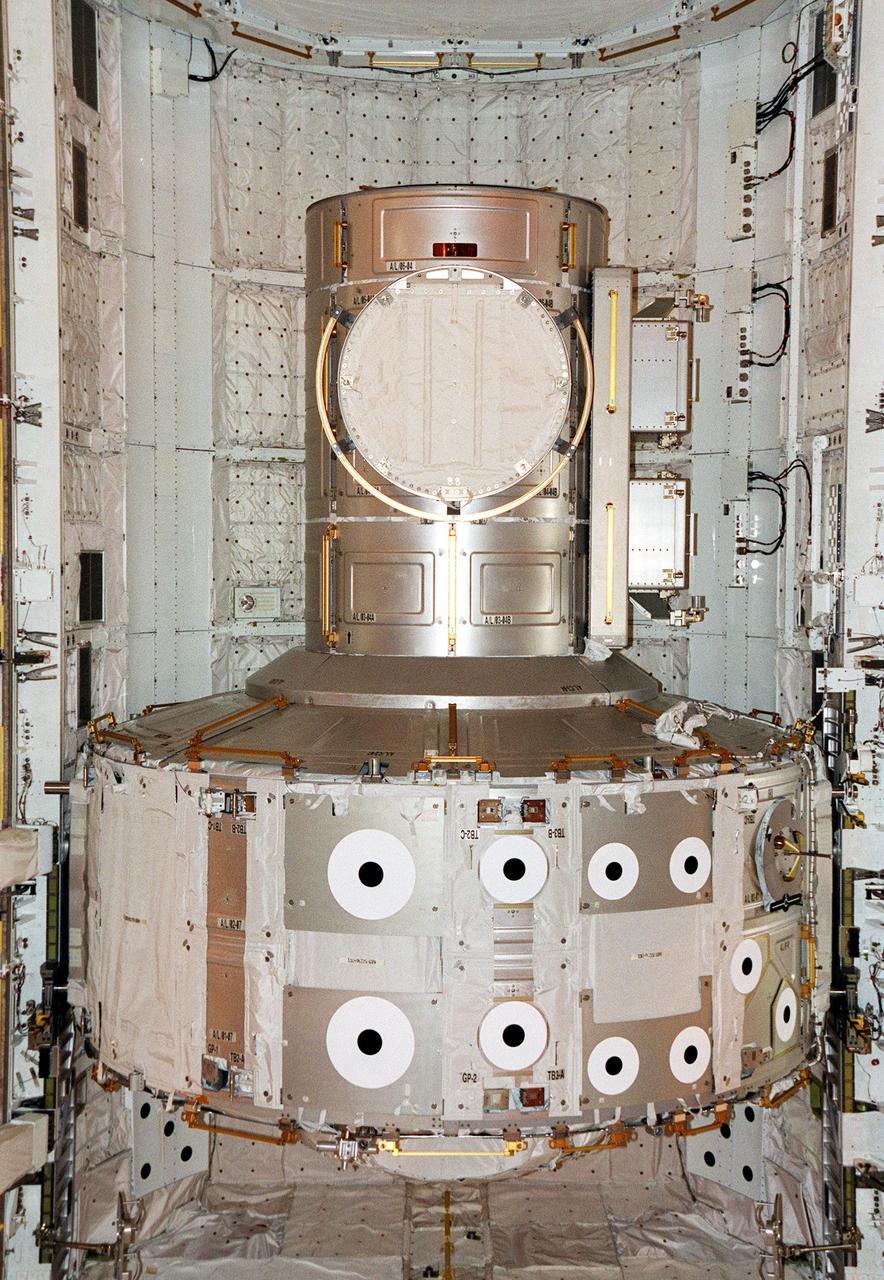
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Joint Airlock Module rests inside Atlantis’s payload bay. The module is the primary payload on mission STS-104, scheduled to be launched July 12 for the International Space Station. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Once installed and activated, the Airlock becomes the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
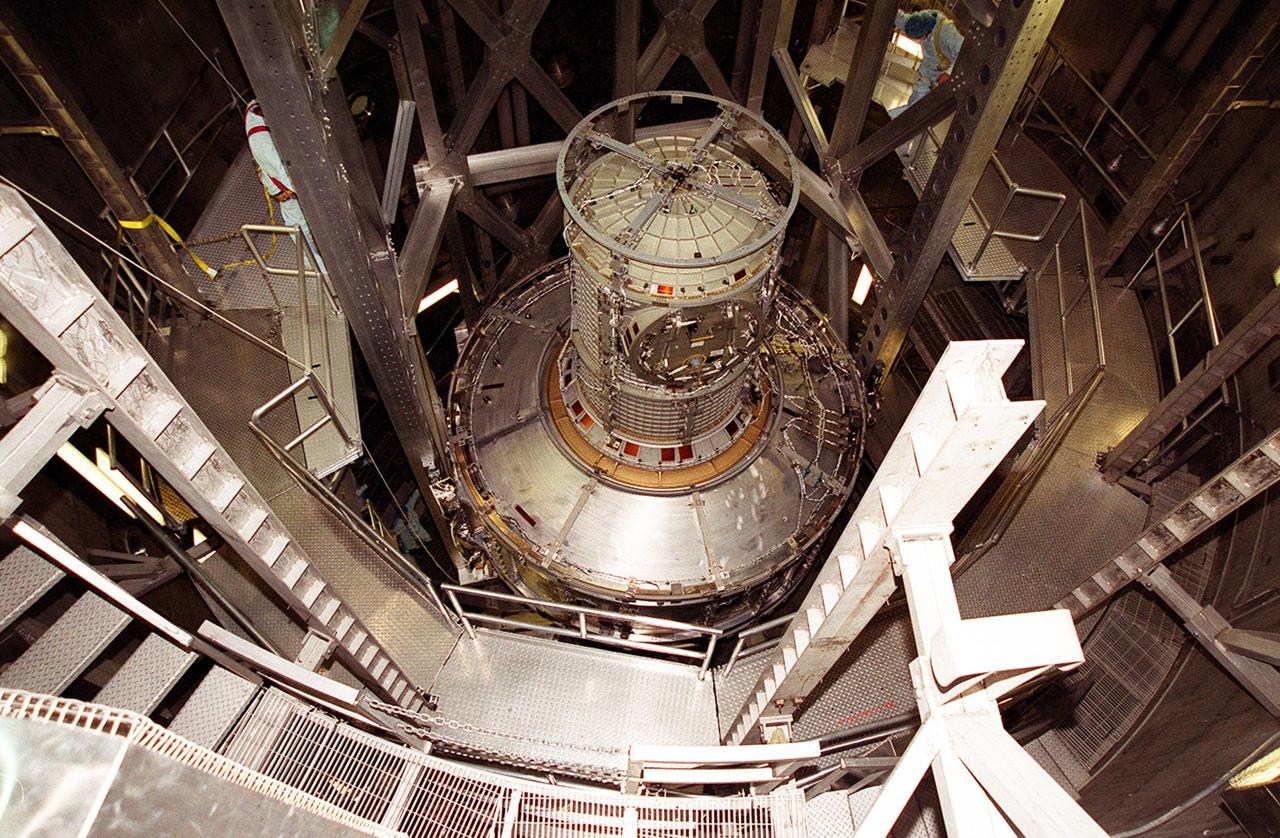
The Joint Airlock Module is fully lowered into the vacuum chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building. Workers on either side check its position. The airlock is being tested for leaks. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module provides a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
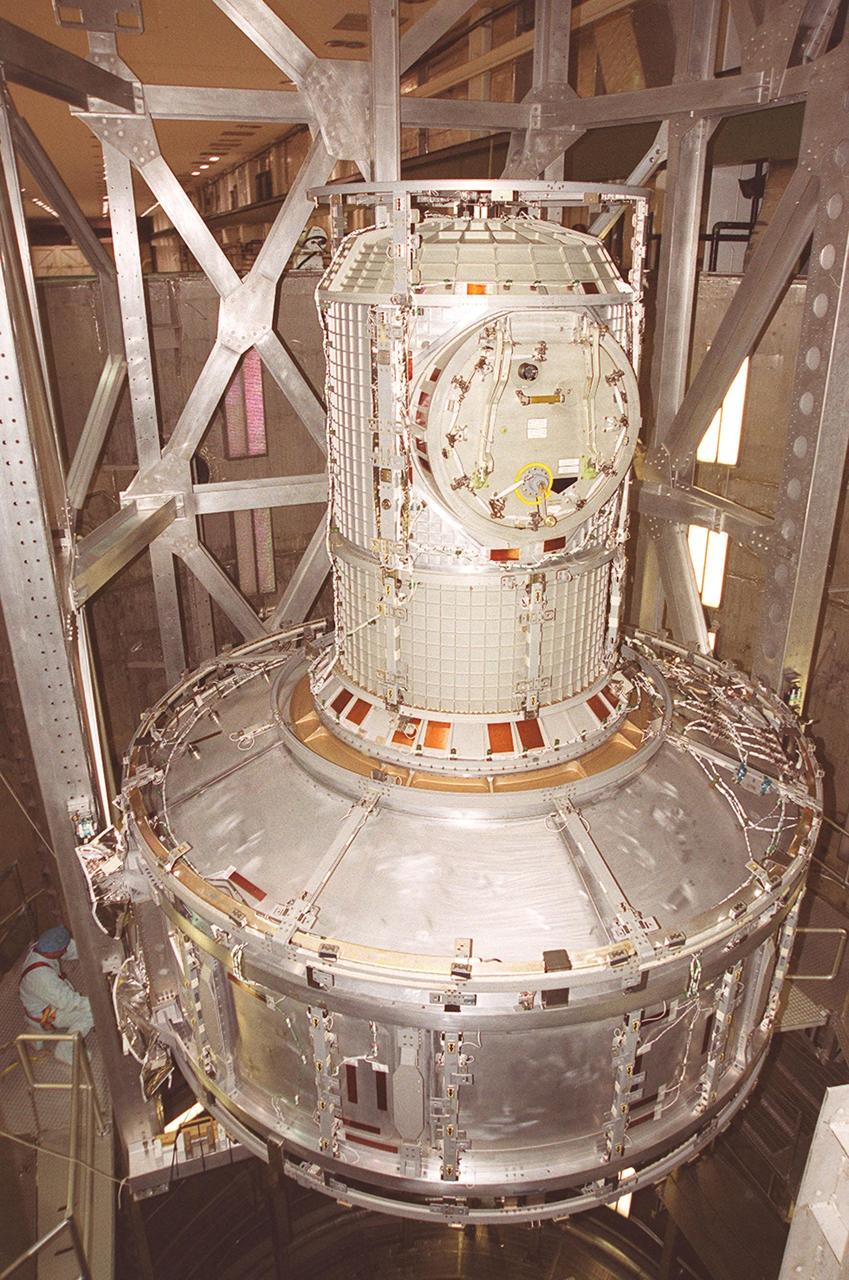
Workers inside the vacuum chamber in the Operations and Checkout Building watch as an overhead crane lowers the Joint Airlock Module inside. The airlock is being tested for leaks. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module provides a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
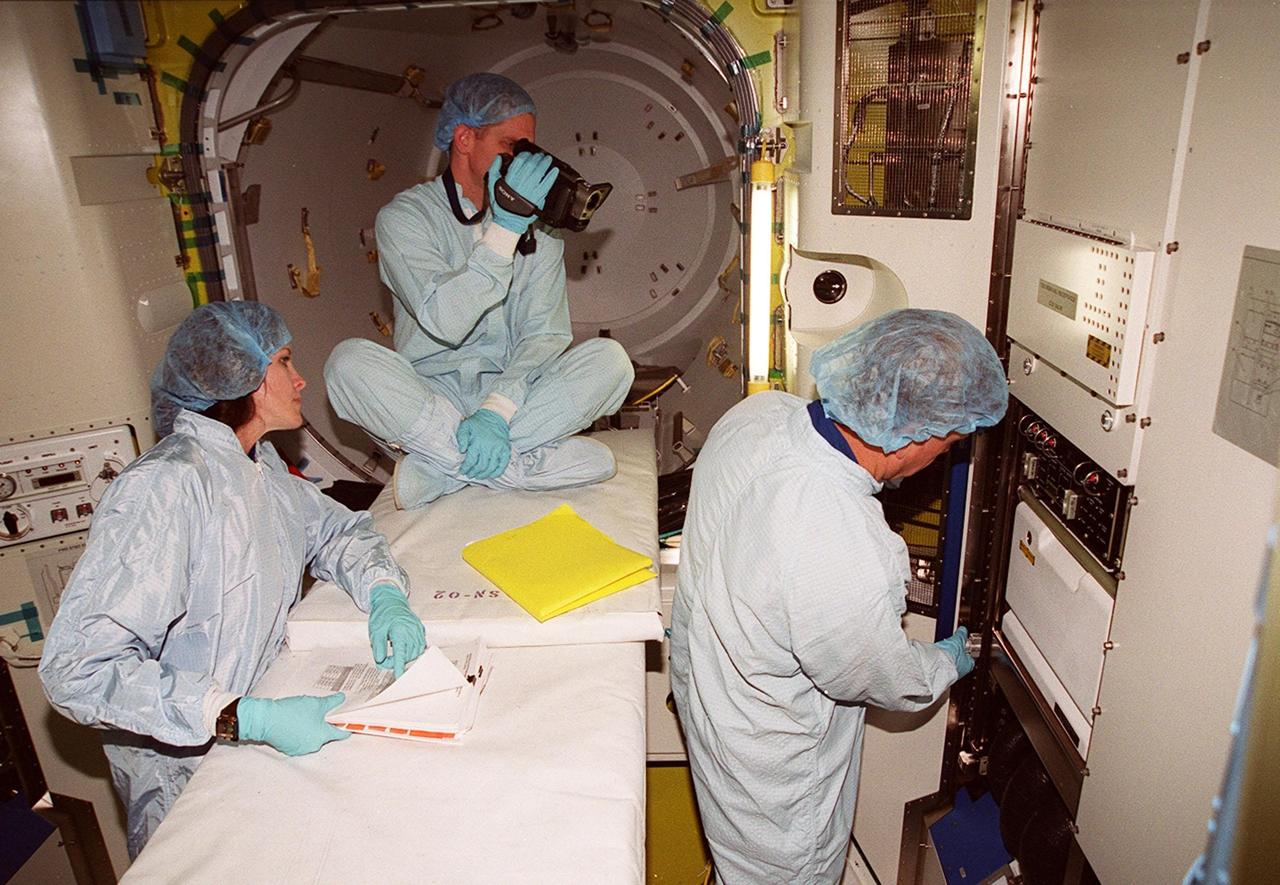
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-104 crew look over equipment inside the equipment lock component of the Joint Airlock Module. At left is Mission Specialist Janet L. Kavandi, and at right Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which also comprises a crew lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
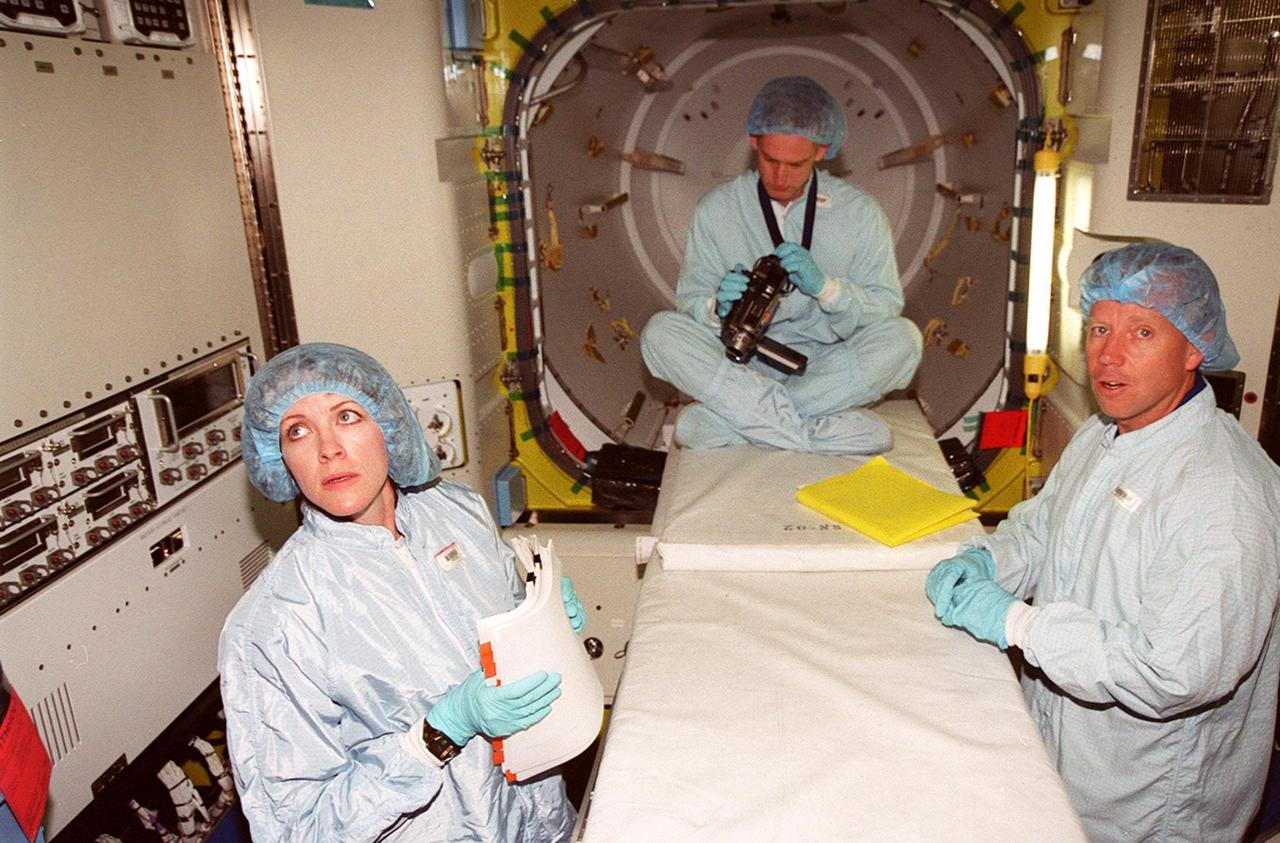
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-104 crew look over equipment inside the equipment lock component of the Joint Airlock Module. At left is Mission Specialist Janet L. Kavandi, and at right Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which also comprises a crew lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
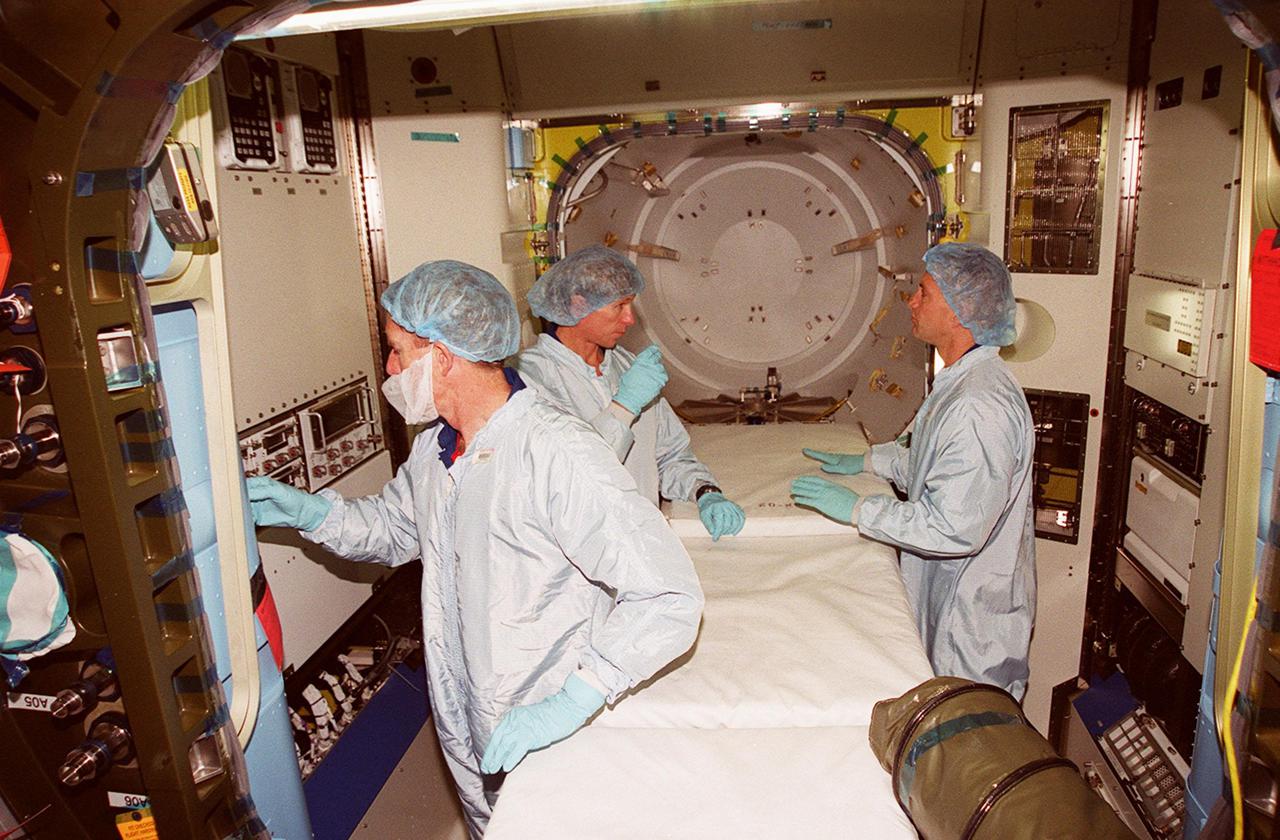

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-104 crew look over equipment inside the equipment lock component of the Joint Airlock Module. At left is Mission Specialist Janet L. Kavandi, and at right Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which also comprises a crew lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module

This artist's concept depicts the separation of the Skylab payload shroud. The payload shroud was both an environmental shield and an aerodynamic fairing. Attached to the forward end of the fixed airlock shroud, it protected the airlock, the docking adapter, and the solar observatory before and during launch. It also provided structural support for the solar observatory in the launch configuration. The payload shroud was jettisoned once Skylab reached orbit after separation of the S-II second stage of the Saturn V vehicle. Five major assemblies clustered together made up the orbiting space station called Skylab. The largest of these was the orbital workshop, that housed the crew quarters and a major experiment area. The airlock module, attached to the forward end of the workshop, enabled crewmembers to make excursions outside Skylab. The docking adapter, attached to the forward end of the airlock module, provided the docking port for the Apollo command and service module. The Apollo Telescope Mount was the first marned astronomical observatory designed for solar research from Earth orbit.
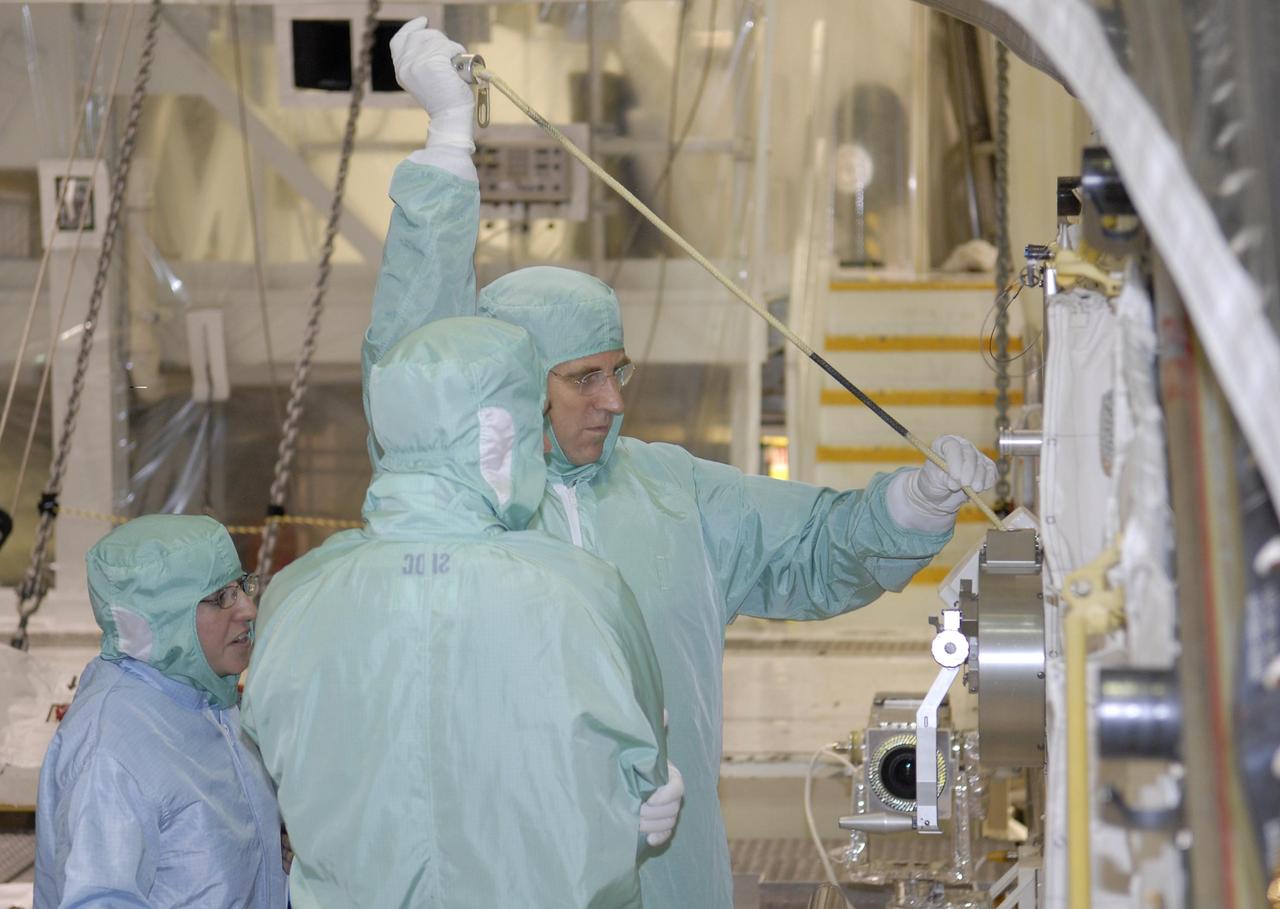

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During crew equipment interface test activities at KSC, STS-118 Mission Specialist Dr. Dafydd Williams (right) maneuvers the latch on the crew airlock module. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. The STS-118 mission will be delivering the third starboard truss segment, the ITS S5, to the International Space Station, as well as the SPACEHAB single cargo module filled with supplies and equipment. Launch aboard Space Shuttle Endeavour is targeted for Aug. 9. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
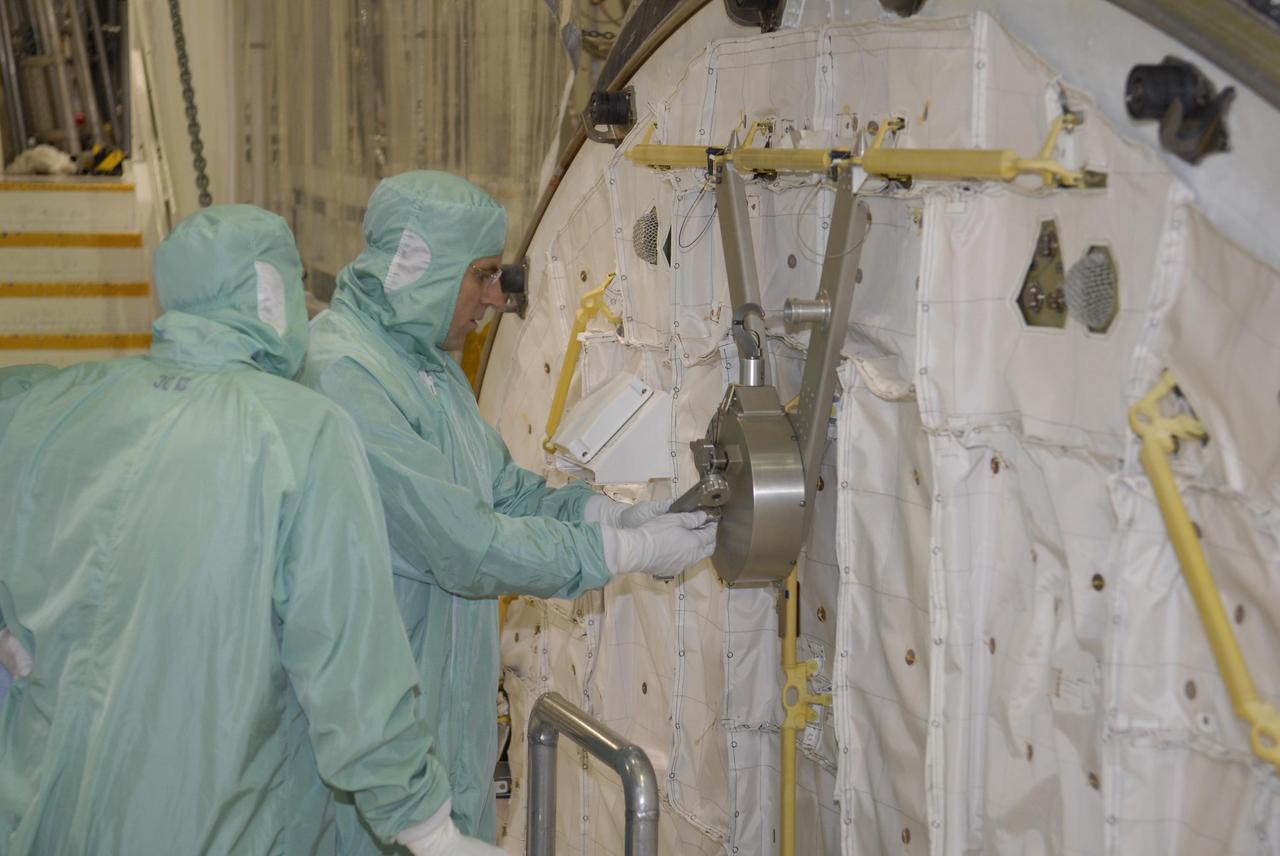

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During crew equipment interface test activities at KSC, STS-118 Mission Specialist Dr. Dafydd Williams (right) maneuvers the latch on the crew airlock module. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. The STS-118 mission will be delivering the third starboard truss segment, the ITS S5, to the International Space Station, as well as the SPACEHAB single cargo module filled with supplies and equipment. Launch aboard Space Shuttle Endeavour is targeted for Aug. 9. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
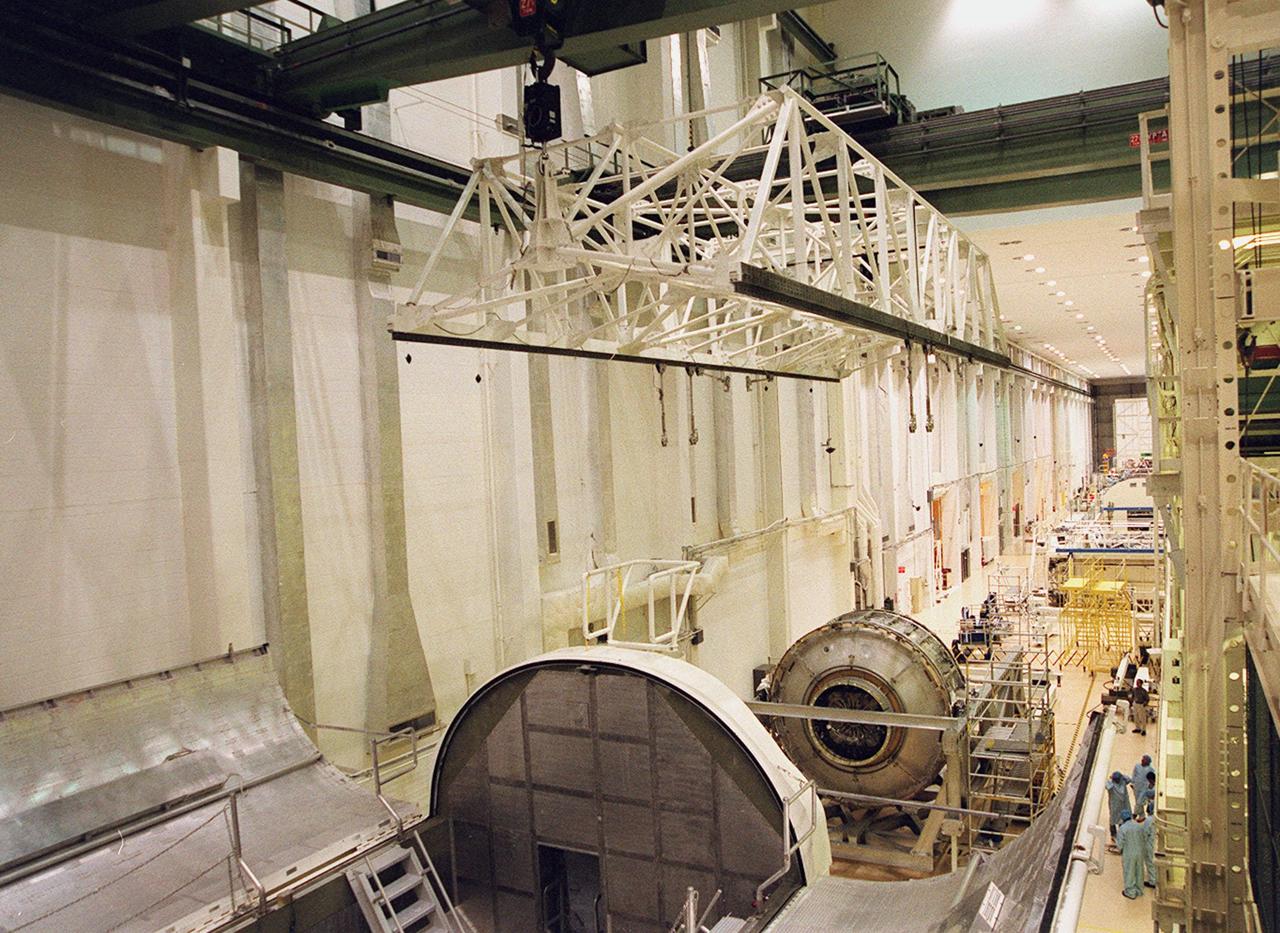
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An overhead crane in the Operations and Checkout Building hovers over the Joint Airlock Module (right) that it will lift and place in the payload canister in the foreground. The canister will transfer the module to the Space Station Processing Facility where it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
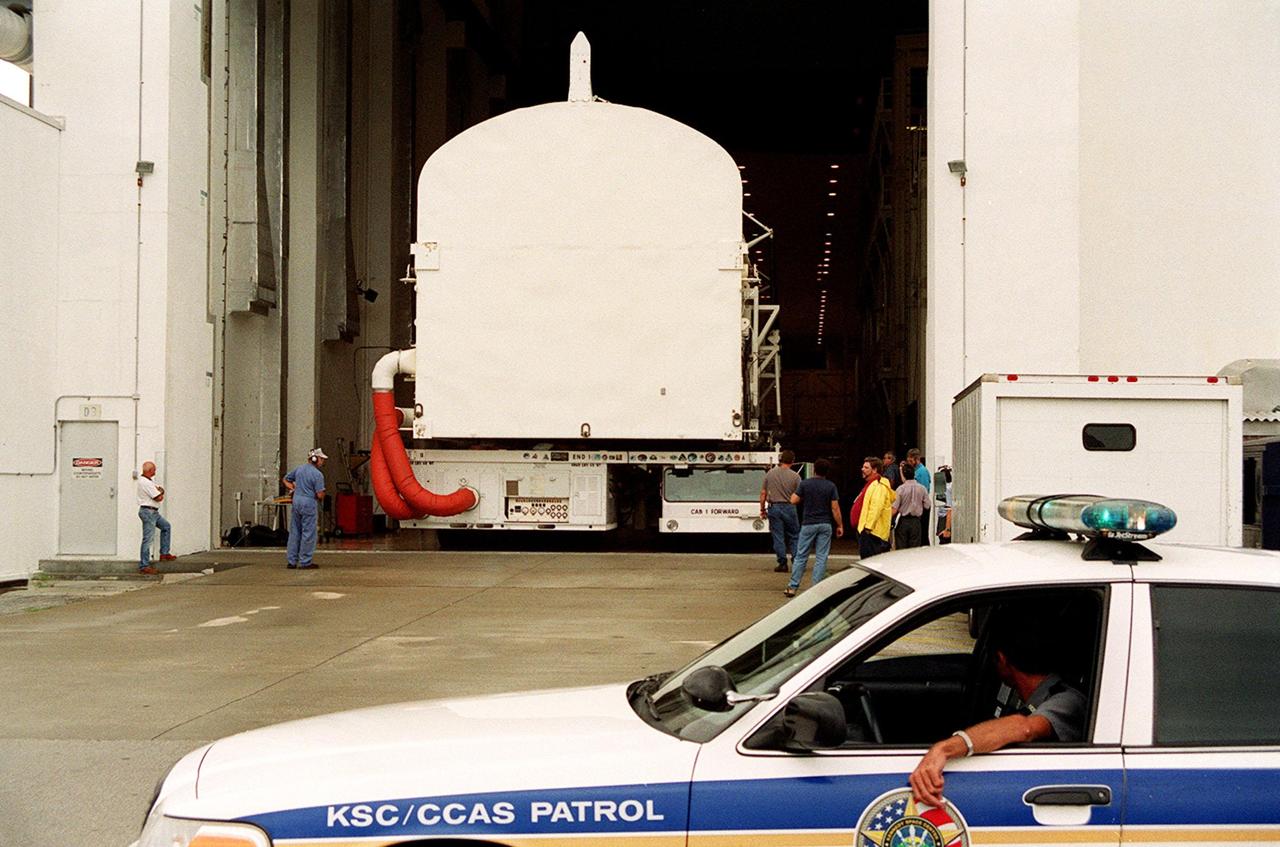

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload canister, with the Joint Airlock Module inside, backs out of the Operations and Checkout Building for a short trip to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload canister, with the Joint Airlock Module inside, backs out of the Operations and Checkout Building for a short trip to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
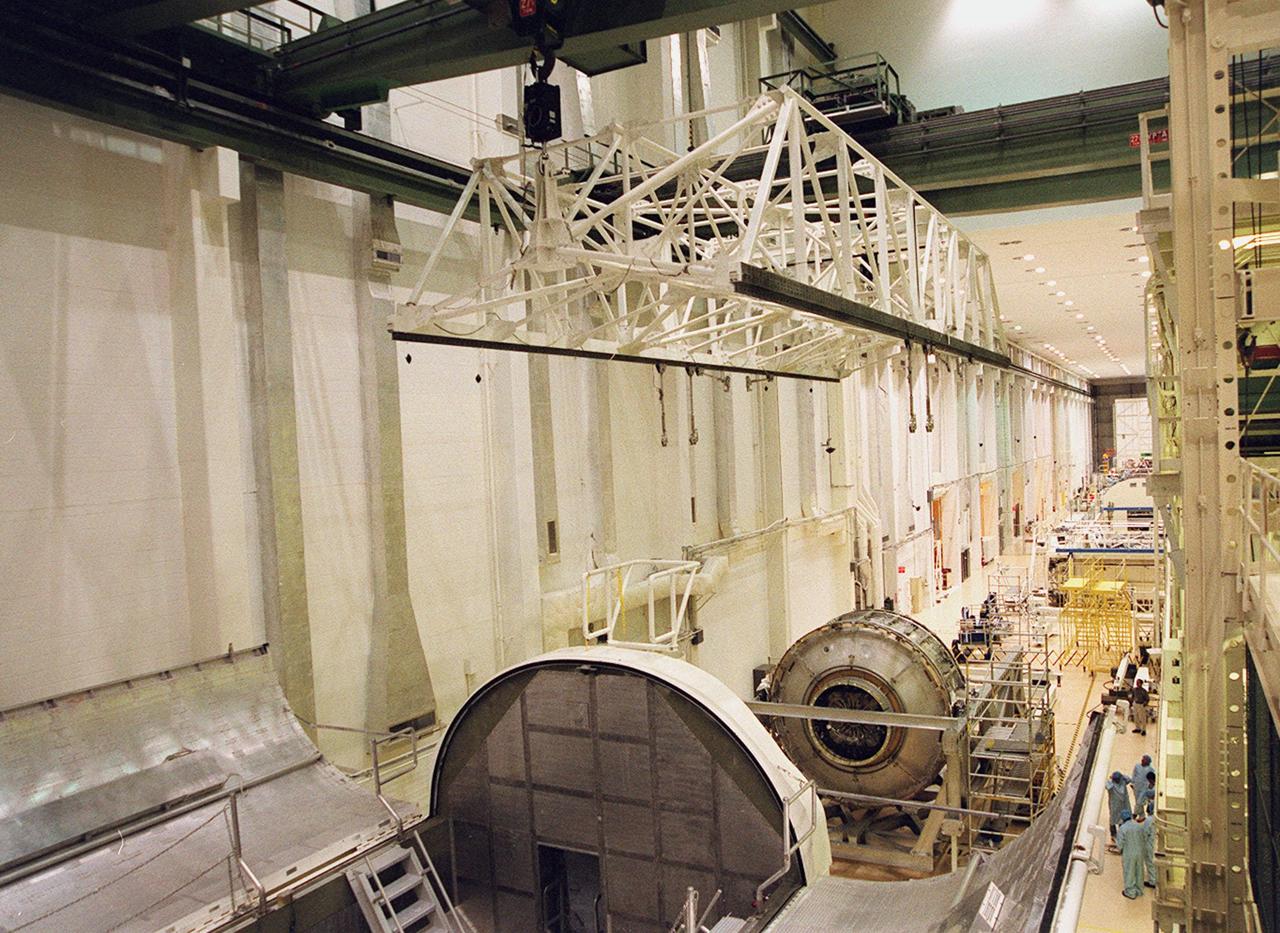
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An overhead crane in the Operations and Checkout Building hovers over the Joint Airlock Module (right) that it will lift and place in the payload canister in the foreground. The canister will transfer the module to the Space Station Processing Facility where it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
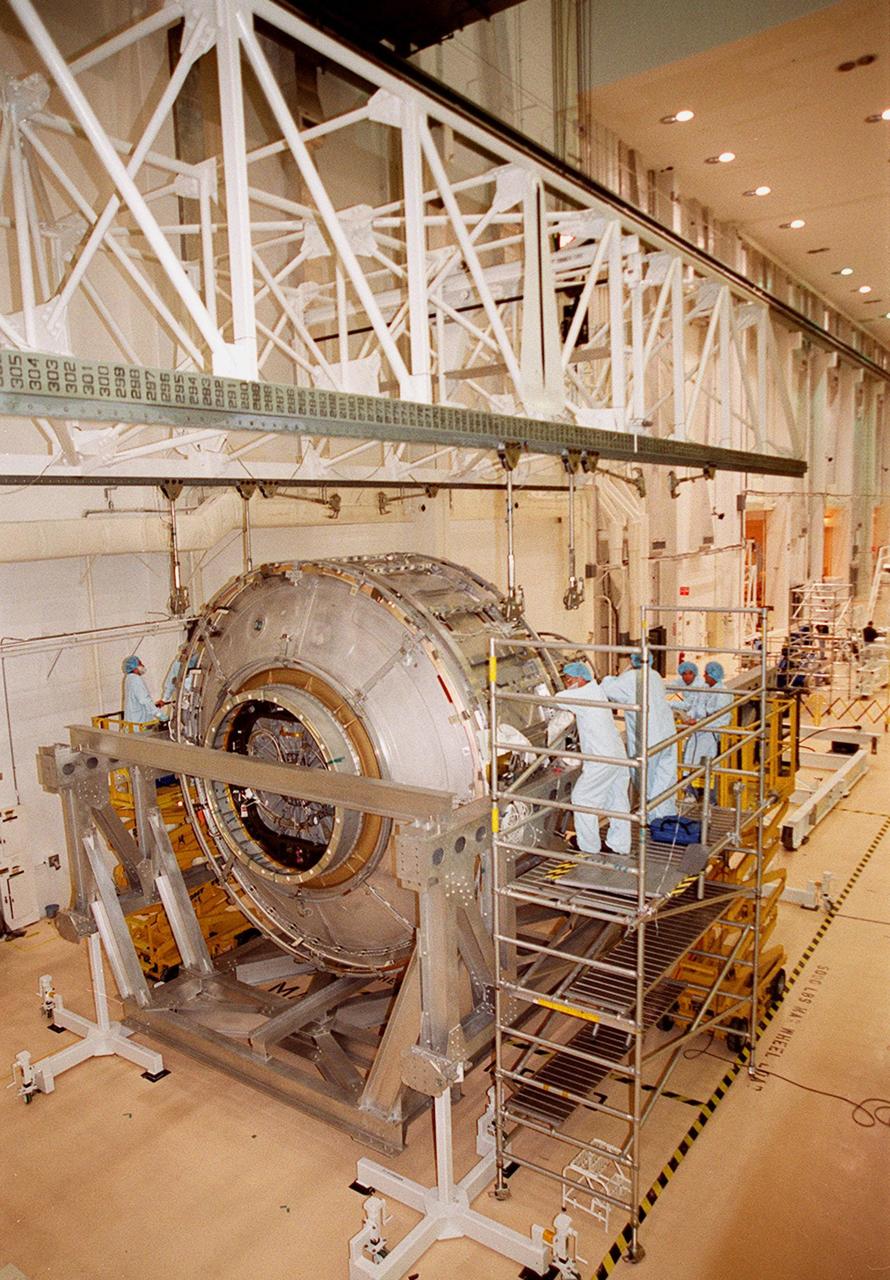
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Operations and Checkout Building keep watch as an overhead crane is lowered toward the Joint Airlock Module that it will lift and place in the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
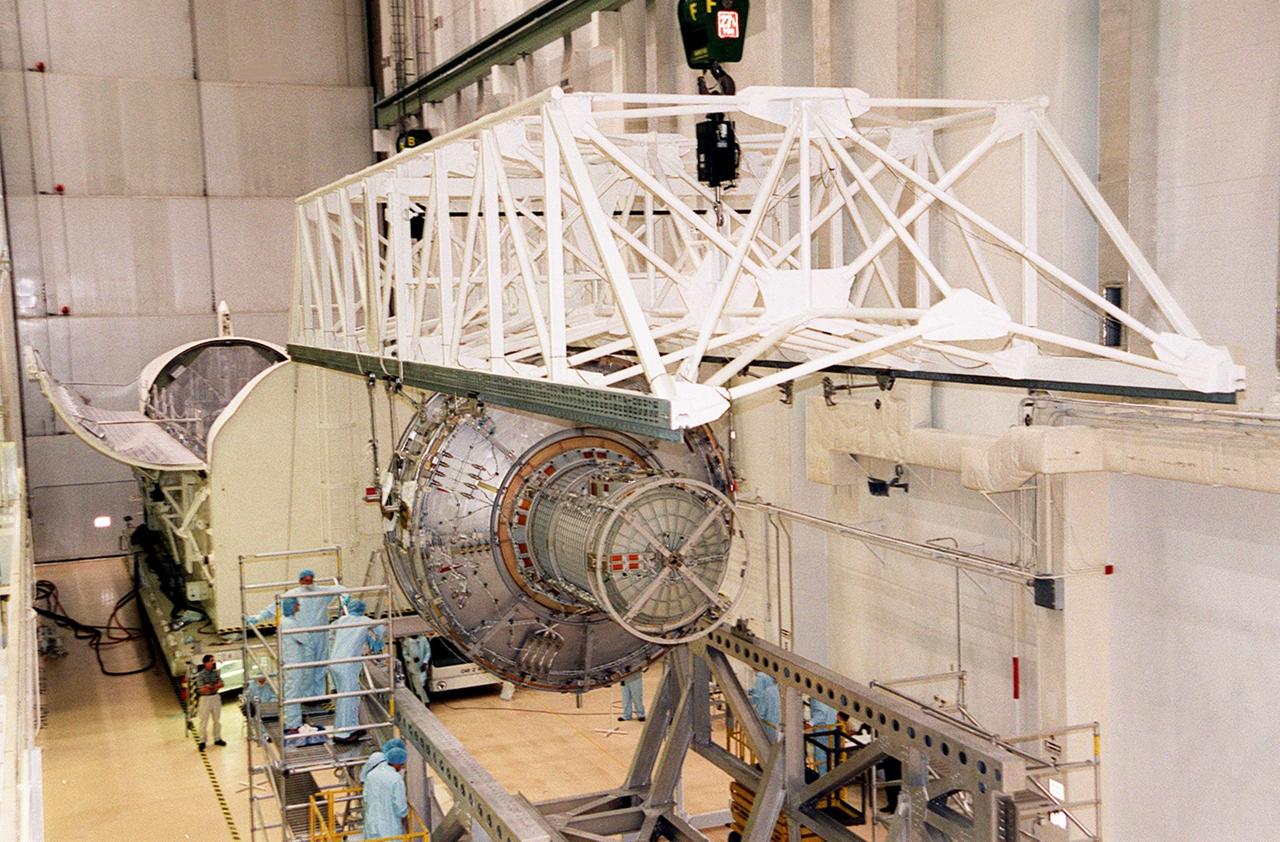
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, an overhead crane lifts the Joint Airlock Module to move and place it into the payload canister at left for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
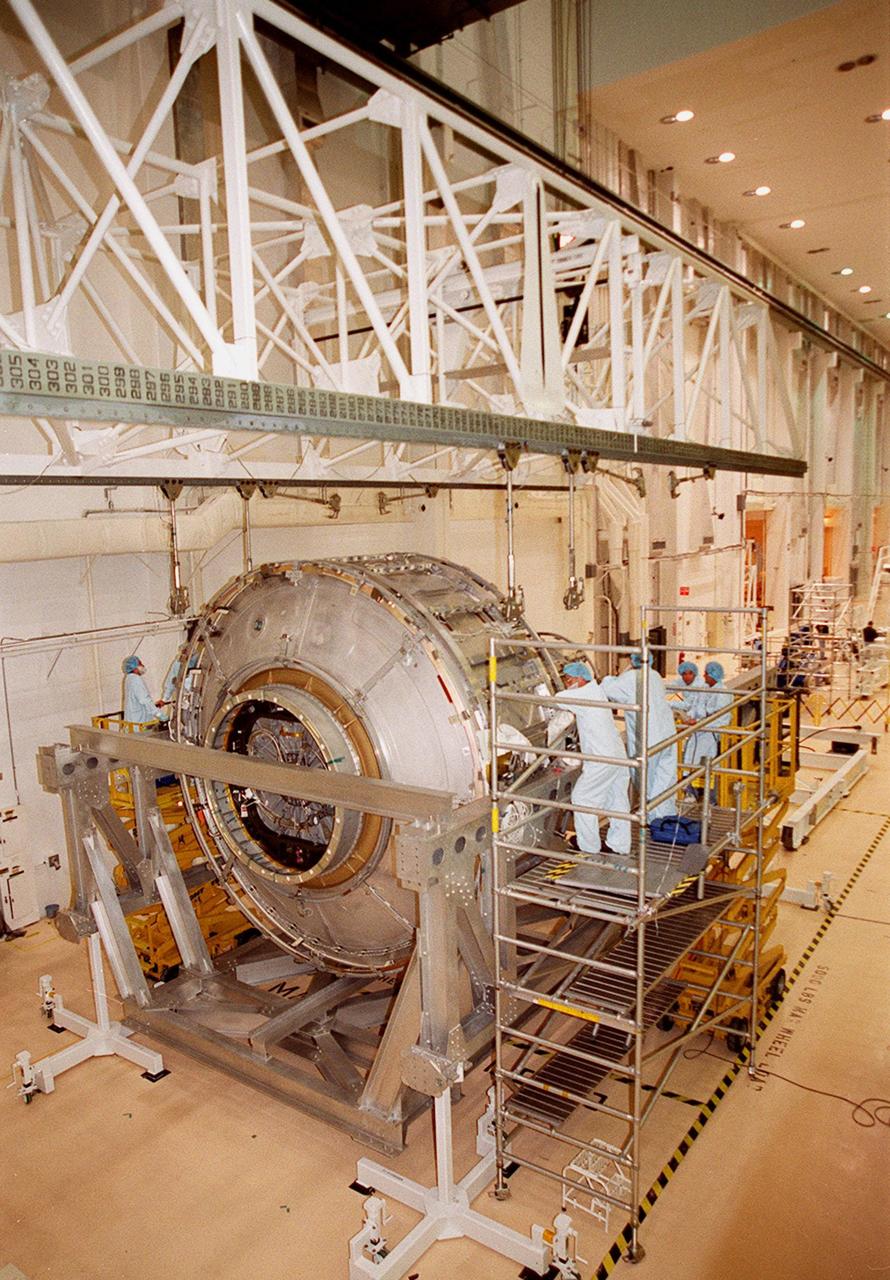
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Operations and Checkout Building keep watch as an overhead crane is lowered toward the Joint Airlock Module that it will lift and place in the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
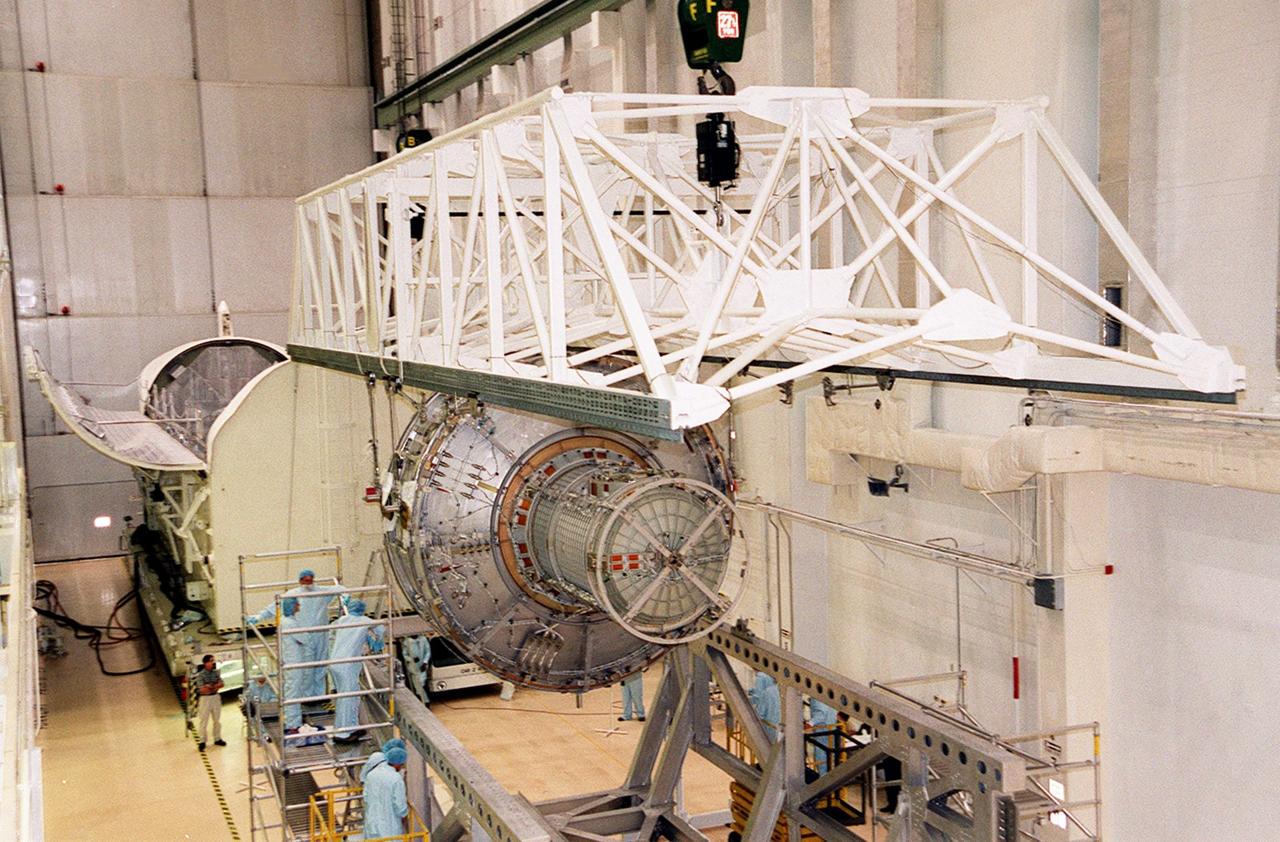
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, an overhead crane lifts the Joint Airlock Module to move and place it into the payload canister at left for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
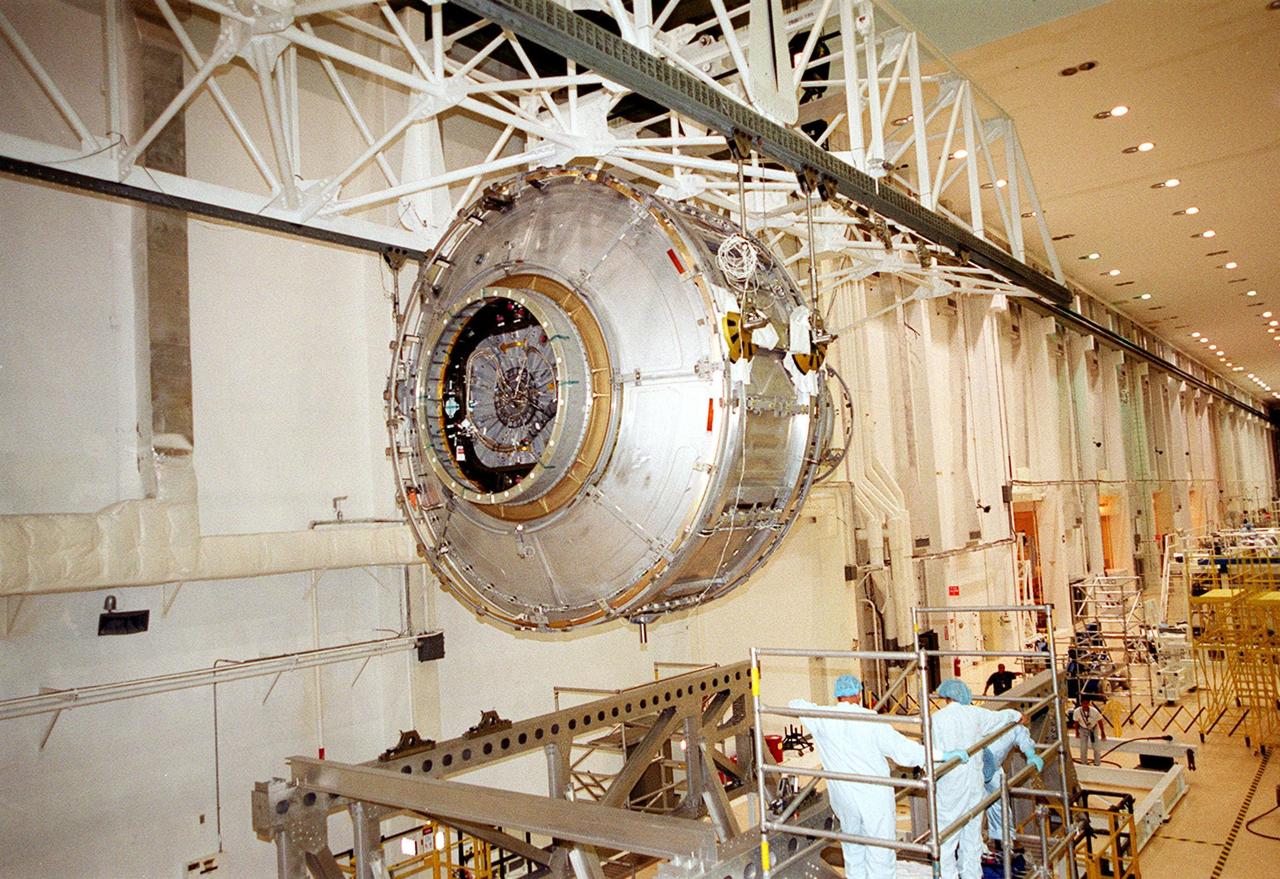
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Joint Airlock Module is suspended by an overhead crane in the Operations and Checkout Building before being moved and placed into the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
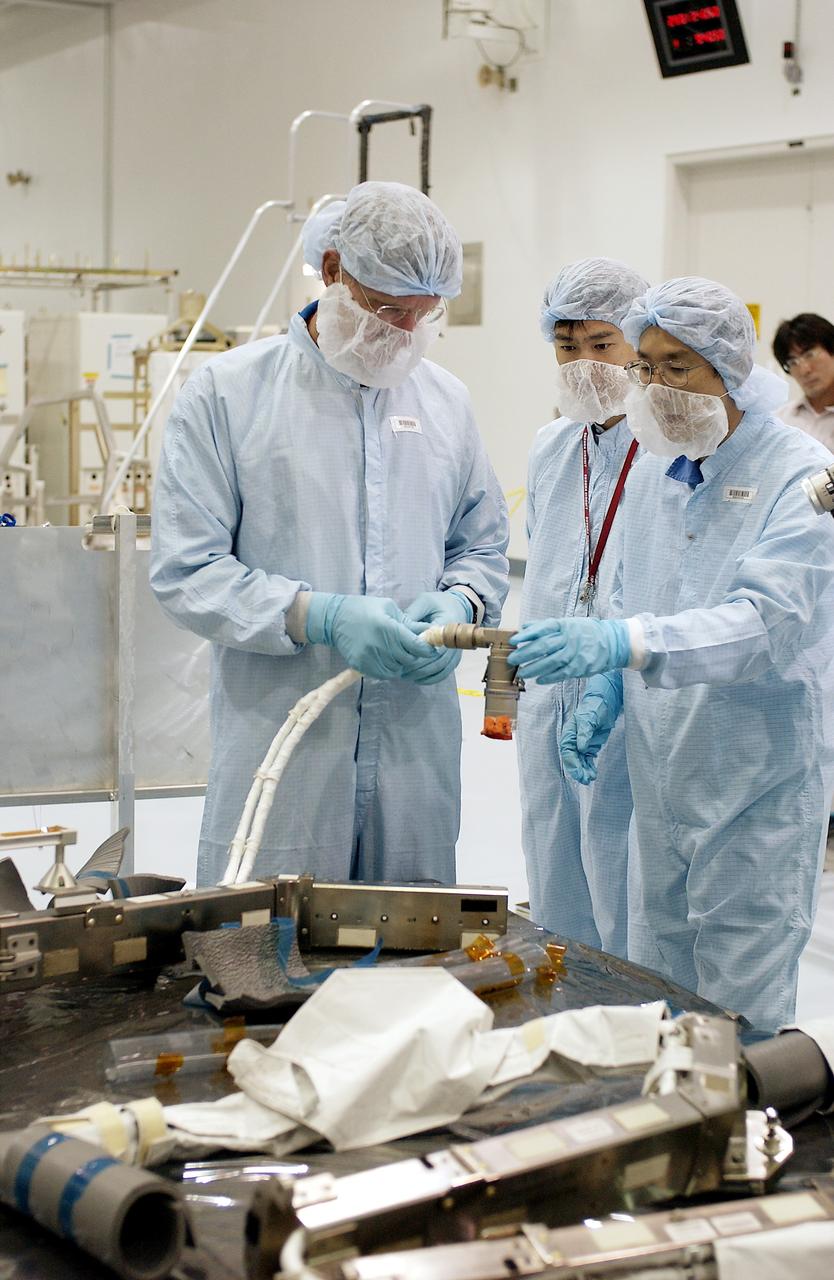

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-115 Mission Specialist Joseph Tanner (left) checks out a camera and cables to be used in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). Known as Kibo, the JEM consists of six components: two research facilities - the Pressurized Module and the Exposed Facility; a Logistics Module attached to each of them; a Remote Manipulator System; and an Inter-Orbit Communication System unit. Kibo also has a scientific airlock through which experiments are transferred and exposed to the external environment of space. The various components of JEM will be assembled in space over the course of three Space Shuttle missions. Equipment familiarization is a routine part of astronaut training and launch preparations.
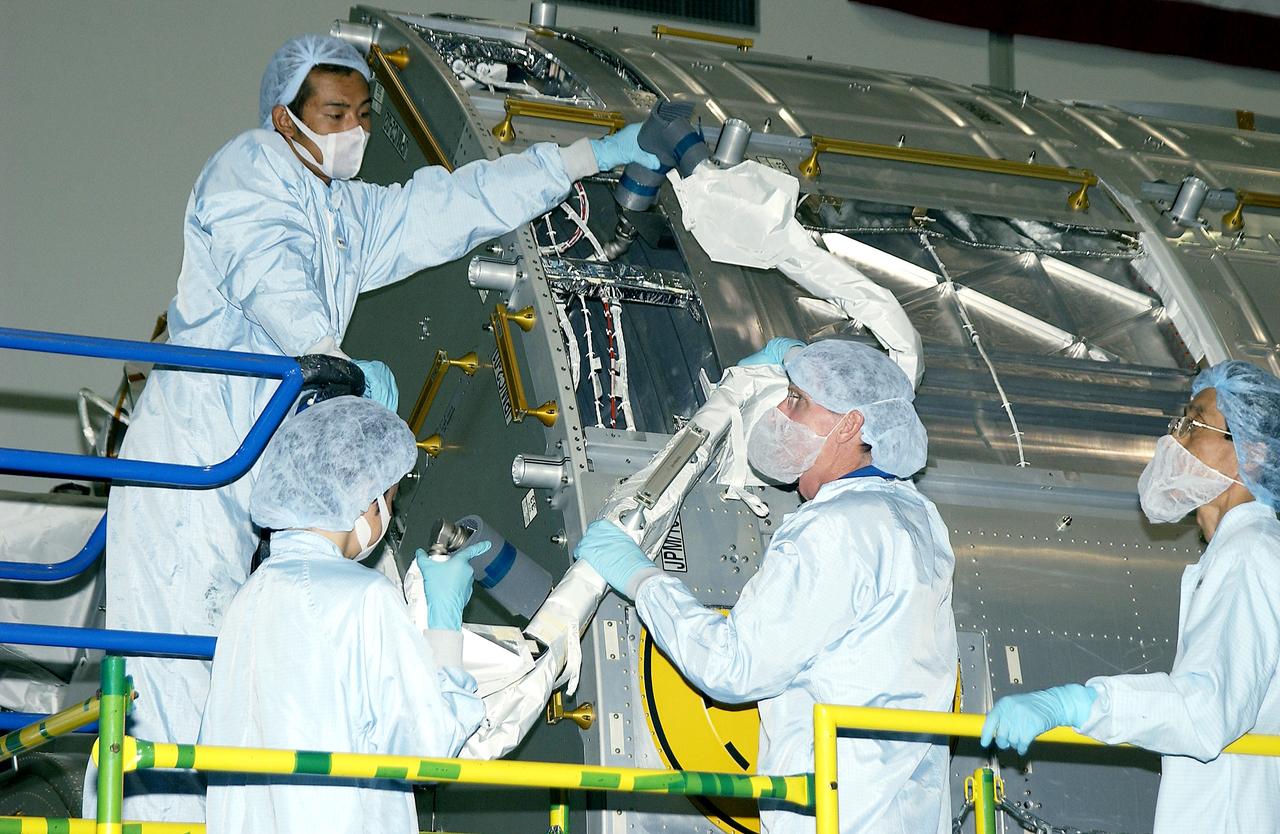

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-115 Mission Specialist Joseph Tanner (center, foreground) works with technicians to learn more about the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), known as Kibo. The JEM consists of six components: two research facilities - the Pressurized Module and the Exposed Facility; a Logistics Module attached to each of them; a Remote Manipulator System; and an Inter-Orbit Communication System unit. Kibo also has a scientific airlock through which experiments are transferred and exposed to the external environment of space. The various components of JEM will be assembled in space over the course of three Space Shuttle missions. Equipment familiarization is a routine part of astronaut training and launch preparations.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-115 Mission Specialist Joseph Tanner (second from right) checks out a camera and cables for the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) in the Space Station Processing Facility. Known as Kibo, the JEM consists of six components: two research facilities - the Pressurized Module and the Exposed Facility; a Logistics Module attached to each of them; a Remote Manipulator System; and an Inter-Orbit Communication System unit. Kibo also has a scientific airlock through which experiments are transferred and exposed to the external environment of space. The various components of JEM will be assembled in space over the course of three Space Shuttle missions. Equipment familiarization is a routine part of astronaut training and launch preparations.
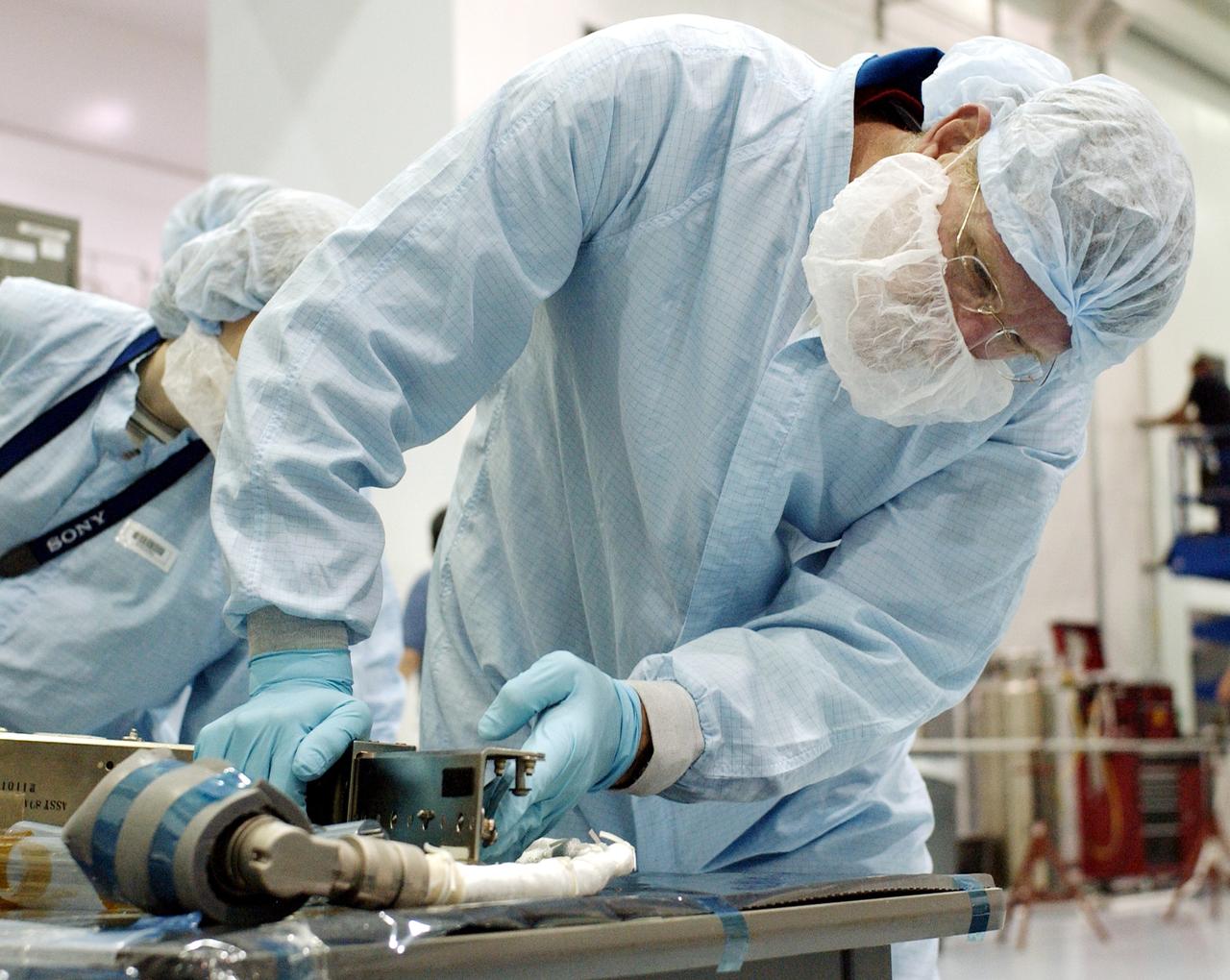

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-115 Mission Specialist Joseph Tanner checks out a camera for the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) in the Space Station Processing Facility. Known as Kibo, the JEM consists of six components: two research facilities -- the Pressurized Module and the Exposed Facility; a Logistics Module attached to each of them; a Remote Manipulator System; and an Inter-Orbit Communication System unit. Kibo also has a scientific airlock through which experiments are transferred and exposed to the external environment of space. The various components of JEM will be assembled in space over the course of three Space Shuttle missions. Equipment familiarization is a routine part of astronaut training and launch preparations.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-115 Mission Specialist Joseph Tanner takes a closer look at the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). Known as Kibo, the JEM consists of six components: two research facilities - the Pressurized Module and the Exposed Facility; a Logistics Module attached to each of them; a Remote Manipulator System; and an Inter-Orbit Communication System unit. Kibo also has a scientific airlock through which experiments are transferred and exposed to the external environment of space. The various components of JEM will be assembled in space over the course of three Space Shuttle missions. Equipment familiarization is a routine part of astronaut training and launch preparations.
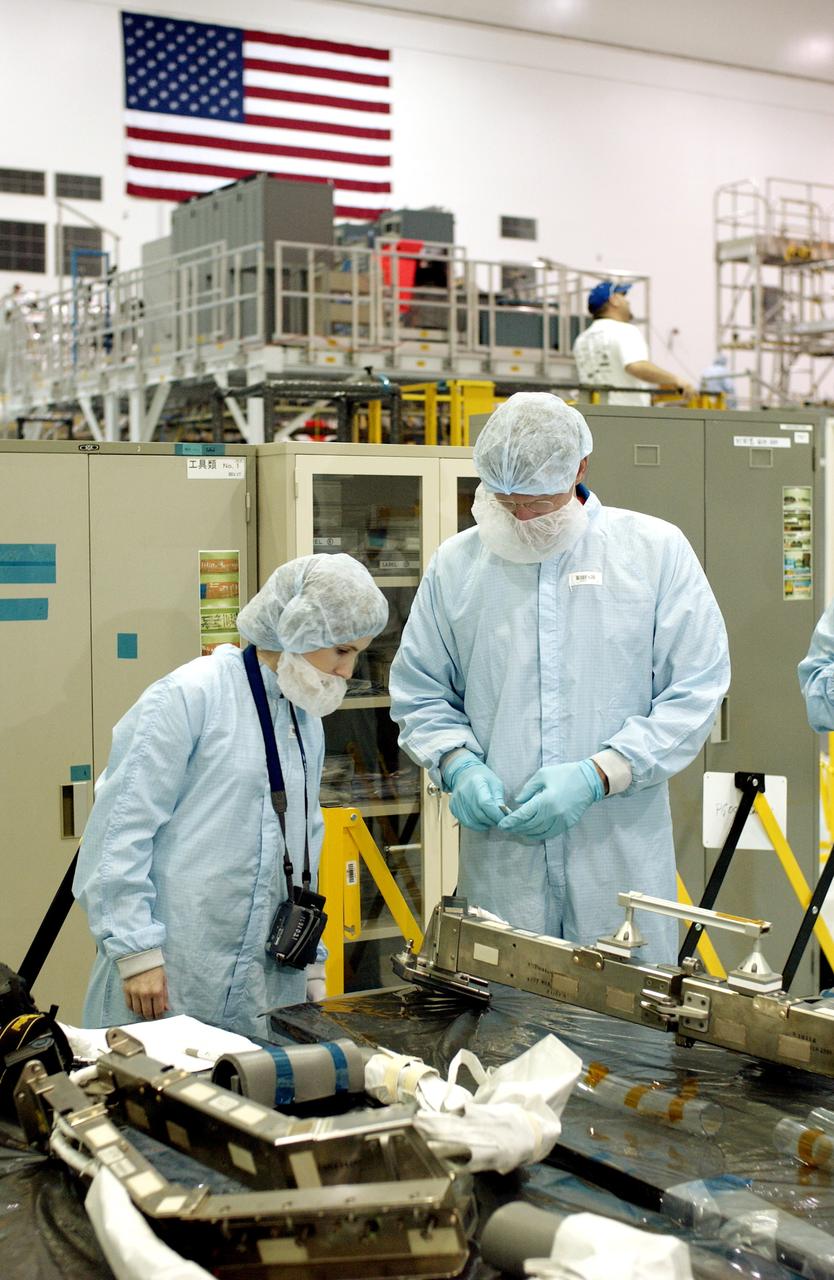

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-115 Mission Specialist Joseph Tanner (right) checks out a camera and cables for the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). Known as Kibo, the JEM consists of six components: two research facilities - the Pressurized Module and the Exposed Facility; a Logistics Module attached to each of them; a Remote Manipulator System; and an Inter-Orbit Communication System unit. Kibo also has a scientific airlock through which experiments are transferred and exposed to the external environment of space. The various components of JEM will be assembled in space over the course of three Space Shuttle missions. Equipment familiarization is a routine part of astronaut training and launch preparations.
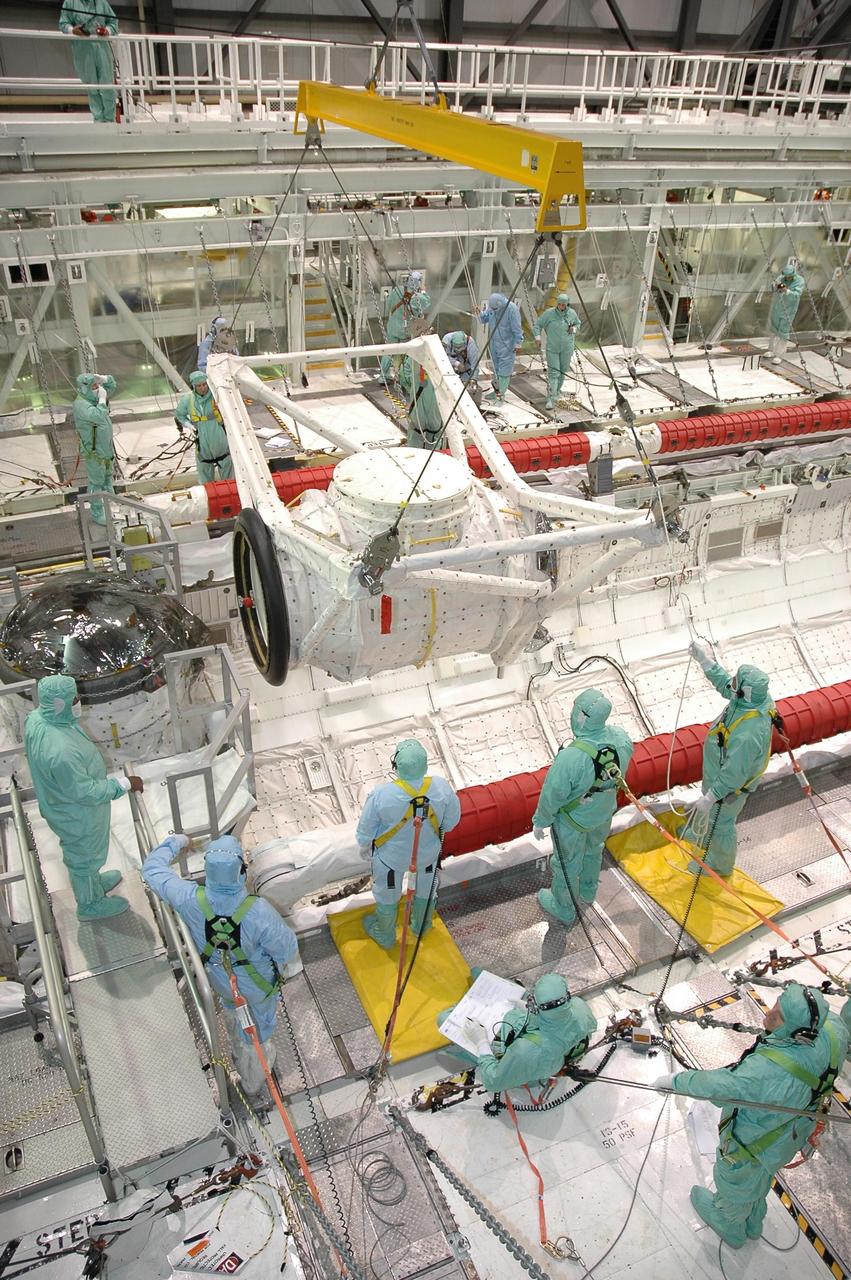
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians control the descent of the crew airlock module into Endeavour's payload bay, where it will be installed. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
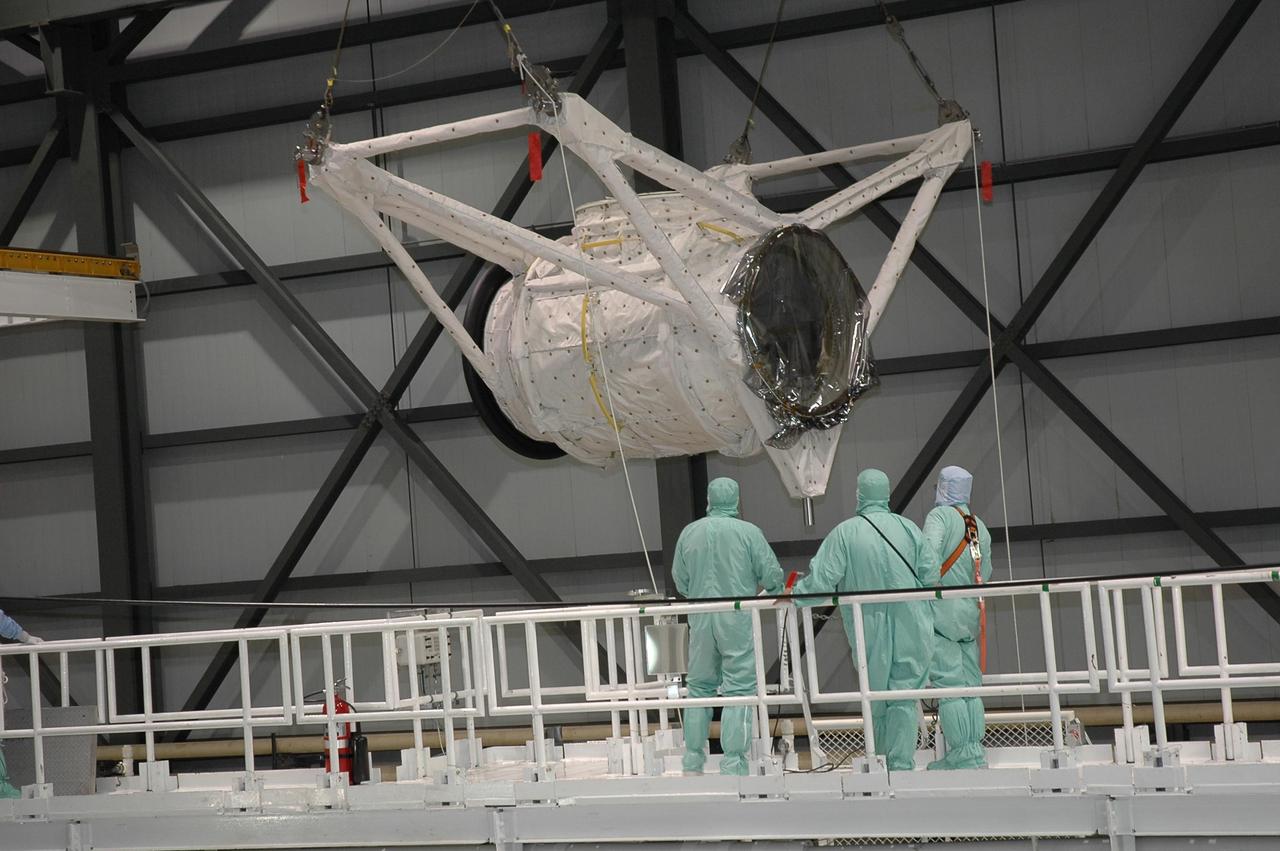

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane moves the crew airlock module toward Endeavour. It will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
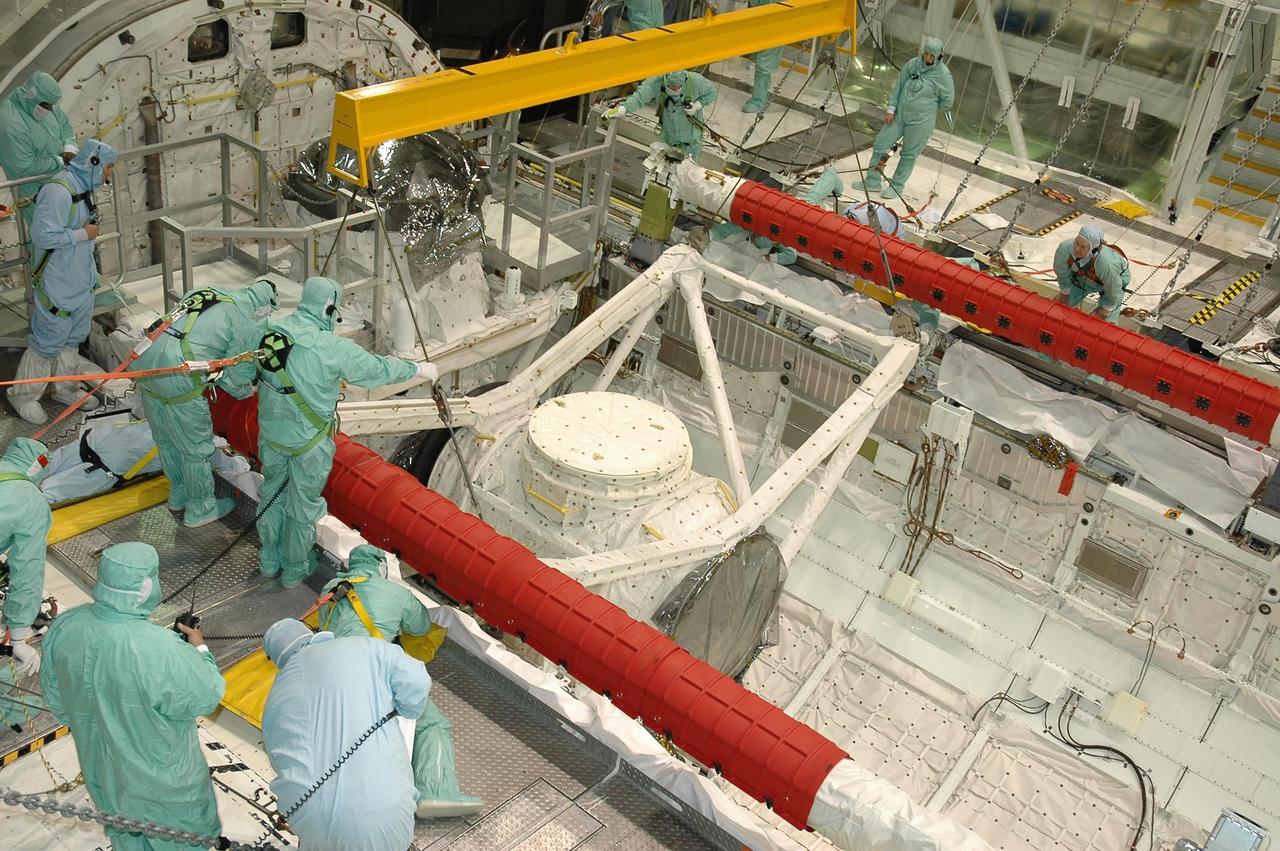
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians direct the placement of the crew airlock module into Endeavour's payload bay, where it will be installed. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
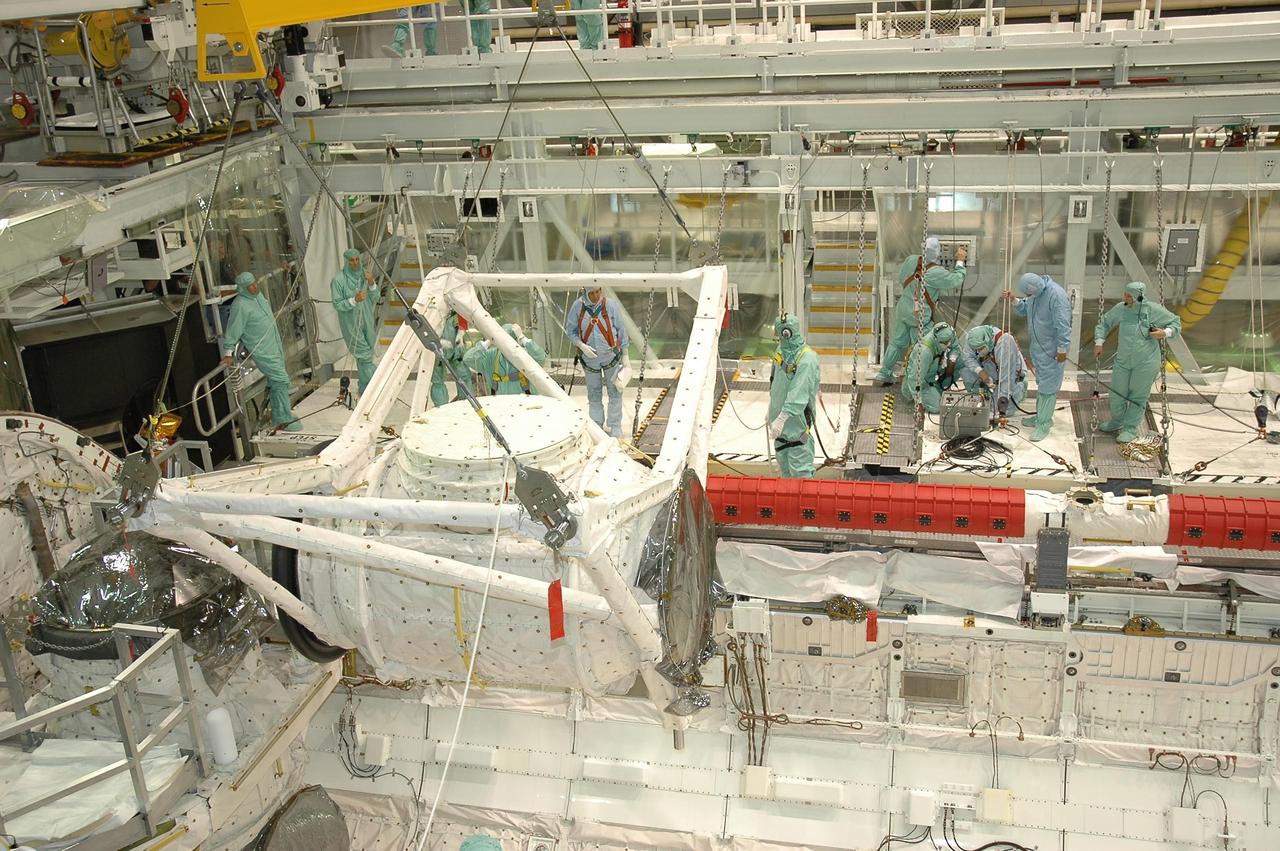

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the crew airlock module is lowered into place in Endeavour's payload bay, where it will be installed. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
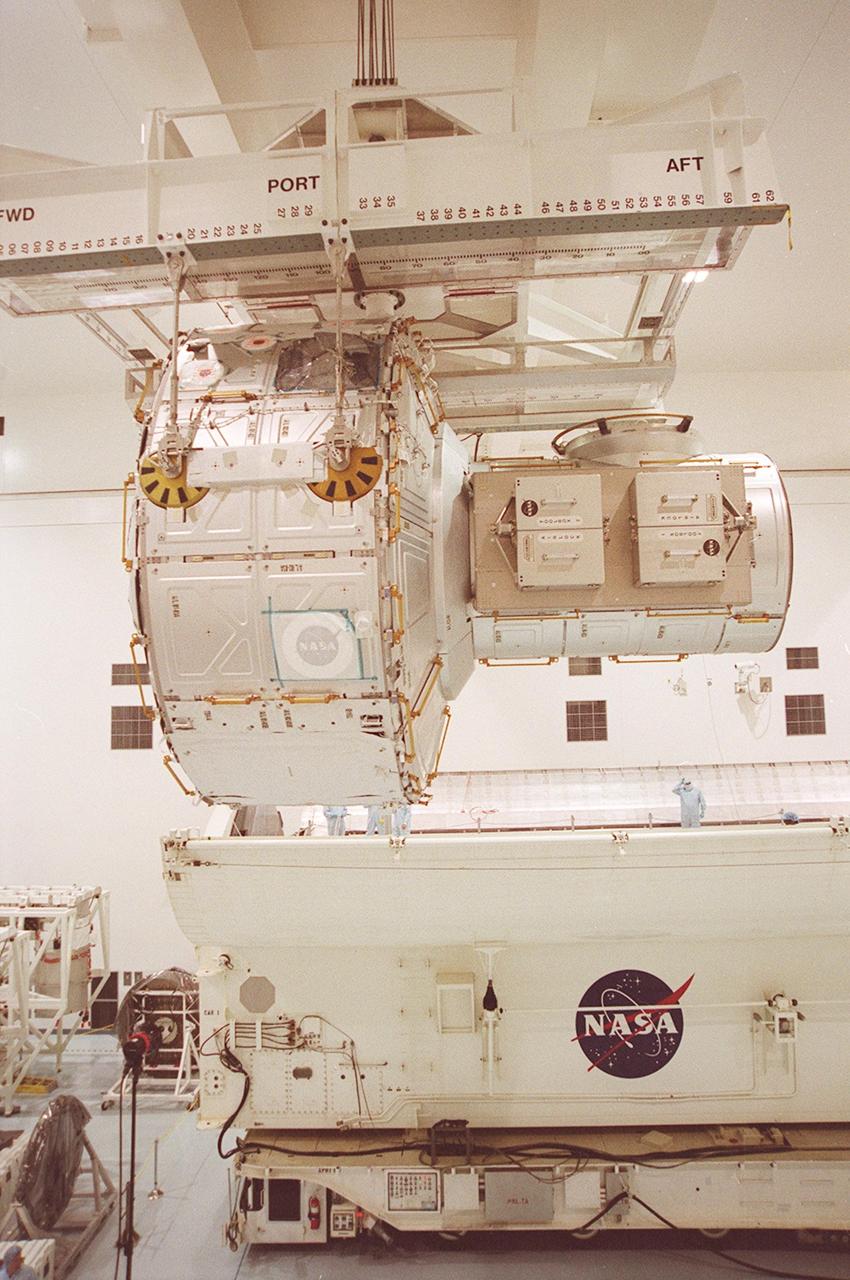
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the Joint Airlock Module is moved closer to the payload canister. The airlock will be installed in the payload bay of Atlantis for mission STS-104 to the International Space Station. The airlock is a pressurized flight element consisting of two cylindrical chambers attached end-to-end by a connecting bulkhead and hatch. Once installed and activated, the Airlock becomes the primary path for spacewalk entry to and departure from the Space Station for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. STS-104 is scheduled for launch June 14 from Launch Pad 39B

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians direct the placement of the crew airlock module into Endeavour's payload bay, where it will be installed. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
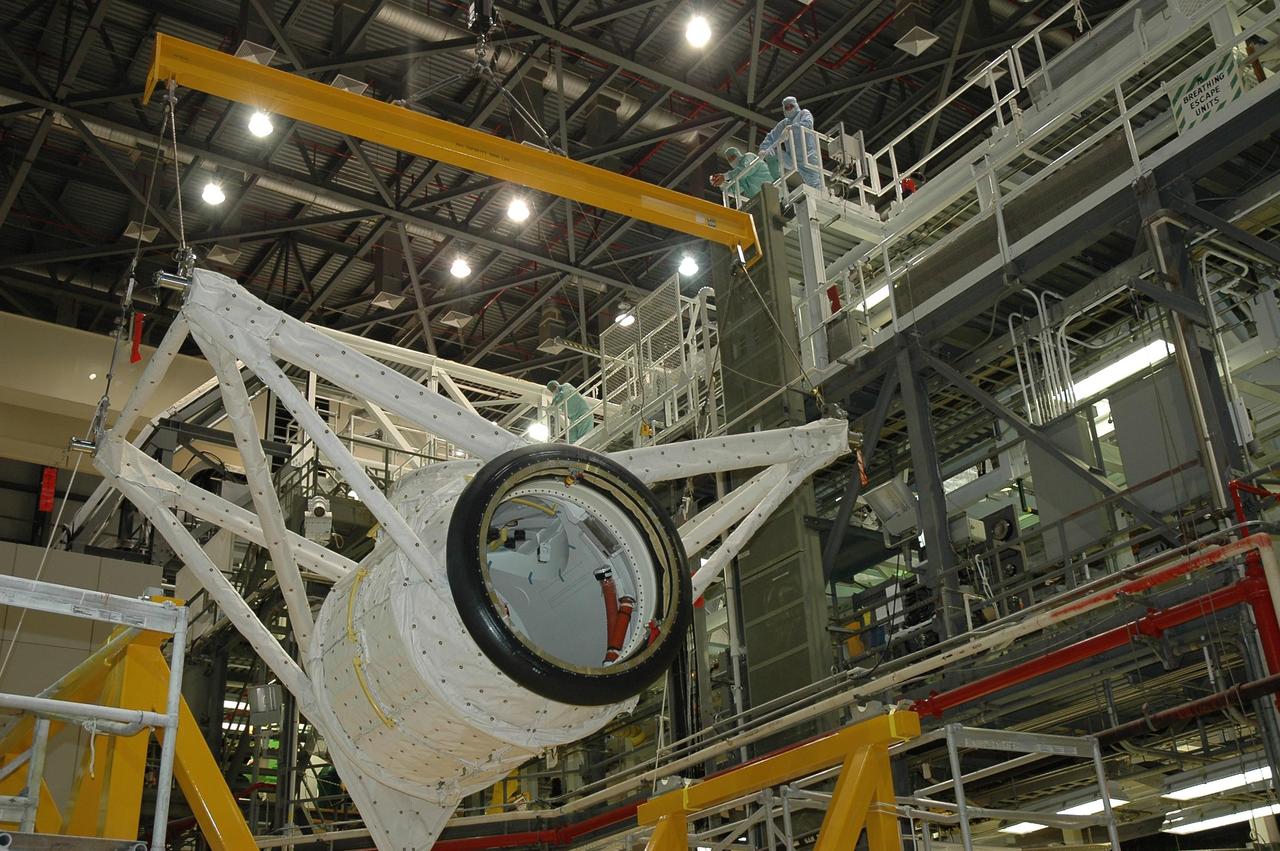

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane moves the crew airlock module across the bay to install it in Endeavour's payload bay. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
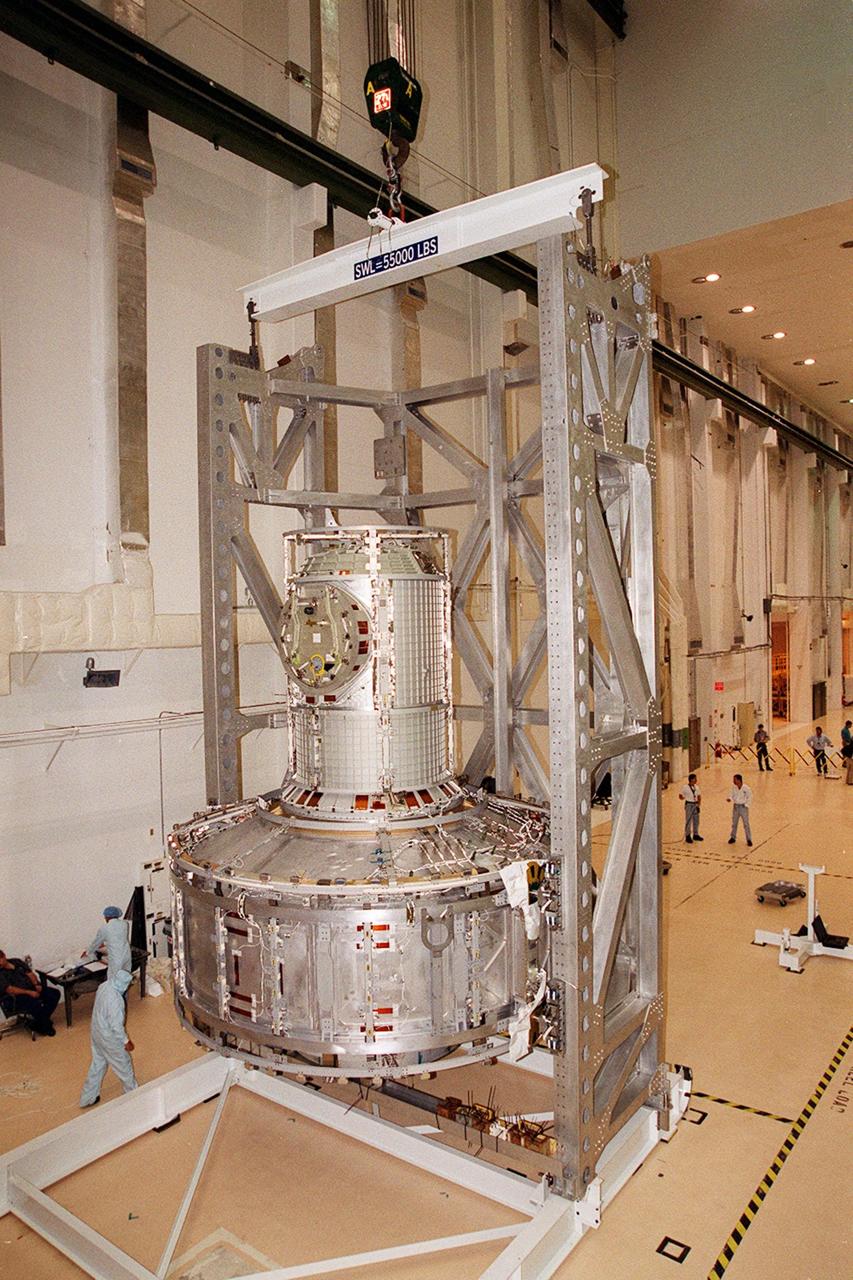

In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module, now in vertical position, is ready to be moved into a vacuum chamber for testing. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module is specially designed to accommodate both suits, providing a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
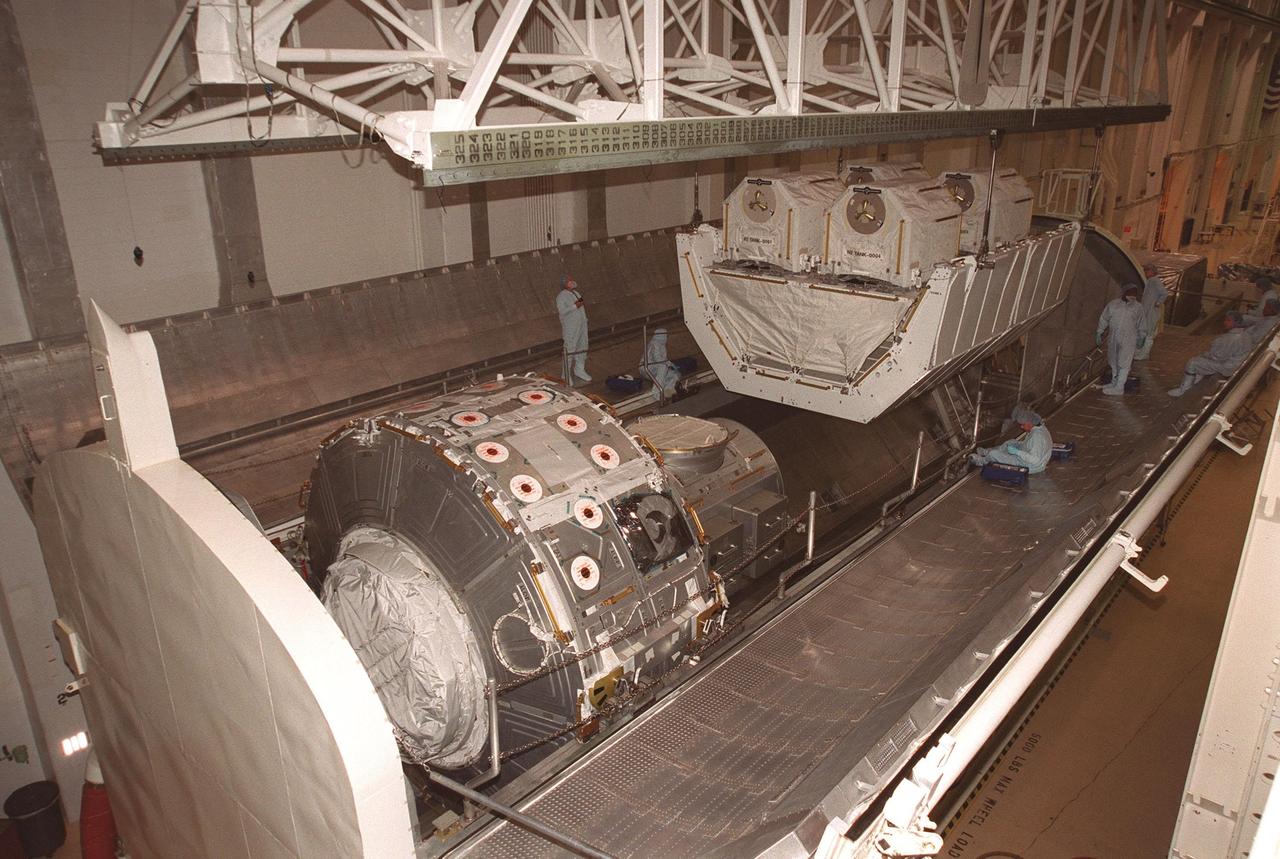

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With workers keeping a close watch, the overhead crane lowers the high pressure gas assembly two gaseous oxygen and two gaseous nitrogen storage tanks into the payload canister. The joint airlock module is already in the canister. The airlock and tanks are part of the payload on mission STS-104 and are being transferred to orbiter Atlantis’s payload bay. The storage tanks will be attached to the airlock during two spacewalks. The storage tanks will support future spacewalk operations from the Station and augment the Service Module gas resupply system. STS-104 is scheduled for launch June 14 from Launch Pad 39B
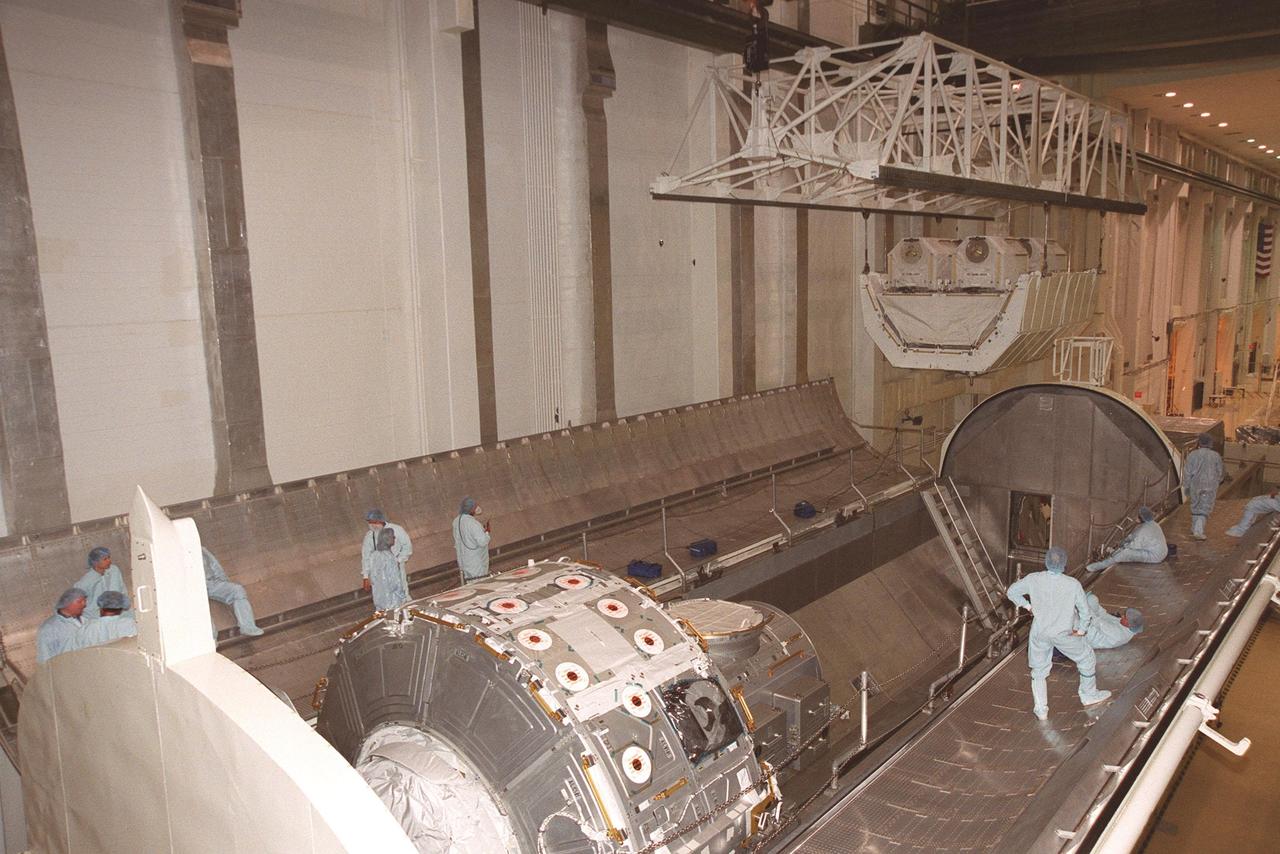
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, workers wait in the payload canister as an overhead crane moves the high pressure gas assembly two gaseous oxygen and two gaseous nitrogen storage tanks toward it. The joint airlock module is already in the canister. The airlock and tanks are part of the payload on mission STS-104 and are being transferred to orbiter Atlantis’s payload bay. The storage tanks will be attached to the airlock during two spacewalks. The storage tanks will support future spacewalk operations from the Station and augment the Service Module gas resupply system. STS-104 is scheduled for launch June 14 from Launch Pad 39B
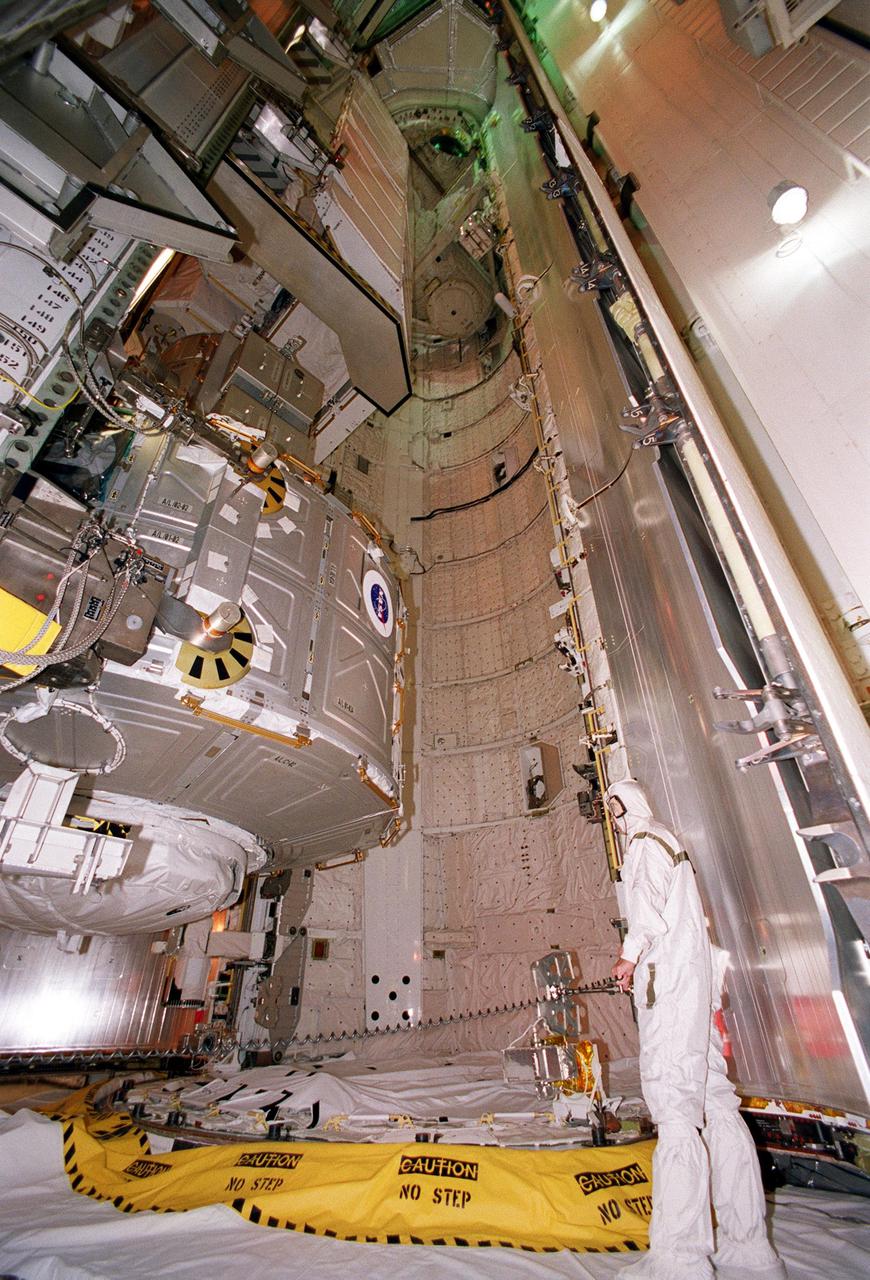
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Joint Airlock Module, sporting a NASA logo, is moved toward the payload bay of Space Shuttle Atlantis for mission STS-104. Once installed and activated, the airlock becomes the primary path for International Space Station spacewalk entry and departure using U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. Launch of Atlantis is scheduled no earlier than July 12 at 5:04 a.m. EDT
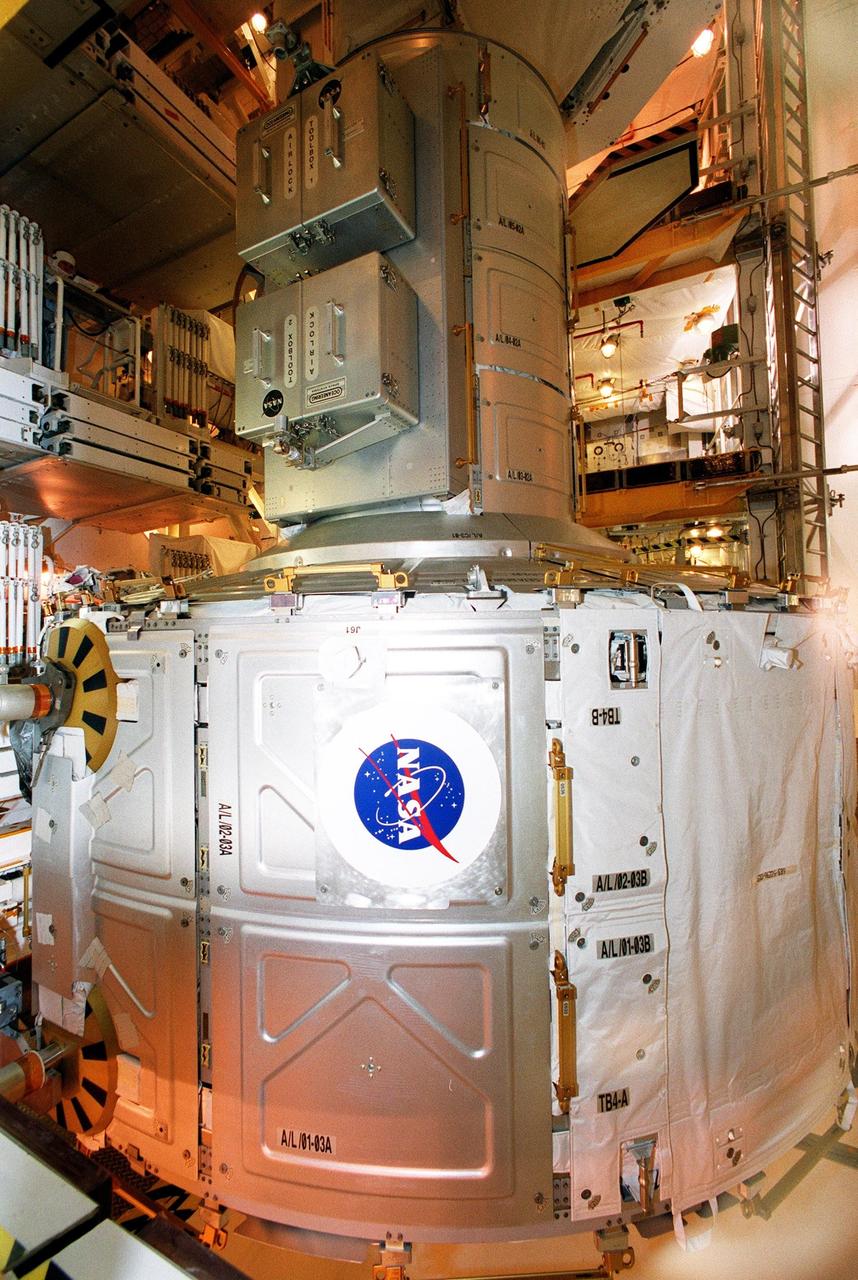

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Joint Airlock Module, sporting a NASA logo, is moved toward the payload bay of Space Shuttle Atlantis for mission STS-104. Once installed and activated, the airlock becomes the primary path for International Space Station spacewalk entry and departure using U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. Launch of Atlantis is scheduled no earlier than July 12 at 5:04 a.m. EDT
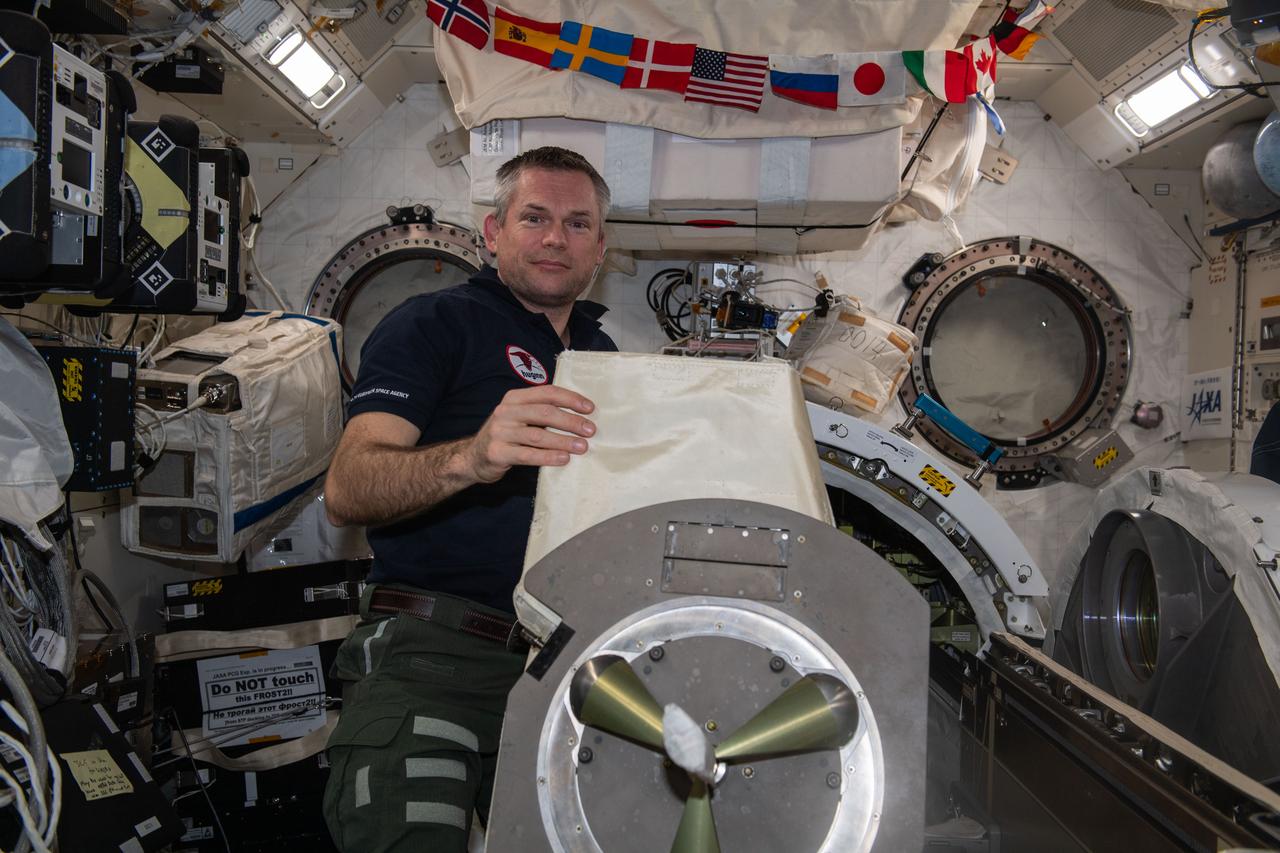

iss070e098166 (Feb. 22, 2024) --- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Expedition 70 Commander Andreas Mogensen removes the multipurpose experiment platform (MPEP) from the Kibo laboratory module's airlock. External science payloads are attached to the MPEP which is then placed inside Kibo's airlock. Next, the airlock is depressurized before the Japanese robotic arm grapples the MPEP and places it on Kibo's Exposed Facility where external science experiments are deployed.
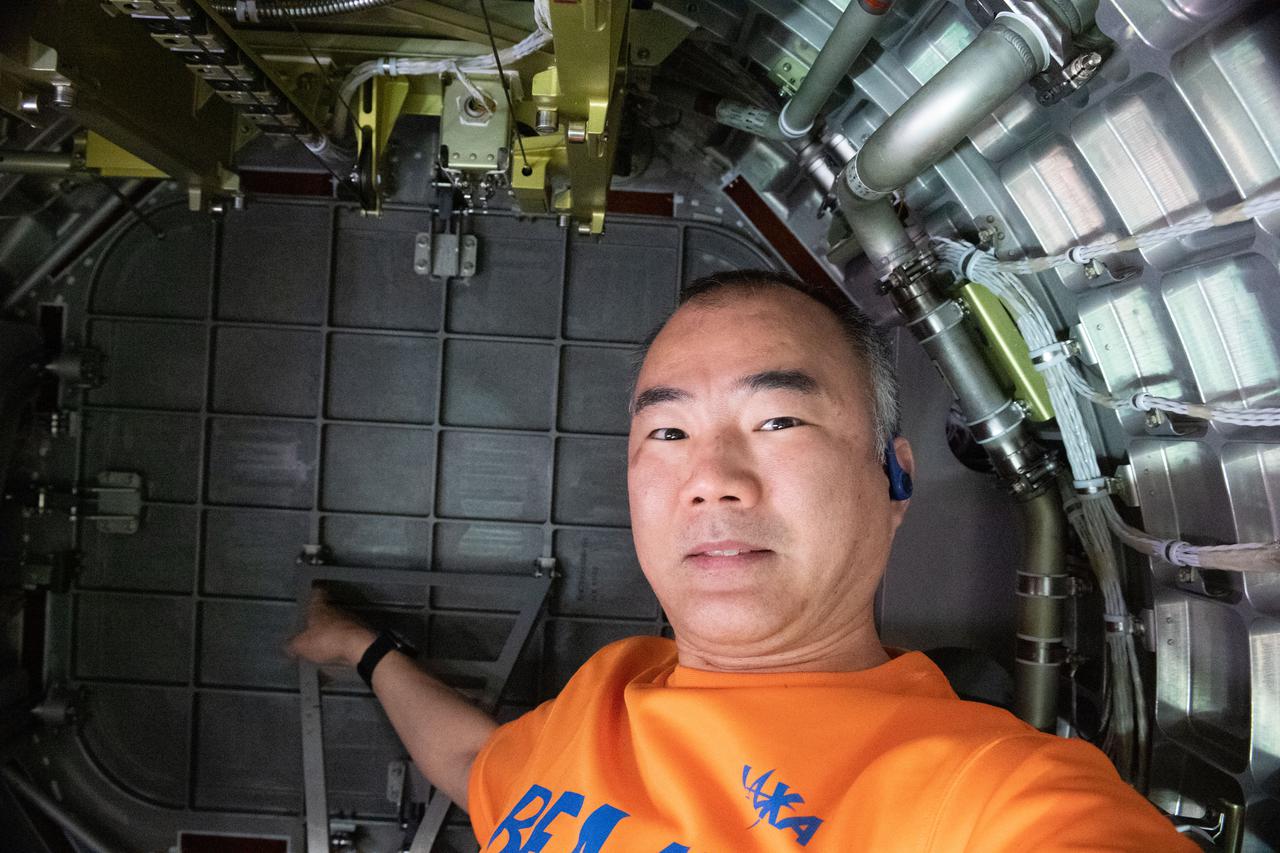

iss064e040776 (March 10, 2021) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Soichi Noguchi is pictured inside the Kibo laboratory module's airlock. Experiments and microsatellites, or CubeSats, are staged inside the airlock for deployment into the external environment of space. The airlock is then closed and depressurized before the Japanese robotic arm grapples the experiments and installs them on an external science platform outside Kibo. The CubeSats are ejected into Earth orbit from a small satellite deployer gripped at the end of the Japanese robotic arm.
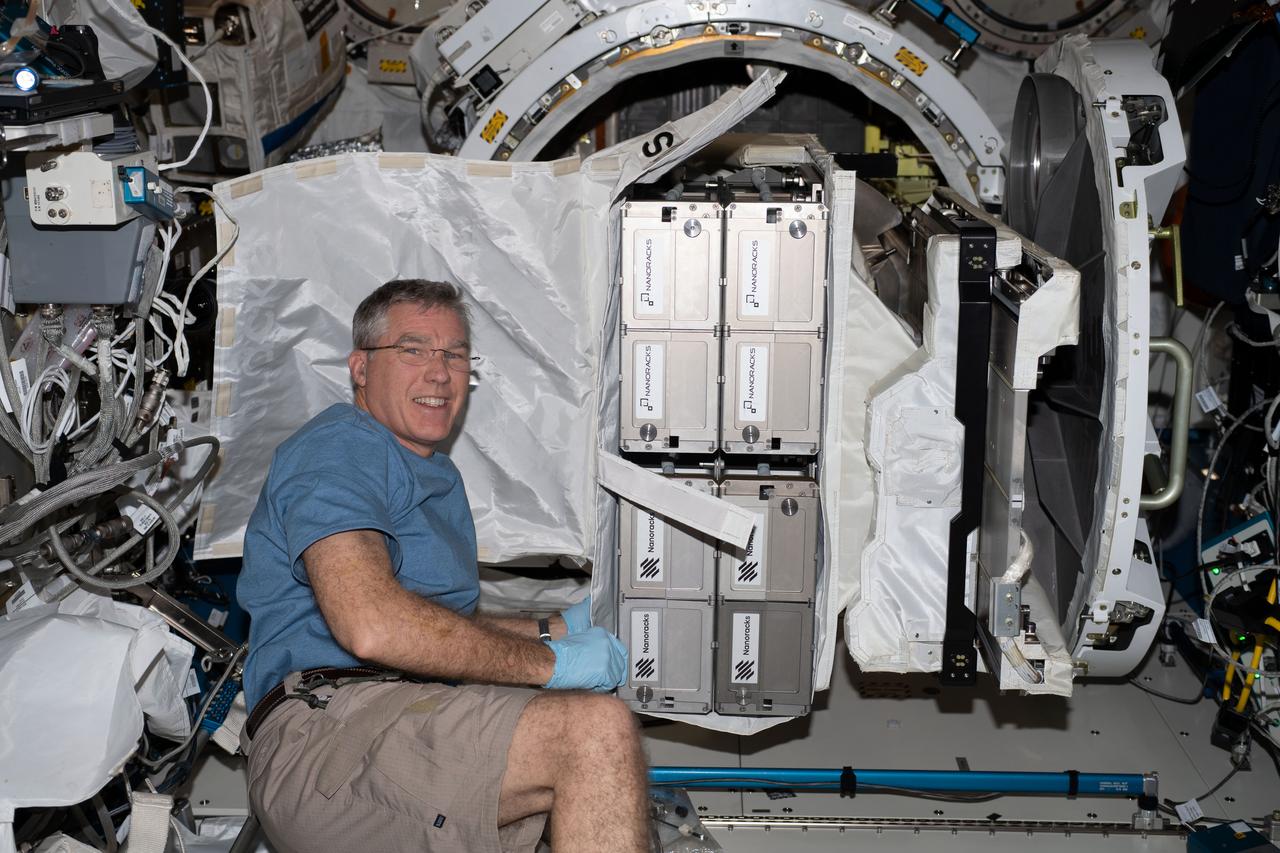

iss069e025743 (June 28, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Stephen Bowen installs the NanoRacks CubeSat Deployer into the Kibo laboratory module's airlock.
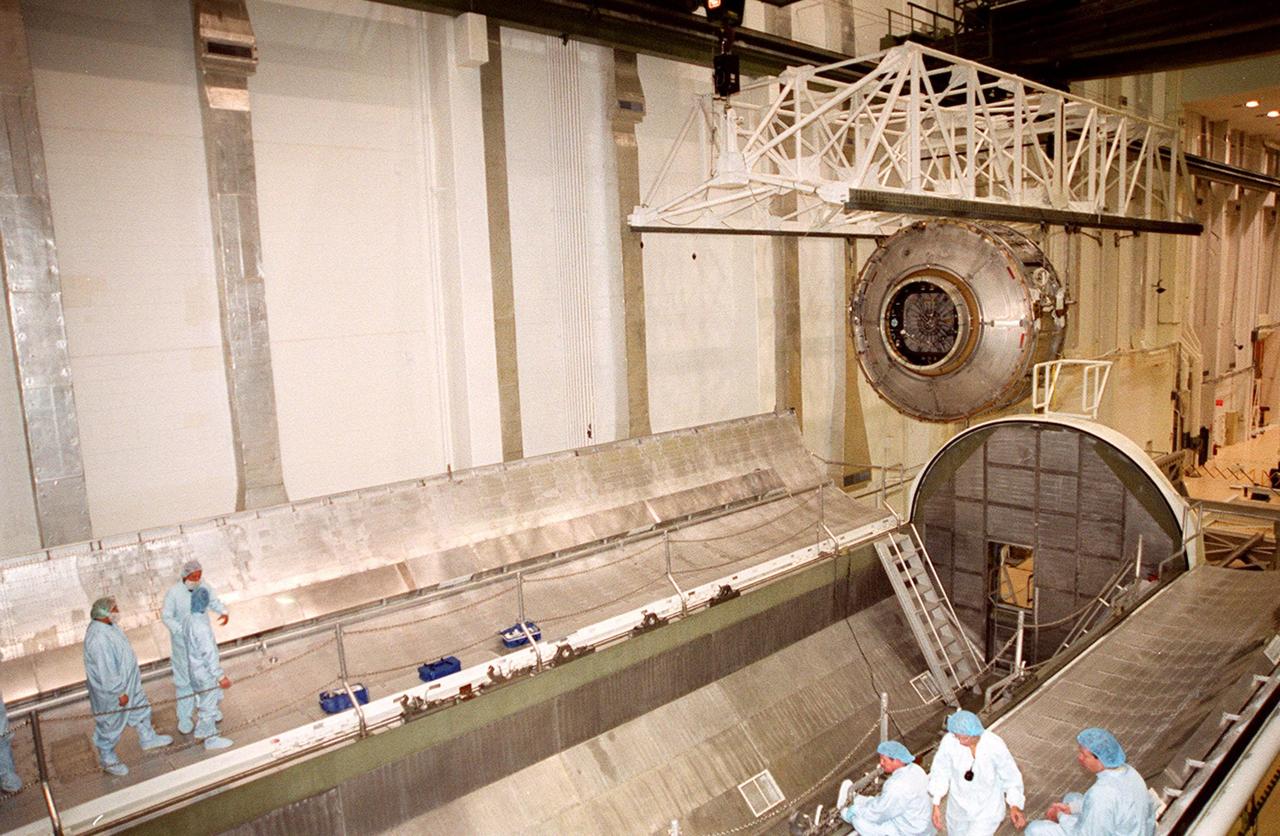
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the foreground, standing or sitting on the doors of the payload canister, wait and watch as the Joint Airlock Module moves toward them. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
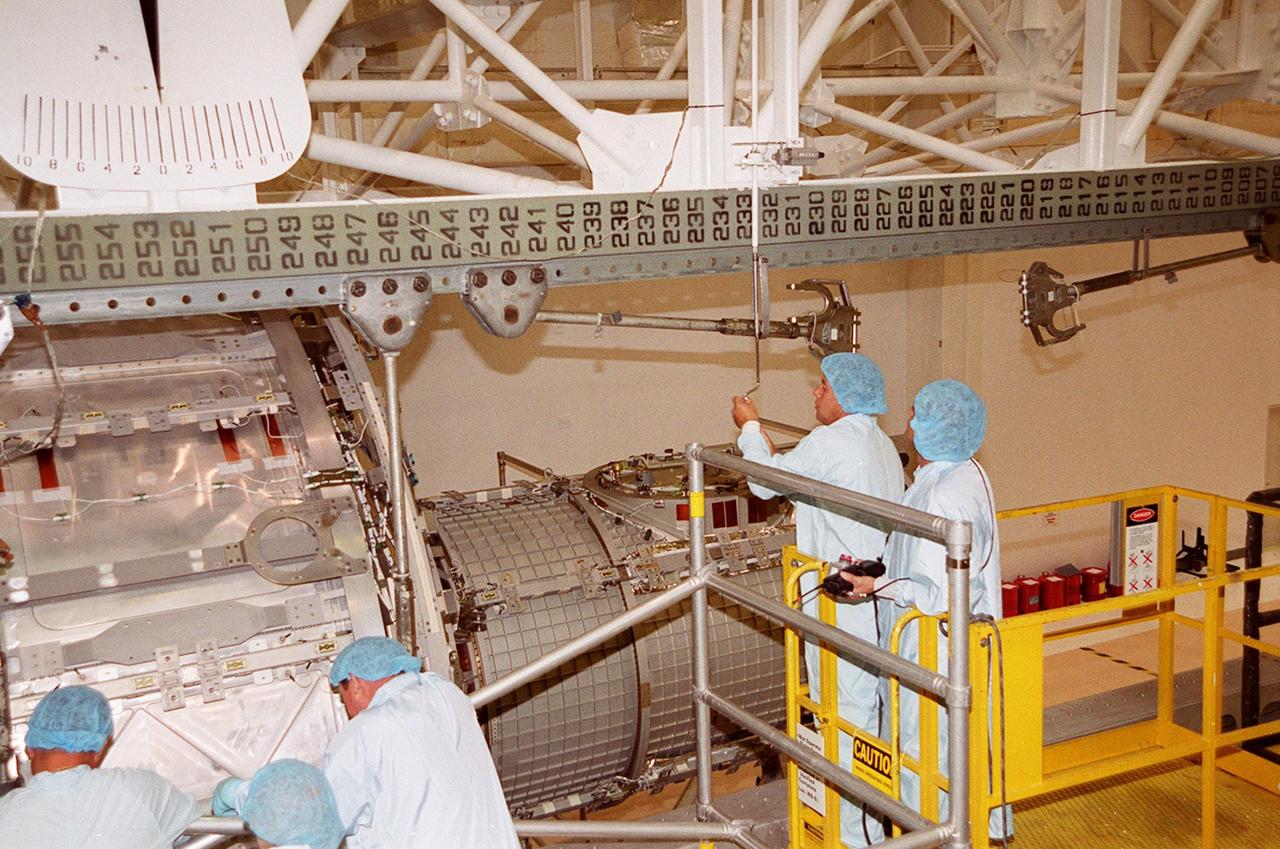
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker in the Operations and Checkout Building attaches the overhead crane to the Joint Airlock Module while another worker controls movement of the crane. The module will be lifted and placed in the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
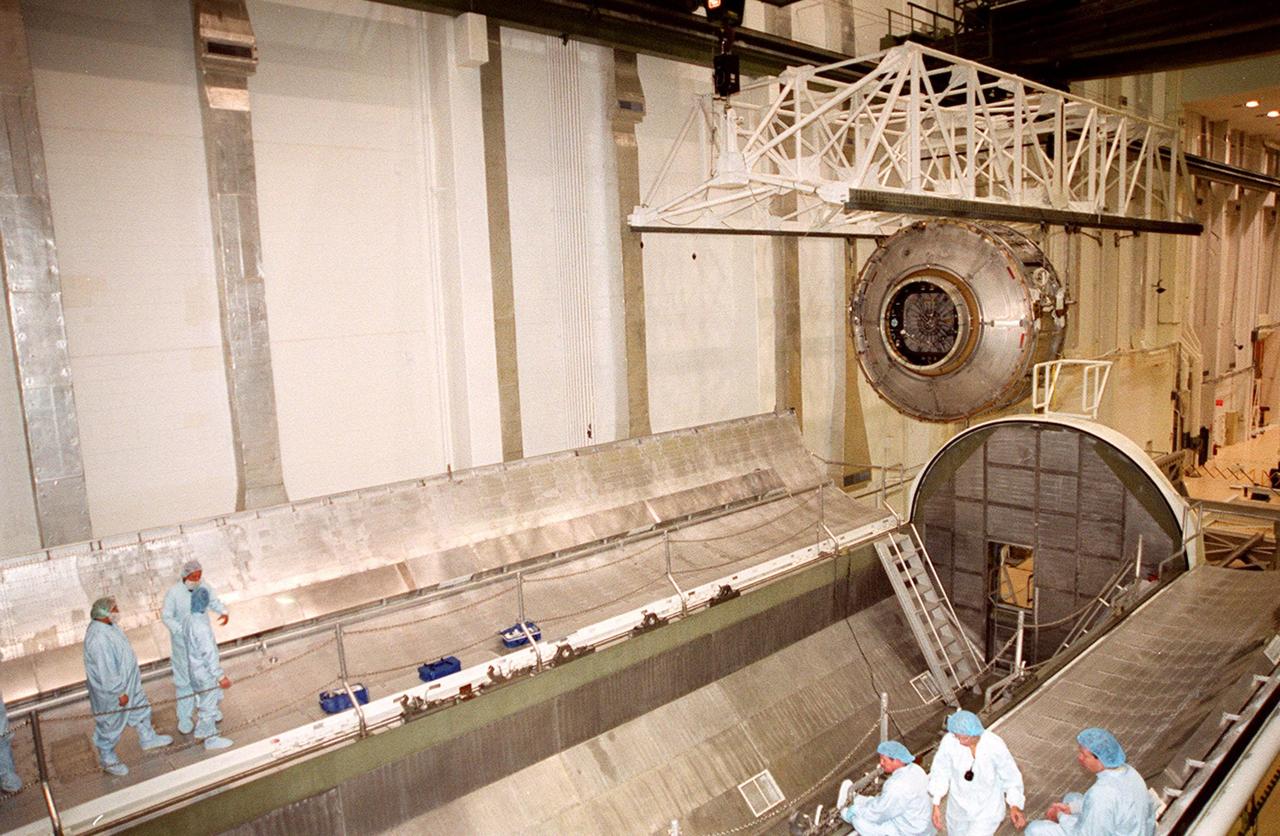
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the foreground, standing or sitting on the doors of the payload canister, wait and watch as the Joint Airlock Module moves toward them. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
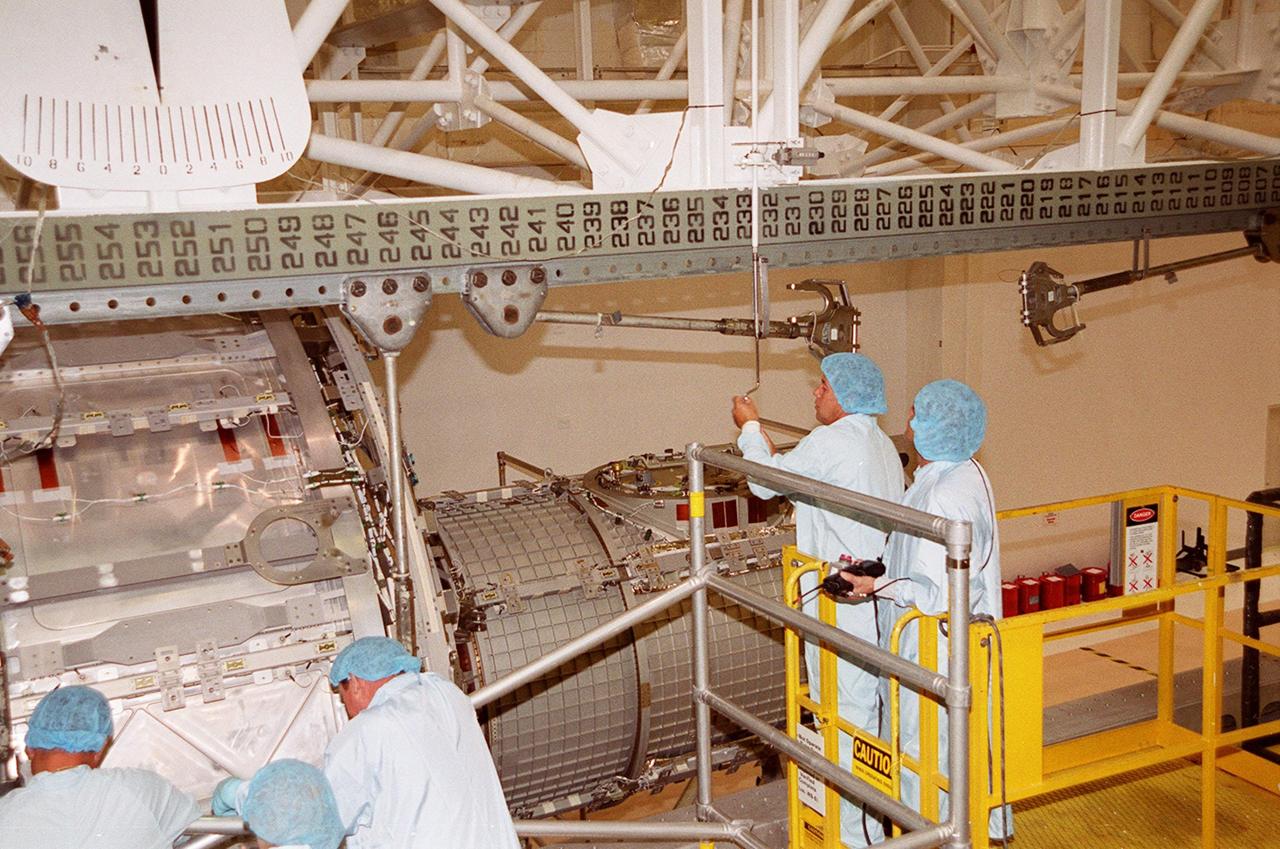
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker in the Operations and Checkout Building attaches the overhead crane to the Joint Airlock Module while another worker controls movement of the crane. The module will be lifted and placed in the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
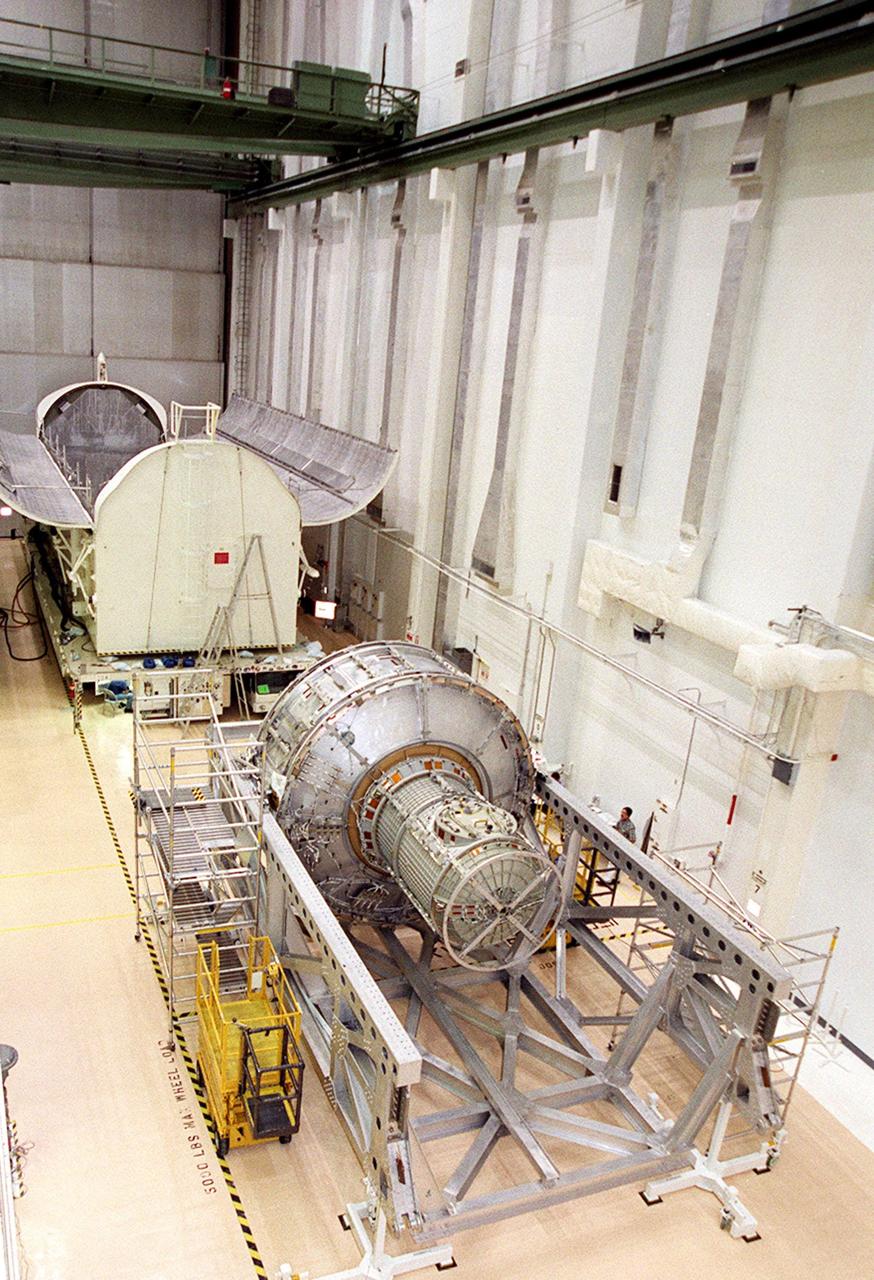

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module waits for transfer to the payload canister behind it after which it will be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility. There it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
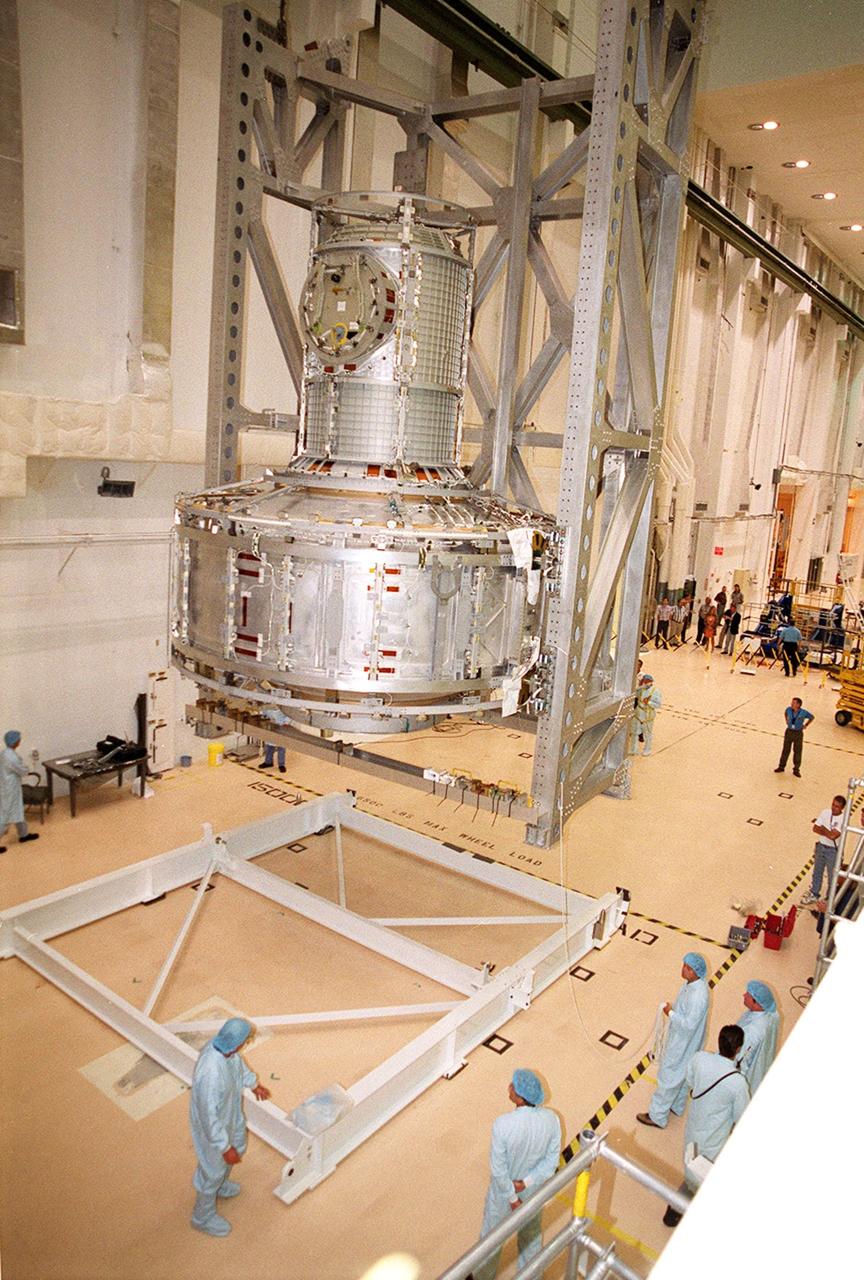
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is lowered toward a stand on the floor where it will be moved to a horizontal position. Then it will be lifted into the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
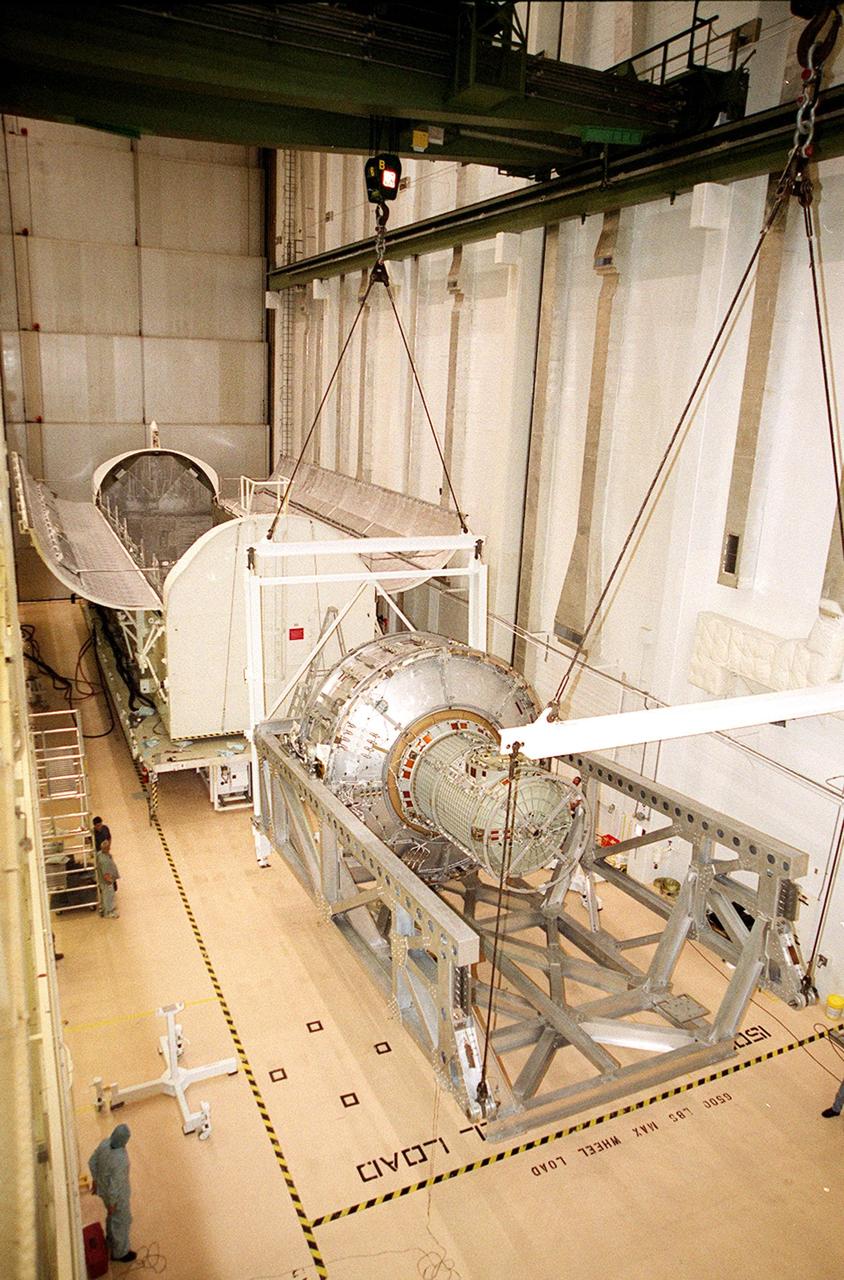

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is placed in a horizontal position to be transferred to the payload canister behind it. Then it will be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility where it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
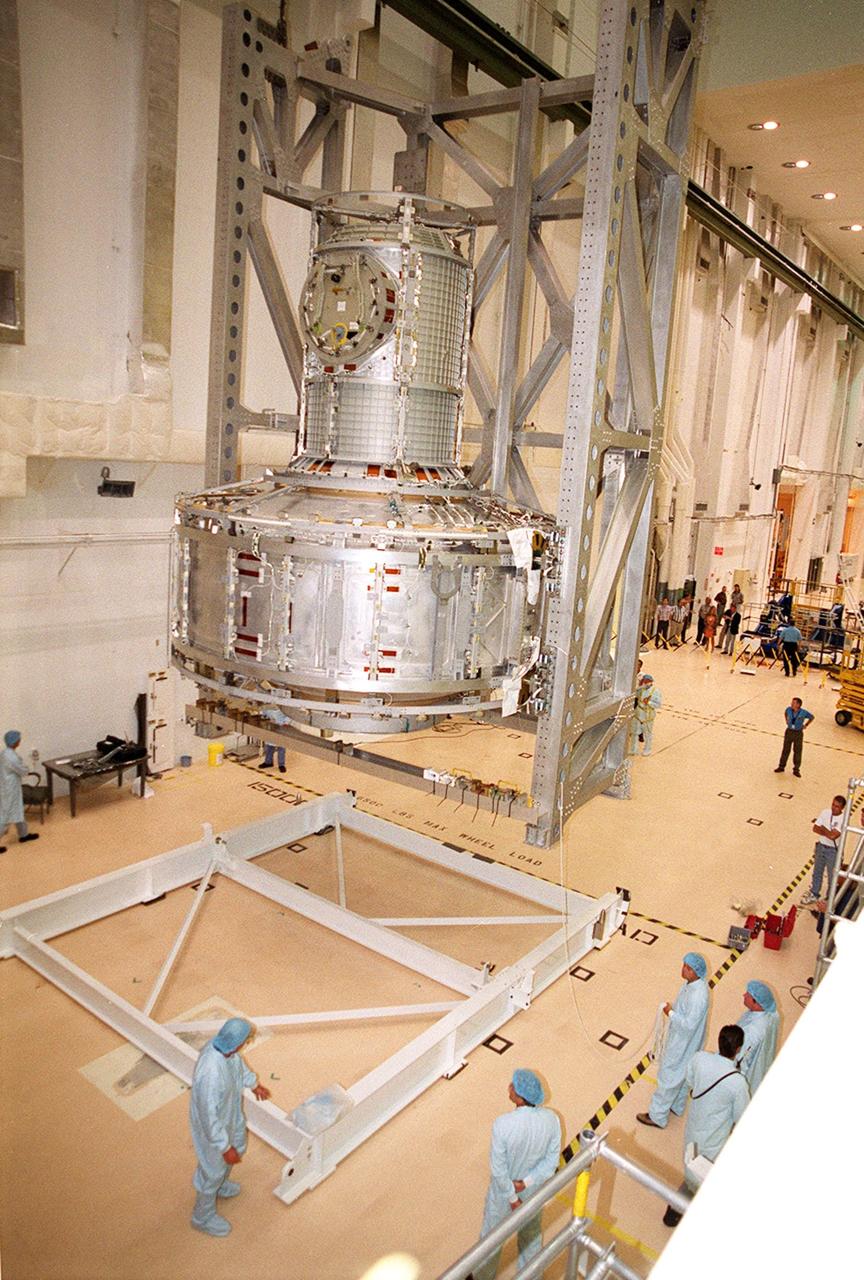
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is lowered toward a stand on the floor where it will be moved to a horizontal position. Then it will be lifted into the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility