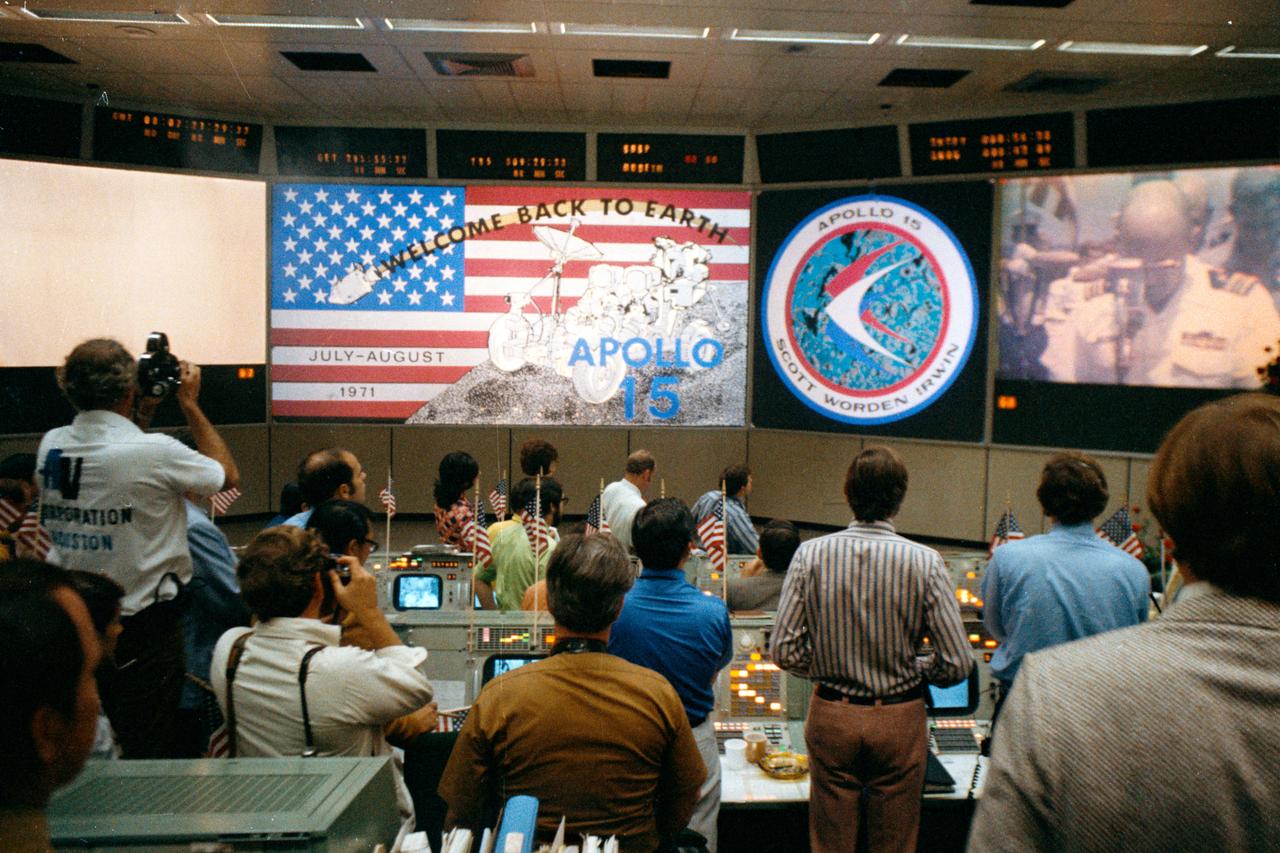

An overall view of activity in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center at the conclusion of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission. The television monitor in the right background shows the welcome ceremonies aboard the prime recovery ship, U.S.S. Okinawa, in the mid-Pacific Ocean.
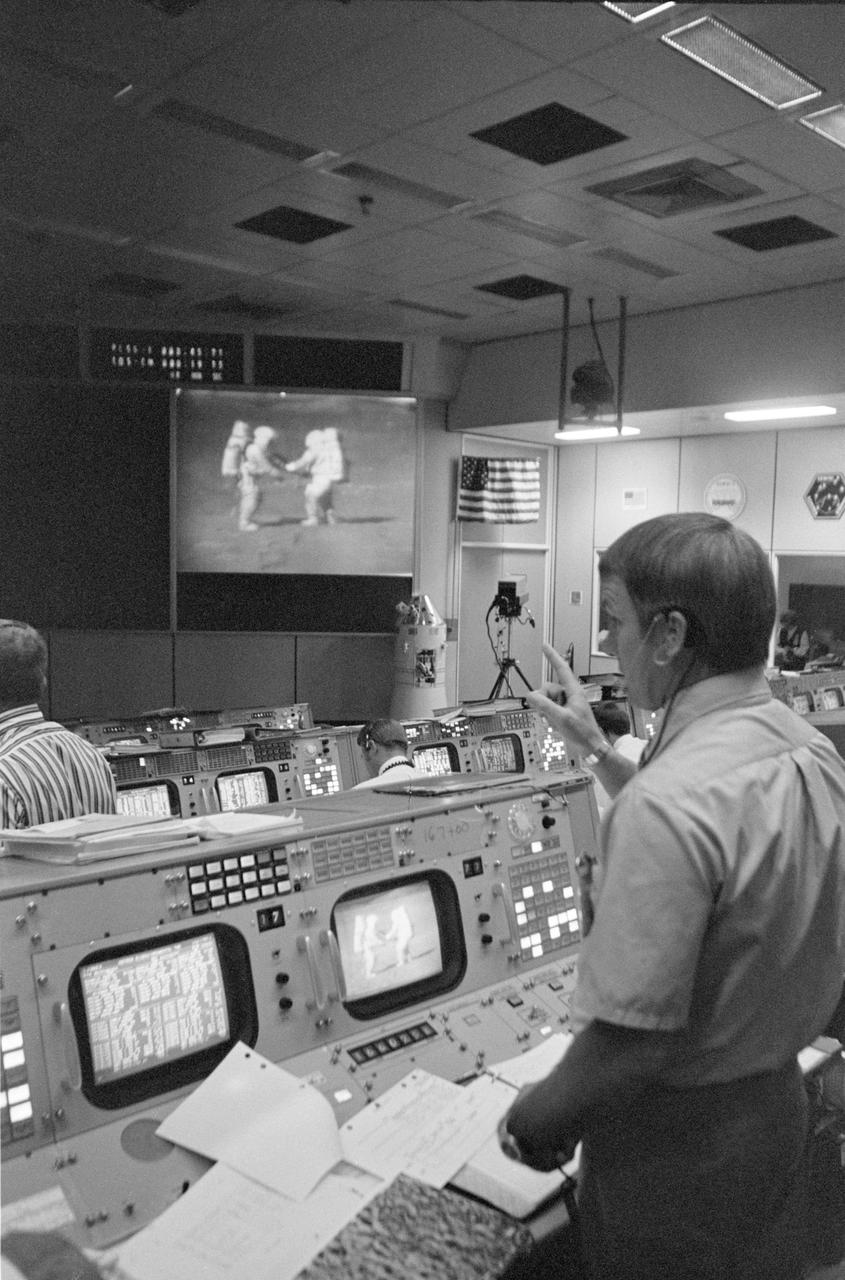

S71-41852 (2 Aug. 1971) --- Gerald D. Griffin, foreground, stands near his console in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) during Apollo 15's third extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. Griffin is Gold Team (Shift 1) flight director for the Apollo 15 mission. Astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin can be seen on the large screen at the front of the MOCR as they participate in sample-gathering on the lunar surface.

S71-41836 (2 Aug. 1971) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Allen, left, directs the attention of astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., to an occurrence out of view at right in the Mission Control Center's (MCC) Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR), while Dr. Donald K. (Deke) Slayton, on right with back to camera, views activity of Apollo 15 on a large screen at the front of the MOCR. Astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin are seen on the screen performing tasks of the mission's third extravehicular activity (EVA), on Aug. 2, 1971. Dr. Slayton is director of Flight Crew Operations, NASA-MSC; Gordon is Apollo 15 backup commander; and Dr. Allen is an Apollo 15 spacecraft communicator.
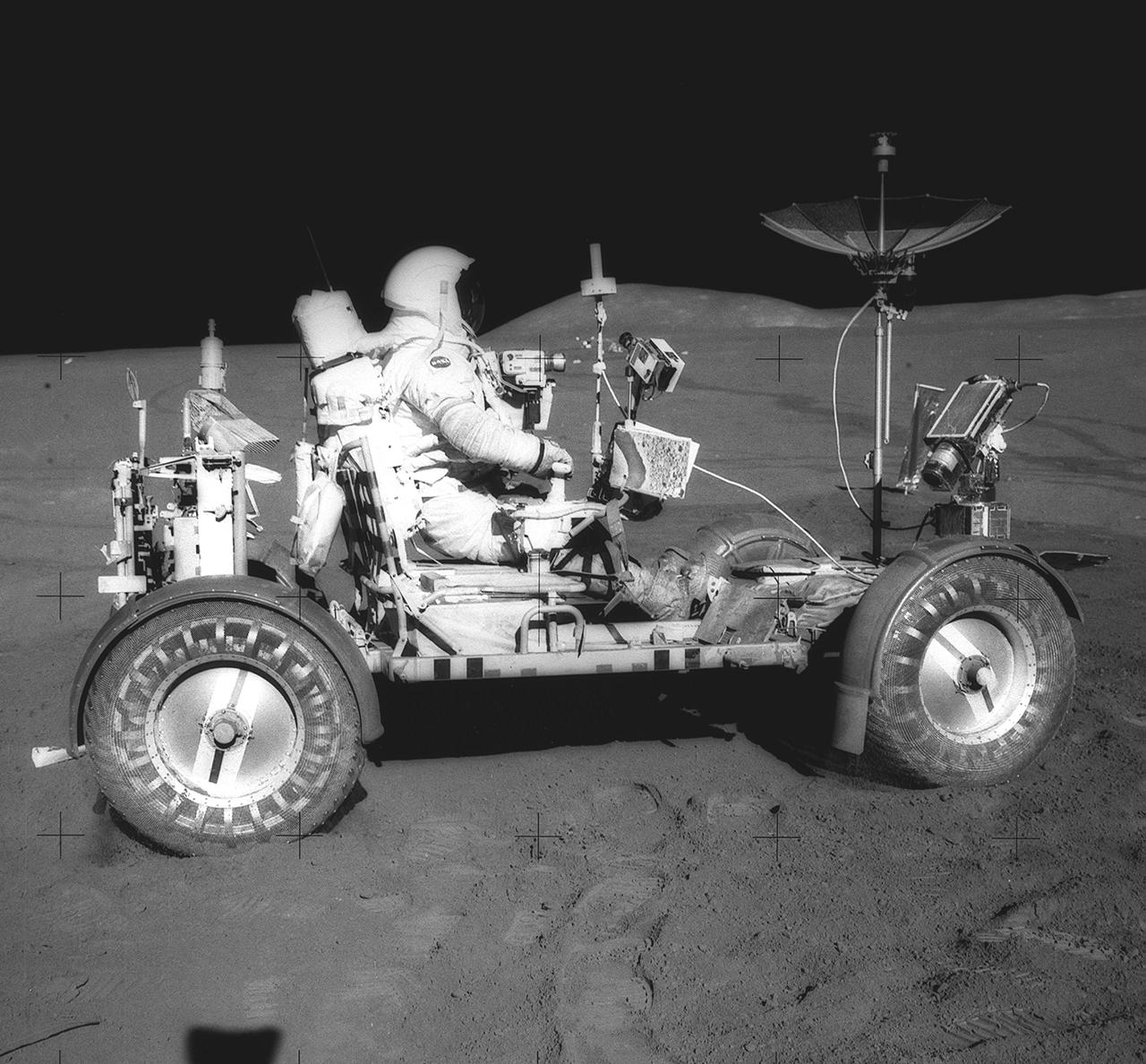

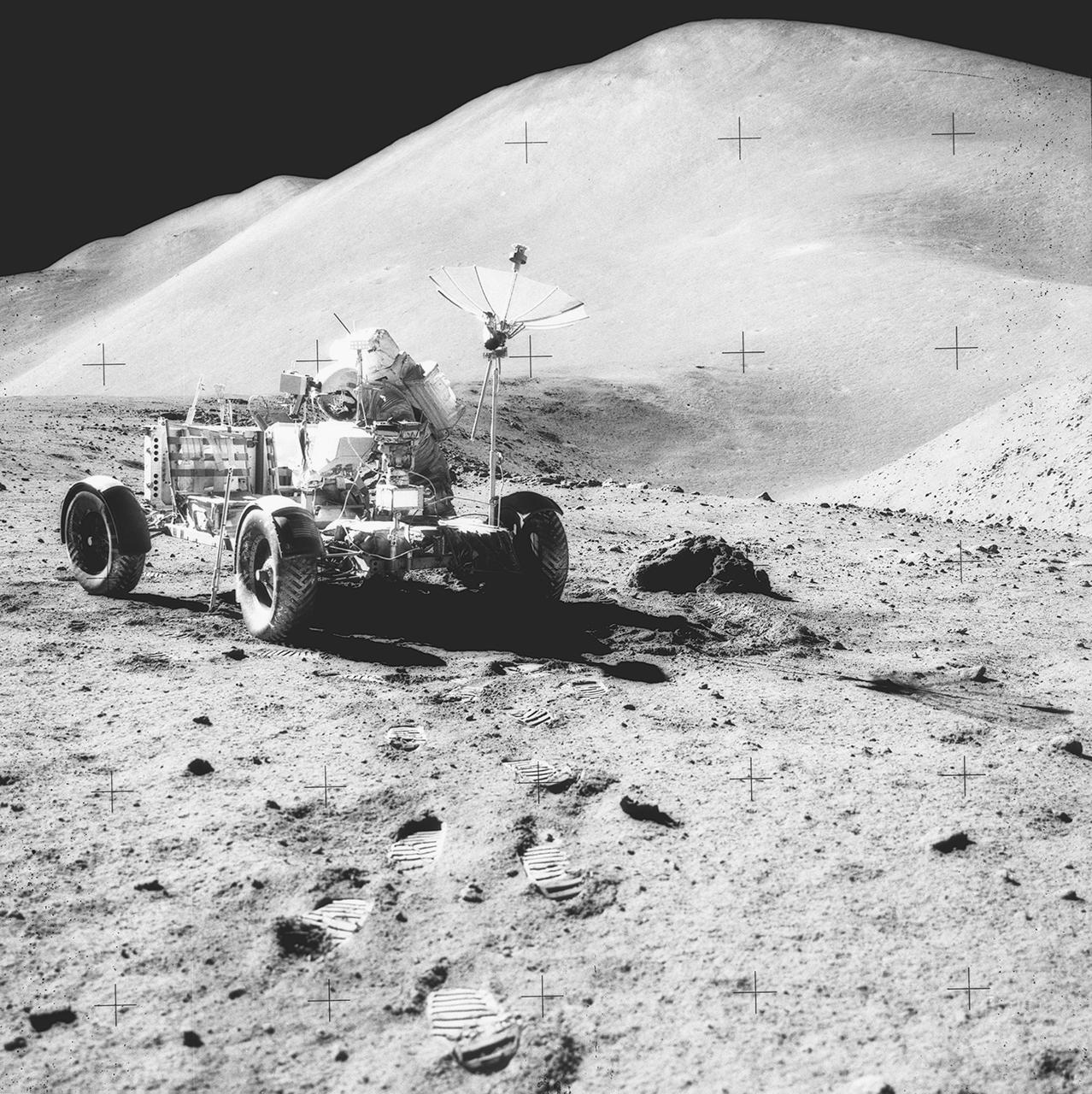
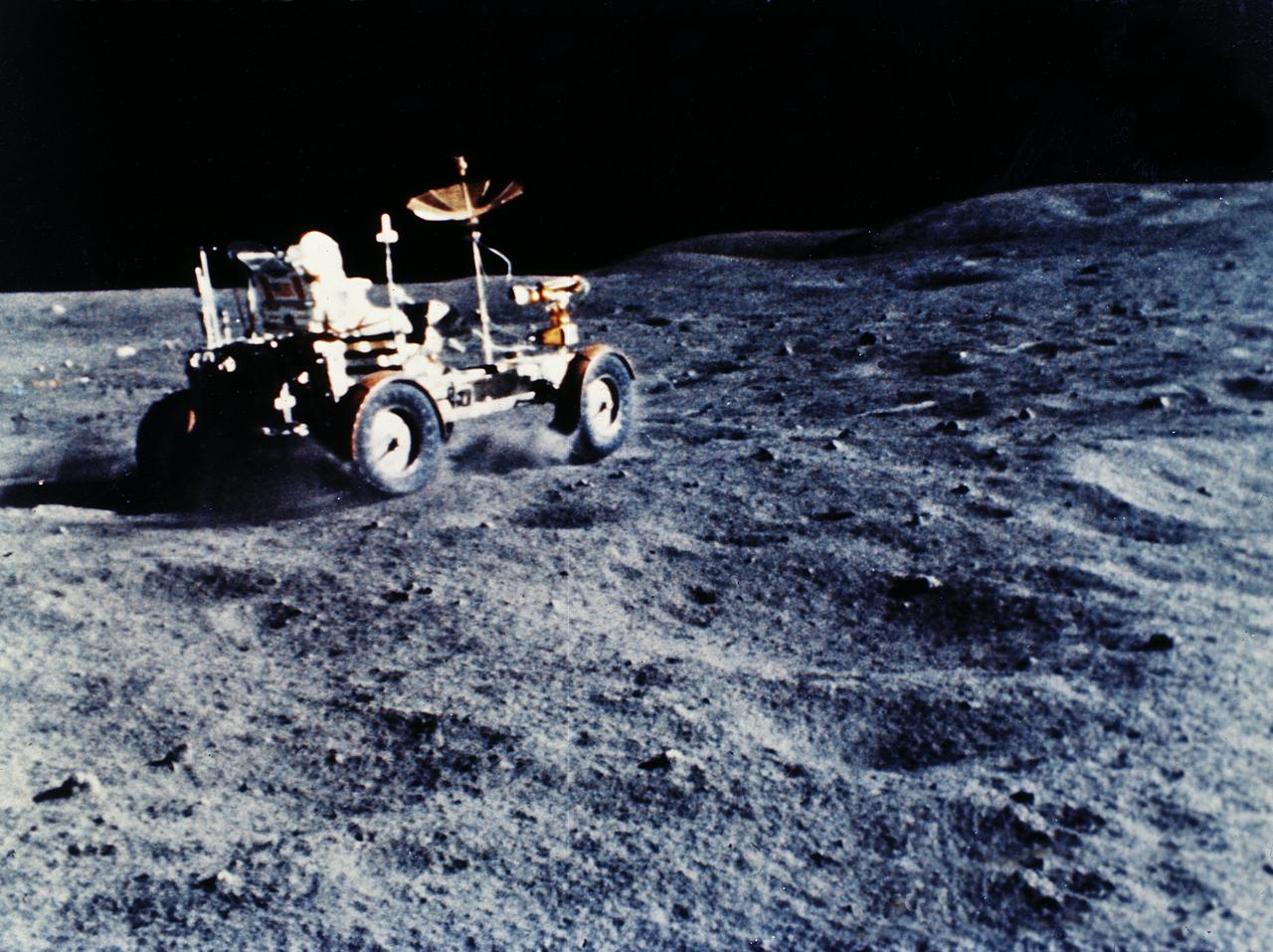
This photograph was taken during the Apollo 15 mission on the lunar surface. Astronaut David R. Scott waits in the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) for astronaut James Irwin for the return trip to the Lunar Module, Falcon, with rocks and soil collected near the Hadley-Apernine landing site. The Apollo 15 was the first mission to use the LRV. Powered by battery, the lightweight electric car greatly increased the range of mobility and productivity on the scientific traverses for astronauts. It weighed 462 pounds (77 pounds on the Moon) and could carry two suited astronauts, their gear and cameras, and several hundred pounds of bagged samples. The LRV's mobility was quite high. It could climb and descend slopes of about 25 degrees. The LRV was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
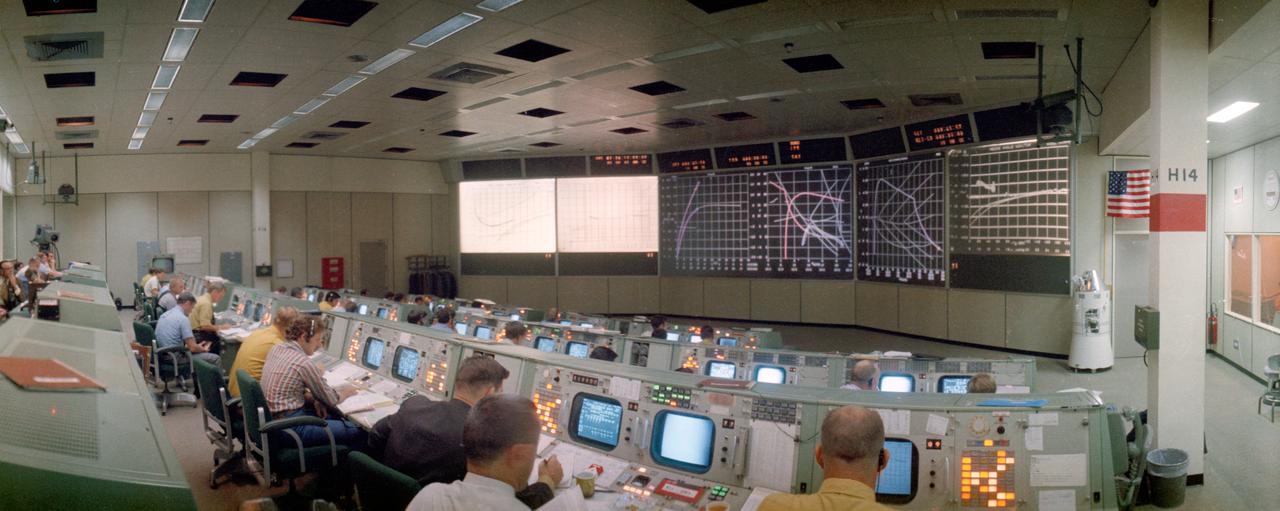

S71-41357 (26 July 1971) --- An overall, wide-angle lens view of activity in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center minutes after the launch of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission. Ground elapsed time was 45 minutes and 42 seconds when this photograph was taken.
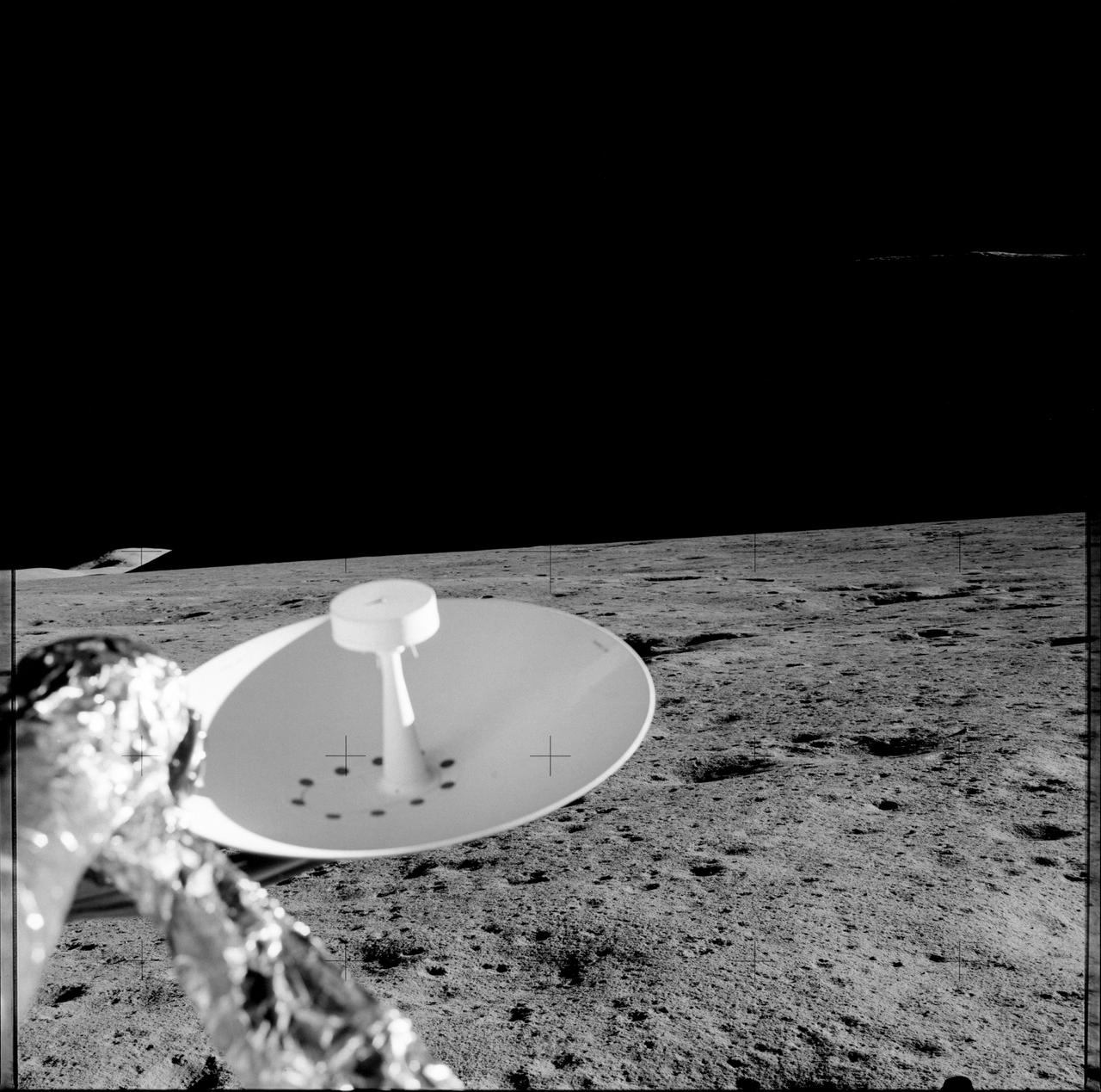

AS15-85-11363 (31 July 1971) --- A 70mm handheld Hasselblad was aimed through the viewing port of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) to record this image of the lunar surface in the vicinity of the Hadley-Apennine landing site. Later, astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, made the mission's first moon walk. The pair had descended from lunar orbit in the LM to explore the moon while astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
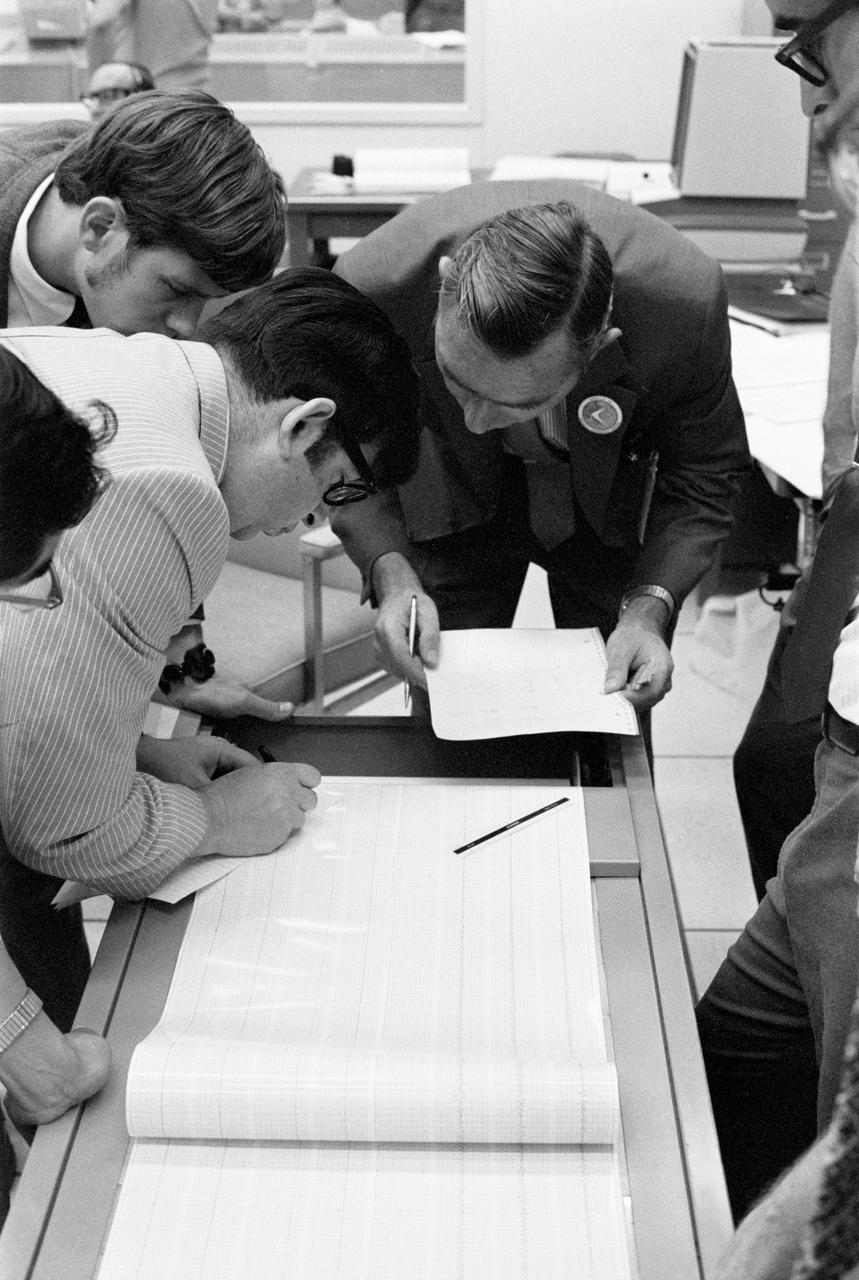

The seismometer reading from the impact made by the Apollo 15 Saturn S-IVB stage when it struck the lunar surface is studied by scientists in the Mission Control Center. Dr. Gary Latham (dark suit, wearing lapel button) of Columbia University is responsible for the design and experiment data analysis of the Passive Seismic Experiment of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiment Package (ALSEP). The man on the left, writing, is Nafi Toksos of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Looking on at upper left is Dave Lamneline, also with Columbia.

jsc2011e118361 - Panorama view of Apollo 15 lunar module pilot James B. Irwin, using a scoop in making a trench in the lunar soil during the second moonwalk of the mission. The panoramas were built by combining Apollo 15 images starting with frame AS15-92-12420 thru end frame AS15-92-12438. The panoramic images received minimal retouching by NASA imagery specialists, including the removal of lens flares that were problematic in stitching together the individual frames and blacking out the sky to the lunar horizon. These adjustments were made based on observations of the Moon walkers who reported that there are no stars visible in the sky due to the bright lunar surface reflection of the Sun.
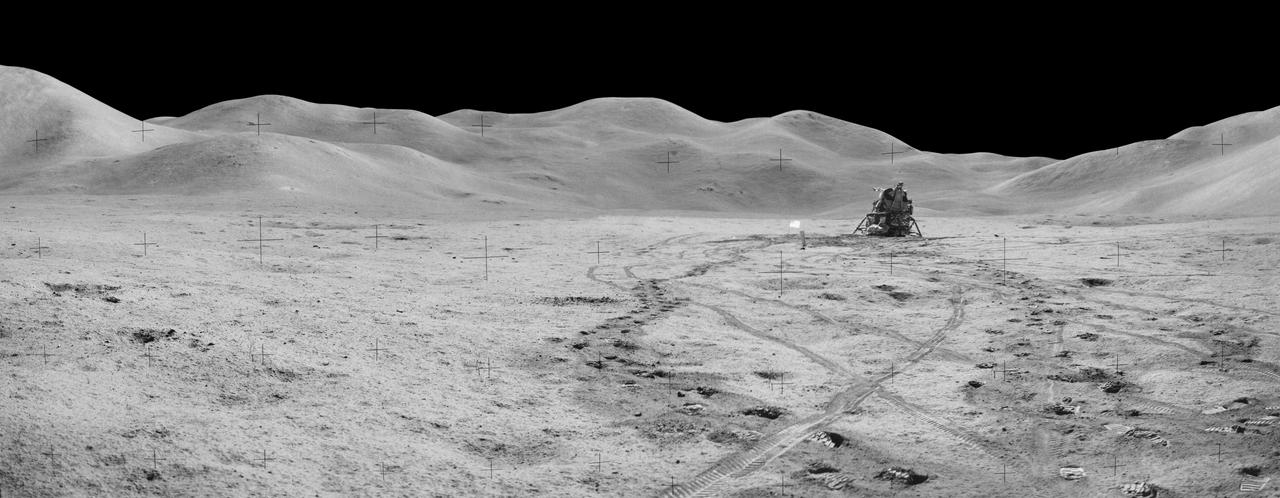

jsc2011e118360 - Panorama view of Station 8 and (Mons) Mt. Hadley taken during the third moonwalk of the Apollo 15 mission. The panoramas were built by combining Apollo 15 images starting with frame AS15-82-11054 thru end frame AS15-82-11058. The panoramic images received minimal retouching by NASA imagery specialists, including the removal of lens flares that were problematic in stitching together the individual frames and blacking out the sky to the lunar horizon. These adjustments were made based on observations of the Moon walkers who reported that there are no stars visible in the sky due to the bright lunar surface reflection of the Sun.
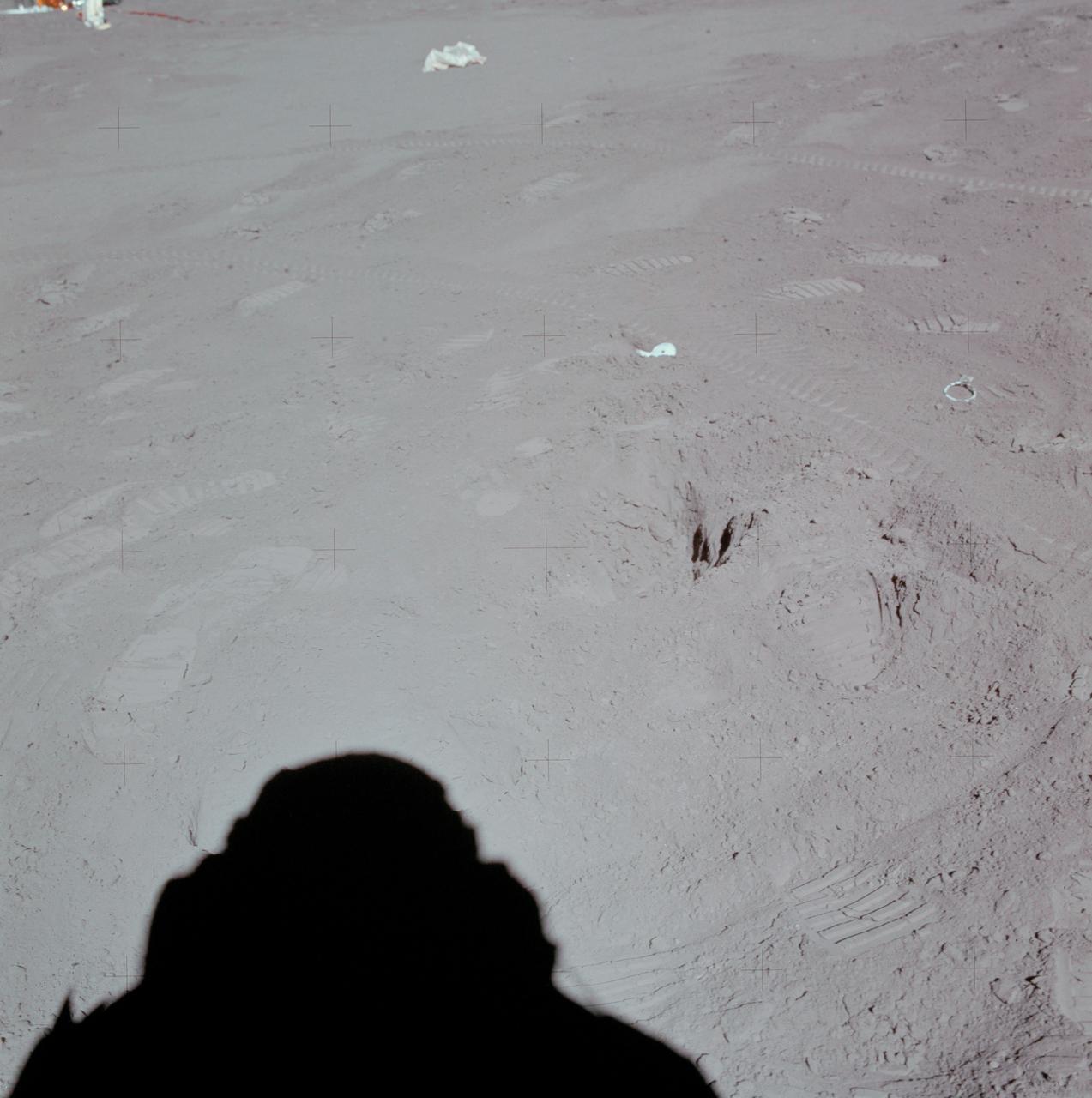

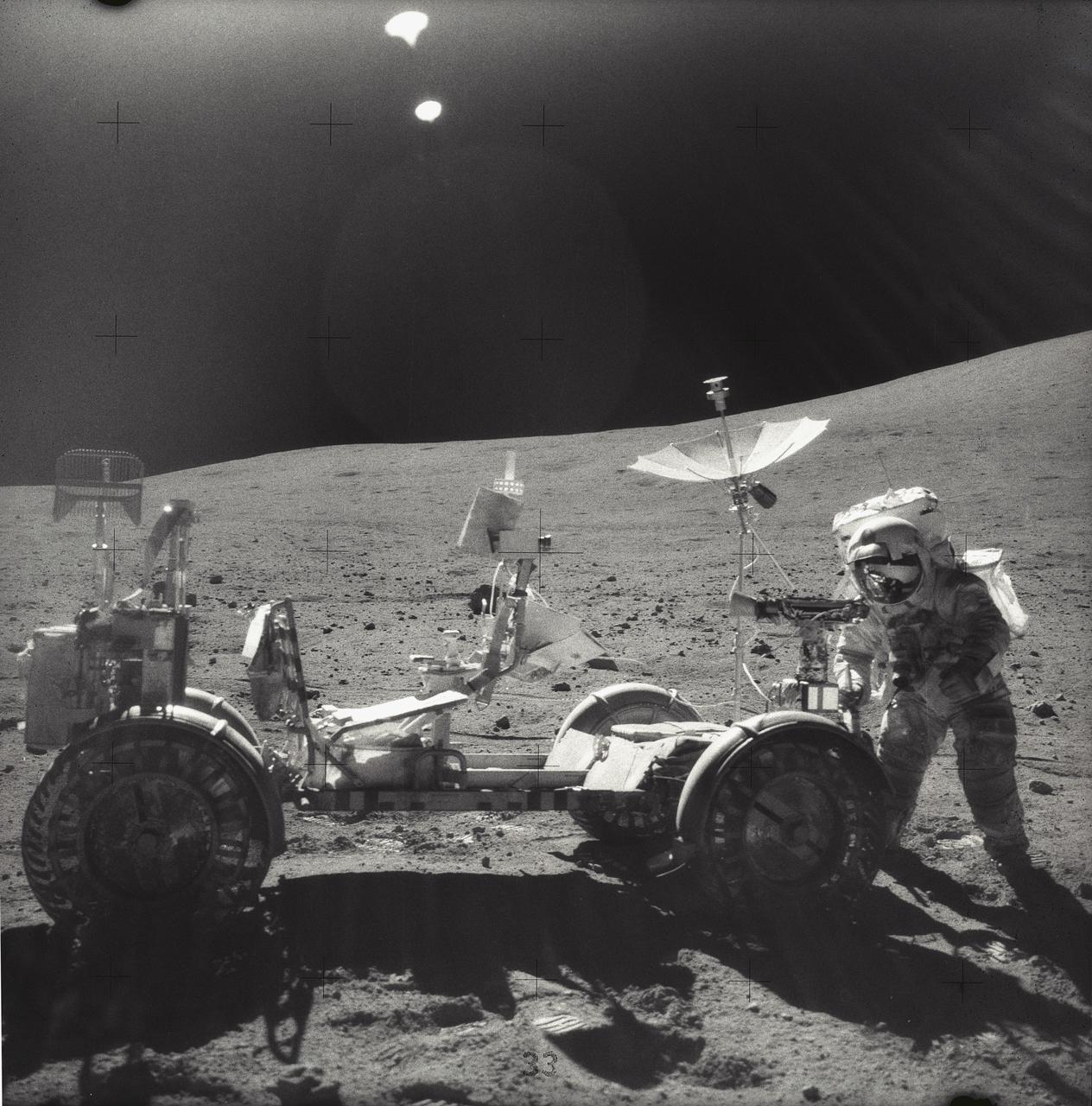
AS15-88-11872 (31 July 1971) --- This north-looking view at Station 8 near the Hadley-Apennine landing site was photographed by one of the missions two moon explorer's (see shadow, foreground) during the third Apollo 15 extravehicular activity (EVA). Prints from the boots of astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, as well as tire tracks from the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) are scattered throughout the view. A small part of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) is in the upper left corner. Lunar samples 15252 and 15253 were removed from this area and returned to Earth for analysis by scientists. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions, Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17, in 1971 and 1972 to permit the crew to travel several miles from the lunar landing site. This photograph was taken during the Apollo 15 mission.
The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17, in 1971 and 1972, to permit the crew to travel several miles from the lunar landing site. This photograph was taken during the Apollo 16 mission.

S71-16722 (January 1971) --- Two members of the prime crew of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission are shown with the Lunar Roving Vehicle "one G" trainer in Building 5, Mission Simulation and Training Facility, Manned Spacecraft Center. Astronaut David R. Scott (on right) is the Apollo 15 commander; and astronaut James B. Irwin is the lunar module pilot. A Lunar Roving Vehicle similar to this trainer will be used by Scott and Irwin during their Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Apollo 15 crew climbs inside the Apollo capsule on launch day before lifting off on a mission to the moon. Photo credit: NASA
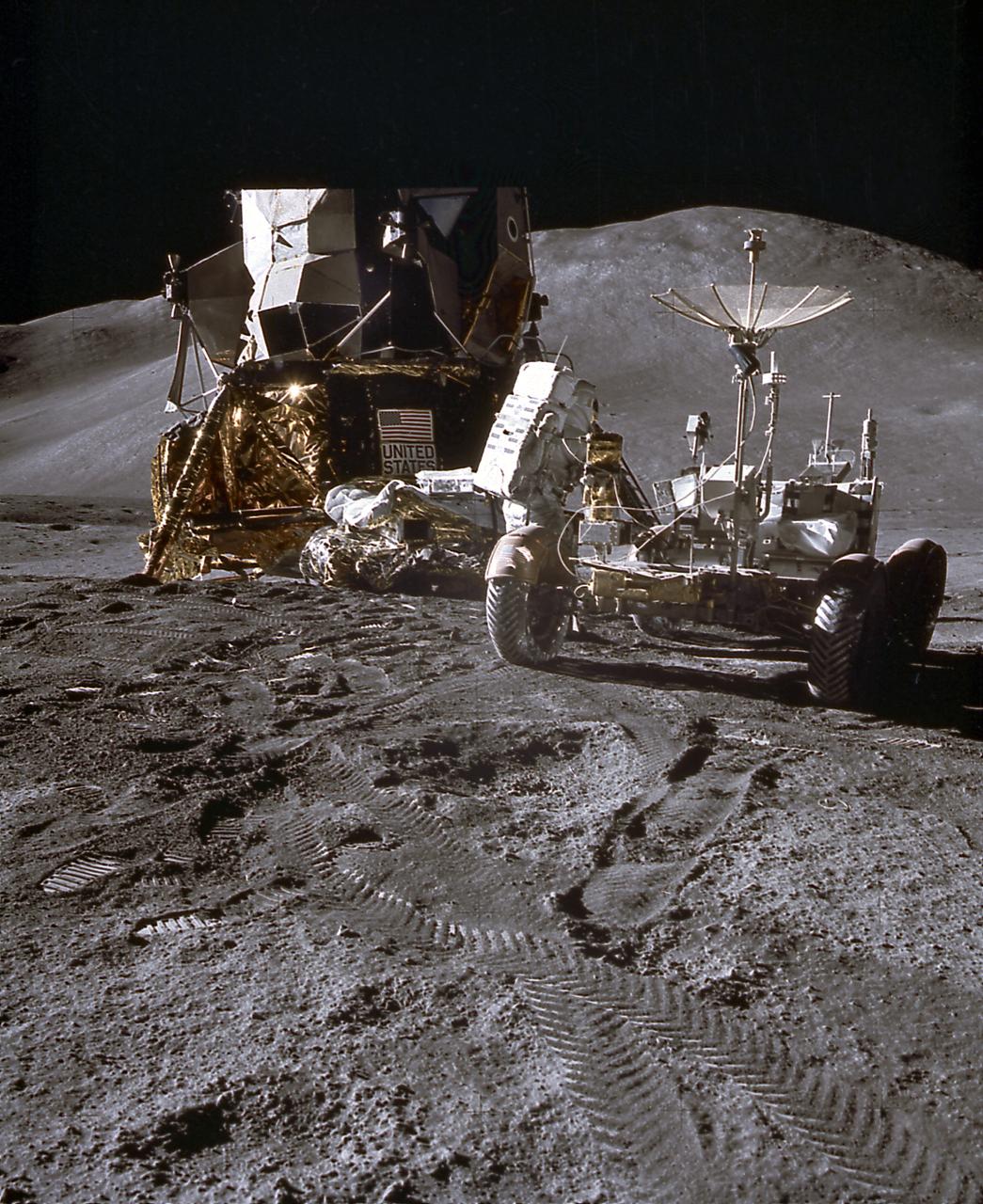

This photograph of an astronaut getting the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) ready for exploration of the lunar surface was taken during activities of the Apollo 15 mission. Designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company, the LRV was first used on the Apollo 15 mission and increased the range of astronauts' mobility and productivity on the lunar surface.
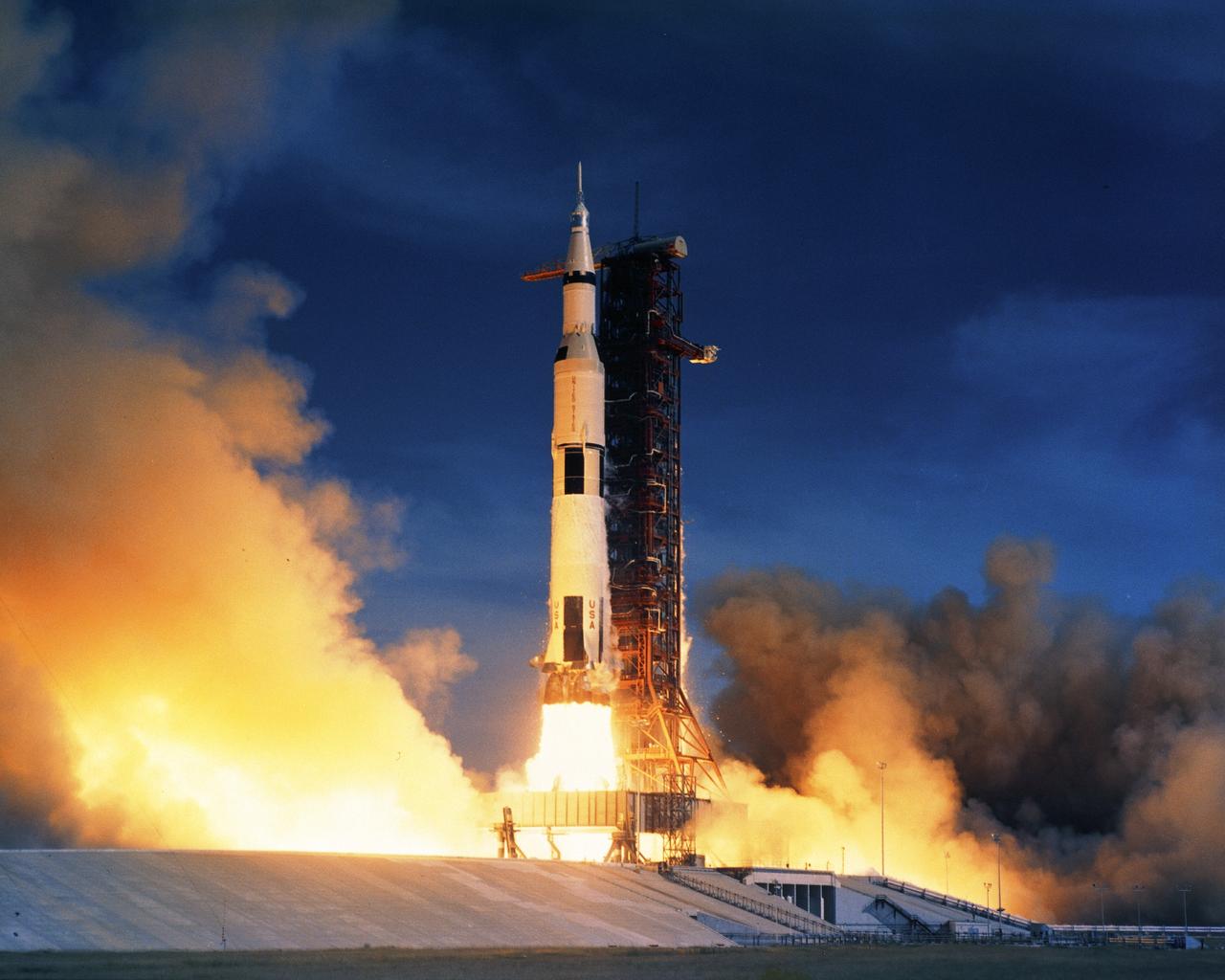

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo 15's Saturn V rocket lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at 9:34 a.m., EDT, July 26, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Aboard the Apollo 15 spacecraft are astronauts David R. Scott, commander, Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. While Apollo 15 astronauts Scott and Irwin will descend in the lunar module to explore the moon's Hadley-Apennine region, astronaut Worden will remain in lunar orbit with the command module. For more information, visit http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/history/apollo/apollo-15/apollo-15.htm Photo credit: NASA
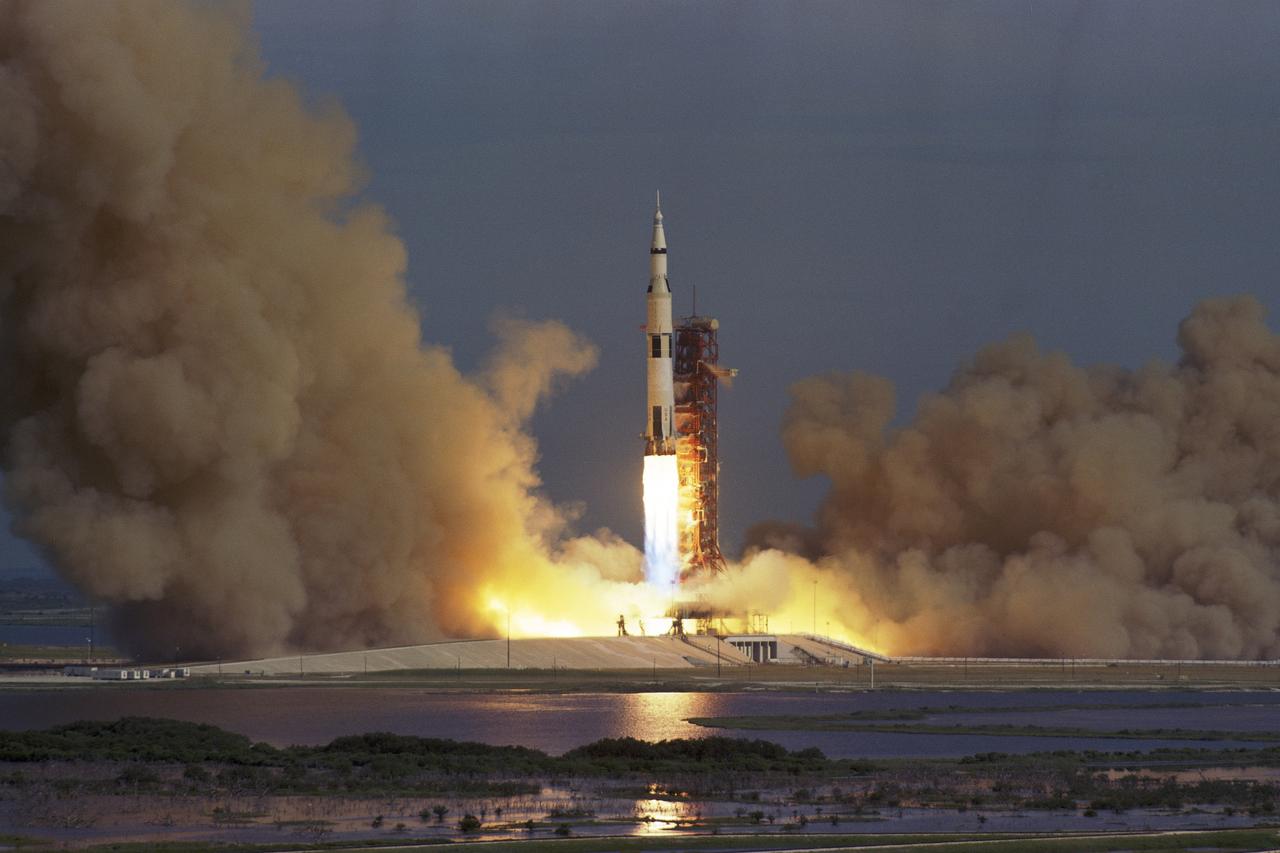

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo 15's Saturn V rocket lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at 9:34 a.m., EDT, July 26, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Aboard the Apollo 15 spacecraft are astronauts David R. Scott, commander, Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. While Apollo 15 astronauts Scott and Irwin will descend in the lunar module to explore the moon's Hadley-Apennine region, astronaut Worden will remain in lunar orbit with the command module. For more information, visit http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/history/apollo/apollo-15/apollo-15.htm Photo credit: NASA
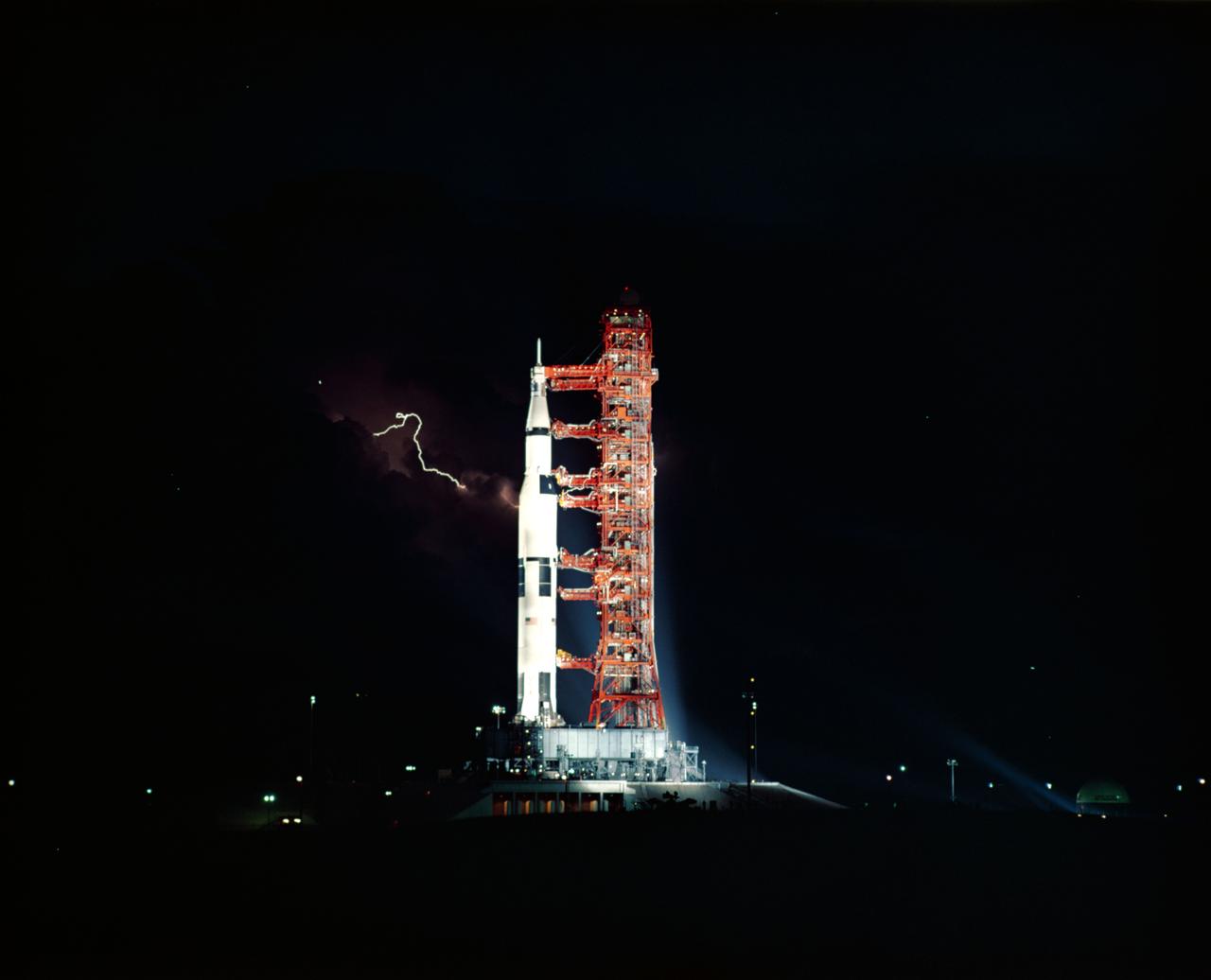

S89-41564 (25 July 1971) --- Lightning streaks through the sky around the Apollo 15 stack of hardware prior to the Apollo 15 launch. The huge 363-feet tall Apollo 15 (Spacecraft 112/Lunar Module 10/Saturn 510) space vehicle is scheduled to launch from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, at 9:34:00:79 p.m. (EDT) on July 26, 1971. The prime crewmembers for the Apollo 15 mission are astronauts David R. Scott, commander; James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot; and Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot.
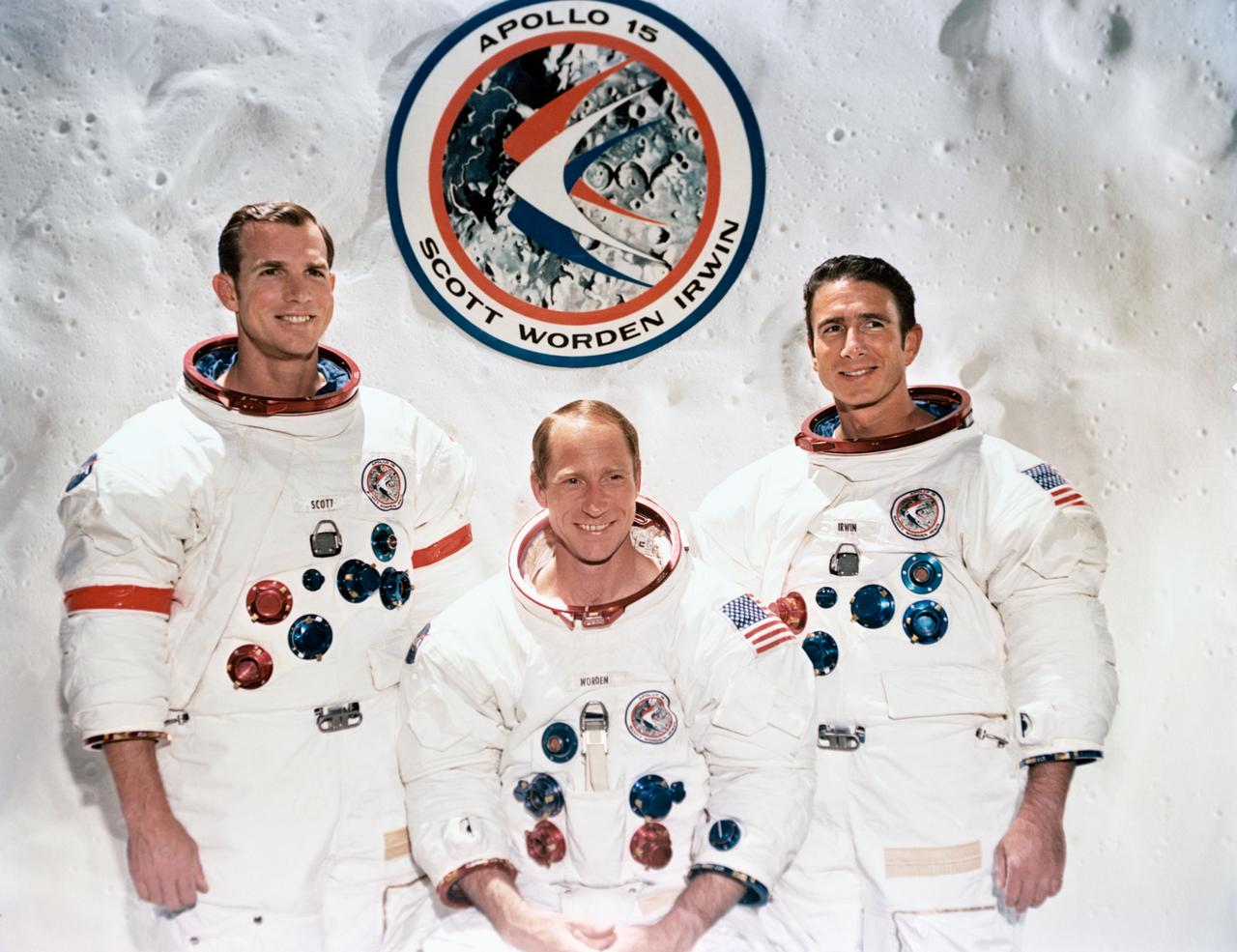

S71-37963 (July 1971) --- These three astronauts are the prime crew of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission. They are, left to right, David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 15 emblem is in the background.
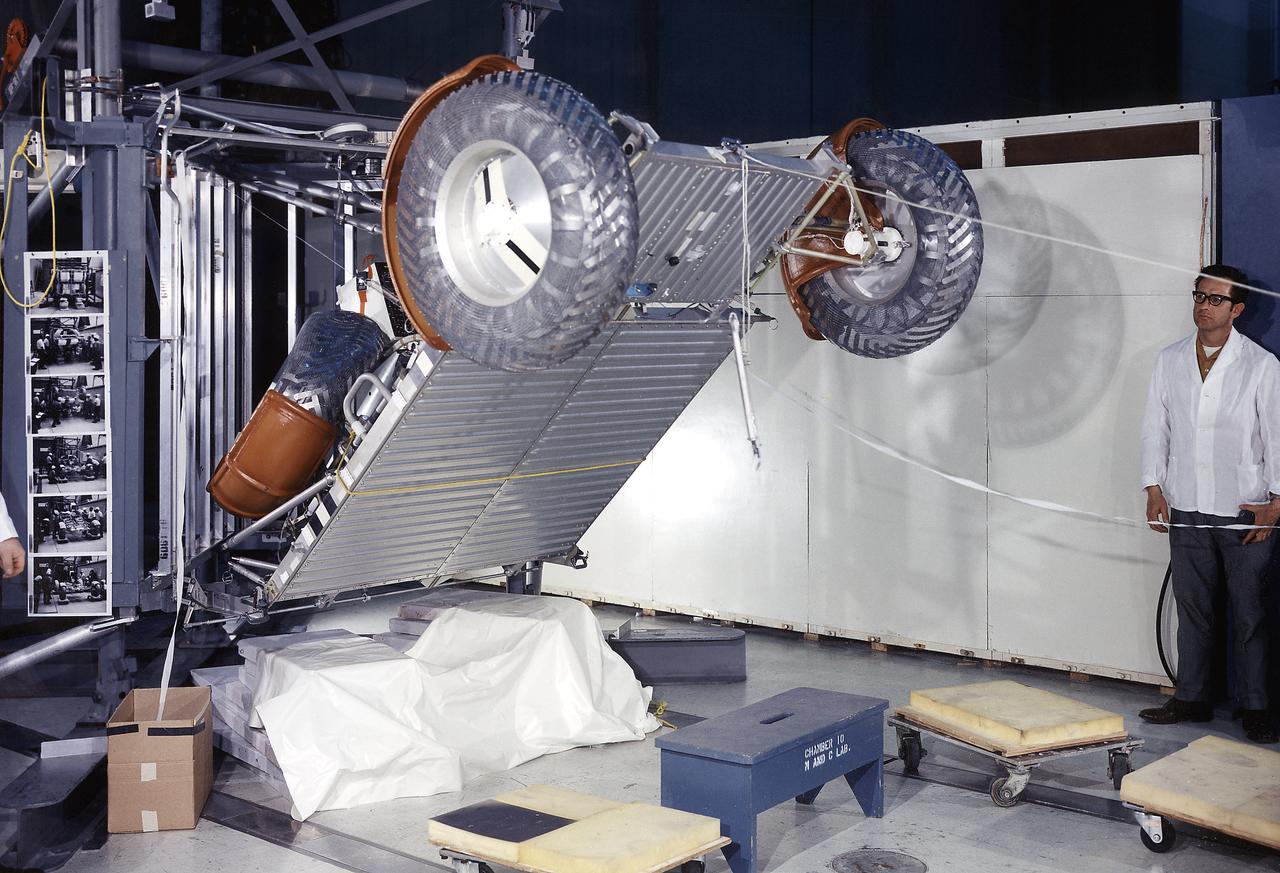
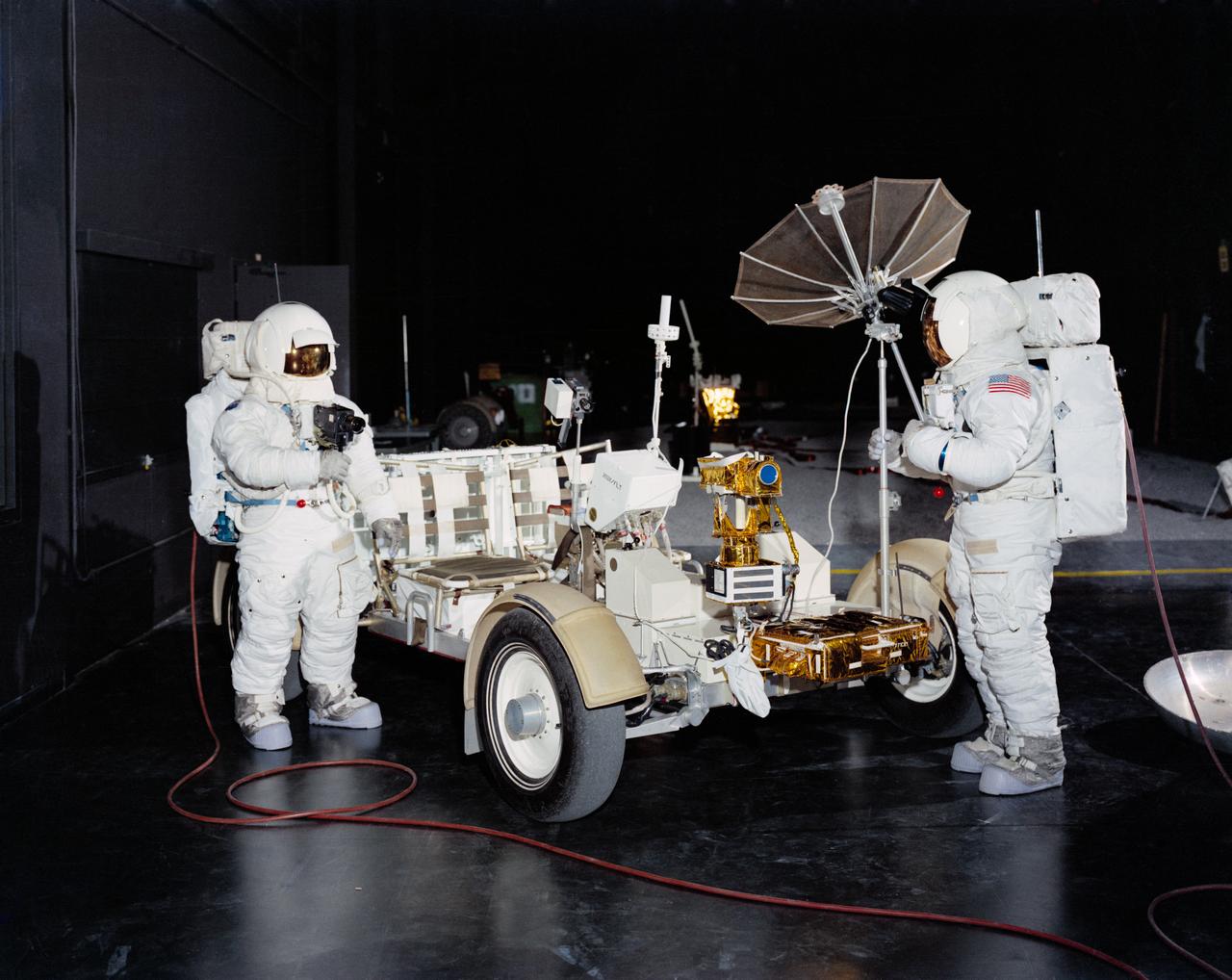
This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
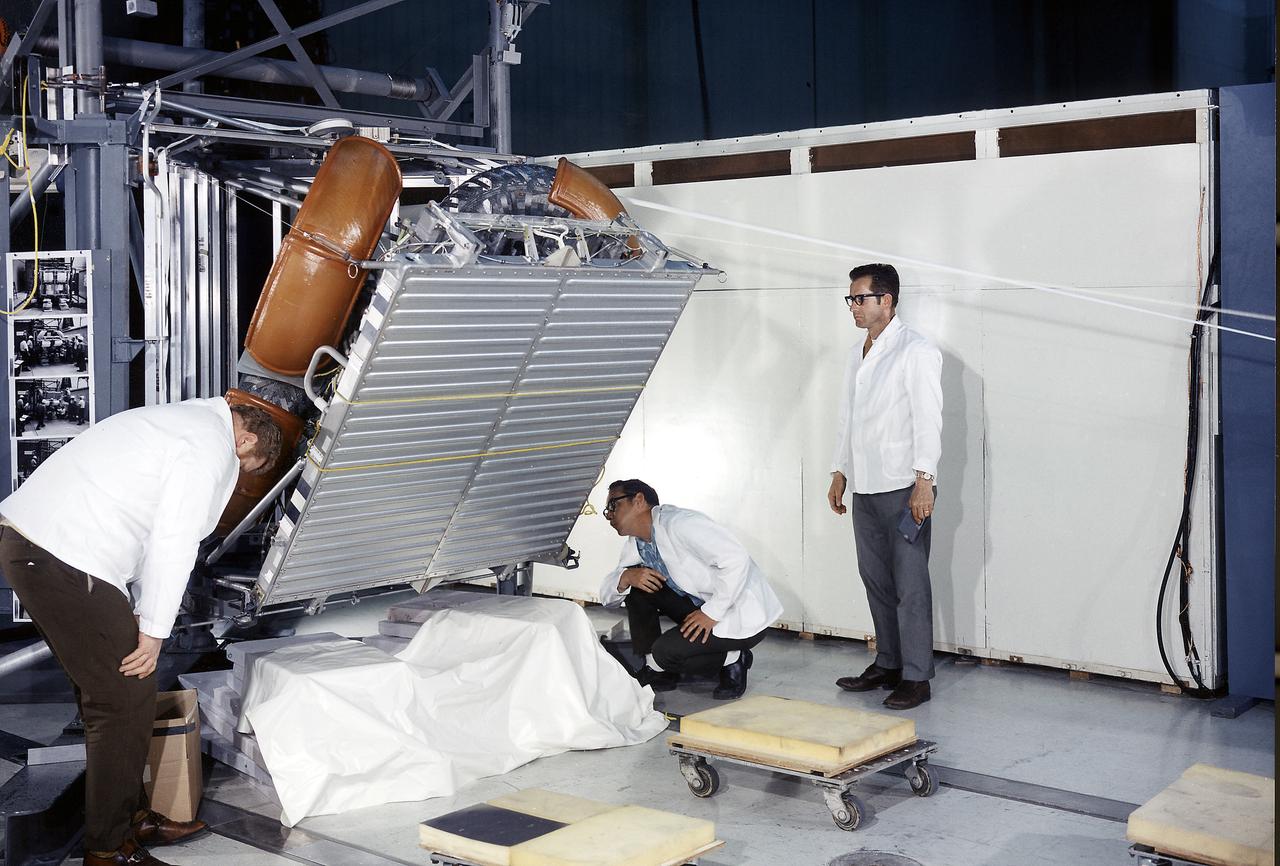

This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
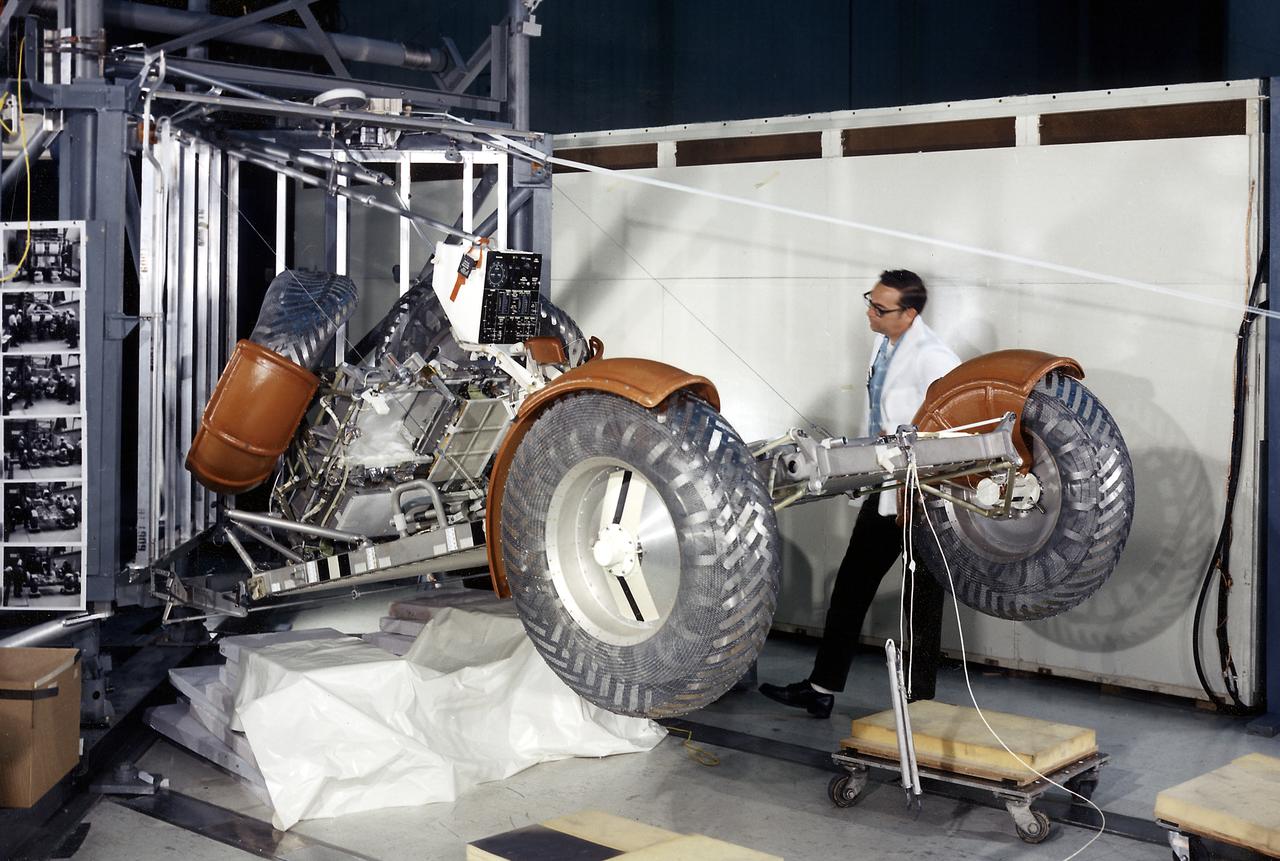

This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
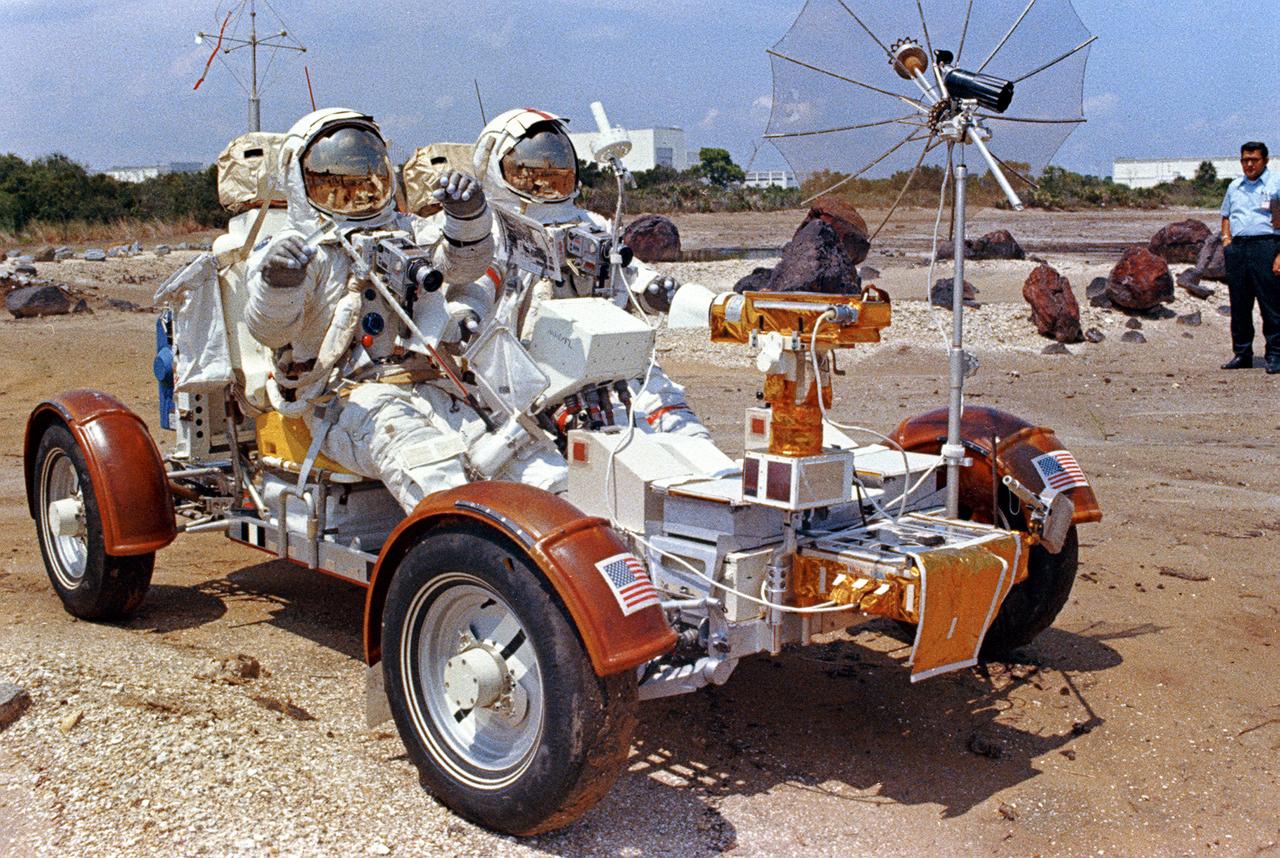
This photograph was taken during the testing of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at the Johnson Space Center. Developed by the MSFC, the LRV was the lightweight electric car designed to increase the range of mobility and productivity of astronauts on the lunar surface. It was used on the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
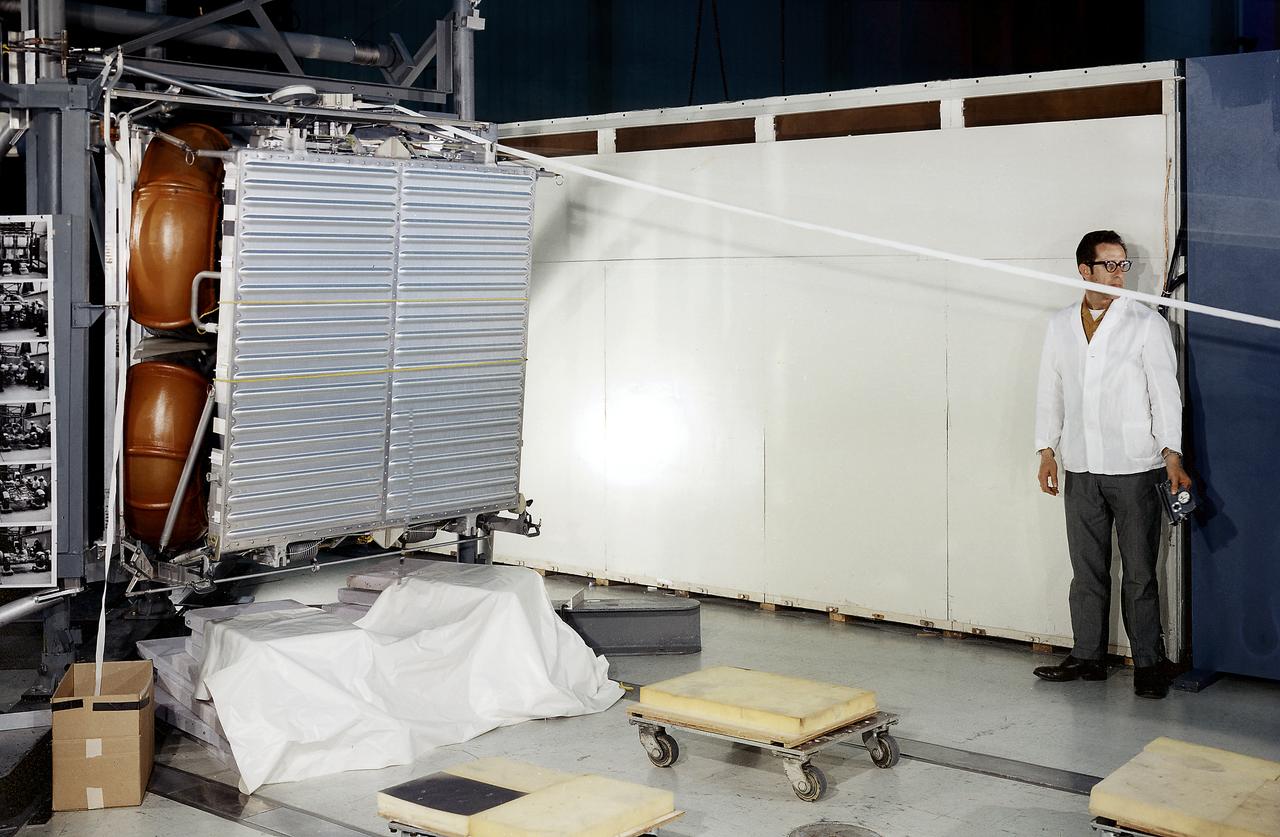

This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.

Apollo astronauts from left, Walt Cunningham (Apollo 17), James Lovell (Apollo 8 Apollo 13), David Scott (Apollo 9 Apollo 15), Buzz Aldrin (Apollo 11), Charles Duke (Apollo 16), Thomas Stafford (Apollo 10) and Eugene Cernan (Apollo 17) are seen during the 40th anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission and the walk on the moon press conference, Monday, July 20, 2009, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
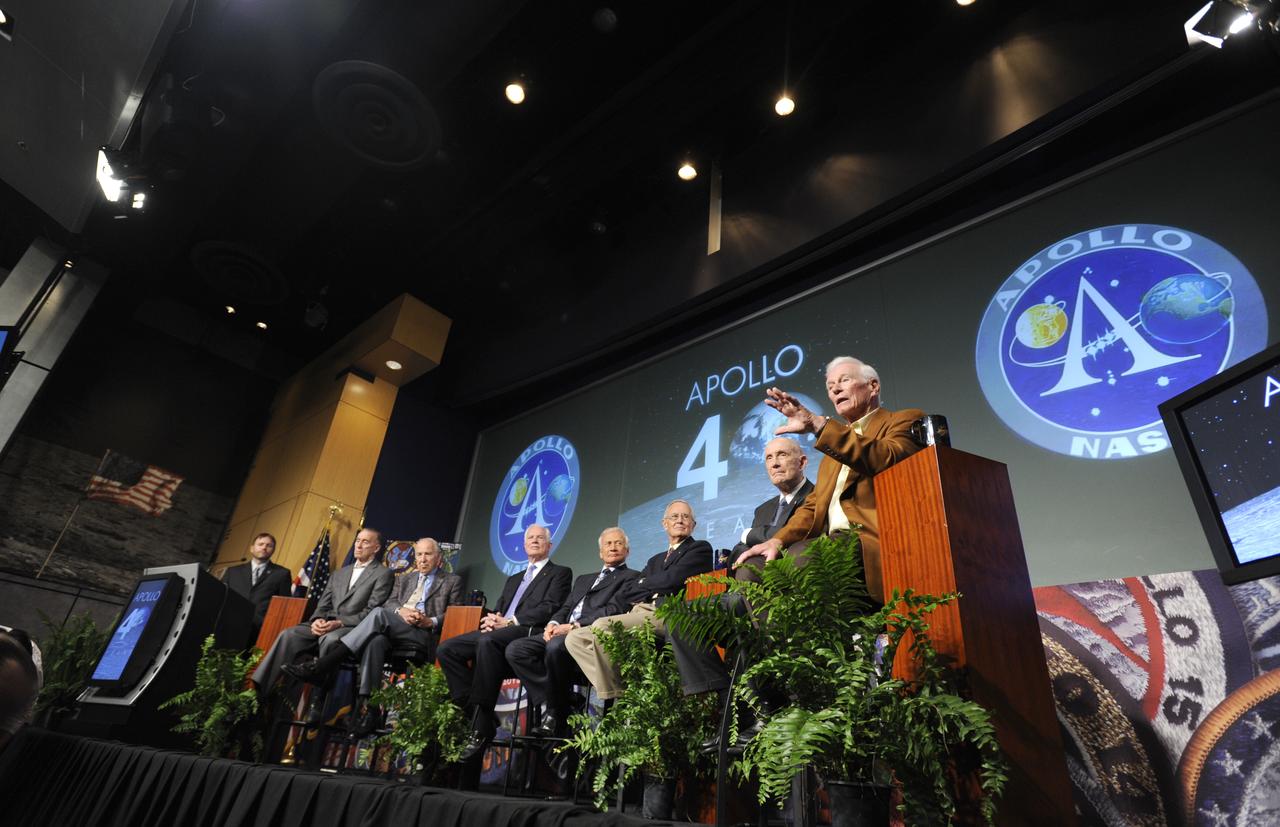

Apollo astronauts from left, Walt Cunningham (Apollo 17), James Lovell (Apollo 8 Apollo 13), David Scott (Apollo 9 Apollo 15), Buzz Aldrin (Apollo 11), Charles Duke (Apollo 16), Thomas Stafford (Apollo 10) and Eugene Cernan (Apollo 17) are seen during the 40th anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission and the walk on the moon press conference, Monday, July 20, 2009, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Apollo astronauts from left, Walt Cunningham (Apollo 17), James Lovell (Apollo 8 Apollo 13), David Scott (Apollo 9 Apollo 15), Buzz Aldrin (Apollo 11), Charles Duke (Apollo 16), Thomas Stafford (Apollo 10) and Eugene Cernan (Apollo 17) are seen during the 40th anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission and the walk on the moon press conference, Monday, July 20, 2009, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
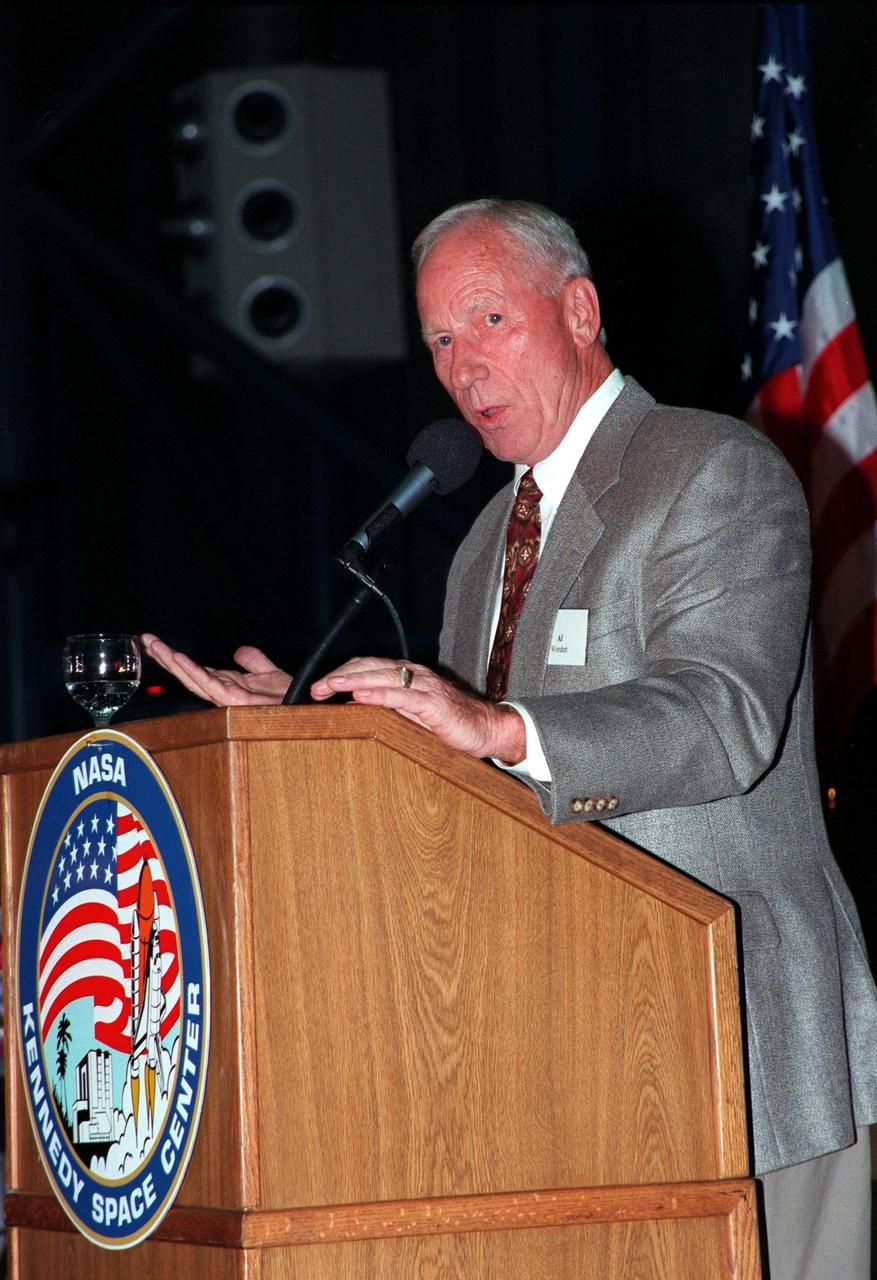

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Former Apollo 15 astronaut Alfred M. Worden relates his experiences in the Apollo Program during a banquet honoring the people who made it all possible. Held on the anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission, which was launched July 16, 1969, and landed on the moon July 20, 1969, the banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center. Worden served as command module pilot on the Apollo 15 mission. Other guests at the banquet were astronauts Neil Armstrong, Wally Schirra, Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin and Walt Cunningham. Armstrong was the first man to walk on the moon; Gene Cernan was the last
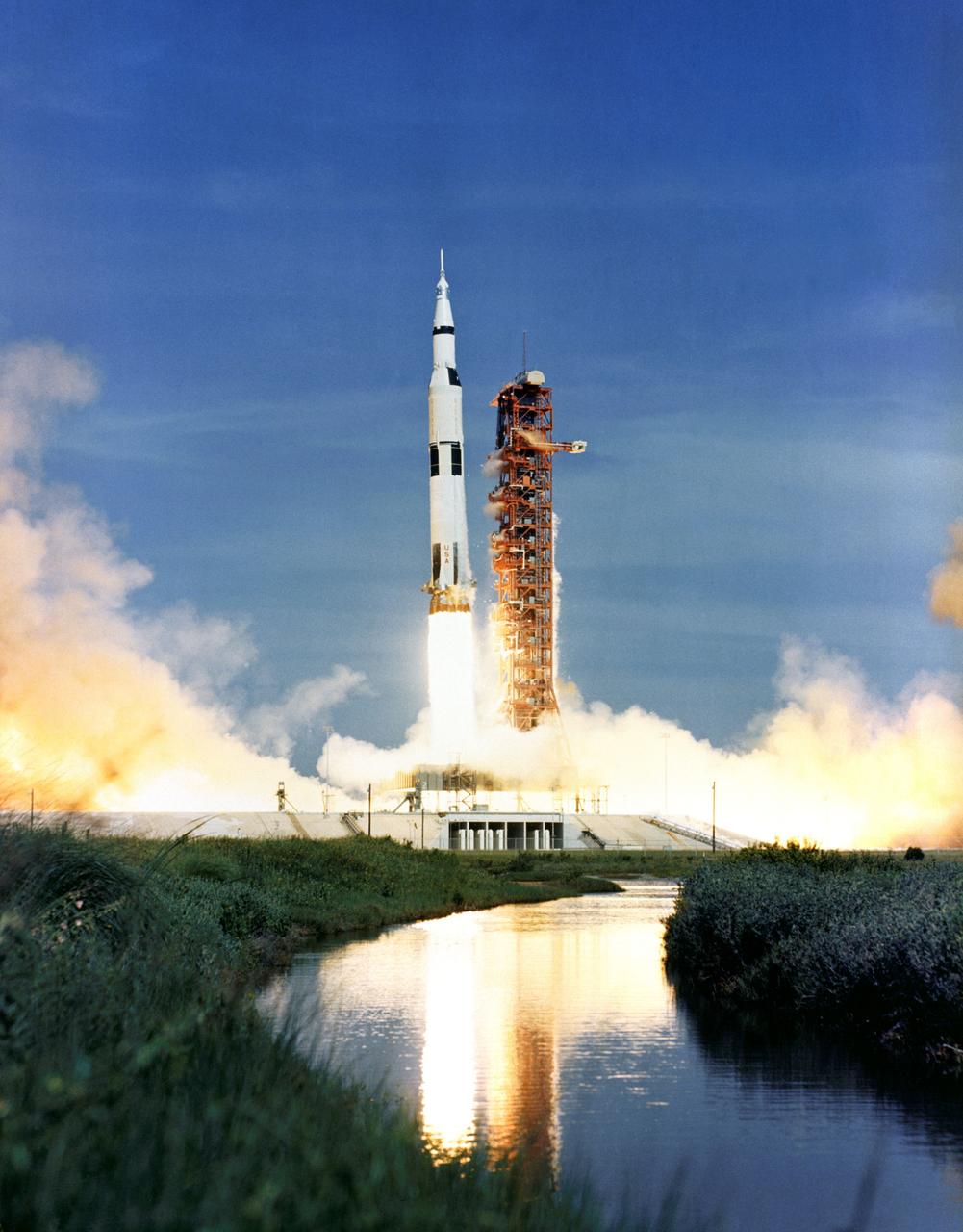

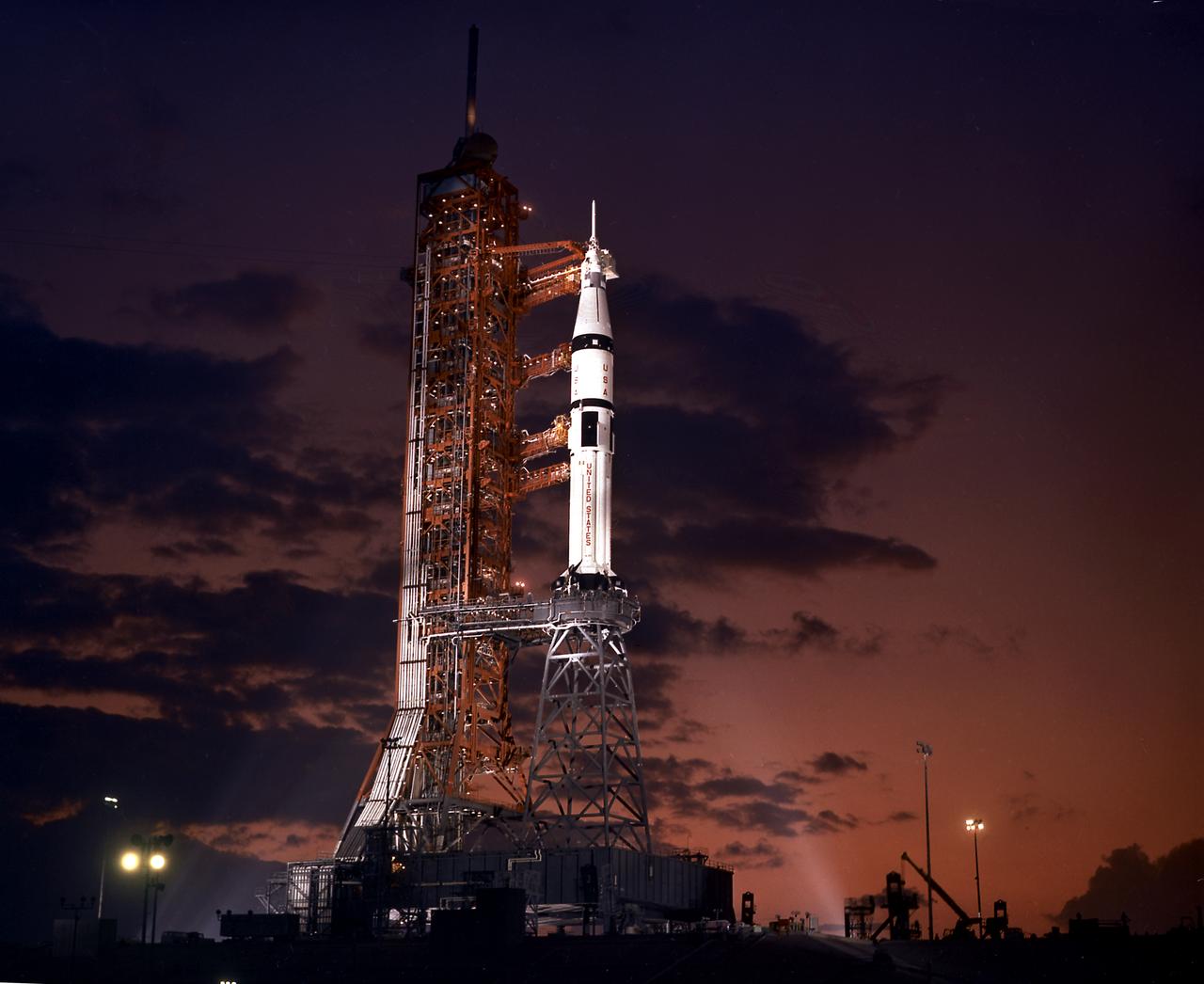
S71-41810 (26 July 1971) --- The 363-feet tall Apollo 15 (Spacecraft 112/Lunar Module 10/Saturn 510) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 9:34:00.79 a.m., July 26, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Aboard the Apollo 15 spacecraft were astronauts David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, commander module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. Apollo 15 is the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) fourth manned lunar landing mission.

The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed by Marshall Space Flight Center to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17, in 1971 and 1972, to permit the crew to travel several miles from the lunar landing site. This photograph was taken during the Apollo 16 mission in 1972.
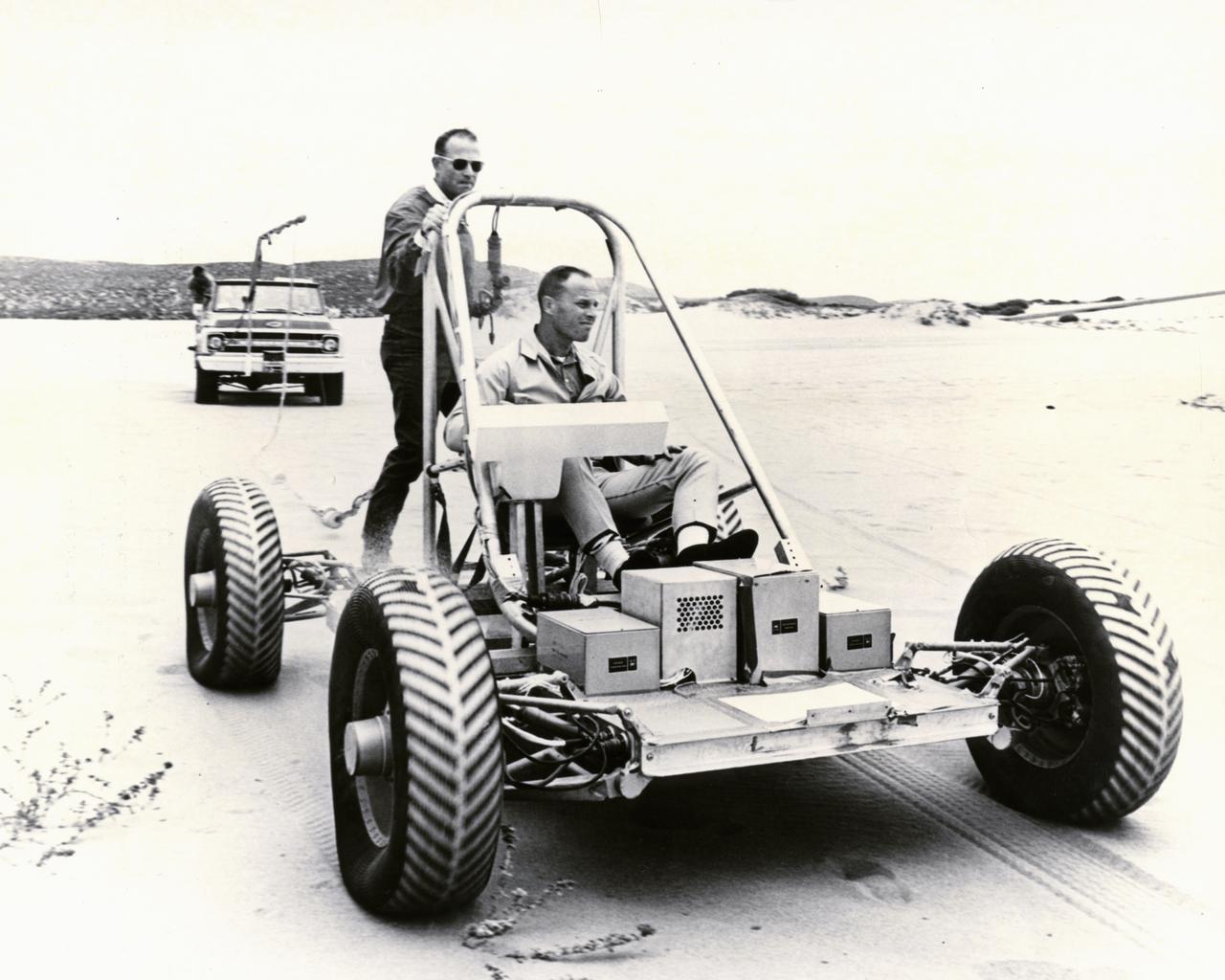

Astronauts Jack Lousma (seated) and Gerald Carr tested the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) training unit on the sands near Pismo Beach. The vehicle was built by the AC Delco electronics division of General Motors Corporation. Under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions. The LRVs were deployed during the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
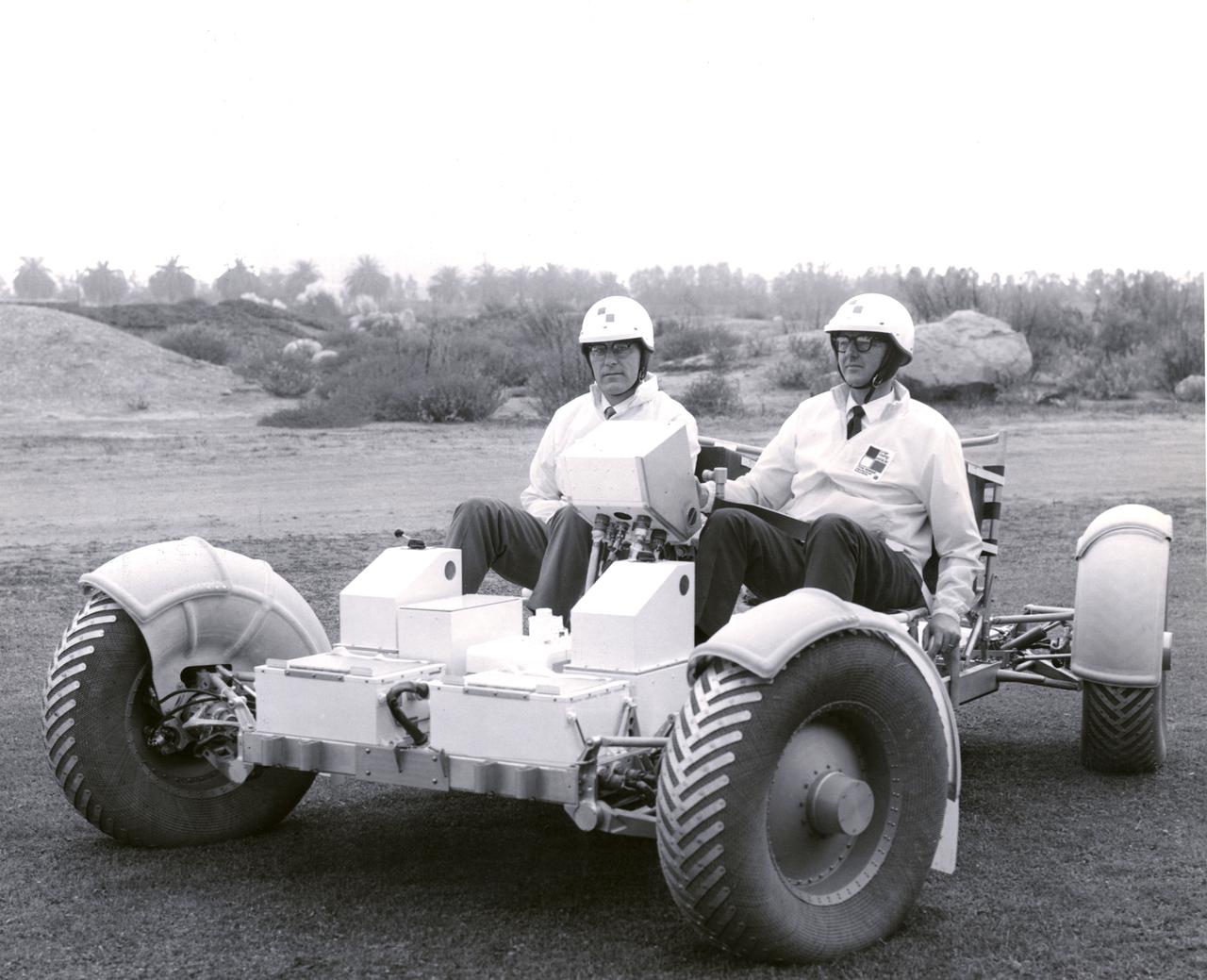

Delco engineers are operating this Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) Trainer. Built by by Delco Electronics Division of the General Motors Corporation, the trainer was shipped to NASA’s Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas for an astronaut training program. Under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions. The LRVs were deployed during the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
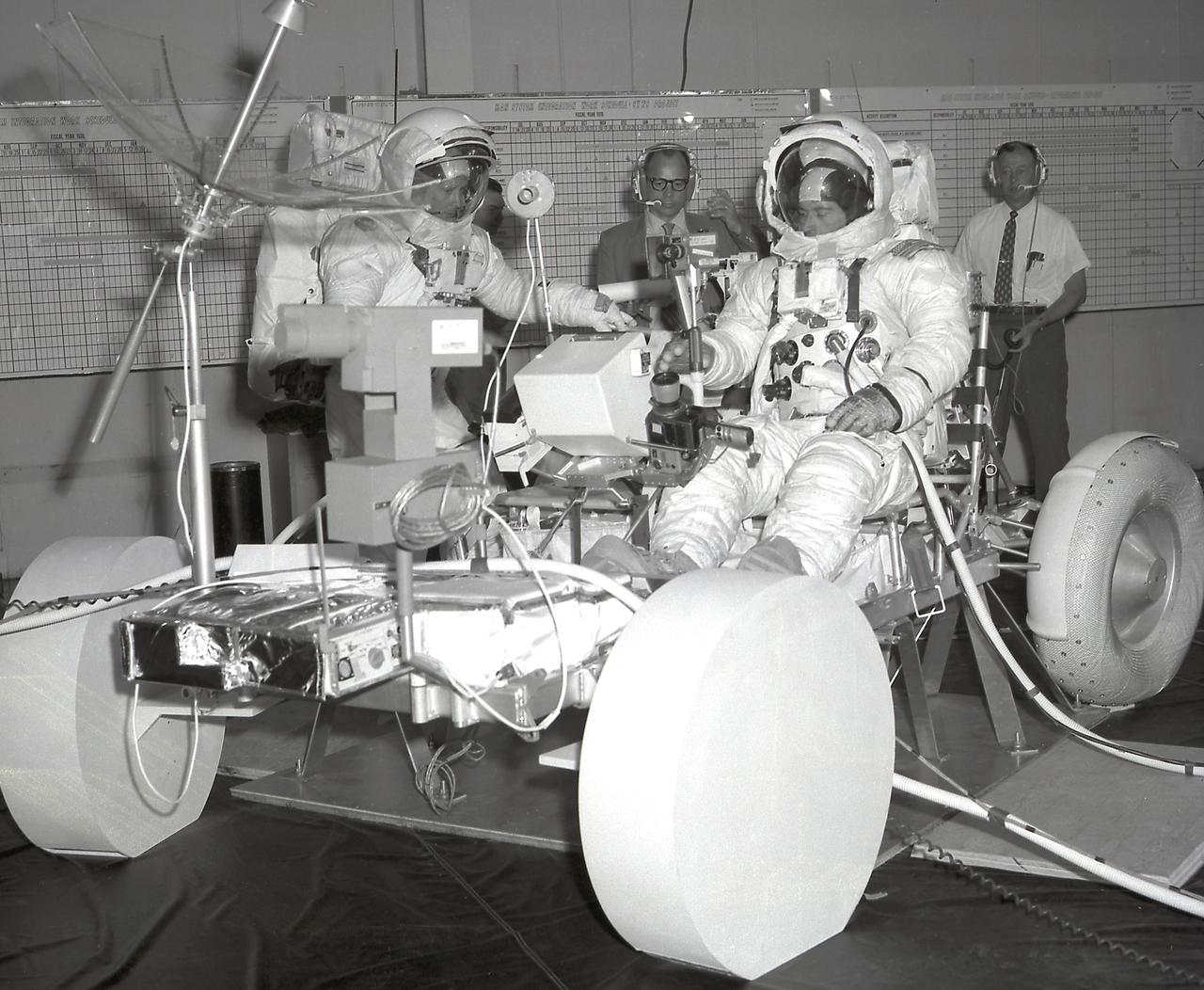
This image depicts the Apollo 16 mission astronauts John Young (right) and Charles Duke (left) in pressure suits during a final crew training on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), building 4619. Developed by the MSFC, the LRV was the lightweight electric car designed to increase the range of mobility and productivity of astronauts on the lunar surface. It was used on the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.

This is a photo of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module, Falcon, on the lunar surface. Apollo 15 launched from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) on July 26, 1971 via a Saturn V launch vehicle. Aboard was a crew of three astronauts including David R. Scott, Mission Commander; James B. Irwin, Lunar Module Pilot; and Alfred M. Worden, Command Module Pilot. The first mission designed to explore the Moon over longer periods, greater ranges and with more instruments for the collection of scientific data than on previous missions, the mission included the introduction of a $40,000,000 lunar roving vehicle (LRV) that reached a top speed of 16 kph (10 mph) across the Moon's surface. The successful Apollo 15 lunar landing mission was the first in a series of three advanced missions planned for the Apollo program. The primary scientific objectives were to observe the lunar surface, survey and sample material and surface features in a preselected area of the Hadley-Apennine region, setup and activation of surface experiments and conduct in-flight experiments and photographic tasks from lunar orbit. Apollo 15 televised the first lunar liftoff and recorded a walk in deep space by Alfred Worden. Both the Saturn V rocket and the LRV were developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center.

Astronaut James Lovell (Apollo 8 Apollo 13), center, flanked by Walt Cunningham (Apollo 7), left, and David Scott (Apollo 9 Apollo 15) responds during the 40th anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission and the walk on the moon press conference, Monday, July 20, 2009, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
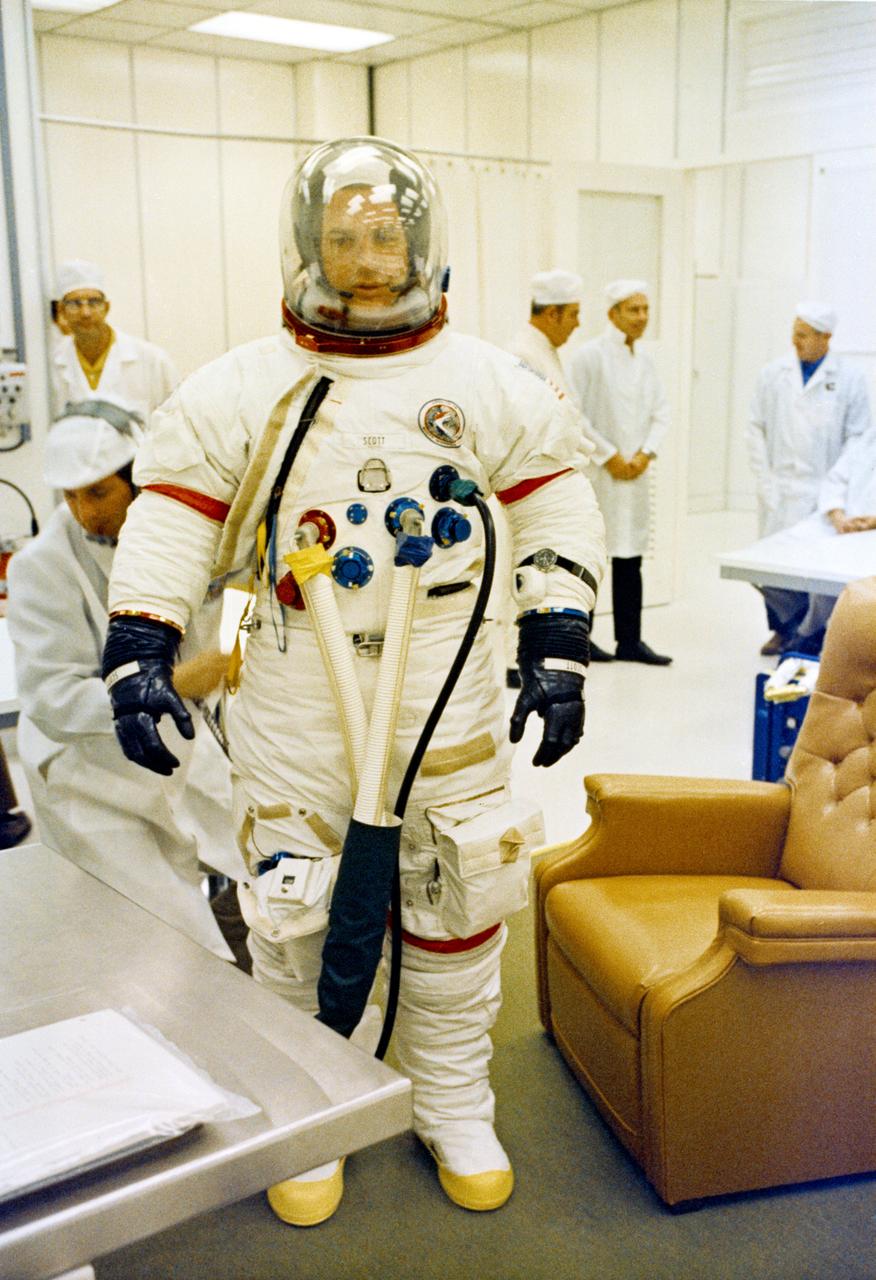

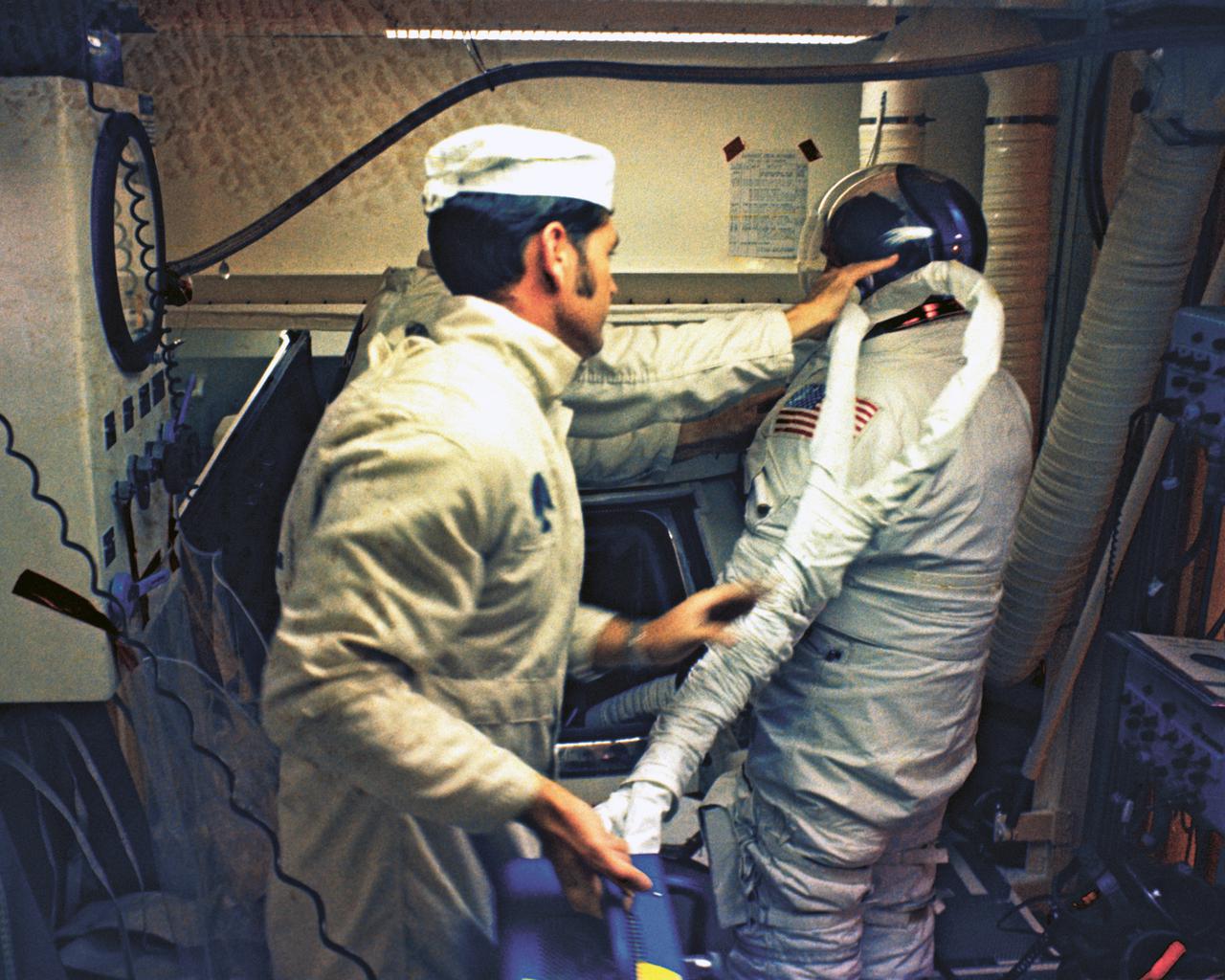
S71-41409 (26 July 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, commander of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission, goes through suiting up operations in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Manned Spacecraft Operations Building (MSOB) during the Apollo 15 prelaunch countdown. Minutes later astronauts Scott; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, rode a special transport van over to Pad A, Launch Complex 39, where their spacecraft awaited them. The Apollo 15 space vehicle was launched at 9:34:00:79 a.m. (EDT), July 26, 1971.
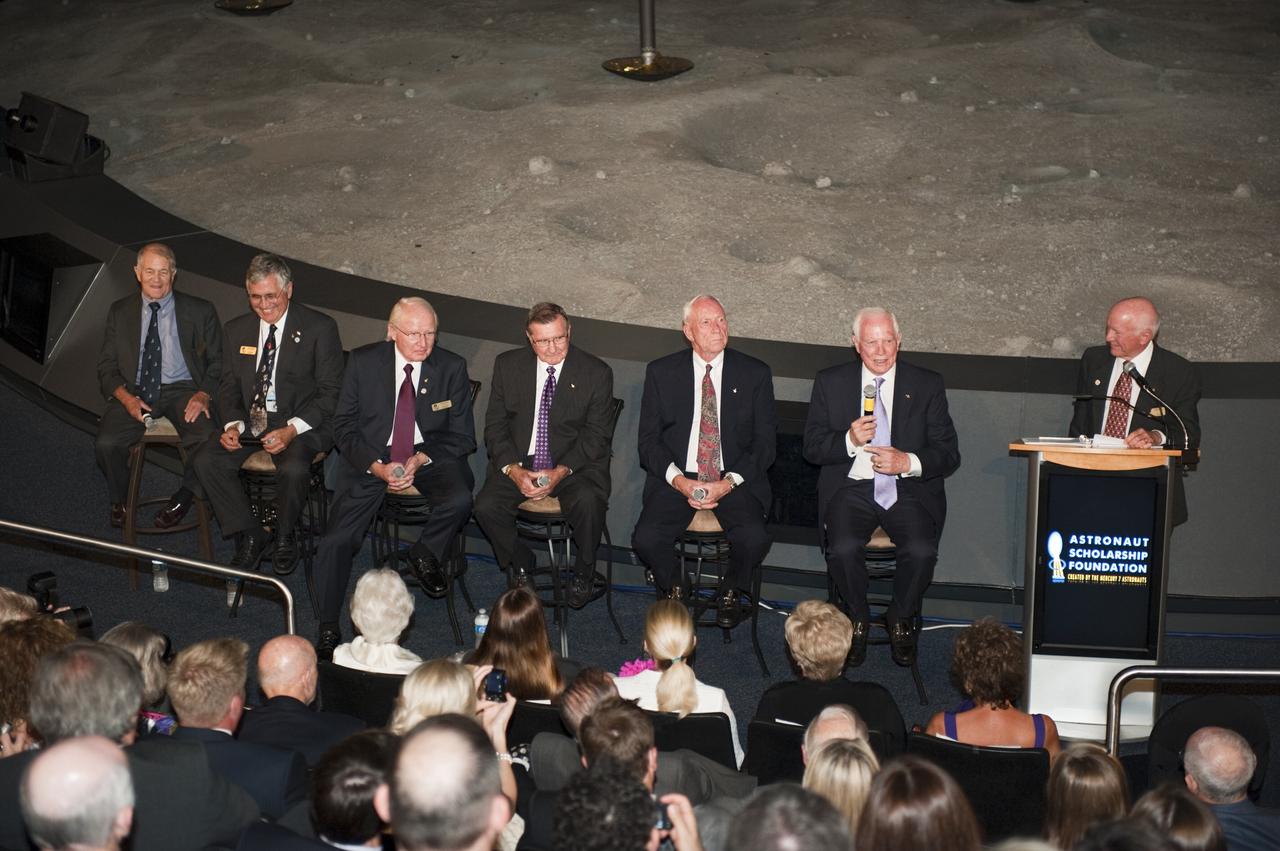

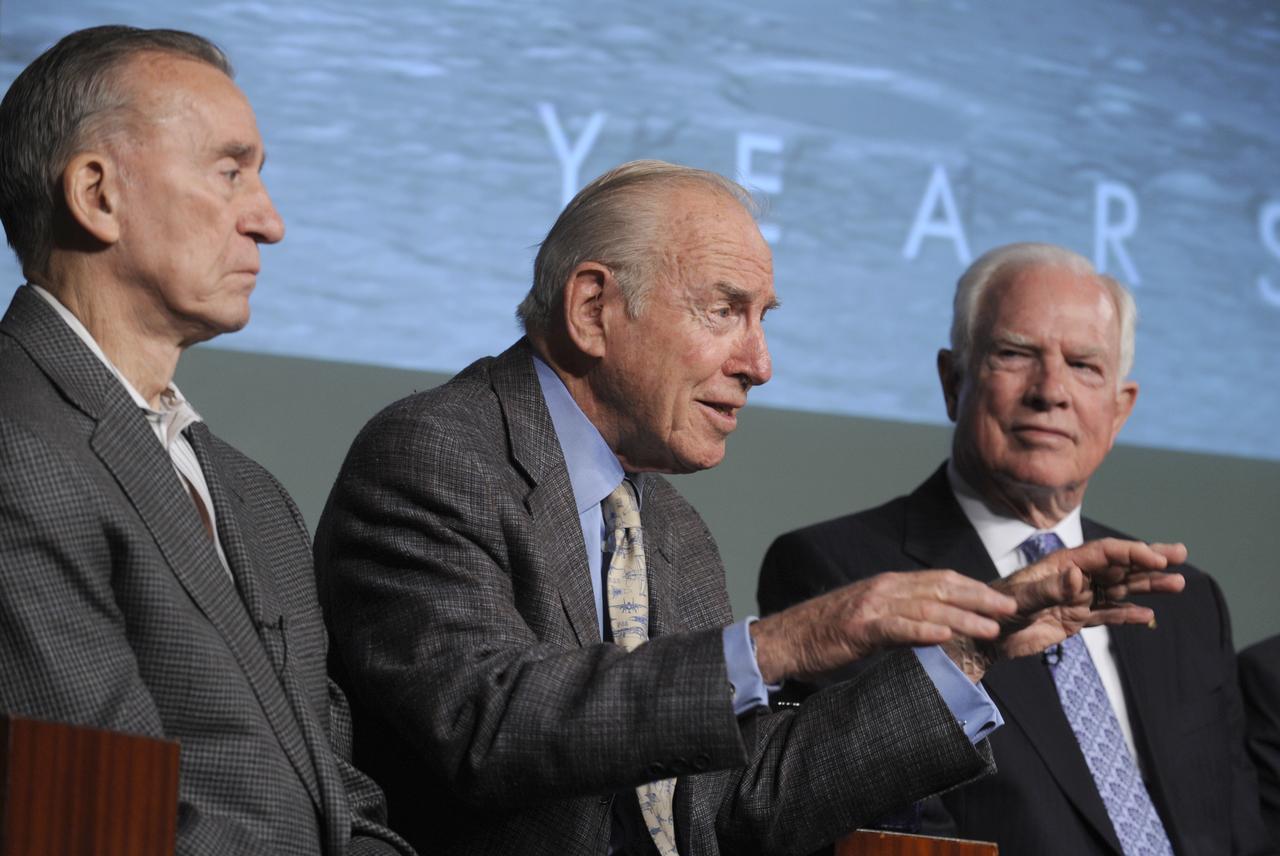
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a celebration on the 40th anniversary of NASA's Apollo 15 mission. An elite gathering of Apollo-era astronauts were on hand for the event and panel discussion. Gerry Griffin, Apollo 15 flight director moderates the question-and-answer period with the panel. From left are: Apollo 15 astronaut backup support crew members, Joe Allen, Jack Schmitt, Vance Brand and Dick Gordon; Al Worden and Dave Scott. Worden circled the moon while Scott and the late Jim Irwin, the Lunar Module commander, made history when they became the first humans to drive a vehicle on the surface of the moon. They also provided extensive descriptions and photographic documentation of geologic features in the vicinity of the Hadley Rille landing site during their three days on the lunar surface. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
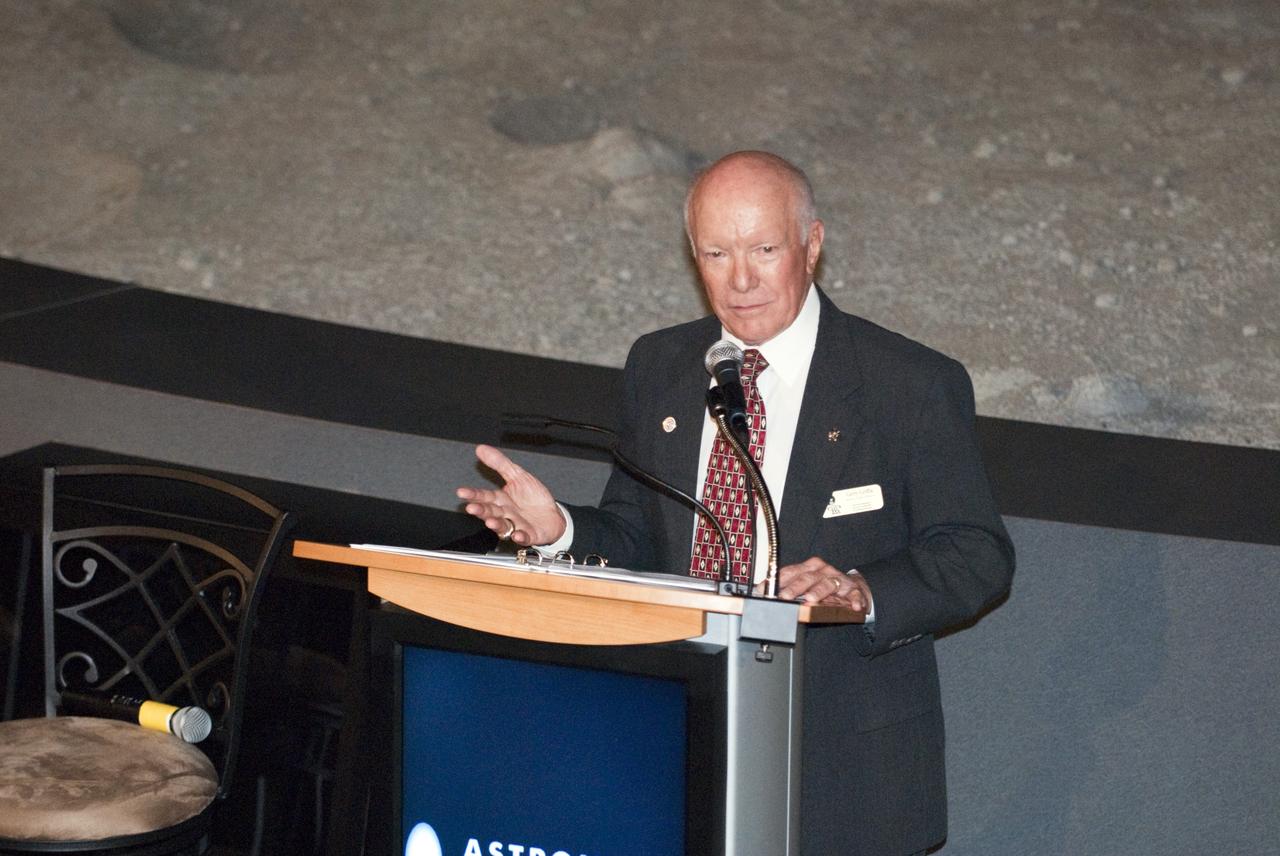

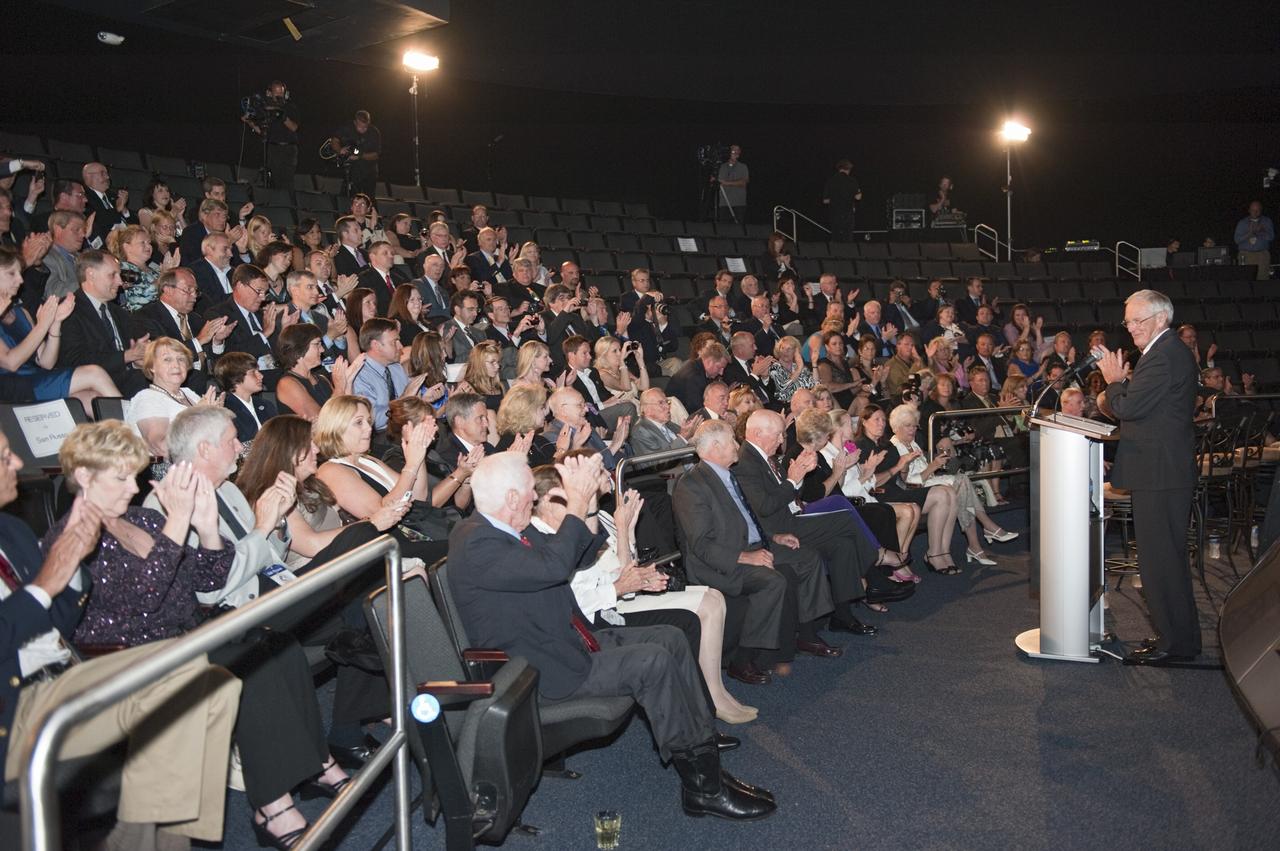
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a celebration on the 40th anniversary of NASA's Apollo 15 mission. Apollo 15 Commander Dave Scott and Command Module Pilot Al Worden and an elite gathering of Apollo-era astronauts were on hand for the event and panel discussion. Here, Gerry Griffin, Apollo 15 flight director, speaks to the invited guests. Worden circled the moon while Scott and the late Jim Irwin, the Lunar Module commander, made history when they became the first humans to drive a vehicle on the surface of the moon. They also provided extensive descriptions and photographic documentation of geologic features in the vicinity of the Hadley Rille landing site during their three days on the lunar surface. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
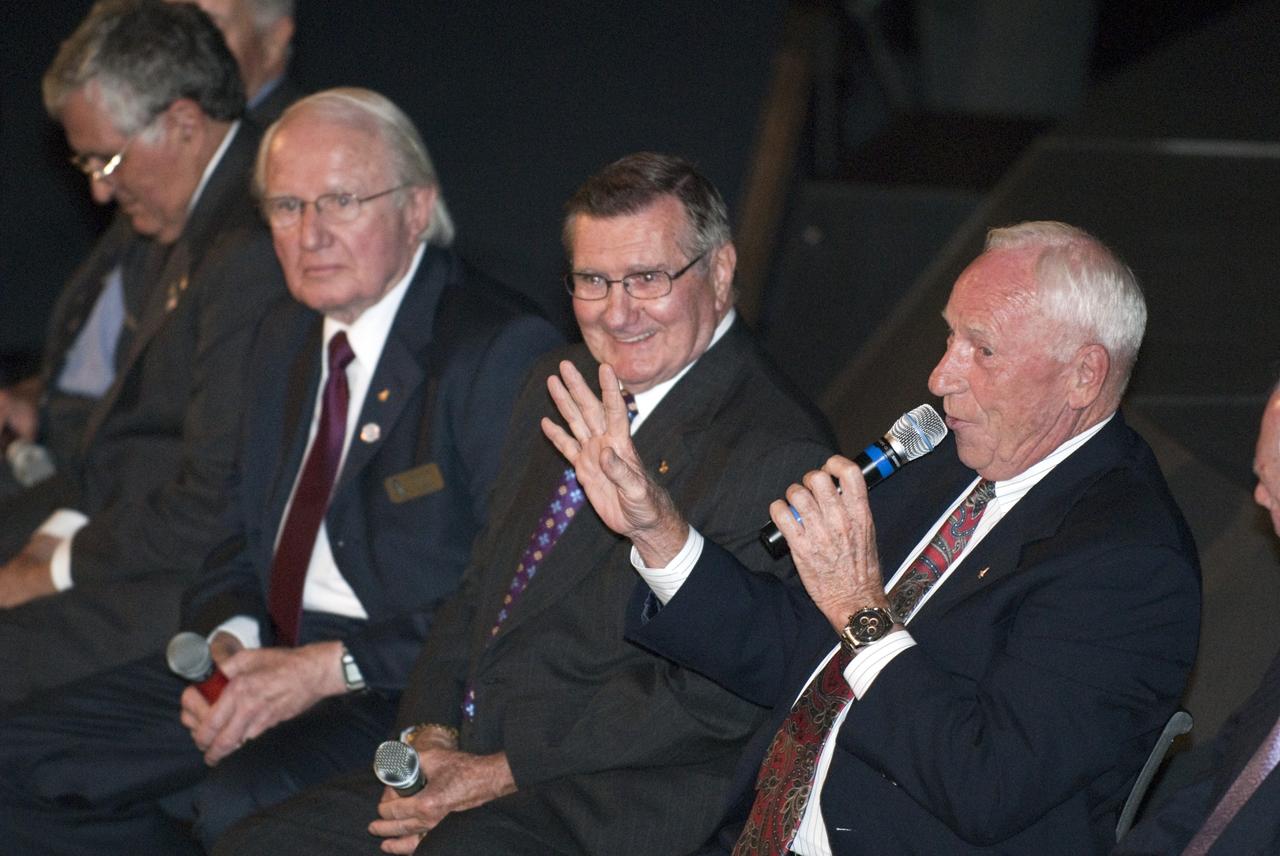

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a celebration on the 40th anniversary of NASA's Apollo 15 mission. Apollo 15 Commander Dave Scott and Command Module Pilot Al Worden and an elite gathering of Apollo-era astronauts were on hand for the event and panel discussion. Seen here are Al Worden (right), and Apollo 15 astronaut backup support crew members, Dick Gordon, Vance Brand and Jack Schmitt. Worden circled the moon while Scott and the late Jim Irwin, the Lunar Module commander, made history when they became the first humans to drive a vehicle on the surface of the moon. They also provided extensive descriptions and photographic documentation of geologic features in the vicinity of the Hadley Rille landing site during their three days on the lunar surface. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
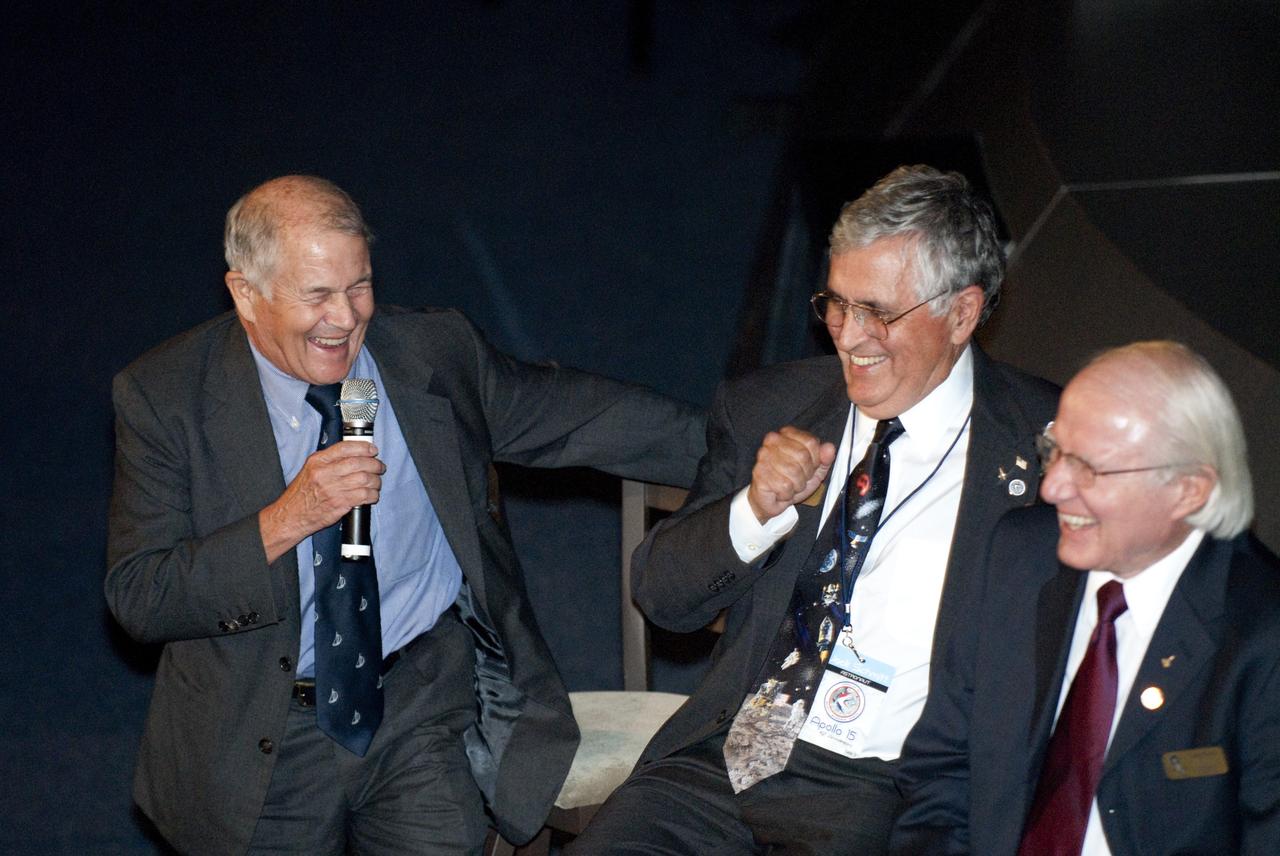

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a celebration on the 40th anniversary of NASA's Apollo 15 mission. Apollo 15 Commander Dave Scott and Command Module Pilot Al Worden and an elite gathering of Apollo-era astronauts were on hand for the event and panel discussion. Here, sharing a light moment are from left, Apollo 15 astronaut support crew members, Joe Allen, Jack Schmitt and Vance Brand. Worden circled the moon while Scott and the late Jim Irwin, the Lunar Module commander, made history when they became the first humans to drive a vehicle on the surface of the moon. They also provided extensive descriptions and photographic documentation of geologic features in the vicinity of the Hadley Rille landing site during their three days on the lunar surface. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
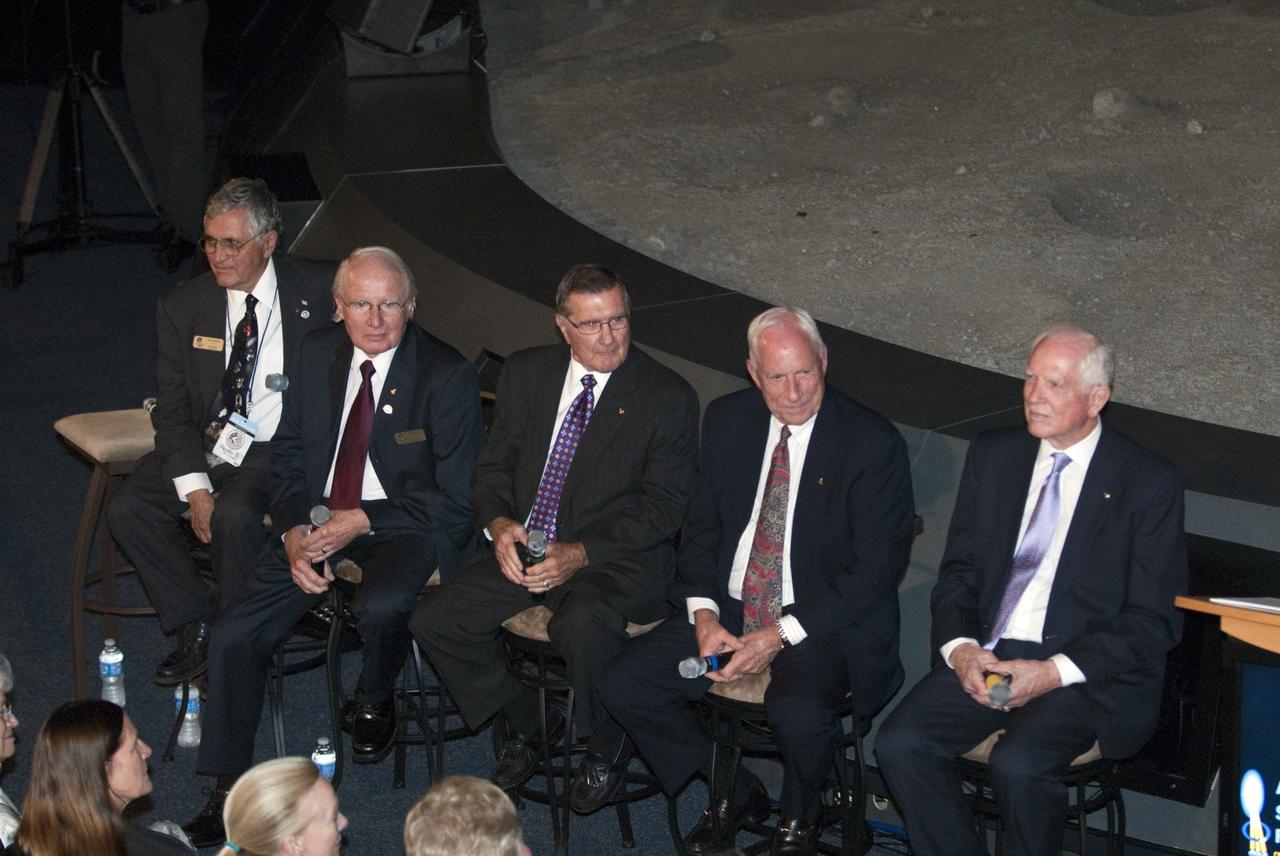

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a celebration on the 40th anniversary of NASA's Apollo 15 mission. Apollo 15 Commander Dave Scott and Command Module Pilot Al Worden and an elite gathering of Apollo-era astronauts were on hand for the event and panel discussion. Seen here are Apollo 15 astronaut backup support crew members, Jack Schmitt (left), Vance Brand and Dick Gordon; Al Worden and Dave Scott. Worden circled the moon while Scott and the late Jim Irwin, the Lunar Module commander, made history when they became the first humans to drive a vehicle on the surface of the moon. They also provided extensive descriptions and photographic documentation of geologic features in the vicinity of the Hadley Rille landing site during their three days on the lunar surface. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
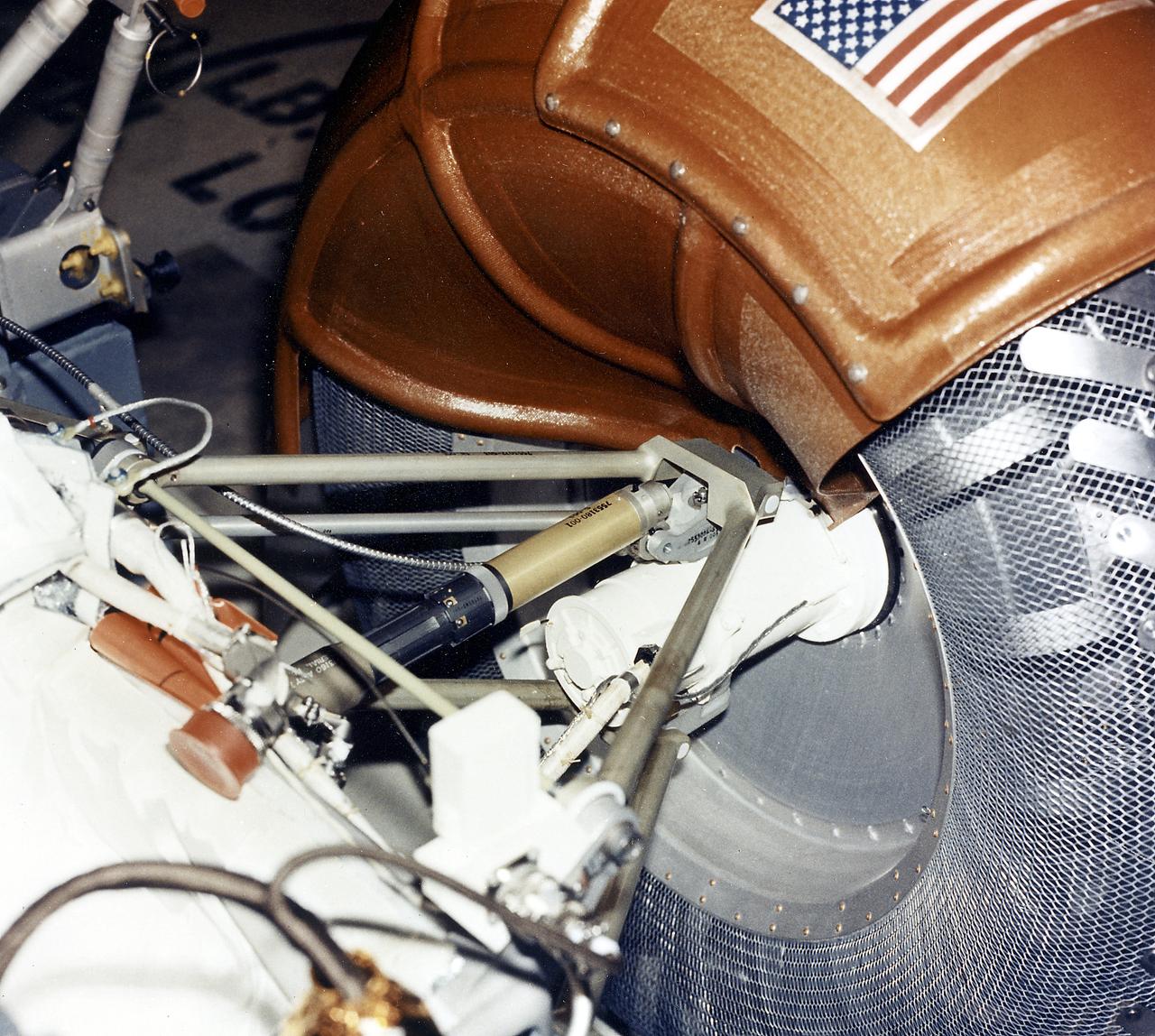
This is a close-up inboard view of a left front wheel of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 1. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater Range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
This is a close-up view of a right rear wheel strut of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 1. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
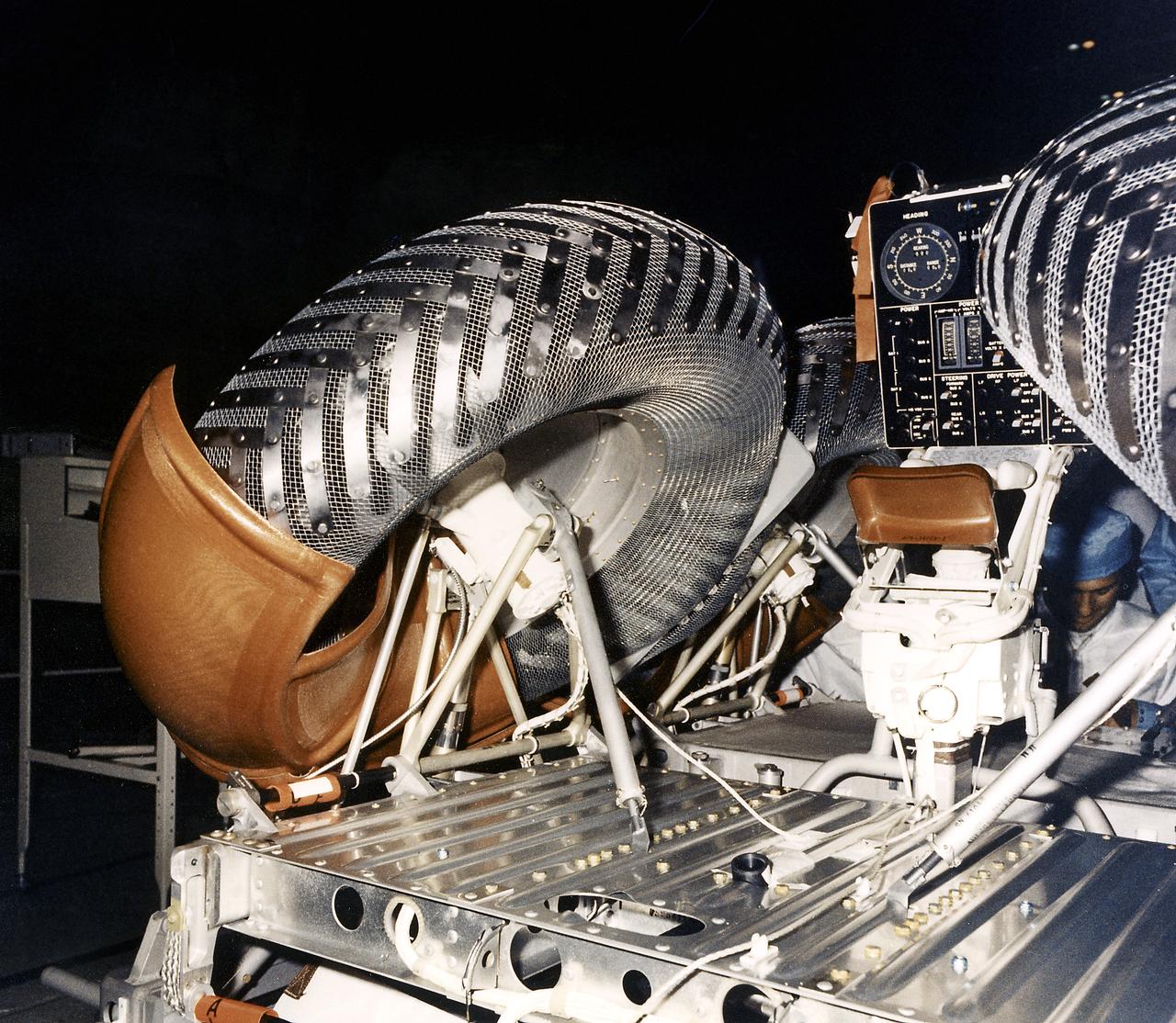
This photograph shows a rear view of a folded configuration of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 2. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
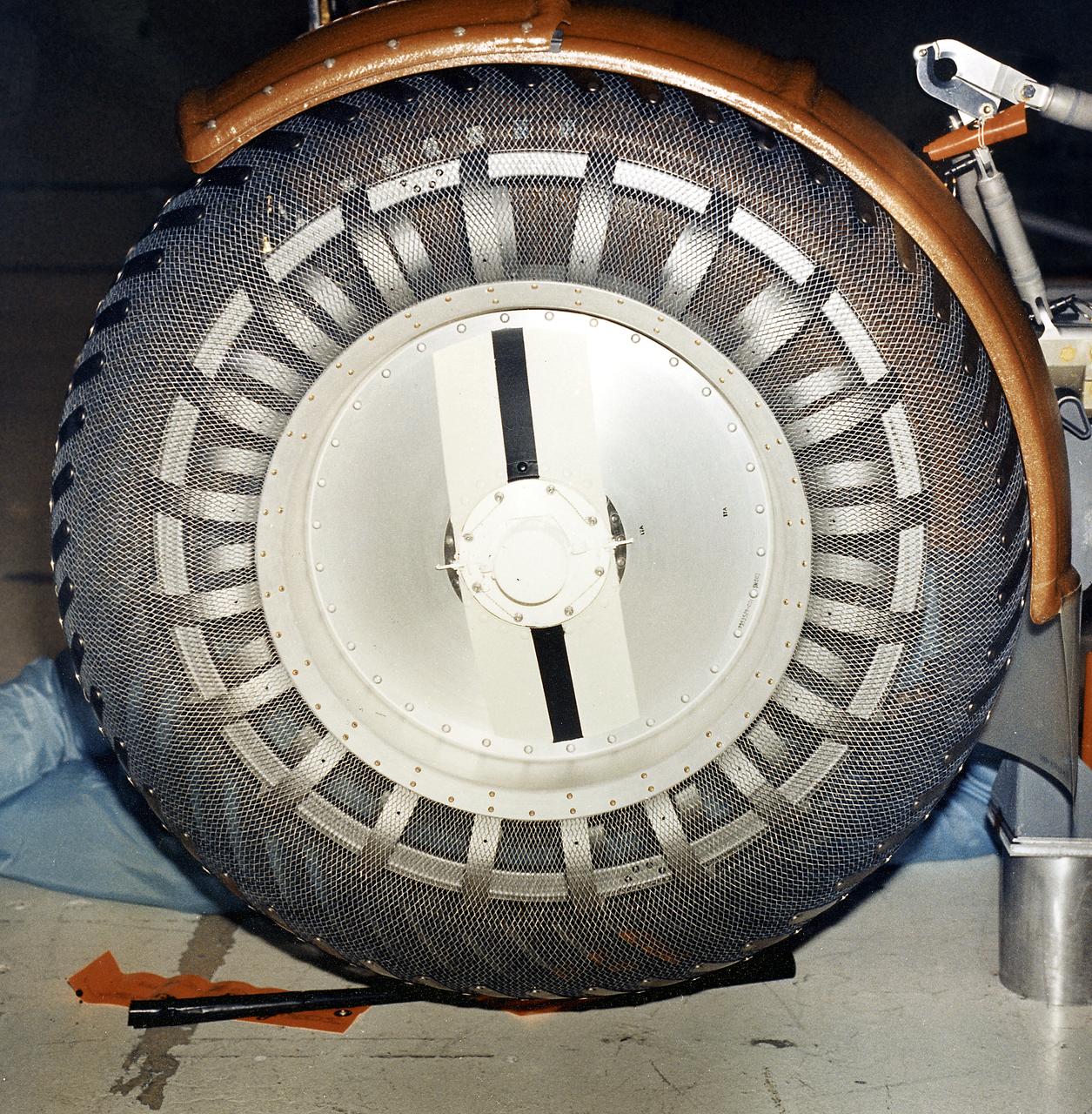

This is a close-up view of a left front wheel of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 1. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
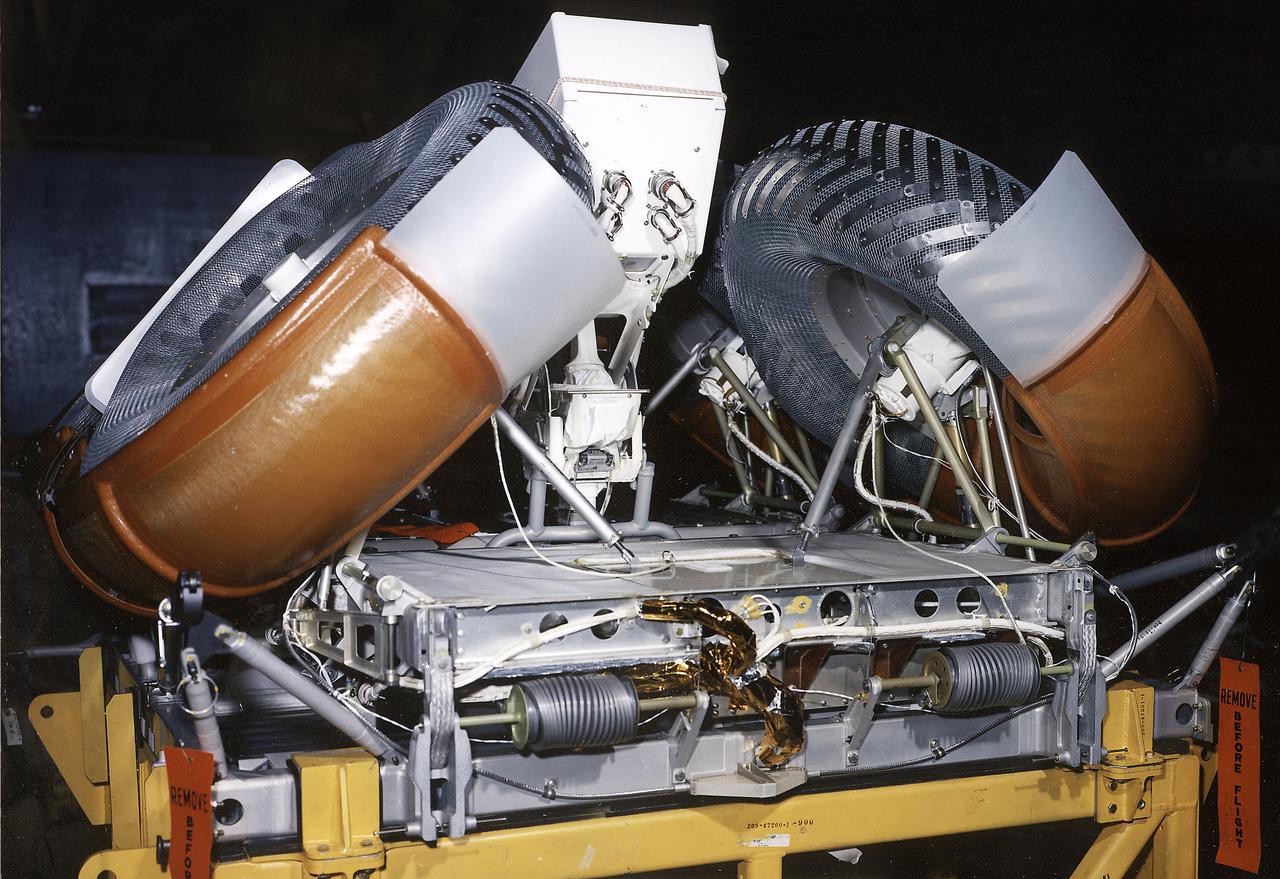
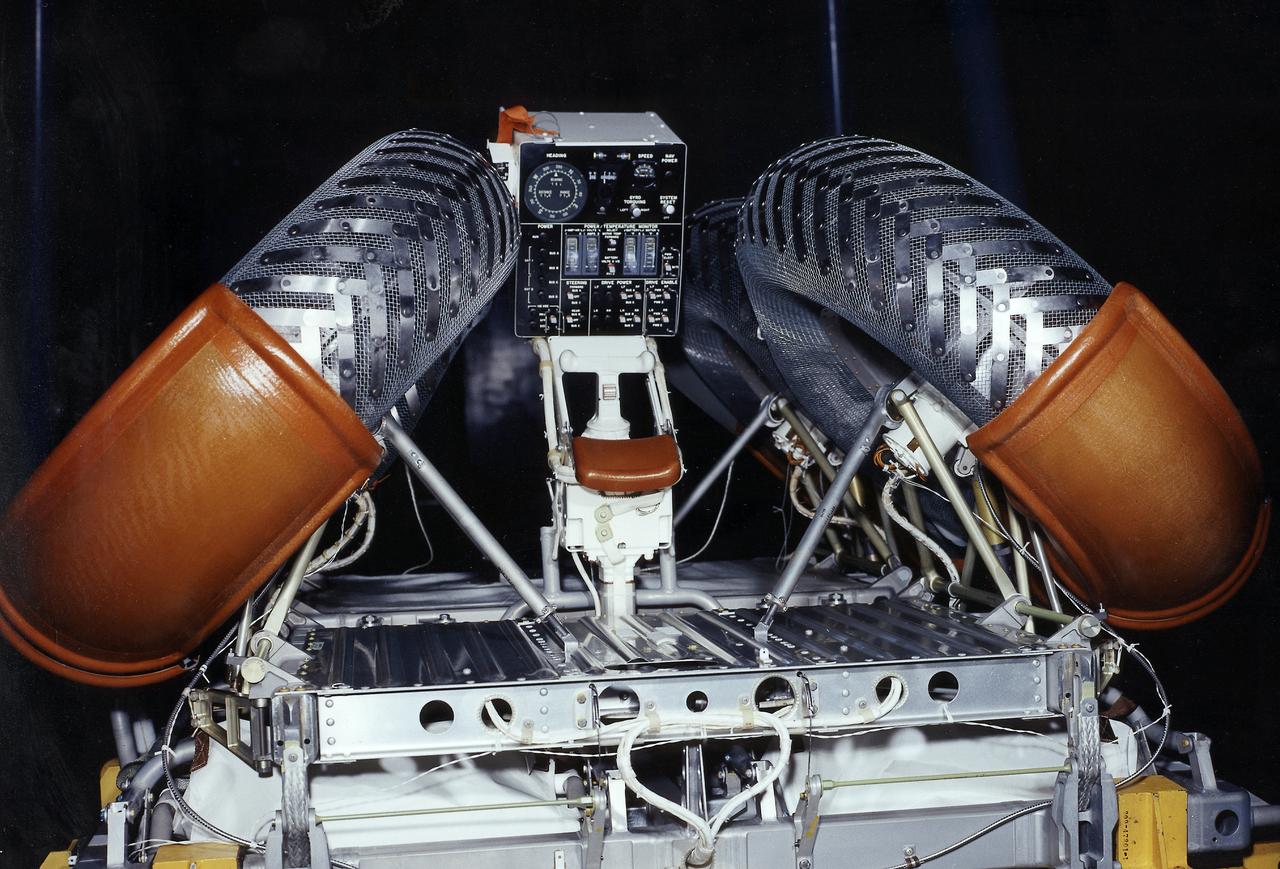
This photograph shows a front view of a folded configuration of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 2. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
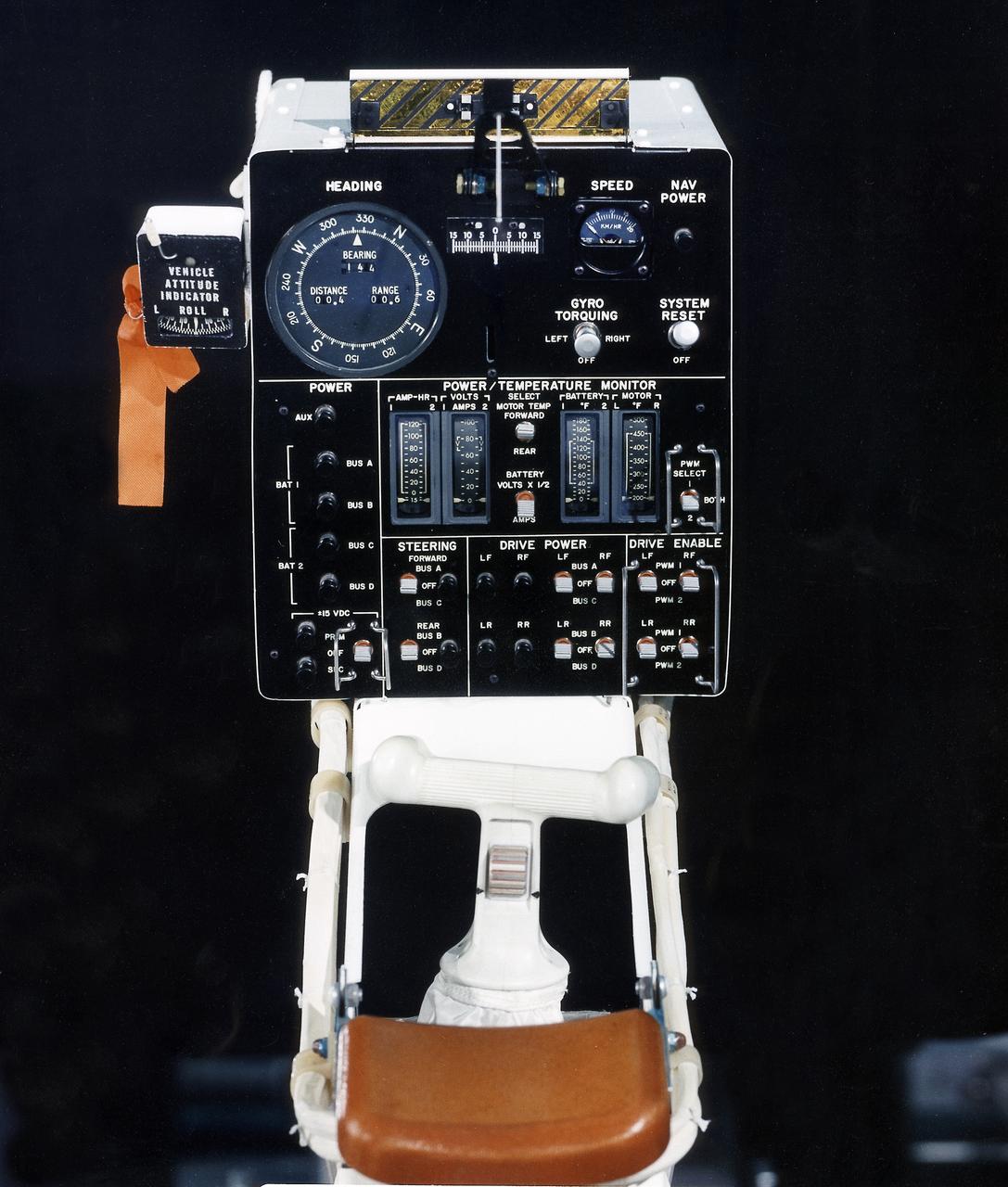
This photograph is a view of a display, control console, and hand controller for the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 2. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
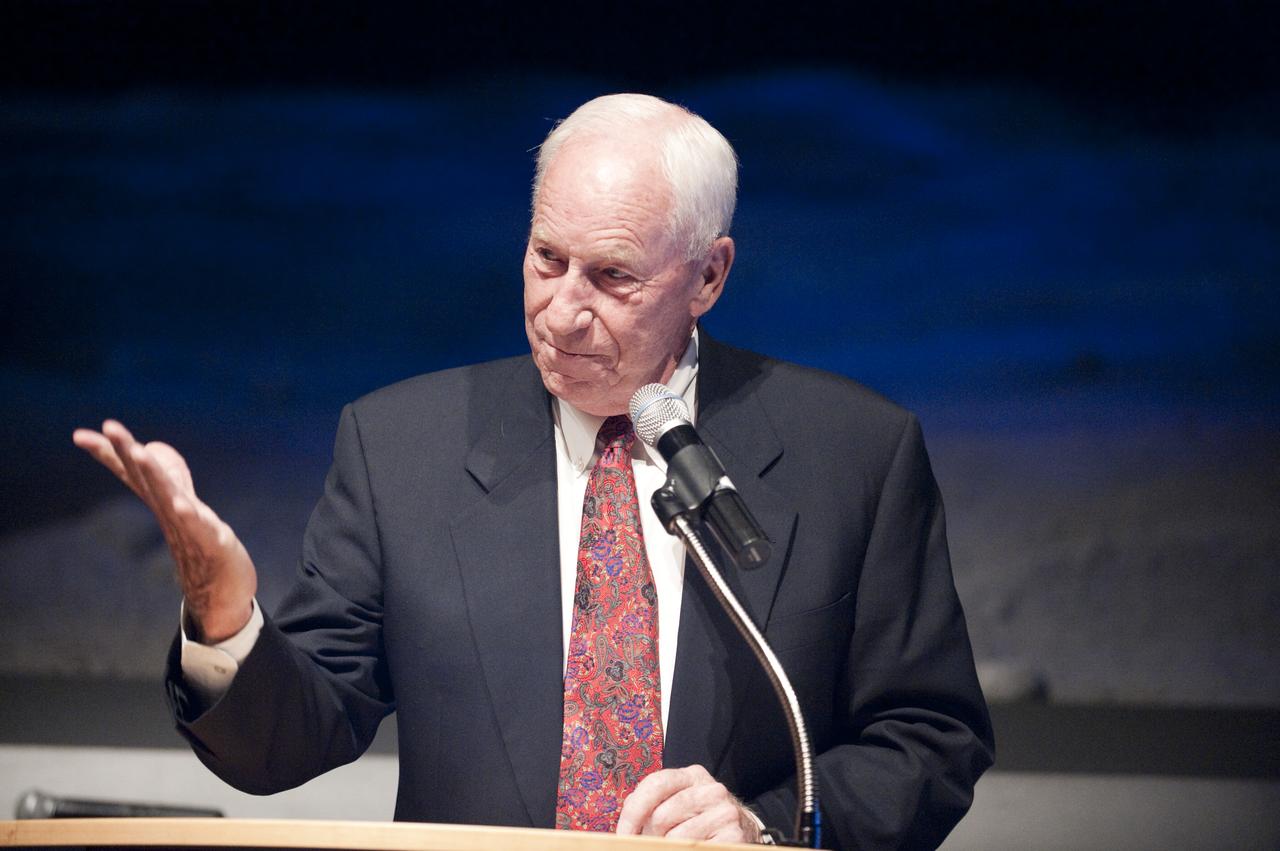

Apollo astronaut Al Worden speaks during a ceremony, Thursday, July 30, 2009, where he was honored with the presentation of the an Ambassador of Exploration Award for his contributions to the U.S. space program at Kennedy Space Center, Fla. Worden served as command module pilot for the Apollo 15 mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
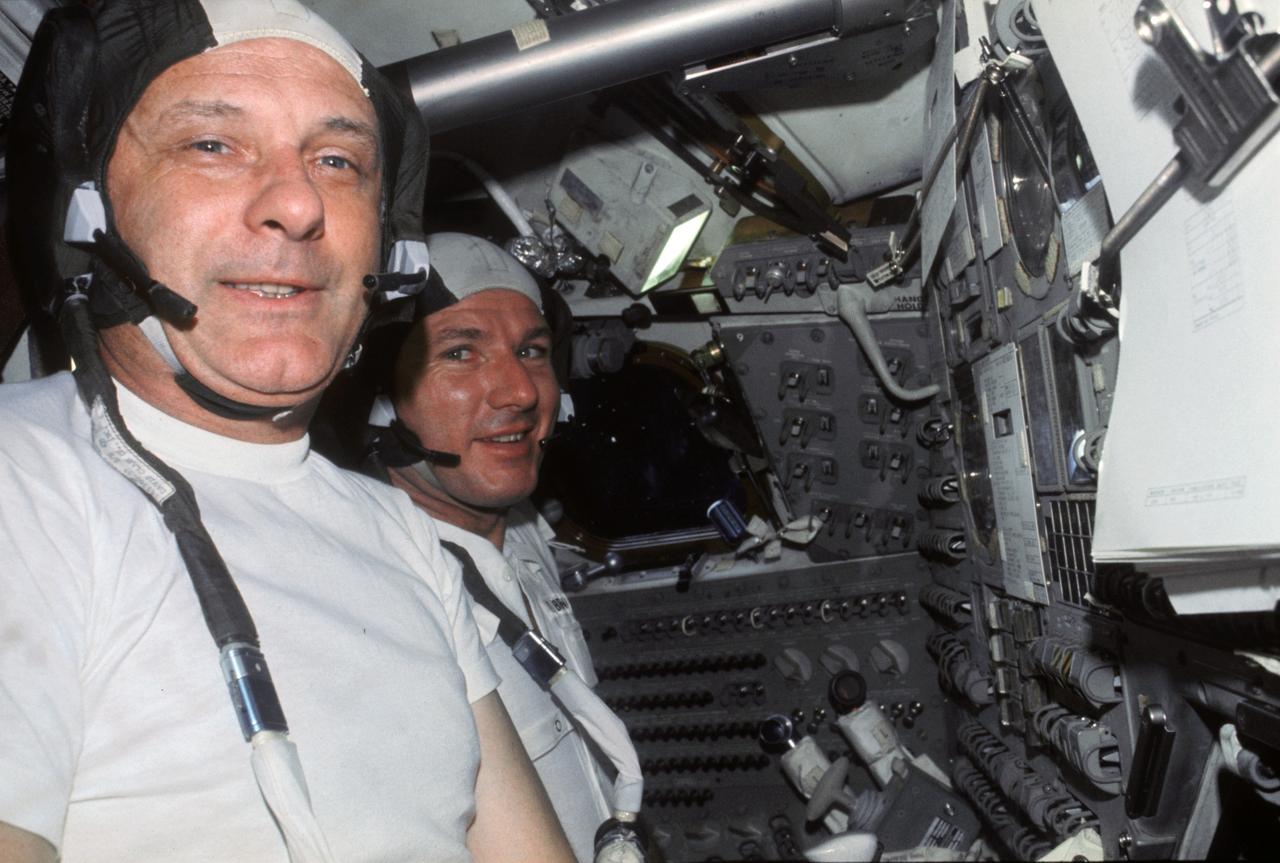

AST-06-344 (15-24 July 1975) --- Two American ASTP crewmen, astronauts Thomas P. Stafford (foreground) and Vance D. Brand are seen in the Apollo Command Module during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. This picture was taken with a 35mm camera.
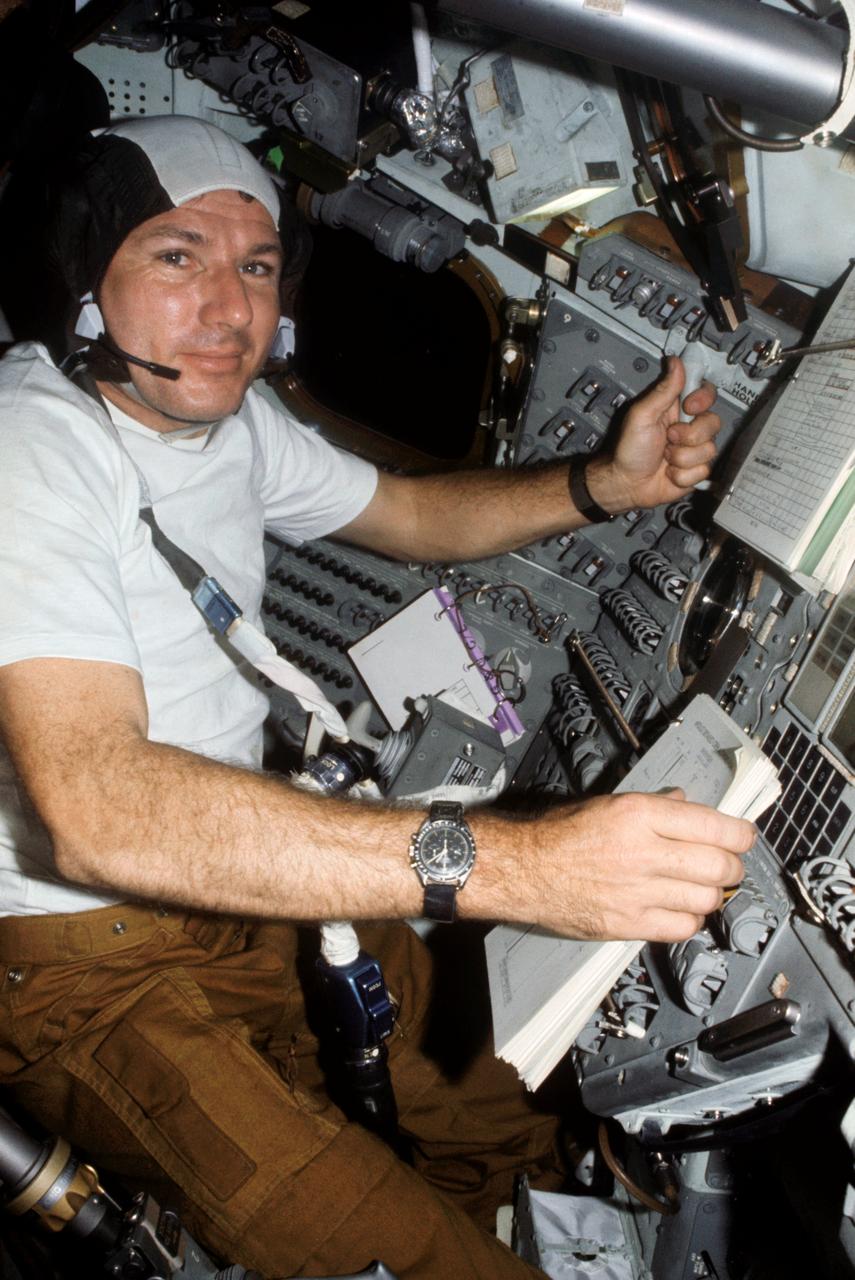

AST-08-499 (15-24 July 1975) --- Astronaut Vance D. Brand, command module pilot of the American ASTP crew, is seen at the controls of the Apollo Command Module during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. This picture was taken with a 35mm camera.
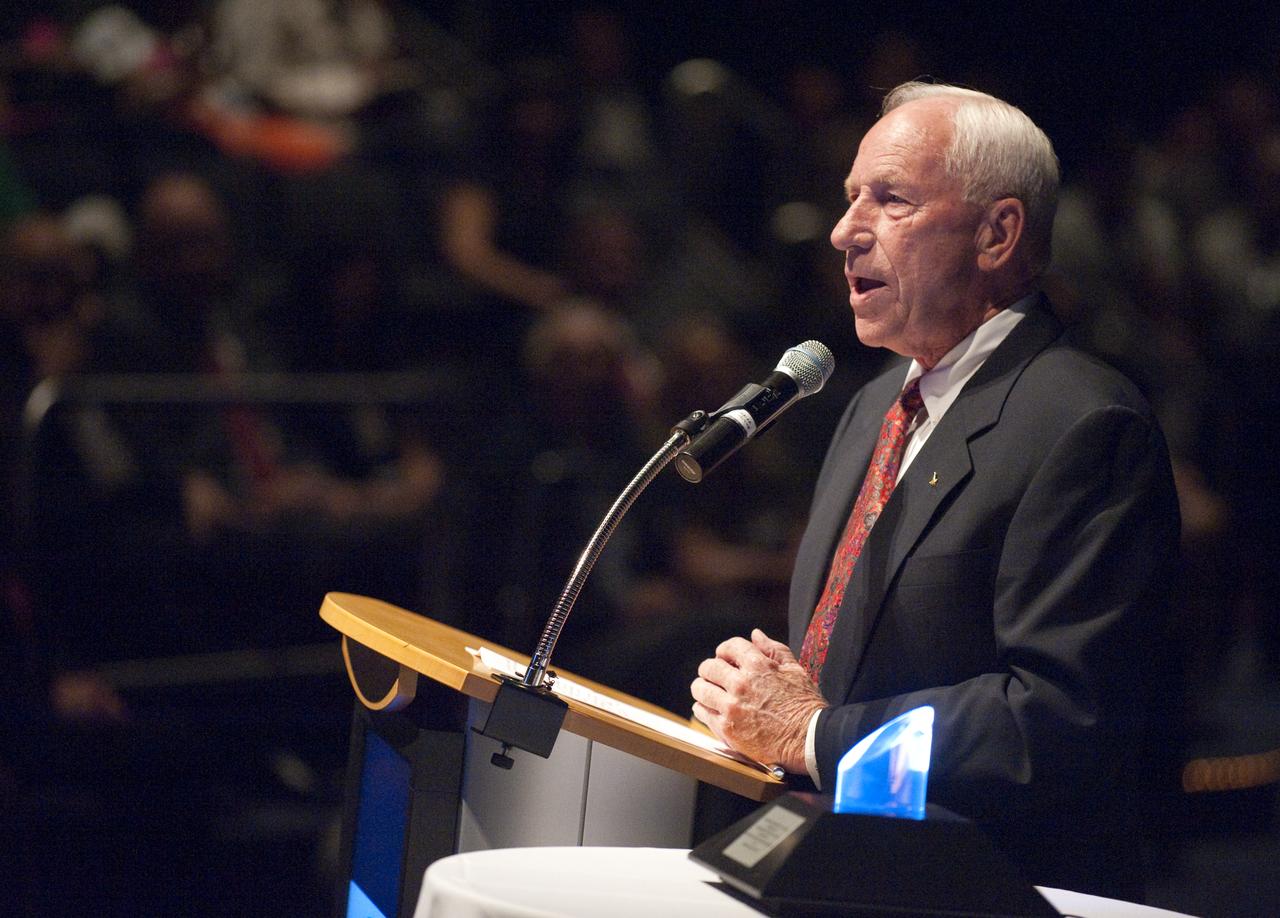

Apollo astronaut Al Worden speaks during a ceremony, Thursday, July 30, 2009, where he was honored with the presentation of the an Ambassador of Exploration Award for his contributions to the U.S. space program at Kennedy Space Center, Fla. Worden served as command module pilot for the Apollo 15 mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a celebration on the 40th anniversary of NASA's Apollo 15 mission. Apollo 15 Commander Dave Scott and Command Module Pilot Al Worden and an elite gathering of Apollo-era astronauts were on hand for the event and panel discussion. Here, Apollo 11 Commander Neil Armstrong speaks to the invited guests. In the background is a model of the Lunar Module, part of the lander portion of the Apollo spacecraft. Worden circled the moon while Scott and the late Jim Irwin, the Lunar Module commander, made history when they became the first humans to drive a vehicle on the surface of the moon. They also provided extensive descriptions and photographic documentation of geologic features in the vicinity of the Hadley Rille landing site during their three days on the lunar surface. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
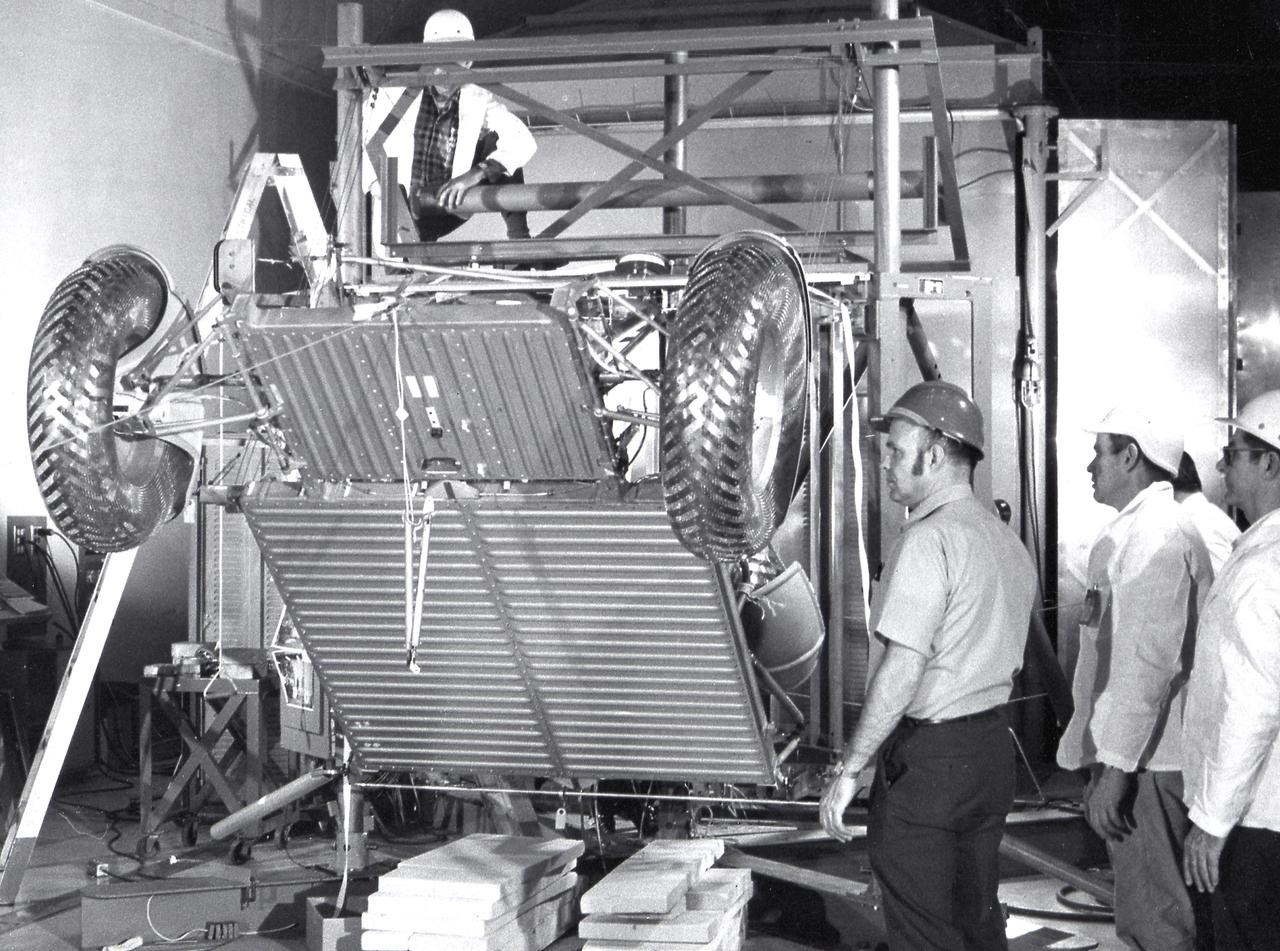
This photograph shows workmen at the Boeing plant in Kent, Washington, performing deployment tests on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility on the lunar surface during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
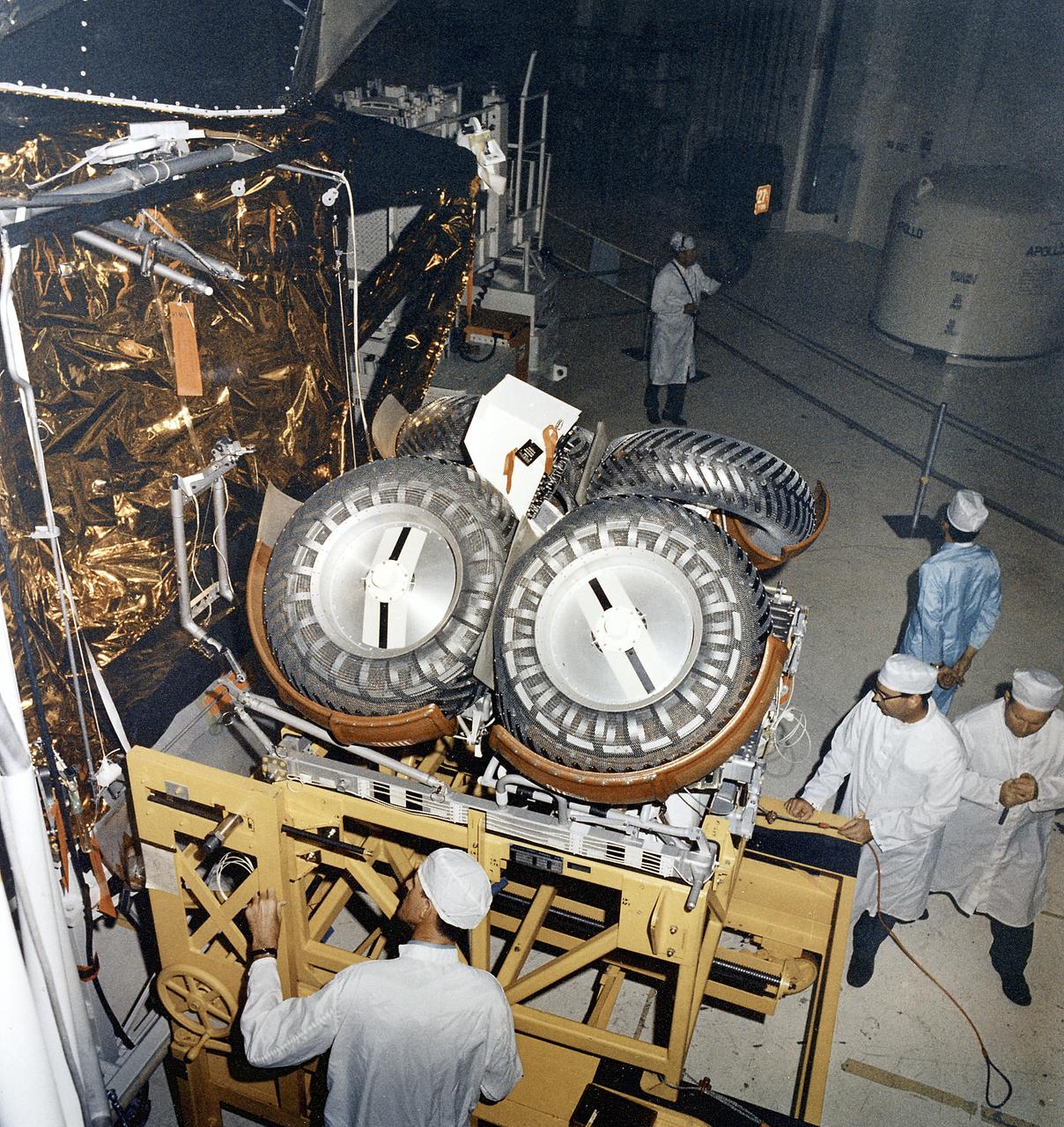
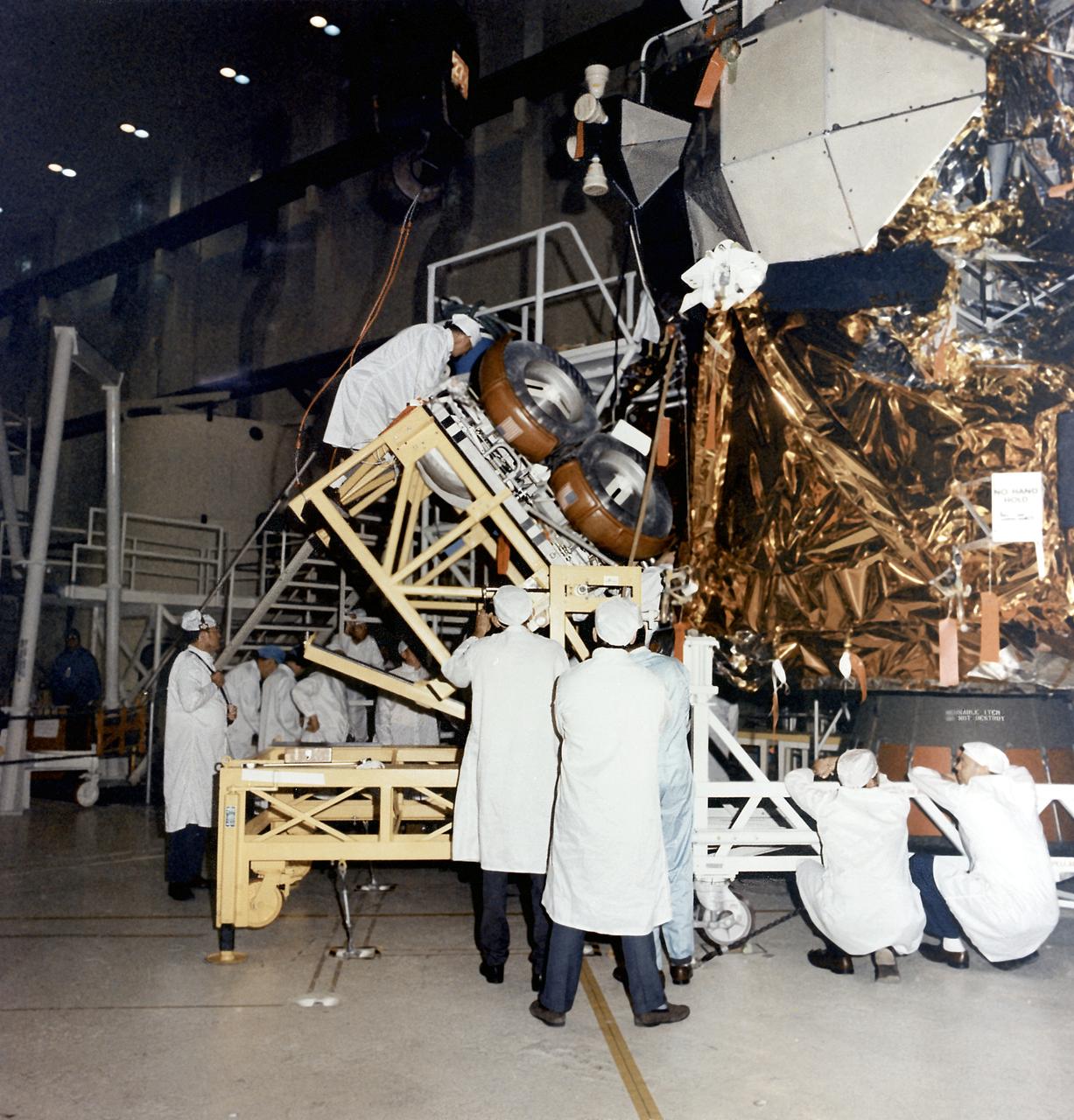
This photograph was taken during the installation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) in the Lunar Module at the Kennedy Space Center. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.

This photograph shows the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) being prepared for installation in the Lunar Module at the Kennedy Space Center. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.

S72-32719 (March 1972) --- With four of the six planned lunar missions completed, this chart has been prepared to show the various areas of the lunar "nearside" to be visited by astronauts representing the NASA Apollo program. Apollo's 11, 12, 14 and 15 are shown at their respective landing points. Apollo 16 and Apollo 17, planned for later this year at Descartes and Taurus Littrow, respectively, also are depicted on the map.

In this November 1971 photograph, (from left to right) Astronauts John Young, Eugene Cernan, Charles Duke, Fred Haise, Anthony England, Charles Fullerton, and Donald Peterson await deployment tests of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) qualification test unit in building 4649 at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The LRV, developed under the direction of the MSFC, was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility on the lunar surface during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.

This photograph was taken during the installation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) in the Lunar Module at the Kennedy Space Center. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
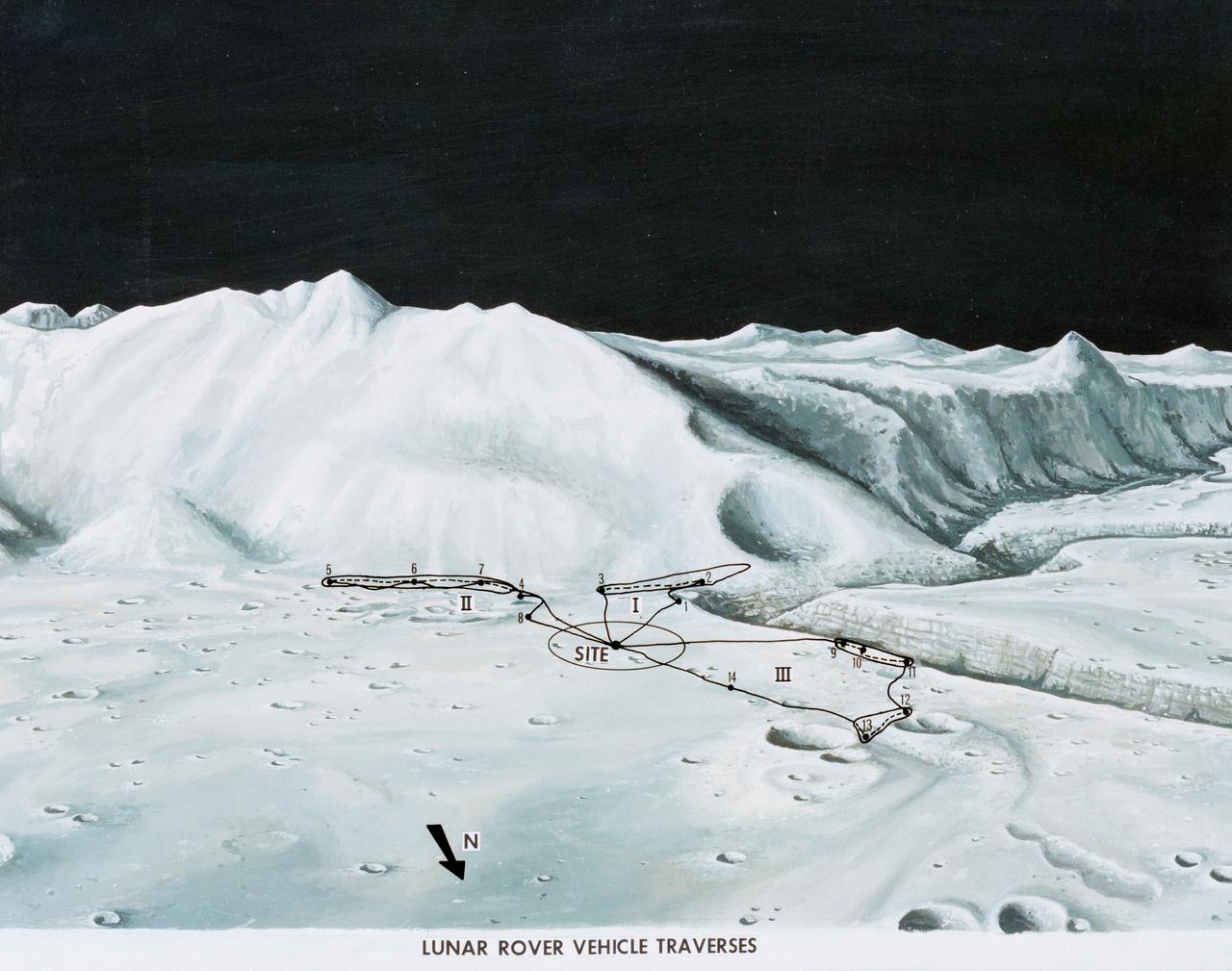

S71-33433 (1 July 1971) --- An artist's concept of the Hadley-Apennine landing site, depicting the traverses planned on the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission using the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The Roman numerals indicate the three periods of extravehicular activity (EVA). The Arabic numbers represent the station stops. This artist's concept was excerpted from "On the Moon with Apollo 15: A Guidebook to Hadley Rille and the Apennine Mountains," by Gene Simmons. The station stops indicated here are keyed to information given in the publication. Artwork by Jerry Elmore.
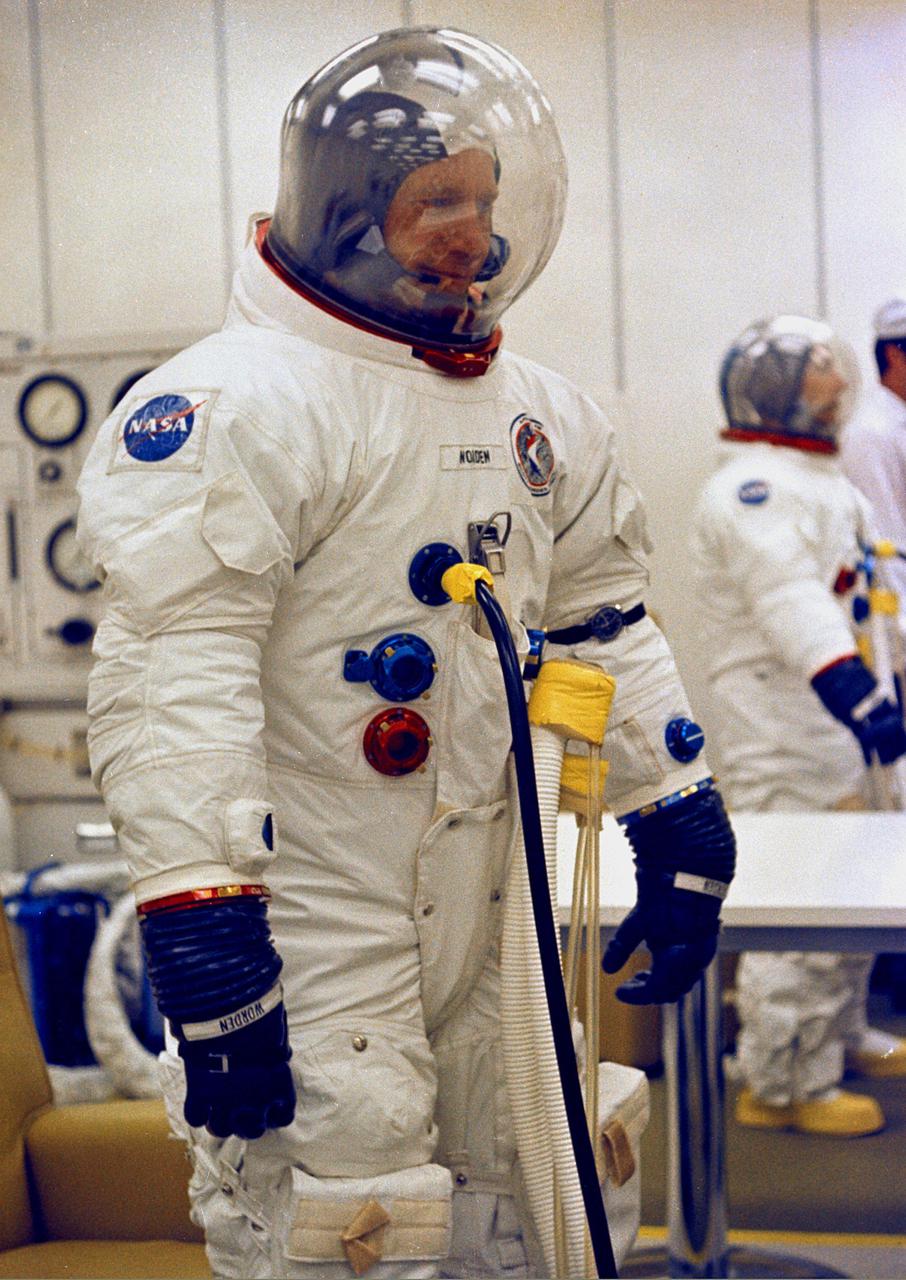

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Apollo 15 Command Module Pilot Alfred M. Worden undergoes spacesuit pressure checks prior to participating in the space vehicle Countdown Demonstration Test. Lunar Module Pilot James B. Irwin is visible in the rear while David R. Scott, the Commander for Apollo 15, is not shown. The test is a rehearsal in preparation for the scheduled Moon mission, scheduled no earlier than July 26, 1971.
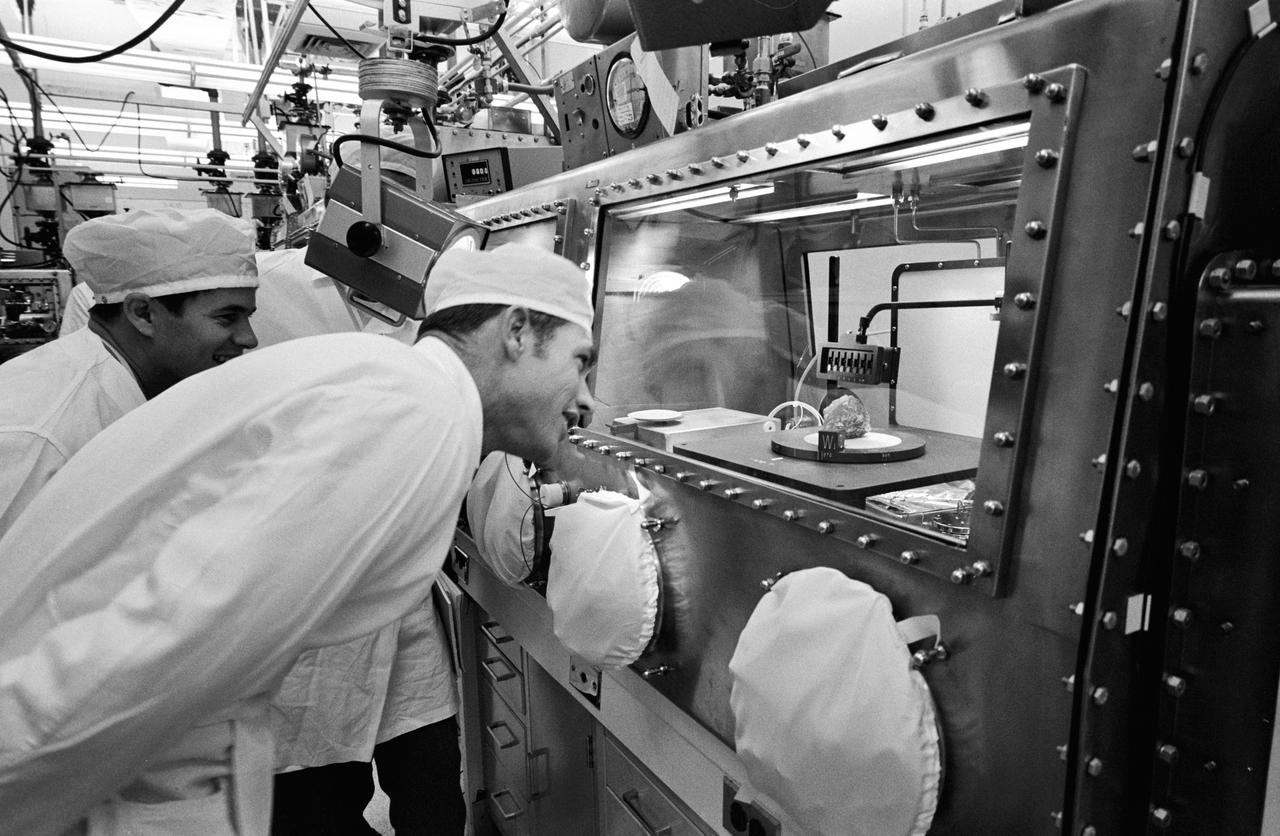

S71-43477 (12 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, right, commander of the Apollo 15 mission, gets a close look at the sample referred to as "Genesis rock" in the Non-Sterile Nitrogen Processing Line (NNPL) in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Allen IV, left, an Apollo 15 spacecraft communicator, looks on with interest. The white-colored rock has been given the permanent identification of 15415.
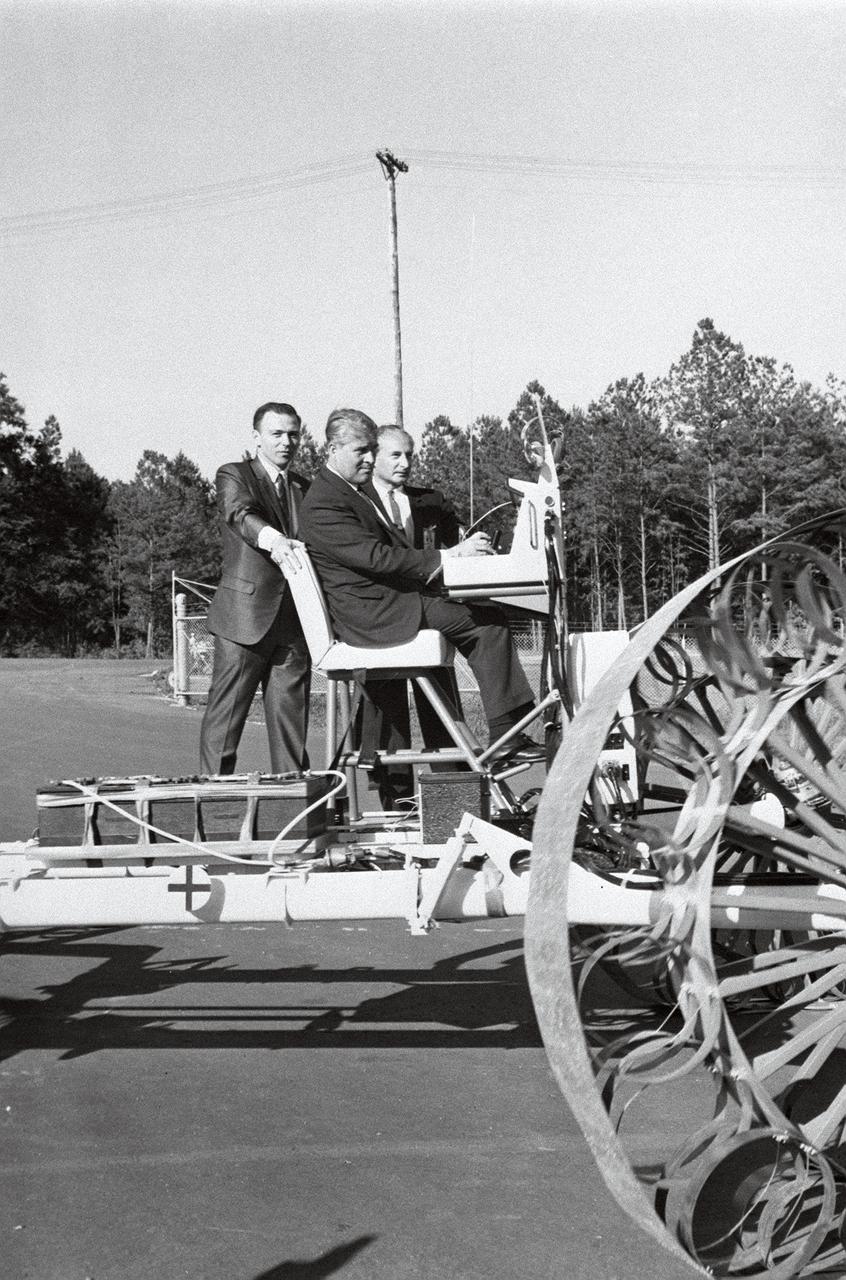

In this June 1966 photograph, Marshall Space Flight Center Director Dr. Wernher von Braun test-drives the Mobility Test Article (MTA), a developmental vehicle built by the Bendix Corporation to test lunar mobility vehicle concepts. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), developed under the direction of the MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions. The LRVs were deployed during the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.

SA-210 Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) awaits the launch scheduled on July 15, 1975 on the launch pad at the Kennedy Space Center, the ASTP mission with astronauts Thomas Stafford, Vance Brand, and Donald "Deke" Slayton. The Saturn IB, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), launched five manned Earth-orbital missions between 1968 and 1975: Apollo 7, Skylab 2, Skylab 3, Skylab 4, and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project .
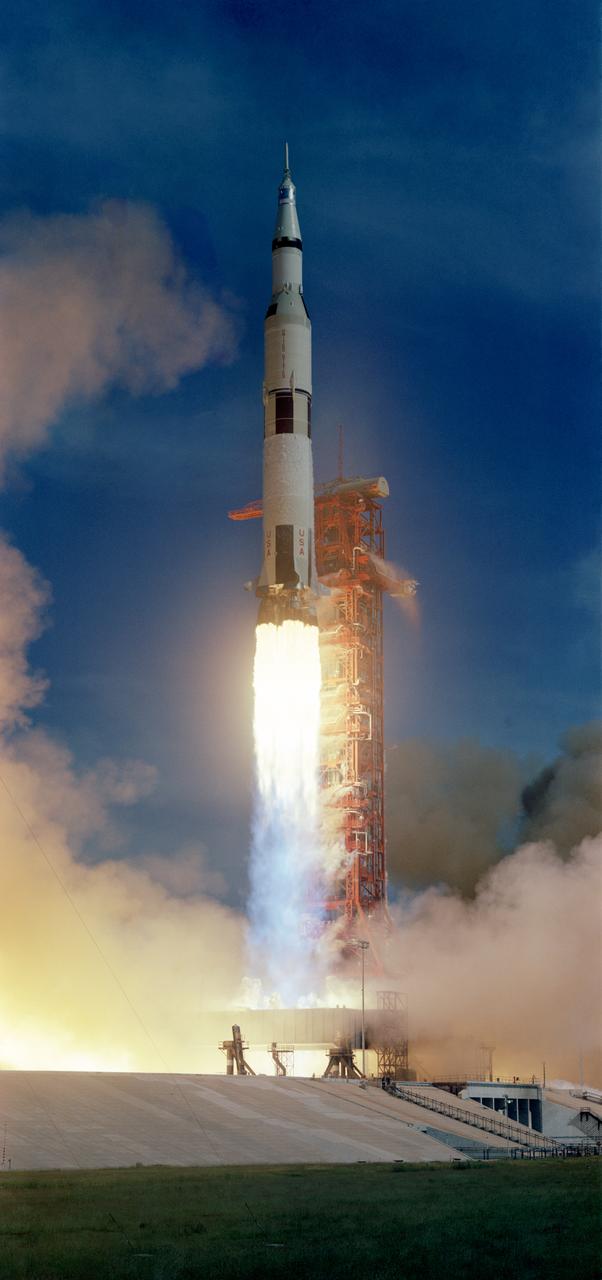

S71-41356 (26 July 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 15 (Spacecraft 112/Lunar Module 10/Saturn 510) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida, at 9:34:00:79 a.m. (EDT), July 26, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Aboard the Apollo 15 spacecraft were astronauts David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. Apollo 15 is the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) fourth manned lunar landing mission. While astronauts Scott and Irwin will descend in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Worden will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
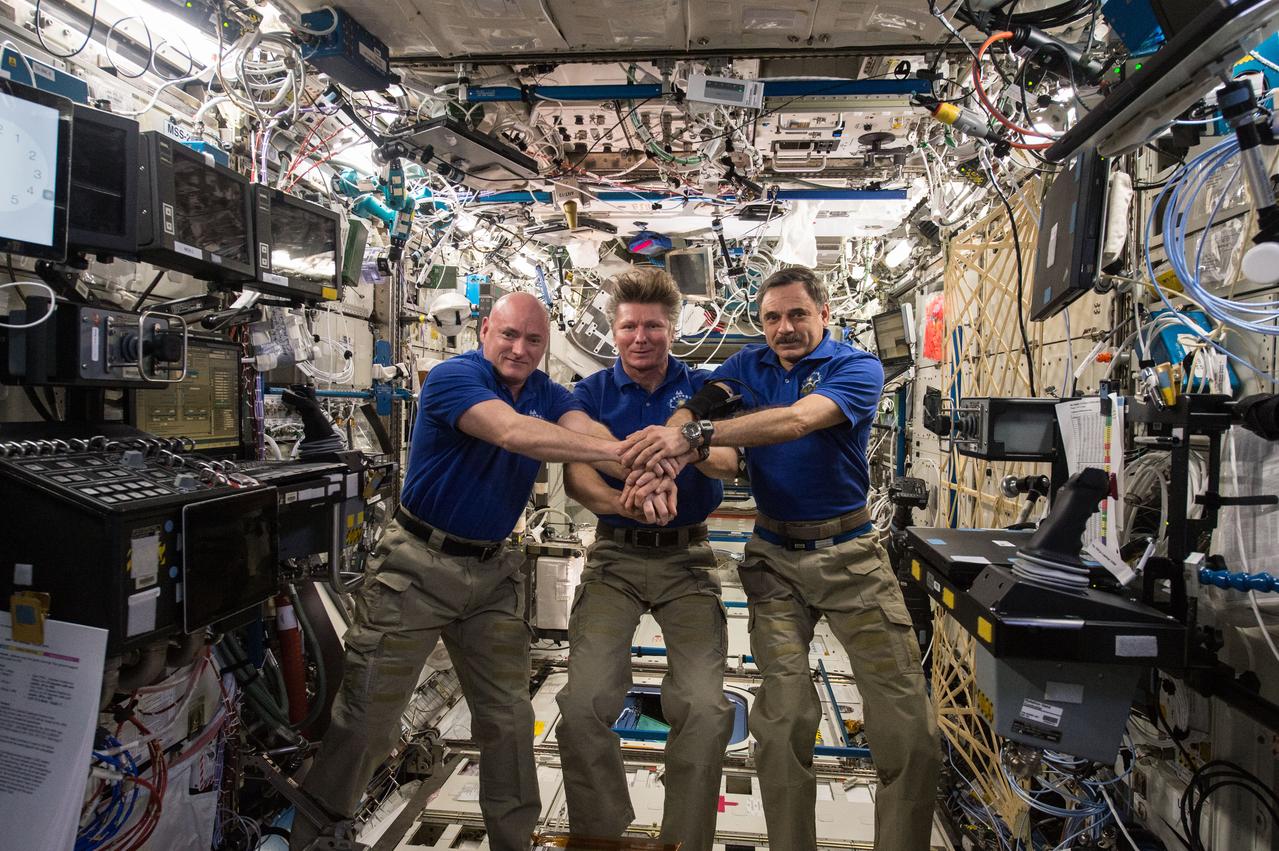

ISS044E013678 (07/15/2015) --- On July 15, 2015 aboard the International Space Station, Expedition 44 crew memebrs Scott Kelly of NASA (left), Expedition Commander and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (middle), and Russian cosmonaut Mikhail Kornienko (right) commemorated the 40th anniversary of the joint Apollo-Soyuz mission.
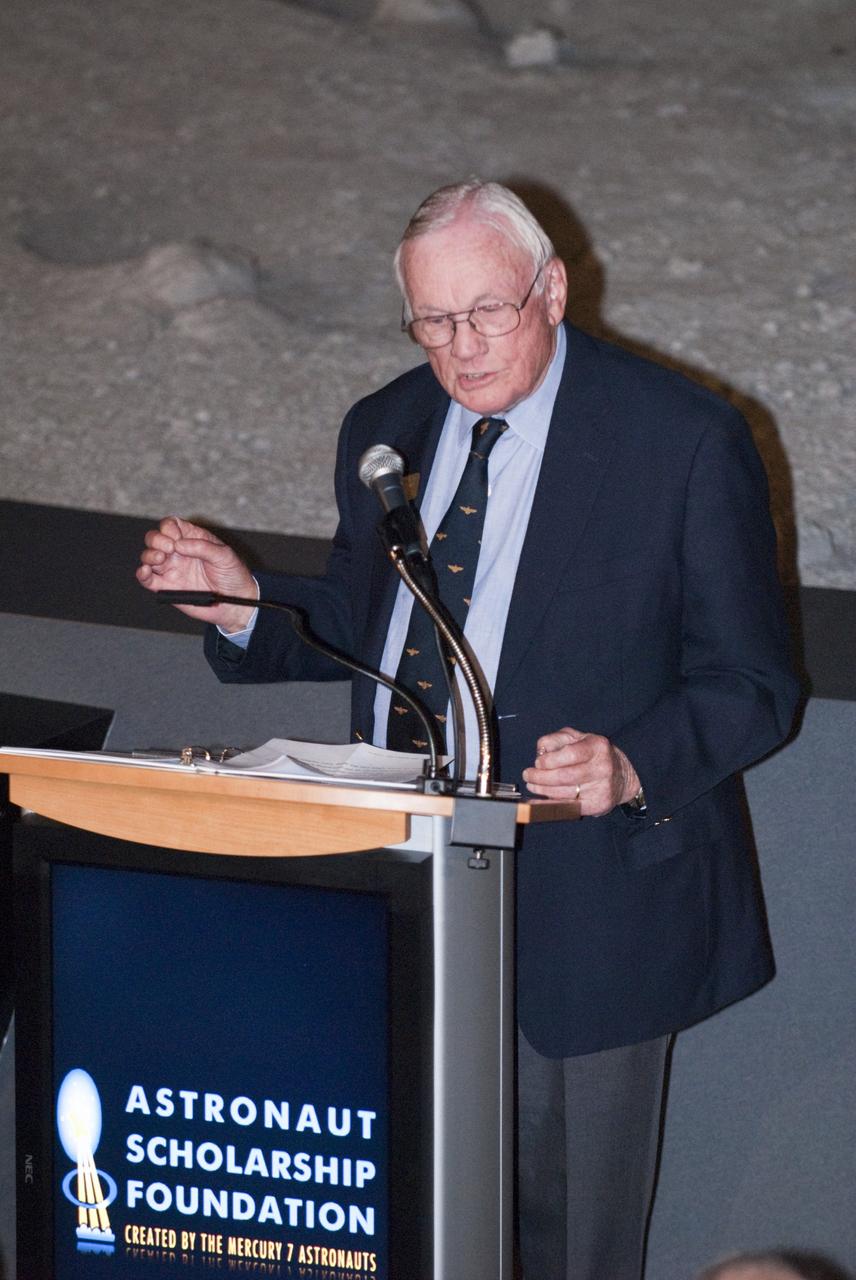

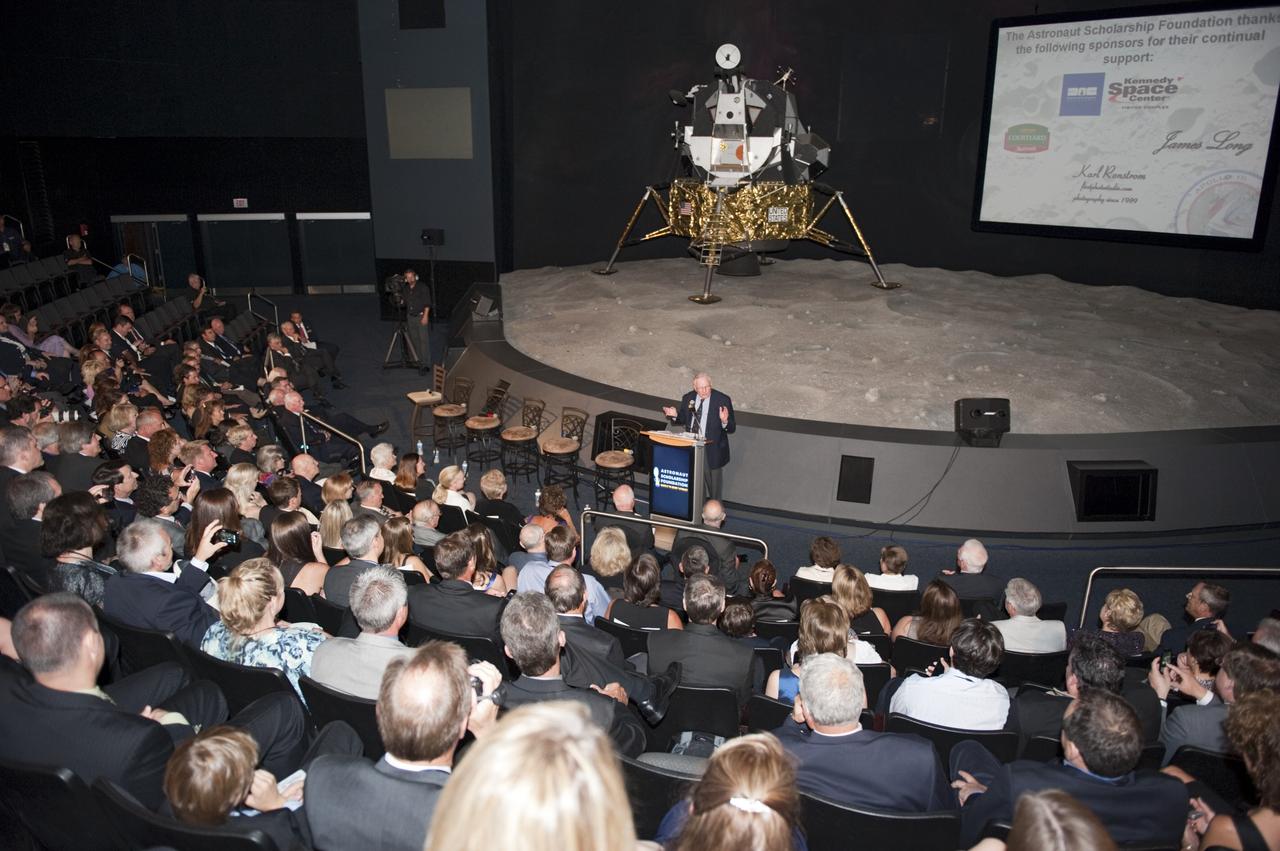
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a celebration on the 40th anniversary of NASA's Apollo 15 mission. Apollo 15 Commander Dave Scott, Command Module Pilot Al Worden and an elite gathering of Apollo-era astronauts were on hand for the event and panel discussion. Here, Apollo 11 Commander Neil Armstrong speaks to the invited guests. Worden circled the moon while Scott and the late Jim Irwin, the Lunar Module commander, made history when they became the first humans to drive a vehicle on the surface of the moon. They also provided extensive descriptions and photographic documentation of geologic features in the vicinity of the Hadley Rille landing site during their three days on the lunar surface. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a celebration on the 40th anniversary of NASA's Apollo 15 mission. Apollo 15 Commander Dave Scott, Command Module Pilot Al Worden and an elite gathering of Apollo-era astronauts were on hand for the event and panel discussion. Here, Apollo 16 Lunar Module Pilot Charlie Duke welcomes the invited guests and introduces the guests of honor. Worden circled the moon while Scott and the late Jim Irwin, the Lunar Module commander, made history when they became the first humans to drive a vehicle on the surface of the moon. They also provided extensive descriptions and photographic documentation of geologic features in the vicinity of the Hadley Rille landing site during their three days on the lunar surface. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
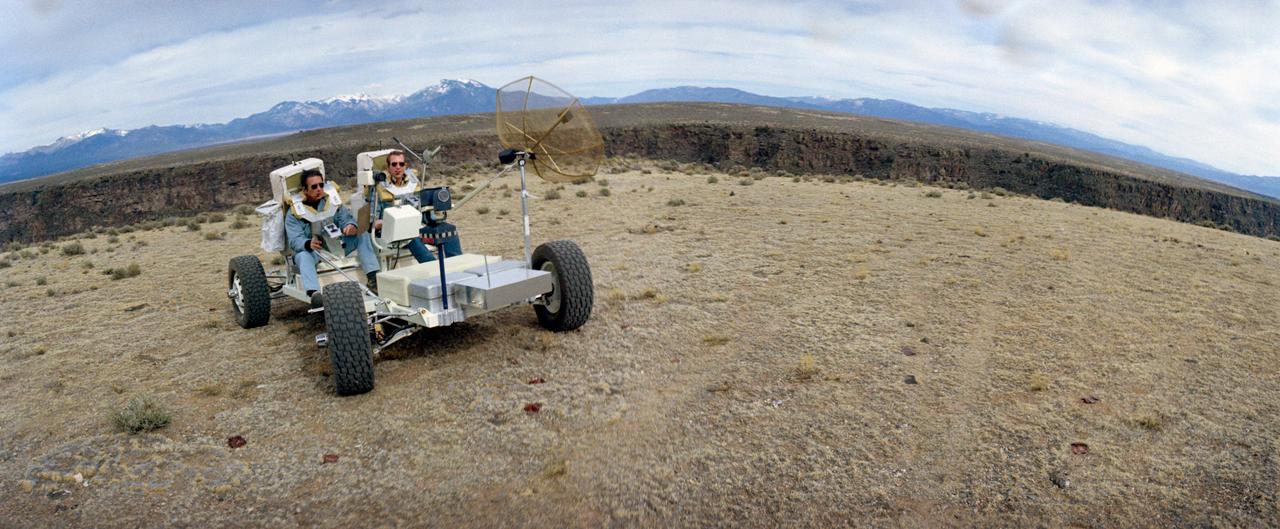

S71-23774 (11-12 March 1971) --- A wide-angle view showing two members of the prime crew of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission riding in a Lunar Roving Vehicle trainer called "Grover" during a simulation of lunar surface extravehicular activity in the Taos, New Mexico area. They are astronauts David R. Scott (riding in left side seat), commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. Apollo 15 will be the first mission to the moon to carry a Lunar Roving Vehicle, which will permit the astronauts to cover a larger area for exploration and sample collecting than on previous missions.
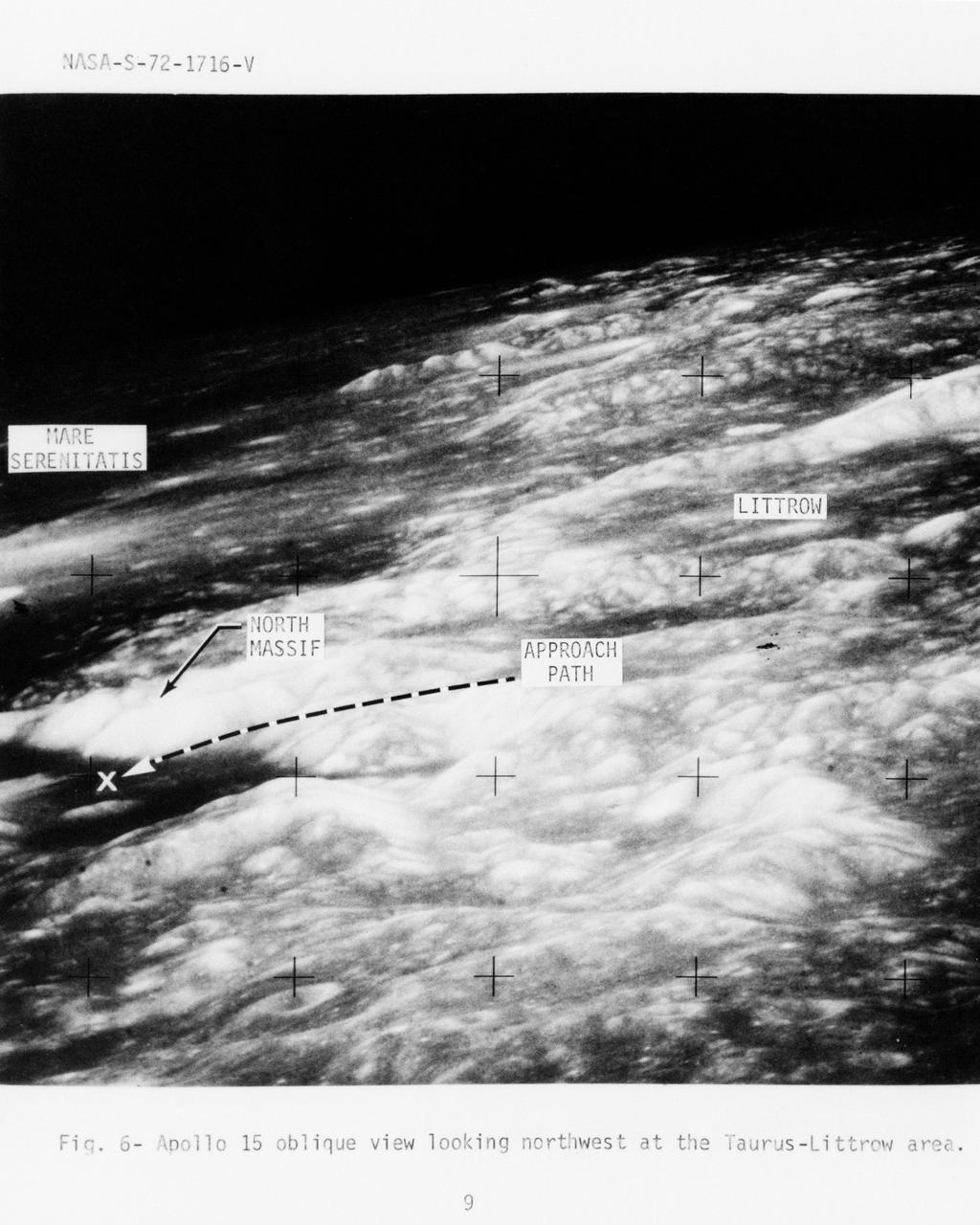
S72-01716 (July 1972) --- An oblique view of the Taurus-Littrow area on the lunar nearside, as photographed from the Apollo 15 spacecraft in lunar orbit. This is an enlarged view. The "X" marks the landing site of the scheduled Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. The overlay points out several features in the photograph. The coordinates of the Apollo 17 touchdown point are 30 degrees 44 minutes 58 seconds east longitude and 20 degrees 9 minutes 50 seconds north latitude.
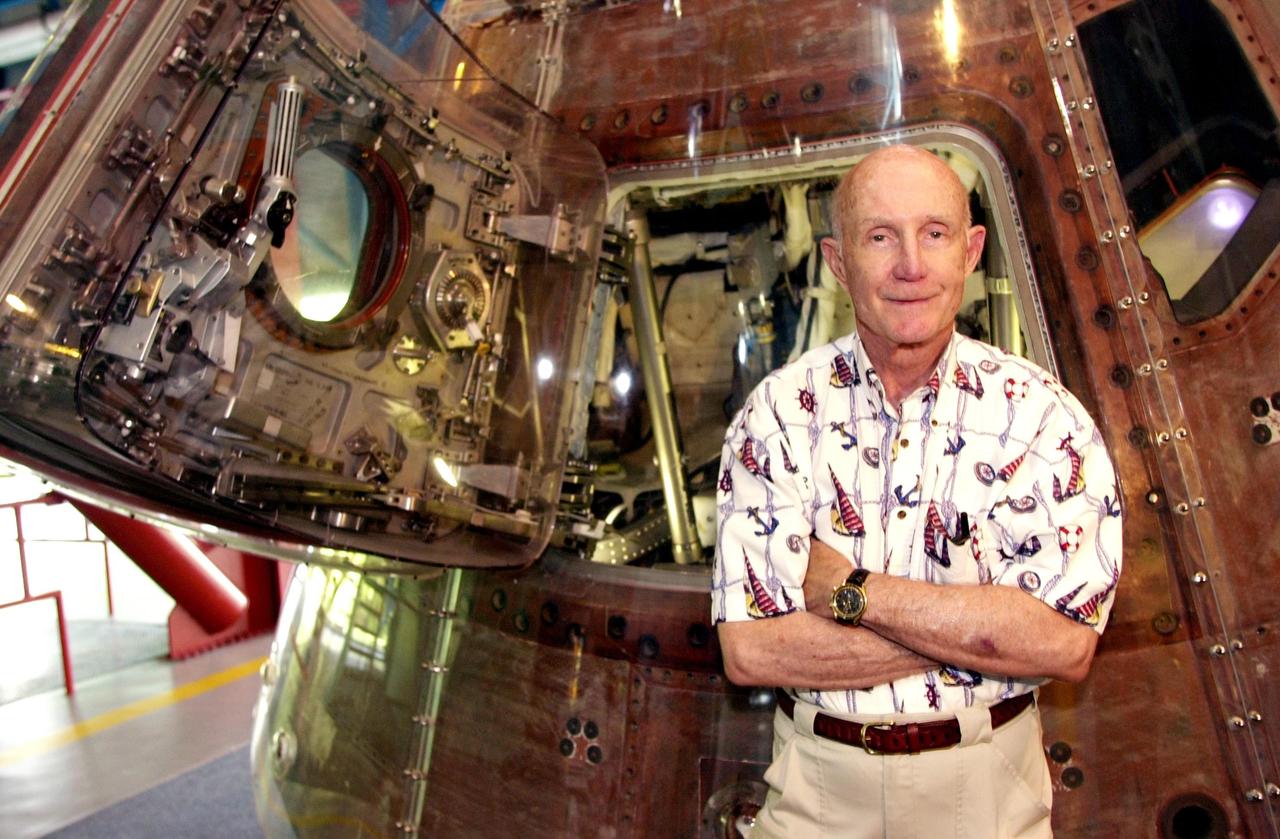

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Former astronaut Thomas Staford visits KSC, shown here at the Apollo Saturn V Center. He is standing in front of the module he flew Stafford logged his fourth space flight as Apollo commander of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) mission, July 15-24, 1975, a joint space flight culminating in the historic first meeting in space between American astronauts and Soviet cosmonauts.
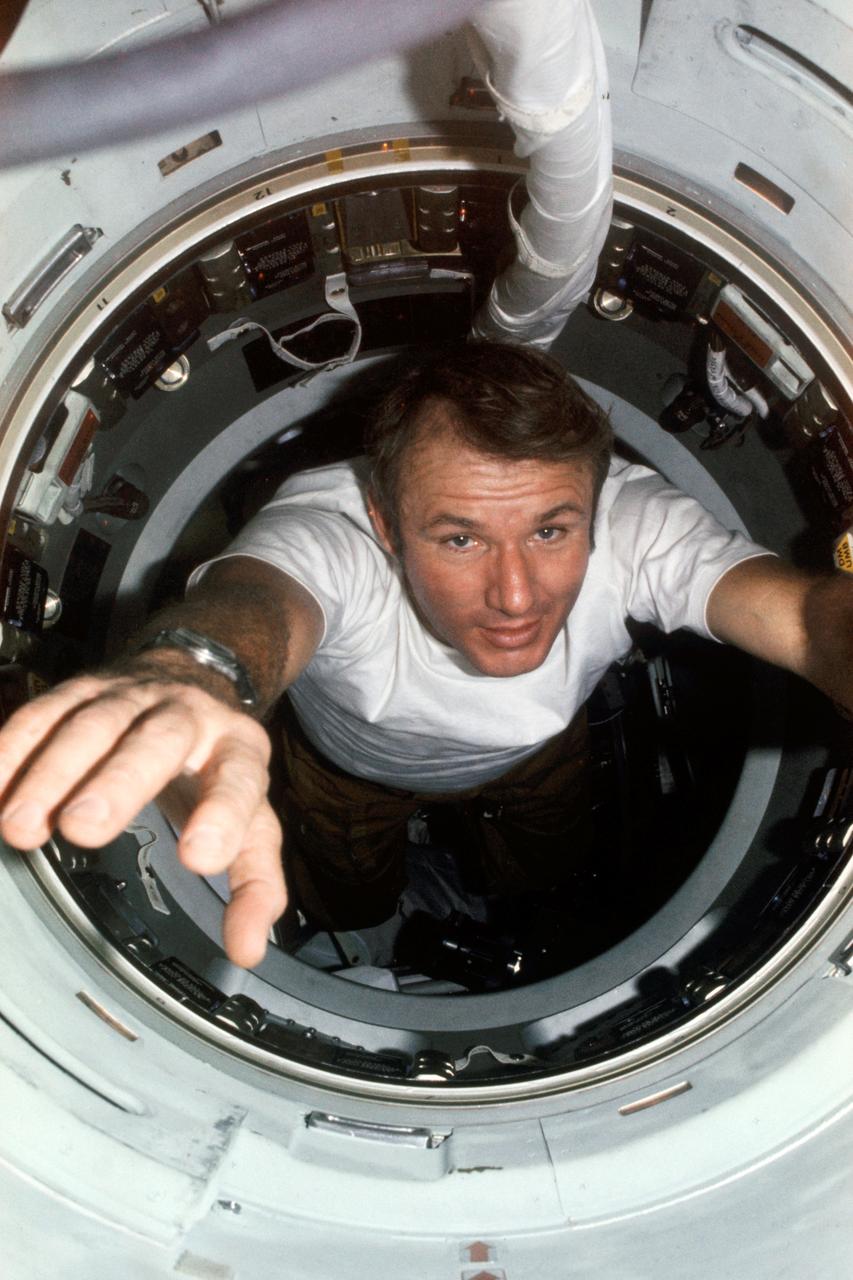

AST-06-318 (15-24 July 1975) --- Astronaut Vance D. Brand, command module pilot of the American ASTP crew, is seen in the hatchway leading from the Apollo Command Module (CM) into the Apollo Docking Module (DM) during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. The 35mm camera is looking from the DM into the CM.
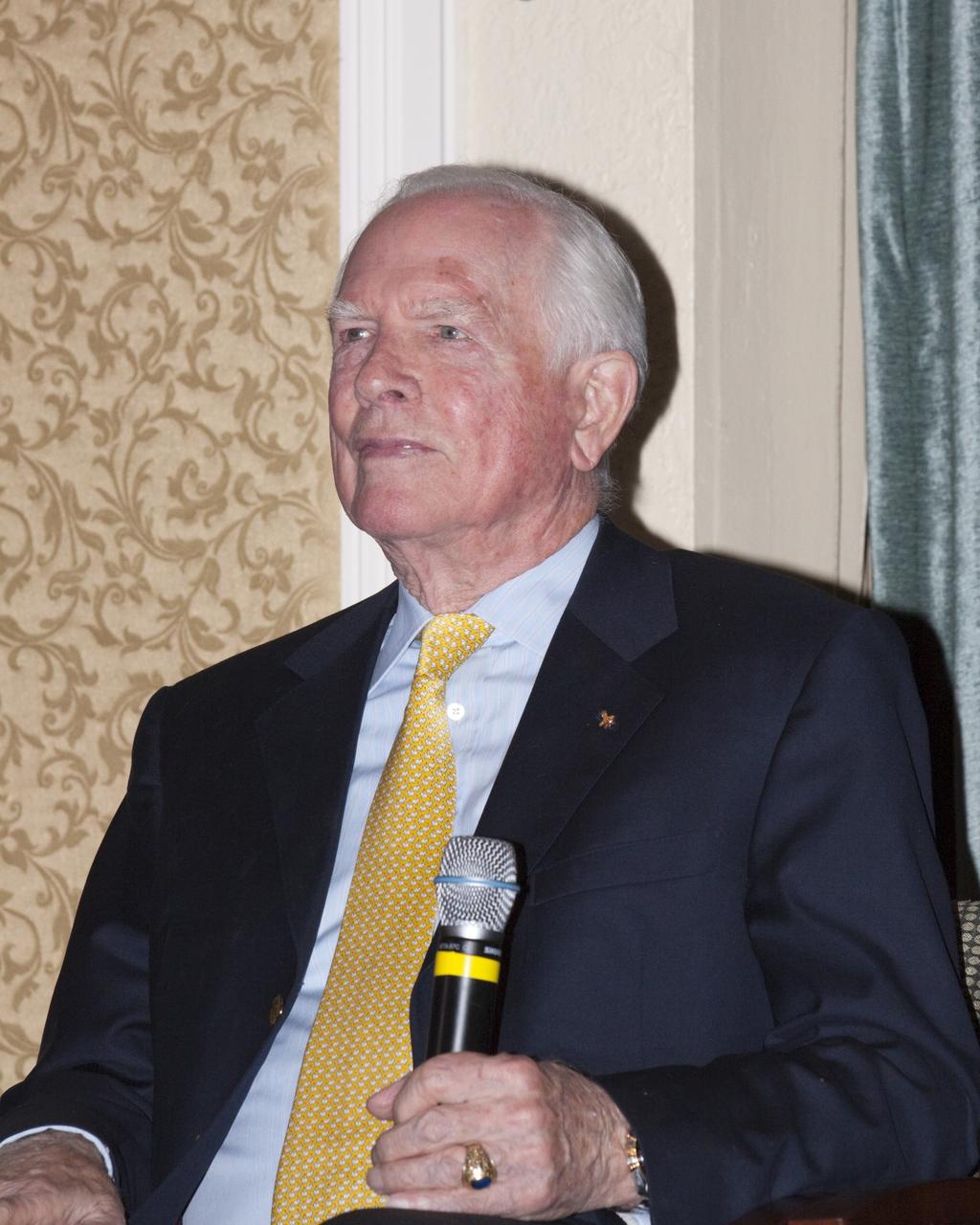

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Gemini 8, Apollo 9 and 15 astronaut David Scott speaks to guests gathered for the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation's dinner at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral celebrating the 40th anniversary of Apollo 17. The gala commemorating the anniversary of Apollo 17 included mission commander Eugene Cernan and other astronauts who flew Apollo missions. Launched Dec. 7, 1972, Cernan and lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt landed in the moon's Taurus-Littrow highlands while command module pilot Ronald Evans remained in lunar orbit operating a scientific instrument module. For more information, visit http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/history/apollo/apollo-17/apollo-17.htm Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
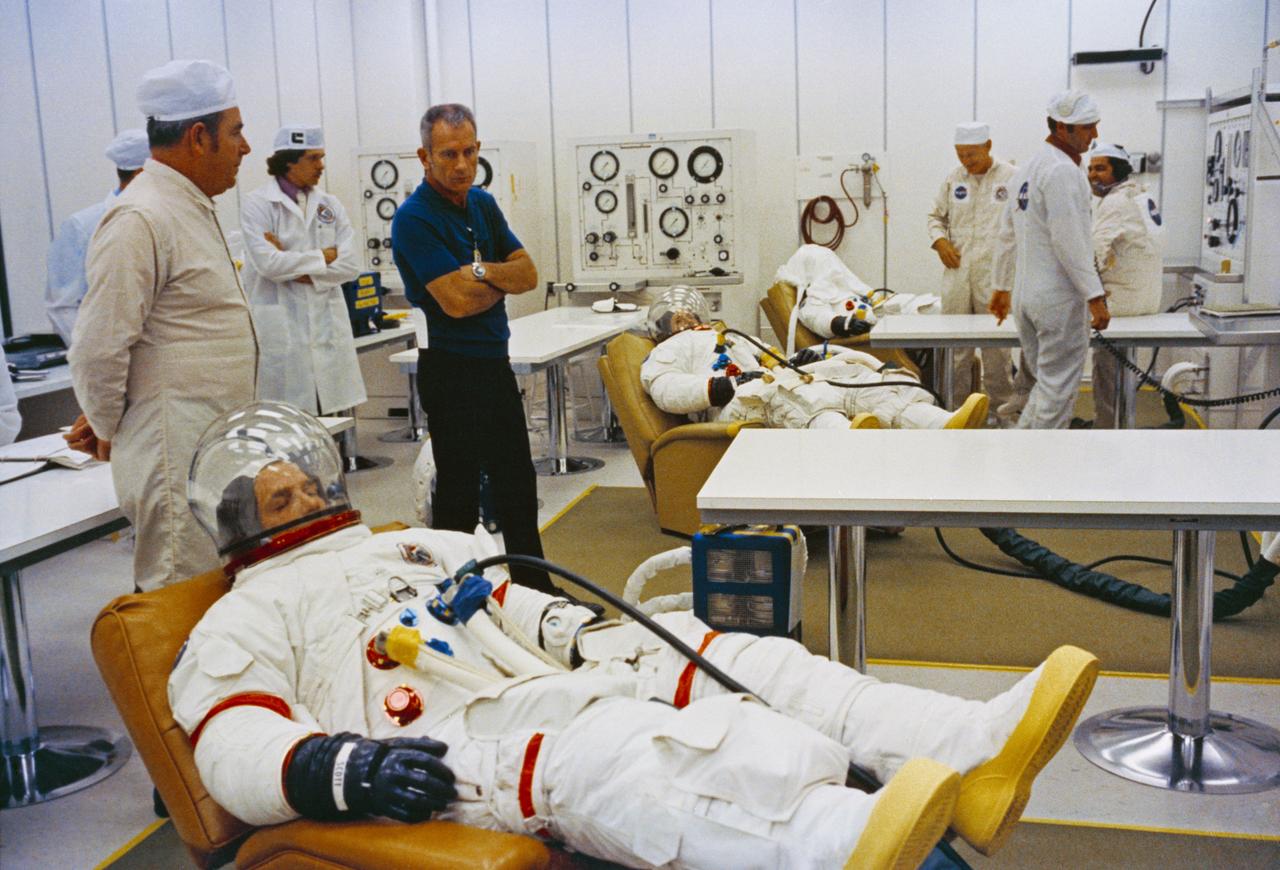

S71-41408 (26 July 1971) --- The three Apollo 15 astronauts go through suiting up operations in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Manned Spacecraft Operations Building (MSOB) during the Apollo 15 prelaunch countdown. They are David R. Scott (foreground), commander; Alfred M. Worden (center), command module pilot; and James B. Irwin (background), lunar module pilot. Minutes later the crew rode a special transport van over to Pad A, Launch Complex 39, where their spacecraft awaited them. With the crew was Dr. Donald (Deke) K. Slayton (wearing dark blue sport shirt), director of Flight Crew Operations, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The Apollo 15 space vehicle was launched at 9:34:00:79 a.m. (EDT), July 26, 1971, on a lunar landing mission.
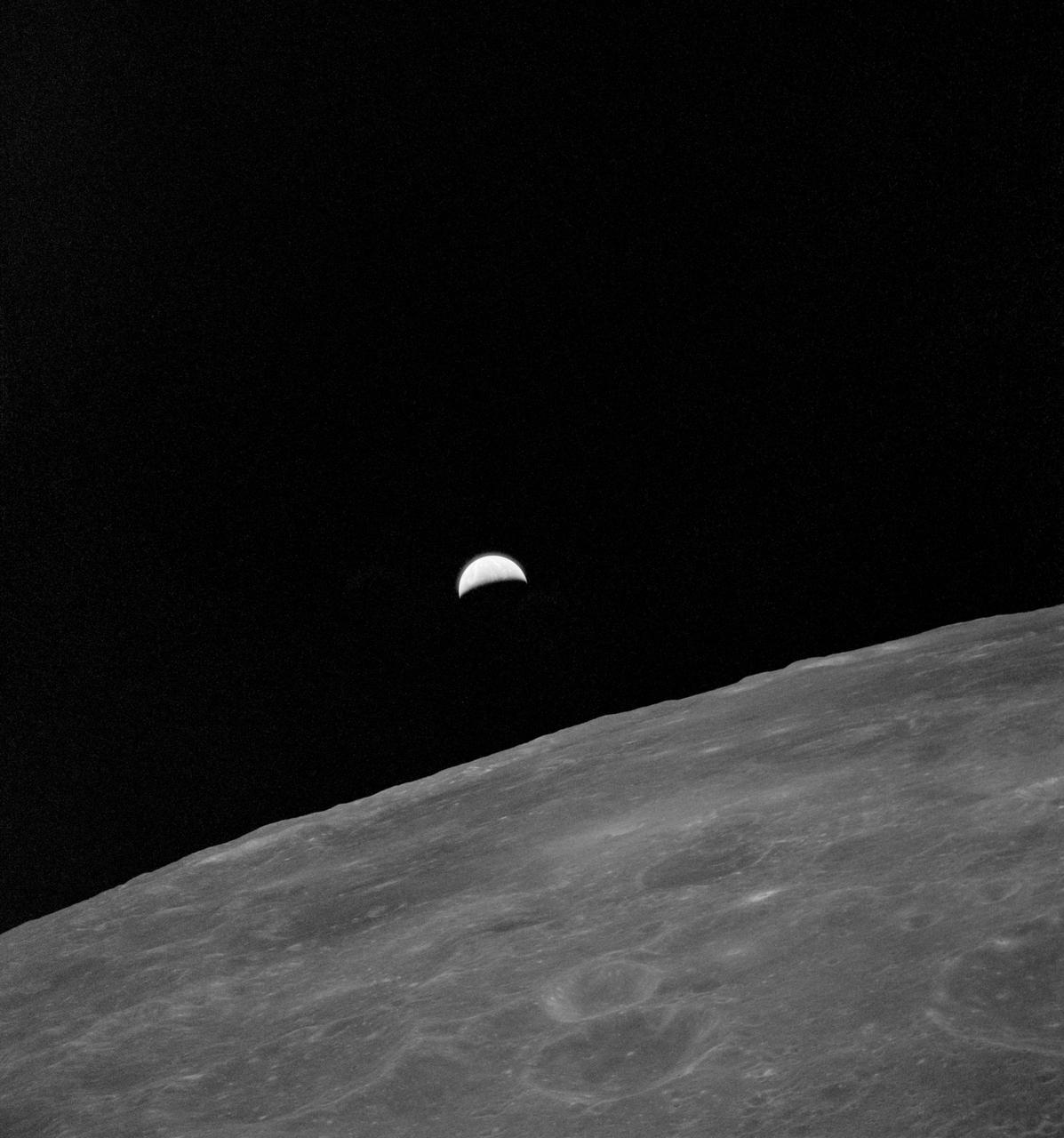

AS15-99-13445 (31 July 1971) --- This ultra violet picture of Earth rising over the lunar surface was taken from the Command Module (CM) Endeavor during the 24th revolution of the moon. Astronaut Alfred M. Worden Jr., Apollo 15 command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon. Photo credit: NASA
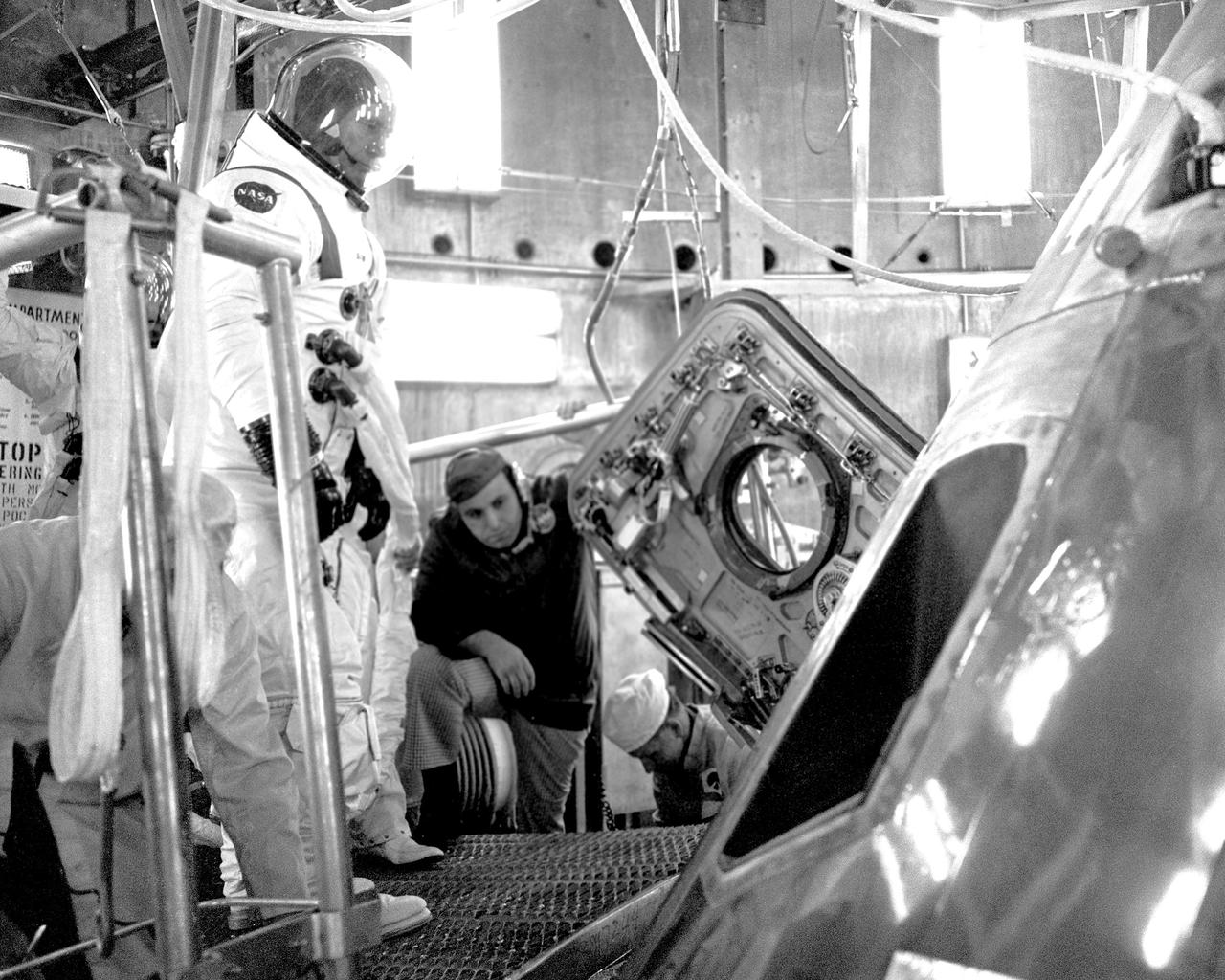

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The docking module and Apollo spacecraft for this summer's joint manned mission with the Soviet were mated in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building today. The docking module will provide a mechanical and electrical link between the Apollo and Soyuz spacecraft while they are docked and also serve as an airlock. On hand to participate in the operation were two members of the Apollo prime crew, Astronauts Donald K. Slayton and Vance D. Brand. Launch of the Saturn 1B/Apollo from Complex 39 is scheduled for July 15. The first international crewed spaceflight was a joint U.S.-U.S.S.R. rendezvous and docking mission. The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, or ASTP, took its name from the spacecraft employed: the American Apollo and the Soviet Soyuz. The three-man Apollo crew lifted off from Kennedy Space Center aboard a Saturn IB rocket on July 15, 1975, to link up with the Soyuz that had launched a few hours earlier. A cylindrical docking module served as an airlock between the two spacecraft for transfer of the crew members. Photo credit: NASA
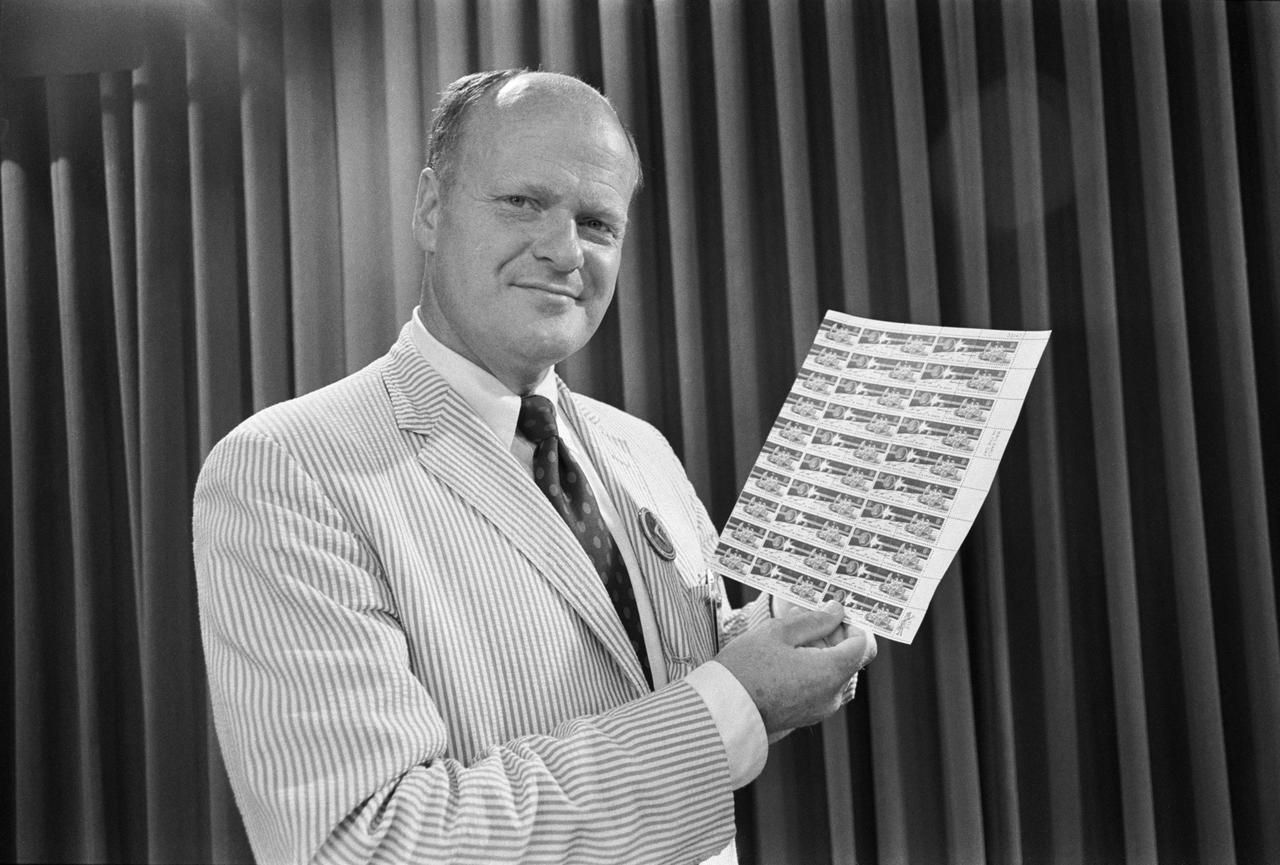

S71-41694 (2 Aug. 1971) --- Artist Robert McCall of Paradise Valley, Arizona, holds a sheet of commemorative postage stamps commemorating the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission. McCall was chose by the U.S. Postal Service to design the eight-cent stamp which heralds: "United States in Space -- A Decade of Achievement." McCall, who has maintained a close tie with the space program for many years, has been commissioned by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration to portray Apollo 15 activities from the Mission Control Center at the Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston, Texas.

S71-22401 (March 1971) --- These three astronauts have been named by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as the prime crew members of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission. They are, left to right, David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. The crew is posed behind the subsatellite that they will deploy from the lunar surface during the Apollo 15 mission. Astronauts Scott and Irwin will descend in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, while astronaut Worden will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
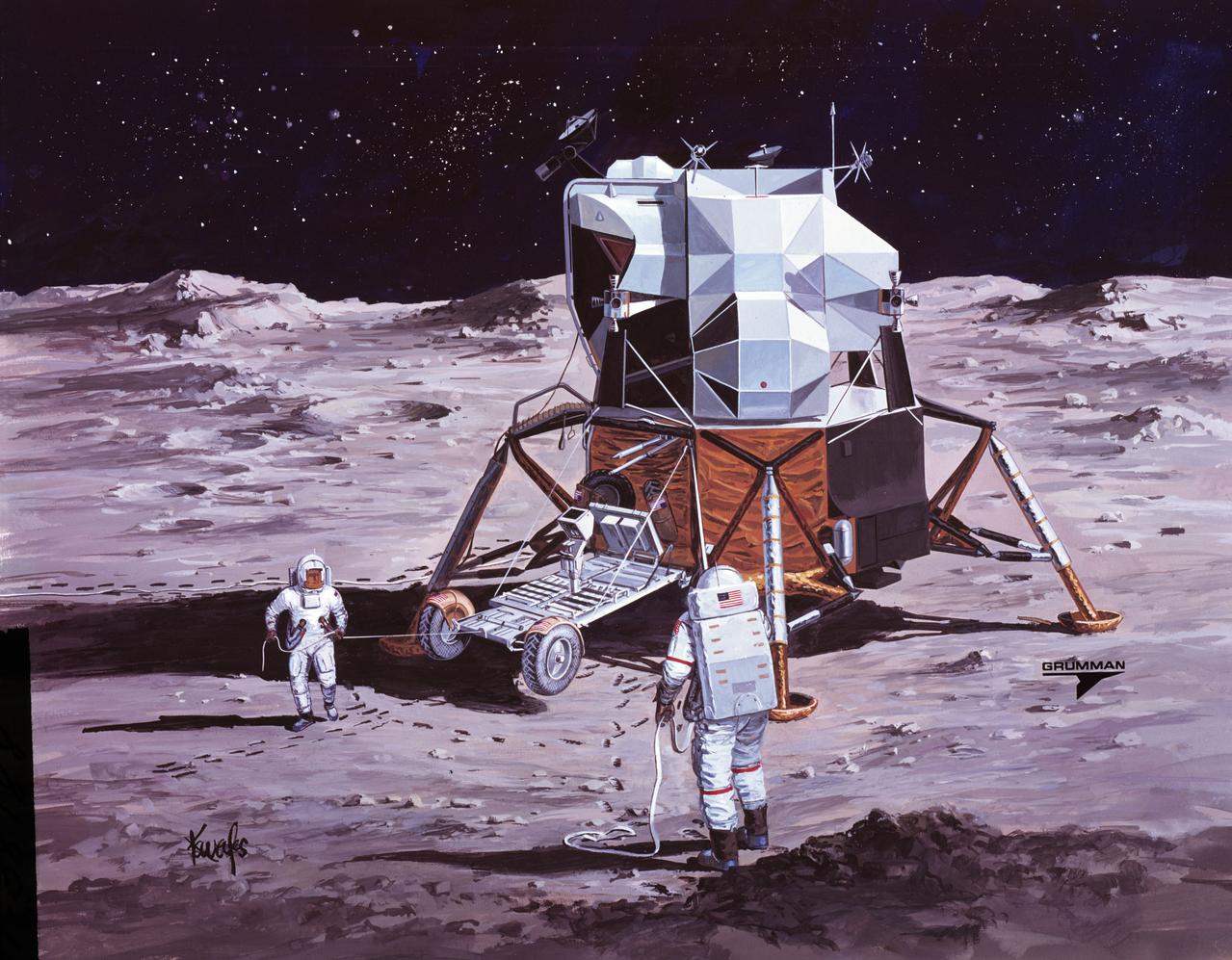
S71-38188 (26 June 1971) --- An artist's concept showing the Apollo 15 mission commander and the lunar module pilot performing deployment of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the lunar surface. The figure on the left represents astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, who here is maintaining a constant pull on the deployment cable to help the LRV unfold, while astronaut David R. Scott (right), commander, pulls the tapes that lower the LRV to the surface. (This is the third in a series of Grumman Aerospace Corporation artist's concepts telling the lunar surface LRV deployment story of the Apollo 15 mission).
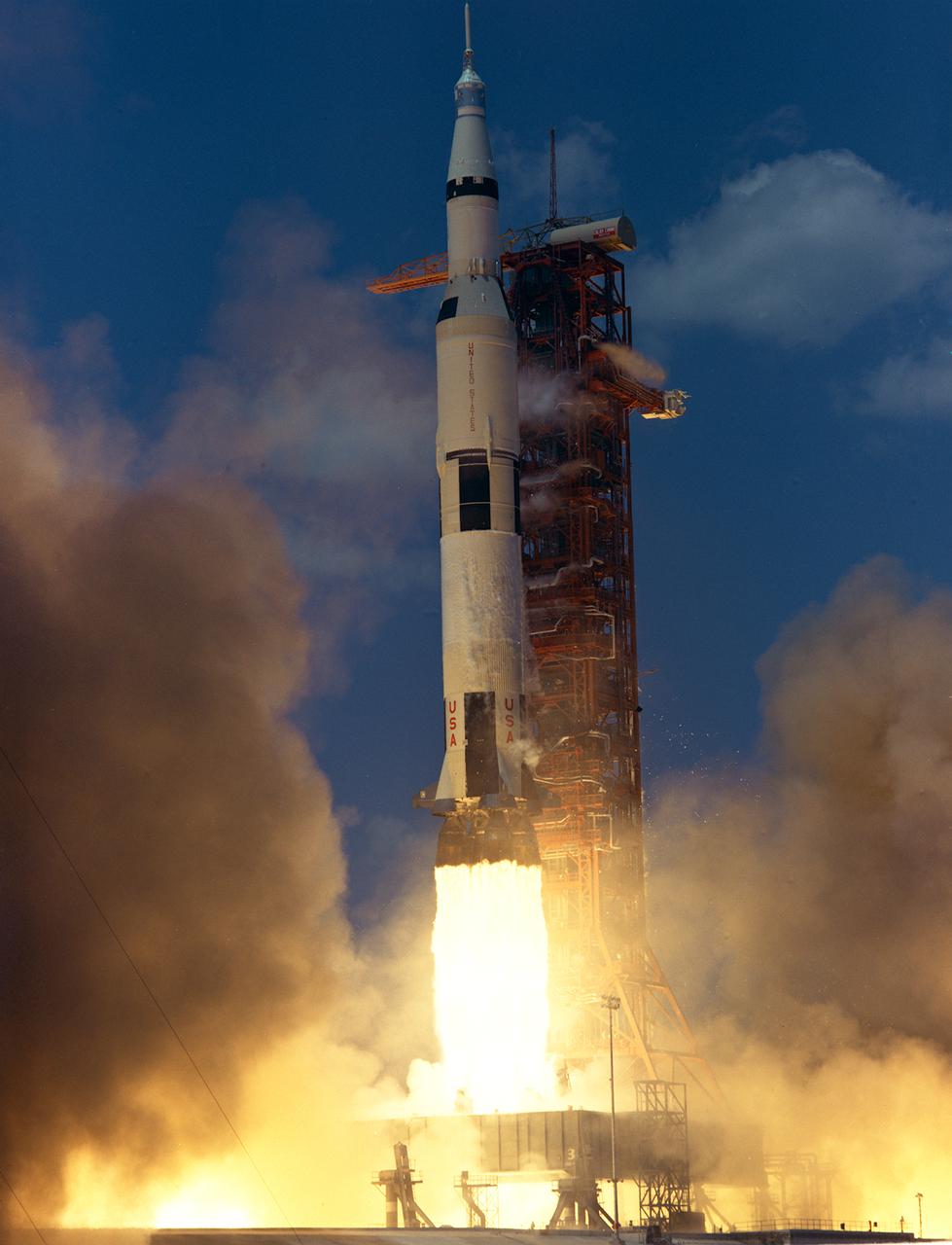

The sixth marned lunar landing mission, the Apollo 16 (SA-511), carrying three astronauts: Mission commander John W. Young, Command Module pilot Thomas K. Mattingly II, and Lunar Module pilot Charles M. Duke, lifted off on April 16, 1972. The Apollo 16 continued the broad-scale geological, geochemical, and geophysical mapping of the Moon's crust, begun by the Apollo 15, from lunar orbit. This mission marked the first use of the Moon as an astronomical observatory by using the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph. It photographed ultraviolet light emitted by Earth and other celestial objects. The Lunar Roving Vehicle was also used. The mission ended on April 27, 1972.
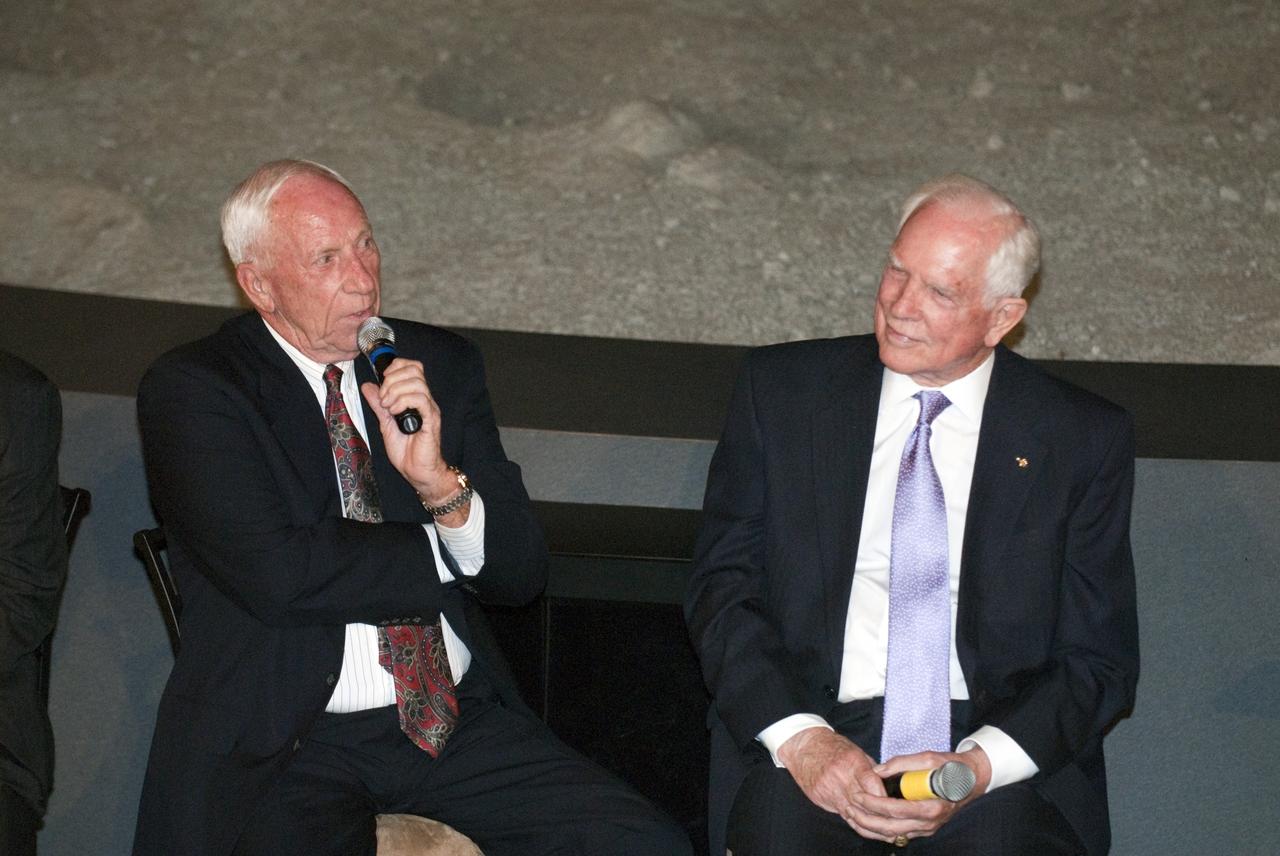

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a celebration on the 40th anniversary of NASA's Apollo 15 mission. Apollo 15 Commander Dave Scott (right) and Command Module Pilot Al Worden and an elite gathering of Apollo-era astronauts were on hand for the event and panel discussion. Worden circled the moon while Scott and the late Jim Irwin, the Lunar Module commander, made history when they became the first humans to drive a vehicle on the surface of the moon. They also provided extensive descriptions and photographic documentation of geologic features in the vicinity of the Hadley Rille landing site during their three days on the lunar surface. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a celebration on the 40th anniversary of NASA's Apollo 15 mission. Apollo 15 Commander Dave Scott and Command Module Pilot Al Worden and an elite gathering of Apollo-era astronauts were on hand for the event and panel discussion. Here, Al Worden with microphone in hand, speaks to the invited guests. Worden circled the moon while Scott and the late Jim Irwin, the Lunar Module commander, made history when they became the first humans to drive a vehicle on the surface of the moon. They also provided extensive descriptions and photographic documentation of geologic features in the vicinity of the Hadley Rille landing site during their three days on the lunar surface. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
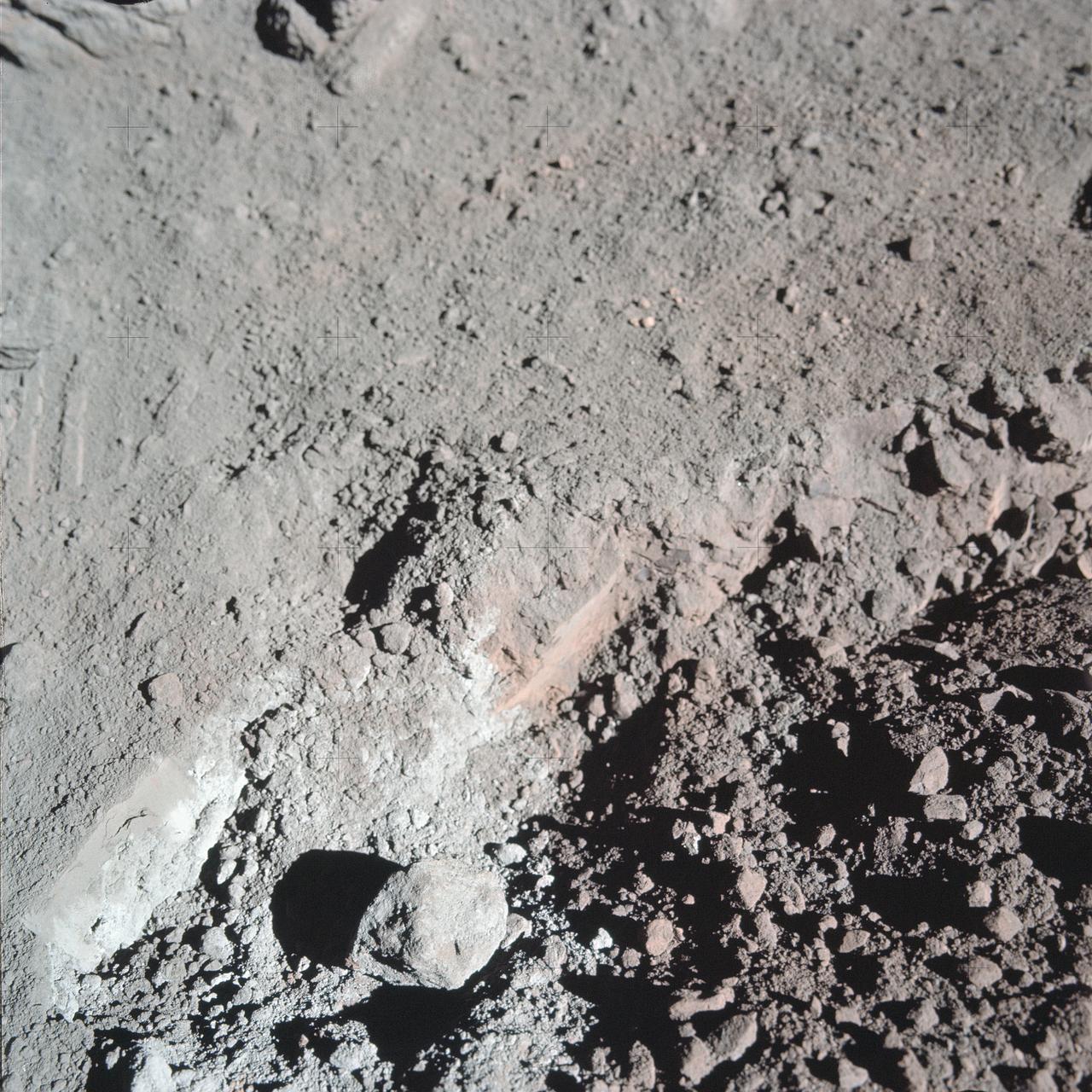

AS17-137-20989 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A close-up view of the much-publicized orange soil which the Apollo 17 crewmen found at Station 4 (Shorty Crater) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The orange soil was first spotted by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt. While astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The orange soil was never seen by the crewmen of the other lunar landing missions - Apollo 11 (Sea of Tranquility); Apollo 12 (Ocean of Storms); Apollo 14 (Fra Mauro); Apollo 15 (Hadley-Apennines); and Apollo 16 (Descartes).

S71-30463 (May 1971) --- This is the insignia designed for the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission. The circular design features the colors red, white and blue. On the outer portion of the patch a narrow band of blue and a narrow band of red encircle a wider band of white. The large disc in the center of the emblem has red, white and blue symbols of flight, superimposed over an artist's concept of the Apollo 15 Hadley-Apennine landing site of gray tone. The surnames of the three names are centered in the white band at the bottom of the insignia. The Apollo 15 prime crew men are David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. This is the official Apollo 15 emblem, property of the government of the United States. It has been authorized only for use by the astronauts. Its production in any form other than in news, information and education media is not authorized without approval. Unauthorized use of the photograph is subject to the provisions of Title 18, U.S. Code, Section 701.

S71-39357 (July 1971) --- A photographic replica of the plaque which the Apollo 15 astronauts will leave behind on the moon during their lunar landing mission. Astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot; will descend to the lunar surface in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon". Astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The seven by nine inch stainless steel plaque will be attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the LM's descent stage. Commemorative plaques were also left on the moon by the Apollo 11, Apollo 12 and Apollo 14 astronauts.

Apollo-Soyuz Test Project: The first international crewed spaceflight was a joint U.S.-U.S.S.R. rendezvous and docking mission. The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, or ASTP, took its name from the spacecraft employed: the American Apollo and the Soviet Soyuz. The three-man Apollo crew lifted off from Kennedy Space Center aboard a Saturn IB rocket on July 15, 1975, to link up with the Soyuz that had launched a few hours earlier. A cylindrical docking module served as an airlock between the two spacecraft for transfer of the crew members. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
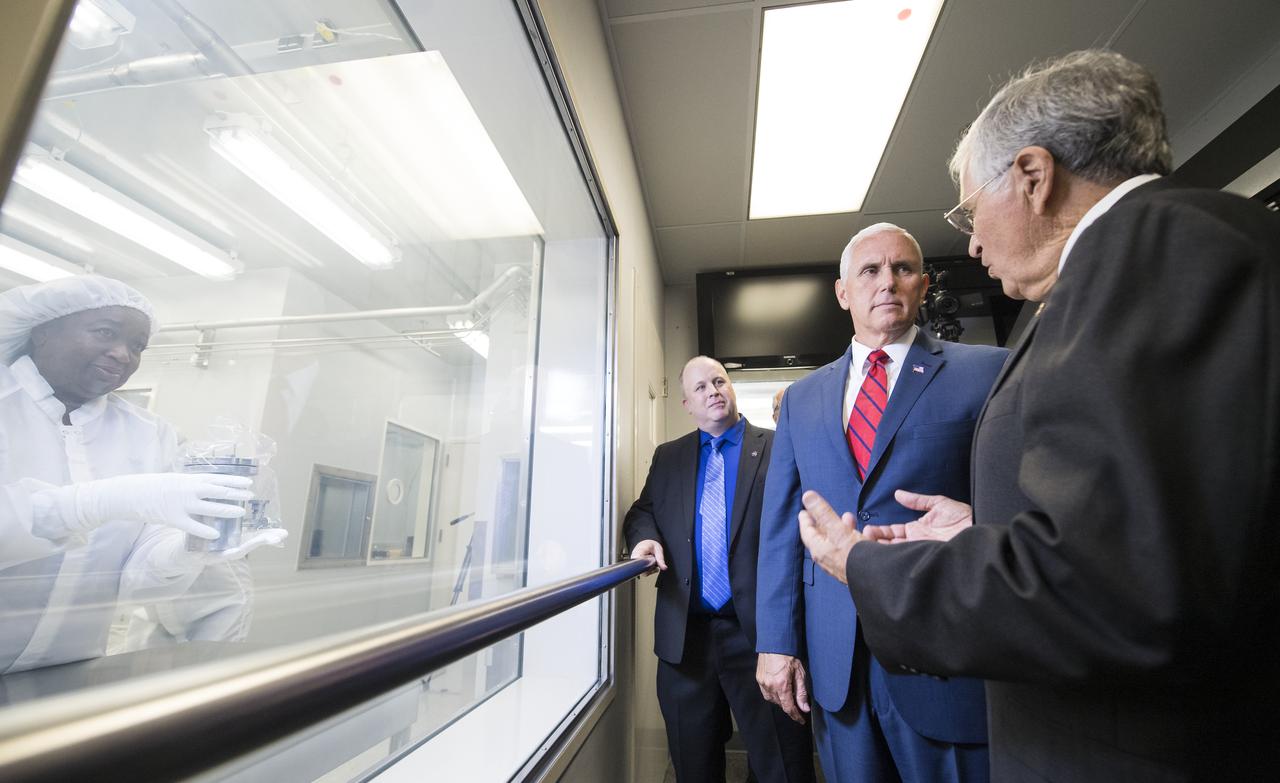

Vice President Mike Pence, center, views Sample 15014, which was collected during Apollo 15 with NASA's Apollo Sample Curator Ryan Zeigler, left, and Apollo 17 astronaut and geologist Dr. Harrison Schmitt, right, in Lunar Curation Laboratory at NASA's Johnson Space Center, Thursday, Aug. 23, 2018 in Houston, Texas. Sample 15014 is one of nine samples out of the 2,196 collected during the Apollo missions that was sealed inside its container on the Moon and still containes gasses from the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
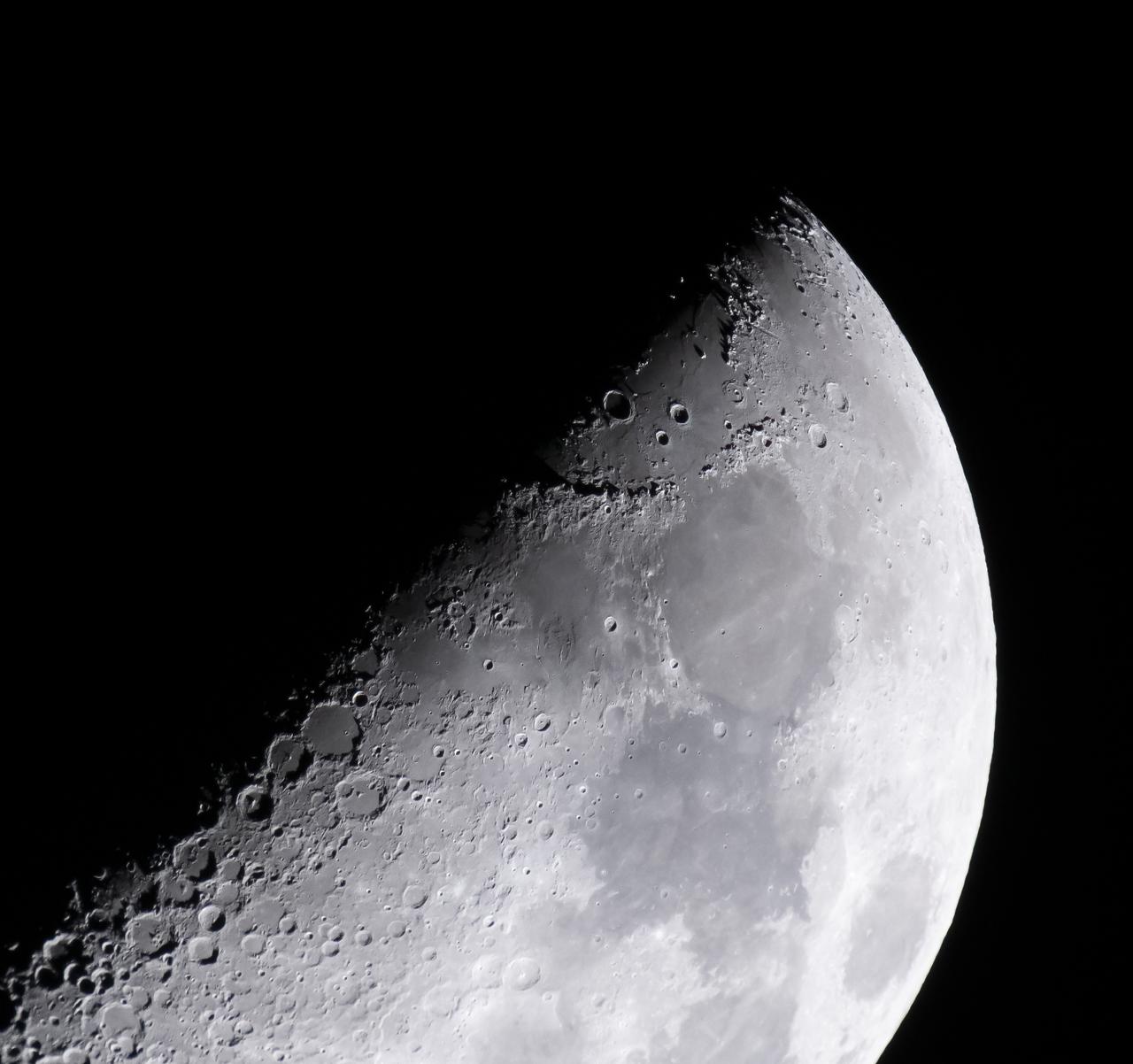

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems’ Program Manager Shawn Quinn captured this image of the Hadley–Apennine region of the moon including the Apollo 15 landing site (very near the edge of the shadow of one of the lunar mountains in the area). Image is a crop of a full frame image. Apollo 11, 16 and 17 landing sites are also visible in this image. Hadley–Apennine is a region on the near side of Earth's Moon that served as the landing site for the American Apollo 15 mission, the fourth crewed landing on the Moon and the first of the "J-missions", in July 1971. The site is located on the eastern edge of Mare Imbrium on a lava plain known as Palus Putredinis. Hadley–Apennine is bordered by the Montes Apenninus (often referred to as "Apennine Front"), a mountain range, and Hadley Rille, a meandering channel, on the east and west, respectively.
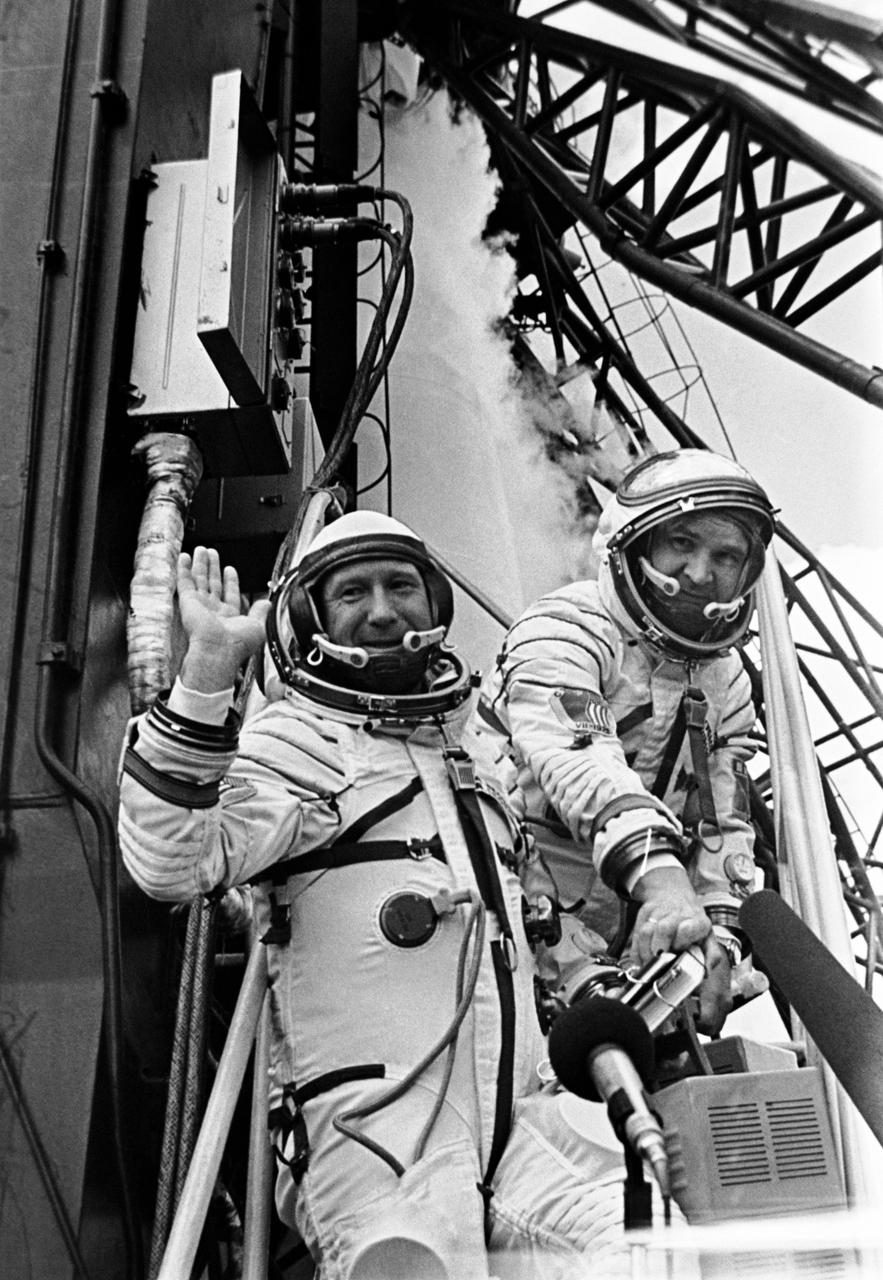

S75-32343 (15 July 1975) --- The two Soviet crewmen for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission are photographed at the launch pad at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on the morning of the Soviet ASTP liftoff on July 15, 1975. They are cosmonauts Aleksey A. Leonov (left), commander; and Valeriy N. Kubasov, flight engineer. Leonov is waving to well-wishers at the launch pad. The Soviet ASTP launch preceded the American ASTP Apollo liftoff by seven and one-half hours. The American and Soviet spacecraft were docked in Earth orbit for a total of about 47 hours on July 17-19, 1975. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
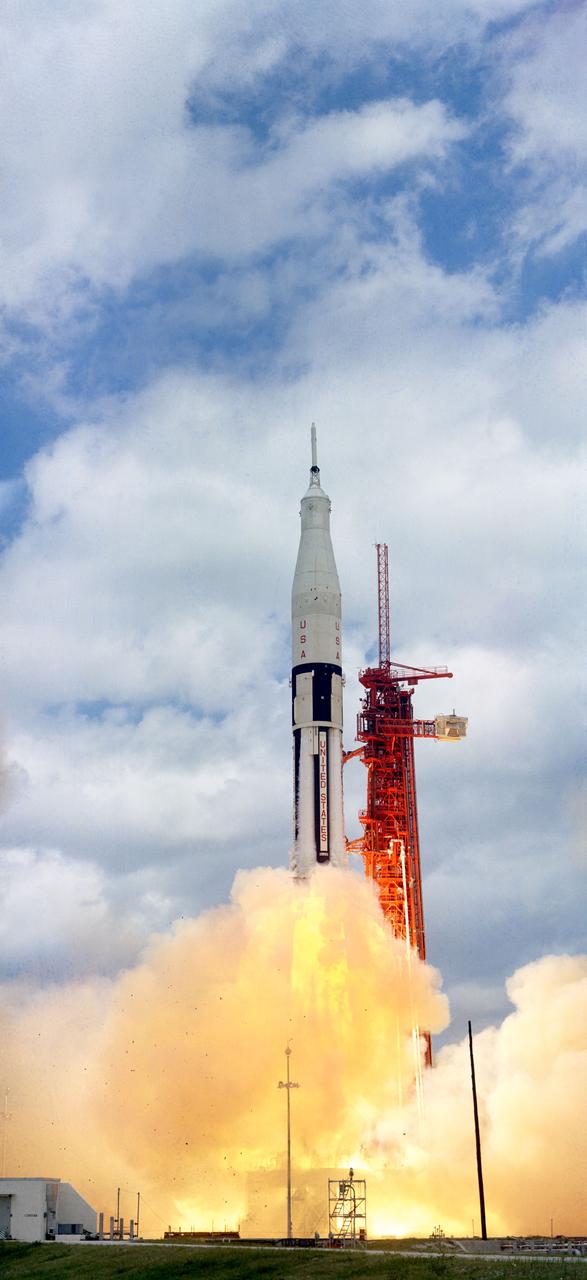

A/S Mission 202 was launched from the KSC Launch Complex (LC)-34 at 12:15 p.m., 08/25/1966. The mission was a step toward qualifying the Apollo Command and Service Modules (CSM)'s and the uprated Saturn I launch vehicle for manned flight. KSC, FL
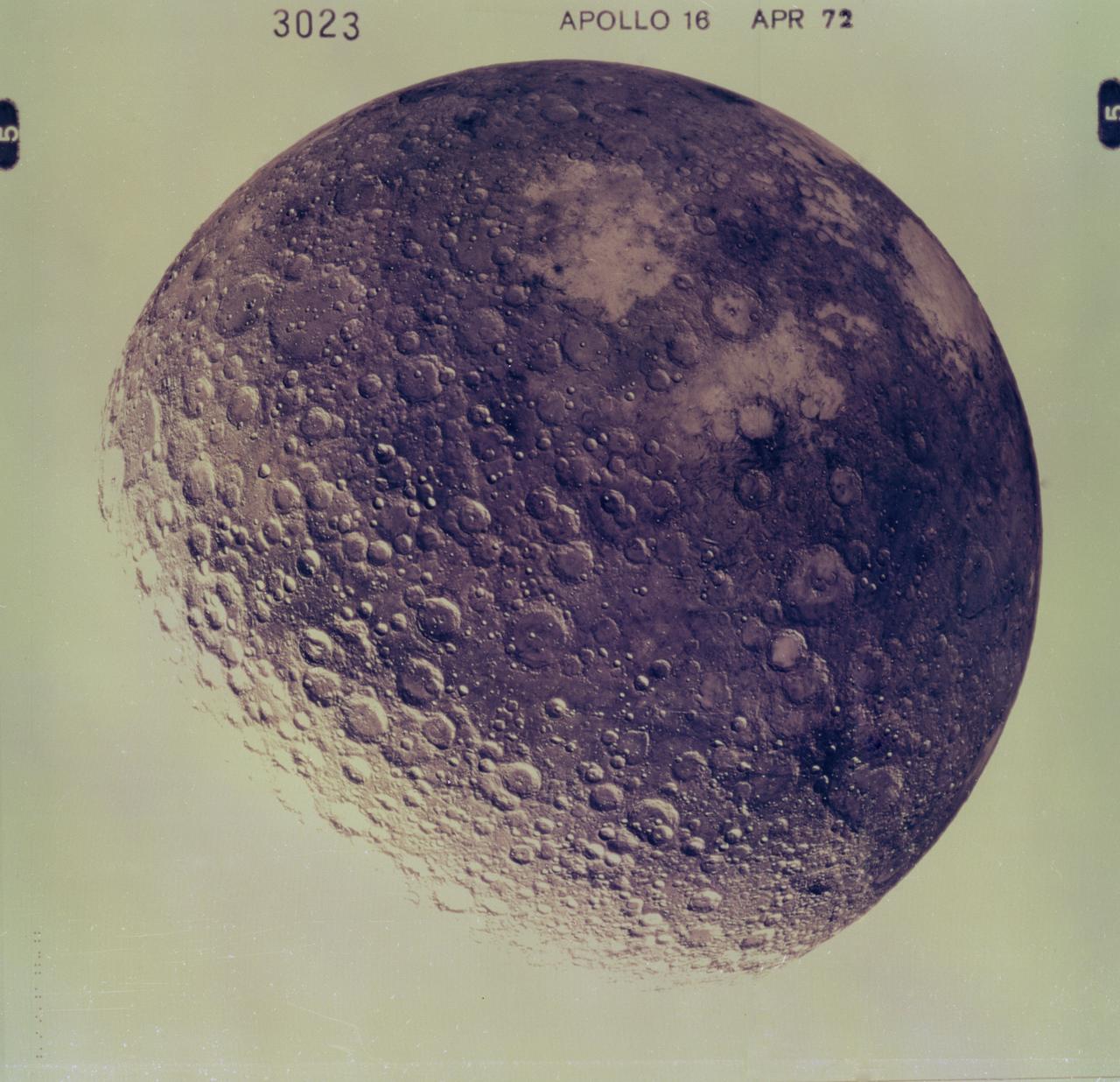

This view of the back side of the Moon was captured by the Apollo 16 mission crew. The sixth manned lunar landing mission, the Apollo 16 (SA-511), carrying three astronauts: Mission Commander John W. Young, Command Module pilot Thomas K. Mattingly II, and Lunar Module pilot Charles M. Duke, lifted off on April 16, 1972. The Apollo 16 continued the broad-scale geological, geochemical, and geophysical mapping of the Moon’s crust, begun by the Apollo 15, from lunar orbit. This mission marked the first use of the Moon as an astronomical observatory by using the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph which photographed ultraviolet light emitted by Earth and other celestial objects. The Lunar Roving Vehicle, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was also used. The mission ended on April 27, 1972.

The Apollo 16 Command Module splashed down in the Pacific Ocean on April 27, 1972 after an 11-day moon exploration mission. The 3-man crew is shown here aboard the rescue ship, USS Horton. From left to right are: Mission Commander John W. Young, Lunar Module pilot Charles M. Duke, and Command Module pilot Thomas K. Mattingly II. The sixth manned lunar landing mission, the Apollo 16 (SA-511) lifted off on April 16, 1972. The Apollo 16 mission continued the broad-scale geological, geochemical, and geophysical mapping of the Moon’s crust, begun by the Apollo 15, from lunar orbit. This mission marked the first use of the Moon as an astronomical observatory by using the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph which photographed ultraviolet light emitted by Earth and other celestial objects. The Lunar Roving Vehicle, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was also used.
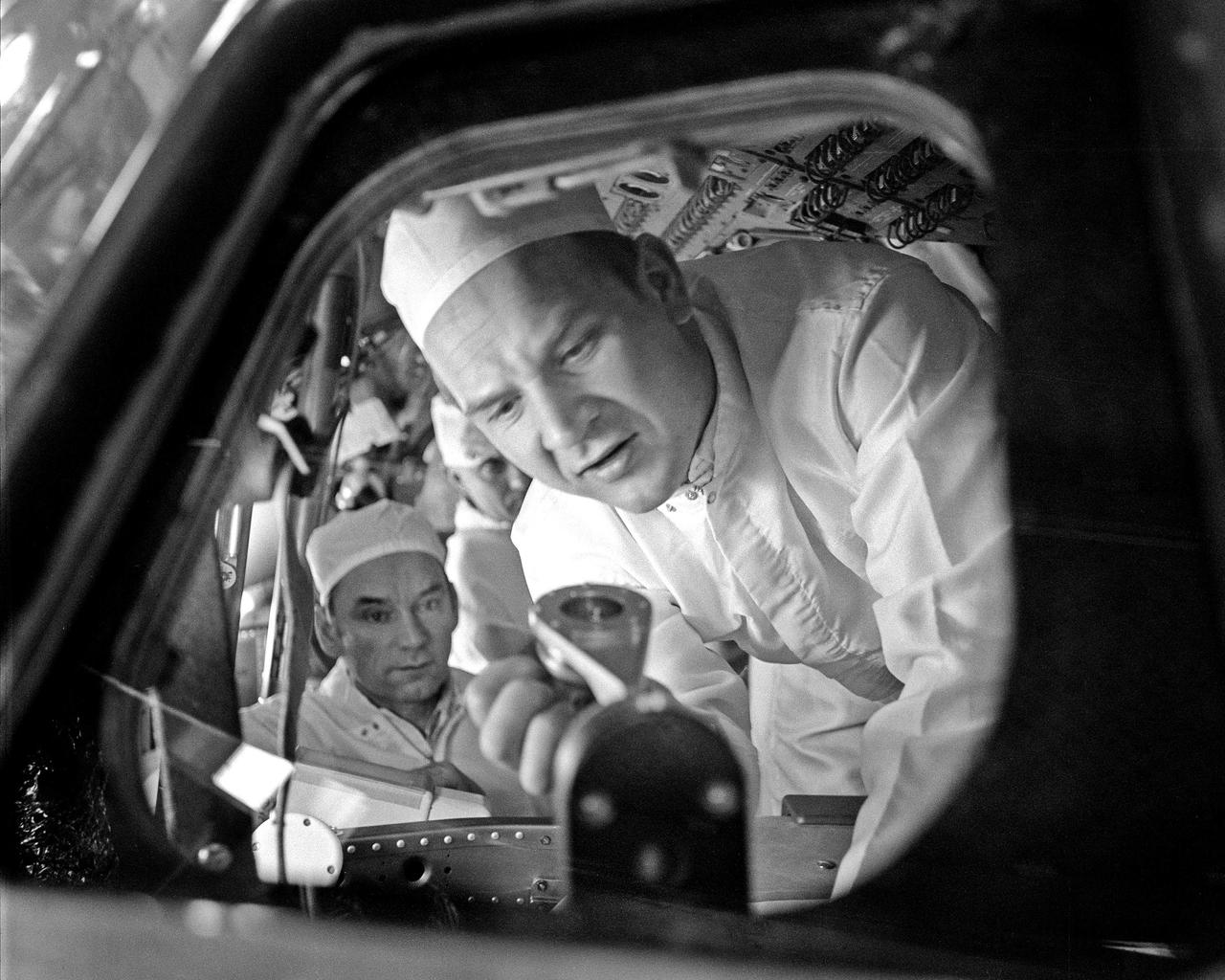

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Soviet Apollo Soyuz Test Project prime crew member Valeriy Kubasov inspects equipment inside the Apollo Command Module. The Soviet and American ASTP crews were at KSC February 8-10 to tour facilities and inspect equipment in preparation for the mid-July joint mission. The first international crewed spaceflight was a joint U.S.-U.S.S.R. rendezvous and docking mission. The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, or ASTP, took its name from the spacecraft employed: the American Apollo and the Soviet Soyuz. The three-man Apollo crew lifted off from Kennedy Space Center aboard a Saturn IB rocket on July 15, 1975, to link up with the Soyuz that had launched a few hours earlier. A cylindrical docking module served as an airlock between the two spacecraft for transfer of the crew members. Photo credit: NASA

The Apollo 16 Command Module splashed down in the Pacific Ocean on April 27, 1972 after an 11-day moon exploration mission. The sixth manned lunar landing mission, the Apollo 16 (SA-511), carrying three astronauts: Mission Commander John W. Young, Command Module pilot Thomas K. Mattingly II, and Lunar Module pilot Charles M. Duke, lifted off on April 16, 1972. The Apollo 16 continued the broad-scale geological, geochemical, and geophysical mapping of the Moon’s crust, begun by the Apollo 15, from lunar orbit. This mission marked the first use of the Moon as an astronomical observatory by using the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph which photographed ultraviolet light emitted by Earth and other celestial objects. The Lunar Roving Vehicle, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was also used.
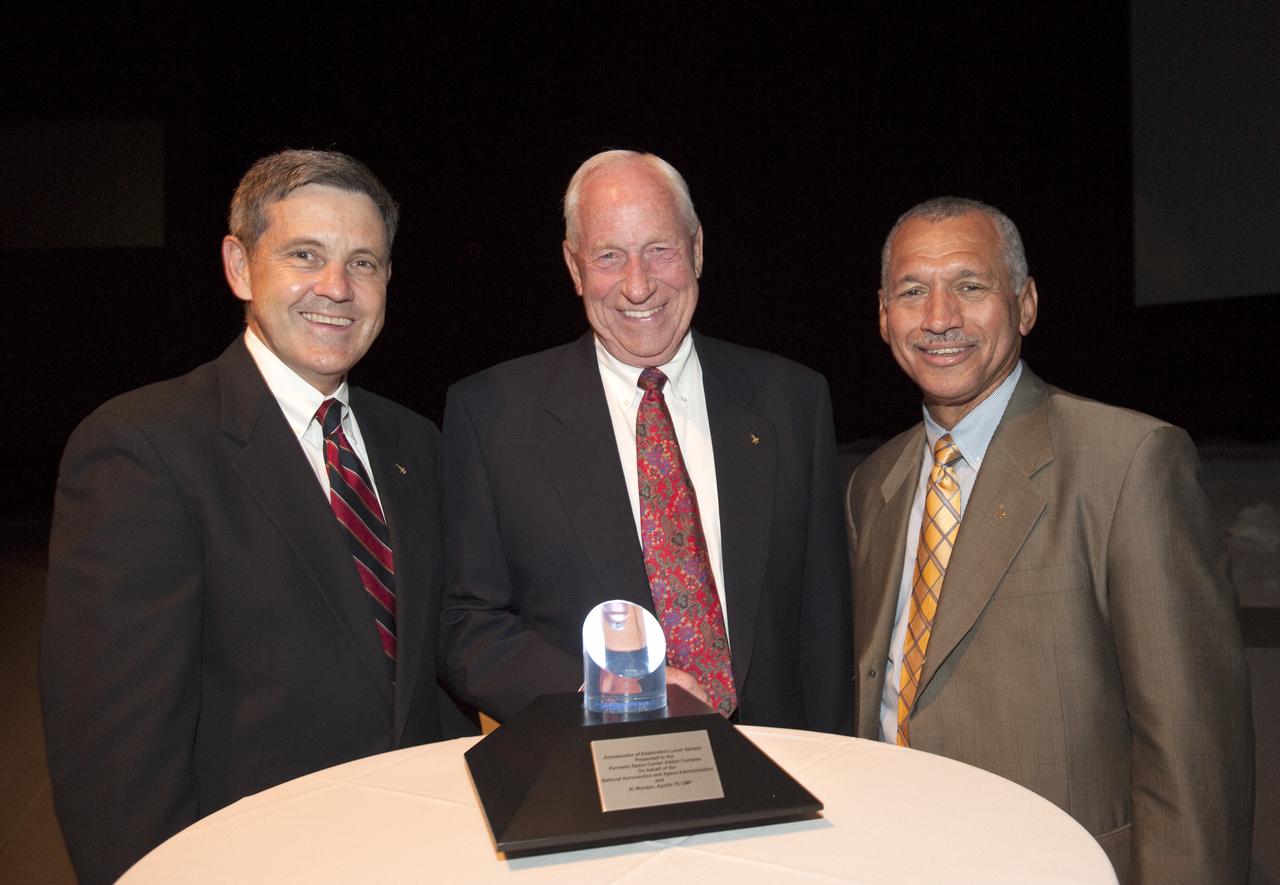

Apollo astronaut Al Worden, center, is flanked by NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, right, and Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana at a ceremony, Thursday, July 30, 2009, where Worden was honored with the presentation of the an Ambassador of Exploration Award for his contributions to the U.S. space program at Kennedy Space Center, Fla. Worden served as command module pilot for the Apollo 15 mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
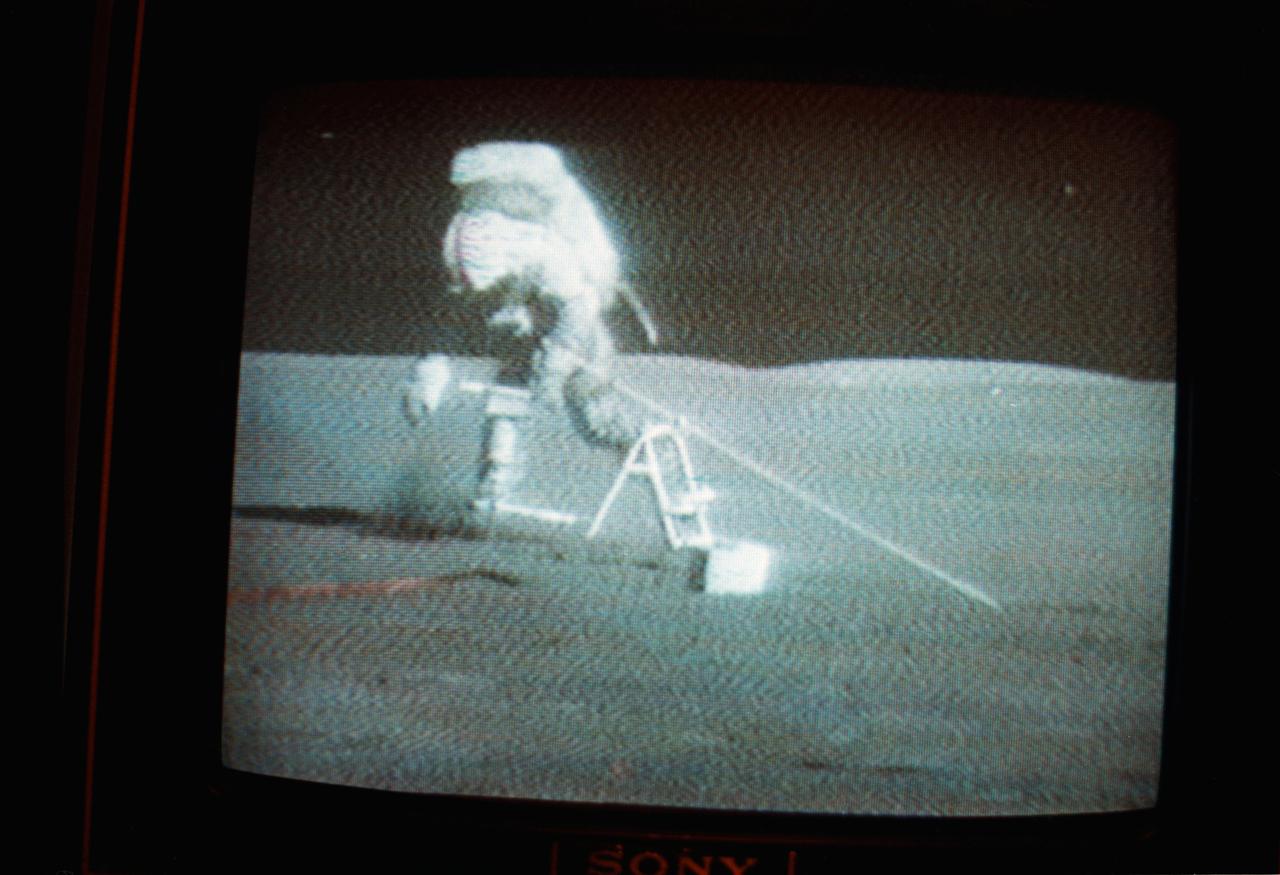

S71-41501 (1 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, Apollo 15 commander, is seen carrying the Apollo Lunar Surface Drill (ALSD) during the second lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) in this black and white reproduction taken from a color transmission made by the RCA color television camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). This transmission was the fourth made during the mission.
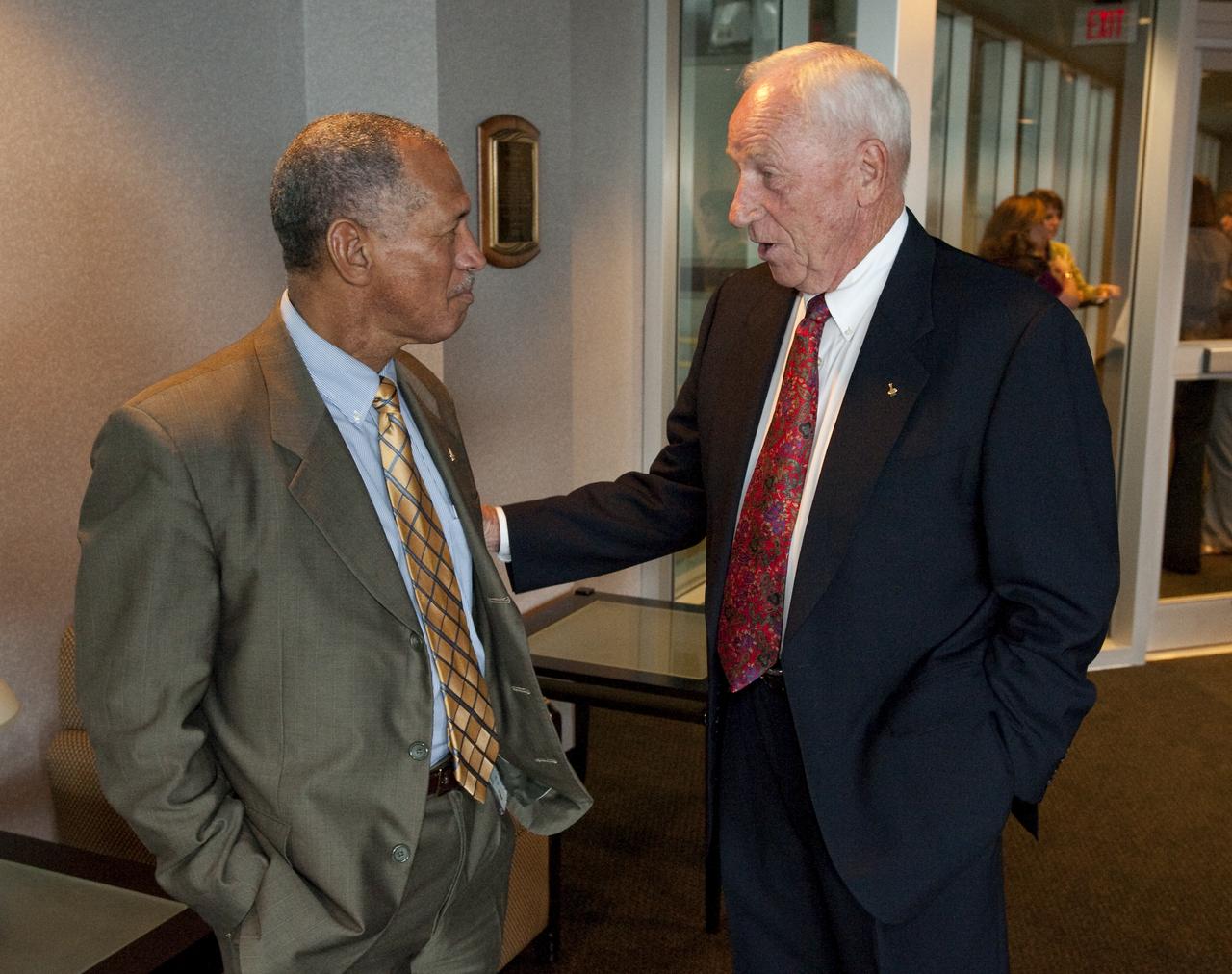

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, visits with Apollo astronaut Al Worden prior to a ceremony, Thursday, July 30, 2009, where Worden was honored with the presentation of the an Ambassador of Exploration Award for his contributions to the U.S. space program at Kennedy Space Center, Fla. Worden served as command module pilot for the Apollo 15 mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
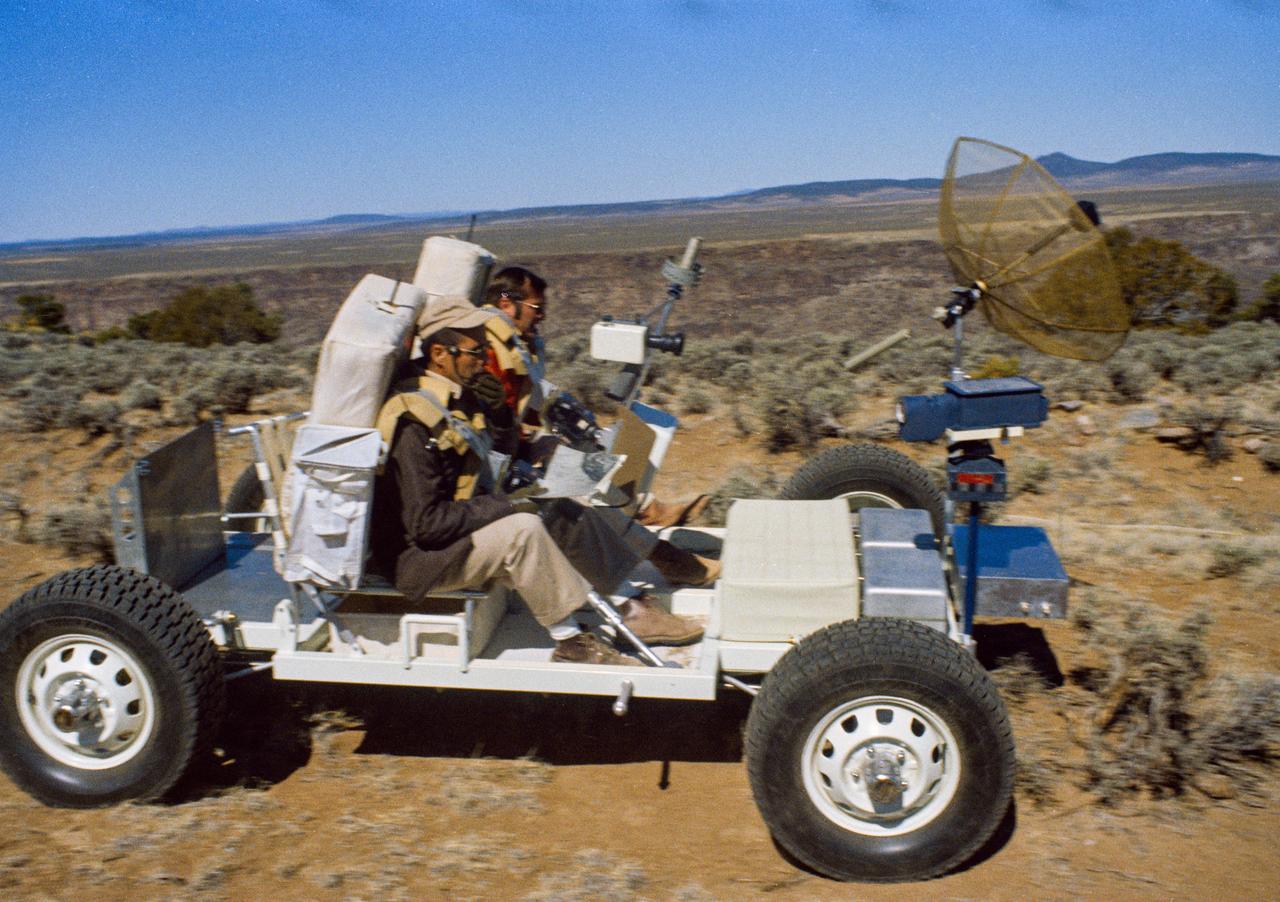

S71-24079 (1971) --- Astronauts Richard F. Gordon Jr., right, and Harrison H. Schmitt ? back-up crew members for the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission -- traverse in an Earth-bound training version of the Apollo Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV or Rover) during geology training in Hawaii. Photo credit: NASA Note: There are elements of this description that have not been confimred. Please hold any release of descriptive information until such can be confirmed.
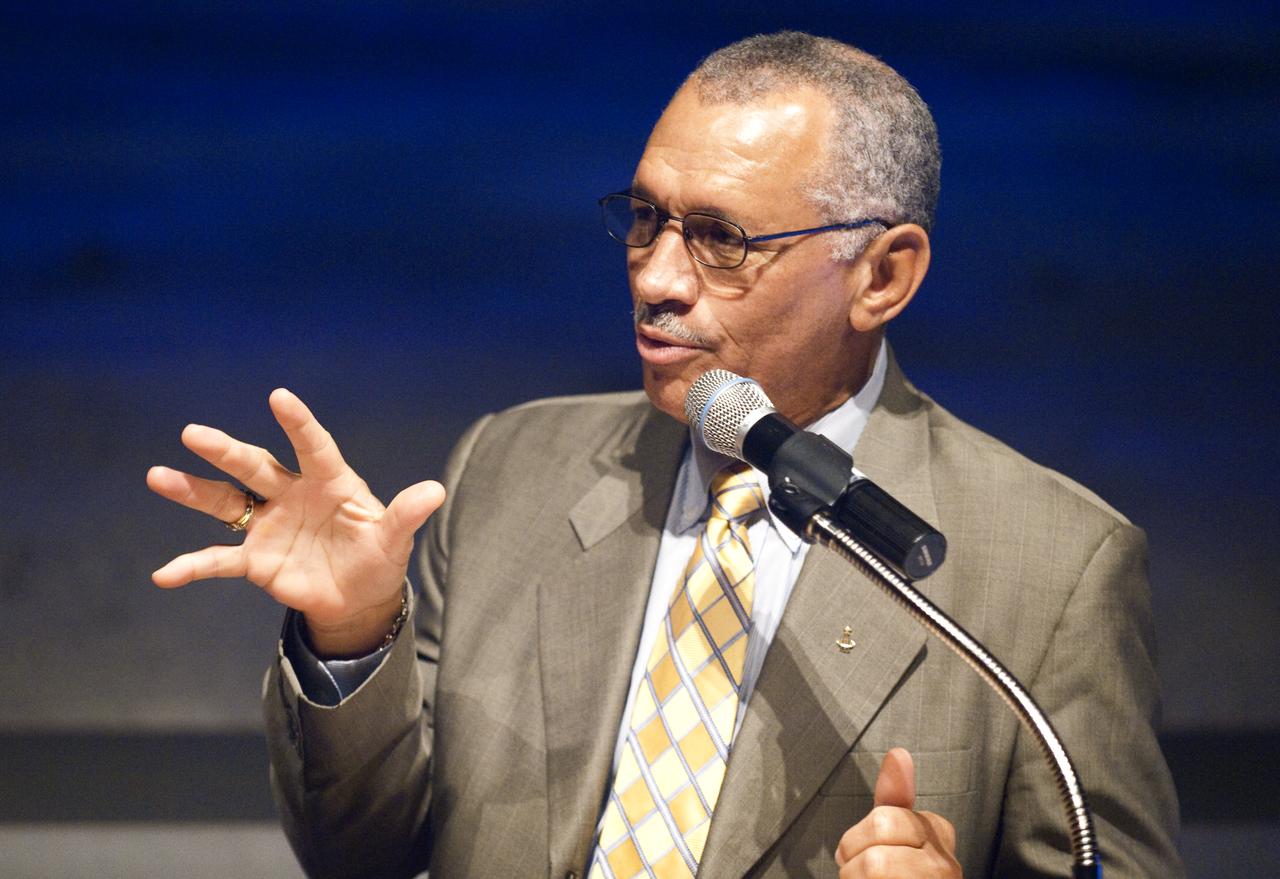

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, talks about Apollo astronaut Al Worden during a ceremony, Thursday, July 30, 2009, where Worden was honored with the presentation of the Ambassador of Exploration Award for his contributions to the U.S. space program at Kennedy Space Center, Fla. Worden served as command module pilot for the Apollo 15 mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
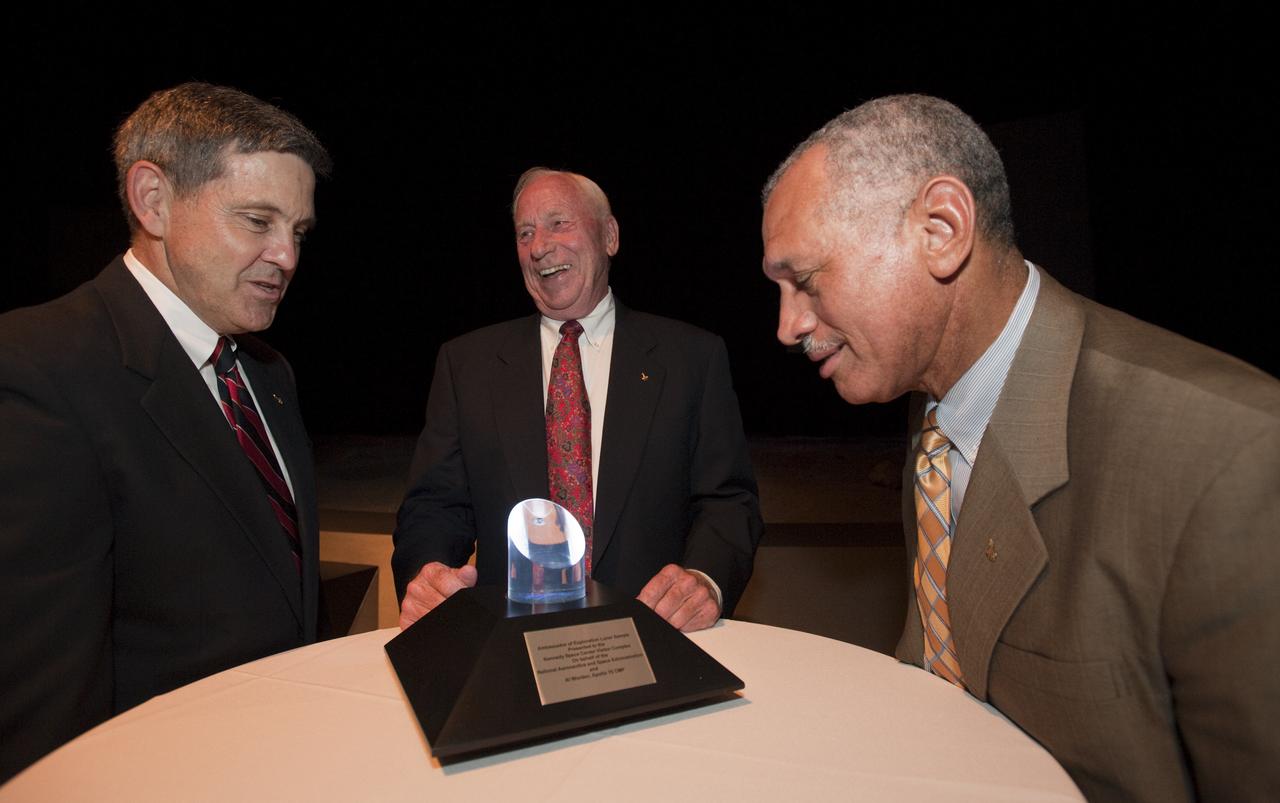

Apollo astronaut Al Worden, center, flanked by NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, right, and Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana following a ceremony, Thursday, July 30, 2009, where Worden was honored with the presentation of the an Ambassador of Exploration Award for his contributions to the U.S. space program at Kennedy Space Center, Fla. Worden served as command module pilot for the Apollo 15 mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
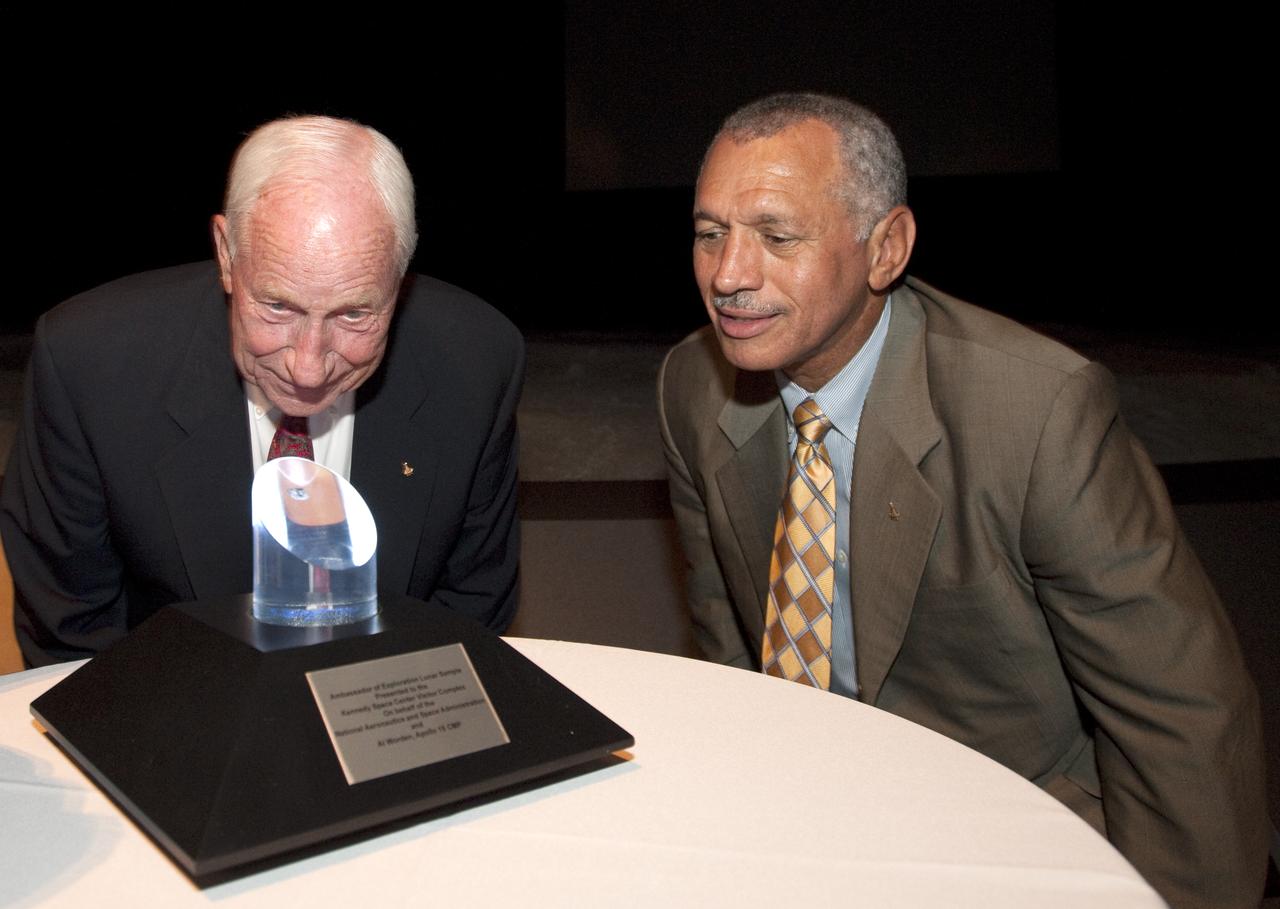

Apollo astronaut Al Worden, left, and NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, take a close look at Worden's Ambassador of Exploration Award for his contributions to the U.S. space program following a ceremony, Thursday, July 30, 2009, where Worden was honored with the presentation of the award at Kennedy Space Center, Fla. Worden served as command module pilot for the Apollo 15 mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)