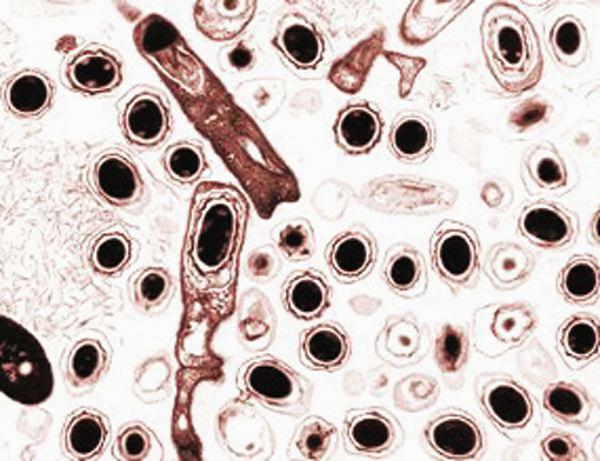
Anthrax spores are inactive forms of Bacillus anthracis. They can survive for decades inside a spore's tough protective coating; they become active when inhaled by humans. A result of NASA- and industry-sponsored research to develop small greenhouses for space research is the unique AiroCide TiO2 system that kills anthrax spores and other pathogens.
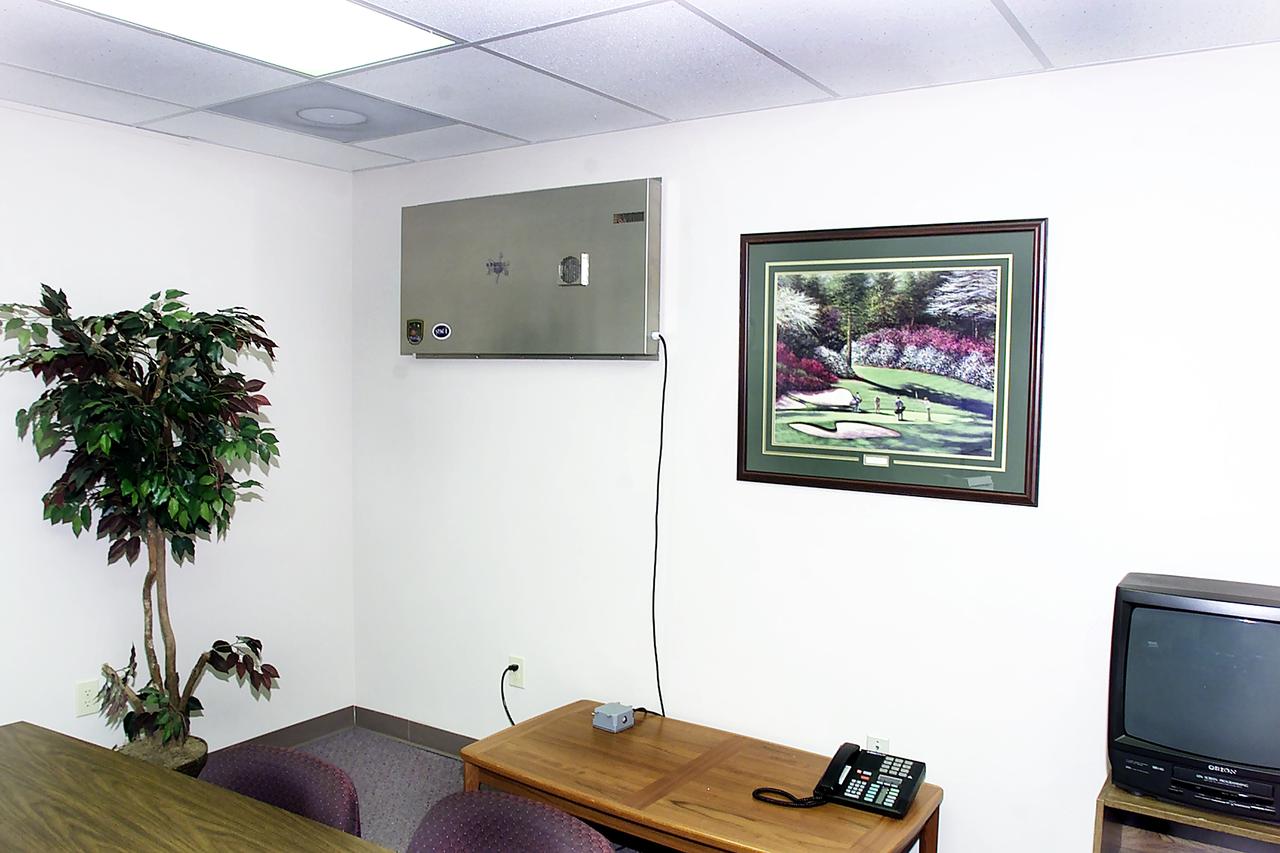

AiroCide Ti02, an anthrax-killing air scrubber manufactured by KES Science and Technology Inc., in Kernesaw, Georgia, looks like a square metal box when it is installed on an office wall. Its fans draw in airborne spores and airflow forces them through a maze of tubes. Inside, hydroxyl radicals (OH-) attack and kill pathogens. Most remaining spores are destroyed by high-energy ultraviolet photons. Building miniature greenhouses for experiments on the International Space Station (ISS) has led to the invention of this device that annihilates anthrax-a bacteria that can be deadly when inhaled. The research enabling the invention started at the University of Wisconsin (Madison) Center for Space Automation and Robotics (WCSAR), one of 17 NASA Commercial Space Centers. A special coating technology used in the anthrax-killing invention is also being used inside WCSAR-built plant growth units on the ISS. This commercial research is managed by the Space Product Development Program at the Marshall Space Flight Center.

This is a photo of a technician at KES Science and Technology Inc., in Kernesaw, Georgia, assembling the AiroCide Ti02, an anthrax-killing device about the size of a small coffee table. The anthrax-killing air scrubber, AiroCide Ti02, is a tabletop-size metal box that bolts to office ceilings or walls. Its fans draw in airborne spores and airflow forces them through a maze of tubes. Inside, hydroxyl radicals (OH-) attack and kill pathogens. Most remaining spores are destroyed by high-energy ultraviolet photons. Building miniature greenhouses for experiments on the International Space Station has led to the invention of this device that annihilates anthrax, a bacteria that can be deadly when inhaled. The research enabling the invention started at the University of Wisconsin's (Madison) Center for Space Automation and Robotics (WCSAR), one of 17 NASA Commercial Space Centers. A special coating technology used in this anthrax-killing invention is also being used inside WCSAR-built plant growth units on the International Space Station. This commercial research is managed by the Space Product Development Program at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
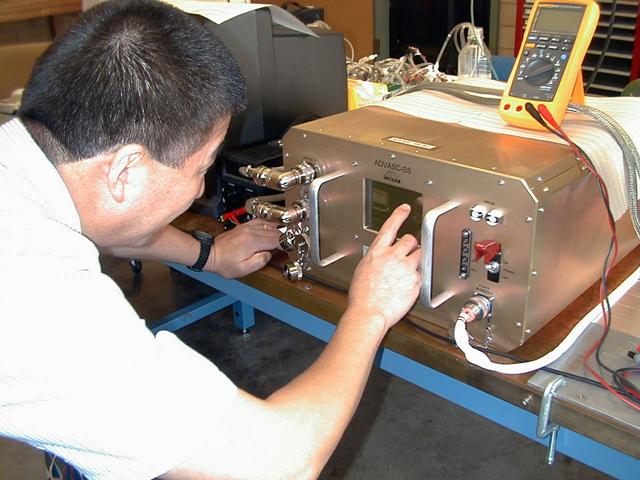

Dr. Weijia Zhou, director of the Wisconsin Center for Space Automation and Robotics at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, inspects the Advanced Astroculture(tm) plant growth unit before its first flight last spring. Coating technology is used inside the miniature plant greenhouse to remove ethylene, a chemical produced by plant leaves that can cause plants to mature too quickly. This same coating technology is used in a new anthrax-killing device. The Space Station experiment is managed by the Space Product Development Program at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. DuPont is partnering with NASA and the Wisconsin Center for Space Automation and Robotics (WCSAR) at the University of Wisconsin-Madison to grow soybeans aboard the Space Station to find out if they have improved oil, protein, carbohydrates or secondary metabolites that could benefit farmers and consumers. Principal Investigators: Dr. Tom Corbin, Pioneer Hi-Bred International Inc., a Dupont Company, with headquarters in Des Moines, Iowa, and Dr. Weijia Zhou, Wisconsin Center for Space Automation and Robotics (WCSAR), University of Wisconsin-Madison.