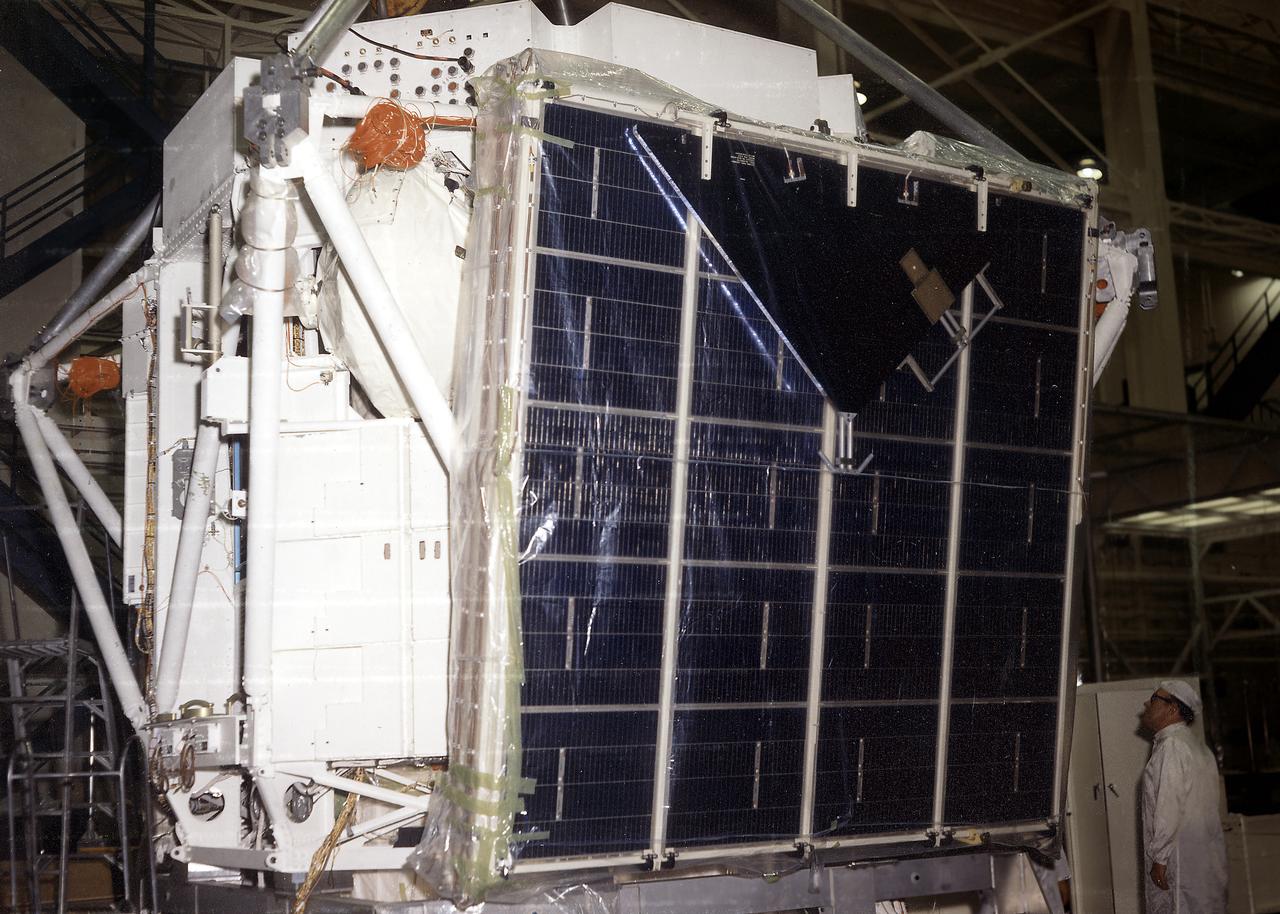

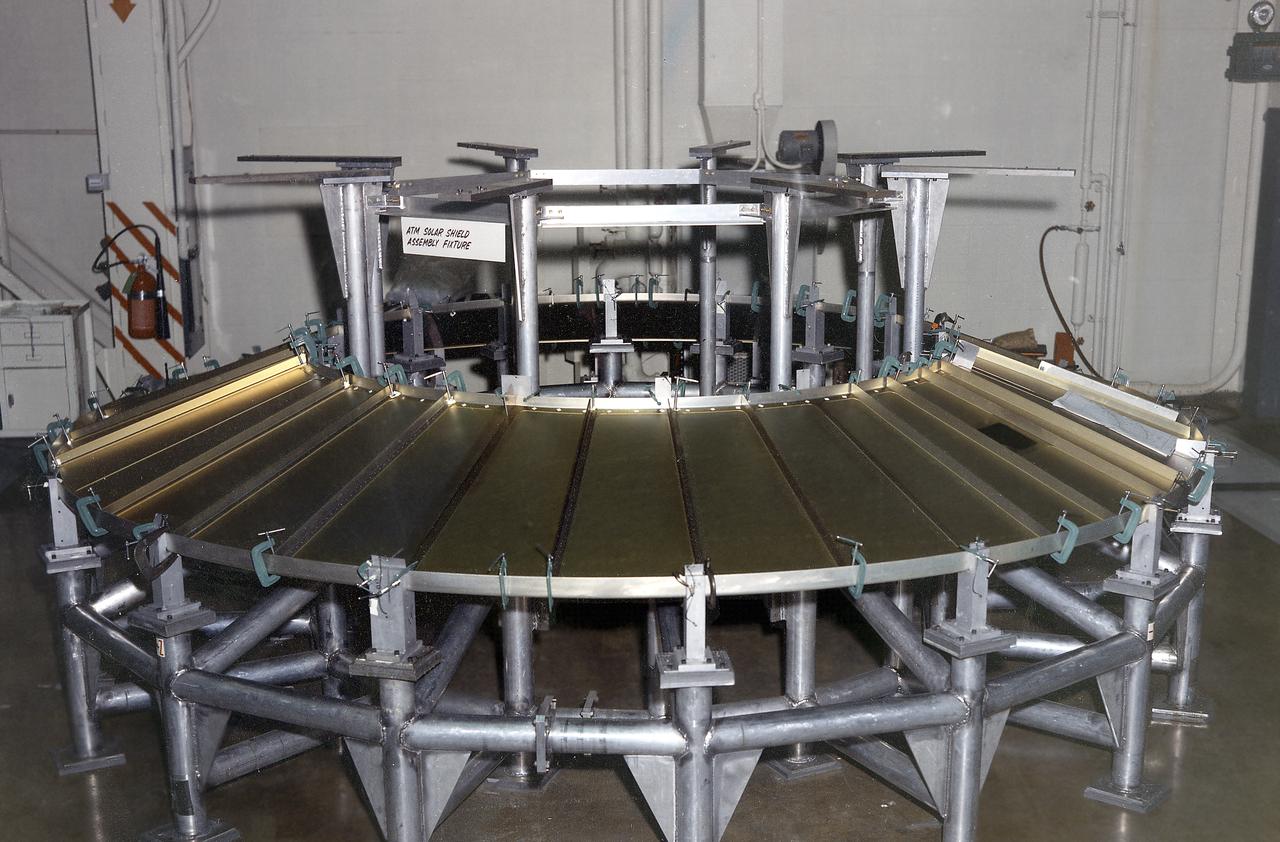
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was one of four major components of Skylab (1973-1979) that were designed and developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center. In this picture, an ATM solar wing prototype is shown during assembly. A total of four solar wings were required to provide power to the ATM.
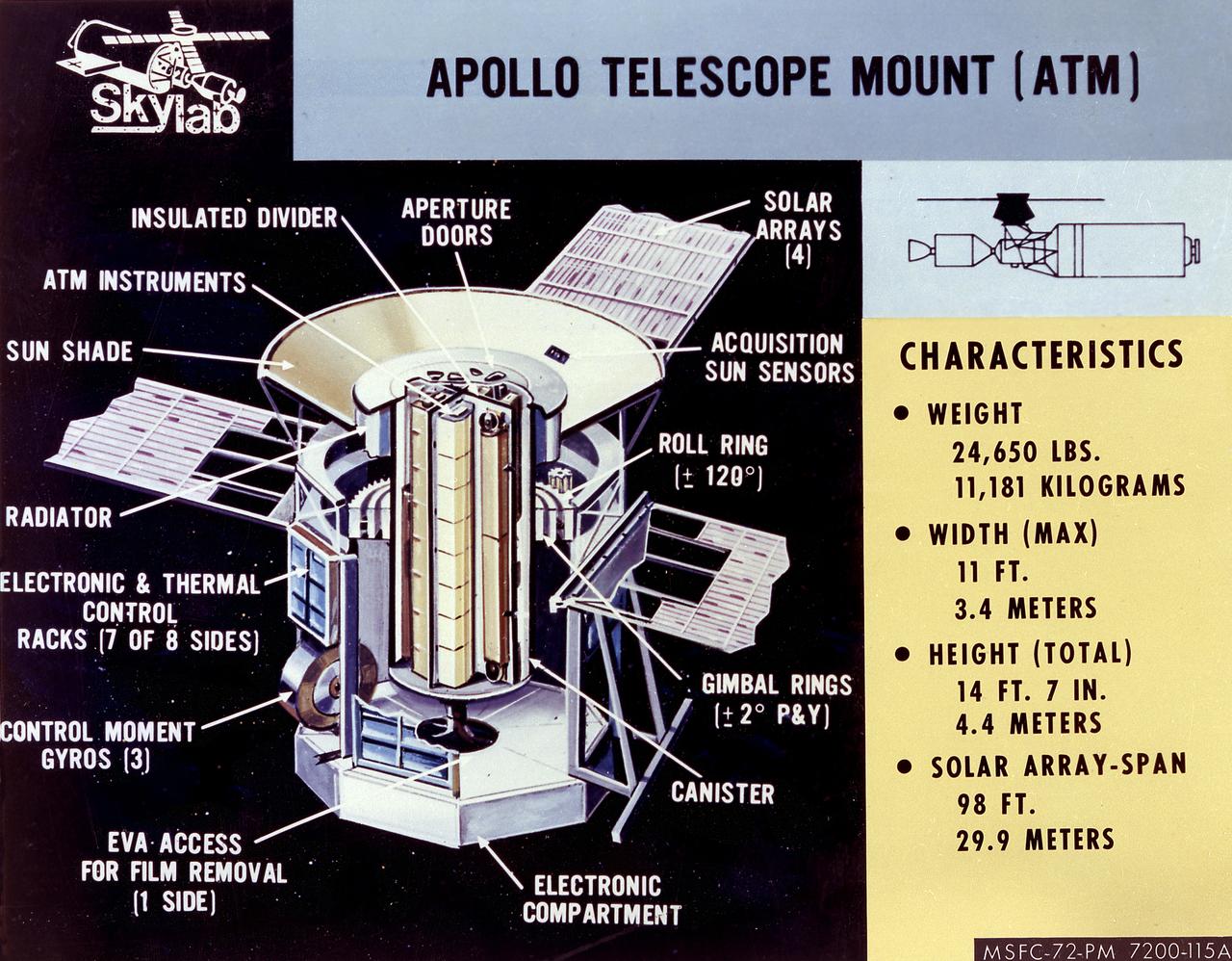
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) served as the first marned astronomical observatory in space. It was designed for solar research from Earth orbit aboard the Skylab. This image is a cutaway illustration of the ATM canister with callouts and characteristics. The ATM was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
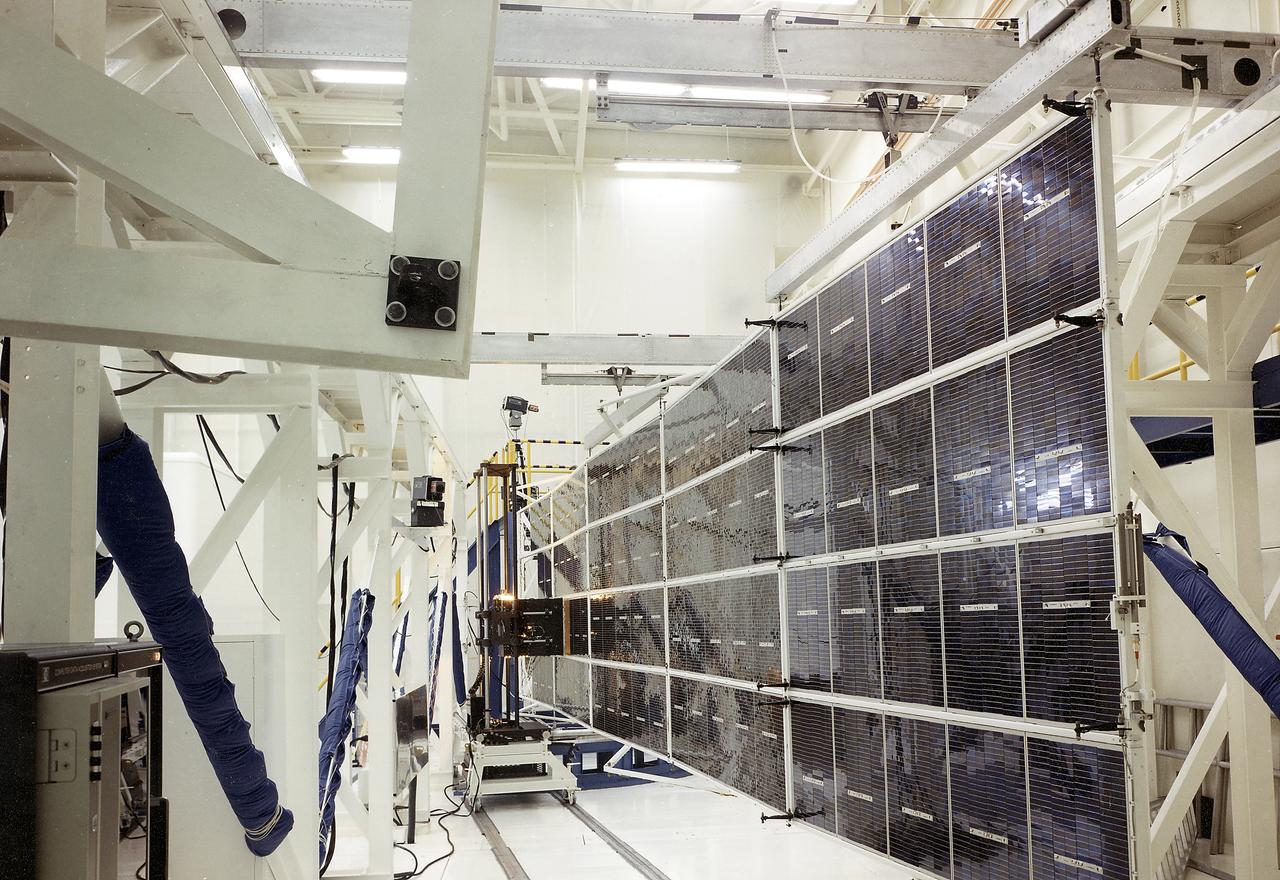

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), one of four major components comprising Skylab, was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. Power to operate the ATM's instruments and experiments was collected by four solar arrays, capable of producing up to 1.1 kilowatts of electricity. This is a photograph of the ATM Solar Array flight unit deployed for illumination testing.
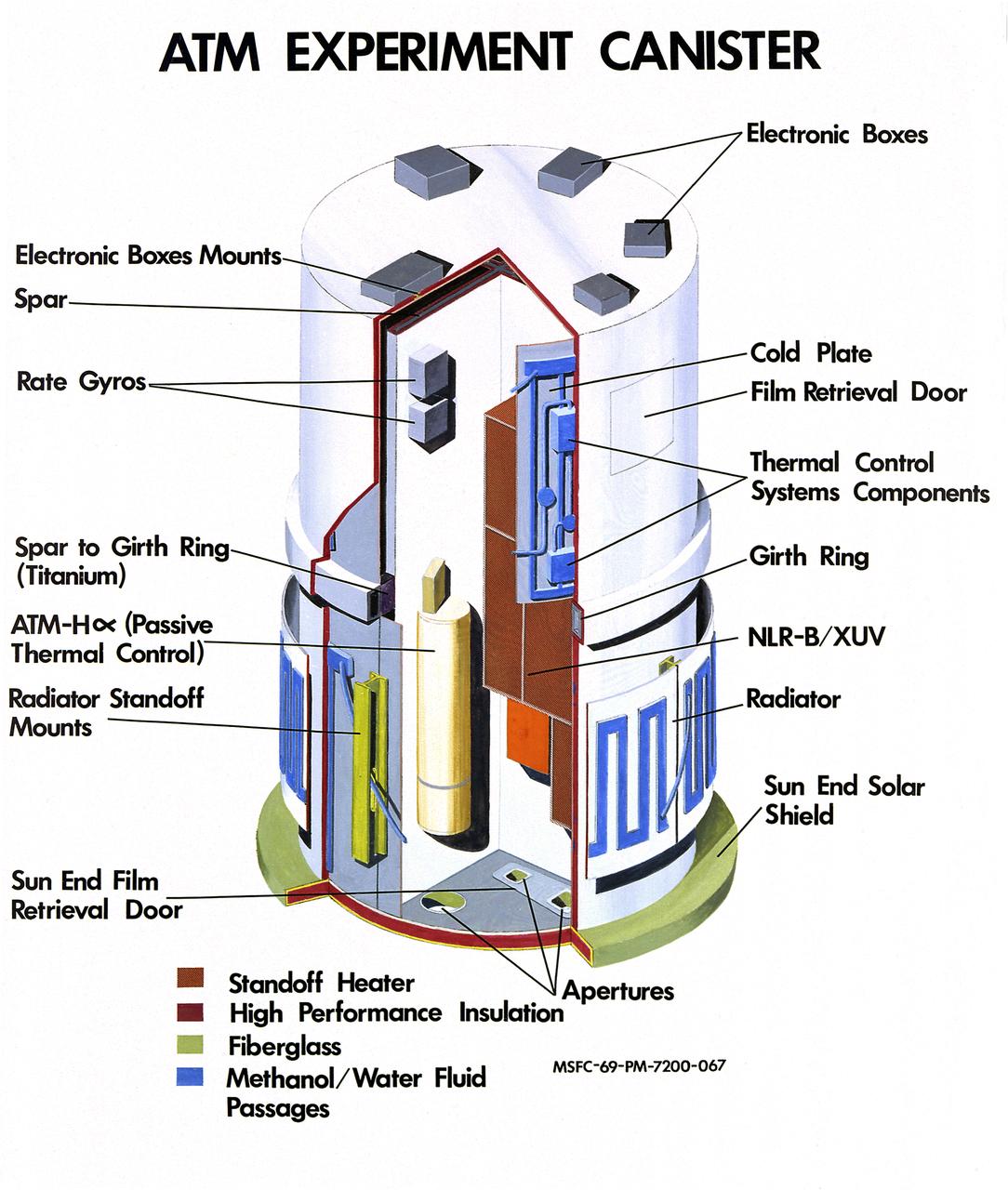
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) served as the first marned astronomical observatory in space. It was designed for solar research from Earth orbit aboard the Skylab. This image is a cutaway illustration of the ATM canister with callouts. The ATM was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
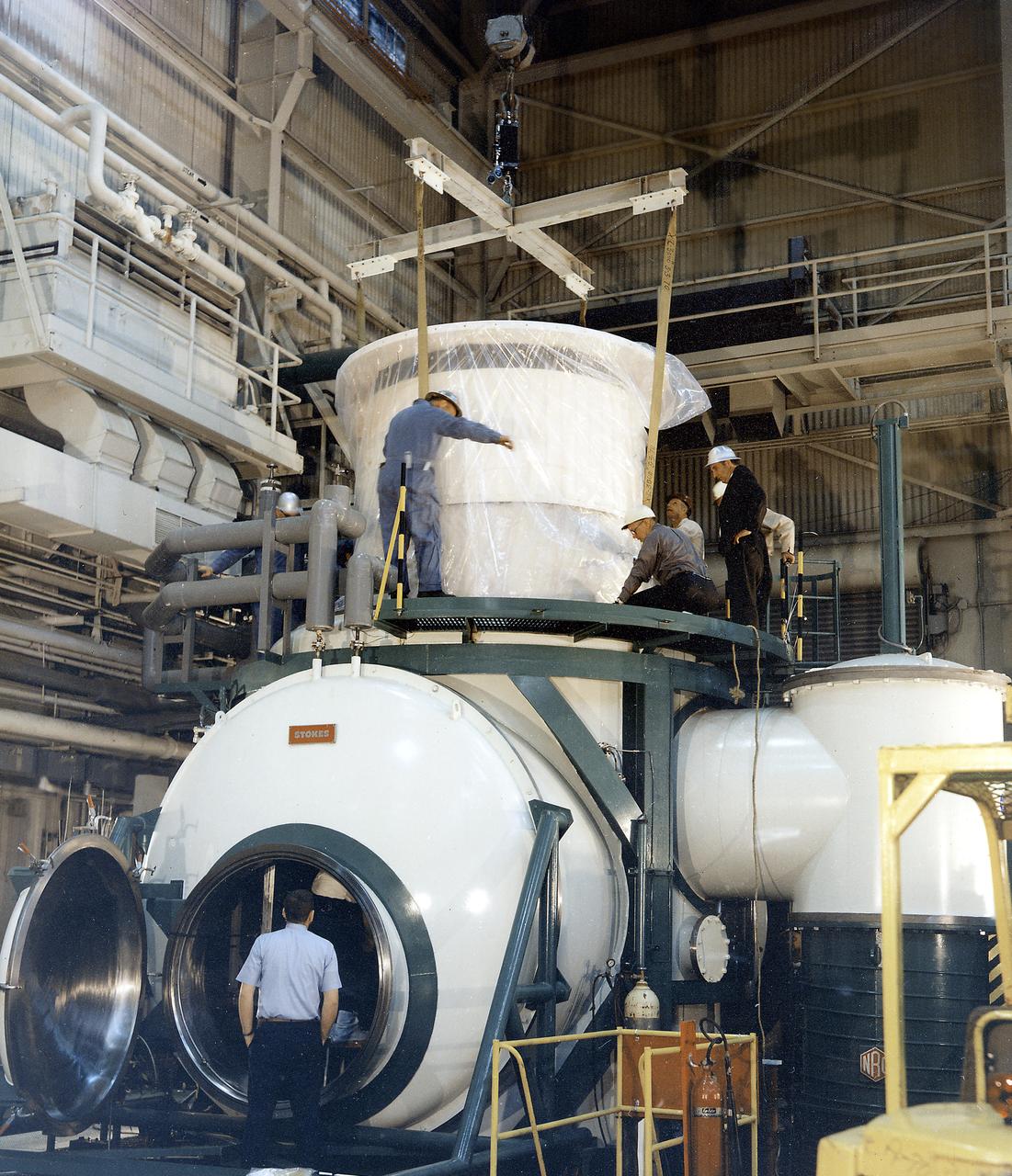

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. In this image, the thermal unit, that controlled the temperature stability of the ATM, is being installed into a vacuum chamber.
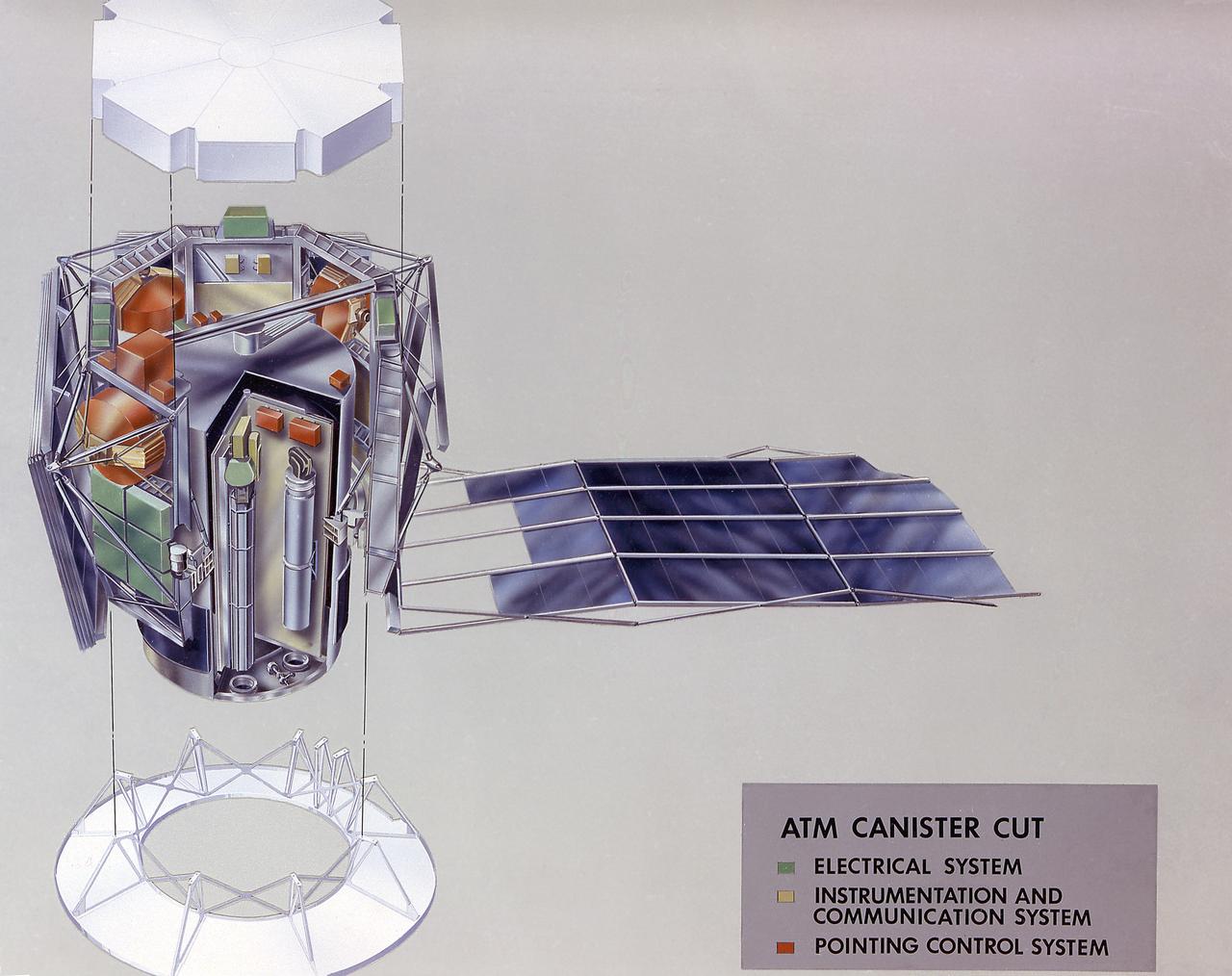
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) served as the first marned astronomical observatory in space. It was designed for solar research from Earth orbit aboard the Skylab. This image is a cutaway illustration of the ATM canister. The ATM was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
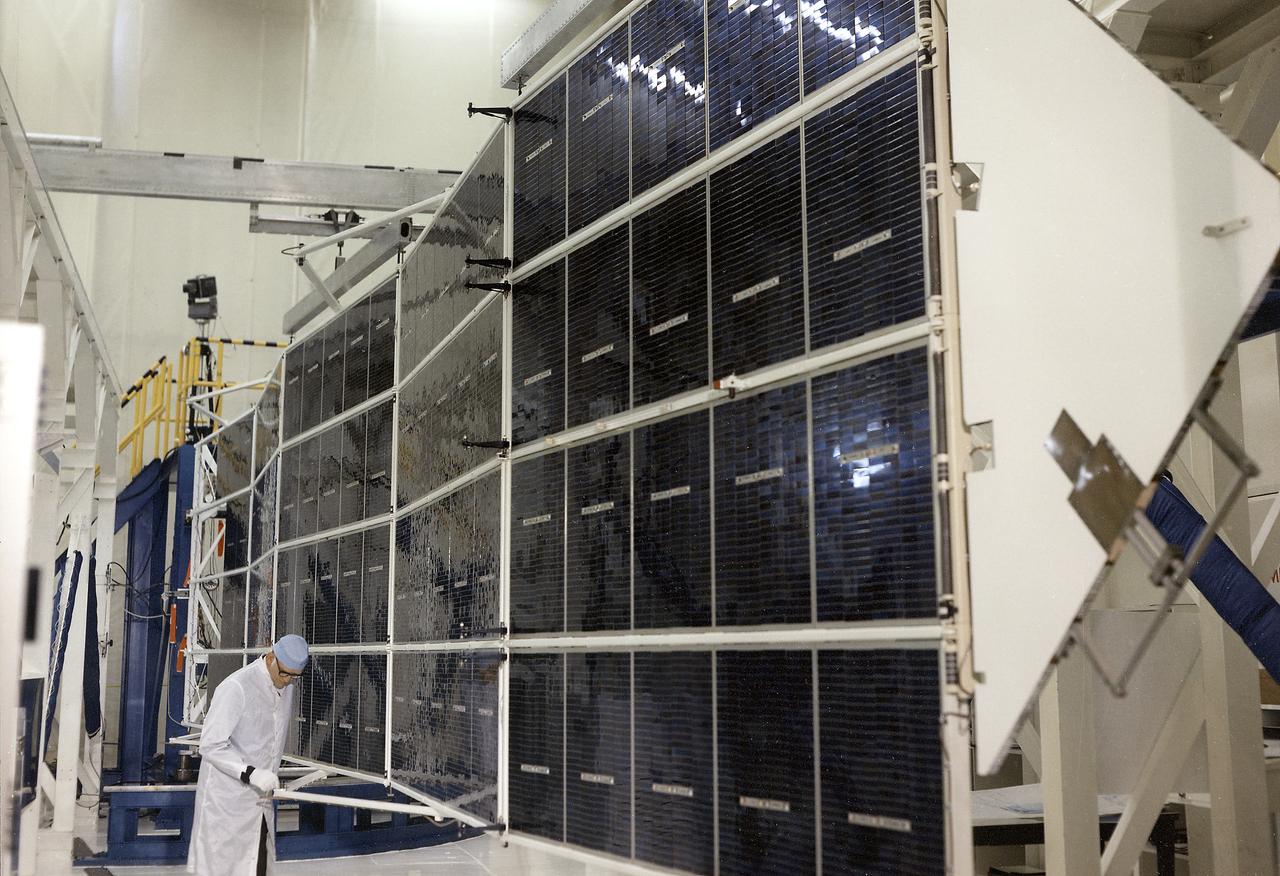

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), one of four major components comprising Skylab, was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. Power to operate the ATM's instruments and experiments was collected by four solar arrays, capable of producing up to 1.1 kilowatts of electricity. This is a photograph of the ATM Solar Array flight unit 1 in the deployed position.
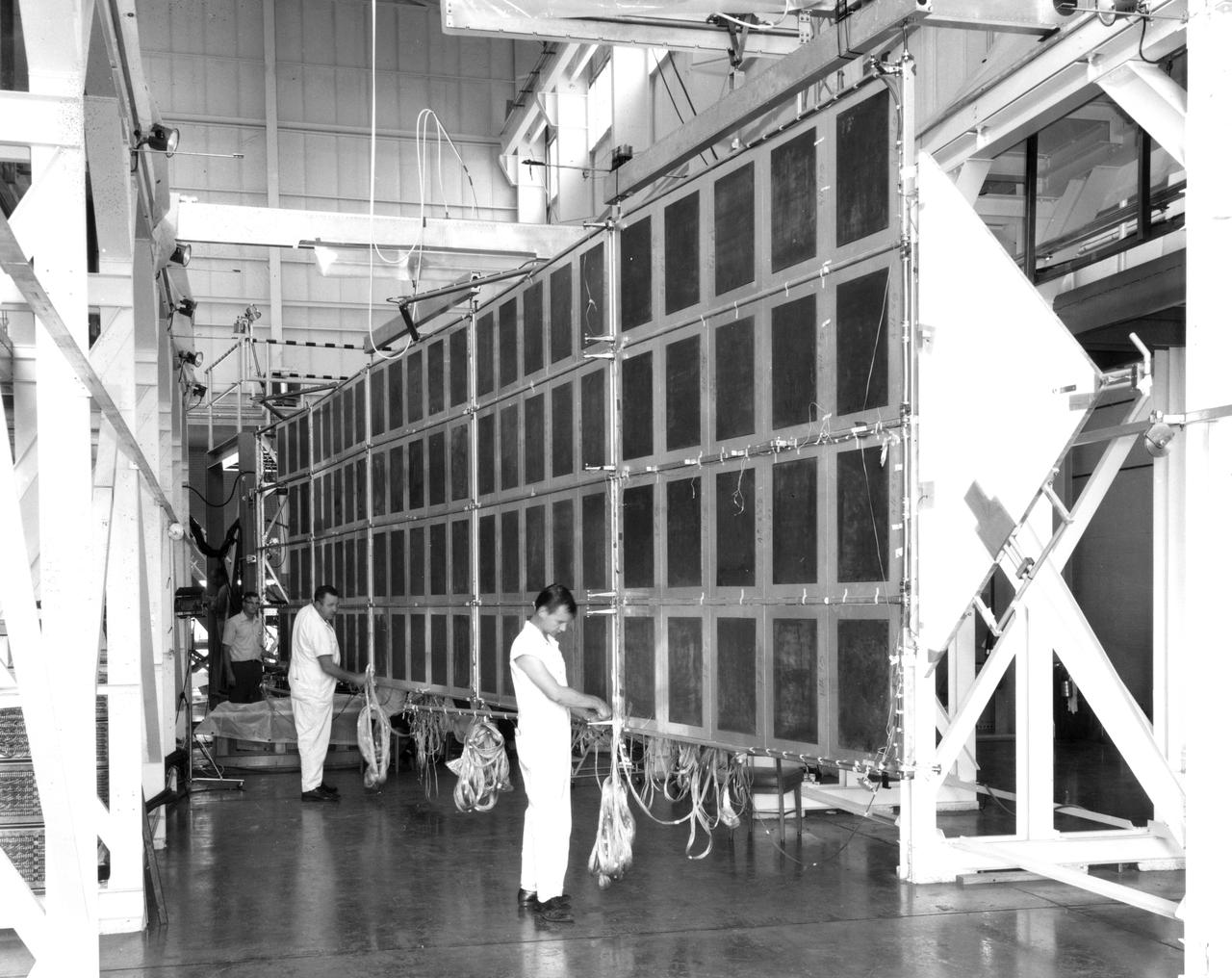

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center check the wiring on a mechanical test article of the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) solar array. Four such arrays were joined in a cross to provide electric power for the ATM in Earth orbit. The deployment mechanism for extending the wing to the fully open position had just been tested when this photograph was taken. The array was suspended from beams riding on air bearings to closely simulate the weightless conditions under which it would be deployed in space. The wings are folded against the sides of the ATM for launch and are deployed by a scissors mechanism in Earth’s orbit.
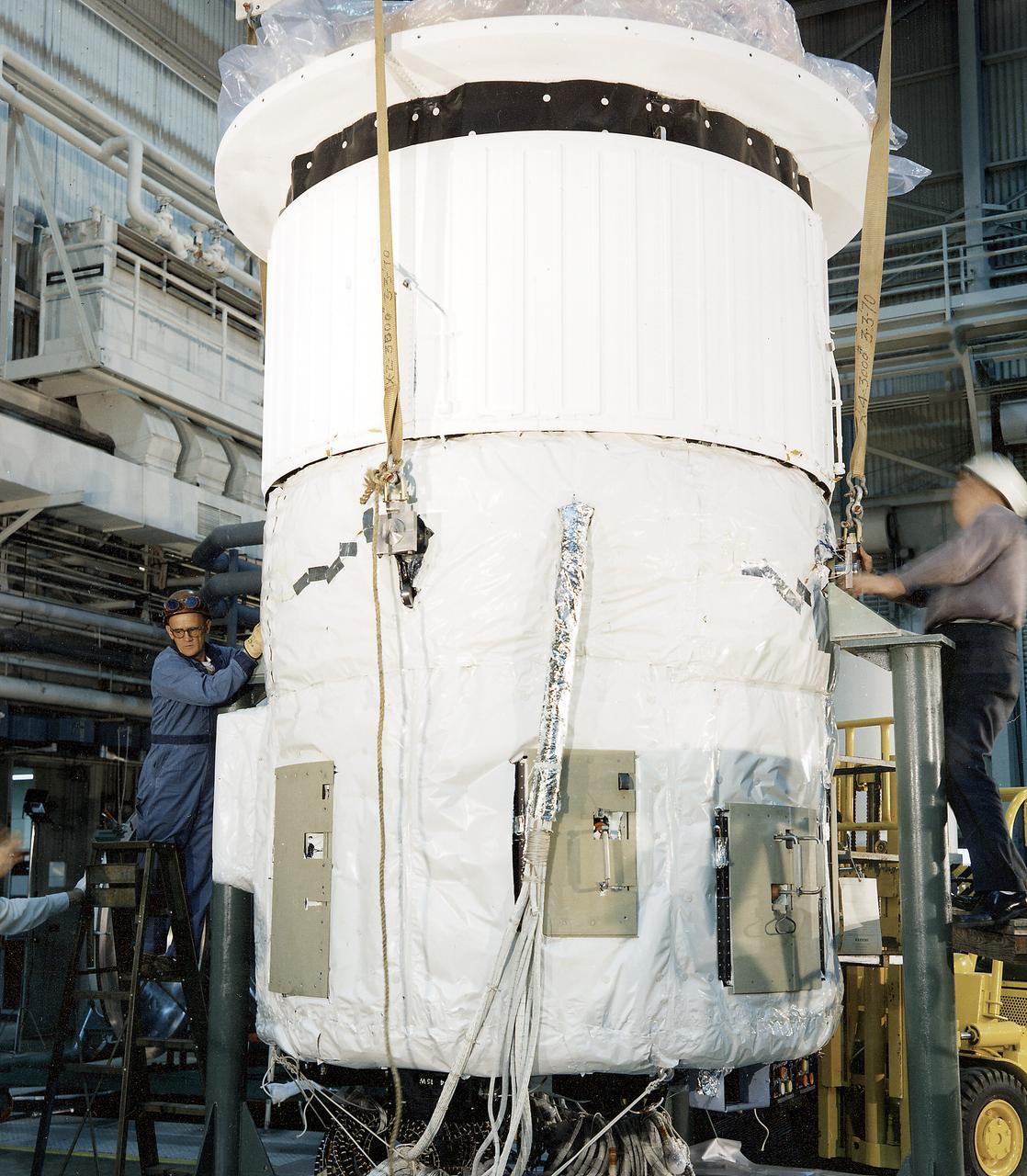

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. This image is of the ATM thermal unit being tested in MSFC's building 4619. The thermal unit consisted of an active fluid-cooling system of water and methanol that was circulated to radiators on the outside of the canister. The thermal unit provided temperature stability to the ultrahigh resolution optical instruments that were part of the ATM.

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). This photograph shows the spar unit, which housed major solar instruments, being lowered into the rack, the outer octagonal complex frame of the ATM flight unit.
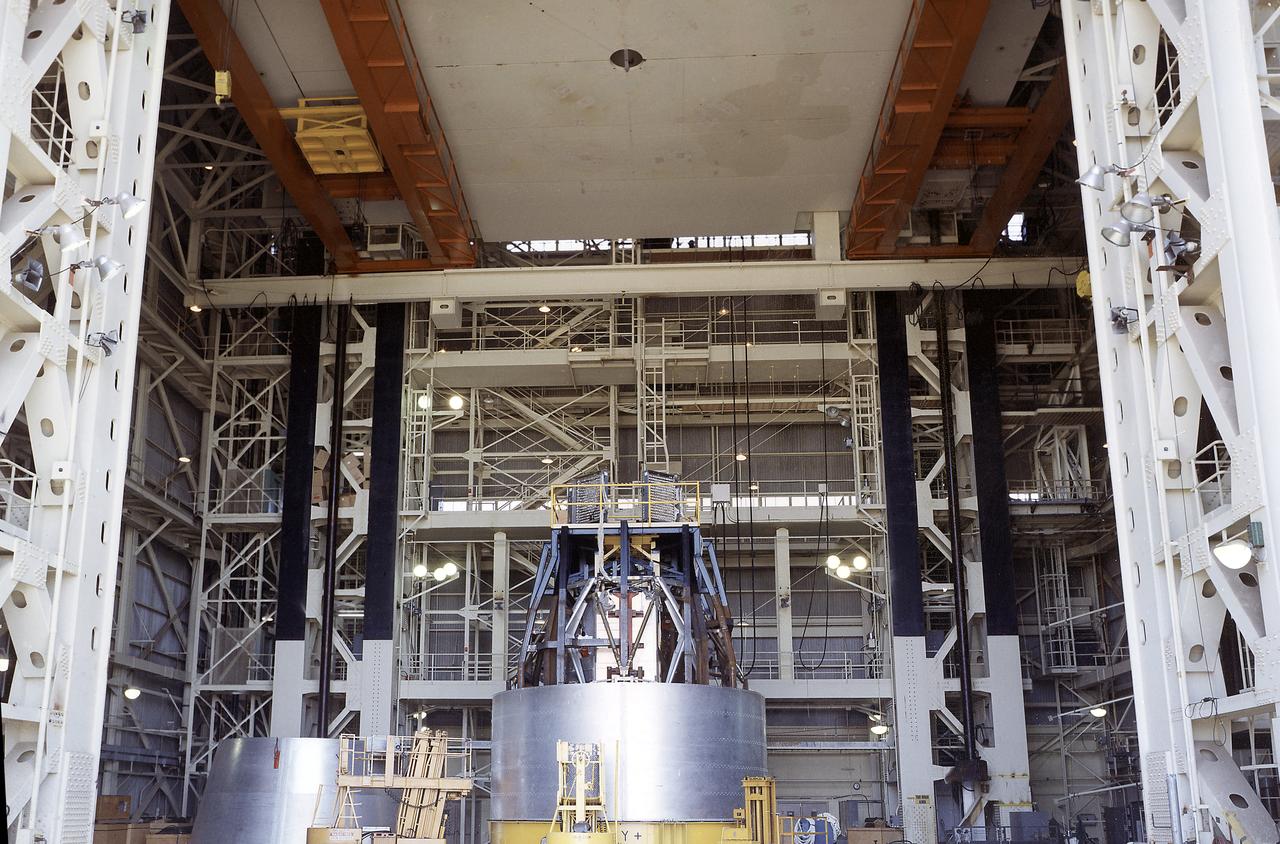

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was one of four major components of Skylab that were designed and constructed under the management of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). In this photograph, an ATM is seen sitting inside the MSFC's Structural Load Test Arnex where the main structural elements were simulated under launch conditions.

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. This is a photograph of the assembly of an ATM flight unit rack. The flight unit rack was an octagonal shaped complex outer frame that housed the canister containing the solar instruments.
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. One scientific instrument was the ATM solar shield that formed the base for the rack/frame instrument and the instrument canister. The solar shield contained aperture doors for each instrument to protect against solar radiation and space contamination.
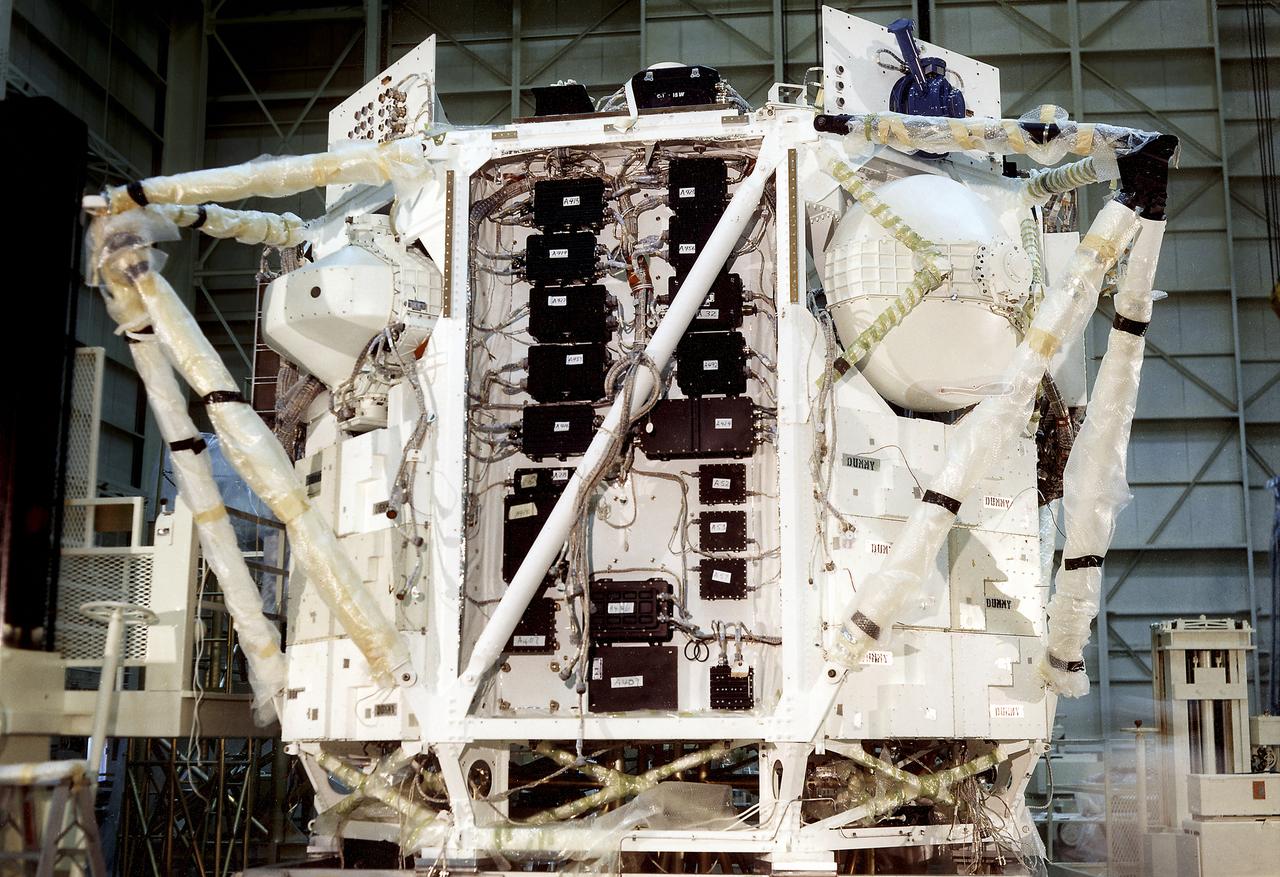
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. This is a photograph of the assembly of an ATM flight unit rack. The flight unit rack was an octagonal shaped complex outer frame that housed the canister containing the solar instruments.
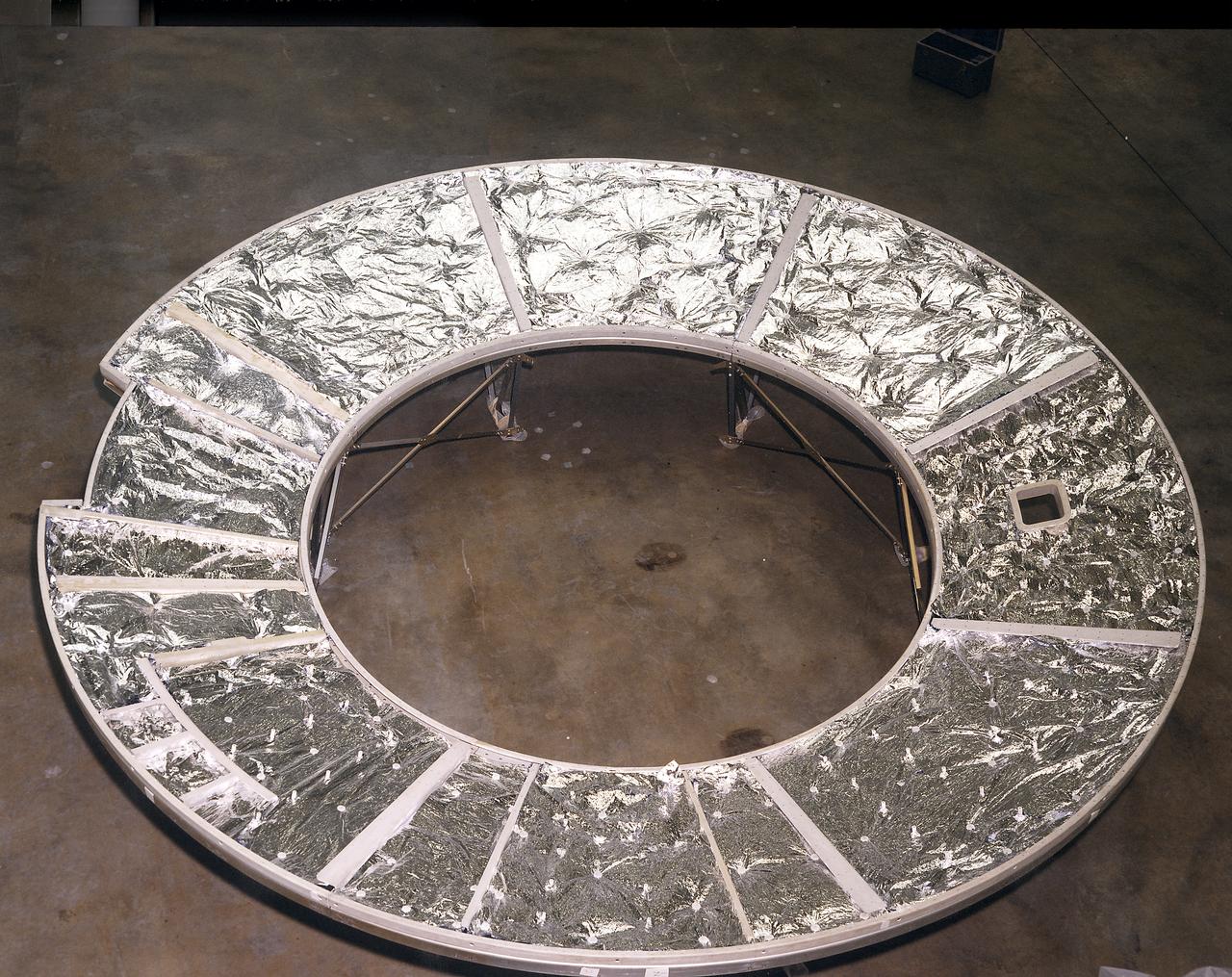

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and constructed at the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab. The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. This photograph shows the flight unit solar shield for the ATM that formed the base for the rack, a complex frame, and the canister that contained the instruments.
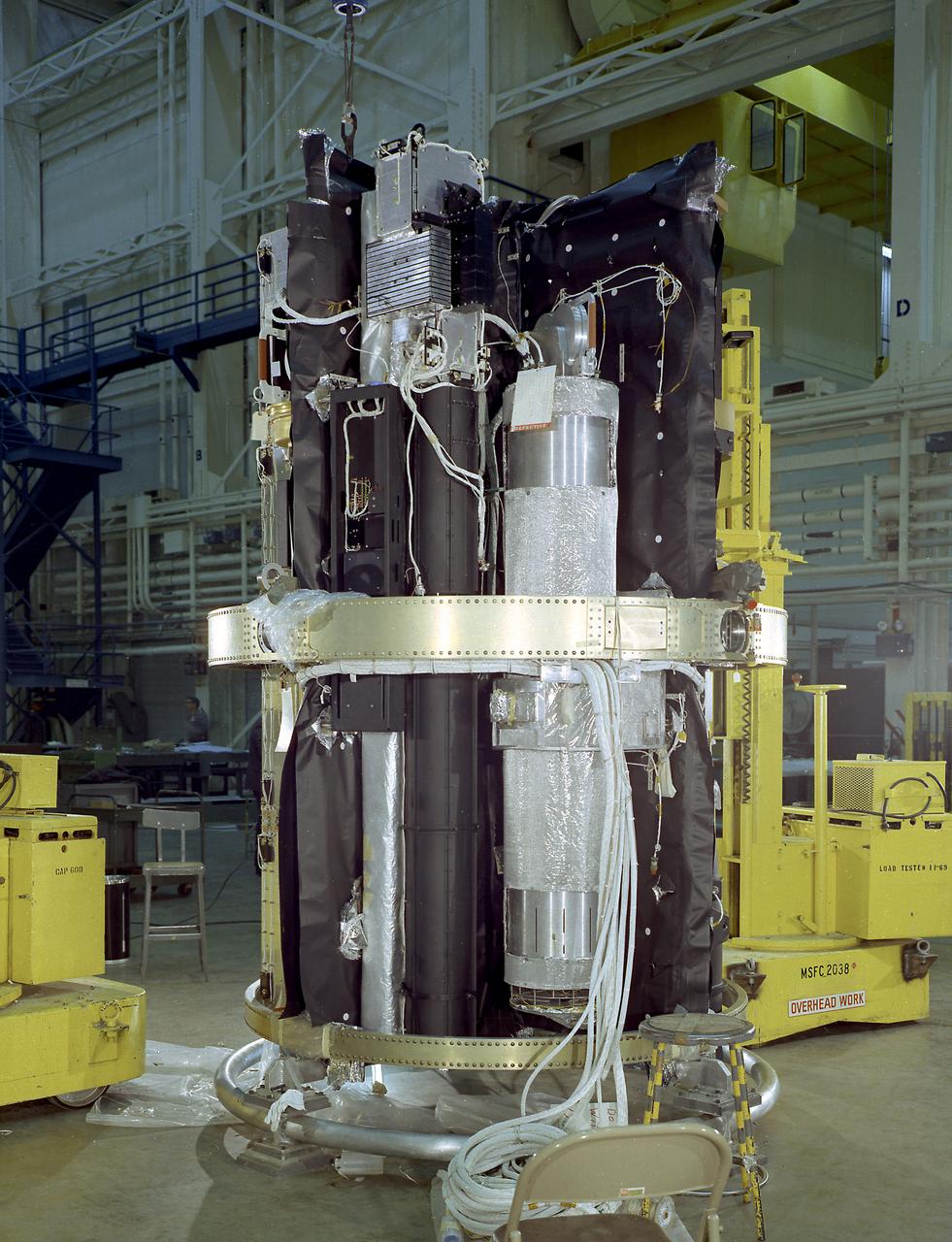
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard the Skylab. The ATM contained eight complex astronomical instruments designed to observe the Sun over a wide spectrum from visible light to x-rays. This image shows the ATM spar assembly. All solar telescopes, the fine Sun sensors, and some auxiliary systems are mounted on the spar, a cruciform lightweight perforated metal mounting panel that divides the 10-foot long canister lengthwise into four equal compartments. The spar assembly was nested inside a cylindrical canister that fit into the rack, a complex frame, and was protected by the solar shield.
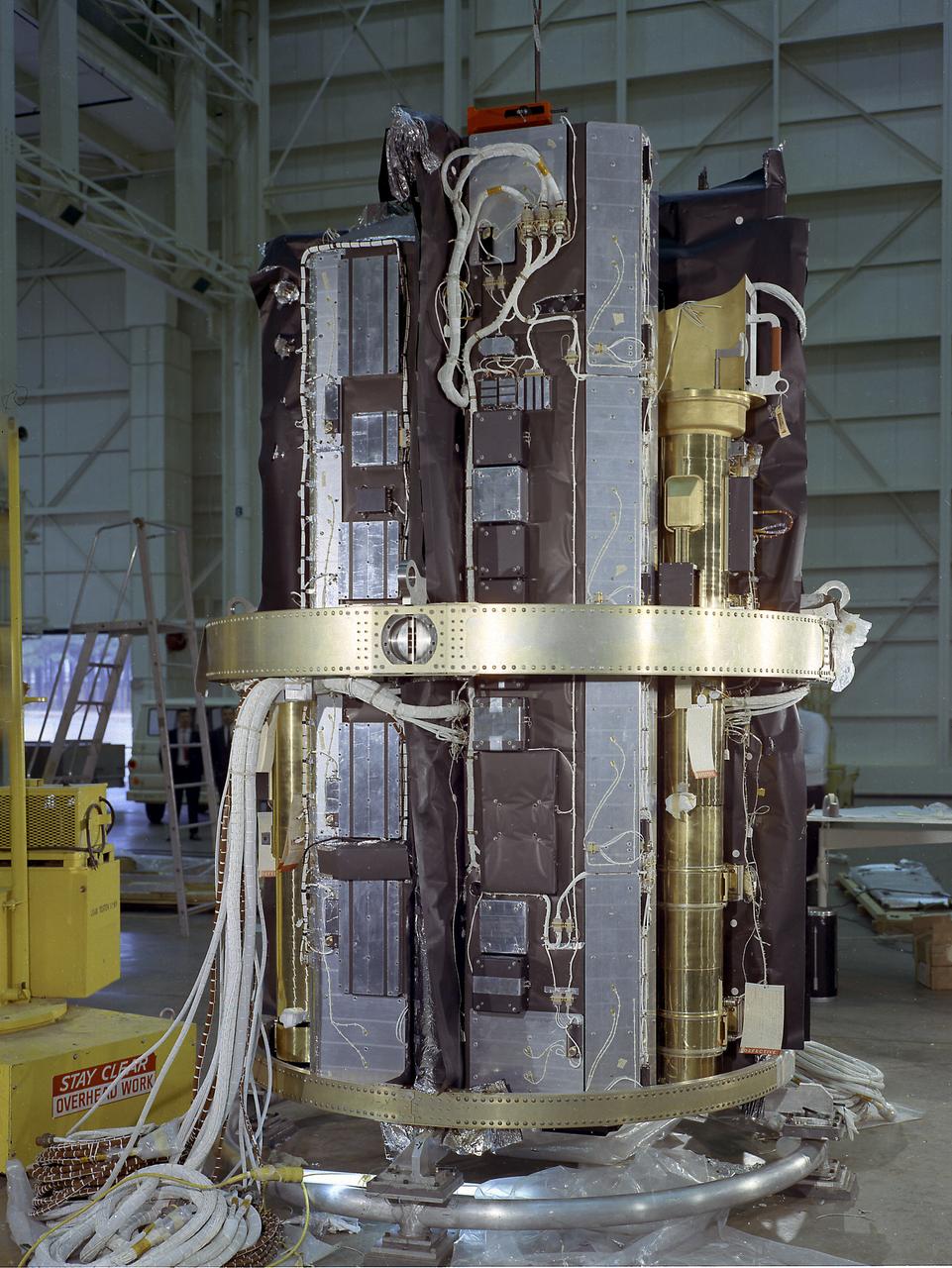
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard the Skylab. The ATM contained eight complex astronomical instruments designed to observe the Sun over a wide spectrum from visible light to x-rays. This image shows the ATM spar assembly. All solar telescopes, the fine Sun sensors, and some auxiliary systems are mounted on the spar, a cruciform lightweight perforated metal mounting panel that divides the 10-foot long canister lengthwise into four equal compartments. The spar assembly was nested inside a cylindrical canister that fit into the rack, a complex frame, and was protected by the solar shield.
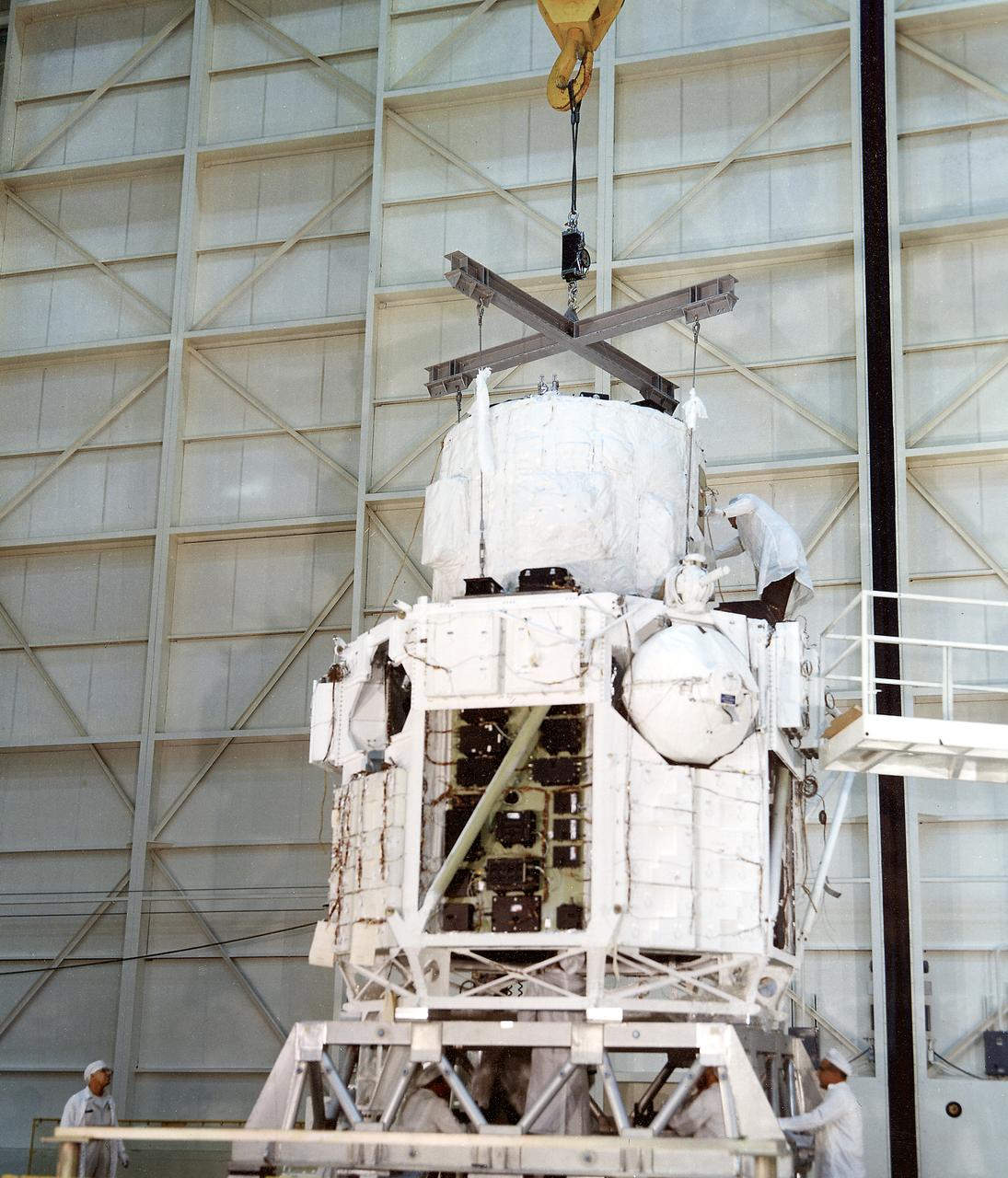
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. In this image, the ATM canister, housing the solar instruments, is mated to the thermal rack that provided thermal stability.
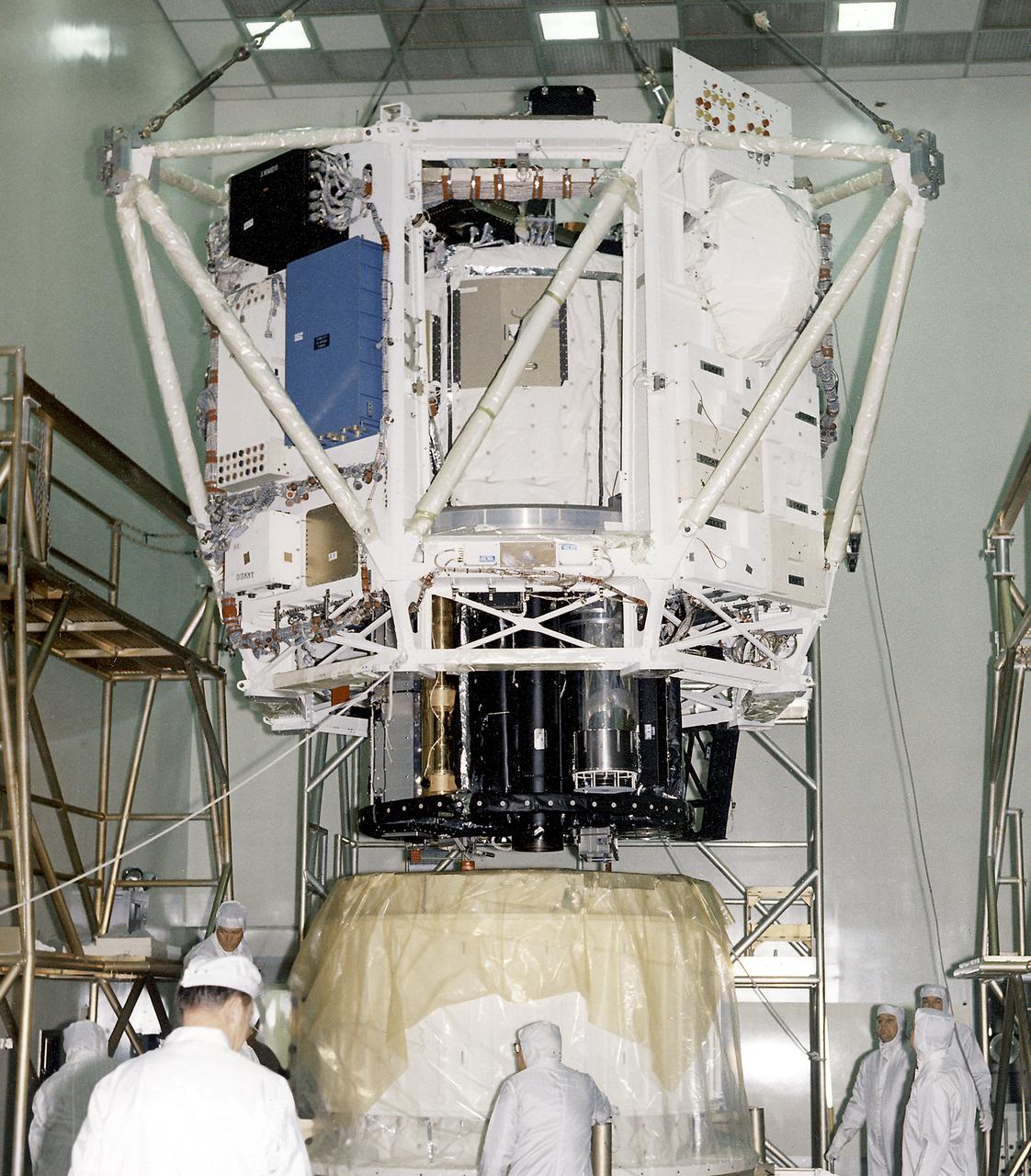
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was one of four major components comprising the Skylab. The ATM housed the first marned scientific telescopes in space. In this photograph, the ATM sun end canister, housing the solar instruments, is being moved to a clean room prior to being mated with the remaining components of the ATM unit.
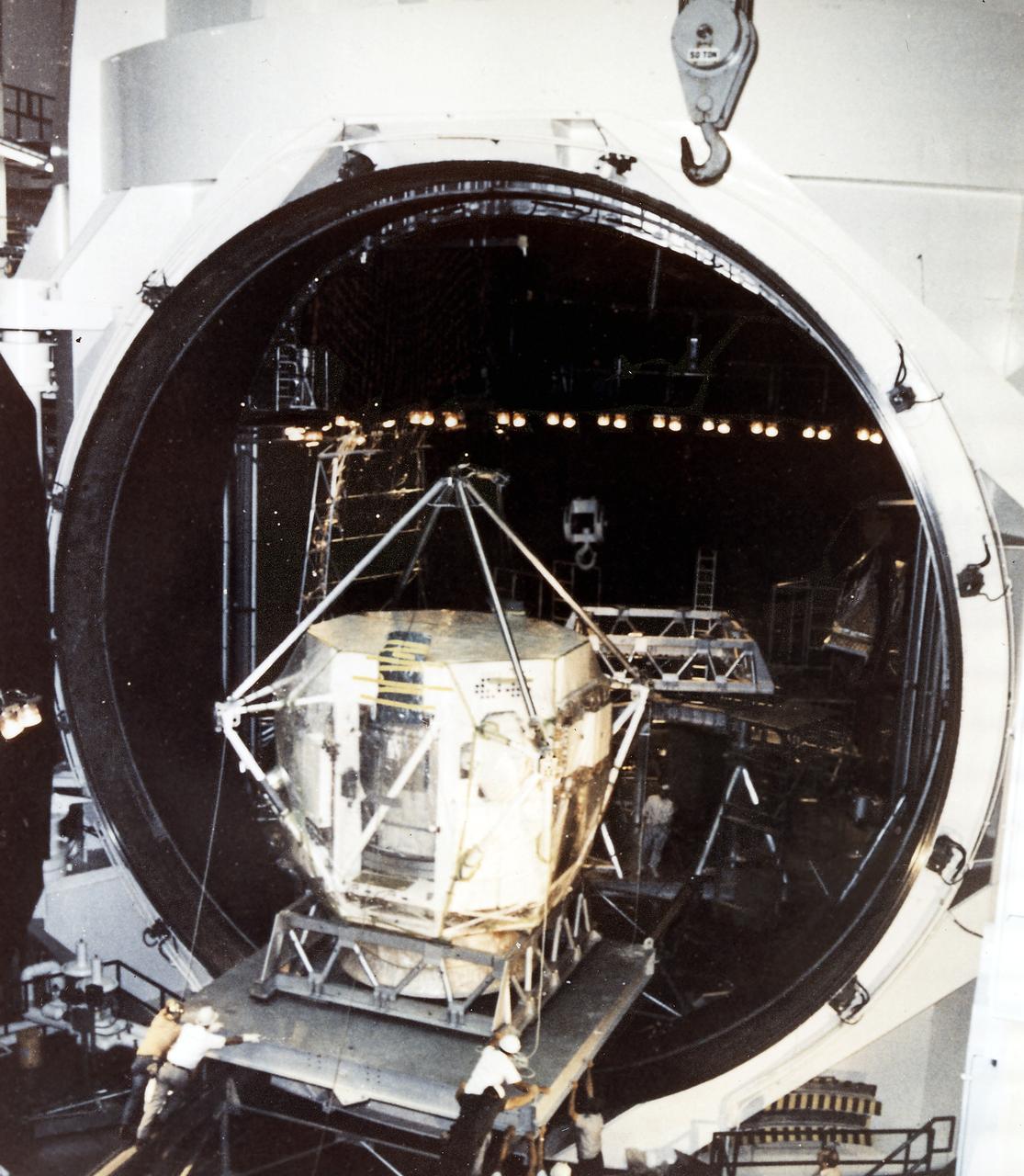
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was one of four major components comprising the Skylab. The ATM housed the first marned scientific telescopes in space. In this photograph, taken at the Manned Spacecraft Center (later renamed the Johnson Space Center), an ATM prototype can be seen in a thermal vacuum chamber that tested the unit's ability to withstand the environment of space.
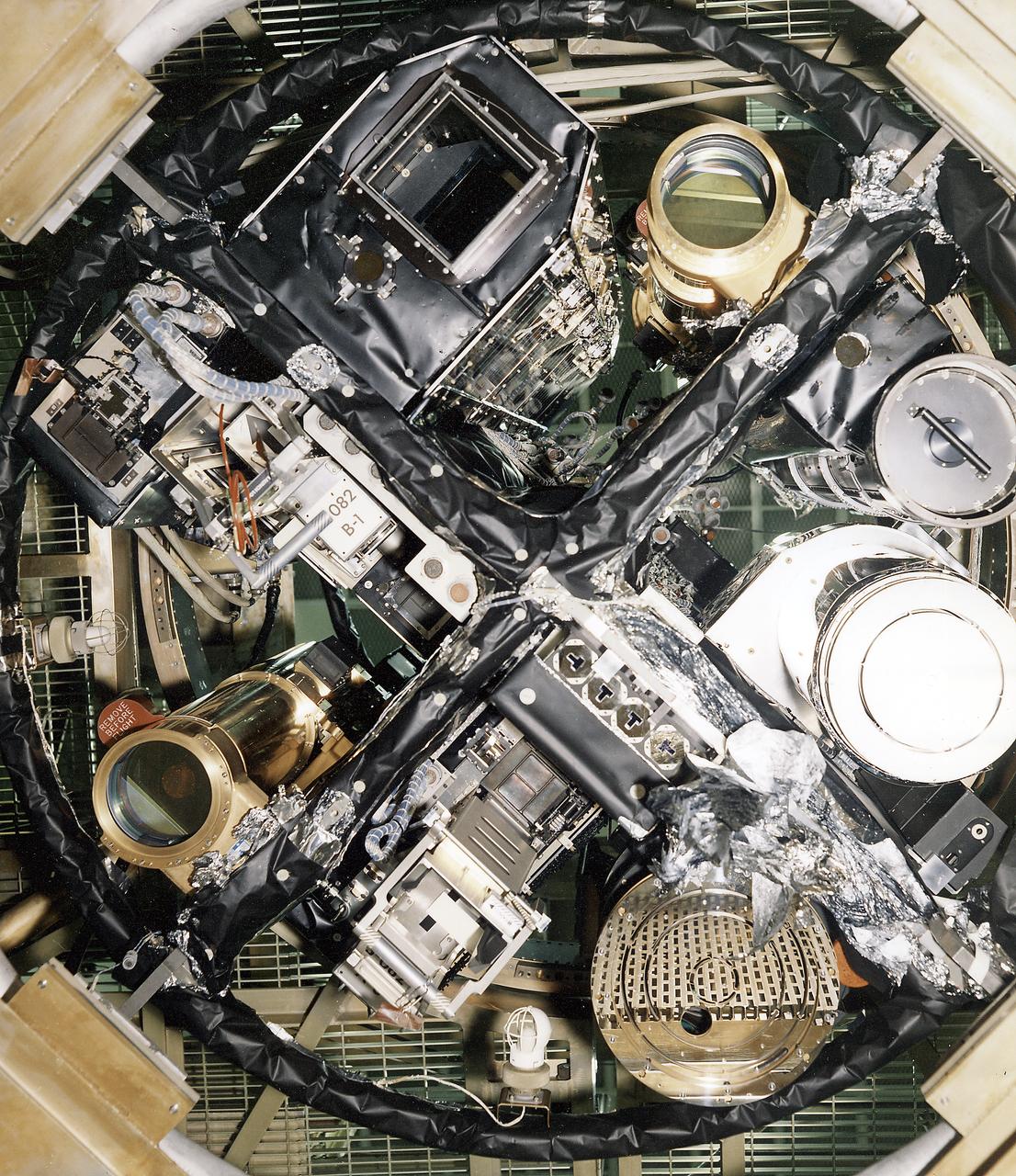
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM contained eight complex astronomical instruments designed to observe the Sun over a wide spectrum from visible light to x-rays. This image depicts the sun end and spar of the ATM flight unit showing individual telescopes. All solar telescopes, the fine Sun sensors, and some auxiliary systems are mounted on the spar, a cruciform lightweight perforated metal mounting panel that divides the canister lengthwise into four equal compartments. The spar assembly was nested inside a cylindrical canister that fit into a complex frame named the rack, and was protected by the solar shield.
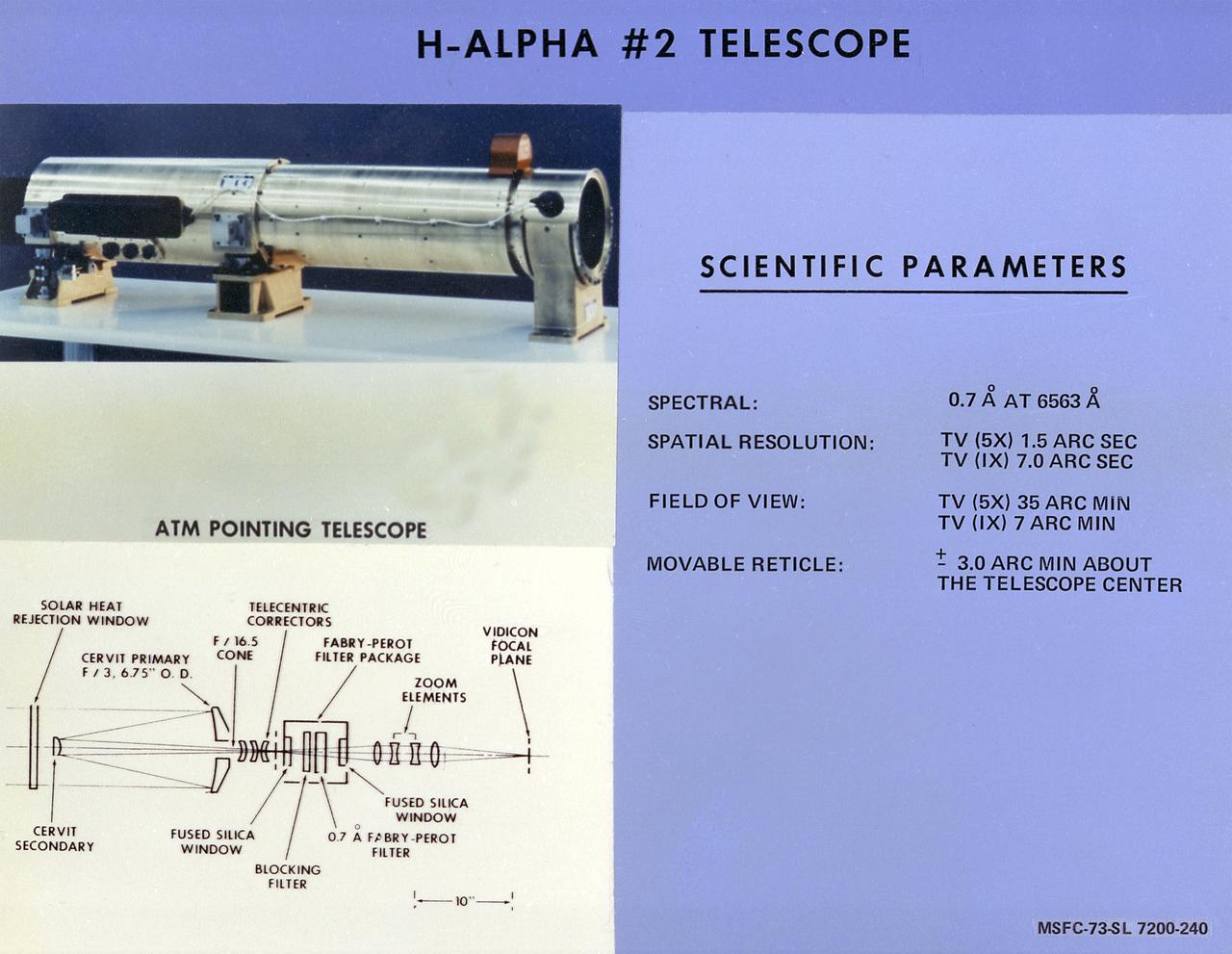
This chart describes the Hydrogen-Alpha (H-Alpha) #2 Telescope, one of eight major solar study facilities on the Skylab Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM). There were two H-Alpha telescopes on the ATM that were used primarily to point the ATM and keep a continuous photographic record during solar observation periods. Both telescopes gave the Skylab astronauts a real-time picture of the Sun in the red light of the H-Alpha spectrum through a closed-circuit television. The H-Alpha #1 telescope provided simultaneous photographic and ultraviolet (UV) pictures, while the #2 telescope operated only in the TV mode. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development of the H-Alpha Telescopes.
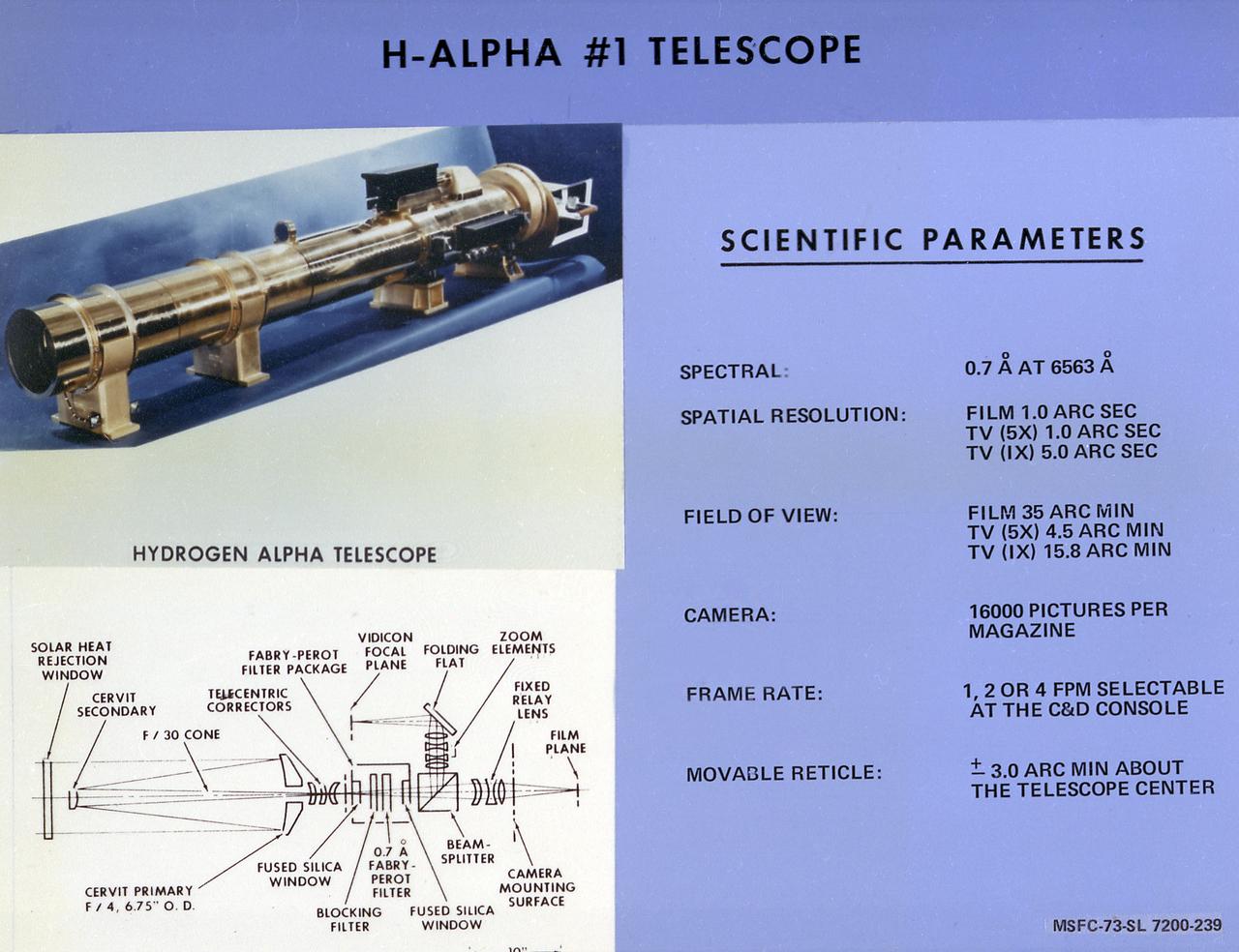
This chart describes the Hydrogen-Alpha (H-Alpha) #1 Telescope, one of eight major solar study facilities on the Skylab Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM). There were two H-Alpha telescopes on the ATM that were used primarily to point the ATM and keep a continuous photographic record during the solar observation periods. Both telescopes gave the Skylab astronauts a real-time picture of the Sun in the red light of the H-Alpha spectrum through a closed-circuit television. The H-Alpha #1 Telescope provided simultaneous photographic and ultraviolet (UV) pictures, while the #2 Telescope operated only in the TV mode. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development of the H-Alpha Telescopes.
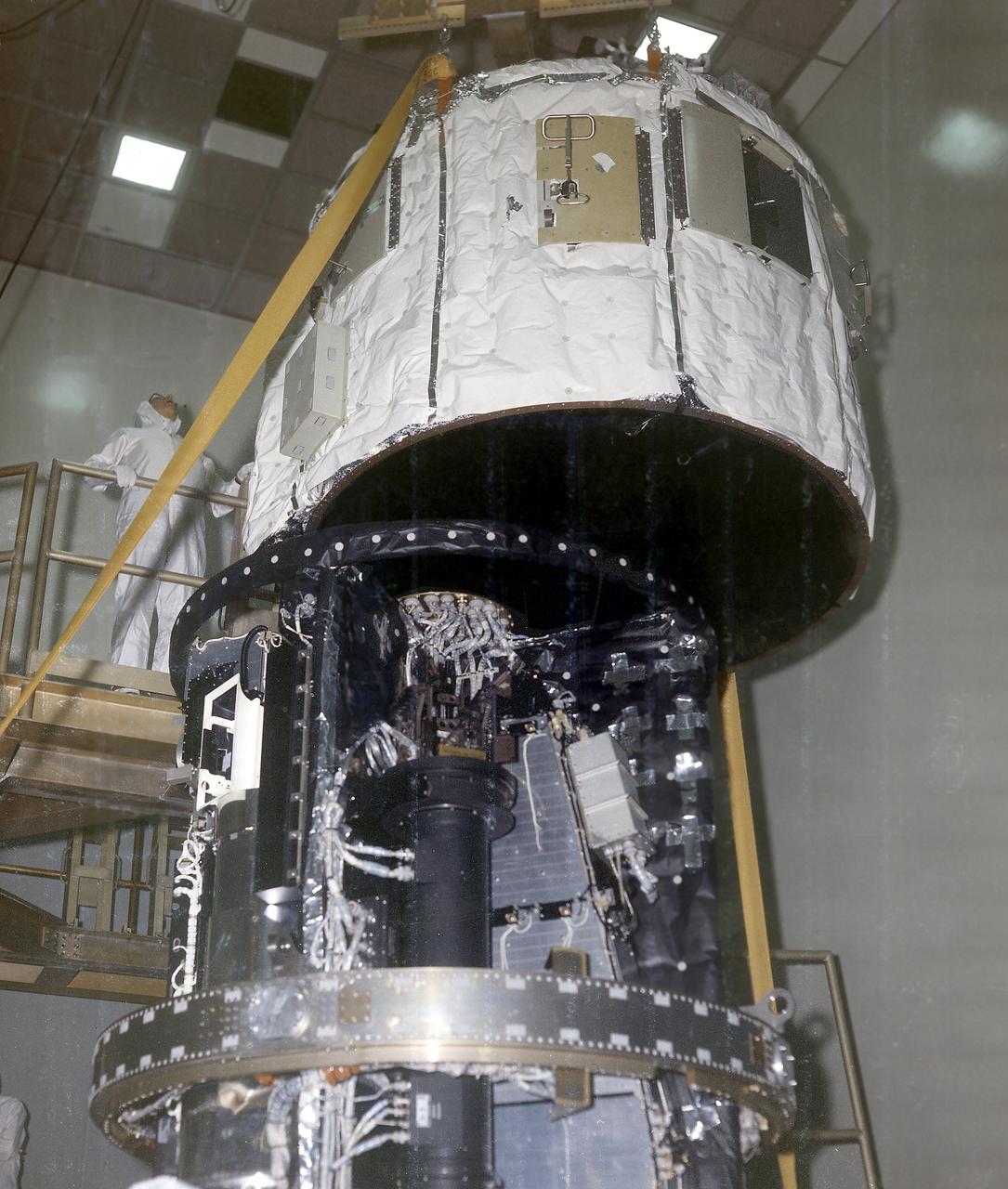
The final version of the Marshall Space Flight Center managed Skylab consisted of four primary parts. One component was the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) that housed the first marned scientific telescopes in space. This picture is a view of the ATM spar, which contained the scientific instruments, as the multiple docking adapter (MDA) canister end is lowered over it. The MDA served to link the major parts of Skylab together.
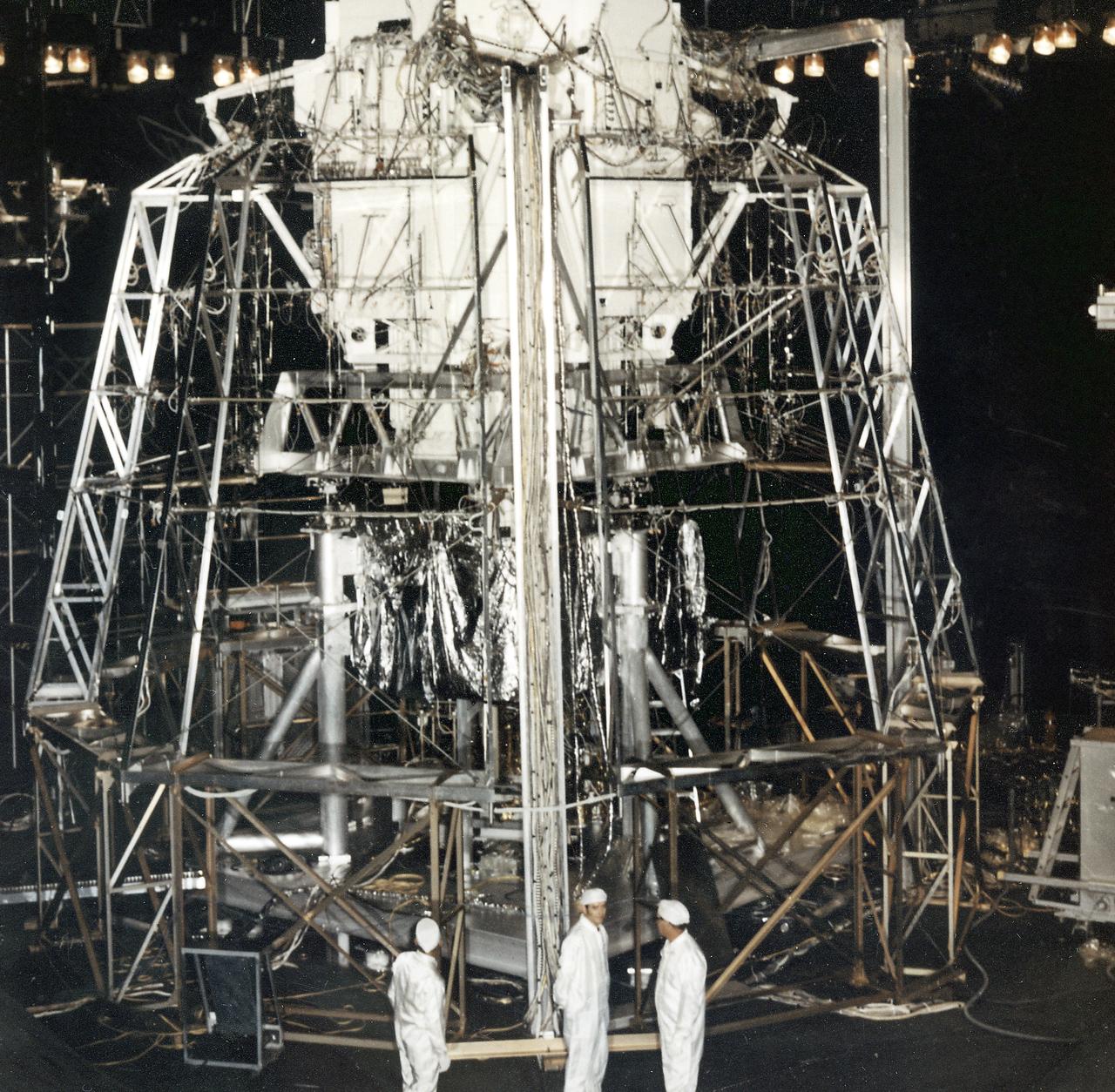
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was one of four major components comprising the Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM housed the first manned scientific telescope in space. This photograph shows the ATM rigged for altitude and space simulation tests at the Space Environment Simulation Laboratory of the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The MSC was renamed the Johnson Space Center (JSC) in early 1973.

This 1970 photograph shows the flight unit for Skylab's White Light Coronagraph, an Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) facility that photographed the solar corona in the visible light spectrum. A TV camera in the instrument provided real-time pictures of the occulted Sun to the astronauts at the control console and also transmitted the images to the ground. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
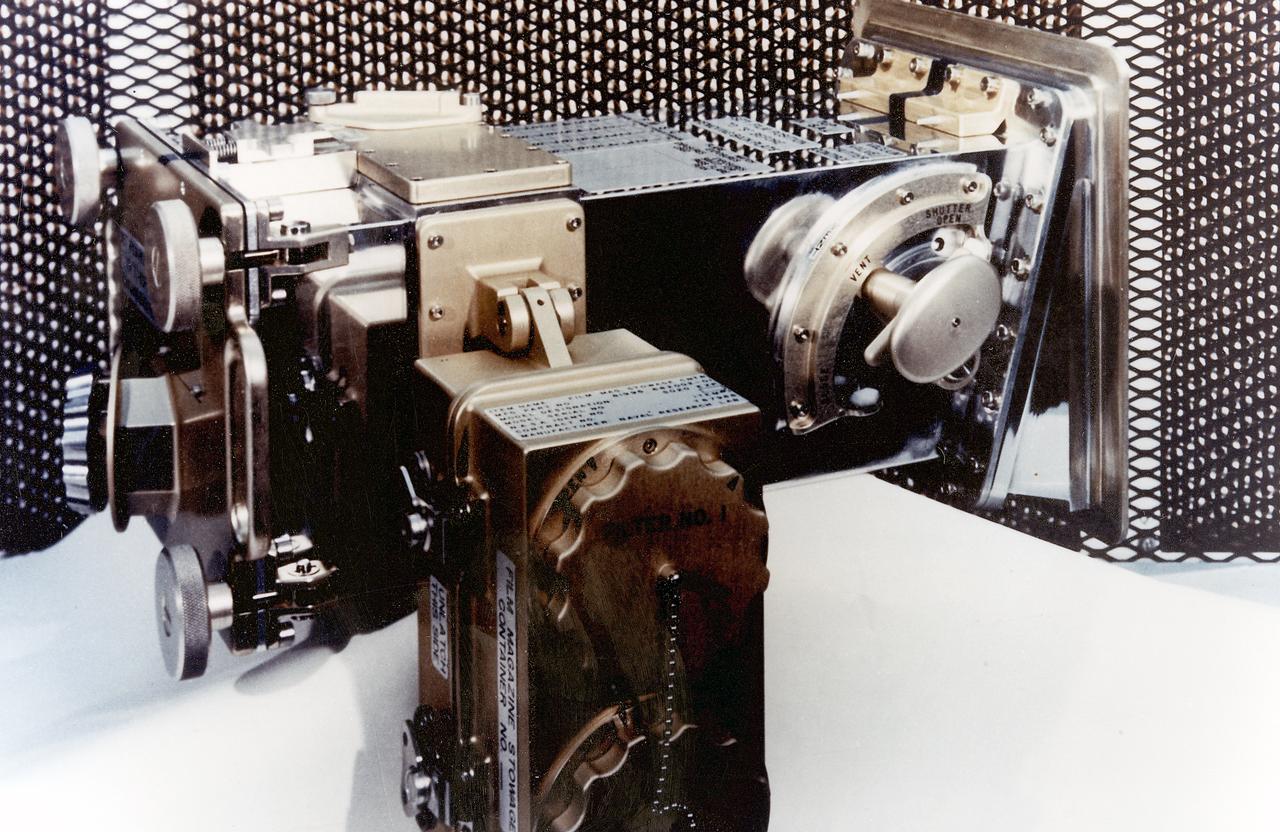
This 1970 photograph shows Skylab's Ultraviolet (UV)/X-Ray Solar Photography instrument, an Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) facility designed to photograph normal and explosive areas in the solar atmosphere in the x-ray and UV spectra. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
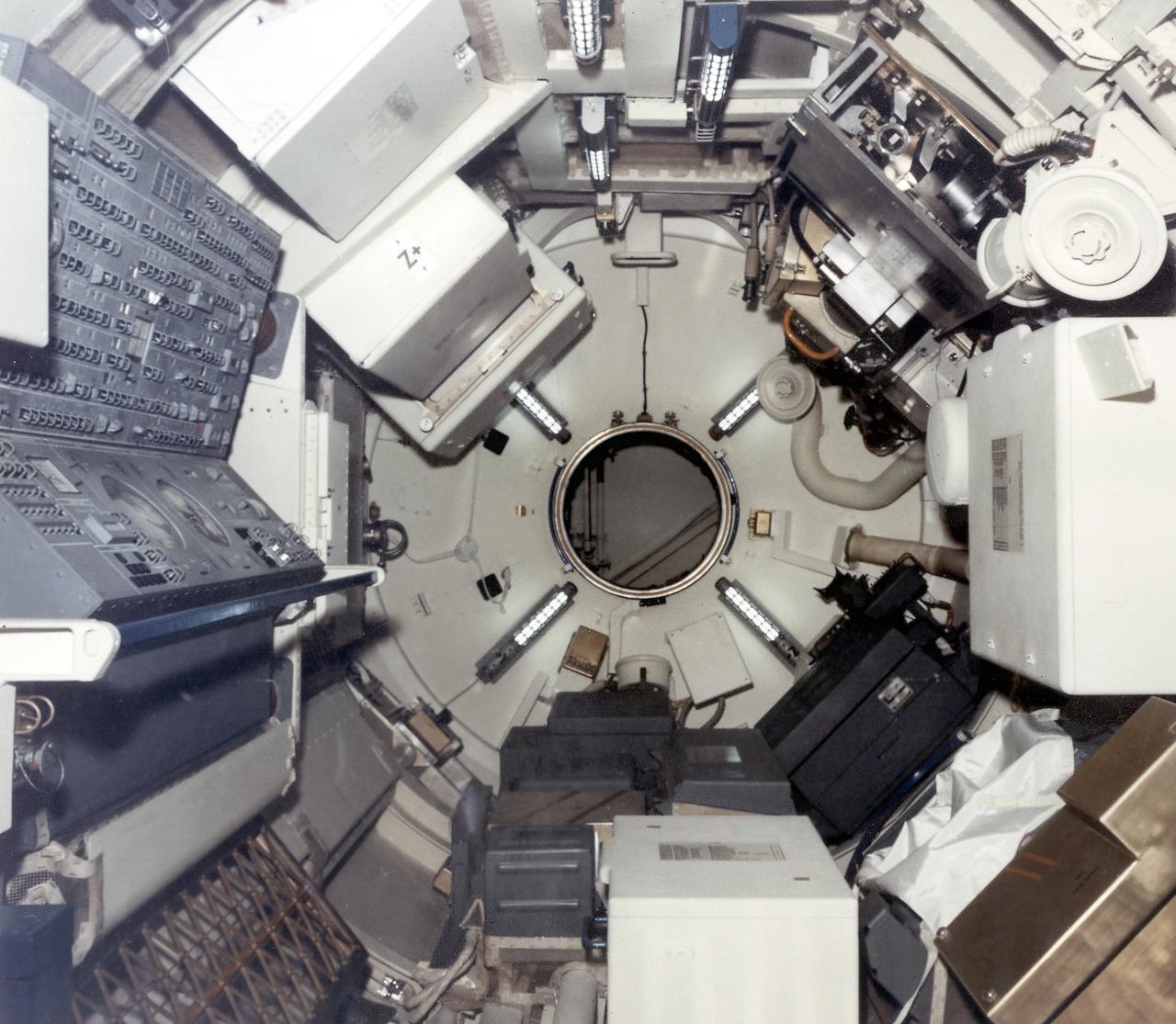

This interior photograph of Skylab's multiple docking adapter (MDA) flight article, then undergoing outfitting at the Martin Marietta Corporation's Space Center facility in Denver, Colorado, shows the forward cone area and docking turnel (center) that attached to the Apollo Command Module. Designed and manufactured by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the MDA housed the control units for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Earth Resources Experiment Package (EREP), and Zero-Gravity Materials Processing Facility and provided a docking port for the Apollo Command Module.
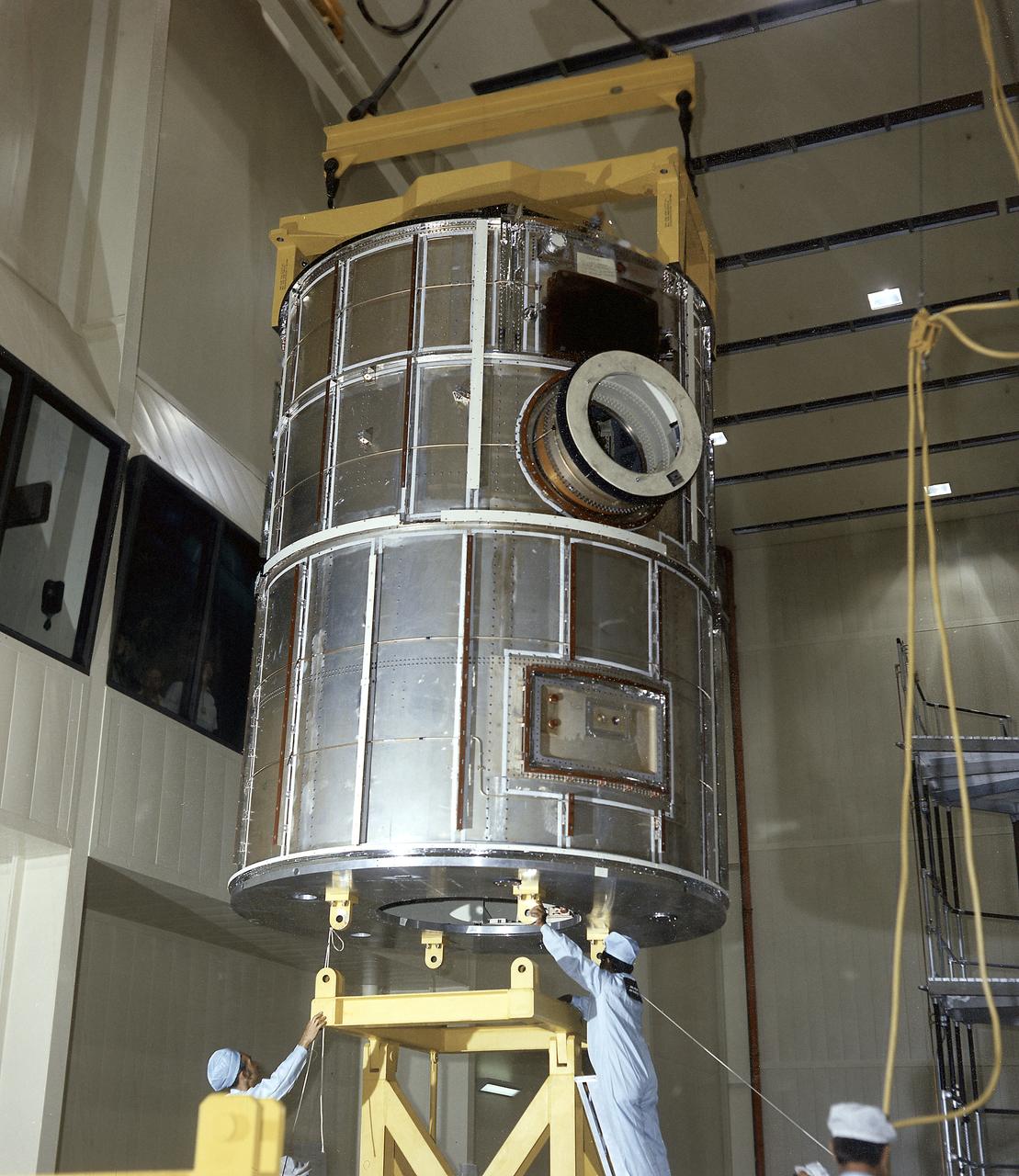

Workmen at the Martin Marietta Corporation's Space Center in Denver, Colorado, position Skylab's Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) flight article in the horizontal transportation fixture. Designed and manufactured by the Marshall Space Flight Center and outfitted by Martin Marietta, the MDA housed the control units for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Earth Resources Experiment Package (EREP), and Zero-Gravity Materials Processing Facility and provided a docking port for the Apollo Command Module.
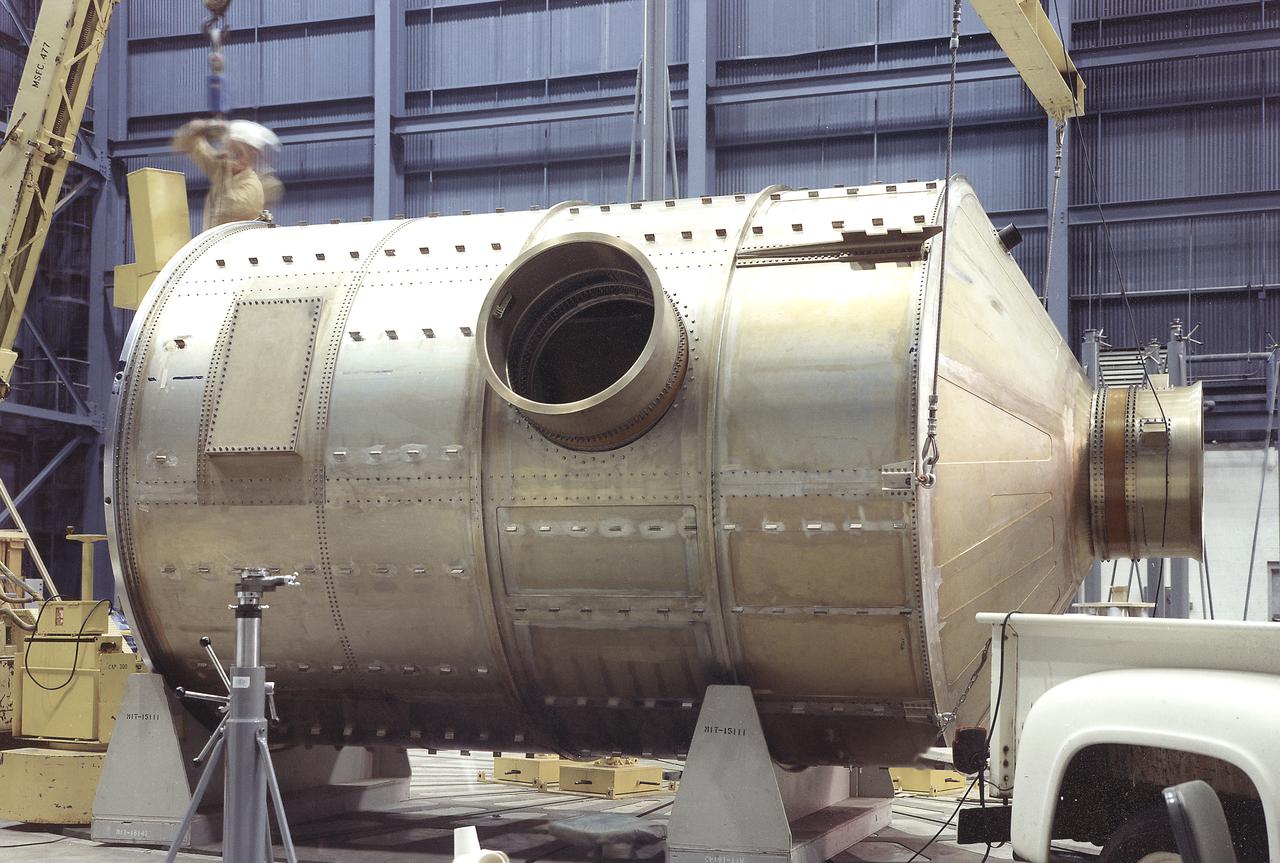
At Marshall Space Flight Center, Skylab's Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) flight article undergoes center-of-gravity testing. Developed and fabricated by MSFC, the MDA housed the control units for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Earth Resources Experiment Package (EREP), and the Zero-Gravity Material Processing Facility and provided a docking port for the Apollo Command Module.
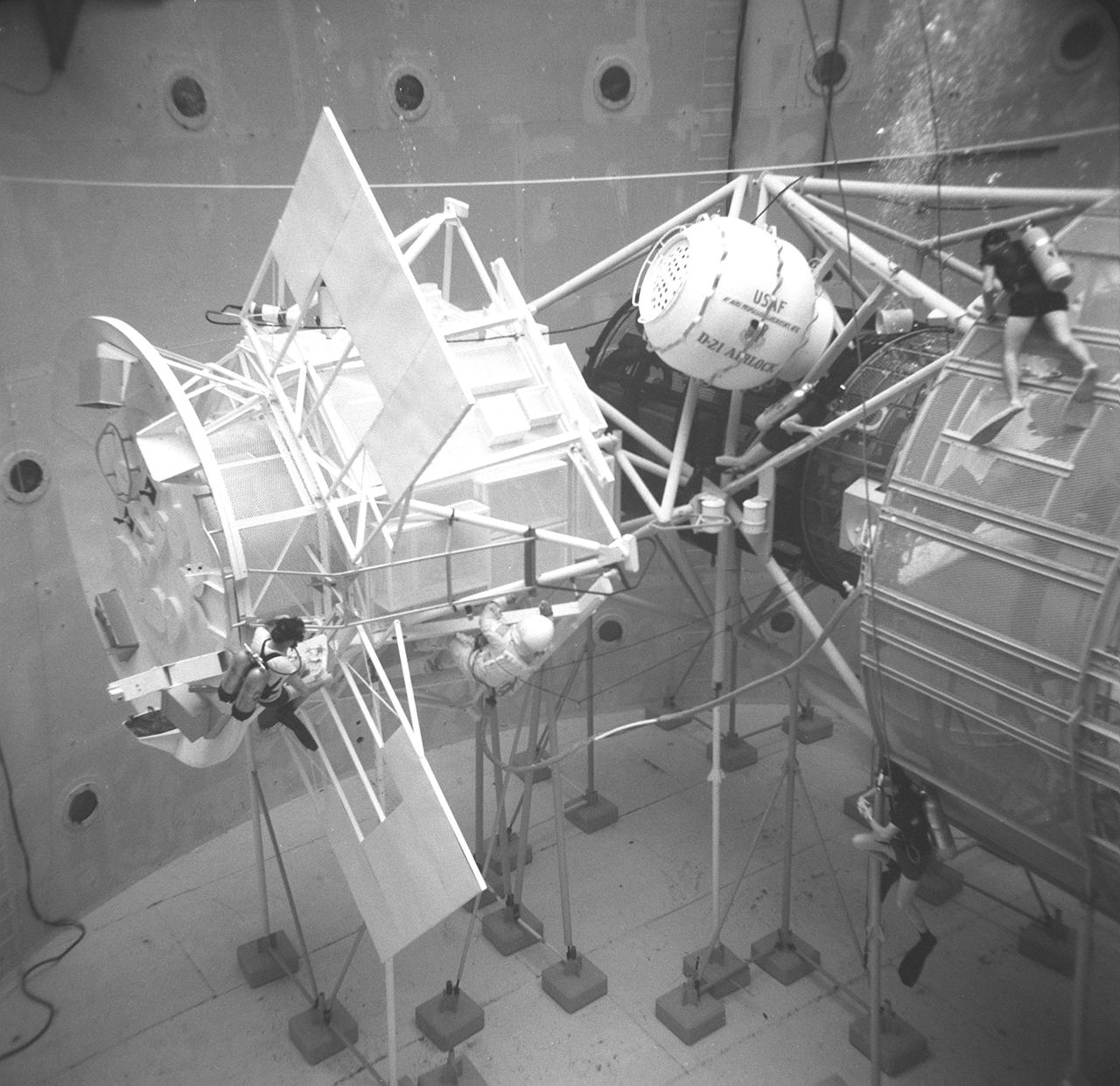

After the end of the Apollo missions, NASA's next adventure into space was the marned spaceflight of Skylab. Using an S-IVB stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle, Skylab was a two-story orbiting laboratory, one floor being living quarters and the other a work room. The objectives of Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. At the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), astronauts and engineers spent hundreds of hours in an MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) rehearsing procedures to be used during the Skylab mission, developing techniques, and detecting and correcting potential problems. The NBS was a 40-foot deep water tank that simulated the weightlessness environment of space. This photograph shows astronaut Ed Gibbon (a prime crew member of the Skylab-4 mission) during the neutral buoyancy Skylab extravehicular activity training at the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) mockup. One of Skylab's major components, the ATM was the most powerful astronomical observatory ever put into orbit to date.
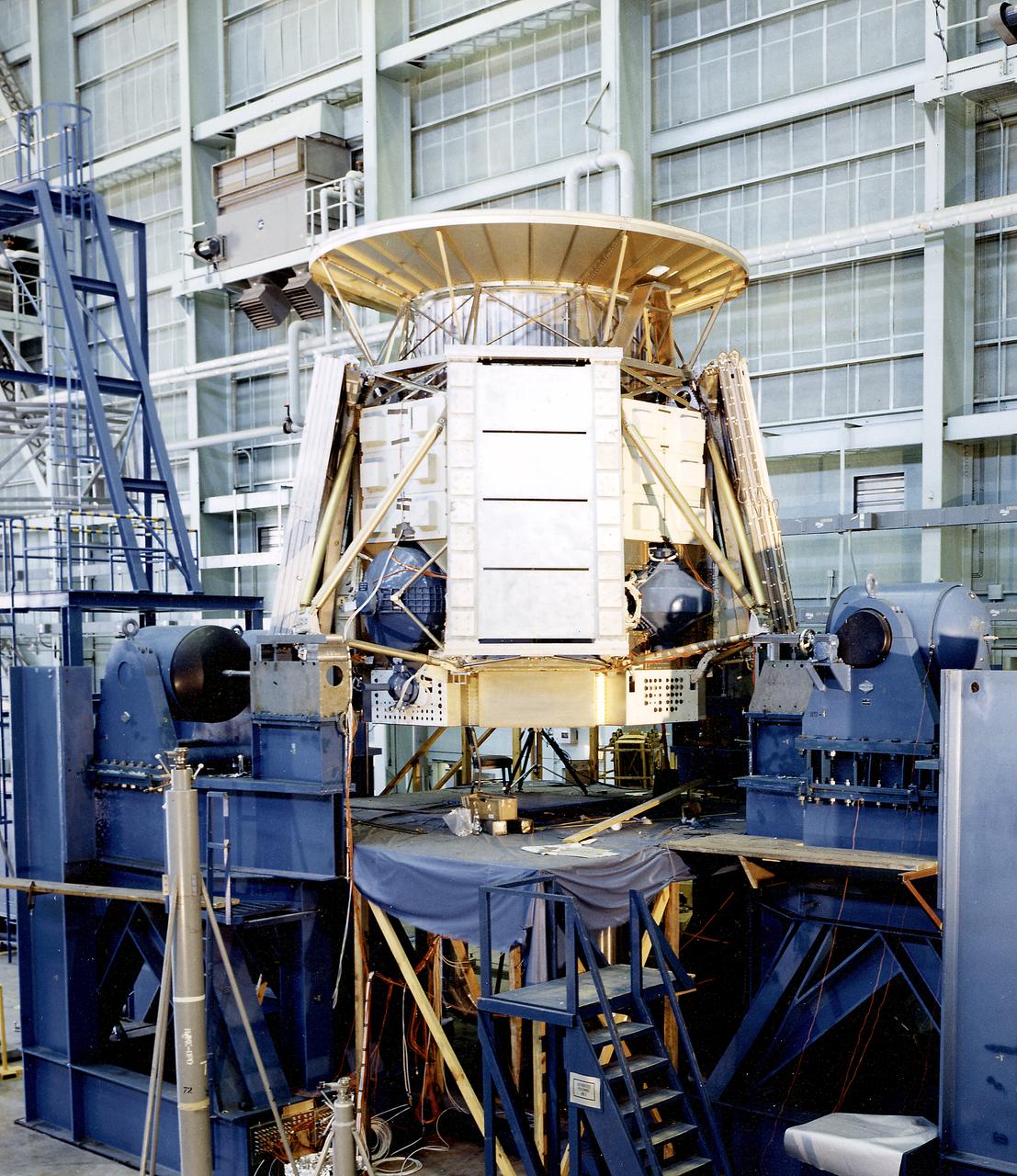

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), one of four major components comprising the Skylab, was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. In this image, the ATM is shown undergoing horizontal vibration testing in a vibration test unit.
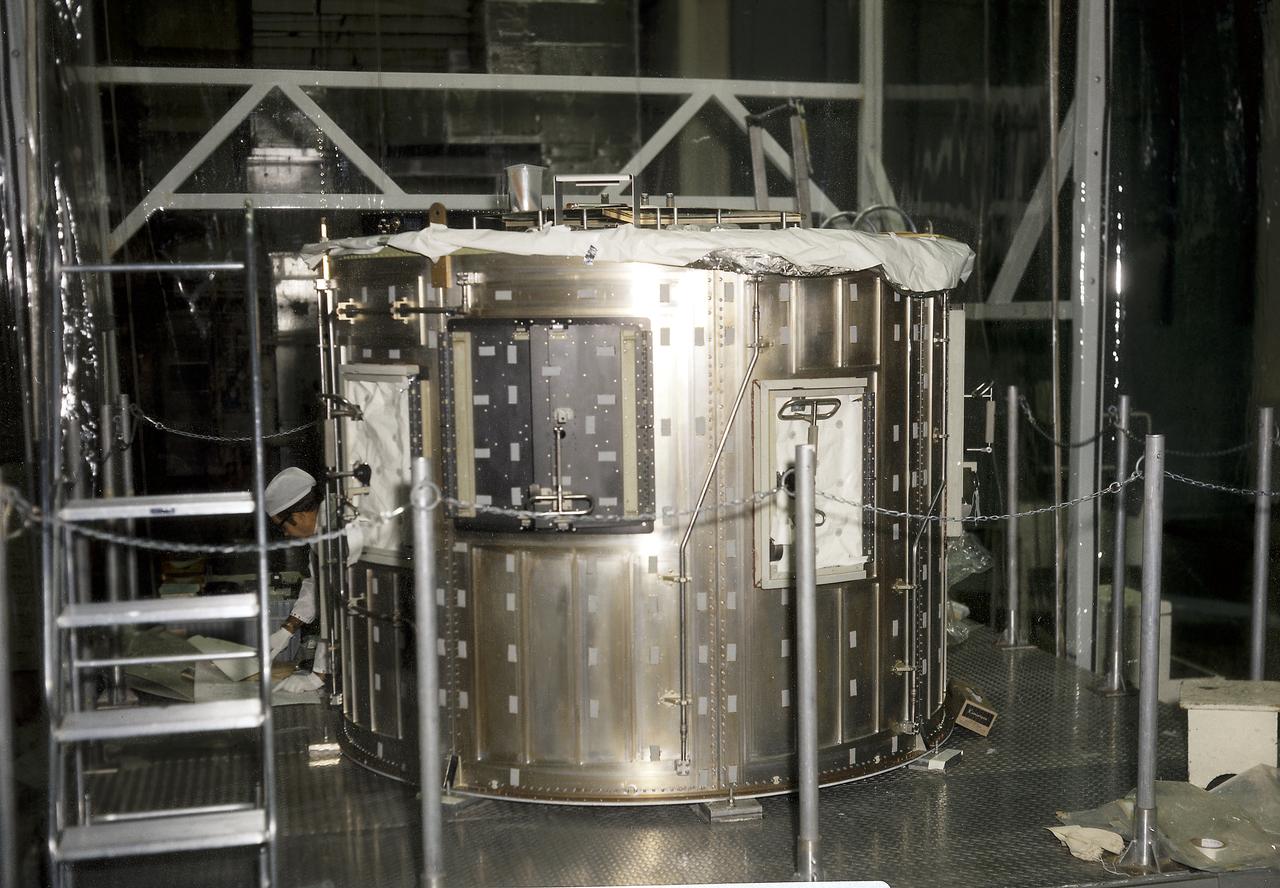
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. This image is of the ATM flight unit sun end canister in MSFC's building 4755.
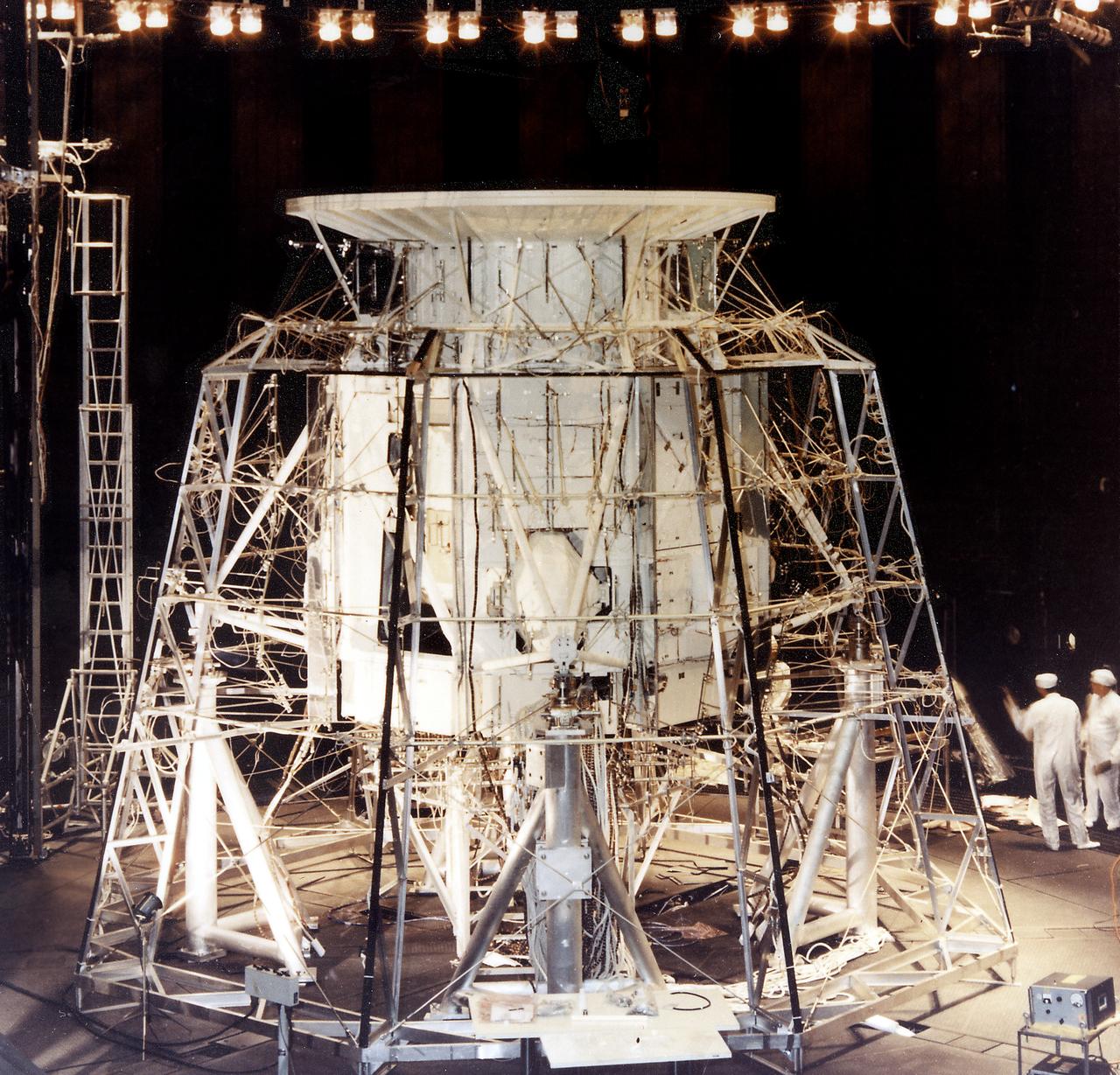

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was one of four major components comprising the Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM housed the first manned scientific telescope in space. This photograph is of the ATM thermal systems unit undergoing testing in the Space Environment Simulation Laboratory of the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The ATM thermal systems unit was used to control the temperatures of space instrument's subsystems during a mission. The MSC was renamed the Johnson Space Center (JSC) in early 1973.

Scientist-Astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot of the Skylab 3 mission, is stationed at the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) console in the Multiple Docking Adapter of the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. From this console the astronauts actively control the ATM solar physics telescope.
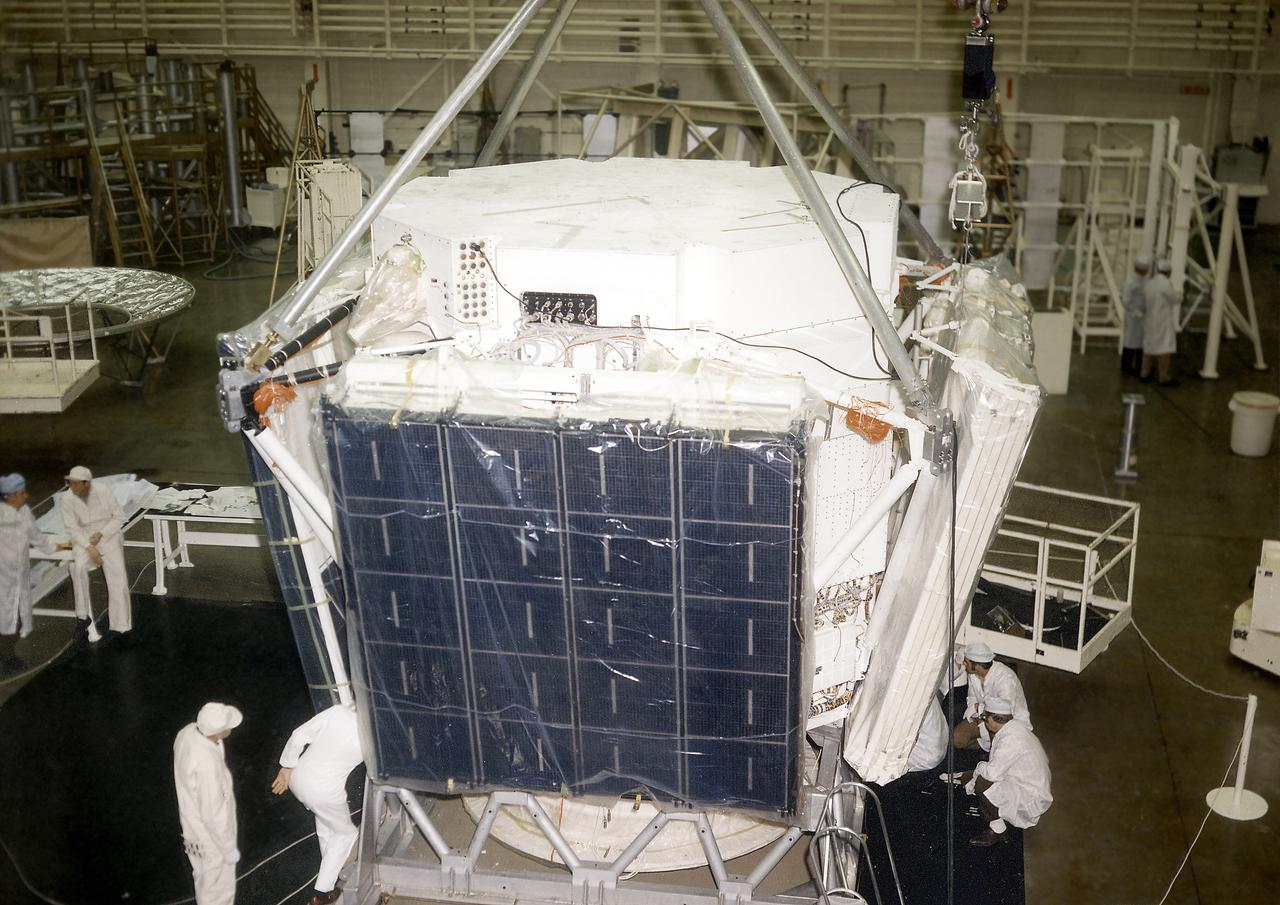

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. In this image, the set of four large solar cell arrays, which could produce up to as much as 1.1 kilowatts of electric power, are being installed on an ATM prototype.
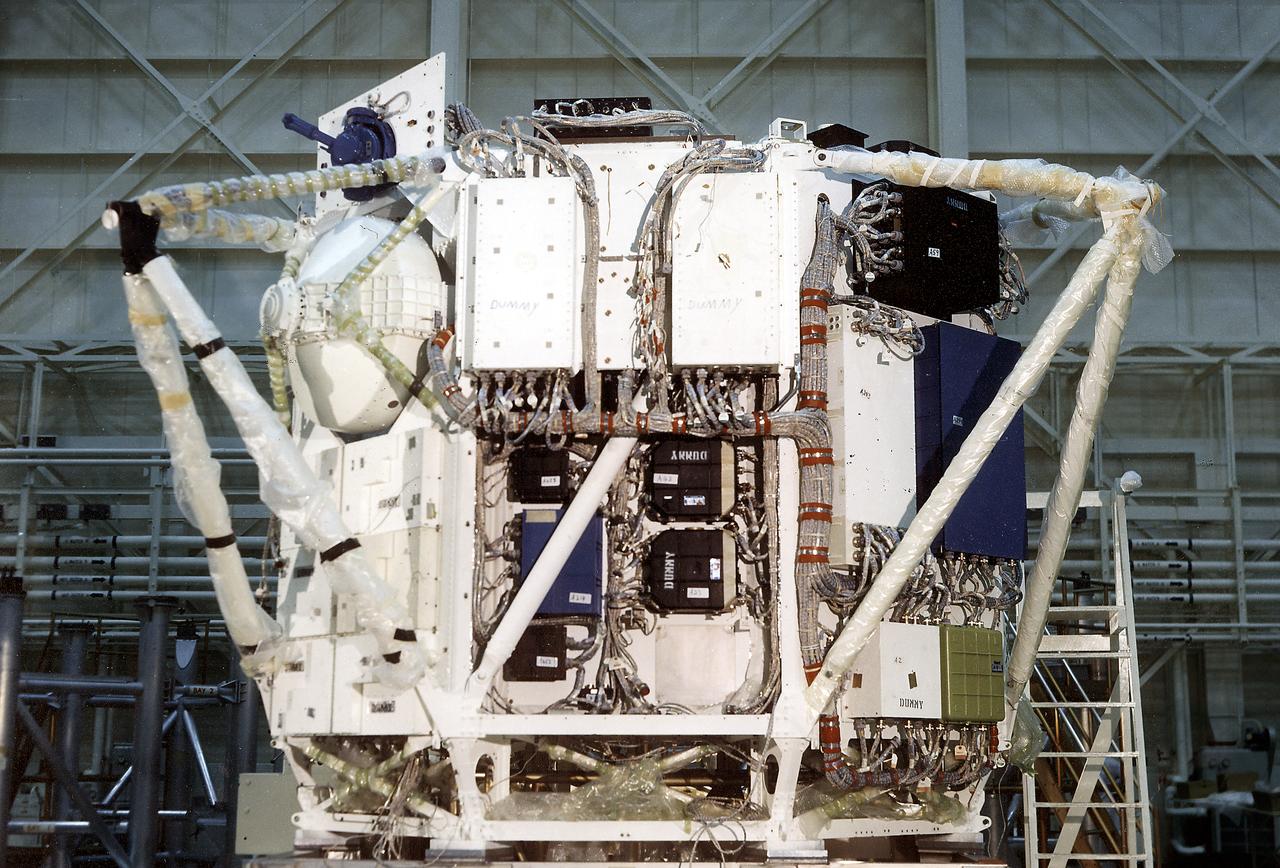
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. This is a photograph of the assembly of an ATM flight unit rack. The flight unit rack was an octagonal shaped complex outer frame that housed the canister containing the solar instruments.
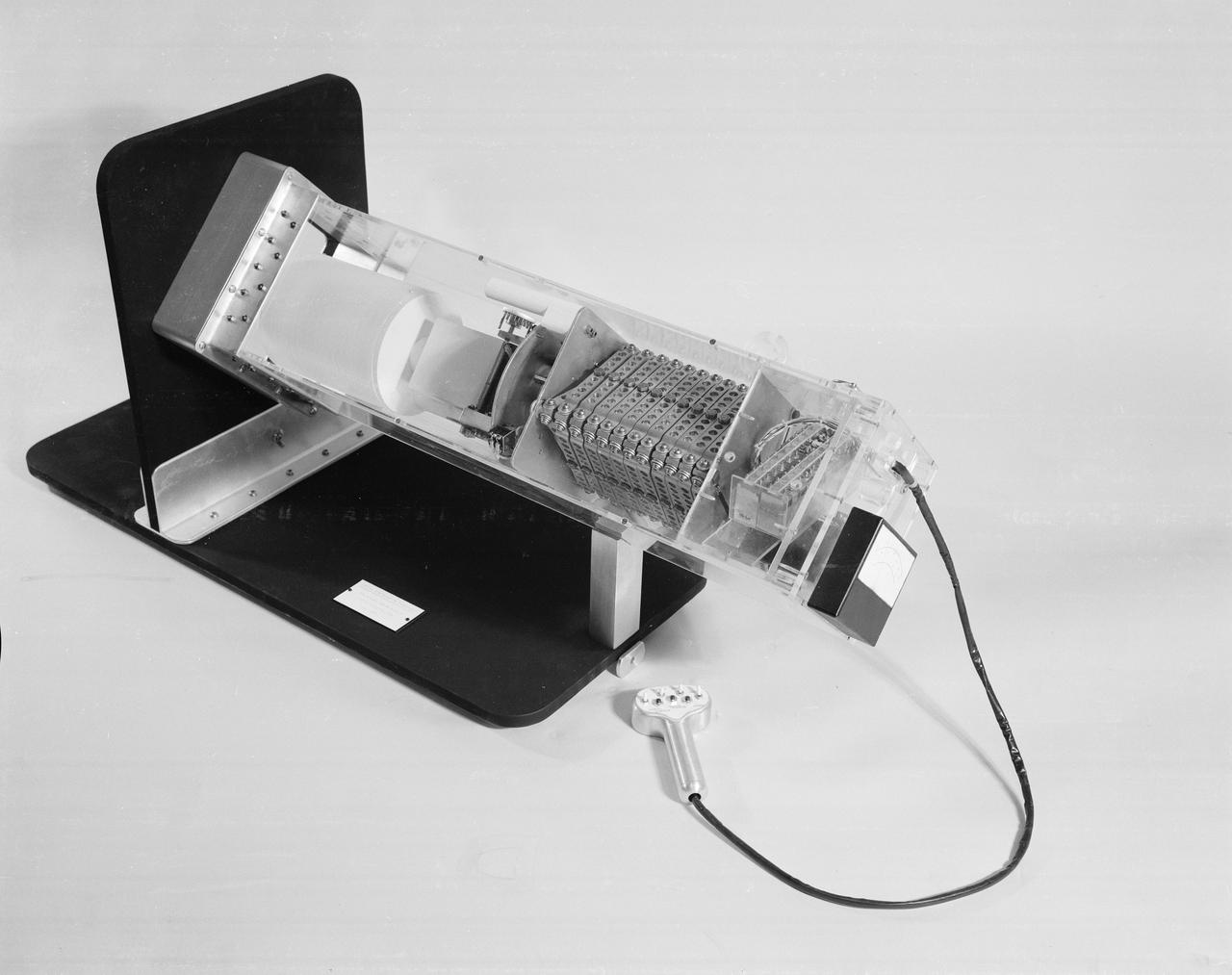
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard the Skylab. The ATM contained eight complex astronomical instruments designed to observe the Sun over a wide spectrum from visible light to x-rays. This angle view is of an ATM contamination monitor meter mockup.
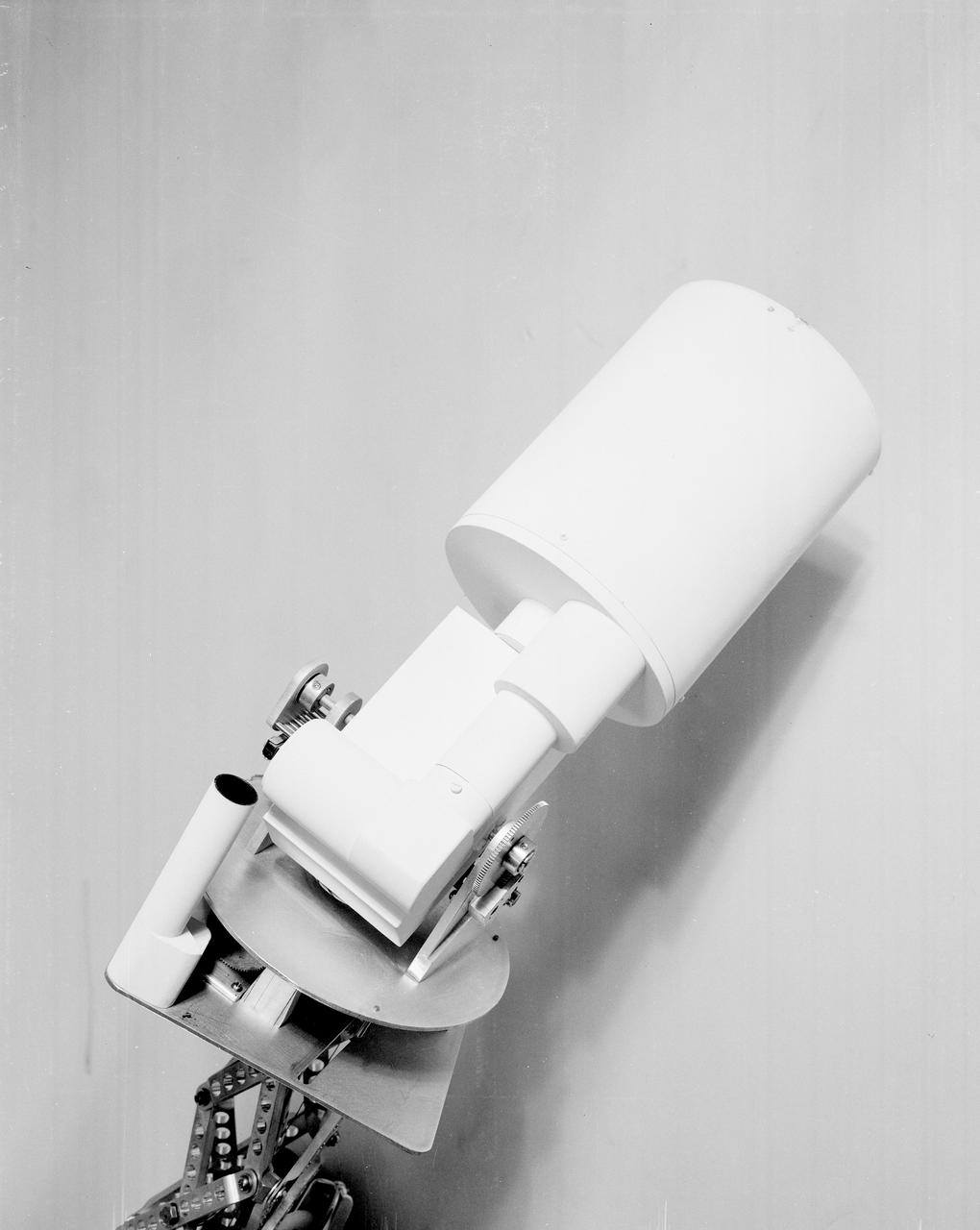

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard the Skylab. The ATM contained eight complex astronomical instruments designed to observe the Sun over a wide spectrum from visible light to x-rays. This photo depicts a mockup of the ATM contamination monitor camera and photometer.
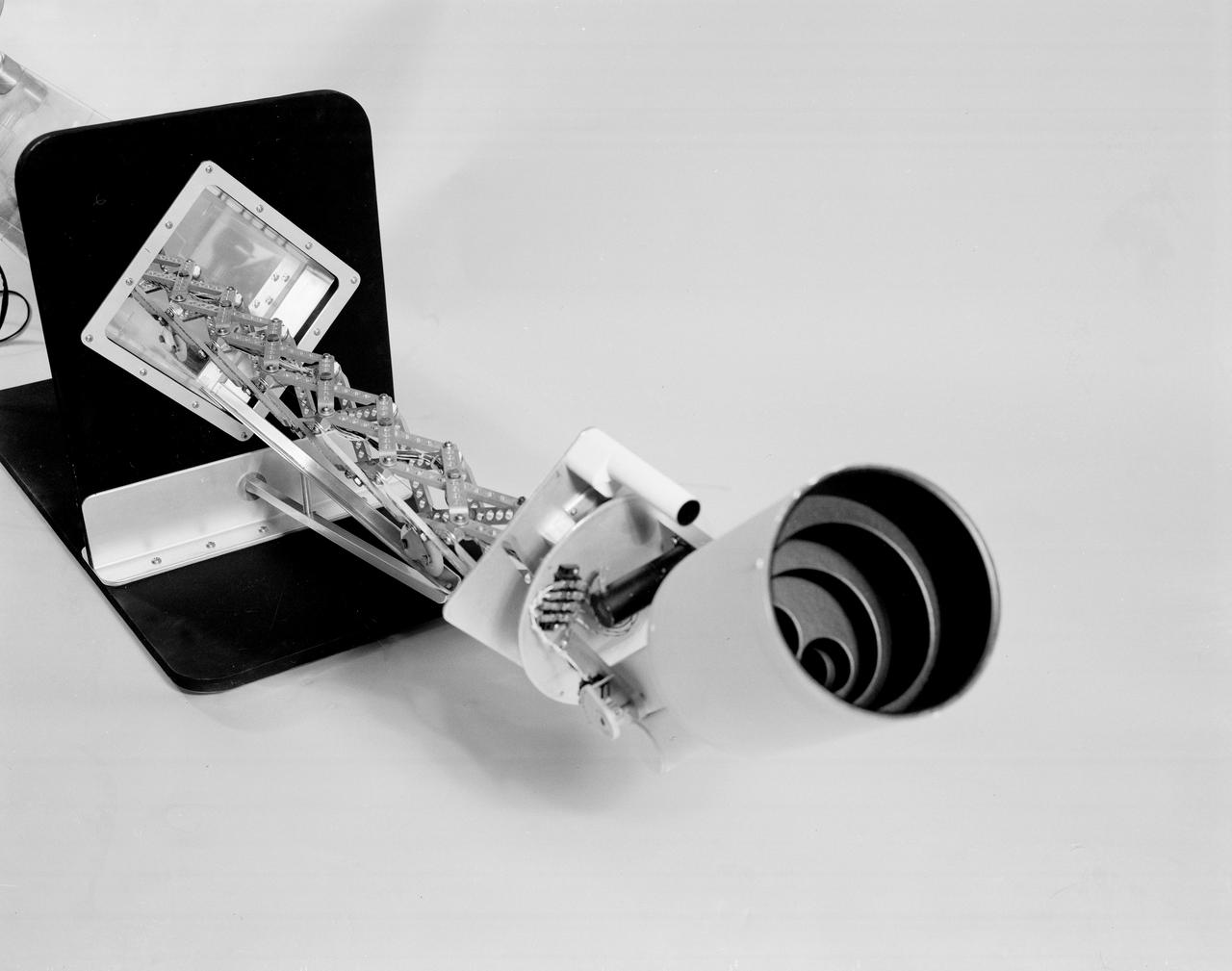

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard the Skylab. The ATM contained eight complex astronomical instruments designed to observe the Sun over a wide spectrum from visible light to x-rays. This photo of the ATM contamination monitor mockup offers an extended view of the sunshield interior.
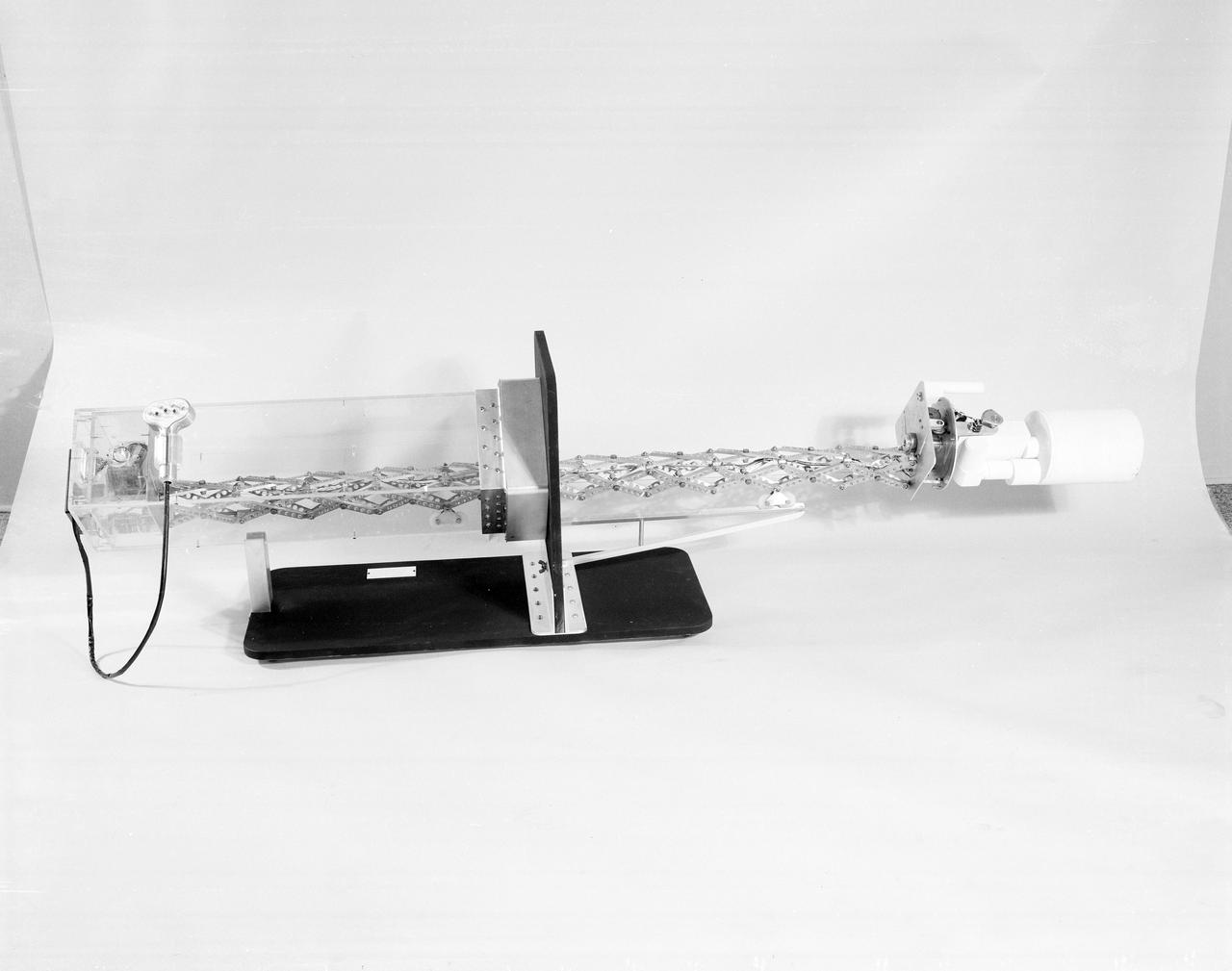

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard the Skylab. The ATM contained eight complex astronomical instruments designed to observe the Sun over a wide spectrum from visible light to x-rays. This photo depicts a side view is of a fully extended ATM contamination monitor mockup.

S74-17306 (5 Dec. 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, Skylab 4 science pilot, stands at the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) console in the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. This picture was taken with a hand-held 35mm Nikon camera. The ATM console was one of the busiest areas of the space station during the 84-day third manned Skylab mission, as Comet Kohoutek and solar activity were closely followed by the ATM and monitored by the crewmen from the ATM console. As Gibson demonstrated during a television transmission on Dec. 5, 1973, the ATM console controls several instruments on the solar telescope. Joining Gibson for the record-setting Skylab 4 mission were astronauts Gerald P. Carr, commander, and William R. Pogue, pilot. Photo credit: NASA
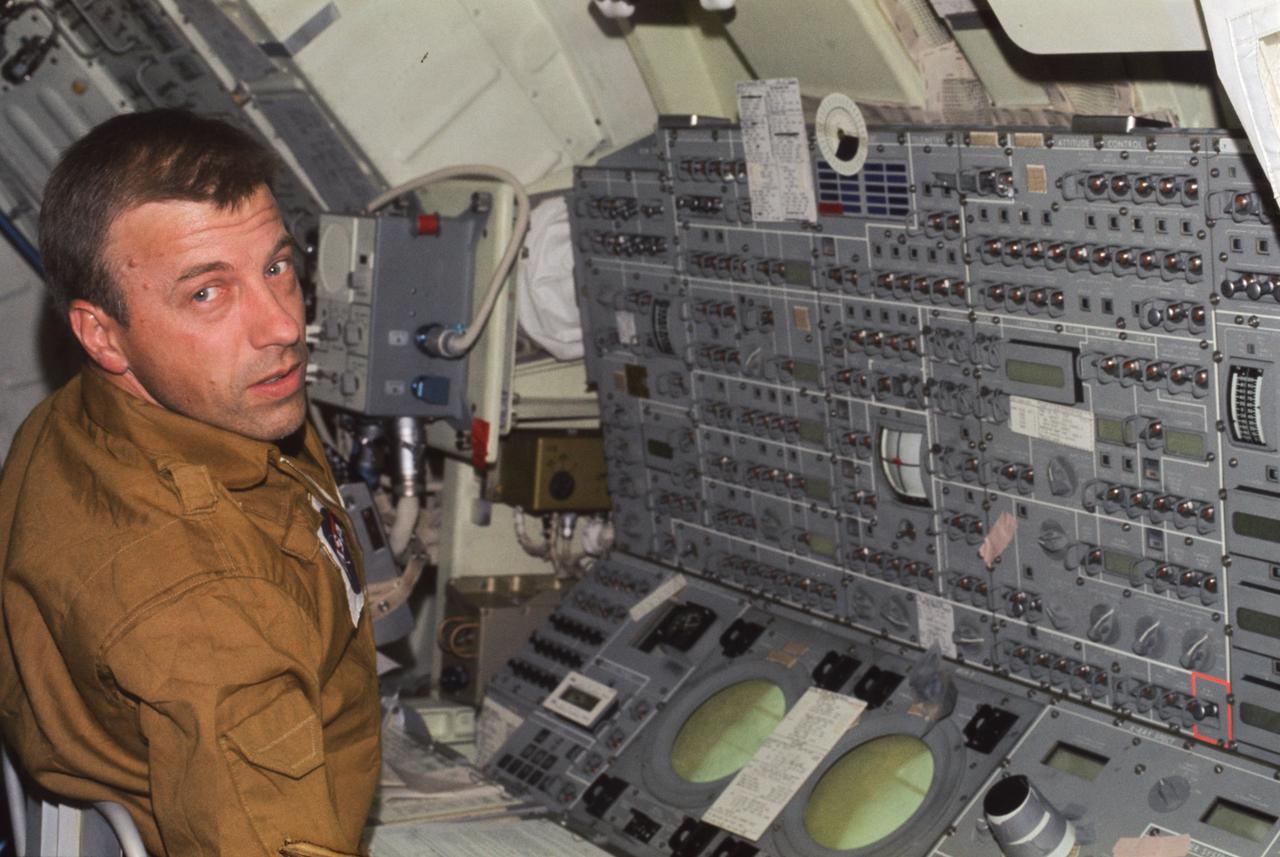

SL2-X9-747 (June 1973) --- Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, Skylab 2 pilot, mans the control and display console of the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) in this onboard view photographed in Earth orbit. The ATM C&D console is located in the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) of the Skylab 1/2 space station. Weitz, along with astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot, went on to successfully complete a 28-day mission in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA
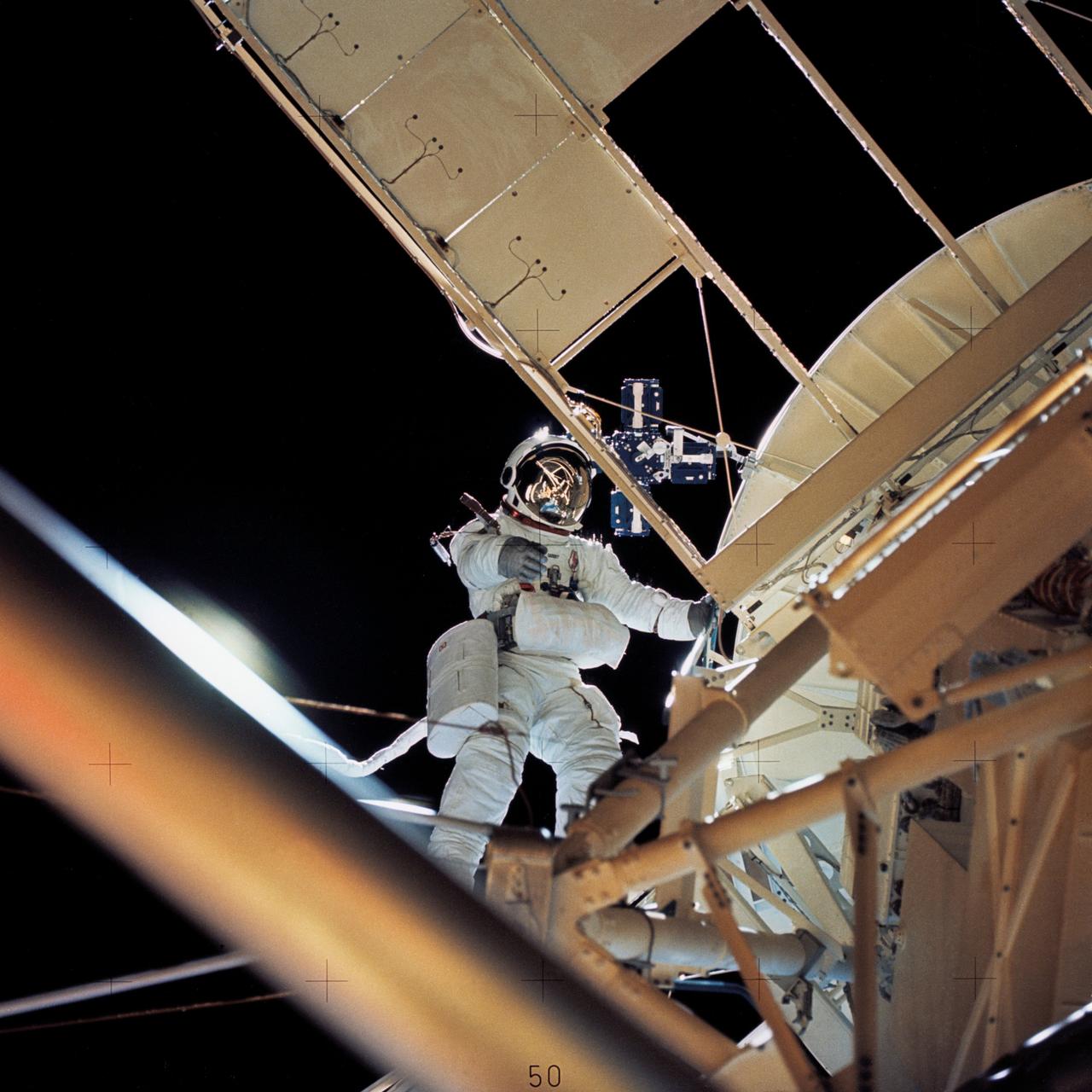

SL3-115-1837 (August 1973) --- Astronaut Owen K. Garriott, Skylab 3 science pilot, retrieves an imagery experiment from the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) attached to the Skylab in Earth orbit. Garriott’s was a special extravehicular activity (EVA) to remove from the attached ATM/orbiting observatory magazines which will be returned to Earth when the second manning of the Skylab space station has been completed. Photo credit: NASA
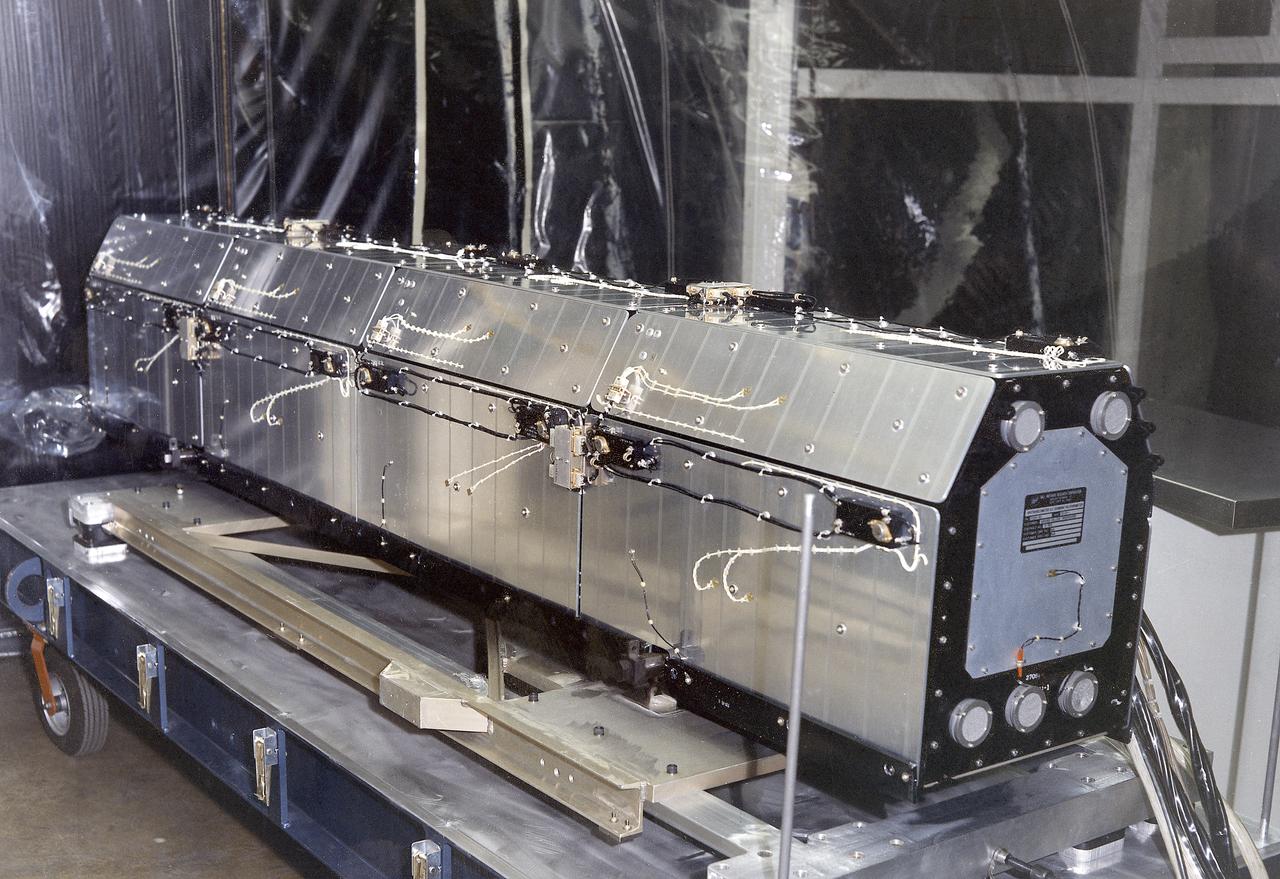
This 1970 photograph shows the flight unit for Skylab's Ultraviolet (UV) Scarning Polychromator Spectroheliometer, an Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) facility. It was designed to observe temporal changes in UV radiation emitted by the Sun's chromosphere and lower corona. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.

S73-32837 (10 Sept. 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, seated, and astronaut William R. Pogue discuss a mission procedure at the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) display and control panel mock-up in the one-G trainer for the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) at Johnson Space Center. Photo credit: NASA
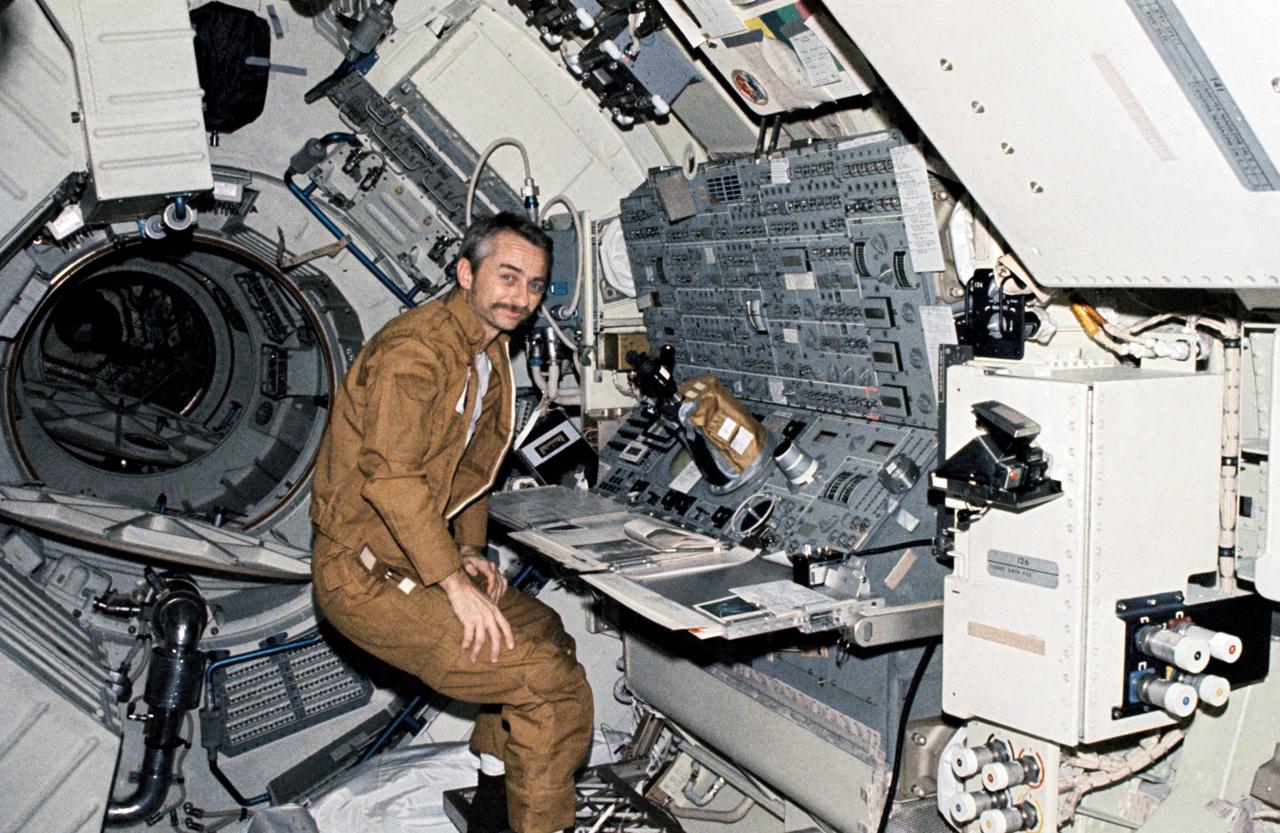

SL3-108-1288 (July-Sept. 1973) --- Astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot of the Skylab 3 mission, is stationed at the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) console in the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) of the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. This picture was taken with a handheld 35mm Nikon camera. Astronauts Garriott, Alan L. Bean and Jack R. Lousma remained with the Skylab space station cluster in orbit for 59 days conducting numerous medical, scientific and technological experiments. In orbit the MDA functions as a major experiment control center for solar observations. From this console the astronauts actively control the ATM solar physics telescopes. Photo credit: NASA
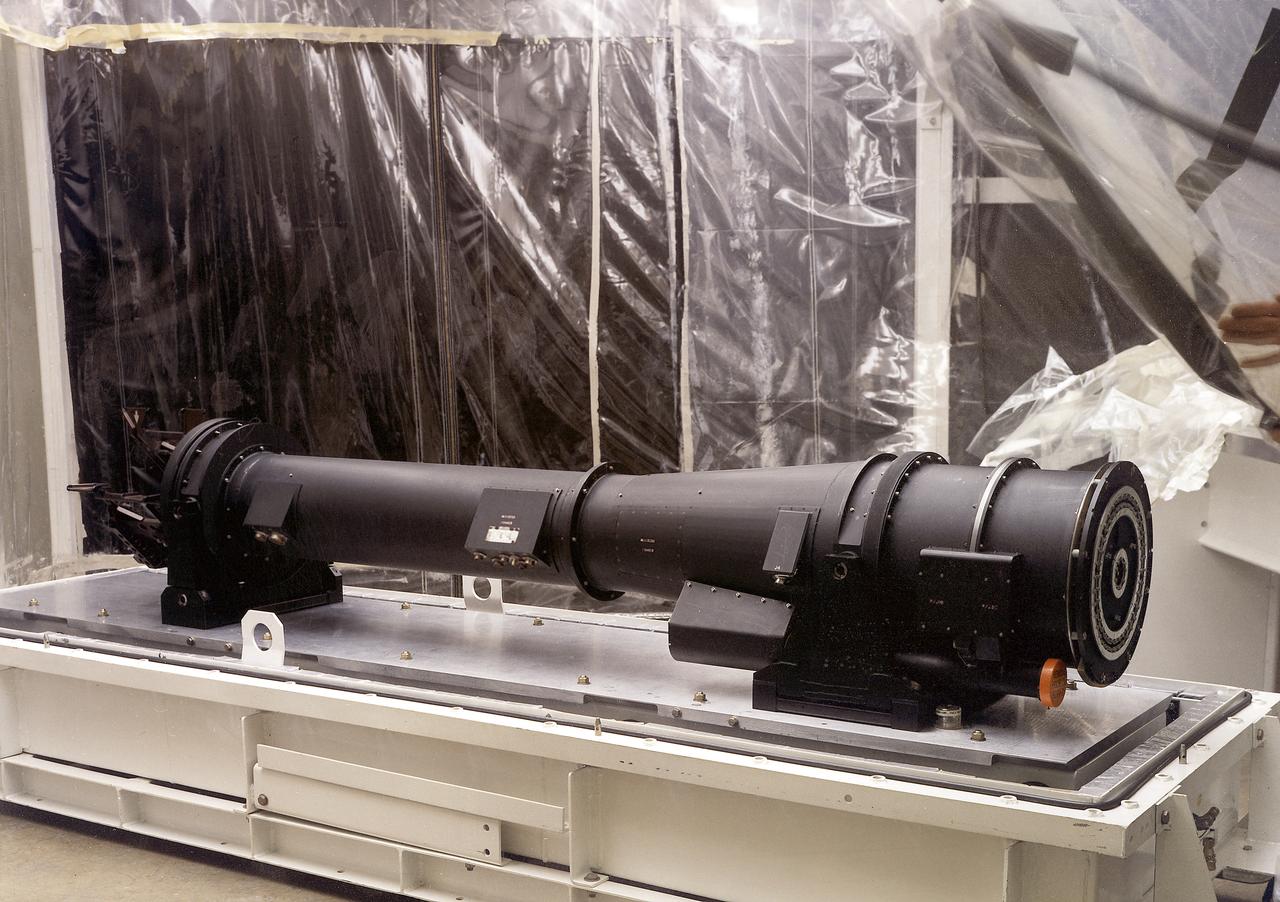

This photograph details Skylab's X-Ray Spectrographic Telescope, an Apollo Telescope Mount facility. It was designed to sequentially photograph solar flares and other active regions in x-ray spectrum. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
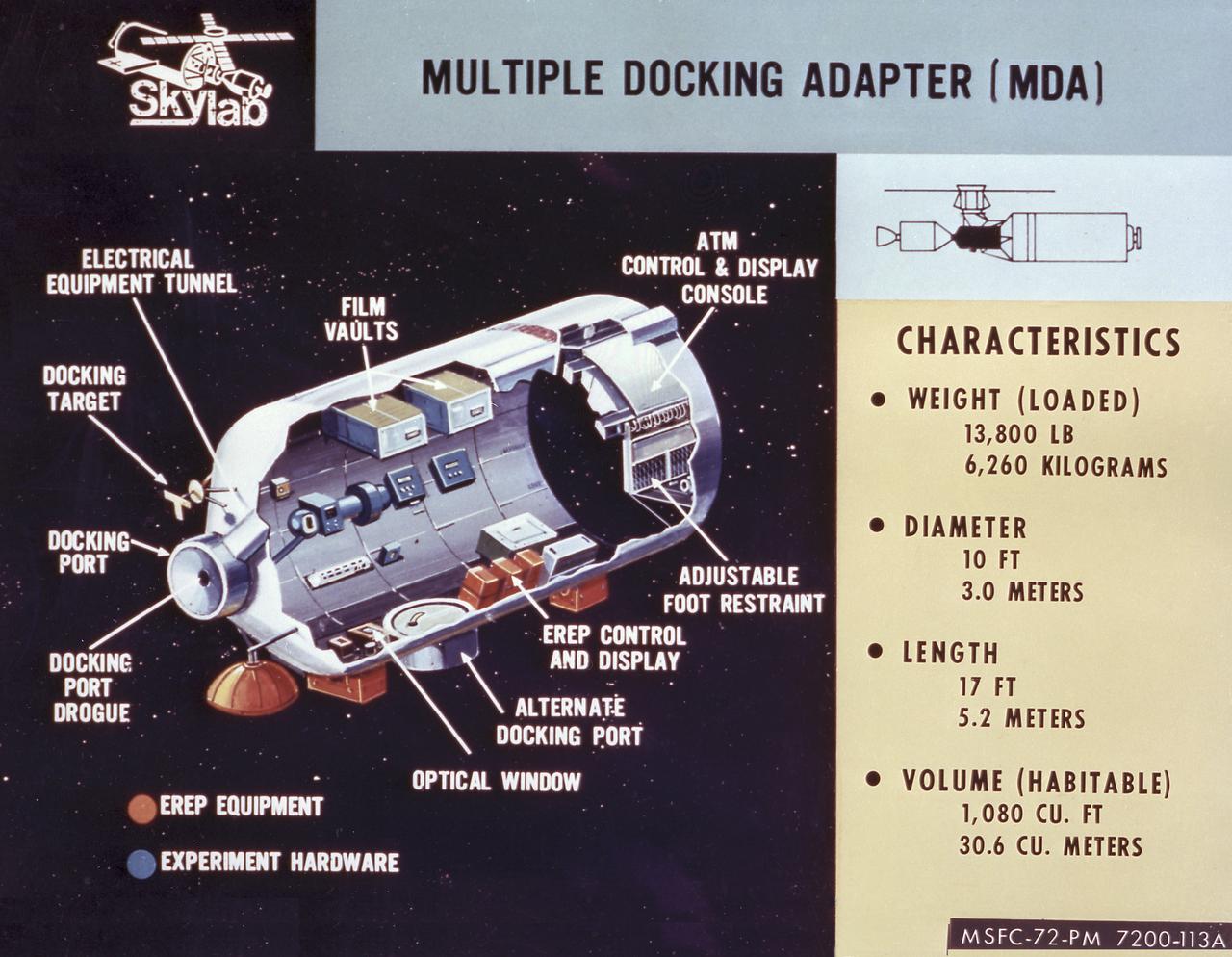
This cutaway drawing details the major characteristics of the Skylab Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA). The MDA, built under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, housed the control units for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Earth Resources Experiment Package (EREP), and Zero-Gravity Materials Processing Facility, and provided a docking port for the Apollo Command Module (CM).

S73-25140 (16 April 1973) --- A ground-level view of Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, showing the 341-feet tall Skylab 1/Saturn V space vehicle on the pad soon after being rolled out from the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The vehicle is composed of the Saturn V first (S-1C) stage, the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), the Airlock Module (AM), and the Orbital Workshop (OWS). Photo credit: NASA
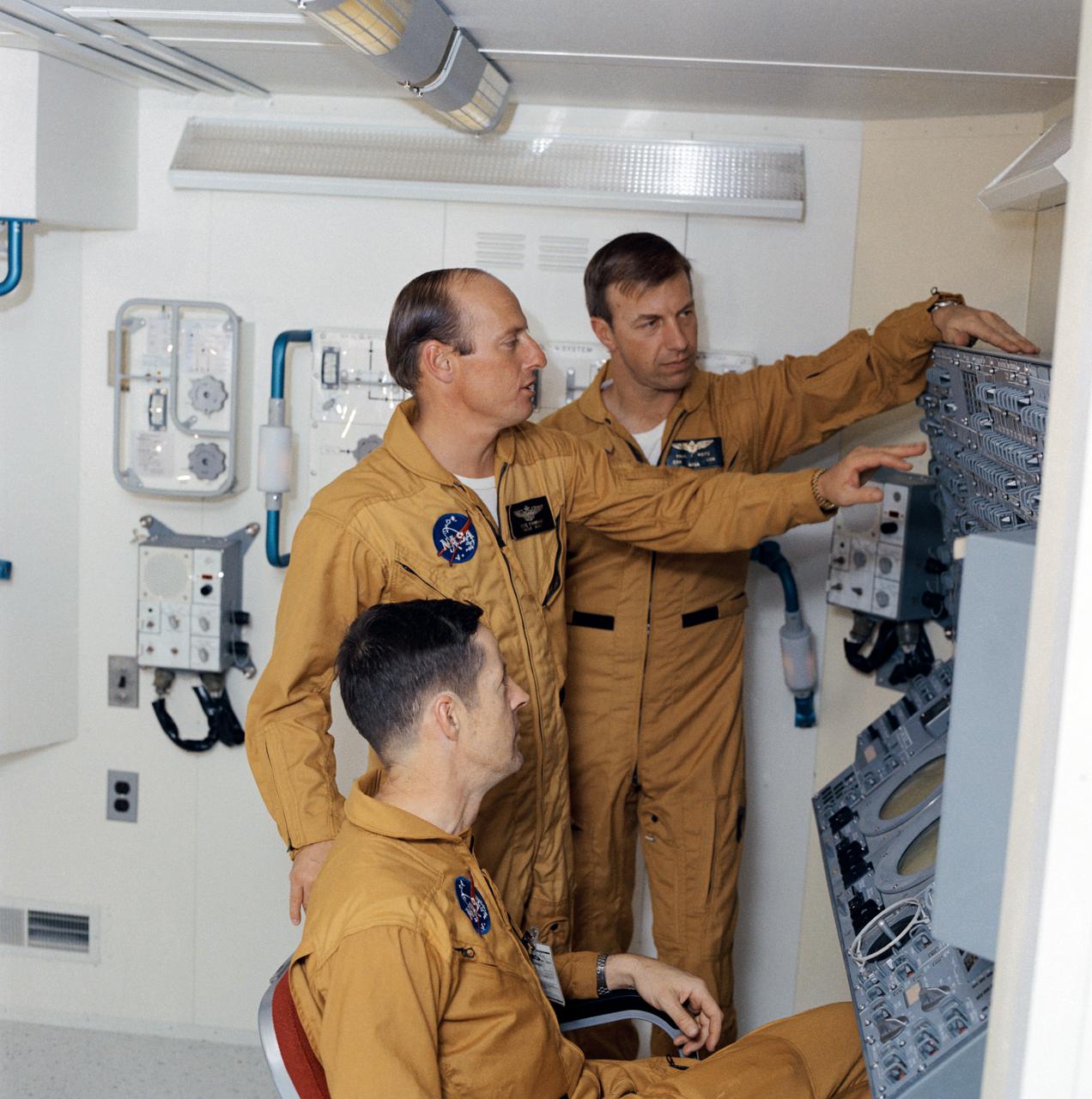

S72-17509 (19 Jan. 1972) --- These three men are the crewmen for the first manned Skylab mission. They are astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, standing left; scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, seated; and astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. They were photographed and interviewed during an "open house" press day in the realistic atmosphere of the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) trainer in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The control and display panel for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) is at right. Photo credit: NASA
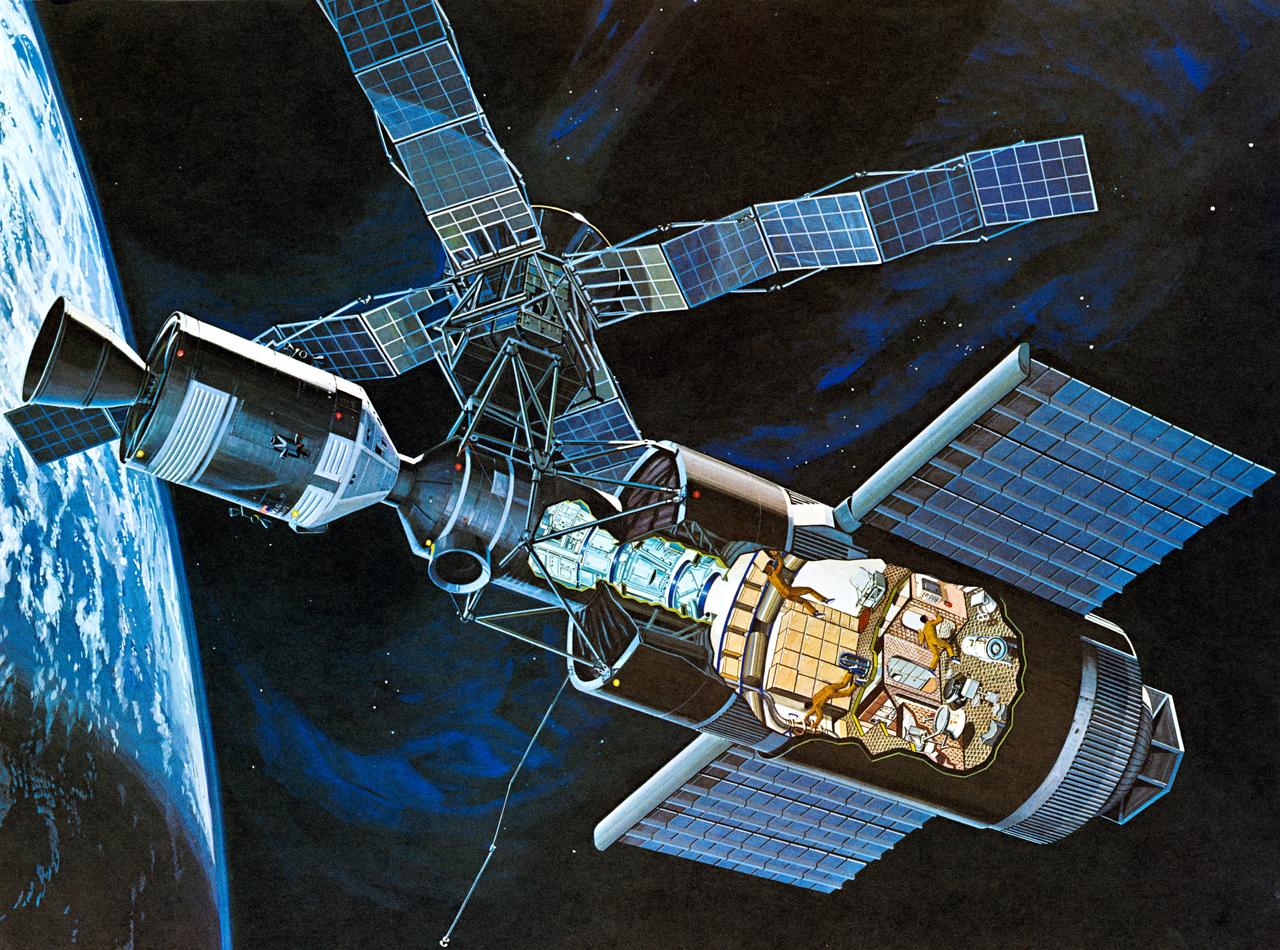

S71-52192 (1971) --- An artist's concept of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth's orbit. The cutaway view shows astronaut activity in the Orbital Workshop (OWS). The Skylab cluster is composed of the OWS, Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), and the Command and Service Module (CSM). Photo credit: NASA
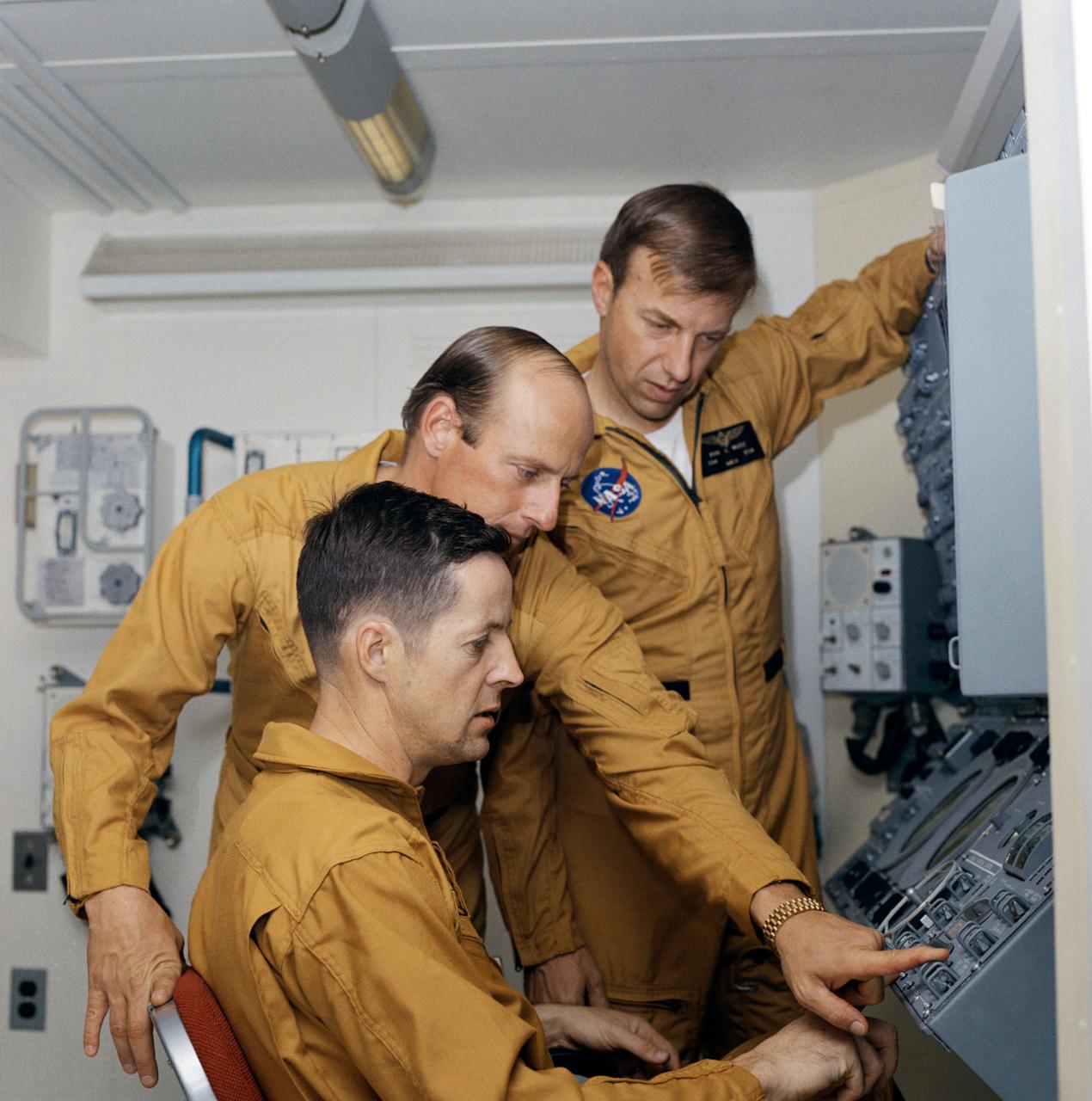

S72-17512 (19 Jan. 1972) --- These three men are the crewmen for the first manned Skylab mission. They are astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, standing left; scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, seated; and astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. They were photographed and interviewed during an "open house" press day in the realistic atmosphere of the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) trainer in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The control and display panel for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) is at right. Photo credit: NASA
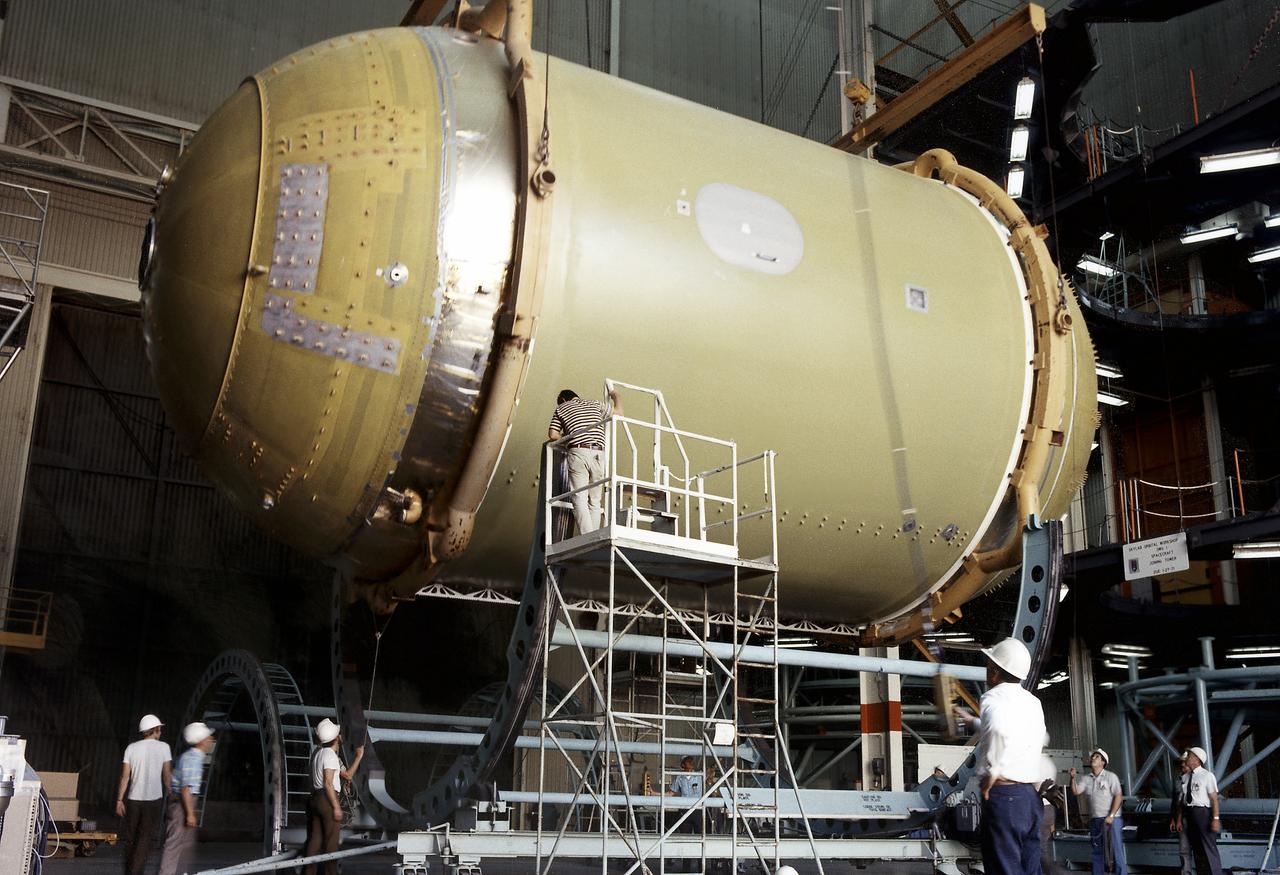

This photographs shows technicians positioning the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) on a rotating work dolly during the assembly phase of the OWS at the McDornell Douglas facility in California. The OWS was the living and working quarters for the astronauts. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments.
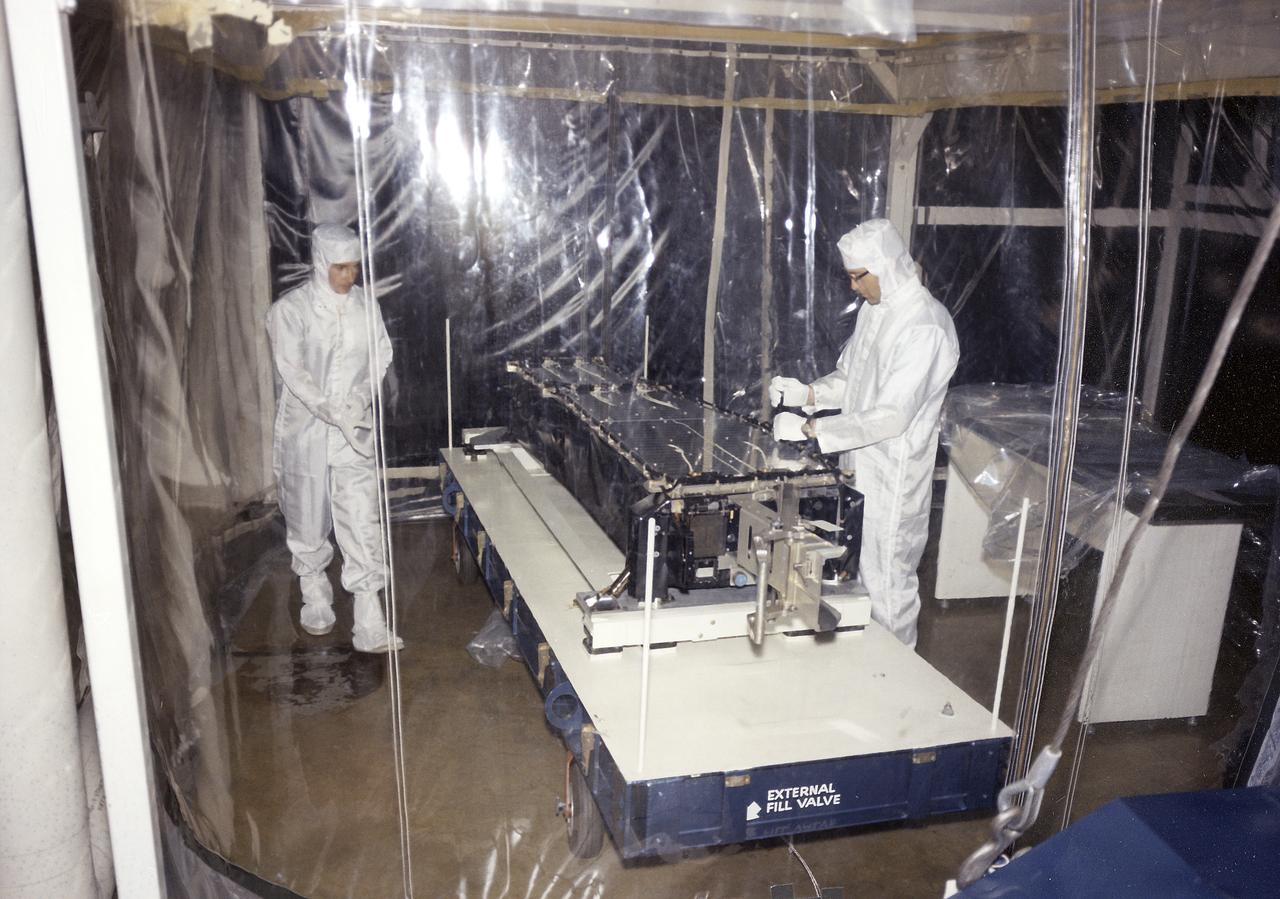

This photograph shows Skylab's Extreme Ultraviolet (XUV) Spectroheliograph during an acceptance test and checkout procedures in April 1971. The unit was an Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) instrument designed to sequentially photograph the solar chromosphere and corona in selected ultraviolet wavelengths. The instrument also obtained information about composition, temperature, energy conversion and transfer, and plasma processes of the chromosphere and lower corona. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
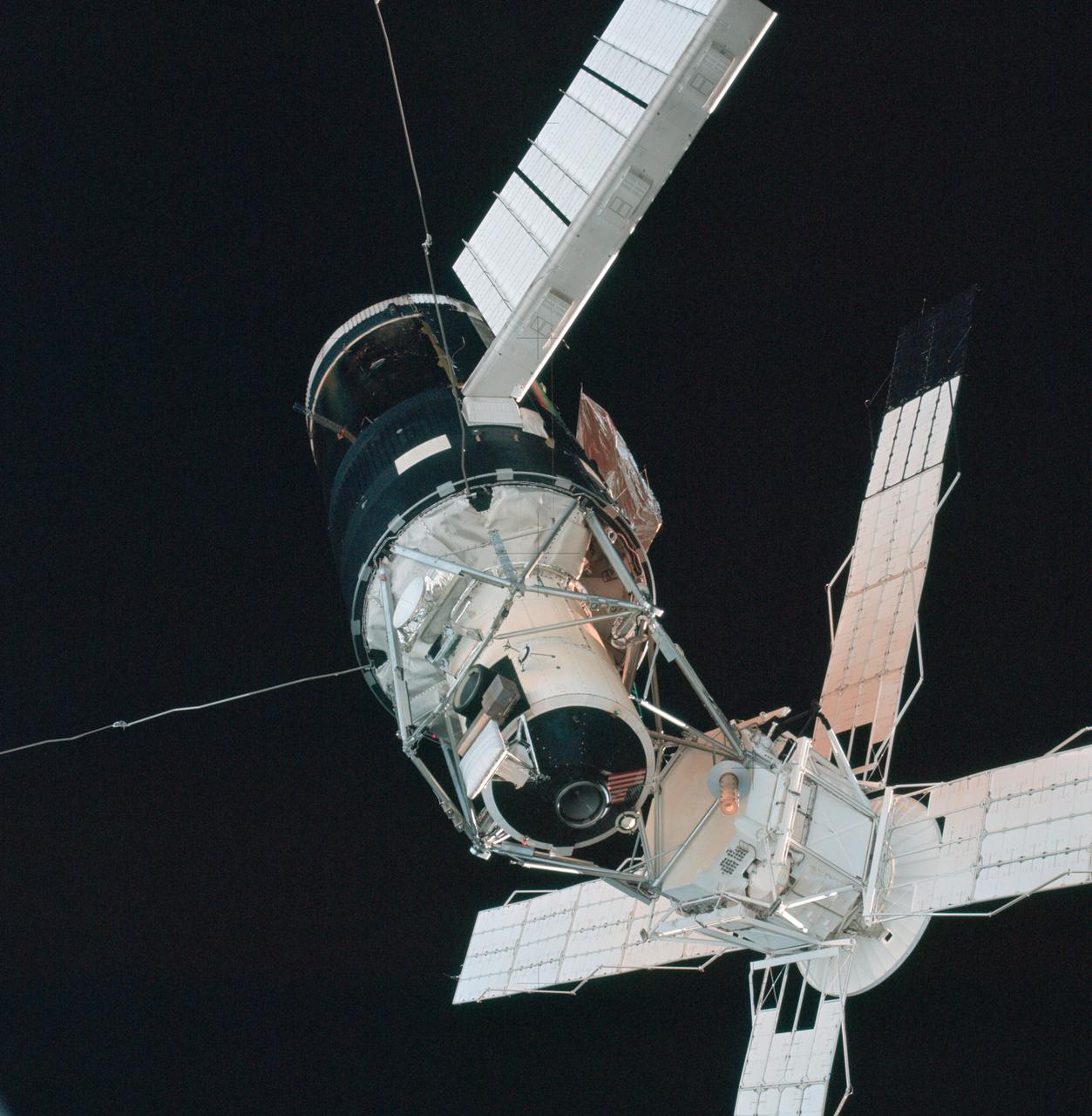
A close-up view of the Skylab space station cluster photographed against a black sky background from the Skylab 3 command module during the "fly around" inspection prior to docking. Note the one solar array system wing on the Orbital Workshop (OWS) which was successfully deployed during EVA on the first manned Skylab mission. The primary docking part at the forward end of the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) is visible below the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM).
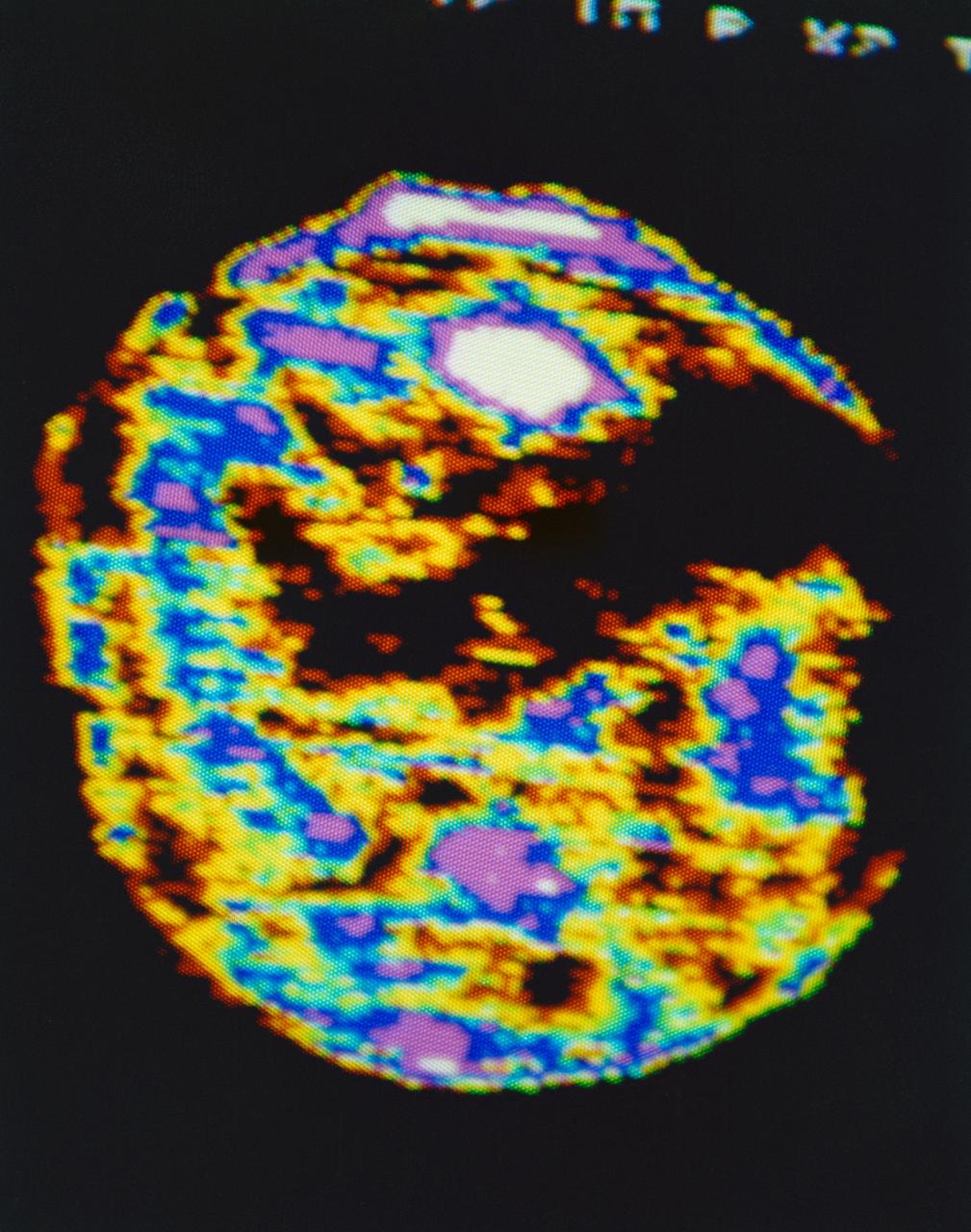
S73-32883 (20 Aug. 1973) --- This false color isophote, processed from an Aug. 20, 1973 television transmission of Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) experiments from Skylab 3, dramatically reveals a significant change in the coronal hole as compared to the previous day. Solar rotation accounts for the new location of the coronal hole. Photo credit: NASA
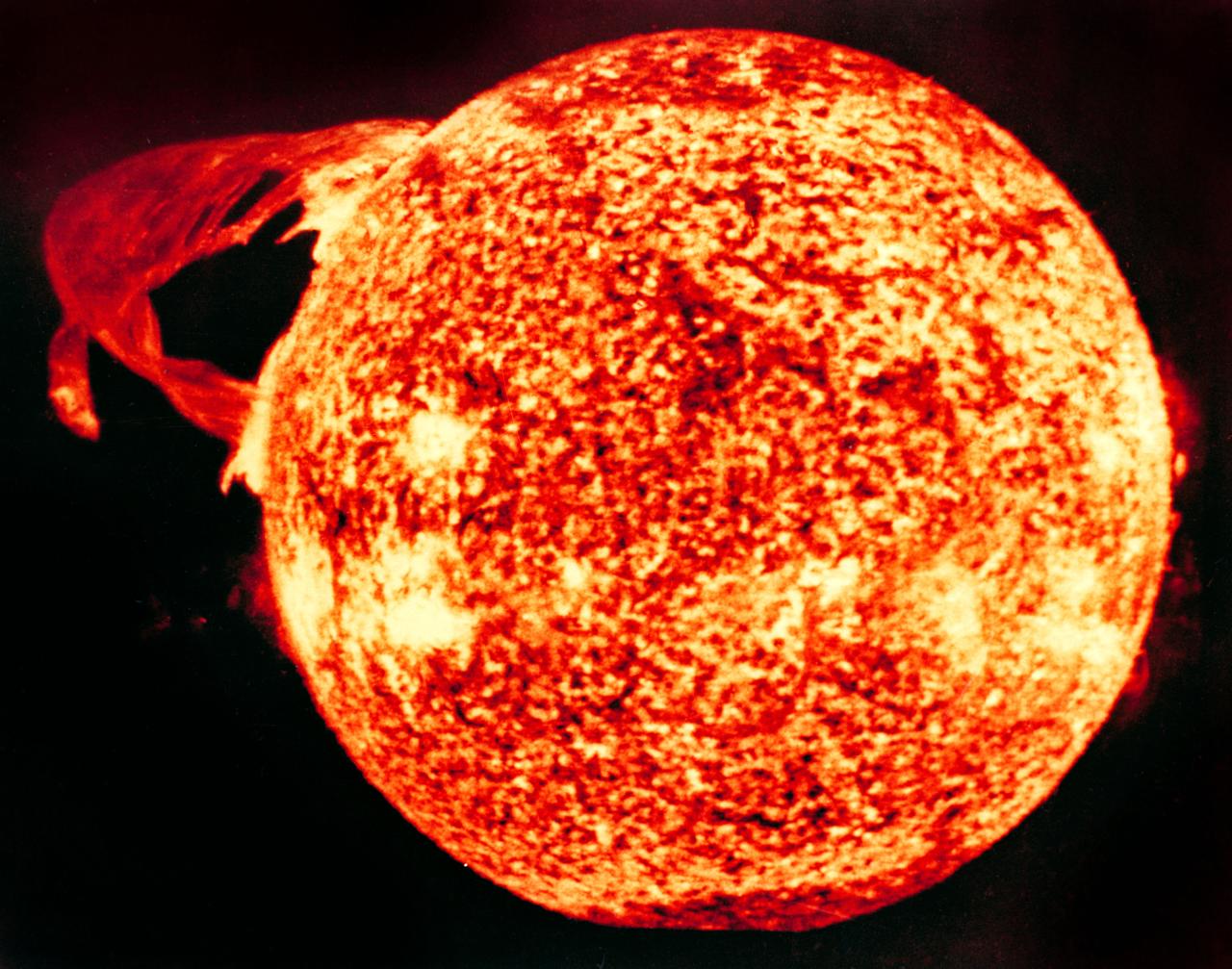
S74-23458 (19 Dec. 1973) --- This photograph of the sun, taken on Dec. 19, 1973, during the third and final manned Skylab mission (Skylab 4), shows one of the most spectacular solar flares ever recorded, spanning more than 588,000 kilometers (365,000 miles) across the solar surface. The last picture, taken some 17 hours earlier, showed this feature as a large quiescent prominence on the eastern side of the sun. The flare gives the distinct impression of a twisted sheet of gas in the process of unwinding itself. Skylab photographs such quiescent features erupt from the sun. In this photograph the solar poles are distinguished by a relative absence of supergranulation network, and a much darker tone than the central portions of the disk. Several active regions are seen on the eastern side of the disk. The photograph was taken in the light of ionized helium by the extreme ultraviolet spectroheliograph instrument of the United States Naval Research Laboratory. Photo credit: NASA
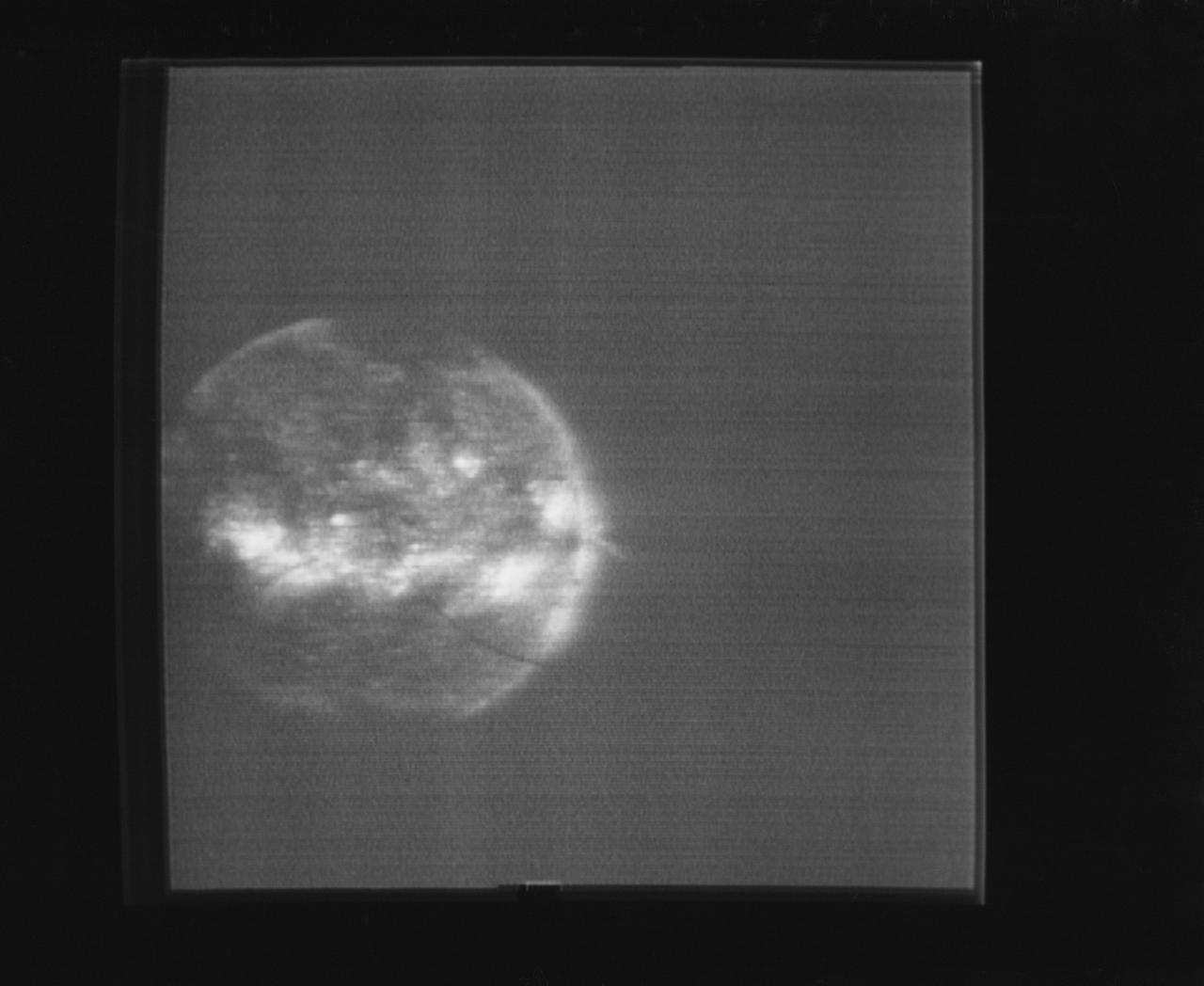
S74-15696 (1974) --- The solar disk photographed through the Skylab S082 Ultraviolet Spectrograph/Heliograph can be seen in this reproduction taken from a television tranmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The S082 experiment is located in the Apollo Telescope Mount. This spectroheliogram shows specific emission features greatly enhanced over photographs of the solar disk in white light. Photo credit: NASA

SL3-122-2611 (22 Sept. 1973) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, Skylab 3 commander, participates in the final extravehicular activity (EVA) for that mission, during which a variety of tasks were performed. Here, Bean is near the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) during final film change out for the giant telescope facility. Astronaut Owen K. Garriott, who took the picture, is reflected in Bean's helmet visor. The reflected Earth disk in Bean's visor is so clear that the Red Sea and Nile River area can delineated. Photo credit: NASA
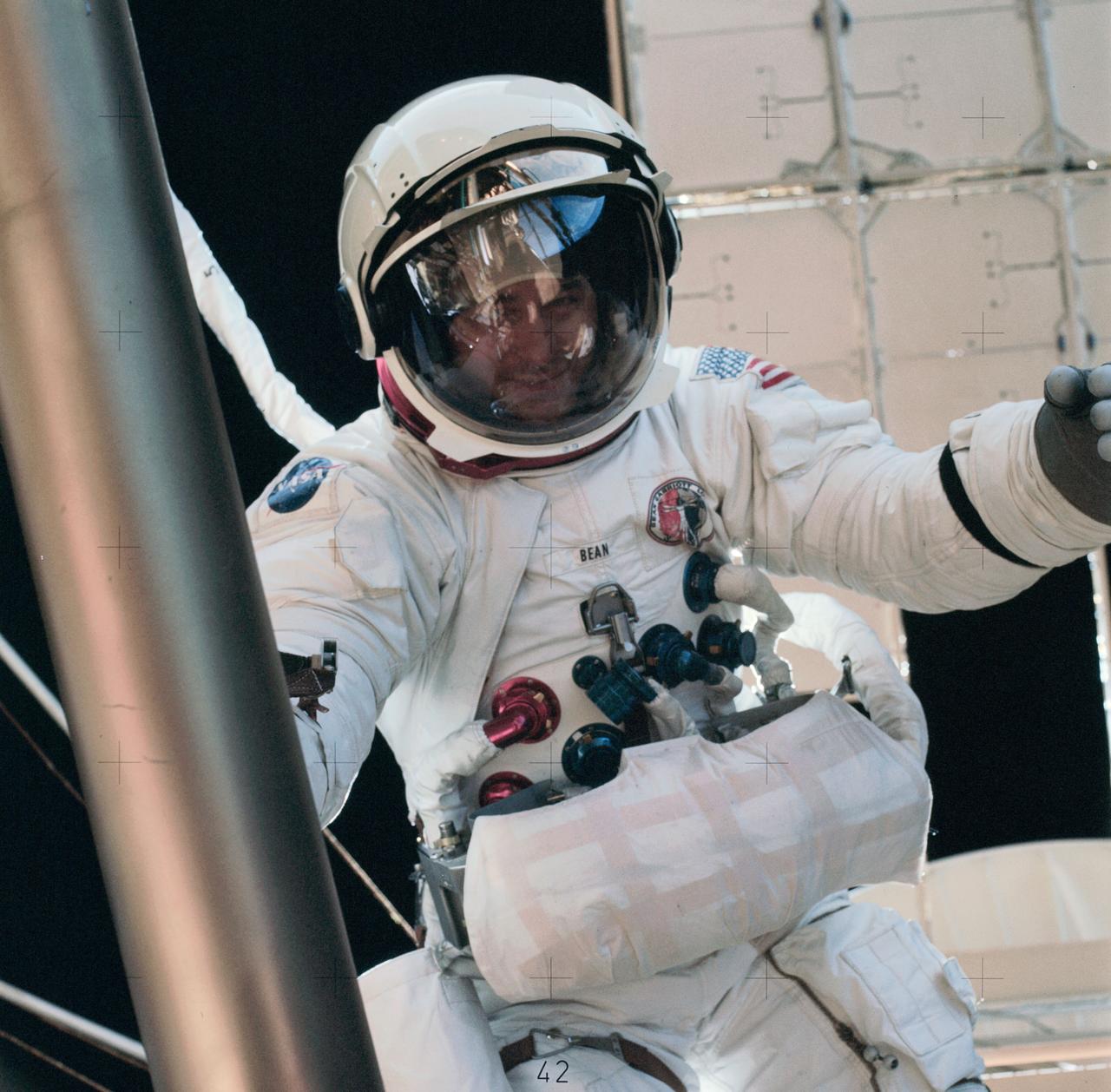

SL3-122-2612 (6 Aug. 1973) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, Skylab 3 commander, participates in the final Skylab 3 extravehicular activity (EVA), during which a variety of tasks were performed. Here, Bean is near the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) during final film change out for the giant telescope facility. Astronaut Owen K. Garriott, who took the picture, is reflected in Bean's helmet visor. The reflected Earth disk in Bean's visor is so clear that the Red Sea and Nile River area can delineated. Photo credit: NASA

S73-32839 (10 Sept. 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot for the third manned Skylab mission (Skylab 4), enters a notation in a manual while seated at the control and display panel for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) during simulations inside the one-G trainer for the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Dr. Gibson will be joined by astronauts Gerald P. Carr, commander, and William R. Pogue, pilot, when the Skylab 4 mission begins in November 1973. Photo credit: NASA
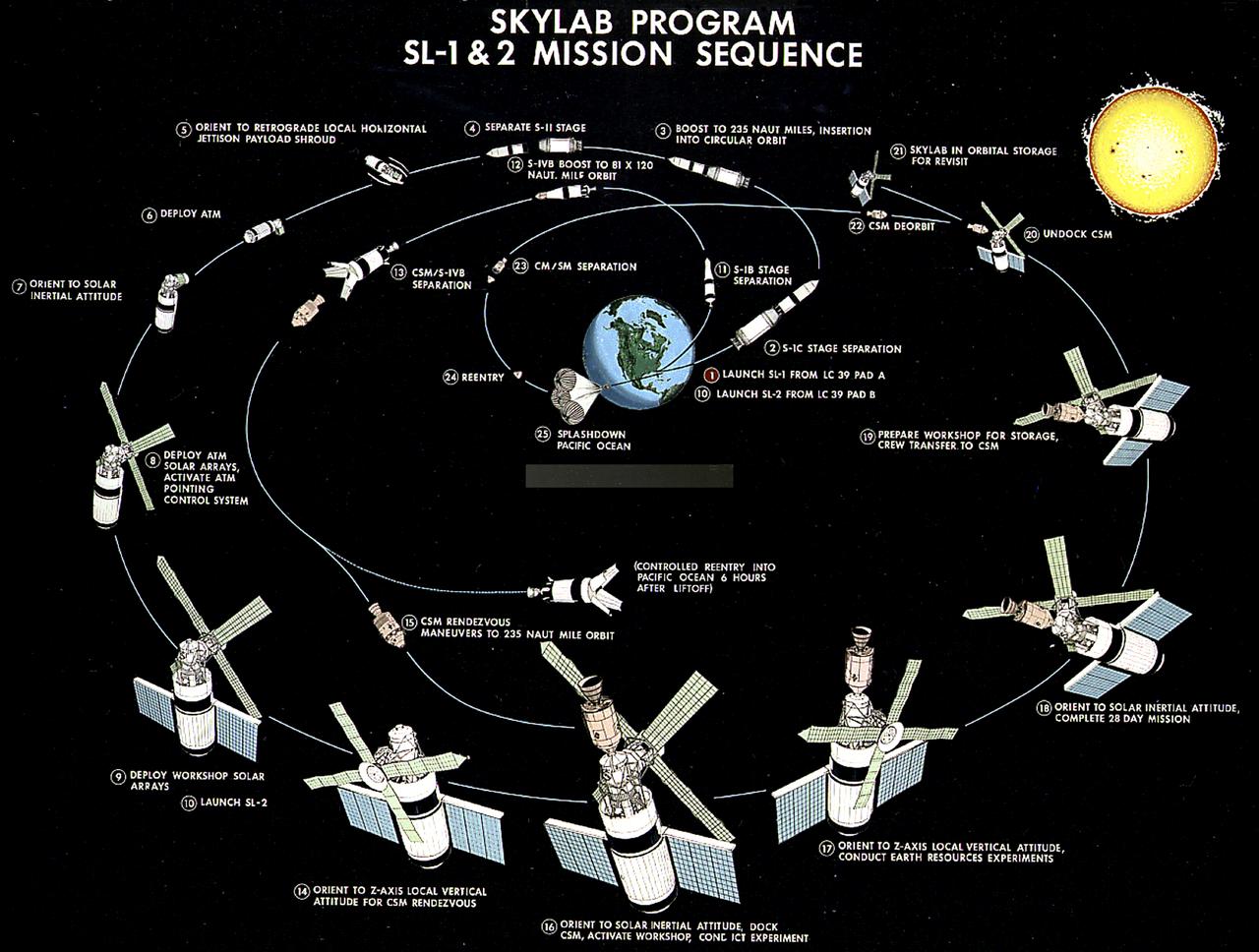
This illustration depicts the Skylab-1 and Skylab-2 mission sequence. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The Skylab also conducted 19 selected experiments submitted by high school students. Skylab's 3 different 3-man crews spent up to 84 days in Earth orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments. MSFC was also responsible for providing the Saturn IB launch vehicles for three Apollo spacecraft and crews and a Saturn V launch vehicle for the Skylab.
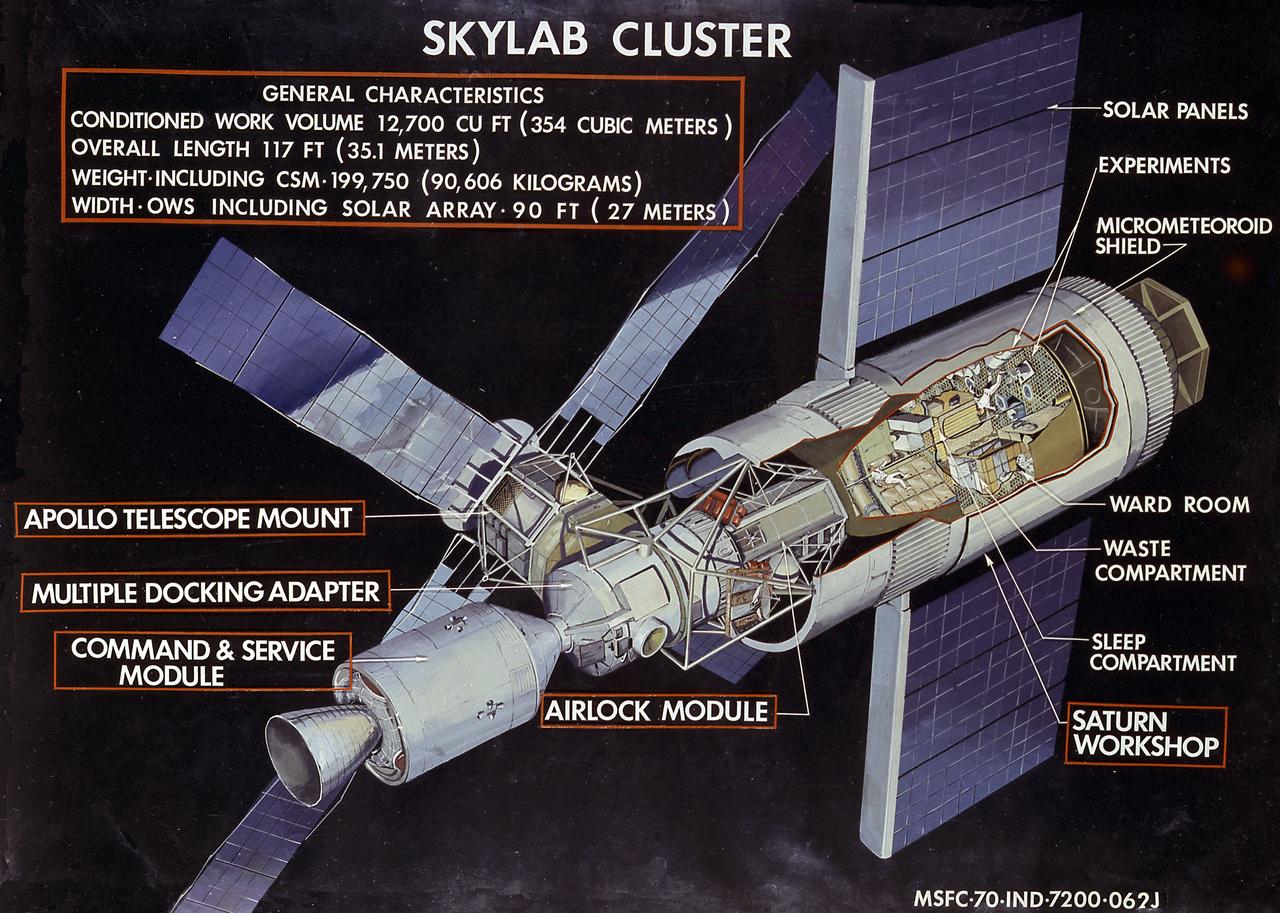
This illustration shows general characteristics of the Skylab with callouts of its major components. In an early effort to extend the use of Apollo for further applications, NASA established the Apollo Applications Program (AAP) in August of 1965. The AAP was to include long duration Earth orbital missions during which astronauts would carry out scientific, technological, and engineering experiments in space by utilizing modified Saturn launch vehicles and the Apollo spacecraft. Established in 1970, the Skylab Program was the forerurner of the AAP. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The Skylab also conducted 19 selected experiments submitted by high school students. Skylab's 3 different 3-man crews spent up to 84 days in Earth orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments. MSFC was also responsible for providing the Saturn IB launch vehicles for three Apollo spacecraft and crews and a Saturn V launch vehicle for the Skylab.
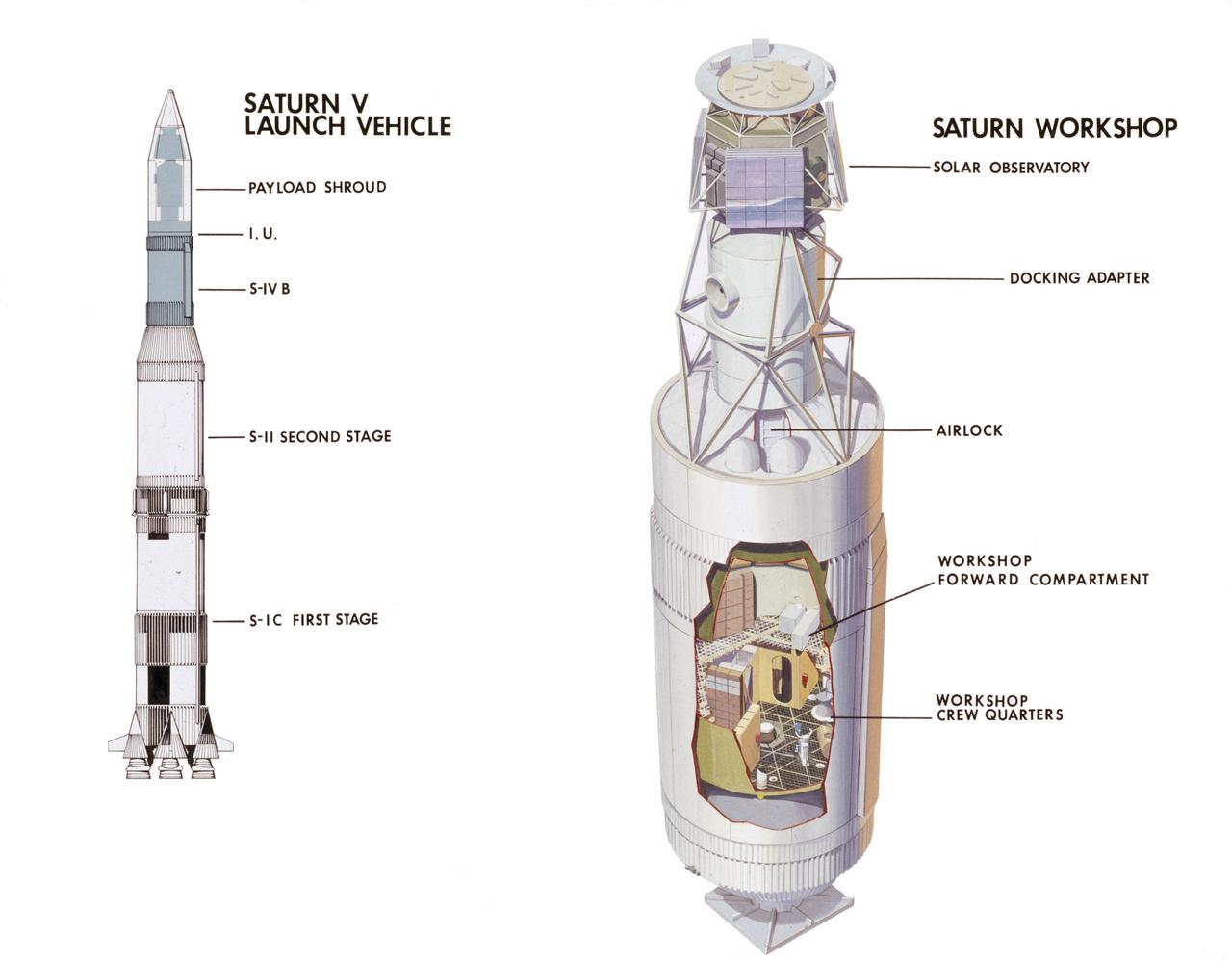
This cutaway drawing illustrates major Skylab components in launch configuration on top of the Saturn V. In an early effort to extend the use of Apollo for further applications, NASA established the Apollo Applications Program (AAP) in August of 1965. The AAP was to include long duration Earth orbital missions during which astronauts would carry out scientific, technological, and engineering experiments in space by utilizing modified Saturn launch vehicles and the Apollo spacecraft. Established in 1970, the Skylab Program was the forerurner of the AAP. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The Skylab also conducted 19 selected experiments submitted by high school students. Skylab's 3 different 3-man crews spent up to 84 days in Earth orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments. MSFC was also responsible for providing the Saturn IB launch vehicles for three Apollo spacecraft and crews and a Saturn V launch vehicle for the Skylab.

This image illustrates major areas of emphasis of the Skylab Program. In an early effort to extend the use of Apollo for further applications, NASA established the Apollo Applications Program (AAP) in August of 1965. The AAP was to include long duration Earth orbital missions during which astronauts would carry out scientific, technological, and engineering experiments in space by utilizing modified Saturn launch vehicles and the Apollo spacecraft. Established in 1970, the Skylab Program was the forerurner of the AAP. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The Skylab also conducted 19 selected experiments submitted by high school students. Skylab's 3 different 3-man crews spent up to 84 days in Earth orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments. MSFC was also responsible for providing the Saturn IB launch vehicles for three Apollo spacecraft and crews and a Saturn V launch vehicle for the Skylab.
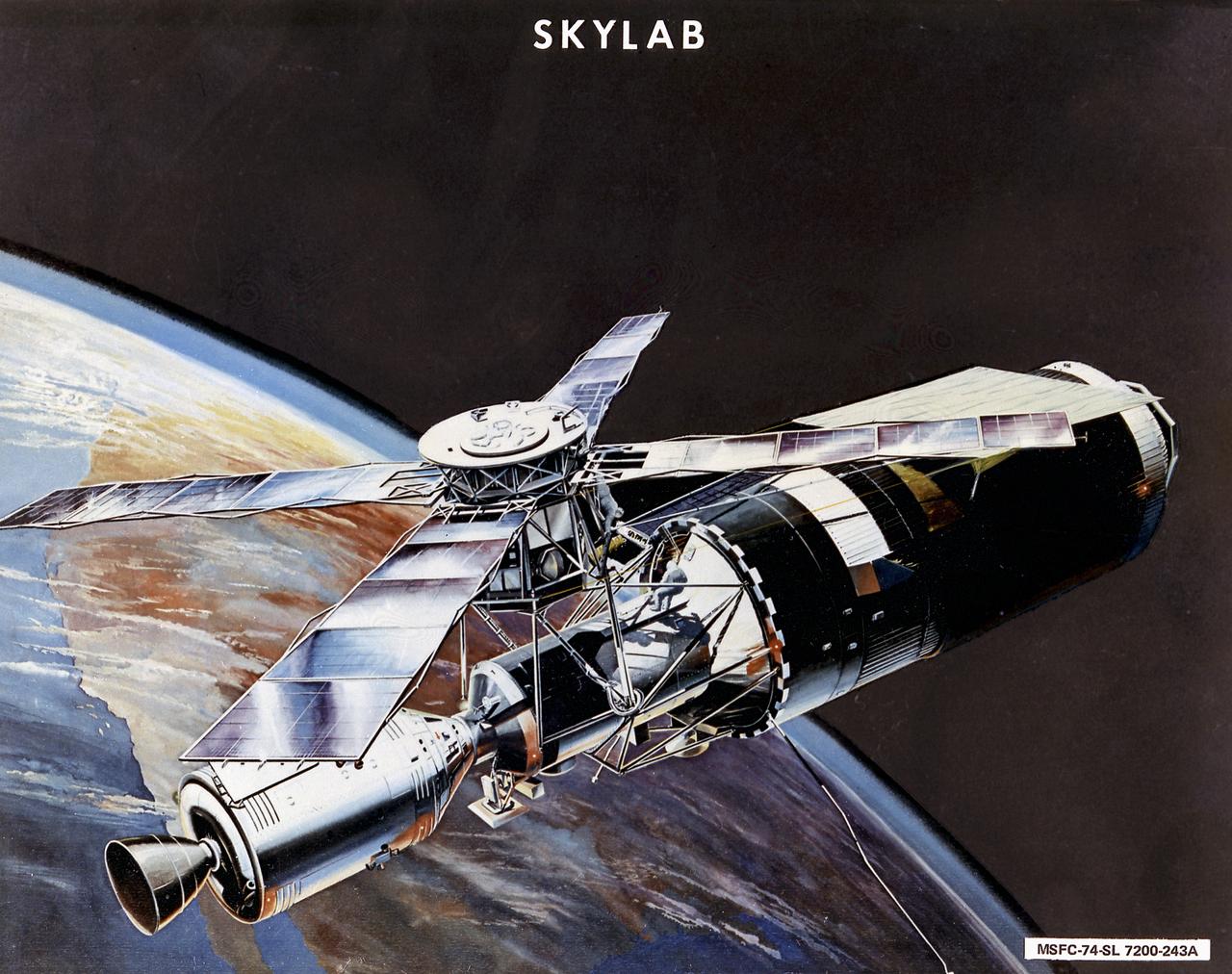

This image is an artist's concept of the Skylab in orbit. In an early effort to extend the use of Apollo for further applications, NASA established the Apollo Applications Program (AAP) in August of 1965. The AAP was to include long duration Earth orbital missions during which astronauts would carry out scientific, technological, and engineering experiments in space by utilizing modified Saturn launch vehicles and the Apollo spacecraft. Established in 1970, the Skylab program was the forerurner of the AAP. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The Skylab also conducted 19 selected experiments submitted by high school students. Skylab's 3 different 3-man crews spent up to 84 days in Earth orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments. MSFC was also responsible for providing the Saturn IB launch vehicles for three Apollo spacecraft and crews and a Saturn V launch vehicle for the Skylab.
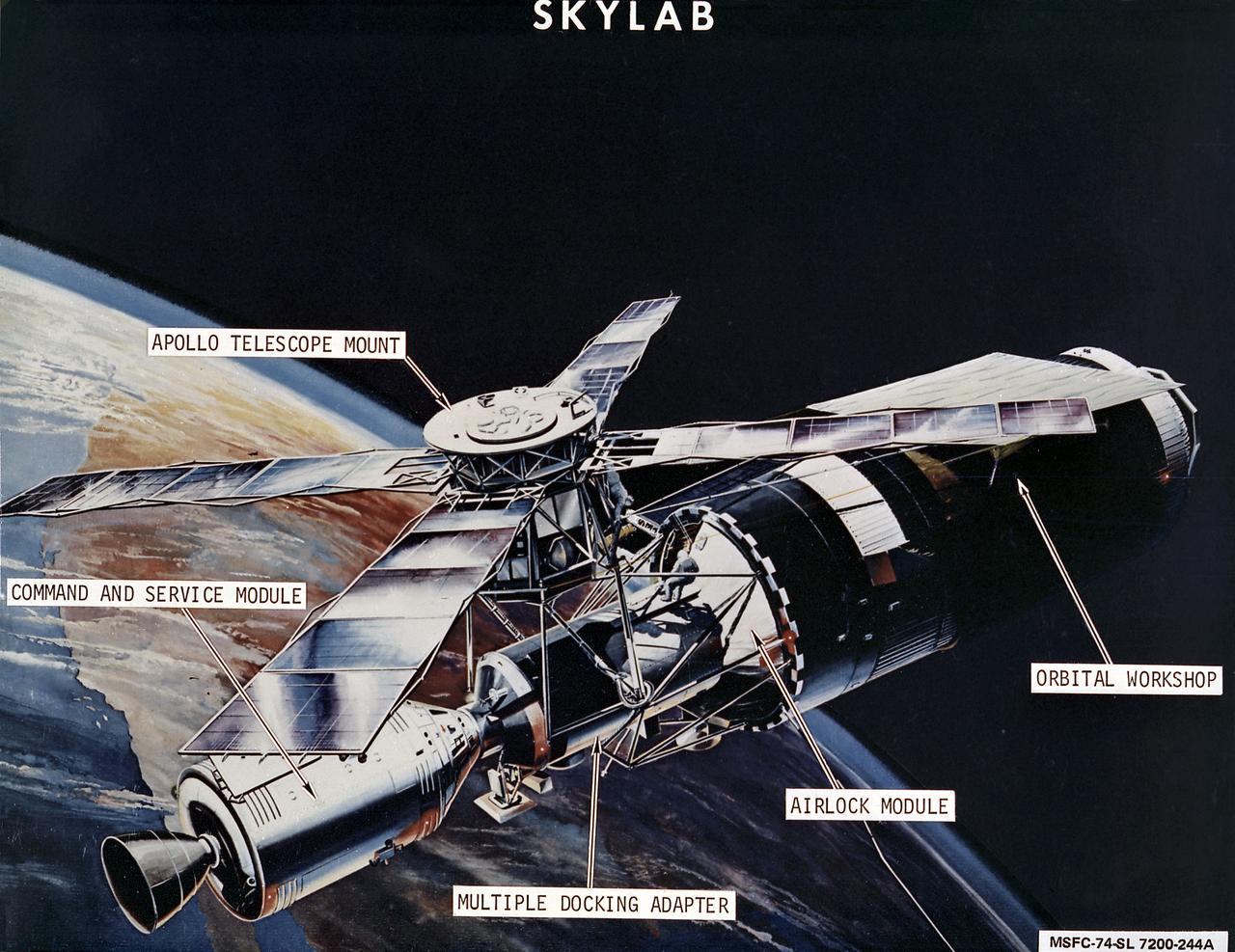
This image is an artist's concept of the Skylab in orbit with callouts of its major components. In an early effort to extend the use of Apollo for further applications, NASA established the Apollo Applications Program (AAP) in August of 1965. The AAP was to include long duration Earth orbital missions during which astronauts would carry out scientific, technological, and engineering experiments in space by utilizing modified Saturn launch vehicles and the Apollo spacecraft. Established in 1970, the Skylab Program was the forerurner of the AAP. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The Skylab also conducted 19 selected experiments submitted by high school students. Skylab's 3 different 3-man crews spent up to 84 days in Earth orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments. MSFC was also responsible for providing the Saturn IB launch vehicles for three Apollo spacecraft and crews and a Saturn V launch vehicle for the Skylab.
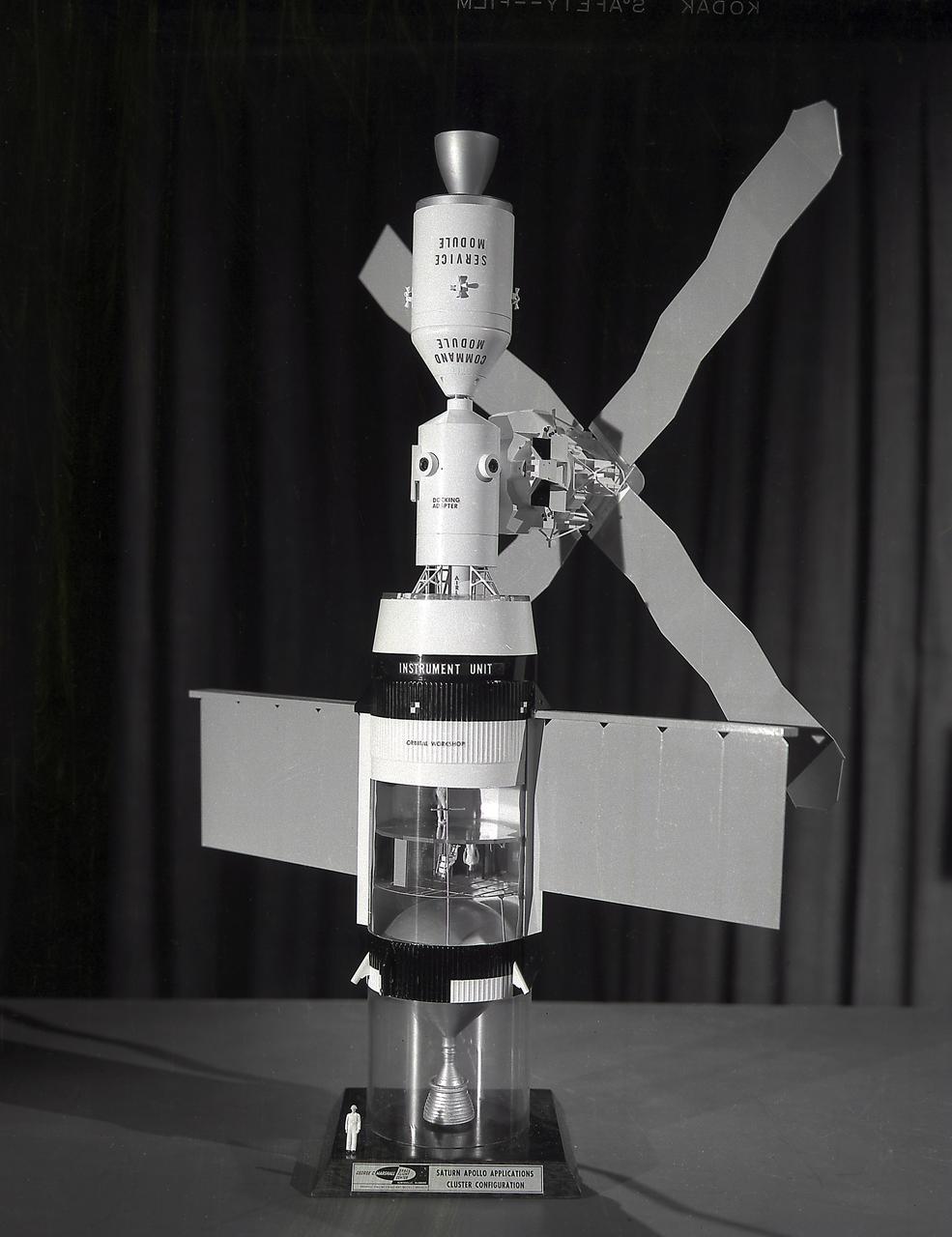
This photograph is of a model of the Skylab with the Command/Service Module being docked. In an early effort to extend the use of Apollo for further applications, NASA established the Apollo Applications Program (AAP) in August of 1965. The AAP was to include long duration Earth orbital missions during which astronauts would carry out scientific, technological, and engineering experiments in space by utilizing modified Saturn launch vehicles and the Apollo spacecraft. Established in 1970, the Skylab Program was the forerurner of the AAP. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The Skylab also conducted 19 selected experiments submitted by high school students. Skylab's 3 different 3-man crews spent up to 84 days in Earth orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments. MSFC was also responsible for providing the Saturn IB launch vehicles for three Apollo spacecraft and crews and a Saturn V launch vehicle for the Skylab.
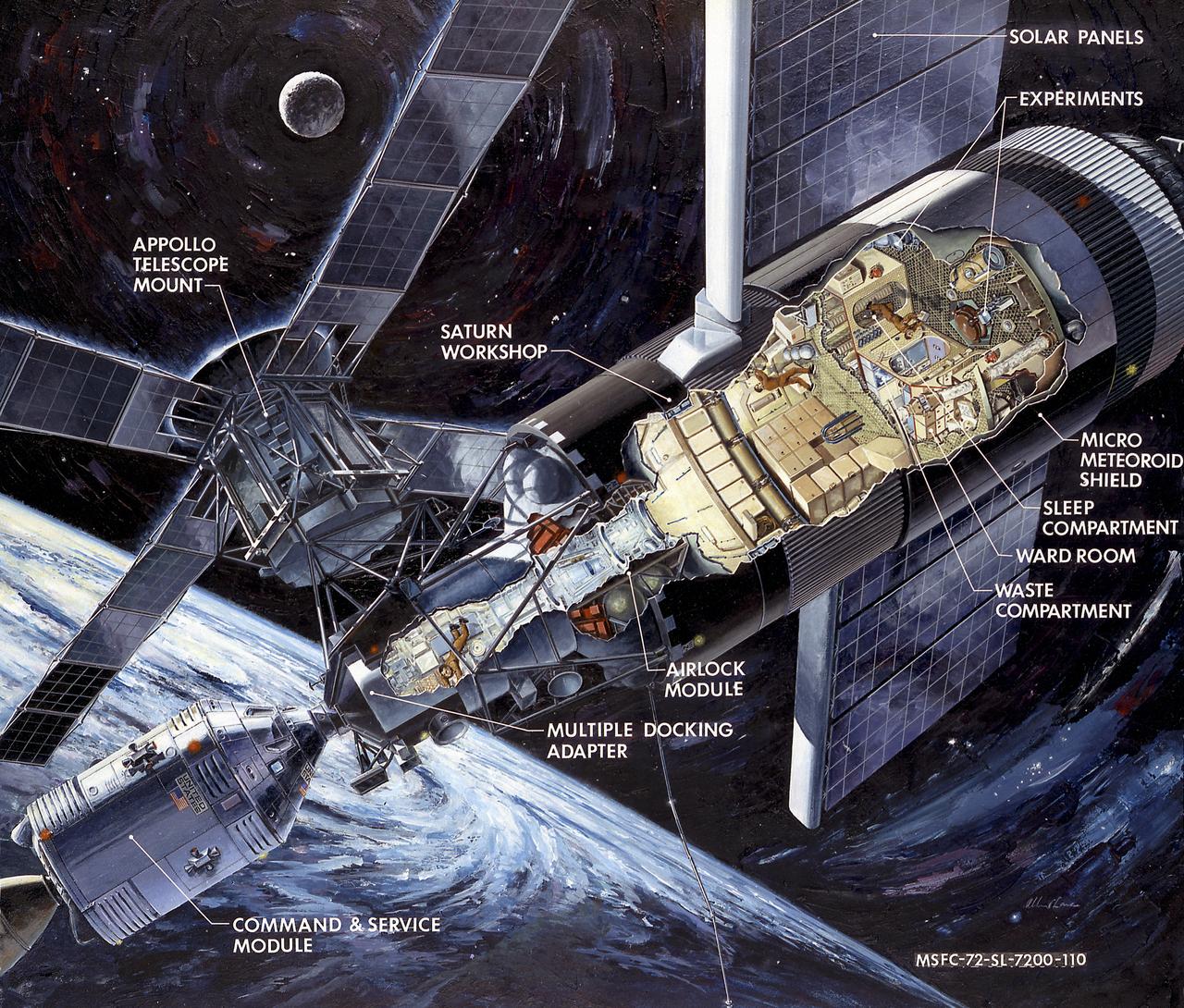
This artist's concept is a cutaway illustration of the Skylab with the Command/Service Module being docked to the Multiple Docking Adapter. In an early effort to extend the use of Apollo for further applications, NASA established the Apollo Applications Program (AAP) in August of 1965. The AAP was to include long duration Earth orbital missions during which astronauts would carry out scientific, technological, and engineering experiments in space by utilizing modified Saturn launch vehicles and the Apollo spacecraft. Established in 1970, the Skylab Program was the forerurner of the AAP. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The Skylab also conducted 19 selected experiments submitted by high school students. Skylab's 3 different 3-man crews spent up to 84 days in Earth orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments. MSFC was also responsible for providing the Saturn IB launch vehicles for three Apollo spacecraft and crews and a Saturn V launch vehicle for the Skylab.

S73-27508 (6 June 1973) --- An artist's concept showing astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Skylab 2 commander, attempting to free the solar array system wing on the Orbital Workshop during extravehicular activity at the Skylab 1 & 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit. The astronaut in the background is Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot. Here, Conrad is pushing up on the Beam Erection Tether (BET) to raise the stuck solar panel. The solar wing is only partially deployed; an aluminum strap is believed to be holding it down. Note the cut aluminum angle. Attach points for the BET are on the vent module of the solar array beam. The other end of the BET is attached to the "A" frame supporting the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) which is out of view. The aluminum strapping is to be out first, freeing the solar array beam. Then, if the beam does not automatically deploy, Conrad will attempt to help by pulling on the BET. The automatic openers may have become too cold to open without assistance. A deployed solar panel of the ATM is at upper left. The EVA is scheduled for Thursday, June 7th. This concept is by artist Paul Fjeld. Photo credit: NASA
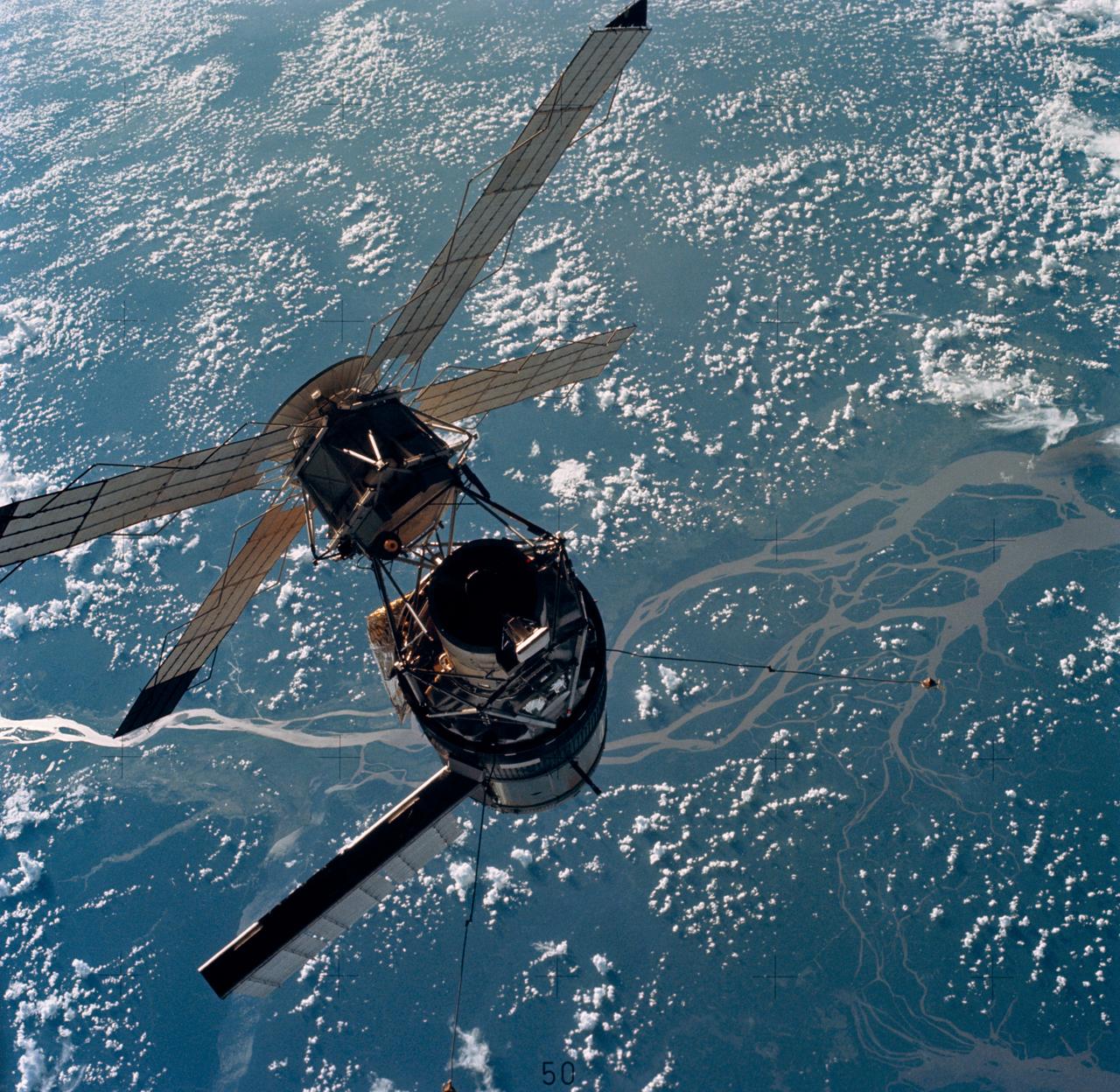

SL3-114-1683 (28 July 1973) --- A close-up view of the Skylab space station photographed against an Earth background from the Skylab 3 Command and Service Modules (CSM) during station-keeping maneuvers prior to docking. Aboard the Command Module (CM) were astronauts Alan L. Bean, Owen K. Garriott and Jack R. Lousma, who remained with the Skylab Space Station in Earth orbit for 59 days. This picture was taken with a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera using a 100mm lens and SO-368 medium speed Ektachrome film. Note the one solar array system wing on the Orbital Workshop (OWS) which was successfully deployed during extravehicular activity (EVA) on the first manned Skylab flight. The parasol solar shield which was deployed by the Skylab 2 crew can be seen through the support struts of the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM). Photo credit: NASA

S74-17456 (3 Feb. 1974) --- Scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson has just egressed the Skylab EVA hatchway in this frame taken from a roll of movie film exposed by a 16mm Maurer camera. Astronaut Gerald P. Carr, Skylab 4 commander, took this picture during the final Skylab extravehicular activity (EVA) which took place on Feb. 3, 1974. Carr was above on the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) when he shot this frame of Gibson. Note Carr's umbilical/tether line extending from inside the space station up toward the camera. Astronaut William R. Pogue, Skylab 4 pilot, remained inside the space station during the EVA by Carr and Gibson. Photo credit: NASA
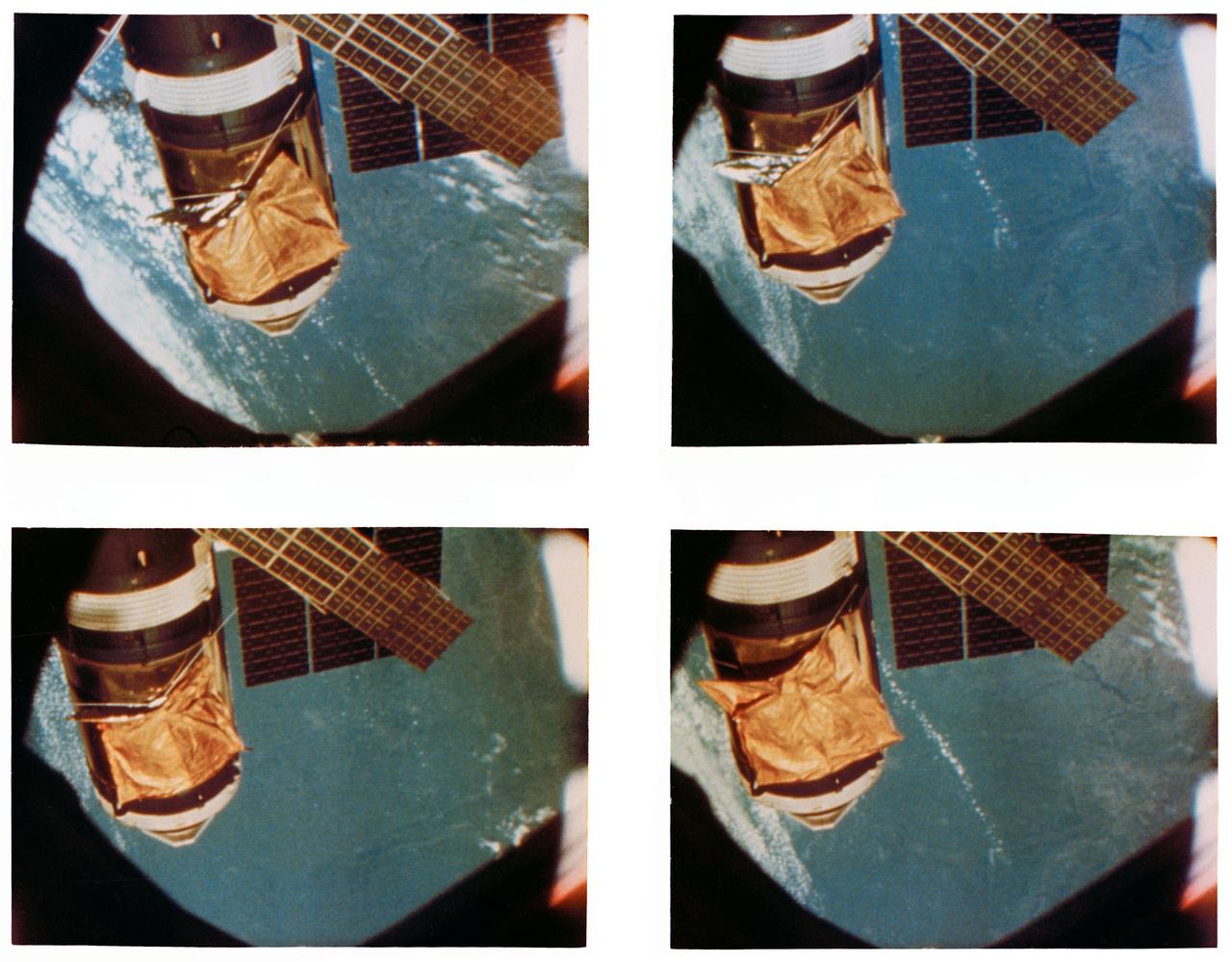
S73-34619 (28 July 1973) --- A composite of four frames taken from 16mm movie camera footage showing an overhead view of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. The Maurer motion picture camera scenes were being filmed during the Skylab 3 Command/Service Module's (CSM) first "fly around" inspection of the space station. Close comparison of the four frames reveals movement of the improvised parasol solar shield over the Orbital Workshop (OWS). The "flapping" of the sun shade was caused from the exhaust of the reaction control subsystem (RCS) thrusters of the Skylab 3 CSM. The one remaining solar array system wing on the OWS is in the lower left background. The solar panel in the lower left foreground is on the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM). Photo credit: NASA

S73-23952 (May 1973) --- This is the official emblem for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Skylab Program. The emblem depicts the United States Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit with the sun in the background. Skylab will evaluate systems and techniques designed to gather information on Earth resources and environmental problems. Solar telescopes will increase man's knowledge of our sun and the multitude of solar influences on Earth environment. Medical experiments will increase knowledge of man himself and his relationship to his earthly environment and adaptability to spaceflight. Additionally, Skylab will experiment with industrial processes which may be enhanced by the unique weightless, vacuum environment of orbital spaceflight. The 100-ton laboratory complex Skylab space station is composed of the Command/Service Module (CSM), Orbital Workshop (OW), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), and Airlock Module (AM). The NASA insignia design for Skylab is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
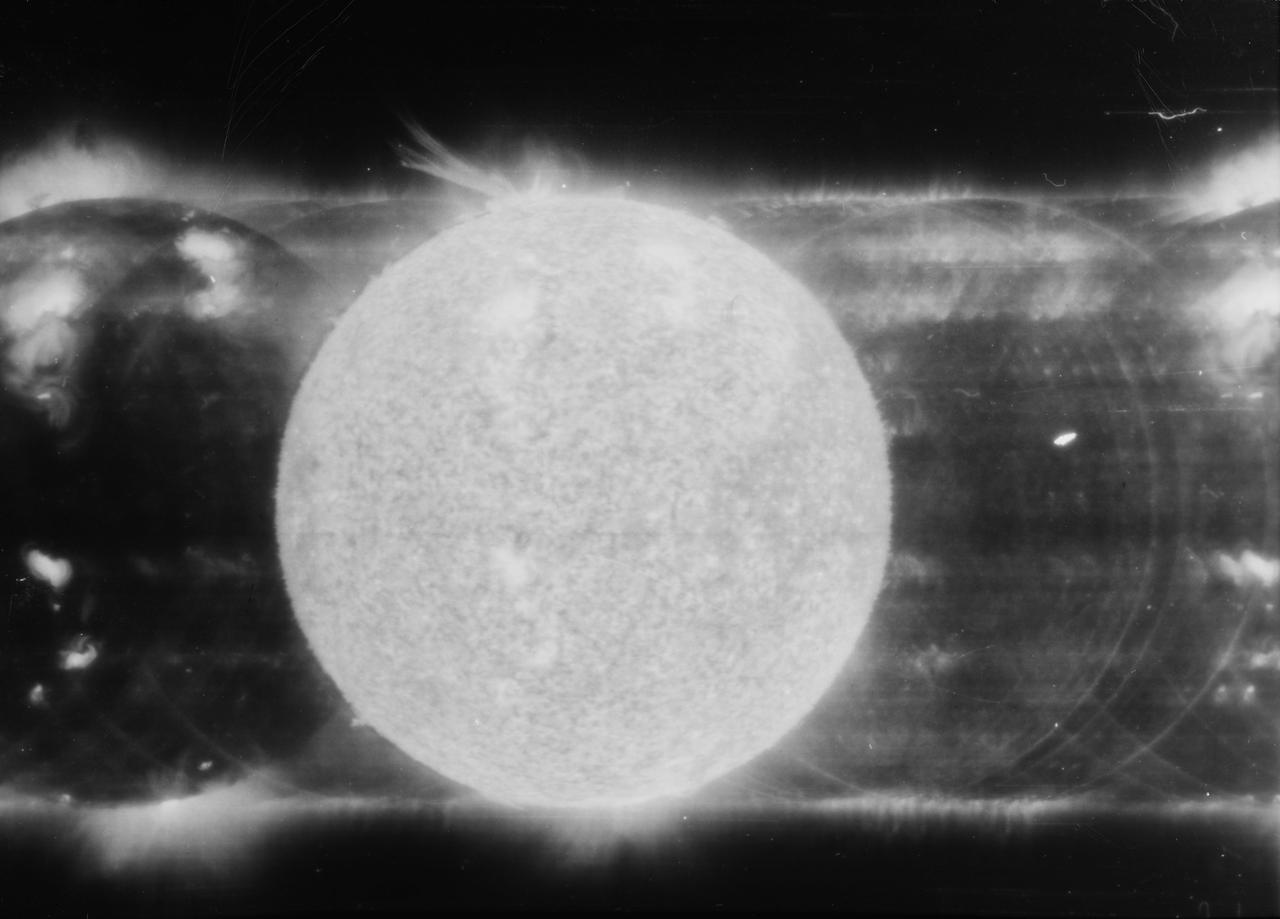

S73-33788 (10 June 1973) --- The solar eruption of June 10, 1973, is seen in this spectroheliogram obtained during the first manned Skylab mission (Skylab 2), with the SO82A experiment, an Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) component covering the wavelength region from 150 to 650 angstroms (EUV). The solid disk in the center was produced from 304 angstrom ultraviolet light from He + ions. At the top of this image a great eruption is visible extending more than one-third of a solar radius from the sun's surface. This eruption preceded the formation of an enormous coronal bubble which extended a distance of several radii from the sun's surface, and which was observed with the coronagraph aboard Skylab. In contrast, the Fe XV image at 285 angstrom just to the right of the 304 angstrom image does not show this event. Instead, it shows the bright emission from a magnetic region in the lower corona. In this picture, solar north is to the right, and east is up. The wavelength scale increases to the left. The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory is principal investigator in charge of the SO82 experiment. Photo credit: NASA
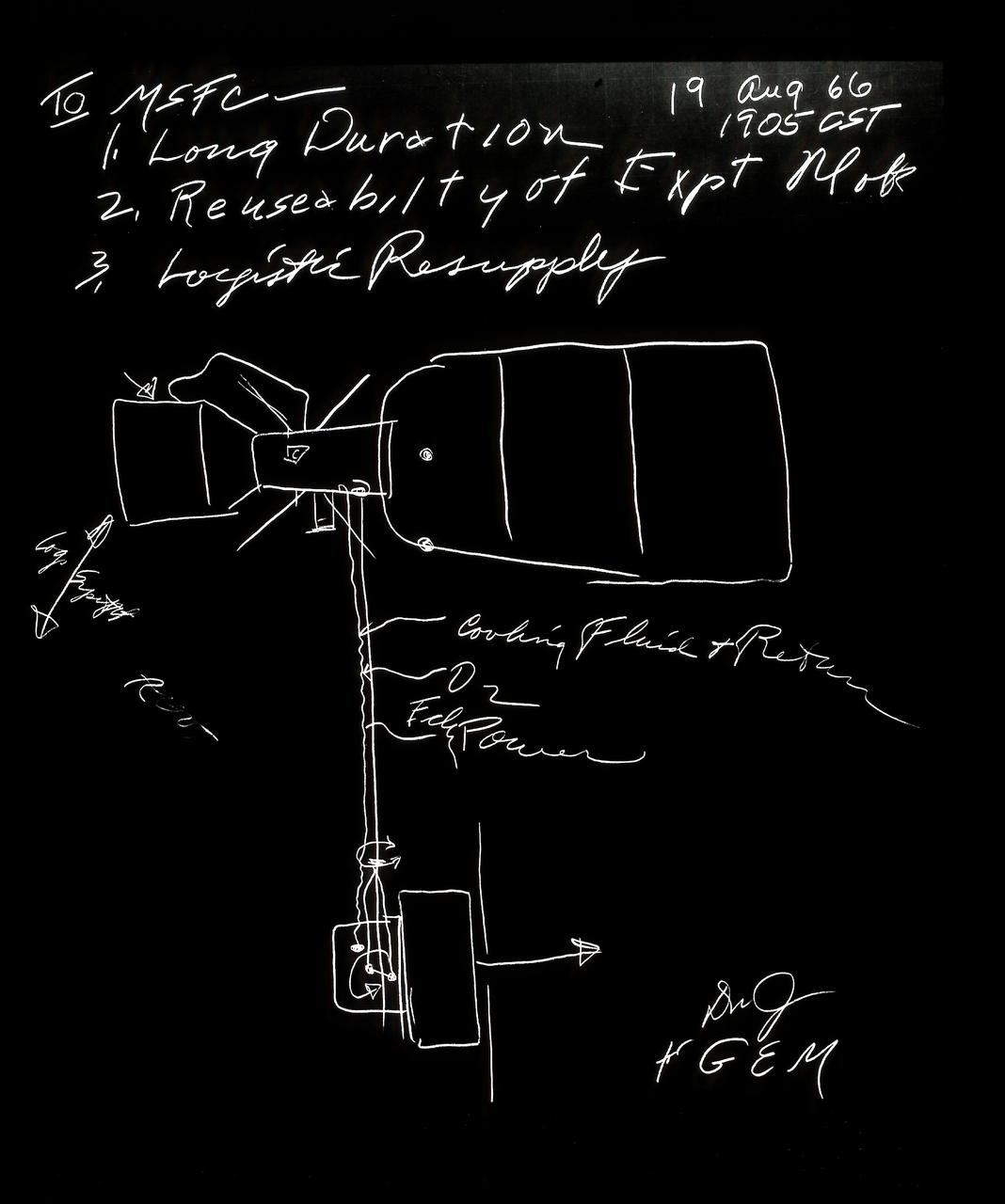
Seldom in aerospace history has a major decision been as promptly and concisely recorded as with the Skylab shown in this sketch. At a meeting at the Marshall Space Flight Center on August 19, 1966, George E. Mueller, NASA Associate Administrator for Marned Space Flight, used a felt pen and poster paper to pin down the final conceptual layout for the budding space station's (established as the Skylab in 1970) major elements. General Davy Jones, first program director, added his initials and those of Dr. Mueller in the lower right corner. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The Skylab also conducted 19 selected experiments submitted by high school students. Skylab's 3 different 3-man crews spent up to 84 days in Earth orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments. MSFC was also responsible for providing the Saturn IB launch vehicles for three Apollo spacecraft and crews and a Saturn V launch vehicle for the Skylab.