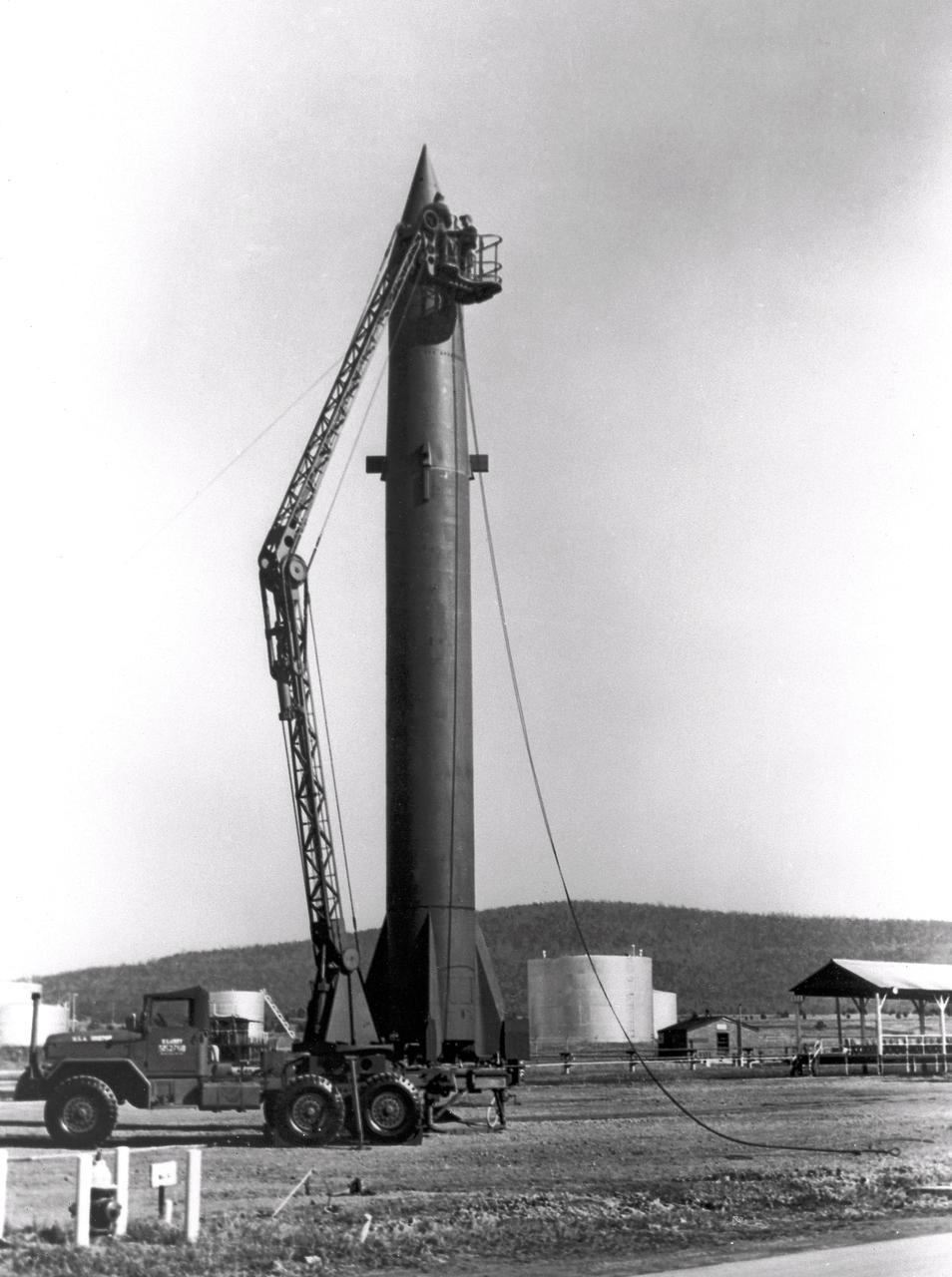

The image depicts Redstone missile being erected. The Redstone ballistic missile was a high-accuracy, liquid-propelled, surface-to-surface missile developed by Army Ballistic Missile Agency, Redstone Arsenal, in Huntsville, Alabama, under the direction of Dr. von Braun. The Redstone engine was a modified and improved version of the Air Force's Navaho cruise missile engine of the late forties. The A-series, as this would be known, utilized a cylindrical combustion chamber as compared with the bulky, spherical V-2 chamber. By 1951, the Army was moving rapidly toward the design of the Redstone missile, and the production was begun in 1952. Redstone rockets became the "reliable workhorse" for America's early space program. As an example of the versatility, Redstone was utilized in the booster for Explorer 1, the first American satellite, with no major changes to the engine or missile
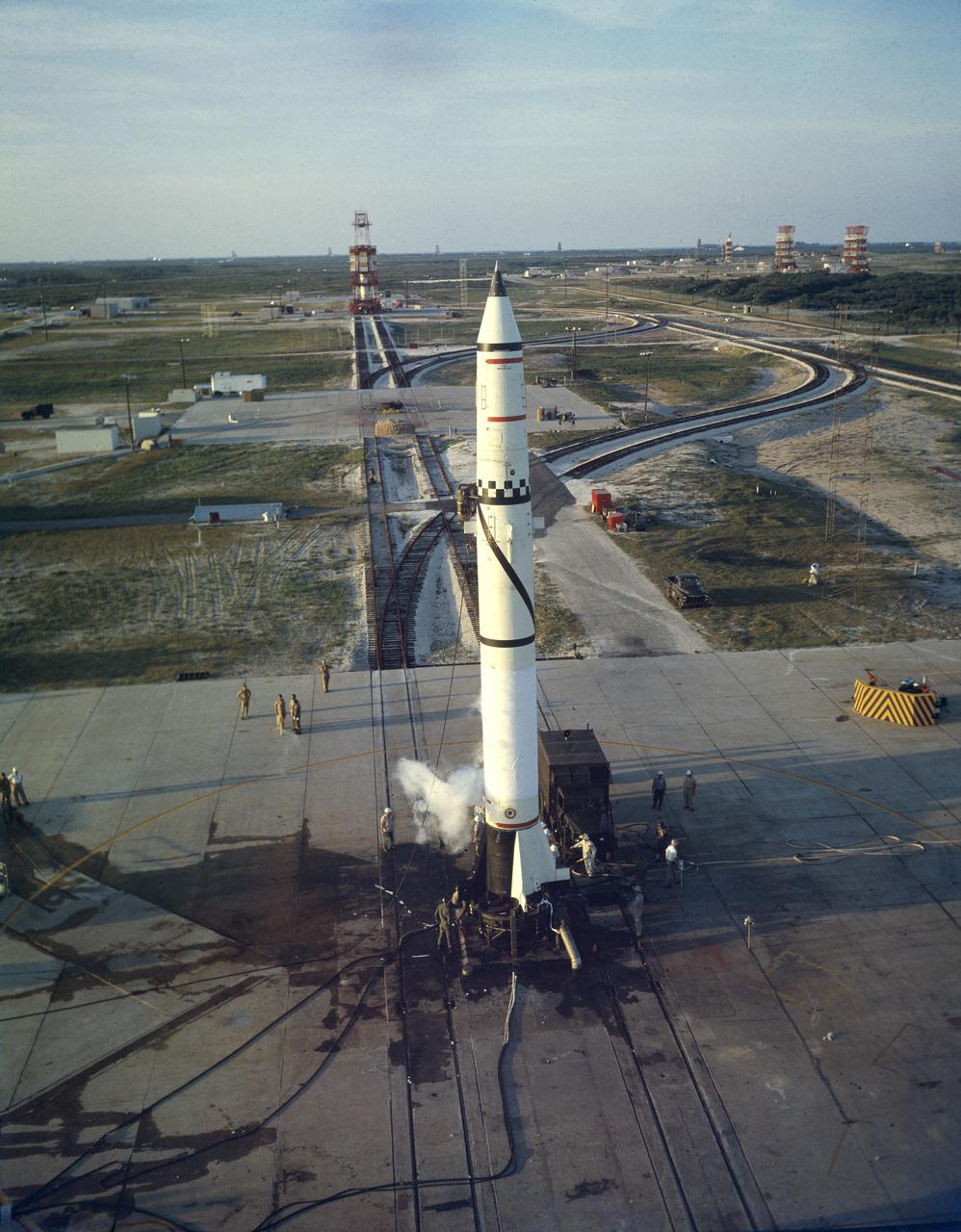

Redstone missile No. 1002 on the launch pad at Cape Canaveral, Florida, on May 16, 1958. The Redstone ballistic missile was a high-accuracy, liquid-propelled, surface-to-surface missile developed by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency, Redstone Arsenal, in Huntsville, Alabama, under the direction of Dr. von Braun. The Redstone engine was a modified and improved version of the Air Force's Navaho cruise missile engine of the late forties. The A-series, as this would be known, utilized a cylindrical combustion chamber as compared with the bulky, spherical V-2 chamber. By 1951, the Army was moving rapidly toward the design of the Redstone missile, and production was begun in 1952. Redstone rockets became the "reliable workhorse" for America's early space program. As an example of the versatility, Redstone was utilized in the booster for Explorer 1, the first American satellite, with no major changes to the engine or missile

The Jupiter rocket was designed and developed by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA). ABMA launched the Jupiter-A at Cape Canaveral, Florida, on March 1, 1957. The Jupiter vehicle was a direct derivative of the Redstone. The Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) at Redstone Arsenal, Alabama, continued Jupiter development into a successful intermediate ballistic missile, even though the Department of Defense directed its operational development to the Air Force. ABMA maintained a role in Jupiter RD, including high-altitude launches that added to ABMA's understanding of rocket vehicle operations in the near-Earth space environment. It was knowledge that paid handsome dividends later.
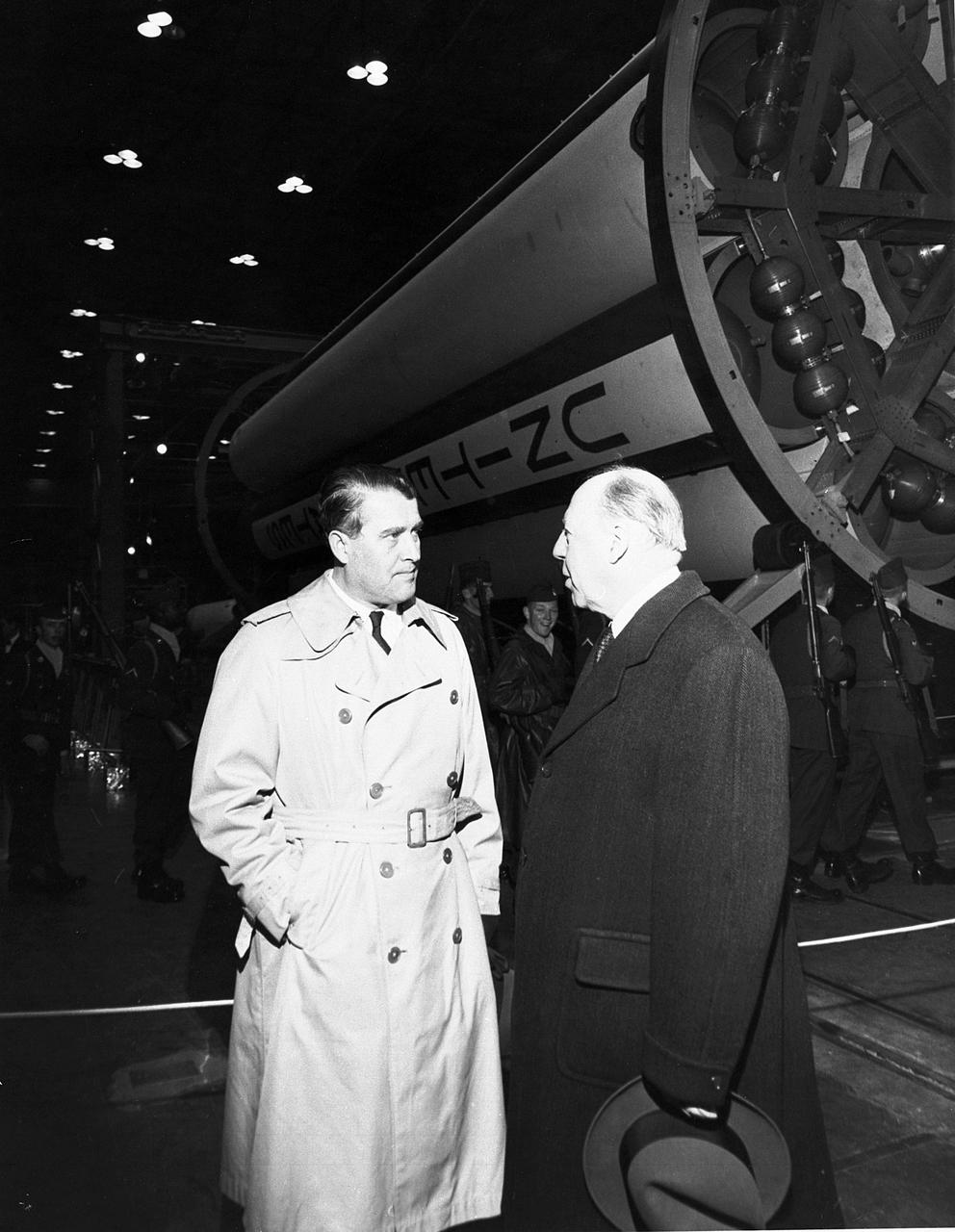

This photograph was taken in 1960 and shows Dr. von Braun, left, and Secretary of the Army, Wilbur Brucker in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) Fabrication Laboratory.
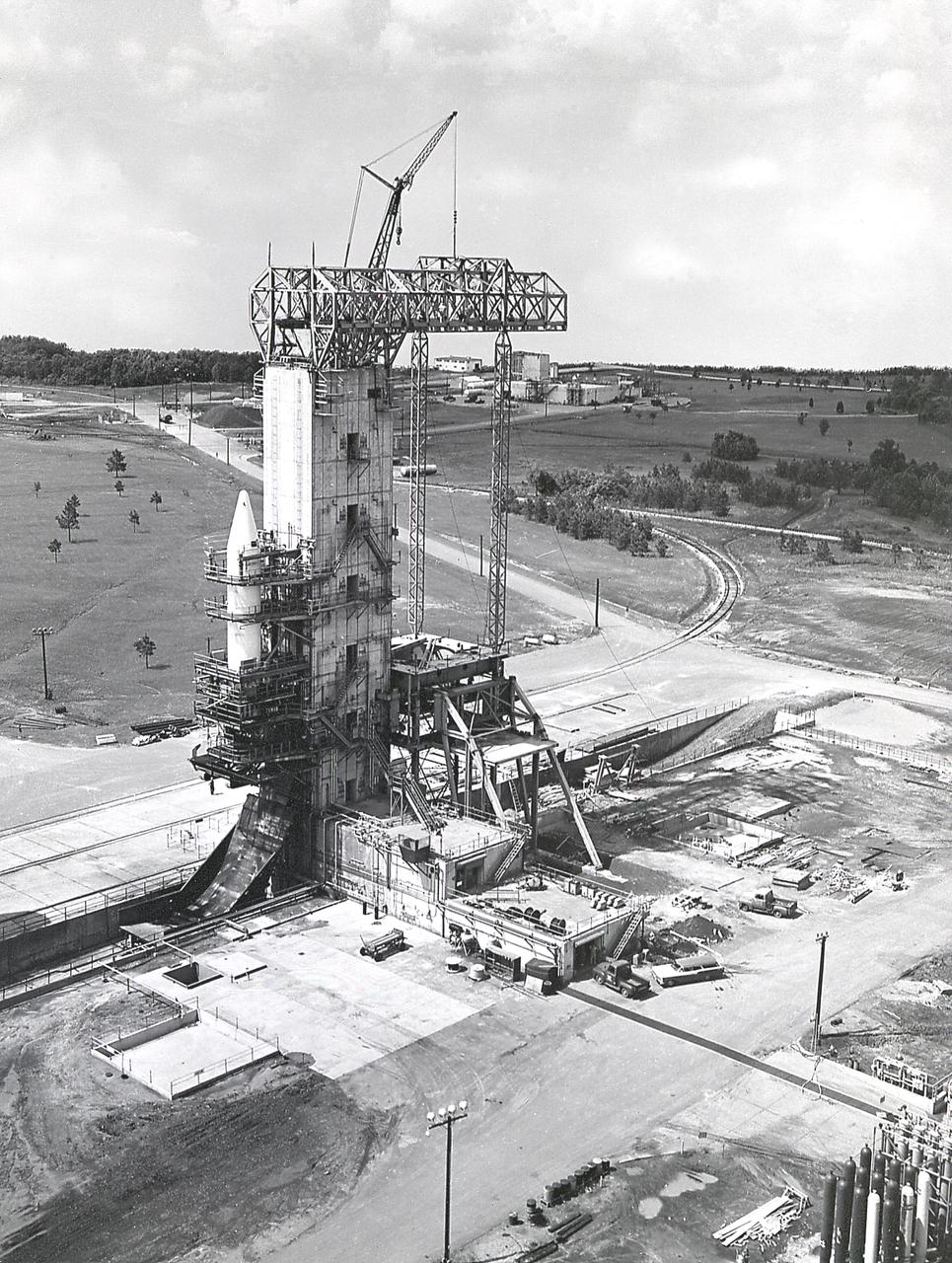
The Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test tower being modified for testing the Saturn booster.
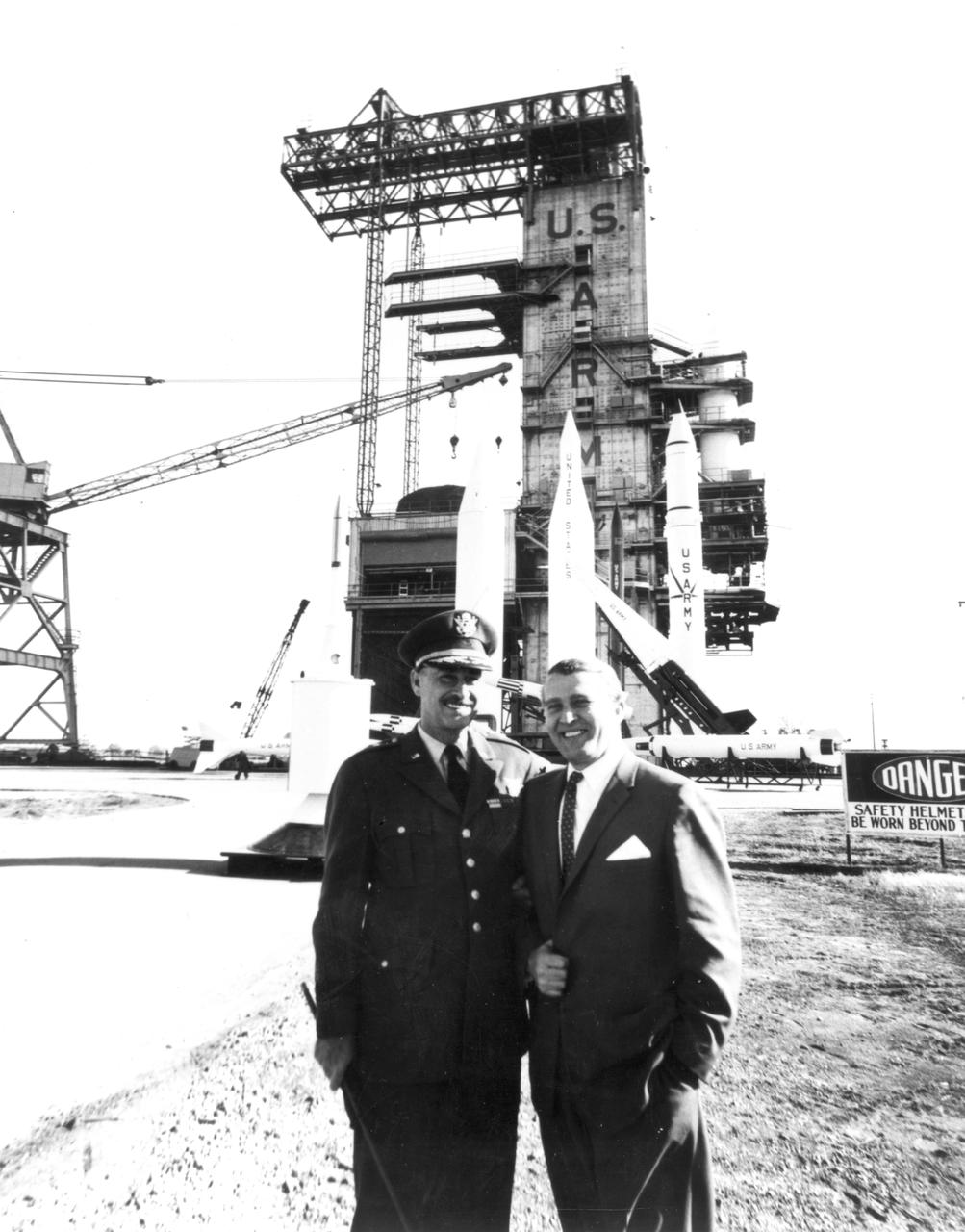

Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC) Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun, is pictured here with Army Ballistic Missile Agency’s (ABMA) Commanding General, J.B. Medaris, before a display of Army missles at the ABMA test lab.
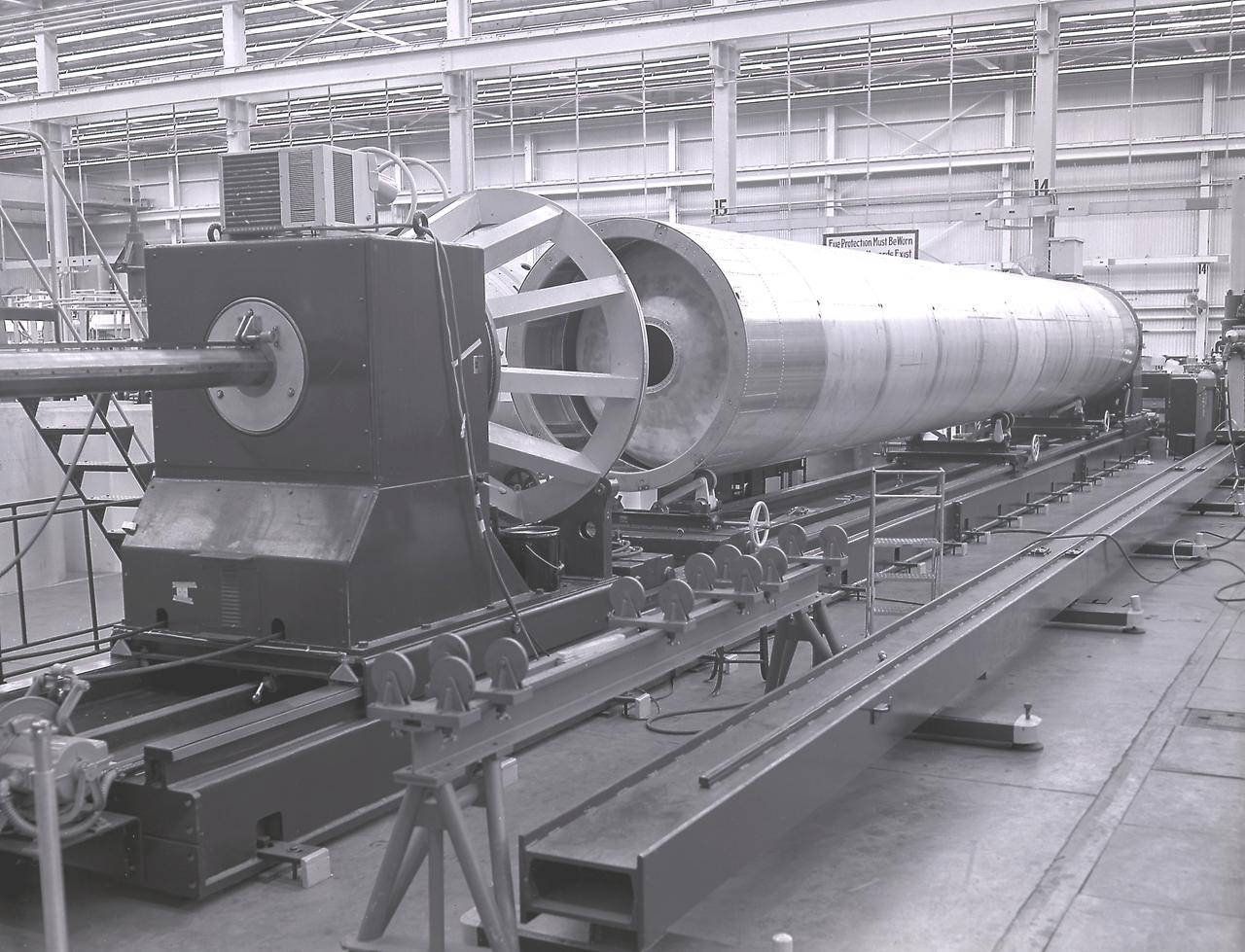
The first circumferential welding being applied on a Saturn fuel container in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) fabrication laboratory, Building 4707, in May 1959.
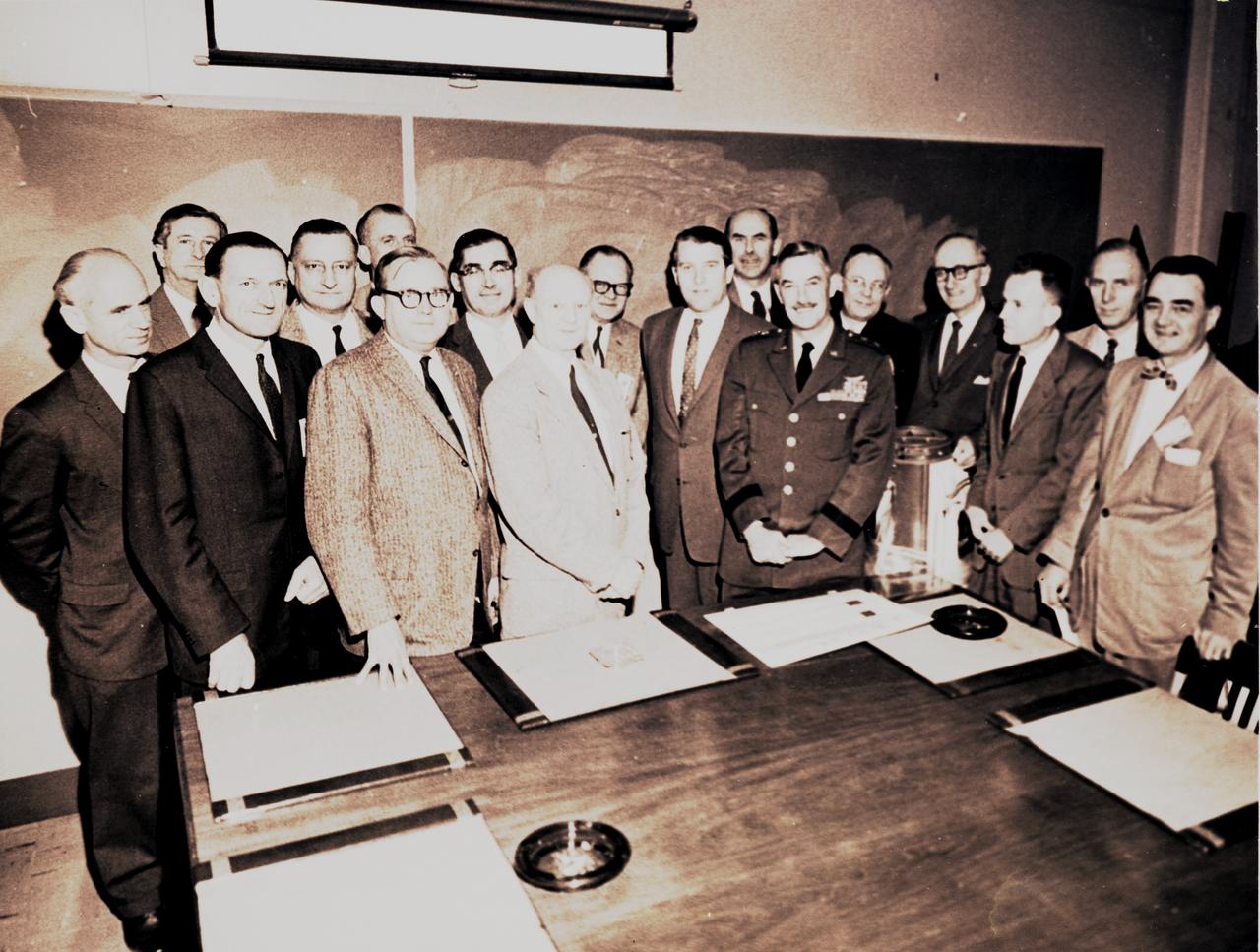

This photograph of Dr. von Braun, shown here to the left of General Bruce Medaris, was taken in the fall of 1959, immediately prior to Medaris' retirement from the Army. At the time, von Braun and his associates worked for the Army Ballistics Missile Agency in Huntsville, Alabama. Those in the photograph have been identified as Ernst Stuhlinger, Frederick von Saurma, Fritz Mueller, Hermarn Weidner, E.W. Neubert (partially hidden), W.A. Mrazek, Karl Heimburg, Arthur Rudolph, Otto Hoberg, von Braun, Oswald Lange, Medaris, Helmut Hoelzer, Hans Maus, E.D. Geissler, Hans Heuter, and George Constan.
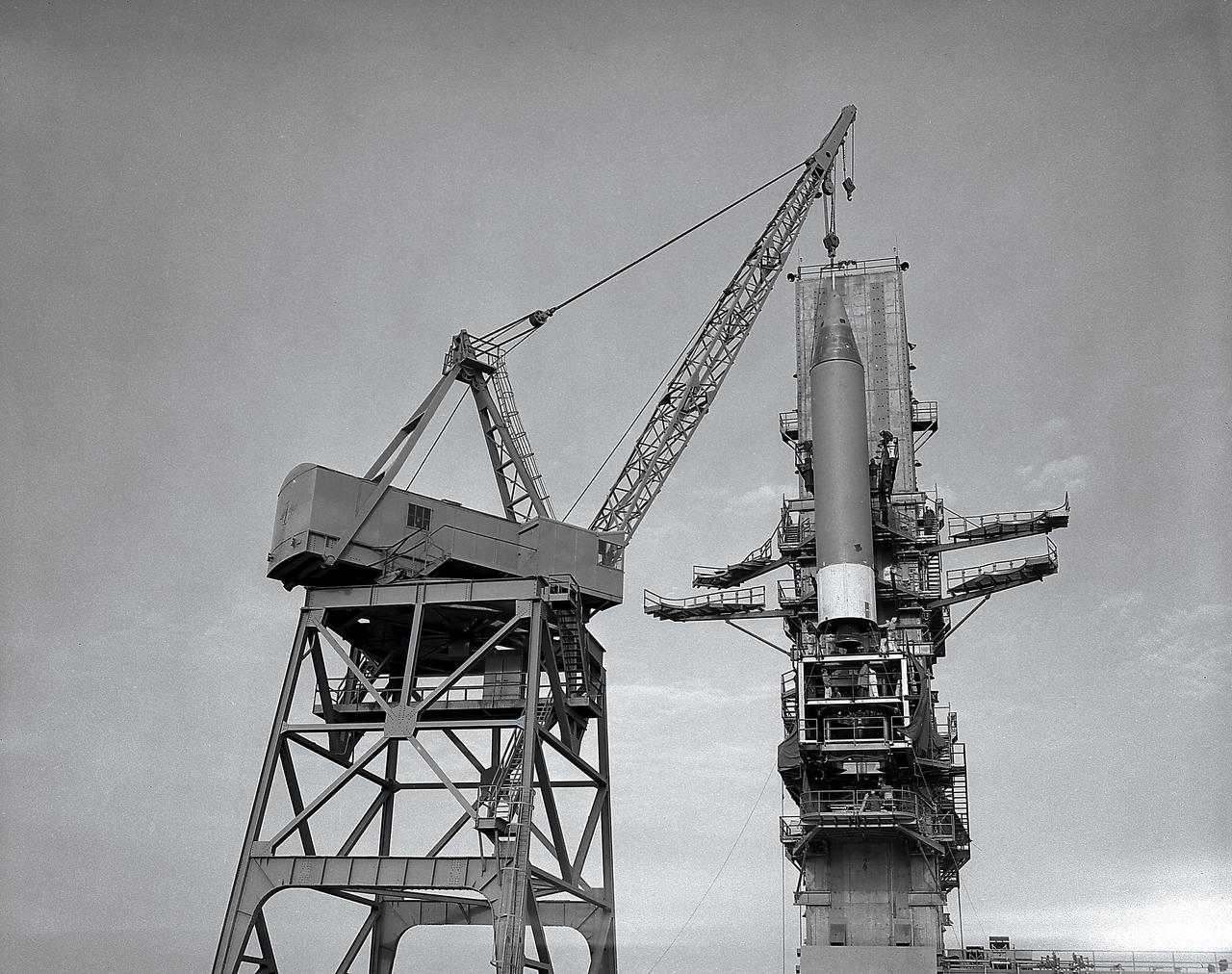

Installation of a Jupiter missile in ABMA (Army Ballistic Missile Agency) West Test Stand, Jan. 16, 1957. Jupiter was a 1500-mile range missile
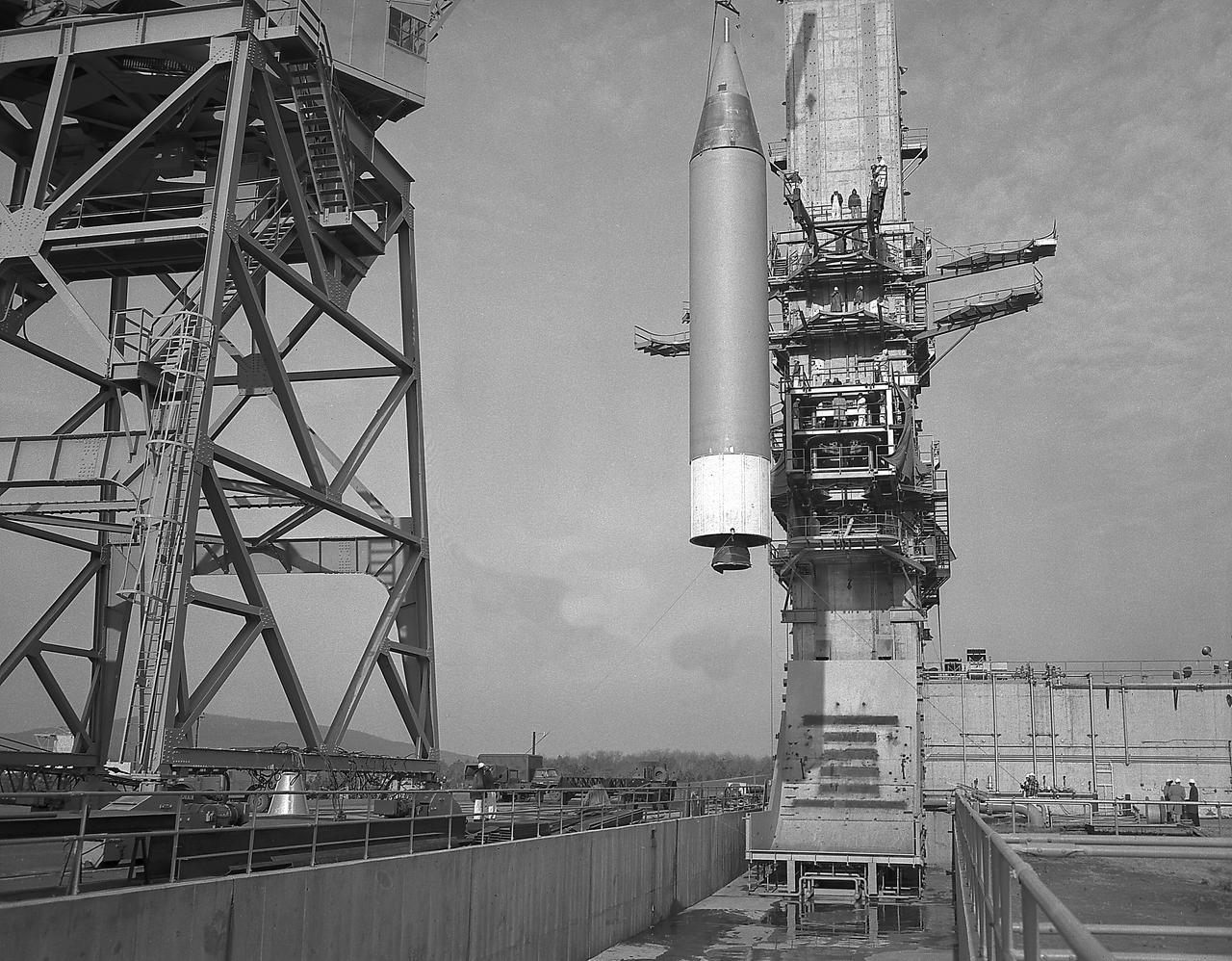

Installation of a Jupiter Missile in ABMA (Army Ballistic Missile Agency) West Test Stand, Jan. 16, 1957. Jupiter was a 1500-mile range missile
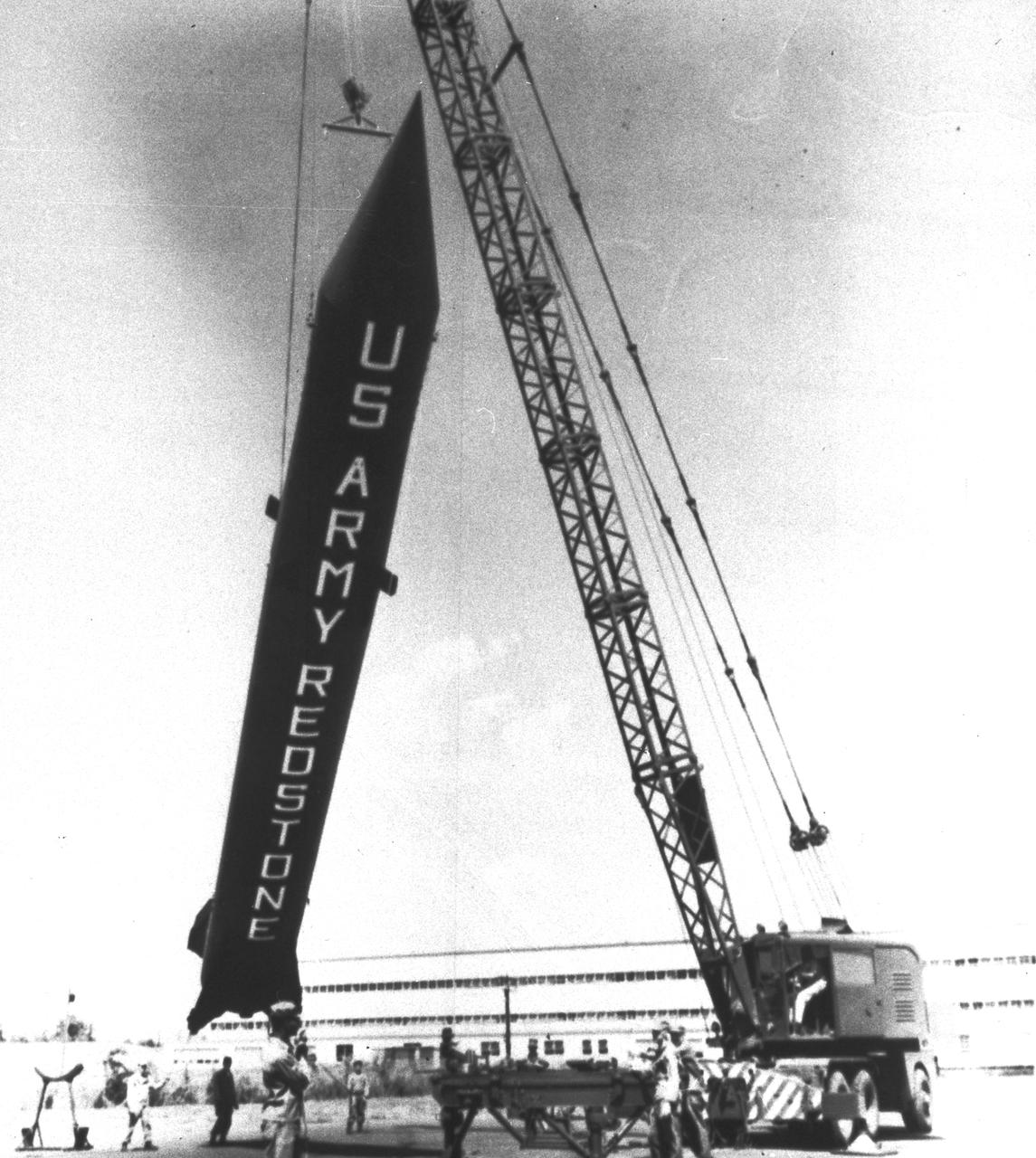

U.S. Army Redstone Rocket: The Redstone ballistic missile was a high-accuracy, liquid-propelled, surface-to-surface missile developed by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency, Redstone Arsenal, in Huntsville, Alabama, under the direction of Dr. von Braun. The Redstone rocket was also known as "Old Reliable" because of its many diverse missions. The first Redstone Missile was launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida on August 30, 1953.
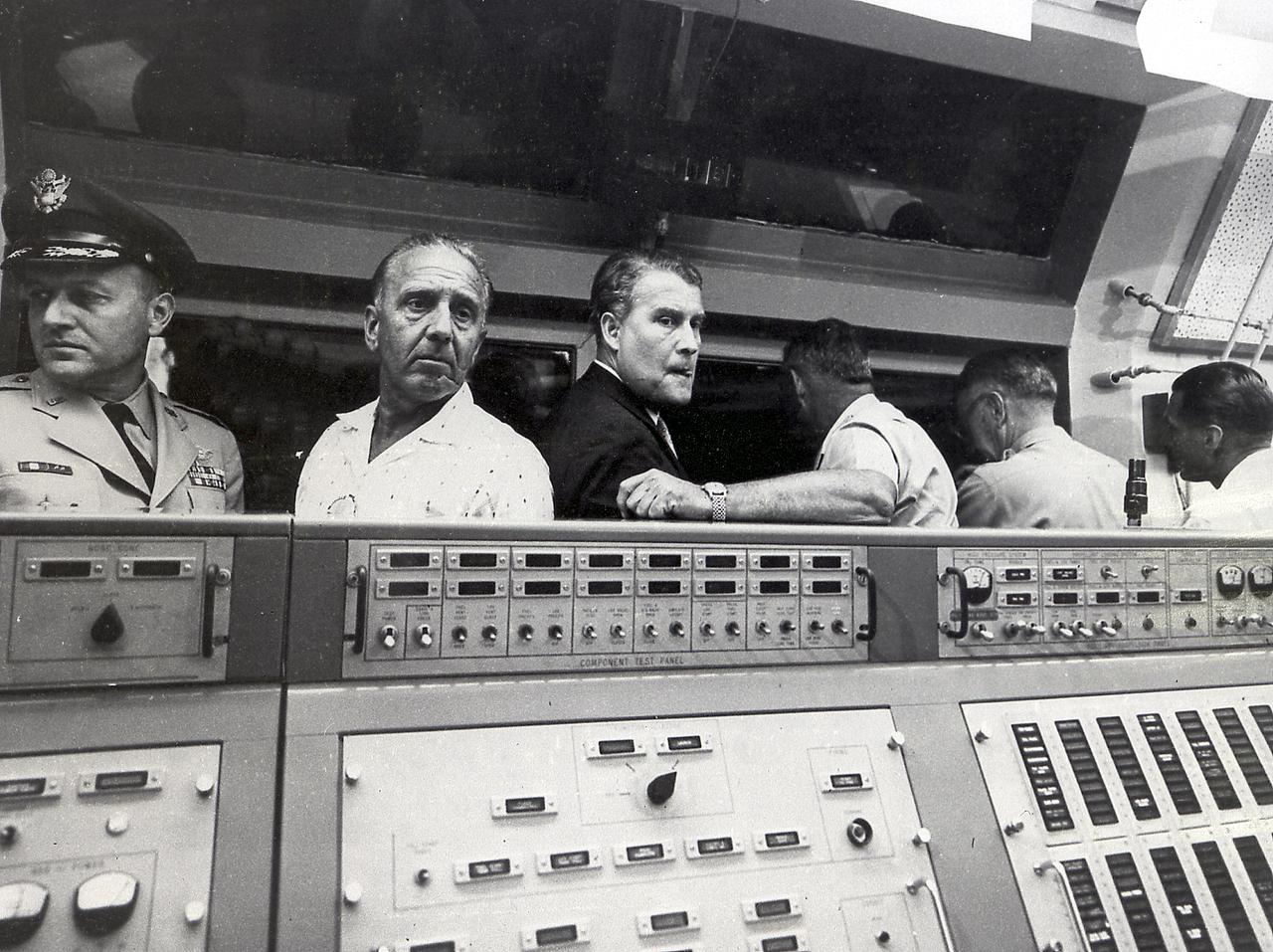

Dr. von Braun, Director of the Development Operations Divisons, and Dr. Debus, Director of the Missile Firing Laboratory; Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA), in the blockhouse during the launch of the Pioneer IV, March 3, 1959.
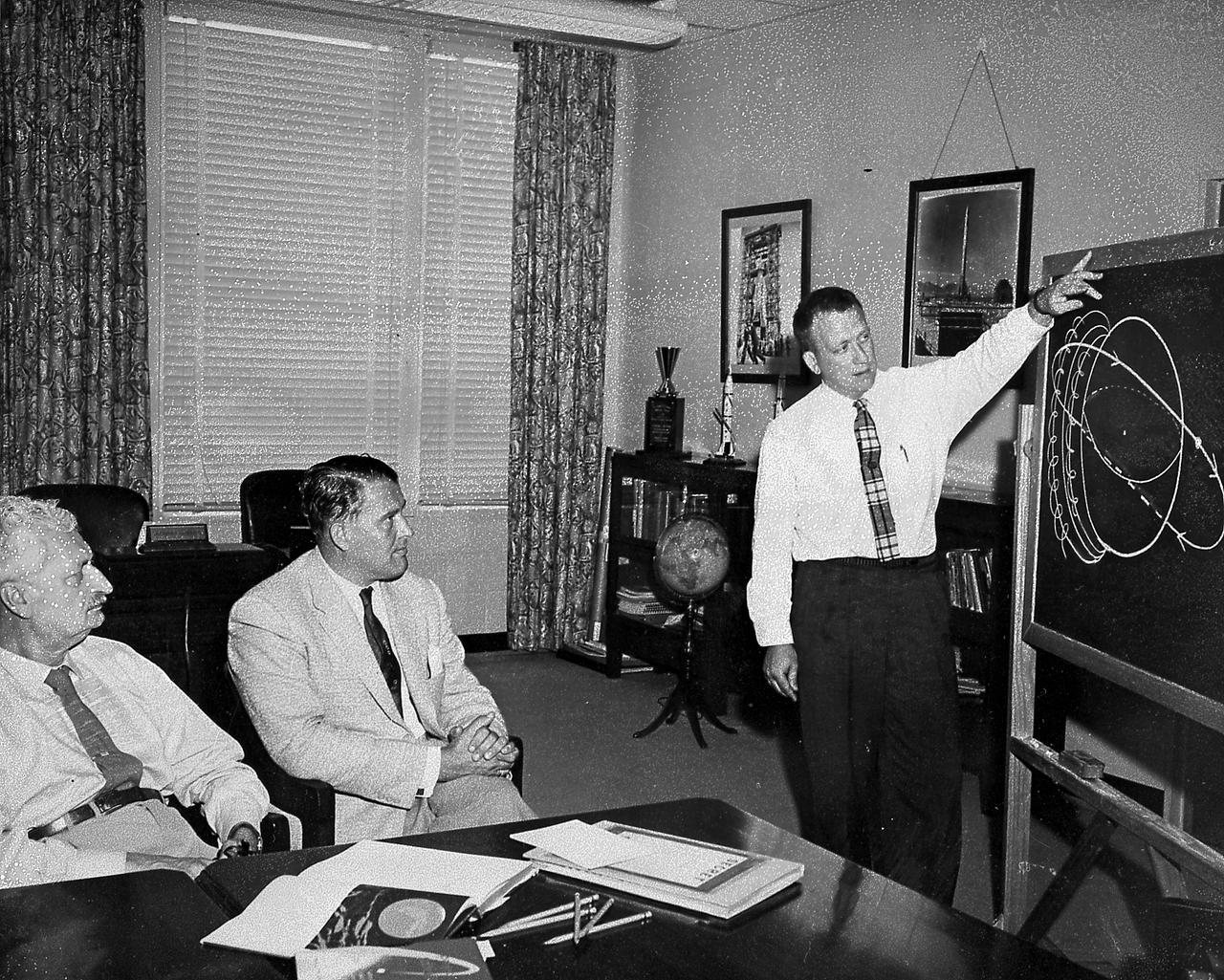

Professor Hermann Oberth and Dr. von Braun are briefed on satellite orbits by Dr. Charles A. Lundquist at Army Ballistic Missile Agency, Redstone Arsenal, Huntsville, Alabama.
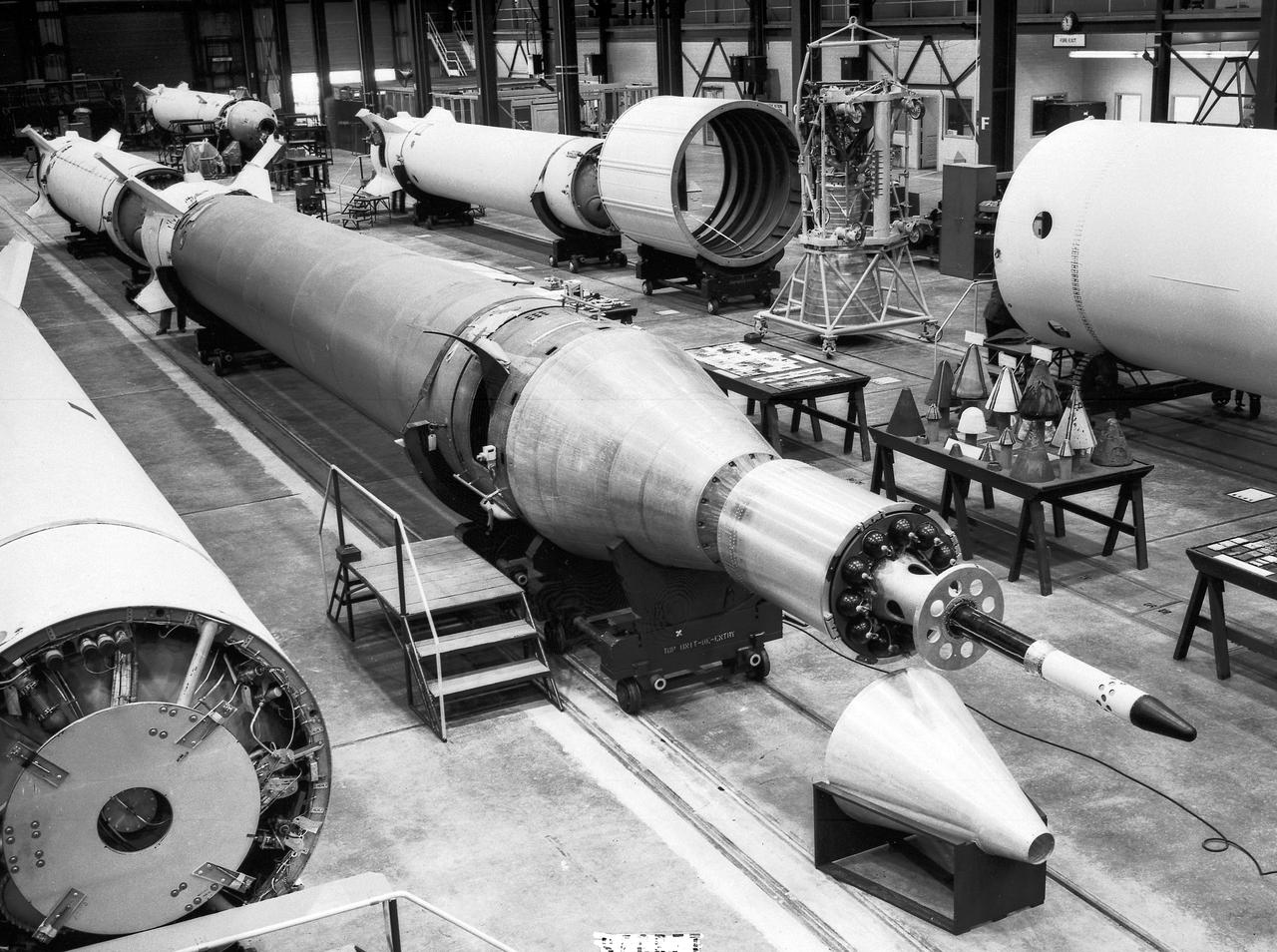

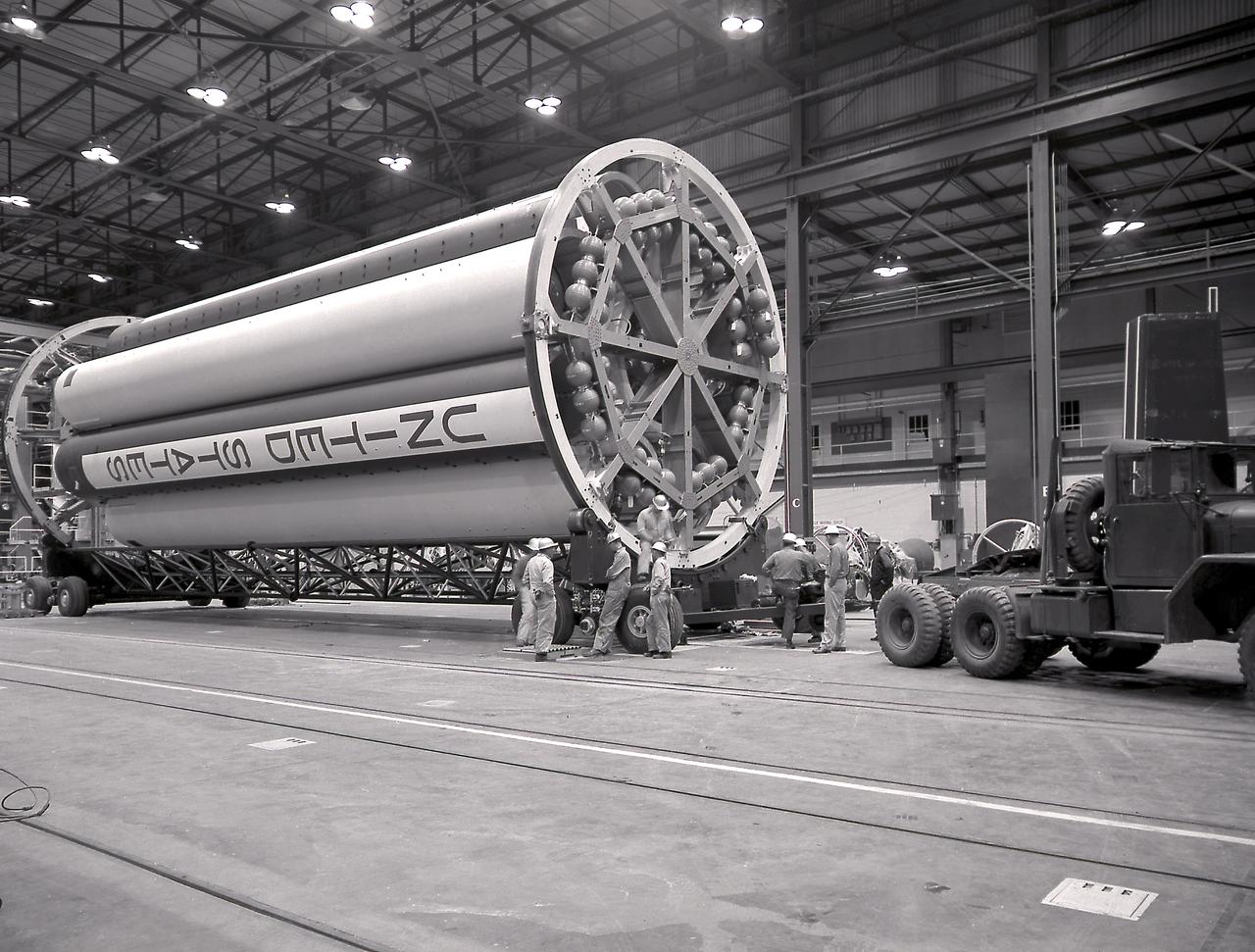
Jupiter-C Missile No. 27 assembly at the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA), Redstone Arsenal, in Huntsville, Aalabama. The Jupiter-C was a modification of the Redstone Missile, and originally developed as a nose cone re-entry test vehicle for the Jupiter Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM). Jupiter-C successfully launched the first American Satellite, Explorer 1, in orbit on January 31, 1958.
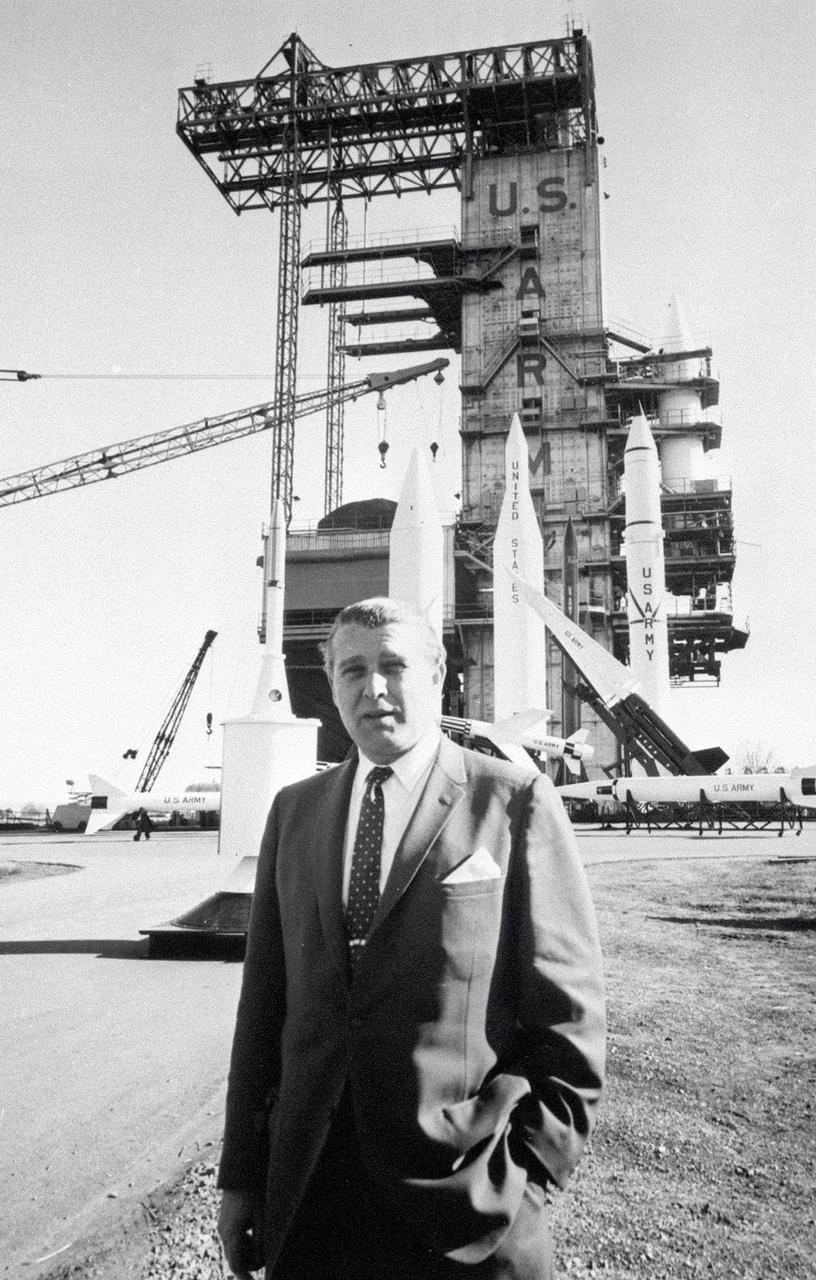

In this photo, Director of the US Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) Development Operations Division, Dr. Wernher von Braun, is standing before a display of Army missiles celebrating ABMA's Fourth Open House. The missiles in the background include (left to right) a satellite on a Juno II shroud with a Nike Ajax pointing left in front of a Jupiter missile. The Lacrosse is in front of the Juno II. The Nike Hercules points skyward in front of the Juno II and the Redstone.
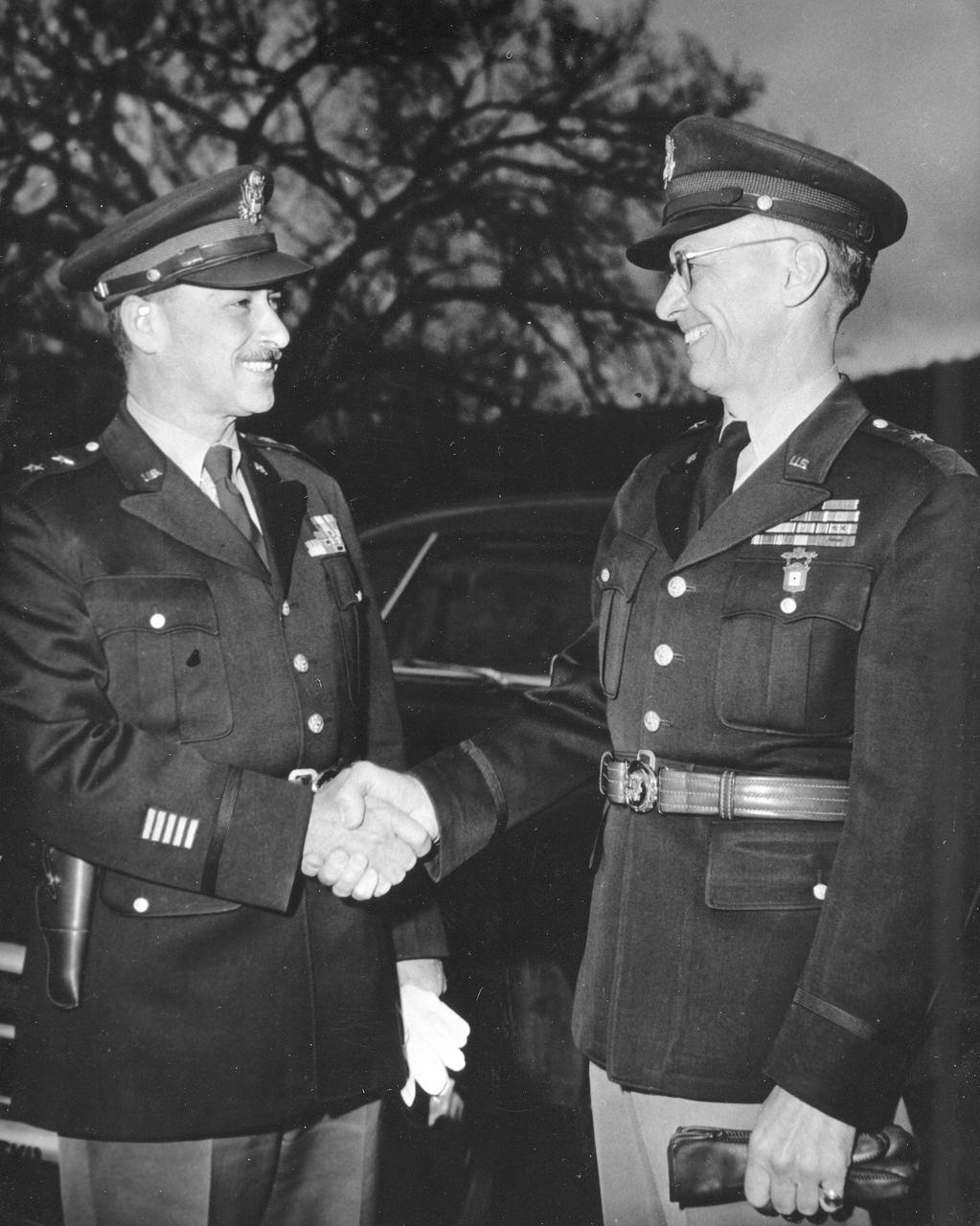

General Medaris, (left) who was a Commander of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama, during 1955 to 1958, shakes hands with Major General Holger Toftoy (right), who consolidated U.S. missile and rocketry development.
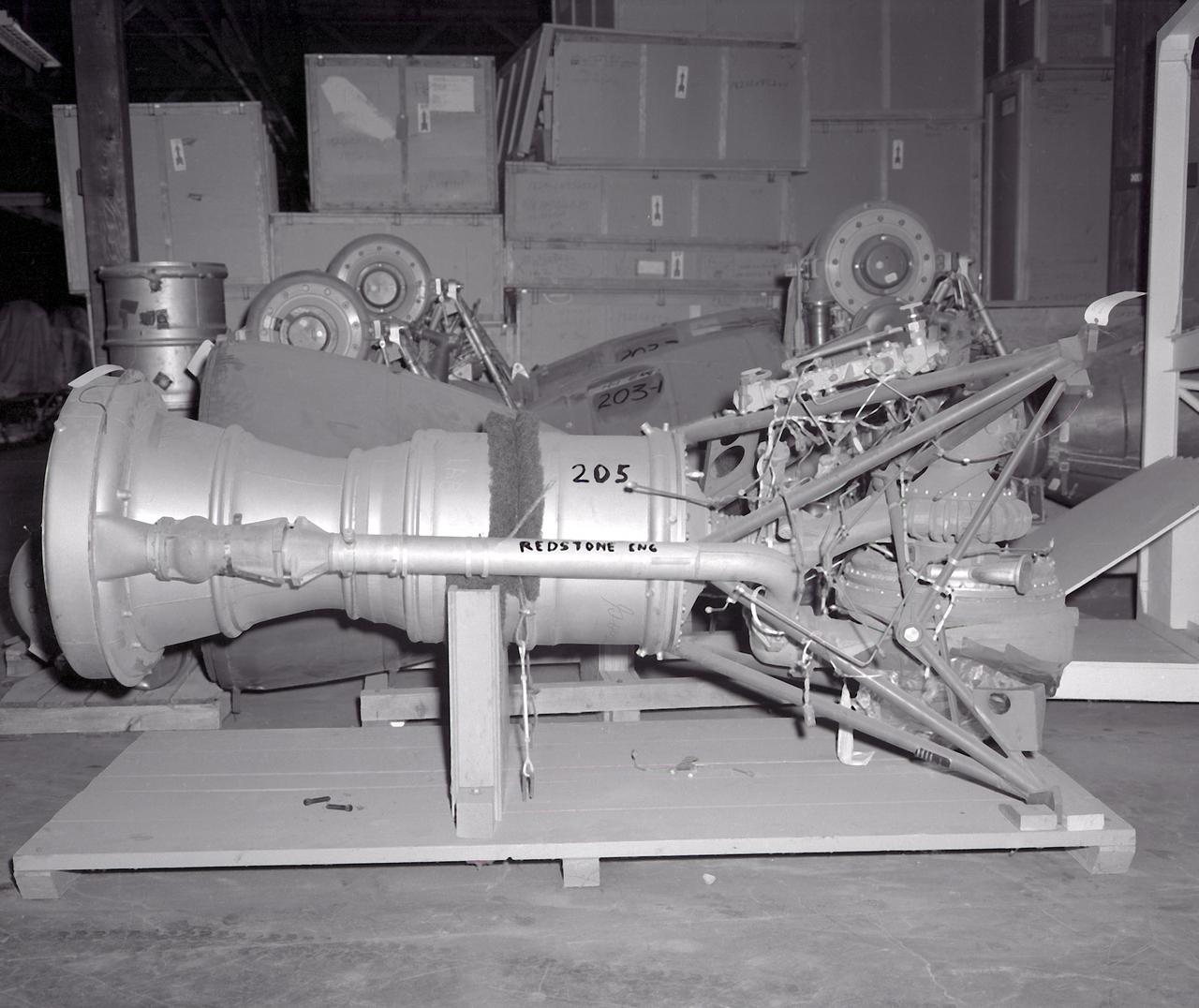
This photograph is of the engine for the Redstone rocket. The Redstone ballistic missile was a high-accuracy, liquid-propelled, surface-to-surface missile developed by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency, Redstone Arsenal, in Huntsville, Alabama, under the direction of Dr. von Braun. The Redstone engine was a modified and improved version of the Air Force's Navaho cruise missile engine of the late forties. The A-series, as this would be known, utilized a cylindrical combustion chamber as compared with the bulky, spherical V-2 chamber. By 1951, the Army was moving rapidly toward the design of the Redstone missile, and the production was begun in 1952. Redstone rockets became the "reliable workhorse" for America's early space program. As an example of its versatility, the Redstone was utilized in the booster for Explorer 1, the first American satellite, with no major changes to the engine or missile.
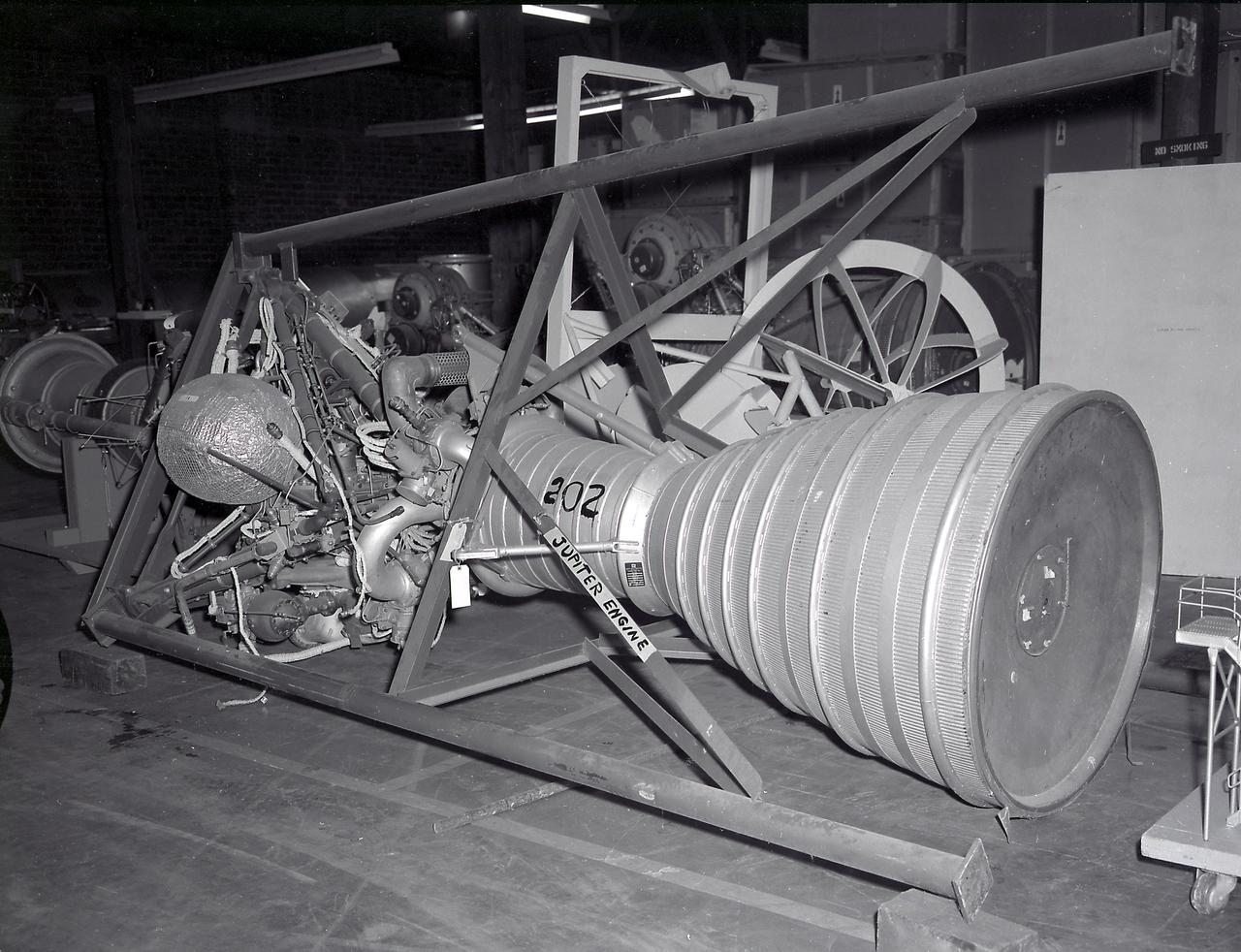
Engine for the Jupiter rocket. The Jupiter vehicle was a direct derivative of the Redstone. The Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) at Redstone Arsenal, Alabama, continued Jupiter development into a successful intermediate ballistic missile, even though the Department of Defense directed its operational development to the Air Force. ABMA maintained a role in Jupiter RD, including high-altitude launches that added to ABMA's understanding of rocket vehicle operations in the near-Earth space environment. It was knowledge that paid handsome dividends later.
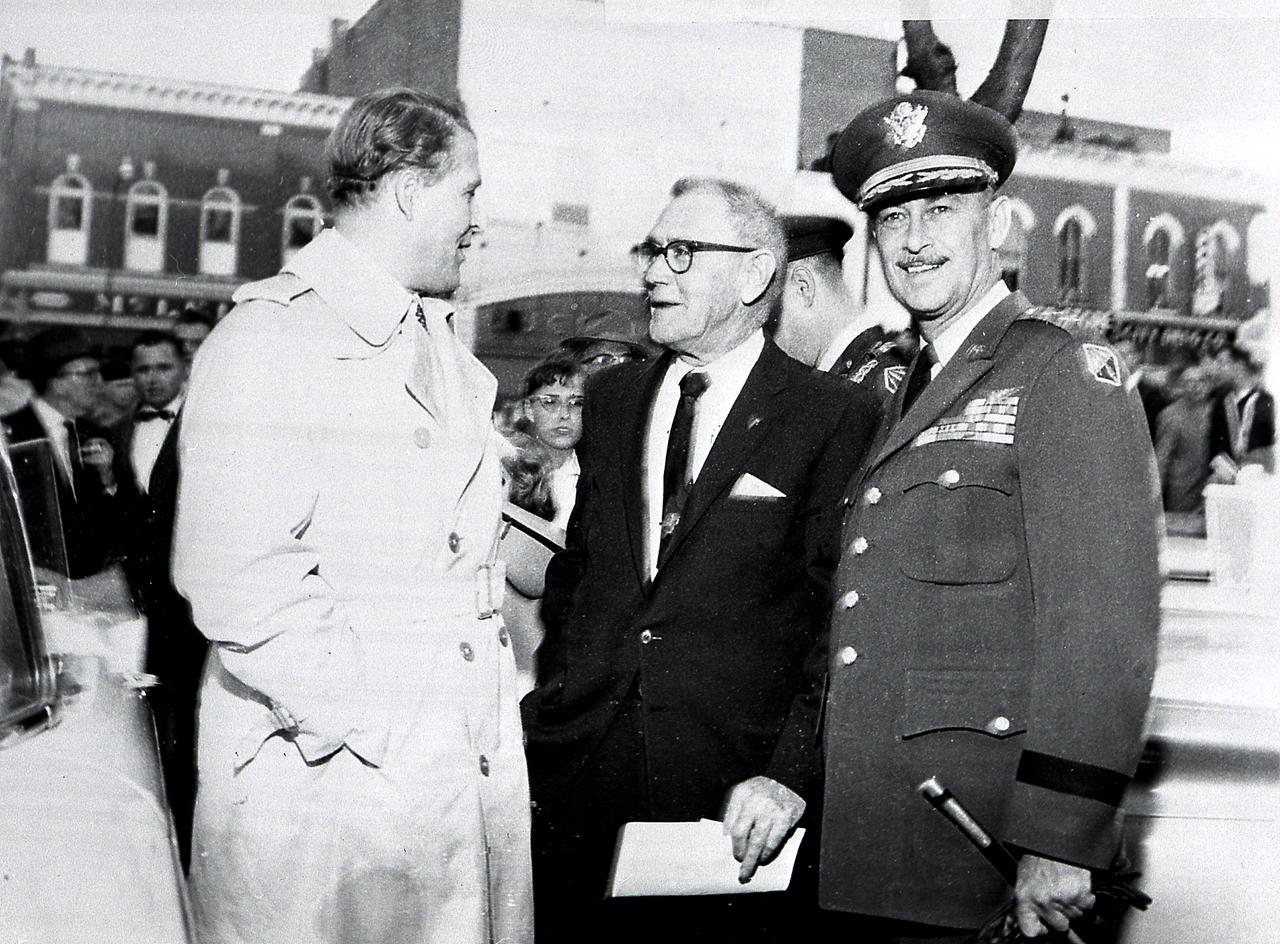

Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director of the U.S. Army Ballistic Missile Agency's (ABMA) Development Operations Division, talks to Huntsville Mayor R. B. "Speck" Searcy, center, and Army Ordnance Missile Command (ARMC) Major General John B. Medaris, right, during "Moon Day" celebrations in downtown Huntsville, Alabama. (Courtesy of Huntsville/Madison County Public Library)
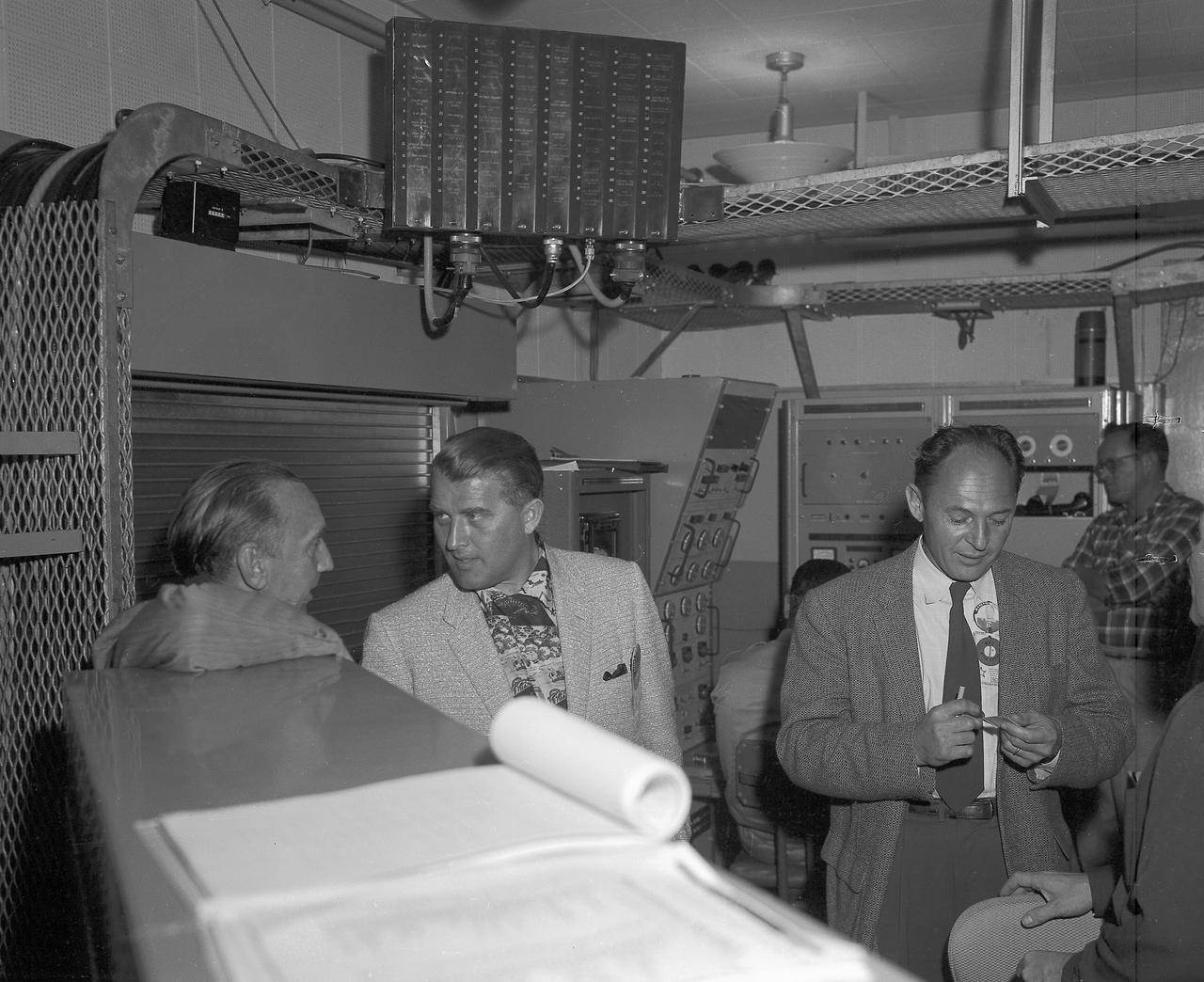

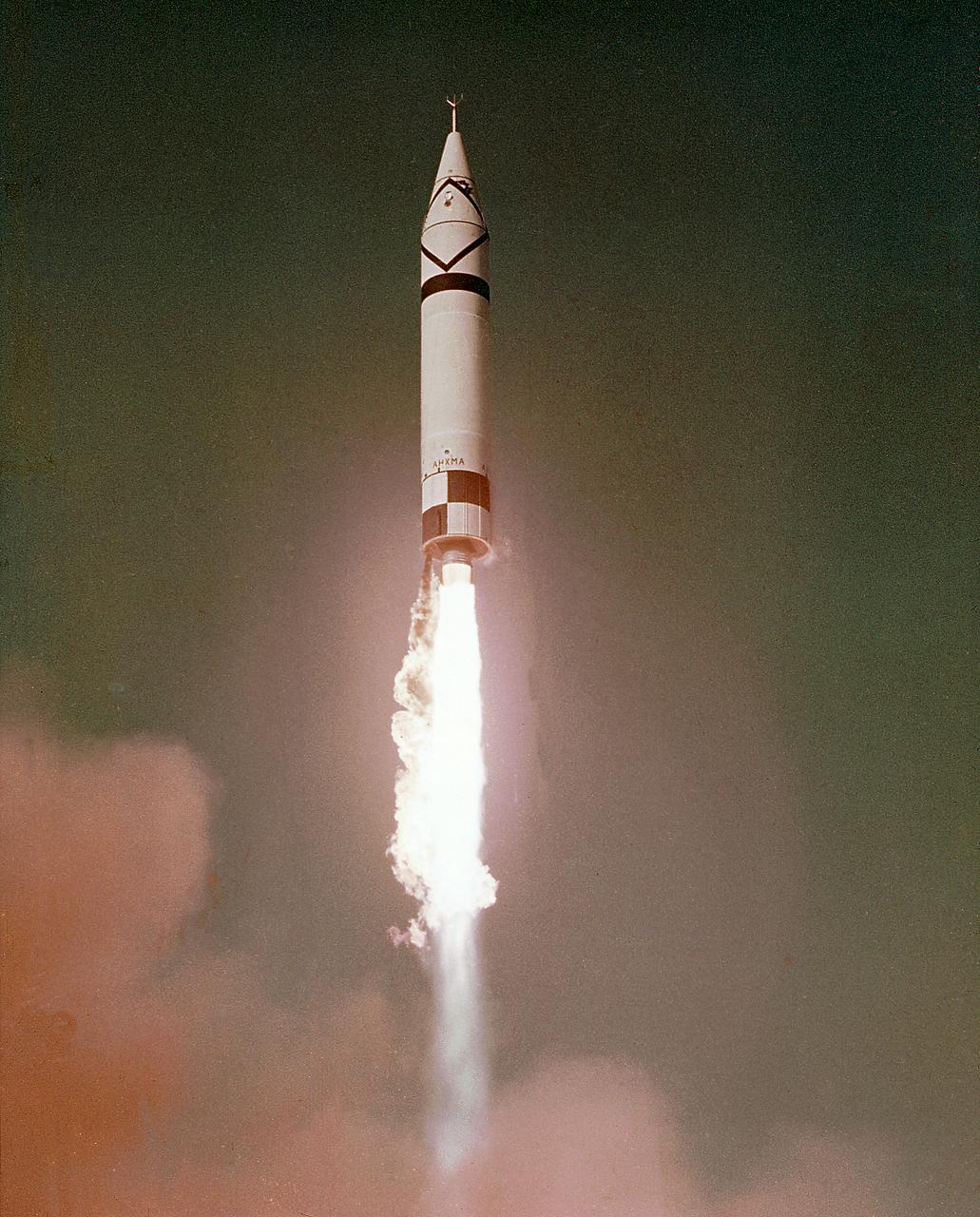
In this photo, (left to right) Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) Missile Firing Laboratory Chief Dr. Kurt Debus, Director of the ABMA Development Operations Division, Dr. von Braun and an unidentified individual in blockhouse during the CM-21 (Jupiter) firing. The Jupiter missile CM-21 became the first Chrysler production qualification missile to be fired and in March 1959 launched the Pioneer IV.
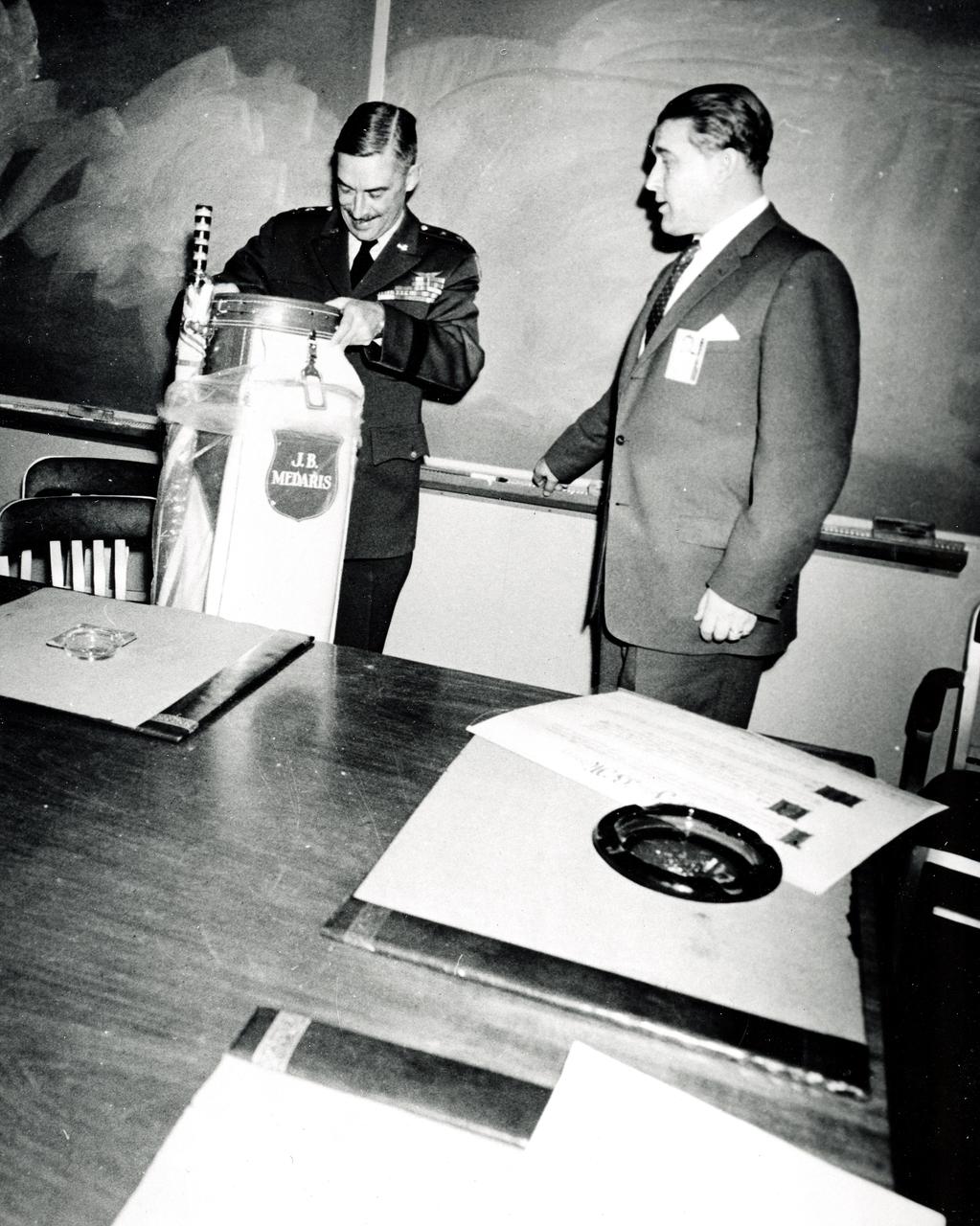

Marshall Space Flight Center Director Wernher von Braun presents General J.B. Medaris with a new golf bag. General Medaris, (left) was a Commander of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama during 1955 to 1958.
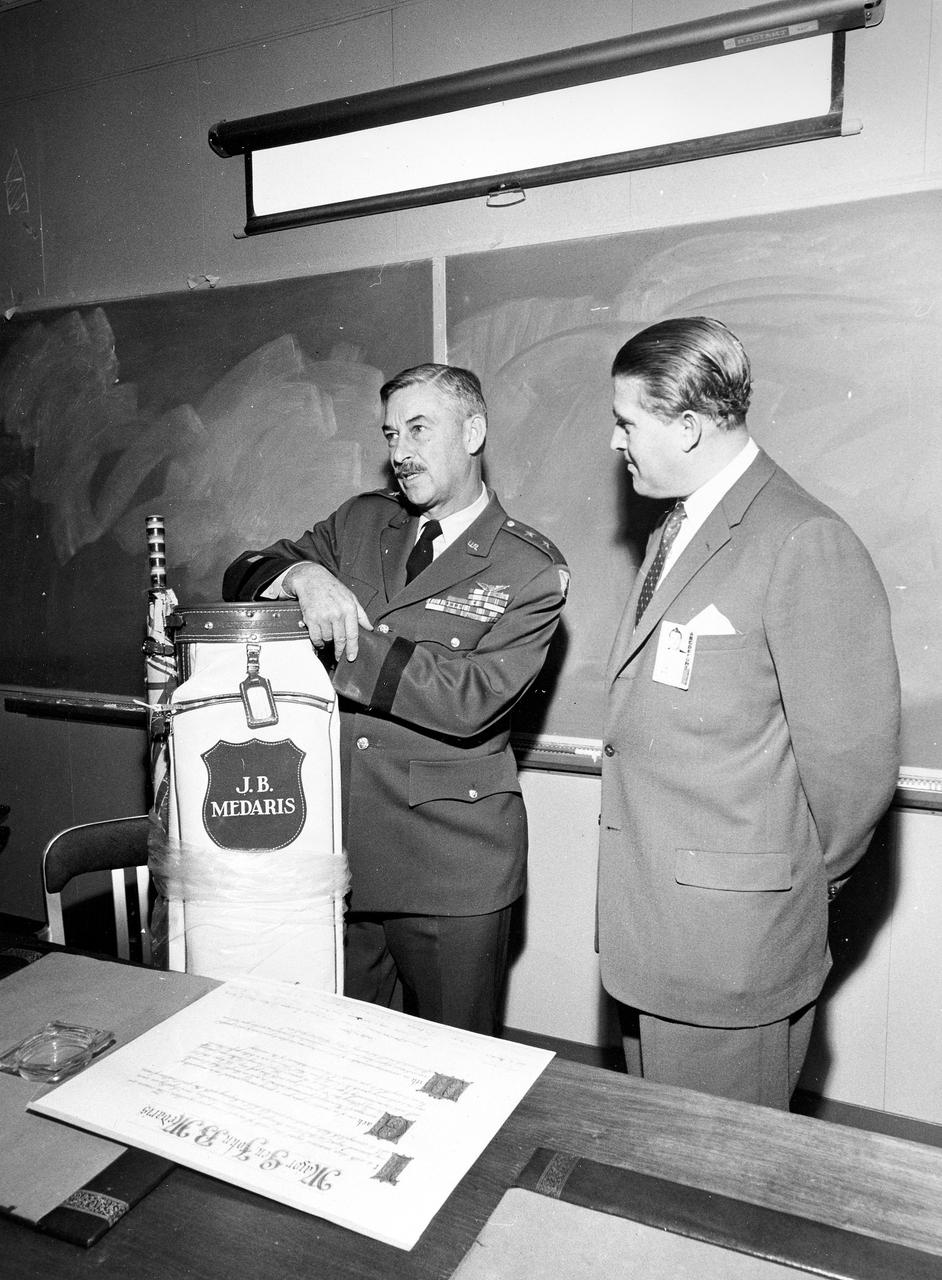

Marshall Space Flight Center Director Wernher von Braun presents General J.B. Medaris with a new golf bag. General Medaris, (left) was a Commander of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama during 1955 to 1958.
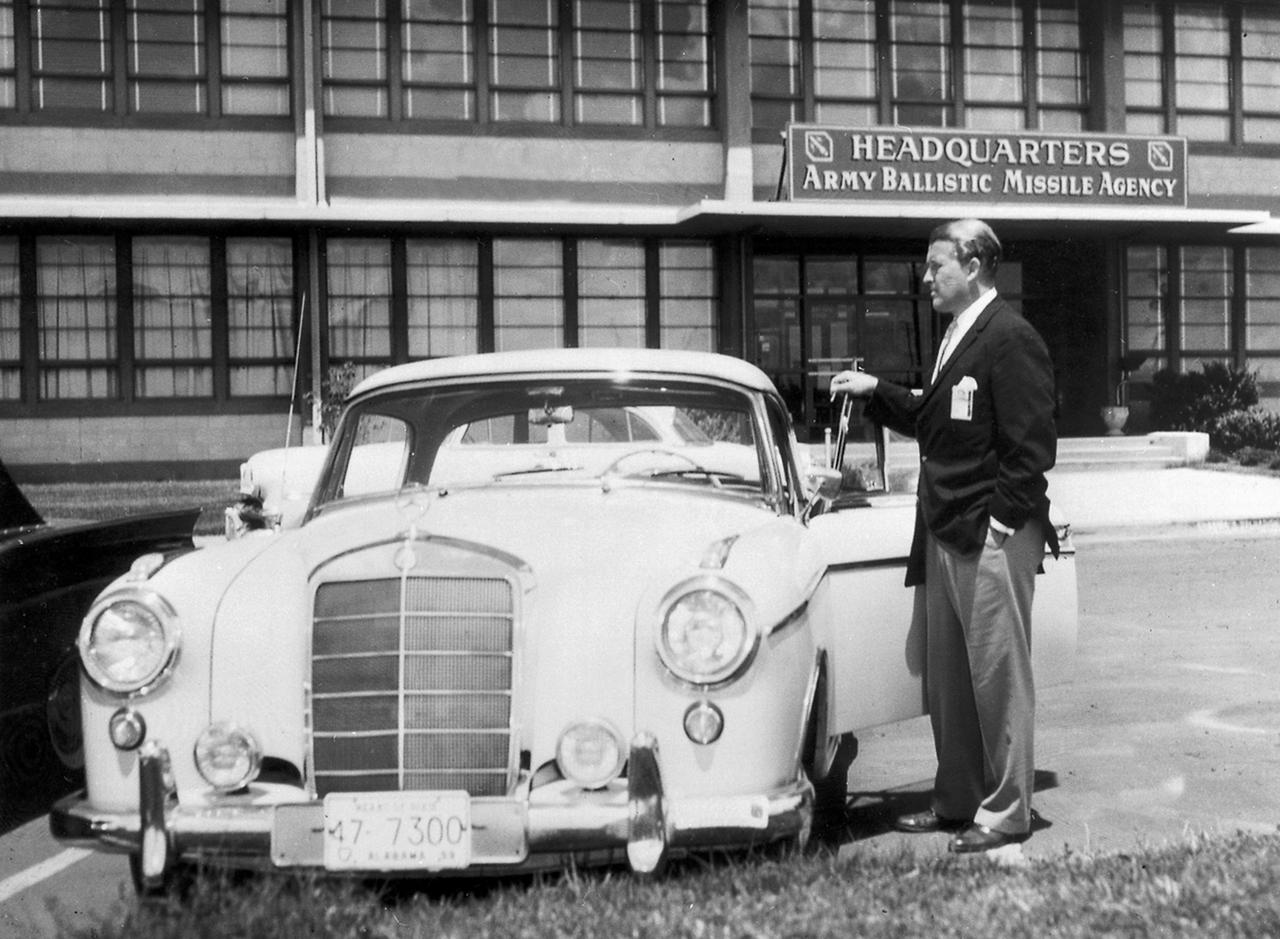

In this picture, Dr. Wernher von Braun, who was serving as Director of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency's (ABMA) Development Operations Division, is shown posed with his Mercedes 220SE automobile in front of Redstone Building 4488, which houses the ABMA.
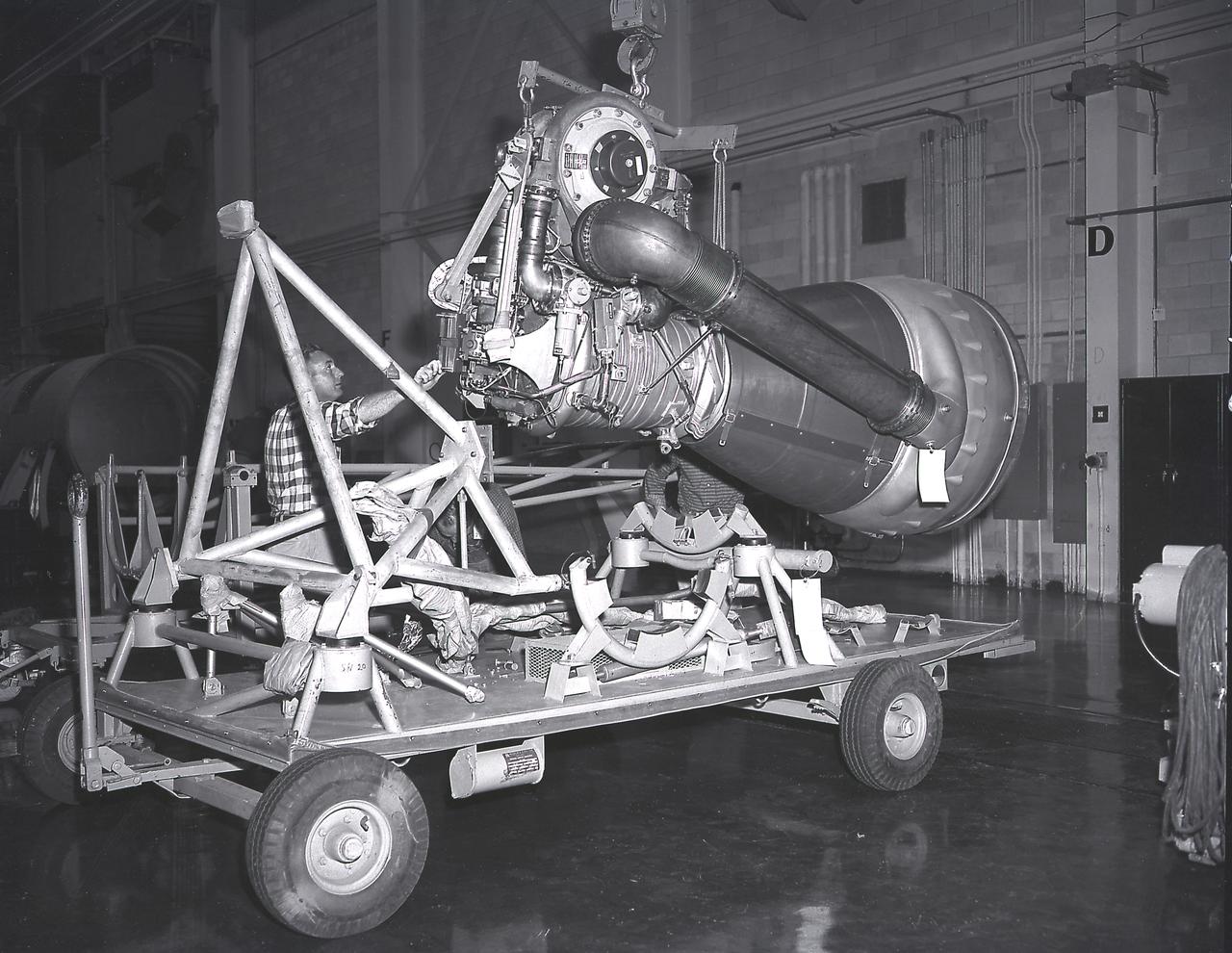
Alignment of the H-1 engine performed in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA ), building 4708, in February 1960. A cluster of eight H-1 engines were used to thrust the first stage of the Saturn I launch vehicle. The H-1 engine was developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
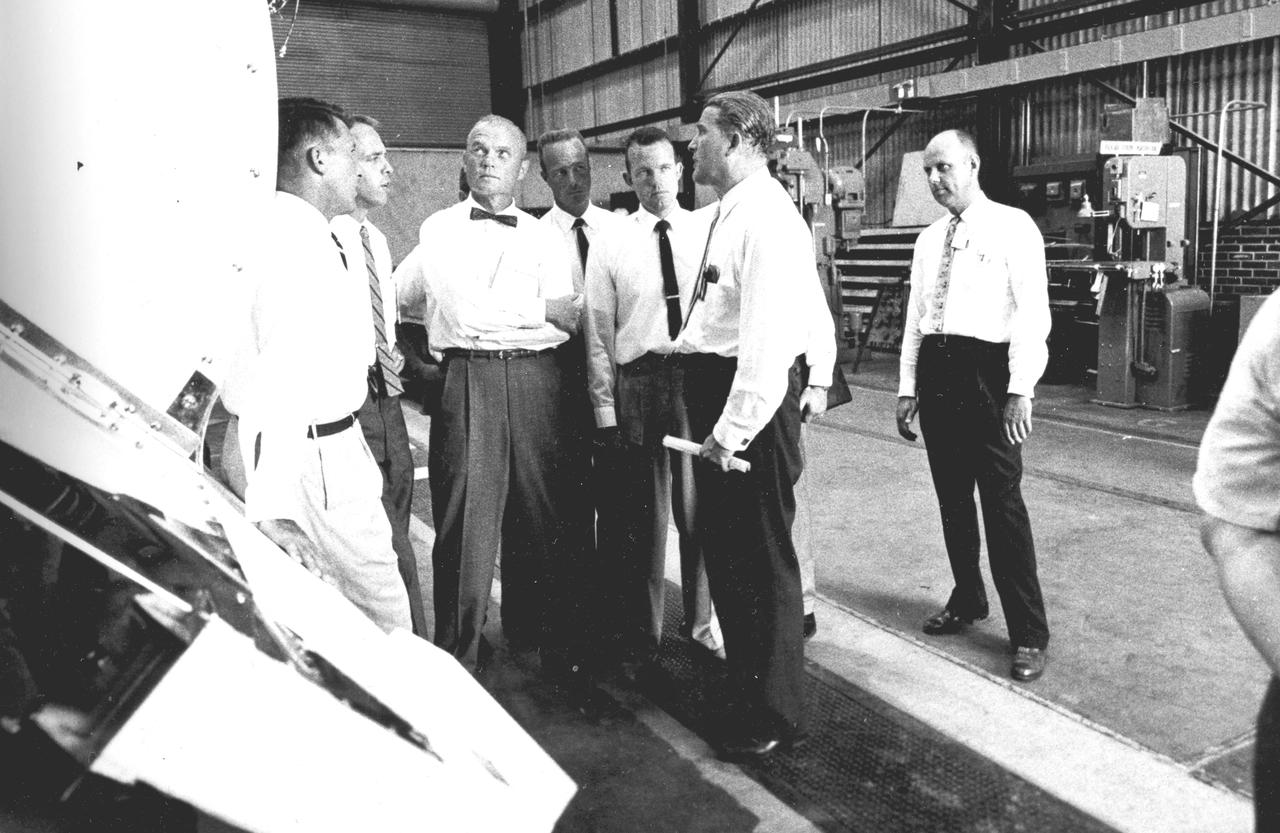

Five of the seven original astronauts are seen with Dr. von Braun inspecting the Mercury-Redstone hardware in the Fabrication Laboratory of Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) in 1959. Left to right: Astronauts Walter Schirra, Alan Shepard, John Glenn, Scott Carpenter, Gordon Cooper, and Dr. von Braun.
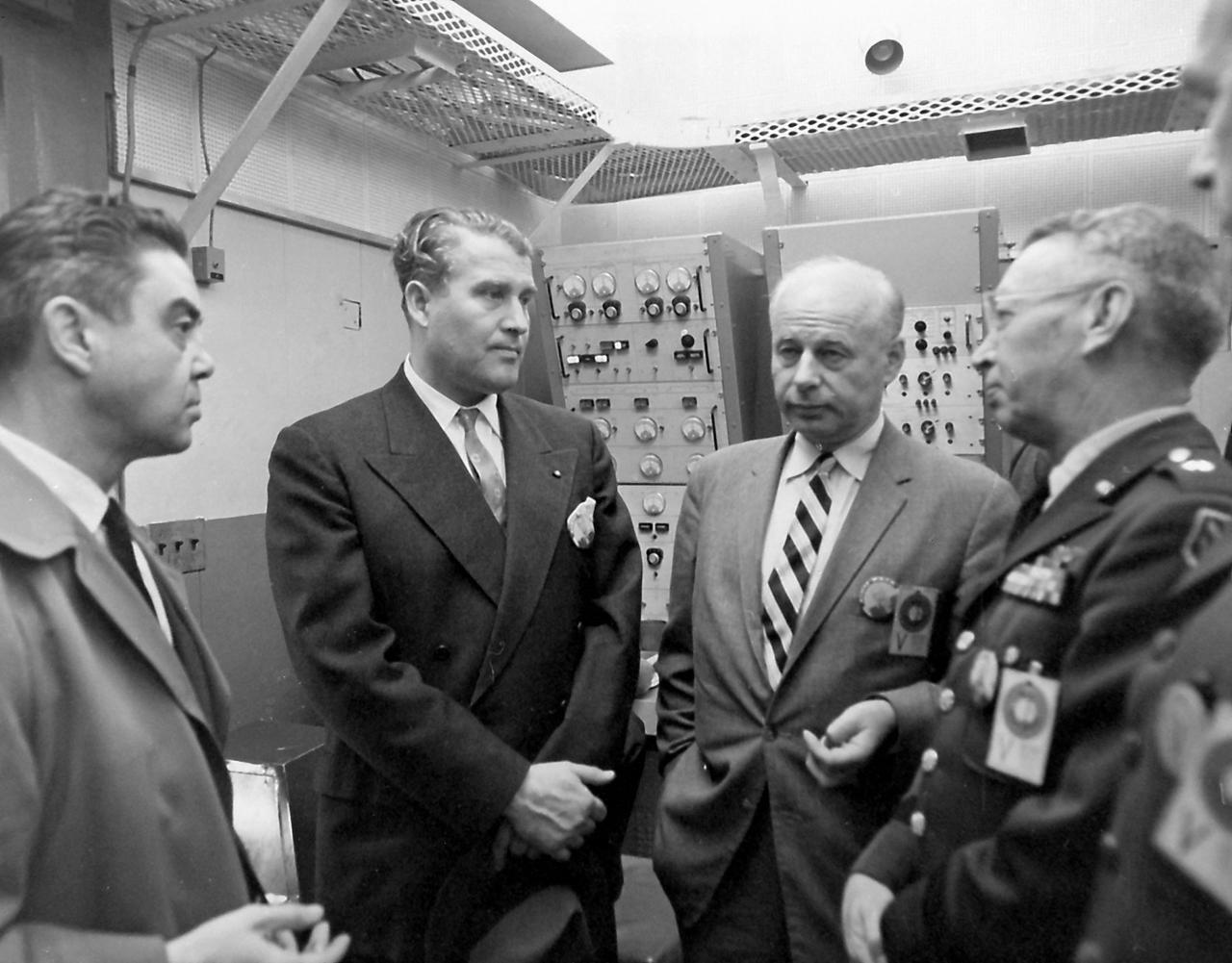

In this 1959 photo, taken at Cape Canaveral, Florida, Dr. von Braun (2nd from left) Director of the U.S. Army Ballistic Missile Agency's (ABMA) Development Operations Division, is shown conferring with Air Force Major General Donald R. Ostrander (left), on assignment at NASA as launch vehicle director; Dr. Eberhard Rees, deputy to Dr. von Braun, and Army Brigadier General John Barclay, commander of the ABMA.
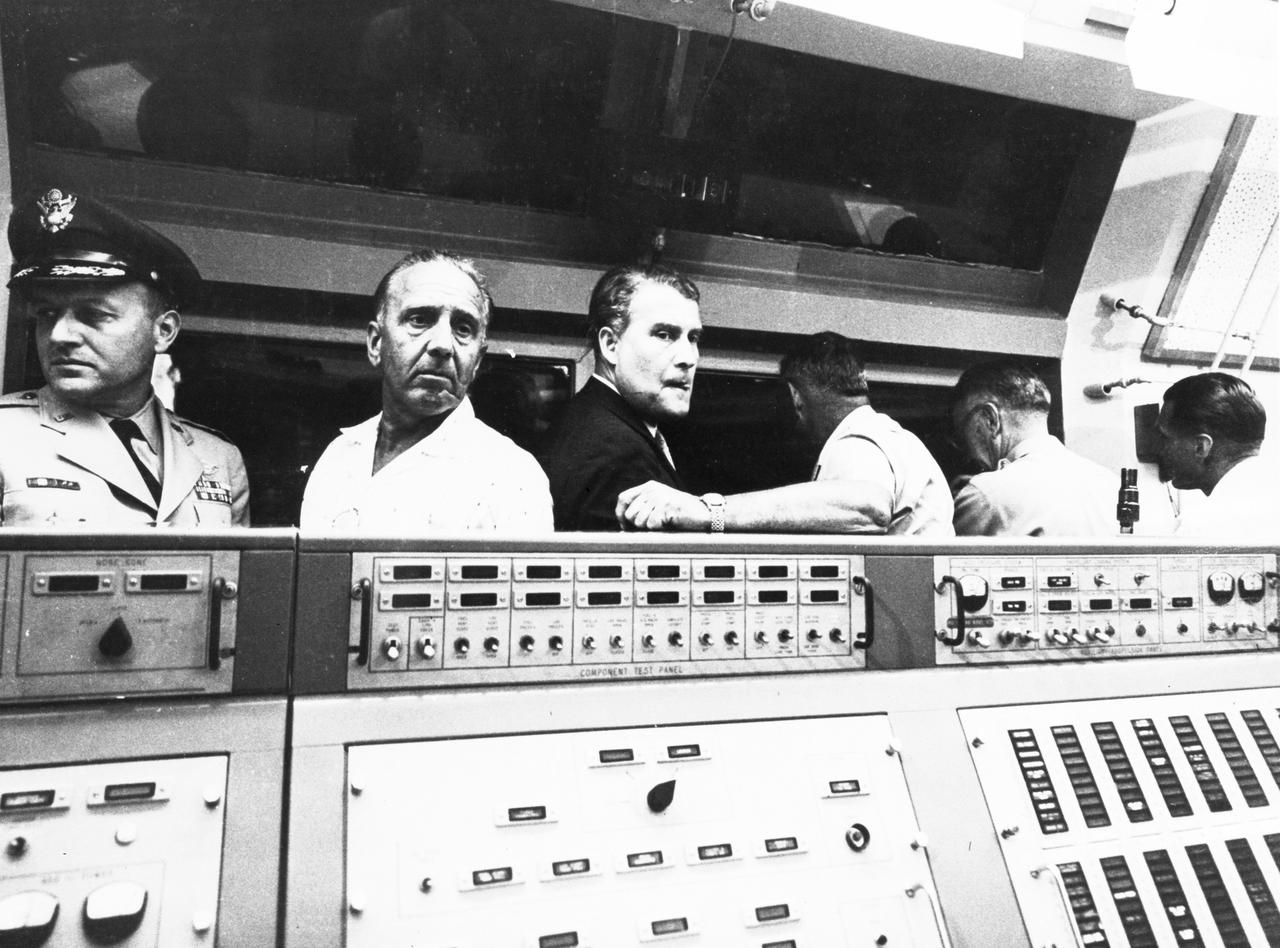

This photograph shows Dr. von Braun, second from the left, in the blockhouse at the Florida launch facilities on March 3, 1959. He and others gathered for the launch of the Pioneer IV satellite. On the left of Dr. von Braun is Kurt Debus, who managed the Florida launch facilities. To the right of Dr. von Braun is Army General John B. Medaris. Next to him is General John Barclay. At this time, Dr. von Braun and his associates were members of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency in Huntsville, Alabama.
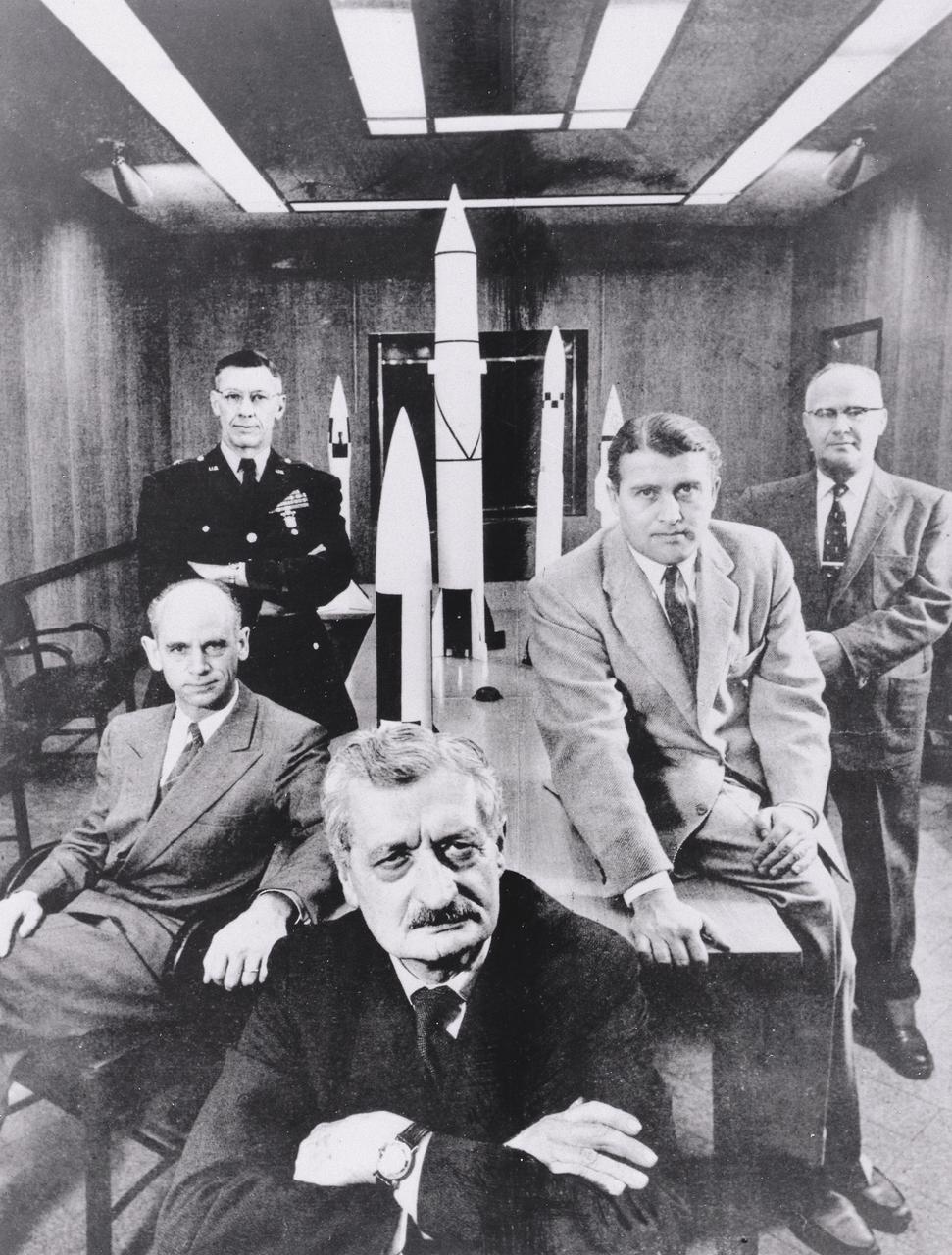
Five pioneers pose with scale models of their missiles they created in the 1950s. From left to right: Dr. Ernst Stuhlinger, a member of the original German rocket team who directed the Research Projects Office, Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA); Major General Holger Toftoy, who consolidated U.S. missile and rocketry development; Professor Herman Oberth, a rocket pioneer and Dr. von Braun's mentor; Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director, Development Operation Division, ABMA; and Dr. Robert Lusser, who served as assistant director for Reliability Engineering for ABMA. This photographis was taken February 1, 1956 by Hank Walker and appeared in February 27, 1956 issue of Life magazine.

Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director of the U.S. Army Ballistic Missile Agency's (ABMA) Development Operations Division, rides with his two daughters, Margrit and Iris, in a parade in downtown Huntsville, Alabama, March 4, 1959. Although the official occasion had been plarned a "Moon Day" weeks before, it was the successful launch of the sun probe Pioneer IV two days previously that increased the celebratory atmosphere.
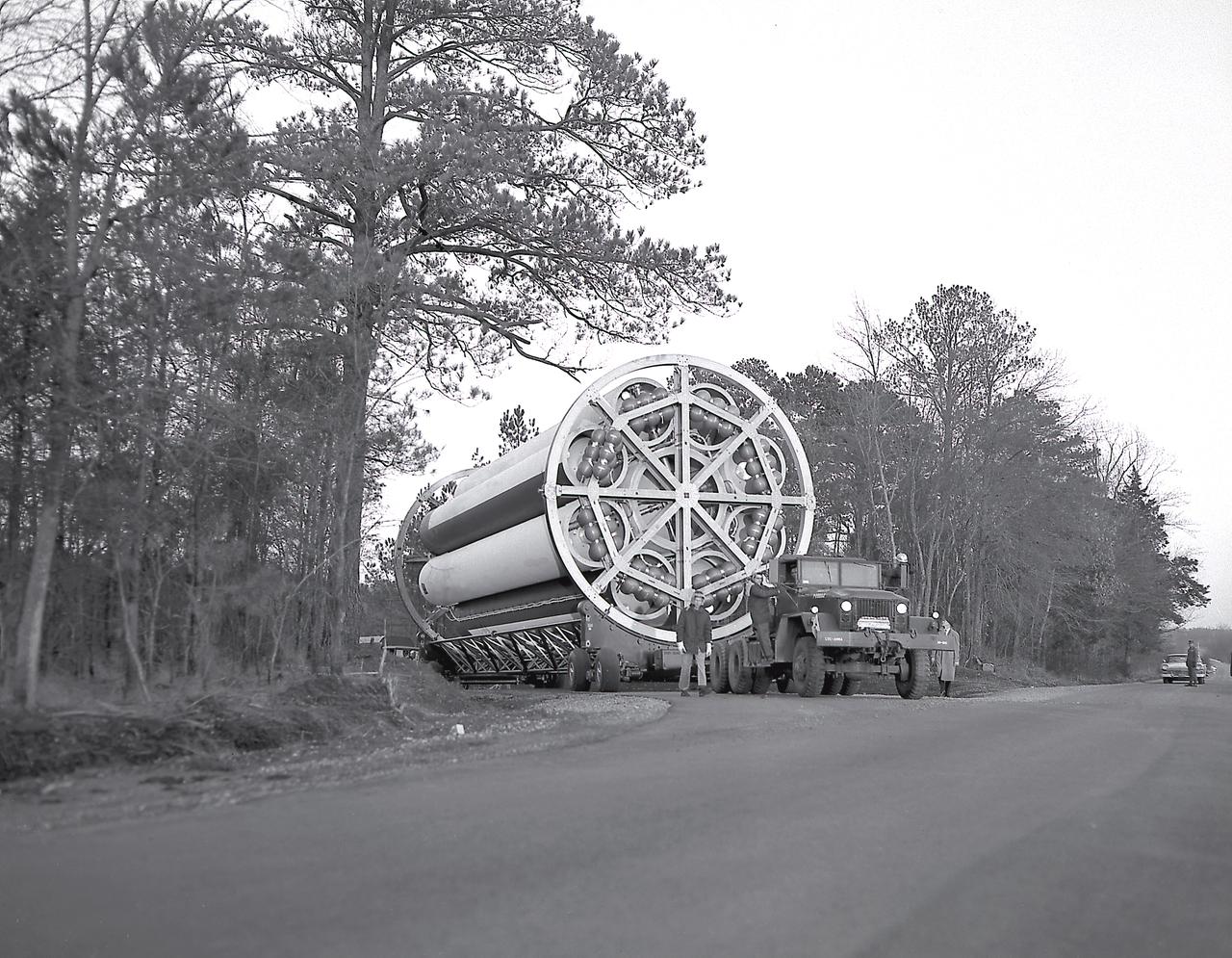

The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960 as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept was well underway at Redstone Arsenal. This photograph depicts a mockup of the Saturn booster (S-I stage) being transported to the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test stand, to check mating of the booster and stand and servicing methods.
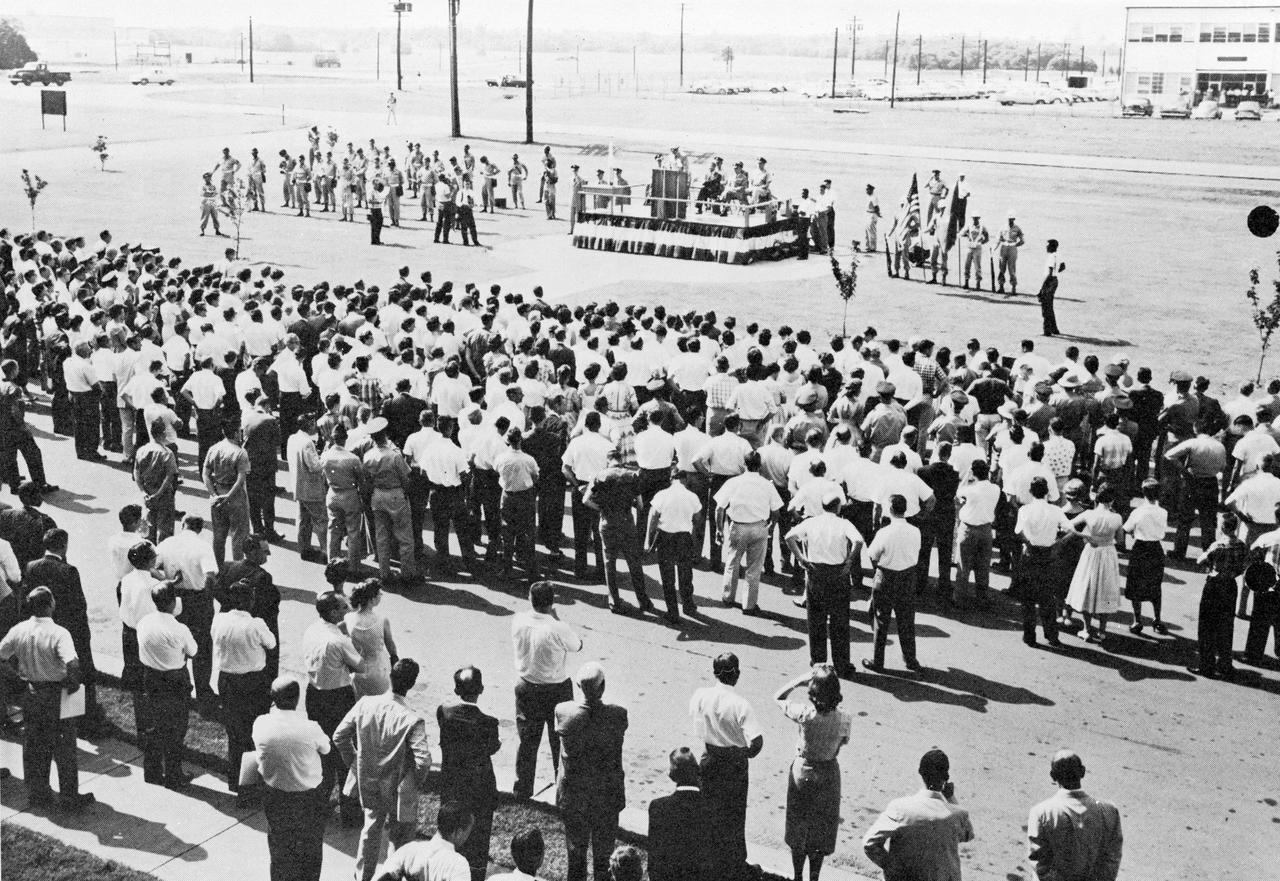

Dr. Wernher von Braun and Maj. Gen. August Schomburg officiate the official transfer of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) to the NASA George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on July 1, 1960. The Official transfer ceremony took place in the front of the ABMA-MSFC joint headquarters, building 4488, Redstone Arsenal, Alabama.
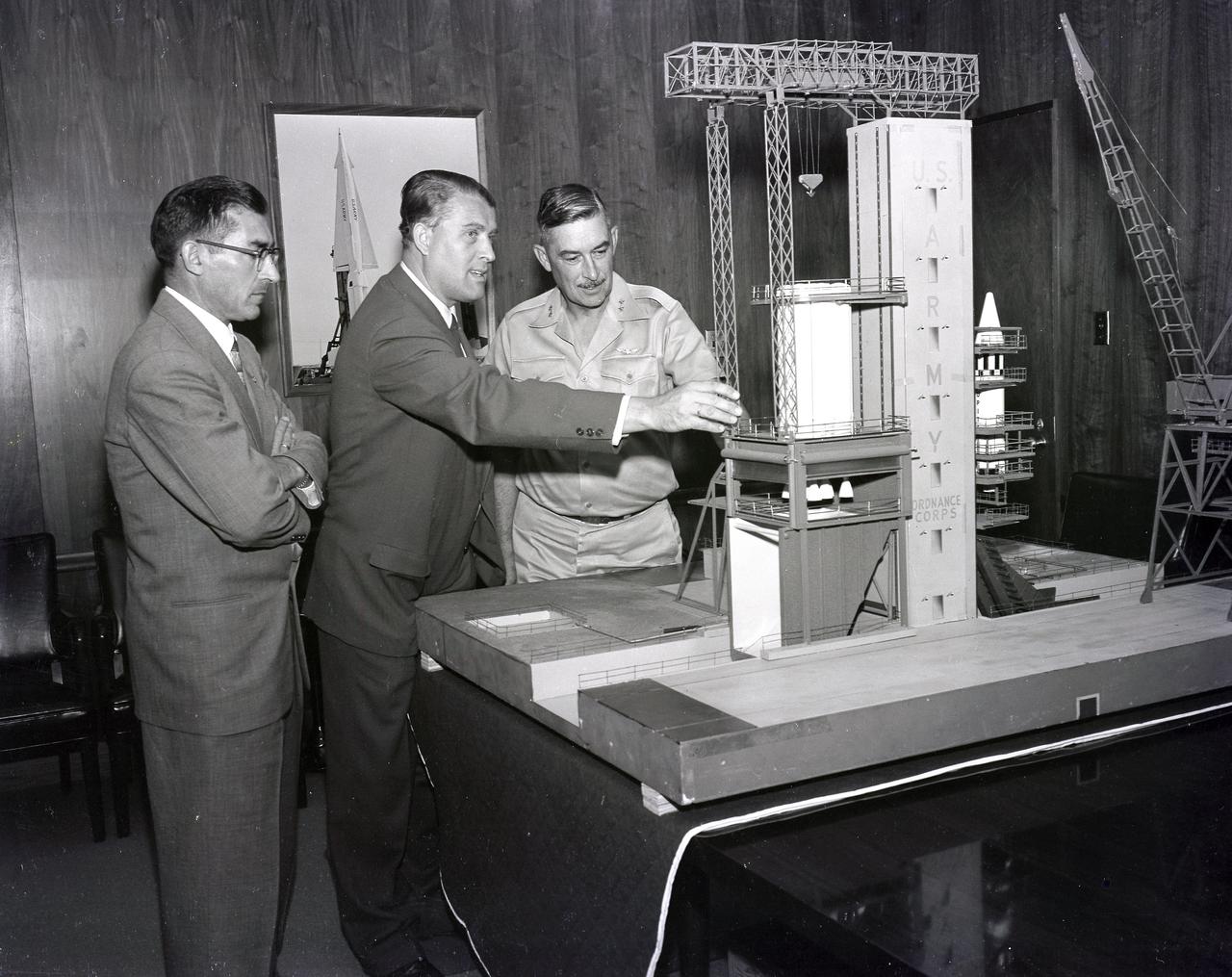

(From left to right) Karl L. Heimburg, Director of the Test Laboratory; Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director of the Development Operation Division; and Major General John B. Medaris with the model of S-1B Test Stand. Gen. Medaris was a Commander of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama, during 1955 to 1958.
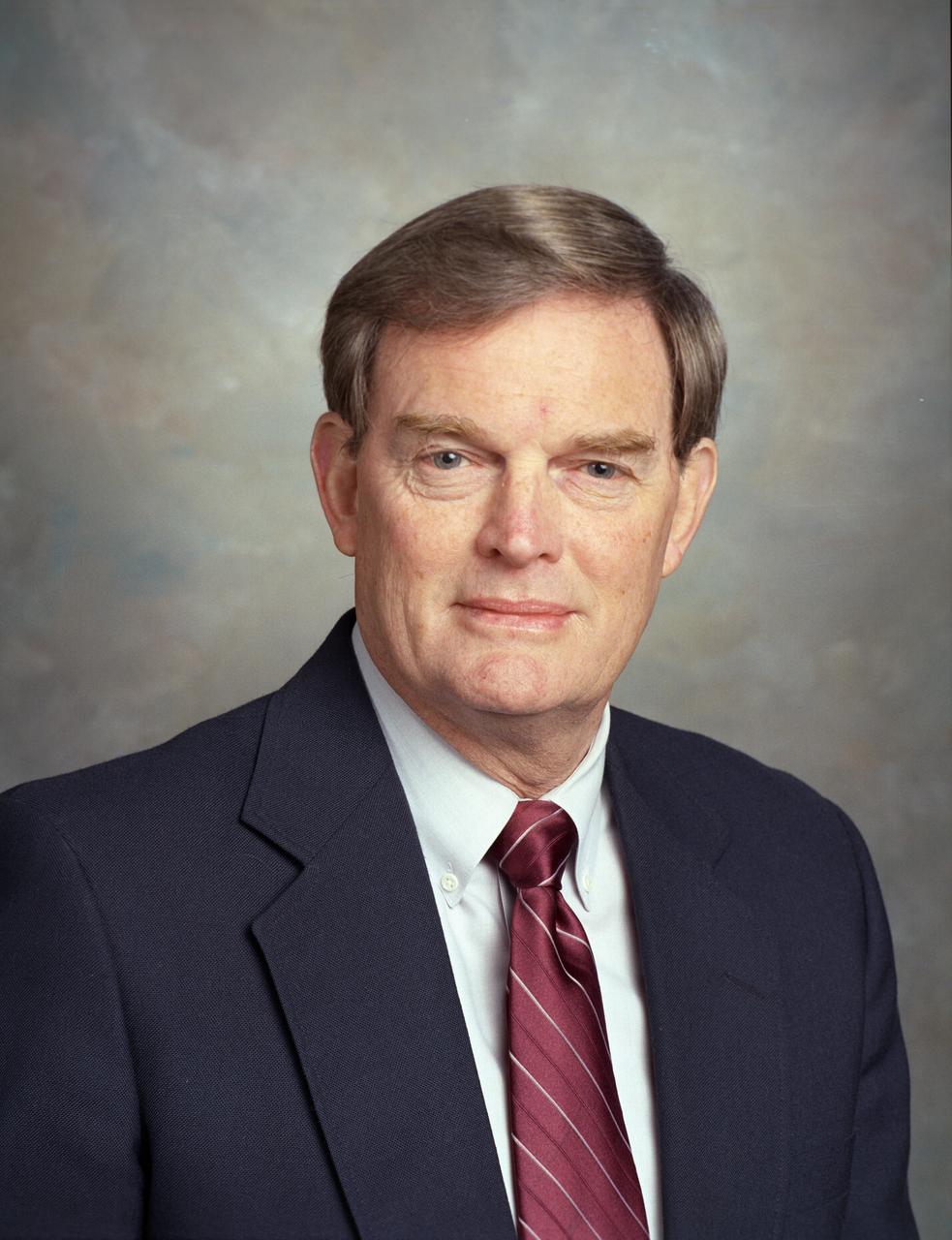

Thomas Jack Lee served as the sixth director of the Marshall Space Flight Center from July 6, 1989 to January 6, 1994. Prior to the appointment, Lee held positions as Center Deputy Director (1980 - 1989) and Spacelab Program Manager (1973 - 1980). Lee began his NASA career in July 1960 when he transferred to the newly formed MSFC from Redstone Arsenal's Army Ballistic Missile Agency.

Dr. von Braun is presented with the front page of the Huntsville Times arnouncing the launch of Explorer I, the first U.S. Earth satellite, which was boosted by the Jupiter-C launch vehicle developed by Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) under the direction of Dr. von Braun. The occasion was the fifth Anniversary of the Explorer I launch in January 1958.
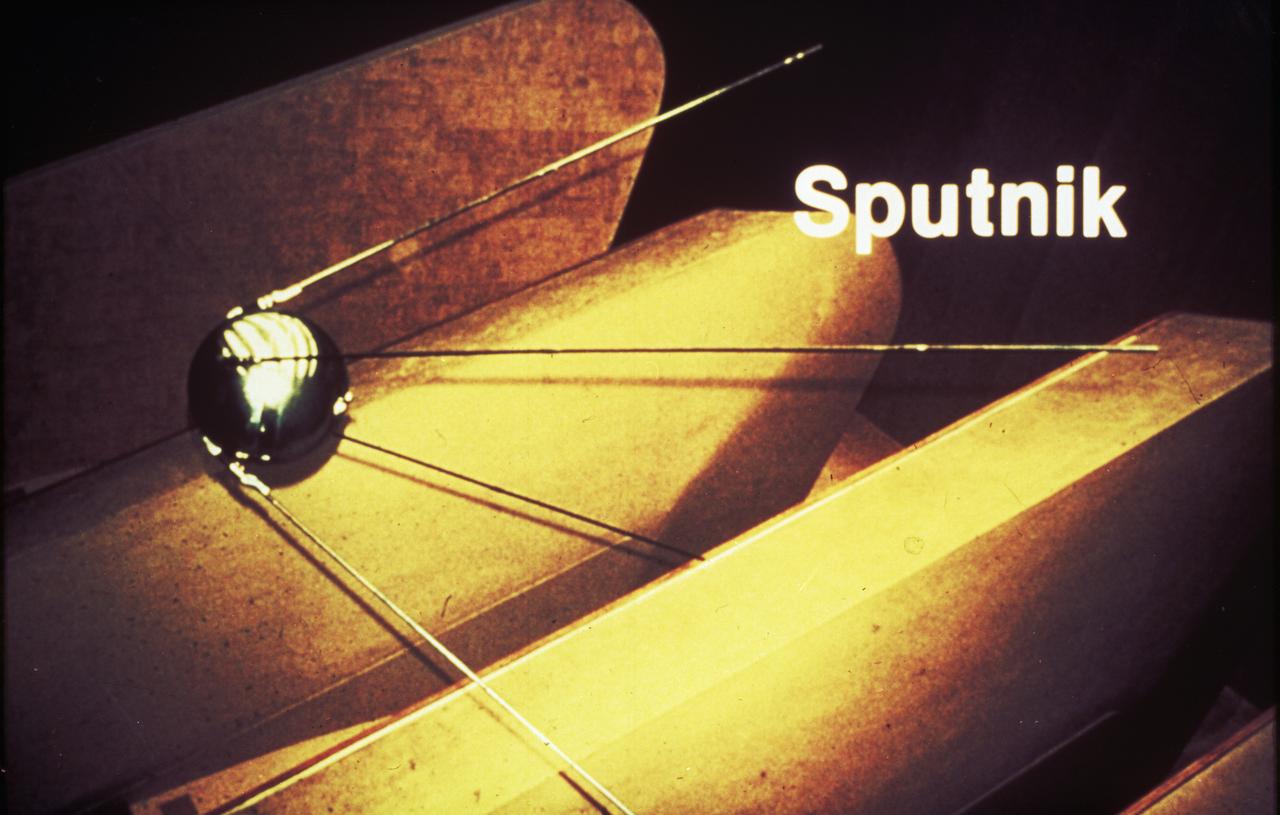
The Army Ballistic Missile Agency incorporated the von Braun team in key positions with Dr. von Braun as a head of the Development Operations Division. On October 4, 1957, the Nation was shocked when the Russians launched Sputnik, the world's first artificial satellite. Two months later, the United States suffered disappointment when a Navy Vanguard rocket, with its satellite payload, failed to develop sufficient thrust and toppled over on the launch pad.
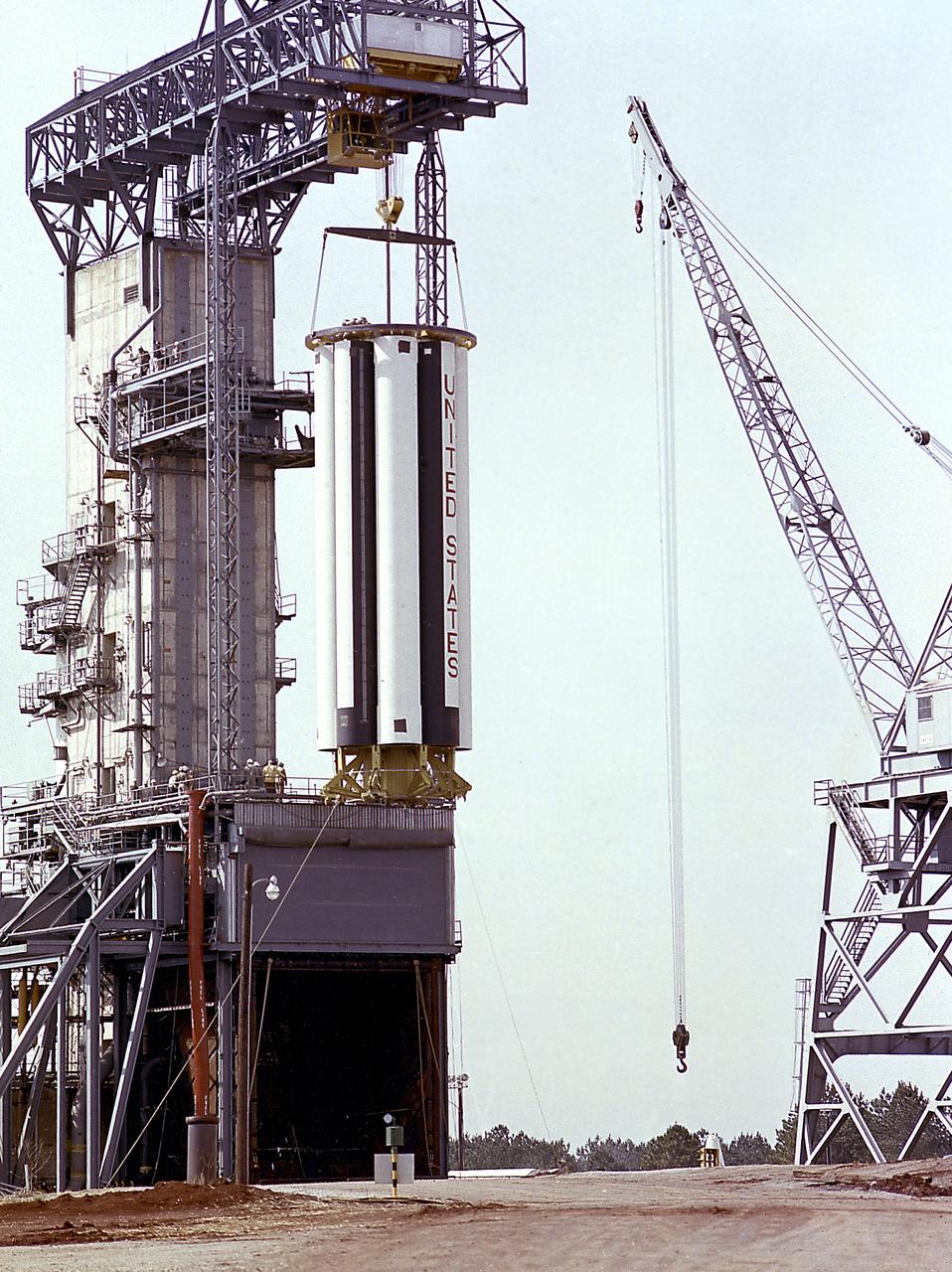

The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960, as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept was well underway at Redstone Arsenal. This photograph depicts a mockup of the Saturn booster (S-I stage) being installed in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test stand, on January 19, 1960, to check mating of the booster and stand and servicing methods.
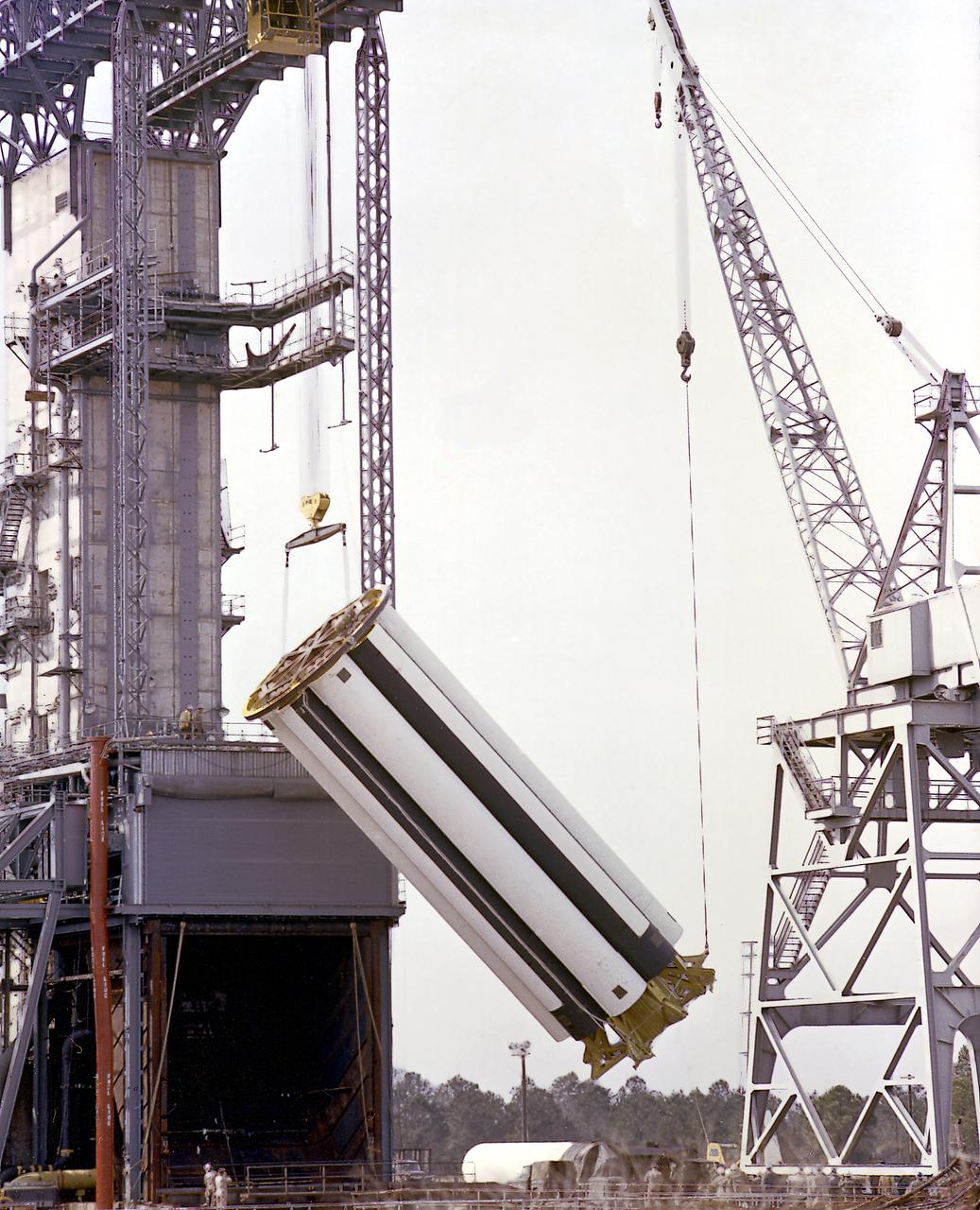

The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960 as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program, to prove out the clustered-booster concept, was well underway at Redstone Arsenal. This photograph depicts a mockup of the Saturn booster (S-I stage) being installed in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test stand, on January 19, 1960, to check mating of the booster and stand and servicing methods.
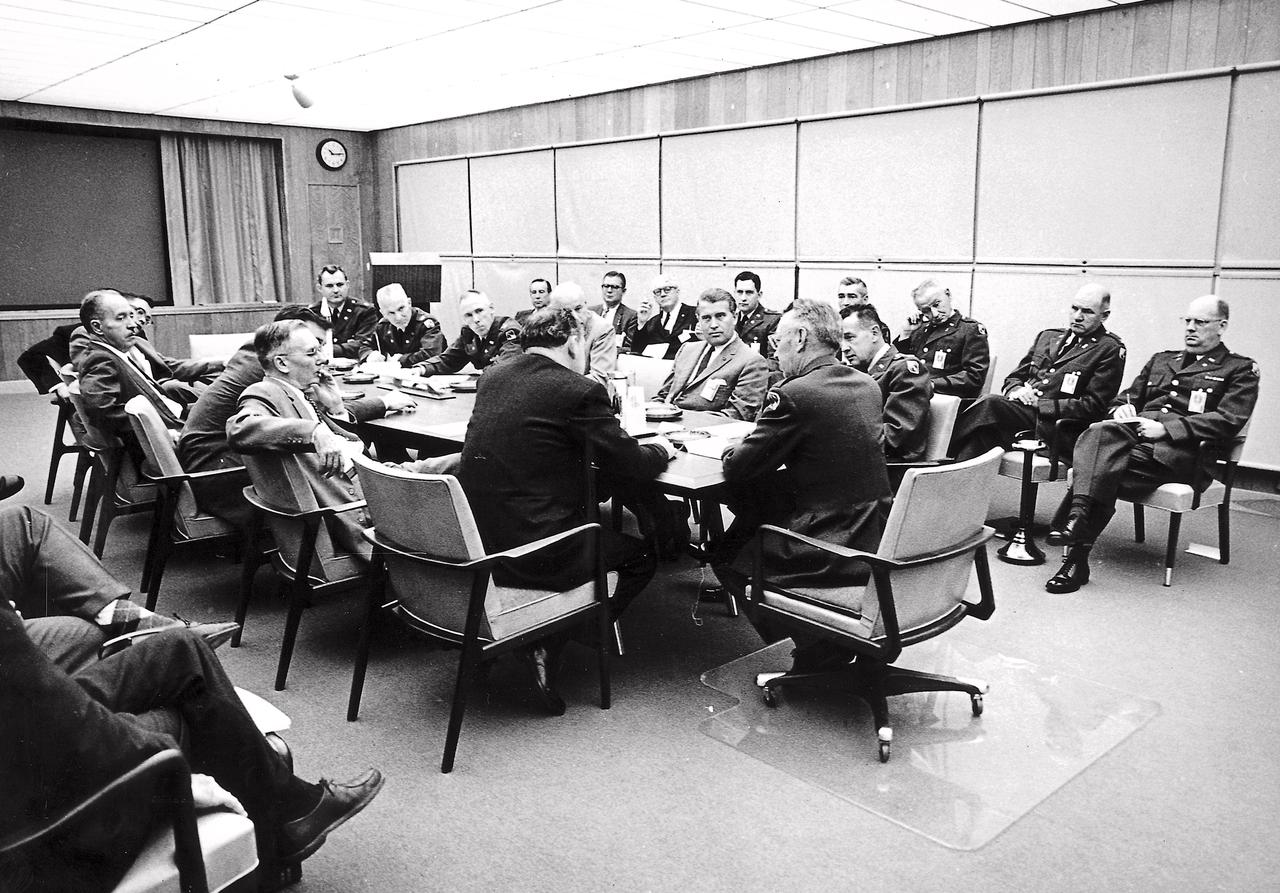

In this picture, negotiations are under way between officials of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) on August 11, 1959. Seated at the table with his back to the camera, is Dr. T. Keith Glernan, NASA Administrator. At the head of the table is Major General John Barclay, Commander of ABMA and at the right side of the table are Colonel John G. Zierdt of ABMA and Dr. von Braun.

The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960 as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept was well underway at Redstone Arsenal. This photograph depicts a mockup of the Saturn booster (S-I stage) being placed on a transporter and later being installed in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test stand, on January 19, 1960, to check mating of the booster and stand and servicing methods.
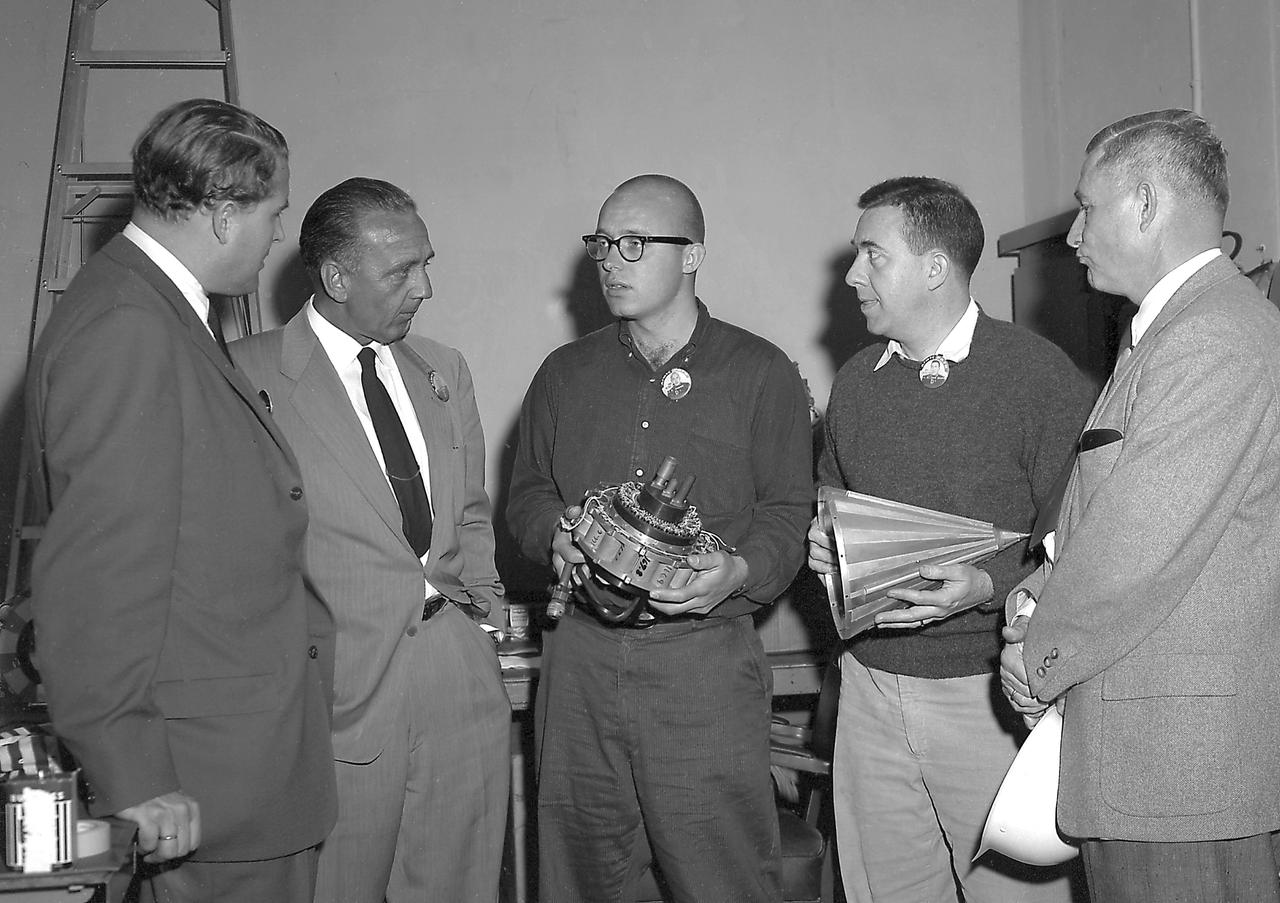

In this photo, Director of the U.S. Army Ballistic Missile Agency's (ABMA) Development Operations Division, Dr. Wernher von Braun, and Director of Missile Firing Division, Dr. Kurt Debus, are shown with unidentified individuals, discussing two components that would make up the Pioneer IV Lunar Probe. The mercury batteries (left) were used to power the radio transmitter, cosmic radiation counter and other instruments in Pioneer IV. The conical shroud placed over the instruments of Pioneer IV was plated with gold to improve conductivity. The metal surface also served as the anterna for the probe's instruments signaling back to the Earth receiving stations.
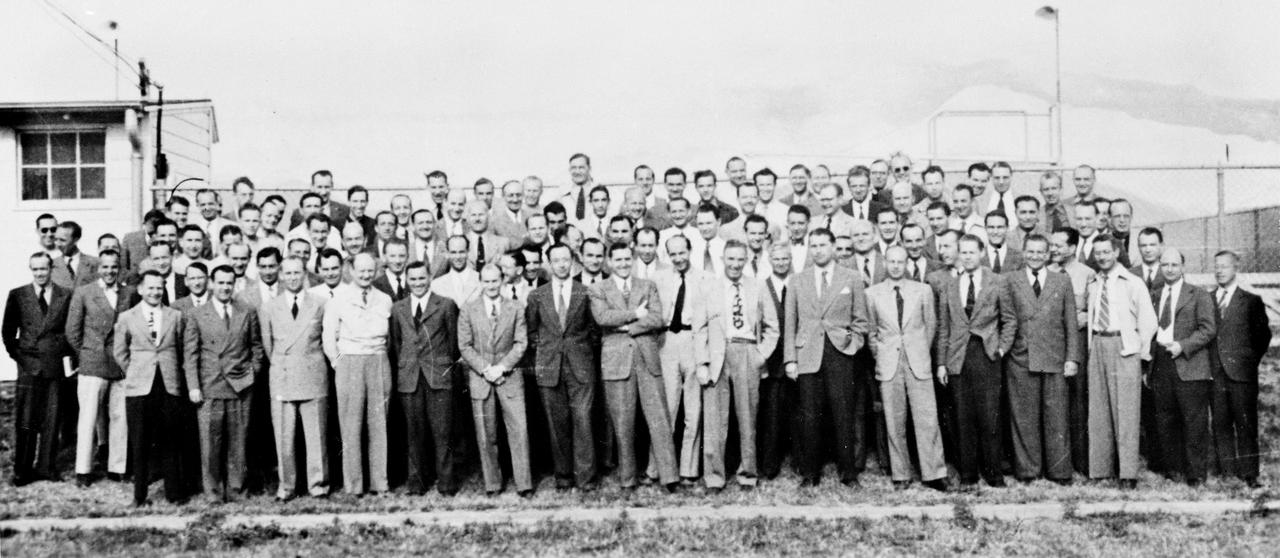

The German Rocket Team, also known as the Von Braun Rocket Team, poses for a group photograph at Fort Bliss, Texas. After World War II ended in 1945, Dr. Wernher von Braun led some 120 of his Peenemuende Colleagues, who developed the V-2 rocket for the German military during the War, to the United Sttes under a contract to the U.S. Army Corps as part of Operation Paperclip. During the following five years the team worked on high altitude firings of the captured V-2 rockets at the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, and a guided missile development unit at Fort Bliss, Texas. In April 1950, the group was transferred to the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) at Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama, and continued to work on the development of the guided missiles for the U.S. Army until transferring to a newly established field center of the National Aeronautic and Space Administration (NASA), George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).

Aerospace pioneers who worked on the launch of Explorer 1 participate in a panel discussion with NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, at far left, at the center's Training Auditorium on Wednesday, May 9, 2018. Panelists, from left are William "Curly" Chandler, firing room engineer; Lionel (Ed) Fannin, mechanical and propulsion systems; Terry Greenfield, blockhouse engineer; Carl Jones, measuring branch engineer; and Ike Rigell, electrical networks systems chief. Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the U.S. It was launched by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency on Jan. 31, 1958 on a Juno I rocket from Launch Complex-26.

Aerospace pioneers who worked on the launch of Explorer 1 participate in a panel discussion with NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, at far left, at the center's Training Auditorium on Wednesday, May 9, 2018. Panelists, from left are William "Curly" Chandler, firing room engineer; Lionel (Ed) Fannin, mechanical and propulsion systems; Terry Greenfield, blockhouse engineer; Carl Jones, measuring branch engineer; and Ike Rigell, electrical networks systems chief. Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the U.S. It was launched by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency on Jan. 31, 1958 on a Juno I rocket from Launch Complex-26.

Aerospace pioneers who worked on the launch of Explorer 1 participate in a panel discussion with NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana at the center's Training Auditorium on Wednesday, May 9, 2018. Panelists, from left are William "Curly" Chandler, firing room engineer; Lionel (Ed) Fannin, mechanical and propulsion systems; Terry Greenfield, blockhouse engineer; Carl Jones, measuring branch engineer; and Ike Rigell, electrical networks systems chief. Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the U.S. It was launched by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency on Jan. 31, 1958 on a Juno I rocket from Launch Complex-26.
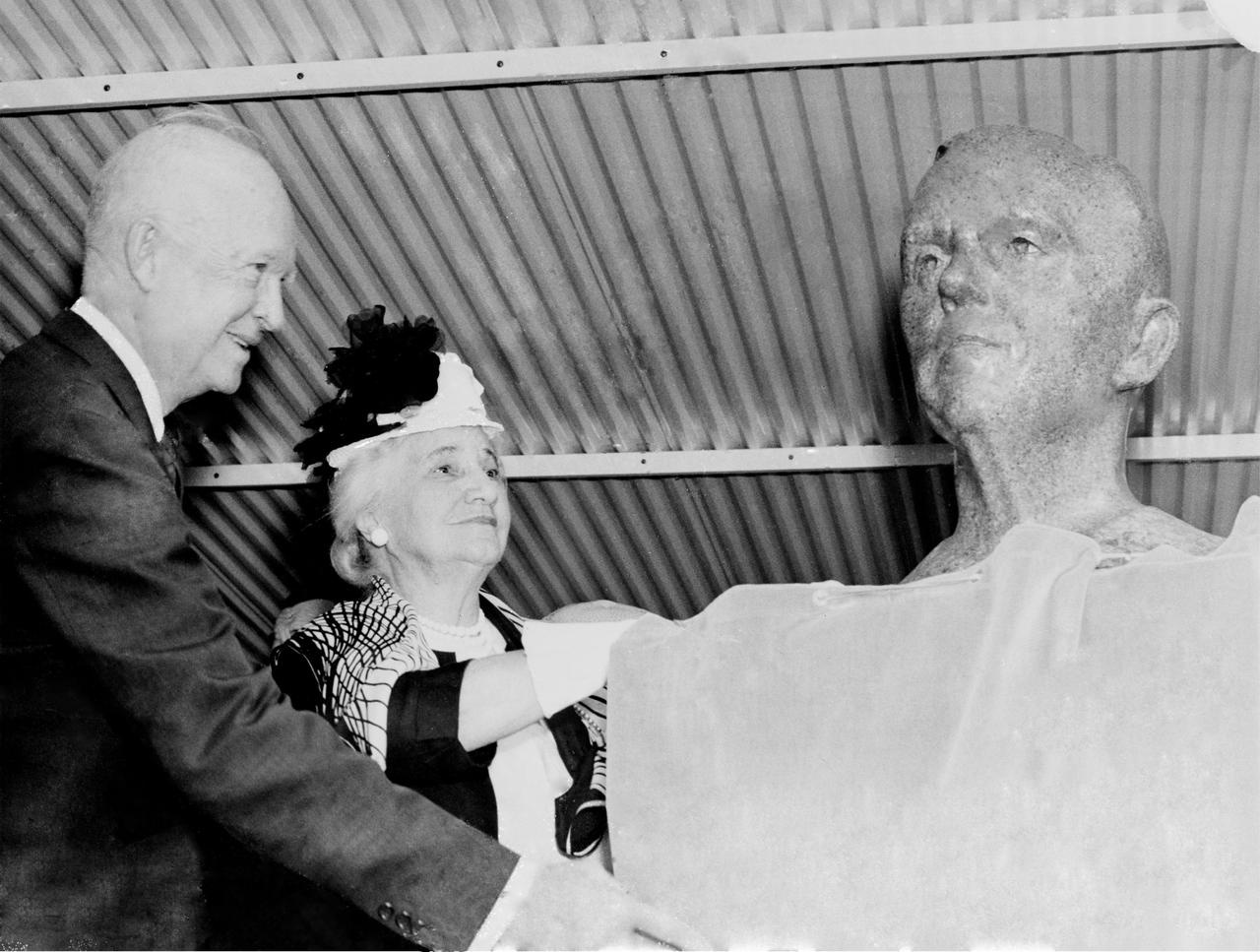

President Dwight D. Eisenhower and Mrs. George C. Marshall unveil the bronze bust of General George C. Marshall during the dedication of the Marshall Space Flight Center. Eisenhower signed an Executive Order on October 21, 1959 directing the transfer of persornel from the Redstone Arsenal's Army Ballistic Missile Agency Development Operations Division to NASA. On March 15, 1960, another Executive Order announced that the space complex formed within the boundaries of Redstone Arsenal would become the George C. Marshall Space Flight Center. The Center was activated on July 1, 1960, with dedication ceremonies taking place September 8, 1960.
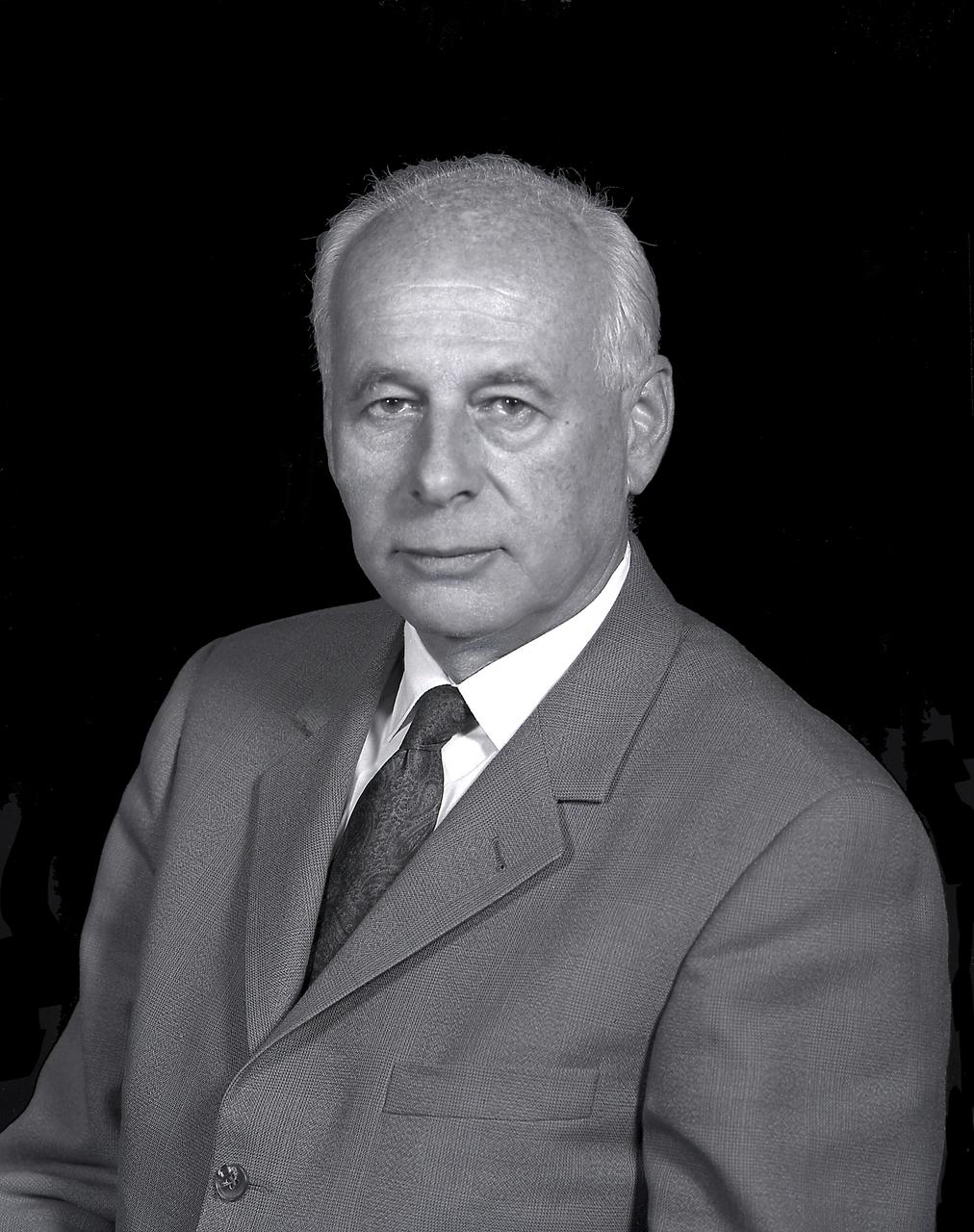

Dr. Eberhard Rees served as director of the Marshall Space Flight Center from March 1, 1970 until January 19, 1973 when he retired from NASA. Prior to his appointment as Director, Rees served as the Center's deputy director under Dr. Wernher von Braun, 1960-1970. Rees came to the United States as part of the Dr. Wernher von Braun's German Rocket team following World War II. He transferred to Huntsville, Alabama from Fort Bliss, Texas in 1950 to work for the Army's rocket program at Redstone Arsenal. From 1956 to 1960 he served as deputy director of development operations at the Army Ballistic Missile Agency under von Braun. In 1960 Rees was transferred to NASA's Marshall Center.
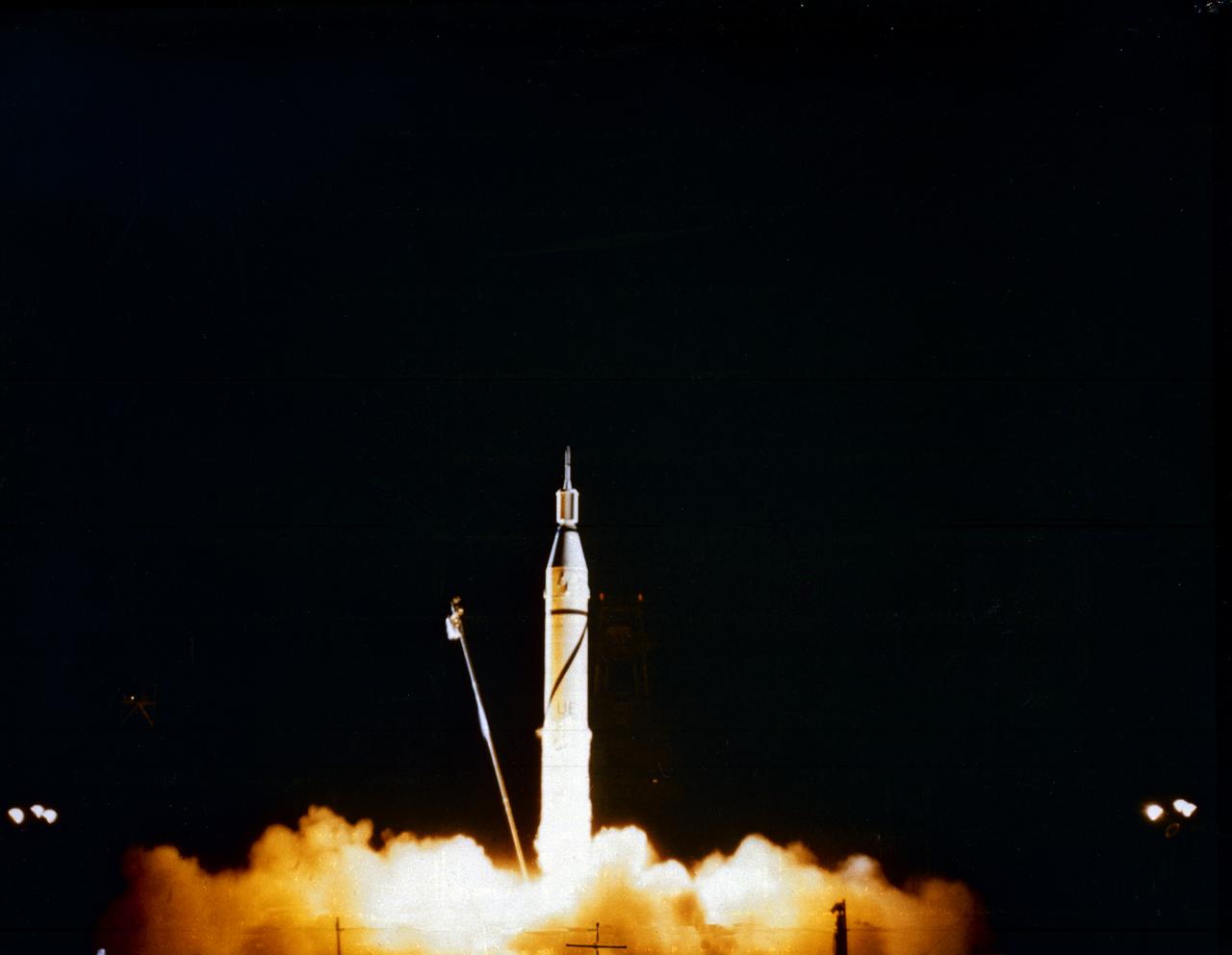

Launch of Jupiter-C/Explorer 1 at Cape Canaveral, Florida on January 31, 1958. After the Russian Sputnik 1 was launched in October 1957, the launching of an American satellite assumed much greater importance. After the Vanguard rocket exploded on the pad in December 1957, the ability to orbit a satellite became a matter of national prestige. On January 31, 1958, slightly more than four weeks after the launch of Sputnik.The ABMA (Army Ballistic Missile Agency) in Redstone Arsenal, Huntsville, Alabama, in cooperation with the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, launched a Jupiter from Cape Canaveral, Florida. The rocket consisted of a modified version of the Redstone rocket's first stage and two upper stages of clustered Baby Sergeant rockets developed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and later designated as Juno boosters for space launches

Launch of Jupiter-C/Explorer 1 at Cape Canaveral, Florida on January 31, 1958. After the Russian Sputnik 1 was launched in October 1957, the launching of an American satellite assumed much greater importance. After the Vanguard rocket exploded on the pad in December 1957, the ability to orbit a satellite became a matter of national prestige. On January 31, 1958, slightly more than four weeks after the launch of Sputnik.The ABMA (Army Ballistic Missile Agency) in Redstone Arsenal, Huntsville, Alabama, in cooperation with the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, launched a Jupiter from Cape Canaveral, Florida. The rocket consisted of a modified version of the Redstone rocket's first stage and two upper stages of clustered Baby Sergeant rockets developed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and later designated as Juno boosters for space launches

This image from March 2, 1959 shows engineers from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory checking NASA's Pioneer 4 spacecraft, the gold-and-black-colored cone sitting atop the white fourth-stage motor of the Juno II launch vehicle in Florida. Launched on March 3, 1959, NASA's Pioneer 4 was the first American mission to escape Earth orbit and the second of two early attempts by the United States to send a spacecraft to the Moon. The spacecraft achieved its primary objective — to put itself on a trajectory from Earth to the Moon. While it flew farther away from the Moon than expected and didn't take the images of the Moon as intended, Pioneer 4 did provide extensive and valuable data on Earth's radiation belt and the tracking of space objects. After 82 hours of transmissions from Pioneer 4's tiny radio and 655,000 miles (1.05 million kilometers) of travel — the farthest tracking distance for a human-made object at the time — contact is lost on March 6, 1959. Pioneer 4 is still in orbit around the Sun. The mission was carried out while JPL was transitioning from being part of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency to NASA. It marked the end of the U.S. Army's pioneering space program and the beginning of NASA's lunar program. JPL, in Pasadena, California, was responsible for mission design and management for both agencies. More information about Pioneer 4 can be found at: https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/pioneer-4/in-depth/ https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23497