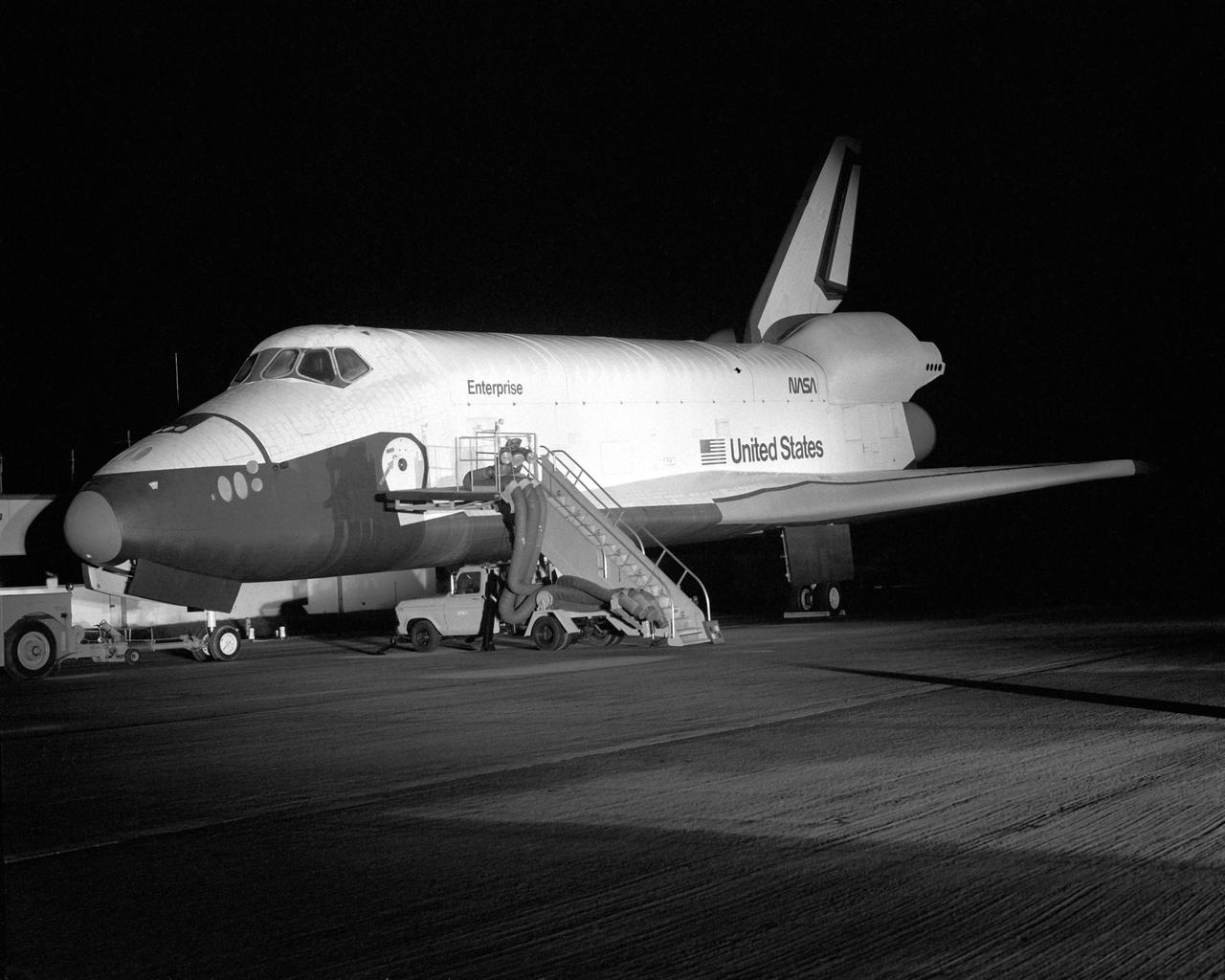

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Space Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise – night landing test. Photo Credit: NASA

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Enterprise in California at VAFB. Photo credit: NASA
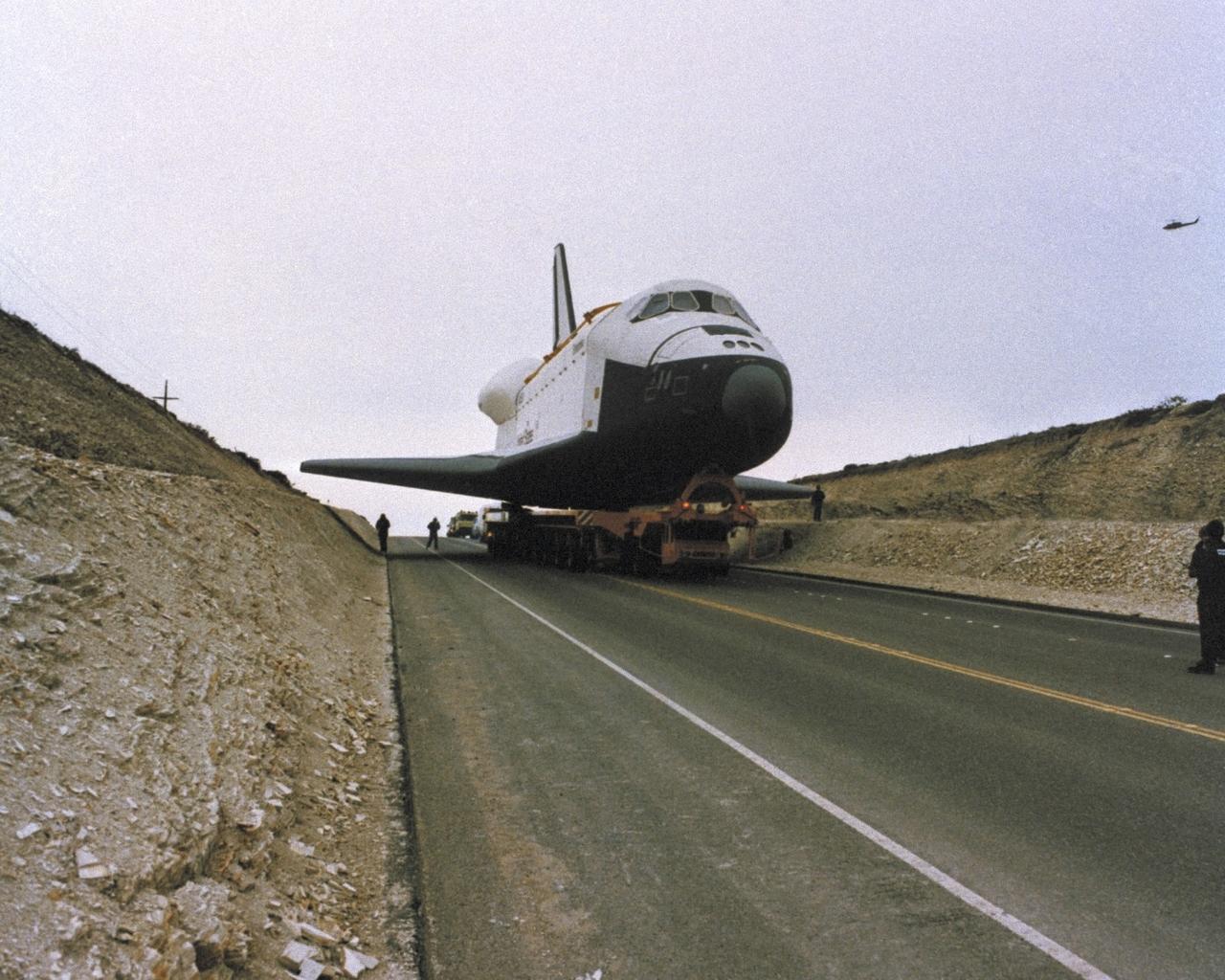

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Enterprise in California at VAFB. Photo Credit: NASA
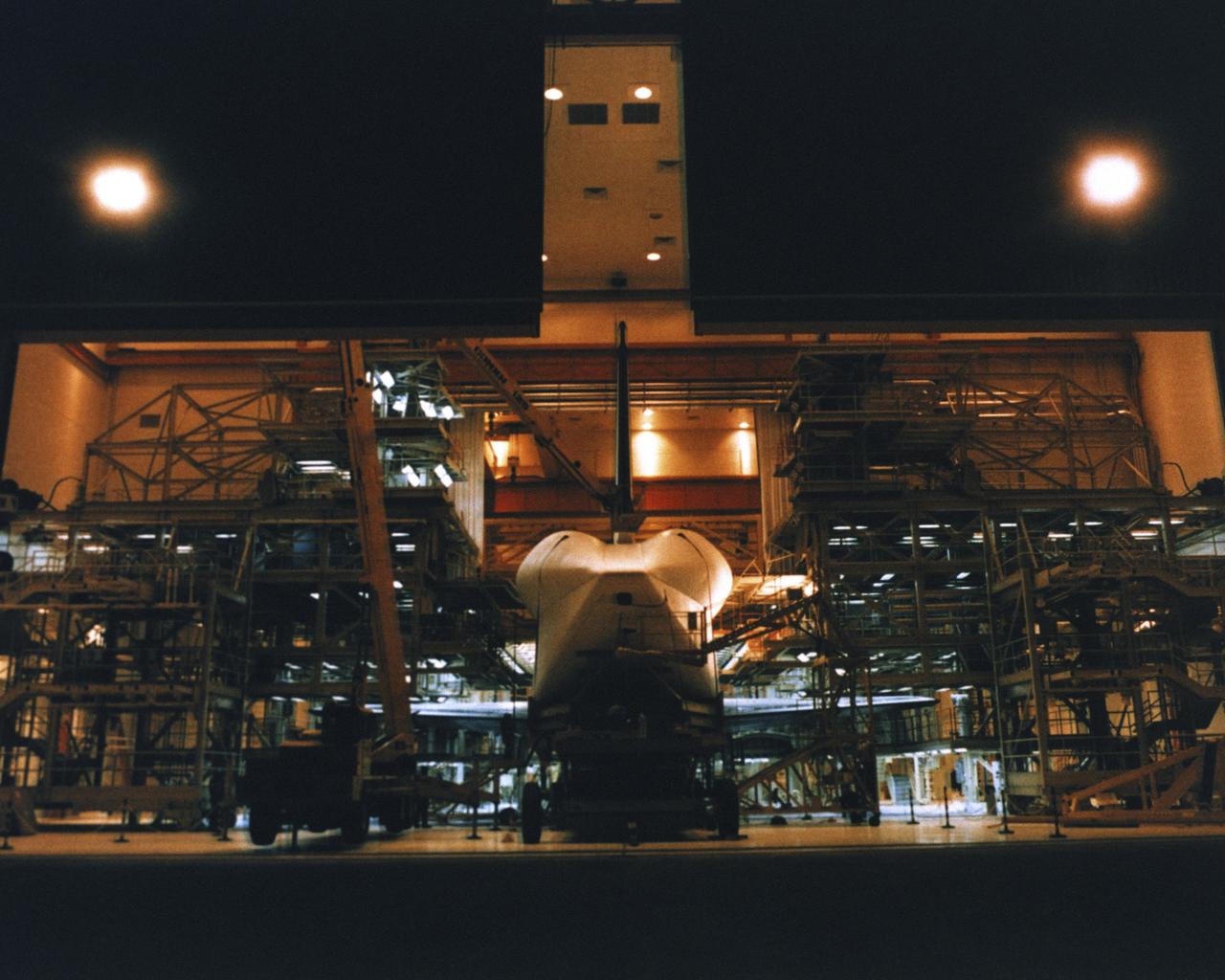

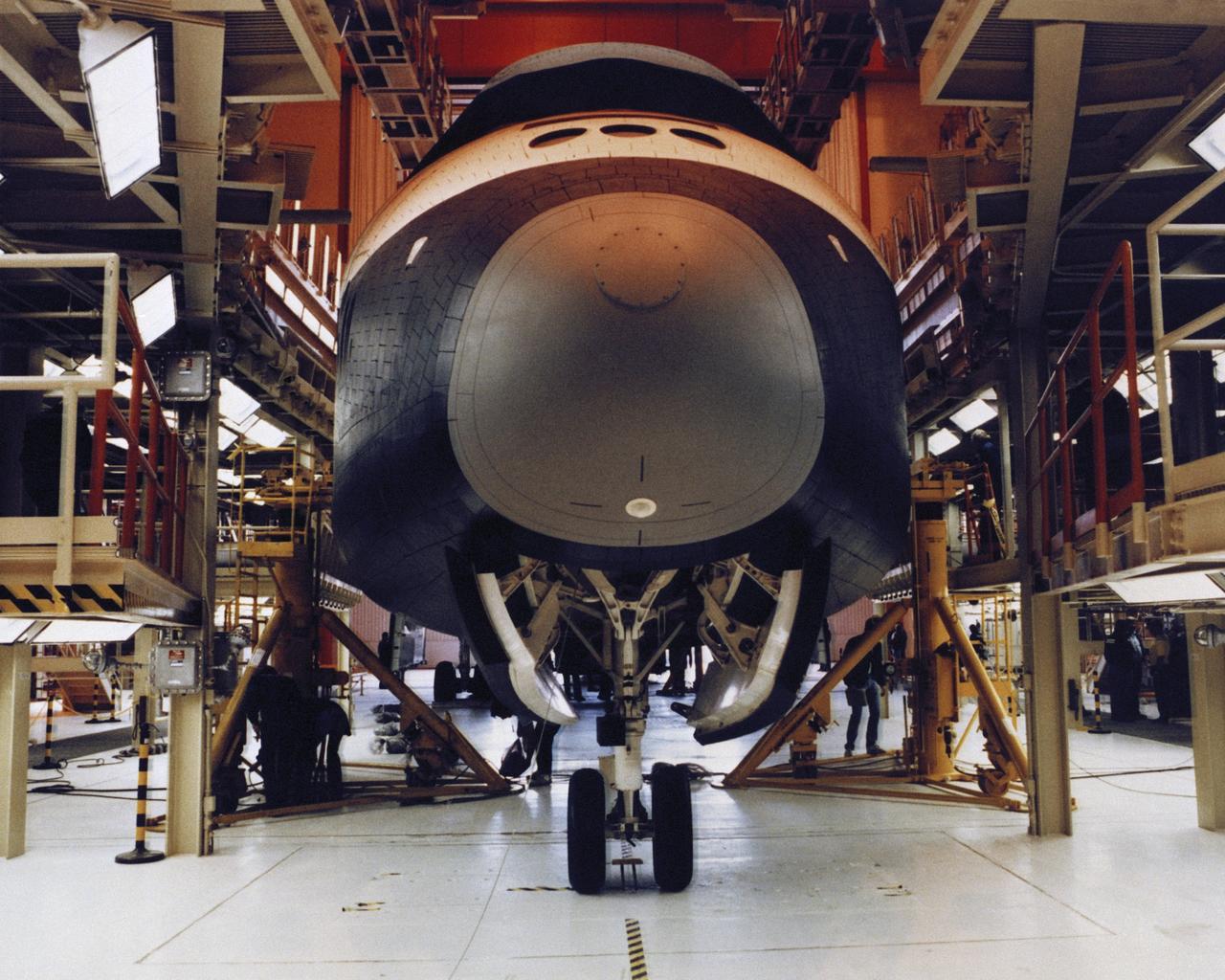
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Enterprise inside the Orbiter Maintenance and Checkout Facility at Vandenberg AFB, California. Photo Credit: NASA

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Enterprise inside the Orbiter Maintenance and Checkout Facility at Vandenberg AFB, California. Photo Credit: NASA

Project LOLA. Test subject sitting at the controls: Project LOLA or Lunar Orbit and Landing Approach was a simulator built at Langley to study problems related to landing on the lunar surface. It was a complex project that cost nearly 2 million dollars. James Hansen wrote: This simulator was designed to provide a pilot with a detailed visual encounter with the lunar surface the machine consisted primarily of a cockpit, a closed-circuit TV system, and four large murals or scale models representing portions of the lunar surface as seen from various altitudes. The pilot in the cockpit moved along a track past these murals which would accustom him to the visual cues for controlling a spacecraft in the vicinity of the moon. Unfortunately, such a simulation--although great fun and quite aesthetic--was not helpful because flight in lunar orbit posed no special problems other than the rendezvous with the LEM, which the device did not simulate. Not long after the end of Apollo, the expensive machine was dismantled. (p. 379) Ellis J. White wrote in his paper, Discussion of Three Typical Langley Research Center Simulation Programs : A typical mission would start with the first cart positioned on model 1 for the translunar approach and orbit establishment. After starting the descent, the second cart is readied on model 2 and, at the proper time, when superposition occurs, the pilot s scene is switched from model 1 to model 2. then cart 1 is moved to and readied on model 3. The procedure continues until an altitude of 150 feet is obtained. The cabin of the LM vehicle has four windows which represent a 45 degree field of view. The projection screens in front of each window represent 65 degrees which allows limited head motion before the edges of the display can be seen. The lunar scene is presented to the pilot by rear projection on the screens with four Schmidt television projectors. The attitude orientation of the vehicle is represented by changing the lunar scene through the portholes determined by the scan pattern of four orthicons. The stars are front projected onto the upper three screens with a four-axis starfield generation (starball) mounted over the cabin and there is a separate starball for the low window. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 379 Ellis J. White, Discussion of Three Typical Langley Research Center Simulation Programs, Paper presented at the Eastern Simulation Council (EAI s Princeton Computation Center), Princeton, NJ, October 20, 1966.
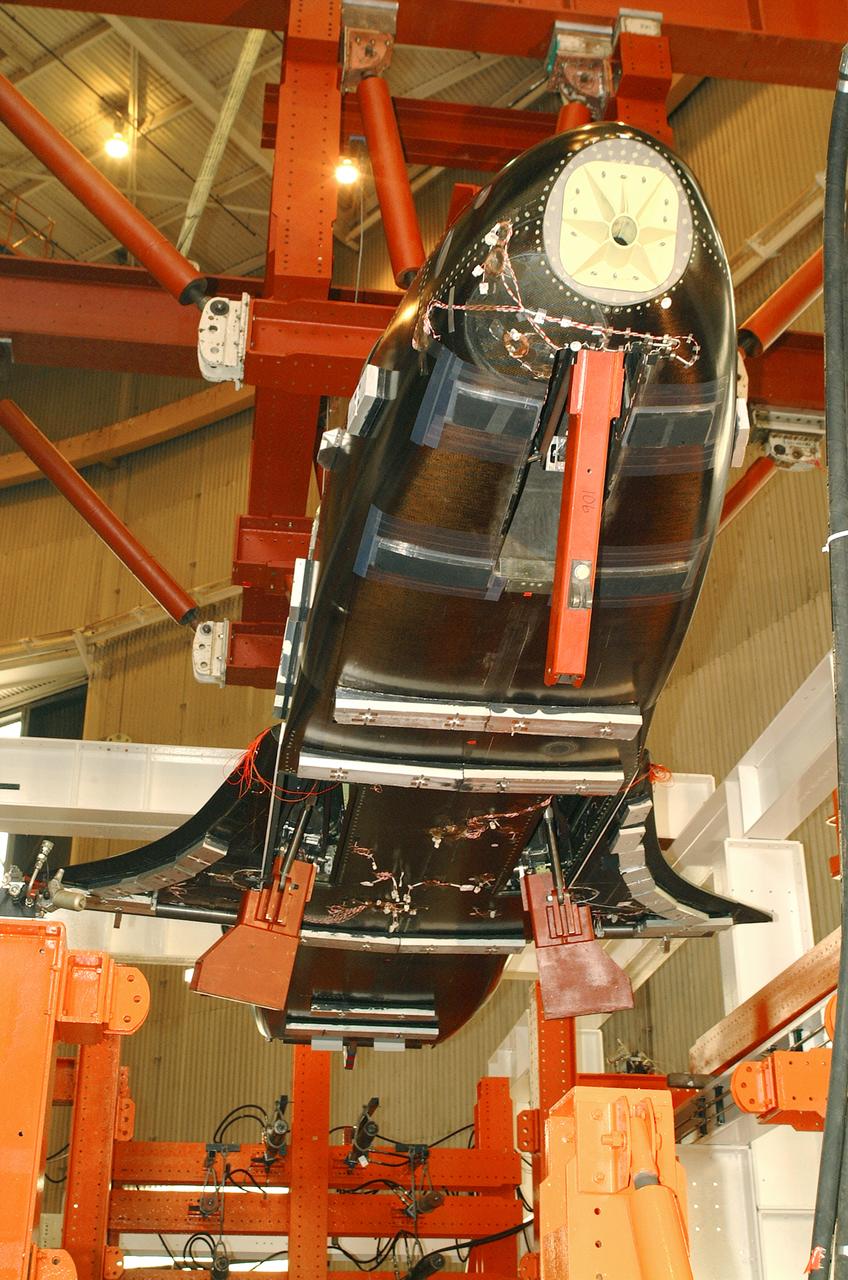

NASA's X-37 Approach and Landing Test Vehicle is installed is a structural facility at Boeing's Huntington Beach, California plant. Tests, completed in July, were conducted to verify the structural integrity of the vehicle in preparation for atmospheric flight tests. Atmospheric flight tests of the Approach and Landing Test Vehicle are scheduled for 2004 and flight tests of the Orbital Vehicle are scheduled for 2006. The X-37 experimental launch vehicle is roughly 27.5 feet (8.3 meters) long and 15 feet (4.5 meters) in wingspan. It's experiment bay is 7 feet (2.1 meters) long and 4 feet (1.2 meters) in diameter. Designed to operate in both the orbital and reentry phases of flight, the X-37 will increase both safety and reliability, while reducing launch costs from $10,000 per pound to $1,000.00 per pound. The X-37 program is managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
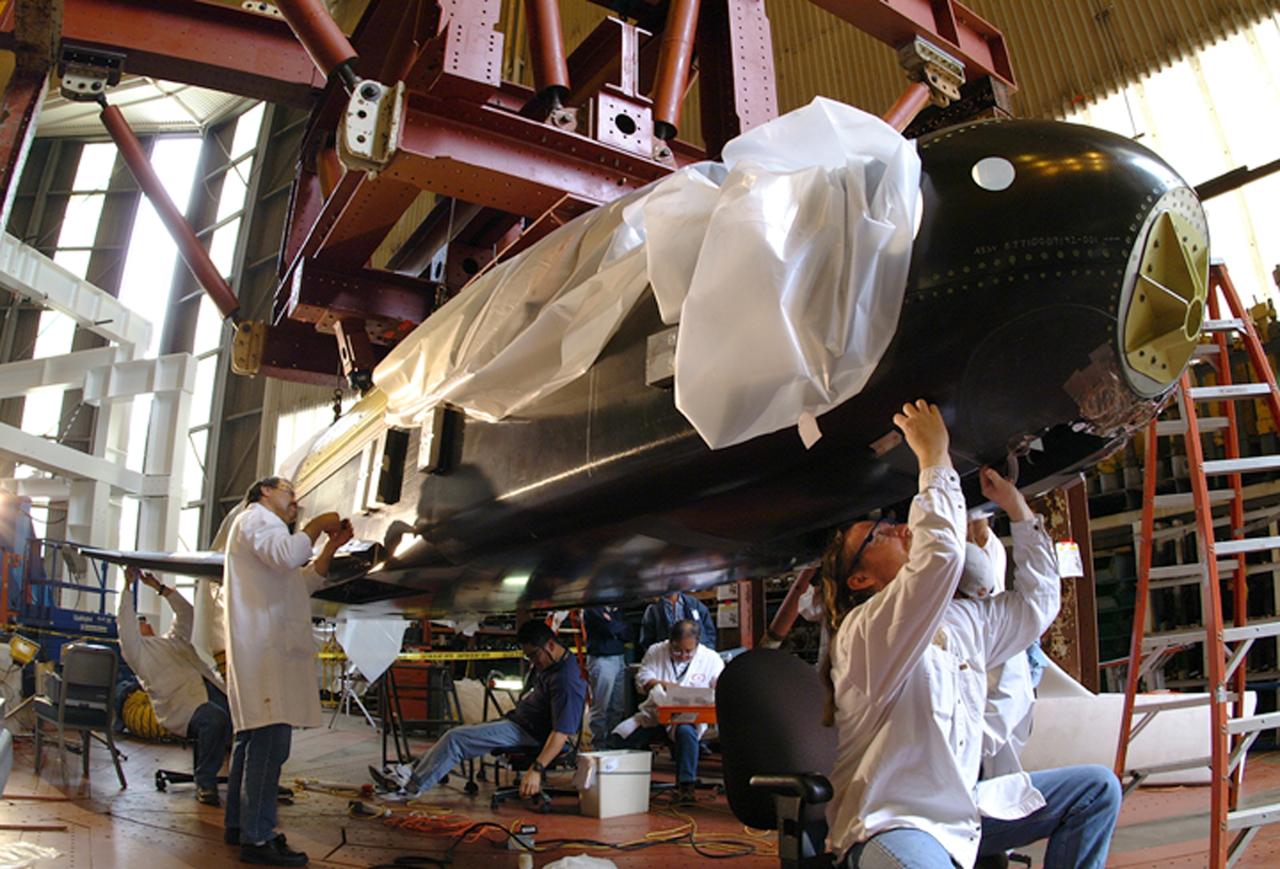

NASA's X-37 Approach and Landing Test Vehicle is installed is a structural facility at Boeing's Huntington Beach, California plant, where technicians make adjustments to composite panels. Tests, completed in July, were conducted to verify the structural integrity of the vehicle in preparation for atmospheric flight tests. Atmospheric flight tests of the Approach and Landing Test Vehicle are scheduled for 2004 and flight tests of the Orbital Vehicle are scheduled for 2006. The X-37 experimental launch vehicle is roughly 27.5 feet (8.3 meters) long and 15 feet (4.5 meters) in wingspan. It's experiment bay is 7 feet (2.1 meters) long and 4 feet (1.2 meters) in diameter. Designed to operate in both the orbital and reentry phases of flight, the X-37 will increase both safety and reliability, while reducing launch costs from $10,000 per pound to $1,000.00 per pound. The X-37 program is managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Dave Sanborn (left) conducts a bond verification test on Thermal Protection System tiles installed on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Dave Sanborn installs Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
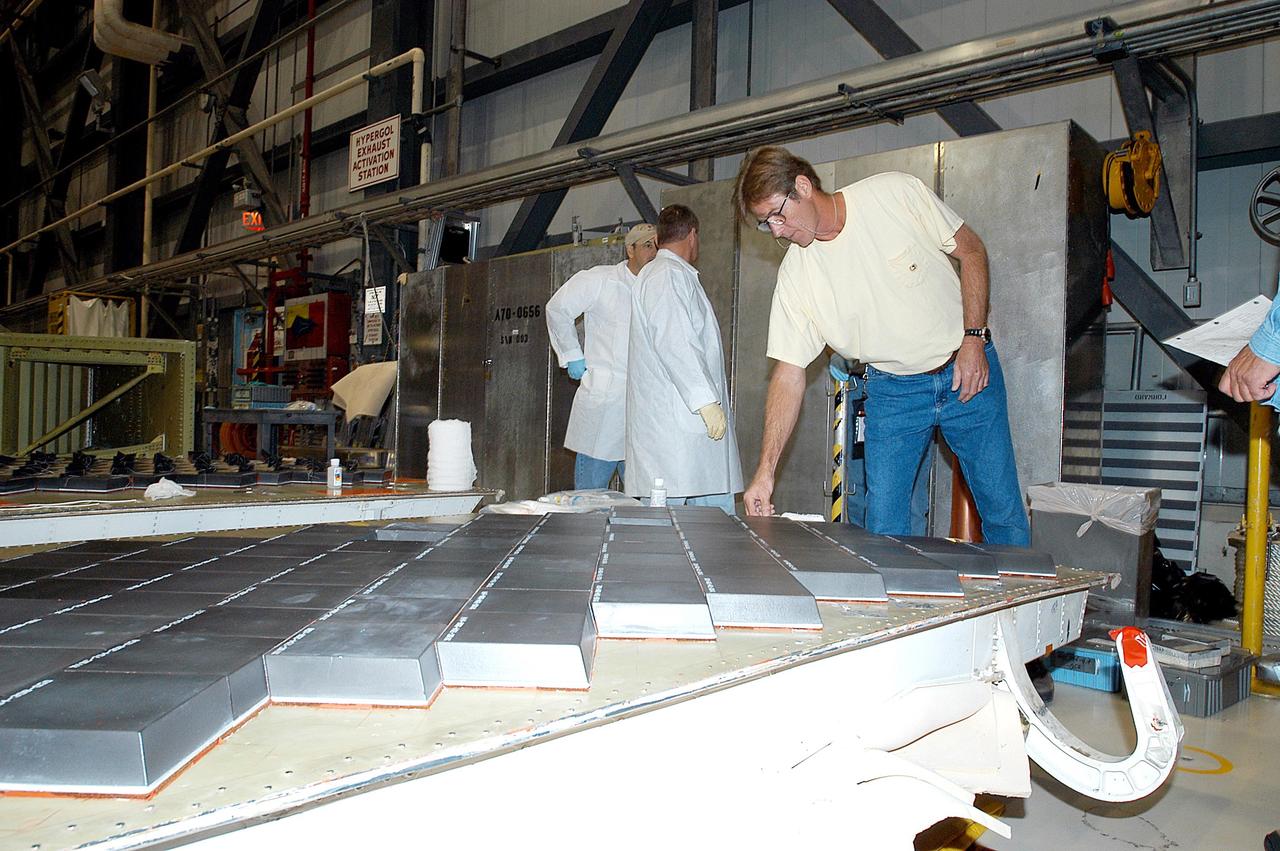

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Harrell Watts (right) installs Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Harrell Watts installs Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
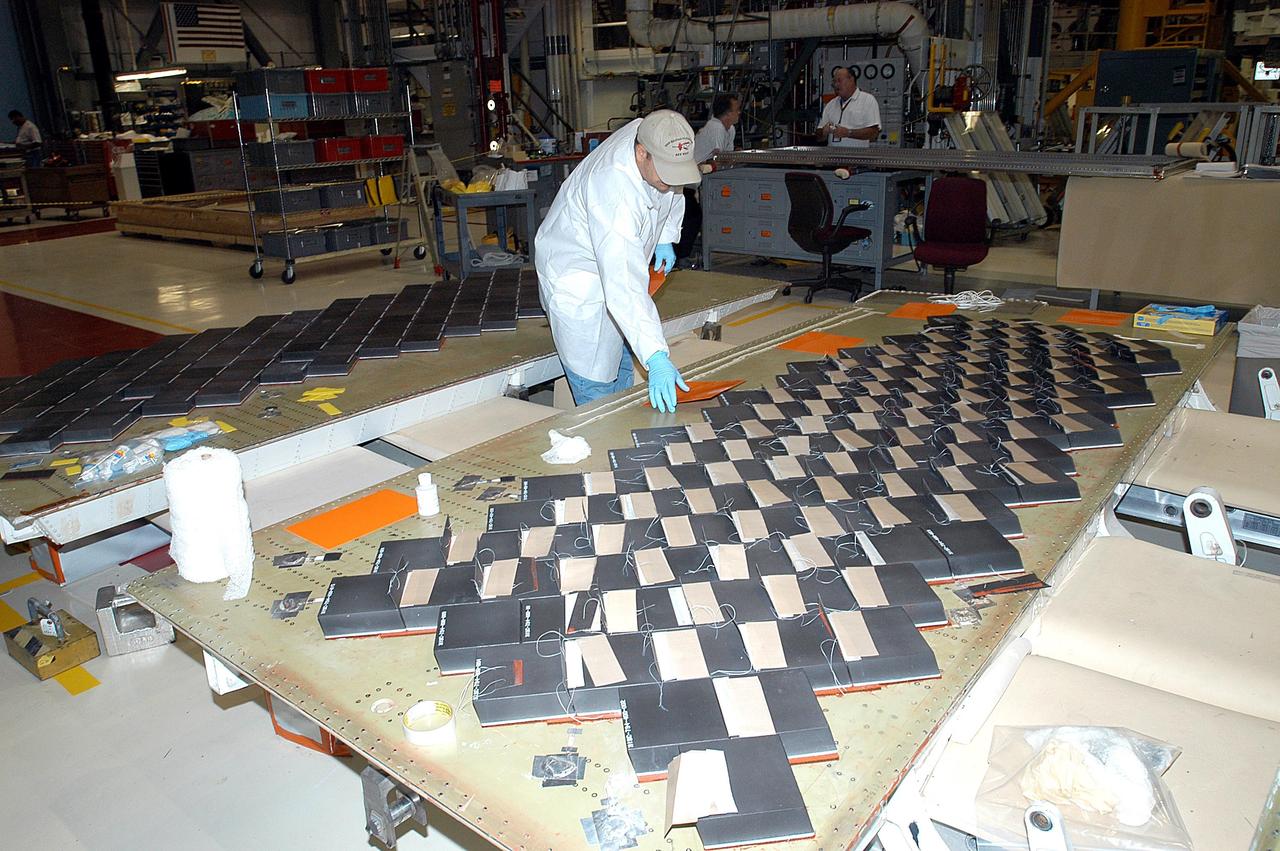

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Mike Cote works on installing Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
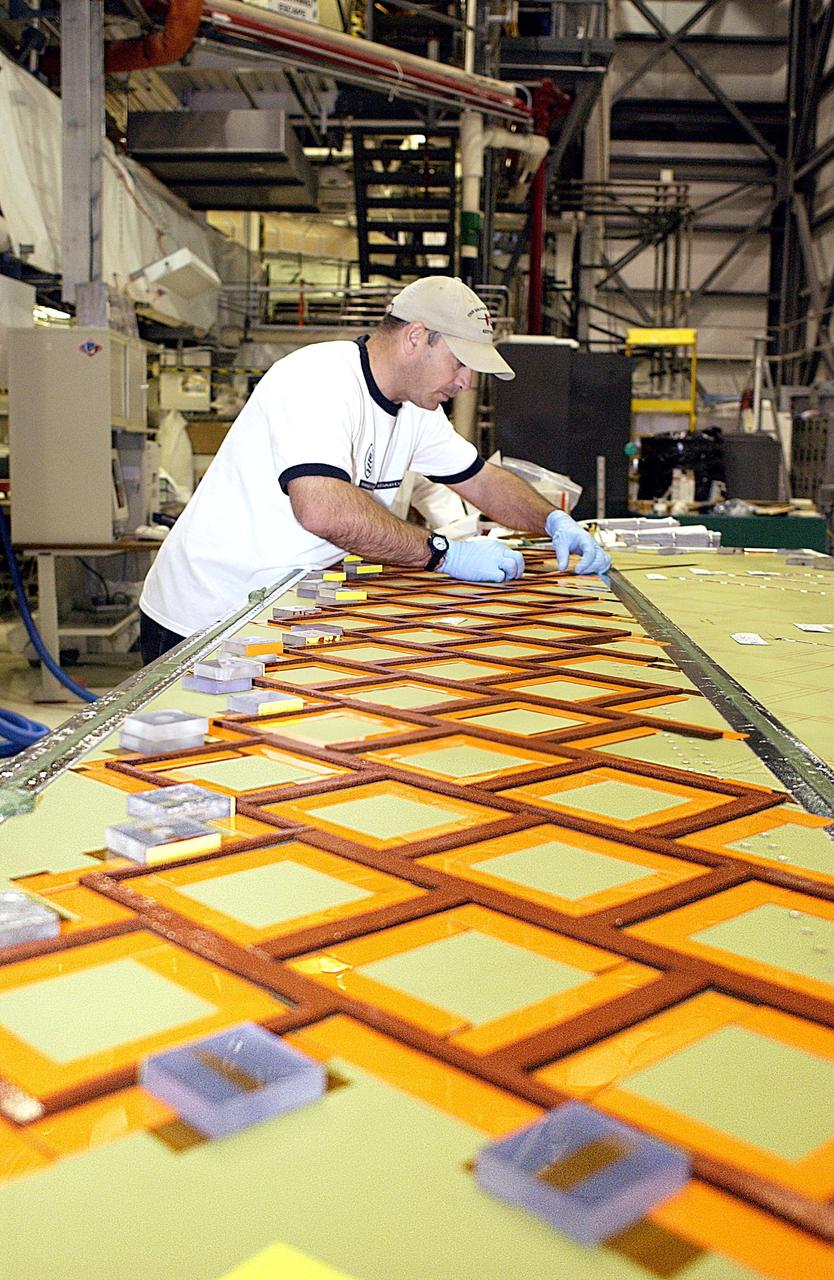

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Mike Cote installs Thermal Protection System tiles on a test panel. The test panel and sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
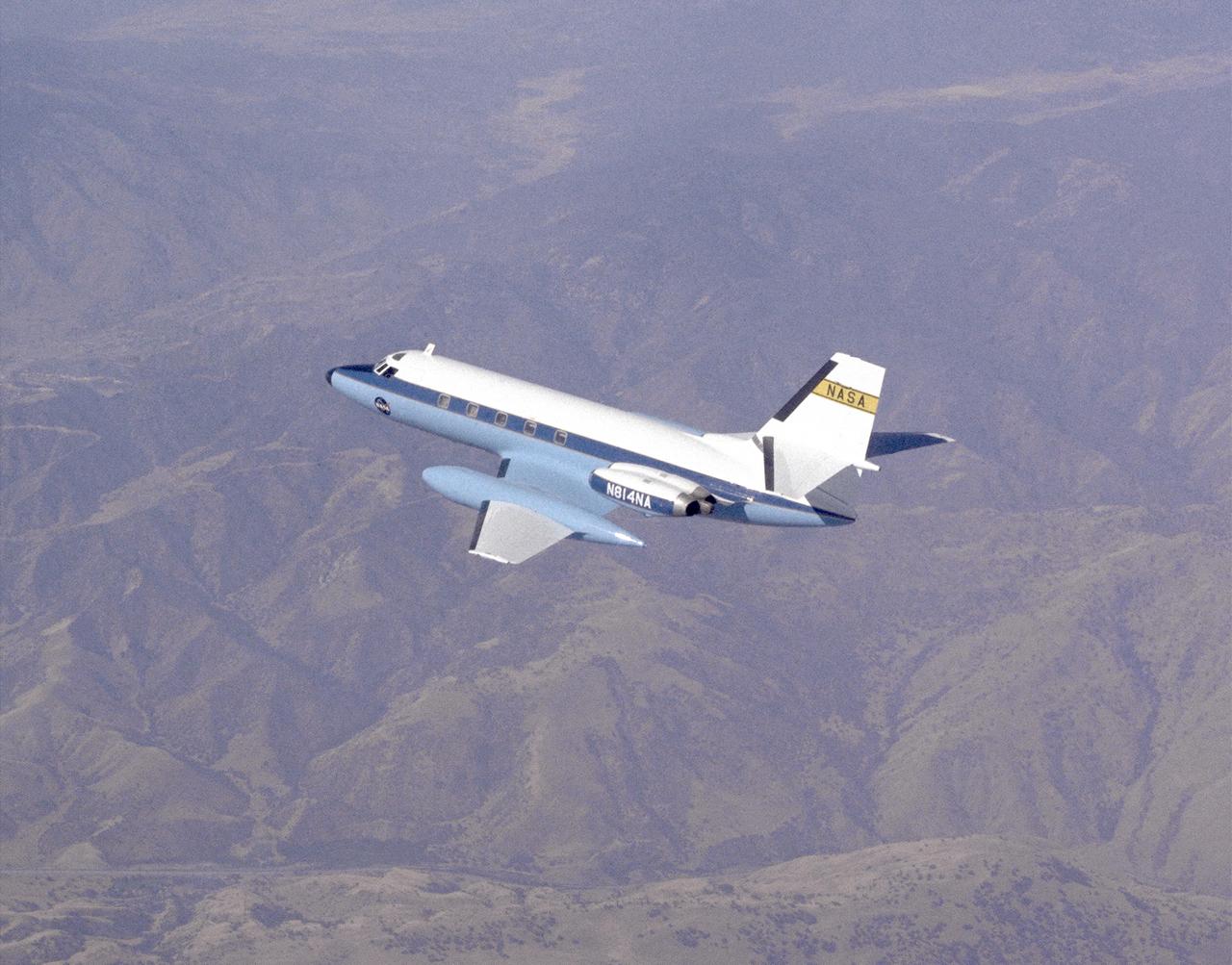

The C-140 JetStar was reconfigured as the General Purpose Airborne Simulator (GPAS) to simulate the flight characteristics of other aircraft. The JetStar was used for research for supersonic transports, general aviation aircraft, and as a training support aircraft for the Space Shuttle Approach and Landing tests at Dryden Flight Research Center (under different names) at Edwards, CA, in 1977. One of the engineers on the GPAS program was Ken Szalai, who later became Dryden's director from 1990 to August 1998.
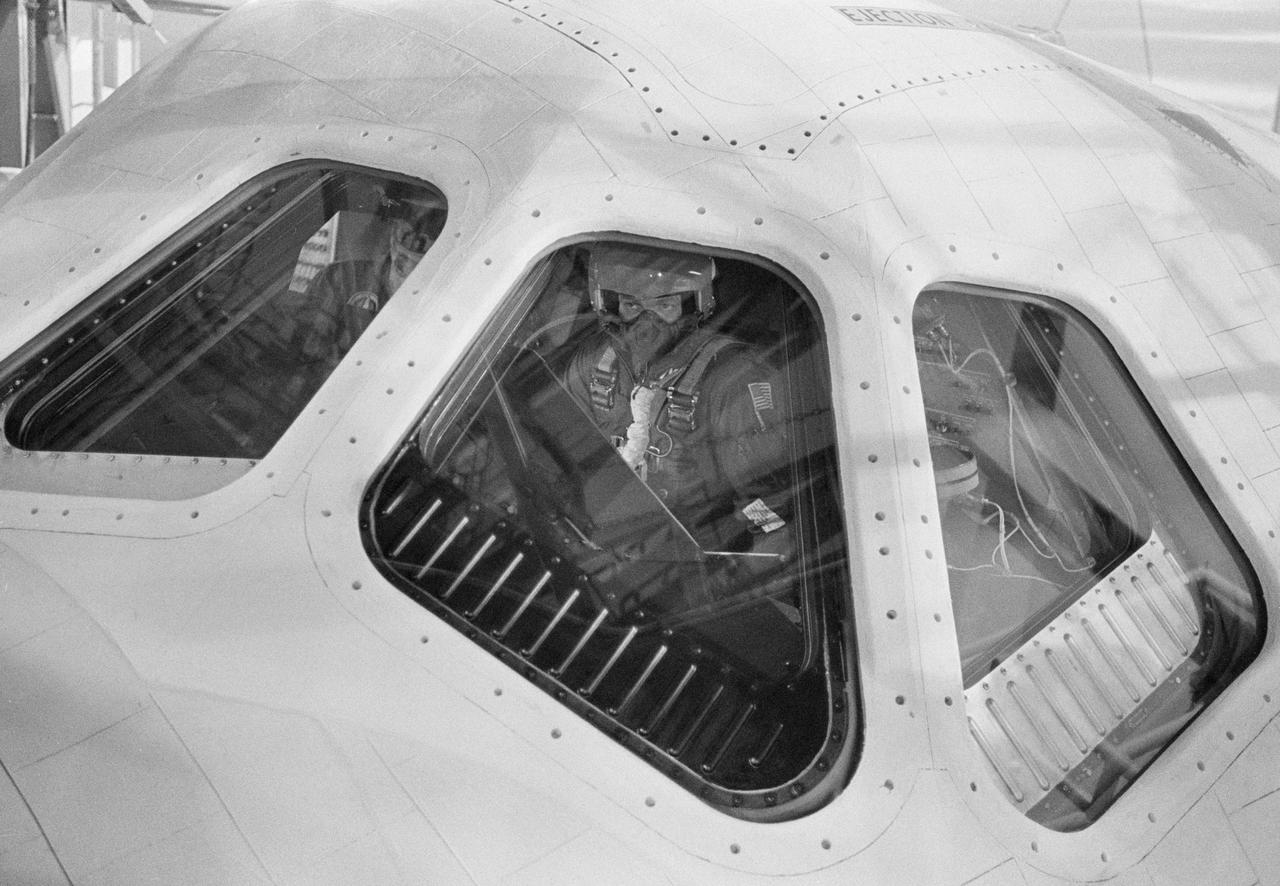

S77-28212 (13 Sept 1977) --- Astronauts Joe H. Engle (right), commander, and Richard H. Truly, pilot, sit in the cockpit of the shuttle Orbiter 101 "Enterprise" at the Dryden Flight Research Center (DFRC) prior to takeoff of the NASA 747 carrier aircraft to which the "Enterprise" was mated. The pair later made a five-minute, 31-second free-flight in the craft, the second in a series of such flights for the Shuttle Approach and Landing Tests (ALT) program. The photograph was made from the Mate-Demate Device (MDD).
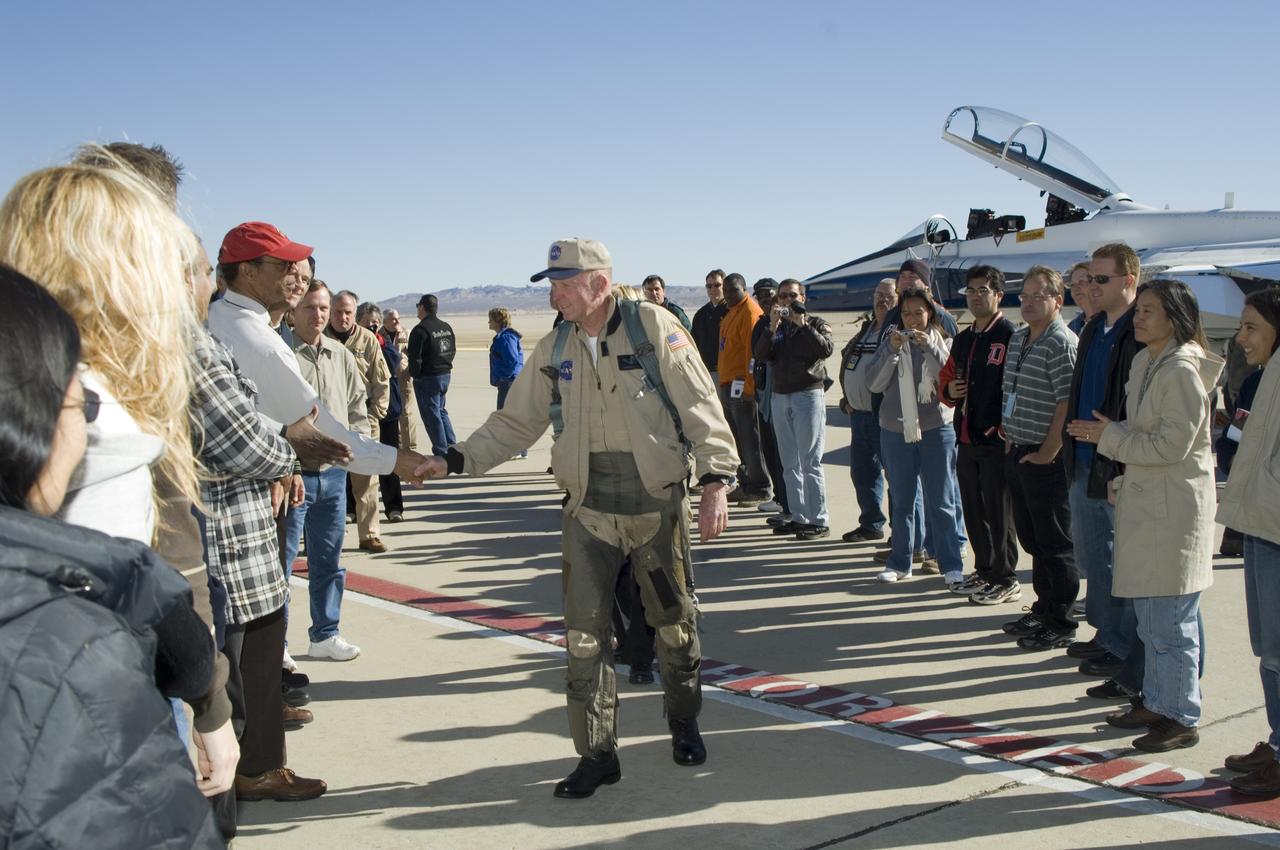

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
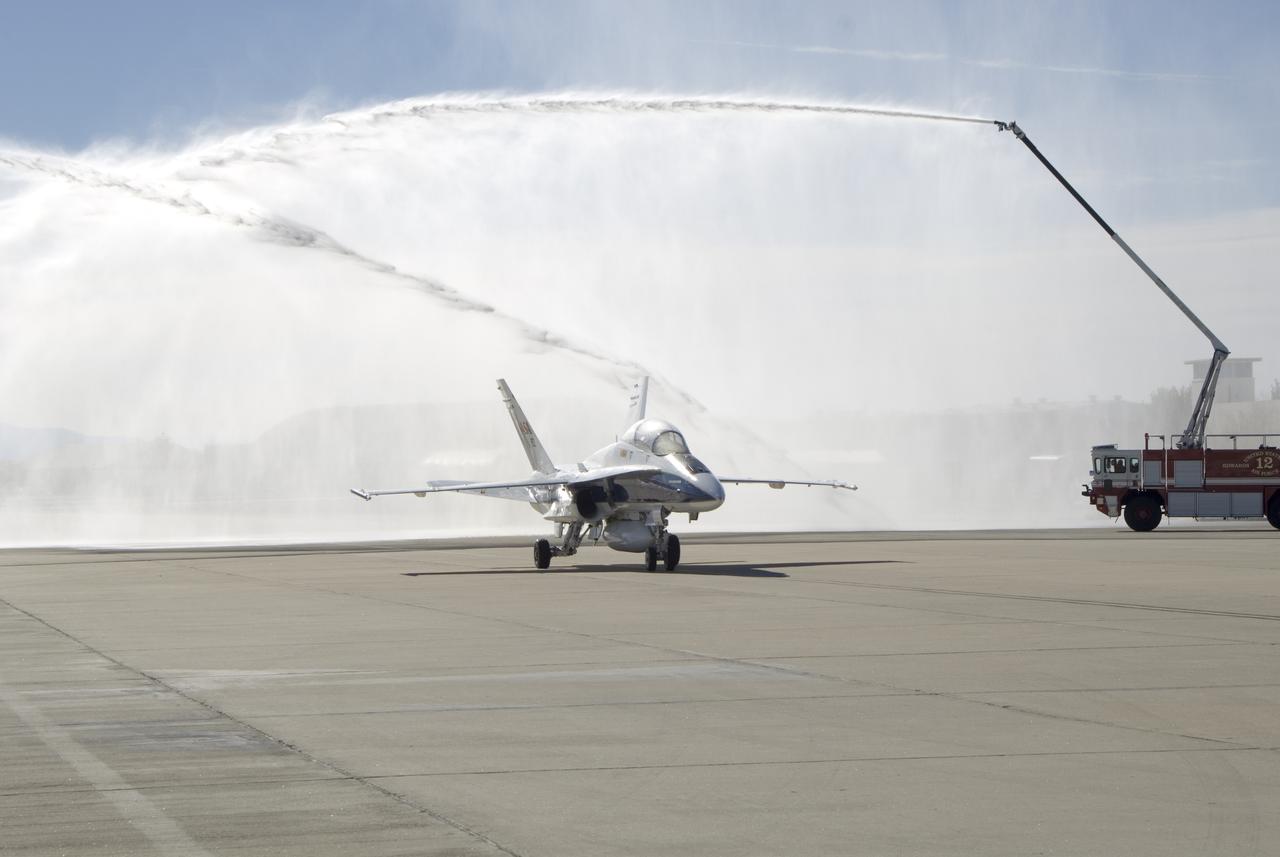

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
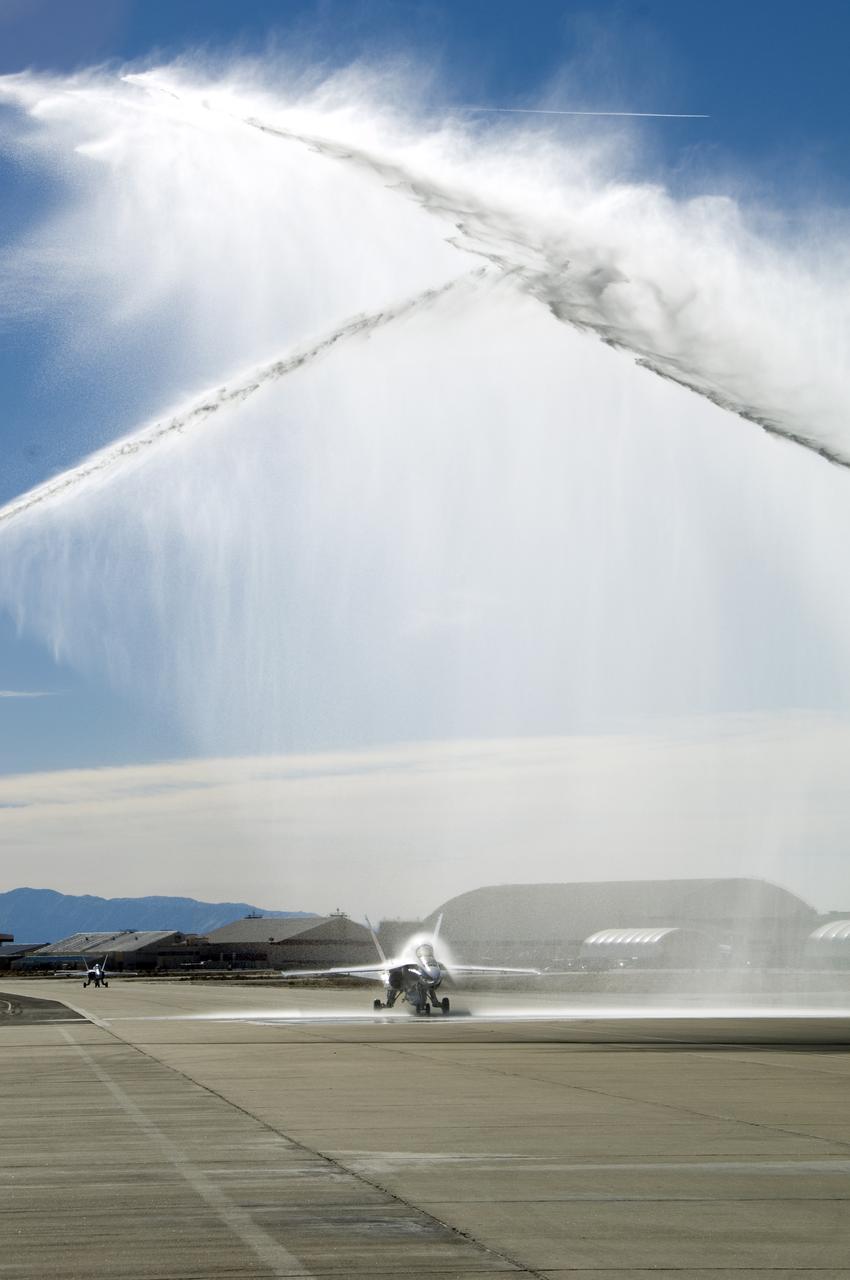

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
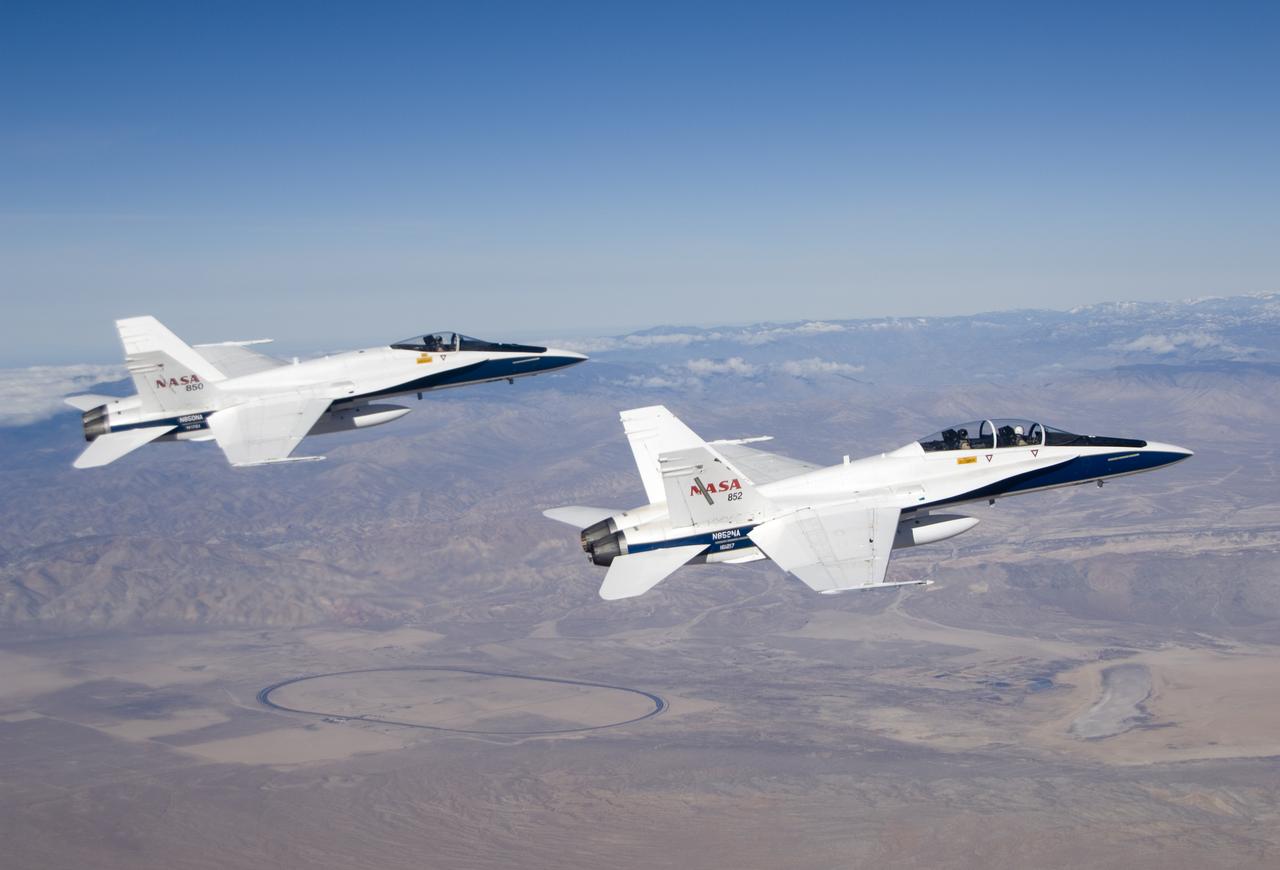

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of sp
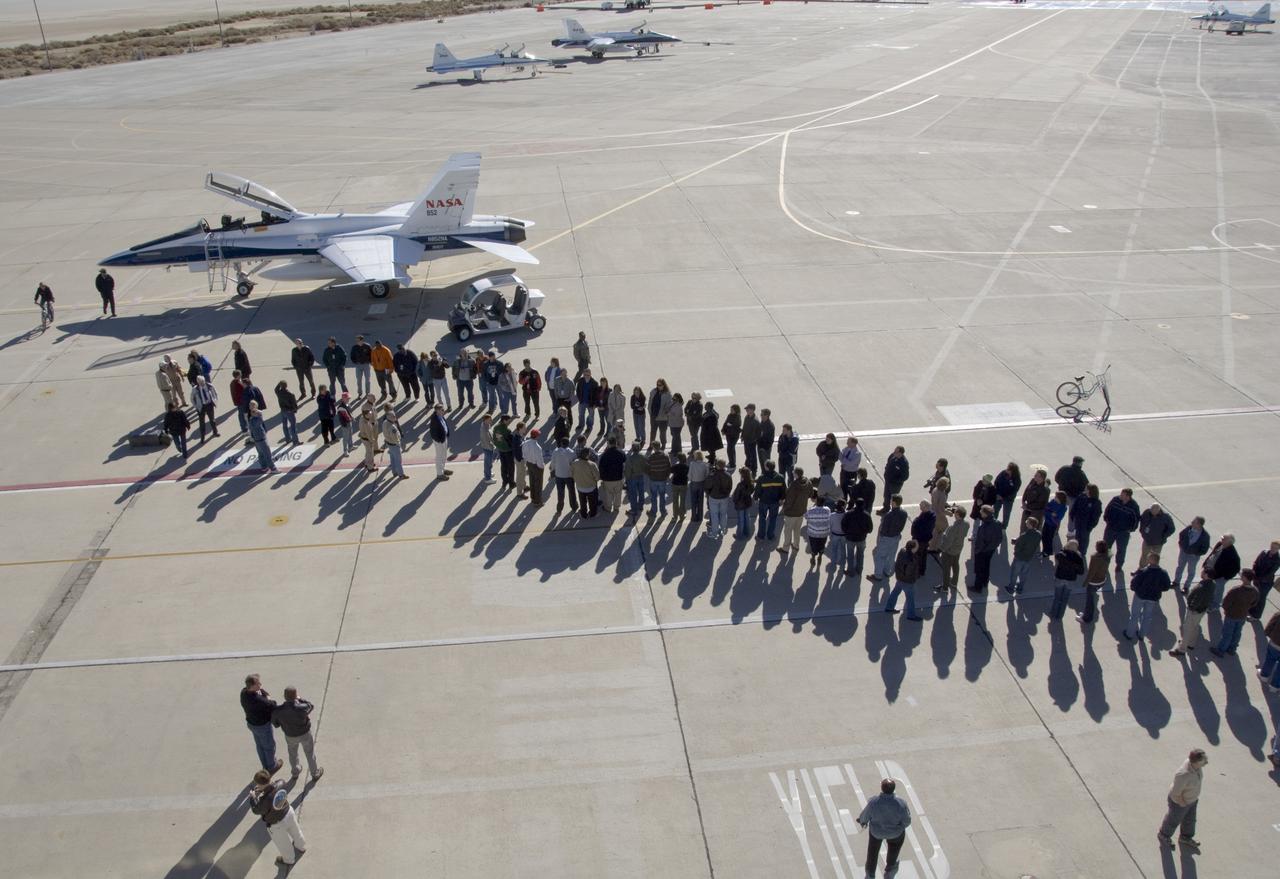

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
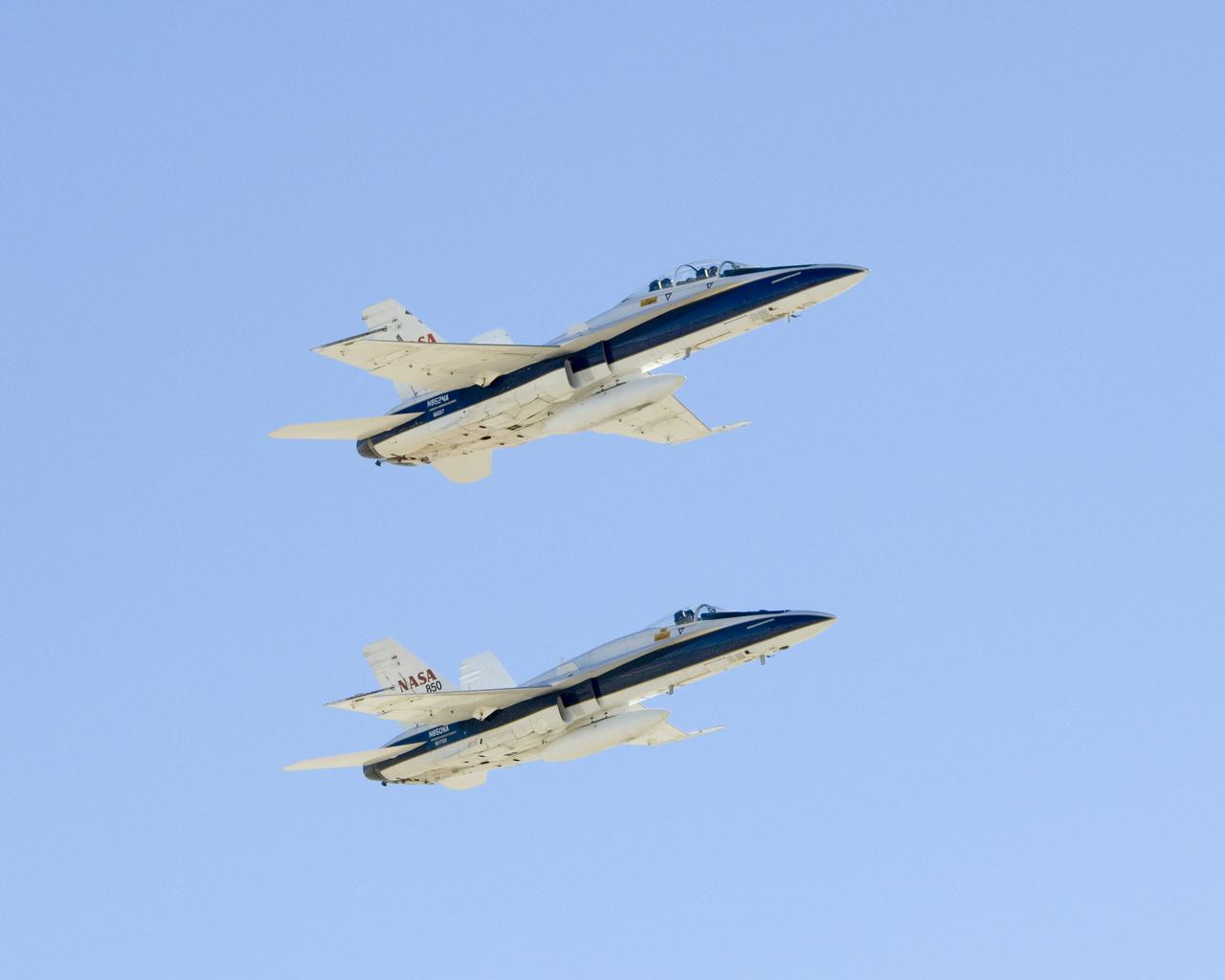

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
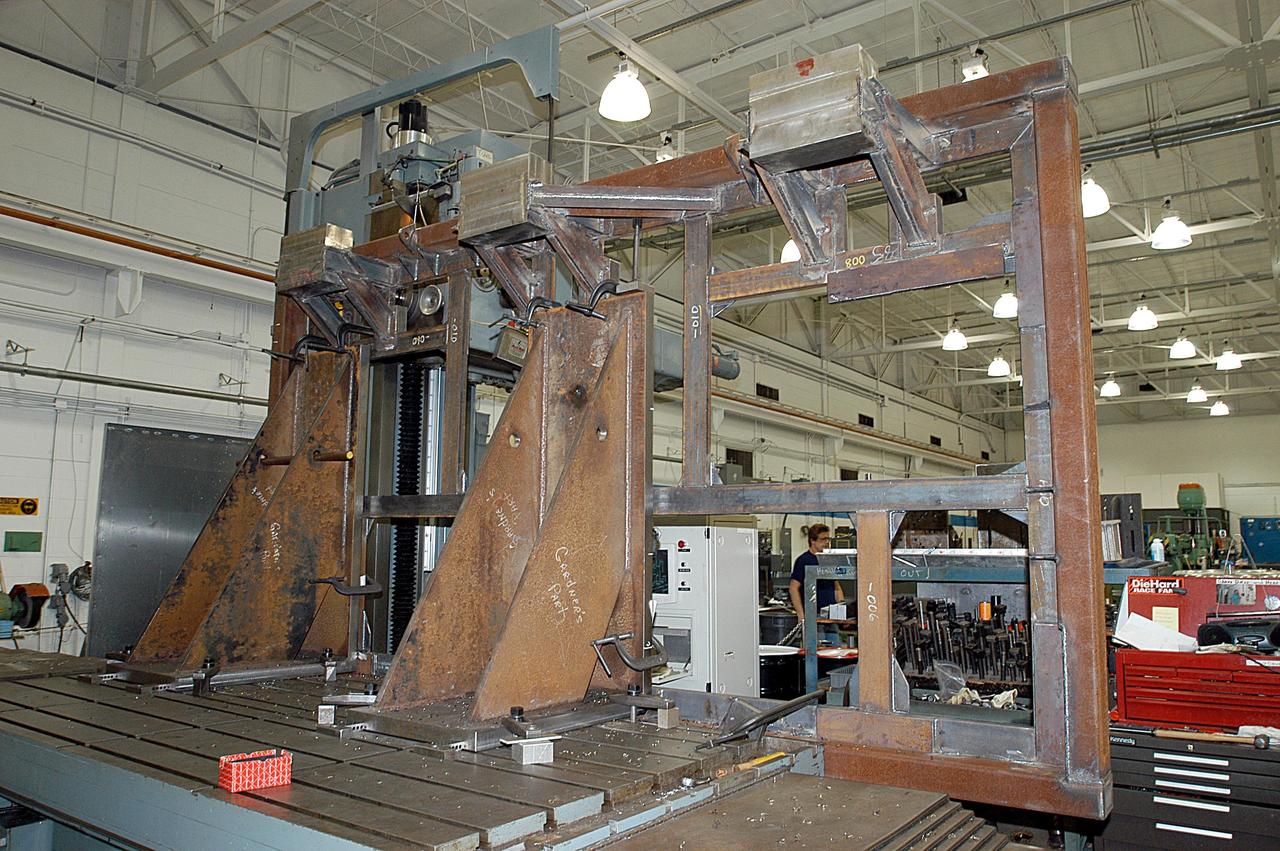

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A main landing gear door mounting fixture in the Launch Equipment Shop is being used to support the Columbia mishap investigation. A simulated orbiter wing and several test panels, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
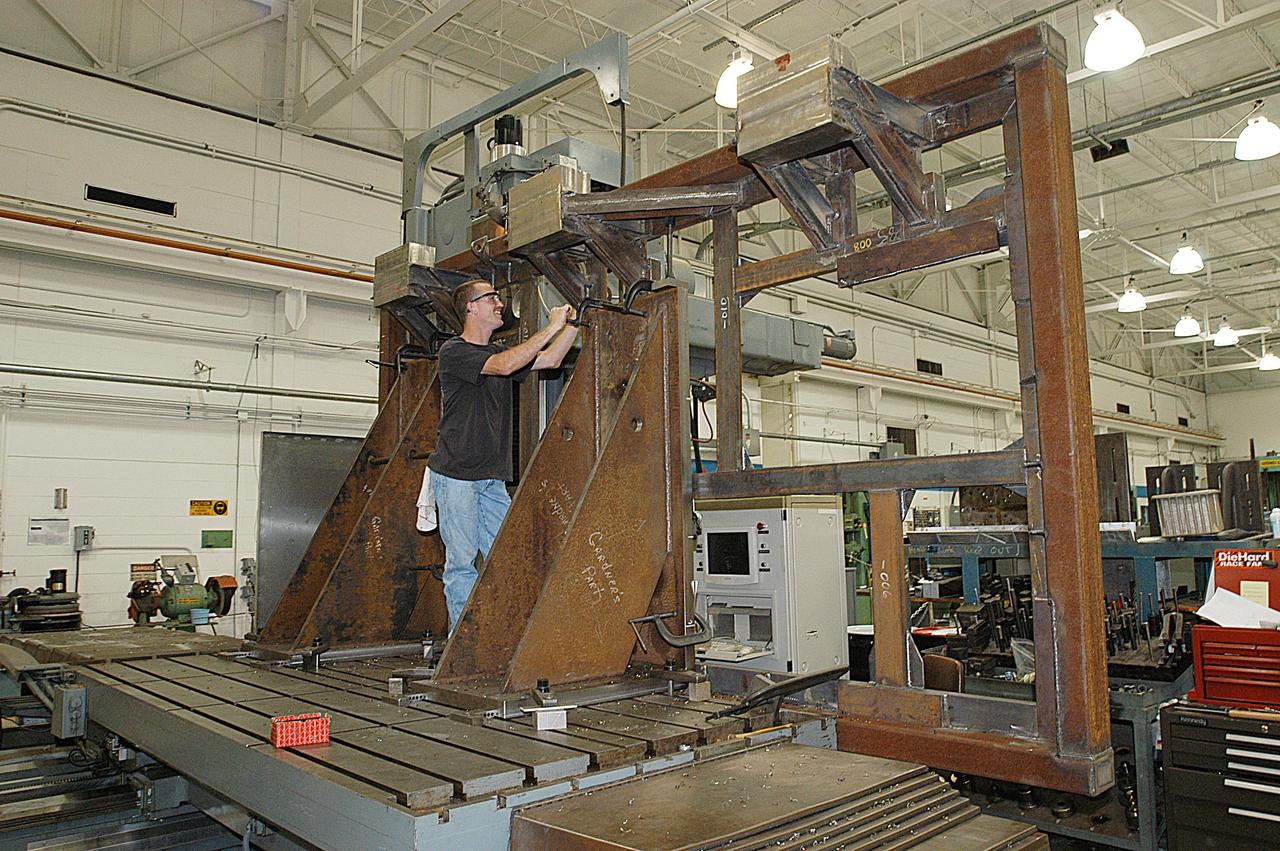

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance technician Matt Boonstra works on a main landing gear door mounting fixture in the Launch Equipment Shop. The fixture is being used to support the Columbia mishap investigation. A simulated orbiter wing and several test panels, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile installation on them is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
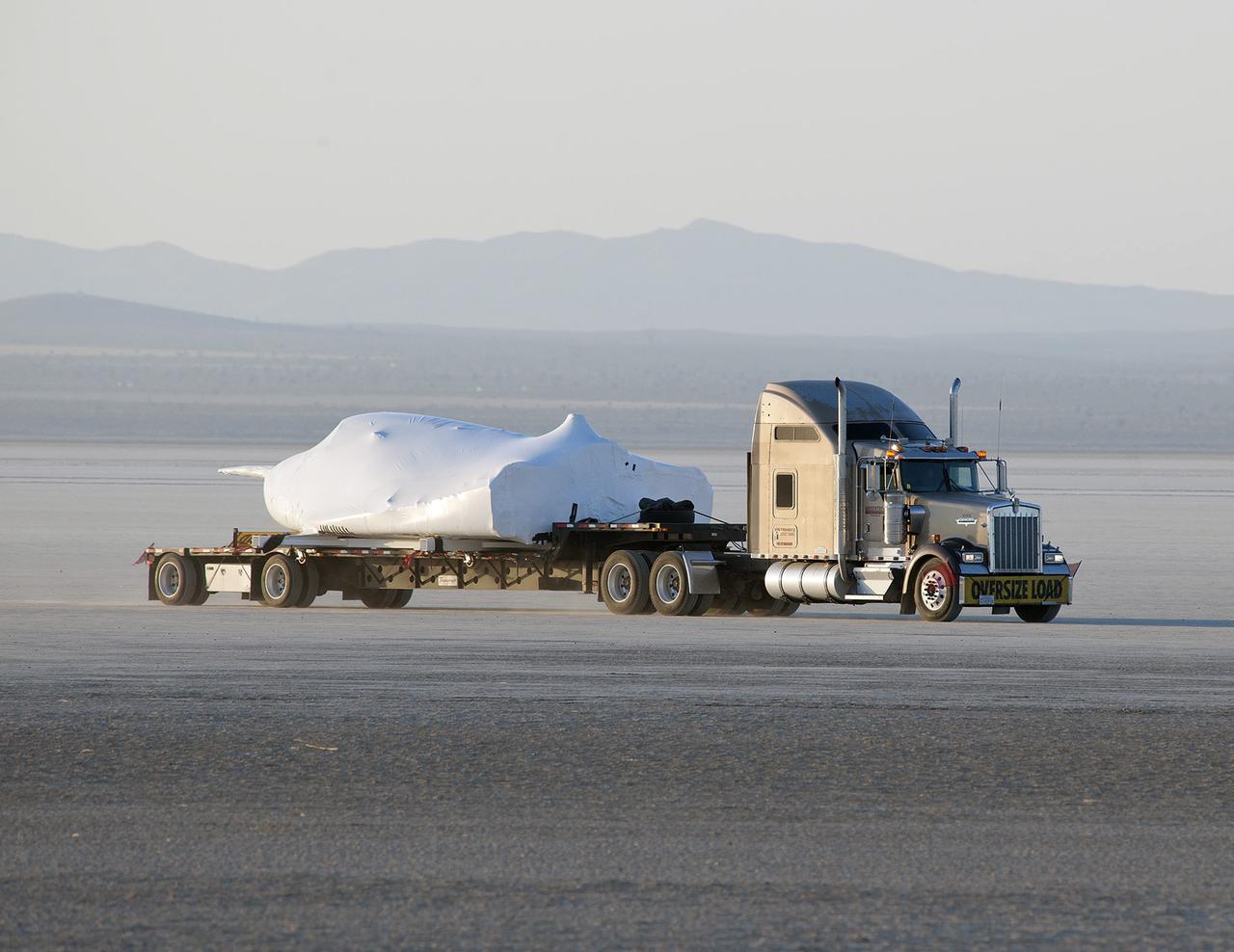

EDWARDS, Calif. – ED13-0142-01: With its wings and tail structure removed and shrouded in plastic wrap for ground transport, Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Space Systems' Dream Chaser engineering test article is hauled across the bed of Rogers Dry Lake at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The Dream Chaser will begin its approach-and-landing flight test program in collaboration with NASA's Commercial Crew Program this summer. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Tom Tschida
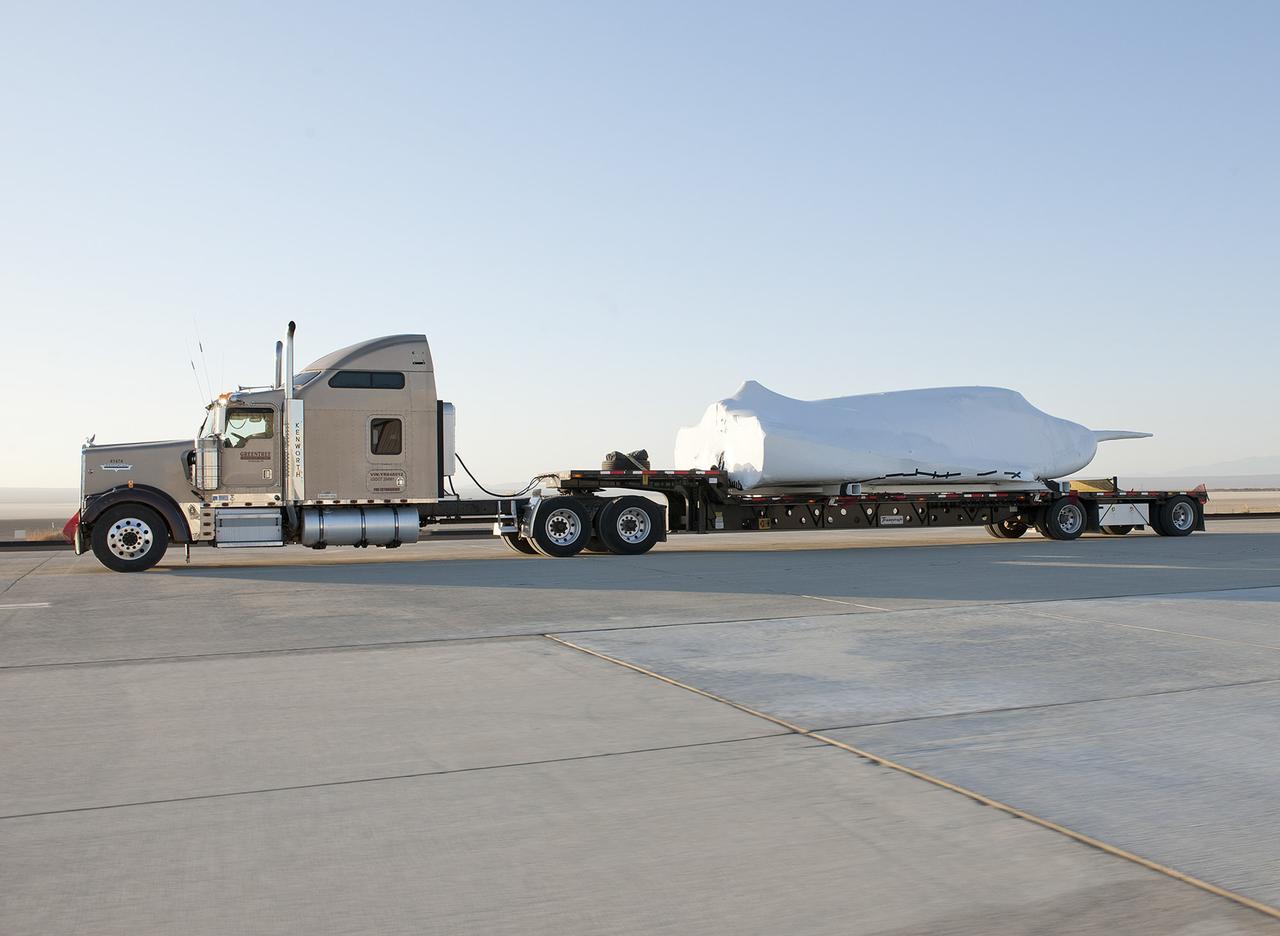

EDWARDS, Calif. – ED13-0142-11: The truck and trailer that transported the Dream Chaser engineering test article from Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Space Systems facility in Louisville, Colo., arrives on the aircraft ramp at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center on Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., early in the morning. Based on NASA's HL-20 lifting body design, the Dream Chaser will begin its approach-and-landing flight test program in collaboration with NASA's Commercial Crew Program this summer. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Tom Tschida
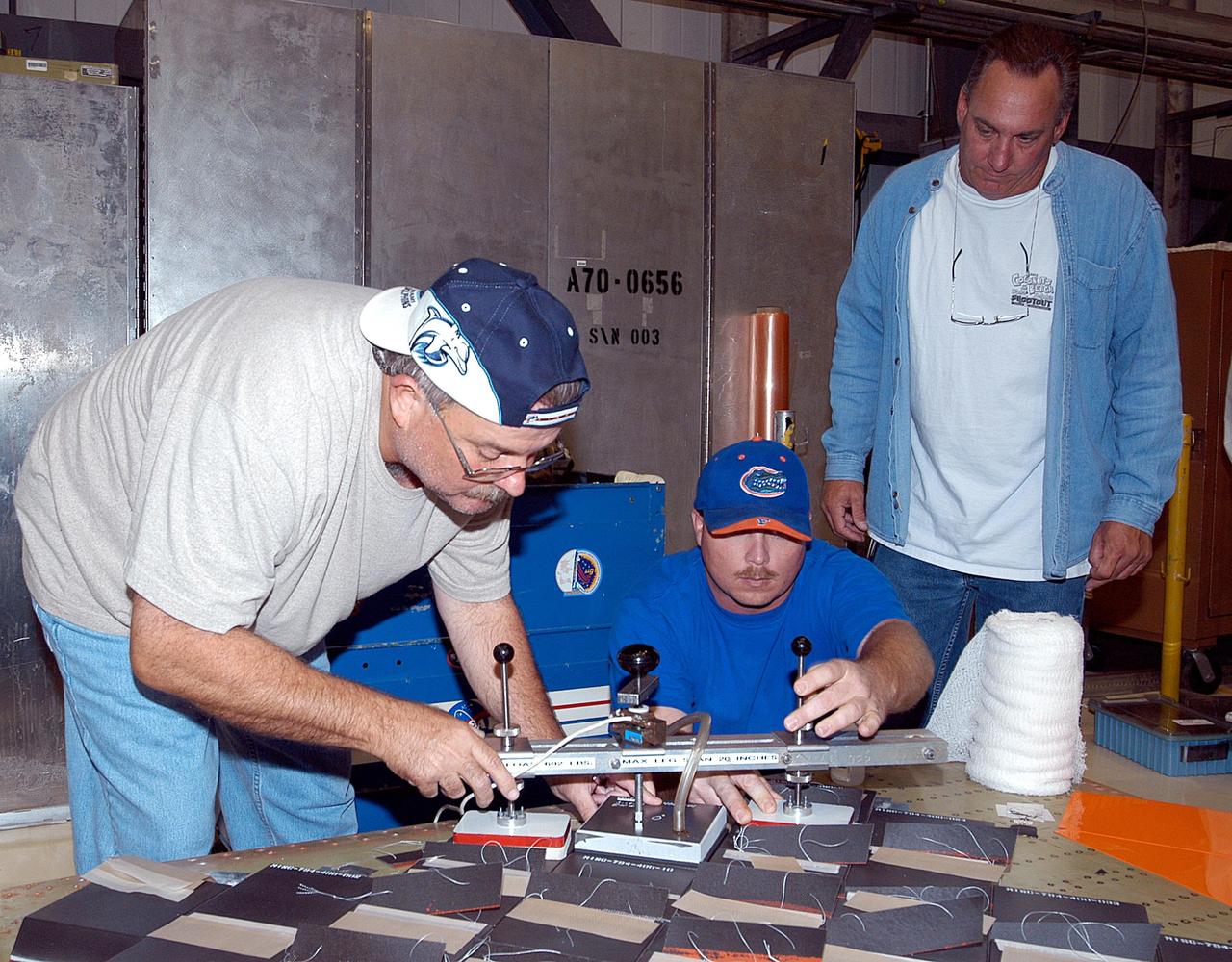

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employees (from left) Dave Sanborn, Butch Lato, and Bill Brooks conduct a bond verification test on Thermal Protection System tiles newly installed on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
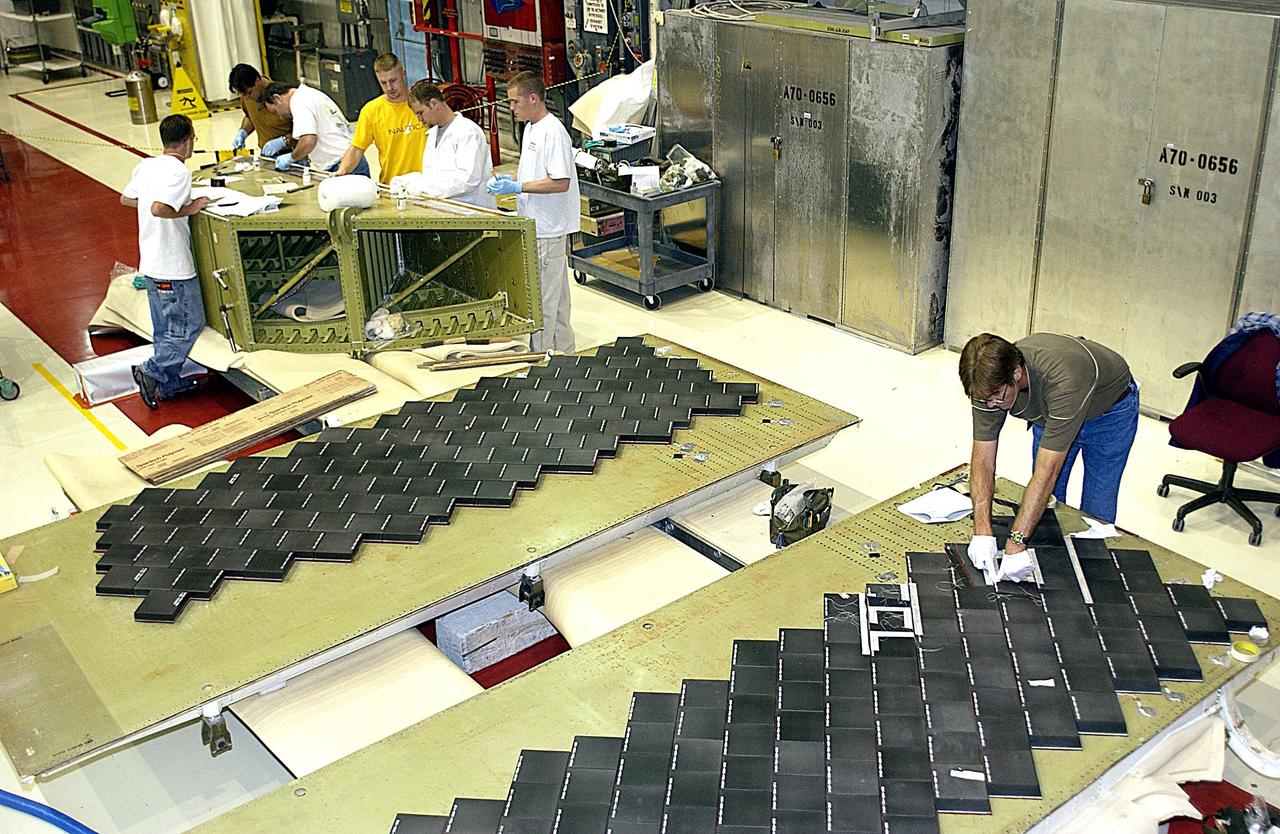

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF), United Space Alliance (USA) employee Harrell Watts (right) installs Thermal Protection System (TPS) tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). In the background, other USA employees, members of the OPF midbody TPS crew, prepare to install TPS tile on a simulated orbiter wing. The wing and the sections of Enterprise will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
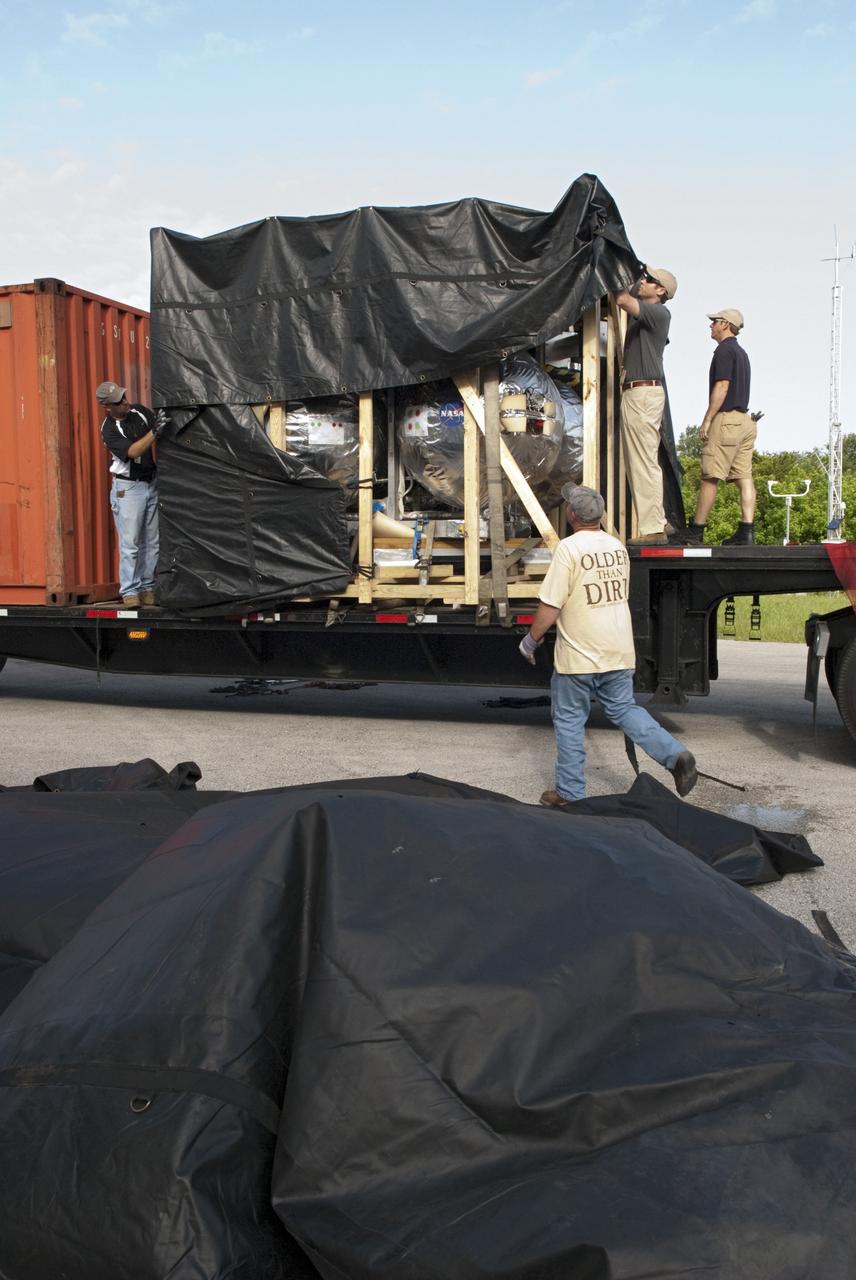

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
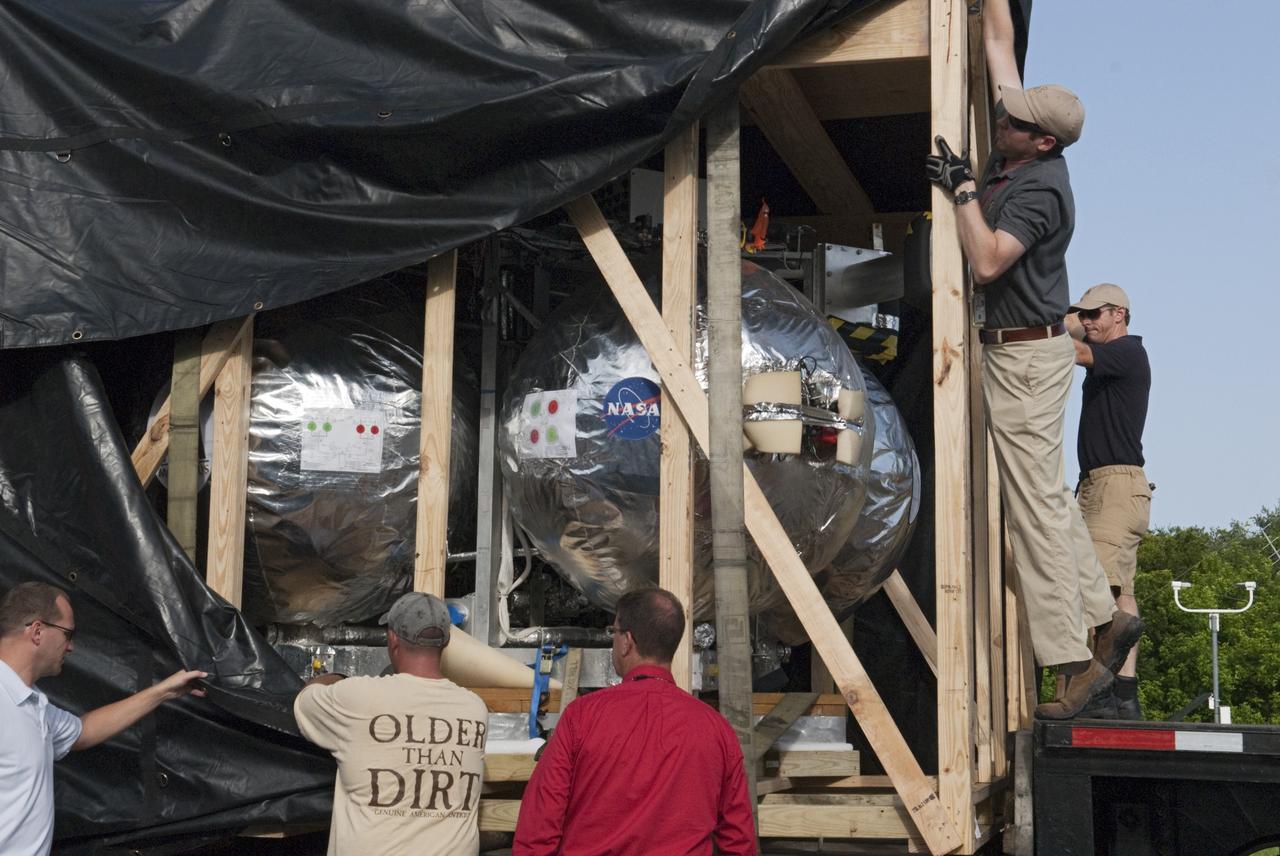

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
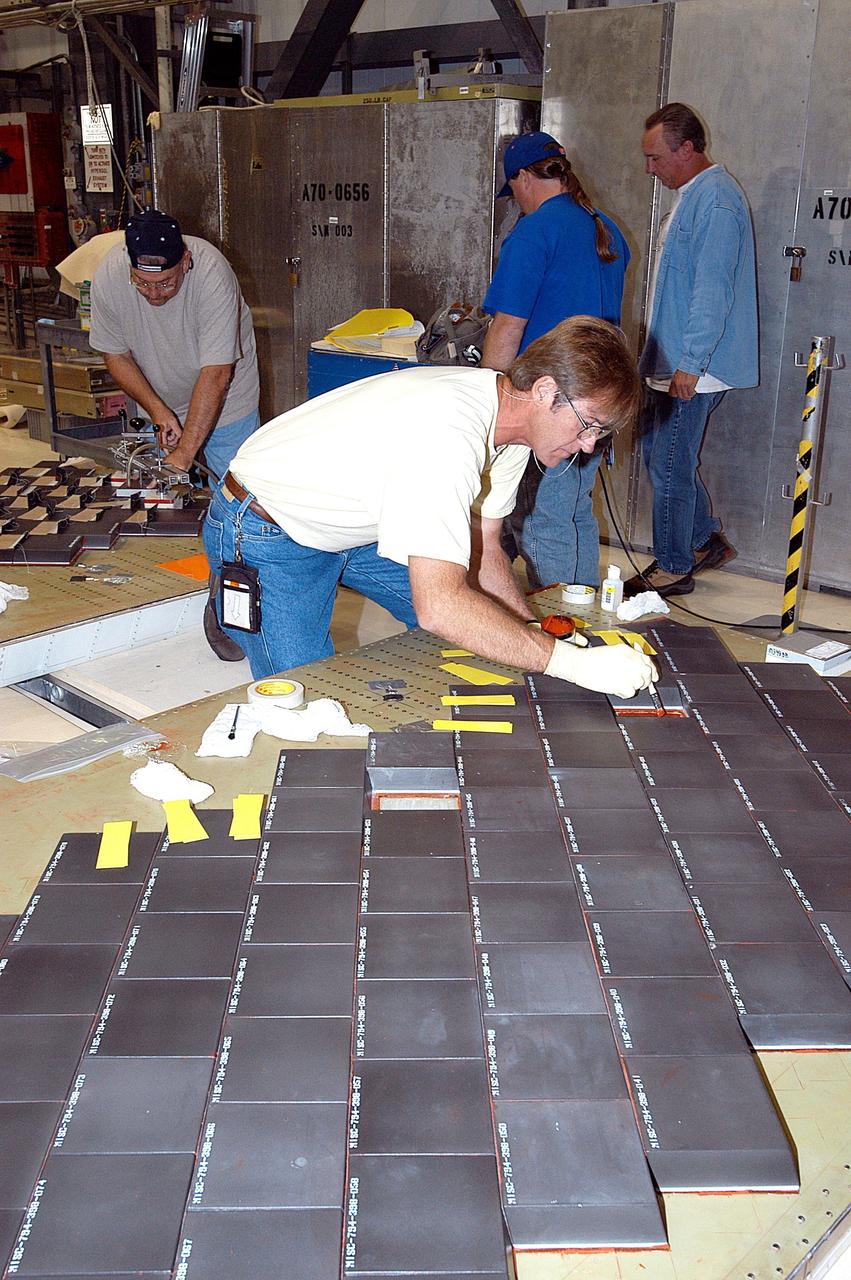

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Harrell Watts applies RTV, a room-temperature vulcanizing silicone adhesive, to a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) on which Thermal Protection System tiles are being installed. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
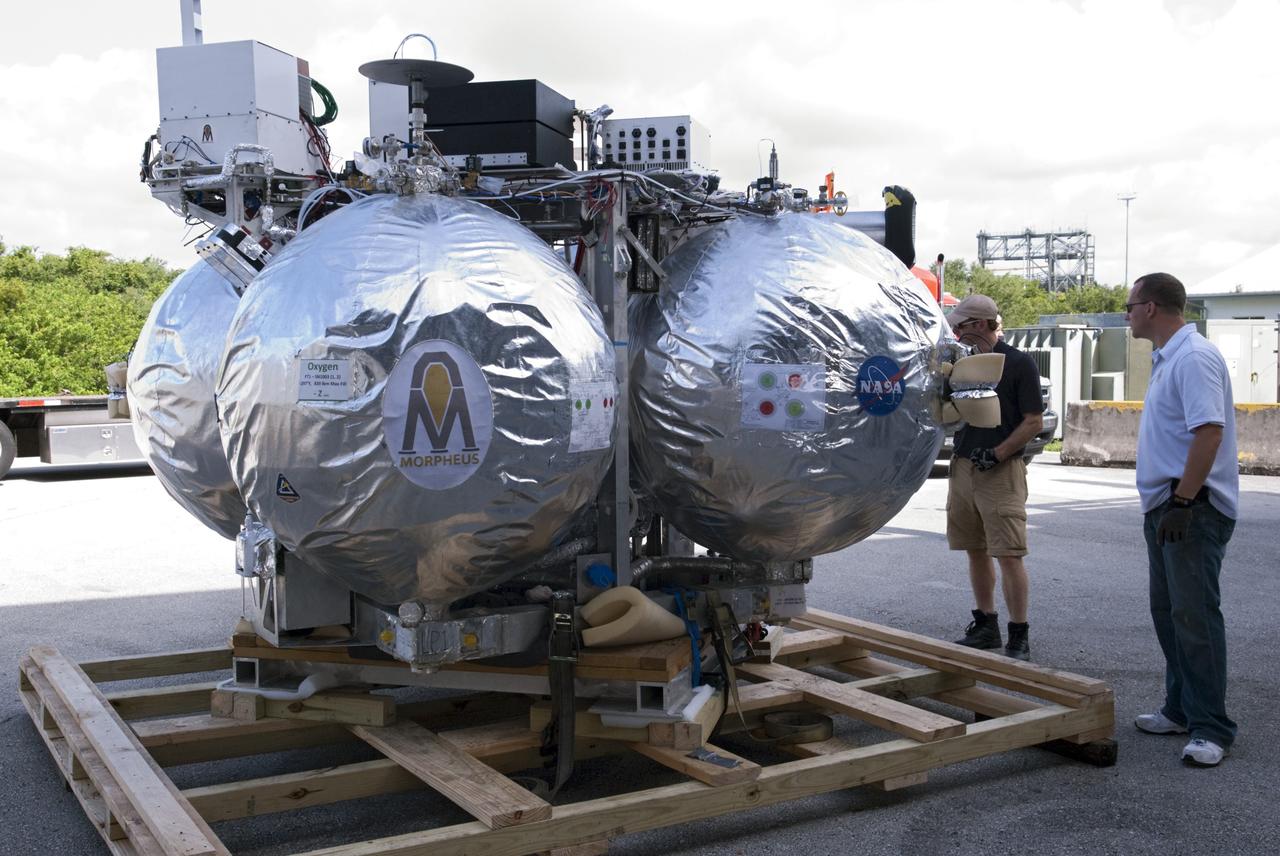

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
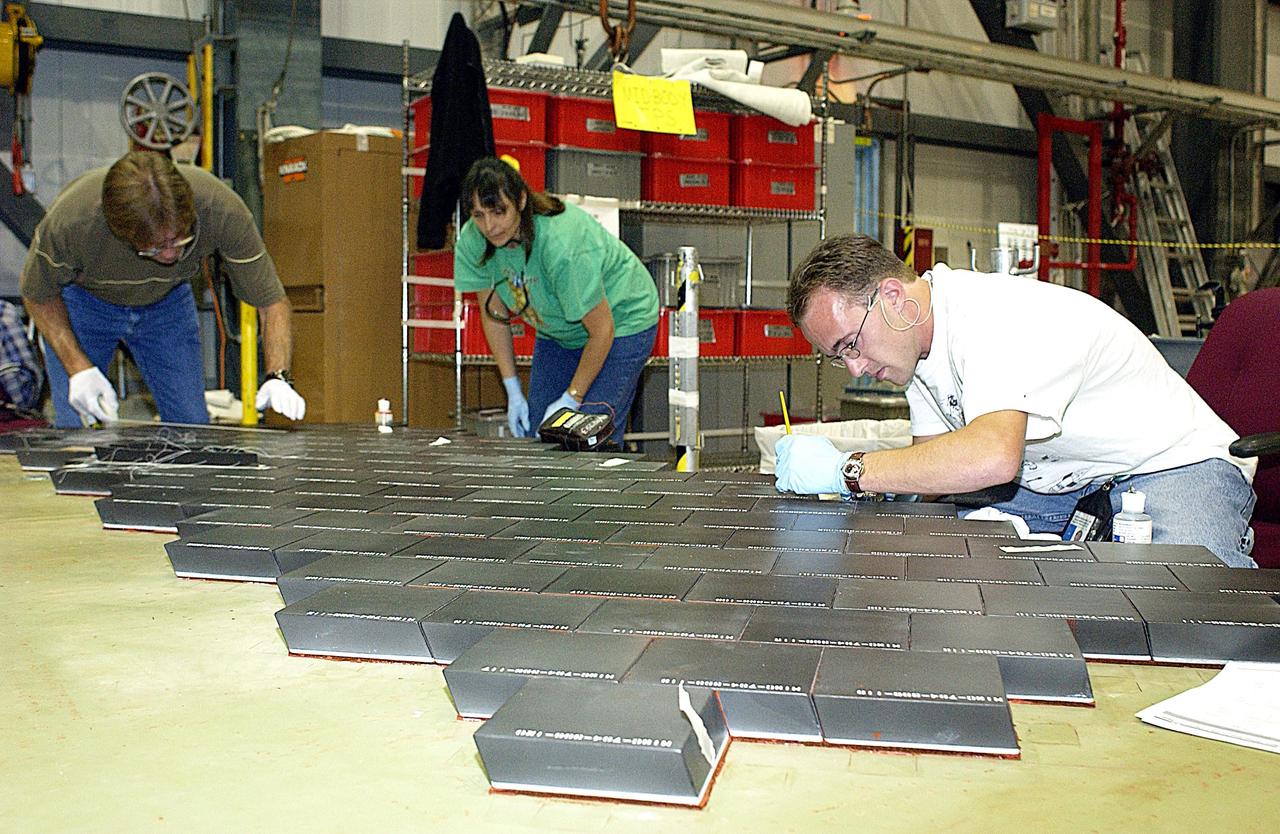

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employees (from left) Harrell Watts, Lynn Wozniak, and Jason Levandusky install Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
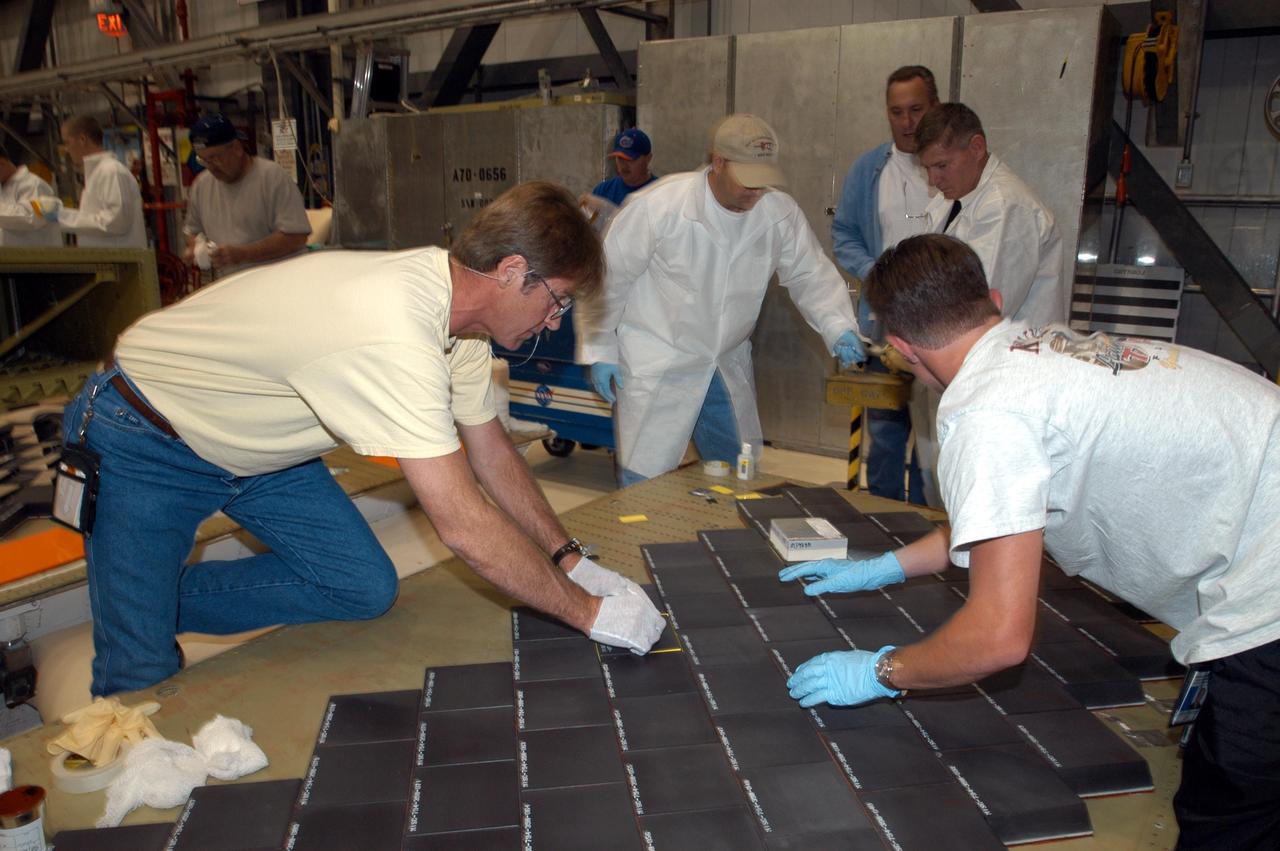

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employees (from left) Harrell Watts, Mike Cote, and Jason Levandusky install Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
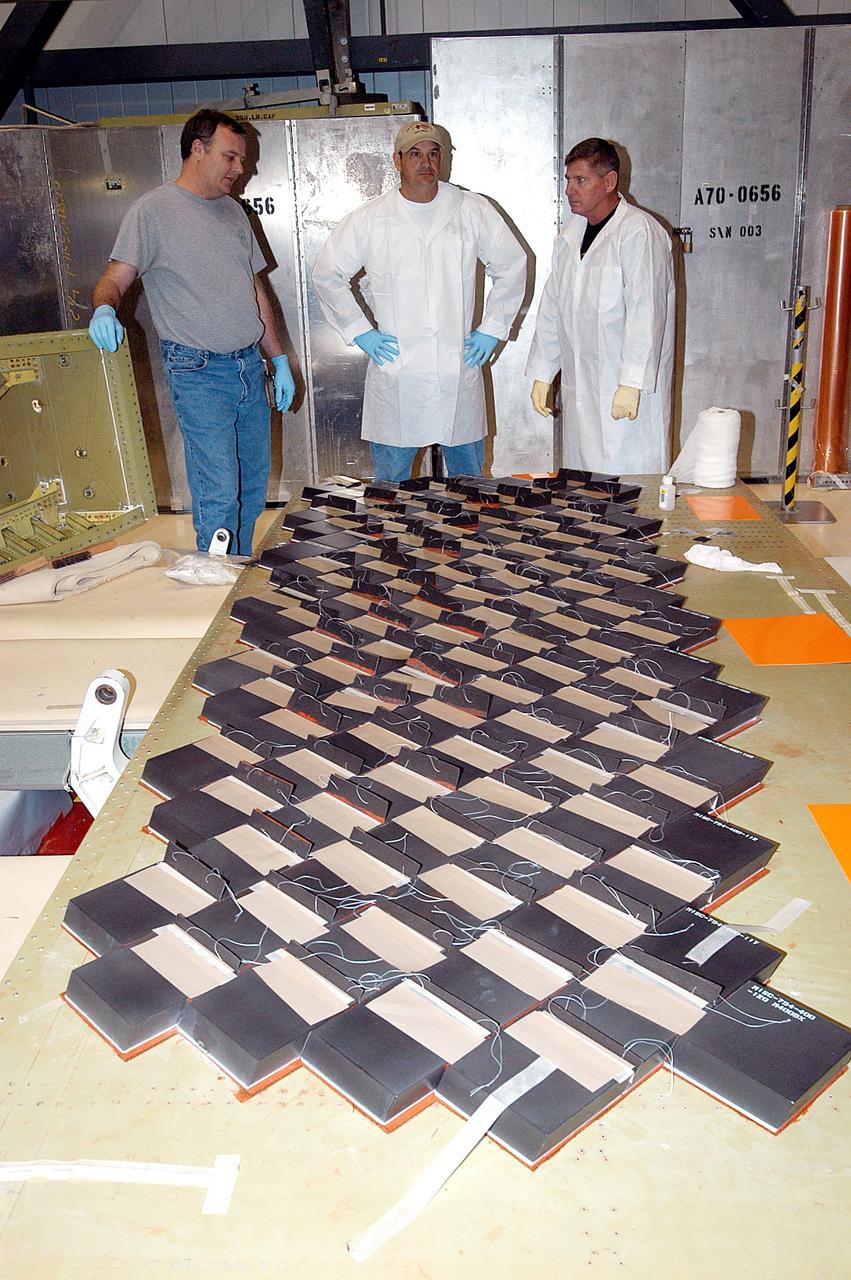

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employees (from left) John Kuhn, Mike Cote, and Tom Baggitt discuss the installation of Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
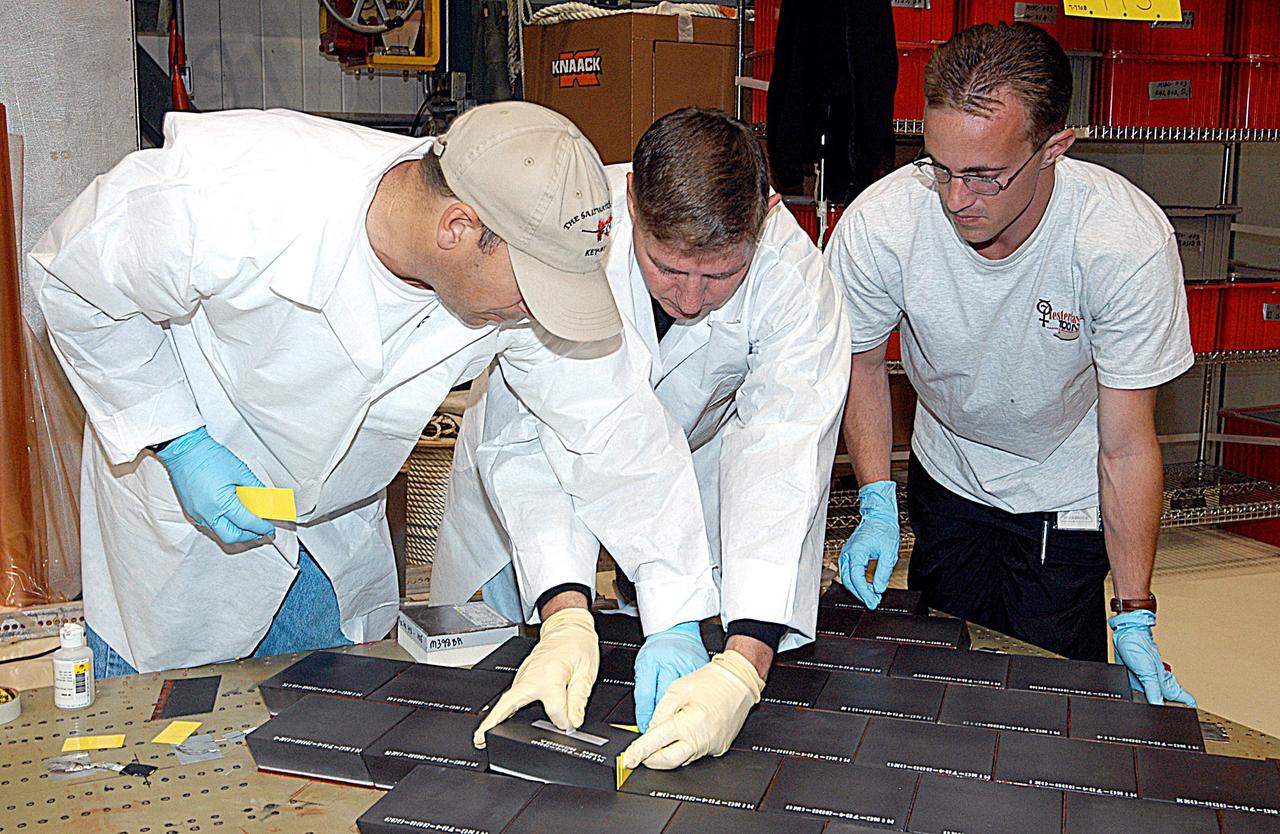

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employees (from left) Mike Cote, Tom Baggitt, and Jason Levandusky install Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.

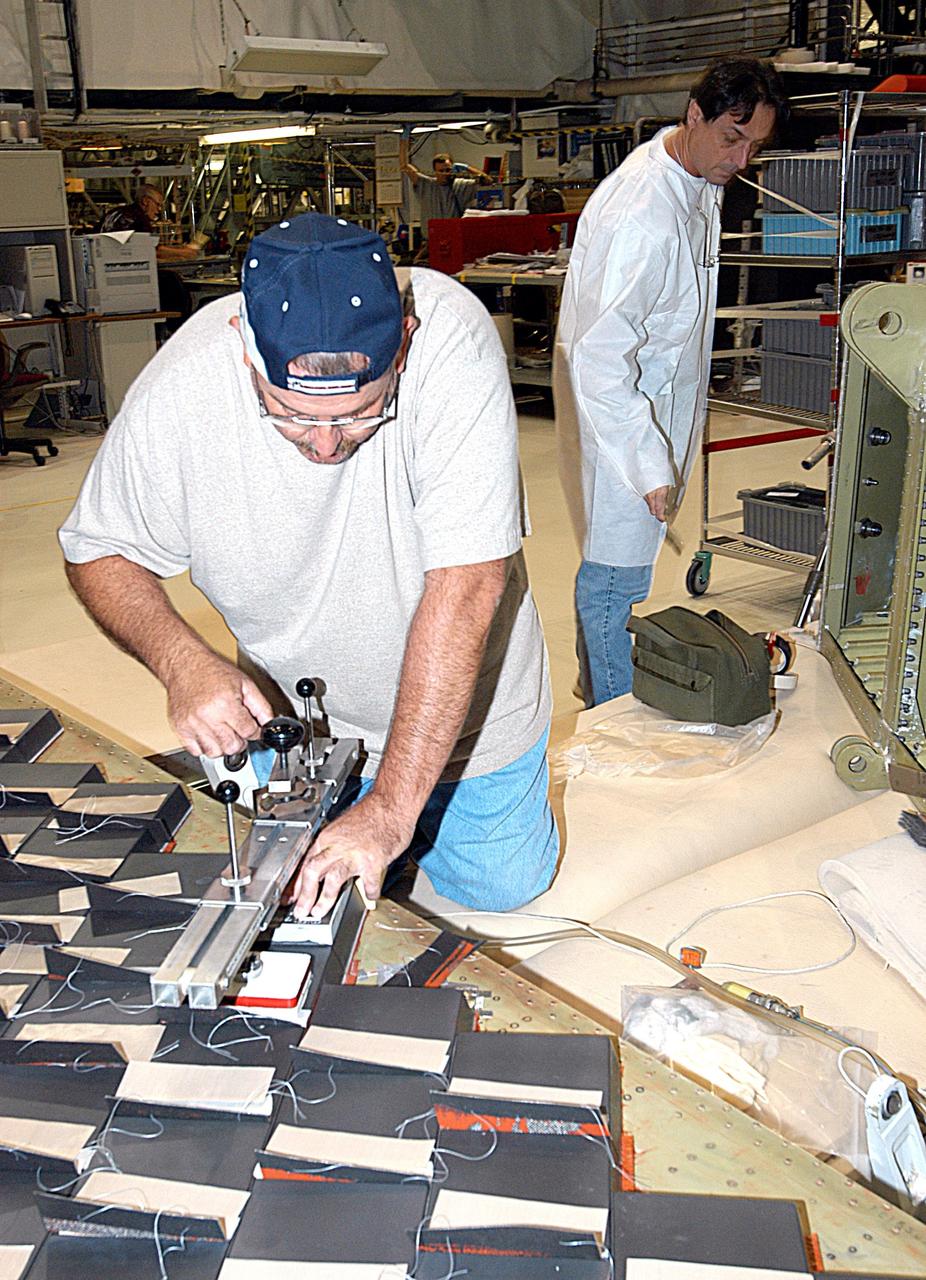
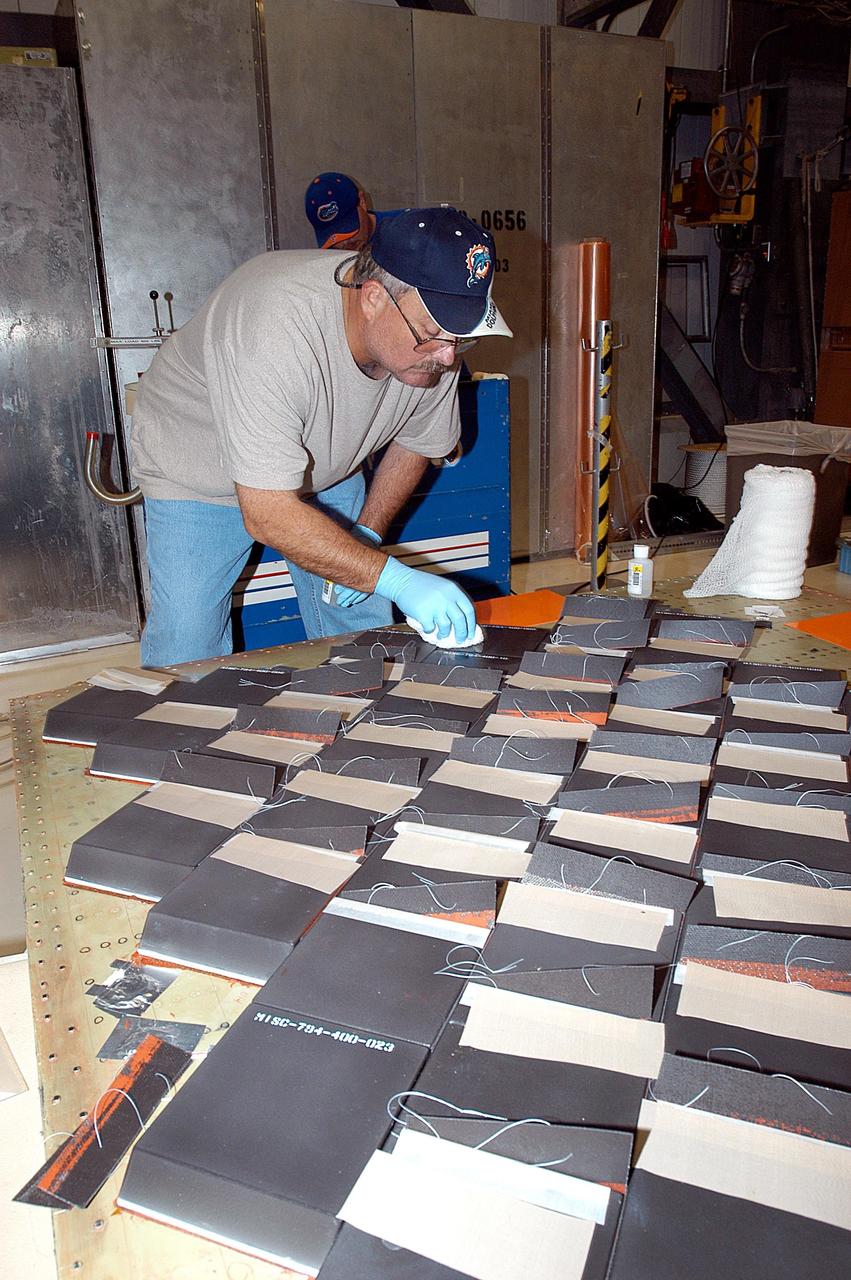
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, employees from The Boeing Co., Huntington Beach, Calif., install a strain gauge on a test panel prior to installation of Thermal Protection System tile on the panel. The test panel and sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
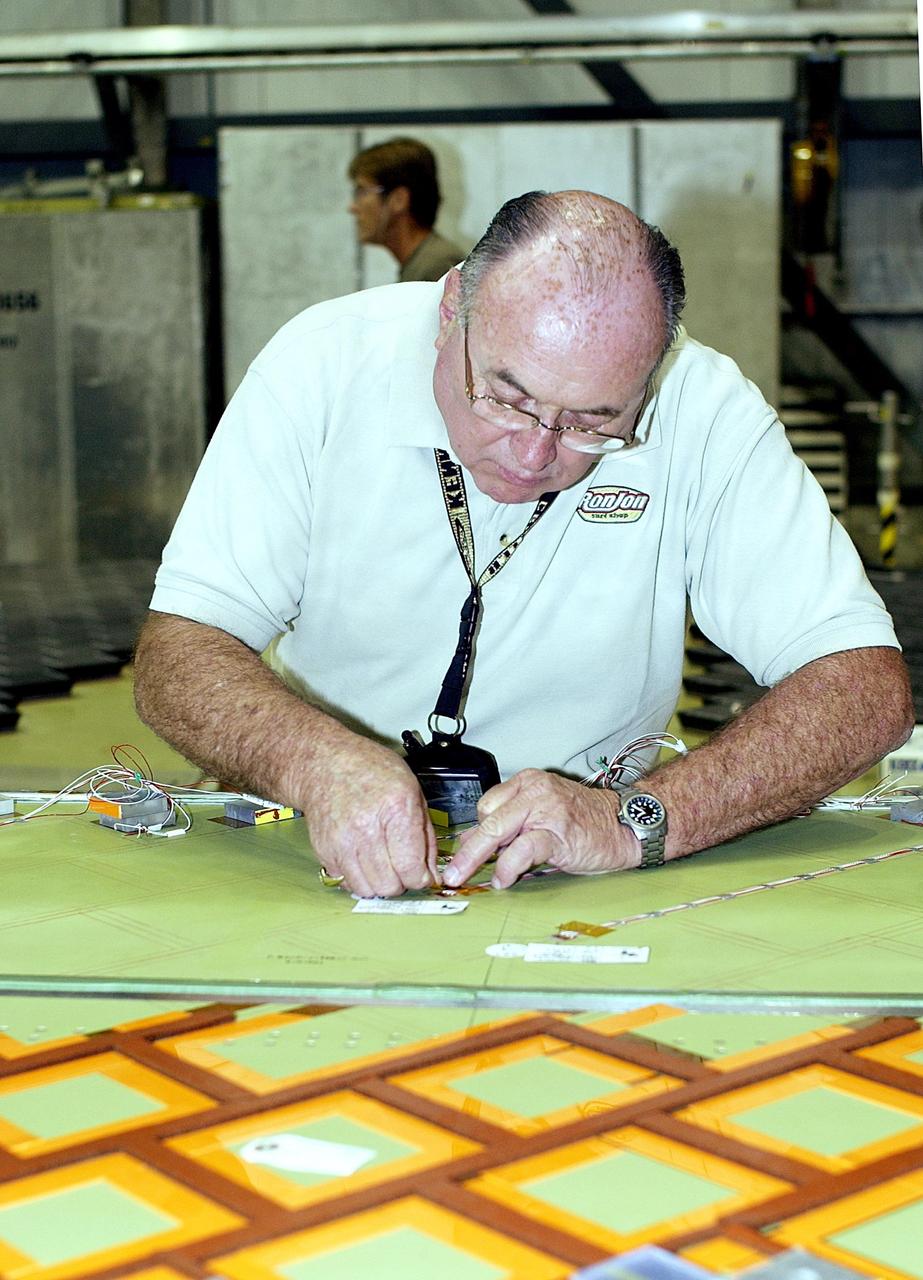

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, an employee from The Boeing Co., Huntington Beach, Calif., installs a strain gauge on a test panel prior to installation of Thermal Protection System tile on the panel. The test panel and sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
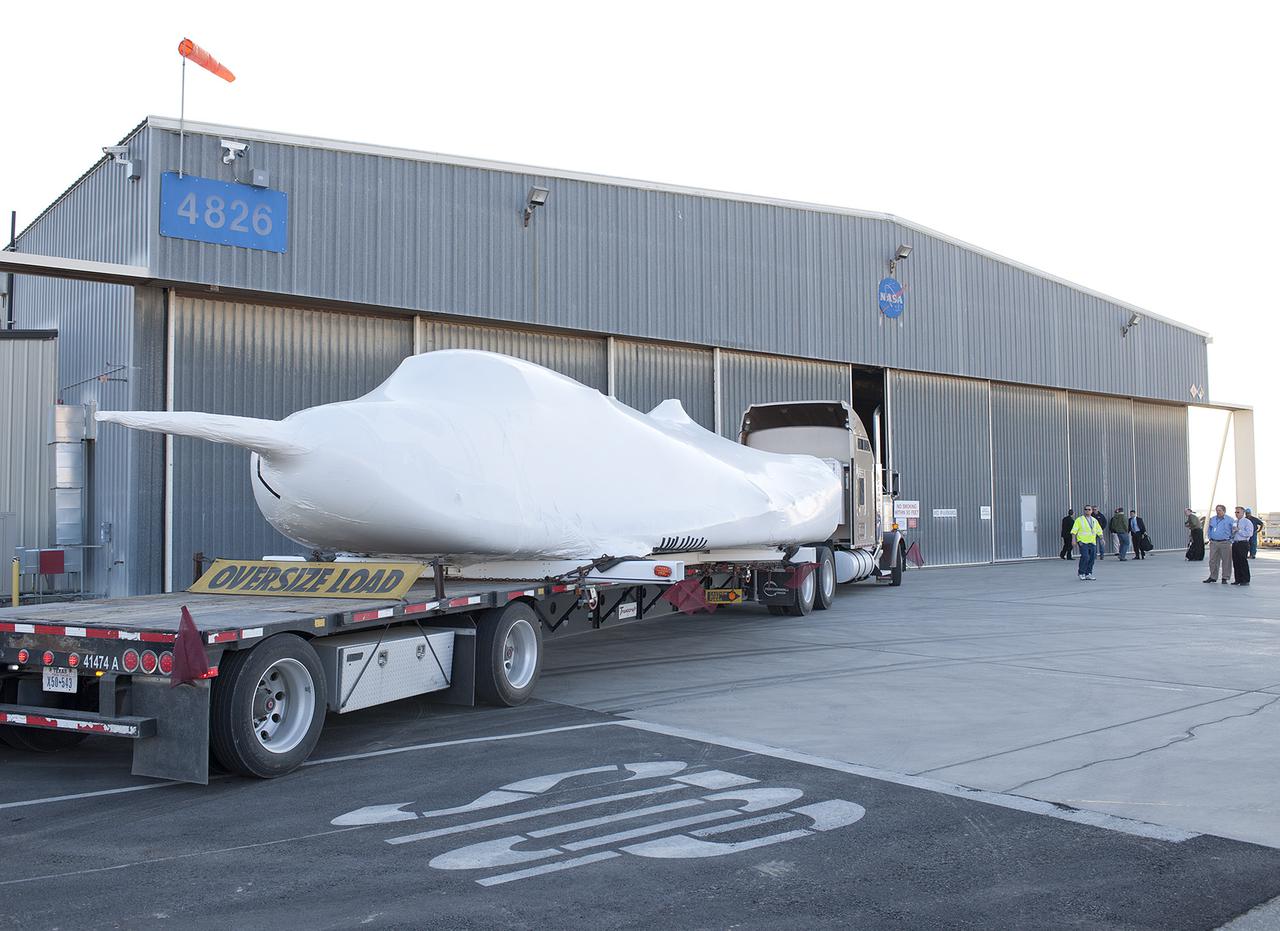

EDWARDS, Calif. – ED13-0142-16: Mounted securely on a flatbed trailer, Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Space Systems' Dream Chaser engineering test article arrives at Hangar 4826 at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center on Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., in the morning. One of three low-Earth orbit space access vehicles being developed under NASA's Commercial Crew Program, the Dream Chaser will undergo ground and approach-and-landing flight tests at NASA Dryden during the next several months. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov_commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA_Tom Tschida
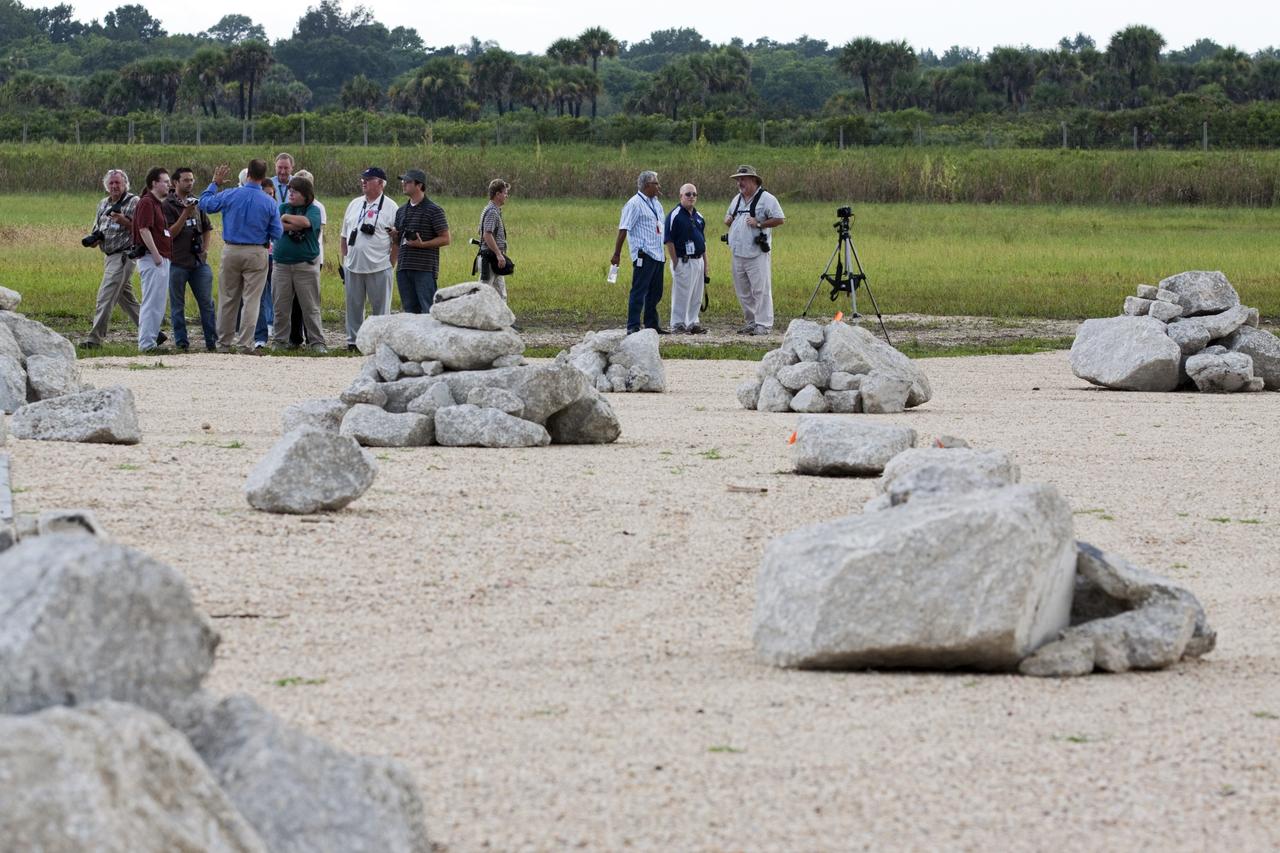

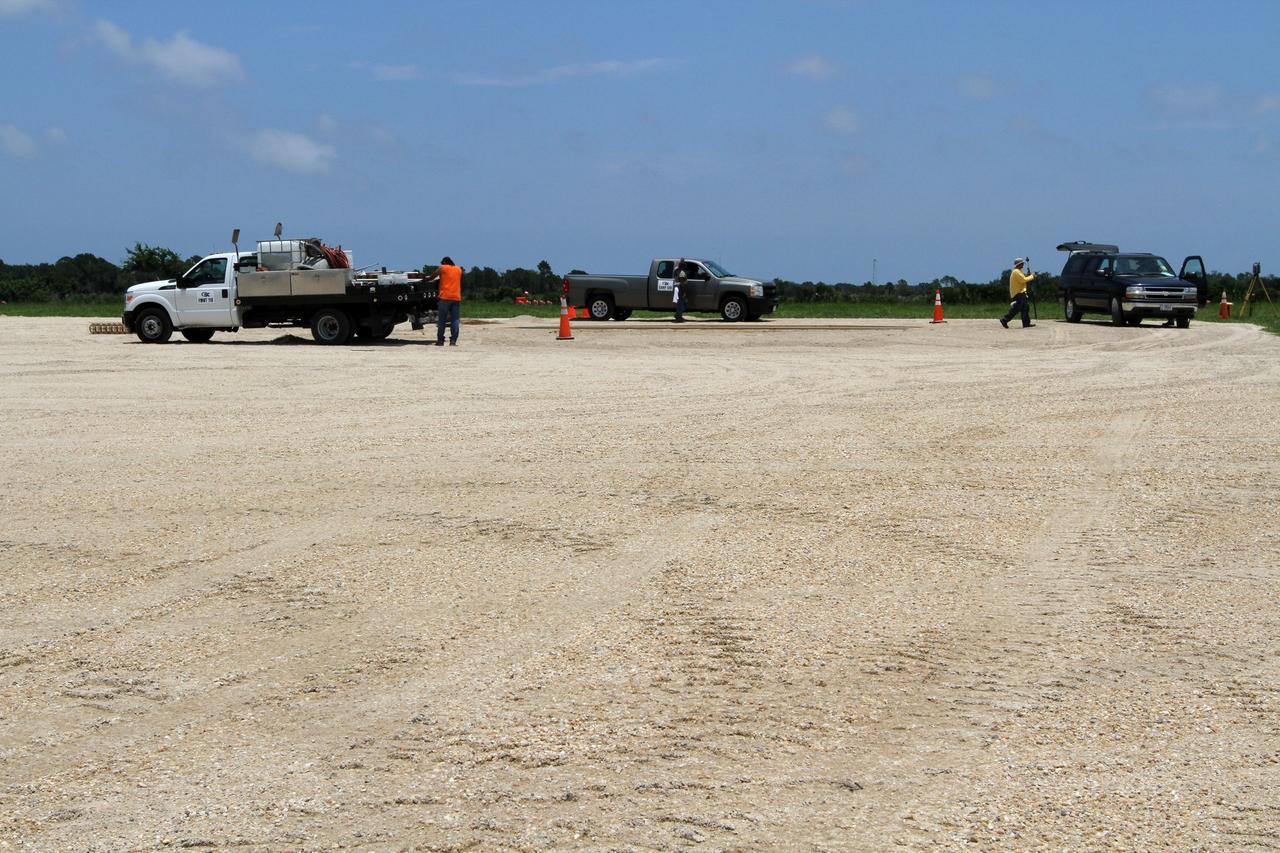
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, field at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media view the hazard field and speak with Morpheus managers. At left, in the blue shirt is Gregory Gaddis, Kennedy Project Morpheus/ALHAT site manager. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
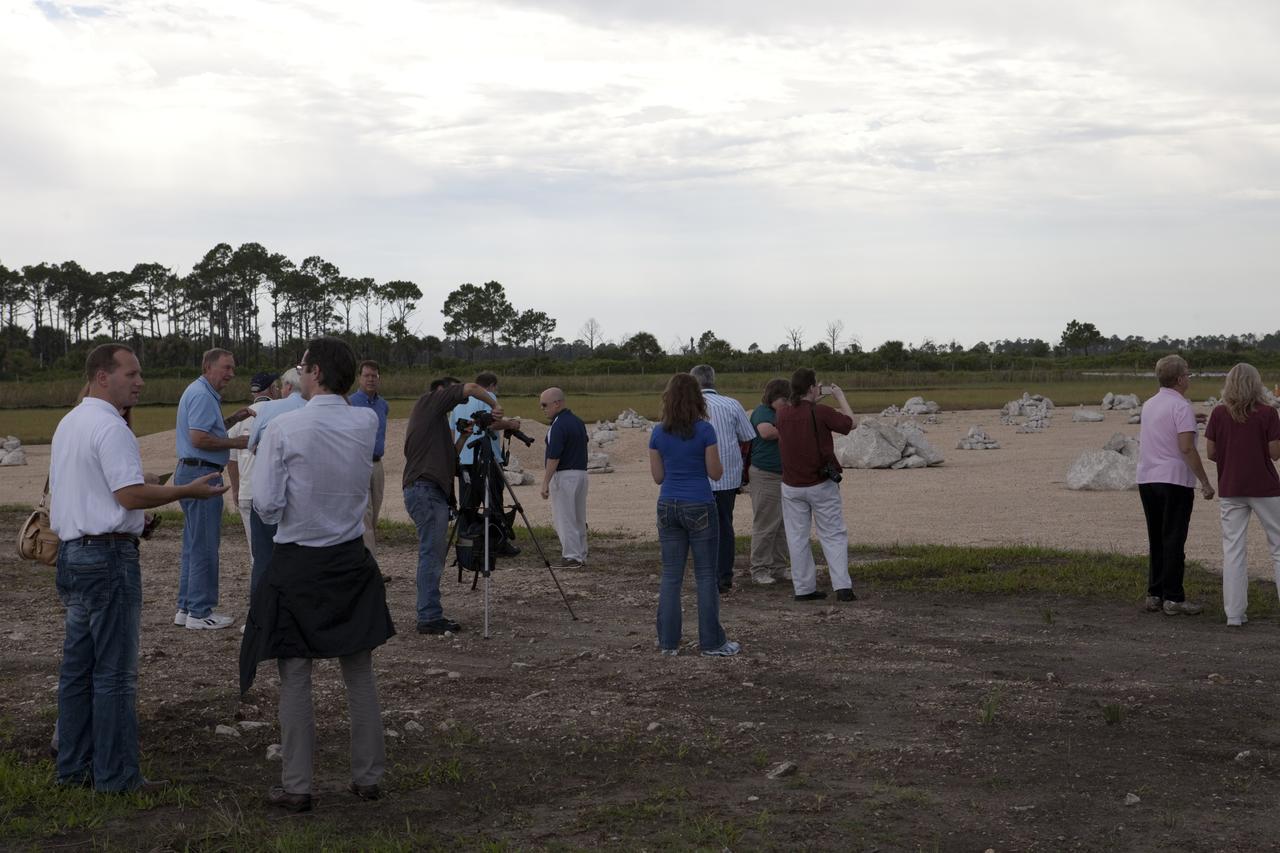

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, field at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media view the hazard field and speak with Morpheus managers. At far left, in the white shirt is Jon Olansen, Johnson Space Center Project Morpheus Manager. At left, in the blue shirt is Chirold Epp, JSC project manager for ALHAT. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
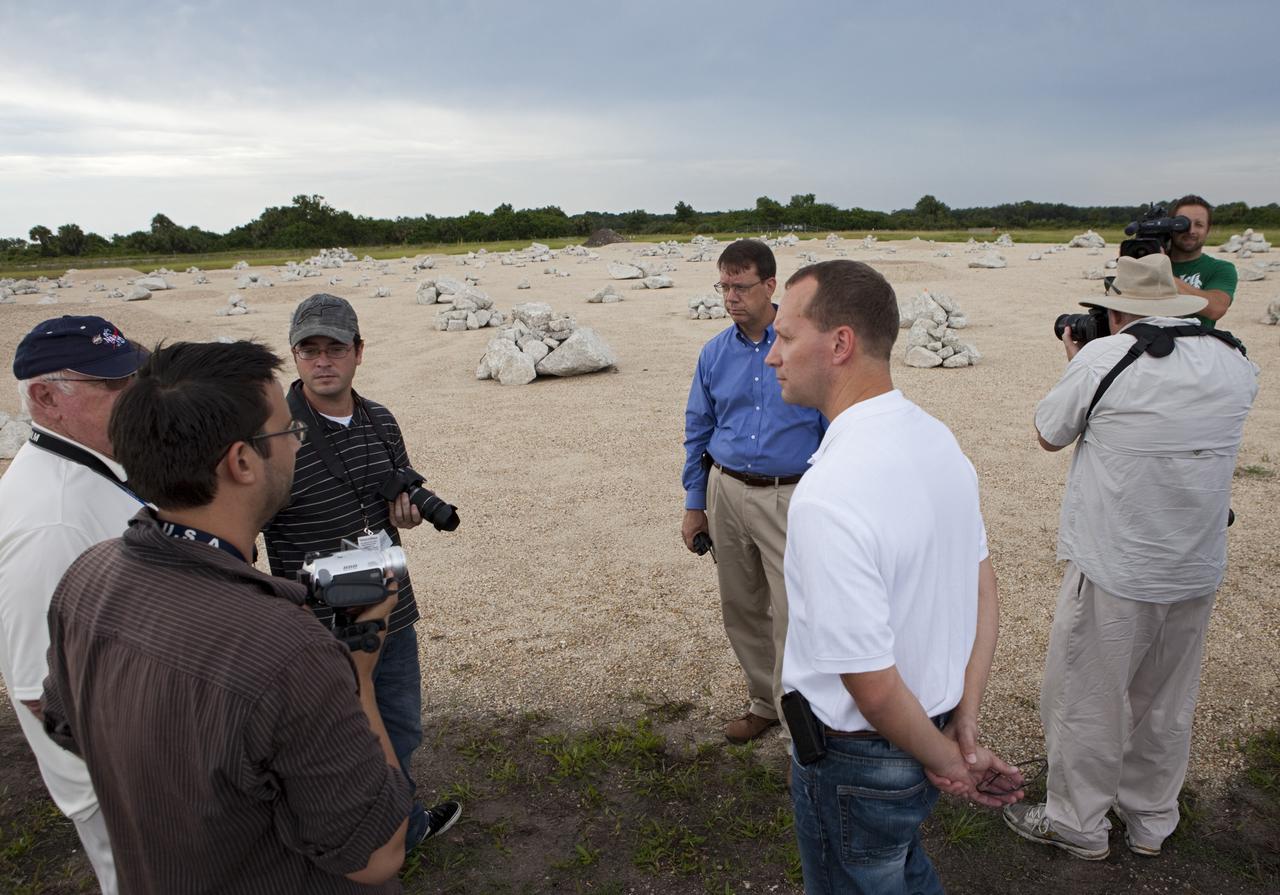

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, field at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media view the hazard field and speak with Morpheus managers. In the white shirt is Jon Olansen, Johnson Space Center Project Morpheus Manager. Behind Olansen is Gregory Gaddis, Kennedy Project Morpheus/ALHAT site manager. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
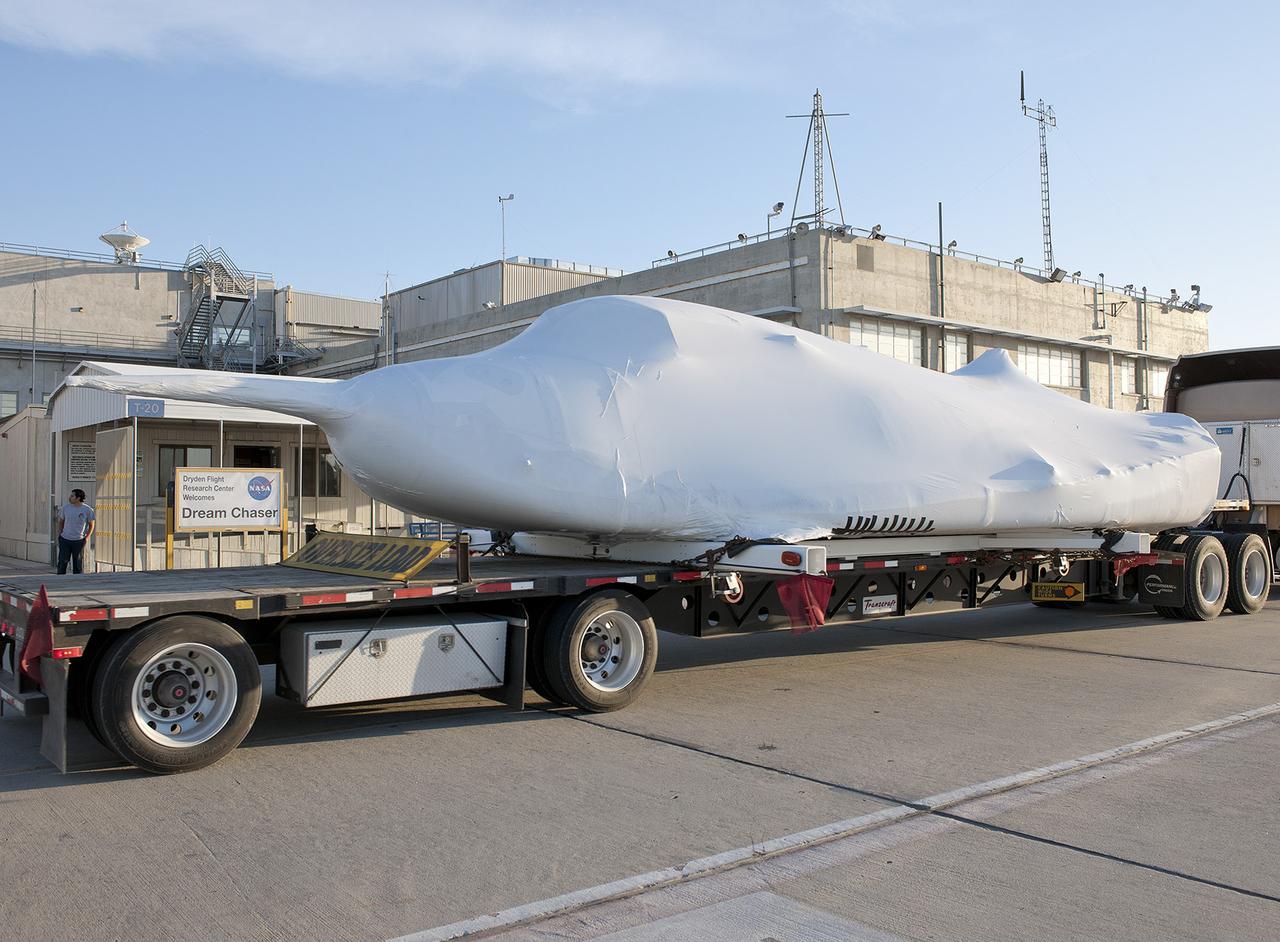

EDWARDS, Calif. – ED13-0142-10: The flatbed truck and trailer that transported Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Space Systems' Dream Chaser engineering test article pauses on the aircraft ramp at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center on Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., upon arrival at the center. Following removal of the protective plastic wrap and reinstallation of its wings and tail structure, the Dream Chaser will begin ground tests in the next few weeks leading to approach and landing flight tests this summer. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Tom Tschida
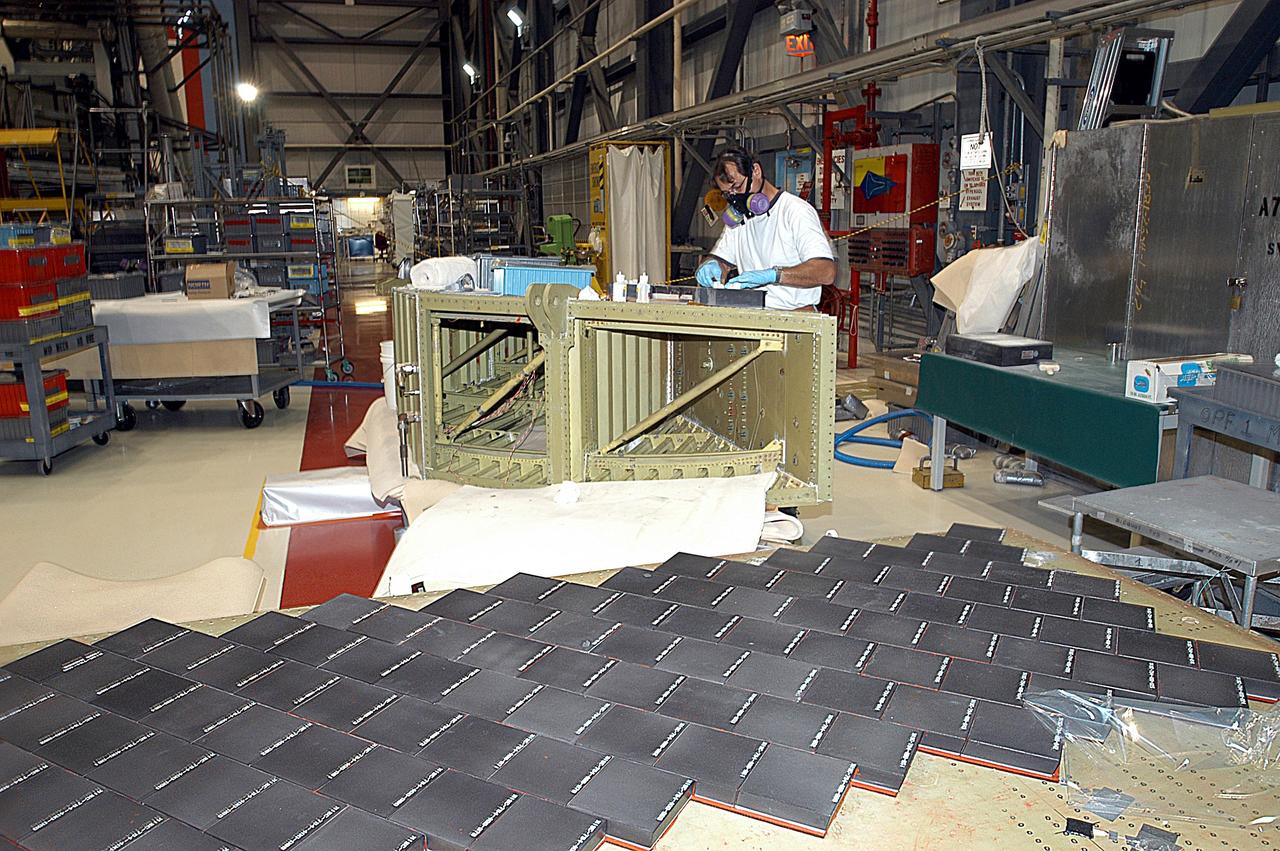

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF), United Space Alliance (USA) technician Mark Jetton installs Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile on a simulated orbiter wing. The wing, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.

NASA Orbiter Transition & Retirement team member Tom Goebel monitors the installation of "rain covers" over space shuttle Enterprise’s vent door openings ahead of the expected rain at Washington Dulles International Airport, Saturday, April 21, 2012, in Sterling, Va. Enterprise, the first orbiter built for the Space Shuttle Program, was used primarily for ground and flight tests within the atmosphere. The initial testing period named Approach and Landing Test (ALT) included a flight on February 18, 1977 atop a Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) to measure structural loads and ground handling and braking characteristics of the mated system. Enterprise will go on permanent display at the Intrepid Sea Air and Space Museum in New York in June. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
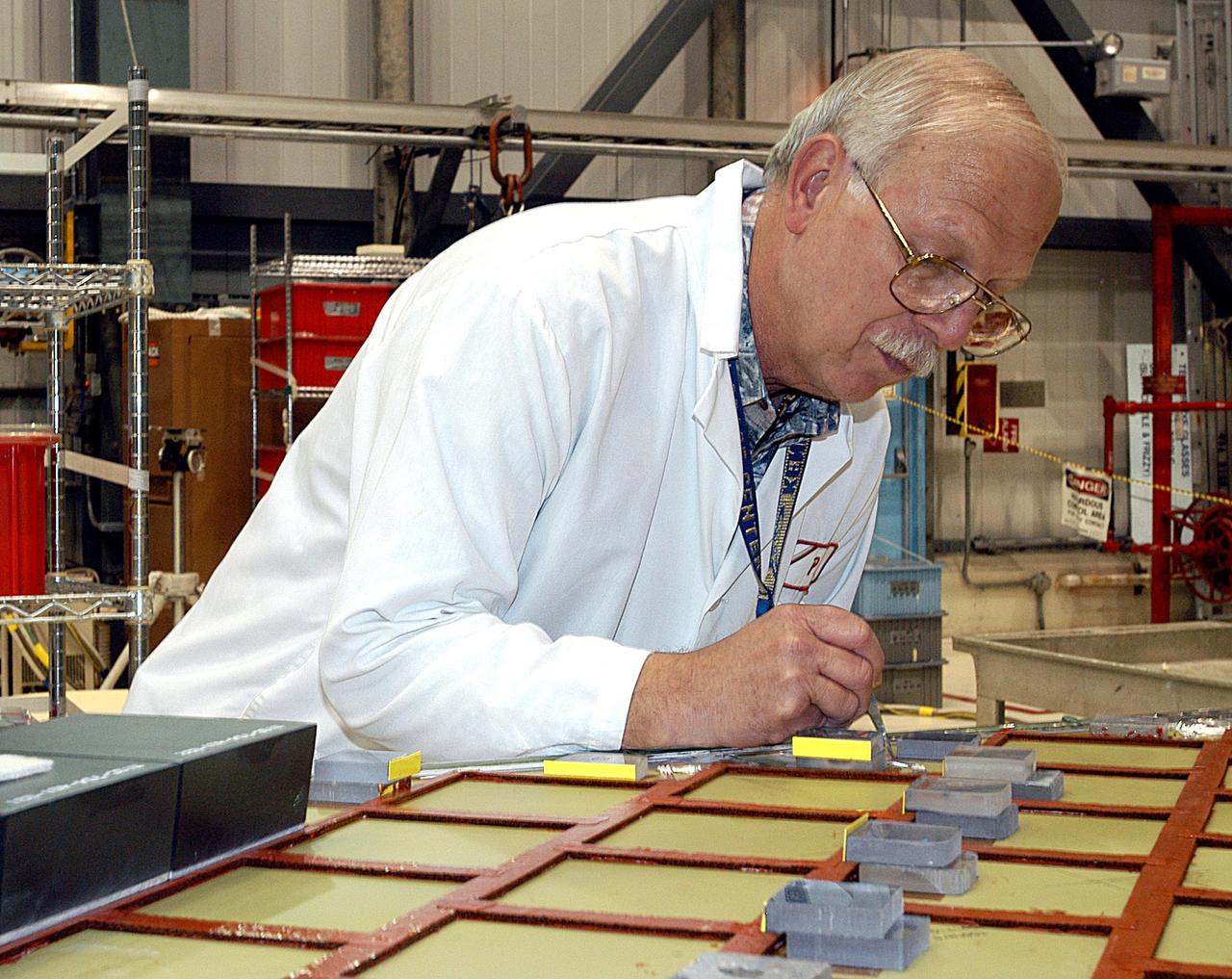

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF), Paul King, an employee of The Boeing Co., Huntington Beach, Calif., installs a strain gauge on a simulated orbiter wing in preparation for Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile installation. The wing, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
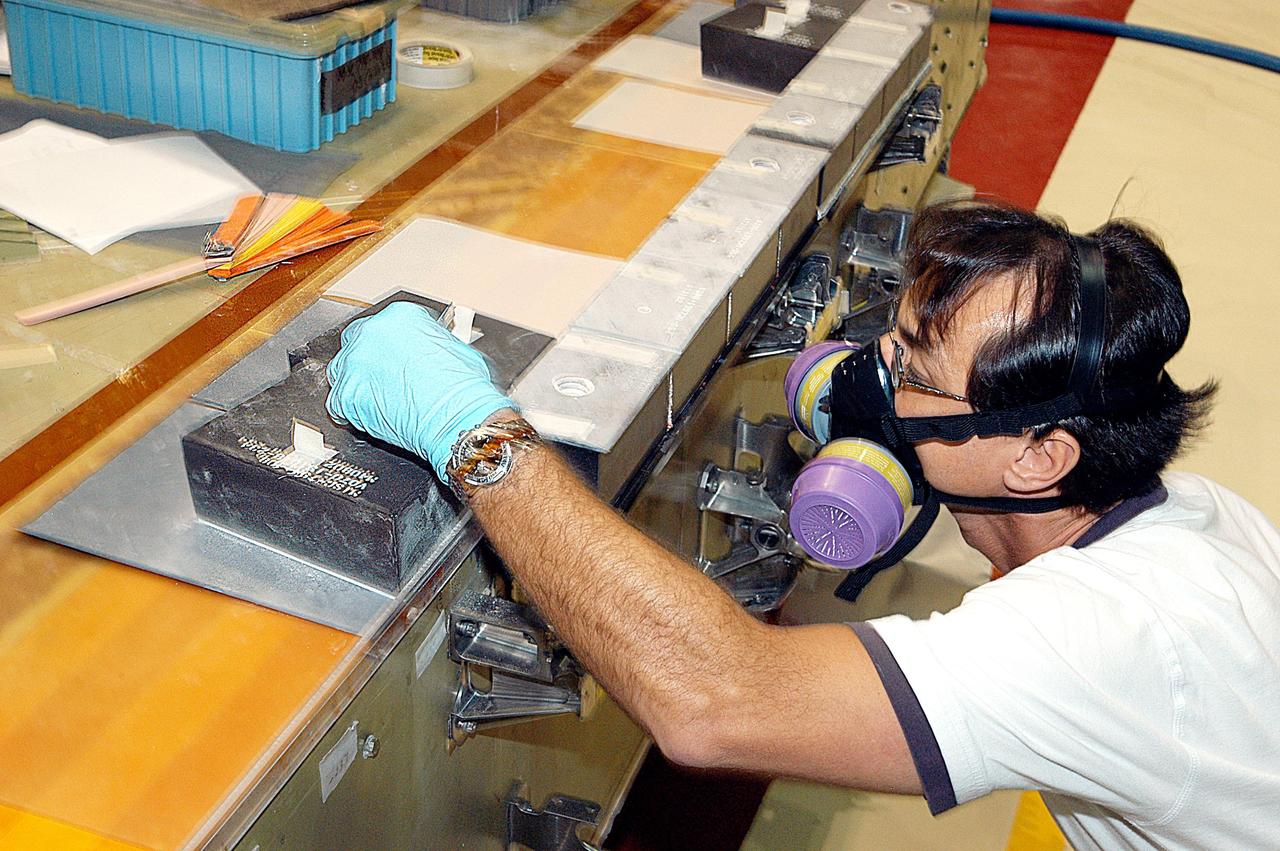

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF), United Space Alliance (USA) technician Mark Jetton installs Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile on a simulated orbiter wing. The wing, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
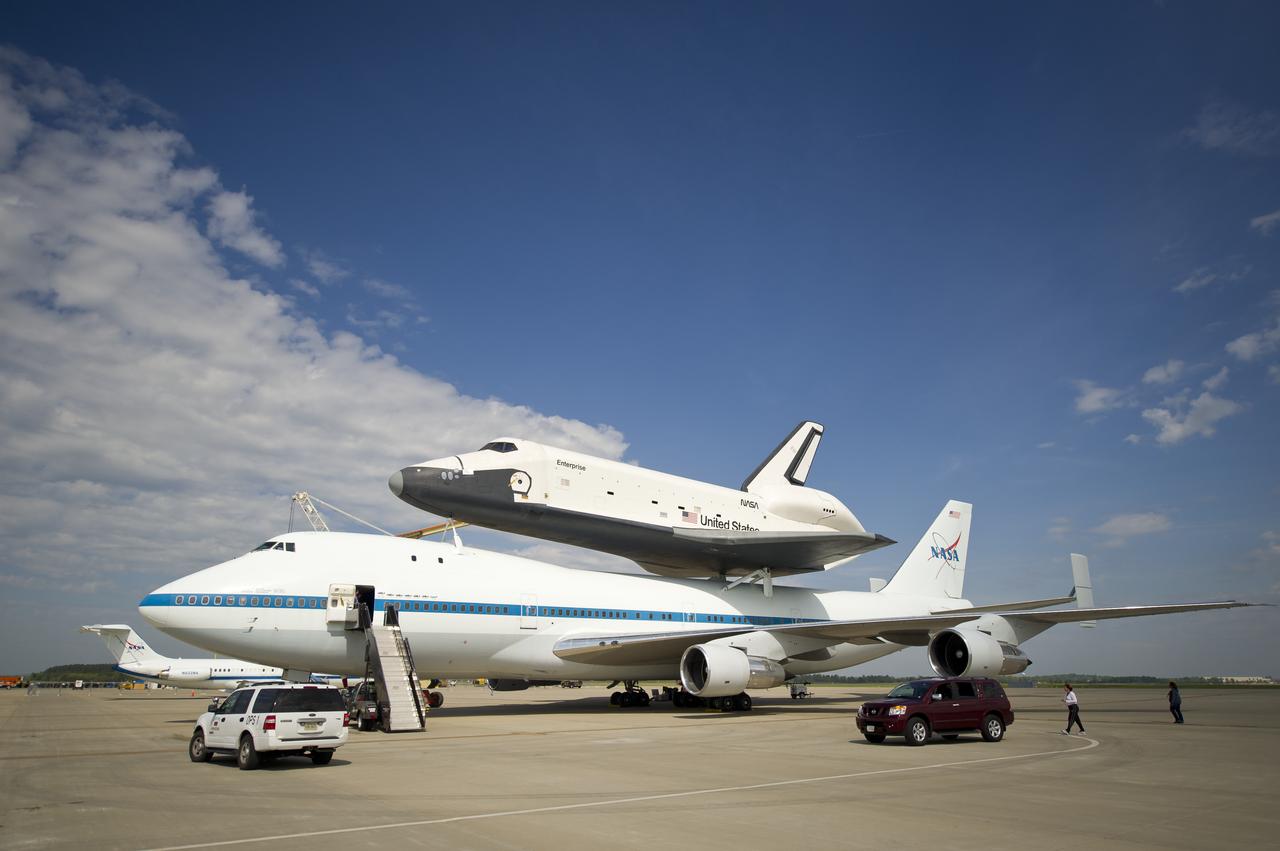

The space shuttle Enterprise is seen mated on top of the NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) at Washington Dulles International Airport, Saturday, April 21, 2012, in Sterling, Va. Space Shuttle Transition and Retirement engineers Saturday completed the final steps to ready Space Shuttle Enterprise for its flight to New York’s John F. Kennedy International Airport while managers continue to evaluate the expected weather that has postponed delivery past Monday. Enterprise, the first orbiter built for the Space Shuttle Program, was used primarily for ground and flight tests within the atmosphere. The initial testing period named Approach and Landing Test (ALT) included a flight on February 18, 1977 atop a Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) to measure structural loads and ground handling and braking characteristics of the mated system. Enterprise will go on permanent display at the Intrepid Sea Air and Space Museum in New York in June. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF), United Space Alliance (USA) technician Mark Jetton installs Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile on a simulated orbiter wing. The wing, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
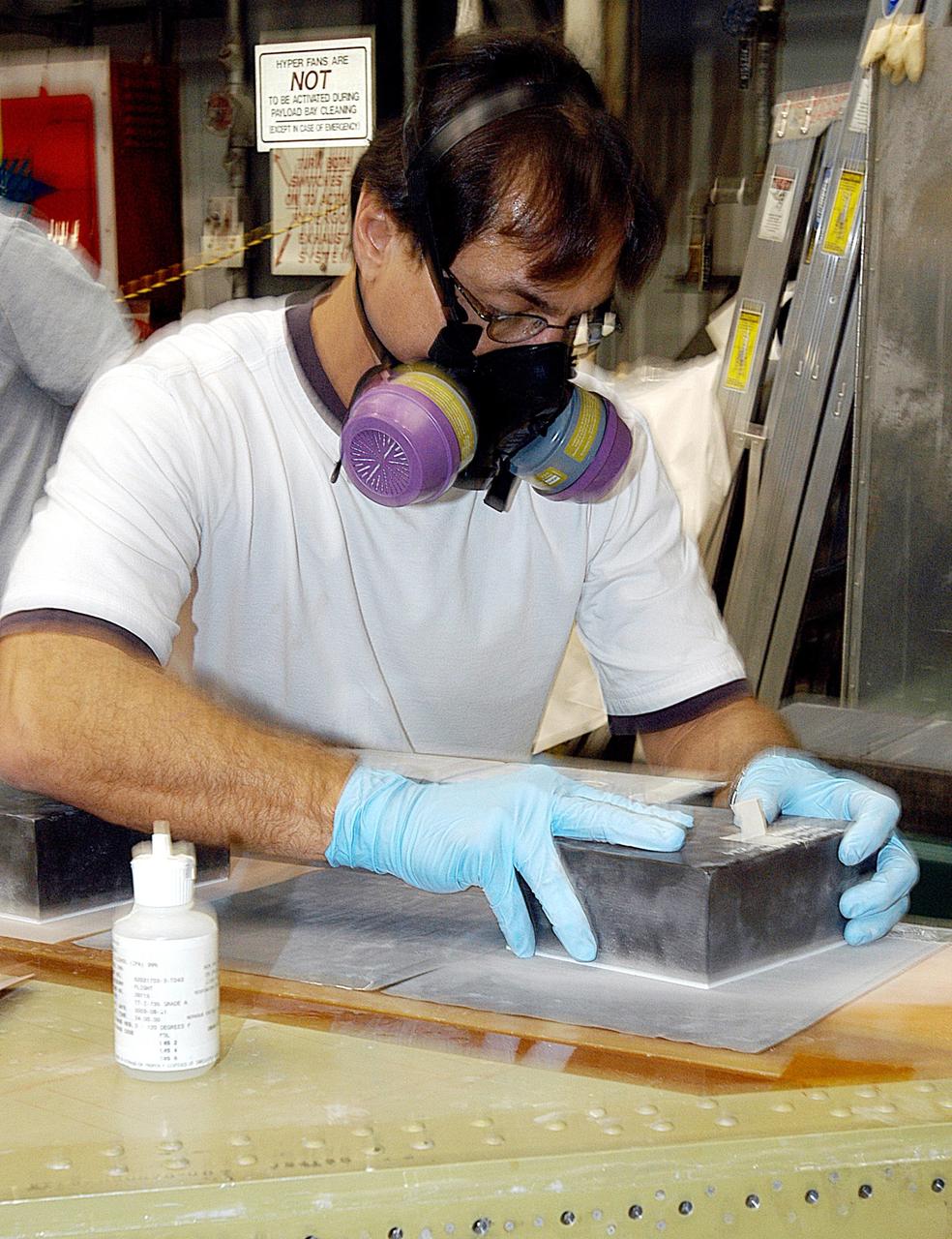

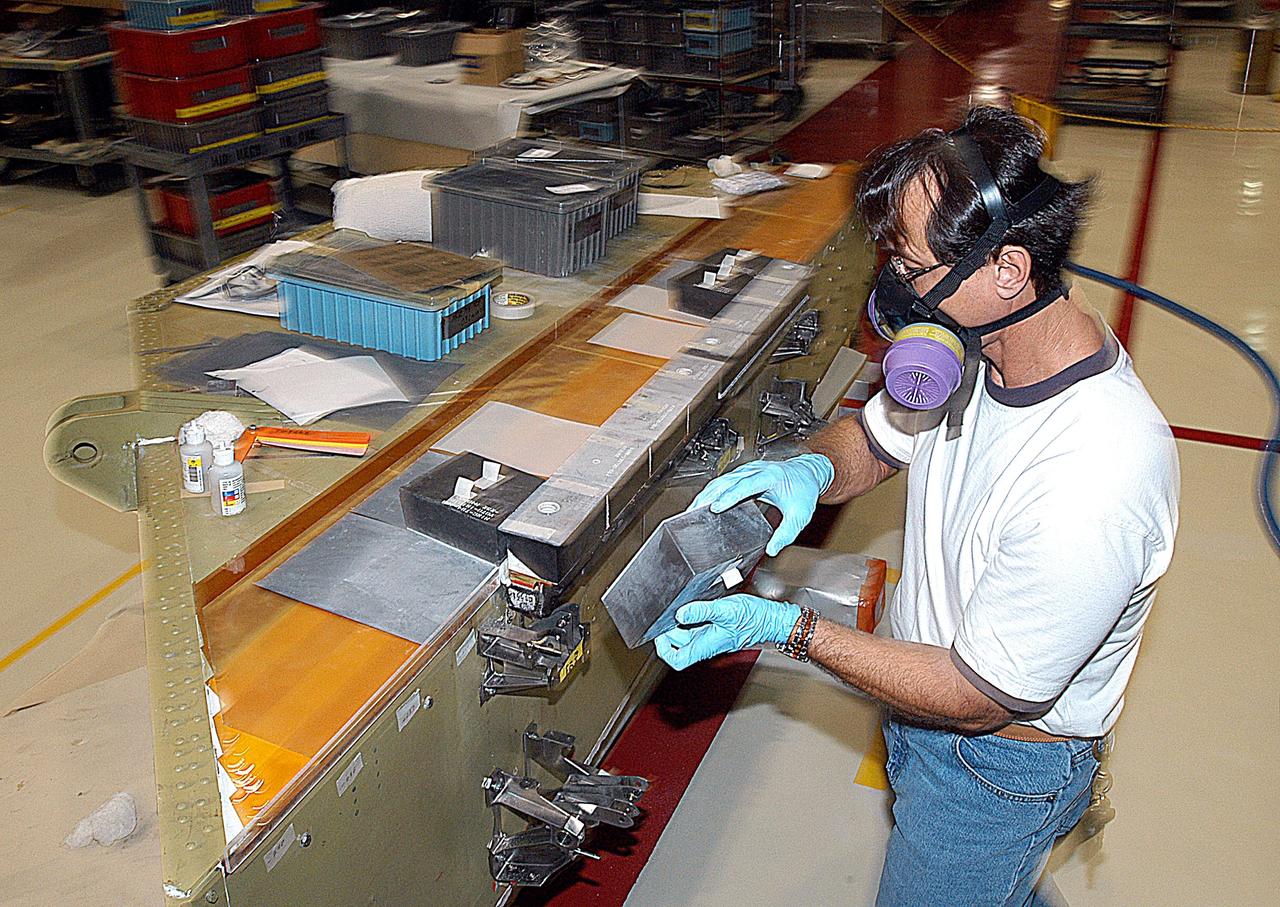
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF), United Space Alliance (USA) technician Mark Jetton installs Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile on a simulated orbiter wing. The wing, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
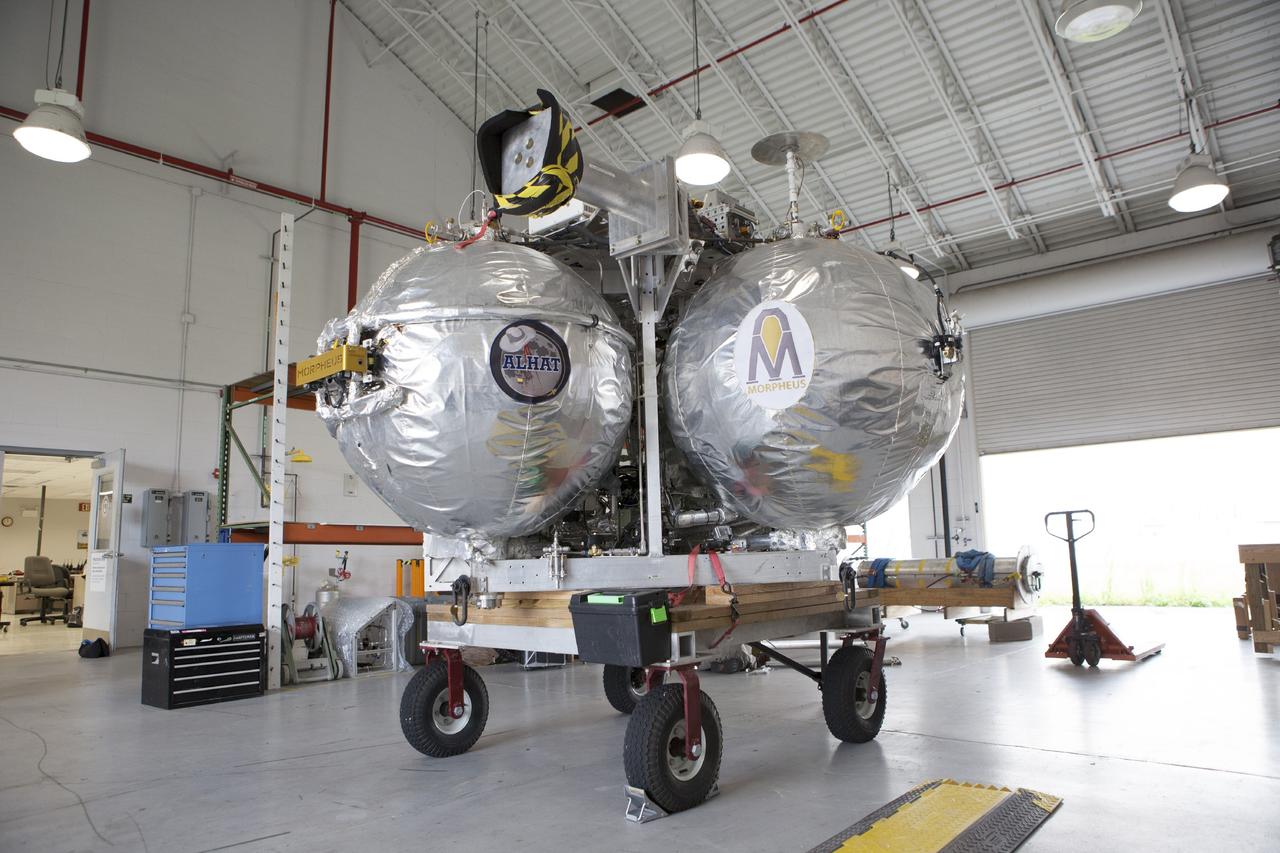

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Project Morpheus lander sits inside the bay of a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
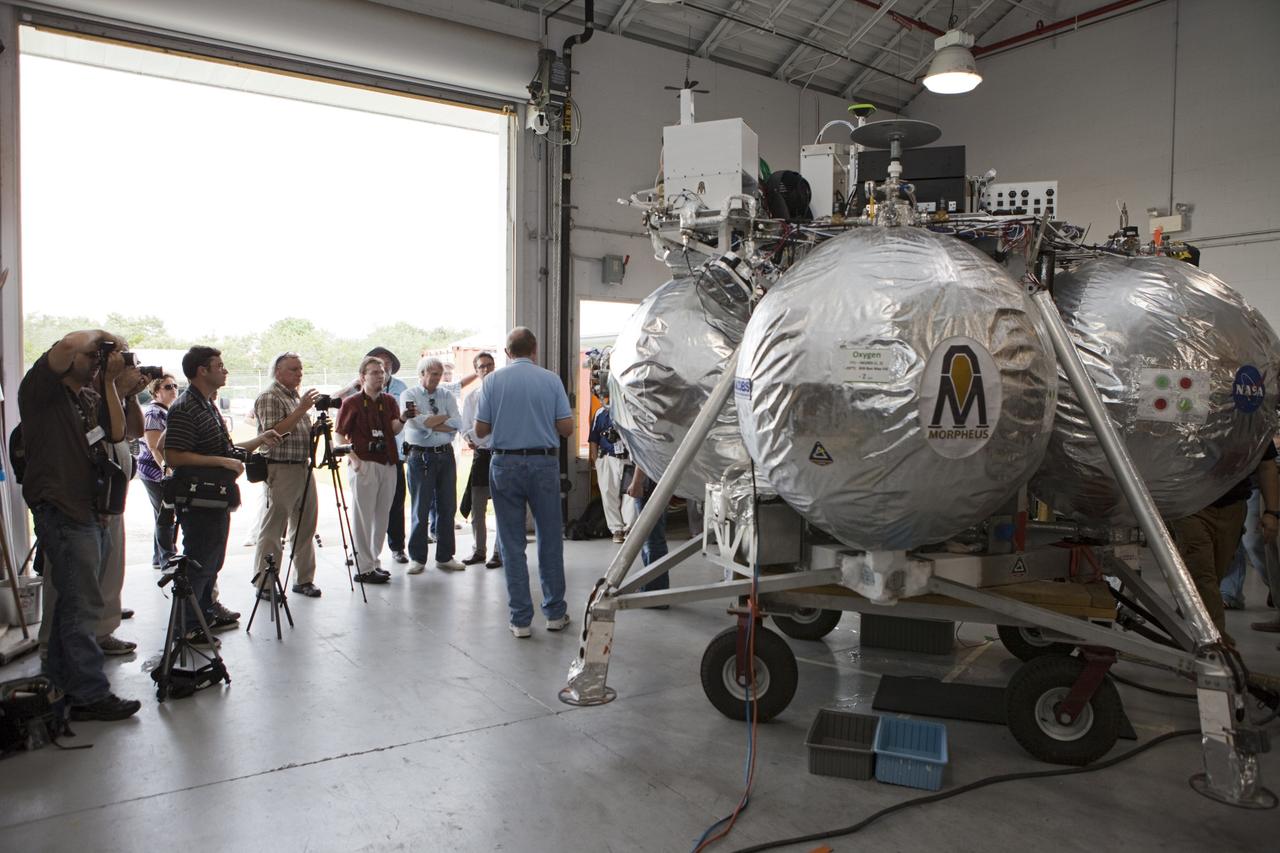

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At a hangar near the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Chirold Epp, Johnson Space Center Project Manager for ALHAT, speaks to members of the media. In the background is the Morpheus prototype lander, which arrived at Kennedy on July 27. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
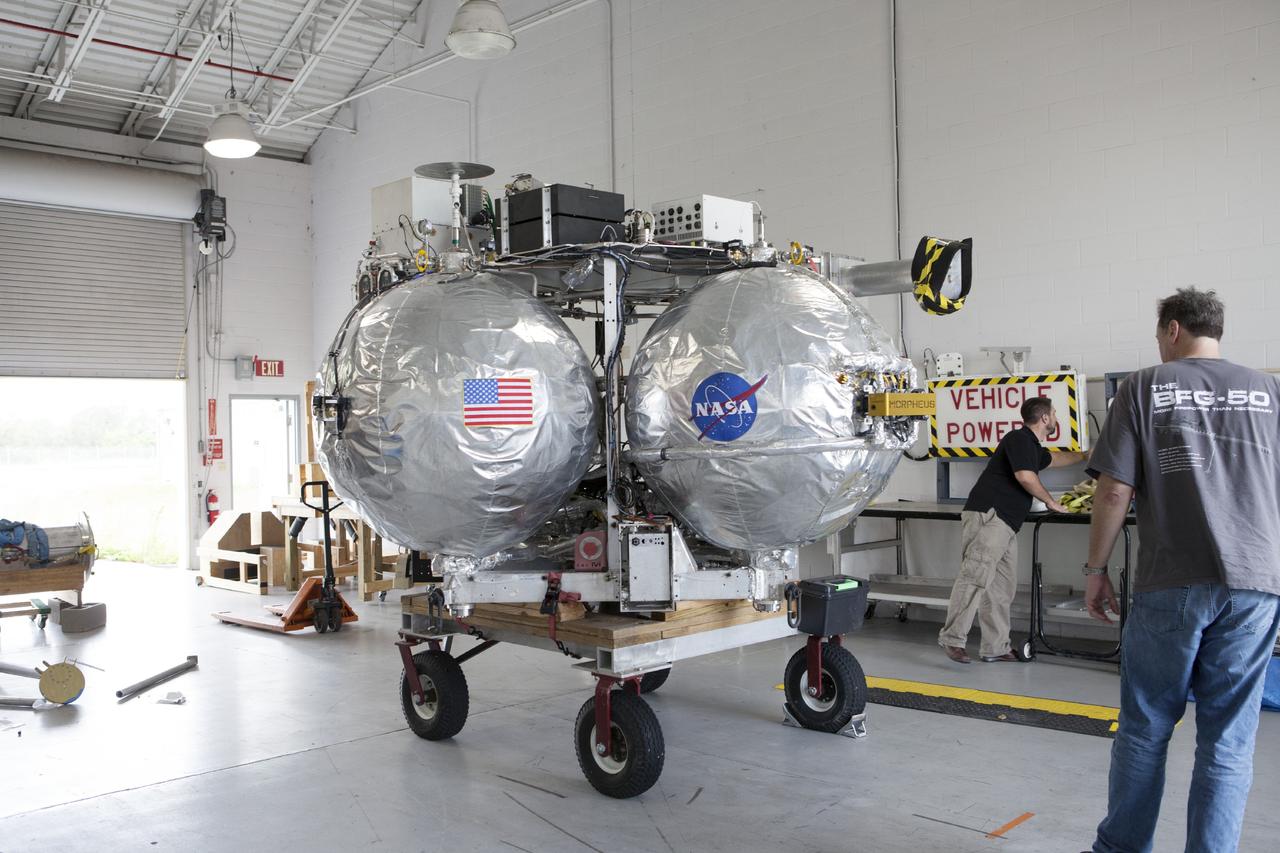

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Project Morpheus lander is moved into the bay of a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
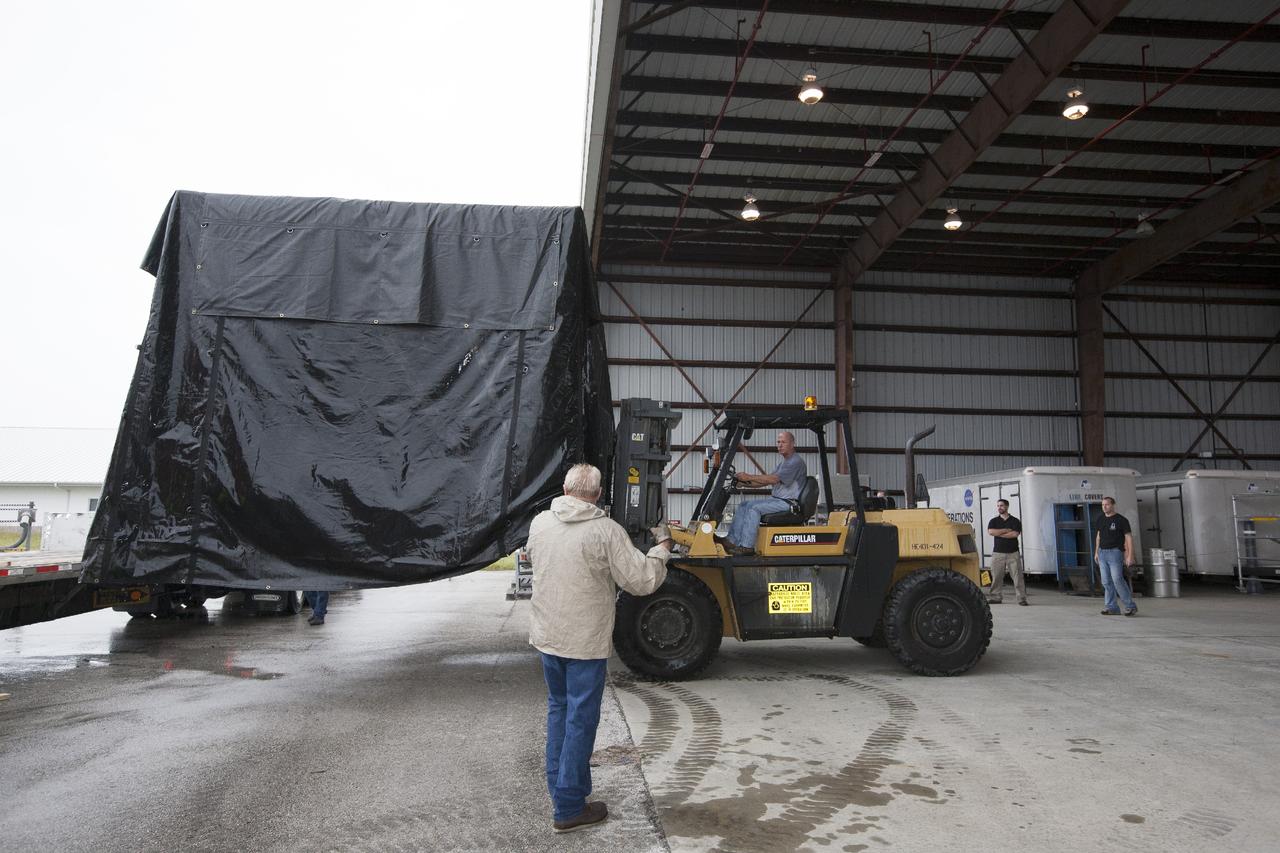

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Project Morpheus lander is moved into a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
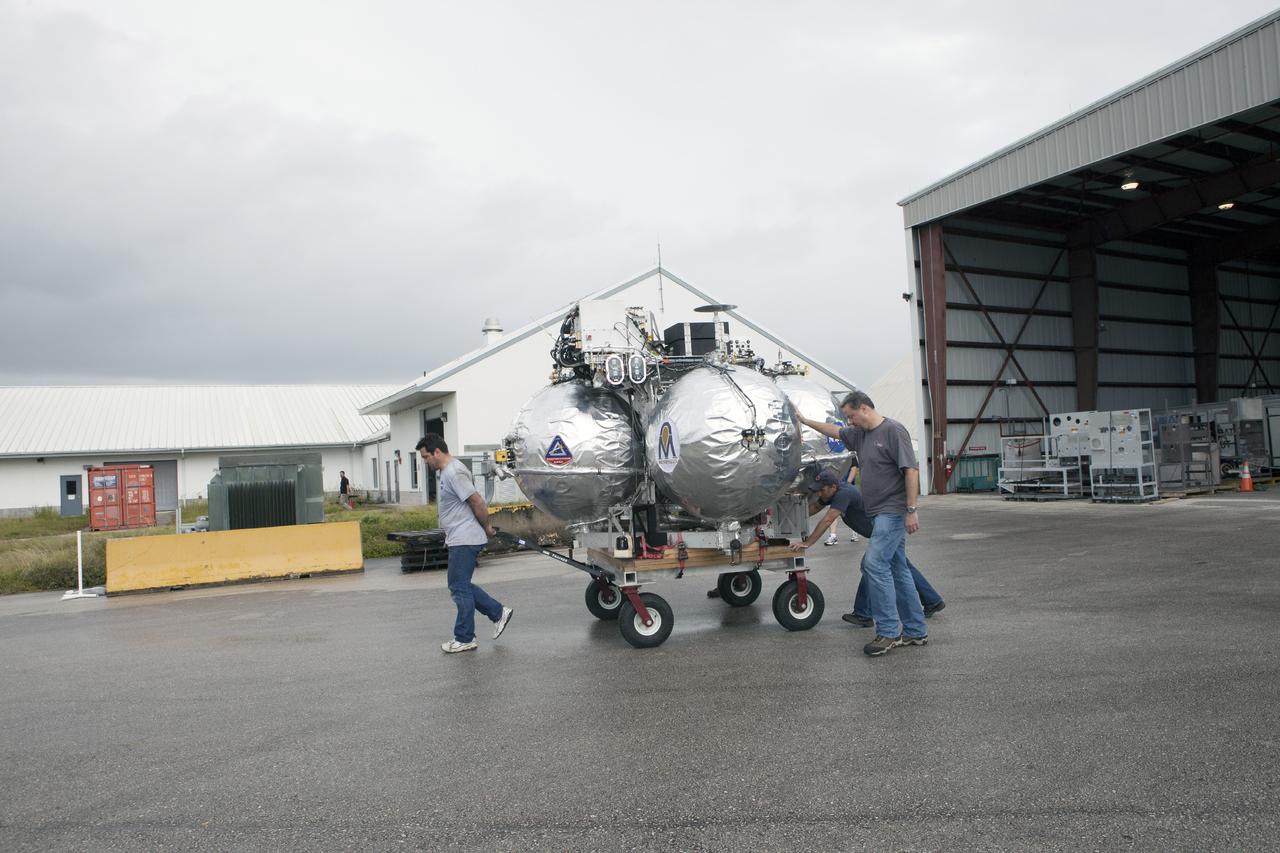

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians move the Project Morpheus lander on a small transporter to a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
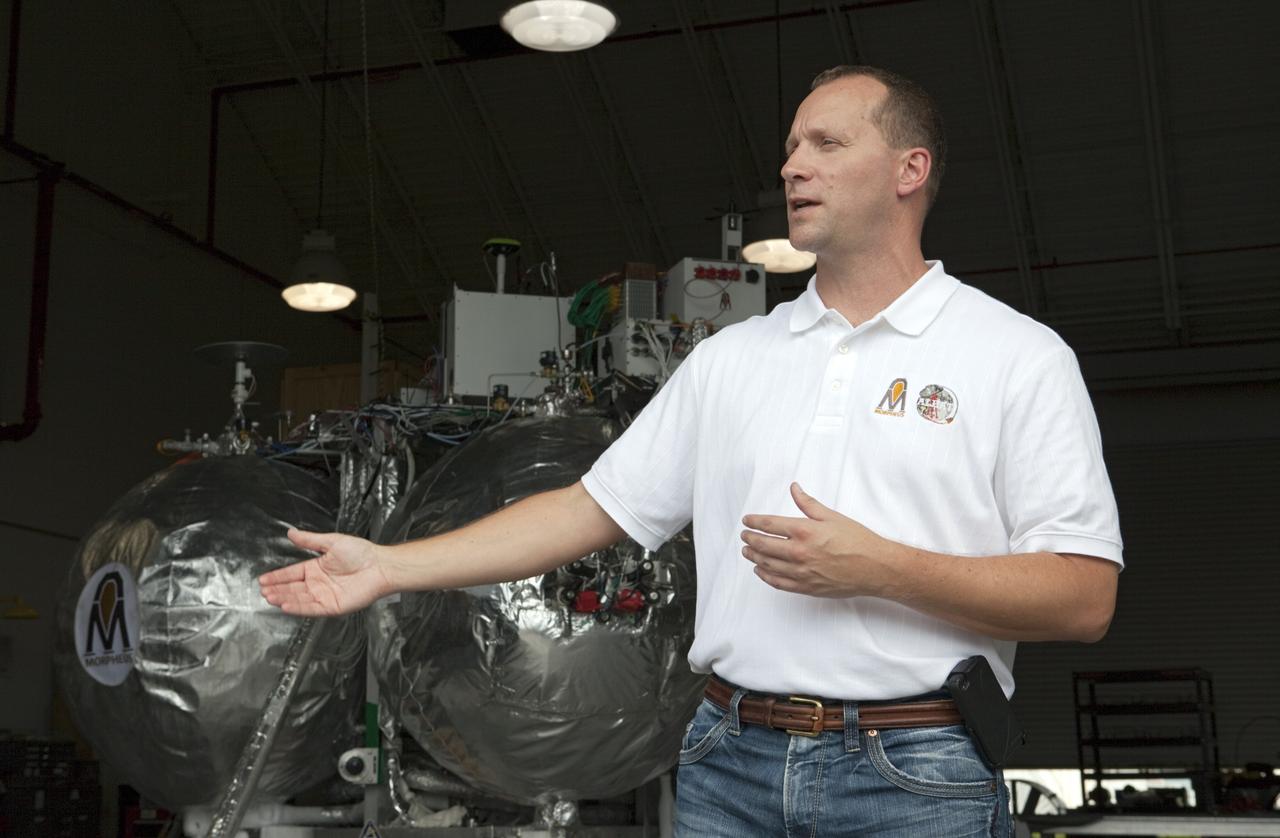

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At a hangar near the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Johnson Space Center Project Morpheus Manager Jon Olansen speaks to members of the media. In the background is the Morpheus prototype lander, which arrived at Kennedy on July 27. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
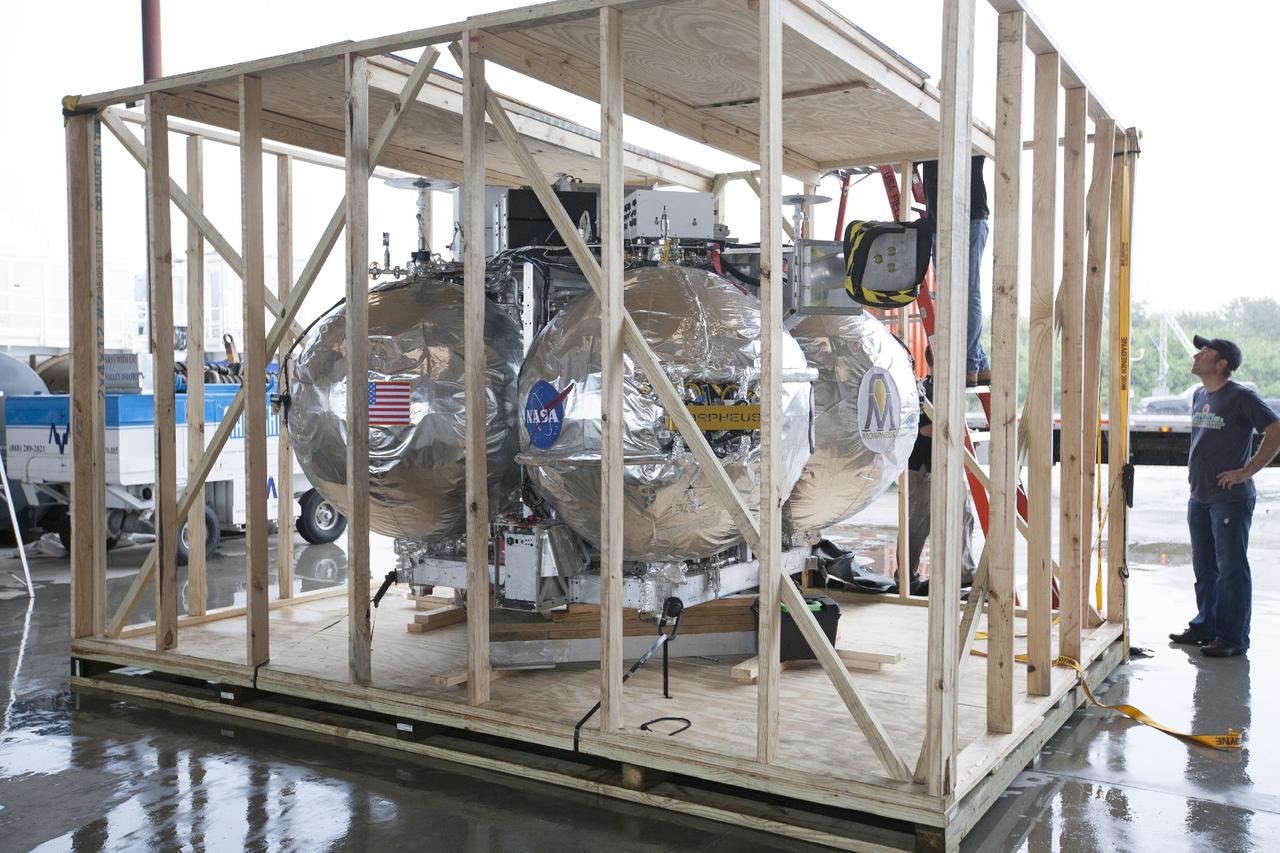
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Project Morpheus lander has been offloaded from a flatbed truck and sits inside a protective crate inside a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
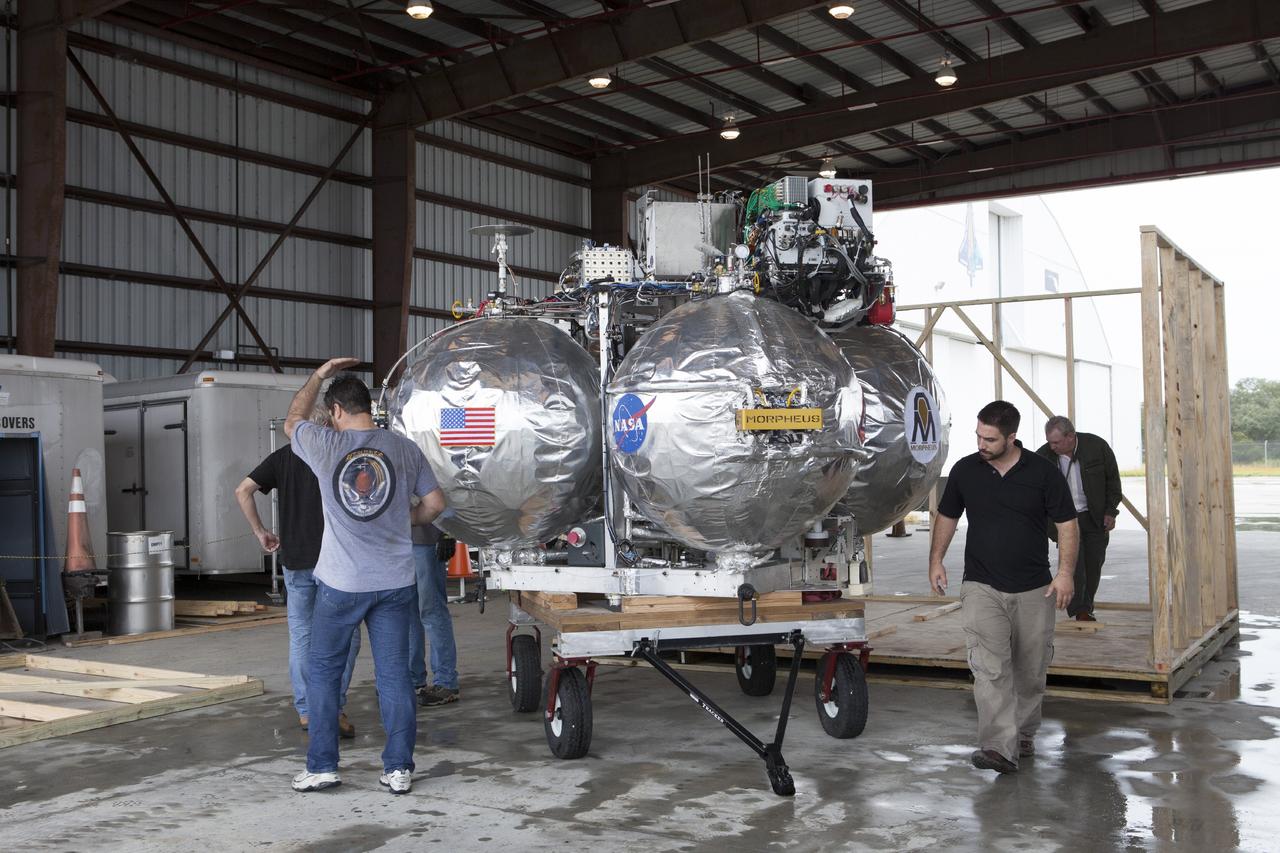

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians position the Project Morpheus lander onto a transporter inside a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
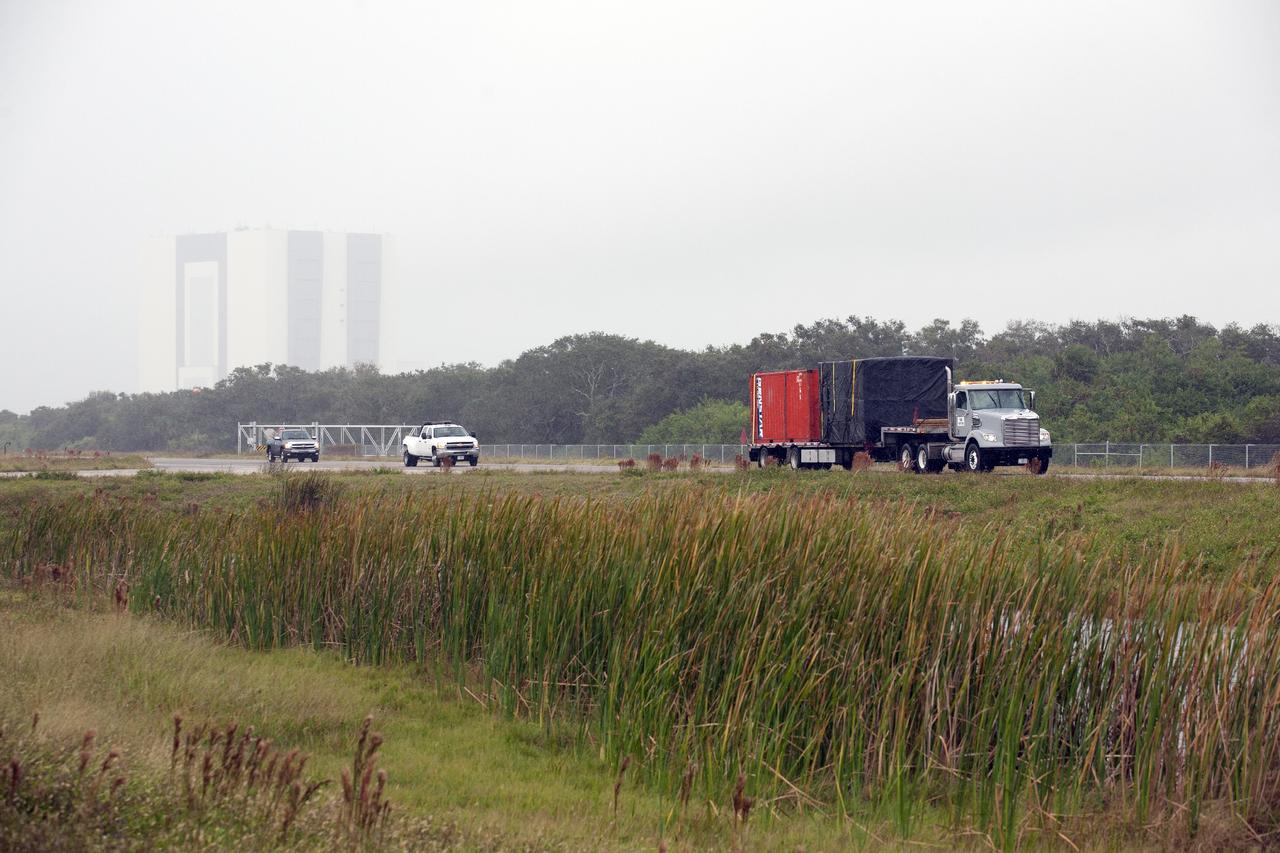

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a flatbed truck carrying the Project Morpheus lander arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
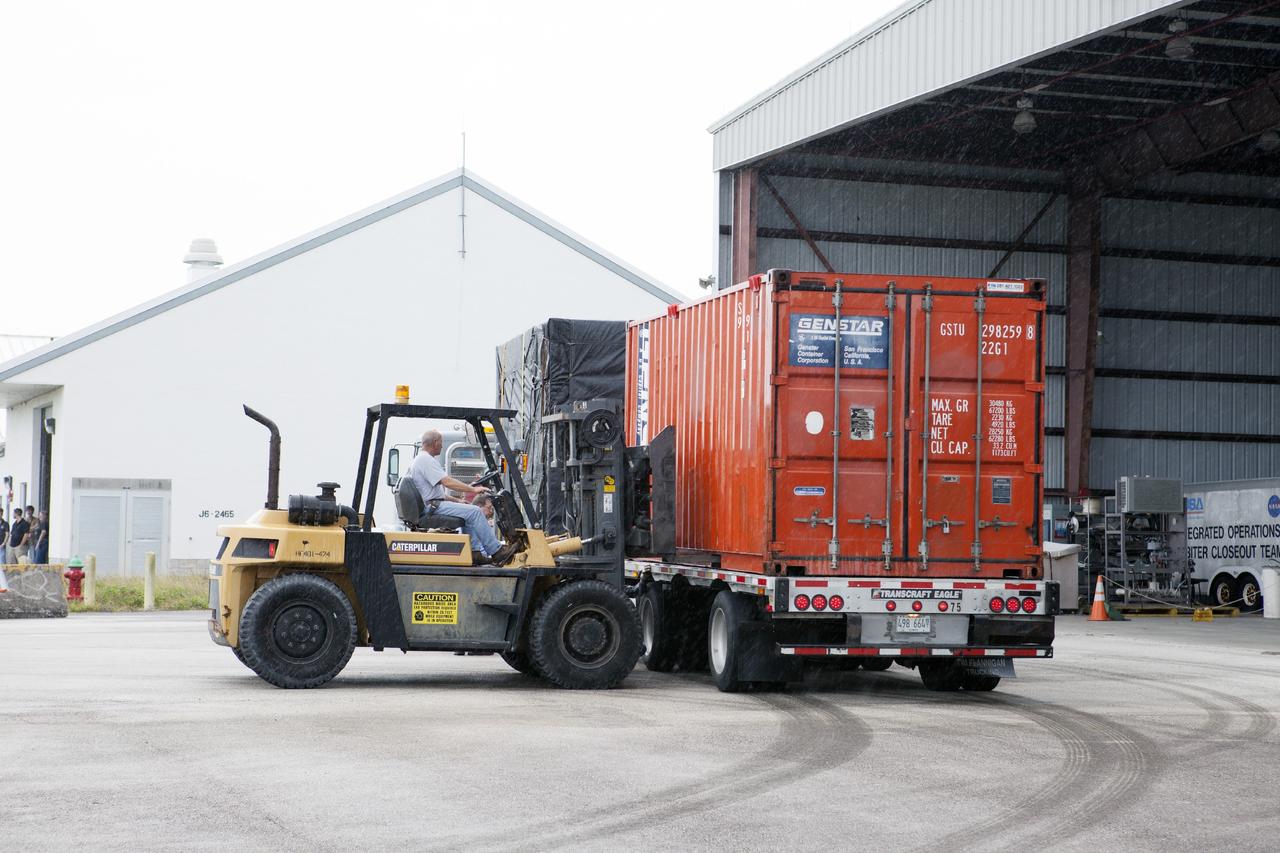

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a flatbed truck carrying the Project Morpheus lander arrives at a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
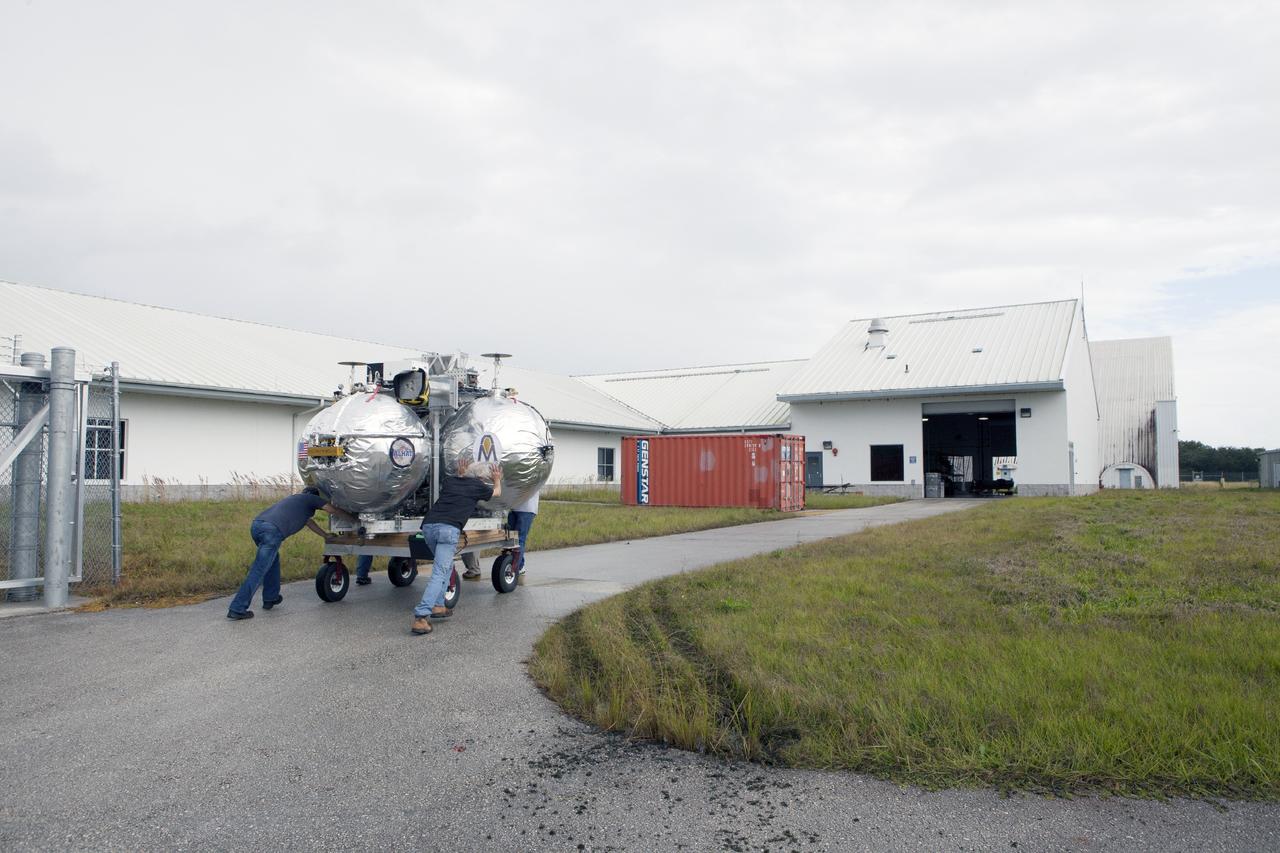

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians move the Project Morpheus lander on a small transporter to a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
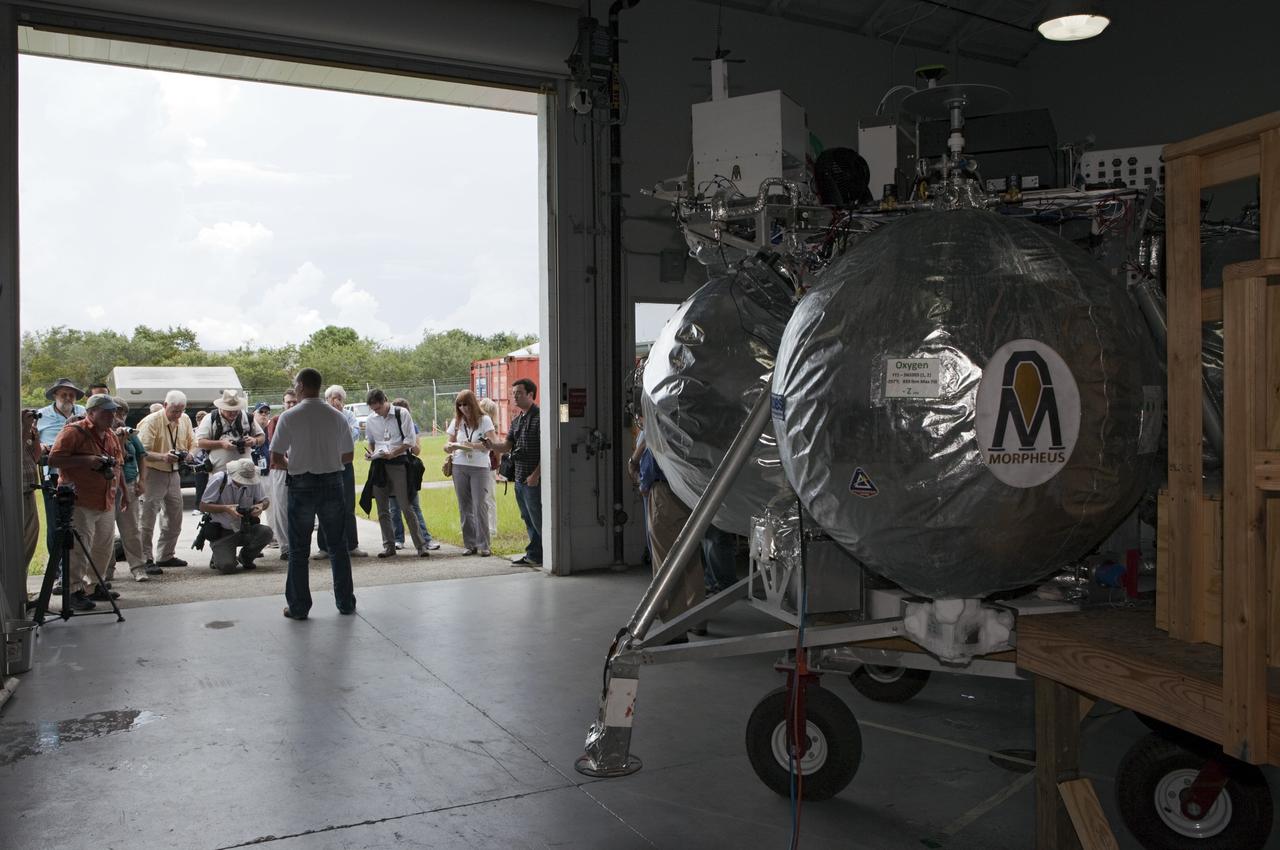

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At a hangar near the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Johnson Space Center Project Morpheus Manager Jon Olansen speaks to members of the media. In the foreground is the Morpheus prototype lander, which arrived at Kennedy on July 27. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
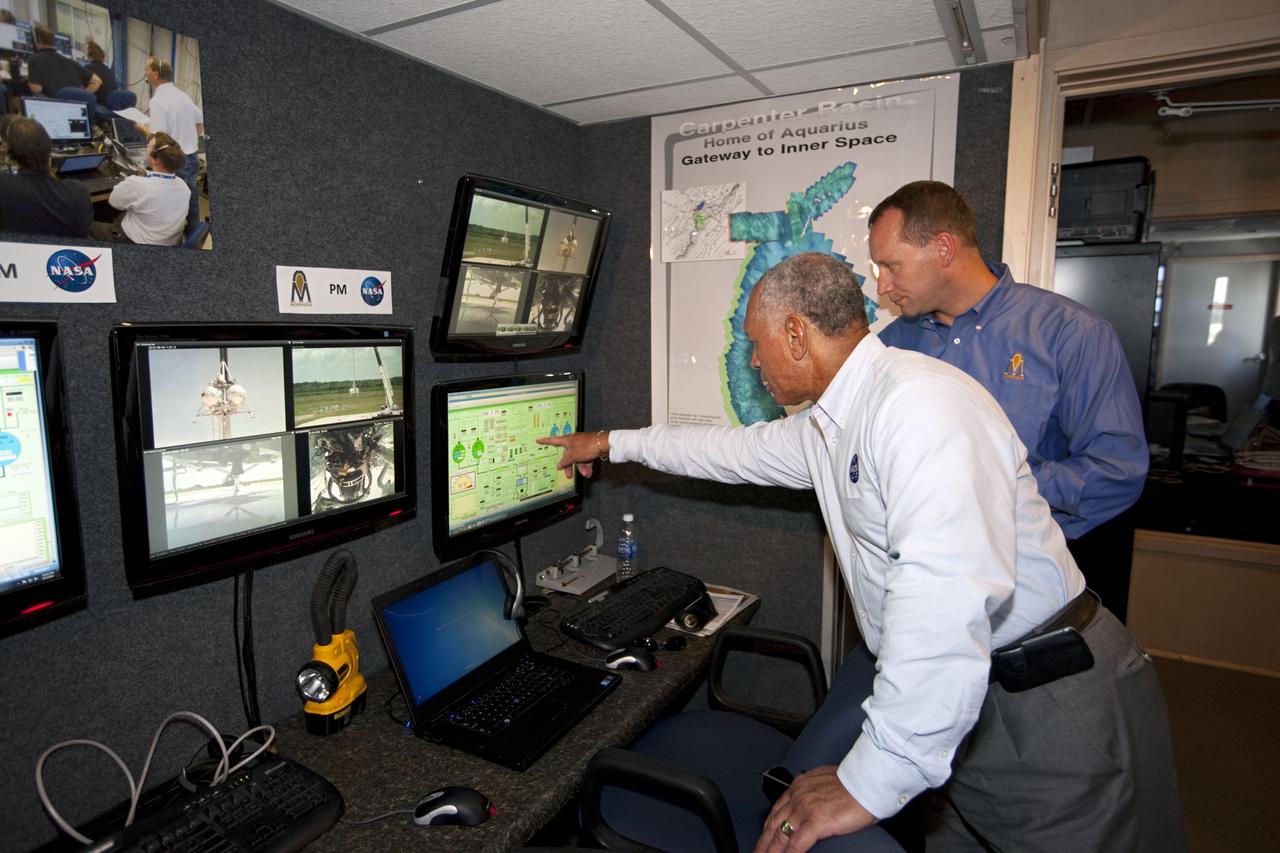

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, joins Dr. Jon Olansen, Morpheus project manager, in the control room at the Shuttle Landing Facility for the first tethered flight of the Morpheus lander. After undergoing testing at Johnson Space Center in Houston for nearly a year, Morpheus arrived at Kennedy on July 27 to begin about three months of tests. A field, replete with boulders, rocks, slopes, craters and hazards to avoid, was created at the north end of Kennedy's runway to provide a realistic landscape for test flights of the lander. Morpheus utilizes autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, to navigate to a safe landing site during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
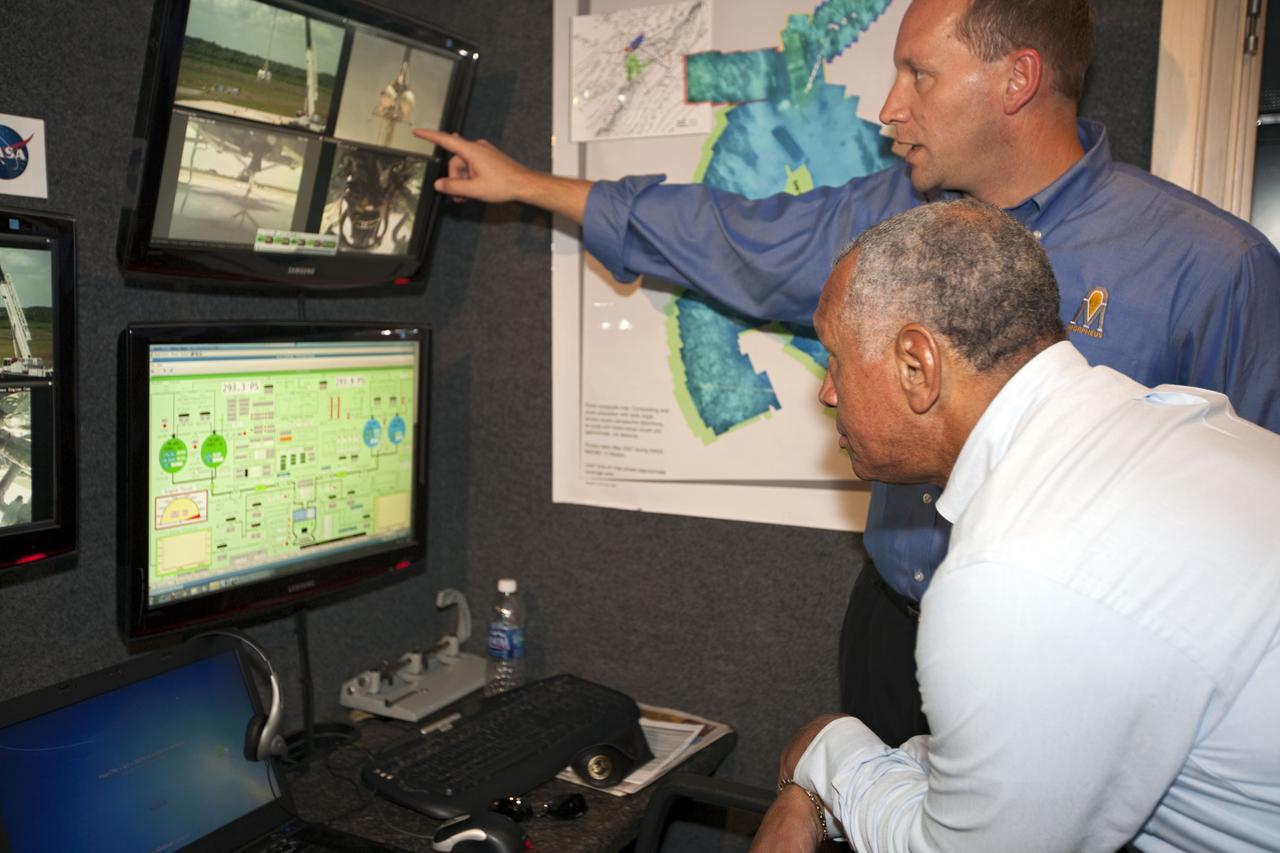

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden joins Morpheus project manager Dr. Jon Olansen, pointing at monitor, in the control room at the Shuttle Landing Facility for the first tethered flight of the Morpheus lander. After undergoing testing at Johnson Space Center in Houston for nearly a year, Morpheus arrived at Kennedy on July 27 to begin about three months of tests. A field, replete with boulders, rocks, slopes, craters and hazards to avoid, was created at the north end of Kennedy's runway to provide a realistic landscape for test flights of the lander. Morpheus utilizes autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, to navigate to a safe landing site during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
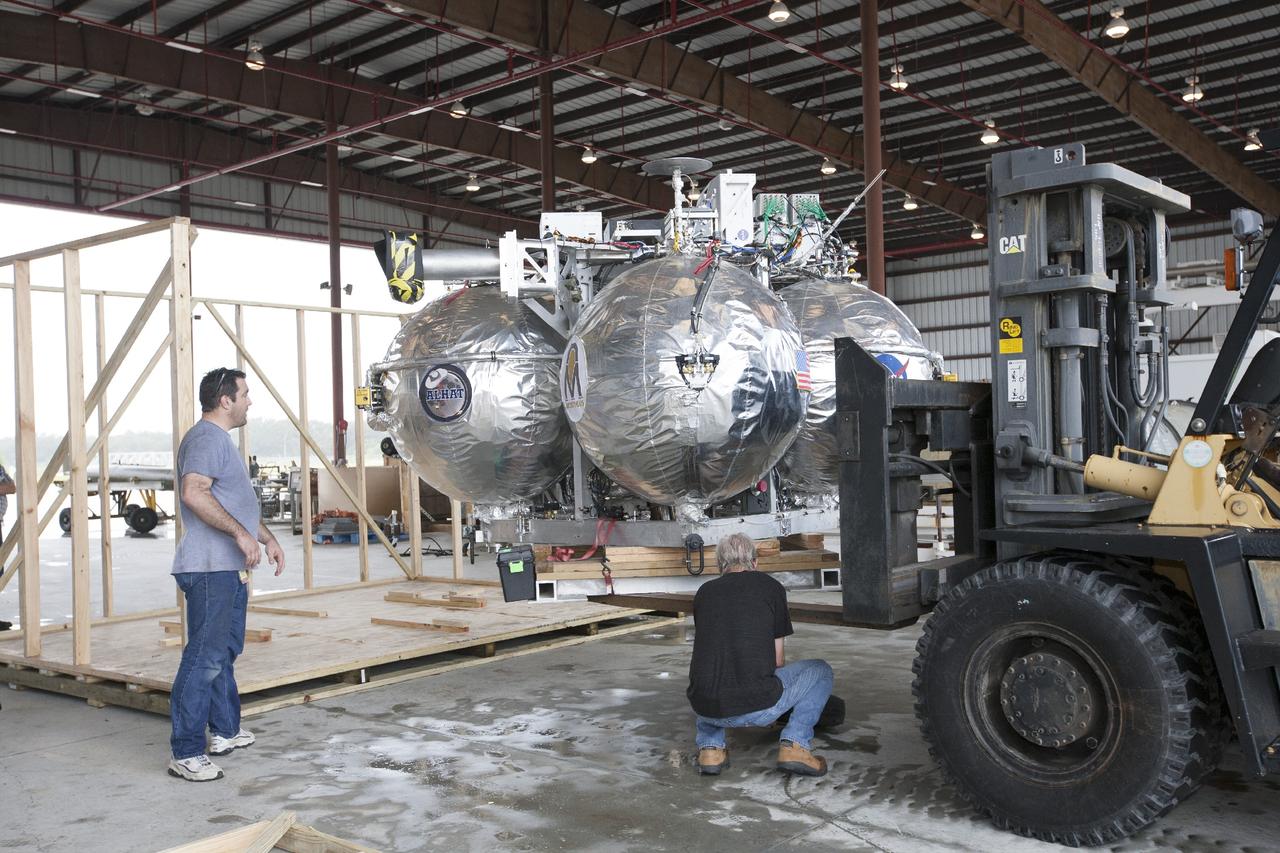

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians remove the Project Morpheus lander from a protective crate inside a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
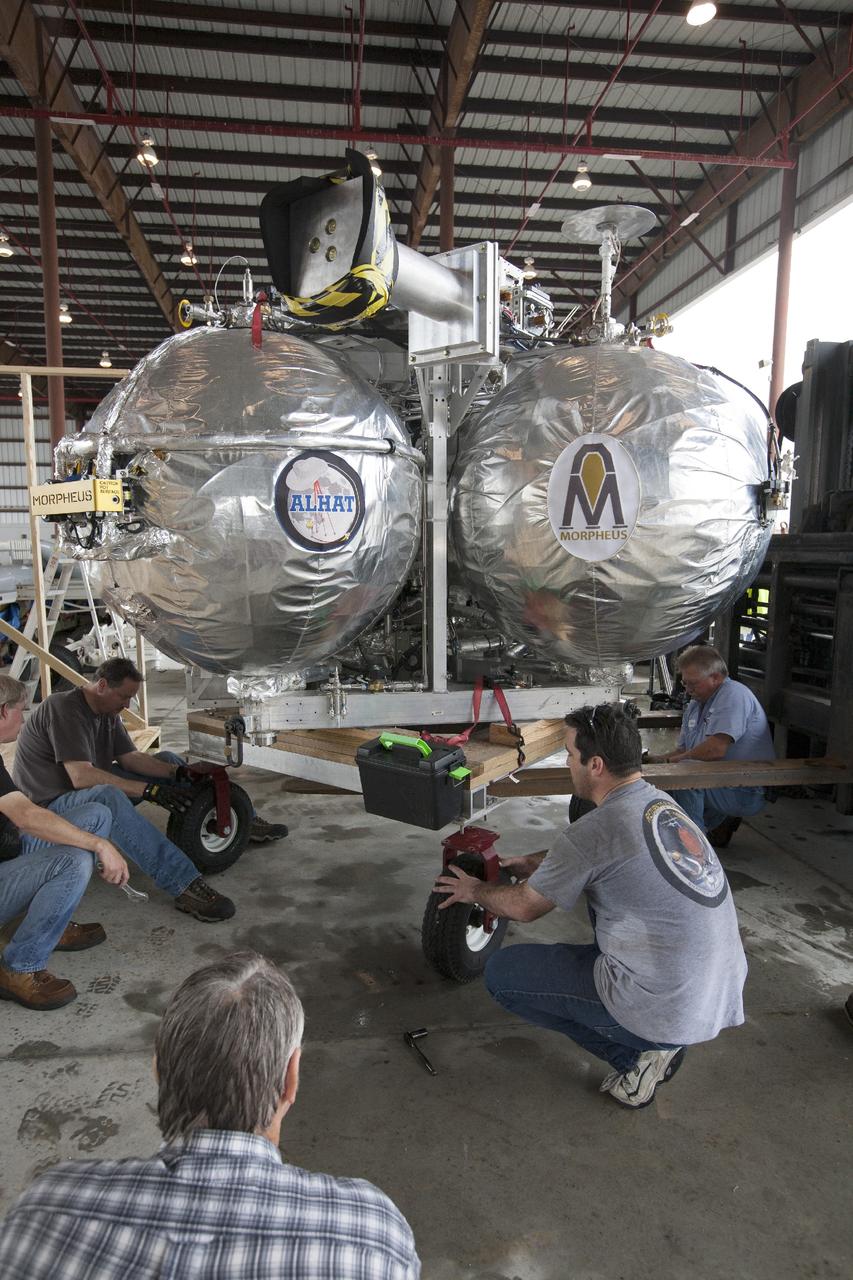

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians position the Project Morpheus lander onto a transporter inside a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
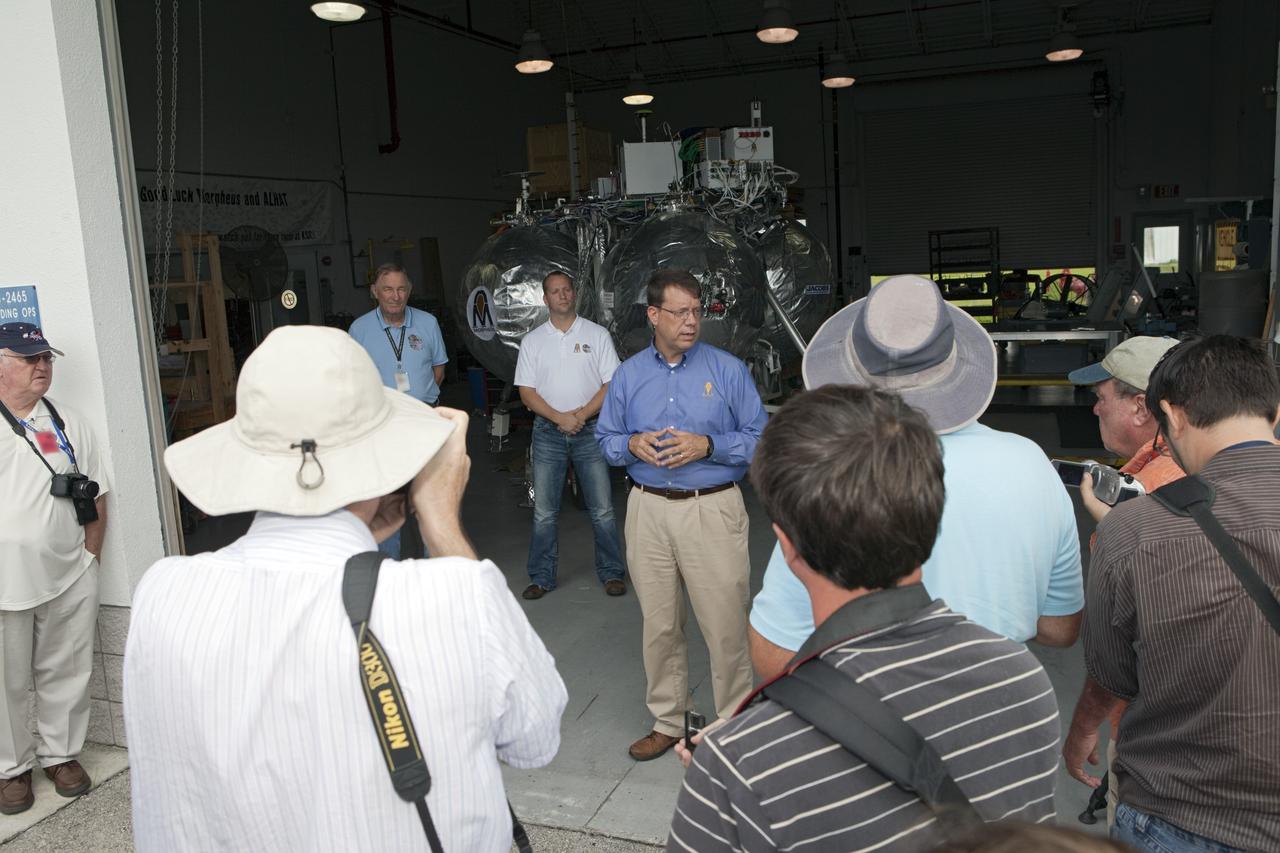

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At a hangar near the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media view the Morpheus prototype lander and speak with Morpheus managers. In front is Gregory Gaddis, Kennedy Project Morpheus/ALHAT site manager. To his left, are Jon Olansen, Johnson Space Center Project Morpheus manager and Chirold Epp, JSC ALHAT project manager. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers set the form for the concrete landing pad during construction of the hazard field for the Project Morpheus lander near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
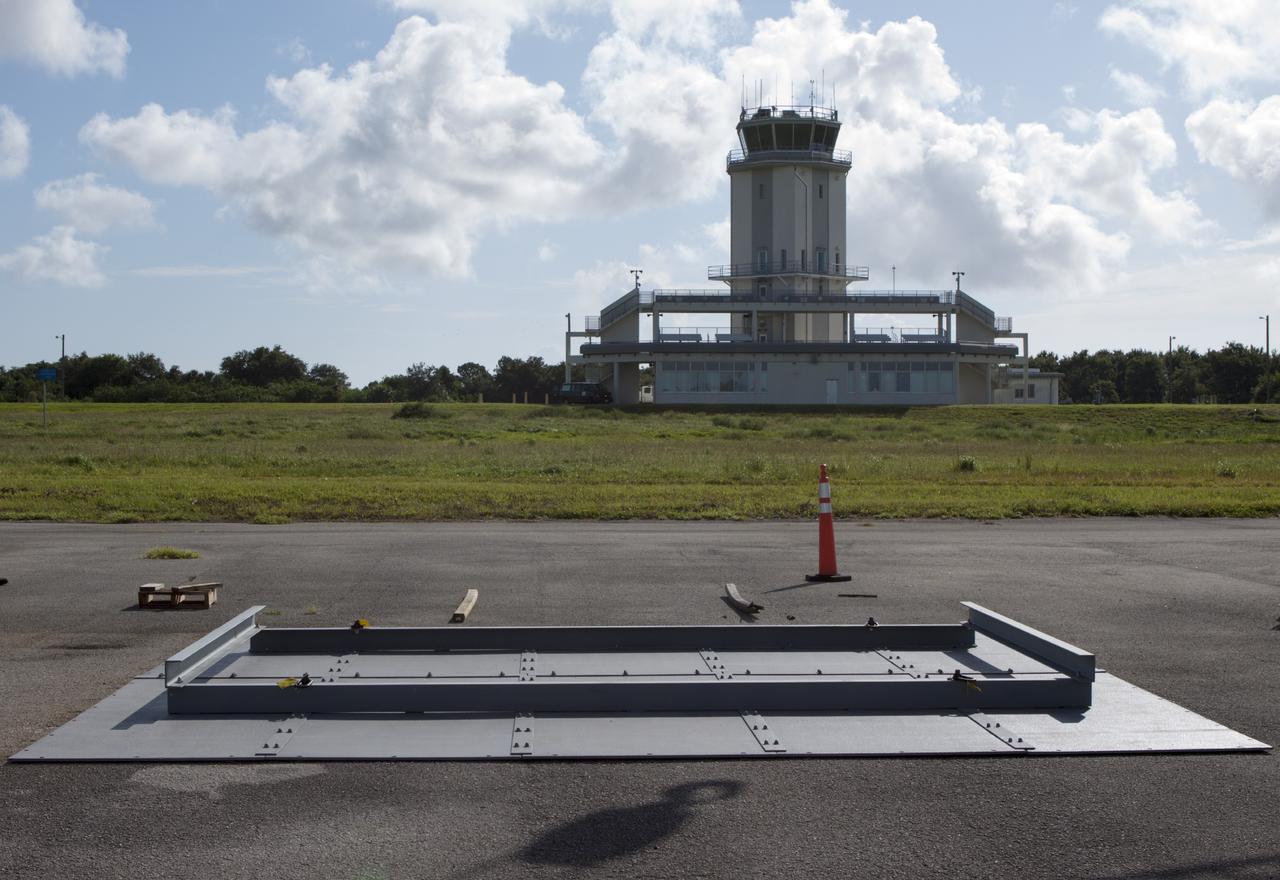

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, buildup continues on the metal landing pad for the Project Morpheus lander at the midfield of the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
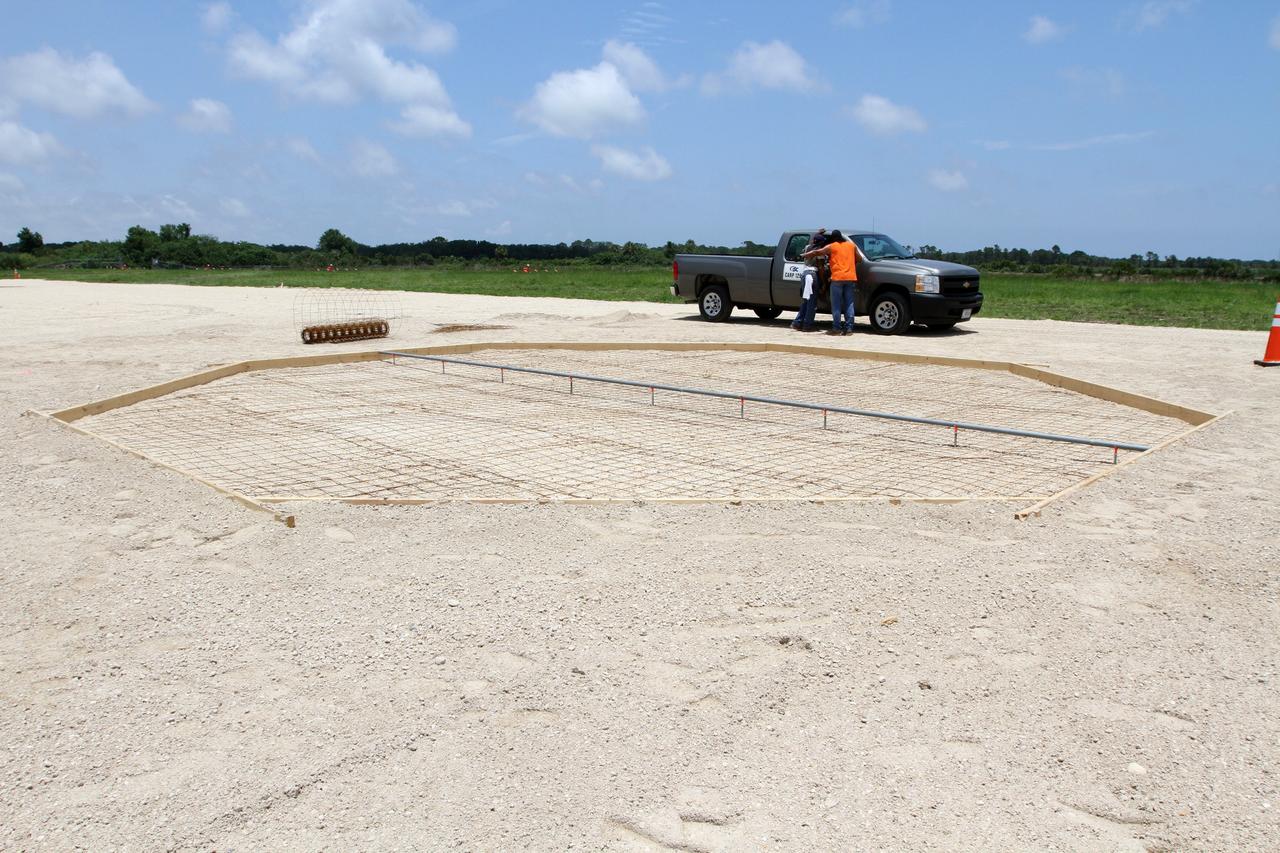

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The form for the concrete landing pad for the Project Morpheus lander is set near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
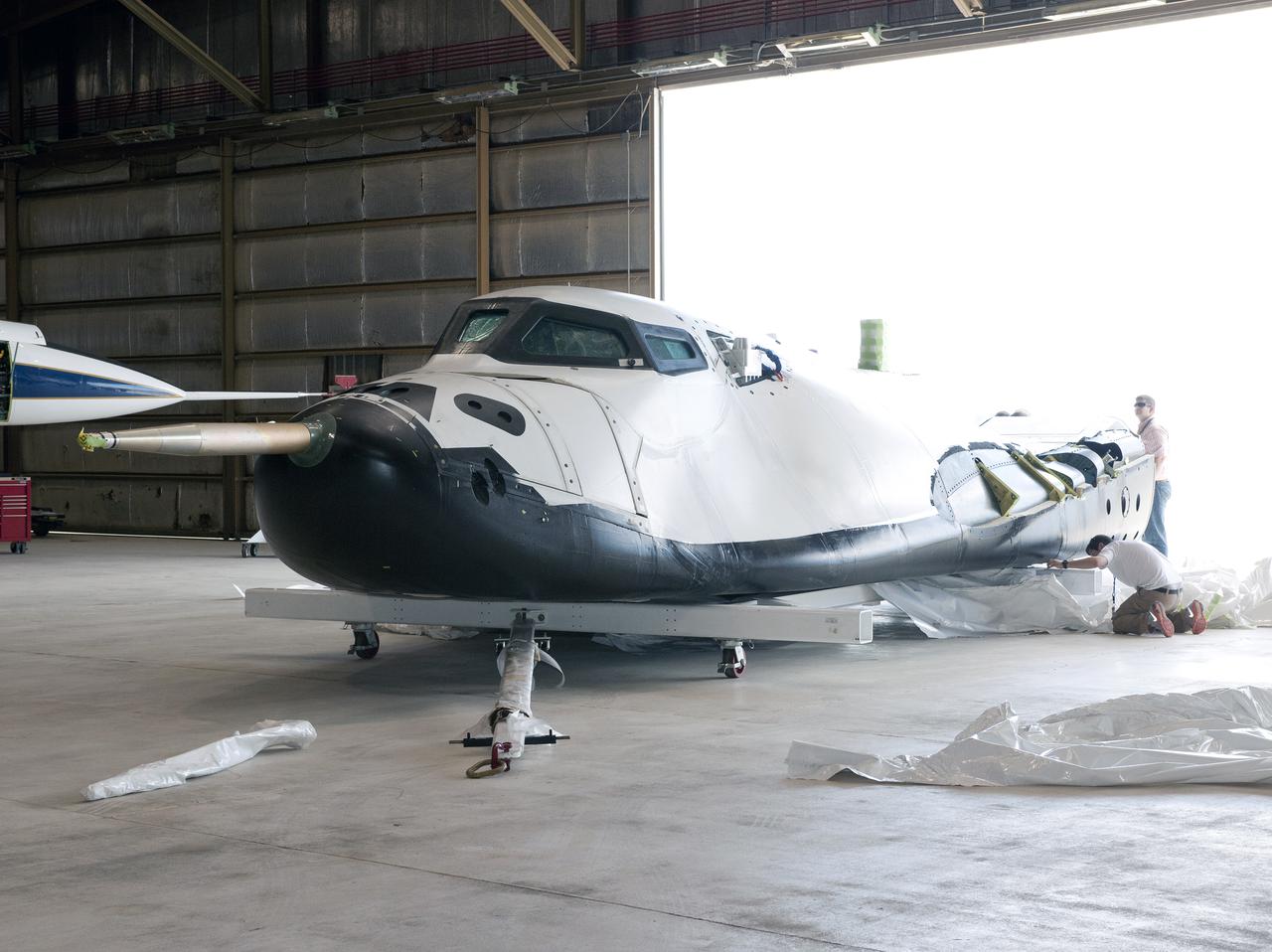

Edwards, Calif. – ED-0144-12 - Plastic wrapping that protected the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight test vehicle during its transport from Colorado is carefully removed by SNC employee Will Armijo following the craft's arrival at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in southern California. The prototype space access vehicle will undergo ground and approach-and-landing flight tests in the coming months at Dryden as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, development work. SNC is one of three companies working with CCP during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov_commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA_Tom Tschida
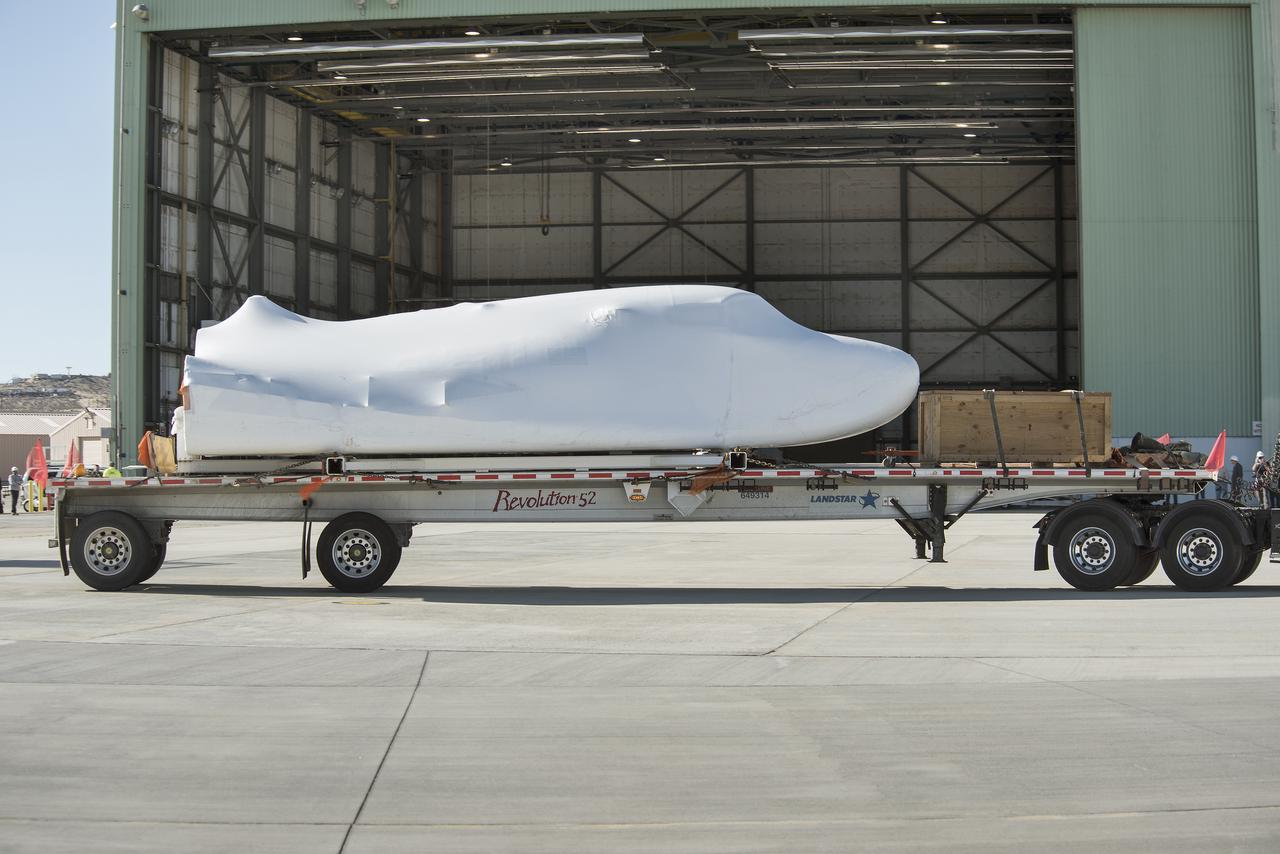

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
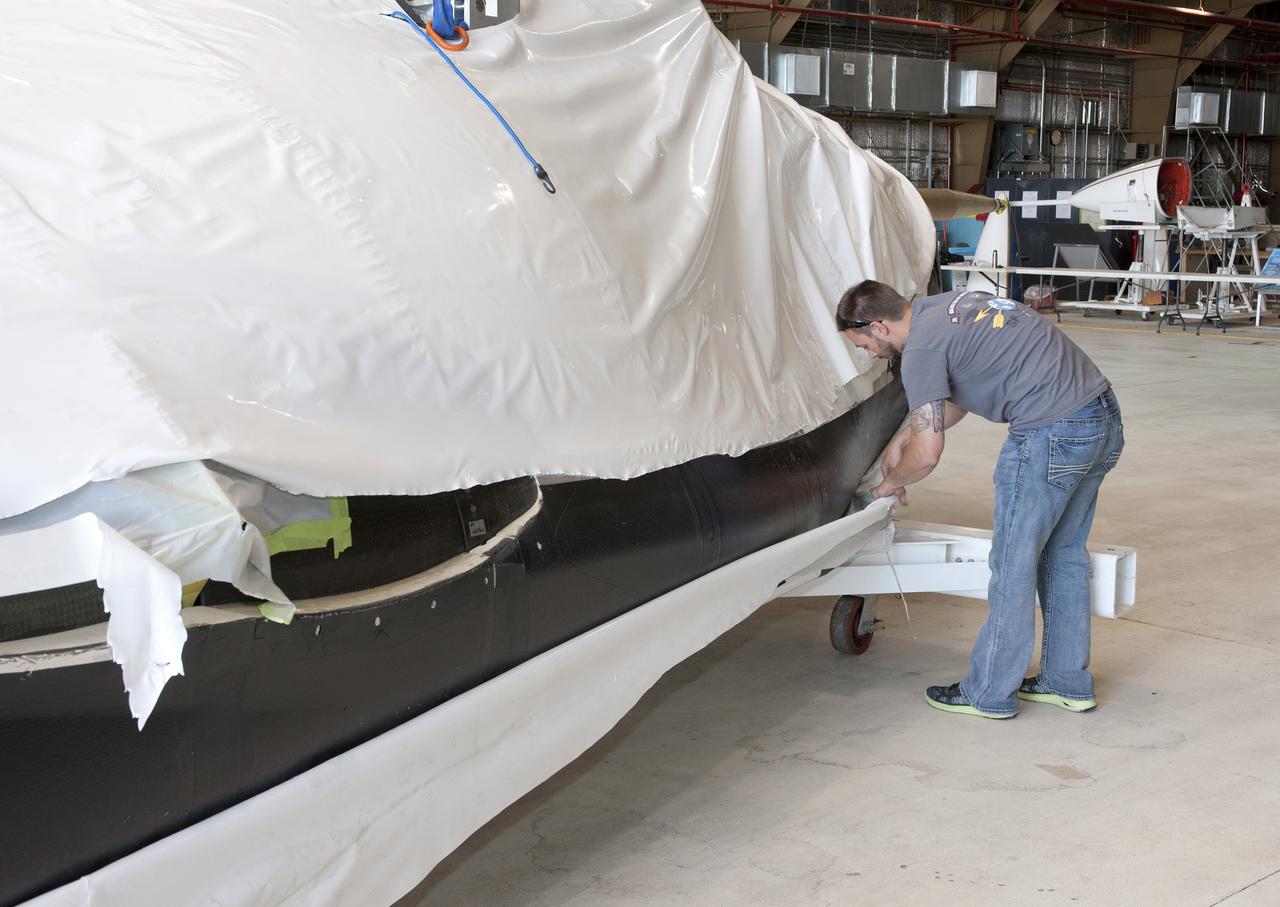

Edwards, Calif. – ED-0144-05 - Plastic wrapping that protected the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight test vehicle during its transport from Colorado is carefully removed by SNC employee Jason Dixon following the craft's arrival at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in southern California. The prototype space access vehicle will undergo ground and approach-and-landing flight tests in the coming months at Dryden as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, development work. SNC is one of three companies working with CCP during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov_commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA_Tom Tschida

Edwards, Calif. – ED-0144-08 - Plastic wrapping that protected the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight test vehicle during its transport from Colorado is carefully removed by SNC Dream Chaser crew chief Christian White, left, and SNC employee Will Armijo following the craft's arrival at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in southern California. The prototype space access vehicle will undergo ground and approach-and-landing flight tests in the coming months at Dryden as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, development work. SNC is one of three companies working with CCP during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov_commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA_Tom Tschida
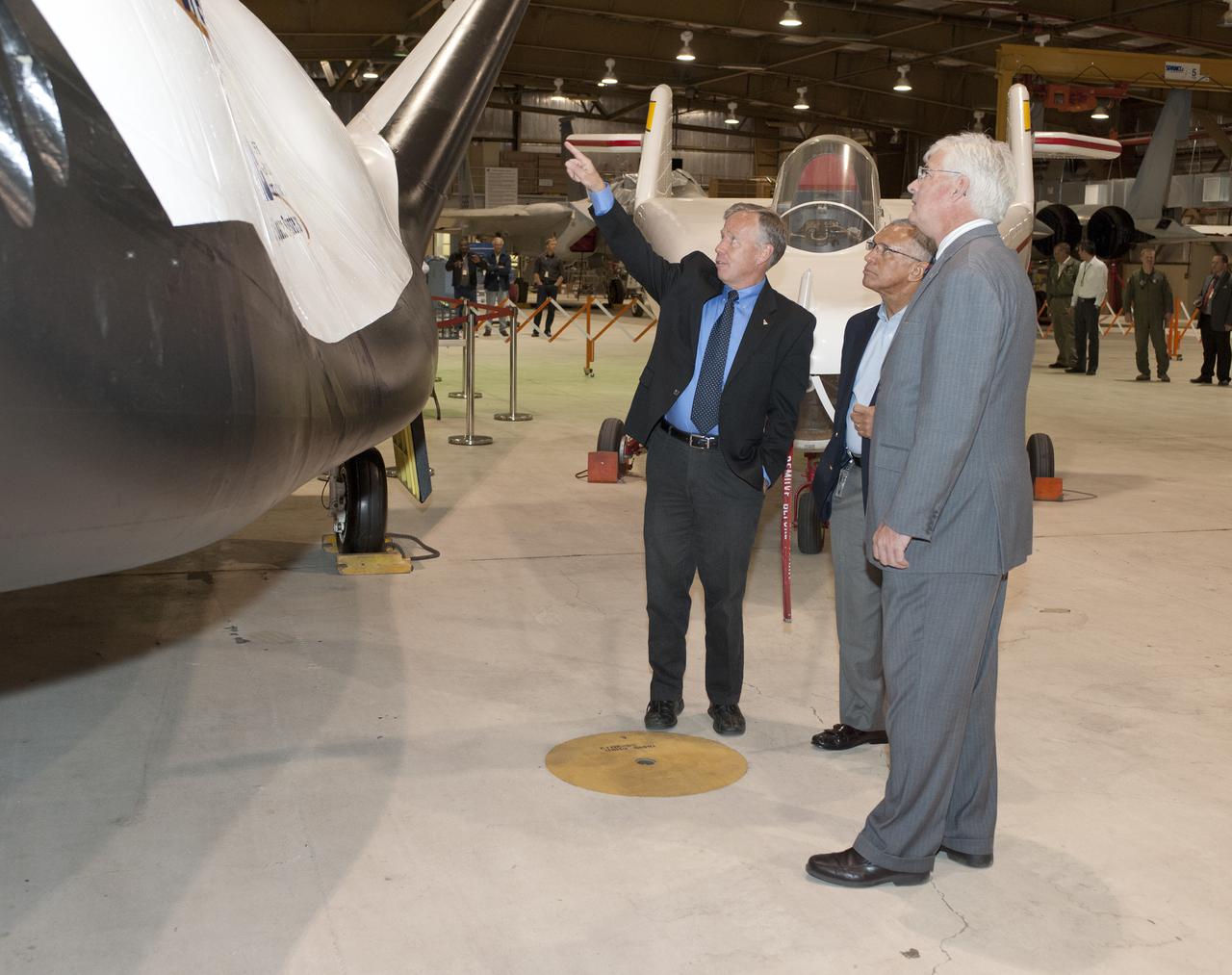

Edwards, Calif. – ED-0155-13 - Steve Lindsey, Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, director of flight operations and former space shuttle astronaut, left, talks to NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, center, and agency Dryden Flight Research Center Deputy Director Patrick Stoliker about the company's Dream Chaser flight test vehicle. It will undergo ground and approach-and-landing flight tests at Dryden in the coming months as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, development work. SNC is one of three companies working with CCP during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov_commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA_Tom Tschida
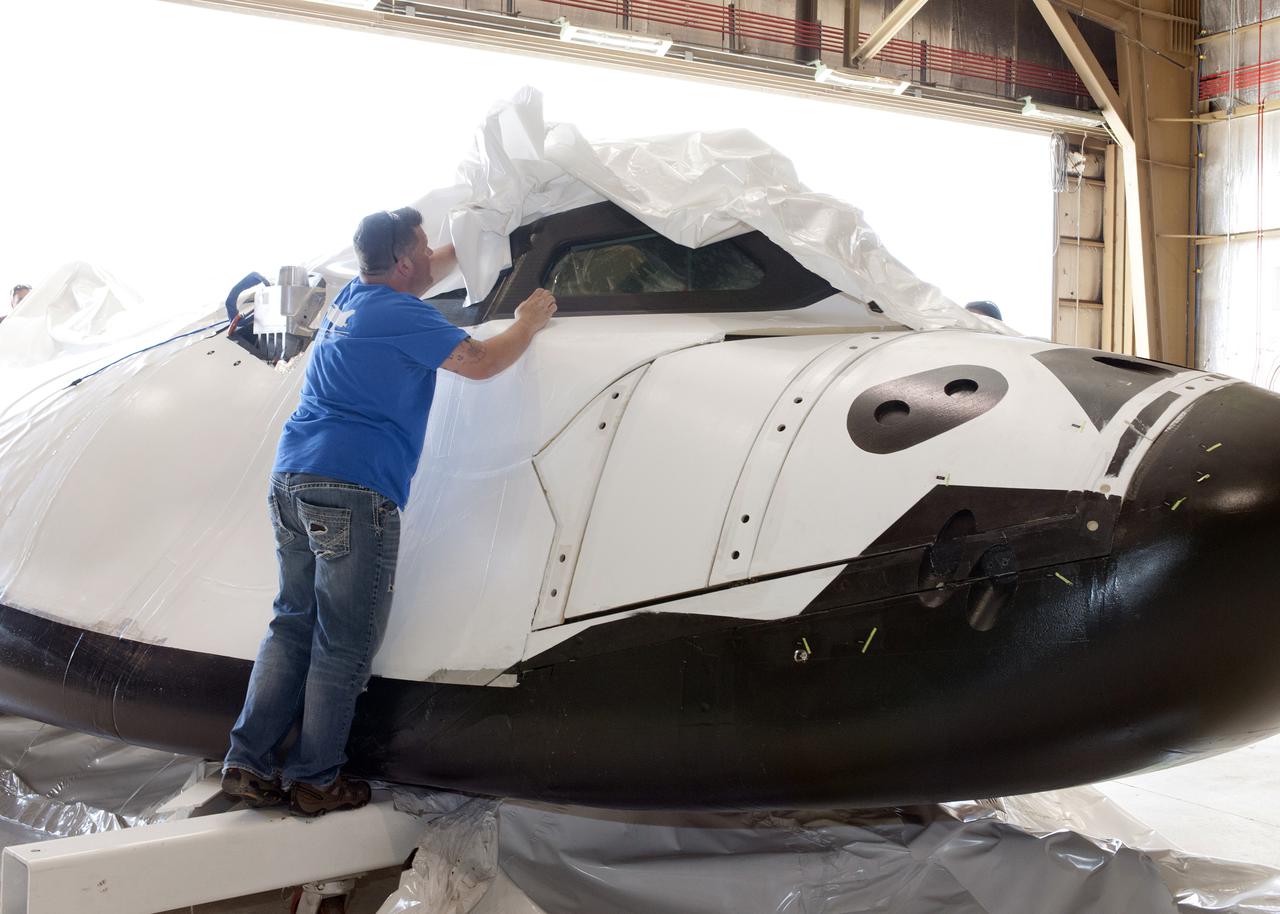

Edwards, Calif. – ED-0144-09 - Plastic wrapping that protected the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight test vehicle during its transport from Colorado is carefully removed by SNC Dream Chaser crew chief Christian White following the craft's arrival at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in southern California. The prototype space access vehicle will undergo ground and approach-and-landing flight tests in the coming months at Dryden as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, development work. SNC is one of three companies working with CCP during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov_commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA_Tom Tschida
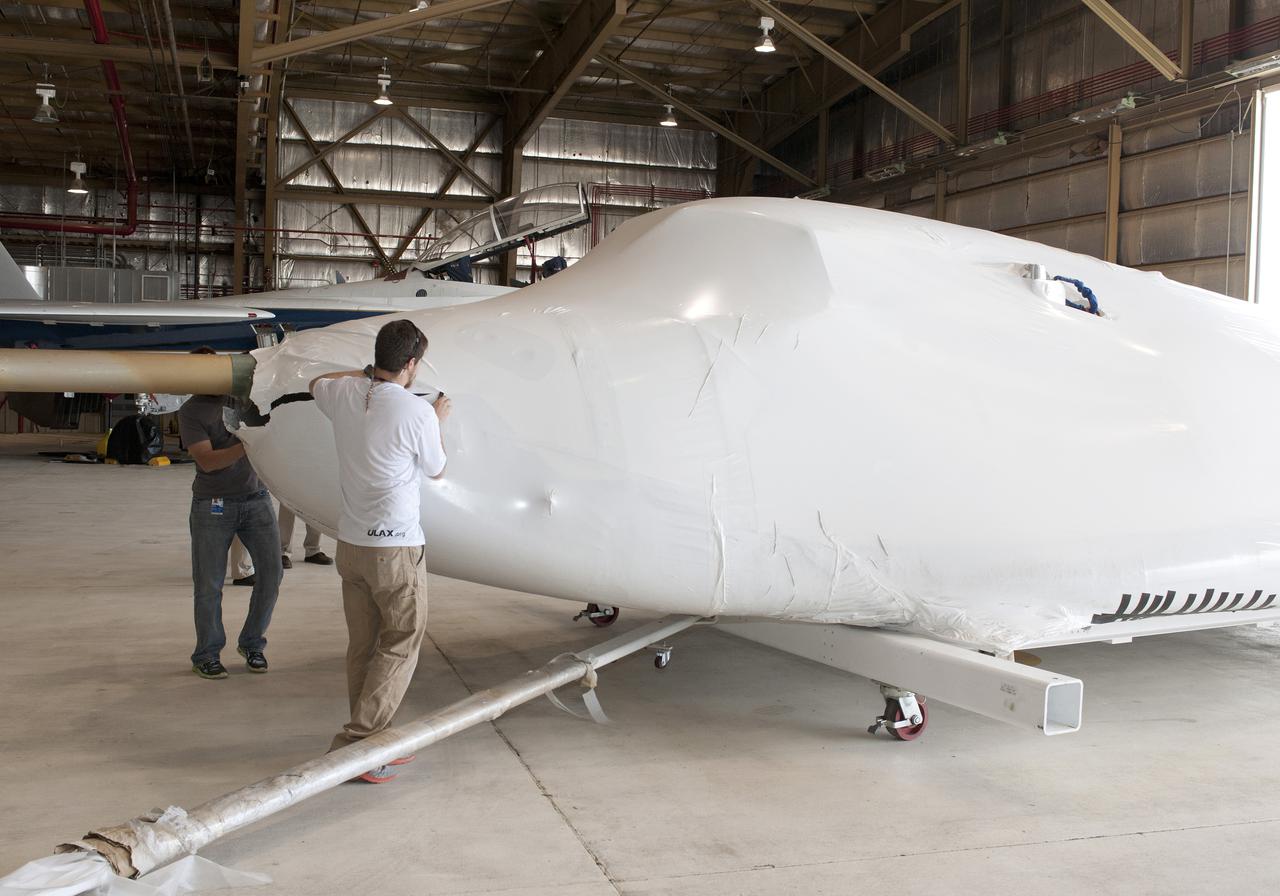

Edwards, Calif. – ED-0144-01 - Plastic wrapping that protected the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight test vehicle during its transport from Colorado is carefully removed by SNC employee Will Armijo following the craft's arrival at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in southern California. The prototype space access vehicle will undergo ground and approach-and-landing flight tests in the coming months as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, development work. SNC is one of three companies working with CCP during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov_commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA_Tom Tschida
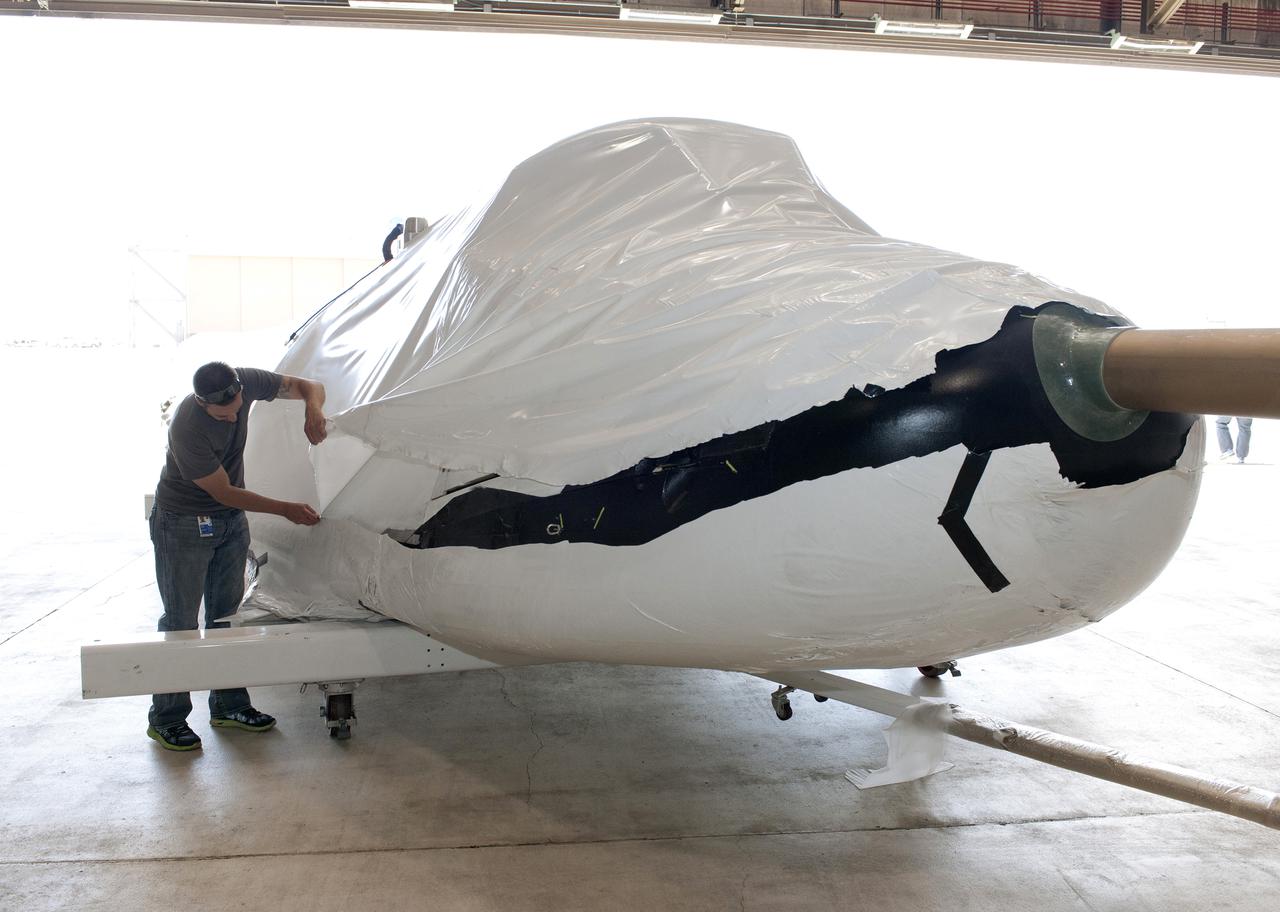

Edwards, Calif. – ED-0144-03 - Plastic wrapping that protected the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight test vehicle during its transport from Colorado is carefully removed by SNC employee Jason Dixon following the craft's arrival at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in southern California. The prototype space access vehicle will undergo ground and approach-and-landing flight tests in the coming months at Dryden as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, development work. SNC is one of three companies working with CCP during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov_commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA_Tom Tschida
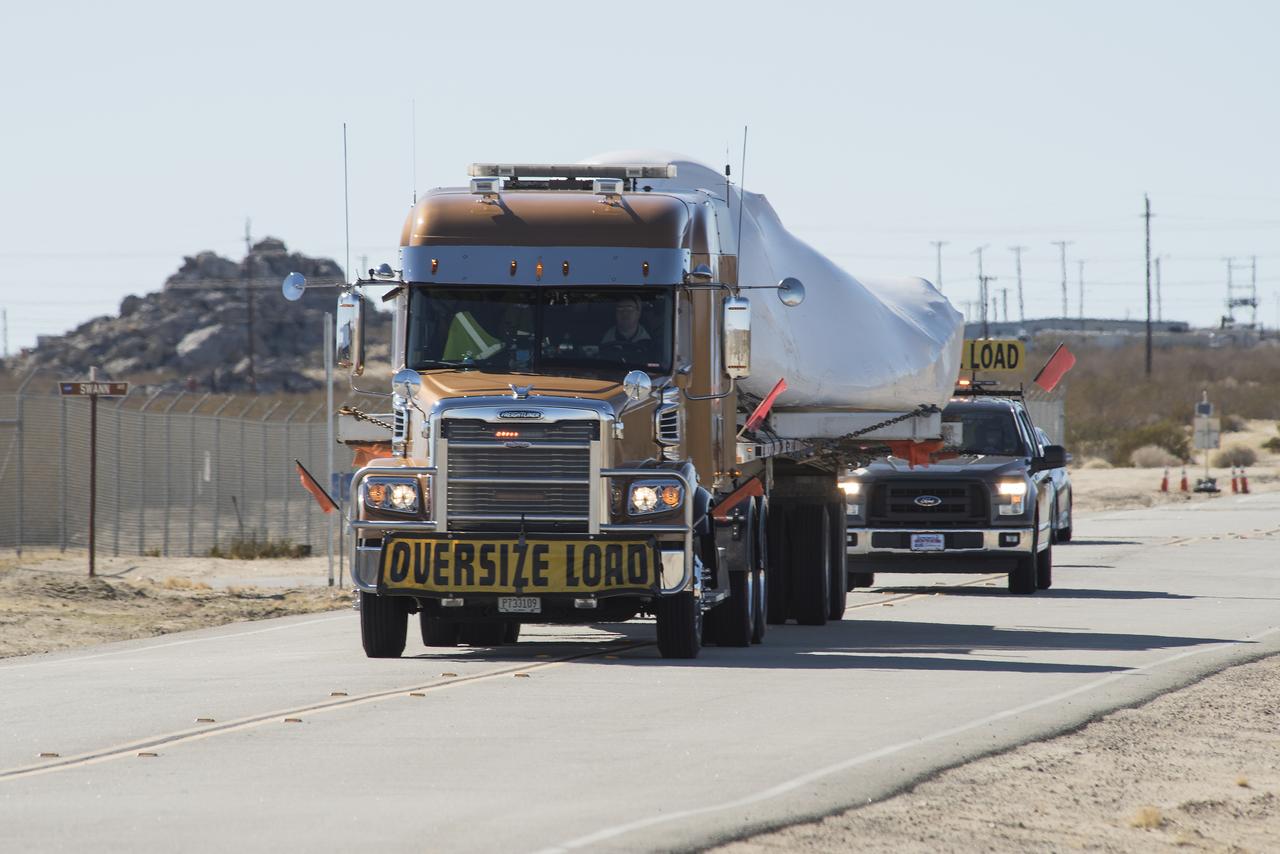

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
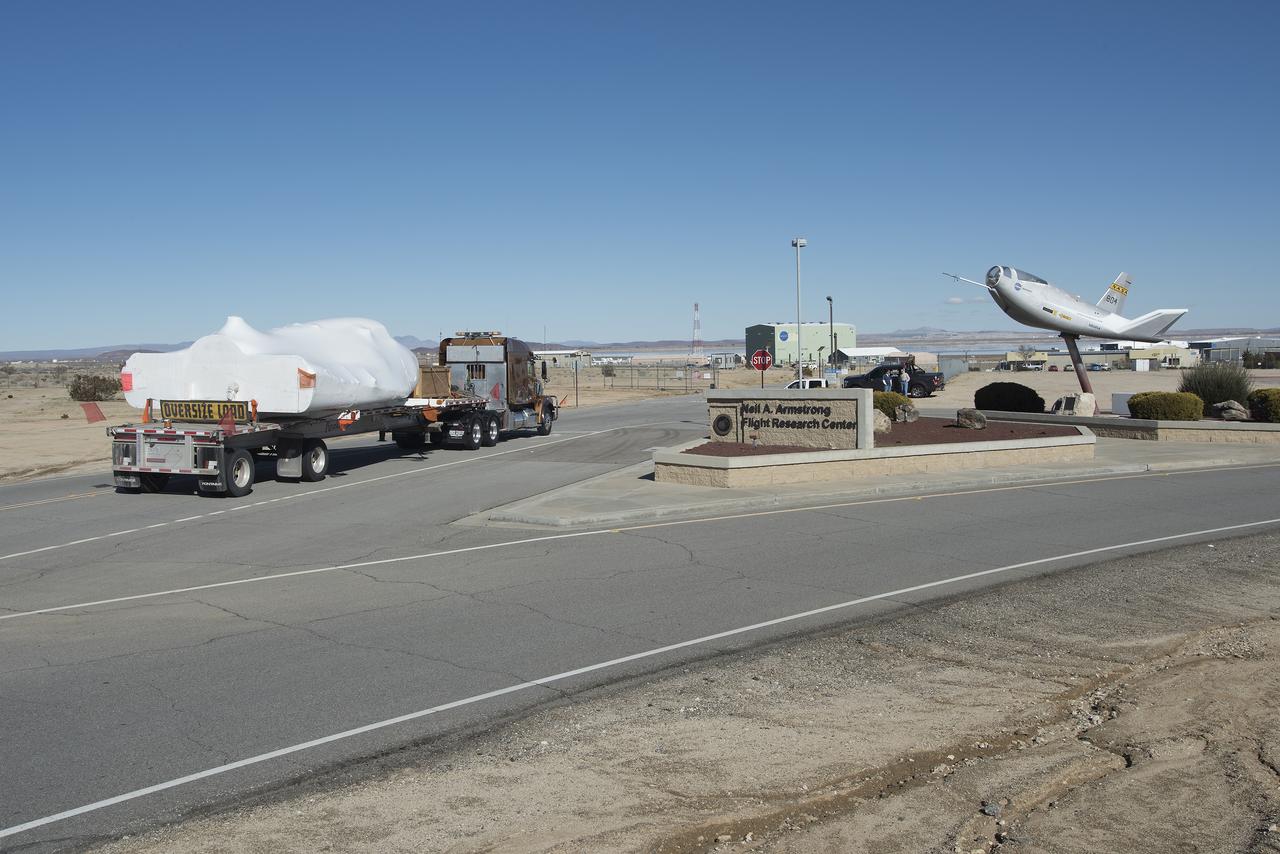

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
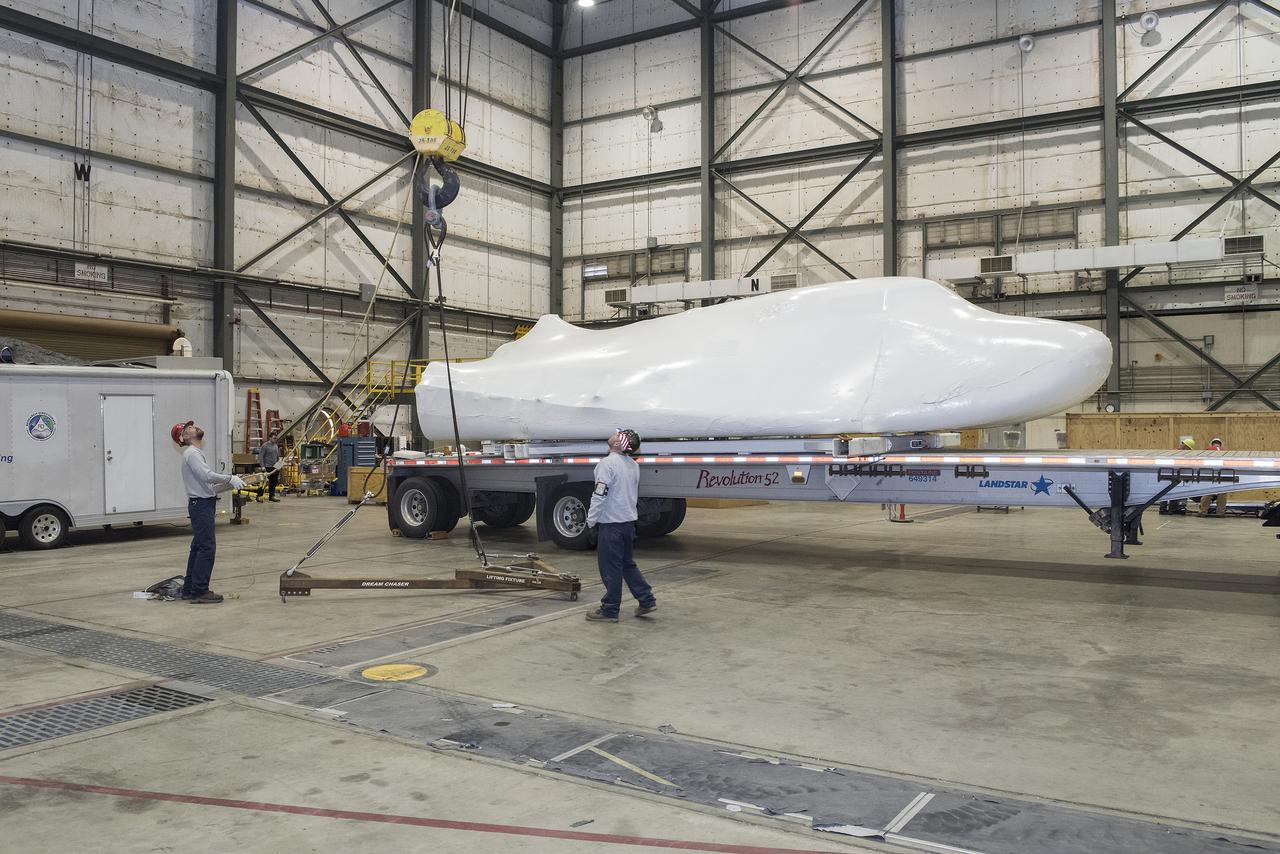

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
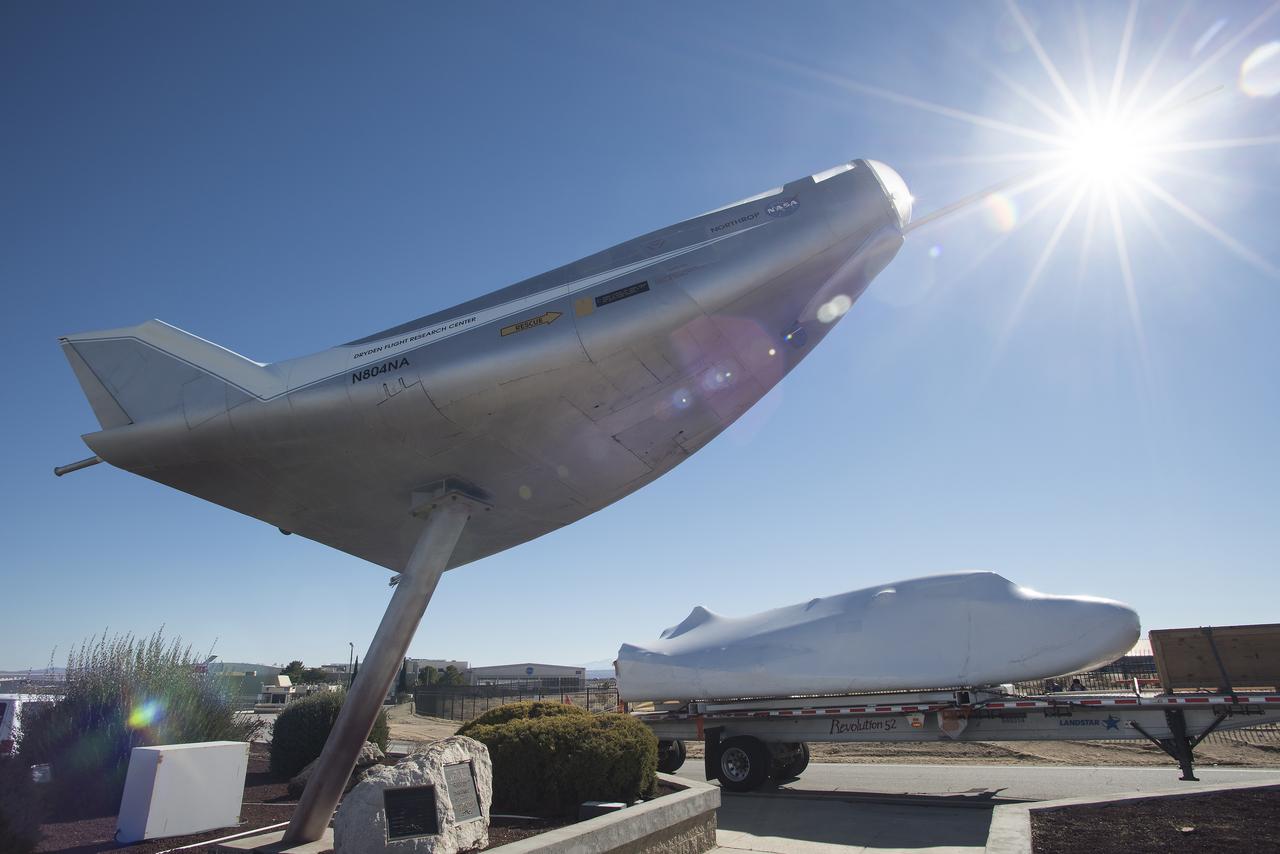

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
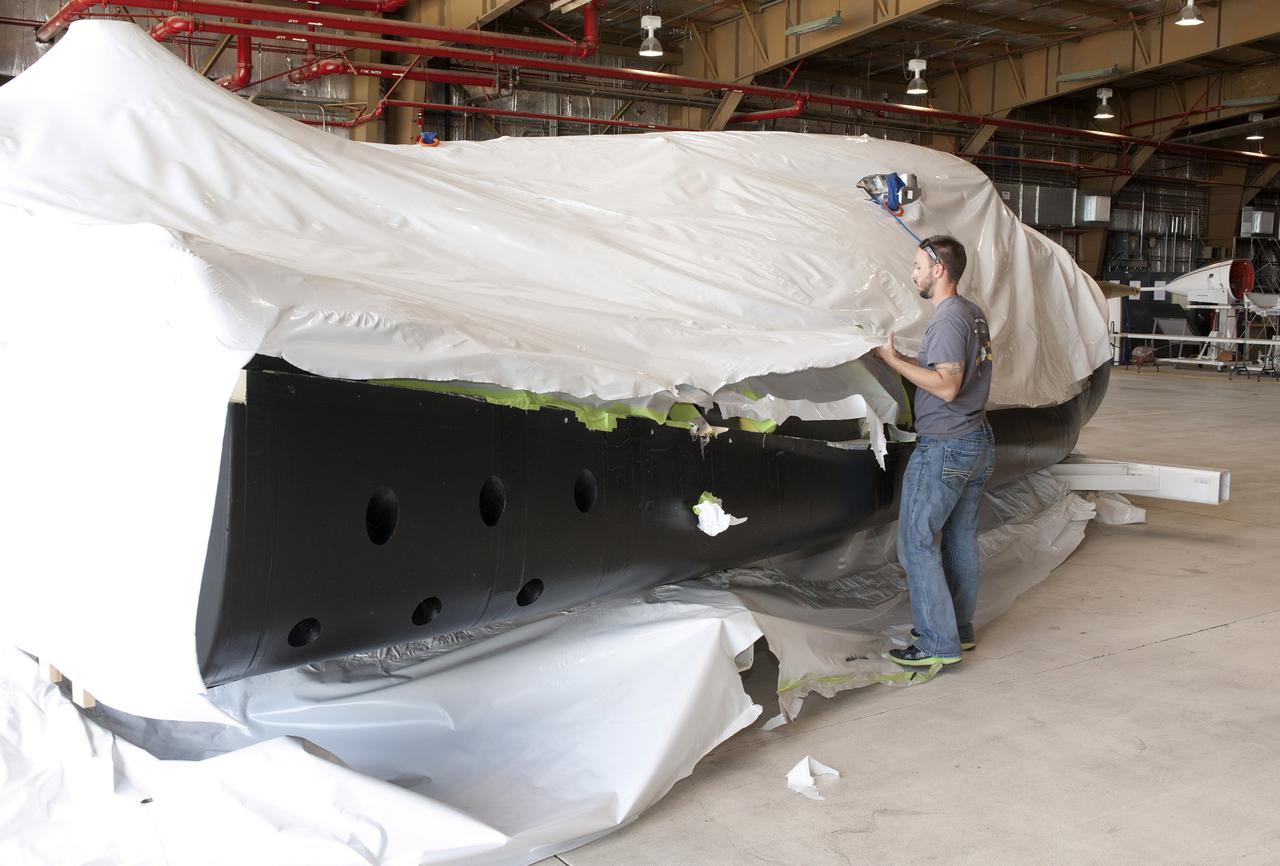

Edwards, Calif. – ED-0144-06 - Plastic wrapping that protected the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight test vehicle during its transport from Colorado is carefully removed by SNC employee Jason Dixon following the craft's arrival at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in southern California. The prototype space access vehicle will undergo ground and approach-and-landing flight tests in the coming months at Dryden as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, development work. SNC is one of three companies working with CCP during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov_commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA_Tom Tschida
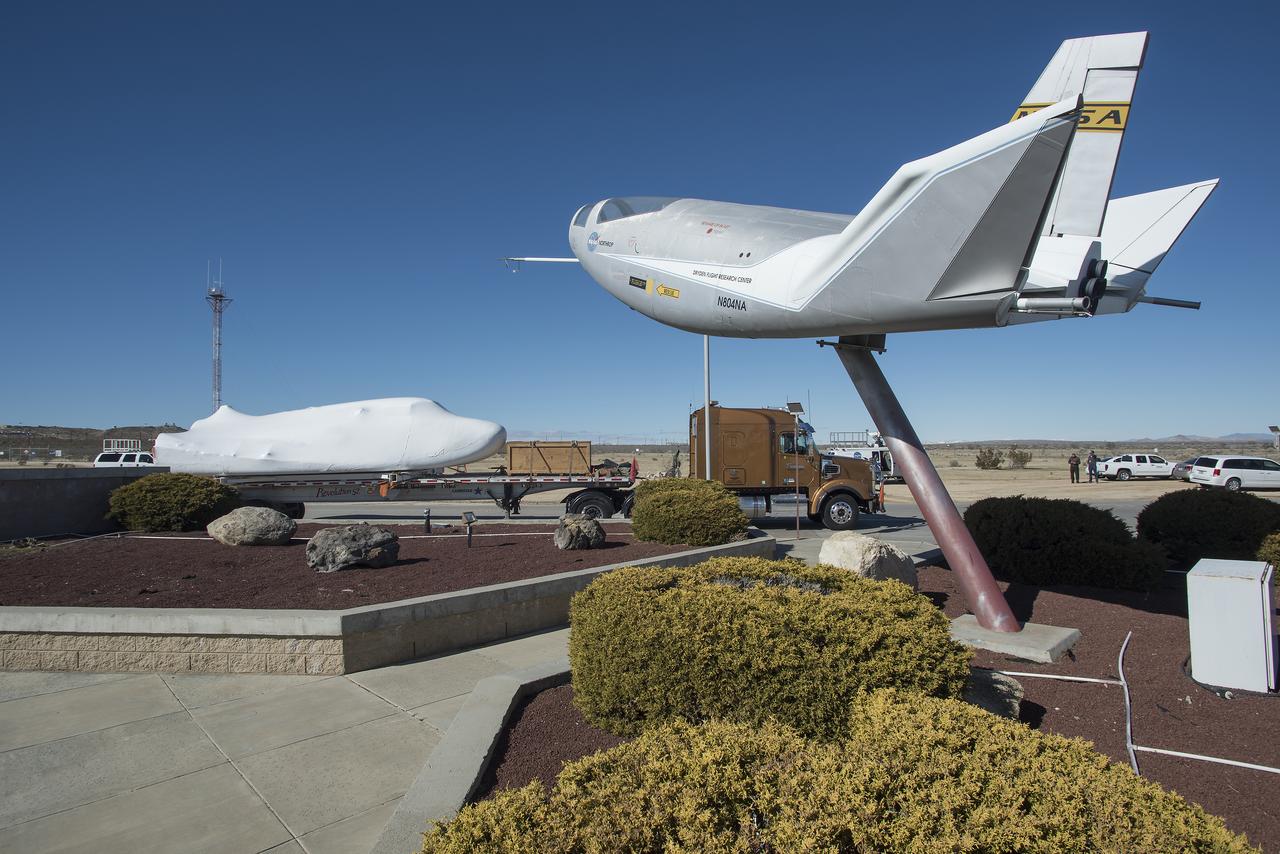

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
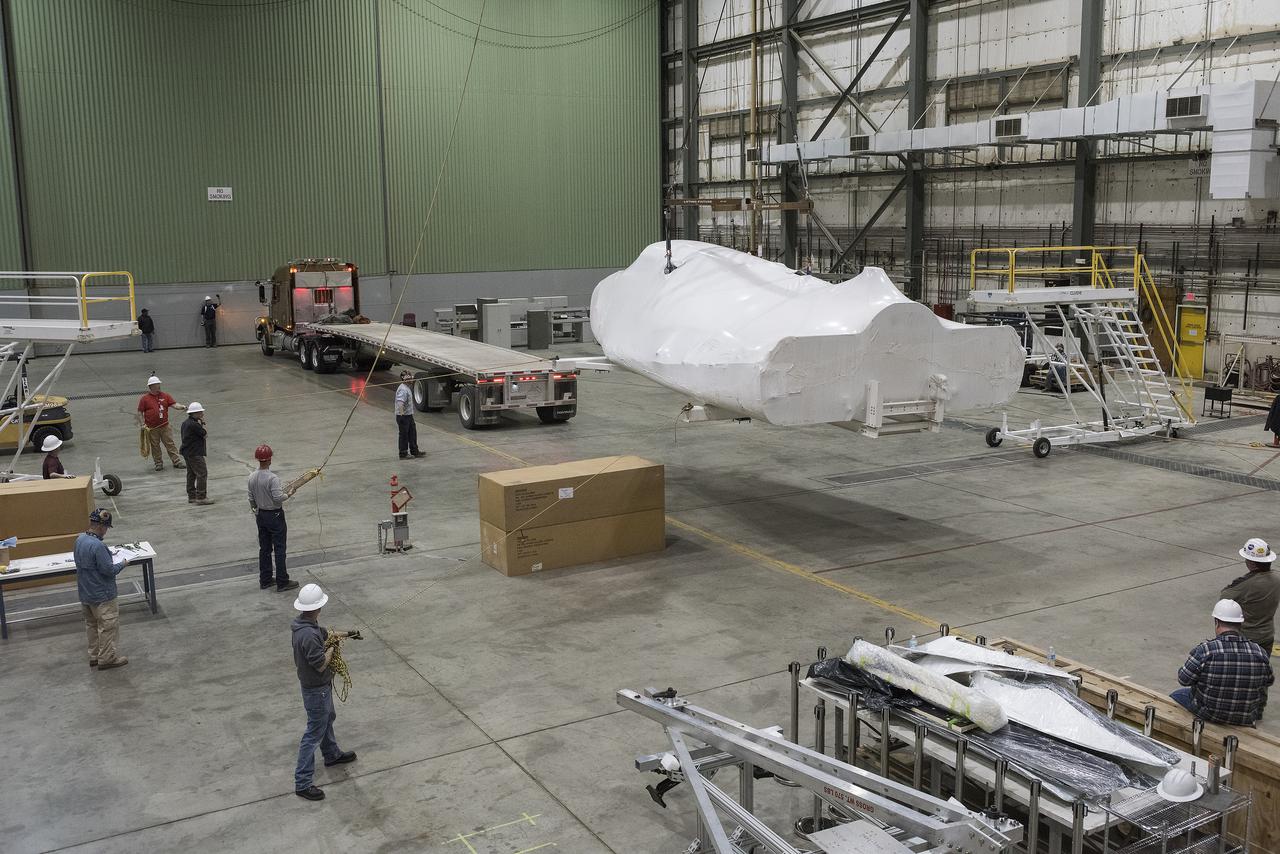

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft is removed from its delivery truck after arriving at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
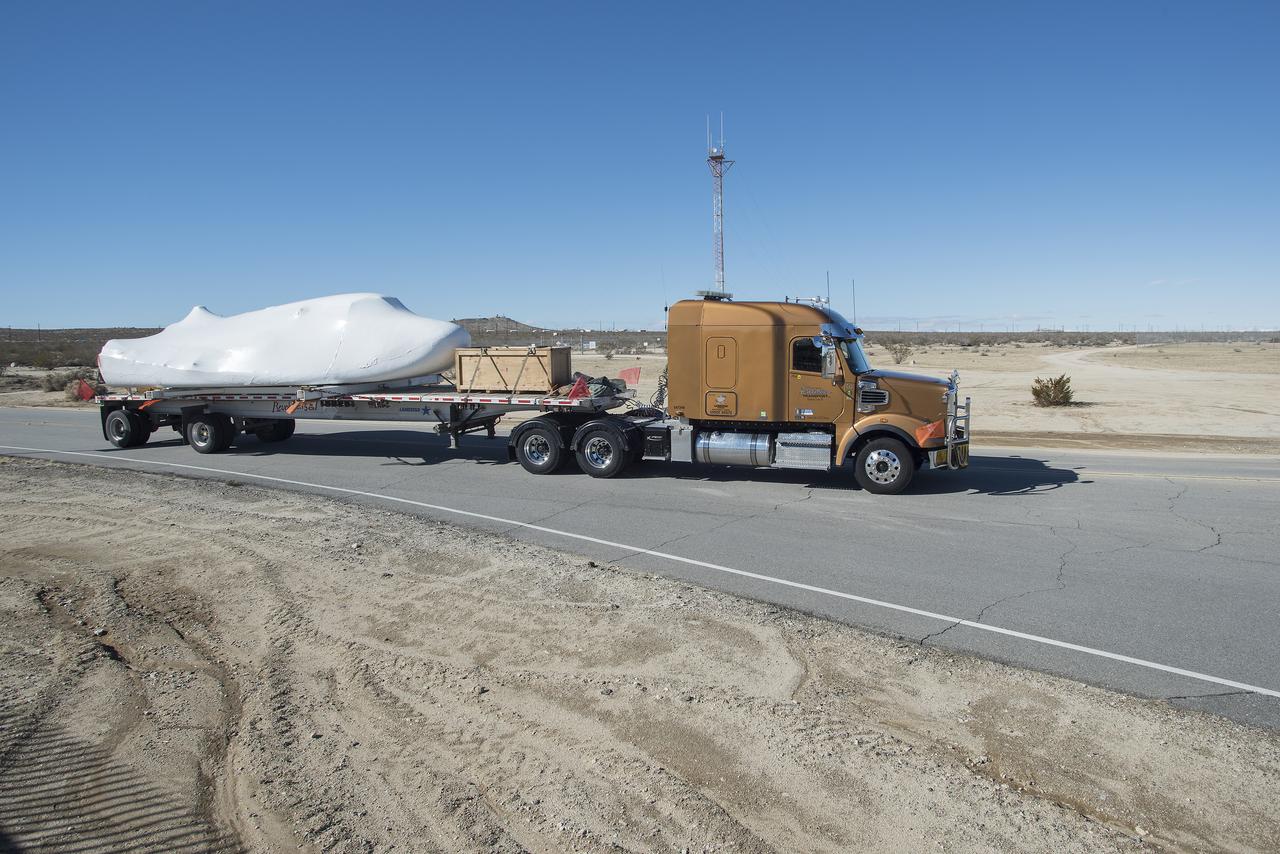

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
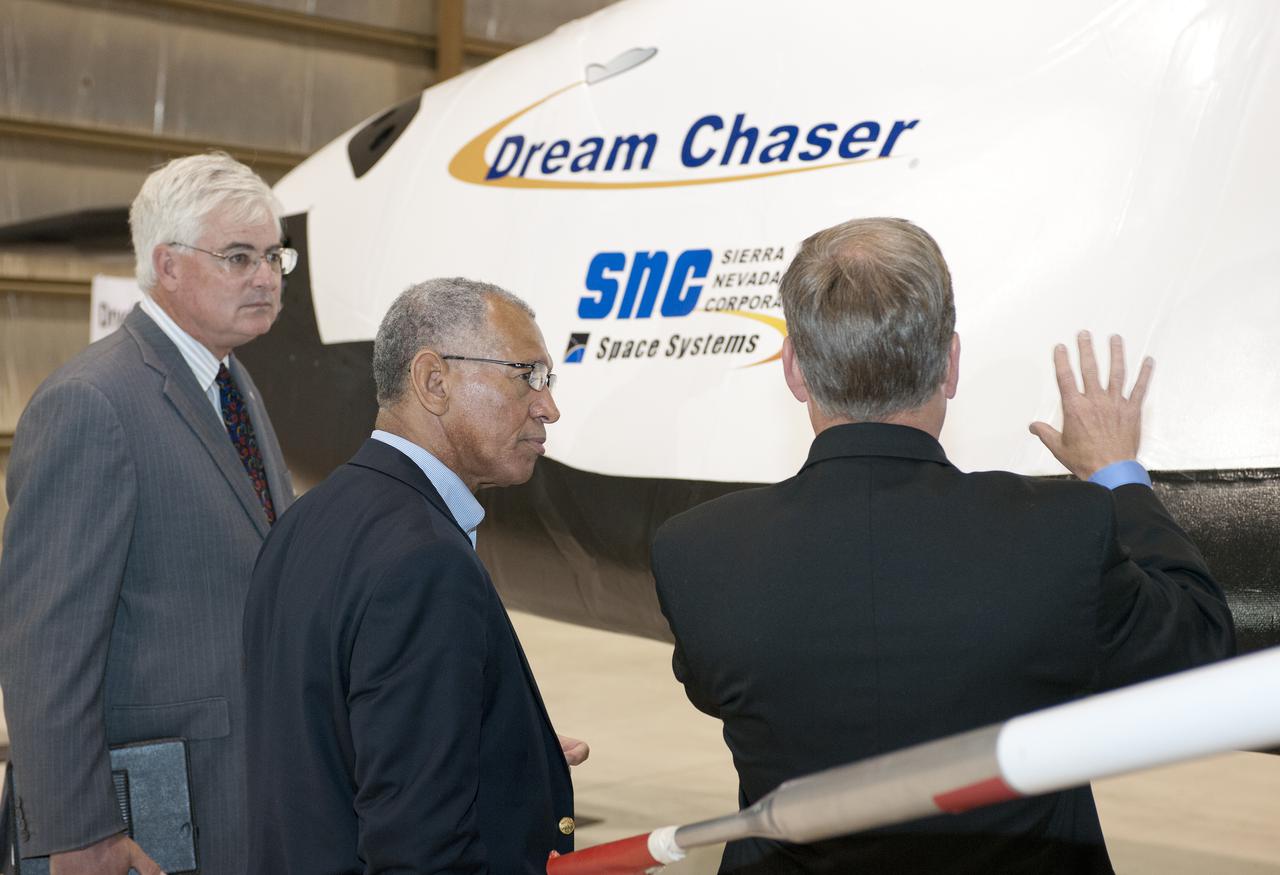

Edwards, Calif. – ED-0155-12 - Steve Lindsey, Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, director of flight operations and former space shuttle astronaut, right, talks to NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, center, and agency Dryden Flight Research Center Deputy Director Patrick Stoliker about the company's Dream Chaser flight test vehicle. It will undergo ground and approach-and-landing flight tests at Dryden in the coming months as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, development work. SNC is one of three companies working with CCP during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov_commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA_Tom Tschida
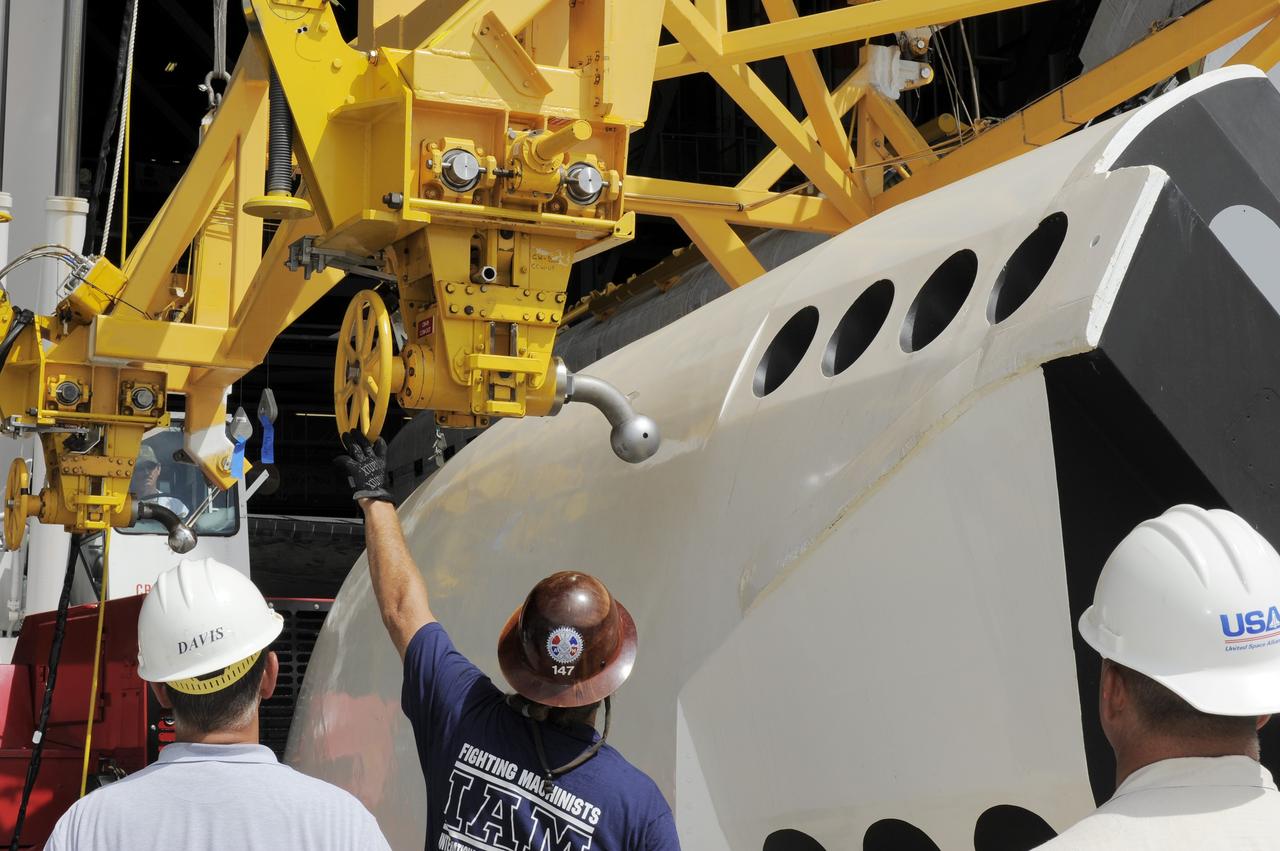

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, raise a cage over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
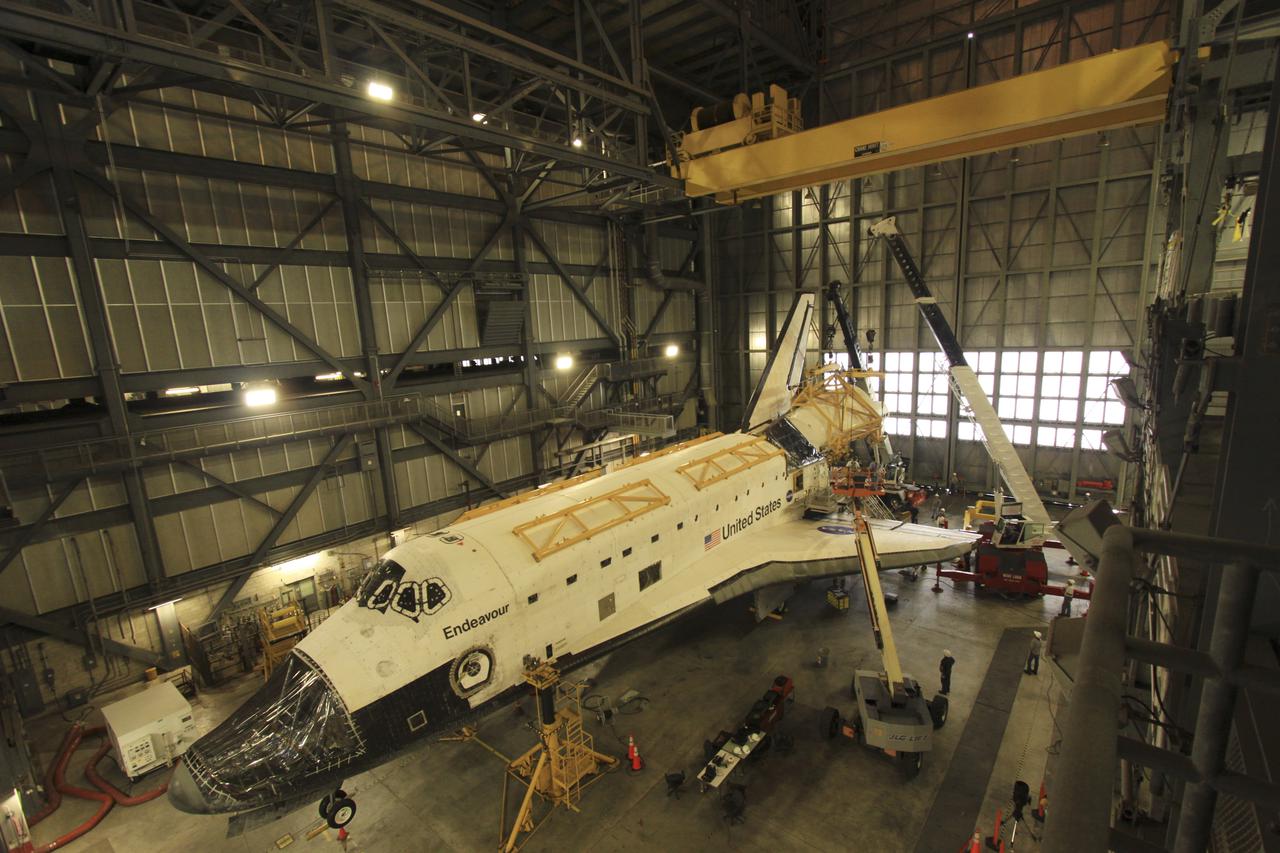

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers lower the cage containing an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod over the rear of space shuttle Endeavour. The ALTA pod is being attached to the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_shuttle. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
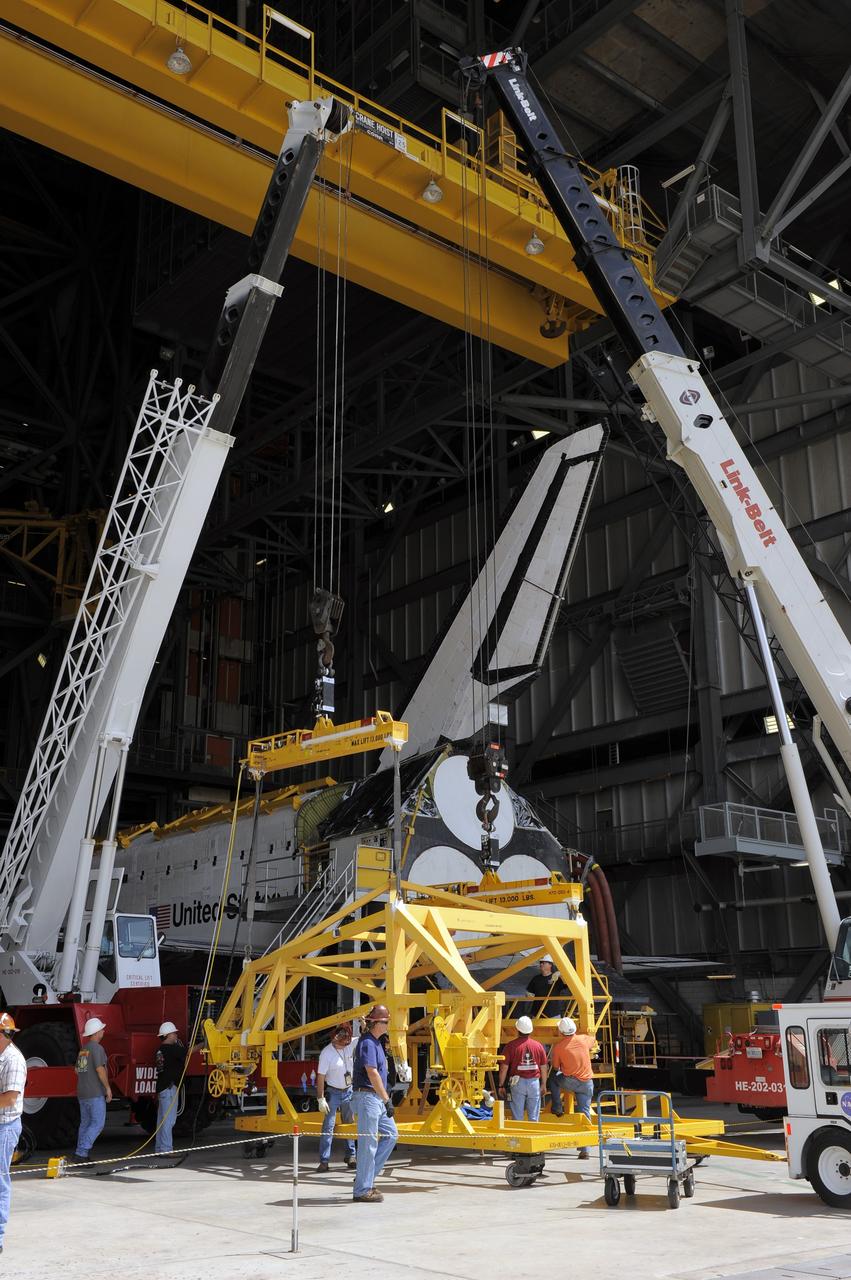

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, begin to raise a cage which will be placed over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
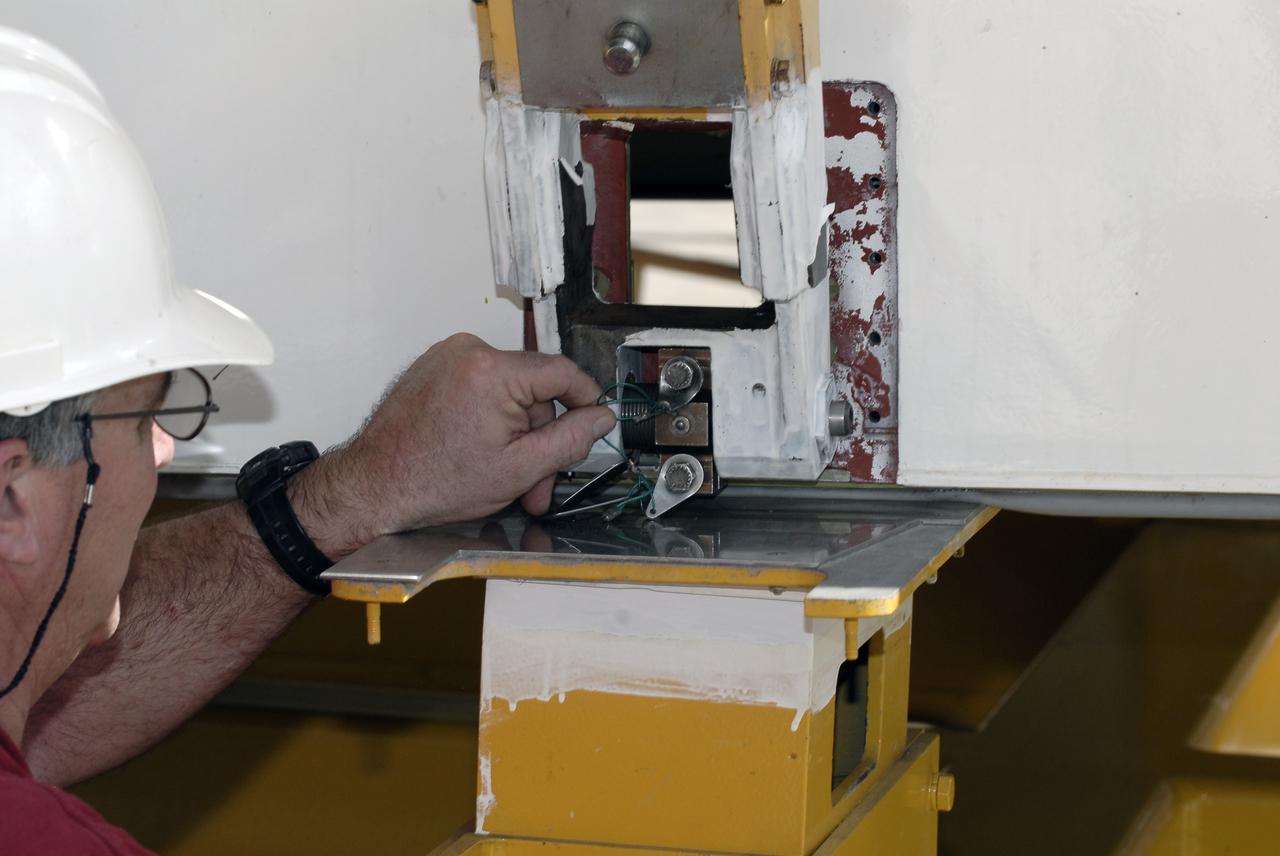

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker connects an aerial lift to the Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The lift will be used to raise the ALTA pod onto space shuttle Endeavour. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
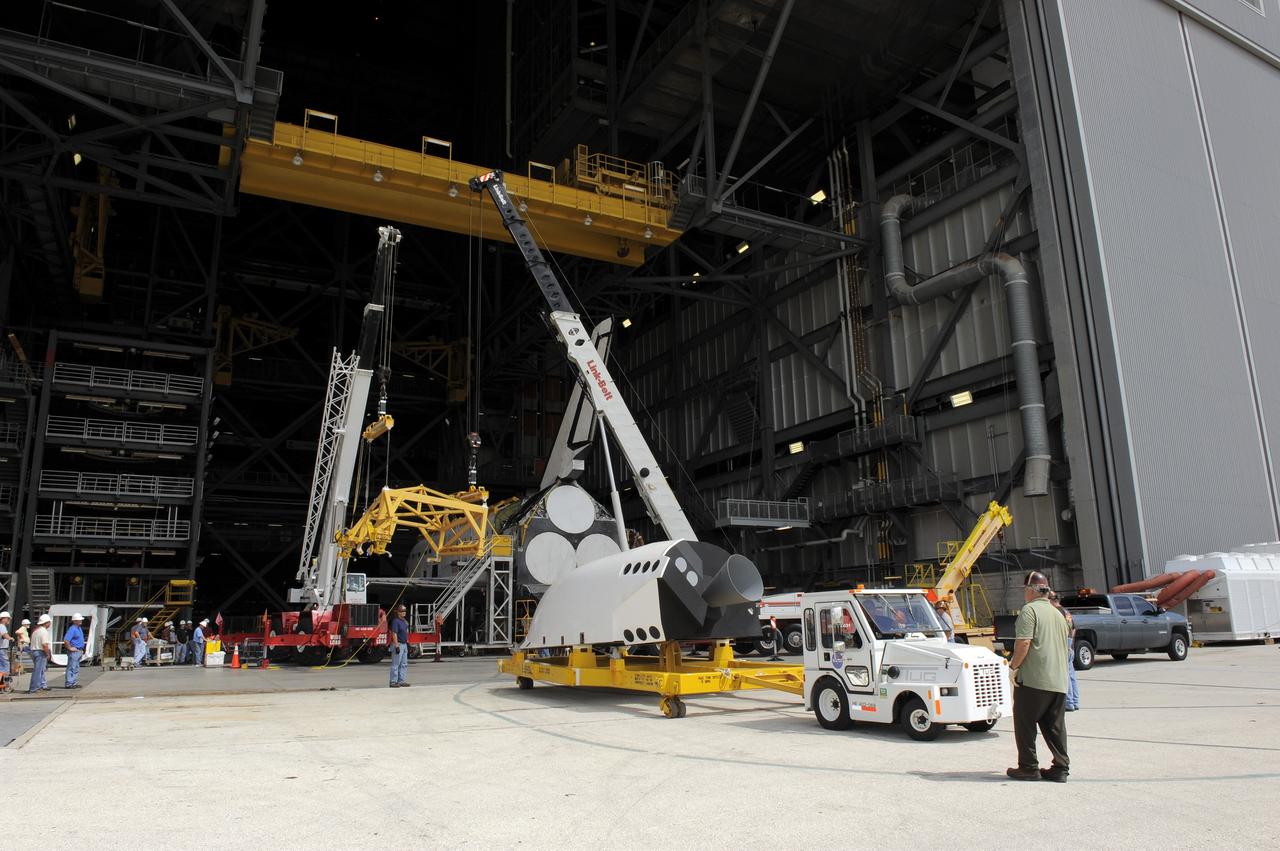

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, raise a cage which will be placed over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod (in the foreground). The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
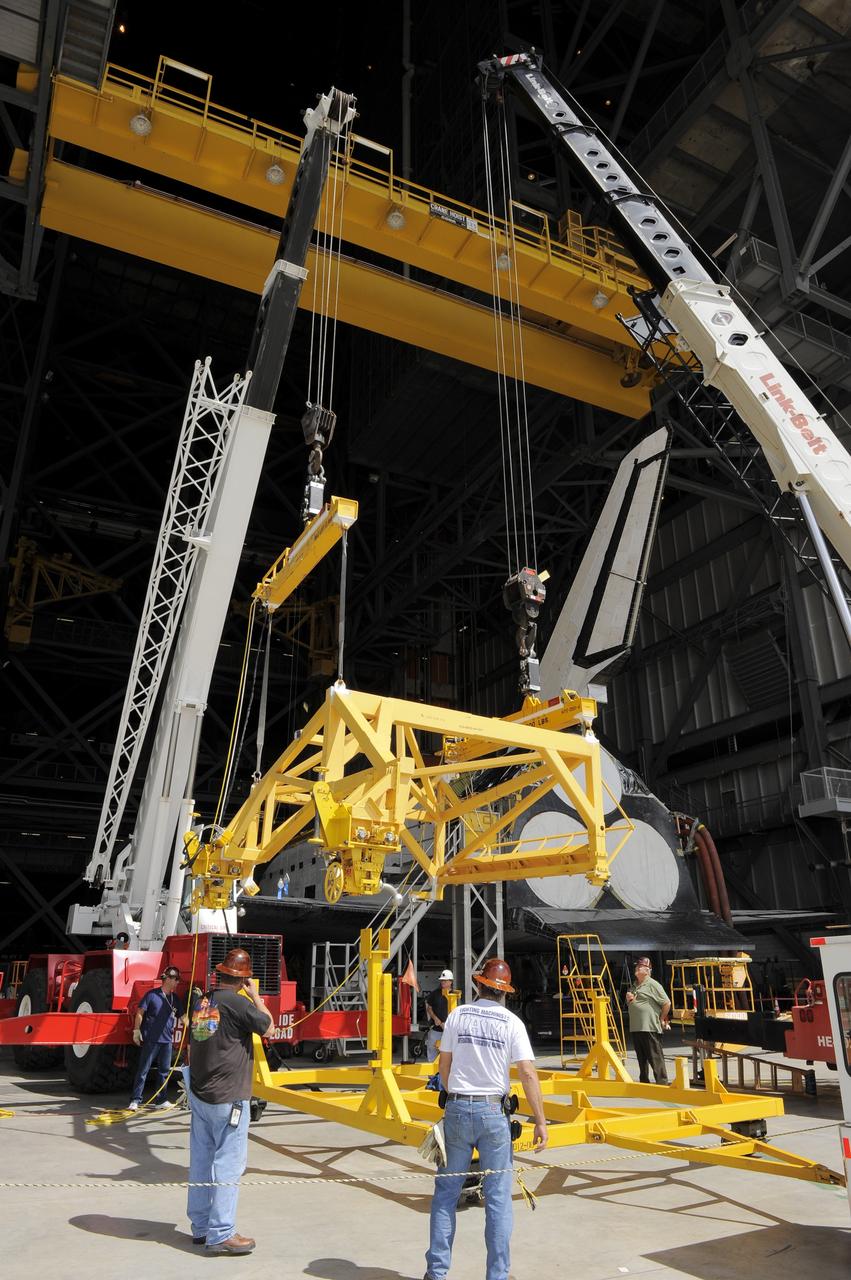

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, raise a cage which will be placed over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
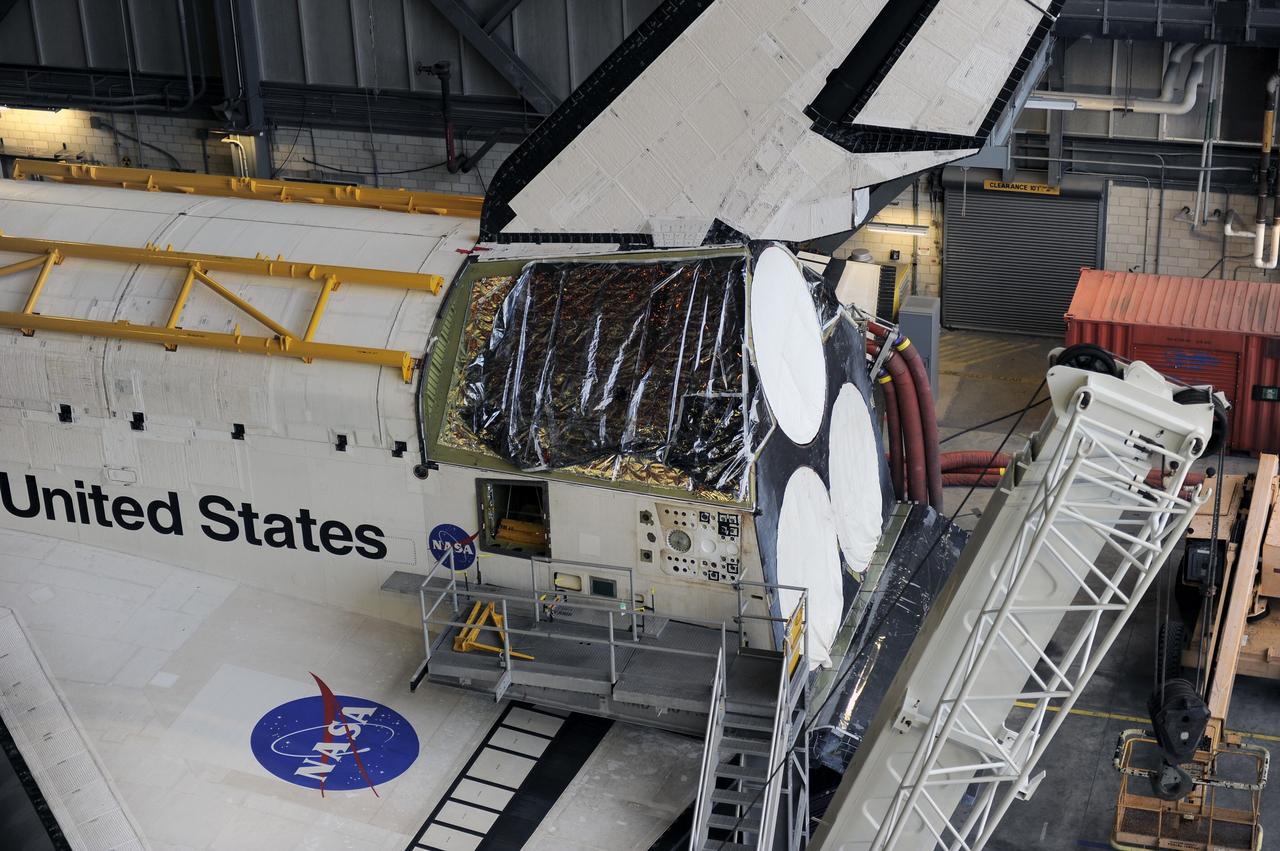

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a rear view of space shuttle Endeavour shows a protective plastic covering the area once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. An aerial lift will raise an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod to fit over the OMS site. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
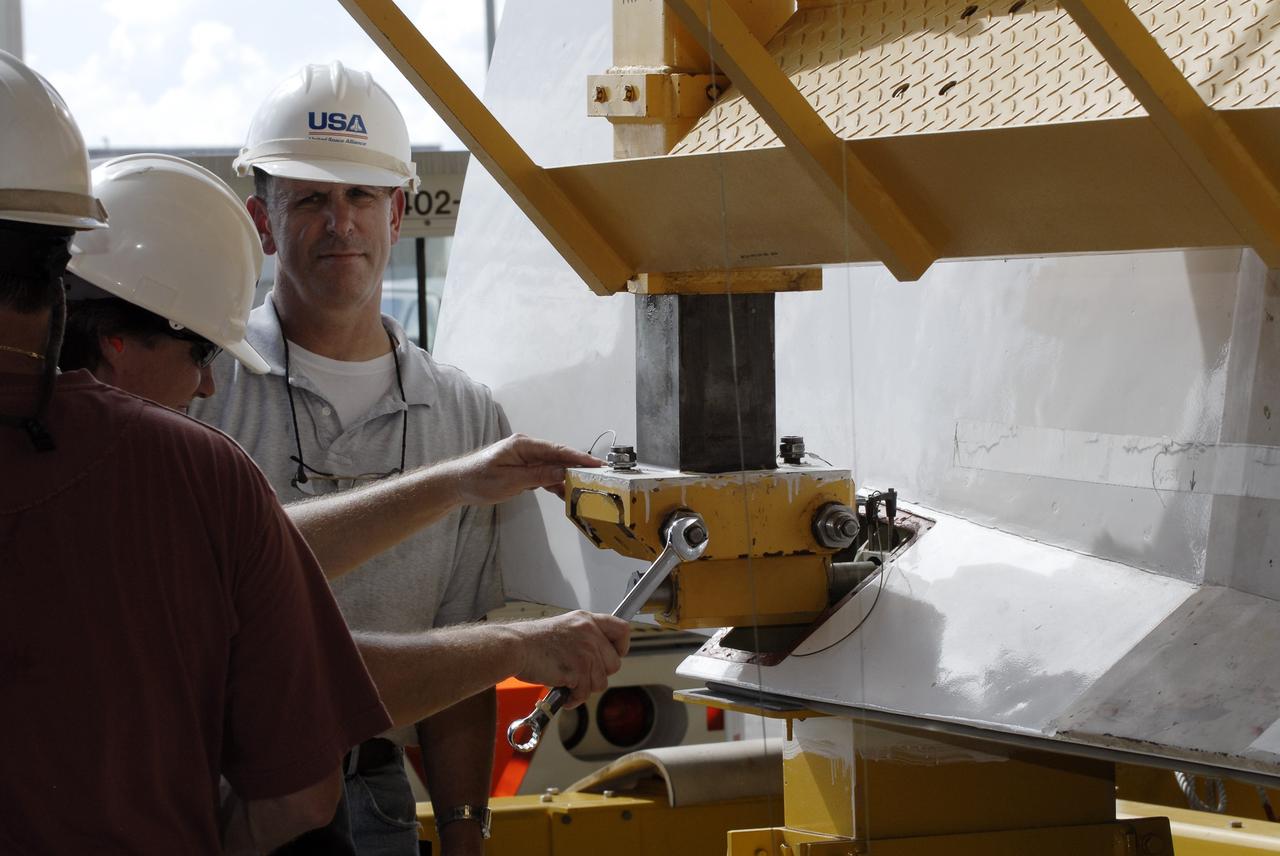

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers use an aerial lift to raise the Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod onto space shuttle Endeavour. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
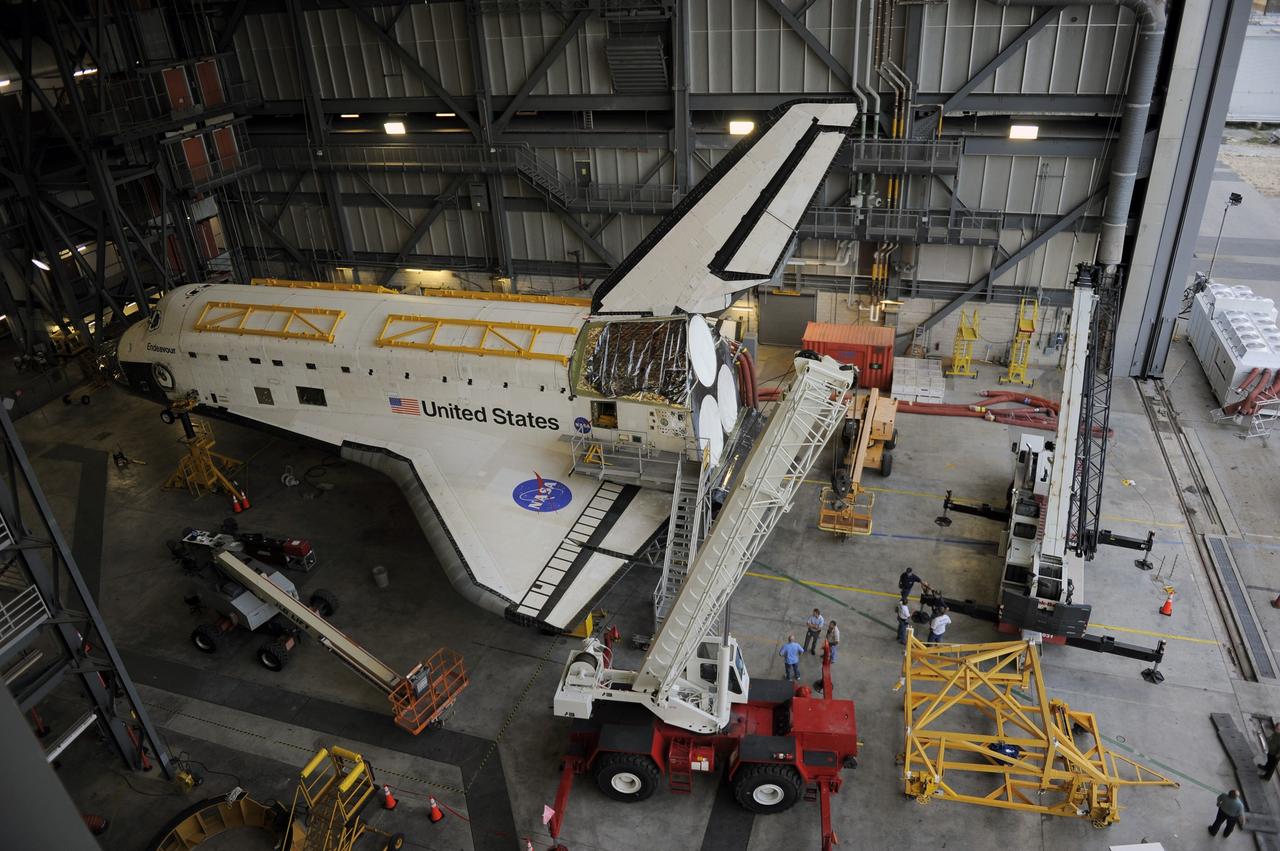

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour sits surrounded by cranes and lifts. Workers are preparing to raise an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod for attachment to the shuttle at the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
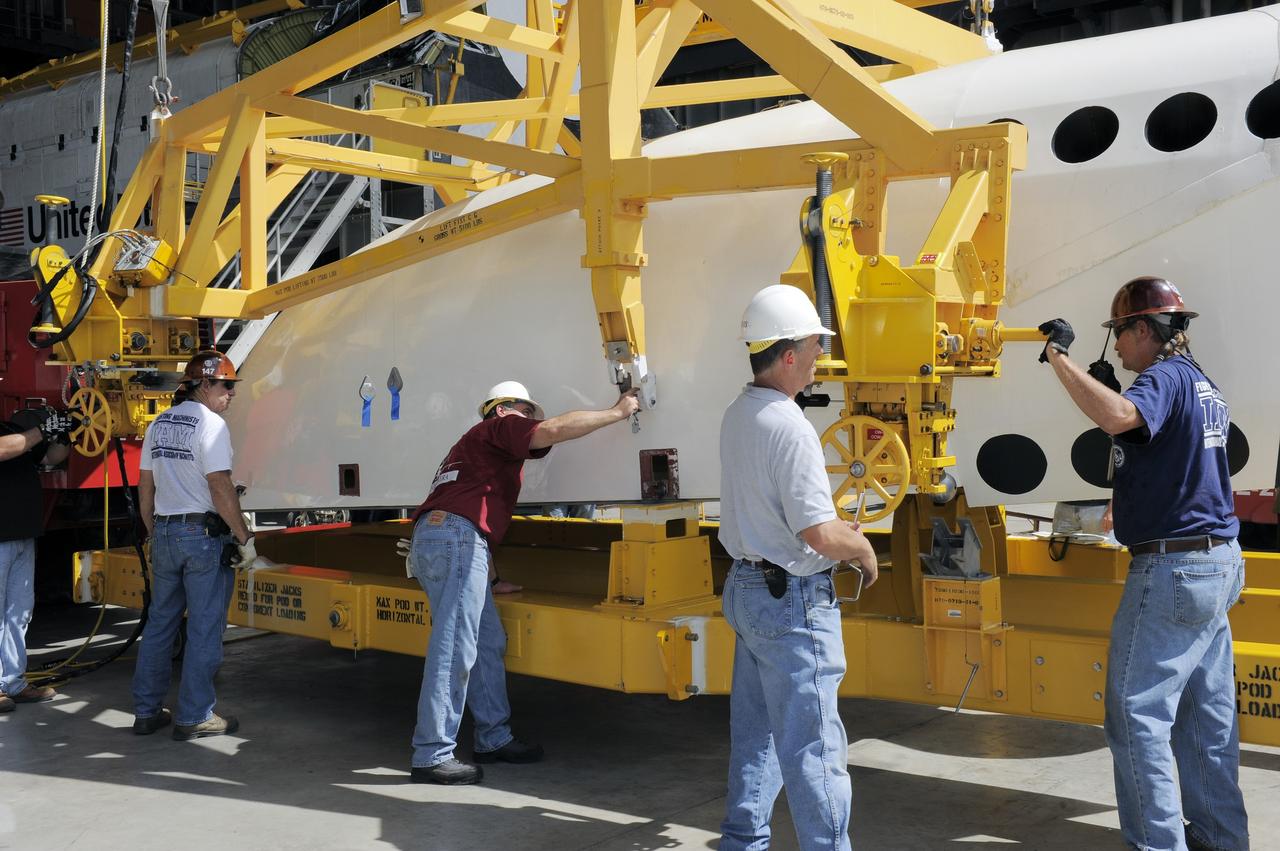

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, lower a cage over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
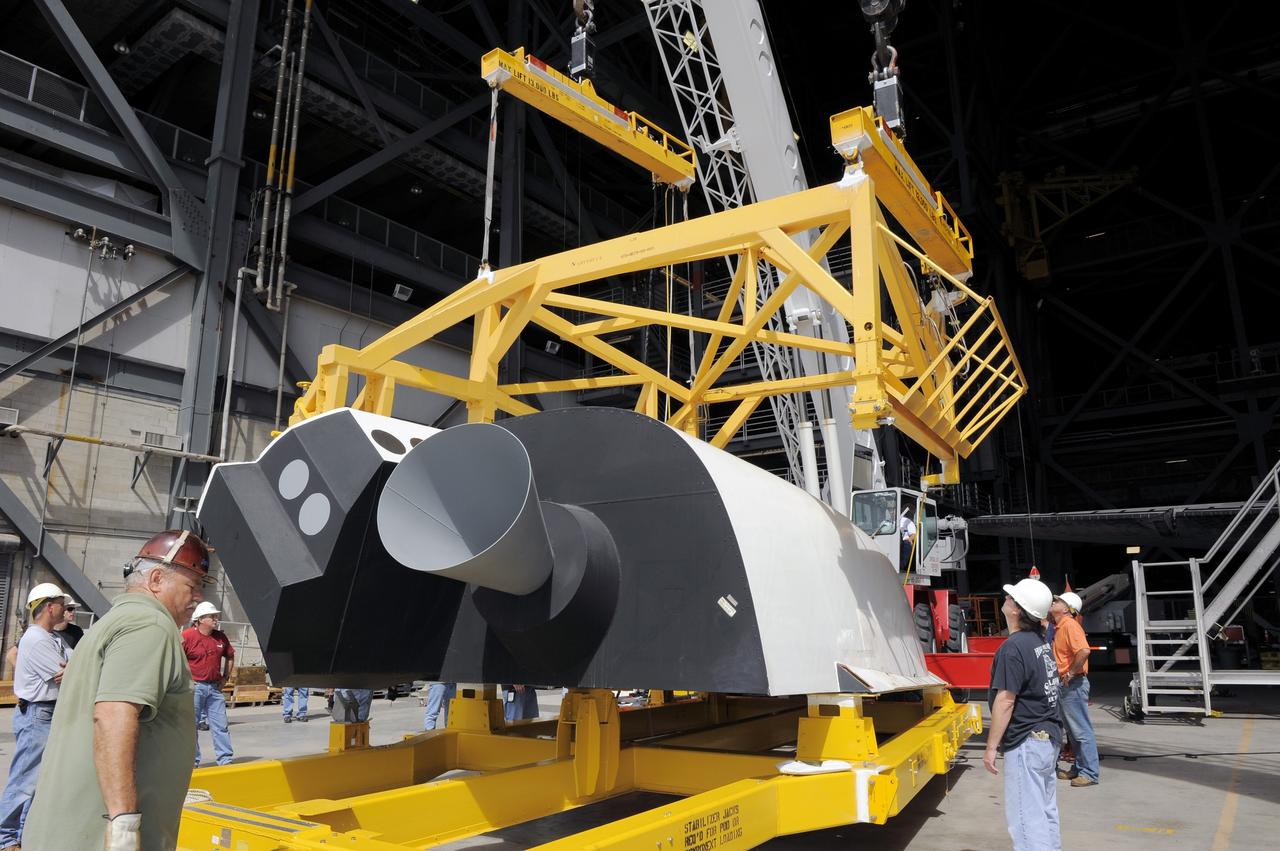

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, raise a cage over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett