
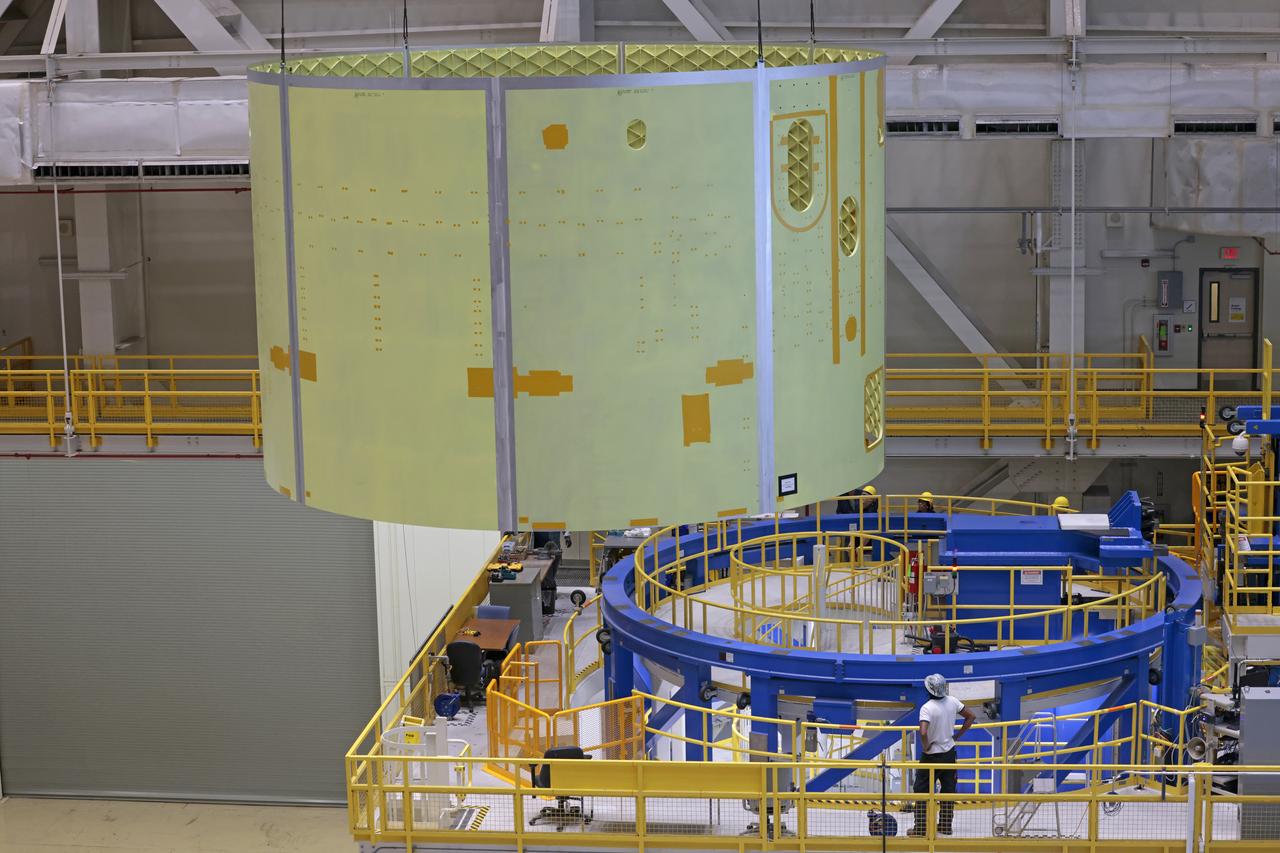
This image shows NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move crew lifting a completed liquid hydrogen tank barrel off the Vertical Weld Center on Feb. 10. The barrel, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, is one of the first pieces of flight hardware manufactured for the agency’s Artemis V mission. The 22-foot-tall barrel section is one of five barrels, which – along with two end domes – make up the 130.8-foot-tall liquid hydrogen fuel tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

This image shows NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move crew lifting a completed liquid hydrogen tank barrel off the Vertical Weld Center on Feb. 10. The barrel, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, is one of the first pieces of flight hardware manufactured for the agency’s Artemis V mission. The 22-foot-tall barrel section is one of five barrels, which – along with two end domes – make up the 130.8-foot-tall liquid hydrogen fuel tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

This image shows NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move crew lifting a completed liquid hydrogen tank barrel off the Vertical Weld Center on Feb. 10. The barrel, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, is one of the first pieces of flight hardware manufactured for the agency’s Artemis V mission. The 22-foot-tall barrel section is one of five barrels, which – along with two end domes – make up the 130.8-foot-tall liquid hydrogen fuel tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon

This image shows NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move crew lifting a completed liquid hydrogen tank barrel off the Vertical Weld Center on Feb. 10. The barrel, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, is one of the first pieces of flight hardware manufactured for the agency’s Artemis V mission. The 22-foot-tall barrel section is one of five barrels, which – along with two end domes – make up the 130.8-foot-tall liquid hydrogen fuel tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

This image shows NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move crew lifting a completed liquid hydrogen tank barrel off the Vertical Weld Center on Feb. 10. The barrel, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, is one of the first pieces of flight hardware manufactured for the agency’s Artemis V mission. The 22-foot-tall barrel section is one of five barrels, which – along with two end domes – make up the 130.8-foot-tall liquid hydrogen fuel tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

This image shows NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move crew lifting a completed liquid hydrogen tank barrel off the Vertical Weld Center on Feb. 10. The barrel, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, is one of the first pieces of flight hardware manufactured for the agency’s Artemis V mission. The 22-foot-tall barrel section is one of five barrels, which – along with two end domes – make up the 130.8-foot-tall liquid hydrogen fuel tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

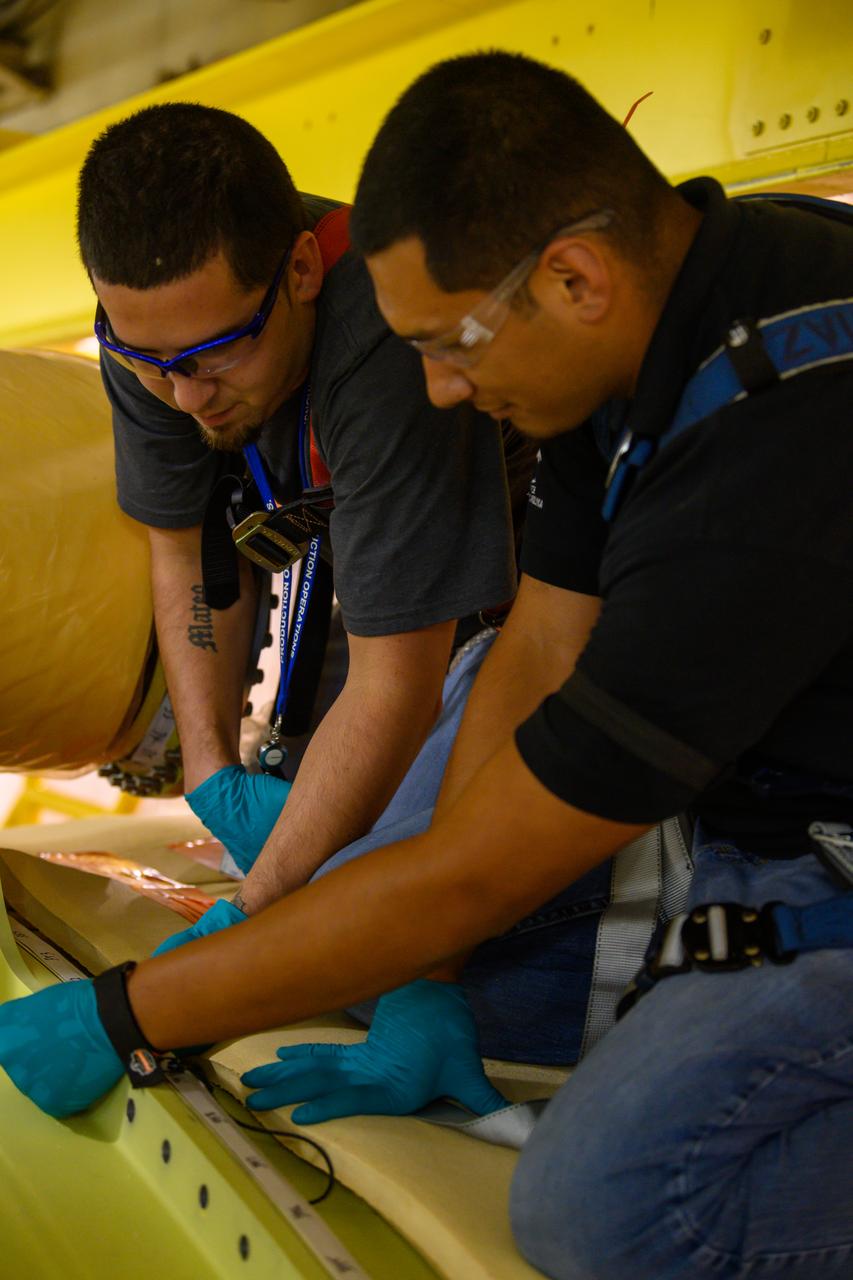
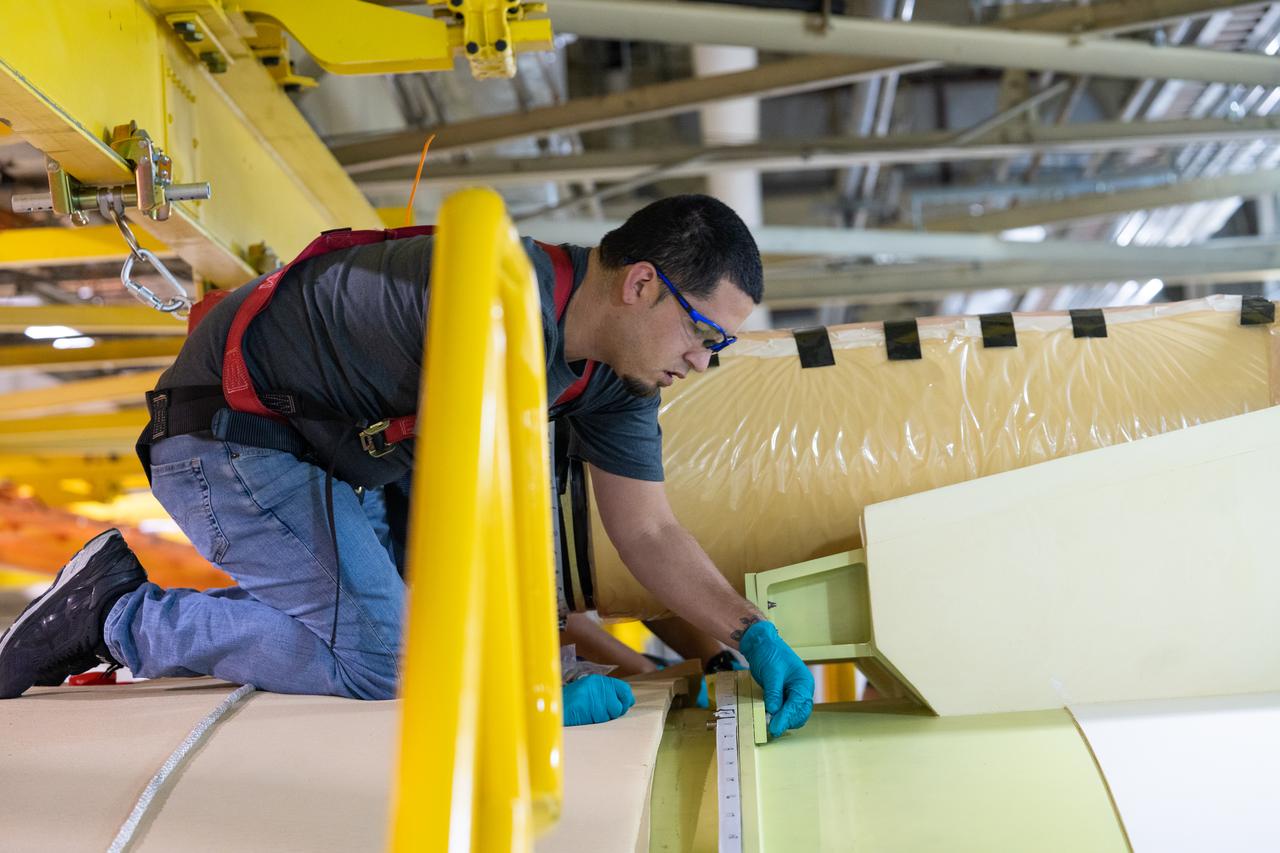
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis V on December 18, 2024, at NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, LA. Throughout 2024, new tooling was erected in bldg. 115 for the upcoming iterations of the Space Launch System (SLS), Exploration Upper Stage (EUS), and the test articles required to develop and assemble each efficiently and effectively. This barrel is the sixty-fourth produced for the Space Launch System program since its inception and is the first barrel weld completed for the core stage of the Artemis V mission. This engine section will be used on the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It is one of the first components that will make up a portion of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis V mission. According to a Boeing engineer, as of this barrel, the VWC has now completed 515 production welds, with friction-stir welding a cumulative distance of 111,568 inches. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis V on December 18, 2024, at NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, LA. Throughout 2024, new tooling was erected in bldg. 115 for the upcoming iterations of the Space Launch System (SLS), Exploration Upper Stage (EUS), and the test articles required to develop and assemble each efficiently and effectively. This barrel is the sixty-fourth produced for the Space Launch System program since its inception and is the first barrel weld completed for the core stage of the Artemis V mission. This engine section will be used on the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It is one of the first components that will make up a portion of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis V mission. According to a Boeing engineer, as of this barrel, the VWC has now completed 515 production welds, with friction-stir welding a cumulative distance of 111,568 inches. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis V on December 18, 2024, at NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, LA. Throughout 2024, new tooling was erected in bldg. 115 for the upcoming iterations of the Space Launch System (SLS), Exploration Upper Stage (EUS), and the test articles required to develop and assemble each efficiently and effectively. This barrel is the sixty-fourth produced for the Space Launch System program since its inception and is the first barrel weld completed for the core stage of the Artemis V mission. This engine section will be used on the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It is one of the first components that will make up a portion of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis V mission. According to a Boeing engineer, as of this barrel, the VWC has now completed 515 production welds, with friction-stir welding a cumulative distance of 111,568 inches. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

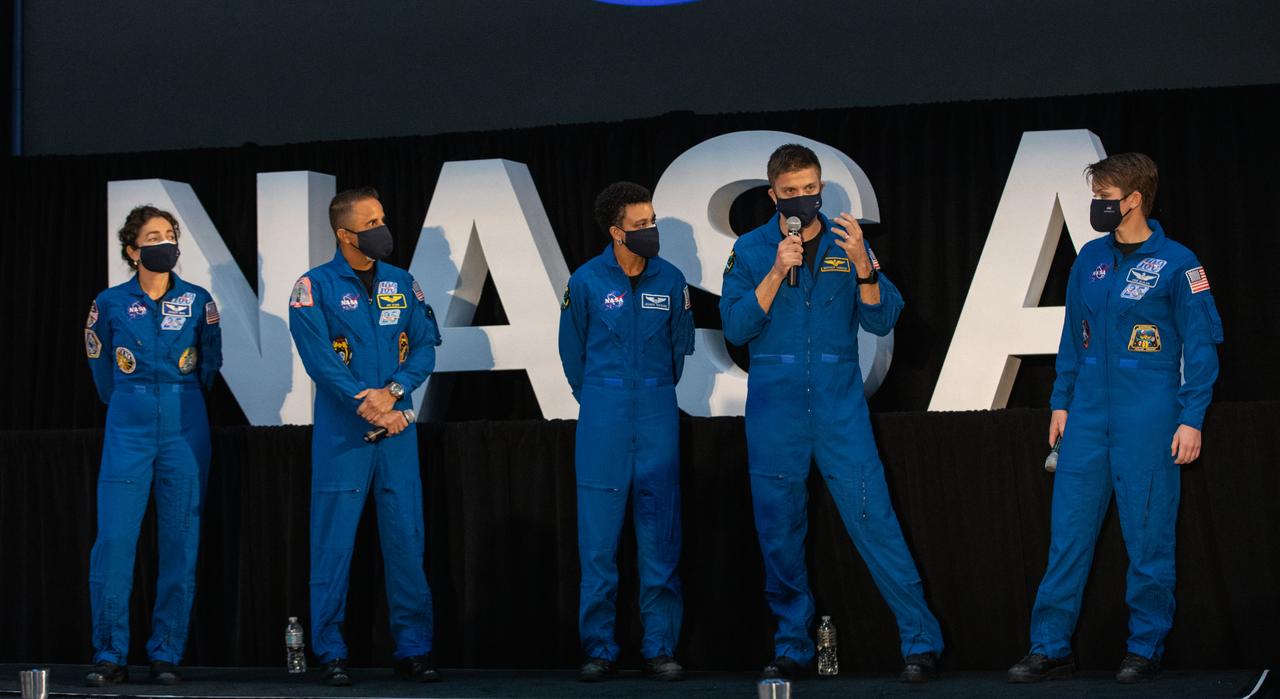
From left, NASA astronauts Jessica Meir, Joseph Acaba, Anne McClain, Matthew Dominick, and Jessica Watkins pose inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. The five are among the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon, announced by Vice President Mike Pence during a meeting of the National Space Council inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
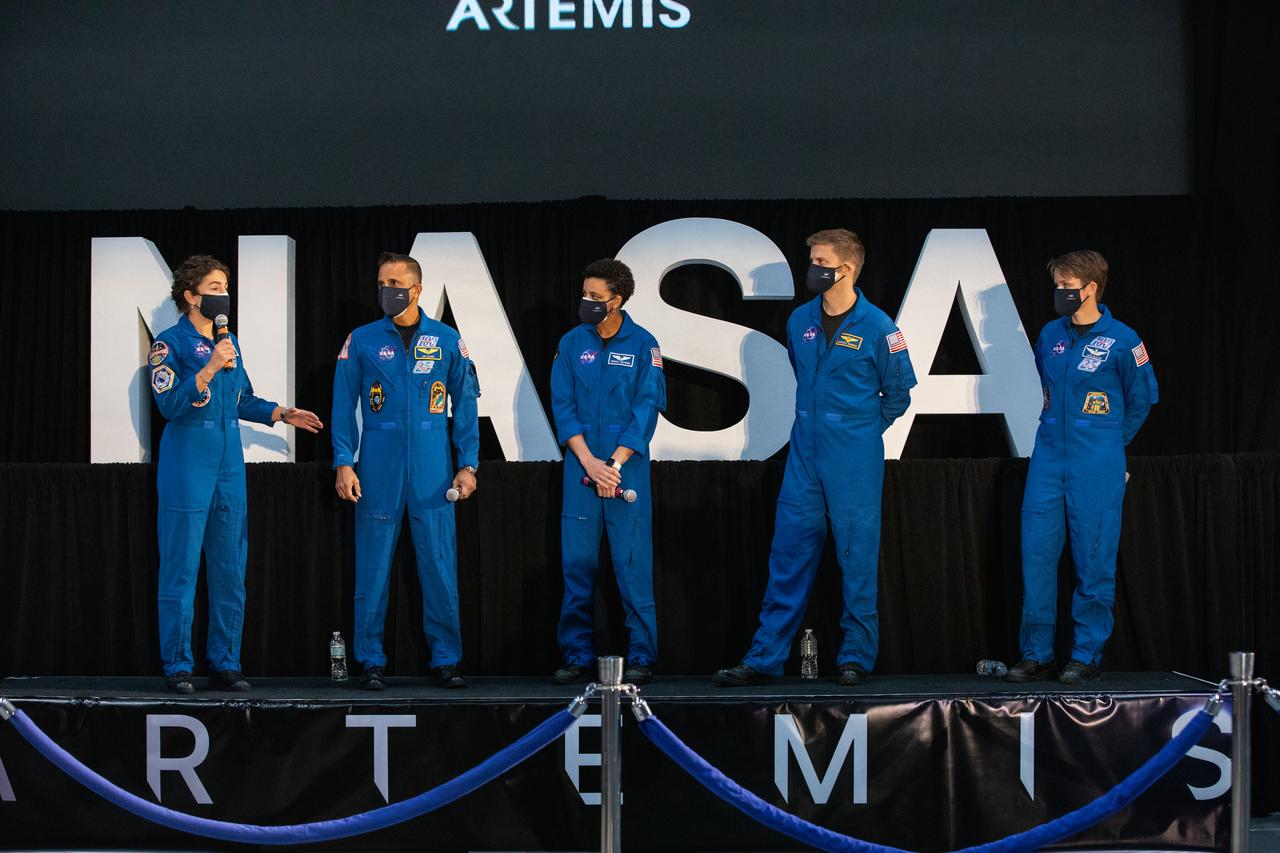

NASA astronaut Jessica Meir speaks to members of the news media during a question-and-answer session Dec. 9, 2020, following a National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. On stage with Meir, from left, are fellow astronauts Joseph Acaba, Jessica Watkins, Matthew Dominick, and Anne McClain. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
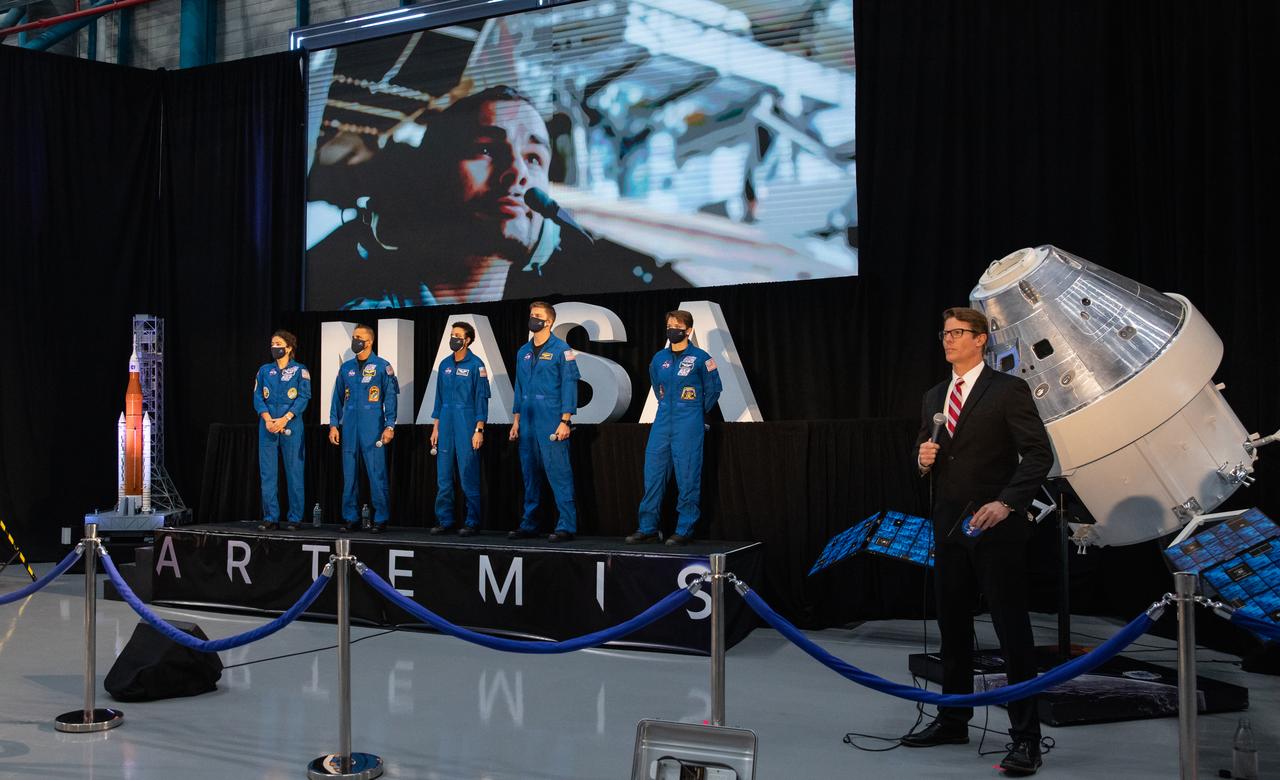

From left, NASA astronauts Jessica Meir, Joseph Acaba, Jessica Watkins, Matthew Dominick, and Anne McClain, along with NASA Communications’ Derrol Nail, listen to a question from a member of the news media during a question-and-answer session Dec. 9, 2020, following a National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
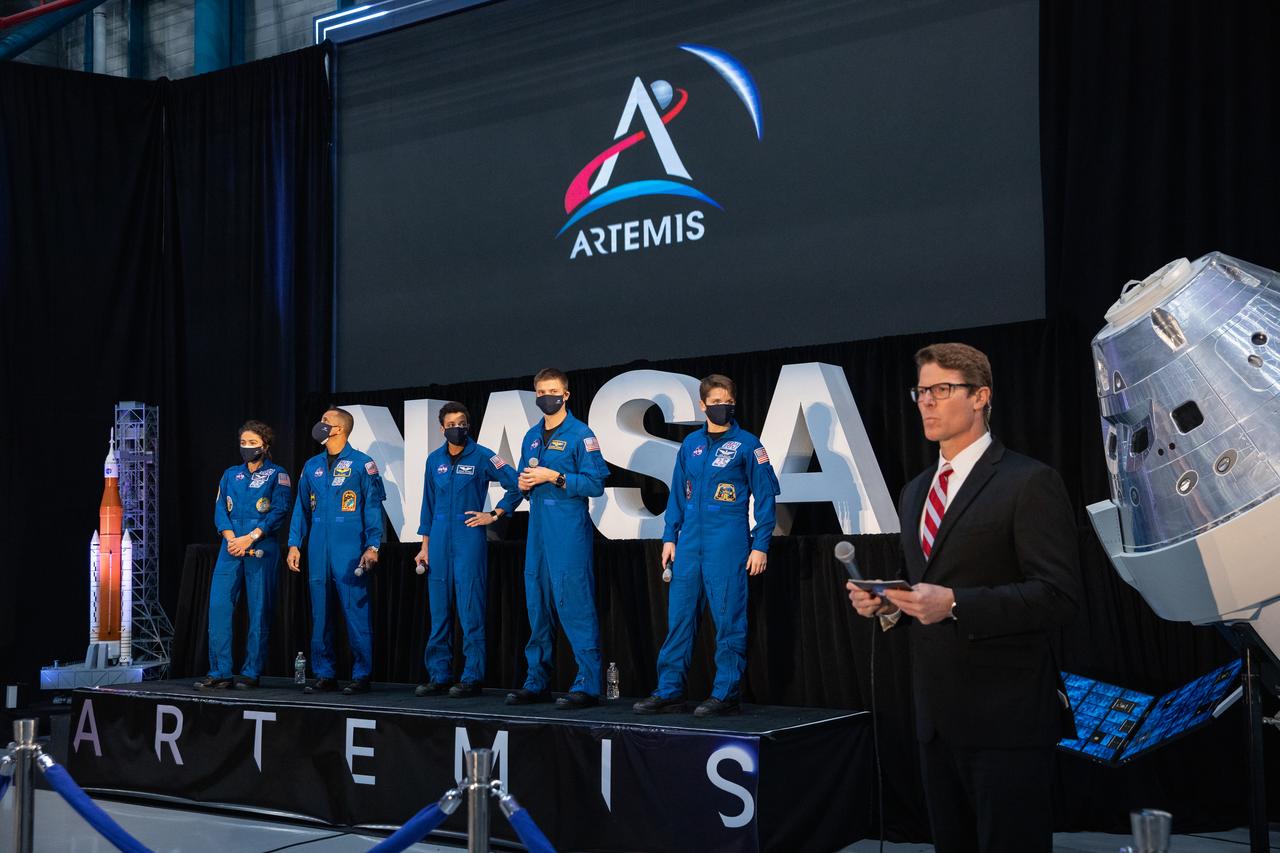

From left, NASA astronauts Jessica Meir, Joseph Acaba, Jessica Watkins, Matthew Dominick, and Anne McClain, along with NASA Communications’ Derrol Nail, listen to a question from a member of the news media during a question-and-answer session Dec. 9, 2020, following a National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
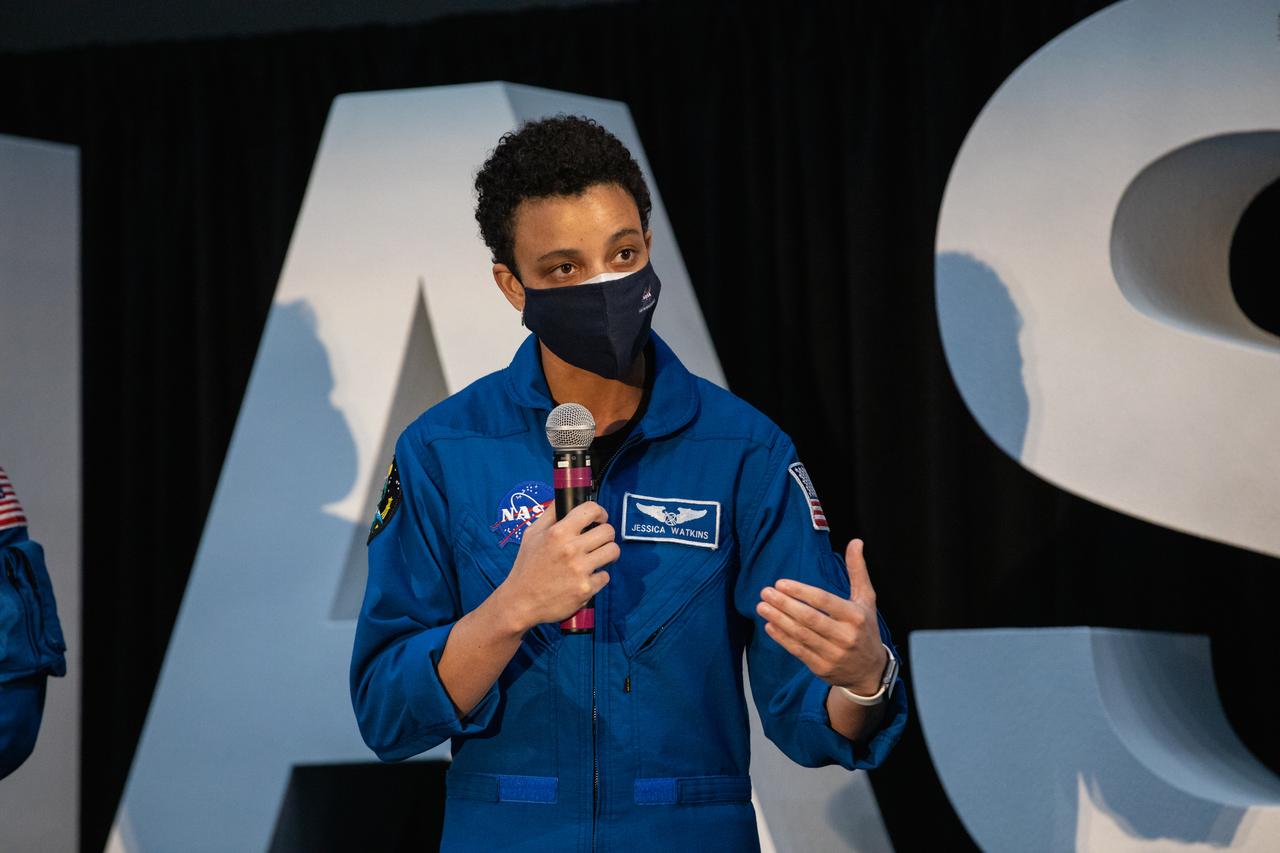

NASA astronaut Jessica Watkins speaks to members of the news media during a question-and-answer session Dec. 9, 2020, following a National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A Colorado native, Watkins was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2017. She was joined at the event by fellow astronauts Joseph Acaba, Matthew Dominick, Jessica Meir, and Anne McClain. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
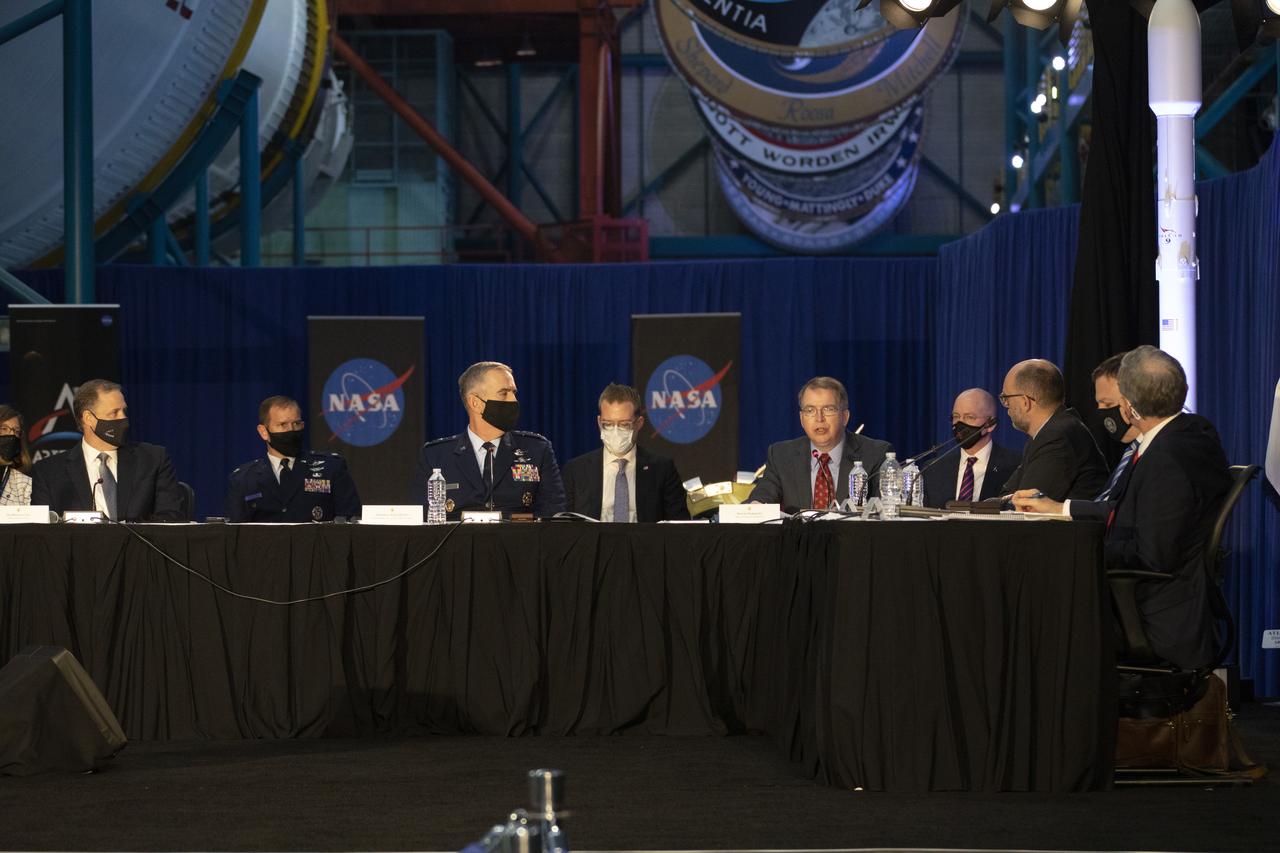

The National Space Council meets inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy and to review the nation's long-range goals for space activities. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
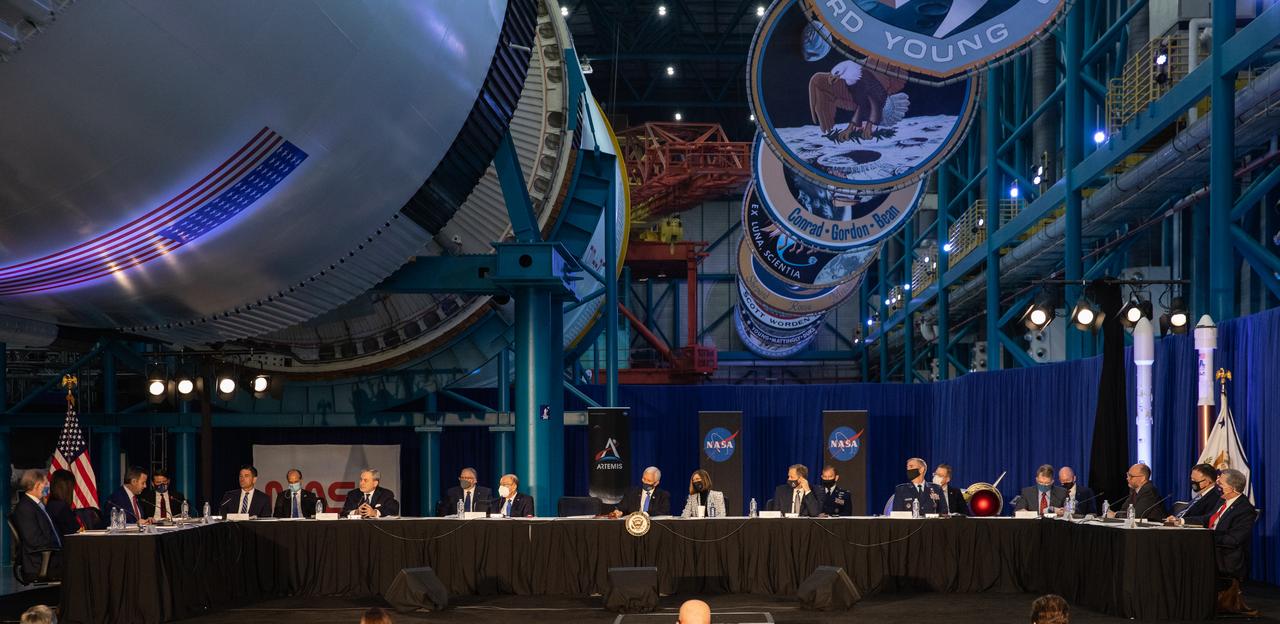

The National Space Council meets inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and to review the nation's long-range goals for space activities. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
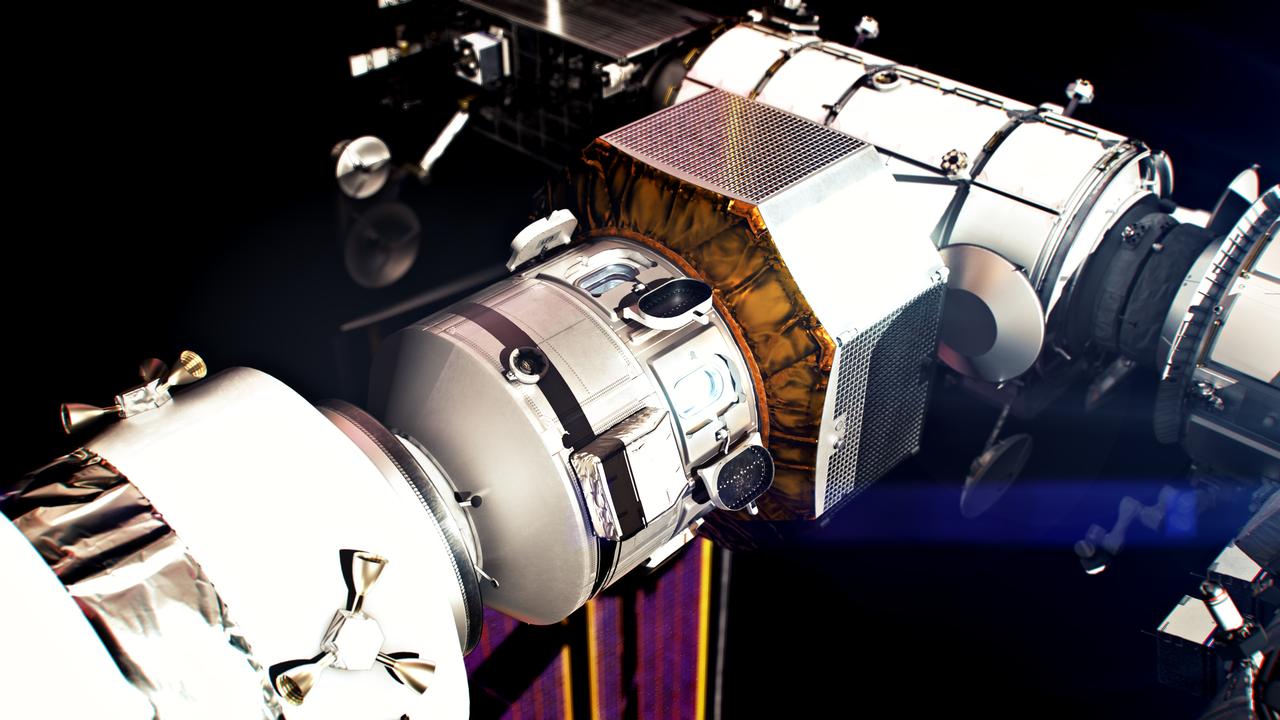

Gateway's ESPRIT Refueling Module, or ERM, will provide refueling capabilities for the space station, cargo storage, and windows for stunning views of the Earth, Moon and deep space. ERM will be delivered to Gateway by the crewed Orion spacecraft on the Artemis V mission after launching on an Space Launch System (SLS) Block 1B rocket.

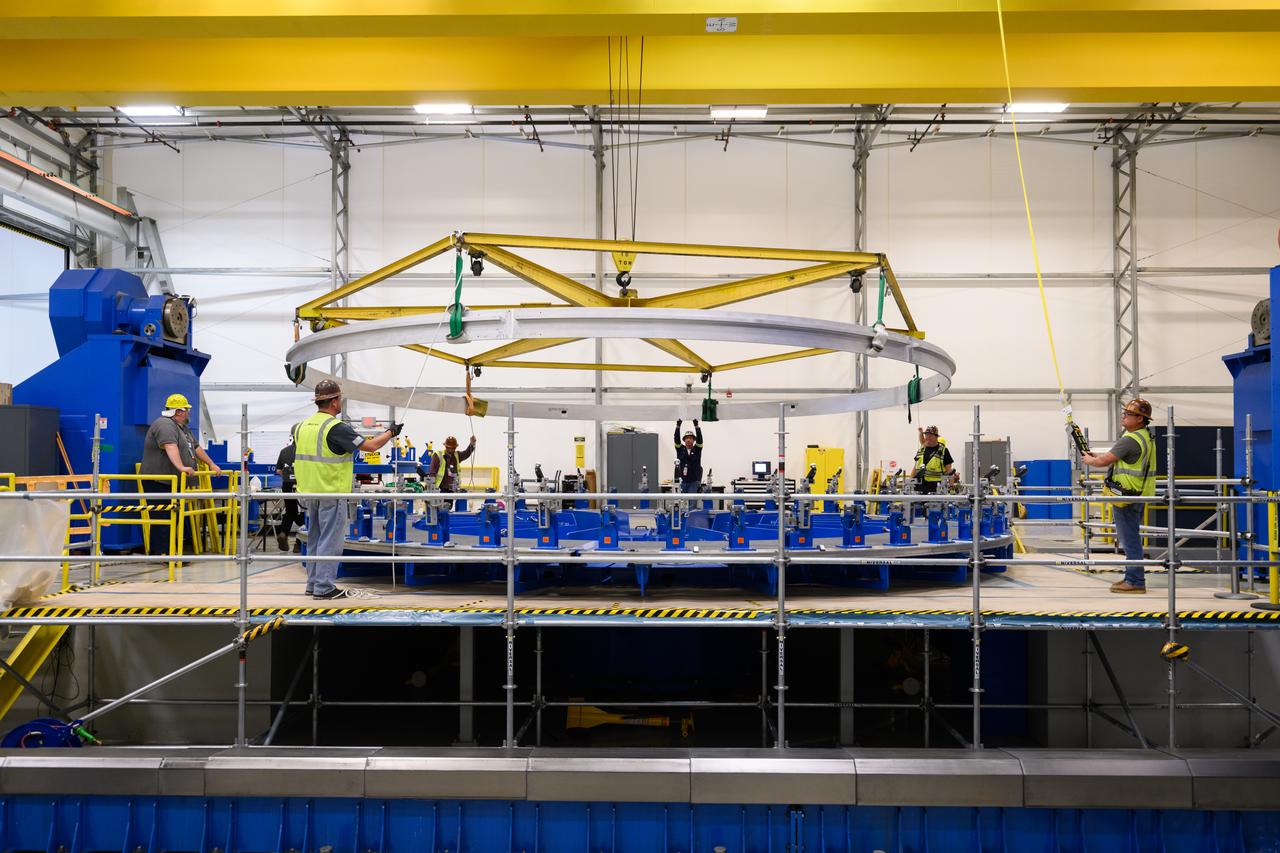
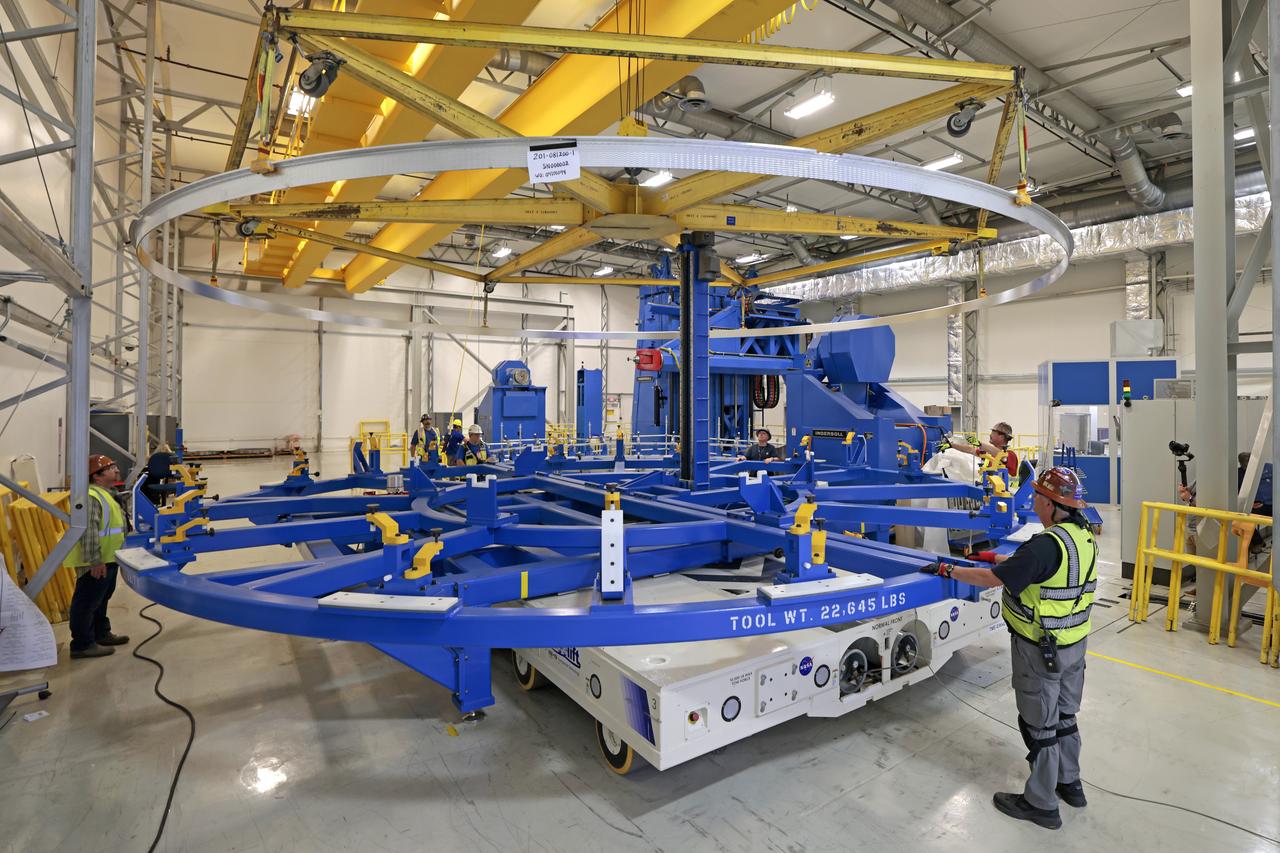
These photos show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans manufactured the Y-ring that will be used on the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It is one of the first components that will make up a portion of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis V mission. The large metal ring will serve as the aft ring for the rocket’s liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage is the backbone of the SLS rocket, stretching 212 feet from top to bottom, and includes four RS-25 engines at its base. At launch, its two huge liquid propellant tanks provide more than 733,000 gallons of fuel to produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust. Michoud Assembly Facility and the SLS Program are managed by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
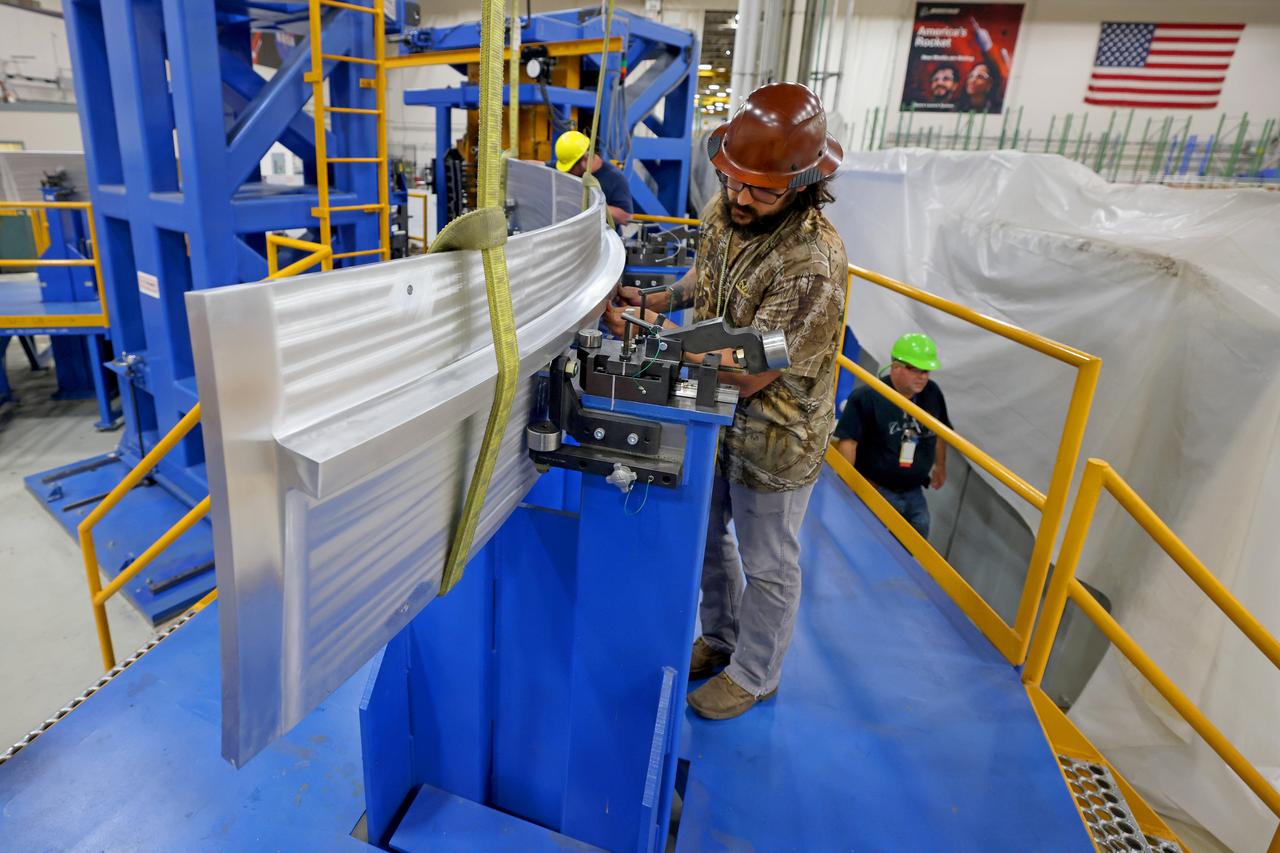

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans manufactured the Y-ring that will be used on the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It is one of the first components that will make up a portion of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis V mission. The large metal ring will serve as the aft ring for the rocket’s liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage is the backbone of the SLS rocket, stretching 212 feet from top to bottom, and includes four RS-25 engines at its base. At launch, its two huge liquid propellant tanks provide more than 733,000 gallons of fuel to produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust. Michoud Assembly Facility and the SLS Program are managed by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
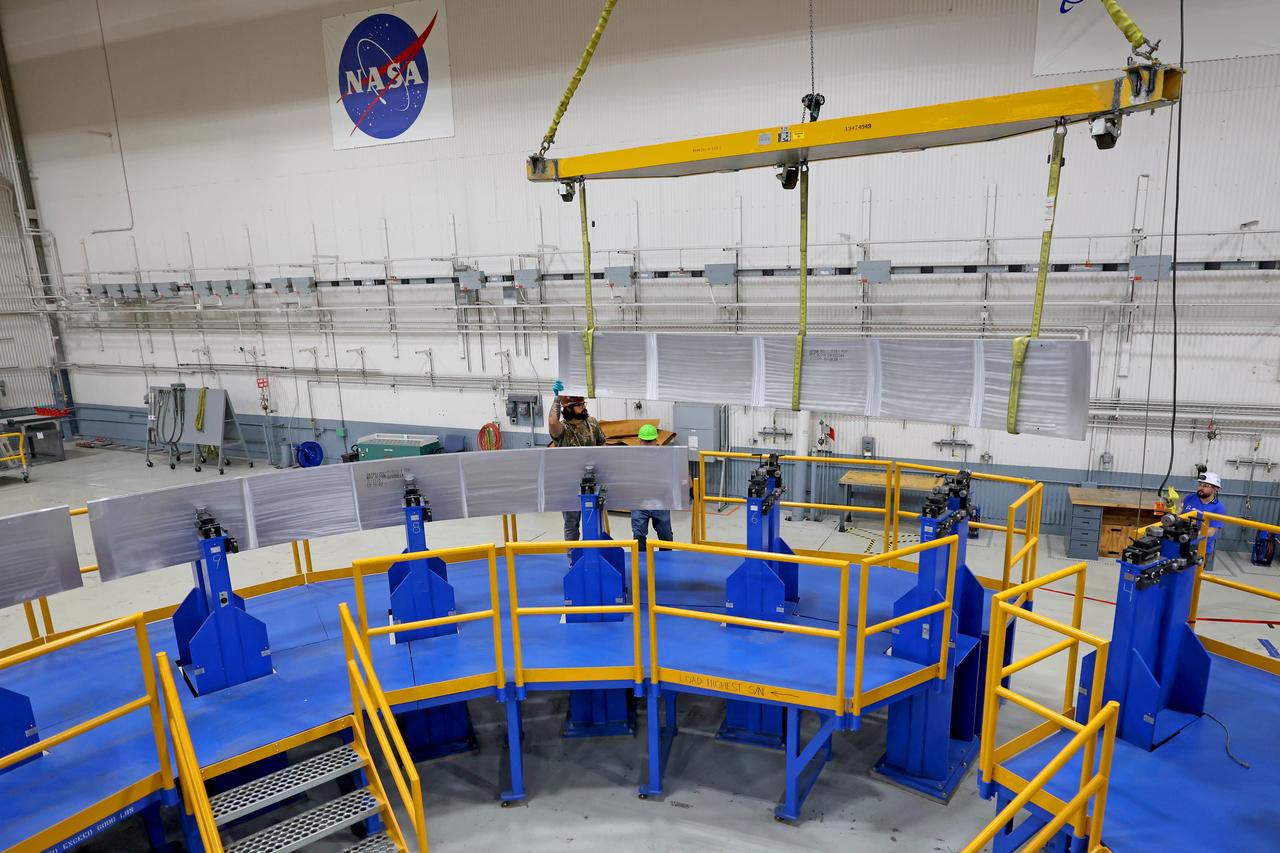

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans manufactured the Y-ring that will be used on the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It is one of the first components that will make up a portion of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis V mission. The large metal ring will serve as the aft ring for the rocket’s liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage is the backbone of the SLS rocket, stretching 212 feet from top to bottom, and includes four RS-25 engines at its base. At launch, its two huge liquid propellant tanks provide more than 733,000 gallons of fuel to produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust. Michoud Assembly Facility and the SLS Program are managed by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
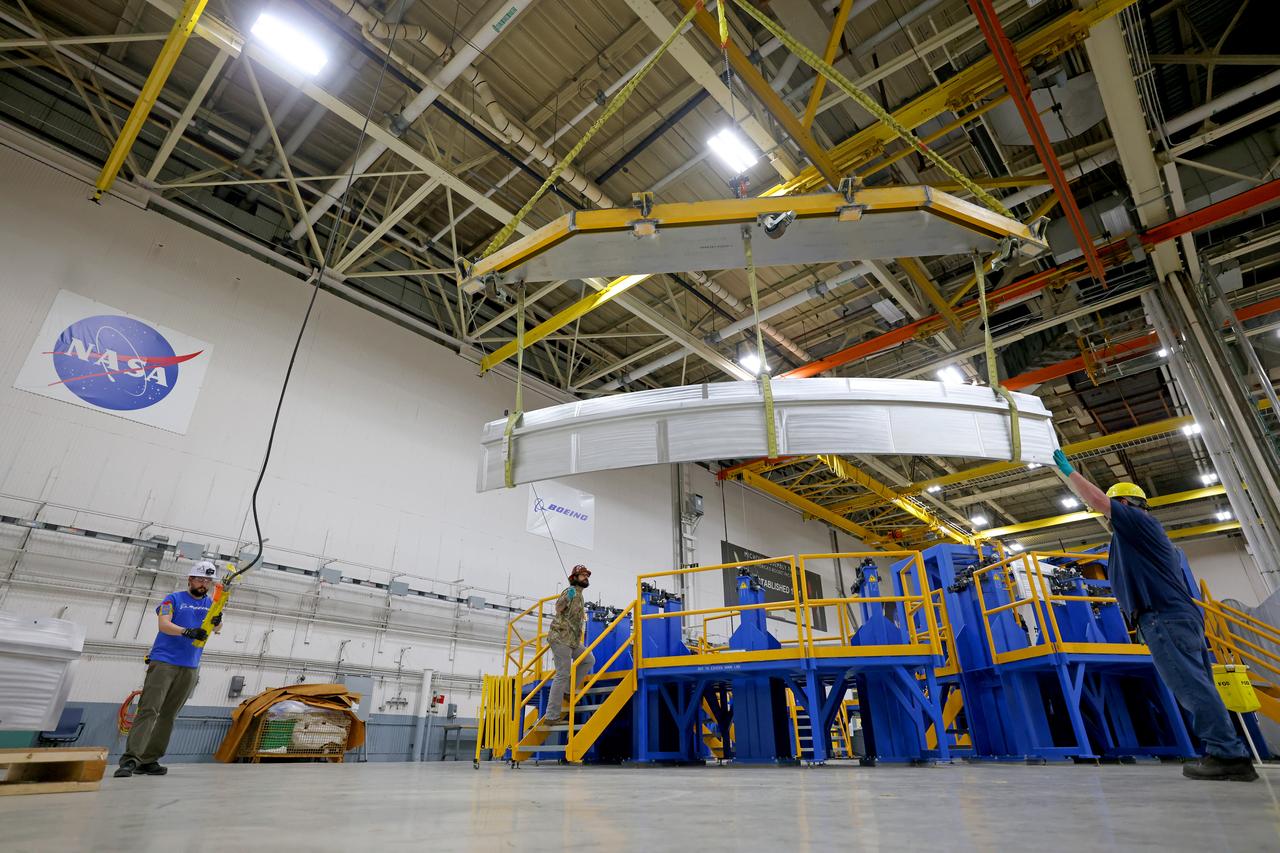

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans manufactured the Y-ring that will be used on the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It is one of the first components that will make up a portion of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis V mission. The large metal ring will serve as the aft ring for the rocket’s liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage is the backbone of the SLS rocket, stretching 212 feet from top to bottom, and includes four RS-25 engines at its base. At launch, its two huge liquid propellant tanks provide more than 733,000 gallons of fuel to produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust. Michoud Assembly Facility and the SLS Program are managed by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
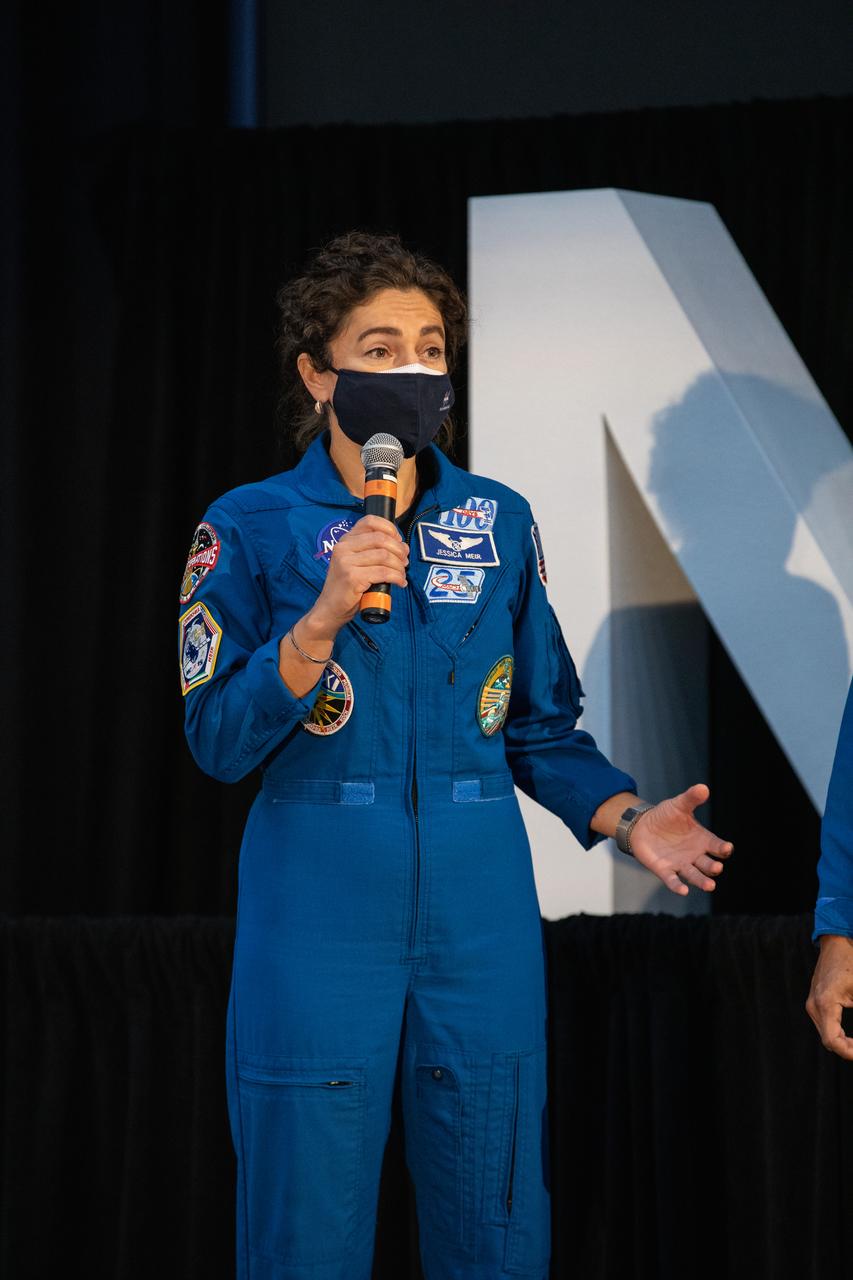

NASA astronaut Jessica Meir speaks to members of the news media during a question-and-answer session Dec. 9, 2020, following a National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A Maine native, Meir was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2013 and has spent 205 days in space on one previous flight. She was joined at the event by fellow astronauts Joseph Acaba, Matthew Dominick, Anne McClain, and Jessica Watkins. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
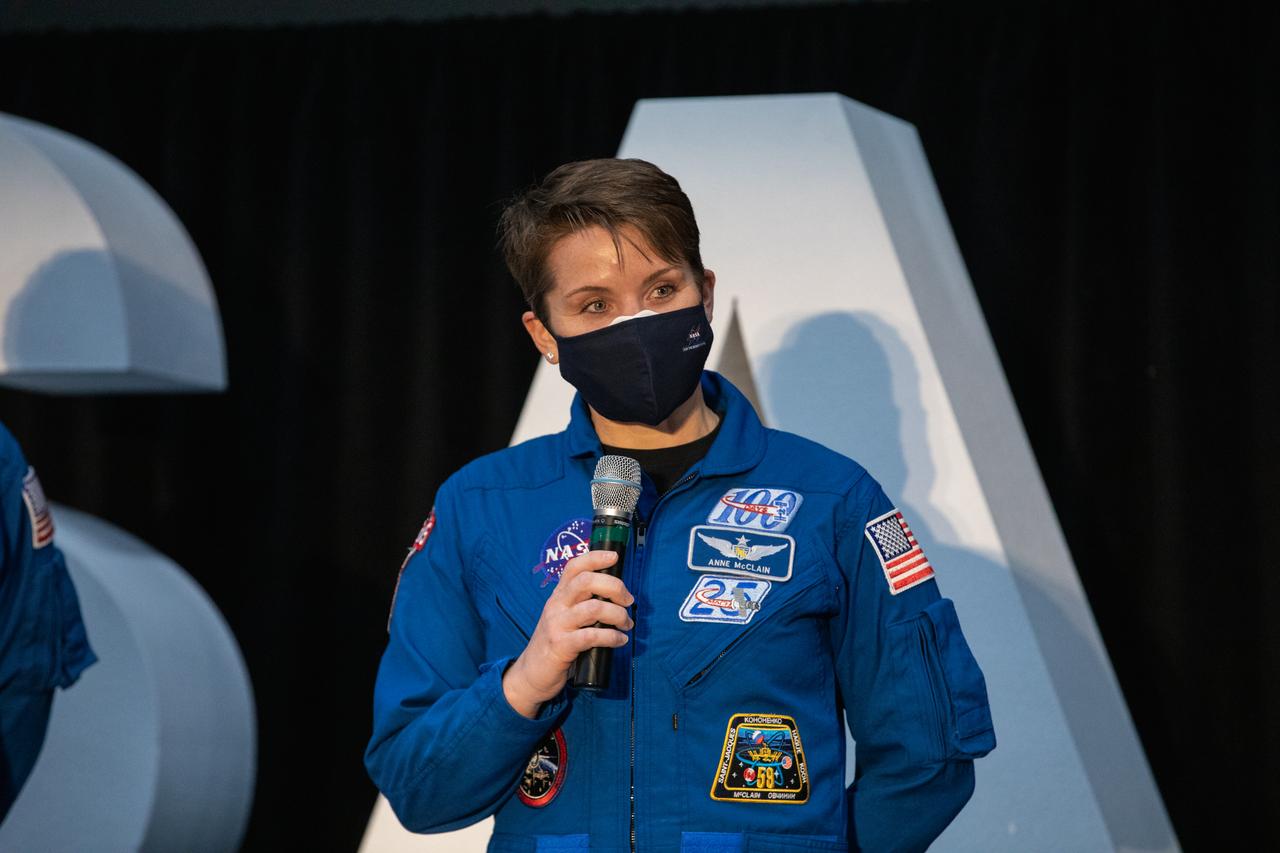

NASA astronaut Anne McClain speaks to members of the news media during a question-and-answer session Dec. 9, 2020, following a National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A native of the state of Washington, McClain was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2013 and has spent 204 days in space on one previous flight. She was joined at the event by fellow astronauts Joseph Acaba, Matthew Dominick, Jessica Meir, and Jessica Watkins. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
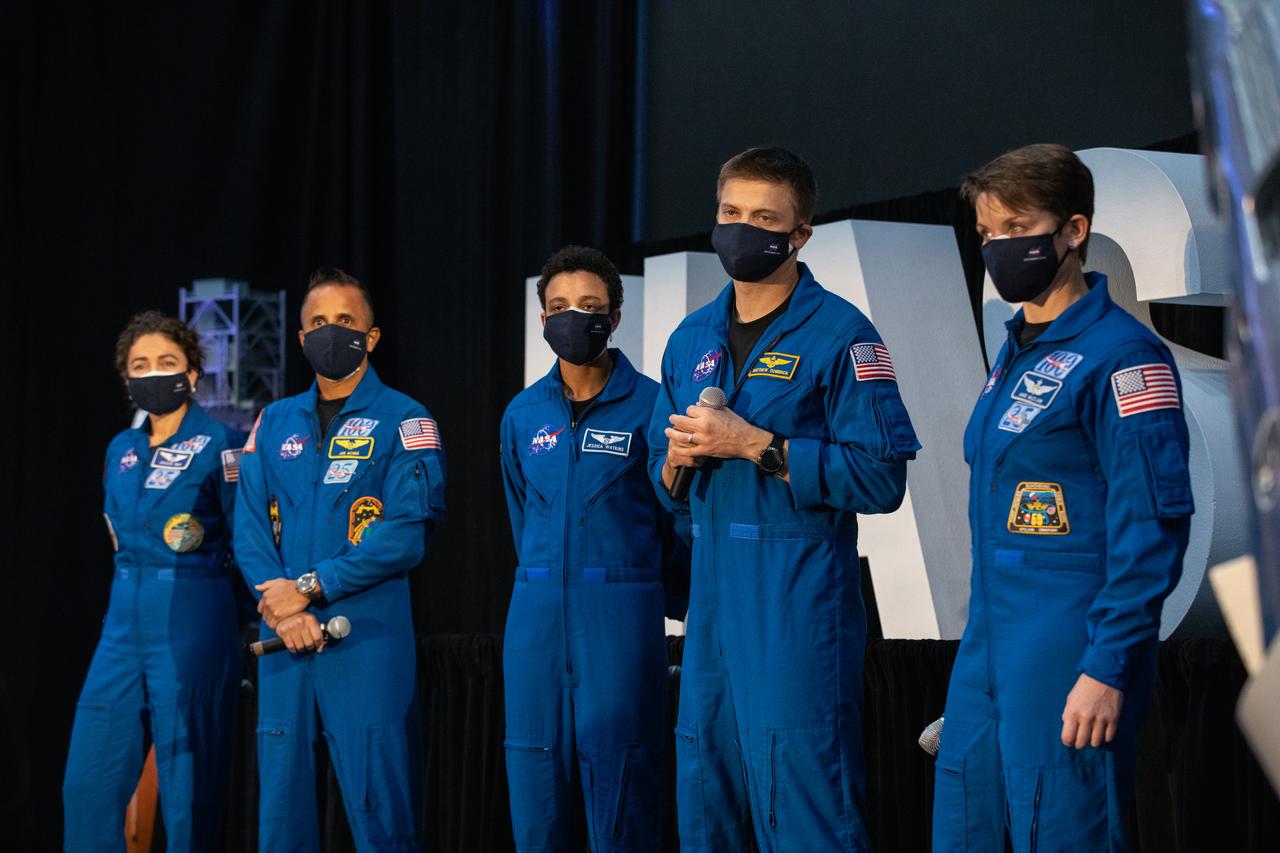

NASA astronaut Matthew Dominick, second from right, listens to a question from a member of the news media during a question-and-answer session Dec. 9, 2020, following a National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A Colorado native, Dominick was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2017. He was joined at the event by fellow astronauts, from left, Jessica Meir, Joseph Acaba, Jessica Watkins, and Anne McClain. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

NASA astronaut Matthew Dominick, second from right, speaks to members of the news media during a question-and-answer session Dec. 9, 2020, following a National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A Colorado native, Dominick was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2017. He was joined at the event by fellow astronauts, from left, Jessica Meir, Joseph Acaba, Jessica Watkins, and Anne McClain. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
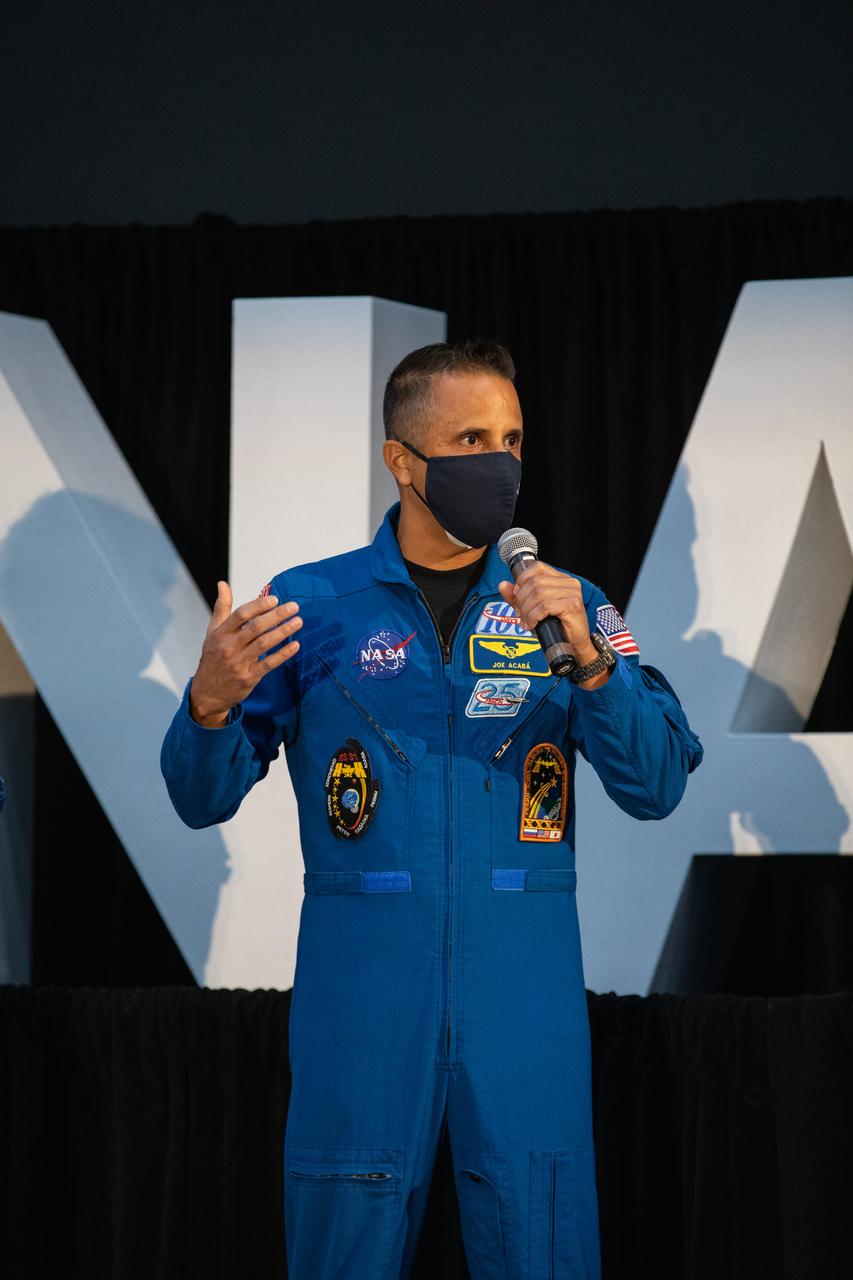

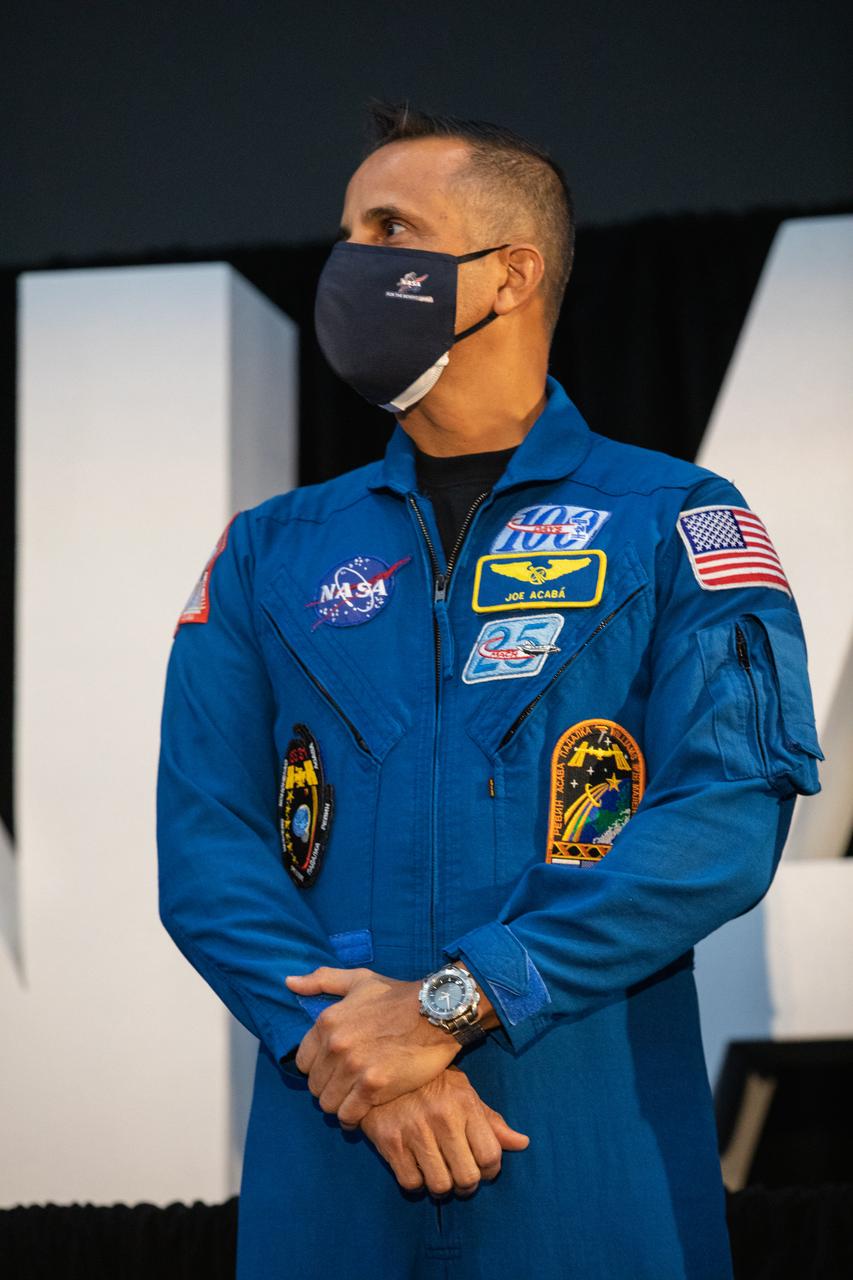
NASA astronaut Joseph Acaba speaks to members of the news media during a question-and-answer session Dec. 9, 2020, following a National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A California native, Acaba was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2004 and has logged a total of 306 days in space on three flights. He was joined at the event by fellow astronauts Matthew Dominick, Jessica Meir, Anne McClain, and Jessica Watkins. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
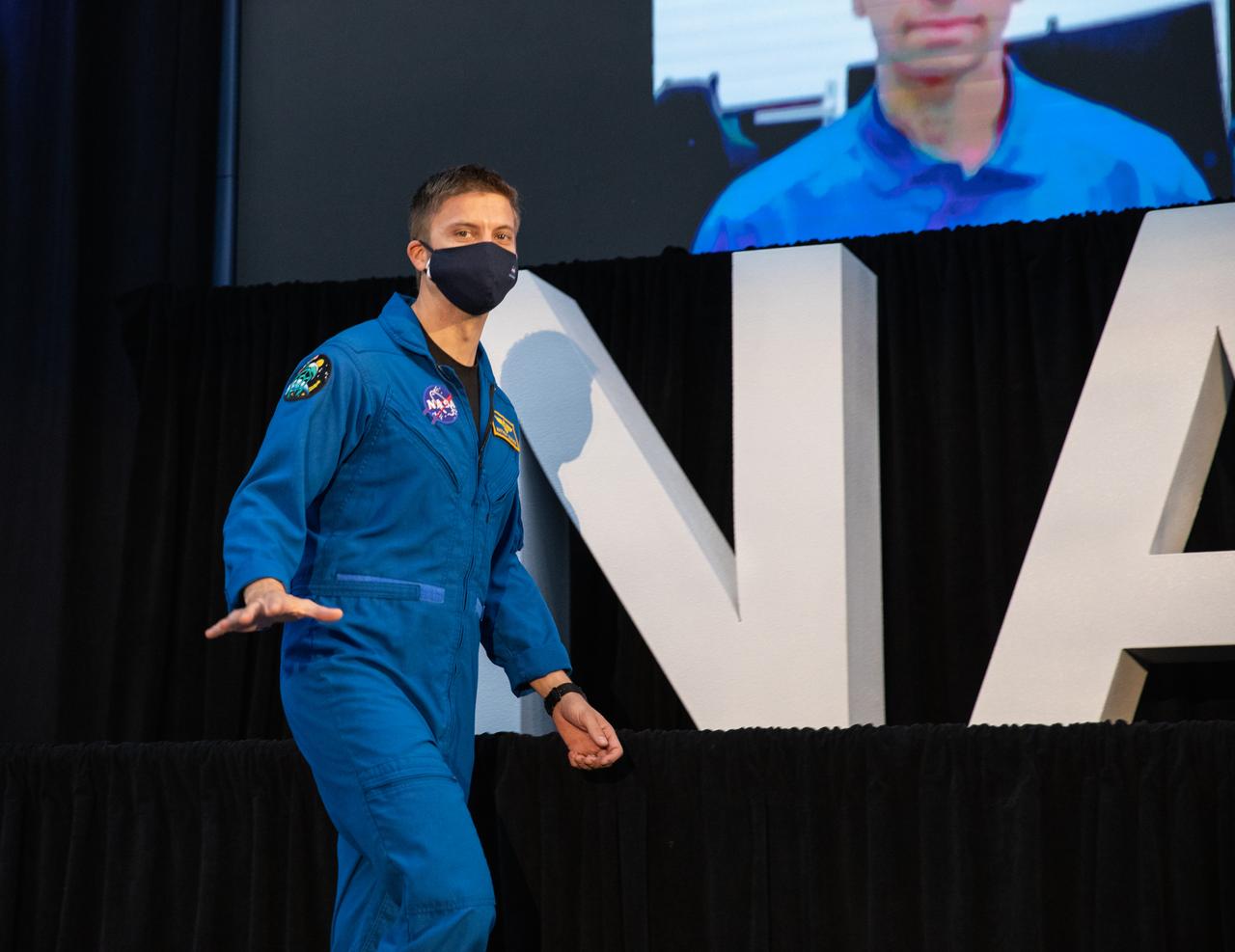

NASA astronaut Matthew Dominick waves during an announcement Dec. 9, 2020, that he is one of the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A Colorado native, Dominick was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2017. Joining him at the event were fellow astronauts Joseph Acaba, Jessica Meir, Anne McClain, and Jessica Watkins. Vice President Mike Pence made the announcement at the close of a National Space Council meeting he chaired in the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
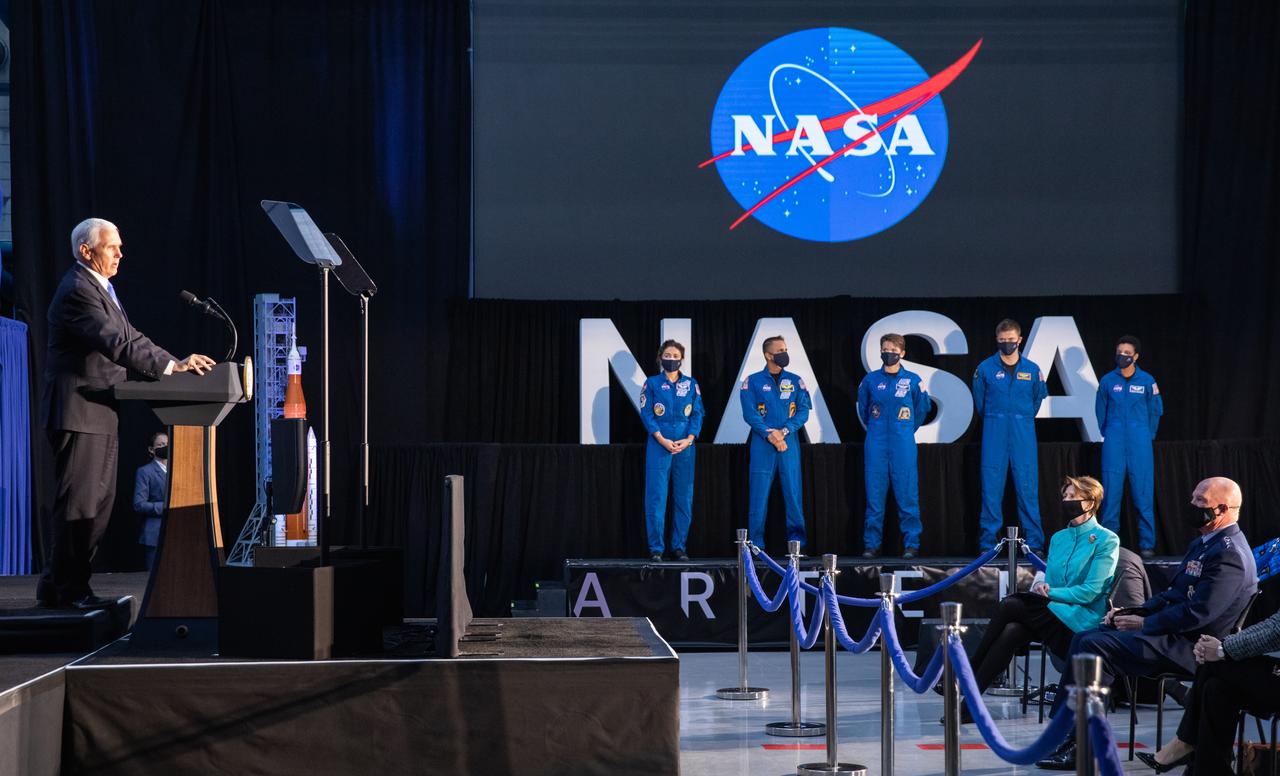

Vice President Mike Pence introduces NASA astronauts, from left, Jessica Meir, Joseph Acaba, Anne McClain, Matthew Dominick, and Jessica Watkins, during a meeting of the National Space Council inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. Meir, Acaba, McClain, Dominick, and Watkins are among the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
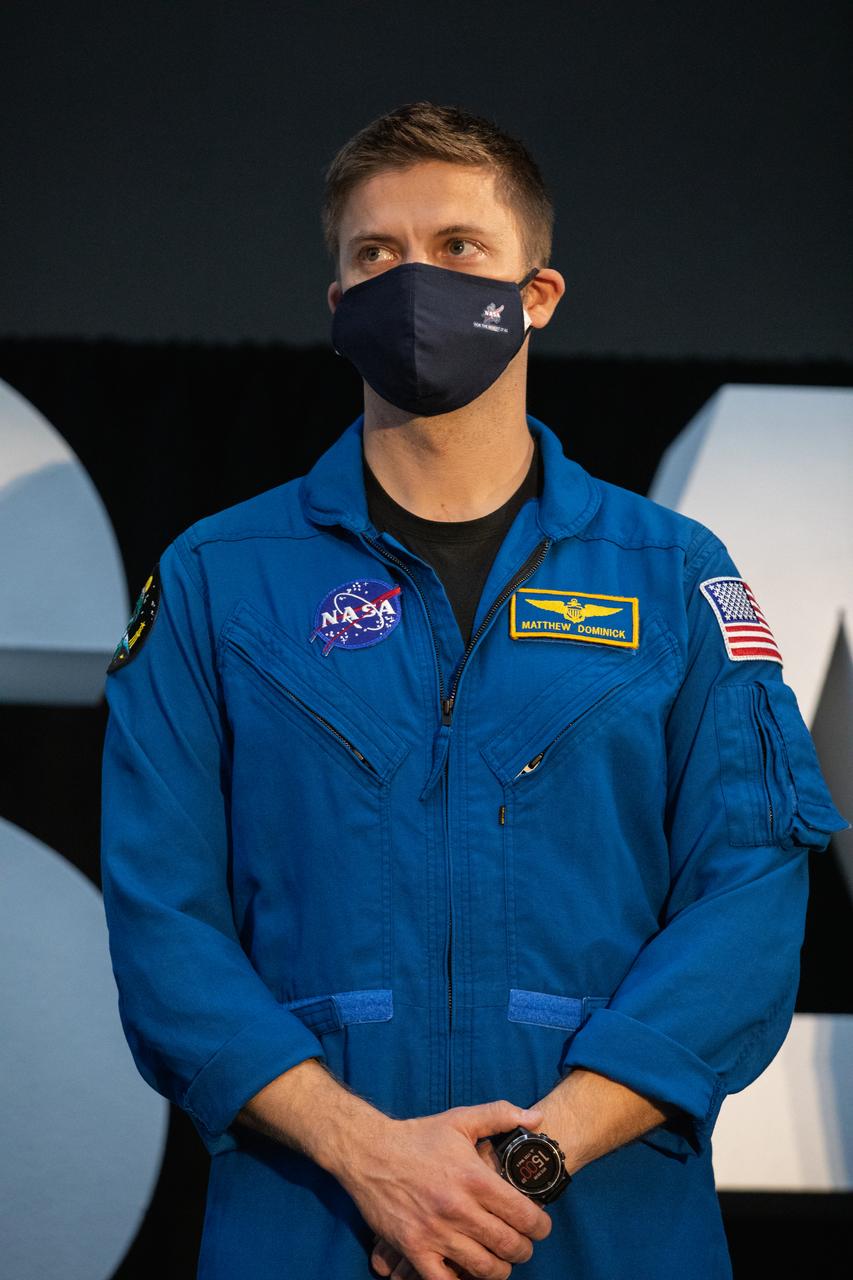

NASA astronaut Matthew Dominick attends an announcement Dec. 9, 2020, that he is one of the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A Colorado native, Dominick was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2017. Joining him at the event were fellow astronauts Joseph Acaba, Jessica Meir, Anne McClain, and Jessica Watkins. Vice President Mike Pence made the announcement at the close of a National Space Council meeting he chaired in the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
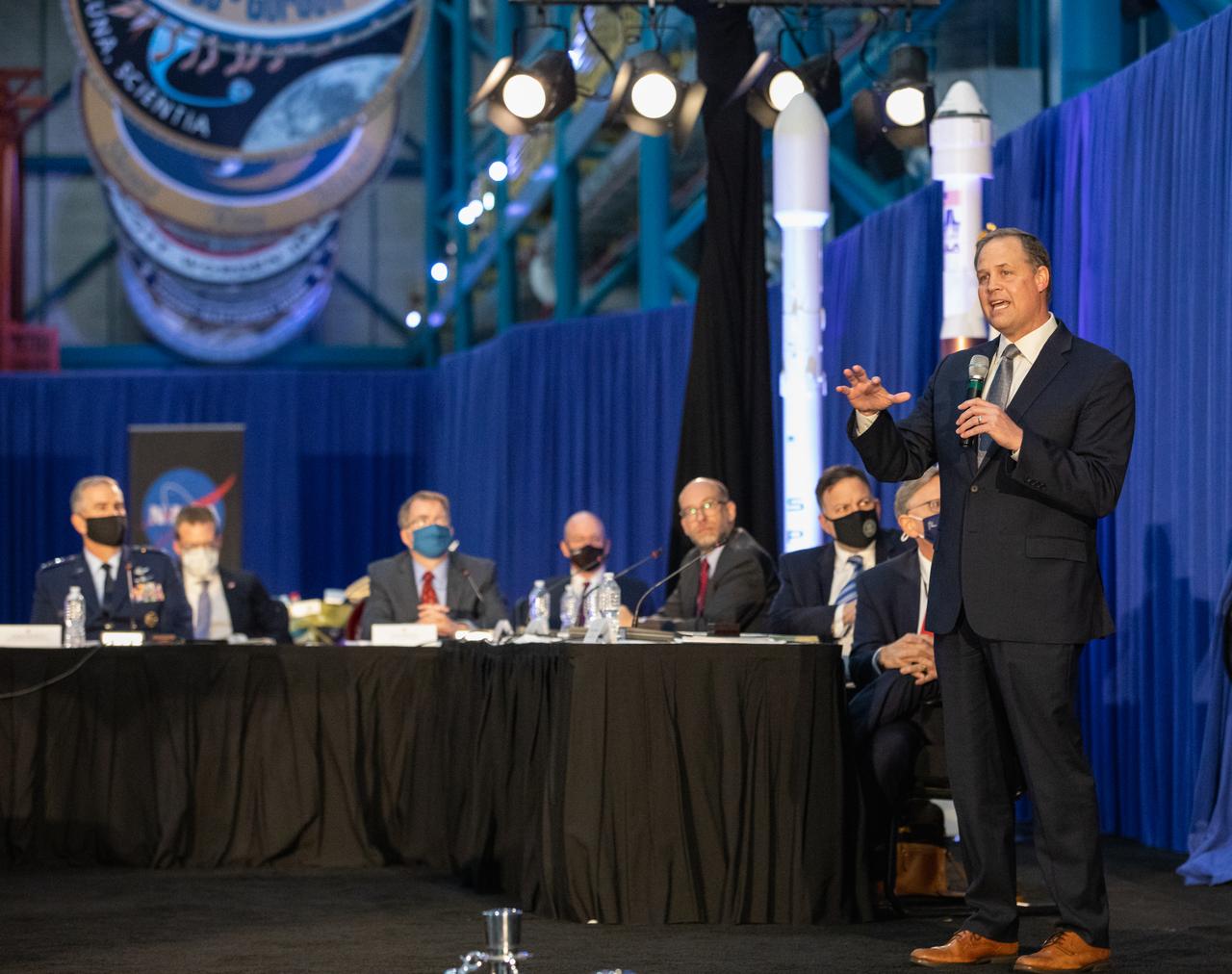

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks during the National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy and to review the nation's long-range goals for space activities. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

From left, Chad Wolf, acting secretary of Homeland Security, and Dan Brouillette, Secretary of Energy, attend a meeting of the National Space Council inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and to review the nation's long-range goals for space activities. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
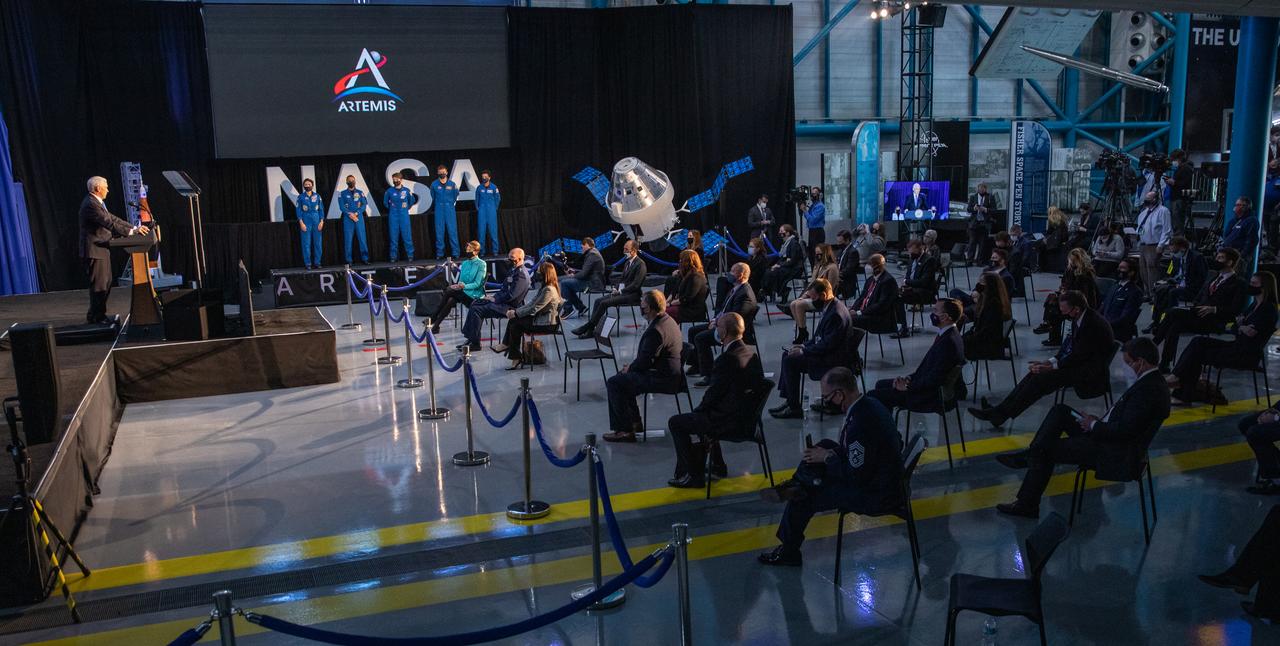

Vice President Mike Pence introduces NASA astronauts, from left, Jessica Meir, Joseph Acaba, Anne McClain, Matthew Dominick, and Jessica Watkins, during a meeting of the National Space Council inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. Meir, Acaba, McClain, Dominick, and Watkins are among the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
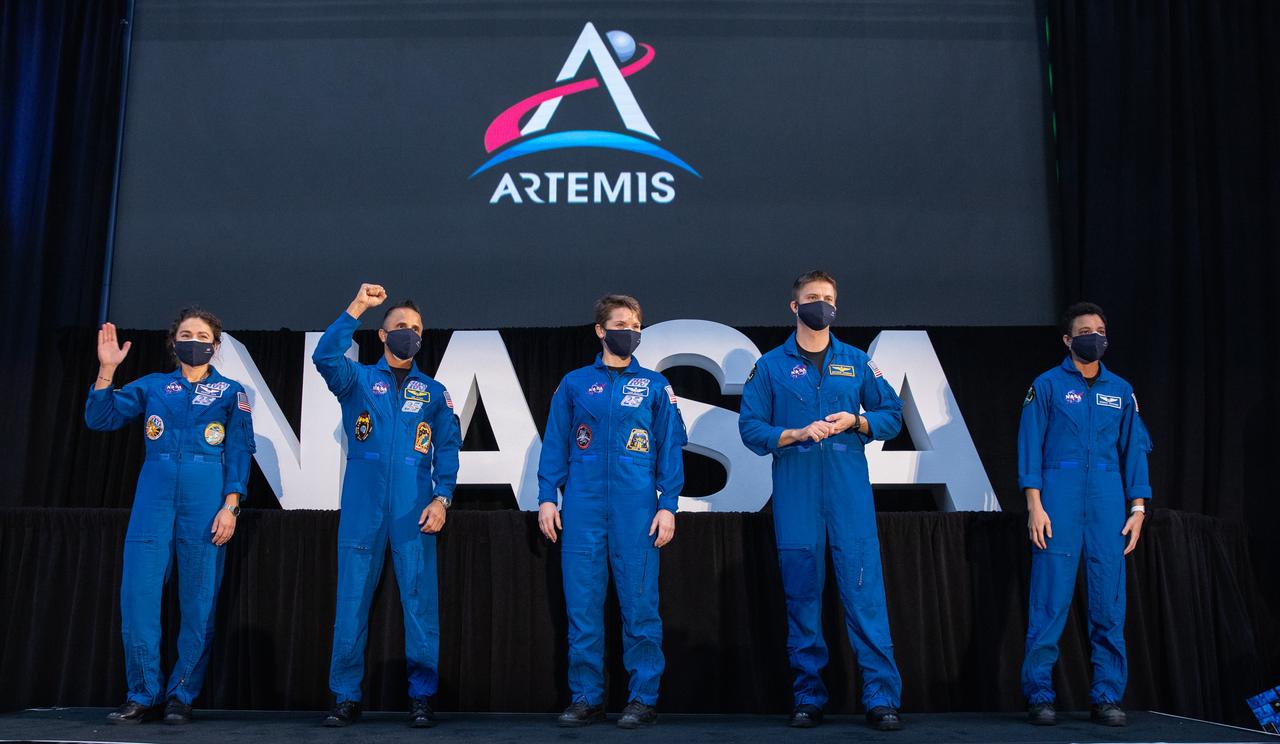

From left, NASA astronauts Jessica Meir, Joseph Acaba, Anne McClain, Matthew Dominick, and Jessica Watkins are introduced during a National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. The five are among an initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Vice President Mike Pence, who chaired the meeting, introduced the astronauts. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks during the National Space Council meeting inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy and to review the nation's long-range goals for space activities. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana attends a meeting of the National Space Council inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy and to review the nation's long-range goals for space activities. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
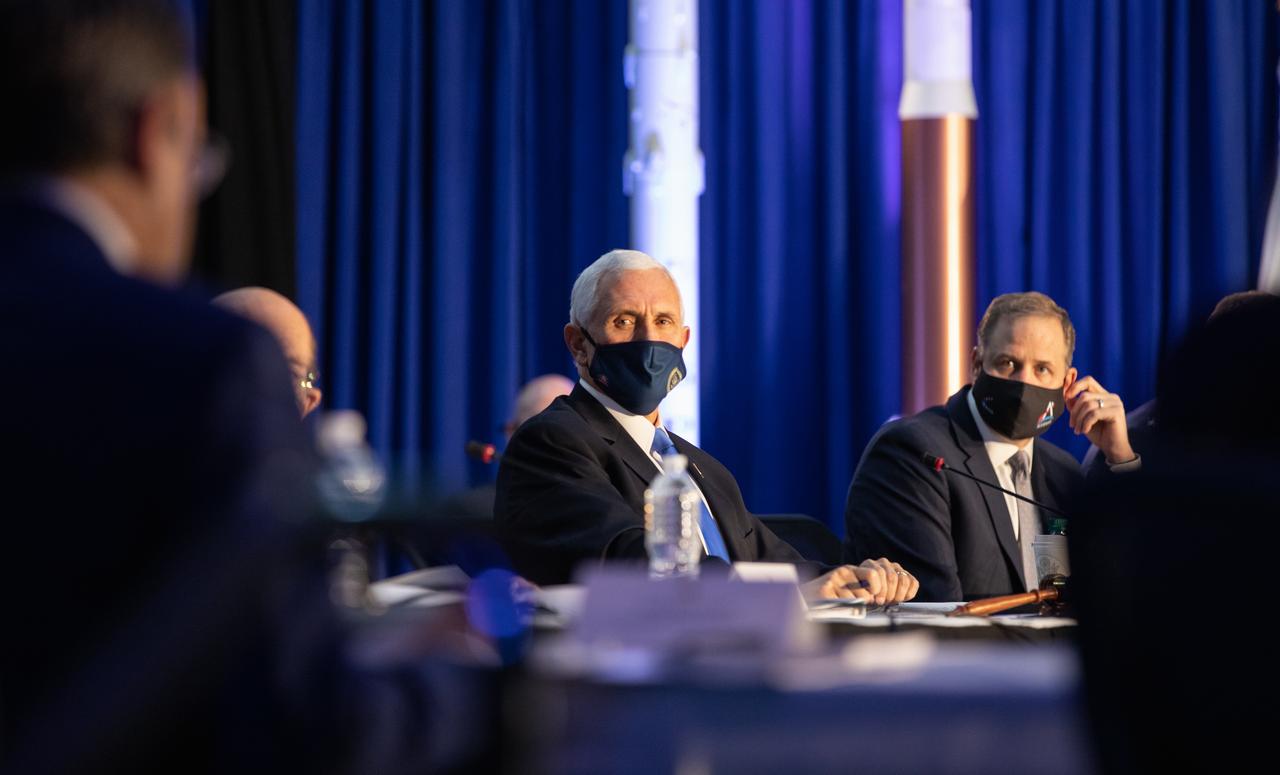

Vice President Mike Pence listens during a meeting of the National Space Council inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy and to review the nation's long-range goals for space activities. At the close of the meeting, Pence announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
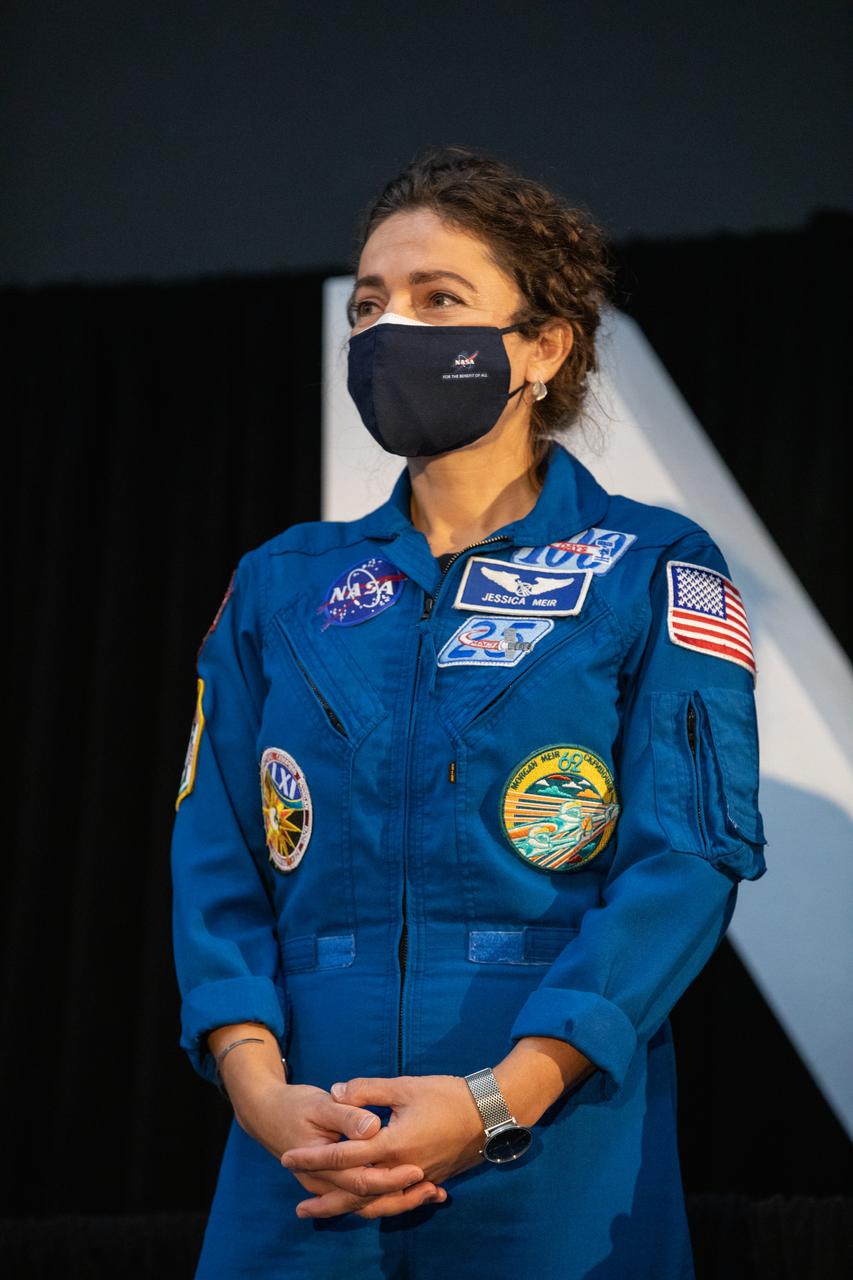

NASA astronaut Jessica Meir attends an announcement Dec. 9, 2020, that she is one of the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A Maine native, Meir was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2013 and has spent 205 days in space on one previous flight. Joining her at the event were fellow astronauts Joseph Acaba, Matthew Dominick, Anne McClain, and Jessica Watkins. Vice President Mike Pence made the announcement at the close of a National Space Council meeting he chaired in the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
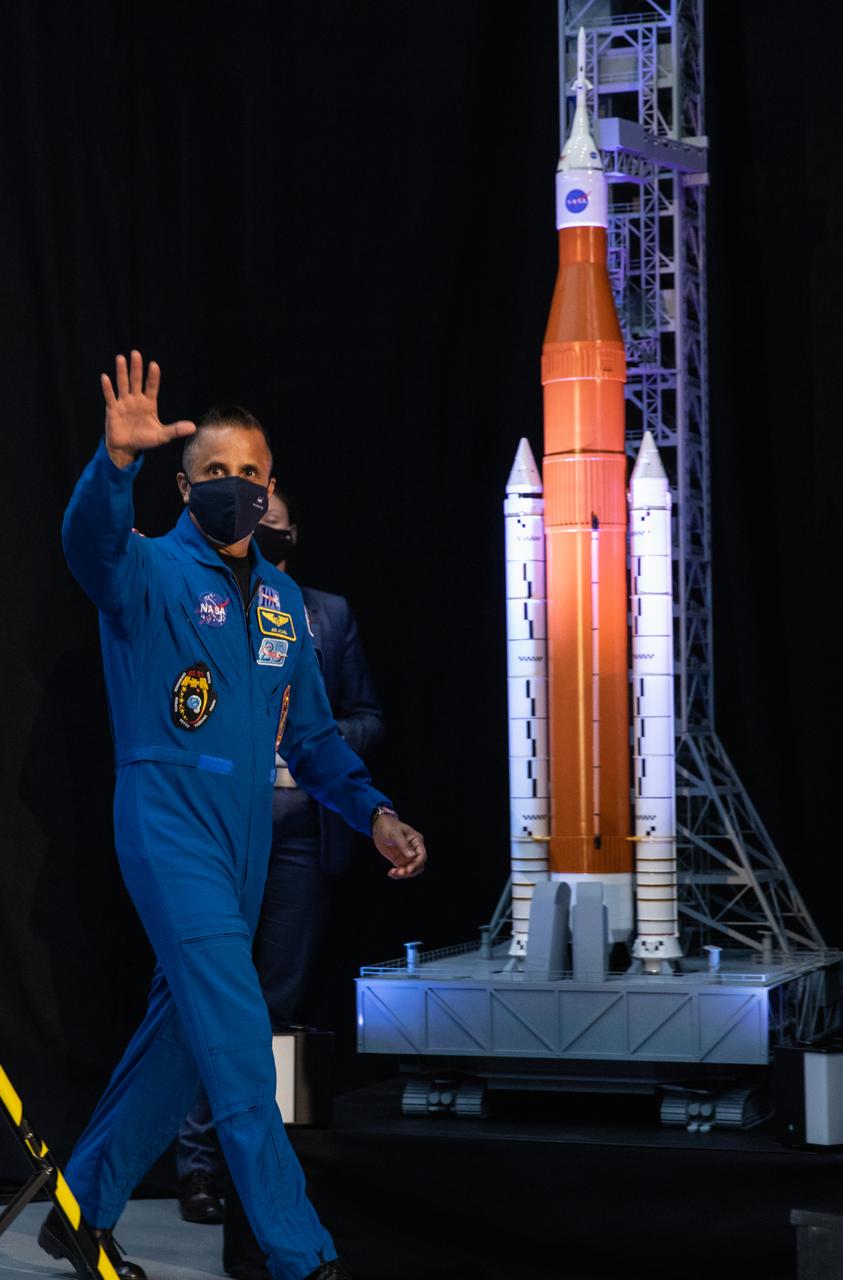

NASA astronaut Joseph Acaba waves during an announcement Dec. 9, 2020, that he is one of the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A California native, Acaba was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2004 and has logged a total of 306 days in space on three flights. Joining him at the event were fellow astronauts Matthew Dominick, Jessica Meir, Anne McClain, and Jessica Watkins. Vice President Mike Pence made the announcement at the close of a National Space Council meeting he chaired in the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

NASA astronaut Joseph Acaba attends an announcement Dec. 9, 2020, that he is one of the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A California native, Acaba was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2004 and has logged a total of 306 days in space on three flights. Joining him at the event were fellow astronauts Matthew Dominick, Jessica Meir, Anne McClain, and Jessica Watkins. Vice President Mike Pence made the announcement at the close of a National Space Council meeting he chaired in the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

NASA astronaut Anne McClain attends an announcement Dec. 9, 2020, that she is one of the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A Washington native, McClain was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2013 and has spent 204 days in space on one previous flight. Joining her at the event were fellow astronauts Joseph Acaba, Matthew Dominick, Jessica Meir, and Jessica Watkins. Vice President Mike Pence made the announcement at the close of a National Space Council meeting he chaired in the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
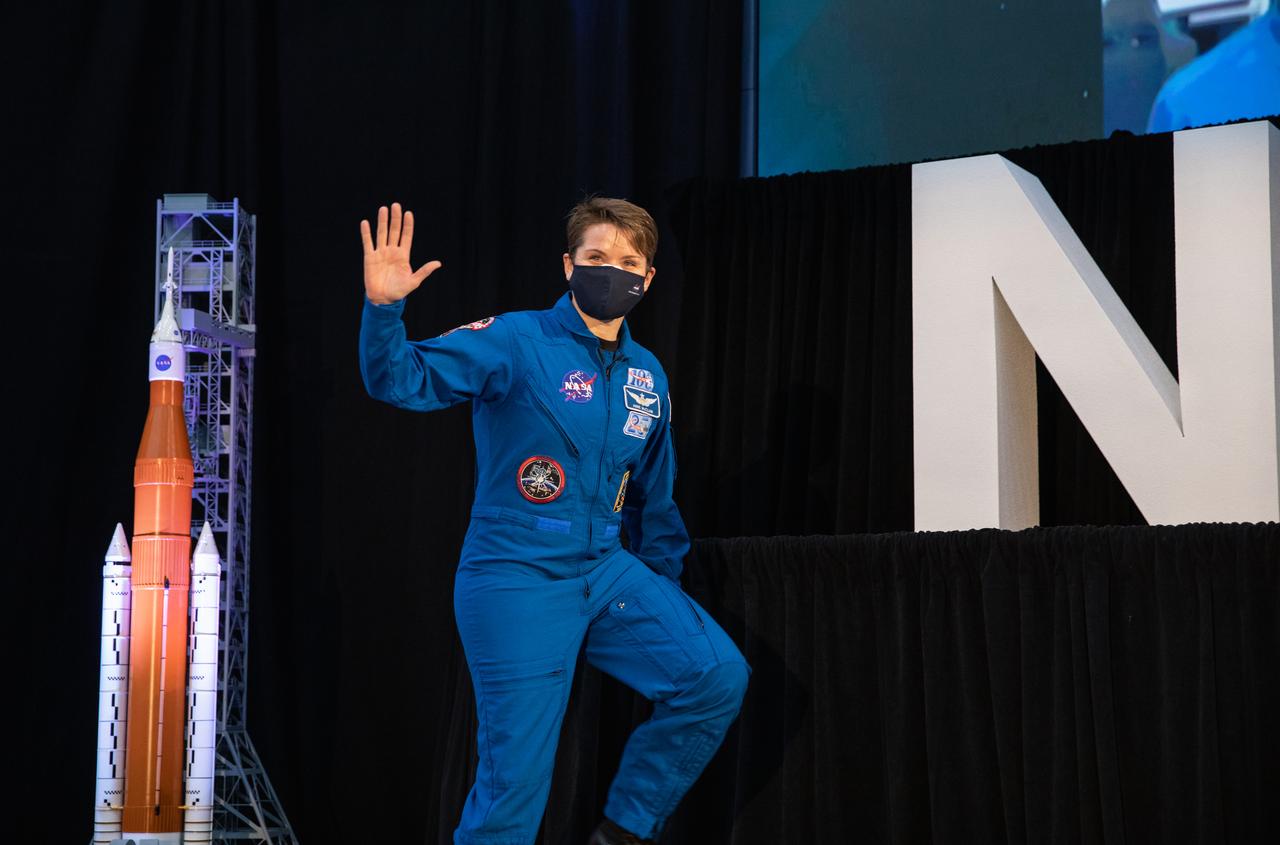

NASA astronaut Anne McClain waves during an announcement Dec. 9, 2020, that she is one of the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. A Washington native, McClain was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2013 and has spent 204 days in space on one previous flight. Joining her at the event were fellow astronauts Joseph Acaba, Matthew Dominick, Jessica Meir, and Jessica Watkins. Vice President Mike Pence made the announcement at the close of a National Space Council meeting he chaired in the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
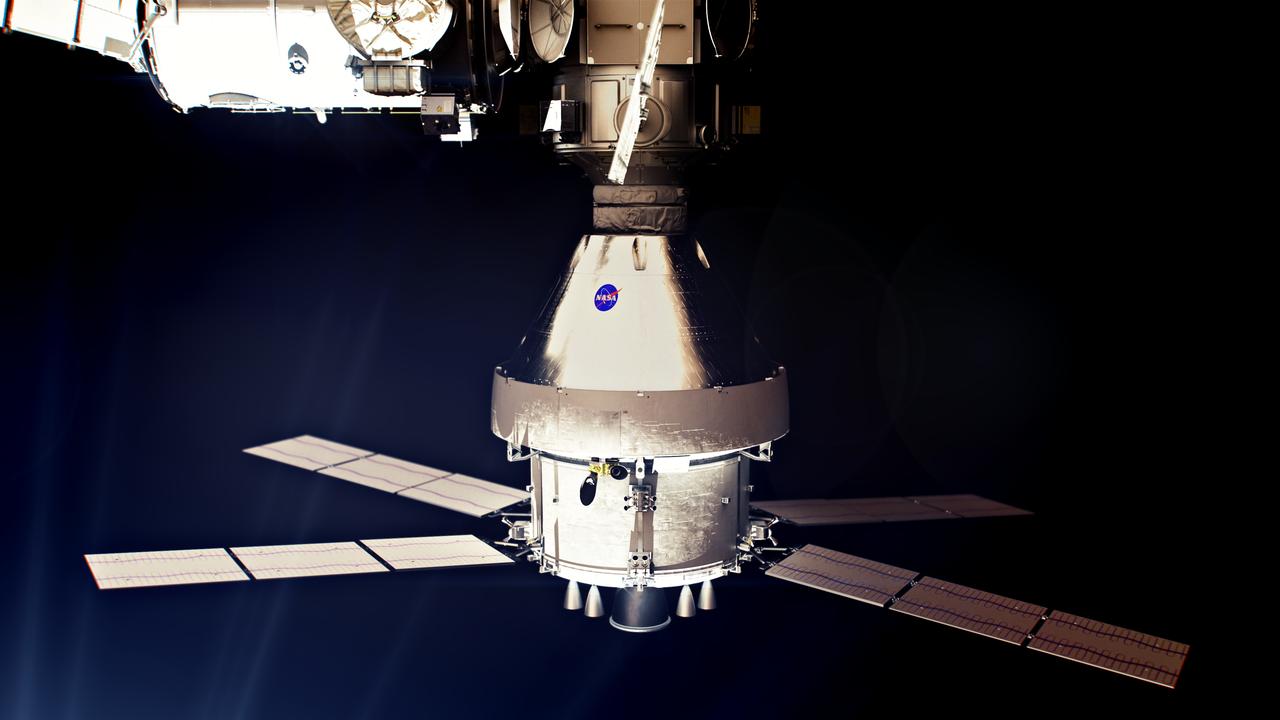
The Orion spacecraft docked to the Gateway space station. Orion will visit Gateway for the first time on the Artemis IV mission when astronauts will use it to deliver the International Habitat (I-Hab) module to Gateway. Orion will return to Gateway to deliver additional elements on Artemis V and VI.
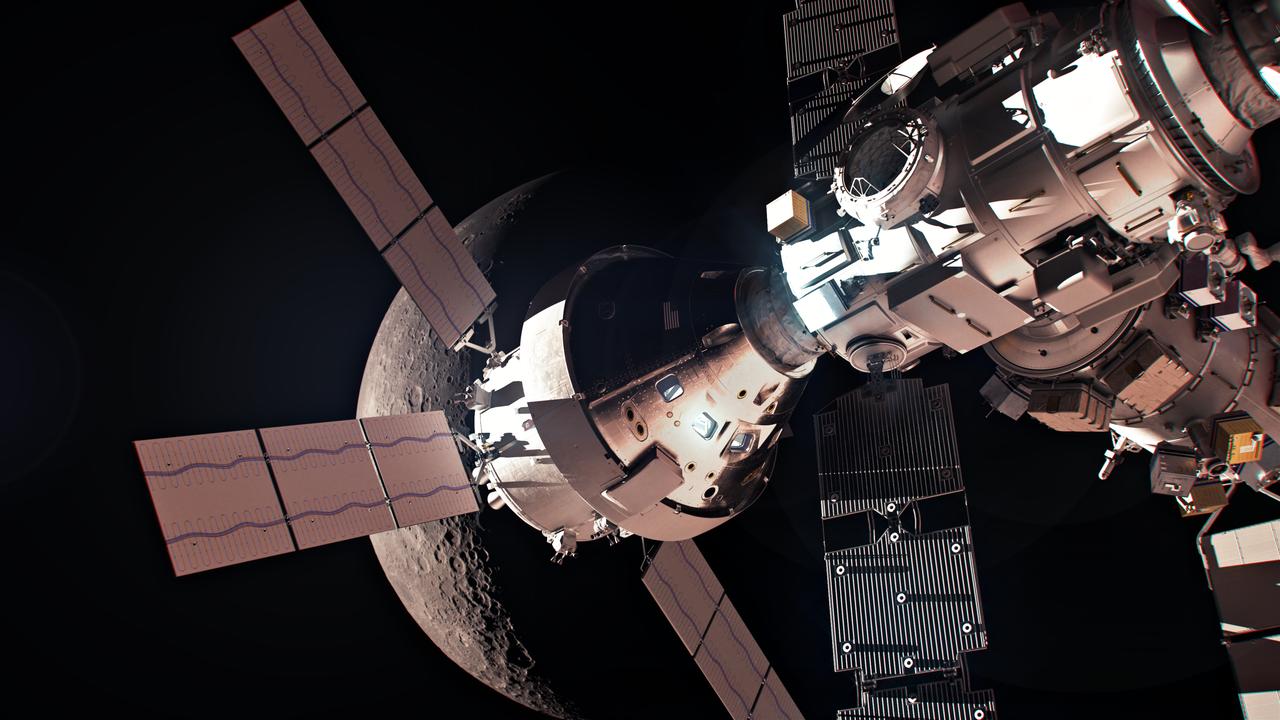

The Orion spacecraft docked to the Gateway space station. Orion will visit Gateway for the first time on the Artemis IV mission when astronauts will use it to deliver the International Habitat (I-Hab) module to Gateway. Orion will return to Gateway to deliver additional elements on Artemis V and VI.
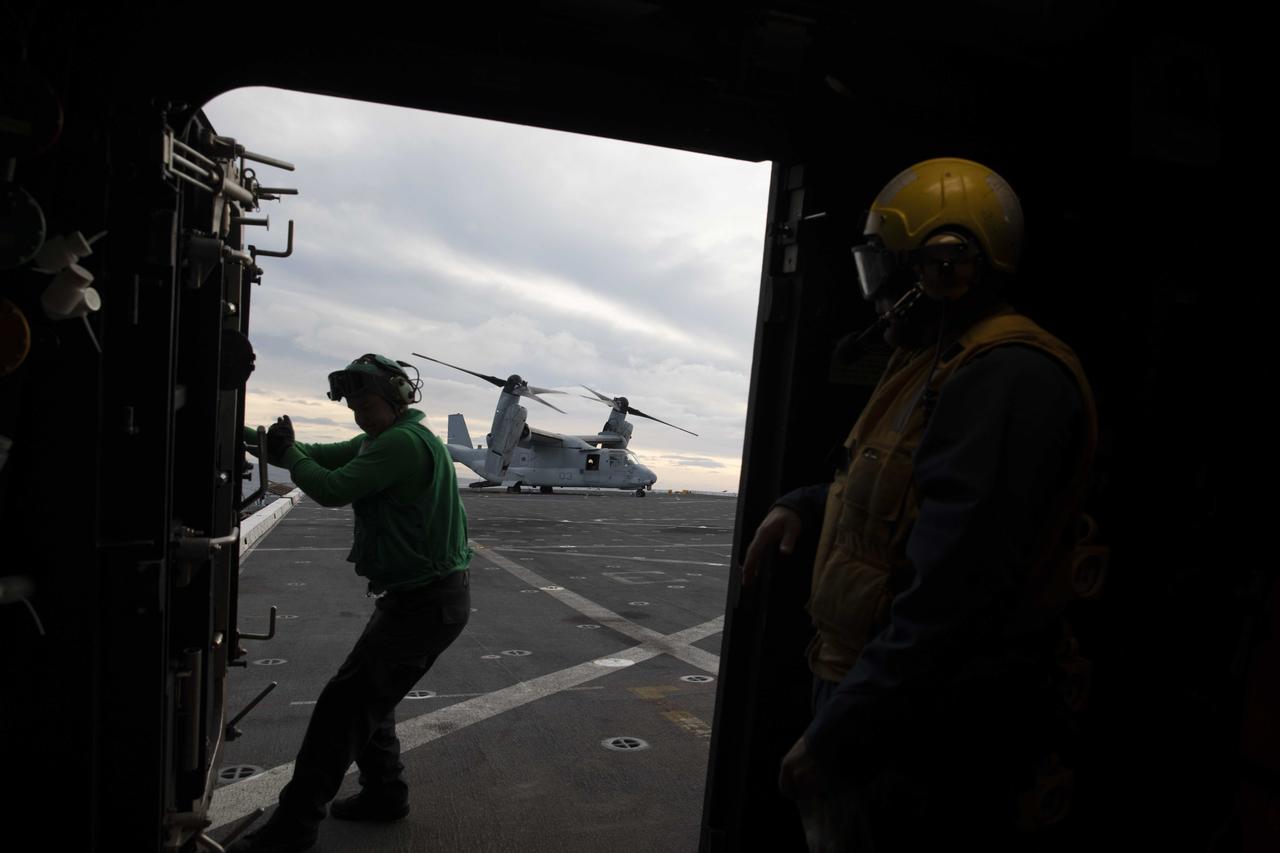

A member of the U.S. Navy helicopter team aboard USS Portland opens a door to the flight deck after a V-22 Osprey lands prior to NASA’s Orion splashdown for the Artemis I mission on Dec. 11, 2022.
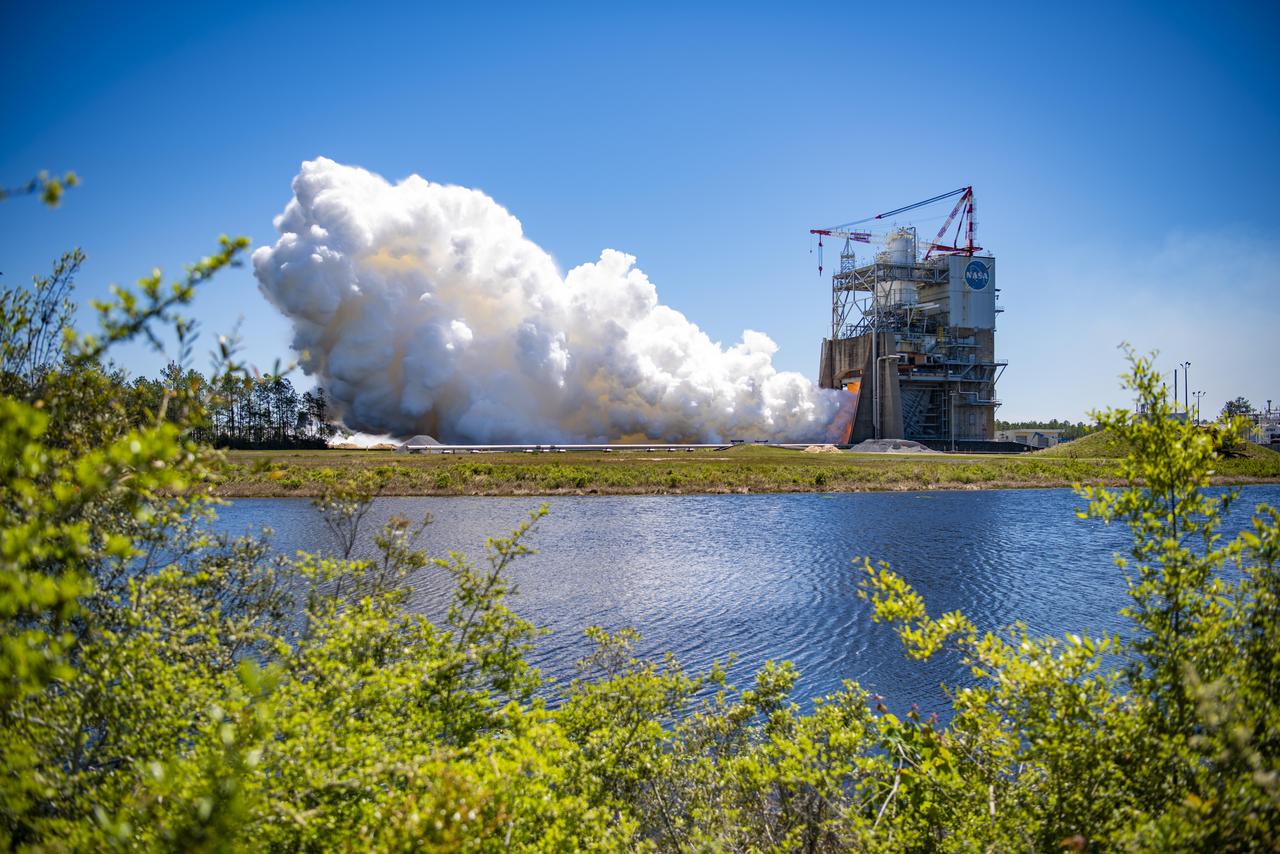

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
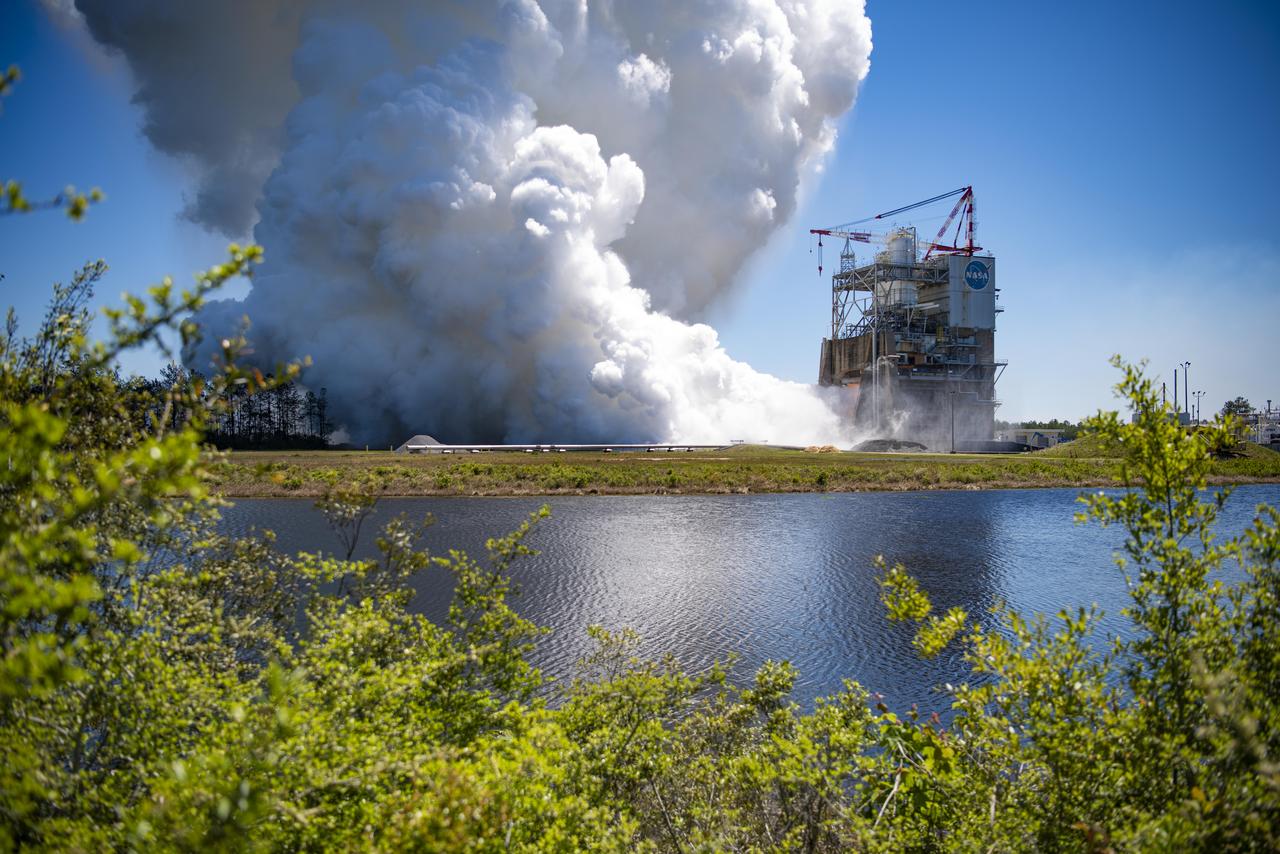

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
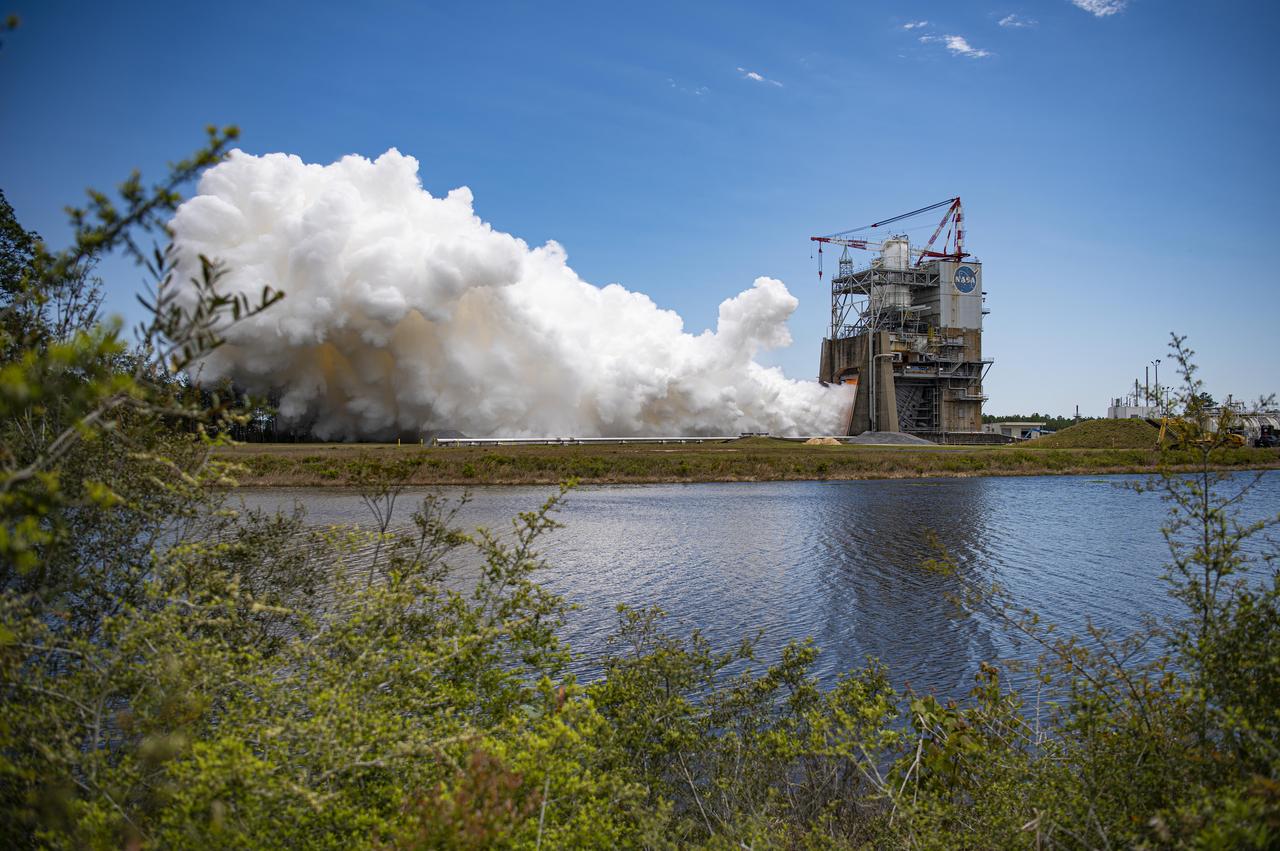

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
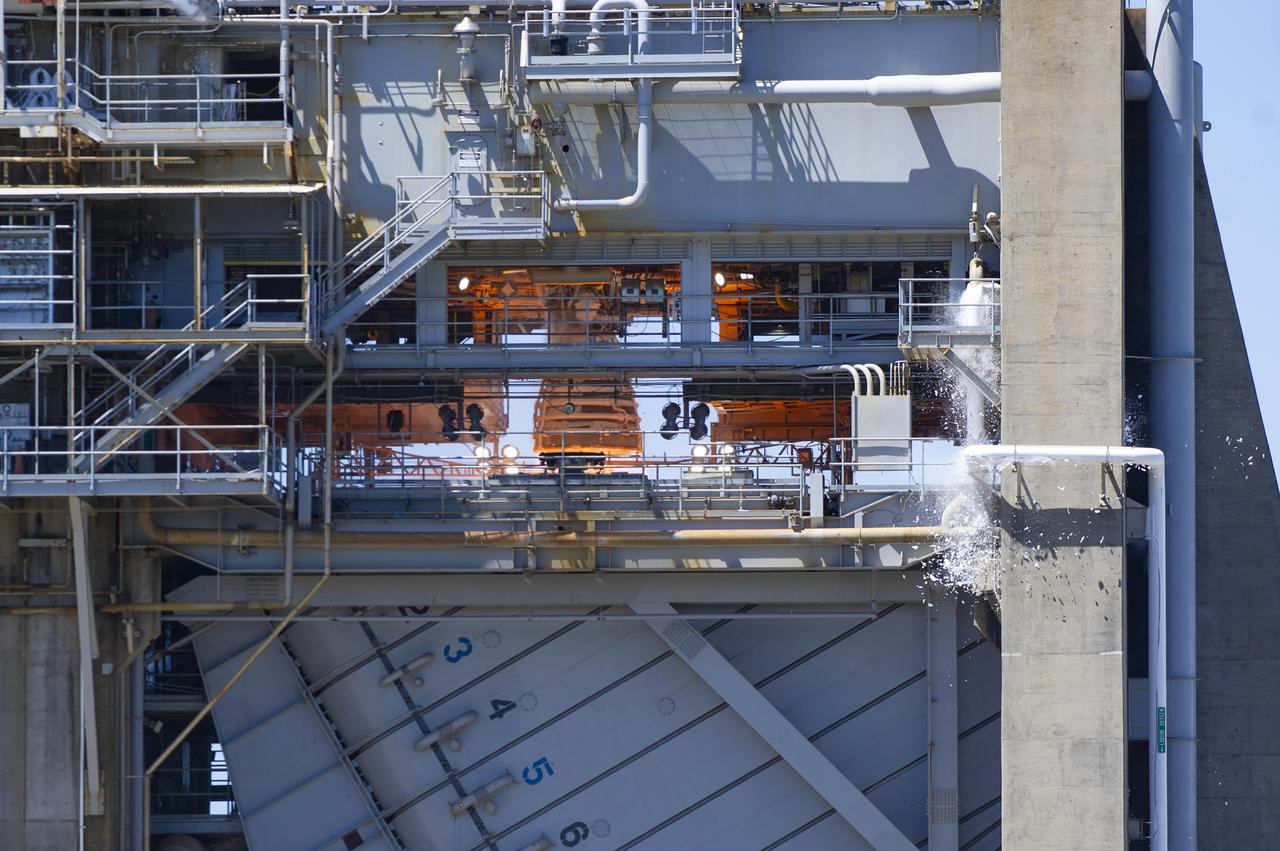

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V
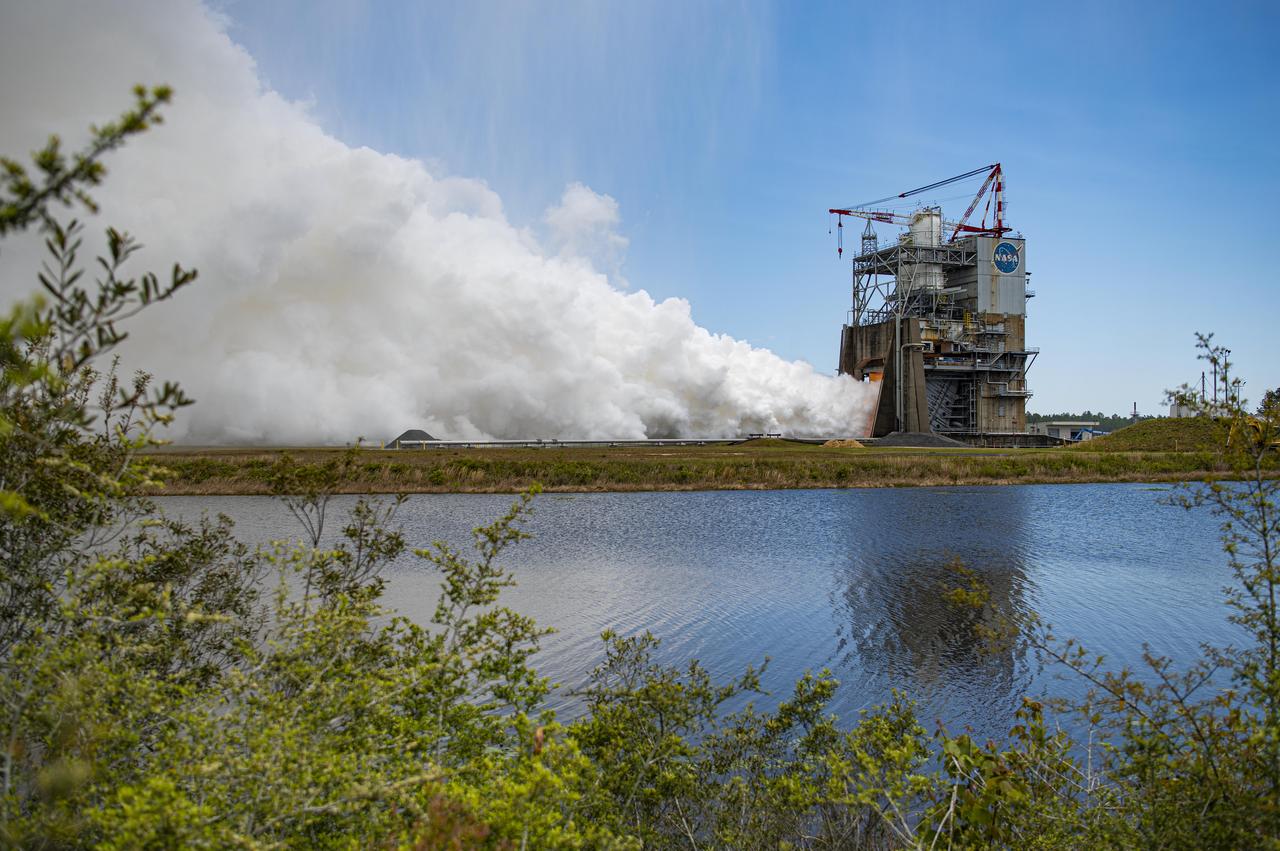

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
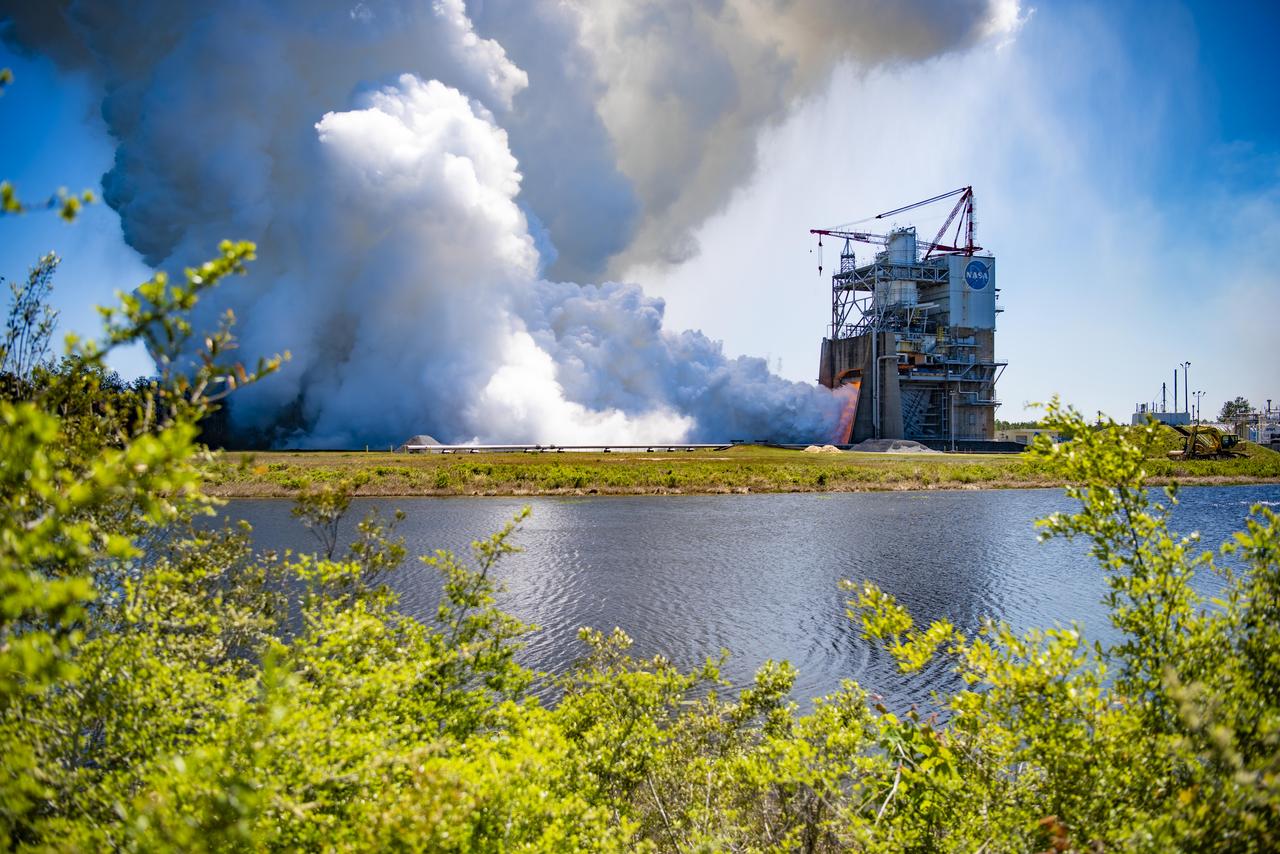

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
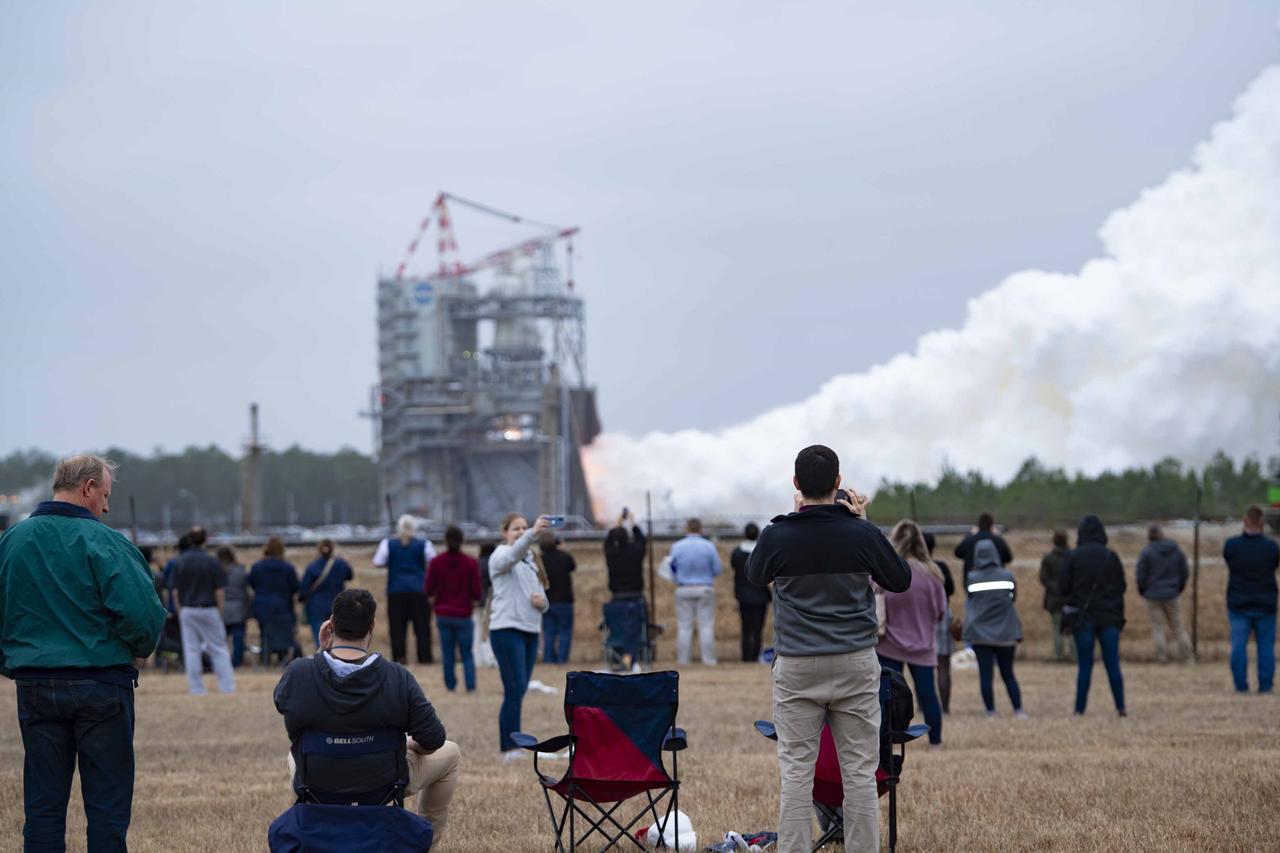

Sitewide employees at NASA’s Stennis Space Center watch the RS-25 test conducted on Jan. 23 as NASA continued a critical test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The full-duration hot fire on the Fred Haise Test Stand is part of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. The new engines will help power SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
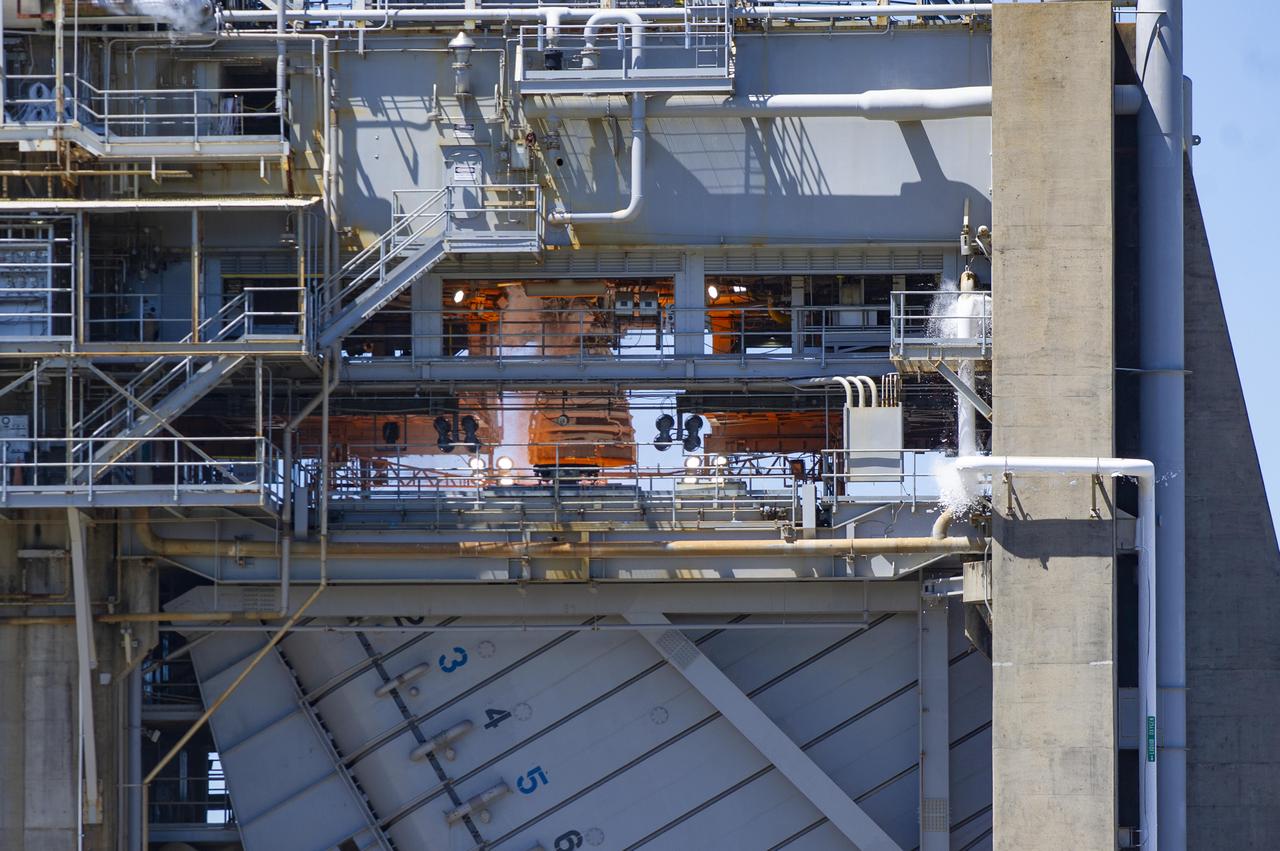

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
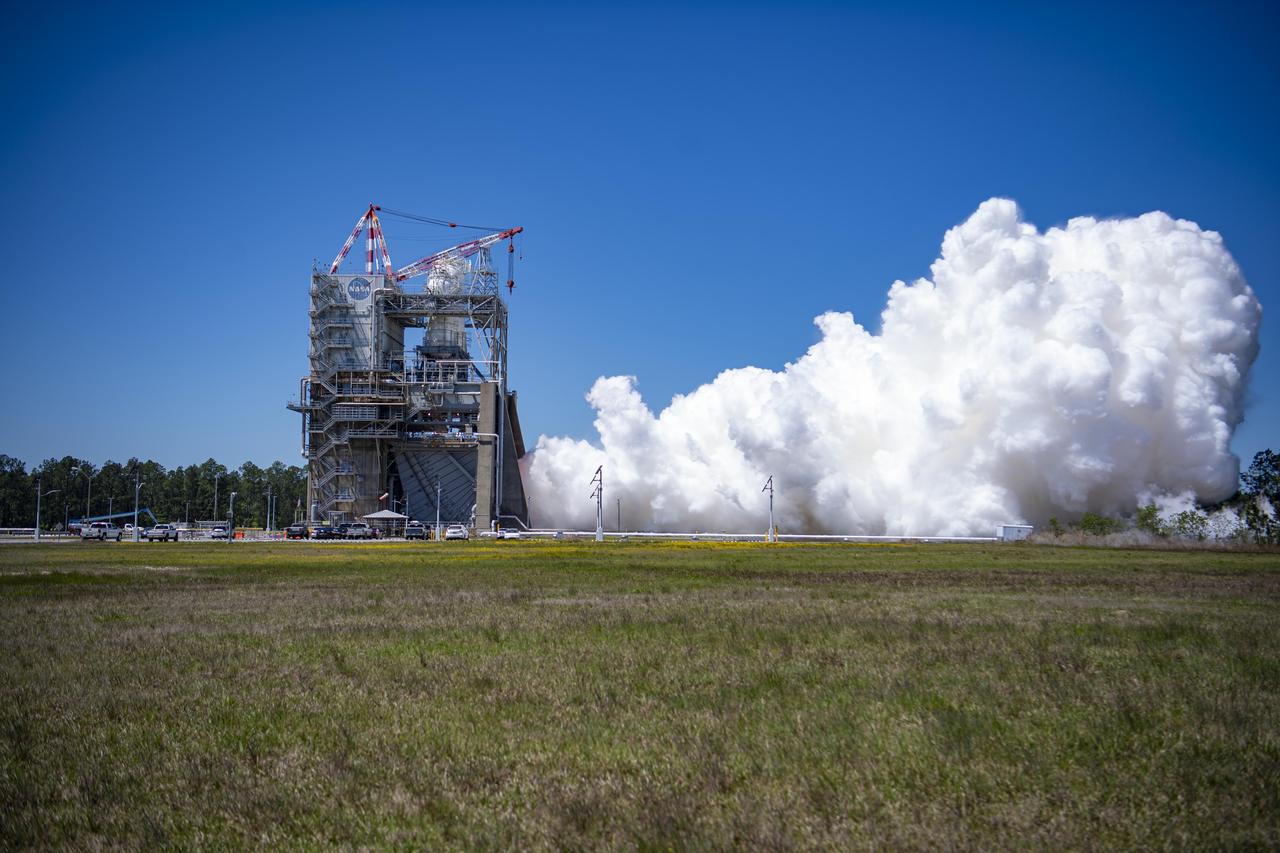

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
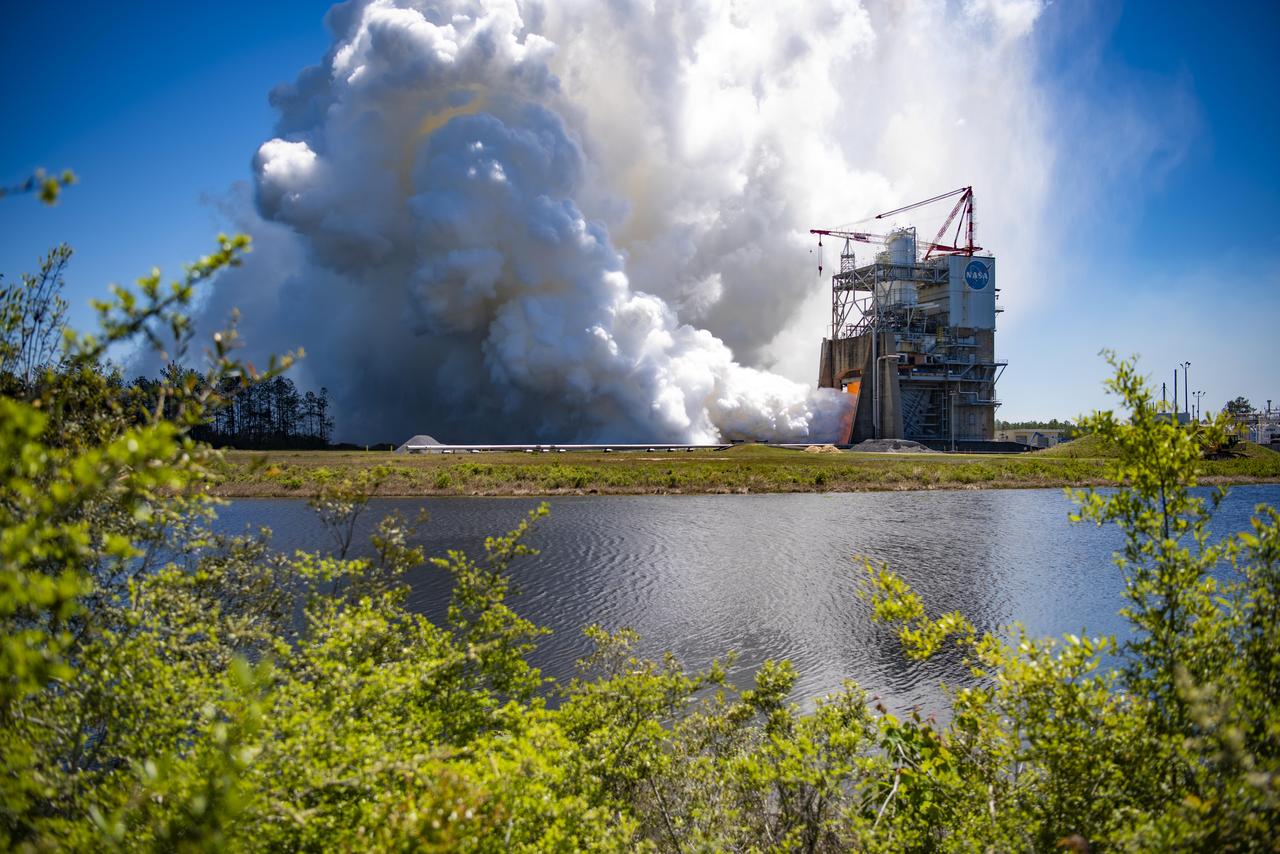

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
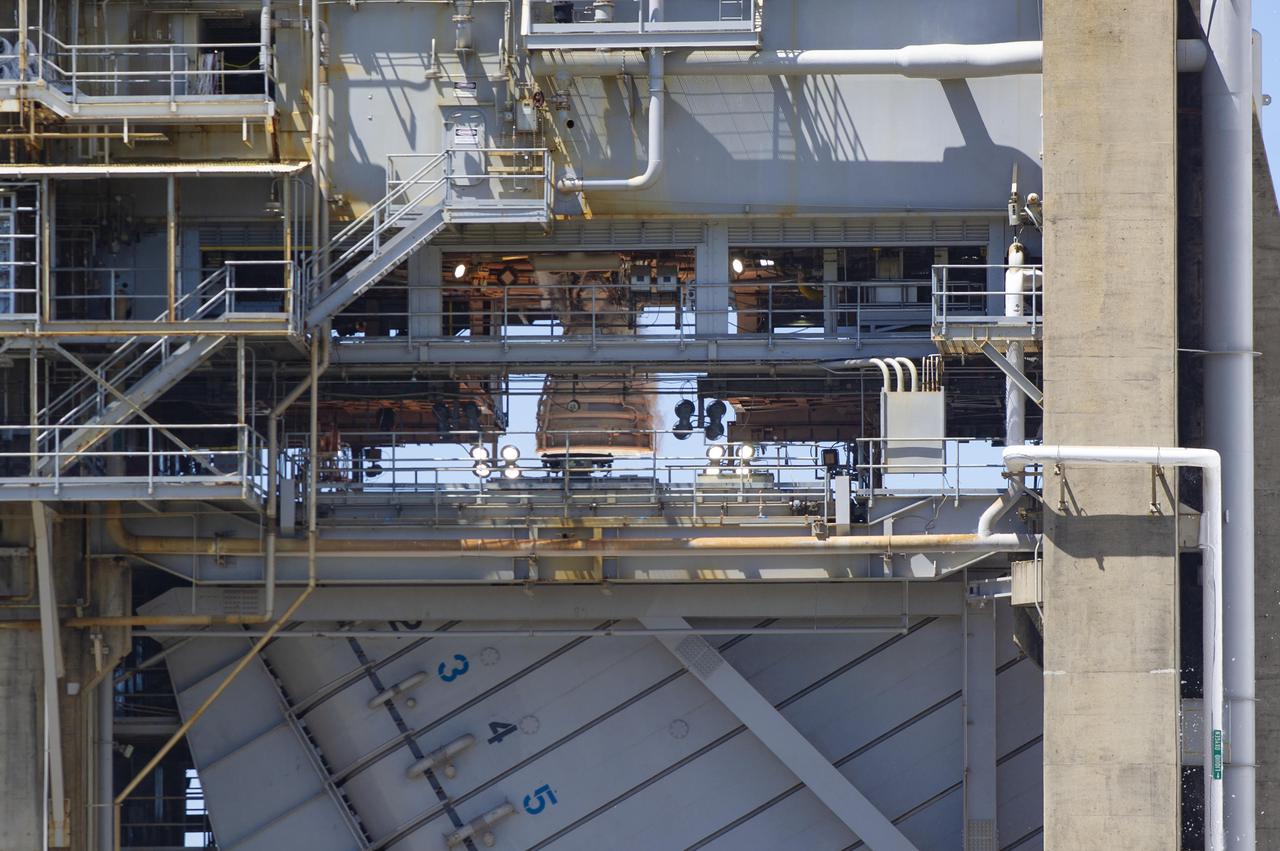

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
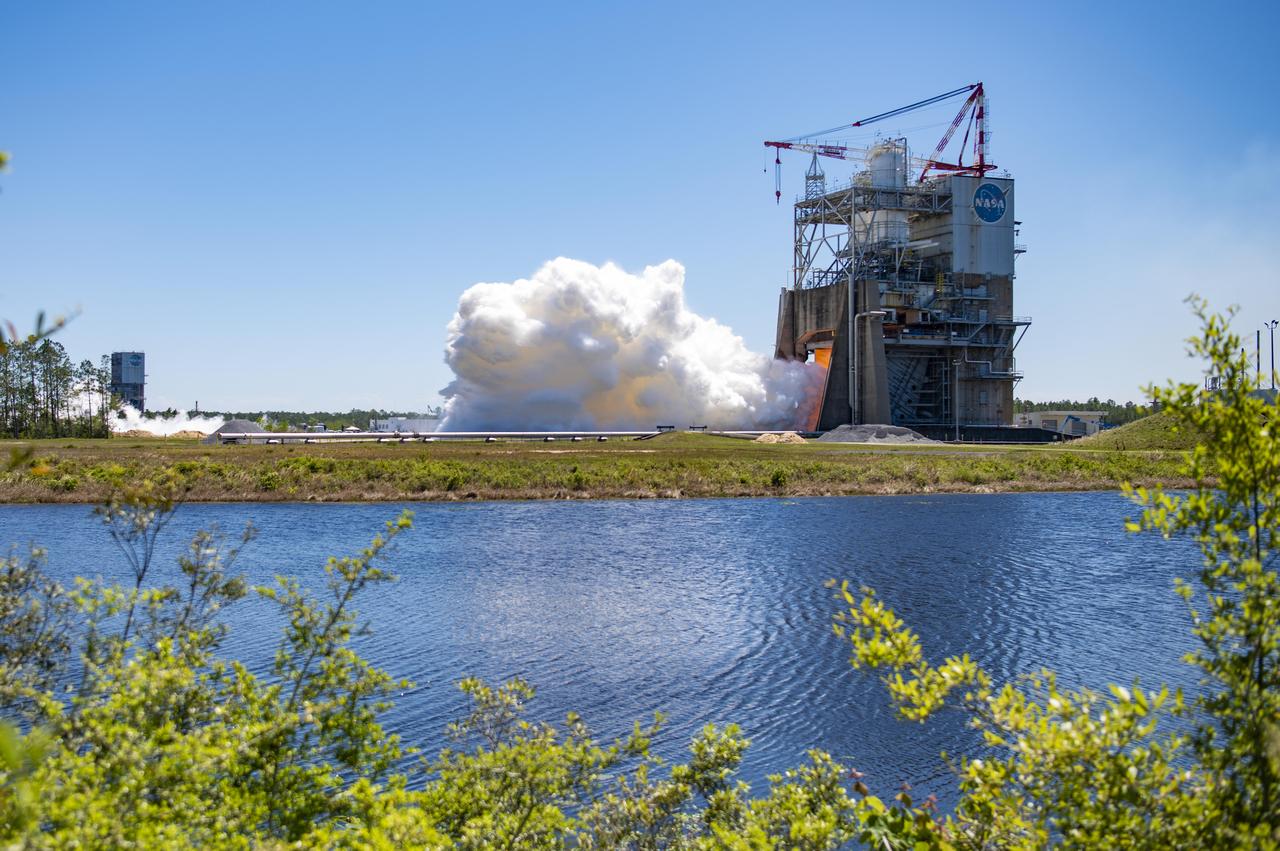

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
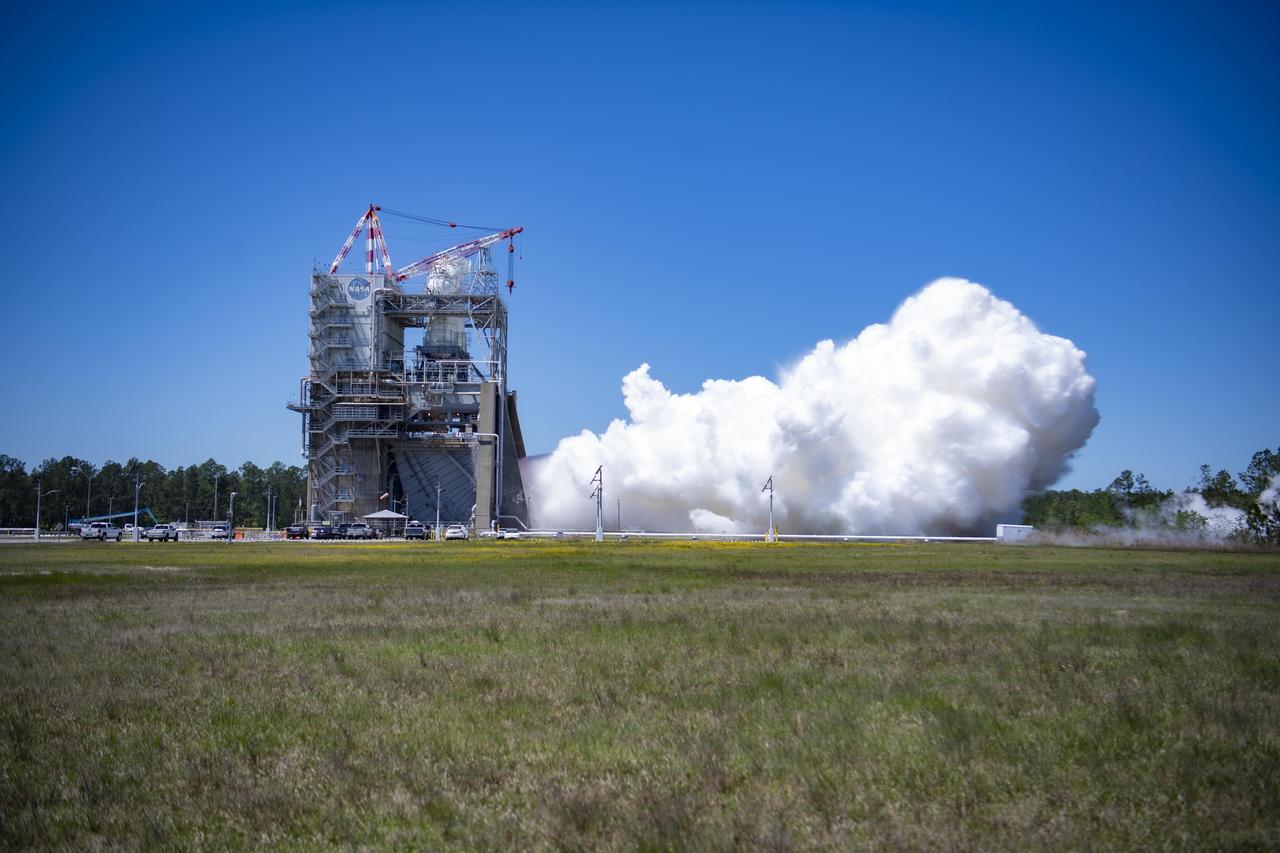

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
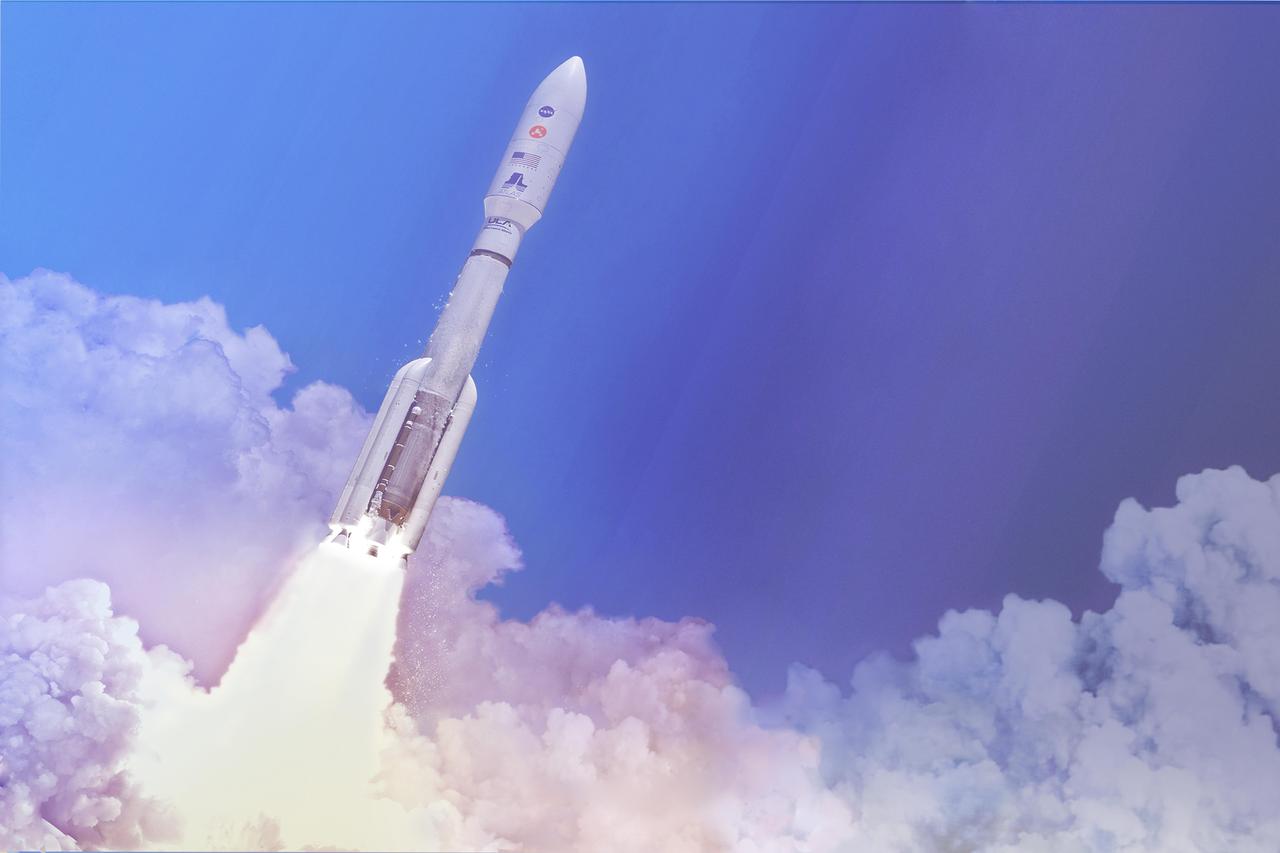

In this artist's concept, a two-stage United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V launch vehicle speeds the Mars 2020 spacecraft toward the Red Planet. The rocket stands at 197 feet (60 meters) tall. This will be the 11th Mars launch on an Atlas rocket and the fifth by the Atlas V following NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2005, Curiosity rover in 2011, MAVEN orbiter in 2013 and InSight lander in 2018. Charged with returning astronauts to the Moon by 2024, NASA will establish a sustained human presence on and around the Moon by 2028 through NASA's Artemis lunar exploration plans. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23922
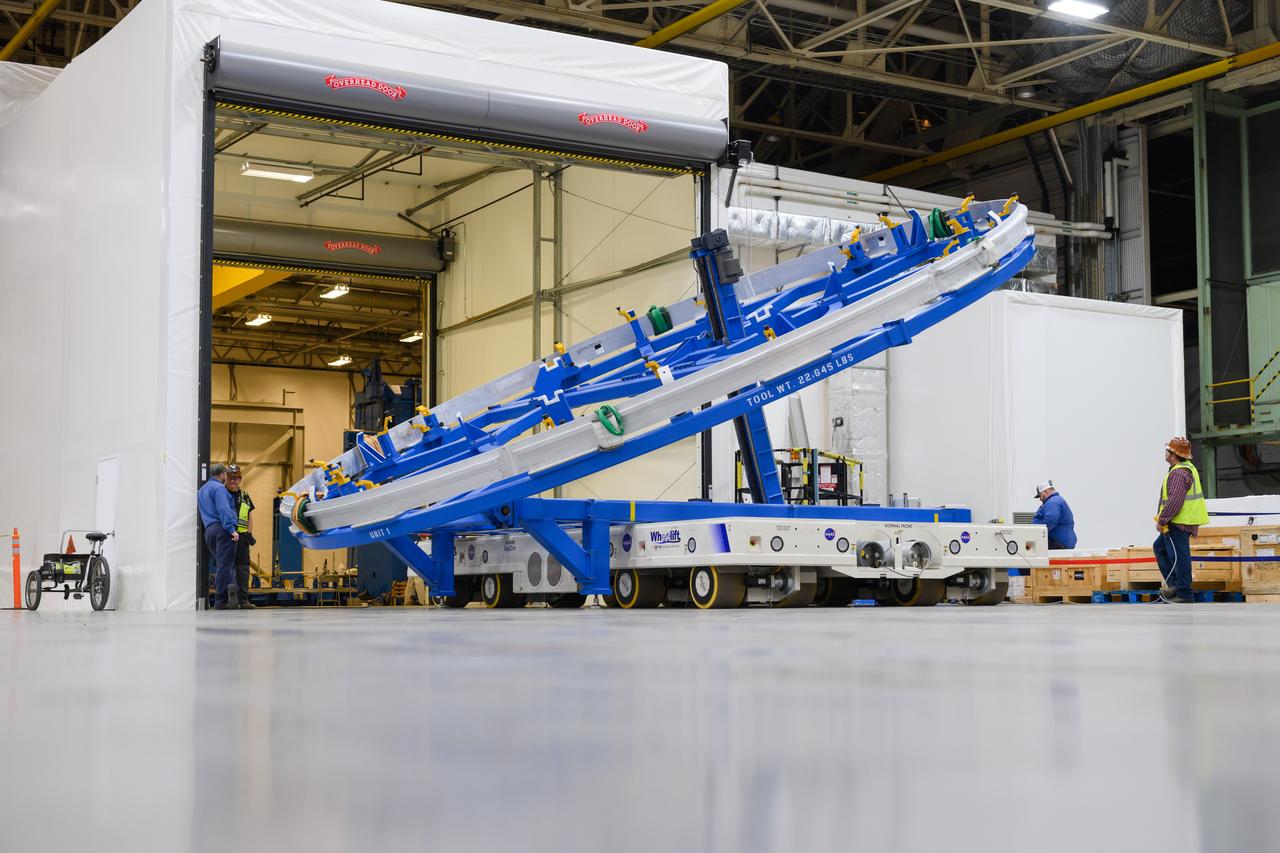

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
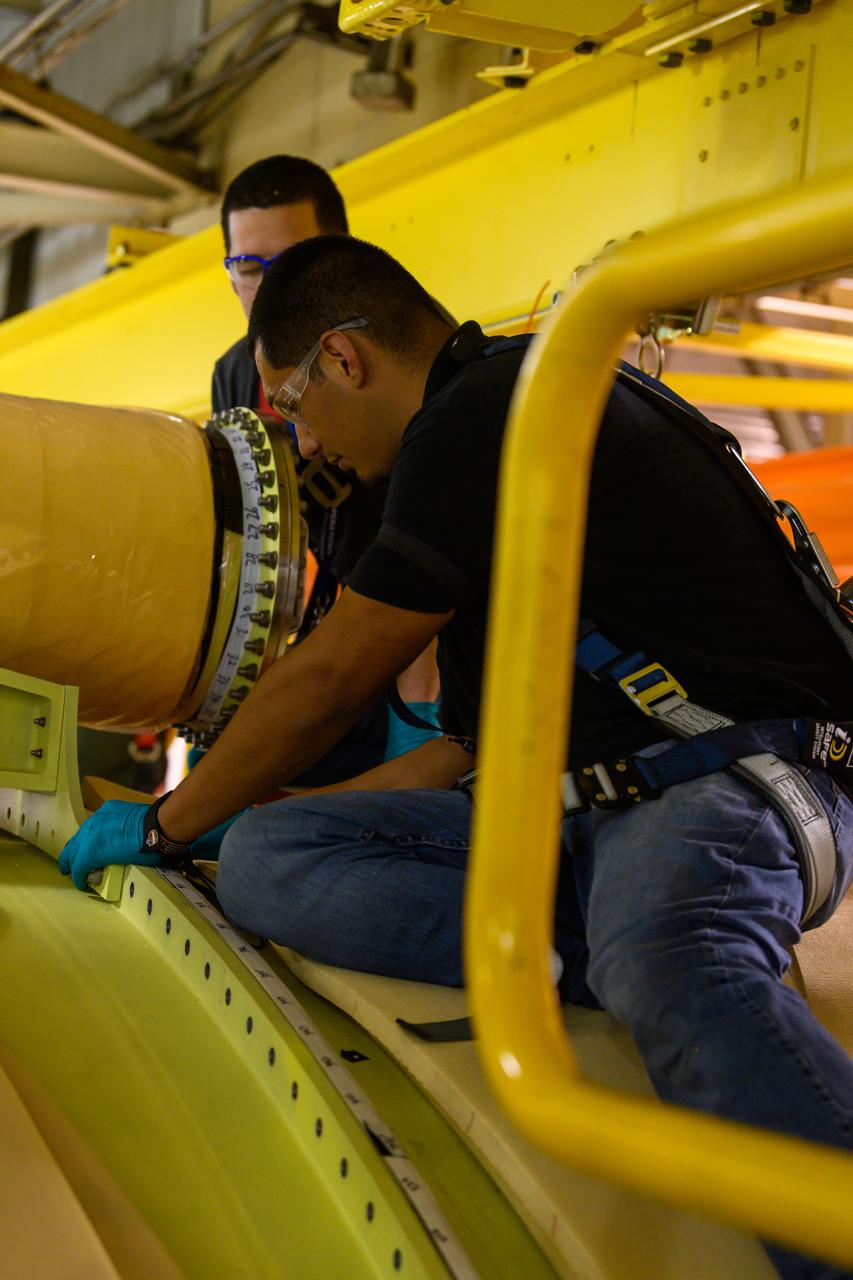

NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
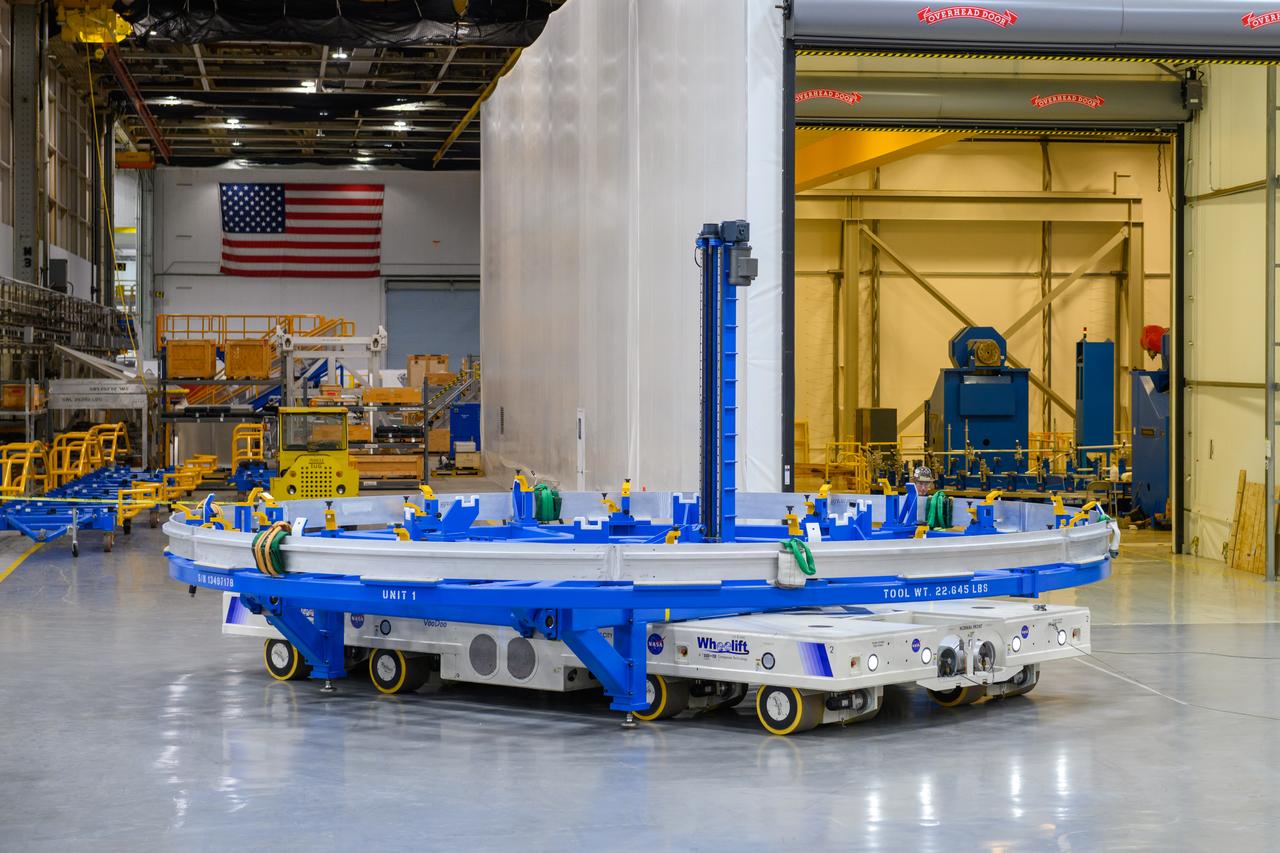

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

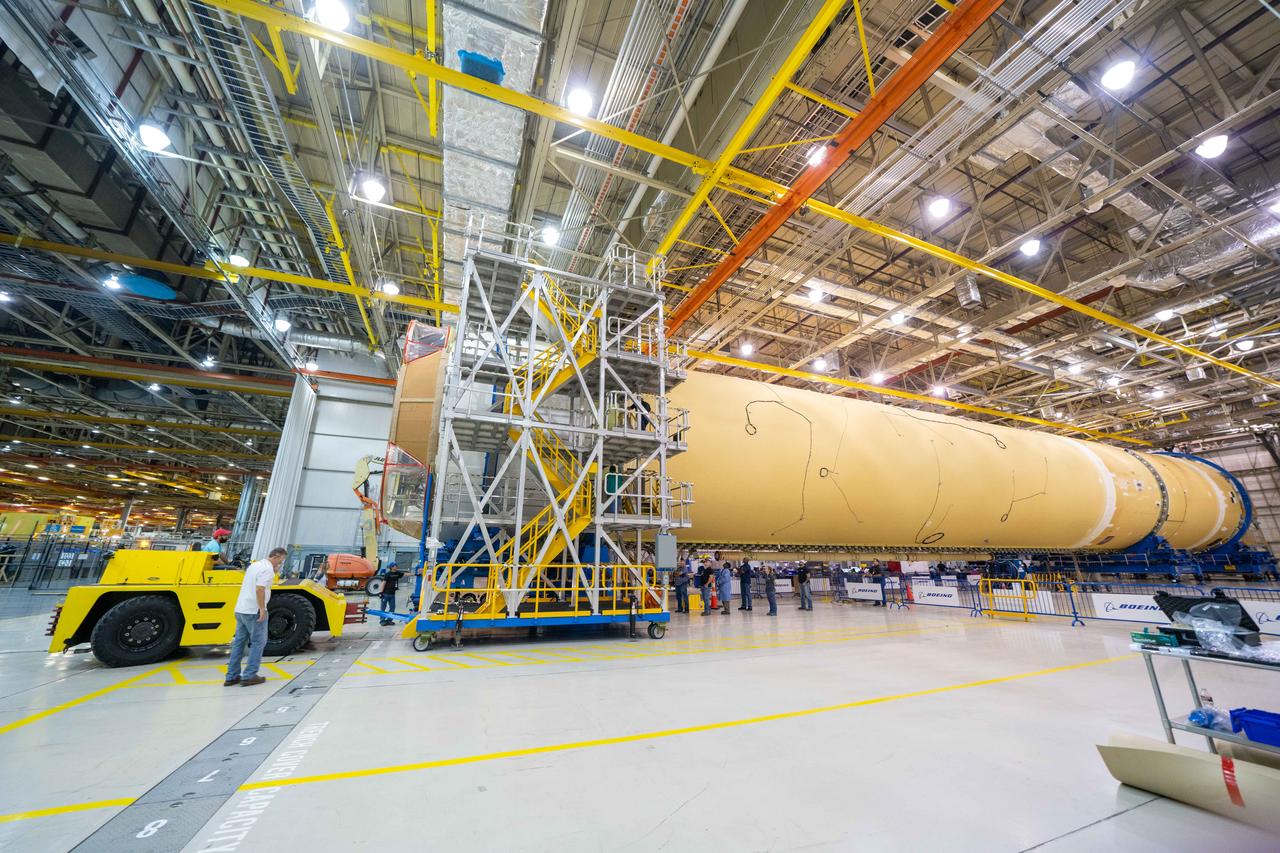
NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
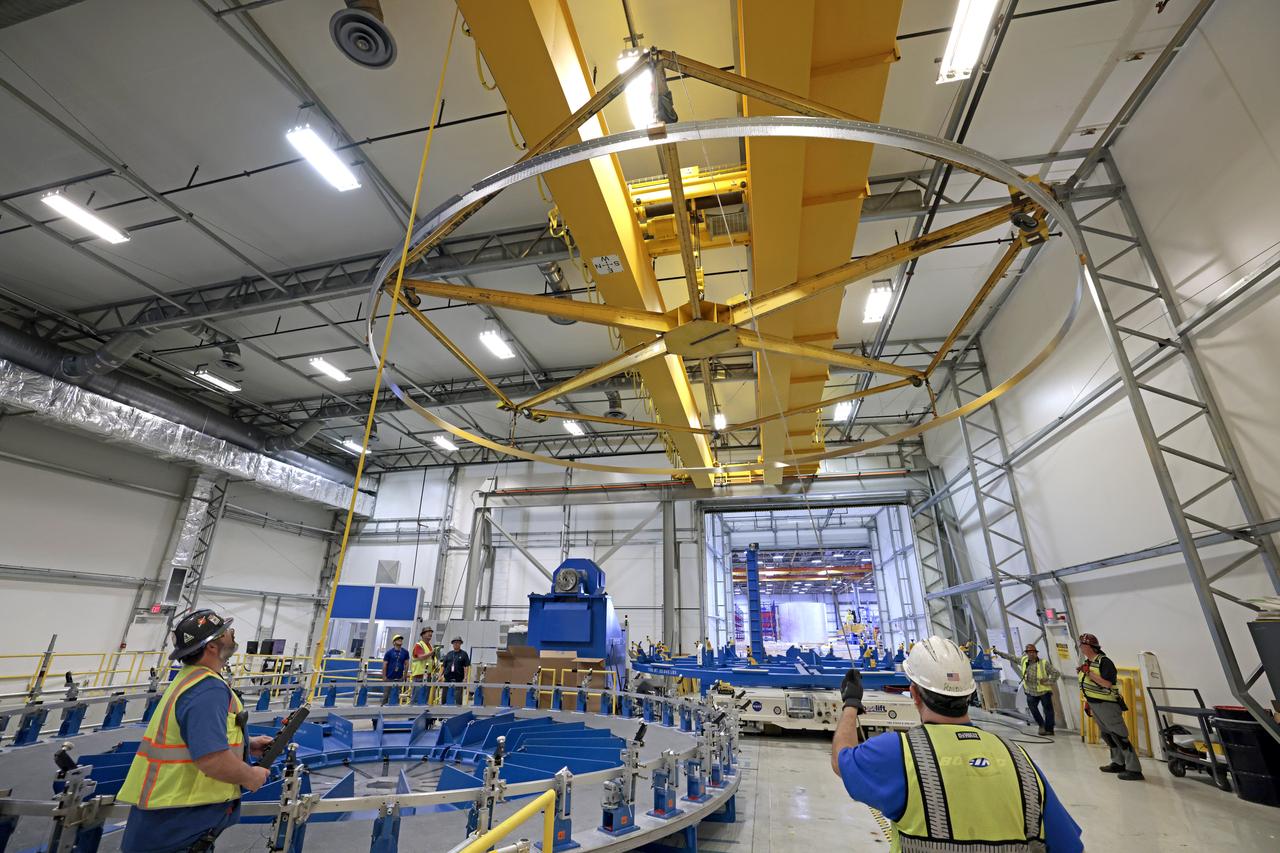

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
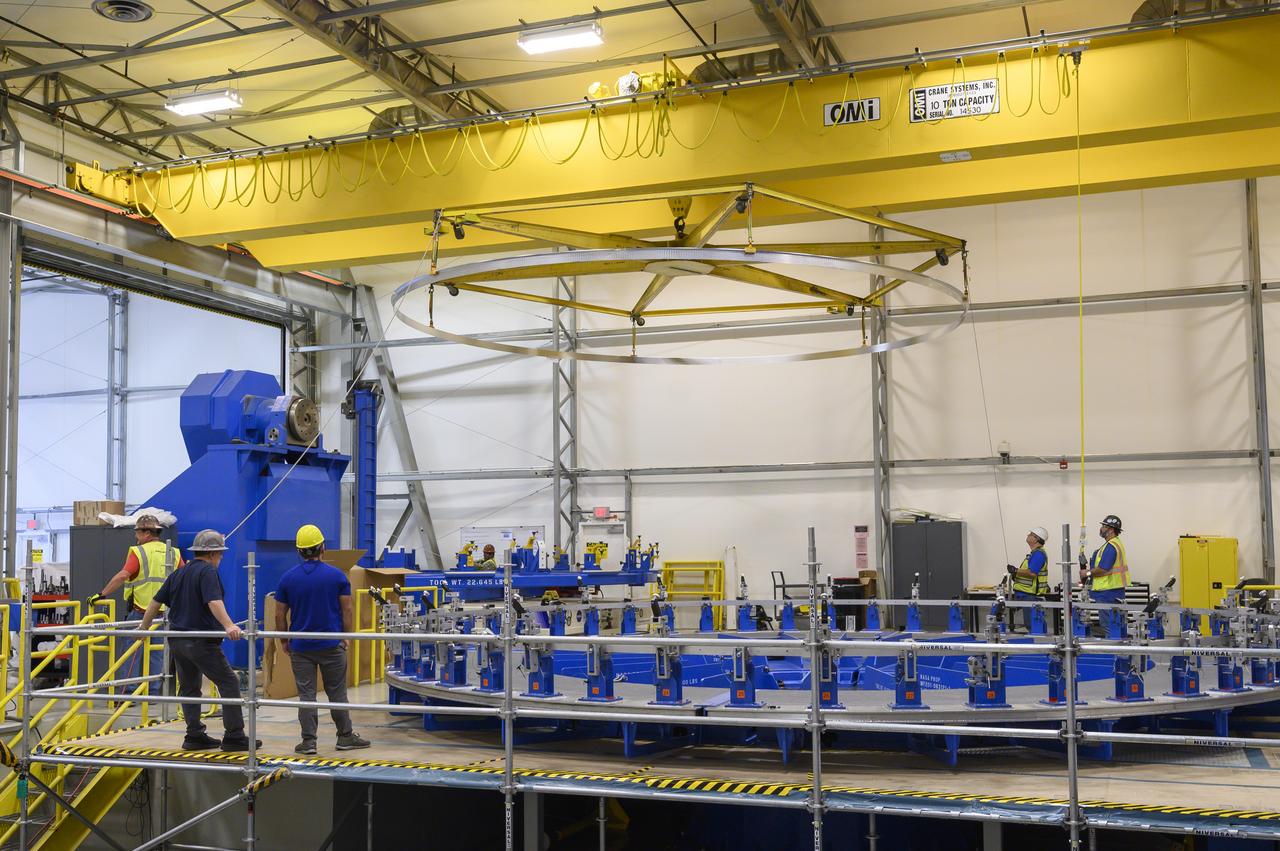

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
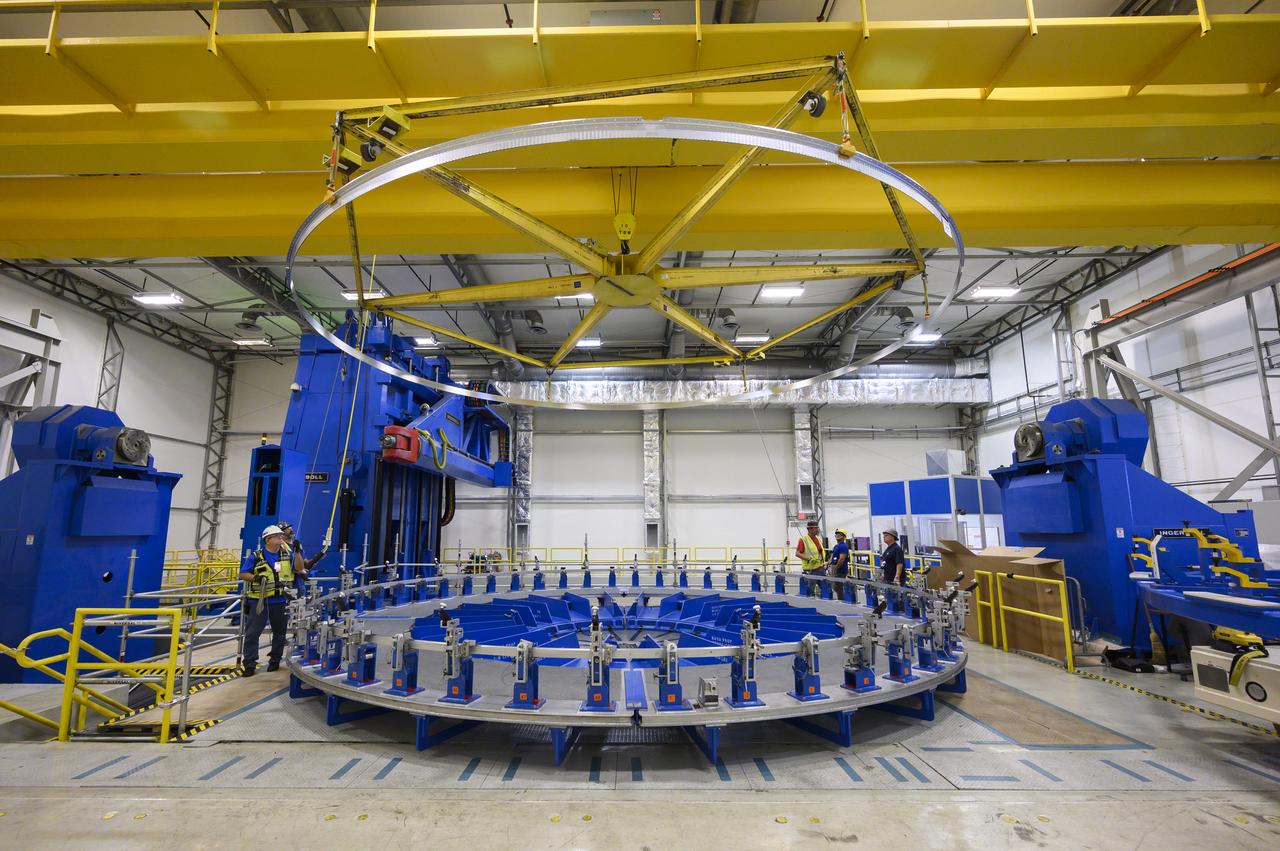

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
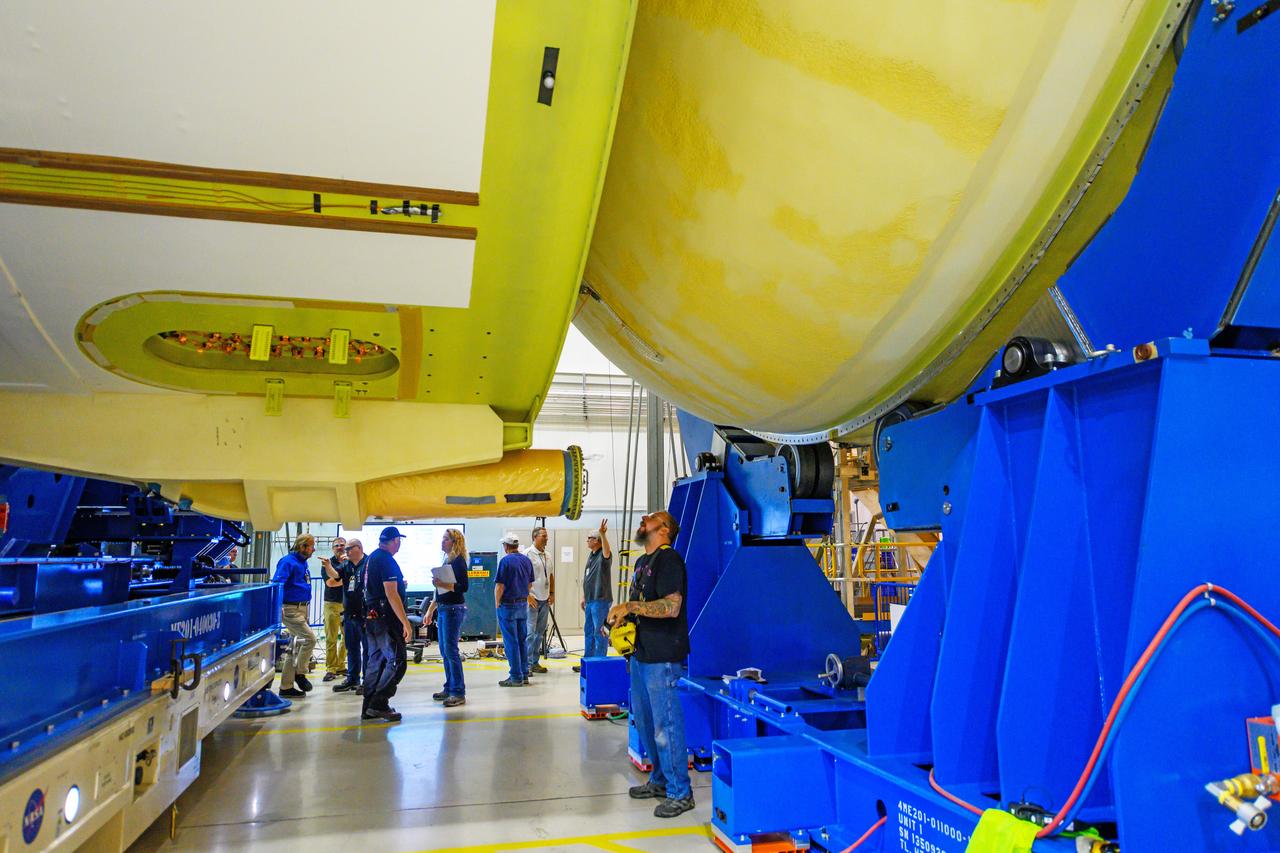

NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
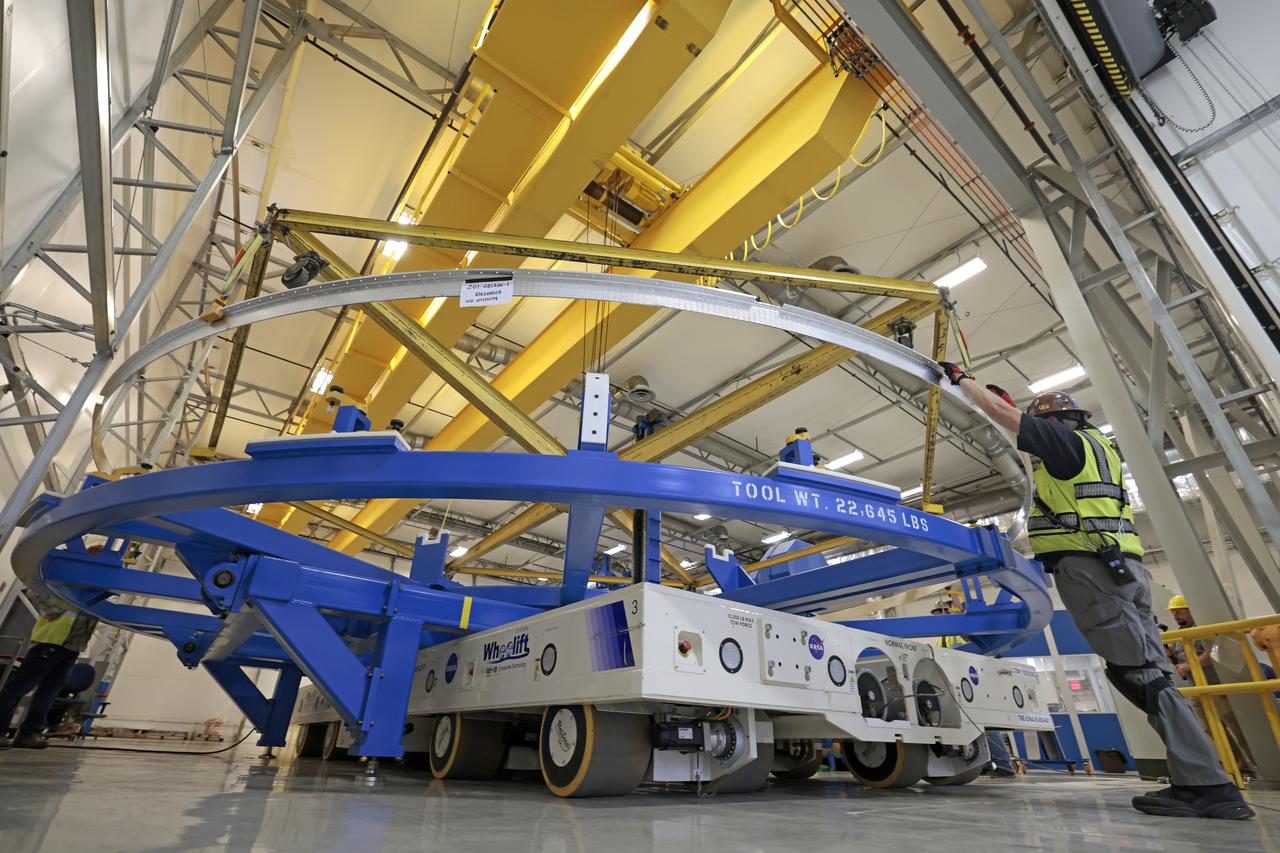

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

A member of the news media asks a question during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
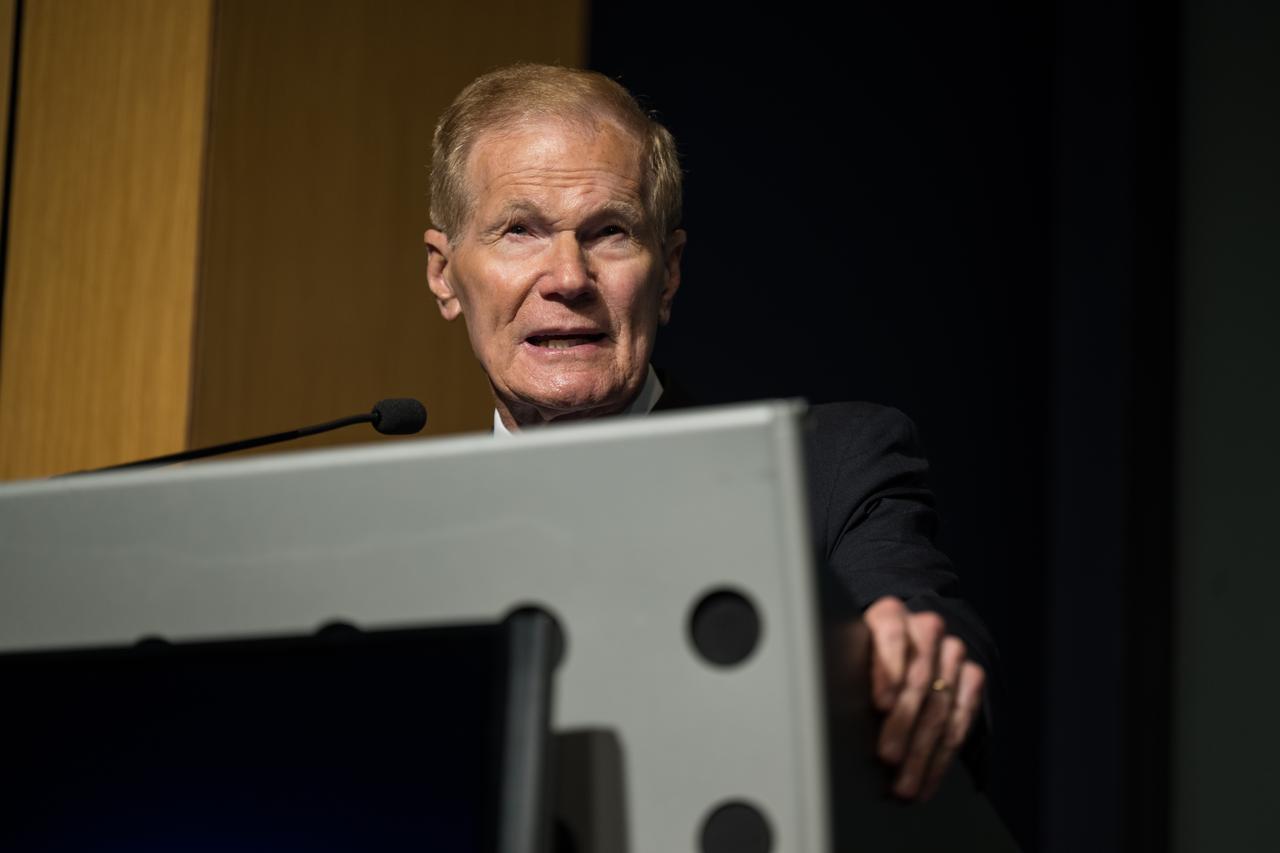

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson announces Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Human Landing System Program Manager Lisa Watson-Morgan gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
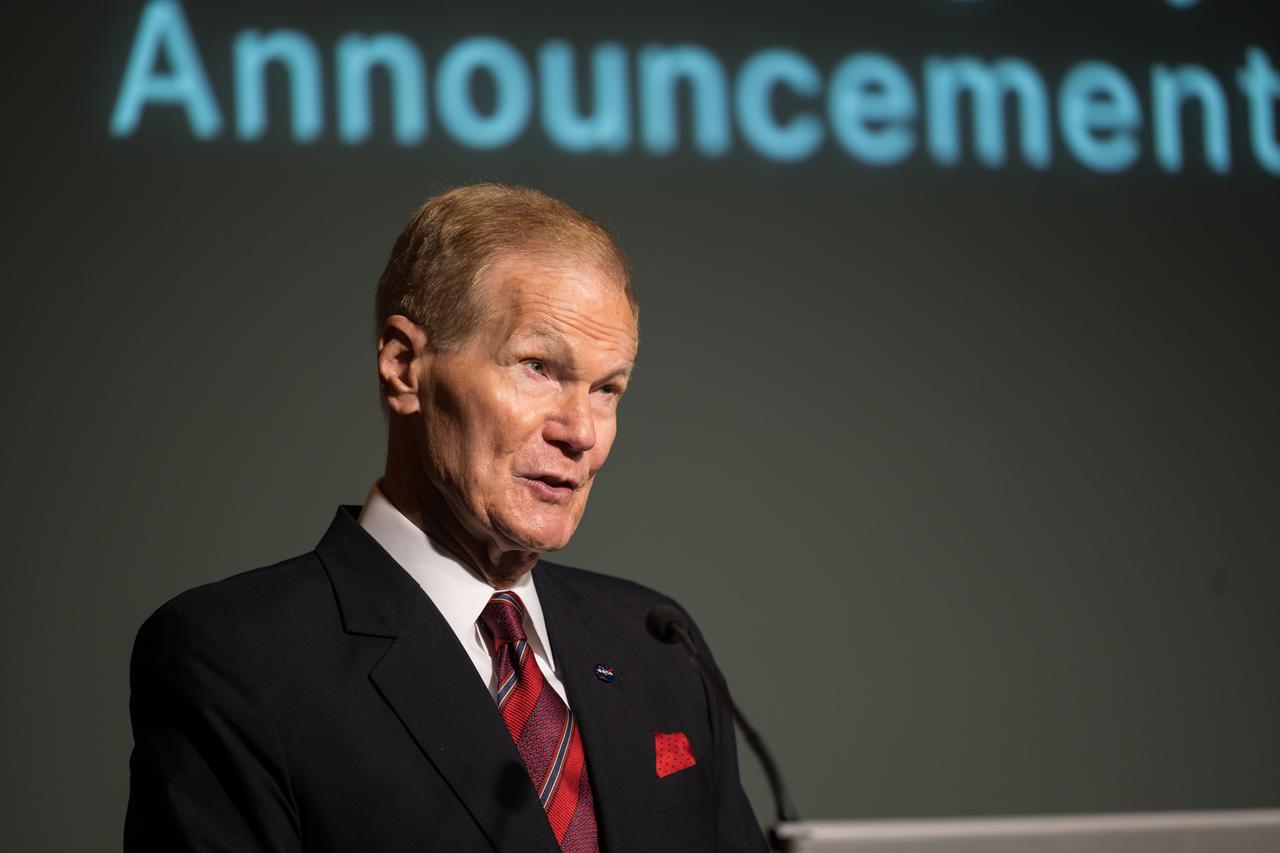

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
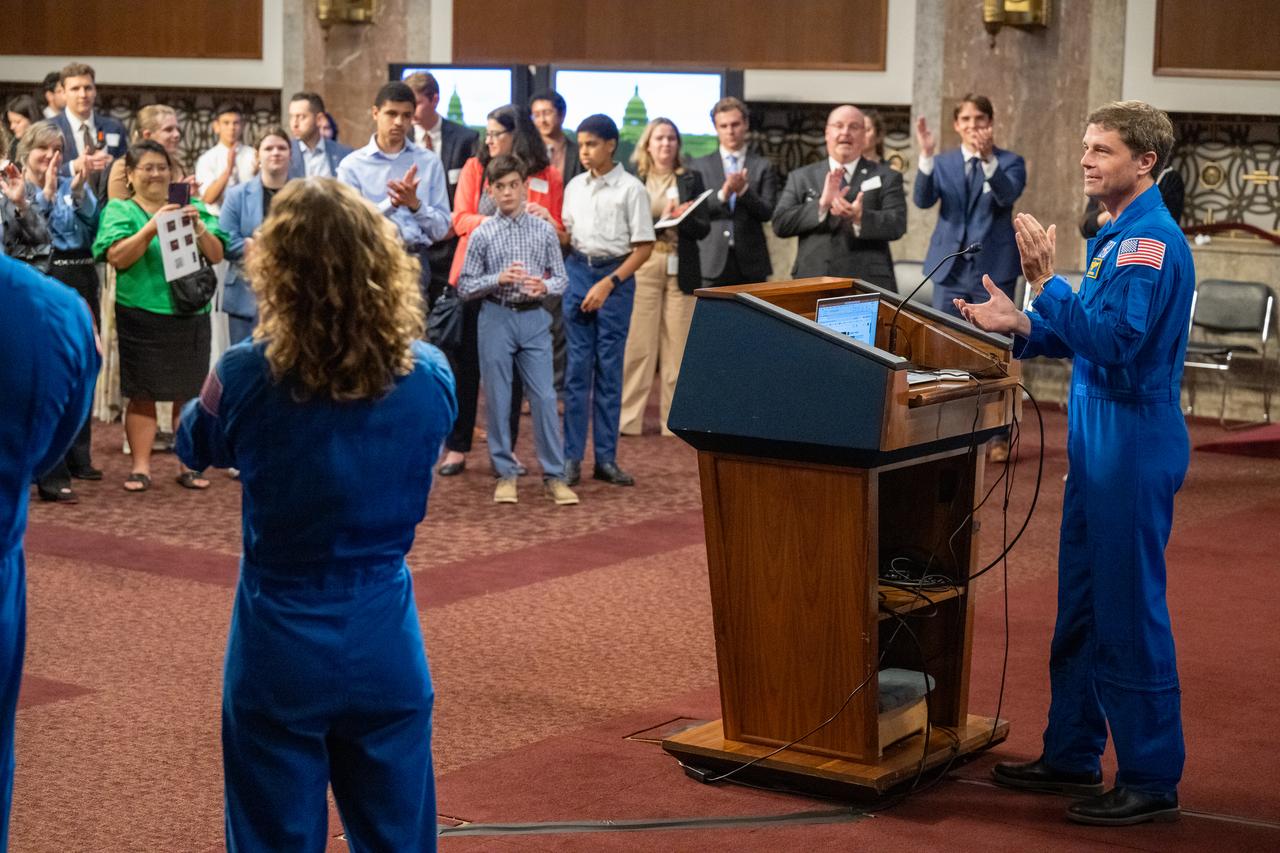

NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman leads a round of applause to recognize the successful launch of United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft aboard earlier that day, during a reception with Artemis II crew members Wednesday, June 5, 2024, at the Dirksen Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson announces Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
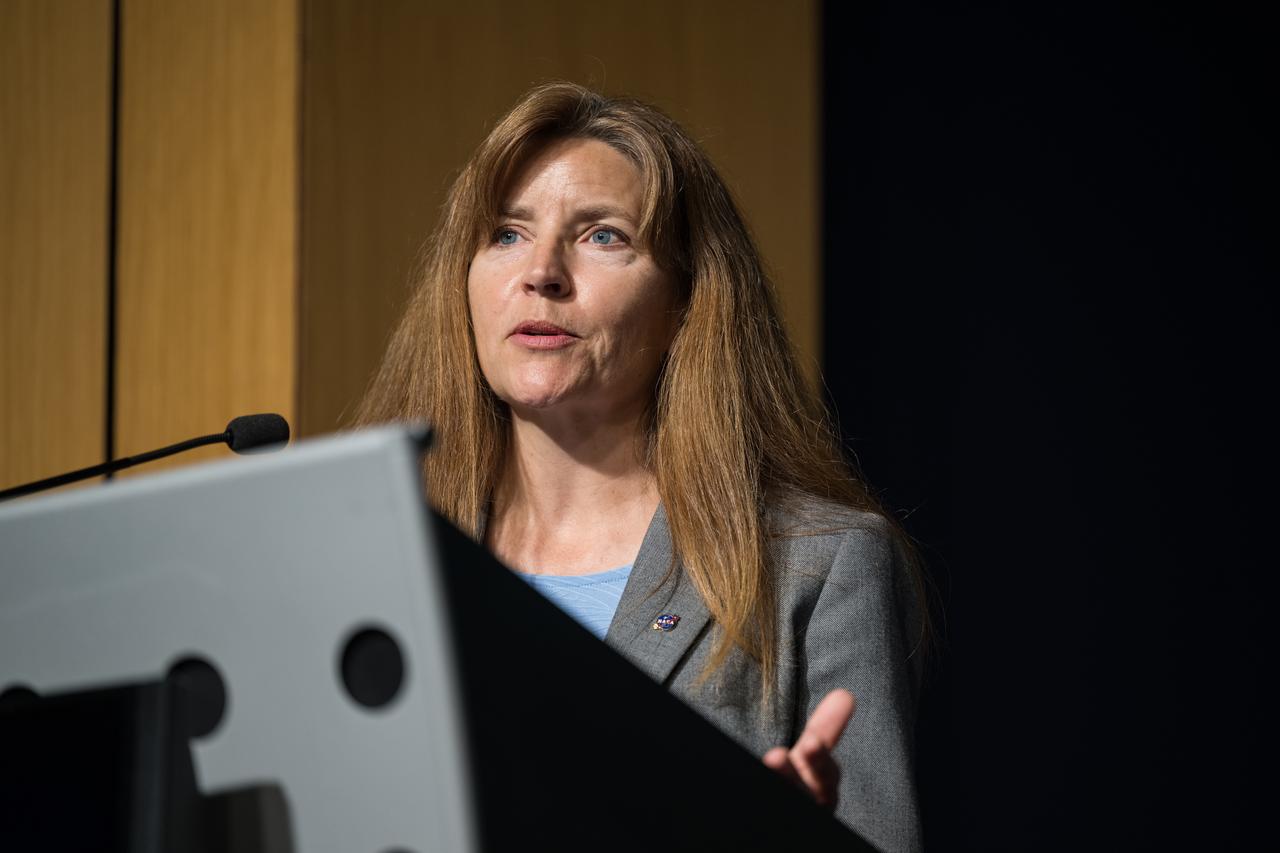

Human Landing System Program Manager Lisa Watson-Morgan gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
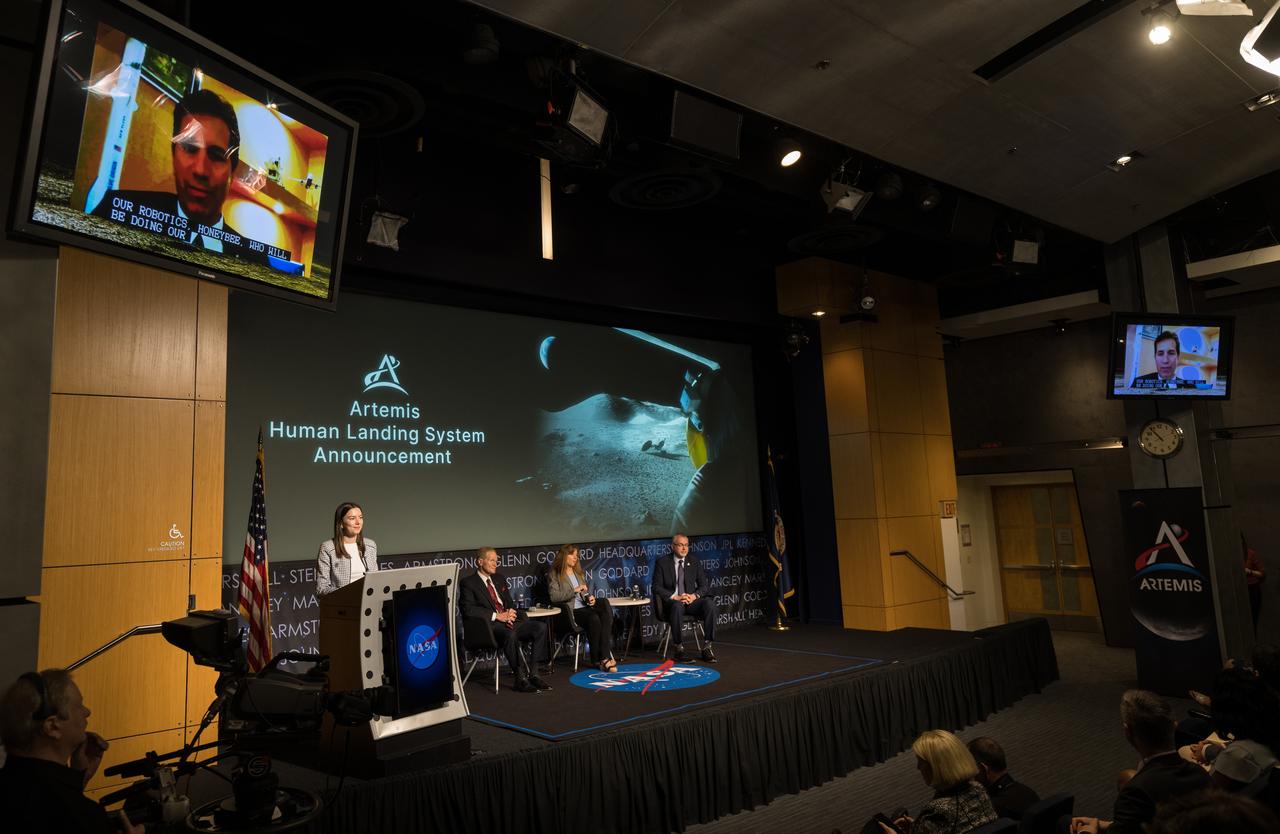

Blue Origin Human Landing System Program Manager, John Couluris, gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
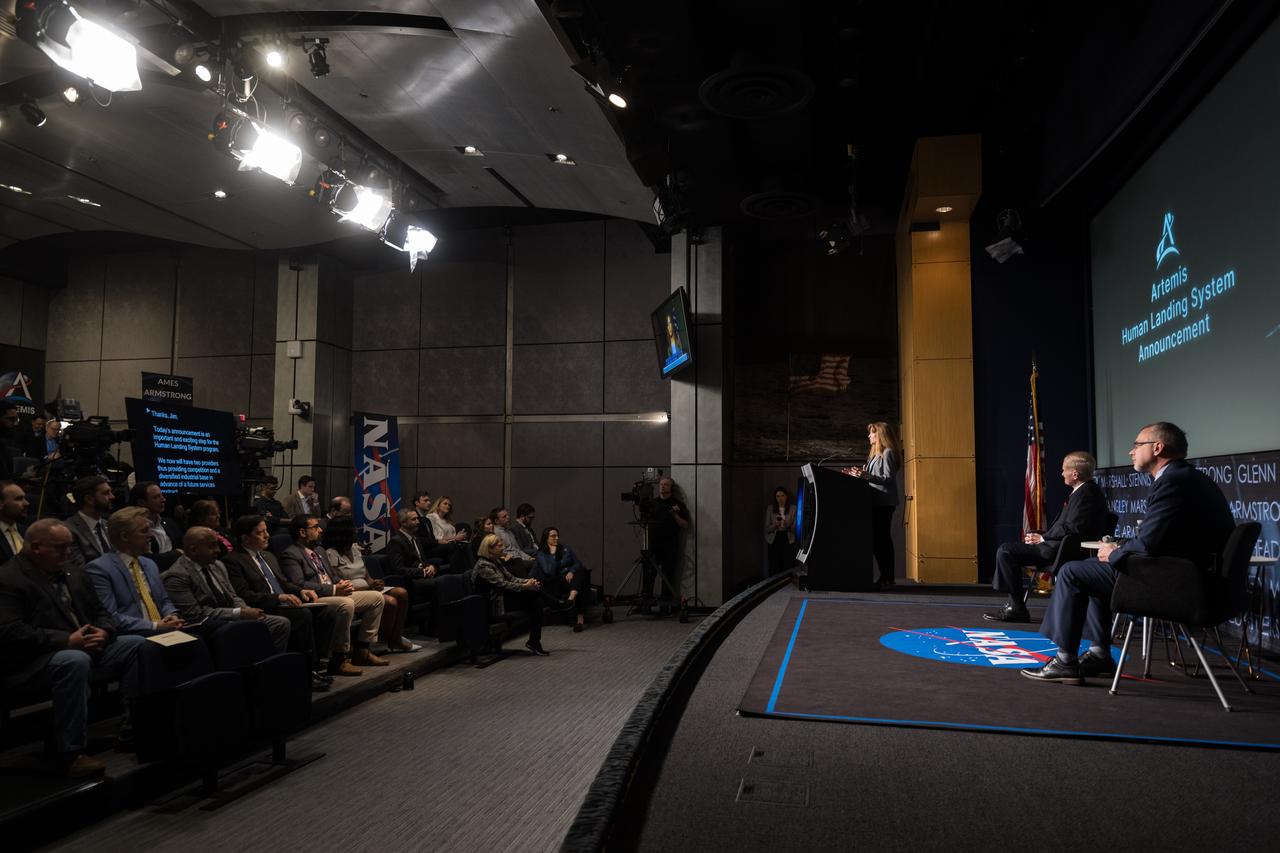

Human Landing System Program Manager Lisa Watson-Morgan gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Press Secretary Jackie McGuinness introduces NASA Administrator Bill Nelson during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson announces Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
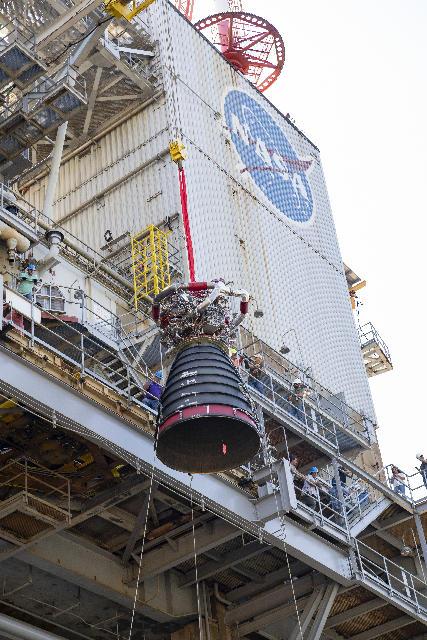

A crane lifts developmental engine E0525 on the west side of the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center on Aug. 30 in preparation for a series of 12 tests that are a key step for lead SLS (Space Launch System) engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to produce engines that will help power the SLS rocket, beginning with Artemis V.

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
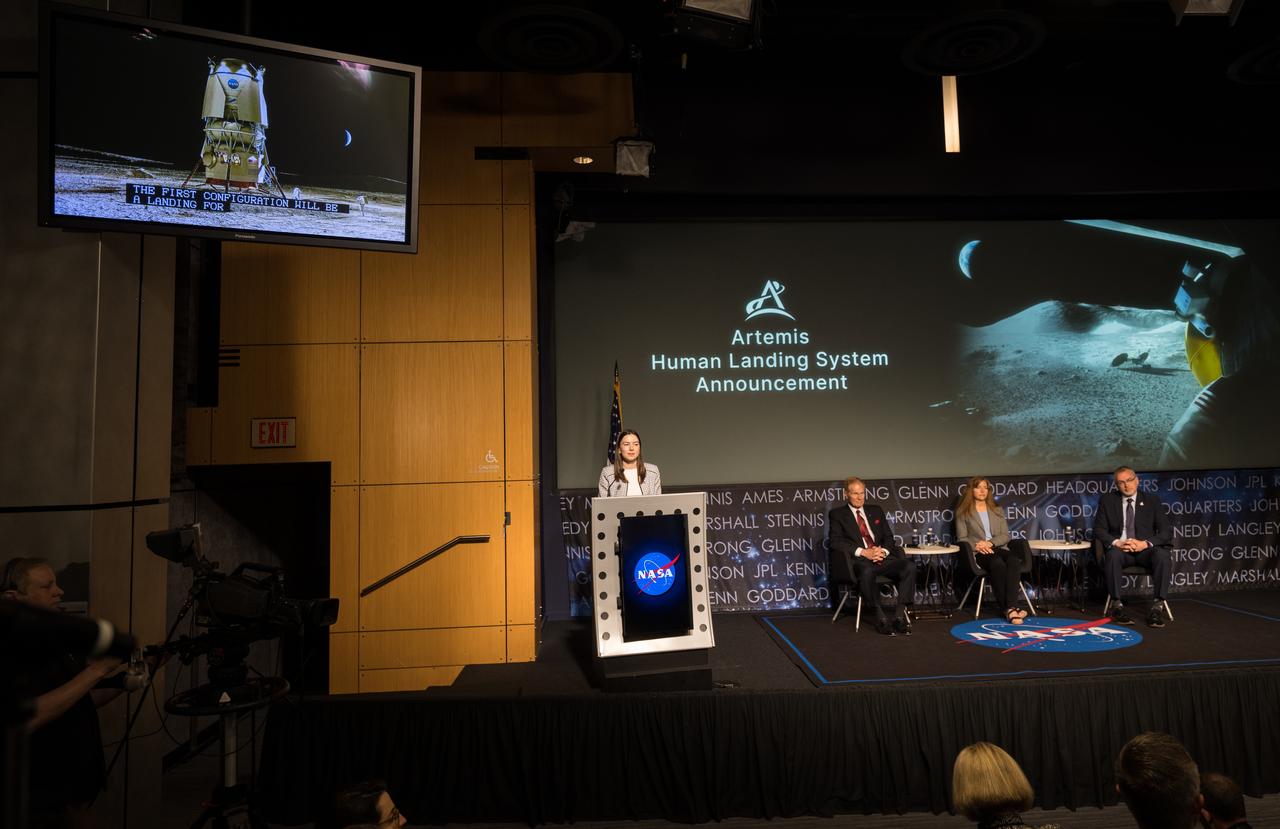

A view of the human landing system is seen on the monitor during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
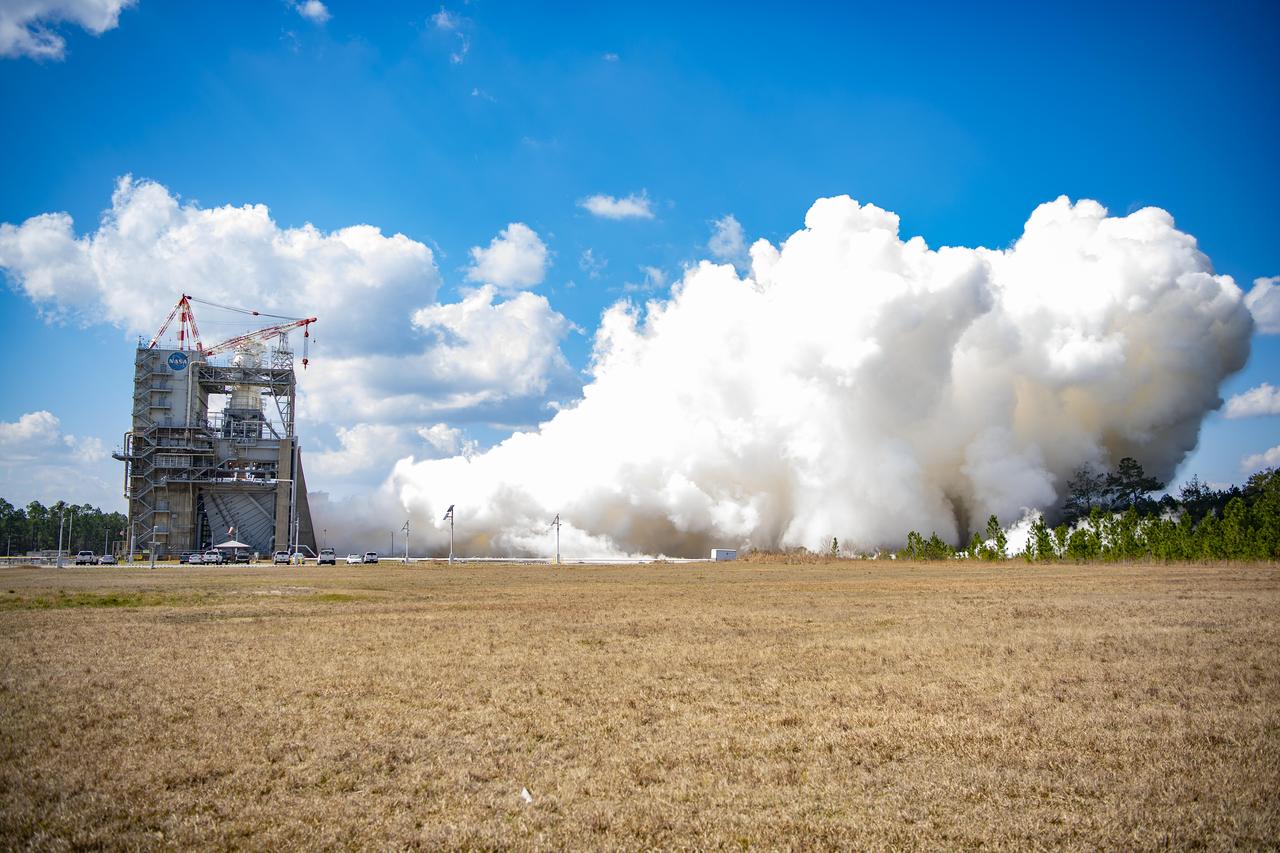

NASA conducts a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 23 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. During the seventh test of the 12-test series, operators fired the certification engine for 550 seconds and up to a 113% power level. The hot fire followed installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. The test series is the second, and final, series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. New engines will help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. NASA and Aerojet Rocketdyne modified 16 former space shuttle engines for use on Artemis missions I through IV. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.

NASA conducts a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 23 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. During the seventh test of the 12-test series, operators fired the certification engine for 550 seconds and up to a 113% power level. The hot fire followed installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. The test series is the second, and final, series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. New engines will help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. NASA and Aerojet Rocketdyne modified 16 former space shuttle engines for use on Artemis missions I through IV. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.
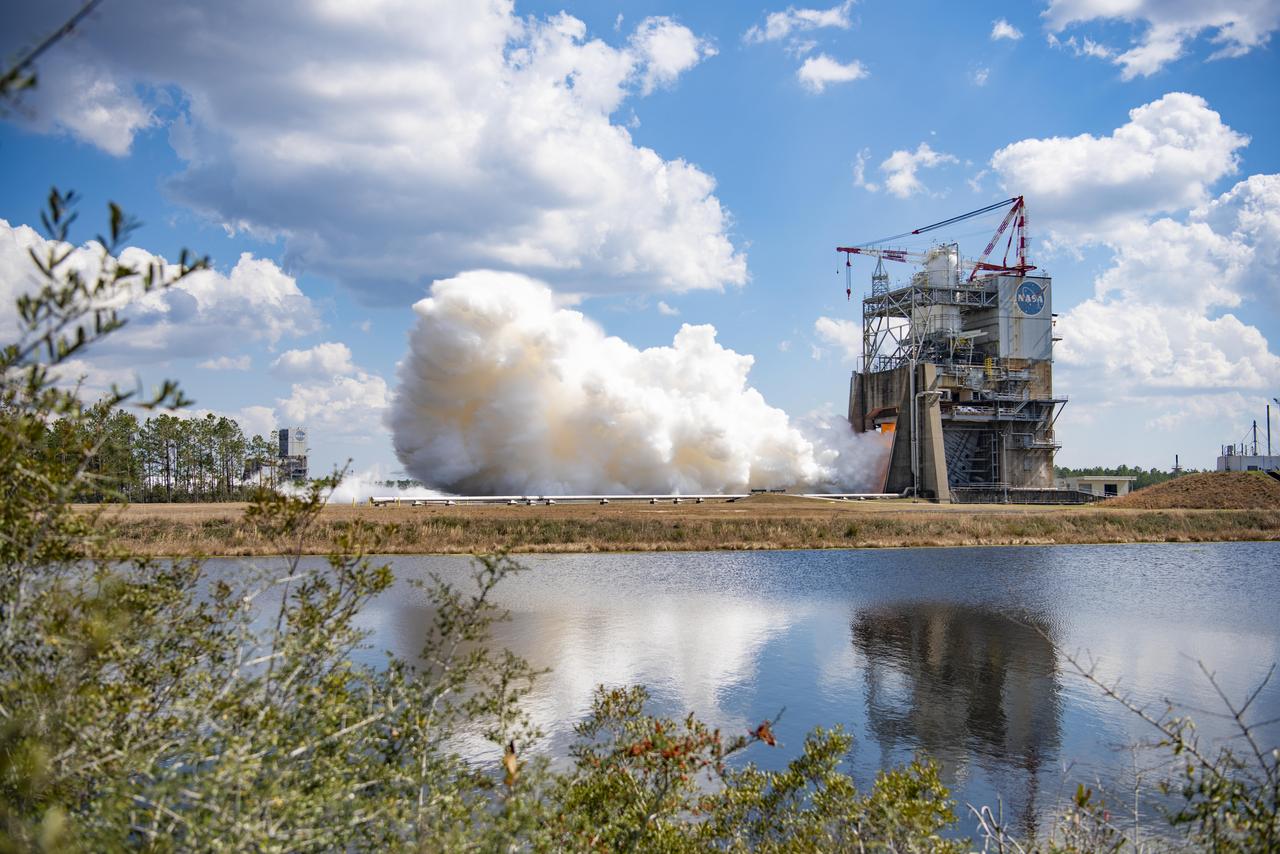

NASA conducts a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 23 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. During the seventh test of the 12-test series, operators fired the certification engine for 550 seconds and up to a 113% power level. The hot fire followed installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. The test series is the second, and final, series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. New engines will help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. NASA and Aerojet Rocketdyne modified 16 former space shuttle engines for use on Artemis missions I through IV. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.
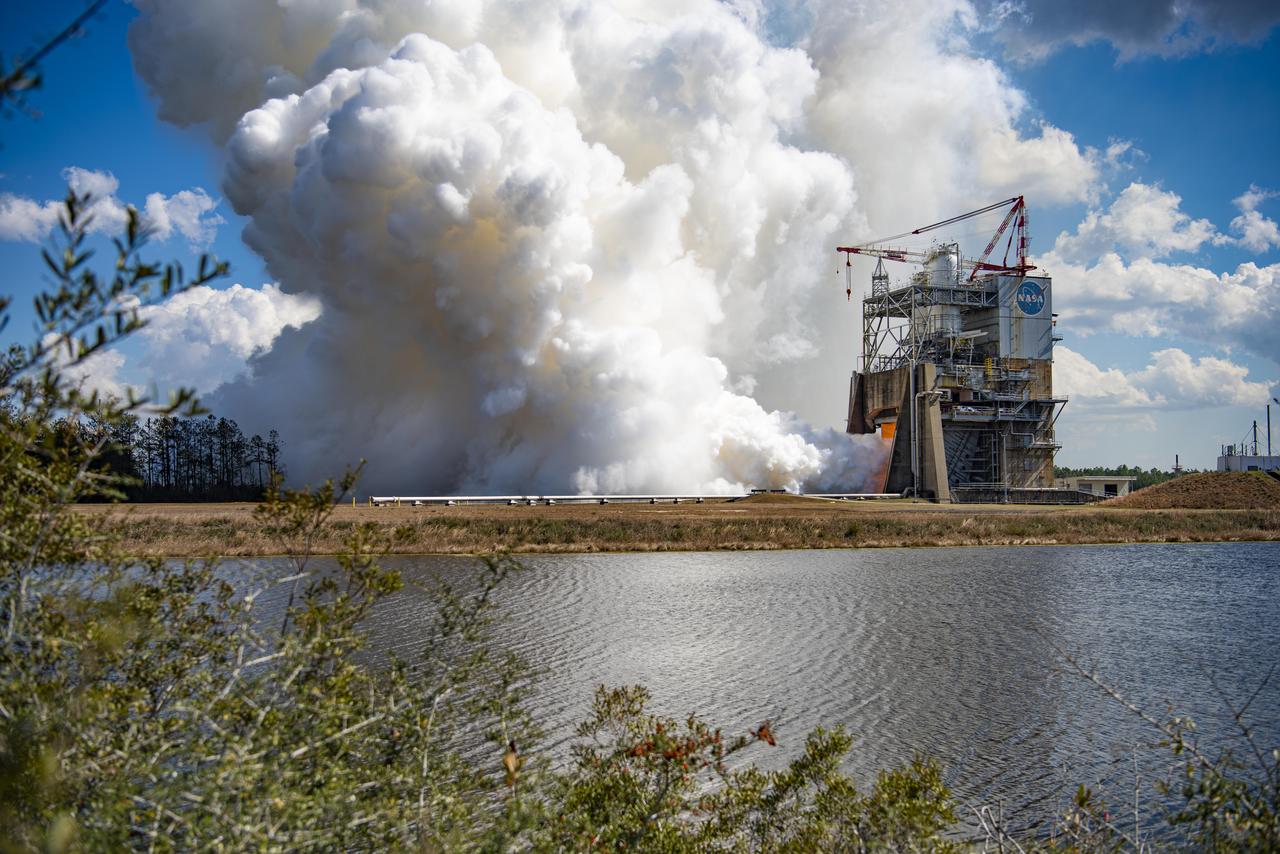

NASA conducts a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 23 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. During the seventh test of the 12-test series, operators fired the certification engine for 550 seconds and up to a 113% power level. The hot fire followed installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. The test series is the second, and final, series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. New engines will help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. NASA and Aerojet Rocketdyne modified 16 former space shuttle engines for use on Artemis missions I through IV. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.
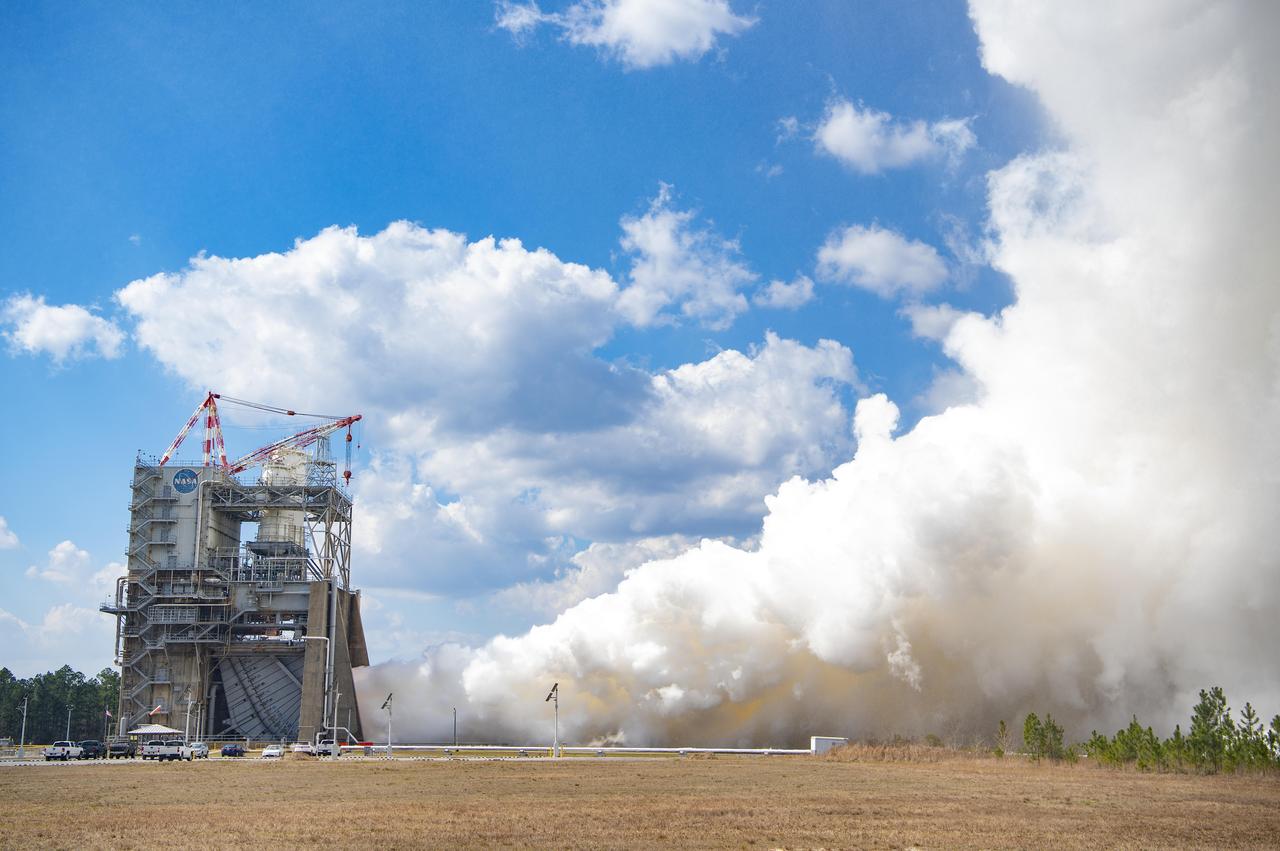

NASA conducts a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 23 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. During the seventh test of the 12-test series, operators fired the certification engine for 550 seconds and up to a 113% power level. The hot fire followed installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. The test series is the second, and final, series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. New engines will help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. NASA and Aerojet Rocketdyne modified 16 former space shuttle engines for use on Artemis missions I through IV. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.
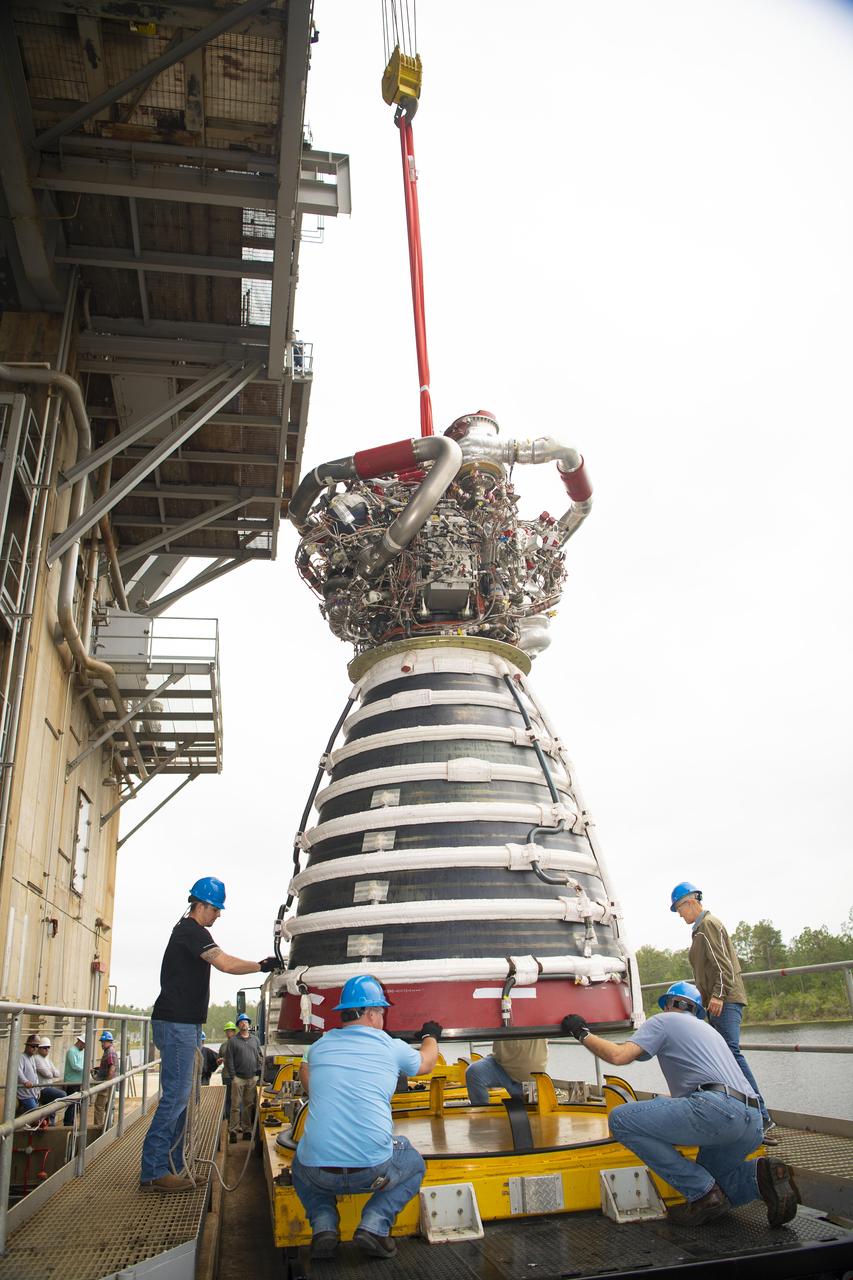

A work crew at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi removes RS-25 developmental engine E0525 from the Fred Haise Test Stand on April 9. Removal of the engine follows completion of the second and final 12-test series for lead engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to certify and build new RS-25 engines for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rockets that will power future lunar missions, beginning with Artemis V. Through Artemis, NASA will establish the foundation for long-term scientific exploration at the Moon; land the first woman, first person of color, and first international partner astronaut on the lunar surface; and prepare for human expeditions to Mars for the benefit of all.
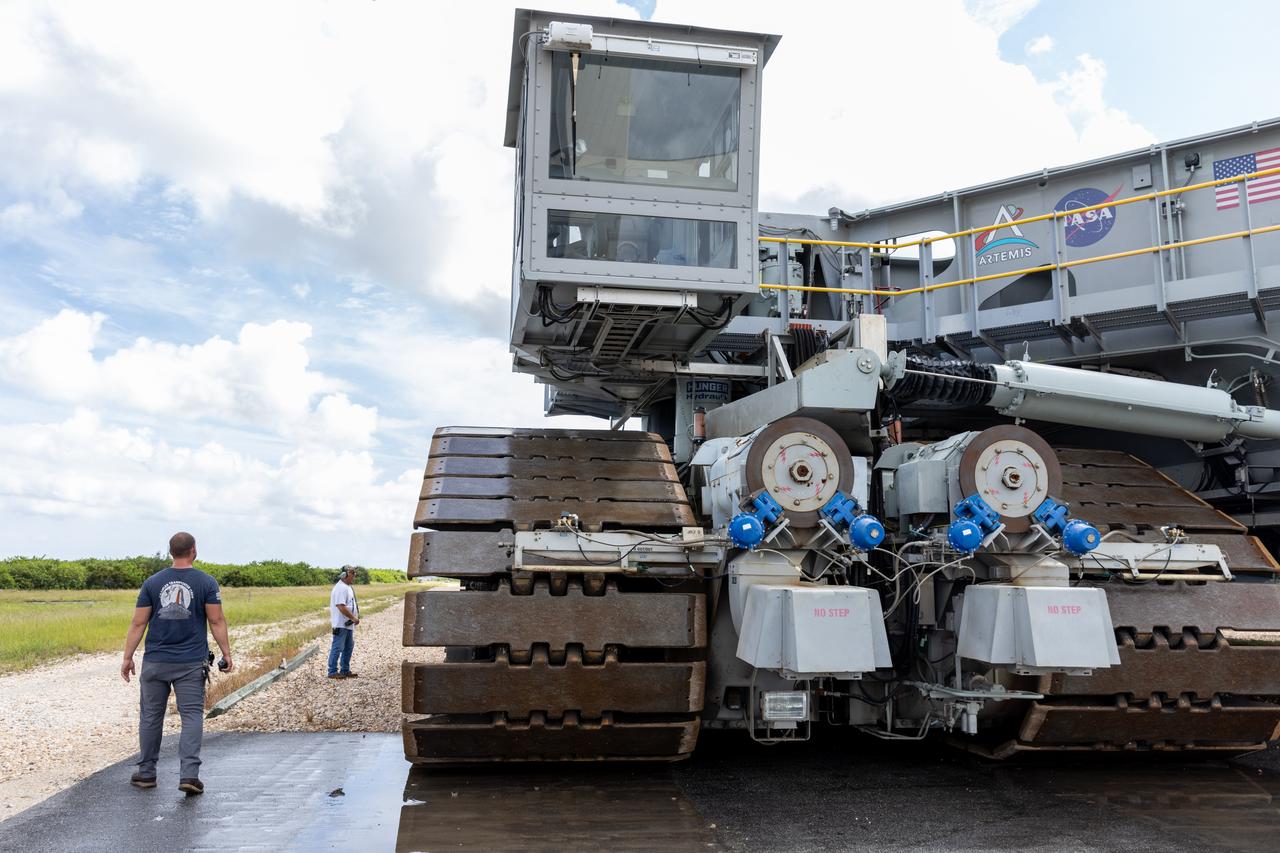

NASA’s crawler-transporter 2 moves slowly along the crawlerway towards Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, after reaching the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida celebrate on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, the agency’s crawler-transporter 2 reaching the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher from Launch Pad 39B back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.

NASA’s crawler-transporter 2 moves slowly along the crawlerway towards Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, after reaching the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.

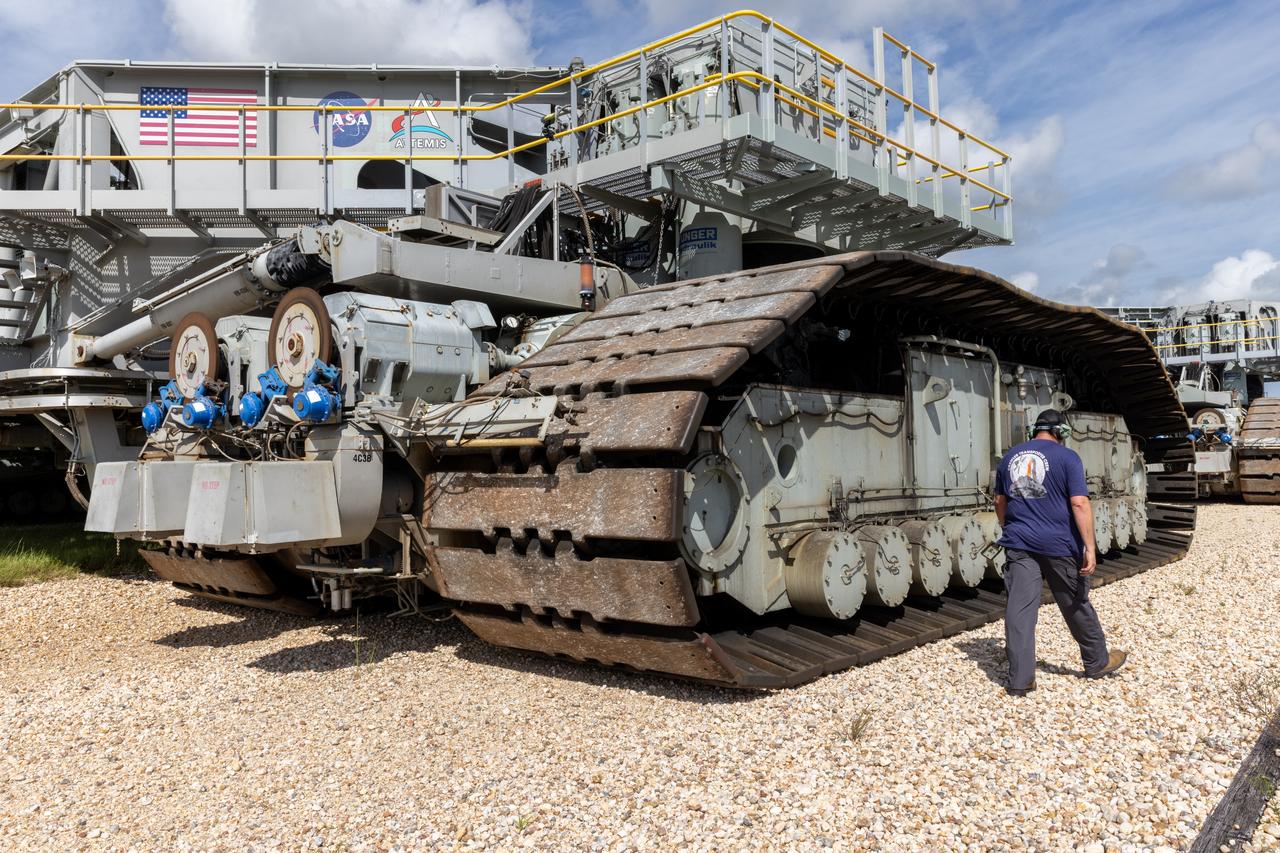
John Giles, crawler element operations manager for NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems, holds a plaque near the odometer of the agency’s crawler-transporter 2, on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, commemorating the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher from Launch Pad 39B back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.
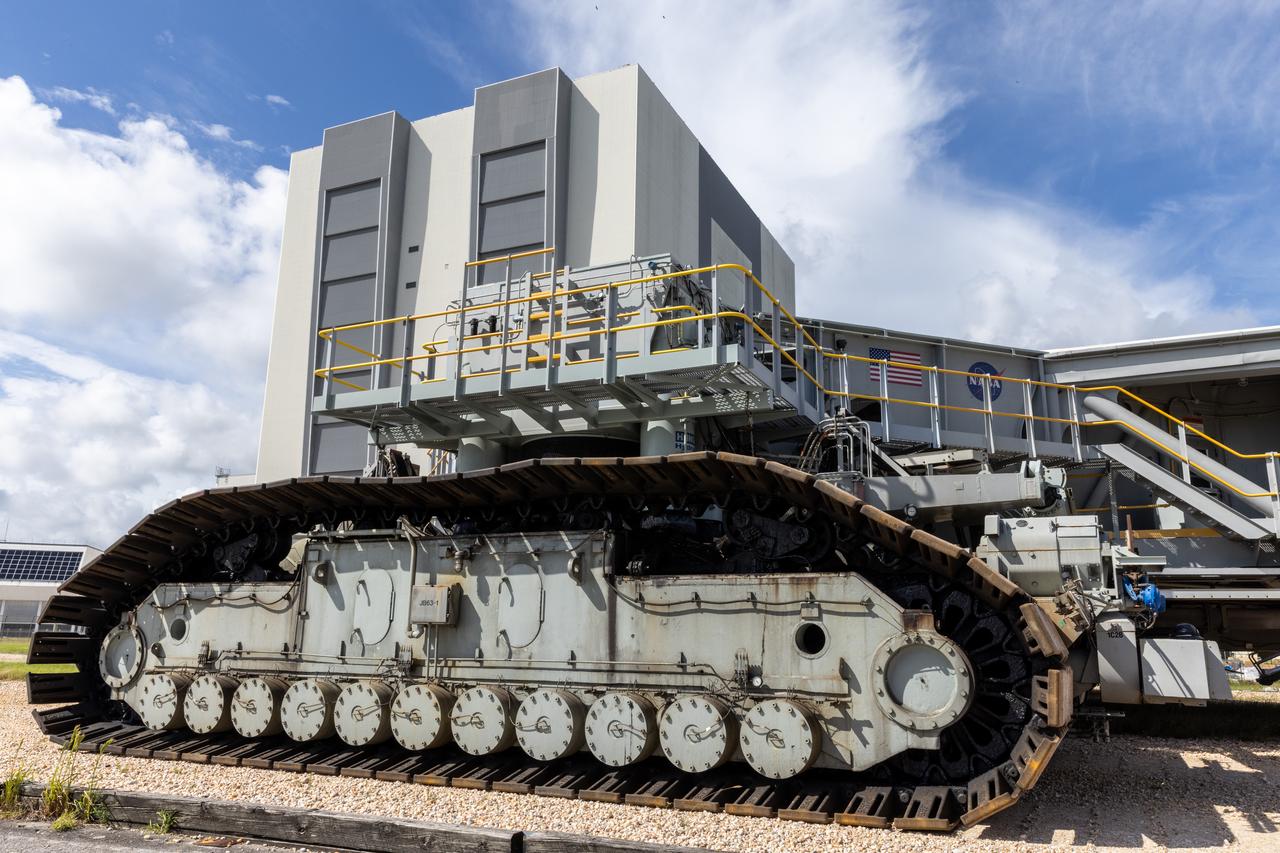

NASA’s crawler-transporter 2 moves slowly along the crawlerway towards Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, after reaching the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.
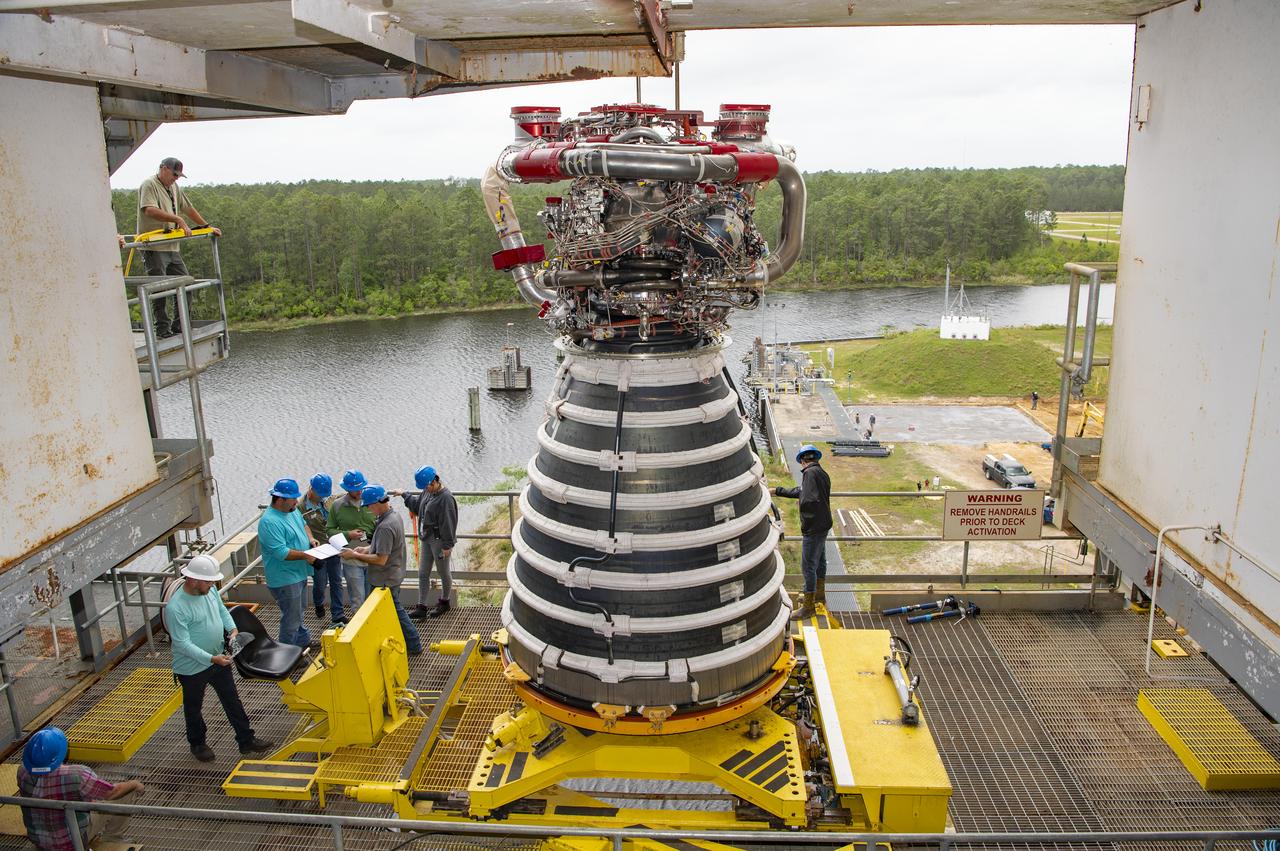

A work crew at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi removes RS-25 developmental engine E0525 from the Fred Haise Test Stand on April 9. Removal of the engine follows completion of the second and final 12-test series for lead engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to certify and build new RS-25 engines for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rockets that will power future lunar missions, beginning with Artemis V. Through Artemis, NASA will establish the foundation for long-term scientific exploration at the Moon; land the first woman, first person of color, and first international partner astronaut on the lunar surface; and prepare for human expeditions to Mars for the benefit of all.