
Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.
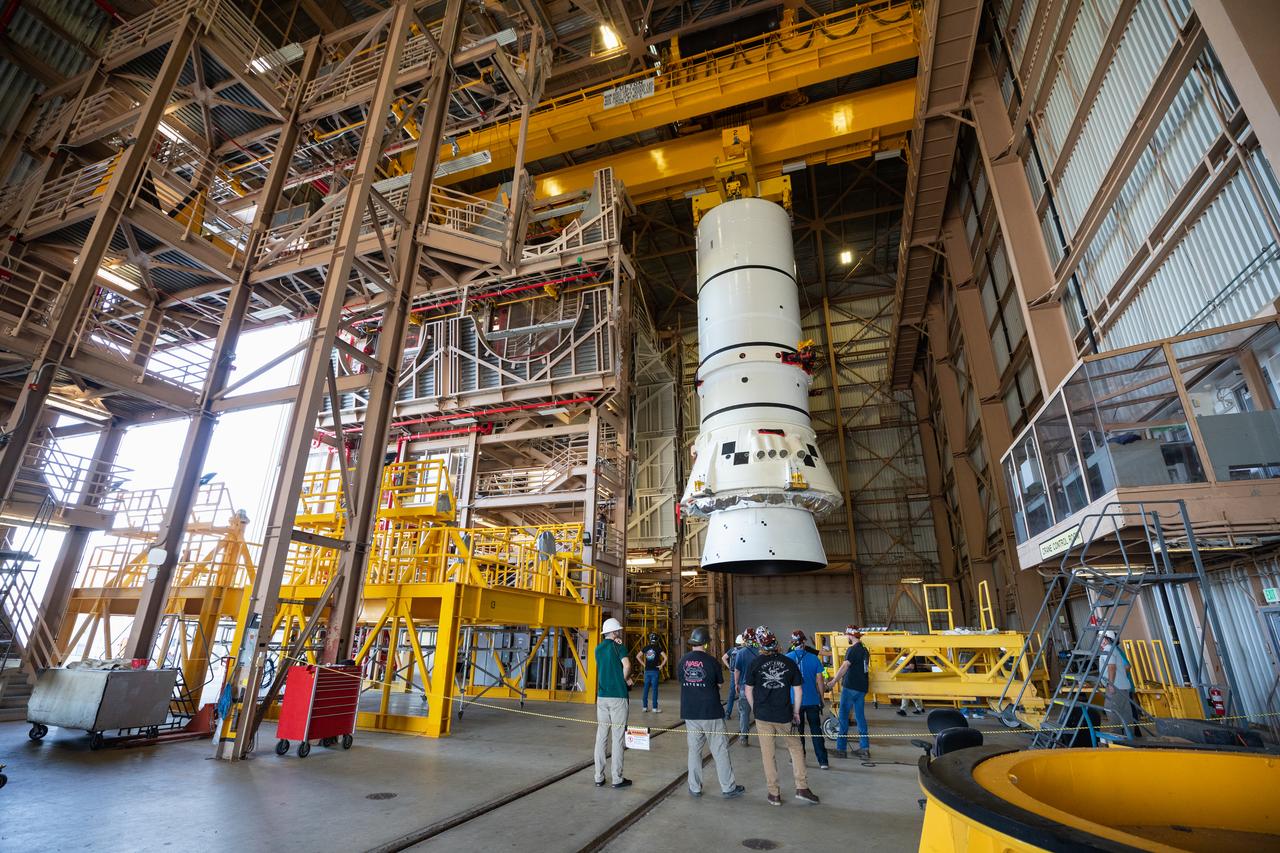

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.
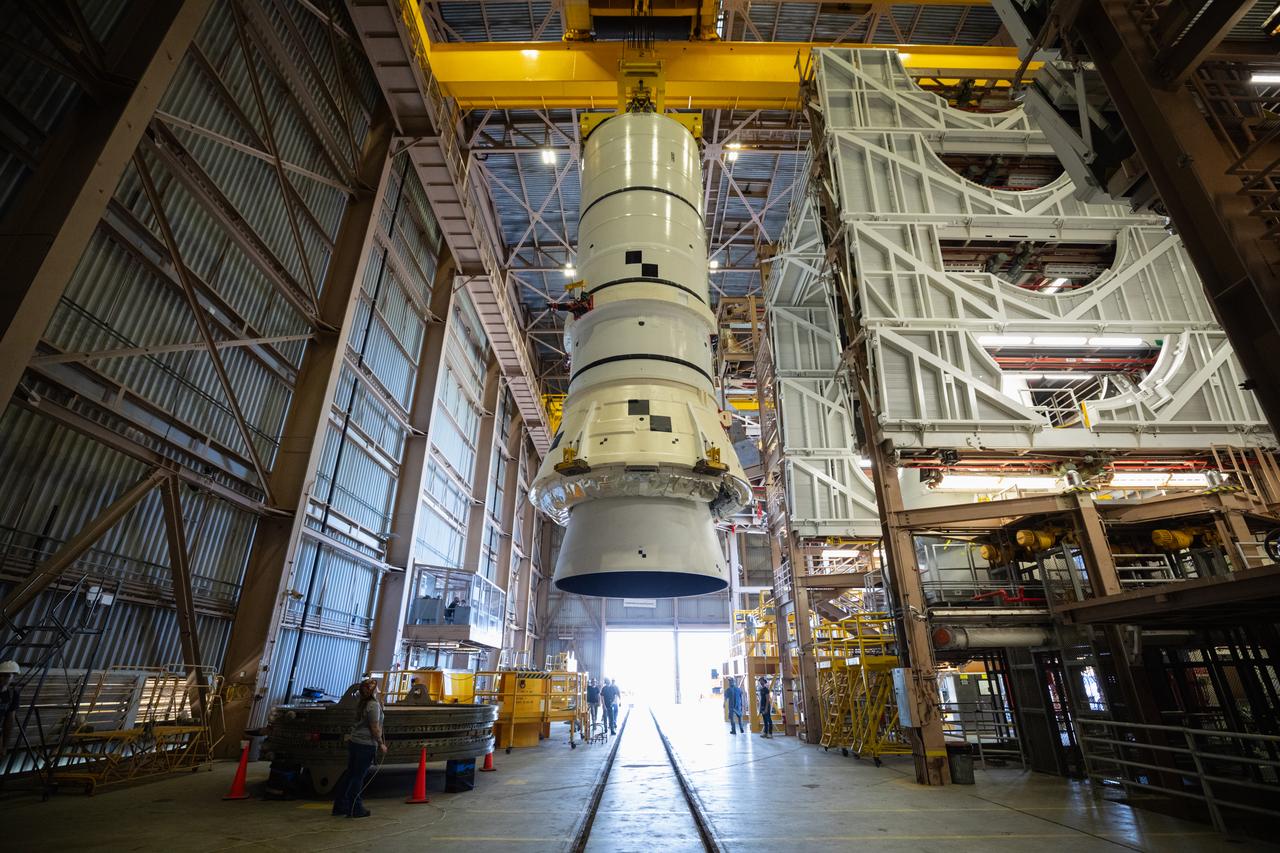

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.
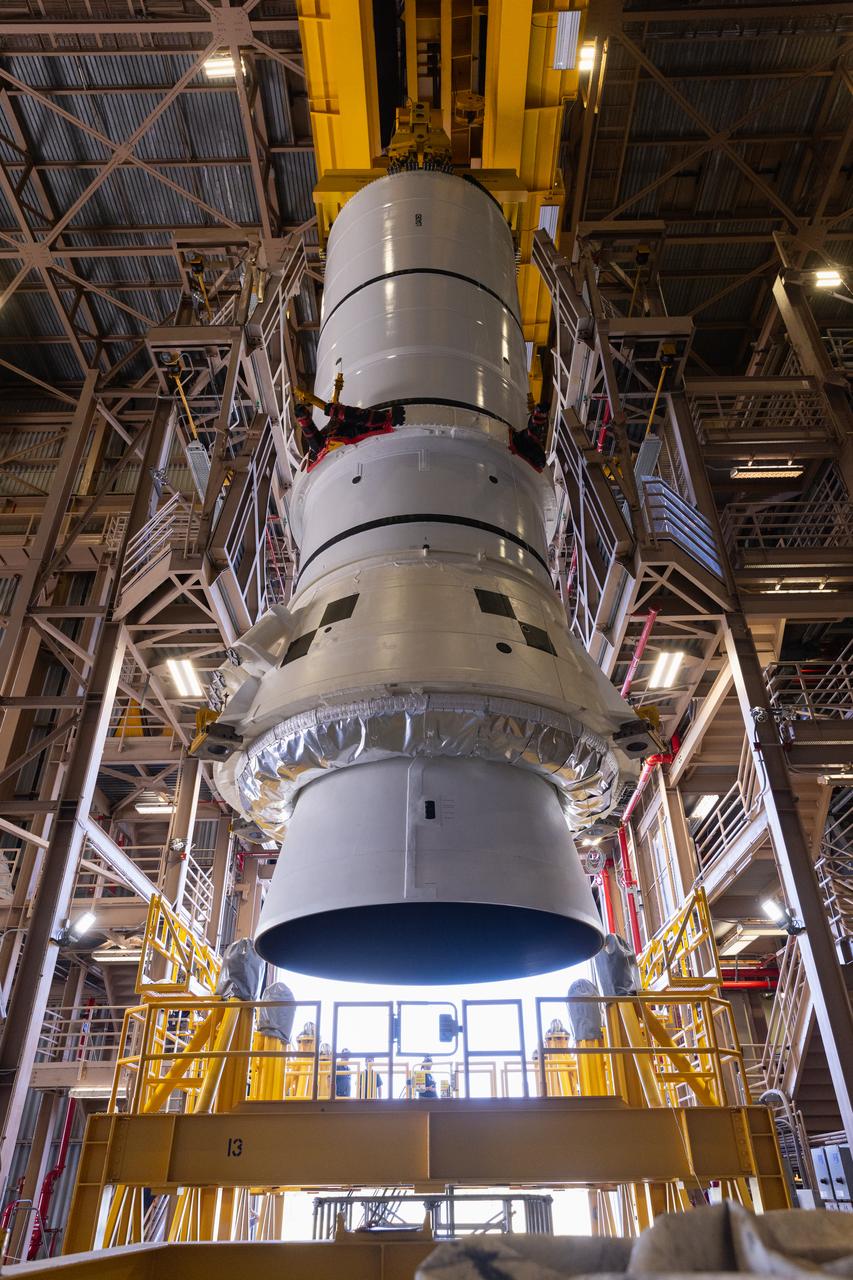

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to move the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.
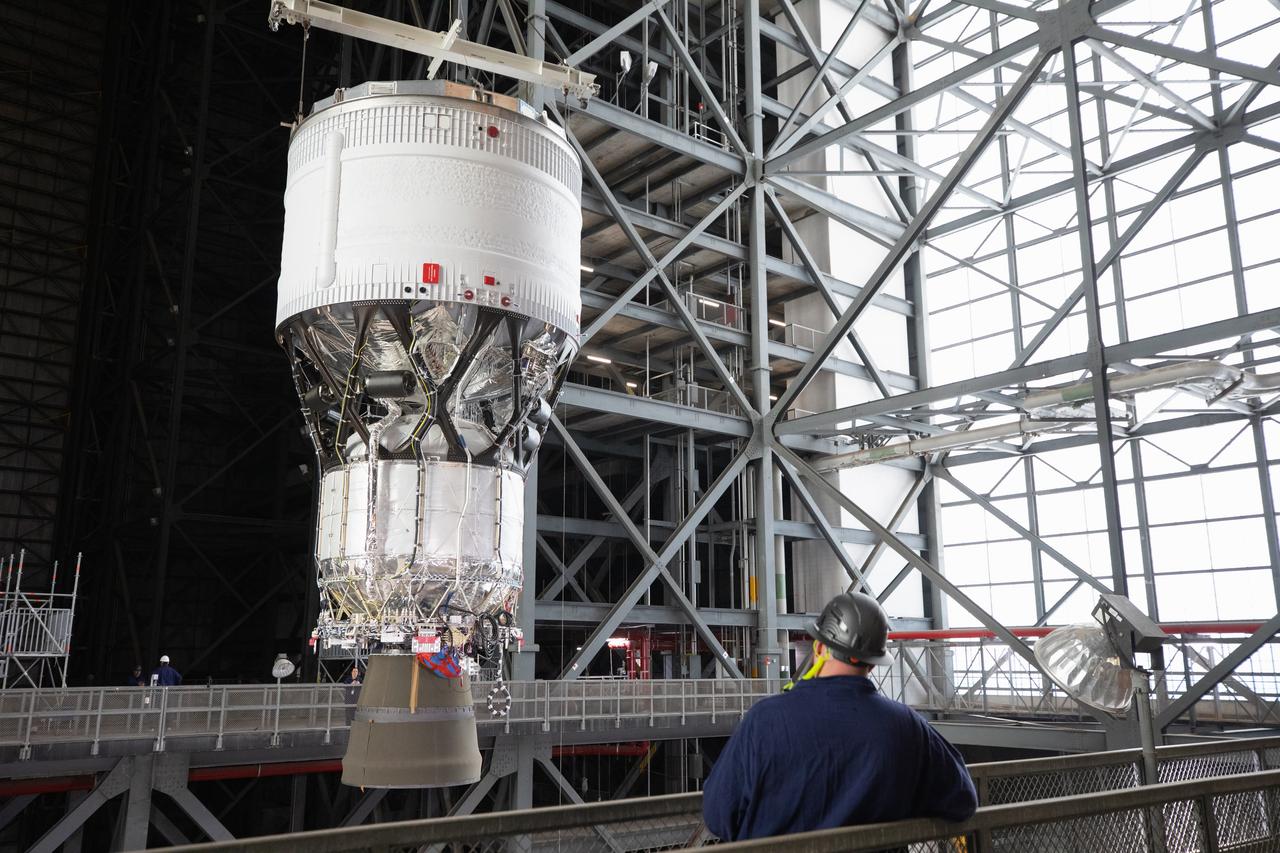

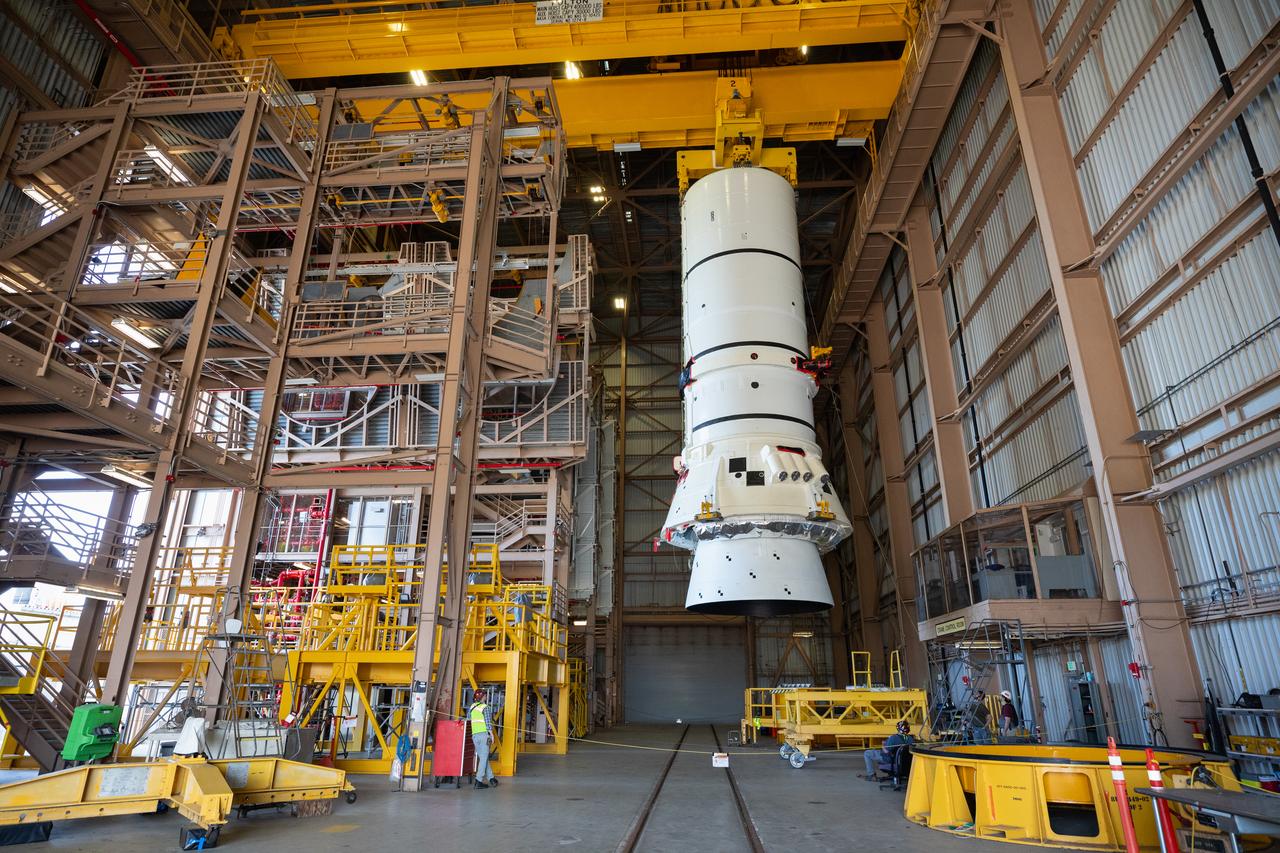
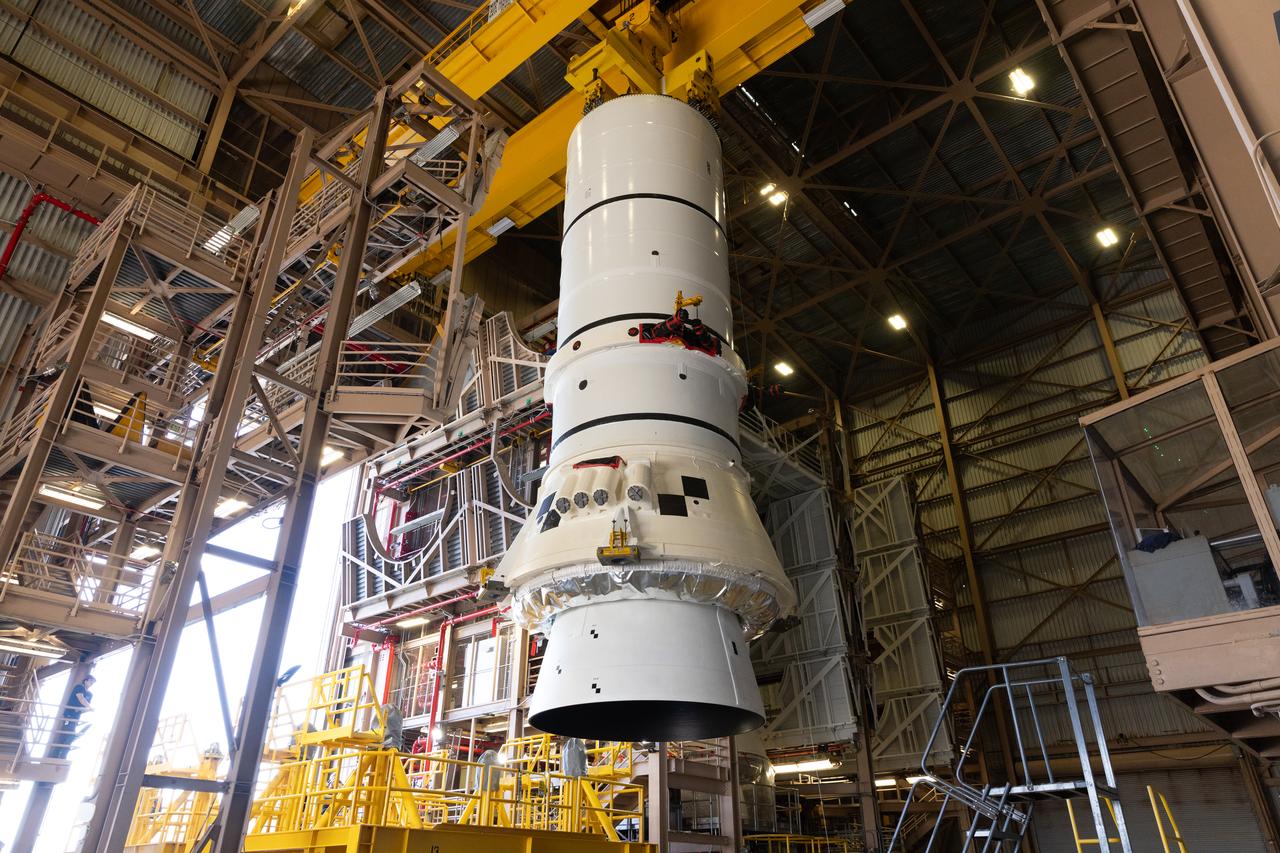
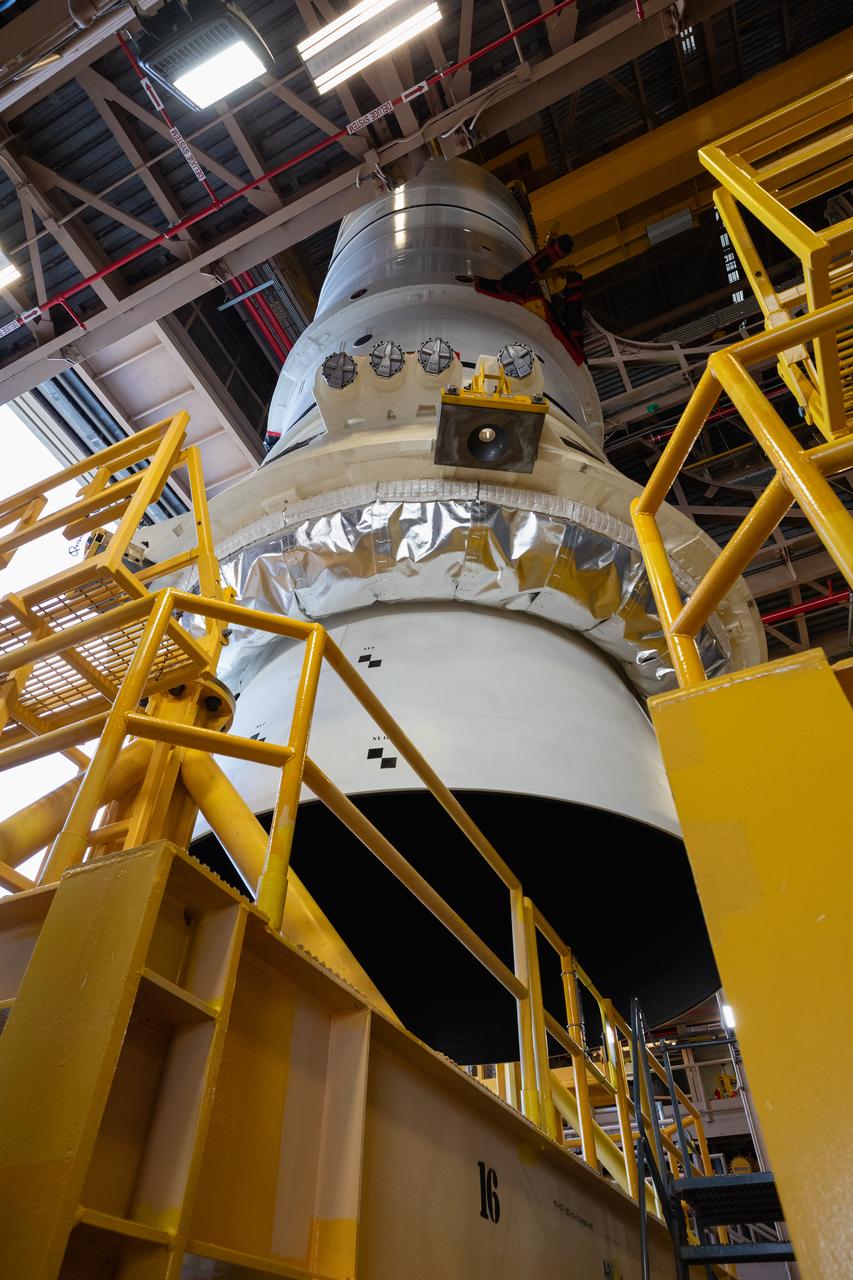
Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.
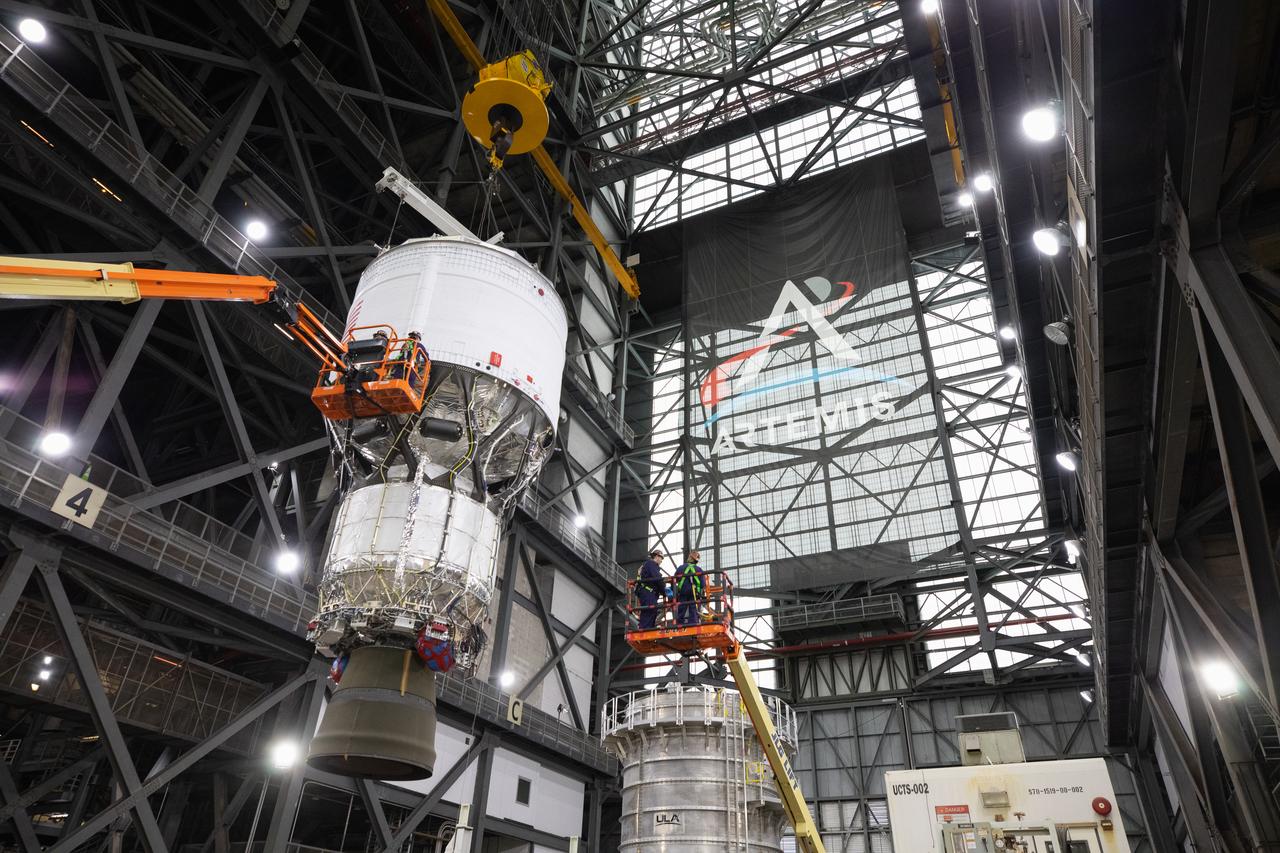

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.
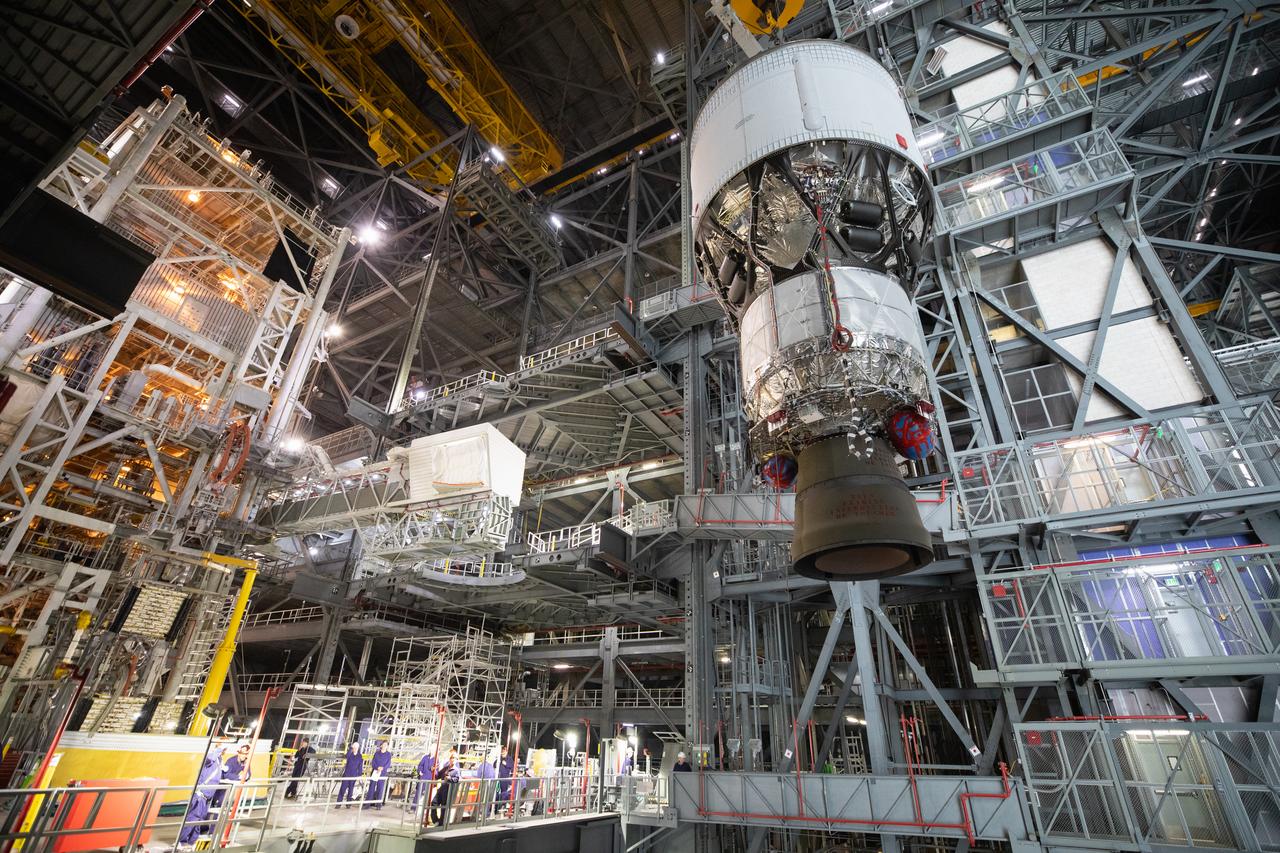

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.
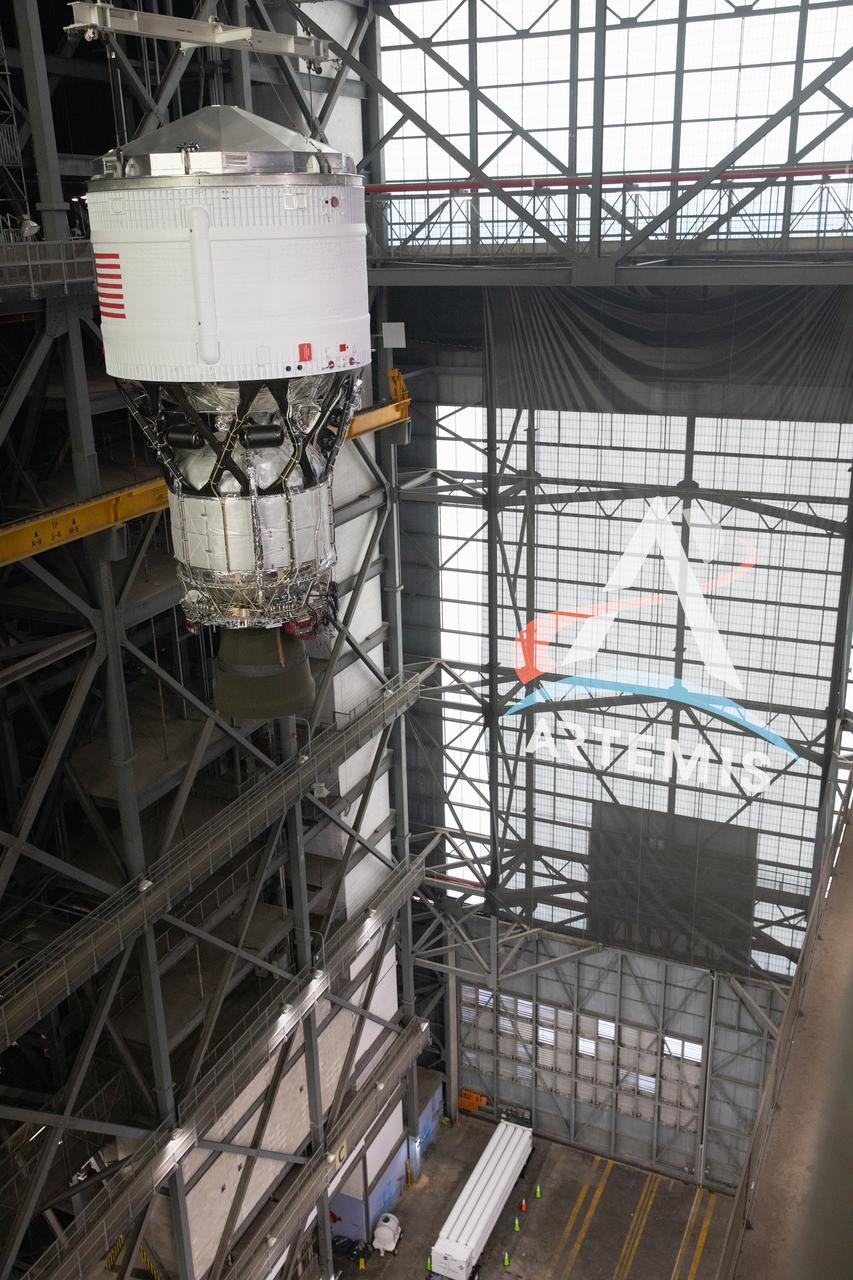

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.

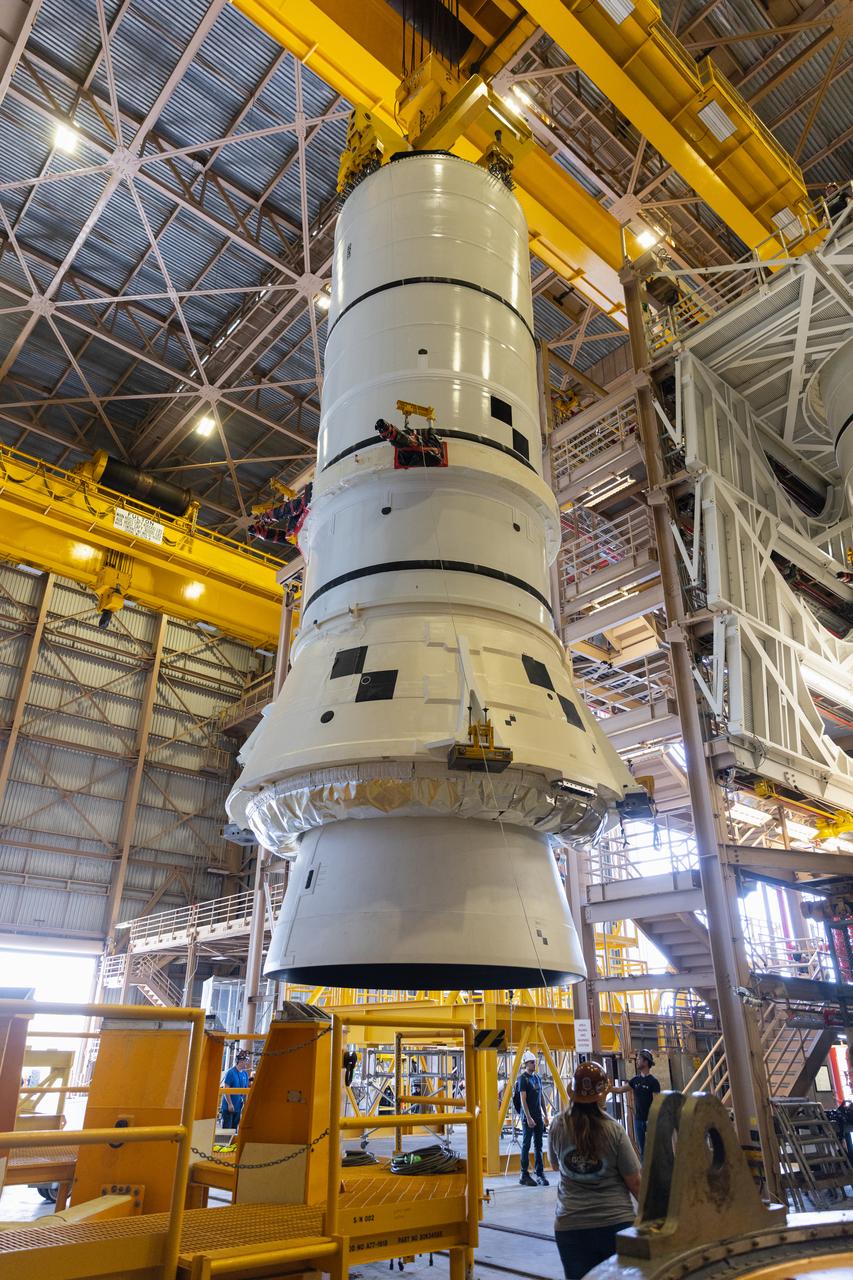
Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program finish integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Thursday, May 1, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program finish integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Thursday, May 1, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.
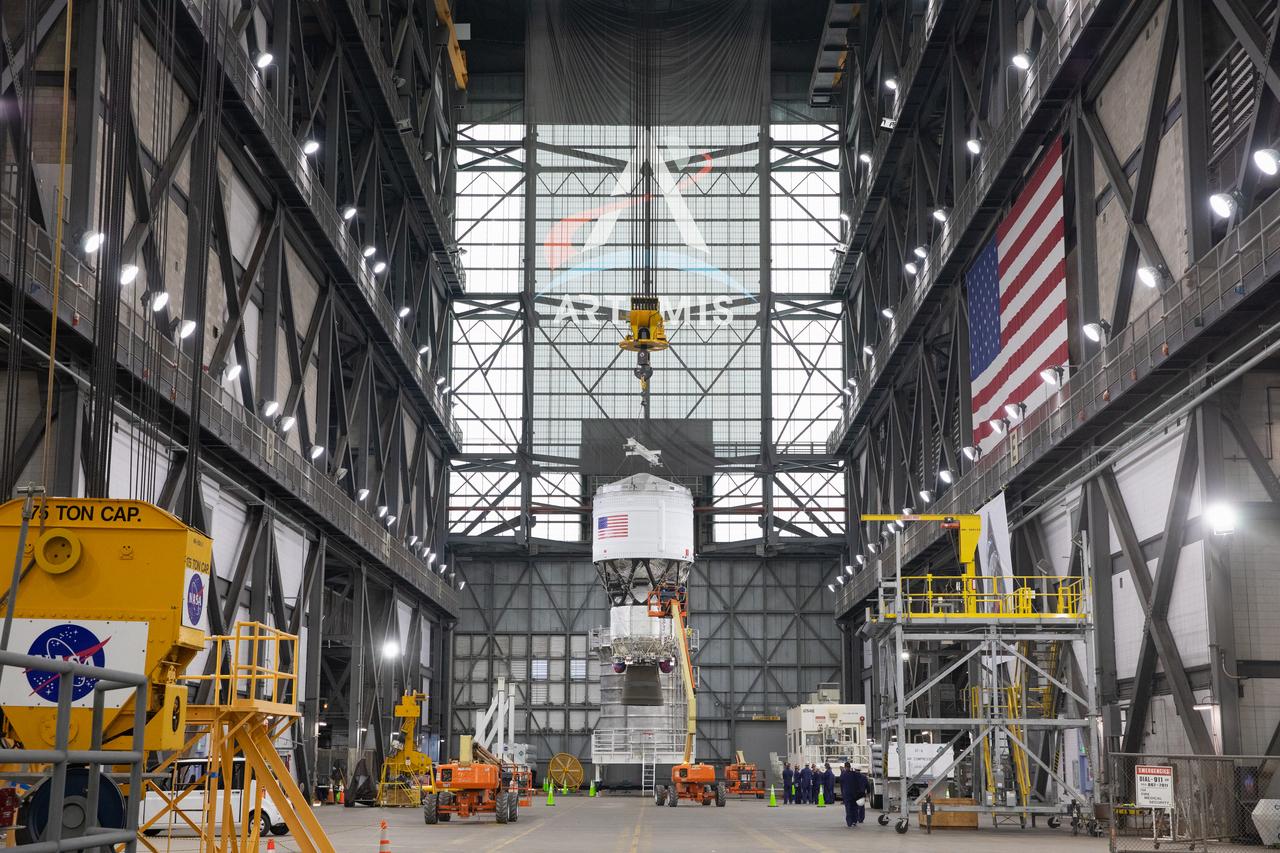

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program finish integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Thursday, May 1, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.
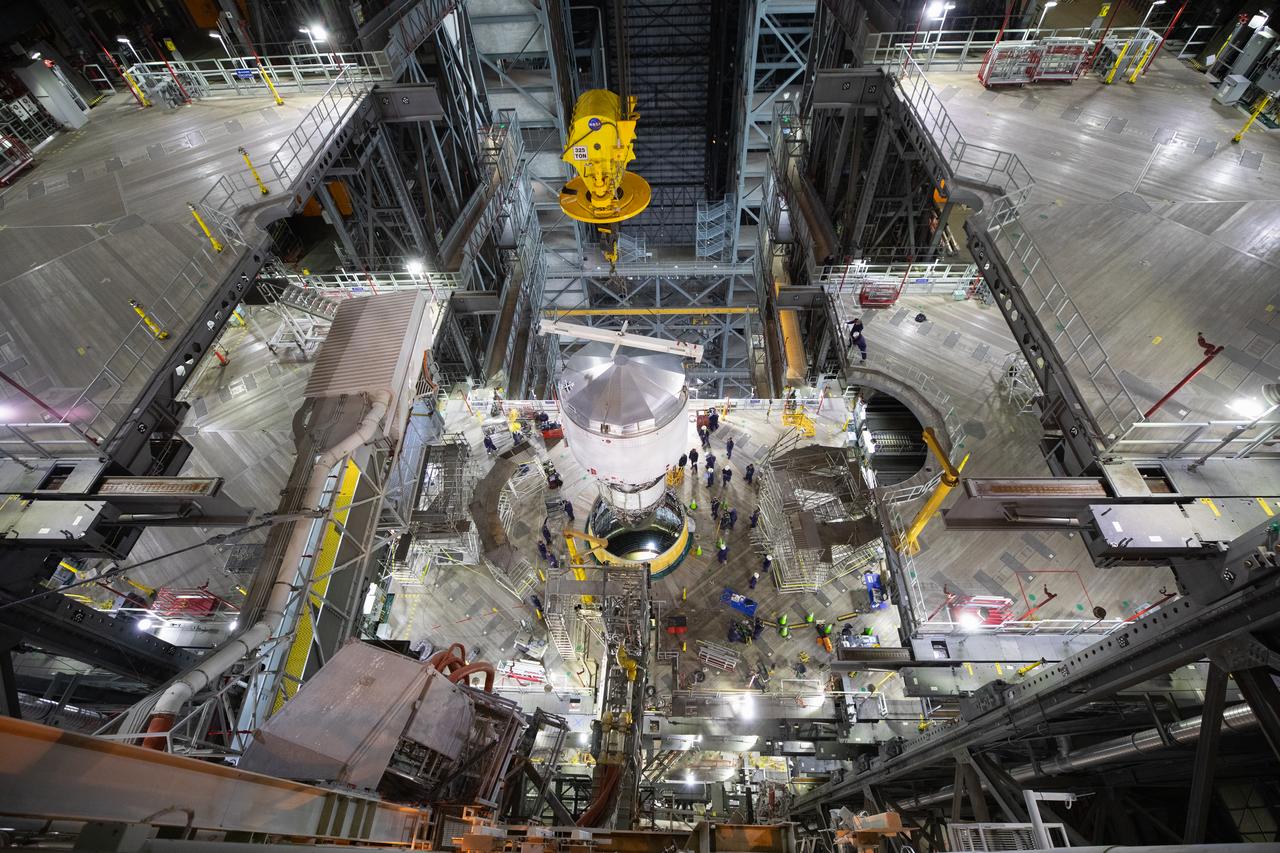

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.
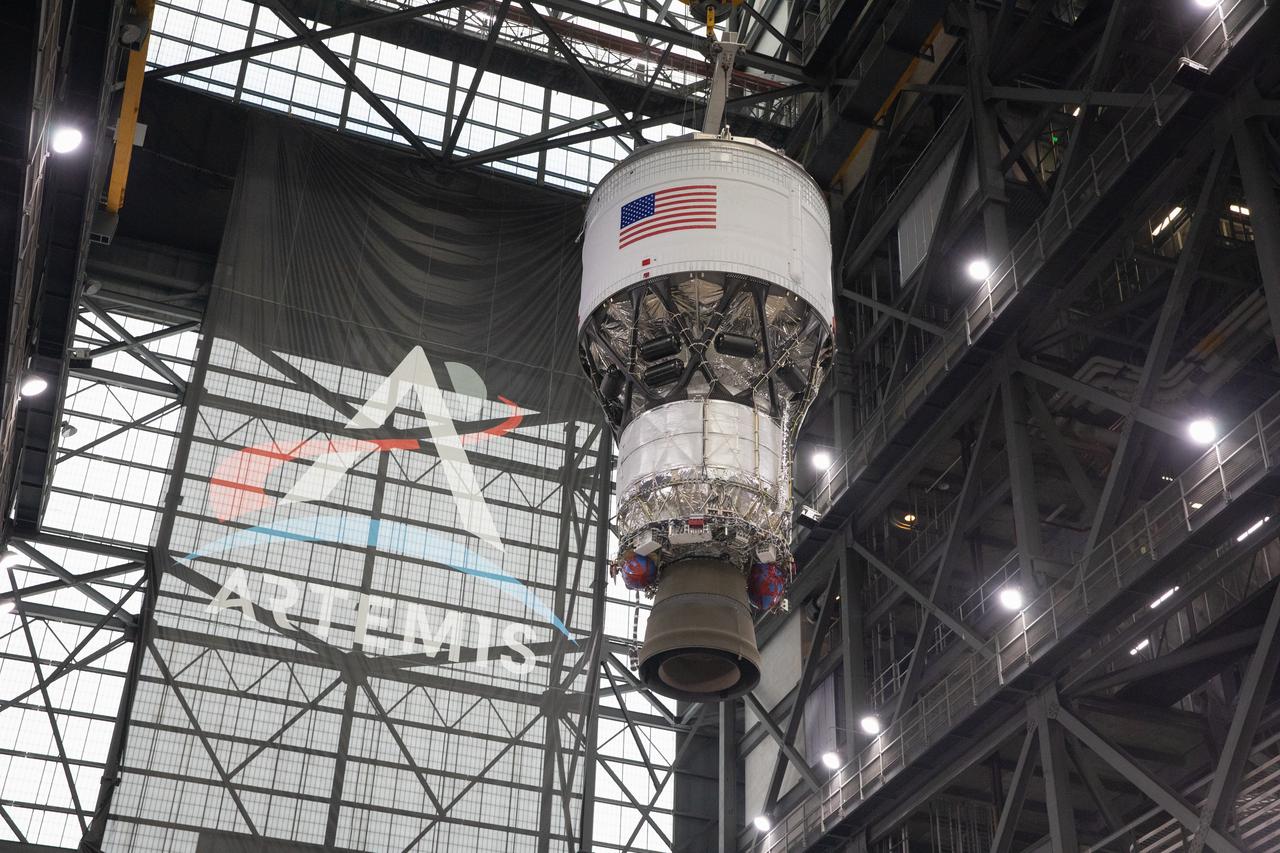

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.
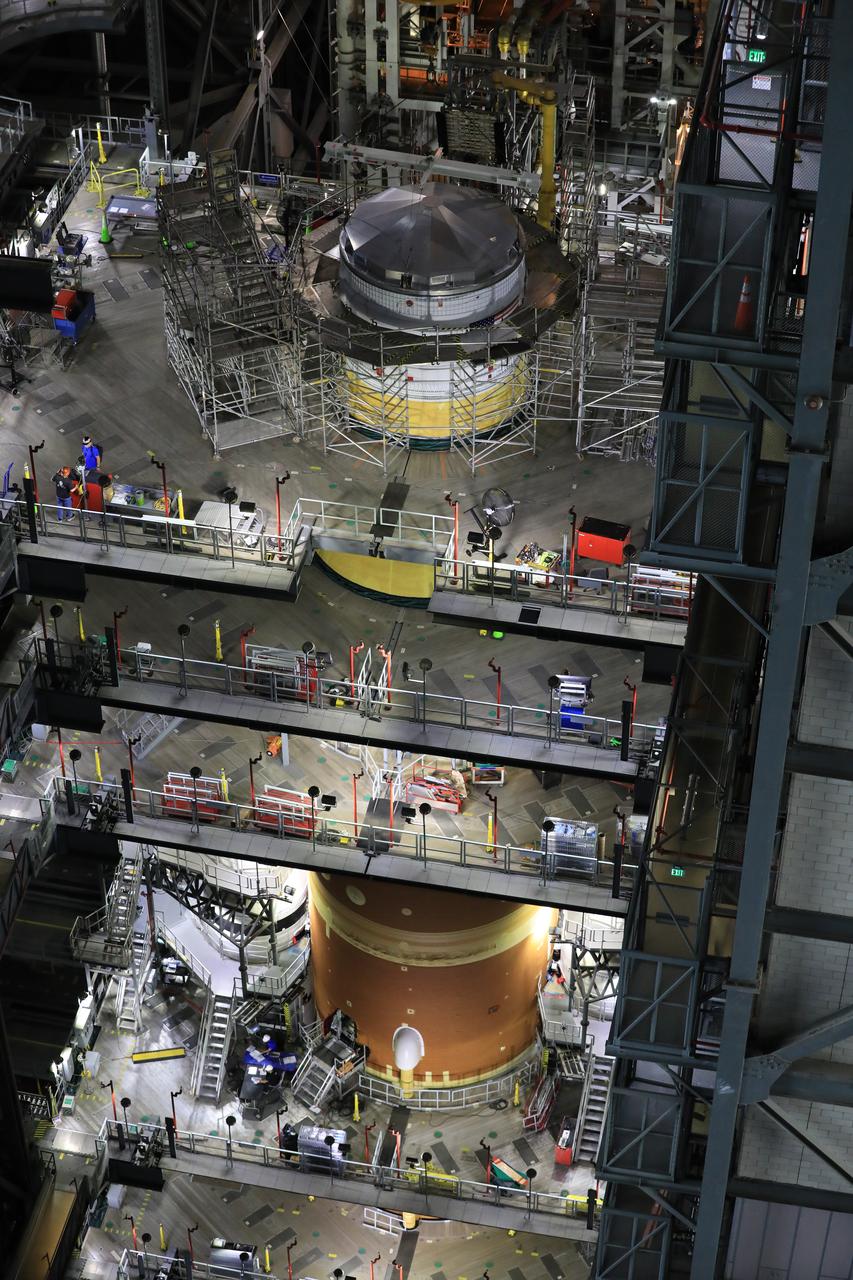

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program finish integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Thursday, May 1, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.
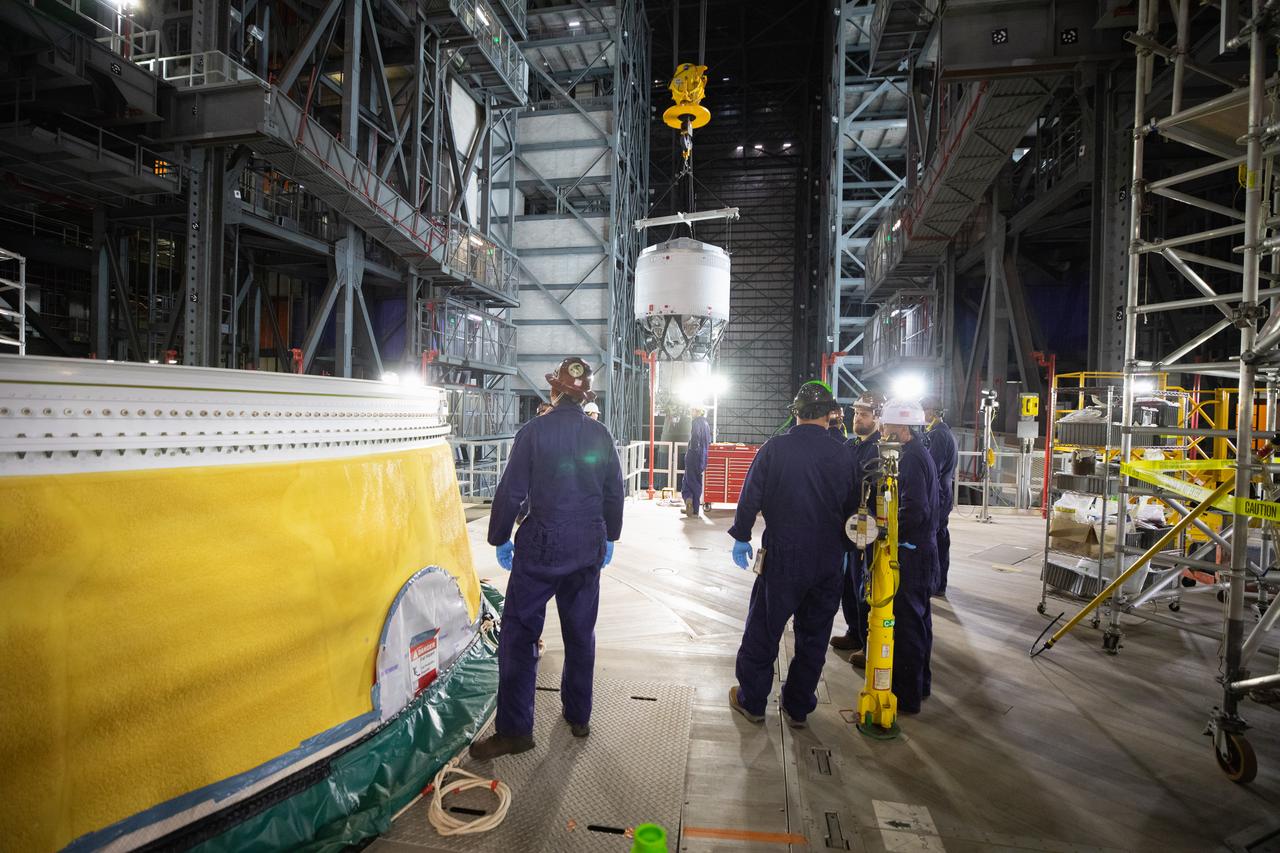

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program begin integrating the interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the SLS (Space Launch System) launch vehicle stage adapter on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four-story propulsion system, built by Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance), is powered by an RL10 engine that will enable the Orion spacecraft to build up enough speed for the push toward the Moon during the Artemis II crewed test flight.
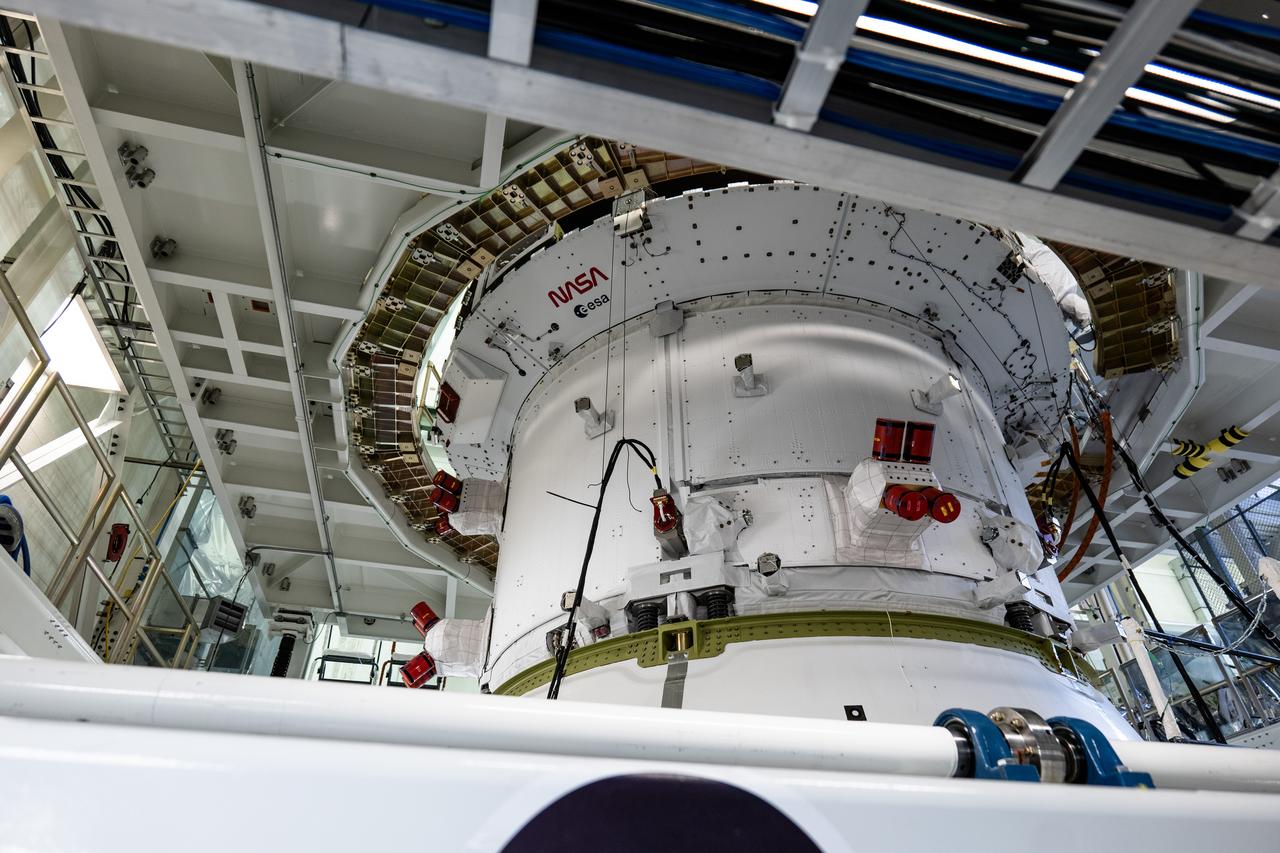

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis II mission undergoes checkouts in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Reid Wiseman, as well as CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen, on a 10-day journey around the Moon and back for the Artemis II test flight.
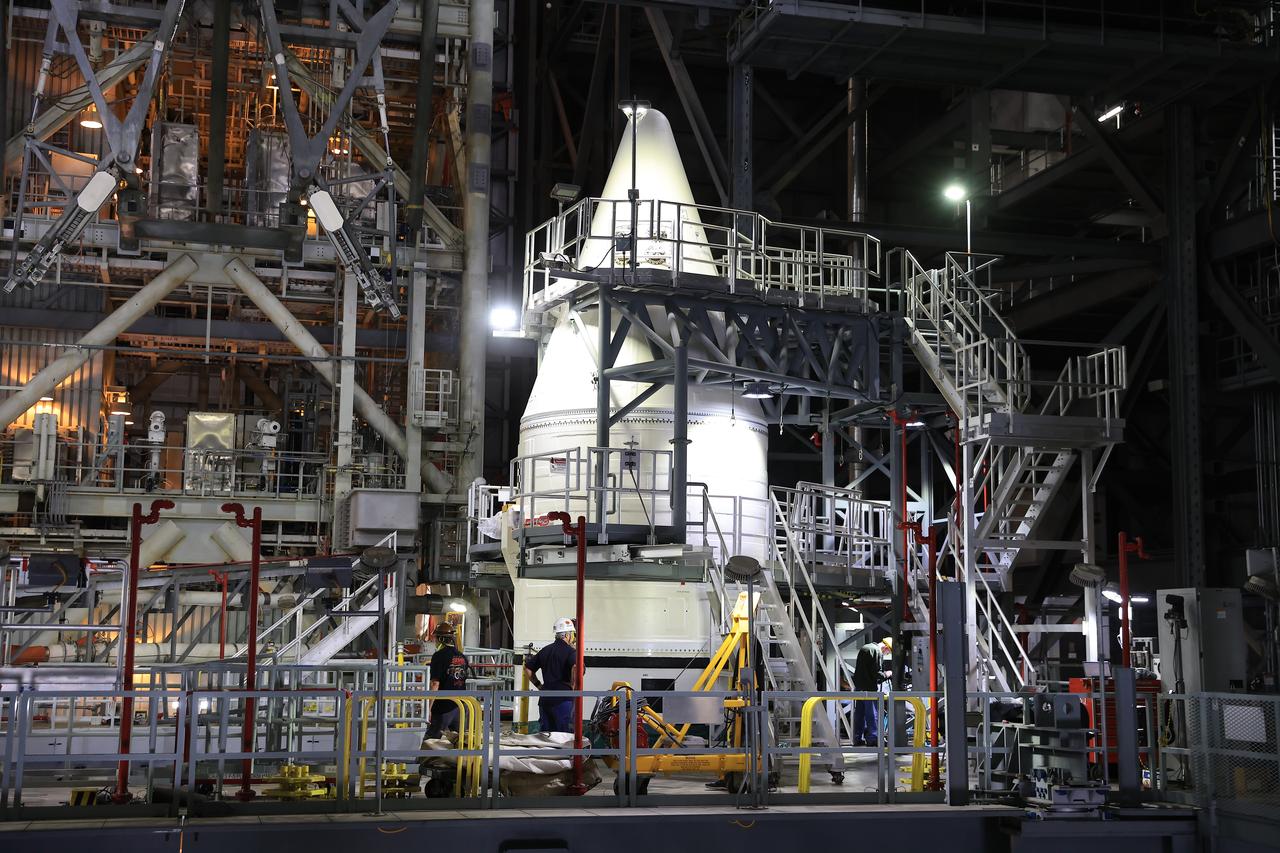

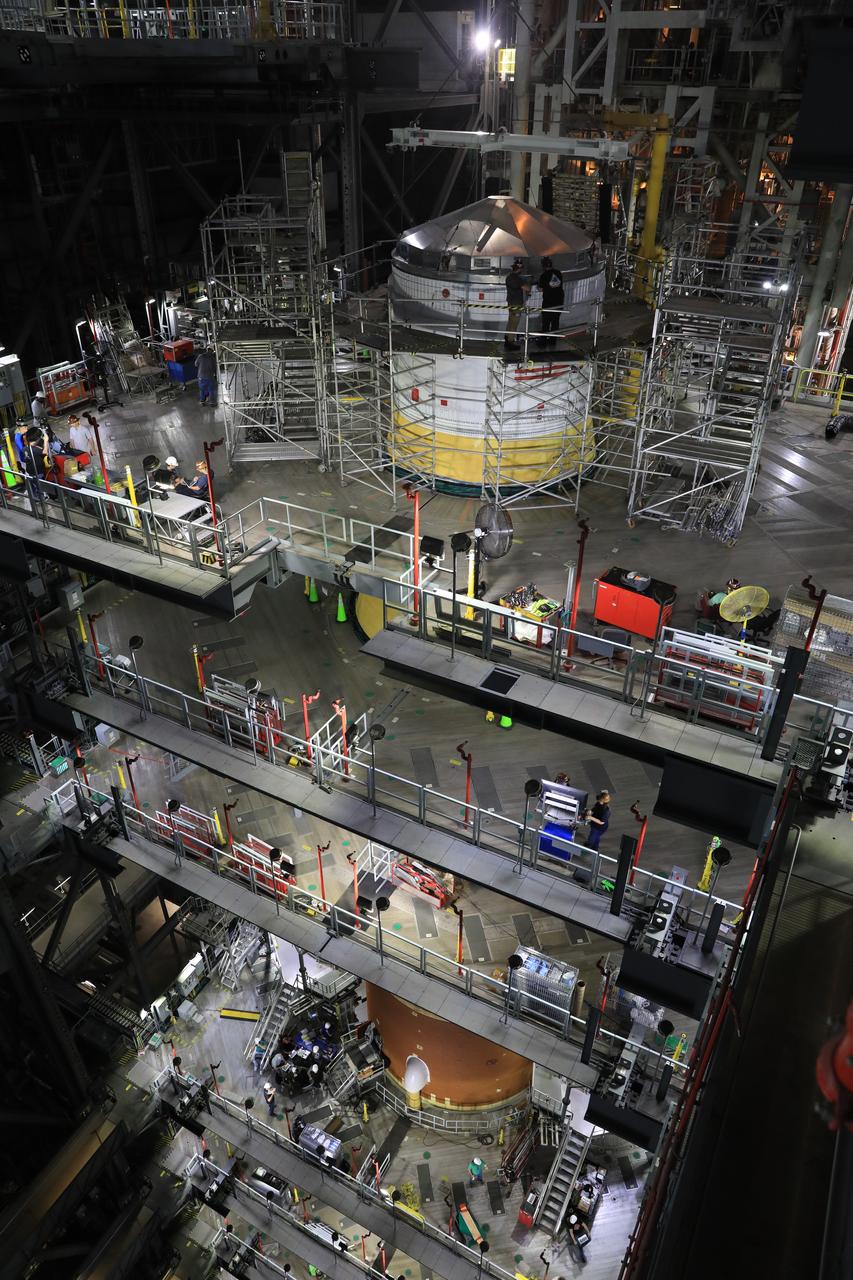
Engineers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems complete stacking operations on the twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for Artemis II by integrating the nose cones atop the forward assemblies inside the Vehicle Assembly Building’s High Bay 3 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 19, 2025. During three months of stacking operations, technicians used a massive overhead crane to lift 10 booster segments – five segments per booster – and aerodynamic nose cones into place on mobile launcher 1. The twin solid boosters will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.

Engineers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems complete stacking operations on the twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for Artemis II by integrating the nose cones atop the forward assemblies inside the Vehicle Assembly Building’s High Bay 3 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 19, 2025. During three months of stacking operations, technicians used a massive overhead crane to lift 10 booster segments – five segments per booster – and aerodynamic nose cones into place on mobile launcher 1. The twin solid boosters will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.
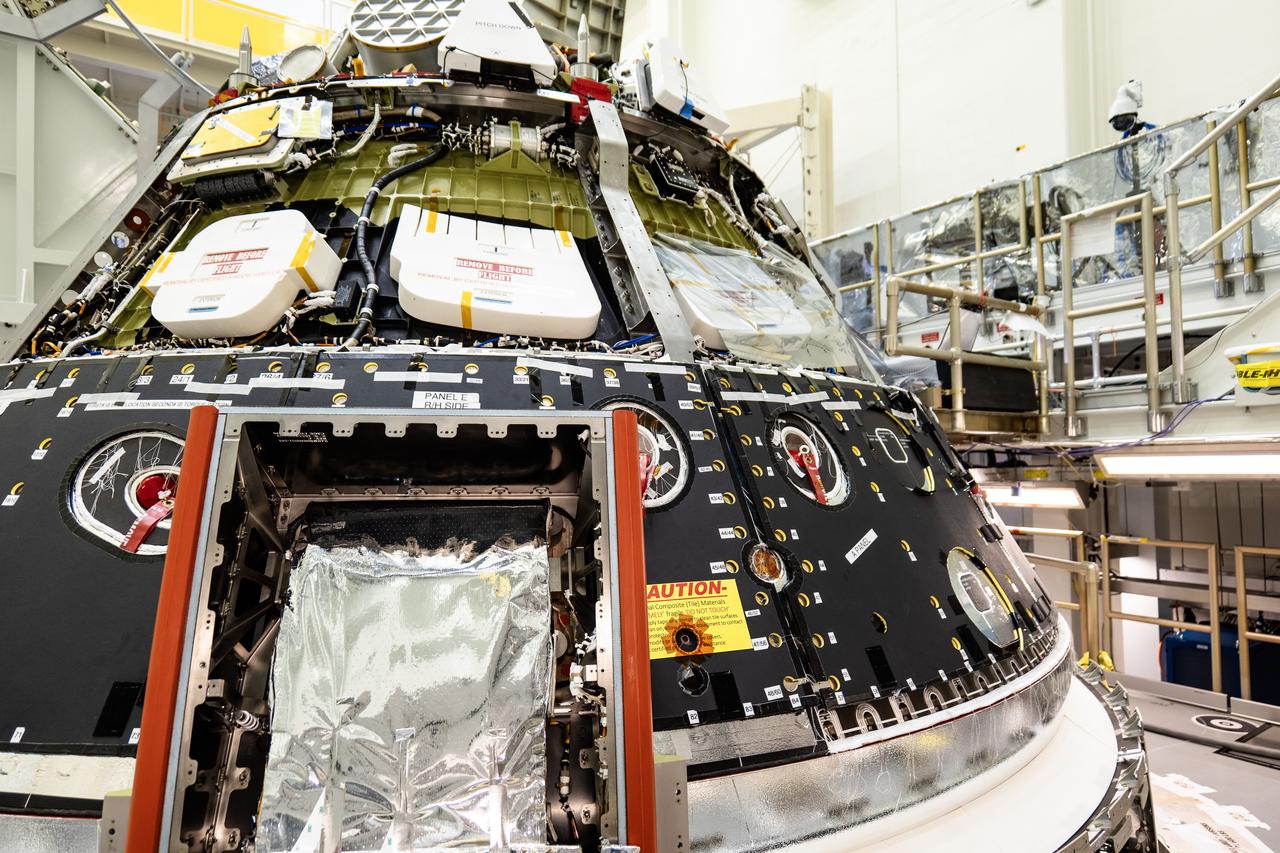

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis II mission undergoes checkouts in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Reid Wiseman, as well as CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen, on a 10-day journey around the Moon and back for the Artemis II test flight.
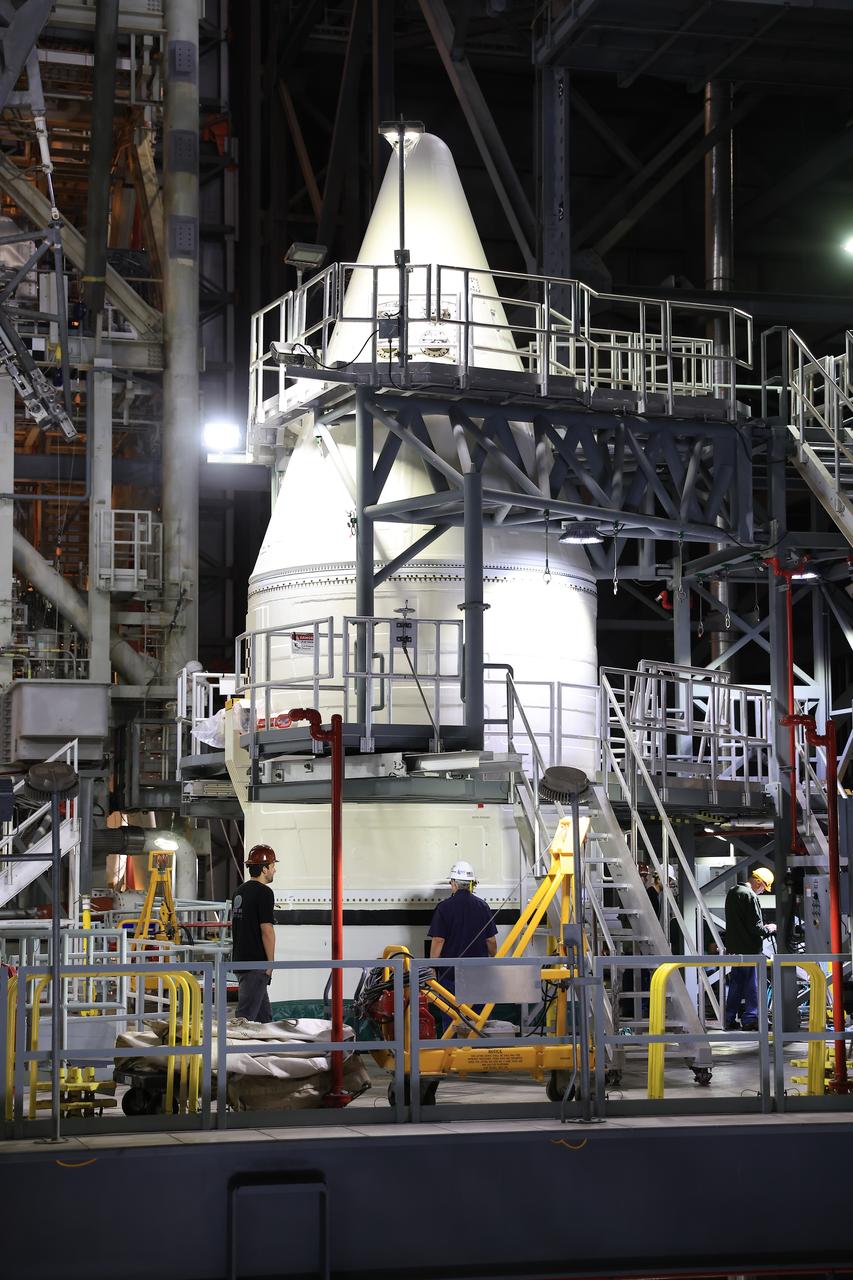

Engineers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems complete stacking operations on the twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for Artemis II by integrating the nose cones atop the forward assemblies inside the Vehicle Assembly Building’s High Bay 3 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 19, 2025. During three months of stacking operations, technicians used a massive overhead crane to lift 10 booster segments – five segments per booster – and aerodynamic nose cones into place on mobile launcher 1. The twin solid boosters will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.
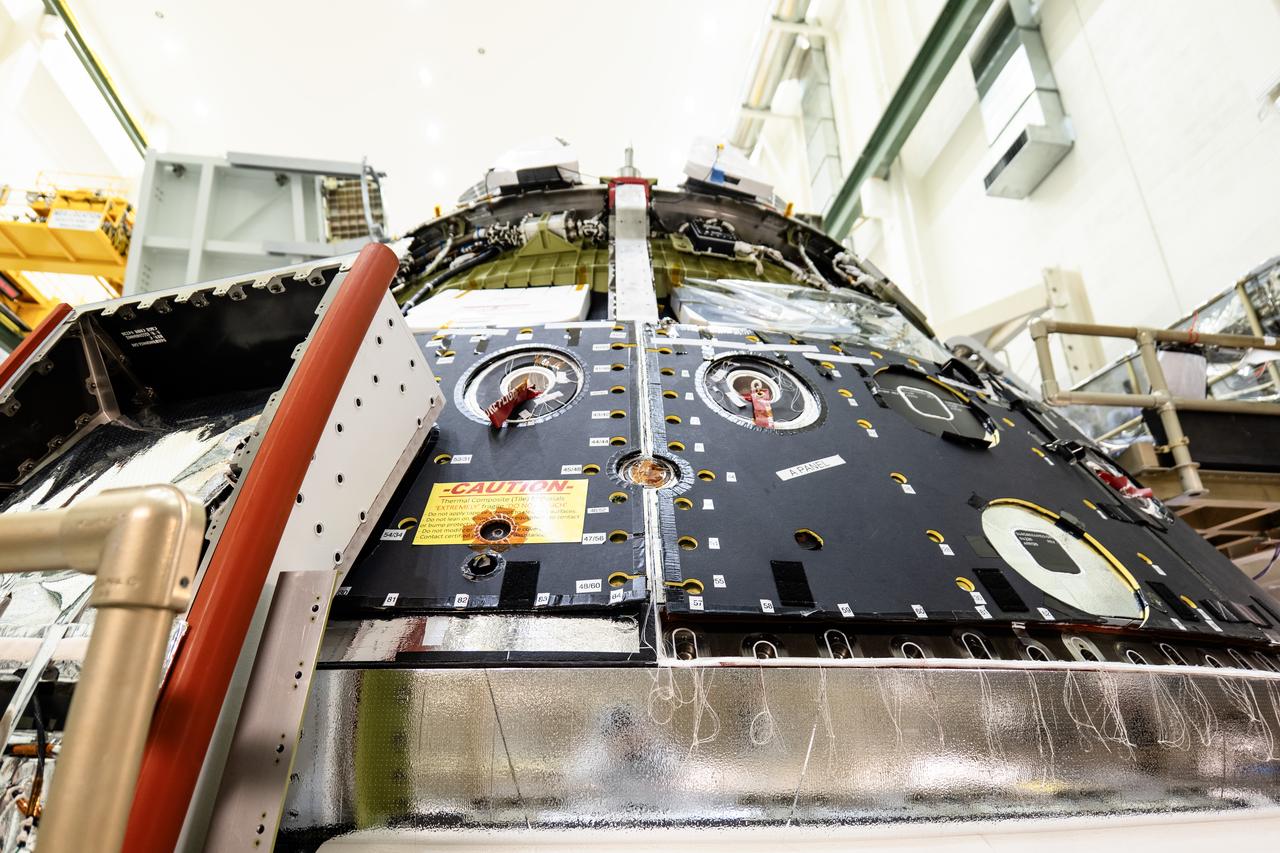
The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis II mission undergoes checkouts in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Reid Wiseman, as well as CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen, on a 10-day journey around the Moon and back for the Artemis II test flight.
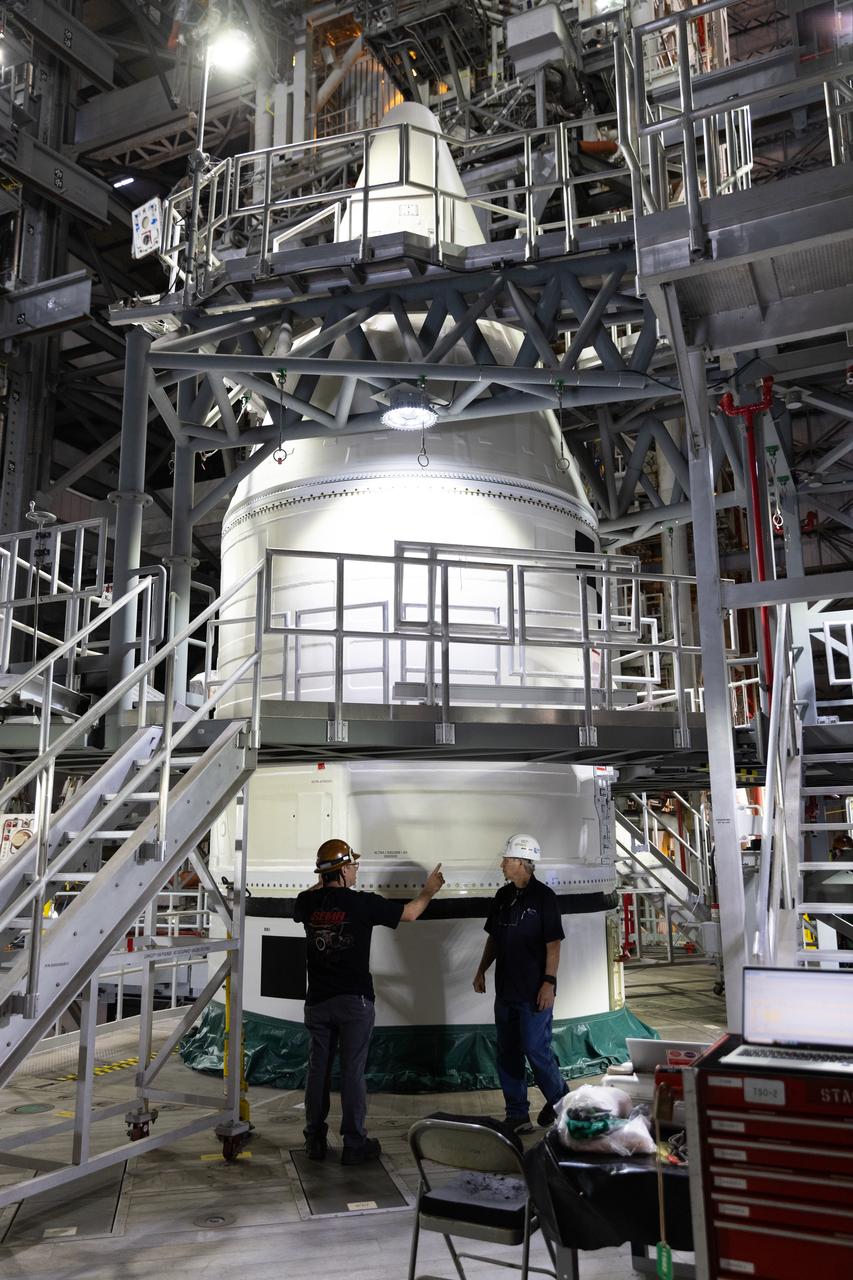

Engineers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems complete stacking operations on the twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for Artemis II by integrating the nose cones atop the forward assemblies inside the Vehicle Assembly Building’s High Bay 3 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 19, 2025. During three months of stacking operations, technicians used a massive overhead crane to lift 10 booster segments – five segments per booster – and aerodynamic nose cones into place on mobile launcher 1. The twin solid boosters will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.
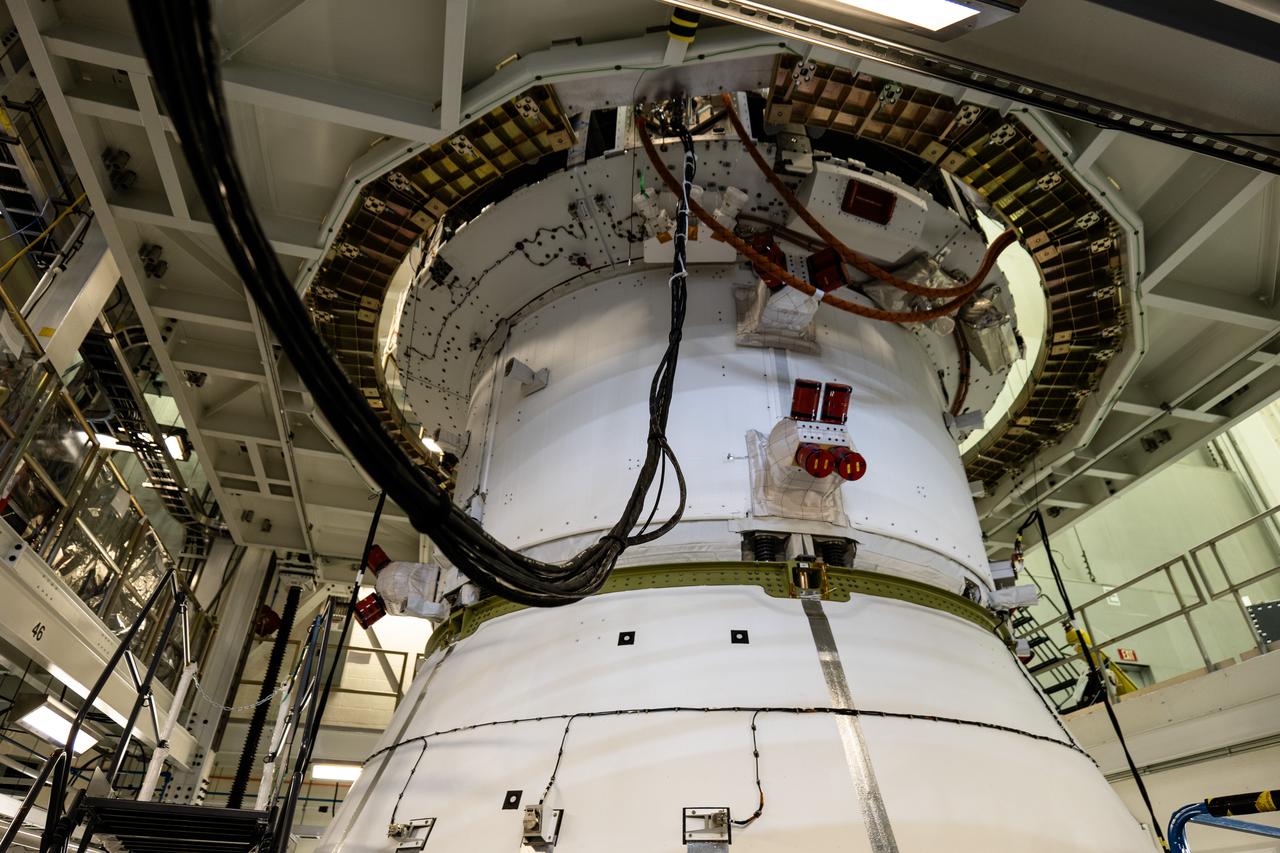

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis II mission undergoes checkouts in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Reid Wiseman, as well as CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen, on a 10-day journey around the Moon and back for the Artemis II test flight.
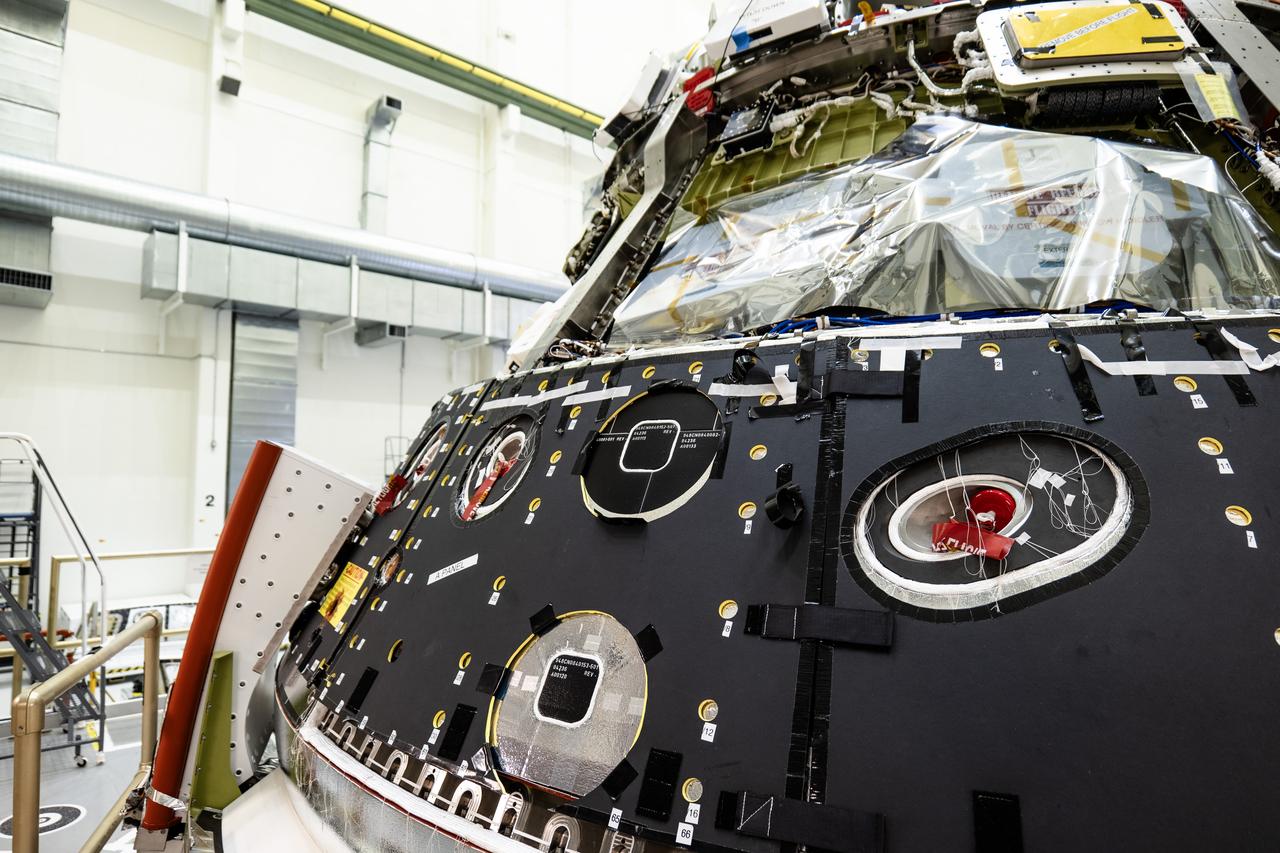
The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis II mission undergoes checkouts in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Reid Wiseman, as well as CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen, on a 10-day journey around the Moon and back for the Artemis II test flight.
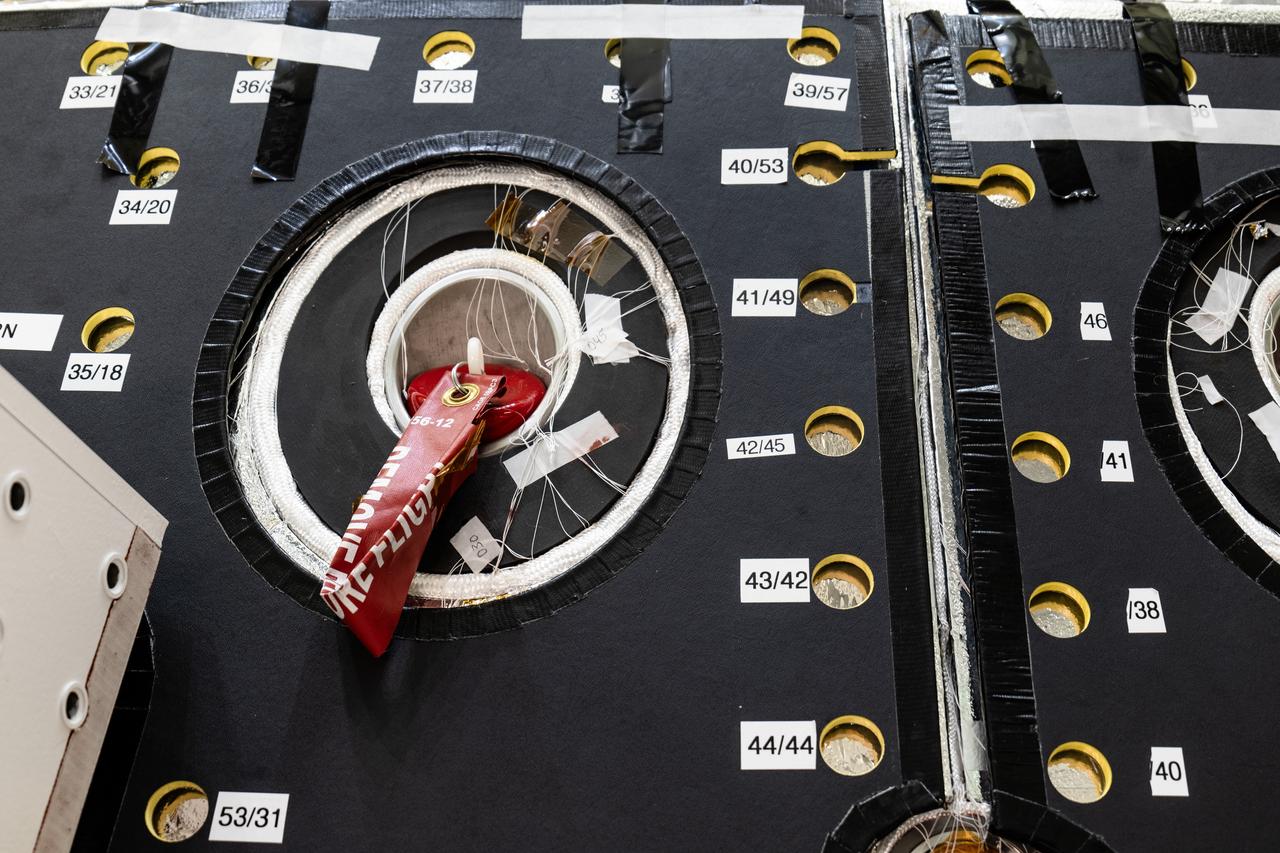
The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis II mission undergoes checkouts in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Reid Wiseman, as well as CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen, on a 10-day journey around the Moon and back for the Artemis II test flight.

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis II mission undergoes checkouts in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Reid Wiseman, as well as CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen, on a 10-day journey around the Moon and back for the Artemis II test flight.
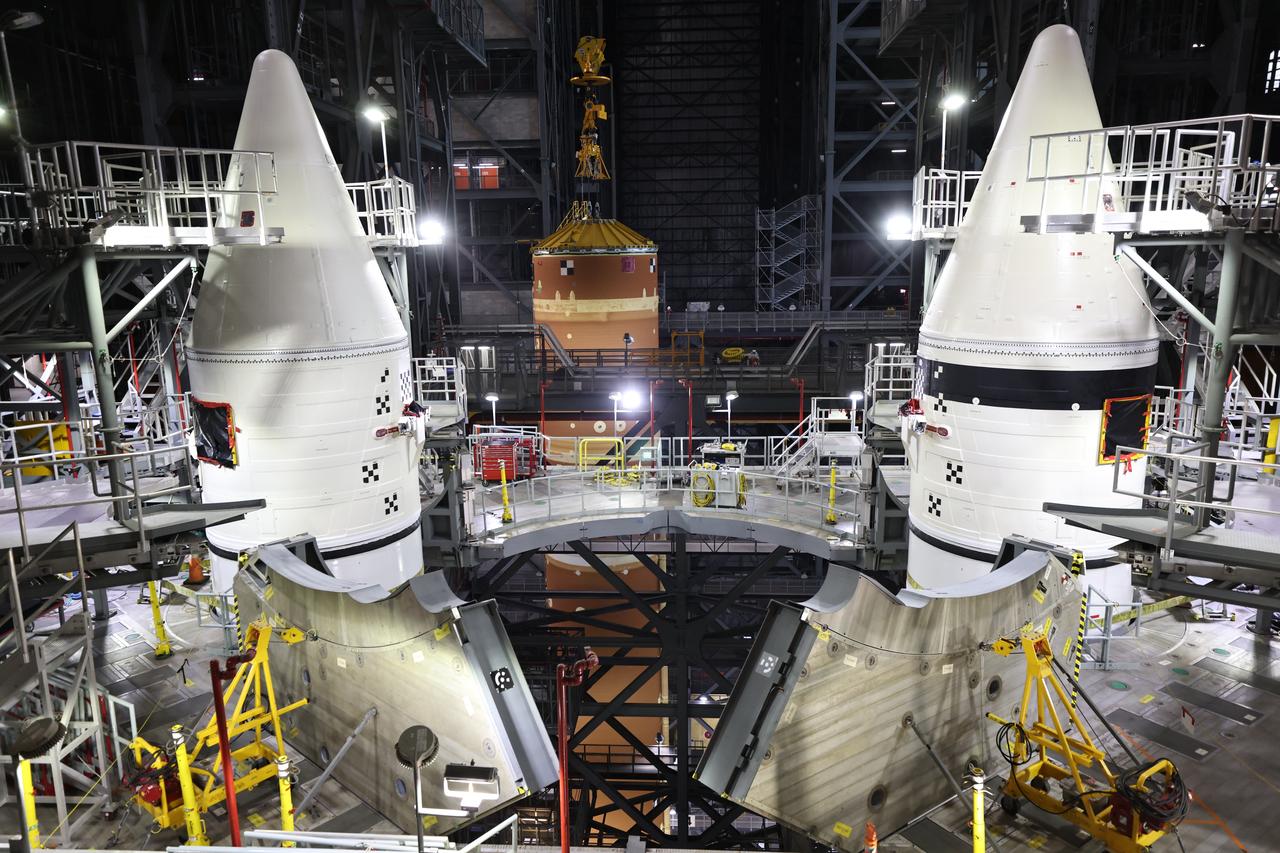

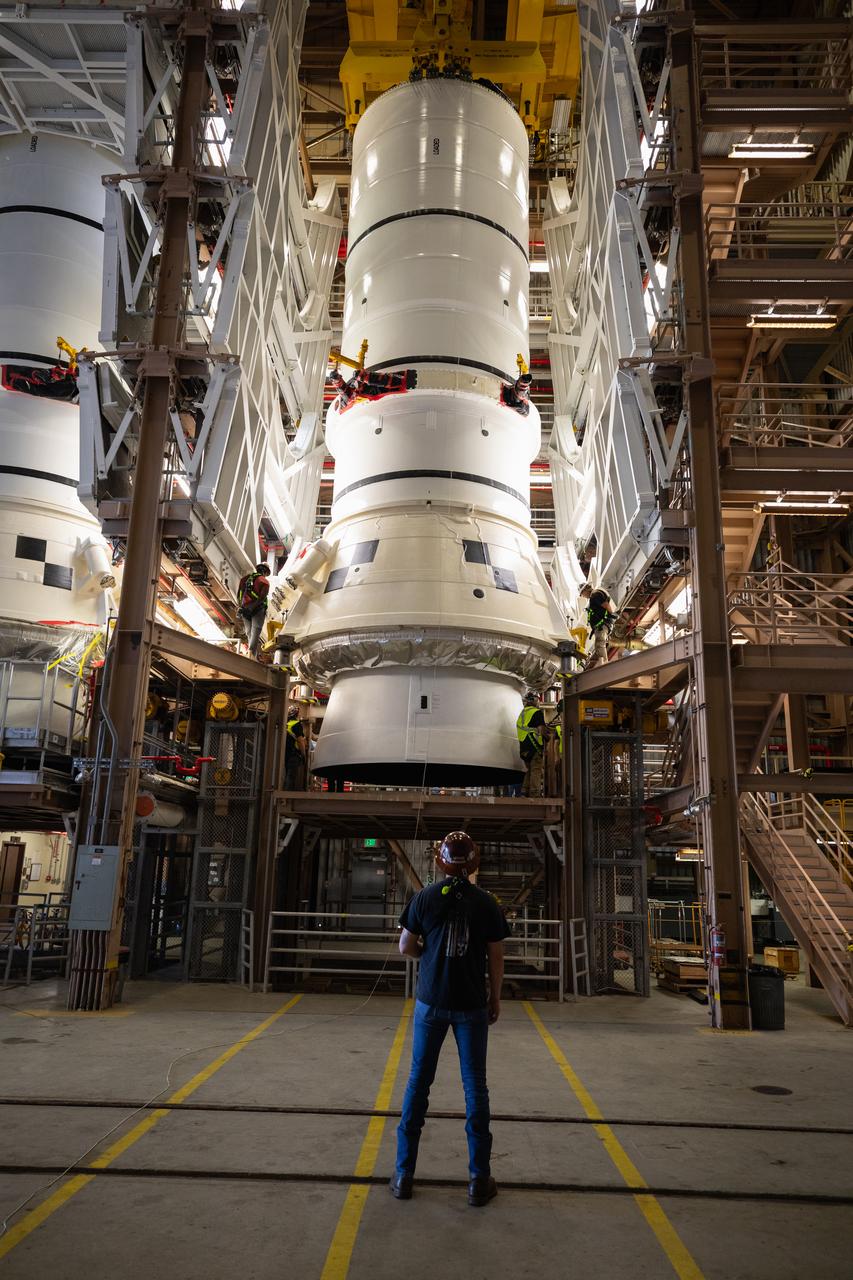
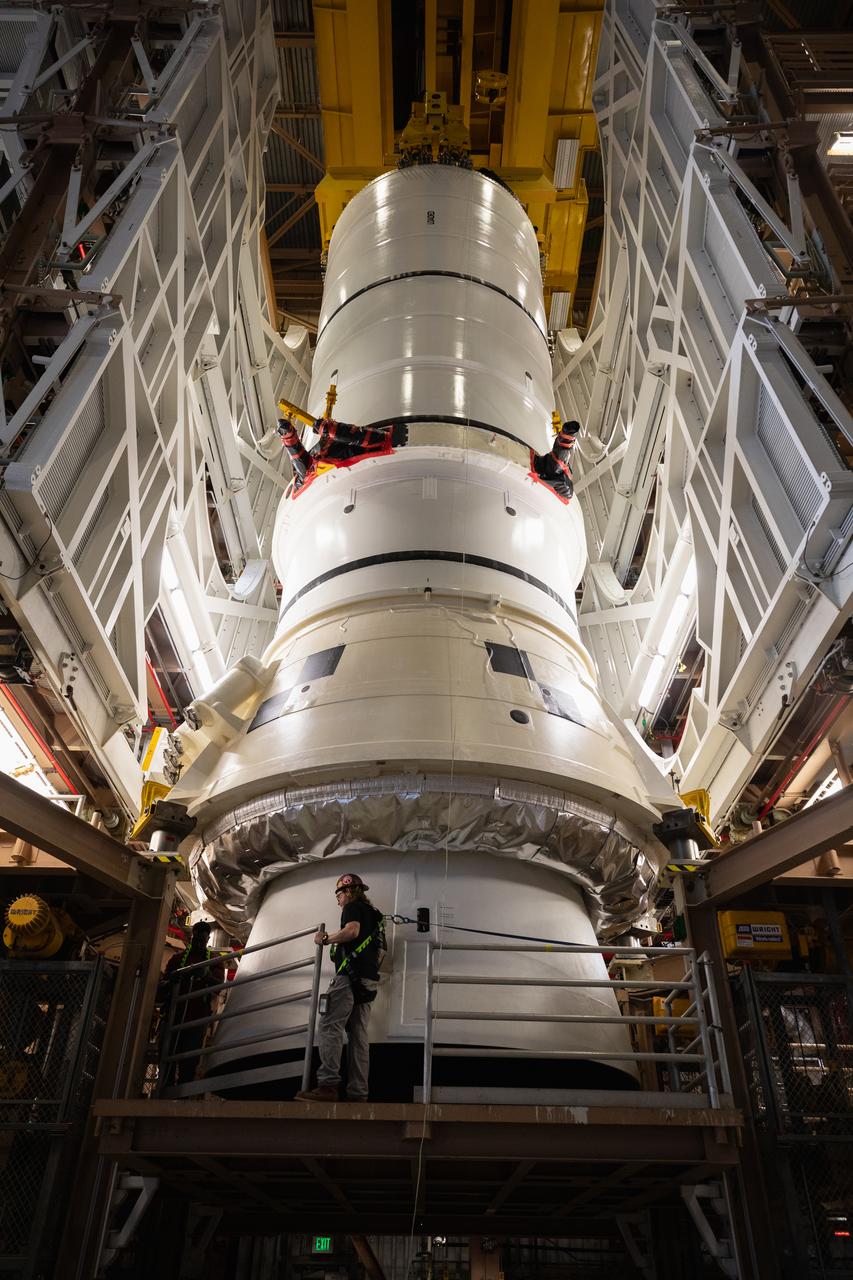
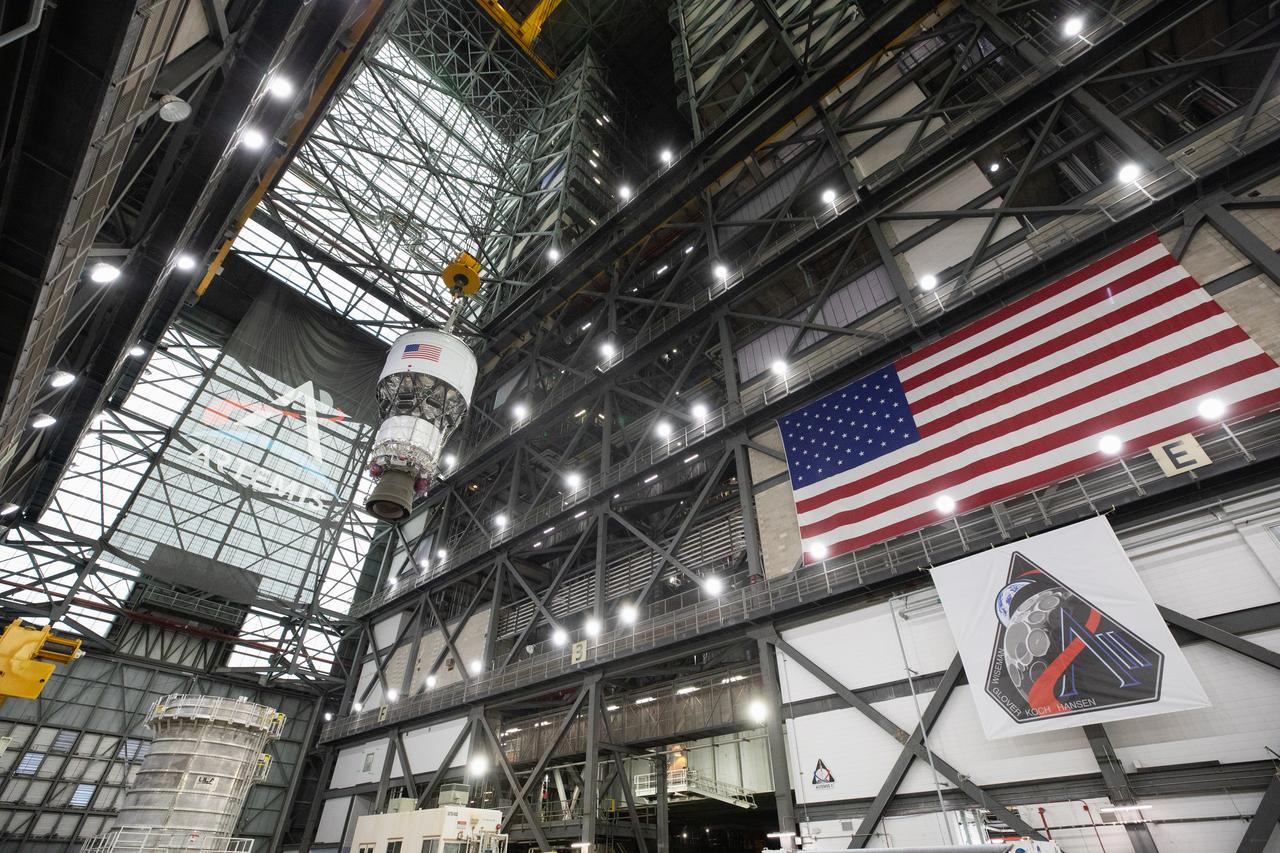
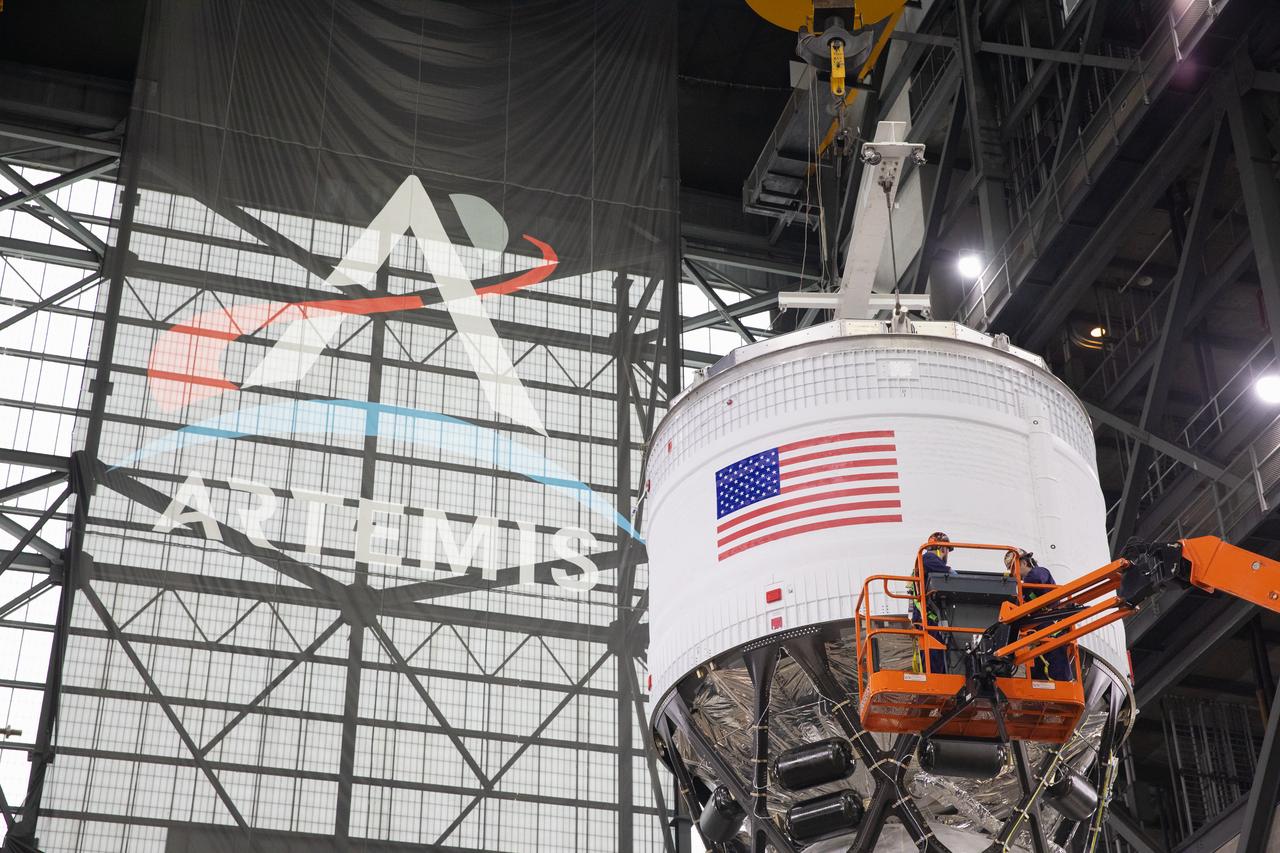
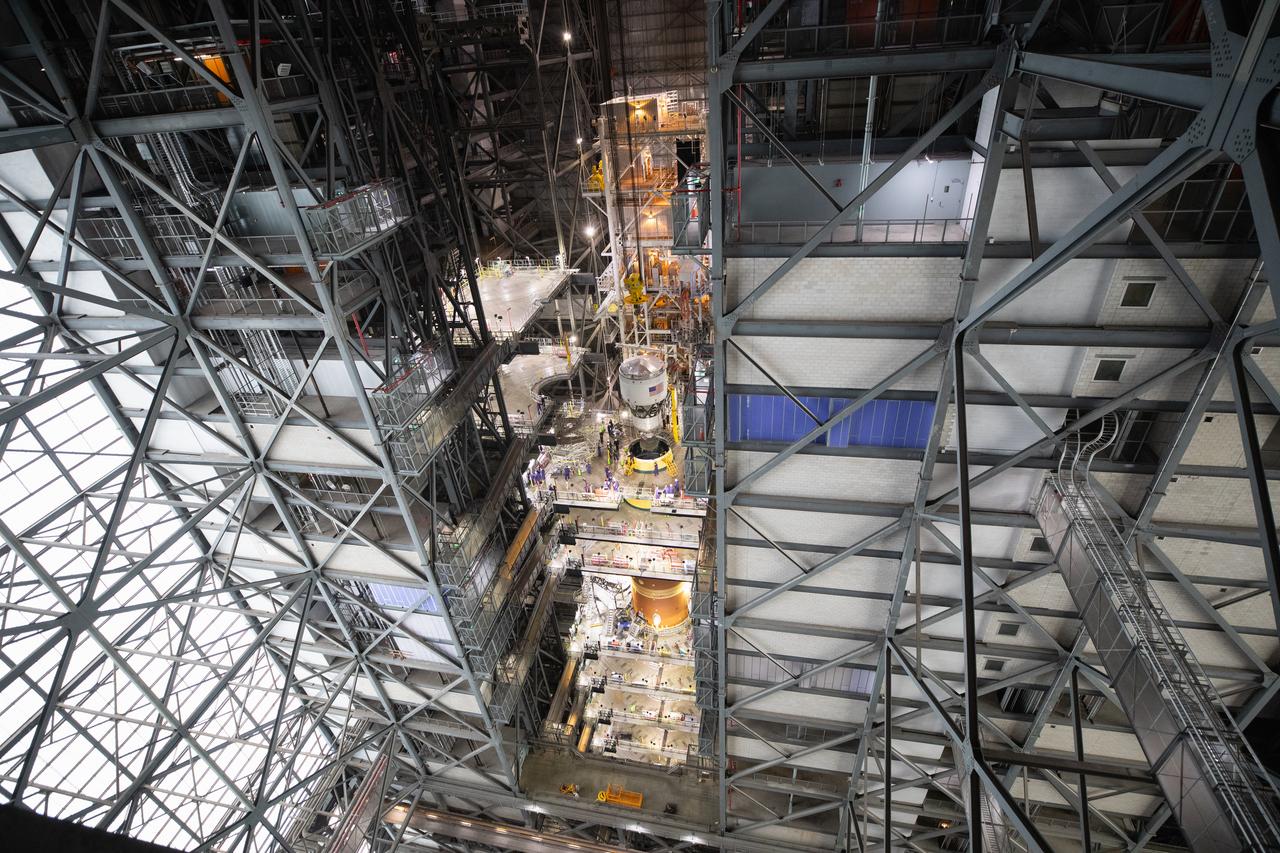
Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor Amentum, integrate the SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket with the solid rocket boosters onto mobile launcher 1 inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Sunday, March 23, 2025. Artemis II is the first crewed test flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
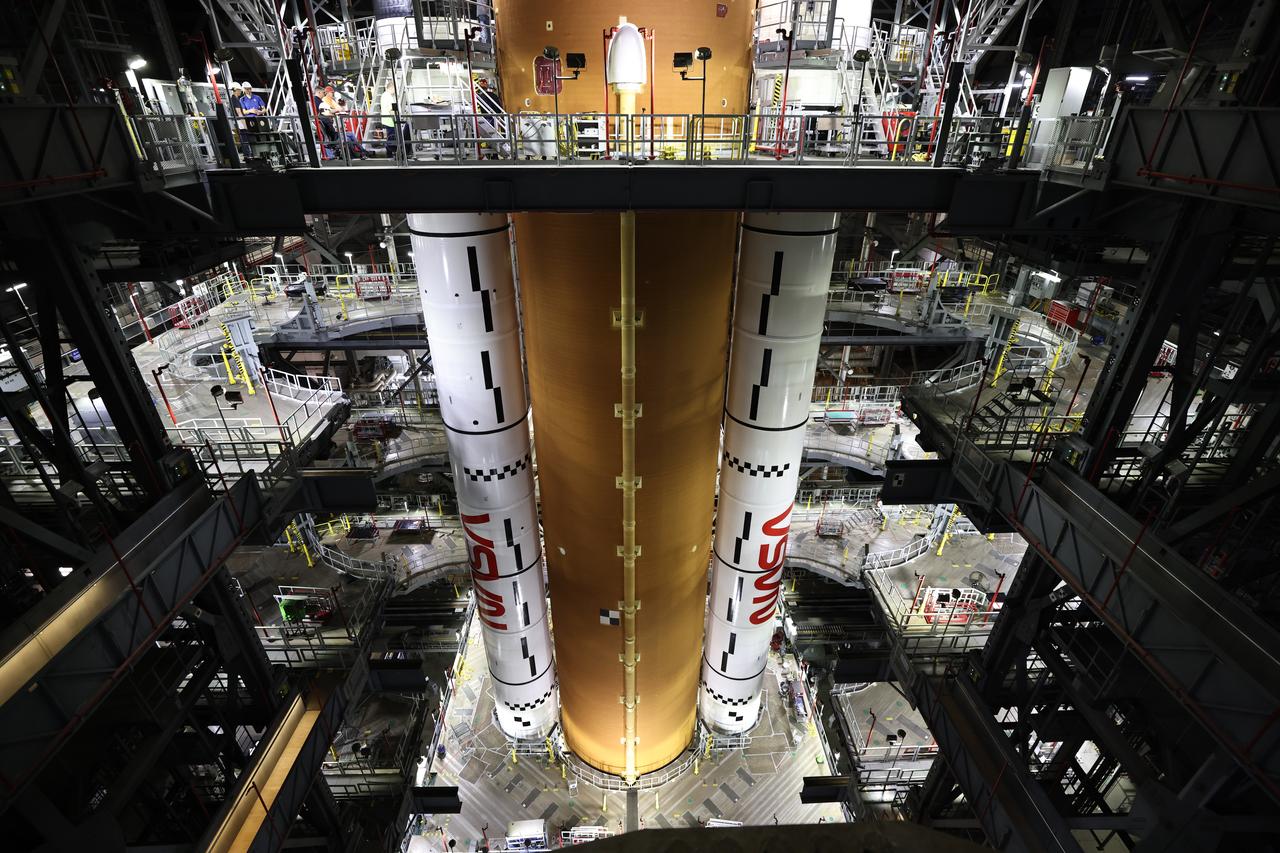
Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor Amentum, integrate the SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket with the solid rocket boosters onto mobile launcher 1 inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Sunday, March 23, 2025. Artemis II is the first crewed test flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
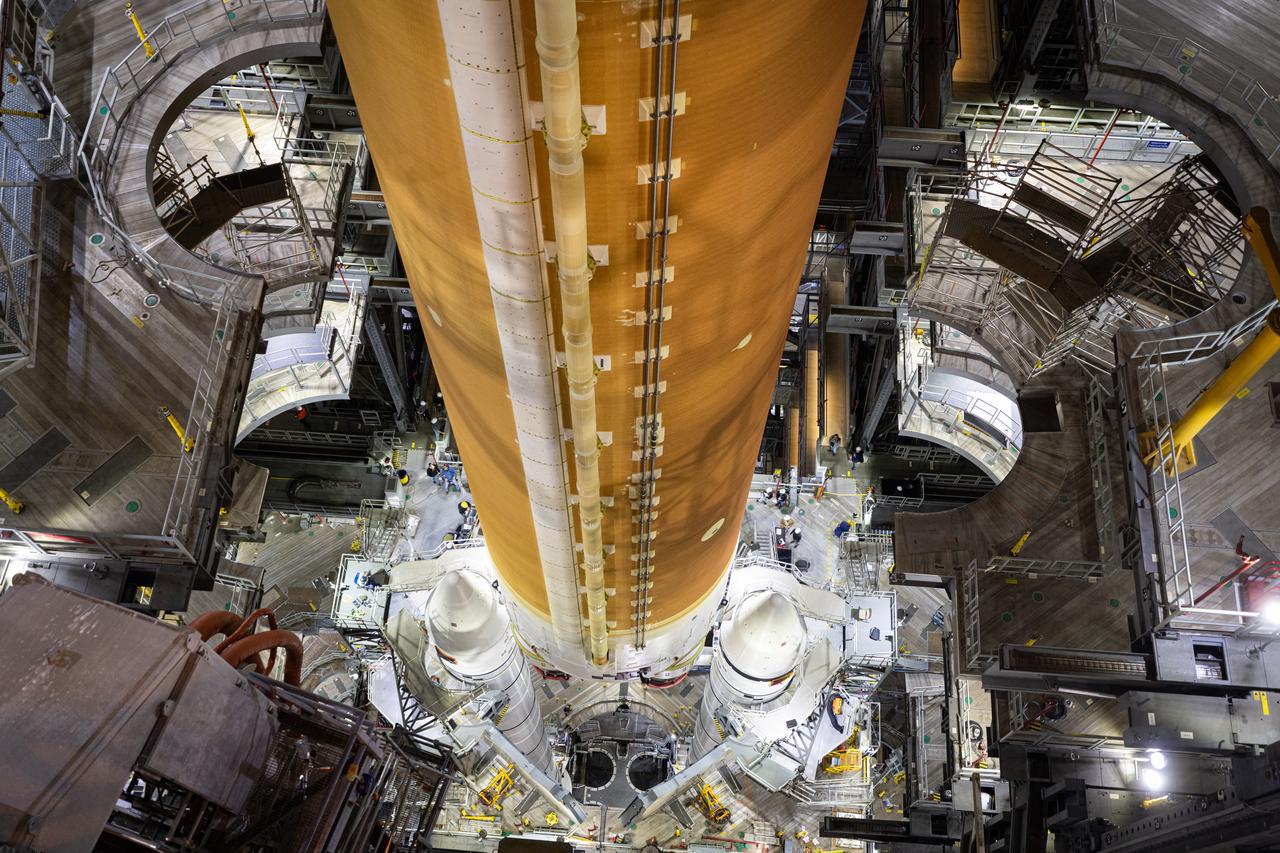

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor Amentum, integrate the SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket with the solid rocket boosters onto mobile launcher 1 inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Sunday, March 23, 2025. Artemis II is the first crewed test flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
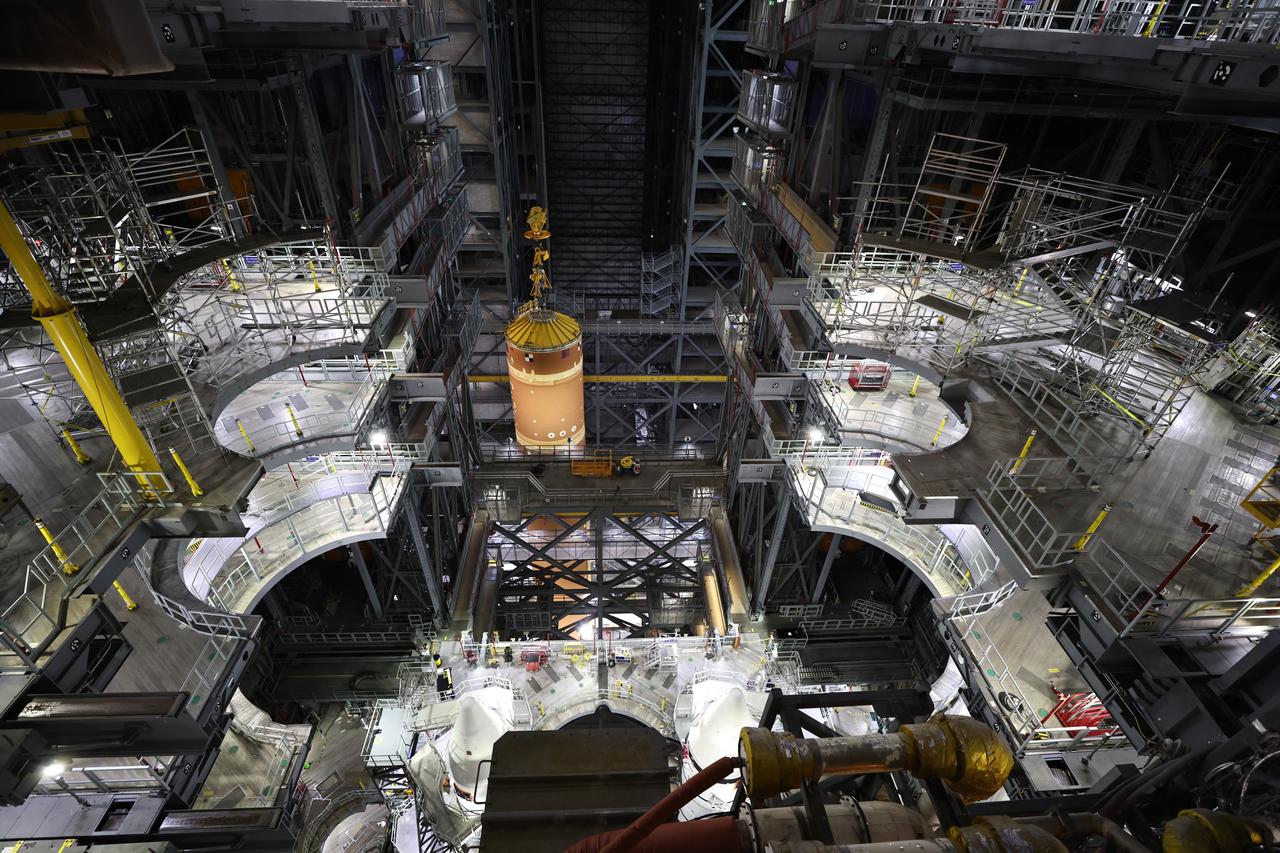

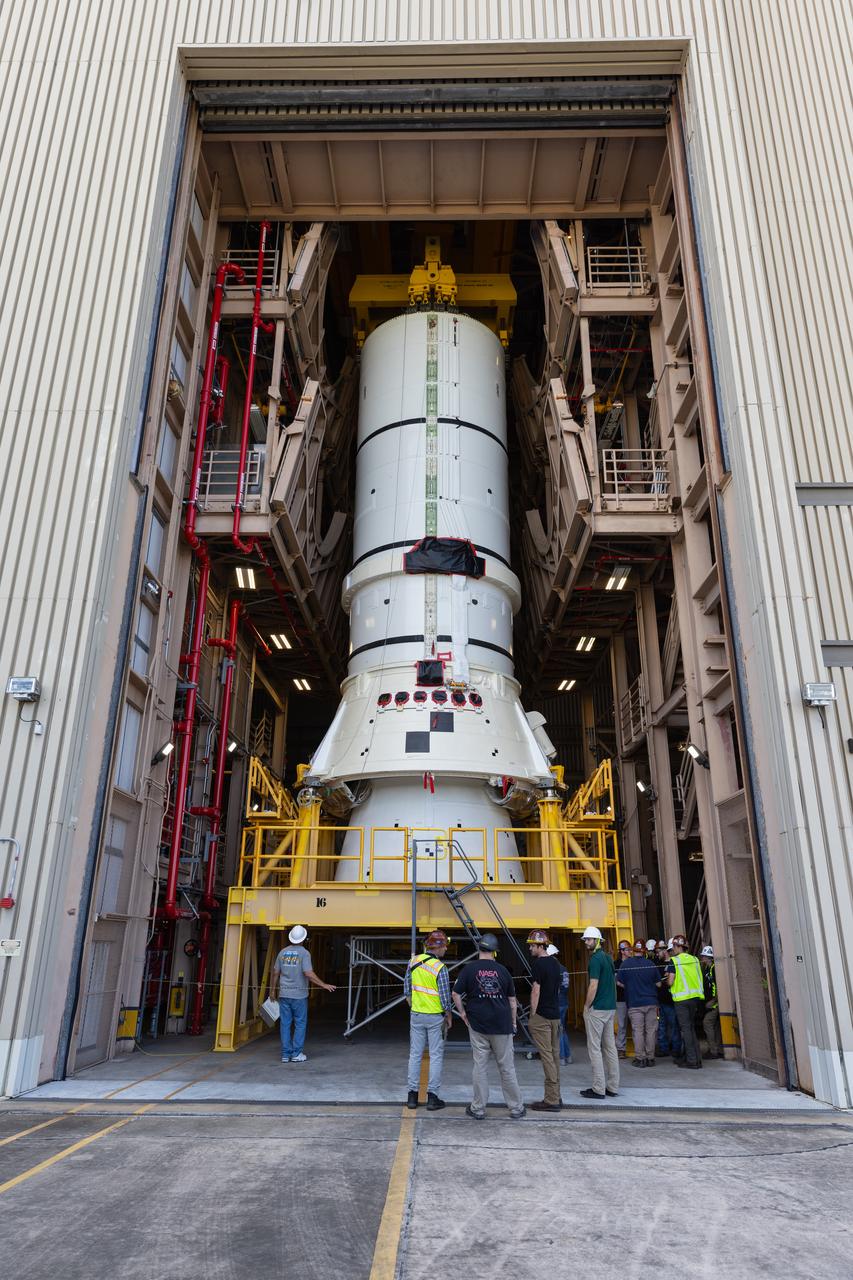
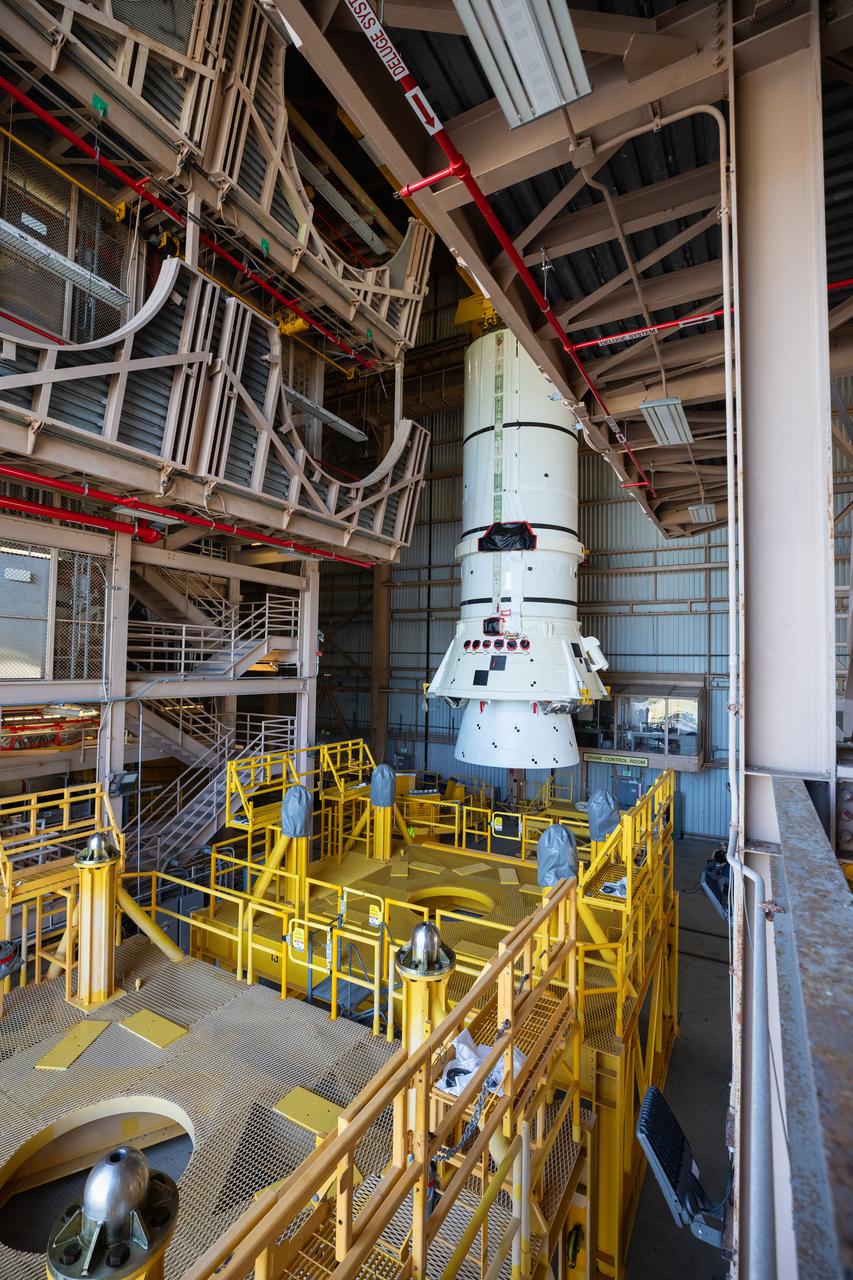
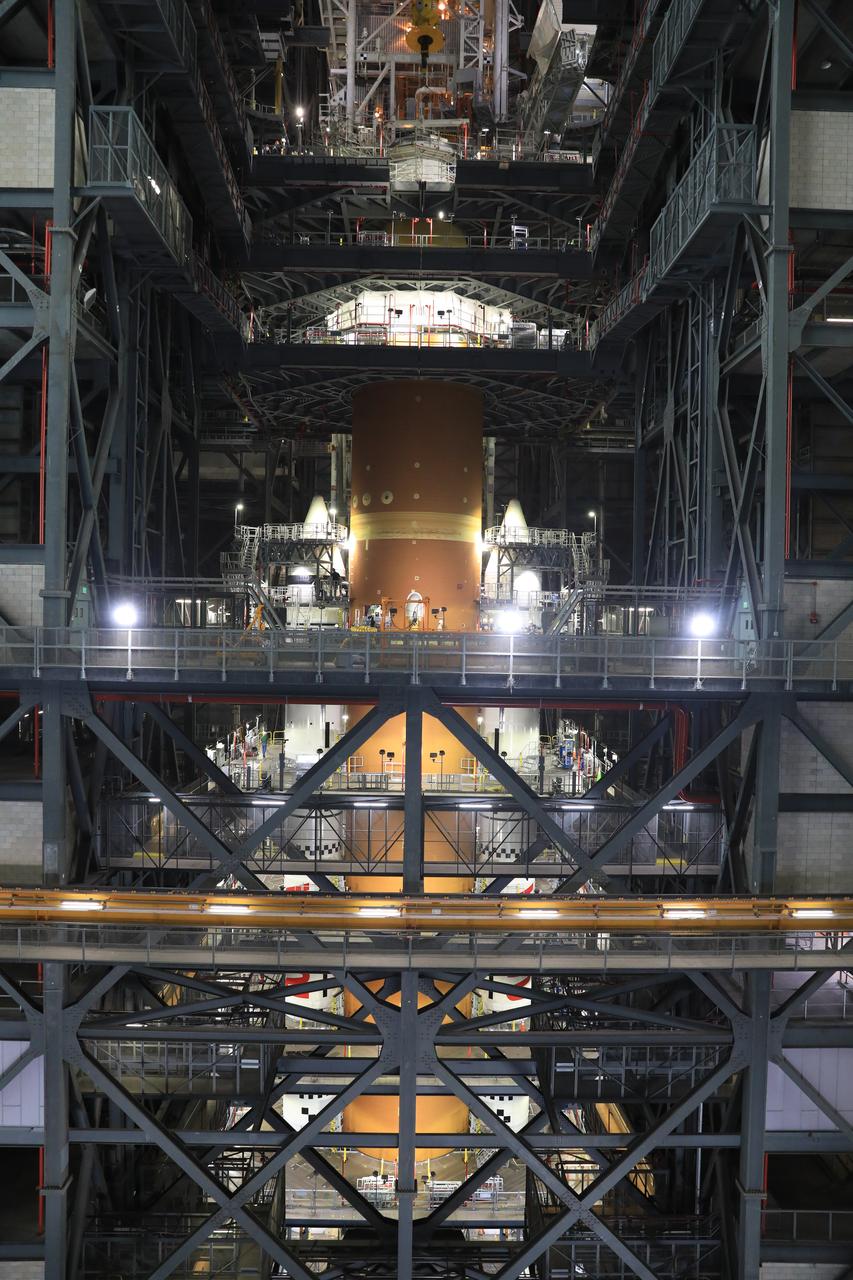
Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor Amentum, use a massive crane to lift to vertical the SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket for Artemis II on Saturday, March 22, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The move from the facility’s transfer aisle into High Bay 3 allows technicians to integrate the 212-foot-tall core stage with the stacked solid rocket boosters onto mobile launcher 1. Artemis II is the first crewed test flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
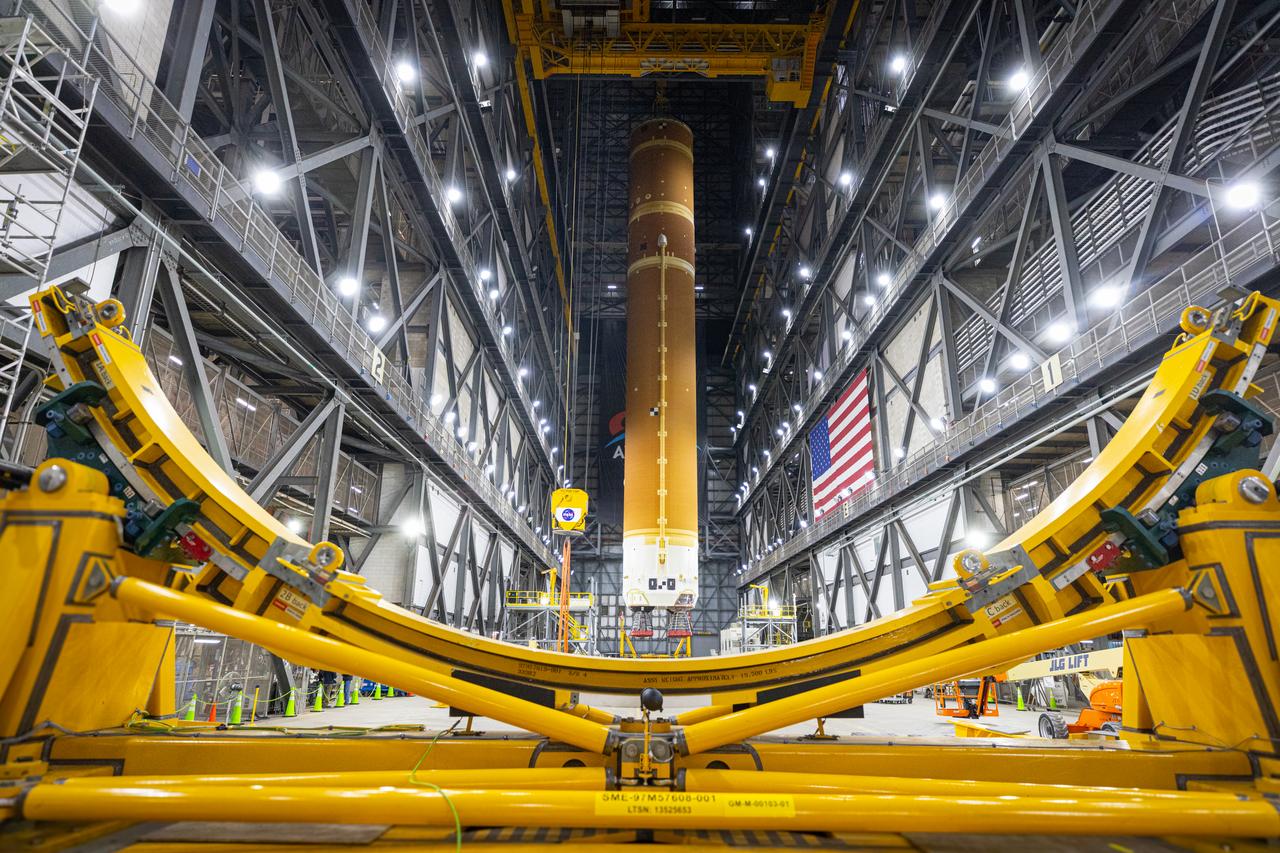

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor Amentum, use a massive crane to lift to vertical the SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket for Artemis II on Saturday, March 22, 2025, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The move from the facility’s transfer aisle into High Bay 3 allows technicians to integrate the 212-foot-tall core stage with the stacked solid rocket boosters onto mobile launcher 1. Artemis II is the first crewed test flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor Amentum, integrate the SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket with the solid rocket boosters onto mobile launcher 1 inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Sunday, March 23, 2025. Artemis II is the first crewed test flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
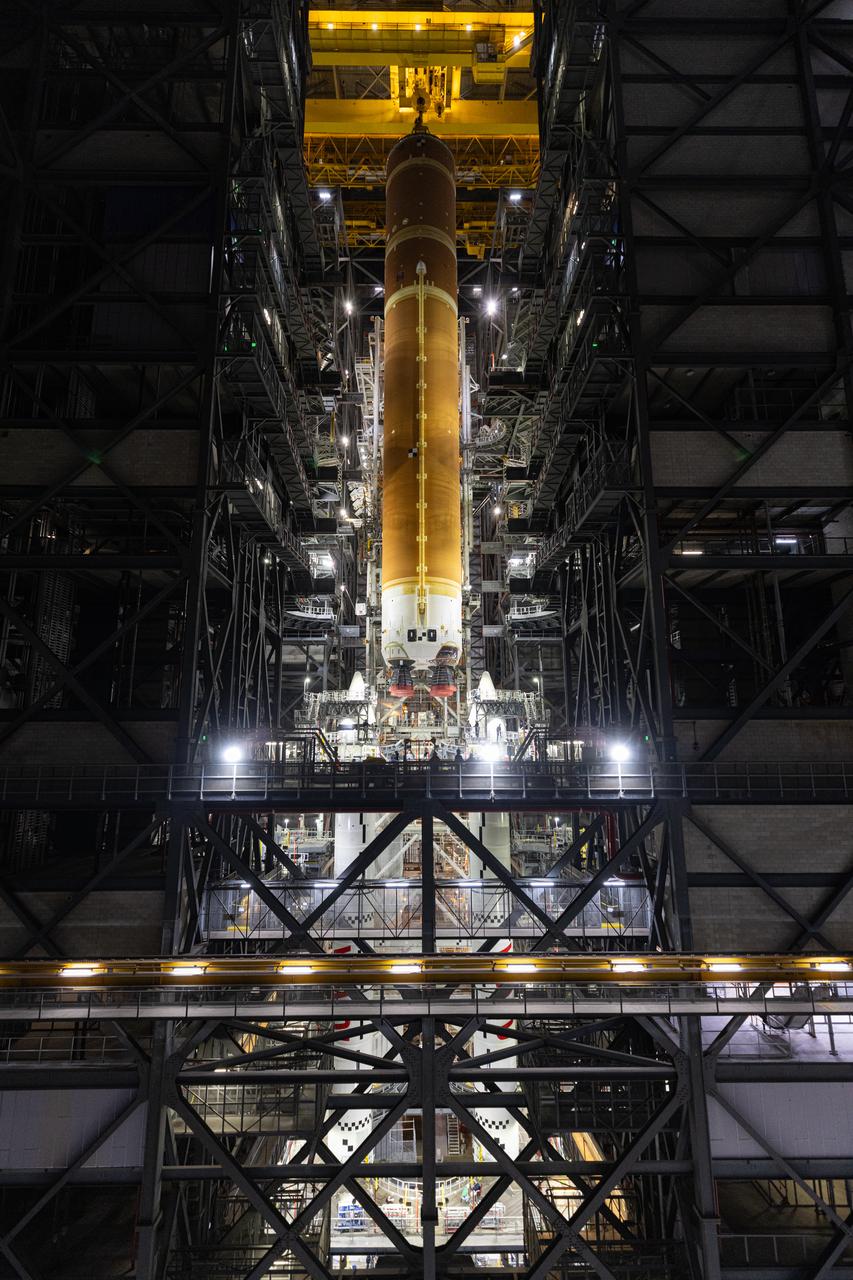

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor Amentum, integrate the SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket with the solid rocket boosters onto mobile launcher 1 inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Sunday, March 23, 2025. Artemis II is the first crewed test flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor Amentum, integrate the SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket with the solid rocket boosters onto mobile launcher 1 inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Sunday, March 23, 2025. Artemis II is the first crewed test flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
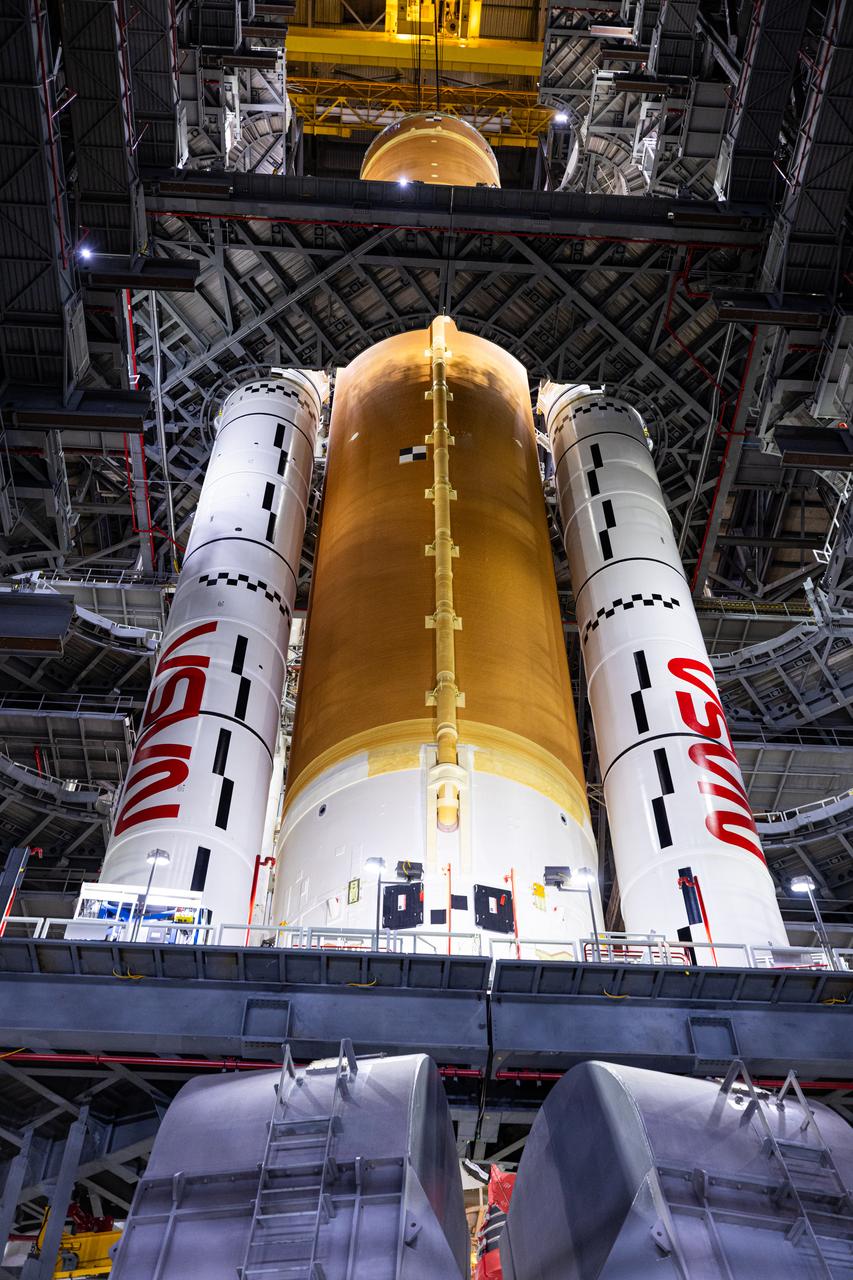

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor Amentum, integrate the SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket with the solid rocket boosters onto mobile launcher 1 inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Sunday, March 23, 2025. Artemis II is the first crewed test flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
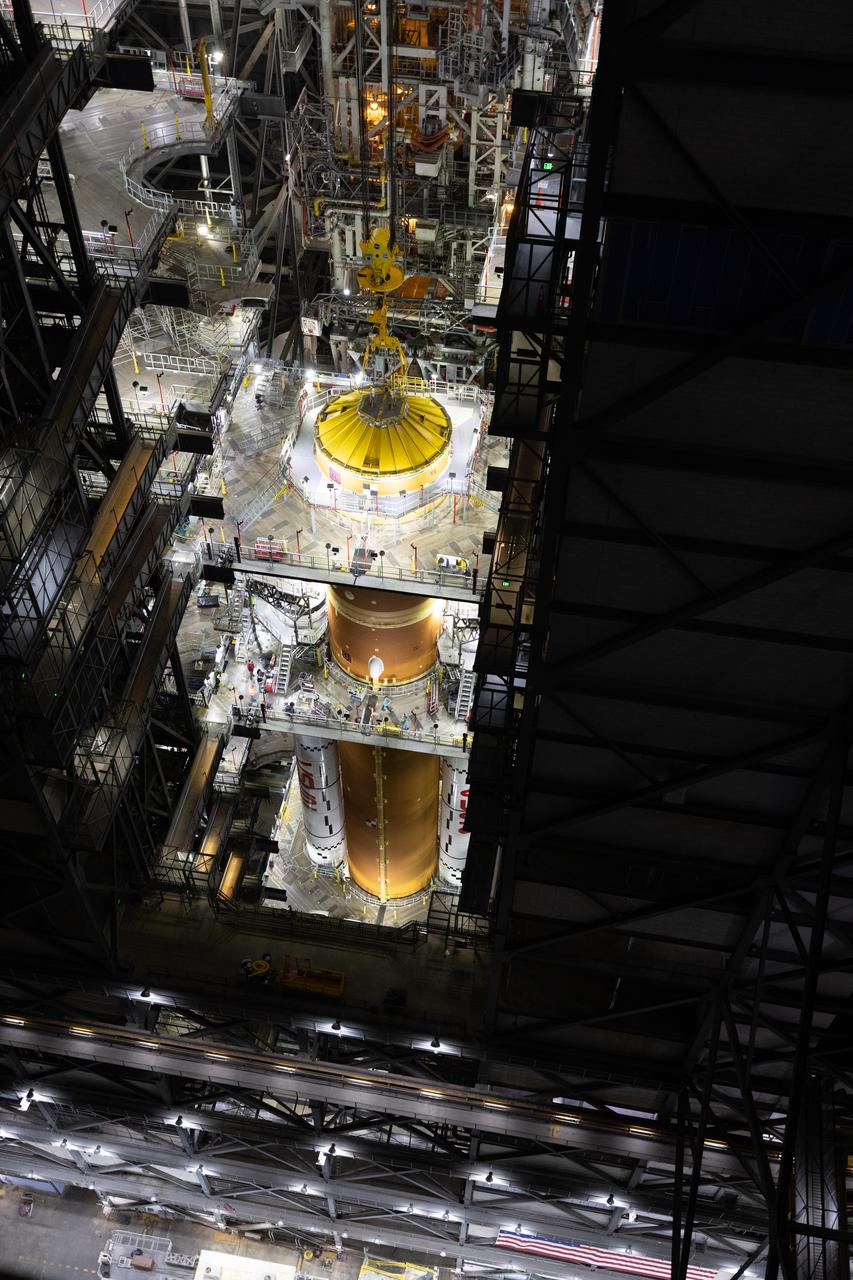
Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor Amentum, integrate the SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket with the solid rocket boosters onto mobile launcher 1 inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Sunday, March 23, 2025. Artemis II is the first crewed test flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
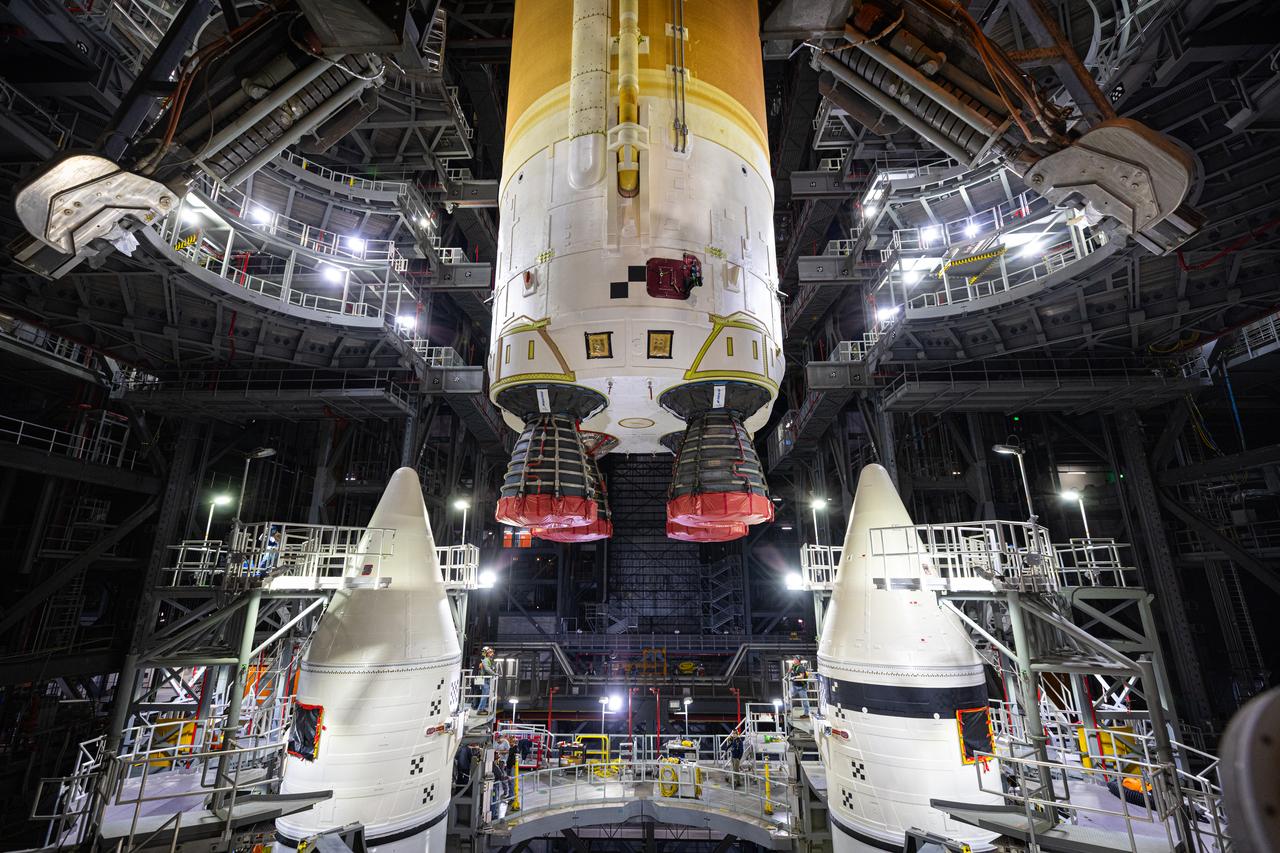

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor Amentum, integrate the SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket with the solid rocket boosters onto mobile launcher 1 inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Sunday, March 23, 2025. Artemis II is the first crewed test flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.