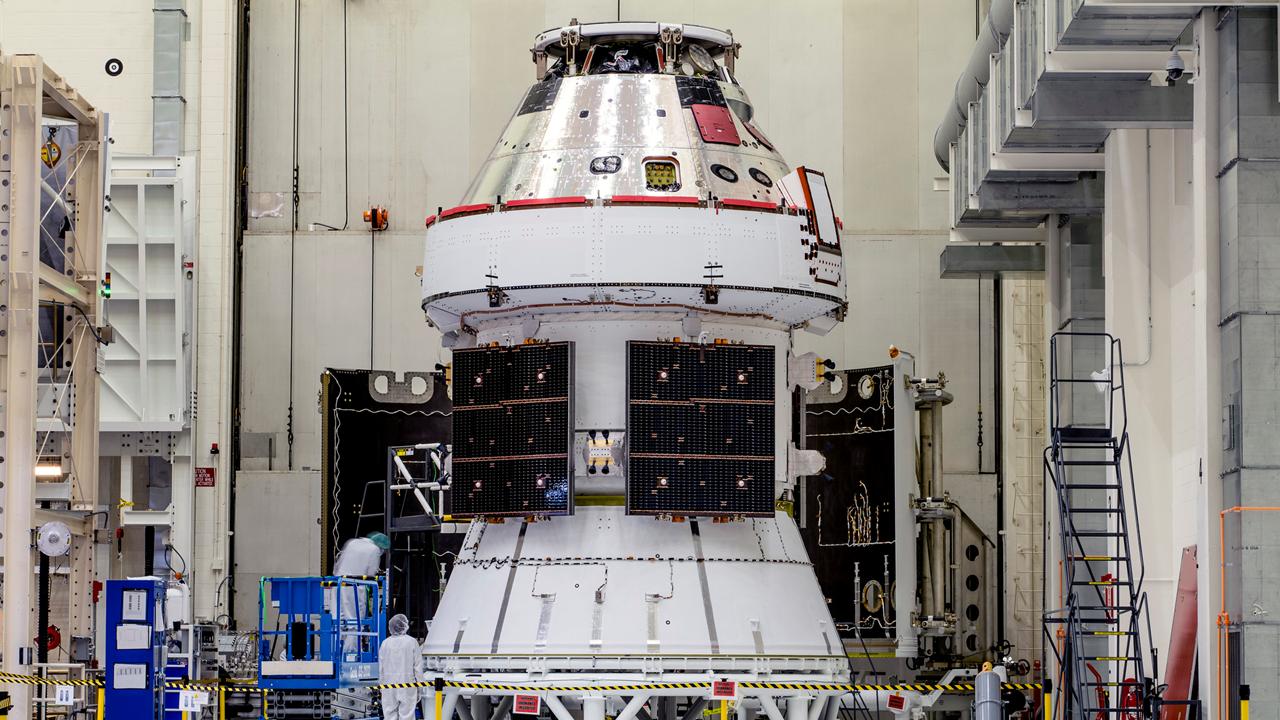
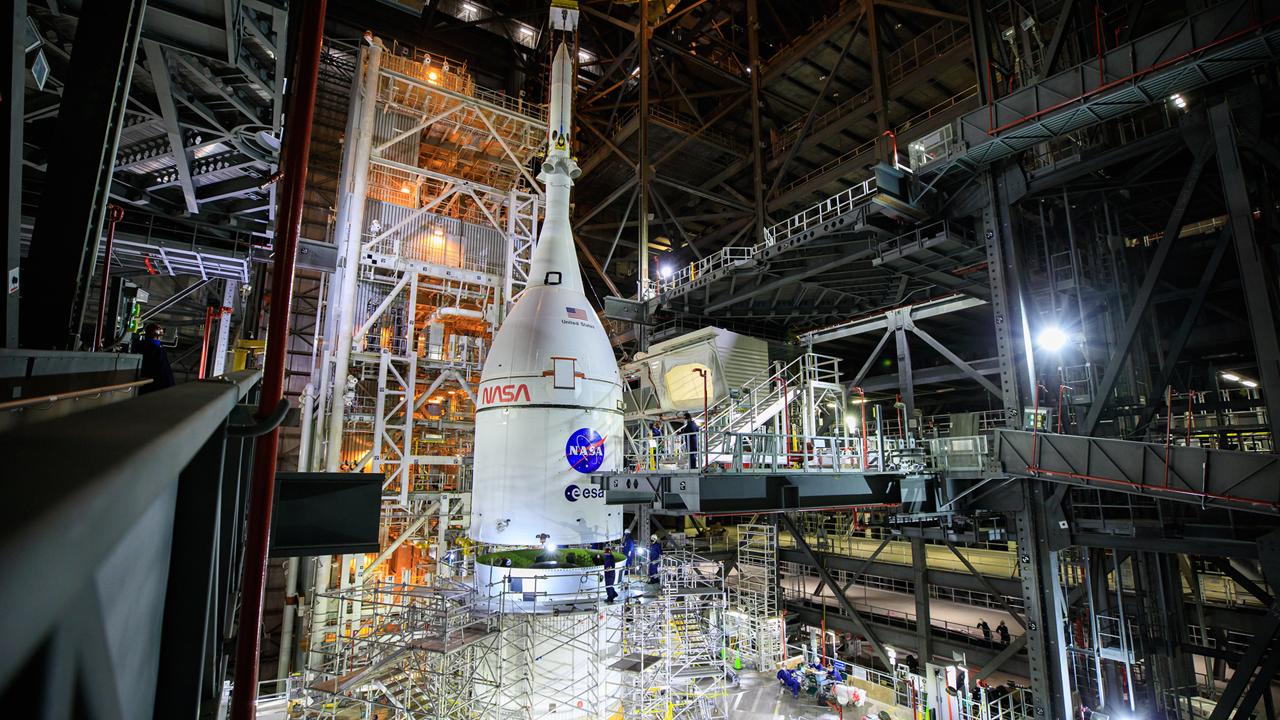
Teams with Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida make upgrades and repairs on mobile launcher 1 at its park site location on July 20, 2023, ahead of the first critical ground testing for Artemis II. Under Artemis, the mobile launcher will transport NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft to Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B for liftoff. Artemis II will be the first Artemis mission flying crew aboard Orion.
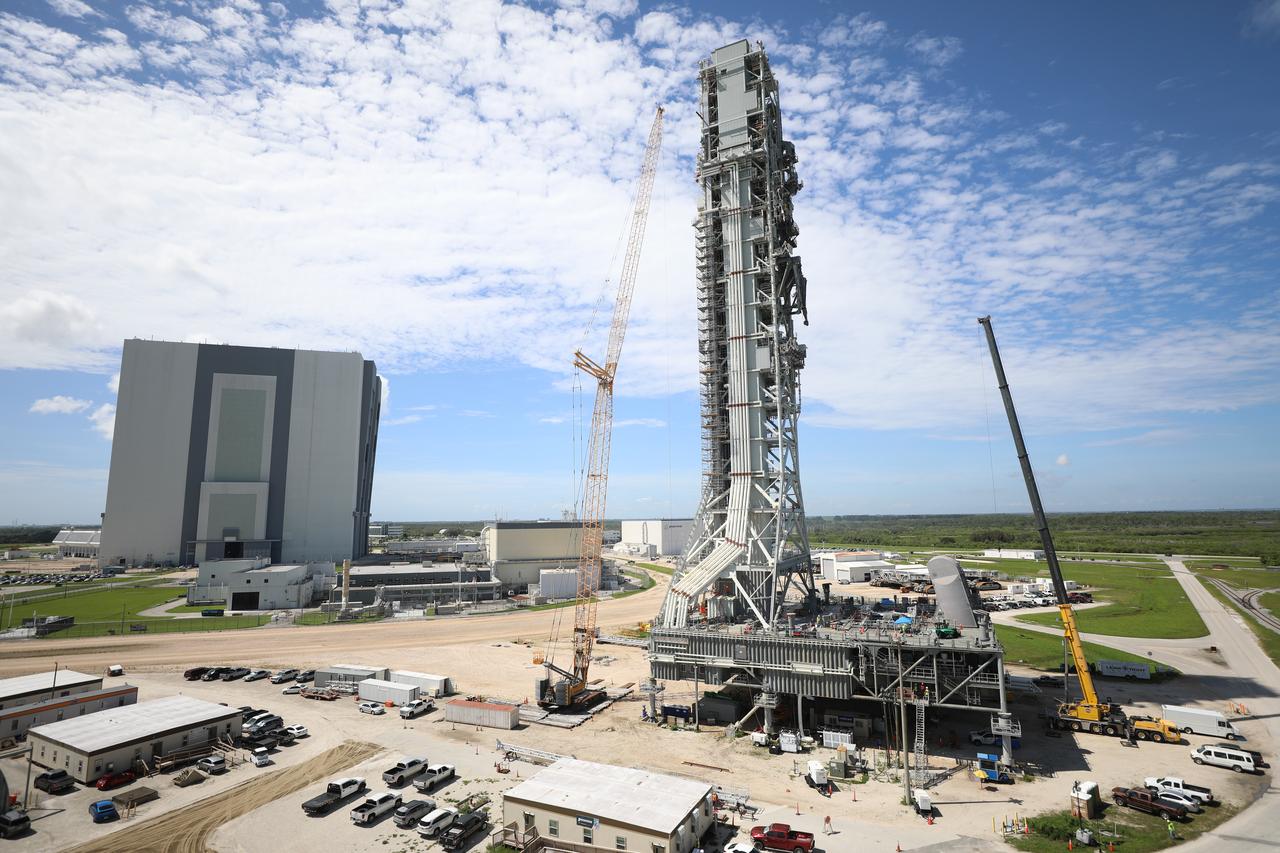

With the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida nearby, teams with Exploration Ground Systems make upgrades and repairs on mobile launcher 1 at its park site location on July 20, 2023, ahead of the first critical ground testing for Artemis II. Under Artemis, the mobile launcher will transport NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft to Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B for liftoff. Artemis II will be the first Artemis mission flying crew aboard Orion.
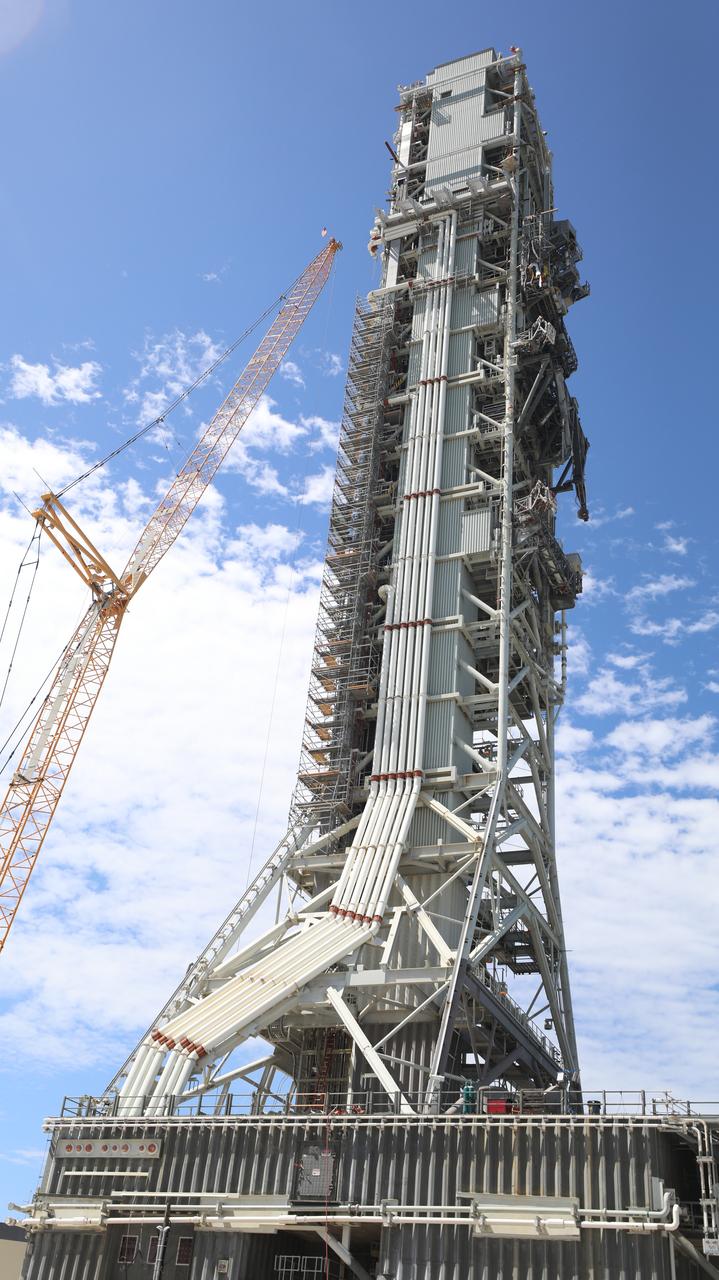

Teams with Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida make upgrades and repairs on mobile launcher 1 at its park site location on July 20, 2023, ahead of the first critical ground testing for Artemis II. Under Artemis, the mobile launcher will transport NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft to Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B for liftoff. Artemis II will be the first Artemis mission flying crew aboard Orion.
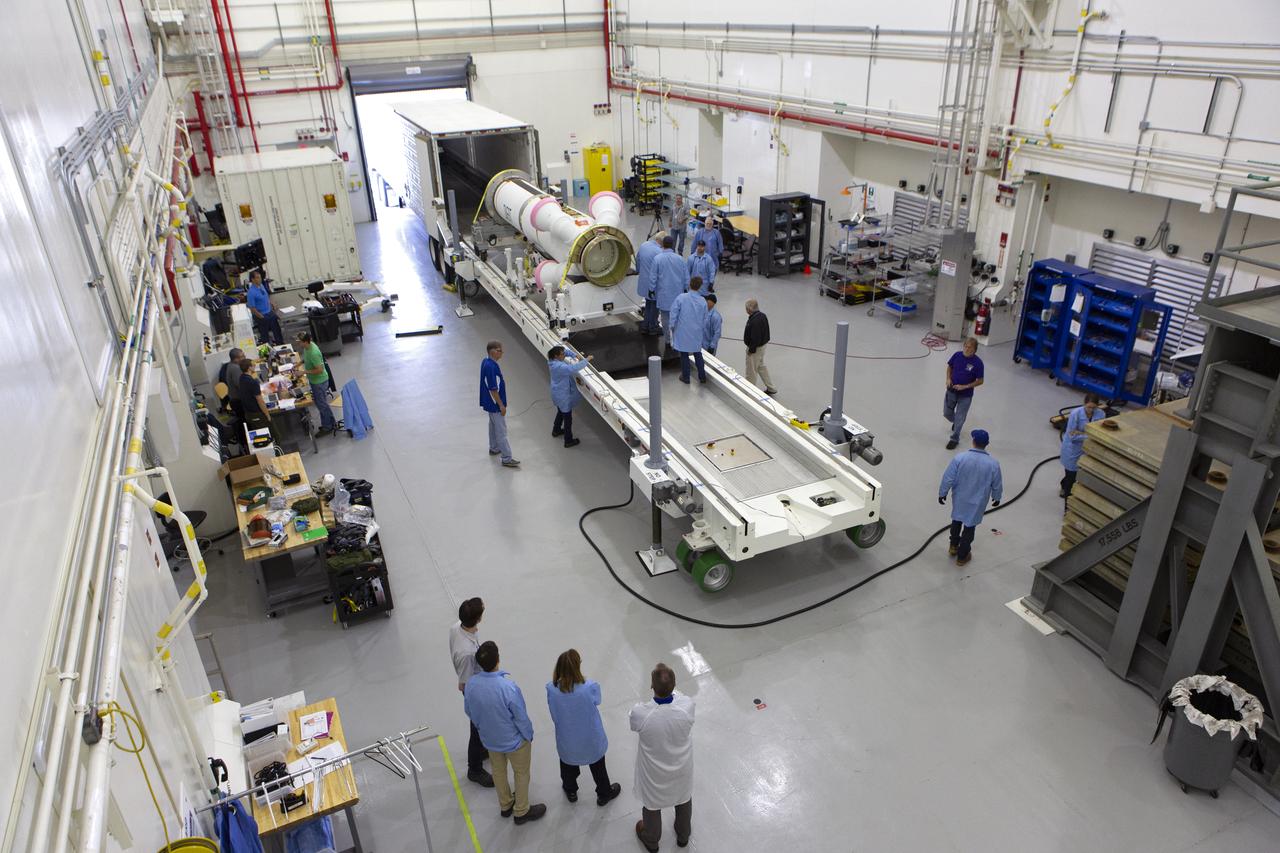

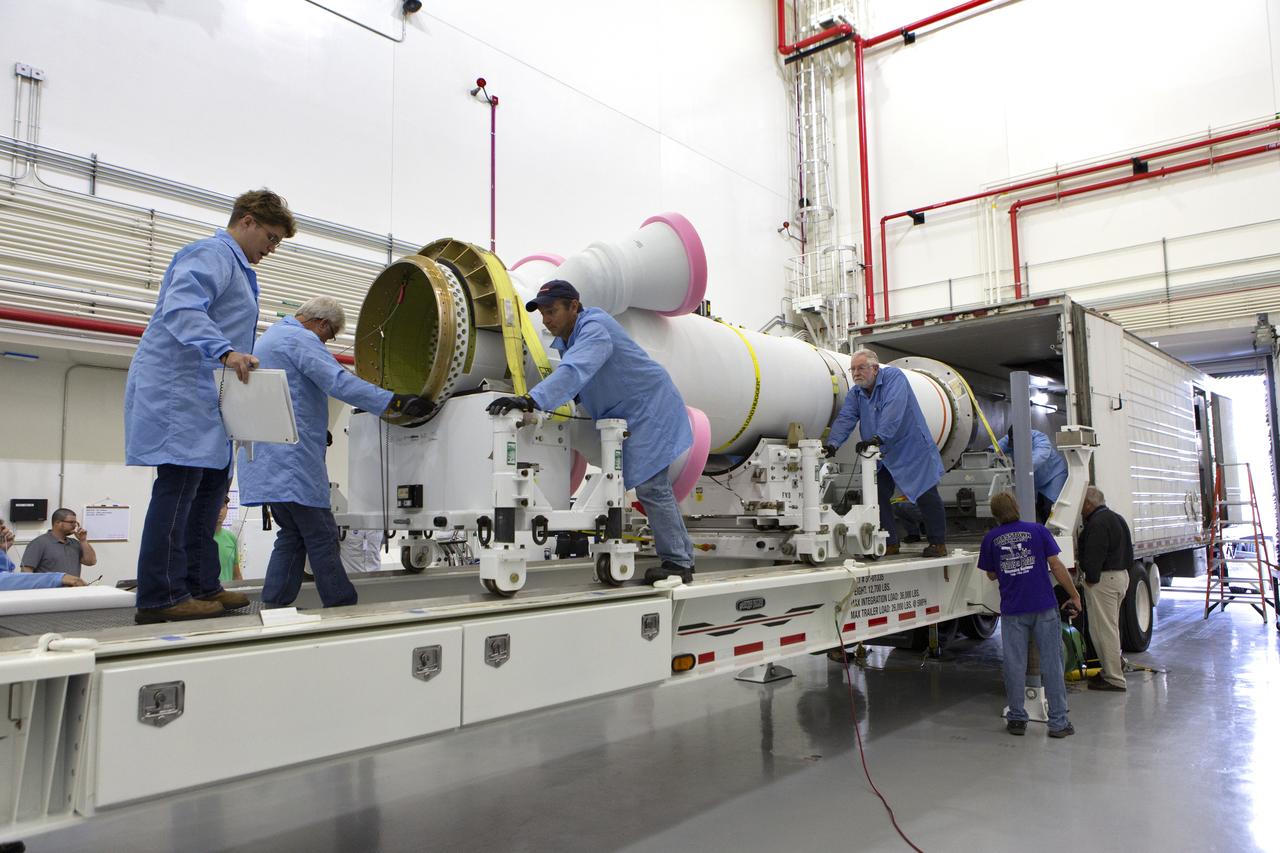
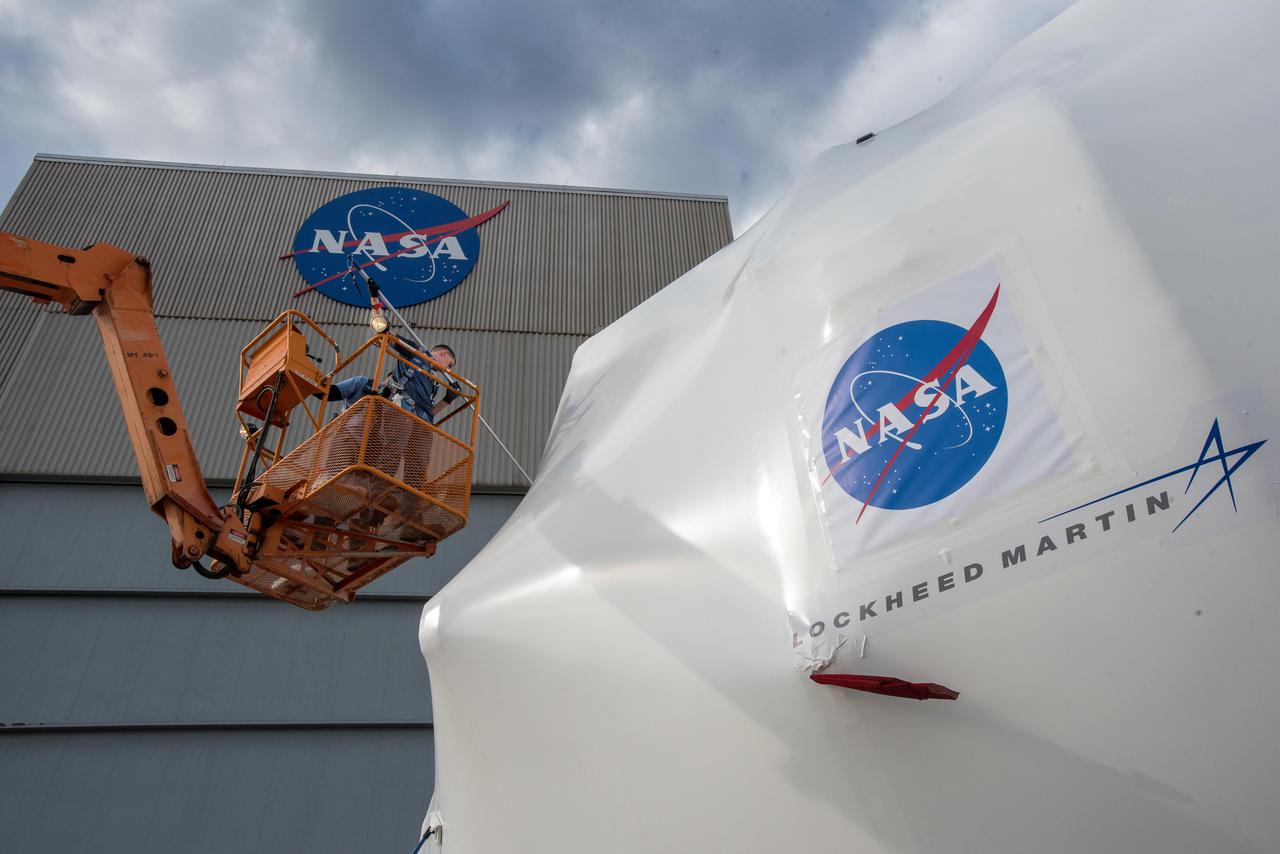
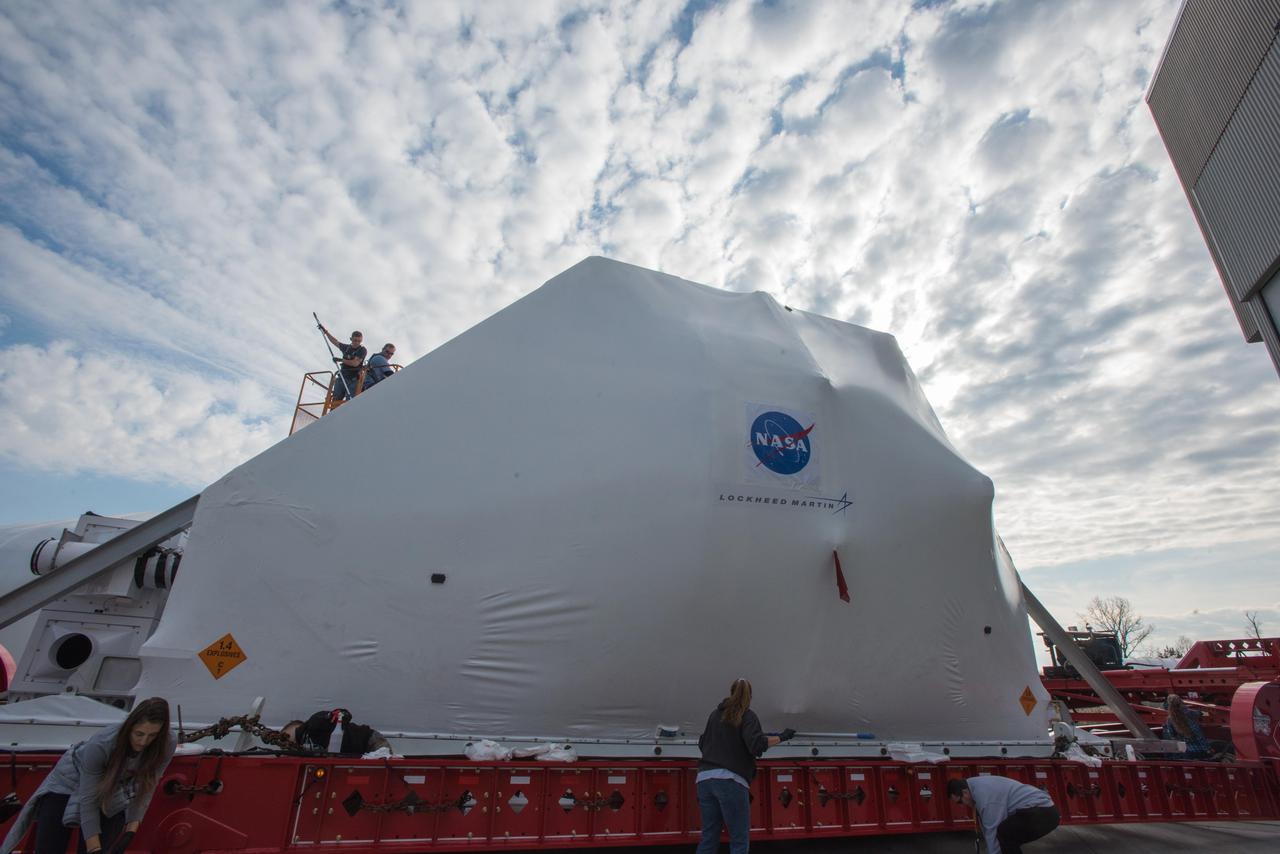
Workers have offloaded the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
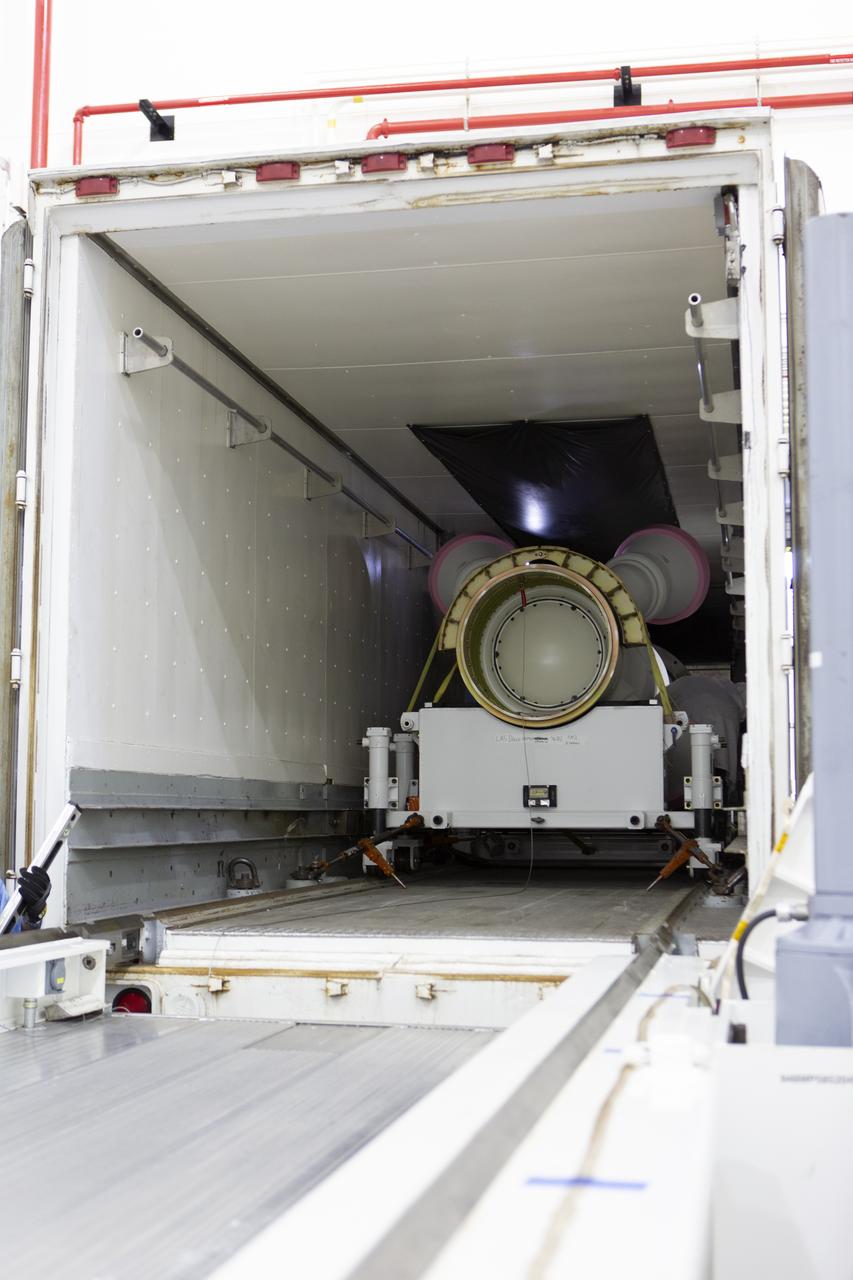

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, is offloaded from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
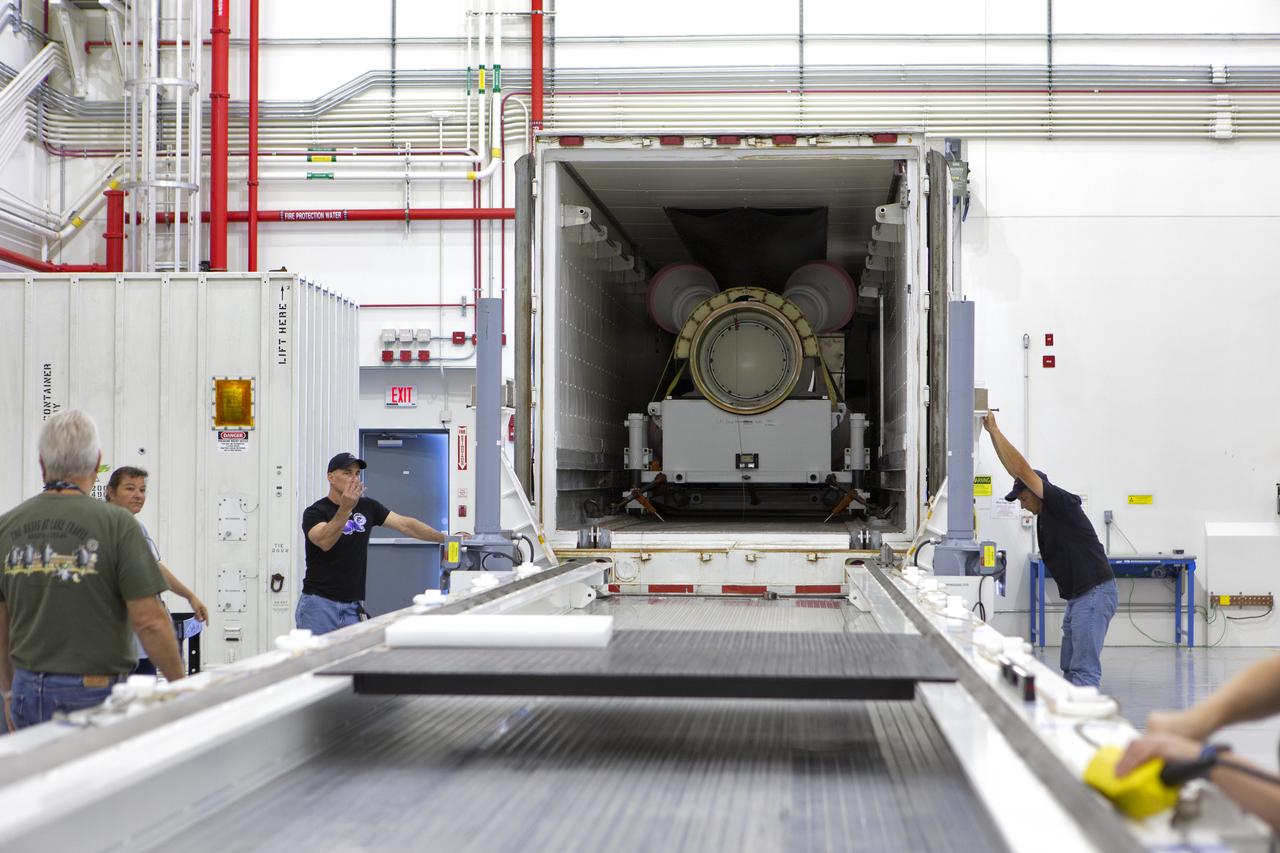

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, is offloaded from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
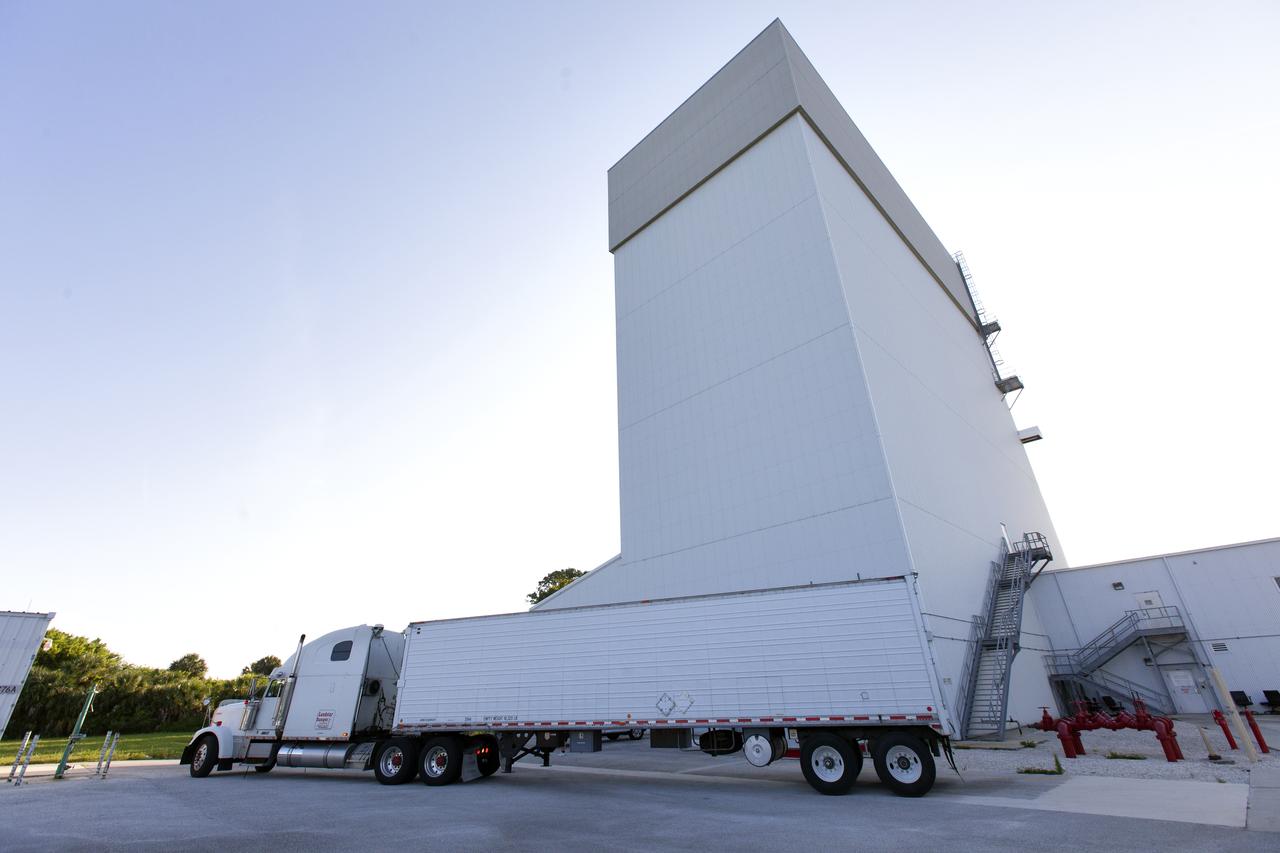

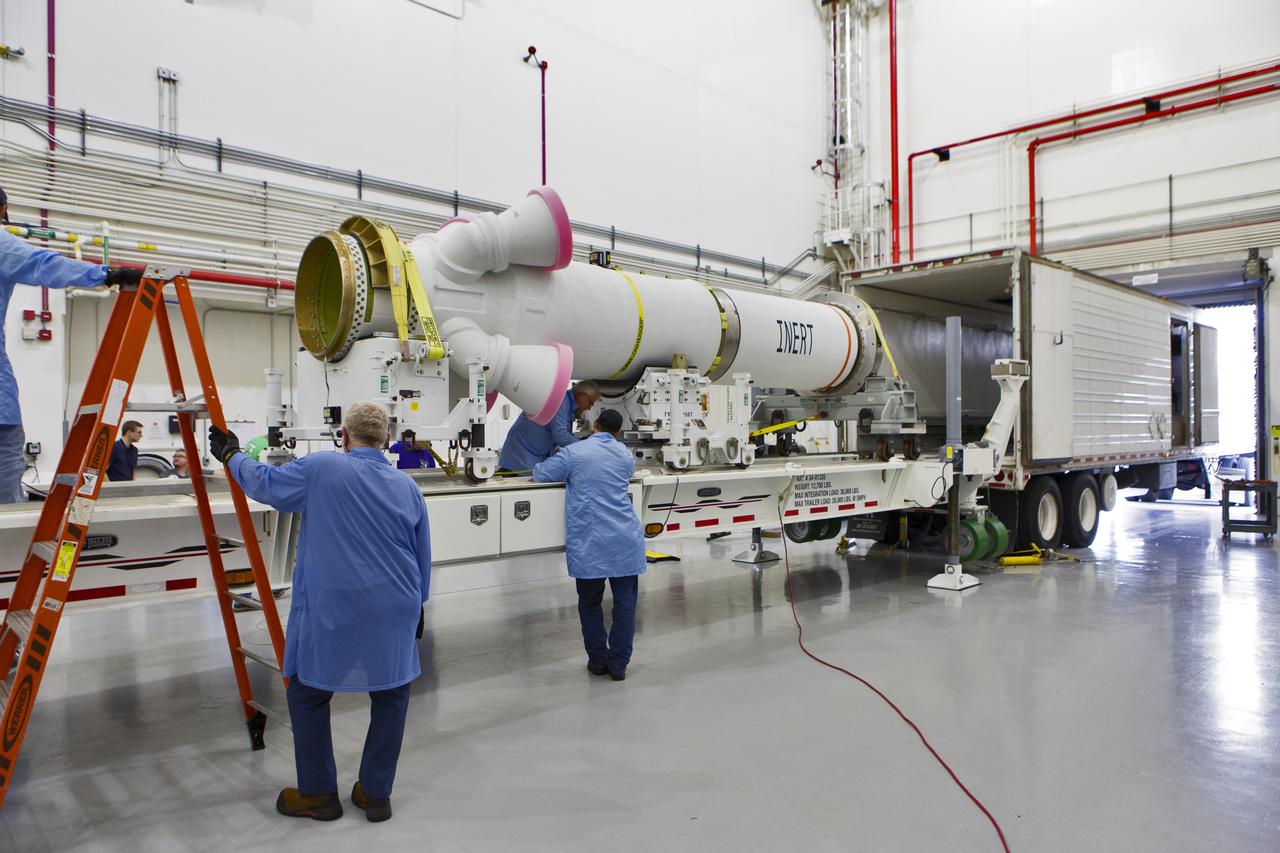
The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, secured in a heavy transport truck, arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be offloaded and moved into the LASF where it will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
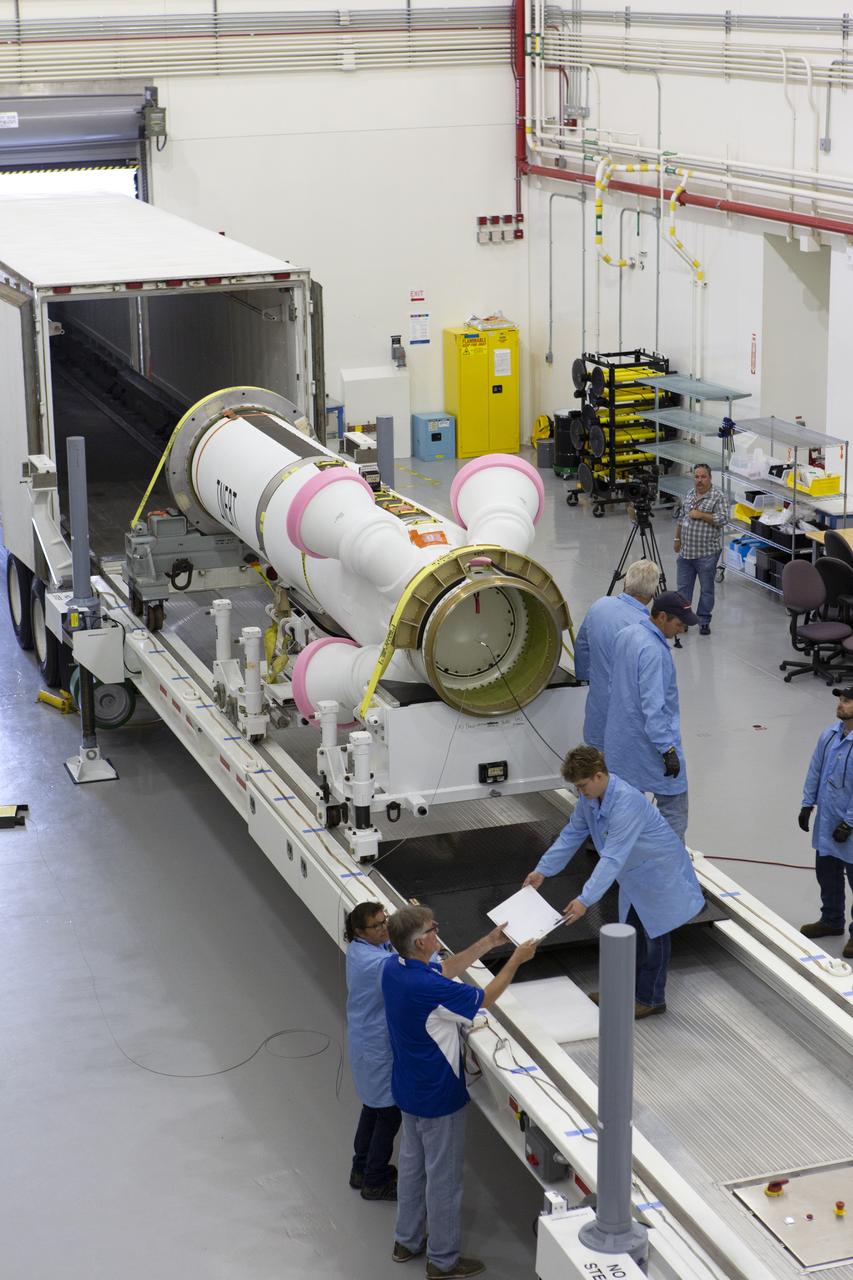

Workers have offloaded the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
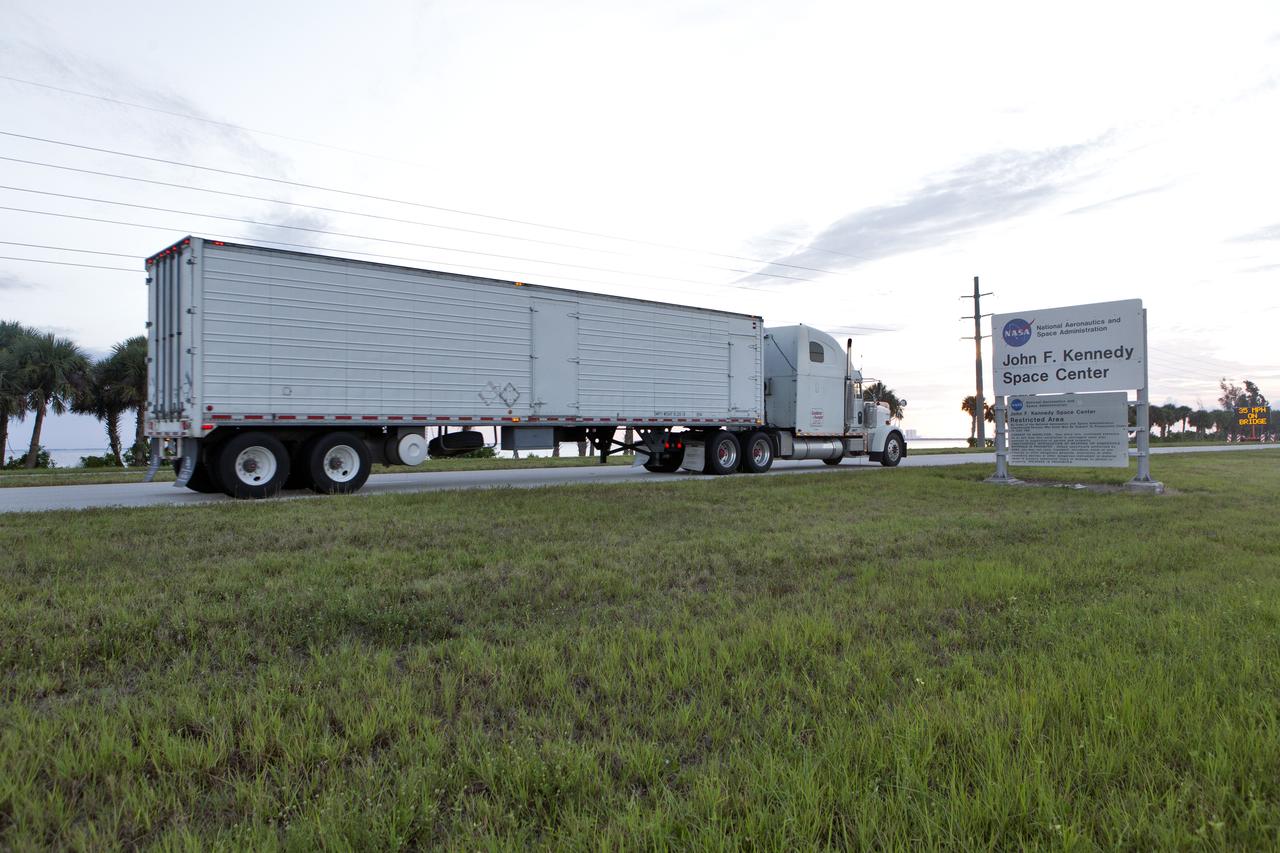

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, secured in a heavy transport truck, arrives at the entrance to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be delivered to the Launch Abort System Facility and integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. It is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.

Workers offload the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.

Workers begin checkouts of the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission is offloaded from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
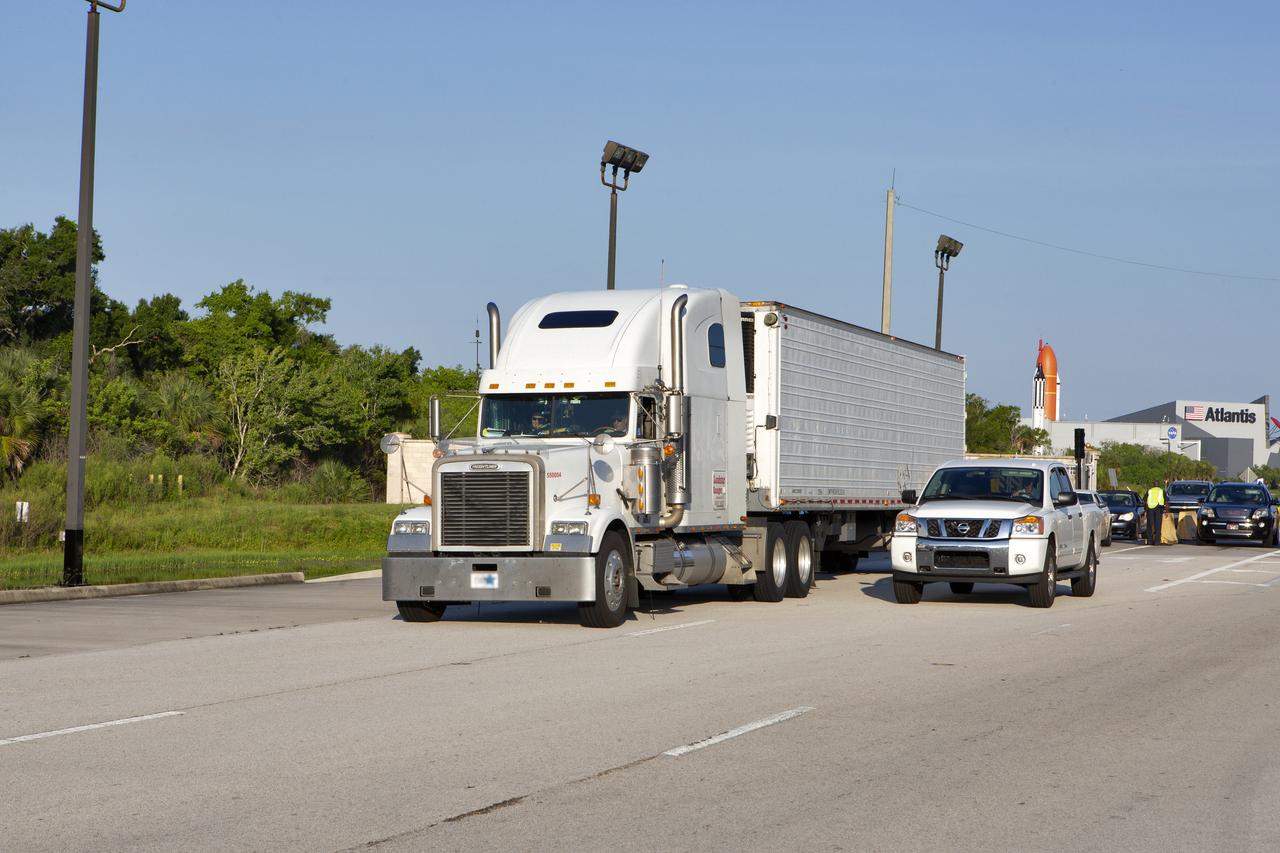

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, secured in a heavy transport truck, arrives at the entrance to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be delivered to the Launch Abort System Facility and integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. It is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
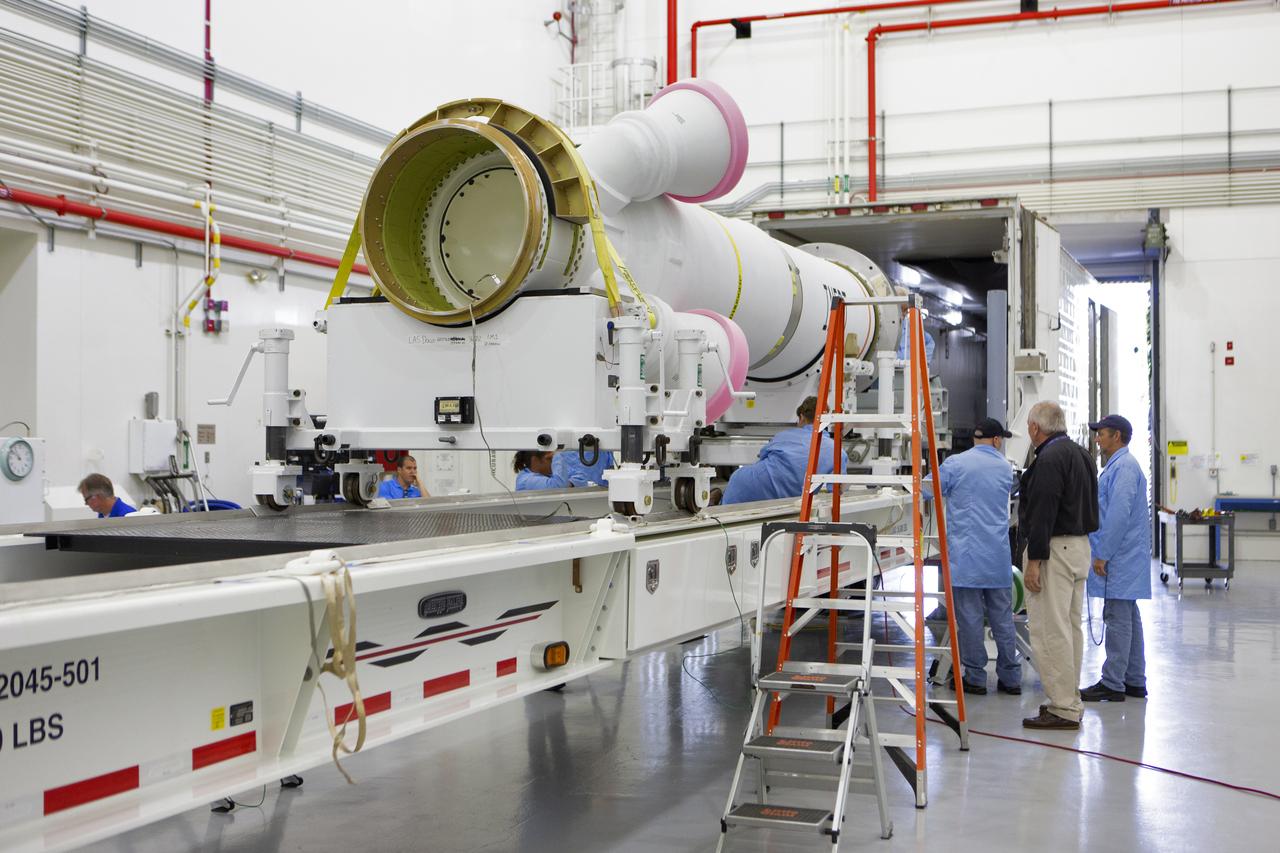

Workers help offload the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
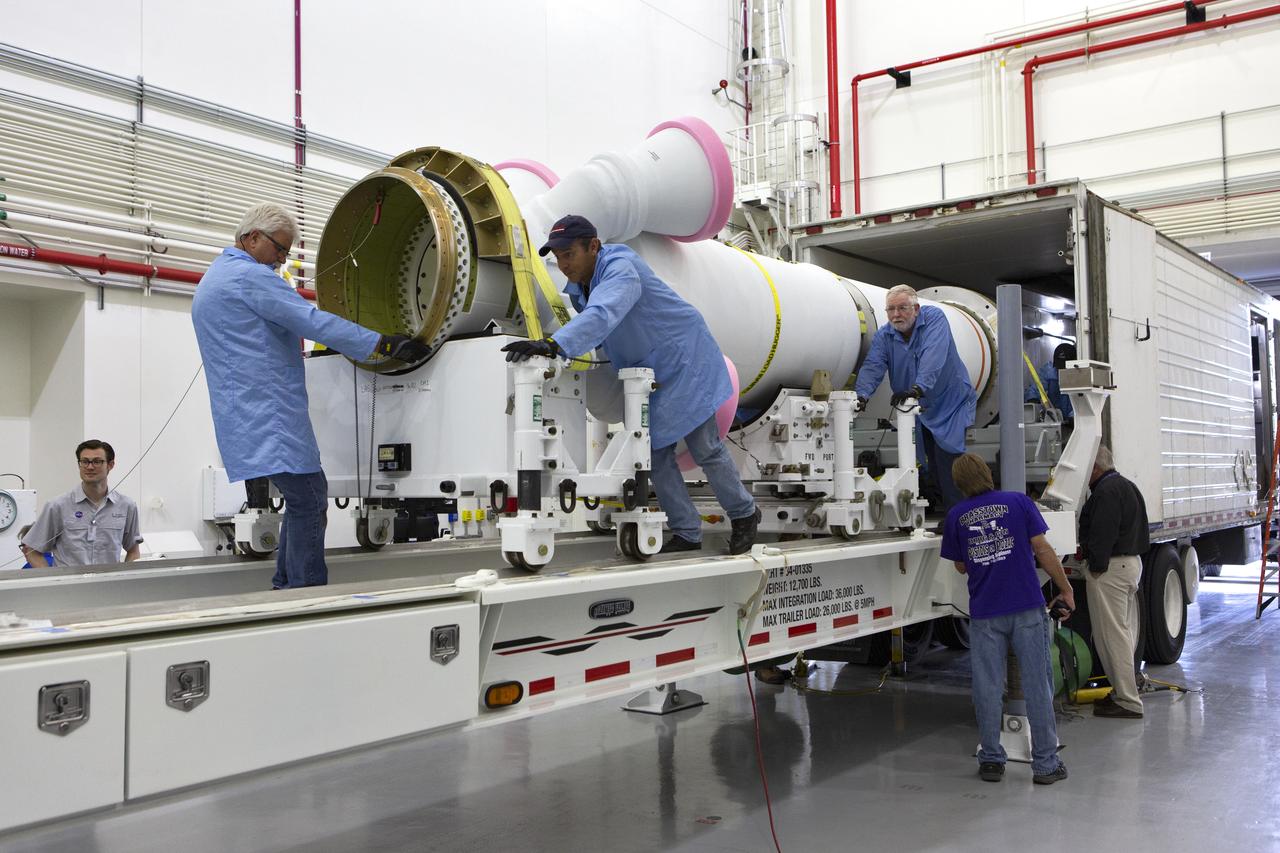

Workers offload the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS). During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
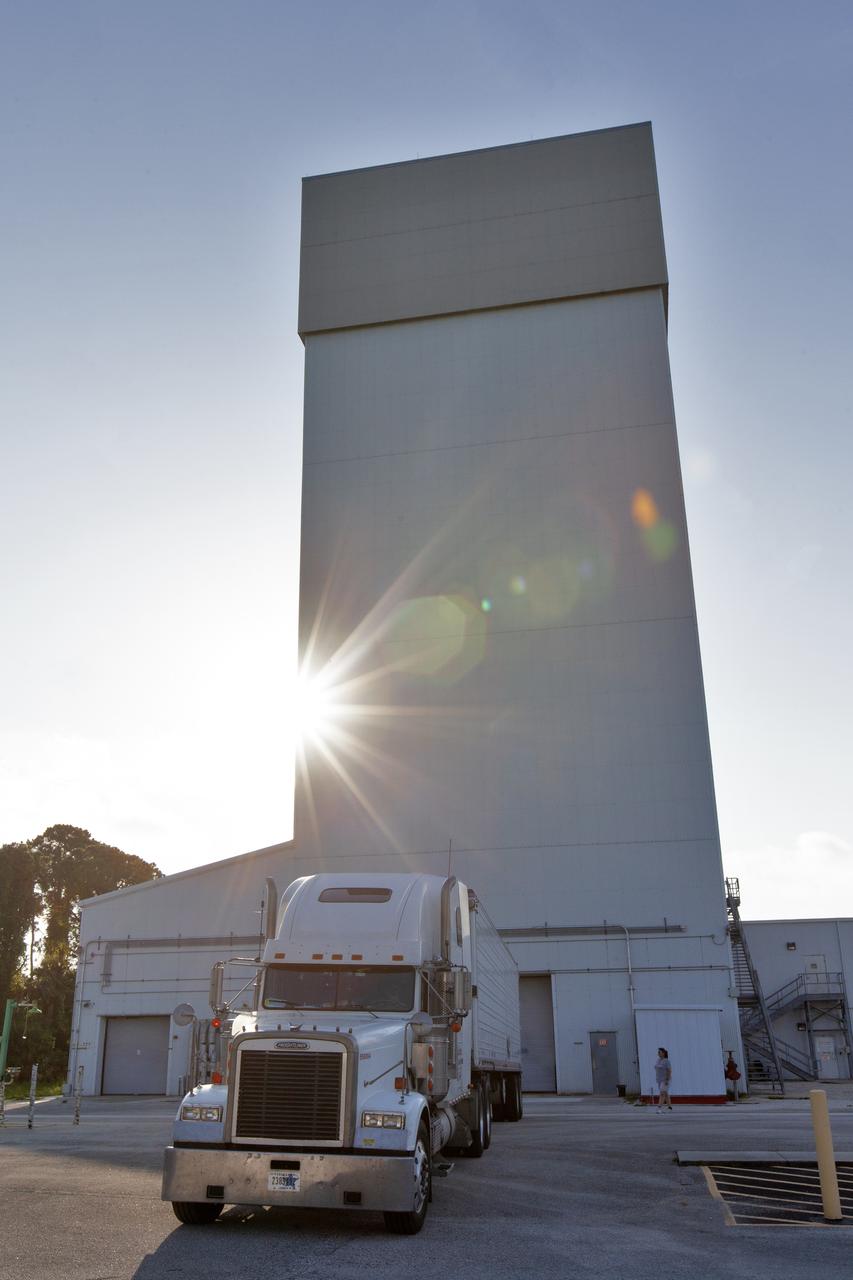

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, secured in a heavy transport truck, arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be offloaded and moved into the LASF where it will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.

Orion - EM-1 - Artemis Spacecraft Arrival at Mansfield Lahm Airport, Transportation to Plum Brook Station and Installation in the Space Environment Complex, SEC Thermal Vacuum Chamber

Orion - EM-1 - Artemis Spacecraft Arrival at Mansfield Lahm Airport, Transportation to Plum Brook Station and Installation in the Space Environment Complex, SEC Thermal Vacuum Chamber

Orion - EM-1 - Artemis Spacecraft Arrival at Mansfield Lahm Airport, Transportation to Plum Brook Station and Installation in the Space Environment Complex, SEC Thermal Vacuum Chamber
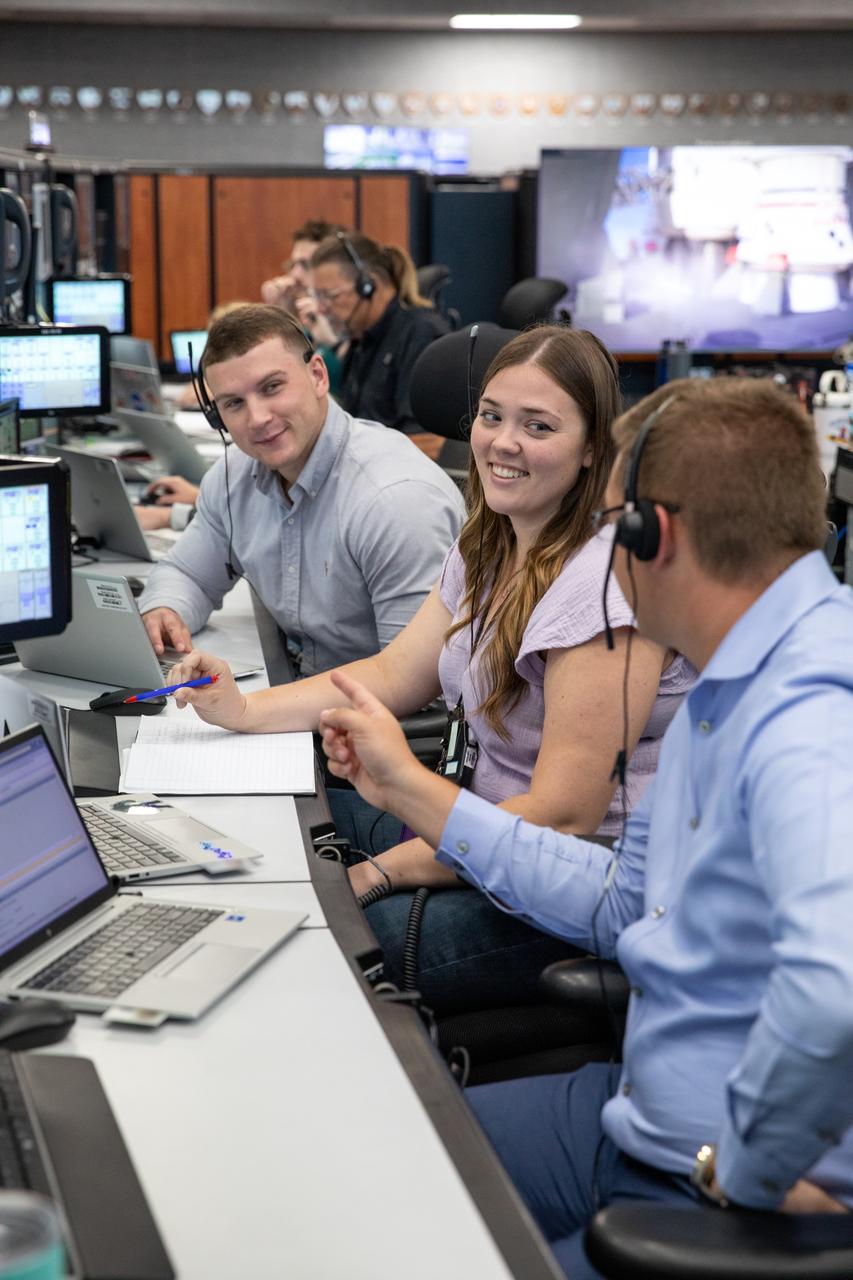

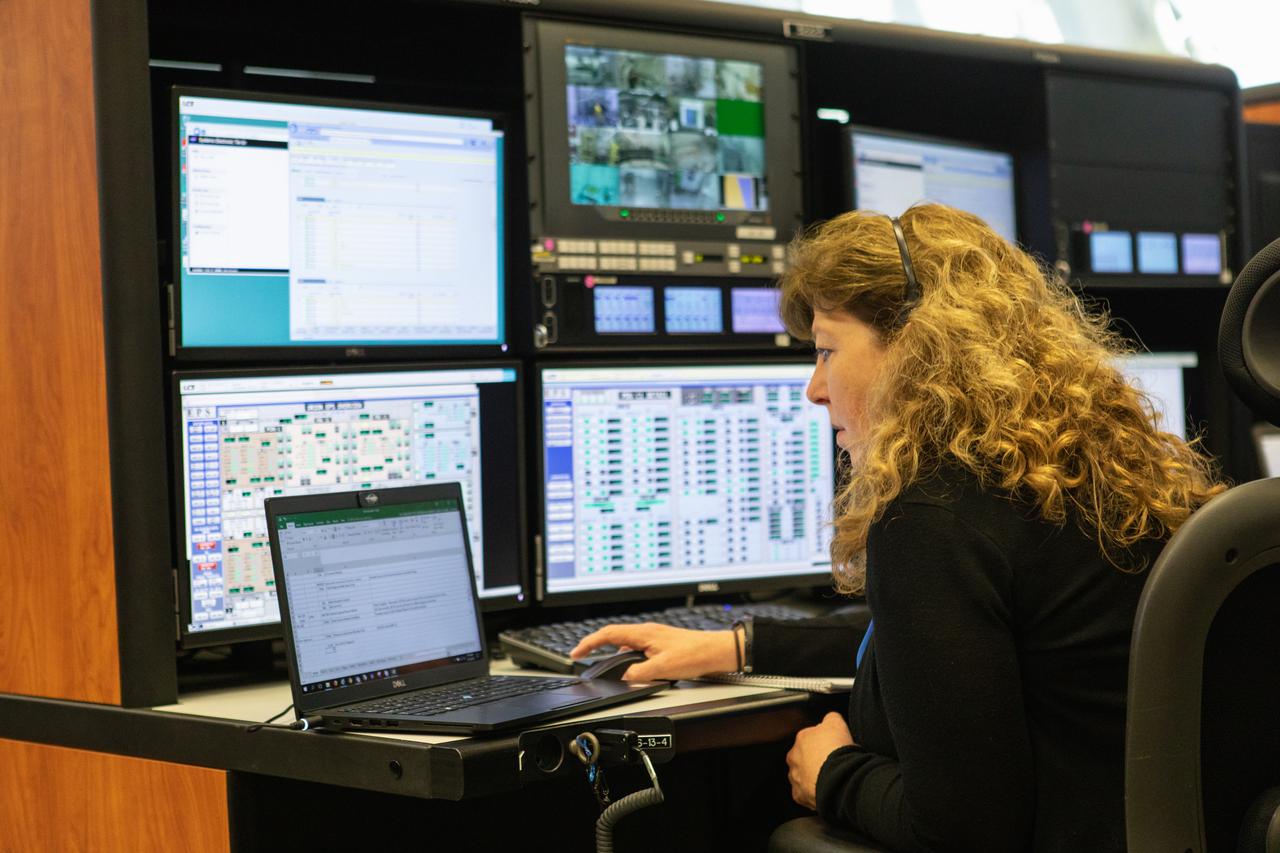
Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs, monitor activities during the Artemis II terminal countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 11, 2023. This is part of a series of simulations to help the team prepare for the launch of Artemis II, the first mission with astronauts under Artemis that will test and check out all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems needed for future crewed missions.
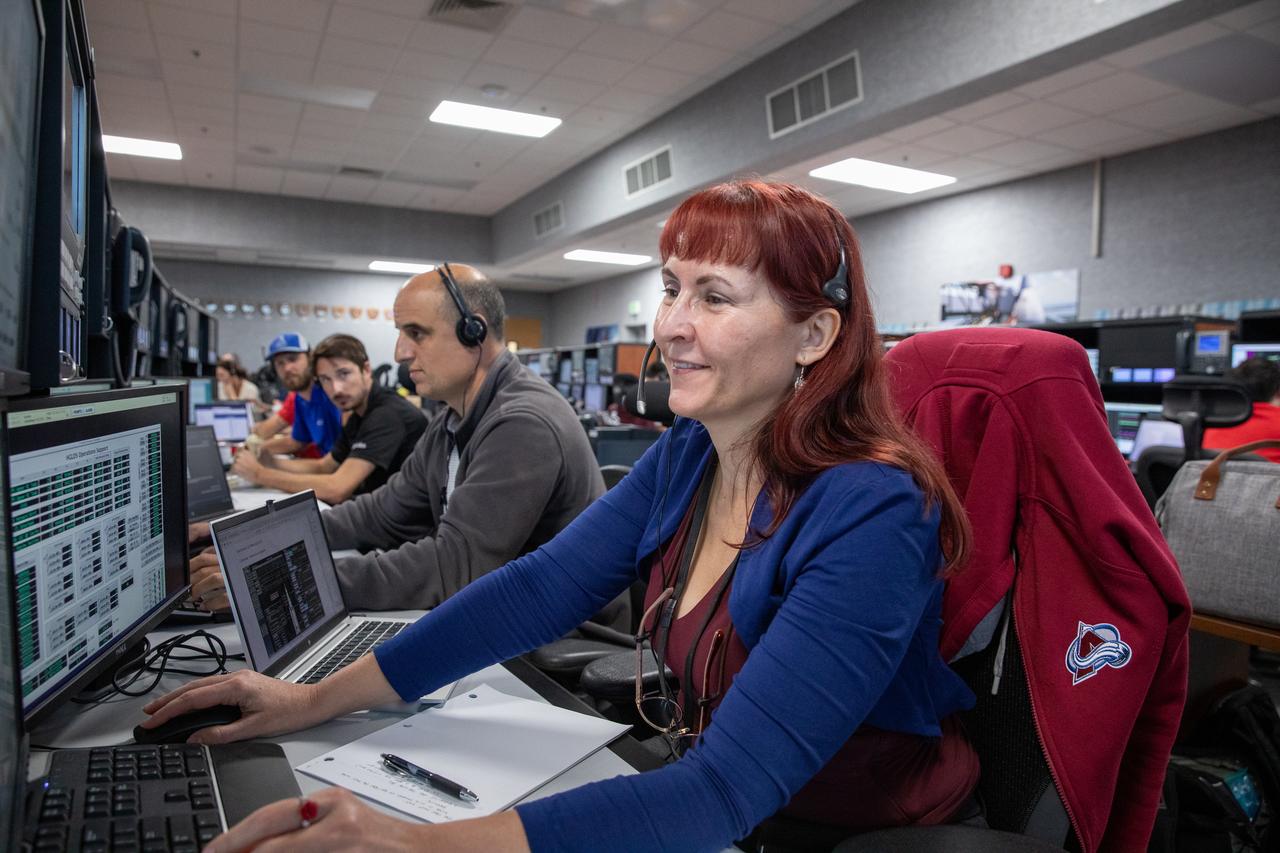

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs, monitor activities during the Artemis II terminal countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 11, 2023. This is part of a series of simulations to help the team prepare for the launch of Artemis II, the first mission with astronauts under Artemis that will test and check out all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems needed for future crewed missions.
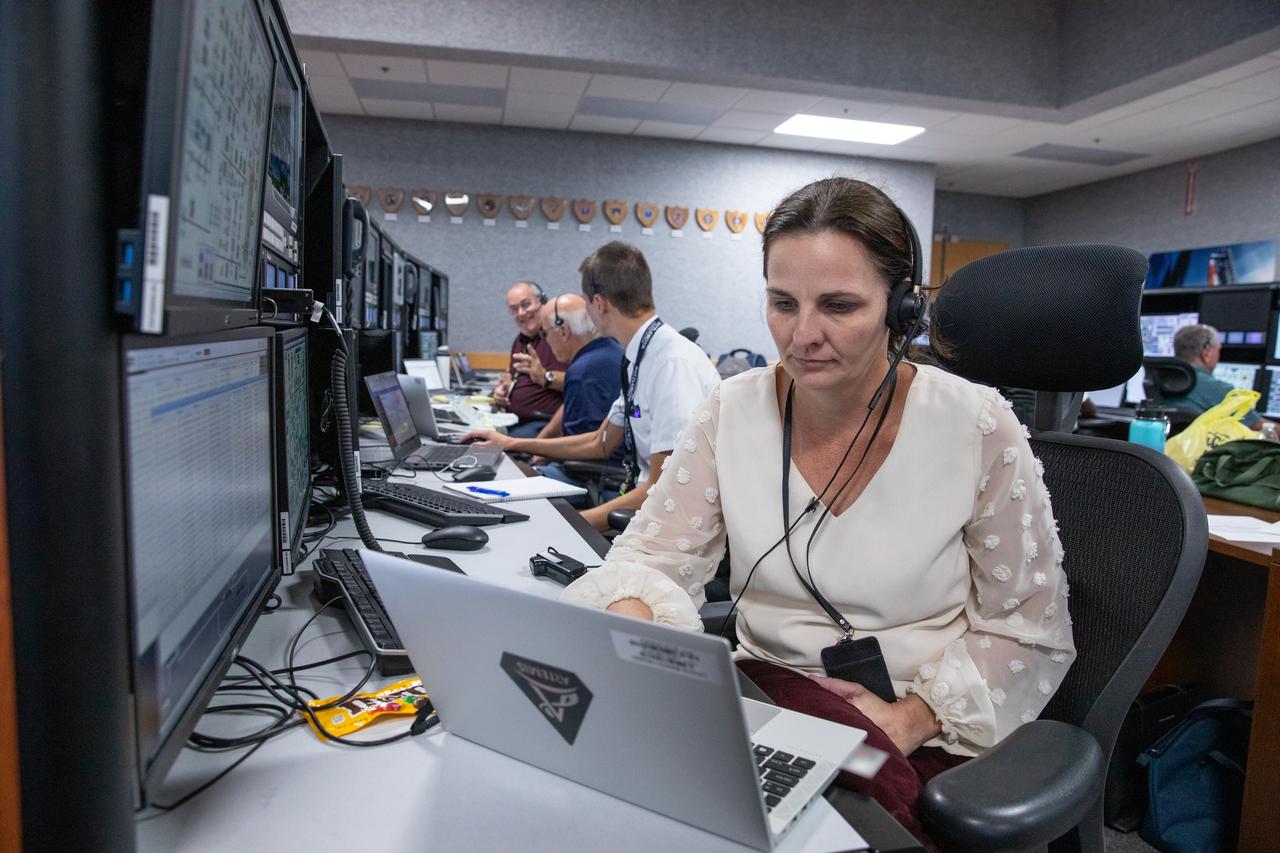

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs, monitor activities during the Artemis II terminal countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 11, 2023. This is part of a series of simulations to help the team prepare for the launch of Artemis II, the first mission with astronauts under Artemis that will test and check out all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems needed for future crewed missions.

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs, monitor activities during the Artemis II terminal countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 11, 2023. This is part of a series of simulations to help the team prepare for the launch of Artemis II, the first mission with astronauts under Artemis that will test and check out all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems needed for future crewed missions.
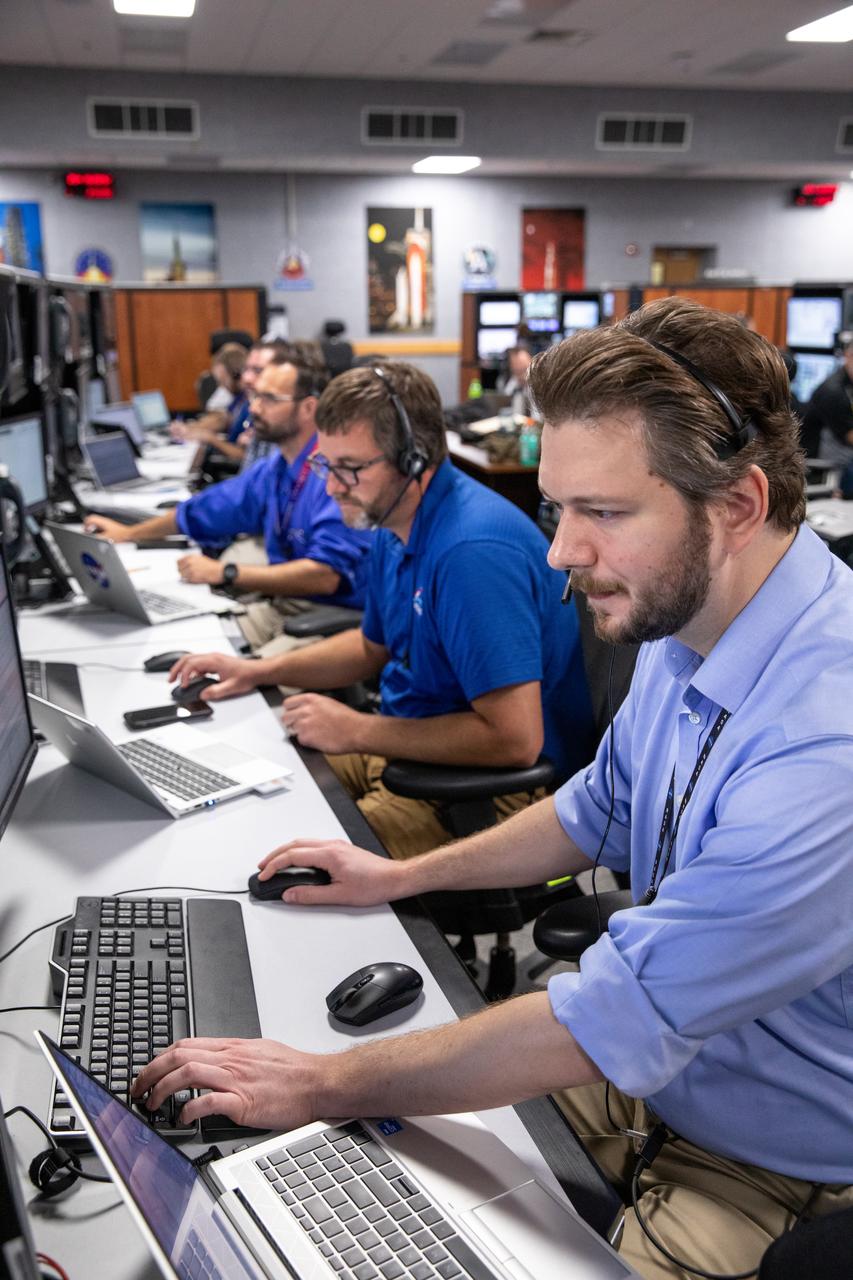

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs, monitor activities during the Artemis II terminal countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 11, 2023. This is part of a series of simulations to help the team prepare for the launch of Artemis II, the first mission with astronauts under Artemis that will test and check out all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems needed for future crewed missions.
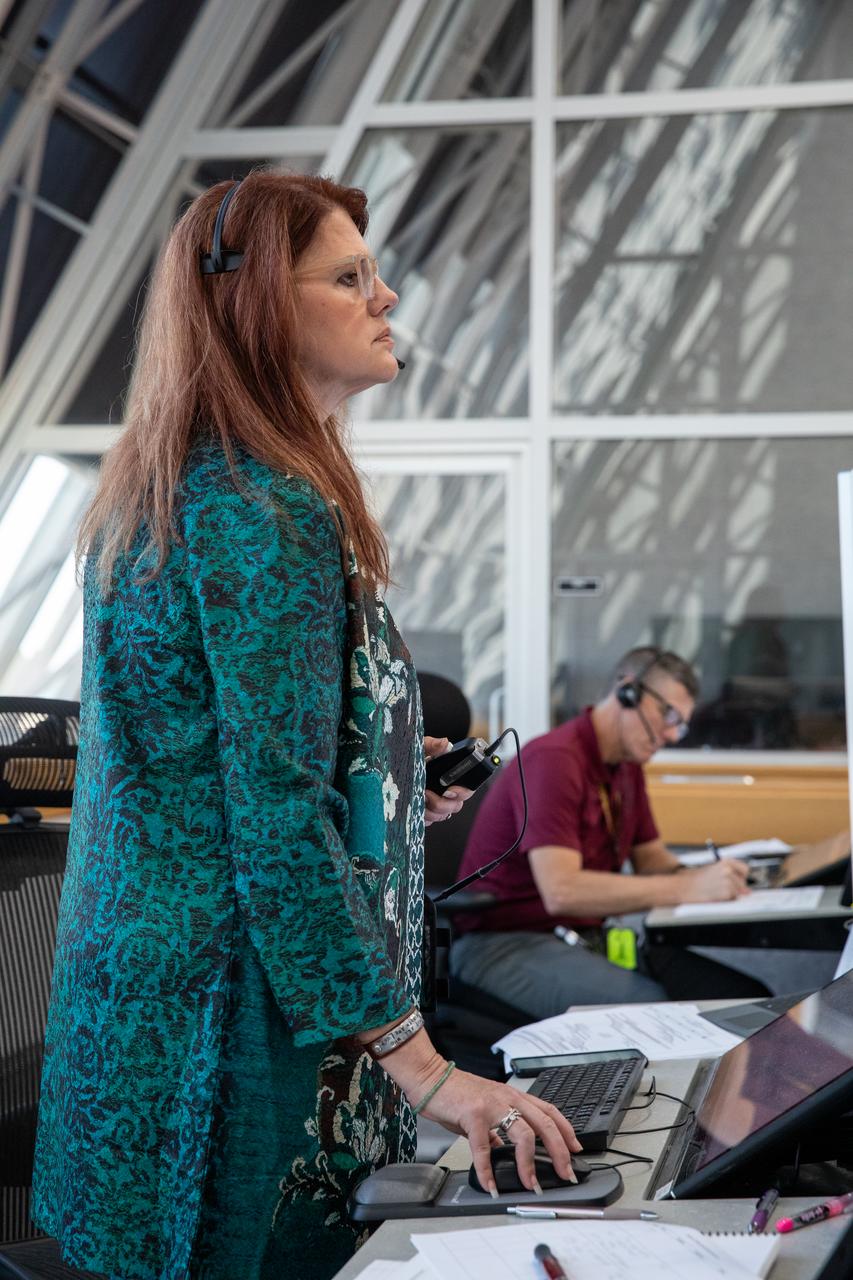

NASA Artemis Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, left, and Assistant Artemis Launch Director Jeremy Graeber monitor activities during the Artemis II terminal countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 11, 2023. Members of the Artemis II launch team include personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs. This is part of a series of simulations to help the team prepare for the launch of Artemis II, the first mission with astronauts under Artemis that will test and check out all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems needed for future crewed missions.
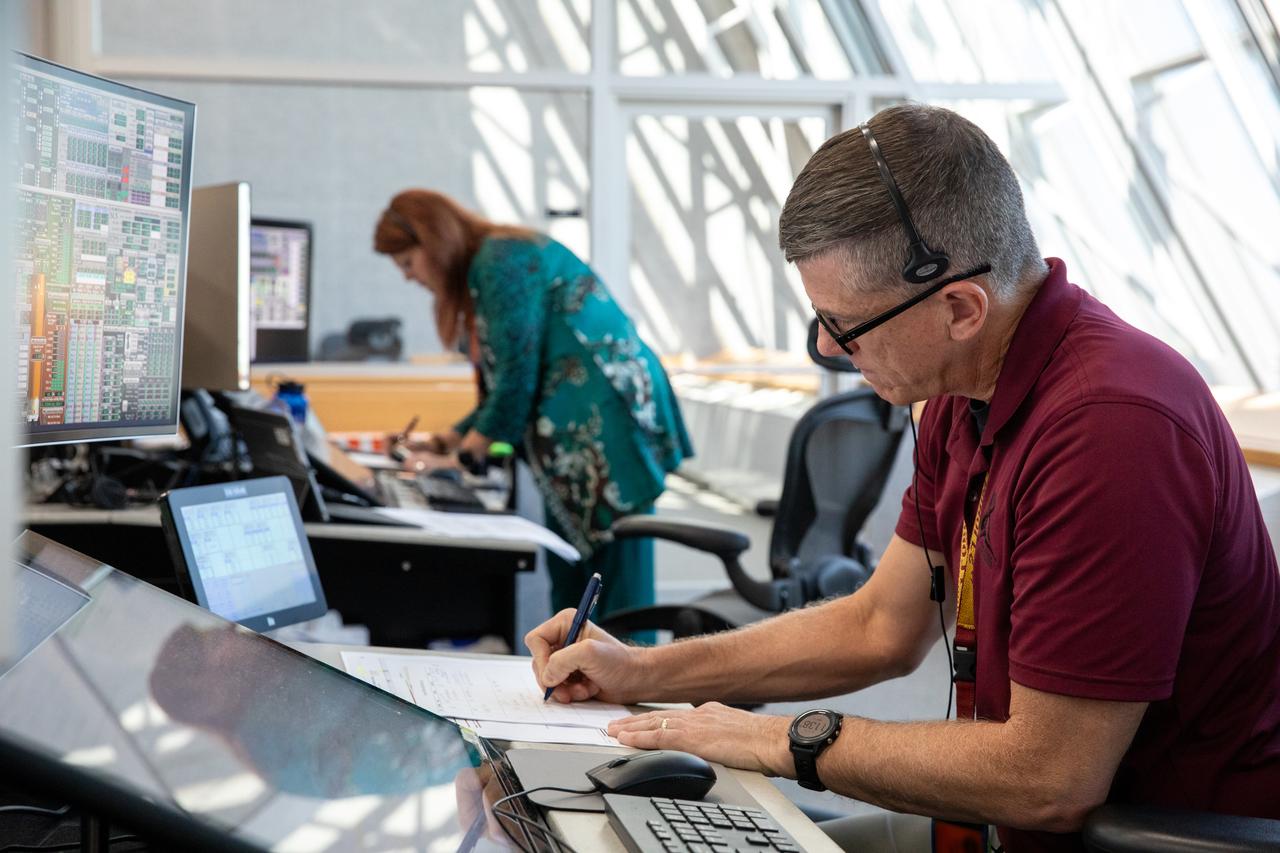

NASA Artemis Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, left, and Assistant Artemis Launch Director Jeremy Graeber monitor activities during the Artemis II terminal countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 11, 2023. Members of the Artemis II launch team include personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs. This is part of a series of simulations to help the team prepare for the launch of Artemis II, the first mission with astronauts under Artemis that will test and check out all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems needed for future crewed missions.
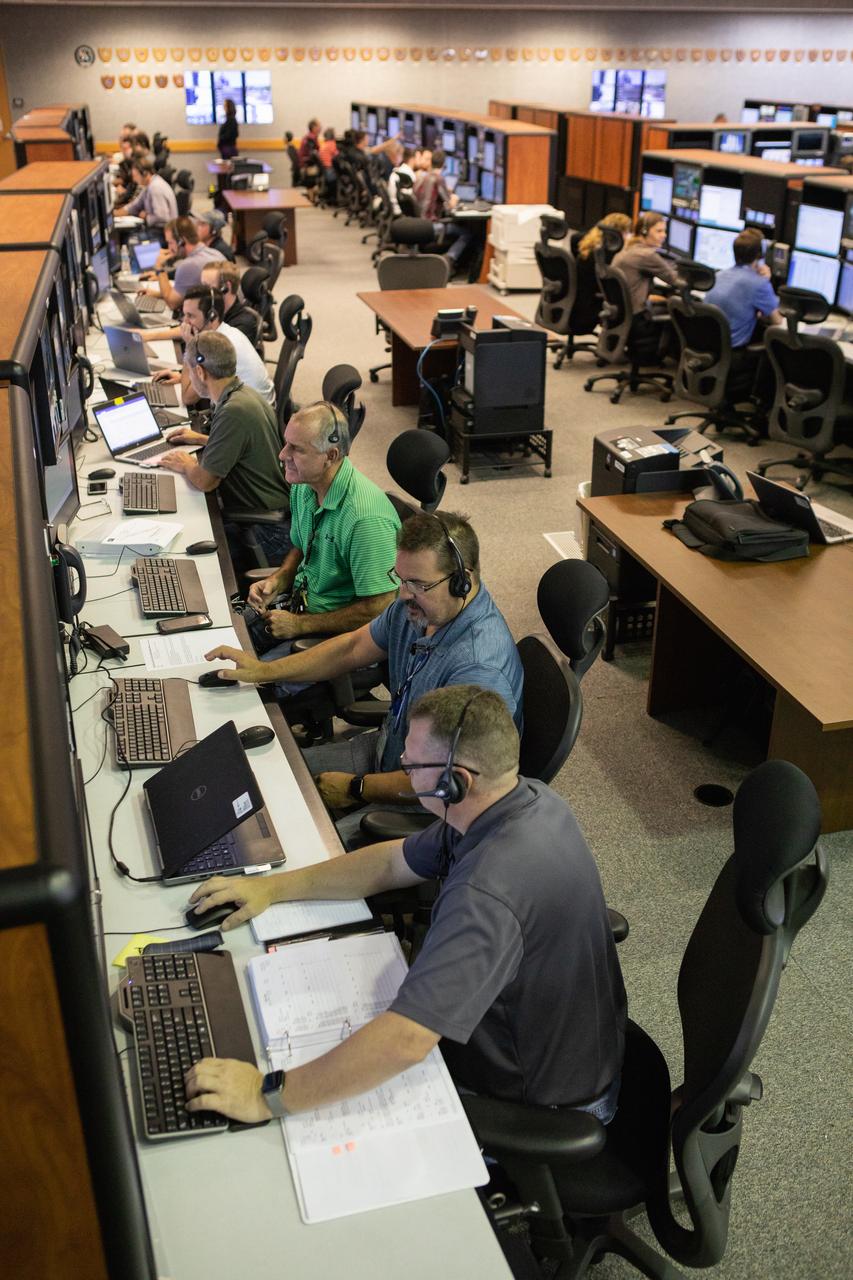

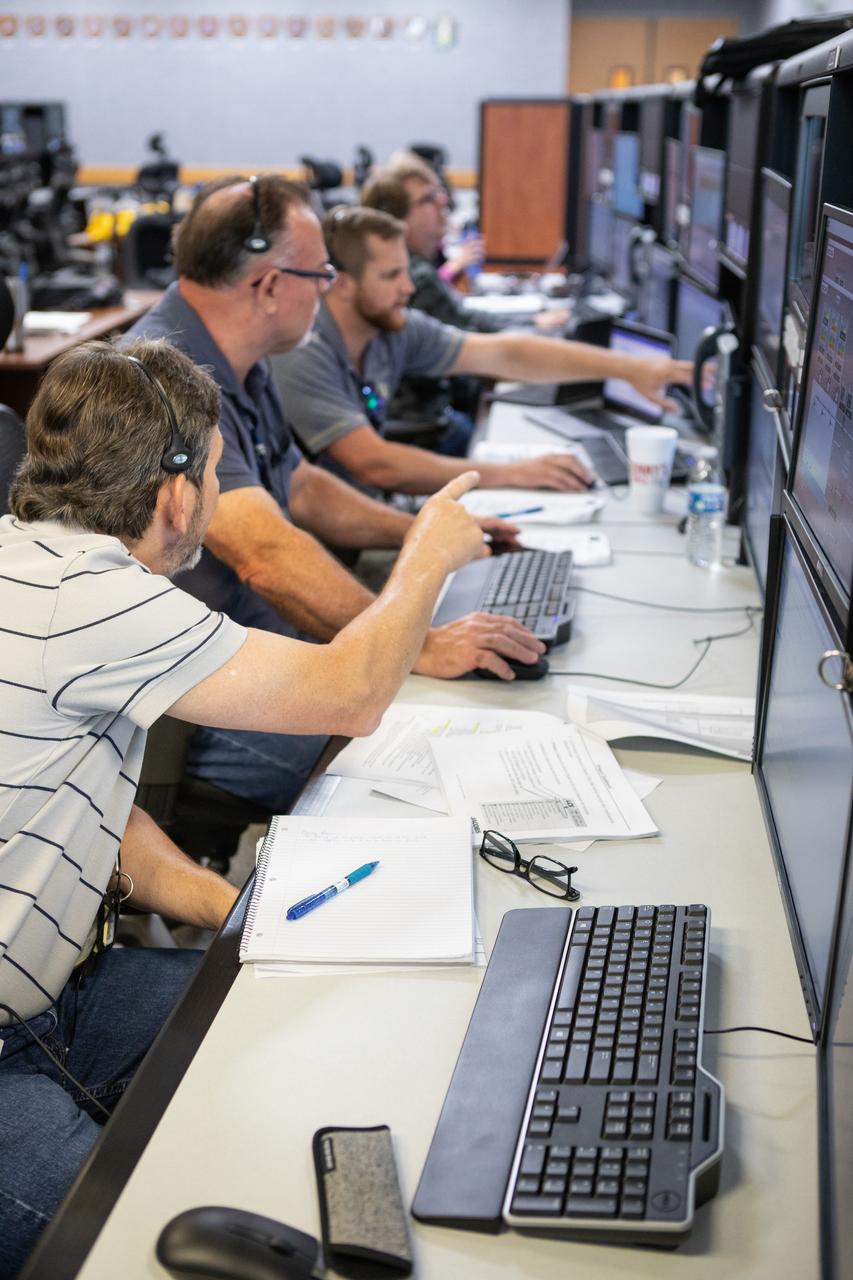
Members of the Artemis 1 launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC), participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
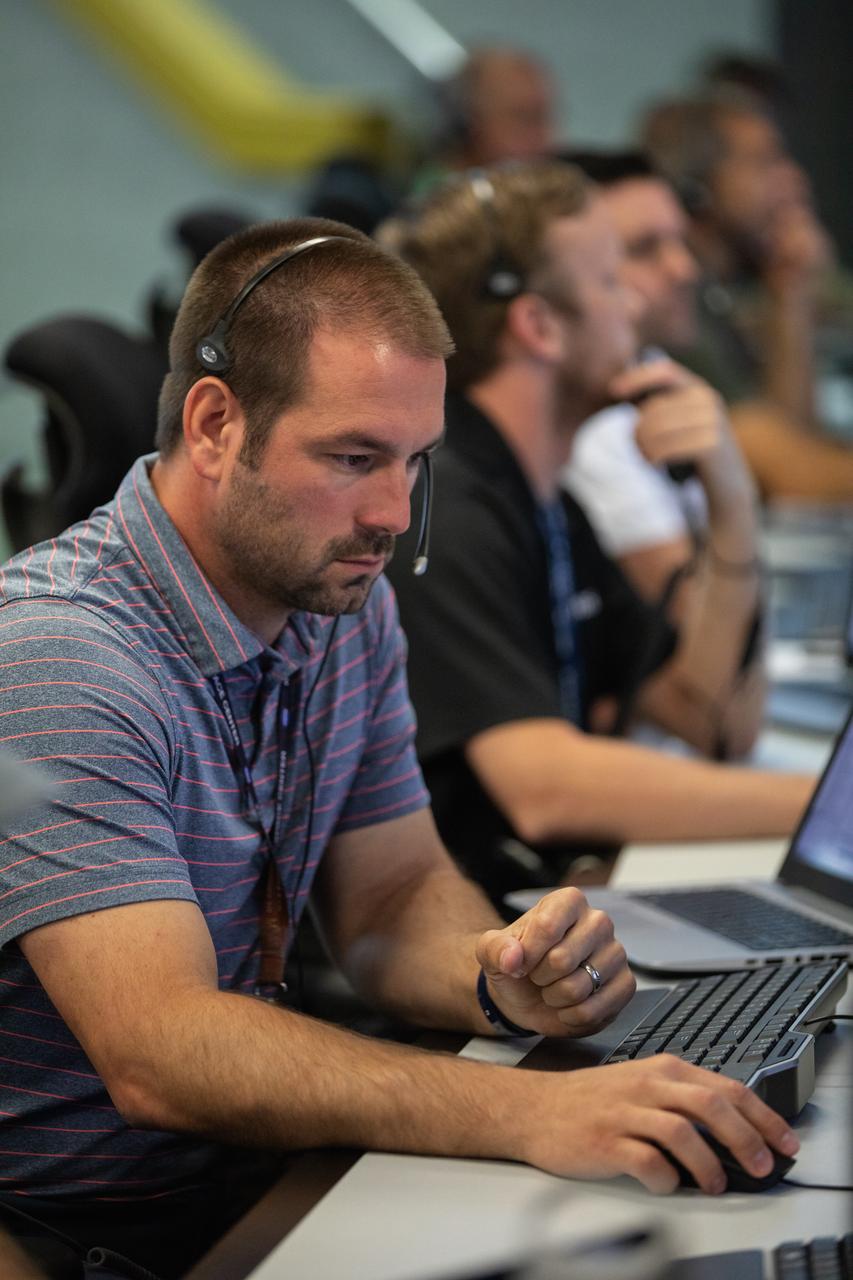

A member of the Artemis 1 launch team participates in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
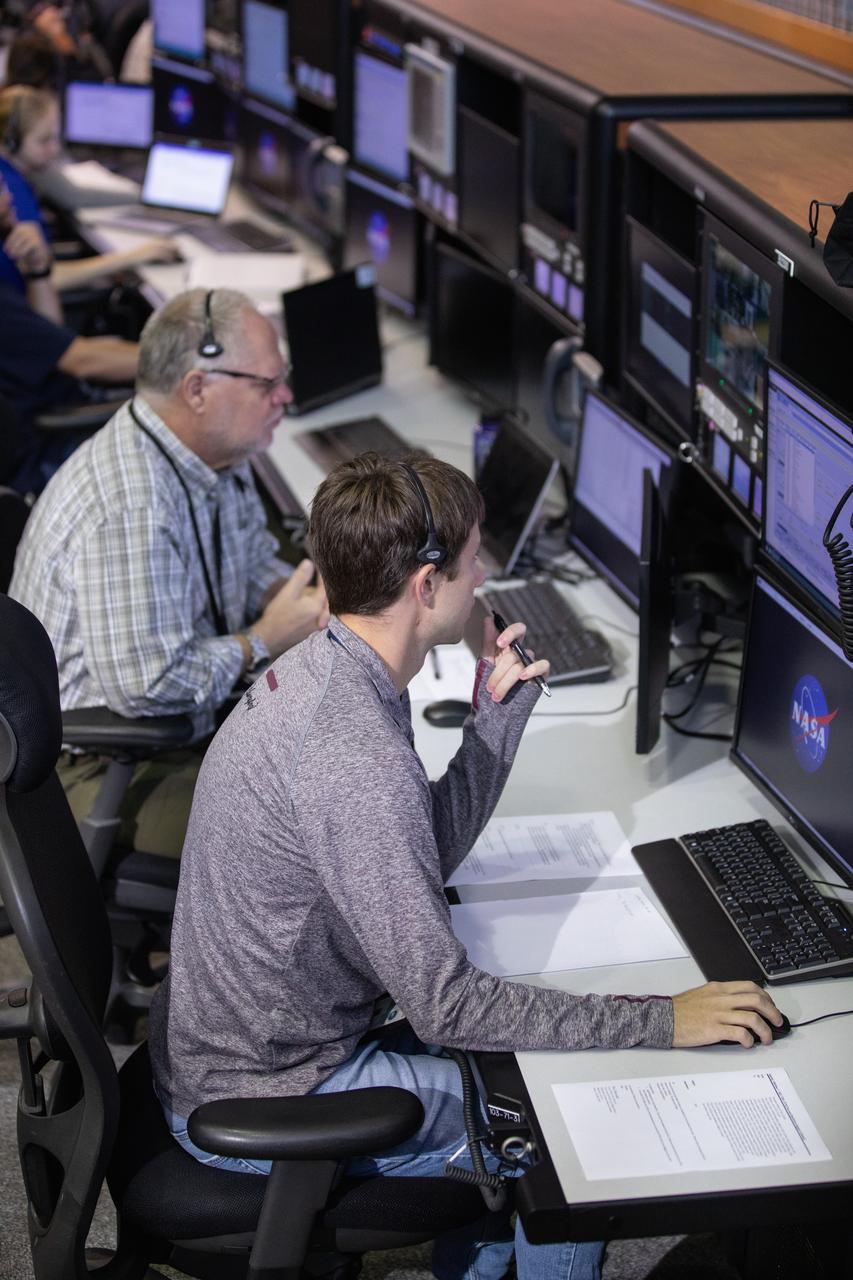

Members of the Artemis 1 launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC), participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS) which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
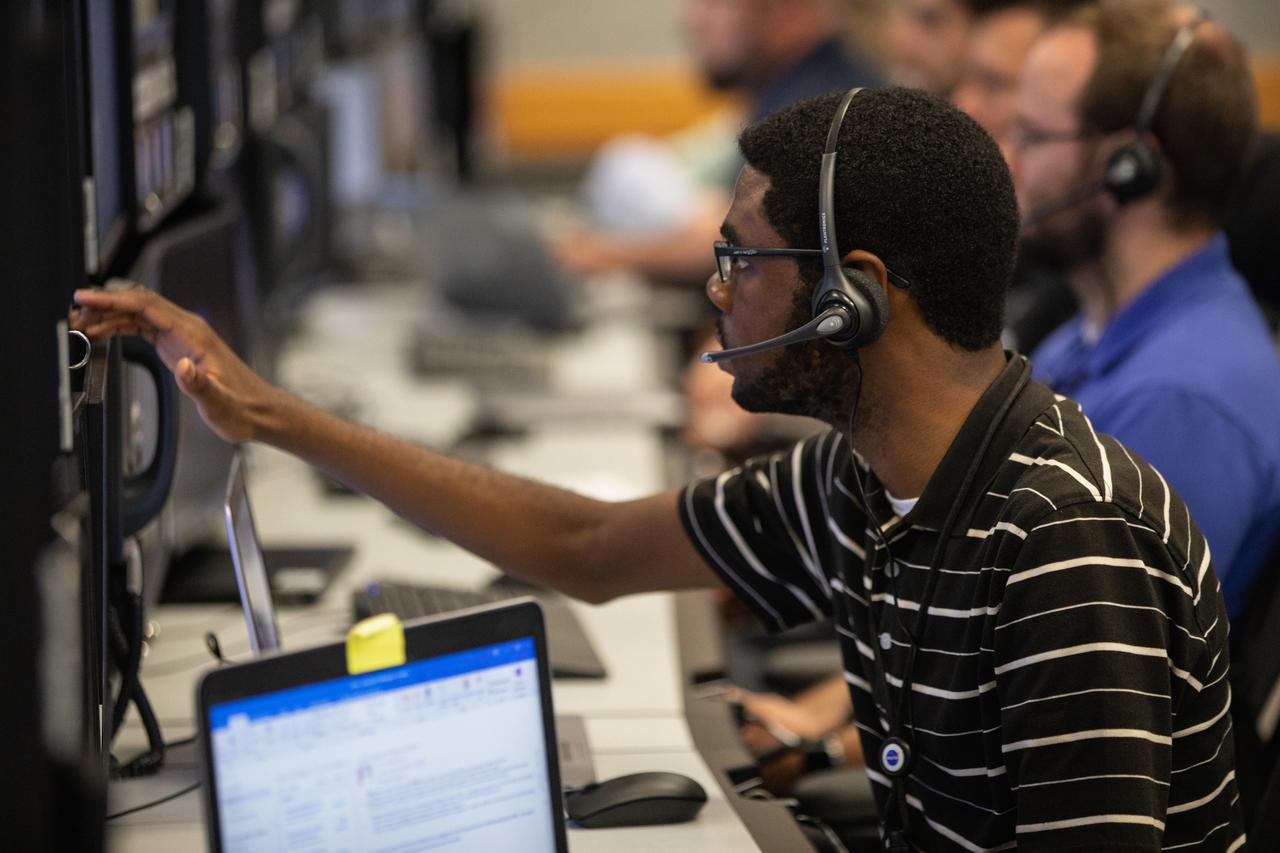

A member of the Artemis 1 launch team participates in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
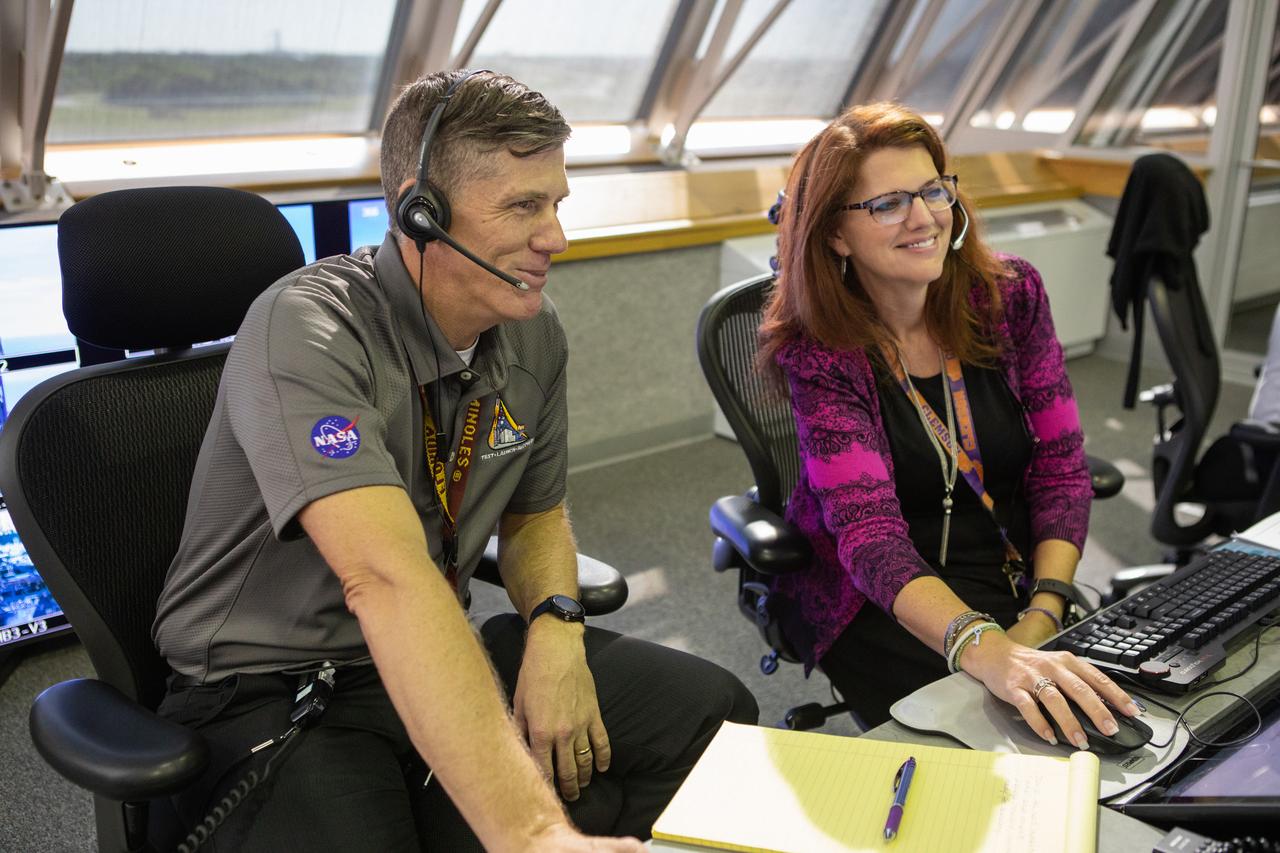

From left, Jeremy Graeber, chief NASA test director, and Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis 1 launch director, participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The launch team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
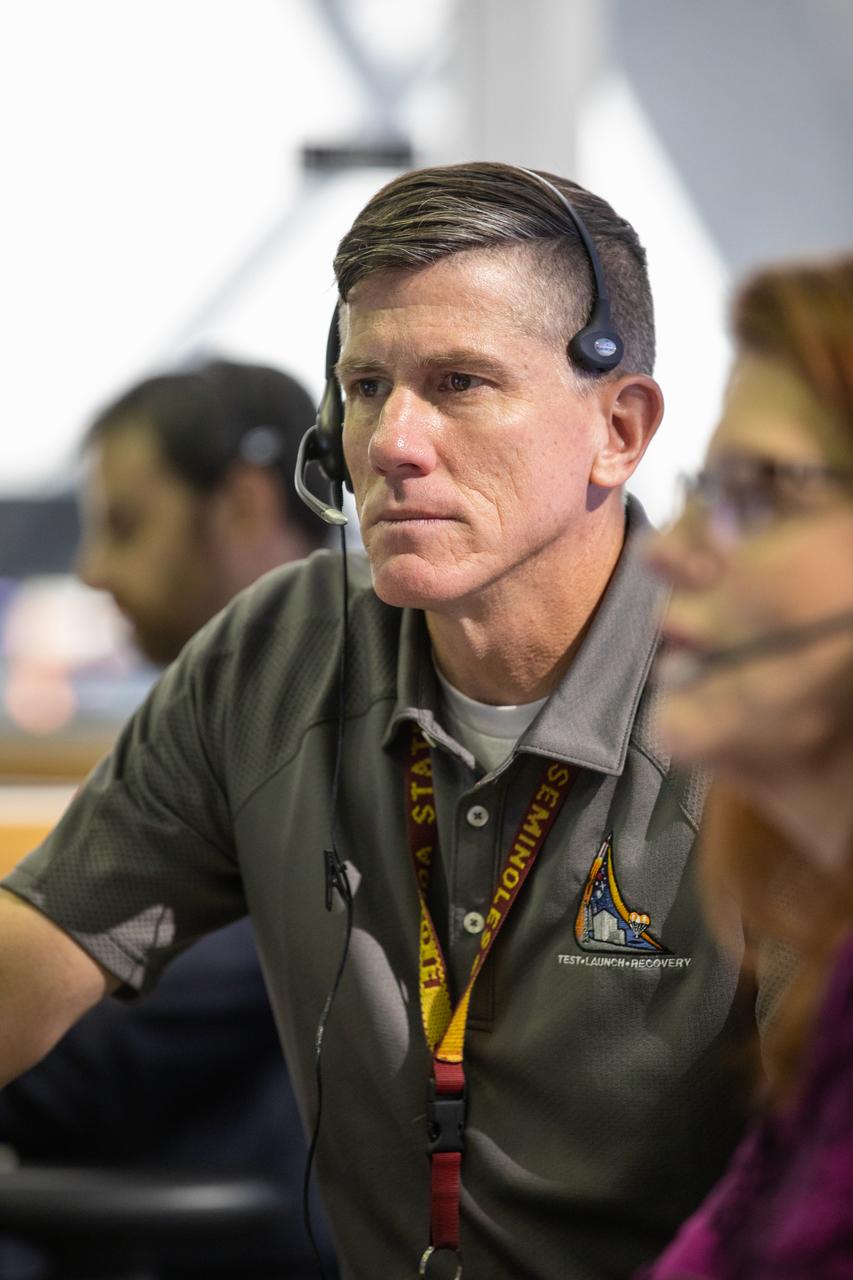

Jeremy Graeber, chief NASA test director, participates in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The Artemis 1 launch team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
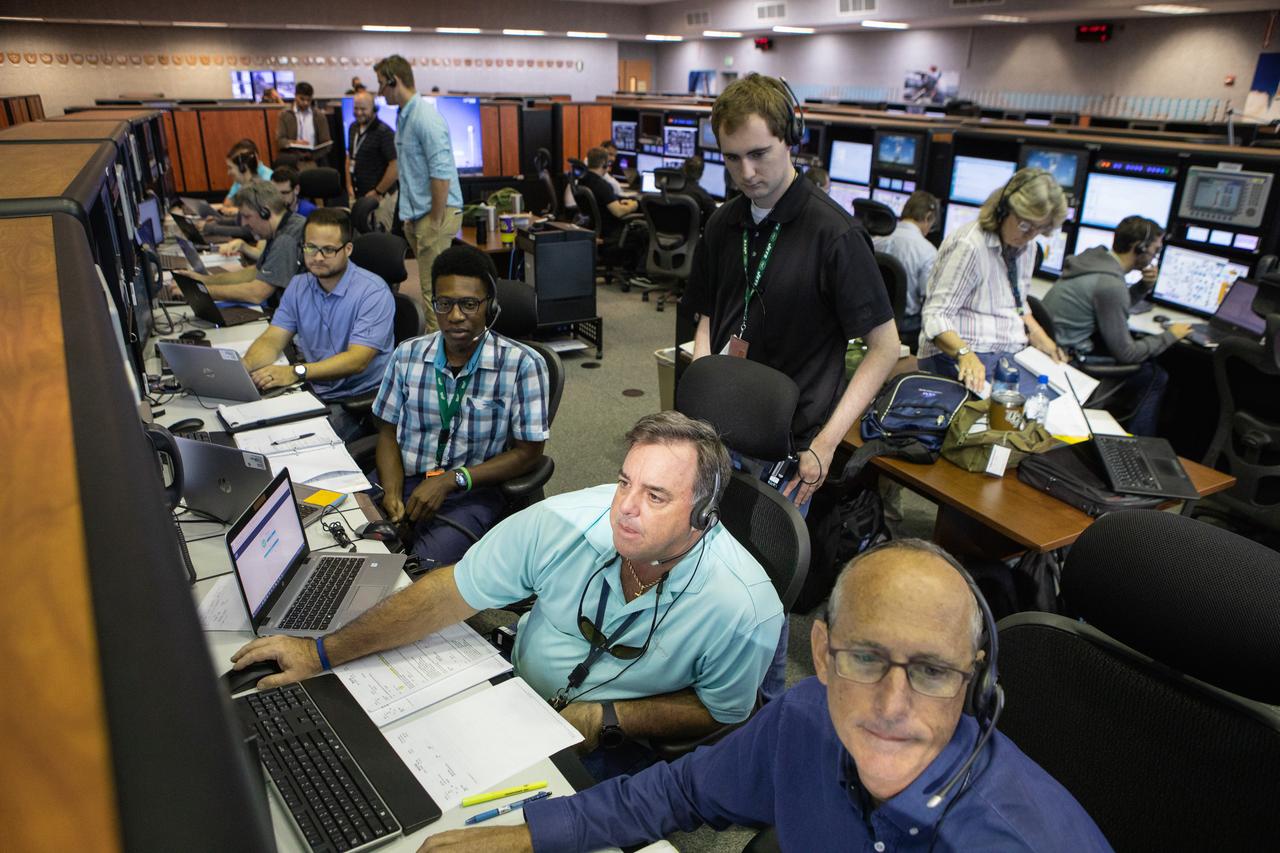

Members of the Artemis 1 launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC), participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.

A member of the Artemis 1 launch team participates in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The launch team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.

Members of the Artemis 1 launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC), participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.

Members of the Artemis 1 launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC), participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.

Members of the Artemis 1 launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC), participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
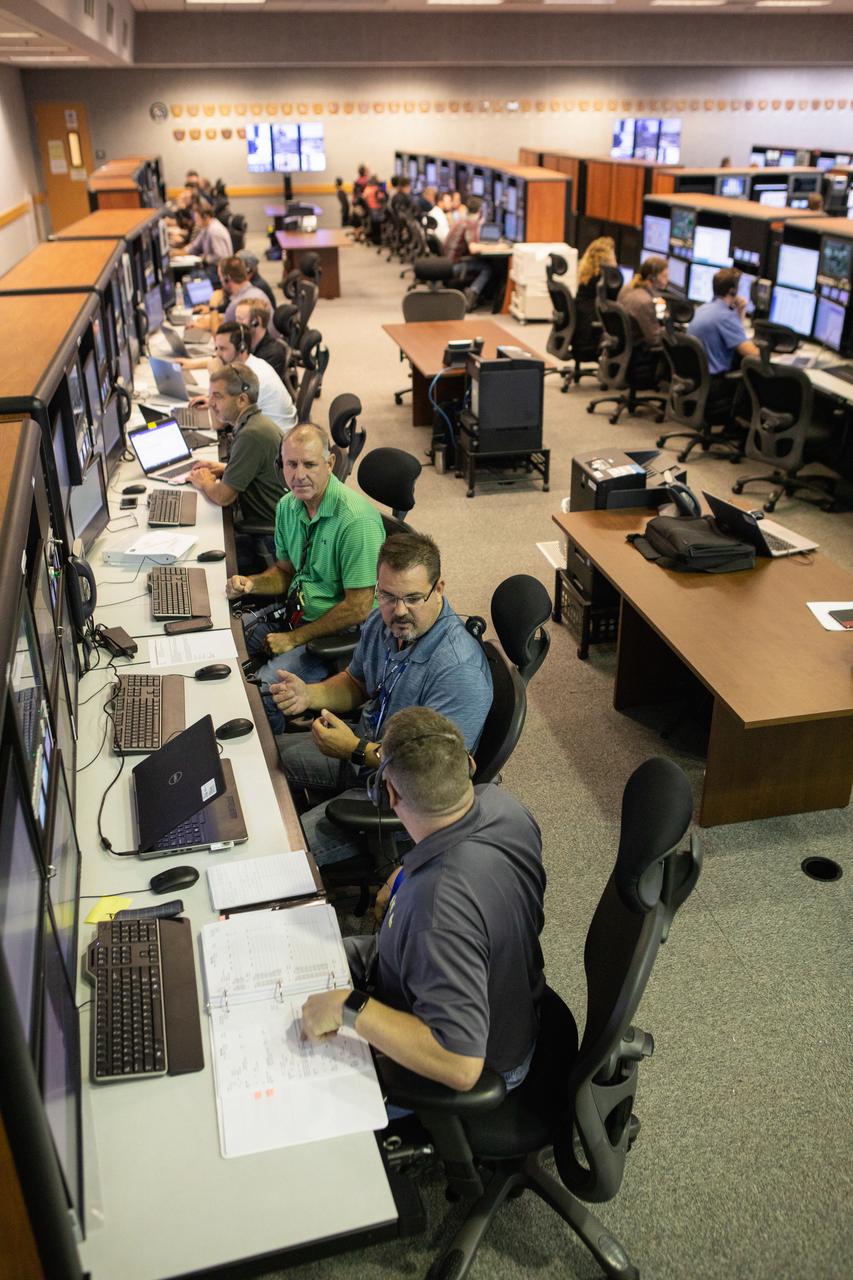

Members of the Artemis 1 launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC), participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
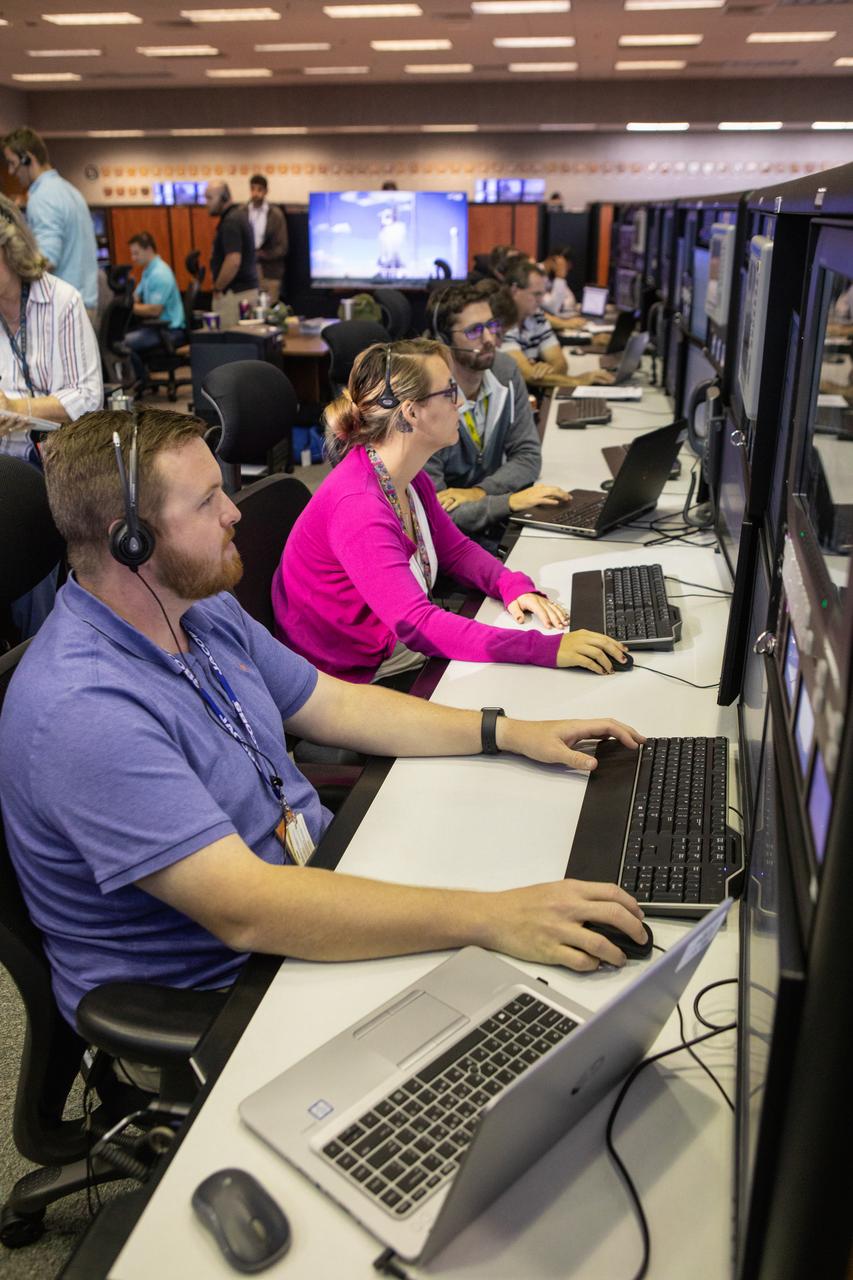

Members of the Artemis 1 launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC), participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.

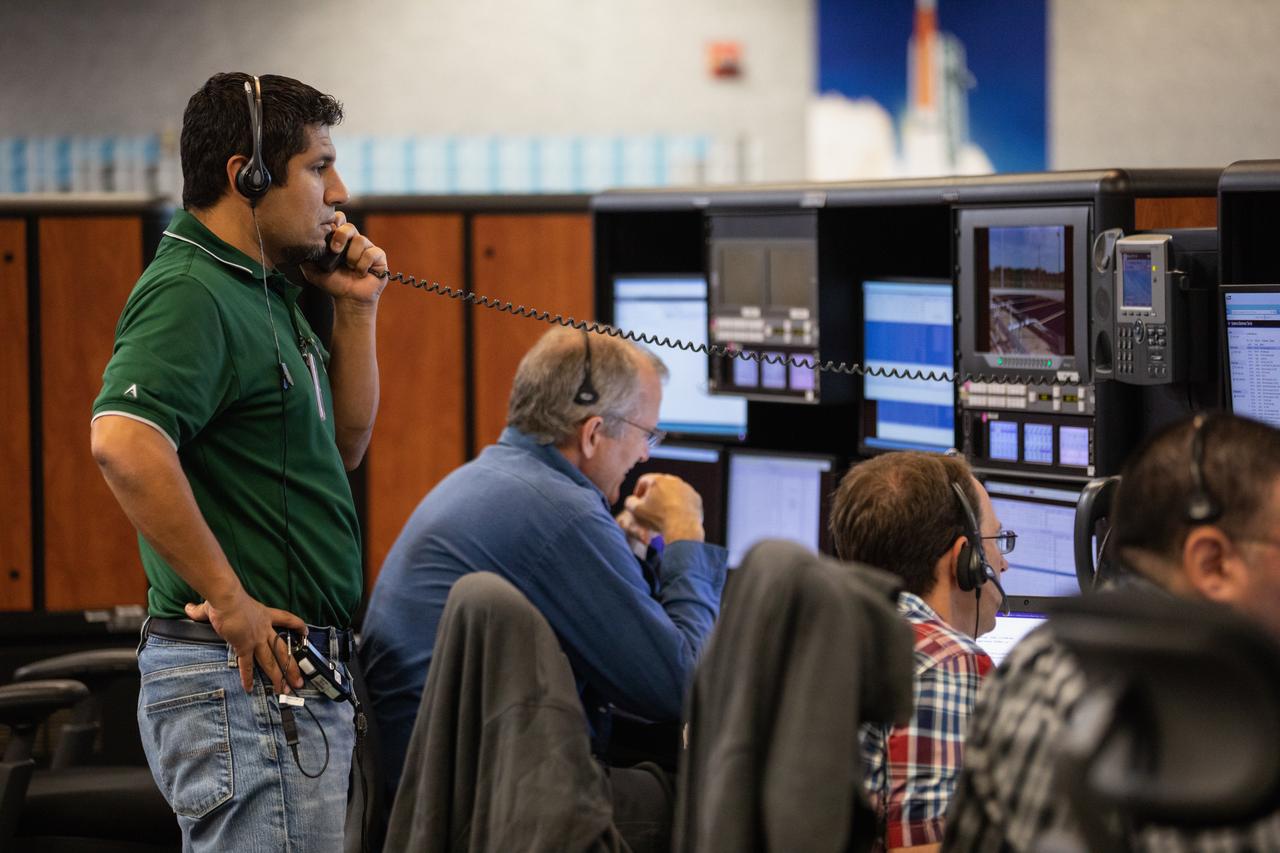
Artemis 1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson leads the launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC), through validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.

Members of the Artemis 1 launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC), participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
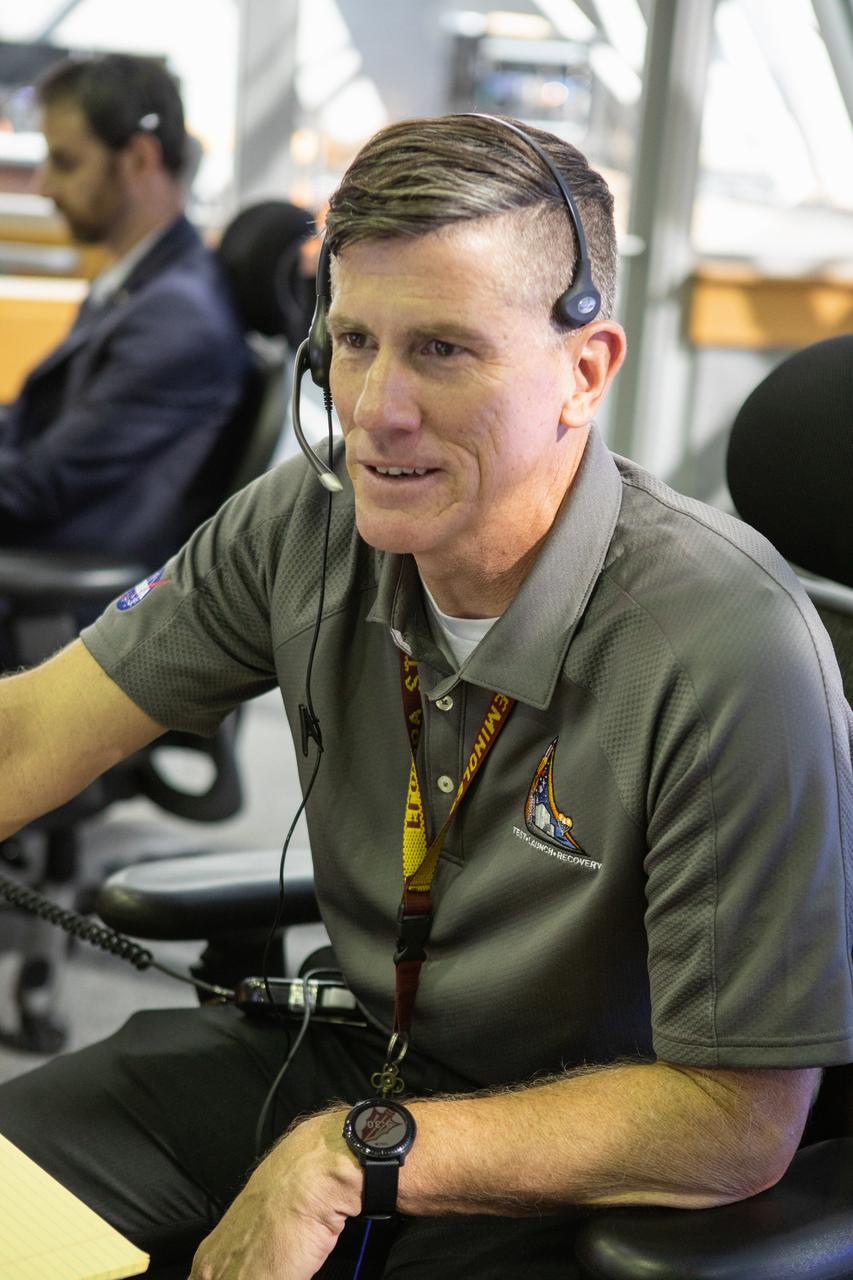

Jeremy Graeber, chief NASA test director, participates in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The Artemis 1 launch team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
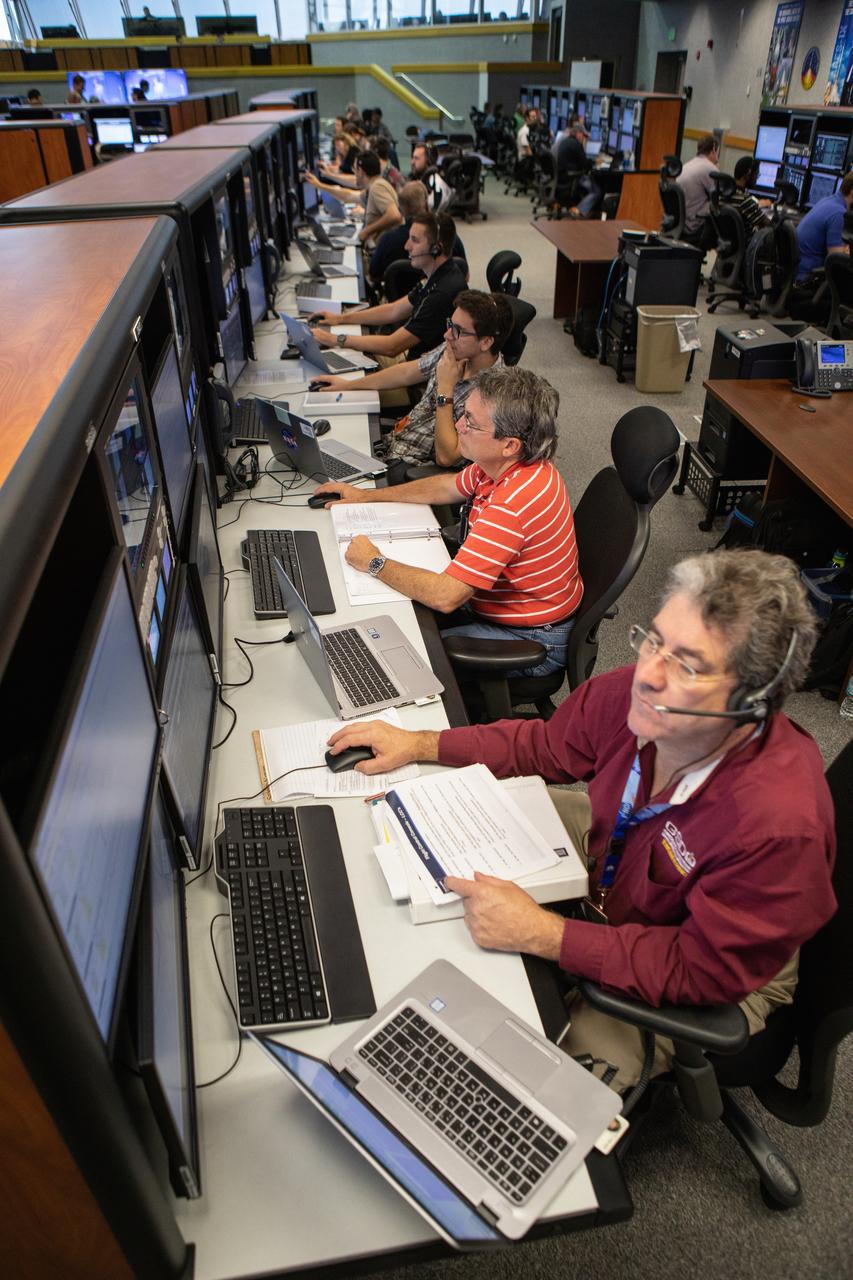

Members of the Artemis 1 launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC), in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
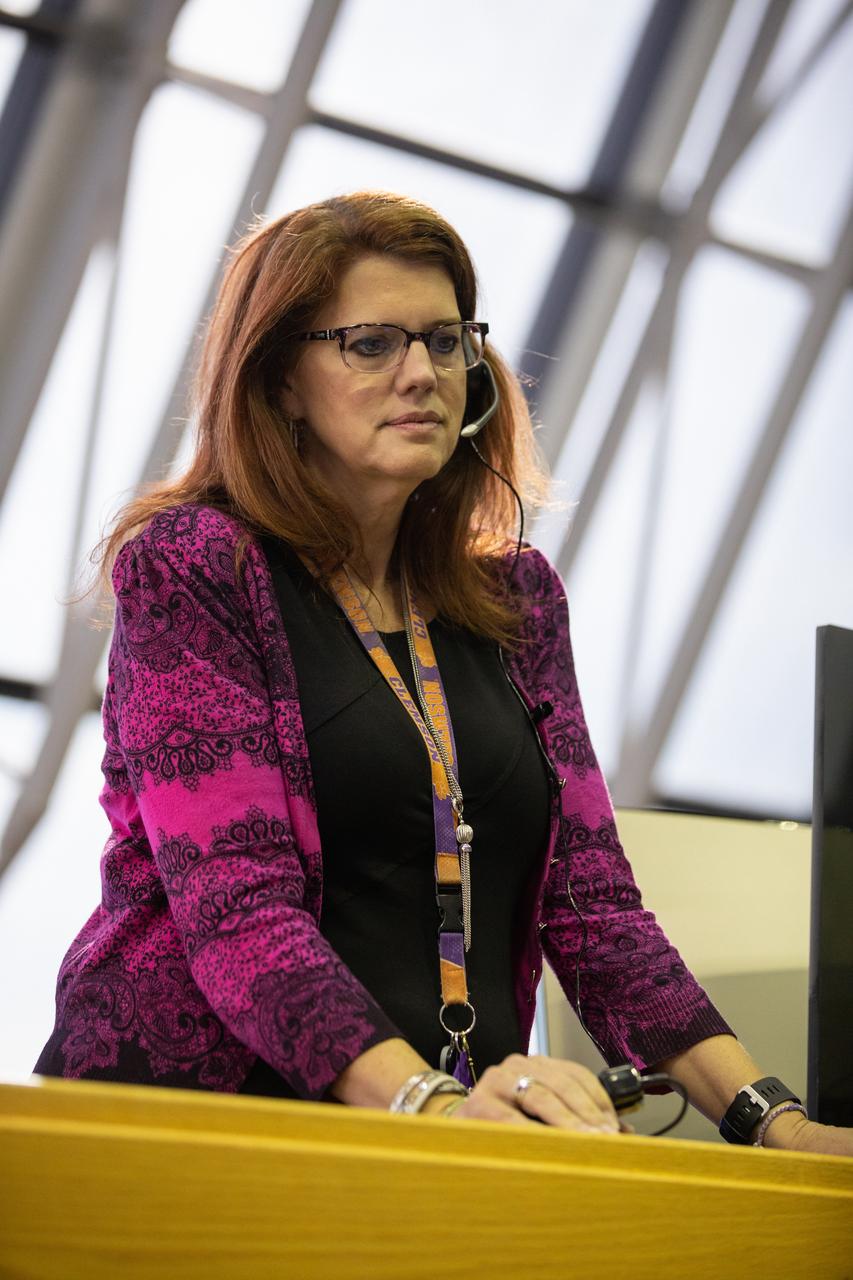

Artemis 1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson leads the launch team through validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
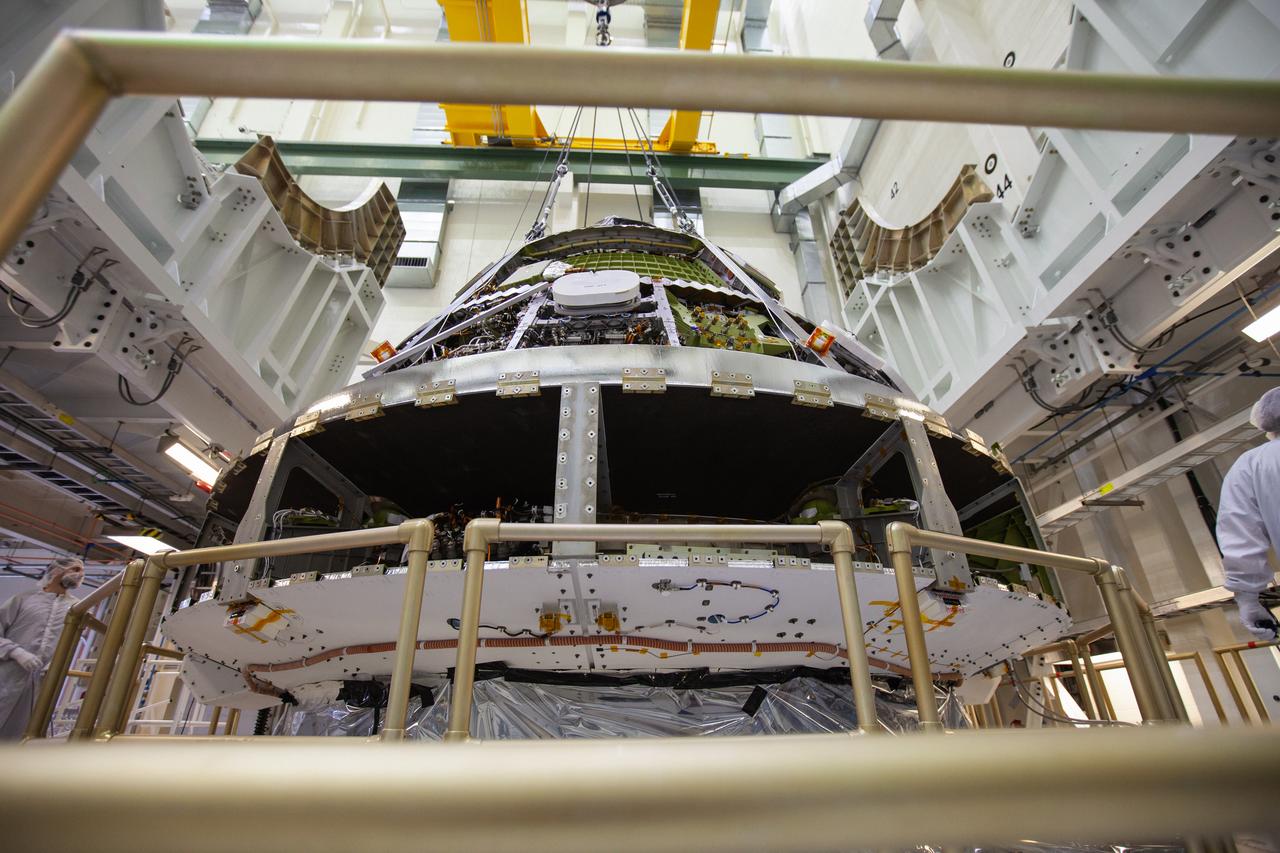

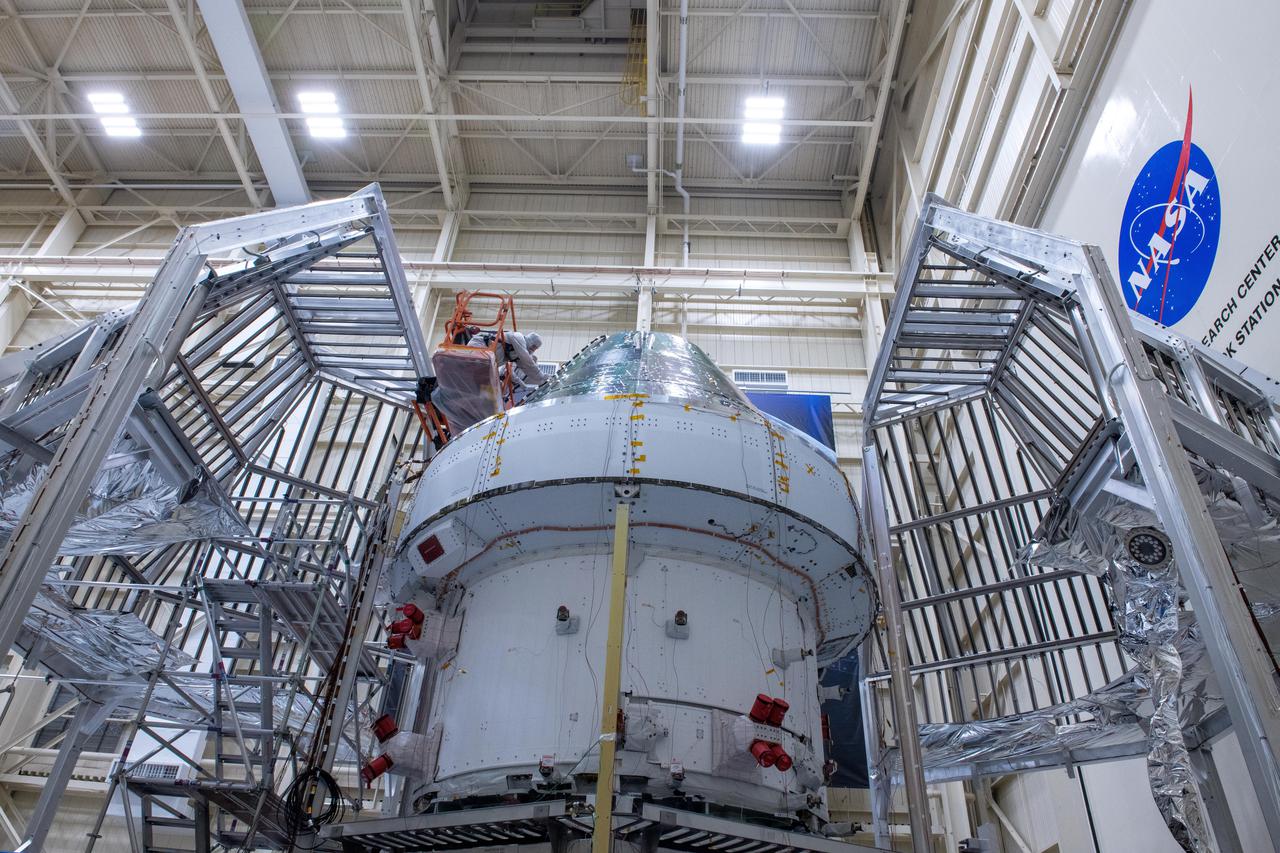
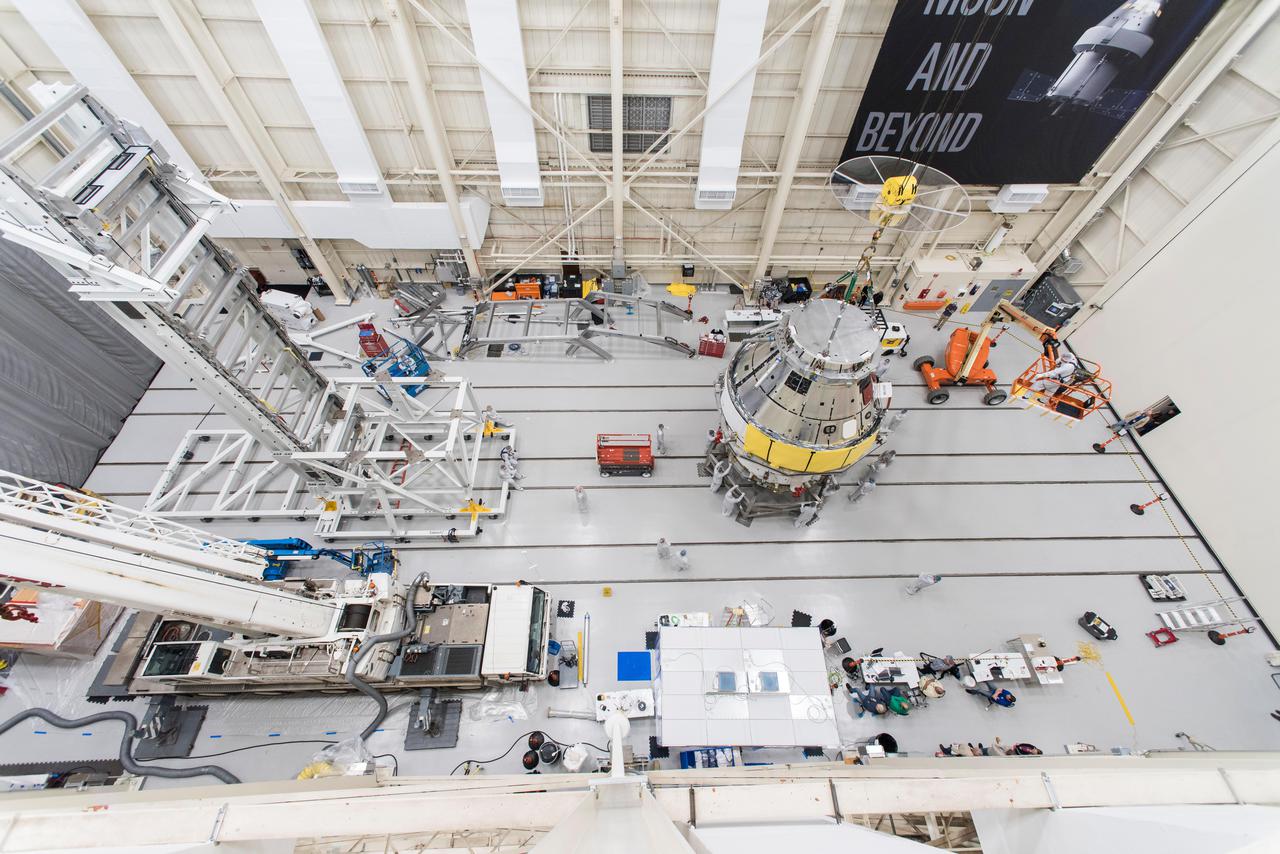
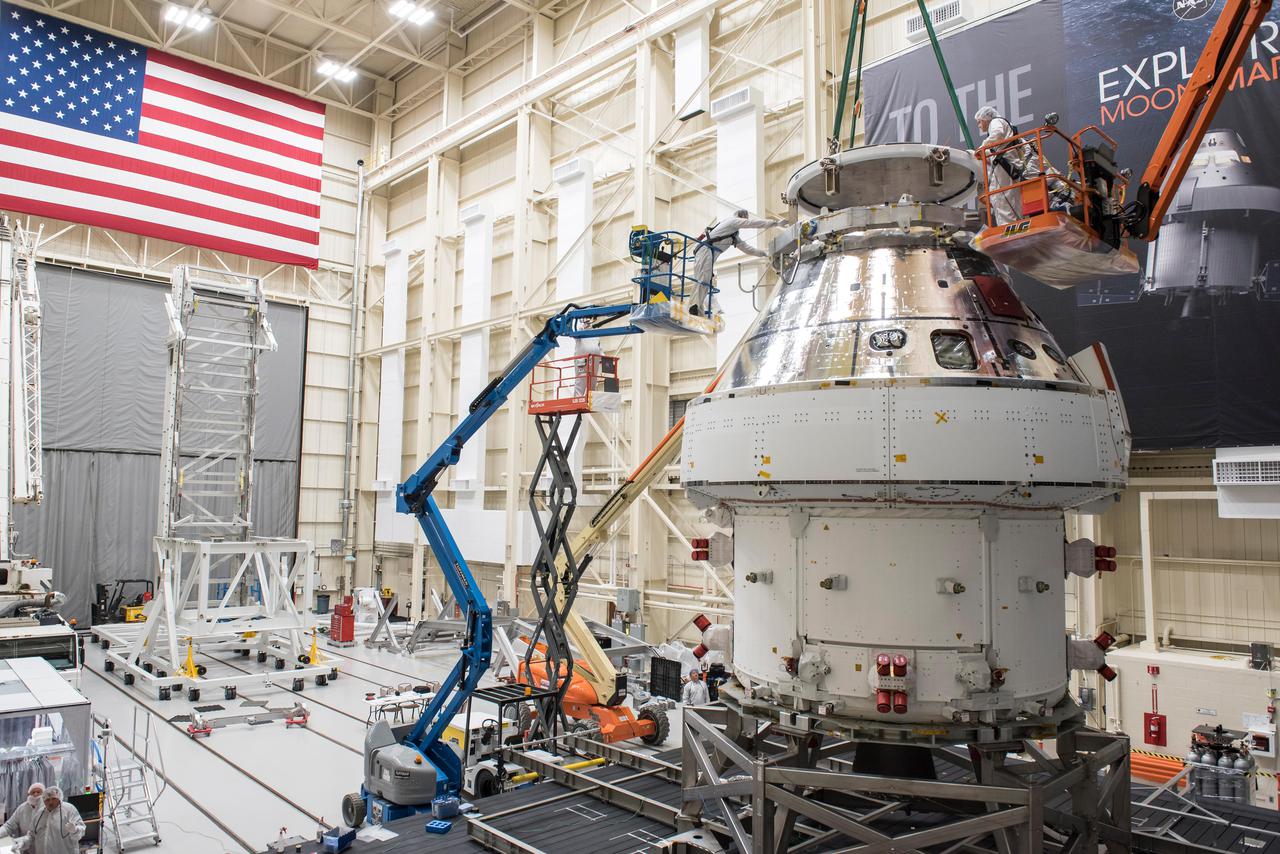
The Orion crew module for Artemis 1 is lifted by crane on July 16, 2019, in the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The crew module will be moved to the final assembly and test cell and work will begin to secure it atop the service module. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its uncrewed test flight atop NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Artemis 1 is the first test flight of the SLS and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system. Orion will travel thousands of miles beyond the Moon during a mission that will test its systems in space. The spacecraft will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean where it will be retrieved and transported back to Kennedy.
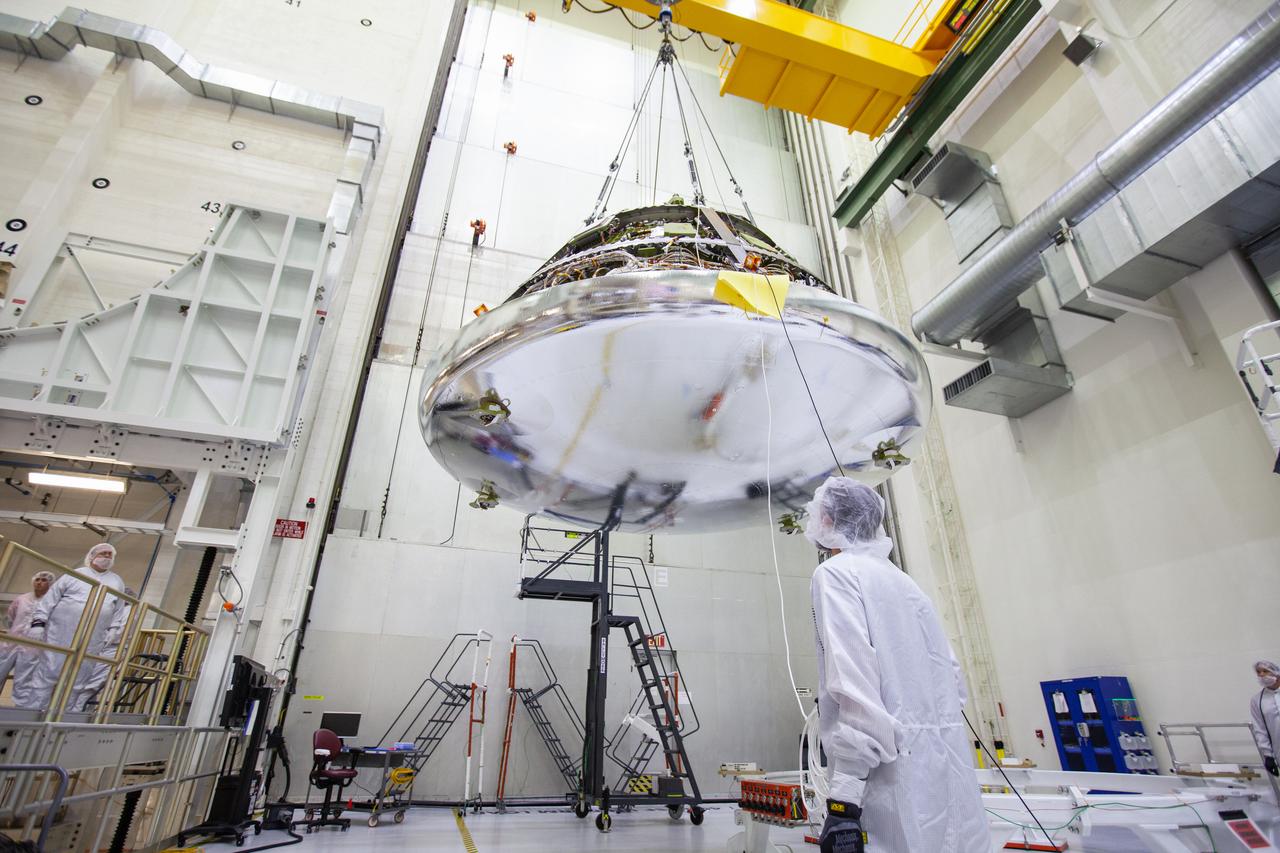

The Orion crew module for Artemis 1 is lifted by crane on July 16, 2019, in the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The crew module is being moved to the final assembly and test cell and work will begin to secure it atop the service module. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its uncrewed test flight atop NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Artemis 1 is the first test flight of the SLS and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system. Orion will travel thousands of miles beyond the Moon during a mission that will test its systems in space. The spacecraft will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean where it will be retrieved and transported back to Kennedy.
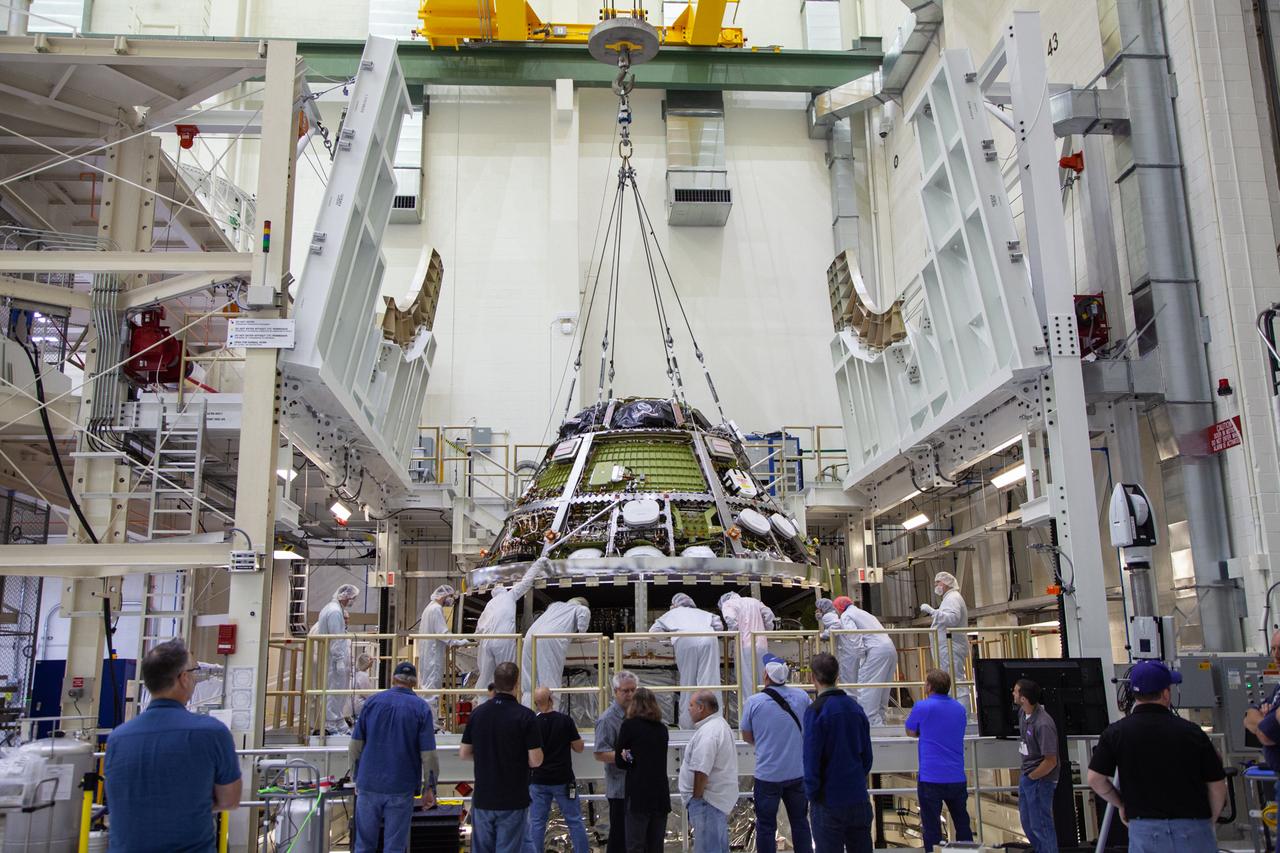

The Orion crew module for Artemis 1 is lowered by crane atop its service module on July 16, 2019, in the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians begin the work to secure the crew module onto the service module in the final assembly and test cell. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its uncrewed test flight atop NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Artemis 1 is the first test flight of the SLS and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system. Orion will travel thousands of miles beyond the Moon during a mission that will test its systems in space and during re-entry. The spacecraft will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean where it will be retrieved and transported back to Kennedy.
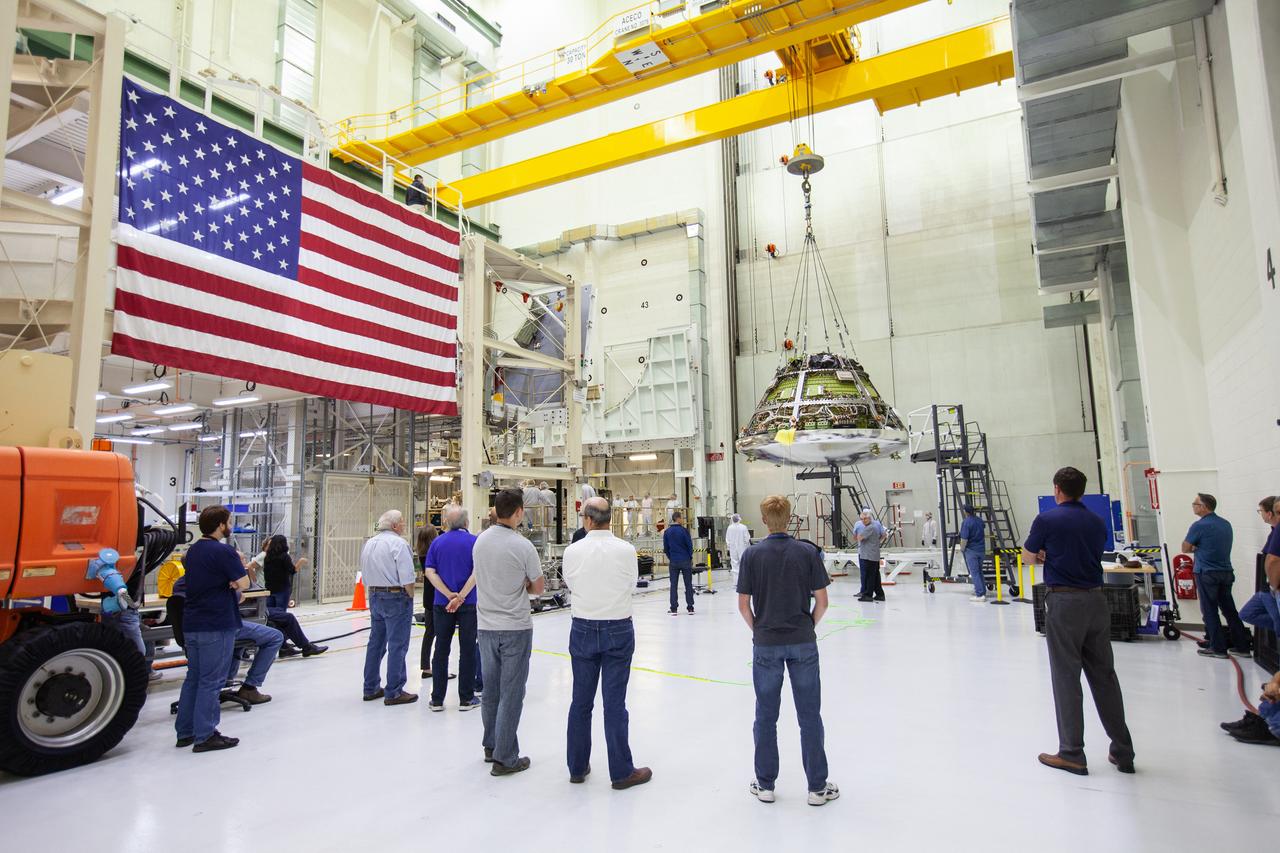

Engineers and technicians monitor the progress as the Orion crew module for Artemis 1 is moved by crane on July 16, 2019, in the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The crew module is being moved to the final assembly and test cell and work will begin to secure it atop the service module. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its uncrewed test flight atop NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Artemis 1 is the first test flight of the SLS and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system. Orion will travel thousands of miles beyond the Moon during a mission that will test its systems in space. The spacecraft will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean where it will be retrieved and transported back to Kennedy.
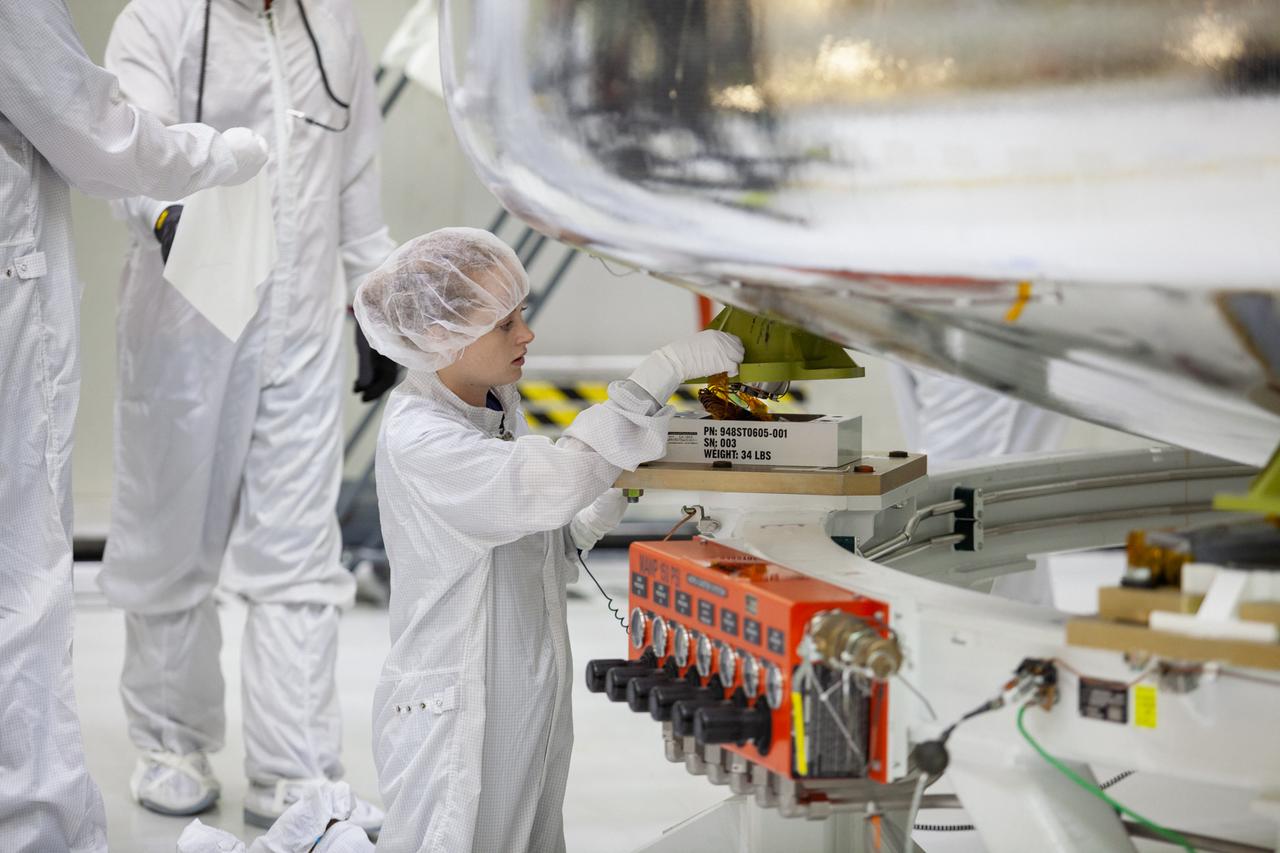

A Lockheed Martin employee works to secure the Orion crew module for the Artemis 1 mission onto a stand inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2019. Work will begin to secure the crew module atop its service module in the final assembly and test cell. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its uncrewed test flight atop NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Artemis 1 is the first test flight of the SLS and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system. Orion will travel thousands of miles beyond the Moon during a mission that will test its systems in space and during re-entry. The spacecraft will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean where it will be retrieved and transported back to Kennedy.
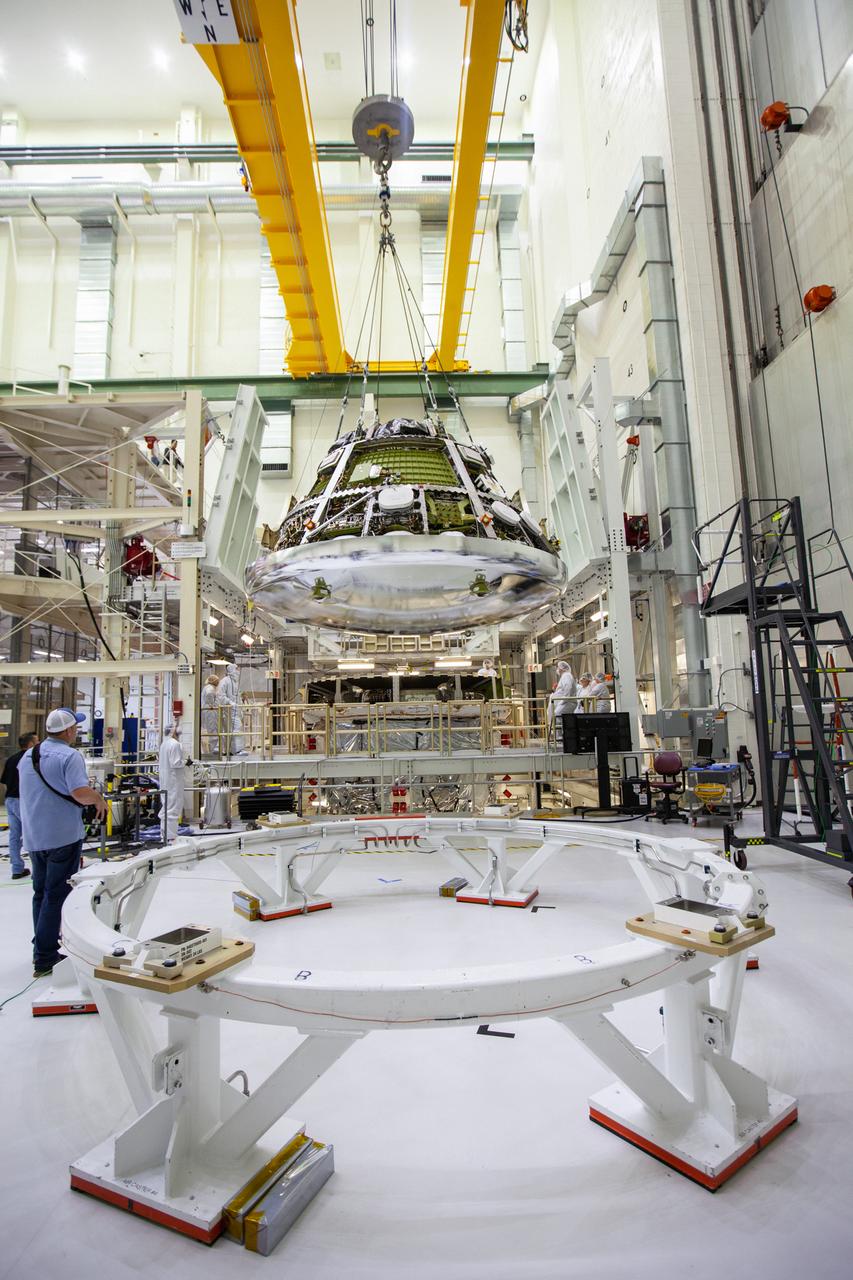

The Orion crew module for Artemis 1 is lifted by crane on July 16, 2019, in the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The crew module is being moved to the final assembly and test cell and work will begin to secure it atop the service module. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its uncrewed test flight atop NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Artemis 1 is the first test flight of the SLS and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system. Orion will travel thousands of miles beyond the Moon during a mission that will test its systems in space. The spacecraft will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean where it will be retrieved and transported back to Kennedy.
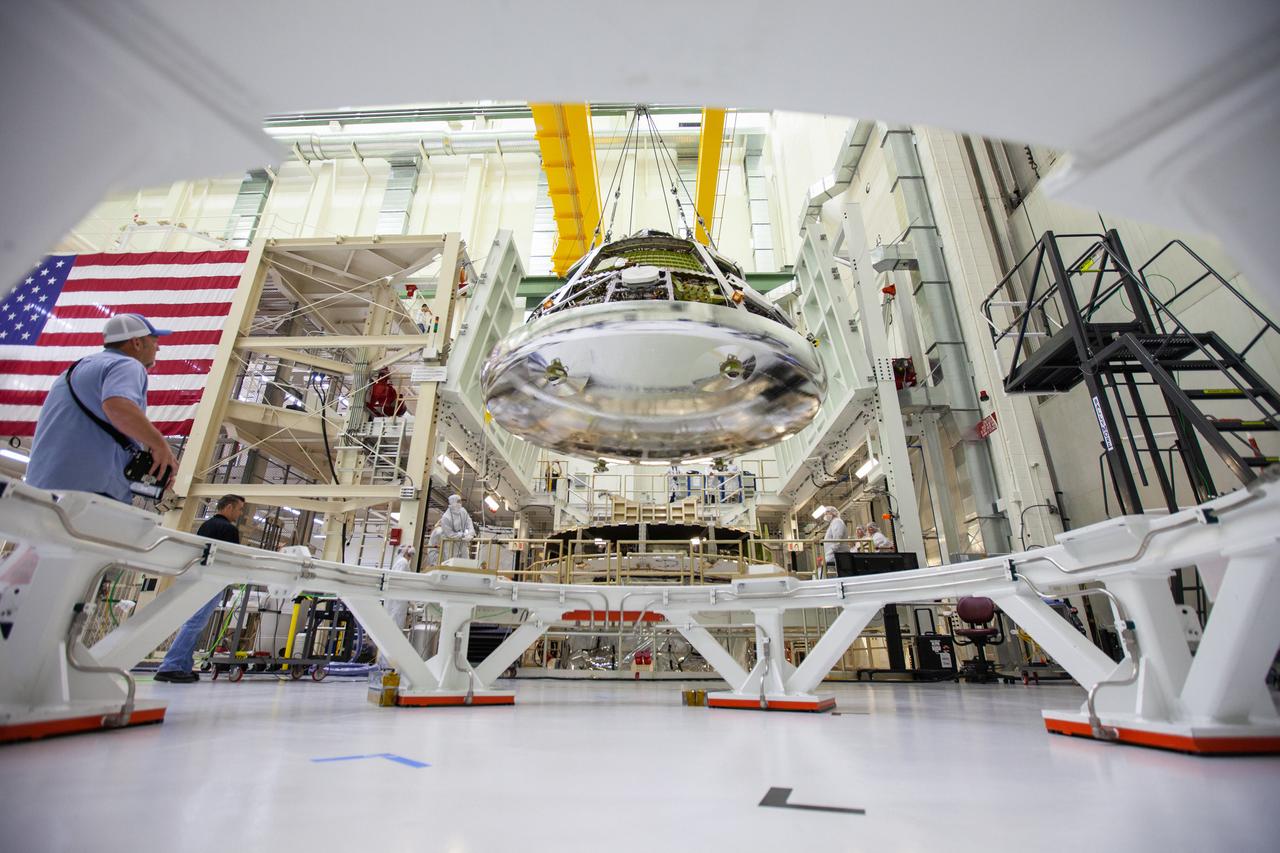

The Orion crew module for Artemis 1 is lifted by crane on July 16, 2019, in the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The crew module will be moved to the final assembly and test cell and work will begin to secure it atop the service module. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its uncrewed test flight atop NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Artemis 1 is the first test flight of the SLS and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system. Orion will travel thousands of miles beyond the Moon during a mission that will test its systems in space. The spacecraft will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean where it will be retrieved and transported back to Kennedy.
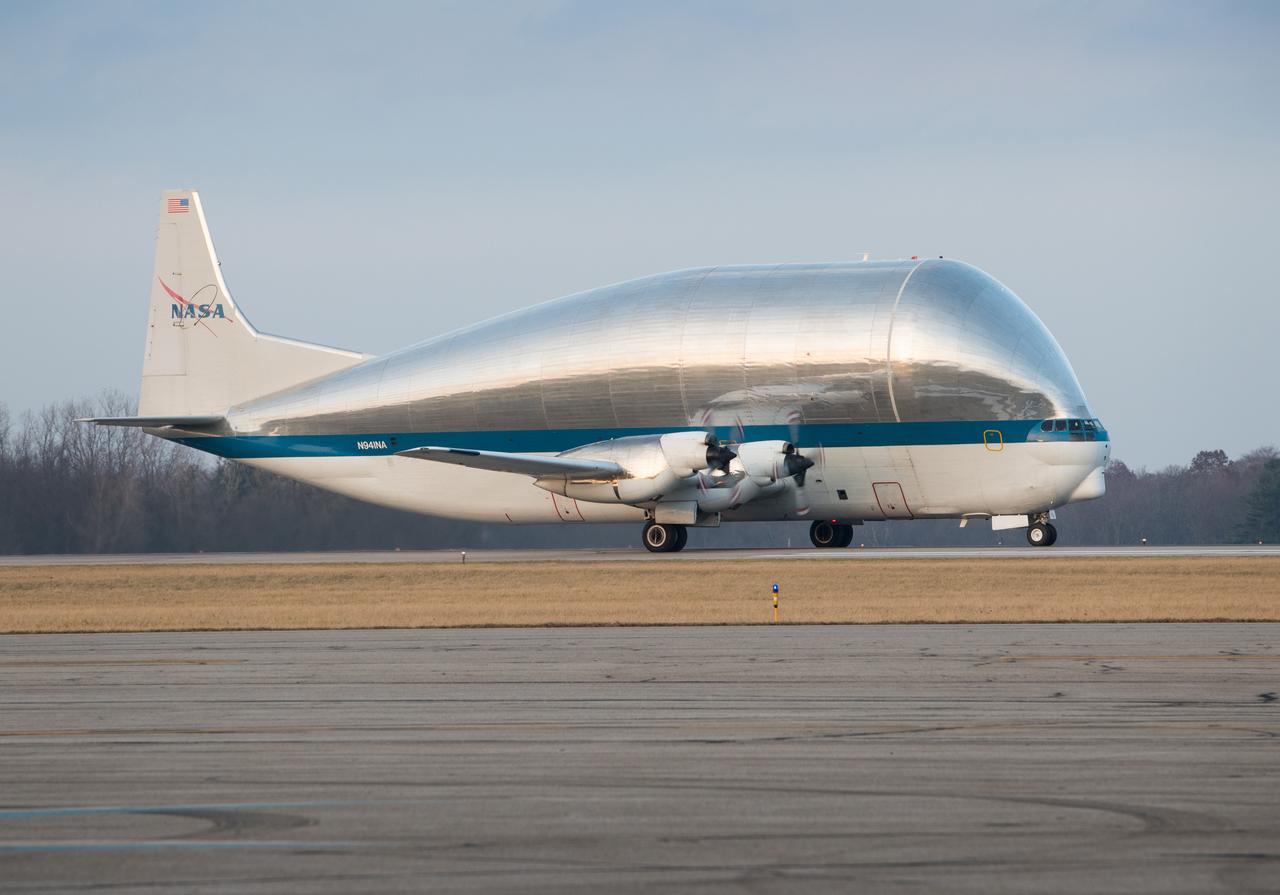

Orion - EM-1 - Artemis Spacecraft Arrival at Mansfield Lahm Airport on Board the Super Guppy Aircraft, Transportation to Plum Brook Station and Installation in the Space Environment Complex, SEC Thermal Vacuum Chamber
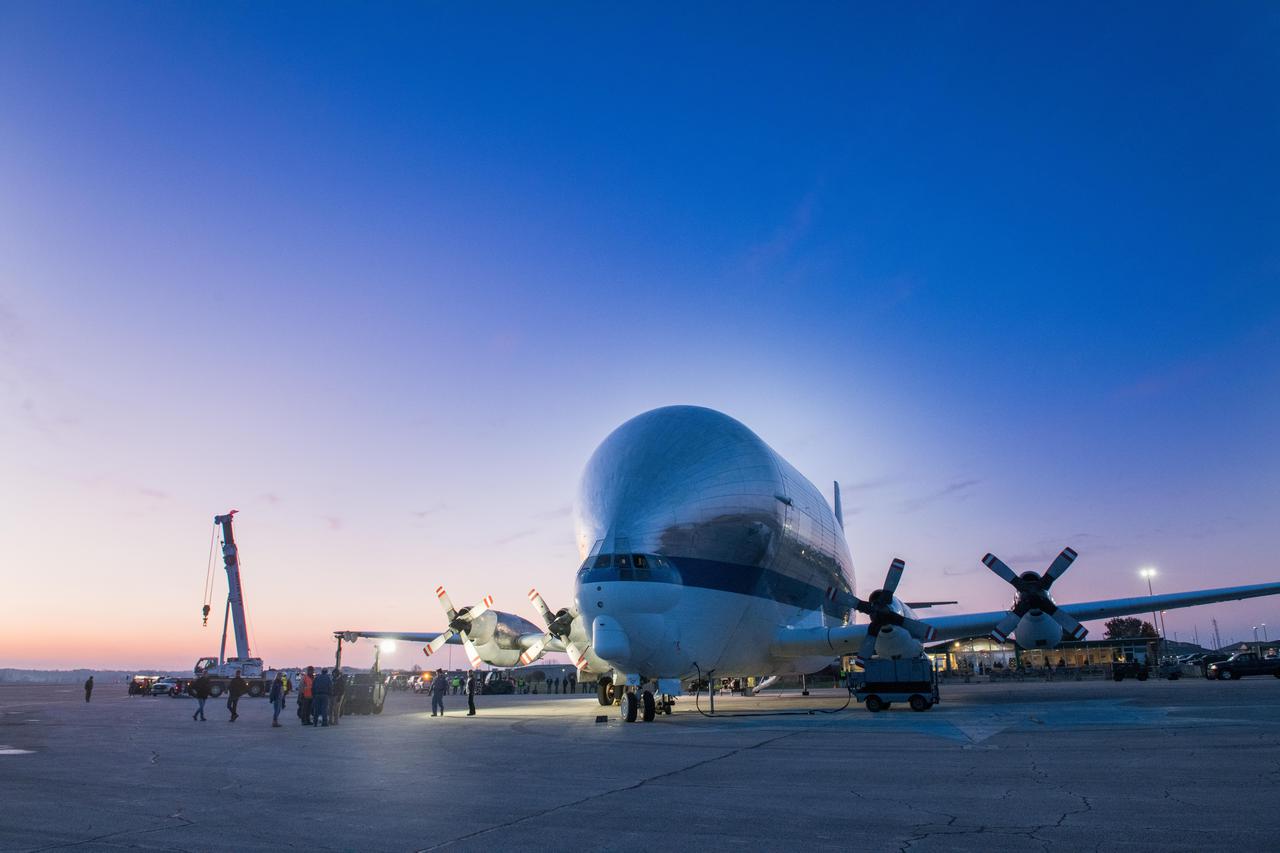

Orion - EM-1 - Artemis Spacecraft Arrival at Mansfield Lahm Airport, Transportation to Plum Brook Station and Installation in the Space Environment Complex, SEC Thermal Vacuum Chamber
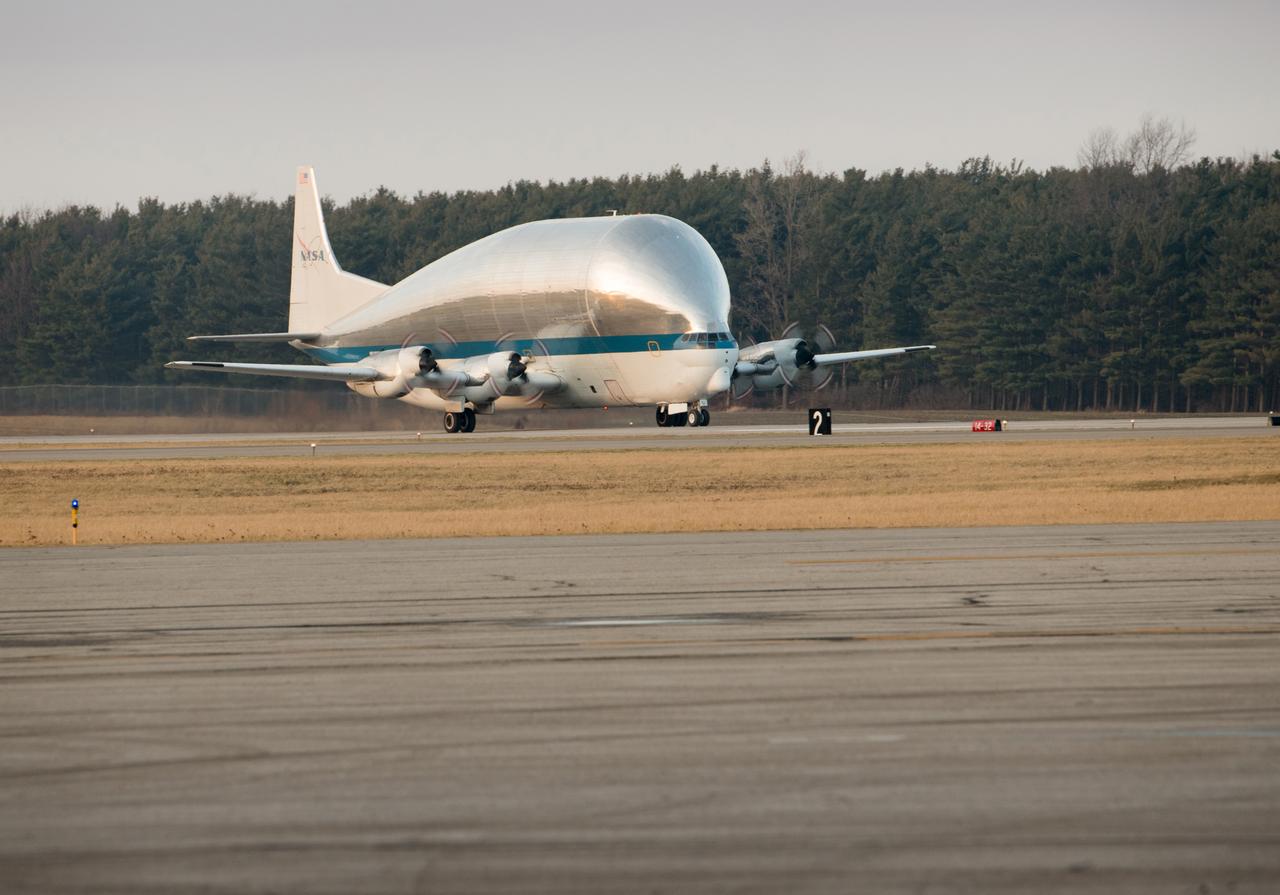

Orion - EM-1 - Artemis Spacecraft Arrival at Mansfield Lahm Airport on board the Super Guppy Aircraft, Transportation to Plum Brook Station and Installation in the Space Environment Complex, SEC Thermal Vacuum Chamber
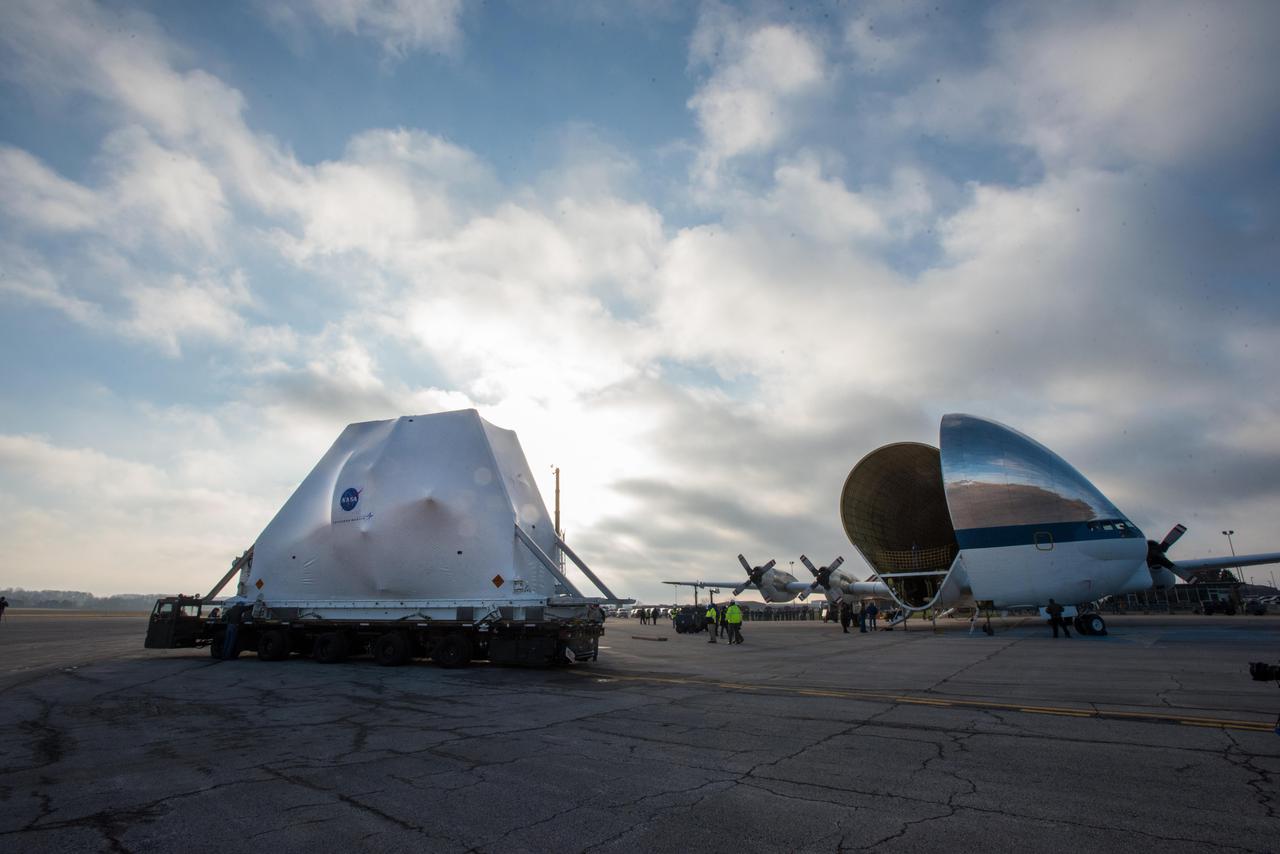

Orion - EM-1 - Artemis Spacecraft Arrival at Mansfield Lahm Airport, Transportation to Plum Brook Station and Installation in the Space Environment Complex, SEC Thermal Vacuum Chamber
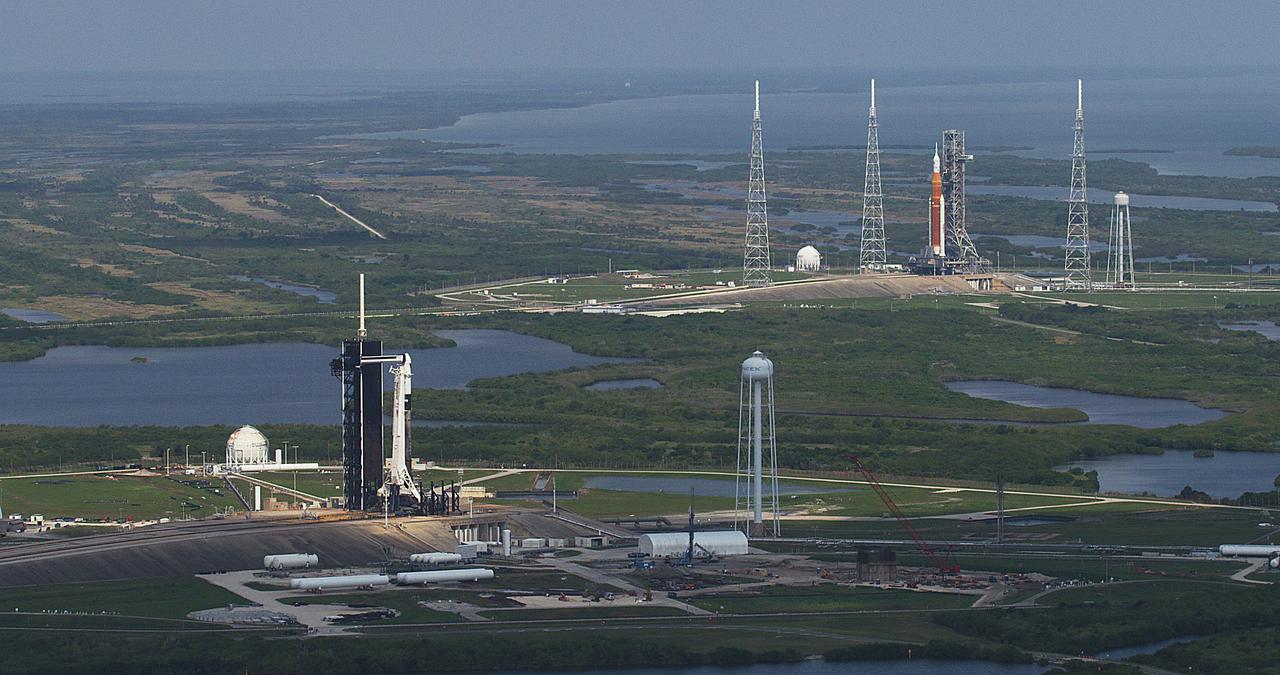

SpaceX’s Axiom-1 is in the foreground on Launch Pad 39A with NASA’s Artemis I in the background on Launch Pad 39B on April 6, 2022. This is the first time two totally different types of rockets and spacecraft designed to carry humans are on the sister pads at the same time—but it won’t be the last as NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida continues to grow as a multi-user spaceport to launch both government and commercial rockets.
Orion - EM-1 - Artemis Spacecraft Departure at the Space Environments Complex, SEC Thermal Vacuum Chamber at the Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility, Transportation to Mansfield Lahm Airport
Orion - EM-1 - Artemis Spacecraft Departure at the Space Environments Complex, SEC Thermal Vacuum Chamber at the Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility, Transportation to Mansfield Lahm Airport
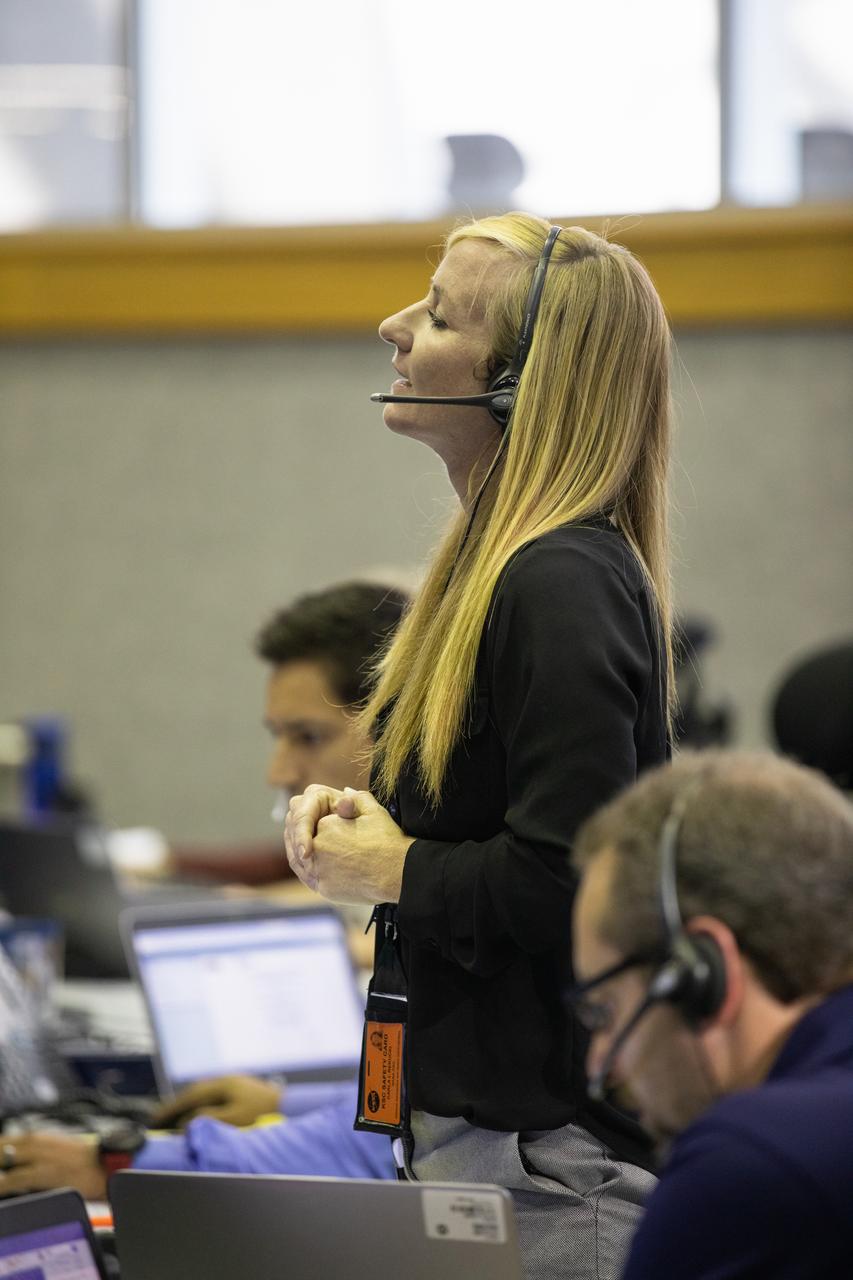

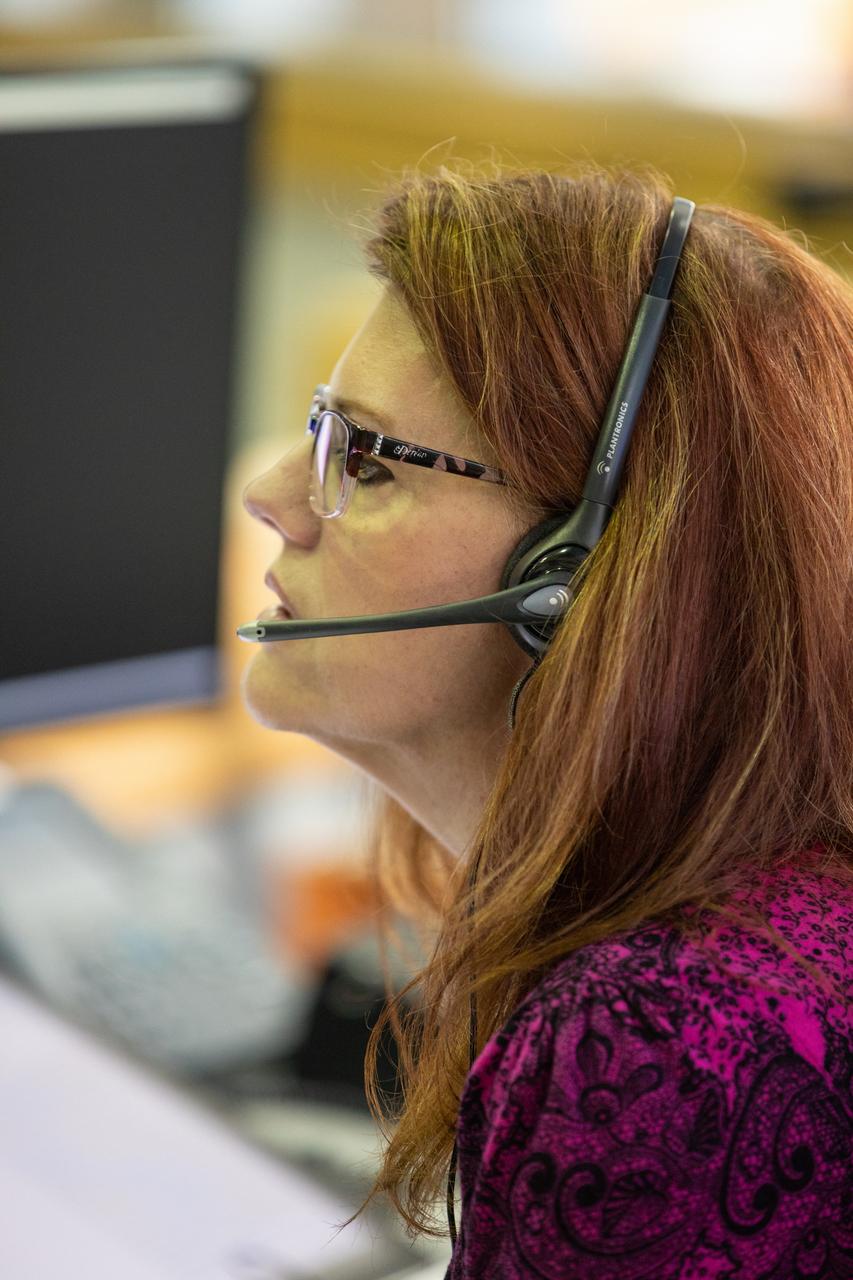
Carla Rekucki, lead NASA test director in NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS), center, and other launch team members participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
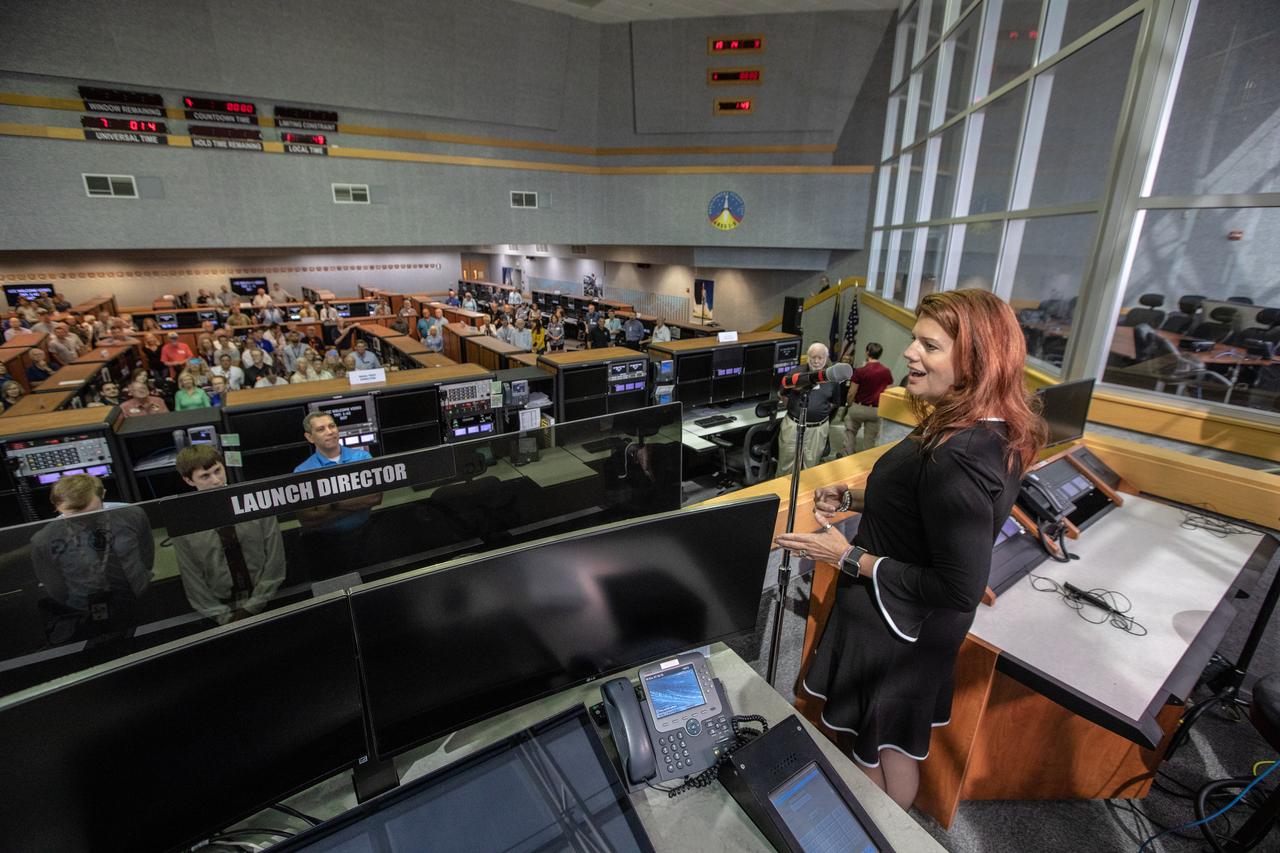

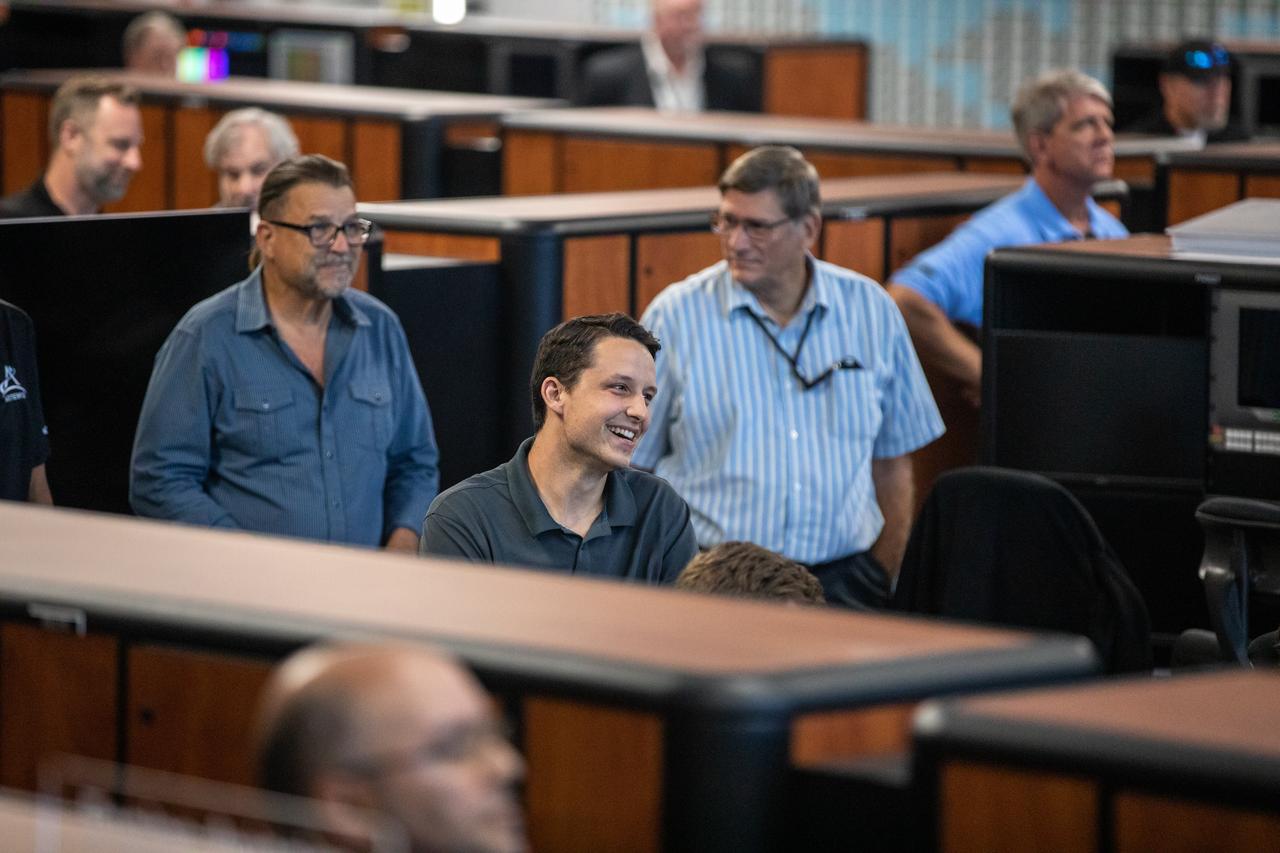
On July 16, 2019, the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch to the Moon, Artemis 1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson stands in Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Floirda. Apollo 11 and Artemis 1 launch team members mingle in the firing room.
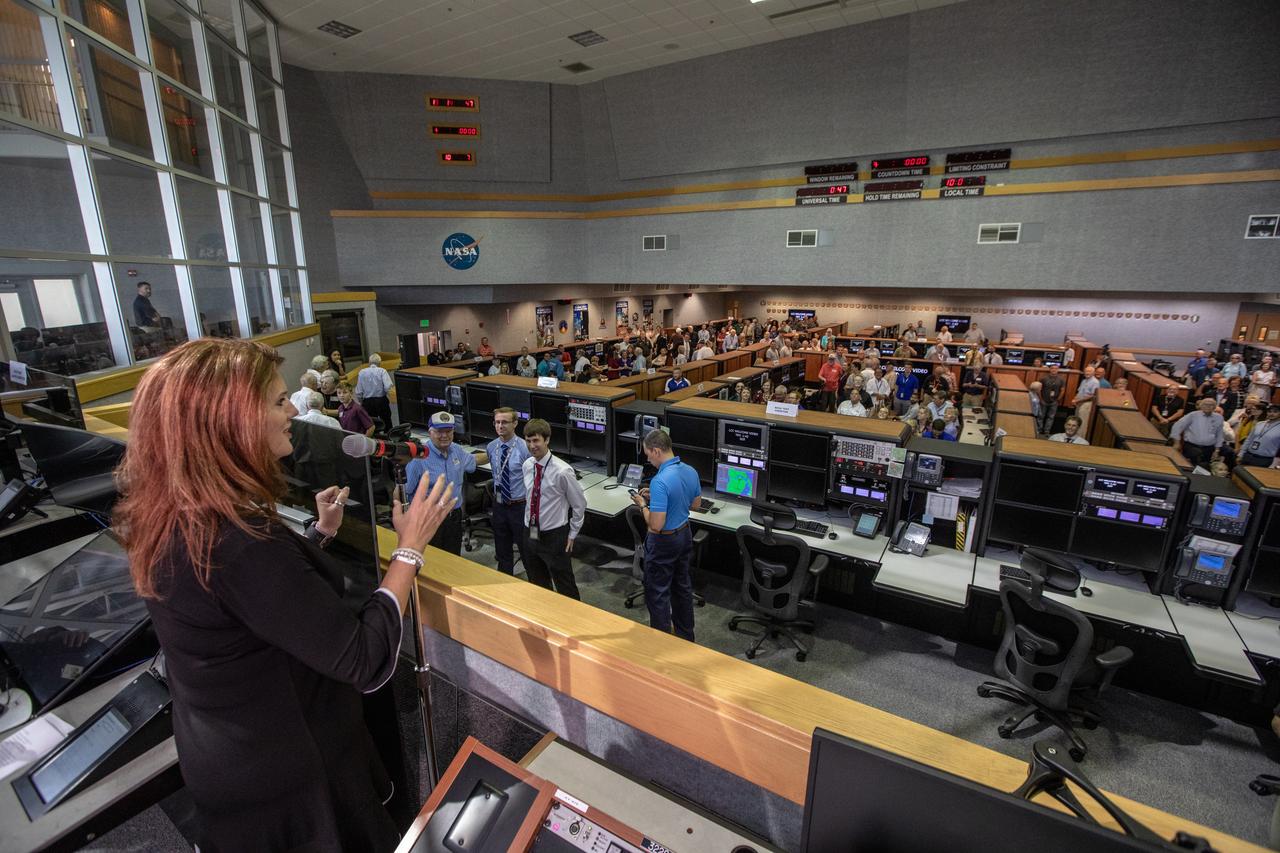

On July 16, 2019, the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch to the Moon, Artemis 1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson stands in Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Floirda. Apollo 11 and Artemis 1 launch team members mingle in the firing room.
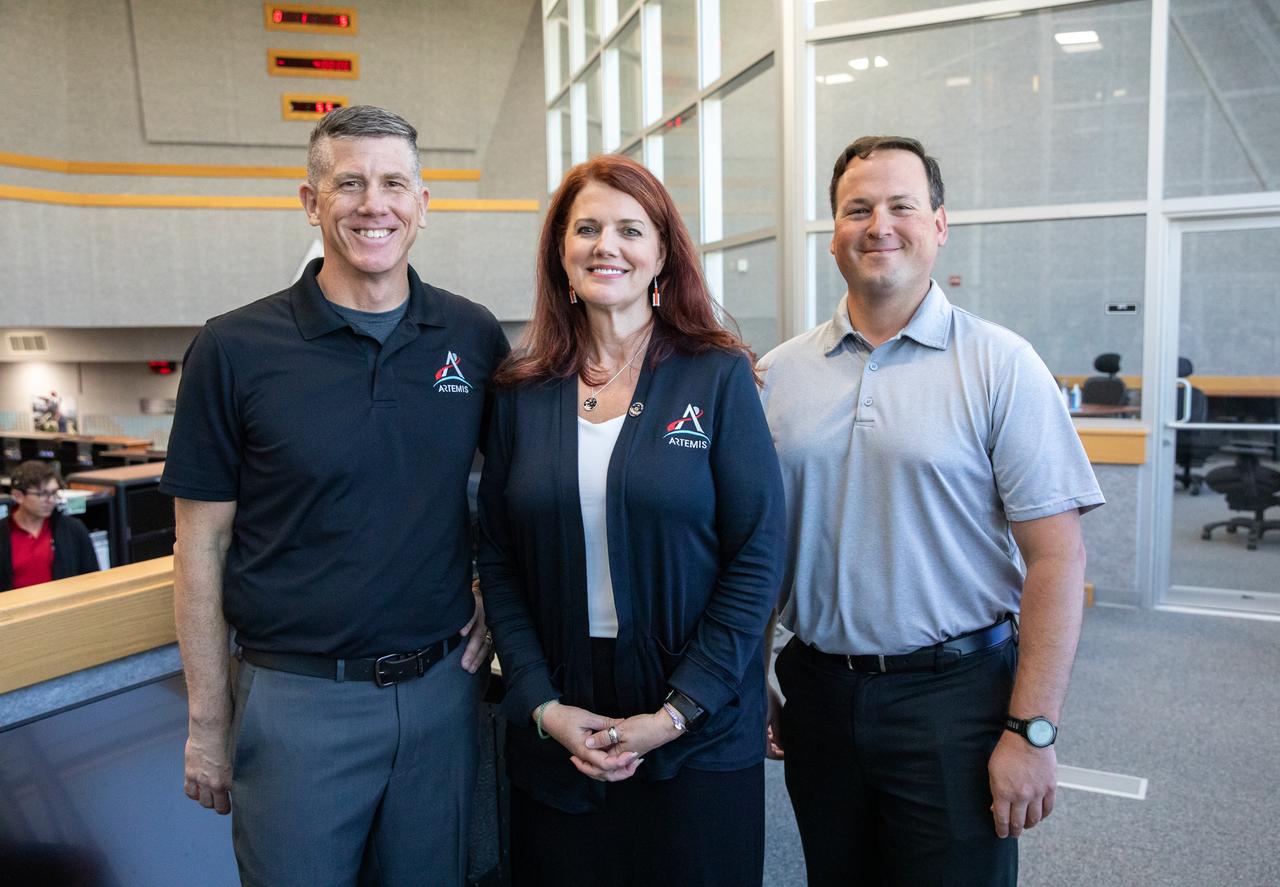

Artemis Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, center, is inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during the inaugural Artemis I launch director awards and plaque ceremony on March 24, 2023. At left is Jeremy Graeber, Artemis assistant launch director. At right is Wes Mosedale, technical assistant to the launch director. Following tradition from the Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs, the Artemis I plaque was added to the wall in Firing Room 1 by Blackwell-Thompson. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I launched successfully from Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2022.

Orion - EM-1 - Artemis Spacecraft Arrival at Mansfield Lahm Airport, Transportation to Plum Brook Station and Installation in the Space Environment Complex, SEC Thermal Vacuum Chamber
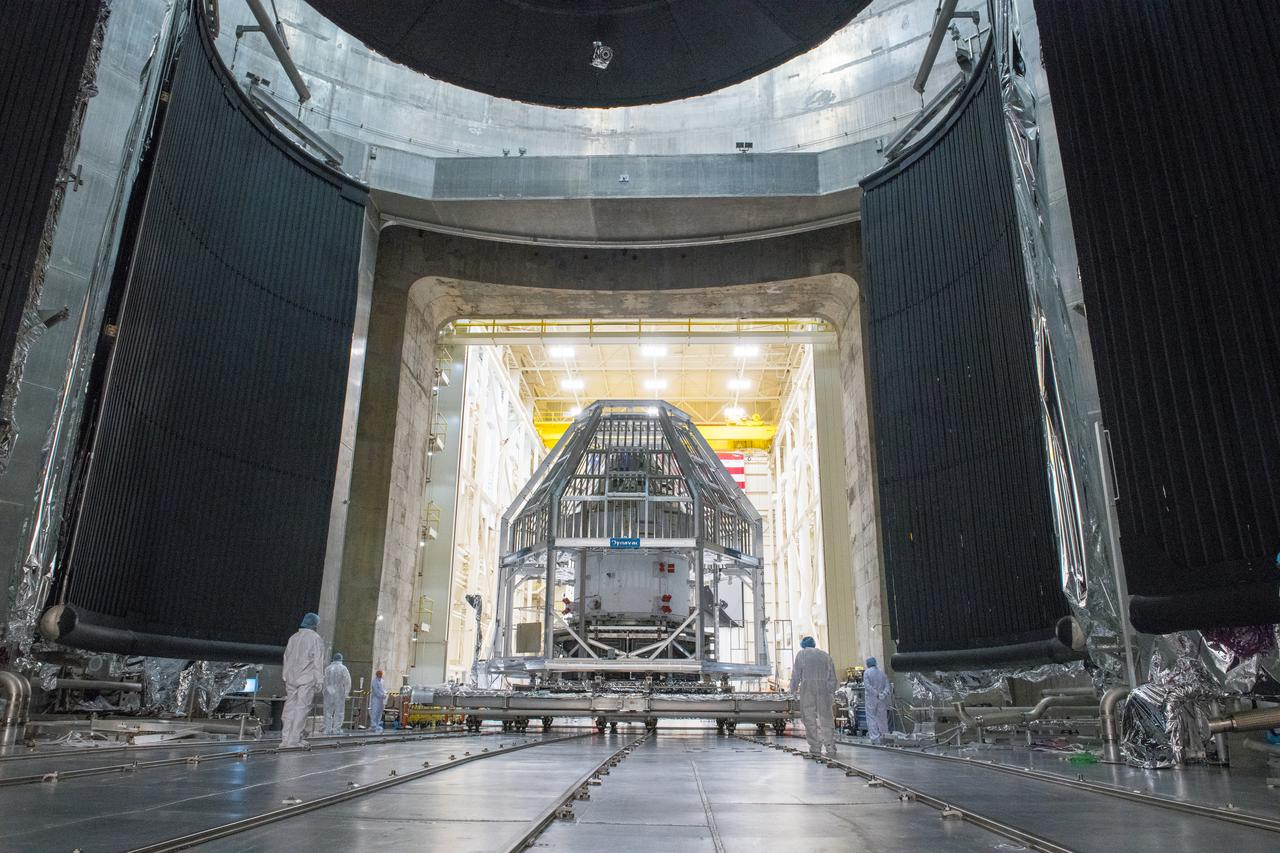

Orion - EM-1 - Artemis Spacecraft Installation in the Space Environment Complex, SEC Thermal Vacuum Chamber
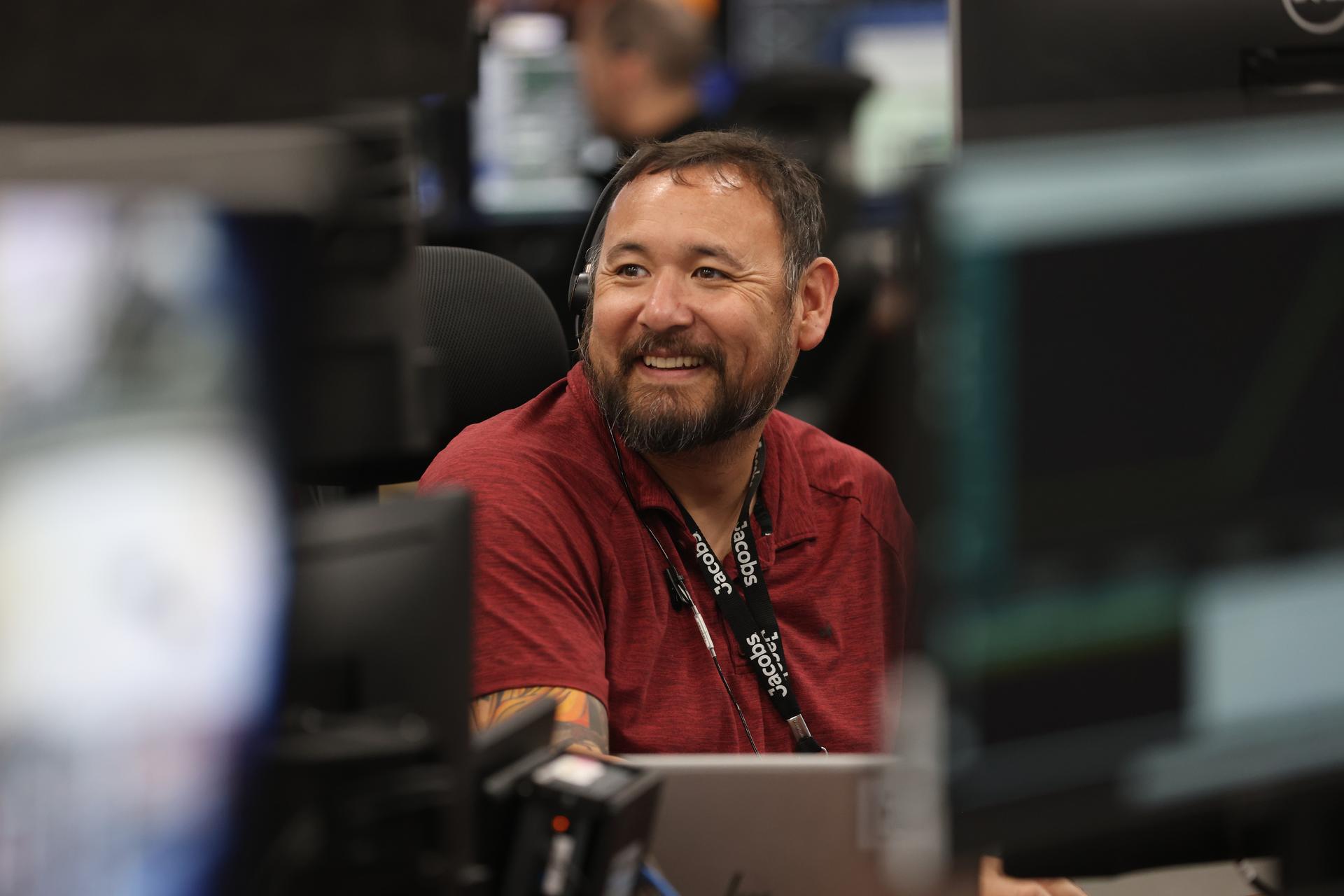

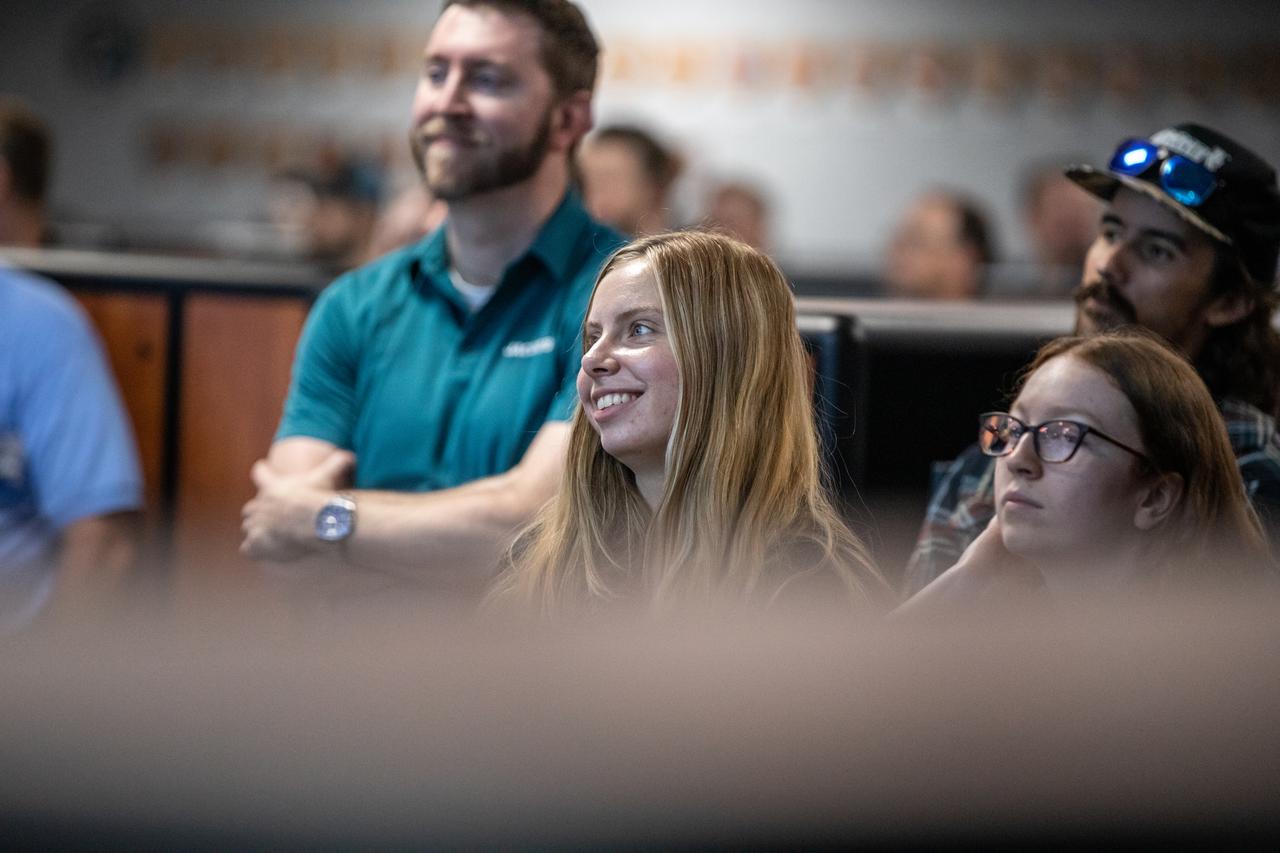
Members of the Artemis launch team participate in an Artemis II launch countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 8, 2025. The simulations go through launch day scenarios to help launch team members test software and make adjustments if needed during countdown operations. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.
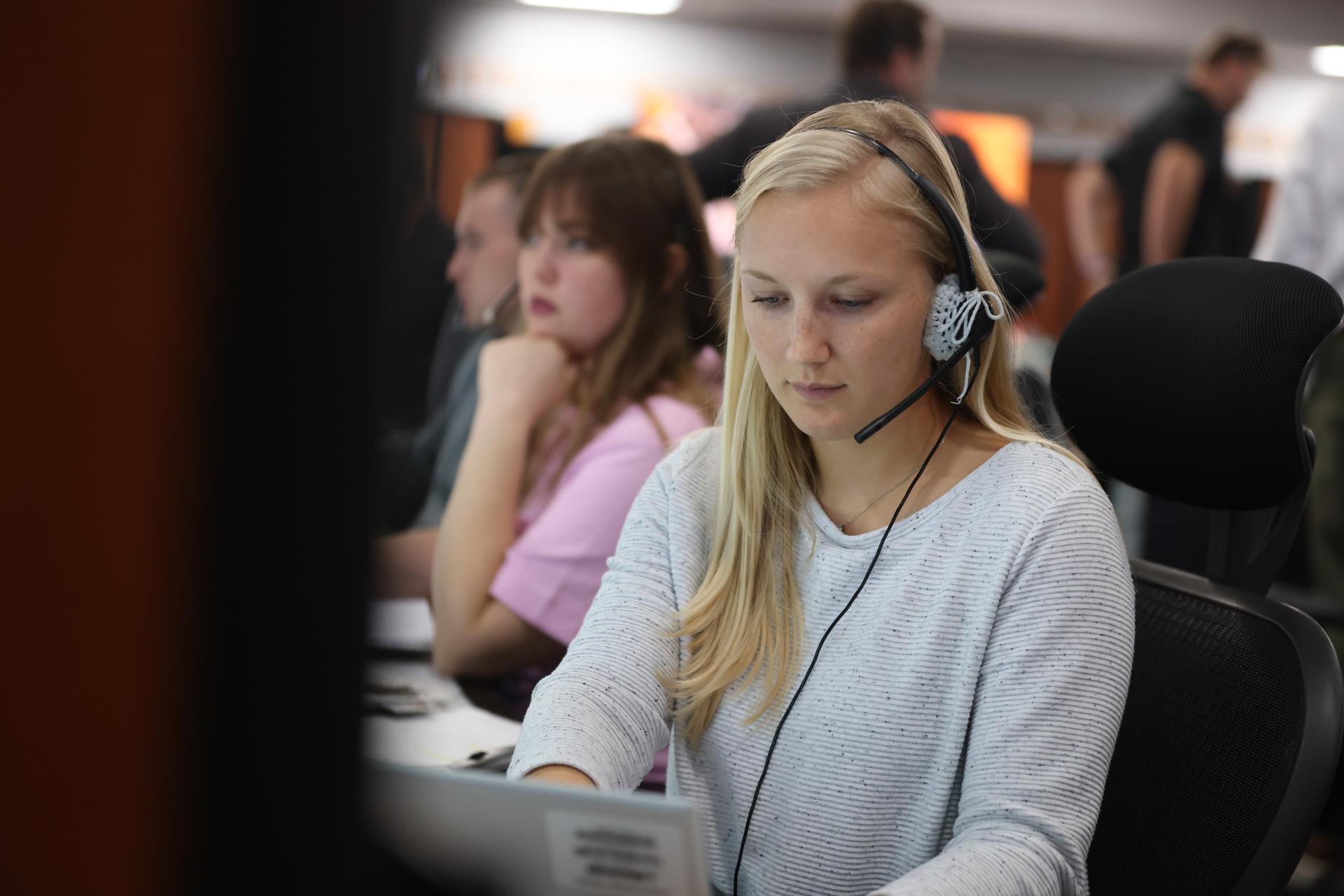

Members of the Artemis launch team participate in an Artemis II launch countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 8, 2025. The simulations go through launch day scenarios to help launch team members test software and make adjustments if needed during countdown operations. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.
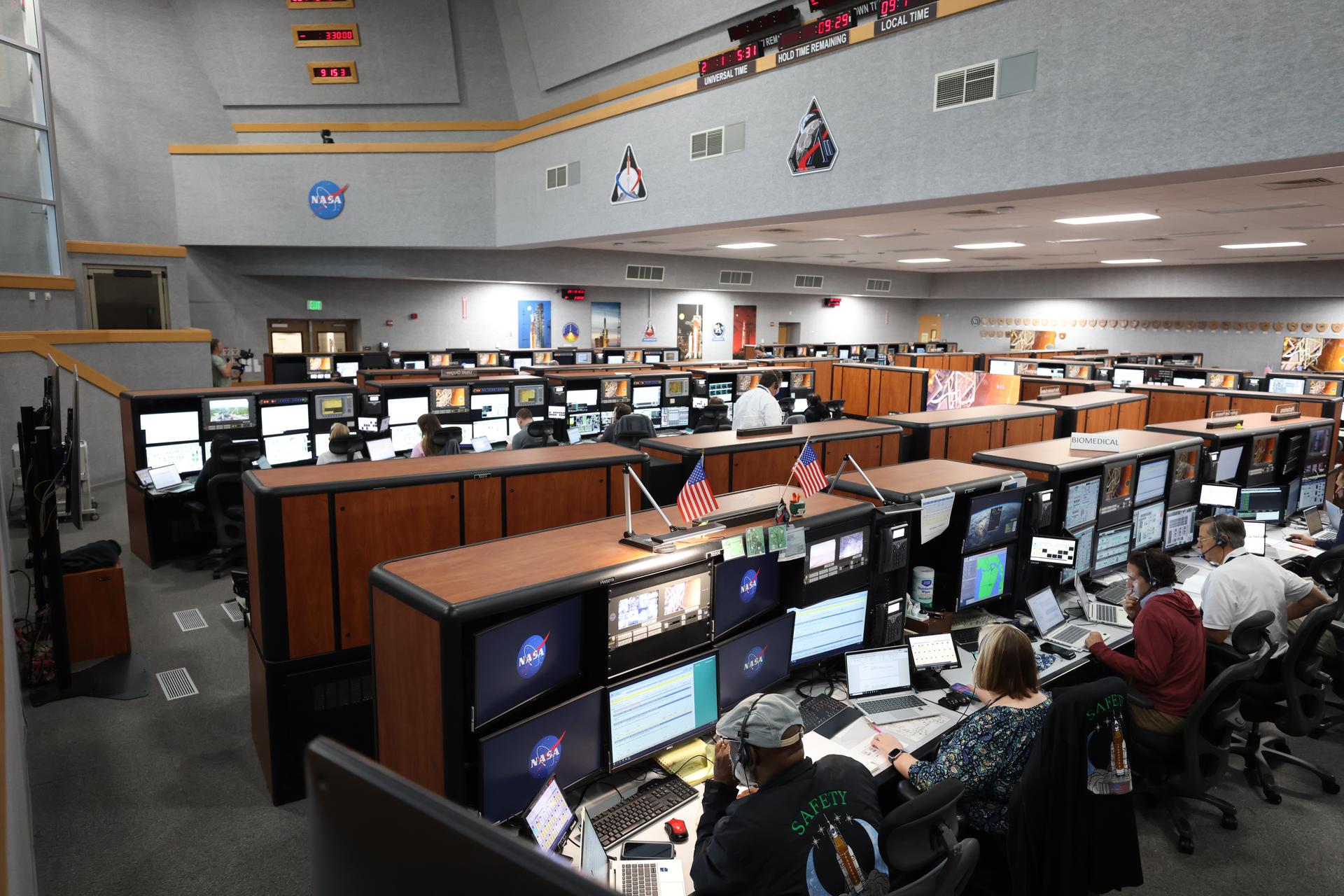

Members of the Artemis launch team participate in an Artemis II launch countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 8, 2025. The simulations go through launch day scenarios to help launch team members test software and make adjustments if needed during countdown operations. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.

Artemis team members gather around Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2023 for the inaugural Artemis Launch Director Awards. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I launched successfully from Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2022.

Artemis team members gather around Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2023 for the inaugural Artemis Launch Director Awards. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I launched successfully from Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2022.
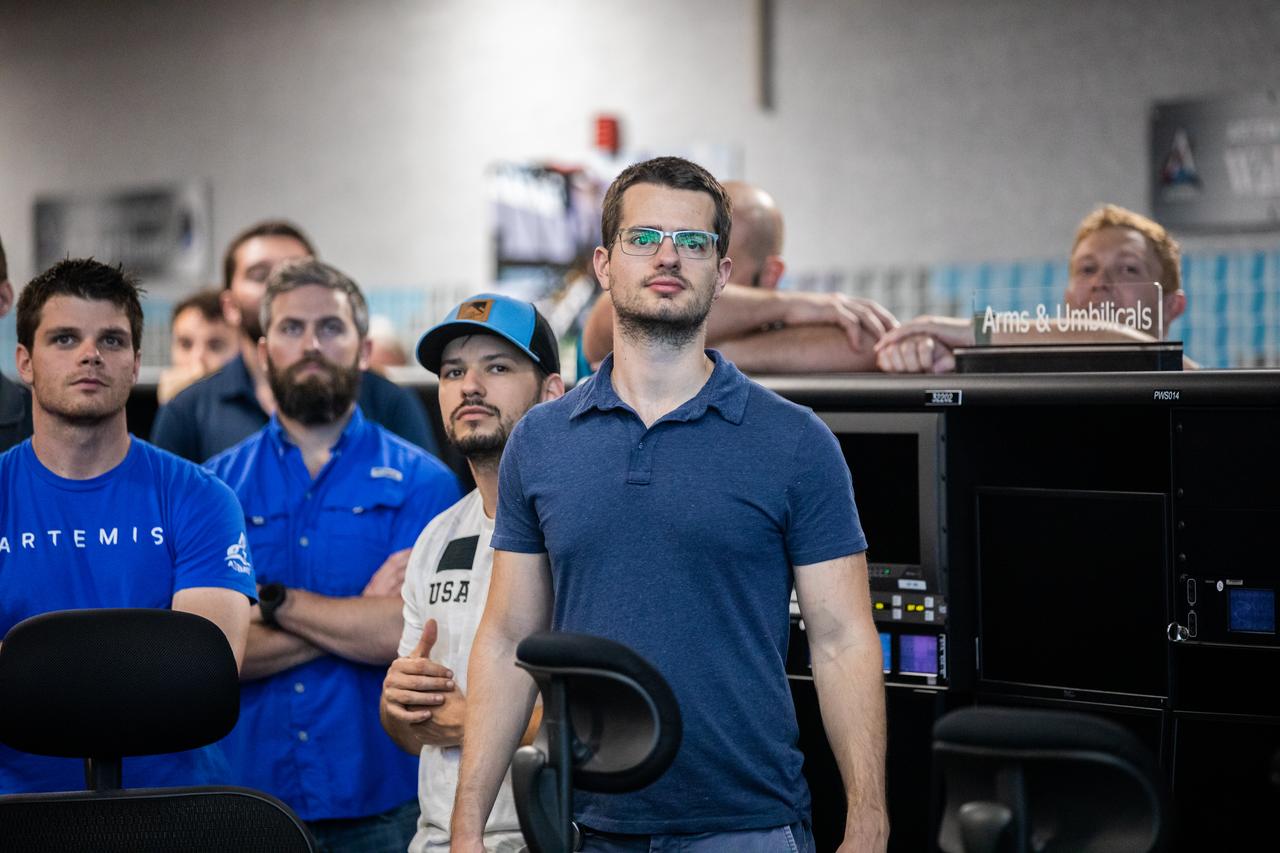

Artemis team members gather around Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2023 for the inaugural Artemis Launch Director Awards. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I launched successfully from Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2022.

Artemis team members gather around Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2023 for the inaugural Artemis Launch Director Awards. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I launched successfully from Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2022.
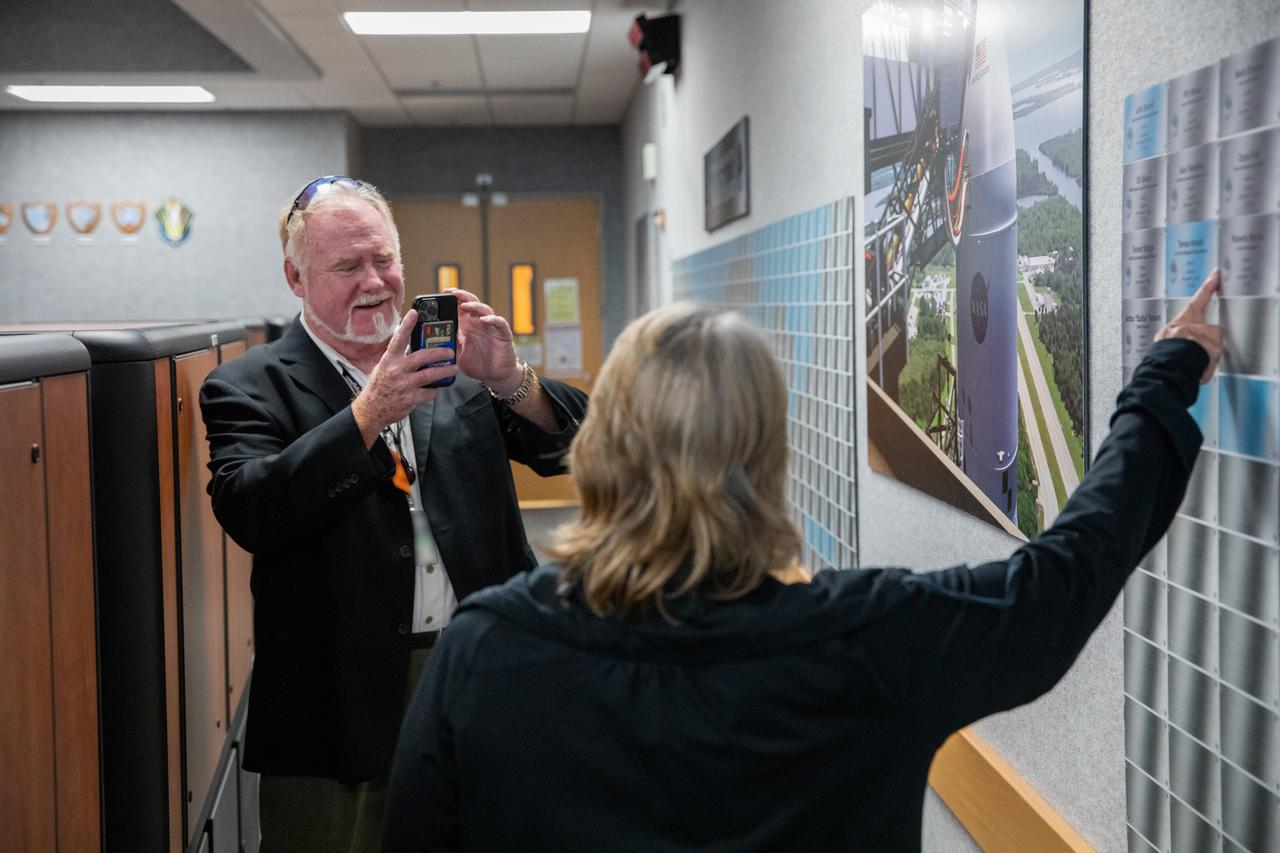

Artemis team members gather around Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2023 for the inaugural Artemis Launch Director Awards. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I launched successfully from Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2022.
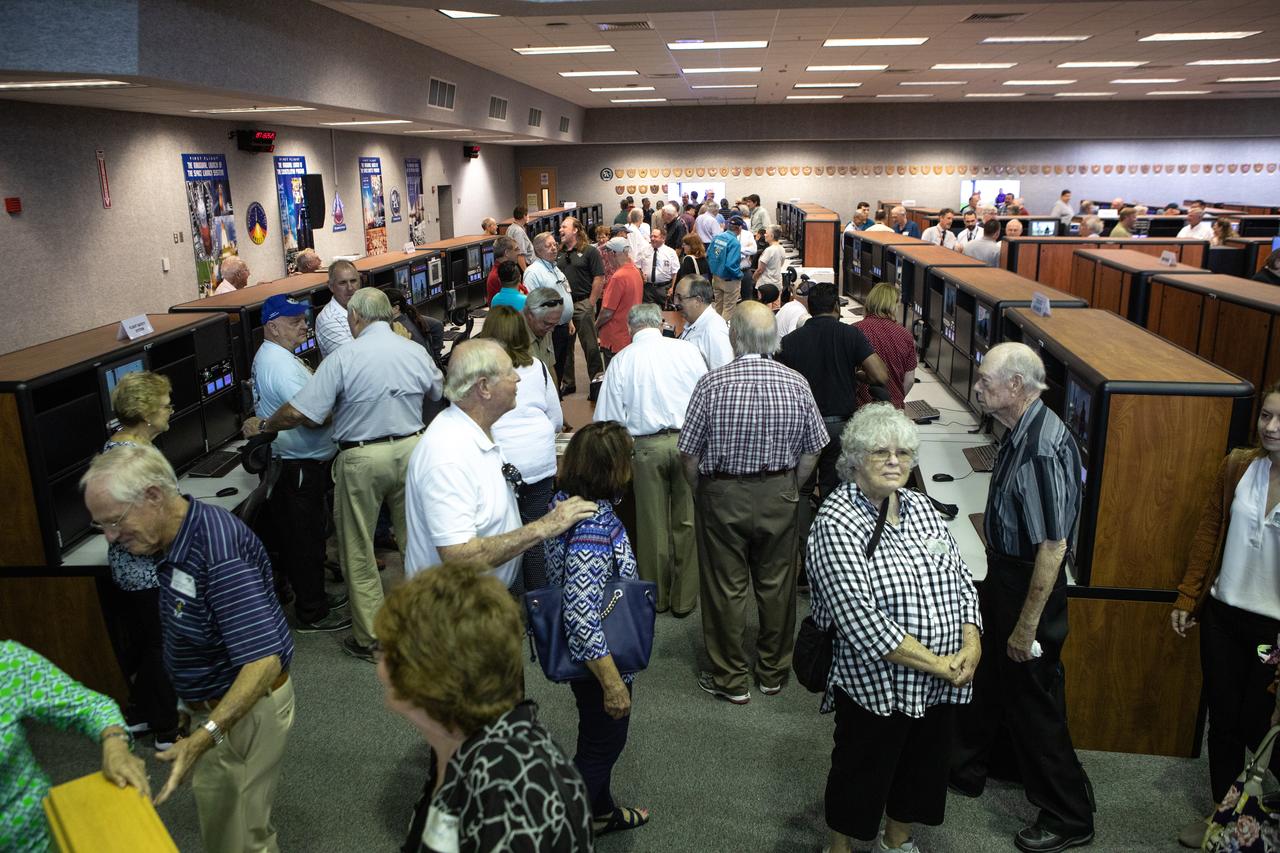

On July 16, 2019, the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch, Apollo-era and Artemis-1 launch team members mingle in Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
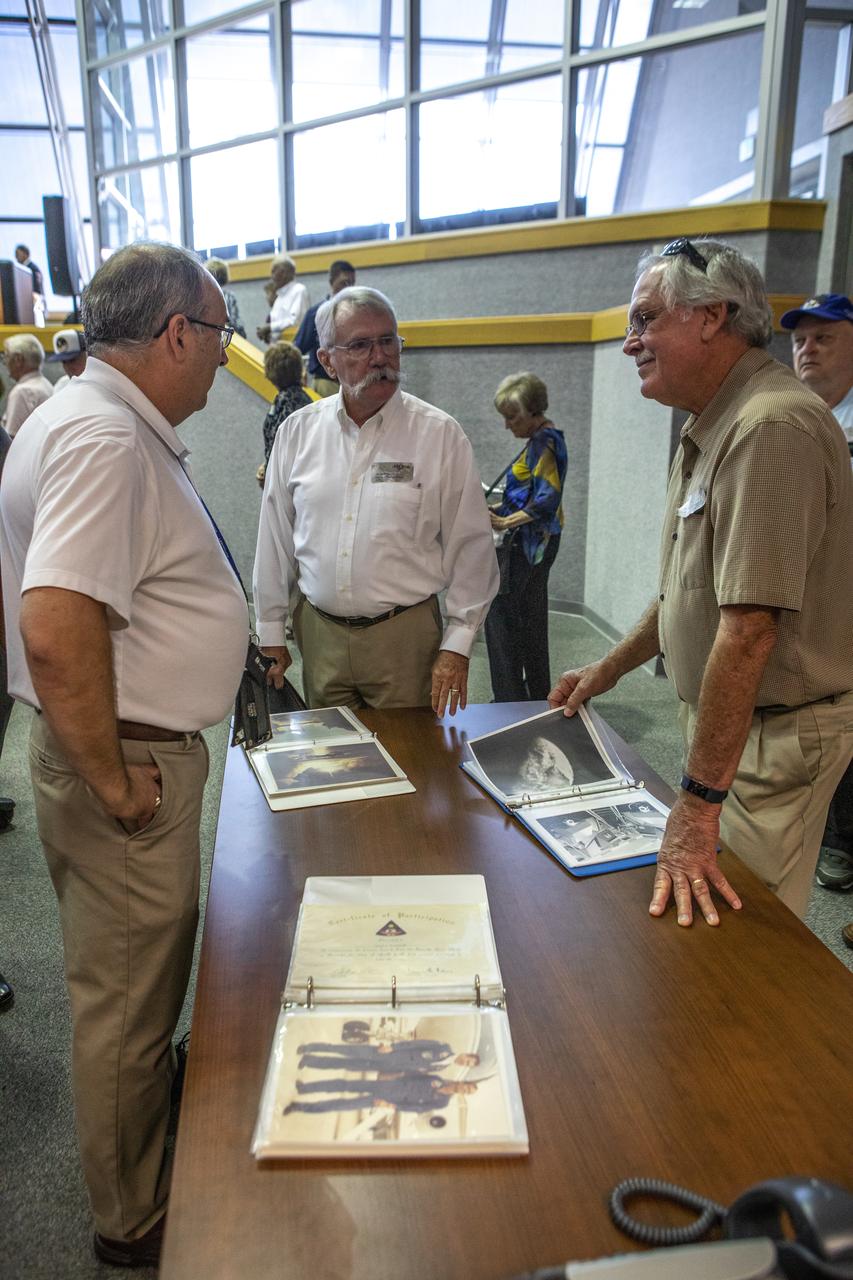

On July 16, 2019, the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch, Apollo-era and Artemis-1 launch team members mingle in Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
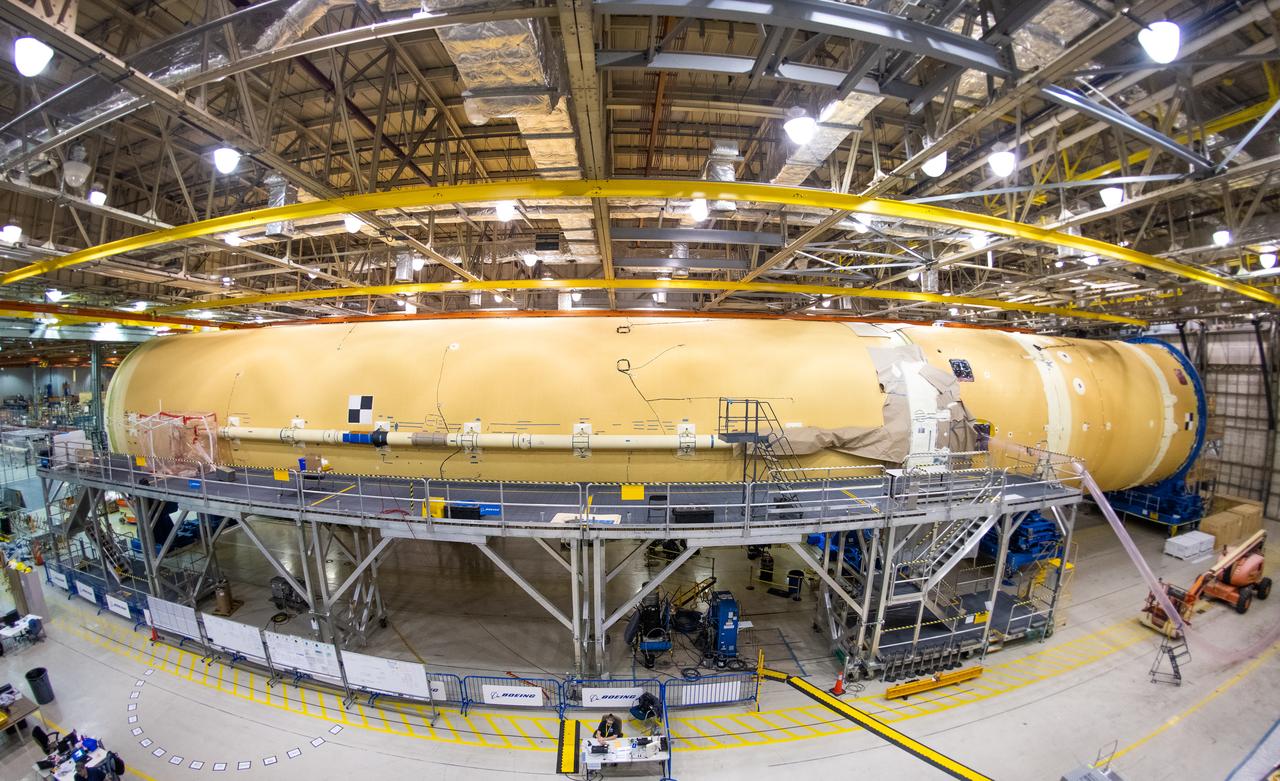

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans completed the “forward join,” which connects structures to form the top part of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage. The first core stage will send Exploration Mission-1, the first integrated flight of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, out beyond the Moon. The forward join mated three structures: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and intertank. This milestone marks the beginning of integration and assembly of the massive, 212-foot-tall SLS core stage, which will include the rocket’s four RS-25 rocket engines, propellant tanks and flight computers. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. These two parts of the core stage will then be assembled to form the largest stage NASA has ever built.
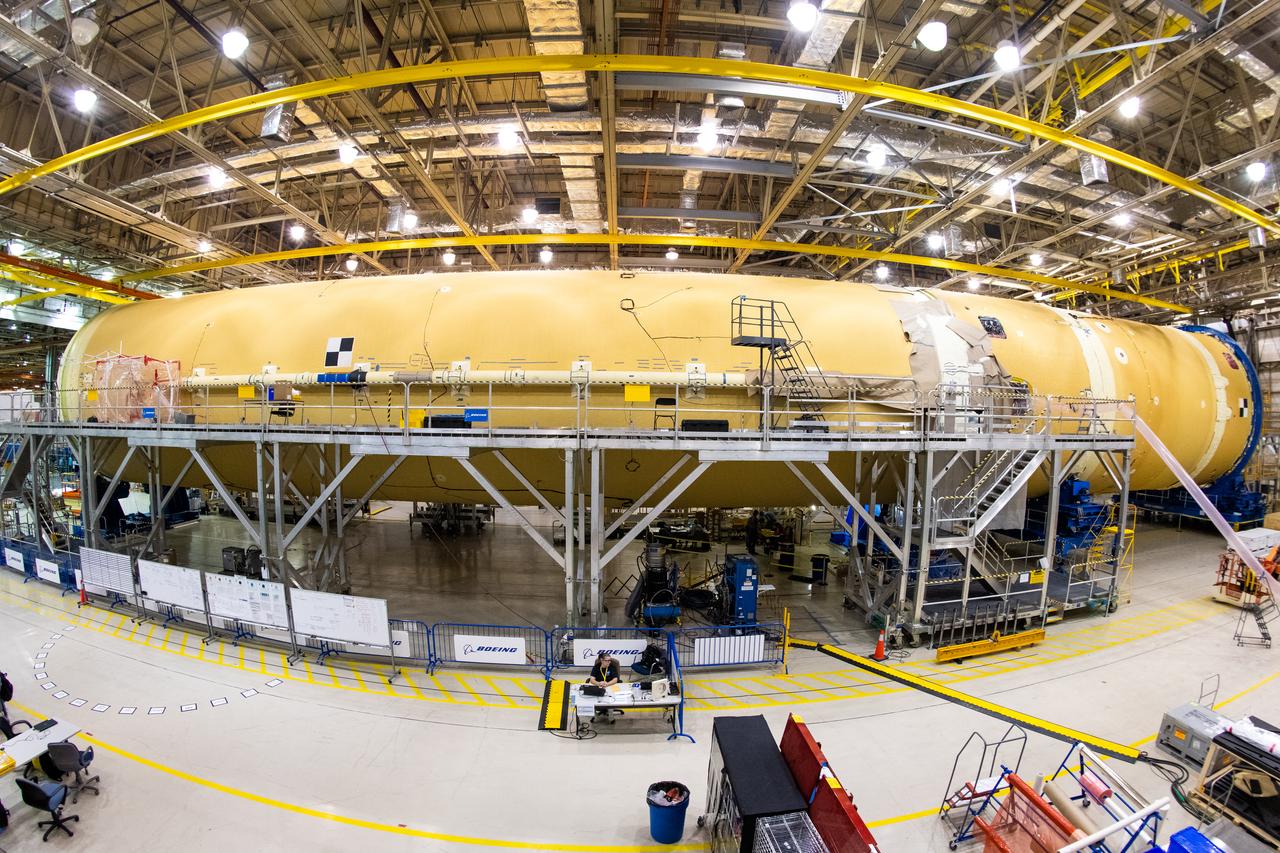

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans completed the “forward join,” which connects structures to form the top part of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage. The first core stage will send Exploration Mission-1, the first integrated flight of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, out beyond the Moon. The forward join mated three structures: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and intertank. This milestone marks the beginning of integration and assembly of the massive, 212-foot-tall SLS core stage, which will include the rocket’s four RS-25 rocket engines, propellant tanks and flight computers. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. These two parts of the core stage will then be assembled to form the largest stage NASA has ever built.
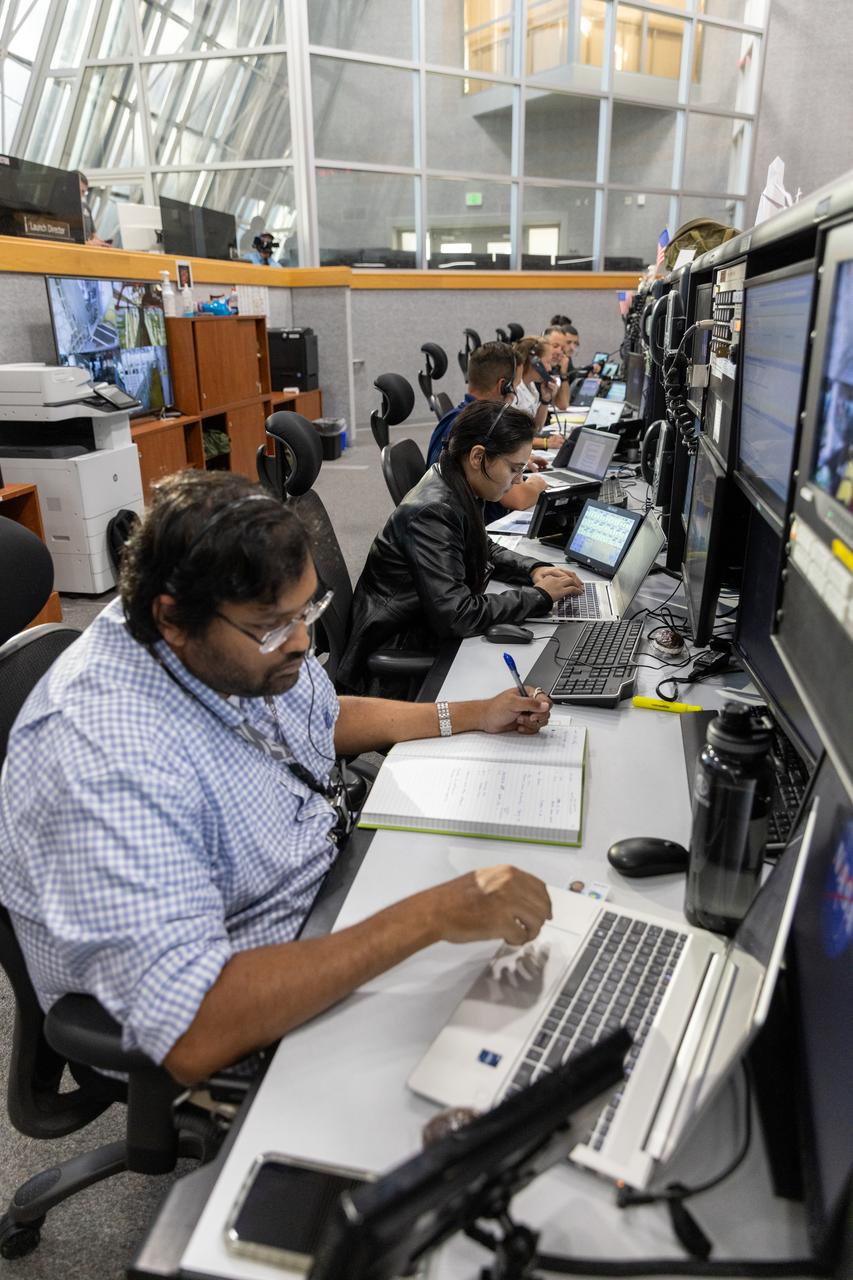

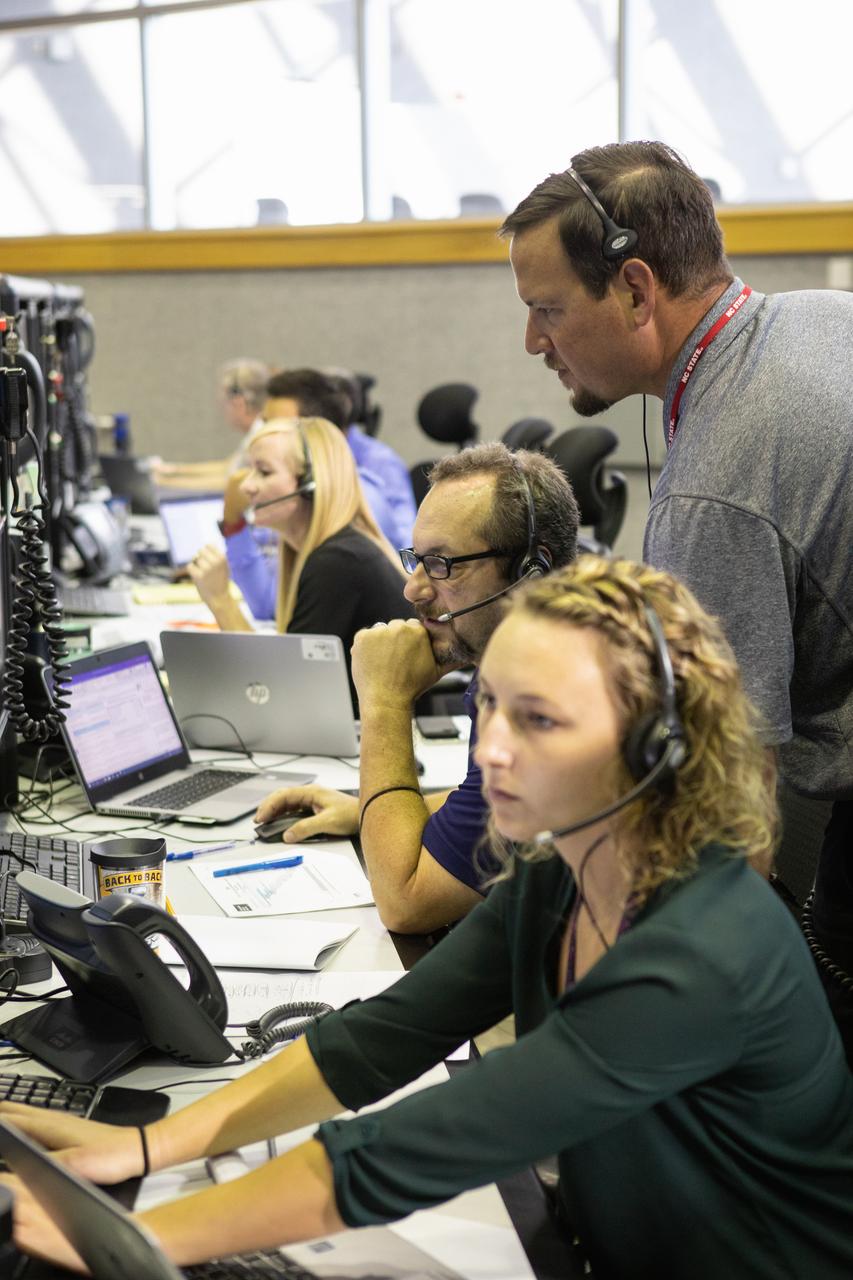
Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems participate in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
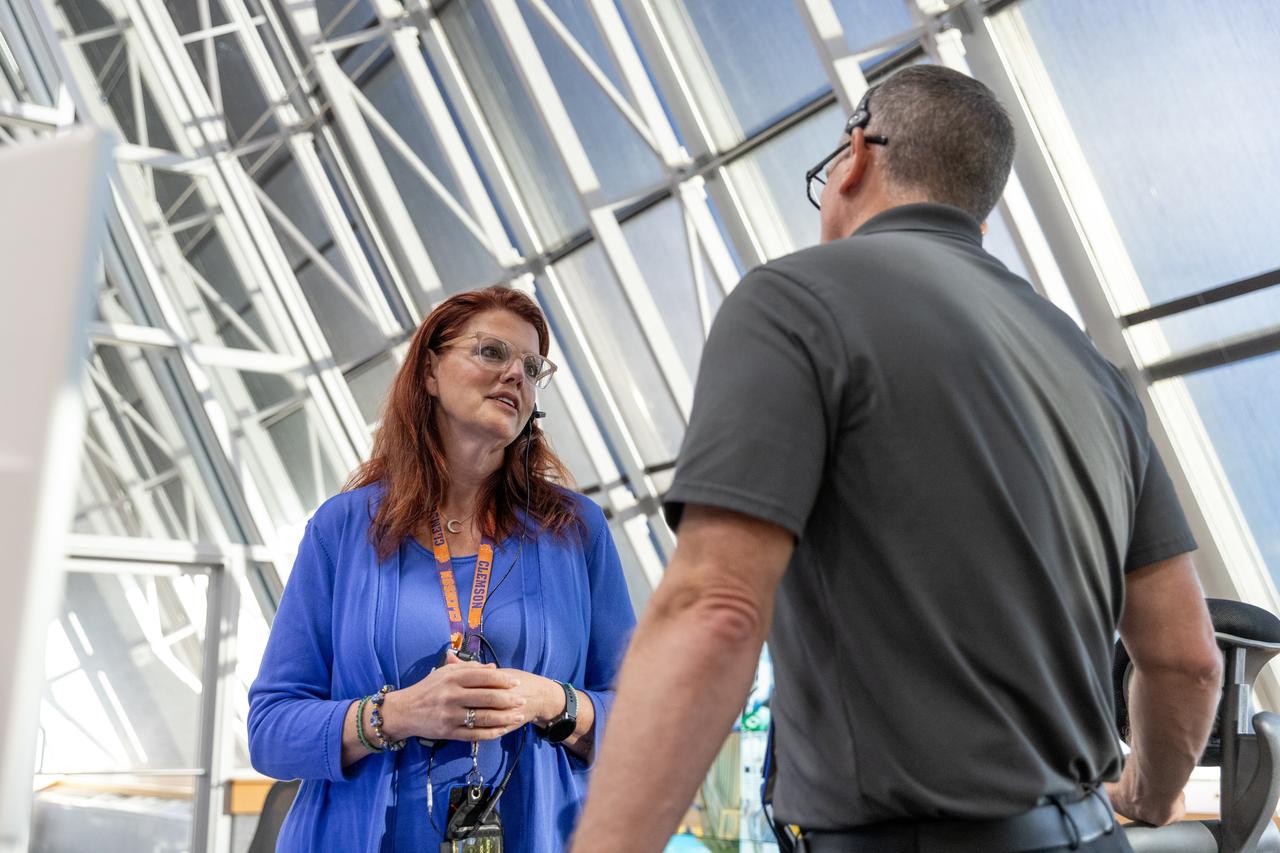

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
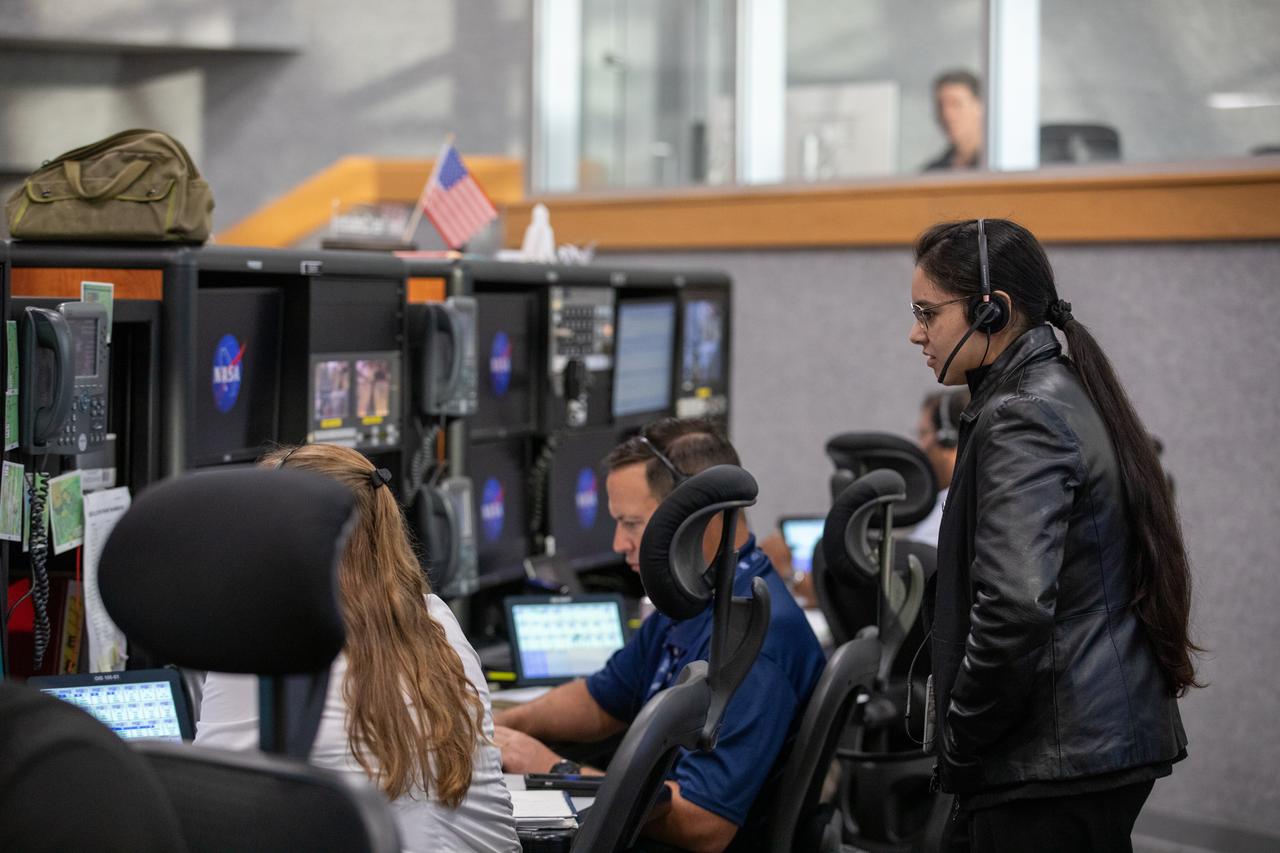

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems participate in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
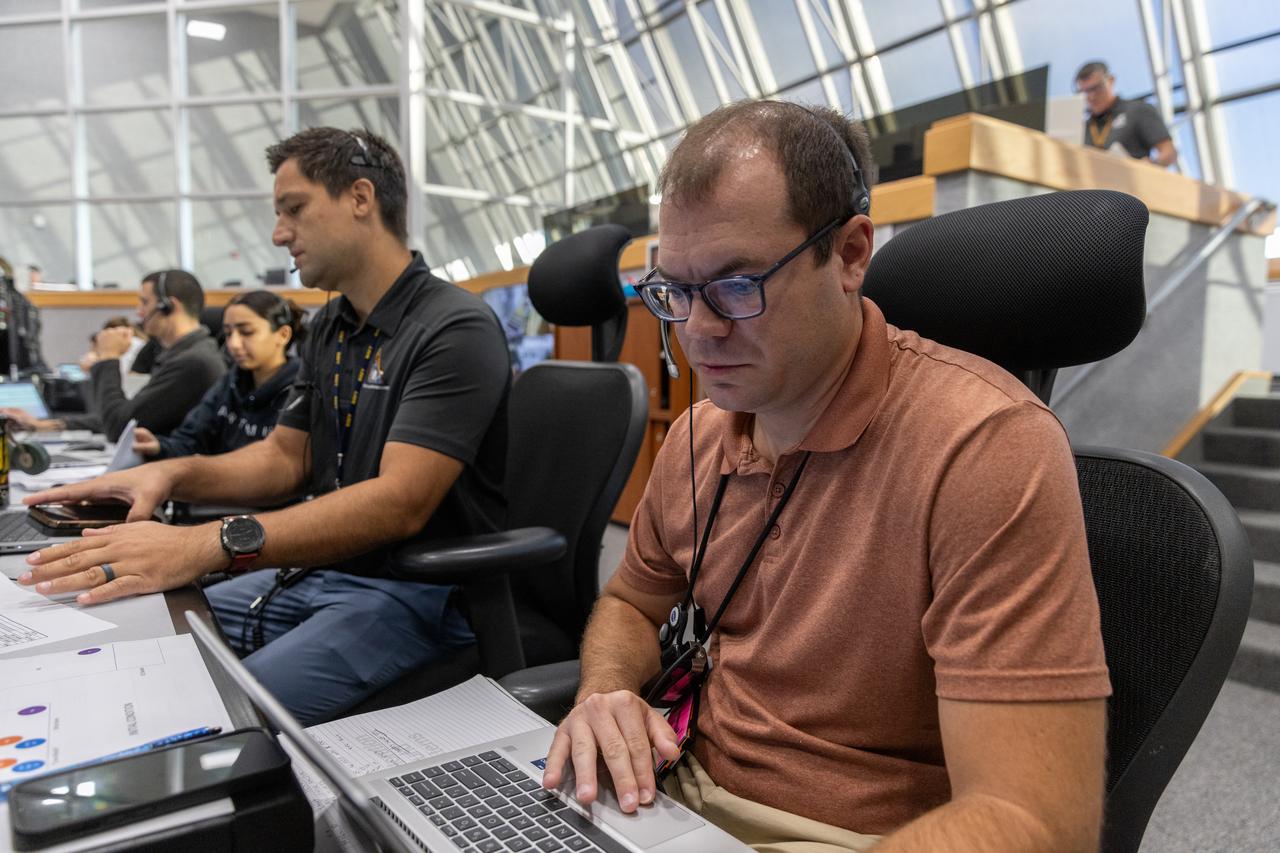

Jeremy Graeber, Artemis assistant launch director, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
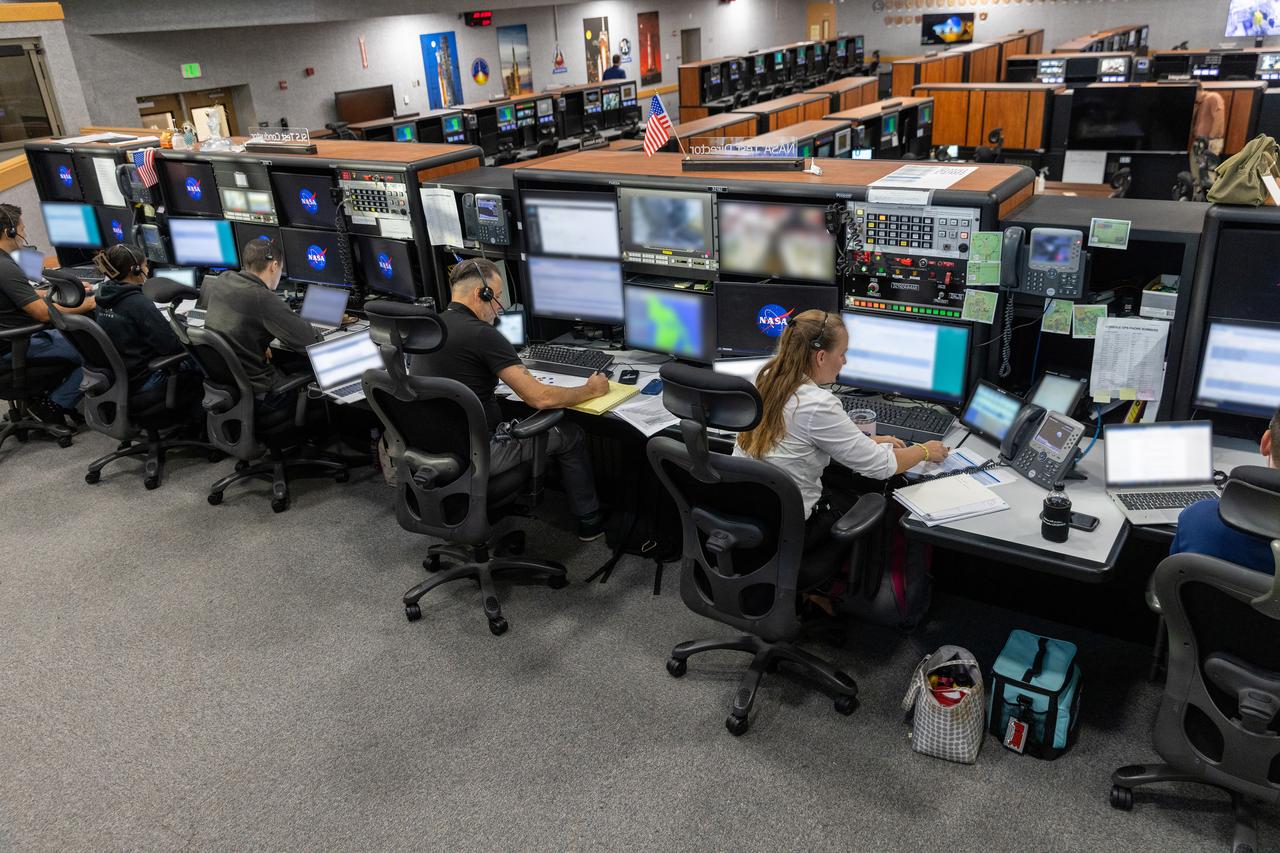

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems participate in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
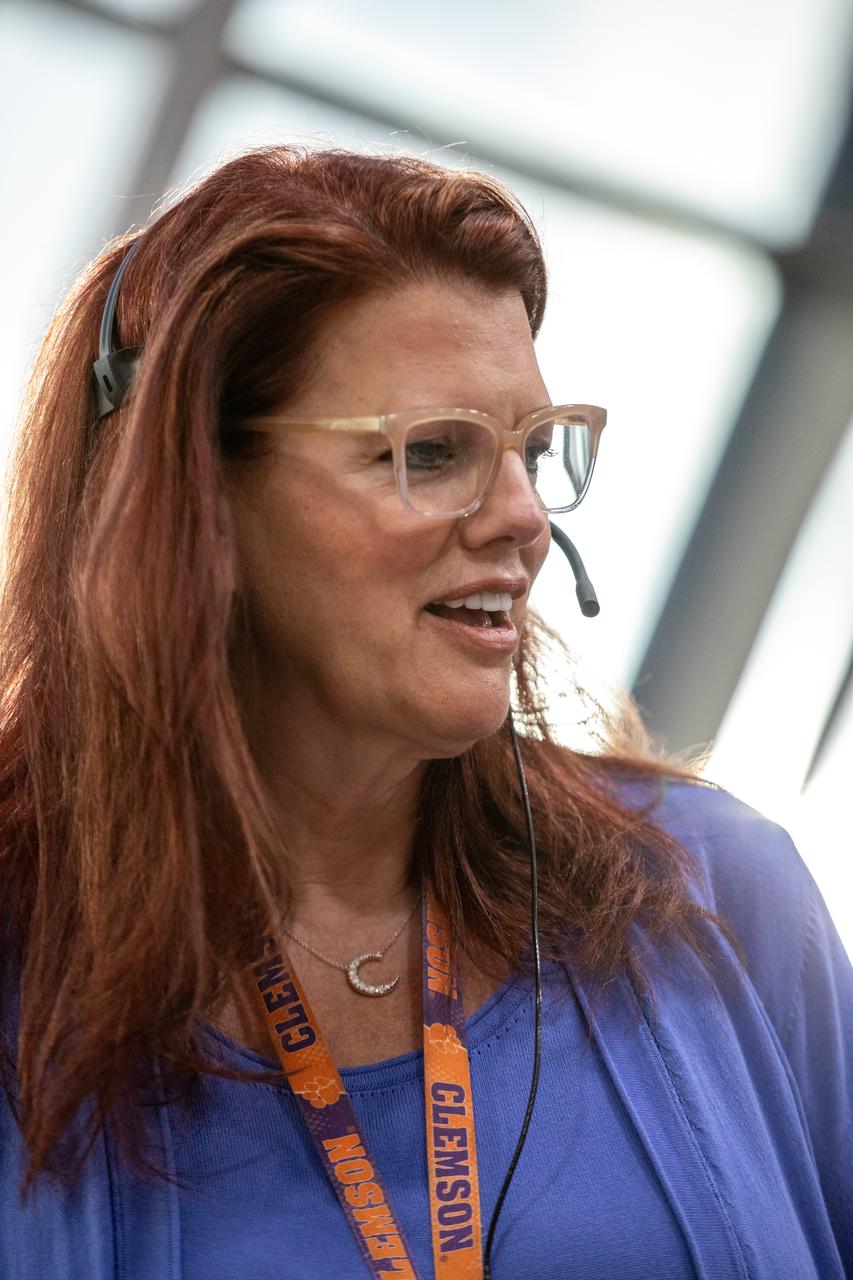

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
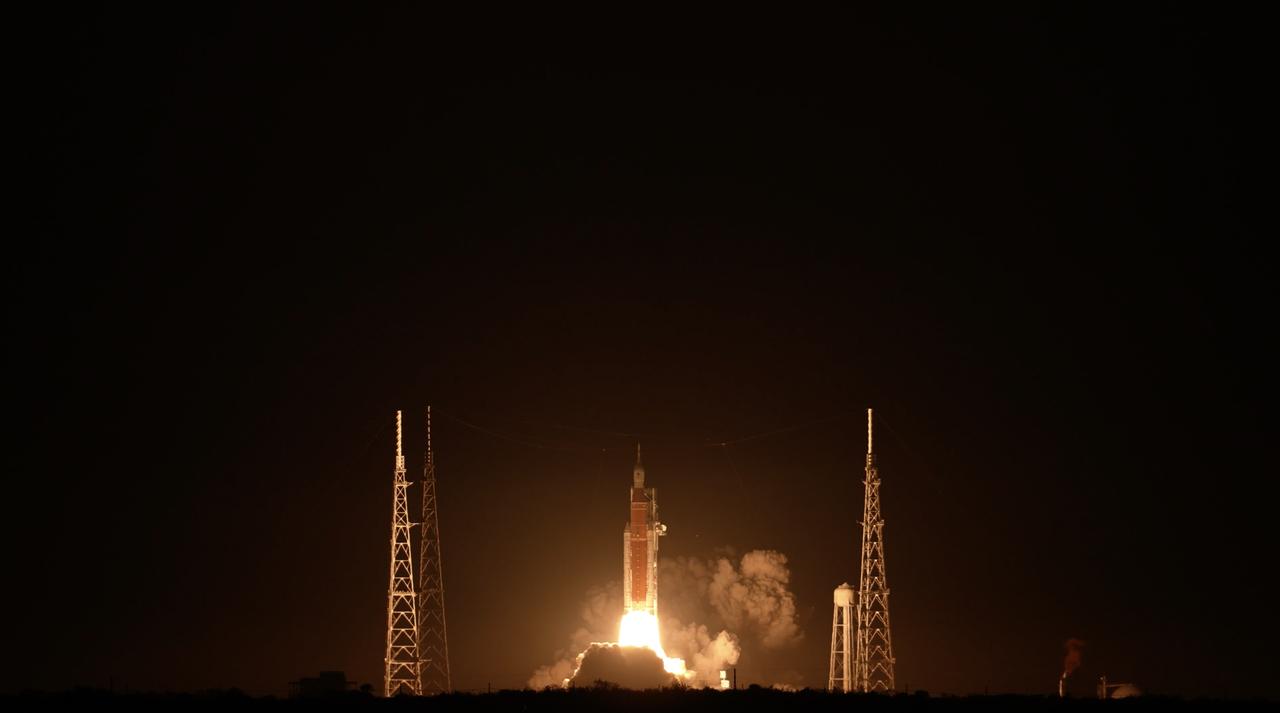

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
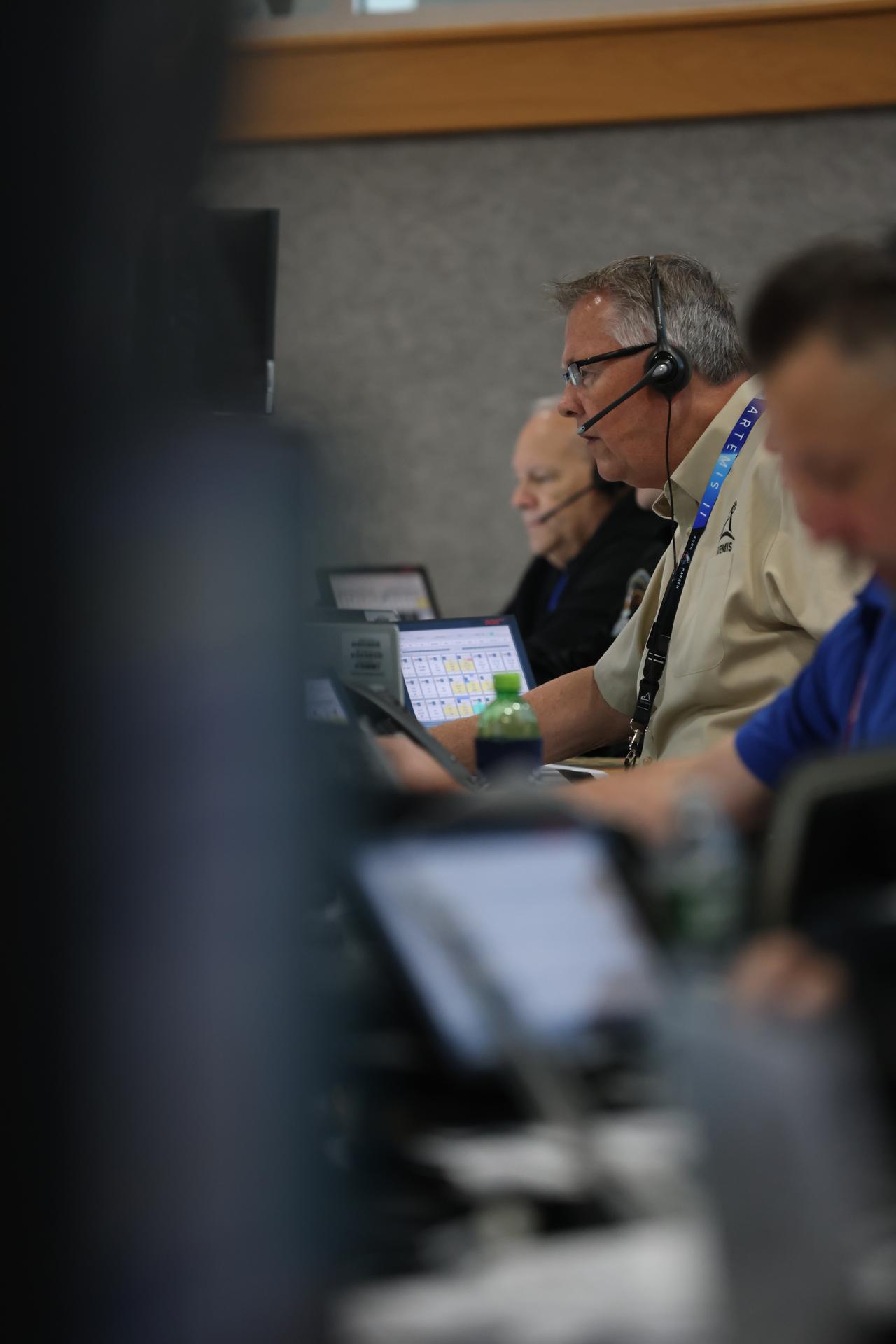

Jeff Spaulding, senior NASA test director for Artemis II at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida participates in an Artemis II launch countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA Kennedy on Wednesday, Oct. 8, 2025. The simulations go through launch day scenarios to help launch team members test software and make adjustments if needed during countdown operations. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.
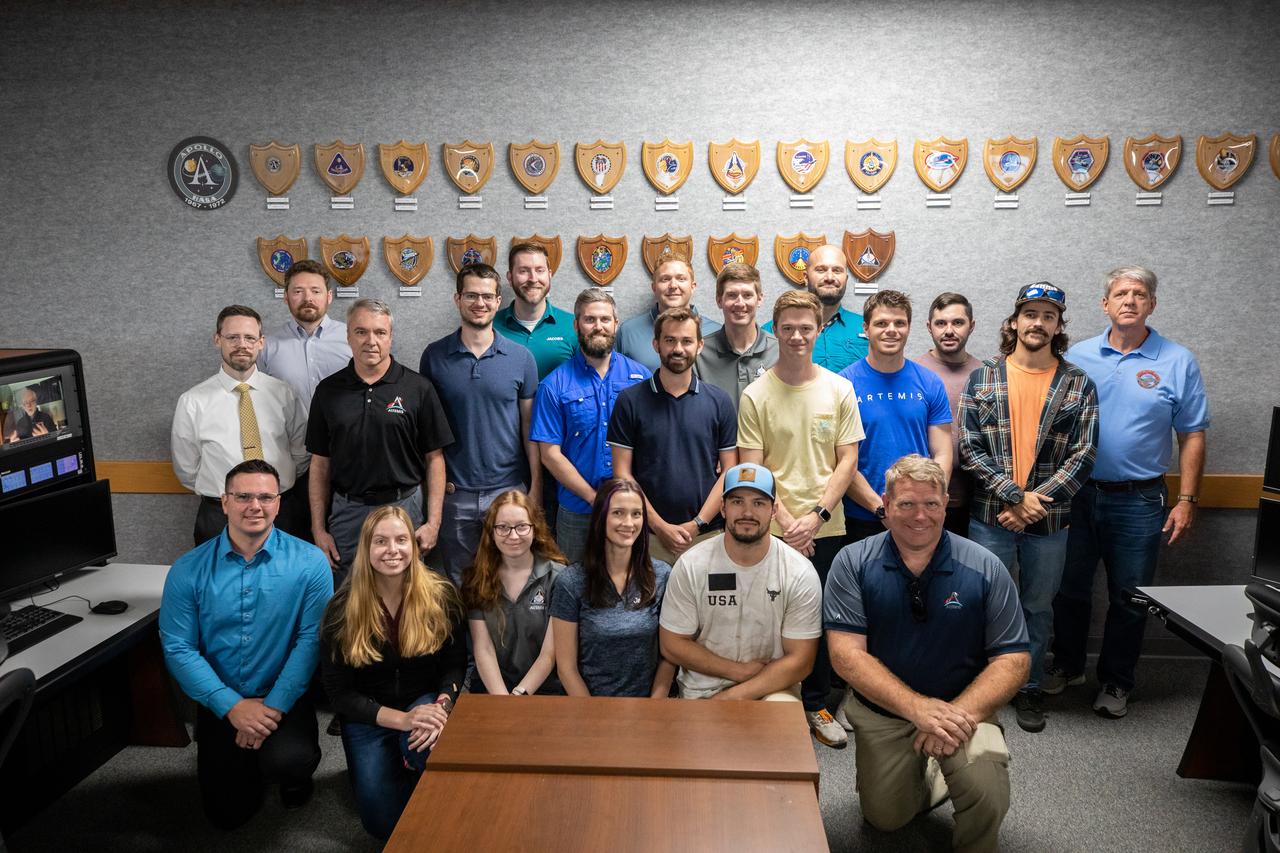
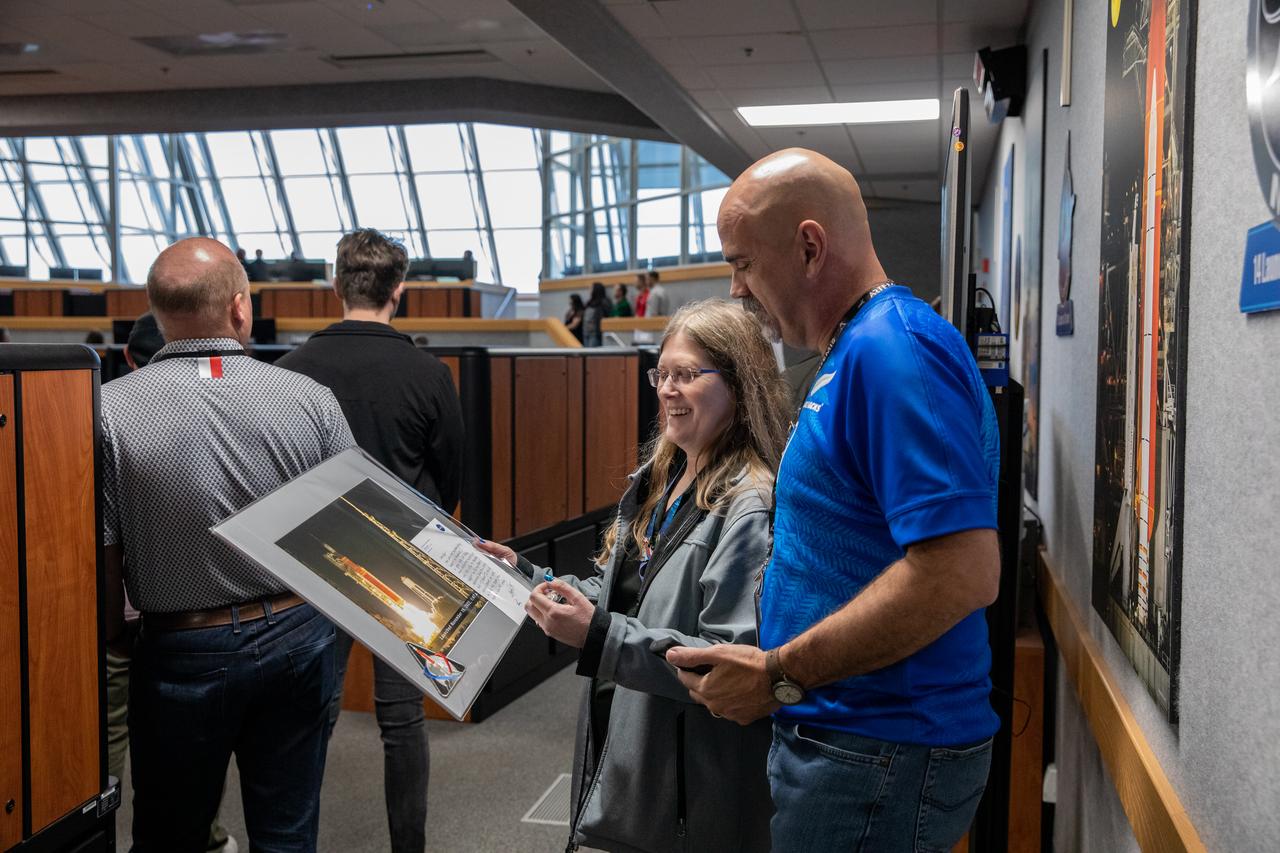
The Arms and Umbilicals (AUS) engineering team gather for a photograph during the Artemis launch director awards and plaque ceremony inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2023. Following tradition from the Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs, the AUS teams hung the Artemis I mission plaque to the wall behind them. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I launched successfully from Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2022.
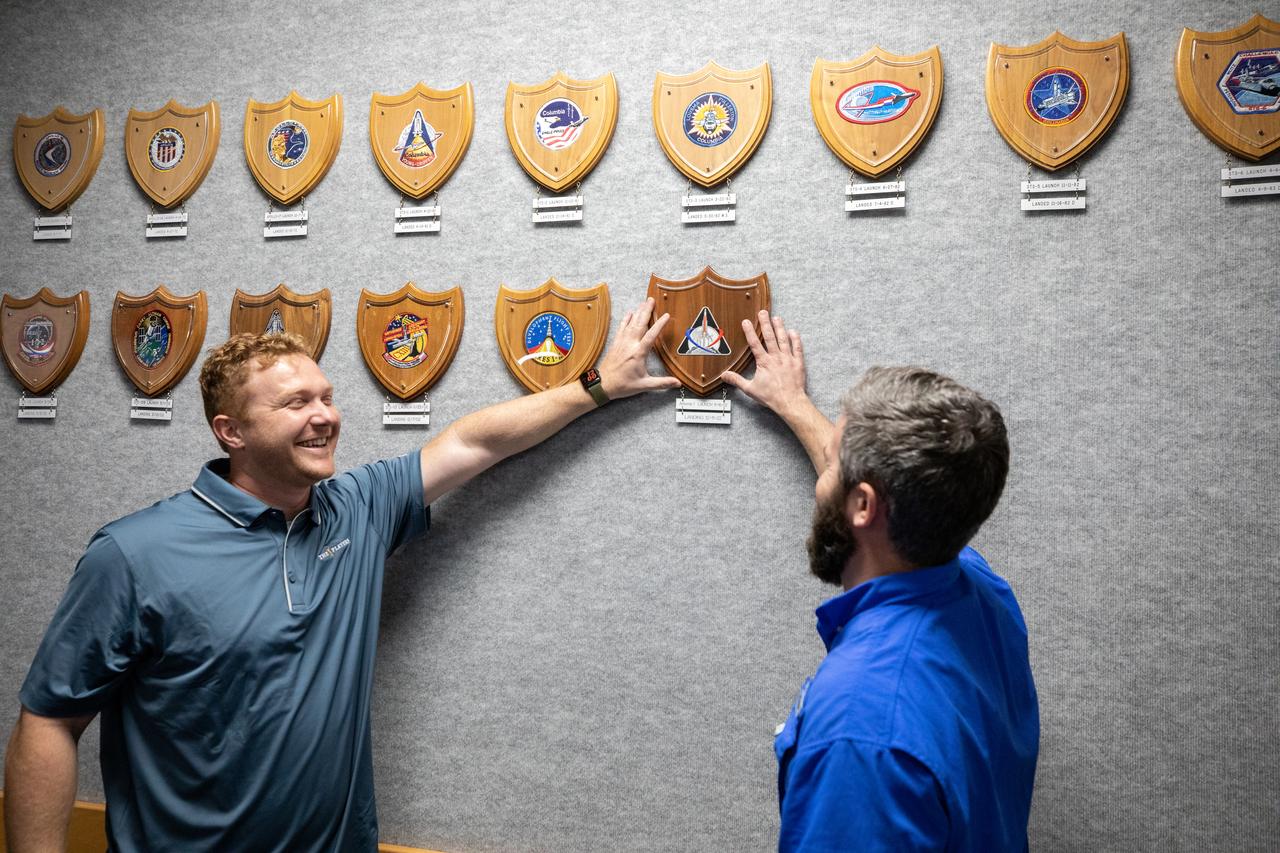

The Artemis plaque is attached to the wall in Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a ceremony on March 24, 2023. Hanging the plaque on the wall are Elliot Payne (left) and Devin Aikman (right), members of the Arms and Umbilicals engineering team. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I launched successfully from Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2022.
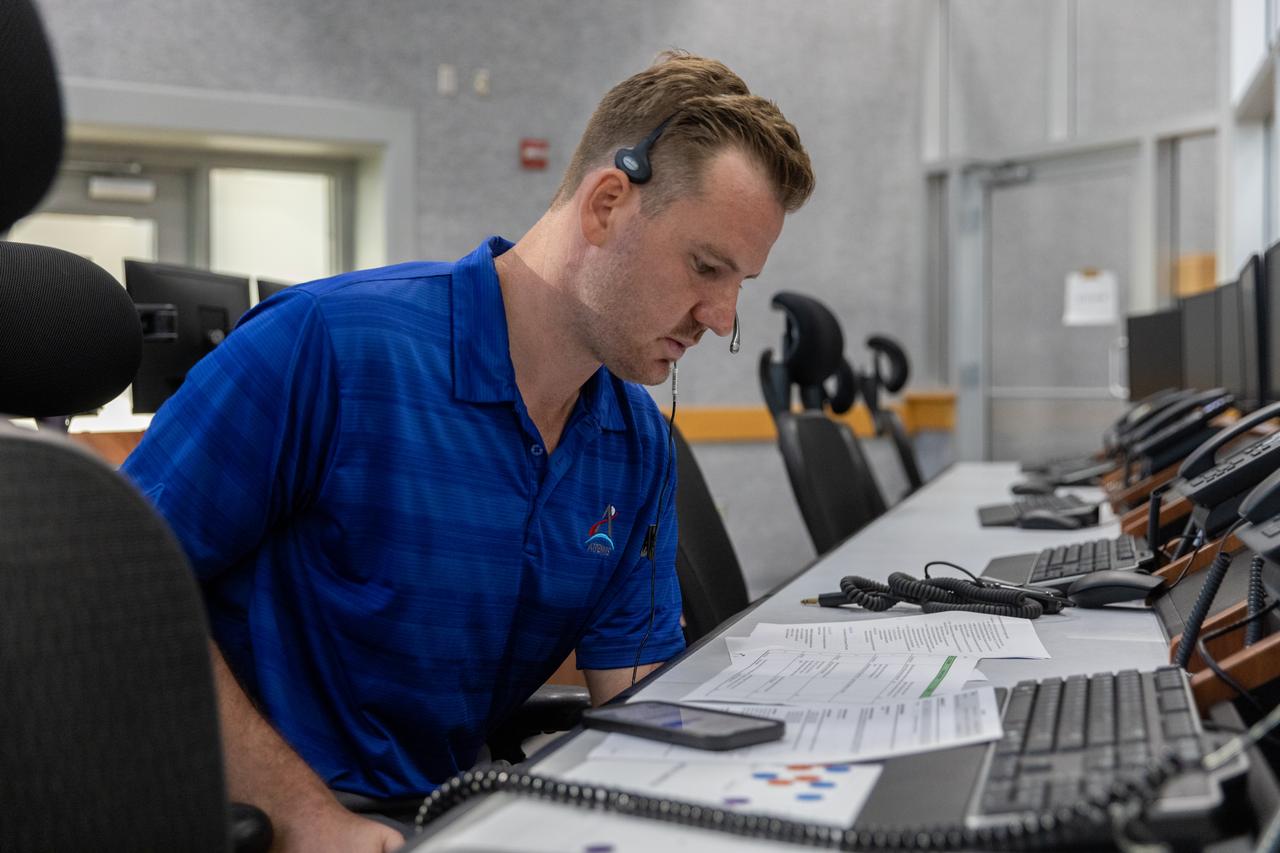

Joseph Pavicic, operations project engineer, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
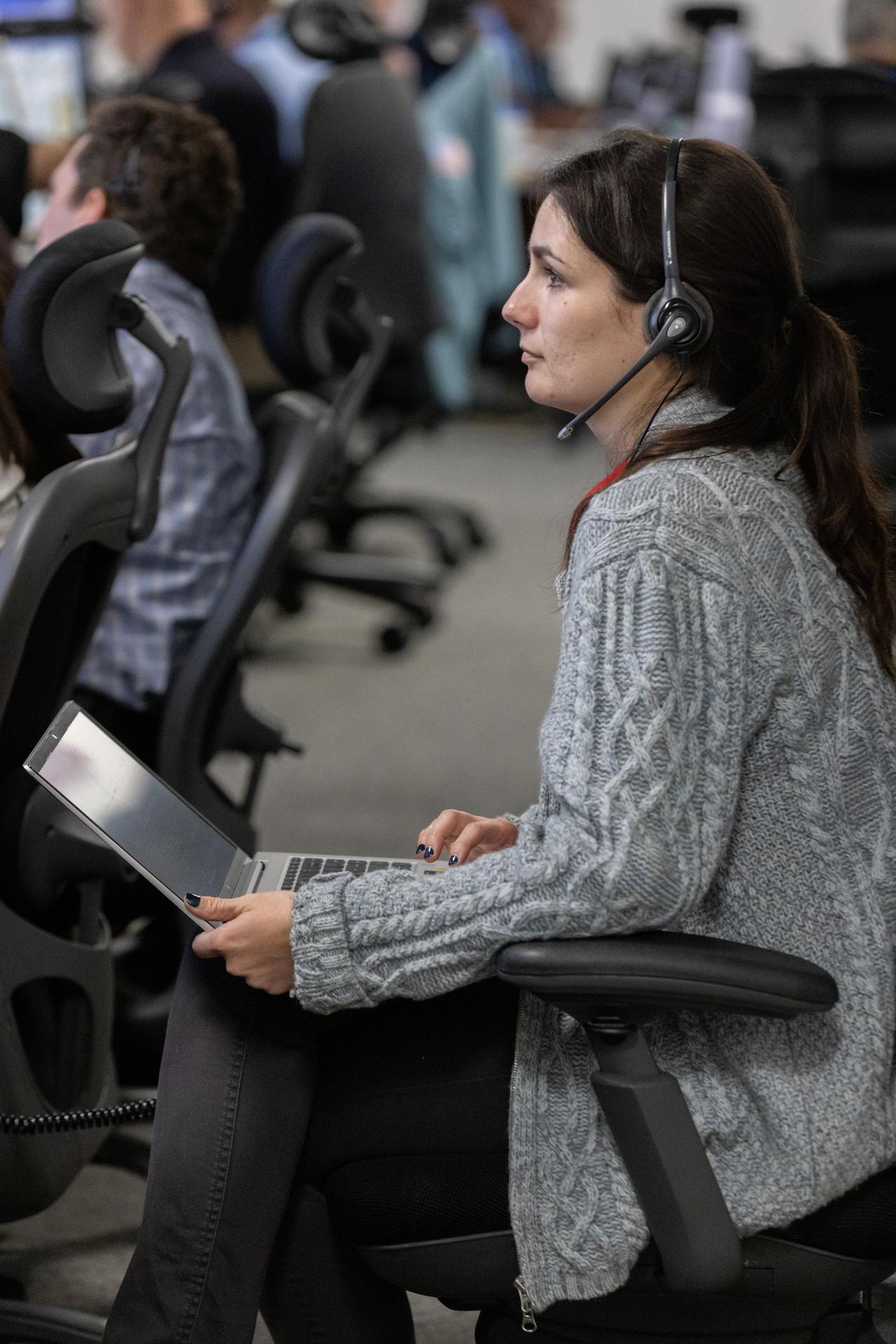

An Artemis launch team member participates in an Artemis II launch countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 5, 2025. The simulations go through launch day scenarios to help launch team members test software and make adjustments if needed during countdown operations. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.
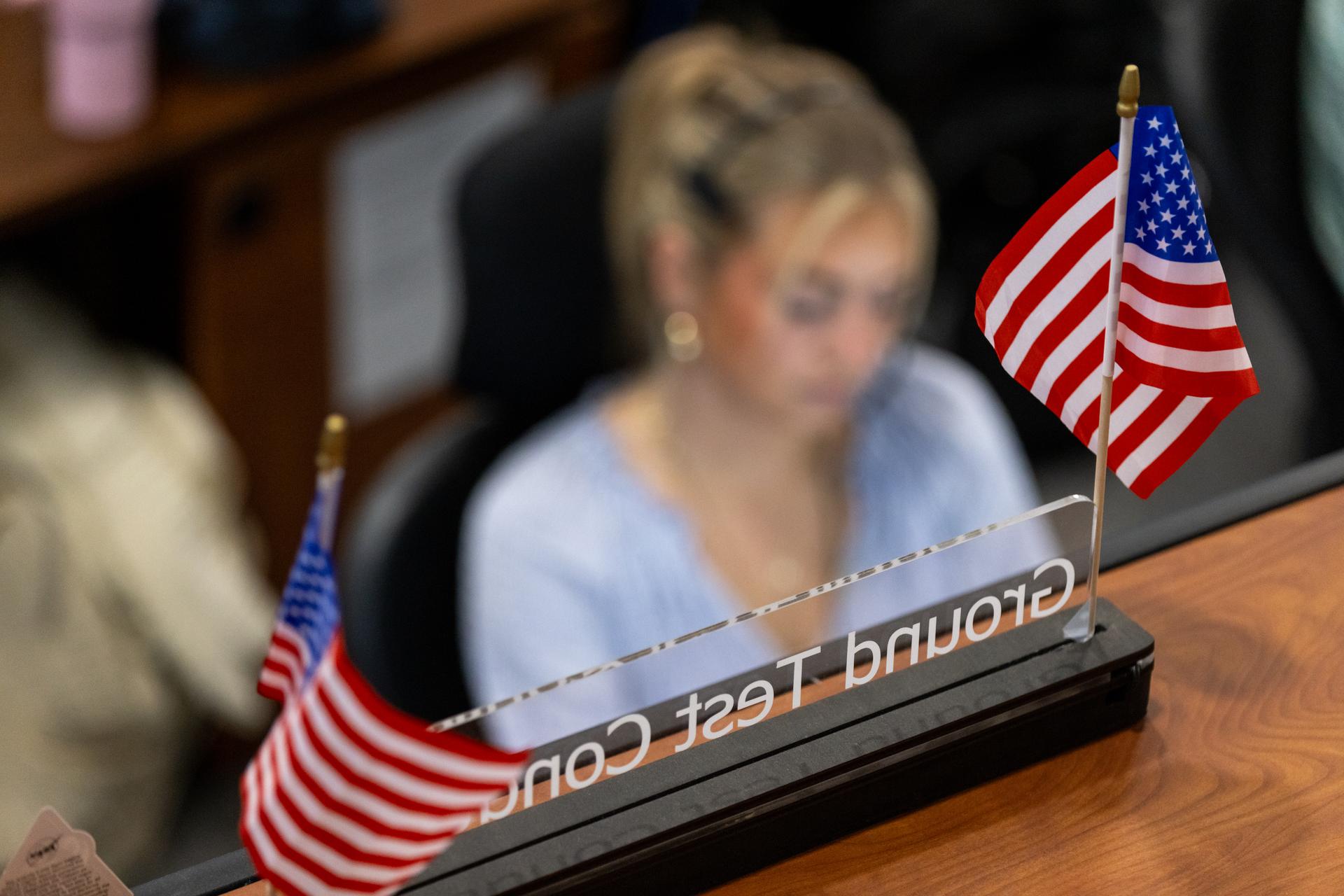

An Artemis launch team member participates in an Artemis II launch countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 5, 2025. The simulations go through launch day scenarios to help launch team members test software and make adjustments if needed during countdown operations. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.
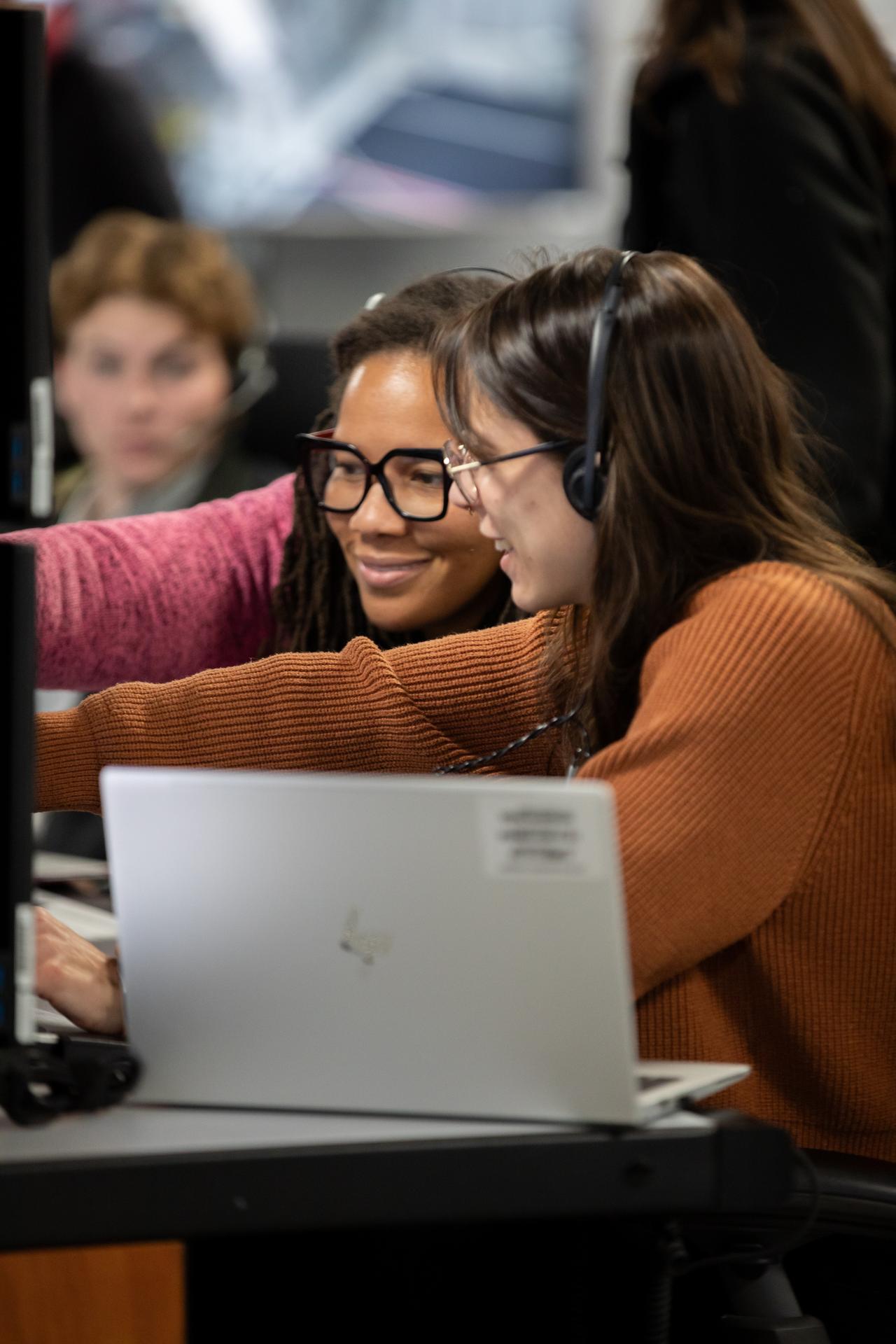

Artemis launch team members participate in an Artemis II launch countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 5, 2025. The simulations go through launch day scenarios to help launch team members test software and make adjustments if needed during countdown operations. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.
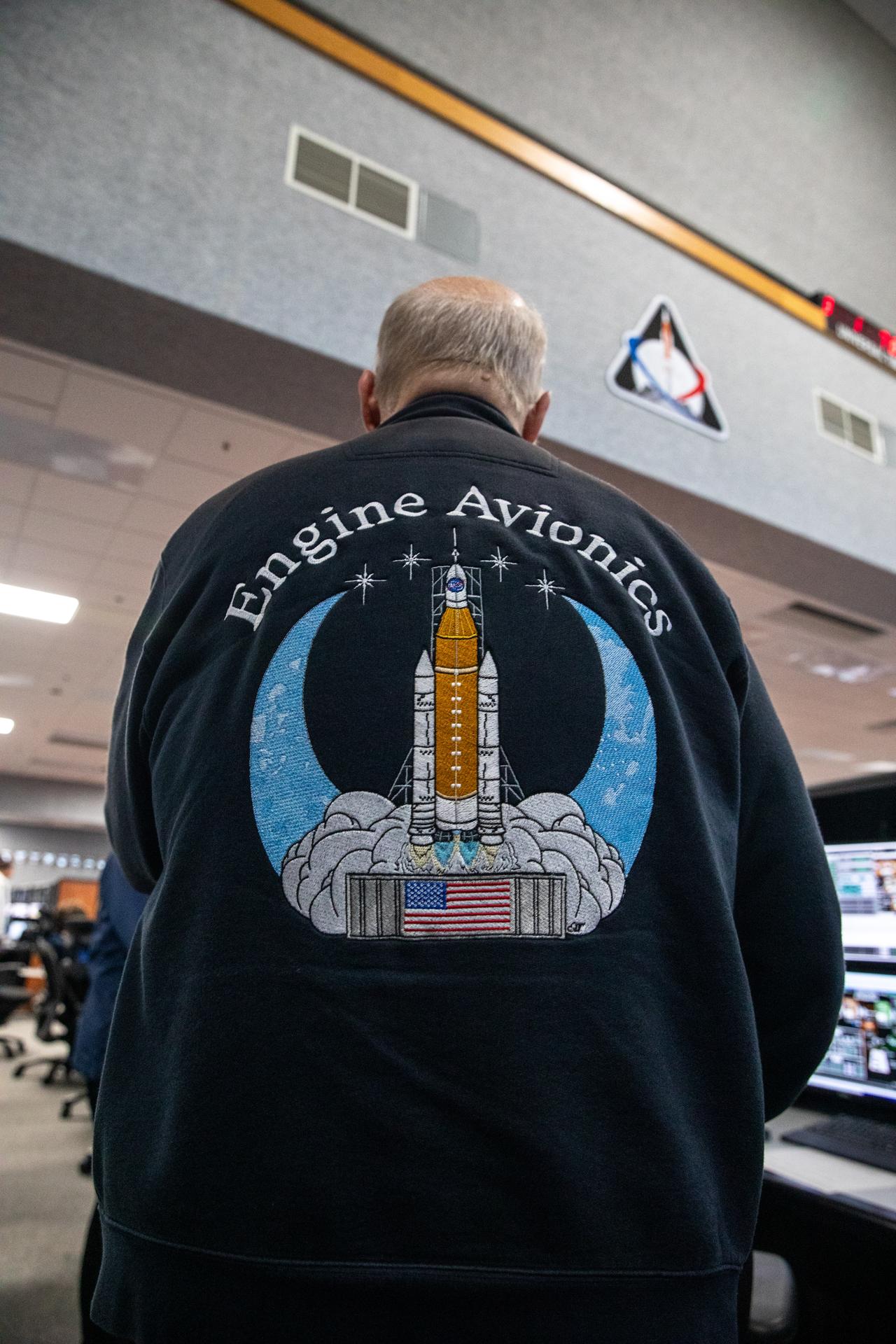

An Artemis launch team member participates in an Artemis II launch countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 5, 2025. The simulations go through launch day scenarios to help launch team members test software and make adjustments if needed during countdown operations. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.
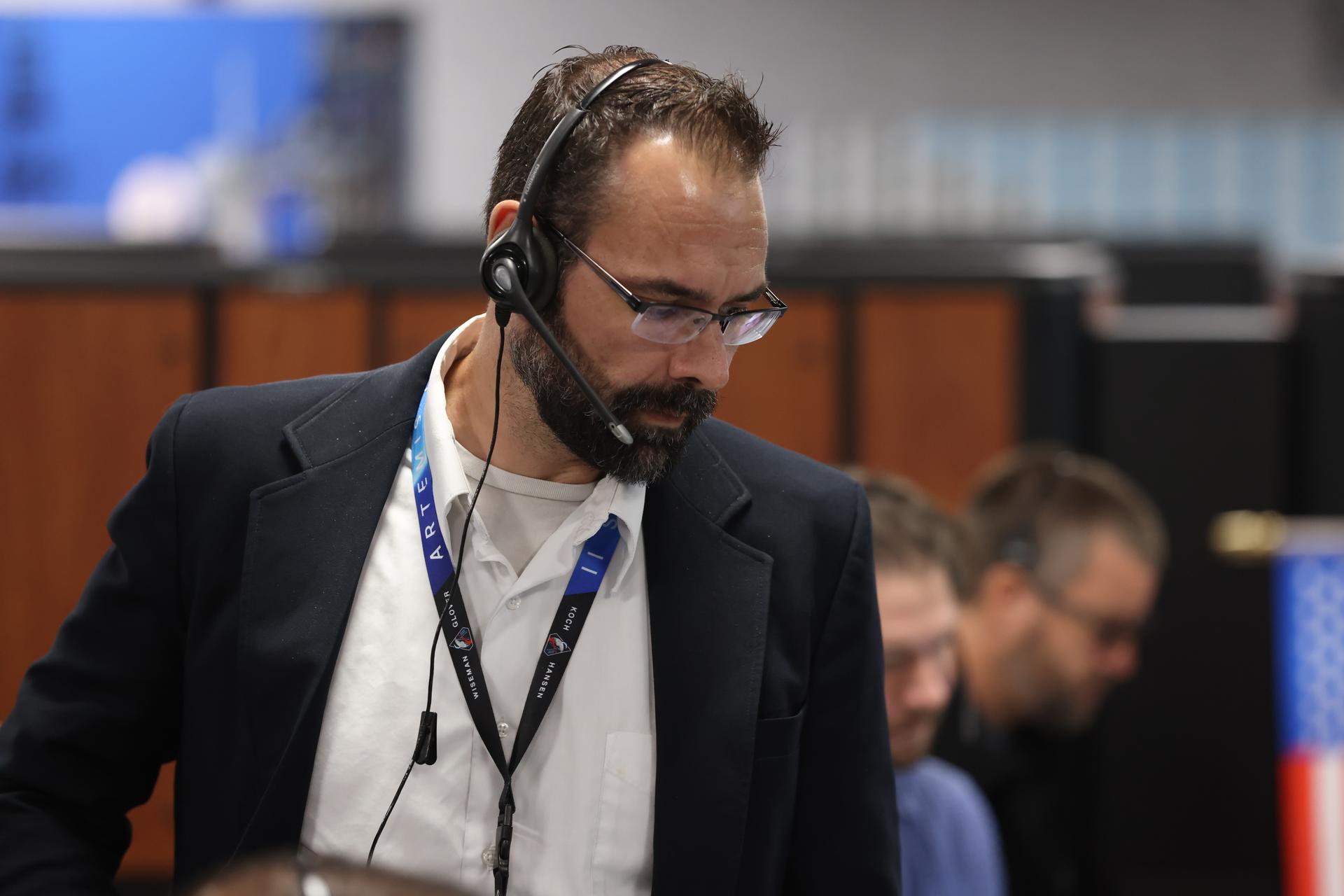

Anton Kiriwas, senior technical integration manager and senior launch project engineer with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program participates in an Artemis II launch countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 8, 2025. The simulations go through launch day scenarios to help launch team members test software and make adjustments if needed during countdown operations. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.

Joe Pavicic, operations project engineer, participates in an Artemis II launch countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 8, 2025. The simulations go through launch day scenarios to help launch team members test software and make adjustments if needed during countdown operations. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.