
S71-52264 (1971) --- Astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin. Photo credit: NASA
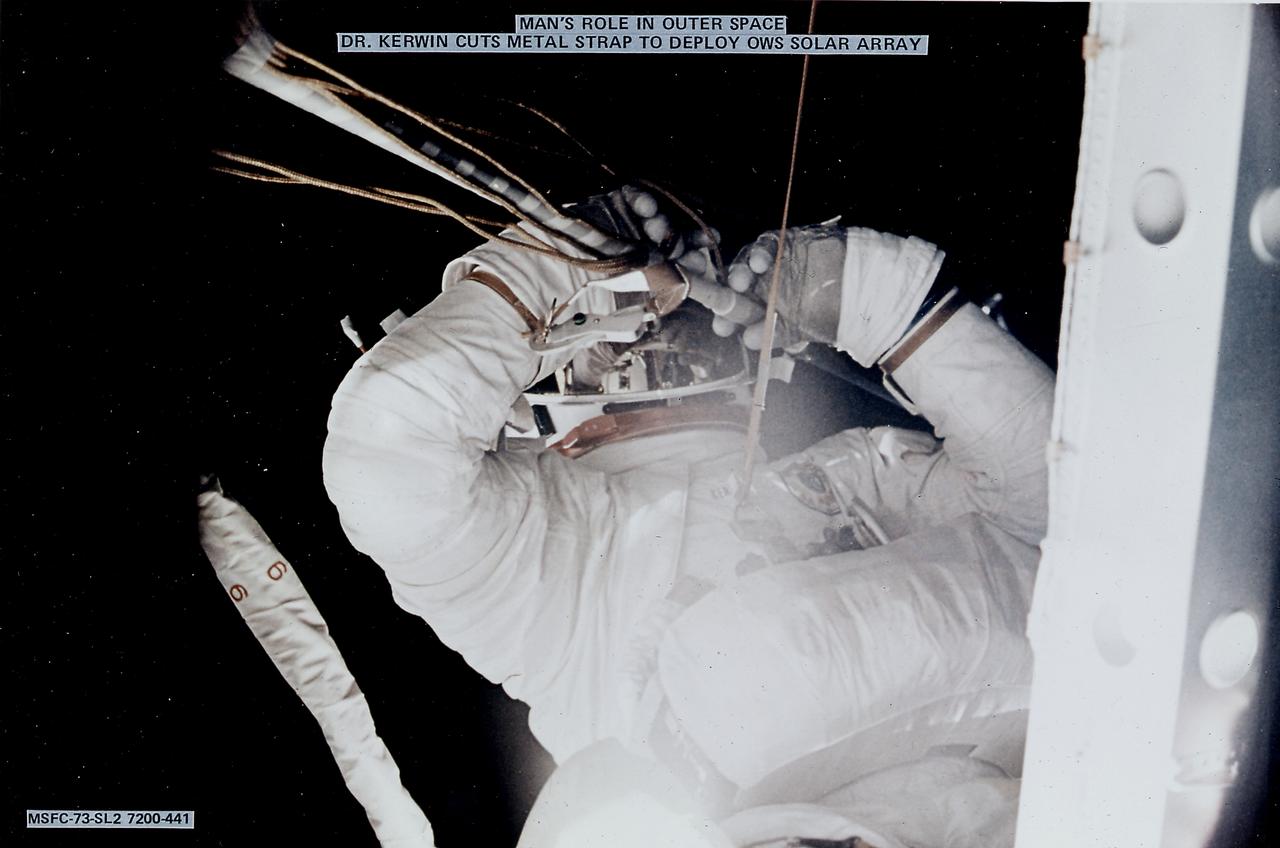

The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into the flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Intrnal temperatures soared, rendering the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image shows astronaut Kerwin cutting the metal strap to free and deploy the Orbital Workshop solar array. Kerwin used special cutting tools developed by engineers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The MSFC had a major role in developing the procedures to repair the damaged Skylab.

S73-27562 (June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, performs extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Skylab 1 and 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the station. Kerwin is just outside the Airlock Module. Kerwin assisted astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Skylab 2 commander, during the successful EVA attempt to free the stuck solar array system wing on the Orbital Workshop. Photo credit: NASA
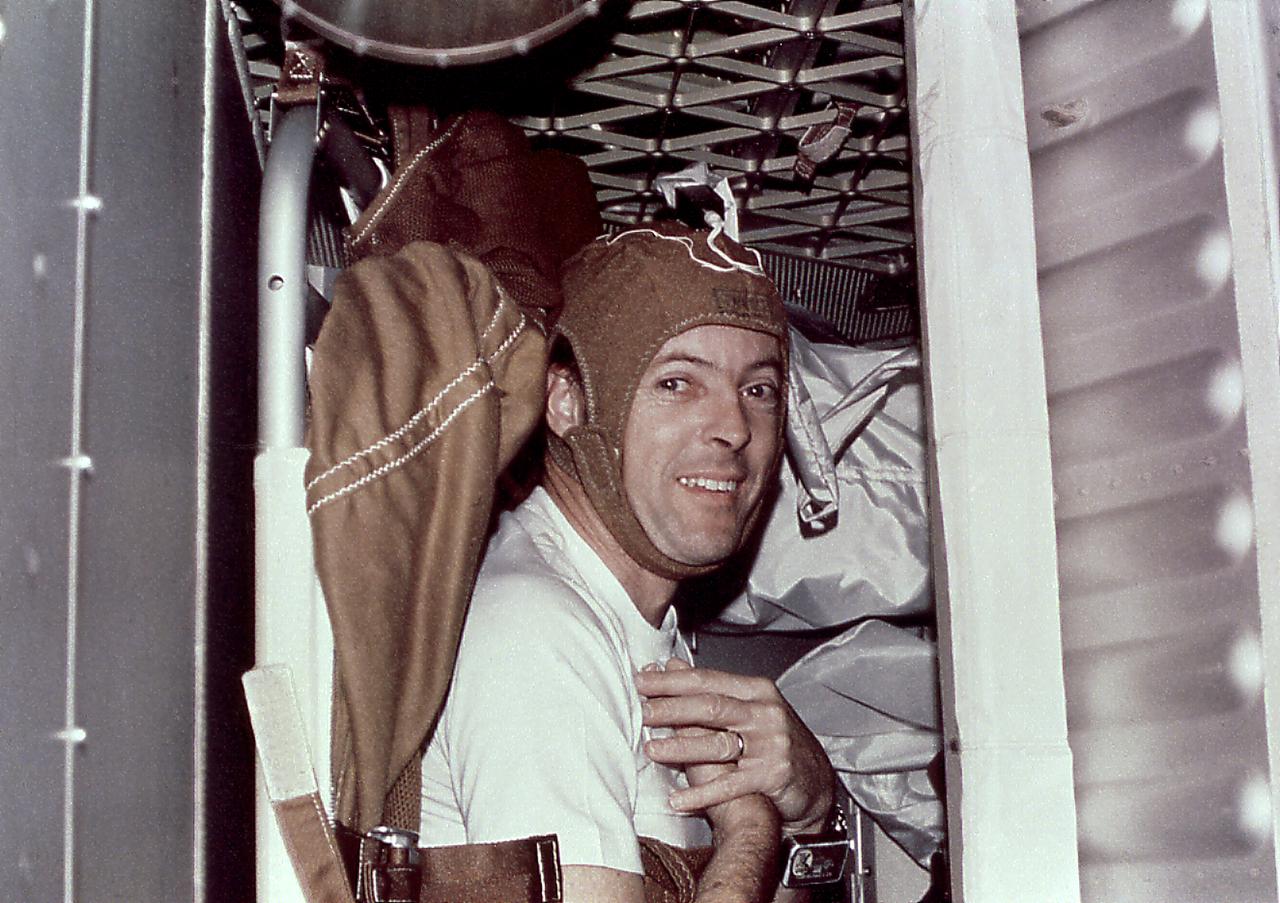

This photograph is of Astronaut Kerwin wearing the Sleep Monitoring cap (Experiment M133) taken during the Skylab-2 mission. The Sleep Monitoring Experiment was a medical evaluation designed to objectively determine the amount and quality of crew members' inflight sleep. The experiment monitored and recorded electroencephalographic (EEG) and electrooculographic (EOG) activity during astronauts' sleep periods. One of the astronauts was selected for this experiment and wore a fitted cap during his sleep periods.

Scientist-Astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, is photographed strapped into the sleep restraint in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 and 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit. Kerwin is wearing the special cap which contains biomedical instrumentation for the M133 Sleep Monitoring Experiment. The purpose of the M133 experiment is to evaluate quantity and quality of sleep during prolonged space flight by the analysis of electroencephalographic (EEG) and electrooculographic (EOG) activity.
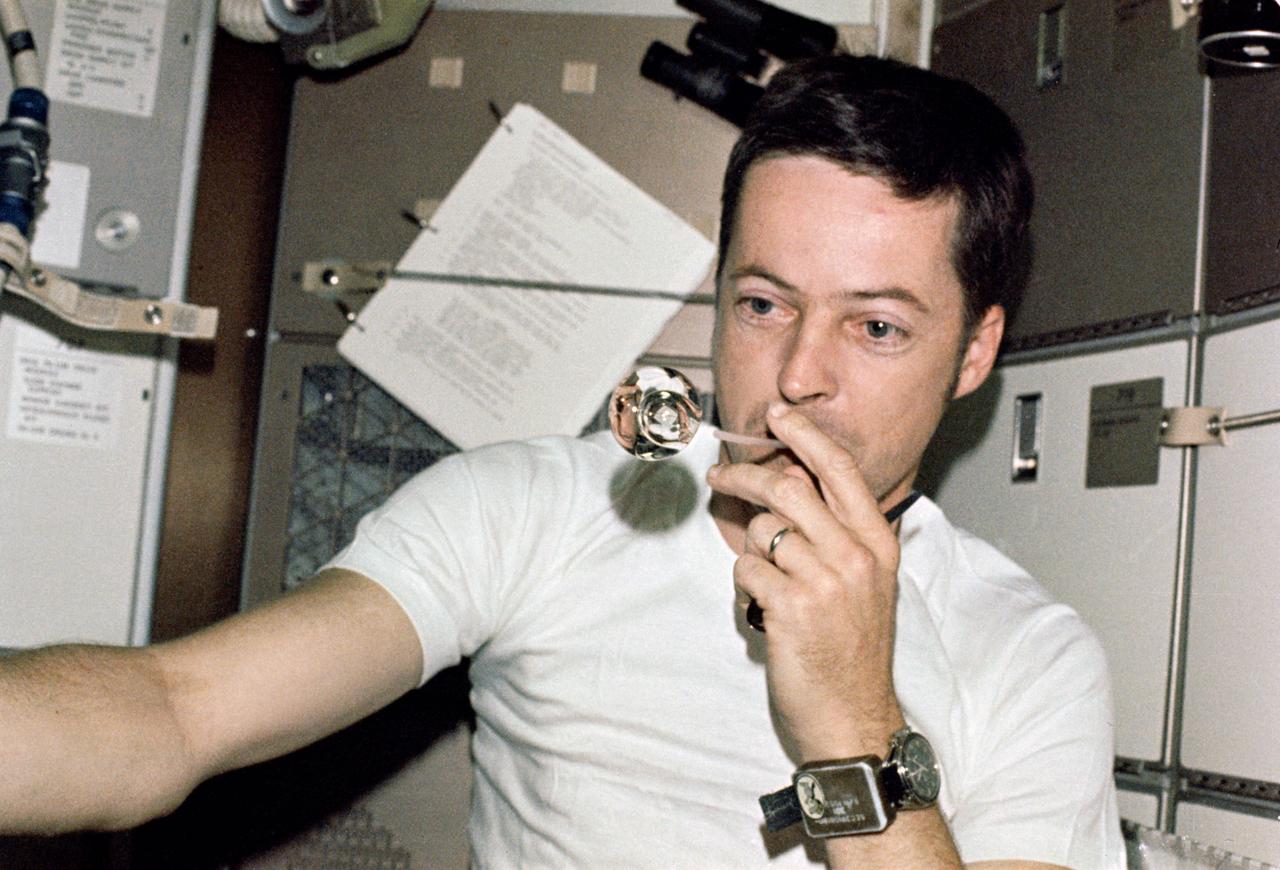

SL2-X9-730 (1 June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, forms a perfect sphere by blowing water droplets from a straw in zero-gravity. He is in the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop. Photo credit: NASA
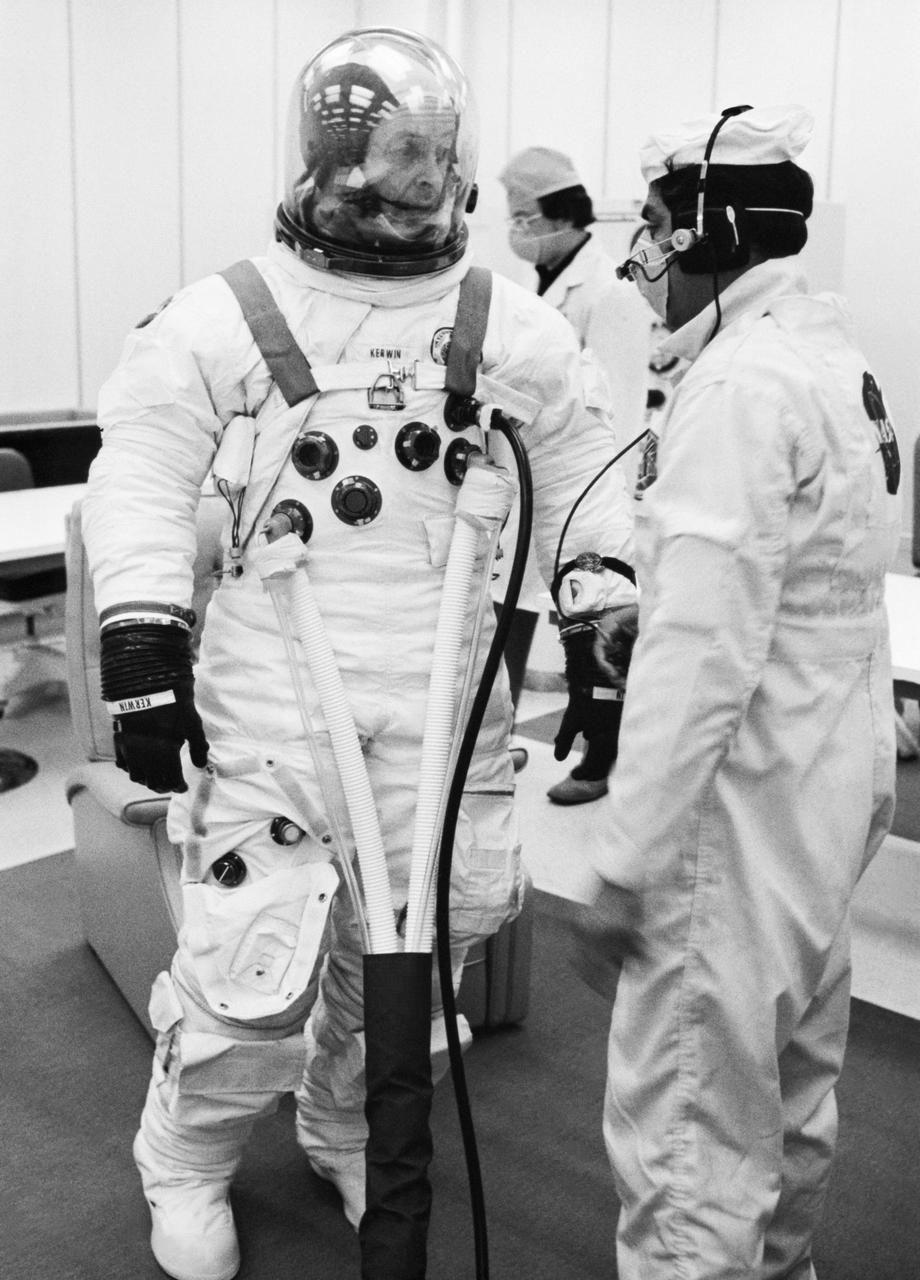

S73-25900 (25 May 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot of the Skylab 2 mission, is suited up in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building at the Kennedy Space Center during Skylab 2 prelaunch preparations. Photo credit: NASA
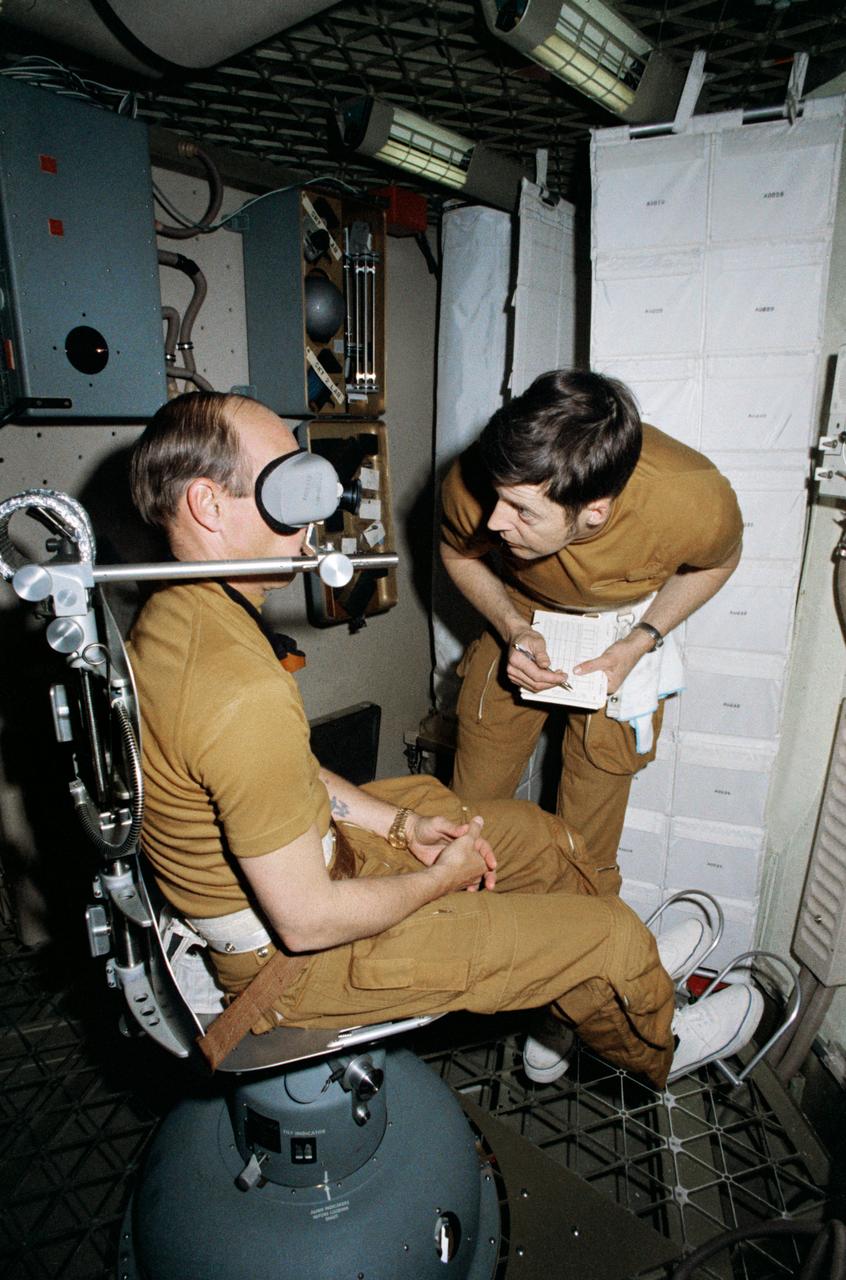
S73-20678 (1 March 1973) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the first manned Skylab mission, checks out the Human Vestibular Function, Experiment M131, during Skylab training at Johnson Space Center. Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot of the mission, goes over a checklist. The two men are in the work and experiments compartment of the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer at JSC. Photo credit: NASA
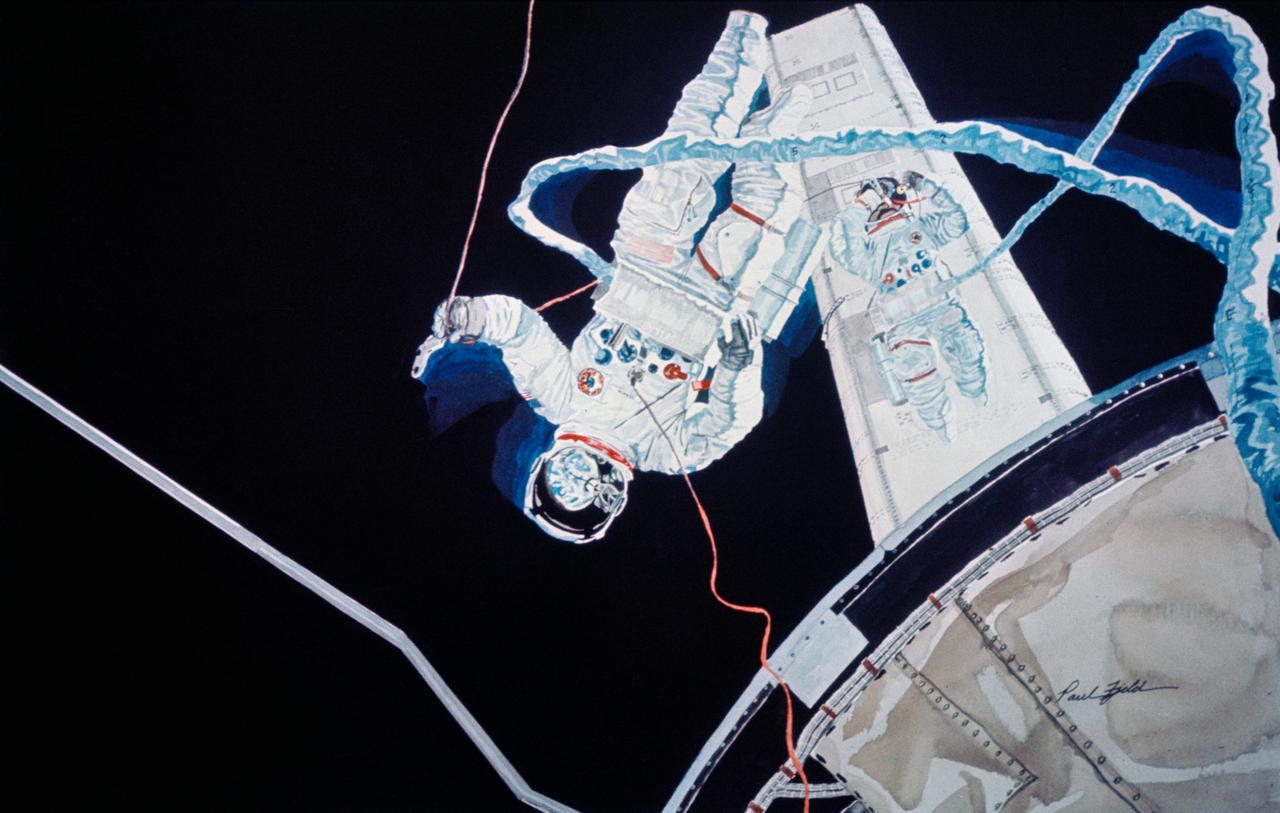
S75-21432 (March 1975) --- An artist's concept illustrating a scene during the June 7, 1973 Skylab 2 extravehicular activity in Earth orbit when astronauts Joseph P. Kerwin (larger figure) and Charles Conrad Jr. cut the aluminum strapping which prevented the Skylab Orbital Workshop solar array system wing from deploying. The solar panel was successfully deployed. The painting is by artist Paul Fjeld. The action portrayed here is about two to four seconds after using the beam erection tether, the two crewmen broke the frozen SAS beam actuators. This artistic effort took weeks to research and a day and a half to paint. Fjeld said that he needed some hundred or so photographs to get all the details for the painting. He struggled through about 300 pages of transcripts from the flight. Also, he used several pages of teleprinter messages which were the actual instructions on the EVA that the two astronauts used in flight. Photo credit: NASA
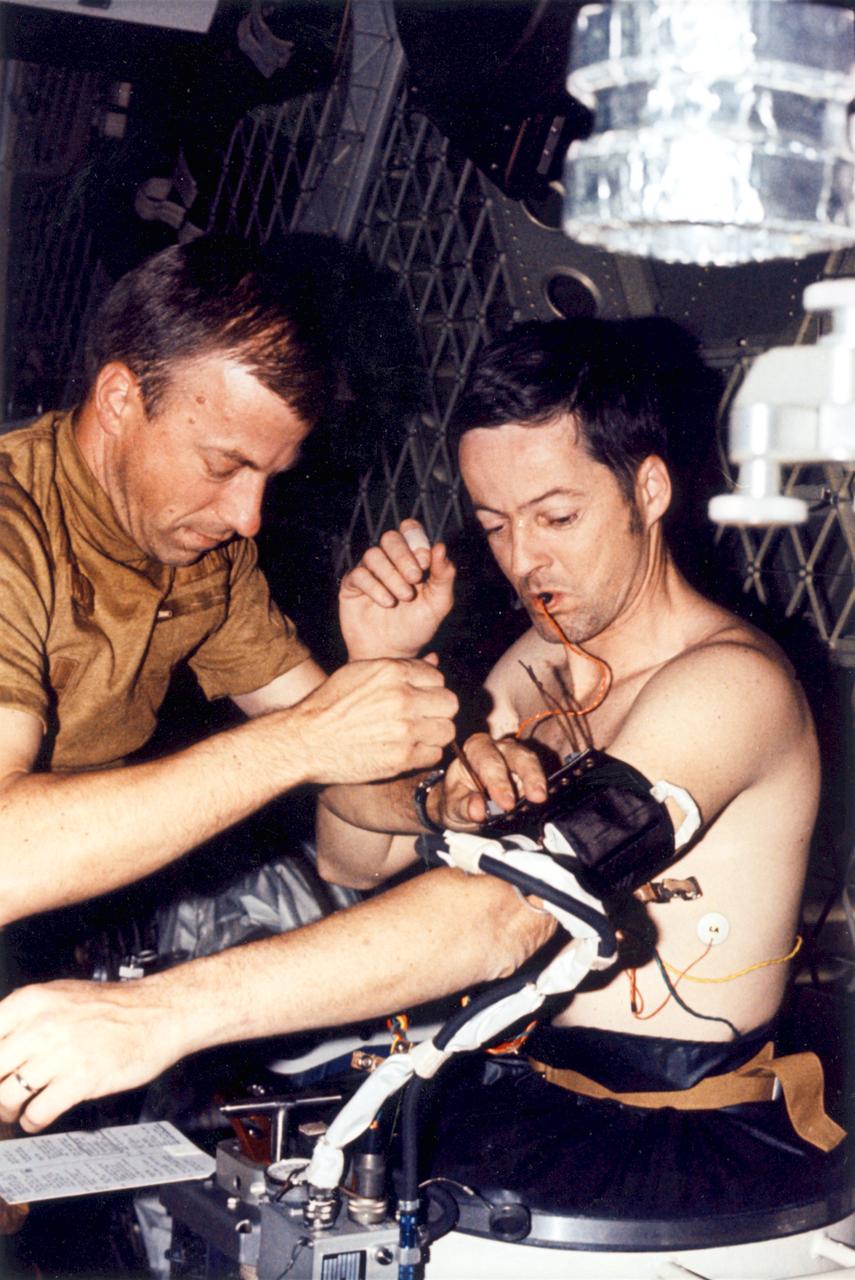
Astronaut Weitz assists Astronaut Kerwin with blood pressure cuff. Skylab-2 mission duration 5/25/73 thru 6/22/73.
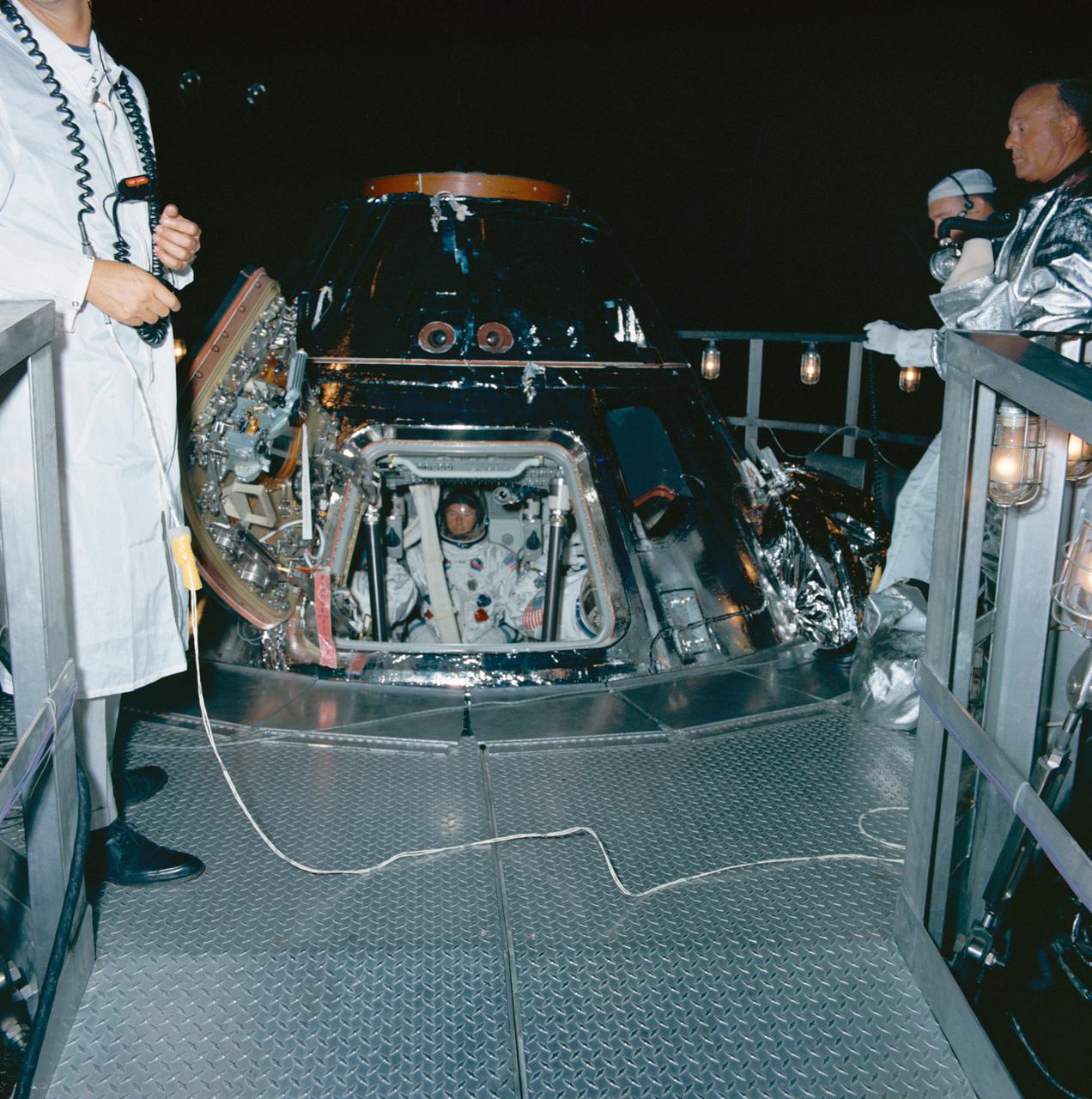
Crew ingress and beginnings of 7 1/2-day Manned Thermal Vacuum Test with Astronauts Joe Engle, Dr. Joseph Kerwin and Brand in the Apollo S/C-2TV-1, Chamber "A", Bldg. 32. Note - 35mm BW (S68-35881 thru S68-35882) - 120 CN (S68-35883 thru S68-35908) 1. ASTRONAUT BRAND, VANCE D. - VACUUM TEST 2. ASTRONAUT KERWIN, JOSEPH - VACUUM TEST 3. ASTRONAUT ENGLE, JOE - VACUUM MSC, HOUSTON, TX
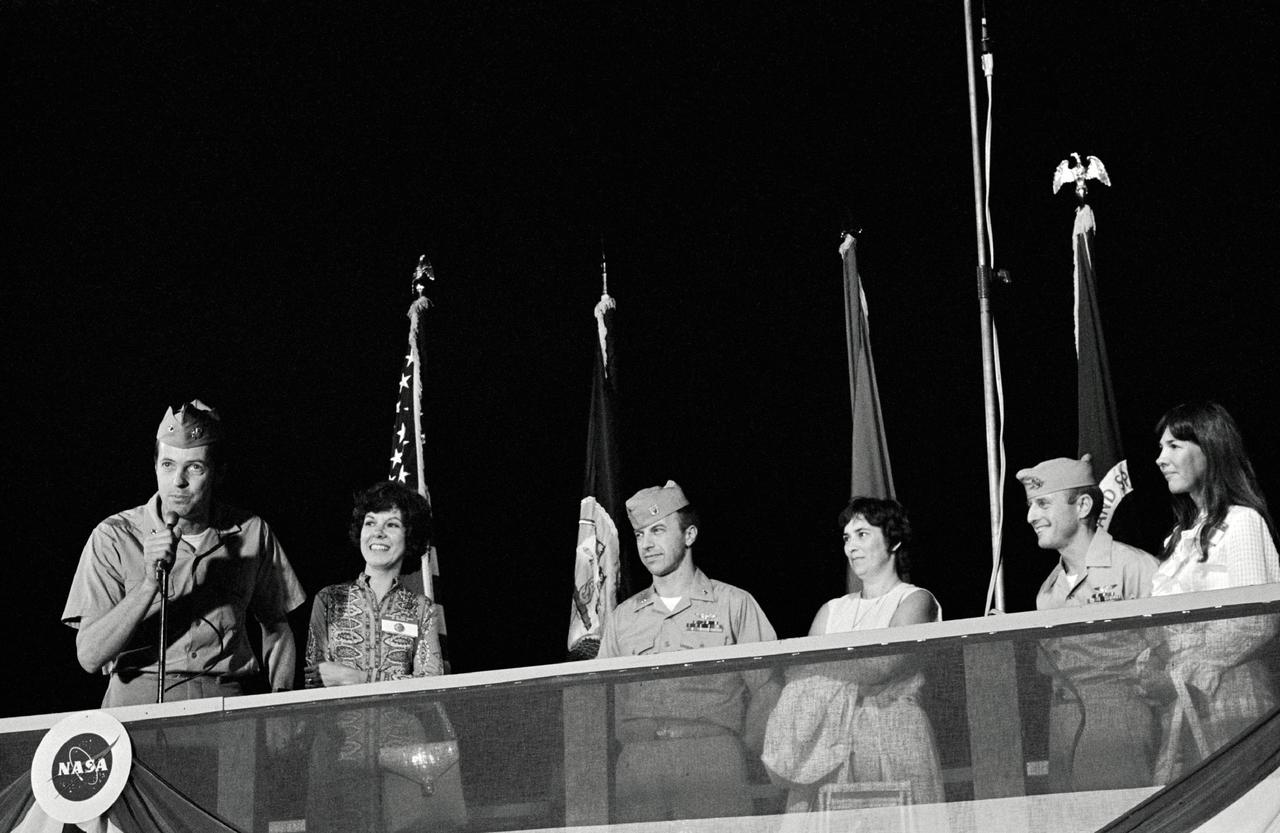

S73-28818 (24 June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot for the Skylab 2 mission, speaks to a crowd at Ellington Air Force Base during welcome home ceremonies for the crew. Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot, is at center; and astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., crew commander, is at right. The wives, standing by their husbands, are (left to right) Shirley Kerwin, Suzanne Weitz and Jane Conrad. Photo credit: NASA
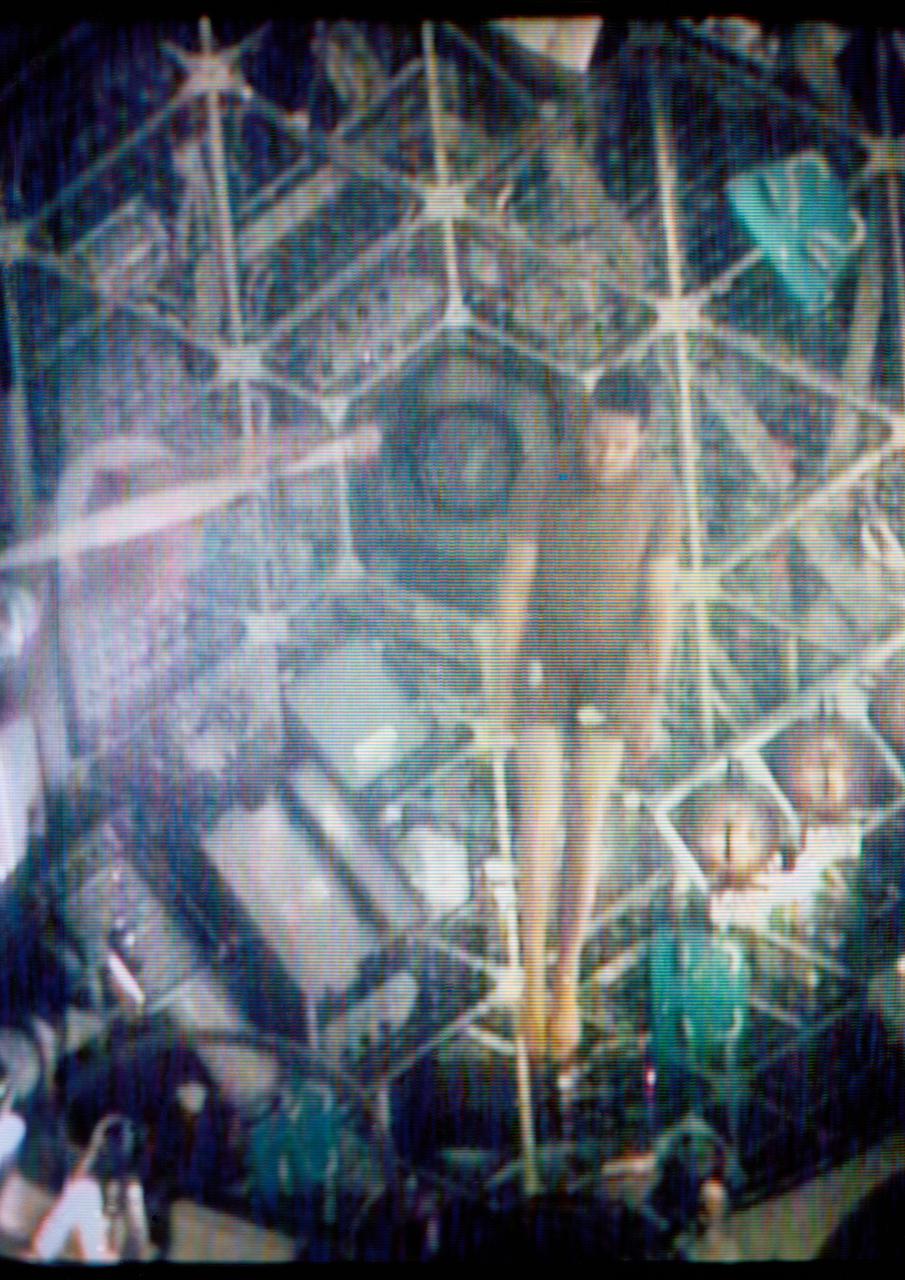

S73-27260 (1 June 1973) --- Two of the three Skylab 2 crewmen demonstrate weightlessness in the forward compartment of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 & 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station. Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot, floats with his body extended. Kerwin is steadied by astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander. The crewmen performed exercises while floating. Photo credit: NASA
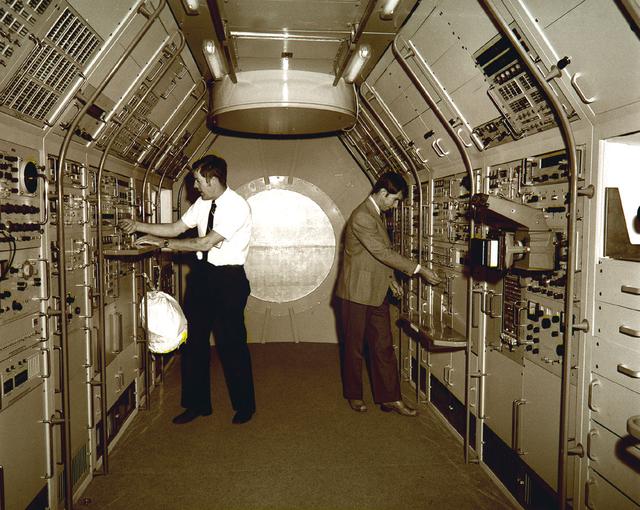

Astronauts Joseph Kerwin (left) and William Lenoir familiarize themselves with equipment aboard the Spacelab mockup during a 1976 visit to the Marshall Space Flight Center. Kerwin and Lenoir were part of an astronaut group briefed on Spacelab subsystems and crew activities by Marshall scientists and engineers. The Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibility for Spacelab.
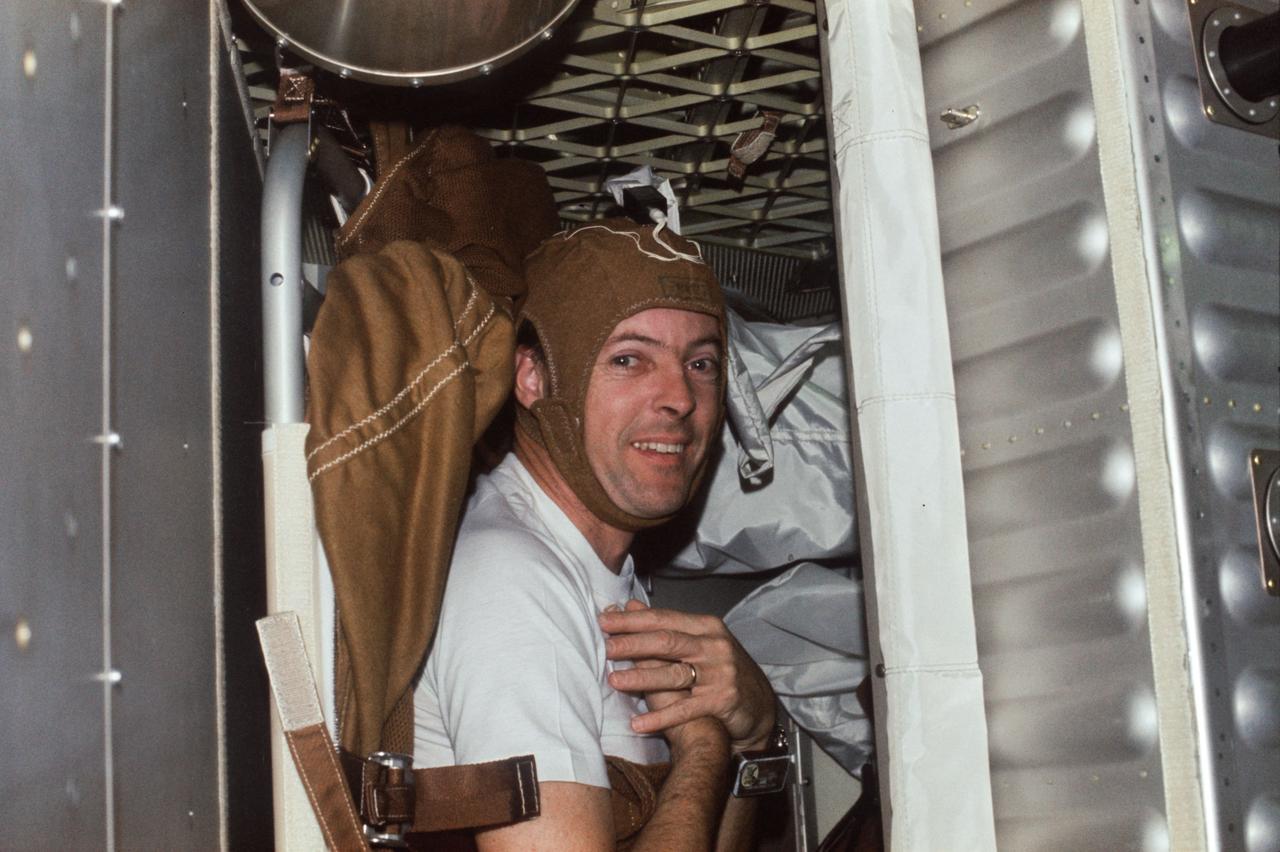

SL2-X3-205 (June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, is photographed strapped into the sleep restraint in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 & 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit. Kerwin is wearing the special cap which contains biomedical instrumentation for the M133 Sleep Monitoring Experiment. The purpose of the M133 experiment is to evaluate quantity and quality of sleep during prolonged space flight by the analysis of electroencephalographic (EEG) and electrooculographic (EOG) activity. Photo credit: NASA
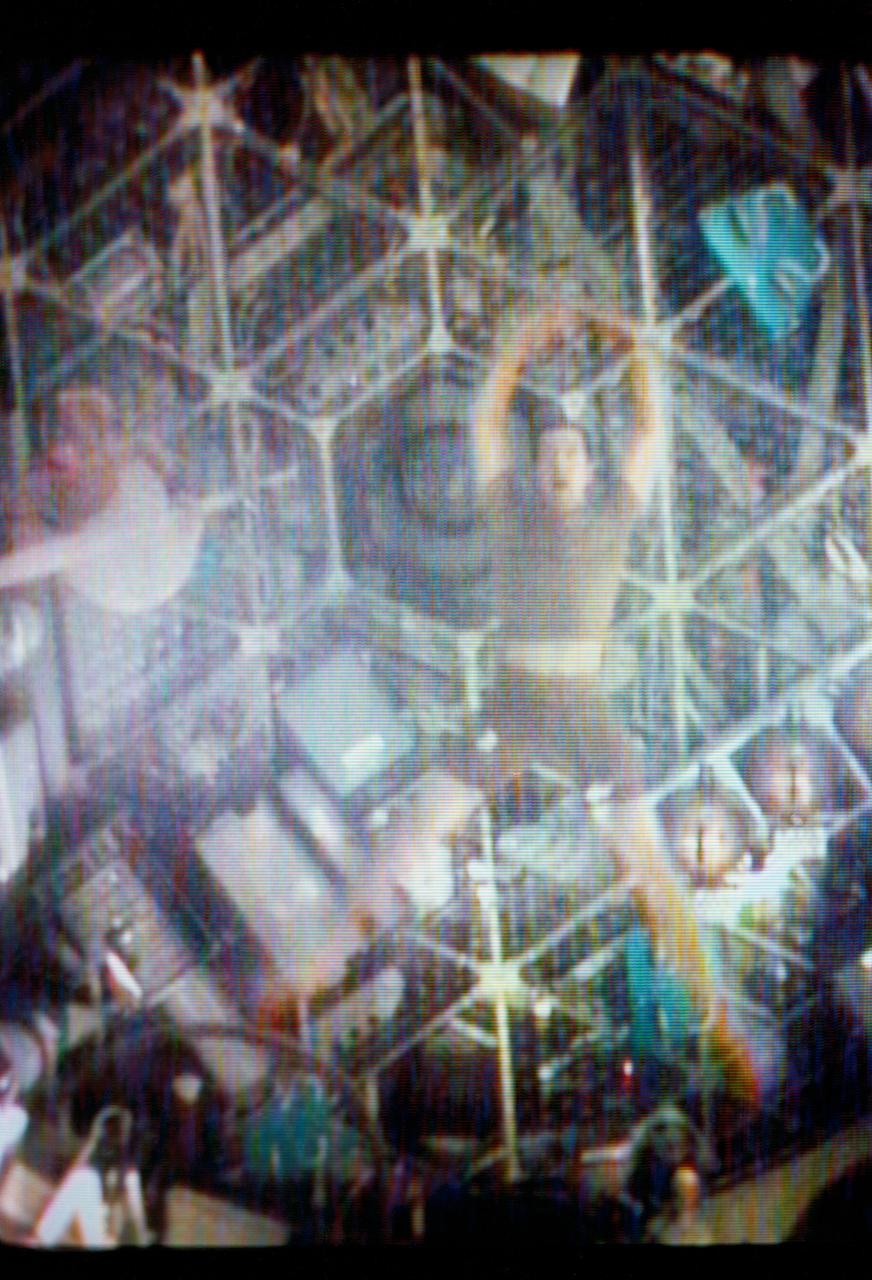

S73-27729 (1 June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, floats with his body outstretched as he demonstrates weightlessness in the forward compartment of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 & 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Skylab 2 commander, is visible on Kerwin's right. The Skylab 2 crewmen performed exercises while floating. Photo credit: NASA
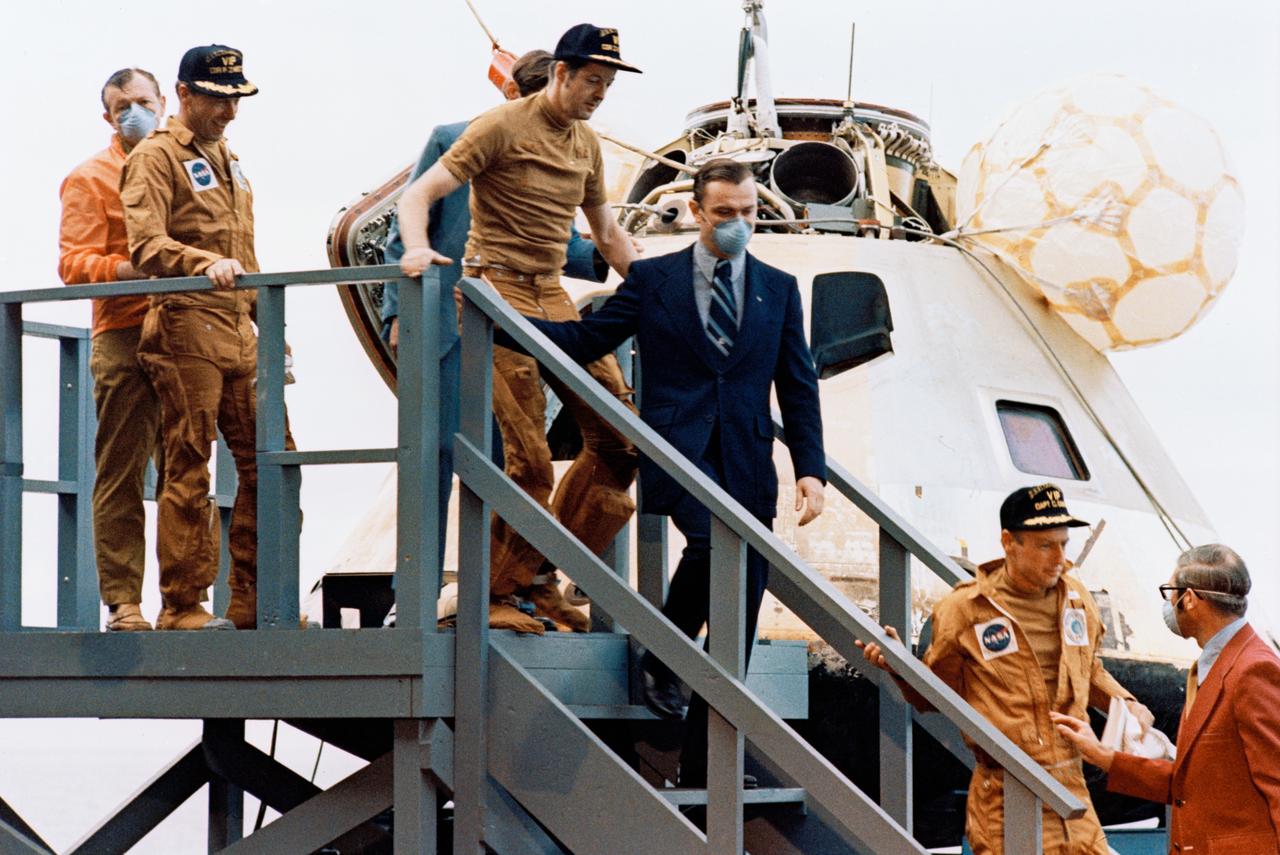

S73-29141 (22 June 1973) --- The three Skylab 2 crewmen arrive on the deck of the prime recovery ship, USS Ticonderoga, following the successful splashdown of the Skylab 2 Command Module about 835 miles southwest of San Diego, California. Leading down the steps is astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, followed by scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot, and astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. Recovery and medical personnel walk down the steps with the astronauts. The crewmen remained inside the spacecraft (seen in background) until it was hoisted aboard the recovery ship. Conrad, Kerwin and Weitz had just completed a 28-day stay with the Skylab 1 space station in Earth orbit conducting numerous medical, scientific and technological experiments. Photo credit: NASA

S73-27734 (11 June 1973) --- Skylab 2 astronaut performs extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Skylab 1 and 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the station. Kerwin is just outside the Airlock Module. Photo credit: NASA
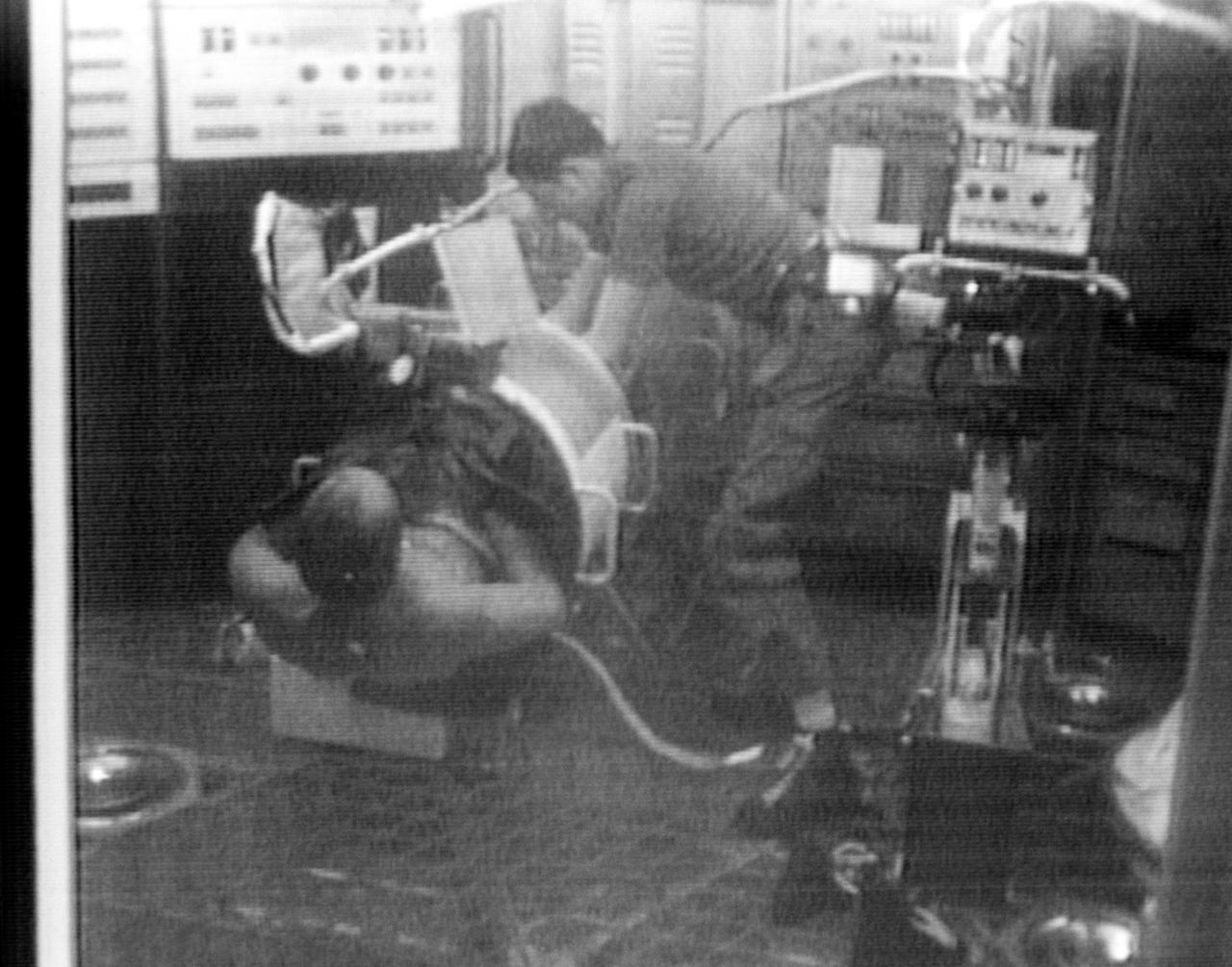
S73-27707 (9 June 1973) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Skylab 2 commander, serves as test subject for the Lower Body Negative Pressure (MO92) Experiment, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab 1/2 space station cluster in Earth orbit. Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, assists Conrad into the LBNP device. Kerwin served as monitor for the experiment. The purpose of the MO92 experiment is to provide information concerning the time course of cardiovascular adaptation during flight, and to provide inflight data for predicting the degree of orthostatic intolerance and impairment of physical capacity to be expected upon return to Earth environment. The data collected in support of MO92 blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature, vectorcardiogram, LBNPD pressure, leg volume changes, and body weight. Photo credit: NASA
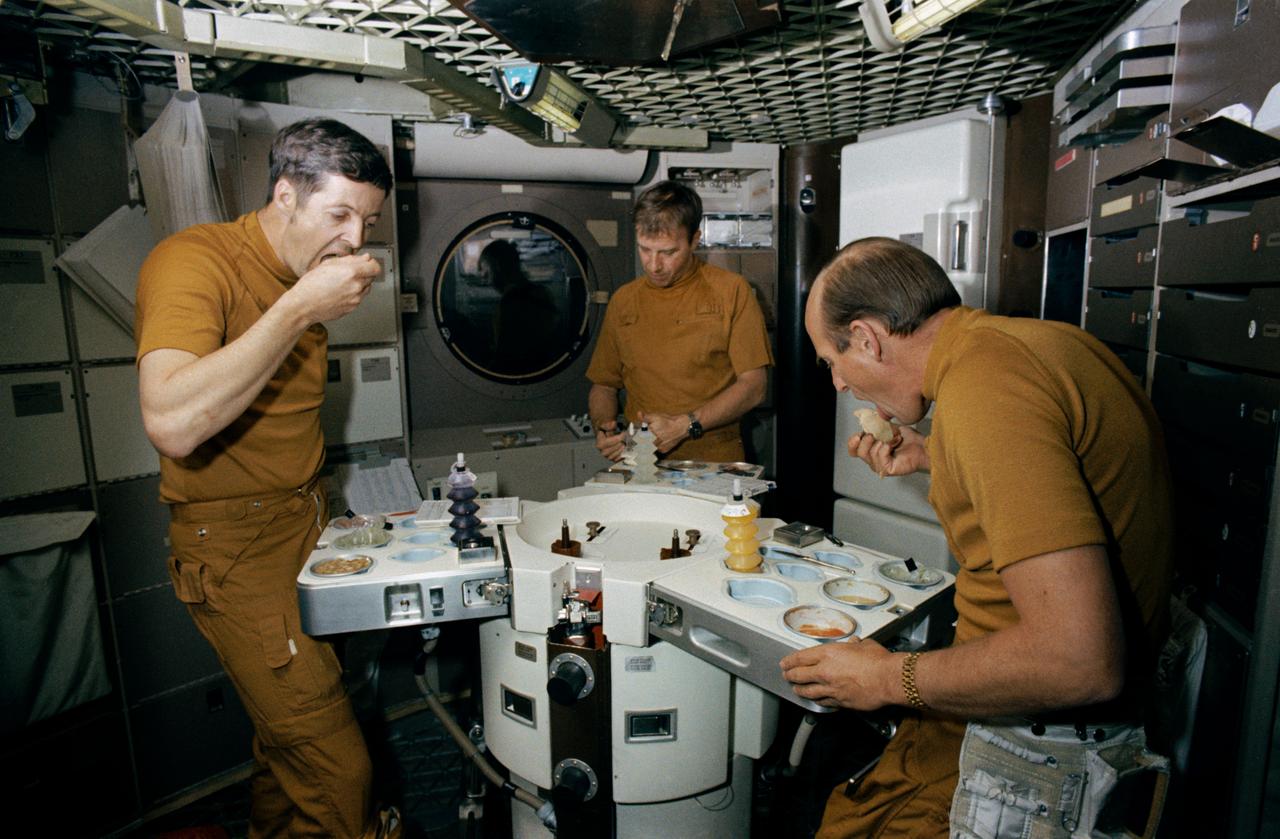

S73-20236 (1 March 1973) --- The three members of the prime crew of the first manned Skylab mission dine on specially prepared Skylab space food in the wardroom of the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer during Skylab training at the Johnson Space Center. They are, left to right, scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot; astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot; and astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander. Photo credit: NASA

S72-17509 (19 Jan. 1972) --- These three men are the crewmen for the first manned Skylab mission. They are astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, standing left; scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, seated; and astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. They were photographed and interviewed during an "open house" press day in the realistic atmosphere of the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) trainer in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The control and display panel for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) is at right. Photo credit: NASA
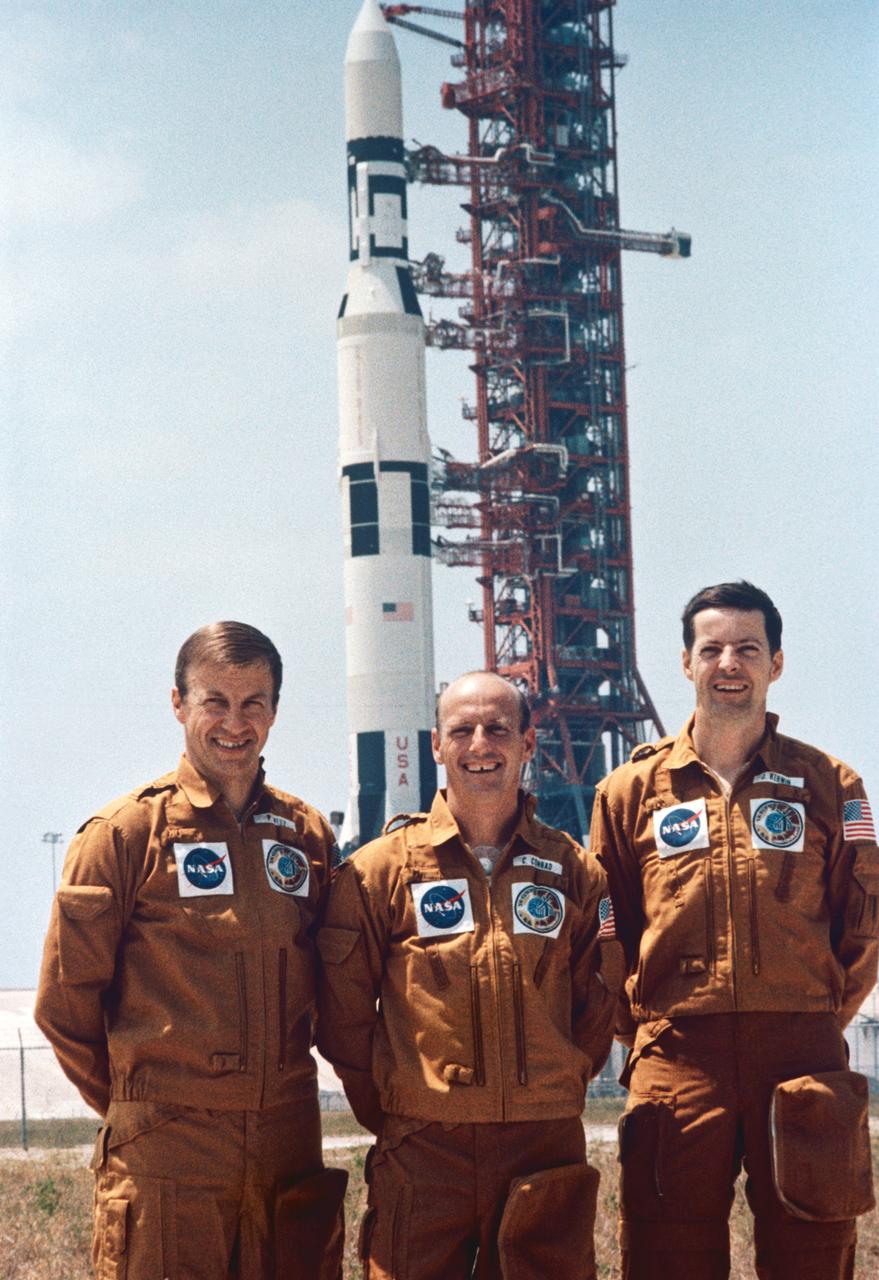

S73-25902 (4 May 1973) --- The three prime crew members of the first manned Skylab mission (Skylab 2) are photographed at Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, during preflight activity. They are, left to right, astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot; astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander; and scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot. In the background is the Skylab 1/Saturn V space vehicle with its Skylab space station payload on Pad A. Photo credit: NASA
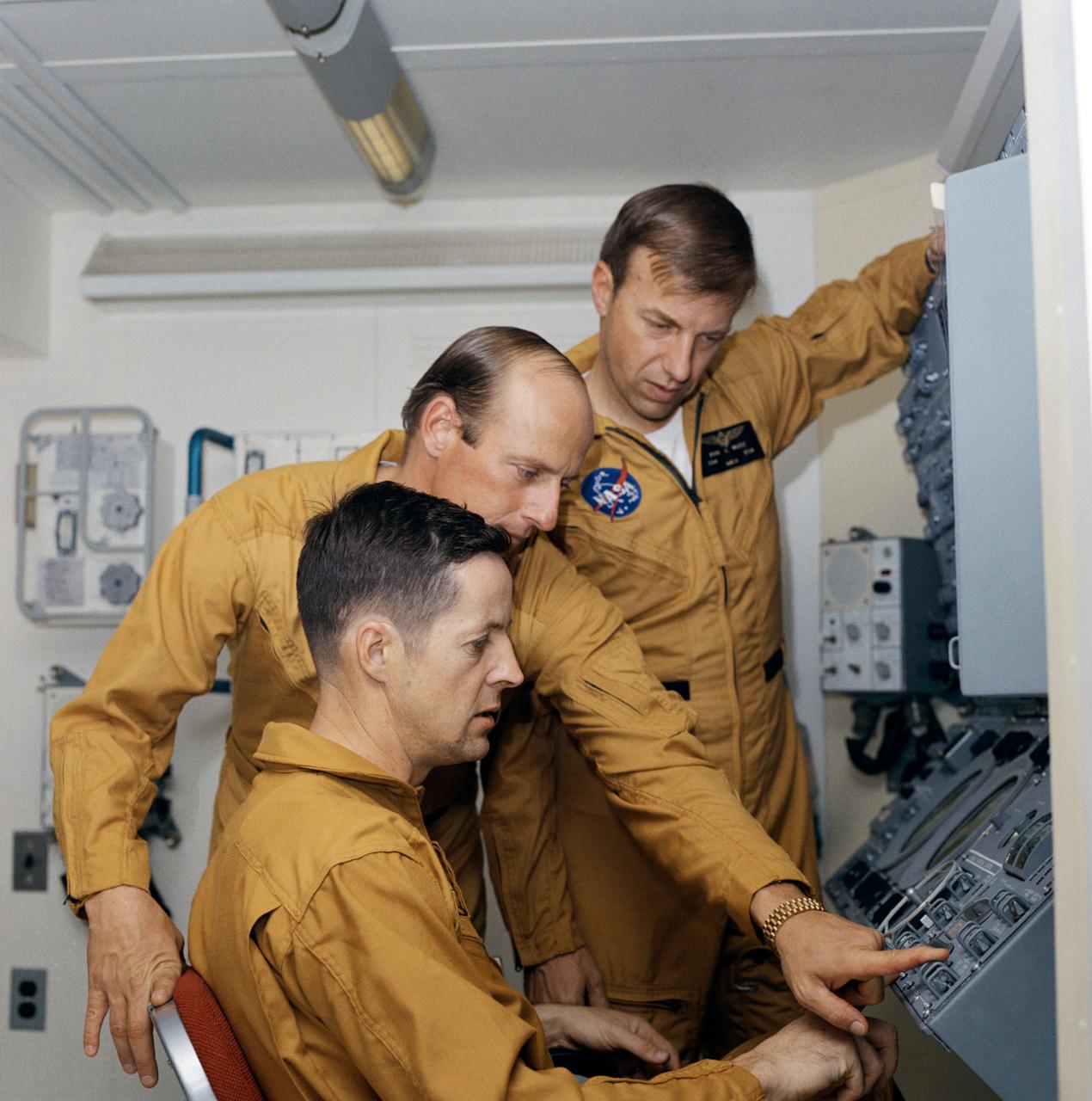

S72-17512 (19 Jan. 1972) --- These three men are the crewmen for the first manned Skylab mission. They are astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, standing left; scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, seated; and astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. They were photographed and interviewed during an "open house" press day in the realistic atmosphere of the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) trainer in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The control and display panel for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) is at right. Photo credit: NASA
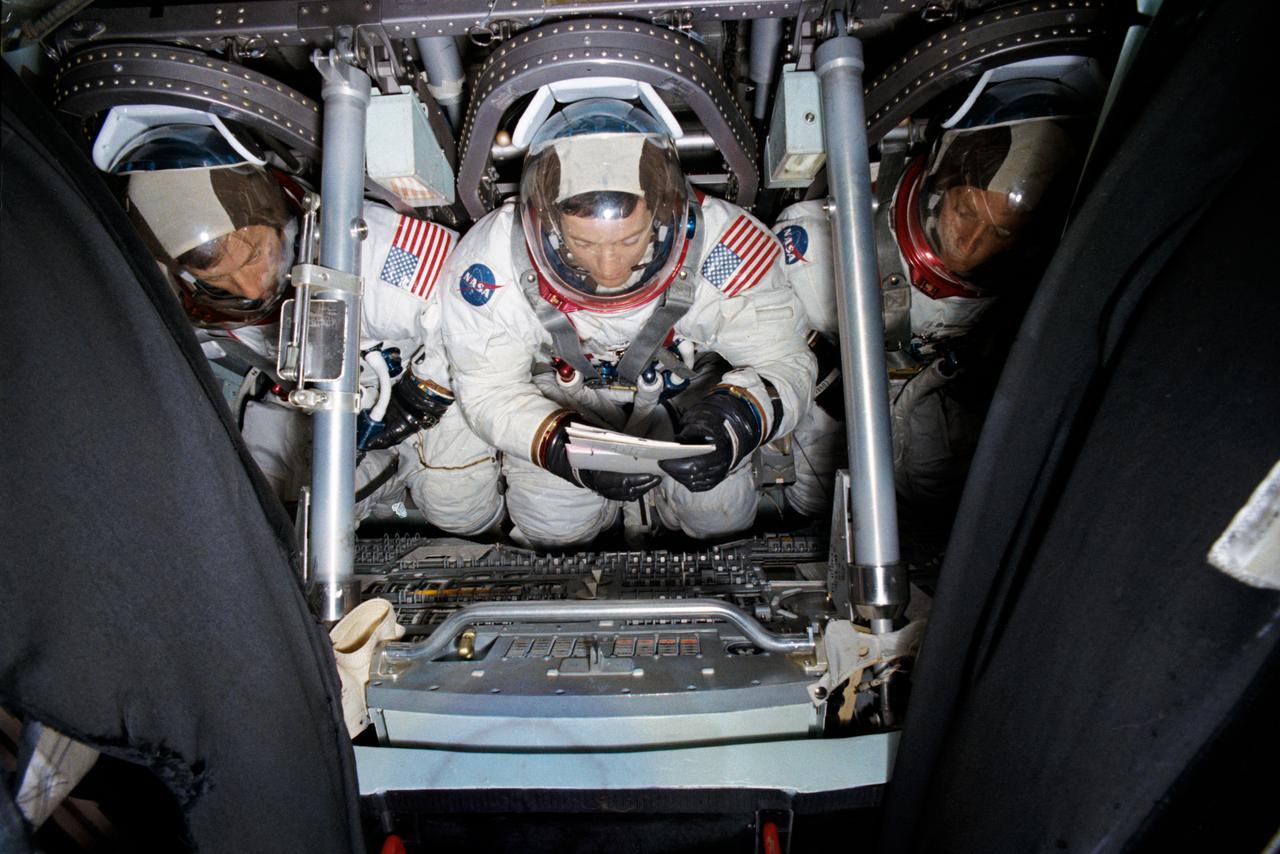

S73-25401 (8 May 1973) --- The members of the prime crew of the first manned Skylab mission go over a checklist during Skylab prelaunch training activity at Johnson Space Center. They are in the Apollo Command Module Mission Simulator in Bldg. 5 at JSC. They are, left to right, astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander; scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot; and astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. Photo credit: NASA

S73-26794 (26 May 1973) --- Two of the three Skylab 2 astronauts are seen in the wardroom of the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 space station cluster in Earth orbit in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station. They are preparing a meal. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, is in the right foreground. In the background is scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot. Photo credit: NASA
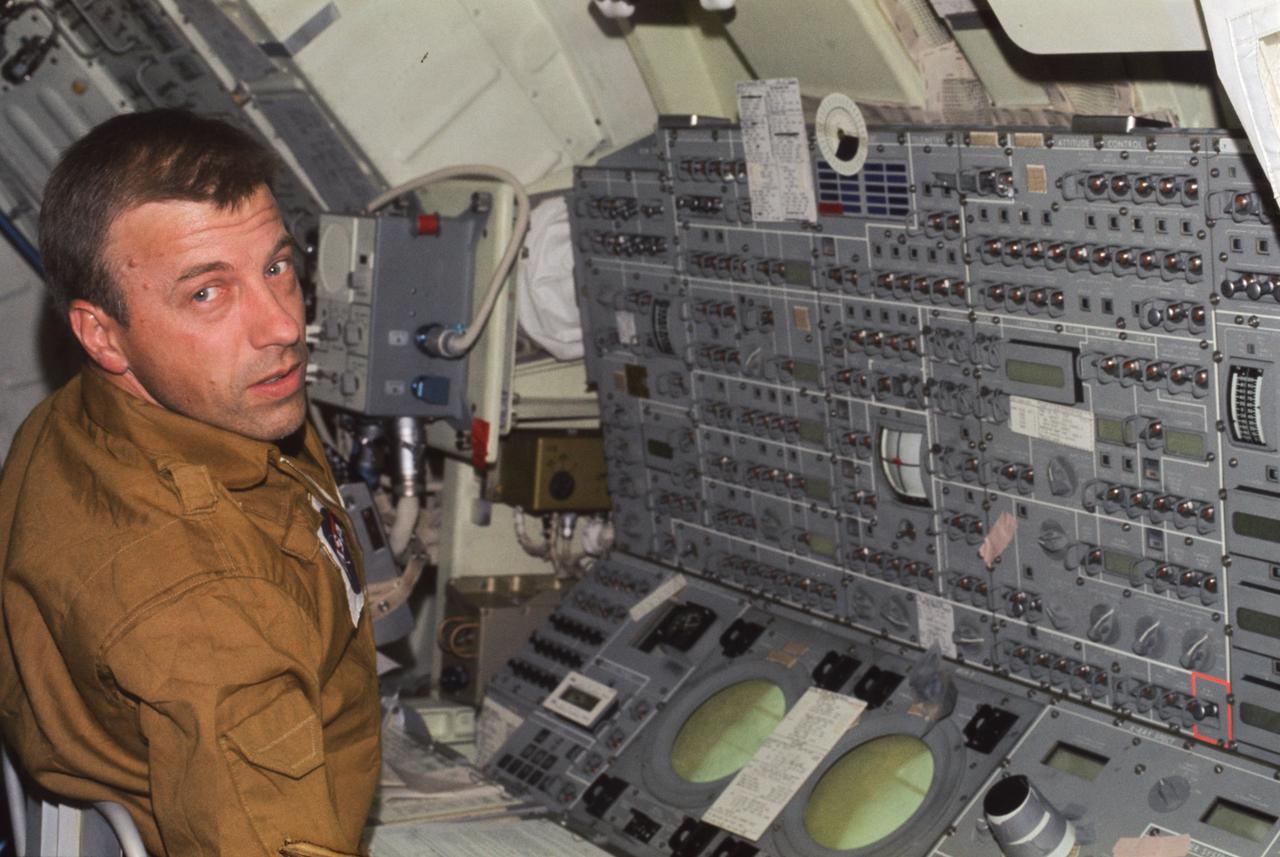

SL2-X9-747 (June 1973) --- Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, Skylab 2 pilot, mans the control and display console of the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) in this onboard view photographed in Earth orbit. The ATM C&D console is located in the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) of the Skylab 1/2 space station. Weitz, along with astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot, went on to successfully complete a 28-day mission in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA
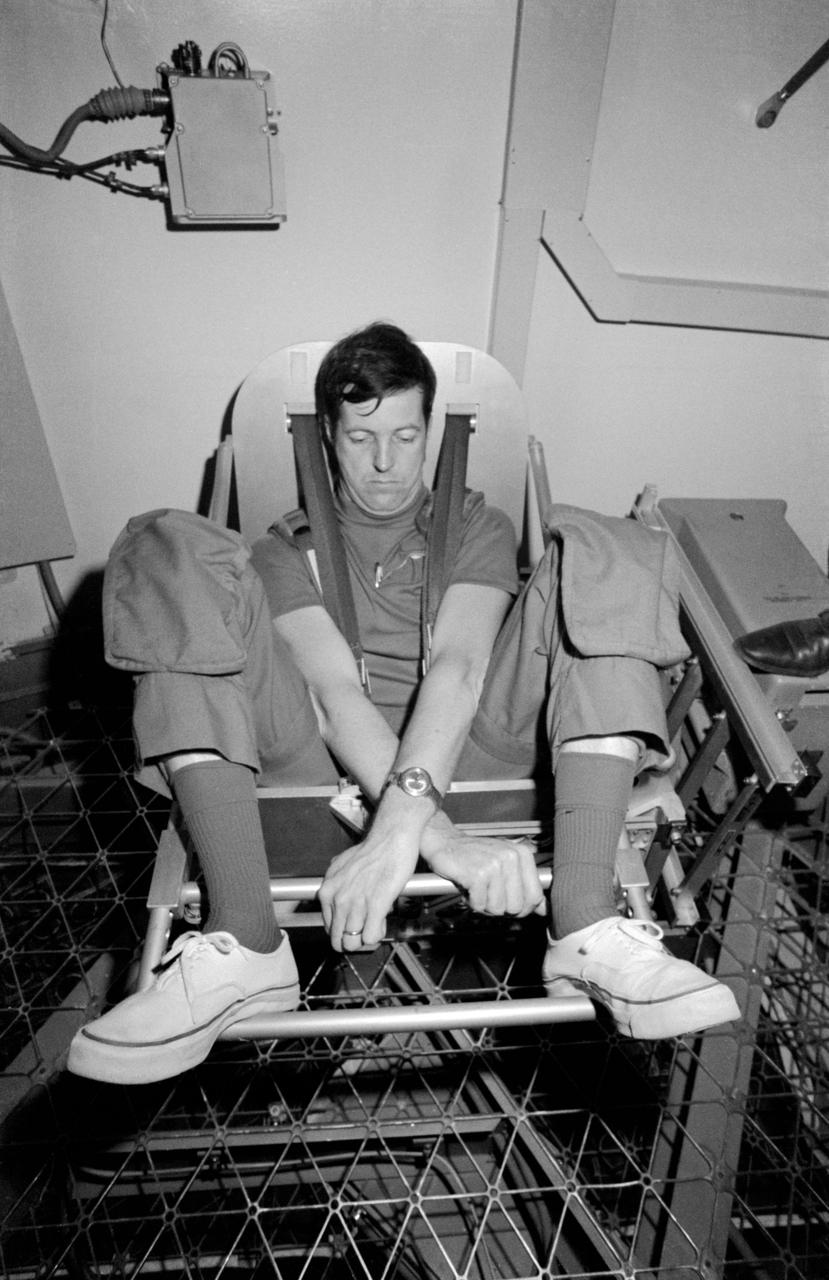

S73-20622 (March 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot of the first manned Skylab mission, demonstrates the Body Mass Measurement Experiment (M172) during Skylab training at the Johnson Space Center. Dr. Kerwin is in the work and experiments area of the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer at JSC. The M172 experiment will demonstrate body mass measurement in a null gravity environment, validate theoretical behavior of this method, and support those medical experiments for which body mass measurements are required. The data to be collected in support of M172 are: preflight calibration of the body mass measurement device and measurements of known masses up to 100 kilograms (220 pounds) three times during each Skylab mission. The device, a spring/flexure pivot-mounted chair, will also be used for daily determination of the crewmen?s weight, which will be manually logged and voice recorded for subsequent telemetered transmission. Photo credit: NASA
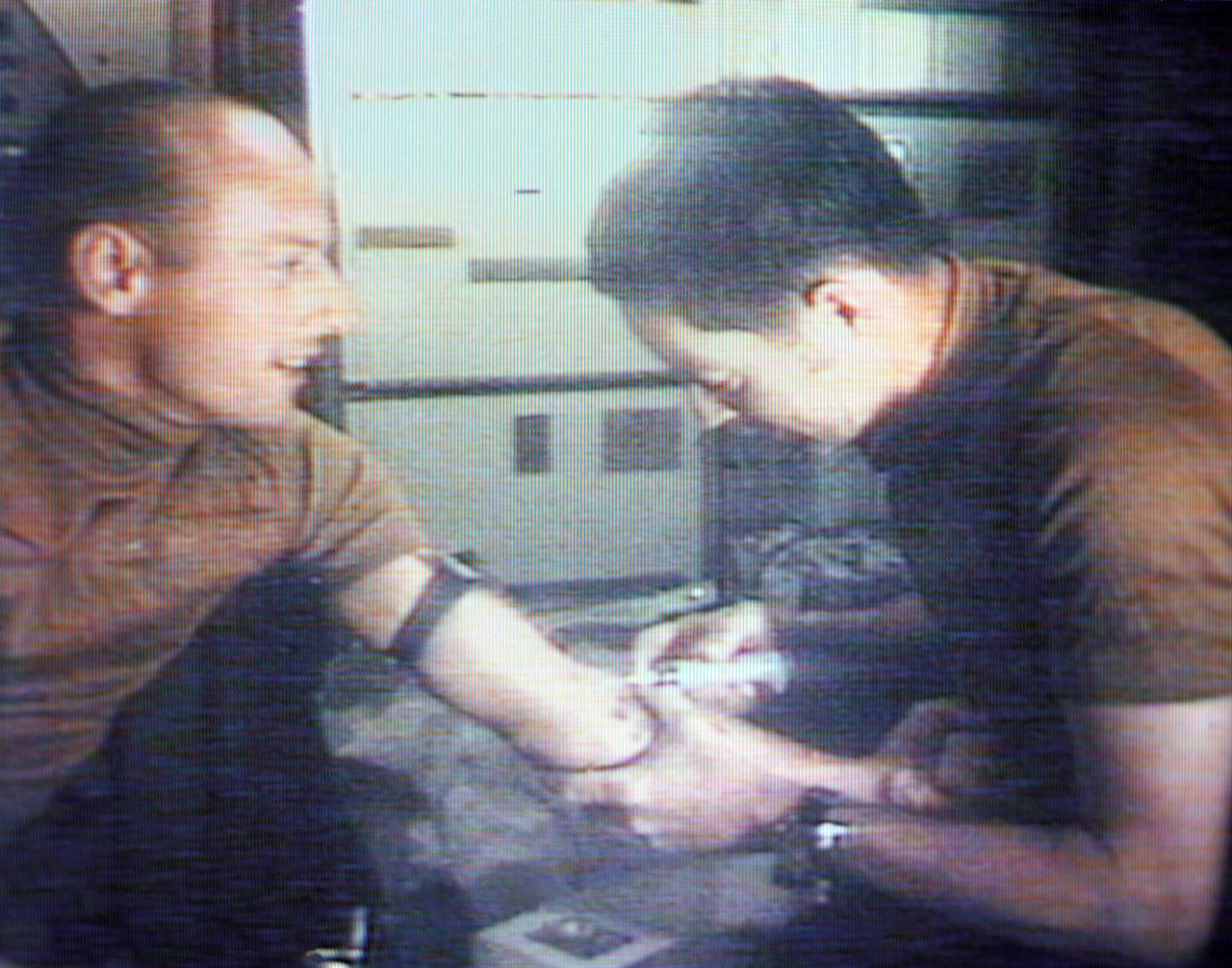
S73-27509 (6 June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin (right), Skylab 2 science pilot and a doctor of medicine, takes a blood sample from astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Skylab 2 commander, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab 1 and 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit. The blood sampling was part of the Skylab Hematology and Immunology Experiment M110 series. Photo credit: NASA

S70-34628 (11 April 1970) --- Astronaut Thomas K. (Ken) Mattingly II, who was scheduled as a prime crew member for the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission but was replaced in the final hours when it was discovered he had been exposed to measles, watches the liftoff phase of the mission. He is seated at a console in the Mission Control Center’s (MCC) Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR). Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, a spacecraft communicator for the mission, looks on at right.
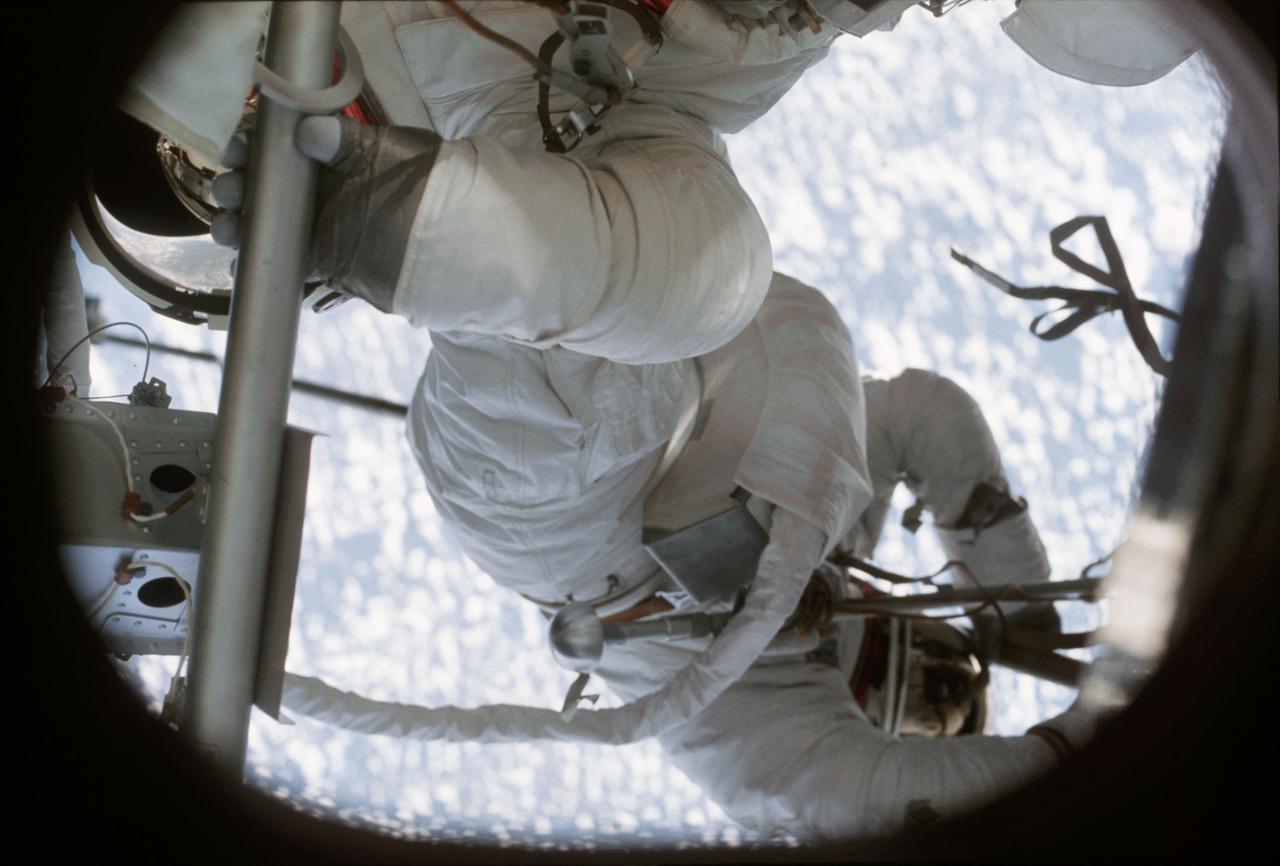

SL2-100-799 (7 June 1973) --- This medium close-up view shows astronauts Charles Conrad, commander for Skylab 2, and Science Pilot Joseph P. Kerwin performing an extravehicular activity (EVA) to repair the damaged and partially deployed solar array system on the Skylab complex. The photo was taken from inside the Orbital Workshop (OWS) by astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. Photo credit: NASA
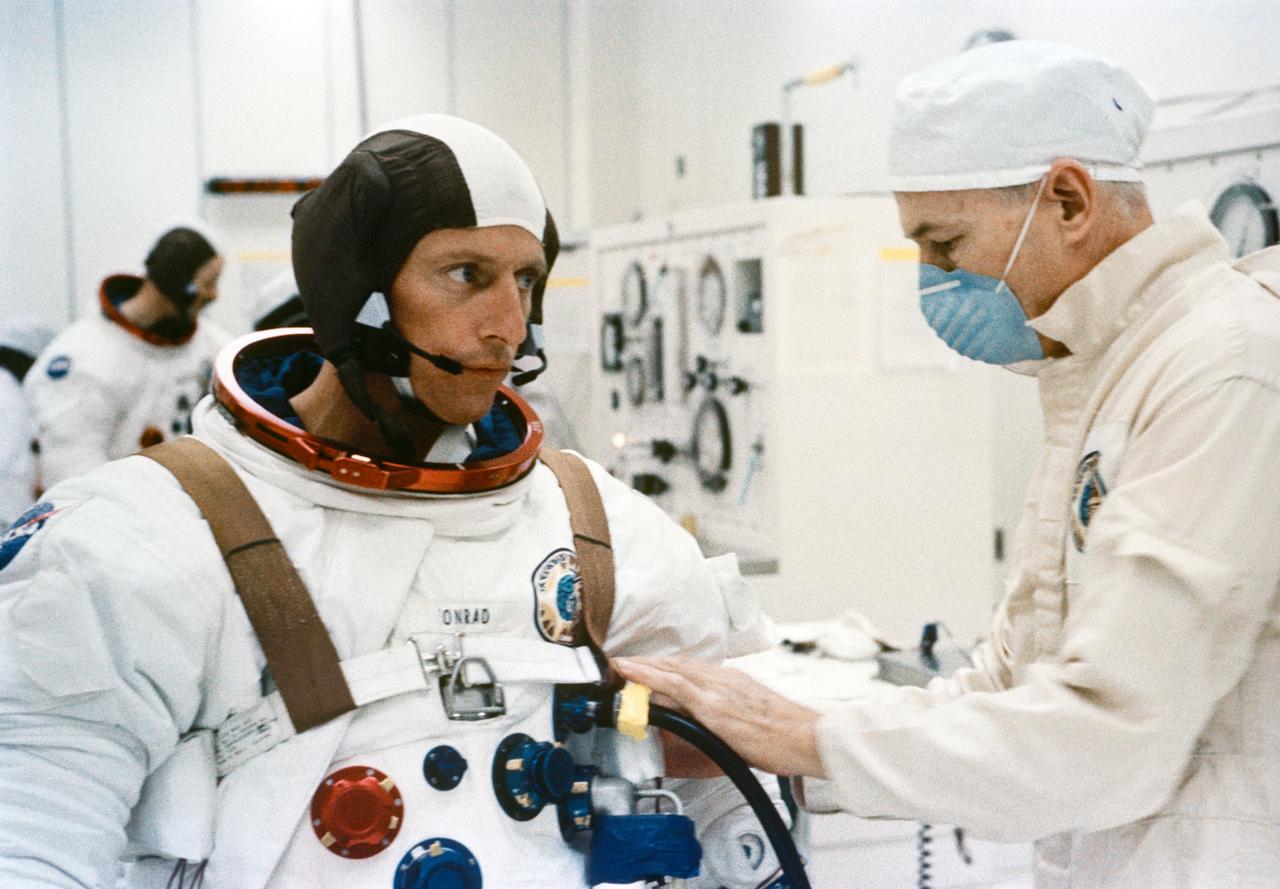
S73-25901 (25 May 1973) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the Skylab 2 mission, is suited up in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building at the Kennedy Space Center during Skylab 2 prelaunch preparations. Skylab 2, with astronauts Conrad, Joseph P. Kerwin and Paul J. Weitz aboard, was launched from KSC's Pad B, Launch Complex 39, at 9:00 a.m. (EDT), May 25, 1973. Photo credit: NASA
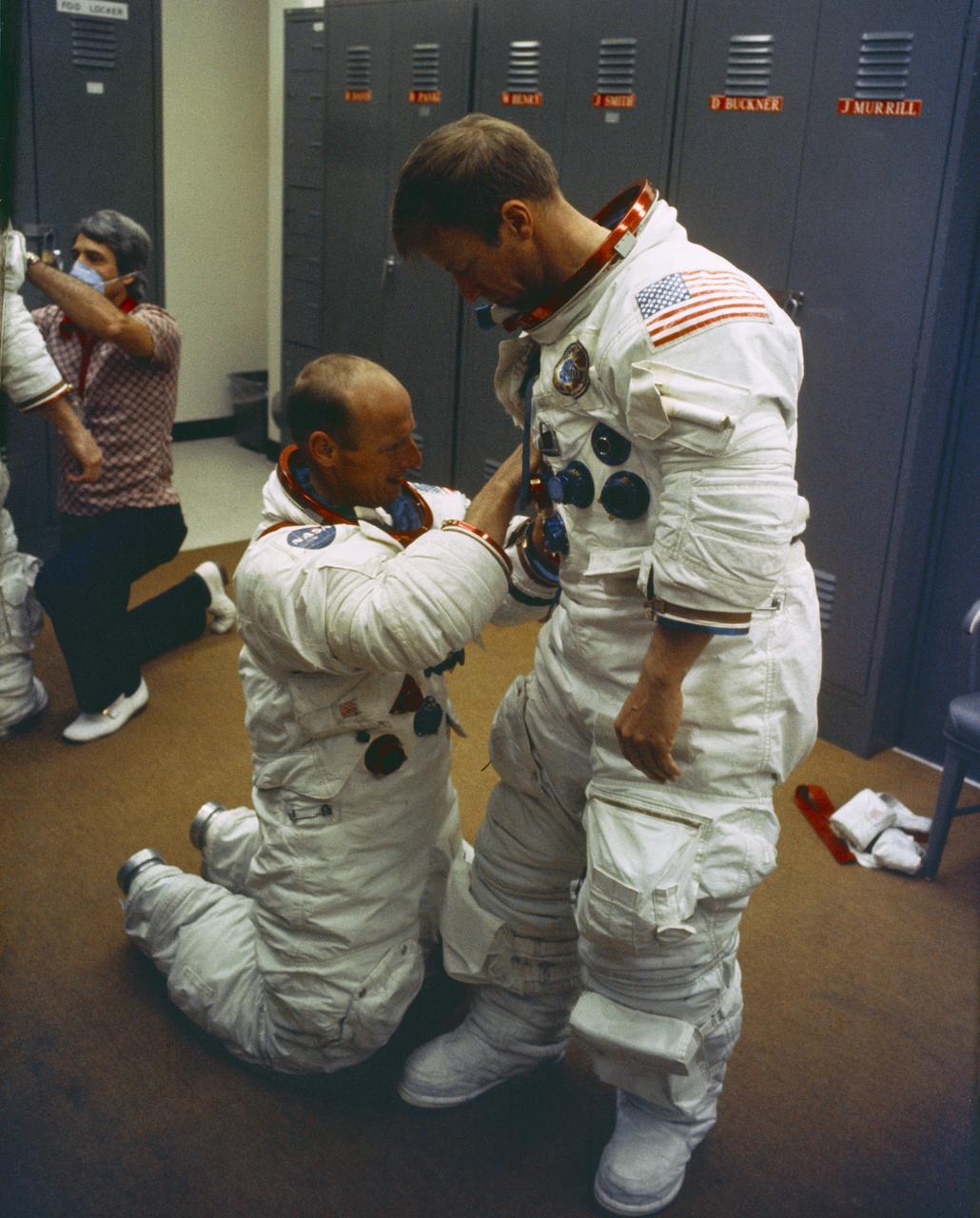

S73-25399 (8 May 1973) --- Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, prime crew pilot of the first manned Skylab mission, is suited up in Bldg. 5 at Johnson Space Center (JSC) during prelaunch training activity. He is assisted by astronaut Charles Conrad, Jr., prime crew commander. The man in the left background is wearing a face mask to insure that Conrad, Joseph Kerwin and Weitz are not exposed to disease prior to launch. Photo credit: NASA
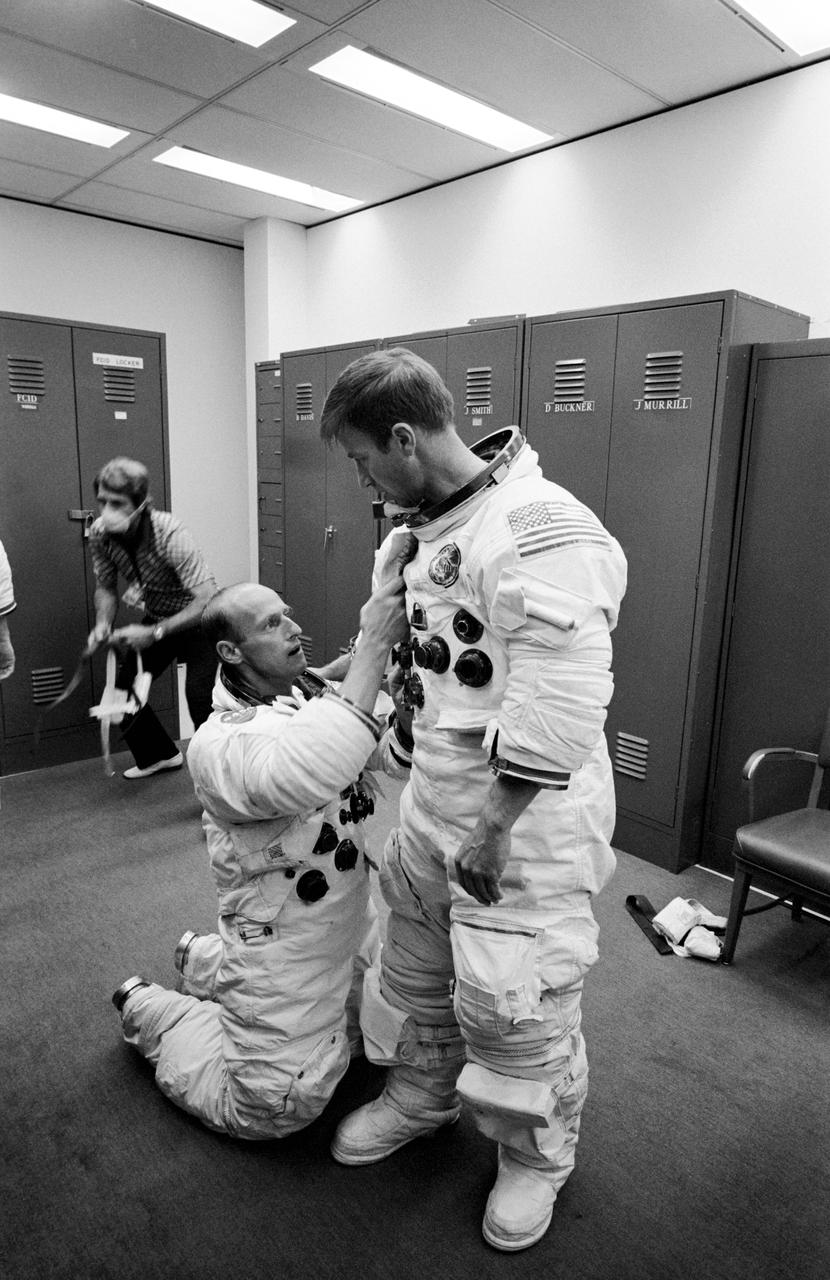

S73-25283 (8 May 1973) --- Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, prime crew pilot of the first manned Skylab mission, is suited up in Bldg. 5 at Johnson Space Center during prelaunch training activity. He is assisted by astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., prime crew commander. The man in the left background is wearing a face mask to insure that Conrad, Joseph Kerwin and Weitz are not exposed to disease prior to launch. Photo credit: NASA
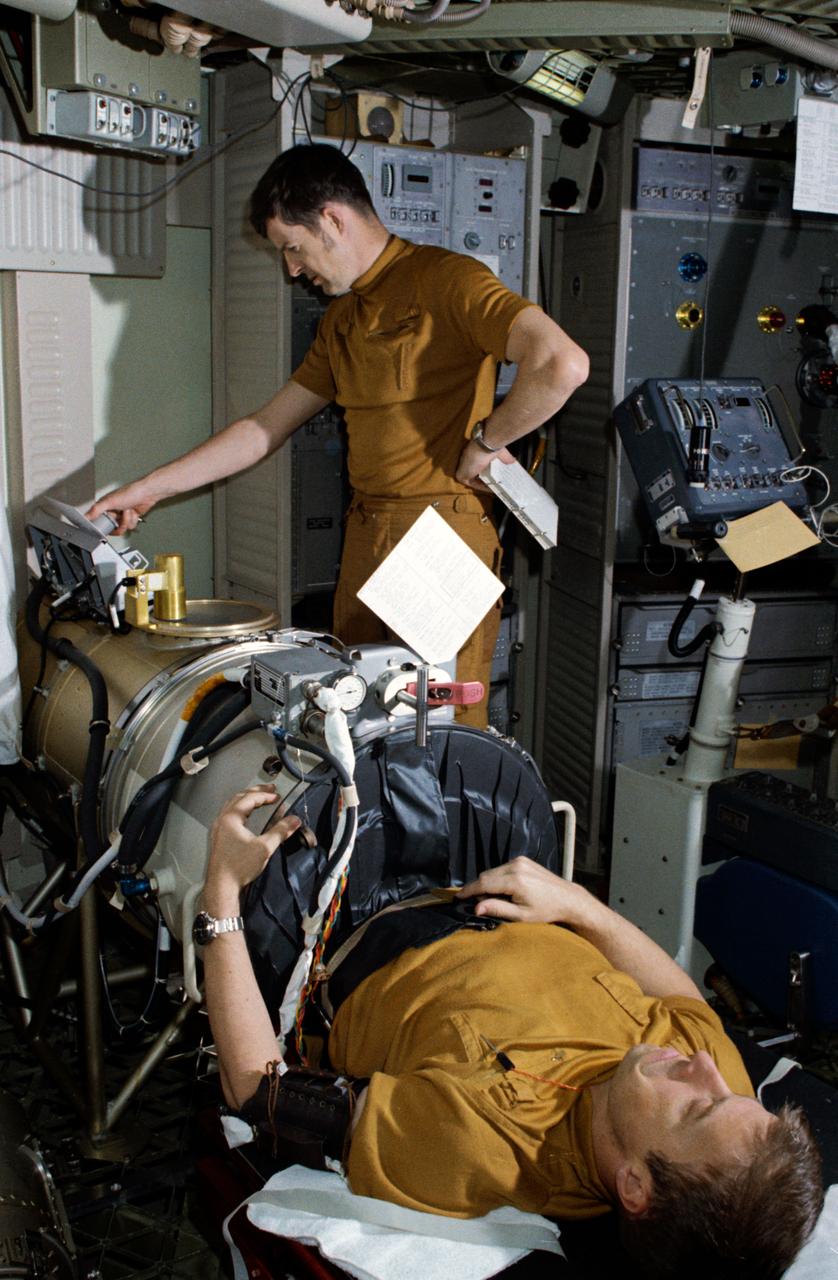

S73-20276 (1 March 1973) --- Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot of the first manned Skylab mission, lies in the lower body negative pressure device during Skylab training at Johnson Space Center. Operating the controls in the background is scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot of the mission. They are in the work and experiments area of the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer at JSC. Photo credit: NASA
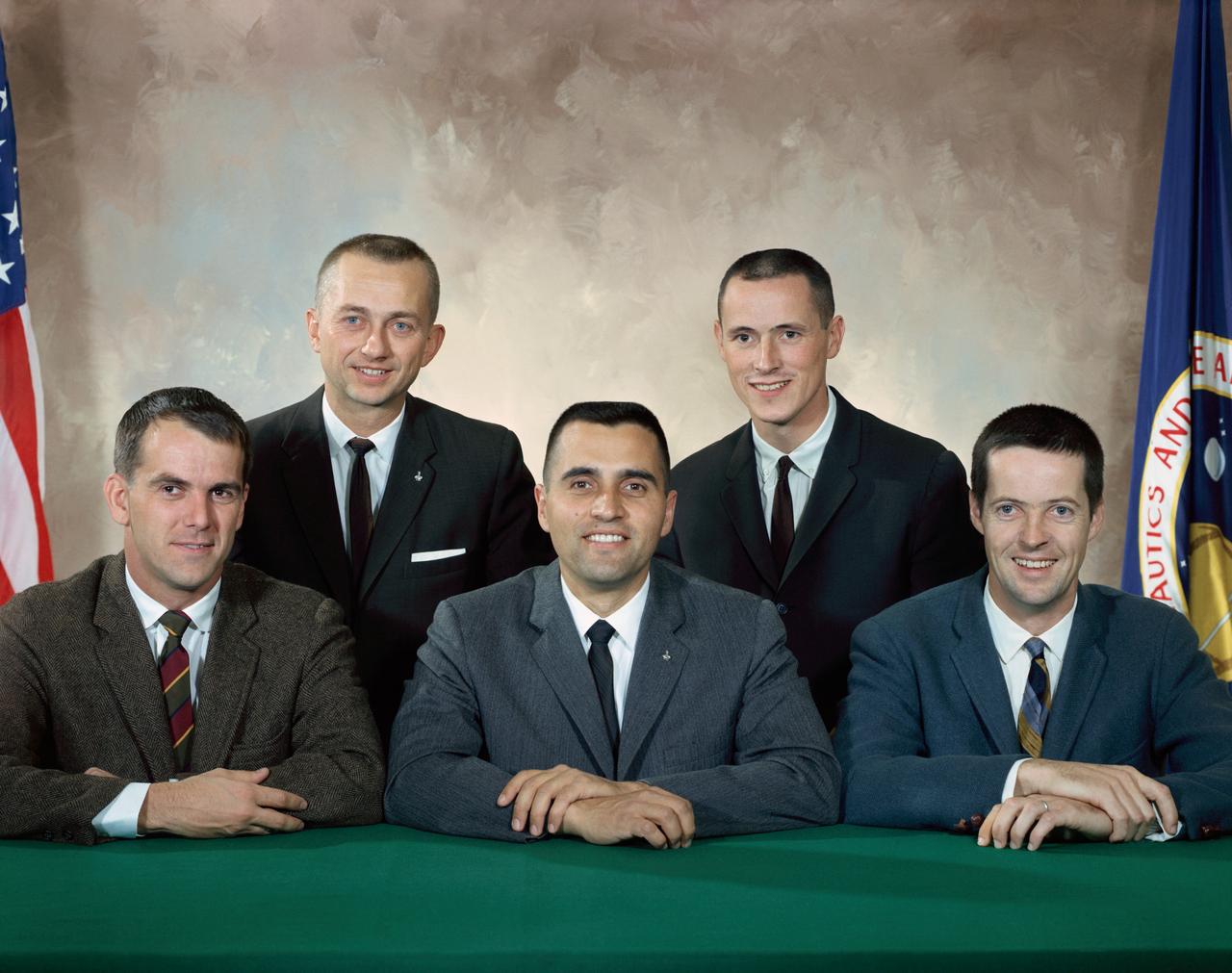

S66-65248 (November 1966) --- Five scientist-astronauts whose selection was announced by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration on June 29, 1969. Front row, left to right, are P. Curtis Michel,(physicist); Harrison H. Schmitt (astrogeologist); and Joseph F. Kerwin (physician). Back row, left to right, are Owen K. Garriott (physicist); and Edward G. Gibson (physicist). Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
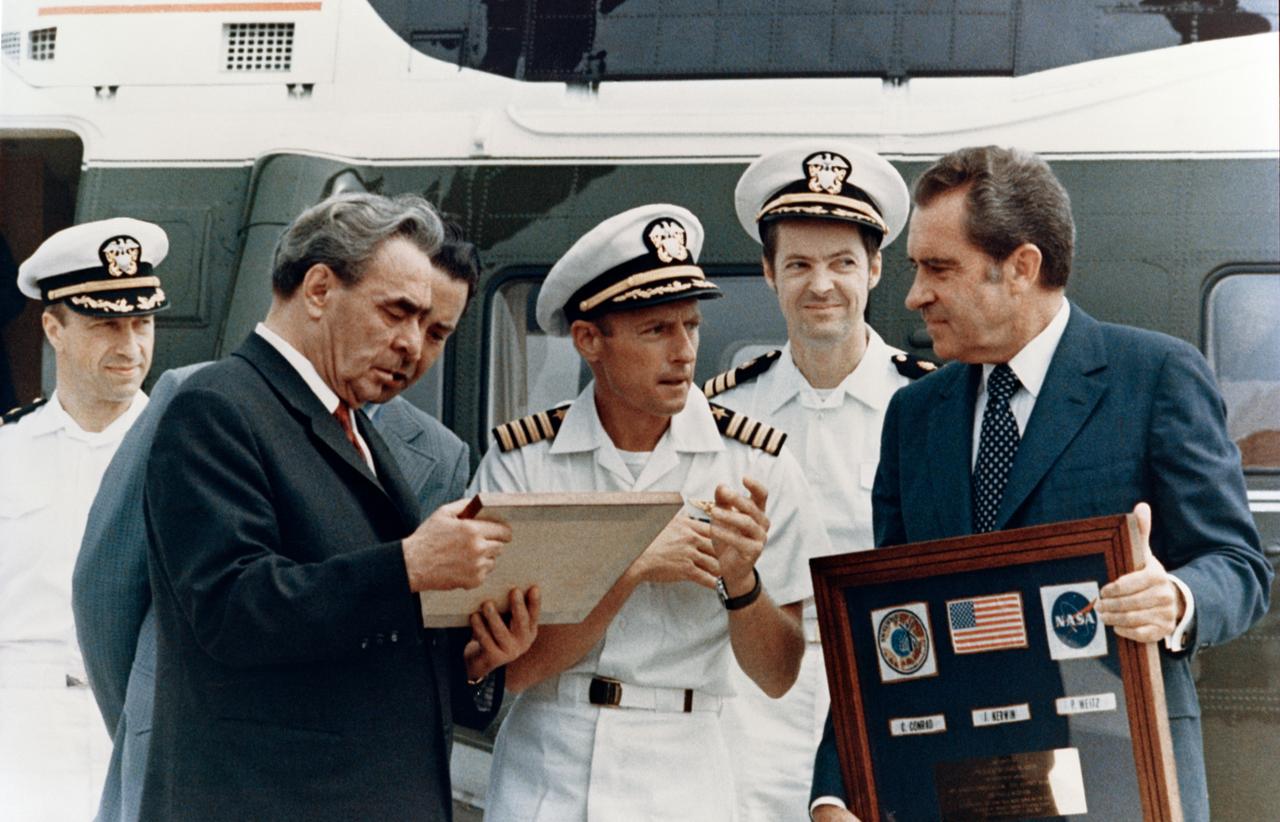

S73-30889 (June 1973) --- Leonid I. Breznev, General Secretary of the Communist Party, Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, and President Richard M. Nixon, during ceremonies at the Western White House in San Clemente, California, examine plaques presented by Skylab astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., center; Joseph P. Kerwin, second from right; and Paul J. Weitz, left. Photo credit: NASA
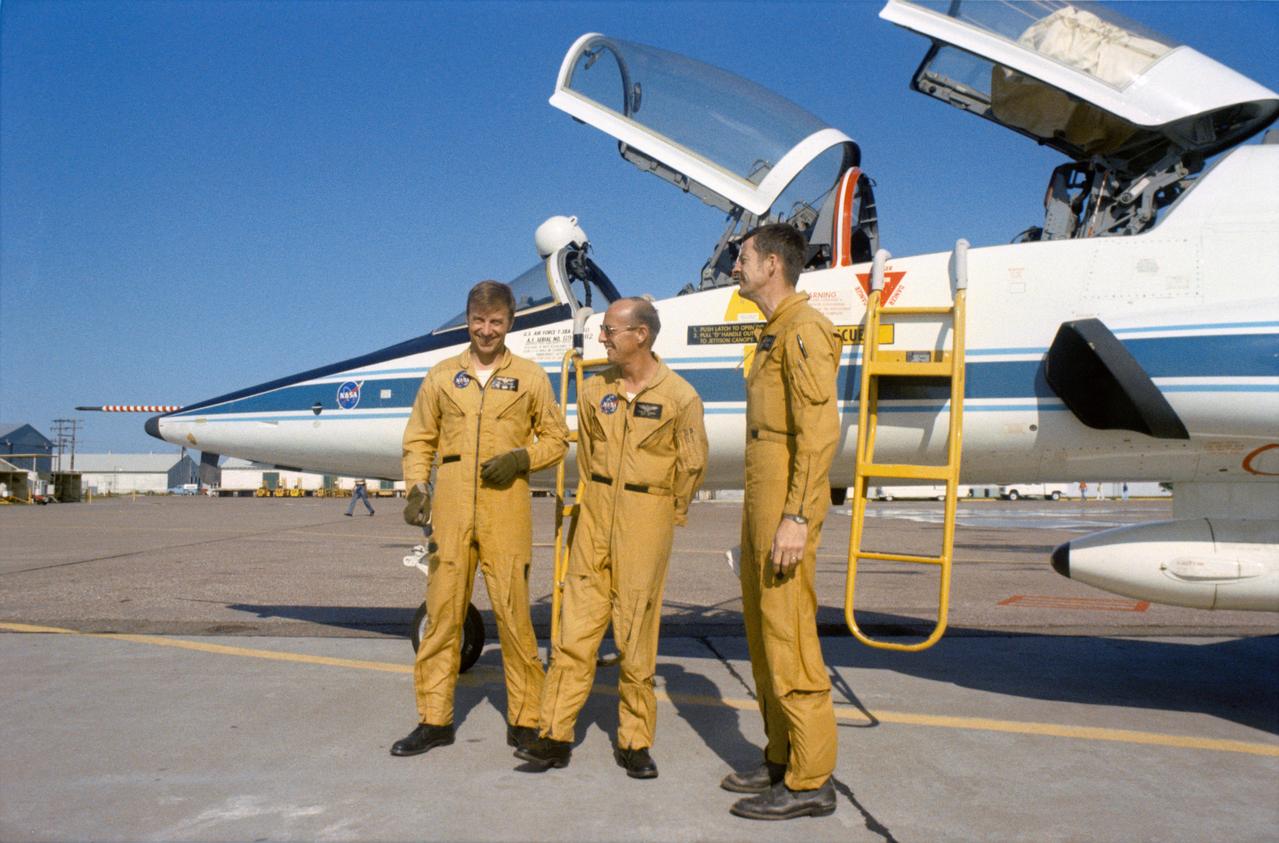

S73-25714 (13 May 1973) --- Members of the prime crew of the first manned Skylab Mission (Skylab 2) stand beside a NASA T-38 jet aircraft trainer at nearby Ellington Air Force Base prior to take off for the Kennedy Space Center, Florida. They are (left to right) astronauts Paul J. Weitz, mission pilot; Charles Conrad Jr., commander; and scientist Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot. The three crewmen have completed their prelaunch training at JSC. Photo credit: NASA

DISCUSSING THEIR EXPERIENCES AND MEMORIES WITH THE MARSHALL TEAM AT THE 40TH ANNIVERSARY CELEBRATION OF SKYLAB JAN. 31 ARE, FROM LEFT, FORMER SKYLAB ASTRONAUTS ED GIBSON, SKYLAB 4 SCIENCE POLOT; PAUL WEITZ, SKYLAB 2 PILOT; WILLIAM POGUE, SKYLAB 4 PILOT; GERALD CARR, SKYLAB 4 COMMANDER; AND JOSEPH KERWIN, SKYLAB 2 SCIENCE PILOT
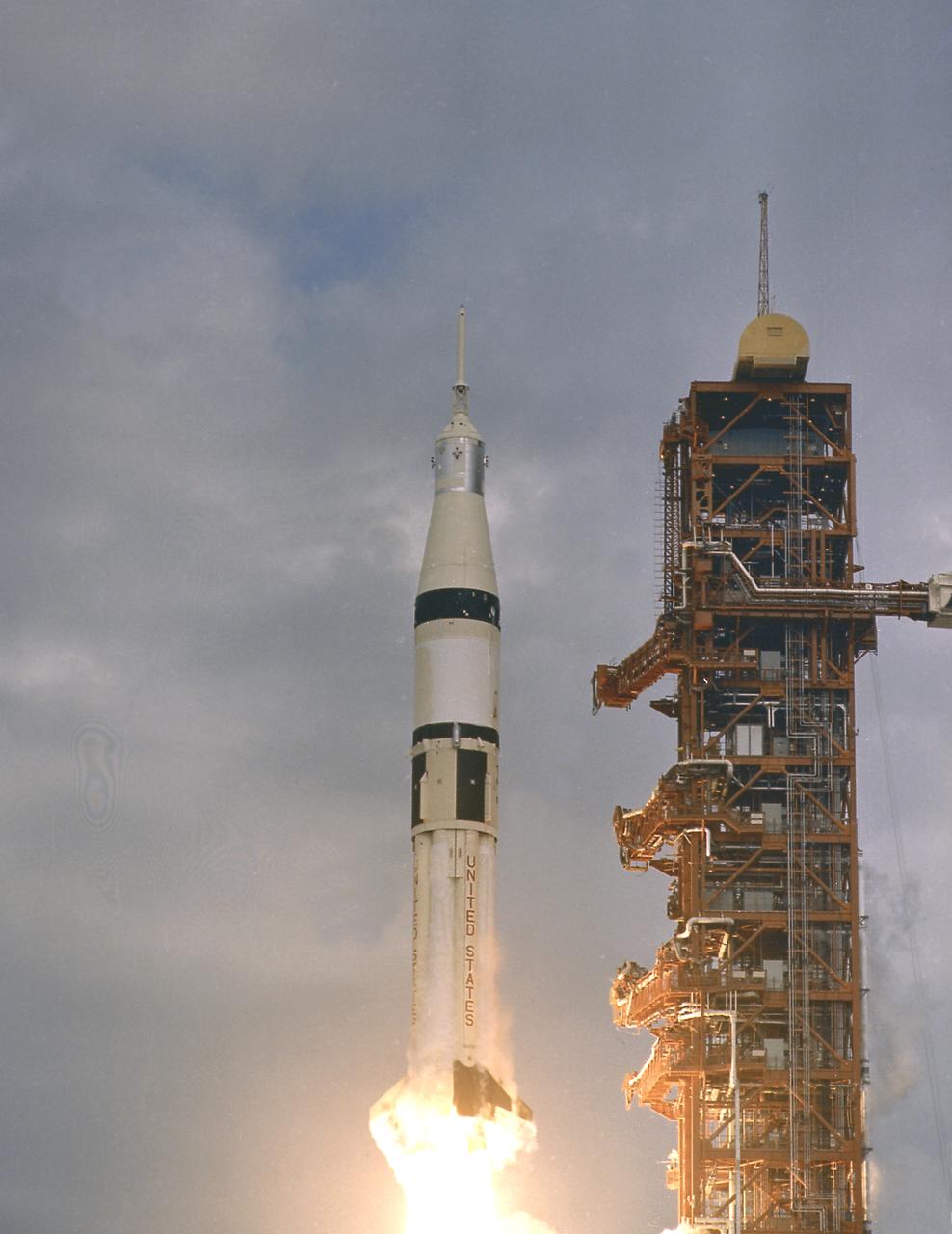
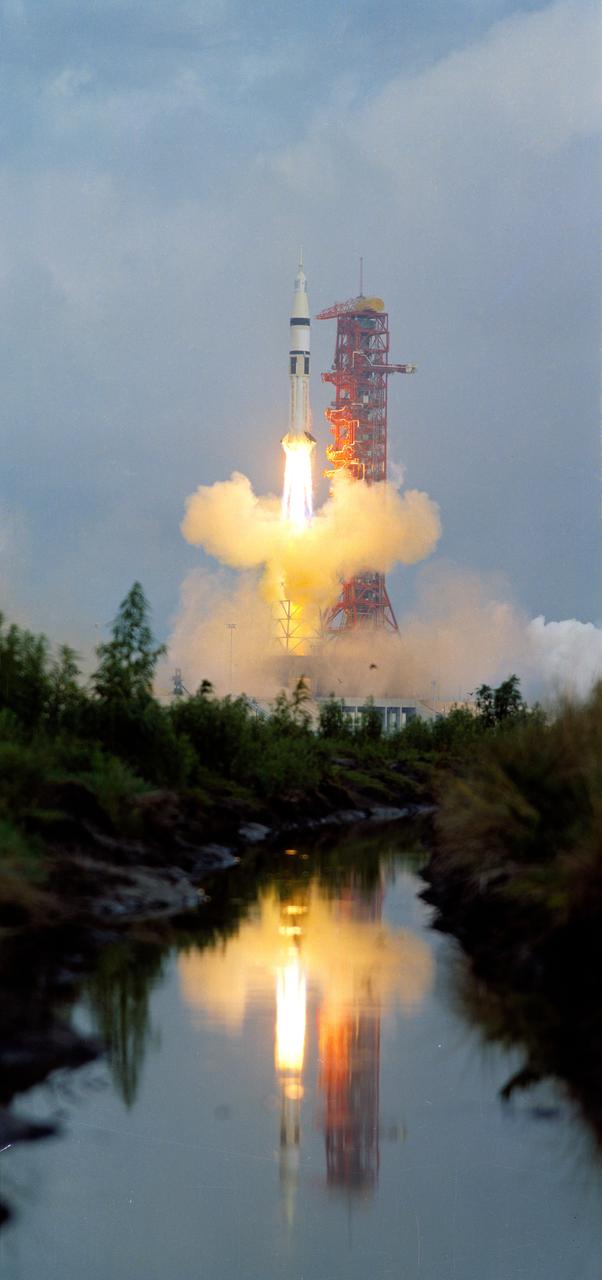
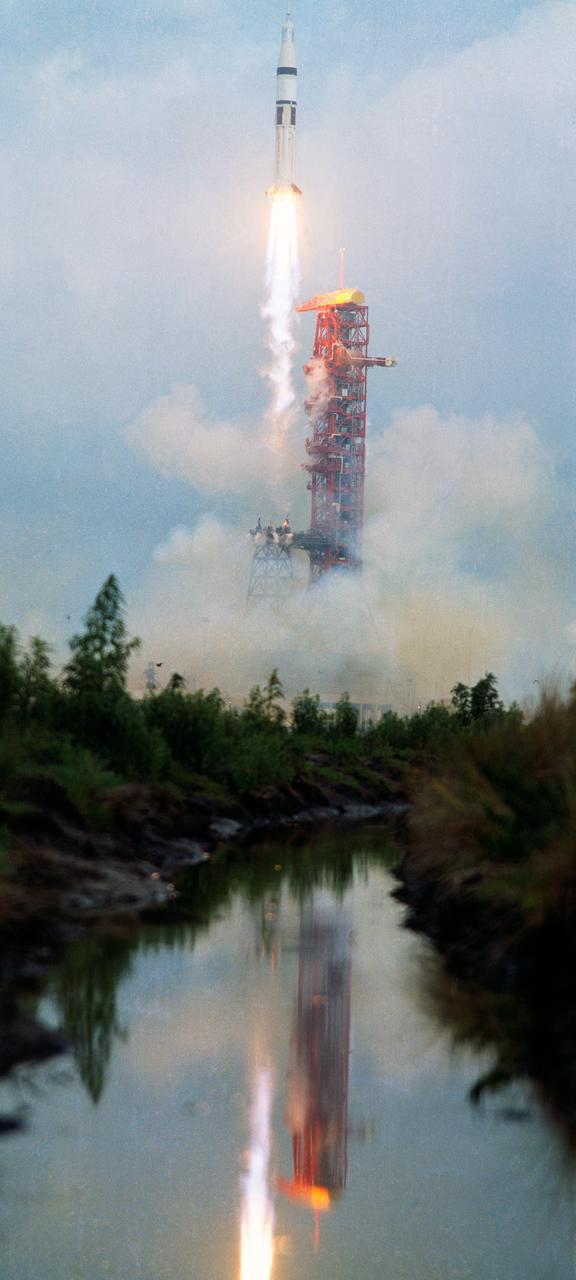
SA-206 lifts off from Kennedy Space Center's launch complex 39B, in Florida, on May 25, 1973, for the first manned Skylab mission (SL-2) with astronauts Pete Conrad, Joseph Kerwin, and Paul Weitz. The Saturn IB, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), launched five manned Earth-orbital missions between 1968 and 1975: Apollo 7, Skylab 2, Skylab 3, Skylab 4, and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP).
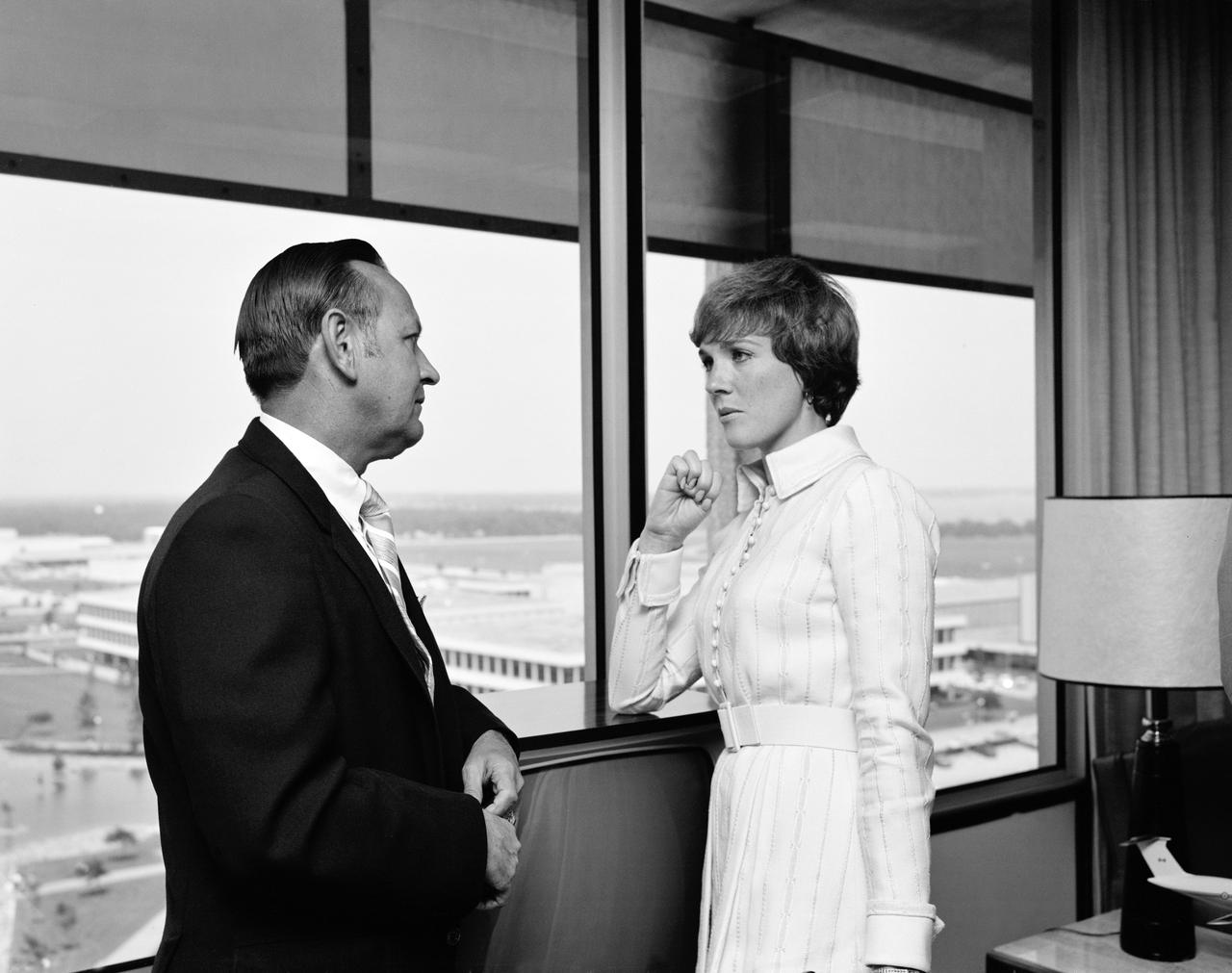

Views of Julie Andrews as she and her entourage visit MSC with Astronauts Thomas Stafford and Joe Kerwin; Public Affairs Officer Brian Duff; James McLane, Bldg. 32; and, Dr. Christopher C. Kraft. 1. KRAFT, C. C., DR. - JULIE ANDREWS TOUR 2. ANDREWS, JULIE - TOUR MSC, HOUSTON, TX

S73-27095 (25 May 1973) --- The Skylab 2 crew, consisting of astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., Joseph P. Kerwin and Paul J. Weitz, inside the command module atop a Saturn IB launch vehicle, heads toward the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The command module was inserted into Earth orbit approximately 10 minutes after liftoff. The three represent the first of three crews who will spend record-setting durations for human beings in space, while performing a variety of experiments. Photo credit: NASA

S73-27096 (25 May 1973) --- The Skylab 2 crew, consisting of astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., Joseph P. Kerwin and Paul J. Weitz, inside the command module atop a Saturn IB launch vehicle, heads toward the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The command module was inserted into Earth orbit approximately 10 minutes after liftoff. The three represent the first of three crews who will spend record-setting durations for human beings in space, while performing a variety of experiments. Photo credit: NASA

S72-52630 (February 1972) --- This is the emblem for the first manned Skylab mission. It will be a mission of up to 28 days. Skylab is an experimental space station consisting of a 100-ton laboratory complex in which medical, scientific and technological experiments will be performed in Earth orbit. The prime crew of this mission will be astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander; scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot; and astronaut Paul J. Weits, pilot. The patch, designed by artist Kelly Freas, shows the Skylab silhouetted against the Earth's globe, which in turn is eclipsing the sun--showing the brilliant signet-ring pattern of the instant before the total eclipse. Photo credit: NASA

S73-27262 (1 June 1973) --- The three Skylab 2 crewmen give a demonstration on the effects of weightlessness in the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 and 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station. Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., Joseph P. Kerwin and Paul J. Weitz are crouched in a fast-start stance to race around the dome area of the OWS forward compartment. The astronauts had ease of motion and good maneuverability in the zero-gravity of space. Photo credit: NASA

S73-27730 (June 1973) --- The Skylab 2 crewmen, astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., Joseph P. Kerwin and Paul J. Weitz, move the S183 Ultraviolet Panorama astrophysics experiment equipment under zero-gravity conditions in space in the foreground compartment of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 & 2 space station in Earth orbit, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station. The S183 equipment includes the S183 spectrograph, the S019 mirror assembly, and a Maurer camera. Photo credit: NASA
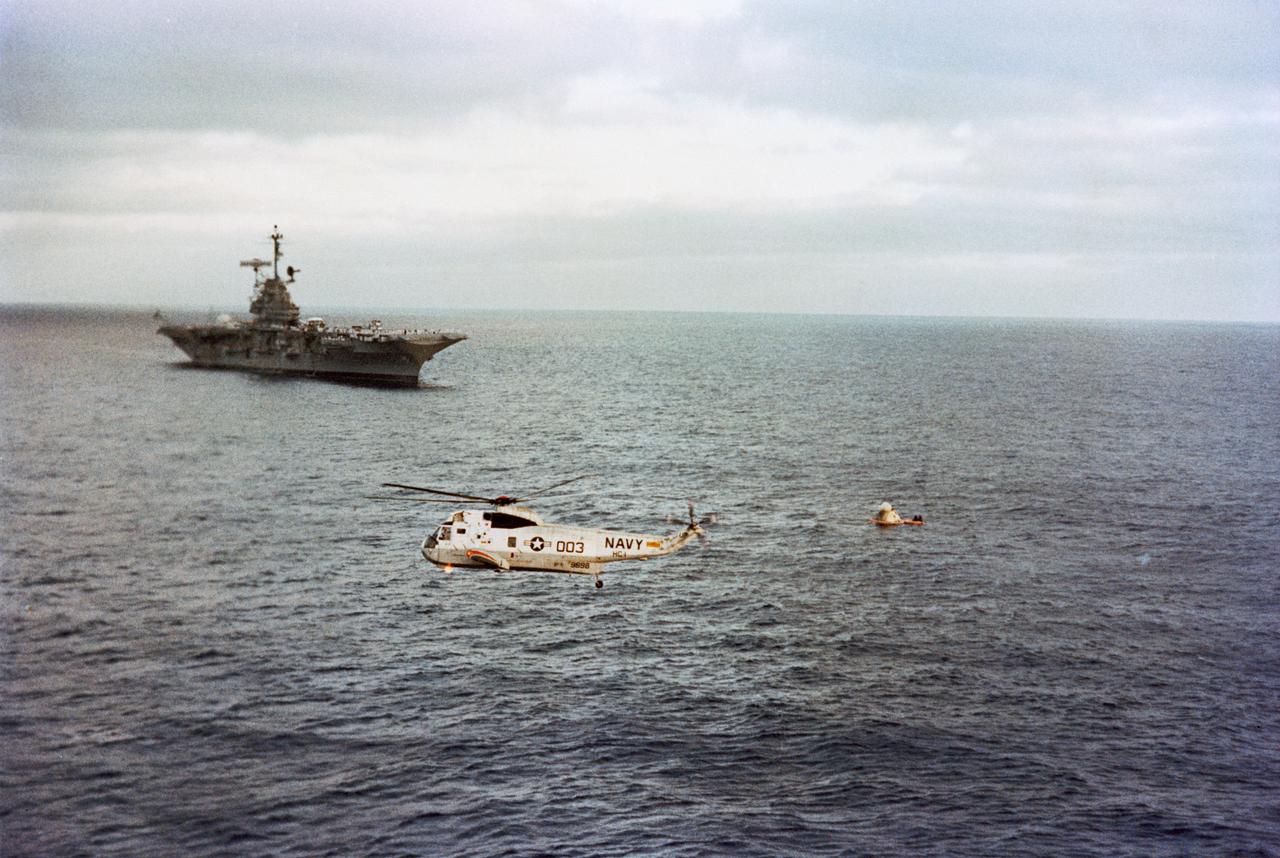

S73-29147 (22 June 1973) --- The Skylab 2 Command Module, with astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., Joseph P. Kerwin and Paul J. Weitz still inside, floats in the Pacific Ocean following successful splashdown about 835 miles southwest of San Diego, California. The prime recovery ship, USS Ticonderoga, approaches from the left background. A recovery helicopter hovers in the foreground. The three Skylab 2 crewmen had just completed a 28-day stay with the Skylab 1 space station in Earth orbit conducting numerous medical, scientific and technological experiments. Photo credit: NASA
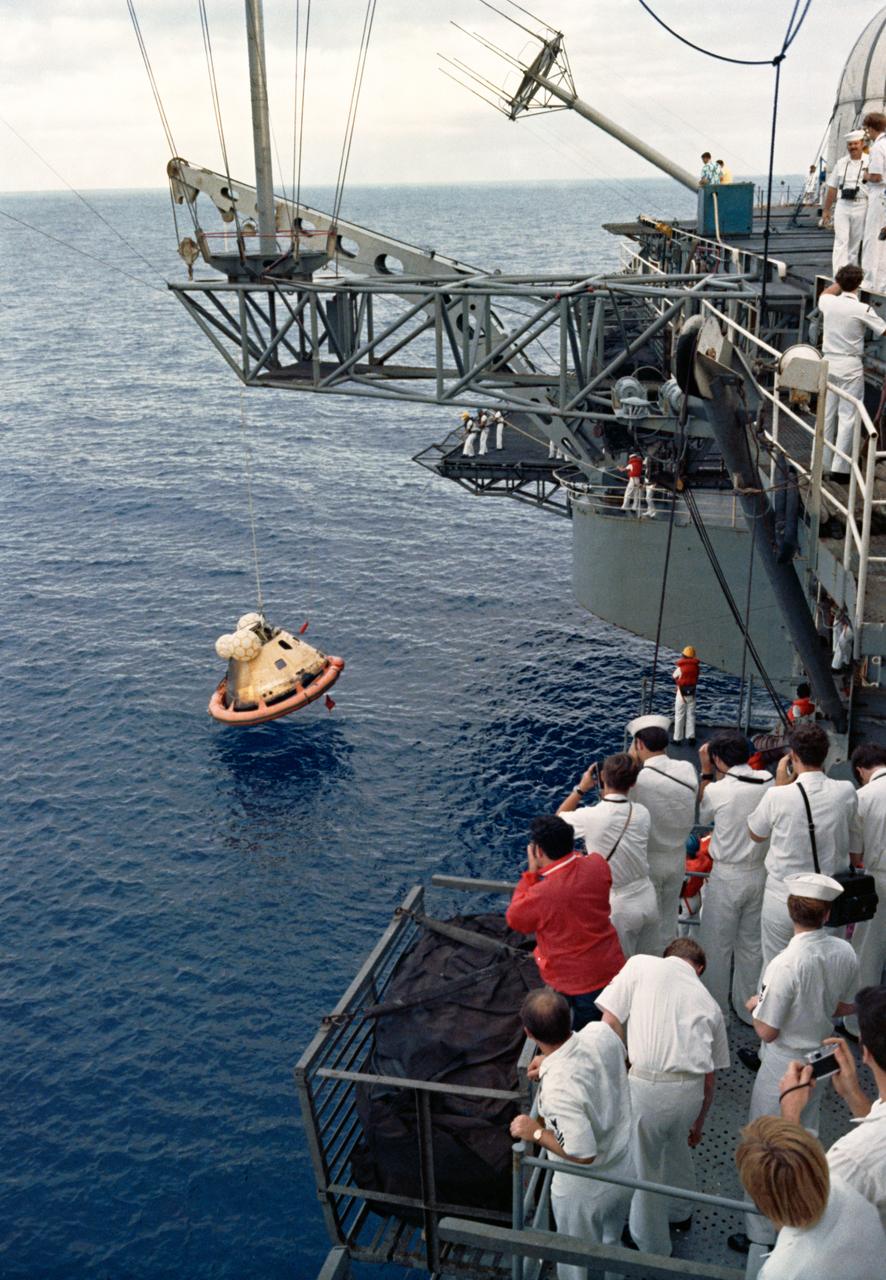

S73-29138 (22 June 1973) --- The Skylab 2 Command Module, with astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., Joseph P. Kerwin and Paul J. Weitz still inside, is hoisted aboard the prime recovery ship, USS Ticonderoga, following successful splashdown in the Pacific Ocean about 835 miles southwest of San Diego, California. The crewmen had just completed a 28-day stay with the Skylab 1 space station in Earth orbit conducting numerous medical, scientific and technological experiments. Note the inflated bags and the floatation collar on the spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA
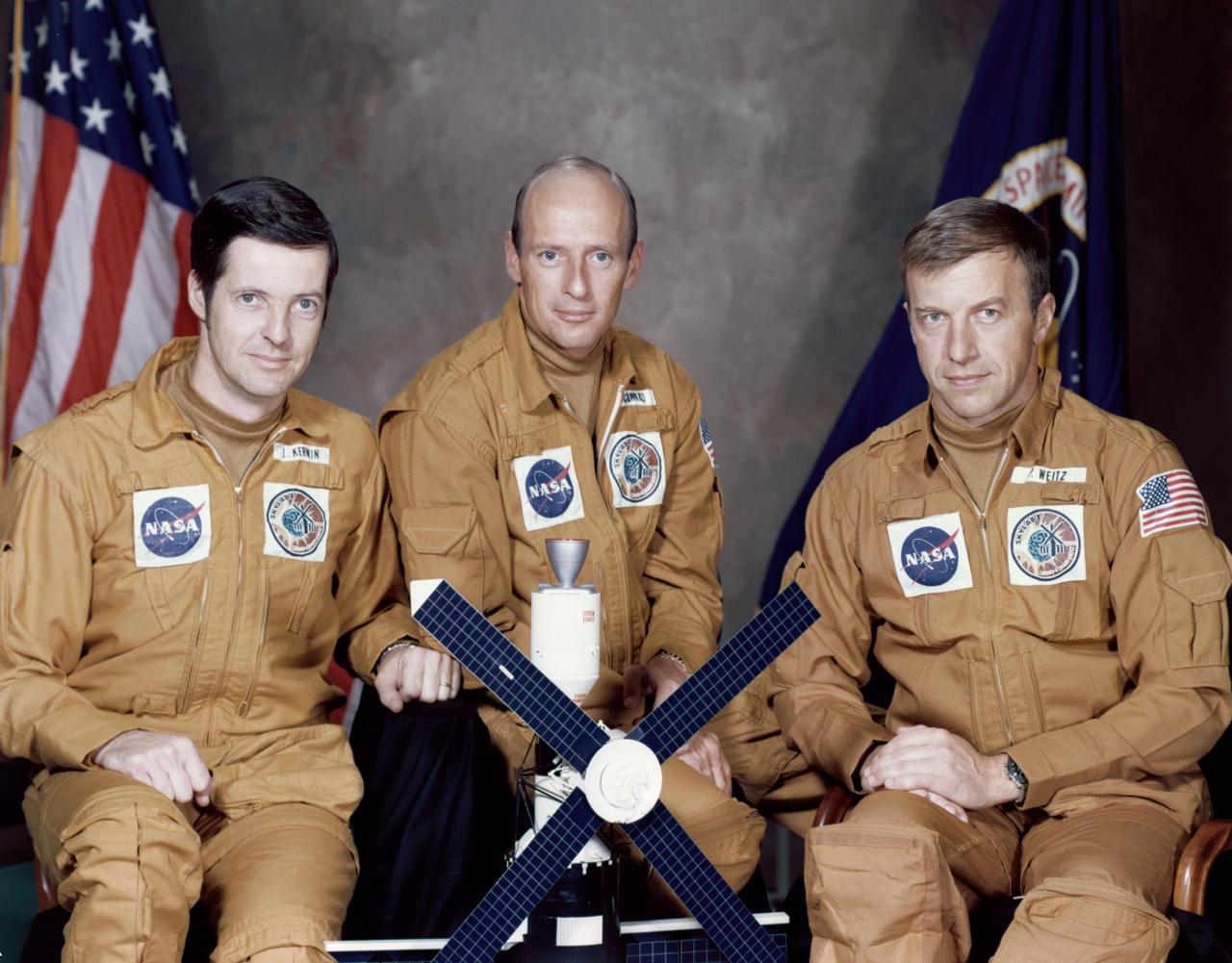

S73-24303 (May 1973) --- These three astronauts have been named by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration as the prime crew of the first manned Skylab mission. They are, left to right, Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot; Charles Conrad Jr., commander; and Paul J. Weitz, pilot. Skylab is a three-part program consisting of one 28-day and two 56-day manned visits spanning an eight-month period. One day prior to the launch of this crew, the unmanned Skylab space station cluster will be launched and placed in Earth orbit. The first manned mission will last up to 28 days. Photo credit: NASA
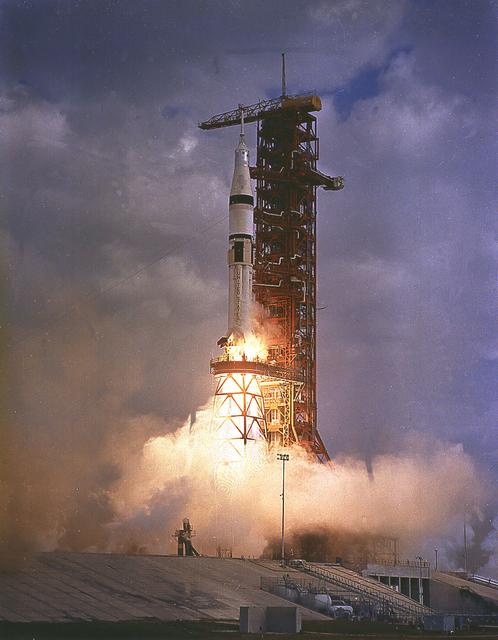
This is an image of the Saturn IB vehicle that lifted off on May 25, 1973, carrying the crew of the Skylab-2 (SL-2) mission. The Saturn IV launch vehicle was used to carry a crew of three astronauts to the Skylab. The SL-2 mission launched the first crew to the Skylab; astronauts Charles "Pete" Conrad, Joseph Kerwin and Paul Weitz. This crew made urgent repair work on the damaged Skylab to make it operational and habitable. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The duration of this mission was 28 days.

A metal strap became tangled over one of the folded solar array panels when Skylab lost its micro meteoroid shield during its launch. Cutters like the ones used to free the solar array were used to cut the ribbon opening to the public a new full-scale Skylab cluster exhibit at the Alabama Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Wielding the cutters are (left to right): Alabama Senator James B. Allen; Marshall Space Flight Center director, Dr. William R. Lucas, Huntsville Mayor, Joe Davis; Madison County Commission Chairman, James Record (standing behind Mayor Davis); and chairman of the Alabama Space Science Exhibit Commission, Jack Giles. Astronauts Conrad and Kerwin used the same type of tool in Earth orbit to cut the aluminum strap which jammed the Skylab solar array.
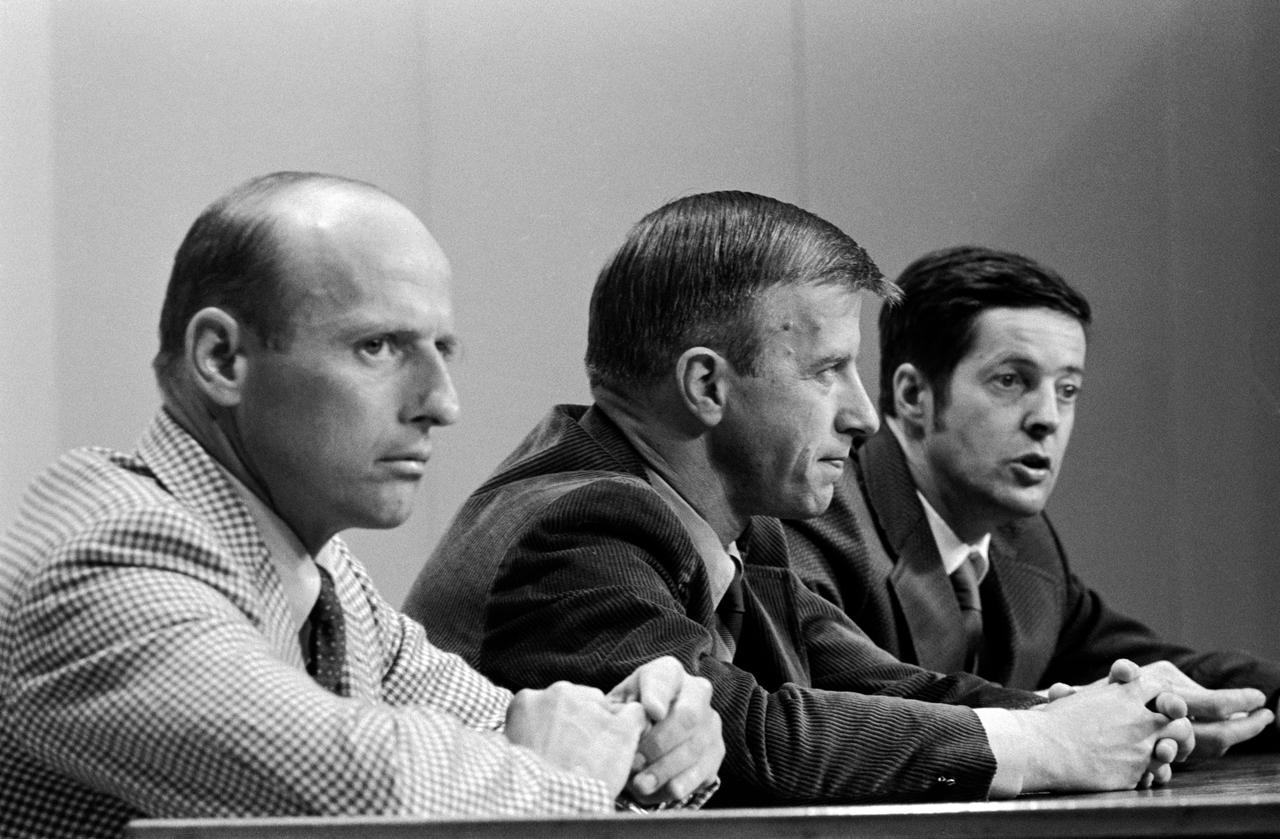

S73-24369 (17 April 1973) --- The three members of the prime crew of the first manned Skylab mission discuss their scheduled flight before a gathering of news media representatives, in building 1 auditorium, April 17, 1973. They are (left to right) astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander; Paul J. Weitz, pilot; and scientist Joseph P. Kerwin, science-pilot. Skylab is a three-part program consisting of one 28-day; and two 56-day manned visits spanning an eight-month period. One day prior to the launch of this crew, the unmanned Skylab Space Station cluster will be launched and placed in Earth orbit. The first manned mission will last up to 28 days. Photo credit: NASA
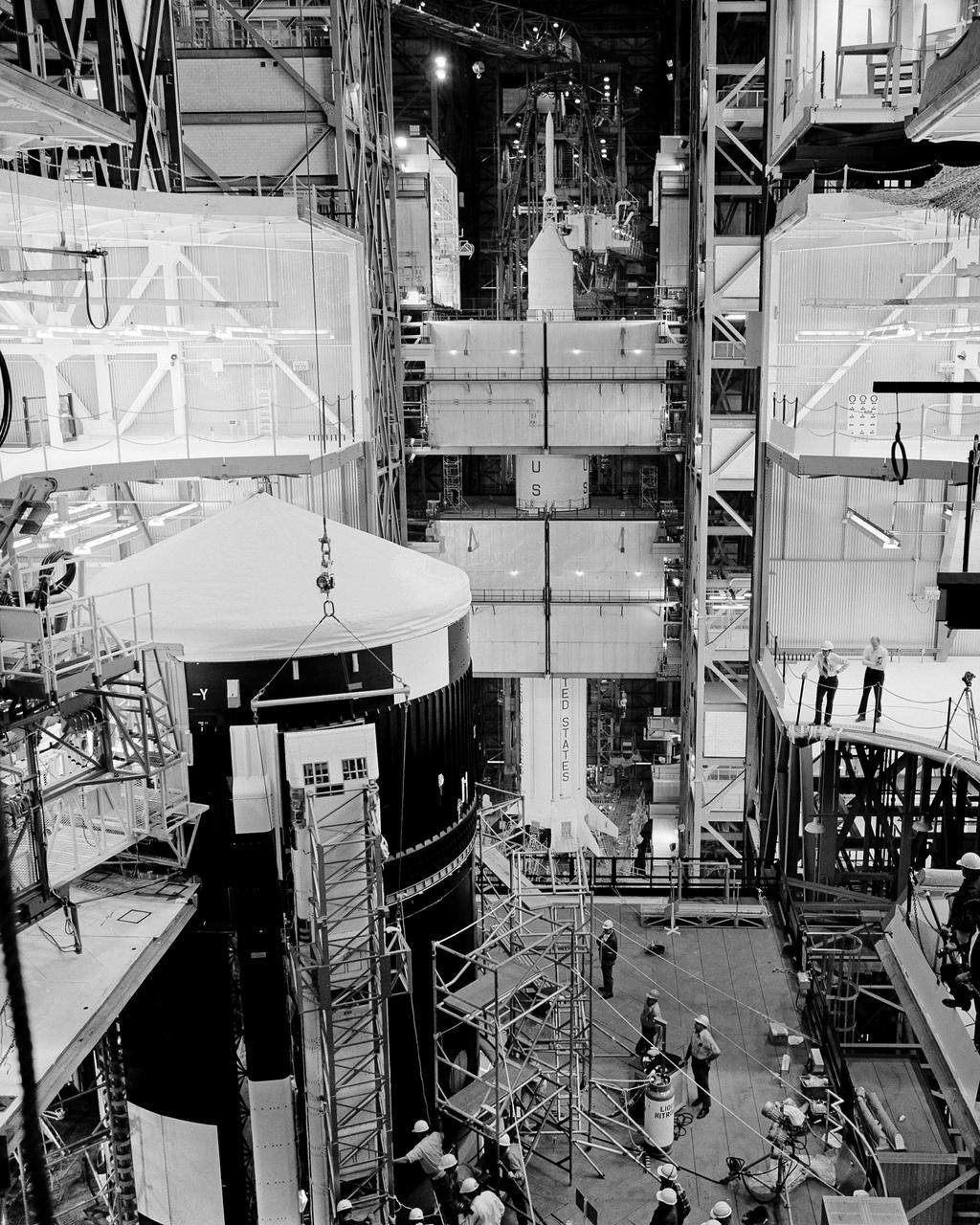
CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of Skylab 1's solar cell arrays is installed on the orbital space station in High Bay 2 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Skylab 2 launch vehicle is in high bay 1, visible in the background. Each of the two solar cell arrays on the space station that will be deployed in orbit is designed to provide 10,500 watts of power. All power needed to operate the station and the Apollo Telescope mount will be taken from the arrays. Each array will have almost 1,177 square feet of surface area to turn sunlight into electrical power. Skylab 1 is schedule for launch April 30, 1973 and Skylab 2, carrying the astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., Dr. Joseph P. Kerwin and Paul J. Weitz to dock with the space station and enter it to live and work for 28 days, will be launched a day later. Photo Credit: NASA
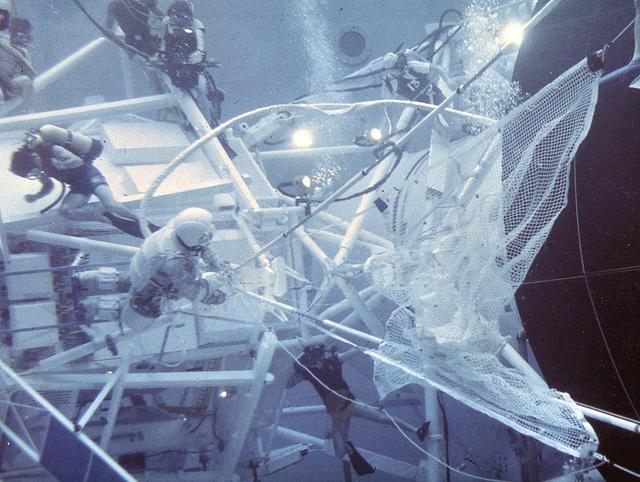

After its launch on May 14, 1973, it was immediately known that there were some major problems with Skylab. The large, delicate, meteoroid shield on the outside of the workshop was ripped off by the vibration of the launch. Its tearing off caused serious damage to the two wings of solar cells that were to supply most of the electric power to the workshop. Once in orbit, the news worsened. The loss of the big shade exposed the metal skin of the workshop to the sun. Internal temperatures soared to 126 degrees F. This heat not only threatened its habitation by astronauts, but if prolonged, would cause serious damage to instruments and film. After twice delaying the launch of the first astronaut crew, engineers worked frantically to develop solutions to these problems and salvage the Skylab. After designing a protective solar sail to cover the workshop, crews needed to practice using the specially designed tools and materials to facilitate the repair procedure. Marshall Space Flight Center's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS), was used to practice these maneuvers. Pictured here are the astronauts in the NBS deploying the protecticve solar sail. On may 25, 1973, an Apollo command and service module was launched and later docked with Skylab. The next day, astronauts Conrad and Kerwin were able to complete the needed repairs to Skylab, salvaging the entire program.
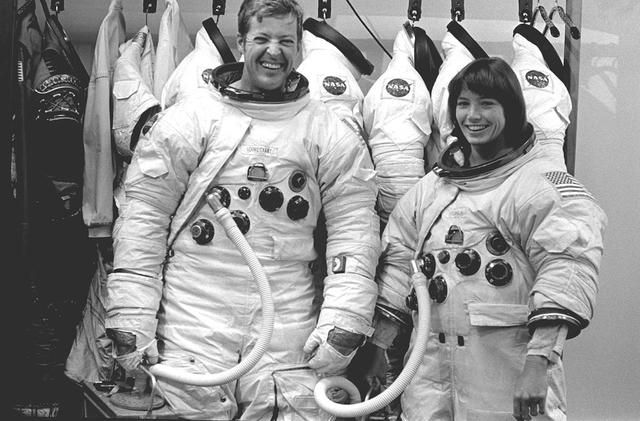

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) that served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown are astronauts Arna Fisher and Joe Kerwin training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument changeout.
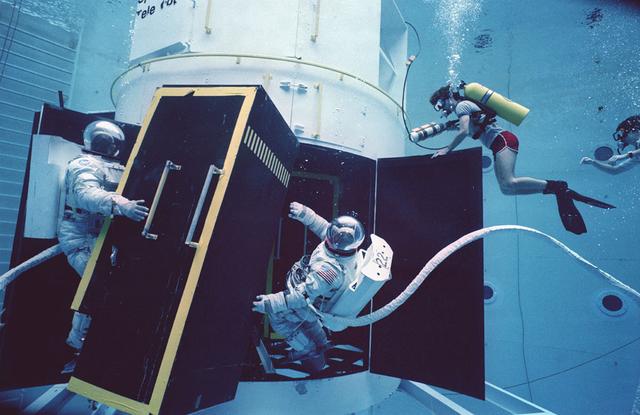
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) that served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown are astronauts Arna Fisher and Joe Kerwin training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument changeout.

S73-27508 (6 June 1973) --- An artist's concept showing astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Skylab 2 commander, attempting to free the solar array system wing on the Orbital Workshop during extravehicular activity at the Skylab 1 & 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit. The astronaut in the background is Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot. Here, Conrad is pushing up on the Beam Erection Tether (BET) to raise the stuck solar panel. The solar wing is only partially deployed; an aluminum strap is believed to be holding it down. Note the cut aluminum angle. Attach points for the BET are on the vent module of the solar array beam. The other end of the BET is attached to the "A" frame supporting the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) which is out of view. The aluminum strapping is to be out first, freeing the solar array beam. Then, if the beam does not automatically deploy, Conrad will attempt to help by pulling on the BET. The automatic openers may have become too cold to open without assistance. A deployed solar panel of the ATM is at upper left. The EVA is scheduled for Thursday, June 7th. This concept is by artist Paul Fjeld. Photo credit: NASA
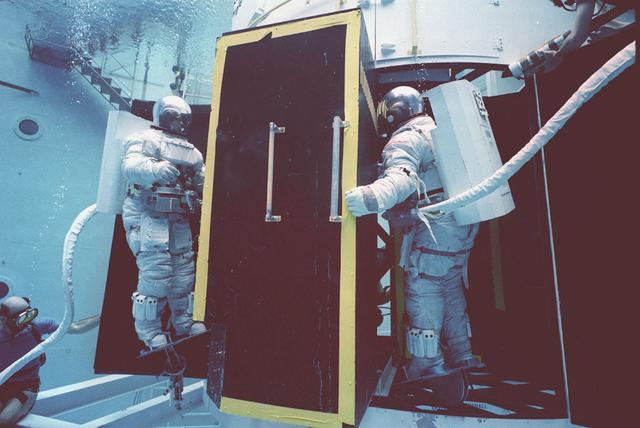

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) that served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown are astronauts Arna Fisher and Joe Kerwin training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument changeout.
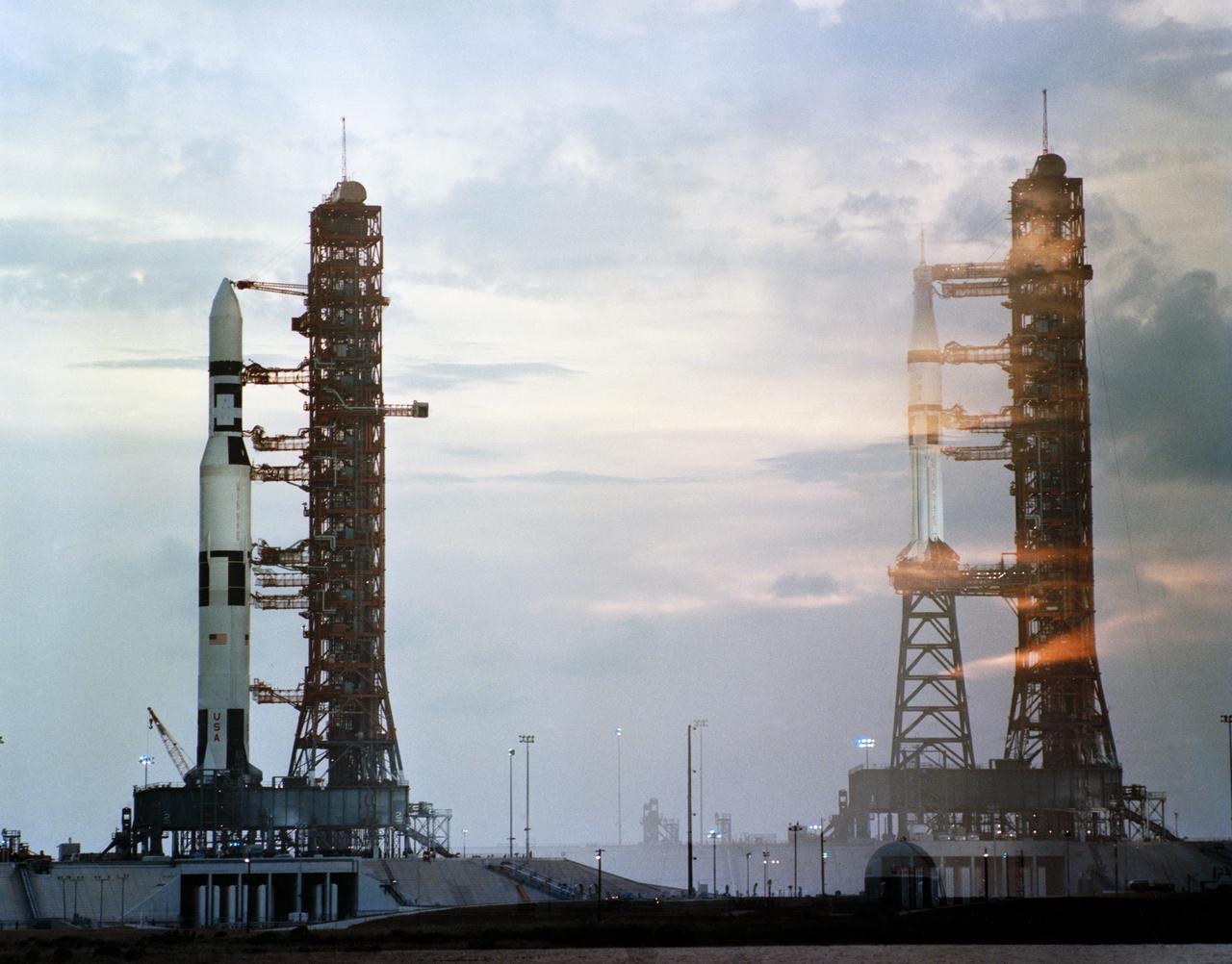

S73-25654 (7 May 1973) --- A deliberate double exposure to help illustrate the comparative sizes and configurations of the Skylab 1 and Skylab 2 space vehicles at Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The double exposure creates an illusion that the rockets are side by side, though actually they are one and a half miles apart. The Skylab 1/ Saturn 1B space vehicle on Pad A is on the left. On the right is the Skylab 2/ Saturn 1B space vehicle on Pad B. The Skylab 1 payload is the space station cluster. The Skylab 2 payload will be an Apollo Command/Service Module (CSM) with astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., Joseph P. Kerwin and Paul J. Weitz aboard. The Saturn V launch vehicle is composed of a Saturn V first (S-1C) stage, a Saturn V second (S-11) stage, and the Skylab payload. The Saturn 1B launch vehicle consists of a Saturn 1B first (S-1B) stage, a Saturn 1B second (S-1VB) stage, and the CSM payload including its launch escape system. Photo credit: NASA

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Skylab space station, atop a modified Saturn V rocket, lifted off May 14, 1973, from Launch Complex 39A, ten minutes later the 100-ton space station reached orbit, where it will be visited by three astronaut crews during the next eight months. The first crew, consisting of Charles Conrad Jr., mission commander, Dr. Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot, and Paul J. Weitz, pilot, will live and work in Skylab nearly a month. NASA directs the Skylab Program, which is designed to gain new knowledge in space for improving life on Earth. Its investigations and experiments will help develop new methods of learning about the Earth's environment and resources. It also will examine man's ability to live and work in space for extended periods, and provide new information about the sun. Two additional manned visits to Skylab will follow in August and November. Photo Credit: NASA