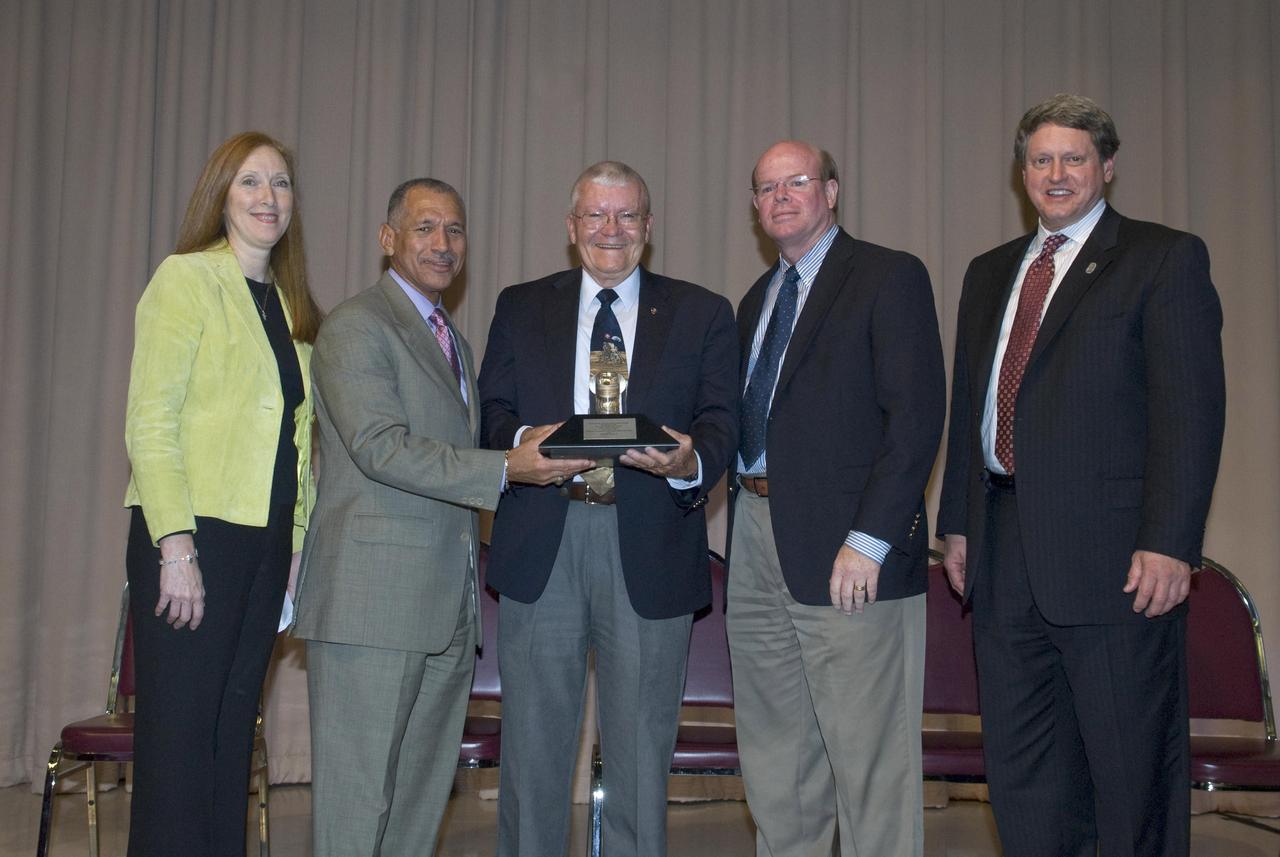

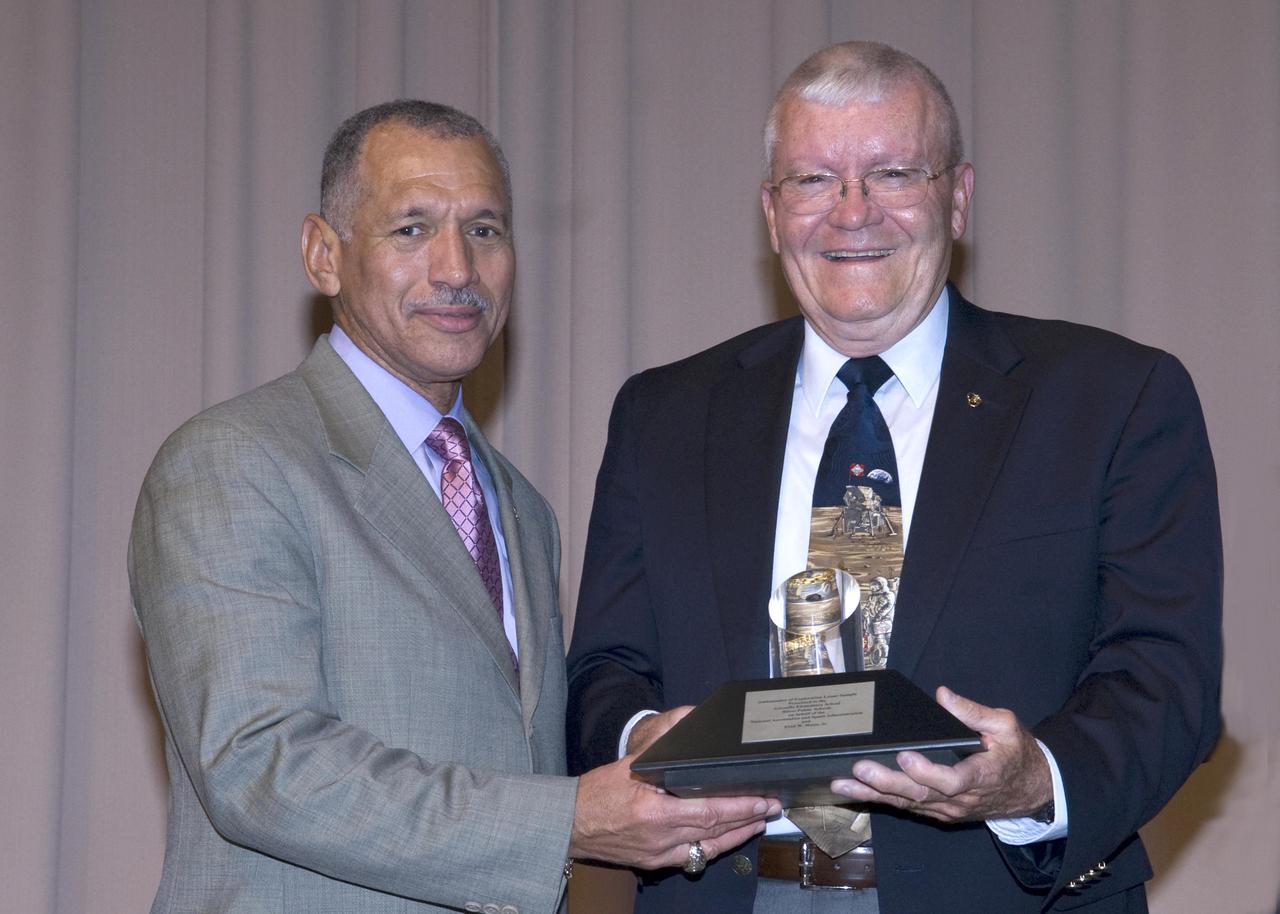
Apollo 13 astronaut and Biloxi native Fred Haise Jr. was honored for a lifetime of achievement with NASA's Ambassador of Exploration Award during a Dec. 2 ceremony at Gorenflo Elementary School in Biloxi. Haise subsequently presented the moon rock award to Gorenflo for display at the school. Participating in the ceremony were (l to r): Gorenflo Principal Tina Thompson, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, Haise, Biloxi Public School District Superintendent Paul Tisdale and Stennis Director Gene Goldman.
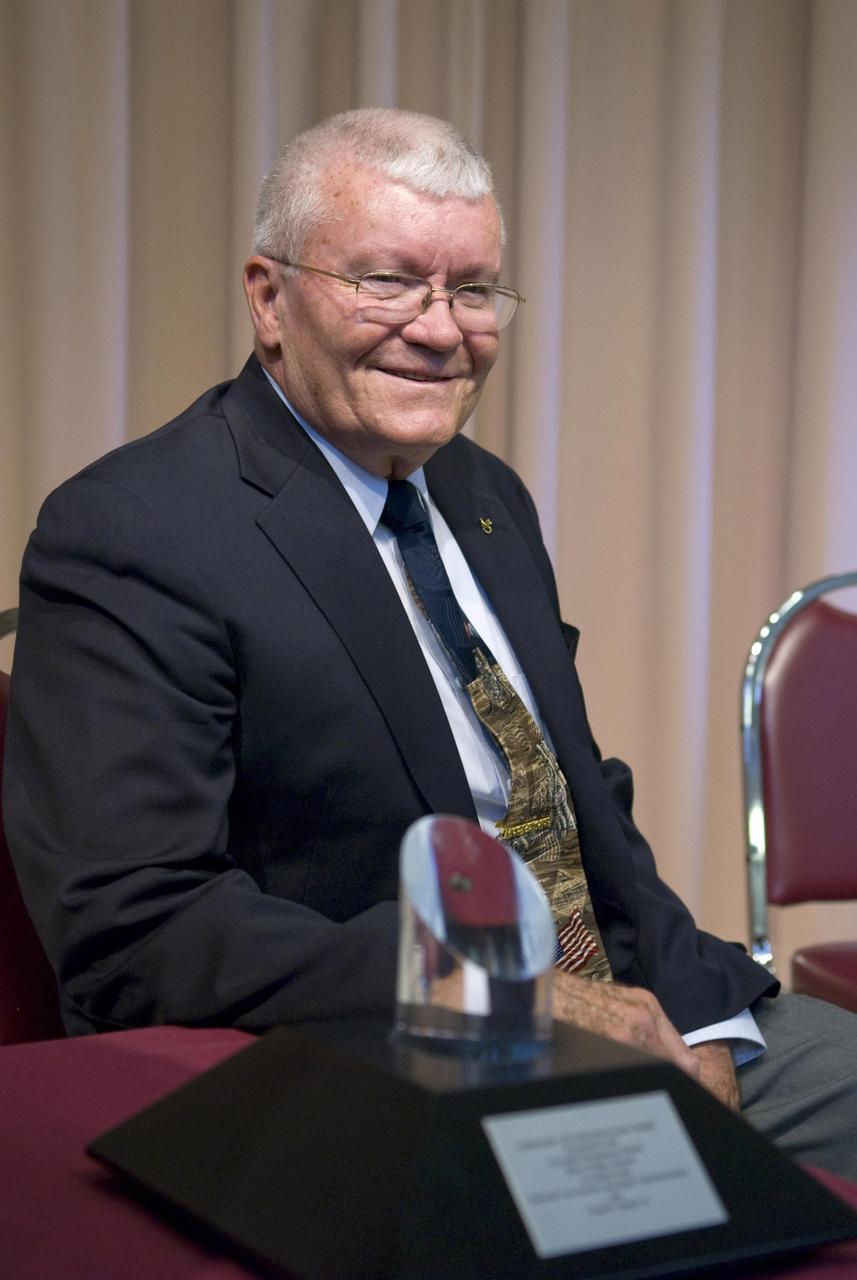

Apollo 13 astronaut and Biloxi native Fred Haise Jr. smiles during a Dec. 2 ceremony at Gorenflo Elementary School in Biloxi honoring his space career. During the ceremony, Haise was presented with NASA's Ambassador of Exploration Award (an encased moon rock). He subsequently presented the moon rock to Gorenflo officials for display at the school. Haise is best known as one of three astronauts who nursed a crippled Apollo 13 spacecraft back to Earth during a perilous 1970 mission. Although he was unable to walk on the moon as planned for that mission, Haise ended his astronaut career having logged 142 hours and 54 minutes in space. During the ceremony, he praised all those who contributed to the space program.
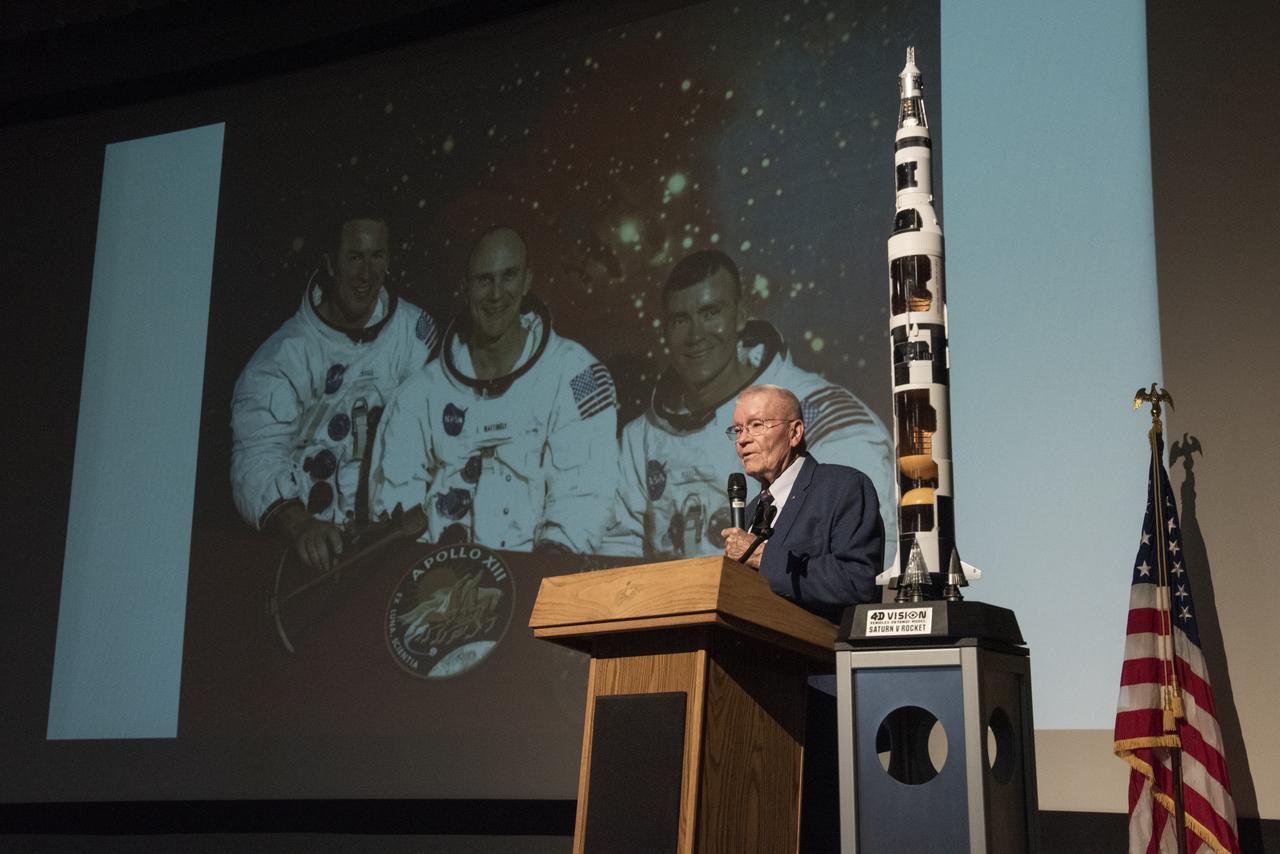

Apollo Astronaut Fred Haise speaks to a crowd of NASA and U.S Air Force employees at the Edwards Air Force Base theater about his career with NASA and as a military pilot. Haise stands on stage with a photo of former astronauts Jim Lovell and Jack Swigert who accompanied him on the Apollo 13 lunar mission in the background with a model of the Saturn V rocket.
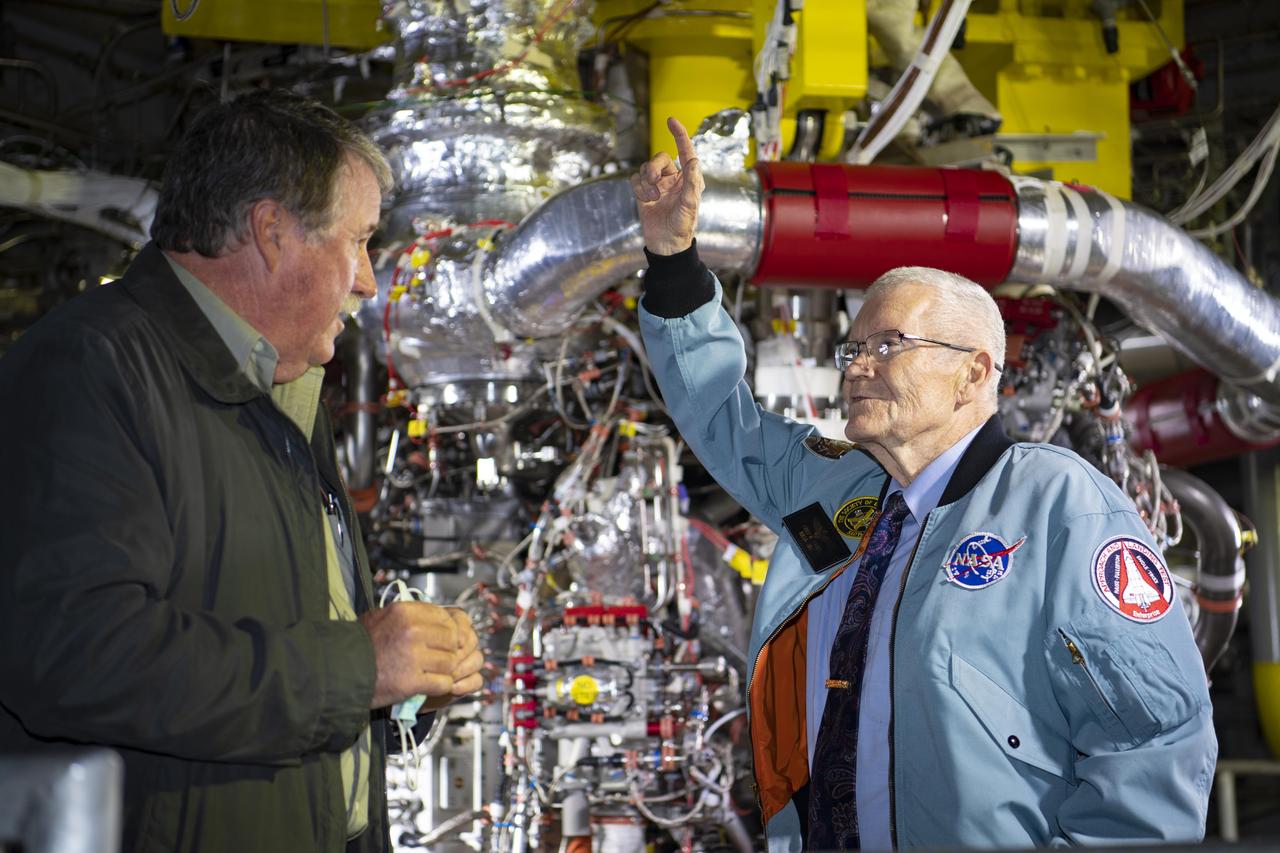

Apollo 13 Astronaut Fred Haise, right, stands in front of an RS-25 rocket engine installed on the A-1 Test Stand along with Jeff Henderson, test director at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The A-1 stand was dedicated to the former astronaut on Dec. 7, 2021 and is now officially known as the Fred Haise Test Stand.
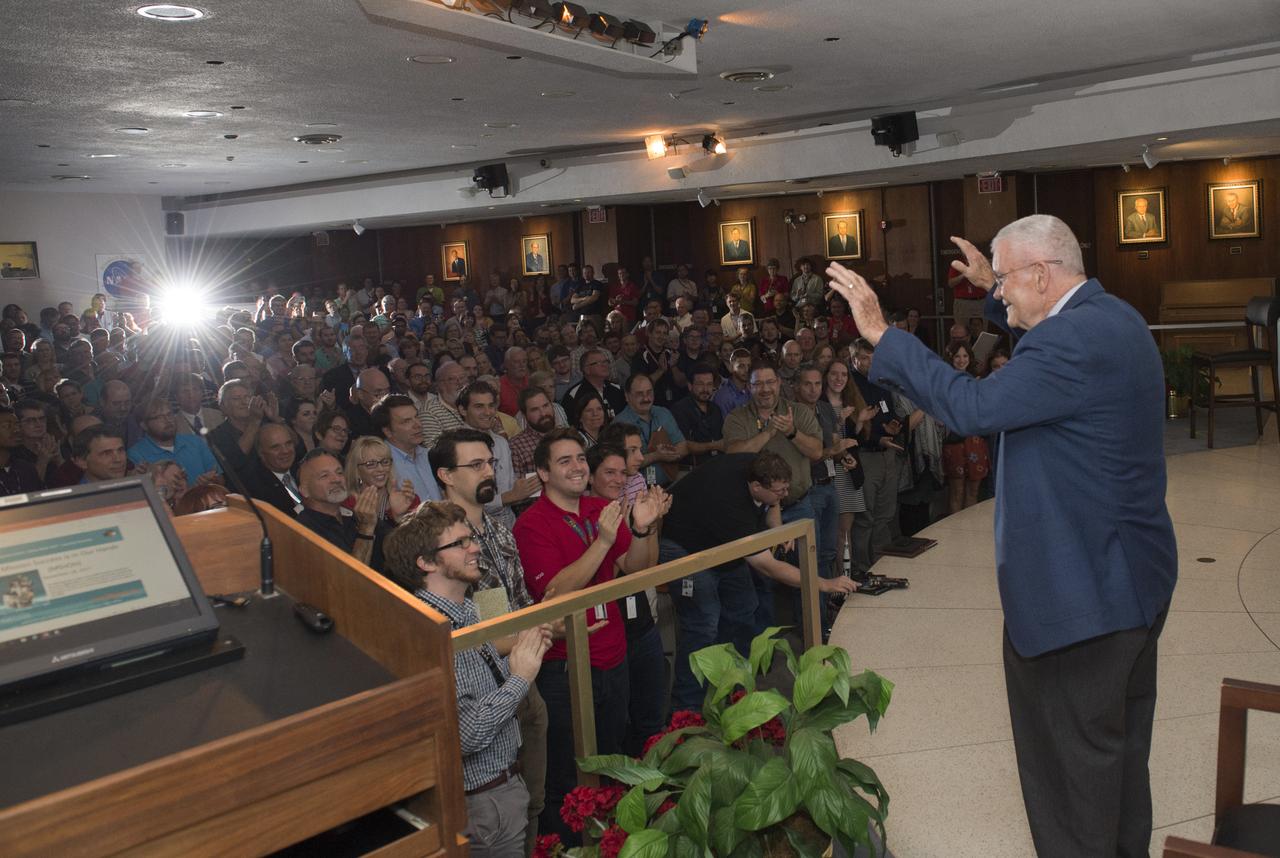

Former NASA astronaut Fred Haise Jr., right, part of the three-man Apollo 13 crew receives a standing ovation from members of the Marshall workforce Sept. 28 in Morris Auditorium.
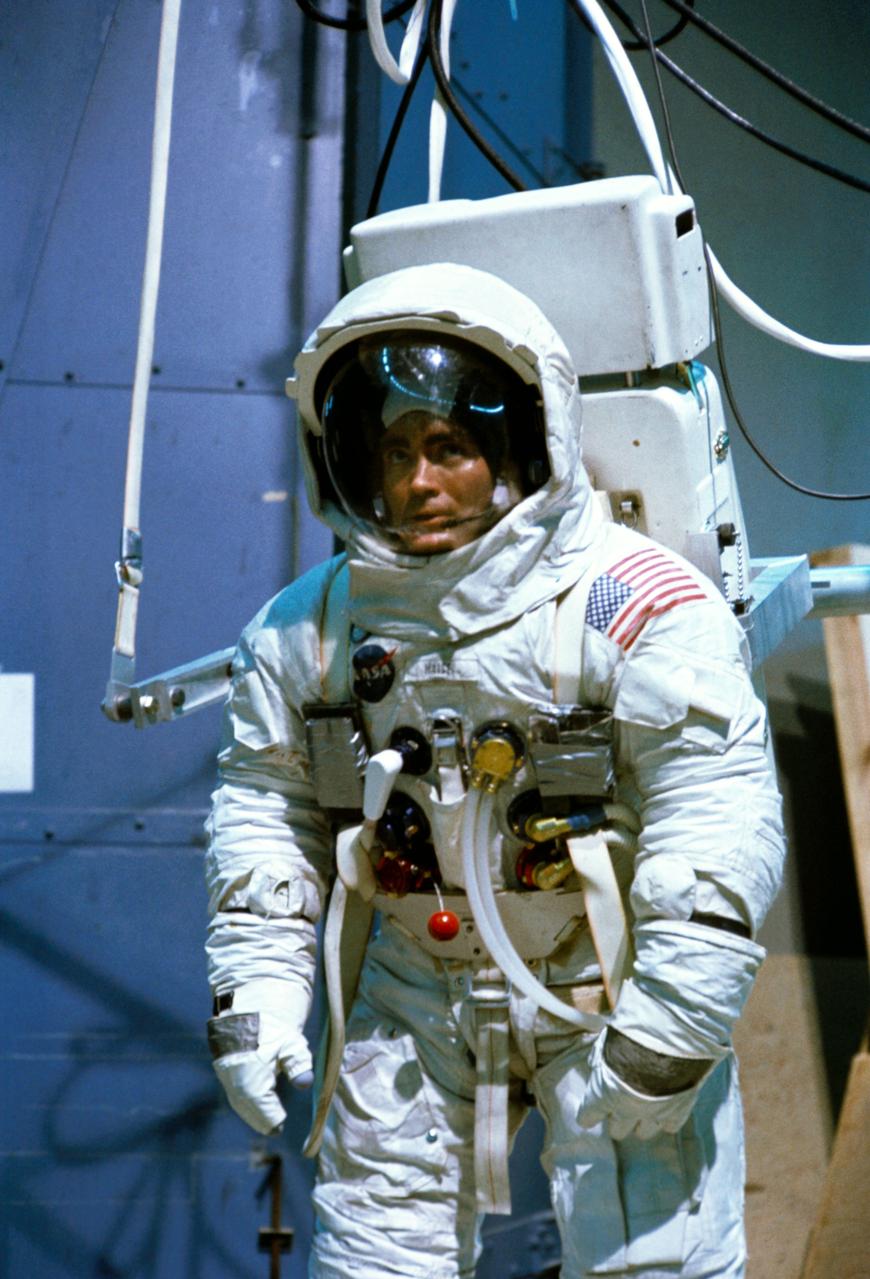

S70-24012 (19 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in lunar surface simulation training at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Haise is attached to a Six Degrees of Freedom Simulator.
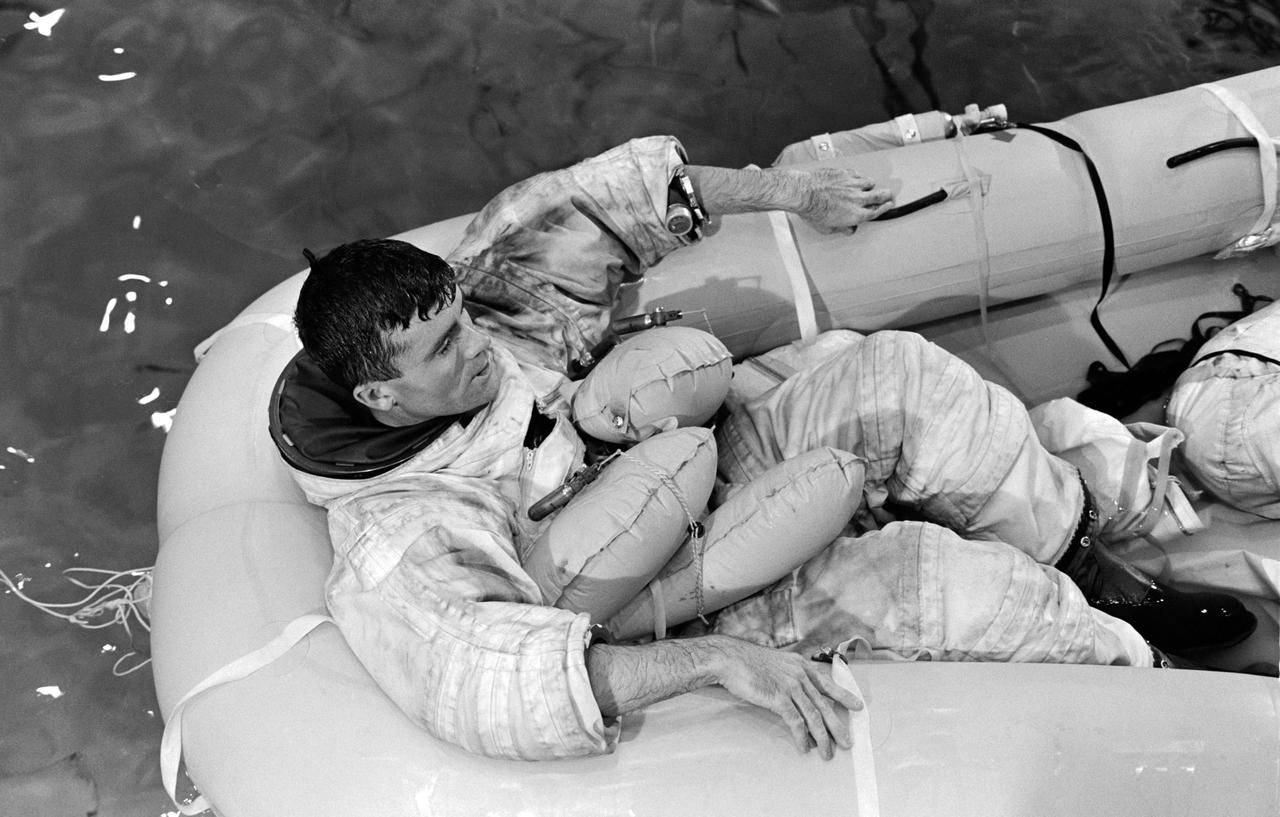

S70-31143 (17 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in water egress training in a water tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center.

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden (left) presents the Ambassador of Exploration Award (an encased moon rock) to Biloxi native and Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise Jr. (right) for his contributions to space exploration. During a Dec. 2 ceremony at Gorenflo elementary School in Biloxi, Miss., Bolden praised Haise for his overall space career and his performance on the Apollo 13 mission that was crippled two days after launch. Haise and fellow crewmembers nursed the spacecraft on a perilous trip back to Earth. 'The historic Apollo 13 mission was as dramatic as any Hollywood production,' Bolden said. 'When an explosion crippled his command module, Fred and his crewmates, Jim Lovell and Jack Swigert, guided their spacecraft around the moon and back to a successful splashdown in the Pacific Ocean - all while the world held its breath. While Fred didn't have the chance to walk on the moon, the cool courage and concentration in the face of crisis is among NASA's most enduring legacies.'
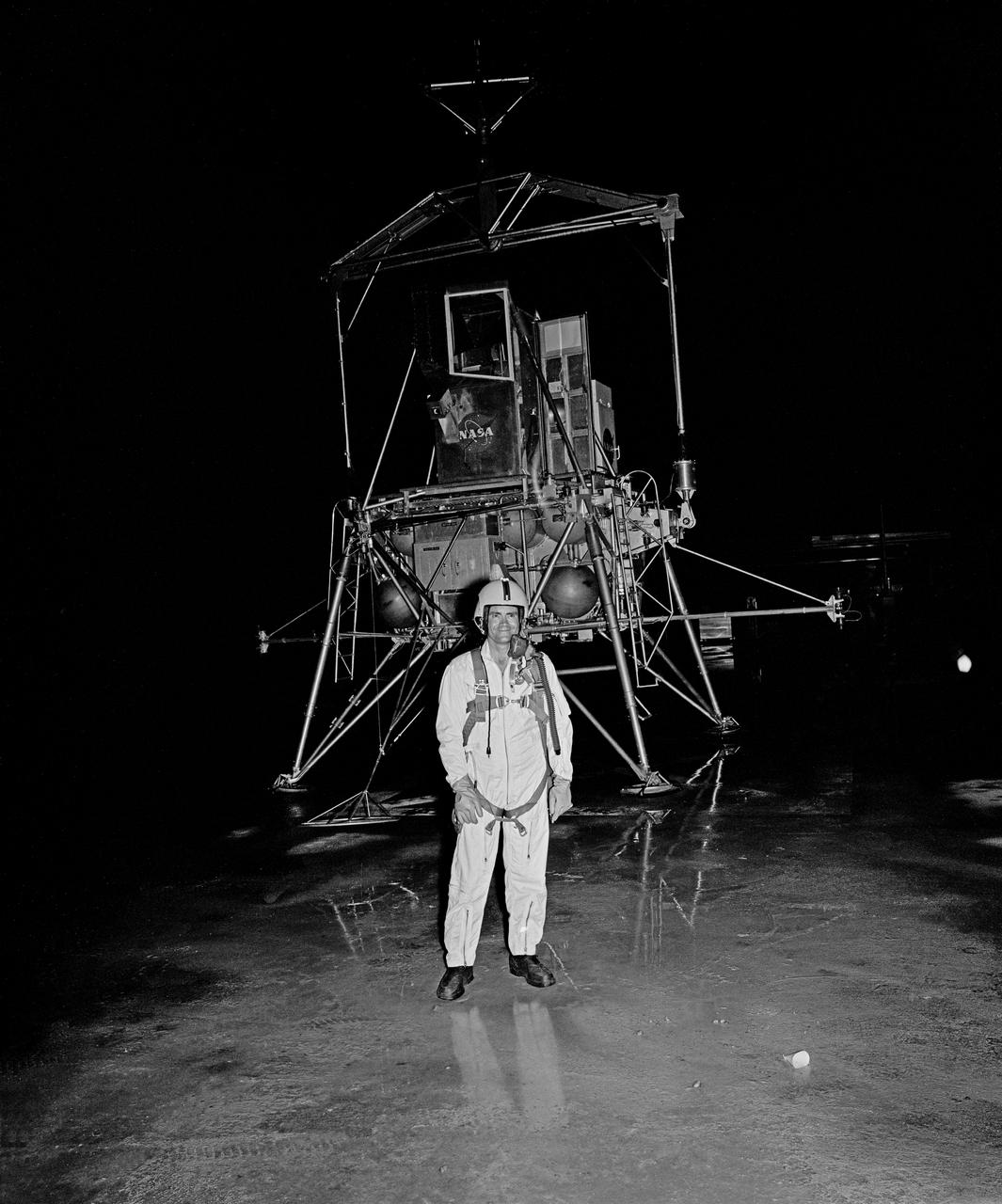

Astronaut Fred Wallace Haise, Jr. at NASA Langley Lunar Research Facility, Gantry test at night. Haise was the lunar module pilot on Apollo 13 (April 11-17, 1970) and has logged 142 hours and 54 minutes in space.
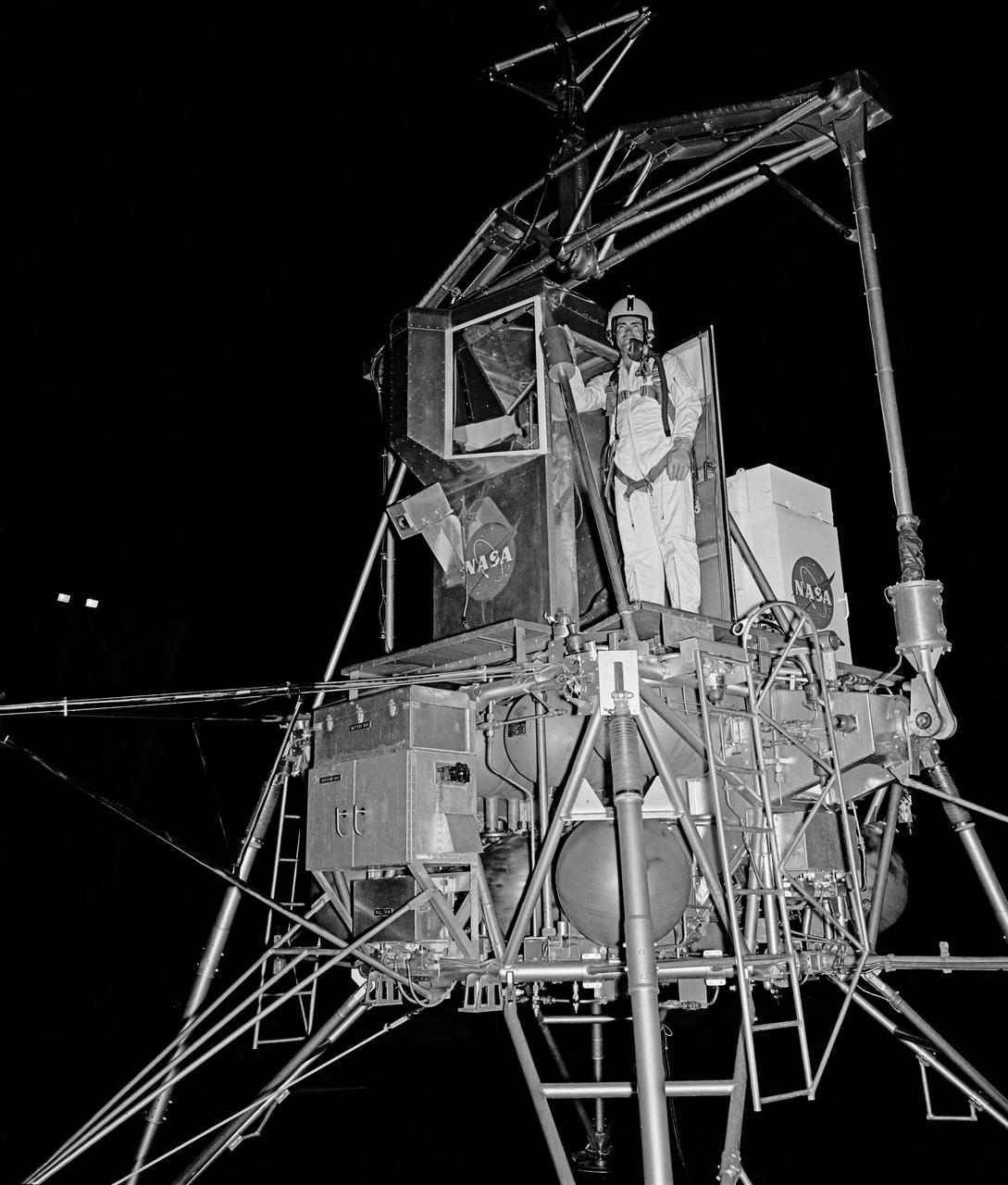

Astronaut Fred Wallace Haise, Jr. at NASA Langley Lunar Research Facility, Gantry test at night. Haise was the lunar module pilot on Apollo 13 (April 11-17, 1970) and has logged 142 hours and 54 minutes in space.
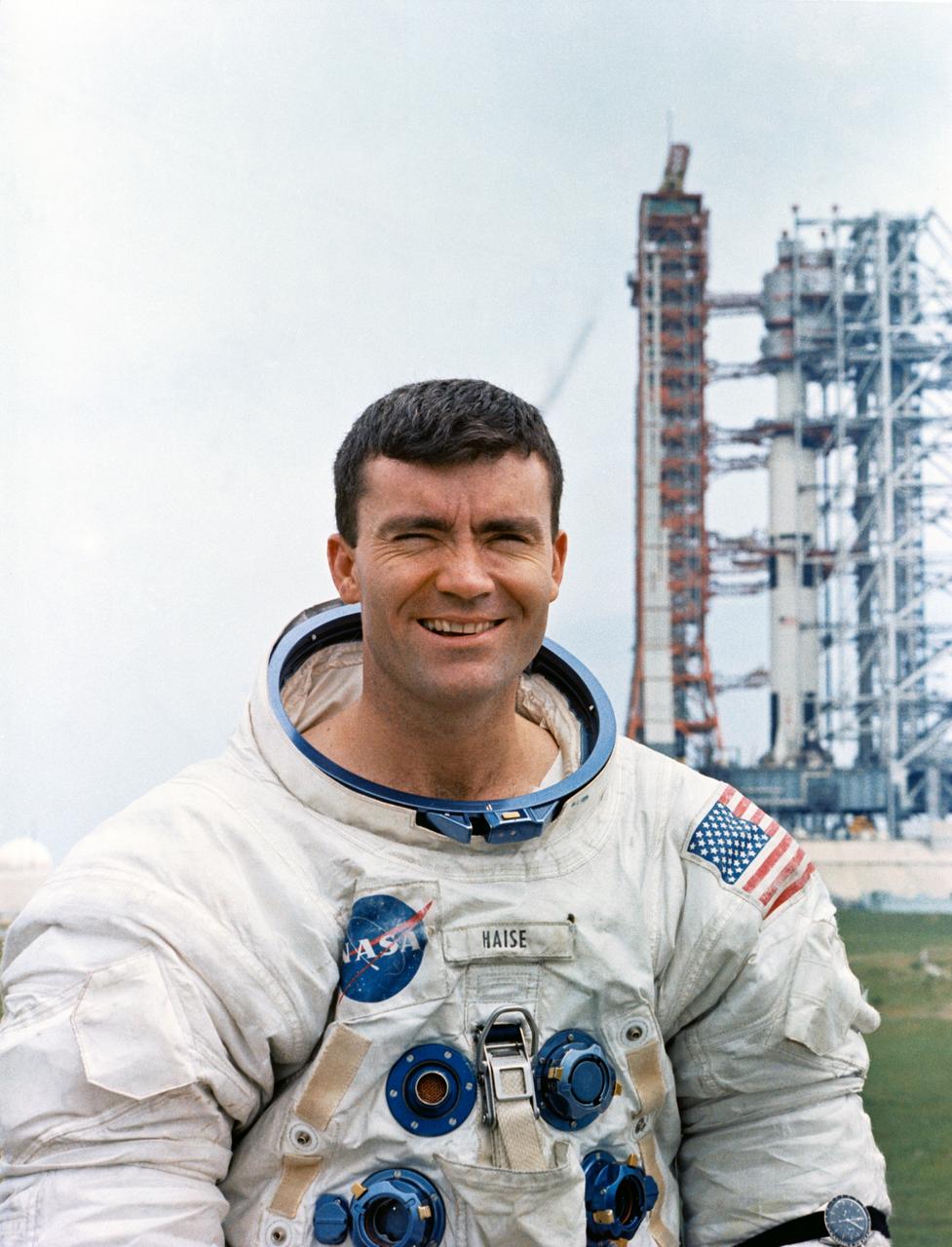

S70-34267 (April 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. Photo credit: NASA (Note, this is not the official Apollo portrait for Fred Haise)
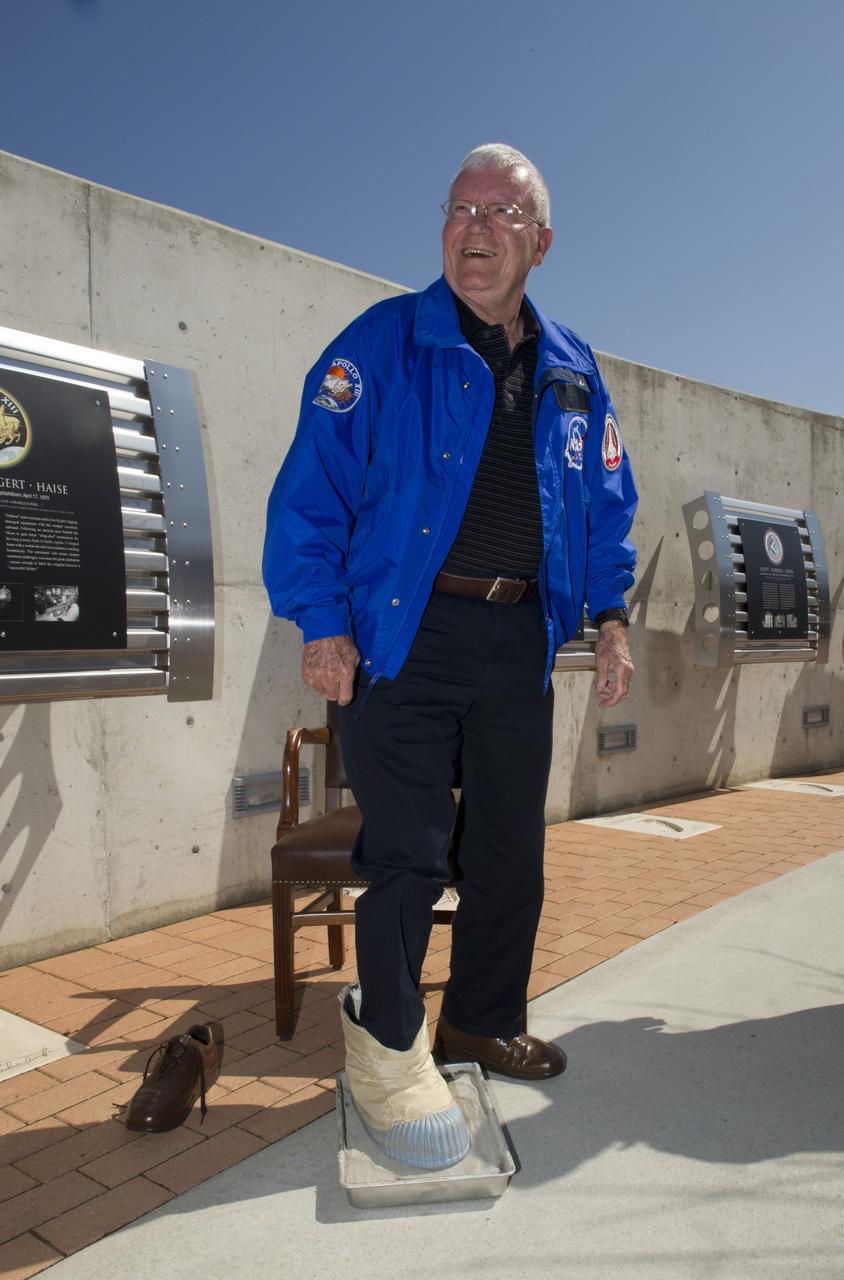

APOLLO 13 ASTRONAUT FRED HAISE CASTS FOOTPRINT AT USSRC DAVIDSON CENTER
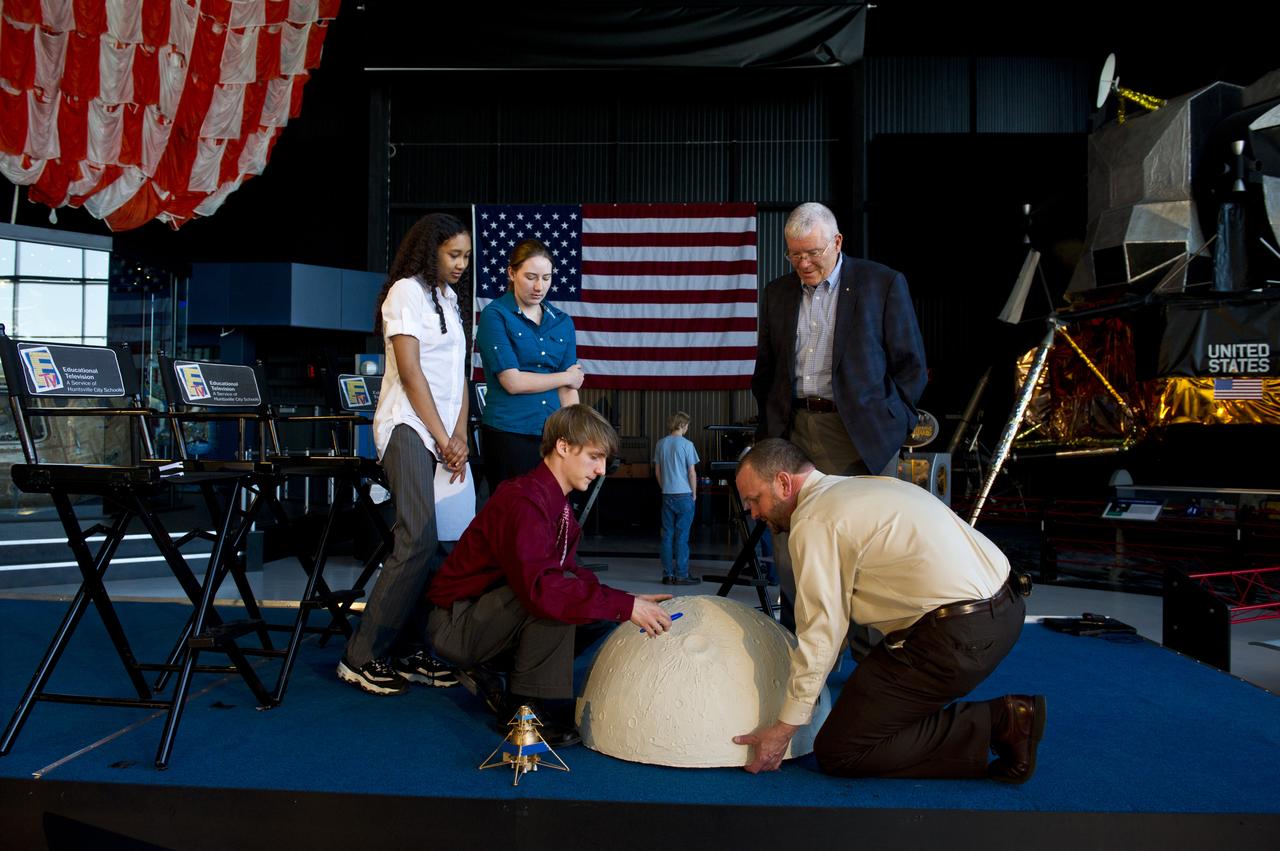

STUDENTS FROM THE CENTER FOR TECHNOLOGY SHOW APOLLO 13 ASTRONAUT FRED HAISE A DISPLAY MODEL FOR A MOON BASED PROJECT THEY ARE DESIGNING FOR COMPETITION WITH OTHER SCHOOLS IN ALABAMA. (L to R) QUIANA HUNT, SARAH FOLSE, MICHAEL HARTMAN, MIKE EVANS (TEACHER), AND FRED HAISE
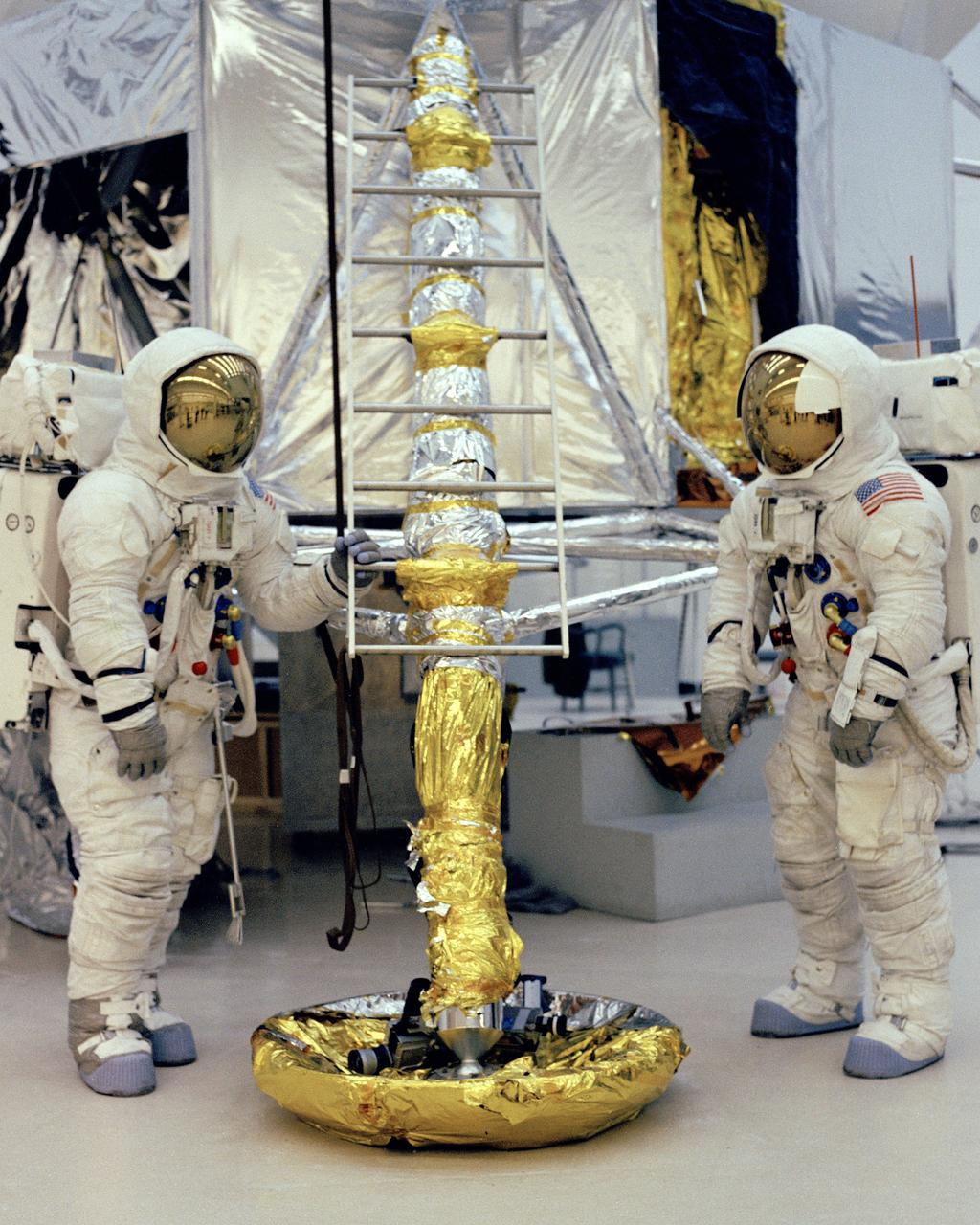

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Apollo 13 astronauts James A. Lovell, Jr., commander, and Fred W. Haise, Jr., lunar module pilot, practice their EVA training in preparation for their mission. Photo credit: NASA
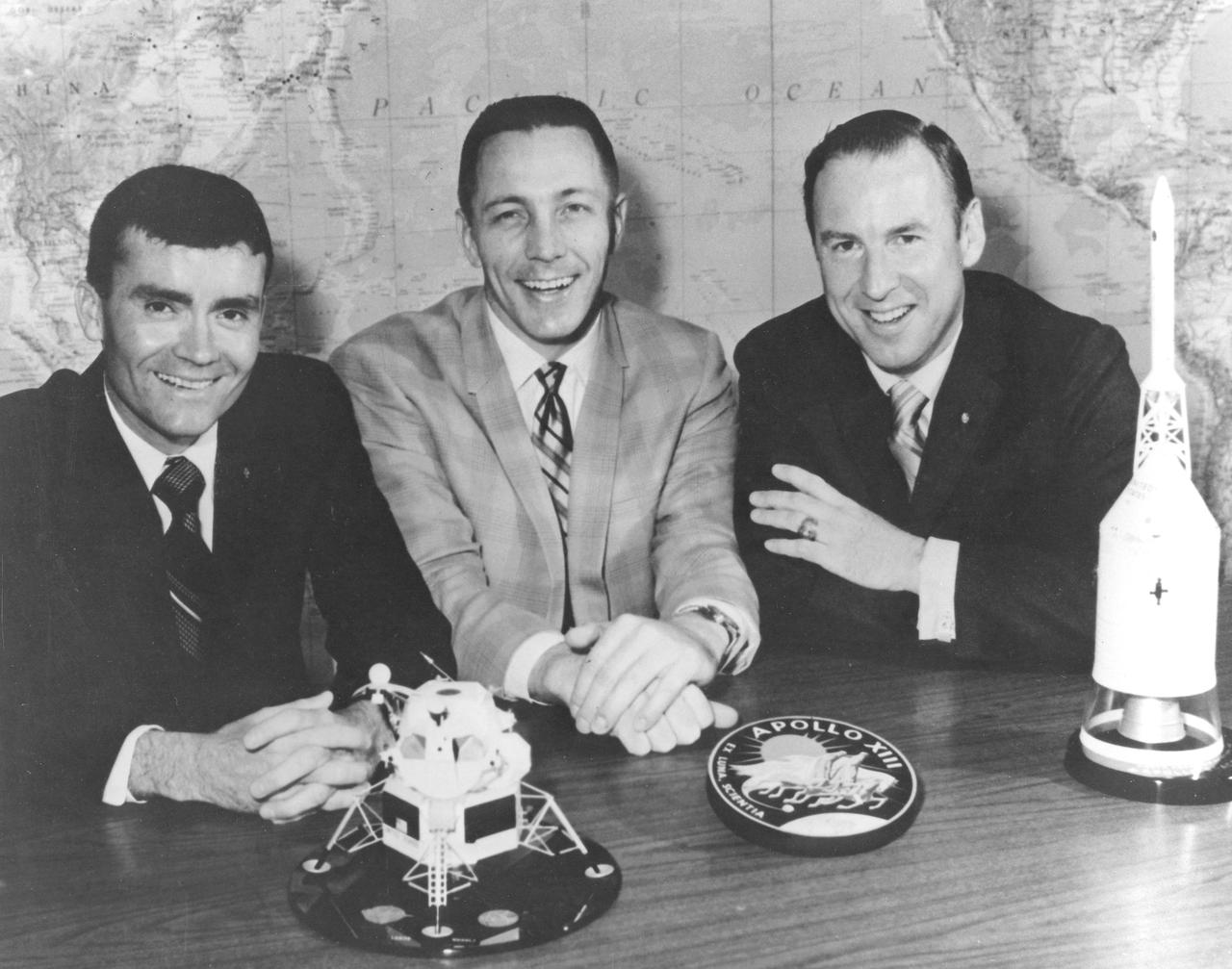

Apollo 13 astronauts Fred Haise, John Swigert, and James Lovell are pictured during the press conference after their ill-fated mission. The Apollo 13 mission (the third lunar landing mission) was aborted after 56 hours of flight, 205,000 miles from Earth, when an oxygen tank in the service module exploded.
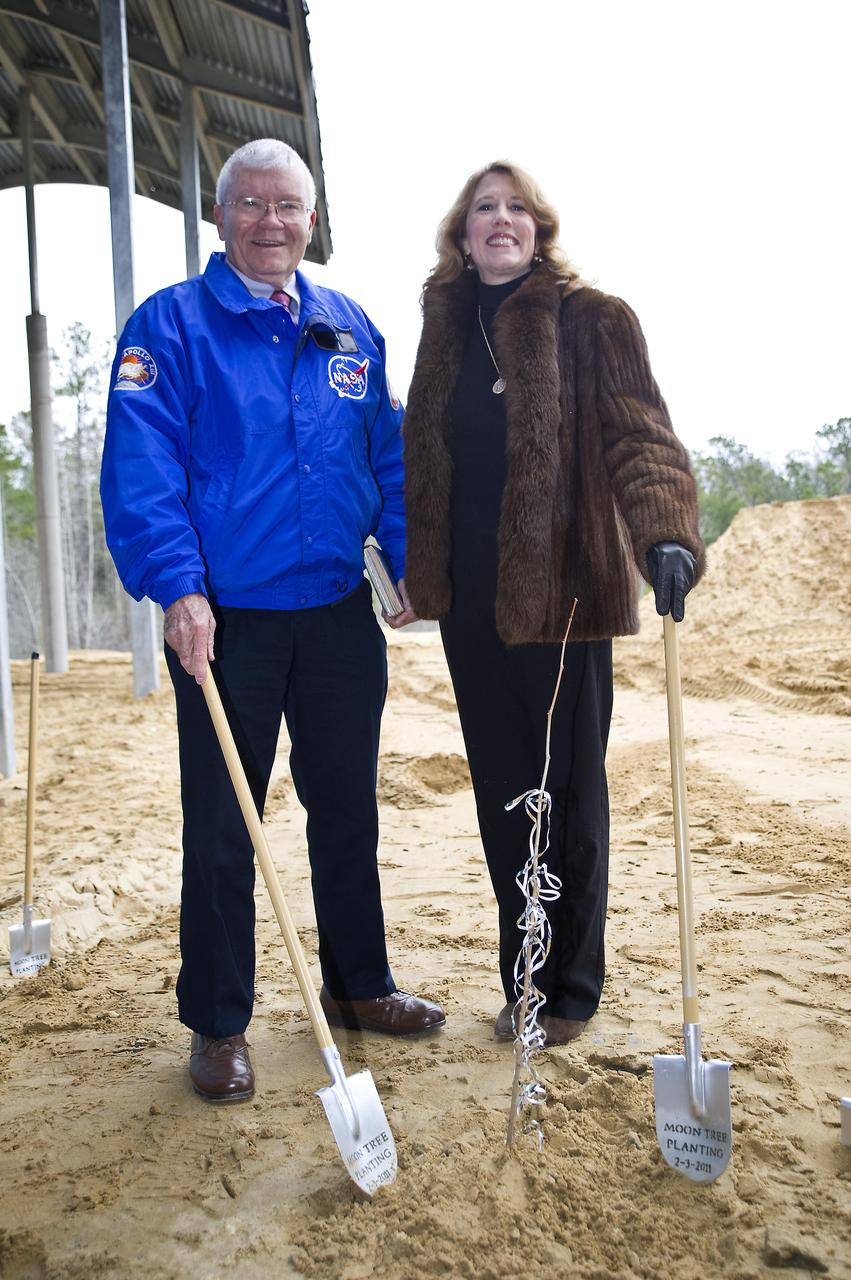

Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise stands with Rosemary Roosa, daughter of late Apollo 14 astronaut Stuart Roosa, beside a 'moon tree' planted at the INFINITY science center on Feb. 3, 2011. The moon tree is a descendent of seeds carried into space by Stuart Roosa on the Apollo 14 mission in 1971.
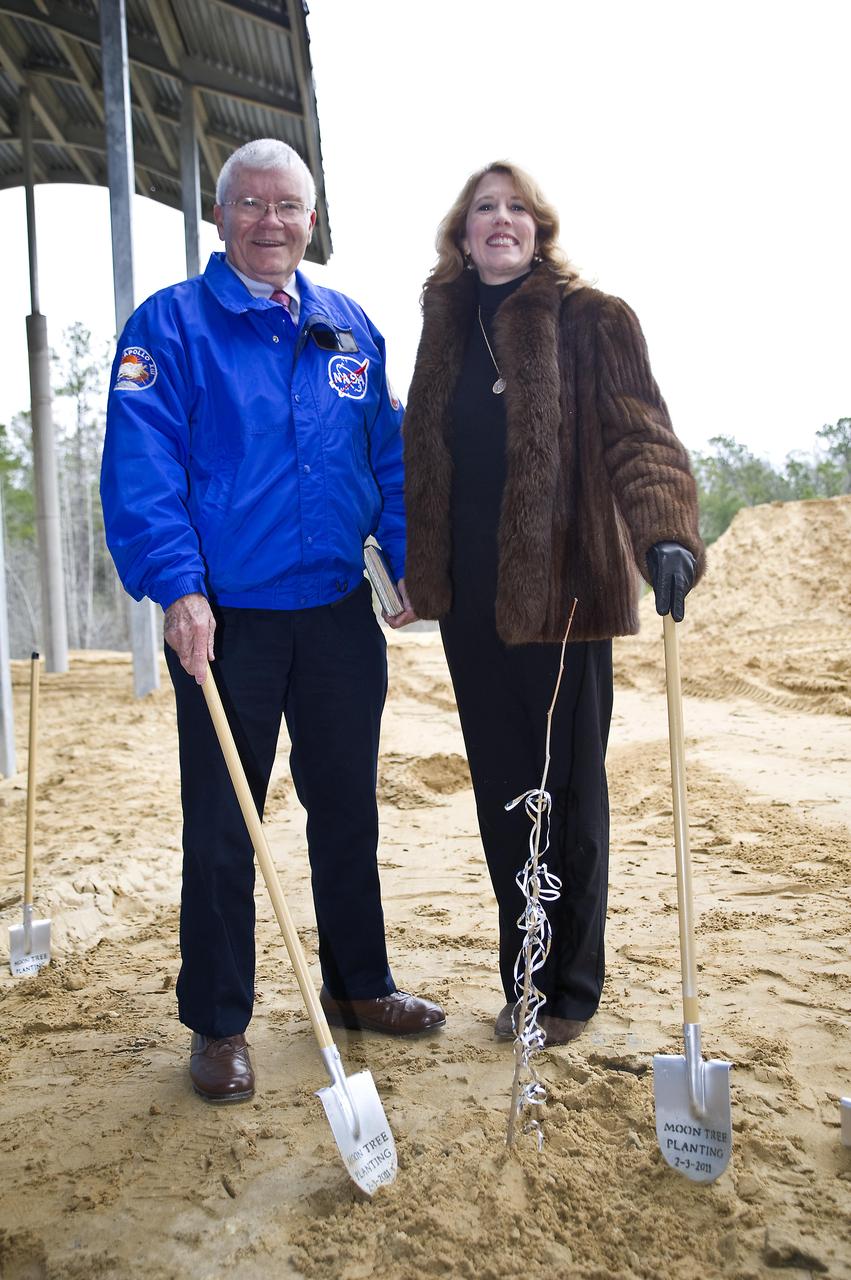

Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise stands with Rosemary Roosa, daughter of late Apollo 14 astronaut Stuart Roosa, beside a 'moon tree' planted at the INFINITY science center on Feb. 3, 2011. The moon tree is a descendent of seeds carried into space by Stuart Roosa on the Apollo 14 mission in 1971.
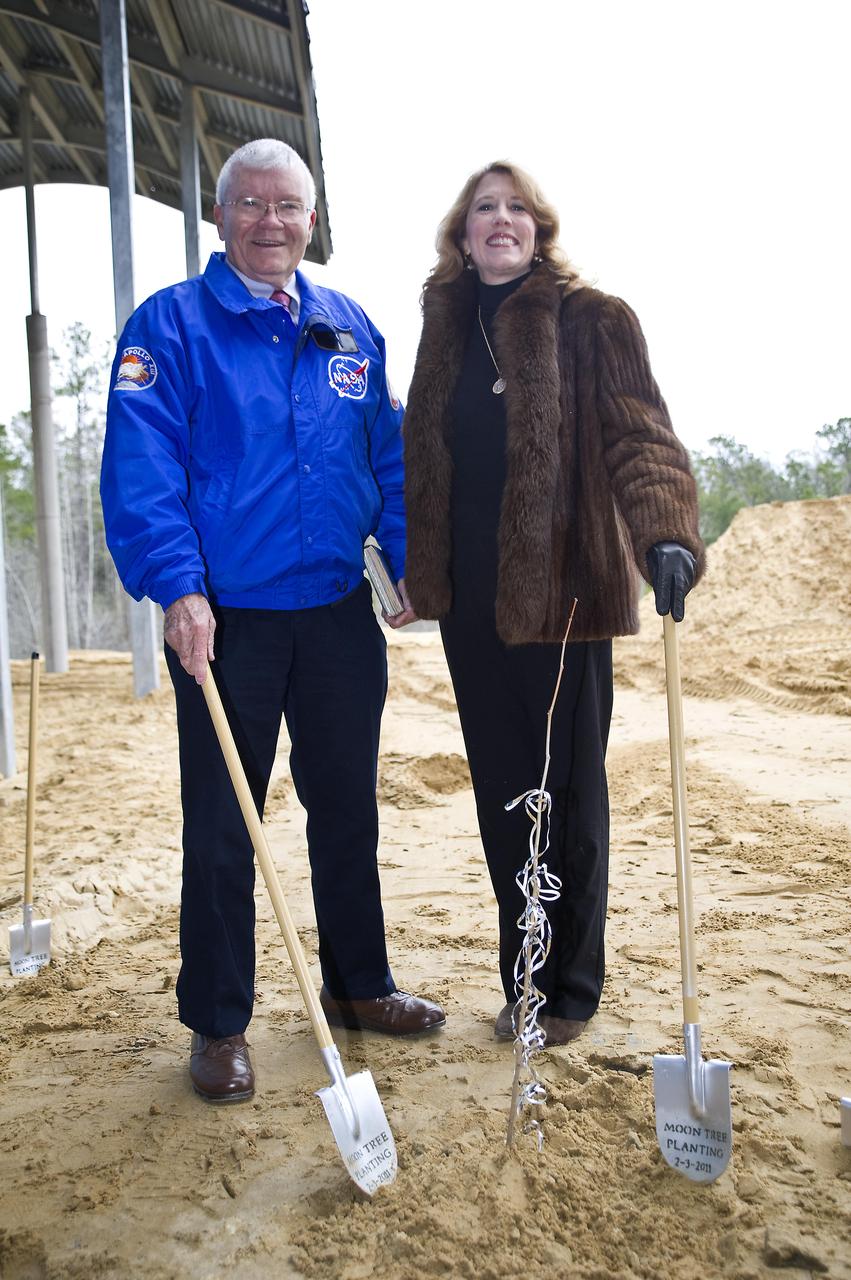

Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise stands with Rosemary Roosa, daughter of late Apollo 14 astronaut Stuart Roosa, beside a 'moon tree' planted at the INFINITY science center on Feb. 3, 2011. The moon tree is a descendent of seeds carried into space by Stuart Roosa on the Apollo 14 mission in 1971.
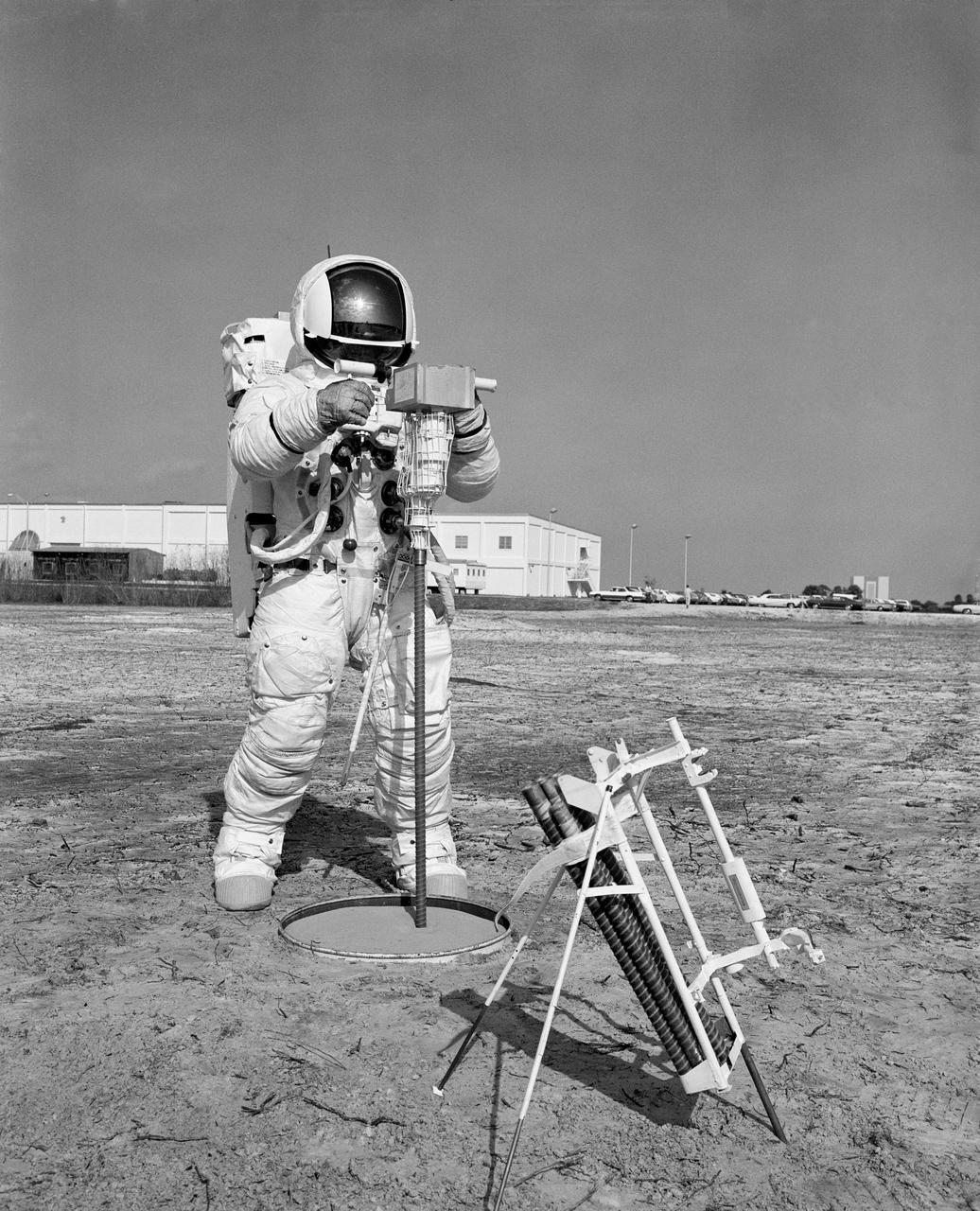

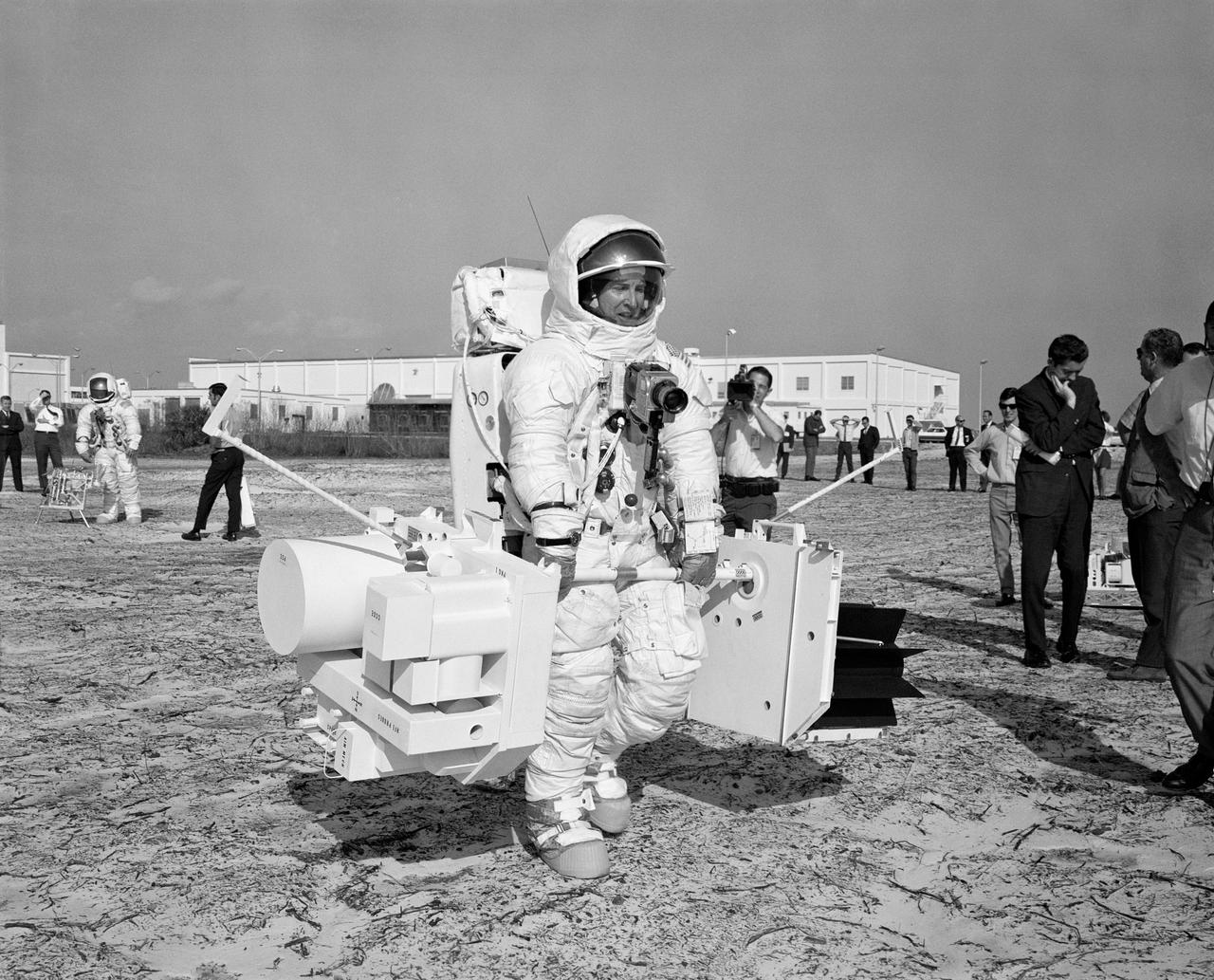
S70-29673 (28 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in a walk-through of the extravehicular activity timeline at the Kennedy Space Center. Here, Haise uses an Apollo Lunar Surface Drill to dig a three-meter heat flow probe hole. The heat flow experiment on Apollo 13 will have an electronic instrument which will measure the outward flux of heat from the moon?s interior.
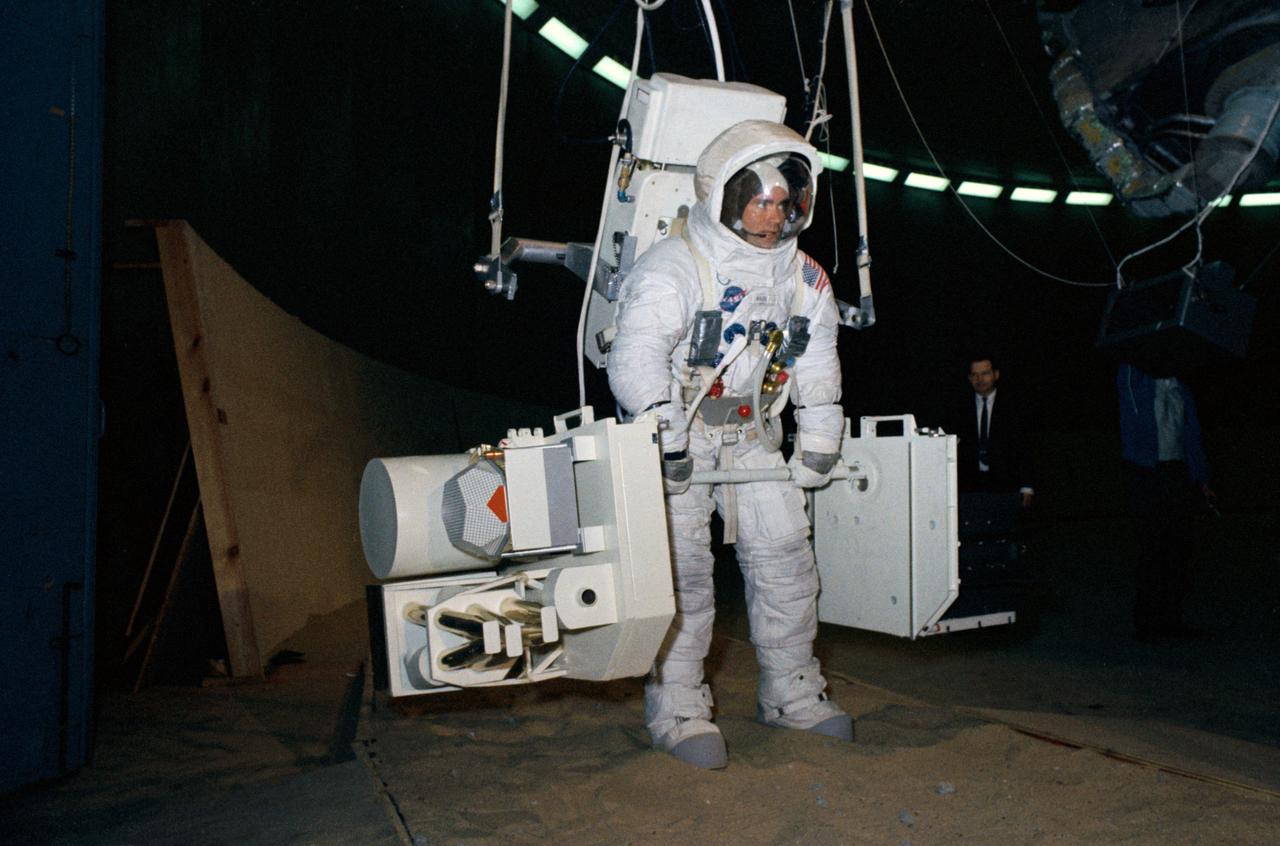

S70-24009 (19 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., Apollo 13 lunar module pilot, trains for his scheduled April lunar space walk at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Haise carries a training version of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP), while connected to a "Six Degrees of Freedom" simulator. Out of frame is astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander, who will share the lunar extravehicular activity (EVA) with Haise. EDITOR'S NOTE: In April 1970 the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) experienced an explosion en route to the moon. The three-man crew was forced to circumnavigate the moon and return to Earth.
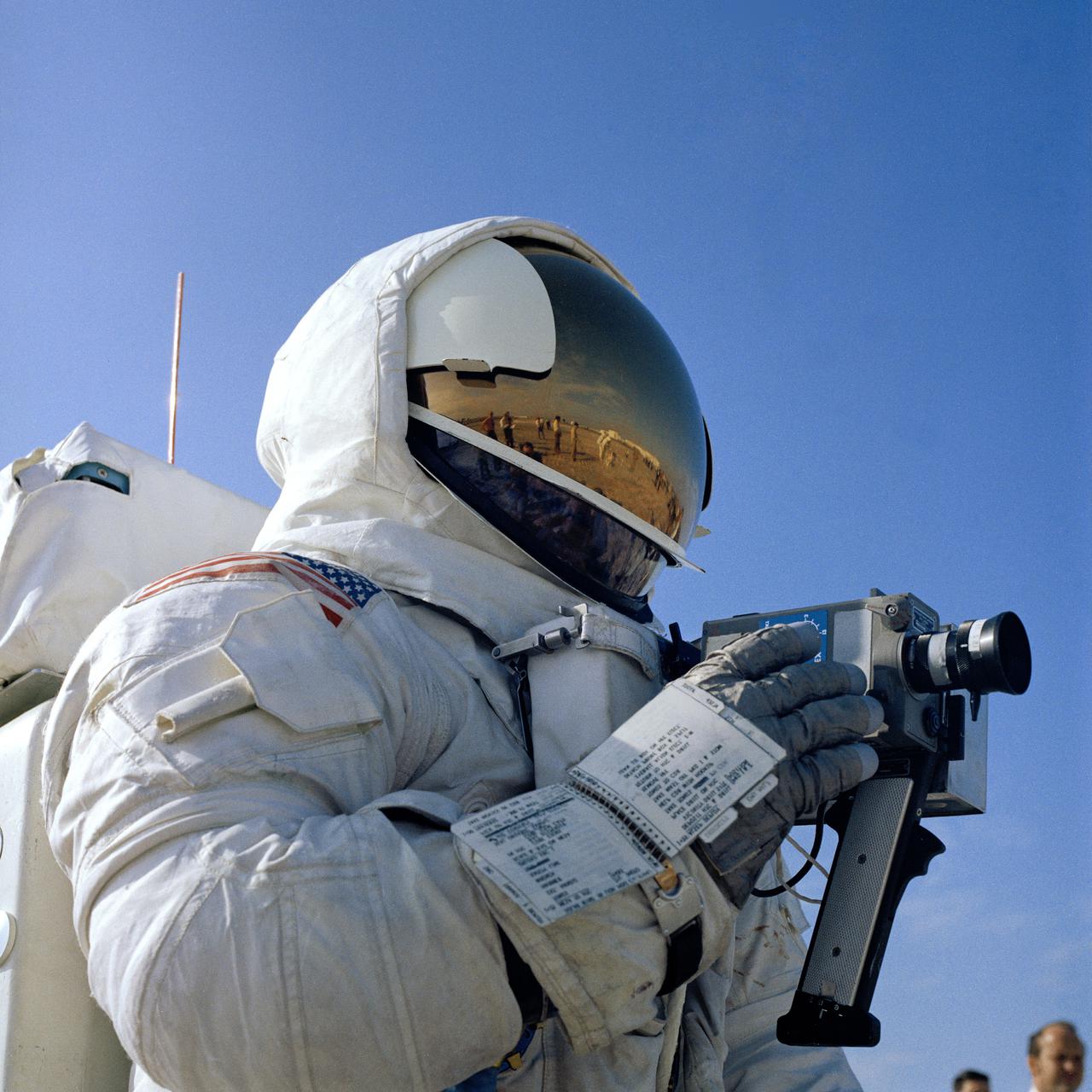

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., Apollo 13 lunar module pilot, practices operation of the 16-millimeter motion picture camera to be used on the lunar surface during the Apollo 13 mission. The Apollo 13 landing is scheduled for the Fra Mauro, a highlands area approximately 95 miles east of the Apollo 12 landing site in November 1969. Apollo 13, scheduled for launch from Kennedy Space Center on April 11, has a prime crew composed of Haise, James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot. Photo credit: NASA
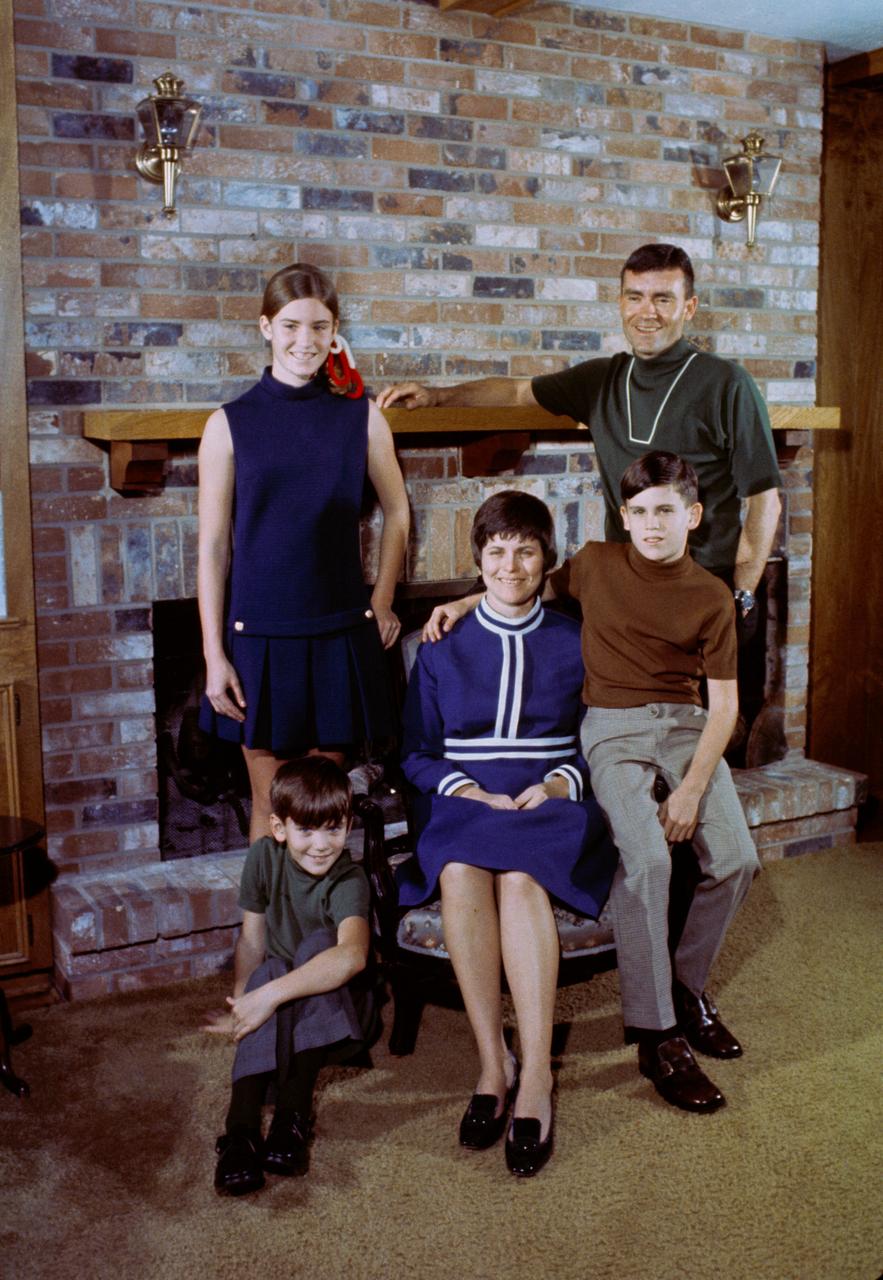

S70-30580 (March 1970) --- This is a family portrait of astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr. and his family. Haise is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. The family includes: Mary M. (standing on left), born on Jan. 25, 1956; Frederick T. (seated on arm of chair), born on May 13, 1958; Stephen W. (seated on floor), born on June 30, 1961; and Mrs. Haise, the former Mary Griffin Grant.
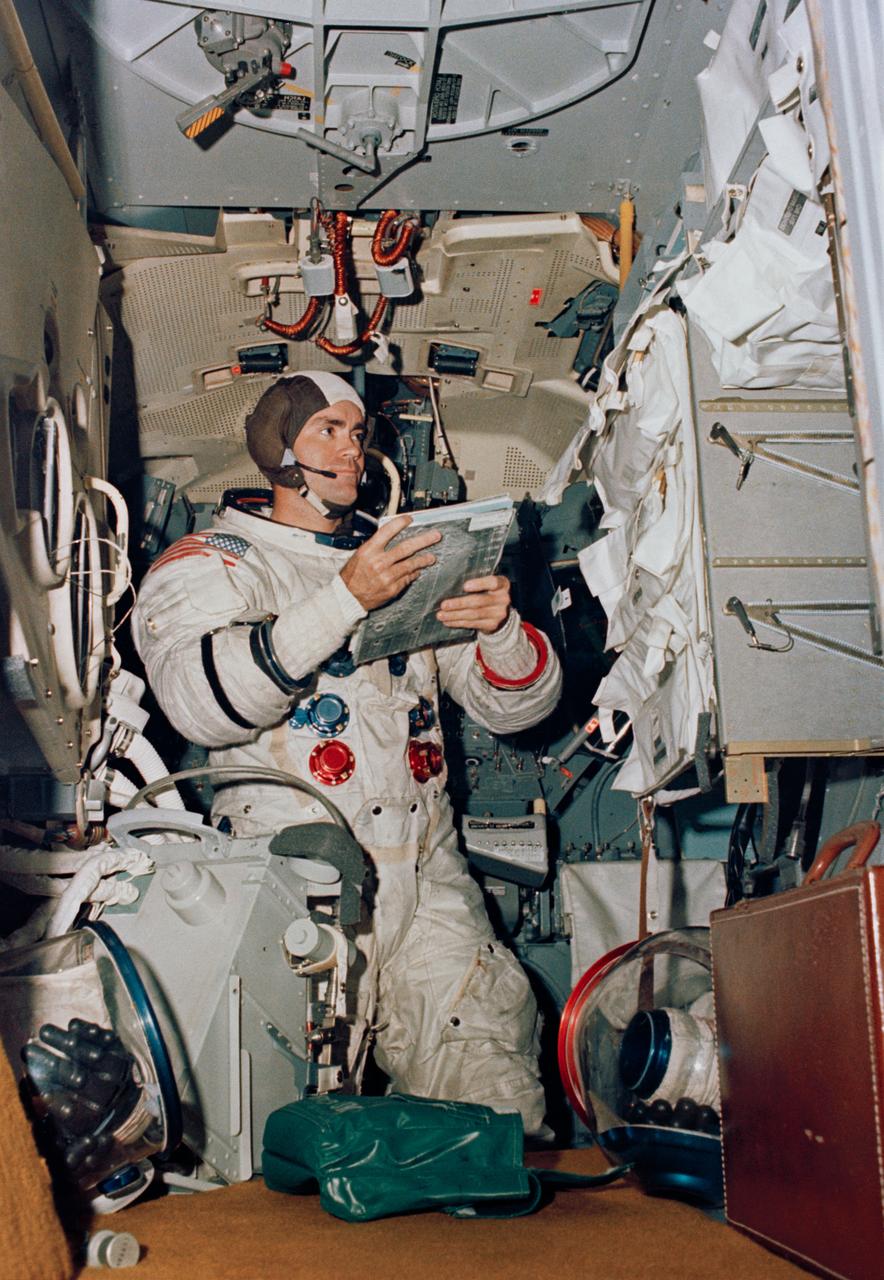

S70-34412 (4 April 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., Apollo 13 lunar module pilot, participates in simulation training in preparation for the scheduled lunar landing mission. He is in the Apollo Lunar Module Mission Simulator in the Kennedy Space Center's Flight Crew Training building.
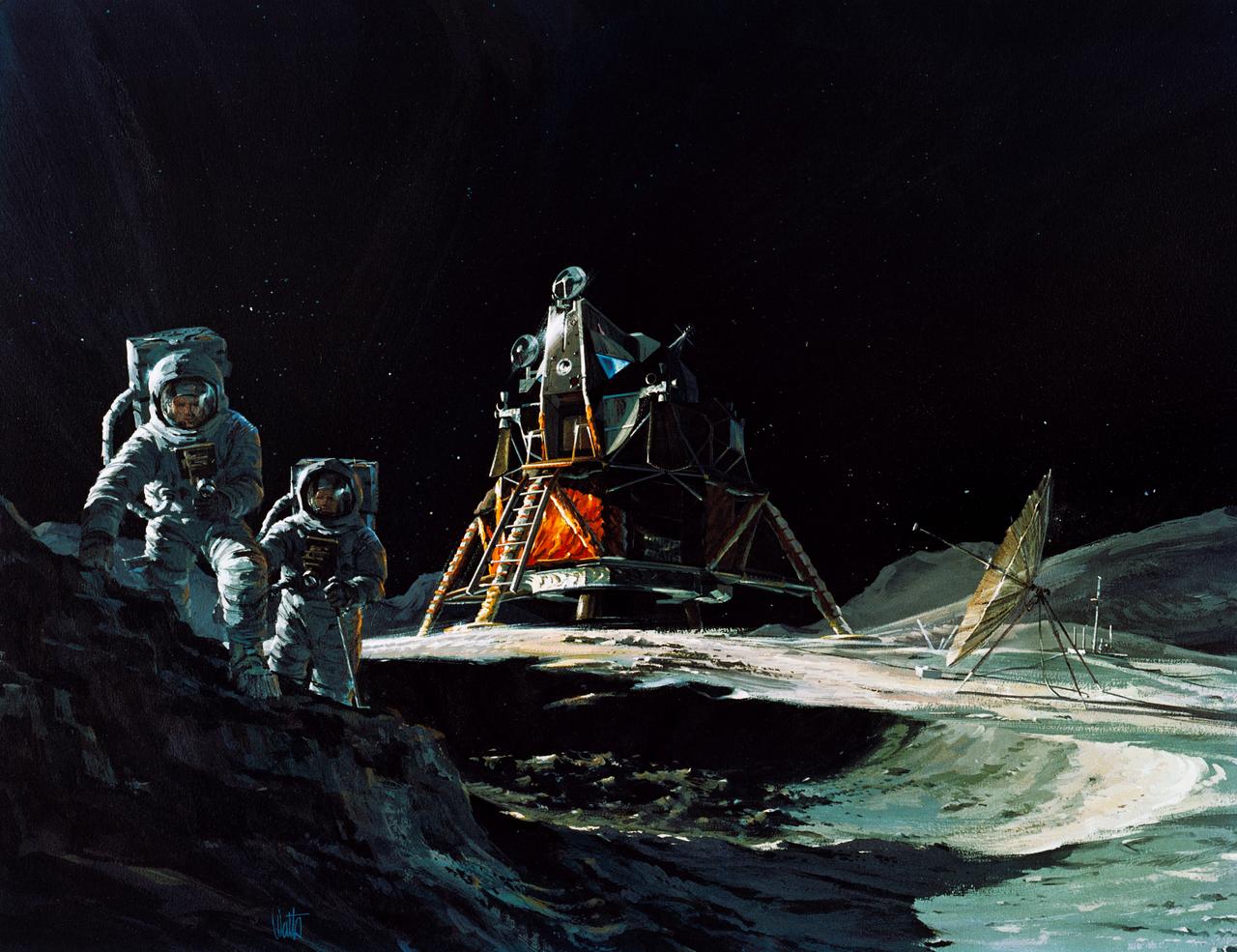

S70-31774 (March 1970) --- An artist's concept by Teledyne Ryan Aeronautical, San Diego, California, showing two Apollo 13 astronauts exploring the surface of the moon. In the center background is the Lunar Module (LM). Apollo 13 will land in the rugged highlands just north of Fra Mauro. The crew of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission will be astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Lovell and Haise are represented by the two men in this picture.
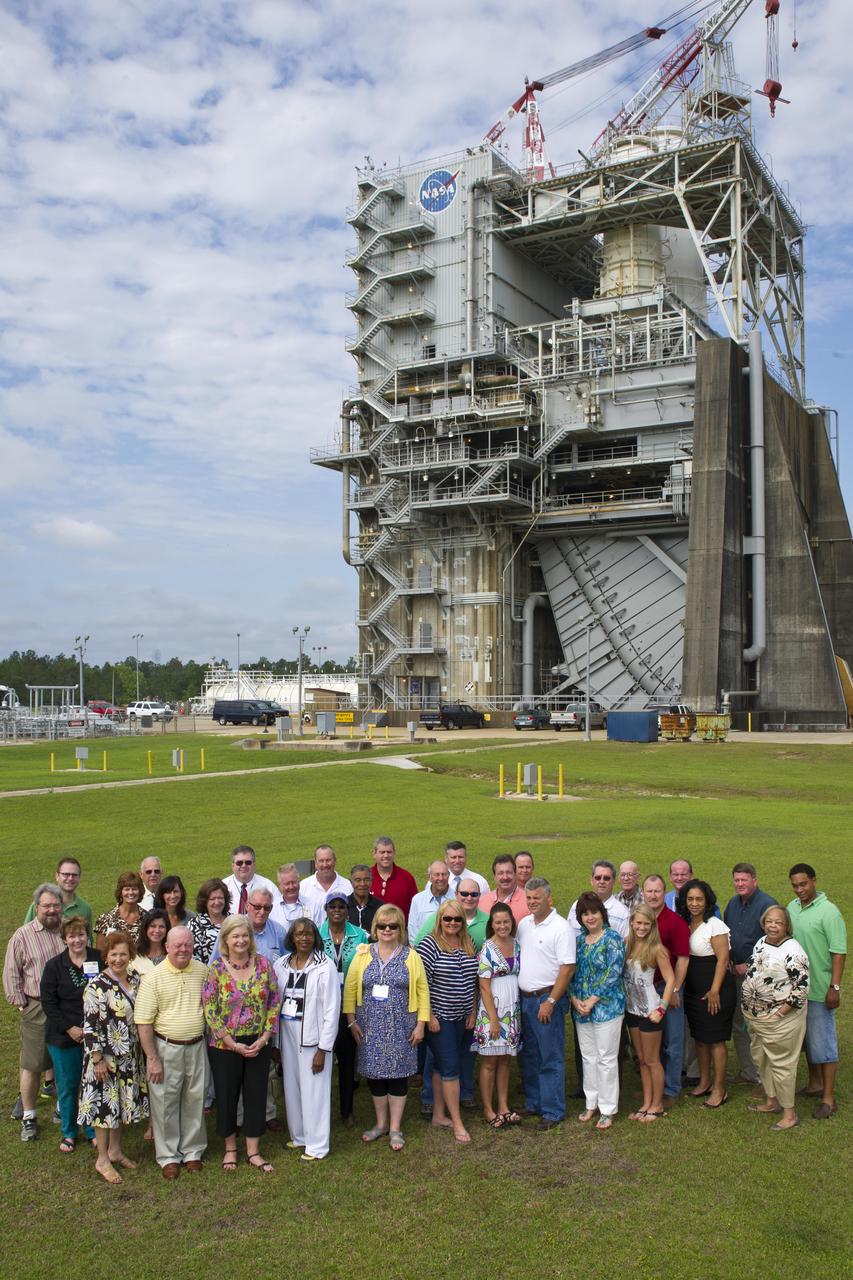

Legislators from across Mississippi visited Stennis Space Center on May 7, 2012, touring various facilities, including the A-1 Test Stand, and learning about work under way at the facility. The legislators also toured the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility and met with Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise.
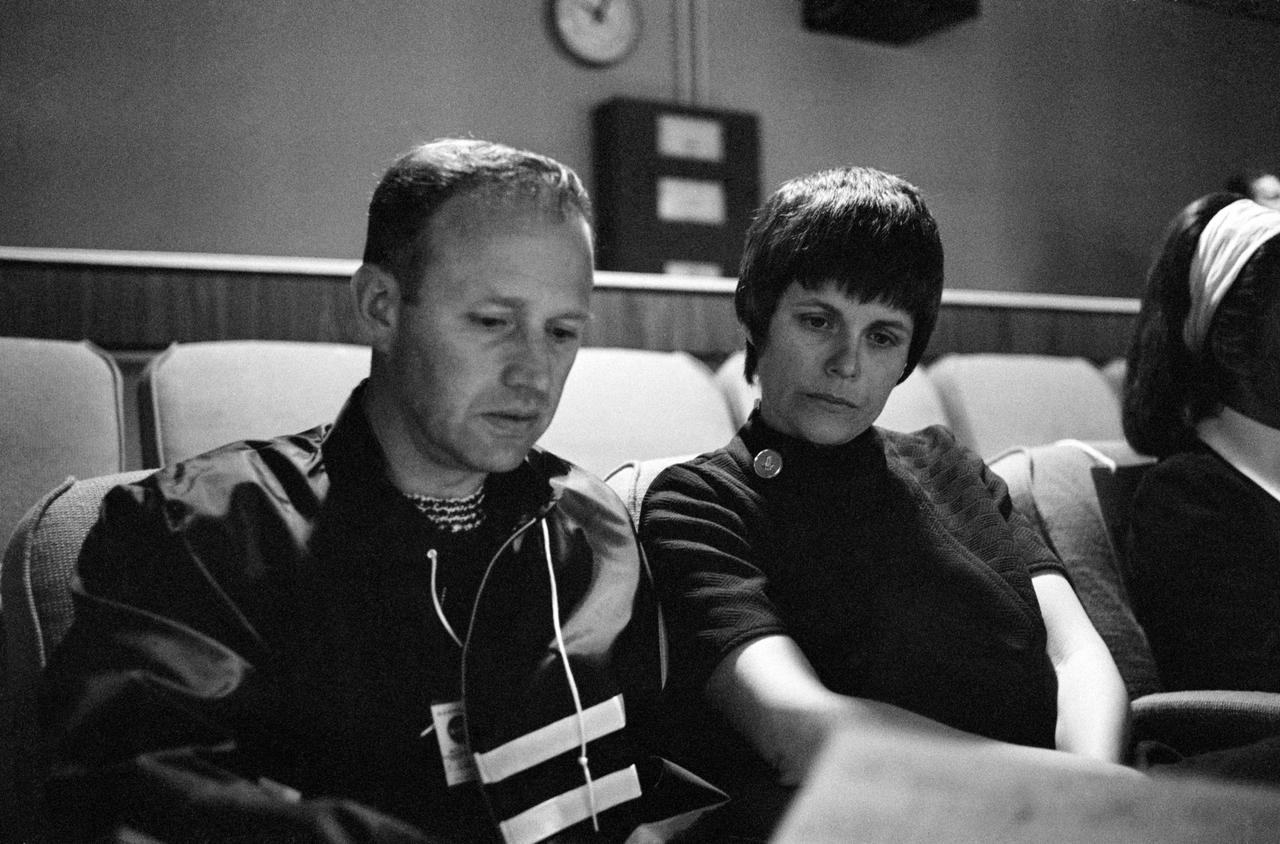

S70-34900 (14 April 1970) --- Mrs. Mary Haise receives an explanation of the revised flight plan of the Apollo 13 mission from astronaut Gerald P. Carr in the viewing room of the Mission Control Center (MCC), Building 30, at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Her husband, astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot for the Apollo 13 mission, was joining fellow crew members, astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., and John L. Swigert Jr. in making correction in their spacecraft following discovery of an oxygen cell failure several hours earlier.

S69-60662 (December 1969) --- This is the insignia of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. The Apollo 13 prime crew will be astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Represented in the Apollo 13 emblem is Apollo, the sun god of Greek mythology, symbolizing how the Apollo flights have extended the light of knowledge to all mankind. The Latin phrase Ex Luna, Scientia means "From the Moon, Knowledge." Apollo 13 will be the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) third lunar landing mission.

NASA's Lunar Lander exhibit is located at the Mississippi I-10 Welcome Center in Hancock County, Miss., just west of Bay St. Louis and 45 miles east of New Orleans on I-10 at Exit 2. The exhibit features a 30-foot-tall replica of a Lunar Lander used as a trainer by the Apollo 13 astronauts. Apollo 13 astronaut and Mississippi native Fred Haise left space-boot prints and signature in concrete at the base of the exhibit.
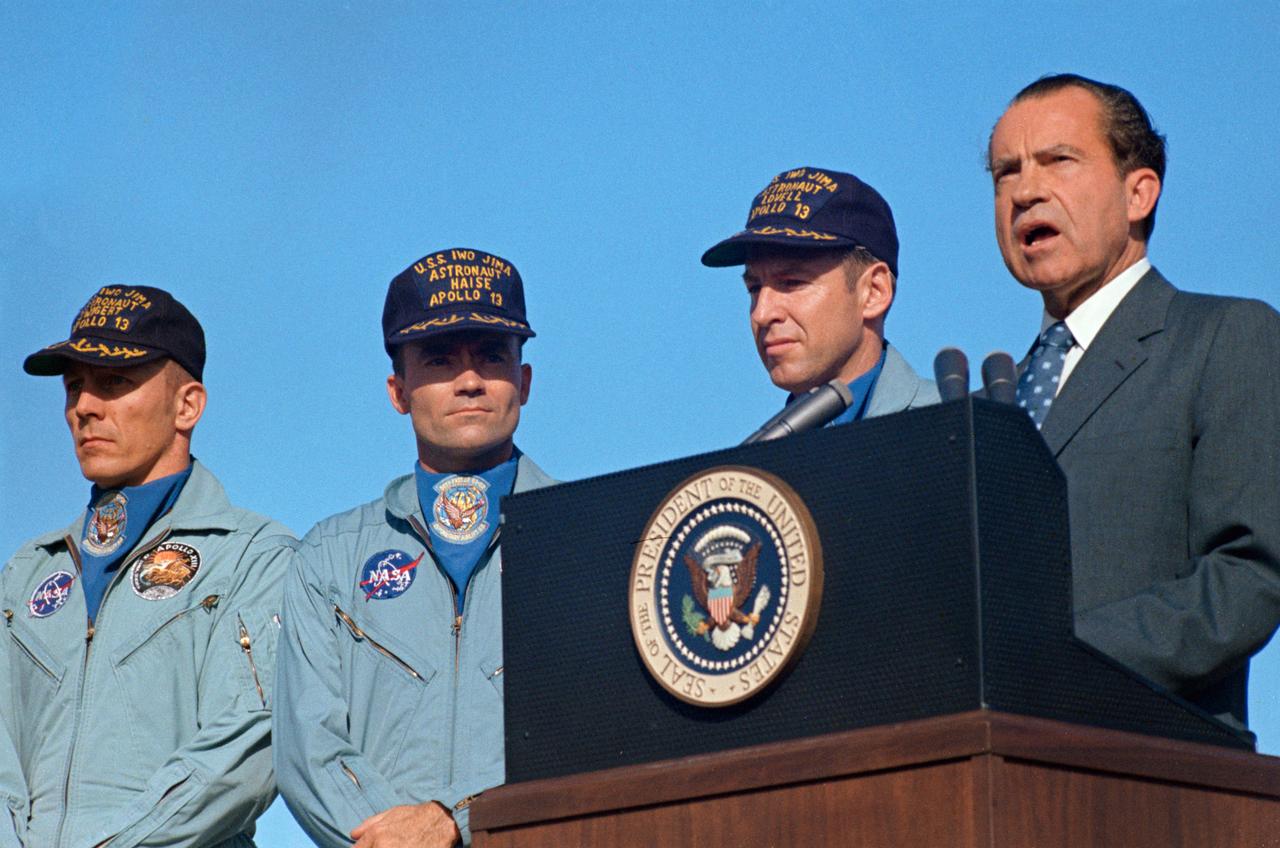

S70-15511 (19 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon speaks at Hickham Air Force Base prior to presenting the nation's highest civilian award to the Apollo 13 crew. Receiving the Presidential Medal of Freedom were astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., (next to the Chief Executive), commander; John L. Swigert Jr. (left), command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Wives of Lovell and Haise and the parents of Swigert accompanied the President to Hawaii. The Apollo 13 splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, about a day and a half prior to the Hickam Air Force Base ceremonies.
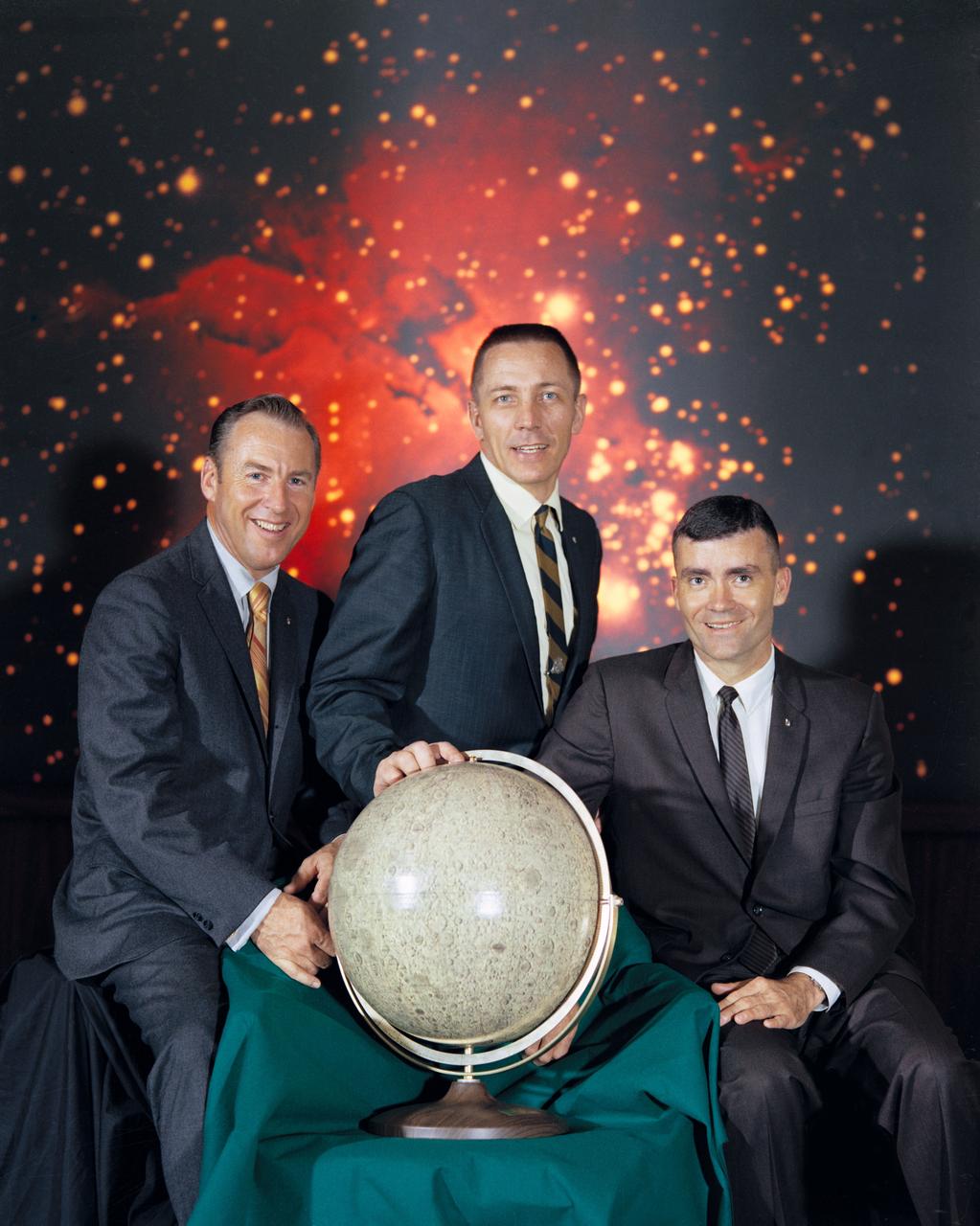

S70-36485 (April 1970) --- These three astronauts are the prime crew of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. Left to right, are James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Apollo 13 will be the United States' third lunar landing mission.
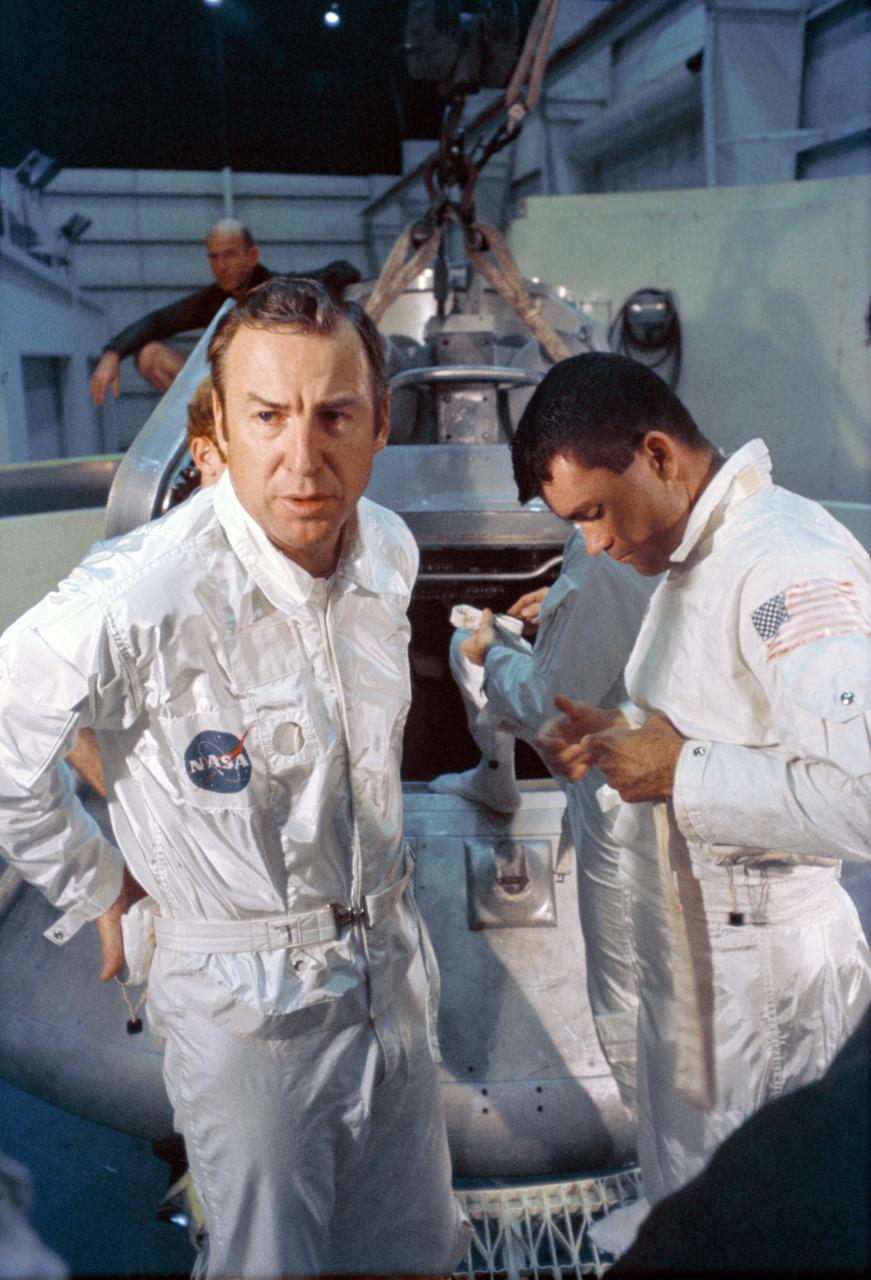

S70-24010 (17 Jan. 1970) --- The three prime crew members of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission stand by to participate in water egress training in a water tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). They are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., (left) commander; Fred W. Haise Jr., (right) lunar module pilot; and Thomas K. Mattingly II (in background, obscured by Haise), command module pilot.
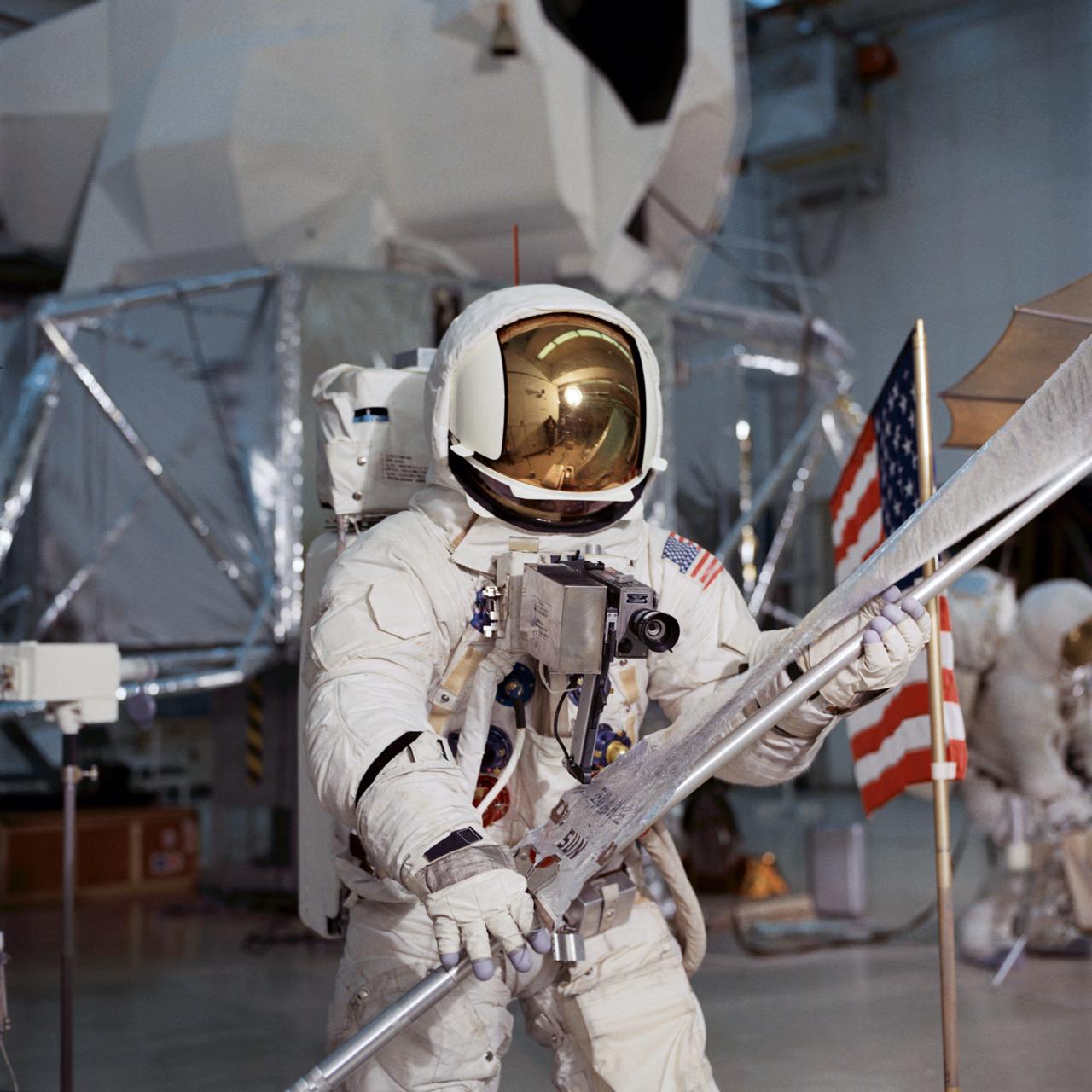

S70-27034 (4 Feb. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, simulates lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) during training exercises in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Flight Crew Training Building (FCTB). Haise, wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), is holding a Solar Wind Composition (SWC) experiment.

S70-15501 (17 April 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 13 mission commander, reads a newspaper account of the safe recovery of the problem plagued mission. Lovell is on board the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for Apollo 13, which was on a course headed for Pago Pago. From Pago Pago the astronauts flew to Hickam Air Force Base, Hawaii, where they were presented the Presidential Medal of Freedom by President Richard M. Nixon. Other Apollo 13 crew members were astronauts John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
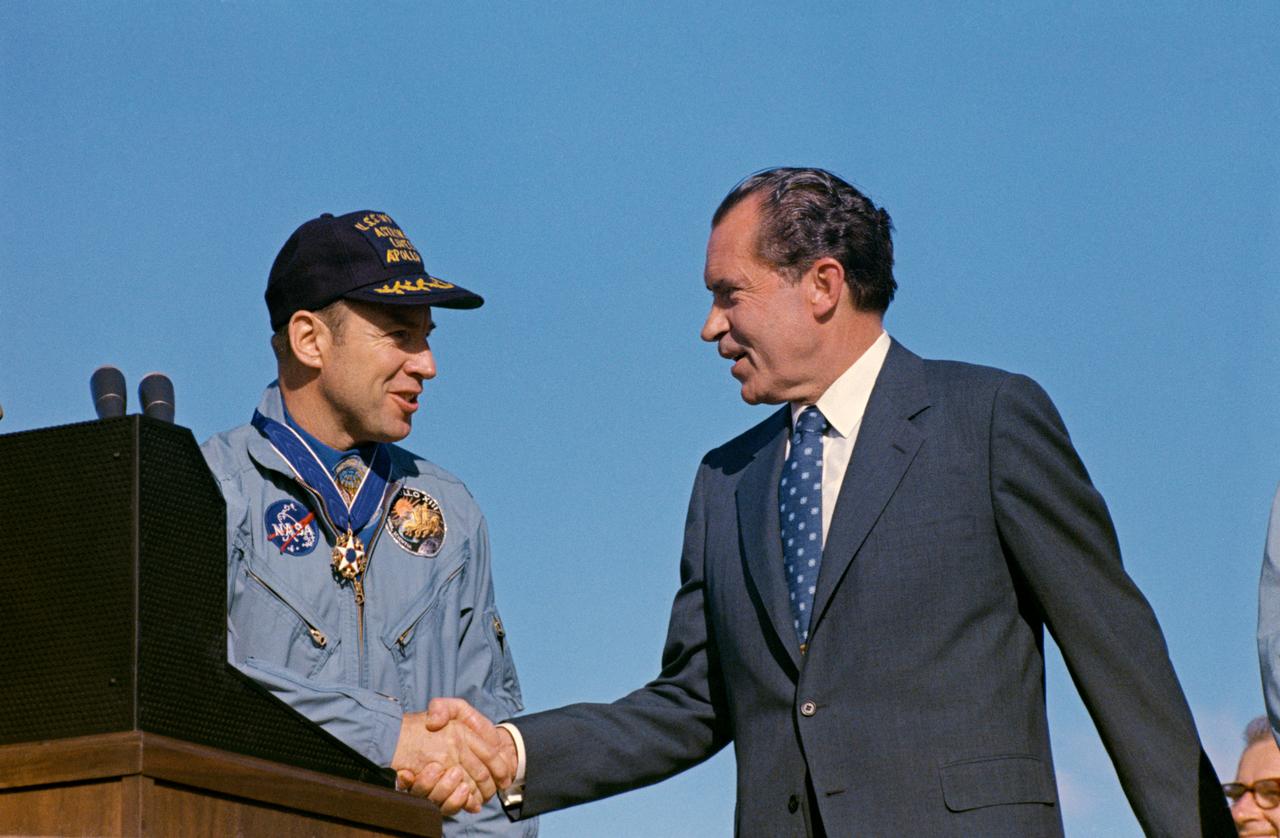

S70-15506 (18 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon and astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 13 commander, shake hands at special ceremonies at Hickam Air Force Base, Hawaii. President Nixon was in Hawaii to present the Apollo 13 crew with the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the nation's highest civilian honor. The wives of astronauts Lovell and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot; and the parents of astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, flew with the Chief Executive to Hickam Air Force Base. The Apollo 13 splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, a day and a half prior to the awards ceremony.
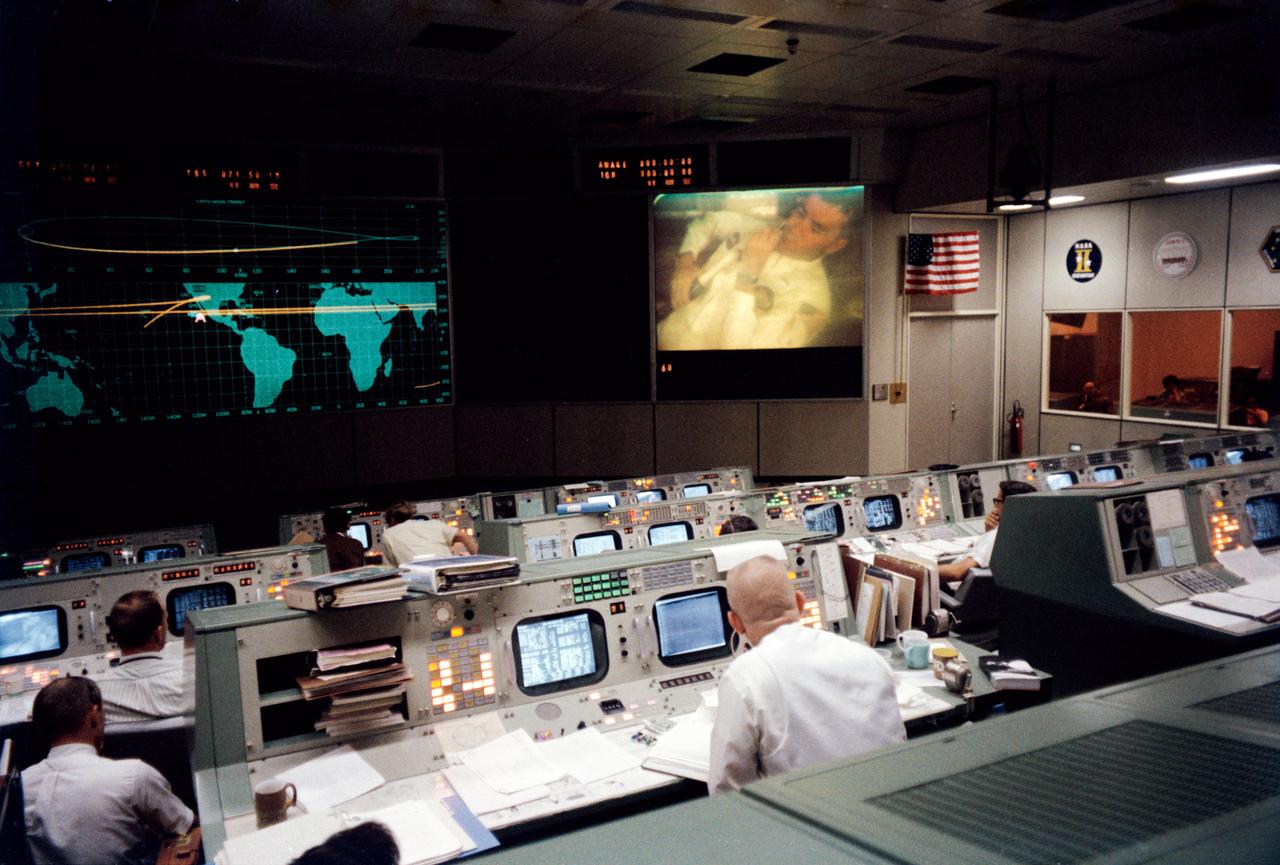

S70-35139 (13 April 1970) --- Overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC) at Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), during the fourth television transmission from the Apollo 13 mission in space. Eugene F. Kranz (foreground, back to camera), one of four Apollo 13 flight directors, views the large screen at front of MOCR, astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, is seen on the screen. The fourth TV transmission from the Apollo 13 mission was on the evening of April 13, 1970.

S70-29672 (28 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in a walk-through of the extravehicular activity timeline at the Kennedy Space Center. Here, Lovell, using mock-ups, traverses with the two subpackages of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP). Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, is standing in the left background.
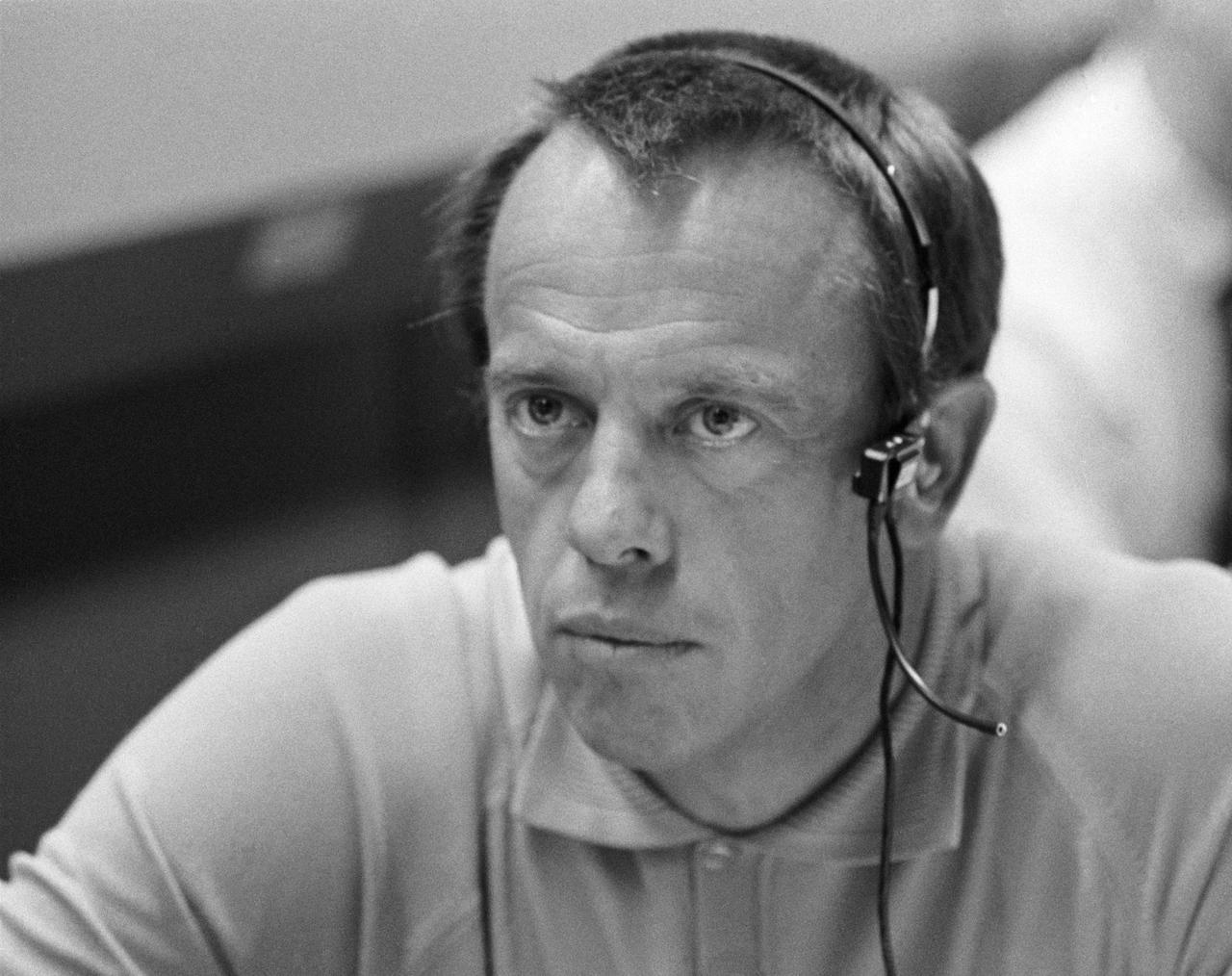

S70-34904 (14 April 1970) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., prime crew commander of the Apollo 14 mission, monitors communications between the Apollo 13 spacecraft and Mission Control Center. He is seated at a console in the Mission Operations Control Room of the MCC, Manned Spacecraft Center. The main concern of the moment was action taken by the three Apollo 13 crewmen - astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., John L. Swigert Jr. and Fred W. Haise Jr. - to make corrections inside the spacecraft following discovery of an oxygen cell failure several hours earlier.

S70-34904 (14 April 1970) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., prime crew commander of the Apollo 14 mission, monitors communications between the Apollo 13 spacecraft and Mission Control Center. He is seated at a console in the Mission Operations Control Room of the MCC, Manned Spacecraft Center. The main concern of the moment was action taken by the three Apollo 13 crewmen - astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., John L. Swigert Jr. and Fred W. Haise Jr. - to make corrections inside the spacecraft following discovery of an oxygen cell failure several hours earlier.
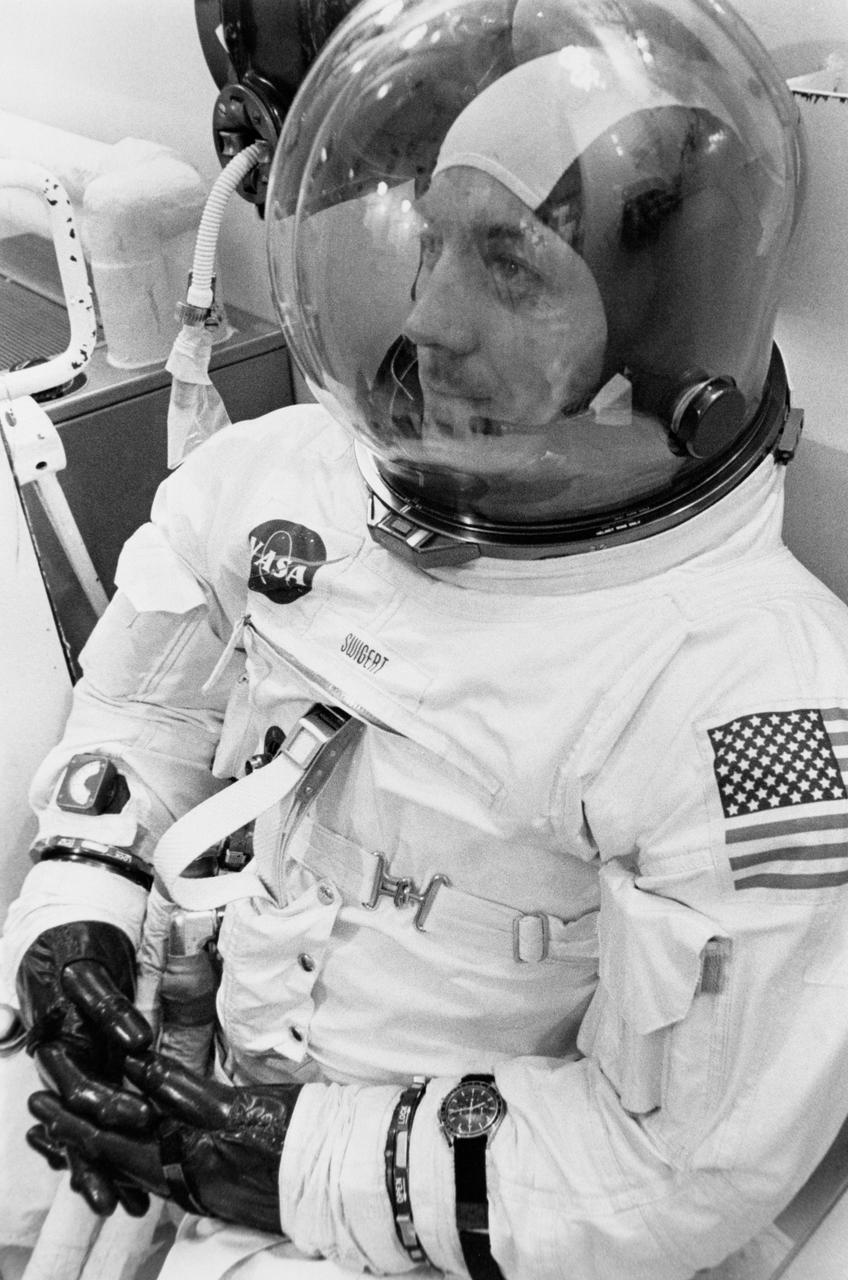

S70-34687 (11 April 1970) --- Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot for the Apollo 13 mission, has just suited up in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Manned Spacecraft Operations Building during the Apollo 13 prelaunch countdown. Minutes later, astronauts Swigert, James A. Lovell Jr. and Fred W. Haise Jr. rode a special transport van over to Pad A, Launch Complex 39, where their spacecraft awaited liftoff. Launch occurred at 2:13 p.m. (EST), April 11, 1970.
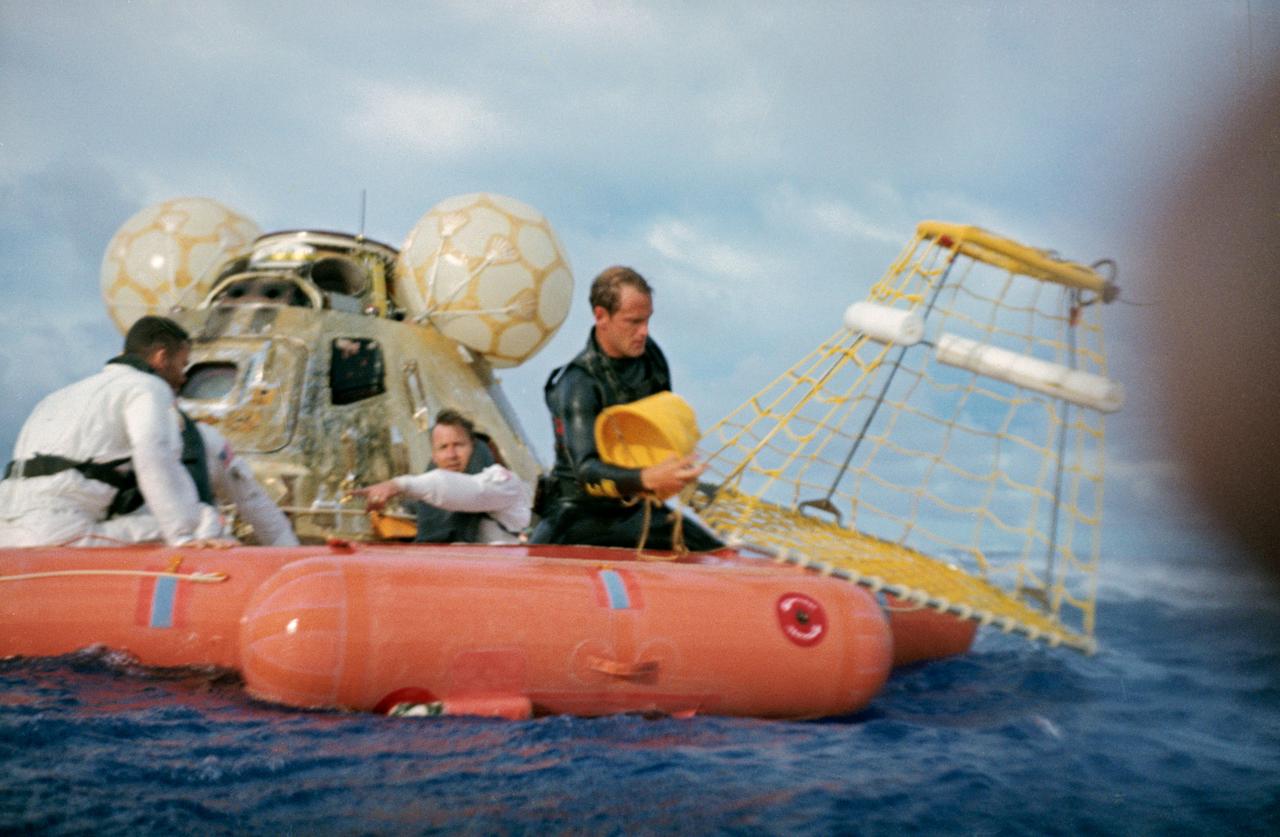

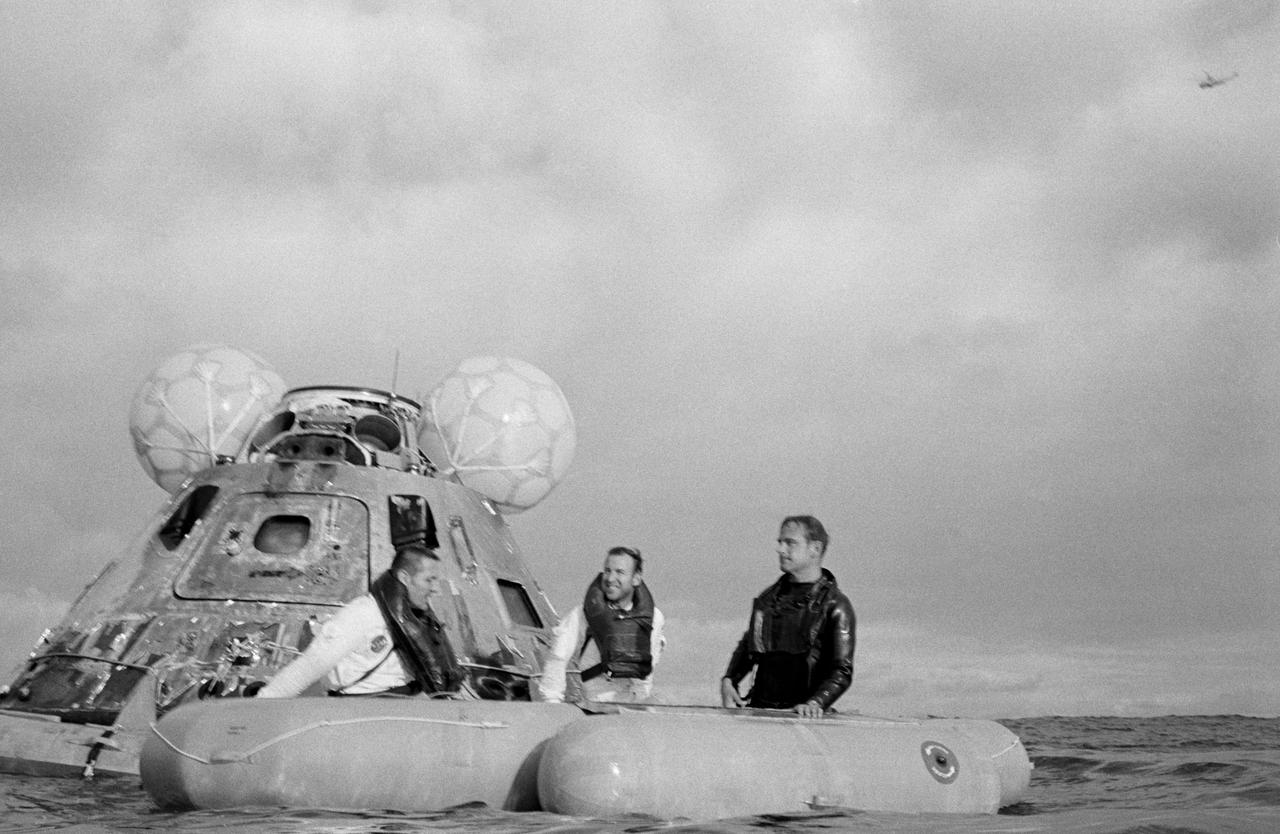
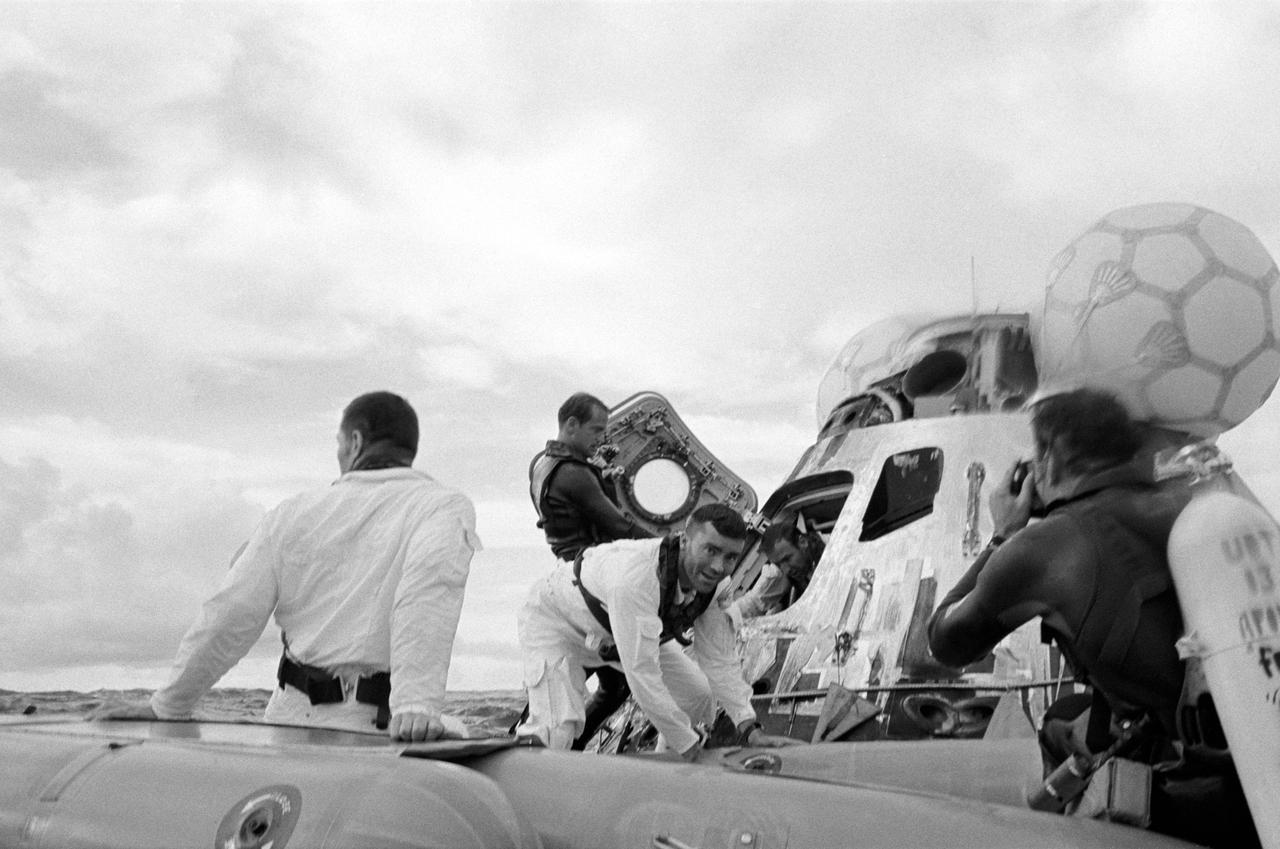
S70-35631 (17 April 1970) --- A water-level view of recovery operations for the Apollo 13 mission in the South Pacific Ocean. The three crewmen have egressed their spacecraft, and are awaiting the readying of the "Billy Pugh" net which will hoist them to a helicopter hovering above. The crewmembers (from the left) are astronauts Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; (only partially visible between Haise and the Command Module (CM)), and James A. Lovell Jr., commander. A U.S. Navy underwater demolition team swimmer prepares to assist Haise into the net. Apollo 13 splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, in the South Pacific, about four miles from the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship.
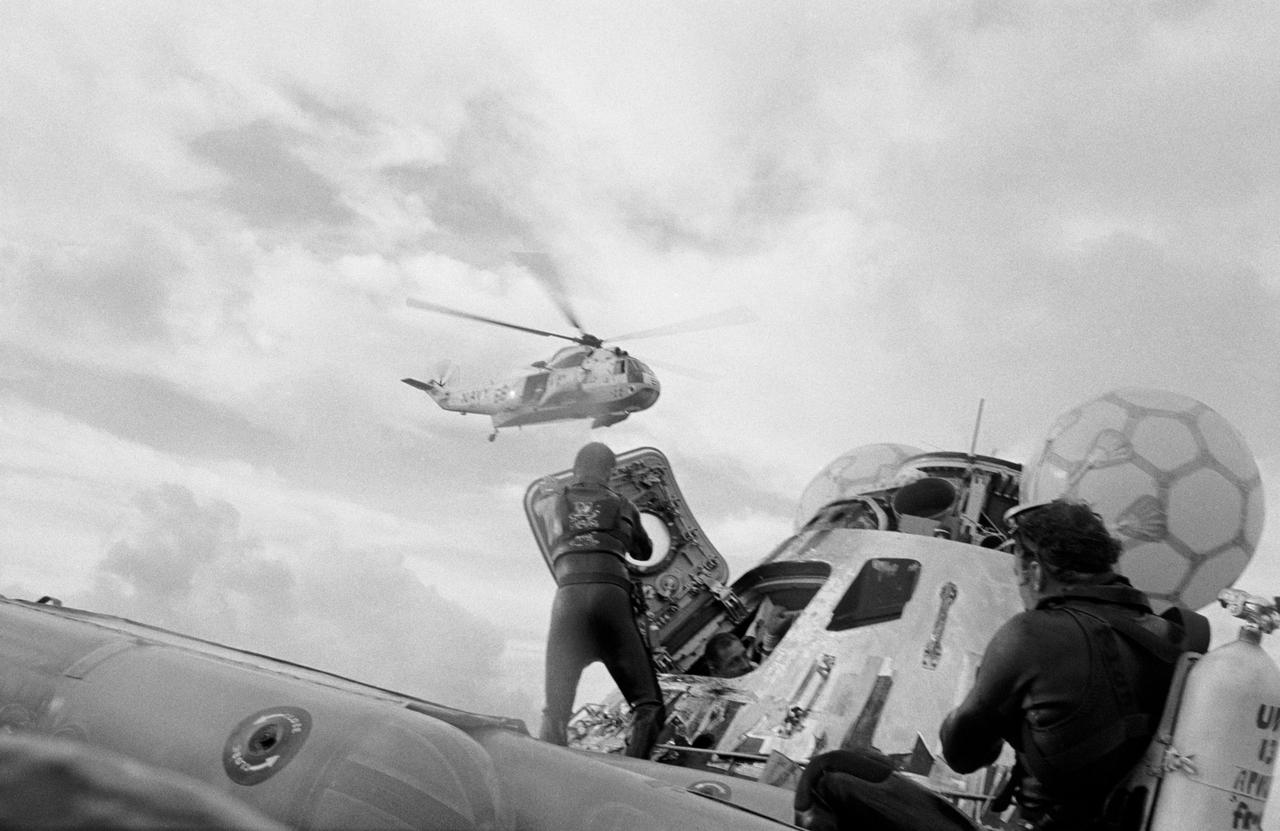

S70-35622 (17 April 1970) --- United States Navy underwater demolition team swimmers assist in the recovery operations of the Apollo 13 crewmembers, shortly after splashdown. The divers prepare to assist the astronauts out of their crippled Command Module (CM), into an awaiting life raft. Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, is preparing to exit the CM. A Navy helicopter is waiting to take the astronauts to the prime recovery ship, the USS Iwo Jima. Apollo 13 splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970. Still aboard the CM are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
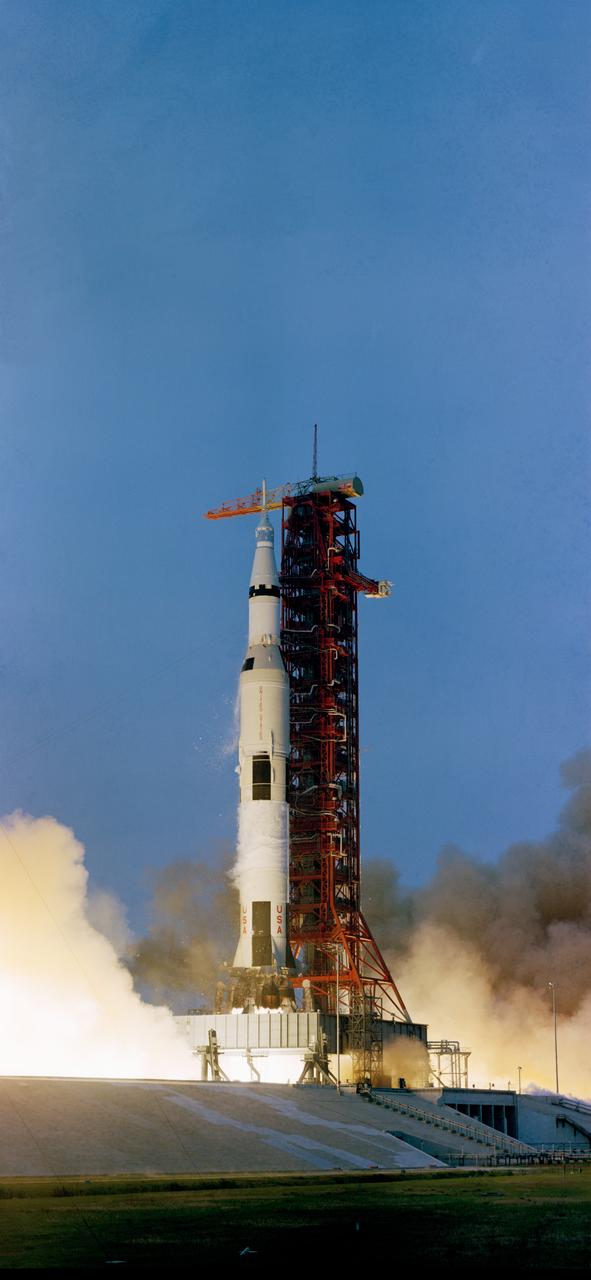

S70-34852 (11 April 1970) --- The Apollo 13 (Spacecraft 109/Lunar Module 7/Saturn 508) space vehicle is launched from Pad A Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), at 2:13 p.m. (EST), April 11, 1970. The crew of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) third lunar landing mission are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
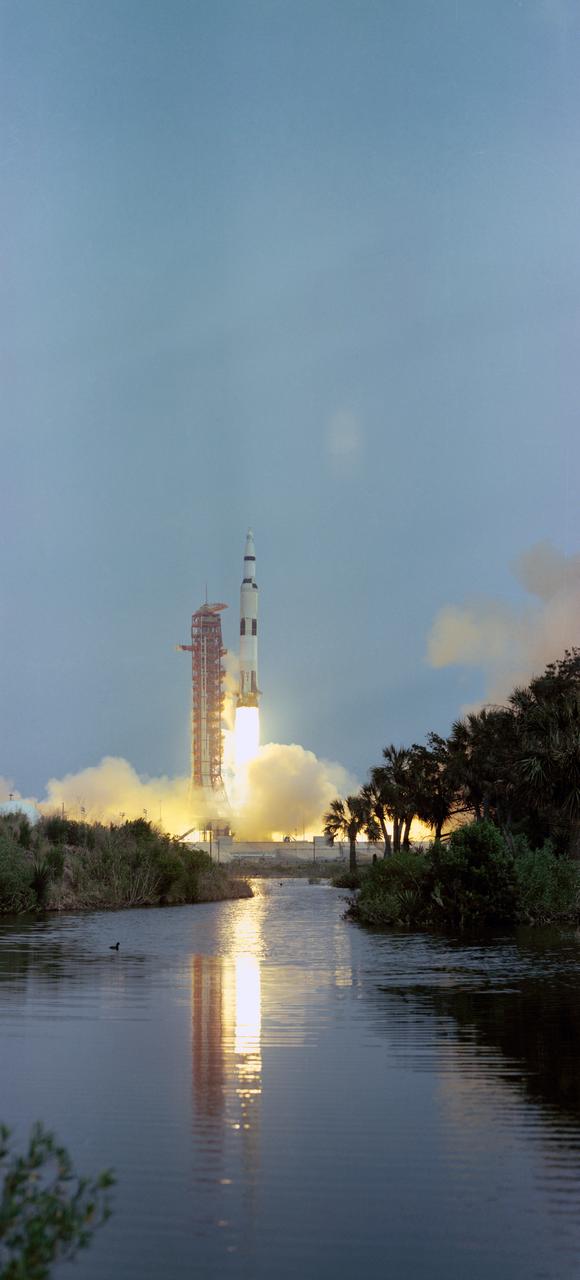

S70-38747 (11 April 1970) --The Apollo 13 (Spacecraft 109/Lunar Module 7/Saturn 508) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), at 2:13 p.m. (EST), April 11, 1970. The crew of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) third lunar landing mission is astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
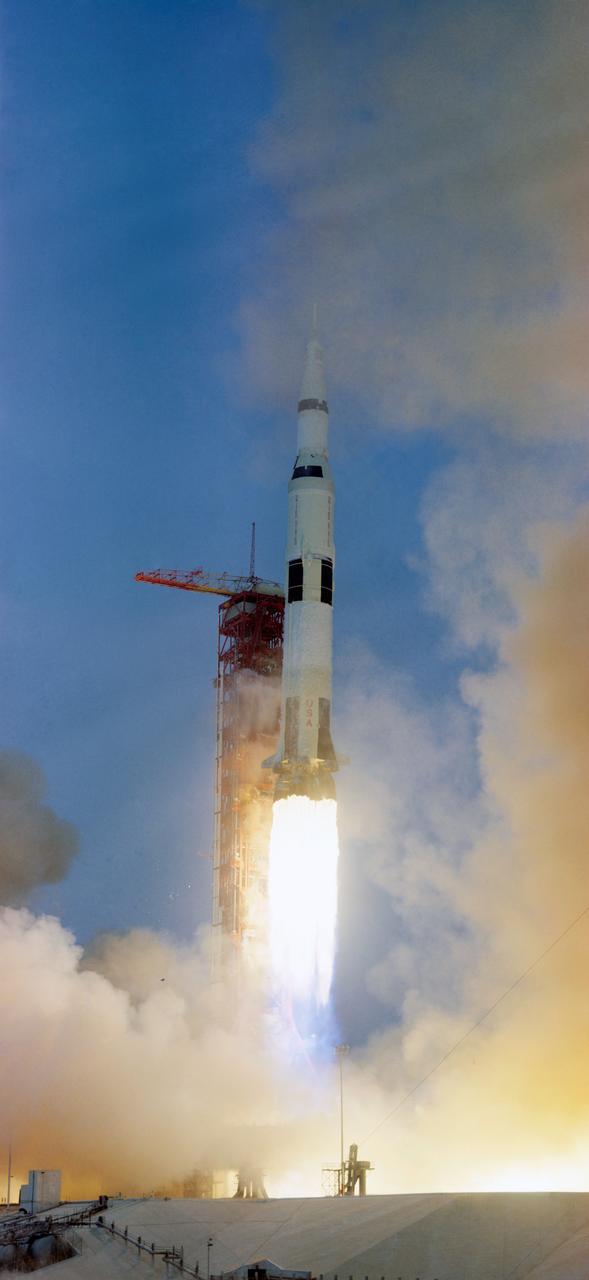

S70-34854 (11 April 1970) --- The Apollo 13 (Spacecraft 109/Lunar Module 7/Saturn 508) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), at 2:13 p.m. (EST), April 11, 1970. The crew of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) third lunar landing mission are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
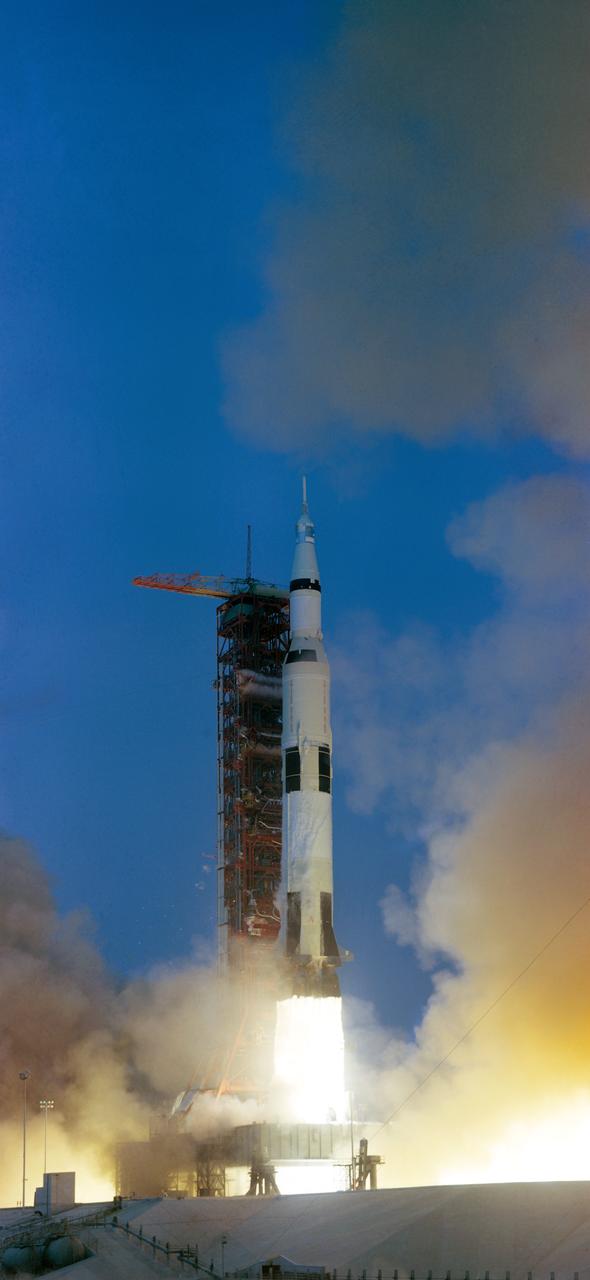

S70-34853 (11 April 1970) --- The Apollo 13 (Spacecraft 109/Lunar Module 7/Saturn 508) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), at 2:13 p.m. (EST), April 11, 1970. The crew of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) third lunar landing mission are astronauts James A., Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.

S70-34855 (11 April 1970) --- The Apollo 13 (Spacecraft 109/Lunar Module 7/Saturn 508) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), at 2:13 p.m. (EST), April 11, 1970. The crew of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) third lunar landing mission are astronauts James A., Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
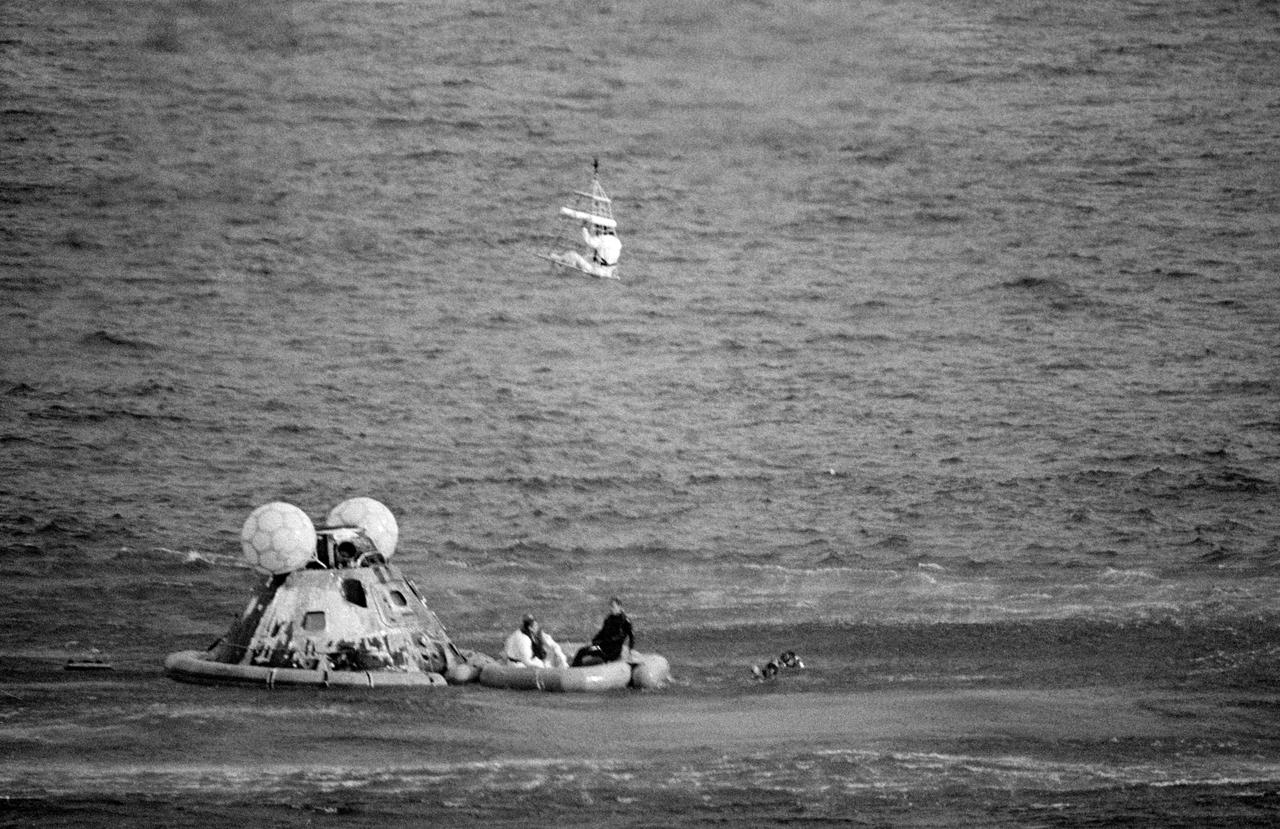

S70-35625 (17 April 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, is hoisted in a "Billy Pugh" net into a Navy helicopter, while United States Navy underwater demolition team swimmers assist in the recovery operations of the Apollo 13 crewmembers. Astronauts John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, and James A. Lovell Jr., commander, are waiting to get hoisted into the helicopter. The helicopter is taking the astronauts to the prime recovery ship, the USS Iwo Jima. Apollo 13 splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970.
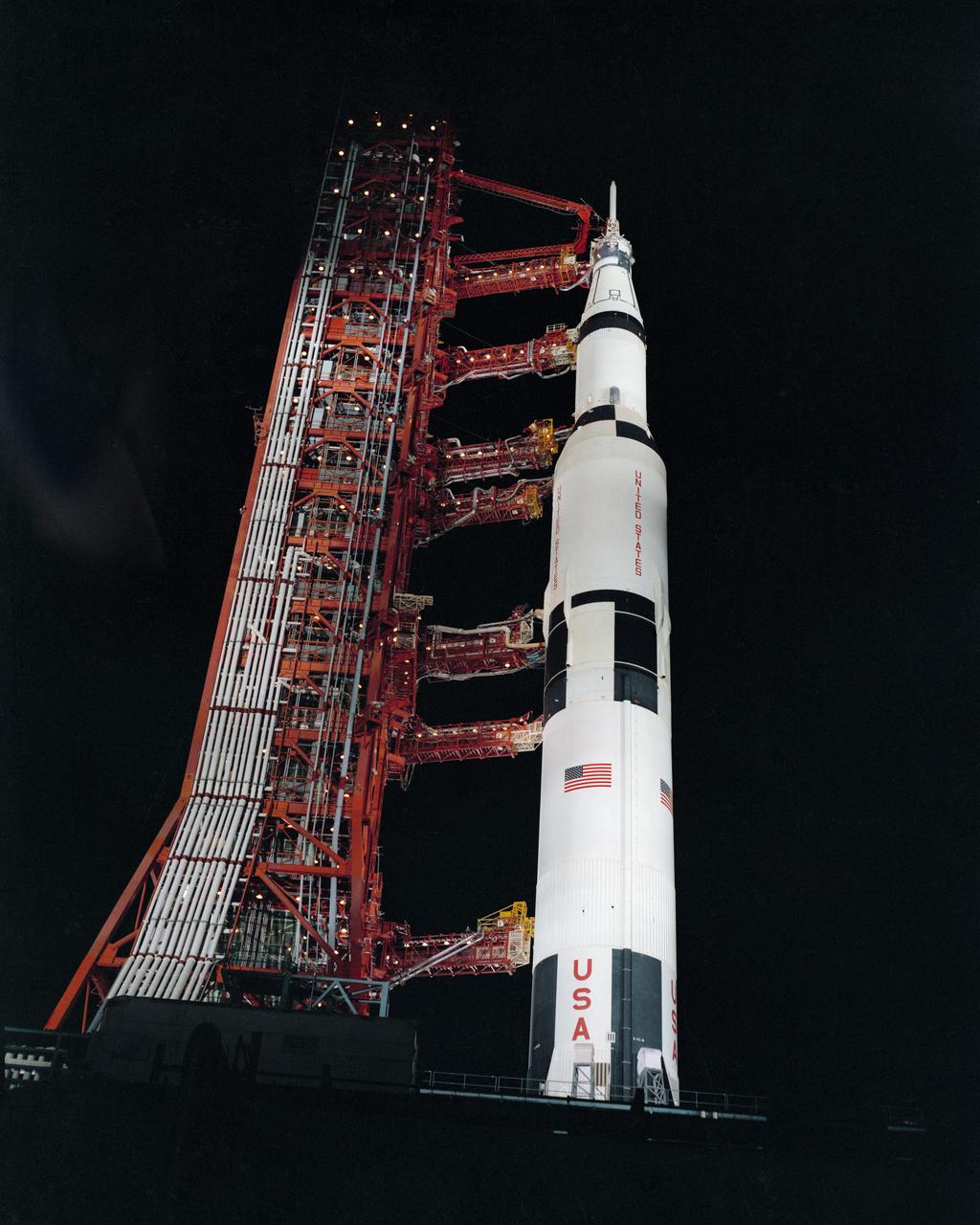

S70-32990 (24 March 1970) --- Nighttime, ground level view of Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), showing the Apollo 13 (Spacecraft 109/Lunar Module 7/Saturn 508) space vehicle during Countdown Demonstration Test (CDDT). The crew of NASA's third lunar landing mission includes astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The Apollo 13 launch has been scheduled for 2:13 p.m. (EST), April 11, 1970.
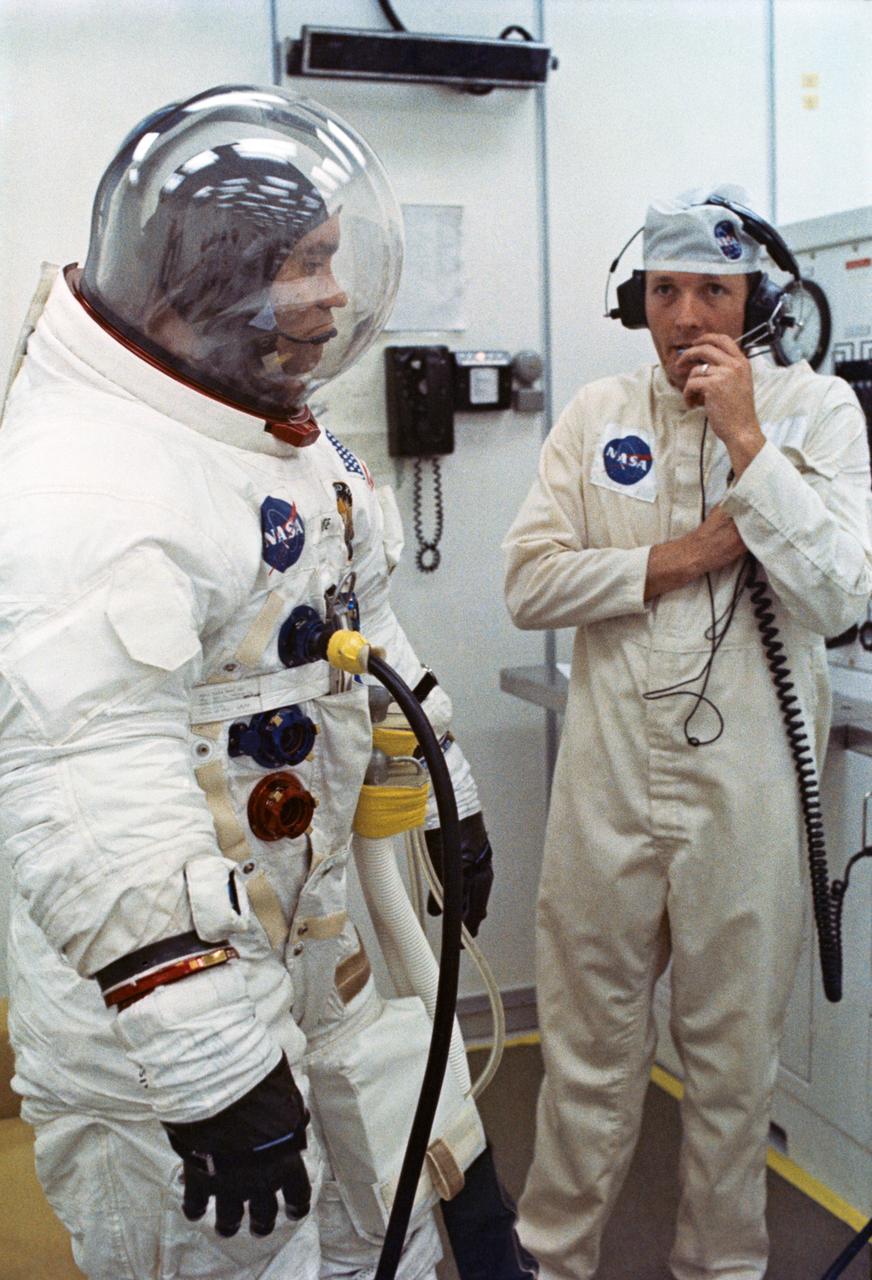

S70-34851 (11 April 1970) --- A space suit technician talks with astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot for NASA's Apollo 13 mission, during suiting up procedures at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Other members of the crew are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot. Swigert replaced astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II as a member of the crew when it was learned he had been exposed to measles.
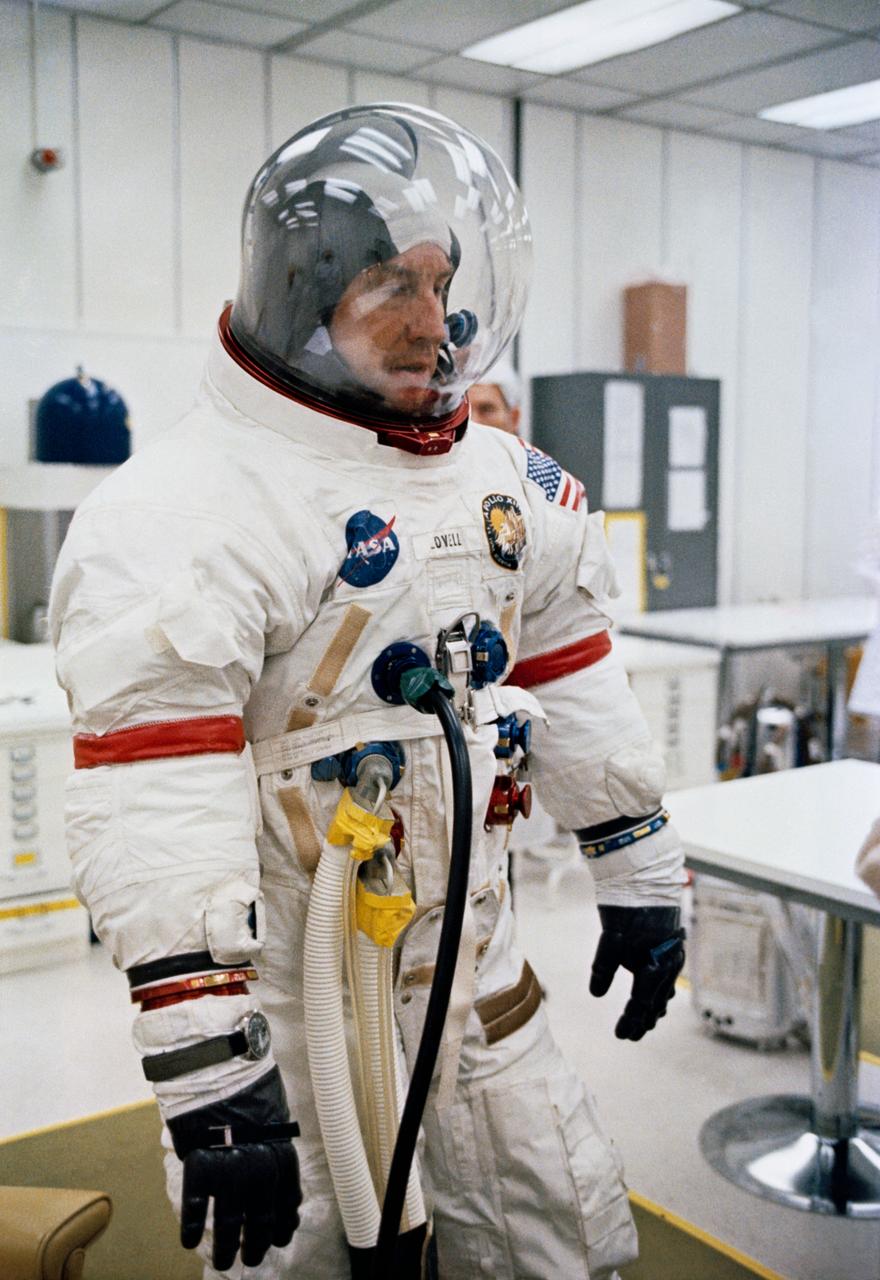

S70-34848 (11 April 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander for NASA's Apollo 13 mission, undergoes space suit checks a few hours before launch. Other members of the crew are astronauts Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, and John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot. Swigert replaced astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II when it was learned he had been exposed to measles.
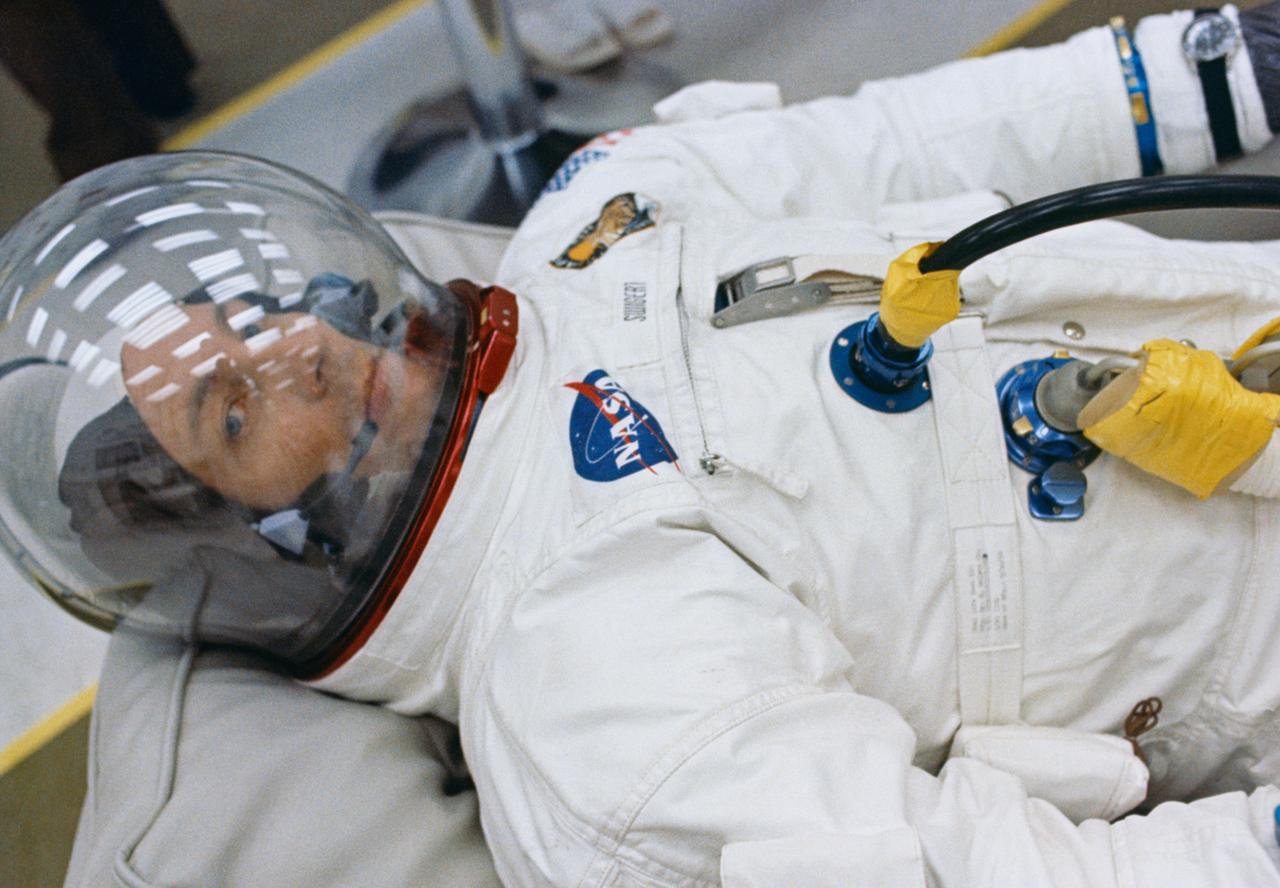

S70-34847 (11 April 1970) --- Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot for NASA?s third lunar landing mission, appears to be relaxing in the suiting room at Kennedy Space Center prior to launch. Other members of the Apollo 13 crew include astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Swigert replaced astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II when it was discovered that Mattingly had been exposed to the measles.

S70-34685 (April 1970) --- A photographic replica of the plaque which the Apollo 13 astronauts will leave behind on the moon during their lunar landing mission. Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, will descend to the lunar surface in the Lunar Module (LM) "Aquarius". Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The plaque will be attached to the ladder of the landing gear strut on the LM?s descent stage. Commemorative plaques were also left on the moon by the Apollo 11 and Apollo 12 astronauts.
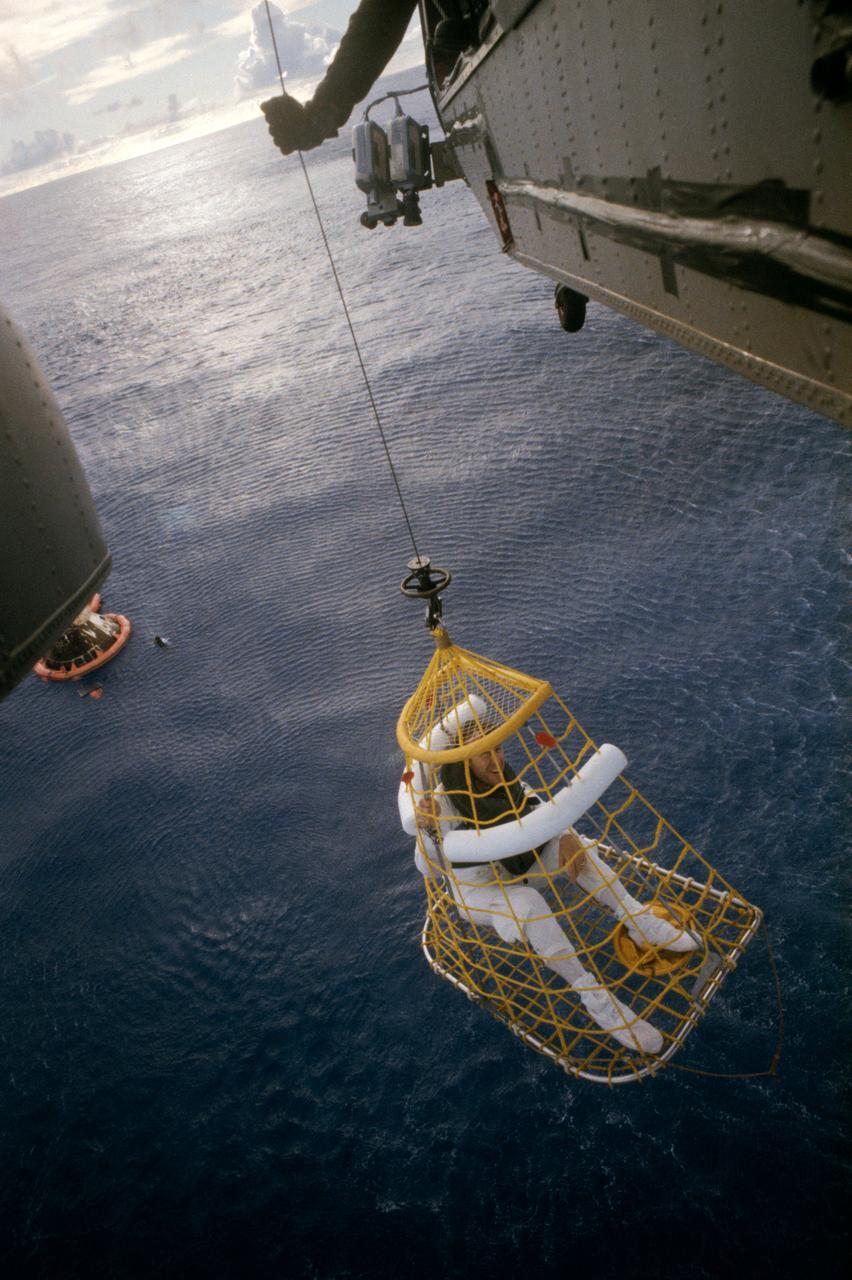

S70-35645 (17 April 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander, is hoisted aboard a helicopter from the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery vessel for the mission. Lovell was the last of the three Apollo 13 crewmembers to egress the Command Module (CM) and the last to be lifted aboard the helicopter. He was preceded by astronauts John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The CM and a U.S. Navy underwater demolition team swimmer can be seen in the ocean background. Apollo 13 splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970.

S70-35747 (20 April 1970) --- The three crew men of the problem plagued Apollo 13 mission are photographed during the first day of their postflight debriefing activity at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Left to right, are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The apparent rupture of oxygen tank number two in the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) and the subsequent damage forced the three astronauts to use the Lunar Module (LM) as a "lifeboat" to return home safely after their moon landing was canceled.
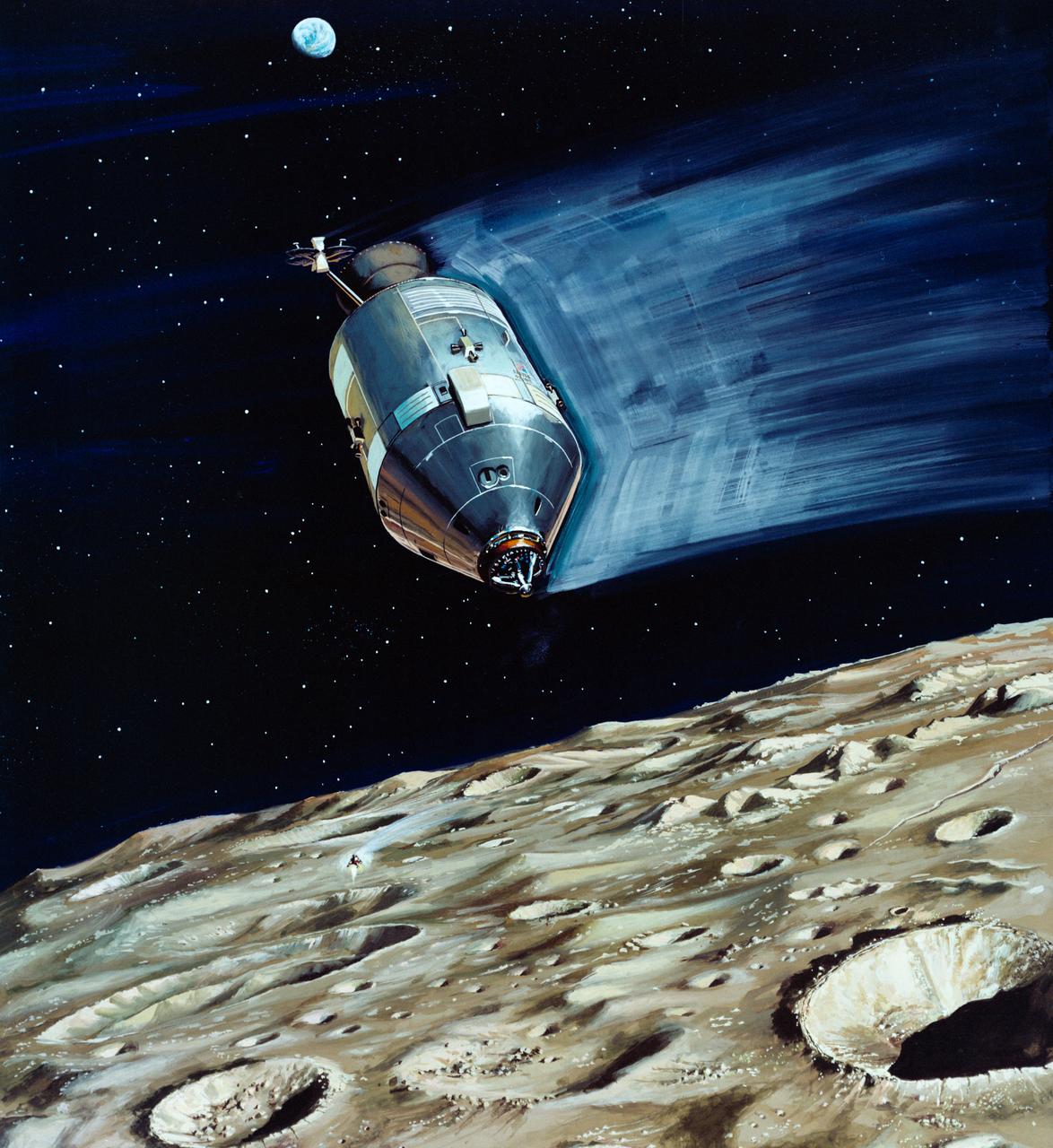

S70-31898 (March 1970) --- A North American Rockwell artist?s concept depicting the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) descending to the Fra Mauro landing site as the Command and Service Module (CSM) remains in lunar orbit. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, will photograph the LM?s descent from the CSM. Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, will descend in the LM to explore the moon. Apollo 13 will be NASA?s third lunar landing mission.
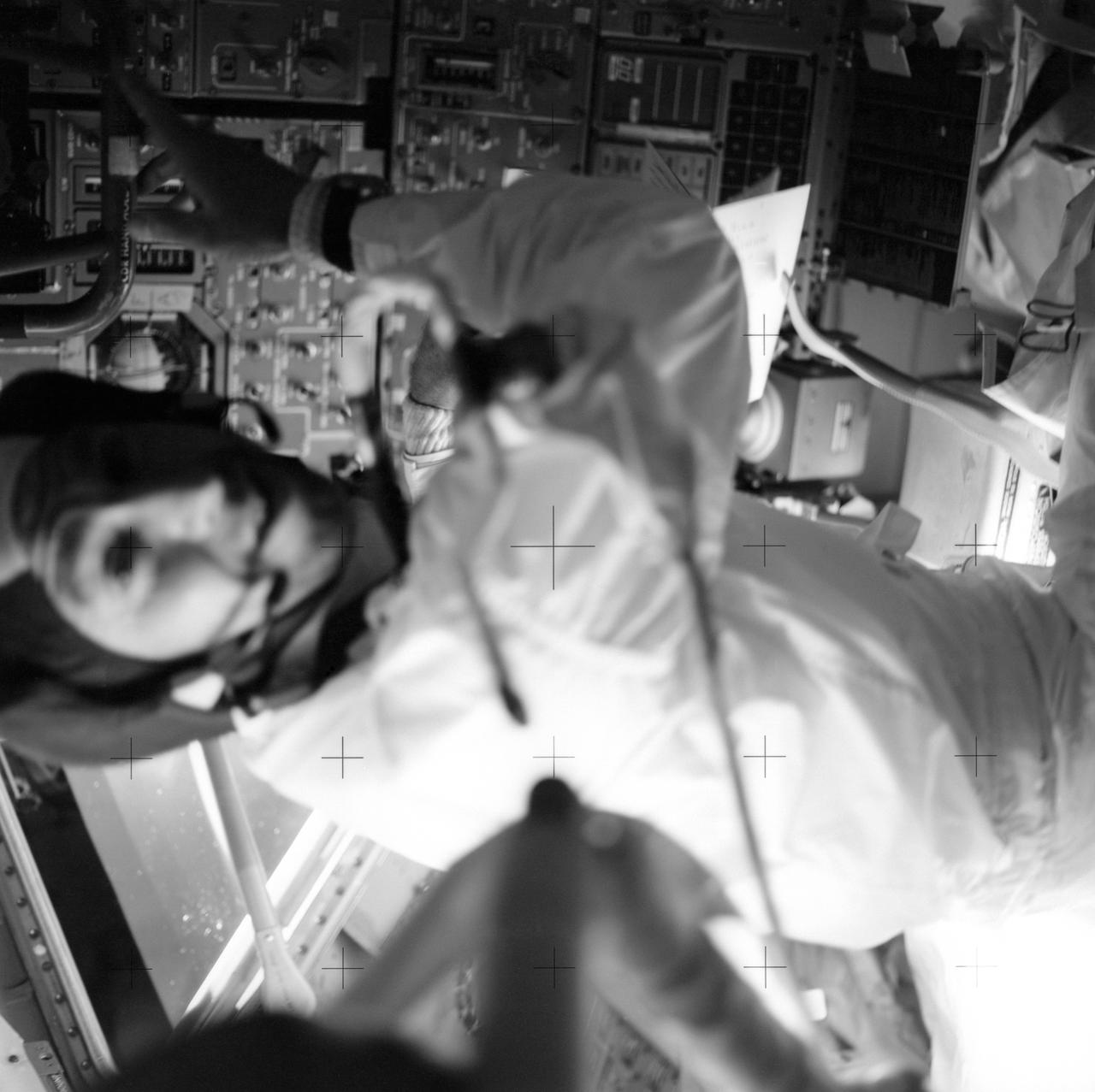

AS13-59-8484 (April 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander, is pictured at his position in the Lunar Module (LM). The Apollo 13 crew of astronauts Lovell; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, relied on the LM as a "lifeboat". The dependence on the LM was caused by an apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two in the Service Module (SM). The LM was jettisoned just prior to Earth re-entry by the Command Module (CM).
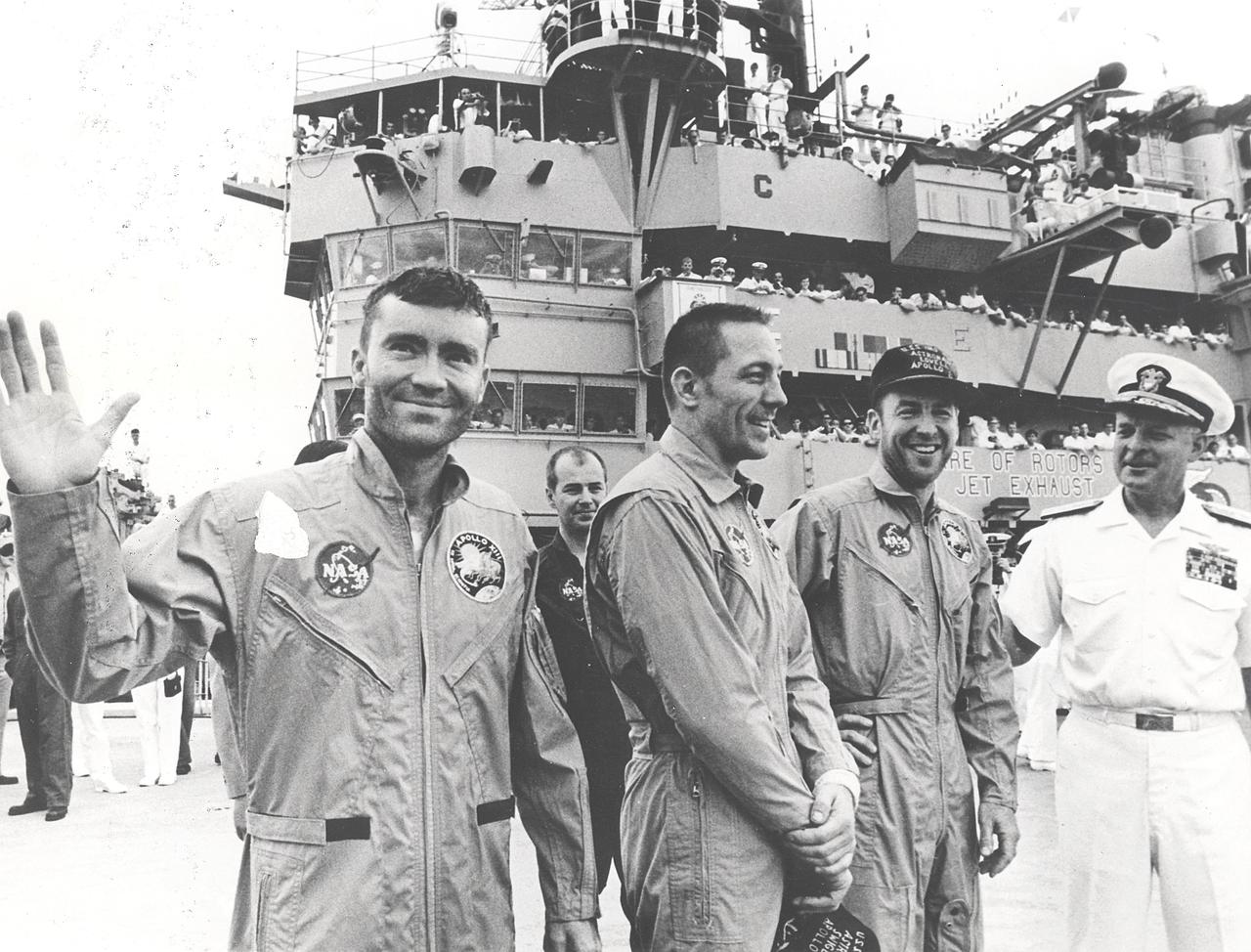

This photograph shows Apollo 13 astronauts Fred Haise, John Swigert, and James Lovell aboard the recovery ship, USS Iwo Jima after safely touching down in the Pacific Ocean at the end of their ill-fated mission. The mission was aborted after 56 hours of flight, 205,000 miles from Earth, when an oxygen tank in the service module exploded. The command module, Odyssey, brought the three astronauts back home safely.
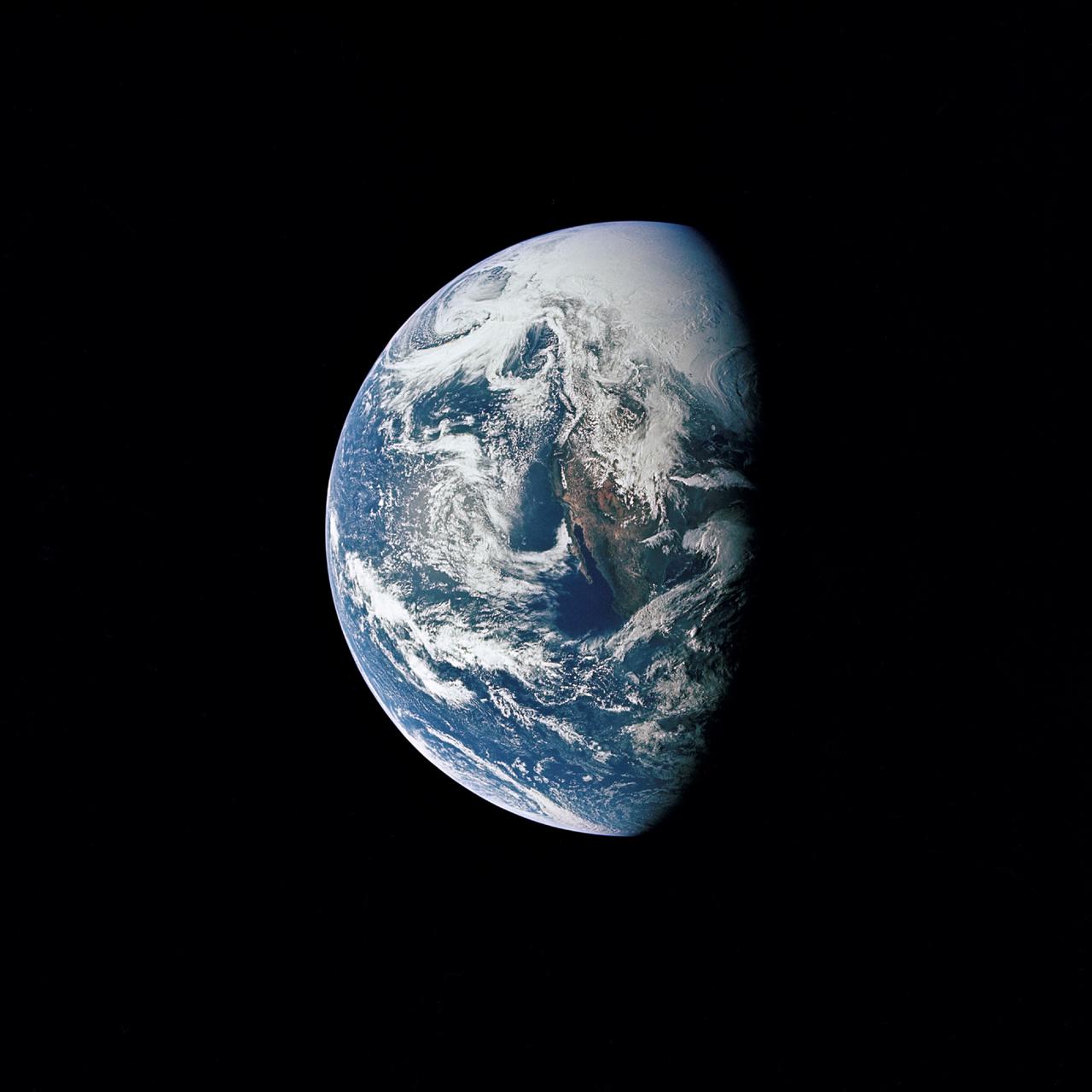

AS13-60-8588 (17 April 1970) --- This photograph of Earth was taken from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Apollo 13 spacecraft during its trans-Earth journey home. The most visible land mass includes southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. The peninsula of Baja California is clearly seen. Most of the land area is under heavy cloud cover. The Apollo 13 crew consisted of astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
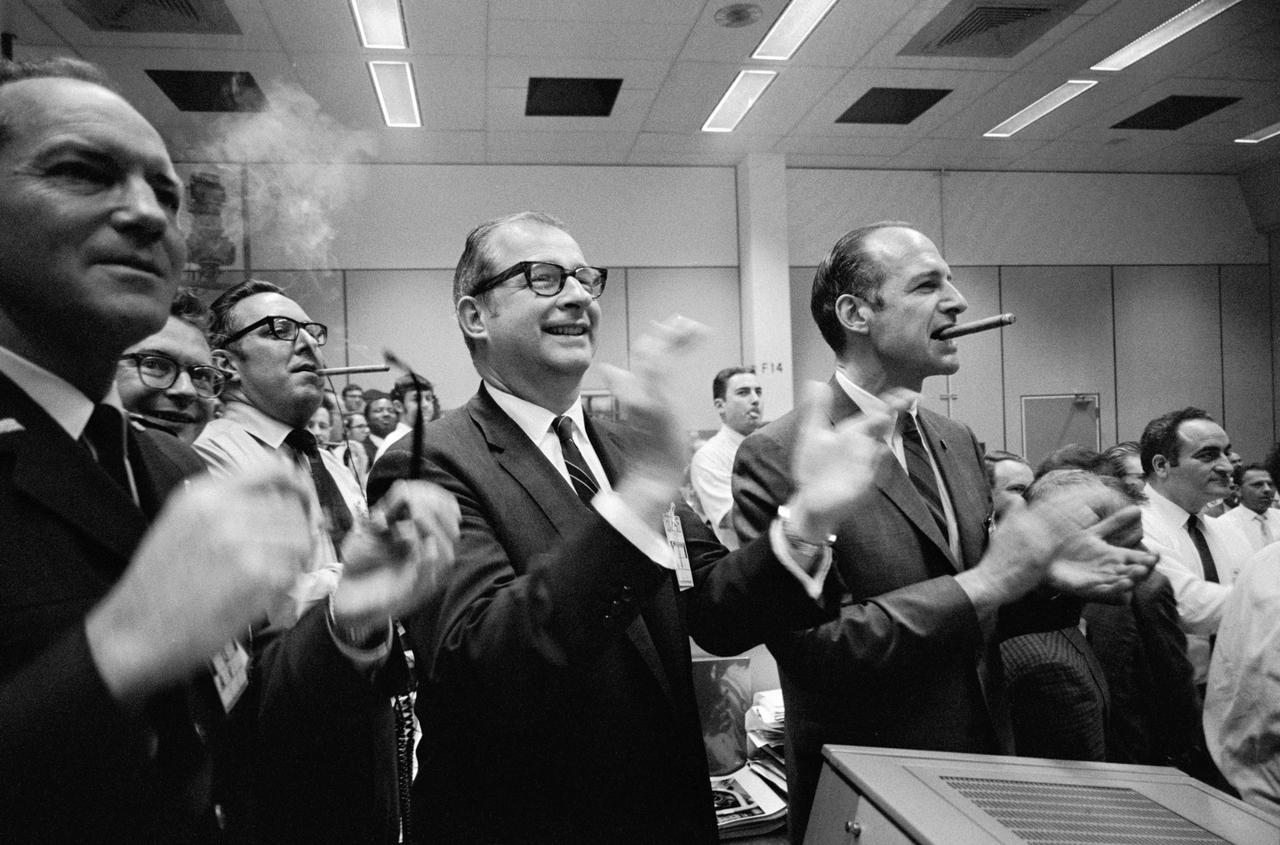

S70-35148 (17 April 1970) --- Staff members from NASA Headquarters (NASA HQ), Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), and Dr. Thomas Paine (center of frame) applaud the successful splashdown of the Apollo 13 mission while Dr. George Low smokes a cigar (right), in the MSC Mission Control Center (MCC), located in Building 30. Apollo 13 crewmembers, astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, in the south Pacific Ocean.
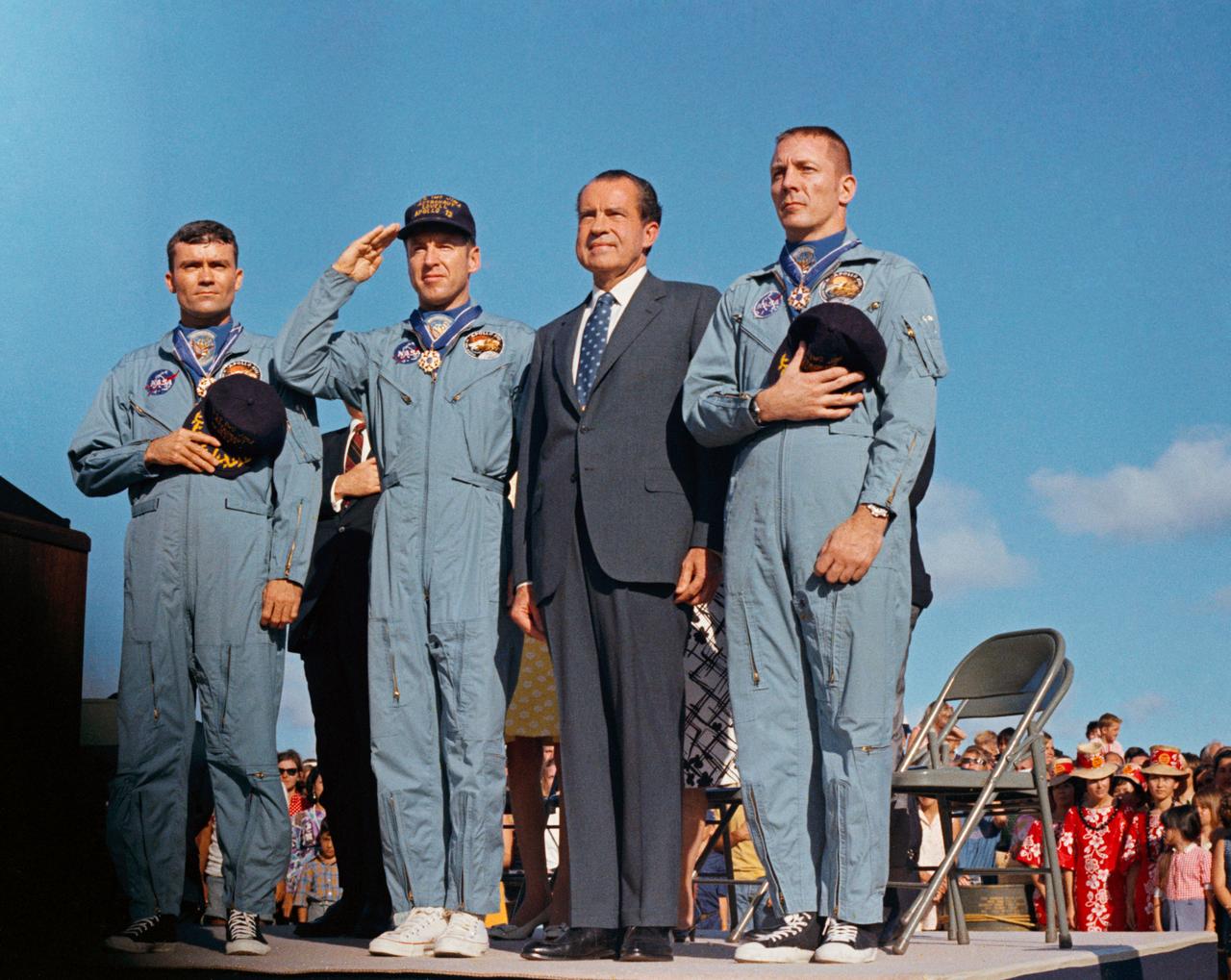

S70-15526 (18 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon and the Apollo 13 crew members pay honor to the United States flag during the post-mission ceremonies at Hickam Air Force Base, Hawaii. Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., (United States Navy Captain, salutes the flag) commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot (right); and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot (left), were presented the Presidential Medal of Freedom by the Chief Executive. The Apollo 13 splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, about a day and a half prior to the award presentation.
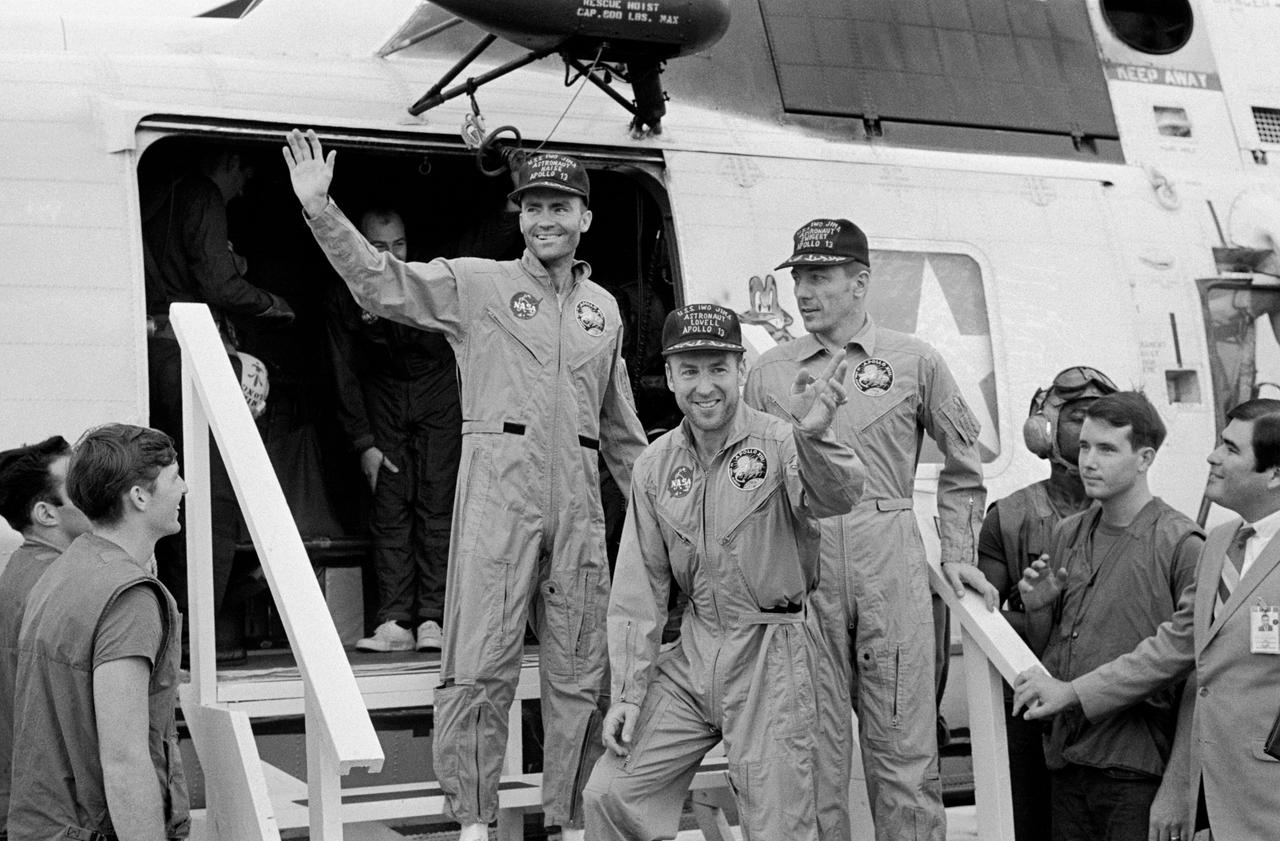

S70-35614 (17 April 1970) --- The crewmembers of the Apollo 13 mission, step aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the mission, following splashdown and recovery operations in the South Pacific Ocean. Exiting the helicopter which made the pick-up some four miles from the Iwo Jima are (from left) astronauts Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot; James A. Lovell Jr., commander; and John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot. The crippled Apollo 13 spacecraft splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970.

S70-35148 (17 April 1970) --- Staff members from NASA Headquarters (NASA HQ), Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), and Dr. Thomas Paine (center of frame) applaud the successful splashdown of the Apollo 13 mission while Dr. George Low smokes a cigar (right), in the MSC Mission Control Center (MCC), located in Building 30. Apollo 13 crewmembers, astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, in the south Pacific Ocean.
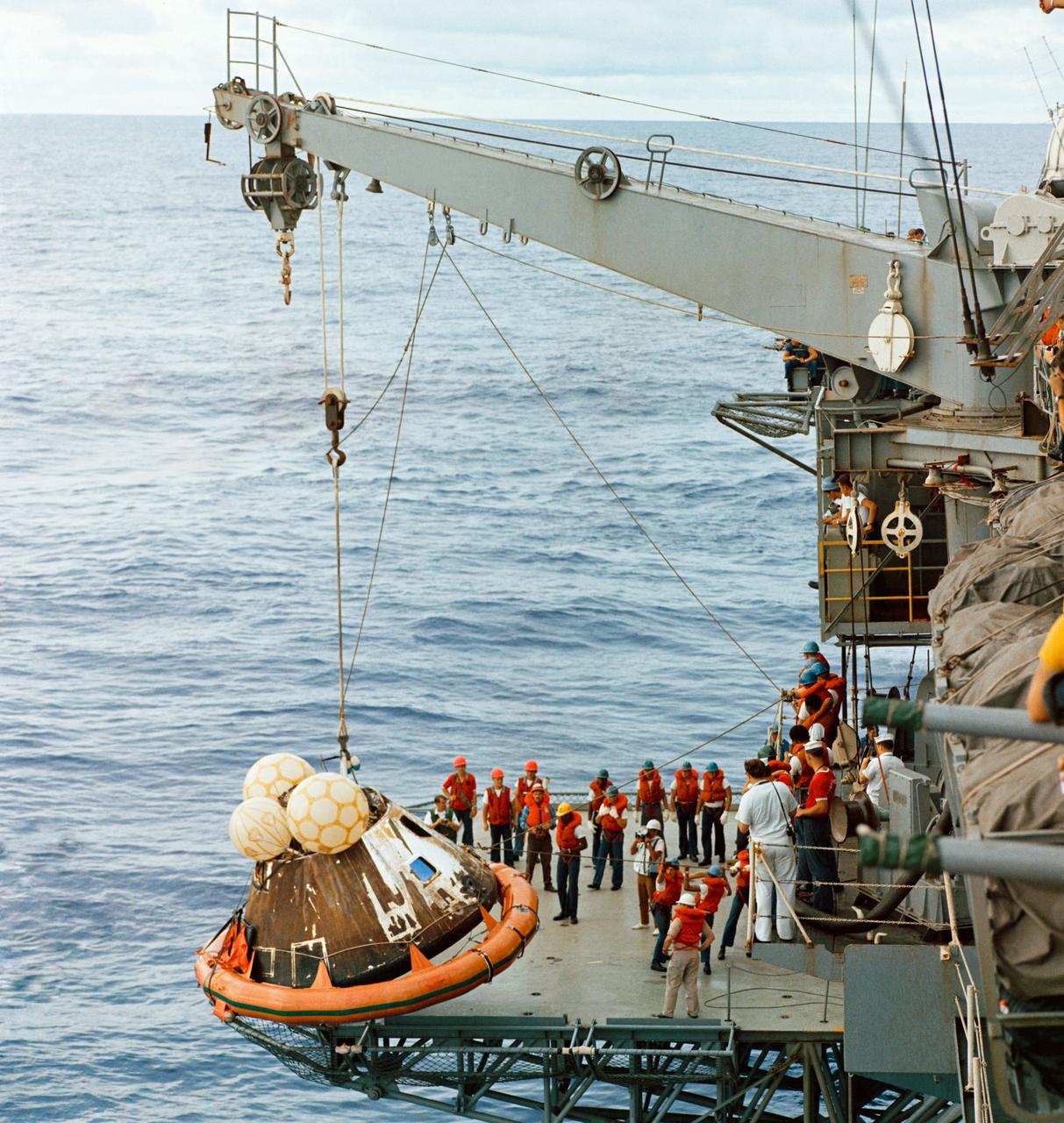

S70-15530 (17 April 1970) --- Crew men aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission, hoist the Command Module (CM) aboard ship. The Apollo 13 crew men, astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., John L. Swigert Jr. and Fred W. Haise Jr., were already aboard the Iwo Jima when this photograph was taken. The CM, with the three tired crew men aboard, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, only about four miles from the recovery vessel in the South Pacific Ocean.
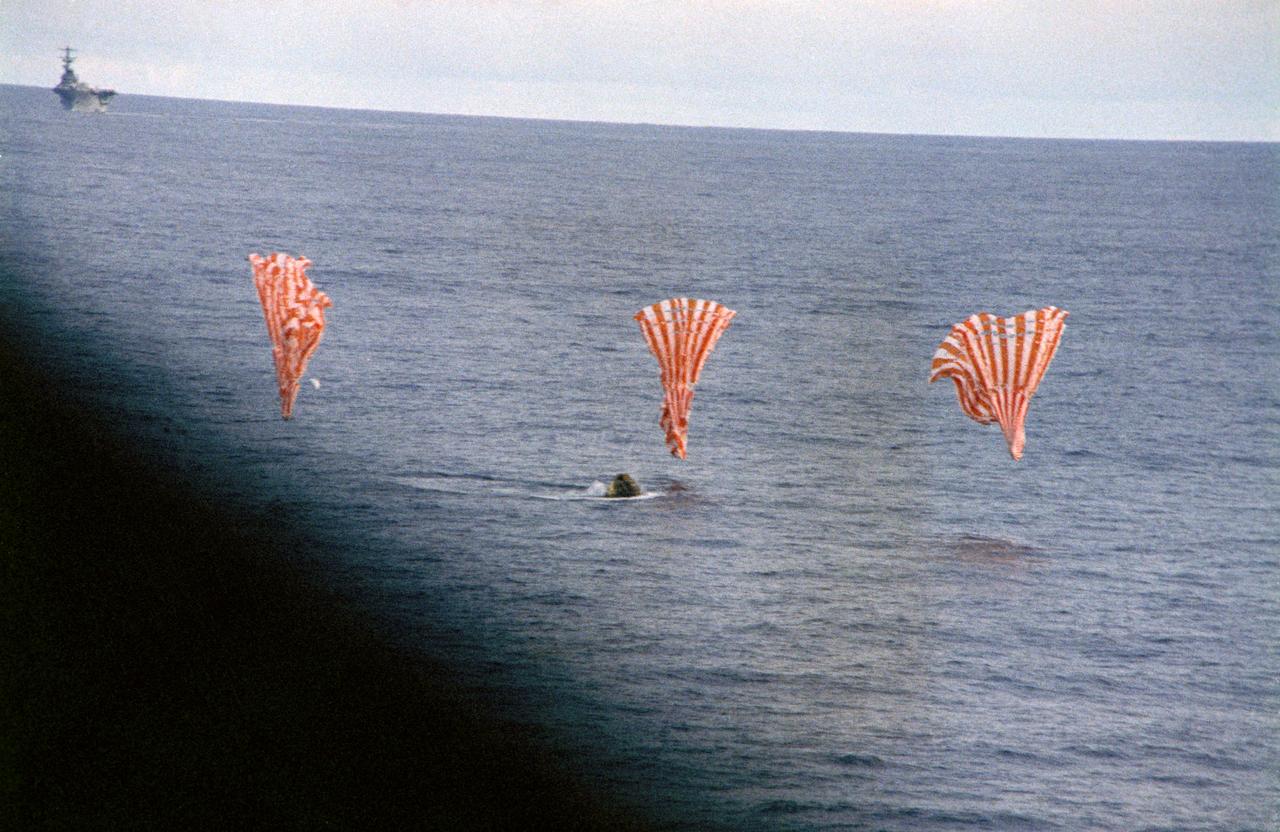

S70-35644 (17 April 1970) --- The Apollo 13 Command Module (CM) splashes down and its three main parachutes collapse, as the week-long problem-plagued Apollo 13 mission comes to a premature, but safe end. The spacecraft, with astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, aboard splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST) April 17, 1970, in the South Pacific Ocean, only about four miles from the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship.
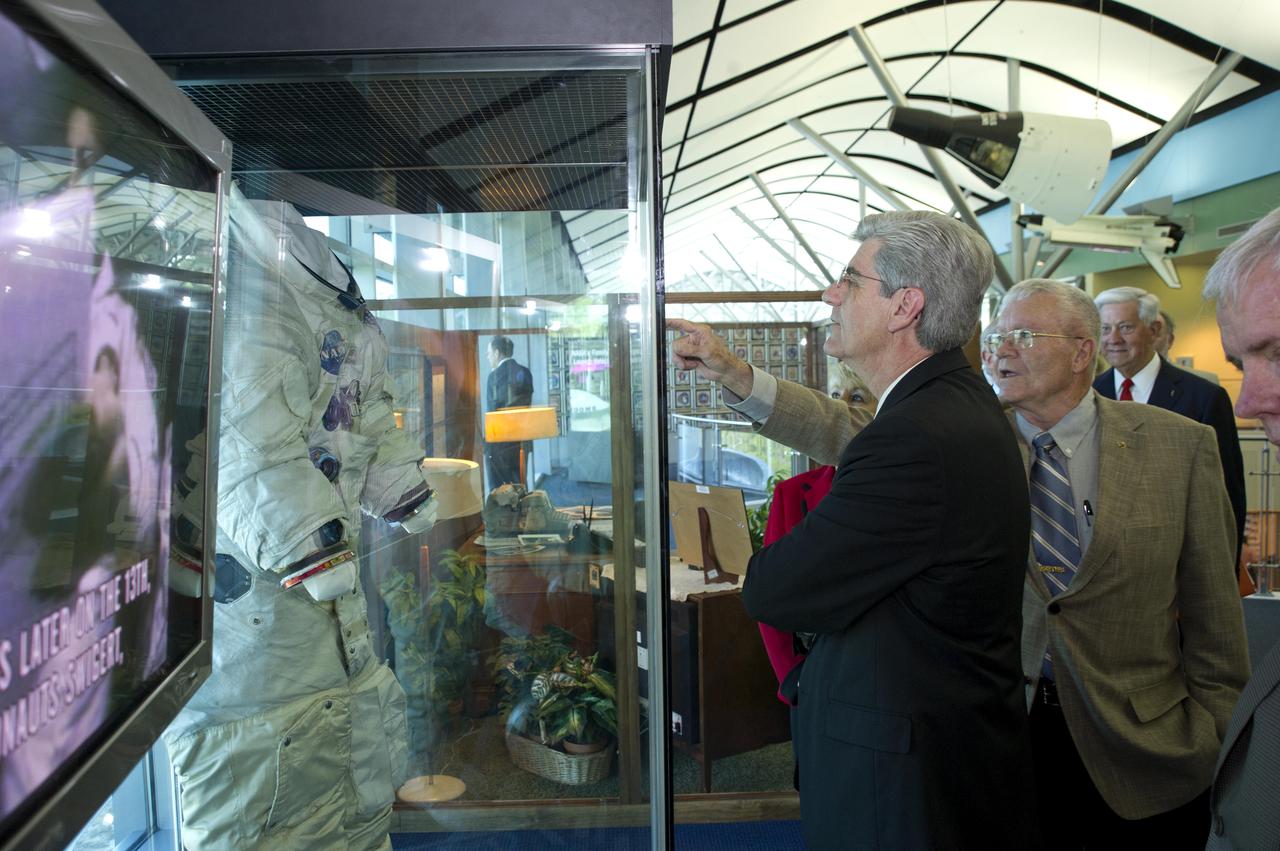

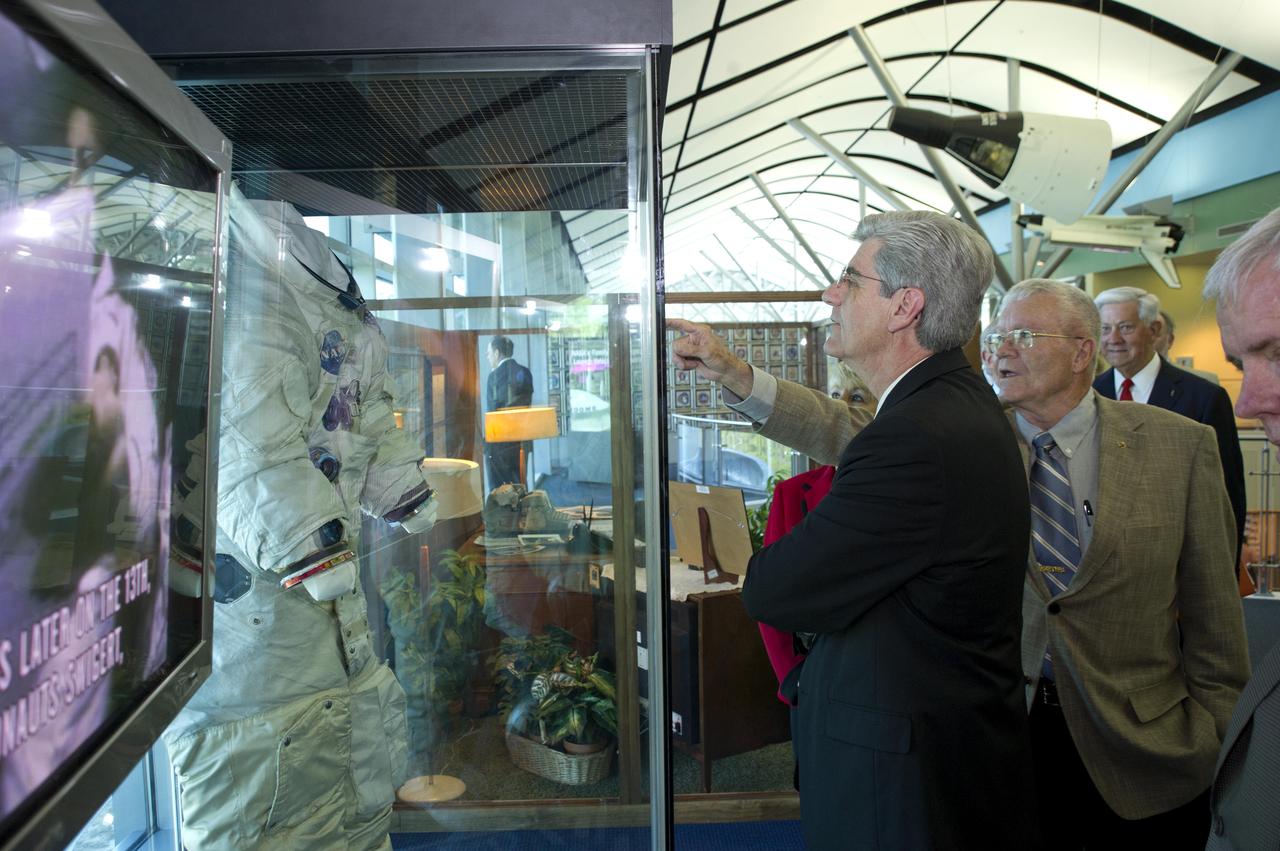
Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant looks on as Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise points out features of the spacesuit he wore on his lunar mission in 1970. The suit is on display at the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center visitor center and museum. The two men toured the facility during ribbon-cutting activities April 11, 2012.
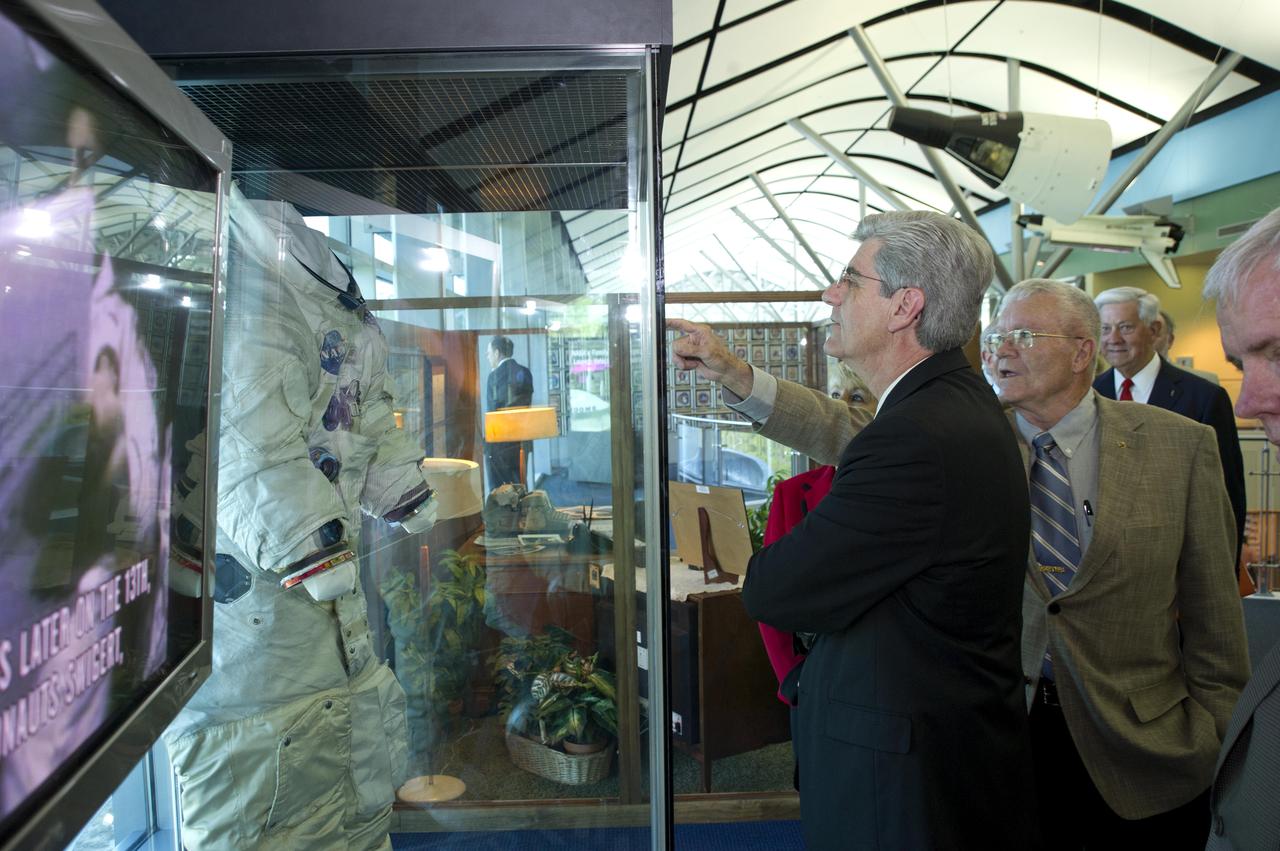

Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant looks on as Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise points out features of the spacesuit he wore on his lunar mission in 1970. The suit is on display at the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center visitor center and museum. The two men toured the facility during ribbon-cutting activities April 11, 2012.

Members of the World Presidents' Organization enjoy exhibits at StenniSphere, the museum and visitor center at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center during a tour of the space facility Jan. 26. WPO members from several states toured Stennis facilities during a daylong visit that included a presentation by Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise of Biloxi.
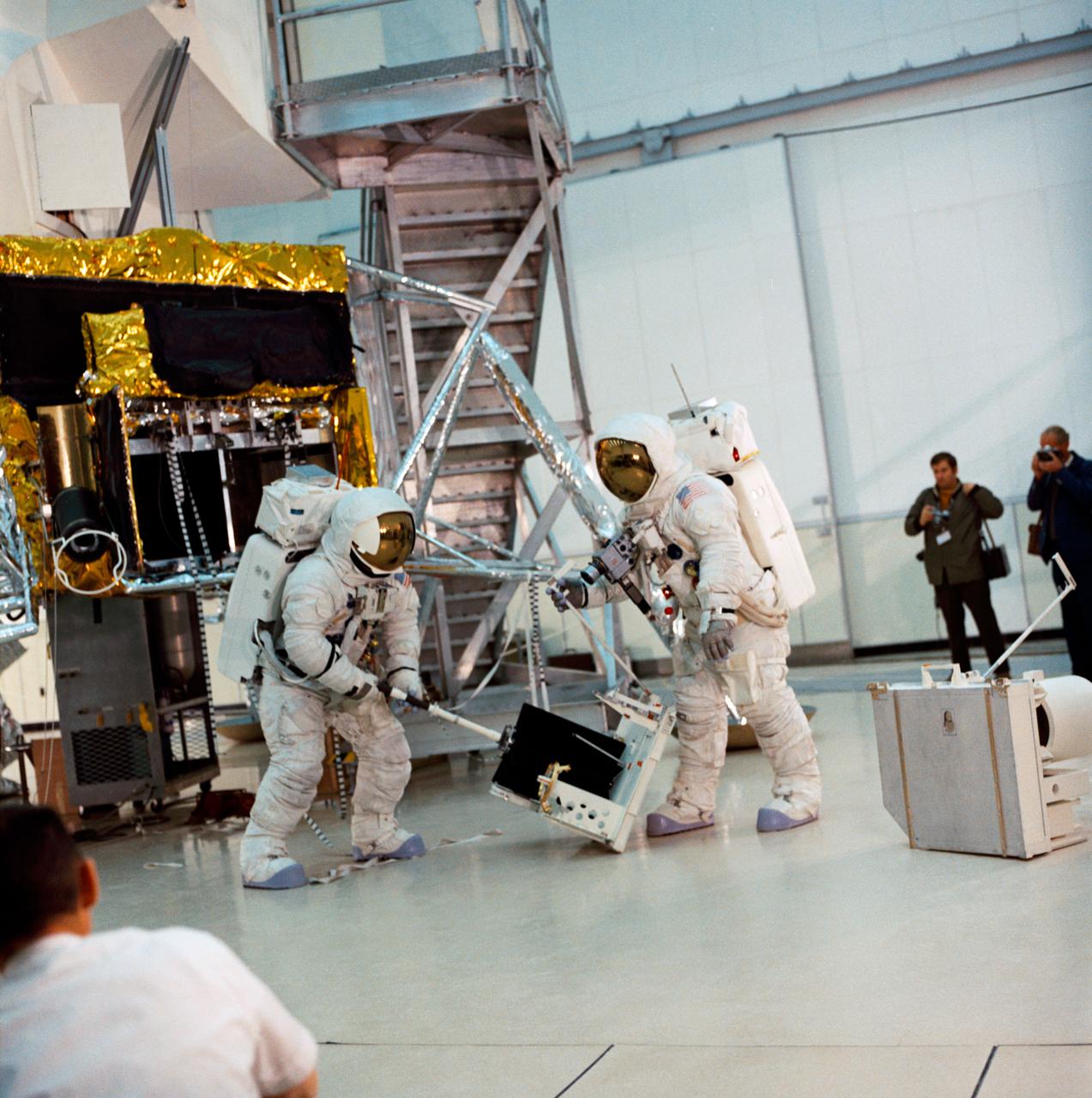

S70-27036 (4 Feb. 1970) --- Two crew men of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission simulate lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) during training exercises in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Flight Crew Training Building. They are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.

Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant looks on as Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise points out features of the spacesuit he wore on his lunar mission in 1970. The suit is on display at the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center visitor center and museum. The two men toured the facility during ribbon-cutting activities April 11, 2012.
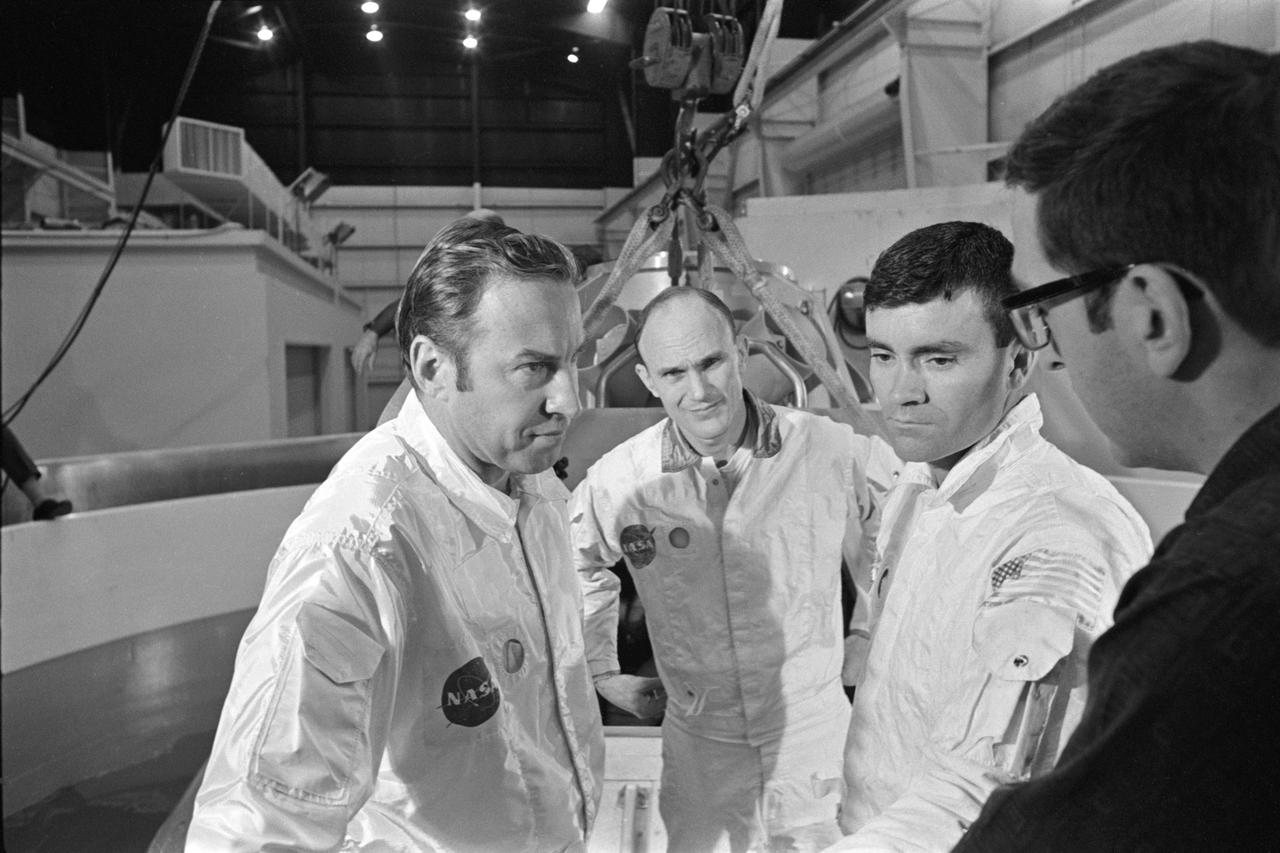

S70-24014 (17 Jan. 1970) --- The three prime crewmen of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission stand by to participate in water egress training in a water tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center. They were (left to right) astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
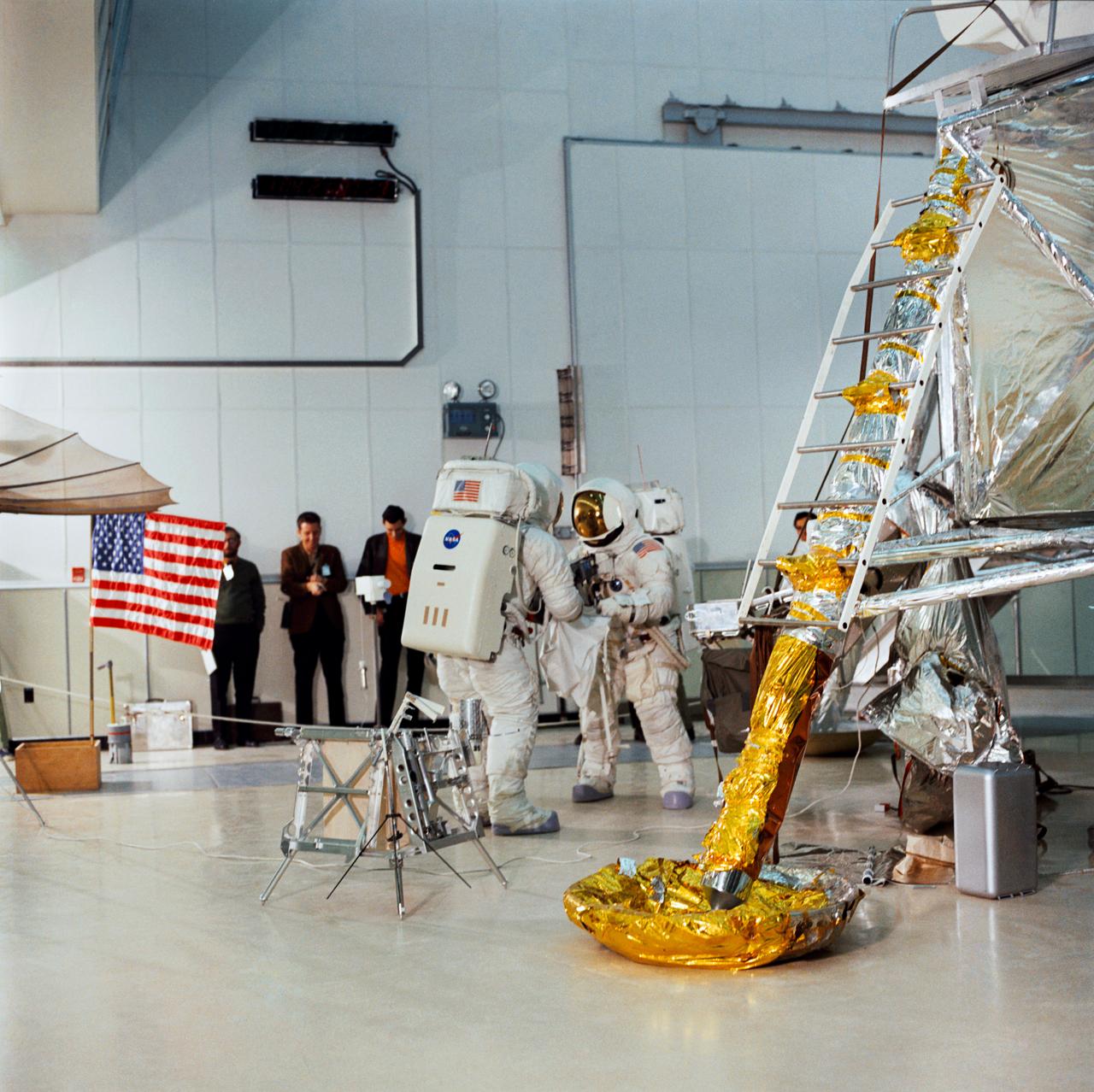

S70-27038 (4 Feb. 1970) --- Two crew men of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission simulate lunar surface Extravehicular Activity (EVA) during training exercises in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Flight Crew Training Building. They are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. (on left, back to camera) commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
S70-35615 (17 April 1970) --- A water level view of the Apollo 13 recovery operations in the South Pacific Ocean. The three astronauts have egressed their spacecraft, and astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, has already ascended to the helicopter. The other two crewmembers await the return of the "Billy Pugh" net. Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr. (center), commander, will remain in the life raft until astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, has boarded the helicopter. A United States Navy underwater demolition team swimmer assist with the recovery operations. The three Apollo 13 crewmembers were flown to the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship. Apollo 13 splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, to safely conclude a perilous space flight.

S70-30534 (9 March 1970) --- A Lunar Landing Training Vehicle (LLTV), piloted by astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., sets down on the runway at the conclusion of a test flight at Ellington Air Force Base. Lovell is the commander of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. Lovell used the LLTV to practice lunar landing techniques in preparation for his scheduled mission. Lovell will be at the controls of the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) when it lands on the moon in the highlands just north of Fra Mauro. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, will remain with the Apollo 13 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Lovell and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, descend in the LM to explore the moon. A hovering helicopter watches the LLTV landing.

S70-35748 (20 April 1970) --- Dr. Donald K. Slayton (center foreground), MSC director of flight crew operations, talks with Dr. Wernher von Braun (right), famed rocket expert, at an Apollo 13 postflight debriefing session. The three crewmen of the problem-plagued Apollo 13 mission (left to right) in the background are astronauts James A Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The apparent rupture of oxygen tank number two in the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) and the subsequent damage forced the three astronauts to use the Lunar Module (LM) as a "lifeboat" to return home safely after their moon landing was canceled. Dr. von Braun is the deputy associate administrator for planning of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
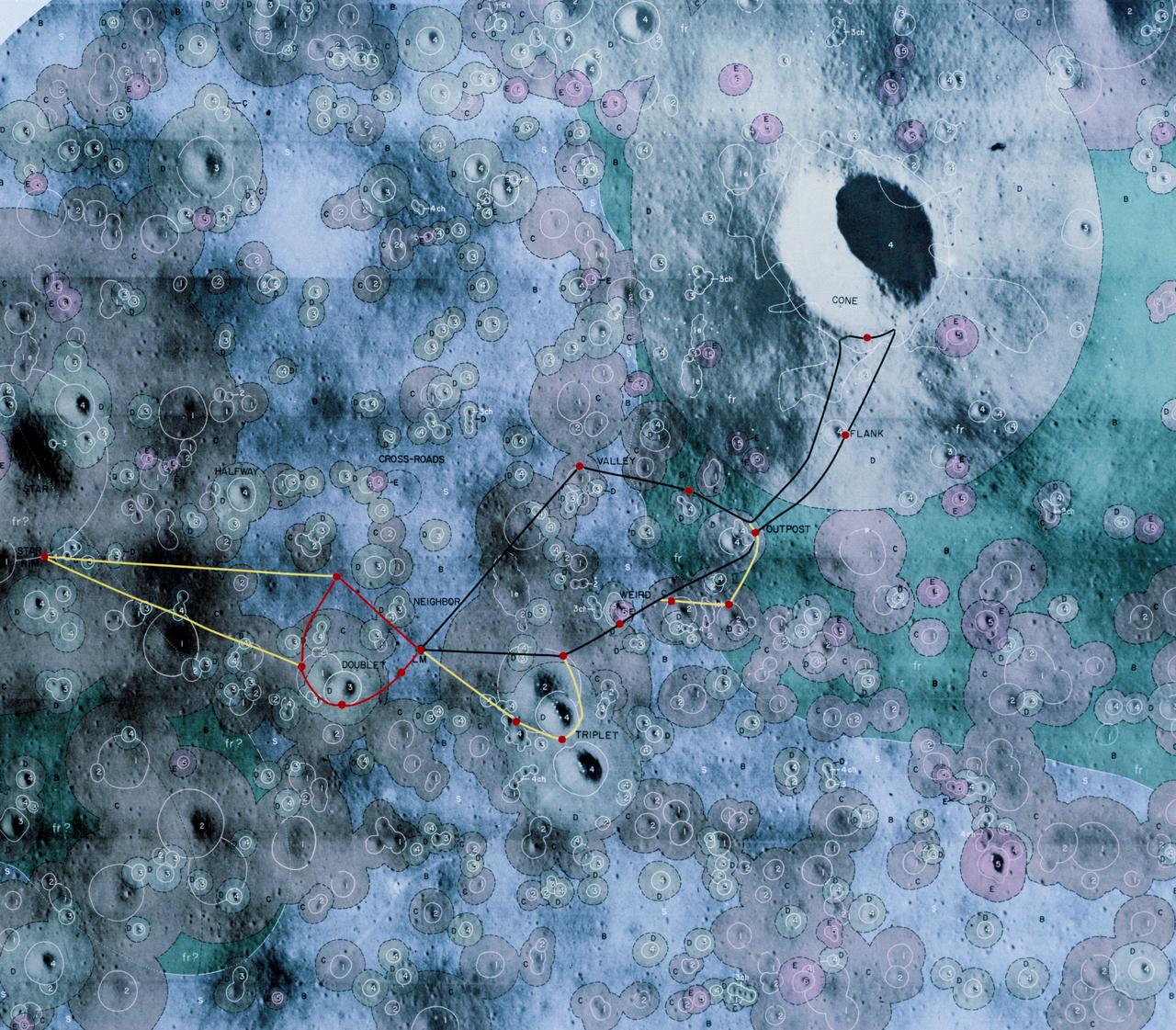

S70-30828 (March 1970) --- A photographic illustration of the Fra Mauro area showing the scheduled traverses planned for the extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. The larger red dot marked LM indicates the landing point of the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM). The red line shows the path of the first EVA traverse. The second EVA traverse is marked with a black line. The yellow line denotes the extension of each traverse in the event a decision is made to do so. The red dots indicate the points of interest for samples and for observation. Participating in the Apollo 13 EVA will be astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II , command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise participates in a presentation to guests gathered for the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation's dinner at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral celebrating the 40th anniversary of Apollo 17. The gala commemorating the anniversary of Apollo 17 included mission commander Eugene Cernan and other astronauts who flew Apollo missions. Launched Dec. 7, 1972, Cernan and lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt landed in the moon's Taurus-Littrow highlands while command module pilot Ronald Evans remained in lunar orbit operating a scientific instrument module. For more information, visit http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/history/apollo/apollo-17/apollo-17.htm Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
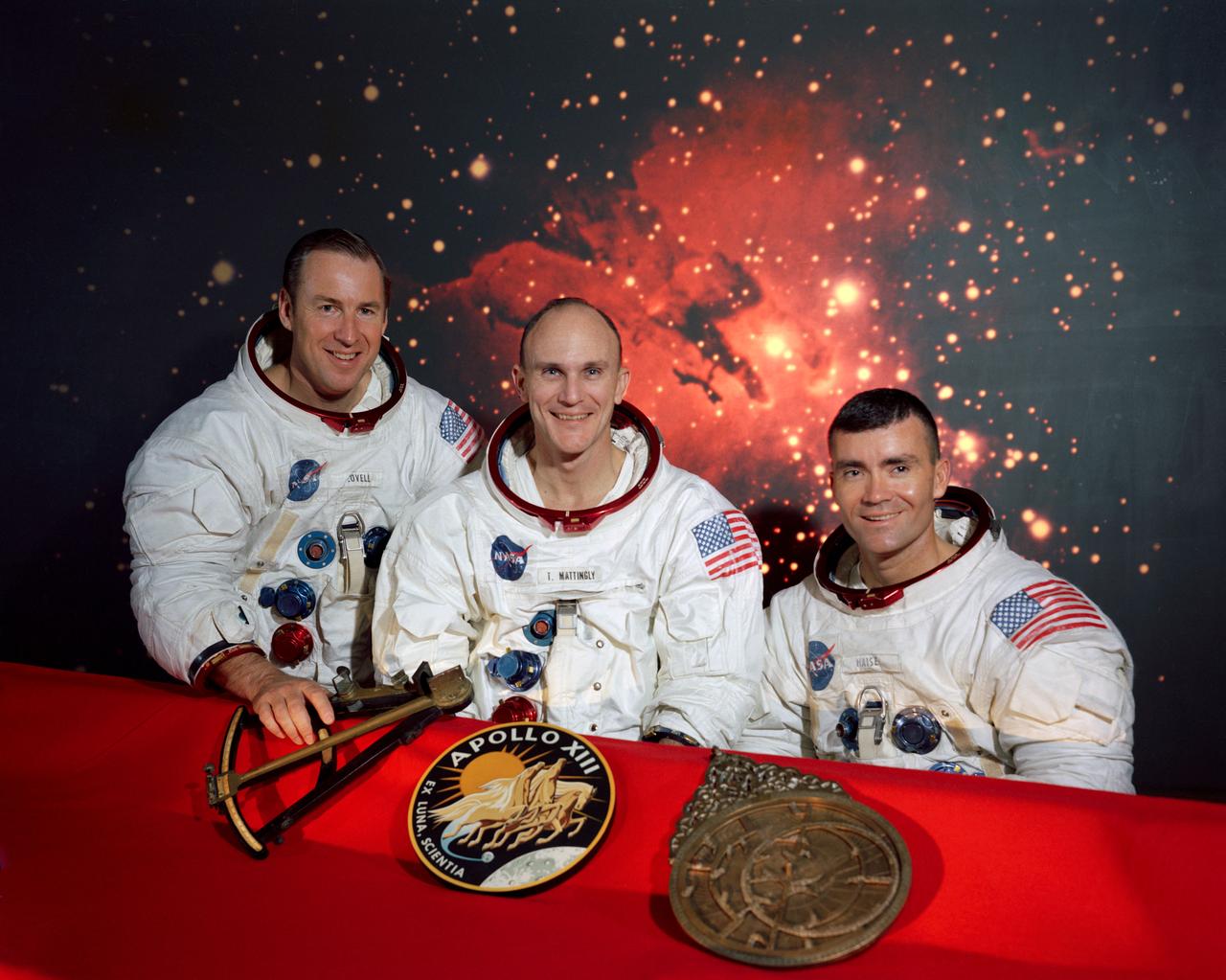

S69-62224 (December 1969) --- The members of the prime crew of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission (left to right) are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. They are seated in front of a scene of the Lagoon Nebula, with the mission insignia and two items of early navigation in the foreground. Represented in the Apollo 13 emblem (center) is Apollo, the sun god of Greek mythology, symbolizing that the Apollo flights have extended the light of knowledge to all mankind. The Latin phrase Ex Luna, Scientia means "From the Moon, Knowledge." The Hindu astrolabe in Sanskrit (on right) was used to predict the position of celestial bodies before the invention of the octant (on left) was used in 1790 to determine the altitude of celestial bodies from aboard ship.

S70-35610 (17 April 1970) --- A water level view of the Apollo 13 recovery operations in the South Pacific Ocean. The three astronauts as seen egressing their spacecraft. John L. Swigert Jr. (back to camera), command module pilot, is already in the life raft. Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, facing camera, is stepping into the life raft. James A. Lovell Jr., commander, is leaving the spacecraft in the background. A United States Navy underwater demolition team assists with the recovery operations. The three crewmembers were picked up by helicopter and flown to the prime recovery ship, USS Iwo Jima. The Apollo 13 Command Module (CM) splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, to conclude safely a perilous space flight. Though the Apollo lunar landing mission was canceled, a disastrous loss of three astronauts was averted.
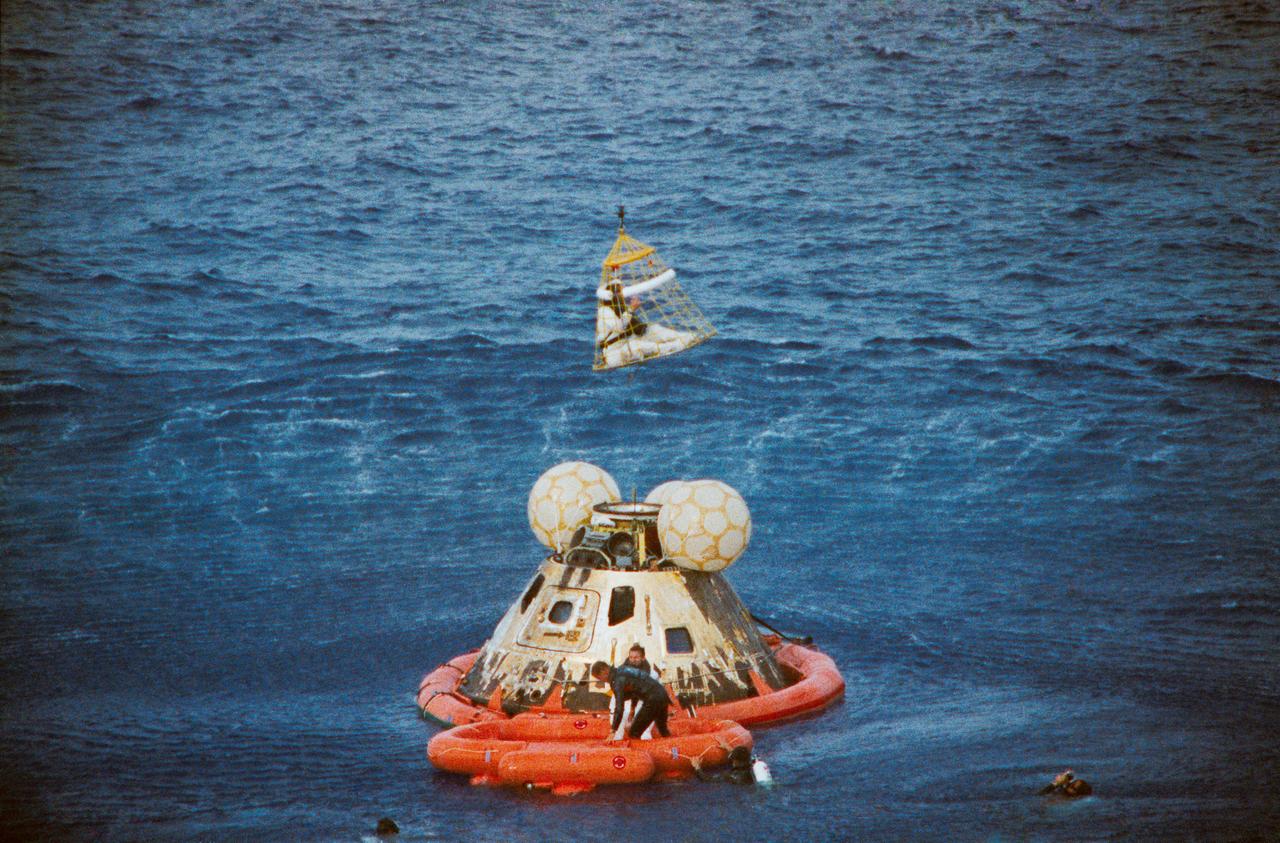

S70-35651 (17 April 1970) --- Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, is lifted aboard a helicopter in a "Billy Pugh" net while astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander, awaits his turn. Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, is already aboard the helicopter. In the life raft with Lovell, and in the water are several U.S. Navy underwater demolition team swimmers, who assisted in the recovery operations. The crew was taken to the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship, several minutes after the Apollo 13 spacecraft splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970.
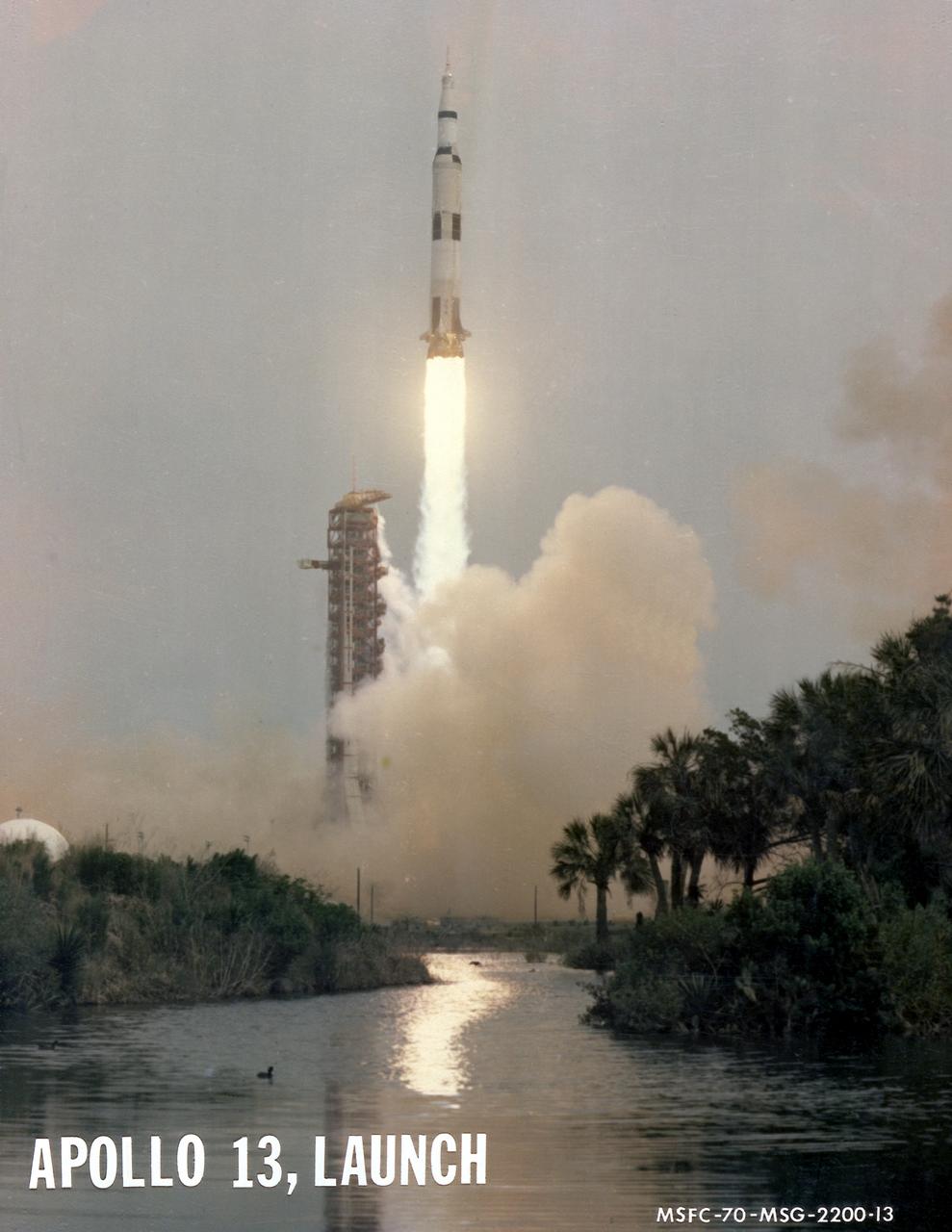

The third marned lunar landing mission, Apollo 13 (SA-508), with three astronauts: Mission commander James A. Lovell Jr., Lunar Module pilot Fred W. Haise Jr., and Command Module pilot John L. Swigert Jr., lifted off from the Kennedy Space Center launch complex 39A on April 11, 1970. The mission was aborted after 56 hours of flight, 205,000 miles from Earth, when an oxygen tank in the service module exploded. The Command Module, Odyssey, carrying the three astronauts, safely splashed down in the Pacific Ocean at 1:08 p.m. EST, April 17, 1970.
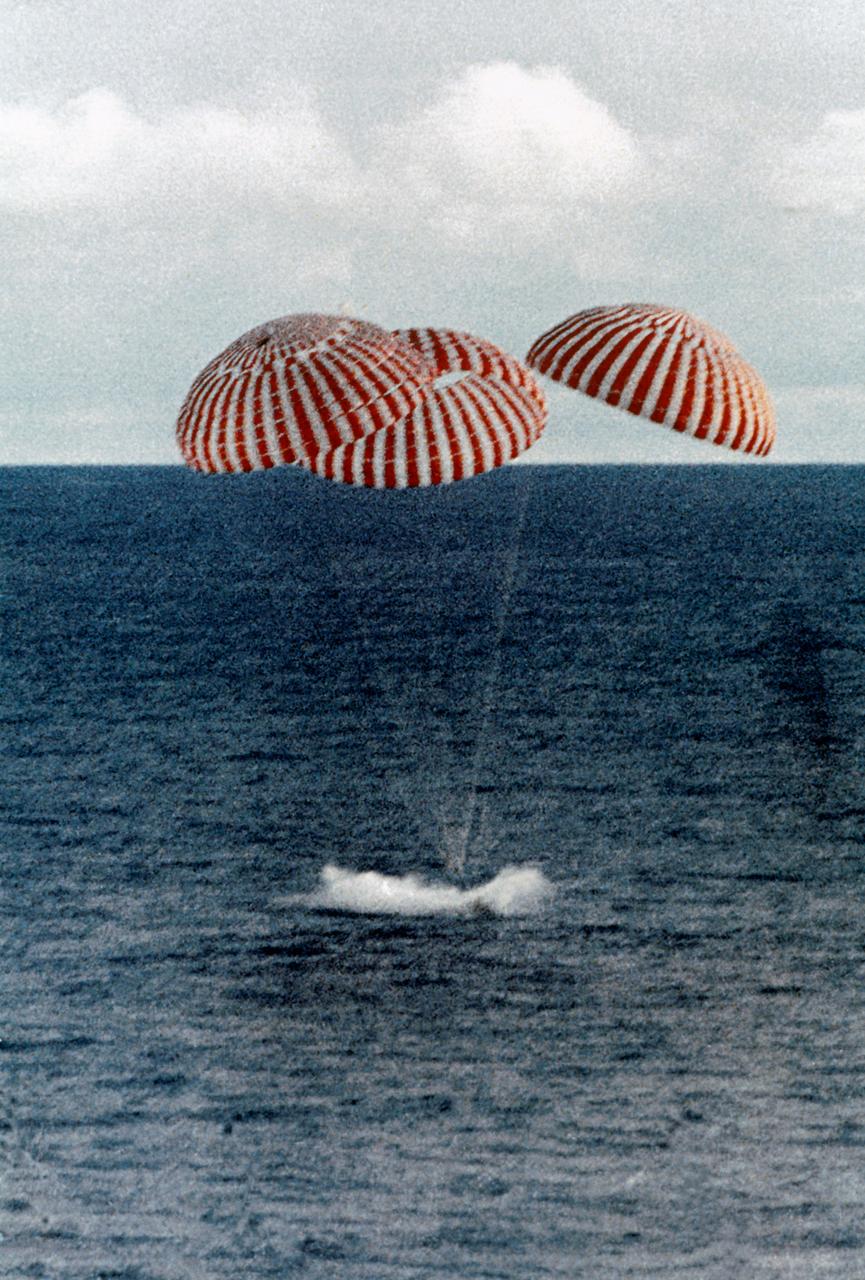

S70-35638 (17 April 1970) --- A perilous space mission comes to a smooth ending with the safe splashdown of the Apollo 13 Command Module (CM) in the South Pacific, only four miles from the prime recovery ship. The spacecraft with astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., John L. Swigert Jr., and Fred W. Haise Jr. aboard, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST) April 17, 1970, to conclude safely the problem-plagued flight. The crewmen were transported by helicopter from the immediate recovery area to the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery vessel.
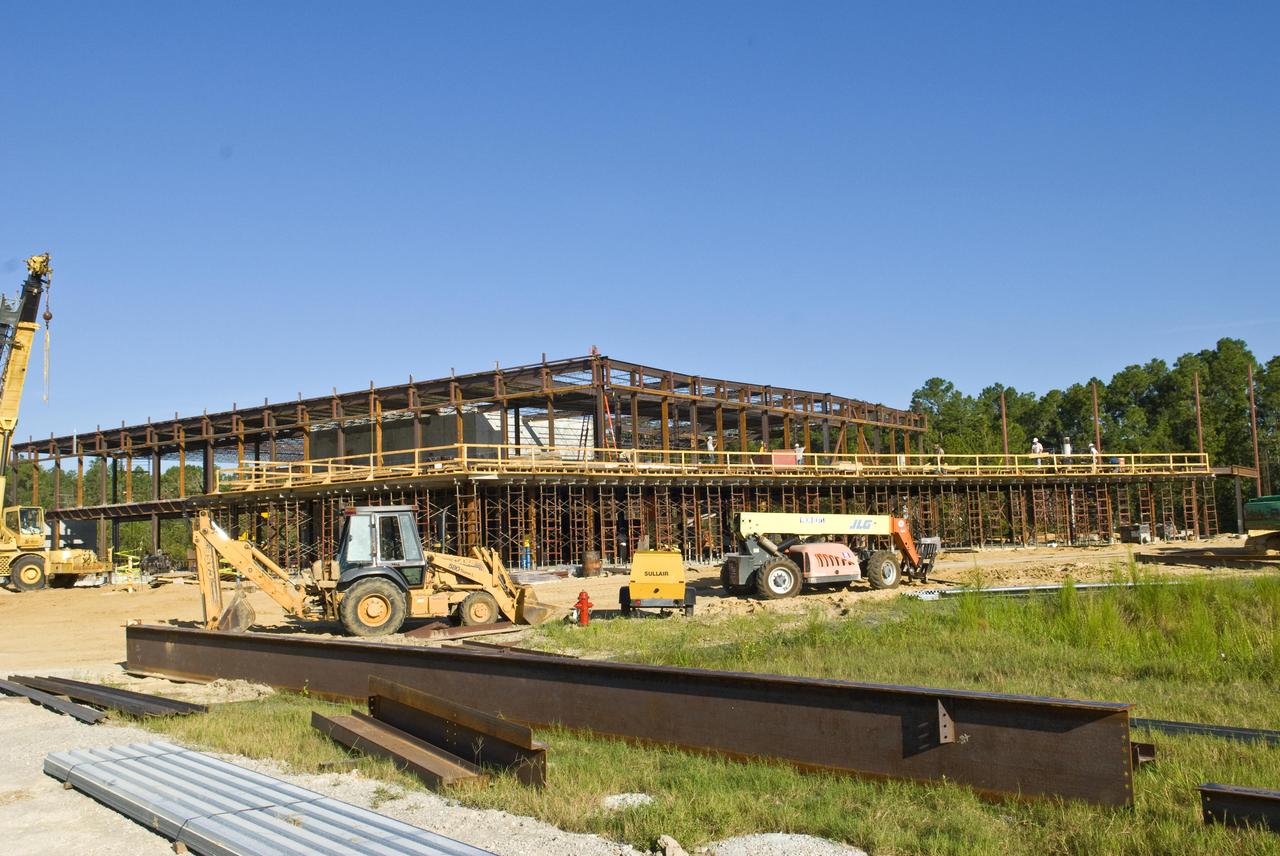

Construction of the new INFINITY Science Center is proceeding just west of the Mississippi Welcome Center at exit 2 on Interstate 10. Roy Anderson Corp. of Gulfport is building the 72,000-squarefoot, $43 million science and education center, which will feature a space gallery and an Earth gallery to showcase the science underpinning missions of the agencies at Stennis Space Center. The project is being spearheaded by INFINITY Science Center, Inc., a non-profit corporation led by Gulfport Mayor George Schloegel and Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise, in partnership with NASA, the state of Mississippi and private donors. When completed, it will serve as the official Stennis visitors center and will be home to the NASA Educator Resource Center.
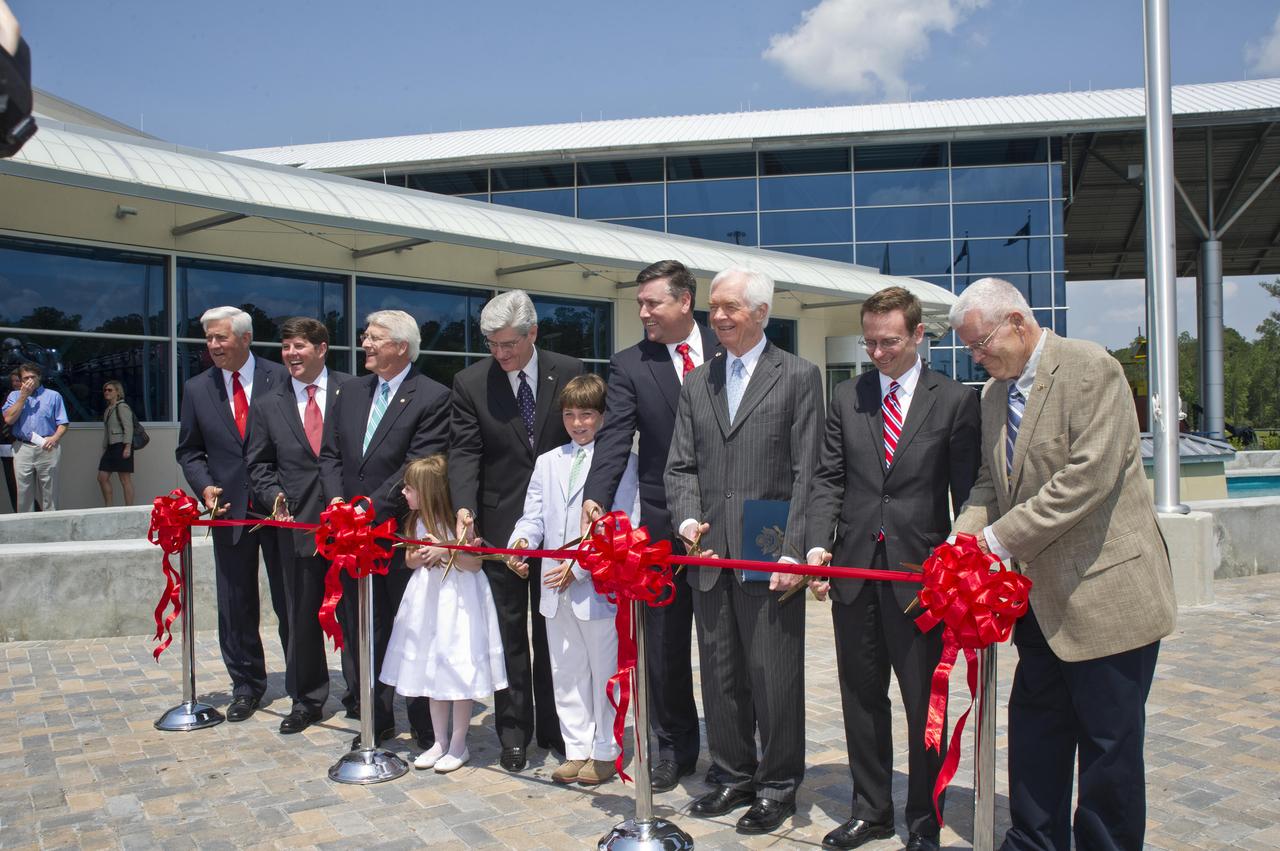

Ceremony participants prepare to cut the ribbon on the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility April 11, 2012. Participating in the ceremony were (l to r): Gulfport Mayor and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Chairman George Schloegel; U.S. Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss.; U.S. Sen. Roger Wicker, R-Miss.; Roy S. Estess granddaughter Lauren McKay; Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant; Leo Seal Jr. grandson Leo Seal IV; Stennis Director Patrick Scheuermann; U.S. Sen. Thad Cochran, R-Miss.; NASA Chief of Staff David Radzanowski; and Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise.
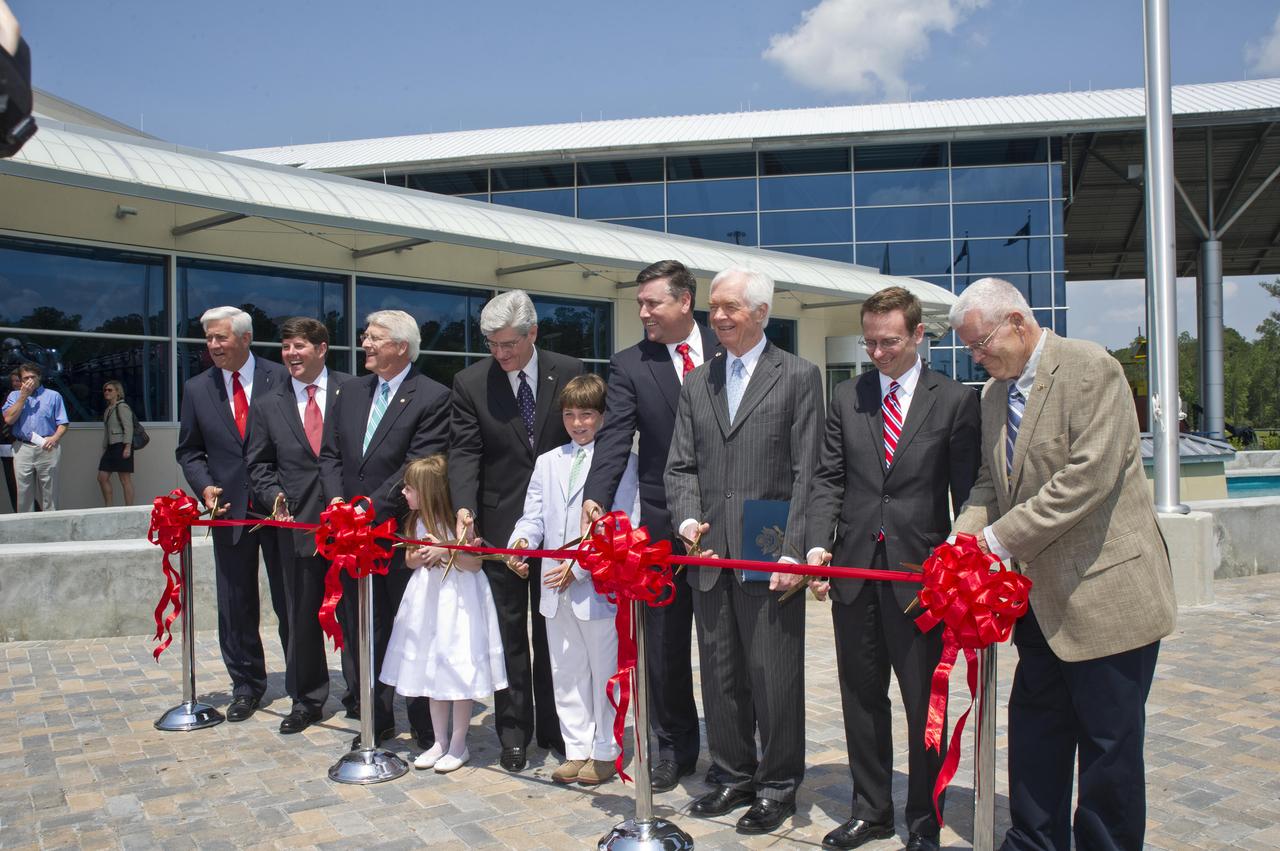

Ceremony participants prepare to cut the ribbon on the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility April 11, 2012. Participating in the ceremony were (l to r): Gulfport Mayor and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Chairman George Schloegel; U.S. Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss.; U.S. Sen. Roger Wicker, R-Miss.; Roy S. Estess granddaughter Lauren McKay; Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant; Leo Seal Jr. grandson Leo Seal IV; Stennis Director Patrick Scheuermann; U.S. Sen. Thad Cochran, R-Miss.; NASA Chief of Staff David Radzanowski; and Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise.
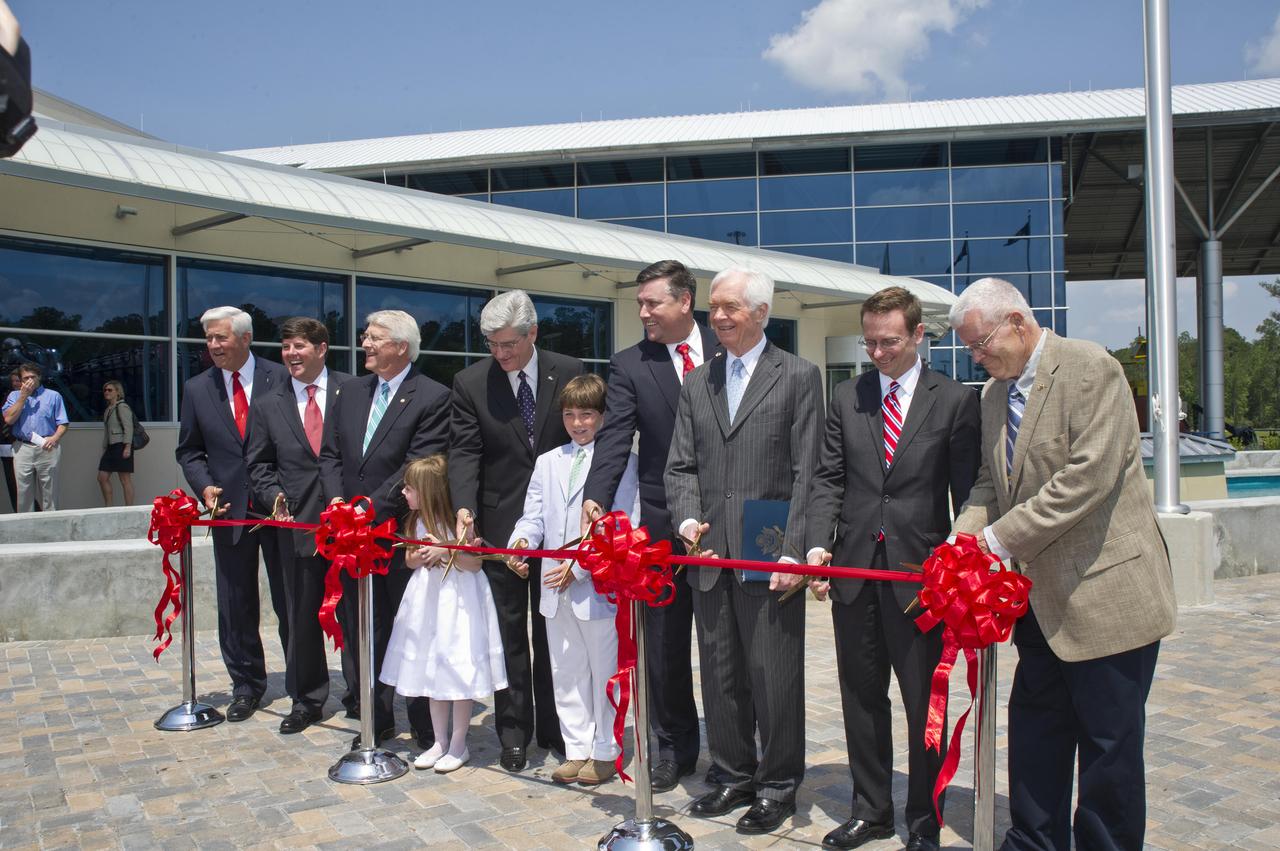

Ceremony participants prepare to cut the ribbon on the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility April 11, 2012. Participating in the ceremony were (l to r): Gulfport Mayor and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Chairman George Schloegel; U.S. Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss.; U.S. Sen. Roger Wicker, R-Miss.; Roy S. Estess granddaughter Lauren McKay; Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant; Leo Seal Jr. grandson Leo Seal IV; Stennis Director Patrick Scheuermann; U.S. Sen. Thad Cochran, R-Miss.; NASA Chief of Staff David Radzanowski; and Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise.
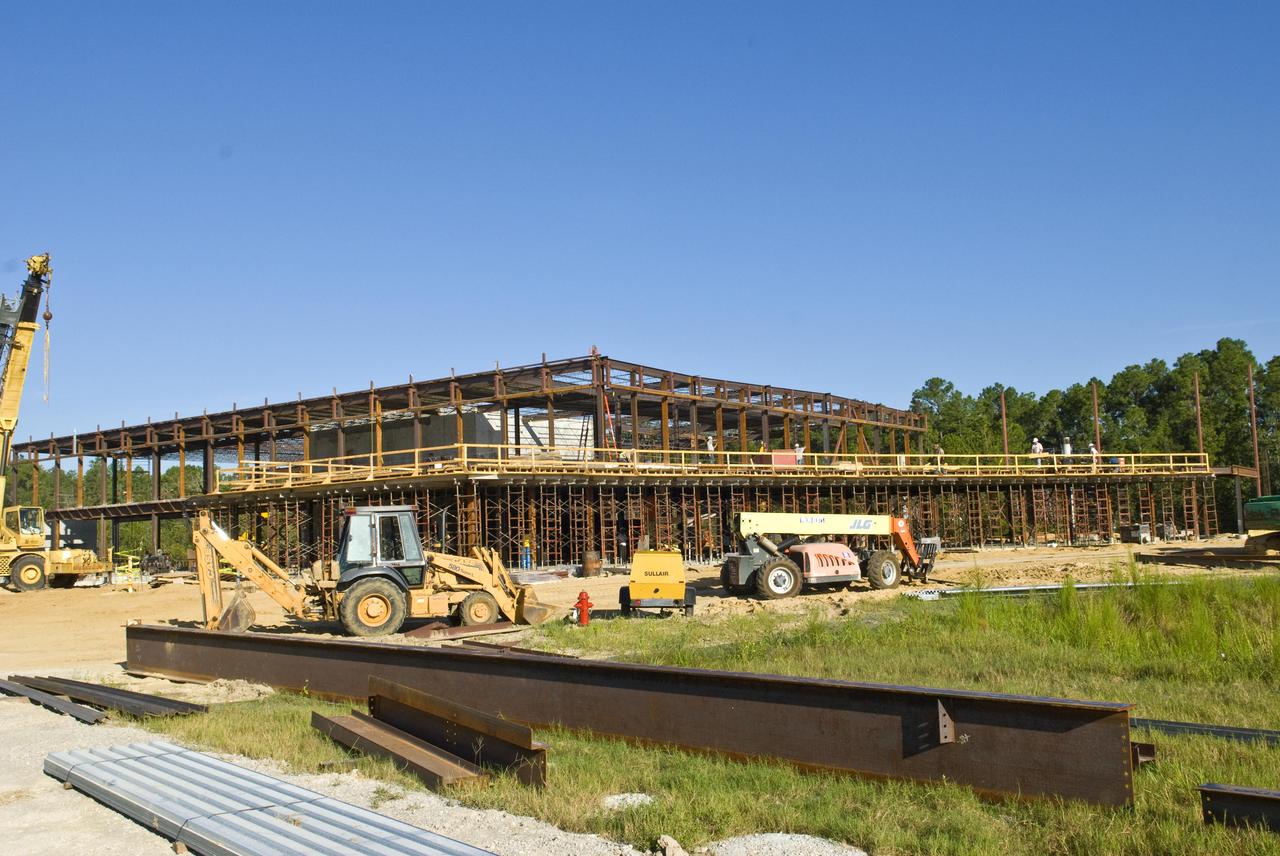

Construction of the new INFINITY Science Center is proceeding just west of the Mississippi Welcome Center at exit 2 on Interstate 10. Roy Anderson Corp. of Gulfport is building the 72,000-squarefoot, $43 million science and education center, which will feature a space gallery and an Earth gallery to showcase the science underpinning missions of the agencies at Stennis Space Center. The project is being spearheaded by INFINITY Science Center, Inc., a non-profit corporation led by Gulfport Mayor George Schloegel and Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise, in partnership with NASA, the state of Mississippi and private donors. When completed, it will serve as the official Stennis visitors center and will be home to the NASA Educator Resource Center.
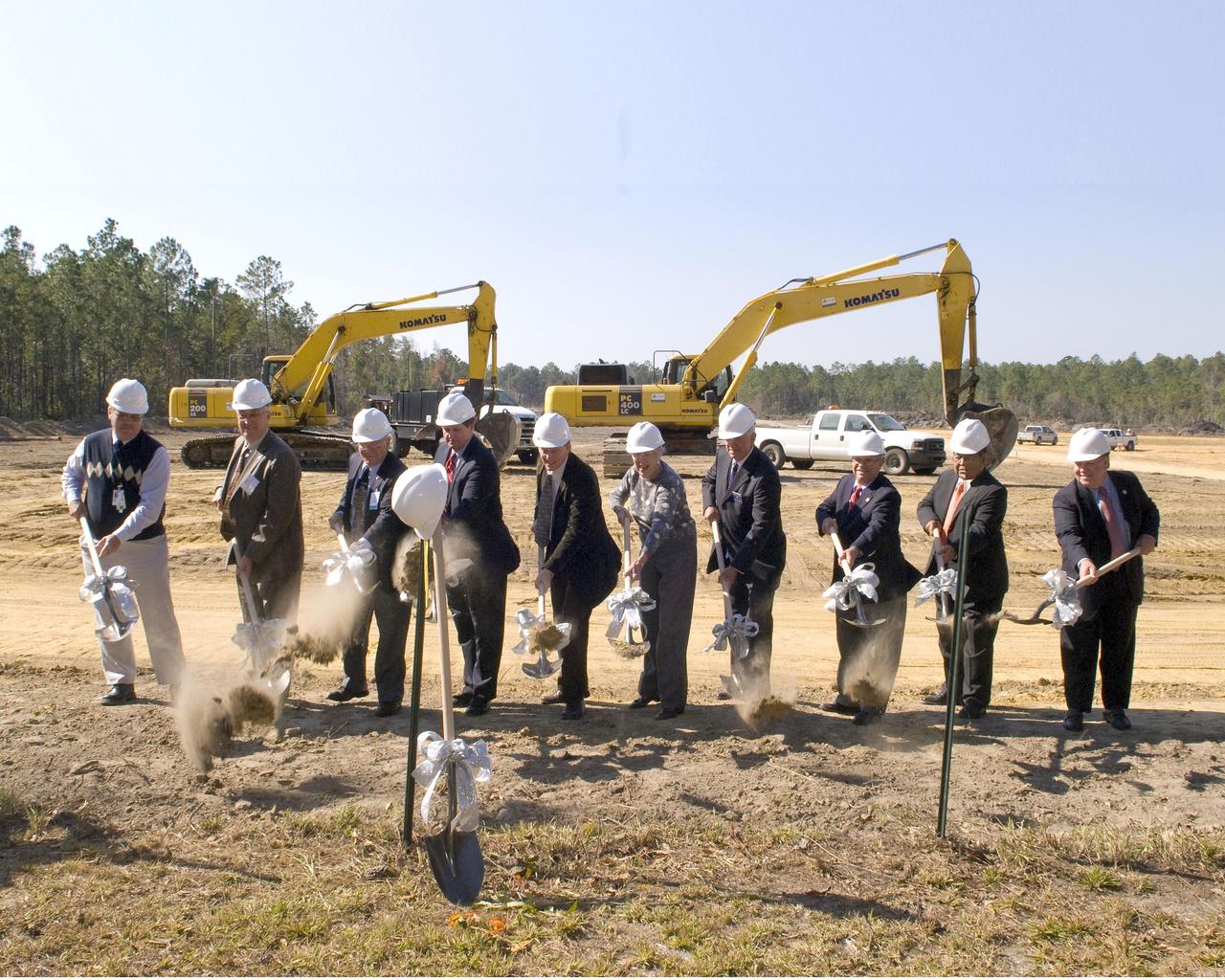

Community leaders from Mississippi and Louisiana break ground for the new INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility during a Nov. 20 ceremony. Groundbreaking participants included (l to r): Gottfried Construction representative John Smith, Mississippi Highway Commissioner Wayne Brown, INFINITY board member and Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise, Stennis Director Gene Goldman, Studio South representative David Hardy, Leo Seal Jr. family representative Virginia Wagner, Hancock Bank President George Schloegel, Mississippi Rep. J.P. Compretta, Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians representative Charlie Benn and Louisiana Sen. A.G. Crowe.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Astronaut Scholarship Foundation helps celebrate the 40th anniversary of Apollo 16's lunar landing, which occurred April 20, 1972, with a soiree at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex's Saturn V Center. Panel members who addressed the audience are, from left, astronaut support crew member for Apollo 16 Hank Hartsfield, Apollo 14 Lunar Module Pilot and Apollo 16 back-up crew member Edgar Mitchell, Apollo 13 Lunar Module Pilot and Apollo 16 back-up crew member Fred Haise, Apollo 16 Lunar Module Pilot Charlie Duke, and Apollo 8 Command Module Pilot and Apollo 13 Commander Jim Lovell. The 11-day Apollo 16 mission featured three moonwalks, including a nearly 17-mile lunar rover road trip to collect more than 200 pounds of moon rocks to return to Earth. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Chamberland
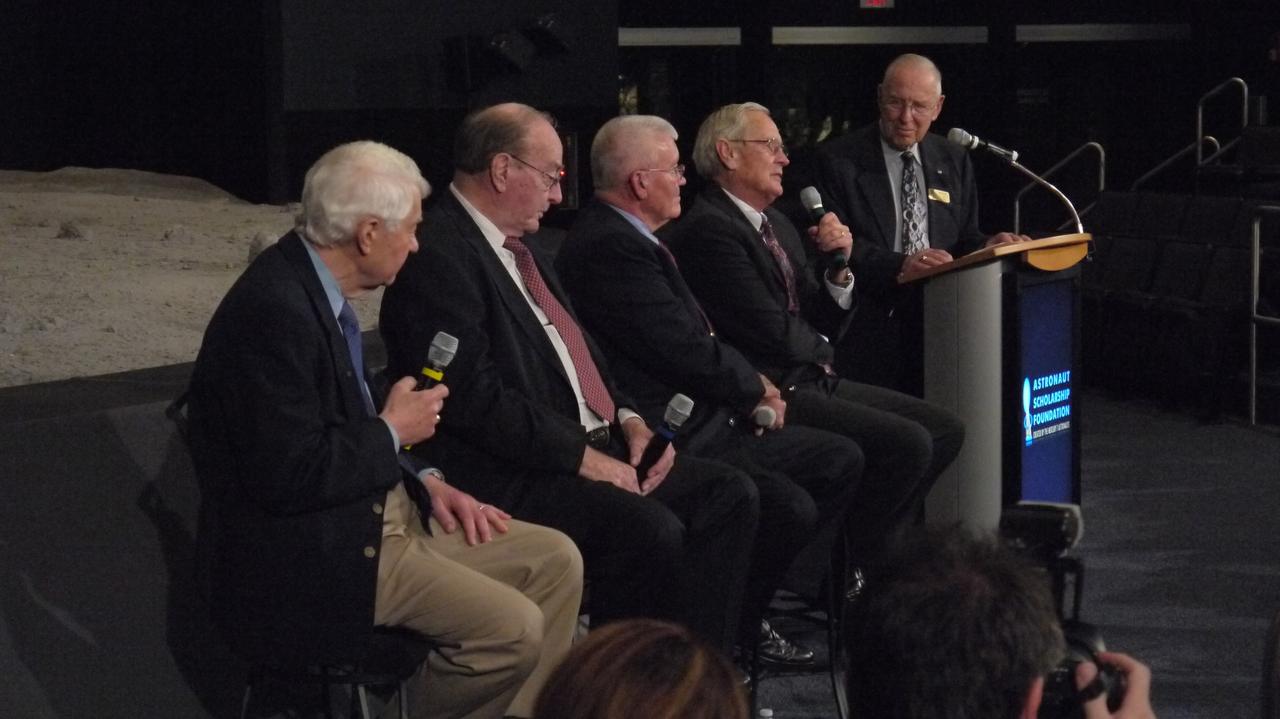

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Astronaut Scholarship Foundation helps celebrate the 40th anniversary of Apollo 16's lunar landing, which occurred April 20, 1972, with a soiree at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex's Saturn V Center. Panel members who addressed the audience are, from left, astronaut support crew member for Apollo 16 Hank Hartsfield, Apollo 14 Lunar Module Pilot and Apollo 16 back-up crew member Edgar Mitchell, Apollo 13 Lunar Module Pilot and Apollo 16 back-up crew member Fred Haise, Apollo 16 Lunar Module Pilot Charlie Duke, and Apollo 8 Command Module Pilot and Apollo 13 Commander Jim Lovell. The 11-day Apollo 16 mission featured three moonwalks, including a nearly 17-mile lunar rover road trip to collect more than 200 pounds of moon rocks to return to Earth. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Chamberland
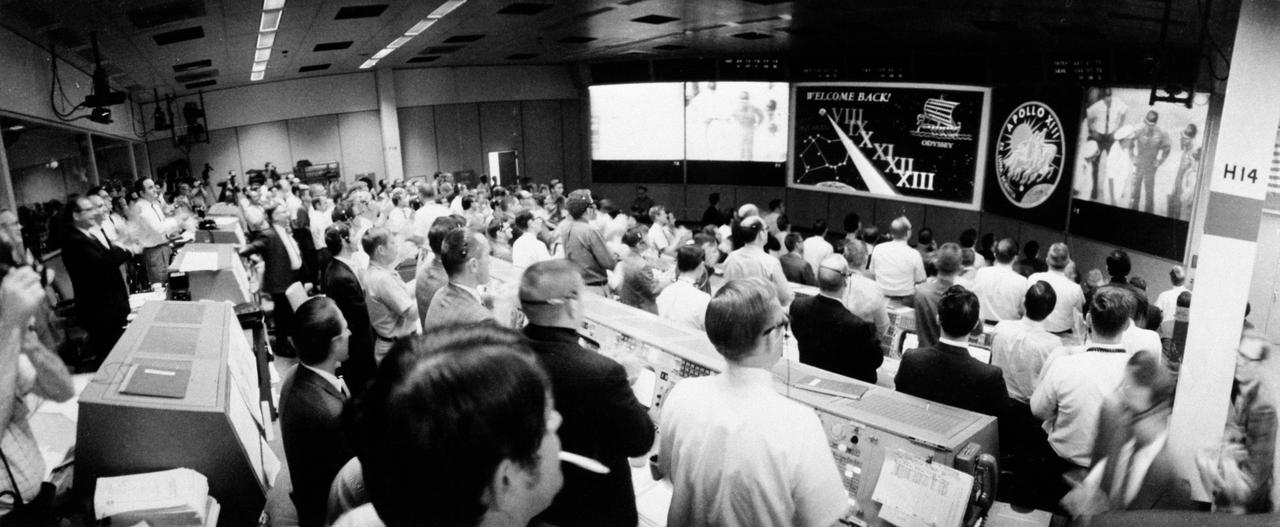

S70-35472 (17 April 1970) --- Overall view of the crowded Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) during post-recovery ceremonies aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission. The Apollo 13 spacecraft, with astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, aboard, splashed down in the South Pacific at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970. The smooth splashdown and recovery operations brought an end to a perilous spaceflight for the crewmembers, and a tiring one for ground crew in MCC.
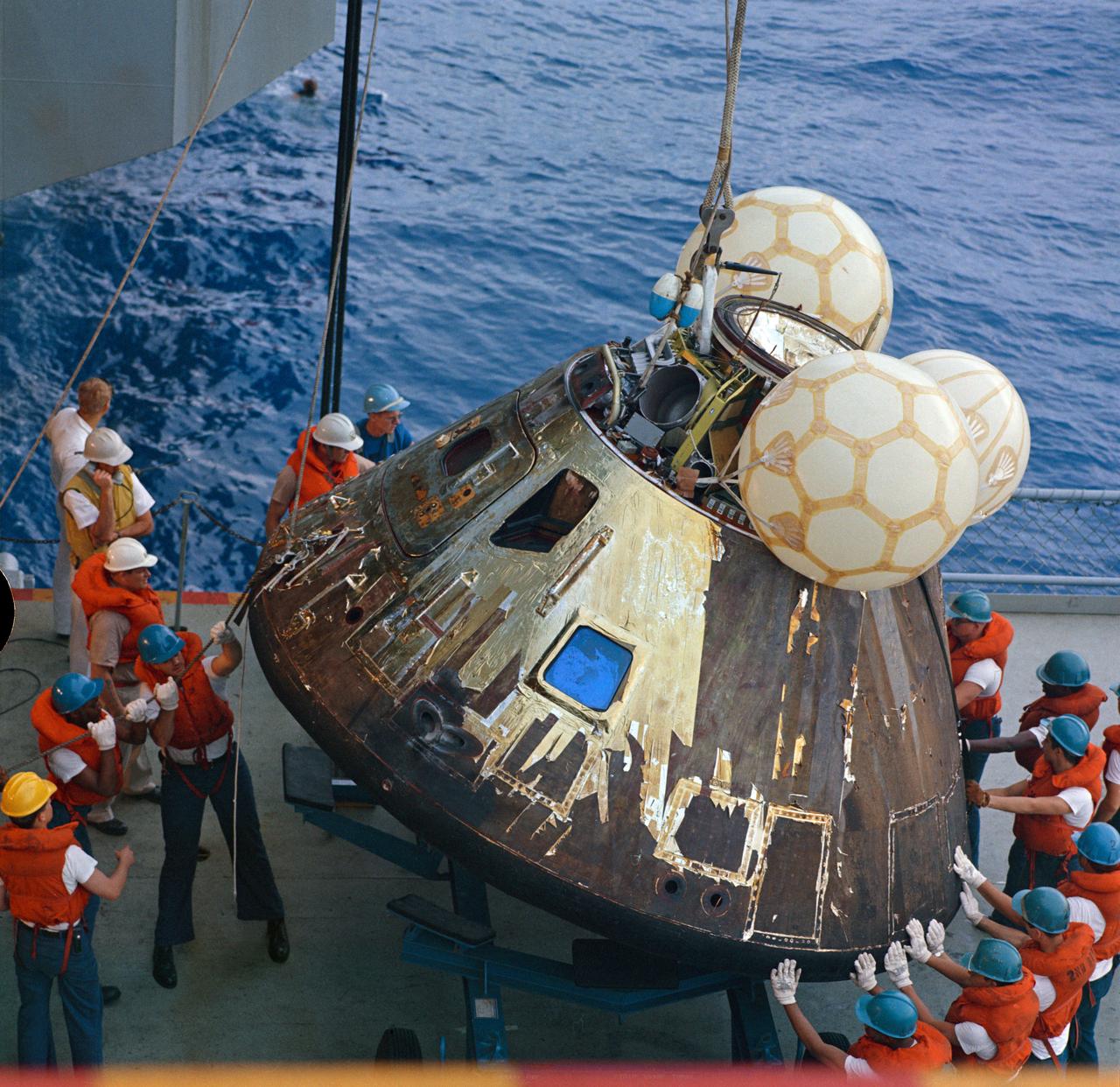

S70-35632 (17 April 1970) --- Crewmen aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission, guide the Command Module (CM) atop a dolly onboard the ship. The CM is connected by strong cable to a hoist on the vessel. The Apollo 13 crewmembers, astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, were already aboard the USS Iwo Jima when this photograph was made. The CM, with the three tired crewmen aboard, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, only about four miles from the recovery vessel in the South Pacific Ocean.
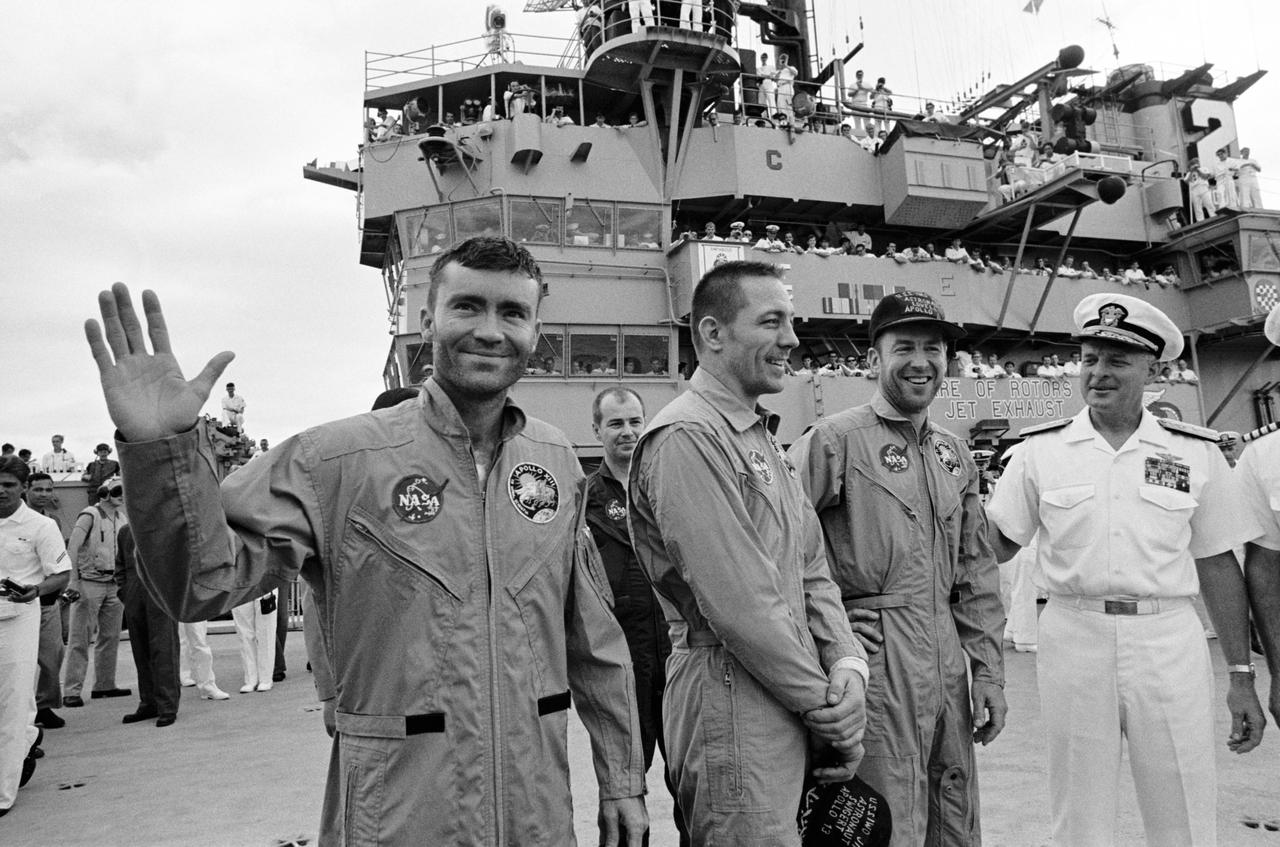

S70-35606 (17 April 1970) --- Rear Admiral Donald C. Davis, Commanding Officer of Task Force 130, the Pacific Recovery Forces for the Manned Spacecraft Missions, welcomes the Apollo 13 crewmembers aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission. The crewmembers (from the left) astronauts Fred W. Haise Jr. (waving), lunar module pilot; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and James A. Lovell Jr., commander; were transported by helicopter to the ship following a smooth splashdown only about four miles from the USS Iwo Jima. Splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, to conclude safely a perilous space flight.
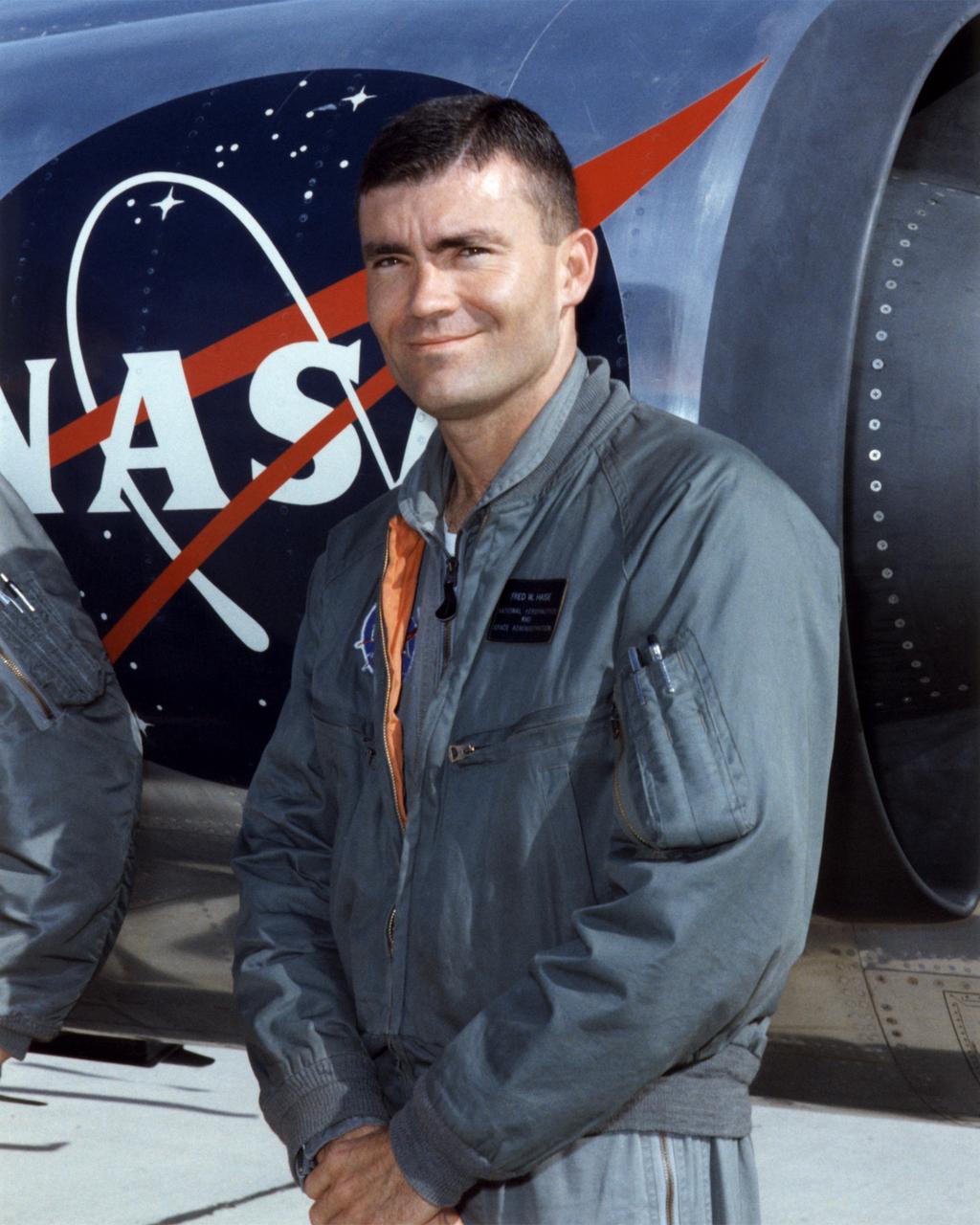

Fred W. Haise Jr. was a research pilot and an astronaut for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration from 1959 to 1979. He began flying at the Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio (today the Glenn Research Center), in 1959. He became a research pilot at the NASA Flight Research Center (FRC), Edwards, Calif., in 1963, serving NASA in that position for three years until being selected to be an astronaut in 1966 His best-known assignment at the FRC (later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center) was as a lifting body pilot. Shortly after flying the M2-F1 on a car tow to about 25 feet on April 22, 1966, he was assigned as an astronaut to the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. While at the FRC he had also flown a variety of other research and support aircraft, including the variable-stability T-33A to simulate the M2-F2 heavyweight lifting body, some light aircraft including the Piper PA-30 to evaluate their handling qualities, the Apache helicopter, the Aero Commander, the Cessna 310, the Douglas F5D, the Lockheed F-104 and T-33, the Cessna T-37, and the Douglas C-47. After becoming an astronaut, Haise served as a backup crewmember for the Apollo 8, 11, and 16 missions. He flew on the aborted Apollo 13 lunar mission in 1970, spending 142 hours and 54 minutes in space before returning safely to Earth. In 1977, he was the commander of three free flights of the Space Shuttle prototype Enterprise when it flew its Approach and Landing Tests at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. Meanwhile, from April 1973 to January 1976, Haise served as the Technical Assistant to the Manager of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Project. In 1979, he left NASA to become the Vice President for Space Programs with the Grumman Aerospace Corporation. He then served as President of Grumman Technical Services, an operating division of Northrop Grumman Corporation, from January 1992 until his retirement. Haise was born in Biloxi, Miss., on November 14, 1933. He underwent flight traini
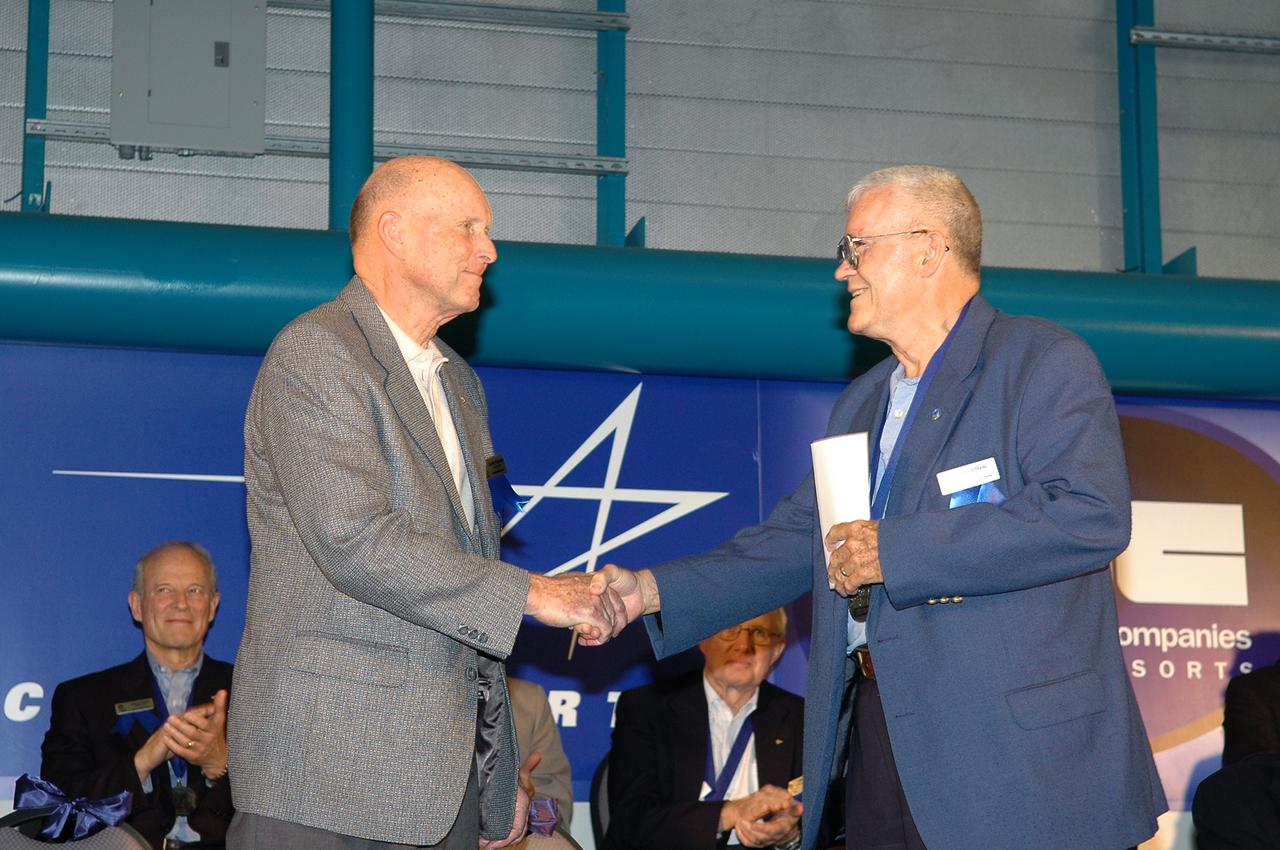

Former astronaut Gordon Fullerton (left), currently chief research pilot at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, is congratulated by former astronaut Fred Haise (right) upon Fullerton's induction into the Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida on April 30, 2005. Fullerton and Haise were one of two flight crews who flew the Approach and Landing Tests of the prototype Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise at Dryden in 1977. Fullerton, who had served on the support crews for four Apollo moon landing missions in the early 1970s, went on to fly two Shuttle missions, STS-3 in 1982 and STS-51F in 1985. STS-3 became the only Shuttle mission to date to land at White Sands, N.M., and STS-51F was completed successfully despite the failure of one of the Shuttle's main engines during ascent to orbit. Haise, a member of the crew on the ill-fated Apollo 13 mission, was also a research pilot at NASA Dryden during his pre-astronaut career. Former astronauts Joseph Allen and Bruce McCandless were also inducted during the 2005 ceremonies at the KSC Visitor Center. In addition to honoring former members of NASA's astronaut corps who have made significant contributions to the advancement of space flight, the annual induction ceremonies serve as a fund-raiser for the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation. The foundation funded 17 $10,000 scholarships to college students studying science and engineering in 2004.
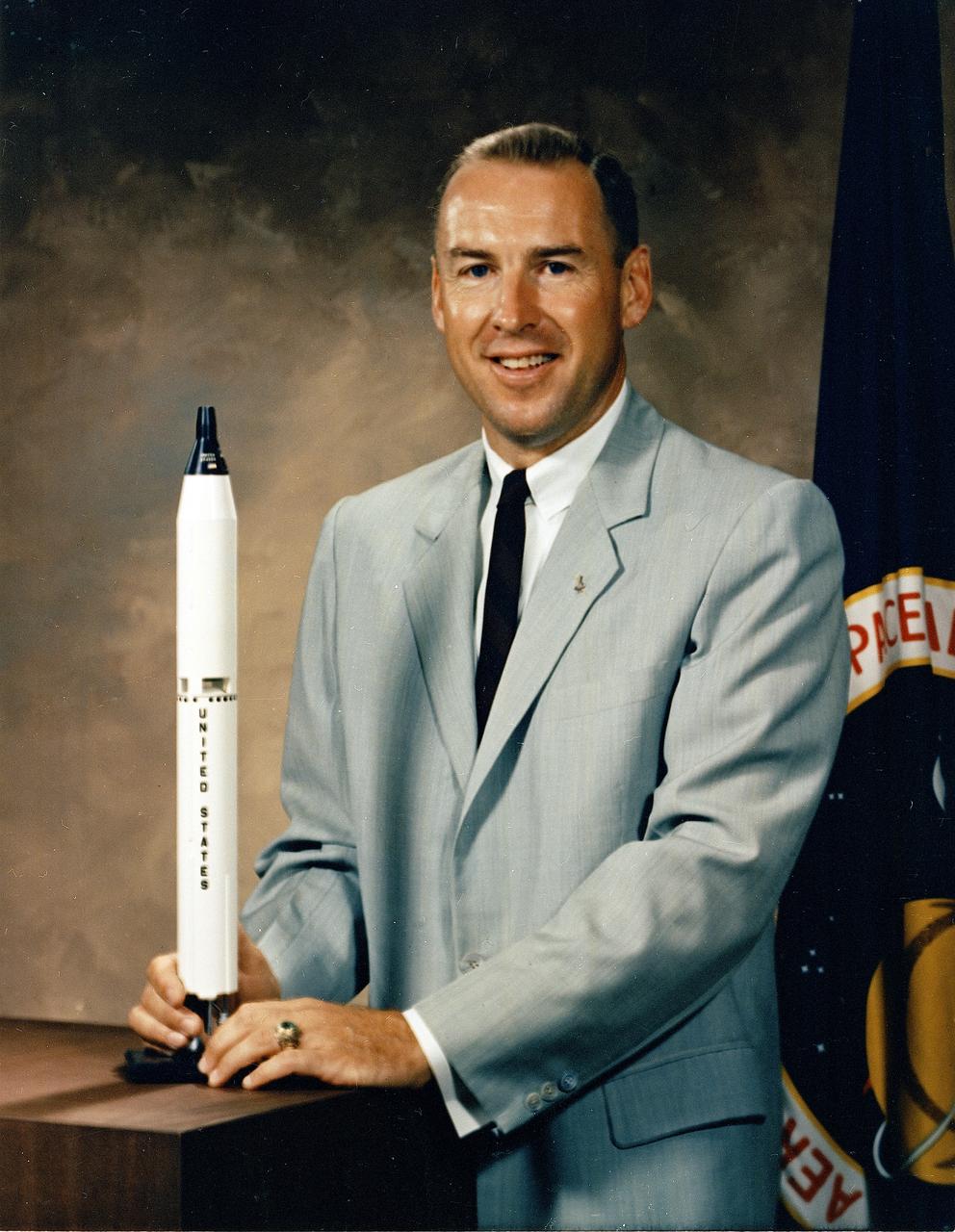

This is the official NASA portrait of astronaut James Lovell. Captain Lovell was selected as an Astronaut by NASA in September 1962. He has since served as backup pilot for the Gemini 4 flight and backup Commander for the Gemini 9 flight, as well as backup Commander to Neil Armstrong for the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. On December 4, 1965, he and Frank Borman were launched into space on the history making Gemini 7 mission. The flight lasted 330 hours and 35 minutes and included the first rendezvous of two manned maneuverable spacecraft. The Gemini 12 mission, commanded by Lovell with Pilot Edwin Aldrin, began on November 11, 1966 for a 4-day, 59-revolution flight that brought the Gemini program to a successful close. Lovell served as Command Module Pilot and Navigator on the epic six-day journey of Apollo 8, the first manned Saturn V liftoff responsible for allowing the first humans to leave the gravitational influence of Earth. He completed his fourth mission as Spacecraft Commander of the Apollo 13 flight, April 11-17, 1970, and became the first man to journey twice to the moon. The Apollo 13 mission was cut short due to a failure of the Service Module cryogenic oxygen system. Aborting the lunar course, Lovell and fellow crewmen, John L. Swigert and Fred W. Haise, working closely with Houston ground controllers, converted their lunar module, Aquarius, into an effective lifeboat that got them safely back to Earth. Captain Lovell held the record for time in space with a total of 715 hours and 5 minutes until surpassed by the Skylab flights. On March 1, 1973, Captain Lovell retired from the Navy and the Space Program.