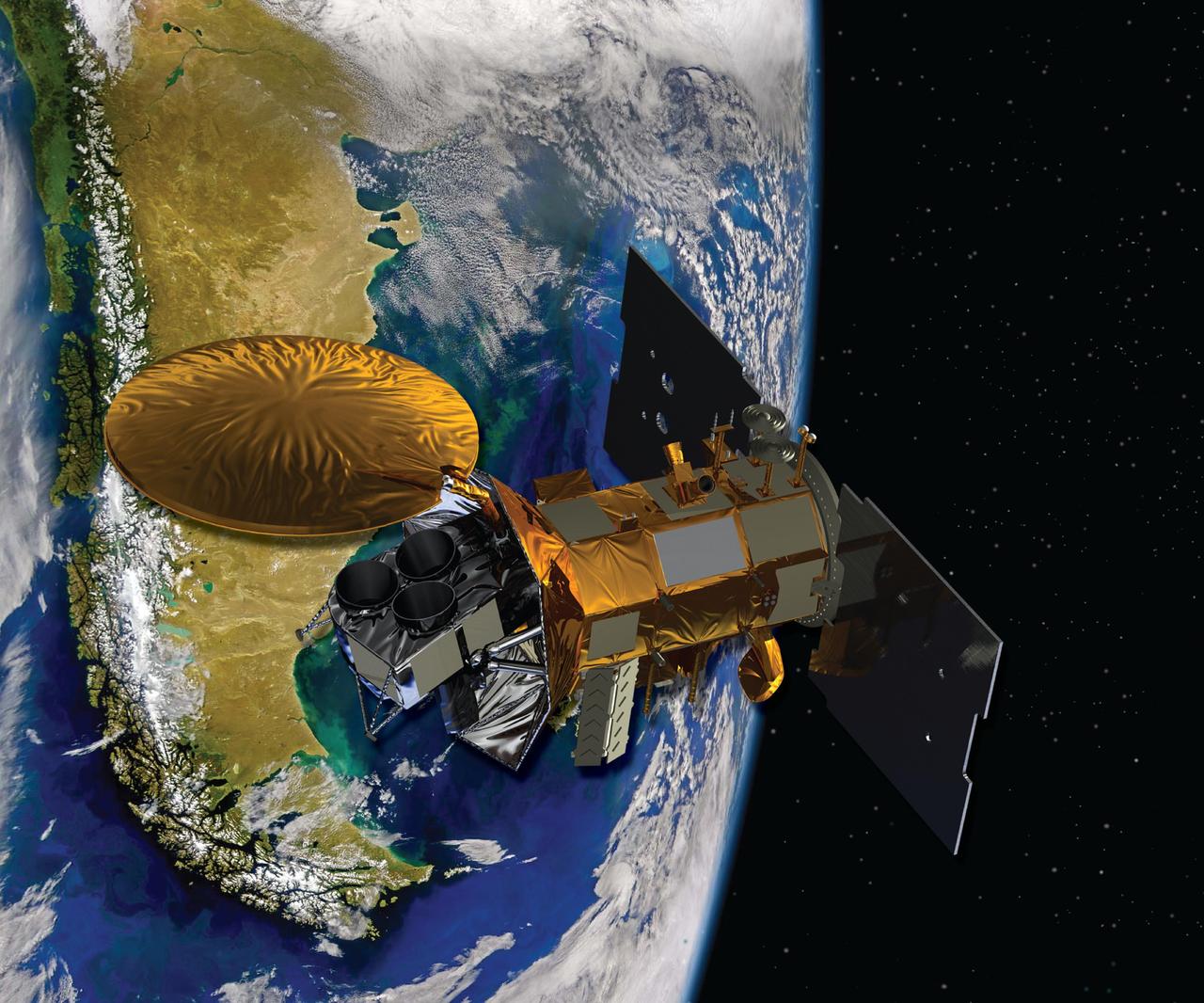

Artist concept of the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft. Aquarius will take NASA first space-based measurements of ocean surface salinity.
NASA Aquarius Principal Investigator Gary Lagerloef photographed in front of the Aquarius/SAC-D satellite observatory as it is being readied for transportation from Brazil to Vandenberg Air Force Base in California for a June 2011 launch.
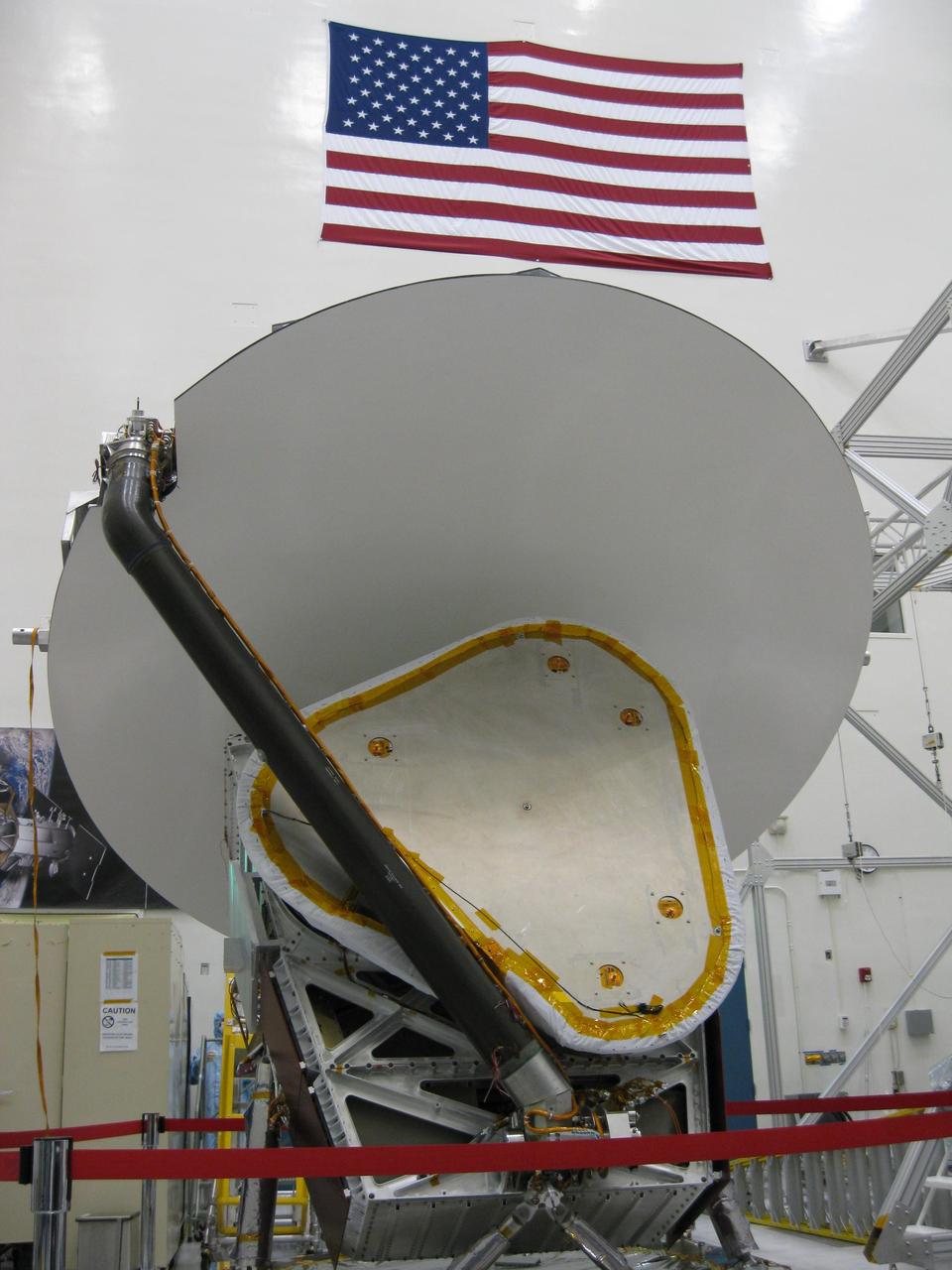

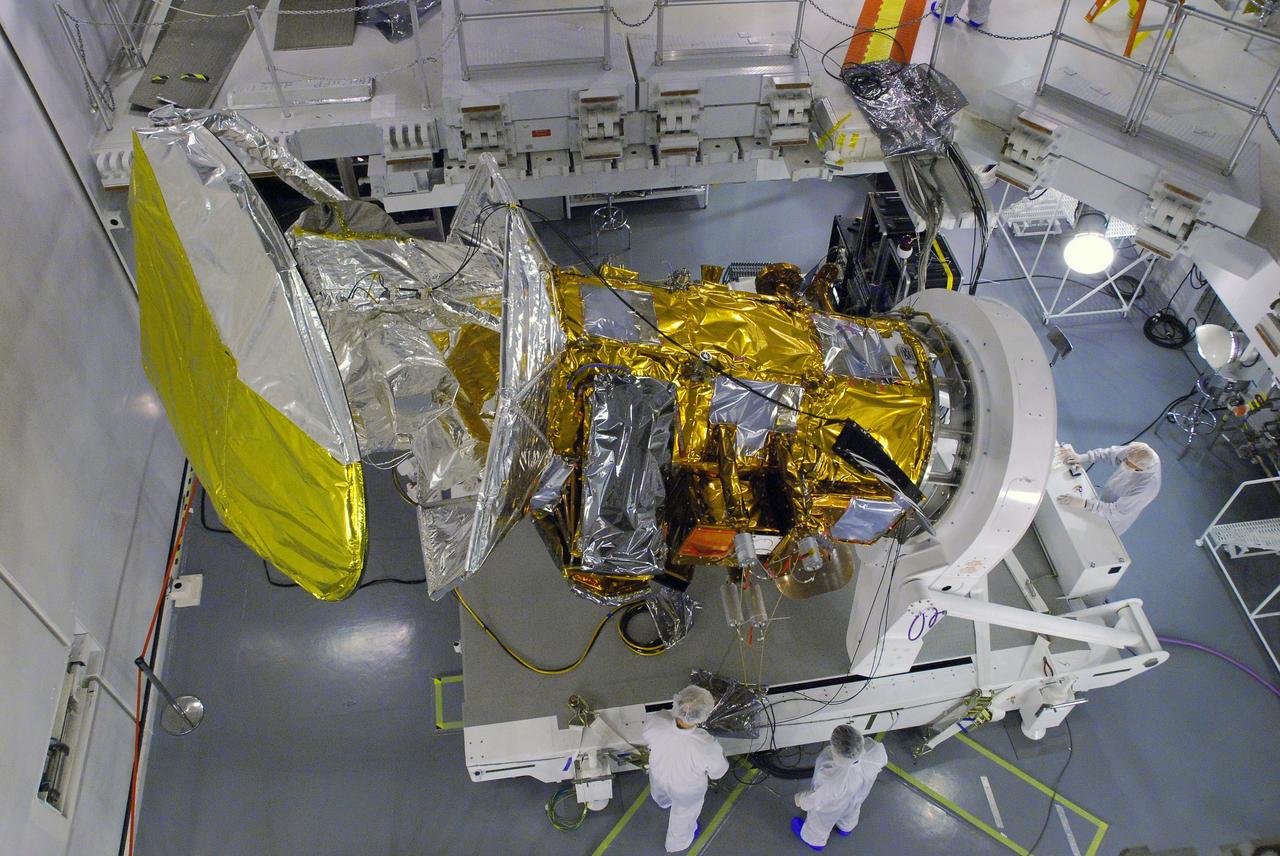
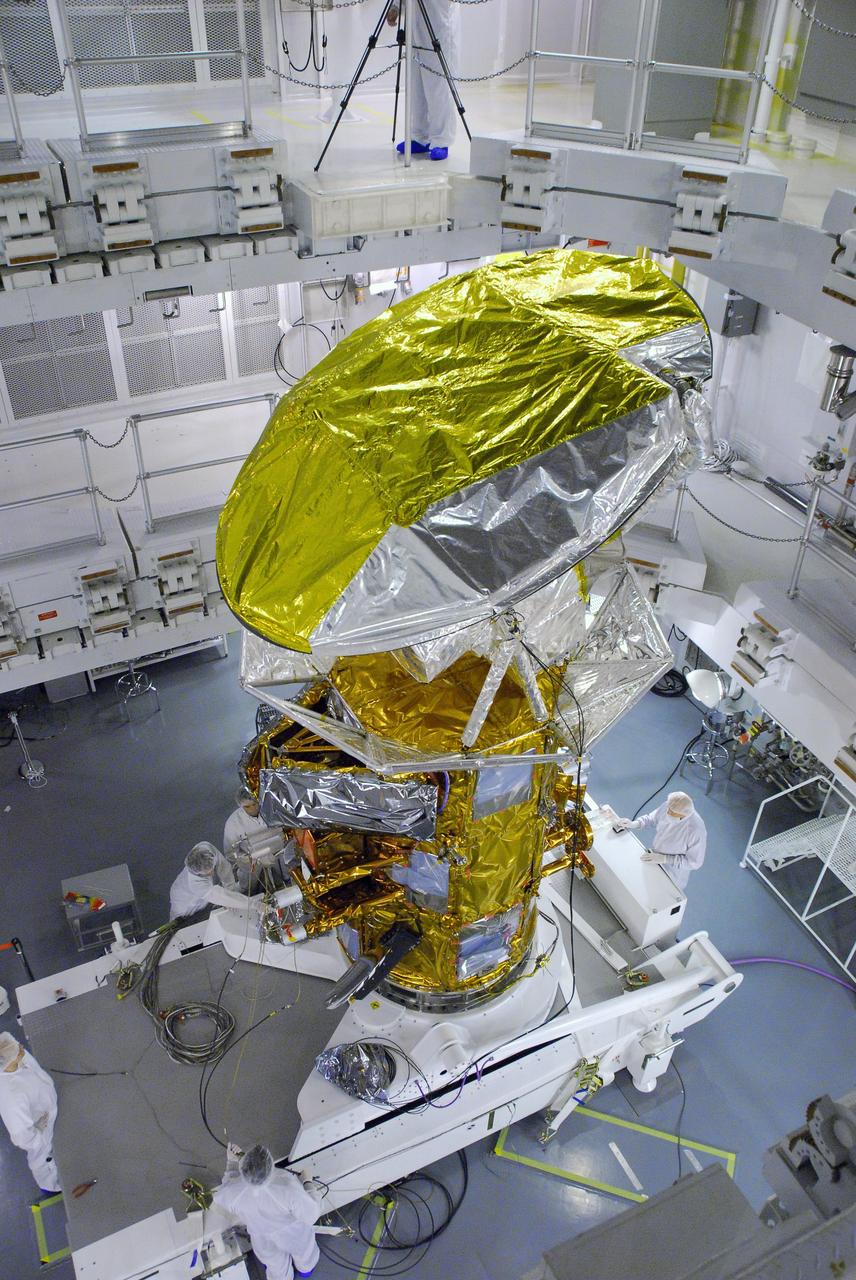
Aquarius instrument, including 2.5 meter reflector, in the clean room at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.
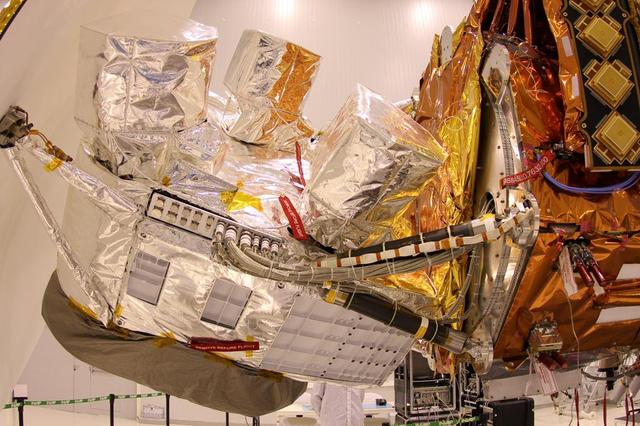

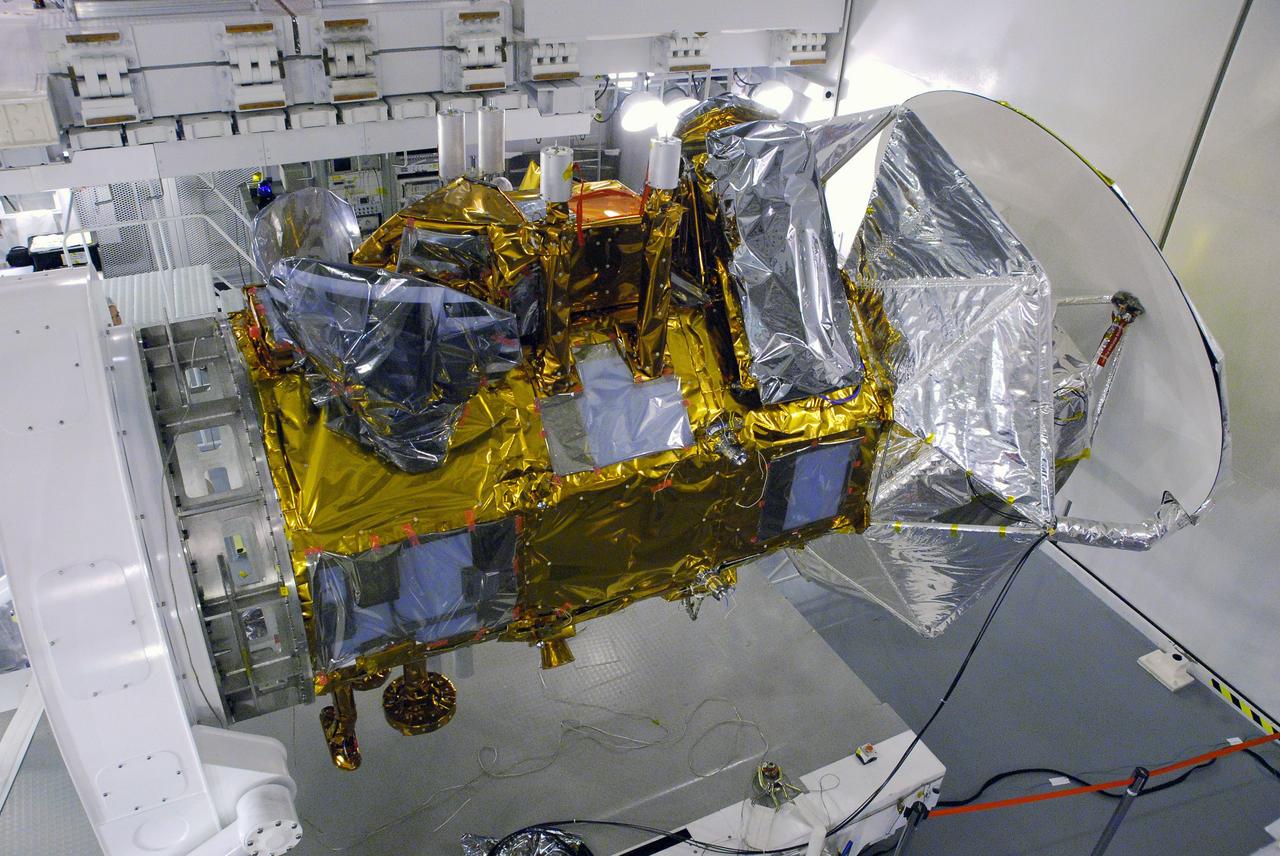
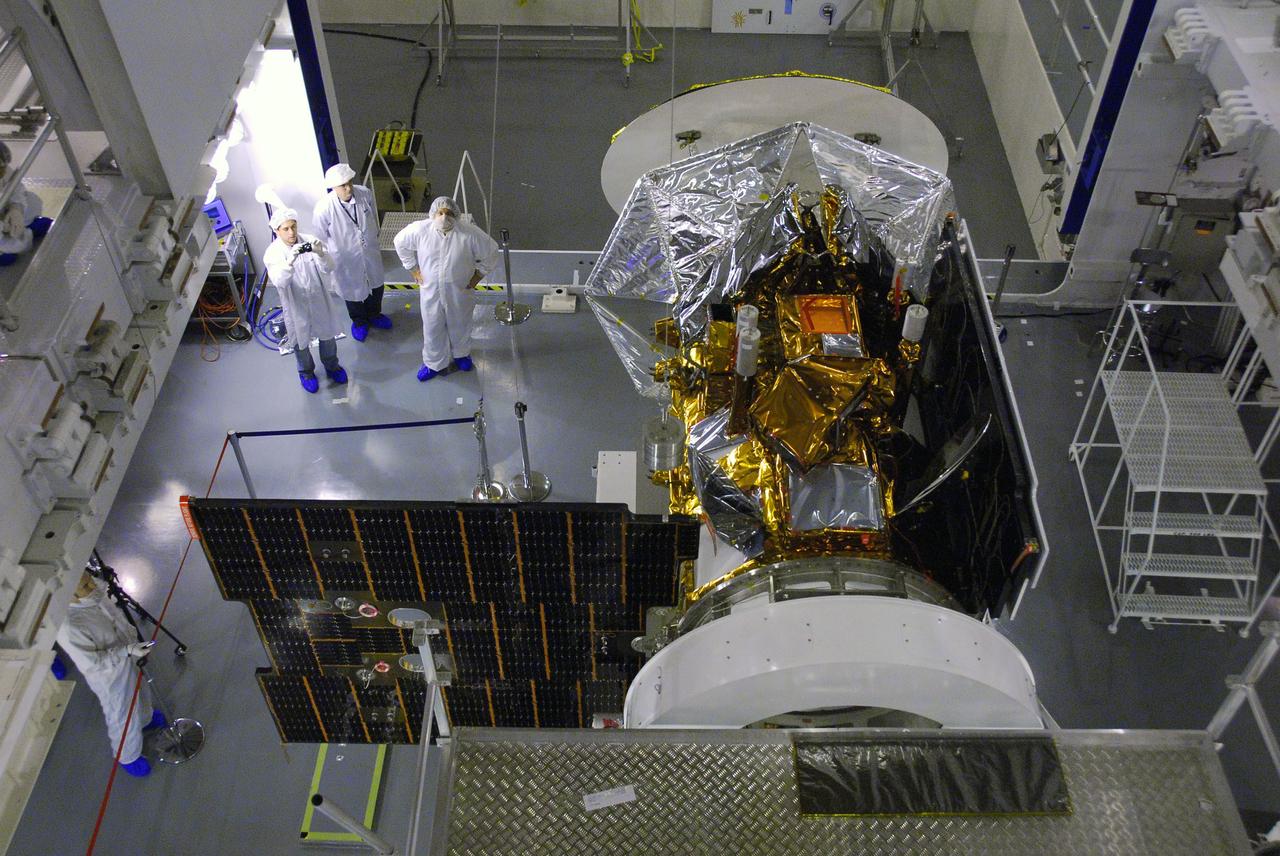
NASA Aquarius instrument, covered in silver foil, is shown attached to the SAC-D satellite bus at INVAP facility.
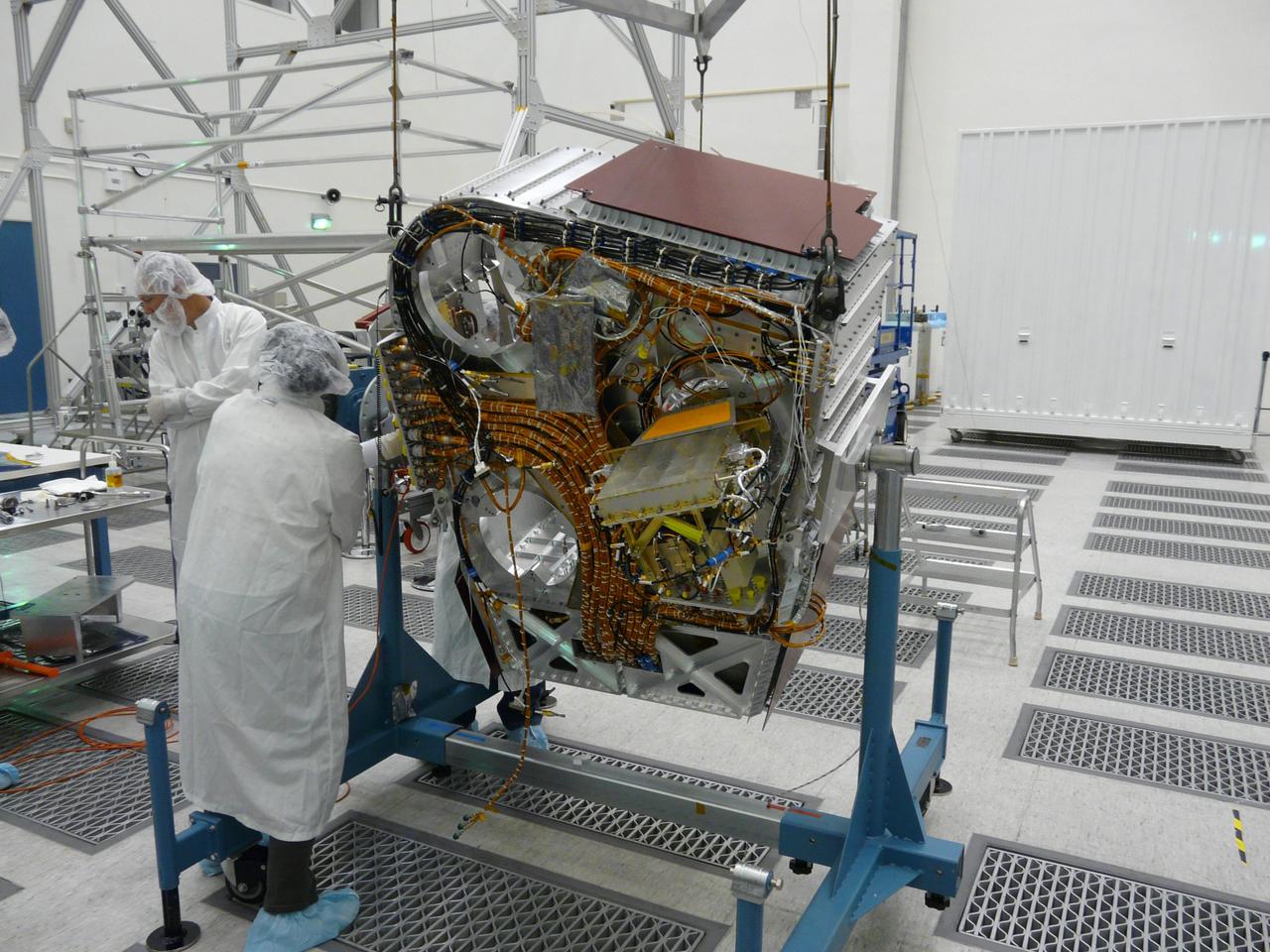

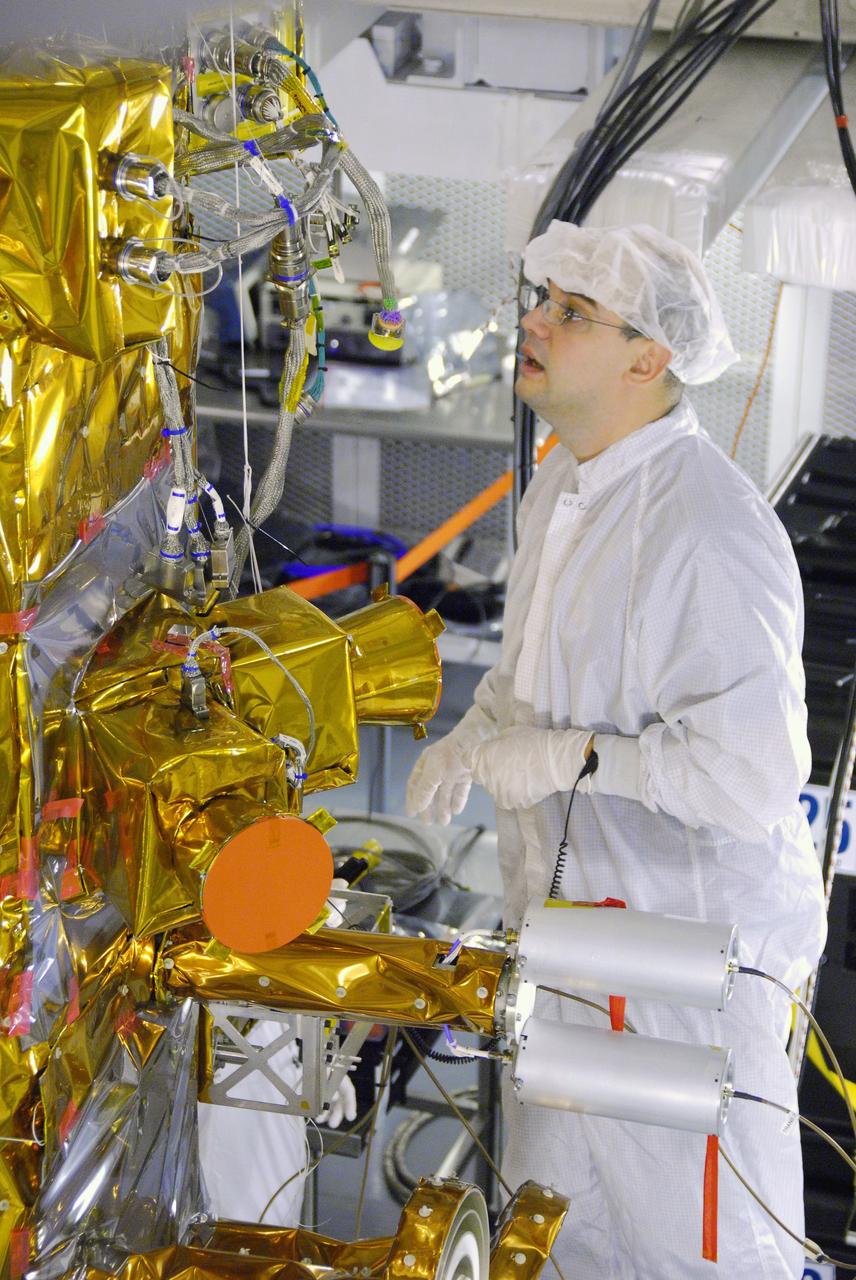
Engineers check cables on back of Aquarius instrument in the clean room at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.
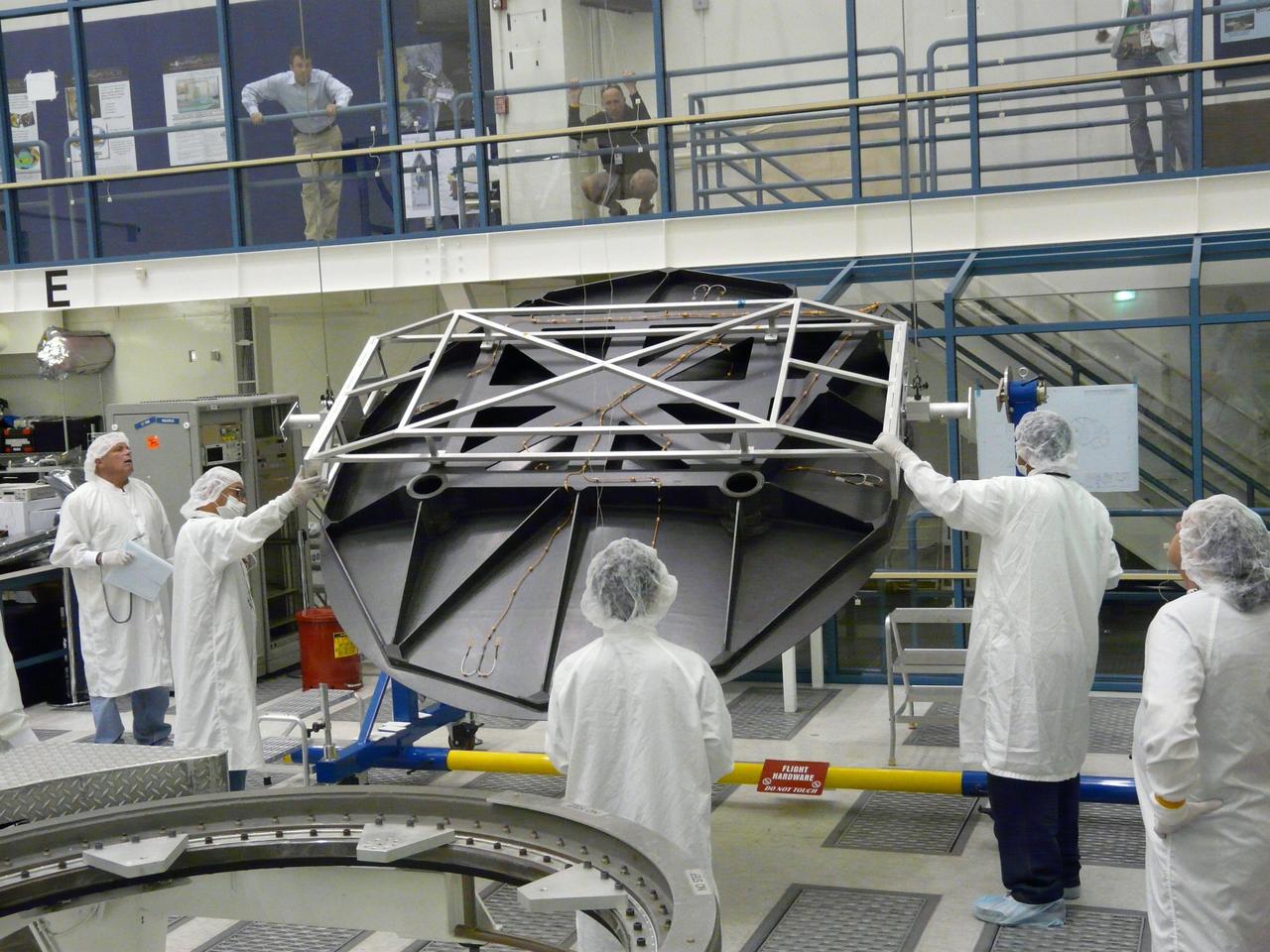

Engineers test Aquarius 2.5 meter reflector in the clean room at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.
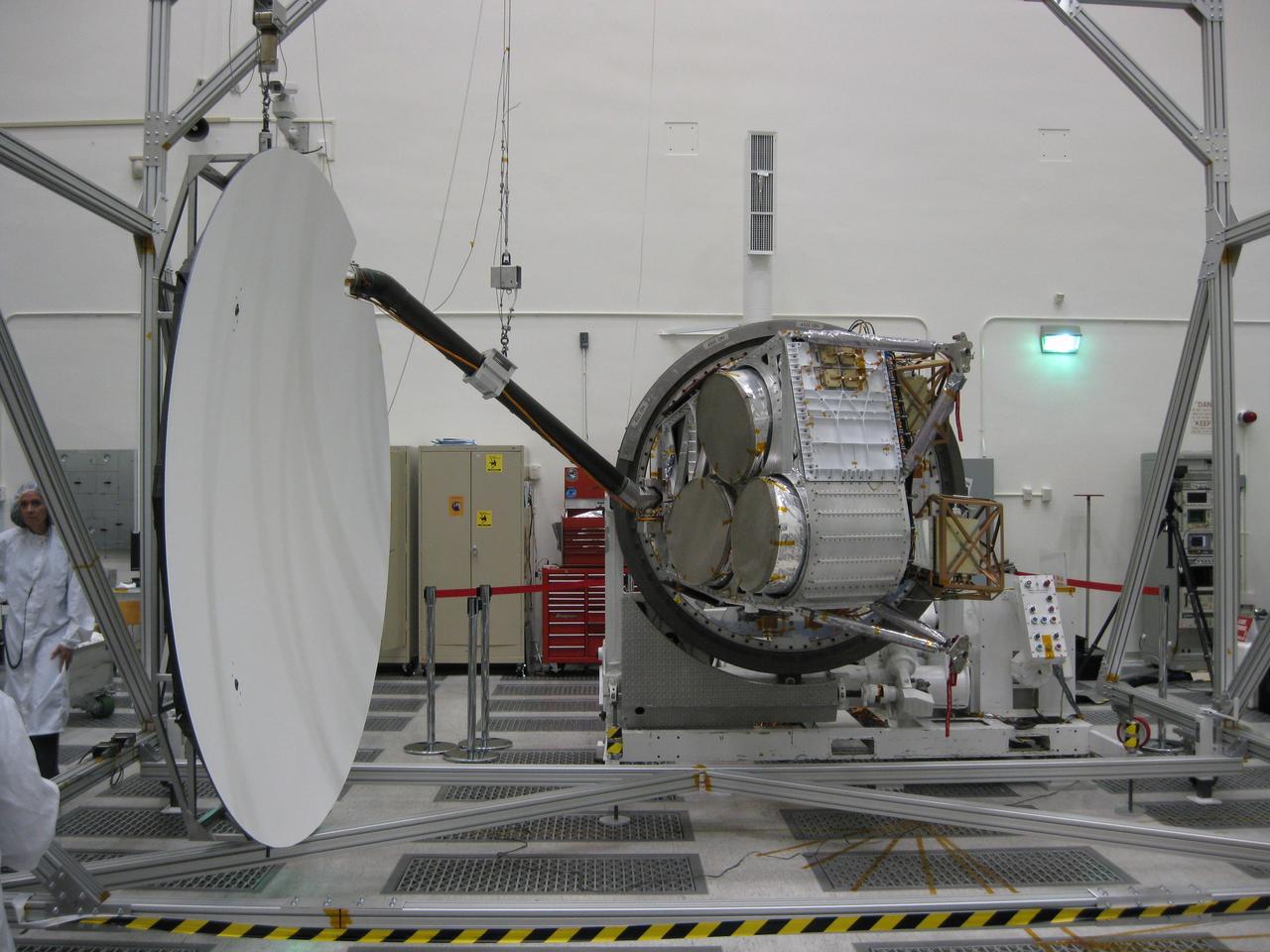

Aquarius reflector deployment is tested in the clean room at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.
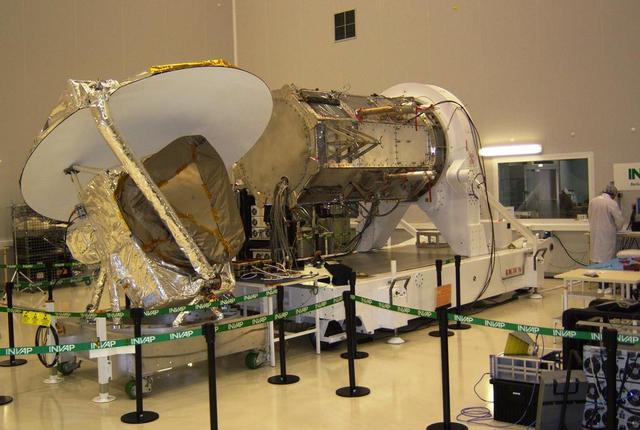

All NASA Aquarius electrical interfaces have successfully been connected to the SAC-D service platform S/P.
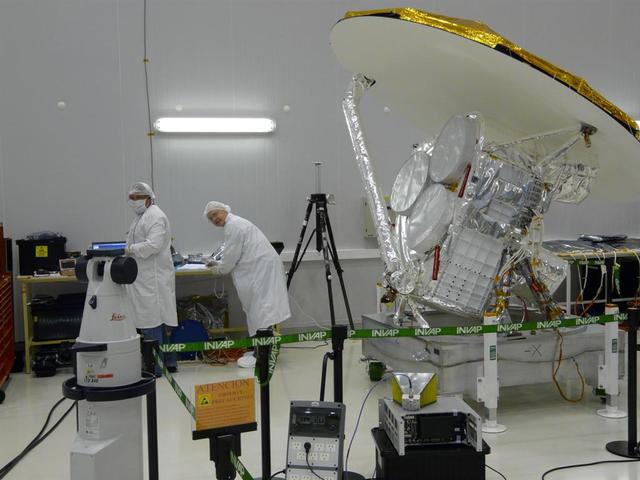

NASA Aquarius instrument power interfaces are tested prior to connection with the SAC-D service platform at the INVAP facility in Bariloche, Argentina.
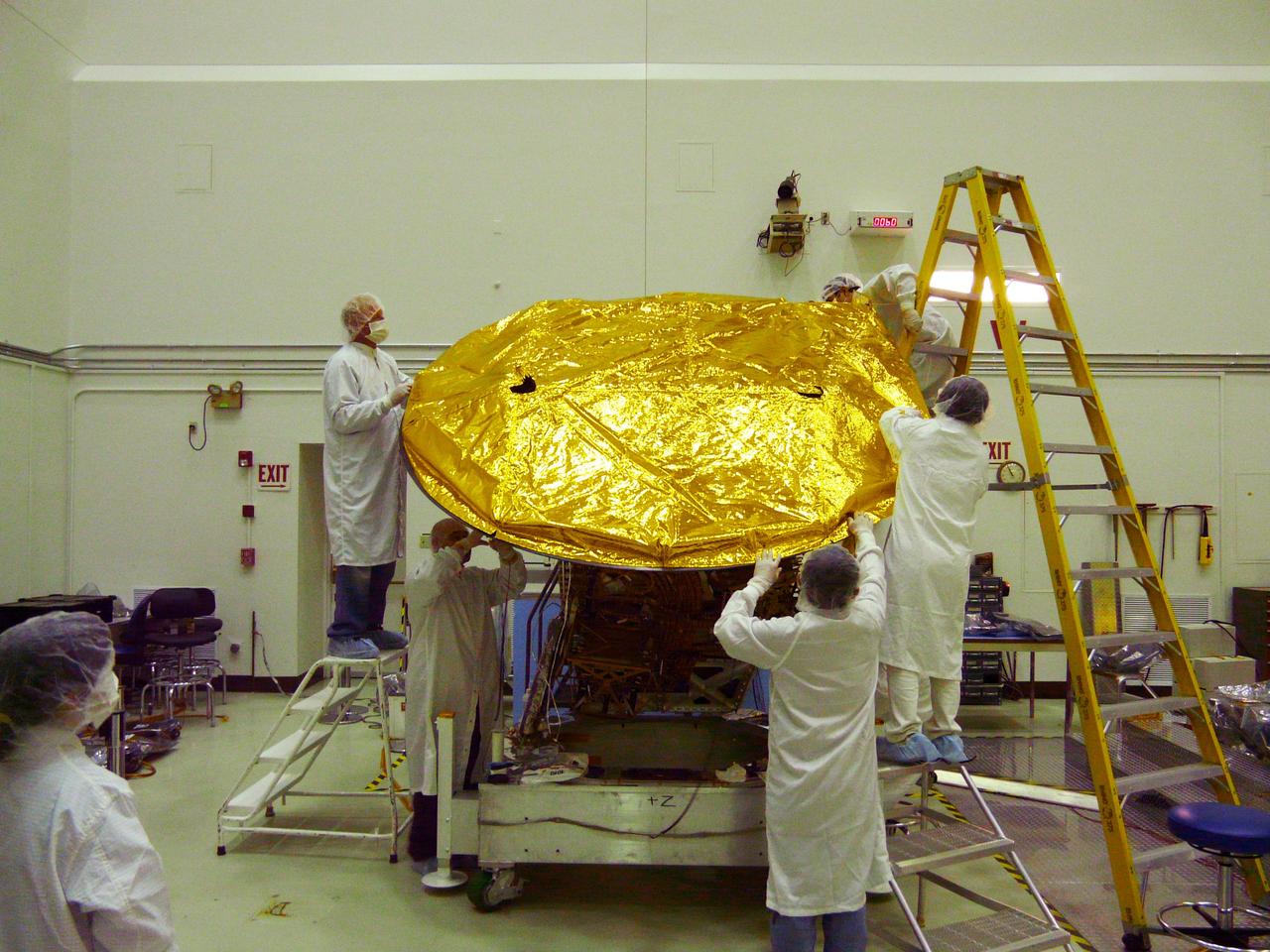

Aquarius 2.5 meter composite reflector being fitted with gold foil covering in the clean room at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.
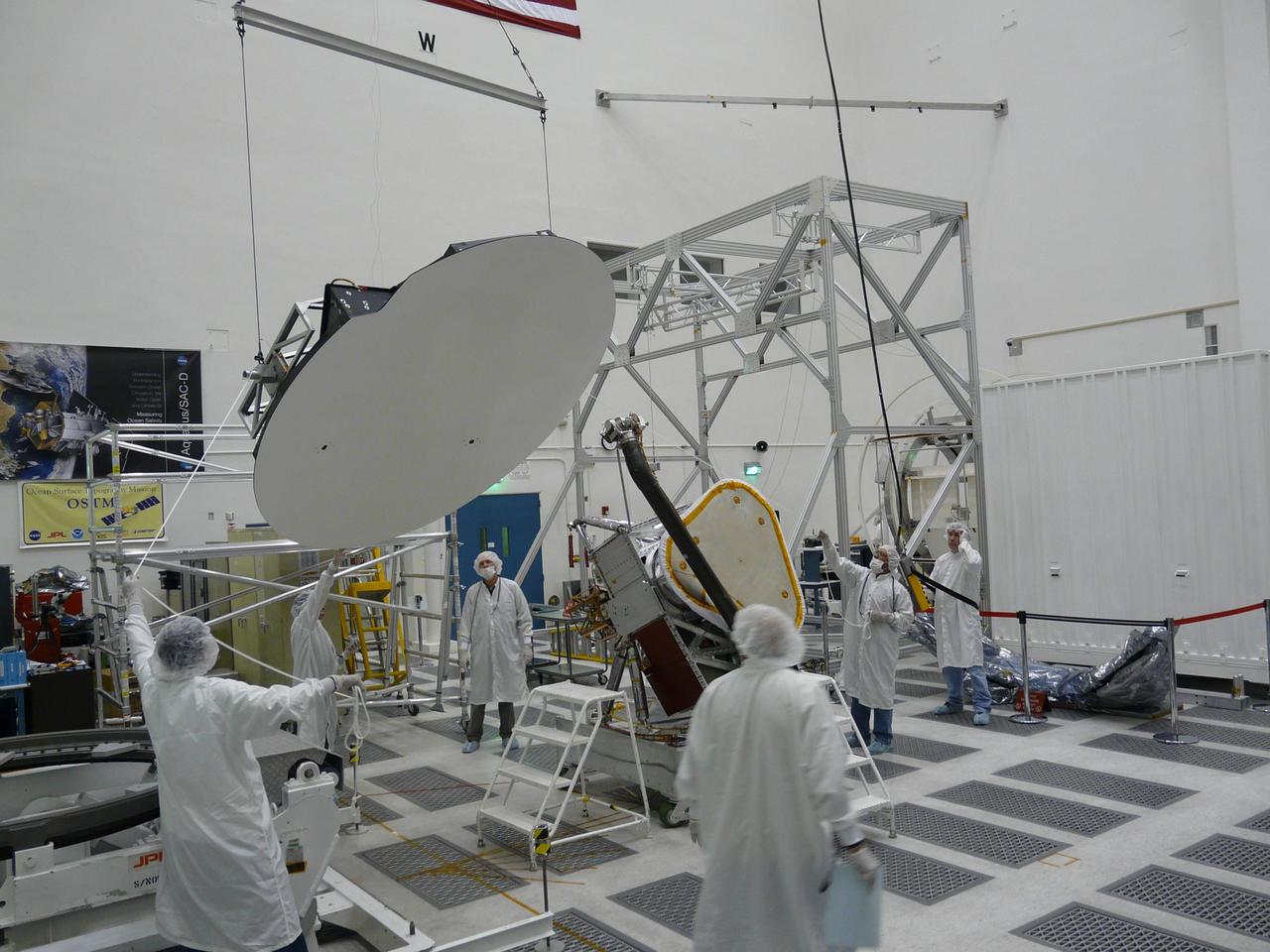

Aquarius 2.5 meter reflector is hoisted before being attached to boom in the clean room at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.

Artist concept of NASA Aquarius/SAC-D observatory. SAC-D observatory will provide NASA first space-based global measurements of salinity at the ocean surface.
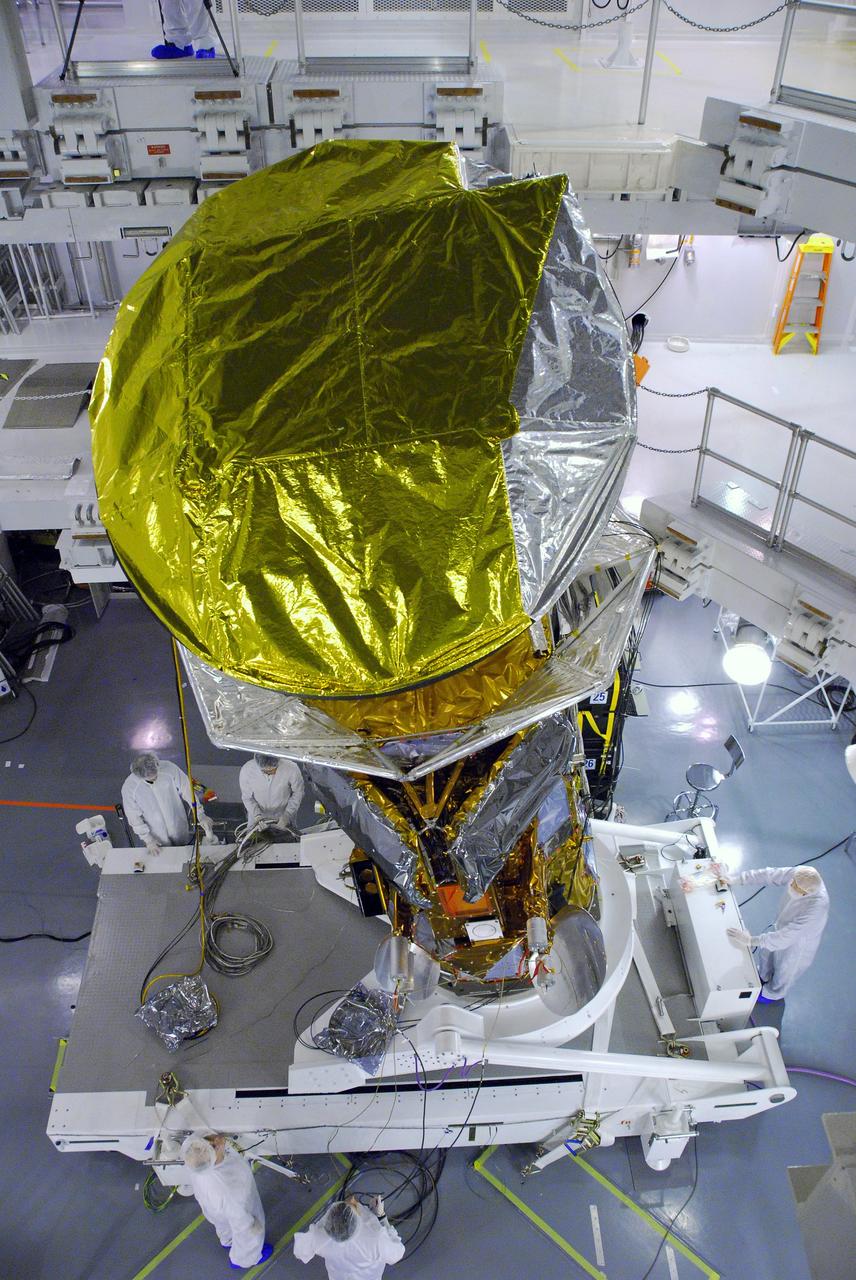
A fit check of half the sunshade is completed to verify the clearance of NASA Aquarius ground lug as well as the blanket interface with the service platform top deck.
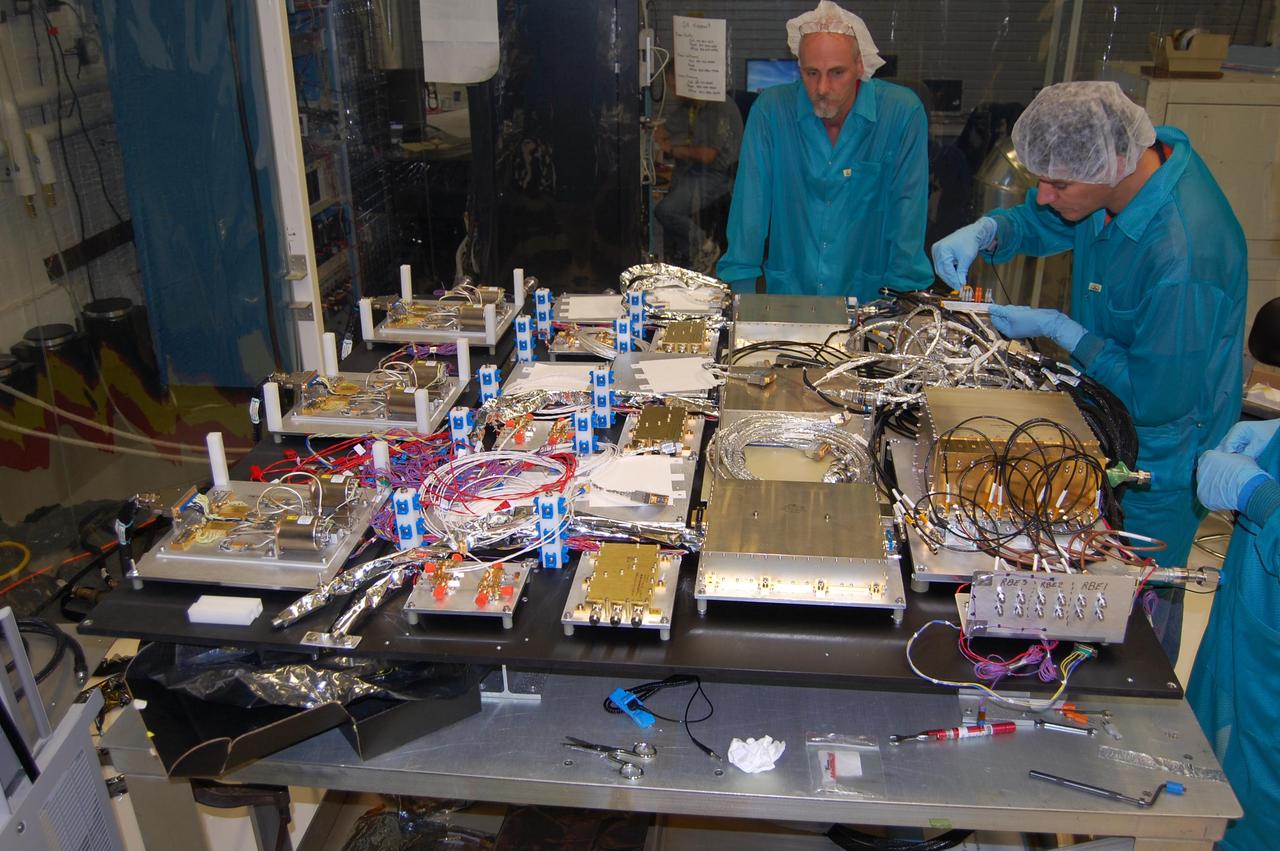

After a four-year development effort, the Goddard Space Flight Center delivered NASA Aquarius radiometer to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., for integration with the Aquarius instrument.
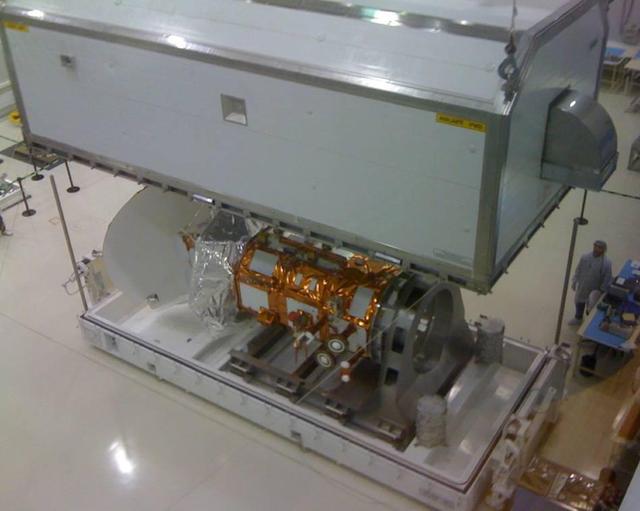

NASA Aquarius/SAC-D being prepared for shipment to Brazil National Institute for Space Research Integration and Testing Lab. At INPE, the Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will undergo its final environmental testing.
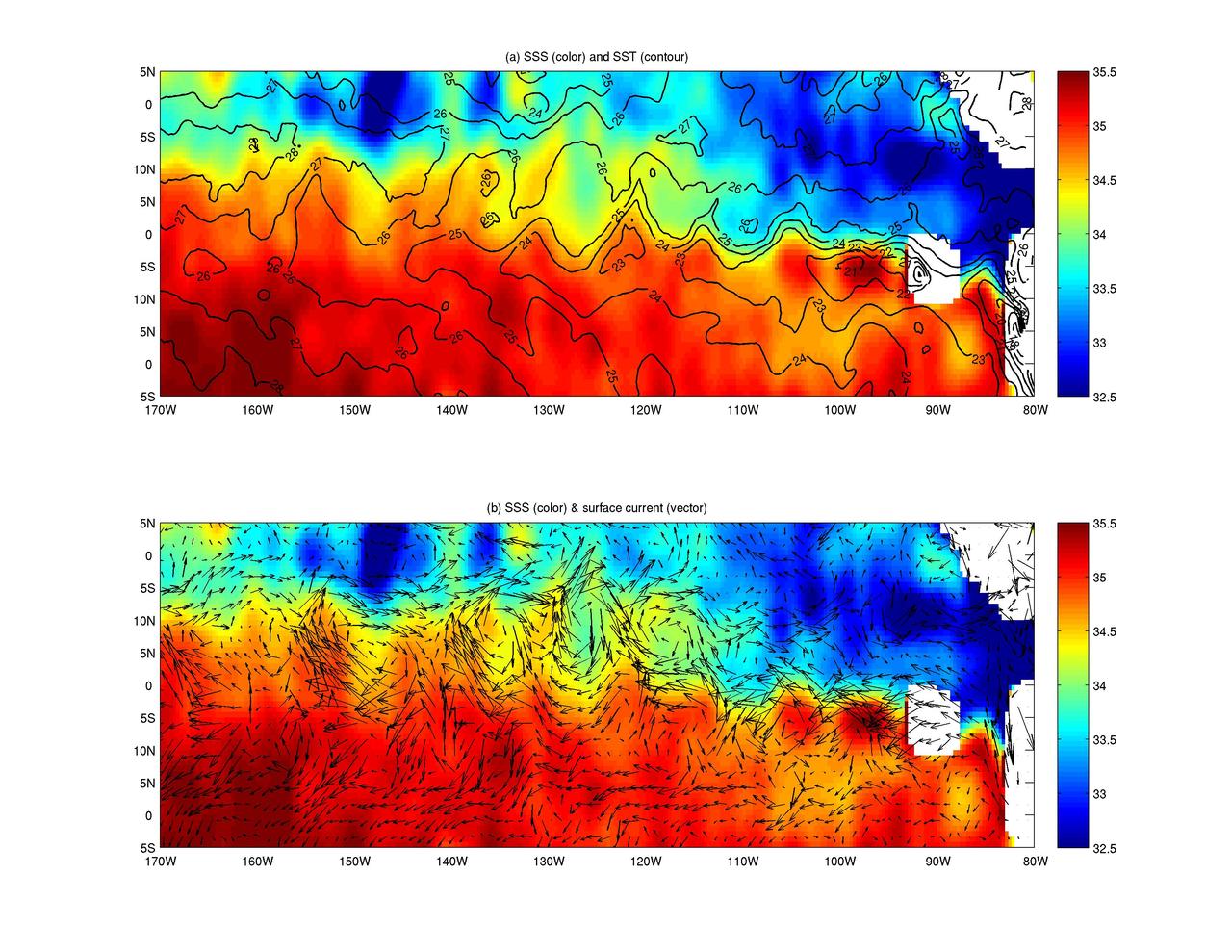
NASA Aquarius instrument on the Aquarius/SAC-D observatory gives an unprecedented look at a key factor involved in the formation of an oceanic wave feature in the tropical Pacific and Atlantic Oceans that influences global climate patterns.
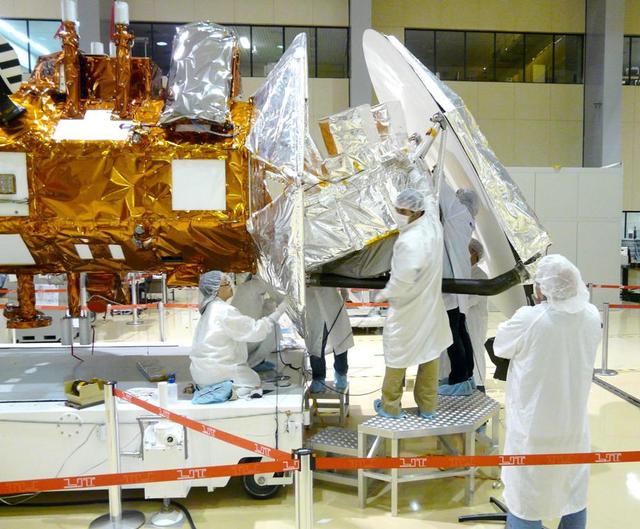

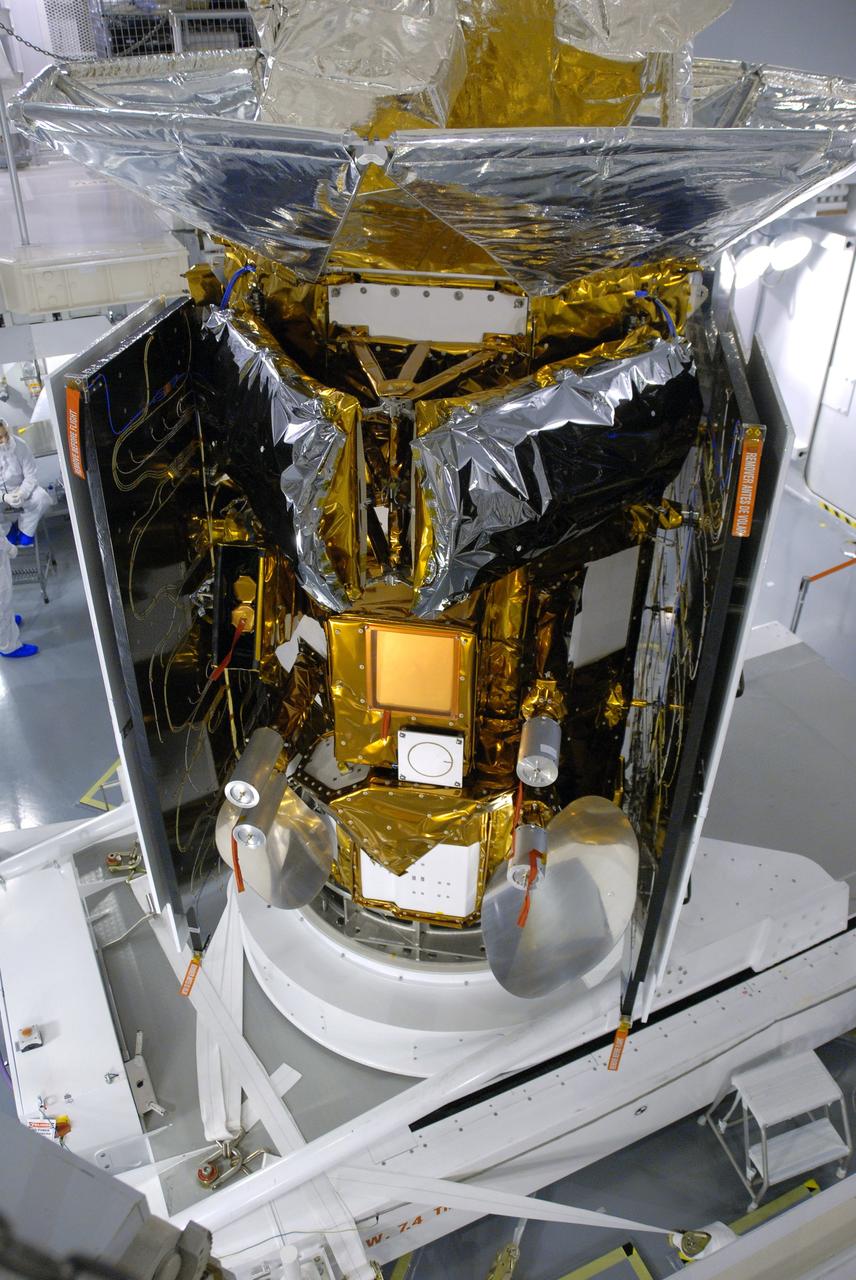
NASA Aquarius instrument thermal blanketing is completed and inspected. In addition, all external surfaces of the satellite are cleaned and inspected with white light to uncover any visible debris.
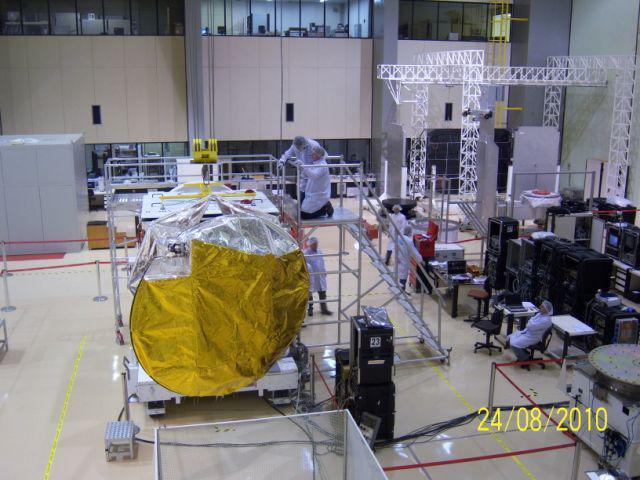

Engineers inspect NASA Aquarius/SAC-D observatory at INVAP facility in Bariloche, Argentina.
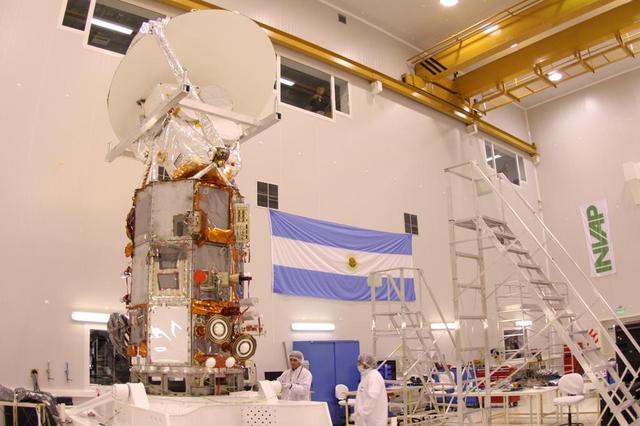

NASA Aquarius instrument on SAC-D sevice platform in INVAP high bay facility for mechanical integration activities.
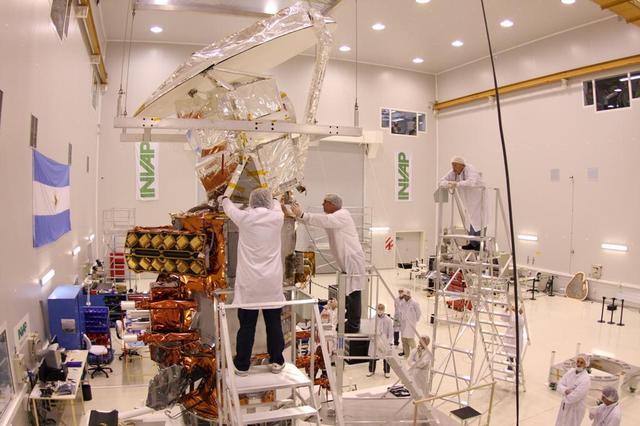

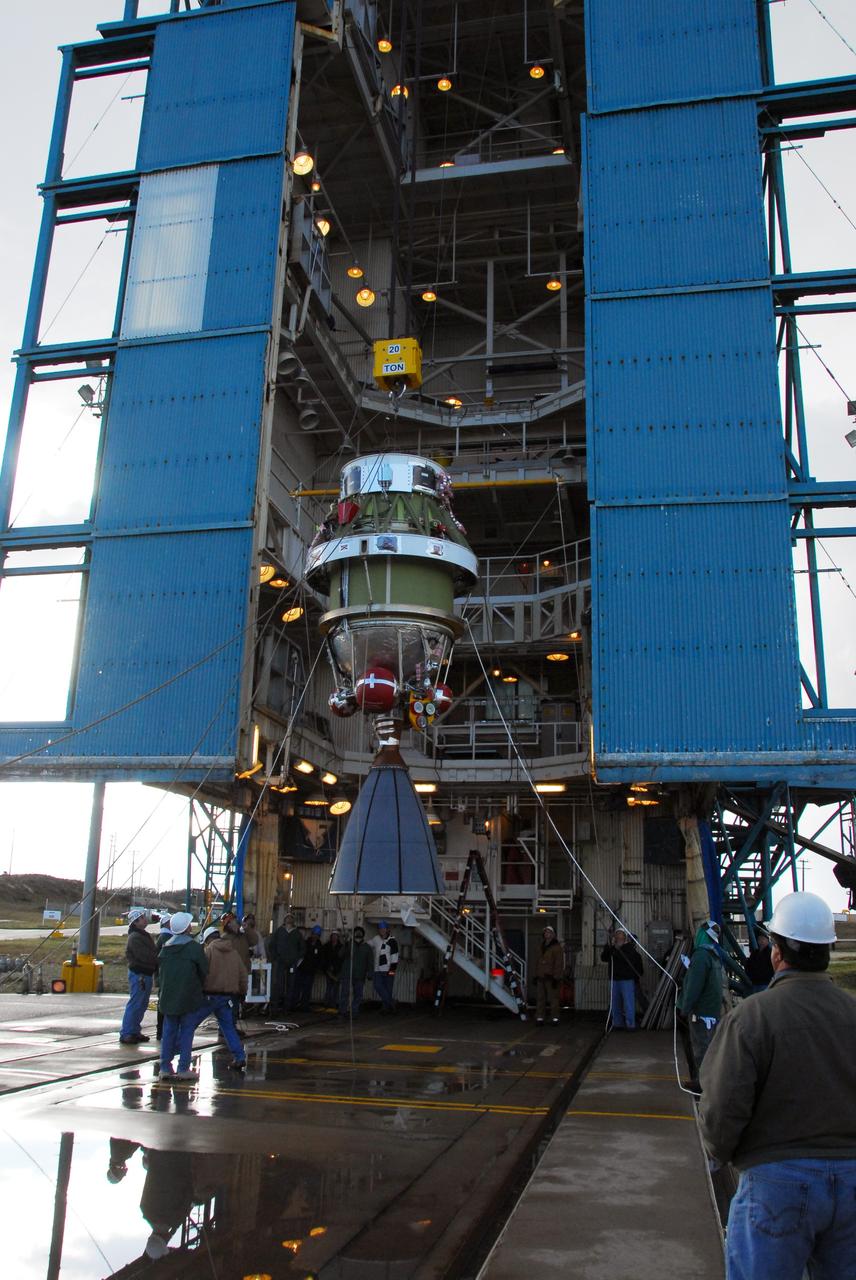
NASA Aquarius instrument is lifted upright onto the SAC-D service platform at the INVAP high bay facility in Bariloche, Argentina.
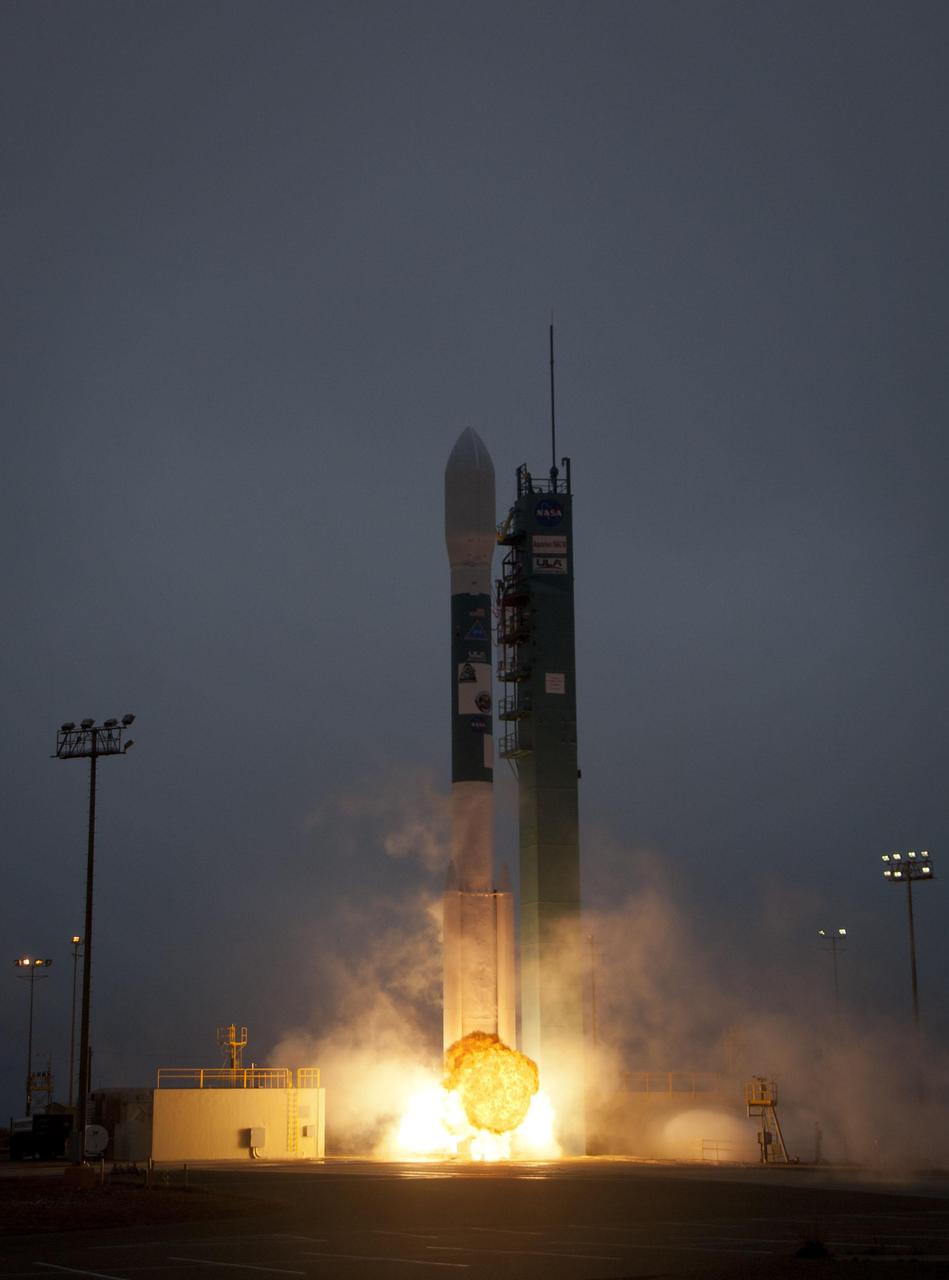

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011.
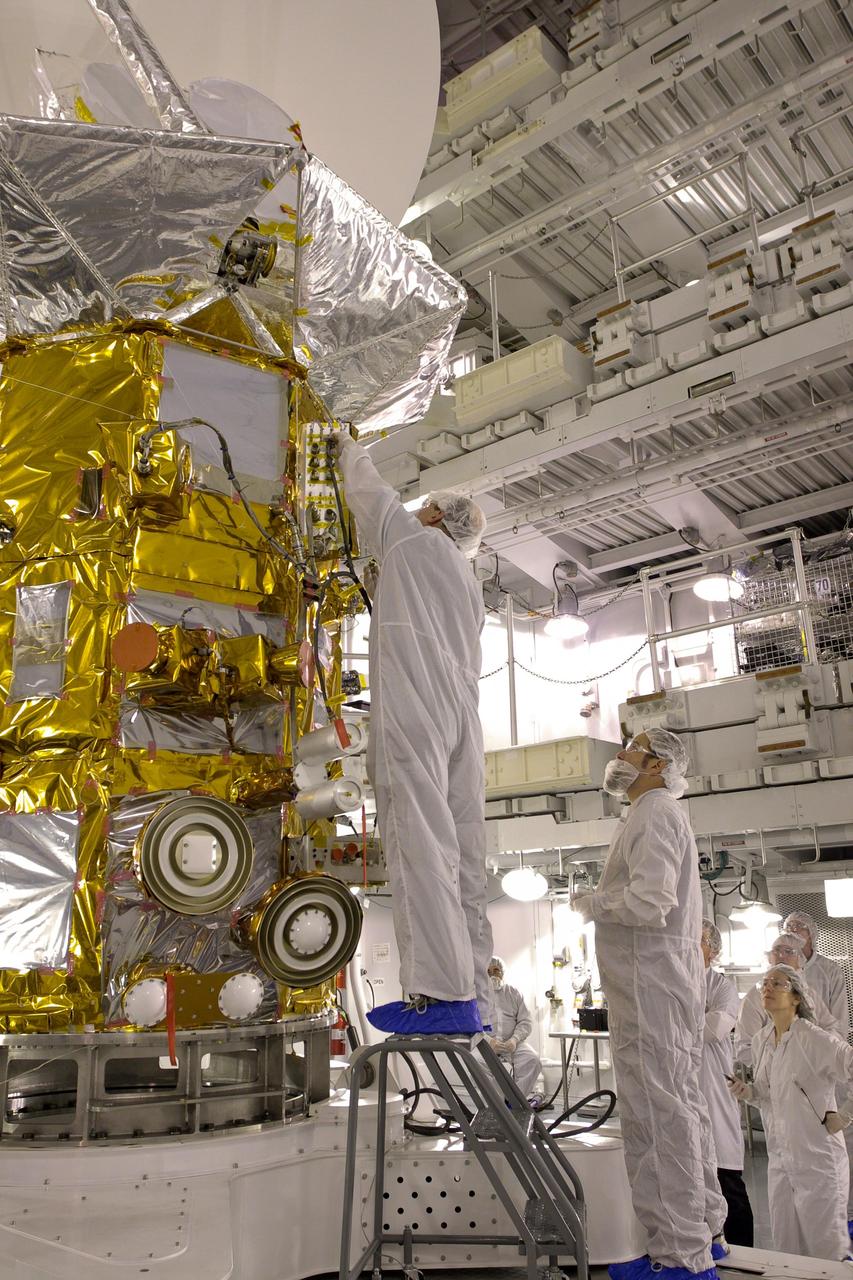

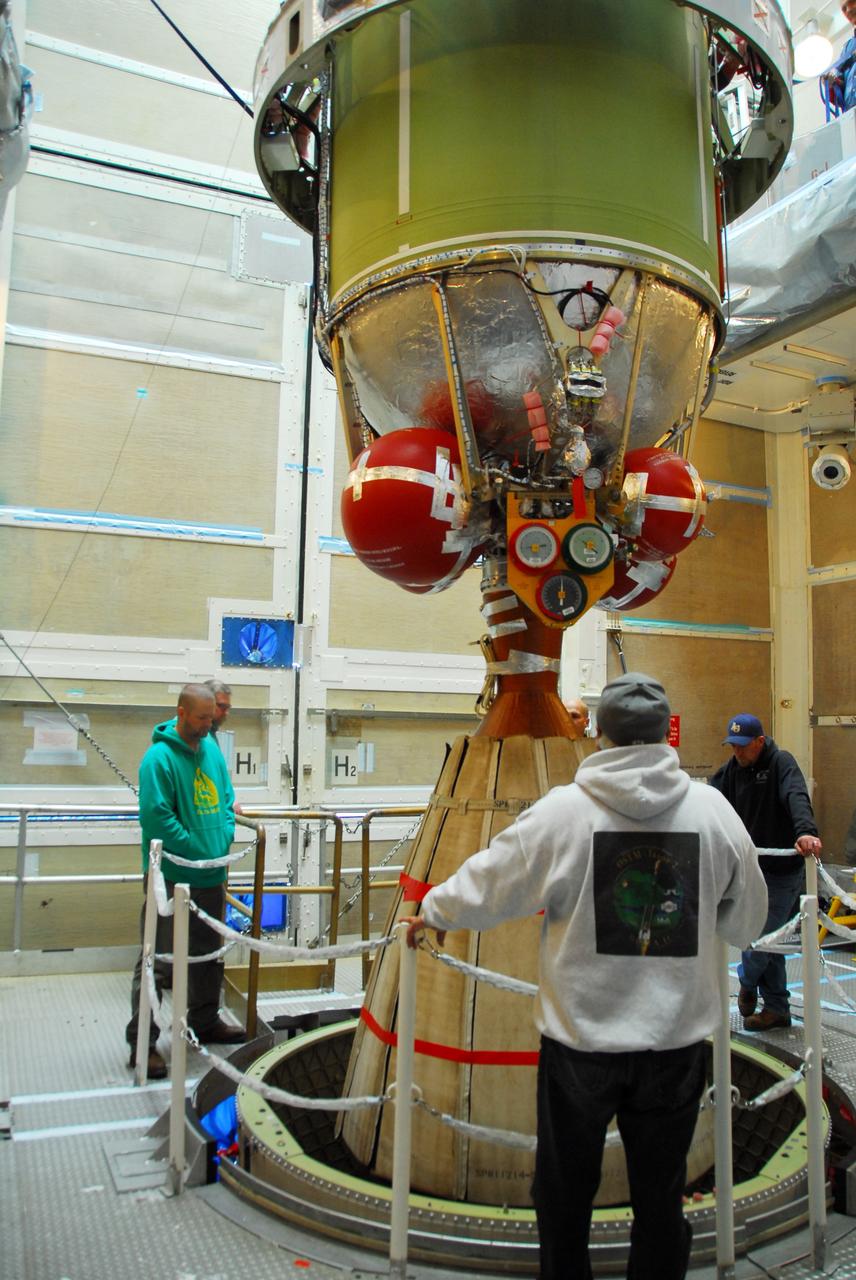
Less than two months before launch, team members conduct their final checks of NASA Aquarius instrument at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. Subsequent final instrument tests will be conducted on the launch pad.

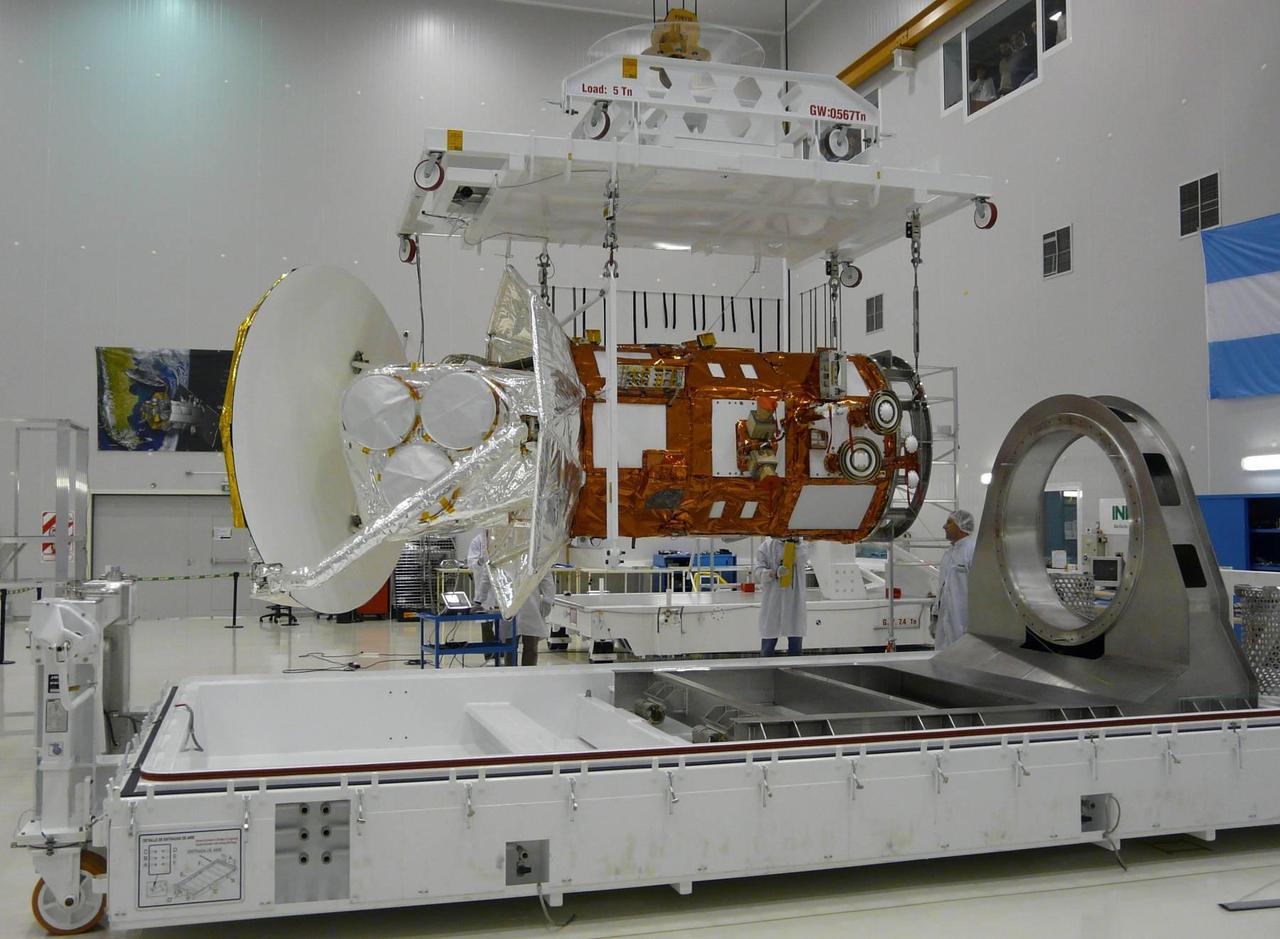
Technicians lower the cover over the shipping container holding the international Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft at Brazil National Institute for Space Research.

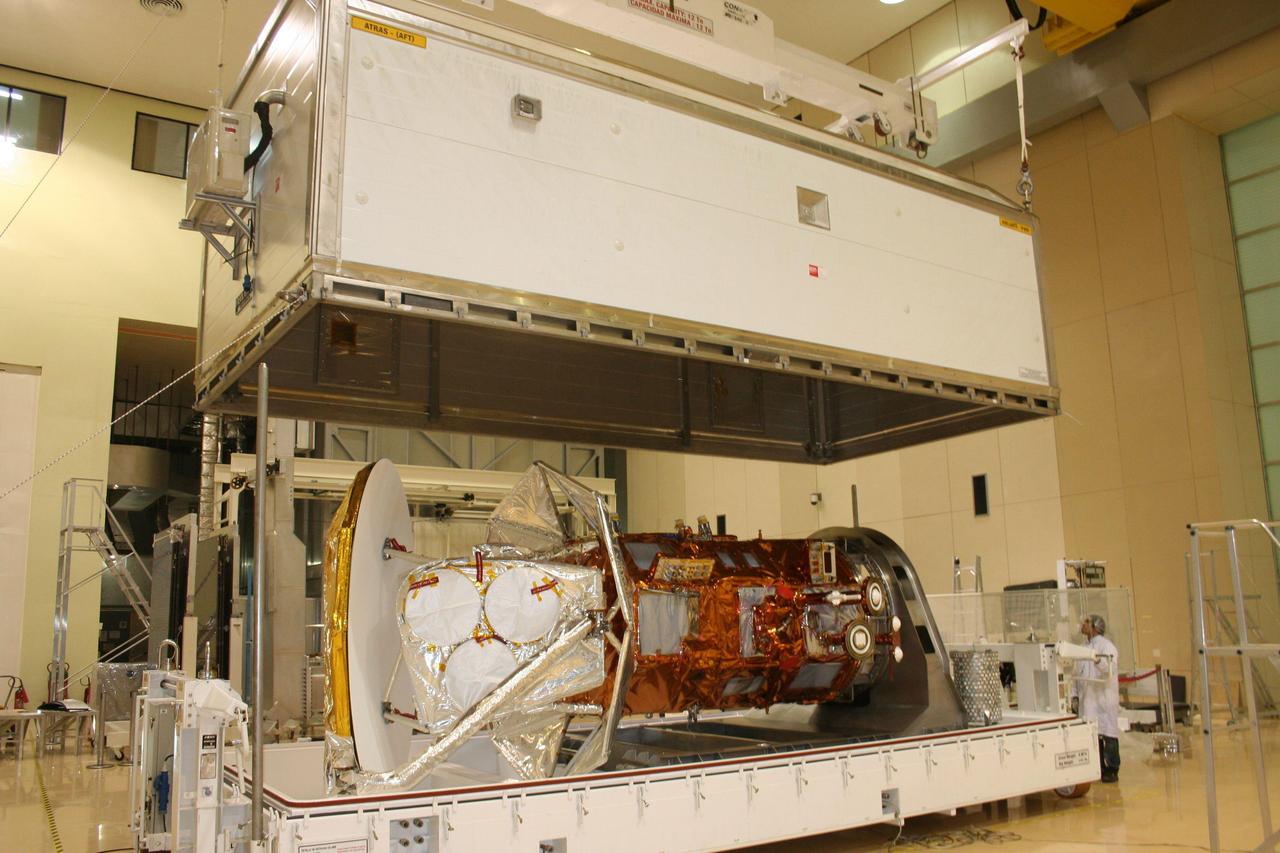
After months of integration and testing at the INVAP facility Bariloche, Argentina, NASA Aquarius/SAC-D is removed from the service platform in preparation for shipping to Brazil.
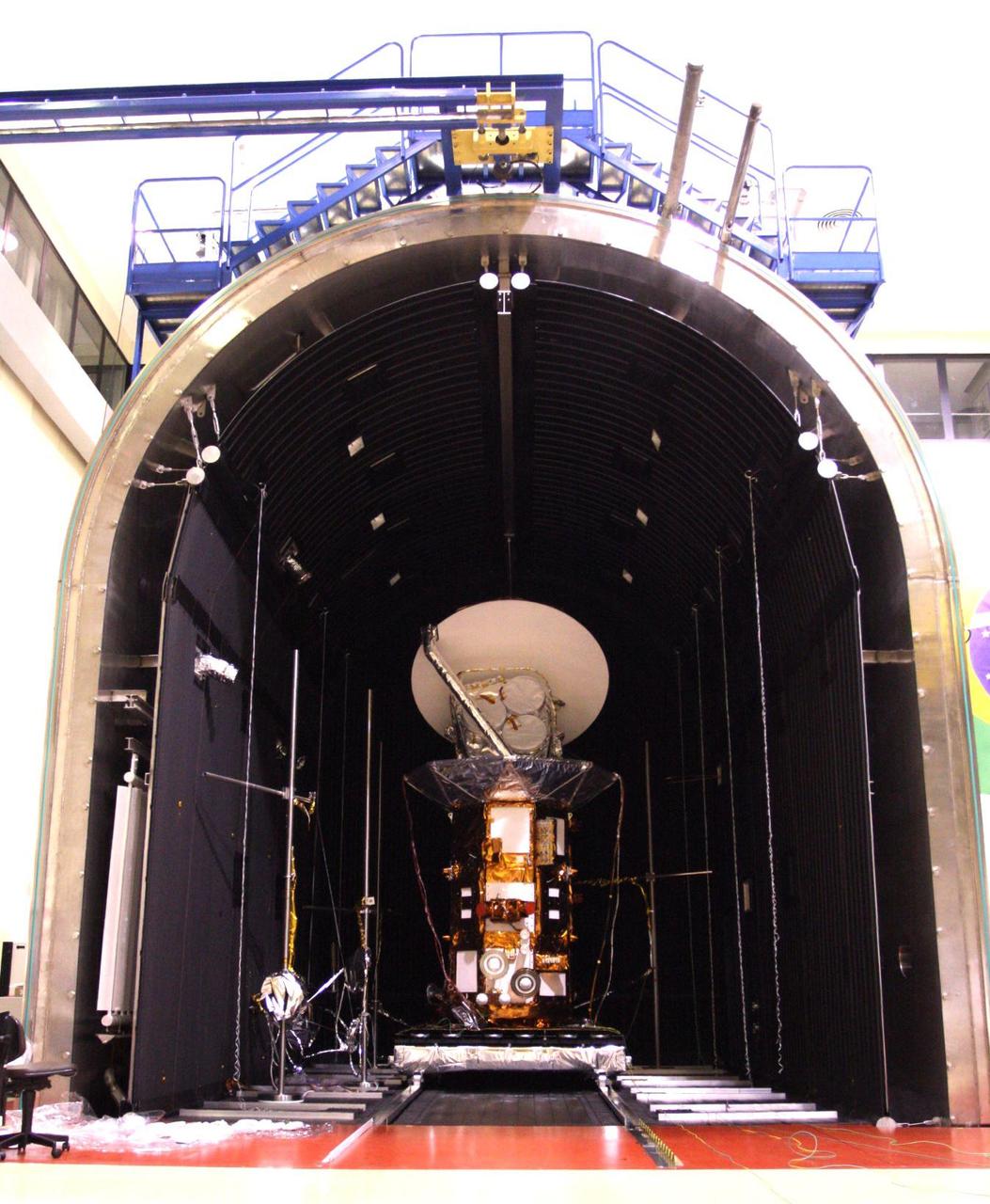

NASA Aquarius/SAC-D observatory is moved into the thermal-vacuum chamber at Brazil National Institute for Space Research.
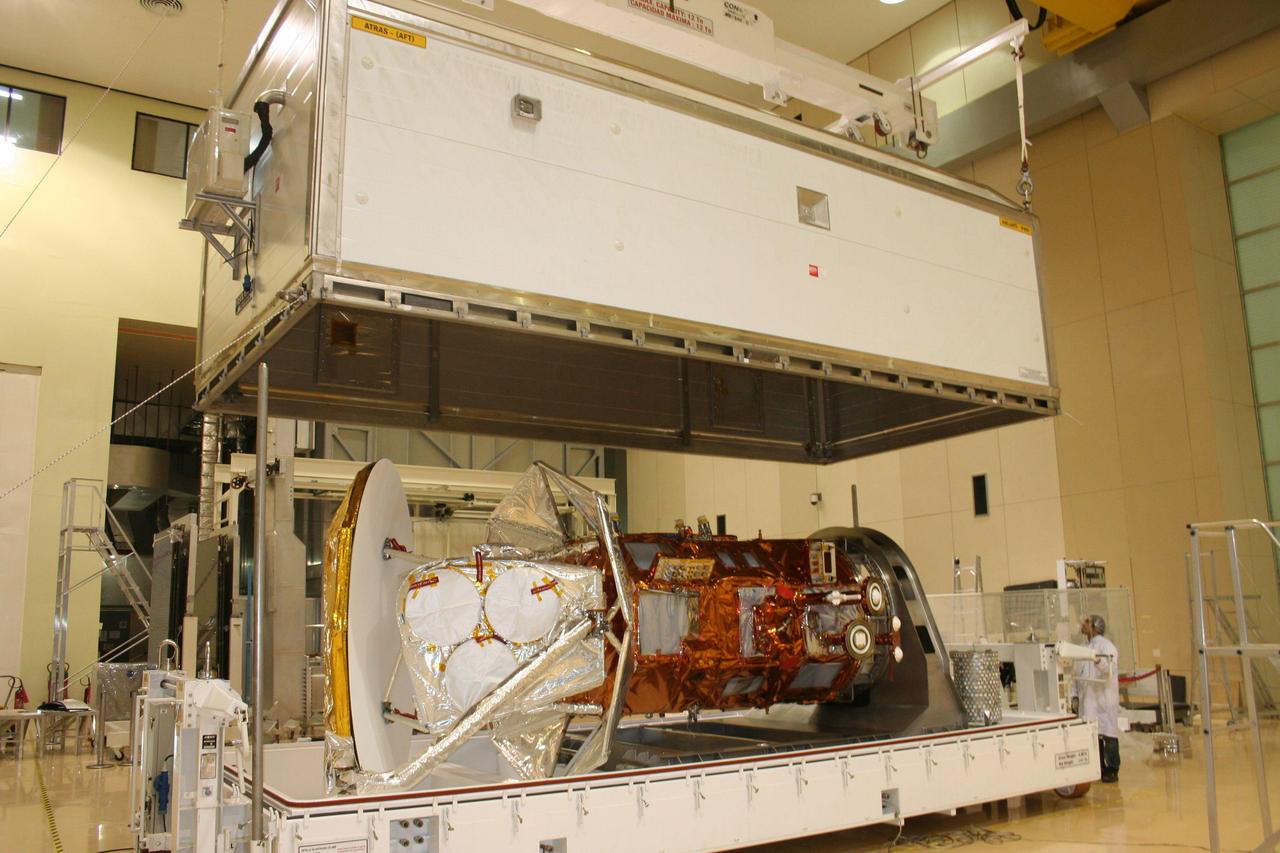

After months of environmental tests at Brazil National Institute for Space Research Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais, INPE, NASA Aquarius/SAC-D observatory is loaded into a crate for shipment to Vandenberg Air Force Base.
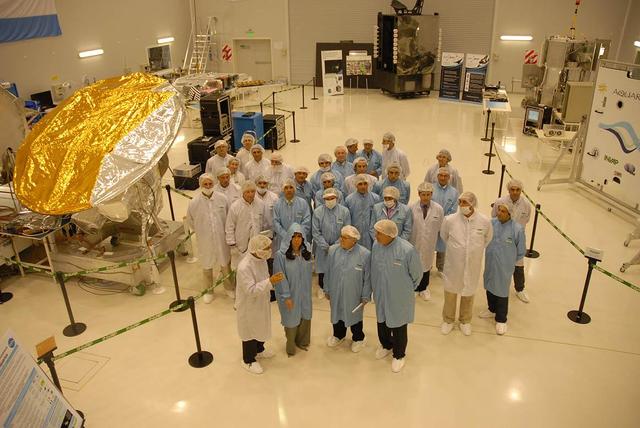

Dr. Cristina Fernández Kirchner, the President of Argentina, visits INVAP for the inauguration of the new facilities including a tour of the high bay where NASA Aquarius/SAC-D satellite is being tested and integrated.
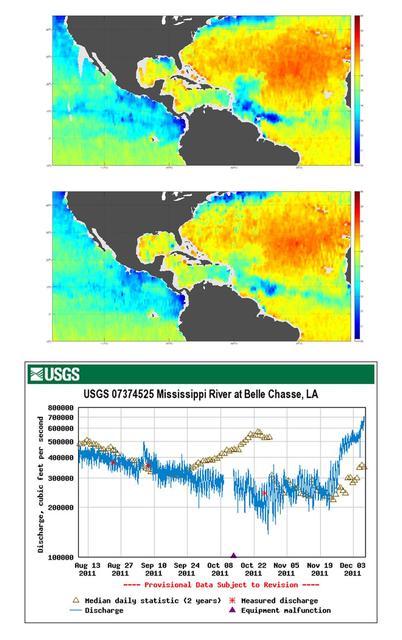
Tropical Storm Lee made landfall over New Orleans on Sept. 2-3, 2011, with predicted rainfall of 15 to 20 inches 38 to 51 centimeters over southern Louisiana. These charts are from NASA Aquarius spacecraft.
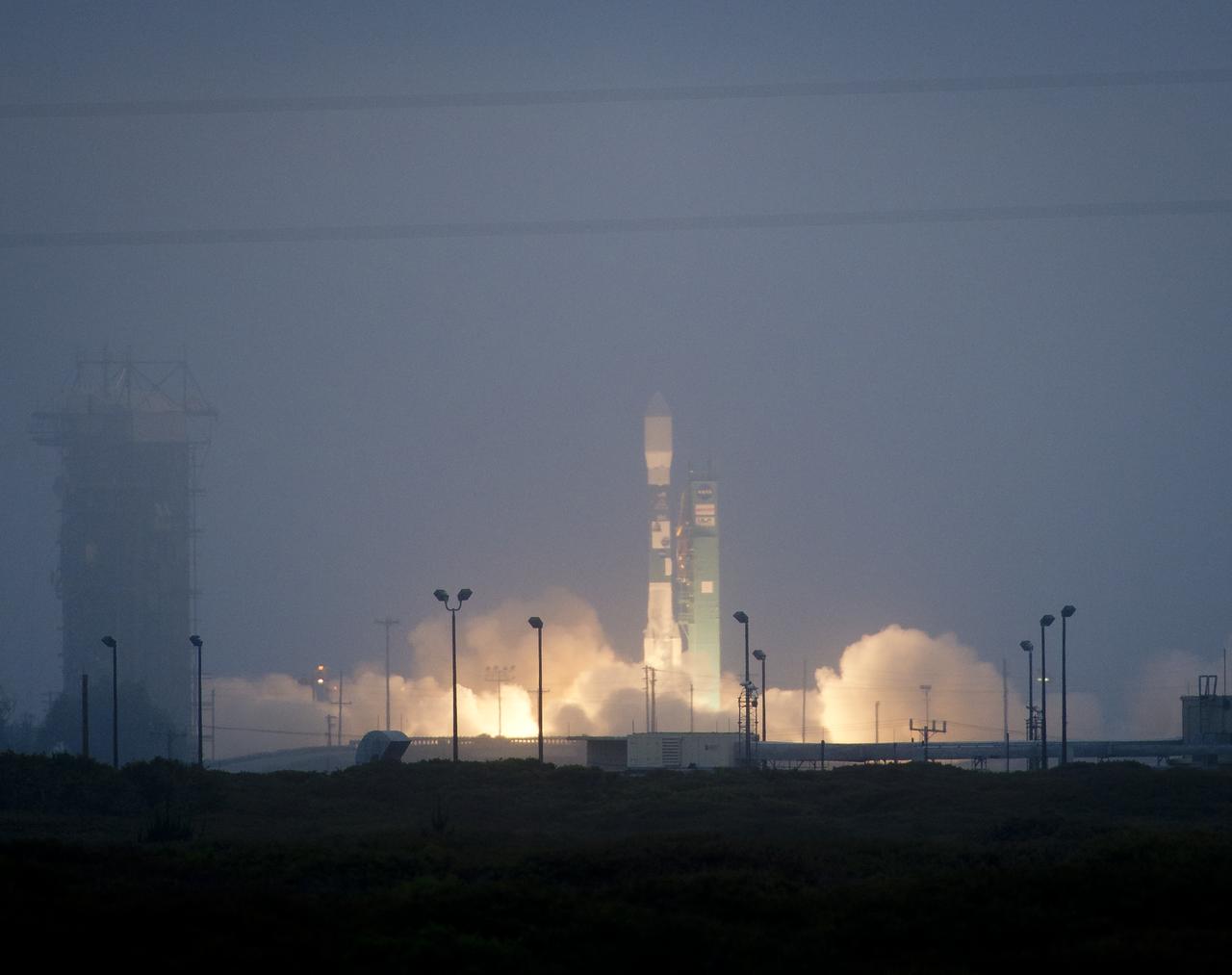

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, set to launch June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
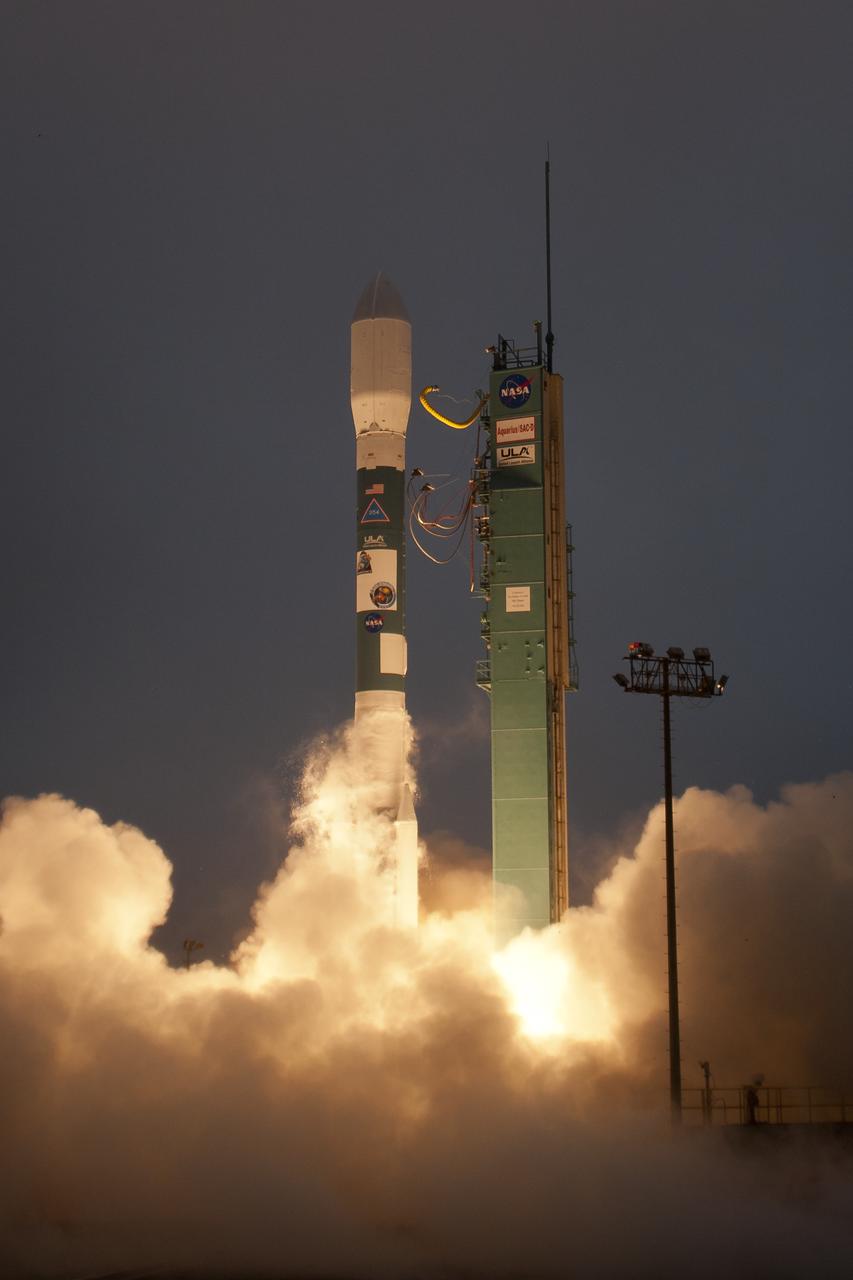

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
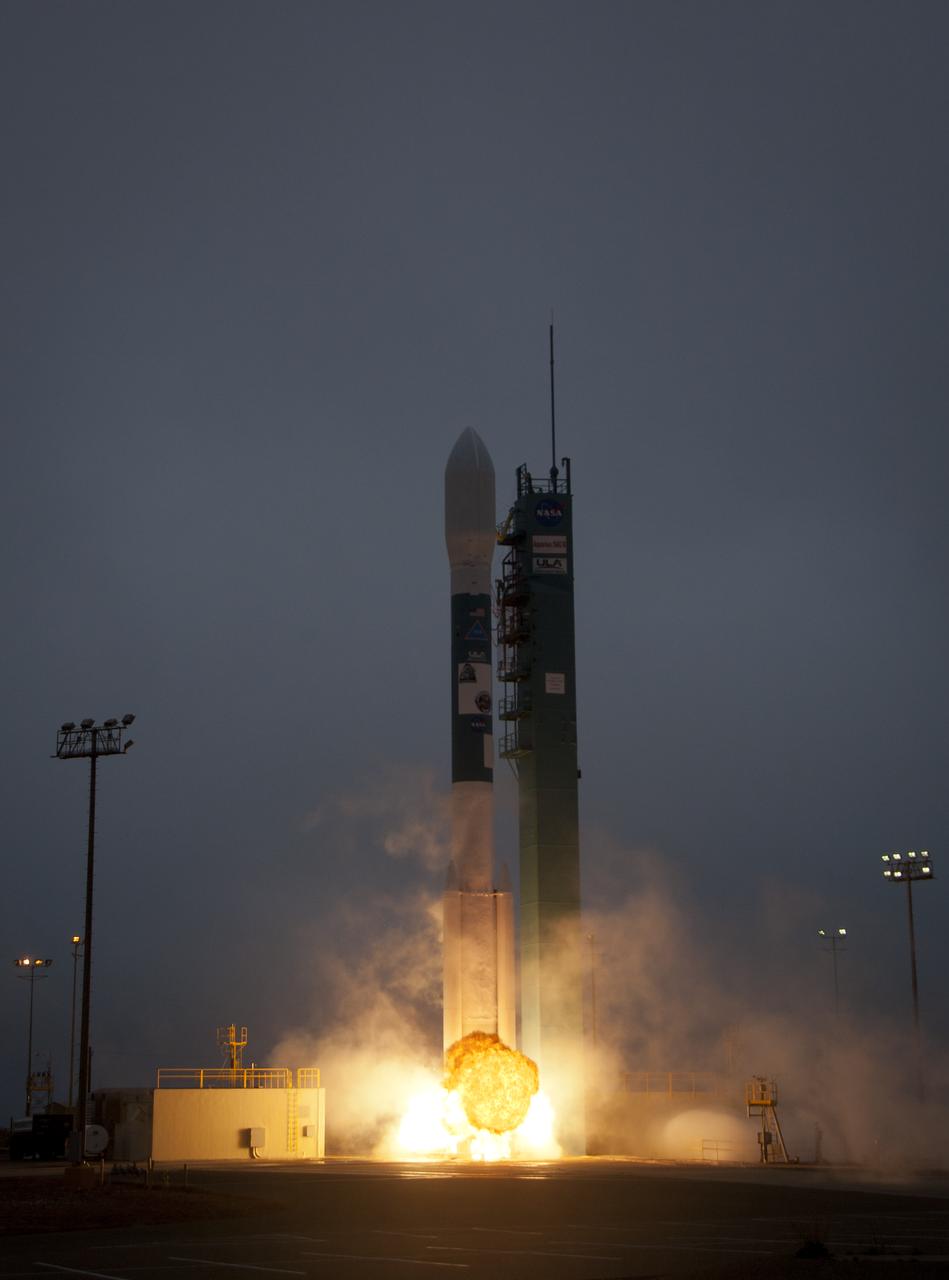

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
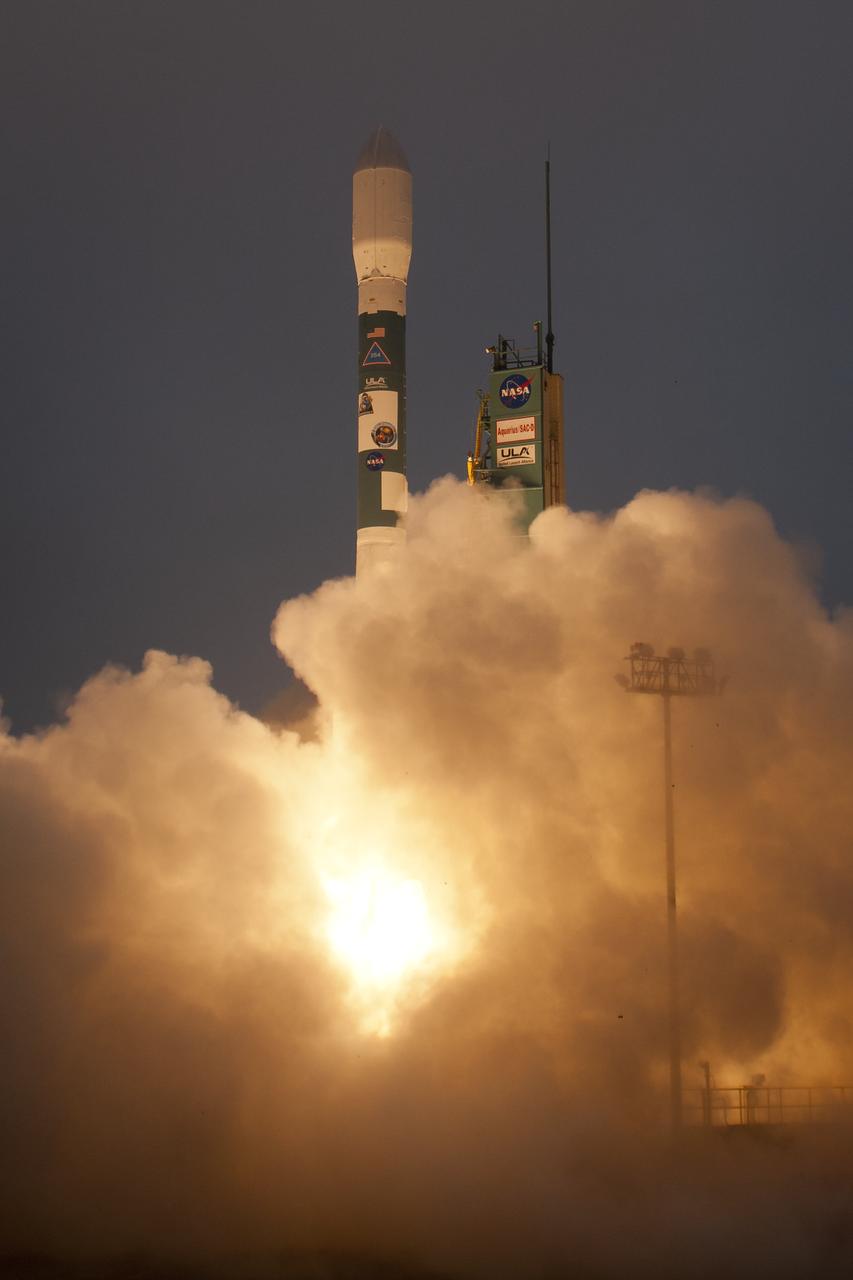

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
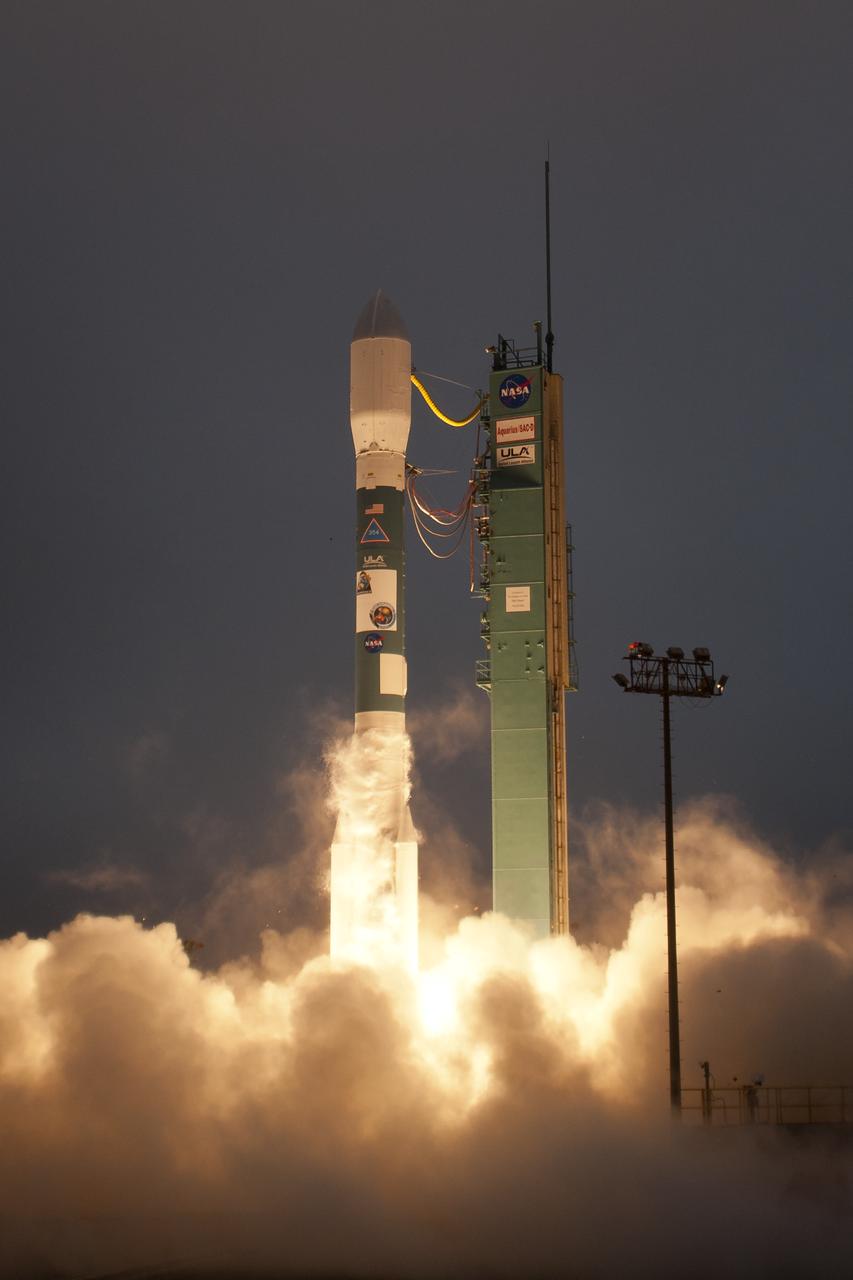

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
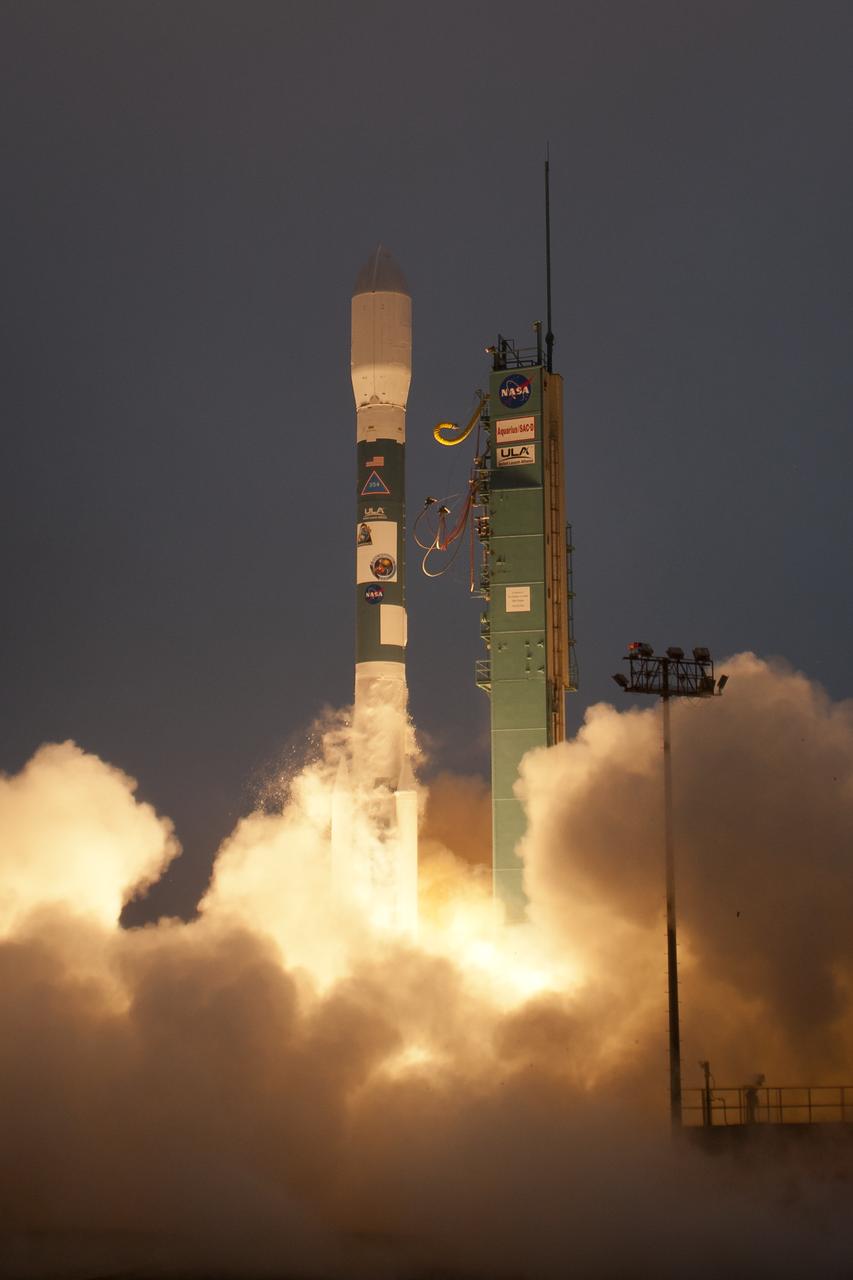

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
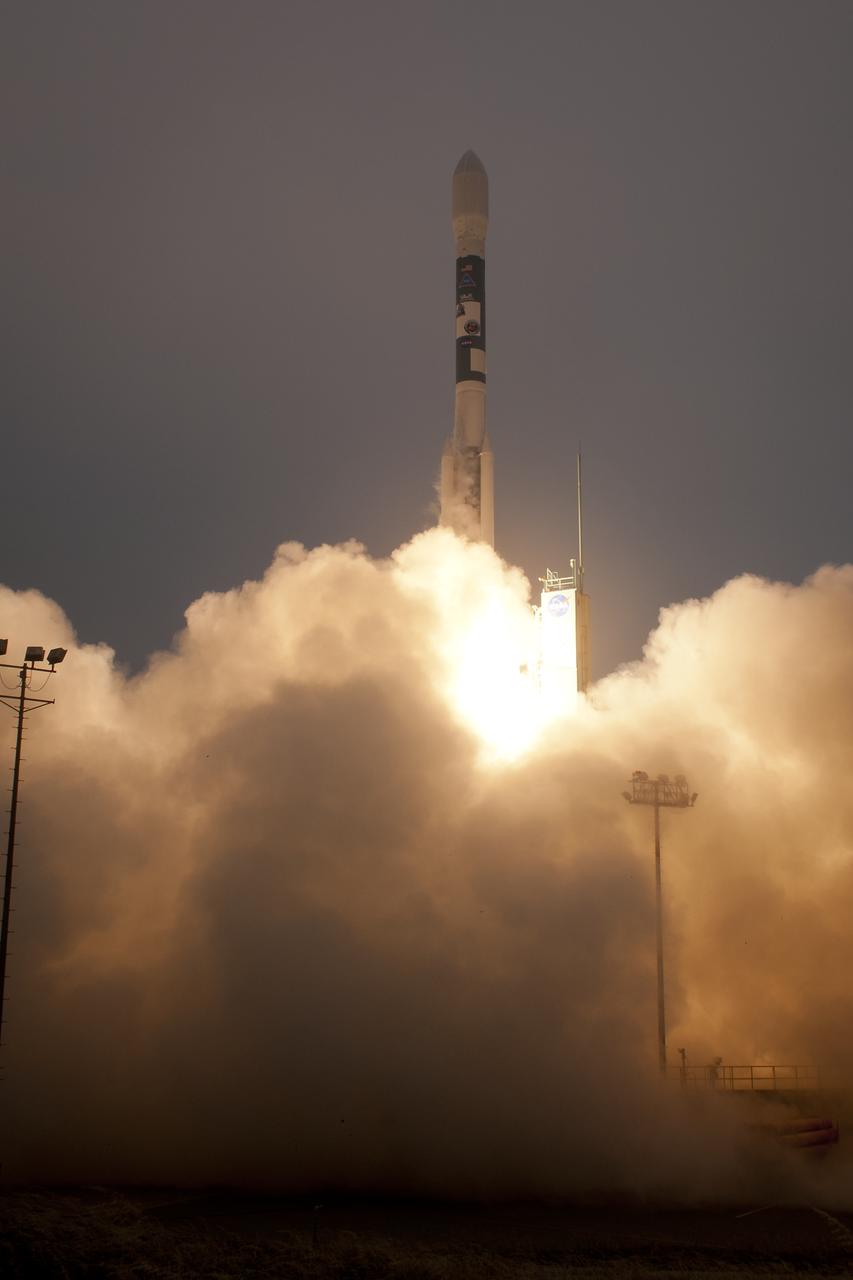

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
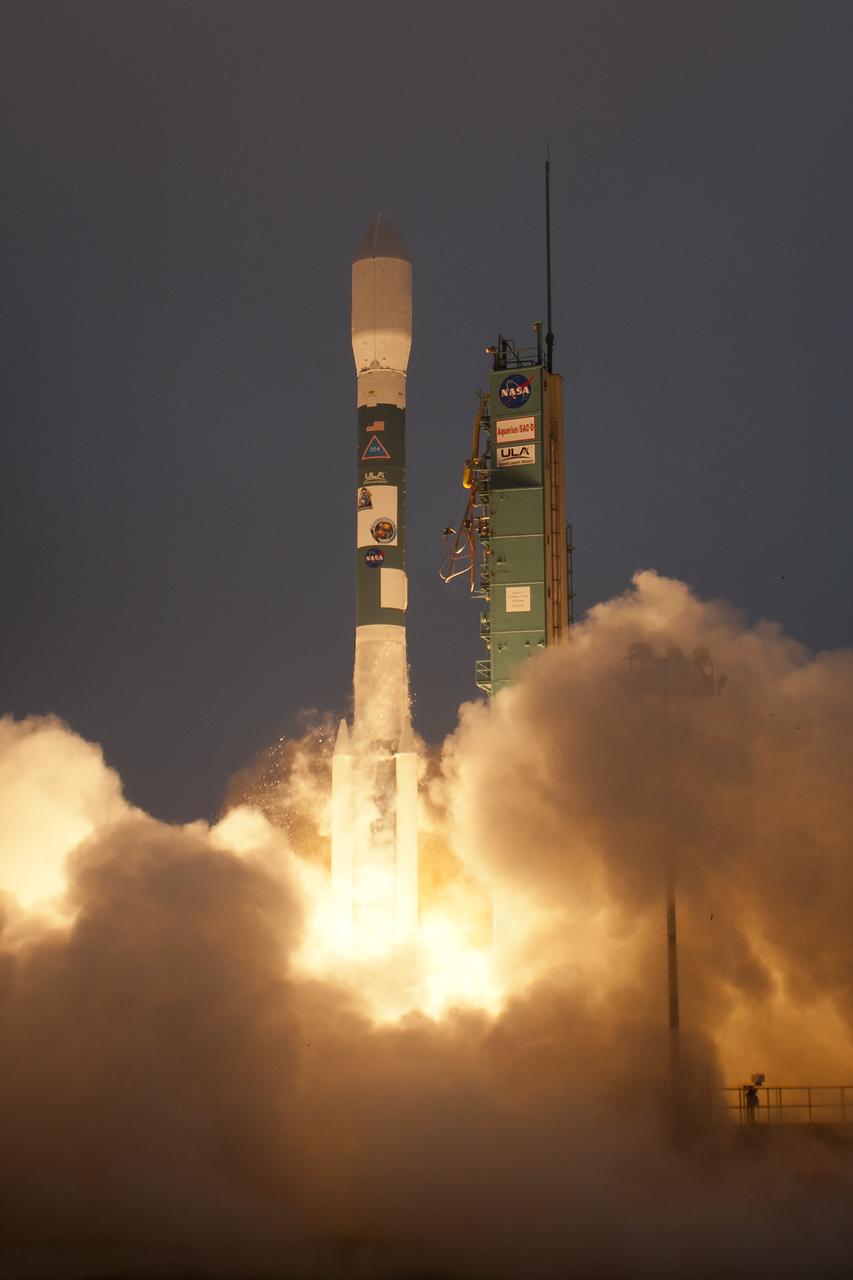

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
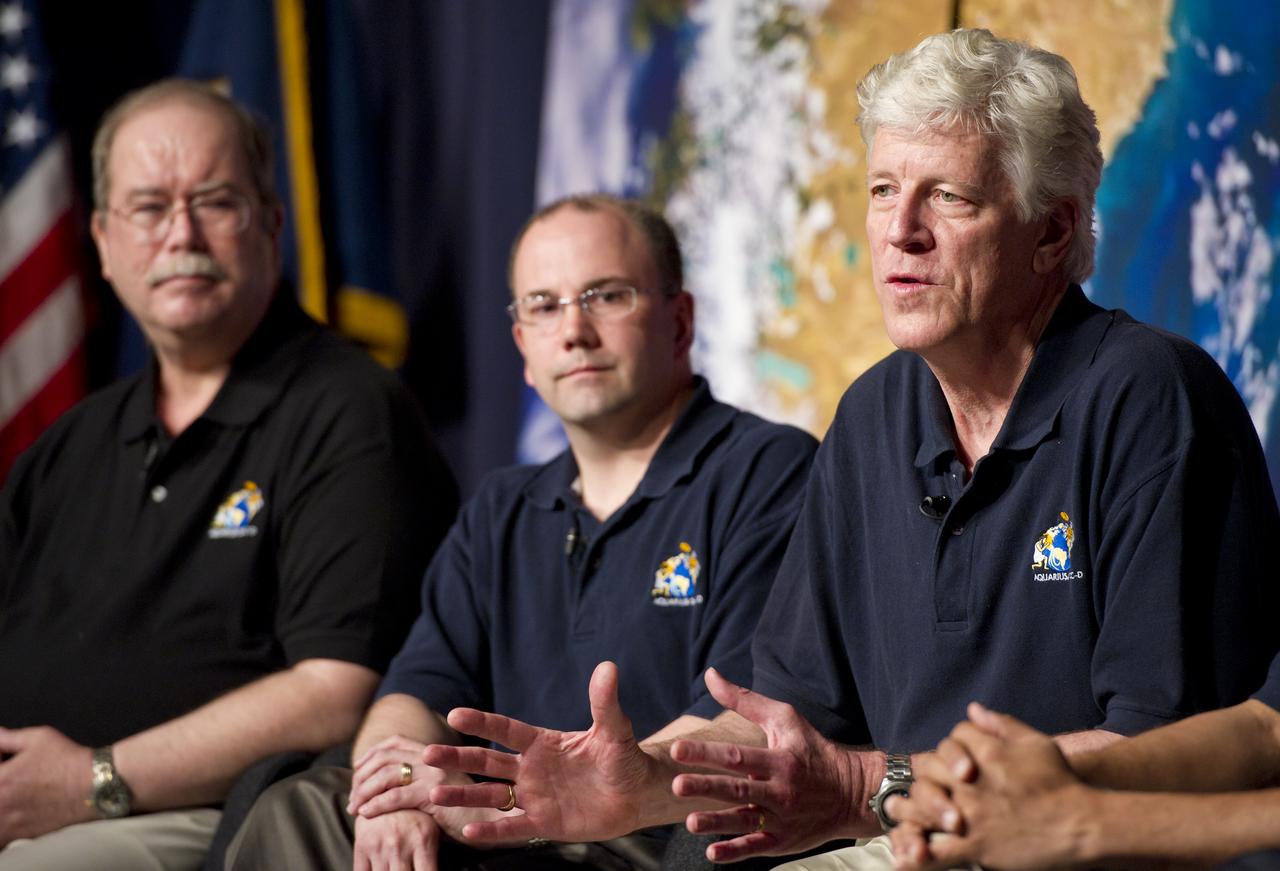

Gary Lagerloef, right, Aquarius Principal Investigator, Earth & Space Research, Seattle, speaks at a press conference on NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D mission to study the salinity of Earth's oceans from space on Tuesday, May 17, 2011 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina's space agency Comision Nacional de Actividades Especiales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. The Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will launch June 9, 2011 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
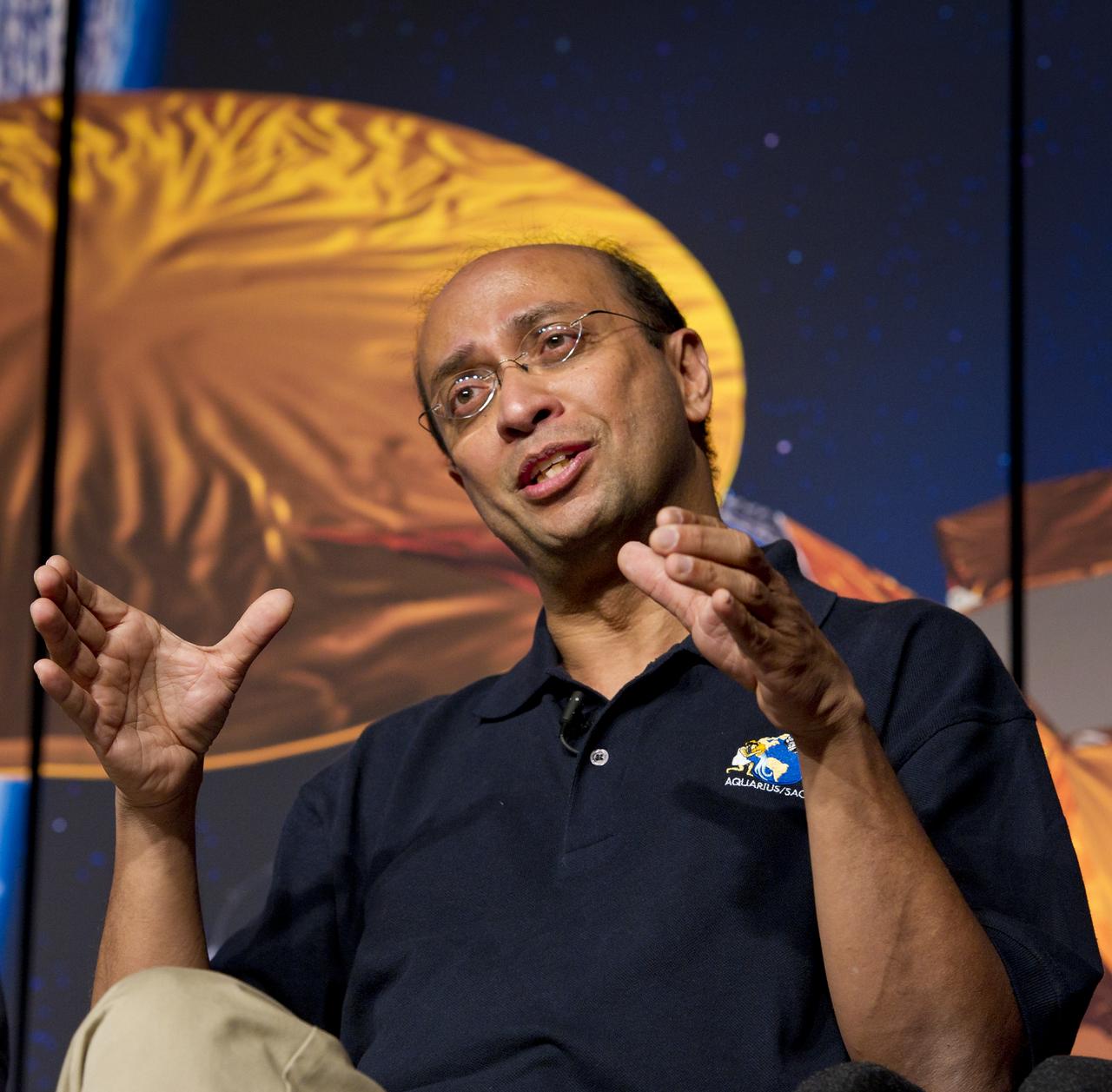

Amit Sen, Aquarius Project Manager, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, speaks at a press conference on NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D mission to study the salinity of Earth's oceans from space on Tuesday, May 17, 2011 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina's space agency Comision Nacional de Actividades Especiales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. The Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will launch June 9, 2011 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
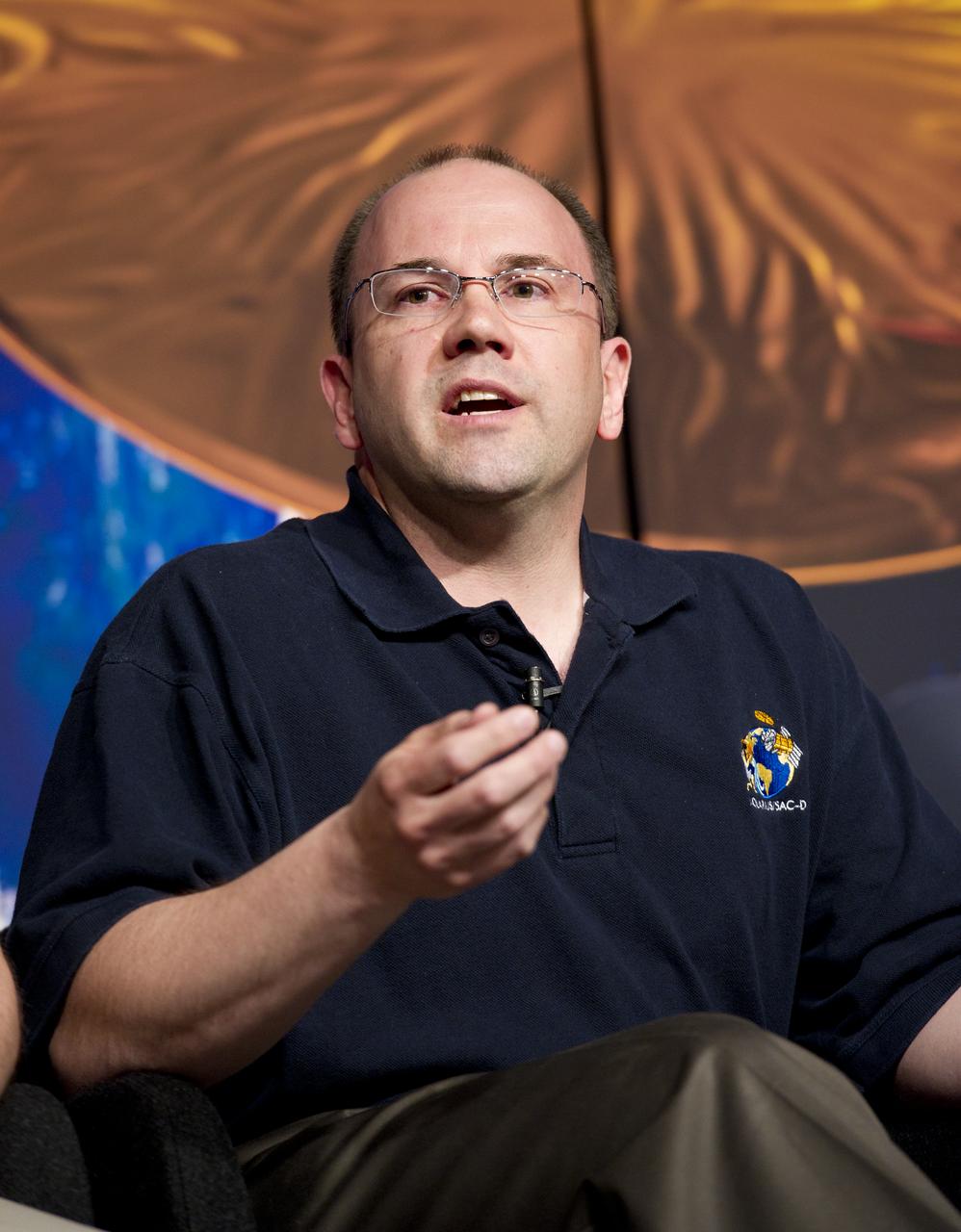

Eric Ianson, Aquarius Program Executive, NASA Headquarters, talks about NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D mission to study the salinity of Earth's oceans from space on Tuesday, May 17, 2011 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina's space agency Comision Nacional de Actividades Especiales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. The Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will launch June 9, 2011 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
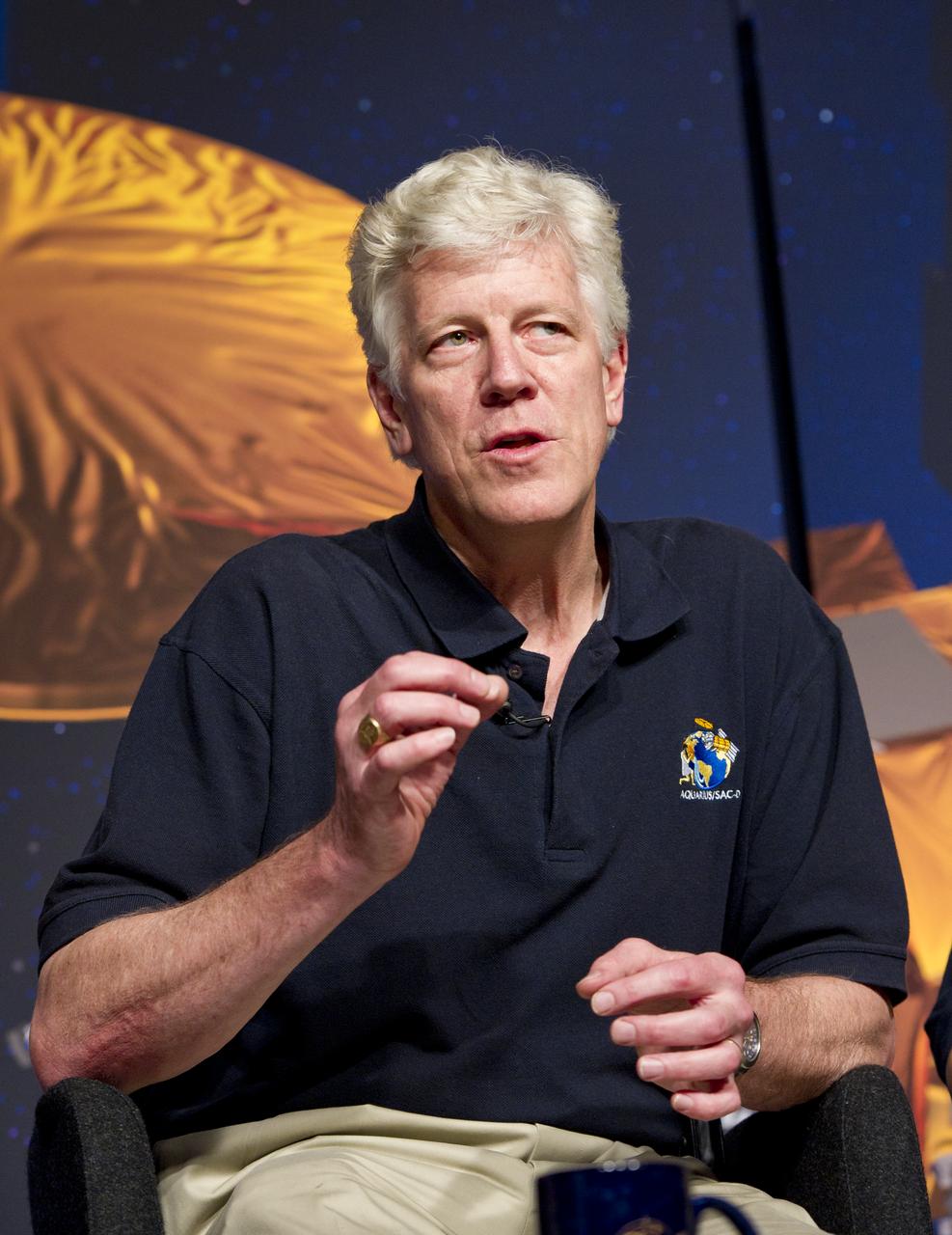

Gary Lagerloef, Aquarius Principal Investigator, Earth & Space Research, Seattle, speaks at a press conference on NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D mission to study the salinity of Earth's oceans from space on Tuesday, May 17, 2011 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina's space agency Comision Nacional de Actividades Especiales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. The Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will launch June 9, 2011 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
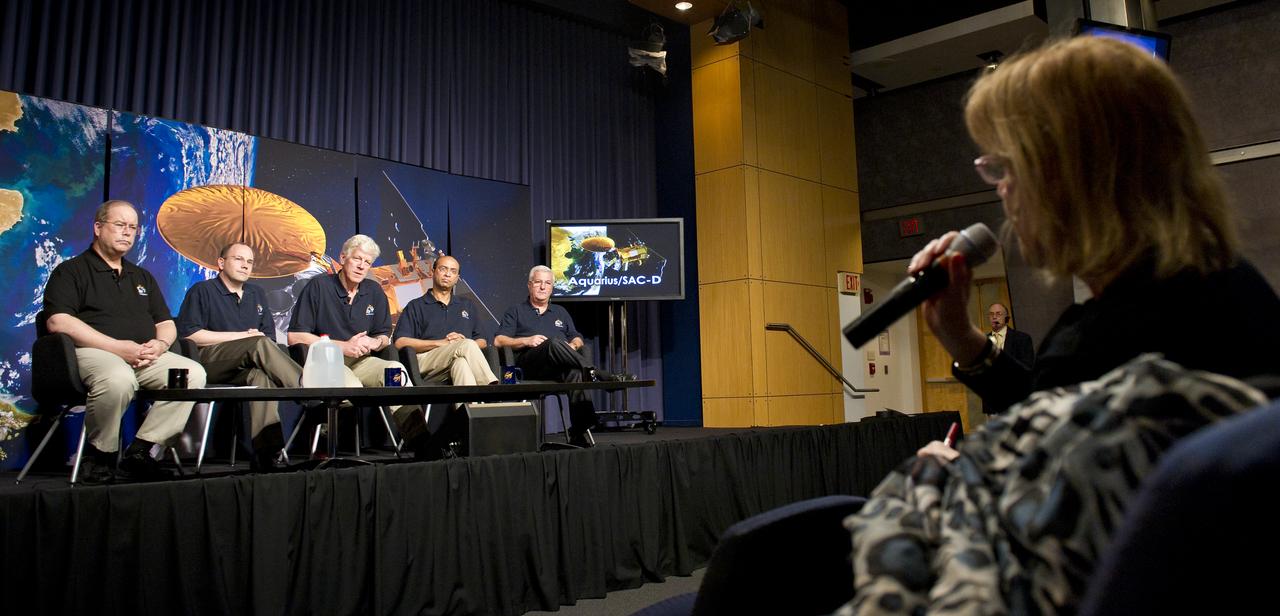

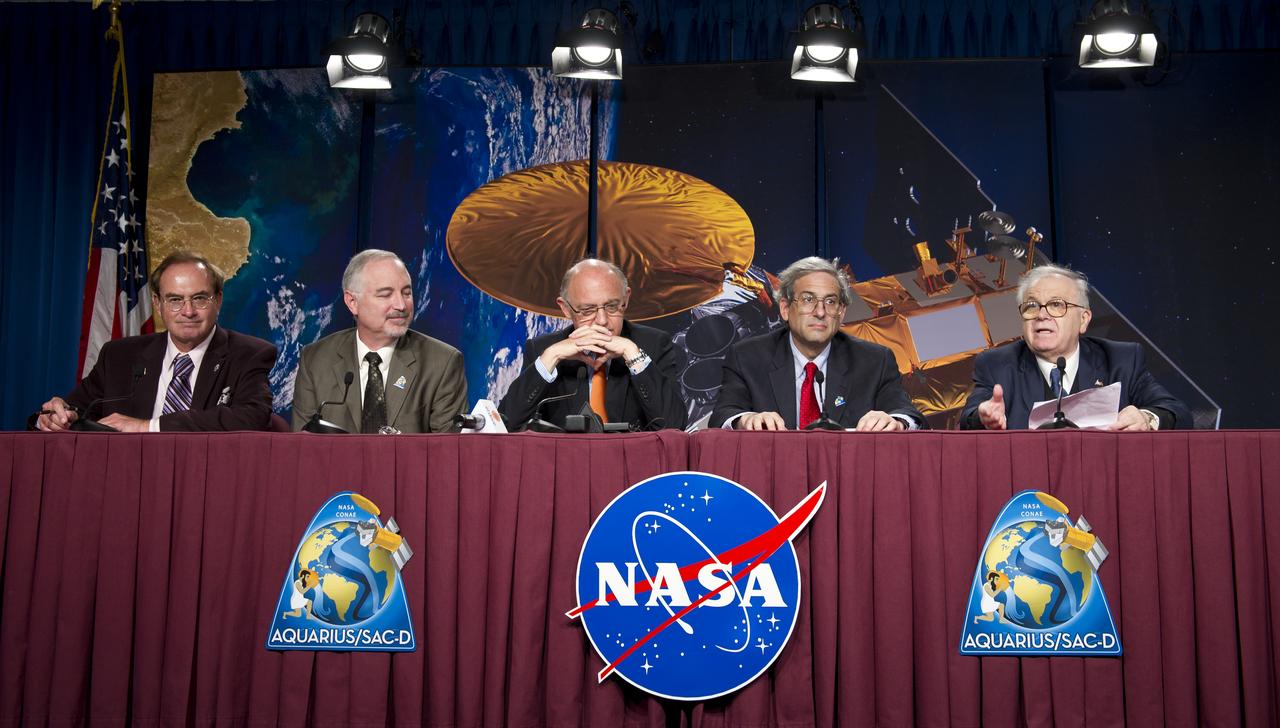
A reporter asks a question to the panel of scientists assembled at the Aquarius/SAC-D press conference on Tuesday, May 17, 2011 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Seated from left are Eric Lindstrom, Aquarius Program Scientist, NASA Headquarters; Eric Ianson, Aquarius Program Executive, NASA Headquarters; Gary Lagerloef, Aquarius Principal Investigator, Earth & Space Research, Seattle; Amit Sen, Aquarius Project Manager, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Daniel Caruso, SAC-D Project Manager, CONAE, Argentina. The mission will study the salinity of the Earth's oceans from space. Aquarius/SAC-D is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina's space agency Comision Nacional de Actividades Especiales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. The Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will launch June 9, 2011 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
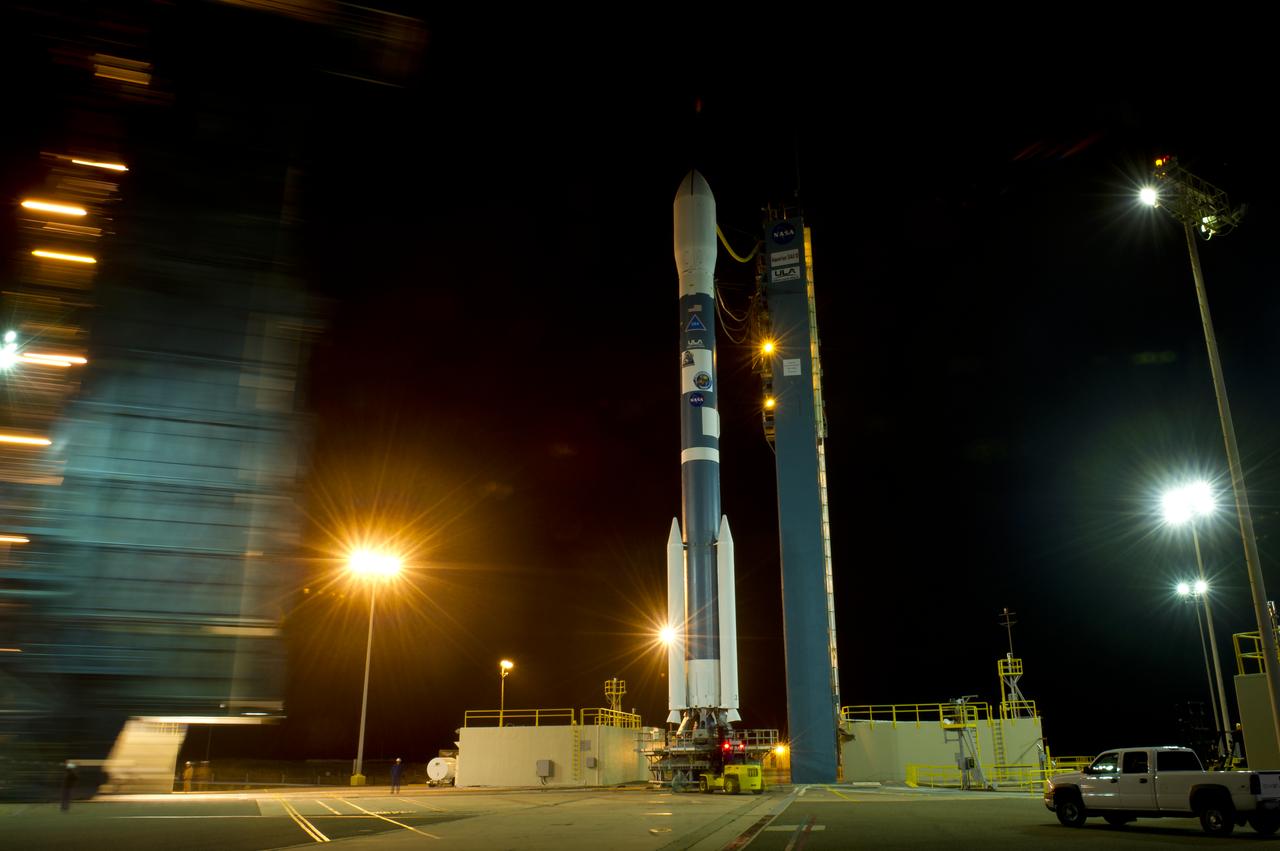

The Delta II rocket with it's Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload is seen as the service structure is rolled back on Thursday, June 9, 2011, at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, set to launch June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
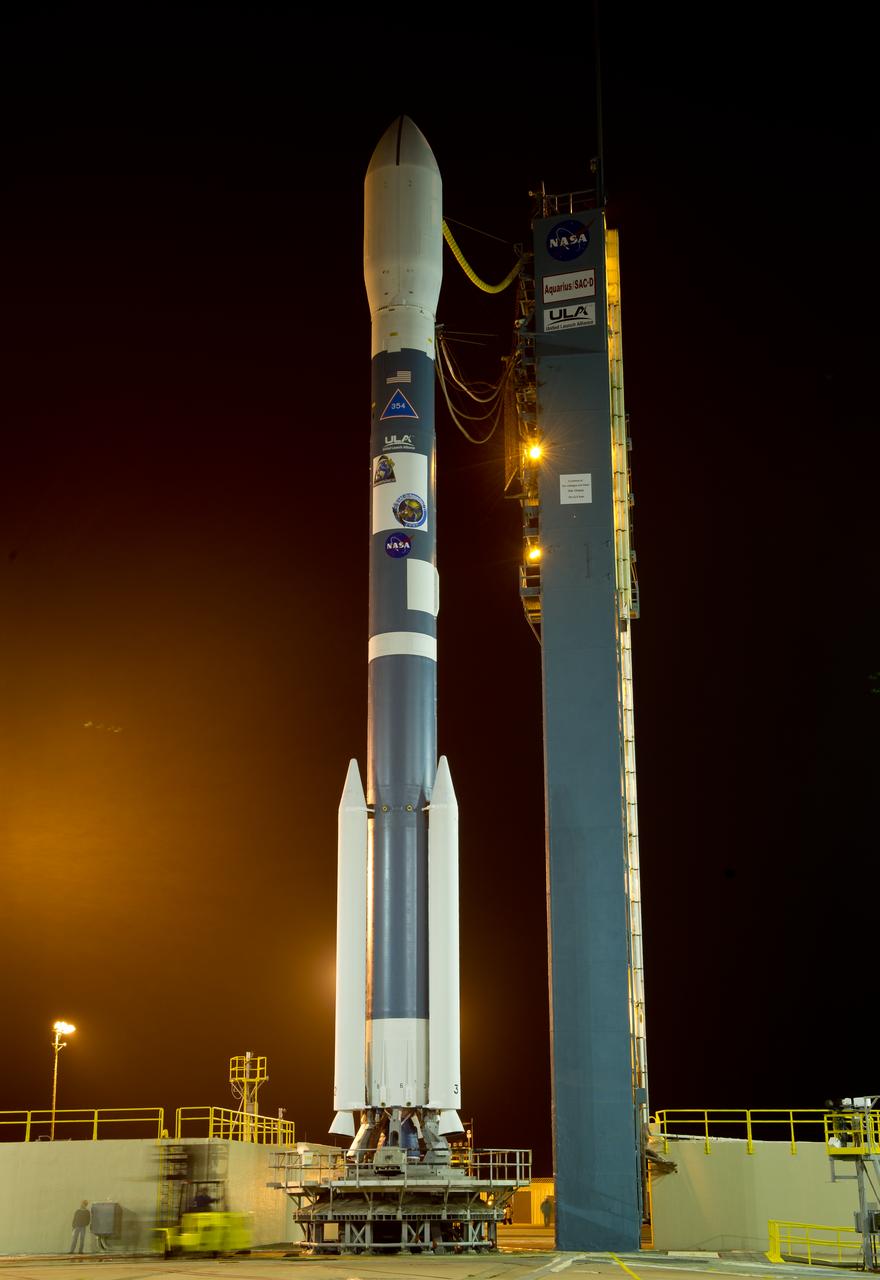

The Delta II rocket with it's Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload is seen shortly after the service structure is rolled back on Thursday, June 9, 2011, at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, set to launch June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Completion of the thermal blanket patterns for the Aquarius bipod after routing the flight harness from the SAC-D service platform.

Gary Lagerloef, left, Aquarius Principal Investigator, Earth & Space Research, Seattle, speaks at a press conference on NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D mission to study the salinity of Earth's oceans from space on Tuesday, May 17, 2011 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina's space agency Comision Nacional de Actividades Especiales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. The Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will launch June 9, 2011 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
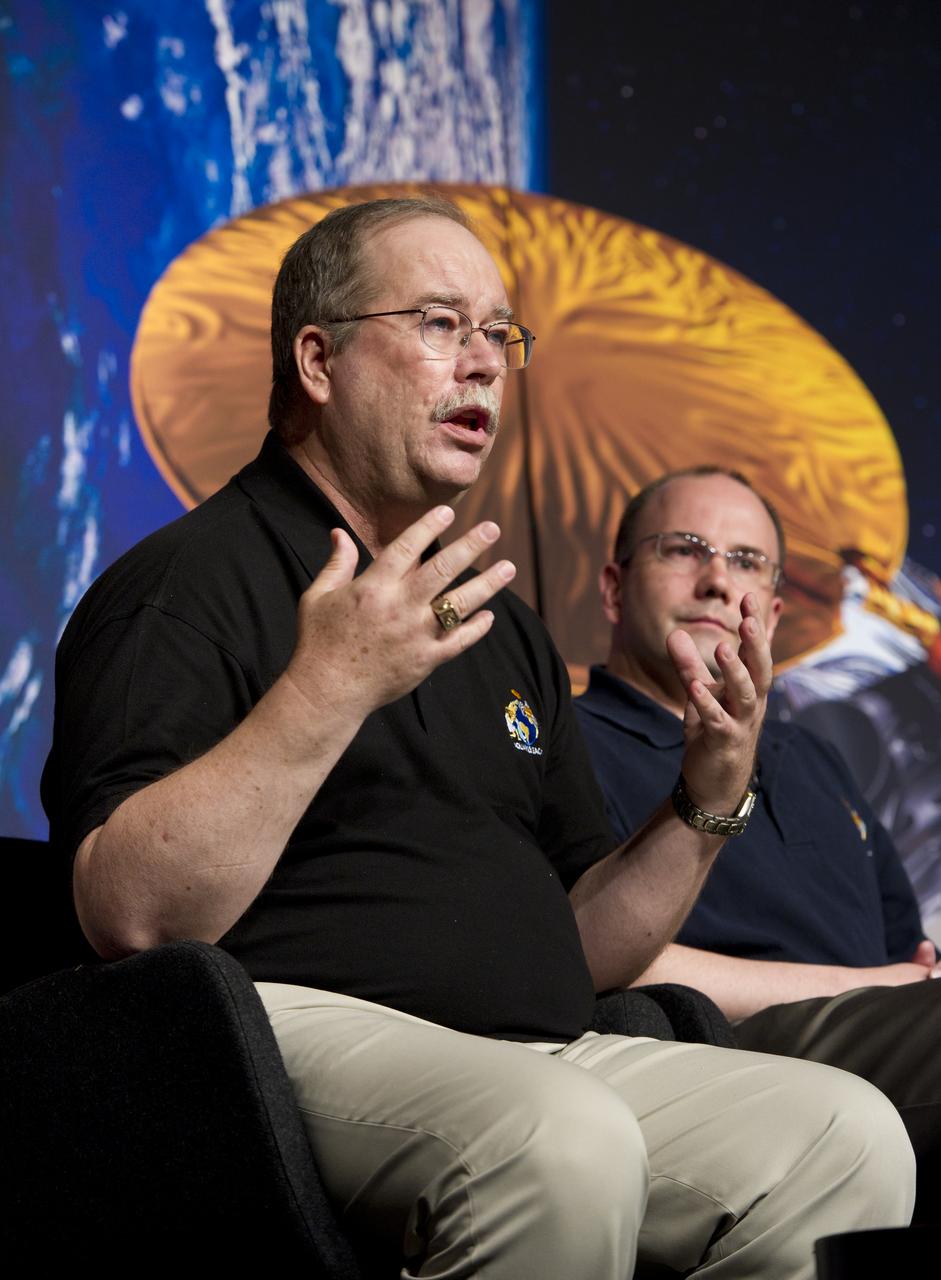

Eric Lindstrom, left, Aquarius Program Scientist, NASA Headquarters, talks about NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D mission to study the salinity of Earth's oceans from space on Tuesday, May 17, 2011 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina's space agency Comision Nacional de Actividades Especiales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. The Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will launch June 9, 2011 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
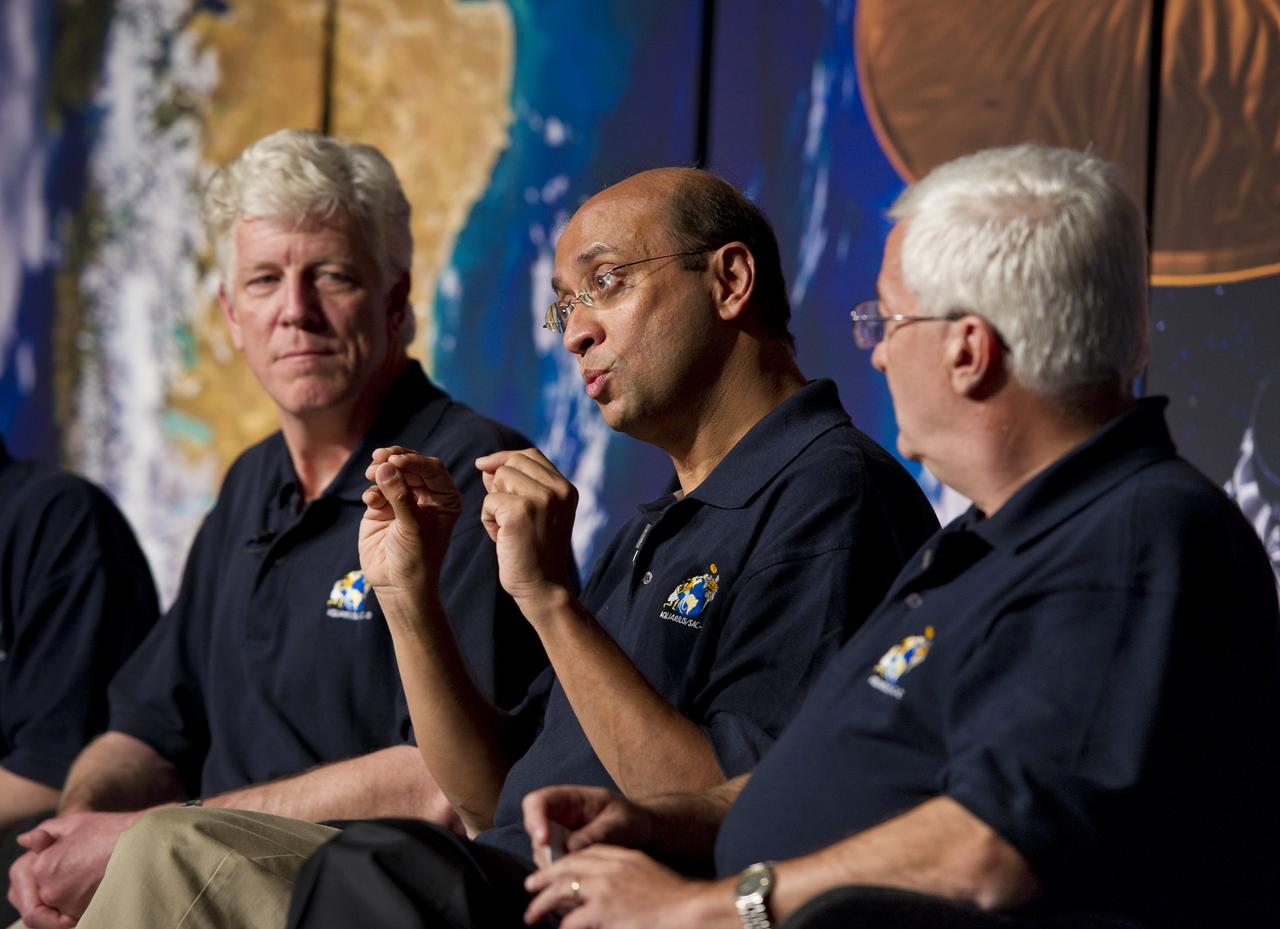

Amit Sen, center, Aquarius Project Manager, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, speaks at a press conference on NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D mission to study the salinity of Earth's oceans from space on Tuesday, May 17, 2011 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina's space agency Comision Nacional de Actividades Especiales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. The Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will launch June 9, 2011 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
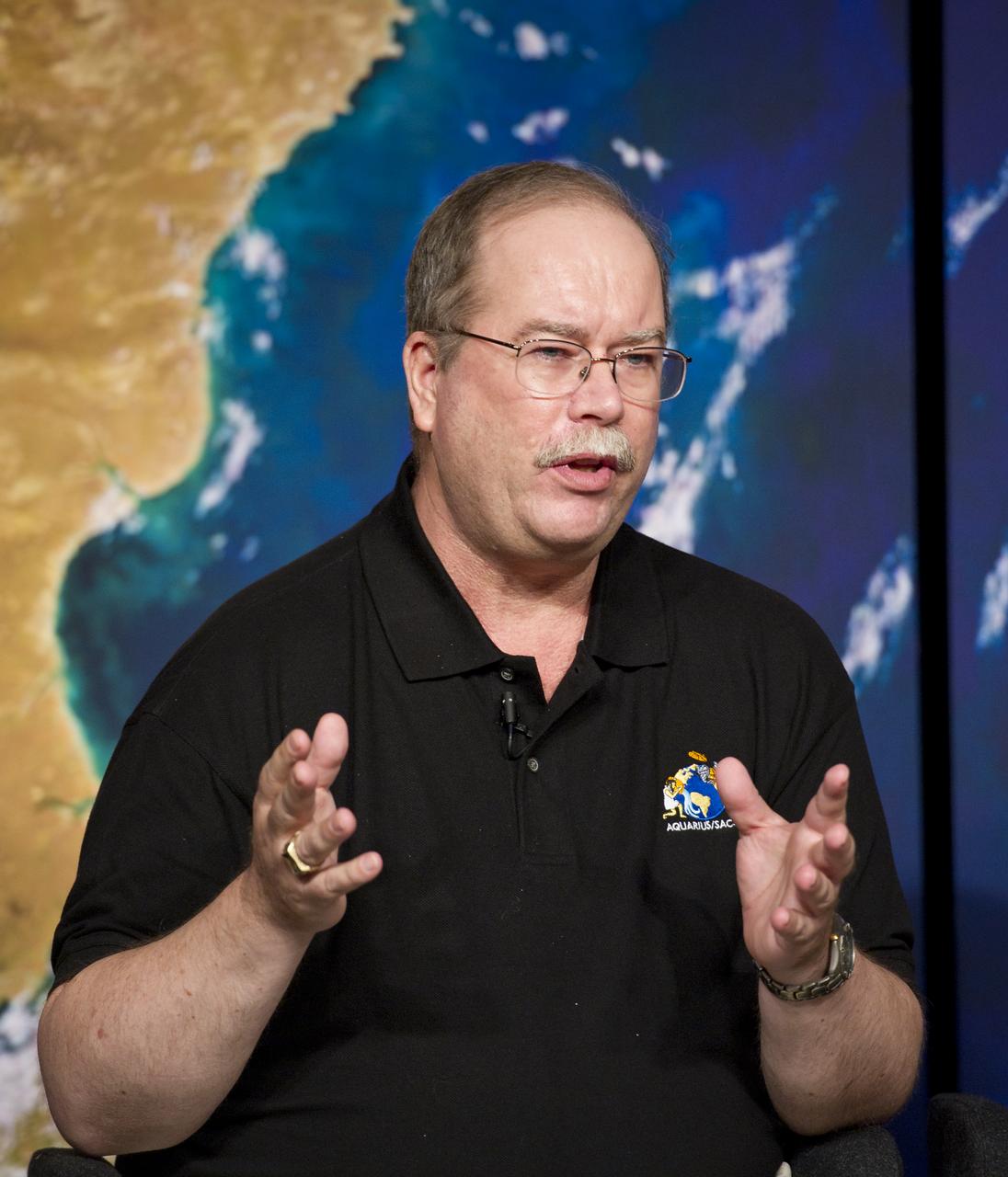

Eric Lindstrom, left, Aquarius Program Scientist, NASA Headquarters, talks about NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D mission to study the salinity of Earth's oceans from space on Tuesday, May 17, 2011 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina's space agency Comision Nacional de Actividades Especiales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. The Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will launch June 9, 2011 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
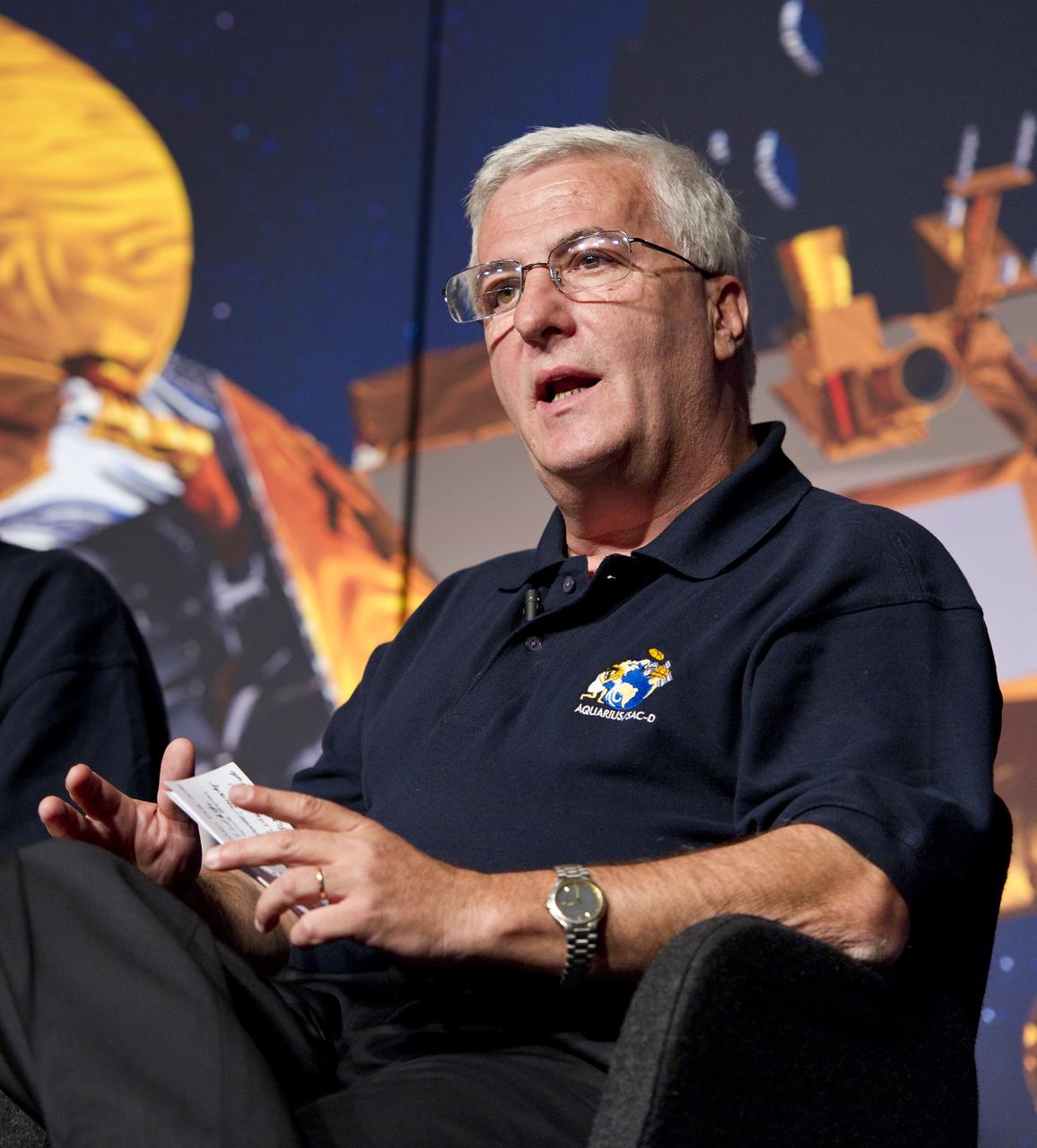

Daniel Caruso, SAC-D Project Manager, CONAE, Argentina, speaks at a press conference on NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D mission to study the salinity of Earth's oceans from space on Tuesday, May 17, 2011 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina's space agency Comision Nacional de Actividades Especiales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. The Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will launch June 9, 2011 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
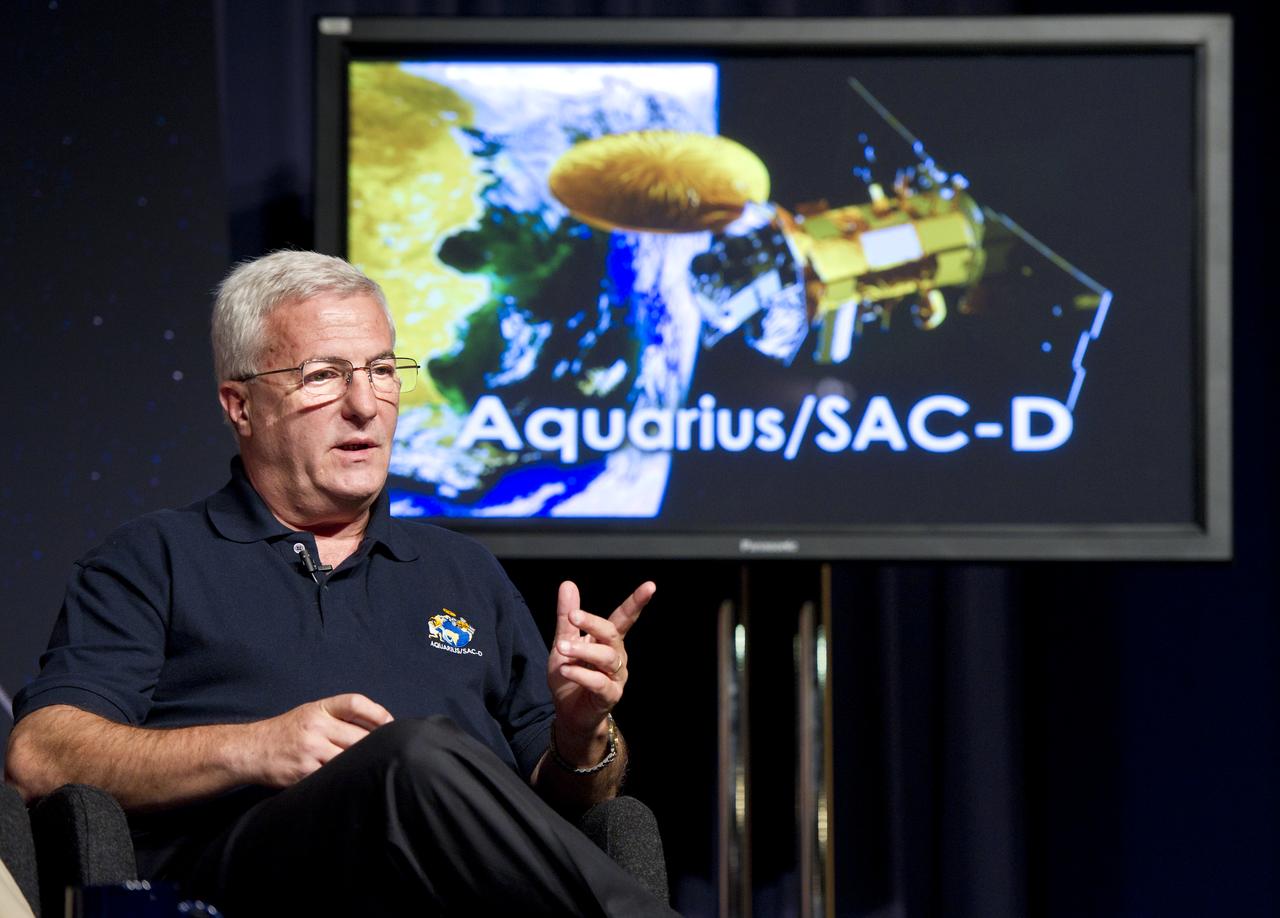

Daniel Caruso, SAC-D Project Manager, CONAE, Argentina, speaks at a press conference on NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D mission to study the salinity of Earth's oceans from space on Tuesday, May 17, 2011 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina's space agency Comision Nacional de Actividades Especiales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. The Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will launch June 9, 2011 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
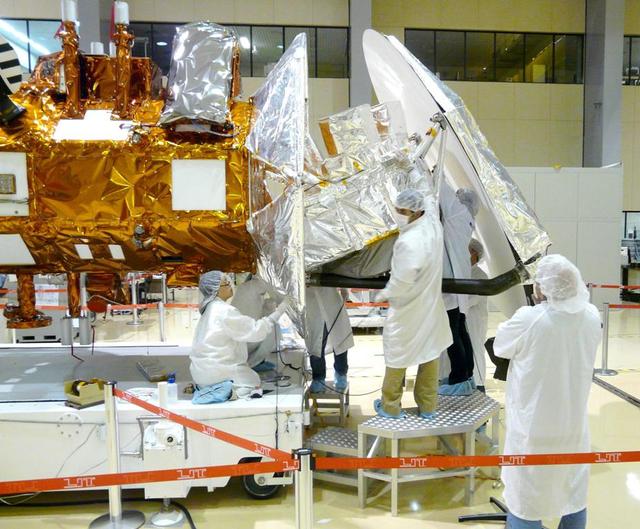

Technicians from NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., install thermal blankets on the Aquarius instrument at Brazil National Institute for Space Research.
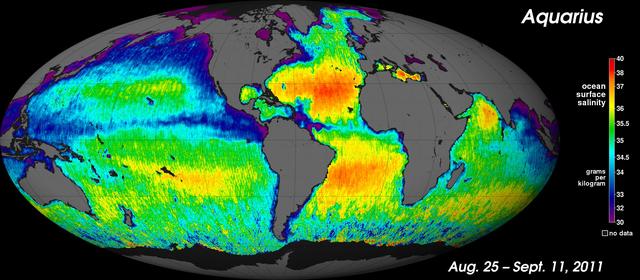
NASA Aquarius instrument has produced its first global map of the salinity, or saltiness, of Earth ocean surface, providing an early glimpse of the mission anticipated discoveries.
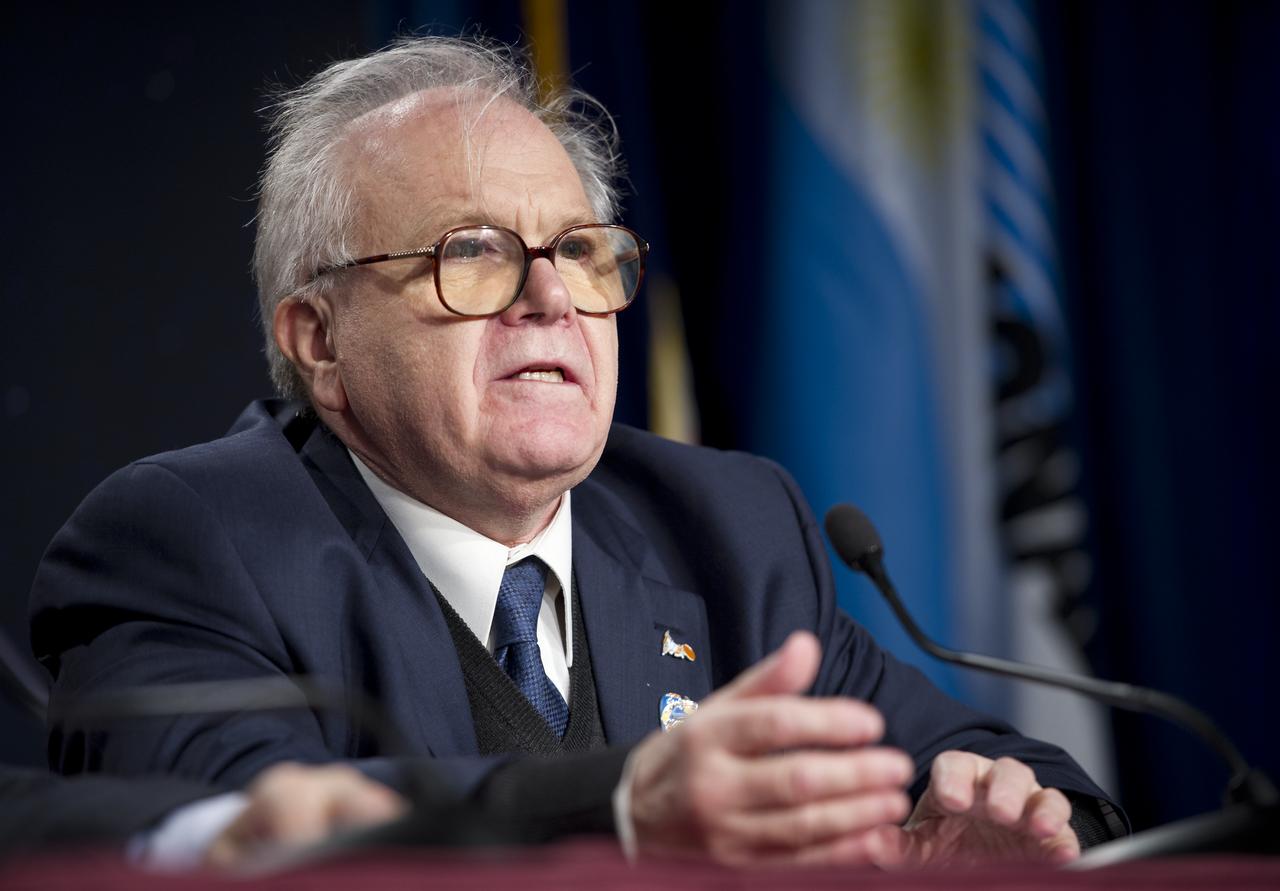

Conrado Varotto, CONAE Executive and Technical Director, Buenos Aires, talks during the Aquarius/SAC-D post-launch press conference on Friday, June 10, 2011 at the NASA Resident Office, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, launched earlier on Friday June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
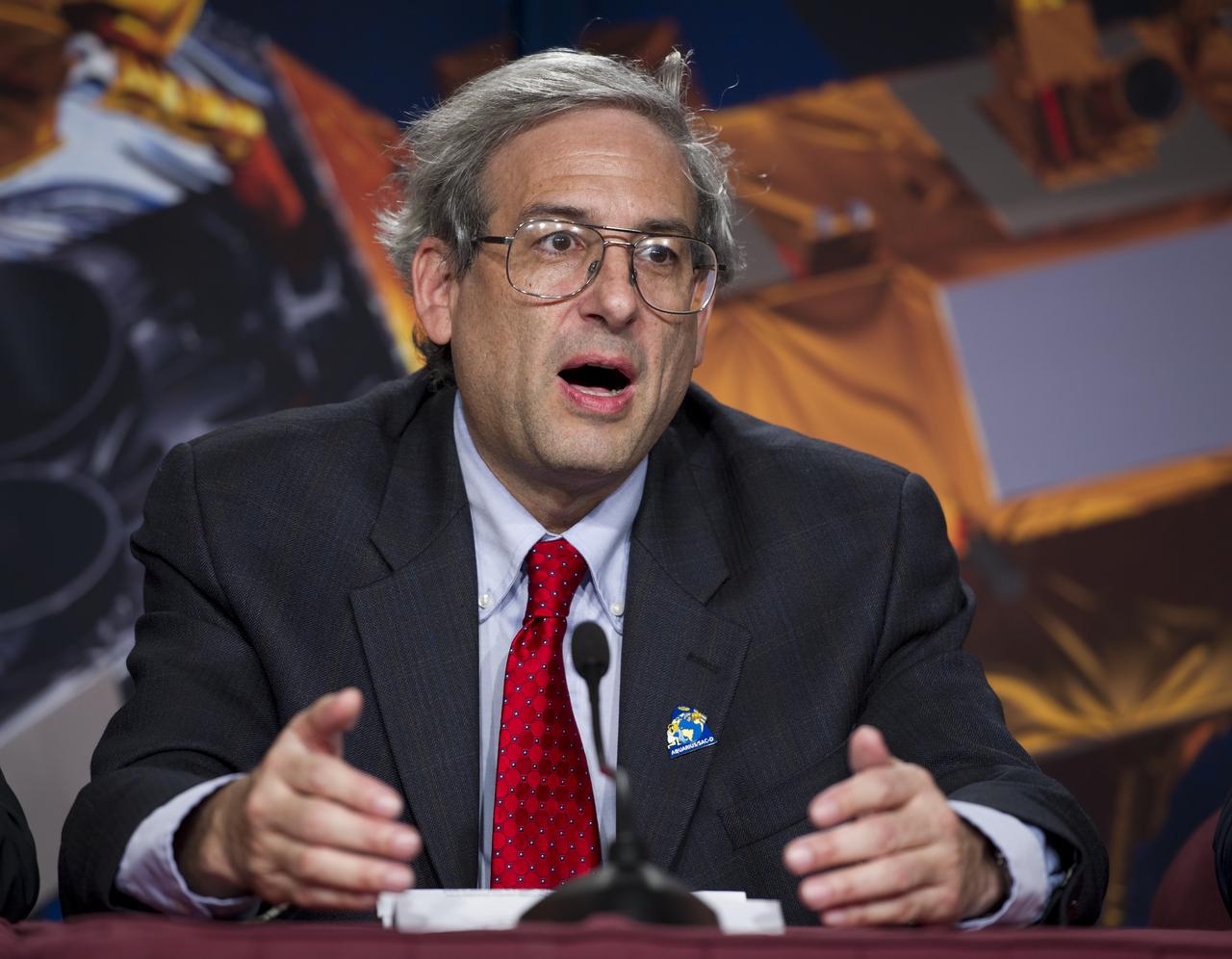

Michael Freilich, NASA Earth Science Division Director, NASA Headquarters, talks during the Aquarius/SAC-D post-launch press conference on Friday, June 10, 2011 at the NASA Resident Office, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, launched earlier on Friday June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
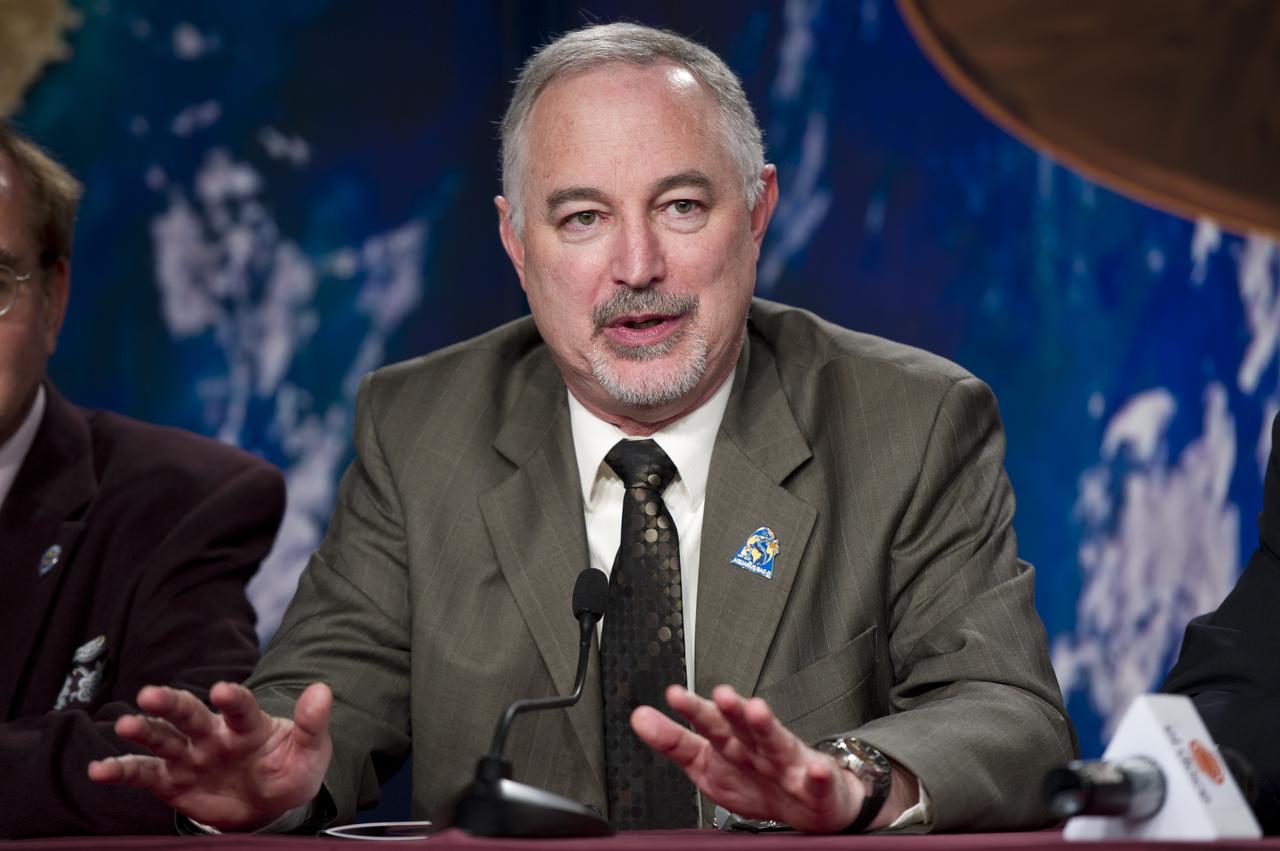

Charles Gay, Deputy Associate Administrator, NASA Science Mission Directorate, talks during the Aquarius/SAC-D post-launch press conference on Friday, June 10, 2011 at the NASA Resident Office, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, launched earlier on Friday June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Michael Freilich, NASA Earth Science Division Director, NASA Headquarters, talks during the Aquarius/SAC-D post-launch press conference on Friday, June 10, 2011 at the NASA Resident Office, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, launched earlier on Friday June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
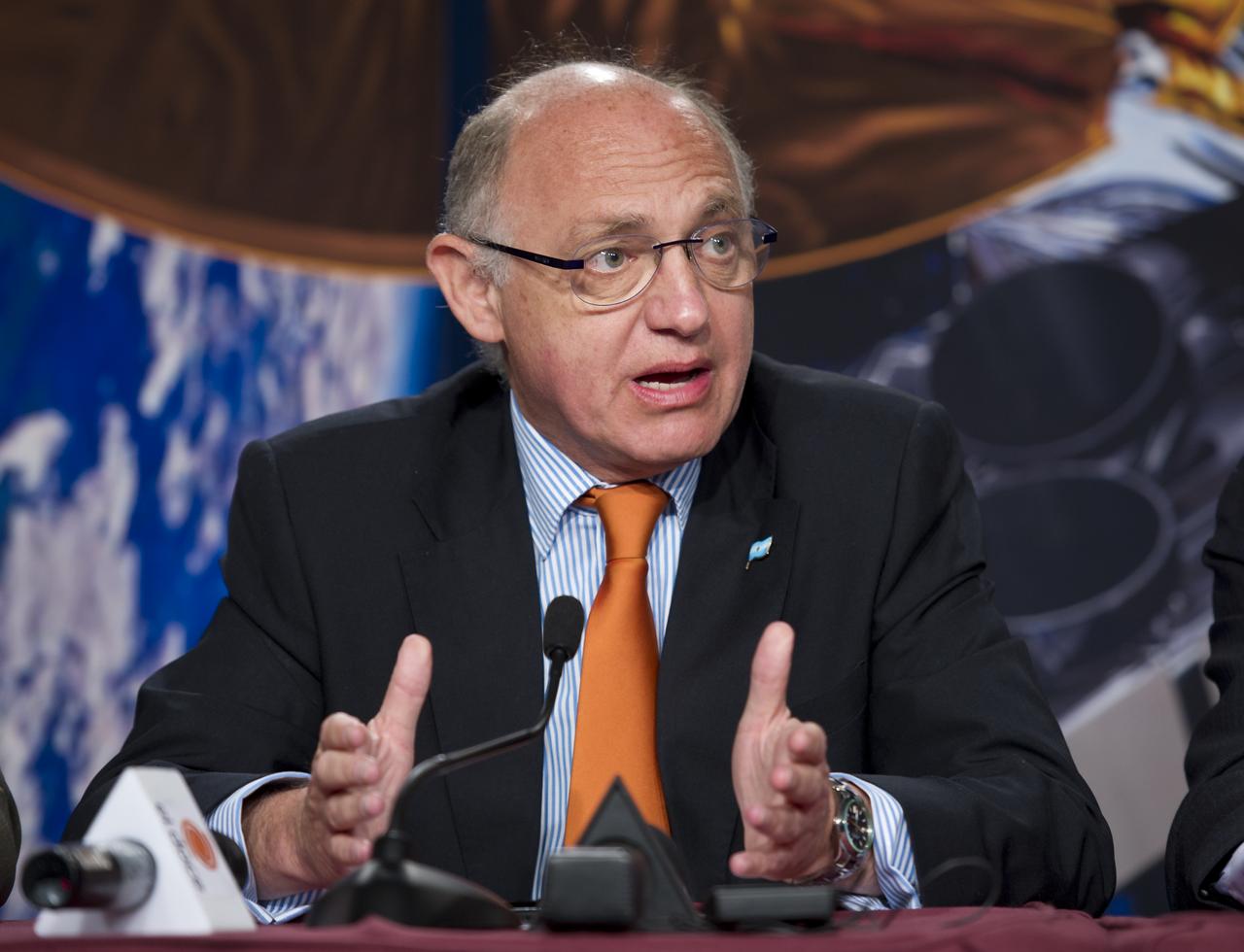

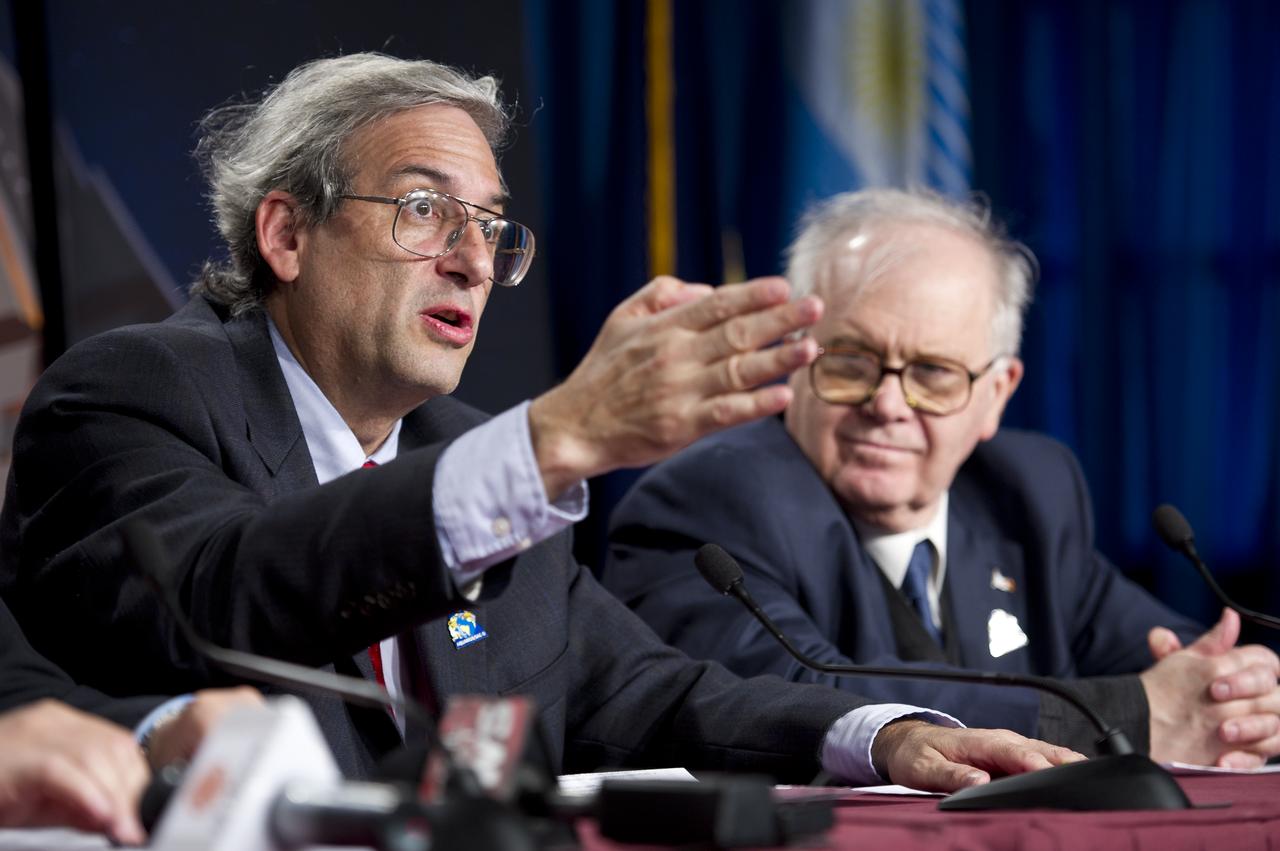
Hector Timerman, Foreign Minister of Argentina, Buenos Aires, talks during the Aquarius/SAC-D post-launch press conference on Friday, June 10, 2011 at the NASA Resident Office, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, launched earlier on Friday June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
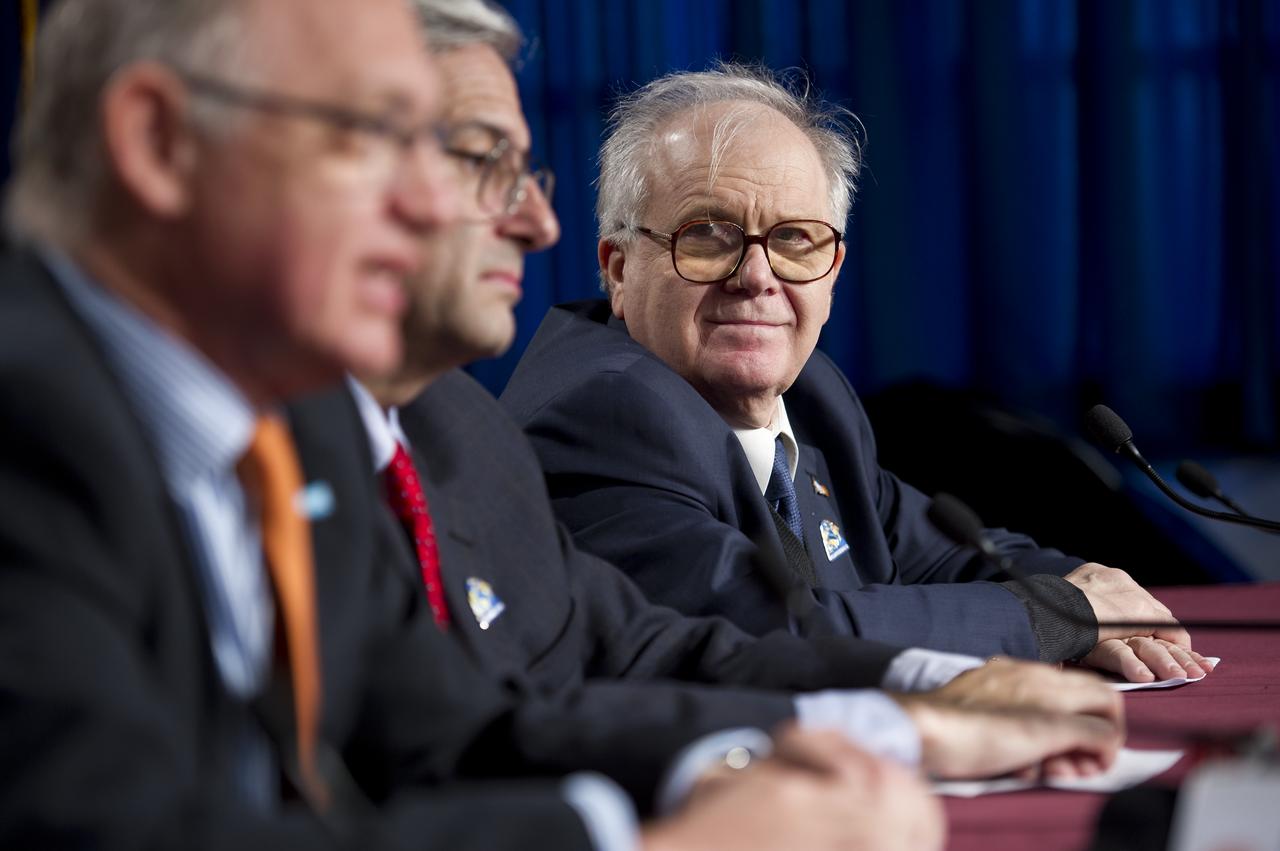

Conrado Varotto, CONAE Executive and Technical Director, Buenos Aires, looks on as other panelest speak during the Aquarius/SAC-D post-launch press conference on Friday, June 10, 2011 at the NASA Resident Office, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, launched earlier on Friday June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
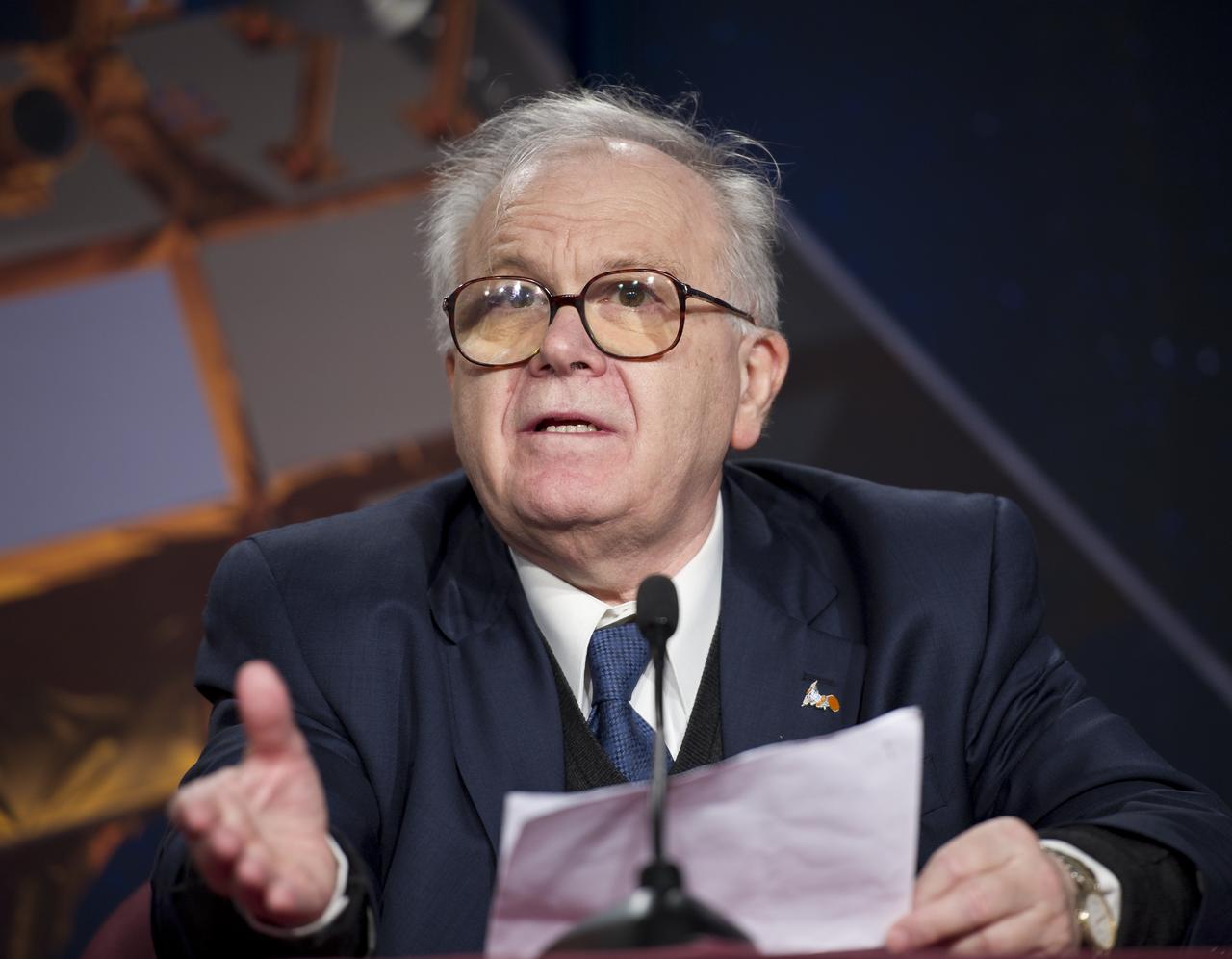

Conrado Varotto, CONAE Executive and Technical Director, Buenos Aires, talks during the Aquarius/SAC-D post-launch press conference on Friday, June 10, 2011 at the NASA Resident Office, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, launched earlier on Friday June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
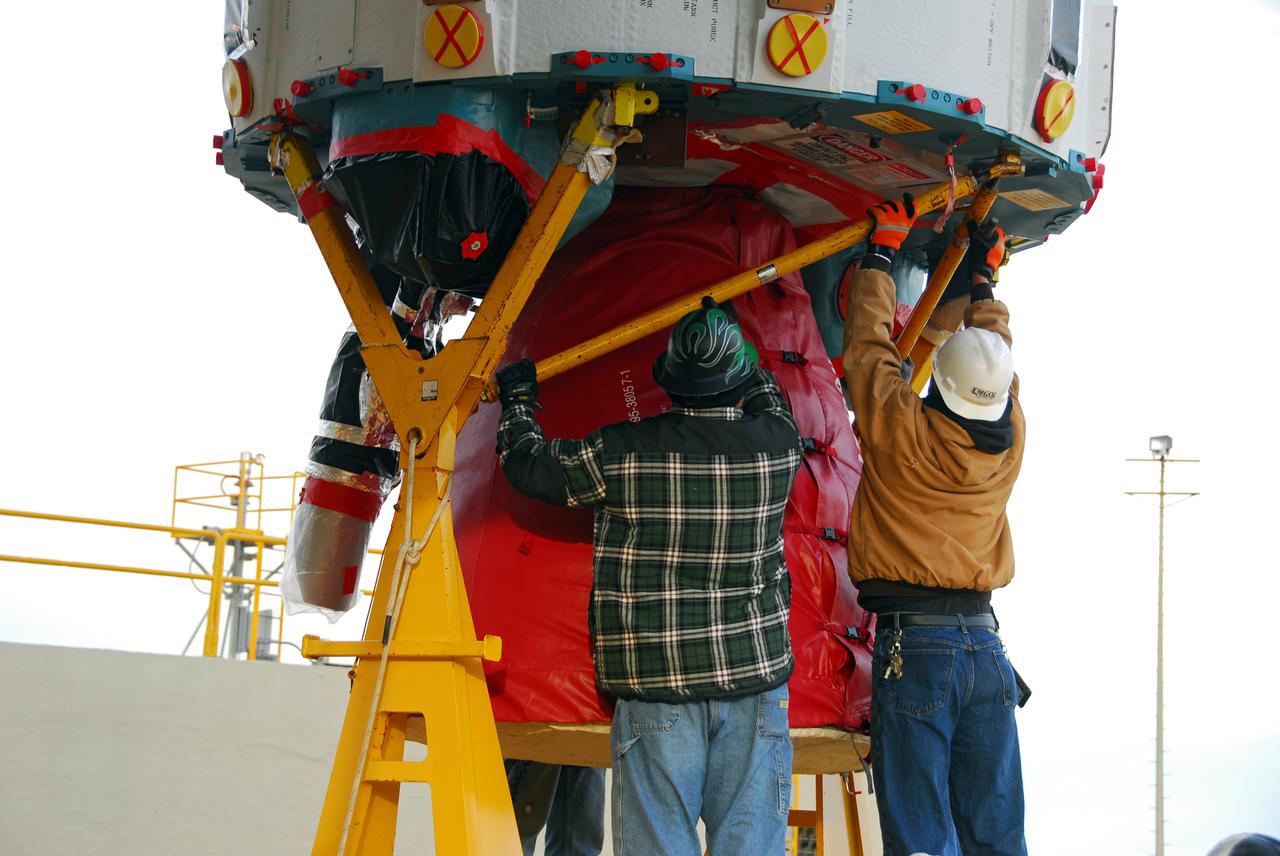

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers guide the first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry the Aquarius_SAC-D spacecraft into low Earth orbit onto the service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, on its three-year mission, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes. Photo credit: NASA_VAFB

Hector Timerman, Foreign Minister of Argentina, Buenos Aires, left, Michael Freilich, NASA Earth Science Division Director, NASA Headquarters, Washington, center, and Conrado Varotto, CONAE Executive and Technical Director, Buenos Aires, laugh at the start of the Aquarius/SAC-D post-launch press conference on Friday, June 10, 2011 at the NASA Resident Office, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, launched earlier on Friday June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

From left, George Diller, NASA Public Affairs Officer; Charles Gay, Deputy Associate Administrator, NASA Science Mission Directorate; Hector Timerman, Foreign Minister of Argentina, Buenos Aires; Michael Freilich, NASA Earth Science Division Director, NASA Headquarters; and Conrado Varotto, CONAE Executive and Technical Director, Buenos Aires, are seen at the Aquarius/SAC-D post-launch press conference on Friday, June 10, 2011 at the NASA Resident Office, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, launched earlier on Friday June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Seated from left, George Diller, NASA Public Affairs Officer; Charles Gay, Deputy Associate Administrator, NASA Science Mission Directorate; Hector Timerman, Foreign Minister of Argentina, Buenos Aires; Michael Freilich, NASA Earth Science Division Director, NASA Headquarters; and Conrado Varotto, CONAE Executive and Technical Director, Buenos Aires, are seen at the Aquarius/SAC-D post-launch press conference on Friday, June 10, 2011 at the NASA Resident Office, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, launched earlier on Friday June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to rotate the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft from a vertical to horizontal position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to rotate the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into a vertical position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians begin to rotate the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into a vertical position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers using an overhead crane lower the United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage motor toward the first stage for mating at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians have rotated the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into a horizontal position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- With the help of an overhead crane workers lift the United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage motor to the top of the service tower for mating with the first stage at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are rotating the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into a vertical position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti, VAFB
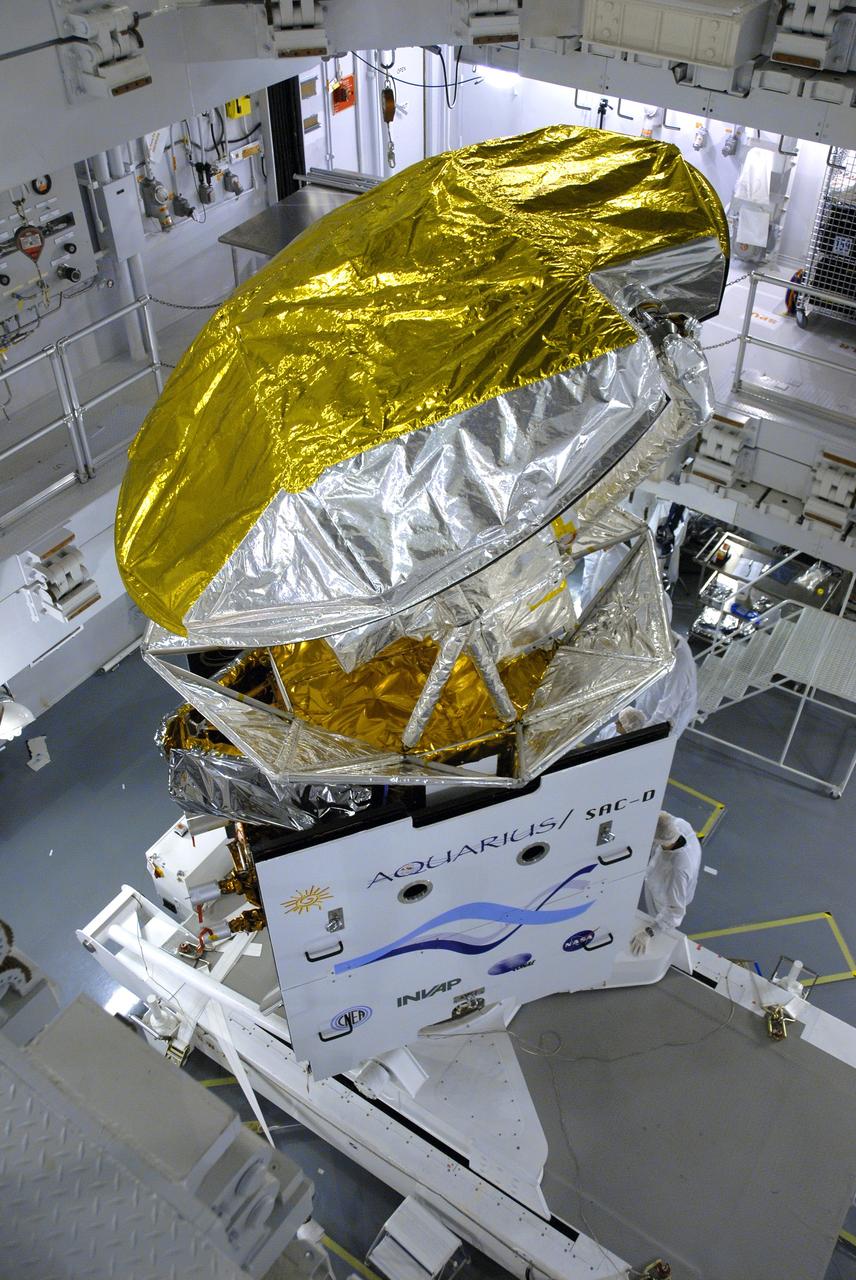

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft is rotated for the final time into a vertical position prior to its installation into a transportation canister. Following delivery to the launch pad, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
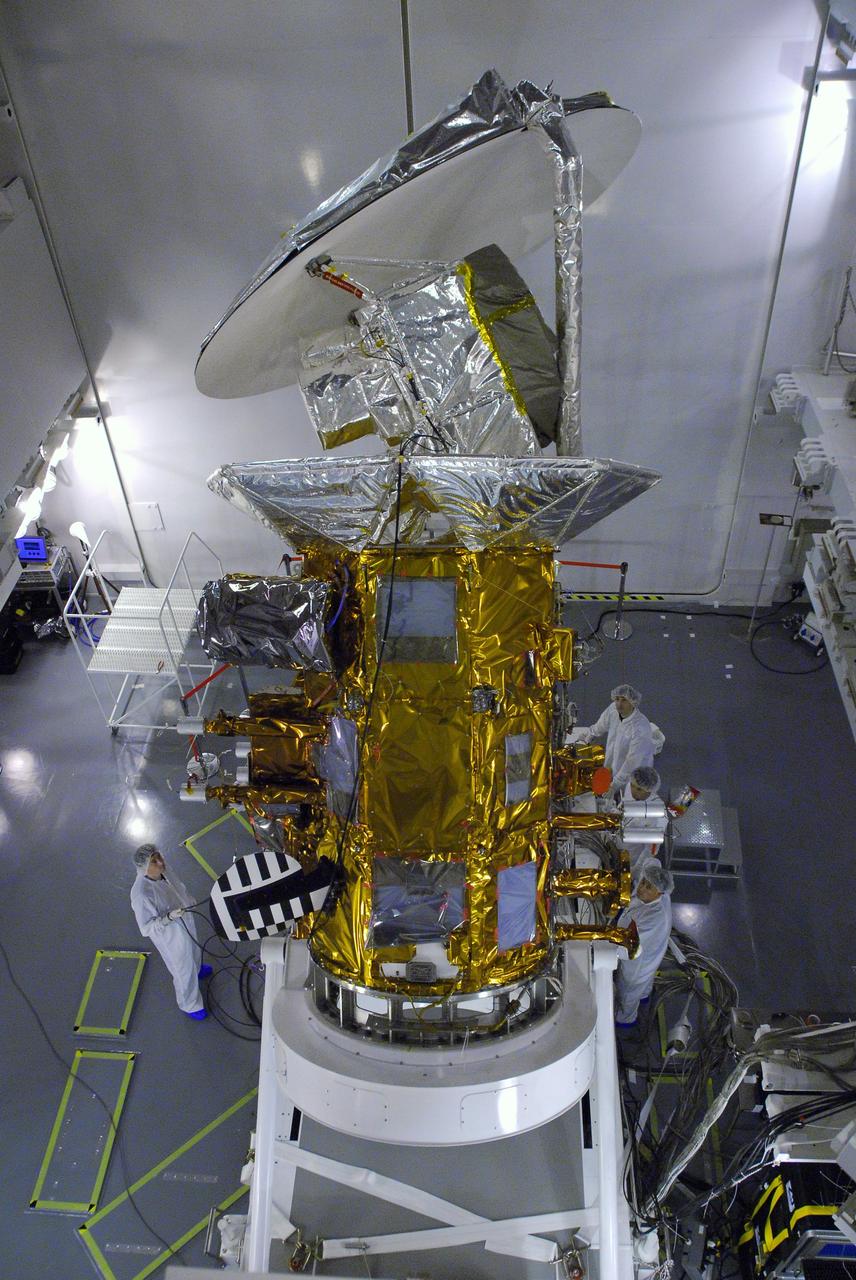

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are rotating the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into a vertical position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti, VAFB
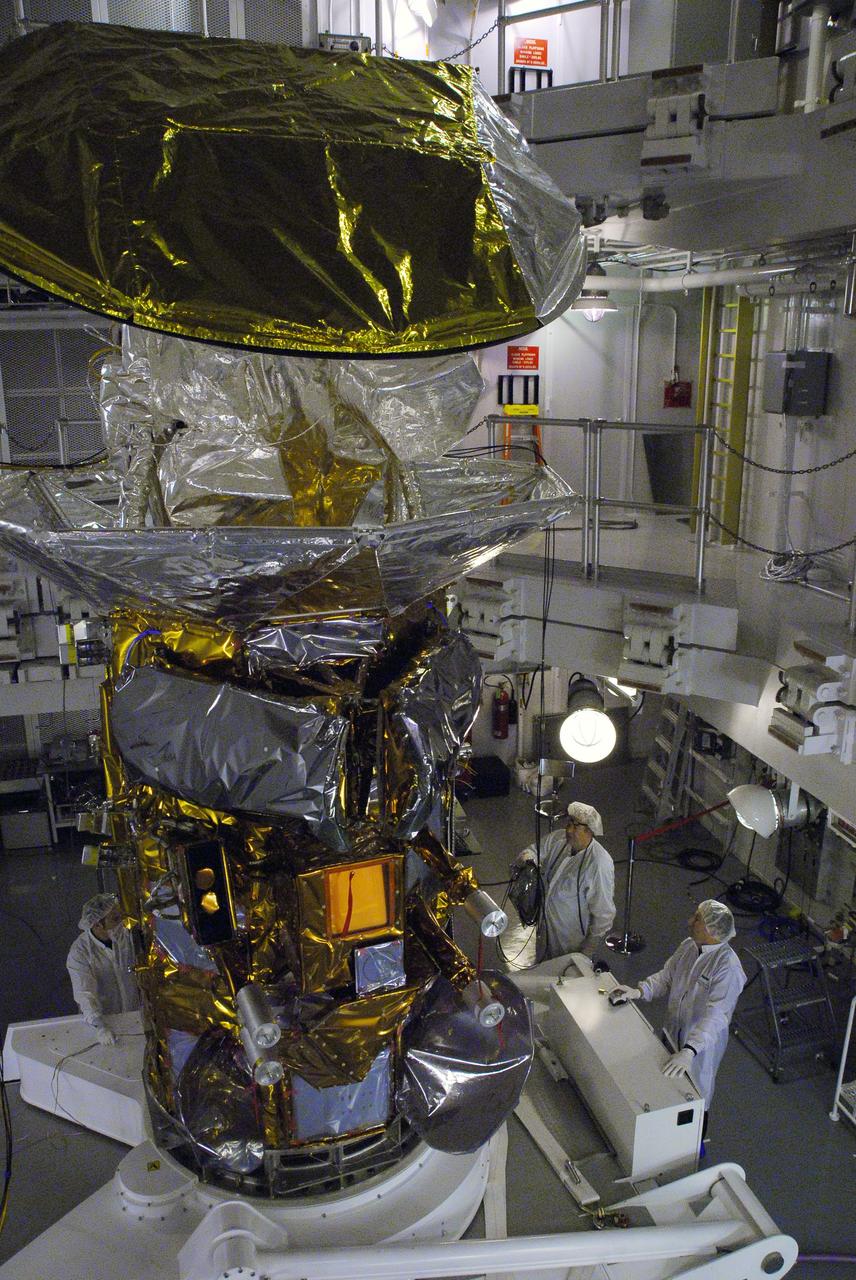

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to rotate the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft from a vertical to horizontal position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
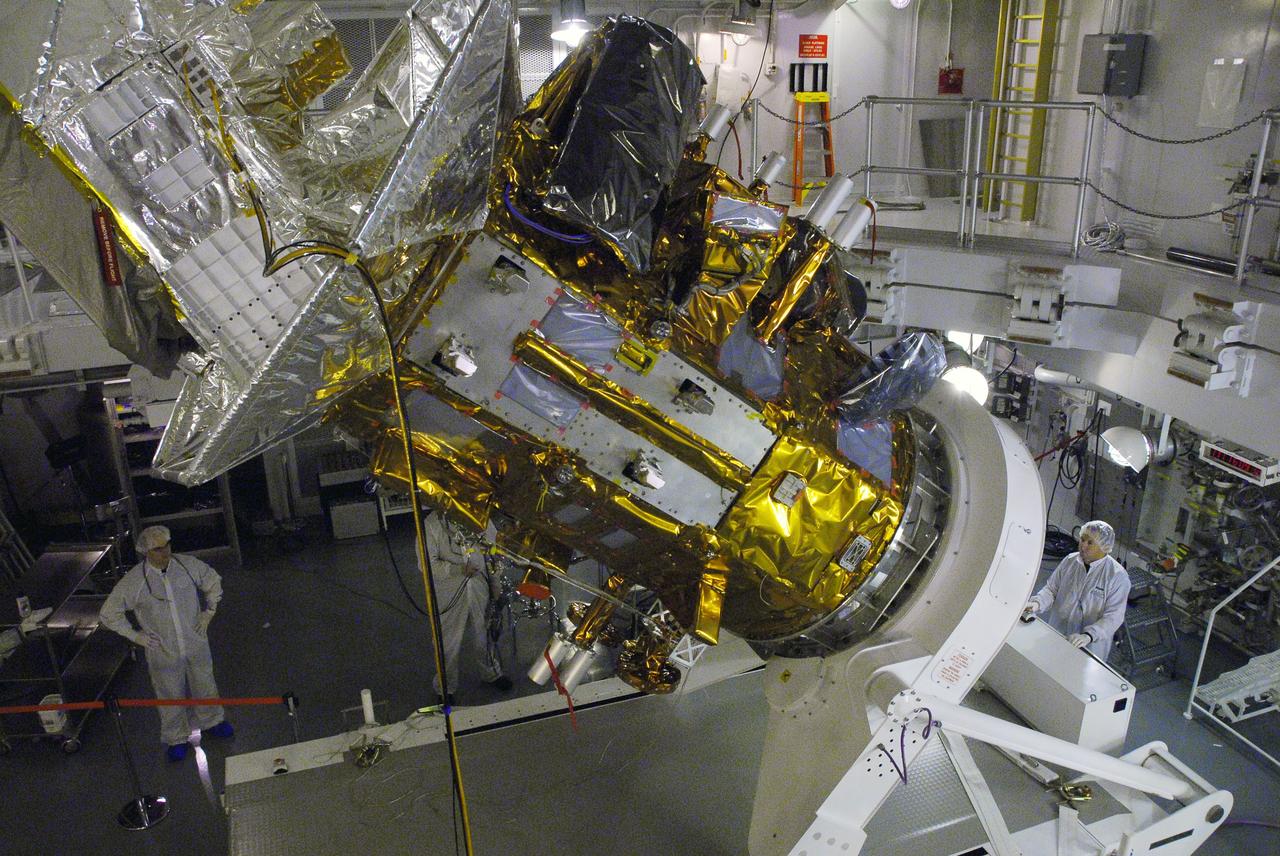
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are rotating the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft from a vertical to horizontal position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
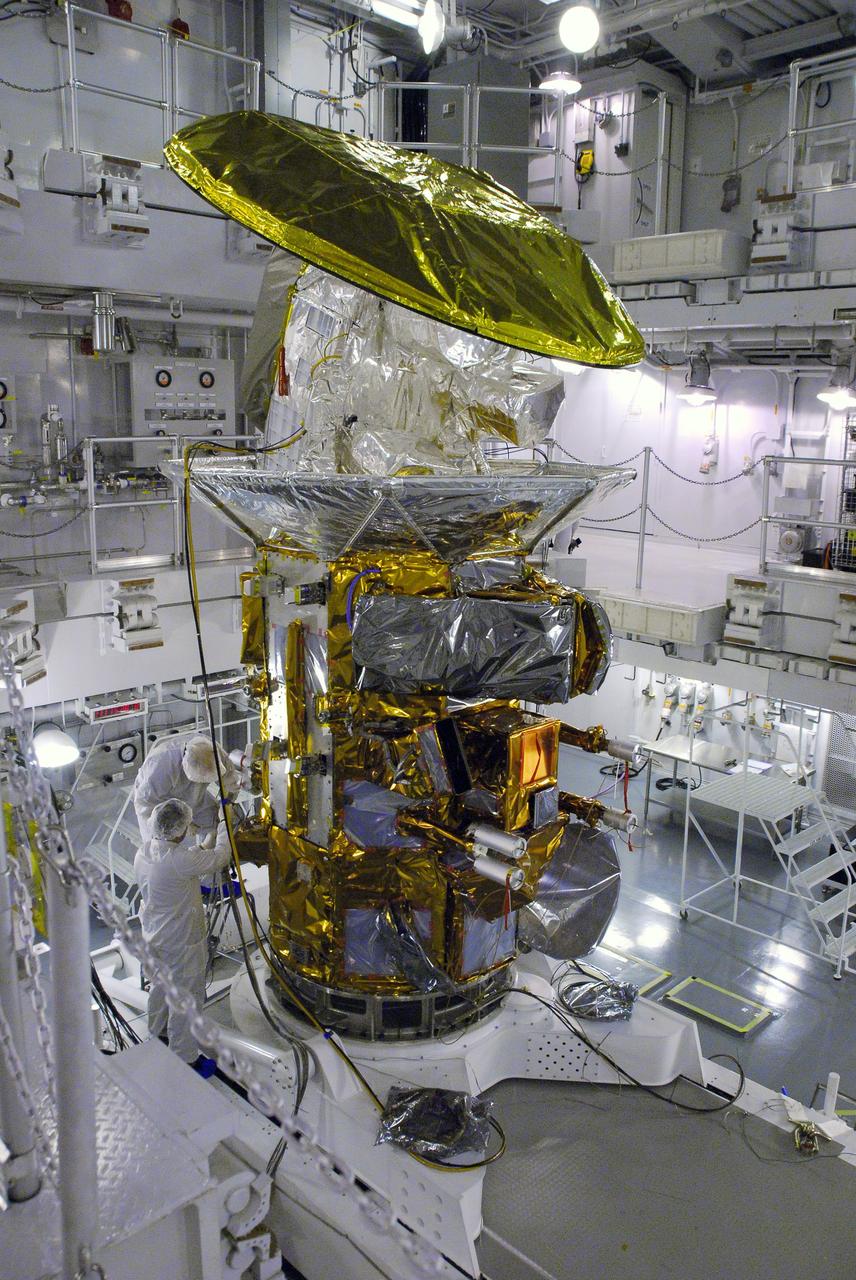

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to rotate the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft from a vertical to horizontal position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
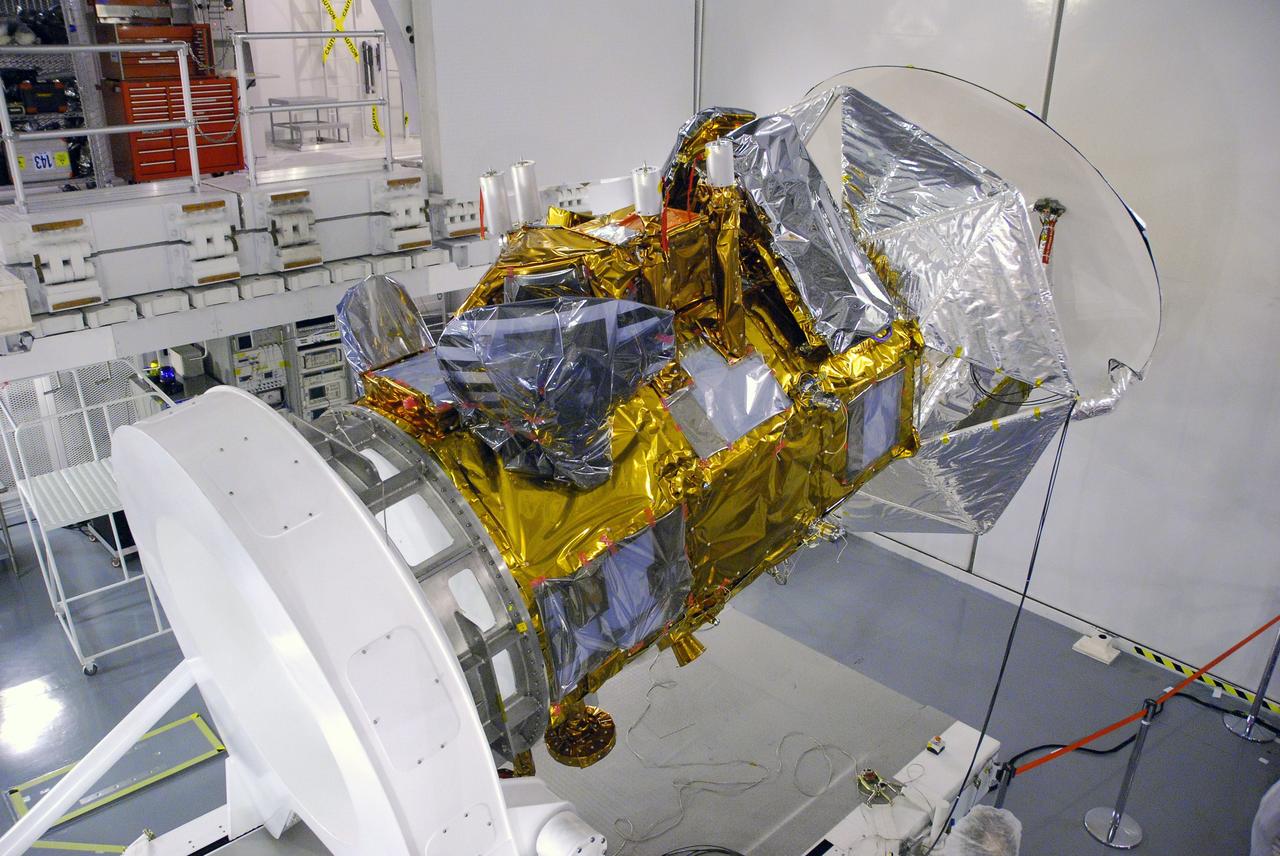

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are rotating the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft from a vertical to horizontal position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
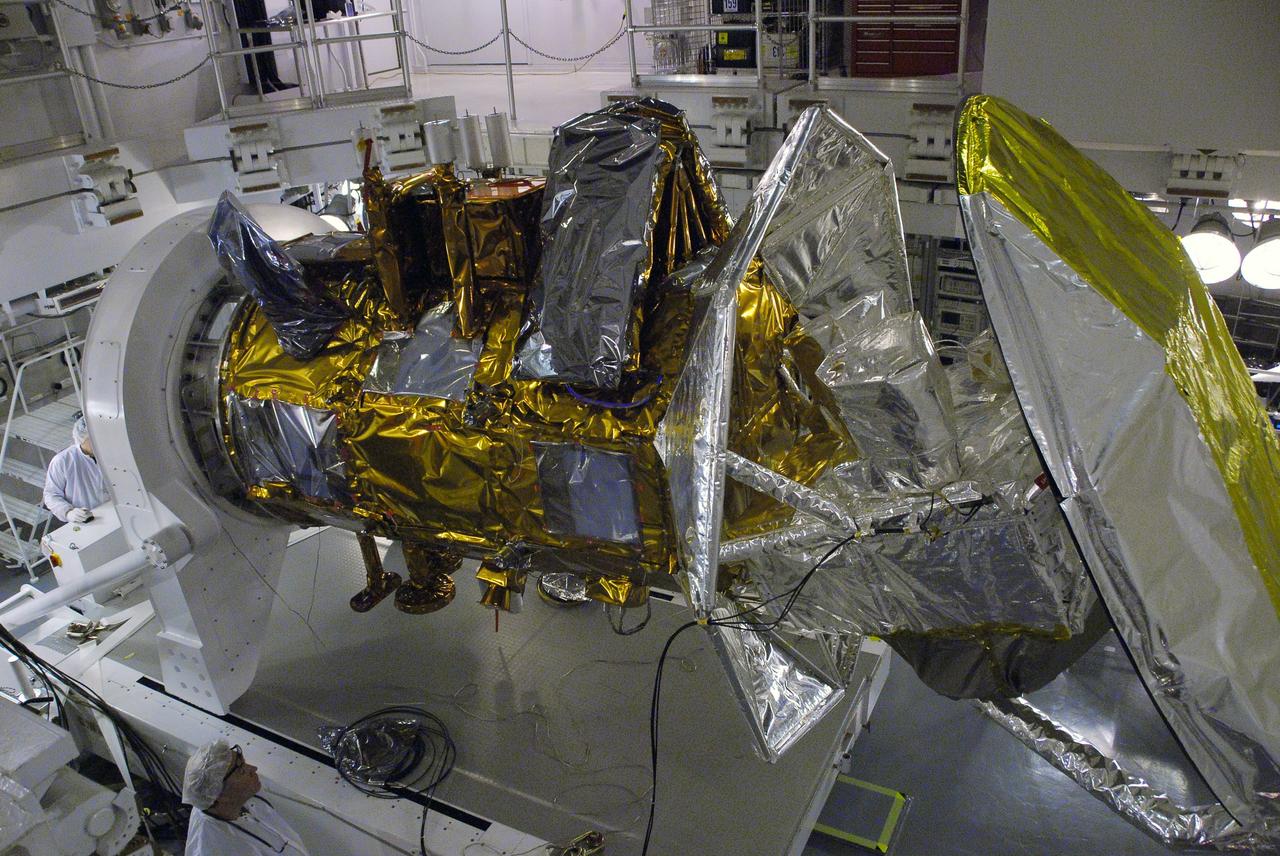
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians have rotated the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into a horizontal position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
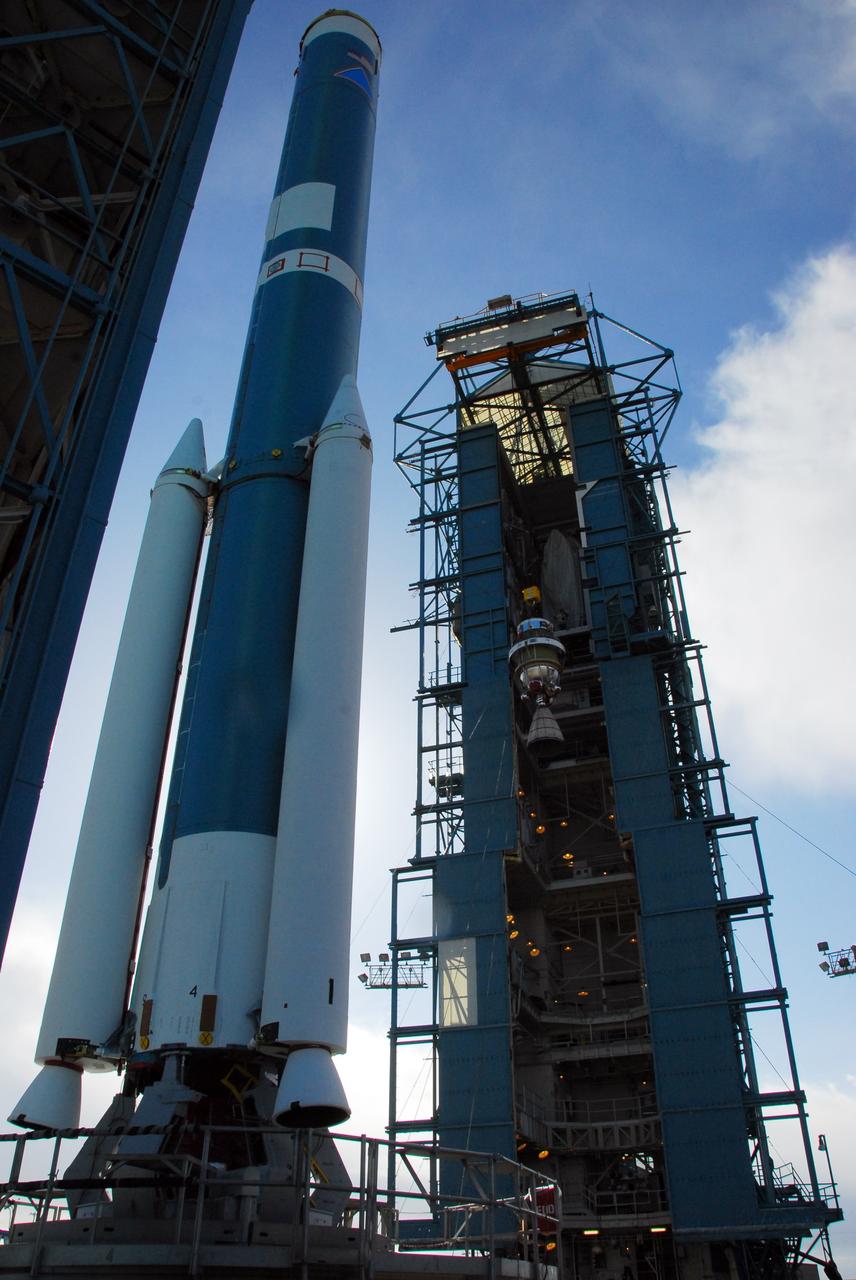

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- With the help of an overhead crane workers lift the United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage motor to the top of the service tower for mating with the first stage at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
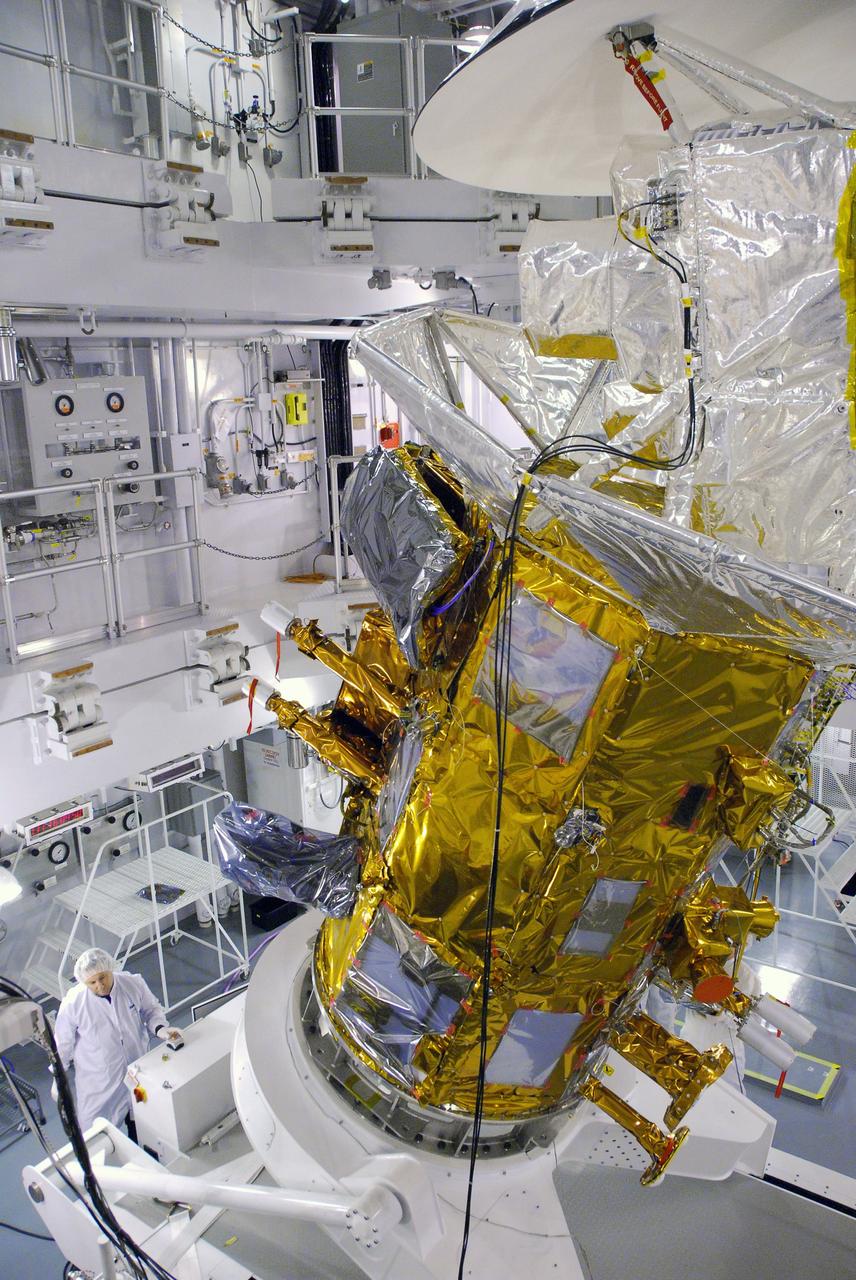

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are rotating the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft from a vertical to horizontal position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
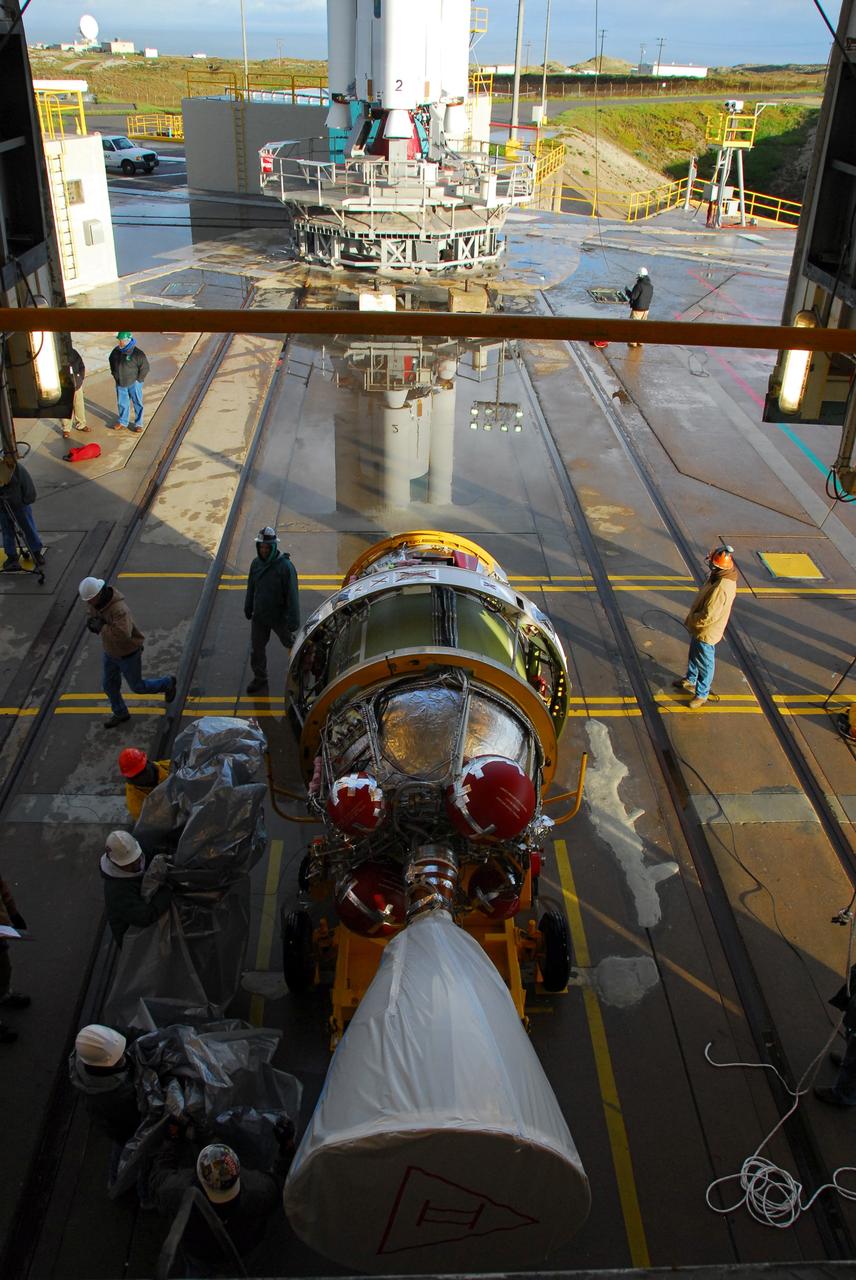

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers prepare the United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage motor for lifting into the service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
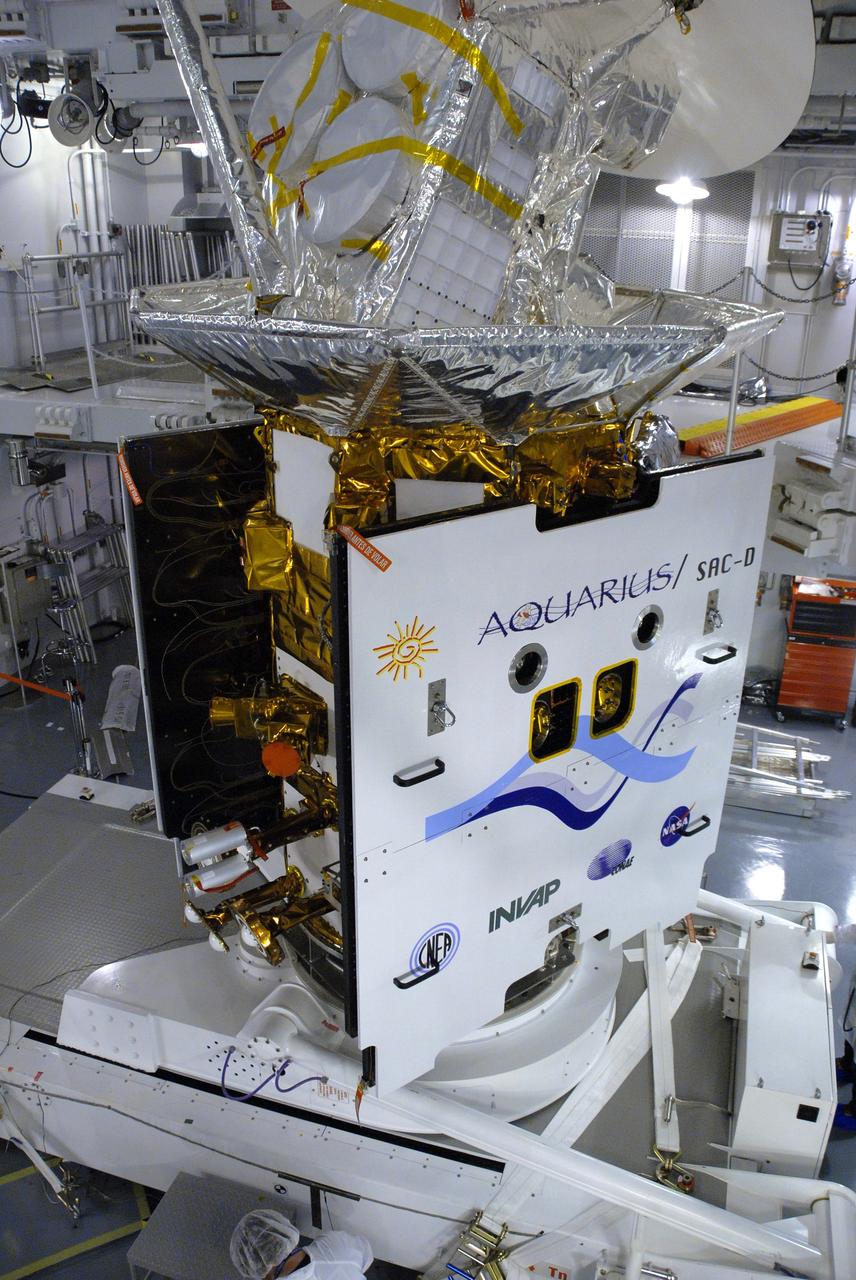

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft is rotated for the final time into a vertical position prior to its installation into a transportation canister. Following delivery to the launch pad, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
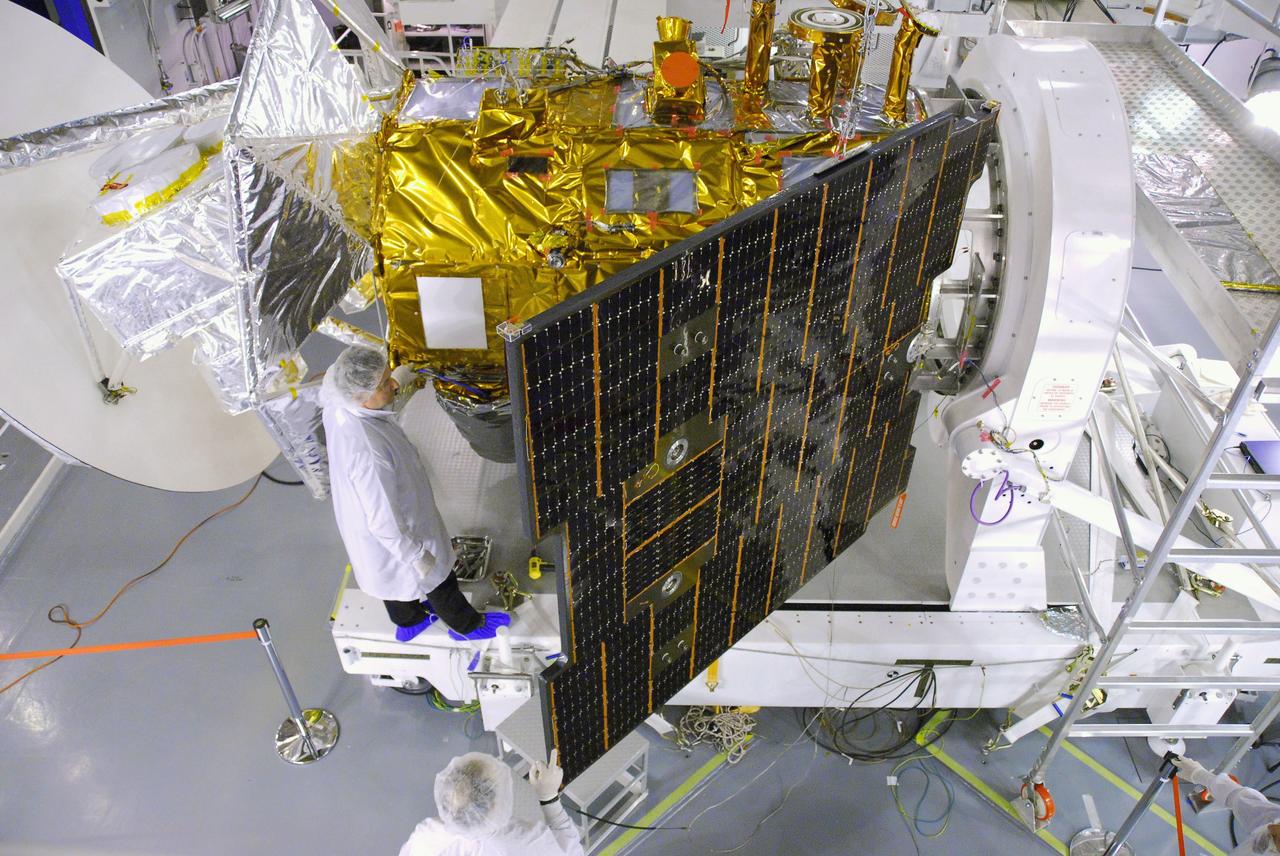

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to close the solar arrays on the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
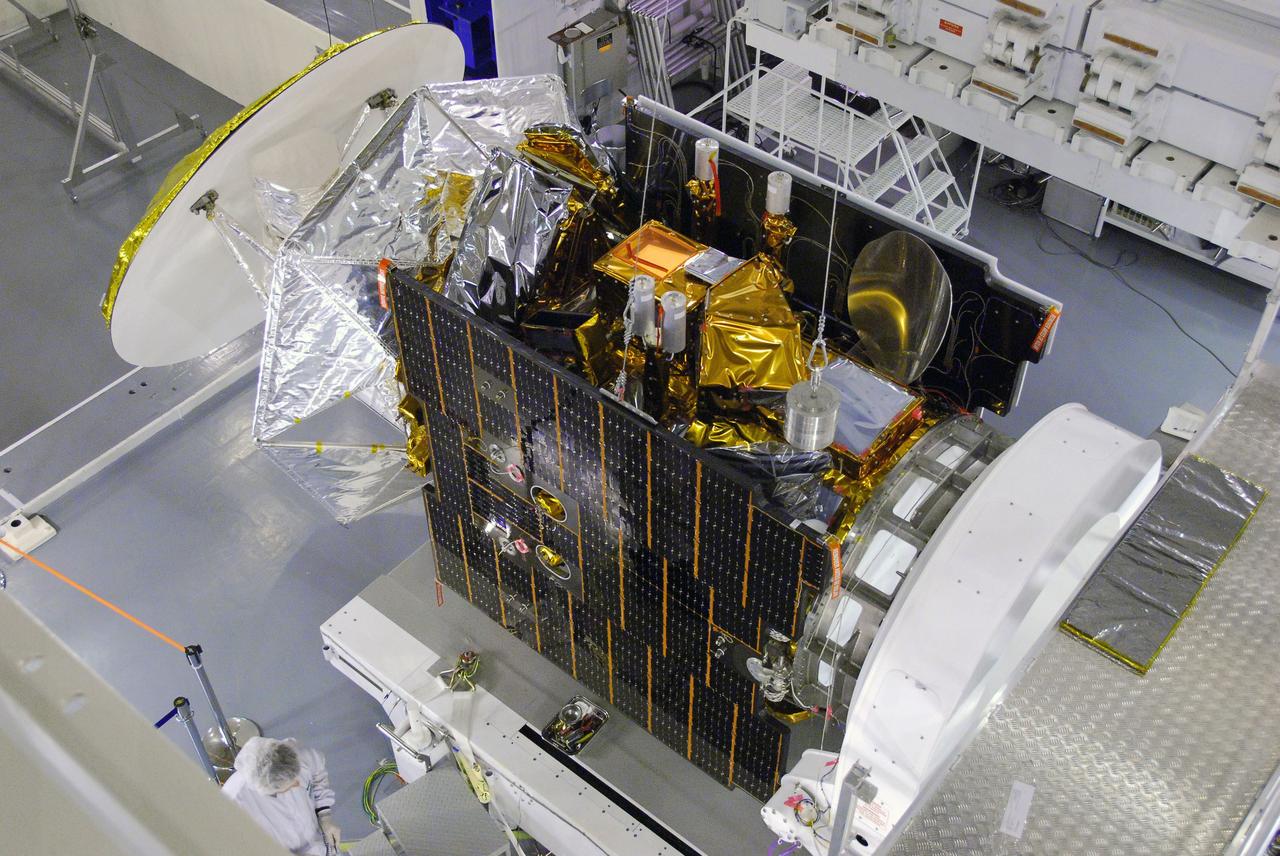

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to test the second solar array after integration to the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
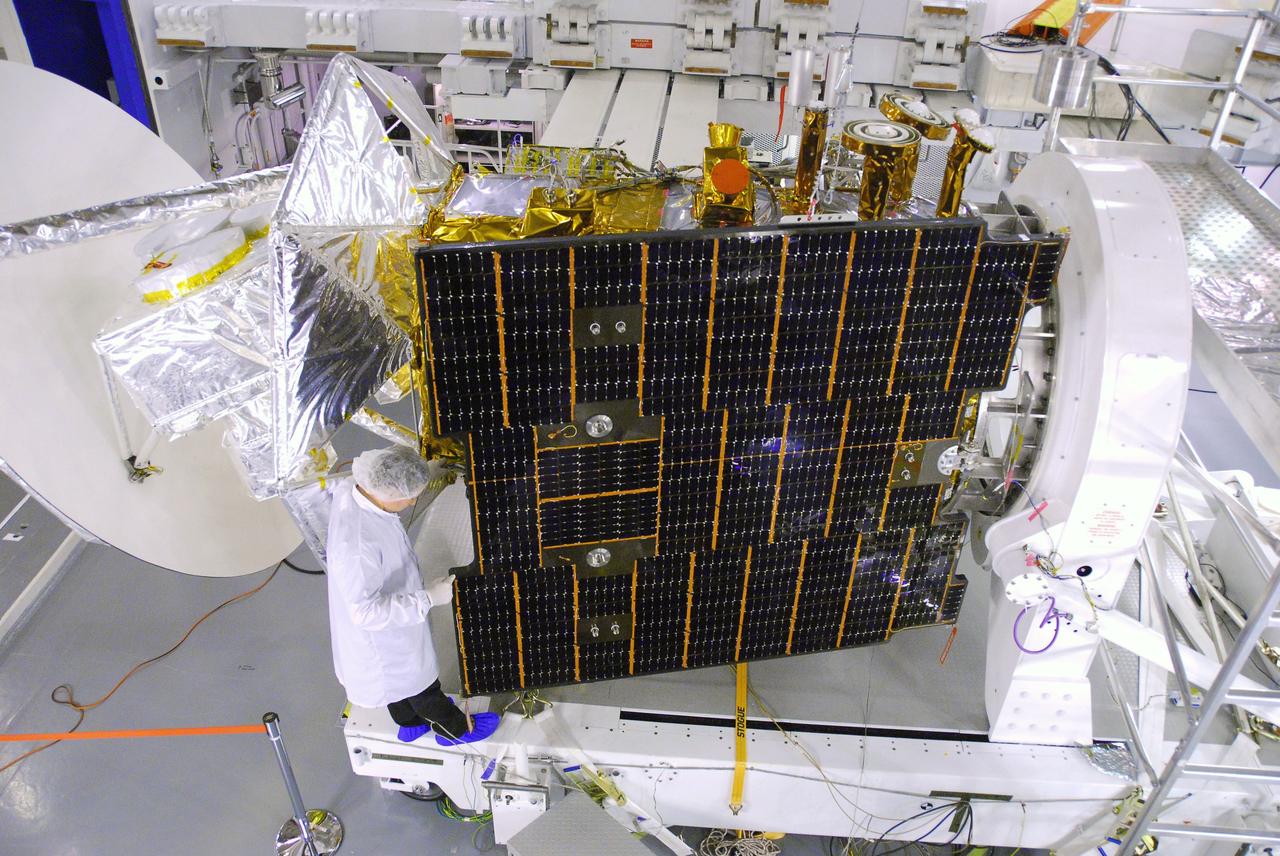

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to close the solar arrays on the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
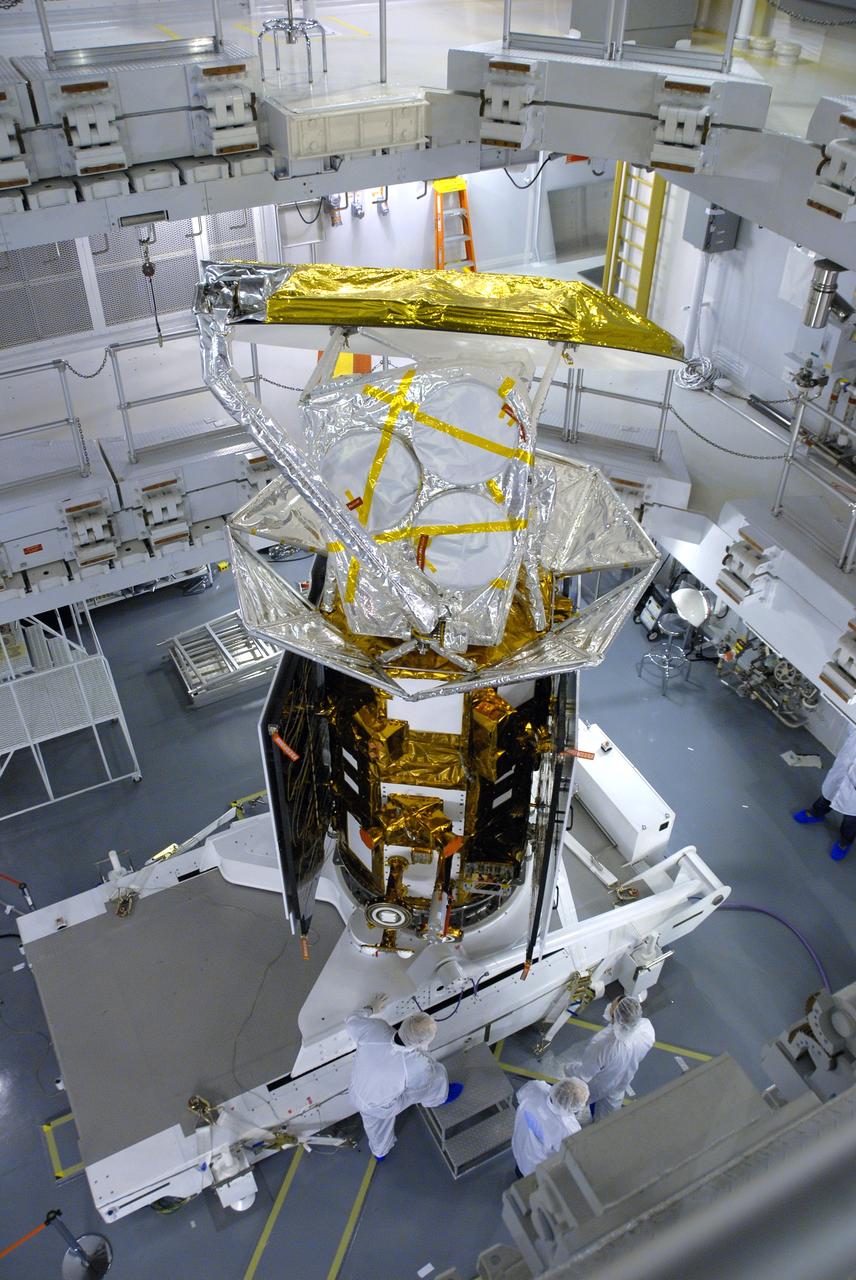

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft is rotated for the final time into a vertical position prior to its installation into a transportation canister. Following delivery to the launch pad, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
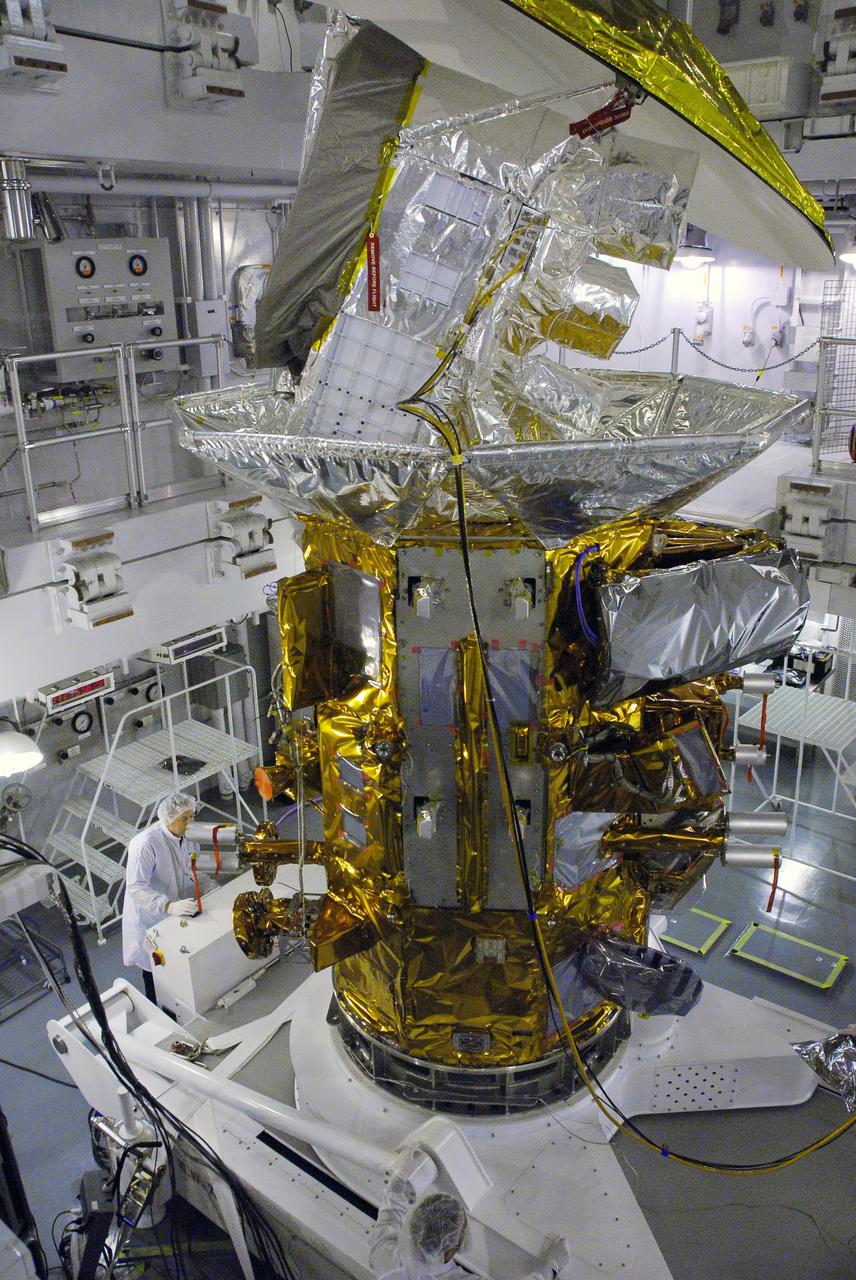

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to rotate the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft from a vertical to horizontal position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
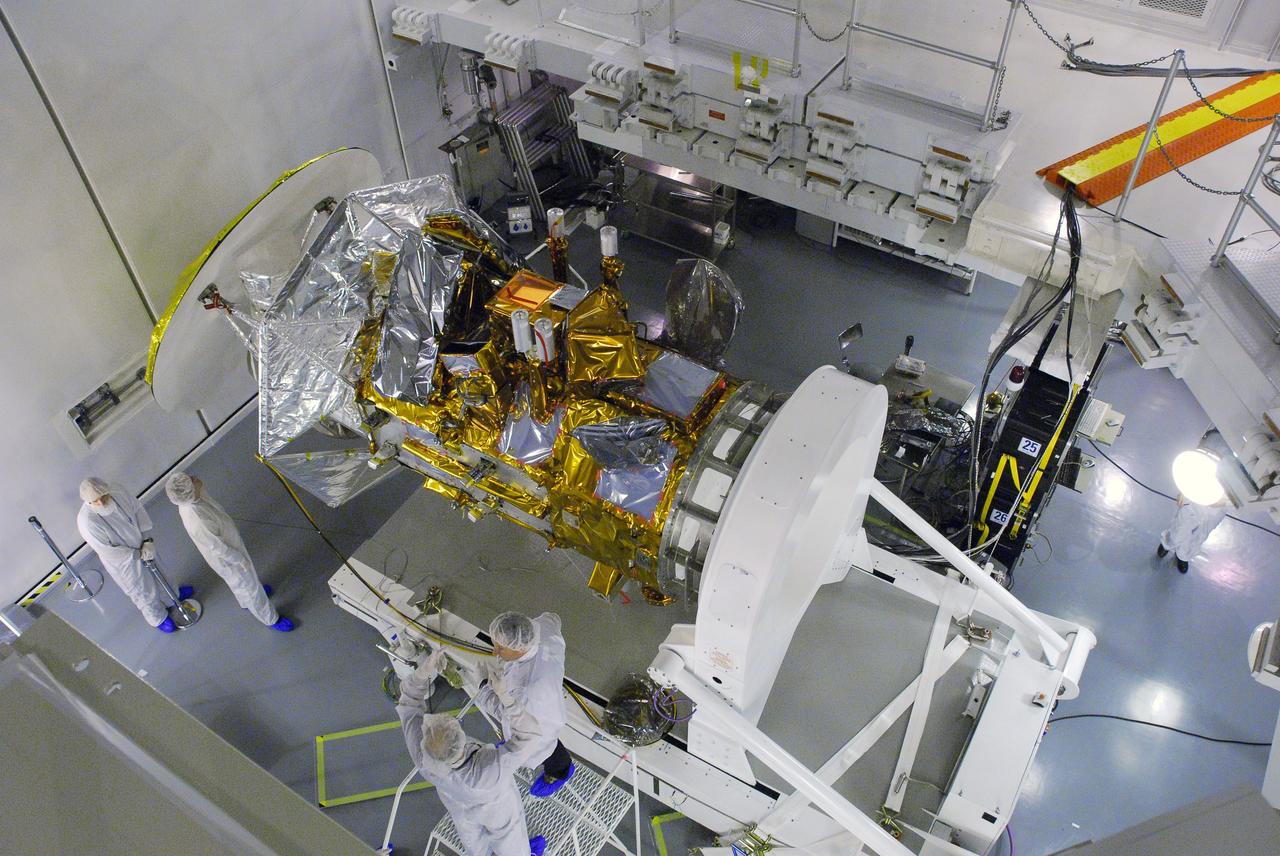

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians have rotated the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into a horizontal position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
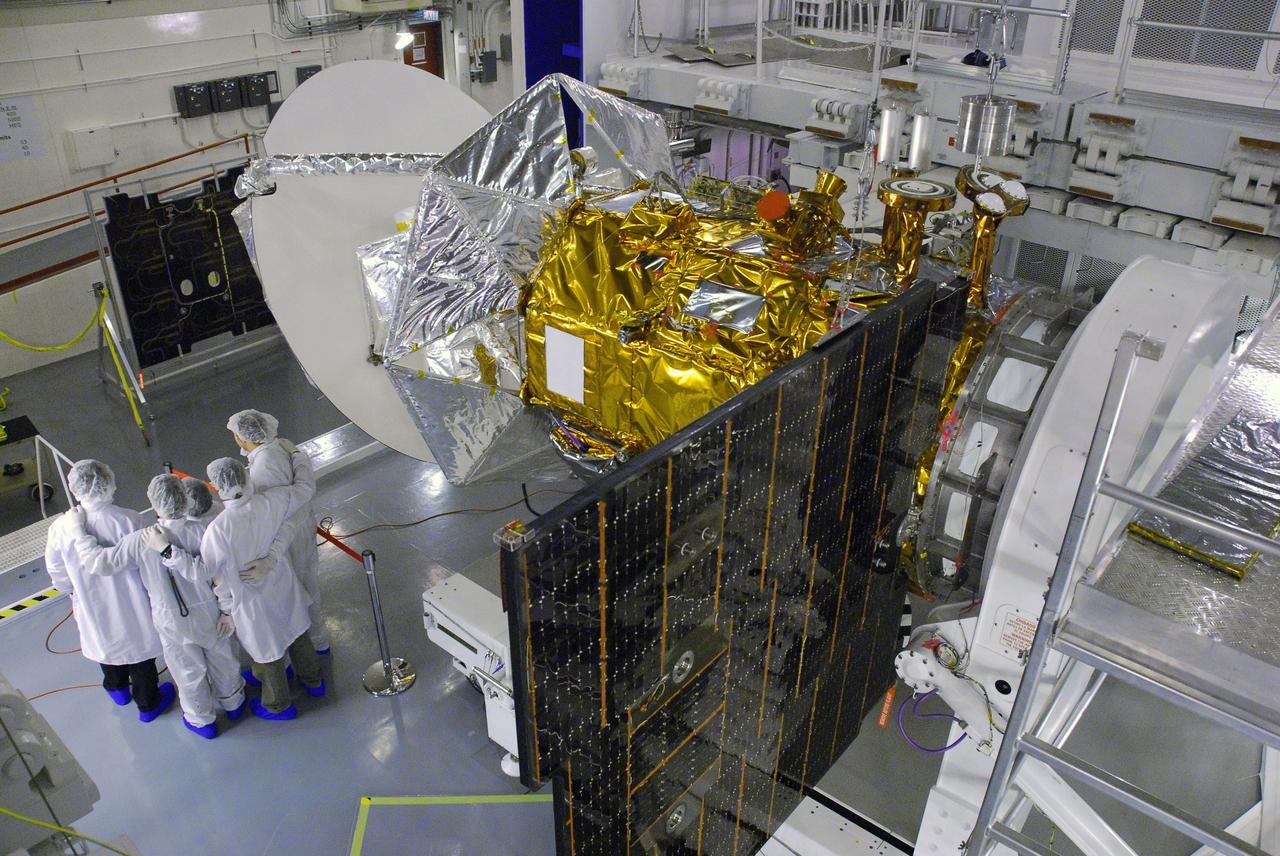

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to close the solar arrays on the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
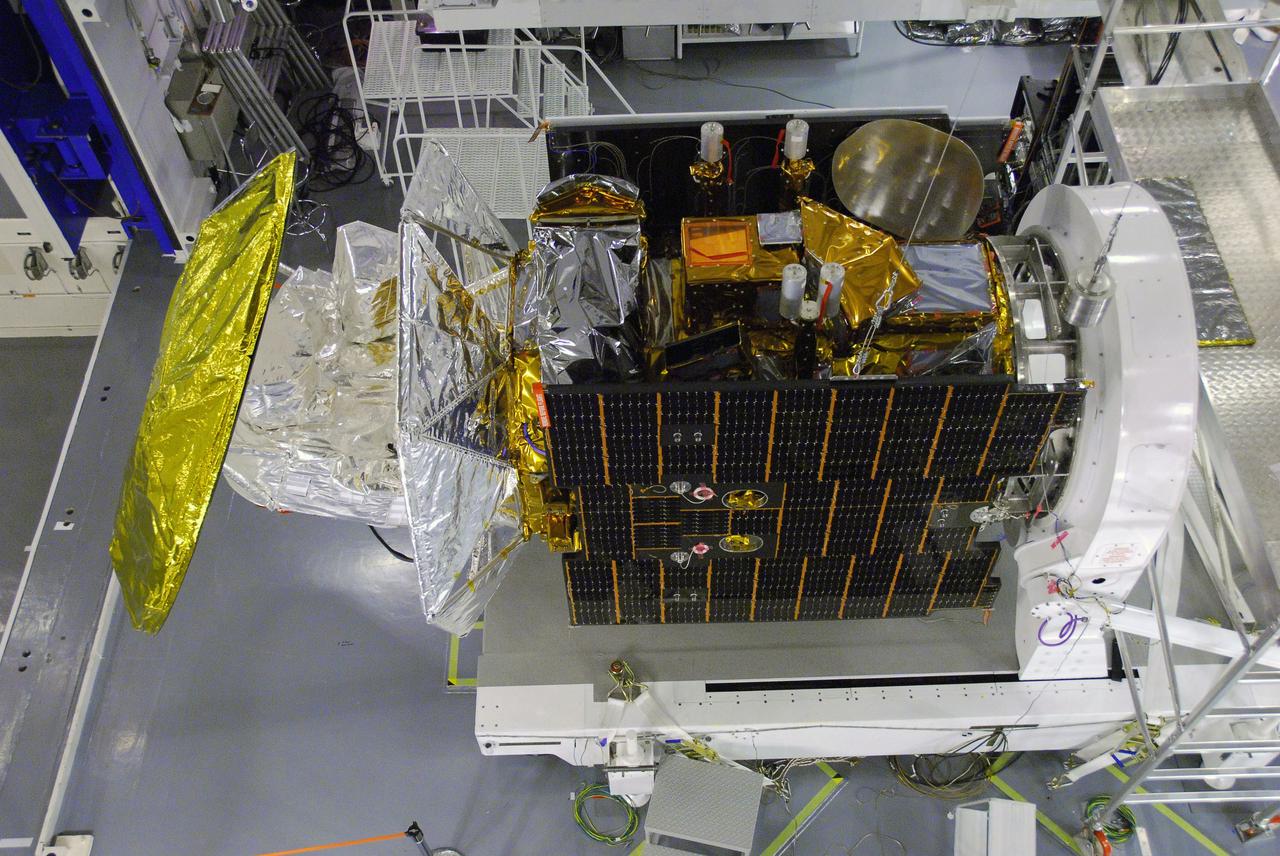
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to test the second solar array after integration to the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
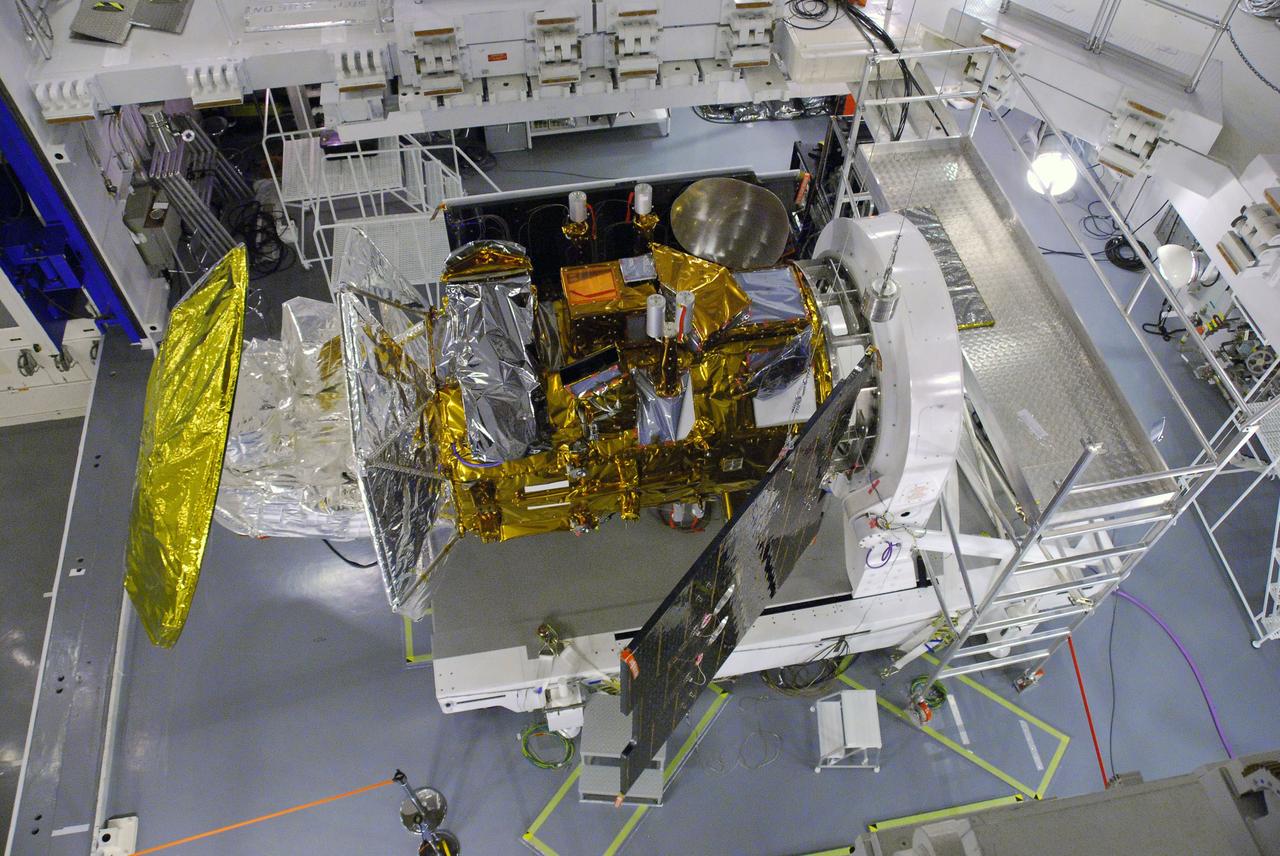
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians extend the second solar array on the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft to test the release mechanism sequence for the array using signal commands. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
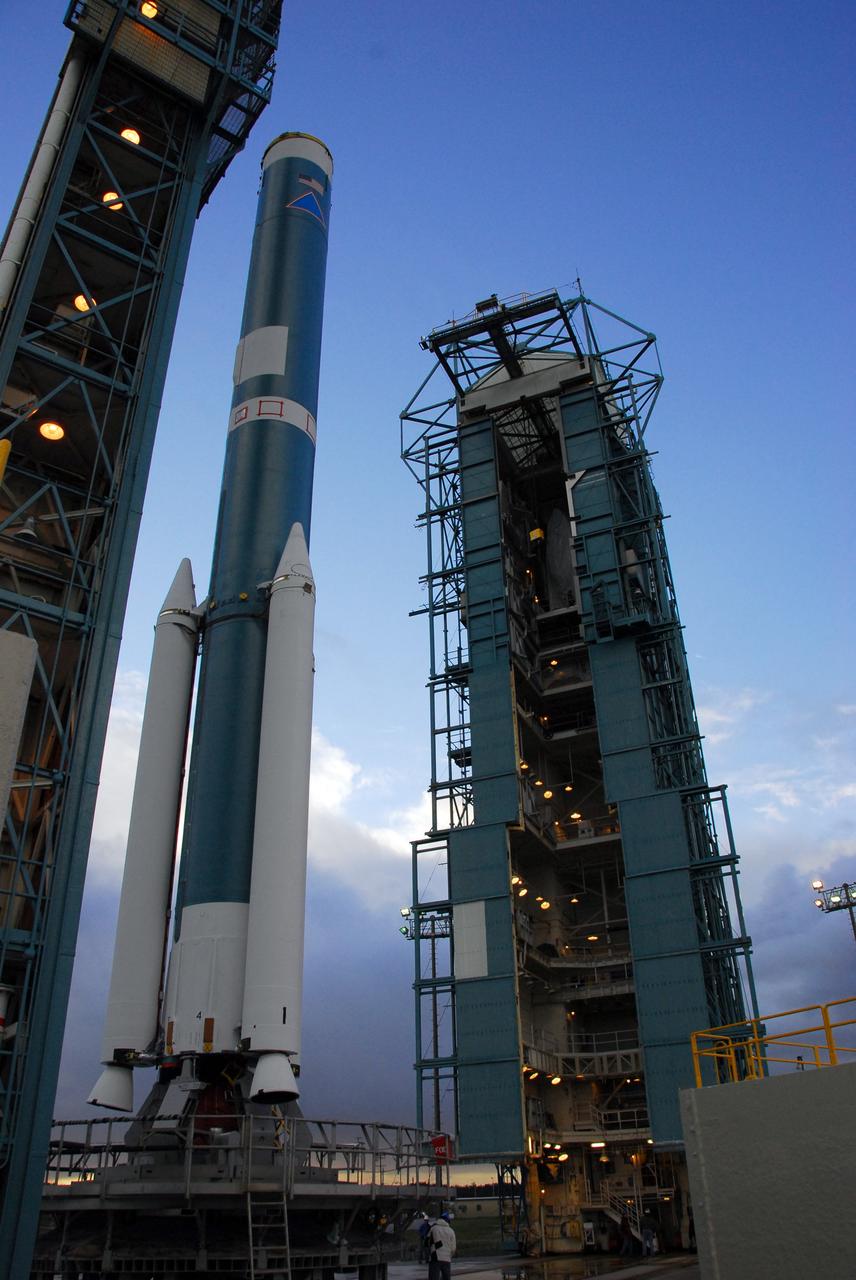

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is moved away from the service tower as workers prepare to lift the second stage to the top of the tower for mating with the first stage at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians have rotated the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into a vertical position for testing. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians extend the second solar array on the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft to test the release mechanism sequence for the array using signal commands. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Space Systems International's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft is rotated for the final time into a vertical position prior to its installation into a transportation canister. Following delivery to the launch pad, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
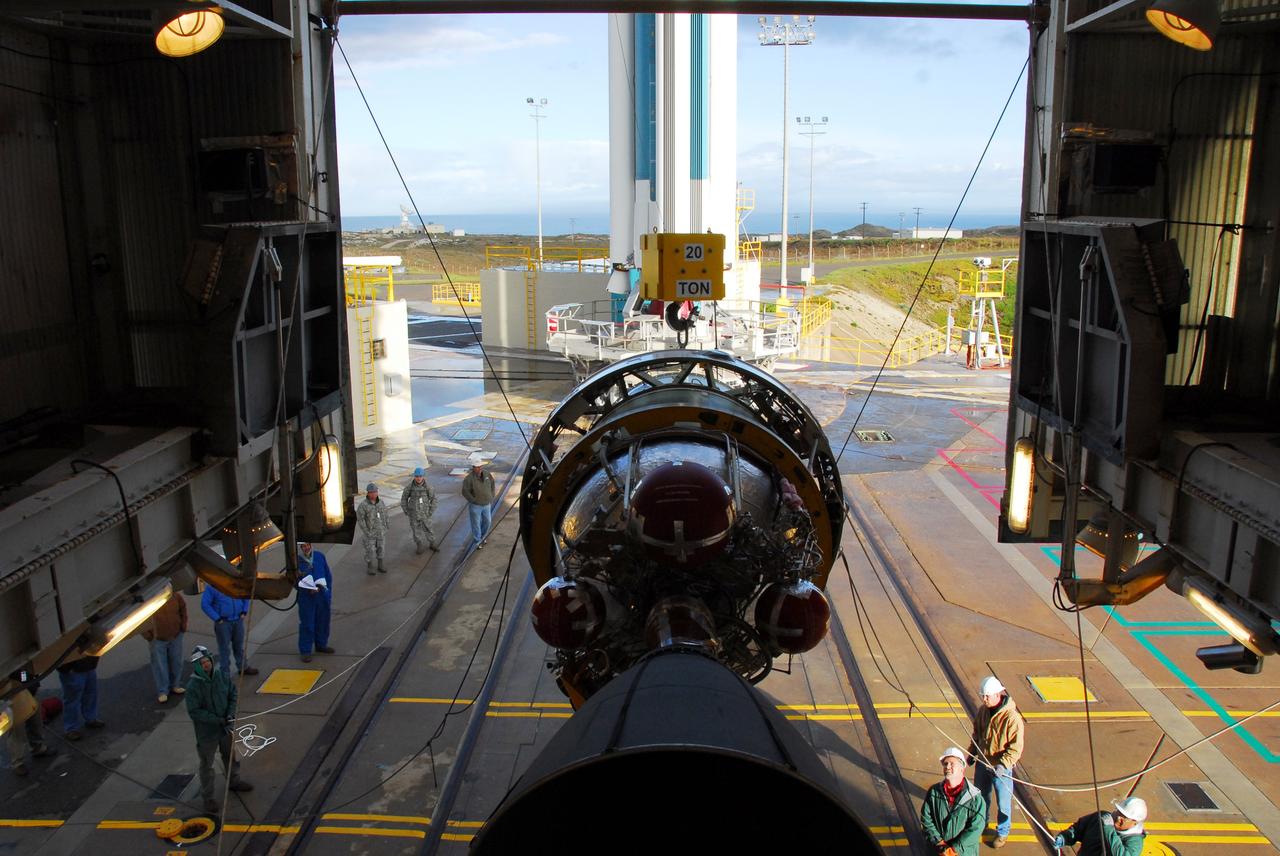

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers attach cables from an overhead crane to the United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage motor for mating to the first stage at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
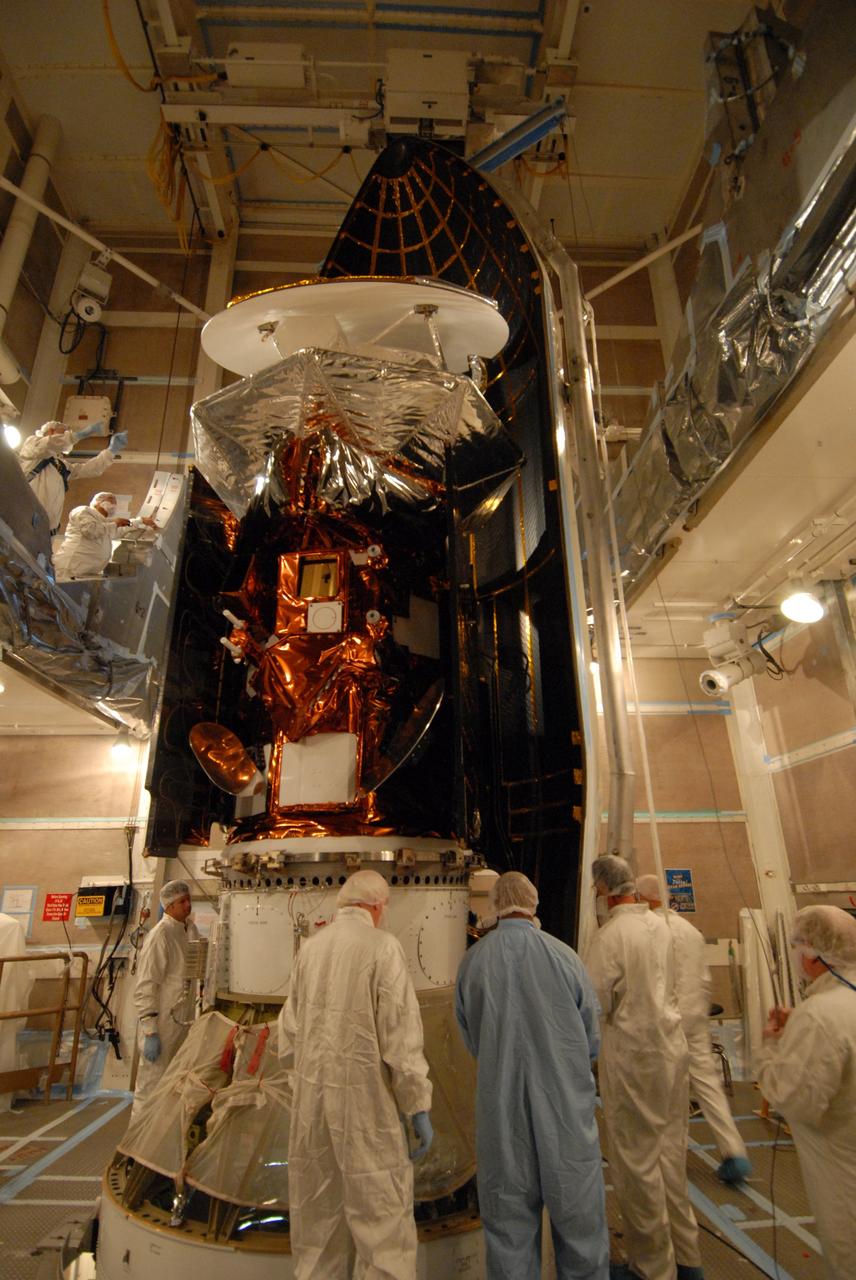

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Inside the mobile service tower at NASA's Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers prepare to install the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into the United Launch Alliance’s Delta II payload fairing. Aquarius will be integrated to the Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June 9 liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Inside the mobile service tower at NASA's Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician secures the United Launch Alliance’s Delta II payload fairing around the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft. Aquarius will be integrated to the Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June 9 liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
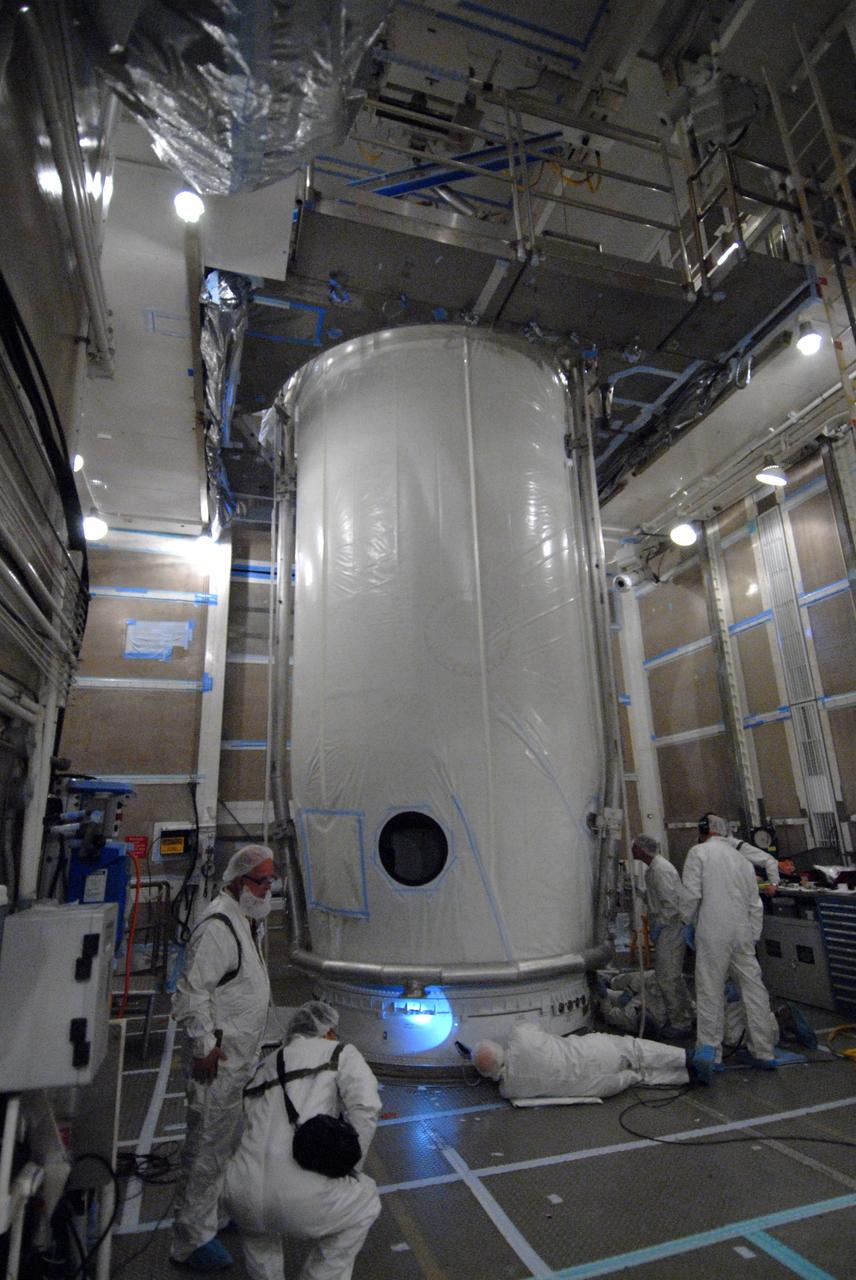

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Inside the mobile service tower at NASA's Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers secure the United Launch Alliance’s Delta II payload fairing around the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft. Aquarius will be integrated to the Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June 9 liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
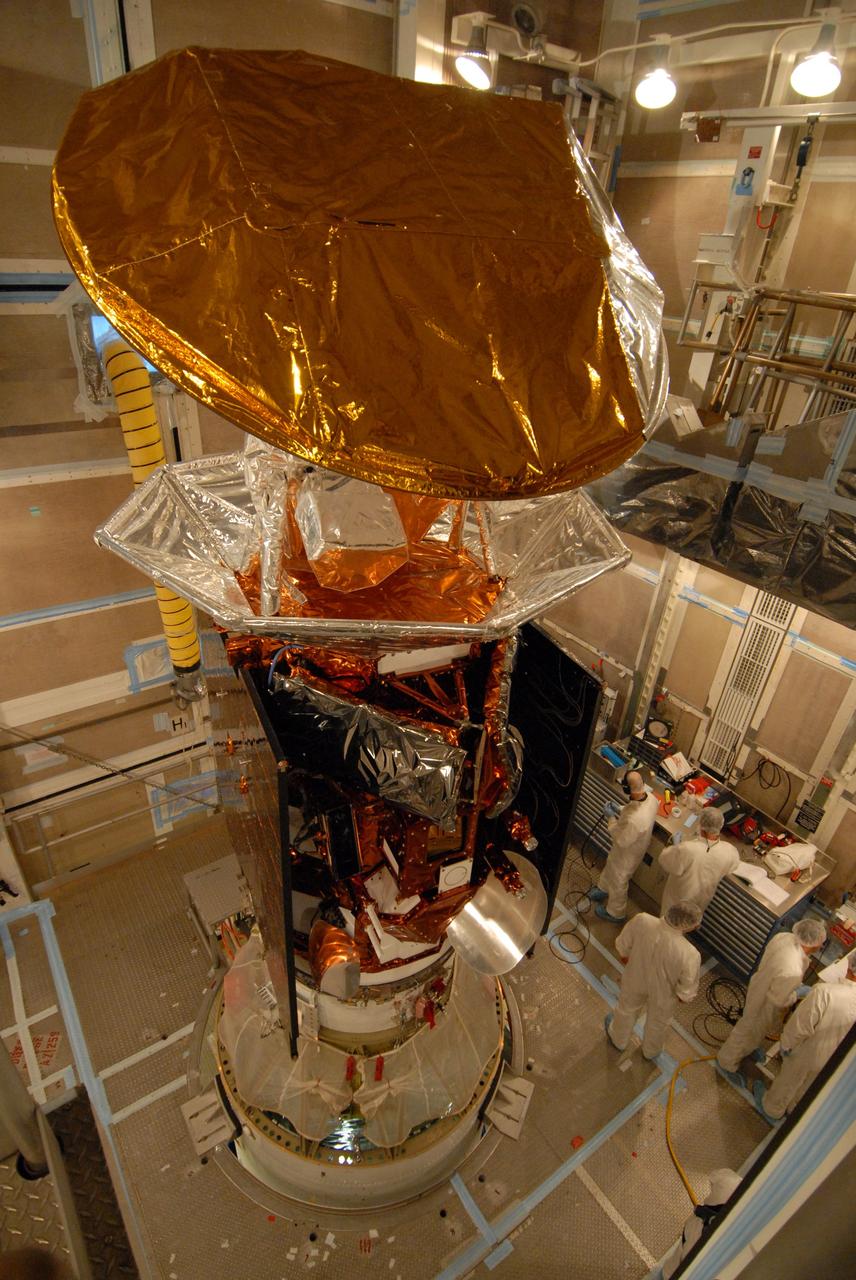

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Inside the mobile service tower at NASA's Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers prepare the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft for fairing installation. Aquarius will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June 9 liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
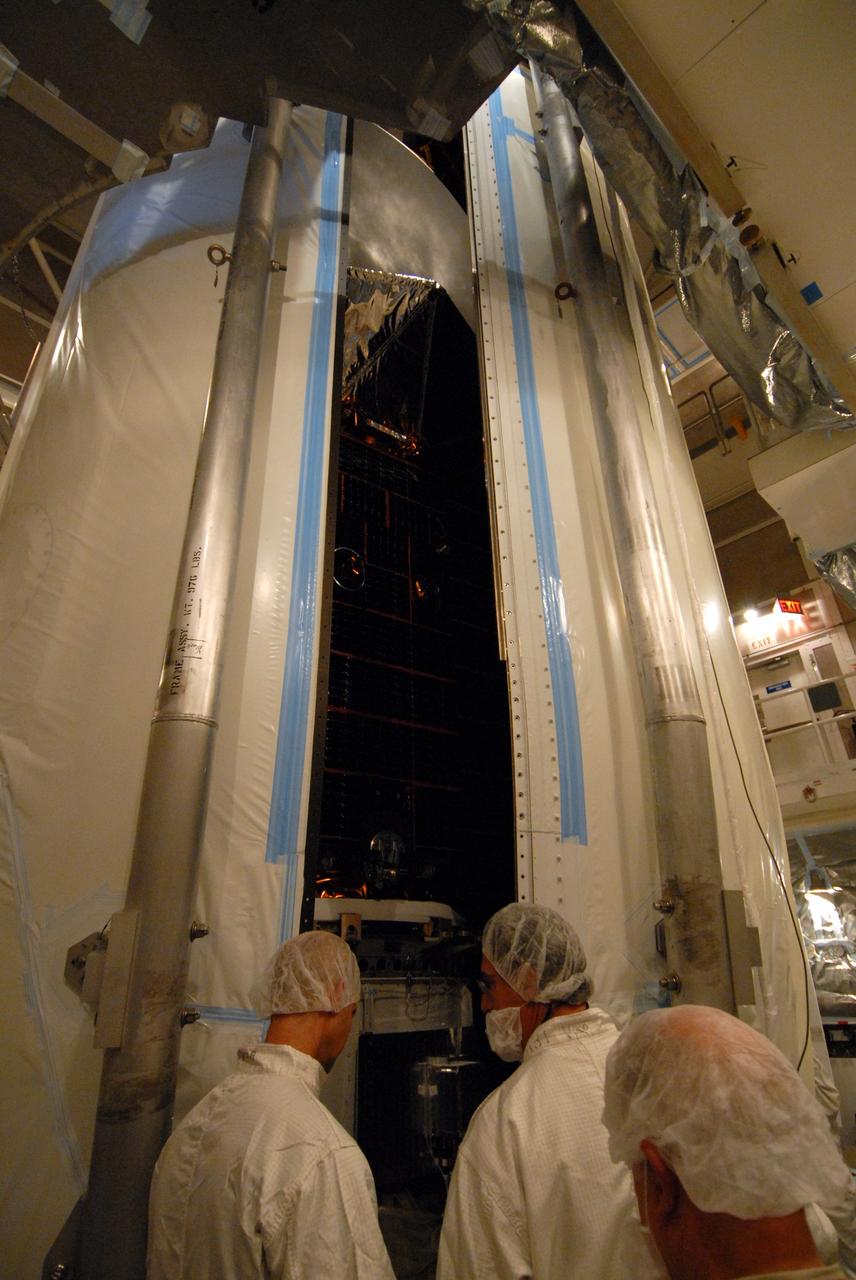
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Inside the mobile service tower at NASA's Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers monitor the progress as the United Launch Alliance’s Delta II payload fairing closes around the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft. Aquarius will be integrated to the Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June 9 liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB