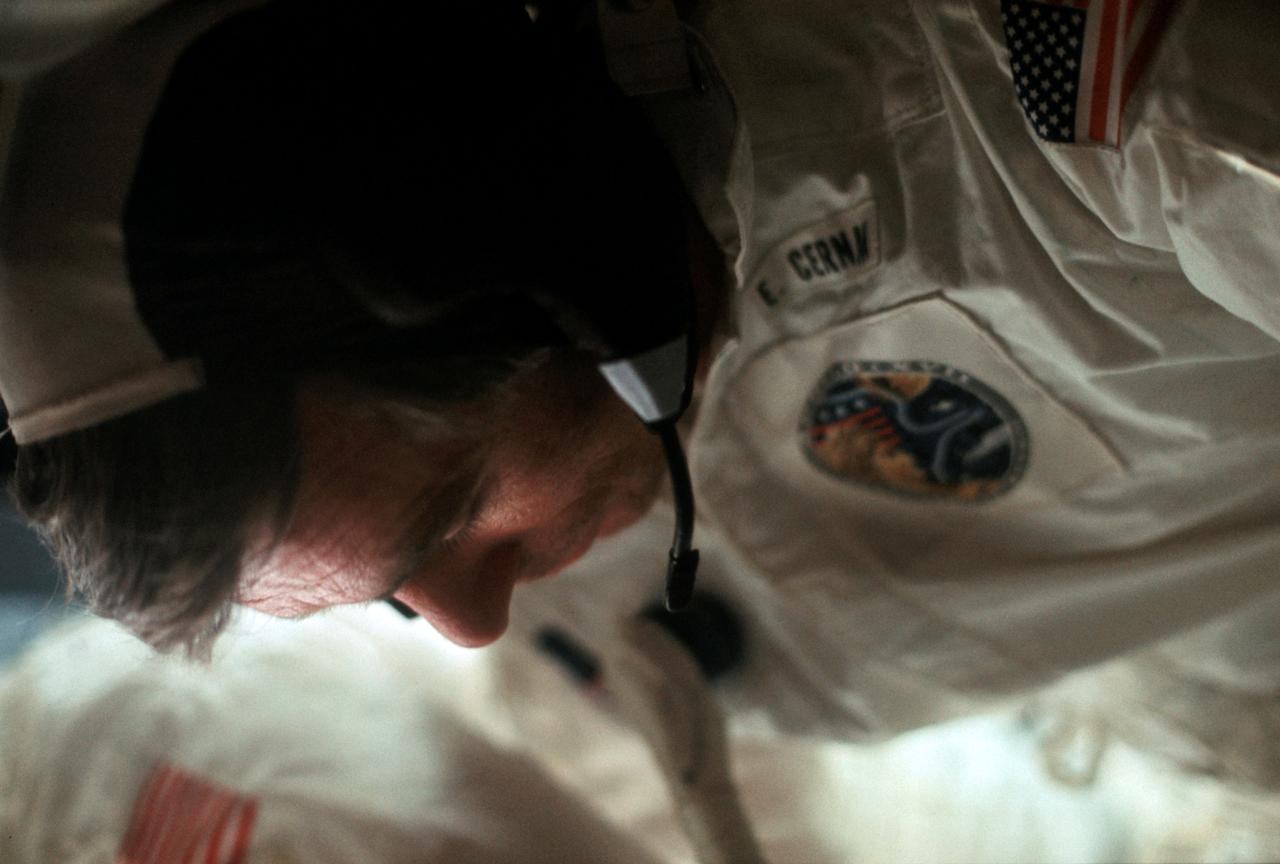

AS17-162-24050 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan appears to be relaxing in this candid photograph taken by a fellow crewman aboard the Apollo 17 spacecraft during the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. Also, aboard Apollo 17 were astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt, lunar module pilot. Cernan was the mission commander.
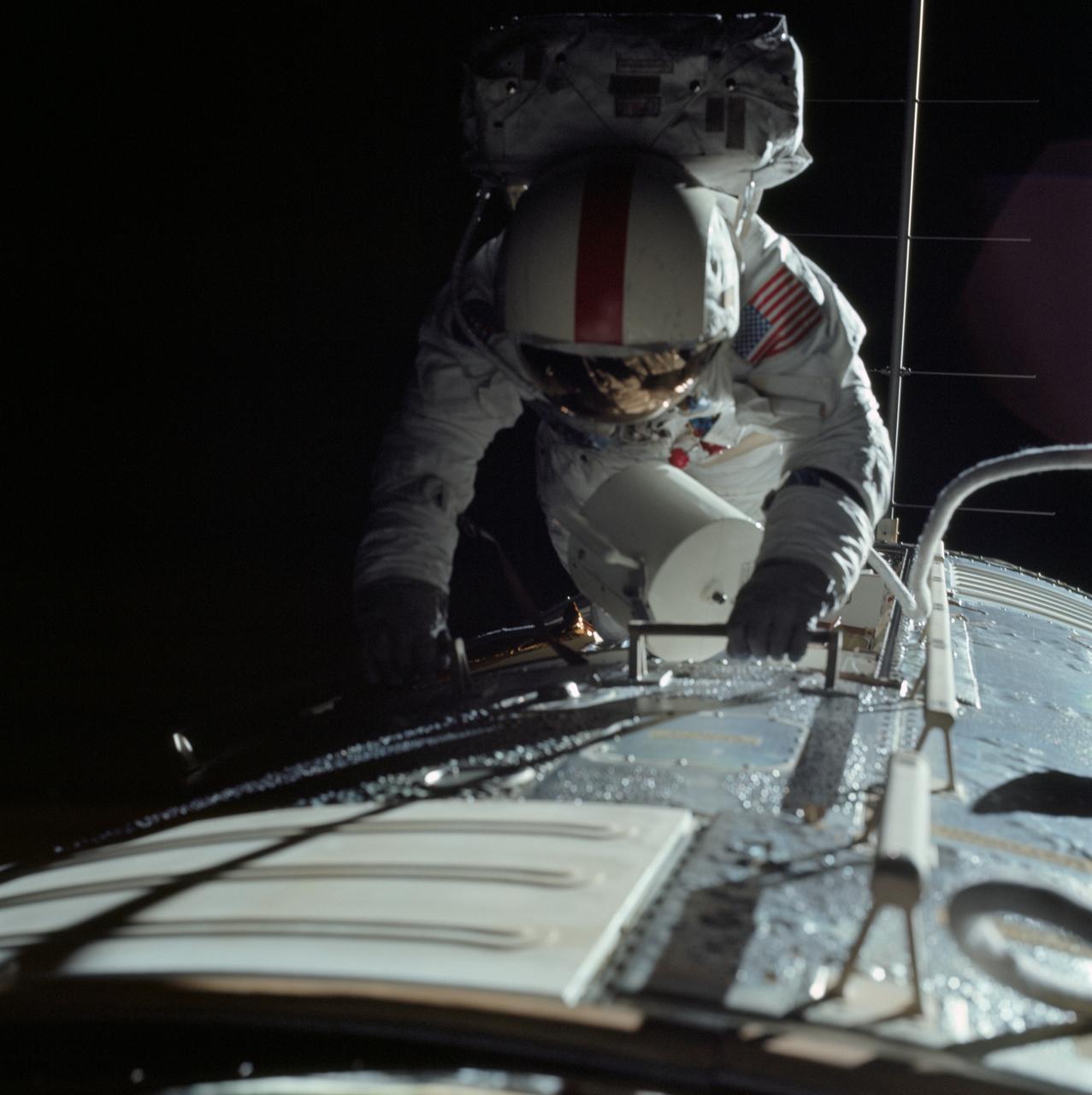

AS17-152-23392 (17 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Ronald E. Evans is photographed performing extravehicular activity during the Apollo 17 spacecraft's trans-Earth coast. During his EVA, command module pilot Evans retrieved film cassettes from the Lunar Sounder, Mapping Camera, and Panoramic Camera. The cylindrical object at Evans' left side is the Mapping Camera cassette. The total time for the trans-Earth EVA was one hour seven minutes 18 seconds, starting at ground elapsed time of 257:25 (2:28 p.m.) and ending at ground elapsed timed of 258:42 (3:35 p.m.) on Sunday, Dec. 17, 1972.
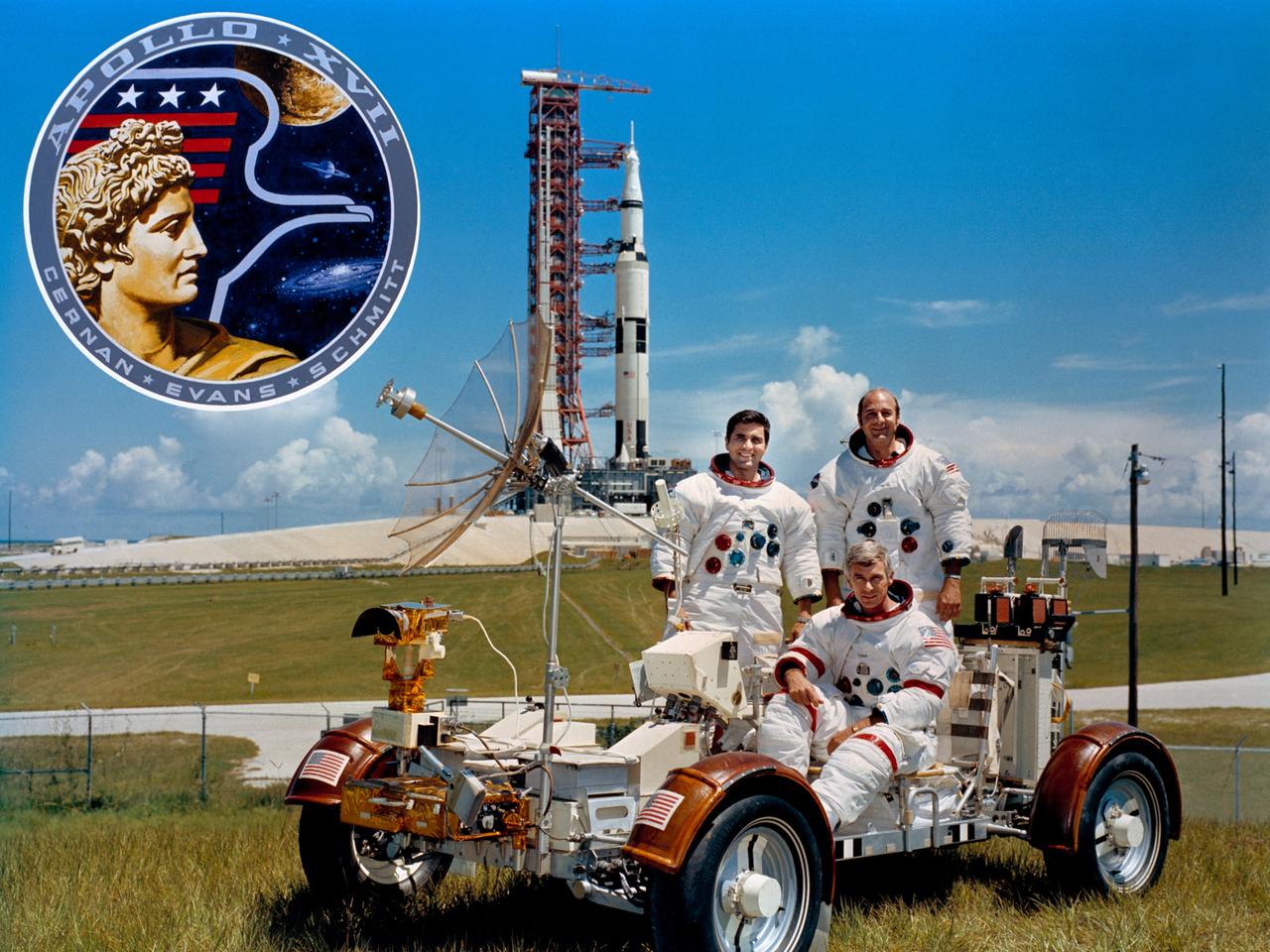

S72-50438 (September 1972) --- These three astronauts are the prime crew members of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. They are Eugene A. Cernan (seated), commander; Ronald E. Evans (standing on right), command module pilot; and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. They are photographed with a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) trainer. Cernan and Schmitt will use an LRV during their exploration of the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The Apollo 17 Saturn V space vehicle is in the background. This picture was taken at Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida. The Apollo 17 insignia is in the photo insert at upper left. The insignia, designed by artist Robert T. McCall in collaboration with the crewmen, is dominated by the image of Apollo, the Greek sun god.
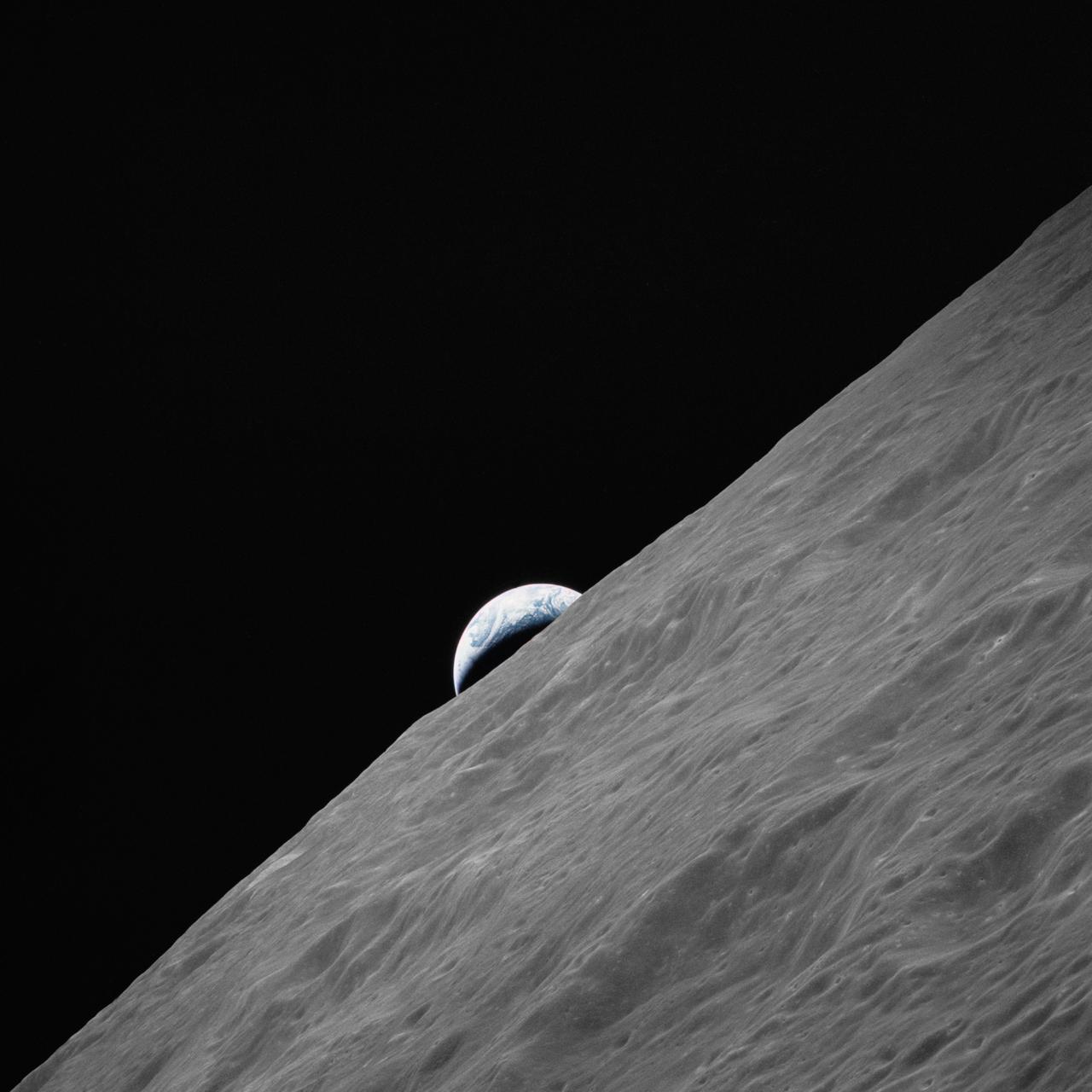

AS17-152-23272 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- The crescent Earth rises above the lunar horizon in this photograph taken from the Apollo 17 spacecraft in lunar orbit during National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) final lunar landing mission in the Apollo program. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.

AS17-140-21497 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt is photographed standing next to a huge, split lunar boulder during the third Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. Schmitt is the Apollo 17 lunar module pilot. This picture was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander. While Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
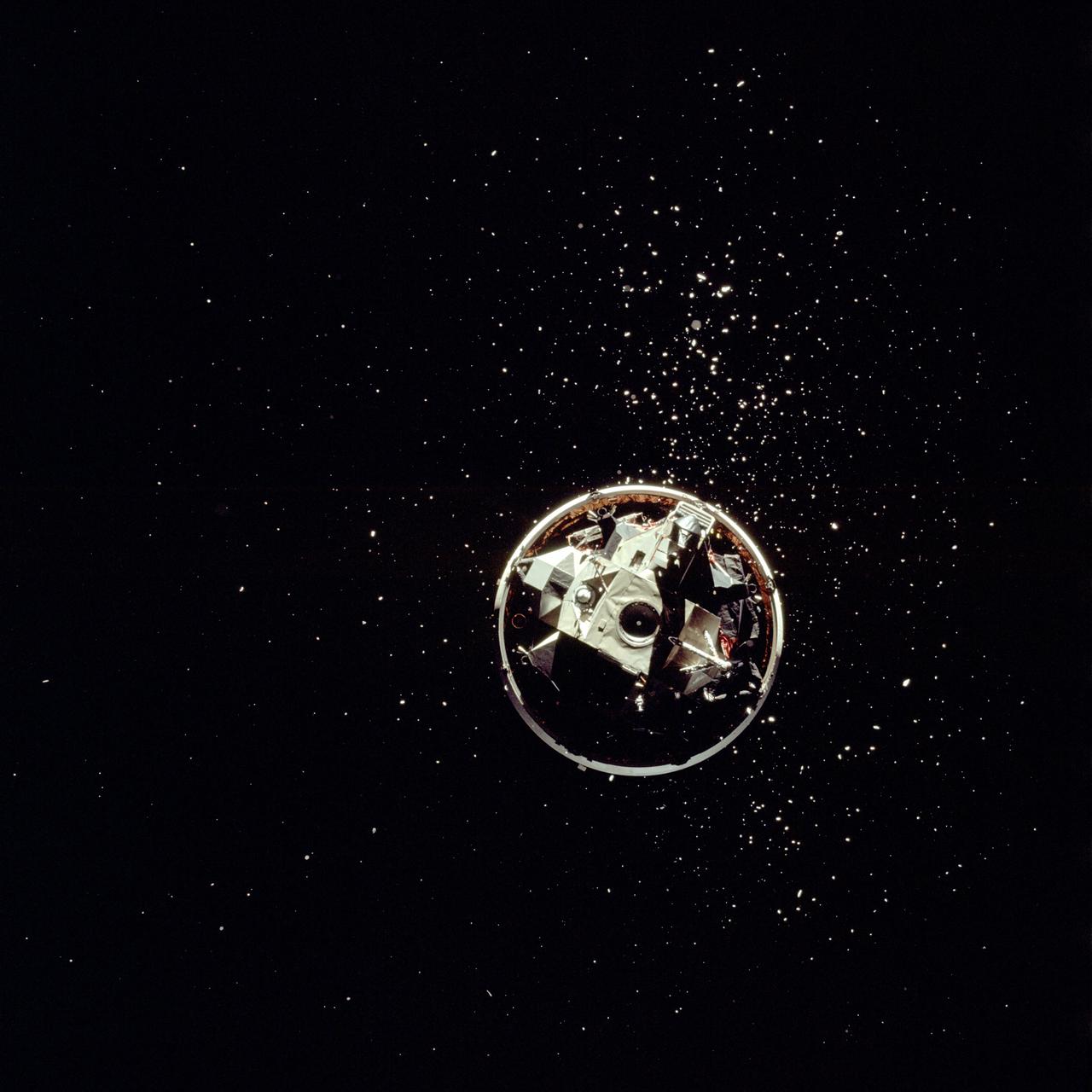

AS17-148-22687 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- View of the Lunar Module from the Apollo 17 spacecraft after transposition/docking maneuvers. The white dots surrounding the Lunar Module are debris from the Saturn S-IVB stage separation.
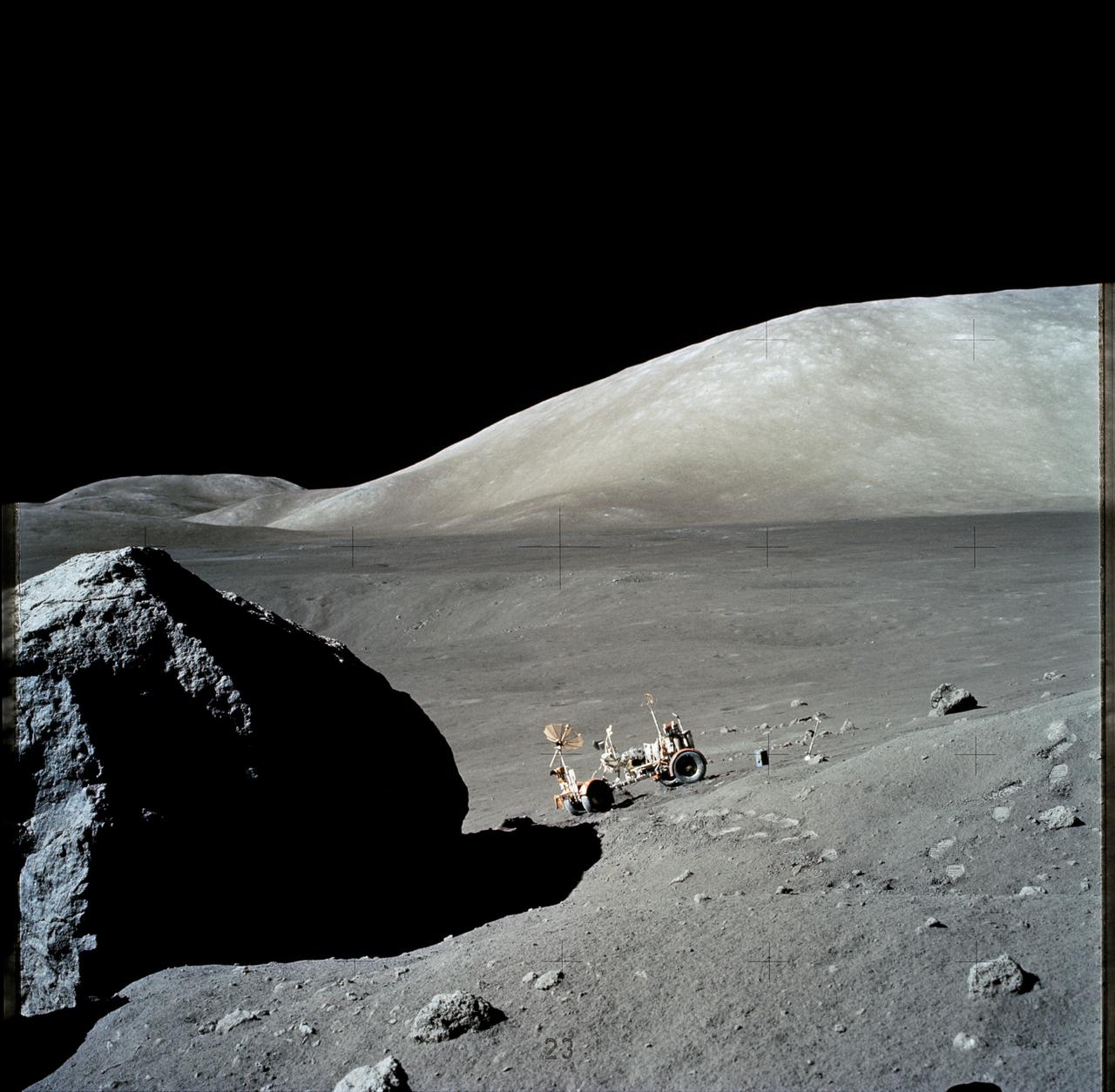

AS17-140-21493 (13 Dec. 1972) --- The Apollo 17 Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is photographed near a large lunar boulder during the third Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. About half of the boulder is captured in this scene, photographed by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander. While astronauts Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS17-137-20972 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This is a close-up view of a lunar rock, showing multi-colored clasts embedded in larger rock. This picture was taken by one of the Apollo 17 astronauts during an extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon surface.

S72-49079 (8 Sept. 1972) --- This is the official emblem of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission which will be flown by astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, Ronald E. Evans and Harrison H. Schmitt. The insignia is dominated by the image of Apollo, the Greek sun god. Suspended in space behind the head of Apollo is an American eagle of contemporary design, the red bars of the eagle's wing represent the bars in the United States flag; the three white stars symbolize the three astronaut crewmen. The background is deep blue space and within it are the moon, the planet Saturn and a spiral galaxy or nebula. The moon is partially overlaid by the eagle's wing suggesting that this is a celestial body that man has visited and in that sense conquered. The thrust of the eagle and the gaze of Apollo to the right and toward Saturn and the galaxy is meant to imply that man's goals in space will someday include the planets and perhaps the stars. The colors of the emblem are red, white and blue, the colors of our flag; with the addition of gold, to symbolize the golden age of space flight that will begin with this Apollo 17 lunar landing. The Apollo image used in this emblem was the famous Apollo of Belvedere sculpture now in the Vatican Gallery in Rome. This emblem was designed by artist Robert T. McCall in collaboration with the astronauts. This is the official Apollo 17 emblem, a property of the government of the United States. It has been authorized only for use by the astronauts. Its reproduction in any form other than in news, information and education media is not authorized without approval. Unauthorized use is subject to the provisions of Title 18, U.S. Code, Section 701.

Apollo 17 astronaut Harrison Schmitt is seen in a video during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
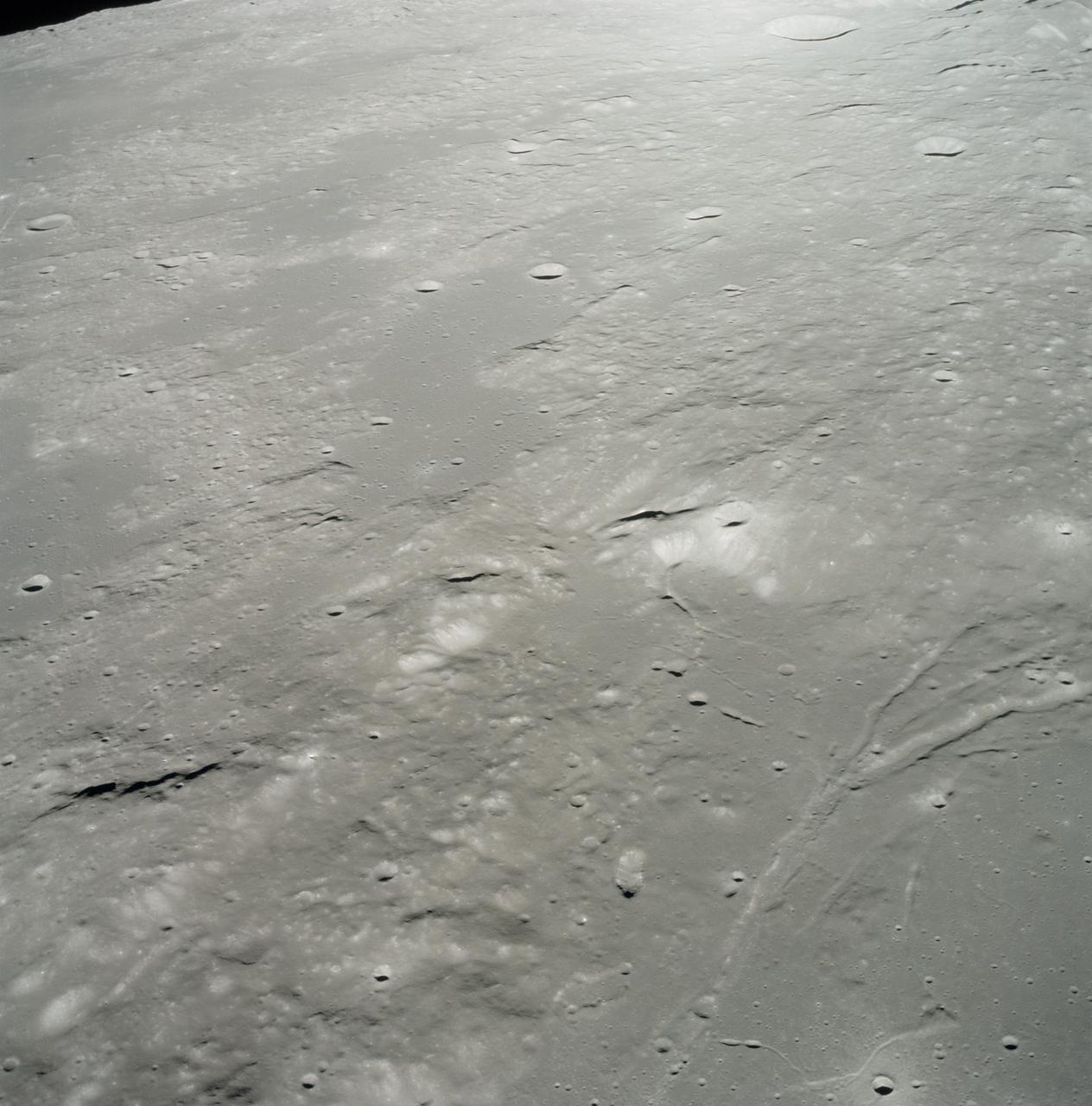

AS17-153-23572 (15 Dec. 1972) --- An oblique view of the Sulpicius Gallus region on the southwestern edge of the Sea of Serenity looking westward across the Haemus Mountains, as photographed from the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules during its 65th revolution of the moon. This photograph shows the slight orange cast which was identified by astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot. The region shown in the picture is about 600 kilometers (360 statute miles) west across Mare Serentatis from the Taurus-Littrow landing site where scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt, lunar module pilot, discovered an orange soil sample composed of fine glass particles rich in iron and titanium. North is toward the right. Rima Sulpicius Gallus is the lunar trench or valley (right foreground) that crosses the edge of the Mare and divides into three branches as it runs to the northwest. The crater Sulpicius Gallus is just off the photograph at the bottom right. Note that several small craters in the dark portion of the picture (east) show a more distinct orange cast. The coordinates of the center of this photograph are about 8.4 degrees east longitude and 19.8 degrees north latitude.

Teasel Muir-Harmony, curator of the Apollo collection at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum, speaks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Teasel Muir-Harmony, curator of the Apollo collection at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum, speaks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Teasel Muir-Harmony, curator of the Apollo collection at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum speaks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Teasel Muir-Harmony, curator of the Apollo collection at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum, speaks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
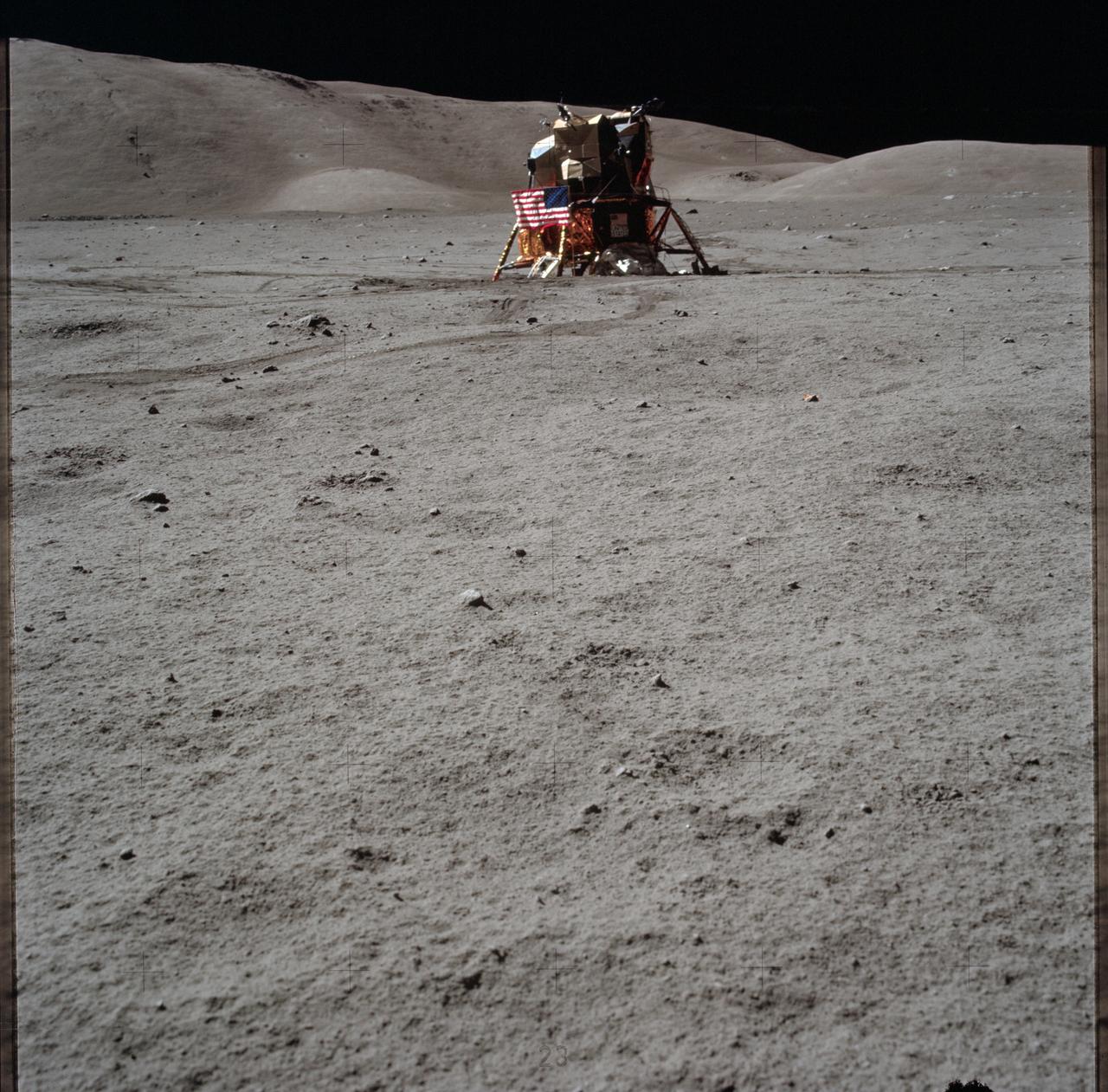

AS17-134-20513 (11 Dec. 1972) --- The Lunar Module (LM) is in the background of this view of the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This was one of the last photographs taken on the lunar surface. The Apollo 17 crewmembers were astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander; Ronald E. Evans, command and service module pilot; and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot.
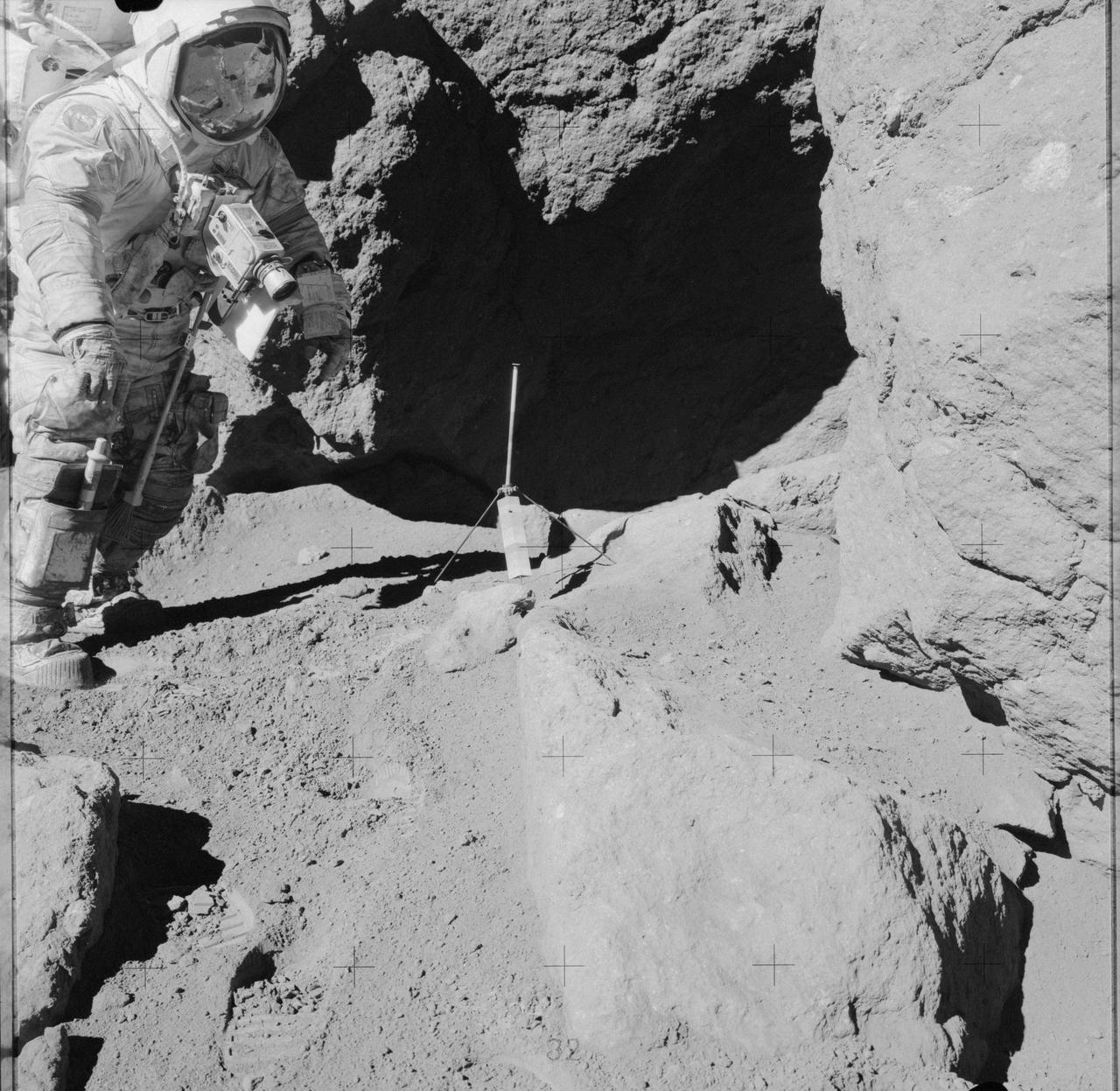

AS17-141-21608 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan stands near an over-hanging rock during the third Apollo 17 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt took this photograph. The tripod-like object just outside the shaded area is the gnomon and photometric chart assembly which is used as a photographic reference to establish local vertical sun angle, scale and lunar color. The gnomon is one of the Apollo Lunar Geology Hand Tools. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module "Challenger" to explore the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.

Robert Lightfoot, executive vice president of Lockheed Martin Space, speaks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson delivers remarks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
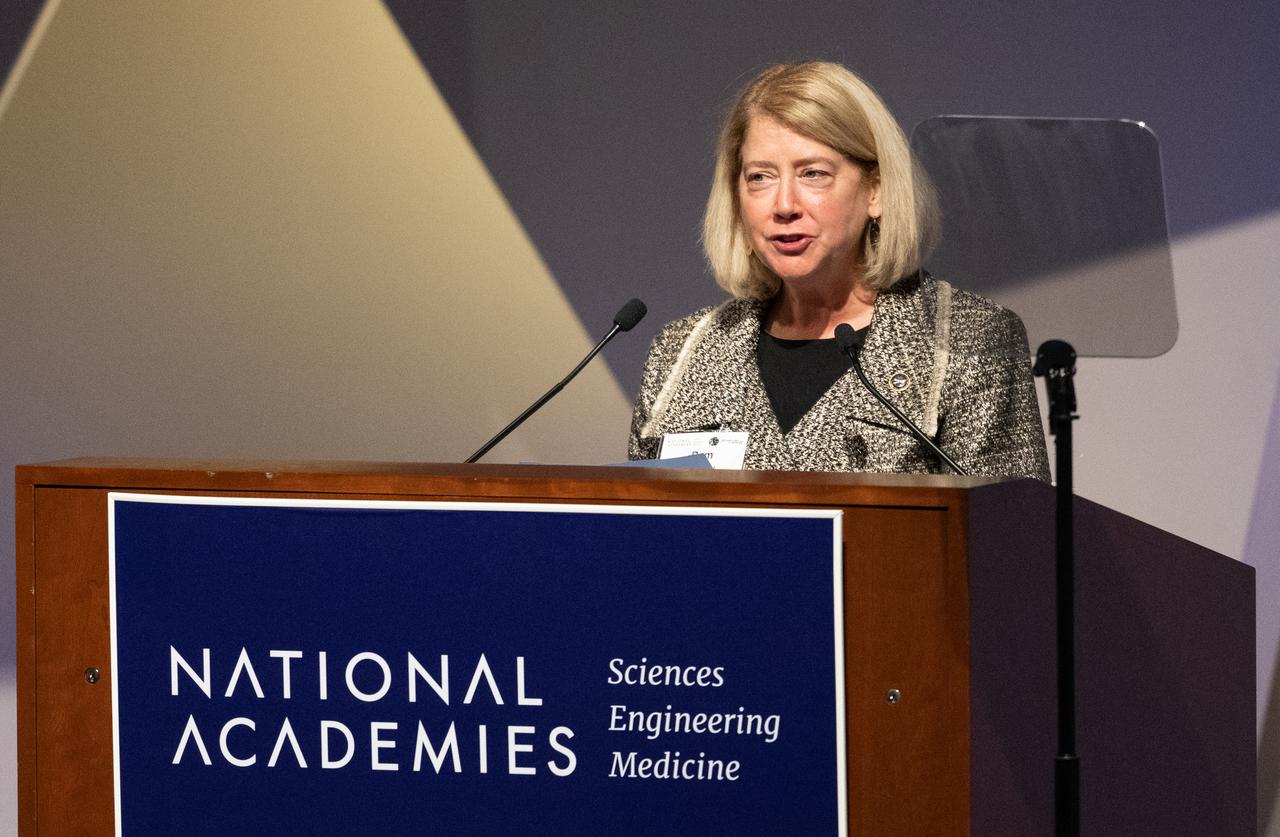

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy delivers remarks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy delivers remarks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
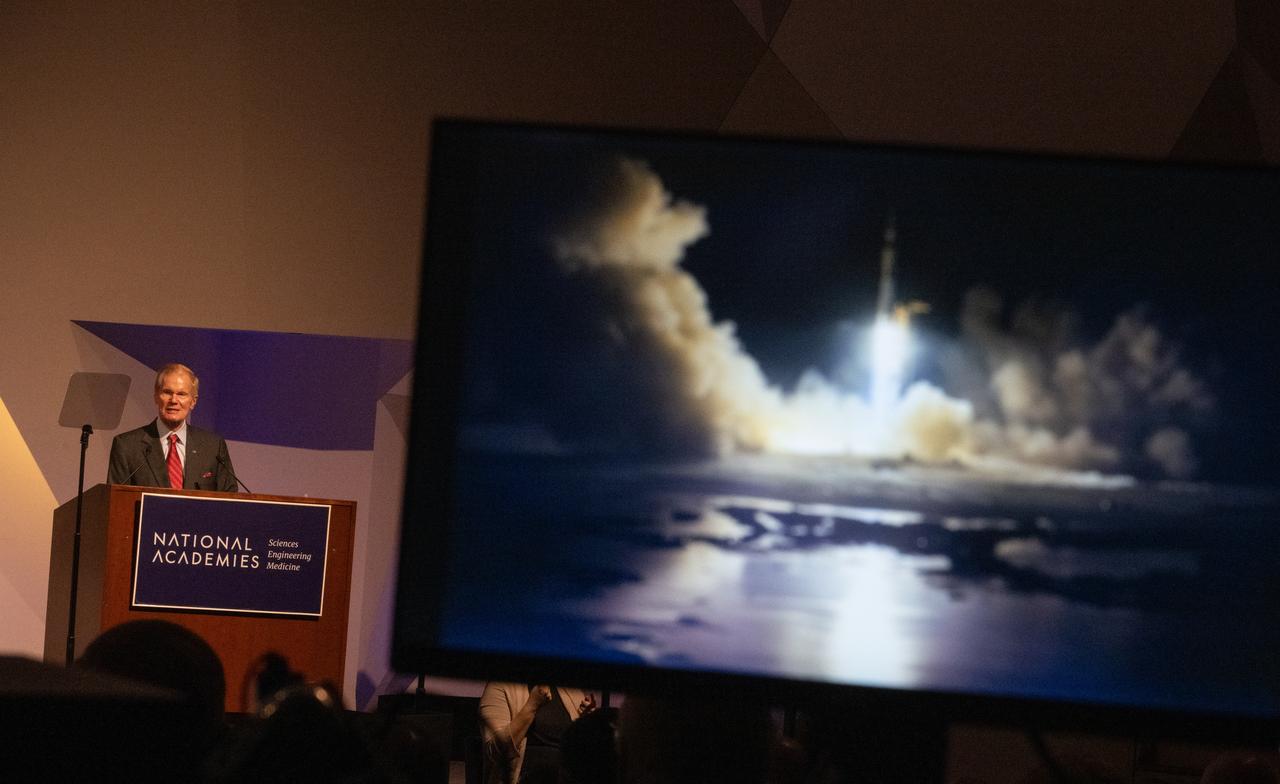

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson delivers remarks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy delivers remarks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
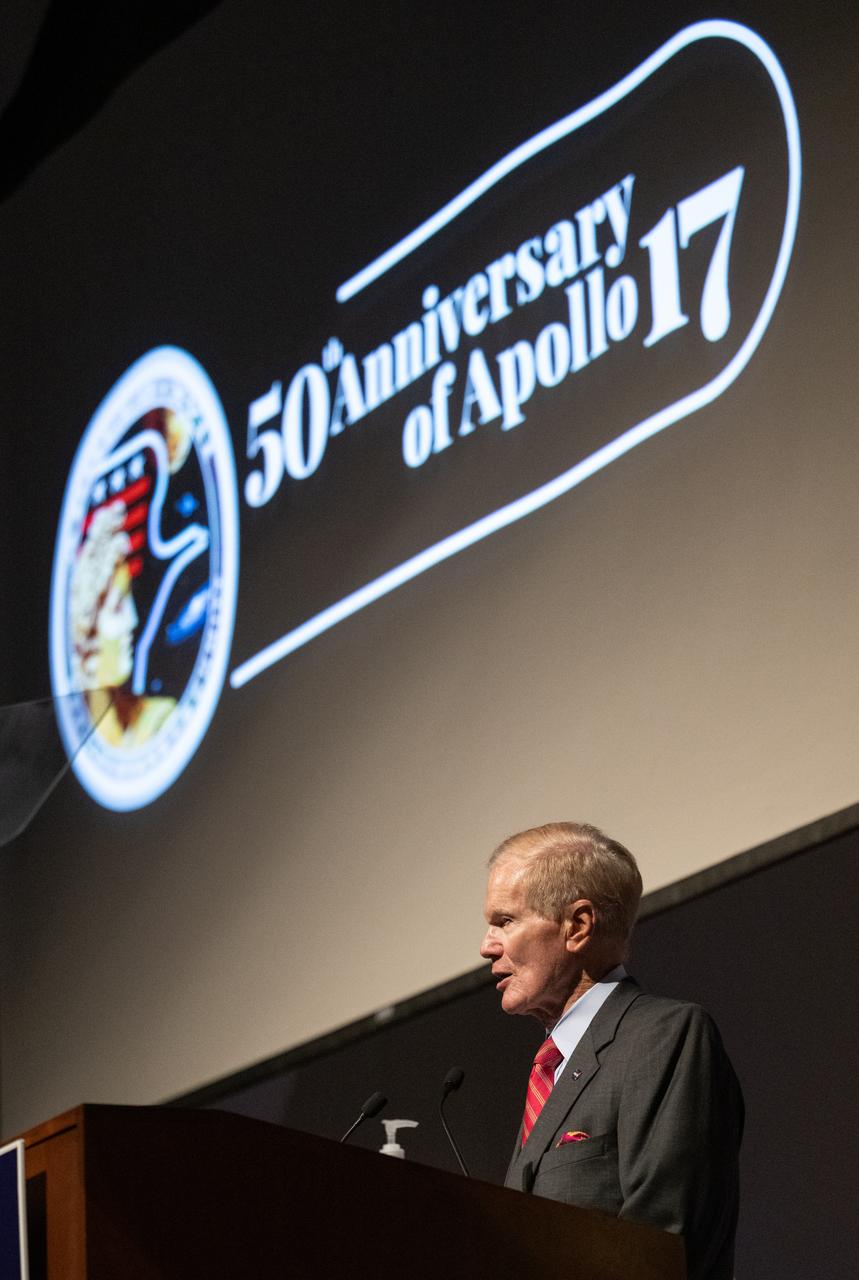

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson delivers remarks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
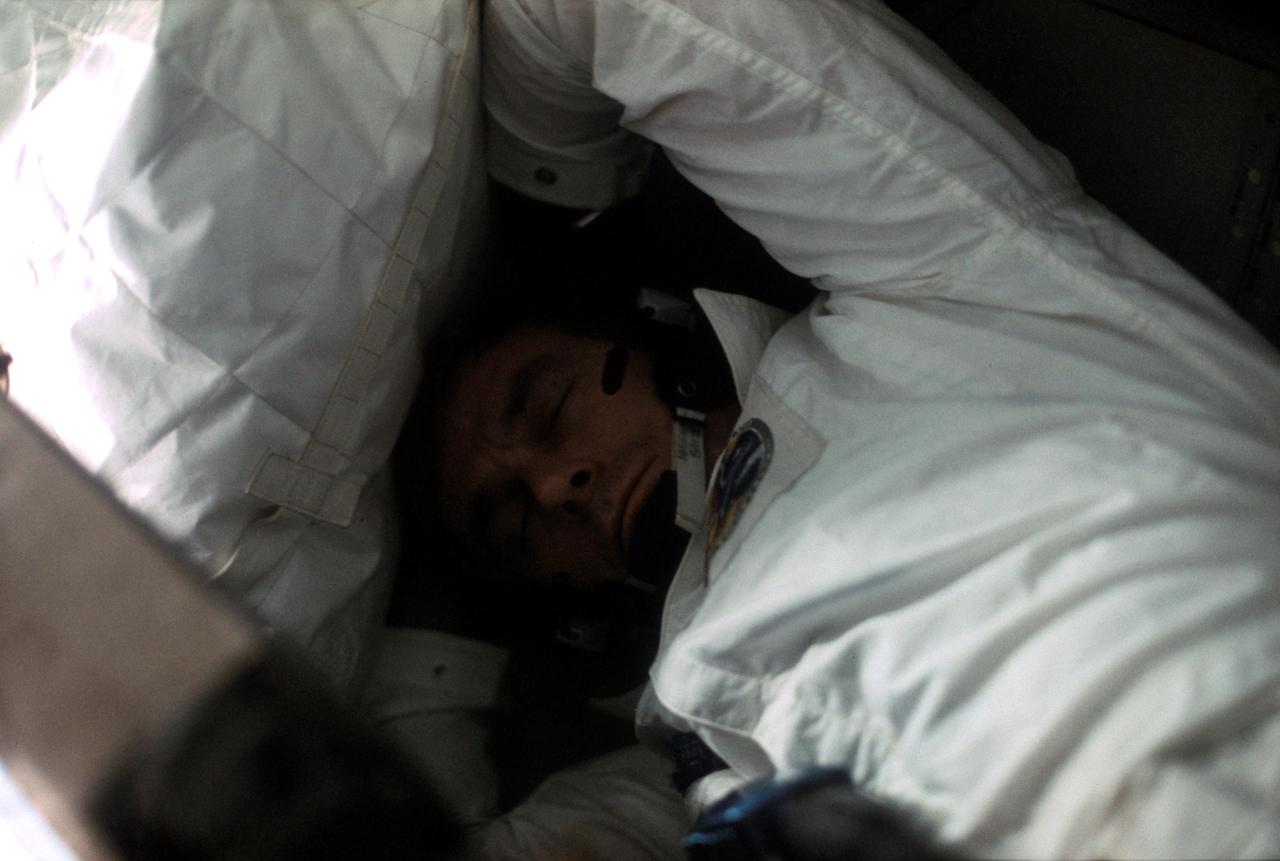

AS17-162-24049 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- A fellow crewman took this picture of astronaut Eugene A. Cernan dozing aboard the Apollo 17 spacecraft during the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. Also, aboard Apollo 17 were astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt, lunar module pilot. Cernan was the mission commander.
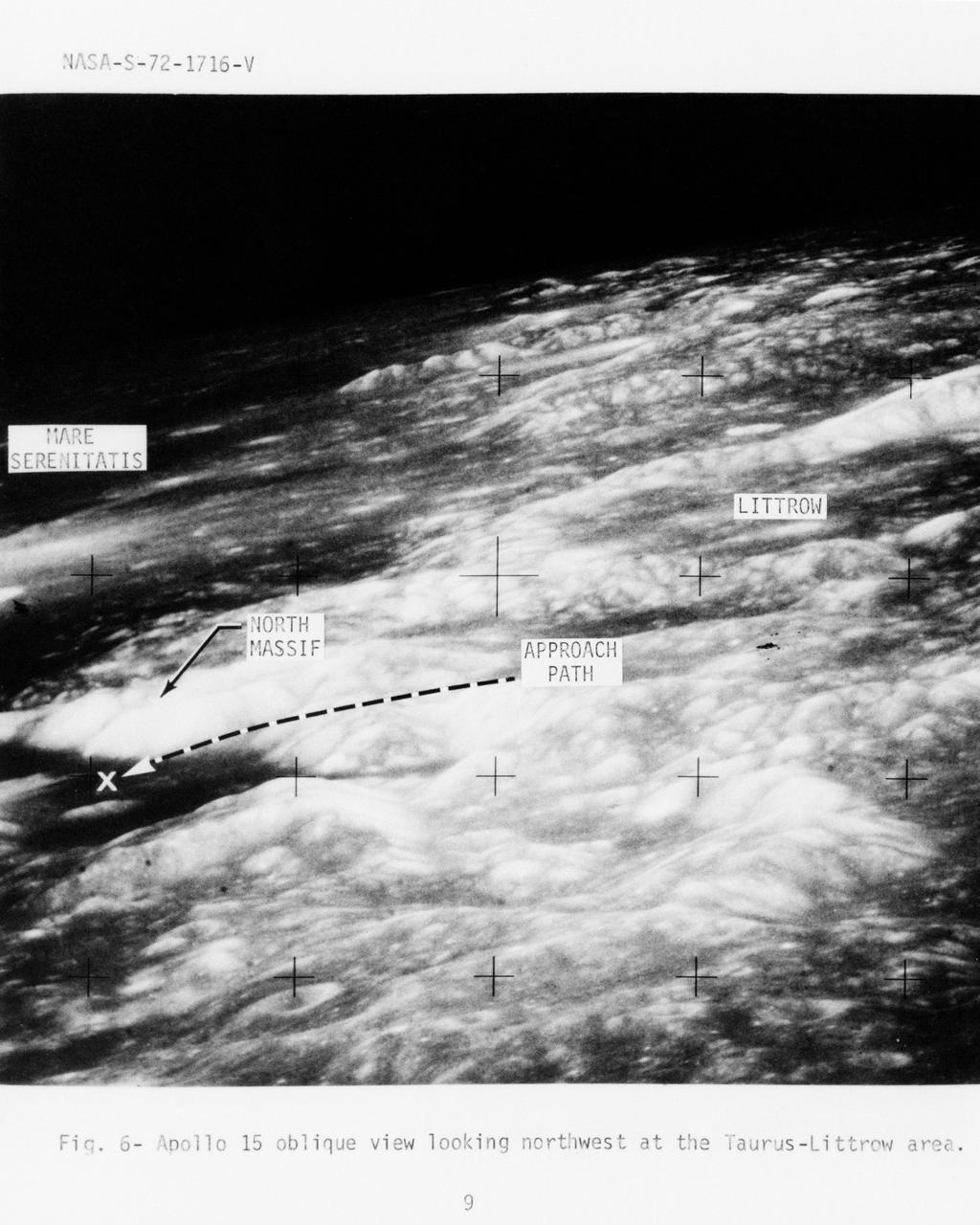
S72-01716 (July 1972) --- An oblique view of the Taurus-Littrow area on the lunar nearside, as photographed from the Apollo 15 spacecraft in lunar orbit. This is an enlarged view. The "X" marks the landing site of the scheduled Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. The overlay points out several features in the photograph. The coordinates of the Apollo 17 touchdown point are 30 degrees 44 minutes 58 seconds east longitude and 20 degrees 9 minutes 50 seconds north latitude.

Panorama view of Apollo 17 Lunar surface photos for use in presentations to NASA management and for Outreach Education in regard to new NASA initiative for human planetary research. Photo numbers used for this panoramic include: Apollo 17 start frame AS17-147-22572 thru end frame AS17-147-22600. View is of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiment Package (ALSEP) Station taken during Extravehicular Activity (EVA) 1.
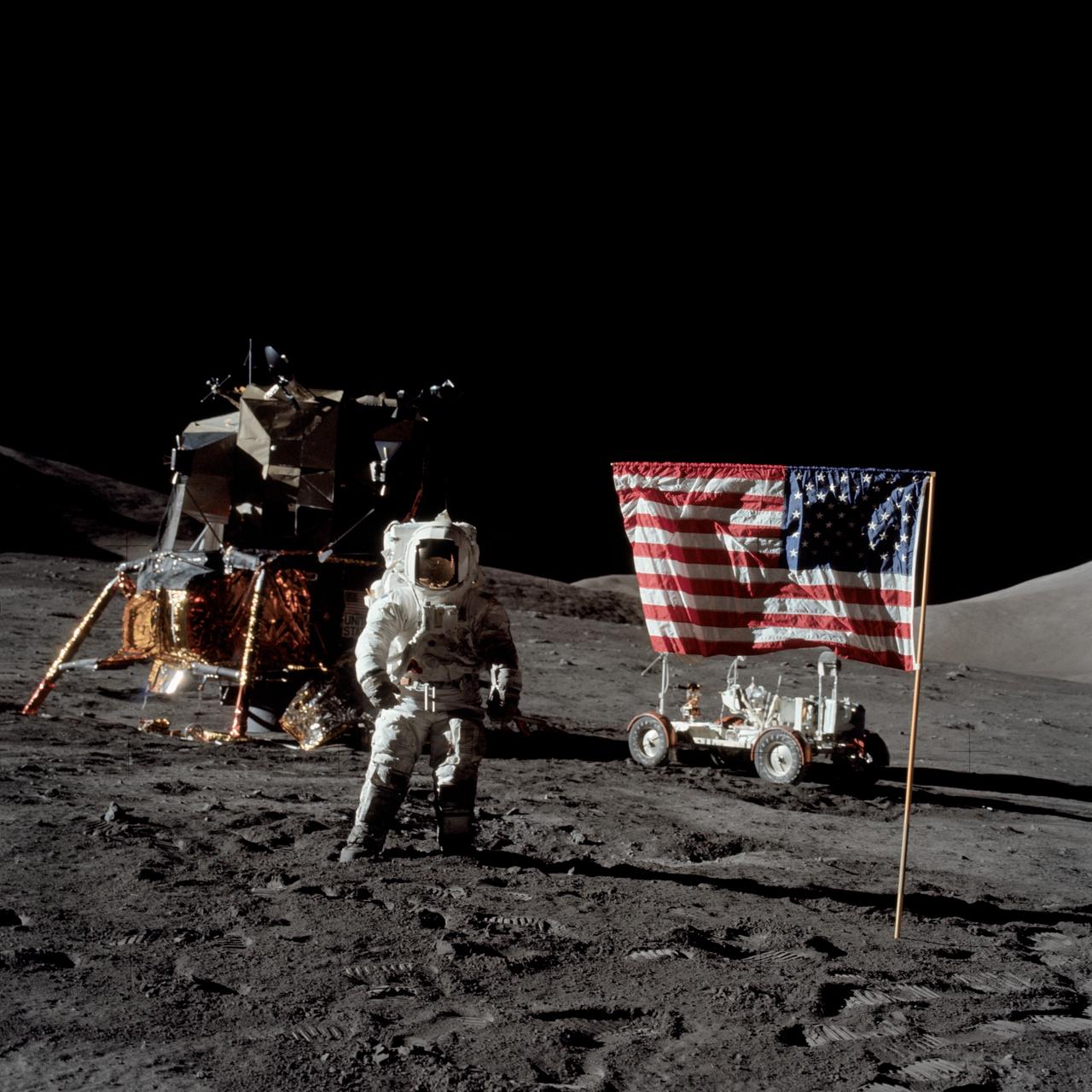

AS17-134-20382 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 lunar module pilot, stands near the deployed United States flag on the lunar surface during extravehicular activity (EVA) of NASA's final lunar landing mission in the Apollo series. The Lunar Module (LM) is at left background and the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at right background (partially obscured). The photo was made by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the LM "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.

Colleen Hartman, director of physics, aeronautics, and space science at the National Academies of Science gives closing remarks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Colleen Hartman, director of physics, aeronautics, and space science at the National Academies of Science gives closing remarks during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Colleen Hartman, director of physics, aeronautics, and space science at the National Academies of Science , left, and NASA Administrator Bill Nelson are seen as they view the NASA Art Program Exhibition “Launching the Future: Looking Back to Look Forward” during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
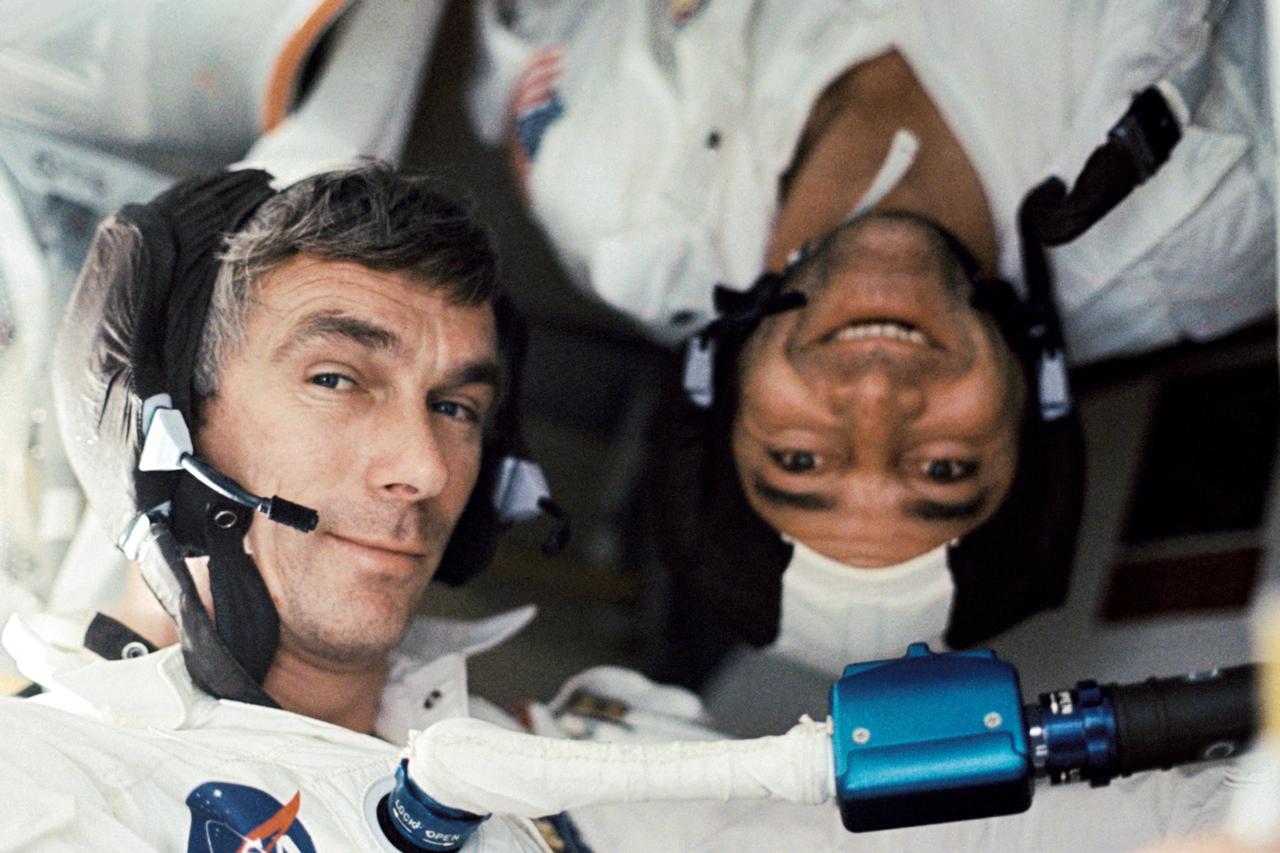

AS17-162-24053 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt, lunar module pilot, took this photograph of his two fellow crew men under zero-gravity conditions aboard the Apollo 17 spacecraft during the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. That is astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander, who is seemingly "right side up." Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, appears to be "upside down." While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Evans remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
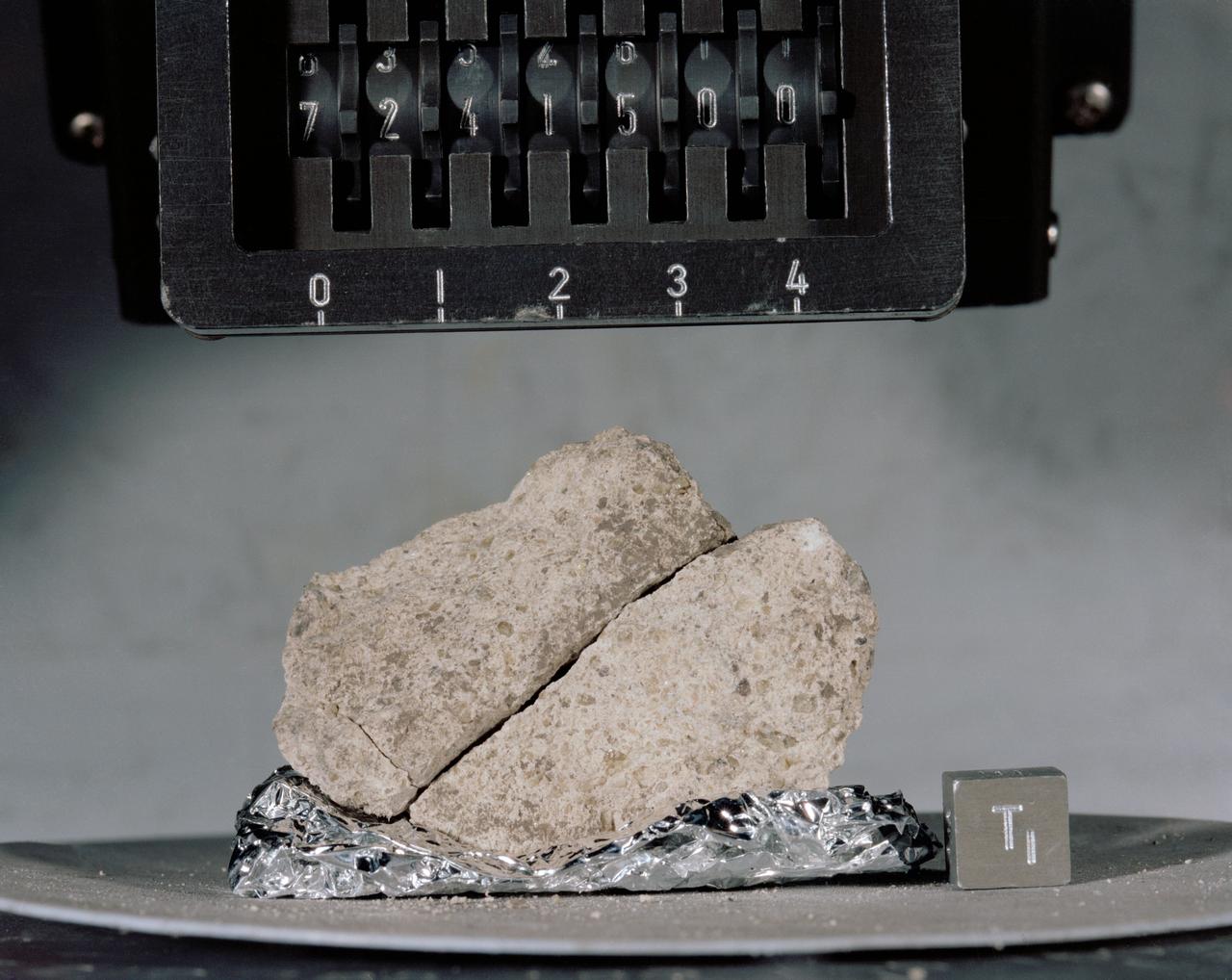

S73-16199 (December 1972) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar sample number 72415,0 which was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. This sample is a brecciated dunite clast weighing a little over 32 grams (about 1.14 ounces). This sample was collected at station 2 (South Massif) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA). IMPORTANT NOTE FOR CREDIT: The view was photographed by Karl Mills, Scientific Photo Arts, Berkeley, California.
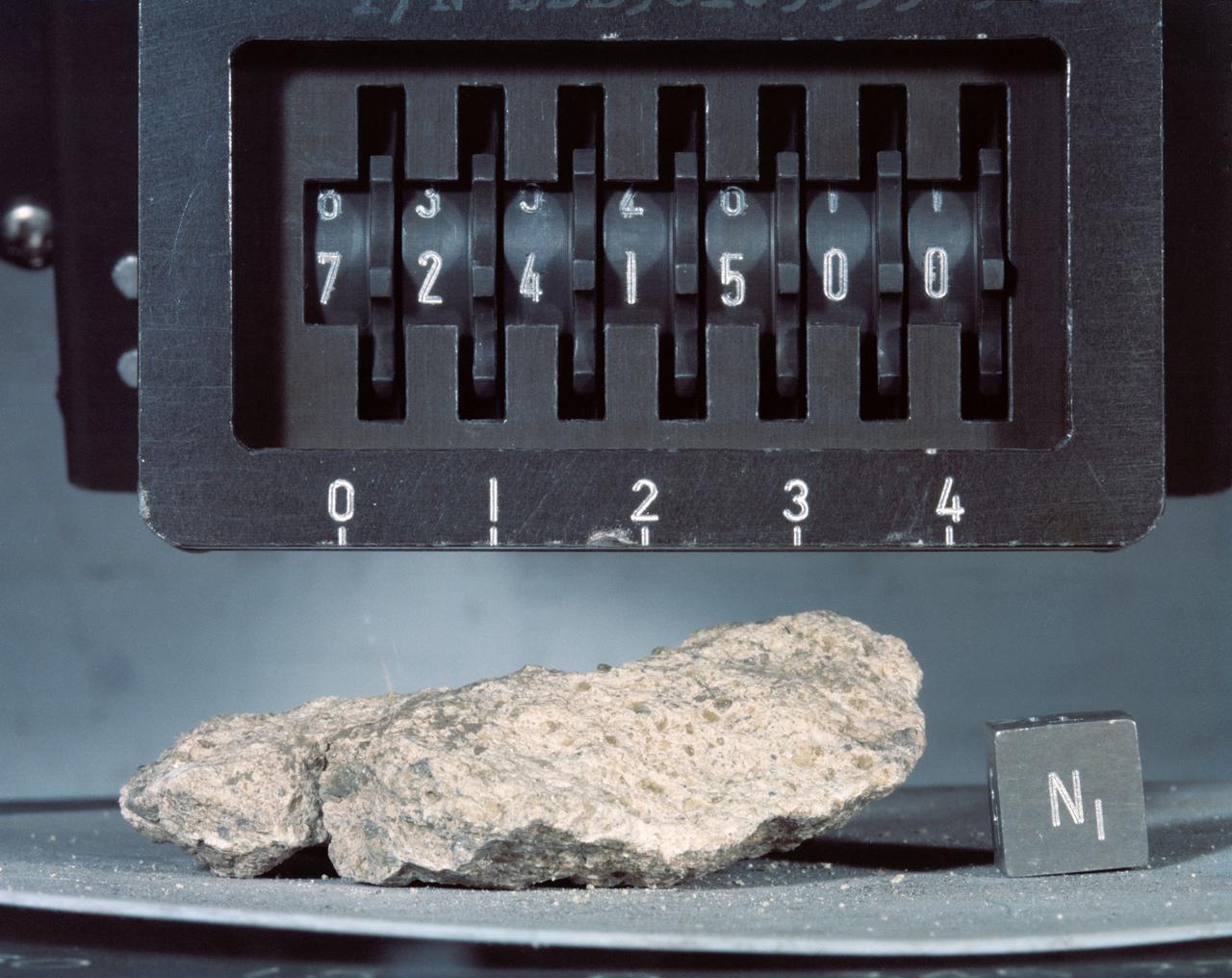

S73-16198 (December 1972) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar sample number 72415,0 which was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. This sample is a brecciated dunite clast weighing a little over 32 grams (about 1.14 ounces). This sample was collected at station 2 (South Massif) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA).
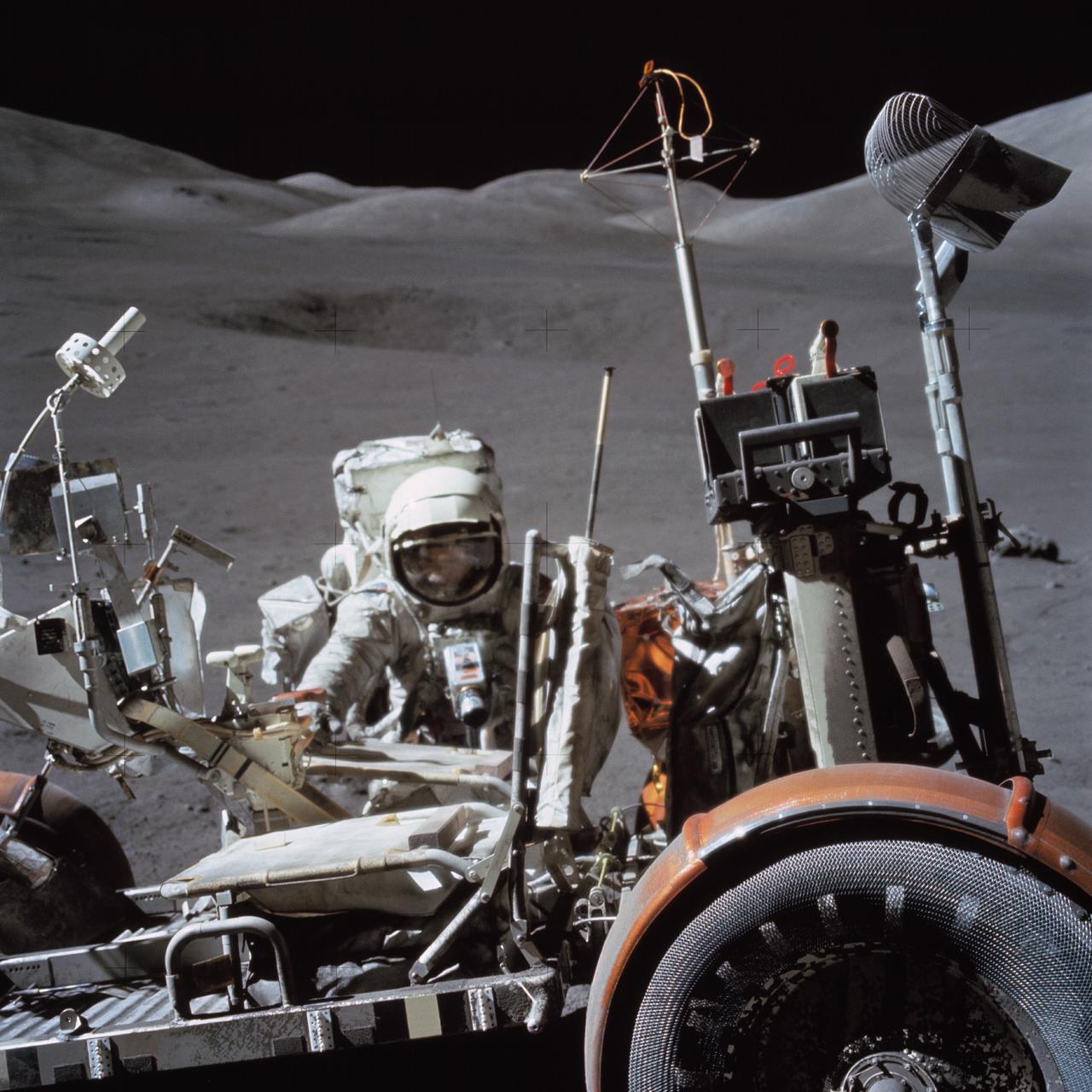
AS17-146-22296 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, works near the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the third Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow site on the lunar surface. The front part of the LRV is out of frame at left, but the seats and several geological tools can be seen. The photo was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander.

Panorama view of Apollo 17 Lunar surface photos for use in presentations to NASA management and for Outreach Education in regard to new NASA initiative for human planetary research. Photo numbers used for this panoramic include: Apollo 17 start frame AS17-146-22339 thru end frame AS17-146-22363. View is of Station 7 Panorama taken during Extravehicular Activity (EVA) 3.
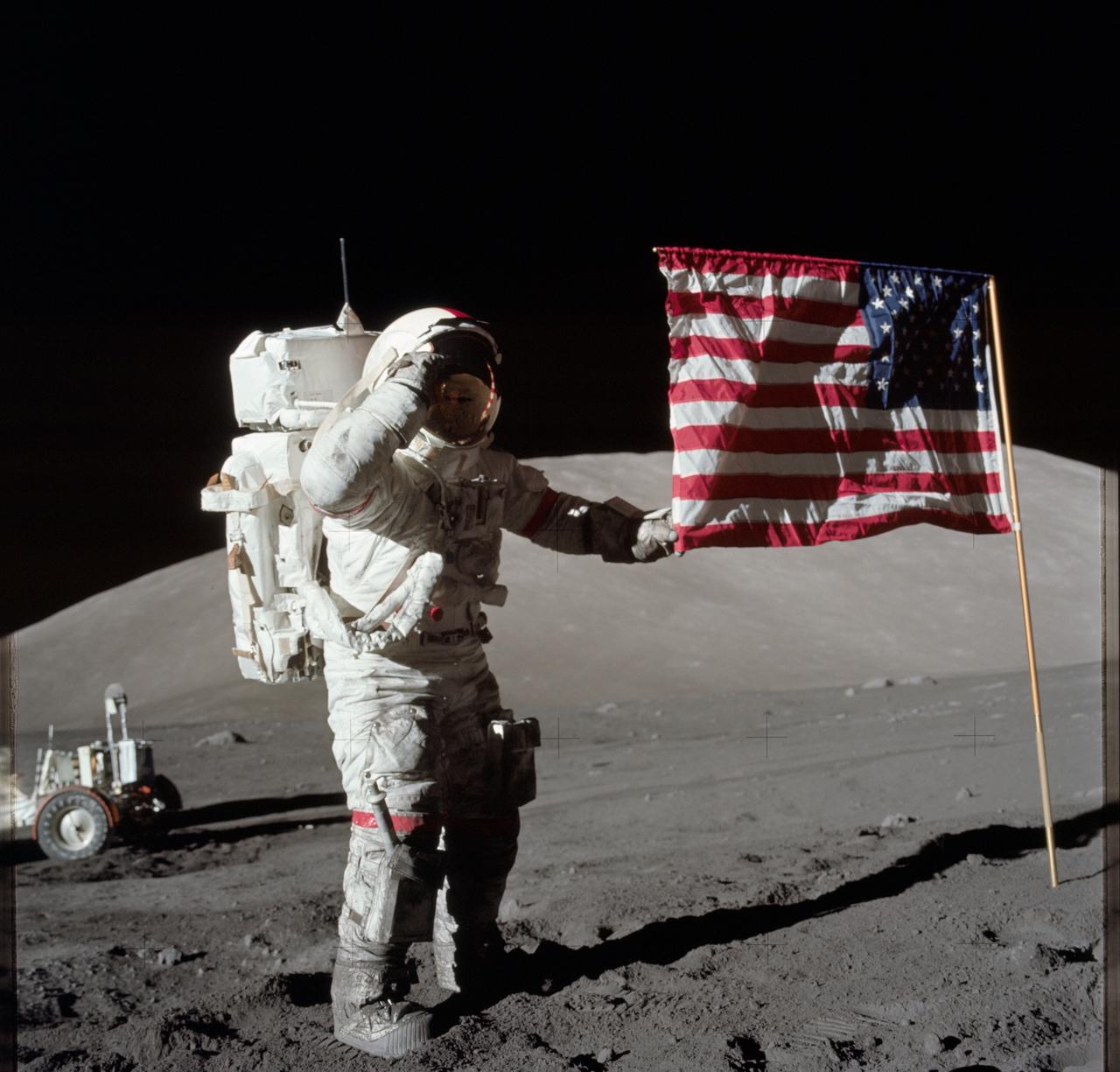

AS17-134-20386 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander, is photographed next to the deployed United States flag during lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The highest part of the flag appears to point toward our planet Earth in the distant background. This picture was taken by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
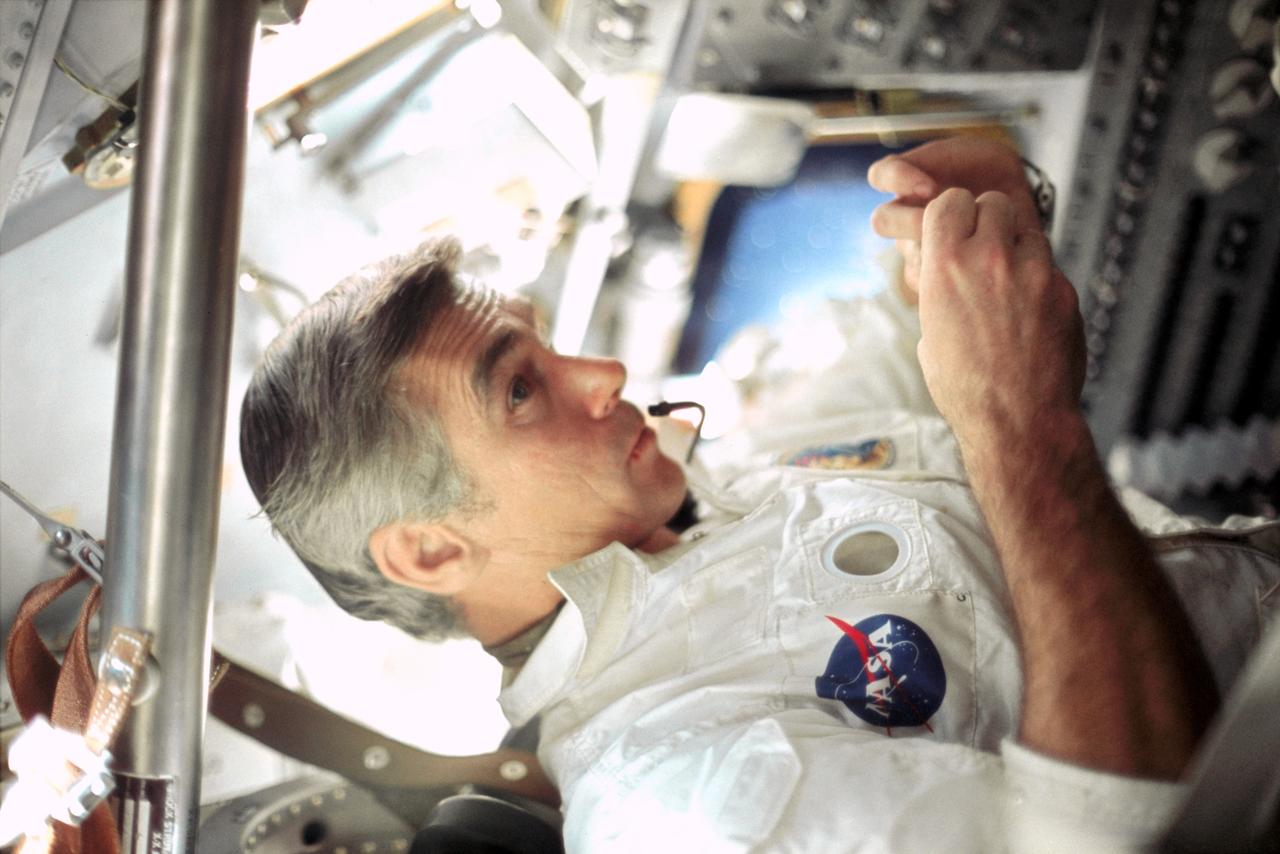

AS17-163-24122 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This candid photograph of astronaut Eugene A. Cernan was taken by a fellow crewman aboard the Apollo 17 spacecraft during the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. Cernan was the mission commander. Also, aboard Apollo 17 were astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt, lunar module pilot.
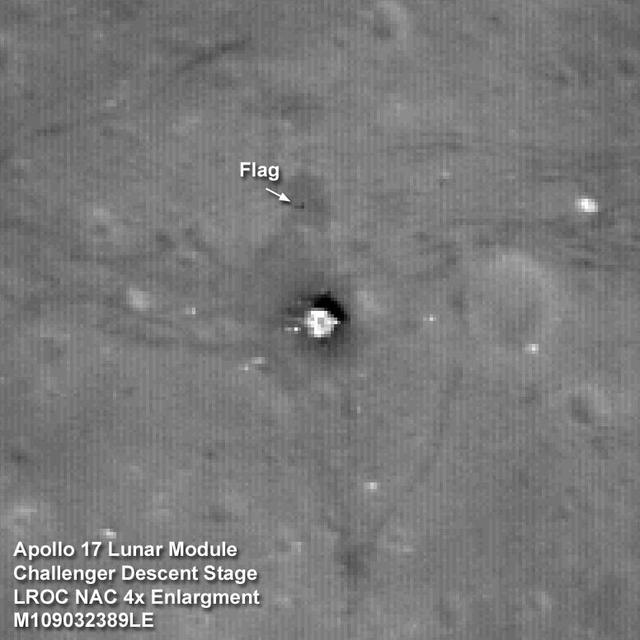
The Apollo 17 Lunar Module Challenger descent stage comes into focus in this image taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
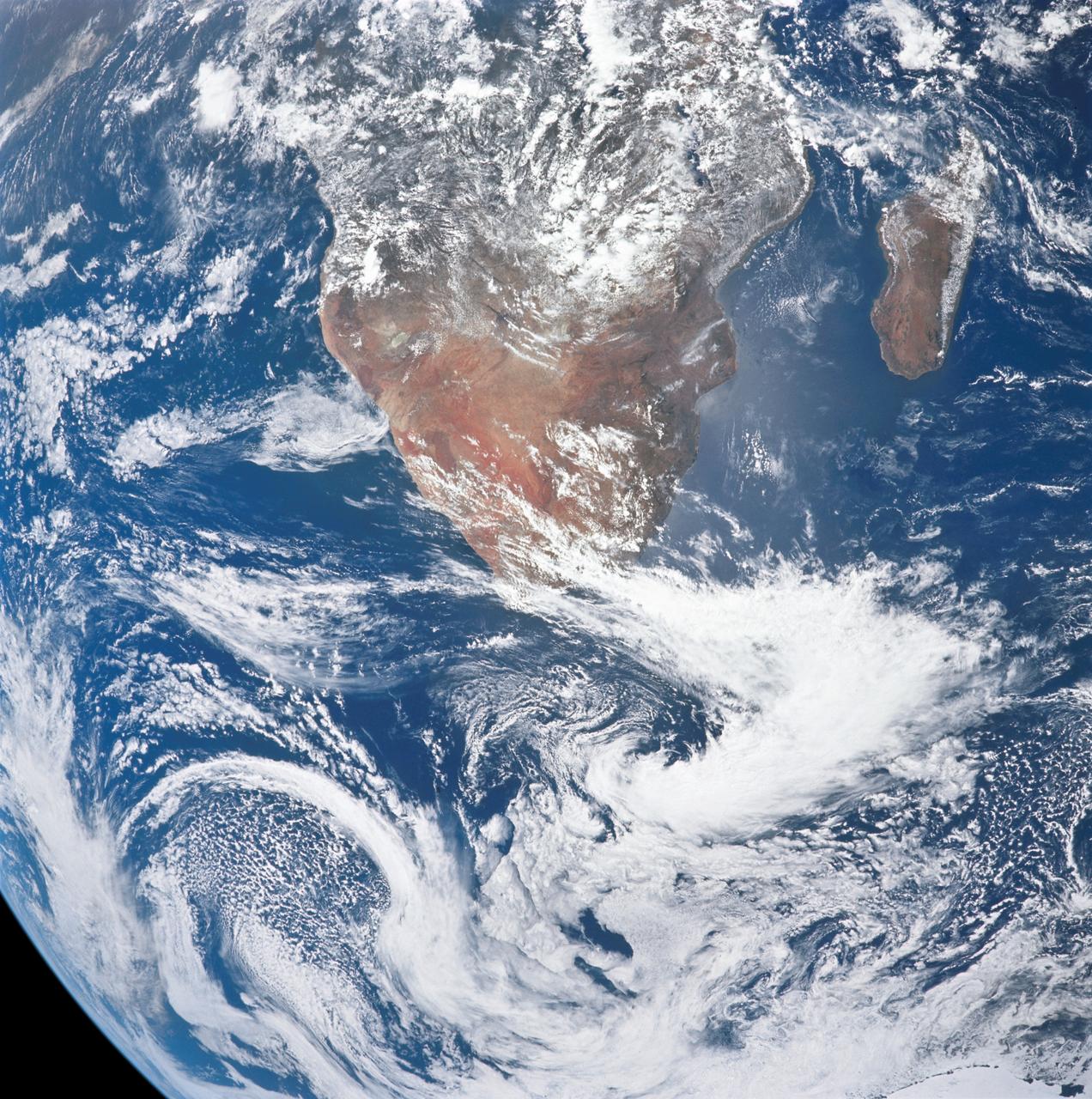

AS17-148-22717 (7 Dec. 1972) --- This view of a portion of Earth was taken from the Apollo 17 spacecraft following trans-lunar insertion during the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo Program. The visible land mass is the southern two-thirds of the African continent, with Madagascar at right. A portion of Antarctica is visible at bottom frame. Onboard the Apollo 17 spacecraft were astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander; Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot; and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Hadley-Apennine region of the moon, astronaut Evans remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
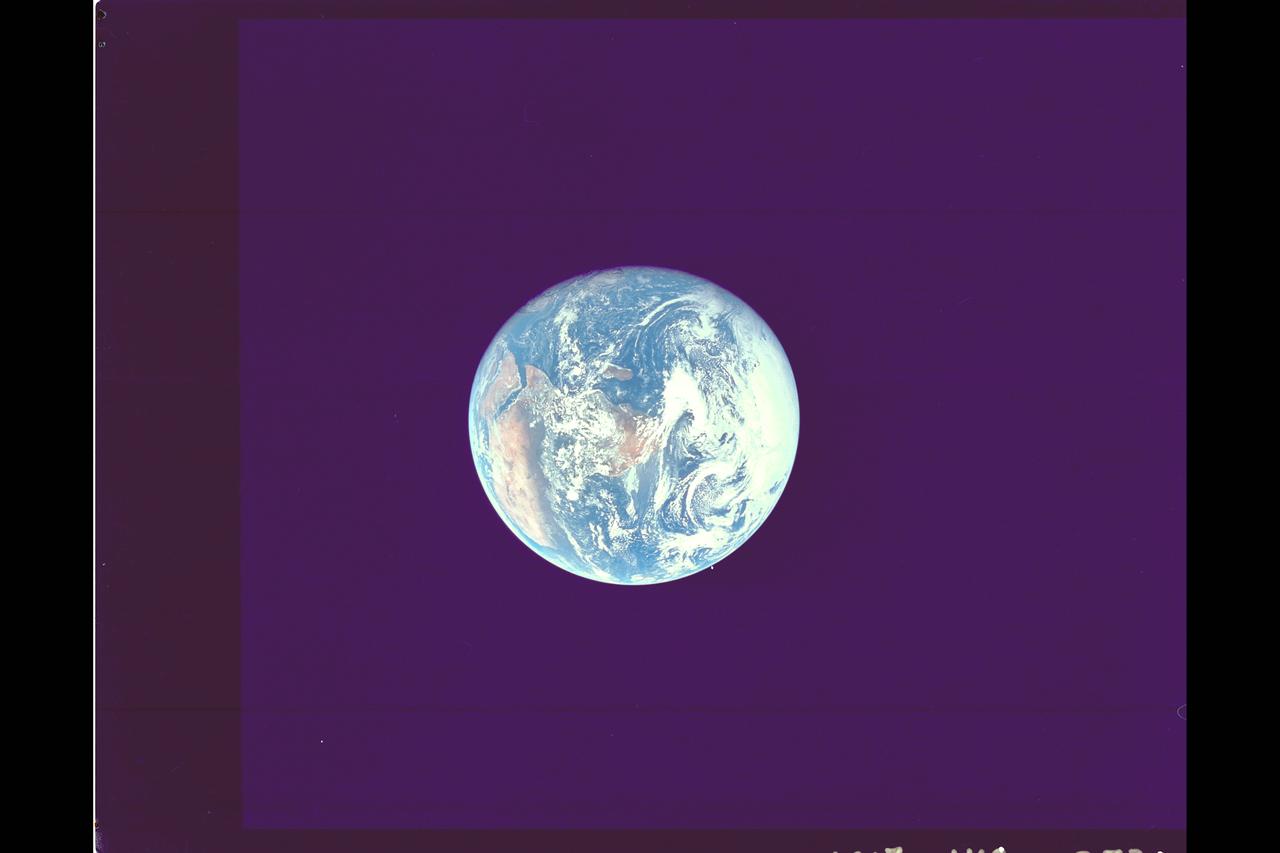

Photo by Apollo 17 Earth
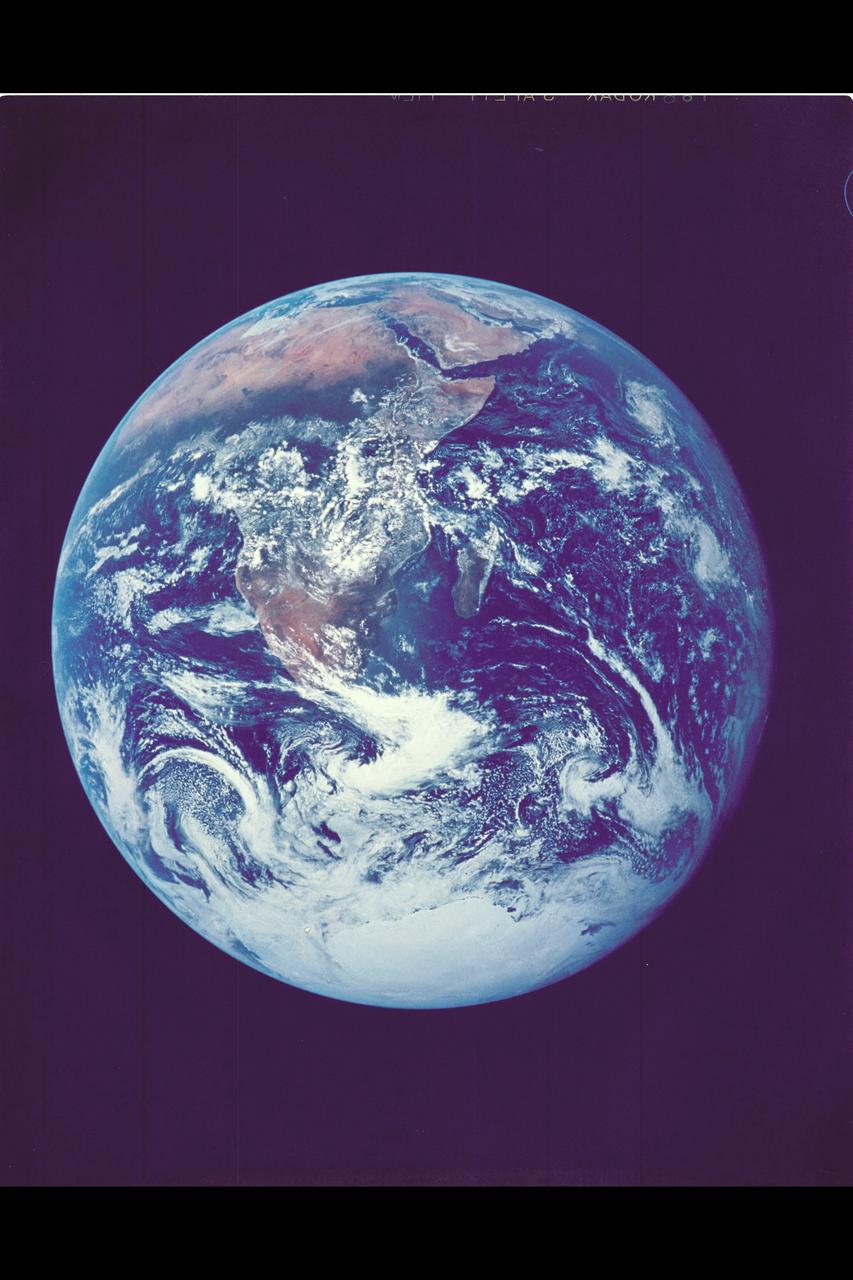

Photo by Apollo 17 Earth
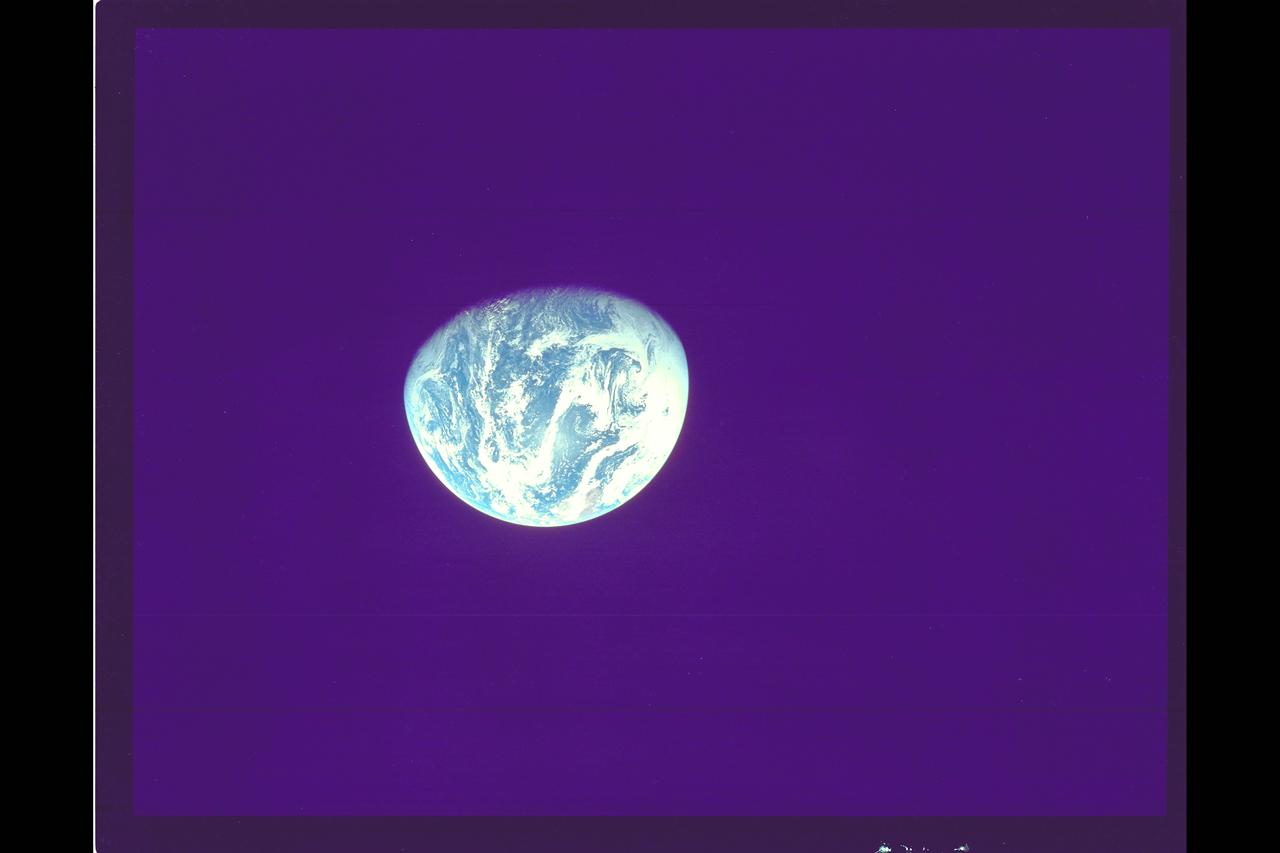

Photo by Apollo 17 Earth

Panorama view of Apollo 17 Lunar surface photos for use in presentations to NASA management and for Outreach Education in regard to new NASA initiative for human planetary research. Photo numbers used for this panoramic include: Apollo 17 start frame AS17-136-20745 thru end frame AS17-136-20759. View is of Station 1, taken during the first Extravehicular Activity (EVA) 1.

Panorama view of Apollo 17 Lunar surface photos for use in presentations to NASA management and for Outreach Education in regard to new NASA initiative for human planetary research. Photo numbers used for this panoramic include: Apollo 17 start frame AS17-138-21053 thru end frame AS17-138-21073. View is of Station 2, taken during the second Extravehicular Activity (EVA) 2.
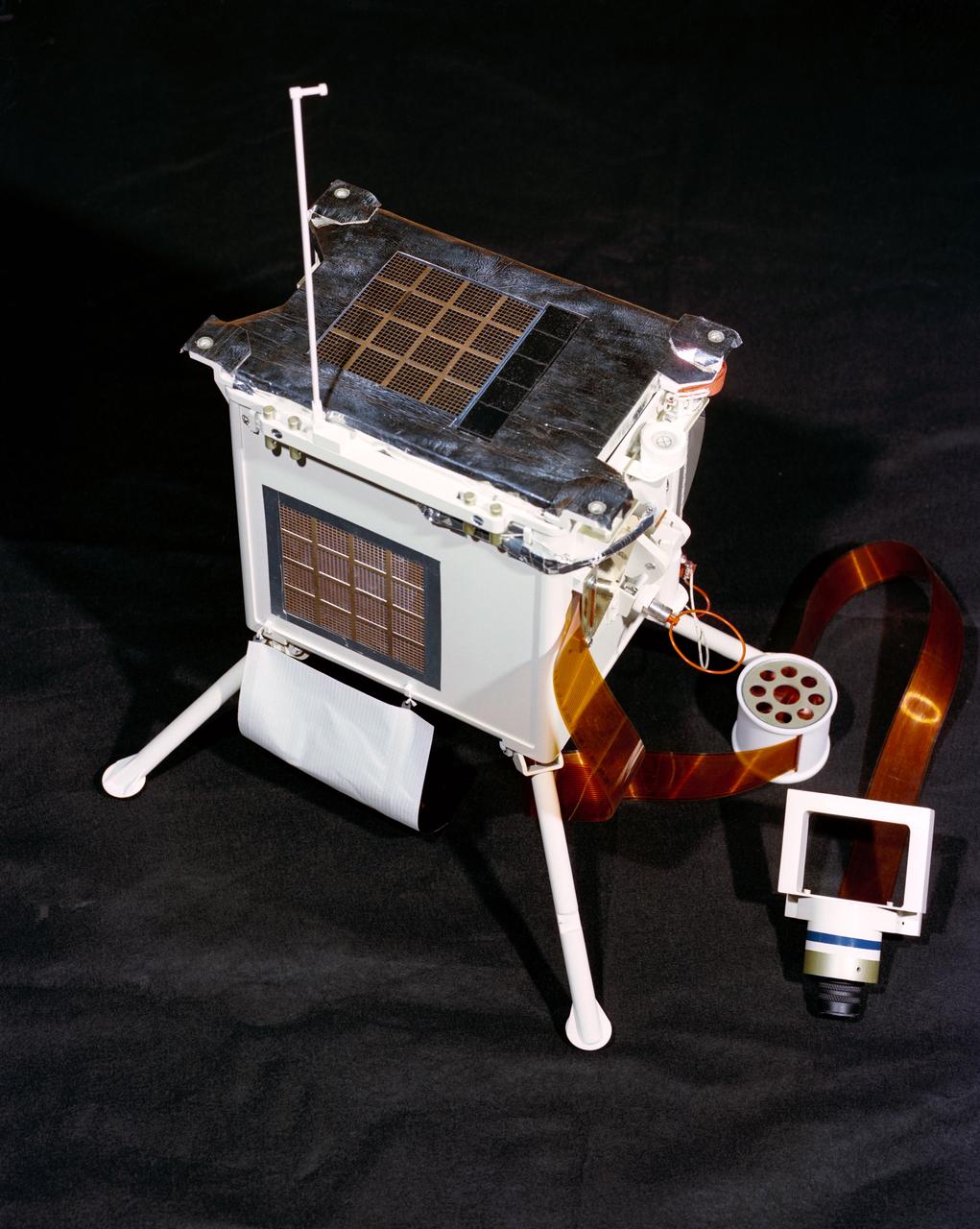

S72-37257 (November 1972) --- The Lunar Ejecta and Meteorites Experiment (S-202), one of the experiments of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package which will be carried on the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. The purpose of this experiment is to measure the physical parameters of primary and secondary particles impacting the lunar surface.

S72-03145 (October 1972) --- A vertical view of the Apollo 17 Taurus-Littrow site with an overlay to illustrate the three planned Apollo 17 traverses using the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The EVA-1 traverse has a single station (1); the EVA-2 traverse has four stations (2,3,4,5); and the EVA-3 traverse has five stations (6,7,8,9,10). Stations 10-A and 10-B are alternate locations for Station 10. In addition to the major stations mentioned above, brief stops are planned for sampling between stations using the LRV sampler tool (note diamond-shaped figures), and for deploying explosive charges associated with the Lunar Seismic Profiling Experiment (LSPE - note black x-marks).
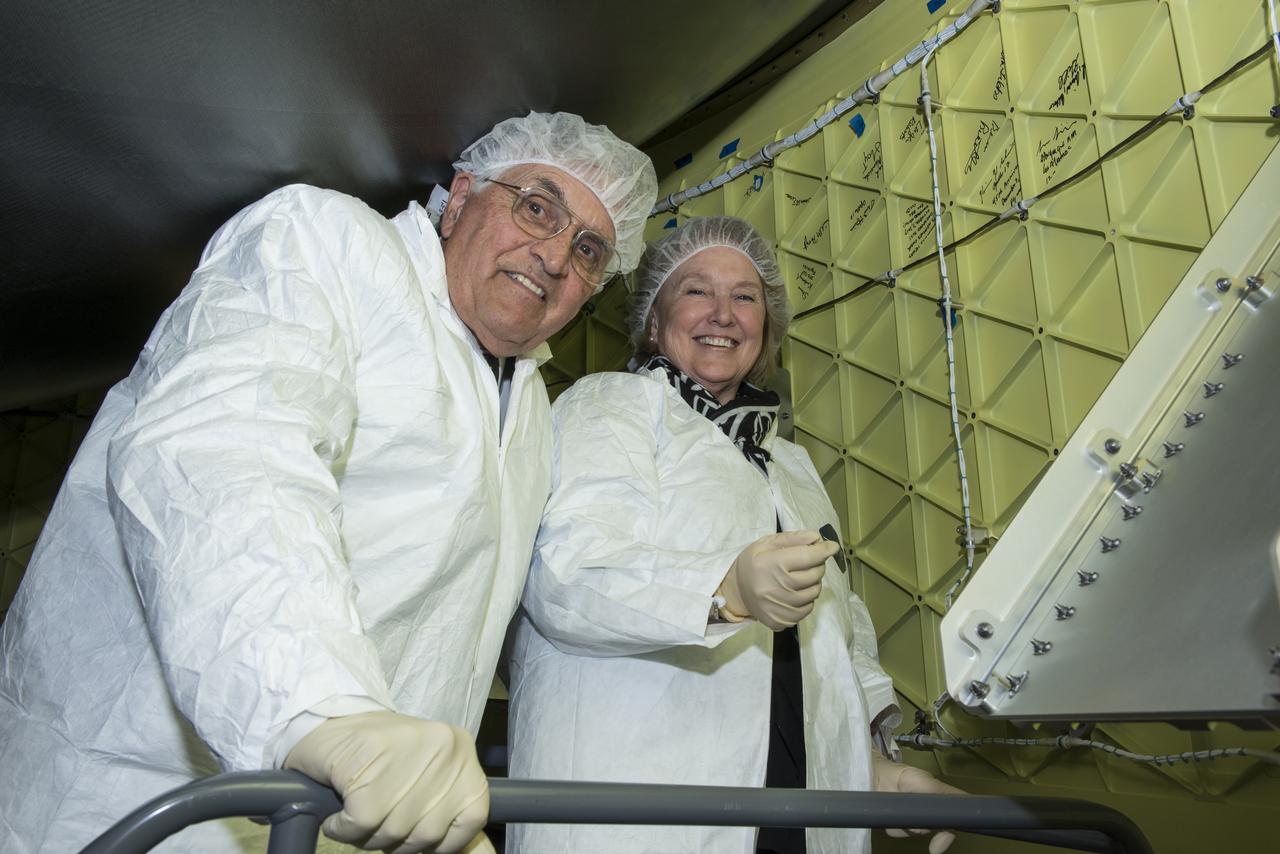

Apollo 17 astronaut Harrison Schmitt and his wife, Teresa, toured the Orion Stage Adapter while at Marshall and signed it before its flight on Exploration Mission-1 in late 2019
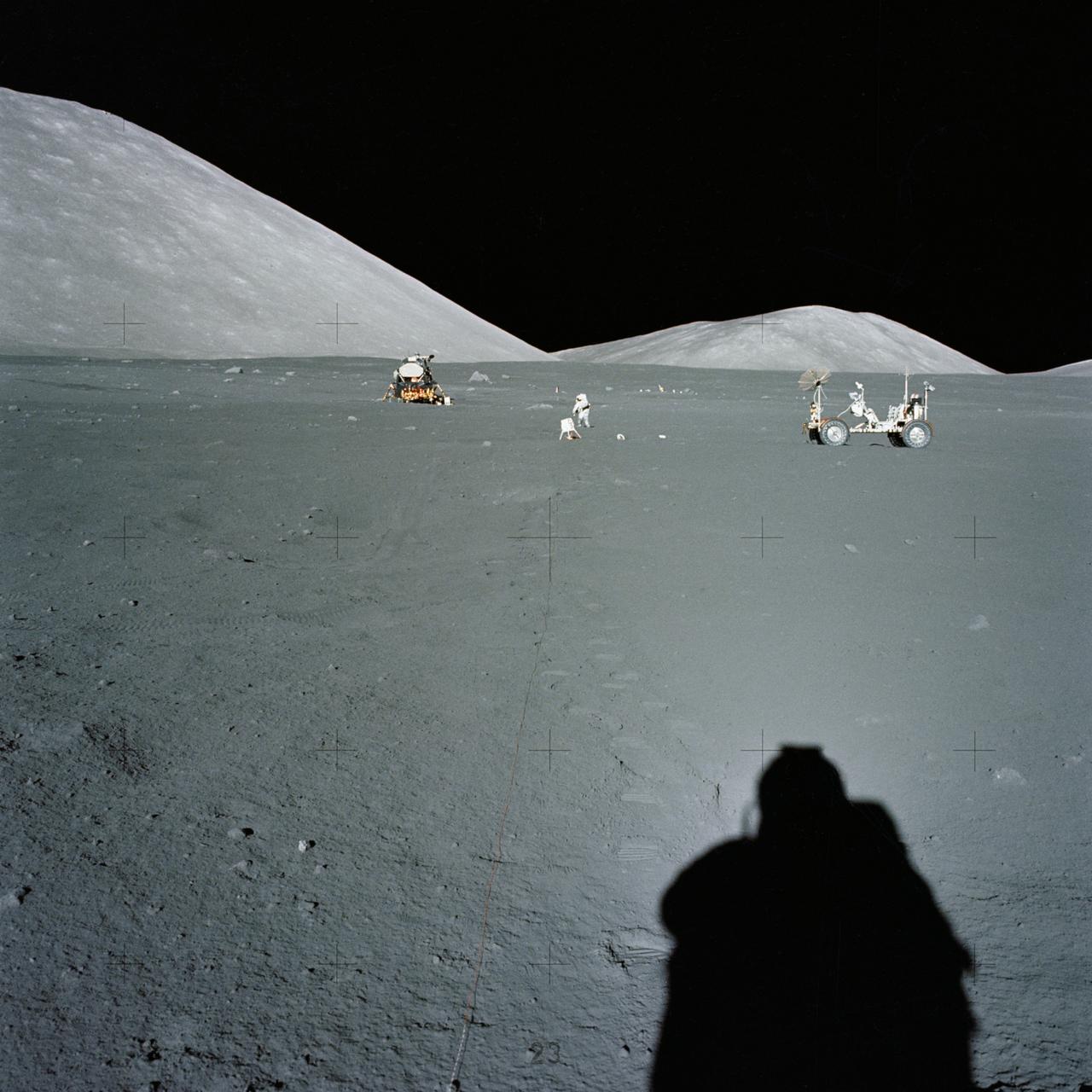

AS17-134-20435 (10 Dec. 1972) --- Wide-angle view of the Apollo 17 Taurus-Littrow lunar landing site. To the left in the background is the Lunar Module. To the right in the background is the Lunar Roving vehicle. An Apollo 17 crewmember is photographed between the two points. The shadow of the astronaut taking the photograph can be seen in the right foreground.
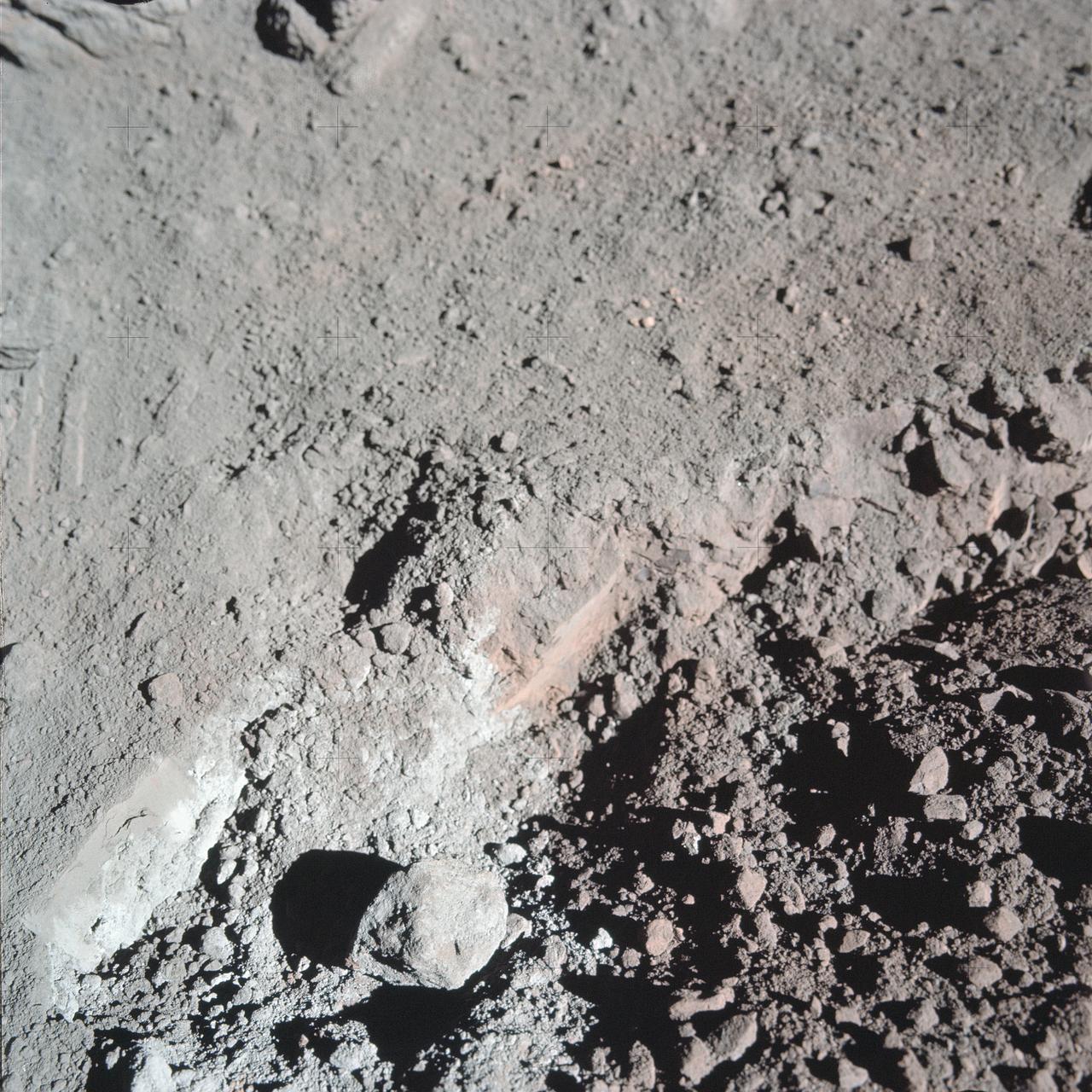

AS17-137-20989 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A close-up view of the much-publicized orange soil which the Apollo 17 crewmen found at Station 4 (Shorty Crater) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The orange soil was first spotted by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt. While astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The orange soil was never seen by the crewmen of the other lunar landing missions - Apollo 11 (Sea of Tranquility); Apollo 12 (Ocean of Storms); Apollo 14 (Fra Mauro); Apollo 15 (Hadley-Apennines); and Apollo 16 (Descartes).
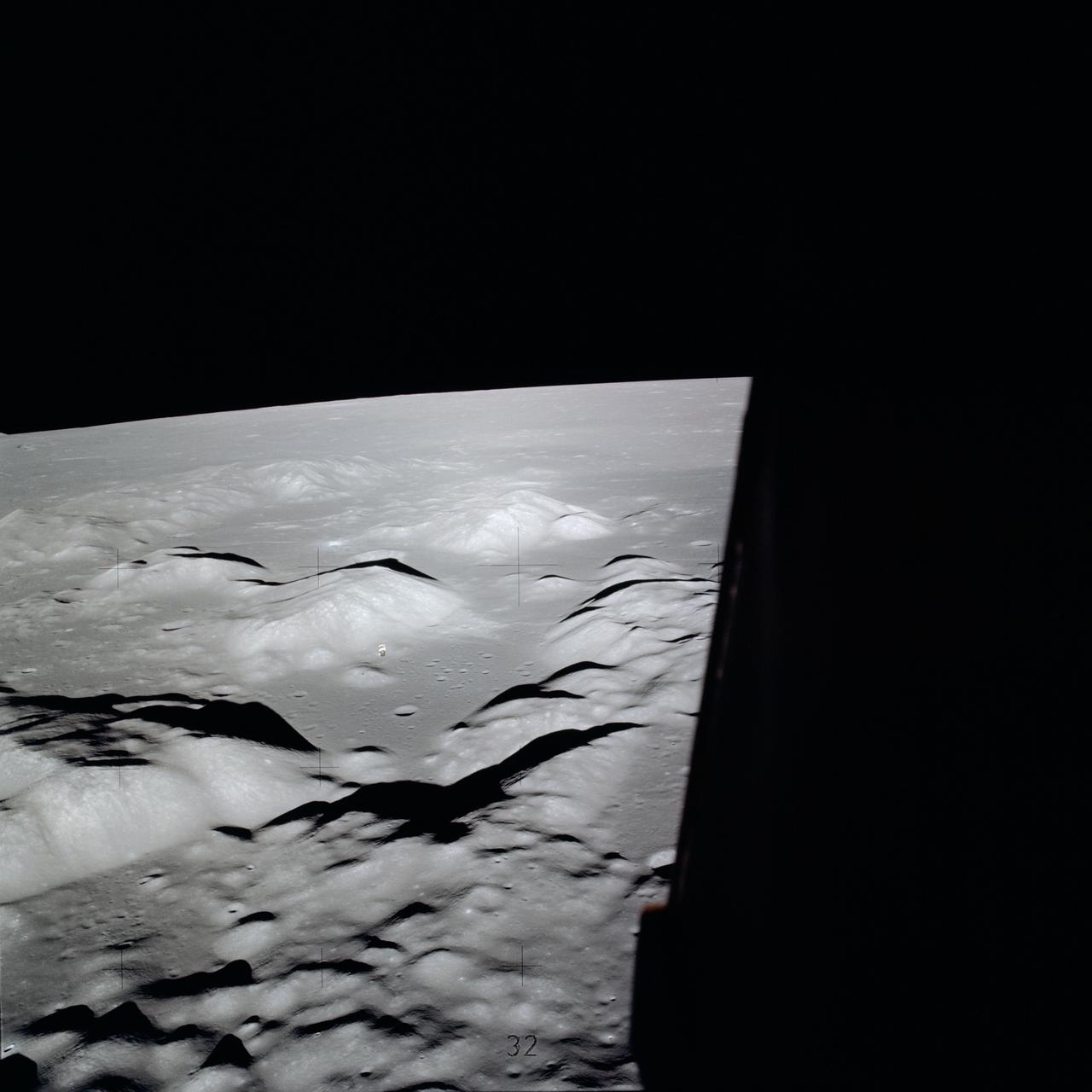

This 70mm frame, showintg the Apollo 17 Command/Service Modules (CSM) backdropped against the Taurus-Littrow landing site, was exposed from the lunar module (LM) prior to the LM's touchdown on the lunar surface.

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut
Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut
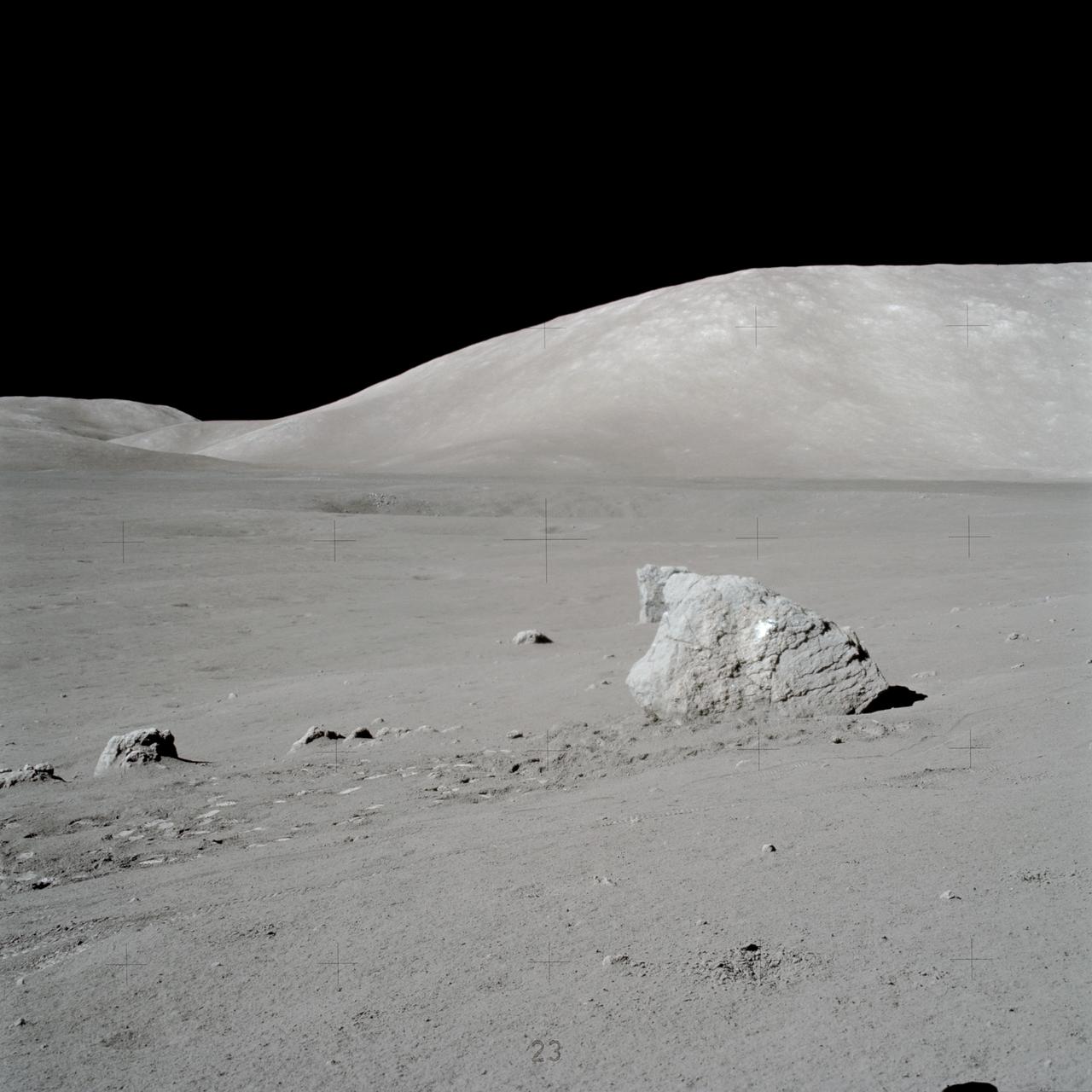

AS17-146-22351 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This view, photographed by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, shows a large boulder which was discovered by astronauts Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt during one of their space walks. The astronauts later pointed out light clasts on the boulder. South Massif is in the background. Tracks left by the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) can be seen near foreground. While astronauts Cernan, commander, and Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
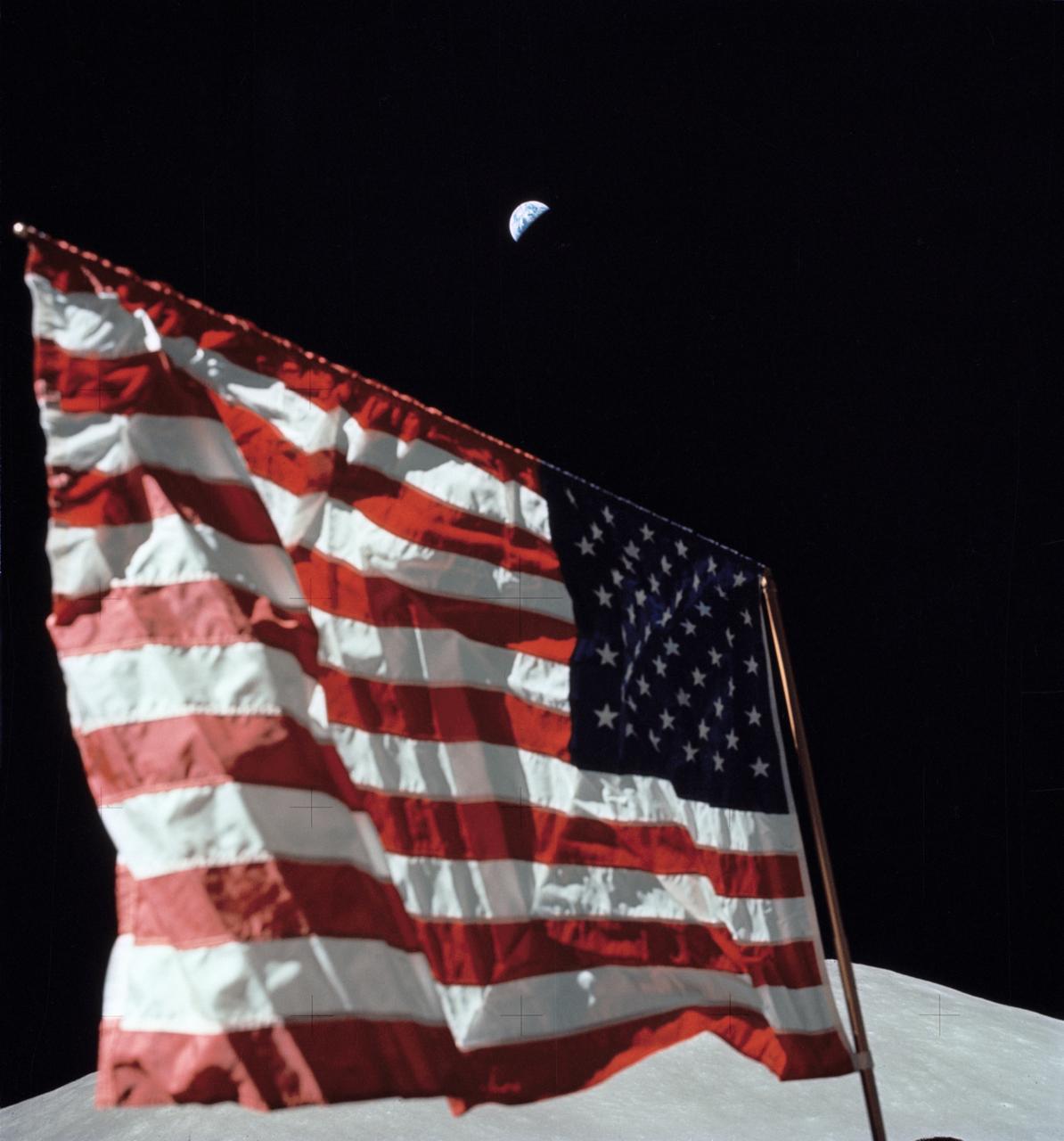

AS17-134-20466 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- A close-up view of the U.S. flag deployed on the moon at the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the crewmen of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. The crescent Earth can be seen in the far distant background above the flag. The lunar feature in the near background is South Massif. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module "Challenger" to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
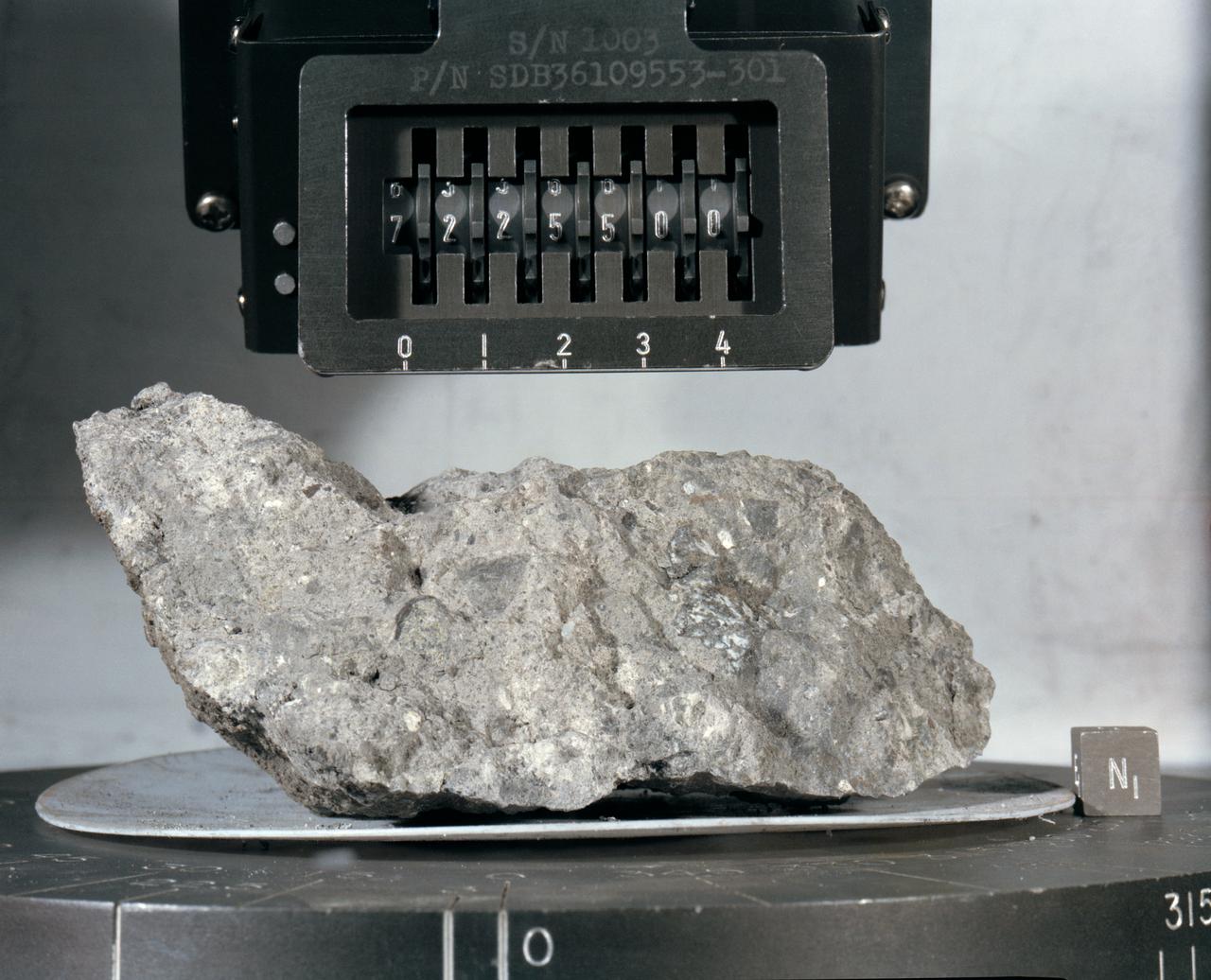

S73-16007 (December 1972) --- A "mug shot" of Apollo 17 lunar sample no. 72255 which was brought back from the lunar surface by the final team of Apollo astronauts. The rock weighs 461.2 grams and measures 2.5 x 9 x 10.5 centimeters. The light grey breccia is sub-rounded on all faces except the top and north sides.
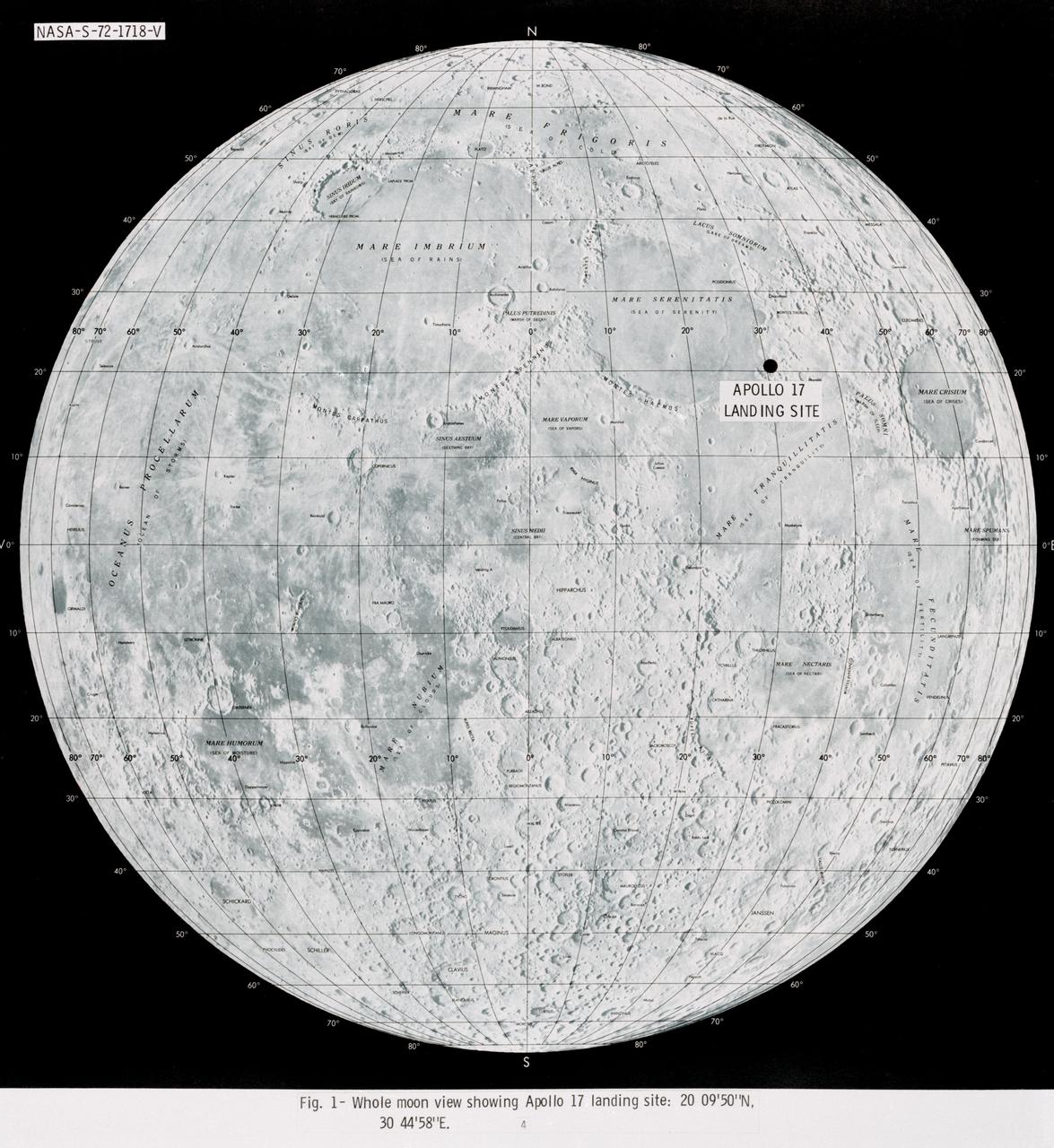

S72-01718 (July 1972) --- A photographic illustration of a full moon showing the location of the Apollo 17 landing site on the lunar nearside. The black dot pinpointing the landing site is in the Taurus-Littrow area at the southeastern edge of the Sea of Serenity. The coordinates of the landing point are 30 degrees 44 minutes 58 seconds east longitude and 20 degrees 9 minutes 50 seconds north latitude.
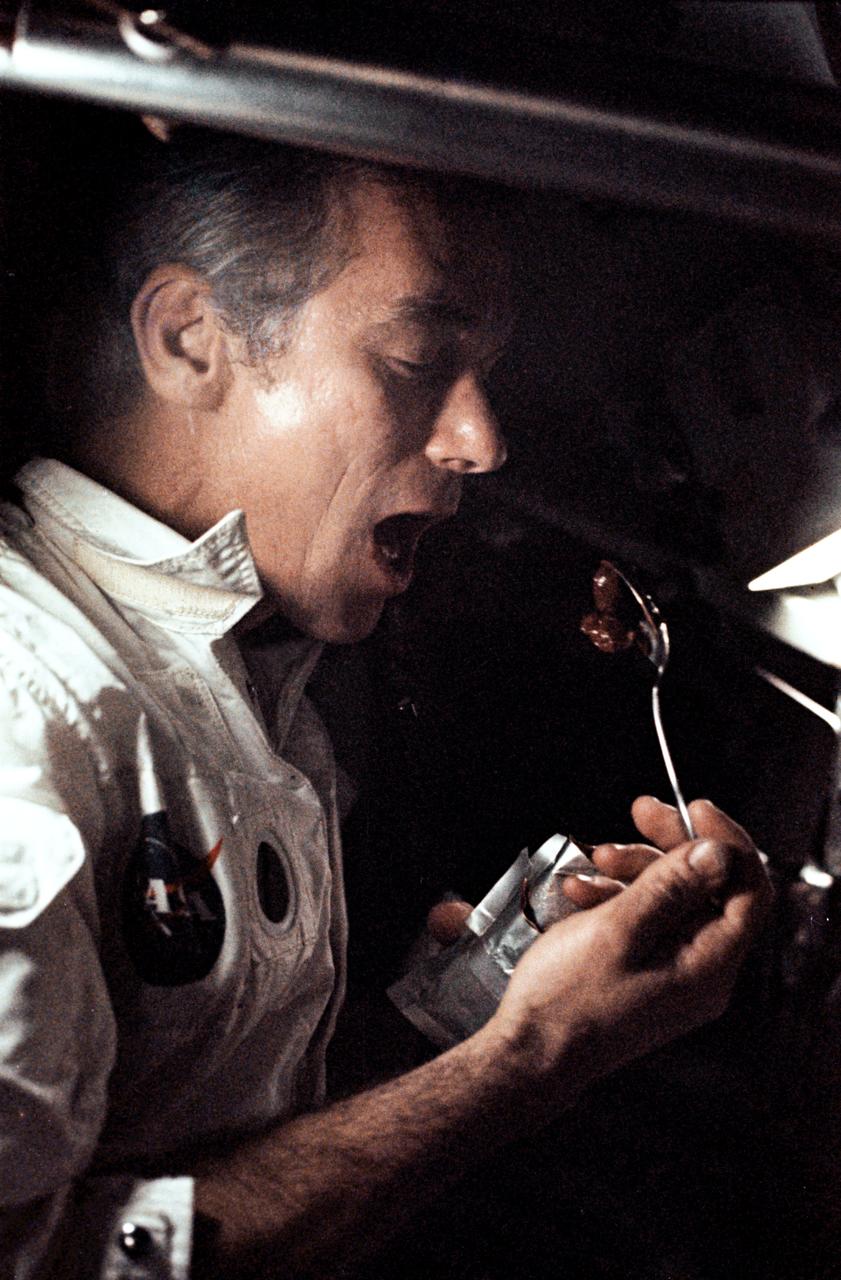

AS17-163-24129 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- A fellow crewman took this photograph of astronaut Eugene A. Cernan eating a meal under weightlessness conditions of space during the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. Also, aboard the Apollo 17 spacecraft were astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt, lunar module pilot. Cernan was the mission commander.
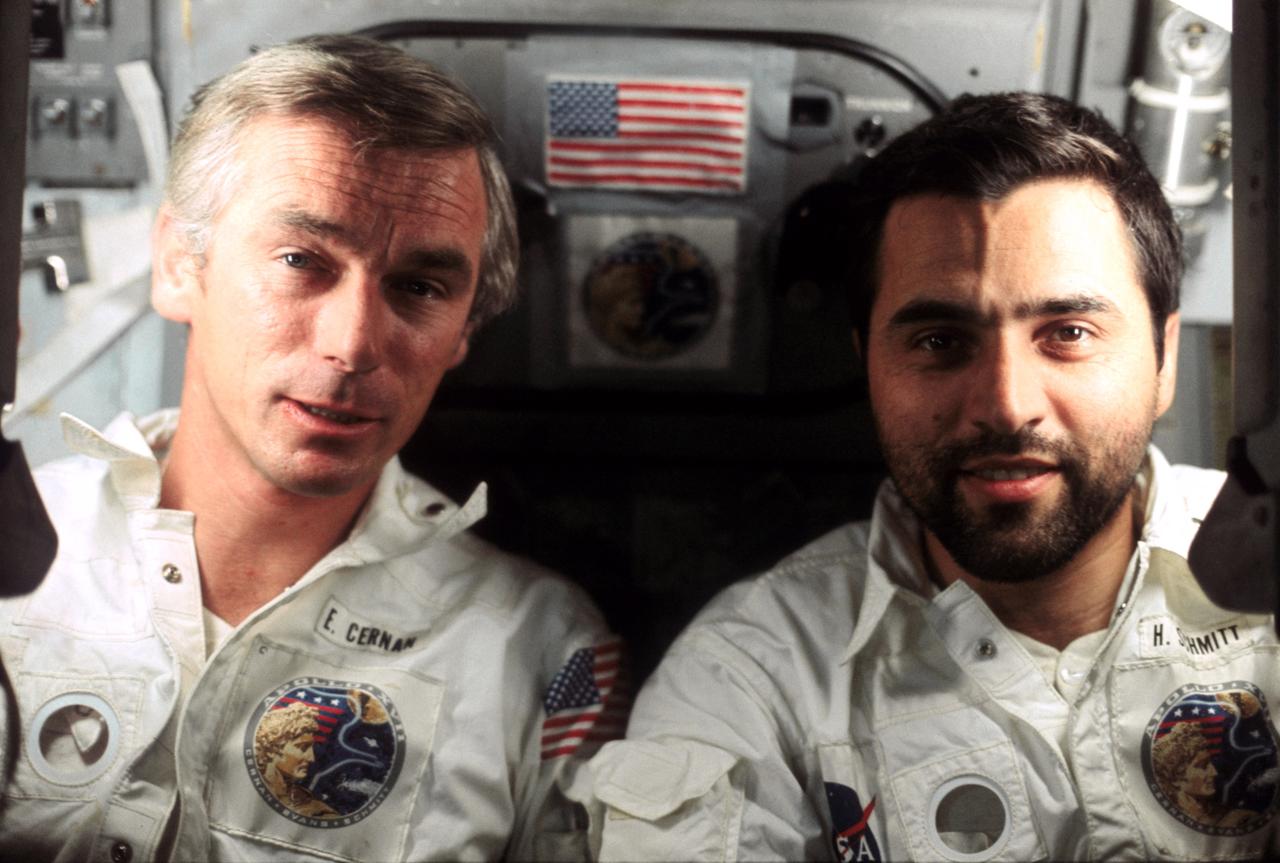

AS17-163-24148 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (left) and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt are photographed by the third crew man aboard the Apollo 17 spacecraft during the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, took this picture. Cernan was the mission commander. Schmitt served as the lunar module pilot.
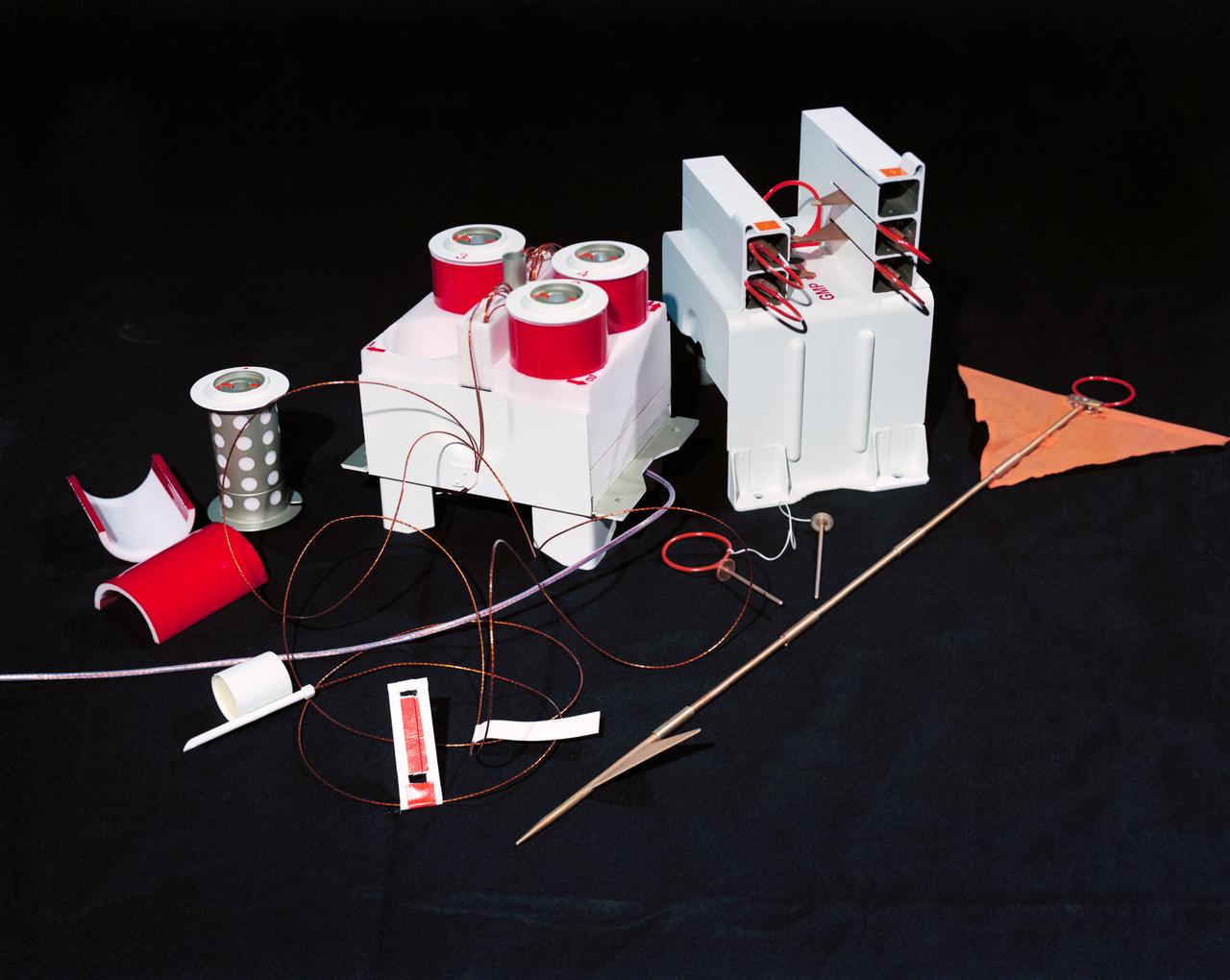
S72-37259 (November 1972) --- The Geophone Module and Cable Reels of the Lunar Seismic Profiling Experiment (S-203), a component of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package which will be carried on the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. LSPE components are four geophones similar to those used in an earlier active seismic experiment, an electronics package in the ALSEP central station, and eight explosive packages which will be deployed during the geology traverse. The four geophones will be placed one in the center and one at each corner of a 90-meter equilateral triangle. Explosive charges placed on the surface will generate seismic waves of varying strengths to provide data on the structural profile of the landing site. After the charges have been fired by ground command, the experiment will settle down into a passive listening mode, detecting moonquakes, meteorite impacts and the thump caused by the Lunar Module ascent stage impact.
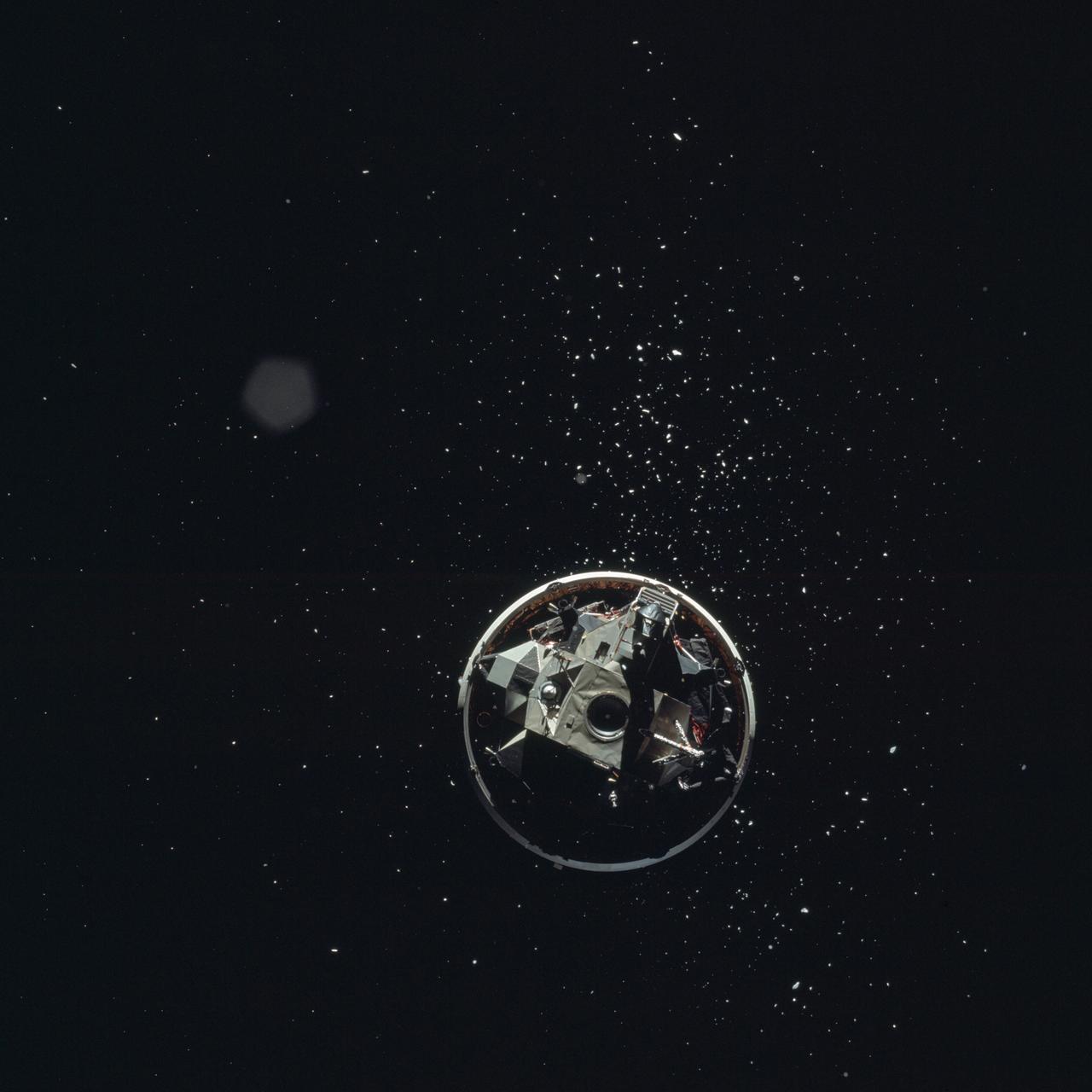

AS17-148-22688 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- View of the Lunar Module from the Apollo 17 spacecraft after transposition/docking maneuvers. The white dots surrounding the Lunar Module are debris from the Saturn S-IVB stage separation.

Apollo 17 lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, left, shared his experiences as an astronaut and lunar geologist during a visit to Marshall Dec. 7, as part of the Shared Experiences Forum. During an interactive Q&A moderated by Marshall Associate Director Jonathan Pettus, right, Schmitt spoke about launching on the Saturn V rocket, exploring the Moon and looking back at the Earth. The day of his visit was the 45th anniversary of the Apollo 17 launch.
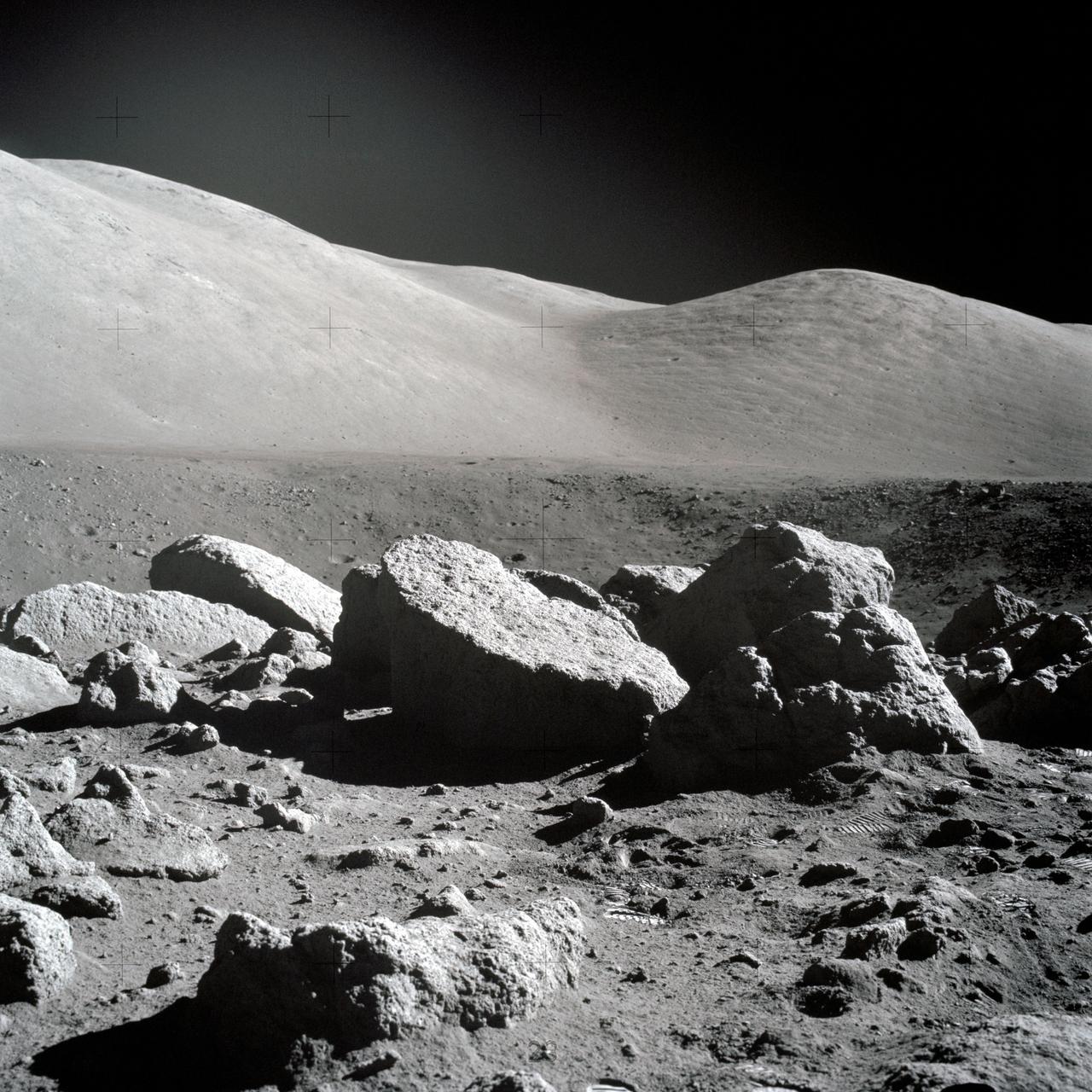

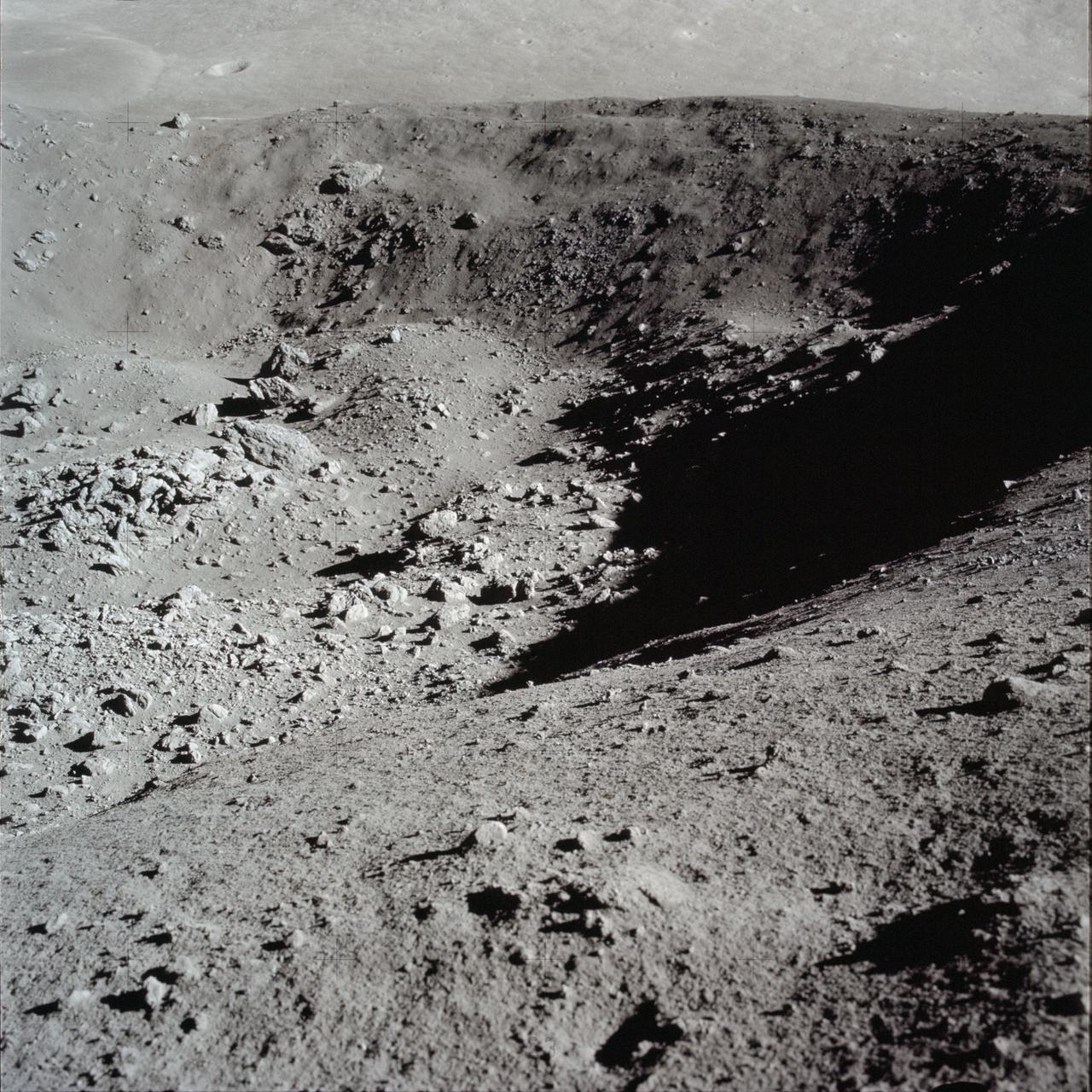
AS17-145-22183 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- One of the Apollo 17 crew took this picture of a large boulder field during lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This view is looking northeast. Apollo 17 was the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo Program. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut
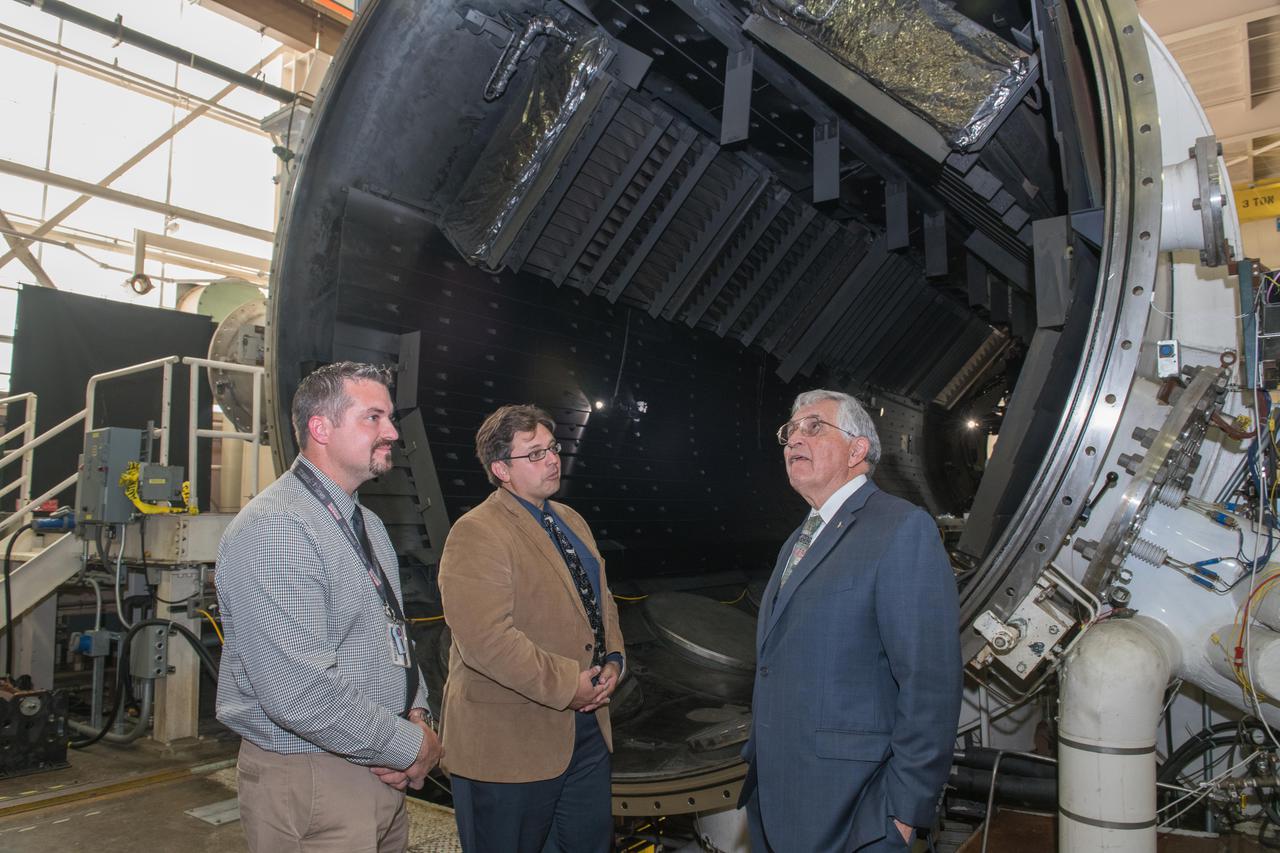

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut
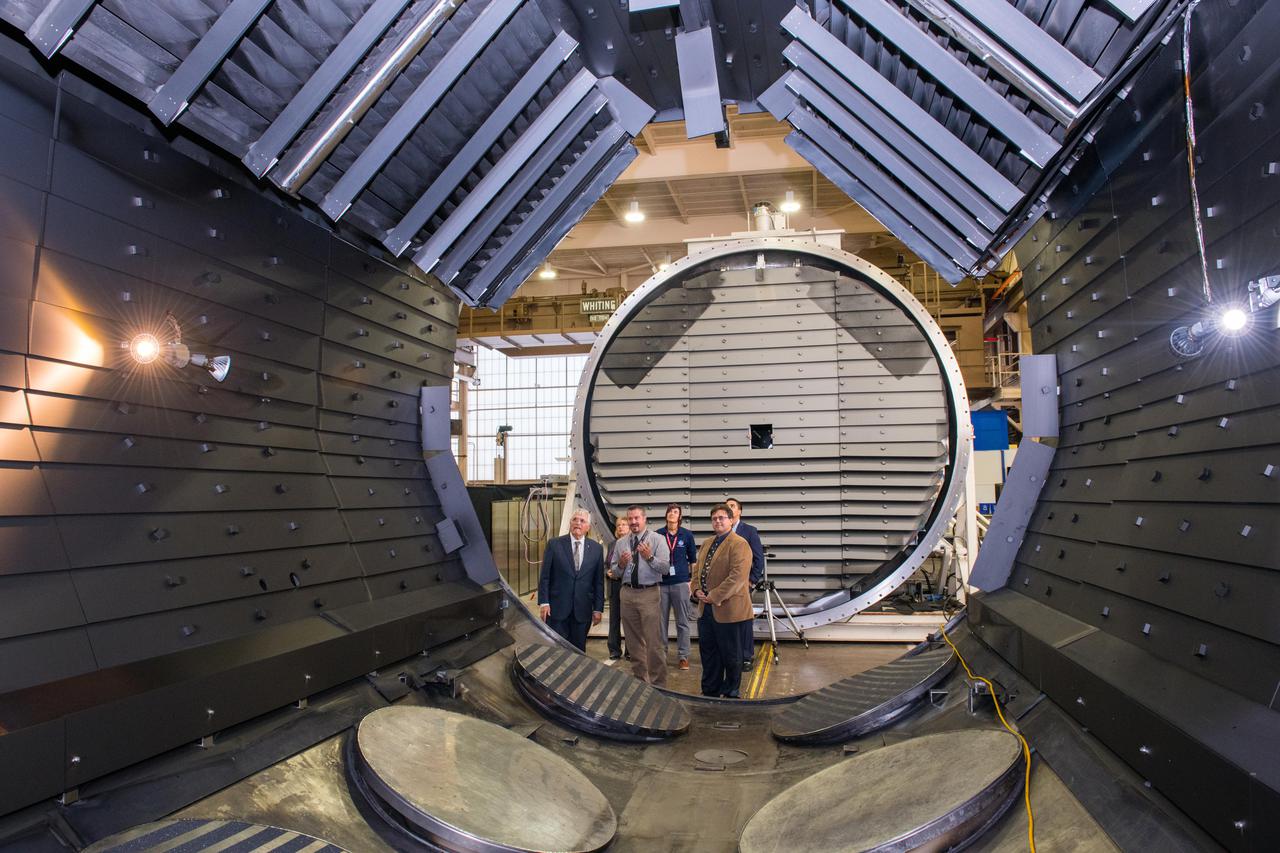

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut
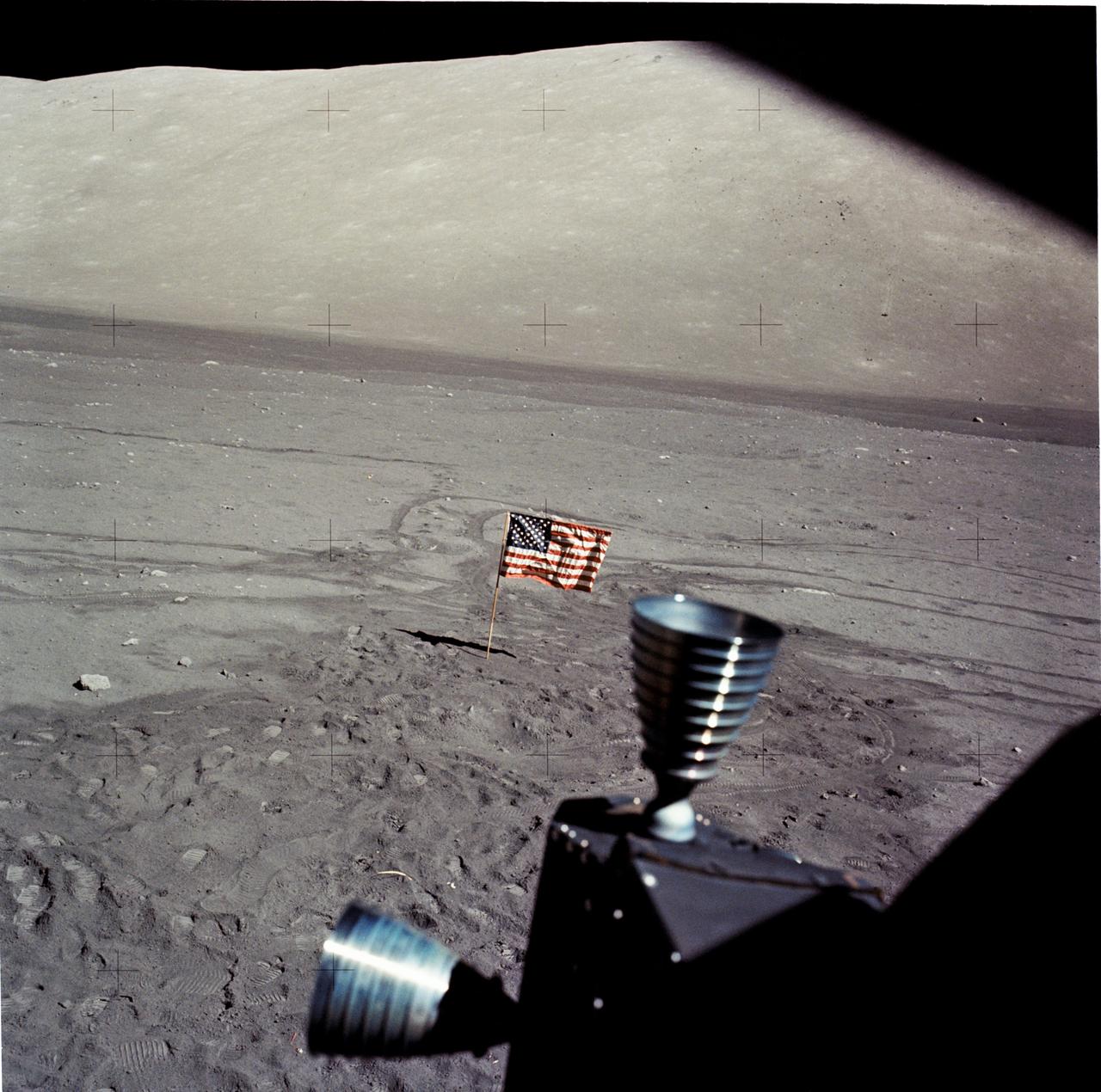

AS17-145-22216 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- In this view looking out the Lunar Module (LM) windows shows the United States Flag on the moon's surface. This view looks toward the north Massif. The LM thrusters can be seen in foreground. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
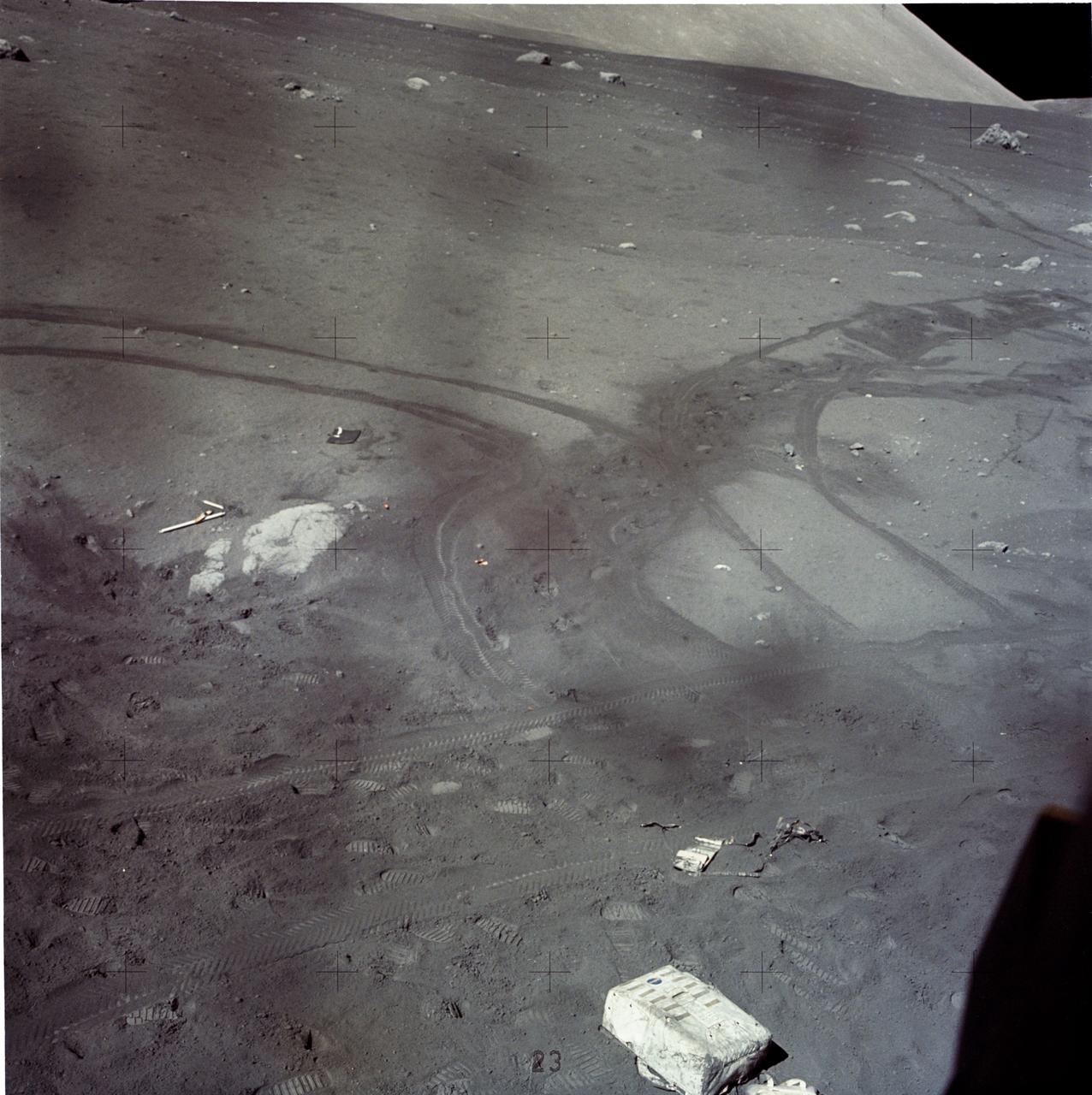

AS17-145-22196 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt's discarded Portable Life Support System (PLSS), along with tracks from the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) and boot prints were photographed through the Lunar Module (LM) window late in the mission. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.

AS17-148-22727 (7 Dec. 1972) --- This view of Earth was seen by the Apollo 17 crew as they traveled toward the moon on their NASA lunar landing mission. This outstanding trans-lunar coast photograph extends from the Mediterranean Sea area to the Antarctica south polar ice cap. This is the first time the Apollo trajectory made it possible to photograph the south polar ice cap. Note the heavy cloud cover in the Southern Hemisphere. Almost the entire coastline of Africa is clearly visible. The Arabian Peninsula can be seen at the northeastern edge of Africa. The large island off the coast of Africa is the Malagasy Republic. The Asian mainland is on the horizon toward the northeast. The Apollo 17 crew consisted of astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander; Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot; and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Evans remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
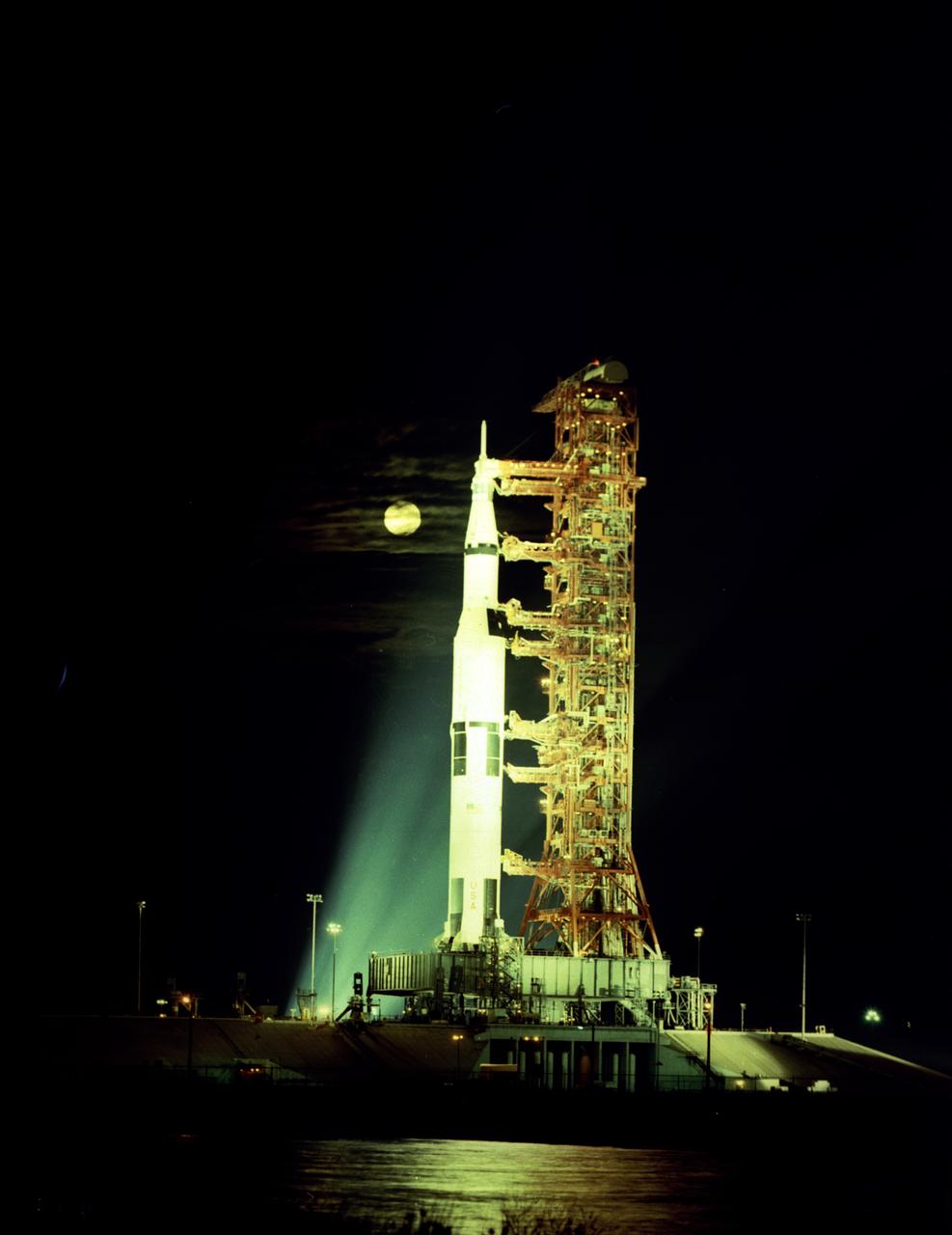

This is a breathtaking moonlit view of Apollo 17 on the Launch Pad at Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC). The seventh and last manned lunar landing and return to Earth mission, the Apollo 17, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Mission Commander Eugene A. Cernan, Lunar Module pilot Harrison H. Schmitt, and Command Module pilot Ronald E. Evans, lifted off on December 7, 1972. The basic objective of the Apollo 17 mission was to sample basin-rim highland material and adjacent mare material, and investigate the geological evolutionary relationship between these two major units. The mission marked the longest Apollo mission, 504 hours, and the longest lunar surface stay time, 75 hours, which allowed the astronauts to conduct an extensive geological investigation. They collected 257 pounds (117 kilograms) of lunar samples with the use of the Marshall Space Flight Center designed Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The mission ended on December 19, 1972
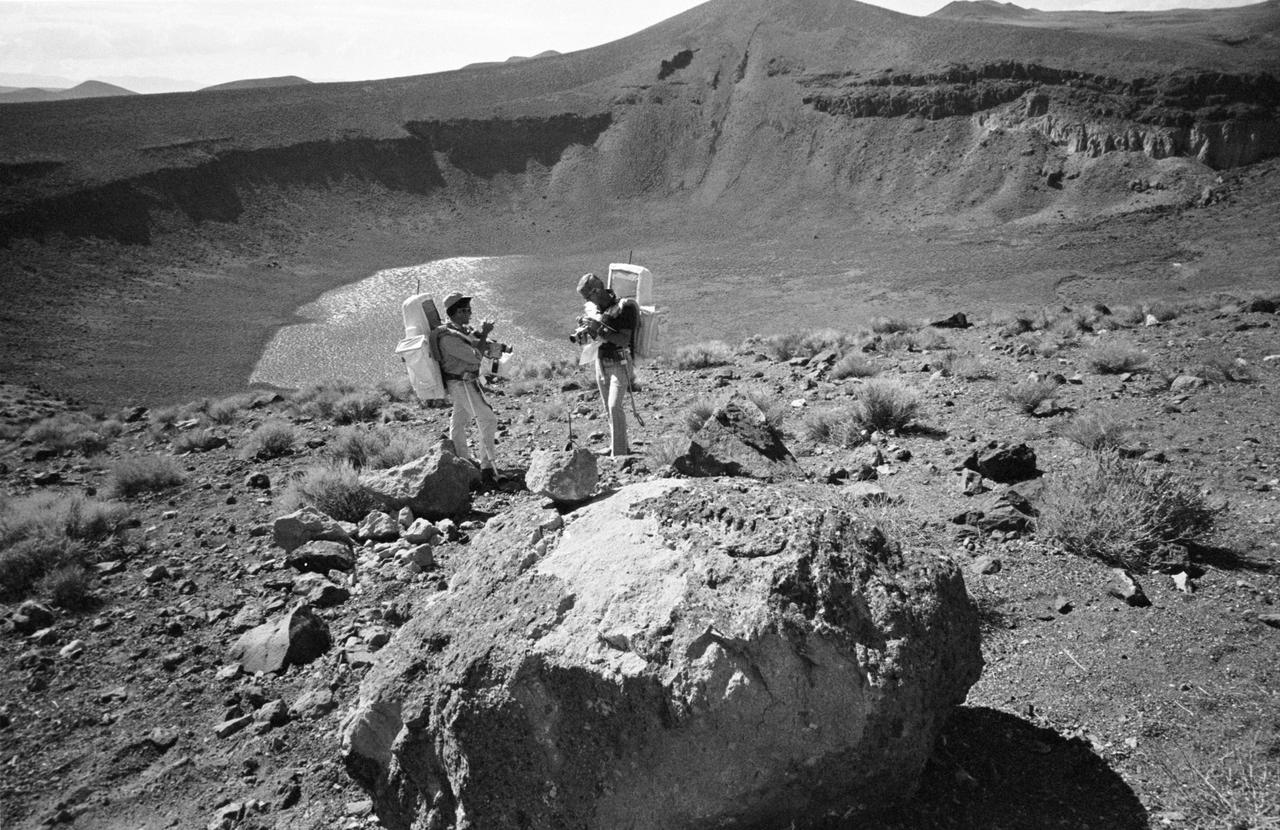

S72-48854 (6 Sept. 1972) --- Two members of the prime crew of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission examine rock specimens during lunar surface extravehicular activity simulation training on a geological field trip to the Pancake Range area of south-central Nevada. They are astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (right), commander; and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. They are standing on the rim of Lunar Crater, which is about 600 feet deep and five-eighths of a mile in diameter. It is a volcanic crater.
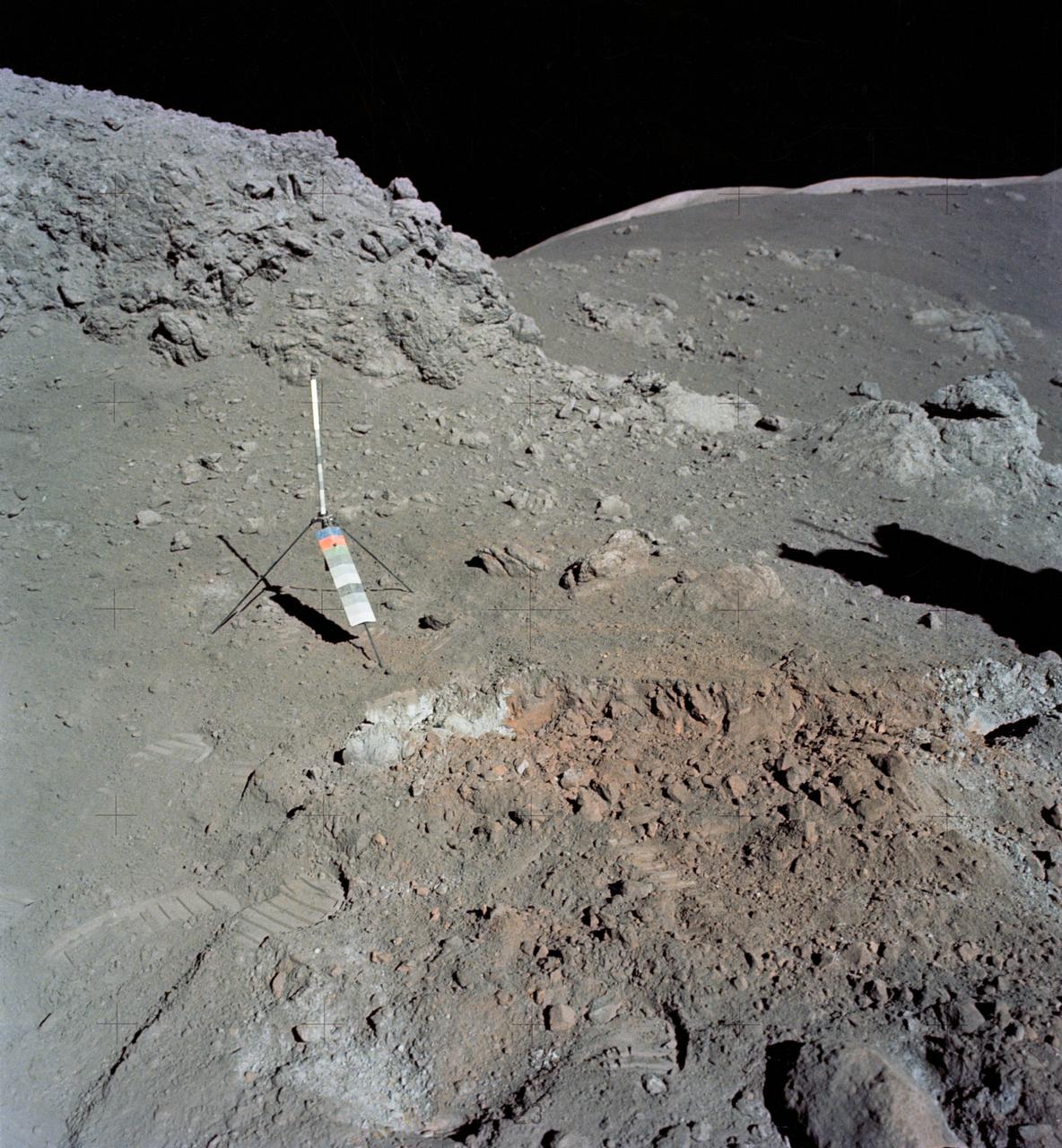

AS17-137-20990 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A view of the area at Station 4 (Shorty Crater) showing the now highly-publicized orange soil which the Apollo 17 crew members found on the moon during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The tripod-like object is the gnomon and photometric chart assembly which is used as a photographic reference to establish local vertical sun angle, scale and lunar color. The gnomon is one of the Apollo lunar geology hand tools. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit. Schmitt was the crew man who first spotted the orange soil.

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut

Visit by Dr. Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 Astronaut
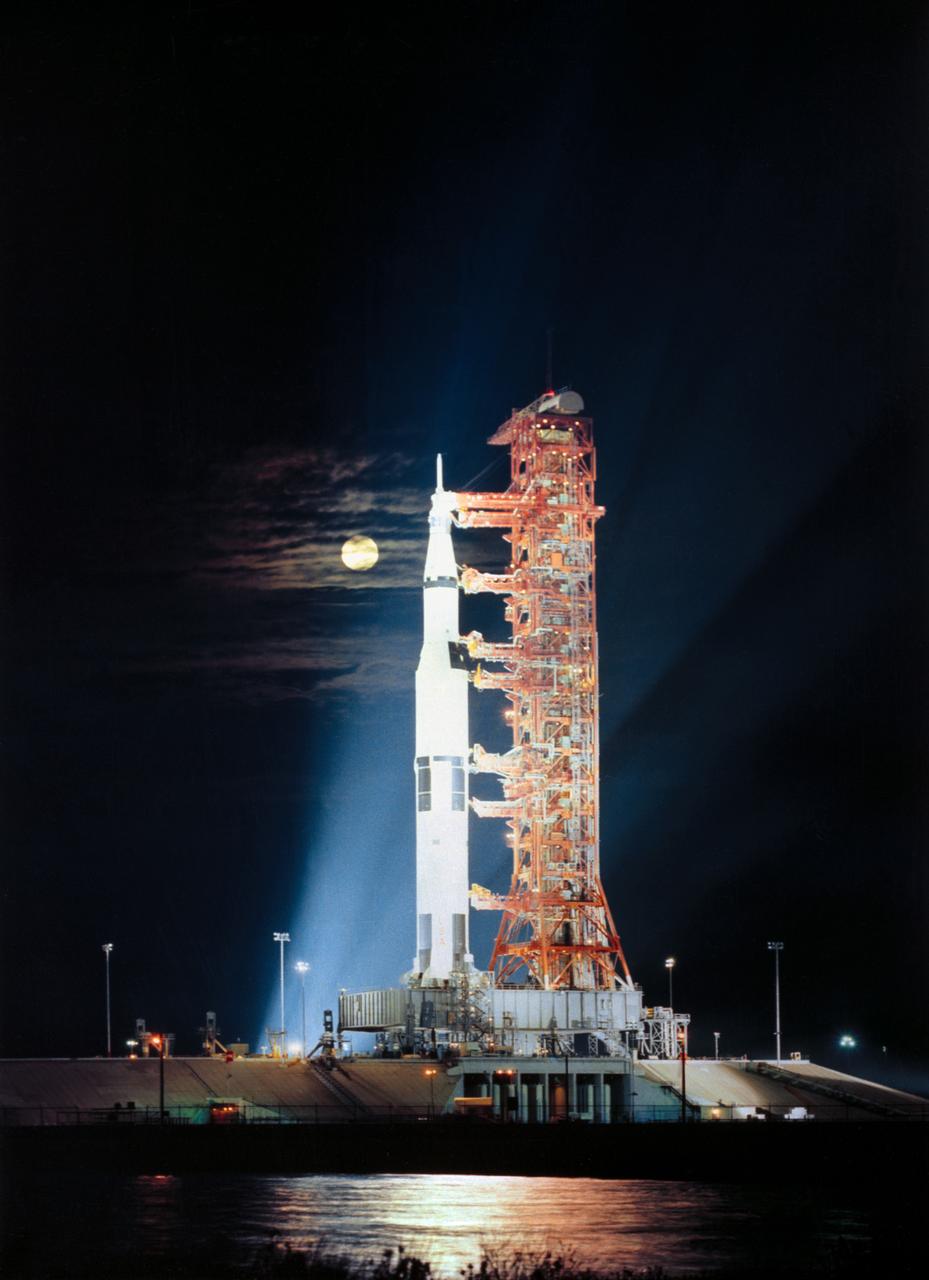

S72-54813 (November 1972) --- Searchlights illuminate this nighttime scene at Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, showing the Apollo 17 (Spacecraft 114/Lunar Module 12/Saturn 512) space vehicle during prelaunch preparations. Apollo 17, the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program, will be the first nighttime liftoff of the huge Saturn V launch vehicle. Apollo 17 is scheduled for launching on the night of Dec. 6, 1972. Aboard the Apollo 17 spacecraft will be astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander; astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot; and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. Note the full moon in the background.
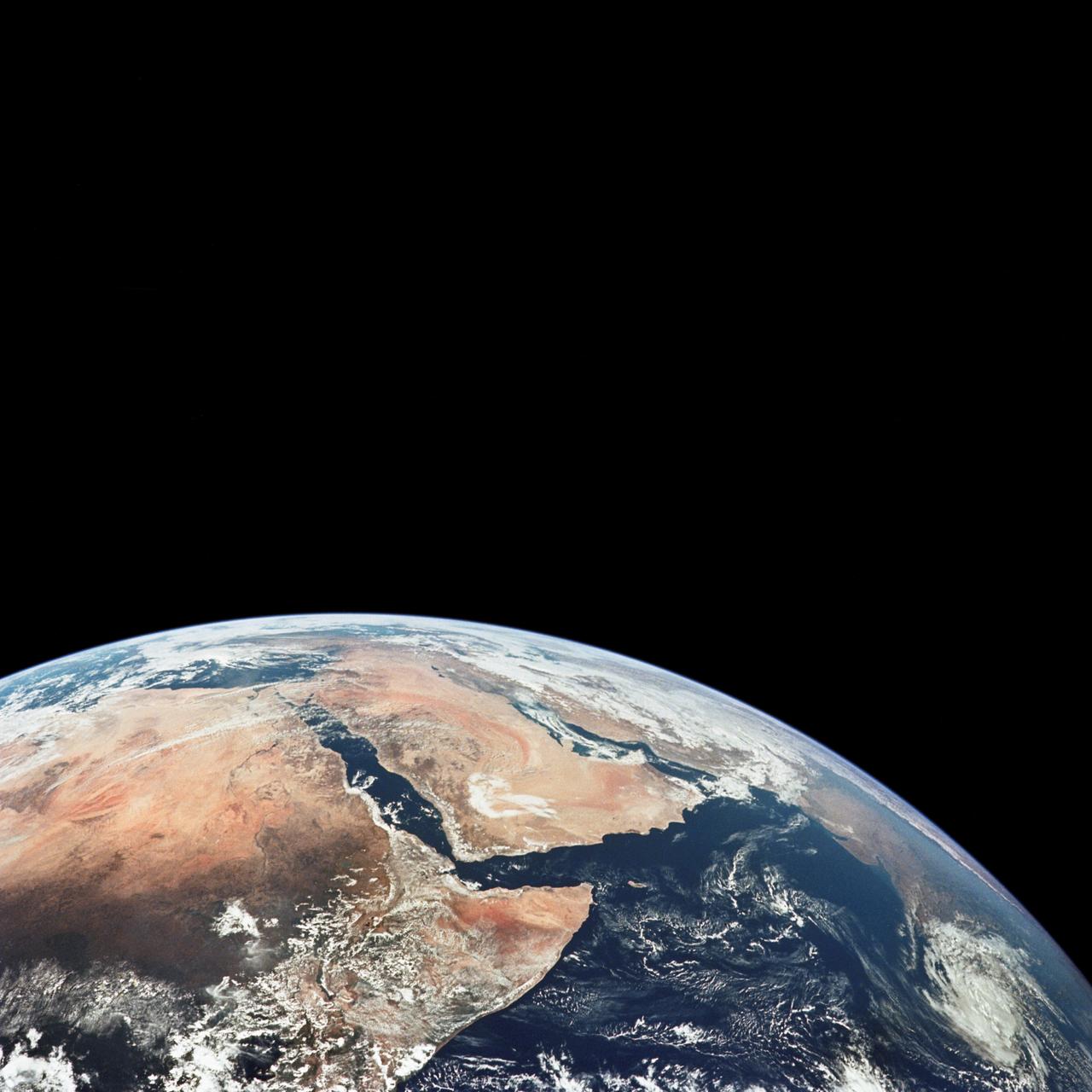

AS17-148-22718 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This excellent view of Saudi Arabia and the north eastern portion of the African continent was photographed by the Apollo 17 astronauts with a hand-held camera on their trans-lunar coast toward man's last lunar visit. Egypt, Sudan, Ethiopia are some of the African nations are visible. Iran, Iraq, Jordan are not so clearly visible because of cloud cover and their particular location in the picture. India is dimly visible at right of frame. The Red Sea is seen entirely in this one single frame, a rare occurrence in Apollo photography or any photography taken from manned spacecraft. The Gulf of Suez, the Dead Sea, Gulf of Aden, Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman are also visible. This frame is one of 169 frames on film magazine NN carried aboard Apollo 17, all of which are SO368 (color) film. A 250mm lens on a 70mm Hasselblad camera recorded the image, one of 92 taken during the trans-lunar coast. Note AS17-148-22727 (also magazine NN) for an excellent full Earth picture showing the entire African continent.

S72-55169 (14 Dec. 1972) --- A photographic replica of the plaque which the Apollo 17 astronauts left behind at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. Apollo 17 is the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. The commemorative plaque was unveiled at the close of the third extravehicular activity (EVA). The plaque is made of stainless steel measuring nine by seven and five-eighths inches, and one-sixteenth inch thick. It is attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the descent stage of Apollo 17 Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger".

AS17-137-20992 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A view looking into Shorty Crater, taken at Station 4, showing the orange soil. Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt found the orange soil on the moon during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
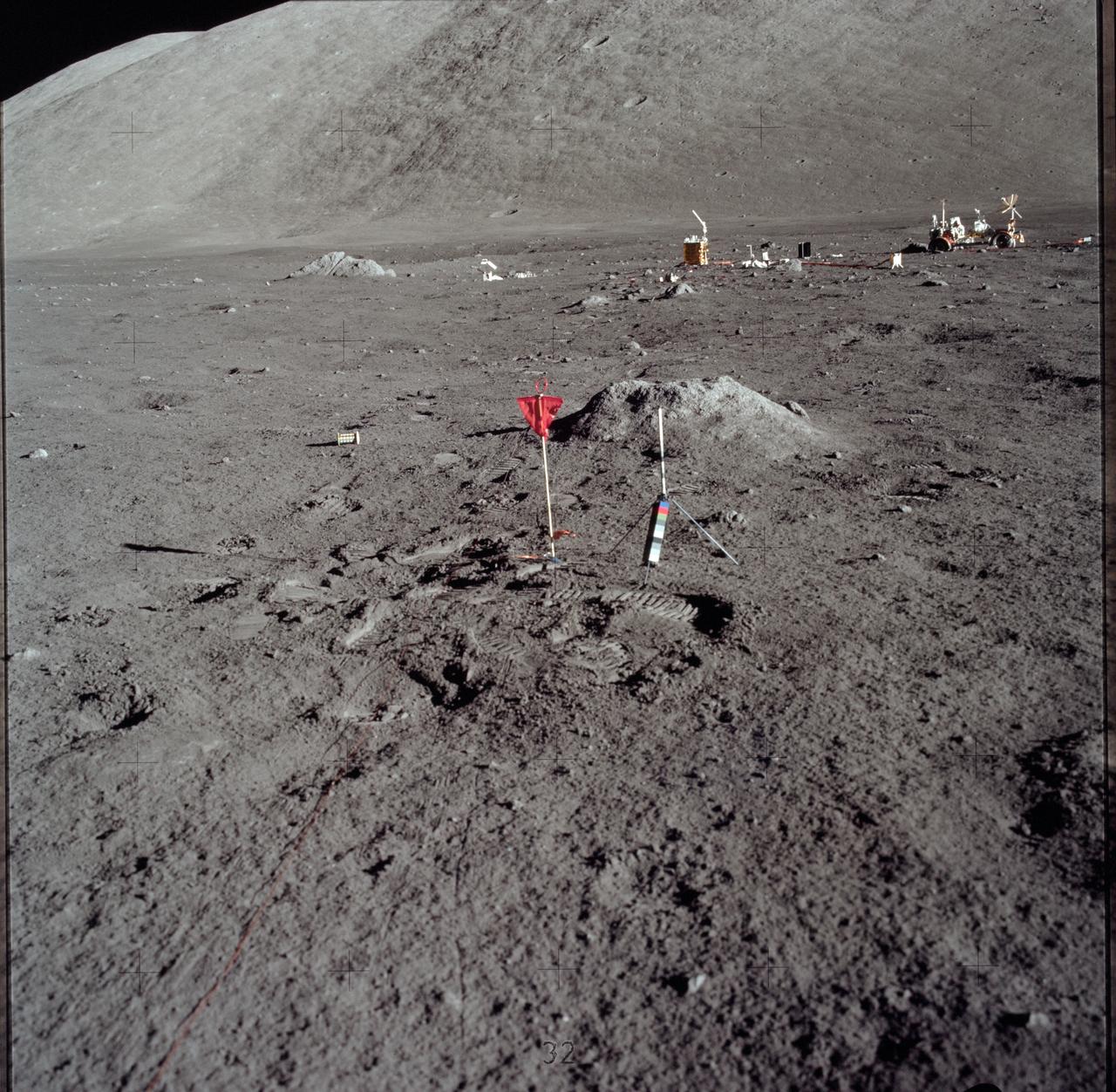

AS17-147-22548 (11 Dec. 1972) --- This is a photograph of the LSP geosphere flag on the lunar surface. The gnomon is in the foreground, while Apollo Lunar Scientific Experiments Package (ALSEP) and north Massif is in the background. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is also seen in the right background. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
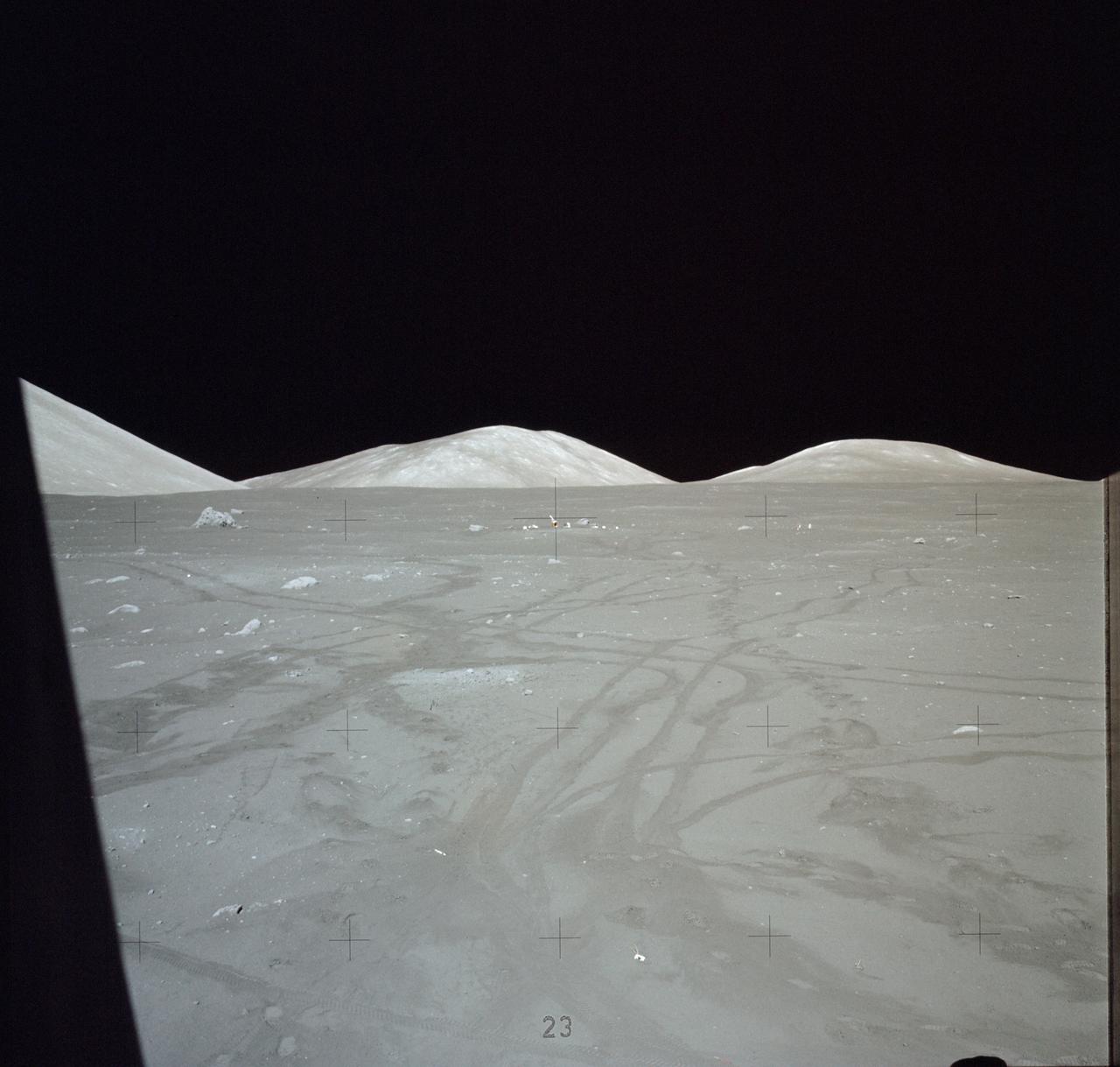

AS17-140-21355 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This picture of the lunar surface was taken from the window of the lunar module at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. Astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt were inside the lunar module preparing for the mission's third spacewalk. Tracks made by lunar roving vehicle (LRV) and the astronauts' bootprints from earlier spacewalks are seen in the foreground.
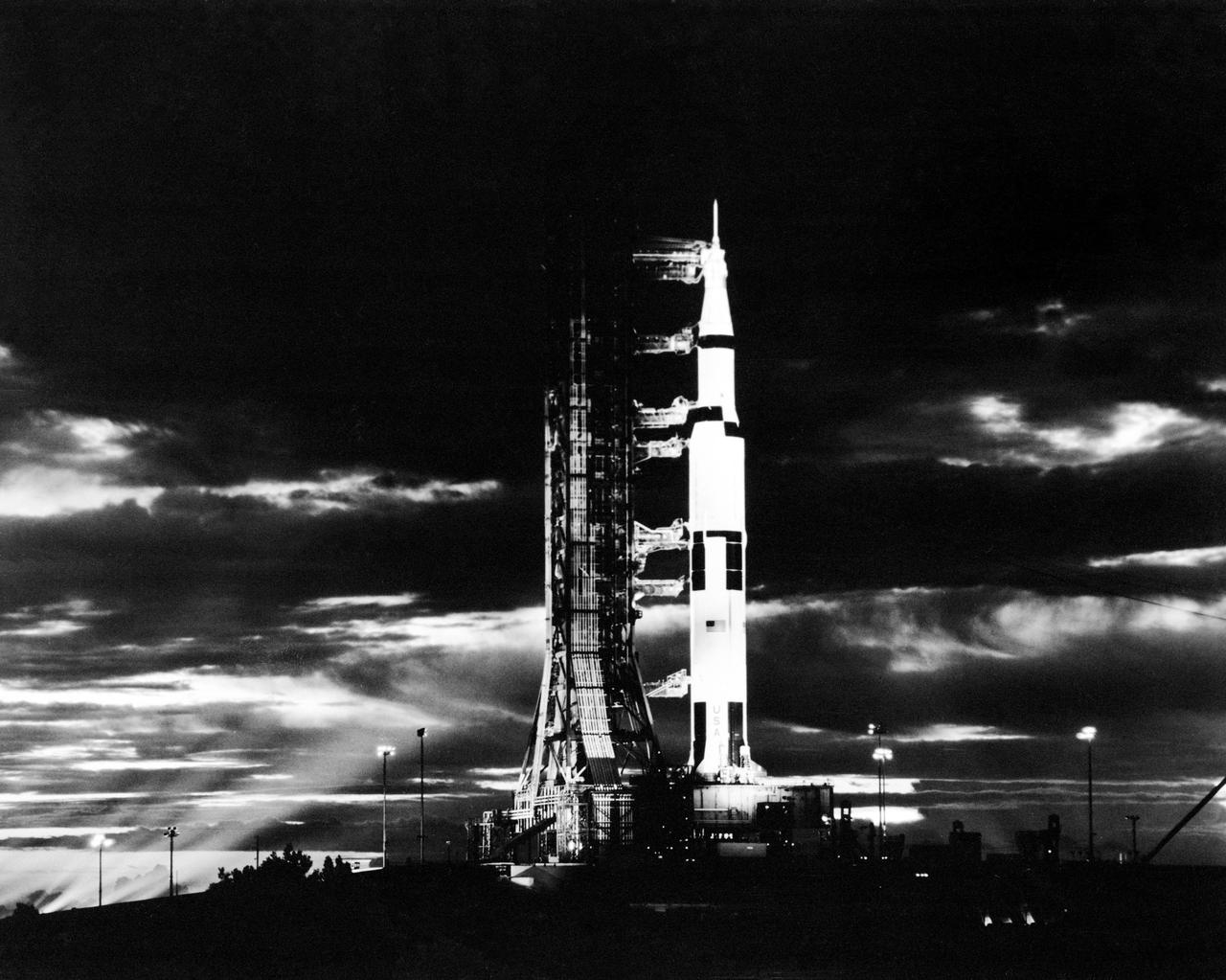

S72-54814 (November 1972) --- Searchlights illuminate this nighttime scene at Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, showing the Apollo 17 (Spacecraft 114/Lunar Module 12/Saturn 512) space vehicle during prelaunch preparations. Apollo 17, the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program, will be the first nighttime liftoff of the huge Saturn V launch vehicle. Apollo 17 is scheduled for launching on the night of Dec. 6, 1972. Aboard the Apollo 17 spacecraft will be astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander; astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot; and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot.
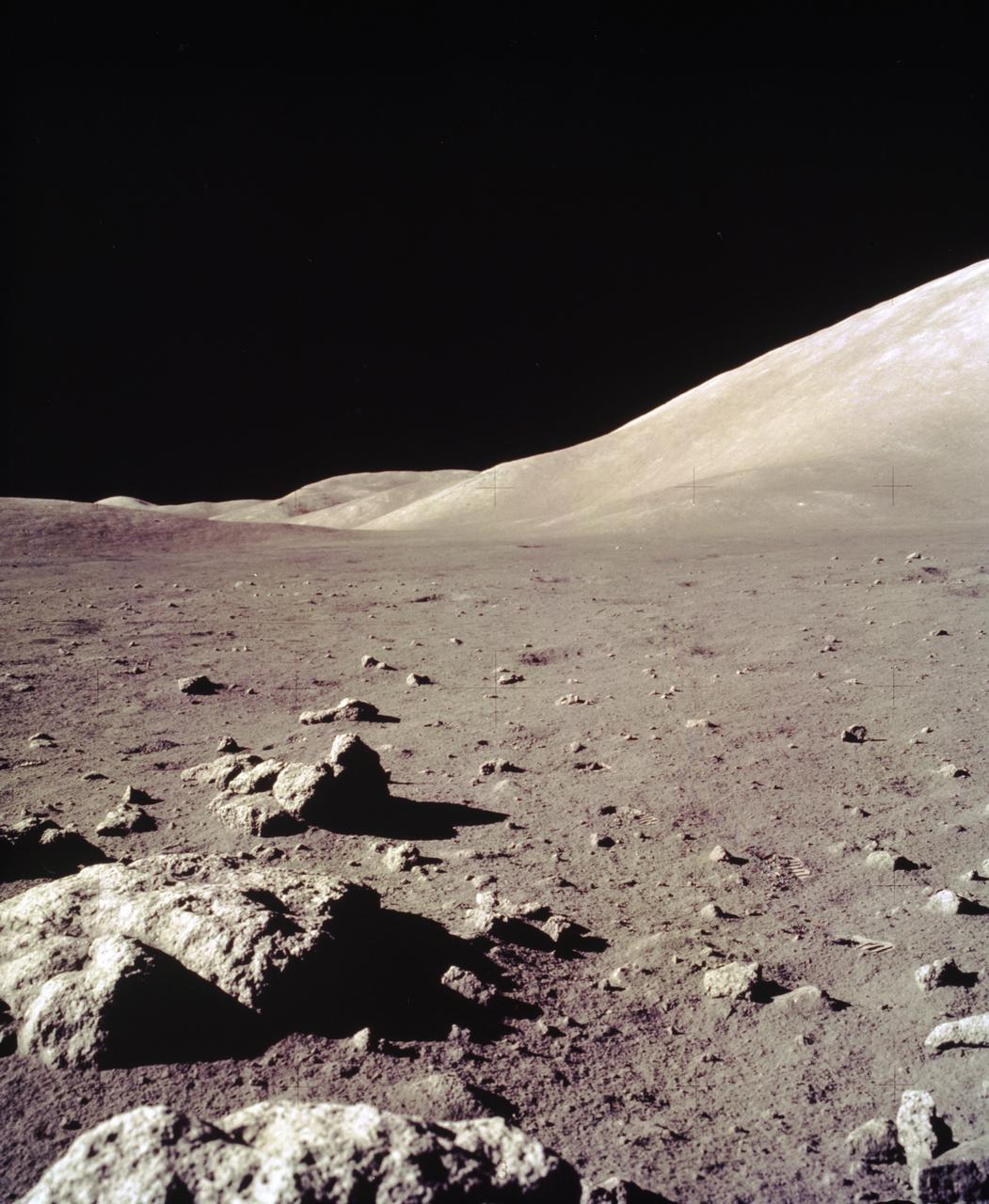

This view of the Lunar surface was taken during the Apollo 17 mission. The seventh and last manned lunar landing and return to Earth mission, the Apollo 17, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Mission Commander Eugene A. Cernan; Lunar Module pilot Harrison H. Schmitt; and Command Module pilot Ronald E. Evans, lifted off on December 7, 1972 from the Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC). Scientific objectives of the Apollo 17 mission included geological surveying and sampling of materials and surface features in a preselected area of the Taurus-Littrow region, deploying and activating surface experiments, and conducting in-flight experiments and photographic tasks during lunar orbit and transearth coast (TEC). These objectives included: Deployed experiments such as the Apollo lunar surface experiment package (ALSEP) with a Heat Flow experiment, Lunar seismic profiling (LSP), Lunar surface gravimeter (LSG), Lunar atmospheric composition experiment (LACE) and Lunar ejecta and meteorites (LEAM). The mission also included Lunar Sampling and Lunar orbital experiments. Biomedical experiments included the Biostack II Experiment and the BIOCORE experiment. The mission marked the longest Apollo mission, 504 hours, and the longest lunar surface stay time, 75 hours, which allowed the astronauts to conduct an extensive geological investigation. They collected 257 pounds (117 kilograms) of lunar samples with the use of the Marshall Space Flight Center designed Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The mission ended on December 19, 1972.
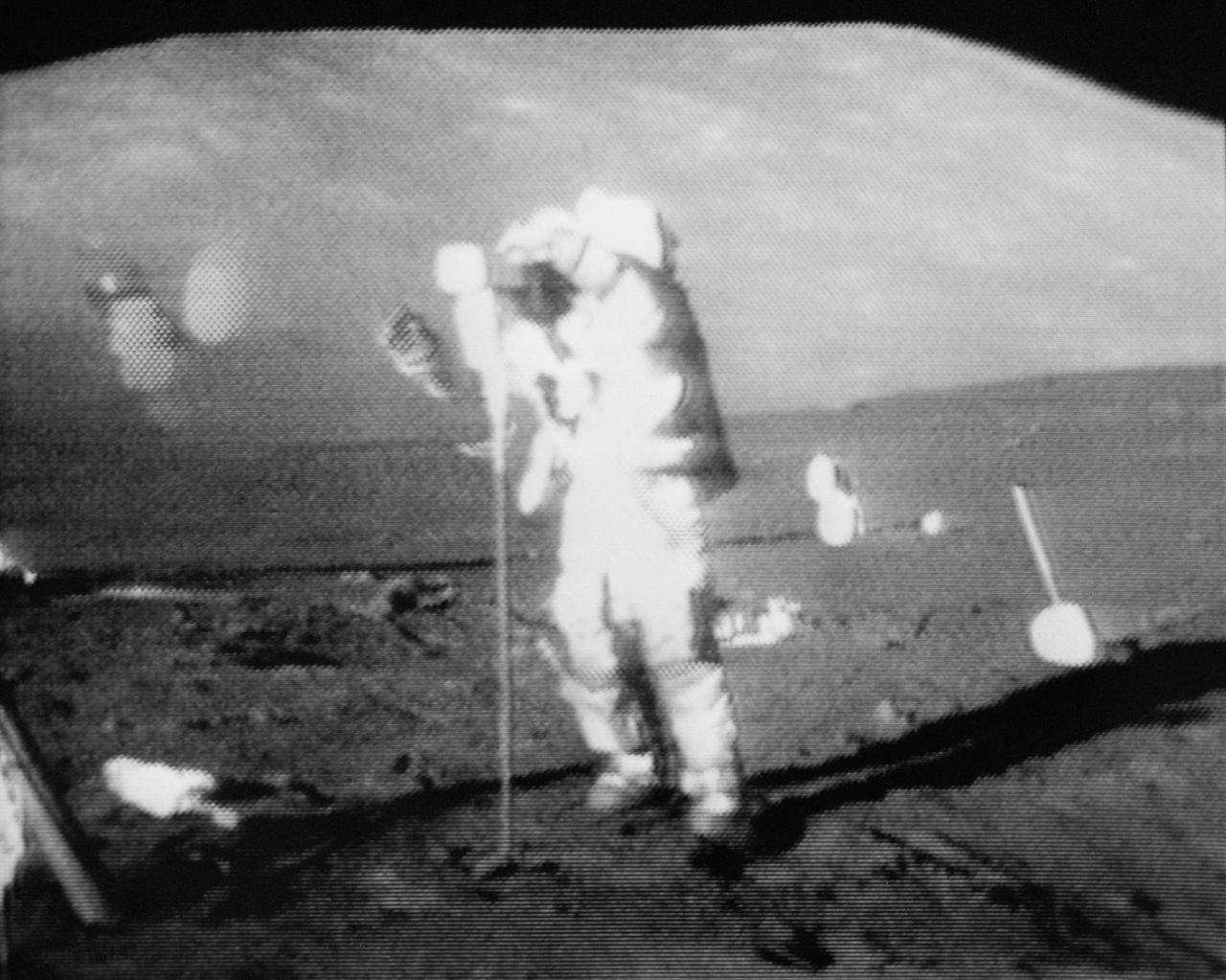

S72-55064 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan operates the Apollo Lunar Surface Drill during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the RCA color TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Cernan is the commander of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronaut Cernan and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the moon.

Young visitors to the INFINITY Science Center, a NASA visitors center, on Dec. 7 enjoy a Living and Working in Space presentation during activities celebrating the Apollo 17 lunar mission in 1972. Visitors were able to learn about the historic mission and to participate in hands-on activities. Apollo 17 was the final mission of America's manned lunar effort.

Young visitors to the INFINITY Science Center, a NASA visitors center, on Dec. 7 enjoy a Living and Working in Space presentation during activities celebrating the Apollo 17 lunar mission in 1972. Visitors were able to learn about the historic mission and to participate in hands-on activities. Apollo 17 was the final mission of America's manned lunar effort.
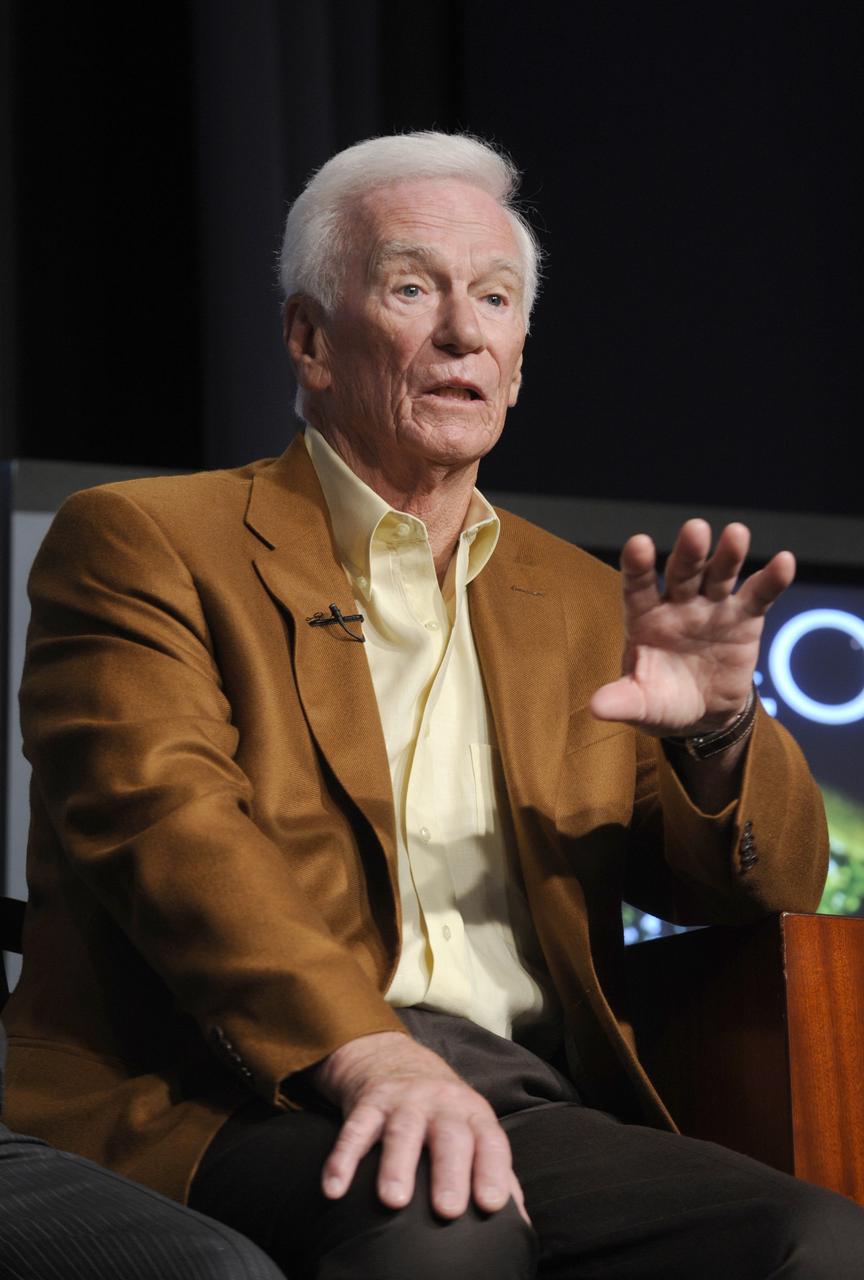

Eugene Cernan (Apollo 17) speaks during the 40th anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission and the walk on the moon press conference, Monday, July 20, 2009, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
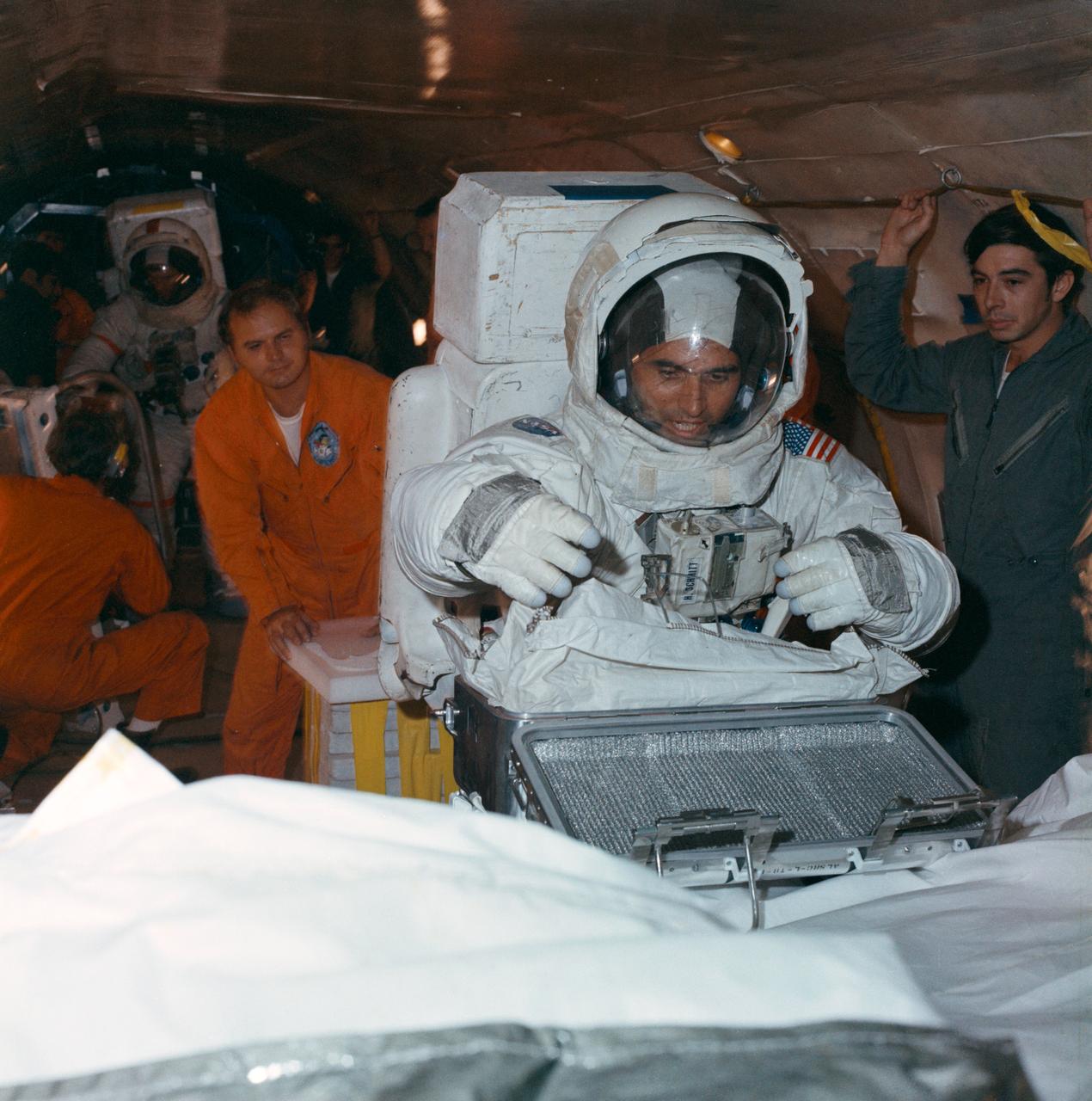

S72-50269 (September 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission, seals an Apollo lunar sample return container during lunar surface extravehicular activity simulation training under one-sixth gravity conditions aboard a U.S. Air Force KC-135 aircraft. Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander, can be seen in the left background.
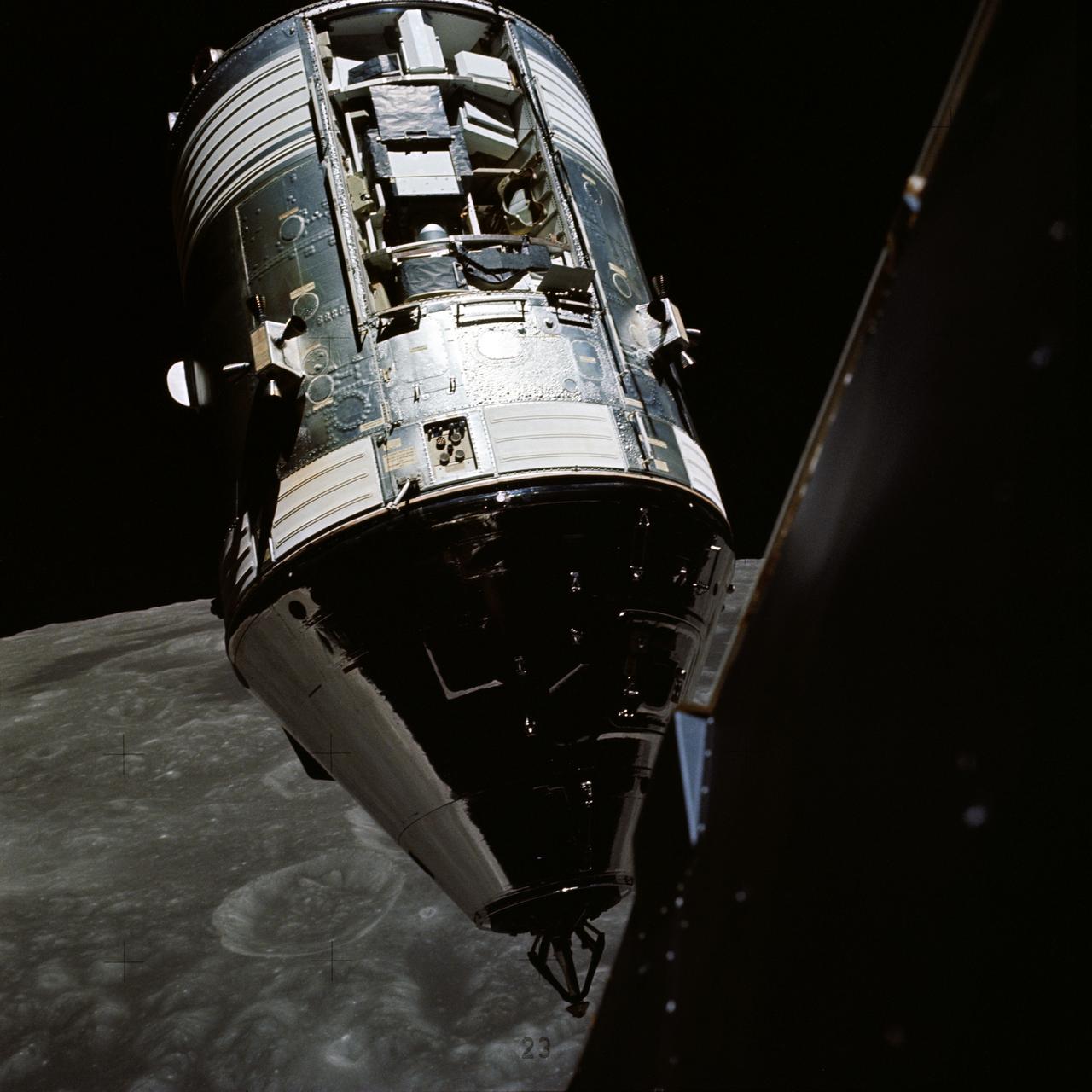

AS17-145-22254 (14 Dec. 1972) --- An excellent view of the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM) photographed from the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" during rendezvous and docking maneuvers in lunar orbit. The LM ascent stage, with astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt aboard, had just returned from the Taurus-Littrow landing site on the lunar surface. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the CSM in lunar orbit. Note the exposed Scientific Instrument Module (SIM) Bay in Sector 1 of the Service Module (SM). Three experiments are carried in the SIM bay: S-209 lunar sounder, S-171 infrared scanning spectrometer, and the S-169 far-ultraviolet spectrometer. Also mounted in the SIM bay are the panoramic camera, mapping camera and laser altimeter used in service module photographic tasks. A portion of the LM is on the right.
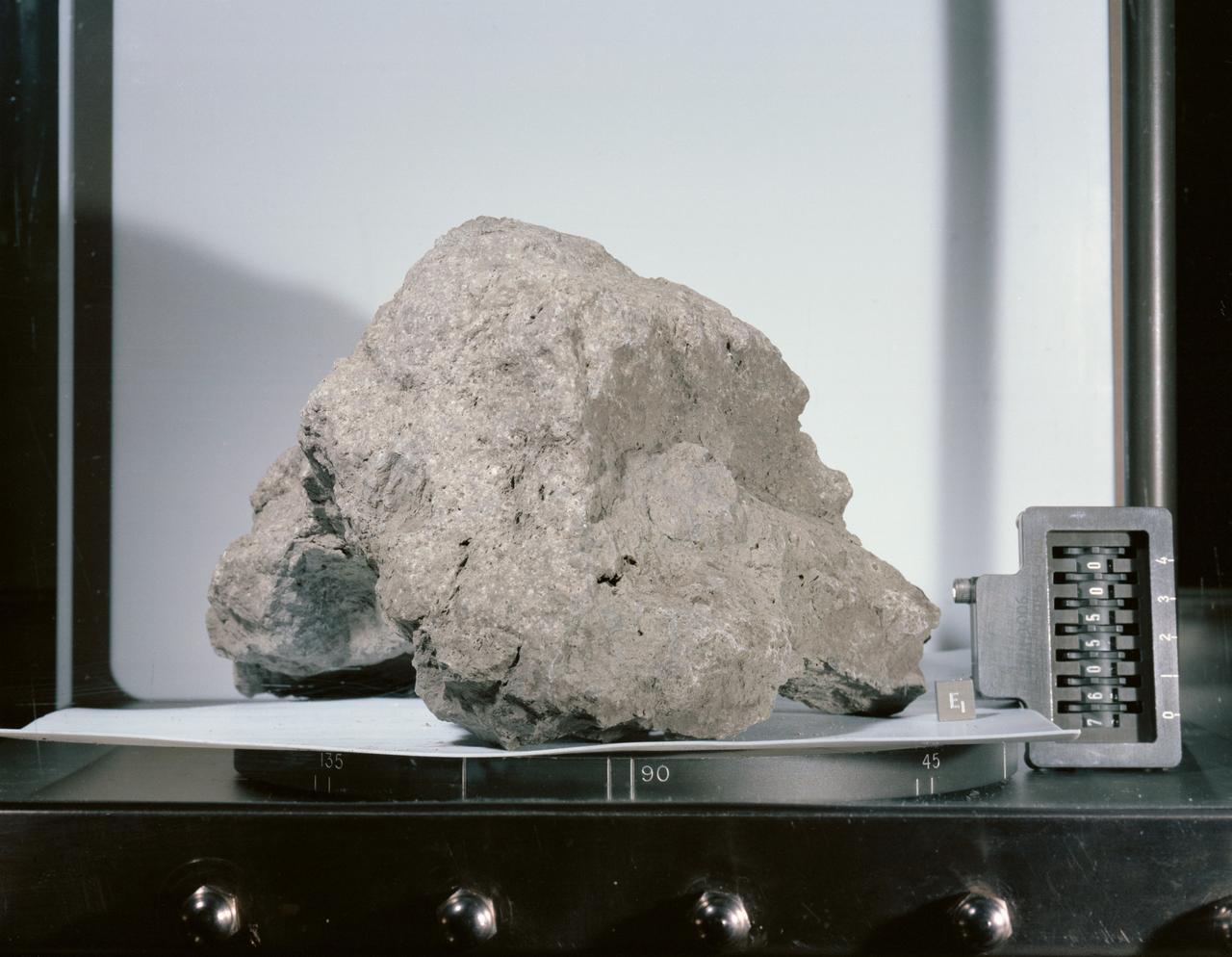

S73-15713 (January 1973) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar rock sample No. 76055 being studied and analyzed in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. This tan-gray irregular, rounded breccia was among many lunar samples brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crew. The rock measures 18 x 20 x 25 centimeters (7.09 x 7.87 x 9.84 inches) and weighs 6,389 grams (14.2554 pounds). The rock was collected from the south side of the lunar roving vehicle while the Apollo 17 astronauts were at Station 7 (base of North Massif).
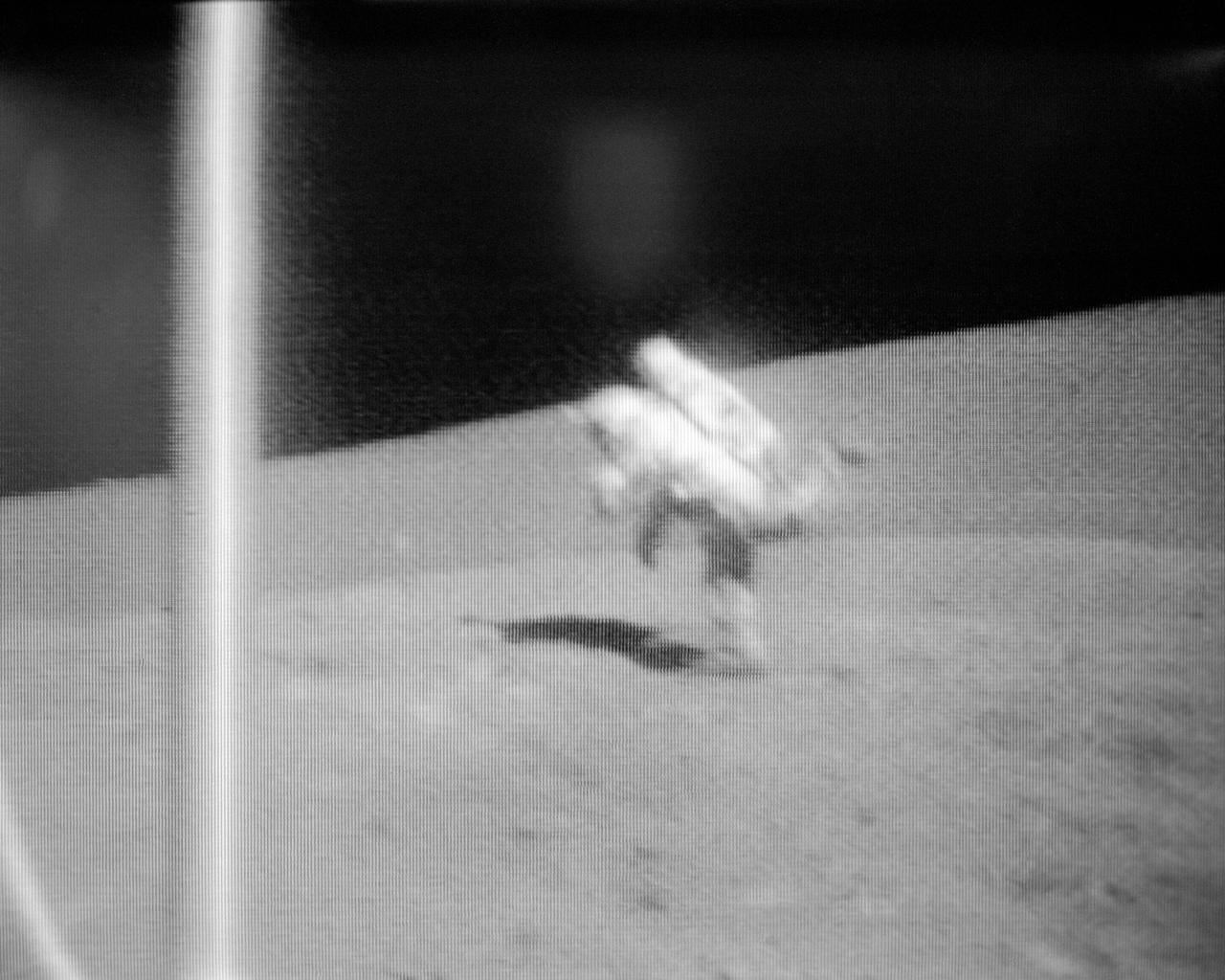

S72-55166 (12 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt loses his balance and heads for a fall during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, as seen in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Schmitt is lunar module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan, commander, descended in the Lunar Module "Challenger" to explore the moon.

S72-55066 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt chips samples from a large boulder during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Schmitt is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan, commander, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the moon.
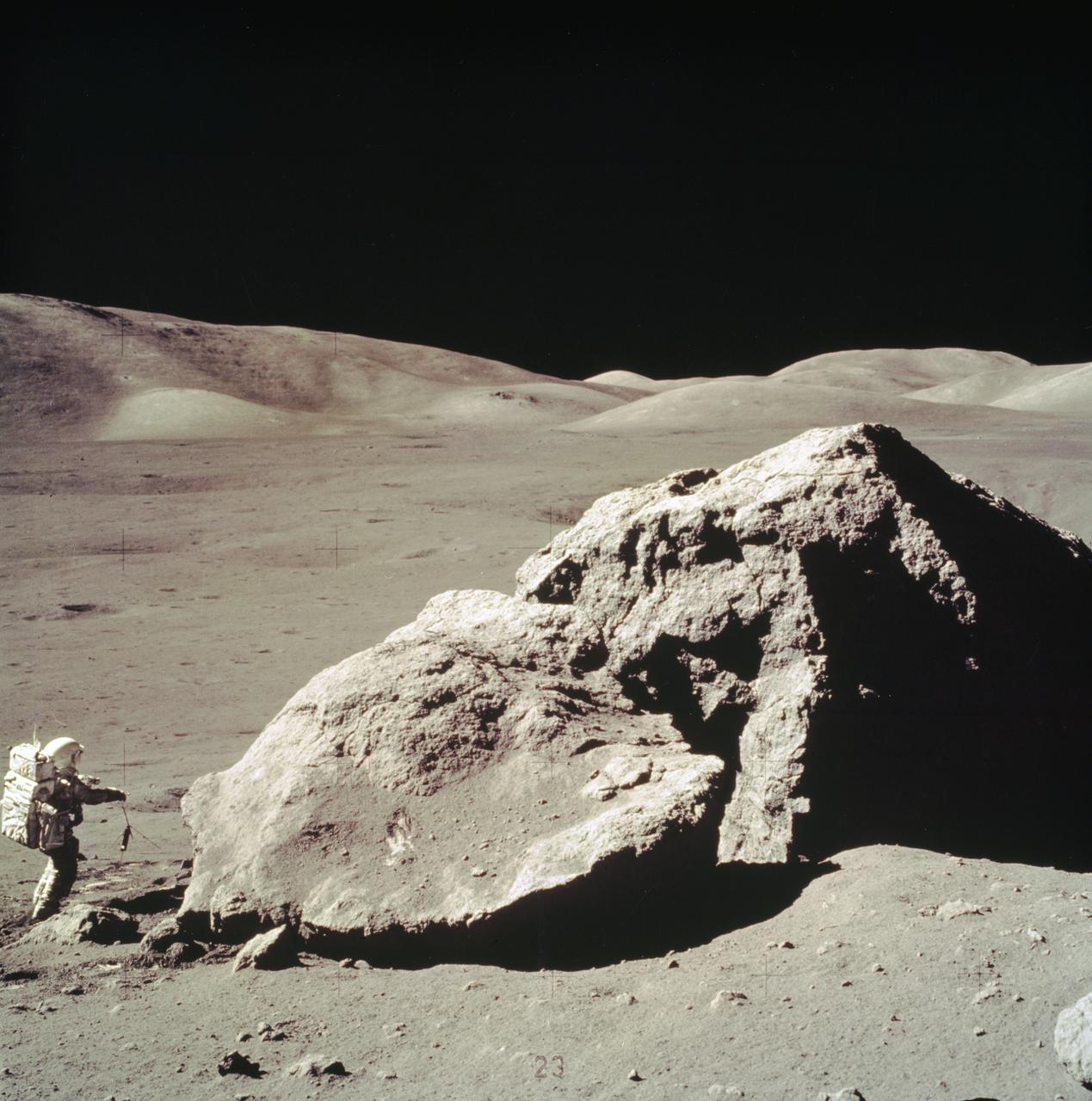

In this Apollo 17 onboard photo, Lunar Module pilot Harrison H. Schmitt collects rock samples from a huge boulder near the Valley of Tourus-Littrow on the lunar surface. The seventh and last manned lunar landing and return to Earth mission, the Apollo 17, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Schmitt; Mission Commander Eugene A. Cernan; and Command Module pilot Ronald E. Evans, lifted off on December 7, 1972 from the Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC). Scientific objectives of the Apollo 17 mission included geological surveying and sampling of materials and surface features in a preselected area of the Taurus-Littrow region, deploying and activating surface experiments, and conducting in-flight experiments and photographic tasks during lunar orbit and transearth coast (TEC). These objectives included: Deployed experiments such as the Apollo lunar surface experiment package (ALSEP) with a Heat Flow experiment, Lunar seismic profiling (LSP), Lunar surface gravimeter (LSG), Lunar atmospheric composition experiment (LACE) and Lunar ejecta and meteorites (LEAM). The mission also included Lunar Sampling and Lunar orbital experiments. Biomedical experiments included the Biostack II Experiment and the BIOCORE experiment. The mission marked the longest Apollo mission, 504 hours, and the longest lunar surface stay time, 75 hours, which allowed the astronauts to conduct an extensive geological investigation. They collected 257 pounds (117 kilograms) of lunar samples with the use of the Marshall Space Flight Center designed Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The mission ended on December 19, 1972
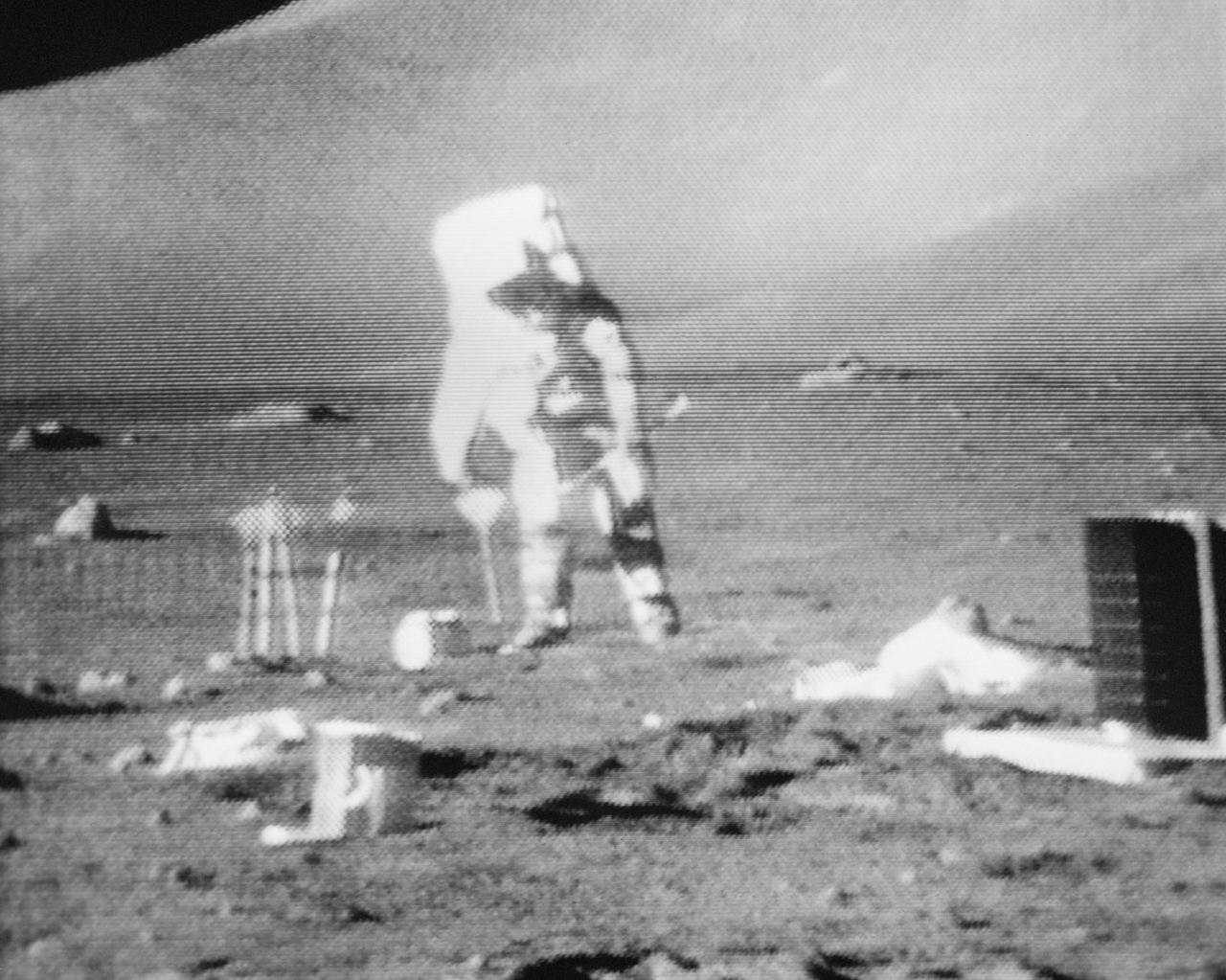

S72-55065 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt is seen anchoring the geophone module with a flag during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, in the black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Schmitt is the lunar module mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Schmitt is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan, commander, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the moon. The geophone module is part of the Lunar Seismic Profiling Experiment (S-203), a component of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP). Other ALSEP components are visible in the picture.