
SCI2017_0004: Artist's illustration of the Epsilon Eridani system showing Epsilon Eridani b, right foreground, a Jupiter-mass planet orbiting its parent star at the outside edge of an asteroid belt. In the background can be seen another narrow asteroid or comet belt plus an outermost belt similar in size to our solar system's Kuiper Belt. The similarity of the structure of the Epsilon Eridani system to our solar system is remarkable, although Epsilon Eridani is much younger than our sun. SOFIA observations confirmed the existence of the asteroid belt adjacent to the orbit of the Jovian planet. Credit: NASA/SOFIA/Lynette Cook
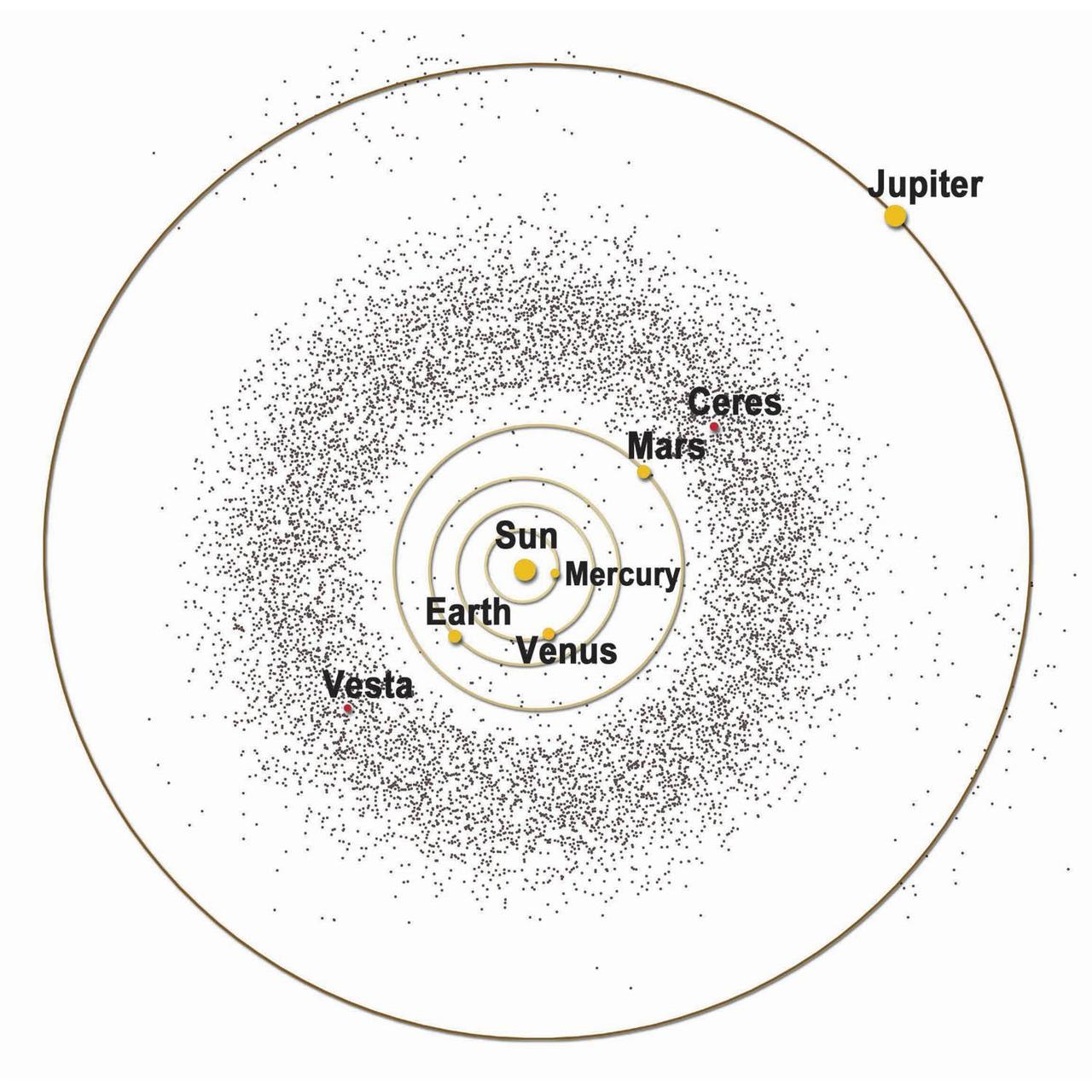
Artist graphic of the asteroid belt, part of Dawn Mission Art series. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19380
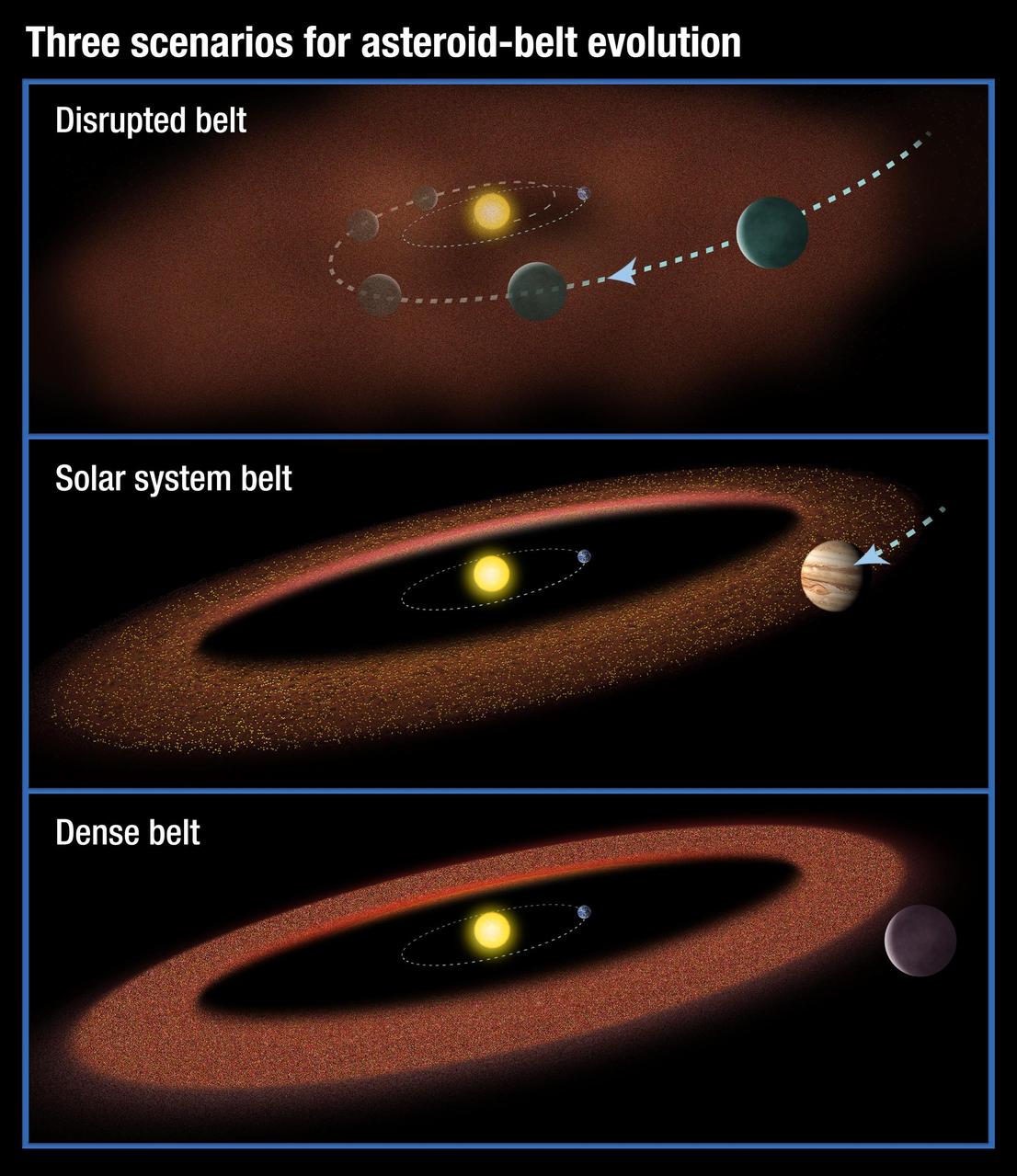
This illustration shows three possible scenarios for the evolution of asteroid belts. At the top, a Jupiter-size planet migrates through the asteroid belt, scattering material and inhibiting the formation of life on planets.
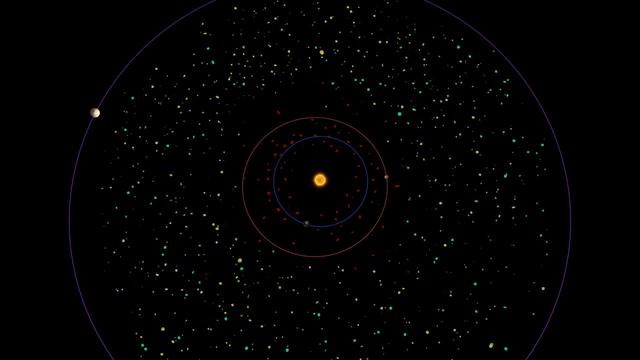
This diagram shows a bird eye view of our asteroid belt, which lies between the orbits of Mars red and Jupiter purple.

Nine Galileo Views in Natural Color of Main-Belt Asteroid Ida http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00330

Nine Galileo Views in Exaggerated Color of Main-Belt Asteroid Ida http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00331
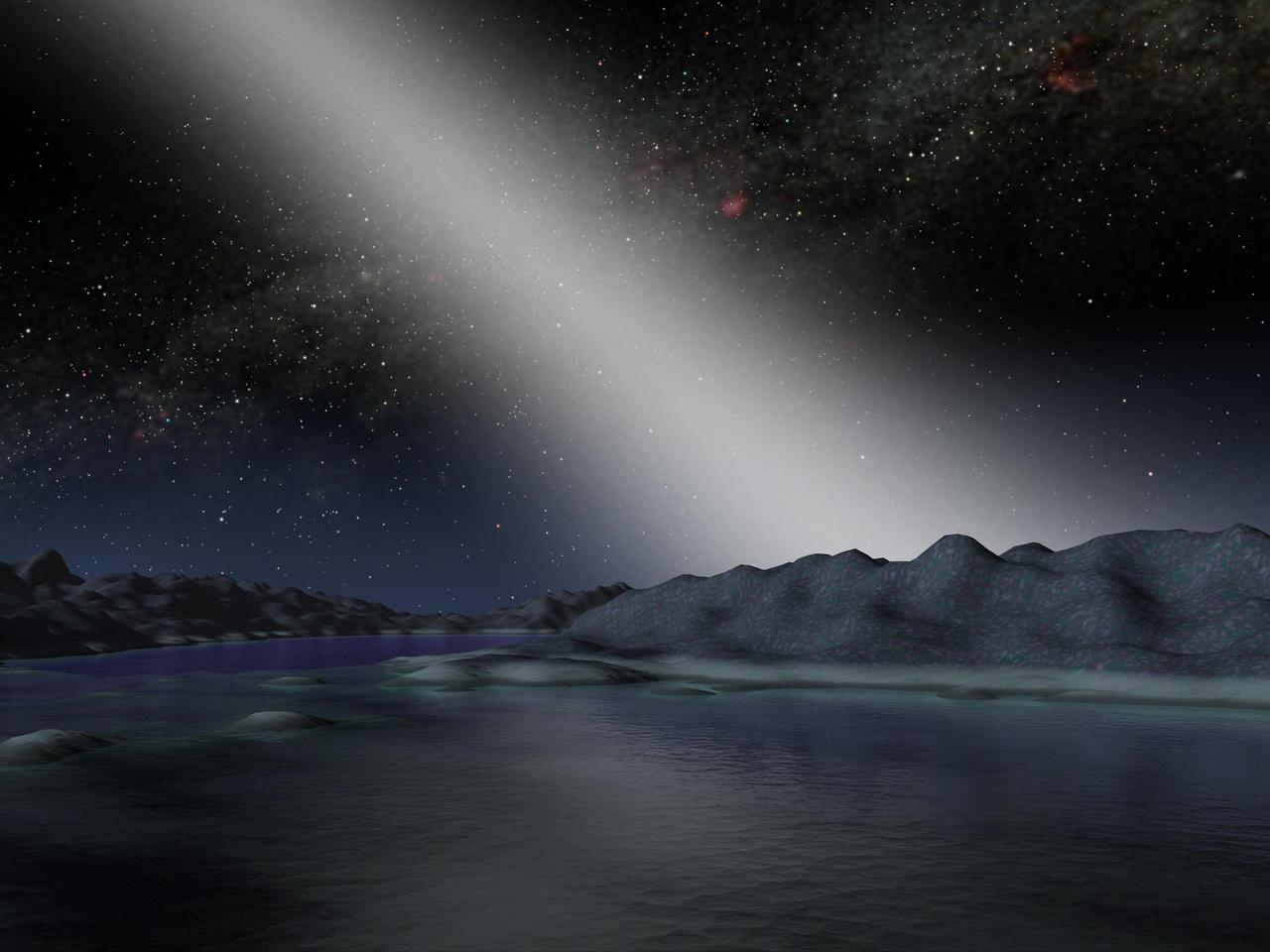

This artist concept shows what the night sky might look like from a hypothetical alien planet in a star system with an asteroid belt 25 times as massive as the one in our own solar system.
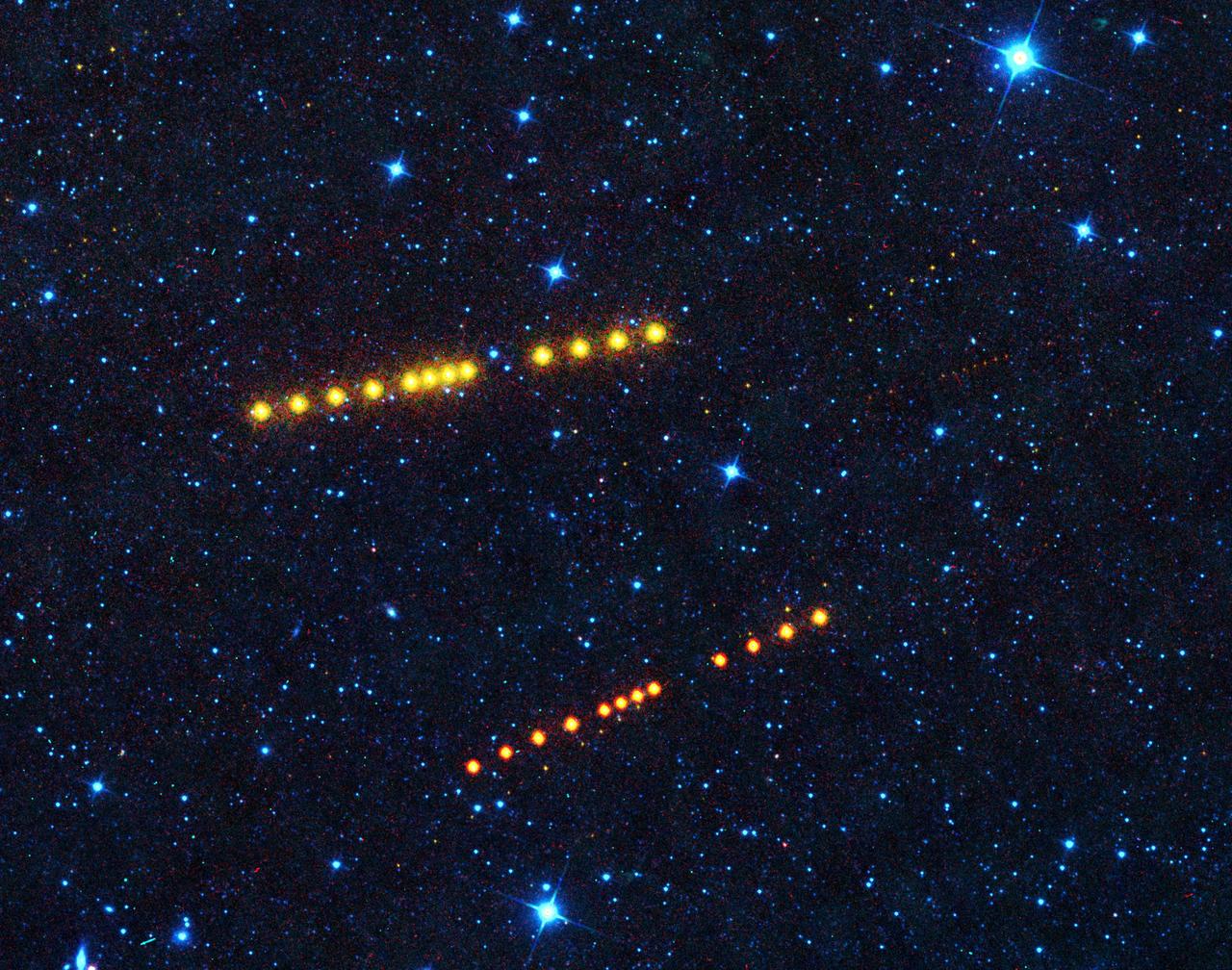

Those aren't Klingon vessels. Appearing as strings of orange dots, the brightest sets of dots belong to asteroids Klotho and Lina. Both orbit out in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, while smaller, more distant asteroids can also be seen passing through the image. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23589

Dwarf planet Ceres is located in the main asteroid belt, between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, as illustrated in this artist conception.

Studying meteorites from the asteroid Vesta helps scientists understand the event known as the lunar cataclysm, when a repositioning of the gas giant planets destabilized a portion of the asteroid belt and triggered a solar-system-wide bombardment.
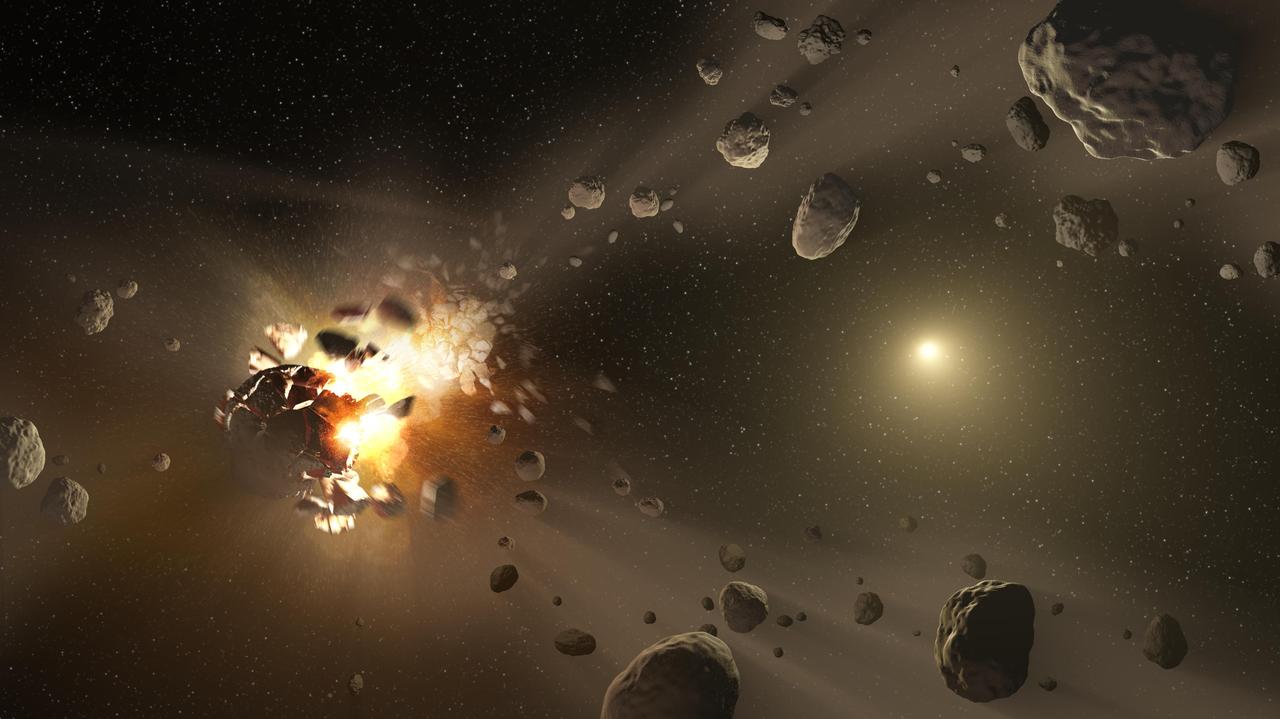

This artist concept catastrophic collisions between asteroids located in the belt between Mars and Jupiter and how they have formed families of objects on similar orbits around the sun.

This is a NASA Hubble Space Telescope color image of dwarf planet Ceres, the largest object in the asteroid belt. The contrast has been enhanced to reveal surface details.
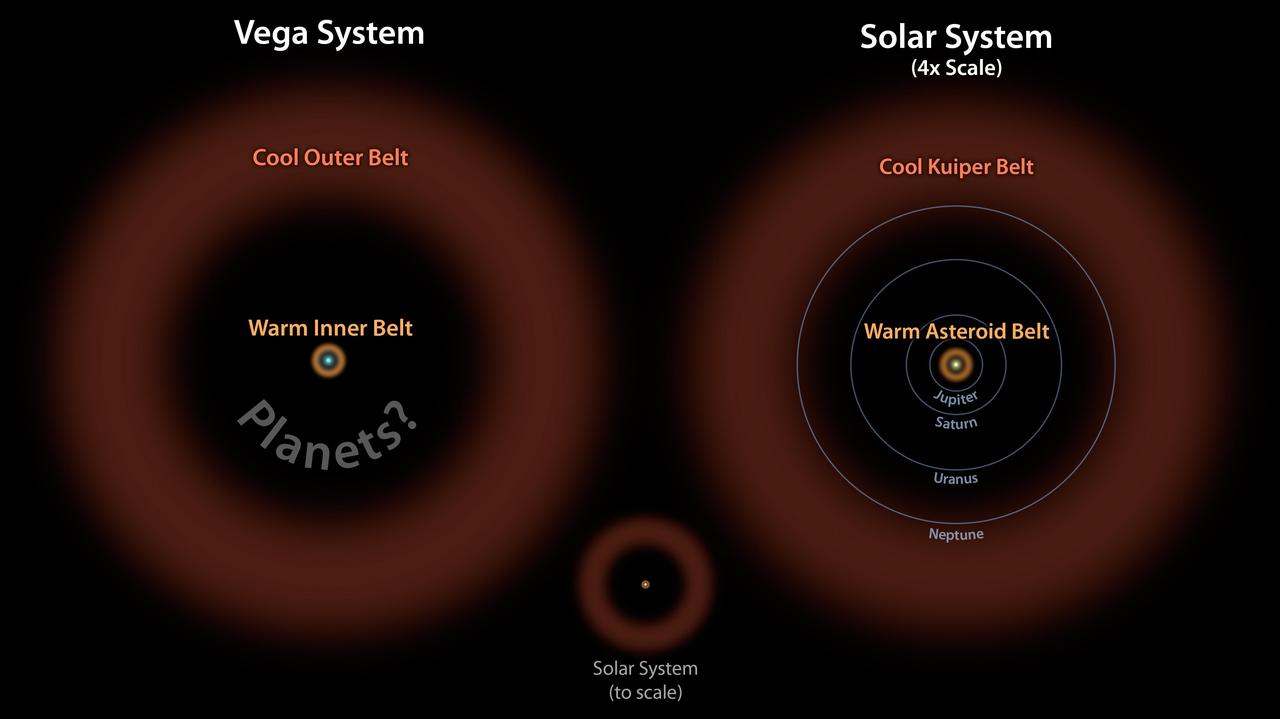
In this diagram, the Vega system, which was already known to have a cooler outer belt of comets orange, is compared to our solar system with its asteroid and Kuiper belts. The ring of warm, rocky debris was detected using NASA Spitzer Space Telescope,
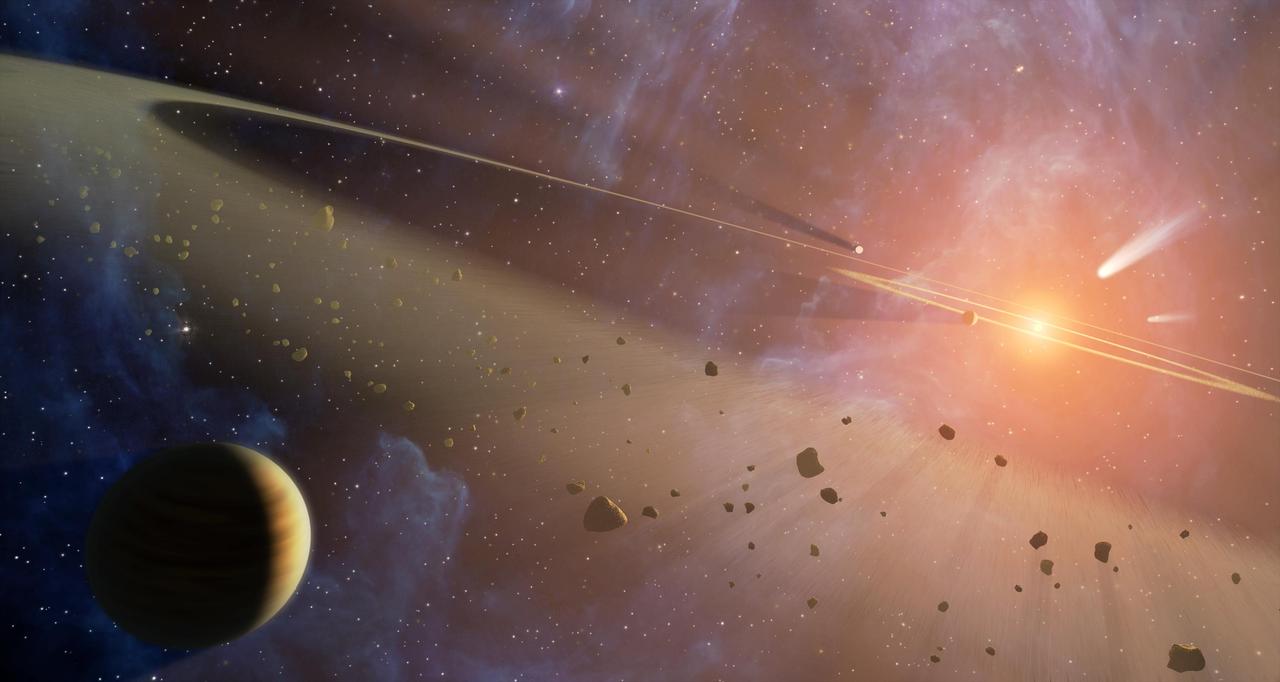

This artist conception shows the closest known planetary system to our own, called Epsilon Eridani. Observations from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope show that the system hosts two asteroid belts.
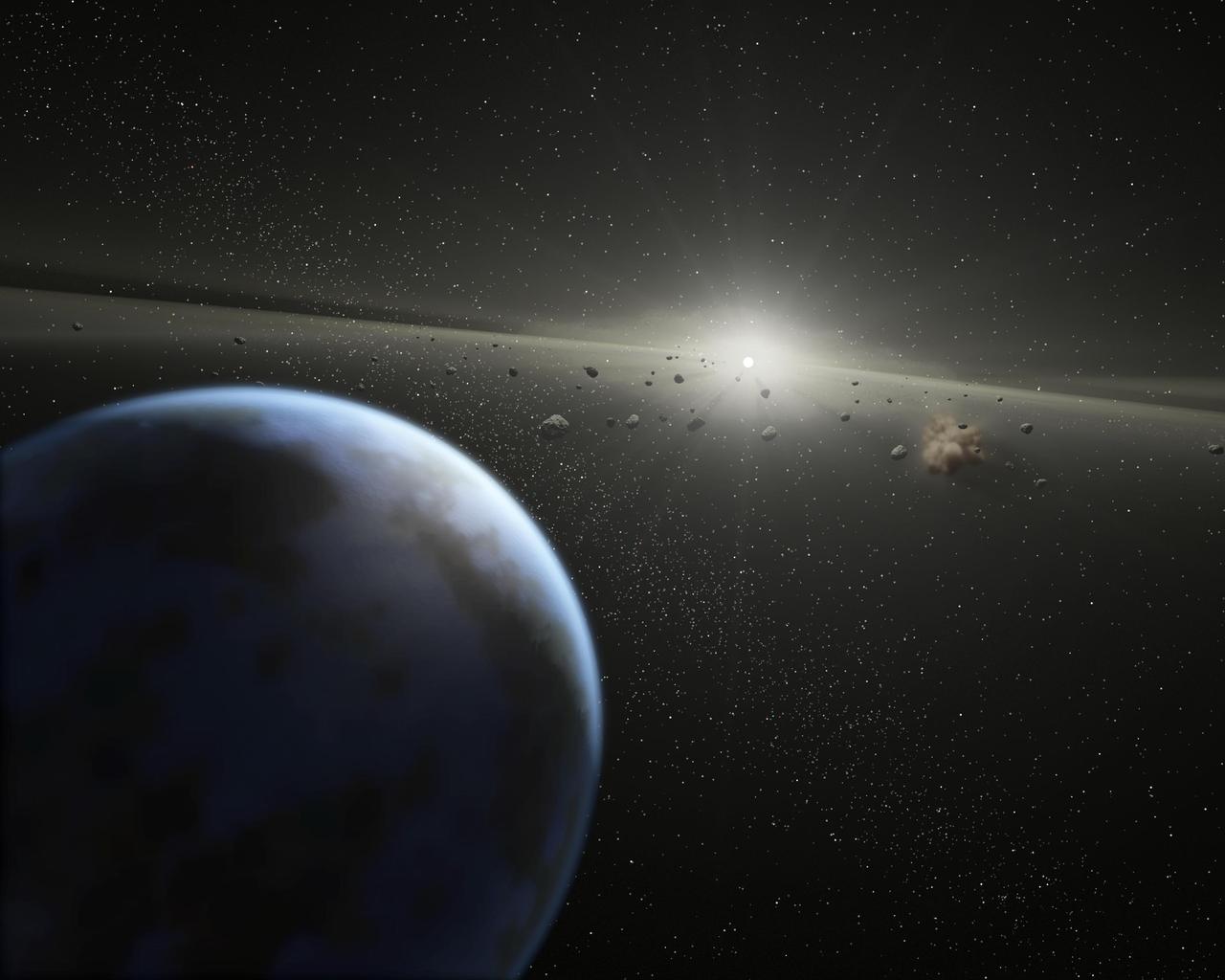

Evidence for this possible belt was discovered by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope when it spotted warm dust around the star, presumably from asteroids smashing together. This is an artist concept.
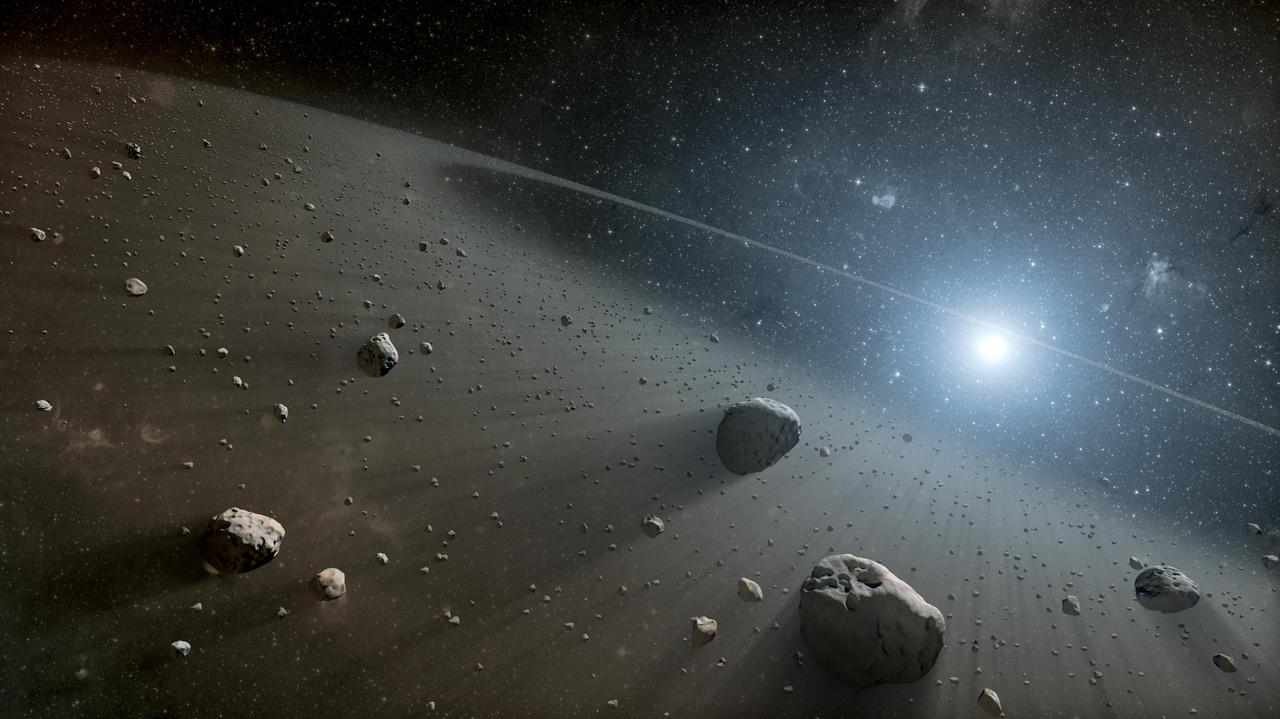

This artist concept illustrates an asteroid belt around the bright star Vega. Evidence for this warm ring of debris was found using NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, and the European Space Agency Herschel Space Observatory.

This artist concept shows NASA Dawn spacecraft arriving at the dwarf planet Ceres, the most massive body in the asteroid belt. Dawn is the first mission to visit a dwarf planet.
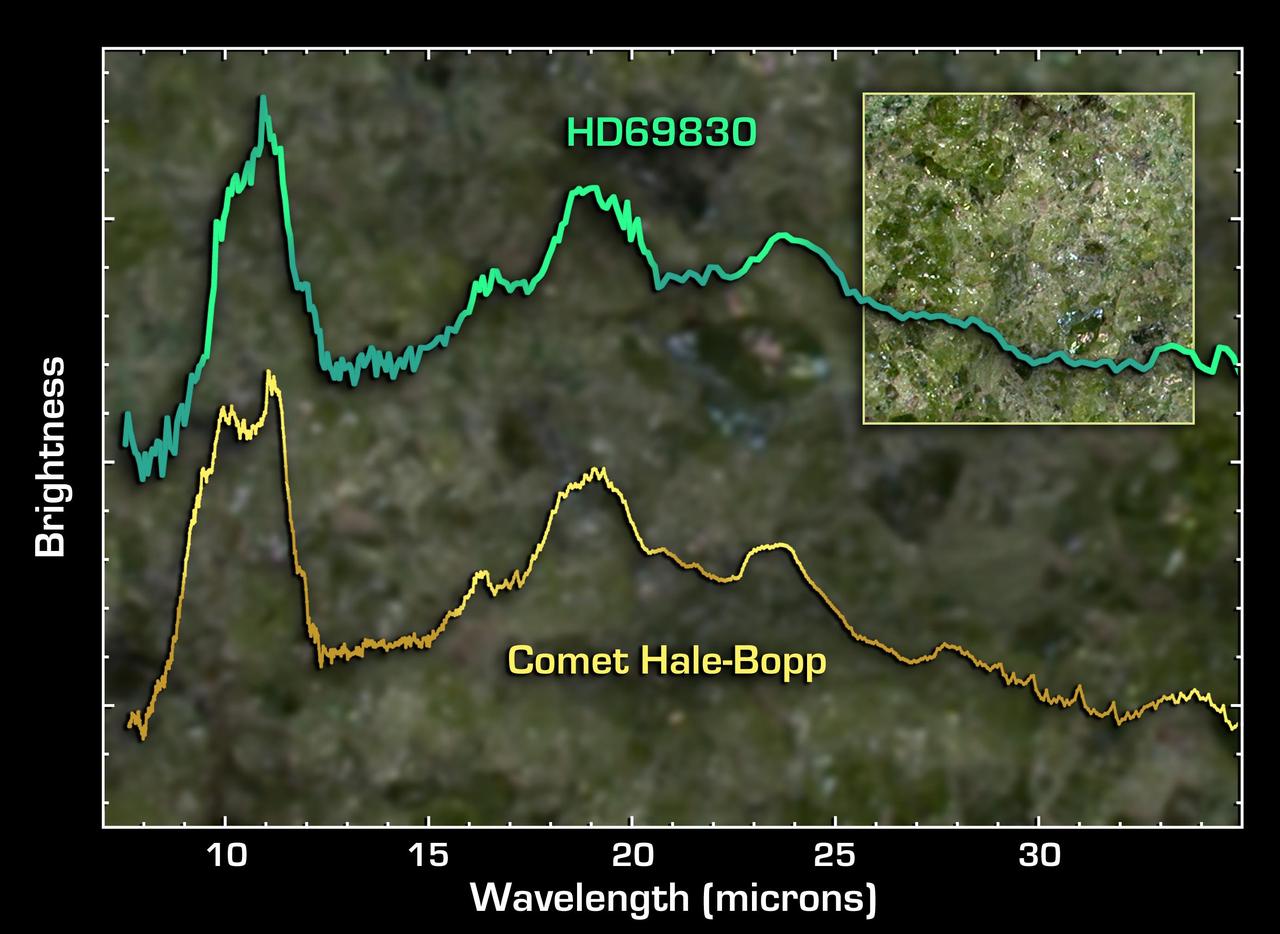
This graph of data from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope demonstrates that the dust around a nearby star called HD 69830 upper line has a very similar composition to that of Comet Hale-Bopp.

This illustration, created in March 2021, depicts the 140-mile-wide (226-kilometer-wide) asteroid Psyche, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Psyche is the focal point of NASA's mission of the same name. The Psyche spacecraft is set to launch in August 2022 and arrive at the asteroid in 2026, where it will orbit for 21 months and investigate its composition. Based on data obtained from Earth, scientists believe Psyche is a mixture of metal and rock. The rock and metal may be in large provinces, or areas, on the asteroid — as illustrated in this rendering. Another possibility is that rock and metal may be intimately mixed on a scale too small to detect from orbit — as depicted in an illustration here: PIA24472. Observing and measuring how the metal and rock are mixed will help scientists determine how Psyche formed. Exploring the asteroid could also give valuable insight into how our own planet and others formed. The Psyche team will use a magnetometer to measure the asteroid's magnetic field. A multispectral imager will capture images of the surface, as well as data about the Psyche's composition and topography. Spectrometers will analyze the neutrons and gamma rays coming from the surface to reveal the elements that make up the asteroid itself. The image was created by Peter Rubin. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24471

This illustration, created in March 2021, depicts the 140-mile-wide (226-kilometer-wide) asteroid Psyche, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Psyche is the focal point of NASA's mission of the same name. The Psyche spacecraft is set to launch in August 2022 and arrive at the asteroid in 2026, where it will orbit for 21 months and investigate its composition. Based on data obtained from Earth, scientists believe Psyche is a mixture of metal and rock. The rock and metal may be in large provinces, or areas, on the asteroid — as depicted in an illustration here: PIA24471. Another possibility is that rock and metal may be intimately mixed on a scale too small to detect from orbit — as depicted in the illustration above. Observing and measuring how the metal and rock are mixed will help scientists determine how Psyche formed. Exploring the asteroid could also give valuable insight into how our own planet and others formed. The Psyche team will use a magnetometer to measure the asteroid's magnetic field. A multispectral imager will capture images of the surface, as well as data about the Psyche's composition and topography. Spectrometers will analyze the neutrons and gamma rays coming from the surface to reveal the elements that make up the asteroid itself. The image was created by Peter Rubin. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24472
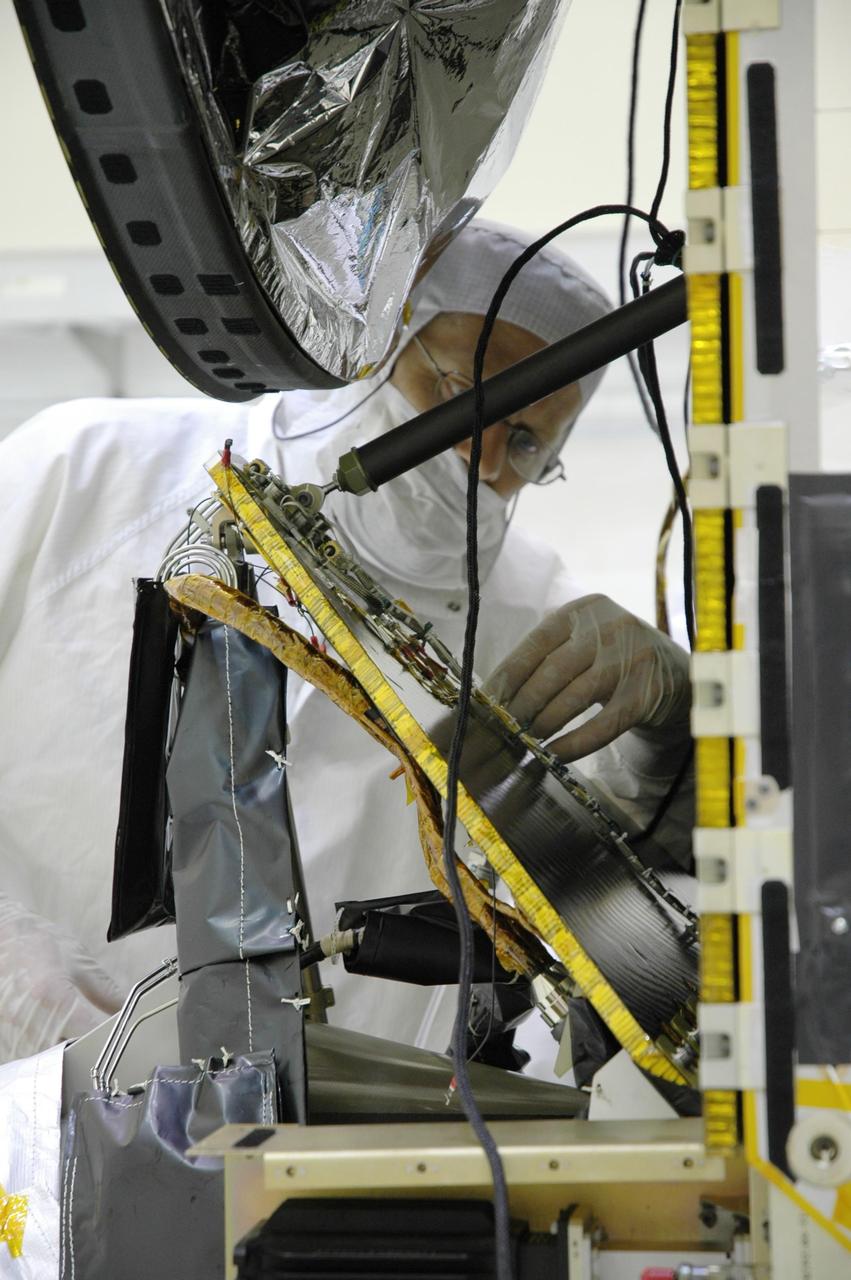

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Astrotech Space Operations facility, Orbital Science technicians install a computer chip on the Dawn spacecraft. The silicon chip holds the names of more than 360,000 space enthusiasts worldwide who signed up to participate in a virtual voyage to the asteroid belt and is about the size of an American five-cent coin. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Astrotech Space Operations facility, Orbital Science technicians verify that a computer chip is securely bonded to a side brace on the Dawn spacecraft. The silicon chip holds the names of more than 360,000 space enthusiasts worldwide who signed up to participate in a virtual voyage to the asteroid belt and is about the size of an American five-cent coin. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Astrotech Space Operations facility, a computer chip is bonded to a side brace on the Dawn spacecraft. The silicon chip holds the names of more than 360,000 space enthusiasts worldwide who signed up to participate in a virtual voyage to the asteroid belt and is about the size of an American five-cent coin. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Astrotech Space Operations facility, a computer chip awaits installation on the Dawn spacecraft. The silicon chip holds the names of more than 360,000 space enthusiasts worldwide who signed up to participate in a virtual voyage to the asteroid belt and is about the size of an American five-cent coin. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

Artist: Rick Guidice Pioneer 10 Crosses the Asteriod Belt: If spacecraft are to visit the outer Solar System, they must cross the asteroid belt between Mars and Jpiter. The Pioneer mission was faced with the question of just how dangerous this astroid belt would be to a spacecraft passing throught it. Note: used in NASA SP-349 'Pioneer Odyssey - Encounter with a Giant' fig. 1-24 and SP-446 ' Pioneer - First to Jupiter, Saturn, and Beyond' fig 1-24
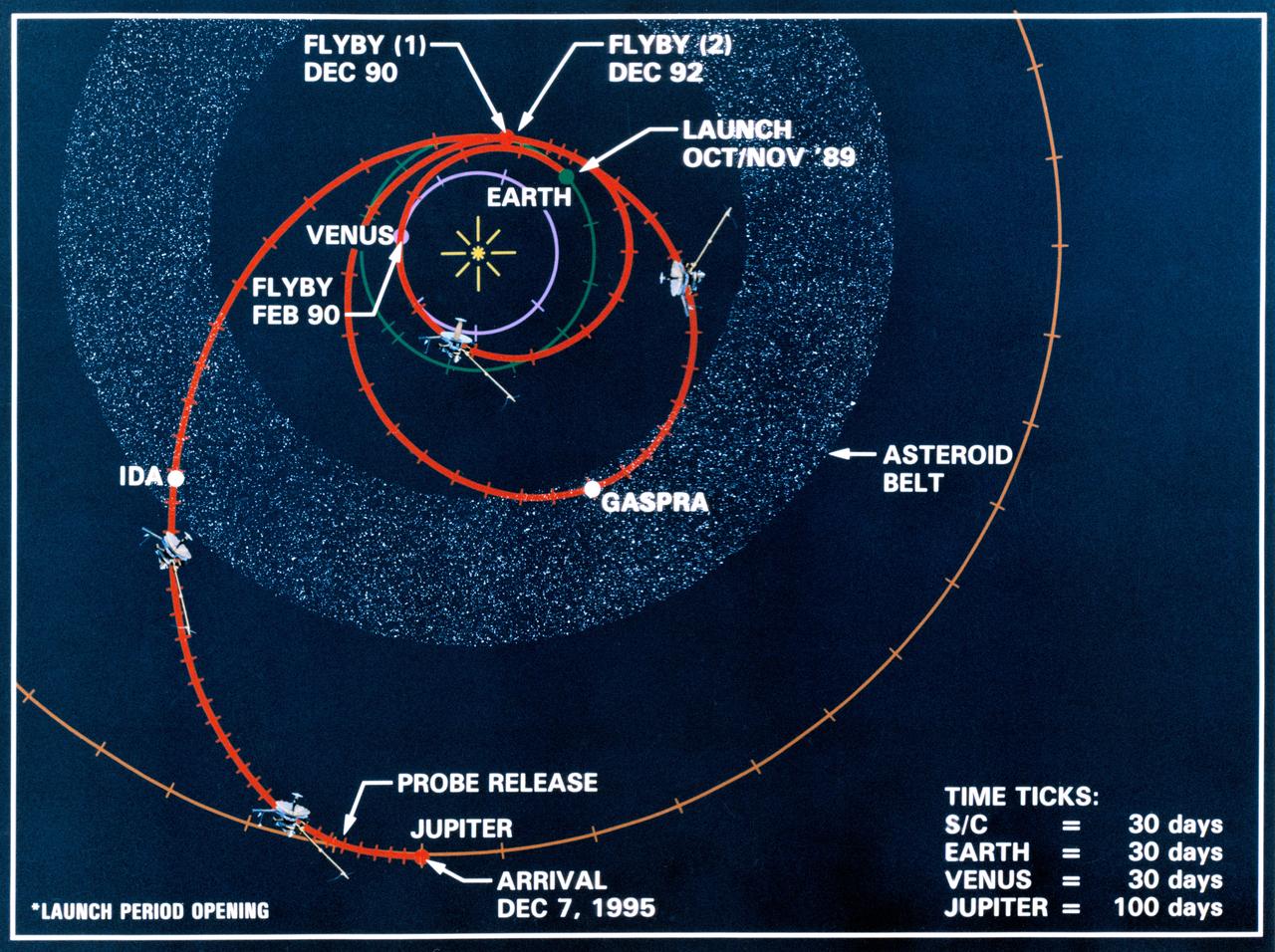
Line drawing charts the Galileo spacecraft's launch from low Earth orbit and its three planetary and two asteroid encounters in the course of its gravity-assisted flight to Jupiter. These encounters include Venus (February 1990), two Earth passes (December 1990 and December 1992), and the asteroids Gaspra and Ida in the asteroid belt. Galileo will release a probe and will arrive at Jupiter, 12-07-95.
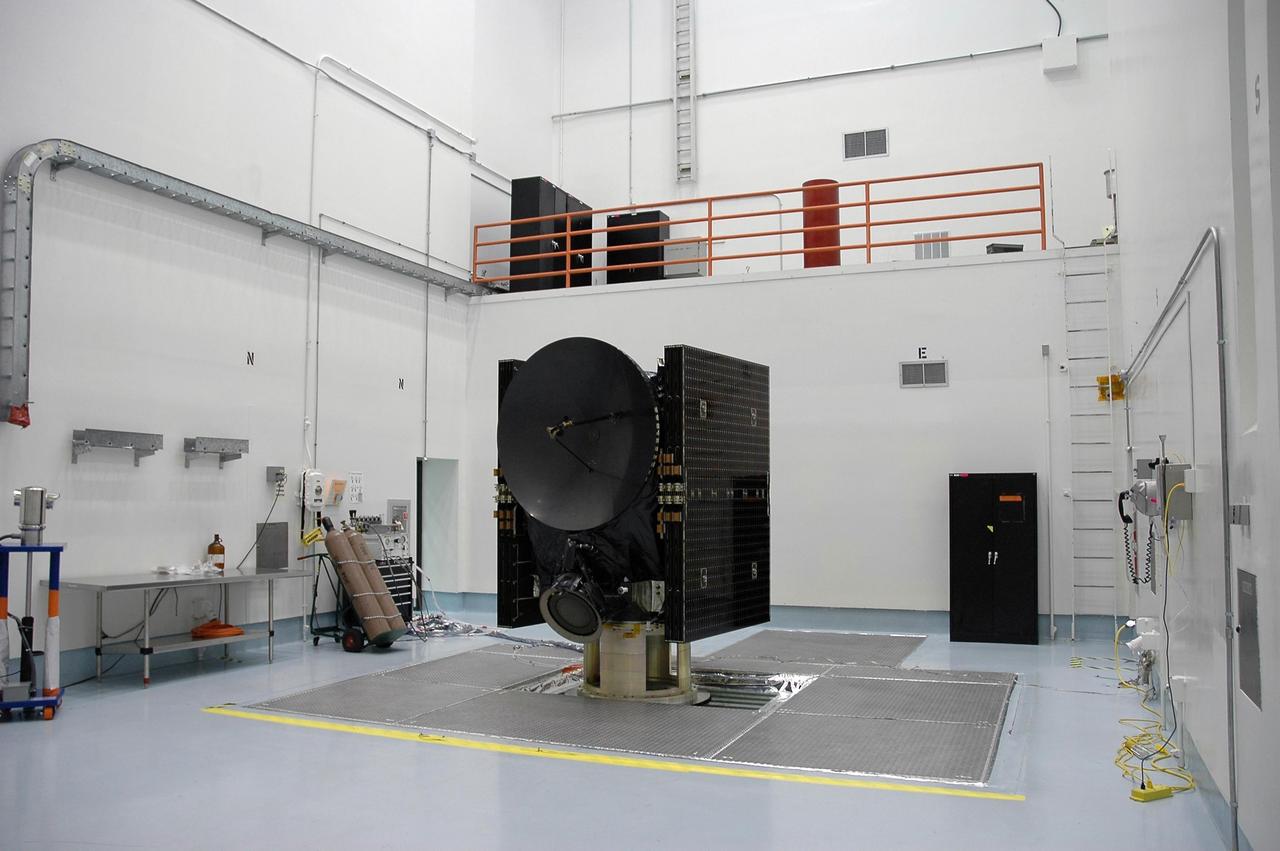

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, the Dawn spacecraft is ready for spin-balance testing. After the test, Dawn will then be mated to the upper stage booster, installed into a spacecraft transportation canister for the trip to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and mated to the Delta II rocket at Launch Pad 17-B. The Dawn spacecraft will employ ion propulsion to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn's goal is to characterize the conditions and processes of the solar system's earliest epoch by investigating in detail these largest protoplanets that have remained intact since their formations. Ceres and Vesta reside in the extensive zone between Mars and Jupiter together with many other smaller bodies, called the asteroid belt. Dawn is scheduled to launch July 7. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians at Astrotech prepare the Dawn spacecraft for spin-balance testing. After the test, Dawn will then be mated to the upper stage booster, installed into a spacecraft transportation canister for the trip to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and mated to the Delta II rocket at Launch Pad 17-B. The Dawn spacecraft will employ ion propulsion to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn's goal is to characterize the conditions and processes of the solar system's earliest epoch by investigating in detail these largest protoplanets that have remained intact since their formations. Ceres and Vesta reside in the extensive zone between Mars and Jupiter together with many other smaller bodies, called the asteroid belt. Dawn is scheduled to launch July 7. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
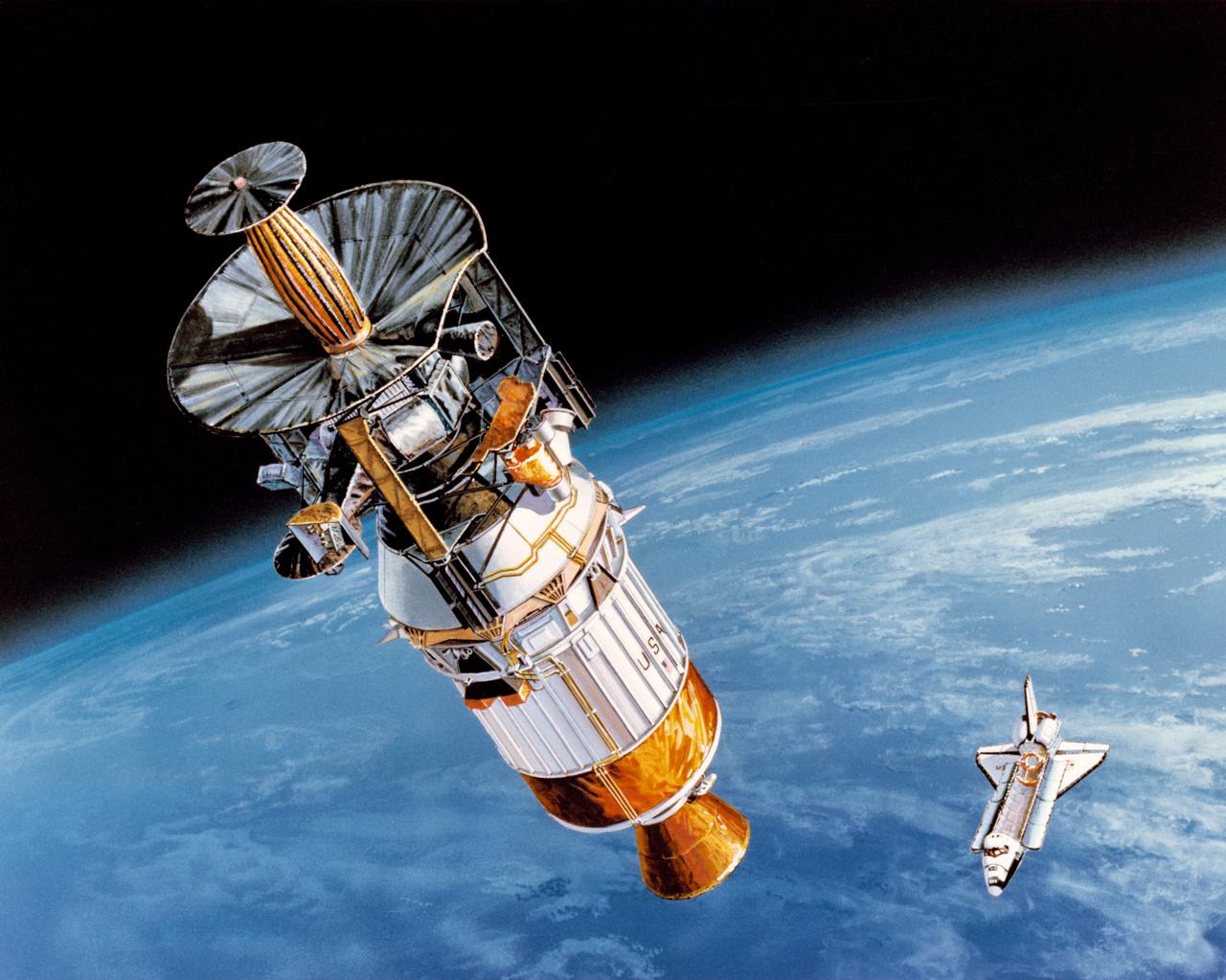

S89-42940 (April 1989) --- In this artist's rendition, the Galileo spacecraft is being boosted into its inter-planetary trajectory by the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) rocket. The Space Shuttle Atlantis, which is scheduled to take Galileo and the IUS from Earth's surface into space, is depicted against the curve of Earth. Galileo will be placed on a trajectory to Venus, from which it will return to Earth at higher velocity and then gain still more energy in two gravity-assist passes, until it has enough velocity to reach Jupiter. Passing Venus, it will take scientific data using instruments designed for observing Jupiter; later, it will make measurements at Earth and the moon, crossing above the moon's north pole in the second pass. Between the two Earth passes, it will edge into the asteroid belt, beyond Mars' orbit; there, the first close-up observation of an asteroid is planned. Crossing the belt later, another asteroid flyby is possible.
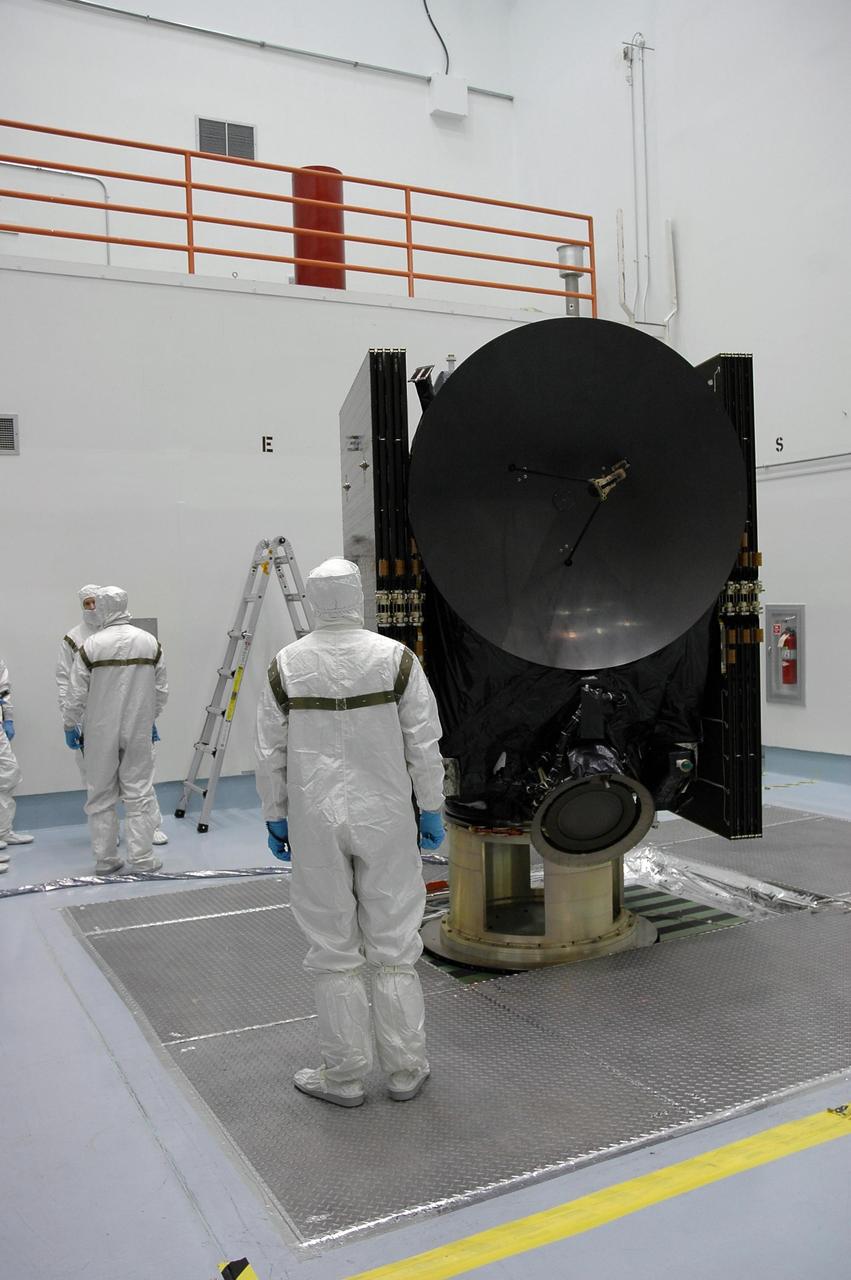

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians at Astrotech are preparing the Dawn spacecraft for spin-balance testing. After the test, Dawn will then be mated to the upper stage booster, installed into a spacecraft transportation canister for the trip to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and mated to the Delta II rocket at Launch Pad 17-B. The Dawn spacecraft will employ ion propulsion to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn's goal is to characterize the conditions and processes of the solar system's earliest epoch by investigating in detail these largest protoplanets that have remained intact since their formations. Ceres and Vesta reside in the extensive zone between Mars and Jupiter together with many other smaller bodies, called the asteroid belt. Dawn is scheduled to launch July 7. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
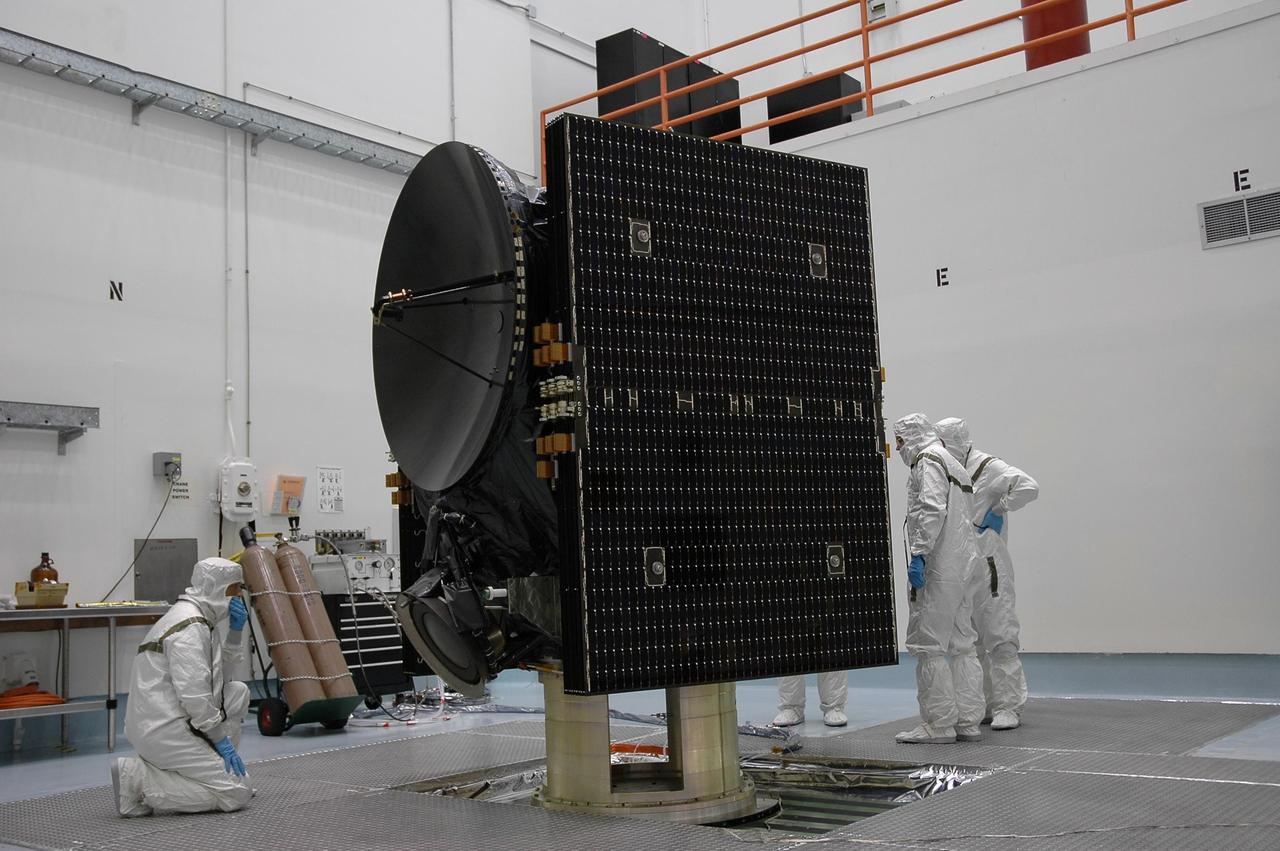

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians at Astrotech check the Dawn spacecraft before spin-balance testing. After the test, Dawn will then be mated to the upper stage booster, installed into a spacecraft transportation canister for the trip to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and mated to the Delta II rocket at Launch Pad 17-B.The Dawn spacecraft will employ ion propulsion to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn's goal is to characterize the conditions and processes of the solar system's earliest epoch by investigating in detail these largest protoplanets that have remained intact since their formations. Ceres and Vesta reside in the extensive zone between Mars and Jupiter together with many other smaller bodies, called the asteroid belt. Dawn is scheduled to launch July 7. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
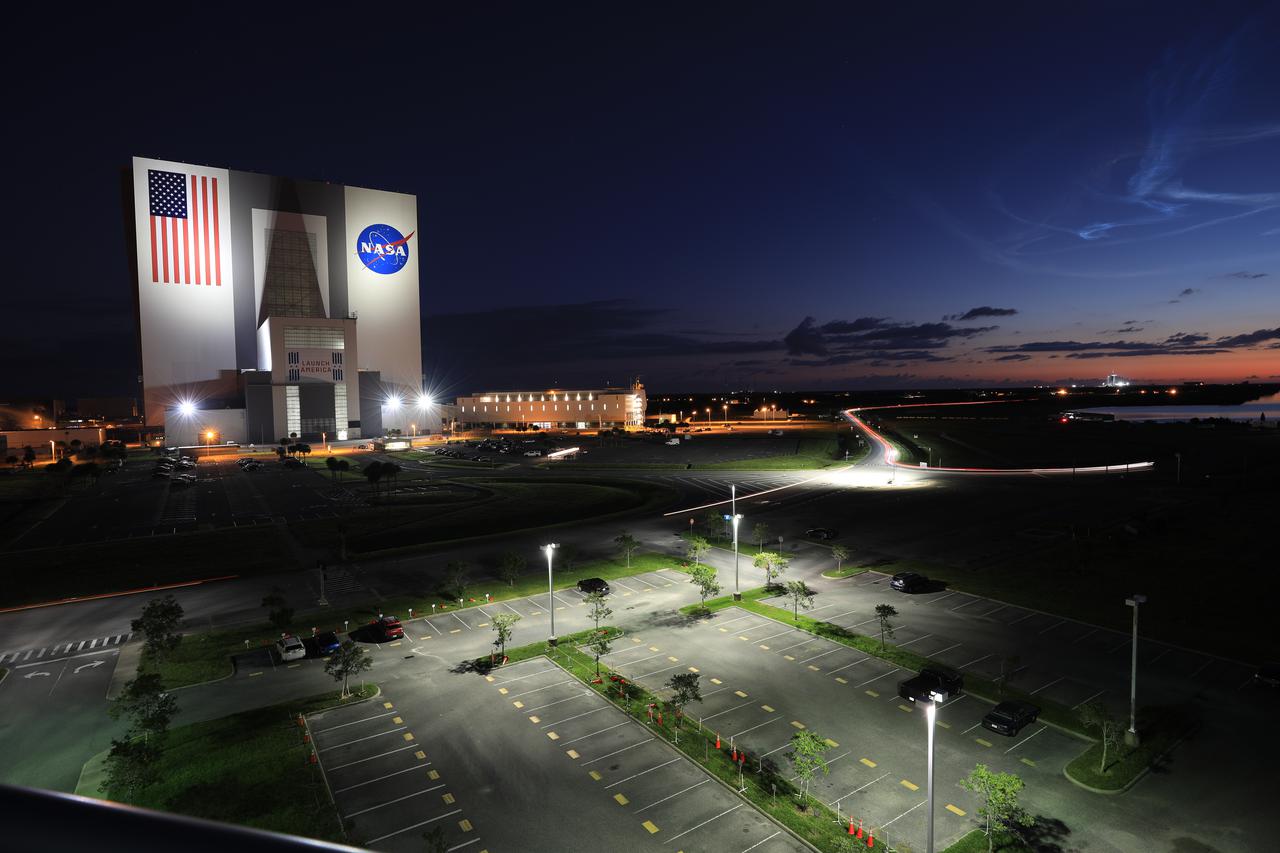

Shown is a view of the Vehicle Assembly at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Oct. 16, 2021 – in the early-morning hours on the day of the Lucy mission. A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket roared off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on at 5:34 a.m. EDT, carrying NASA’s Lucy spacecraft into space. During its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Lucy is the first space mission to study the Trojan asteroids, which hold vital clues to the formation of our solar system.

This artist's concept depicts the 140-mile-wide (226-kilometer-wide) asteroid Psyche, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Psyche is the focal point of NASA's mission of the same name. The Psyche spacecraft is set to launch in August 2022 and arrive at the asteroid in 2026, where it will orbit for 21 months and investigate its composition. Scientists think that Psyche, unlike most other asteroids that are rocky or icy bodies, is made up of mostly iron and nickel — similar to the Earth's core. Exploring the asteroid could give valuable insight into how our own planet and others formed. The Psyche team will use a magnetometer to measure the asteroid's magnetic field. A multispectral imager will capture images of the surface, as well as data about the Psyche's composition and topography. Spectrometers will analyze the neutrons and gamma rays coming from the surface to reveal the elements that make up the asteroid itself. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23876
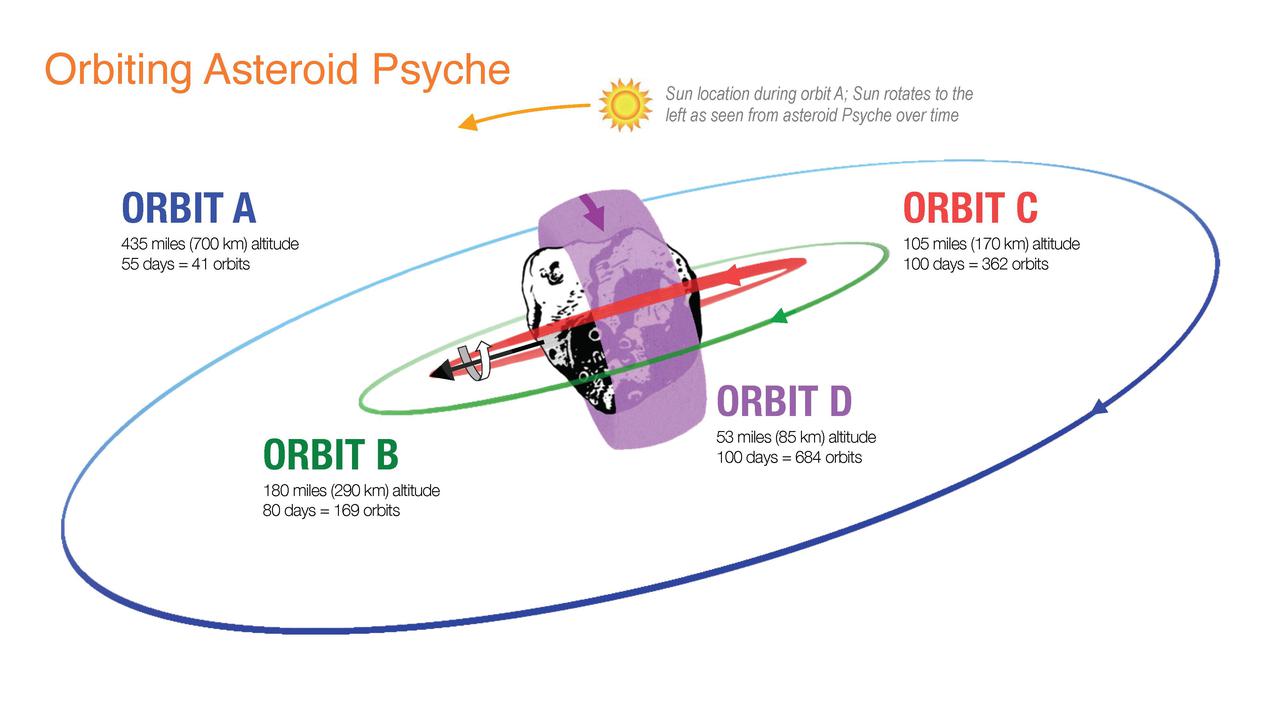
This illustration shows how NASA's Psyche spacecraft will explore the asteroid Psyche, beginning with Orbit A when it arrives at the asteroid in early 2026. The initial orbit is designed to be at a high altitude – about 435 miles (700 kilometers) above the asteroid's surface. Over the following 20 months, the spacecraft will use its electric propulsion system to dip into lower and lower orbits as it conducts its science investigation. Eventually, the spacecraft will establish a final orbit (Orbit D) about 53 miles (85 kilometers) above the surface. Set to launch in August 2022, Psyche will investigate a metal-rich asteroid of the same name, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Scientists believe the asteroid could be part or all of the iron-rich interior of an early planetary building block that was stripped of its outer rocky shell as it repeatedly collided with other large bodies during the early formation of the solar system. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24896
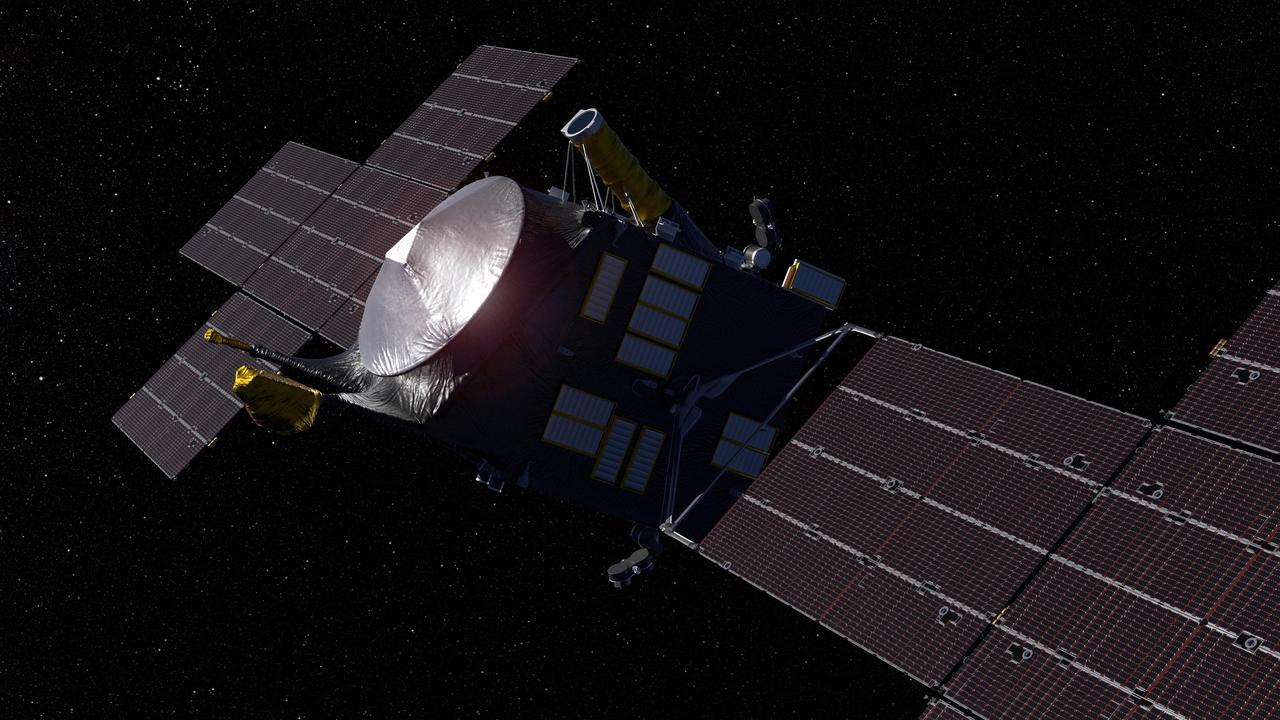

This artist's concept, updated as of June 2020, depicts NASA's Psyche spacecraft. Set to launch in August 2022, the Psyche mission will explore a metal-rich asteroid of the same name that lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The spacecraft will arrive in early 2026 and orbit the asteroid for nearly two years to investigate its composition. Scientists think that Psyche, unlike most other asteroids that are rocky or icy bodies, is made up of mostly iron and nickel — similar to the Earth's core. The Psyche team will use a magnetometer to measure the asteroid's magnetic field. A multispectral imager will capture images of the surface, as well as data about the Psyche's composition and topography. Spectrometers will analyze the neutrons and gamma rays coming from the surface to reveal the elements that make up the asteroid itself. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23875
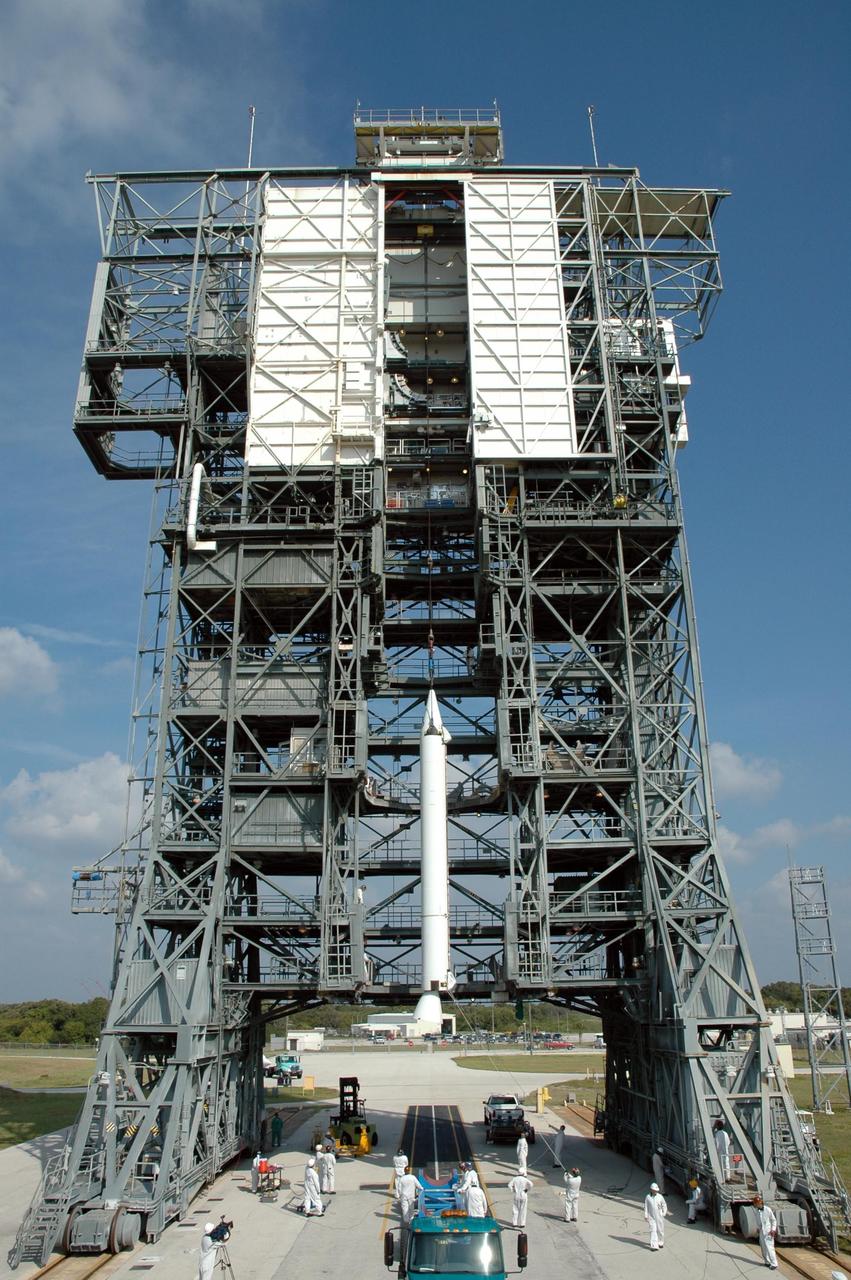

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, one of nine solid rocket boosters is lifted into the mobile service tower. It will be attached to the Delta II first stage for the launch of the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
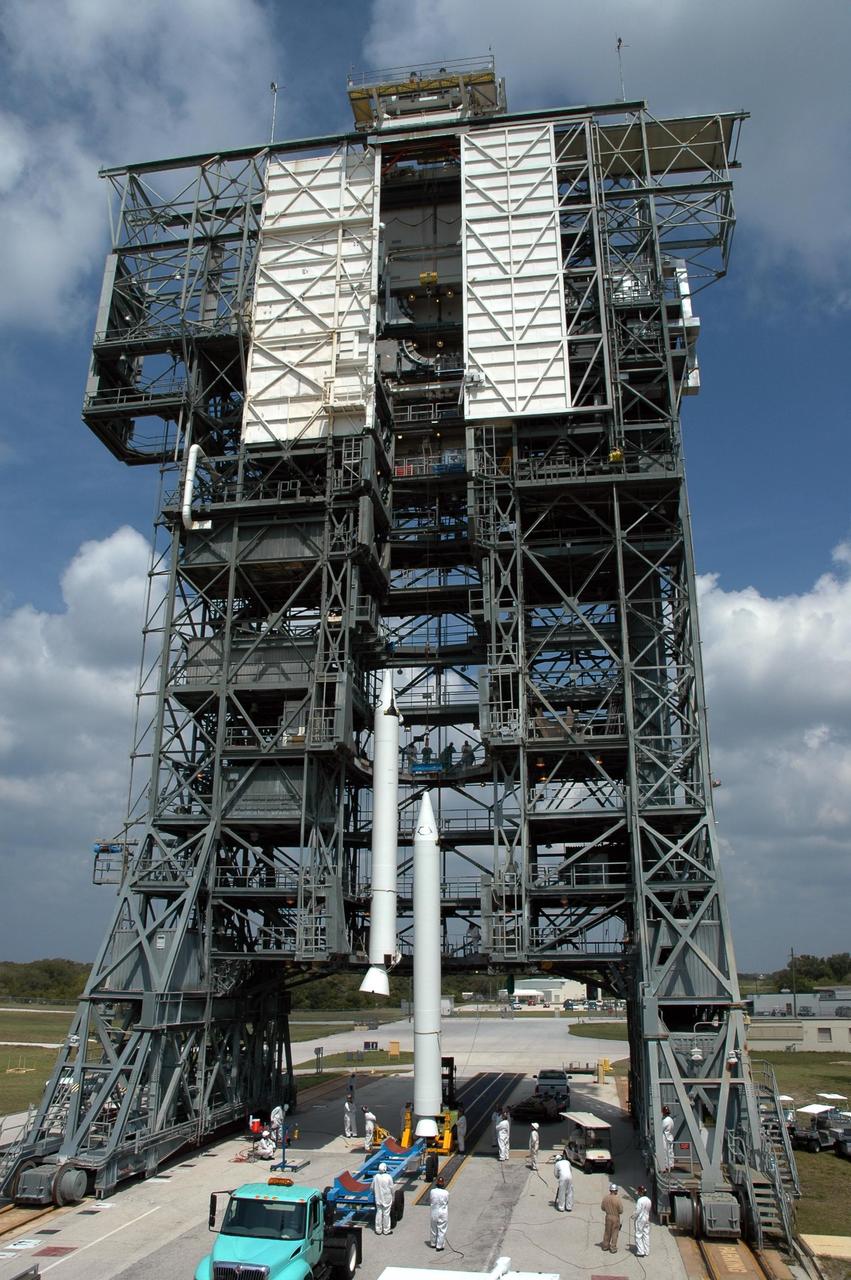

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a second solid rocket booster is ready to be lifted into the mobile service tower. It will be attached to the Delta II first stage for the launch of the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
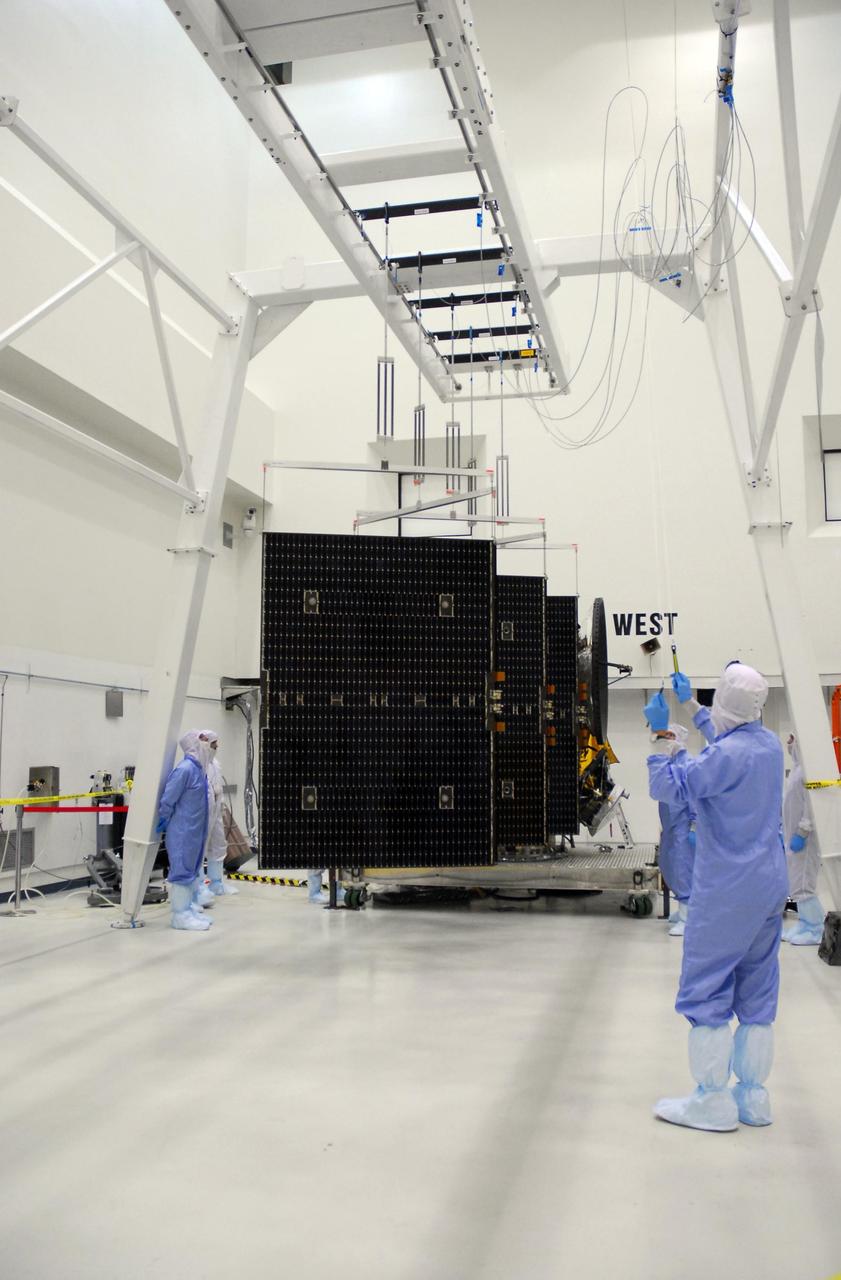

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, the more than 32-foot-long solar panels on one side of the Dawn spacecraft glide open during a test deployment. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
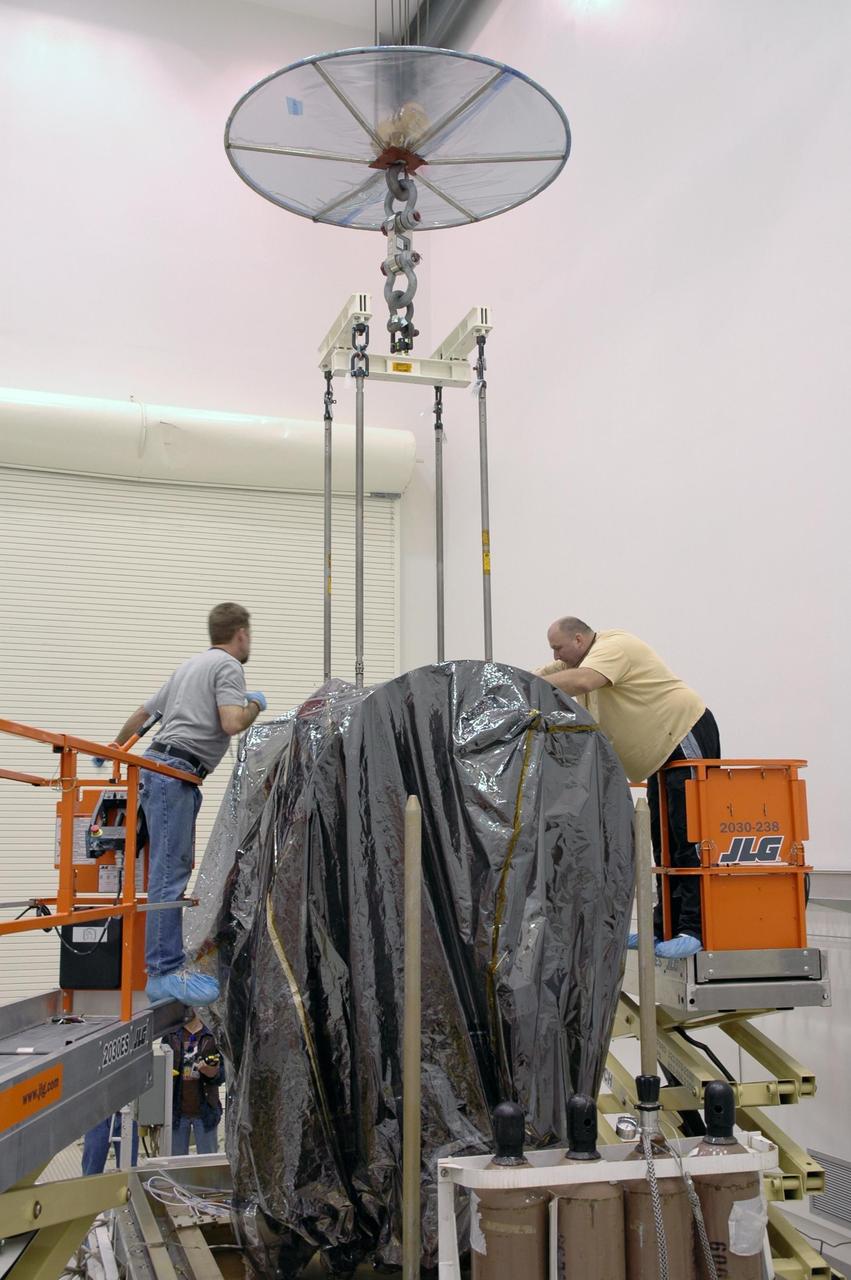

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a crane is being attached to the Dawn spacecraft to lift it from the transporter. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
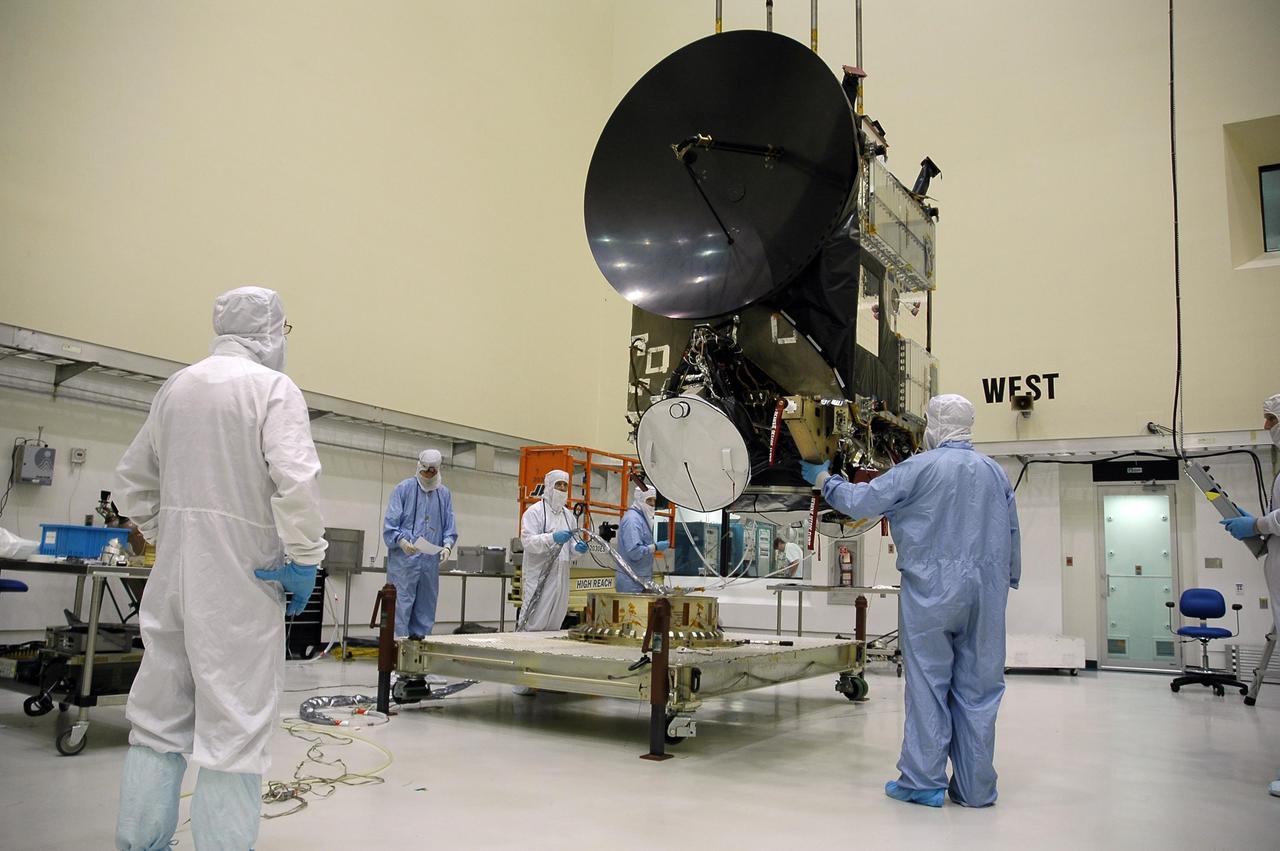

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In a clean room at Astrotech, the Dawn spacecraft is lowered toward a work stand for solar panel installation. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
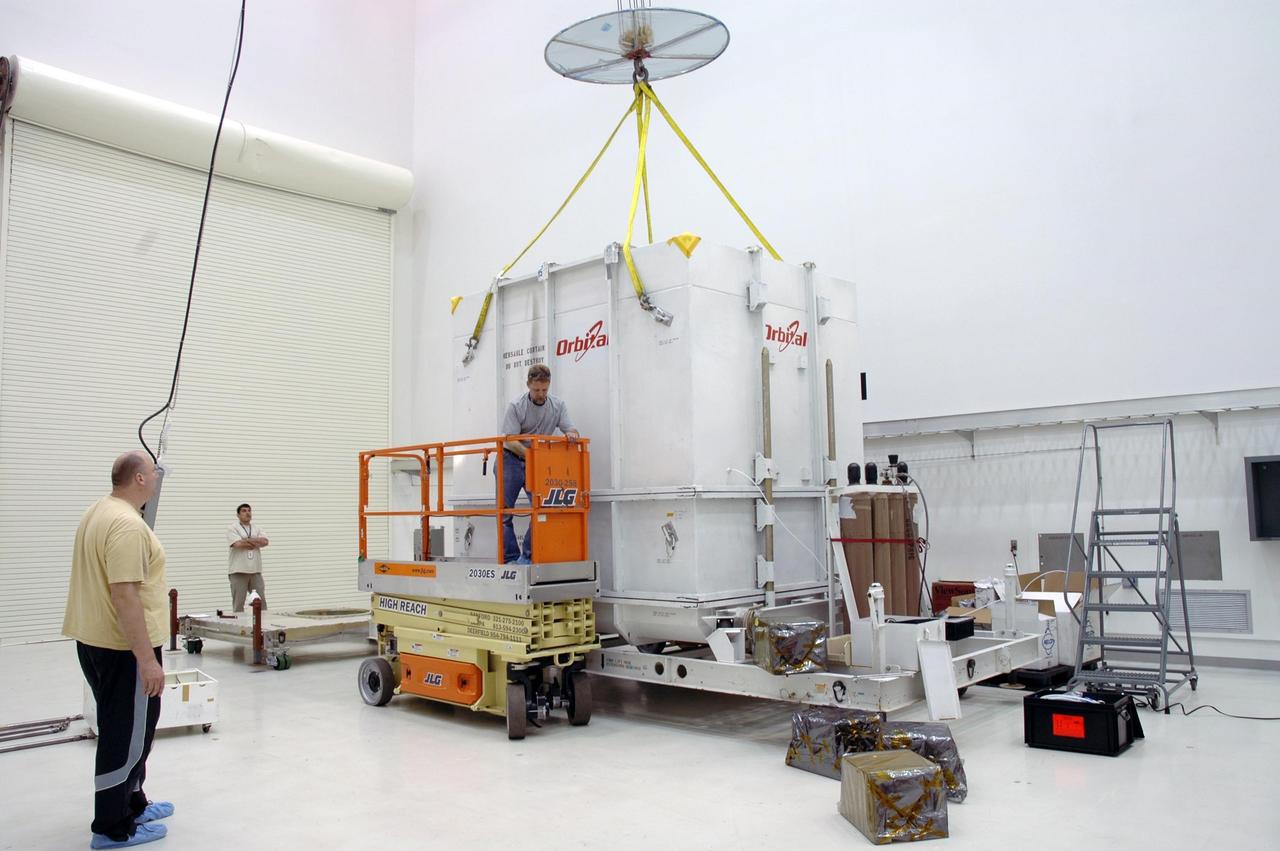

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a crane is attached to the shipping container to remove it from around the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, workers fold the large solar array panels on one side of the Dawn spacecraft. The panels will be tested for deployment and stowage. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
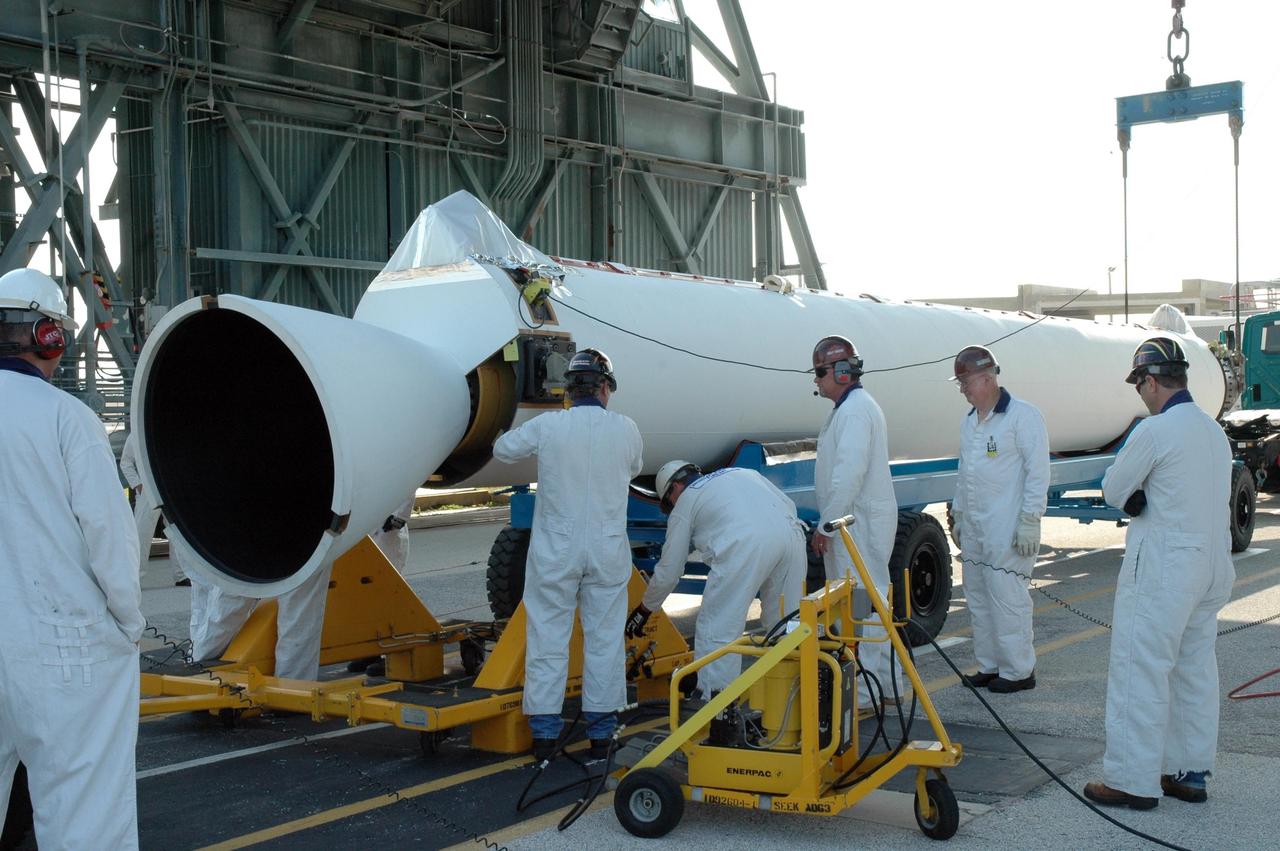

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers prepare the solid rocket booster to be raised off the transporter. The SRB is one of nine to be mated to the Delta II rocket that will launch the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
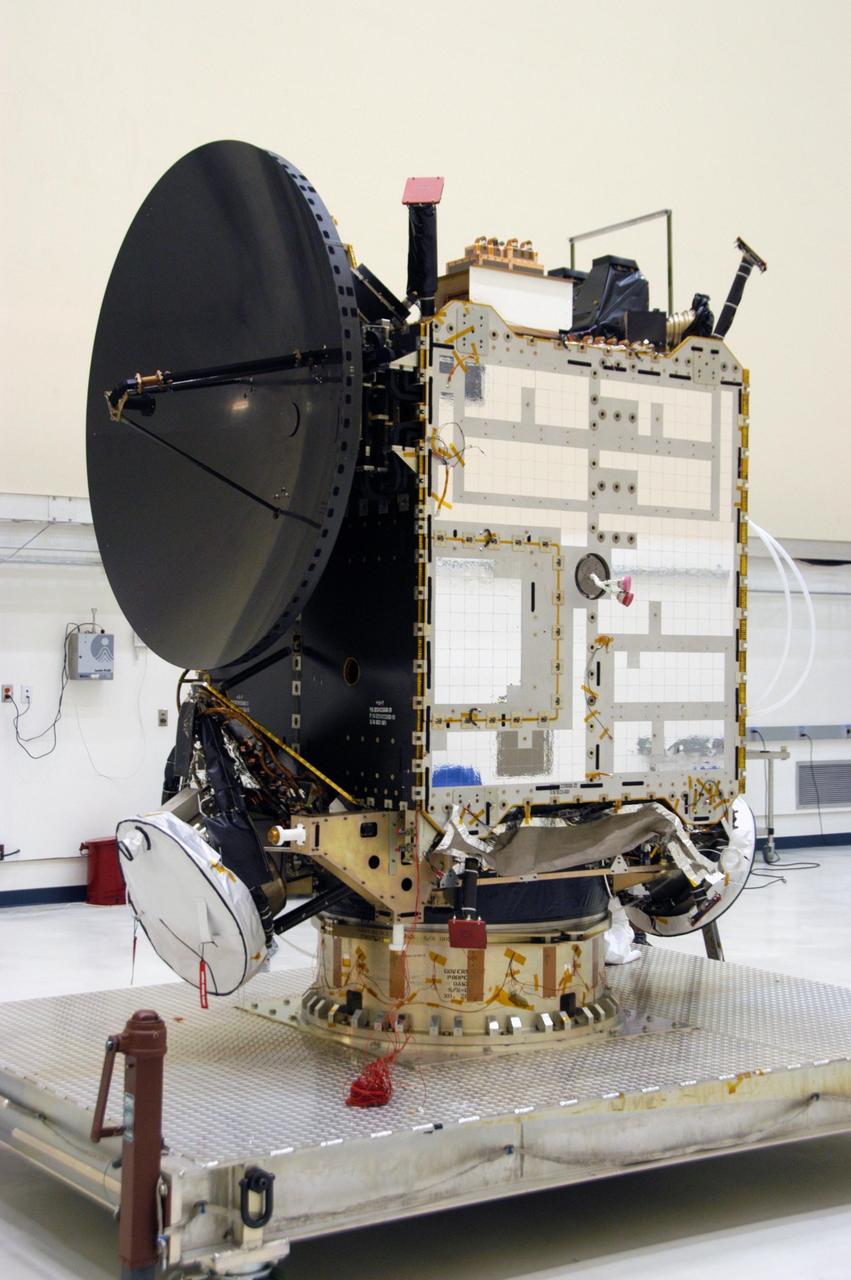
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Dawn spacecraft is seen here in clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility. In the clean room, the spacecraft will undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
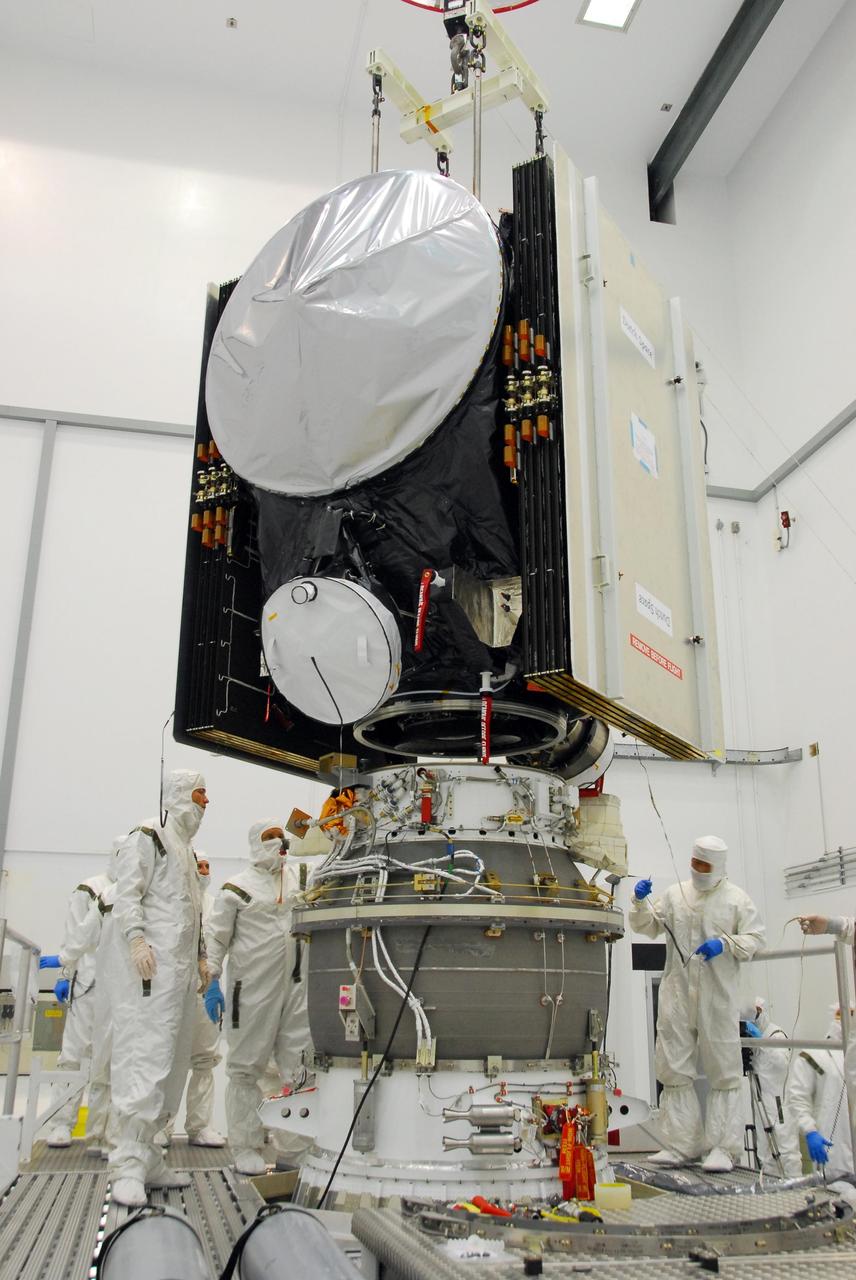

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, workers check the progress of the Dawn spacecraft being lowered toward the upper stage booster below. The two elements will be mated for launch. Dawn's goal is to characterize the conditions and processes of the solar system's earliest epoch by investigating in detail the largest protoplanets that have remained intact since their formations: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. They reside in the extensive zone between Mars and Jupiter together with many other smaller bodies, called the asteroid belt. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
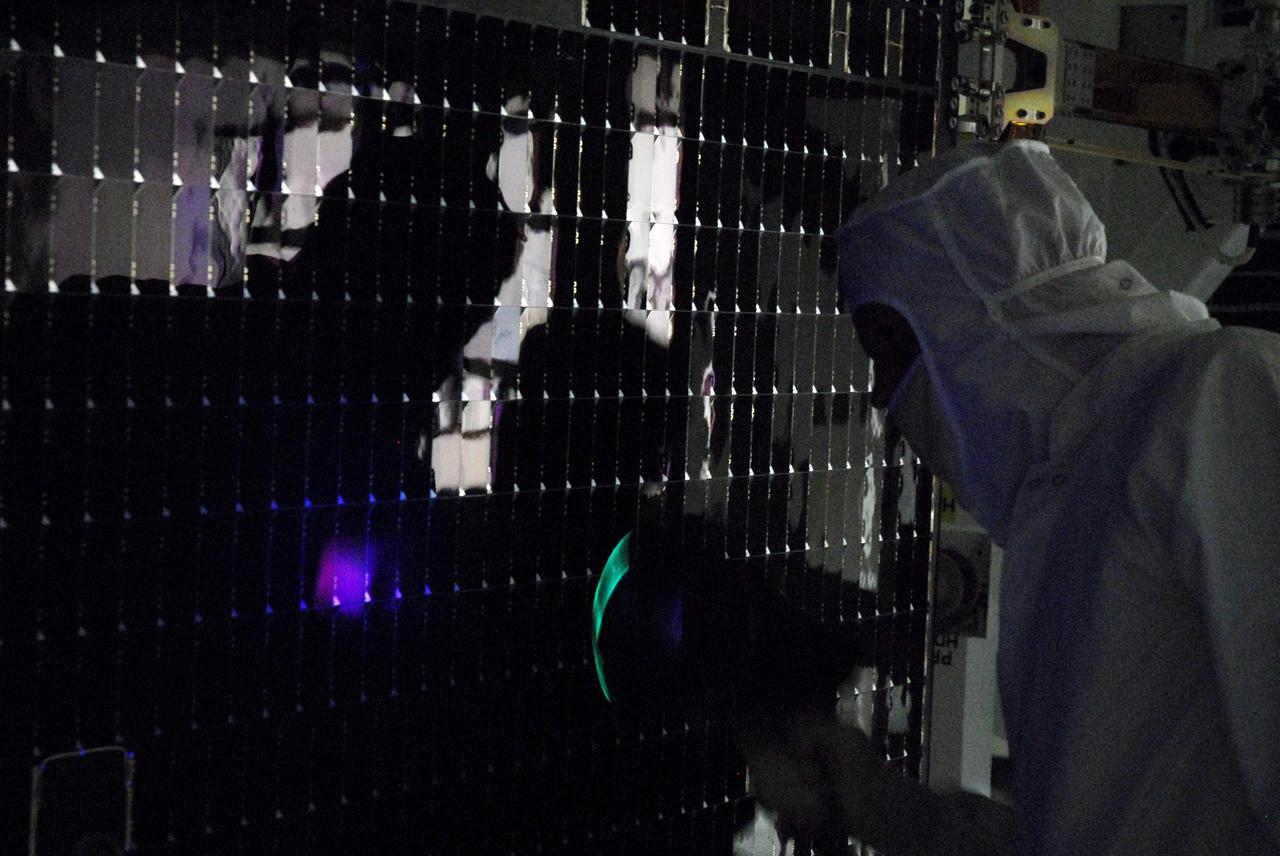

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In a clean room at Astrotech, workers begin black light testing on the solar panels of the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
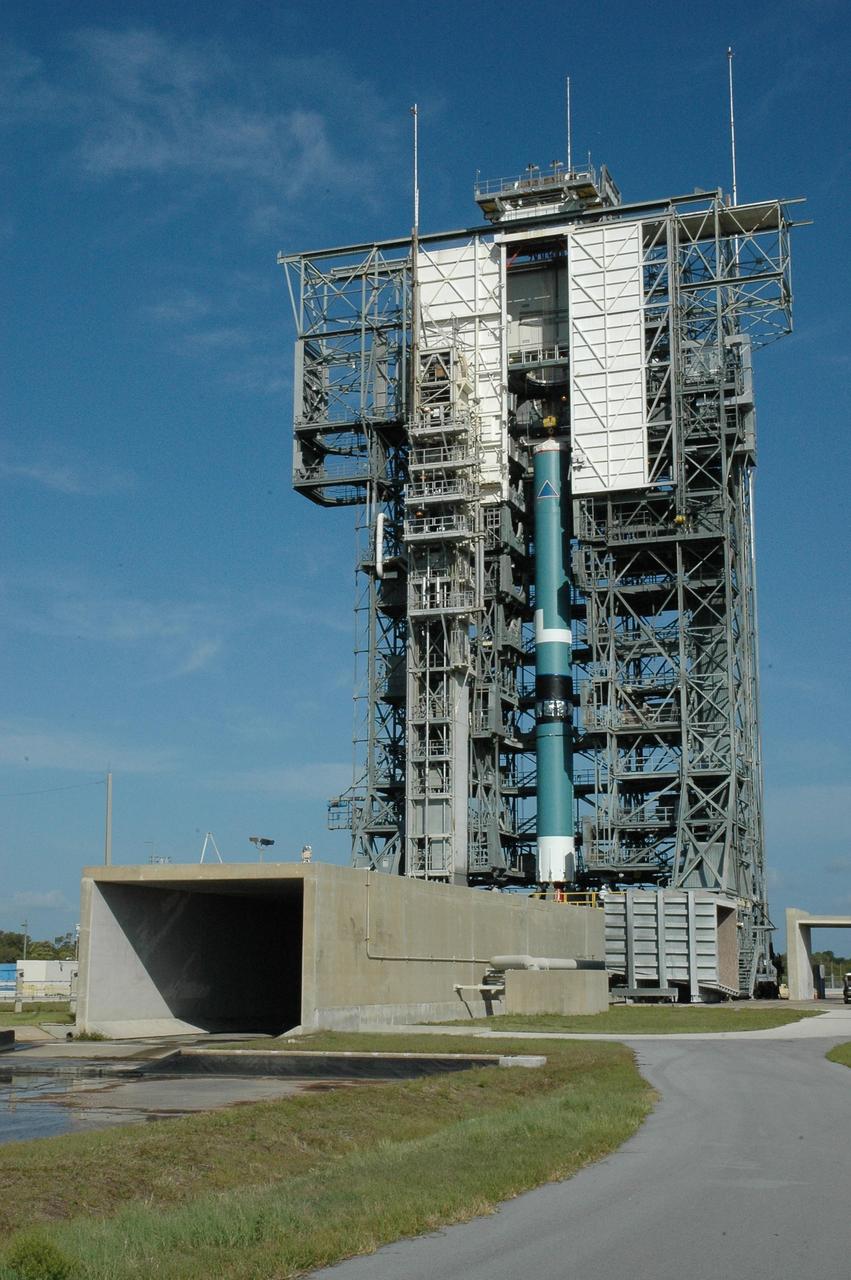

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II first stage is ready to receive the upper stages and solid rocket boosters for launch. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Dawn spacecraft, targeted for liftoff on June 30. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, an external cover is removed from around the shipping container holding the Dawn spacecraft. The container will then be moved into the high bay of the Payload Processing Facility and the spacecraft removed. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
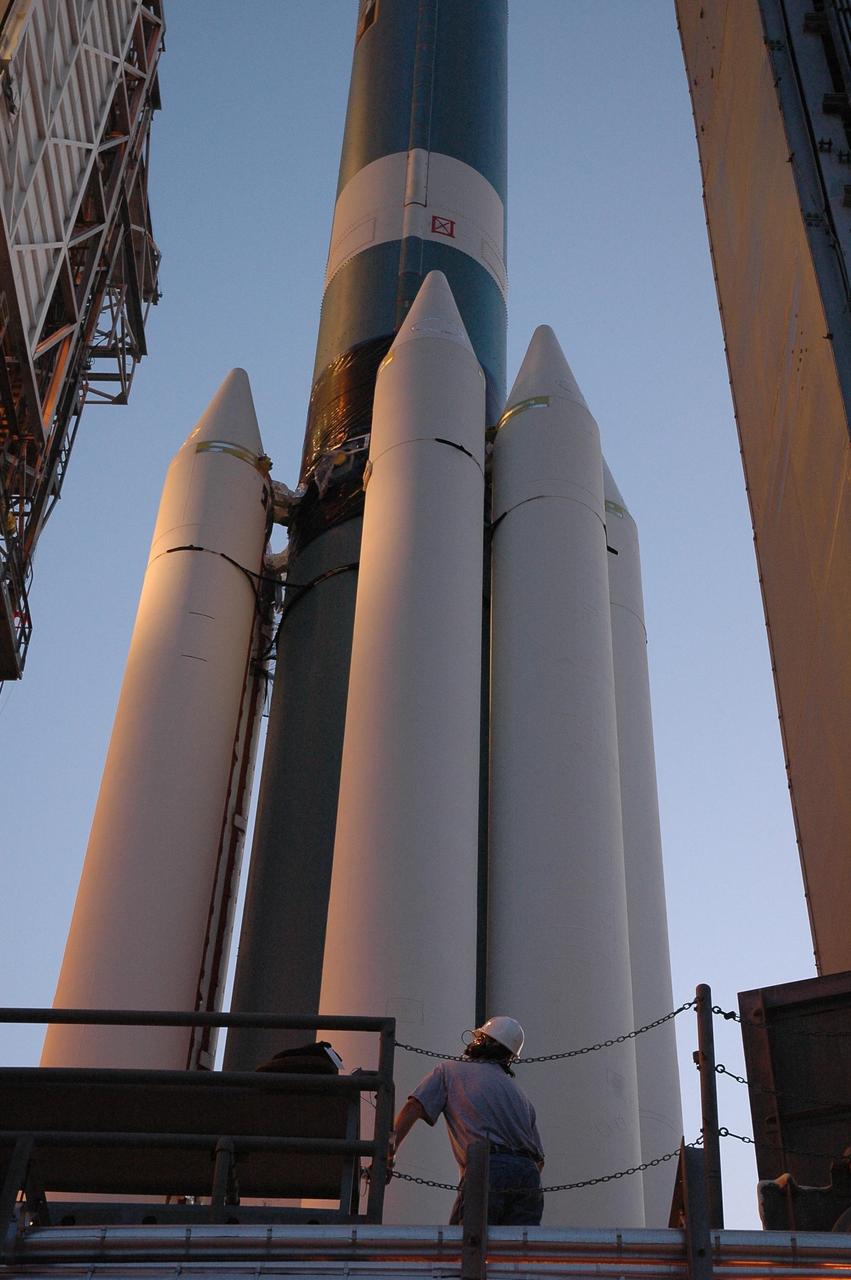

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This closeup shows four of the nine solid rocket boosters being mated to the Delta II first stage on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for launch of the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's goal is to characterize the conditions and processes of the solar system's earliest epoch 4.5 billion years ago by investigating in detail two of the largest asteroids, Ceres and Vesta. They reside between Mars and Jupiter in the asteroid belt. Launch is targeted for July 7. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In a clean room at Astrotech, workers prepare the Dawn spacecraft to be moved to a work stand for solar panel installation. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, technicians dressed in "bunny suits," or clean-room attire, begin working on the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.
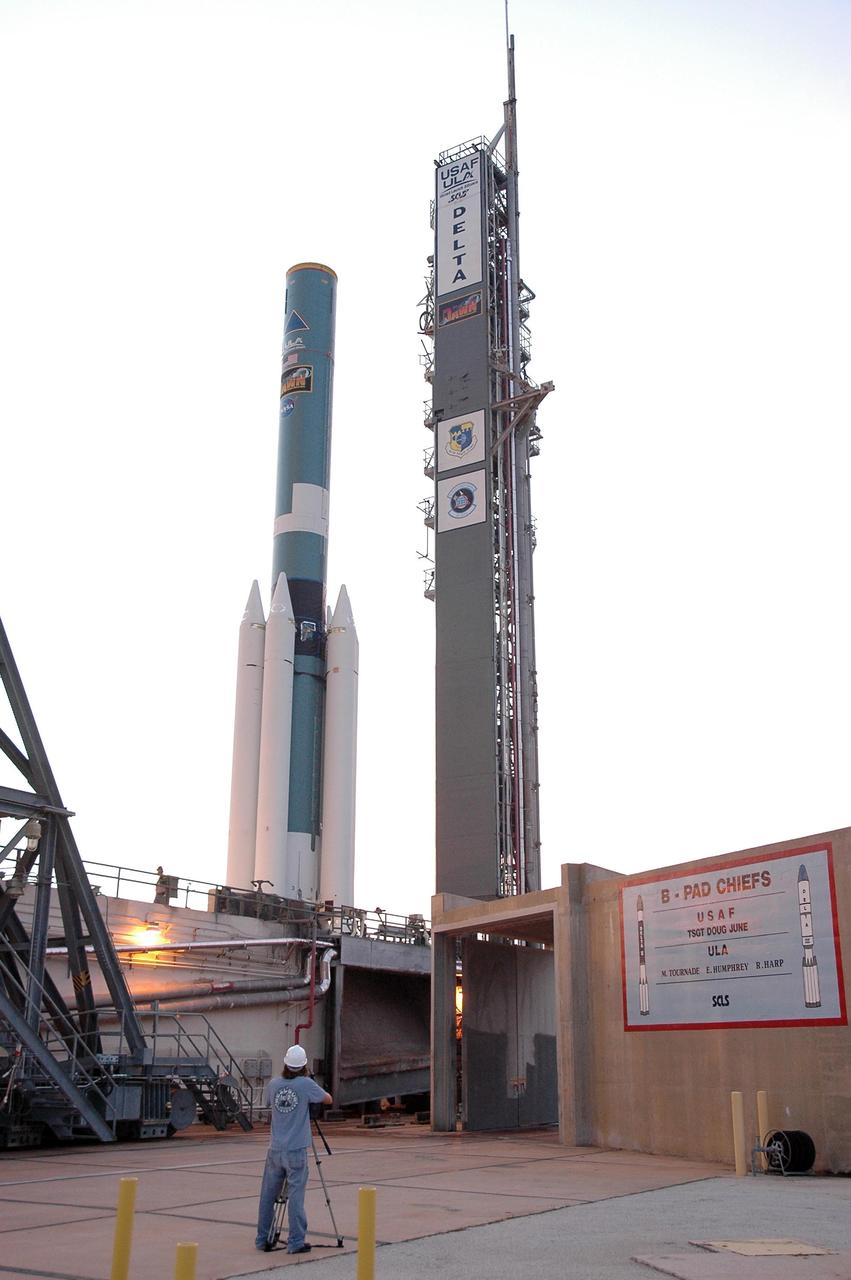

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II first stage waits for the mating of additional solid rocket boosters for launch of the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's goal is to characterize the conditions and processes of the solar system's earliest epoch 4.5 billion years ago by investigating in detail two of the largest asteroids, Ceres and Vesta. They reside between Mars and Jupiter in the asteroid belt. Launch is targeted for July 7. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In a clean room at Astrotech, workers prepare the Dawn spacecraft for installation of its solar array panels. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
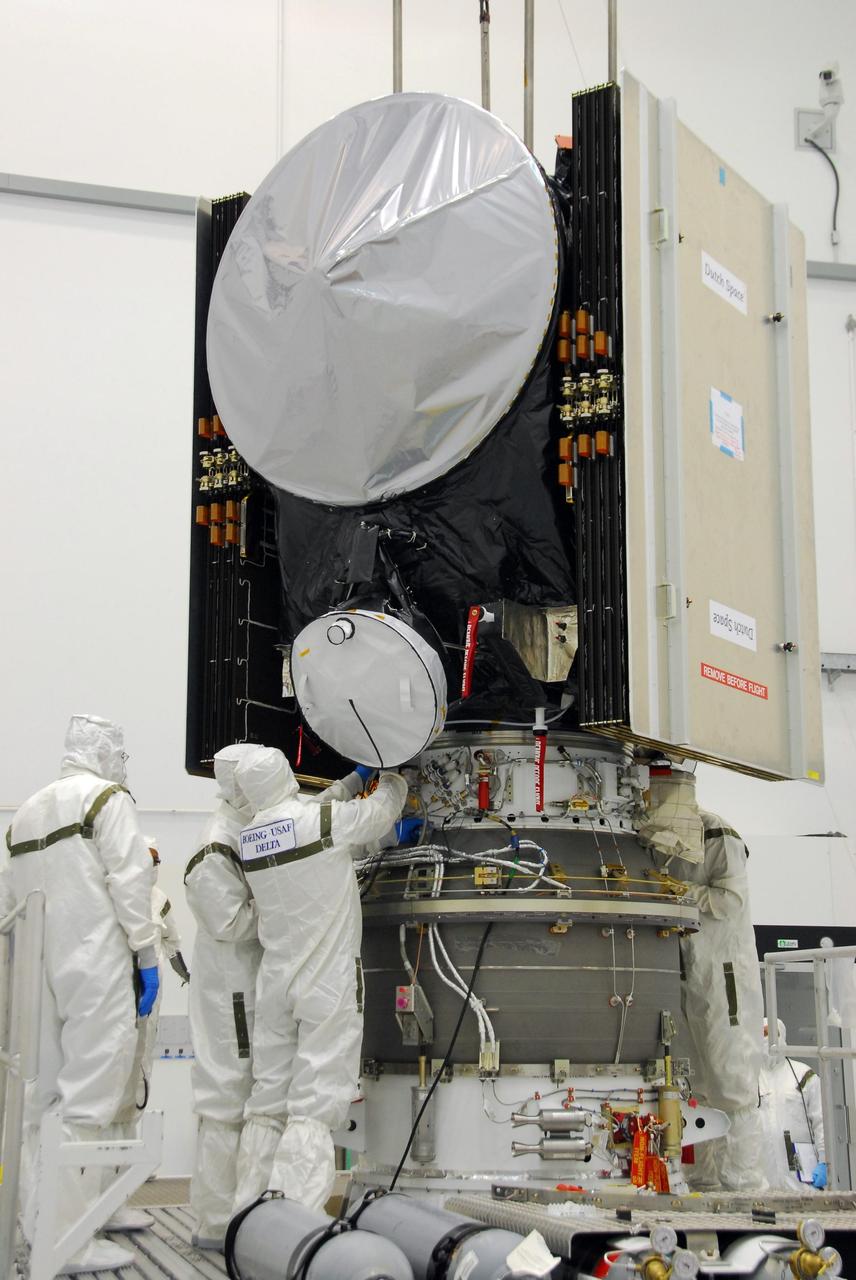

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, workers secure the attachments of the Dawn spacecraft onto the upper stage booster. The two elements are being mated for launch. Dawn's goal is to characterize the conditions and processes of the solar system's earliest epoch by investigating in detail the largest protoplanets that have remained intact since their formations: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. They reside in the extensive zone between Mars and Jupiter together with many other smaller bodies, called the asteroid belt. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
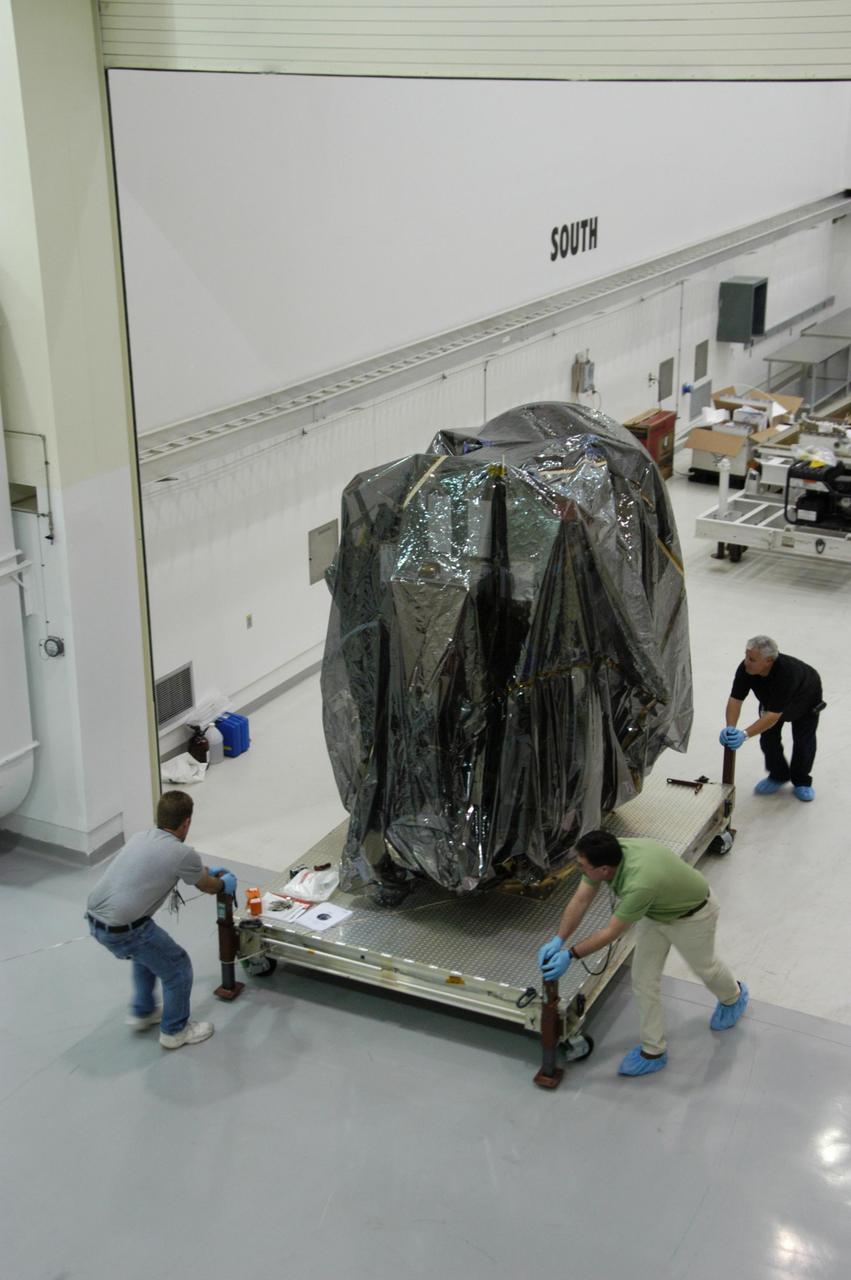

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, technicians roll the Dawn spacecraft into clean room C for unbagging and further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

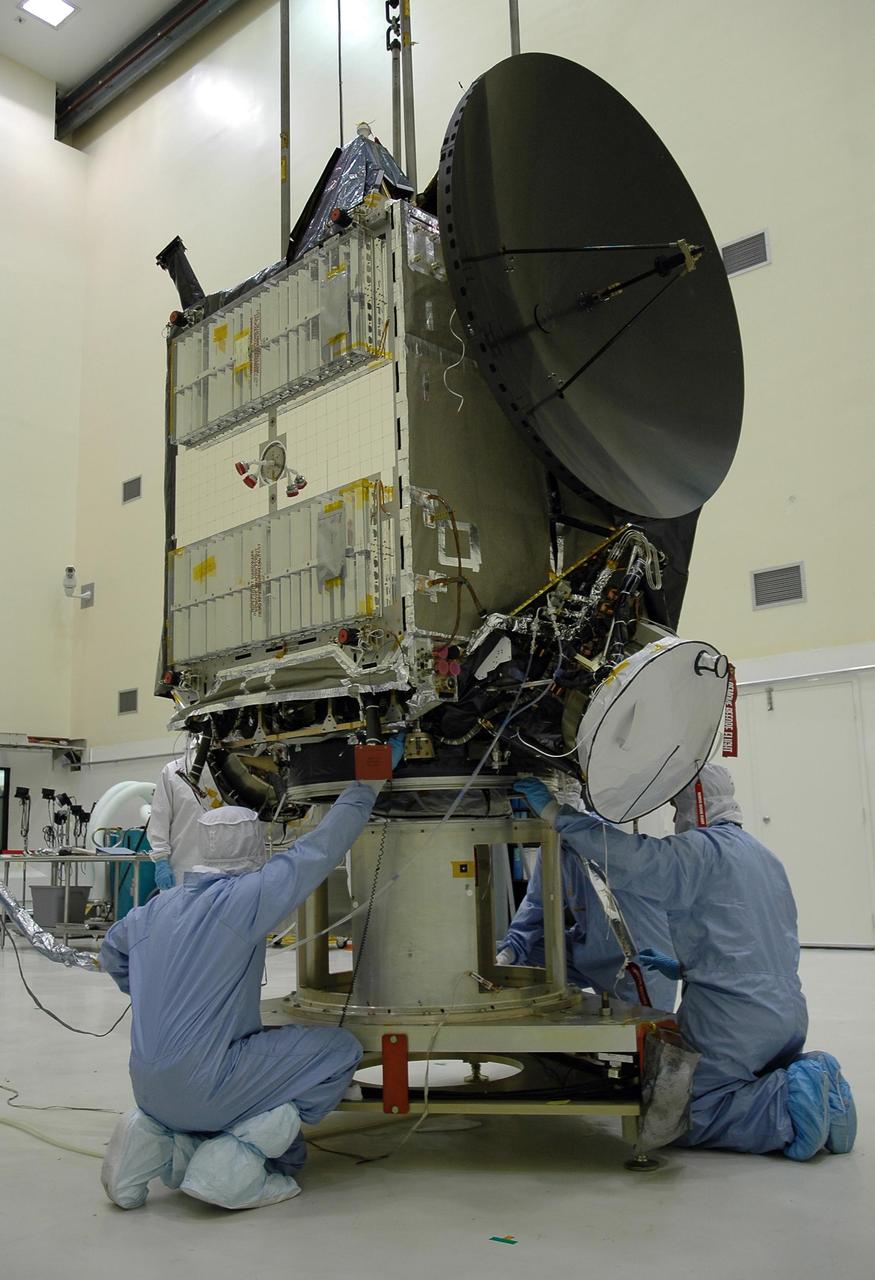
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, two Dutch technicians examine the Dawn spacecraft after deployment of the solar panels on one side. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
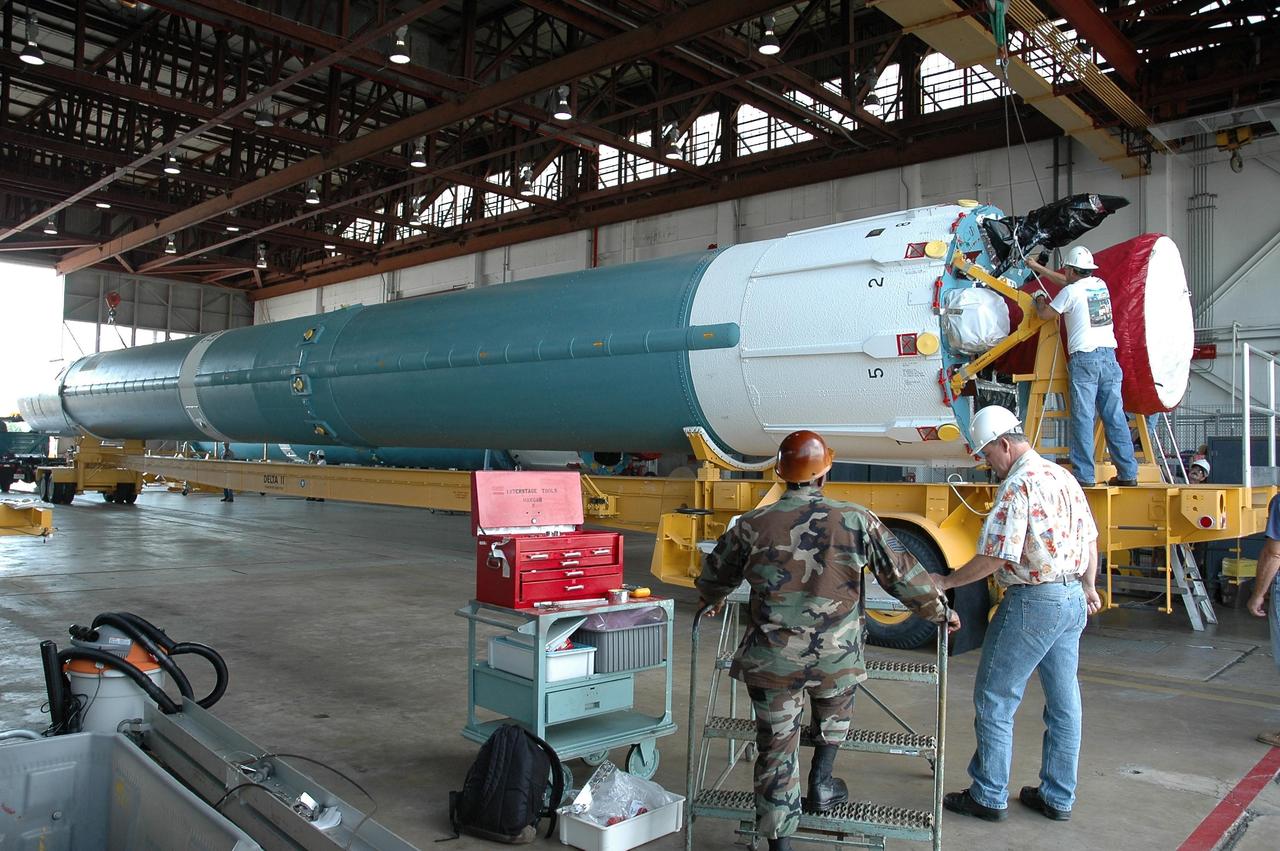

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After its successful transfer to a transporter, the Delta II first stage is ready to move out of Hangar M on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
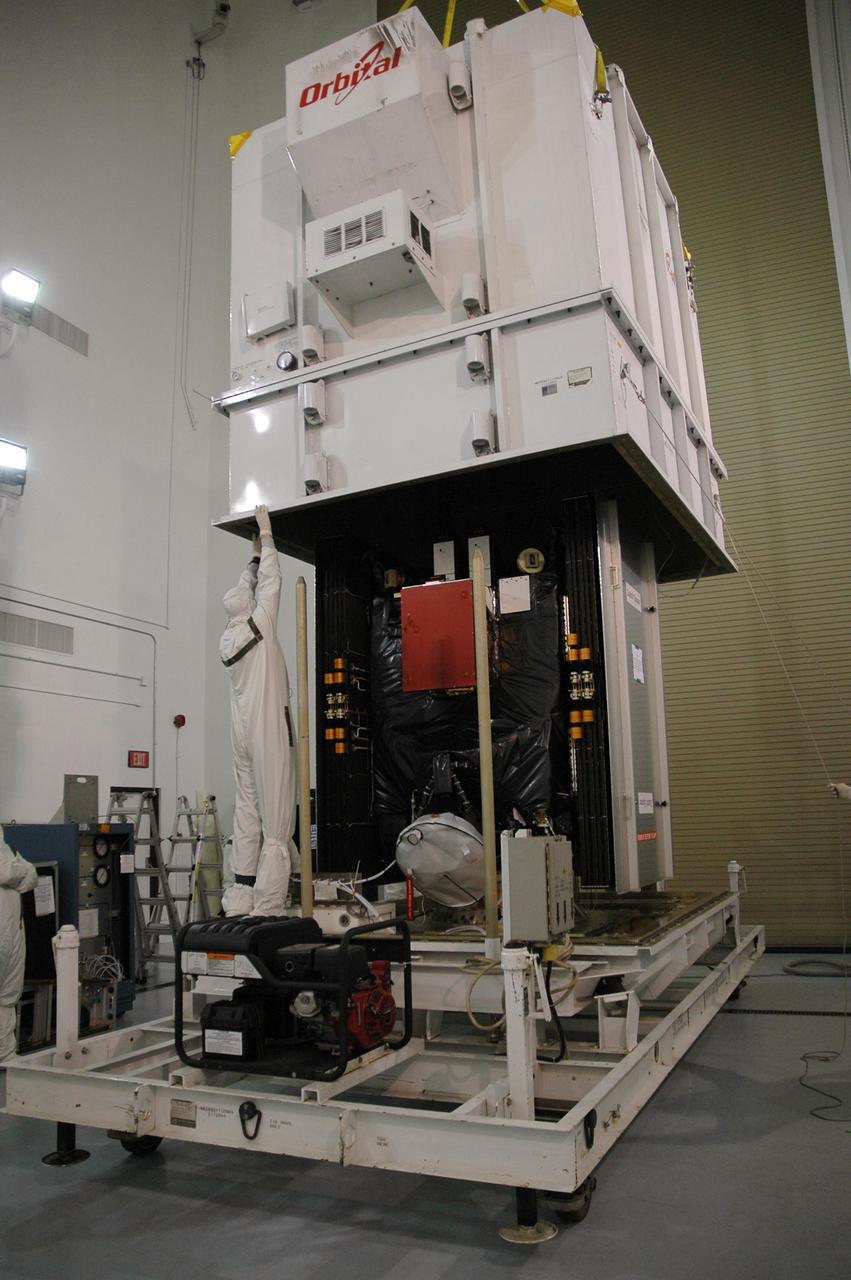

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside Astrotech's Hazardous Processing Facility, the shipping container is removed from around the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn will be moved to a scale for weighing and then prepared for fueling. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a worker wears a "bunny suit," or clean-room attire, next to the Dawn spacecraft, which will be unbagged and undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.
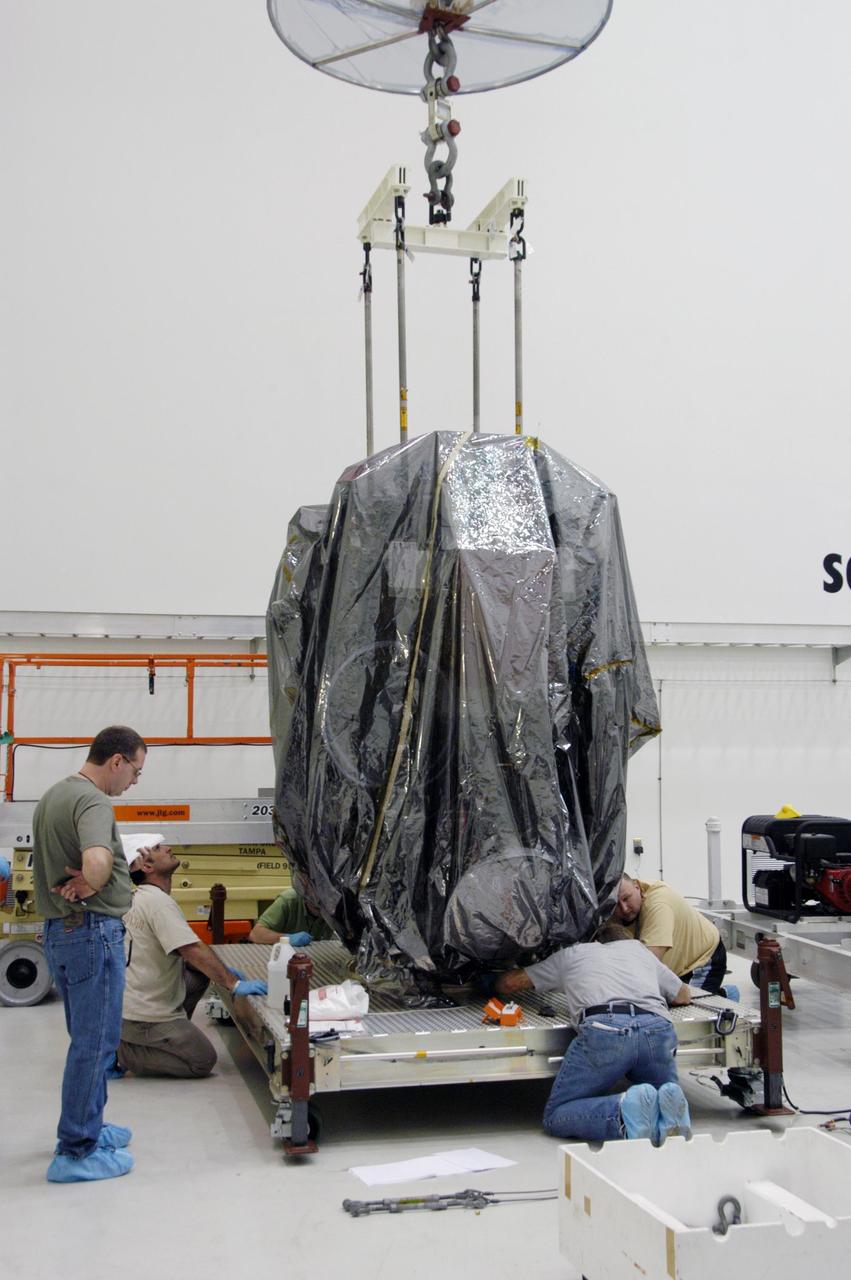

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, technicians help secure the Dawn spacecraft onto a moveable stand. Dawn will be moved into clean room C for unbagging and further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
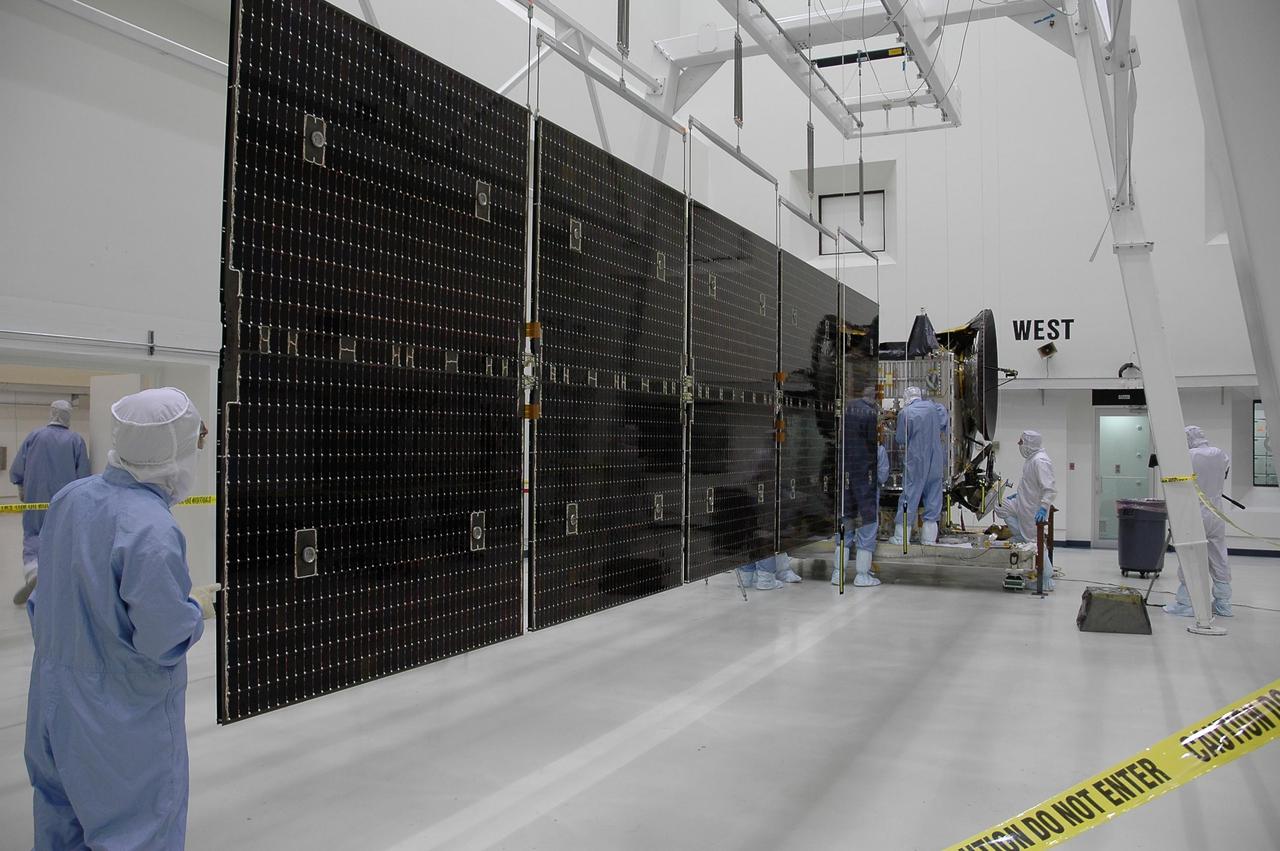

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In a clean room at Astrotech, the solar array panels at left are being installed on the Dawn spacecraft, in the background. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
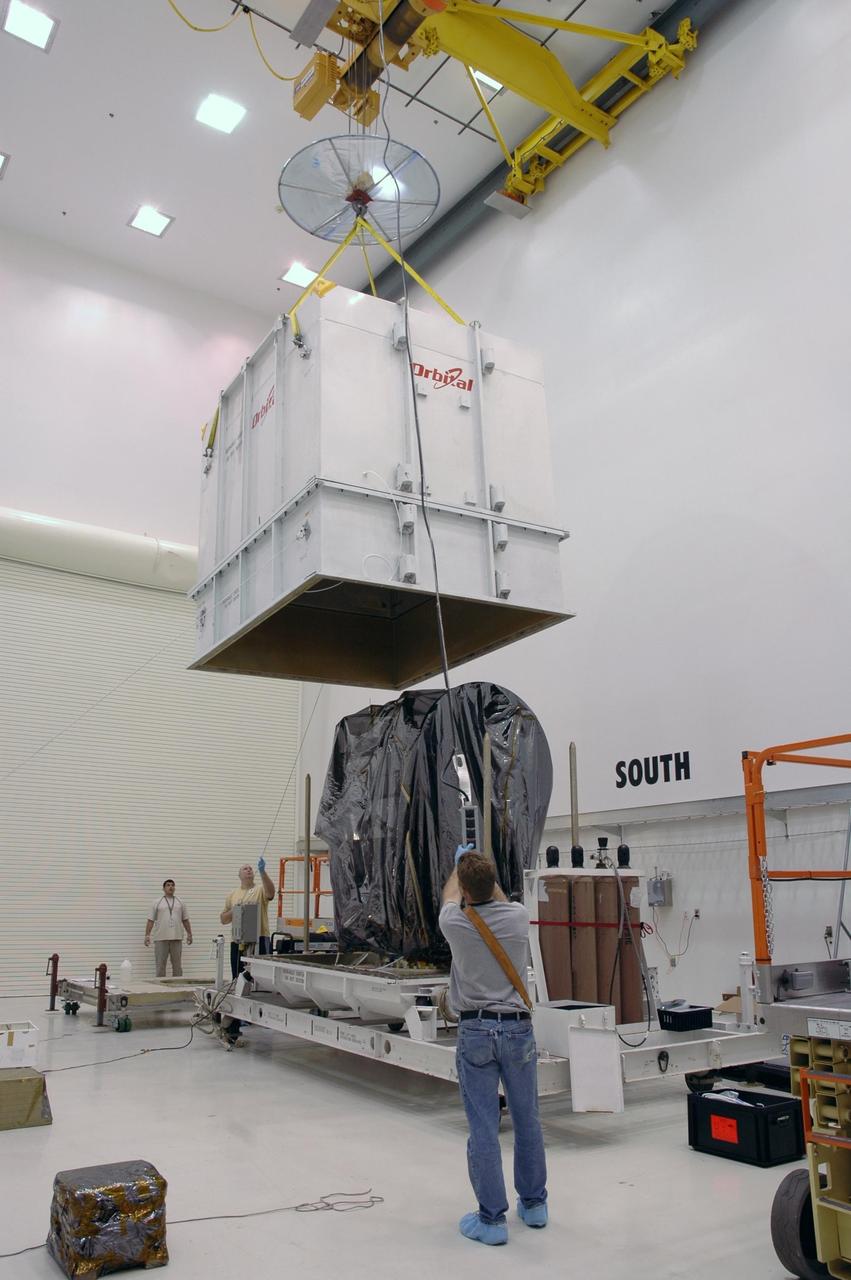

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a crane lifts the shipping container from the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
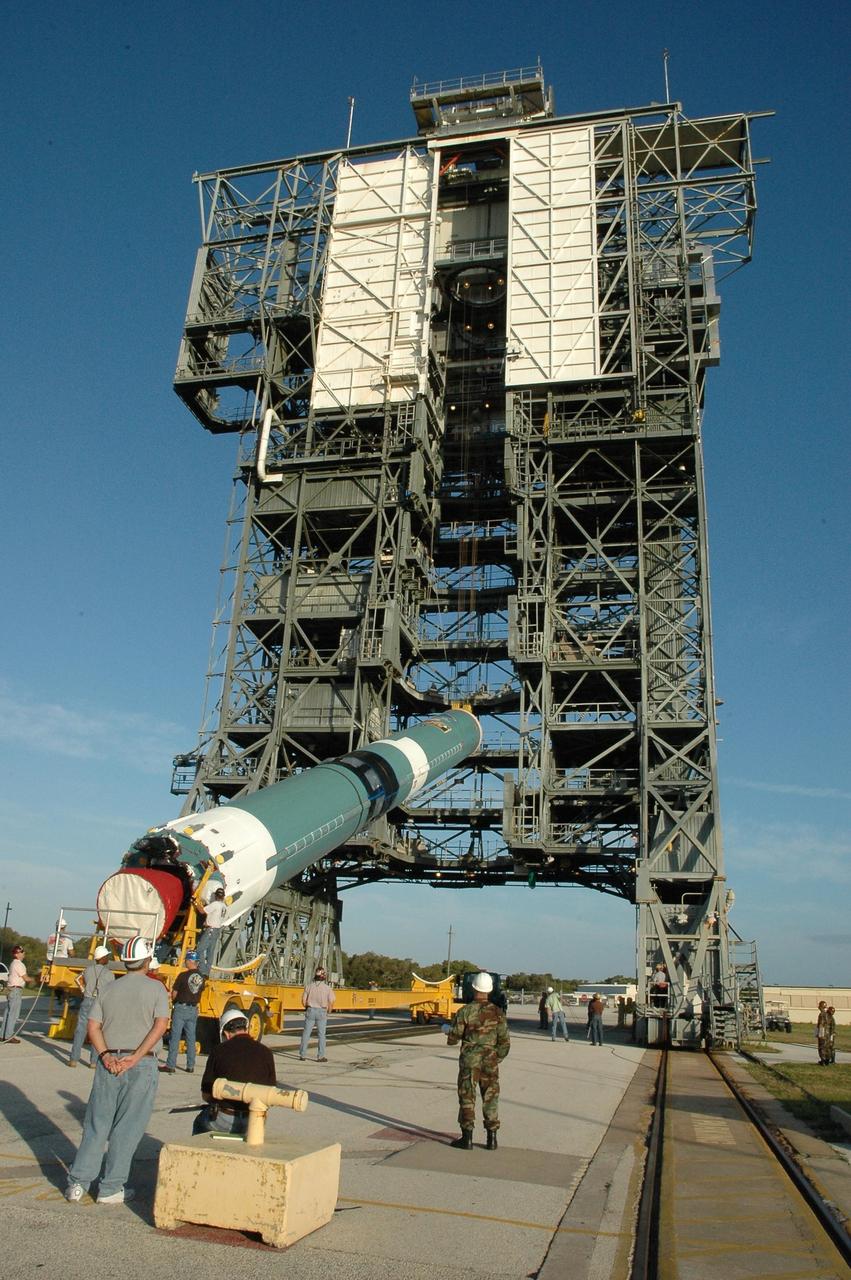
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first stage of a Delta II rocket is being raised off its transporter into a vertical position. Once vertical, the rocket will be lifted up into the mobile service tower. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Dawn spacecraft, targeted for liftoff on June 30. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, technicians dressed in "bunny suits," or clean-room attire, begin working on the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
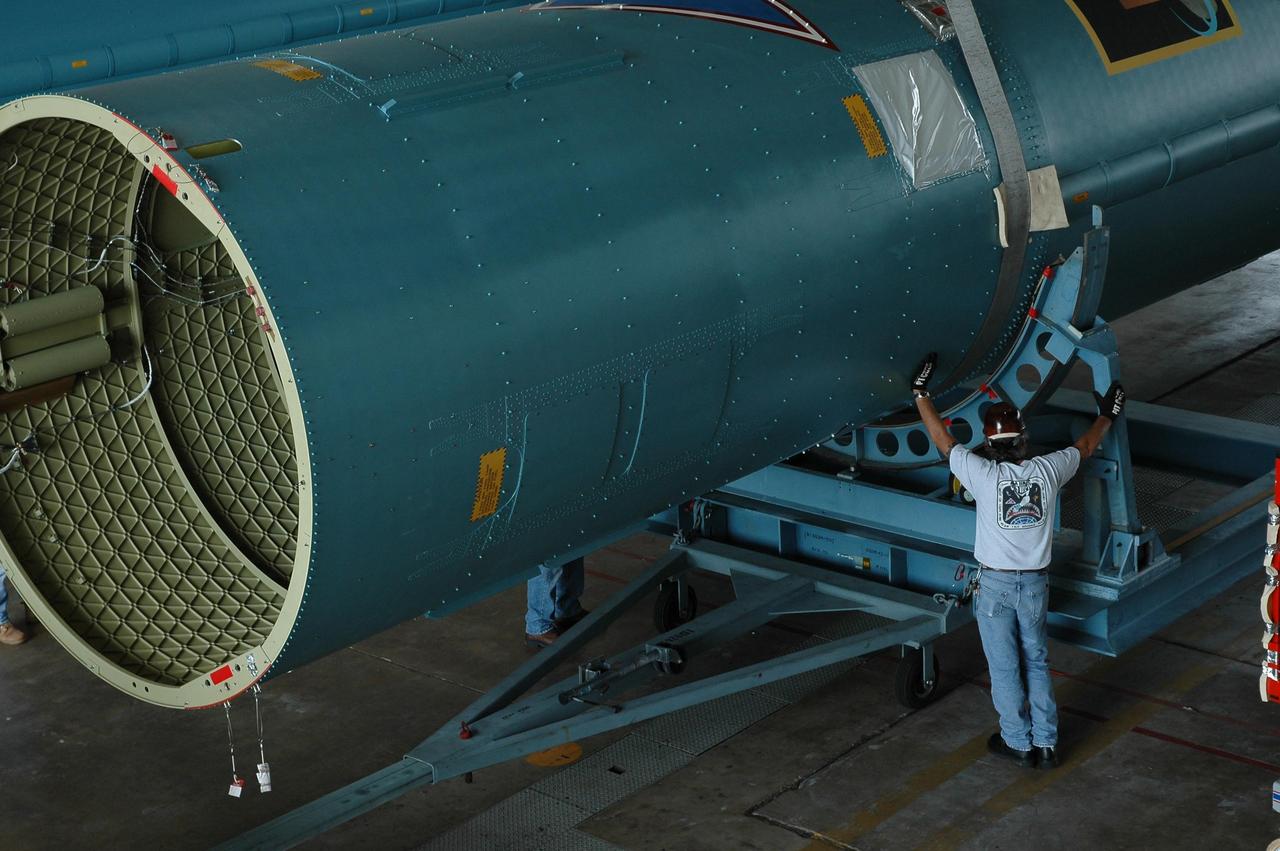

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Hangar M on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers secure straps to an overhead crane around the Delta II rocket's first stage. It will be lifted and placed onto a transporter for its move to the launch pad. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
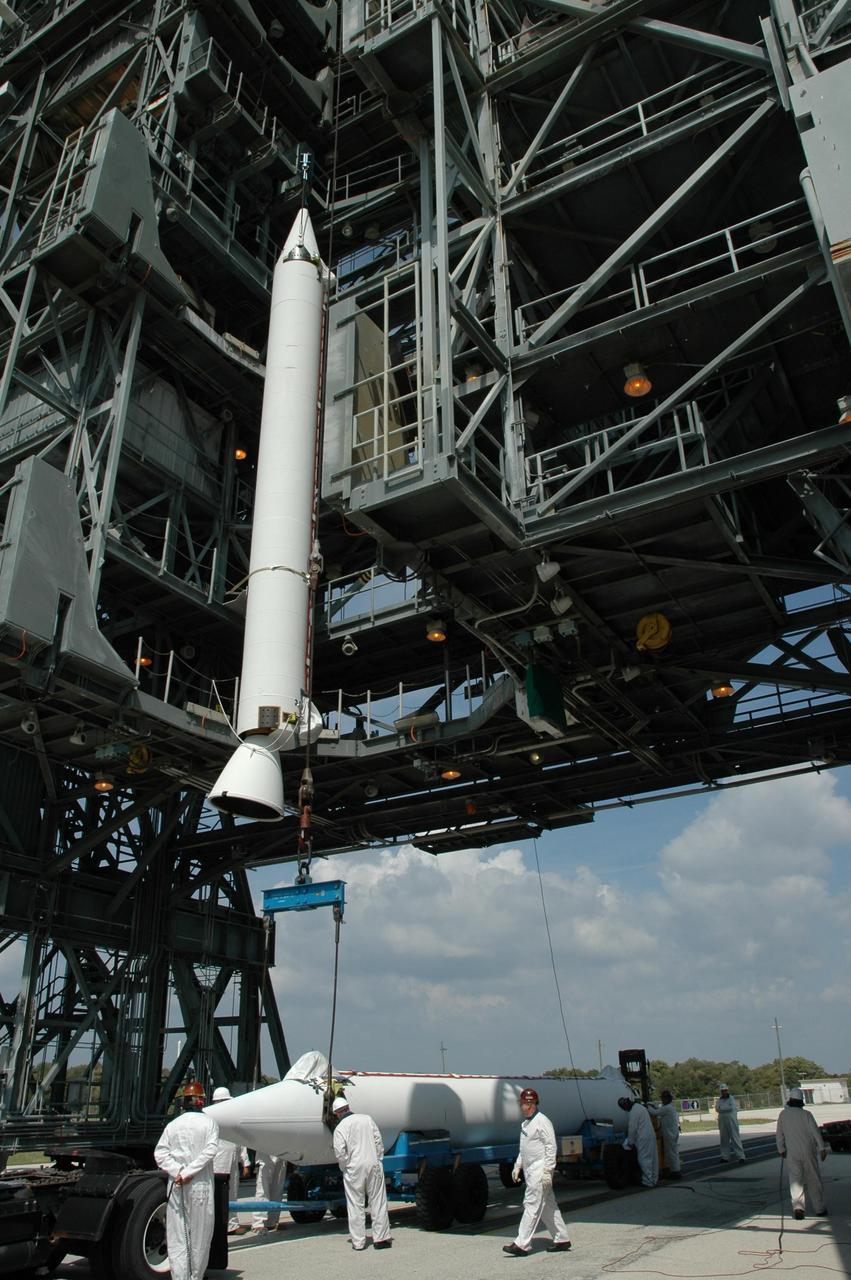

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a second solid rocket booster arrives under the mobile service tower. It will join the first, seen above, and be attached to the Delta II first stage for the launch of the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
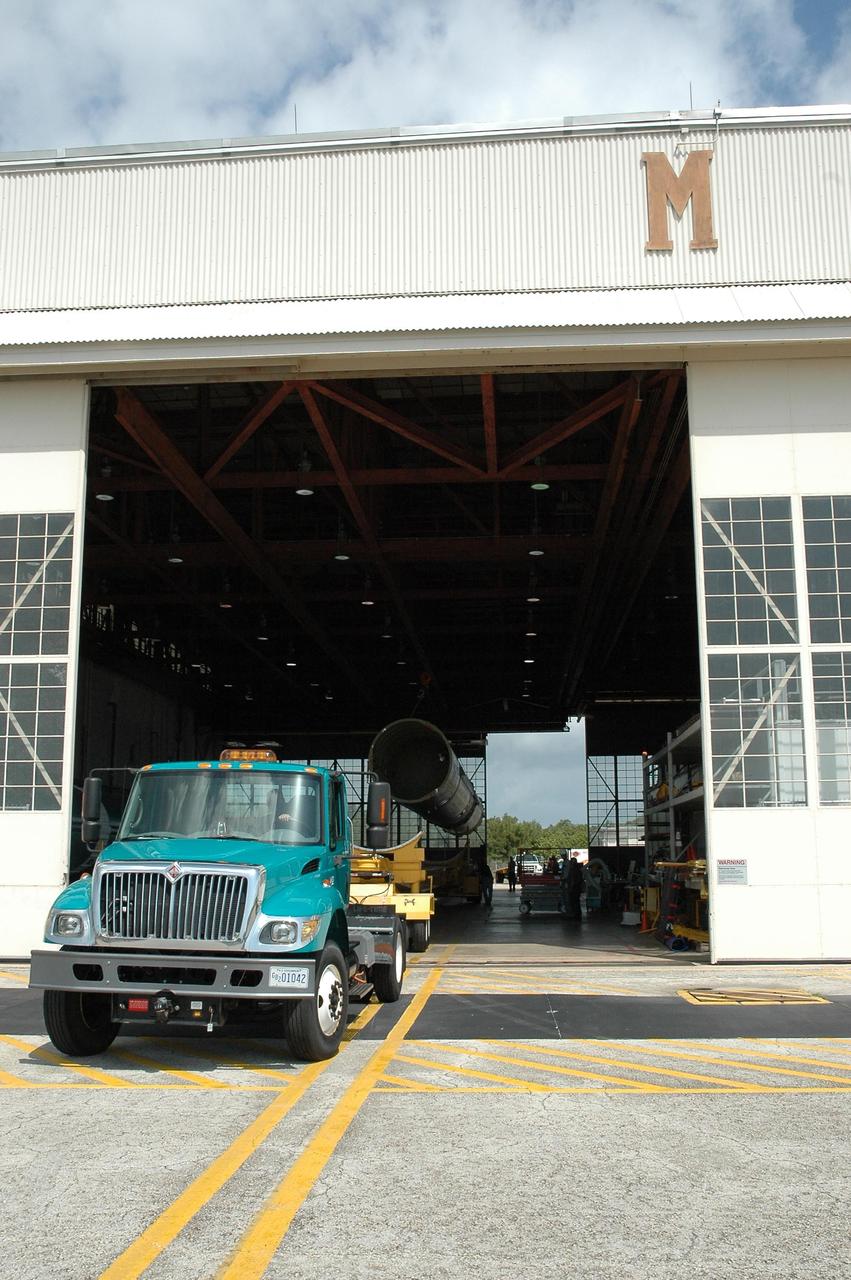

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With the transporter in place inside Hangar M on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the suspended Delta II first stage can be placed on it. The Delta will be moved to the launch pad. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, workers prepare the Dawn spacecraft before test deploying its large solar panels on one side. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the Dawn spacecraft from its transporter. Dawn will be moved into clean room C for unbagging and further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C
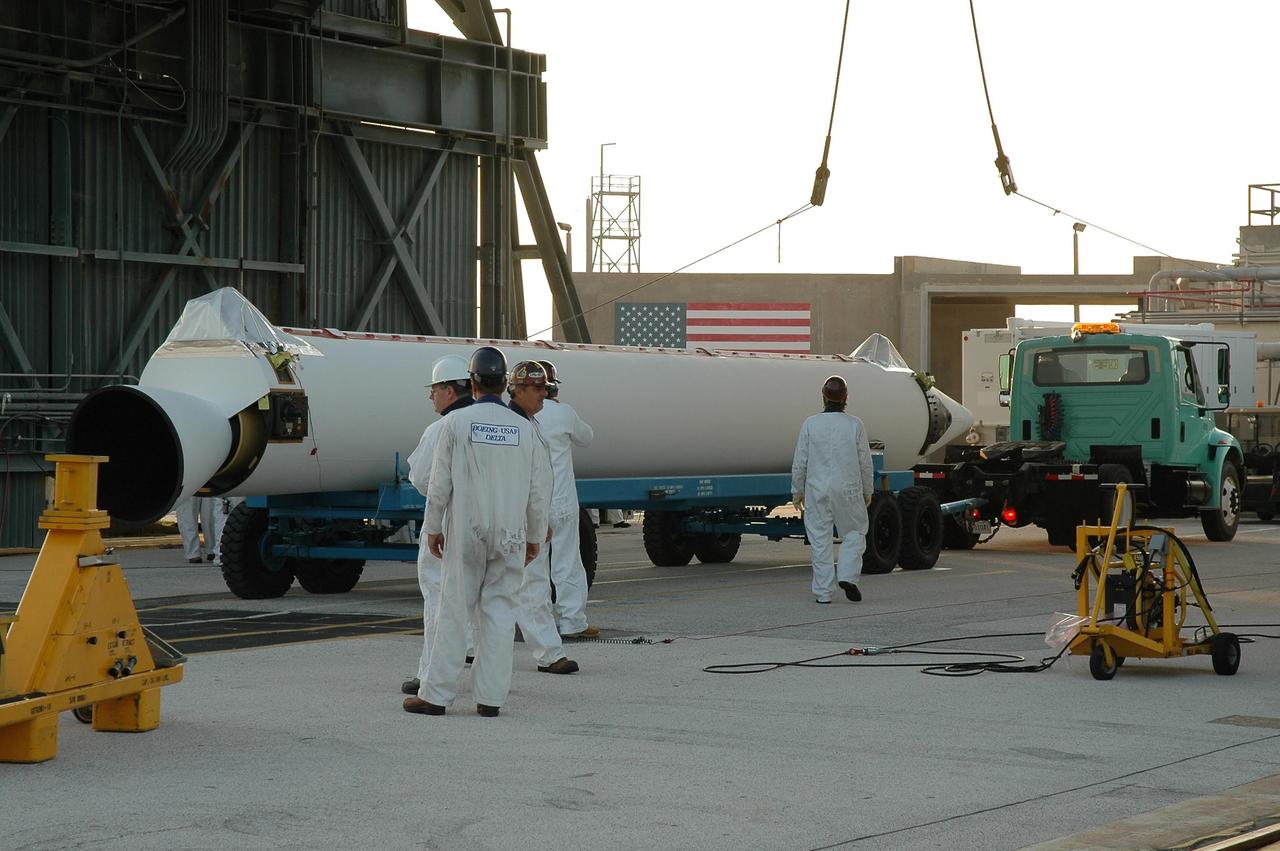

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Another solid rocket booster arrives on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station to be mated to the Delta II first stage. The Delta is the launch vehicle for the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's goal is to characterize the conditions and processes of the solar system's earliest epoch 4.5 billion years ago by investigating in detail two of the largest asteroids, Ceres and Vesta. They reside between Mars and Jupiter in the asteroid belt. Launch is targeted for July 7. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
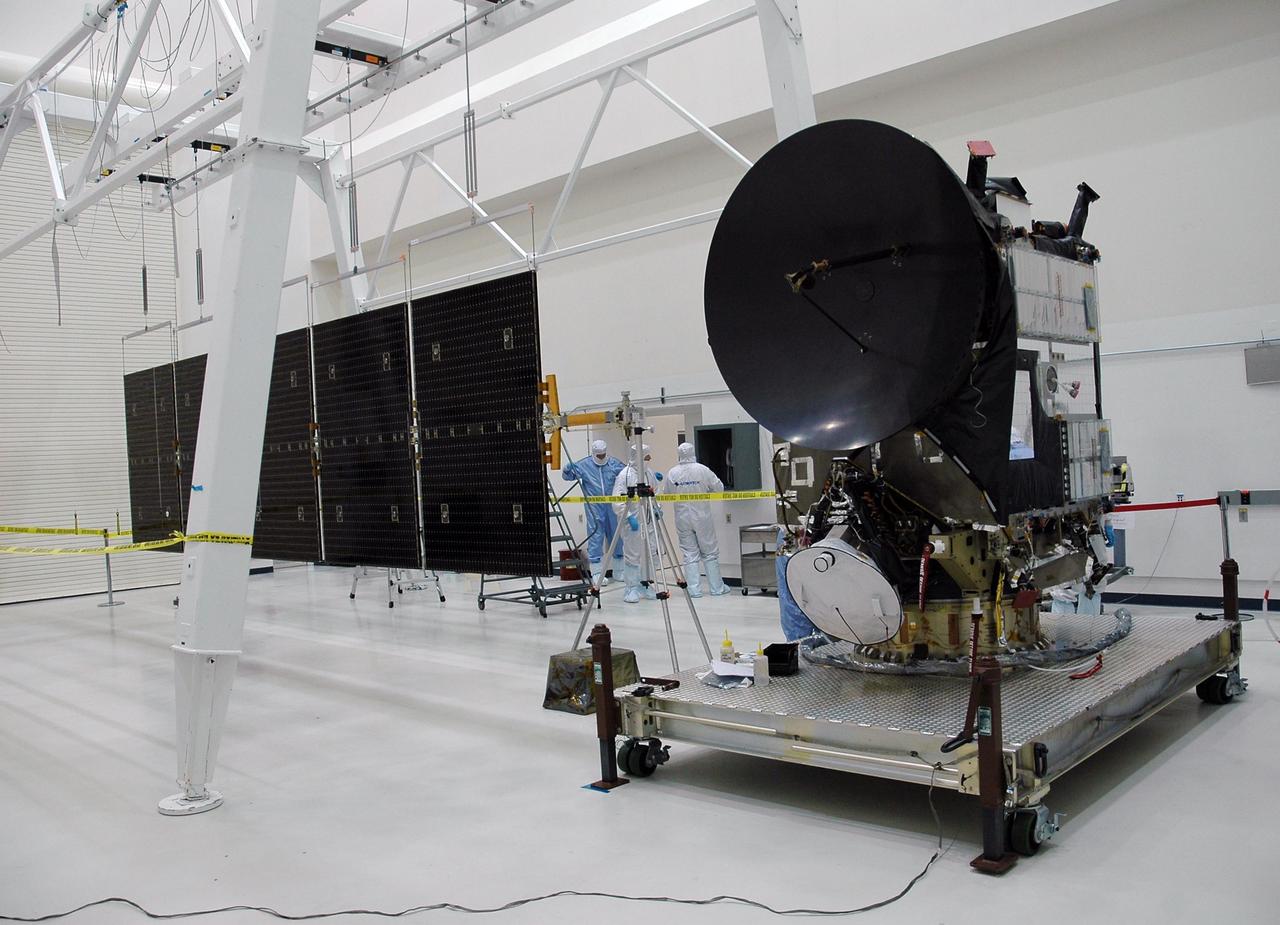
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In another clean room at Astrotech, solar array panels at left are ready to be installed on the Dawn spacecraft, at right. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
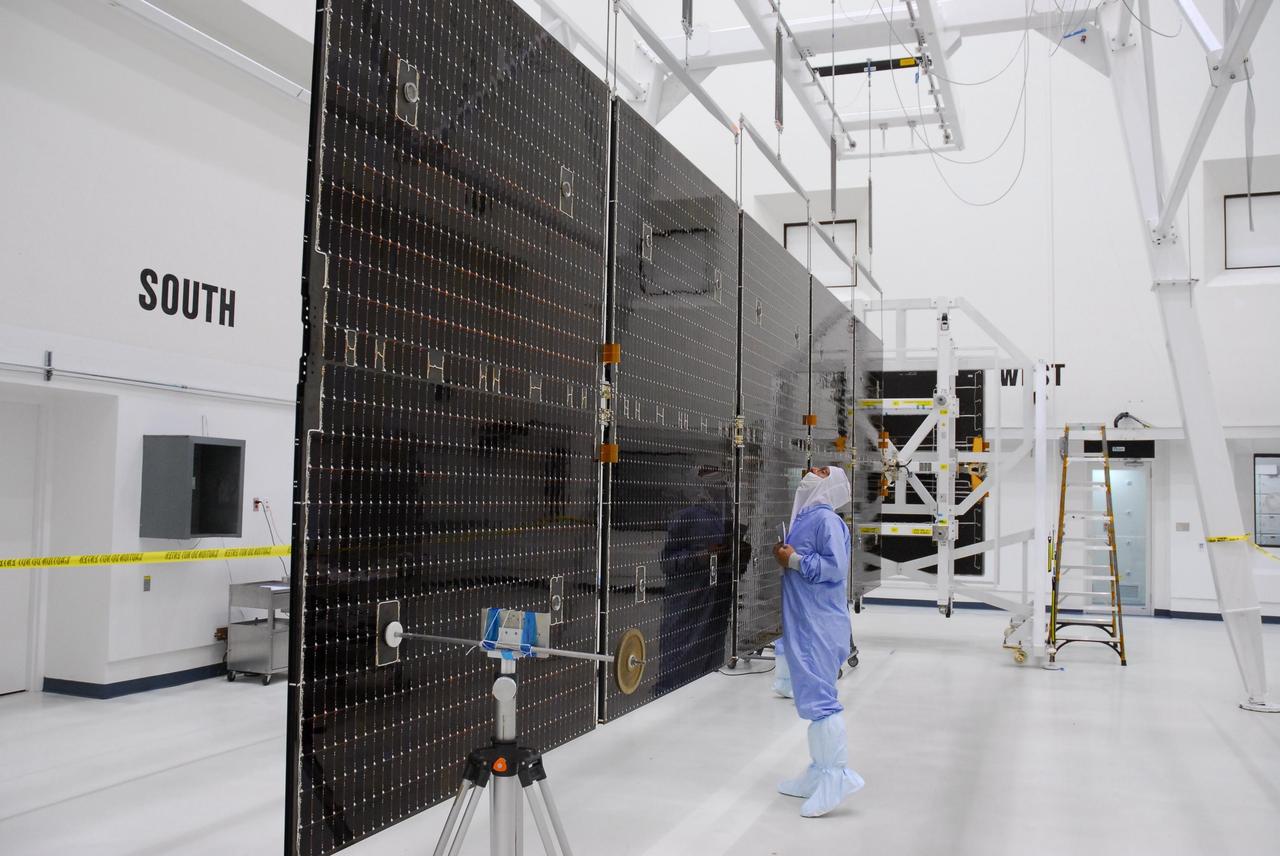

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In a clean room at Astrotech, workers begin checking the solar panels of the Dawn spacecraft. The panels will also undergo black light inspection. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
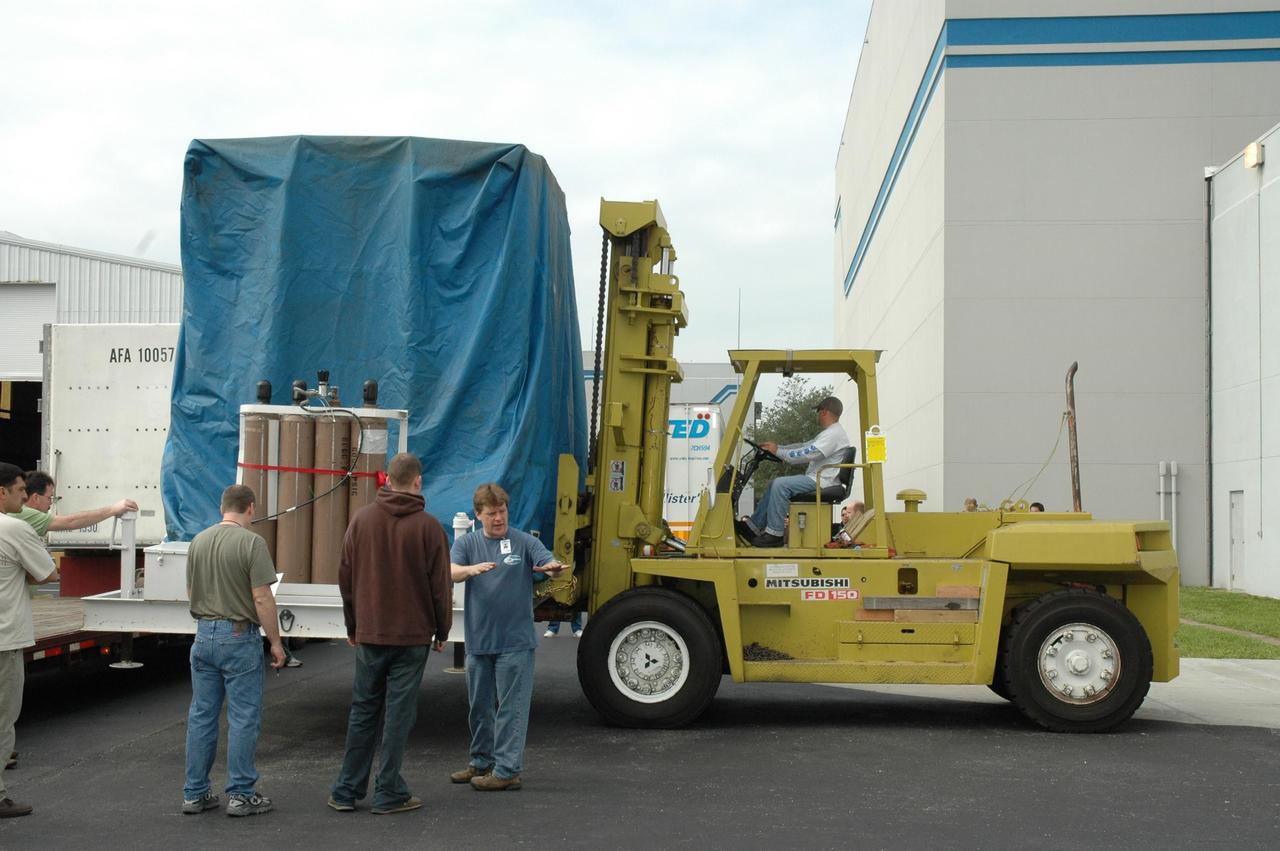

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, the shipping container holding the Dawn spacecraft is removed from the truck. The container will then be moved into the high bay of the Payload Processing Facility and the spacecraft removed. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
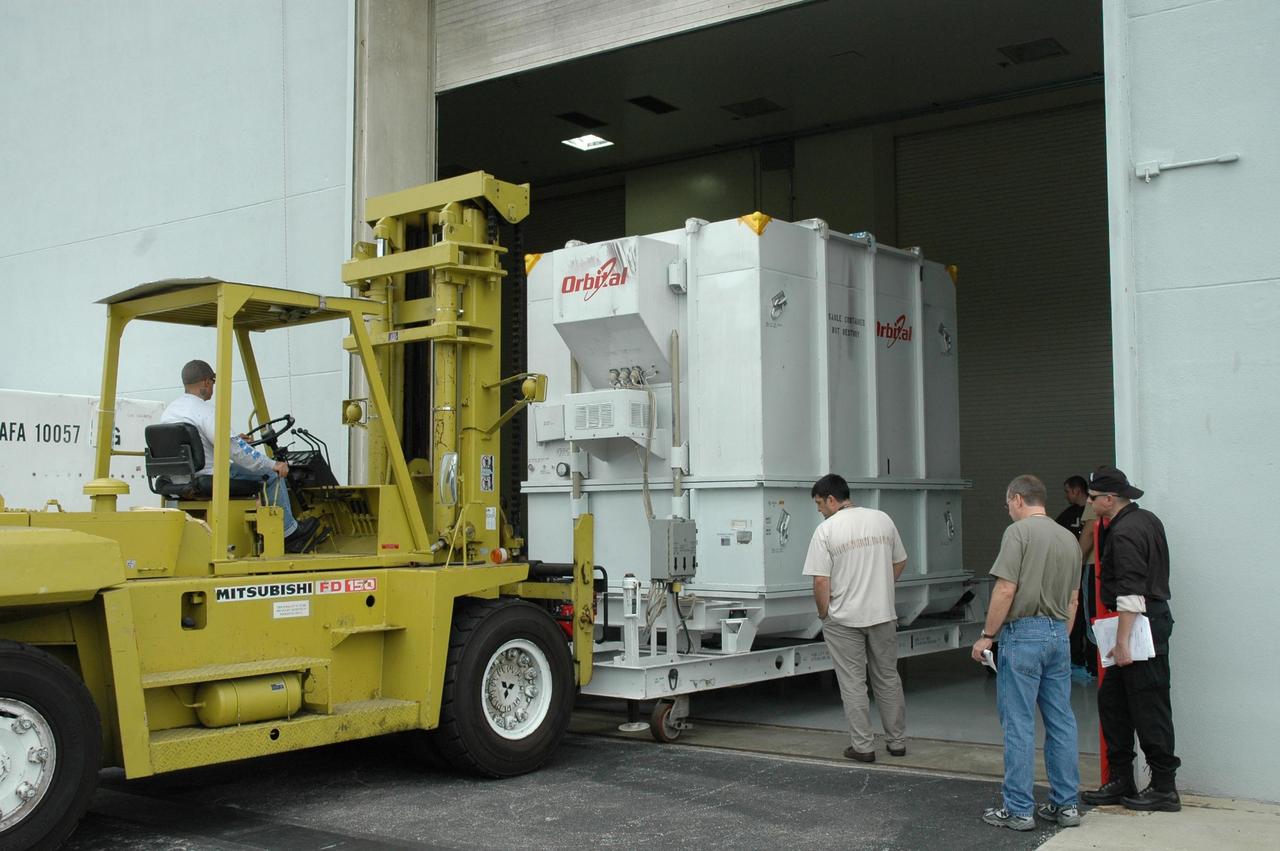

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, the shipping container holding the Dawn spacecraft is moved into the high bay of the Payload Processing Facility. The spacecraft will next be removed from the container. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a worker wearing a "bunny suit," or clean-room attire, looks over the Dawn spacecraft after removing the protective cover, at bottom right. In the clean room, the spacecraft will undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.
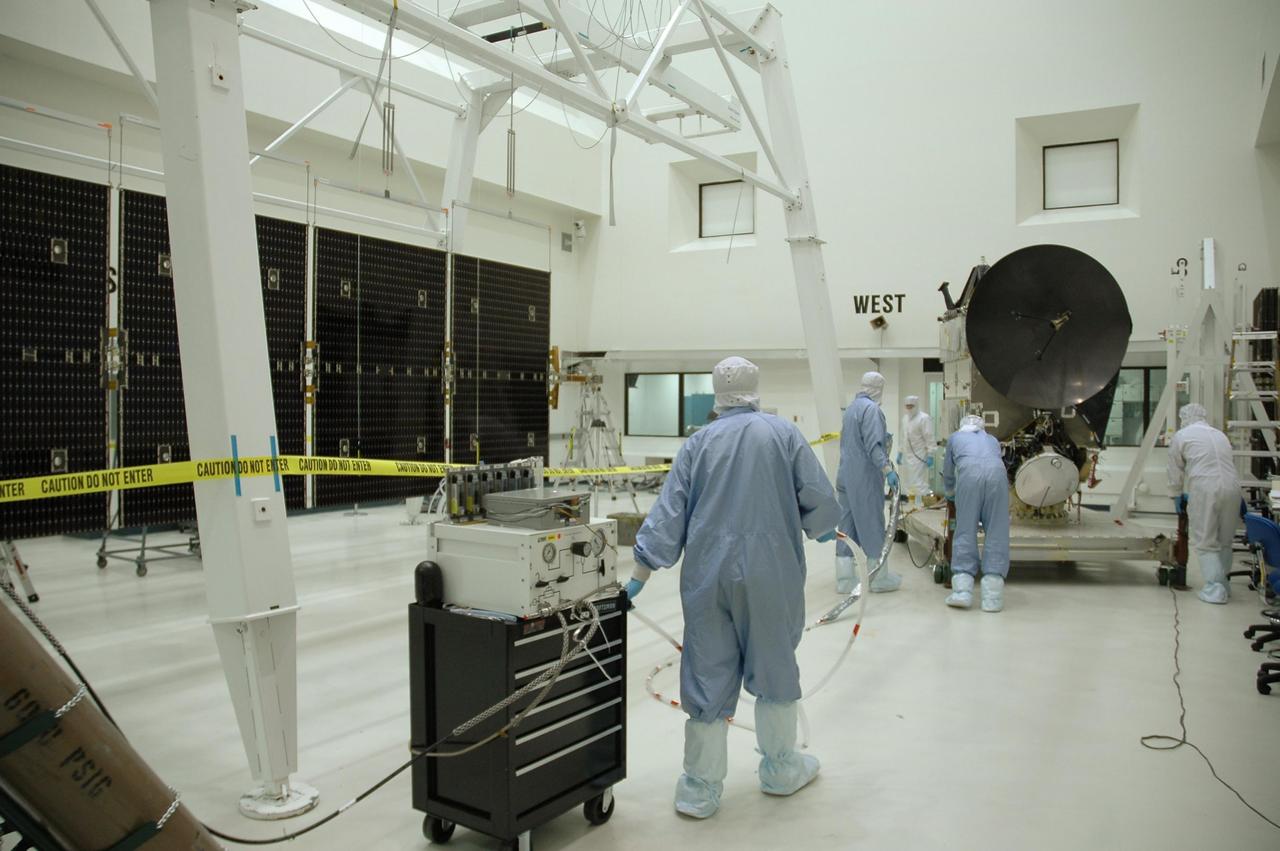

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In another clean room at Astrotech, solar array panels are lined up at left to be installed on the Dawn spacecraft, at right. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
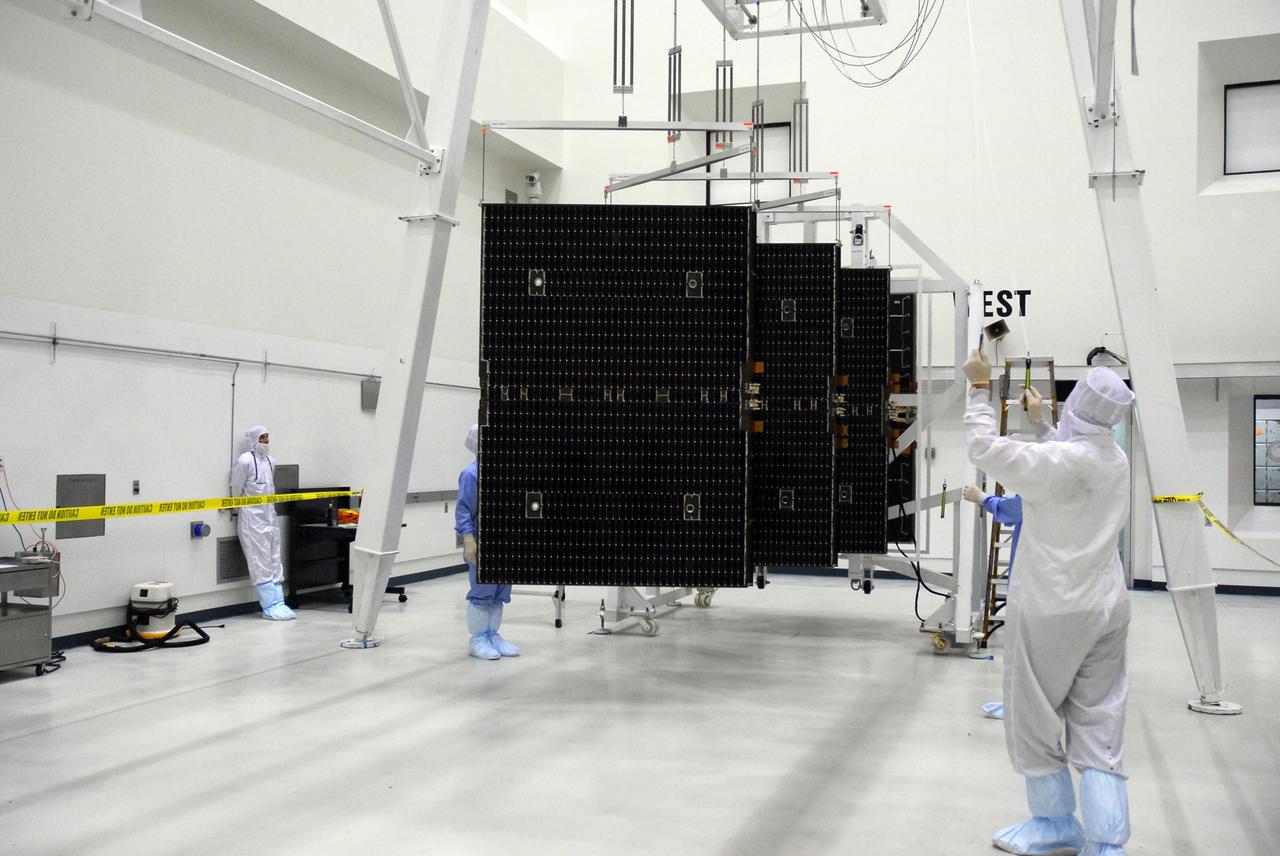

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In a clean room at Astrotech, workers deploy the solar panels of the Dawn spacecraft. The panels will be tested and undergo black light inspection. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
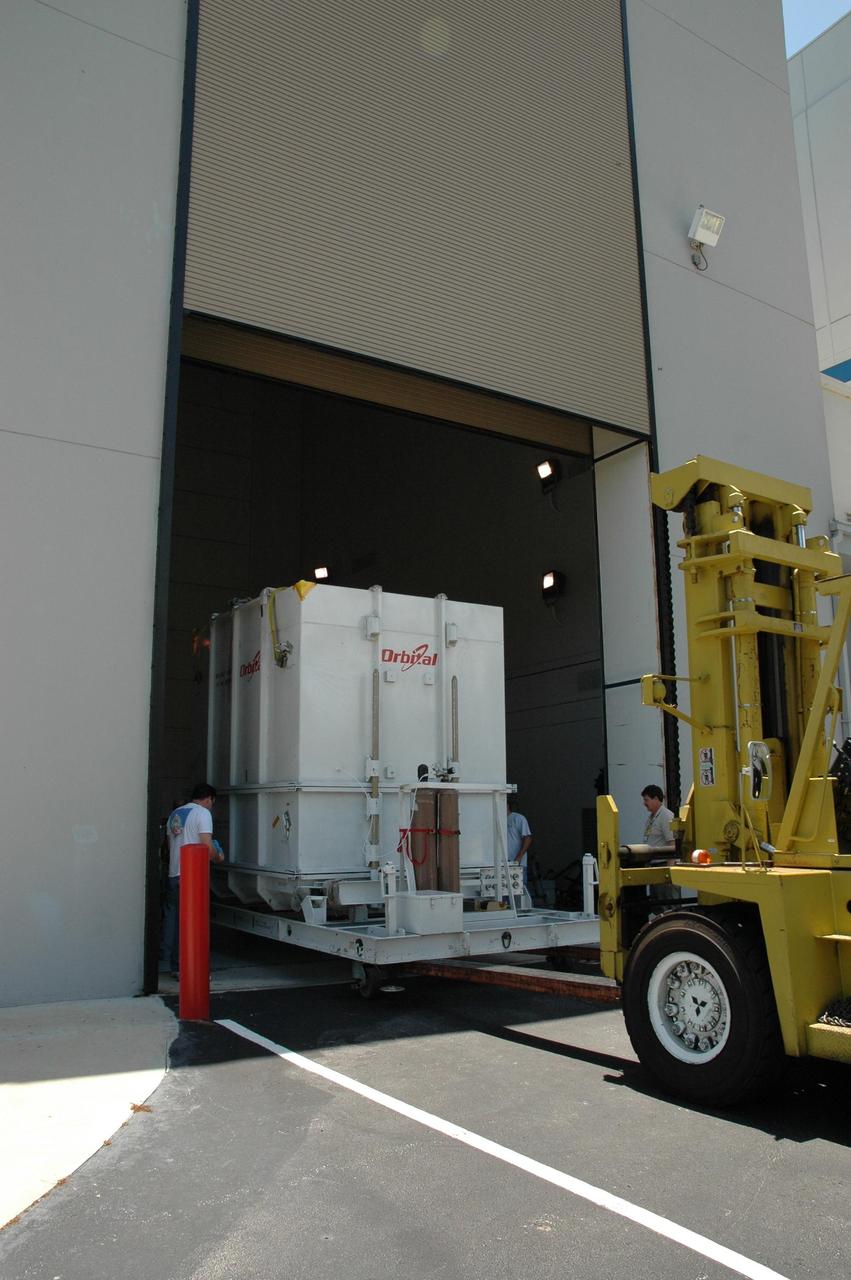

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Dawn spacecraft, inside its shipping container, is moved out of the Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility for transfer to the Hazardous Processing Facility for fueling. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, technicians help secure the Dawn spacecraft onto a moveable stand. Dawn will be moved into clean room C for unbagging and further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.
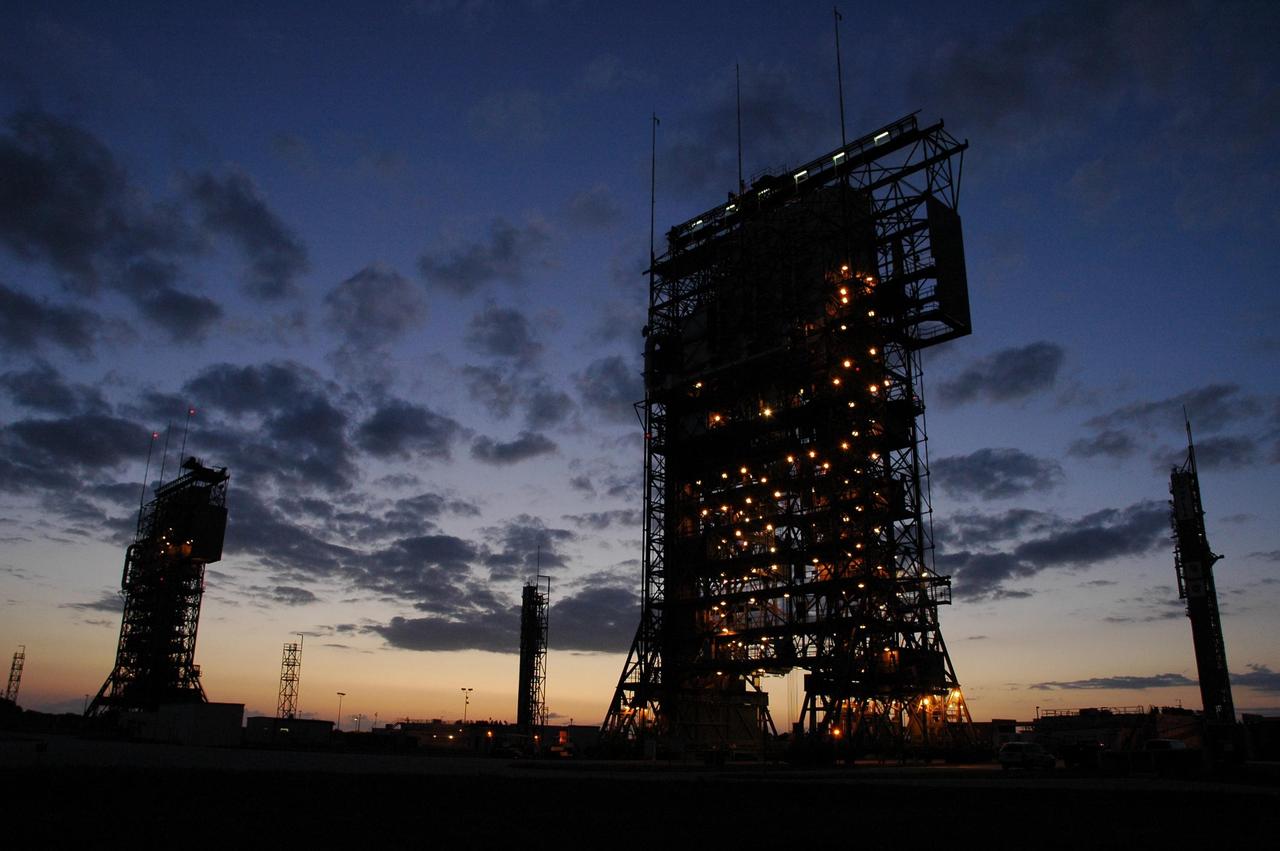

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The mobile service towers on Launch Pads 17-A (left) and 17-B (right) are silhouetted against the pre-dawn sky at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. In the background are the launch gantries. Pad 17-B is the site for the launch of the Dawn spacecraft on June 30. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
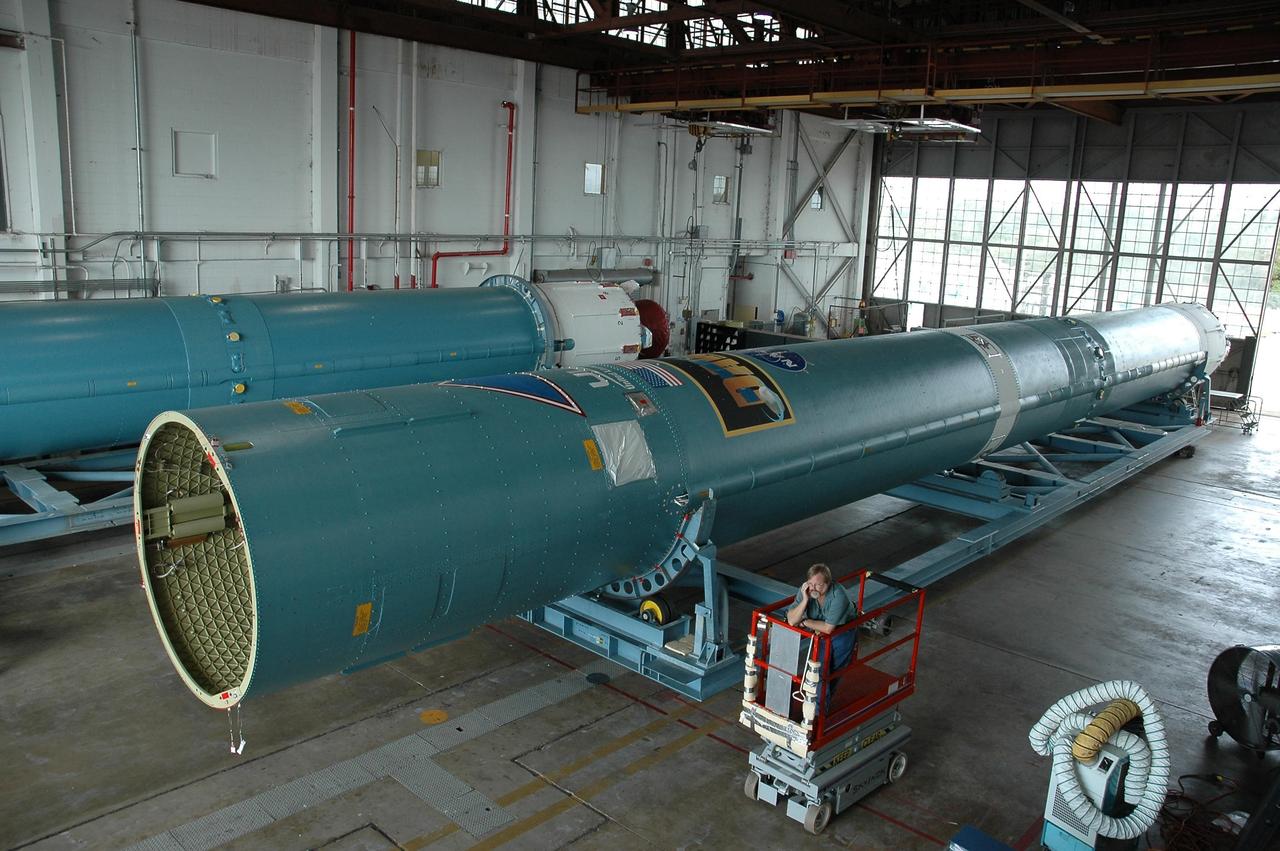

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Hangar M on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first stage of the Delta II rocket that will launch the Dawn spacecraft is ready to be transferred to a transporter for its move to the launch pad. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, the solar panels on the Dawn spacecraft are stowed in preparation for Dawn's transfer to a transporter and move to the Hazardous Processing Facility for fueling. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside Astrotech's Hazardous Processing Facility, technicians check the progress of the Dawn spacecraft as it is lifted off the transporter. Dawn will be moved to a scale for weighing and then prepared for fueling. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
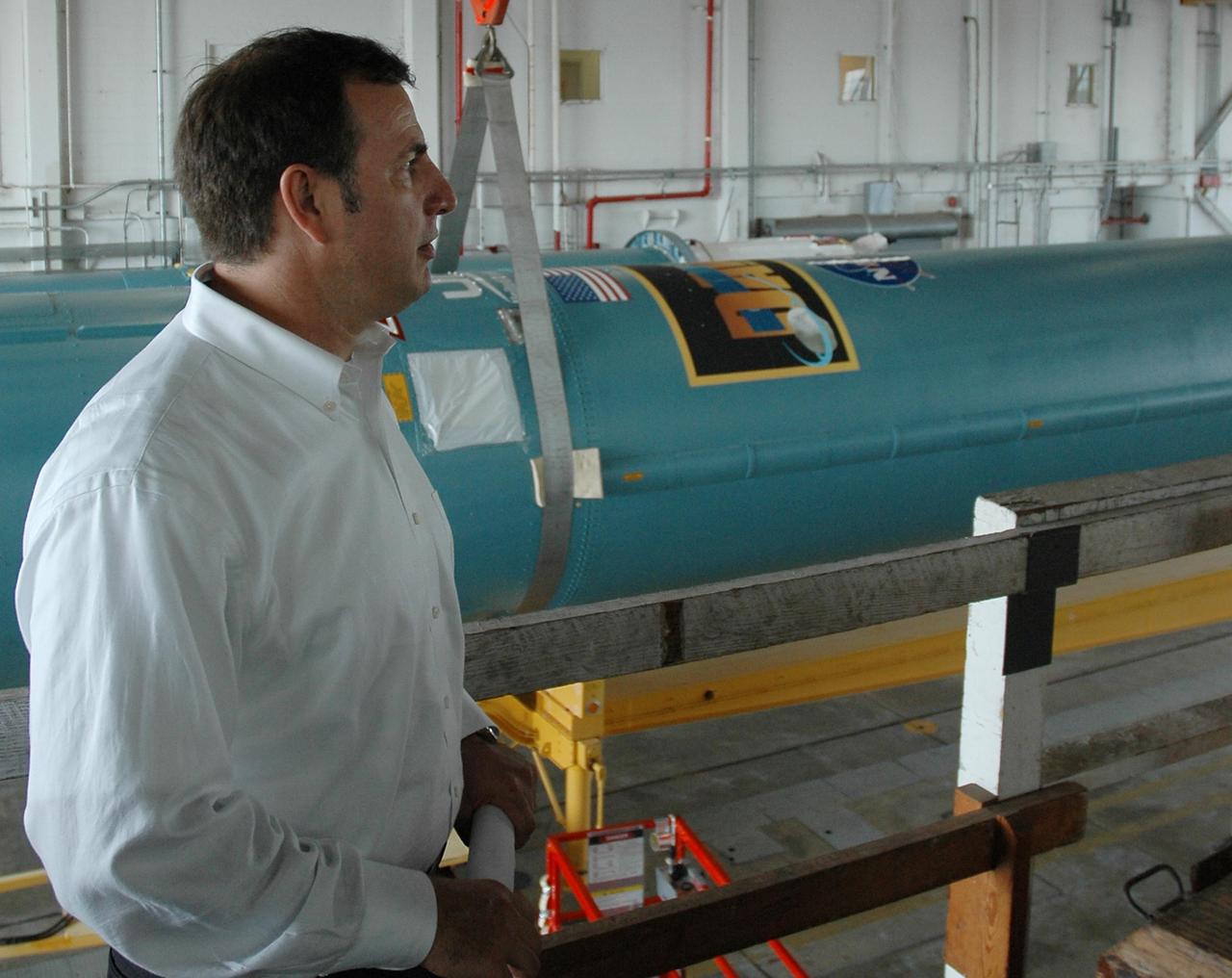

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside Hangar M on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Larry Penepent, manager of Launch Operations Engineering with United Launch Alliance, oversees the transfer of the Delta II first stage onto a transporter. The Delta will be moved to the launch pad. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
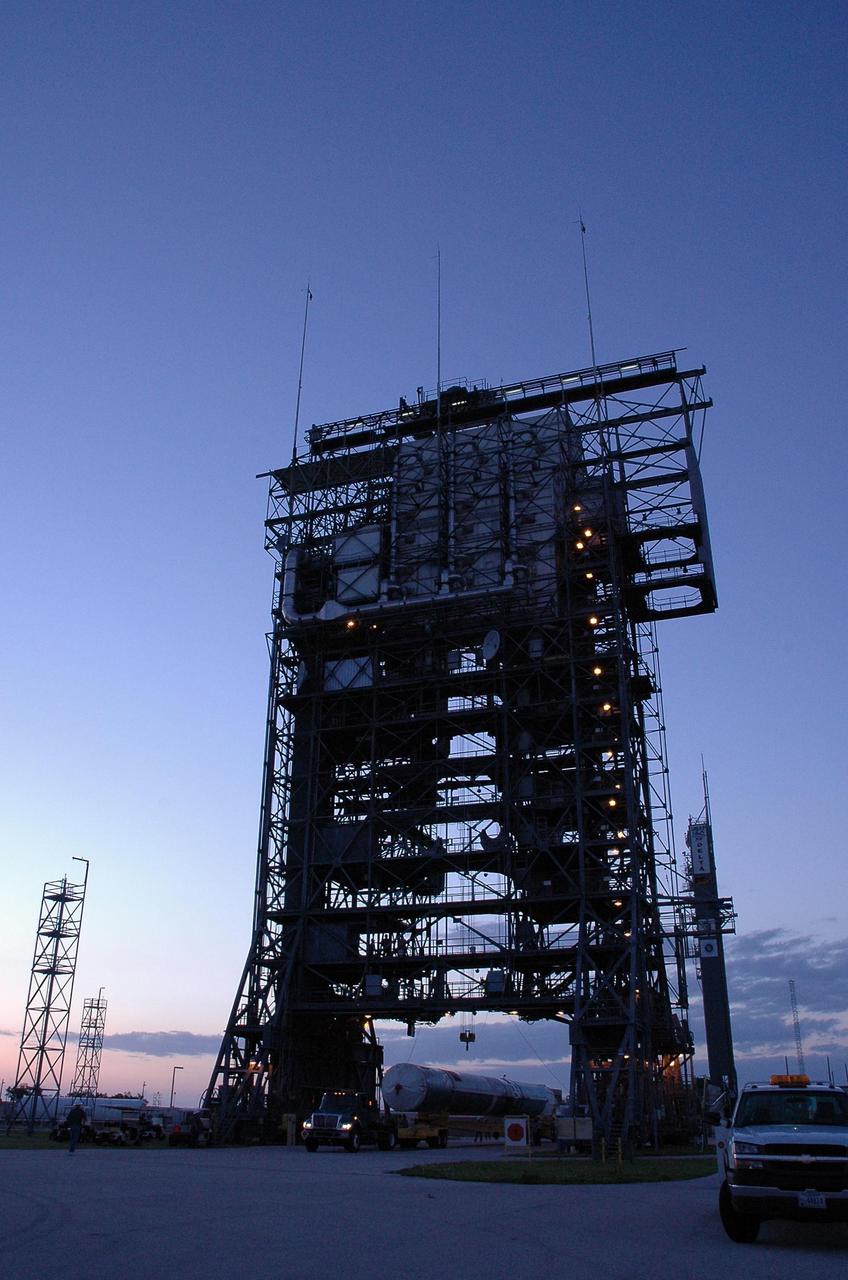

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The first stage of a Delta II rocket rolls under the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Dawn spacecraft, targeted for liftoff on June 30. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Hangar M on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers secure straps to an overhead crane around the Delta II rocket's first stage. It will be lifted and placed onto a transporter for its move to the launch pad. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
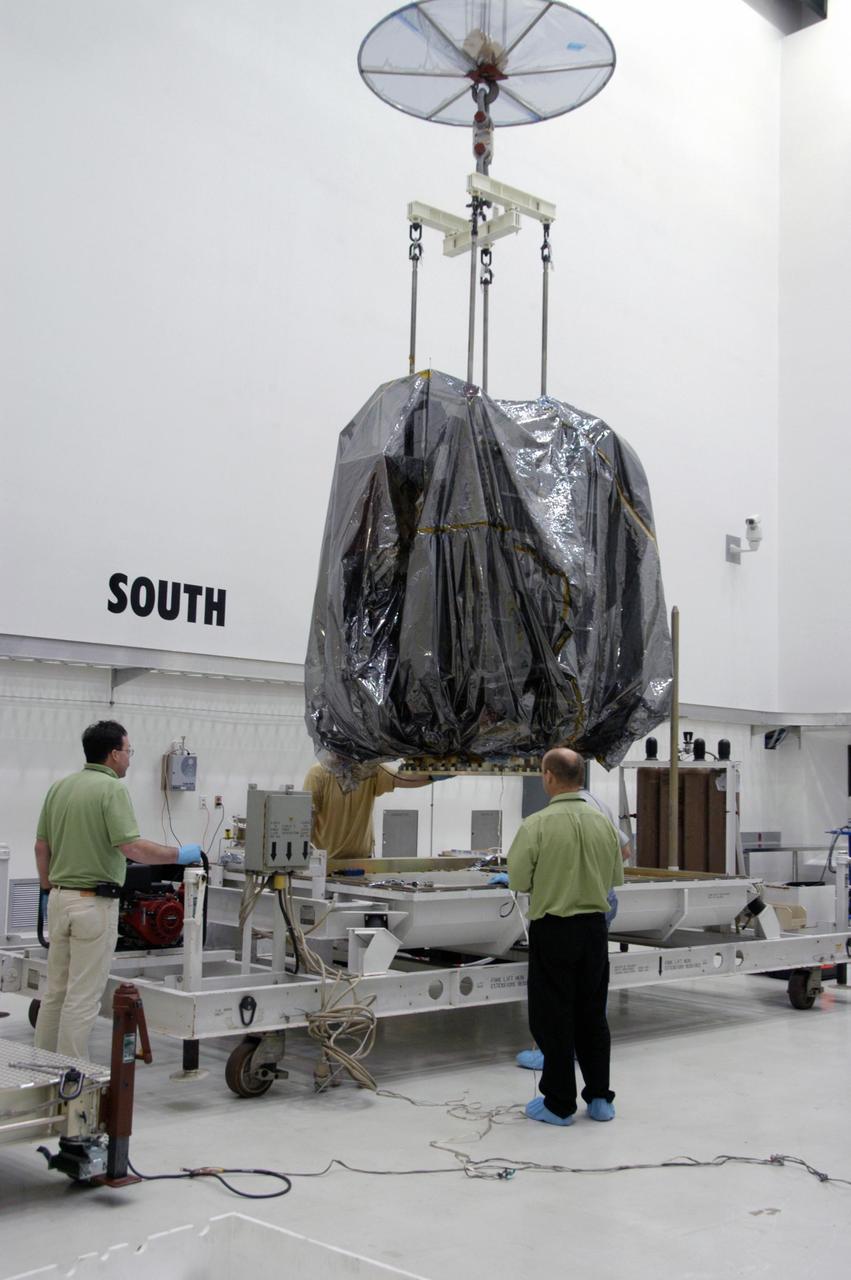

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the Dawn spacecraft from its transporter. Dawn will be moved into clean room C for unbagging and further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
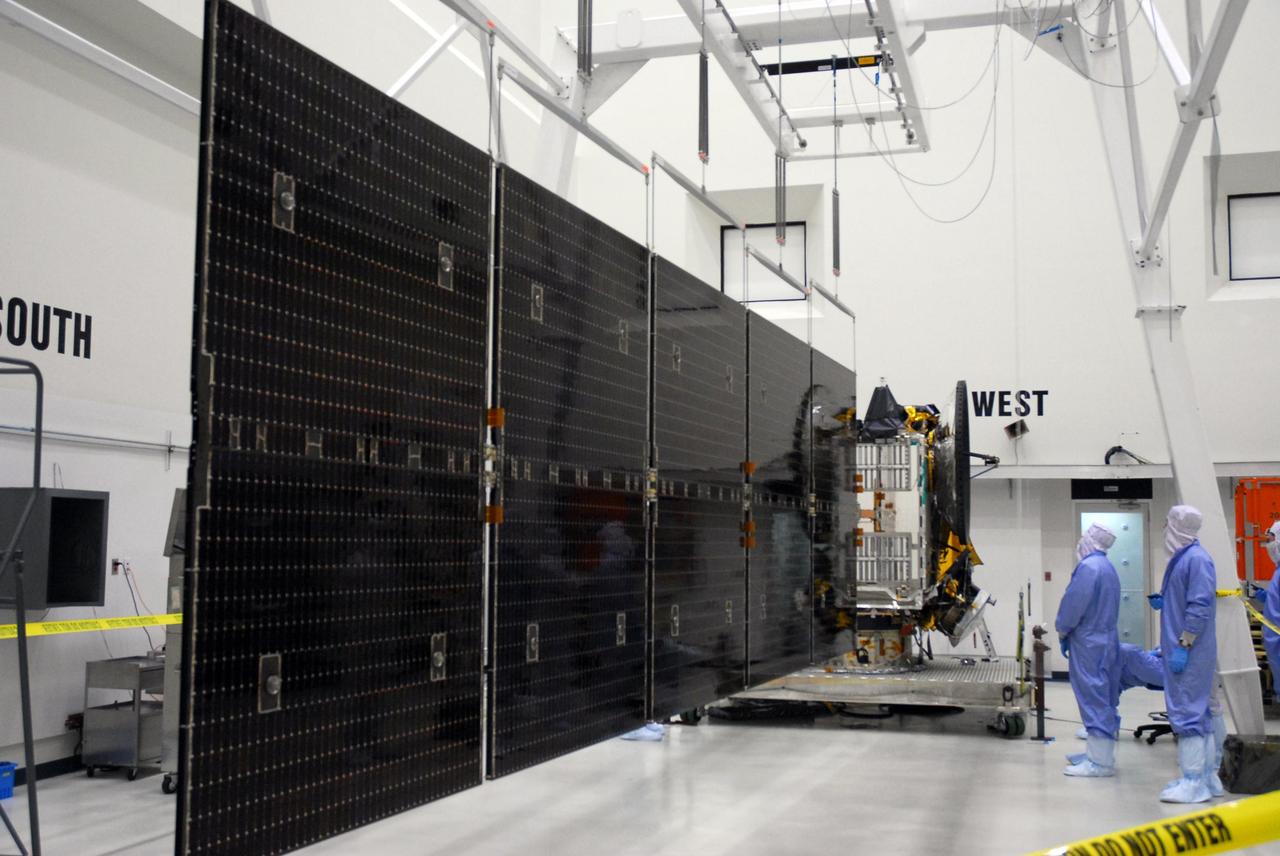

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, the more than 32-foot-long solar panels on one side of the Dawn spacecraft are fully deployed during a test. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
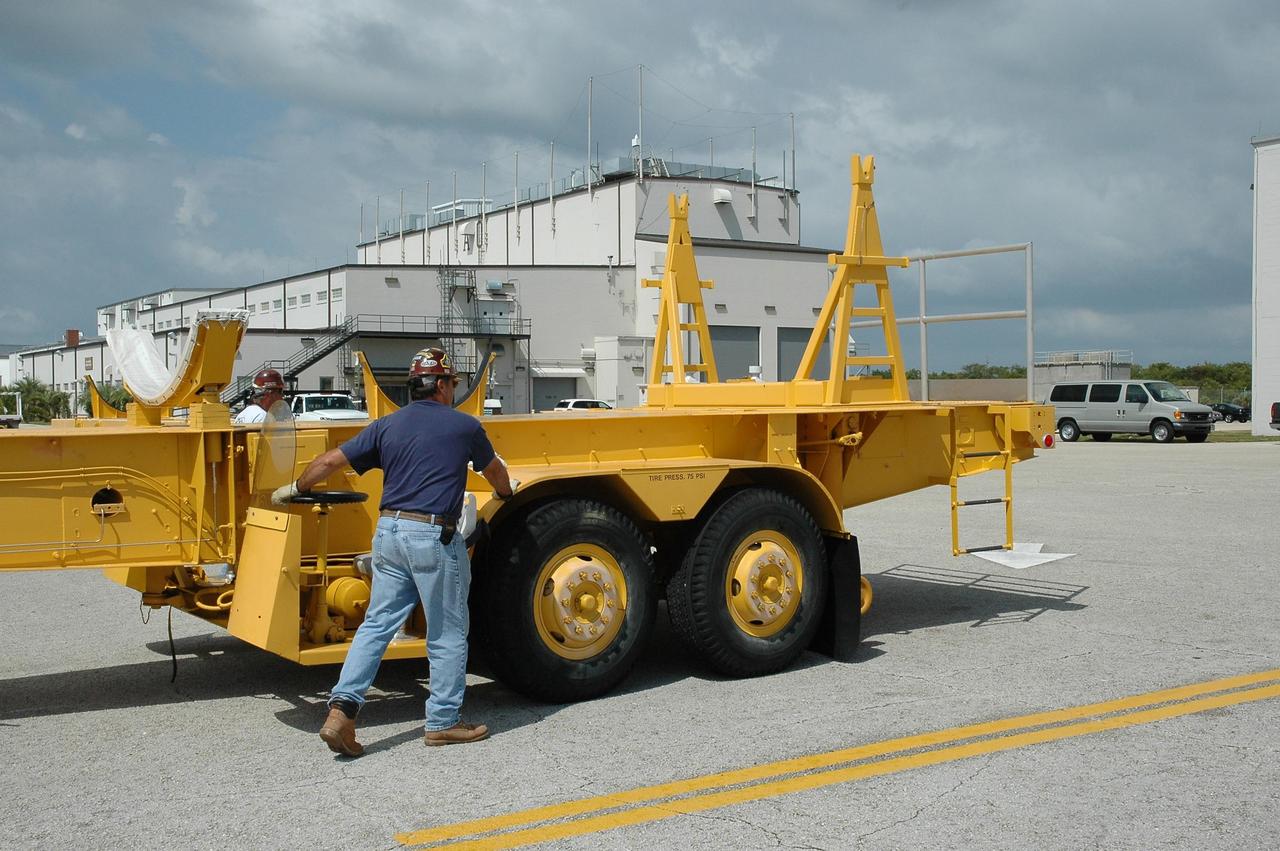

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Hangar M on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a worker guides a transporter into place to receive the Delta II first stage. The Delta will be moved to the launch pad. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In a clean room at Astrotech, workers prepare to deploy the solar panels of the Dawn spacecraft. The panels will be tested and undergo black light inspection. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

The Dawn spacecraft is seen here in clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility. In the clean room, the spacecraft will undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.
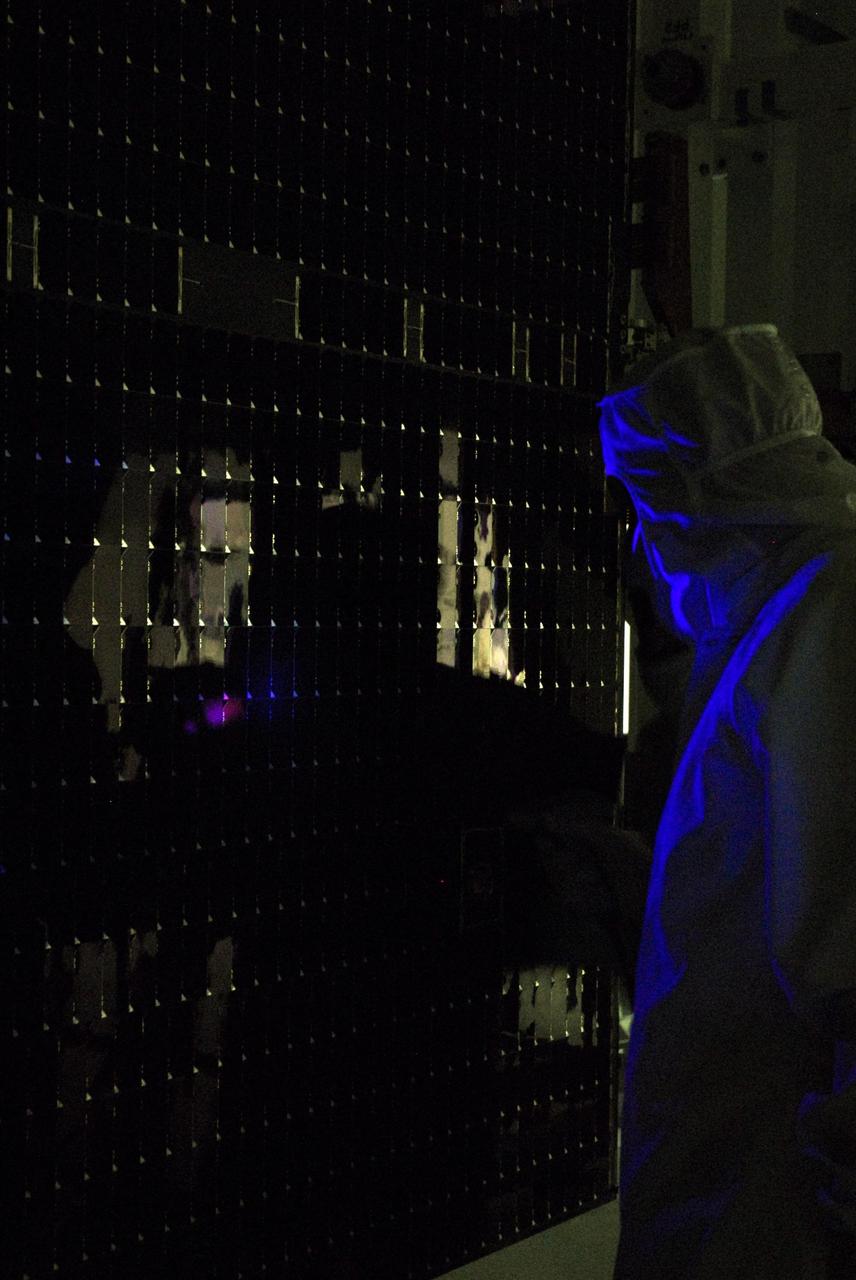

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In a clean room at Astrotech, workers begin black light testing on the solar panels of the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
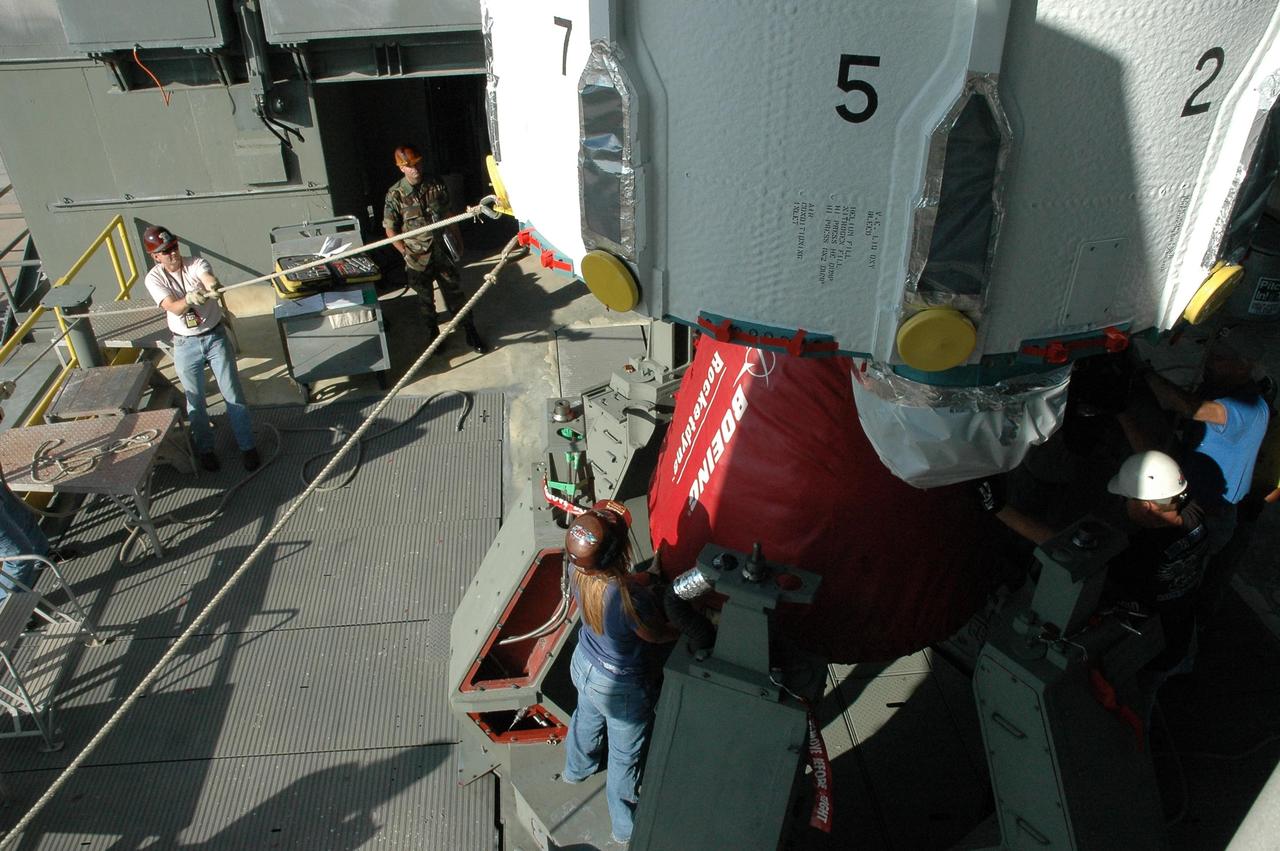

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers make final checks of the Delta II rocket in the mobile service tower. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Dawn spacecraft, targeted for liftoff on June 30. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
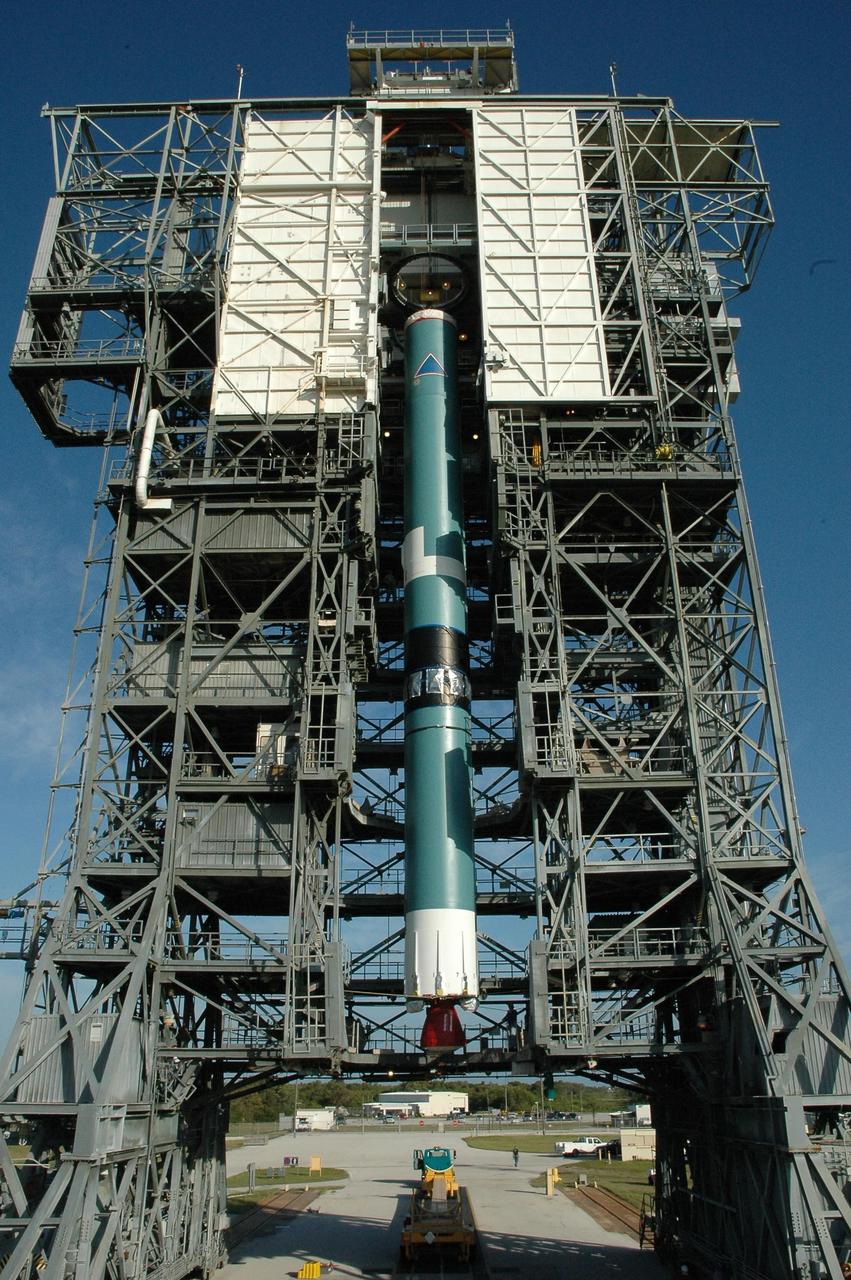

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first stage of a Delta II rocket is placed in the mobile service tower. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Dawn spacecraft, targeted for liftoff on June 30. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
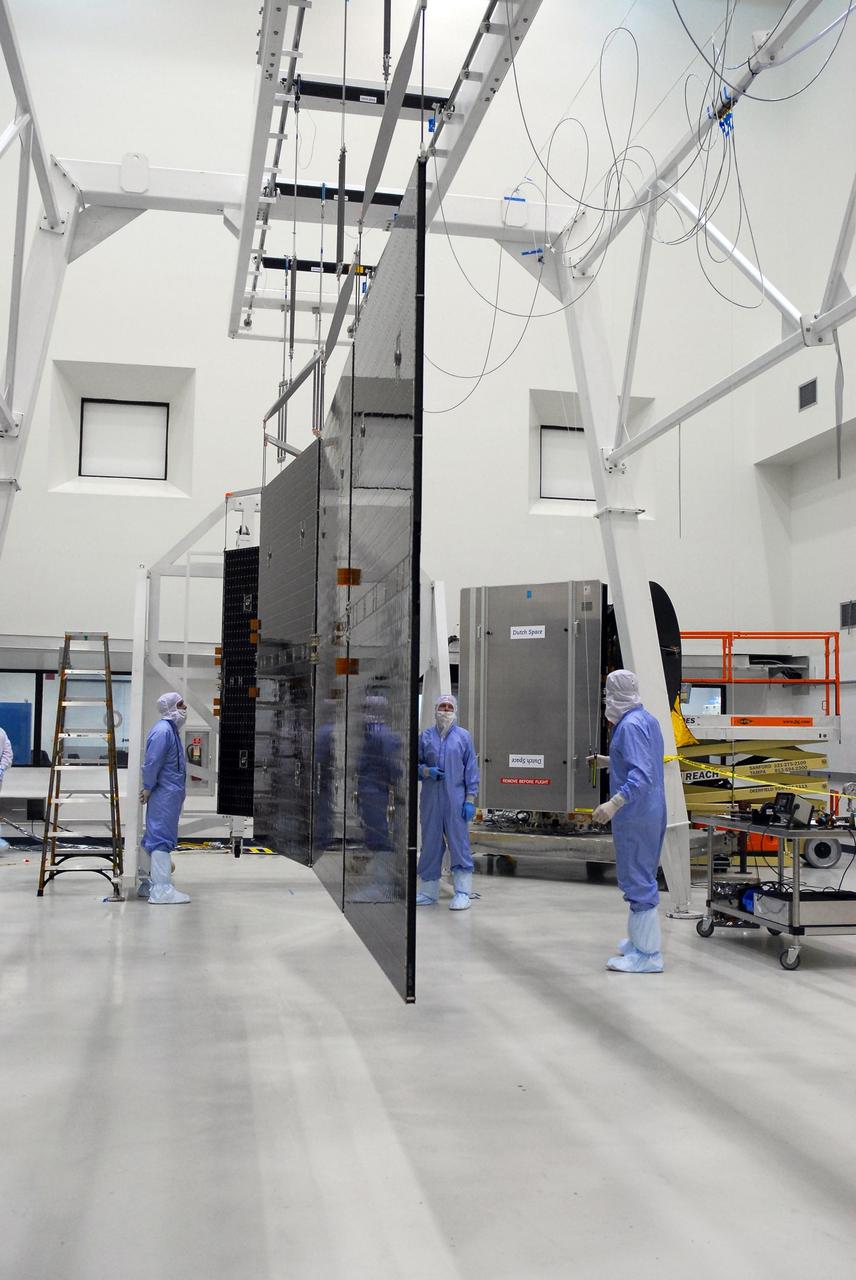

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, a suspended set of solar array panels is opened prior to installation on the Dawn spacecraft. Another set was installed previously. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
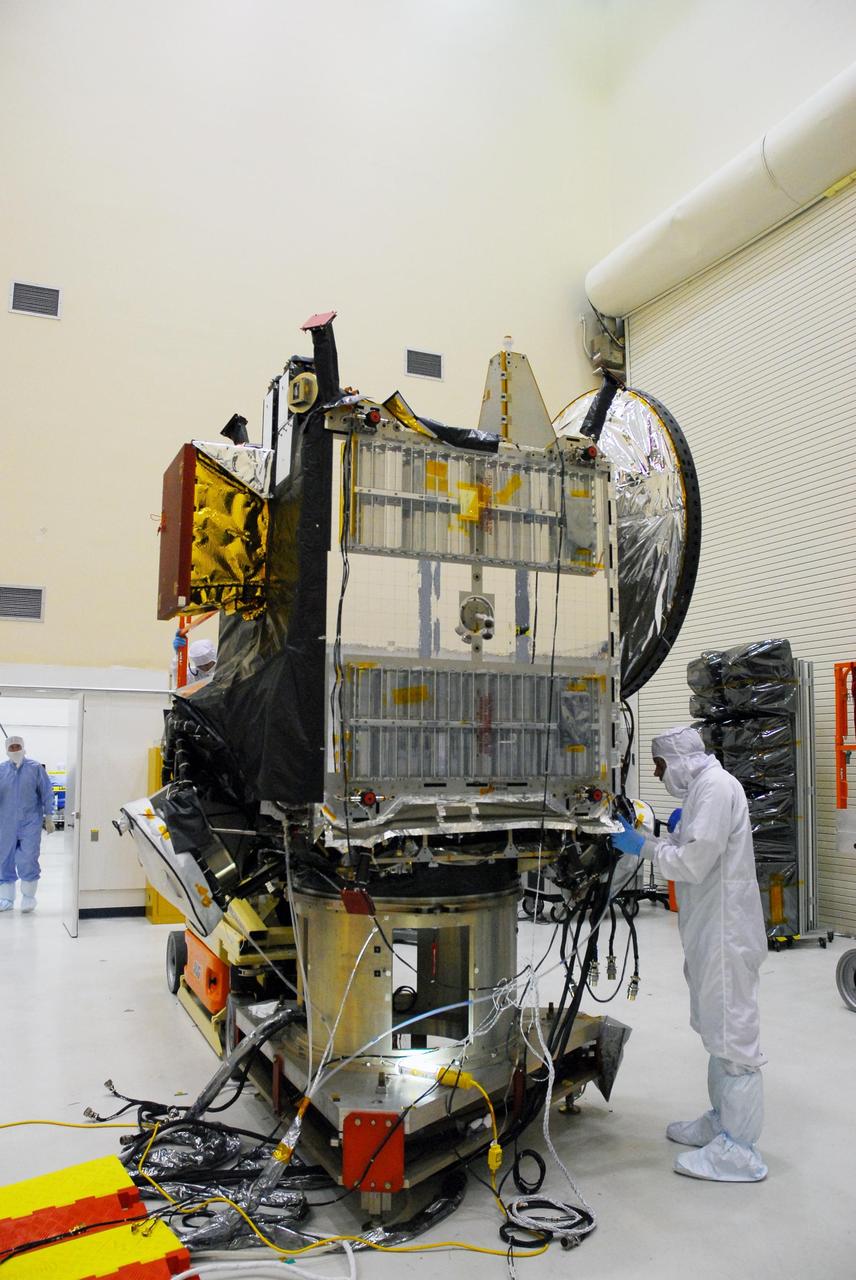

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In a clean room at Astrotech, workers prepare the Dawn spacecraft for thermal blanket installation. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 from Launch Complex 17-B. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
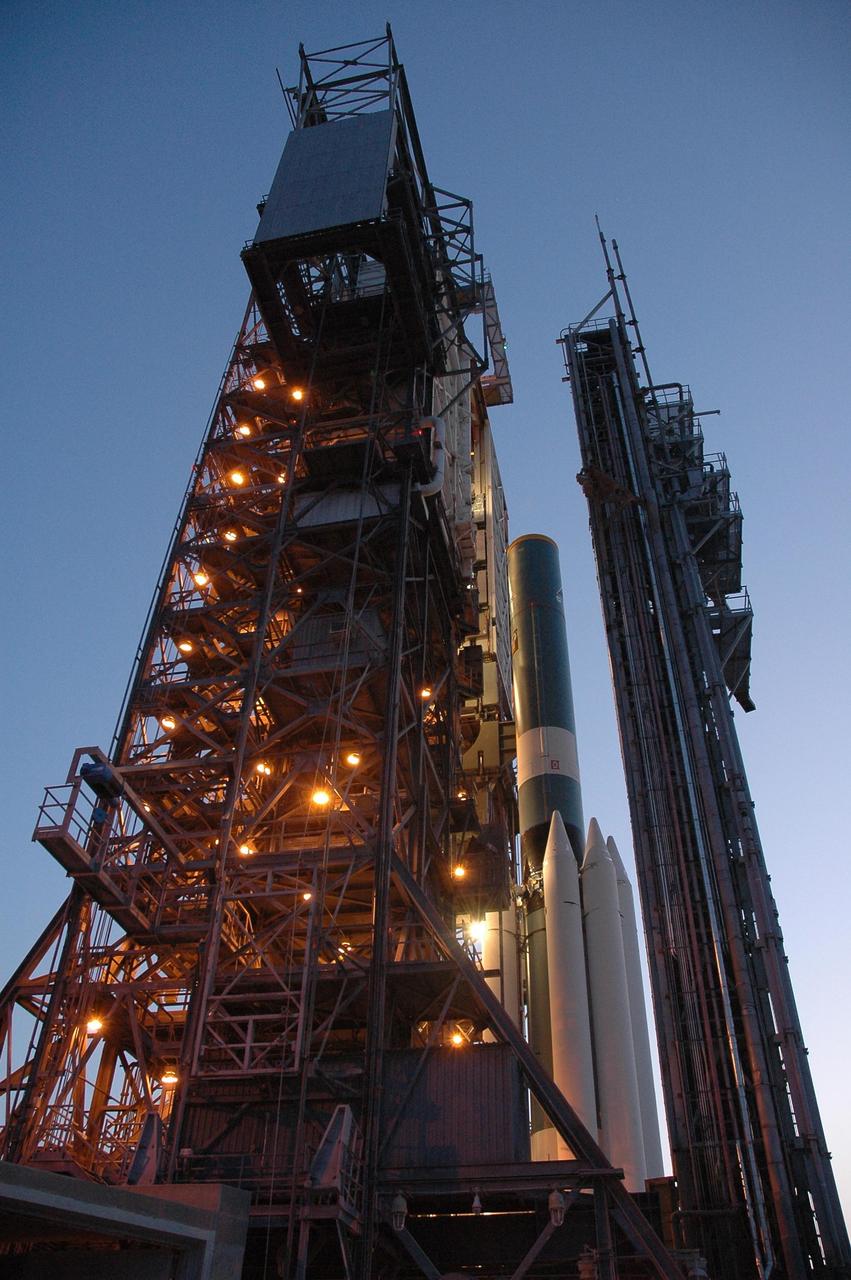

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Next to the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II first stage is being mated to the solid rocket boosters for launch of the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's goal is to characterize the conditions and processes of the solar system's earliest epoch 4.5 billion years ago by investigating in detail two of the largest asteroids, Ceres and Vesta. They reside between Mars and Jupiter in the asteroid belt. Launch is targeted for July 7. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, workers help guide the Dawn spacecraft toward the upper stage booster below. The two elements will be mated for launch. Dawn's goal is to characterize the conditions and processes of the solar system's earliest epoch by investigating in detail the largest protoplanets that have remained intact since their formations: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. They reside in the extensive zone between Mars and Jupiter together with many other smaller bodies, called the asteroid belt. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, workers get ready to test deploy the large solar array panels on one side of the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn is scheduled to launch June 30 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
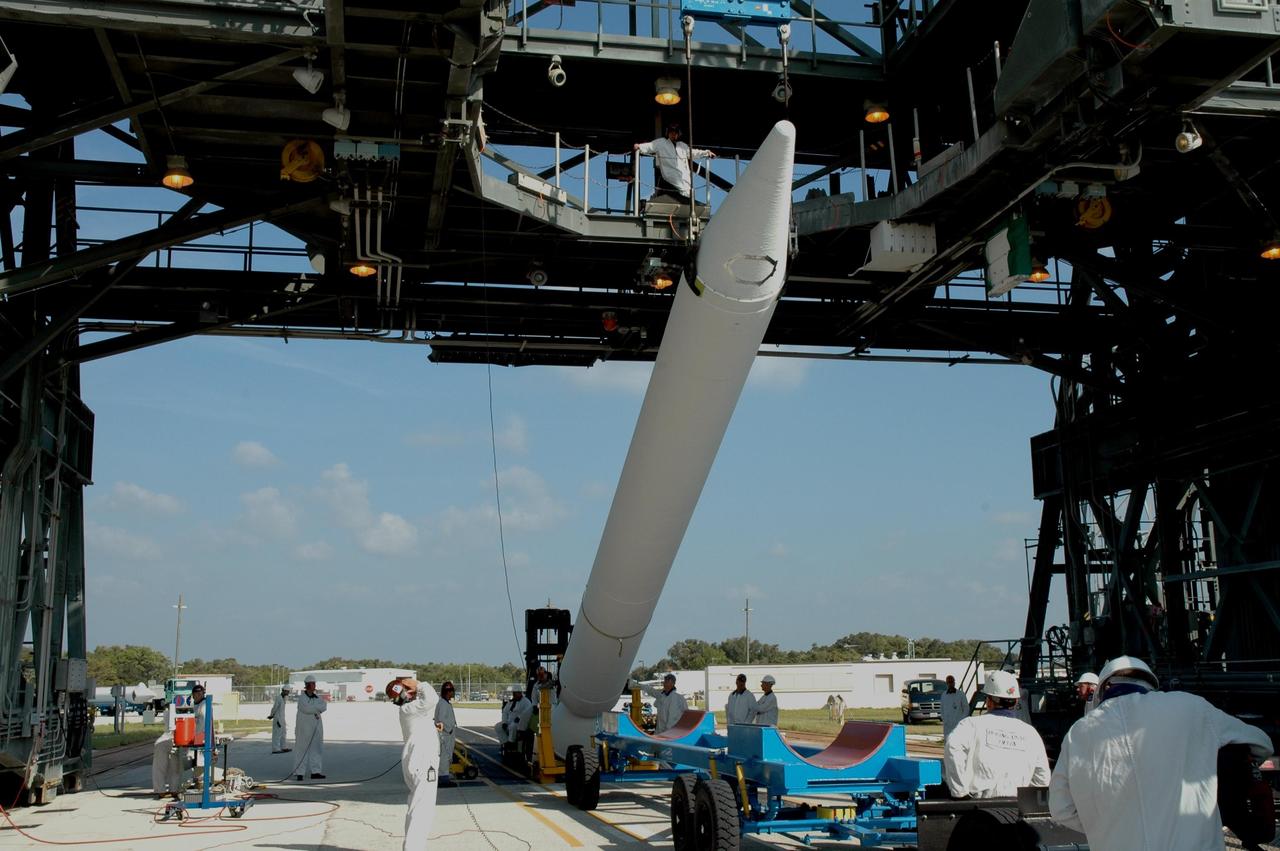

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, one of nine solid rocket boosters is raised off the transporter. It will be lifted into the mobile service tower for attachment around the Delta II first stage. The SRB is one of nine to be attached for the launch of the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann