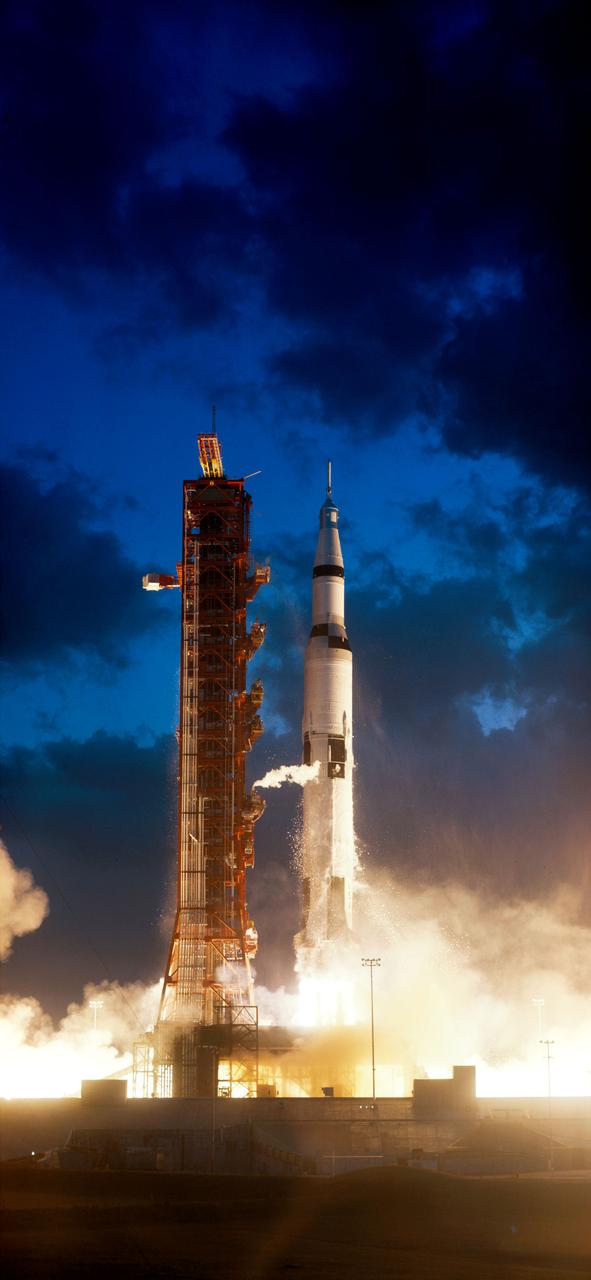

S67-50903 (9 Nov. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) space mission was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The liftoff of the huge 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle was at 7:00:01 a.m. (EST), Nov. 9, 1967. The successful objectives of the Apollo 4 Earth-orbital unmanned space mission obtained included (1) flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, subsystem operation, emergency detection subsystem, and (2) evaluation of the Apollo Command Module heat shield under conditions encountered on return from a moon mission.

AS04-01-200 (9 Nov. 1967) --- Coastal Brazil, Atlantic Ocean, West Africa, Sahara, looking northwest, as photographed from the unmanned Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) earth-orbital space mission. This picture was taken when the Spacecraft 017 and the Saturn IVB stage were orbiting Earth at an altitude of 9,060 nautical miles.

AS04-01-750 (9 Nov. 1967) --- Atlantic Ocean, Antarctica, looking west, as photographed from the Earth-orbital Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) unmanned space mission. This picture was taken when the Spacecraft 017 and the Saturn S-IVB (third) stage was orbiting Earth at an altitude of 8,628 nautical miles.

AS04-01-580 (9 Nov. 1967) --- Earth as viewed from 10,000 miles. In 1969, the Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) unmanned test flight made a great ellipse around Earth as a test of the translunar motors and of the high speed entry required of a manned flight returning from the moon. A 70mm camera was programmed to look out a window toward Earth, and take a series of photographs from "high apogee". Coastal Brazil, Atlantic Ocean, West Africa, Antarctica, looking west. This photograph was made when the Apollo 4 spacecraft, still attached to the S-IVB (third) stage, was orbiting Earth at an altitude of 9,544 miles.

This photograph shows an early moment of the first test flight of the Saturn V vehicle for the Apollo 4 mission, photographed by a ground tracking camera, on the morning of November 9, 1967. This mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmarned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield.

S67-36022 (20 June 1967) --- Apollo Spacecraft 017 is moved into position in the Vehicle Assembly Building's high bay area for mating with the Saturn V launch vehicle. S/C 017 will be flown on the Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501 (Apollo 4) space mission.

S67-49447 (9 Nov. 1967) --- Close-up view of the charred heat shield of the Apollo Spacecraft 017 Command Module aboard the USS Bennington. The damage was caused by the extreme heat of reentry. The carrier Bennington was the prime recovery ship for the Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) unmanned, Earth-orbital space mission. Splashdown occurred at 3:37 p.m. (EST), Nov. 9, 1967, 934 nautical miles northwest of Honolulu, Hawaii.

S67-49423 (9 Nov. 1967) --- The Apollo Spacecraft 017 Command Module, with flotation collar still attached, is hoisted aboard the USS Bennington, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) unmanned, Earth-orbital space mission. The Command Module splashed down at 3:37 p.m. (EST), Nov. 9, 1967, 934 nautical miles northwest of Honolulu, Hawaii, in the mid-Pacific Ocean. Note charred heat shield caused by extreme heat of reentry.

AS04-01-410 (9 Nov. 1967) --- Coastal Brazil, Atlantic Ocean, West Africa, Sahara, Antarctica, looking west, as photographed from the Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) unmanned, Earth-orbital space mission. This picture was taken when the Spacecraft 017 and Saturn S-IVB (third) stage were orbiting Earth at an altitude of 9,745 nautical miles.

This photograph depicts the Saturn V vehicle (SA-501) for the Apollo 4 mission in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). After the completion of the assembly operation, the work platform was retracted and the vehicle was readied to rollout from the VAB to the launch pad. The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.

S67-49969 (9 Nov. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) space mission was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The liftoff of the huge 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle was at 7:00:01 a.m. (EST), Nov. 9, 1967. The successful objectives of the Apollo 4 Earth-orbital unmanned space mission obtained included (1) flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, subsystem operation, emergency detection subsystem operation, and (2) evaluation of the Apollo Command Module heat shield under conditions encountered on return from a moon mission.
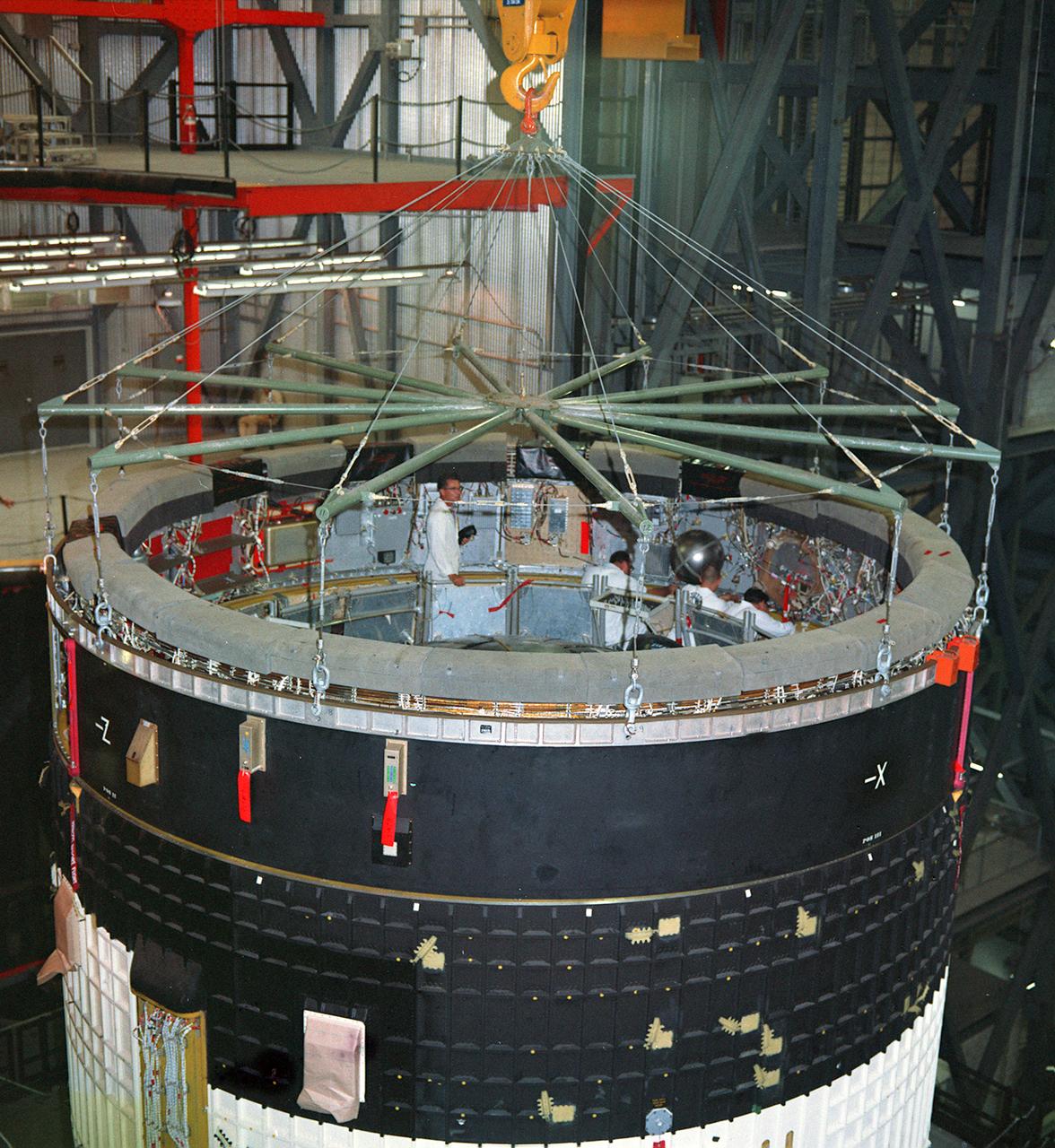

This photograph was taken during the final assembly operation of the Saturn V launch vehicle for the Apollo 4 (SA 501) mission. The instrument unit (IU) was mated atop the S-IC/S-II assembly in the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay at the Kennedy Space Center. The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.
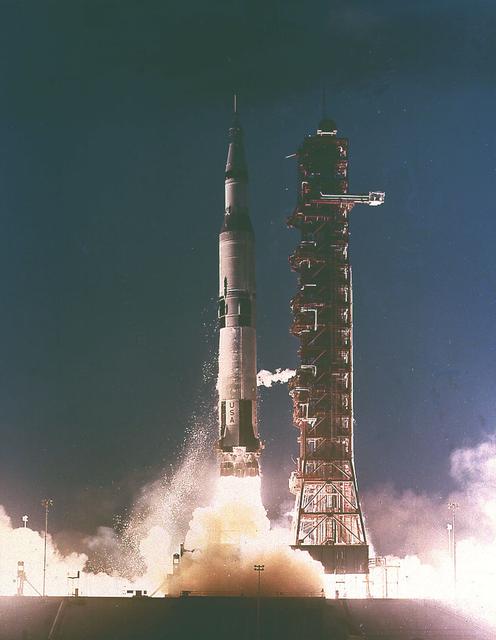
AS-501, the first flight of the Saturn V launch vehicle, takes flight from Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A on November 9, 1967. The unmanned mission, also designated Apollo 4, marked the first test flight of the S-IC and S-II stages, developed for the Saturn program under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
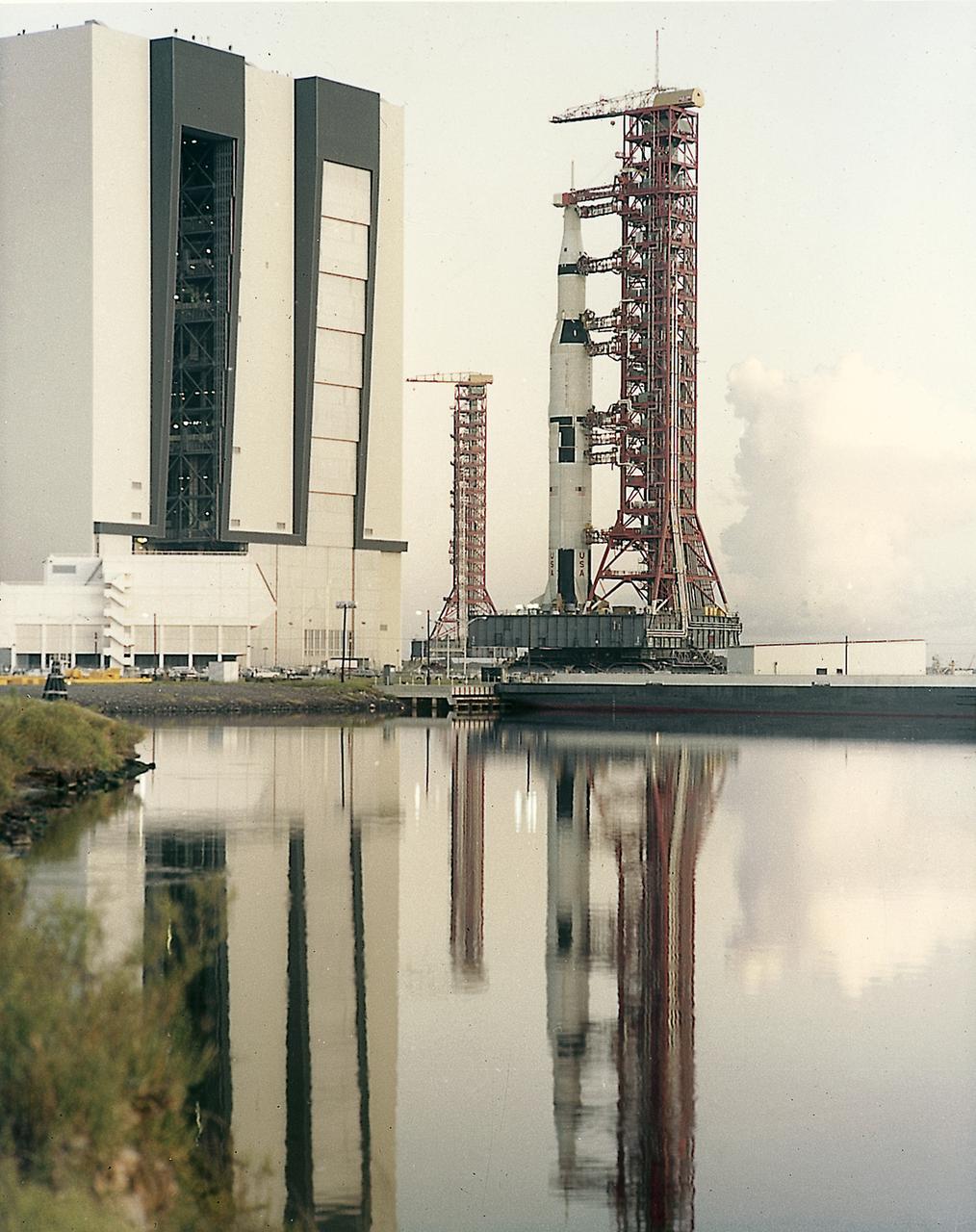

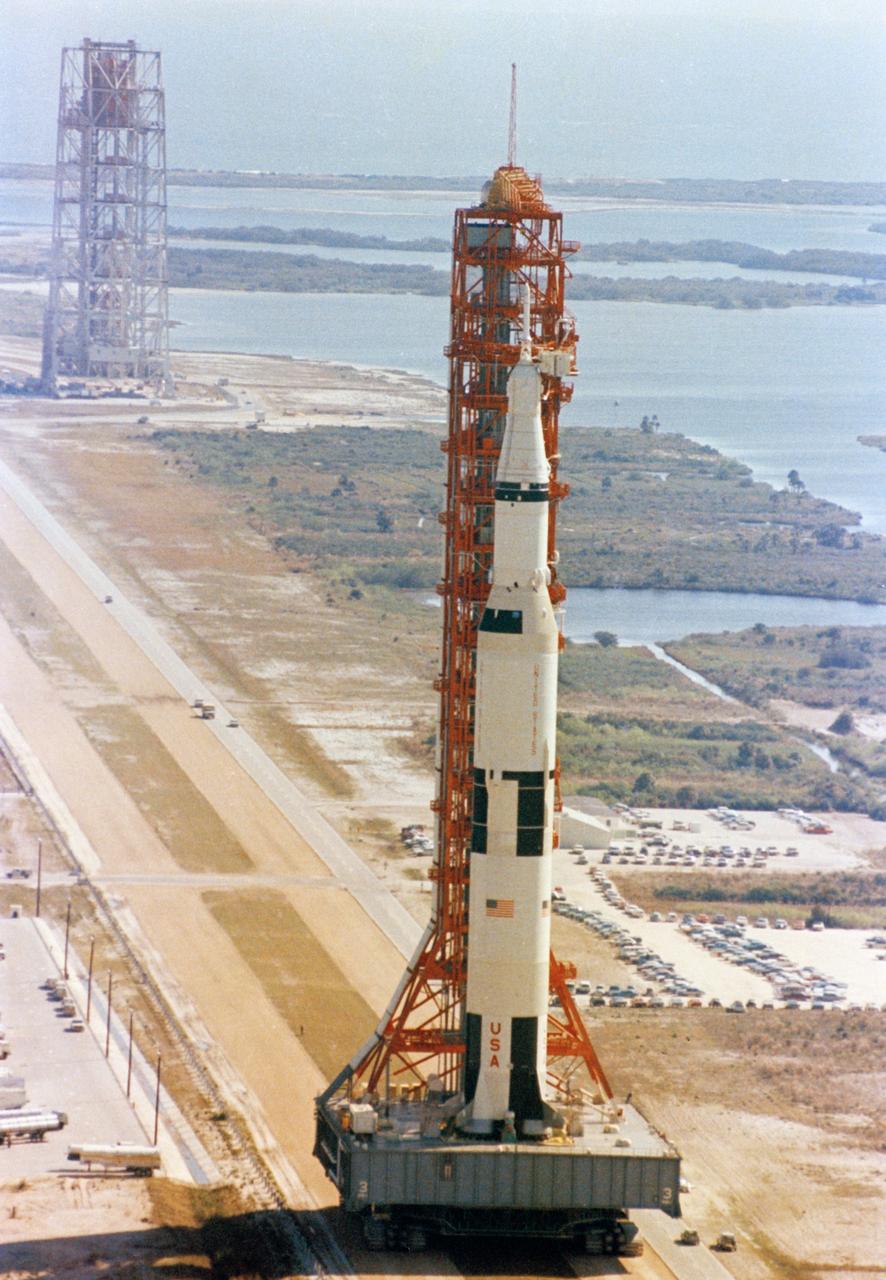
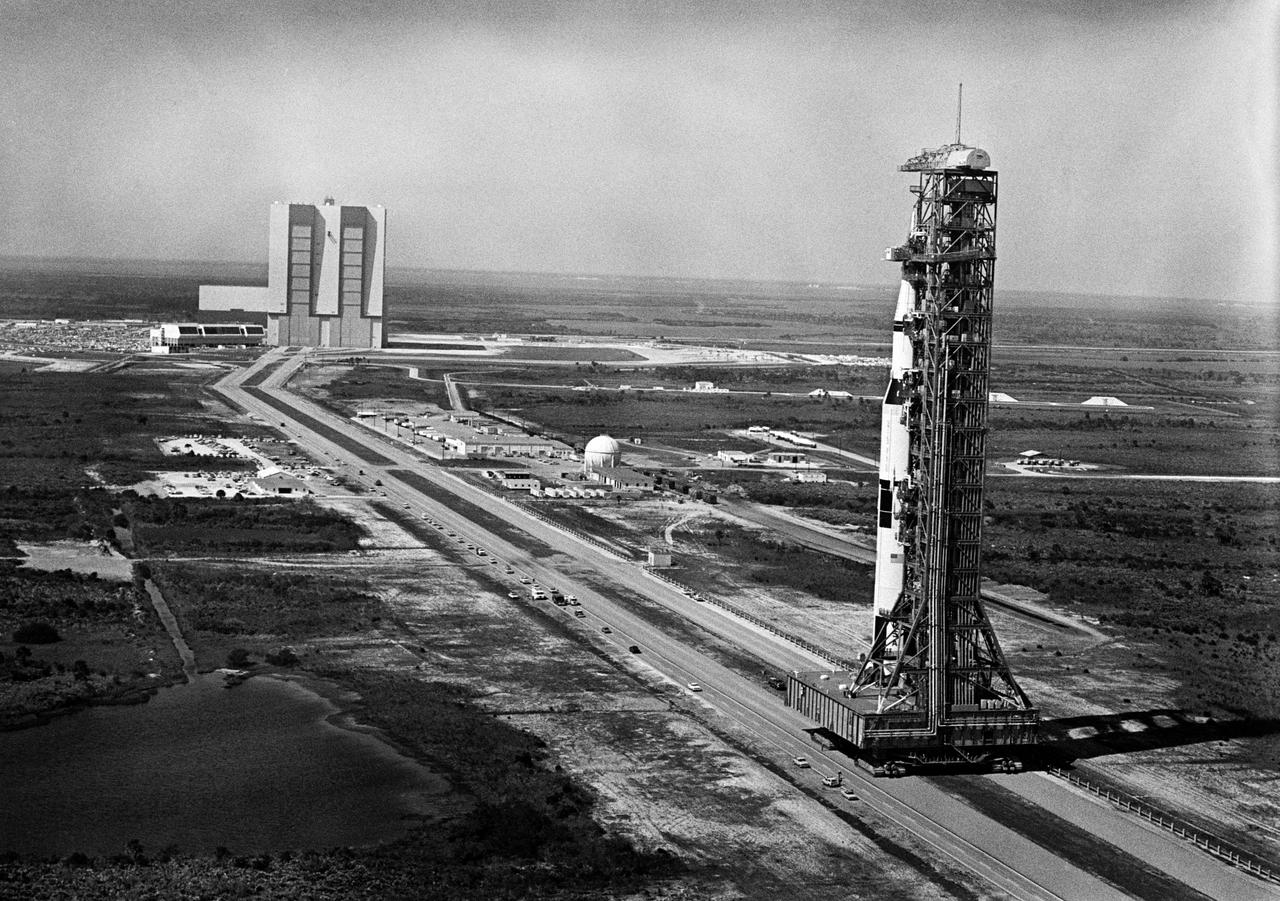
This picture shows the Saturn V vehicle (AS-501), for the Apollo 4 mission on the Crawler Transporter Vehicle. It was rolled out from the Vehicle Assembly Building and slowly (1 mph) moved to the launch pad at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.
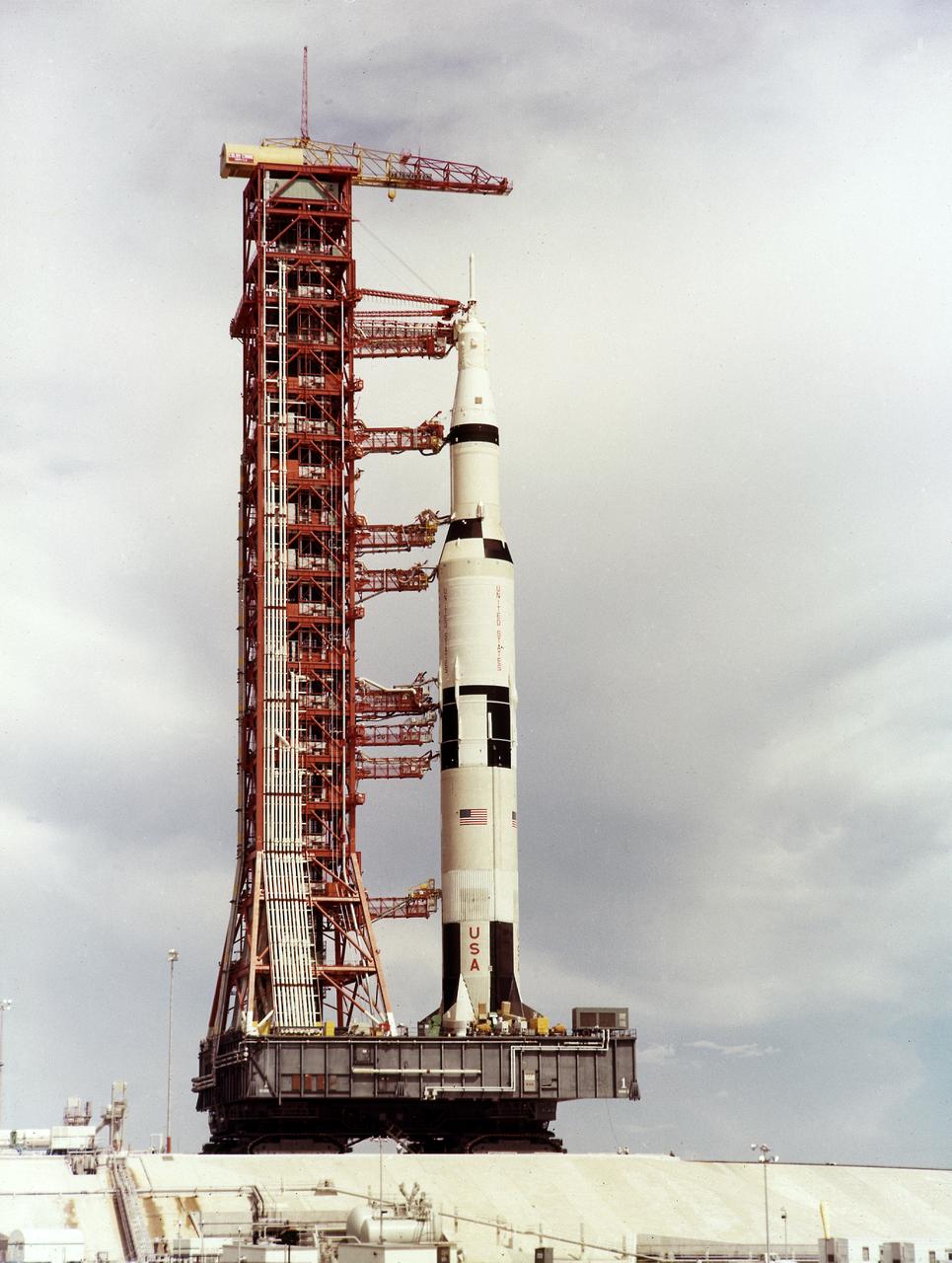
This is a view of the the first test flight of the Saturn V vehicle (SA-501) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) launch complex 39A, awaiting the scheduled launch on November 9, 1967. Designated as Apollo 4, this mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield.
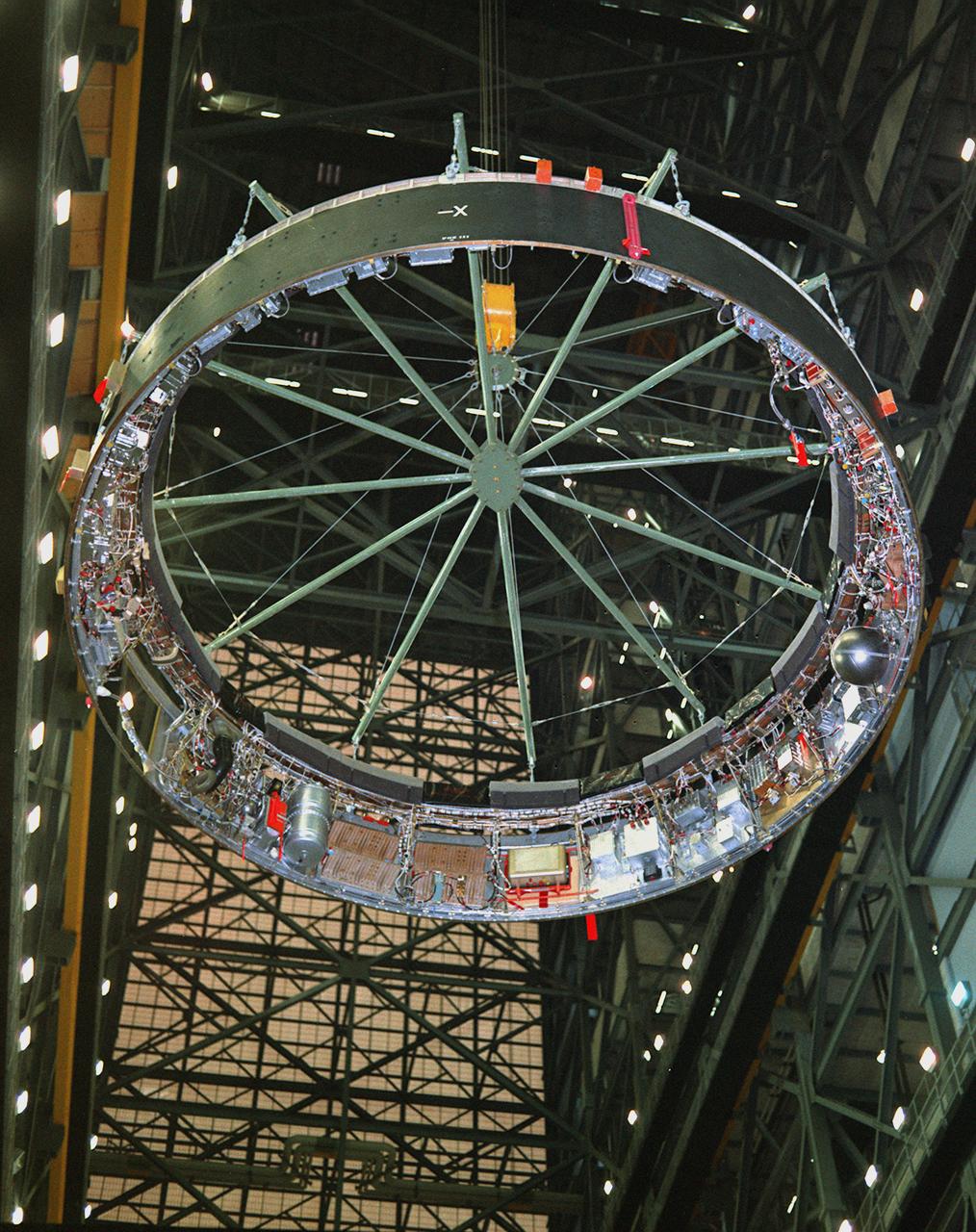

This photograph was taken during the final assembly operation of the Saturn V launch vehicle for the Apollo 4 (SA 501) mission. The instrument unit (IU) was hoisted to be mated to the S-IC/S-II assembly in the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay at the Kennedy Space Center. The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.
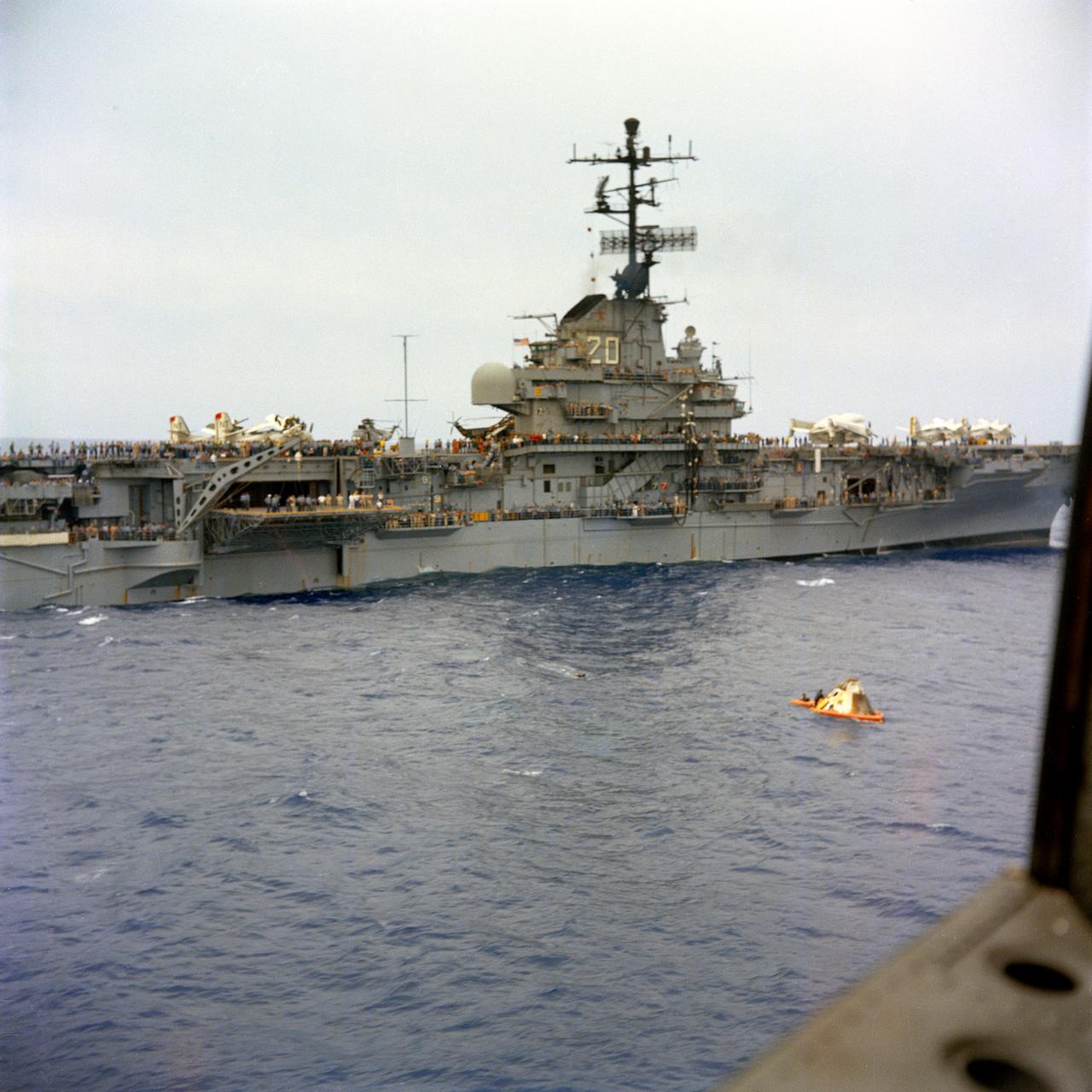

U.S.S. Bennington comes alongside the floating Apollo spacecraft 017 Command Module during recovery operations in the mid-Pacific Ocean. The Command Module splashed down at 3:37 p.m., November 9, 1967, 934 nautical miles northwest of Honolulu, Hawaii.

This photograph shows a test firing of a Saturn V second stage (S-II) on the S-IC test stand at the Propulsion Test Facility near New Orleans, Louisiana. This second stage component was used in the unmarned test flight of Apollo 4.

This spectacular view is a color-enhanced ultraviolet exposure of a colossal eruption, photographed during the Skylab-4 mission by the Apollo Telescope Mount facility on December 19, 1973. This giant prominence, one of the mightiest in 25 years, sparned a third of a million miles into space, roughly the distance between Earth and the Moon.
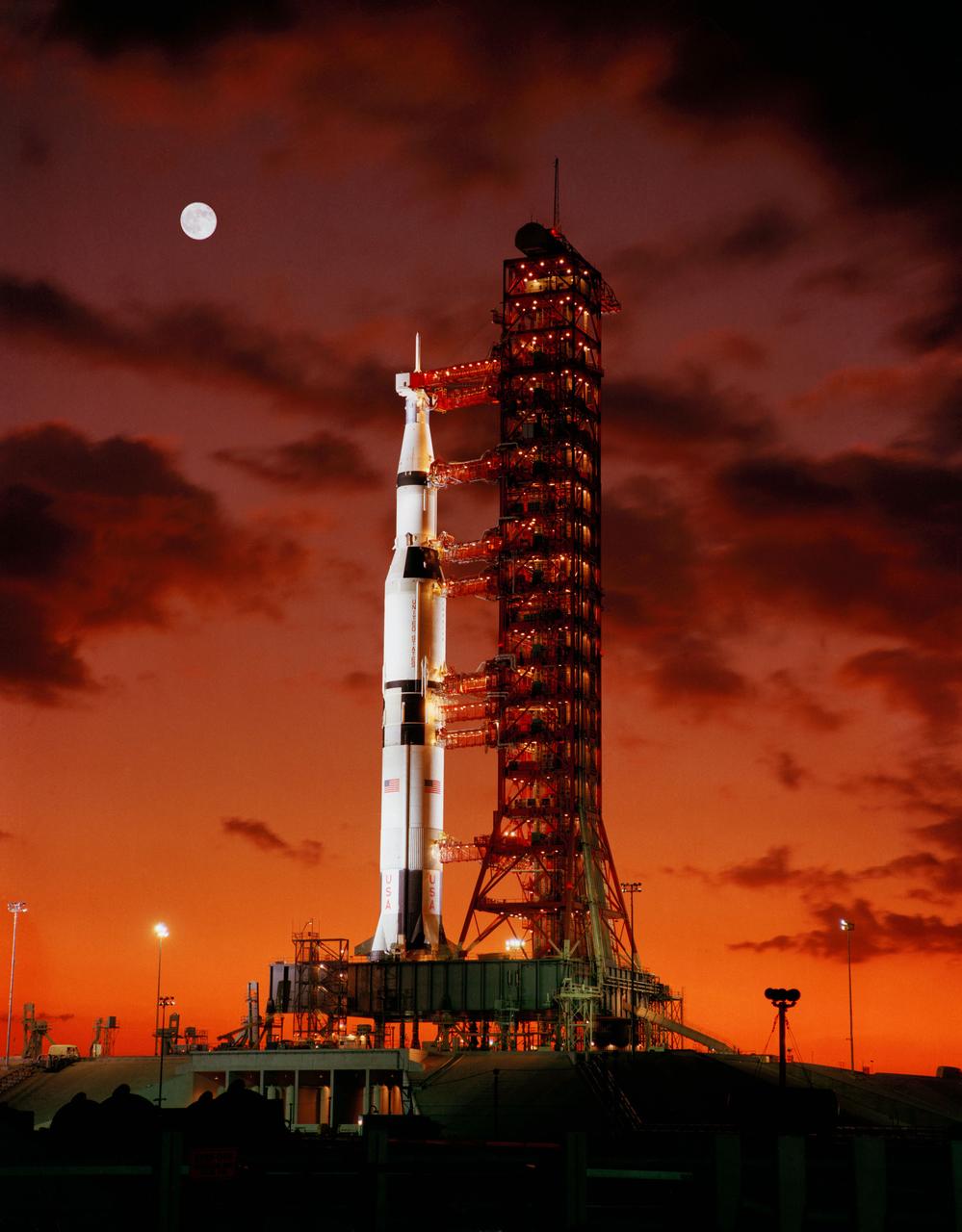

Early morning view of Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, showing Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) unmanned, earth-orbital space mission ready for launch, with a full moon in the upper left part of the image. The 363-foot tall Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle was launched at 7:00:01 AM (EST), November 9, 1967.
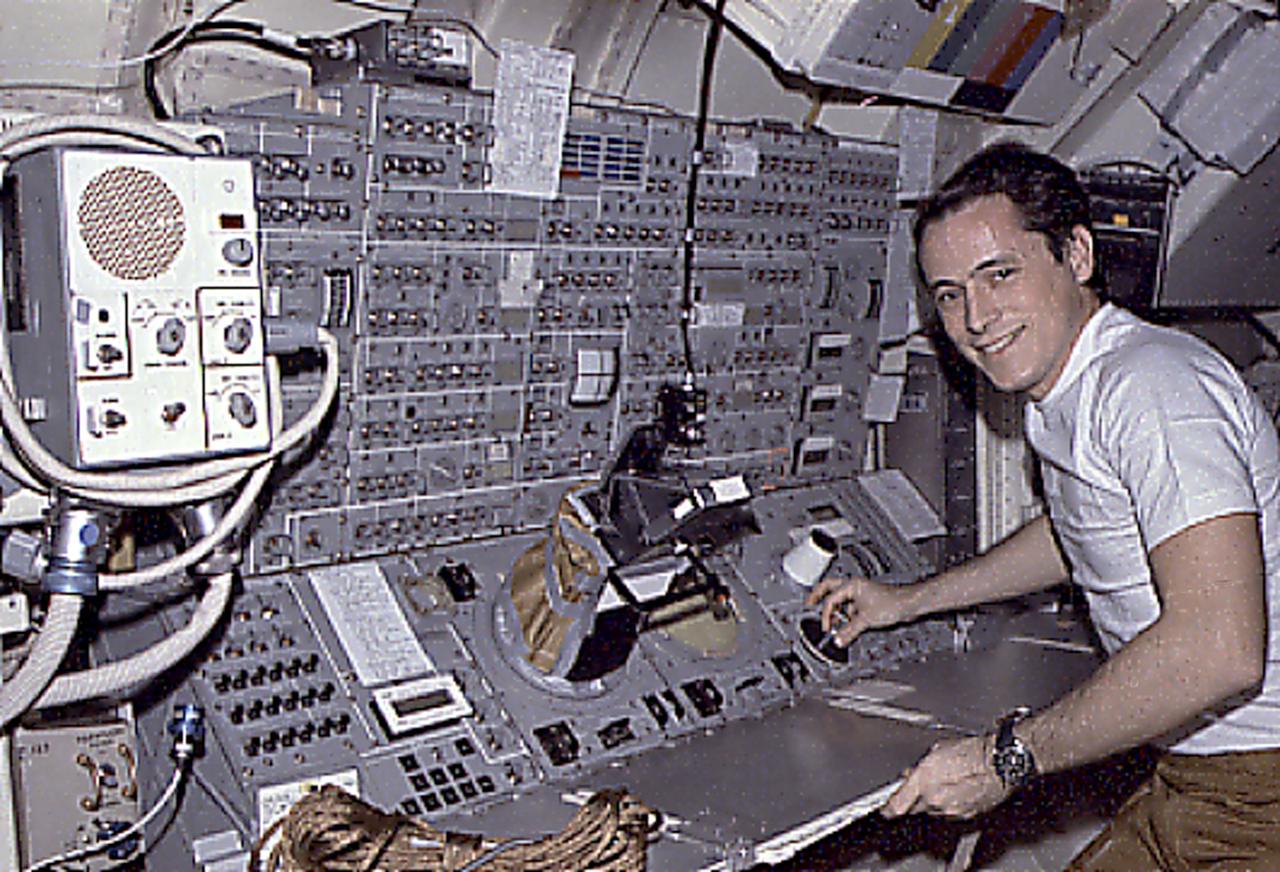
This Skylab-4 mission onboard photograph shows Astronaut Ed Gibson at the complex control and display console for the Apollo Telescope Mount solar telescopes located in the Skylab Multiple Docking Adapter. Astronauts watched the Sun, and photographed and recorded the solar activities, such as the birth of a solar flare.
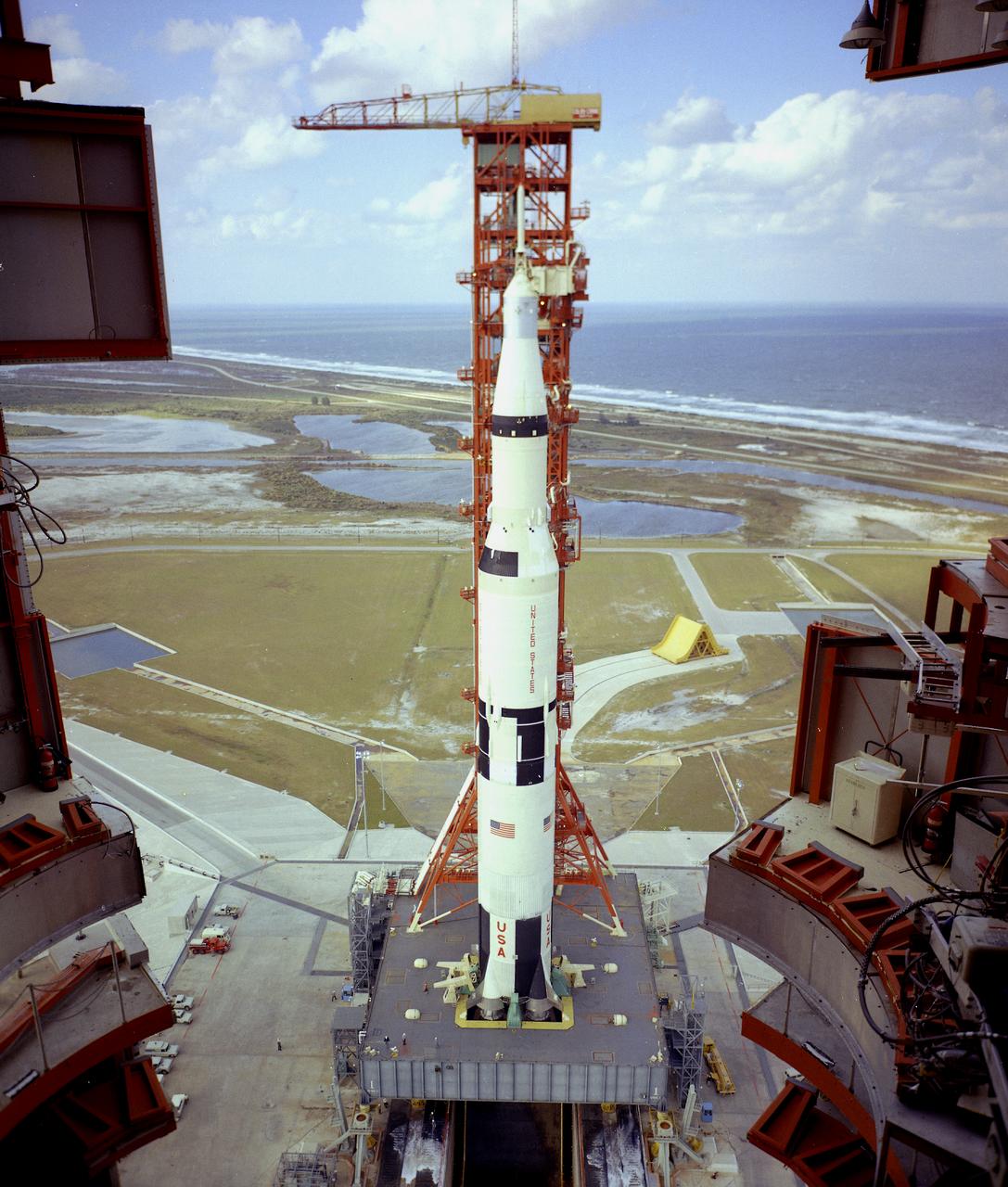

This is a view of the the first test flight of the Saturn V vehicle (SA-501) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) launch complex 39A. The thrust chambers of the first stage's five engines extend into the 45-foot-square hole in the mobile launcher platform. Until liftoff, the flames impinged downward onto a flame deflector that diverted the blast lengthwise in the flame trench. Here, a flame deflector, coated with a black ceramic, is in place below the opening, while a yellow (uncoated) spare deflector rests on its track in the background. It took a tremendous flow of water (28,000 gallons per minute) to cool the flame deflector and trench. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.
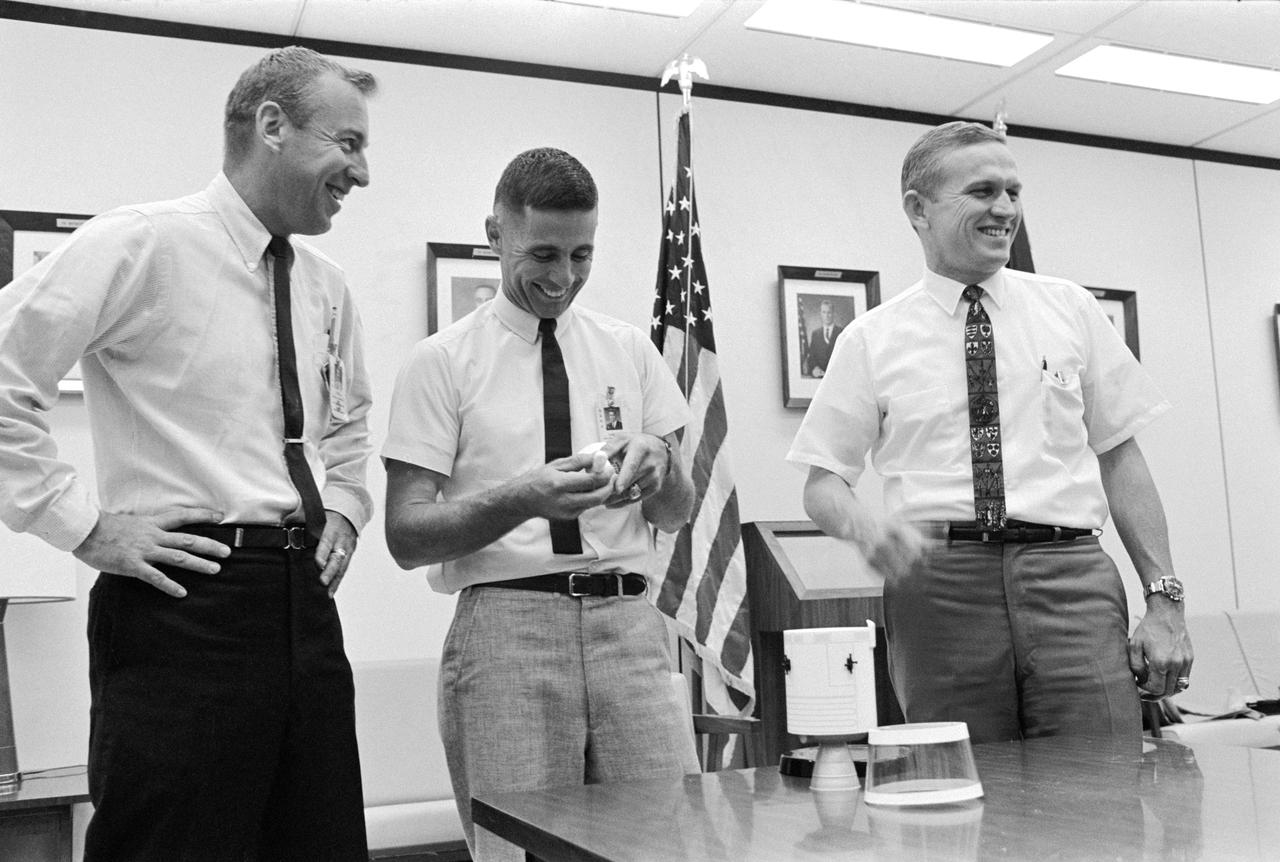

S68-50646 (18 Oct. 1968) --- The prime crew of the Apollo 8 mission is photographed in Building 4, at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), where they are participating in classroom work in burn test review and procedures review. Left to right, are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., William A. Anders, and Frank Borman.
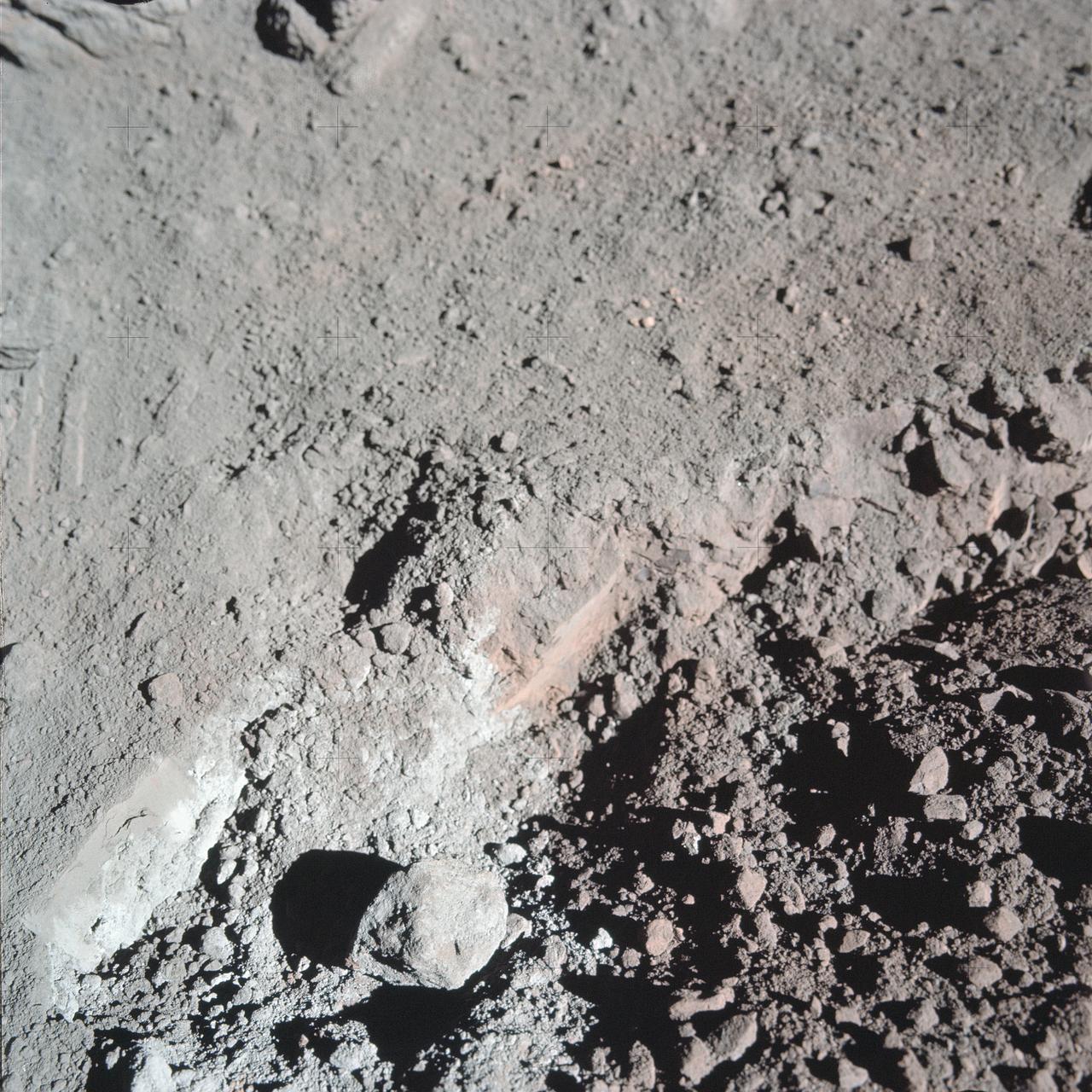

AS17-137-20989 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A close-up view of the much-publicized orange soil which the Apollo 17 crewmen found at Station 4 (Shorty Crater) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The orange soil was first spotted by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt. While astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The orange soil was never seen by the crewmen of the other lunar landing missions - Apollo 11 (Sea of Tranquility); Apollo 12 (Ocean of Storms); Apollo 14 (Fra Mauro); Apollo 15 (Hadley-Apennines); and Apollo 16 (Descartes).

AS17-137-20992 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A view looking into Shorty Crater, taken at Station 4, showing the orange soil. Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt found the orange soil on the moon during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.

Apollo 17 astronaut, Harrison Schmitt, right, is interviewed by Kennedy Space Center public affairs officer, Megan Cruz, at the Operations Support Building II prior to the launch of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the company's Crew Dragon spacecraft on NASA’s SpaceX Crew-4 mission with NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren, Robert Hines, Jessica Watkins, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti onboard, Wednesday, April 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-4 mission is the fourth crew rotation mission of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Lindgren, Hines, Watkins, and Cristoforetti launched at 3:52 a.m. ET from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center to begin a six month mission onboard the orbital outpost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Apollo 17 astronaut, Harrison Schmitt, right, is interviewed by Kennedy Space Center public affairs officer, Megan Cruz, at the Operations Support Building II prior to the launch of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the company's Crew Dragon spacecraft on NASA’s SpaceX Crew-4 mission with NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren, Robert Hines, Jessica Watkins, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti onboard, Wednesday, April 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-4 mission is the fourth crew rotation mission of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Lindgren, Hines, Watkins, and Cristoforetti launched at 3:52 a.m. ET from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center to begin a six month mission onboard the orbital outpost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
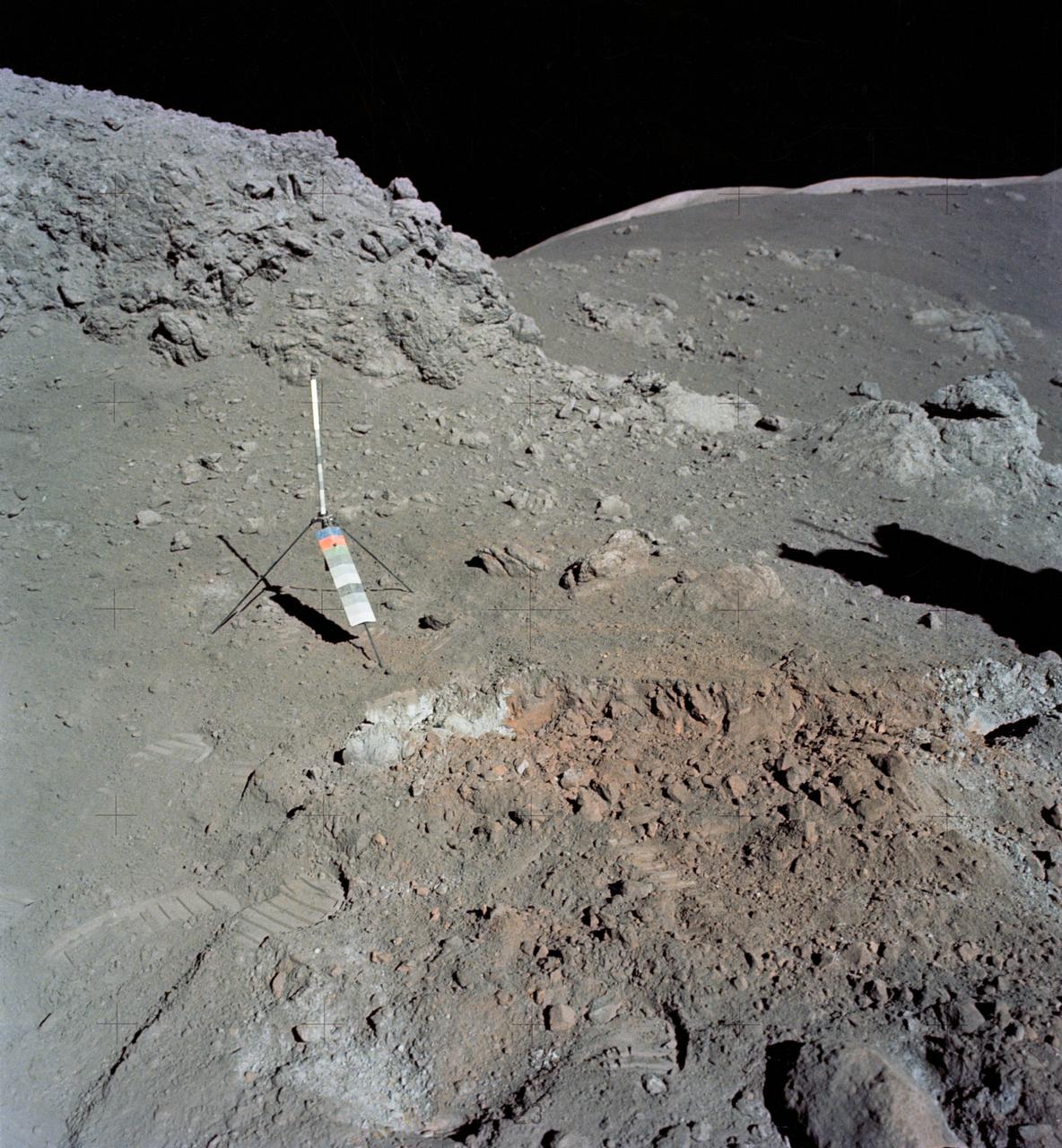

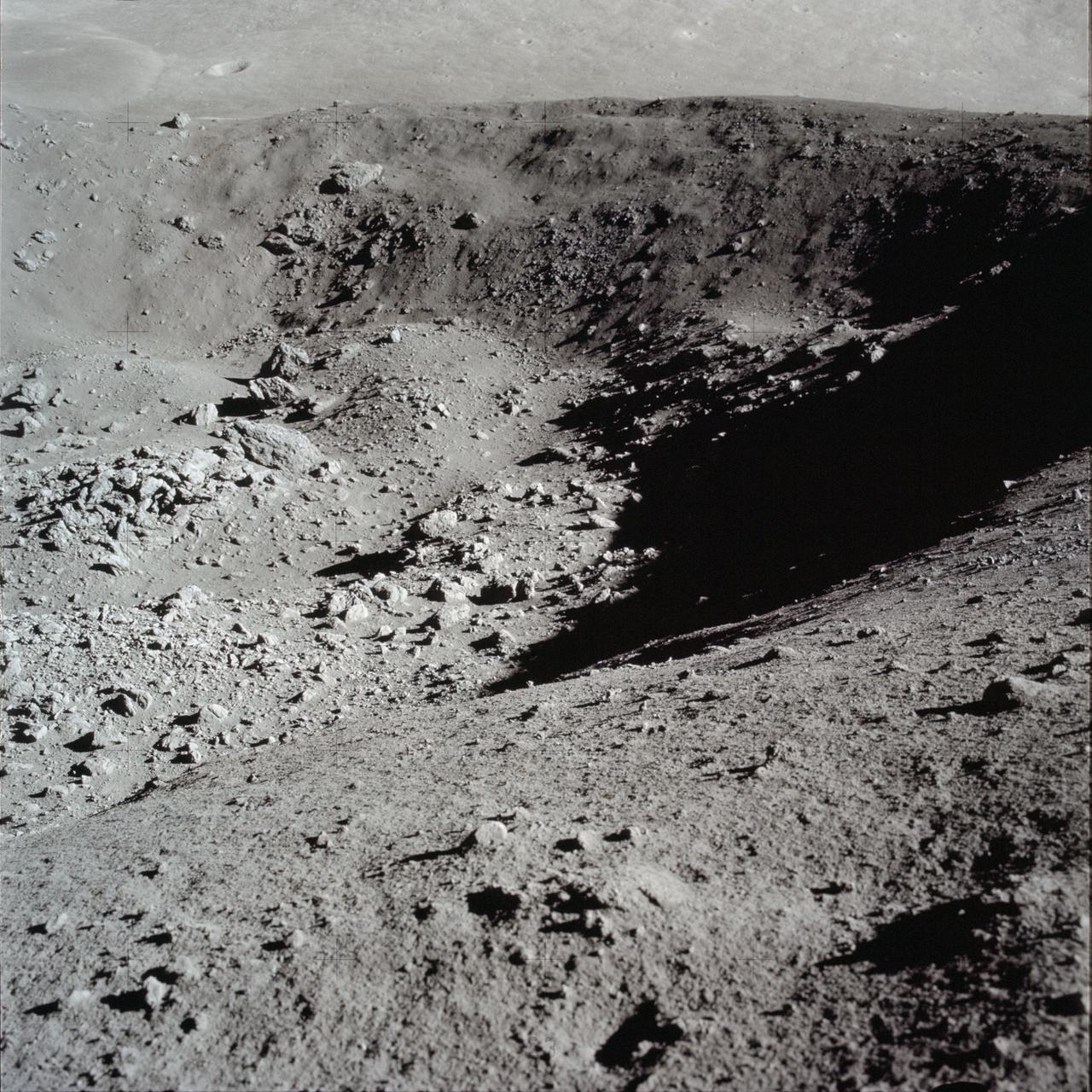
AS17-137-20990 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A view of the area at Station 4 (Shorty Crater) showing the now highly-publicized orange soil which the Apollo 17 crew members found on the moon during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The tripod-like object is the gnomon and photometric chart assembly which is used as a photographic reference to establish local vertical sun angle, scale and lunar color. The gnomon is one of the Apollo lunar geology hand tools. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit. Schmitt was the crew man who first spotted the orange soil.

Yankee Clipper crater on Mars carries the name of the command and service module of NASA 1969 Apollo 12 mission to the moon. NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity recorded this stereo view on Nov. 4, 2010. 3D glasses are necessary.
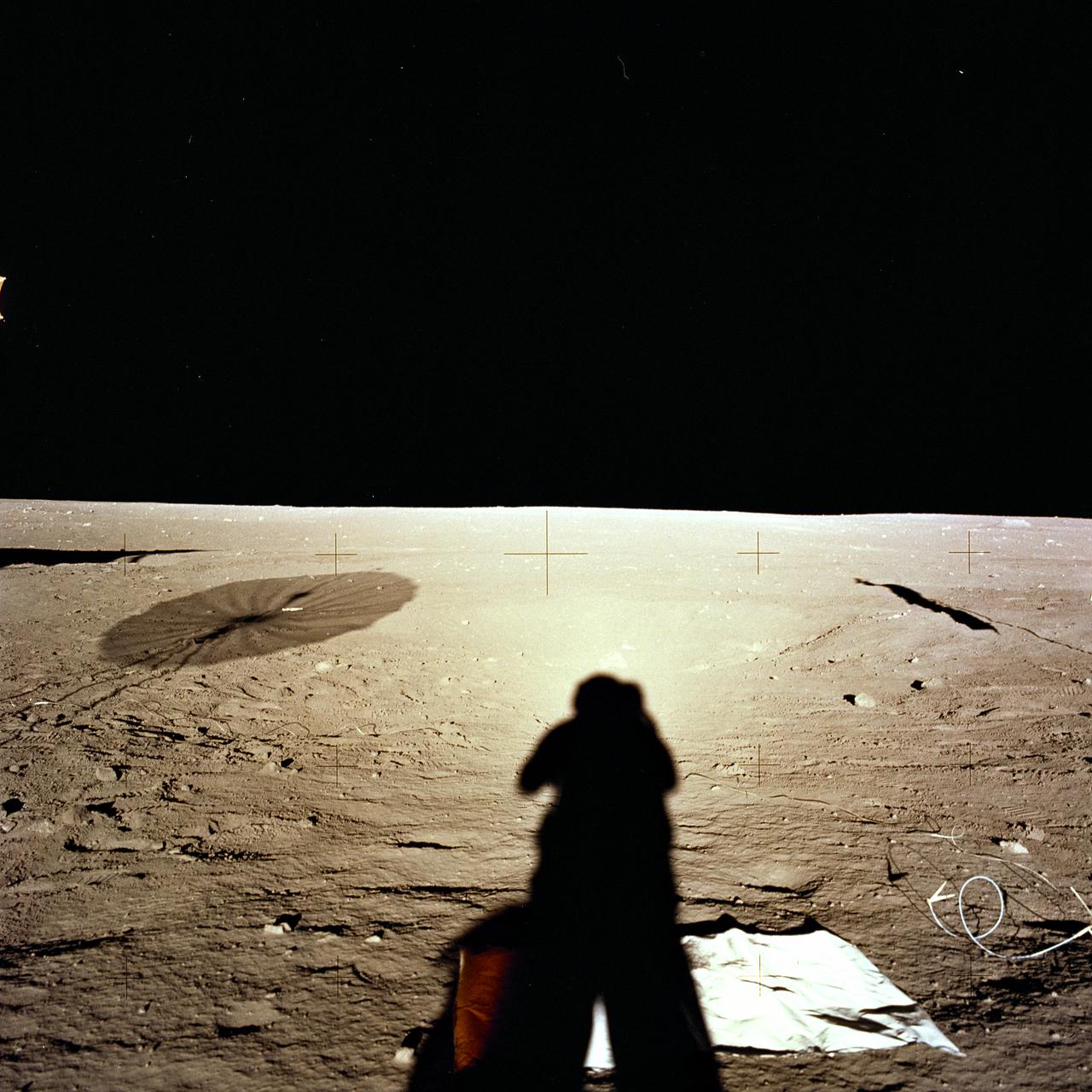

The second manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 12 launched from launch pad 39-A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on November 14, 1969 via a Saturn V launch vehicle. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard Apollo 12 was a crew of three astronauts: Alan L. Bean, pilot of the Lunar Module (LM), Intrepid; Richard Gordon, pilot of the Command Module (CM), Yankee Clipper; and Spacecraft Commander Charles Conrad. The LM, Intrepid, landed astronauts Conrad and Bean on the lunar surface in what’s known as the Ocean of Storms while astronaut Richard Gordon piloted the CM, Yankee Clipper, in a parking orbit around the Moon. Lunar soil activities included the deployment of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP), finding the unmanned Surveyor 3 that landed on the Moon on April 19, 1967, and collecting 75 pounds (34 kilograms) of rock samples. This is the fourth of 25 images captured by the crew in attempt to provide a 360 degree Lunar surface scene. Apollo 12 safely returned to Earth on November 24, 1969.
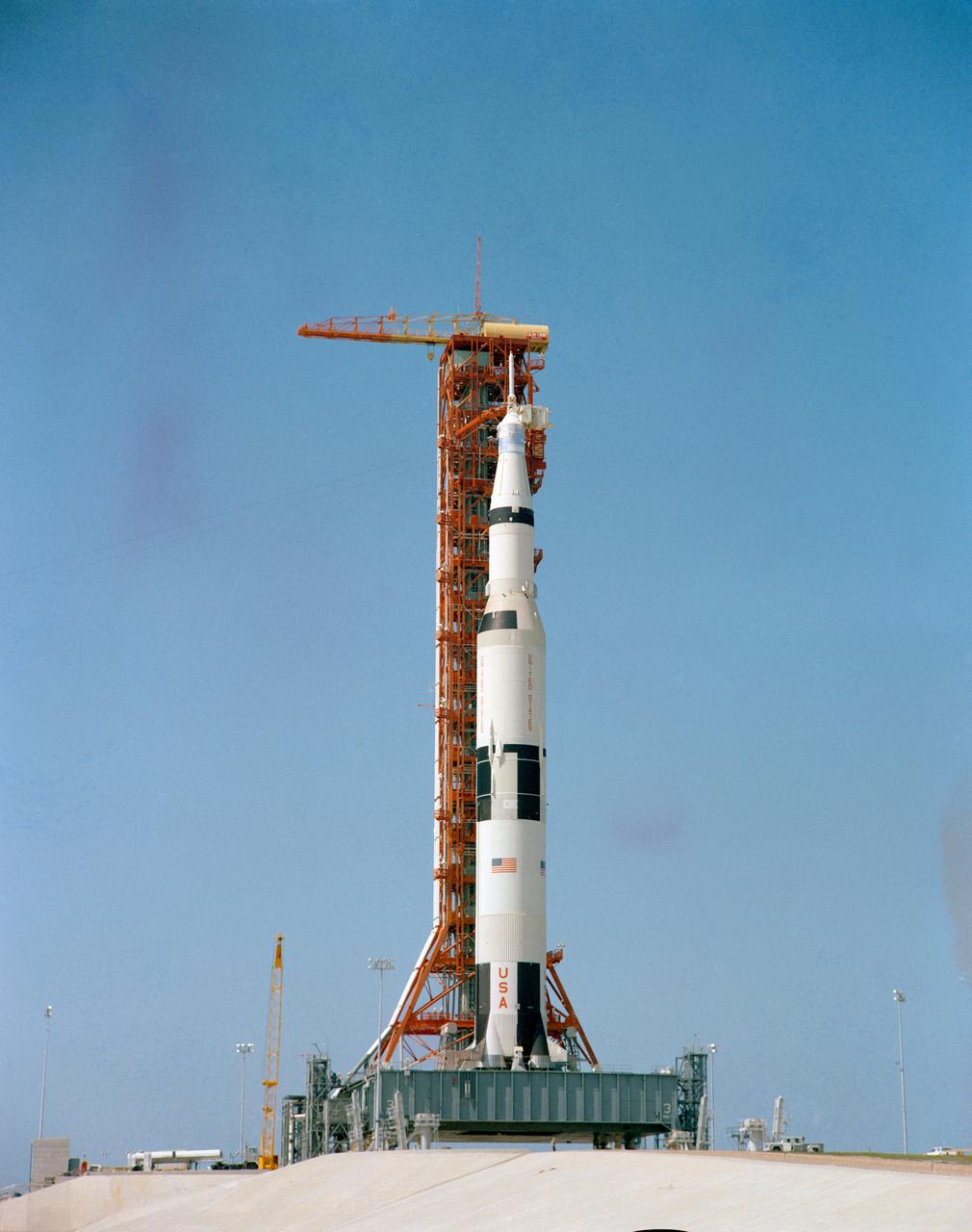

S69-33853 (4 May 1969) --- Ground-level view of the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. This photograph of the 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V stack was taken during Countdown Demonstration Test (CDDT) activity. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
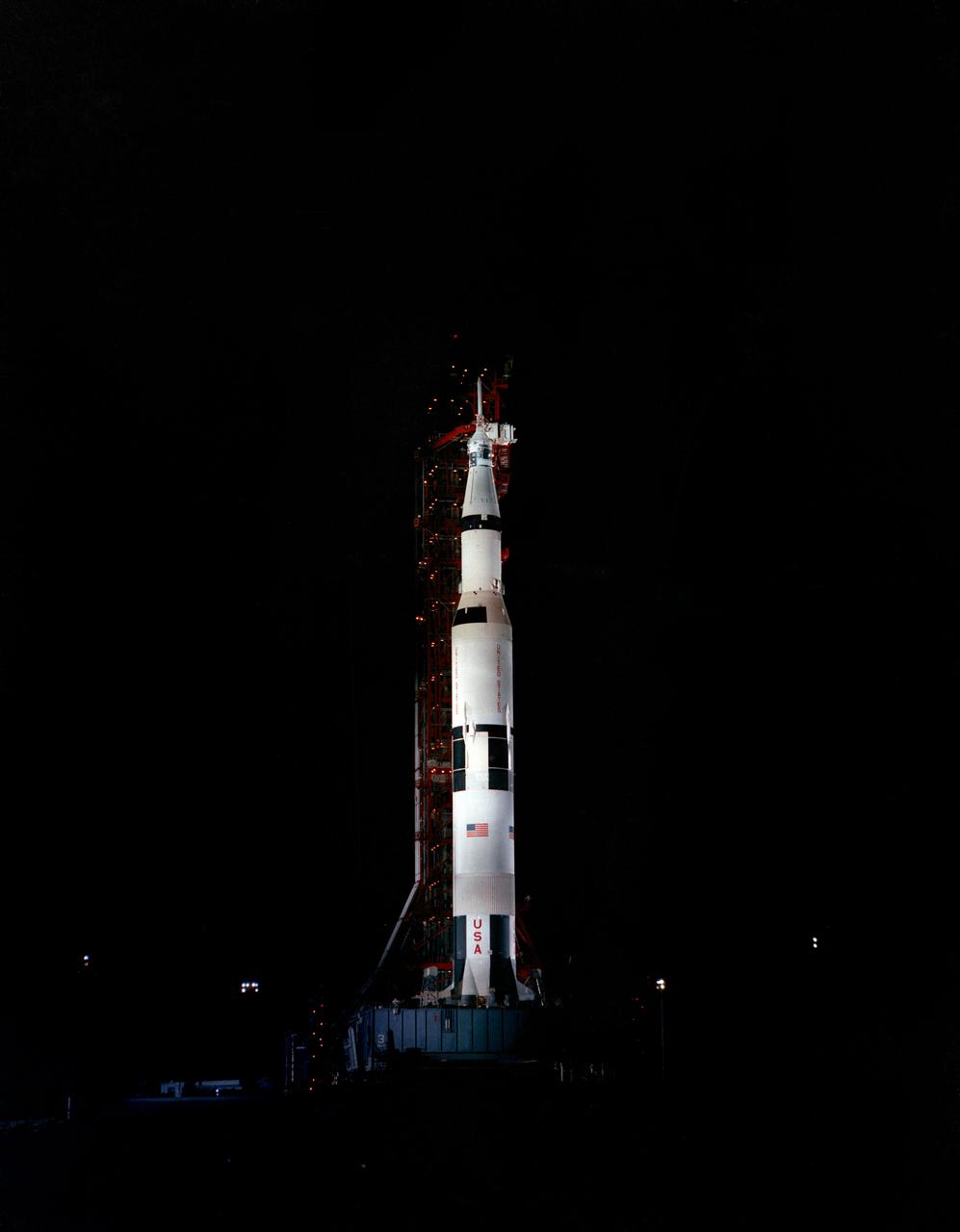

S69-33855 (4 May 1969) --- Nighttime, ground-level view of the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center. This photograph of the 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V stack was taken during pull back of the mobile service structure. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, John W. Young, and Eugene A. Cernan.
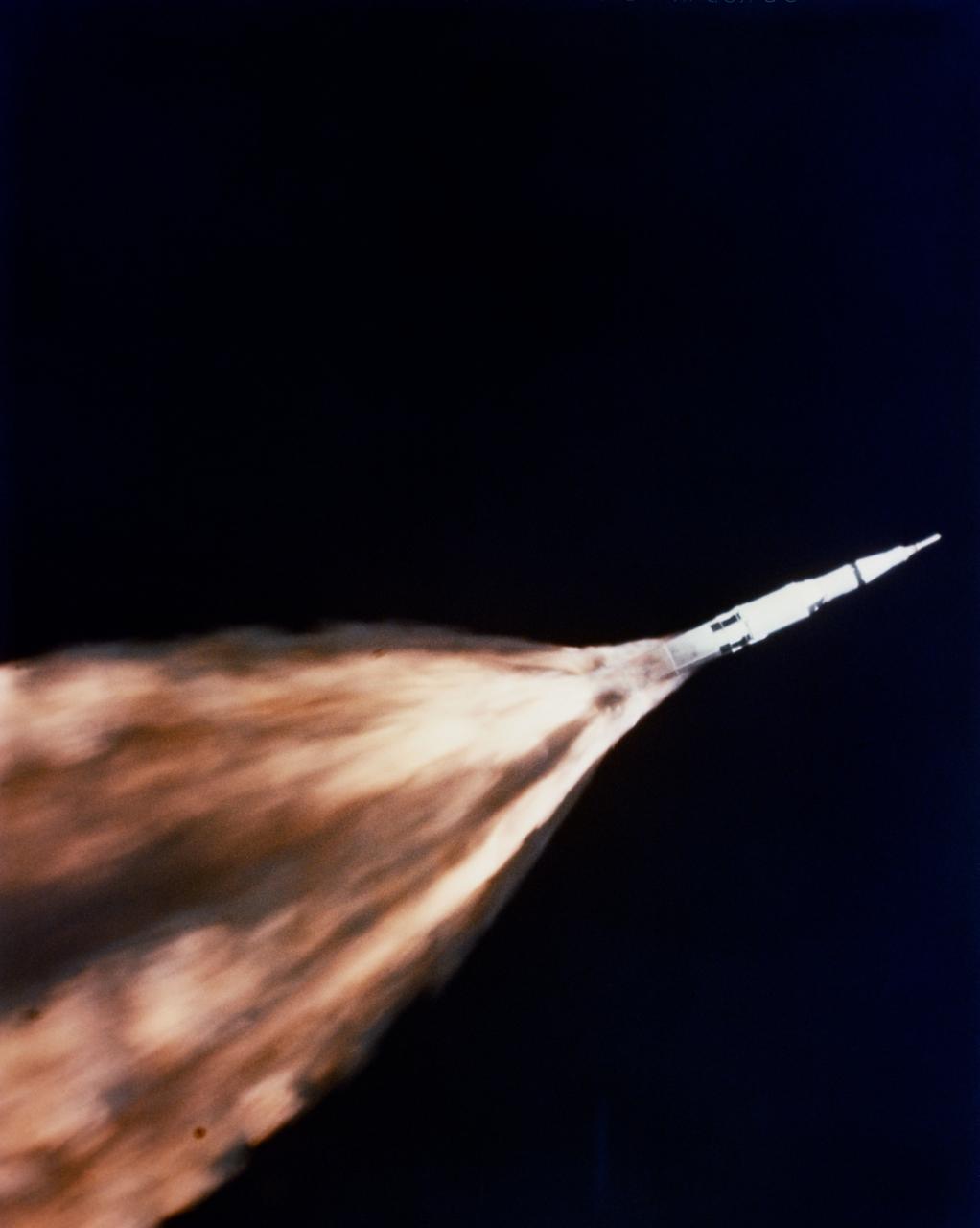

S68-27365 (4 April 1968) --- The five F-1 engines of the huge Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle's first (S-IC) stage leave a gigantic trail of flame in the sky above the Kennedy Space Center seconds after liftoff. The launch of the Apollo 6 (Spacecraft 020/Saturn 502) unmanned space mission occurred at 07:00:01.5 (EST), April 4, 1968. This view of the Apollo 6 launch was taken from a chase plane.
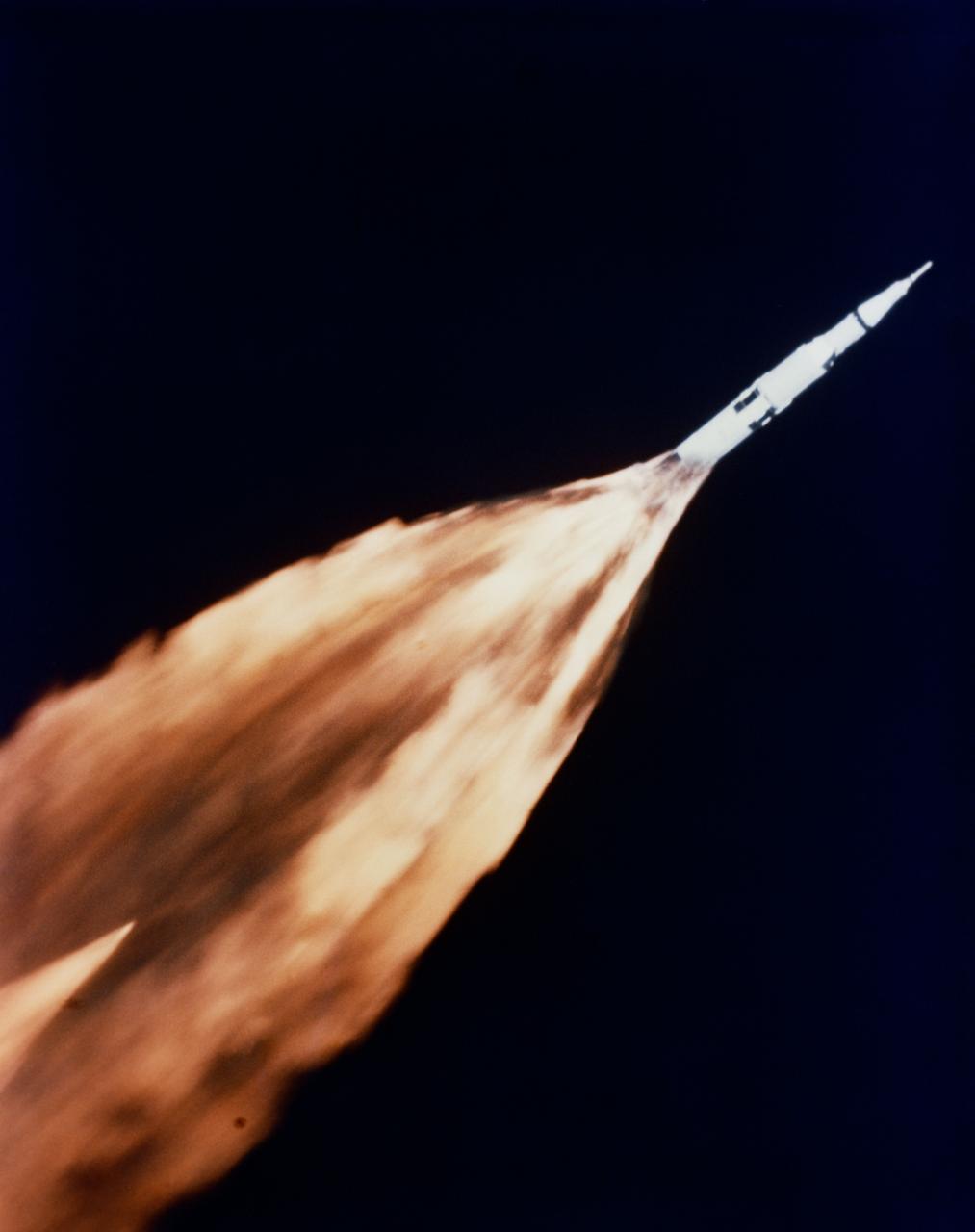

S68-27366 (4 April 1968) --- The five F-1 engines of the huge Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle's first (S-IC) stage leave a gigantic trail of flame in the sky above the Kennedy Space Center seconds after liftoff. The launch of the Apollo 6 (Spacecraft 020/Saturn 502) unmanned space mission occurred at 07:00:01.5 (EST), April 4, 1968. This view of the Apollo 6 launch was taken from a chase plane.
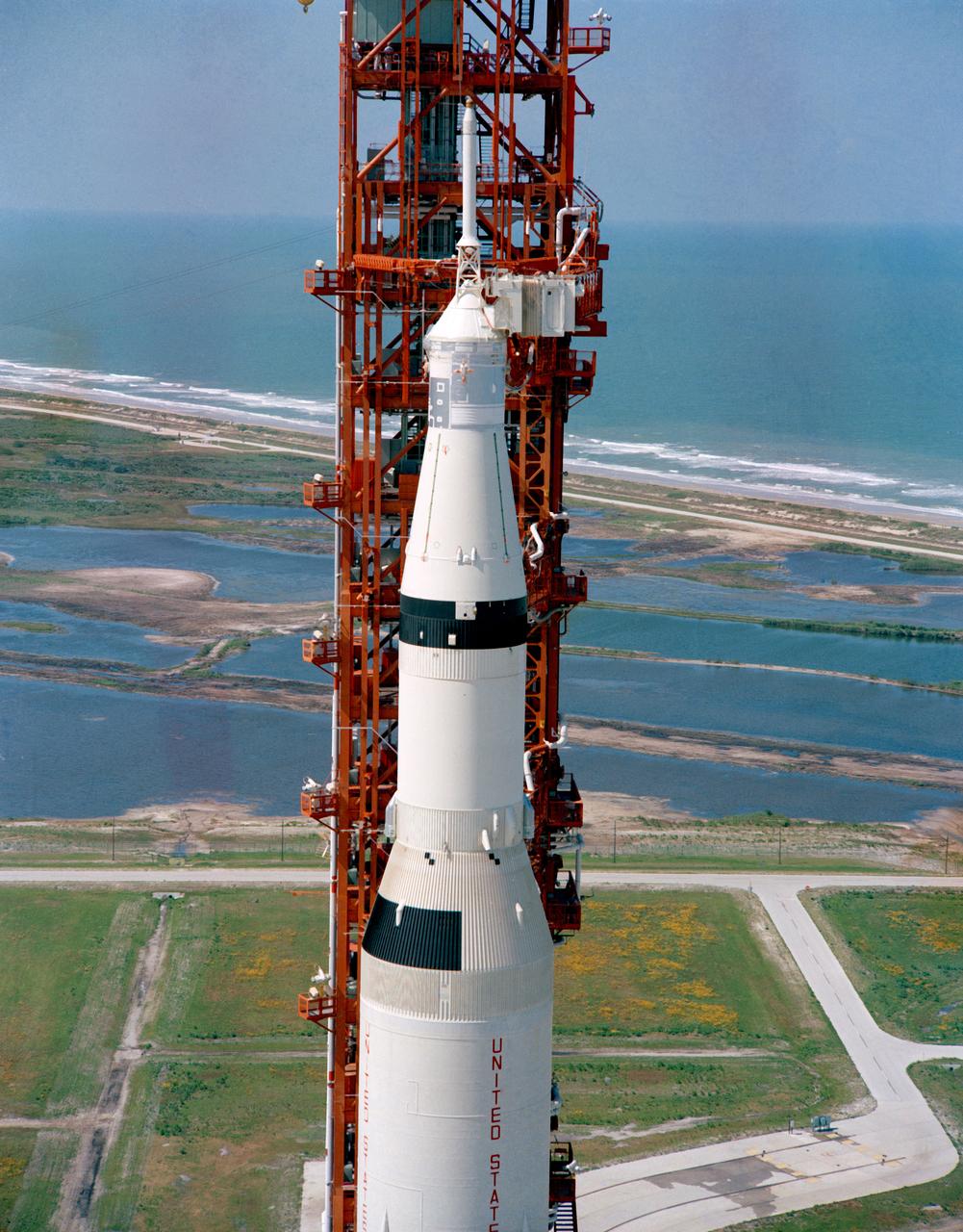

S69-33854 (4 May 1969) --- Aerial (high-angle, clasp) view of the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center. This photograph of the 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V stack was taken during pull back of the mobile service structure. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, John W. Young, and Eugene A. Cernan.
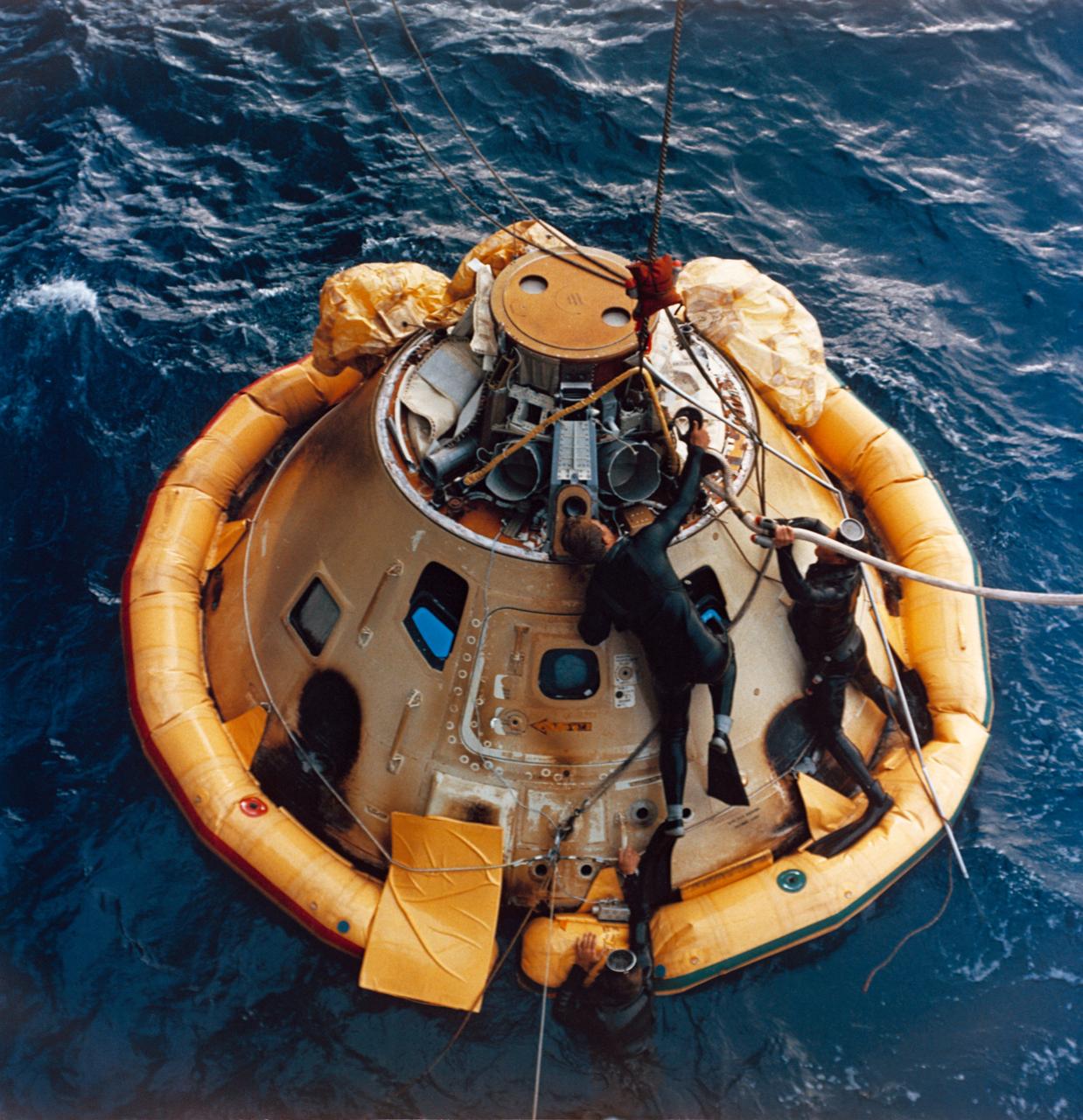

S68-27884 (4 April 1968) --- A U. S. Navy frogman team prepares the Apollo Spacecraft 020 Command Module (CM) for hoisting aboard the USS Okinawa. The USS Okinawa was the prime recovery ship for the Apollo 6 (Spacecraft 020/Saturn 502) unmanned space mission. Splashdown occurred at 4:58:45 p.m. (EST), April 4, 1968, at 375 nautical miles north of Honolulu, Hawaii.

S68-26989 (4 April 1968) --- The Apollo 6 Spacecraft 020 Command Module is hoisted aboard the USS Okinawa.
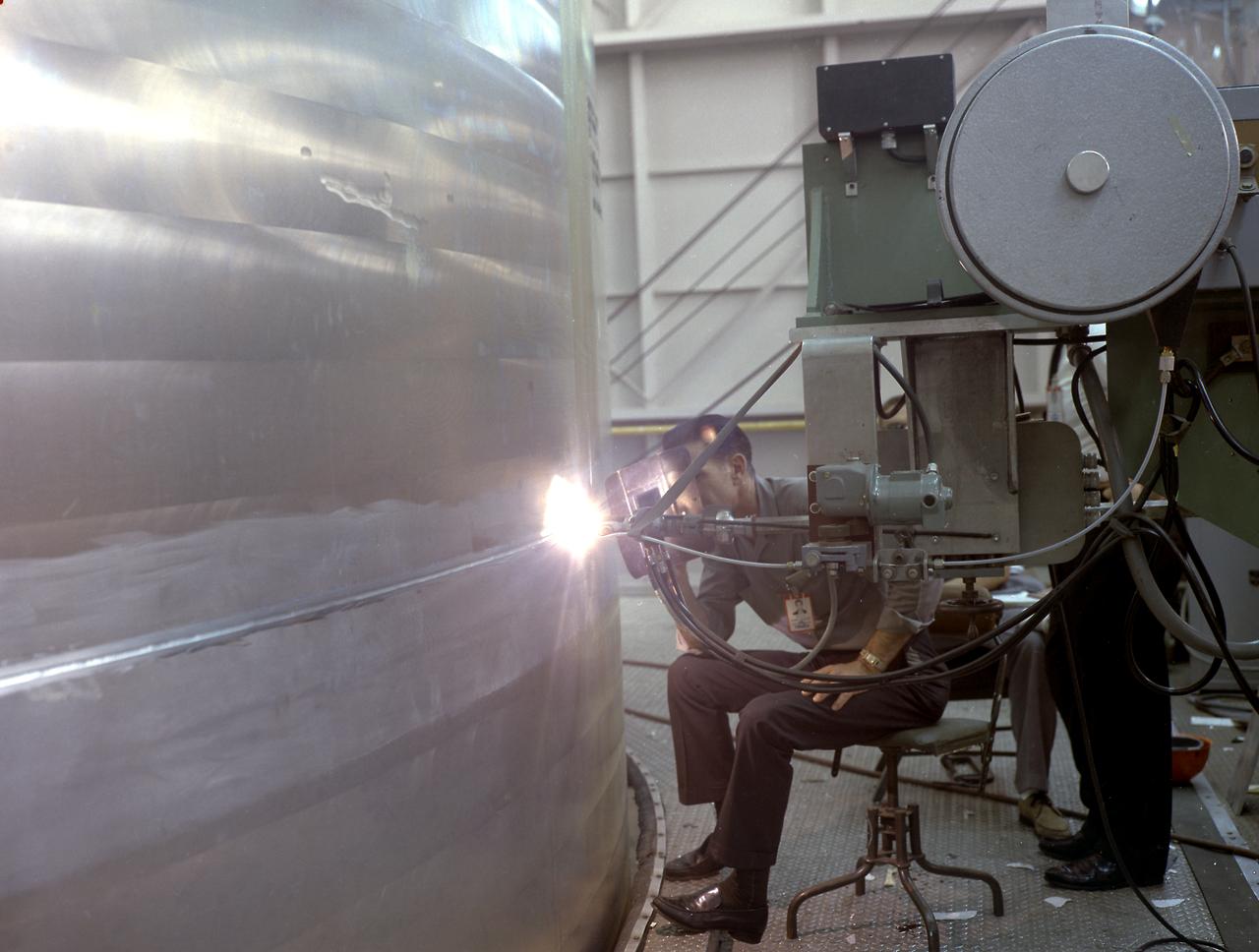

This photo shows the closeout welding operation of the liquid oxygen (LOX) tank for the Saturn V SA-501 vehicle for the Apollo 4 mission.

S68-27364 (4 April 1968) --- The Apollo 6 (Spacecraft 020/Saturn 502) unmanned space mission was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida. The liftoff of the huge Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle occurred at 7:00:01.5 a.m. (EST), April 4, 1968.
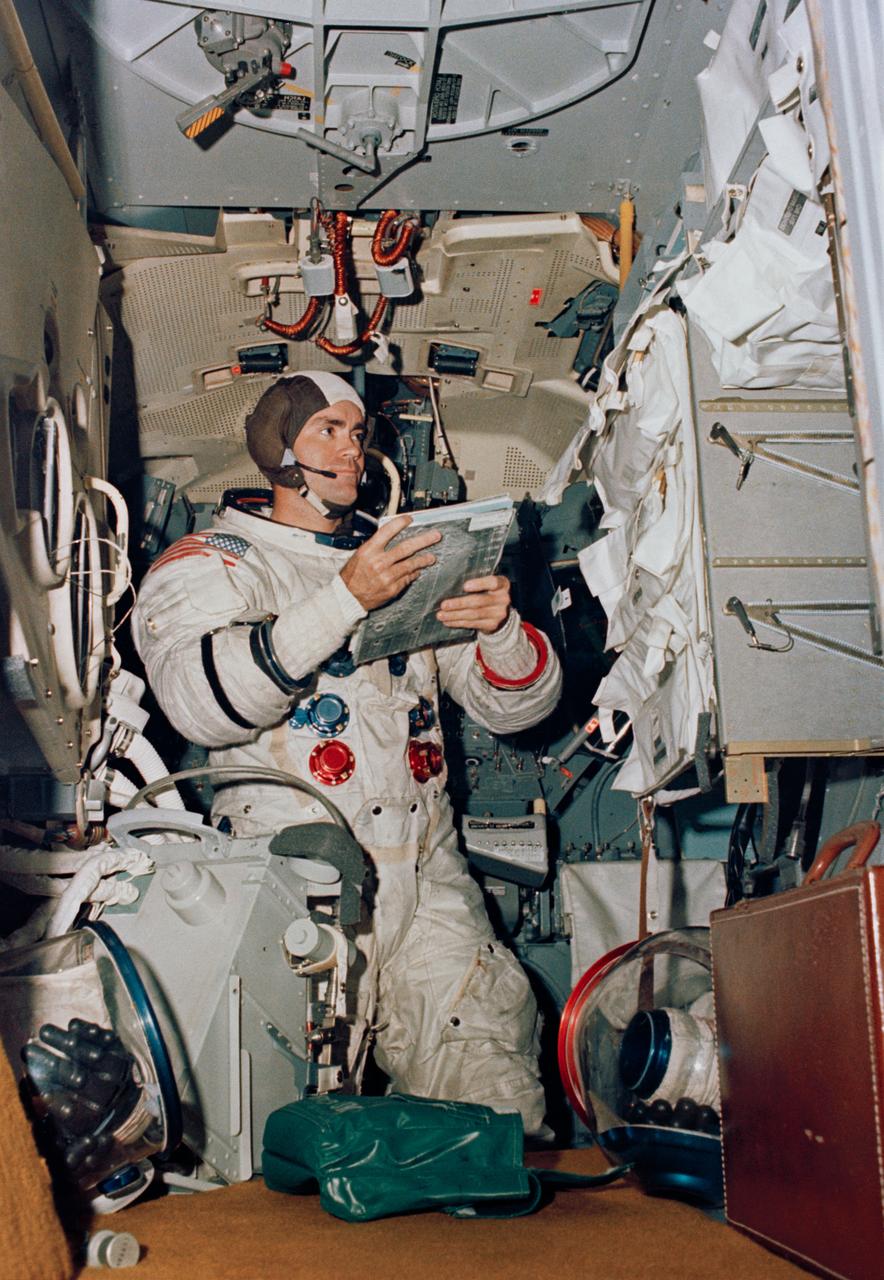

S70-34412 (4 April 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., Apollo 13 lunar module pilot, participates in simulation training in preparation for the scheduled lunar landing mission. He is in the Apollo Lunar Module Mission Simulator in the Kennedy Space Center's Flight Crew Training building.
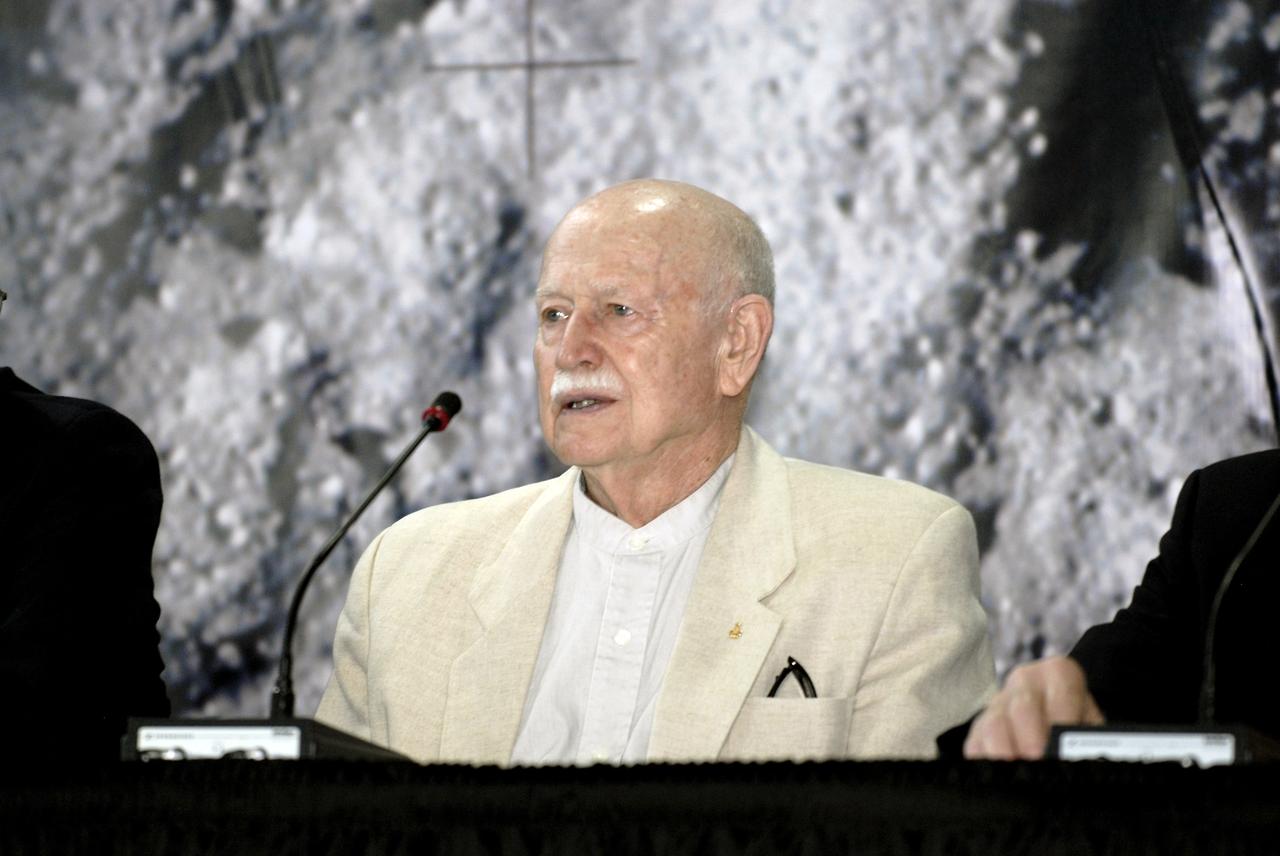

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo astronaut Gerald Carr shares his experiences with spectators crowd gathered for NASA's 40th Anniversary of Apollo Celebration of the July 1969 launch and landing on the moon. Carr served as CAPCOM for the Apollo 8 and 12 flights, and was involved in the development and testing of the lunar roving vehicle which was used on the lunar surface by Apollo flight crews. He also was commander of Skylab 4 launched in 1973 on the third and final manned visit to the Skylab Orbital Workshop. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
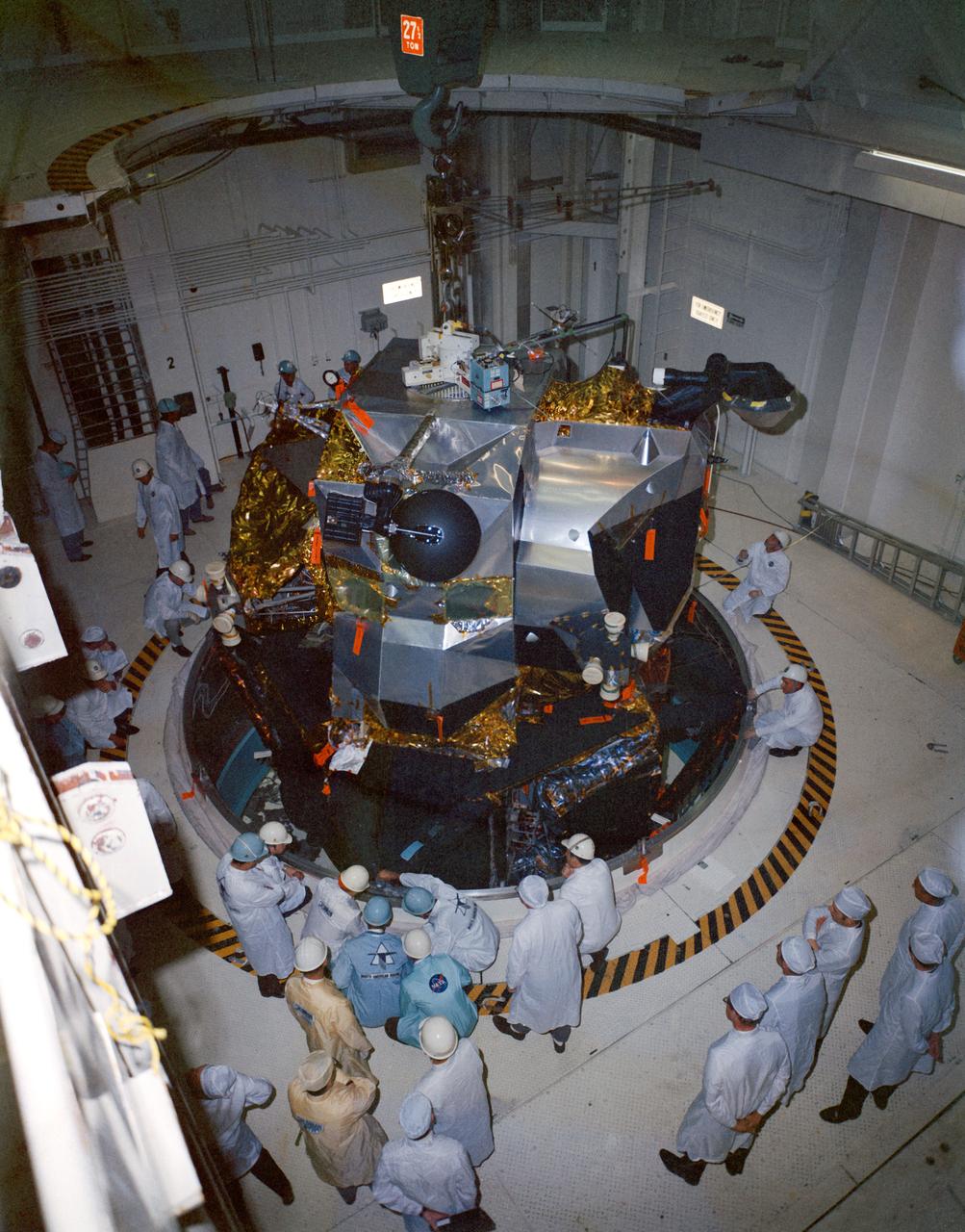
S69-17809 (13 Jan. 1969) --- Lunar Module 4 in the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building being moved into position for mating with Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) 13. Lunar Module 4 will be flown on the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Saturn 505) lunar orbit mission.
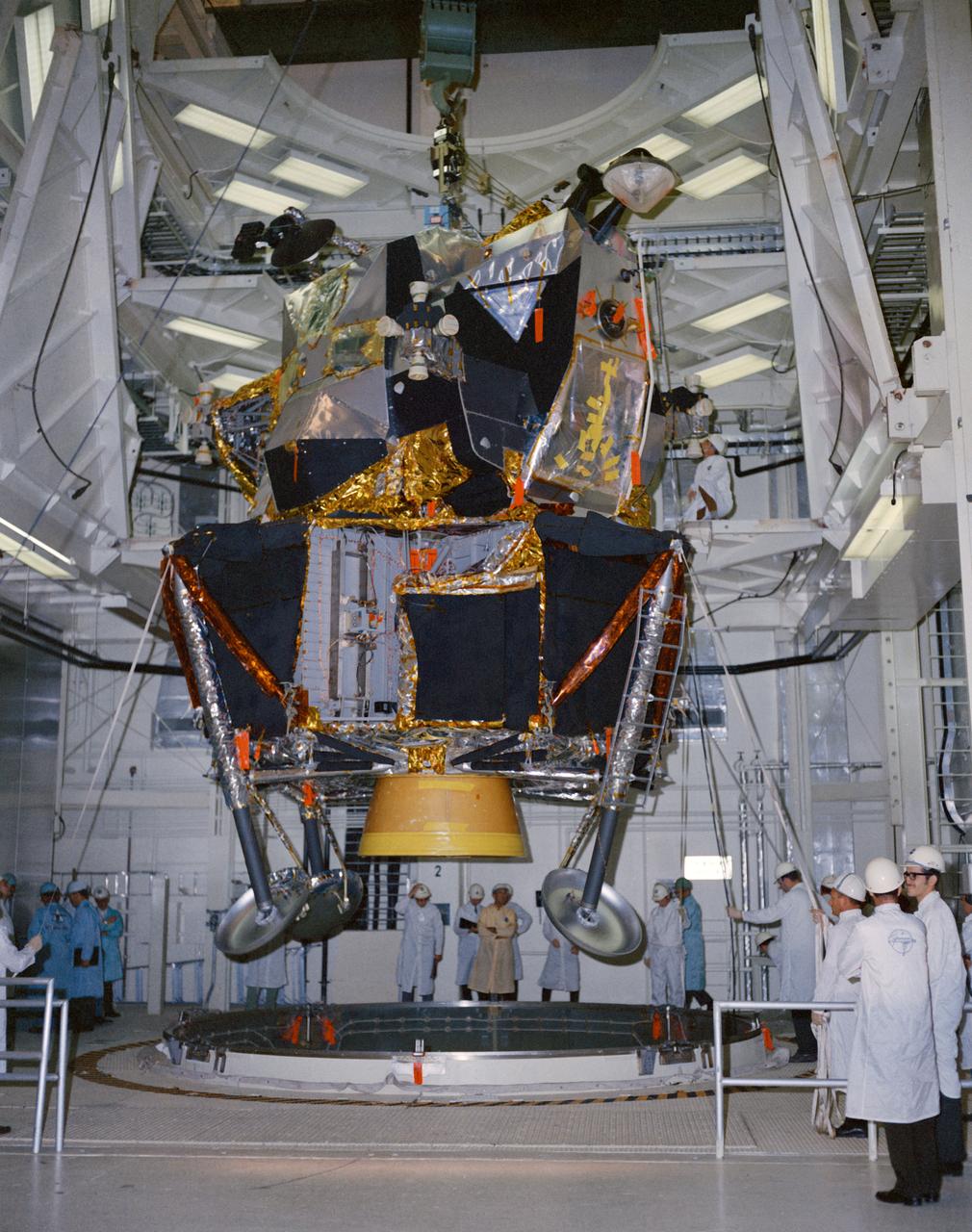

S69-17807 (13 Jan. 1969) --- Lunar Module 4 in the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building being moved into position for mating with Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) 13. Lunar Module 4 will be flown on the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Saturn 505) space mission.
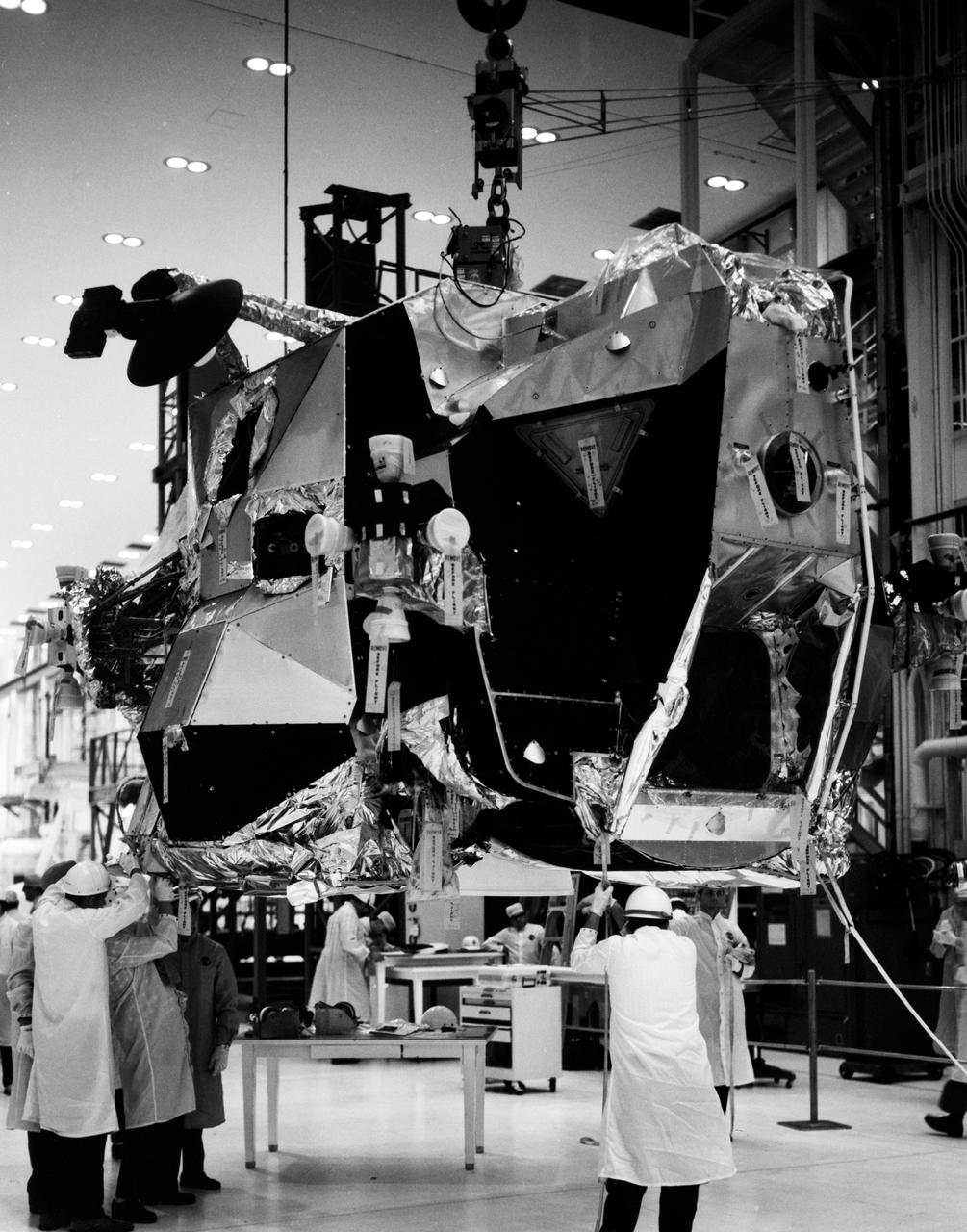

S69-25979 (December 1968) --- The ascent stage of Lunar Module-4 is moved from work stand into altitude chamber in the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building. Lunar Module-4 will be flown on the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Saturn 505) lunar orbit mission.
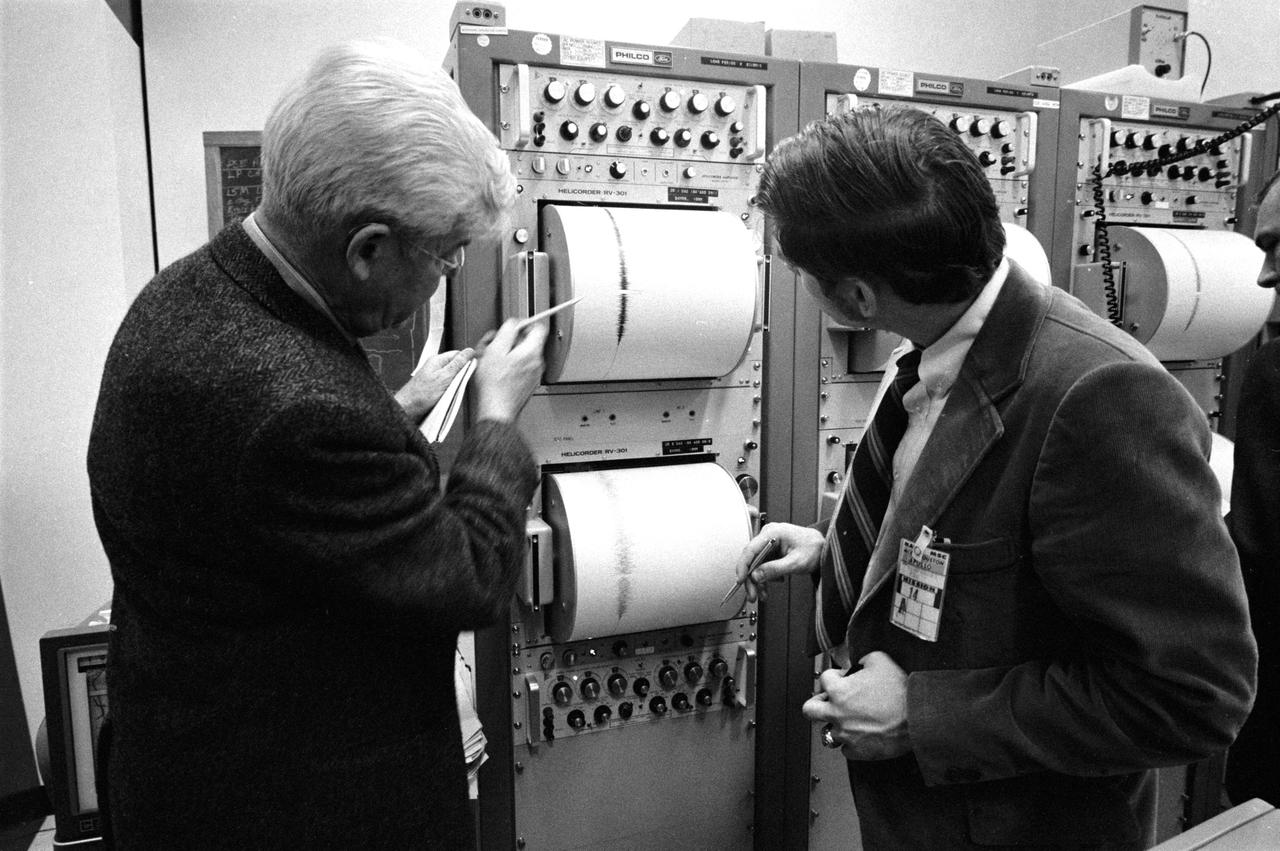

S71-17609 (4 Feb. 1971) --- These two individuals are examining a seismic reading in the Mission Control Center's ALSEP Room during the Apollo 14 S-IVB impact on the moon. Dr. Maurice Ewing (left) is the director of the Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory at Columbia University. David Lammlein, a Columbia graduate student, is on the right. The Apollo 14 Saturn IVB stage impacted on the lunar surface at 1:40:54 a.m. (CST), Feb. 4, 1971, about 90 nautical miles south-southwest of the Apollo 12 passive seismometer. The energy release was comparable to 11 tons of TNT. Dr. Gary Latham of the Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory is the principal investigator for the Passive Seismic Experiment, a component of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package.
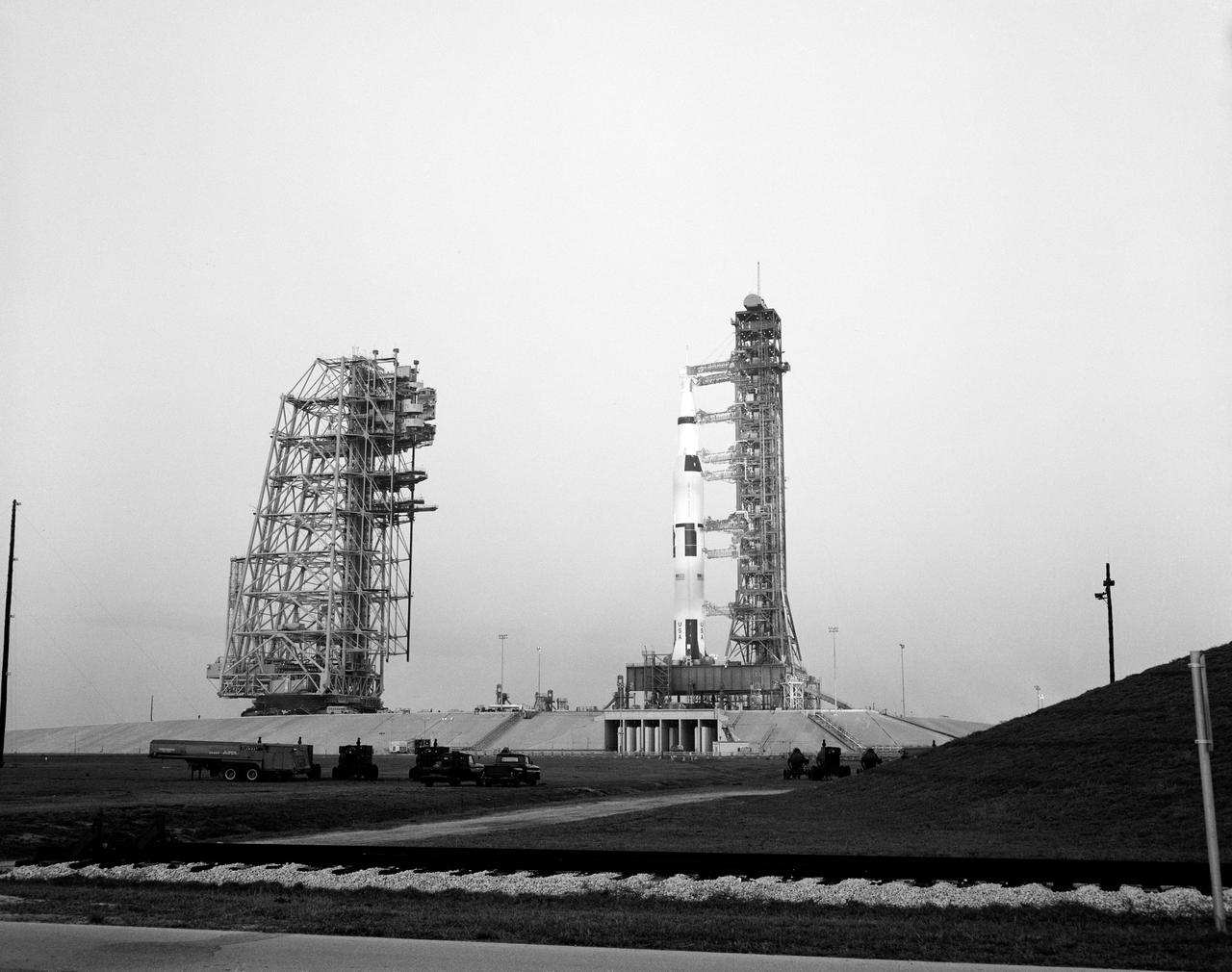

S69-27089 (11 March 1969) --- Overall view of Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, showing the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module-4/Saturn 505) space vehicle during a Countdown Demonstration Test. The Apollo 10 flight is scheduled as a lunar orbit mission. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
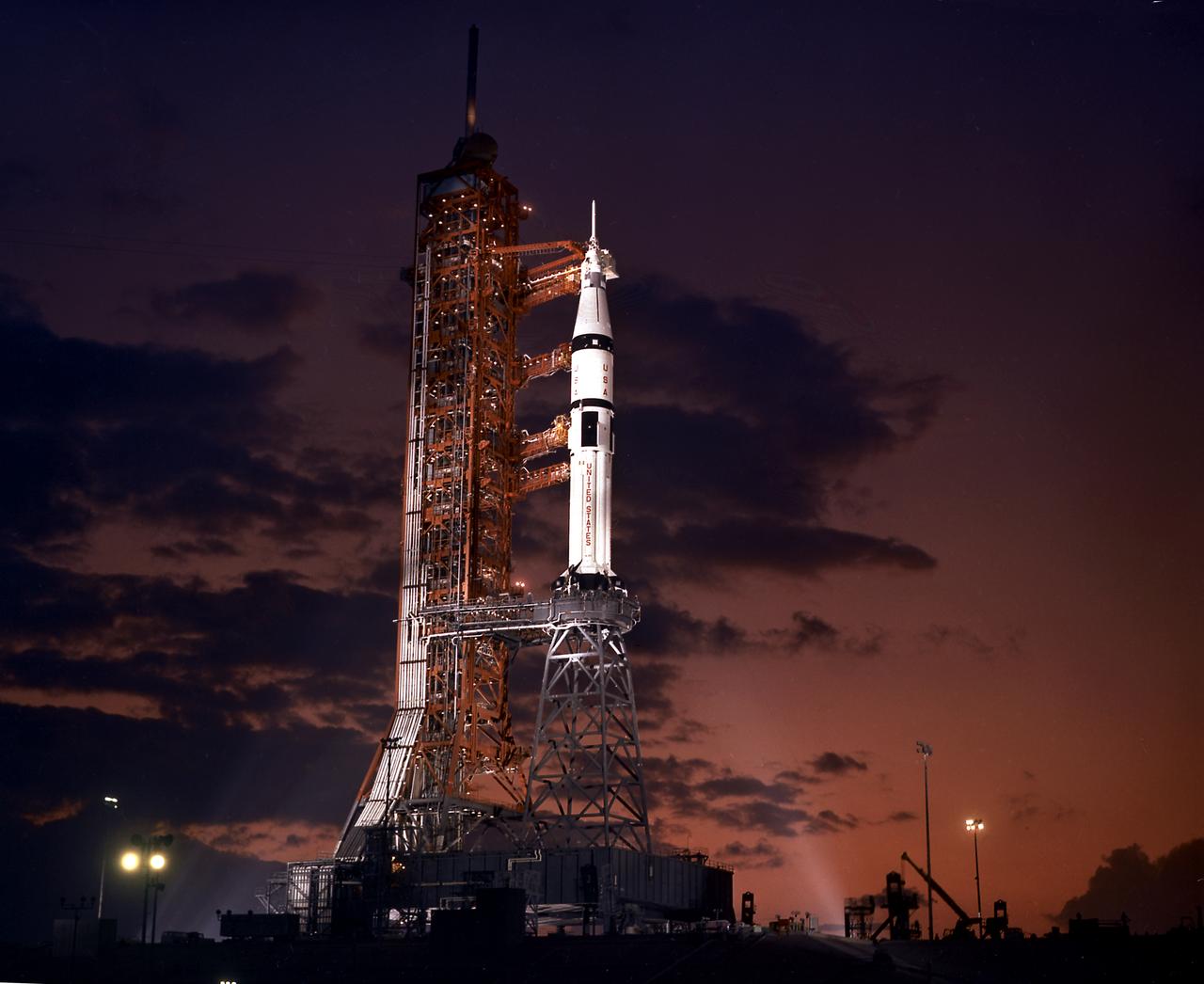

SA-210 Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) awaits the launch scheduled on July 15, 1975 on the launch pad at the Kennedy Space Center, the ASTP mission with astronauts Thomas Stafford, Vance Brand, and Donald "Deke" Slayton. The Saturn IB, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), launched five manned Earth-orbital missions between 1968 and 1975: Apollo 7, Skylab 2, Skylab 3, Skylab 4, and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project .
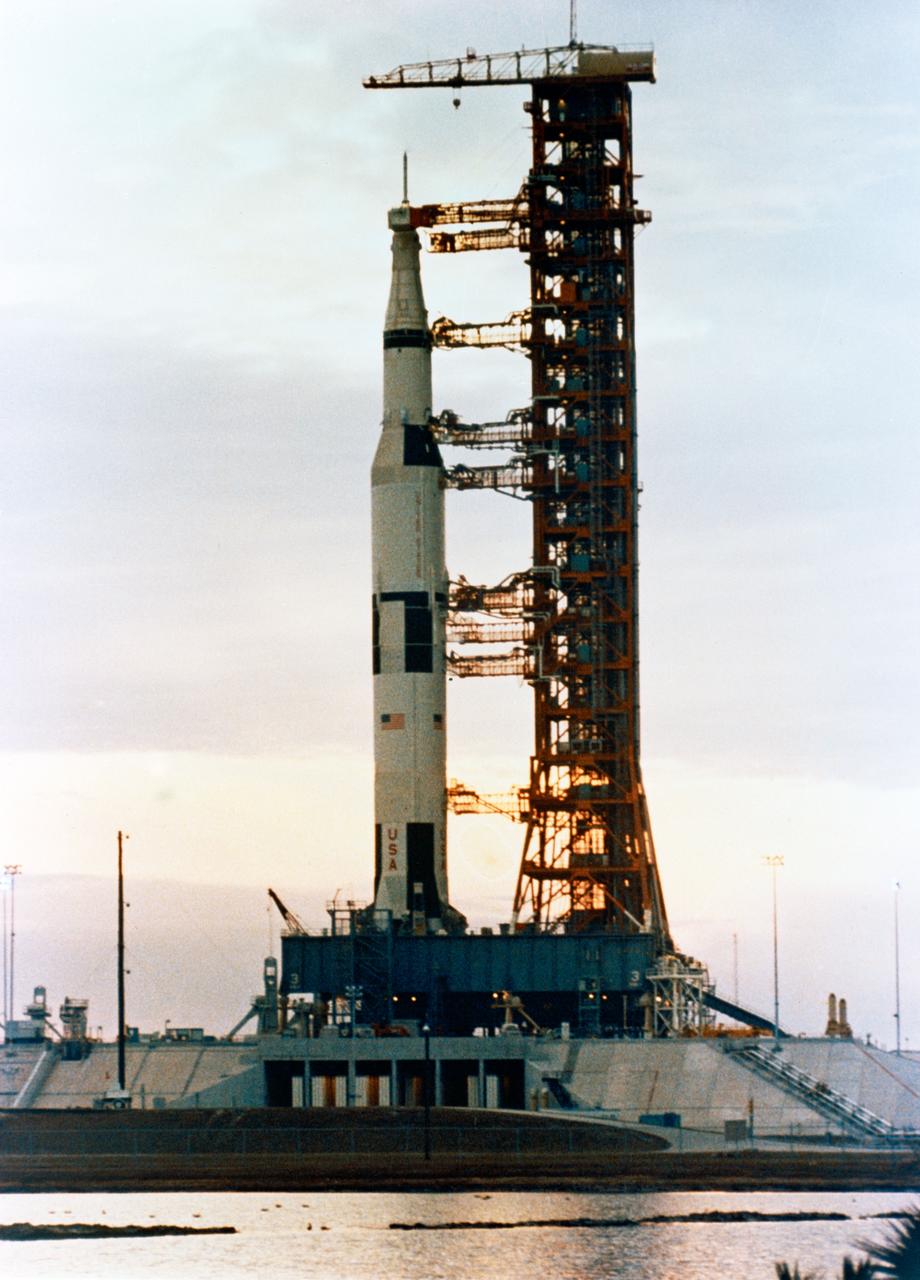
S69-34318 (11 March 1969) --- Ground-level view at sunset of the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle at Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center. The Apollo 10 stack had just been positioned after being rolled out from the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
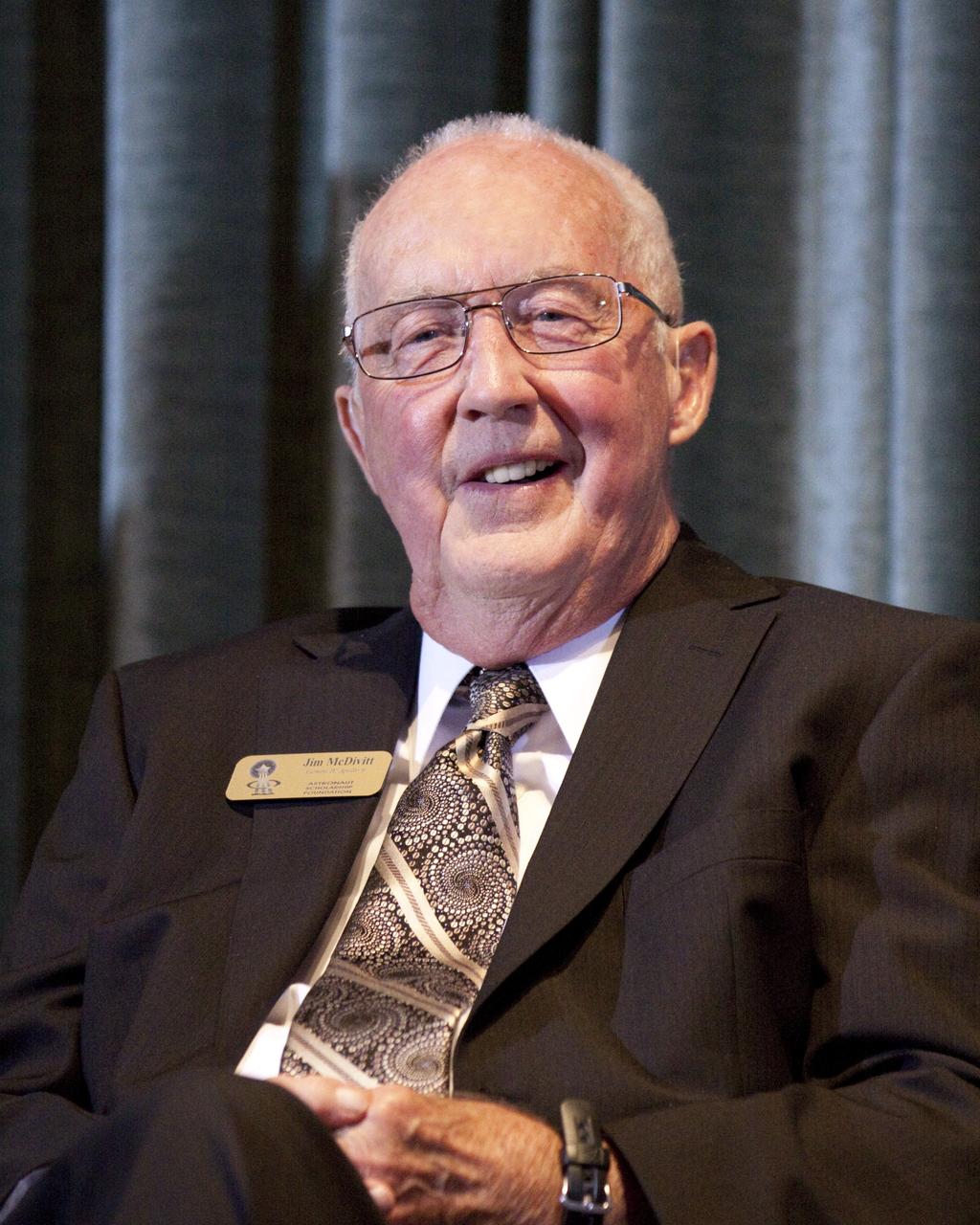

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Gemini 4 and Apollo 9 astronaut James McDivitt speaks to guests gathered for the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation's dinner at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral celebrating the 40th anniversary of Apollo 17. The gala commemorating the anniversary of Apollo 17 included mission commander Eugene Cernan and other astronauts who flew Apollo missions. Launched Dec. 7, 1972, Cernan and lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt landed in the moon's Taurus-Littrow highlands while command module pilot Ronald Evans remained in lunar orbit operating a scientific instrument module. For more information, visit http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/history/apollo/apollo-17/apollo-17.htm Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
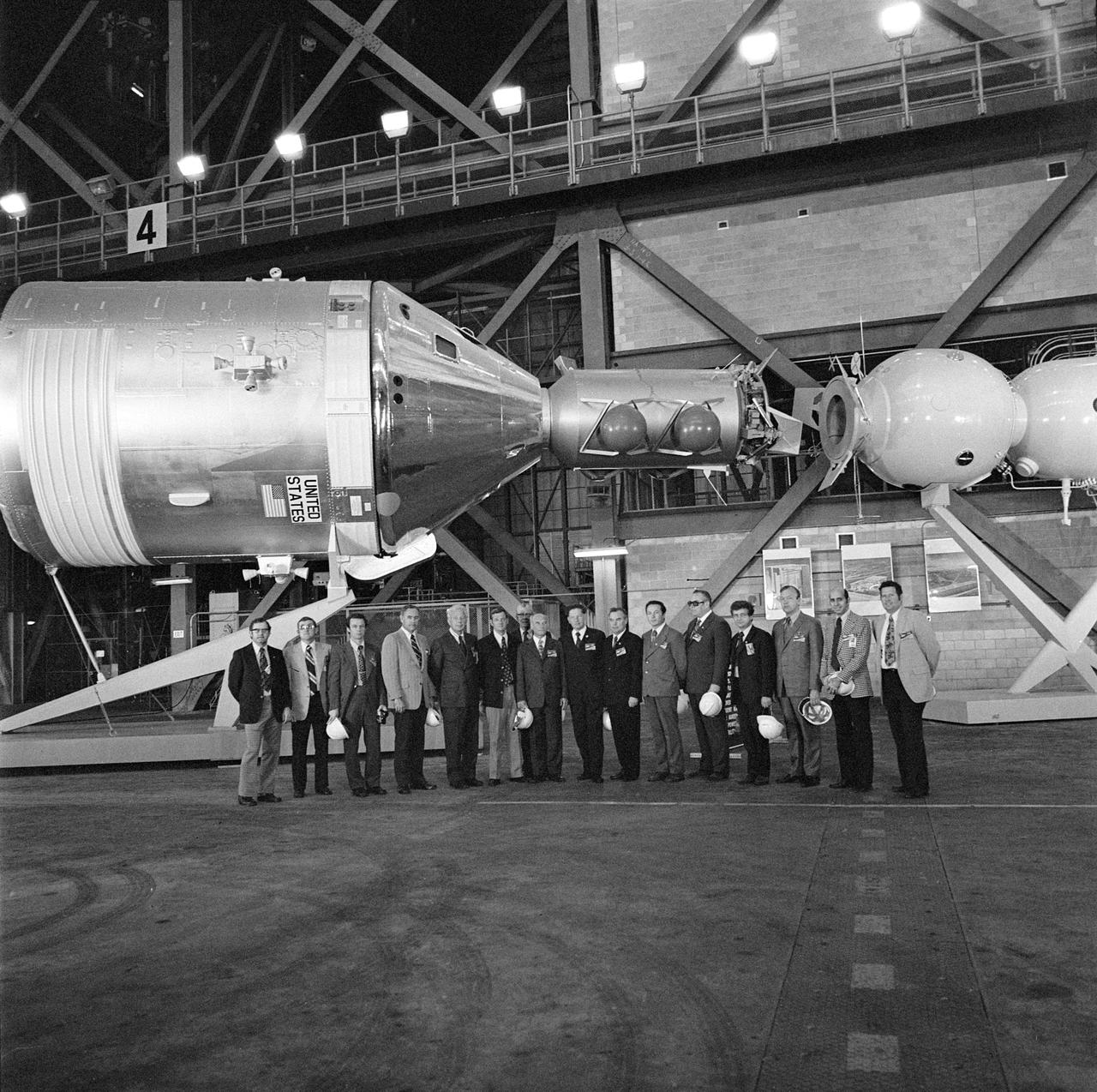

S75-24026 (4 Feb. 1975) --- A group of Soviet and American ASTP officials during a tour of the Kennedy Space Center. They were photographed next to the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking in Earth orbit mock-up at KSC.
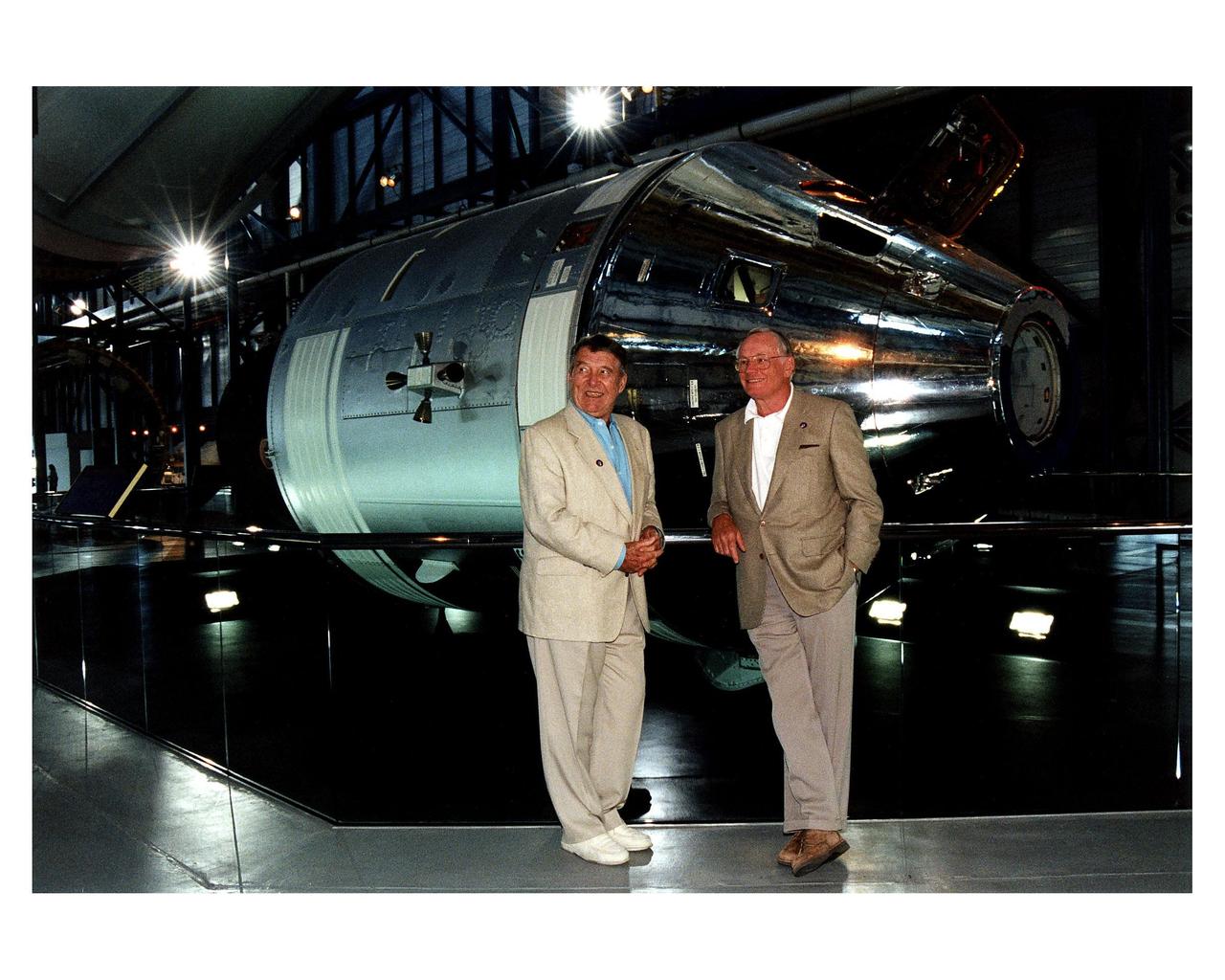

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Among the many special NASA STS-83 launch guests who witnessed the liftoff of the Space Shuttle Columbia April 4 were Apollo 7 Commander Walter M. "Wally" Schirra (left ) and Apollo l1 Commander Neil A. Armstrong. The two former astronauts are posing in front of the Apollo Command and Service Module in the Apollo/Saturn V Center at KSC. Columbia took off from Launch Pad 39A at 2:20:32 p.m. EST to begin the 16-day Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission
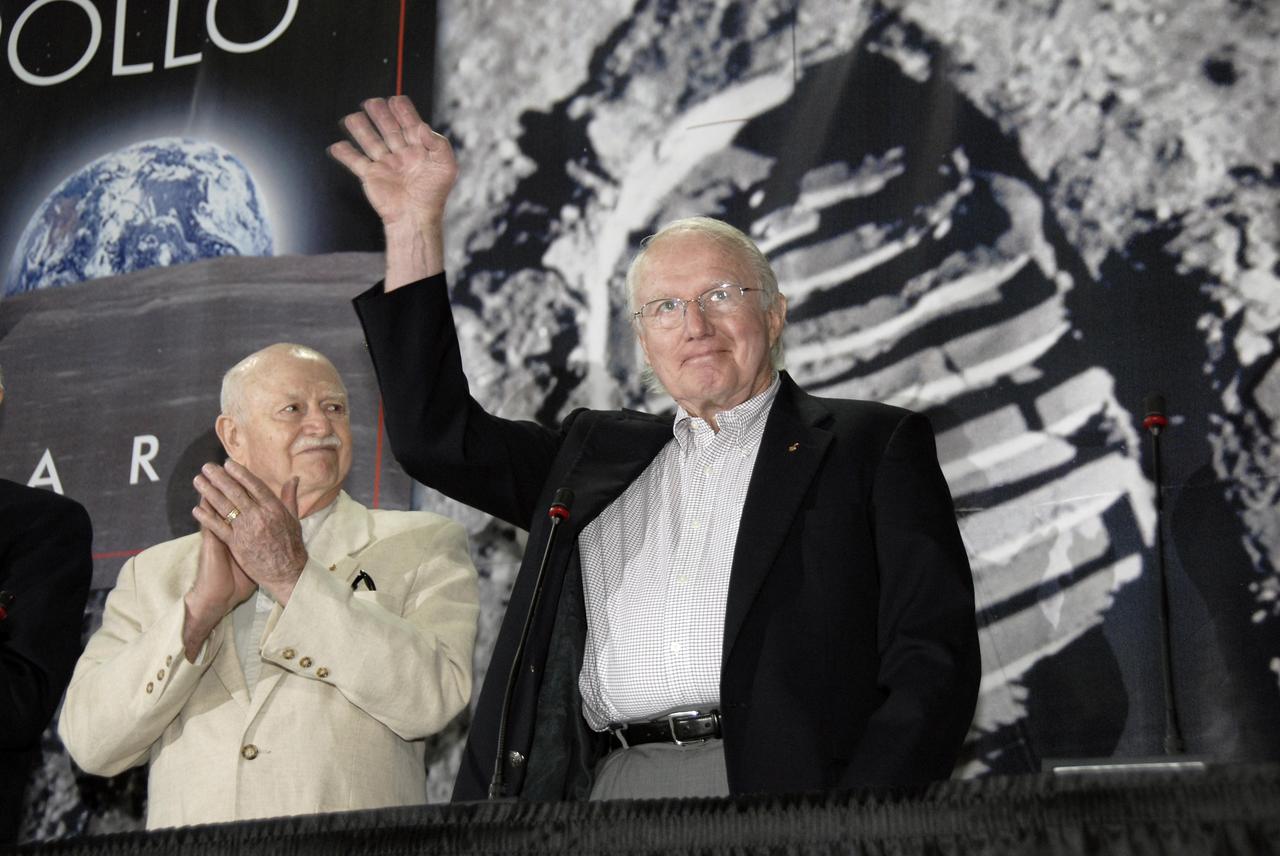

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo astronaut Gerald Carr (right) joins Vance Brand (left) and six other Apollo astronauts for NASA's 40th Anniversary of Apollo Celebration of the July 1969 launch and landing on the moon. Carr served as CAPCOM for the Apollo 8 and 12 flights, and was involved in the development and testing of the lunar roving vehicle which was used on the lunar surface by Apollo flight crews. He also was commander of Skylab 4 launched in 1973 on the third and final manned visit to the Skylab Orbital Workshop. It was the longest manned flight (84 days, 1 hour, 15minutes) in history at that date. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
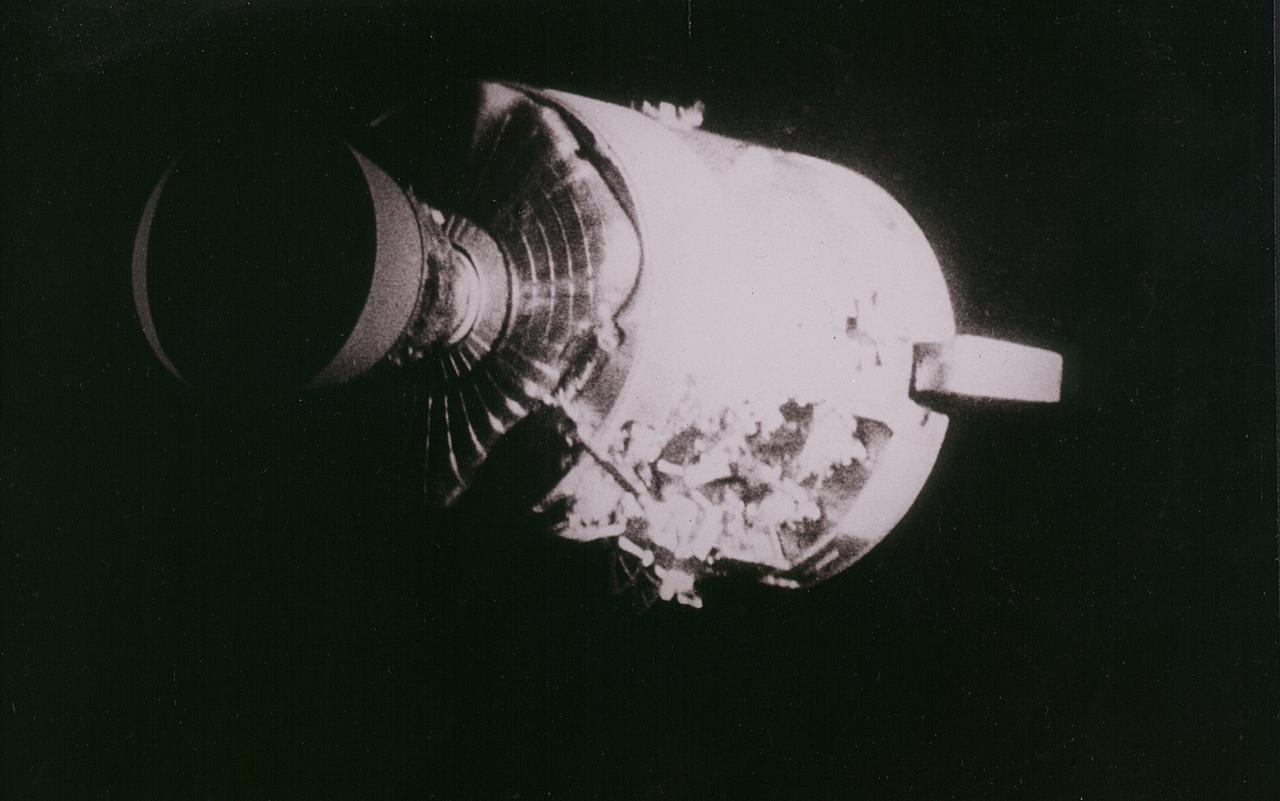
Apollo 13 onboard photo: This view of the severely damaged Apollo 13 Service Module was photographed from the Lunar Module/Command Module following the jettison of the Service Module. As seen here, an entire panel of the Service Module was blown away by the apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two located in Sector 4 of the Service Module. Two of the three fuel cells are visible just forward (above) the heavily damaged area. Three fuel cells, two oxygen tanks, and two hydrogen tanks, are located in Sector 4. The damaged area is located above the S-band high gain anterna. Nearest the camera is the Service Propulsion System (SPS) engine and nozzle. The damage to the Service Module caused the Apollo 13 crewmen to use the Lunar Module as a lifeboat. The Lunar Module was jettisoned by the Command Module just prior to Earth re-entry.

S69-27916 (11 March 1969) --- Aerial view at Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, showing the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module-4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on its way to Pad B. The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower are atop a huge crawler-transporter. The Apollo 10 flight is scheduled as a lunar orbit mission. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
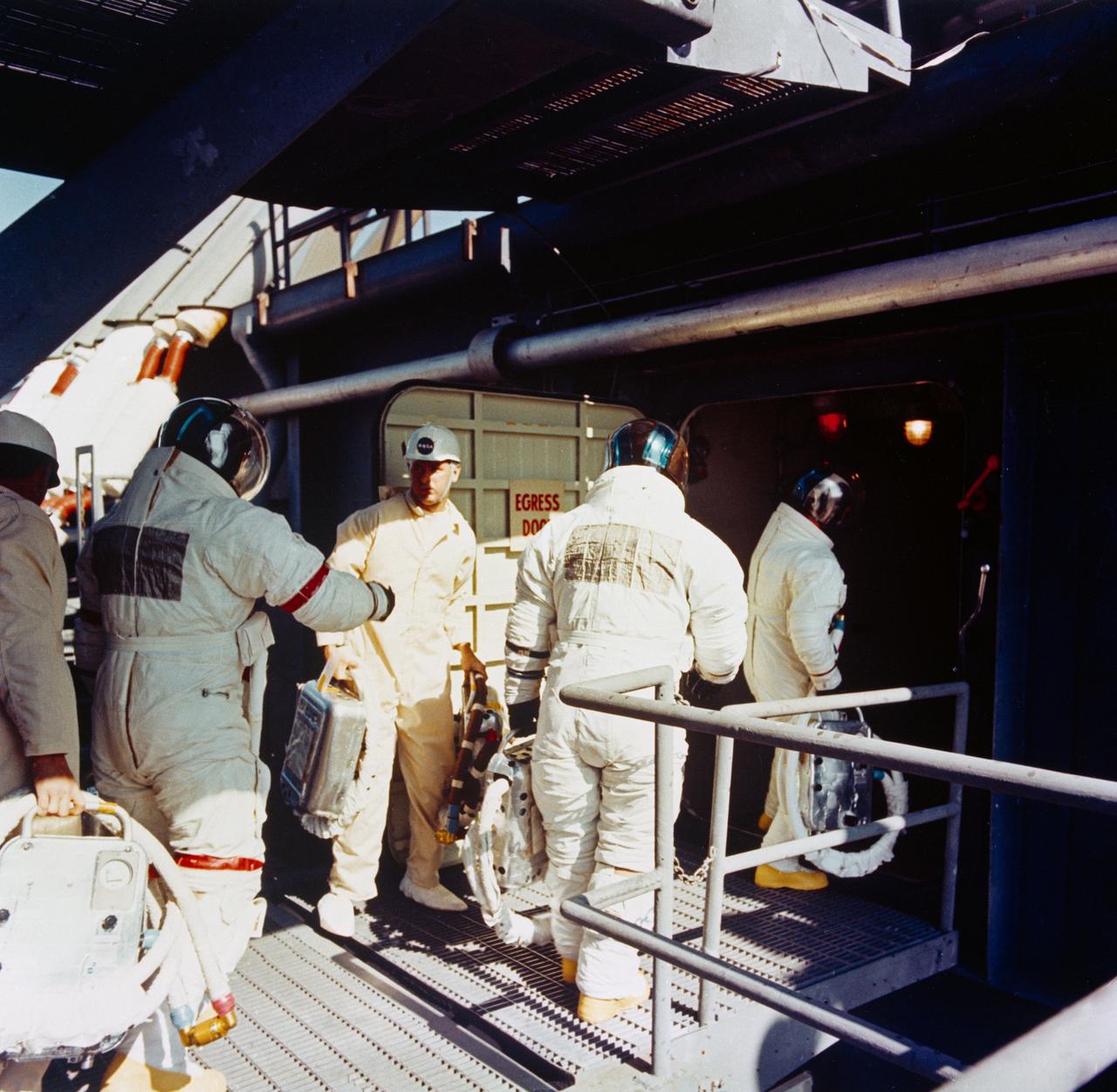

S71-16635 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The three Apollo 14 astronauts arrive at the White Room atop Pad A, Launch Complex 39, during the Apollo 14 prelaunch countdown. Apollo 14, with Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, aboard was launched at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Note identifying bands on the sleeve and leg of Shepard. Standing in the center foreground is astronaut Thomas P. Stafford, chief of the MSC Astronaut Office.

AS13-58-8458 (17 April 1970) --- This view of the severely damaged Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) was photographed from the Lunar Module/Command Module (LM/CM) following SM jettisoning. An entire SM panel was blown away by the apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two. Two of the three fuel cells are visible at the forward portion of the opening. The hydrogen tanks are located in Sector 4 of the Apollo 13 SM. The apparent rupture of the oxygen tank caused the Apollo 13 crew members to use the LM as a "lifeboat." The LM was jettisoned just prior to Earth re-entry by the CM.

S69-27915 (11 March 1969) --- Aerial view at Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, showing a close-up of the 363-feet tall Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on its way to Pad B. The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower are atop a huge crawler-transporter. The Apollo 10 flight is scheduled as a lunar orbit mission. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.

S69-27741 (11 March 1969) --- Aerial view at Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, showing the 363-feet tall Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module-4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on its way to Pad B. The Vehicle Assembly Building is in the background. The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower are atop a huge crawler-transporter. The Apollo 10 flight is schedule as a lunar orbit mission. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
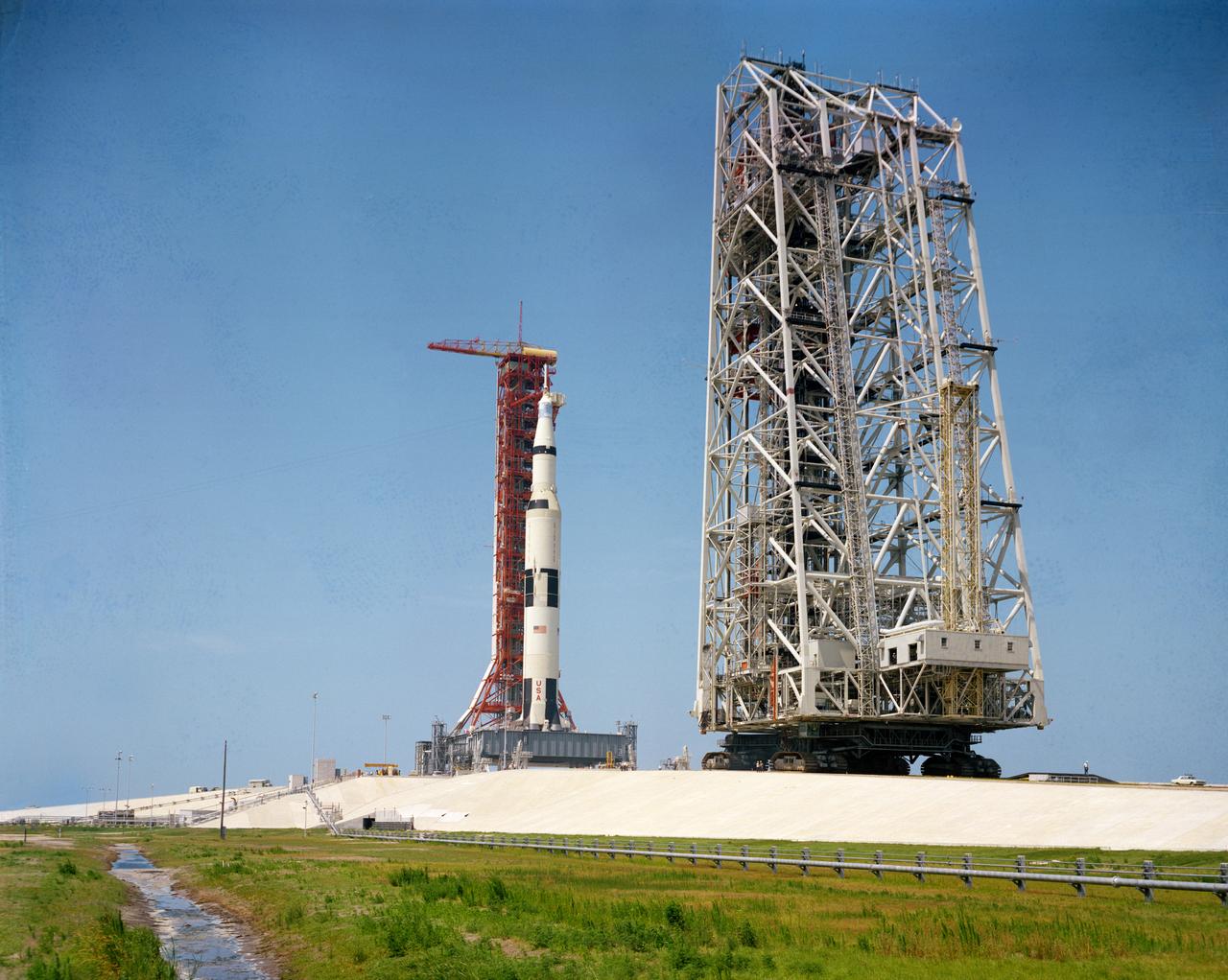

S69-34320 (17 May 1969) --- Ground level view of the 363-feet tall Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center. The service structure is in the right foreground. The crew of the Apollo 10 lunar orbit mission will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
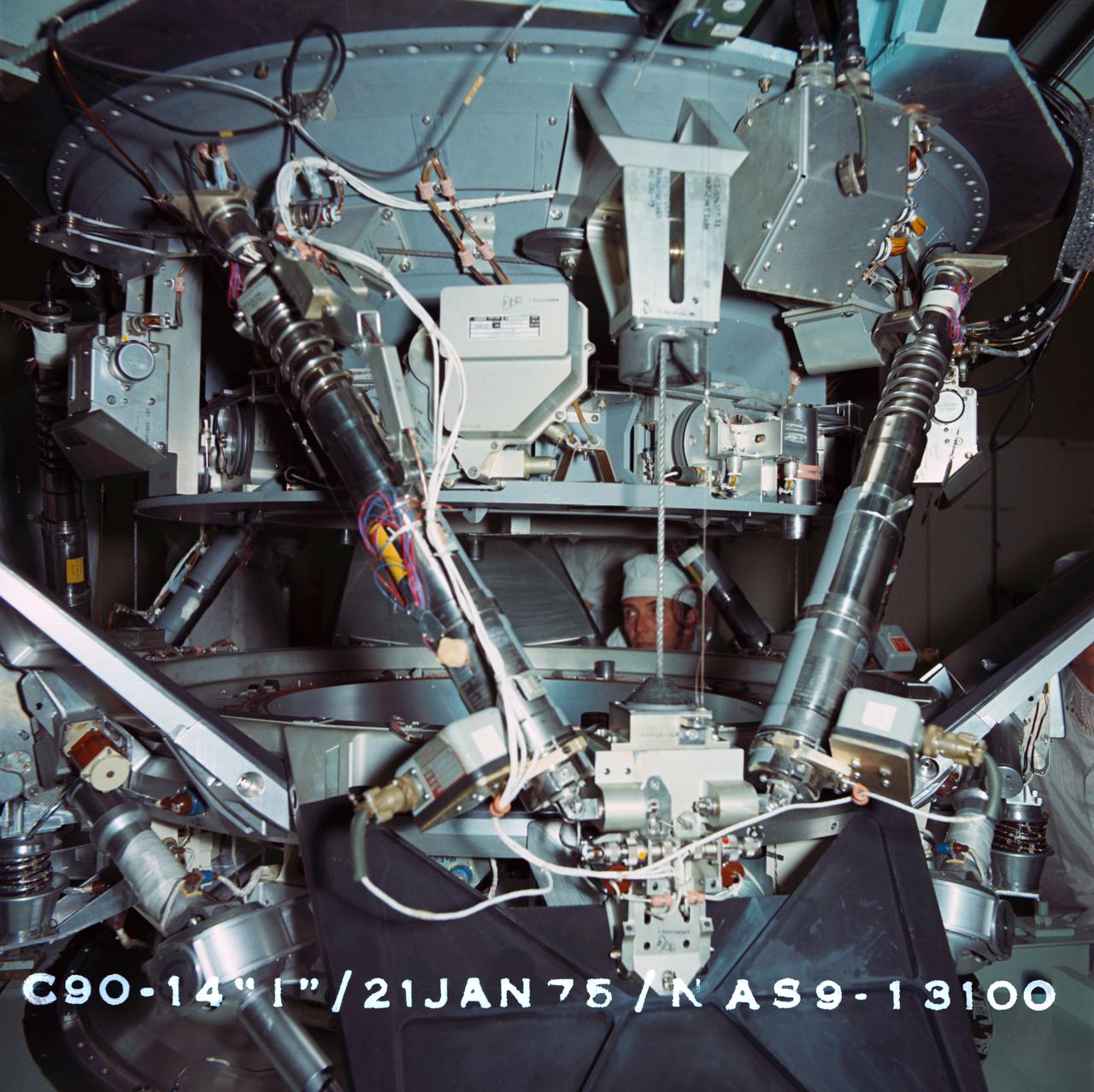
S95-02815 (21 Jan. 1975) --- Soviet junior researcher Y.G. Pobrov observes testing of the Apollo-Soyuz docking system at Rockwell International's plant in Downey, California. The United States' Docking System 3 (DS-3) here is being positioned onto the USSR's CA-4 system during a Pin and Socket Alignment Test. DS-5 has been designated as the prime flight article for the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) docking mission in Earth orbit, scheduled for July 1975.

S69-19197 (1969) --- Interior view of the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Manned Spacecraft Operations Building (MSOB) showing Apollo Spacecraft 106 Command and Service Modules (CSM) being moved to integrated work stand number one for mating to Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) 13. Spacecraft 106 will be flown on the Apollo 10 (Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space mission.

AS13-58-8464 (17 April 1970) --- This view of the severely damaged Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) was photographed from the Lunar Module/Command Module (LM/CM) following SM jettisoning. Nearest the camera is the Service Propulsion System (SPS) engine and nozzle. An entire SM panel was blown away by the apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two located in Sector 4 of the SM. The apparent rupture of the oxygen tank caused the Apollo 13 crew men to use the Lunar Module (LM) as a "lifeboat".
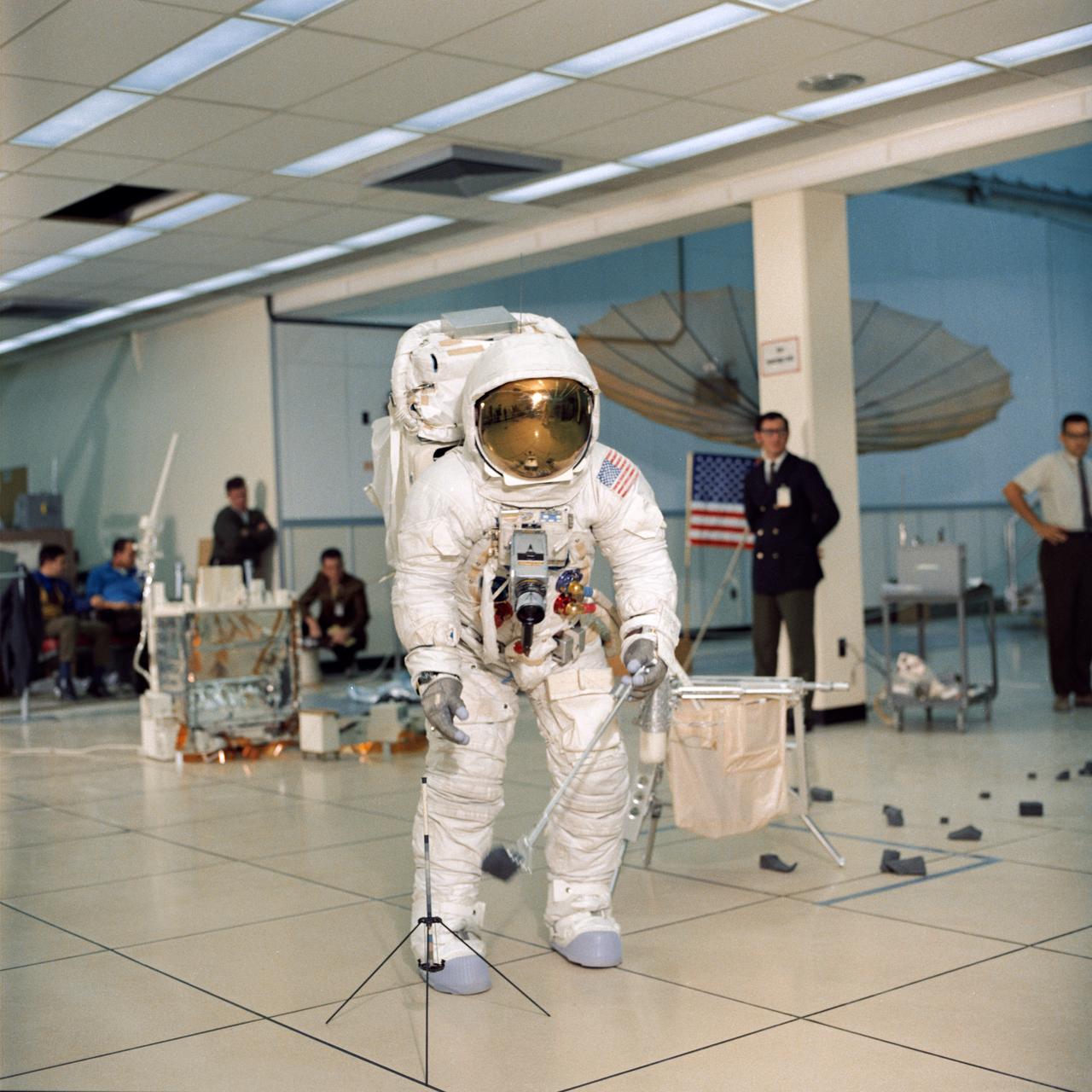

S70-27037 (4 Feb. 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, simulates lunar surface extravehicular activity during training exercises in the Kennedy Space Center’s Flight Crew Training Building. Lovell, wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), is holding an Apollo Lunar Hand Tool (a set of tongs) in his left hand. A gnomon is in front of his right foot. A tool carrier is in the right background.
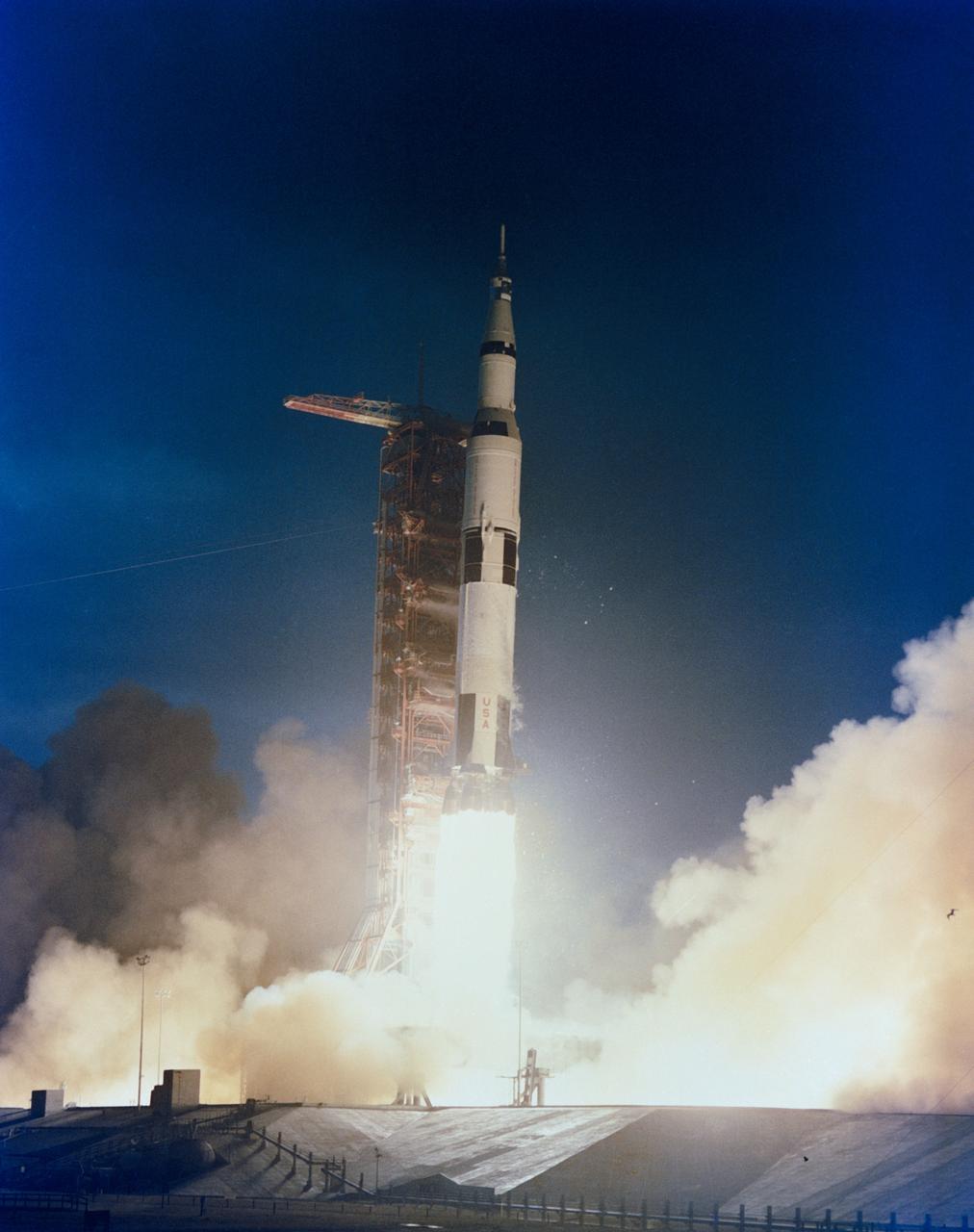

S71-17621 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1981, on a lunar landing mission. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.
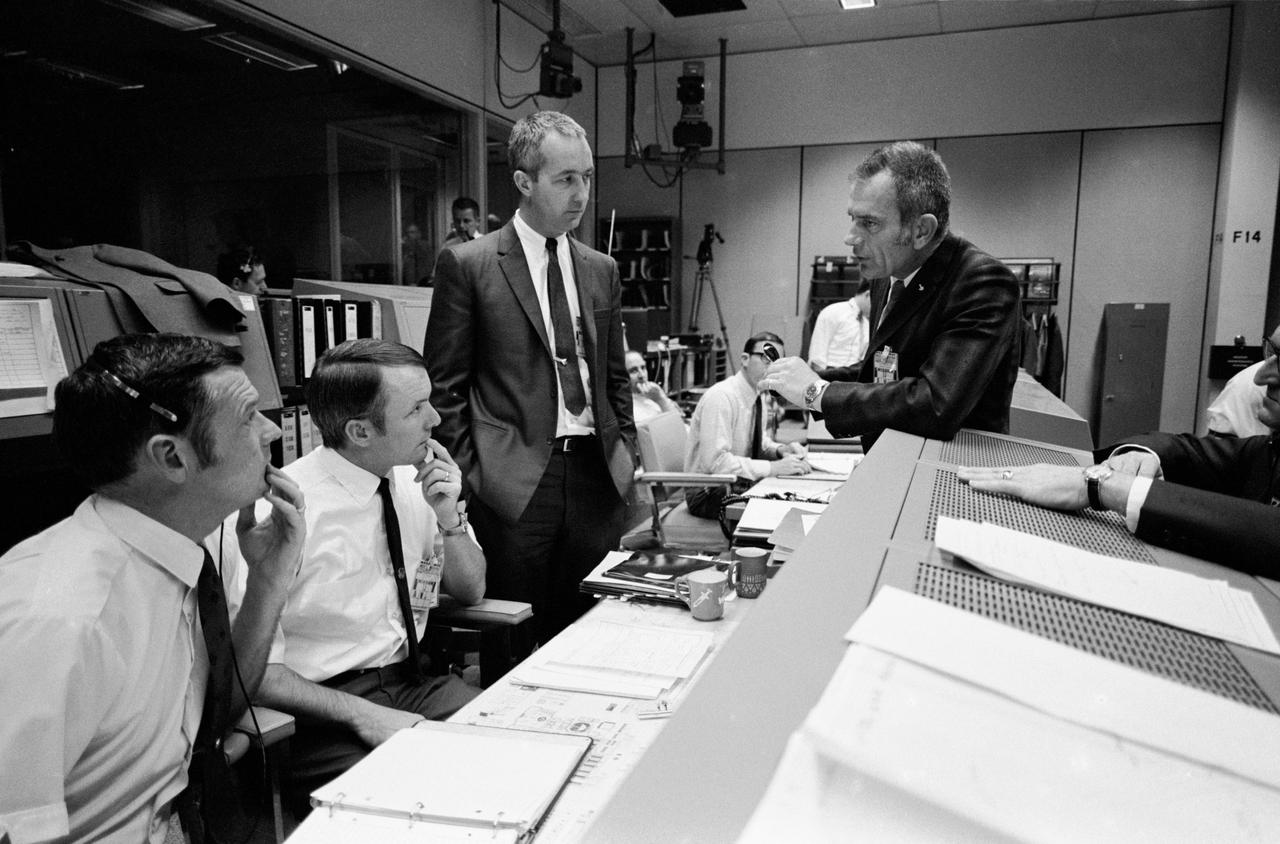

S70-35369 (16 April 1970) --- Discussion in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) dealing with the Apollo 13 crewmen during their final day in space. From left to right are Glynn S. Lunney, Shift 4 flight director; Gerald D. Griffin, Shift 2 flight director; astronaut James A. McDivitt, manager, Apollo Spacecraft Program, MSC; Dr. Donald K. Slayton, director of Flight Crew Operations, MSC; and Dr. Willard R. Hawkins, M.D., Shift 1 flight surgeon.
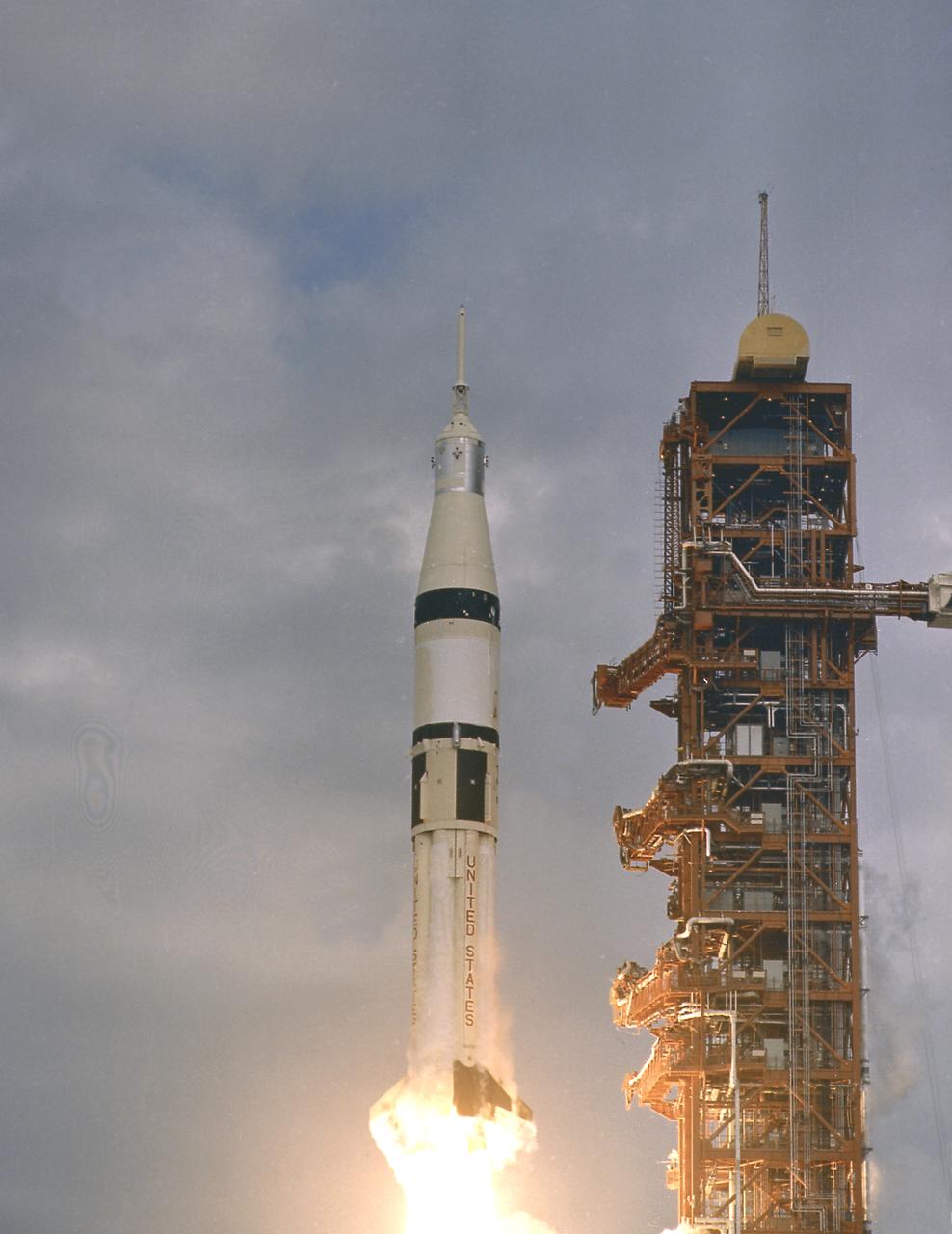
SA-206 lifts off from Kennedy Space Center's launch complex 39B, in Florida, on May 25, 1973, for the first manned Skylab mission (SL-2) with astronauts Pete Conrad, Joseph Kerwin, and Paul Weitz. The Saturn IB, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), launched five manned Earth-orbital missions between 1968 and 1975: Apollo 7, Skylab 2, Skylab 3, Skylab 4, and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP).
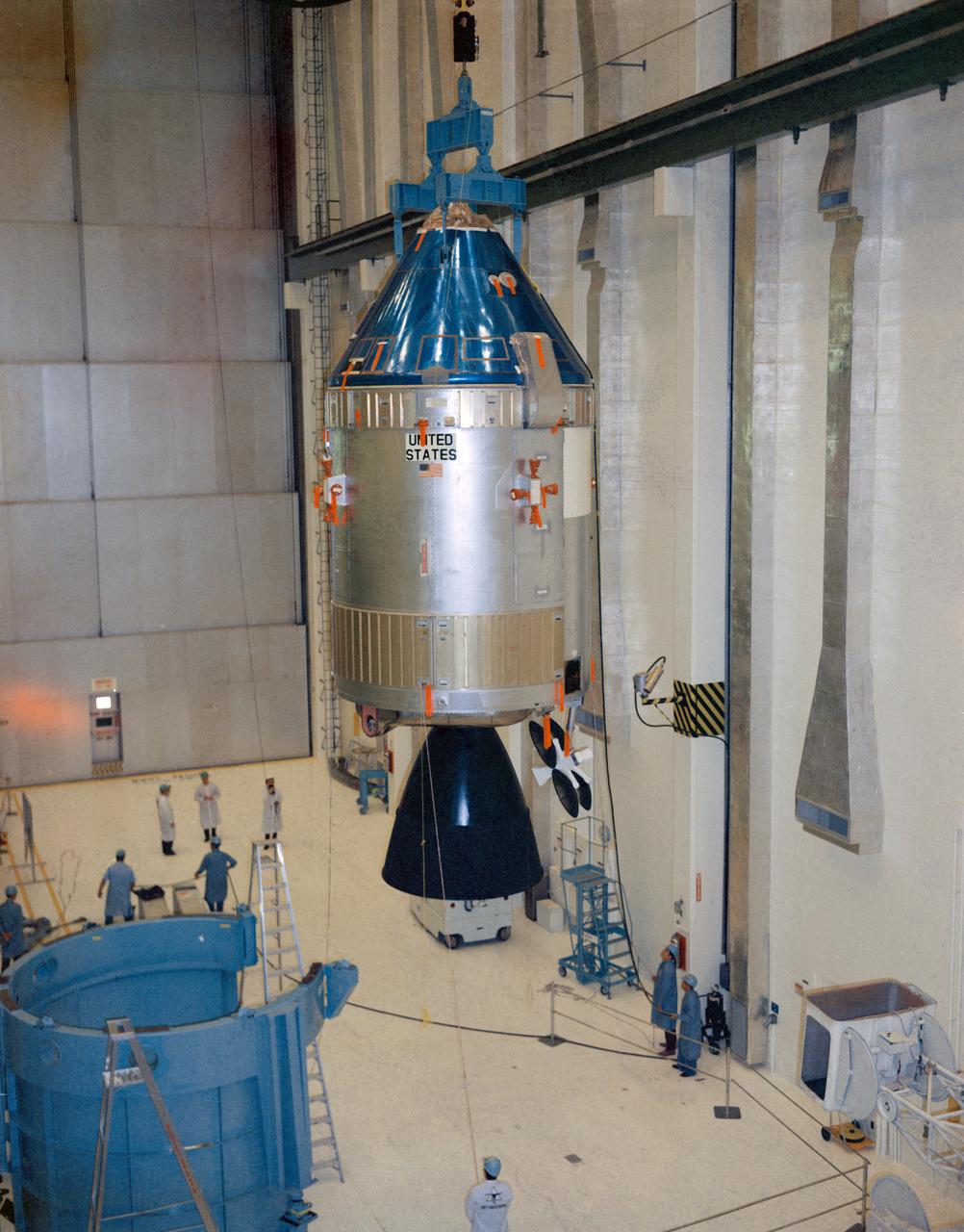

S69-19190 (31 Jan. 1969) --- Interior view of the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building showing Apollo Spacecraft 106/Command/Service Module being moved to integrated work stand number one for mating to Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) 13. Spacecraft 106 will be flown on the Apollo 10 (Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space mission.
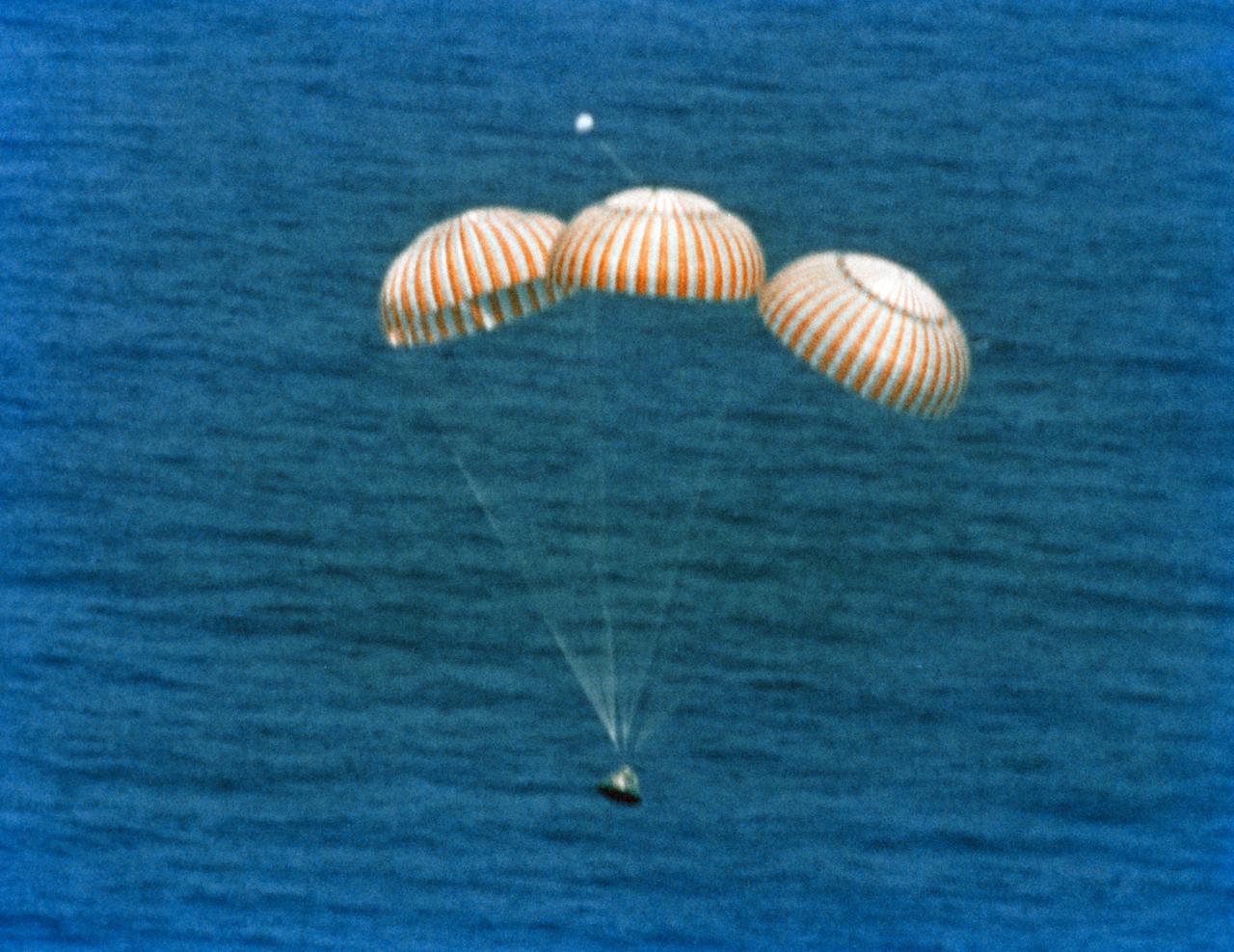

S75-29719 (24 July 1975) --- The ASTP Apollo Command Module, with astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. Slayton aboard, nears a touchdown in the Central Pacific Ocean to conclude the historic joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. The spacecraft splashed down in the Hawaiian Islands area at 4:18 p.m. (CDT), July 24, 1975.
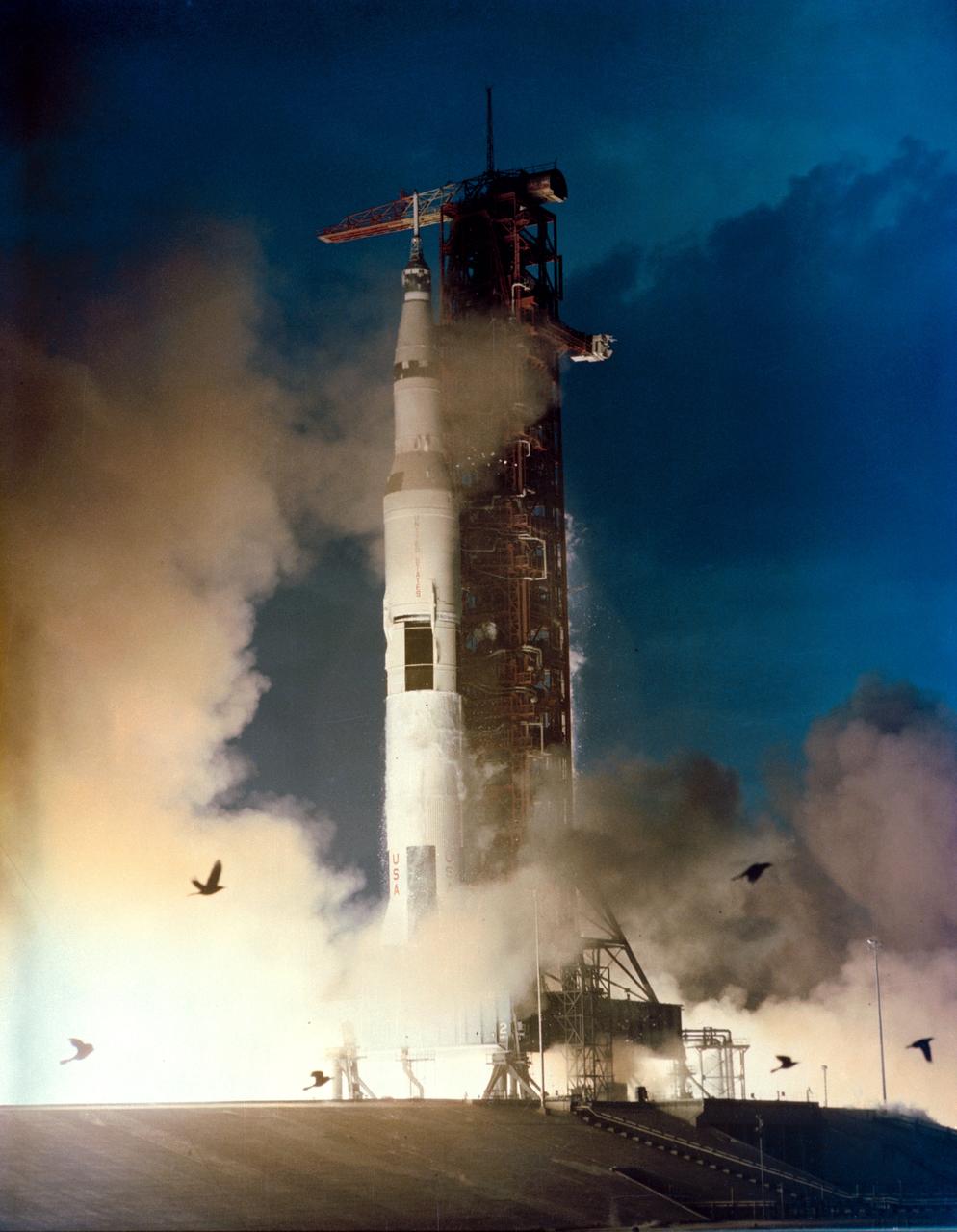

S71-18395 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.
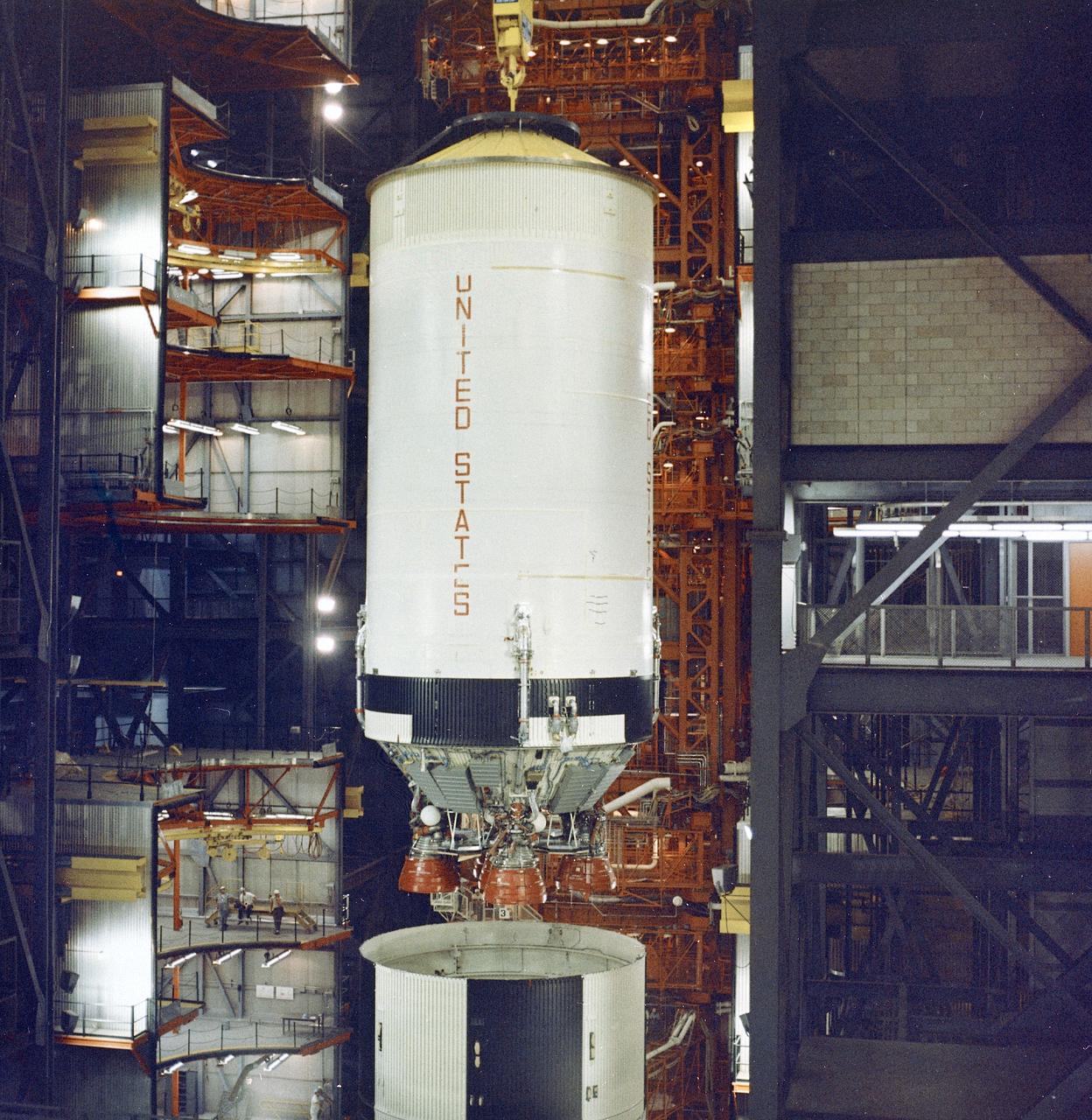
This photograph shows the Saturn V S-II (second) stage of the Apollo 6 mission being lowered atop of the S-IC (first) stage during the final assembly operations in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the Kennedy Space Center. The Apollo 6 mission was the second Saturn V unmanned flight for testing an emergency detection system. The launch occurred on April 4, 1968.
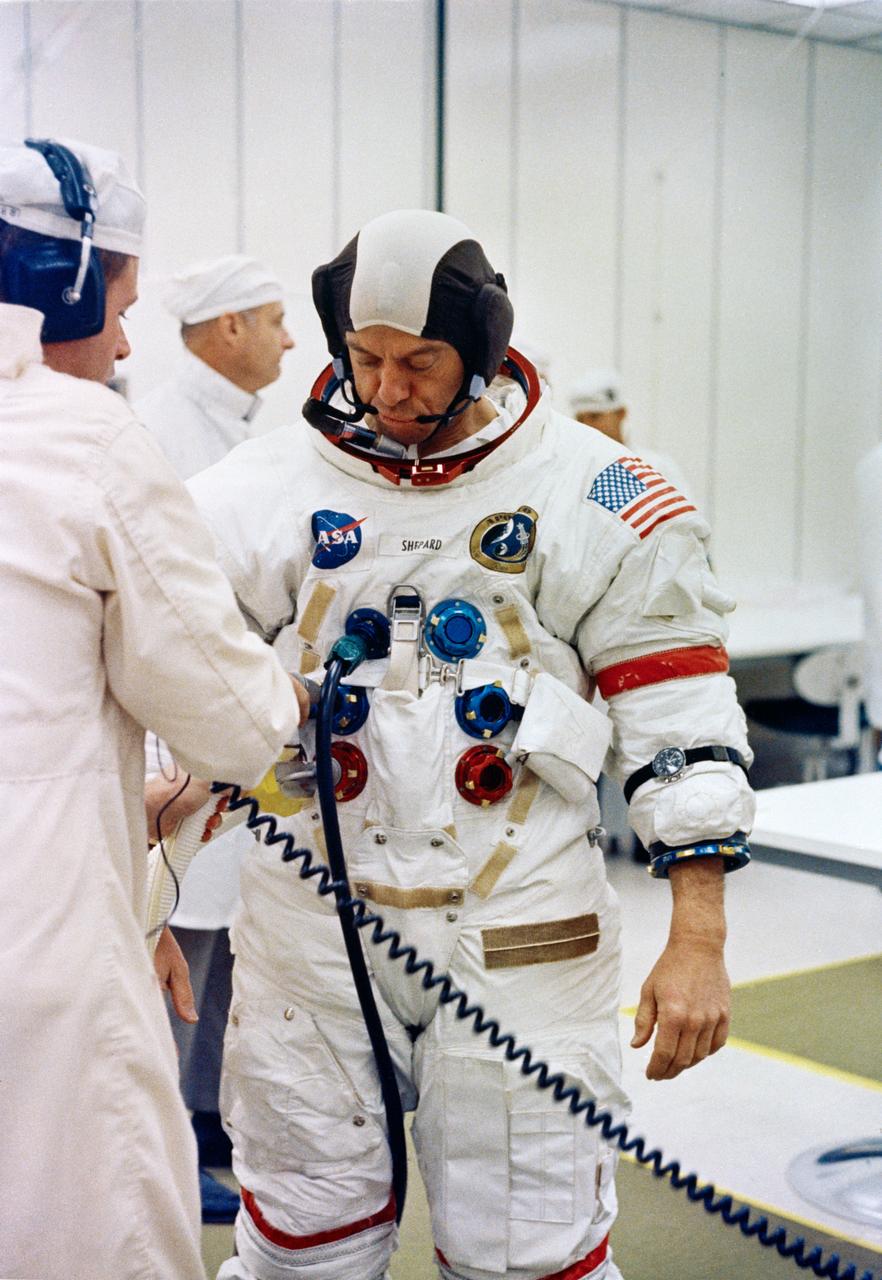

S71-16638 (31 Jan. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, undergoes suiting up operations at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) during the Apollo 14 prelaunch countdown. Apollo 14, with astronauts Shepard; Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; and Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; aboard was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39 at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971.

S69-34328 (17 May 1969) --- Ground level view of the 363-feet tall Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
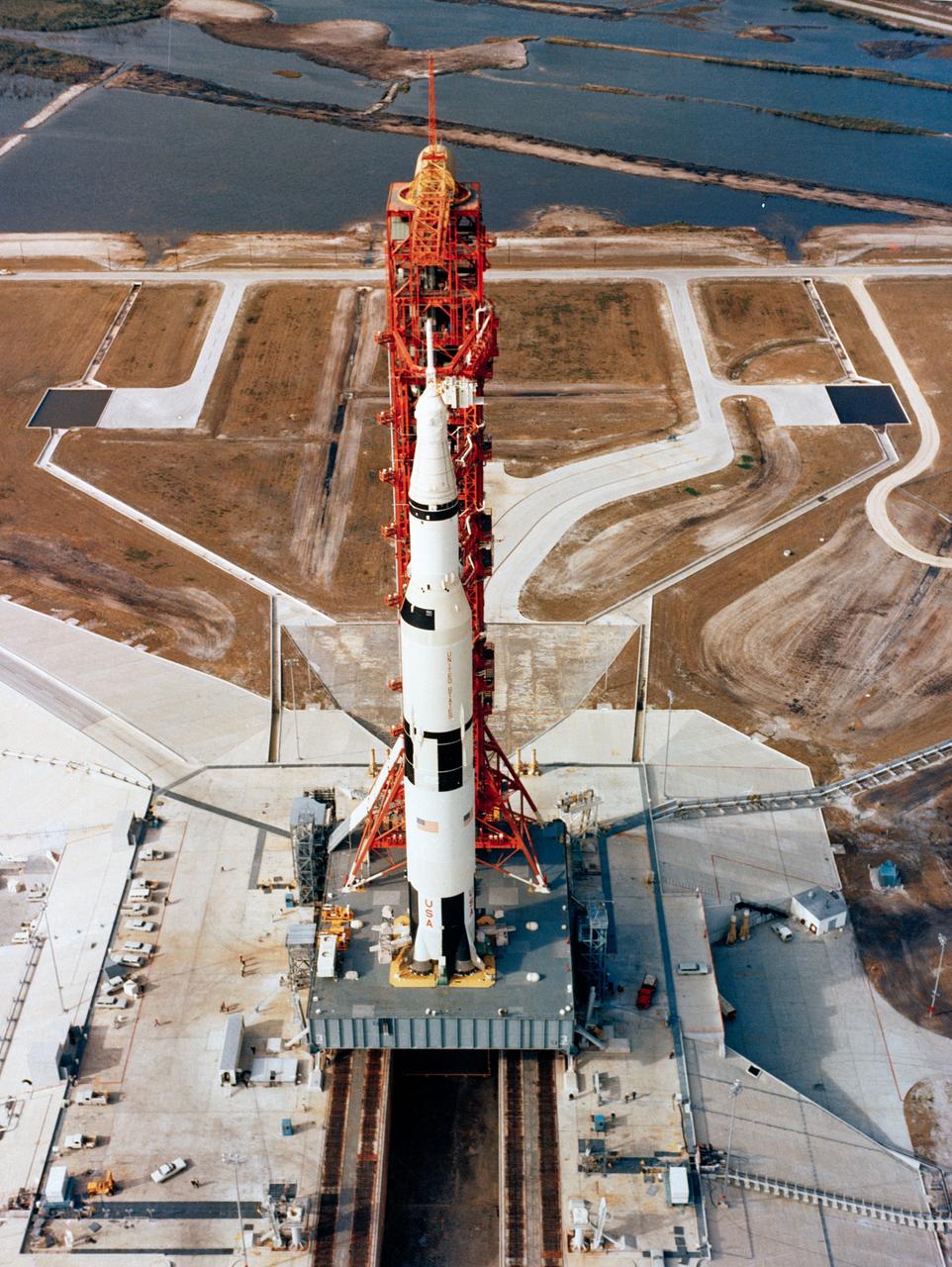

S69-34327 (13 May 1969) --- Aerial, high-angle, view of the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle at Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The crew of the Apollo 10 lunar orbit mission will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
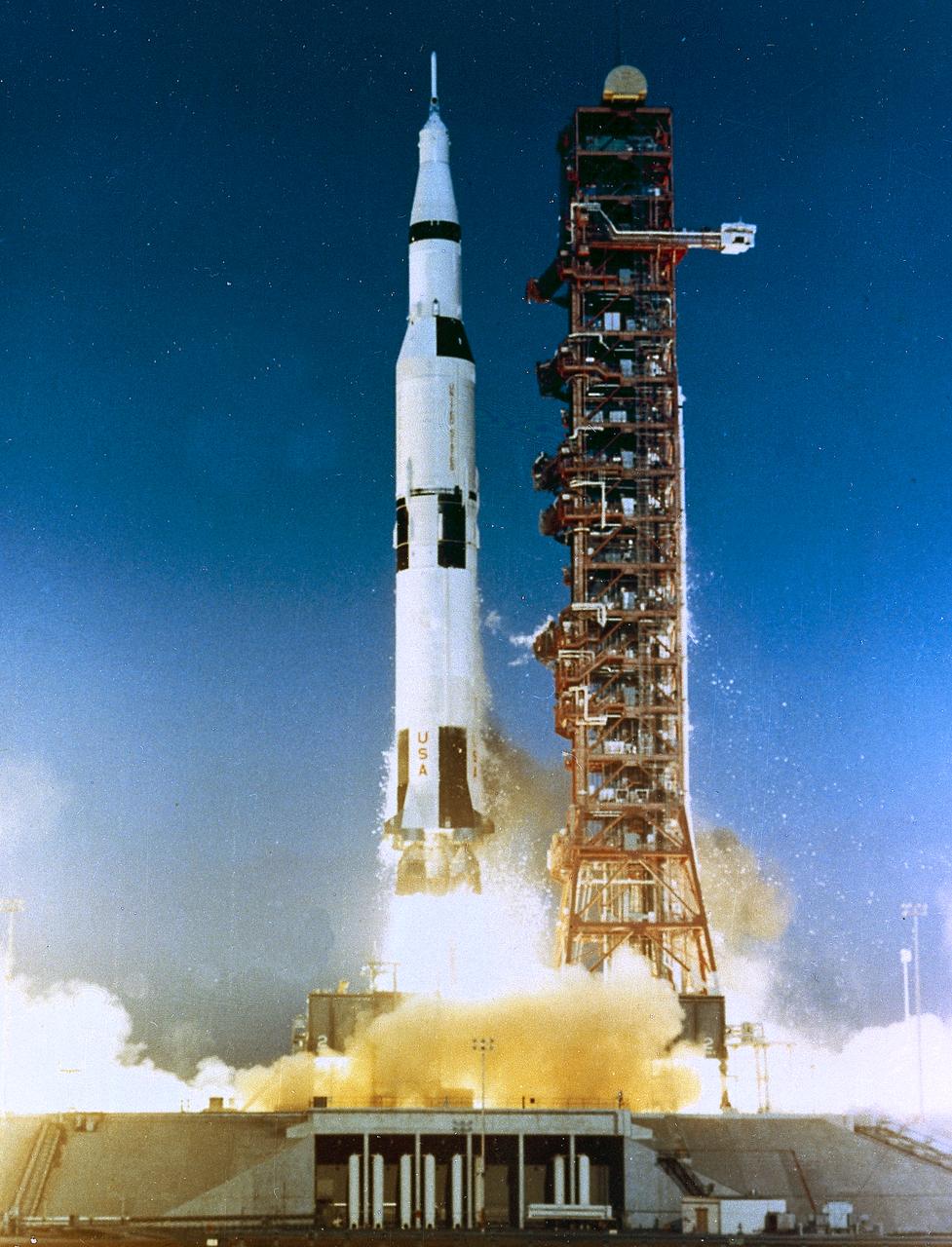
The second Saturn V launch vehicle (SA-502) for the Apollo 6 mission lifted off from the Kennedy Space Center launch complex on April 4, 1968. This unmanned Saturn V launch vehicle tested the emergency detection system in closed loop configuration.
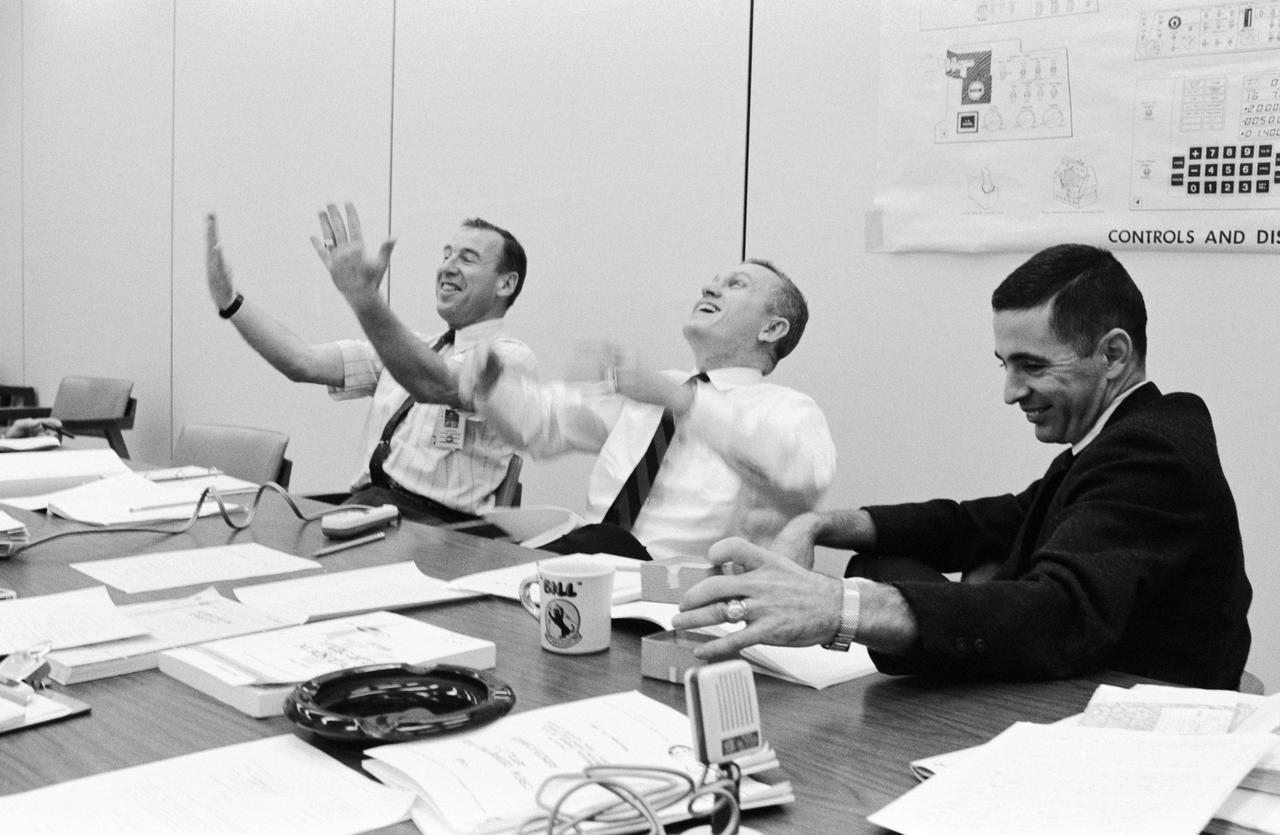

S68-56530 (30 Dec. 1968) --- The crew of the historic Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission participates in a technical de-briefing session in Building 4. Left to right, are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., command module pilot; Frank Borman, commander; and William A. Anders, lunar module pilot.
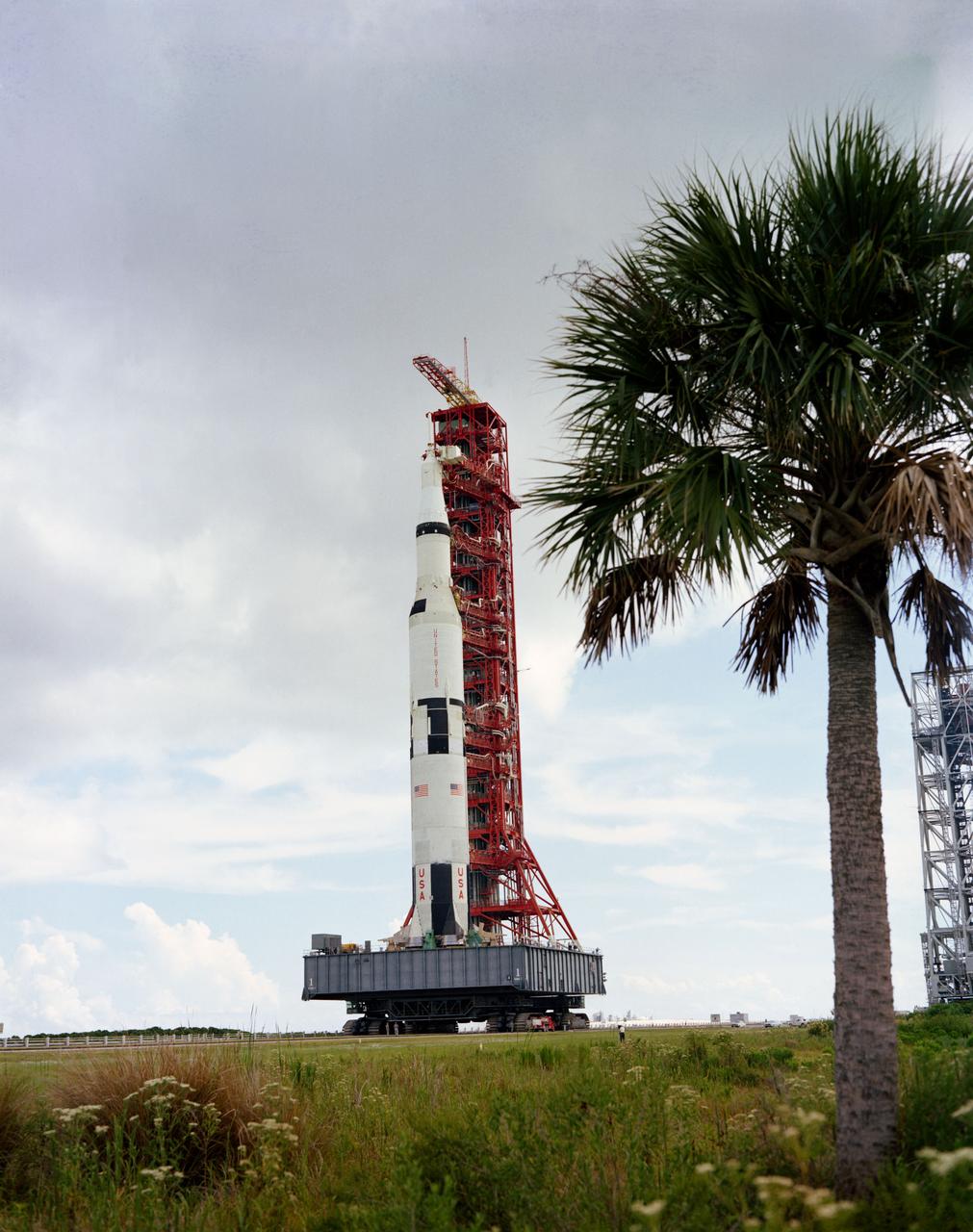

S67-43595 (26 Aug. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) stack and its mobile launch tower atop a crawler-transporter moving from the Vehicle Assembly Building toward Pad A, Launch Complex 39.

AS6-02-1455 (4 April 1968) --- Texas is photographed from the Apollo 6 (Spacecraft 020/Saturn 502) unmanned space mission. Seen in this photograph are Midland, Brownfield, Big Spring, J. B. Thomas Lake, headwaters of Colorado and Brazos Rivers, and the west Texas gas and oil fields.
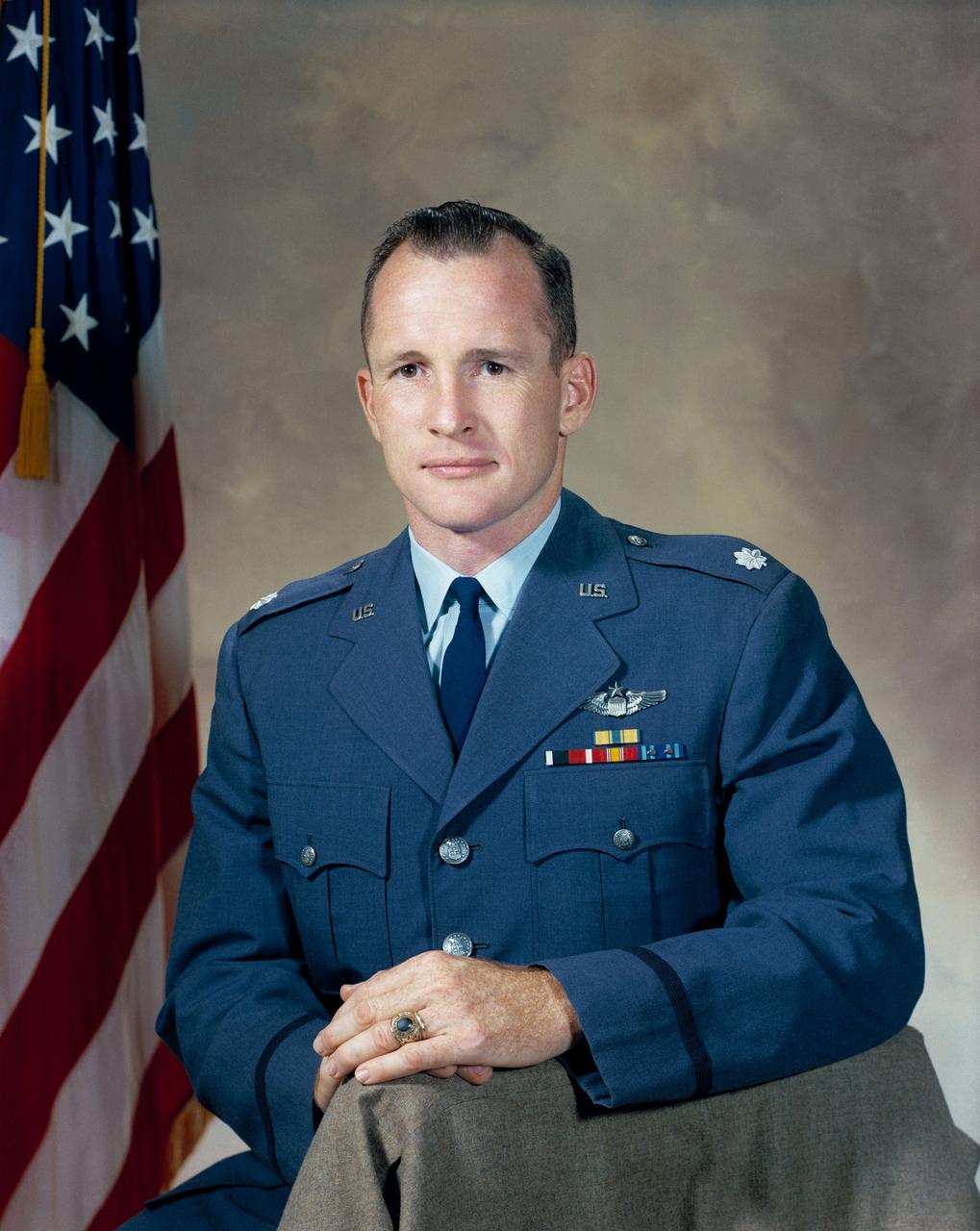

S66-35219 (1966) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II (United States Air Force Lieutenant Colonel), Gemini 4 pilot. Editor's Note: Since this portrait was taken astronaut White lost his life on Jan. 27, 1967, in the Apollo 1/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy, KSC, Florida.
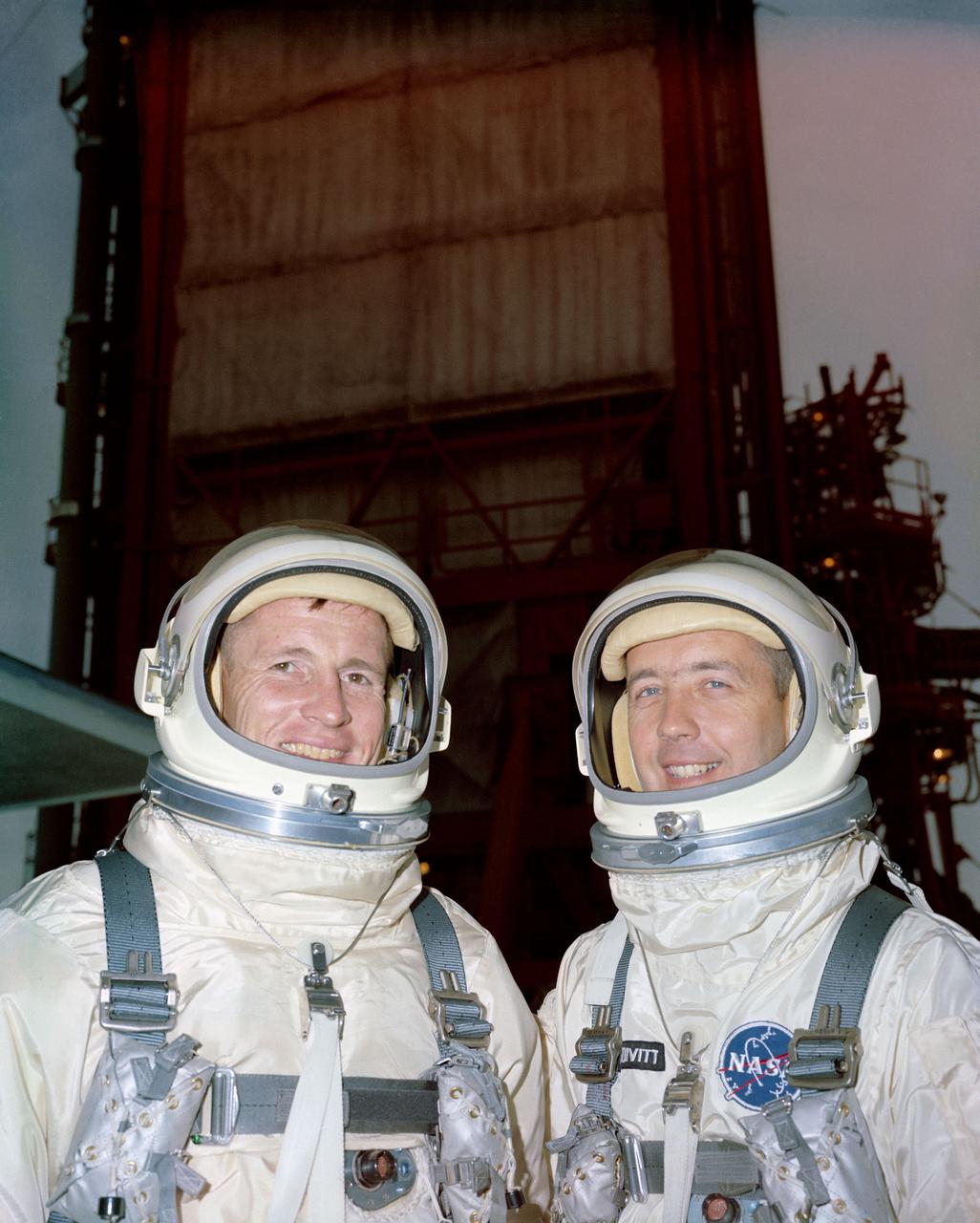

S65-19528 (1 June 1965) --- Astronauts Edward H. White II (left), Gemini-Titan 4 pilot; and James A. McDivitt, command pilot. EDITOR?S NOTE: Astronaut White died in the Apollo 1/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy on Jan. 27, 1967.

Originally devised to observe Saturn stage separation during Apollo flights, Marshall Space Flight Center's Miniature Television Camera, measuring only 4 x 3 x 1 1/2 inches, quickly made its way to the commercial telecommunications market.
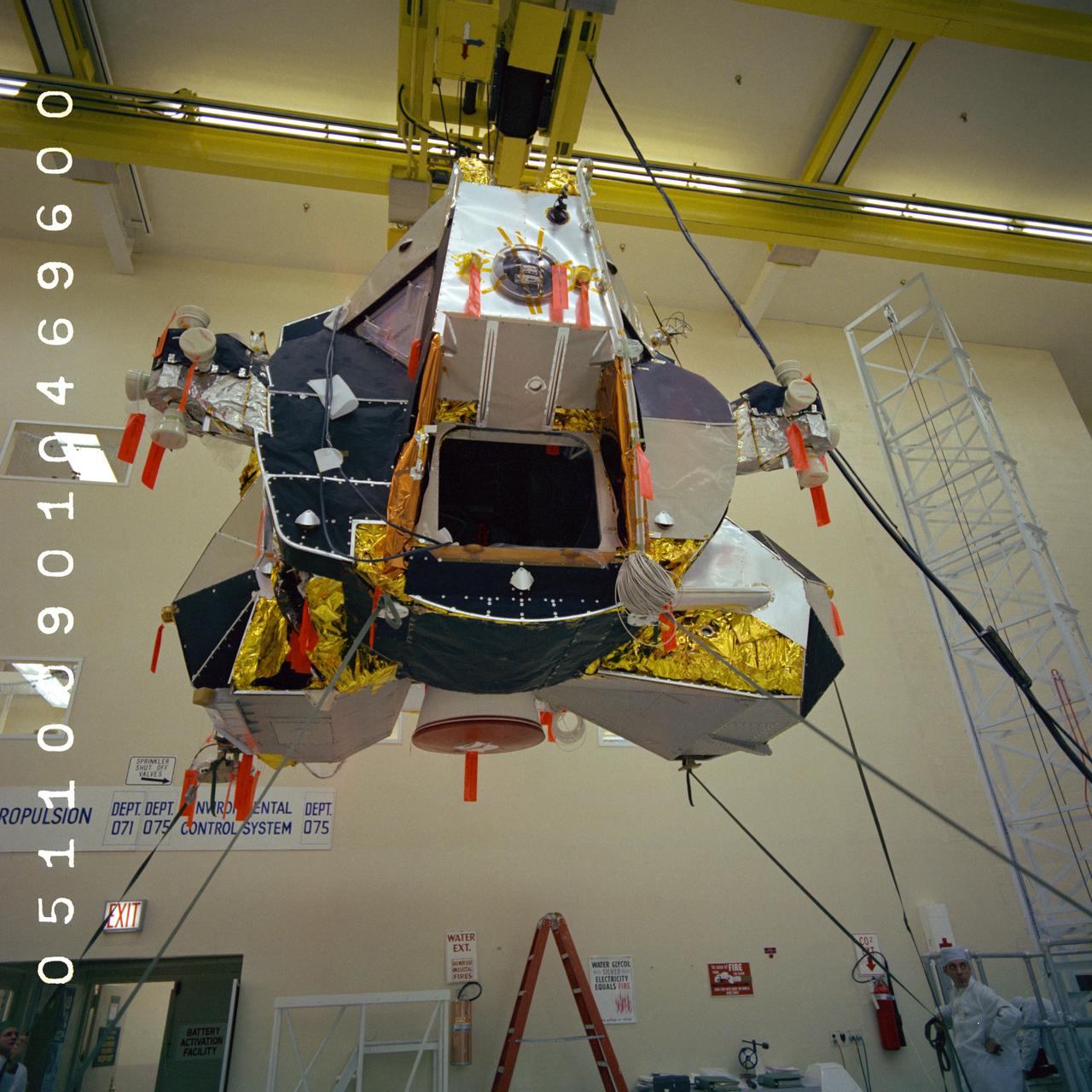

S69-19644 (4 Jan. 1969) --- Lunar Module (LM) 5 ascent stage in Final Assembly Area on overhead hoist being moved to dolly for roll-out inspection. LM-5 will be flown on the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. Photo credit: NASA/Grumman
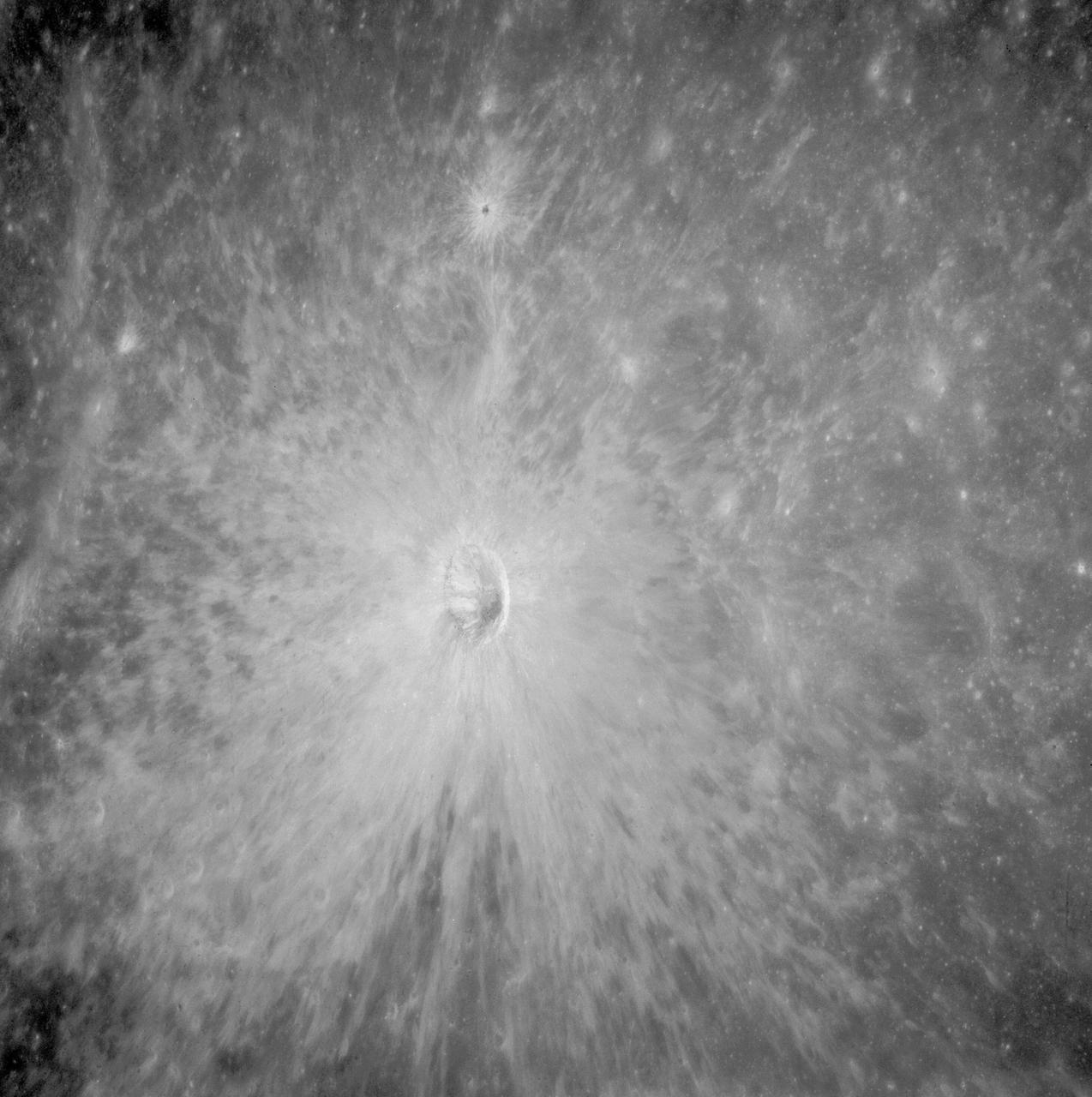

AS11-42-6285 (July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 view of a bright rayed crater on the lunar farside. The crater is unnamed. The center of this photograph is located at 100 degrees southeast longitude and 4 degrees 30 minutes north latitude. This area is just east of Smyth's Sea.
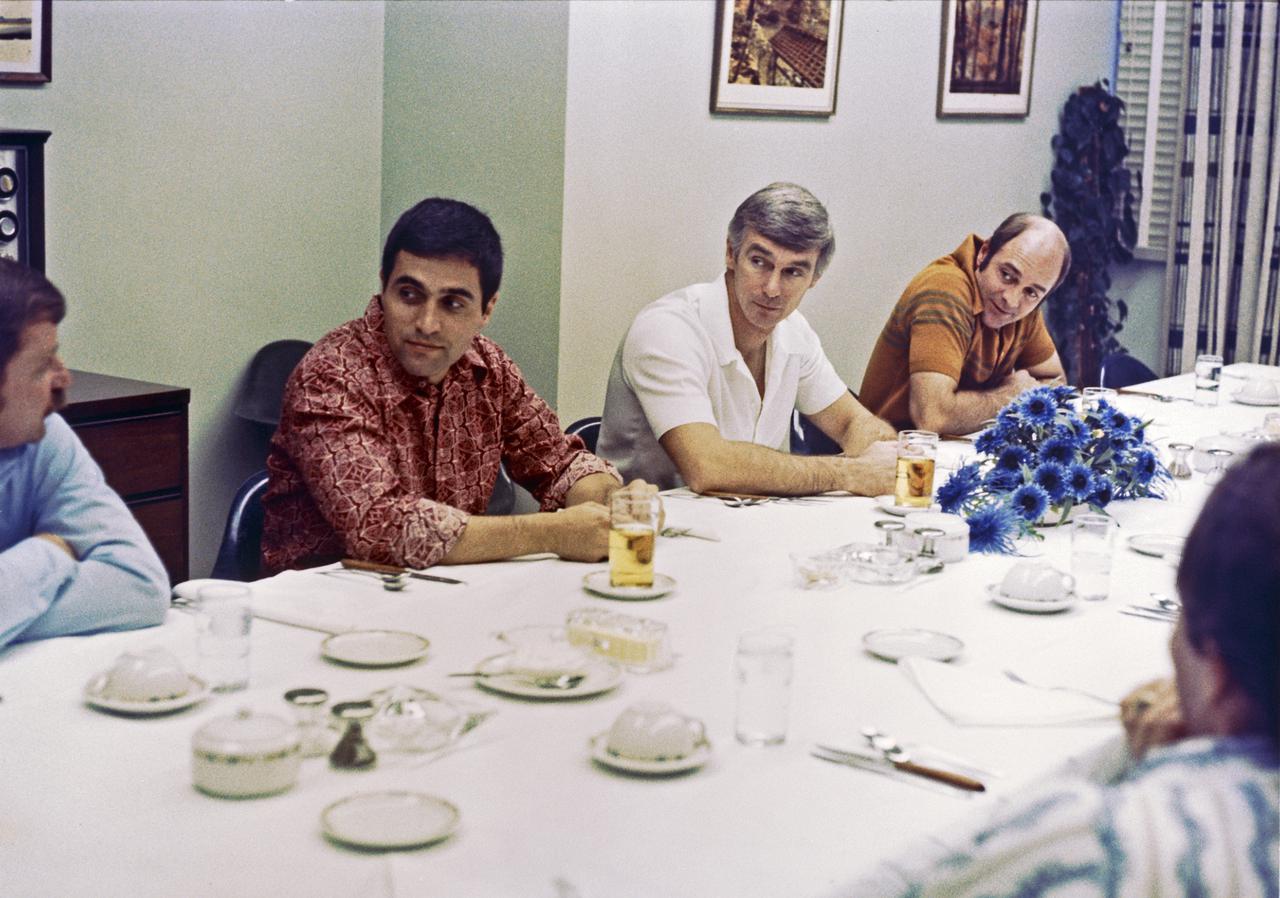

About 4 1_2 hours prior to launch to the Moon from Kennedy Space Center, the Apollo 17 astronauts relax in crew quarters during dinner. They are, left to right, Harrison H. Schmitt, Eugene A. Cernan and Ronald E. Evans.
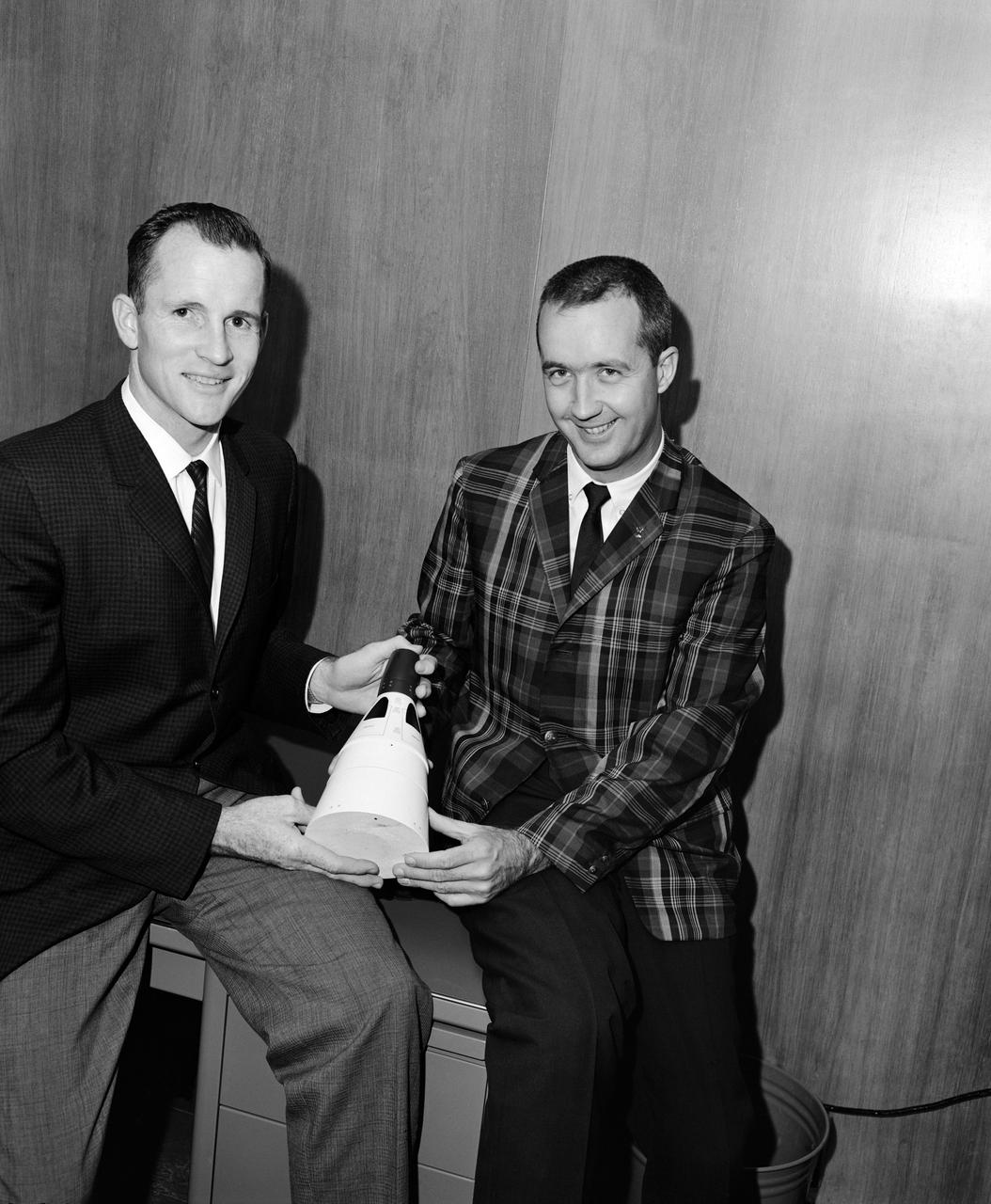

S62-04515 (1962) --- Astronauts Edward H. White II (left), Gemini-Titan 4 (GT-4) pilot, and James A. McDivitt, command pilot, pose for a photo holding a Gemini model. EDITOR?S NOTE: Jan. 27, 1967, astronaut White lost his life in the Apollo/Saturn 204 accident at Cape Canaveral, Florida.
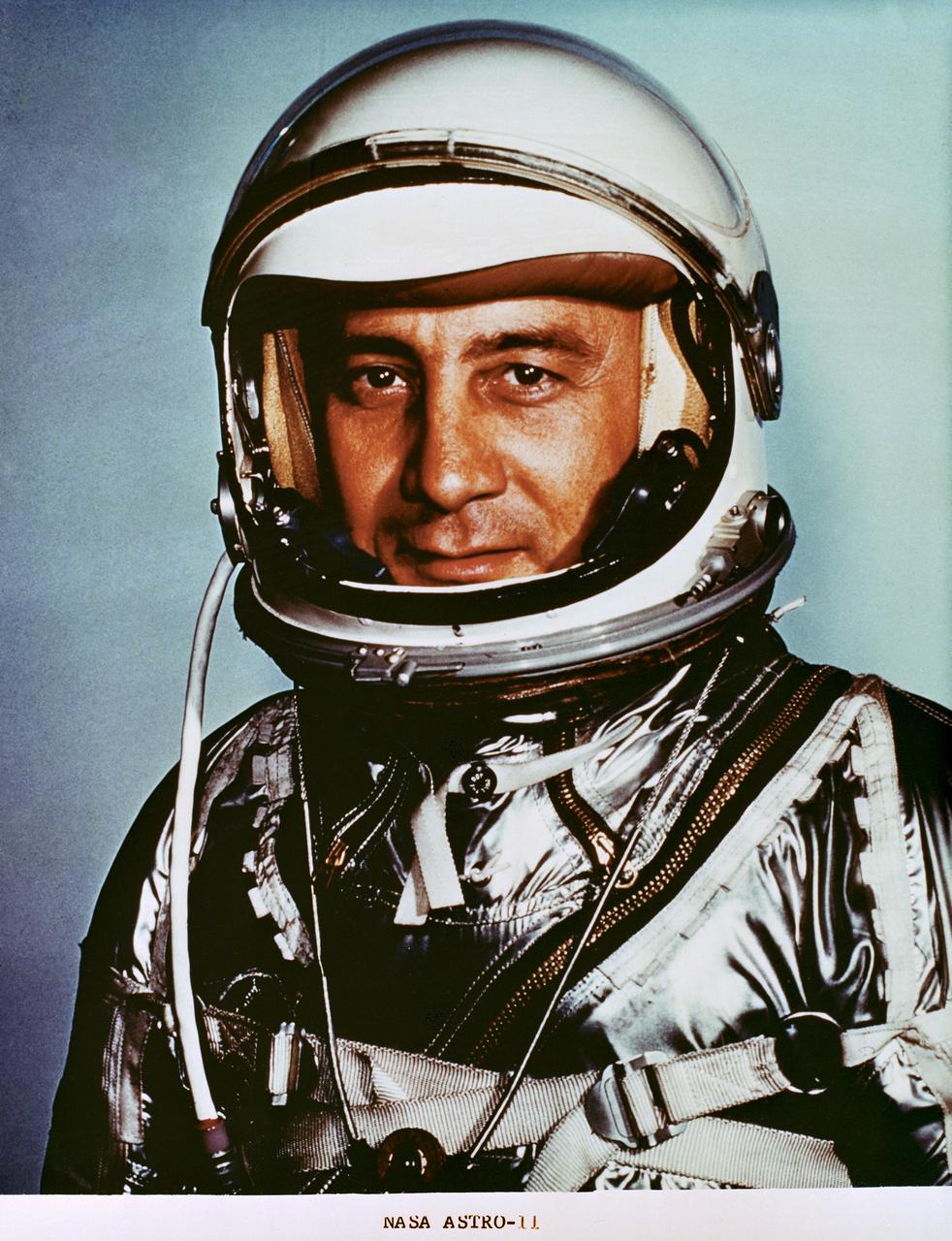

S88-55873 (1961) --- Astronaut Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom, pilot of the Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) spaceflight. (NOTE: Astronaut "Gus" Grissom, one of the original seven astronauts, died Jan. 27, 1967, at NASA?s John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Cape Canaveral Florida, in the Apollo 1 spacecraft fire.) Photo credit: NASA
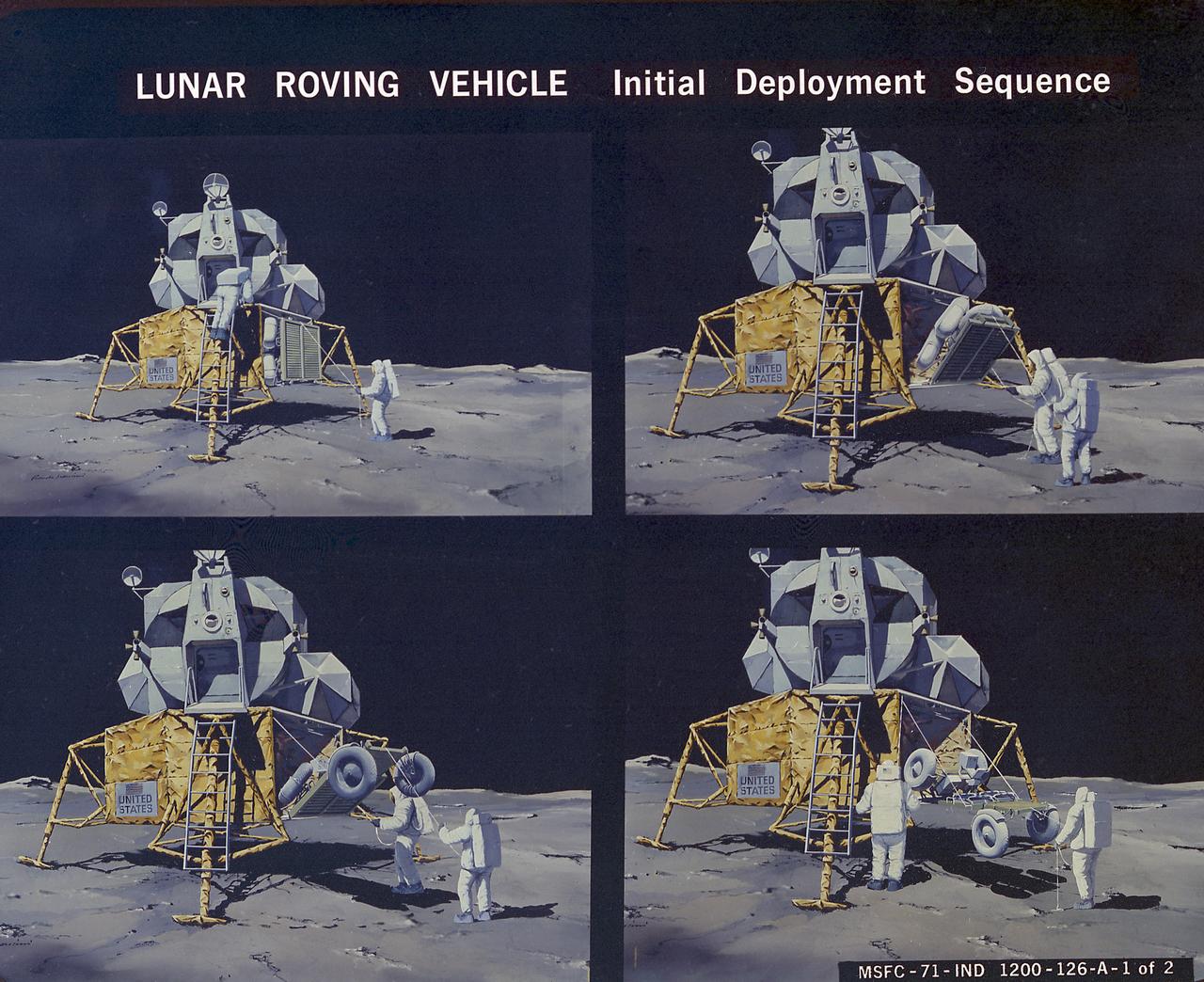
This artist's concept illustrates the deployment sequence of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Moon. The LRV was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
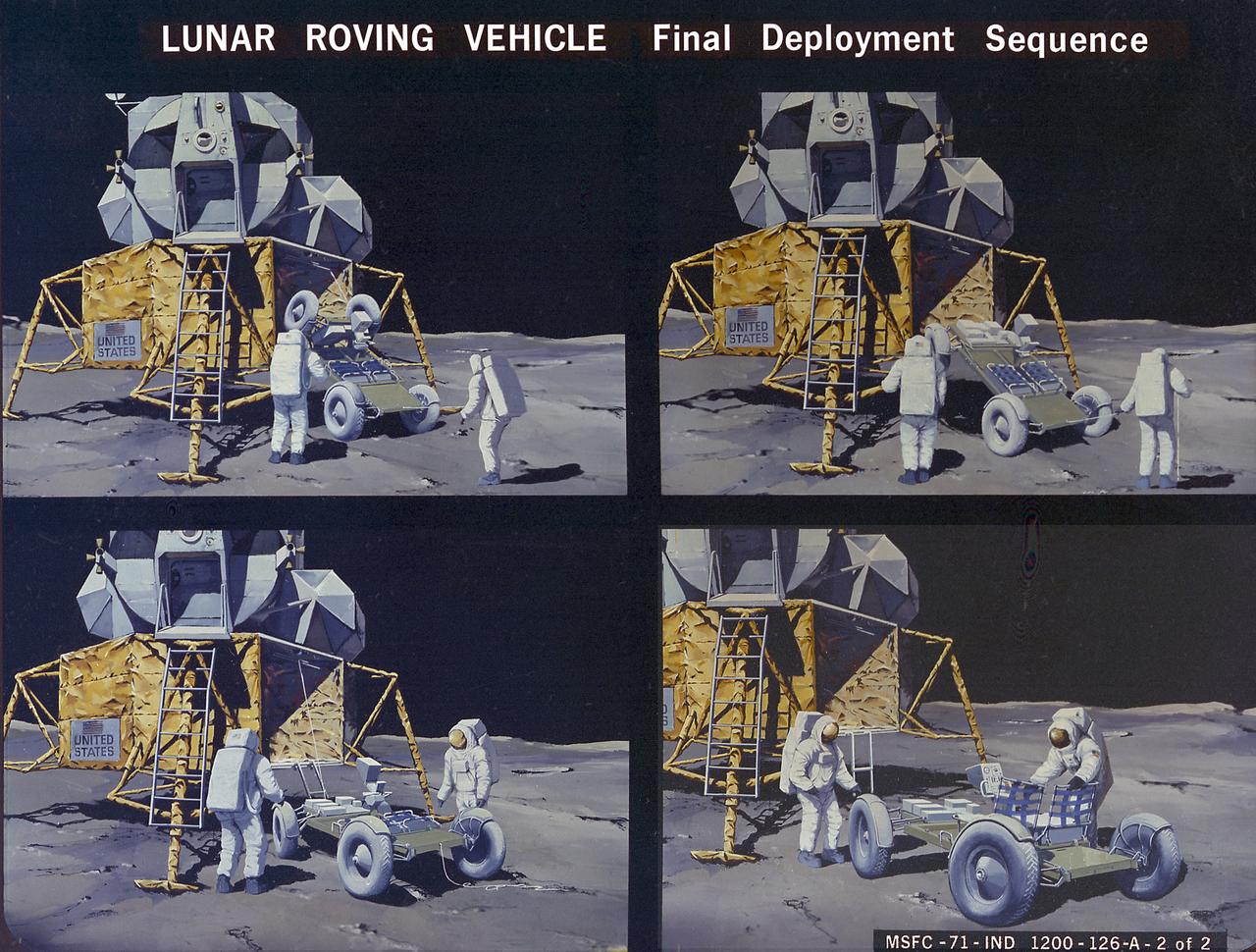
This artist's concept illustrates the deployment sequence of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Moon. The LRV was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.

The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
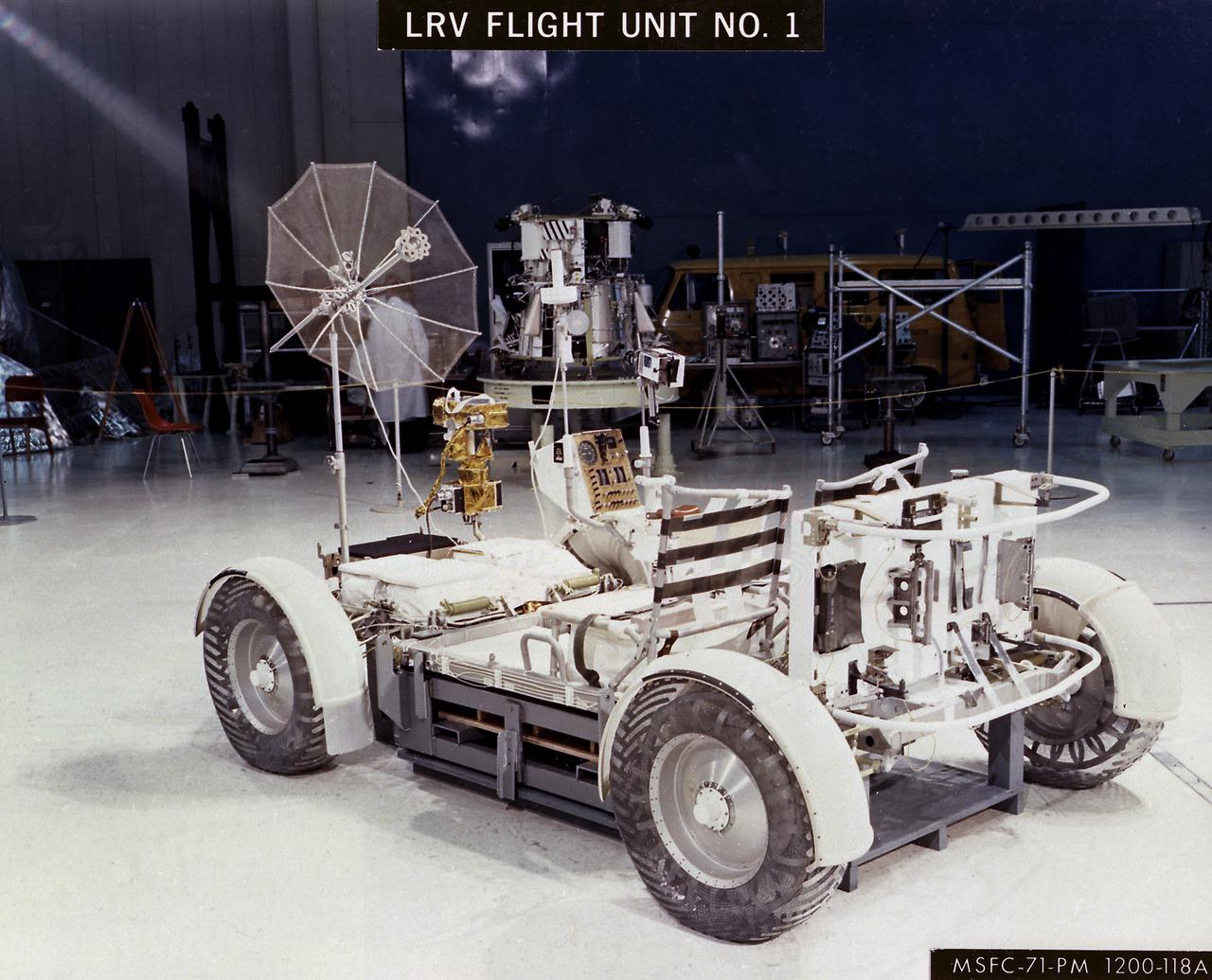
The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crews to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
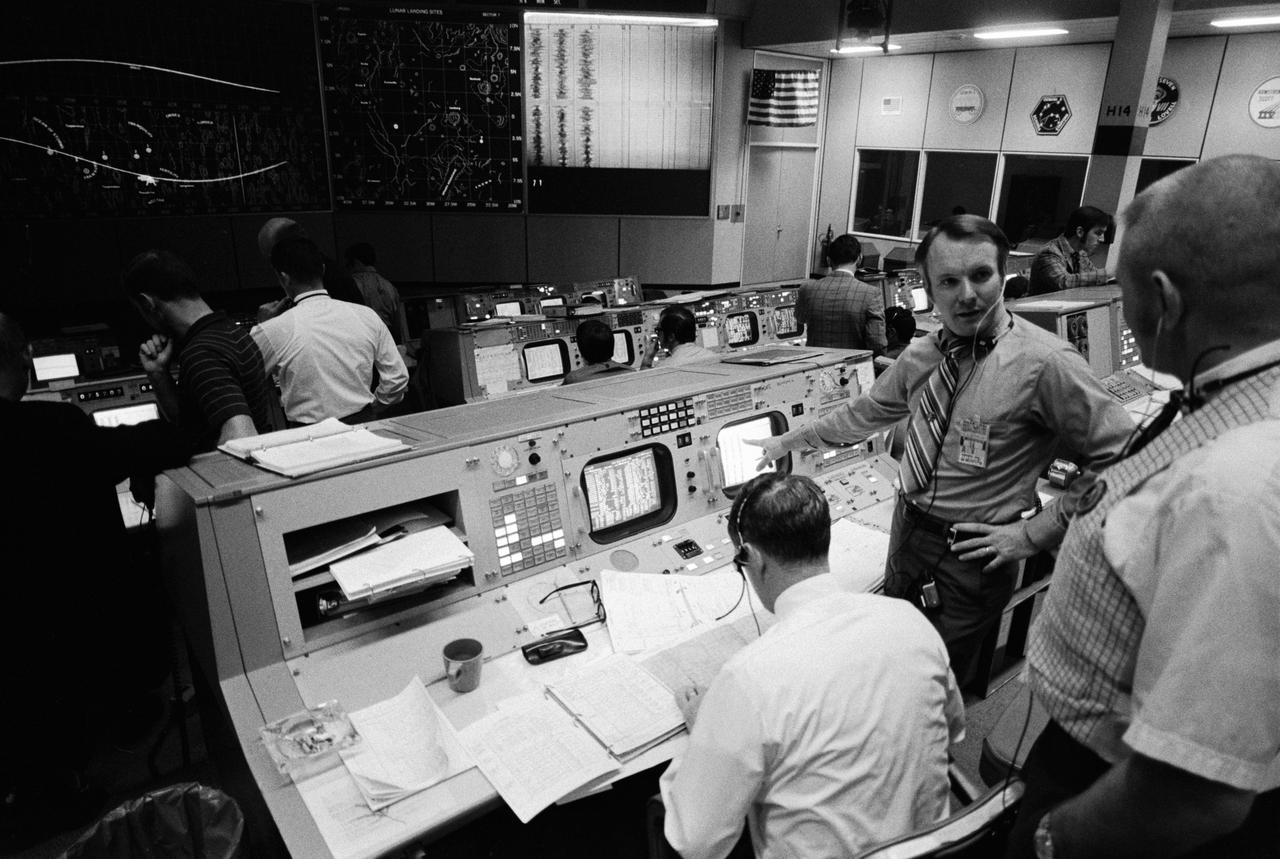

S71-17610 (4 Feb. 1971) --- Partial view of activity in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center at the time the Apollo 14 S-IVB stage impacted on the lunar surface. The flight director's console is in the foreground. Eugene F. Kranz, chief of the MSC Flight Control Division, is in the right foreground. Seated at the console is Glynn S. Lunney, head of the Flight Director Office, Flight Control Division. Facing the camera is Gerald D. Griffin, flight director of the Third (Gold) Team. A seismic reading from the impact can be seen in the center background. The S-IVB impacted on the lunar surface at 1:40:54 a.m. (CST), Feb. 4, 1971, about 90 nautical miles south-southwest of the Apollo 12 passive seismometer. The energy release was comparable to 11 tons of TNT.
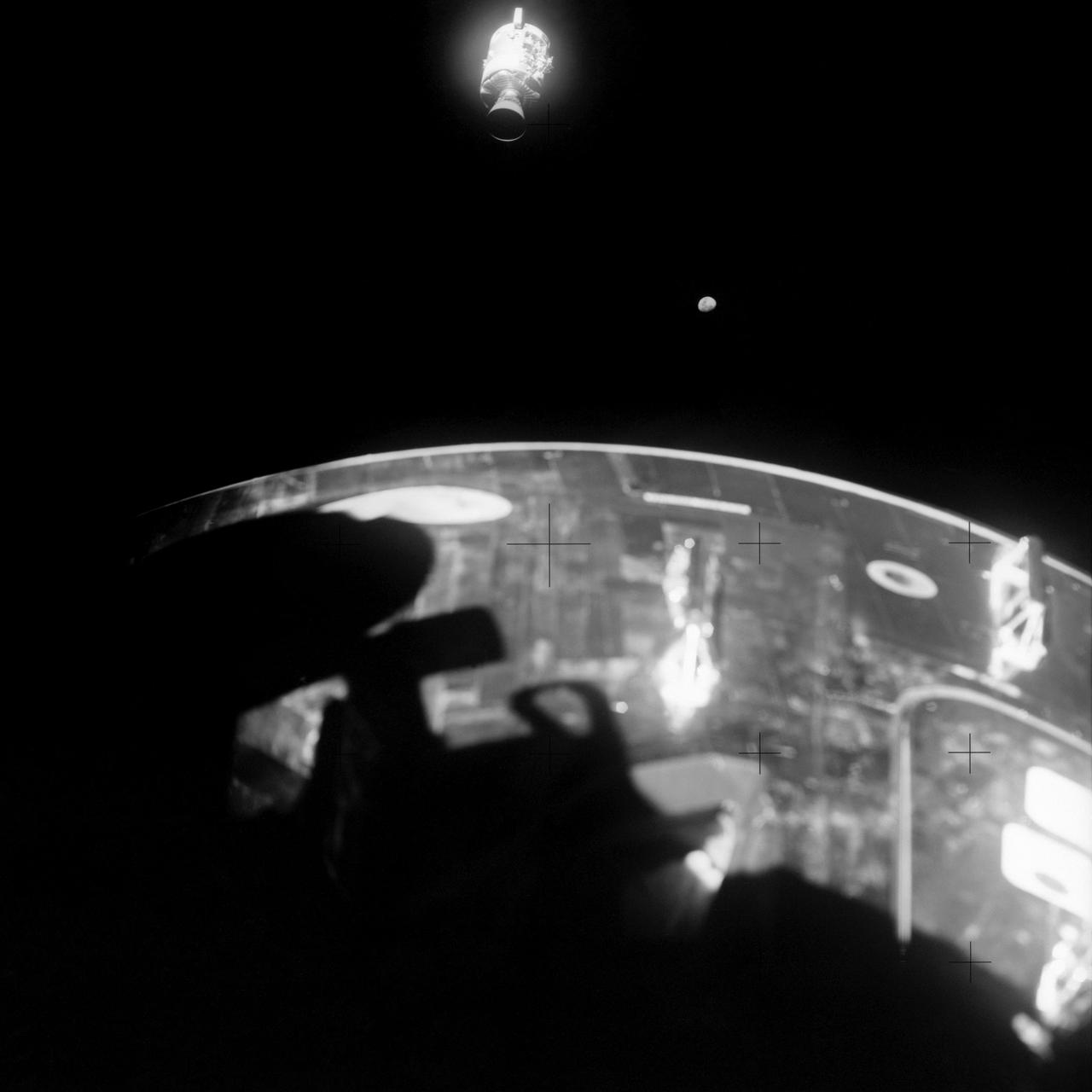

AS13-59-8501 (17 April 1970) --- This view of the severely damaged Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) was photographed from the Lunar Module/Command Module (LM/CM) following SM jettisoning. As seen here, an entire panel on the SM was blown away by the apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two located in Sector 4 of the SM. Two of the three fuel cells are visible just forward (above) the heavily damaged area. Three fuel cells, two oxygen tanks, and two hydrogen tanks are located in Sector 4. The damaged area is located above the S-Band high gain antenna. Nearest the camera is the Service Propulsion System (SPS) engine and nozzle. The damage to the SM caused the Apollo 13 crew men to use the LM as a "lifeboat." The LM was jettisoned just prior to Earth re-entry by the CM.
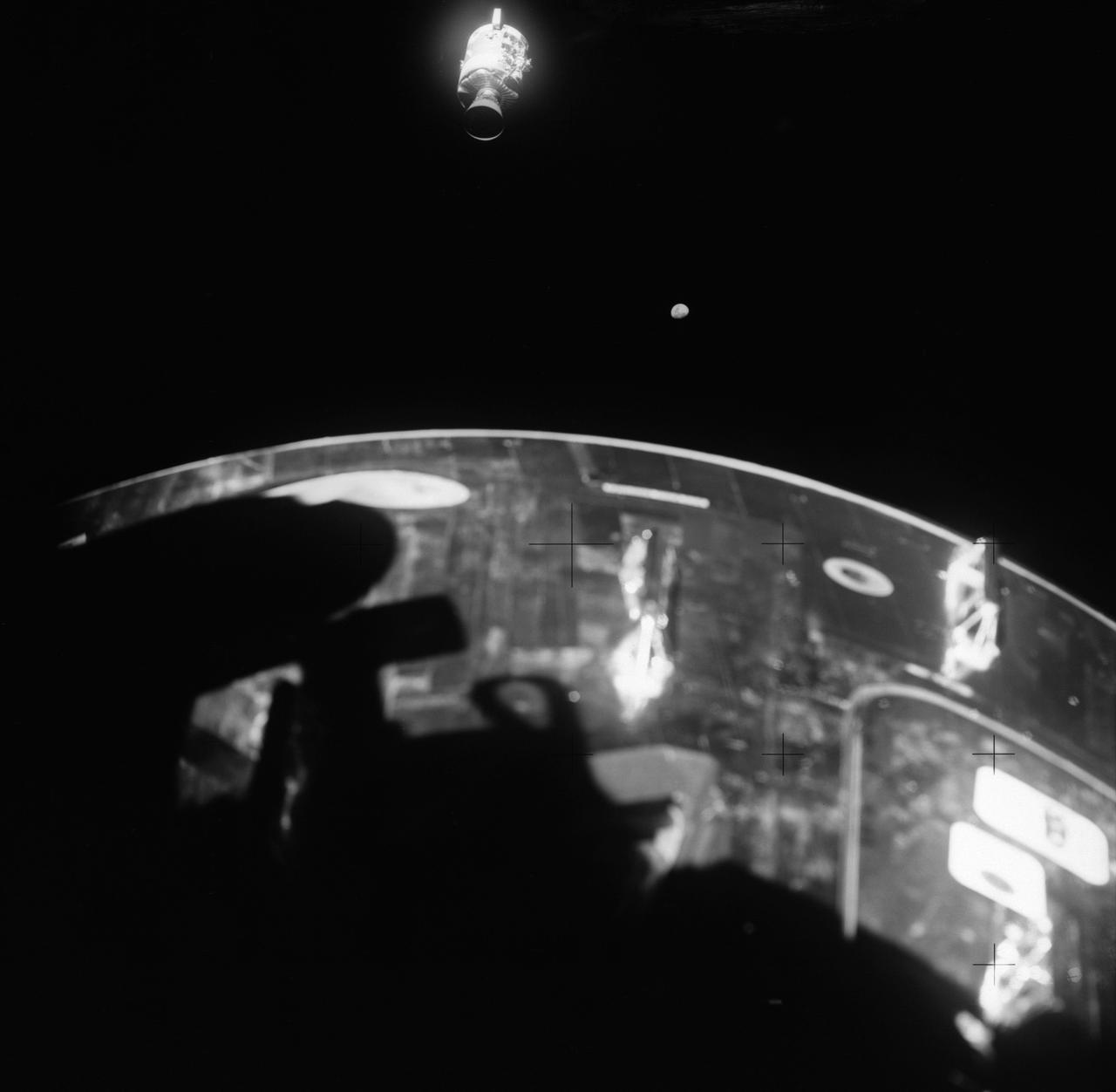

This view of the damaged Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) was photographed from the Lunar Module/Command Module following SM jettisoning. As seen here, an entire panel on the SM was blown away by the apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two located in Sector 4 of the SM. Two of the three fuel cells are visible just forward (above) the heavily damaged area. Three fuel cells, two oxygen tanks, and two hydrogen tanks are locate in Sector 4. The damaged area is located above the S-band high gain antenna. Nearest the camera is the Service Propulsion System (SPS) engine and nozzle. The damage to the SM caused the Apollo 13 crewmen to use the Lunar Module (LM) as a "lifeboat". The LM was jettisoned just prior to Earth reentry by the Command Module.
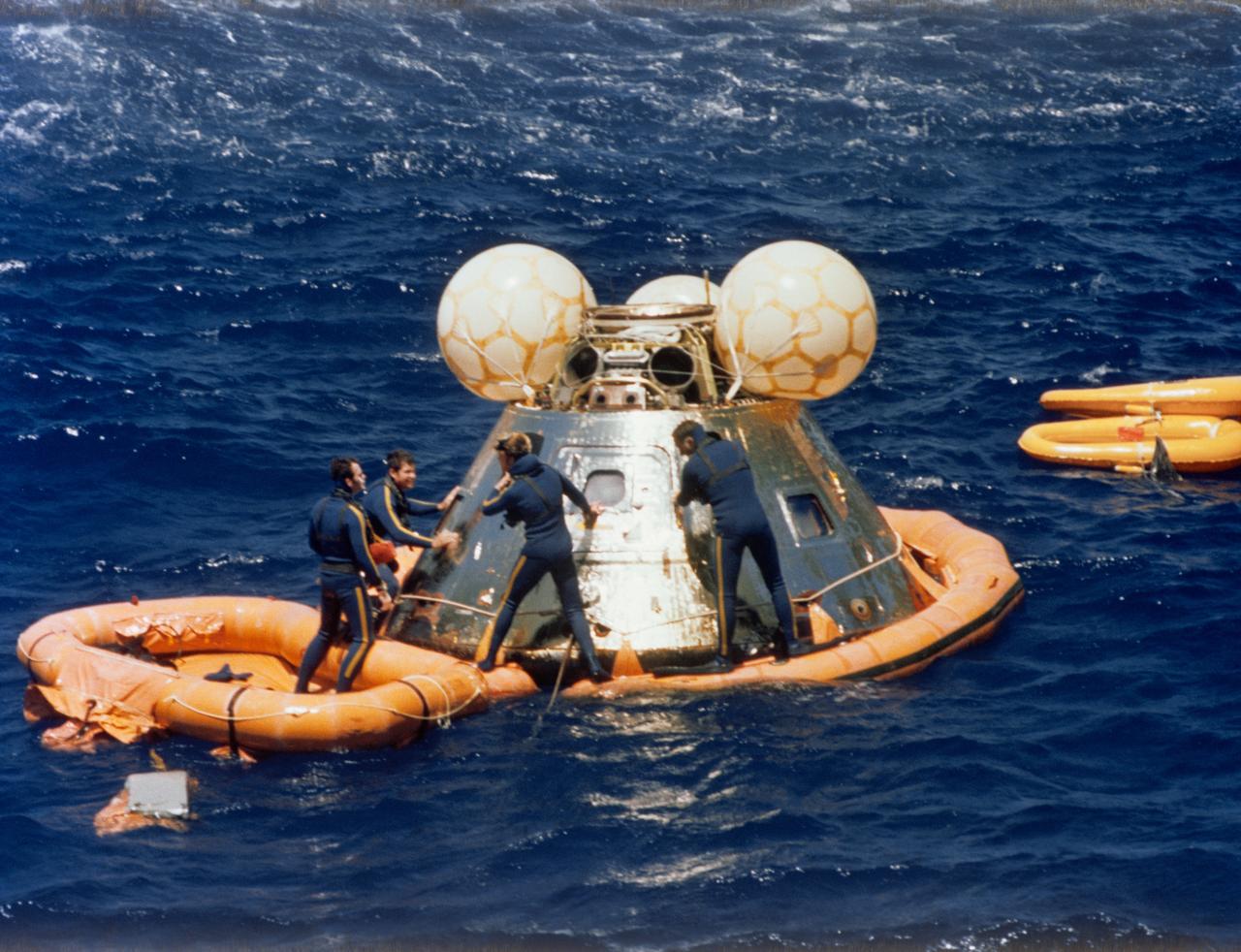

S75-29715 (24 July 1975) --- A team of U.S. Navy swimmers assists with the recovery of the ASTP Apollo Command Module following its splashdown in the Central Pacific Ocean to conclude the historic joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. The swimmers have already attached a flotation collar to the spacecraft. The CM touched down in the Hawaiian Islands area at 4:18 p.m. (CDT), July 24, 1975. The crewmen, astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. Slayton, remained in the CM until it was hoisted aboard the prime recovery ship, the USS New Orleans.
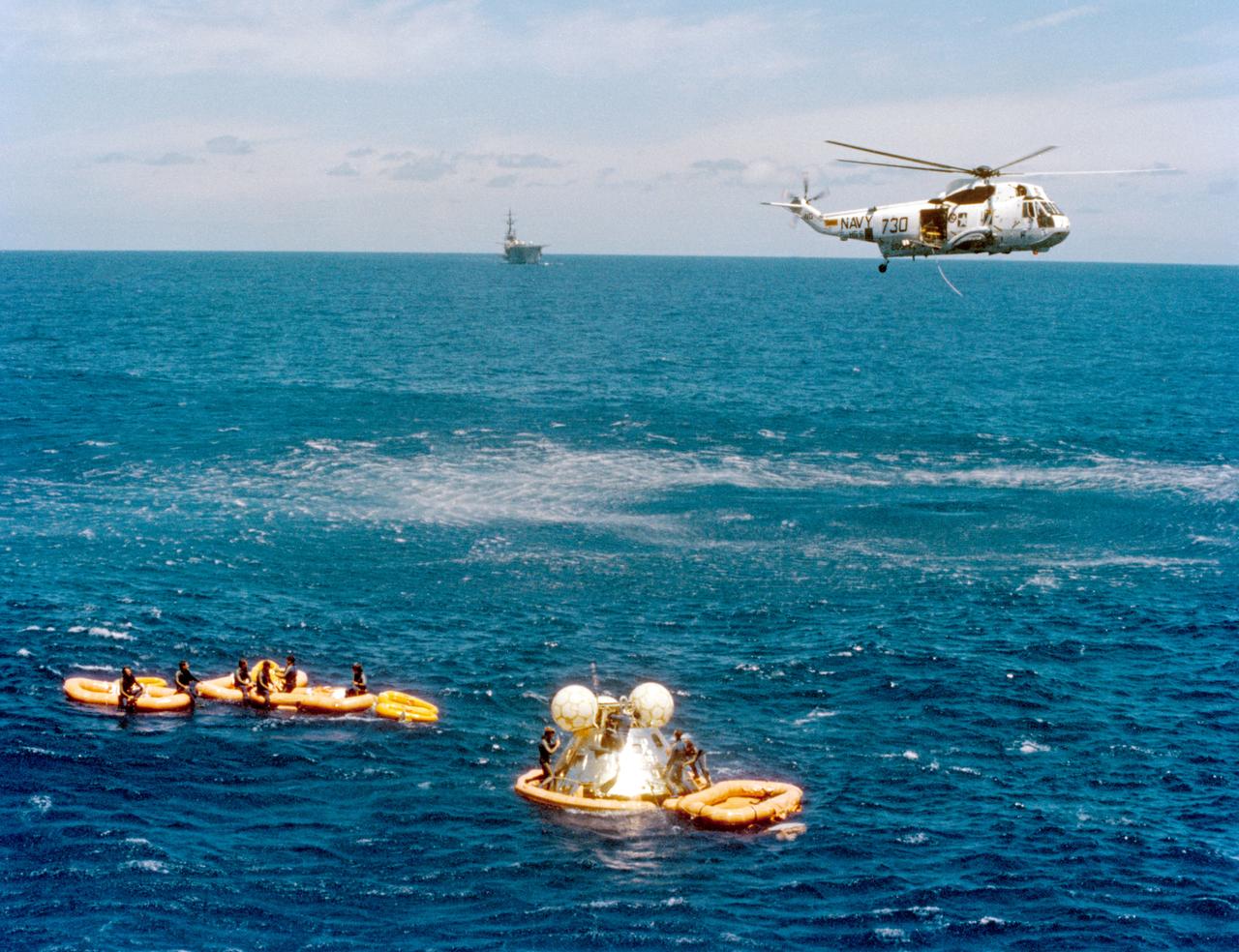

S75-29717 (24 July 1975) --- The ASTP Apollo Command Module, with astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. Slayton still inside, awaits pickup by the prime recovery ship, the USS New Orleans, following splashdown in the Central Pacific Ocean to conclude the historic joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. The CM touchdown occurred in the Hawaiian Islands area at 4:18 p.m. (CDT), July 24, 1975. A team of U.S. Navy swimmers assists with the recovery operations. A recovery helicopter hovers overhead.
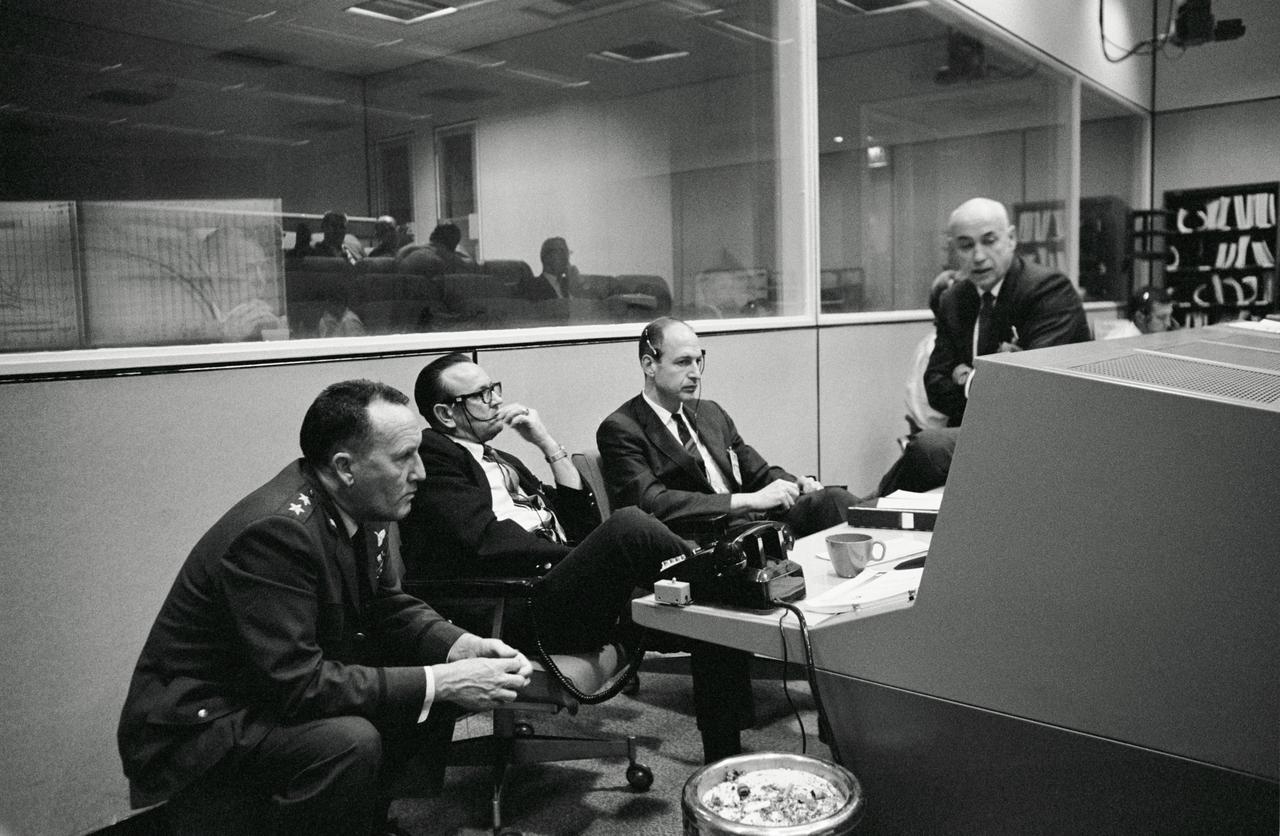

S68-20986 (4 April 1968) --- Scene at the flight operations director's console in the Mission Control Center, Building 30, during the Apollo 6 (Spacecraft 020/Saturn 520) unmanned space flight. Left to right, are Air Force Maj. Gen. Vincent G. Huston, DOD Manager, Manned Space Flight Operations, Andrews Air Force Base, Washington, D.C.; Dr. Christopher C. Kraft Jr., MSC director of flight operations; George M. Low, manager, MSC Apollo Spacecraft Program Office; and Dr. Robert R. Gilruth, MSC Director.
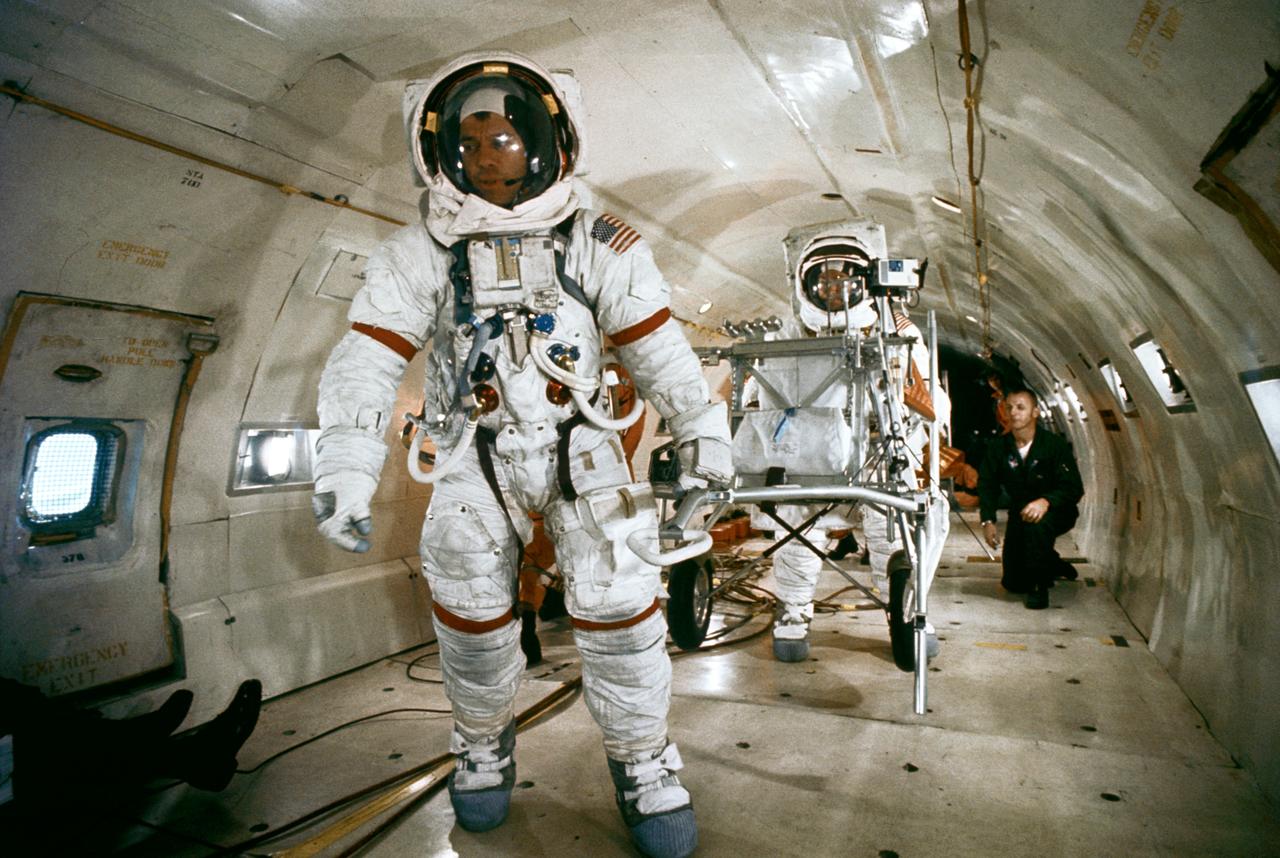

S70-53479 (4 Nov. 1970) -- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., Apollo 14 commander, pulls the modular equipment transporter (MET) under weightless conditions aboard an Air Force KC-135 out of Patrick Air Force Base. Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, Apollo 14 lunar module pilot, is behind the MET. The KC-135 aircraft, flying a parabolic curve, creates a weightless environment providing a training exercise in preparation for the astronauts' extravehicular activities (EVA) on the lunar surface. This training simulates the 1/6 gravity the astronauts will encounter on the moon.
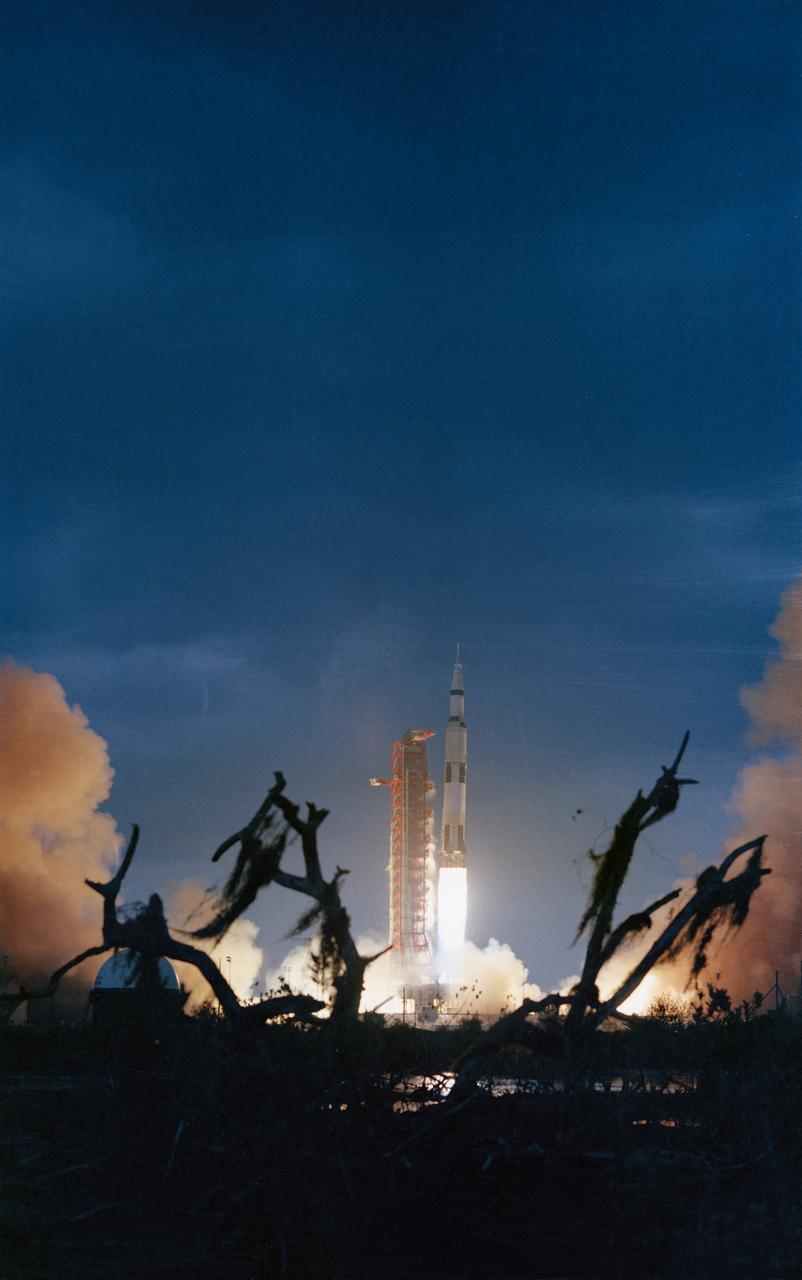

S71-18399 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. This view is framed by moss-covered dead trees in the dark foreground. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.
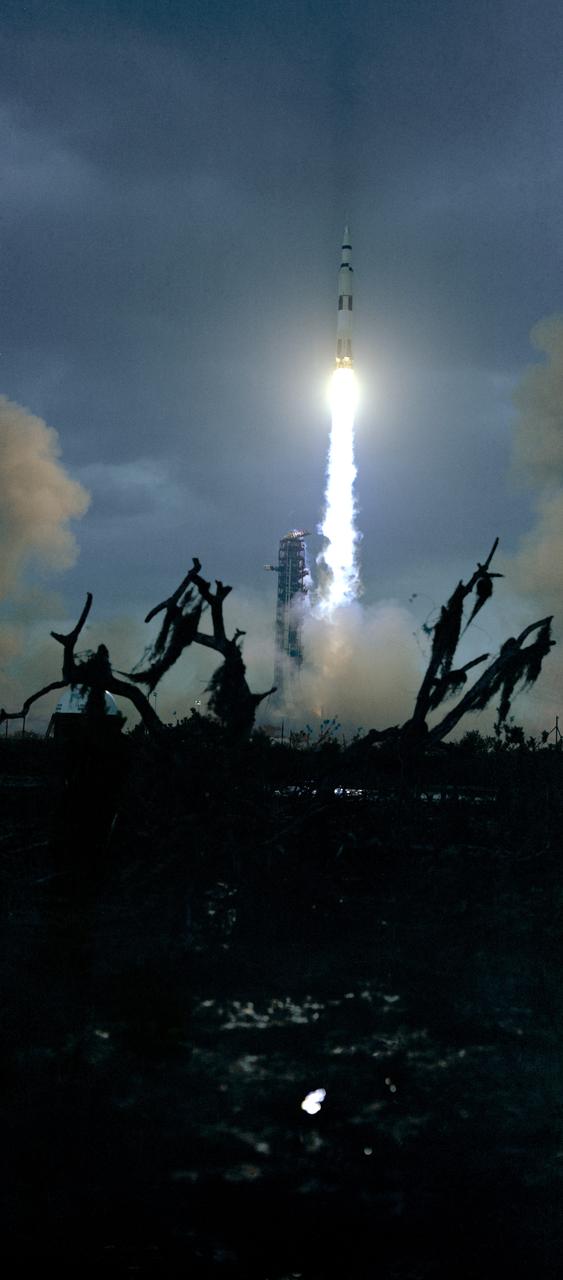

S71-18398 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. This view is framed by moss-covered dead trees in the dark foreground. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.

AS06-02-1462 (4 April 1968) --- View of the Dallas-Fort Worth, Texas, area as photographed from the unmanned Apollo 6 (Spacecraft 020/Saturn 502) space mission. The highway and expressway system in and around both cities is clearly visible. North is toward left side of picture. Grapevine Reservoir and Garza-Little Elm Reservoir are to the north-west of Dallas. The city of Denton can be seen in left center of picture at conjunction of highways leading to both Fort Worth and Dallas. The Brazos River is in lower right corner. This photograph was made three hours and nine minutes after liftoff of the Apollo 6 space flight.
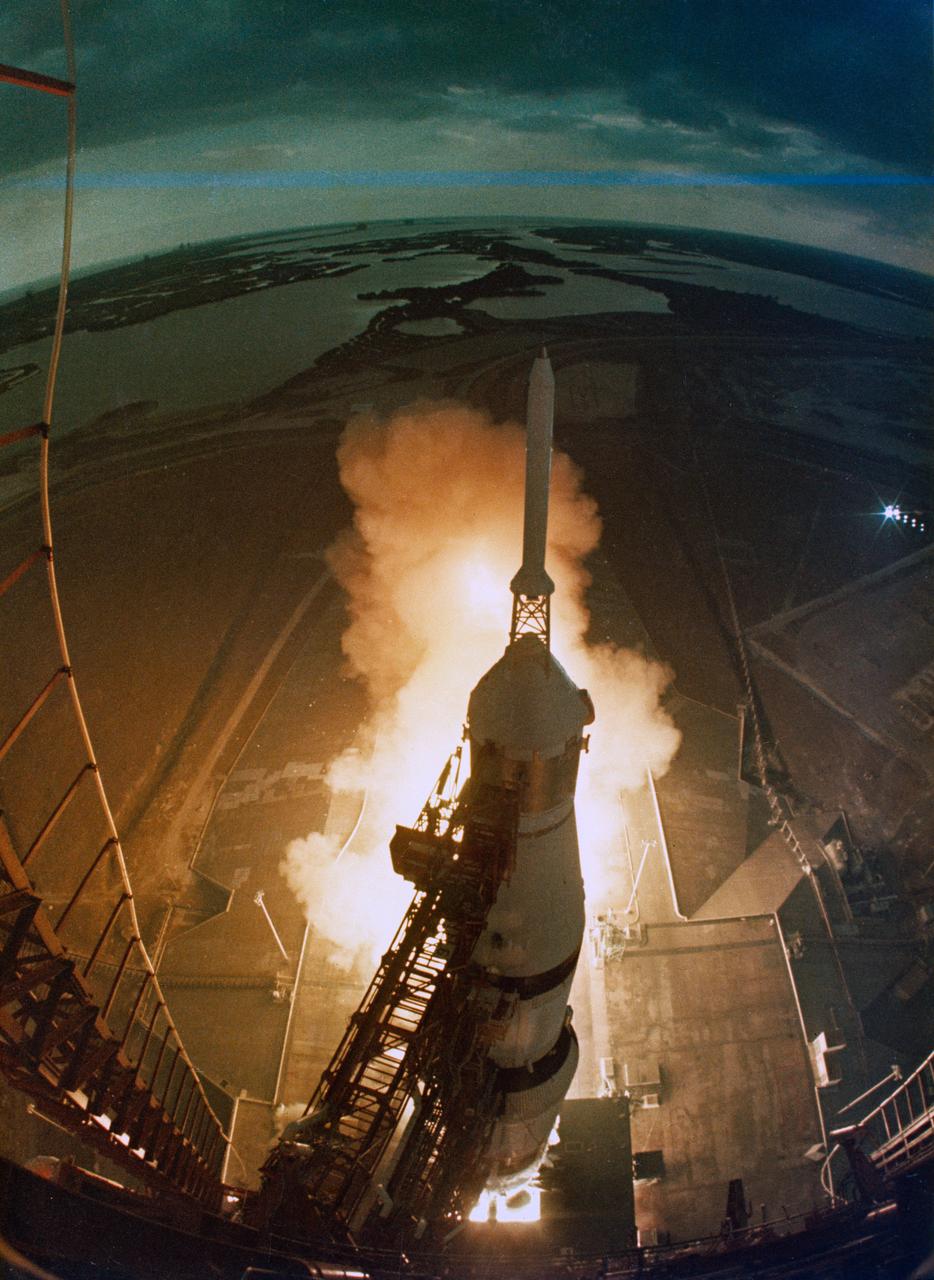

S71-17620 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1981, on a lunar landing mission. This view of the liftoff was taken by a camera mounted on the mobile launch tower. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.