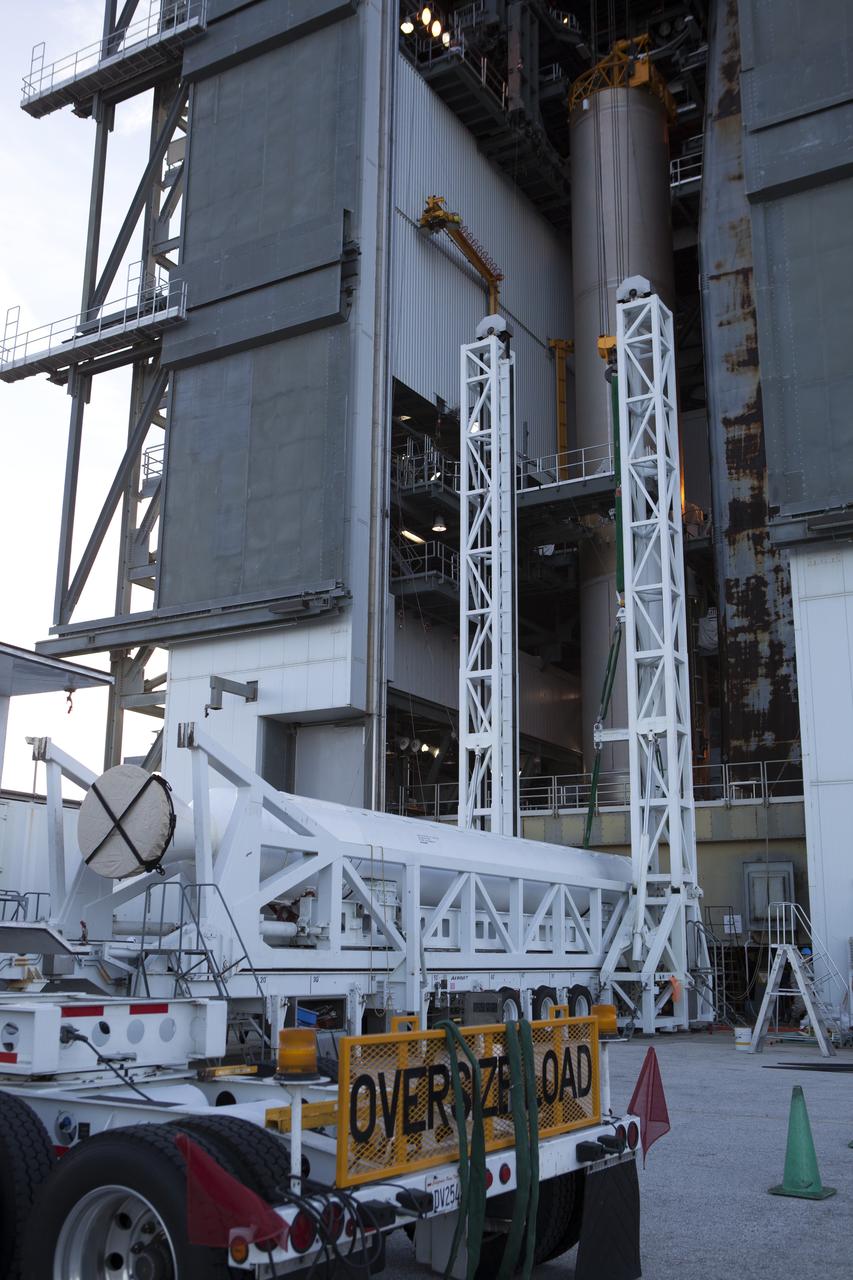

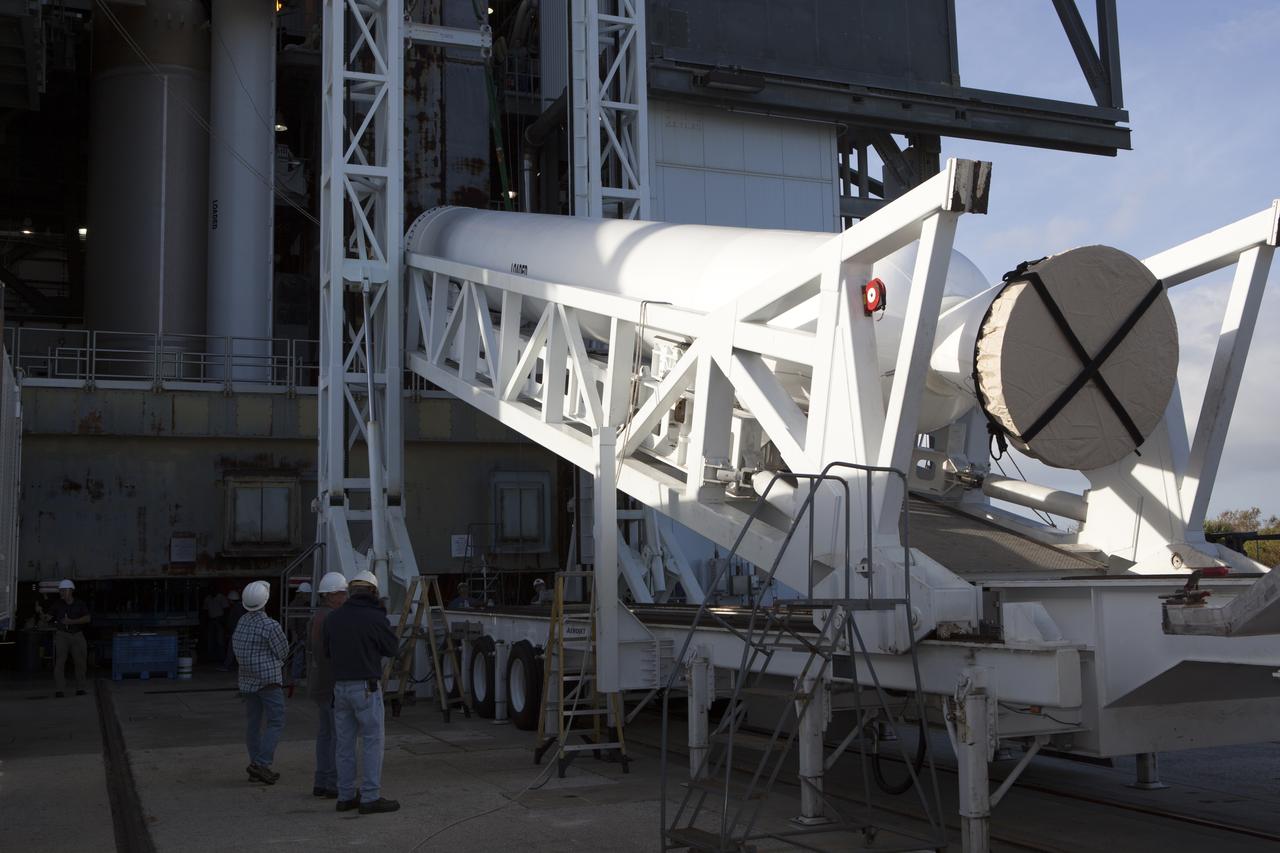
Preparations are underway to lift the solid rocket motor up from its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
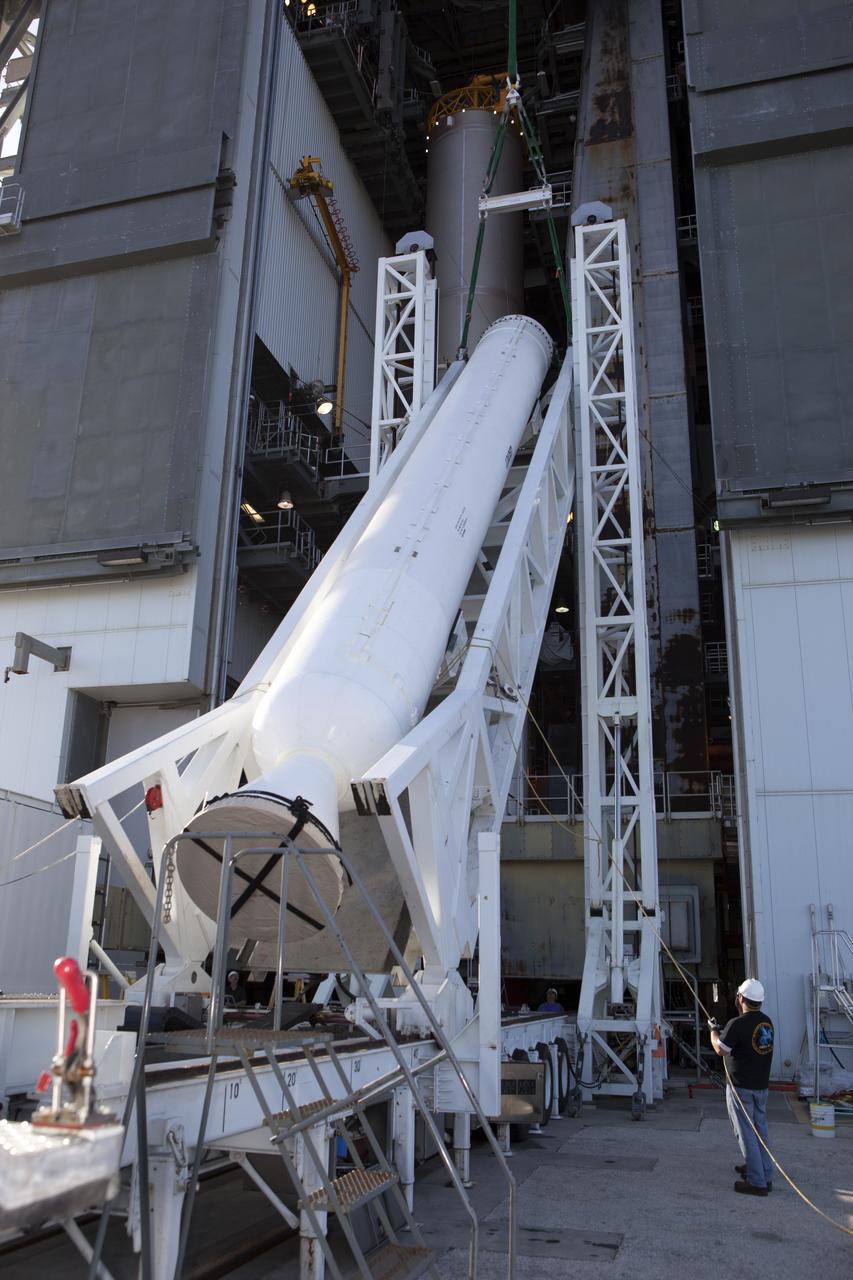

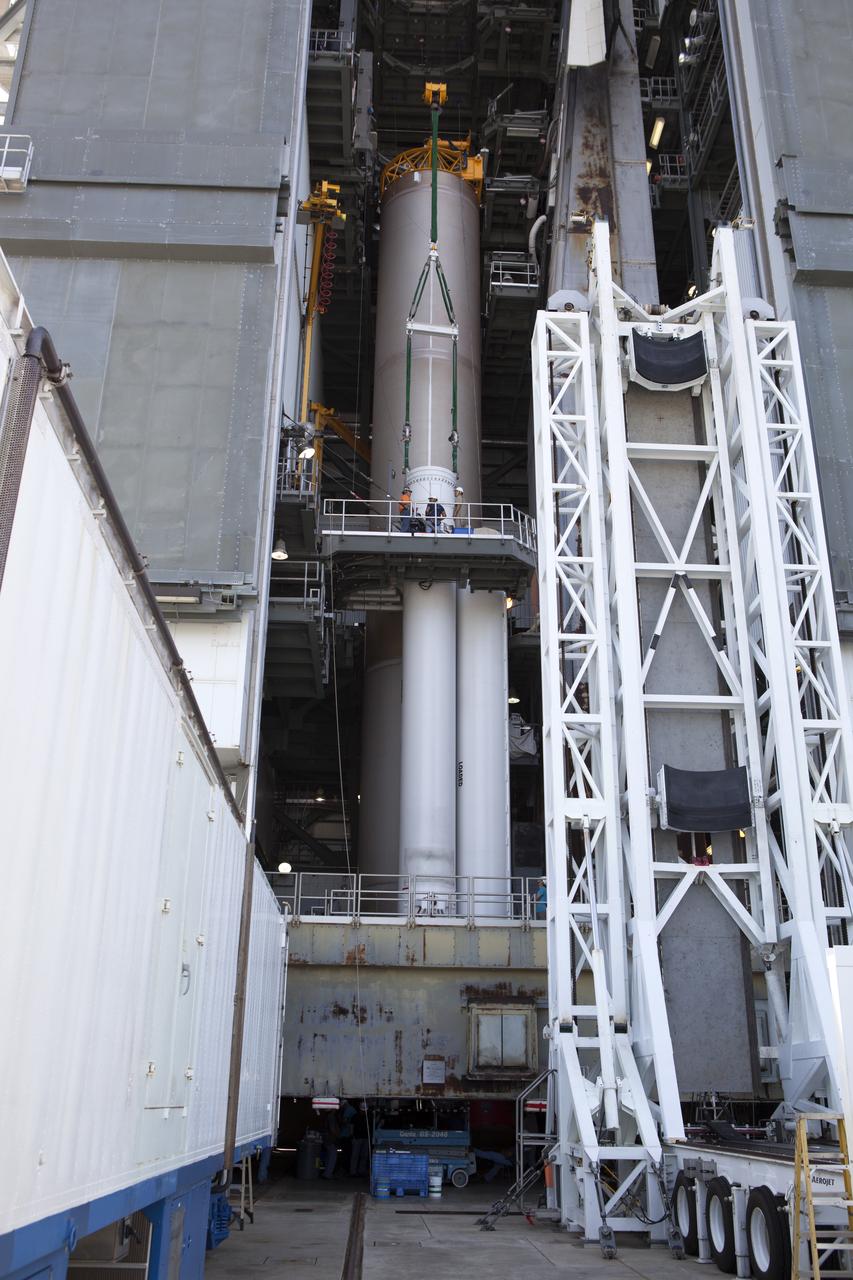
The solid rocket motor is lifted on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

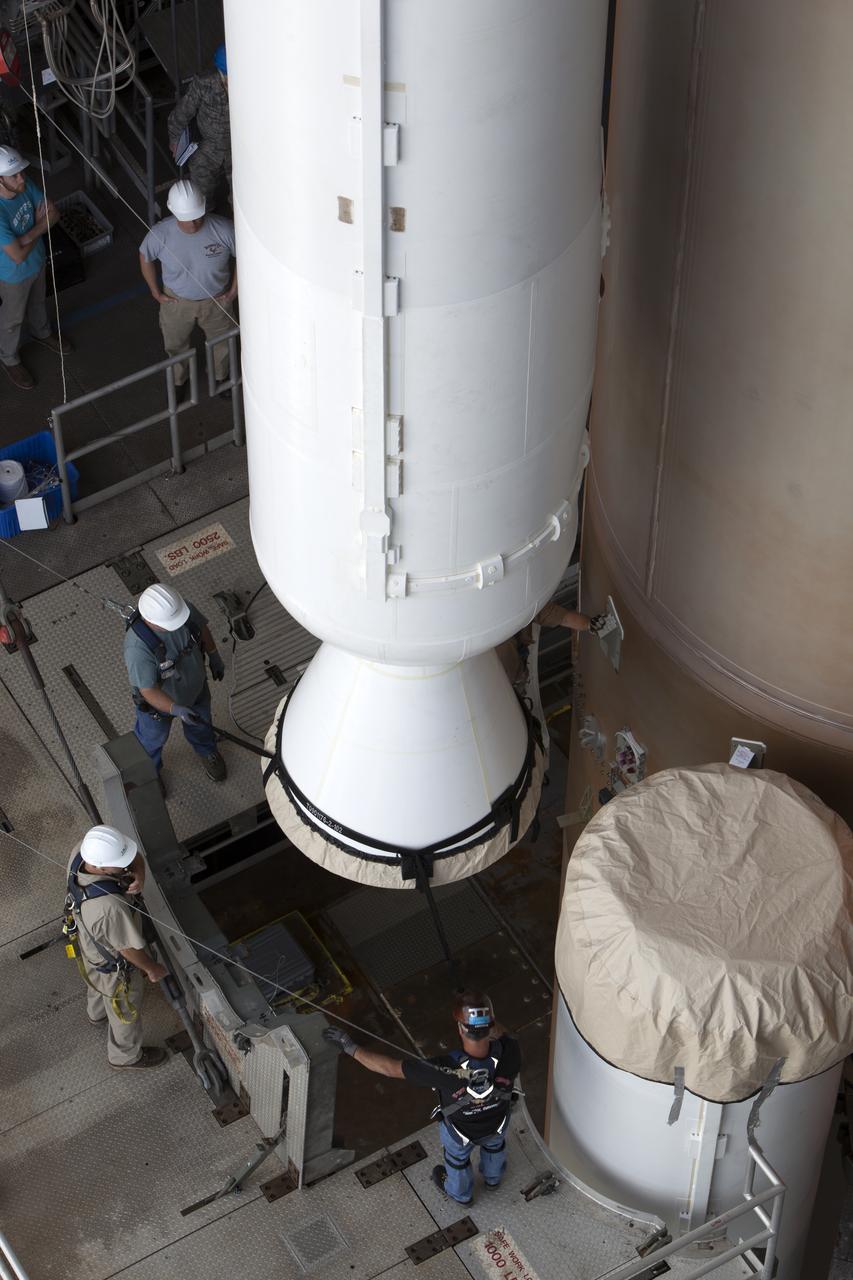
Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the solid rocket motor is being mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for its upcoming launch. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

Technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) monitor the progress as the solid rocket motor is mated to the ULA Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

The solid rocket motor is lifted on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the solid rocket motor is mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for its upcoming launch. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position and moved into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
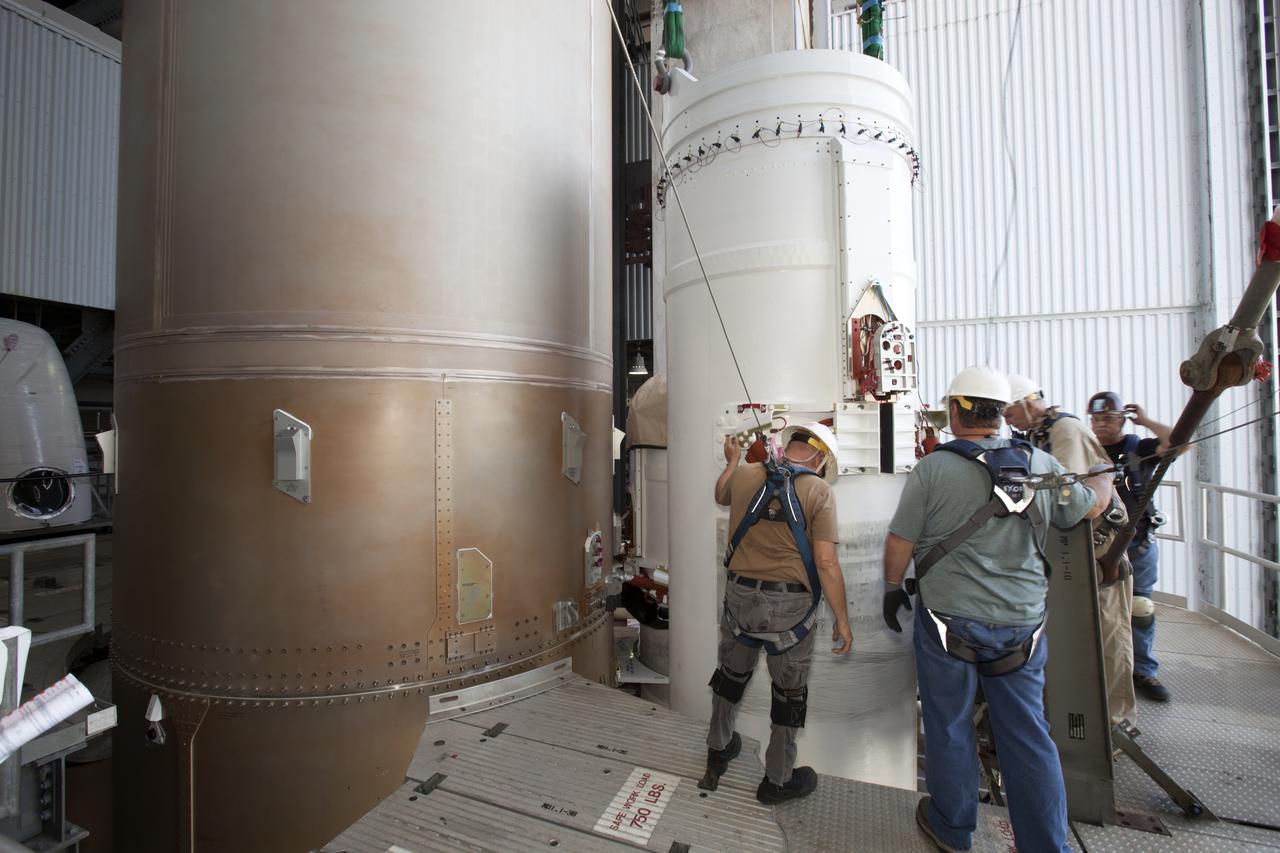

Technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) assist as the solid rocket motor is mated to the ULA Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
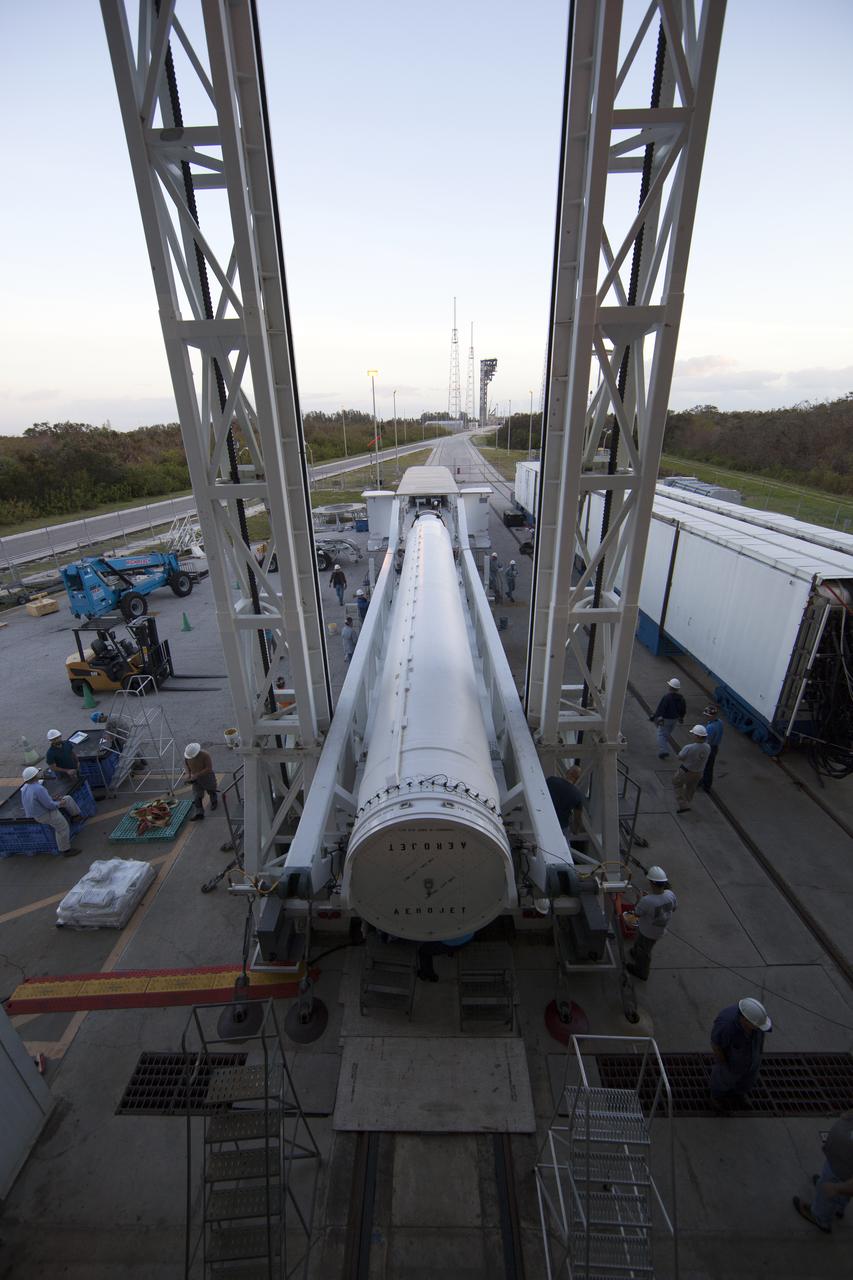

Preparations are underway to lift the solid rocket motor up from its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
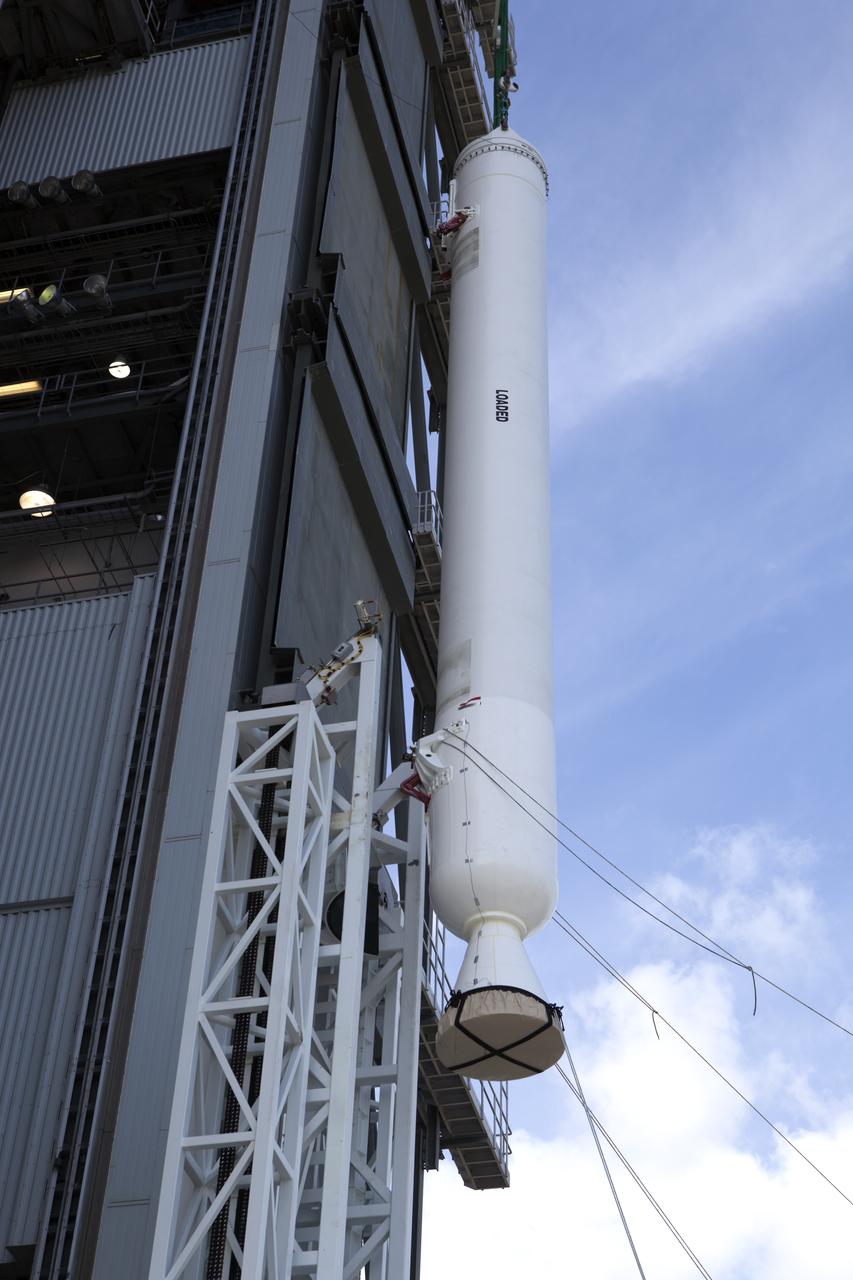

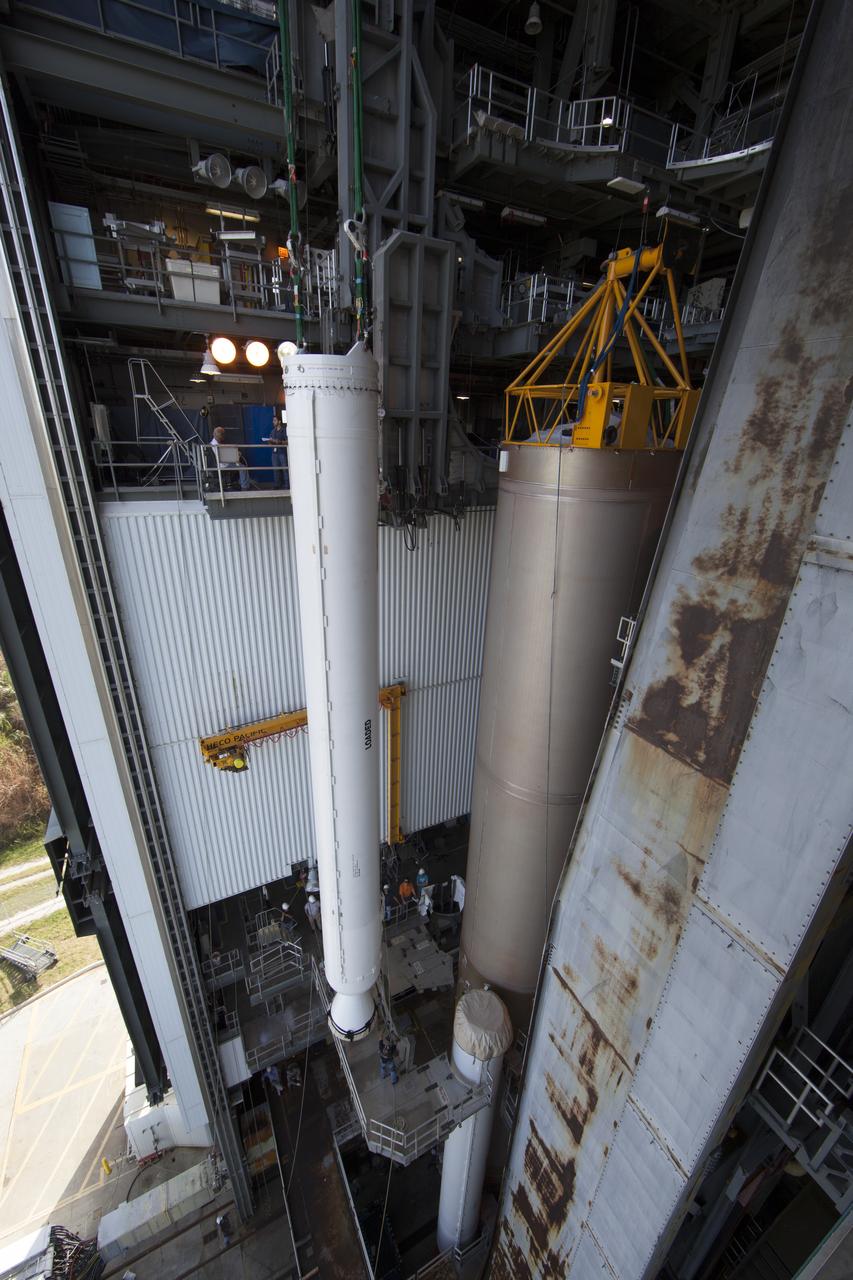
The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
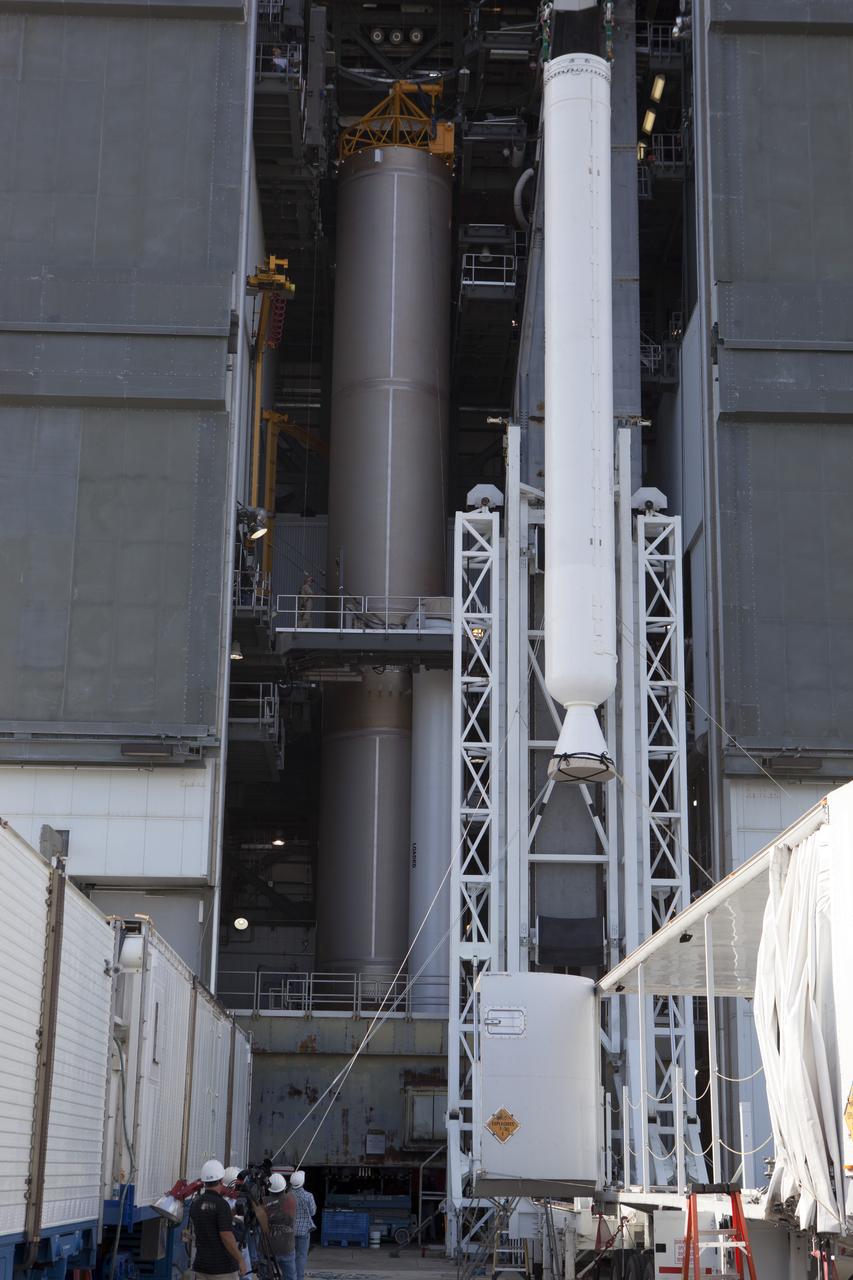

The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
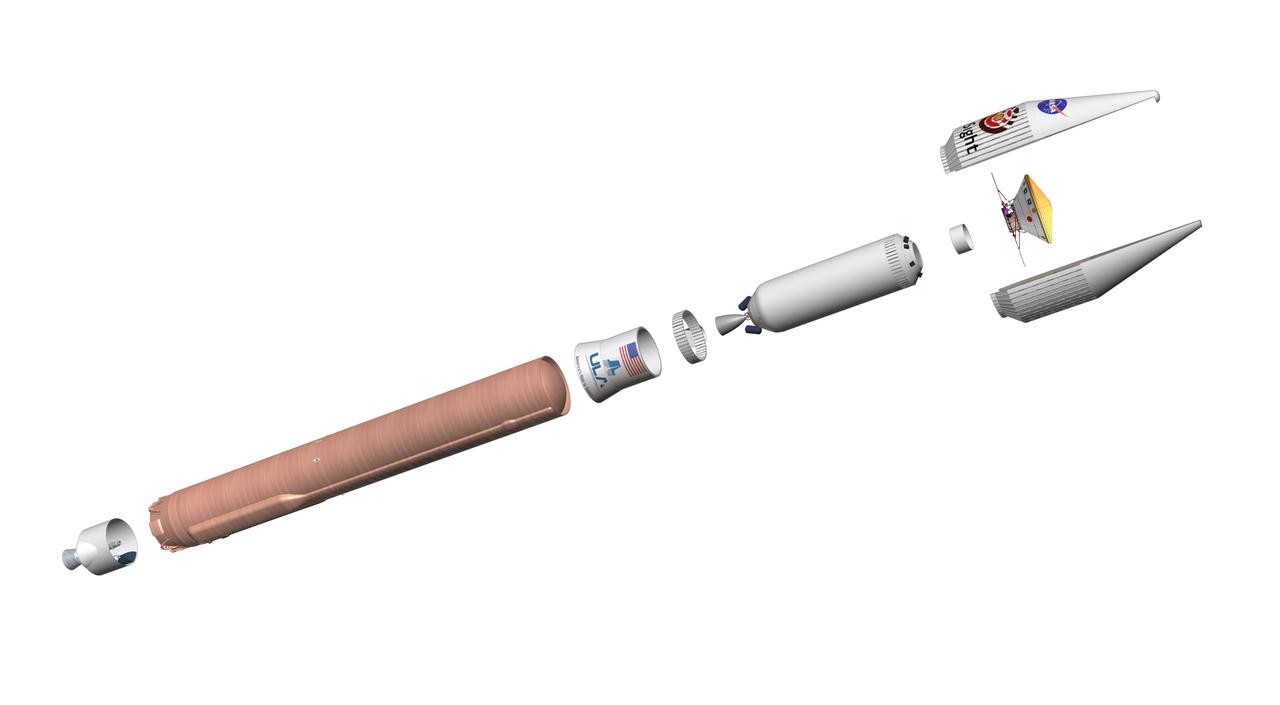
Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, is scheduled to launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base on California's Pacific coast between May 5 and June 8, 2018. The lander will launch to Mars aboard an Atlas V-401 launch vehicle, one of the biggest rockets available for interplanetary flight. It stands 188 feet (57.3 meters) tall, or about as tall as a 19-story building. Fully stacked, with the spacecraft, the Atlas V-401 weighs about 730,000 pounds (333,000 kilograms). That's about 14 big rigs, fully loaded with cargo! The three numbers in the 401 designation signify: 4: a payload fairing -- or nose cone -- that is about 13 feet (4 meters) in diameter 0: solid-rocket boosters supplementing the main booster 1: the upper stage, which has one engine https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22231

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) technician inspects the solid rocket motor for the ULA Atlas V rocket on its transporter near the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solid rocket motor will be lifted and mated to the rocket in preparation for the launch of NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
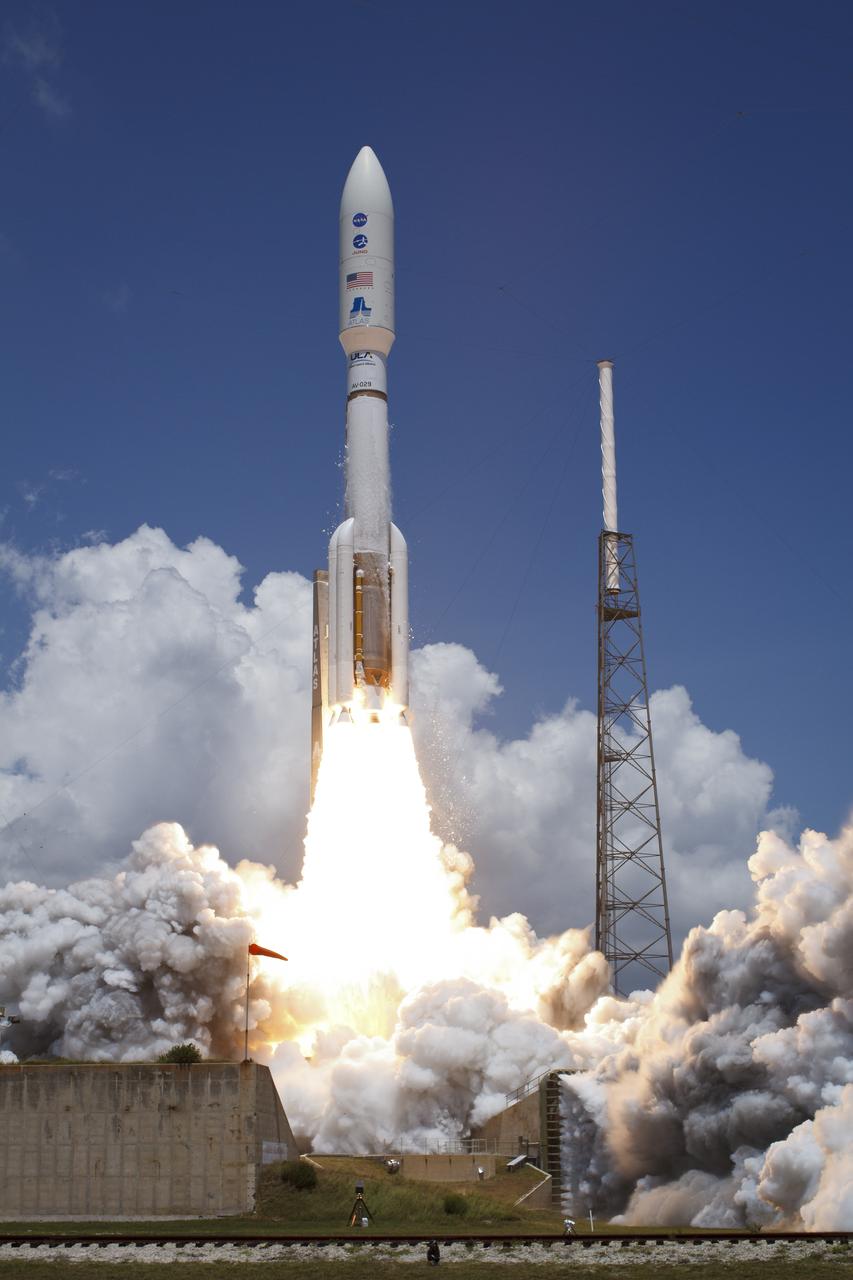

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
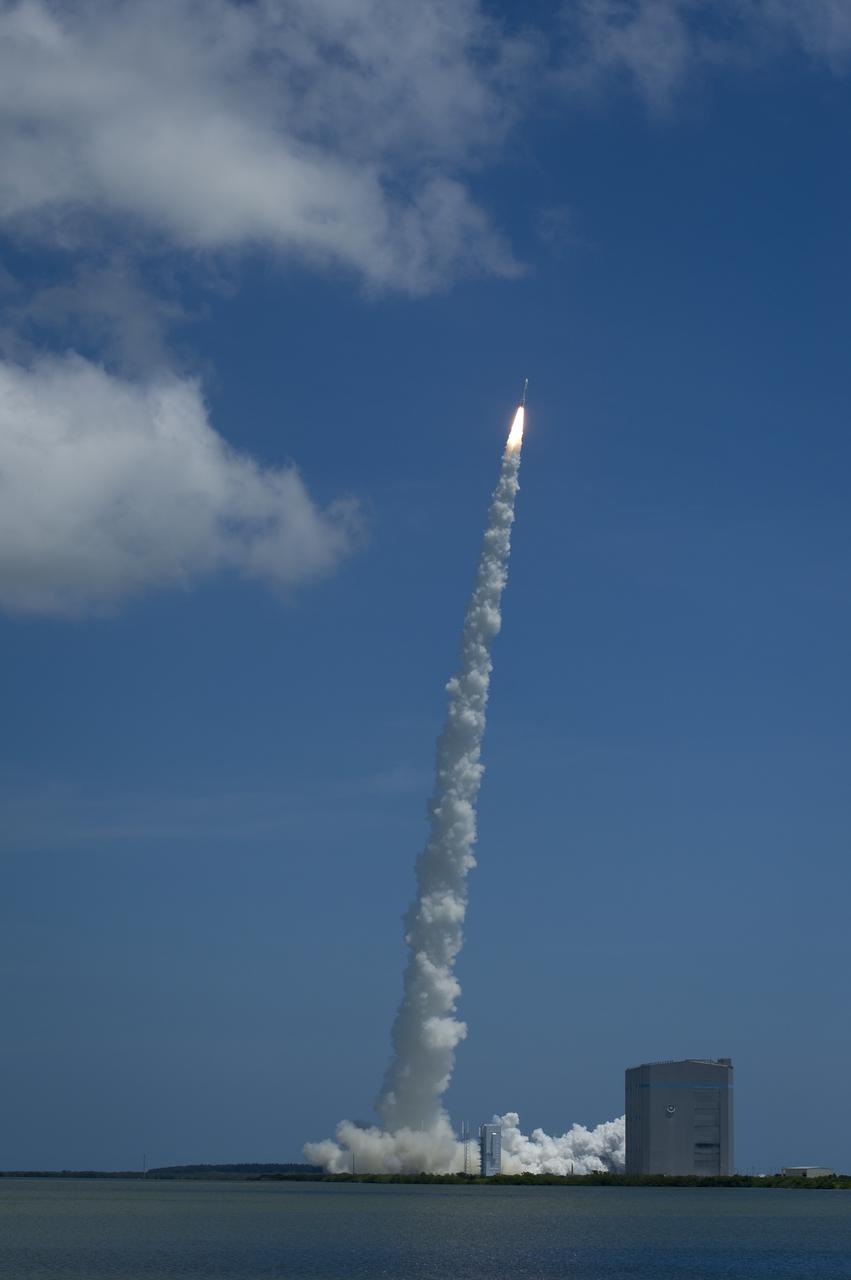

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
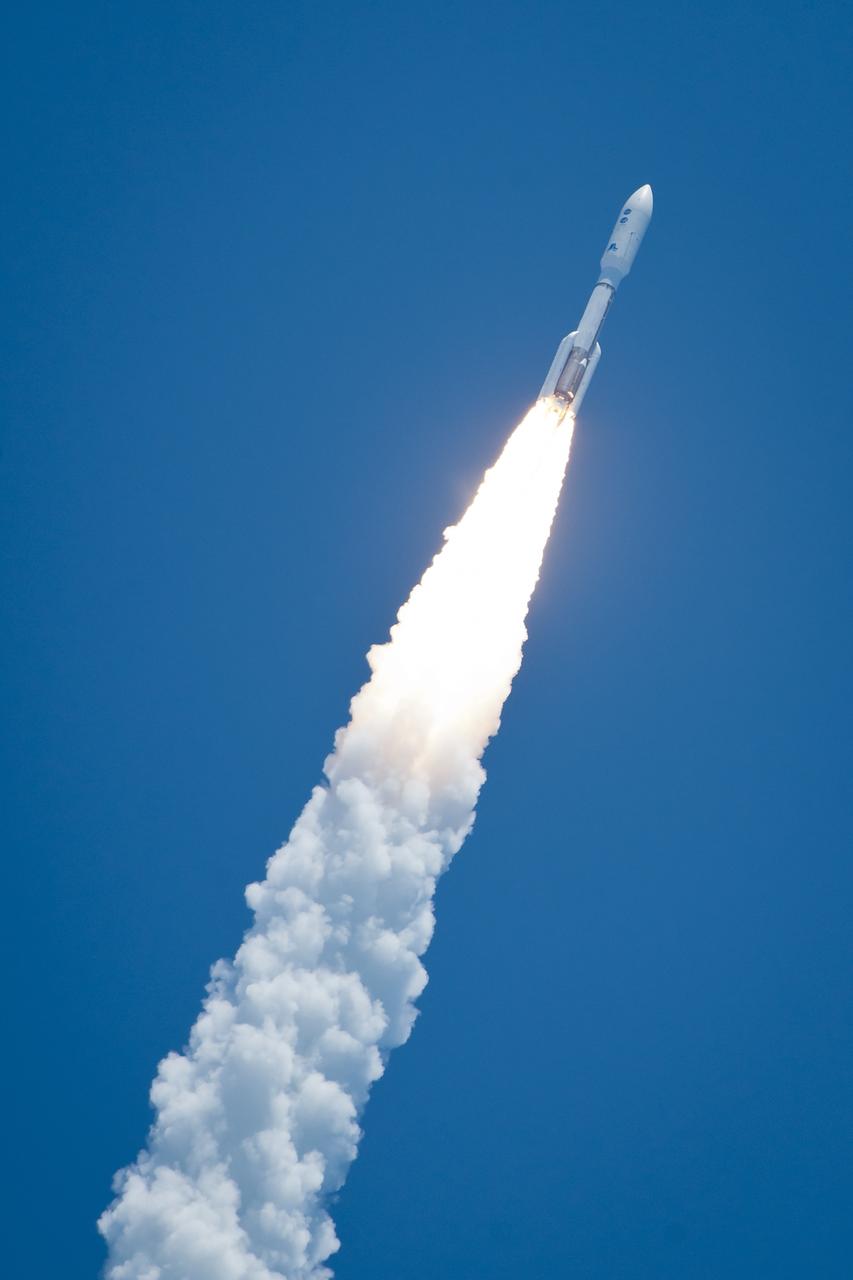

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
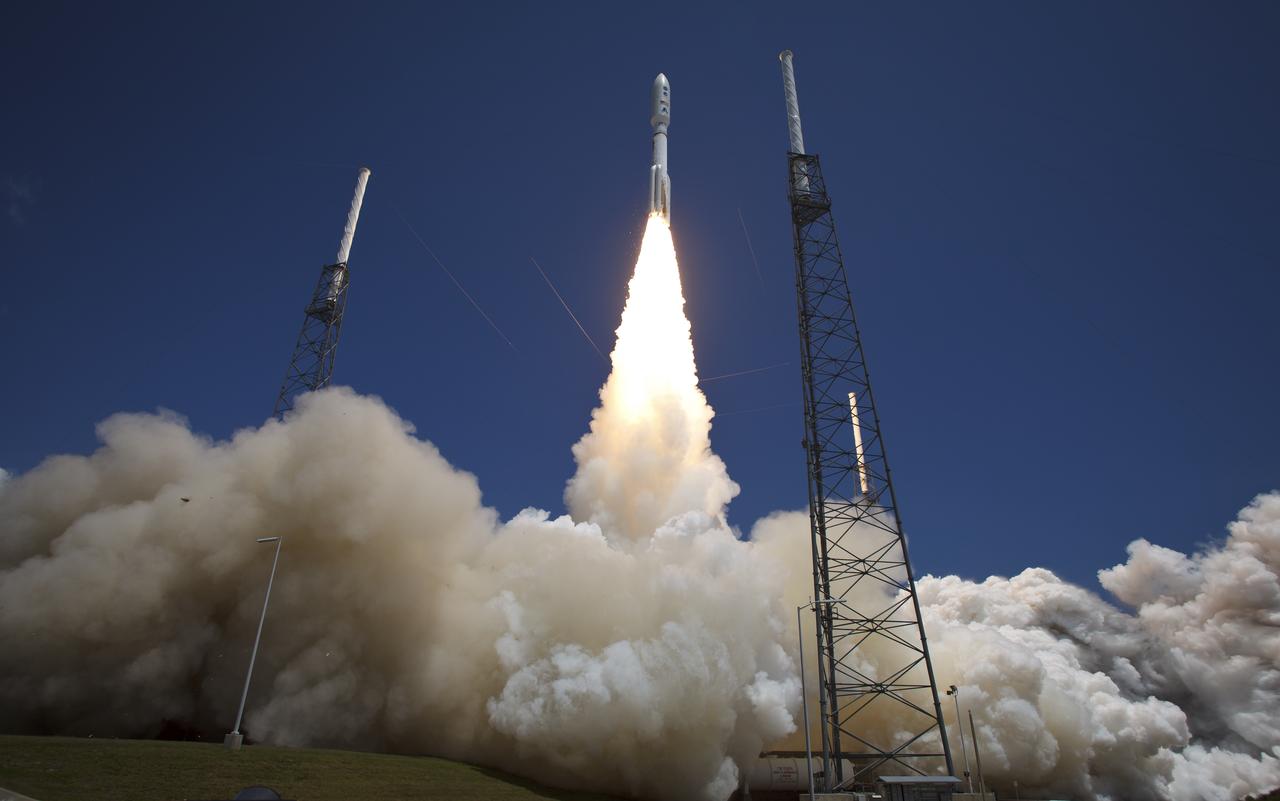

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
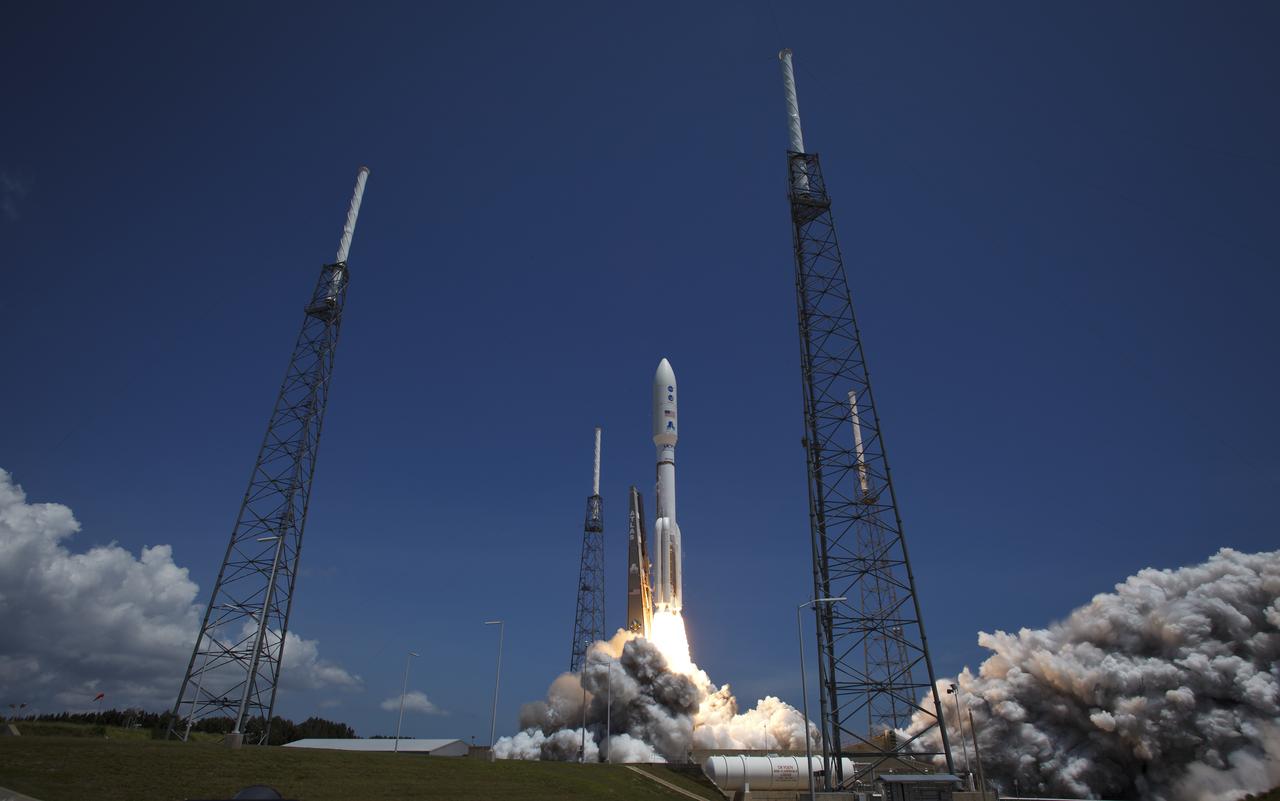

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
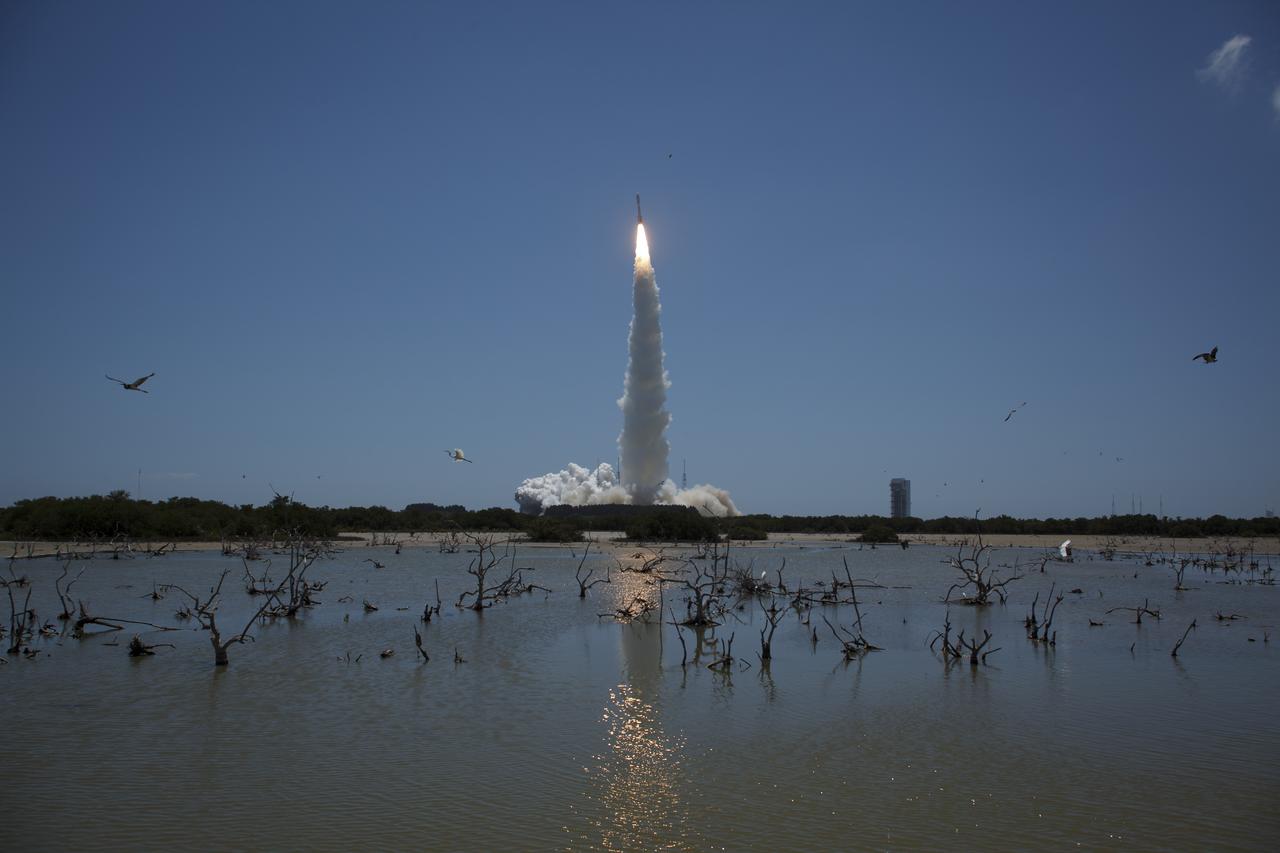

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
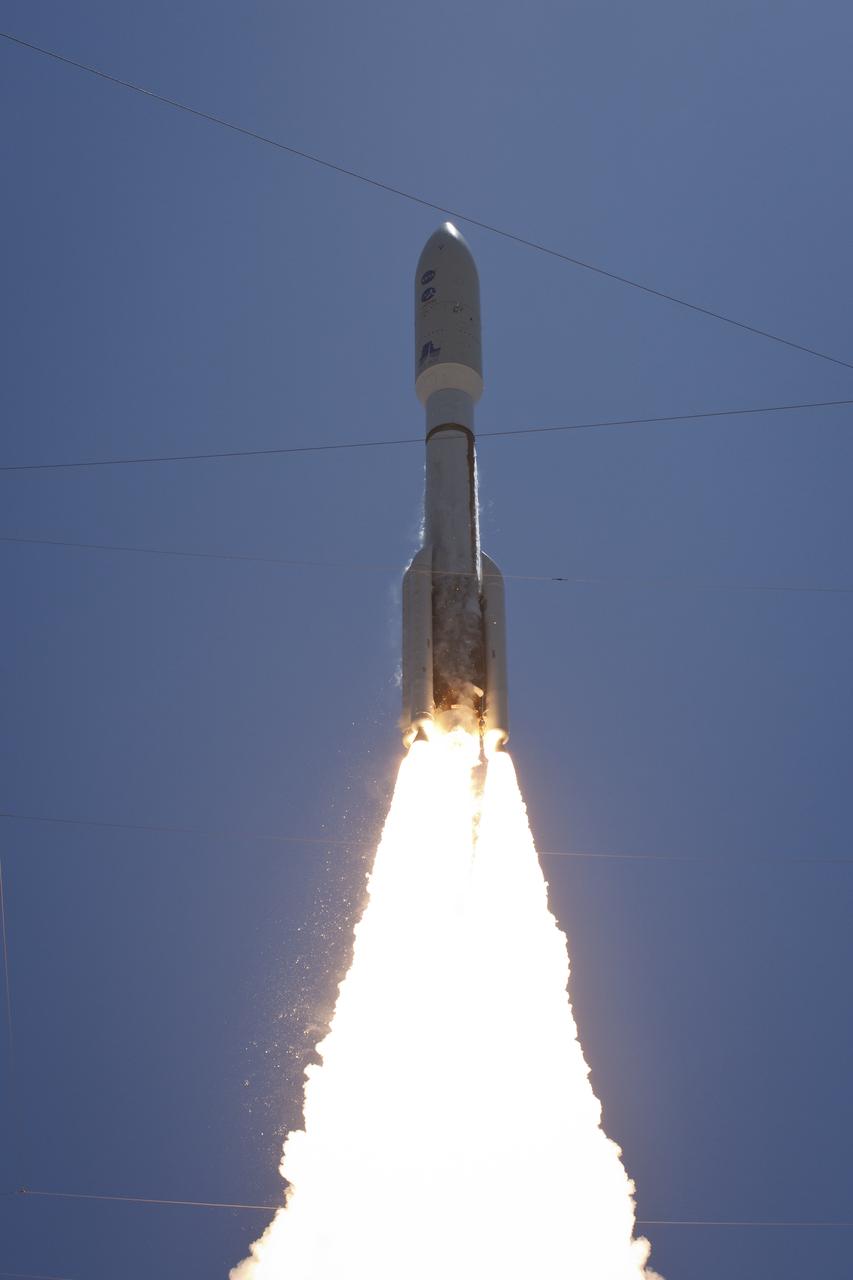

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
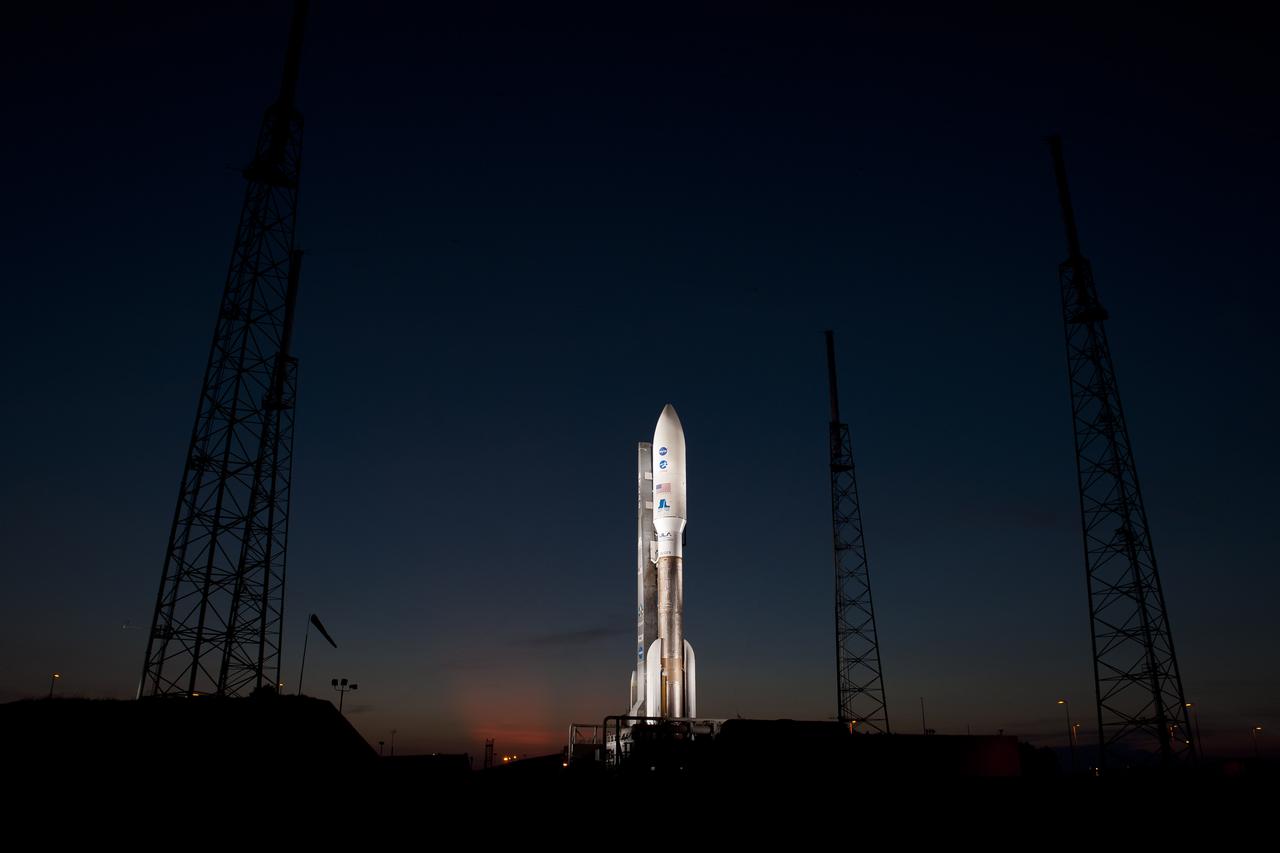

An Atlas V rocket with NASA's Juno spacecraft payload is seen the evening before it's planned launch at Space Launch Complex 41 of the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Thursday, August 4, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
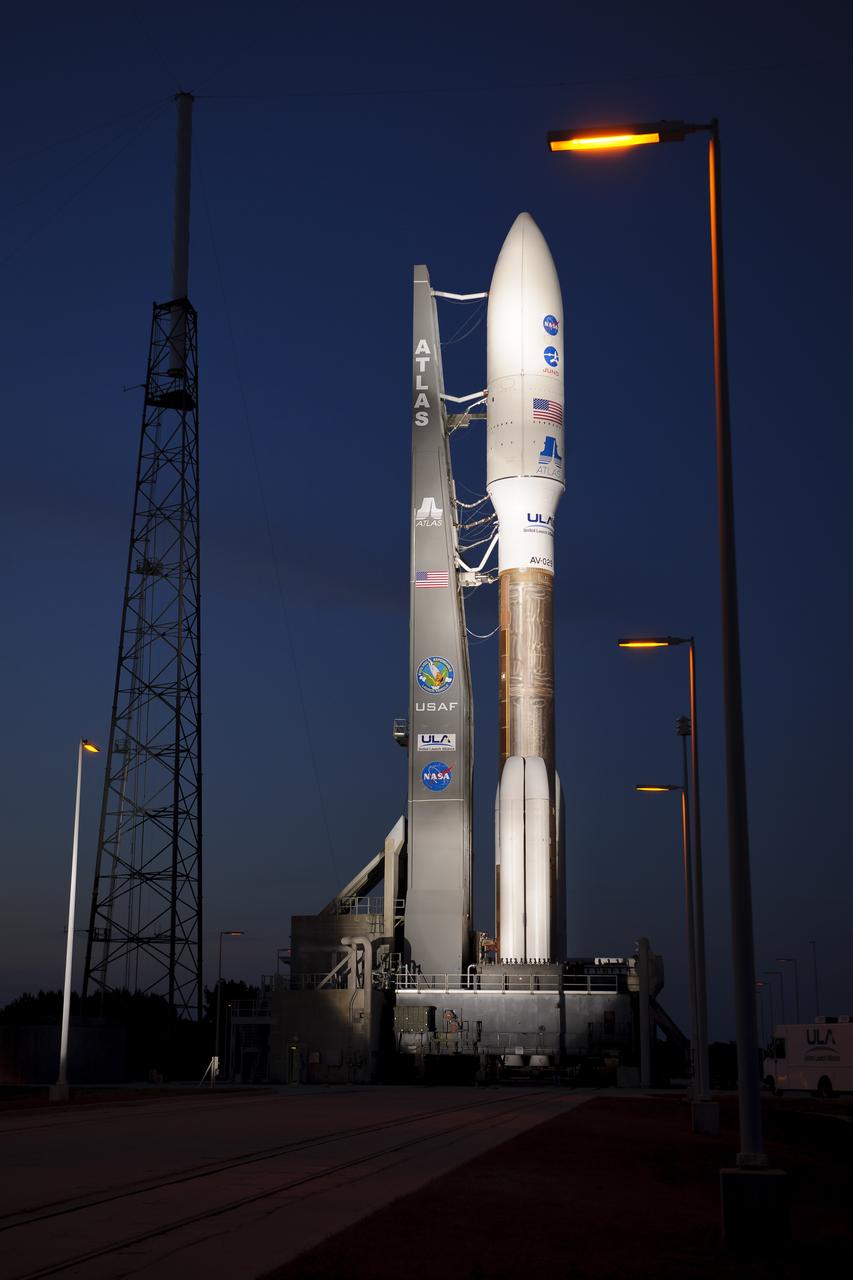

An Atlas V rocket with NASA's Juno spacecraft payload is seen the evening before it's planned launch at Space Launch Complex 41 of the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Thursday, August 4, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
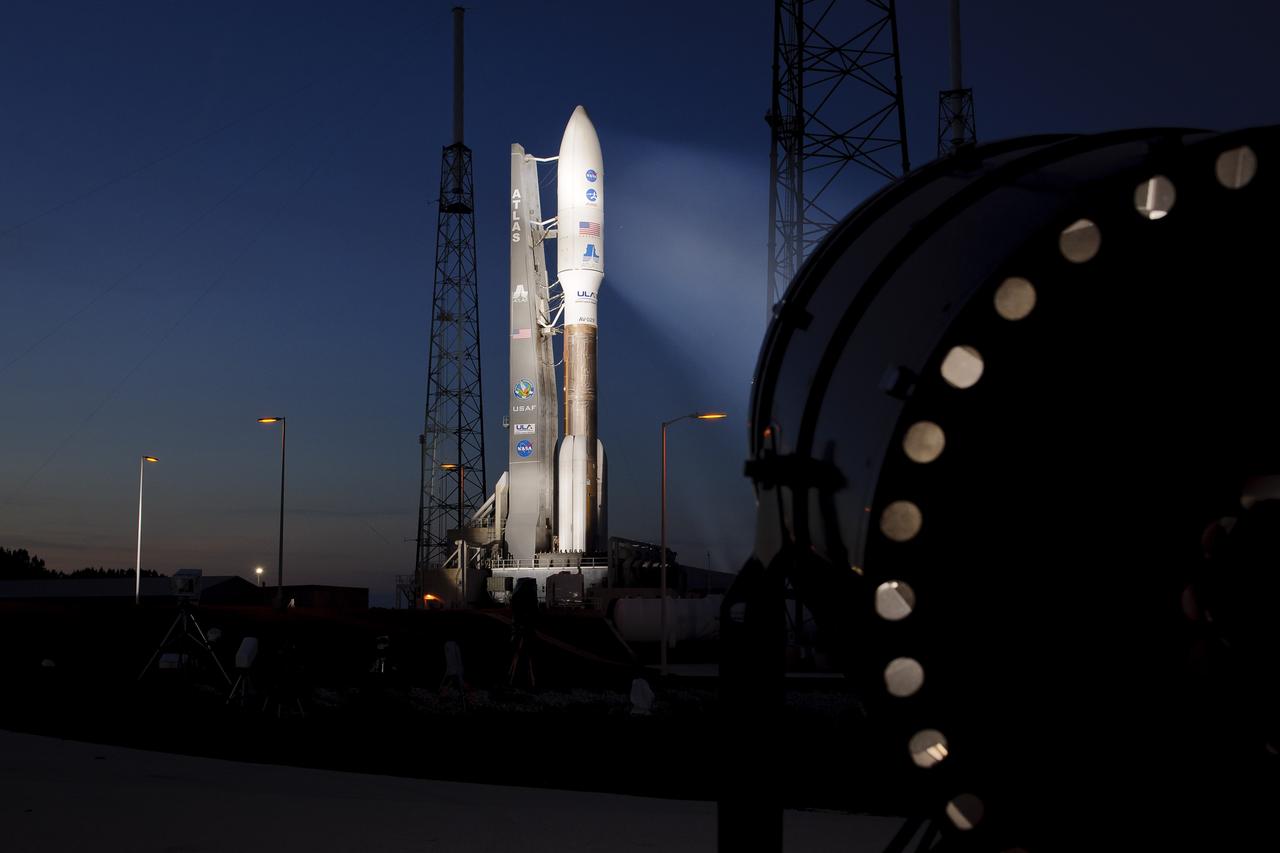

An Atlas V rocket with NASA's Juno spacecraft payload is seen the evening before it's planned launch at Space Launch Complex 41 of the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Thursday, August 4, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
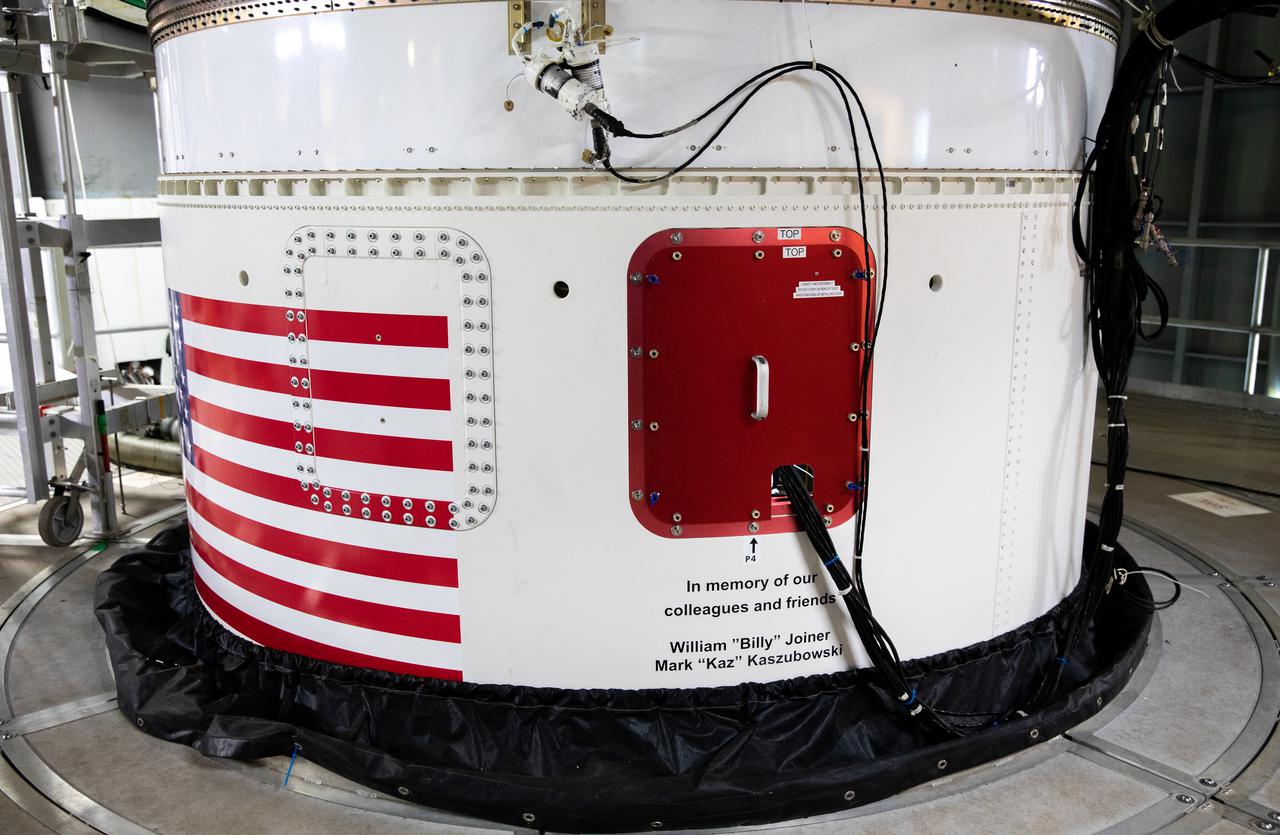
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
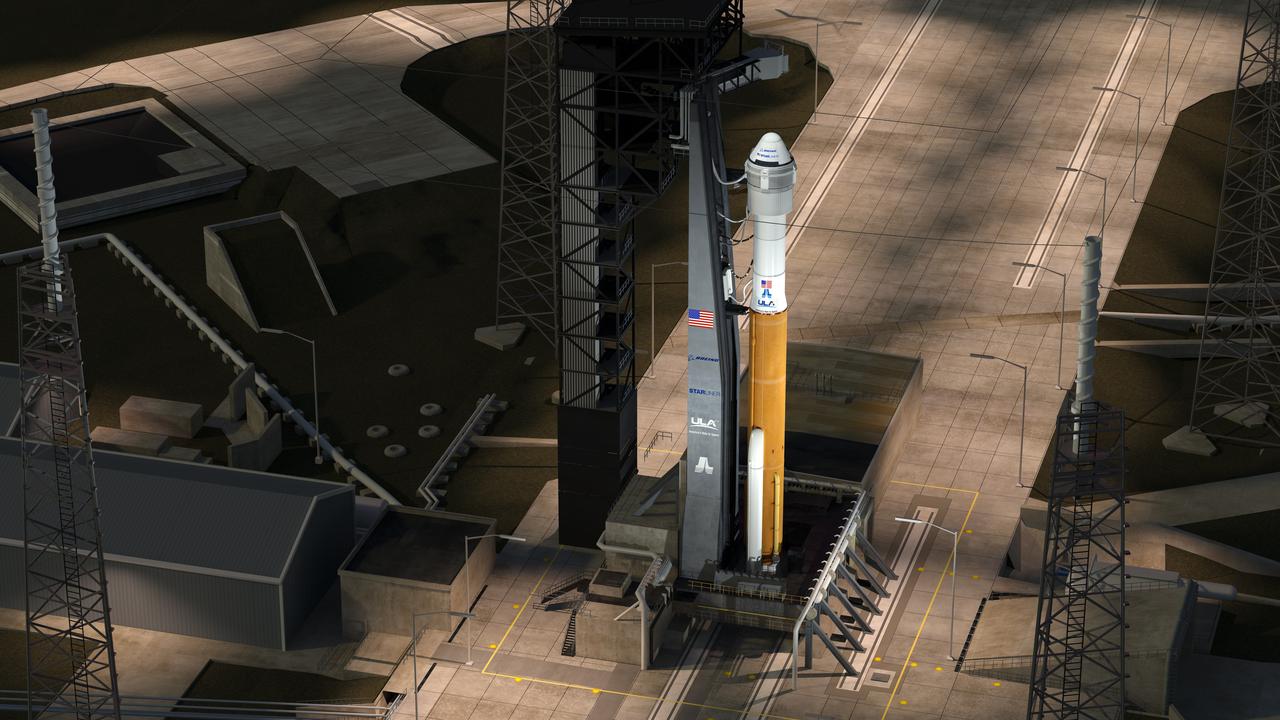

This artist concept shows a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a Boeing CST-100 Starliner capsule at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Starliner/Atlas V system is under development by Boeing and ULA in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to launch astronauts to the International Space Station.
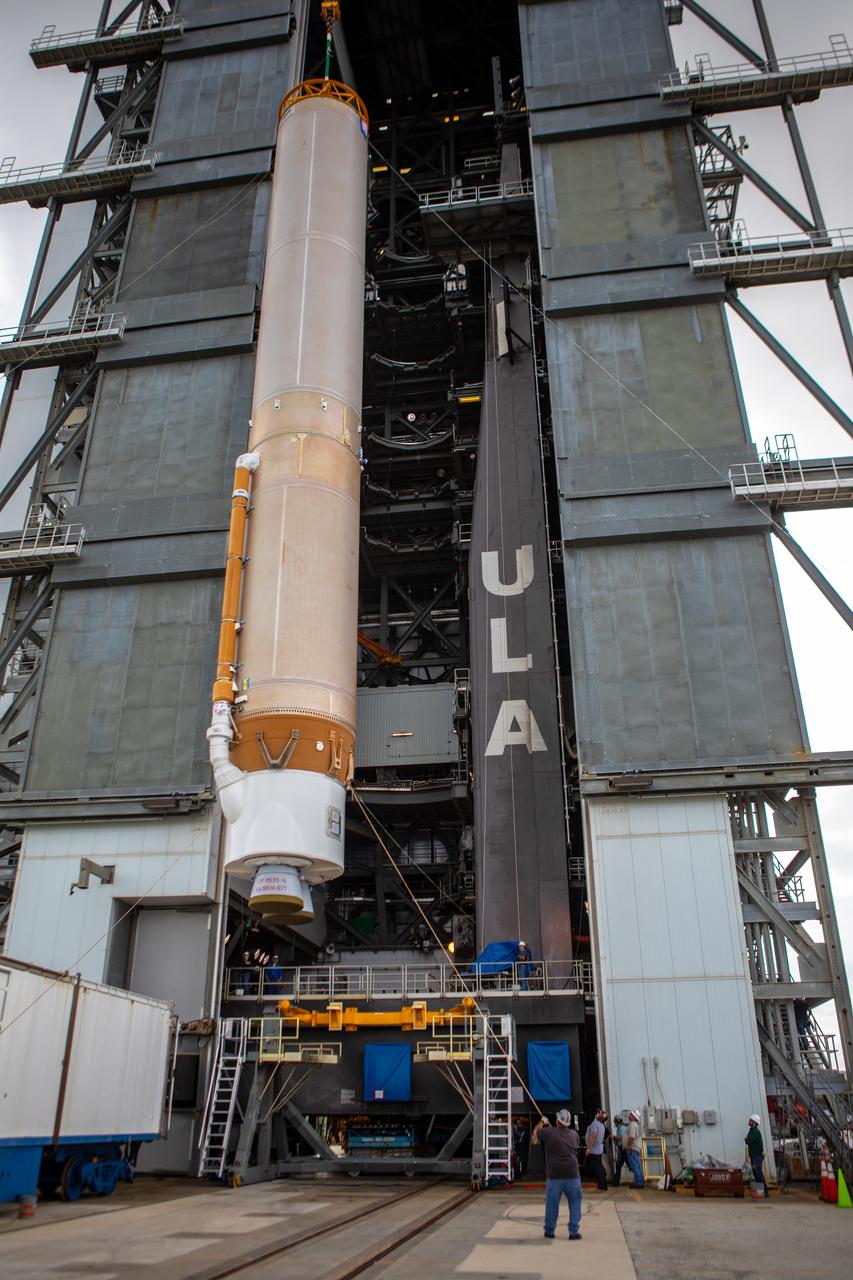

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
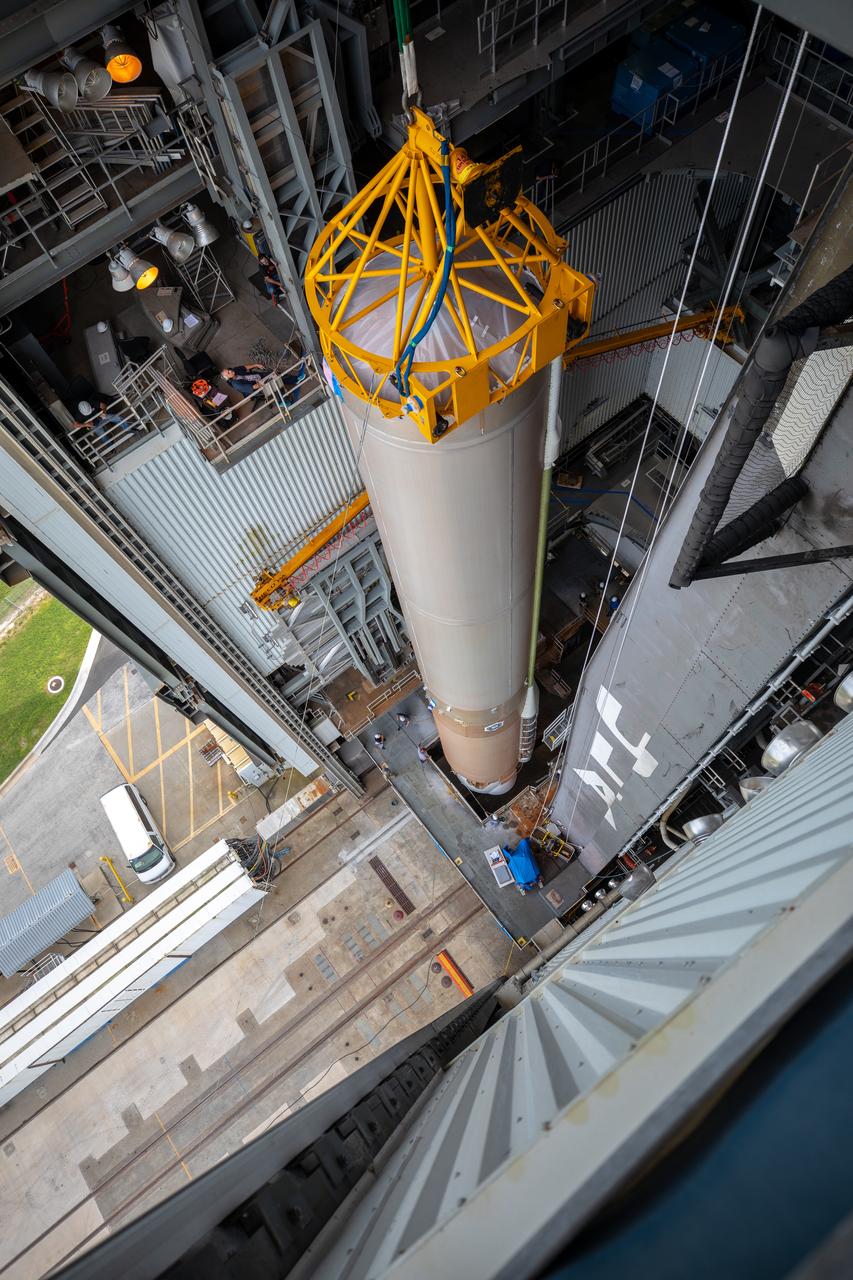

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
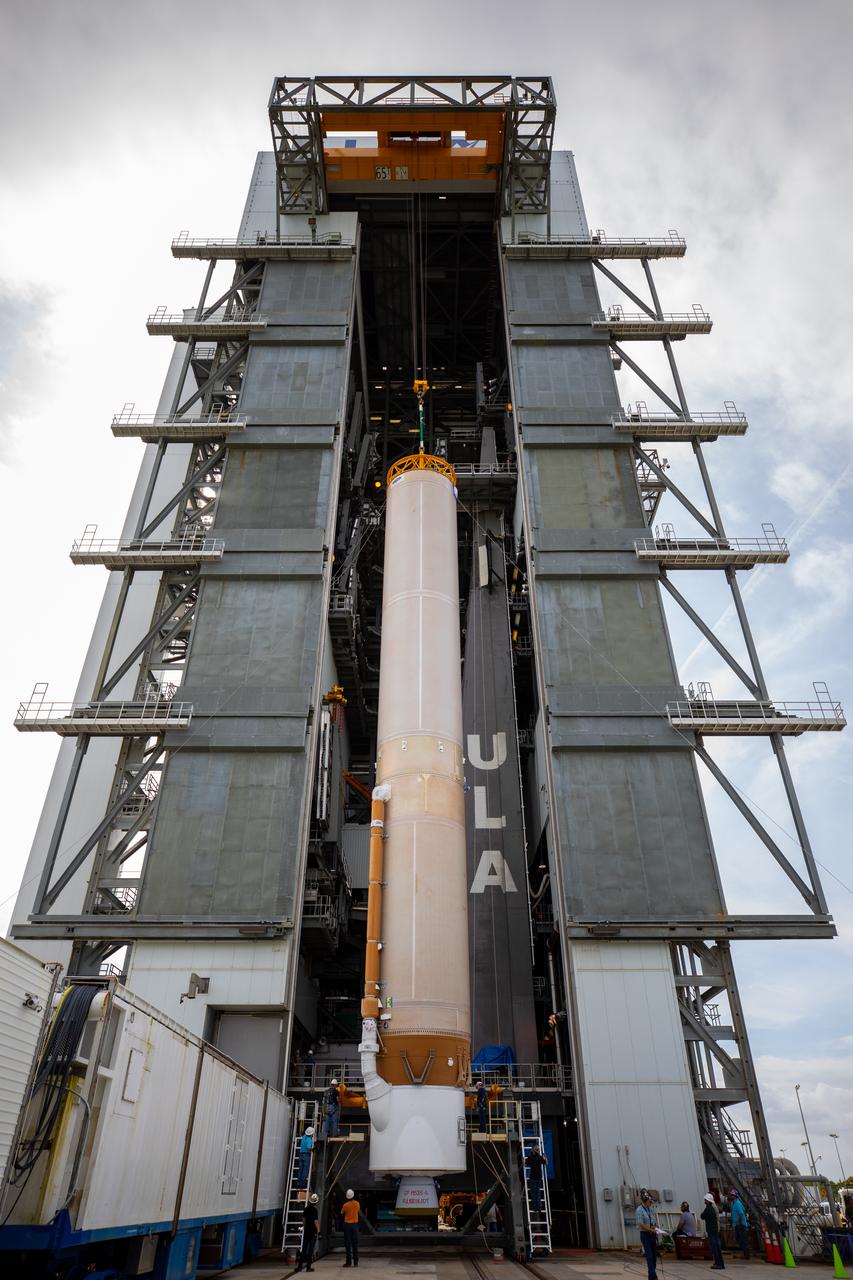

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
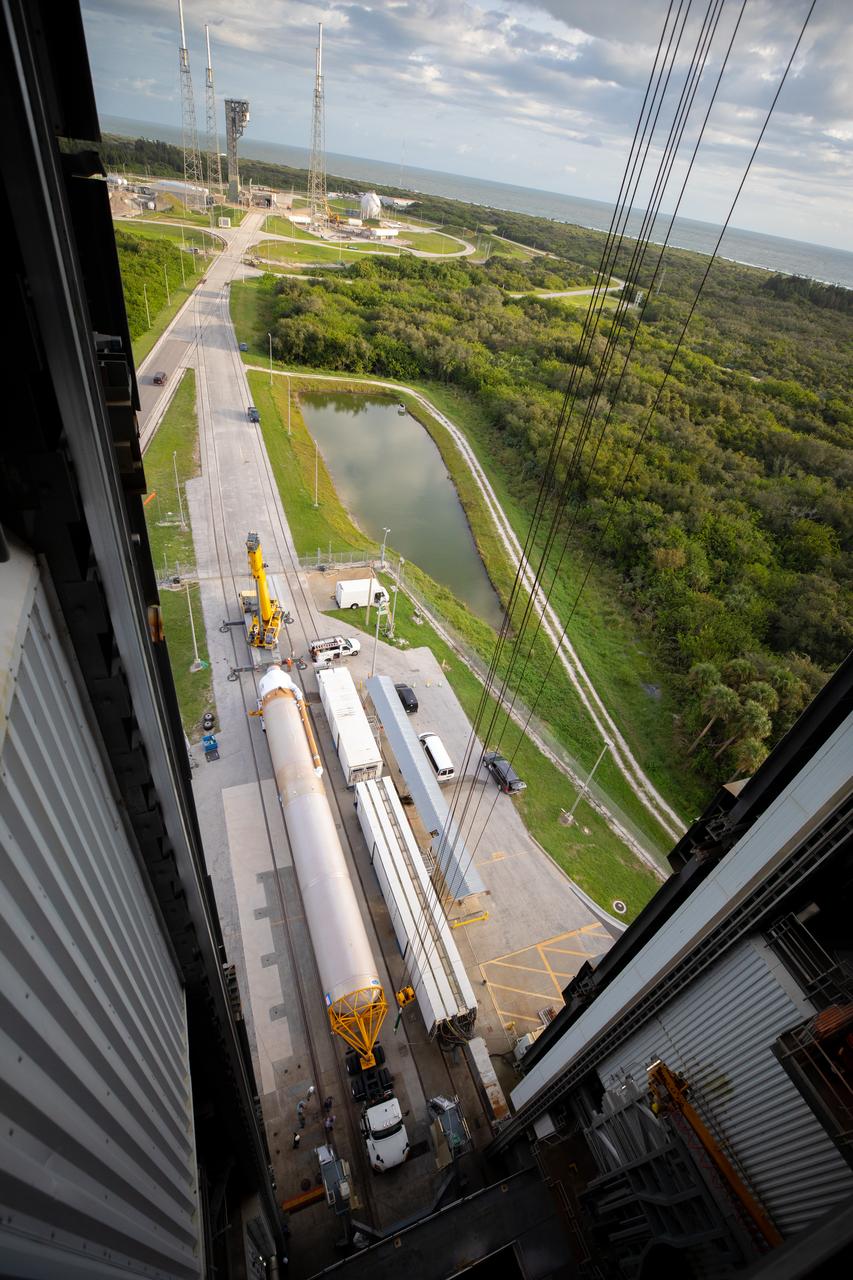

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
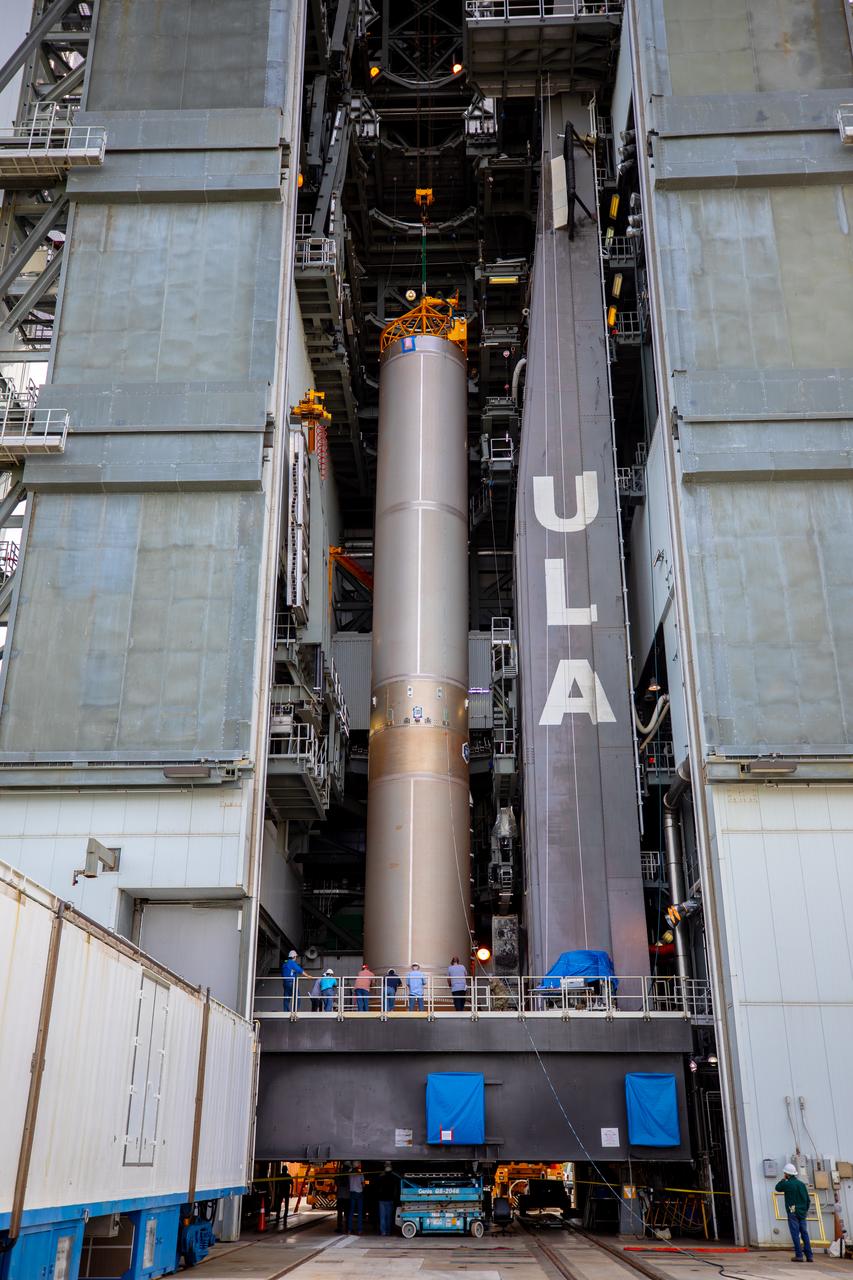

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
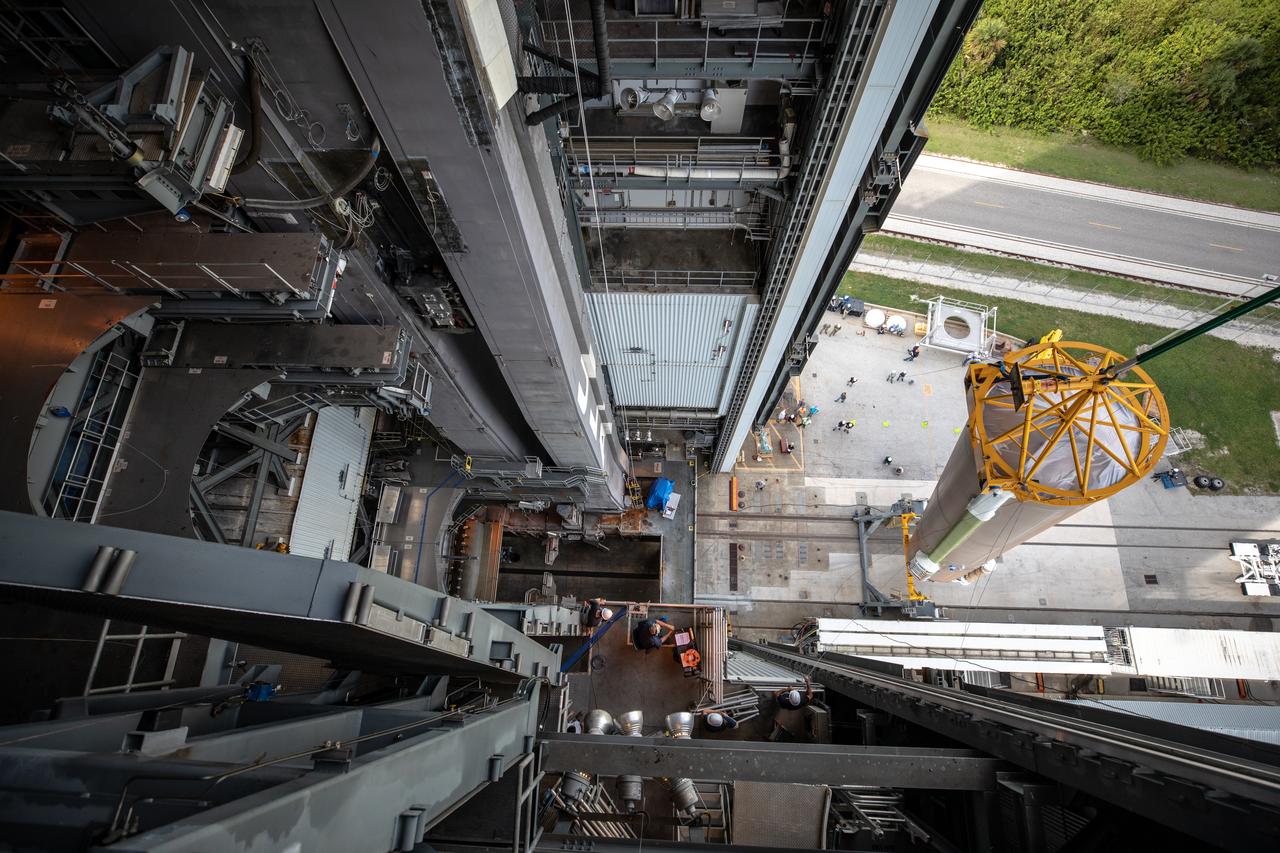

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
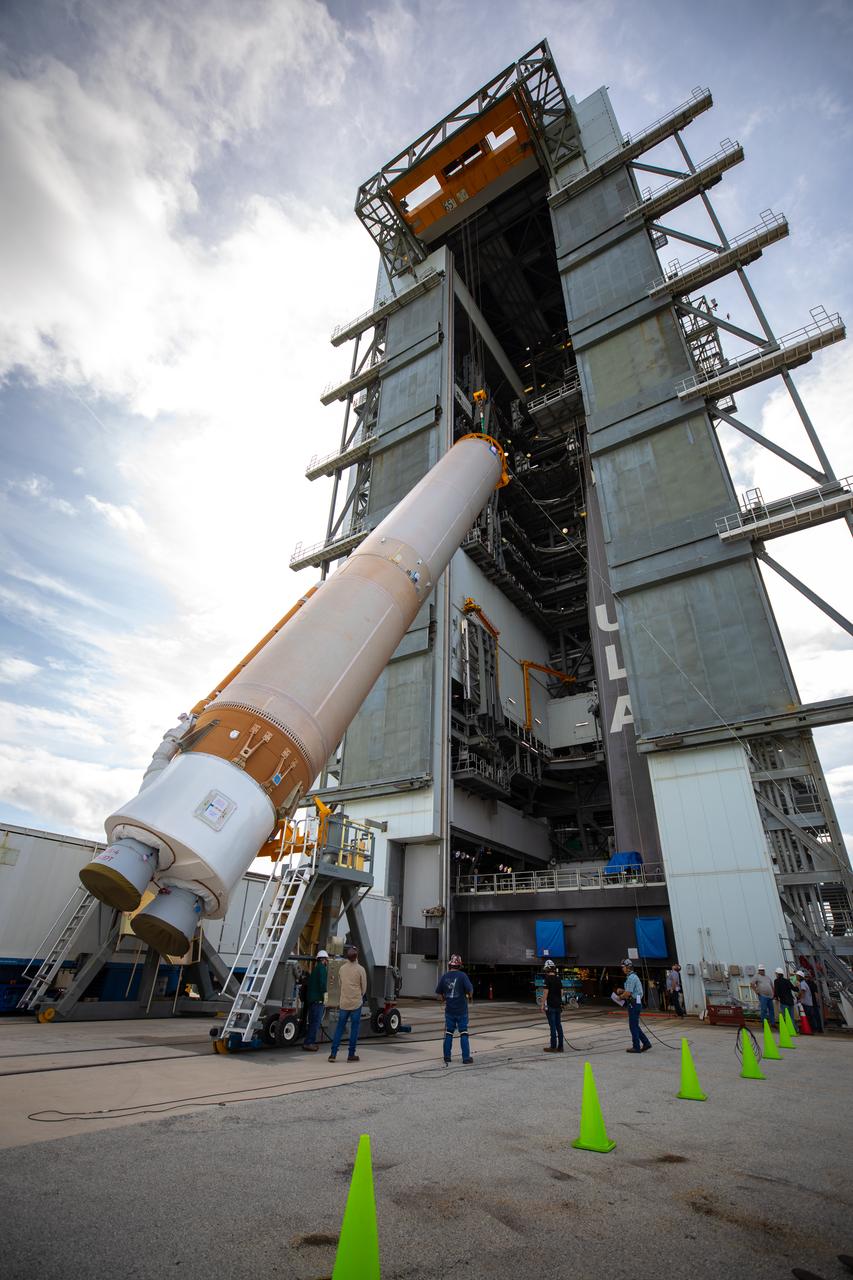

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
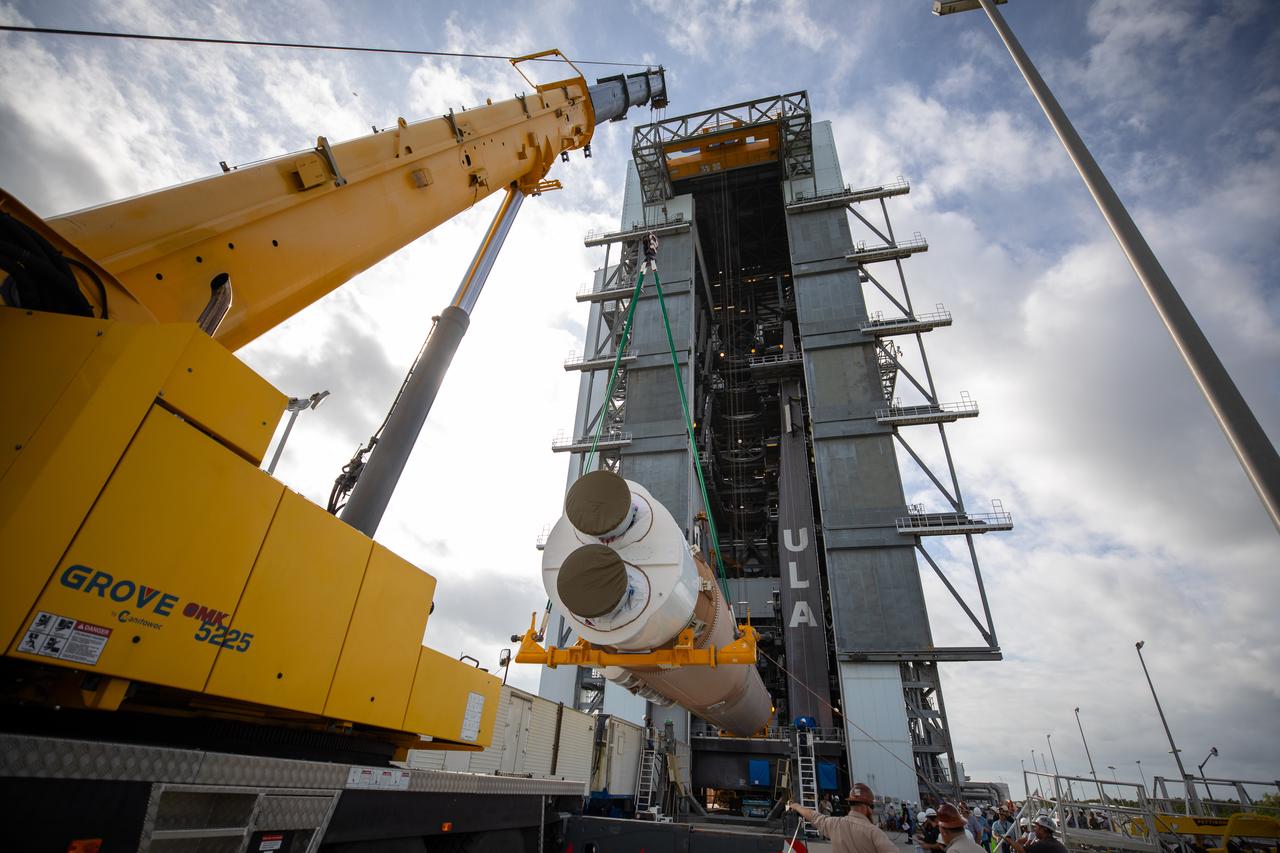

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
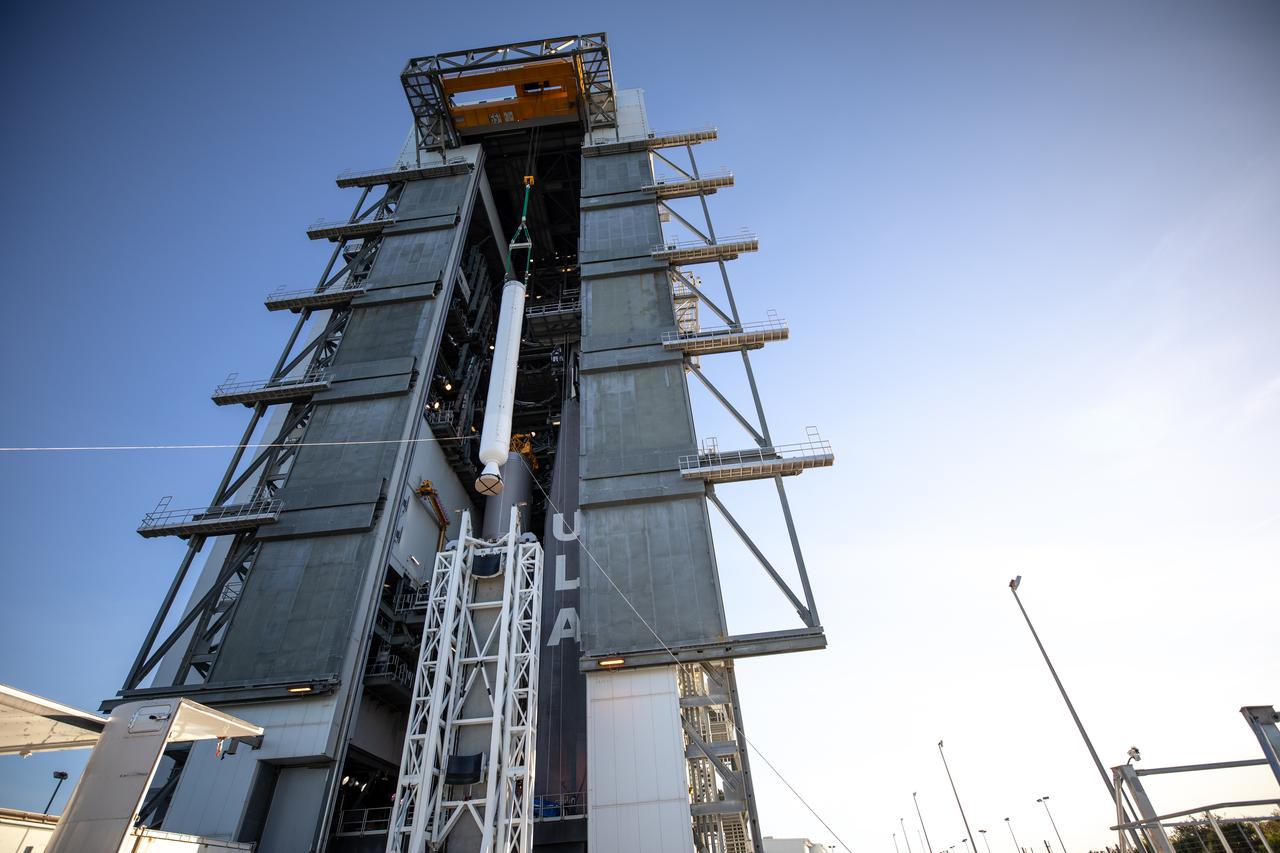

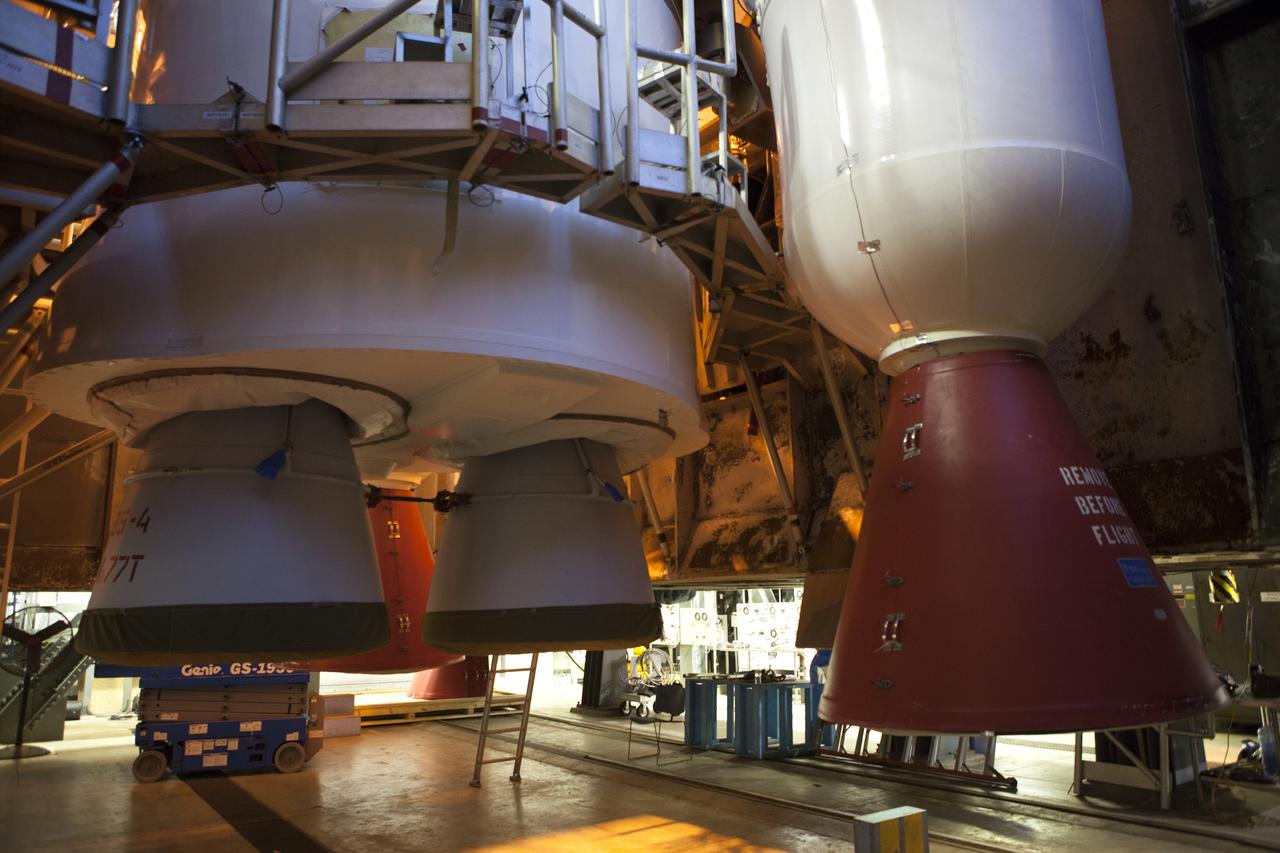
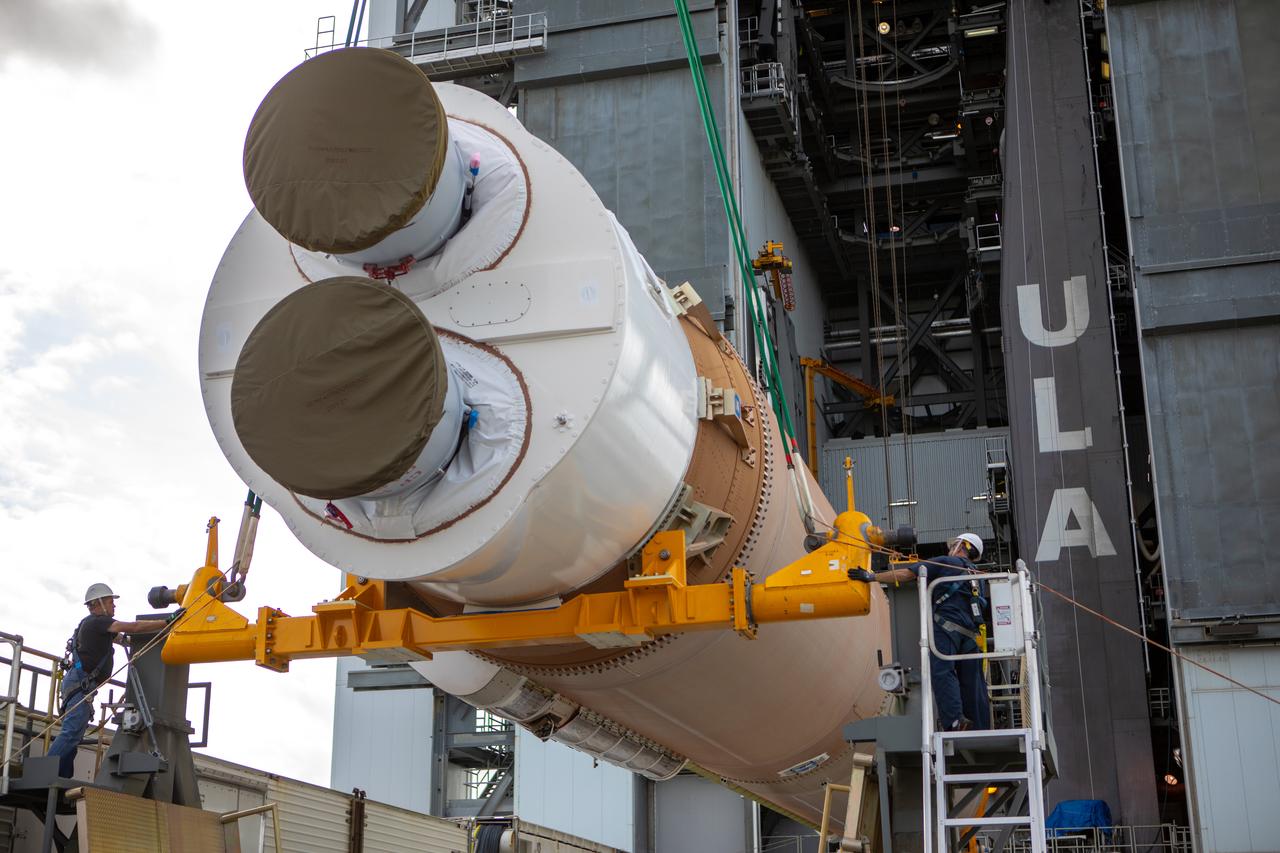
Two solid rocket boosters are mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
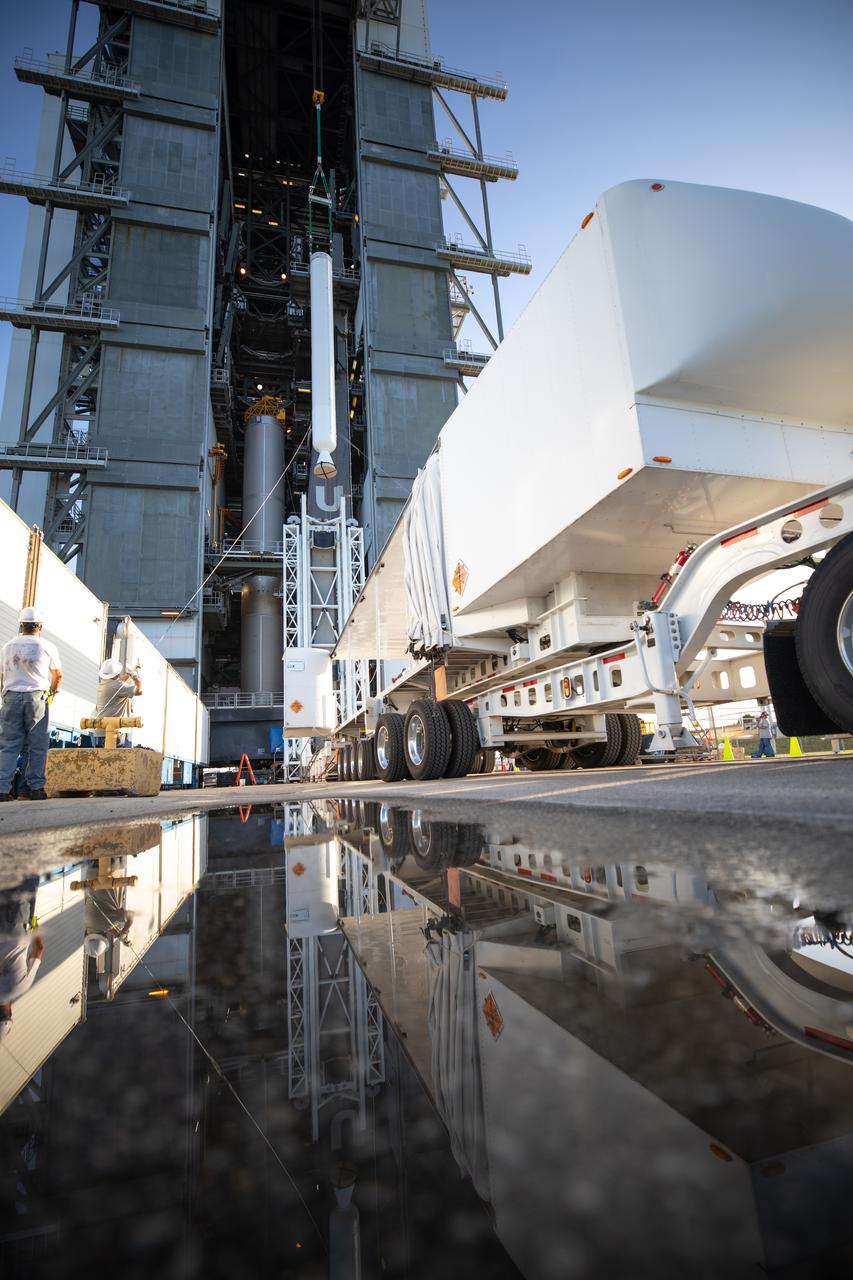

Two solid rocket boosters are mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
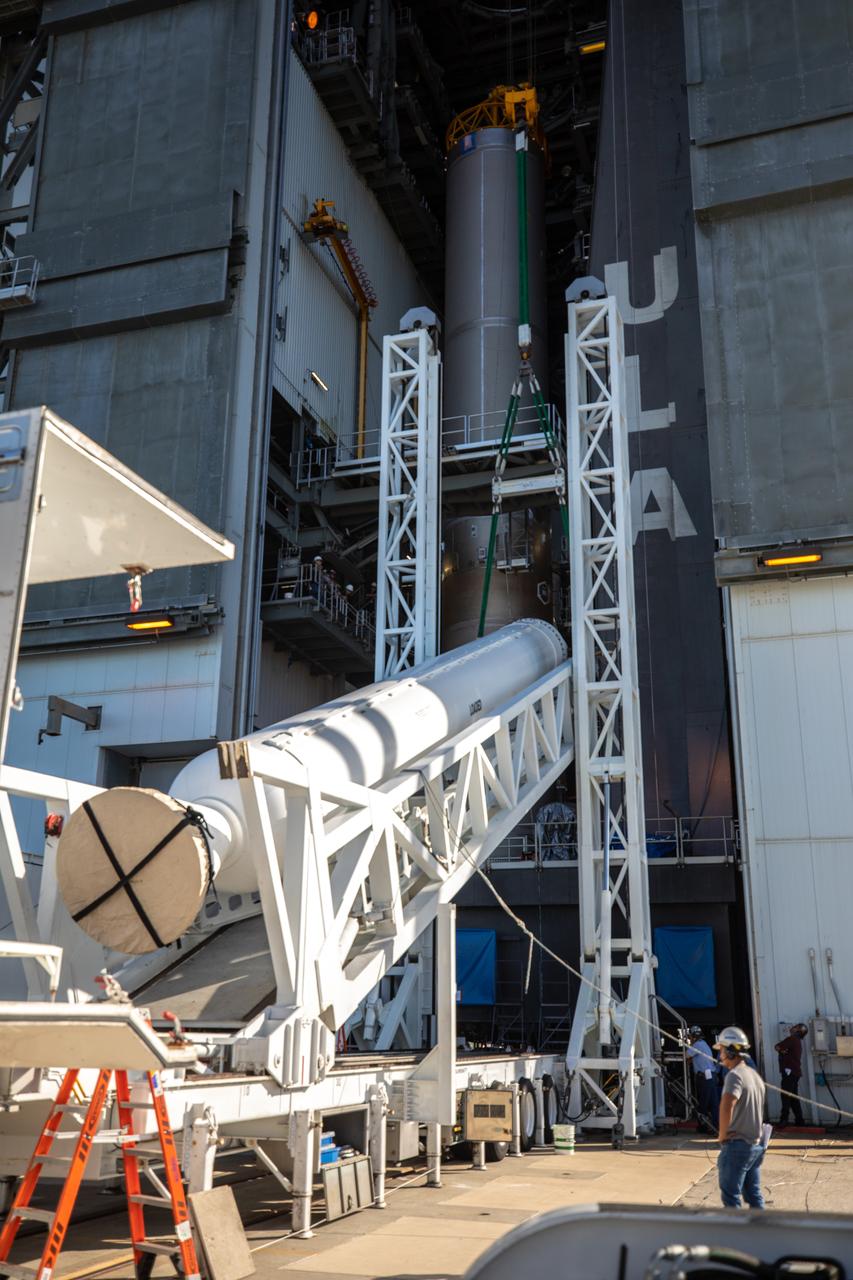

Two solid rocket boosters are mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
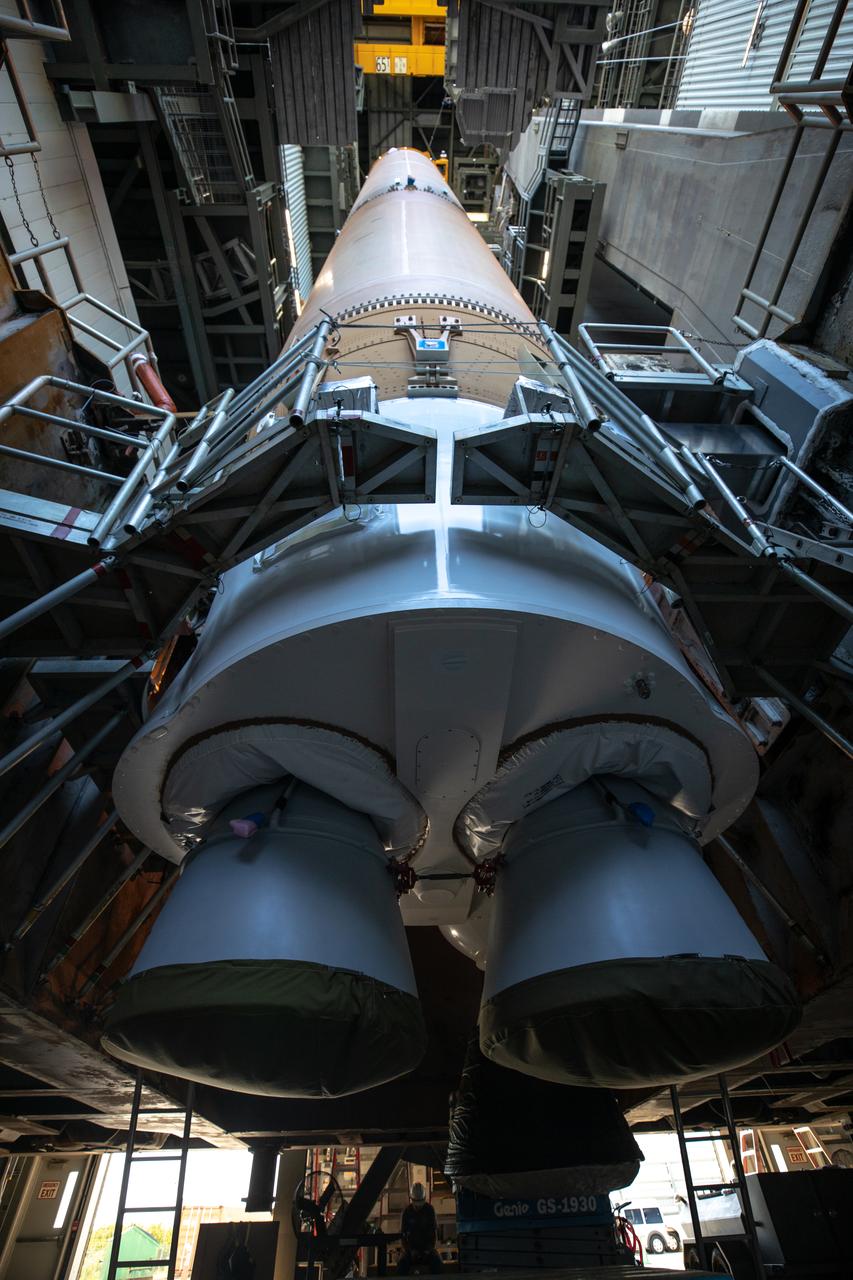

Two solid rocket boosters are mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
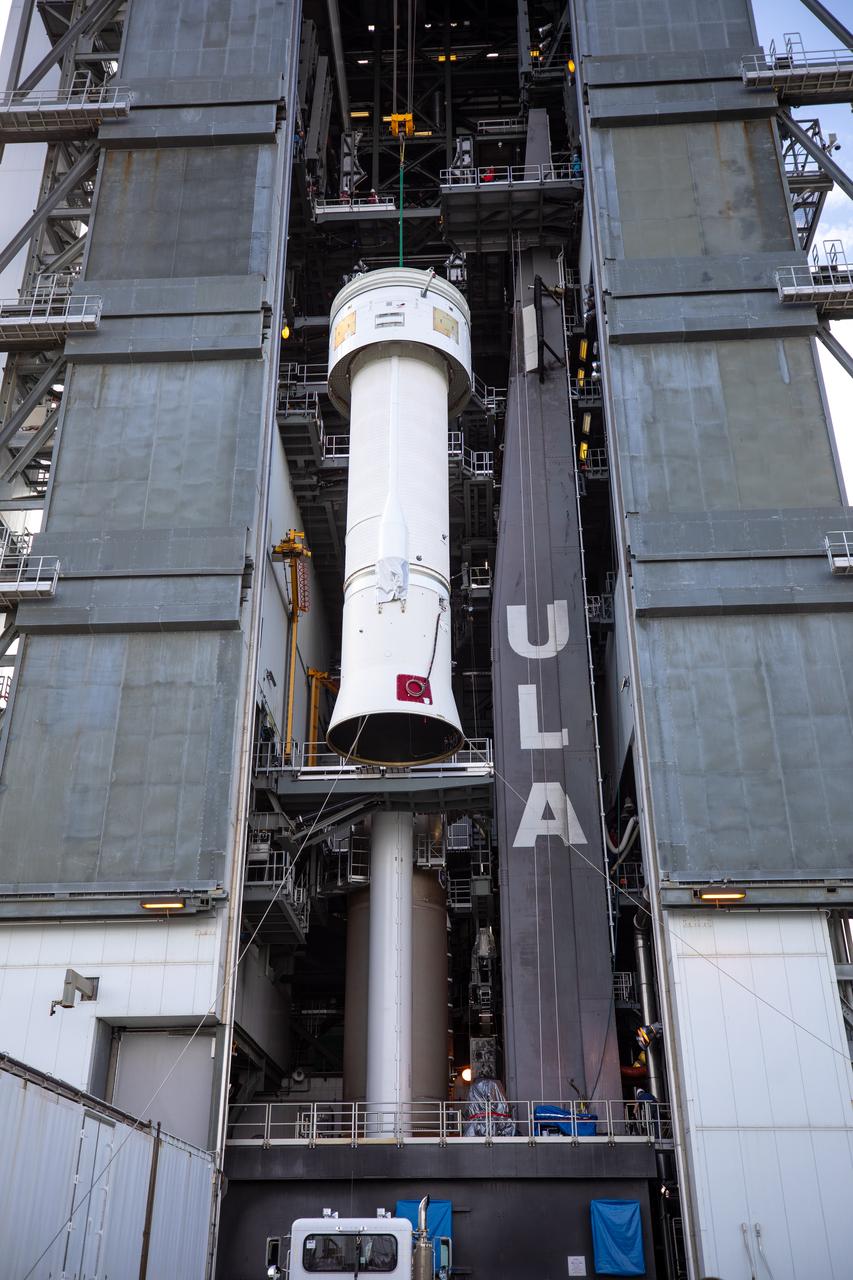

A Centaur upper stage is lifted at the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 8, 2019, for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
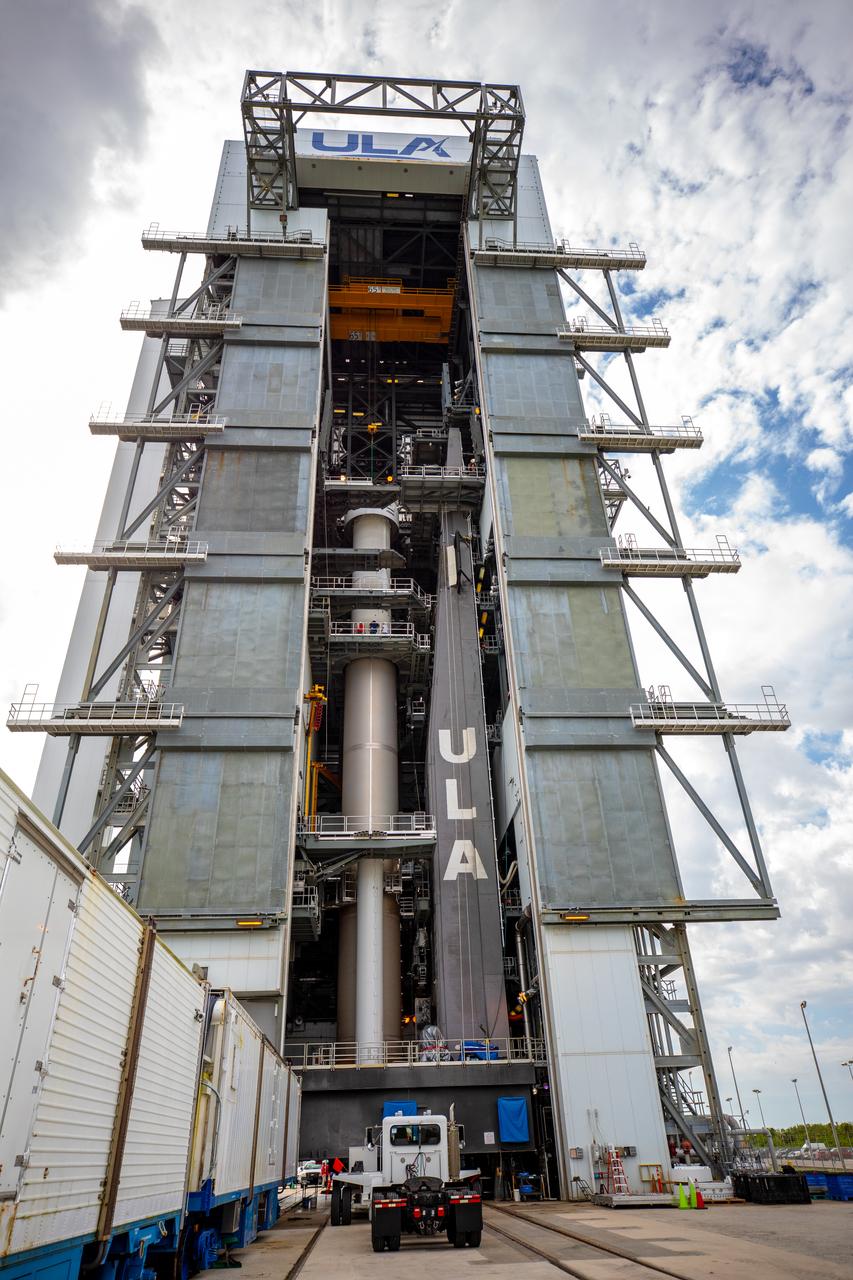

A Centaur upper stage is mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 8, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
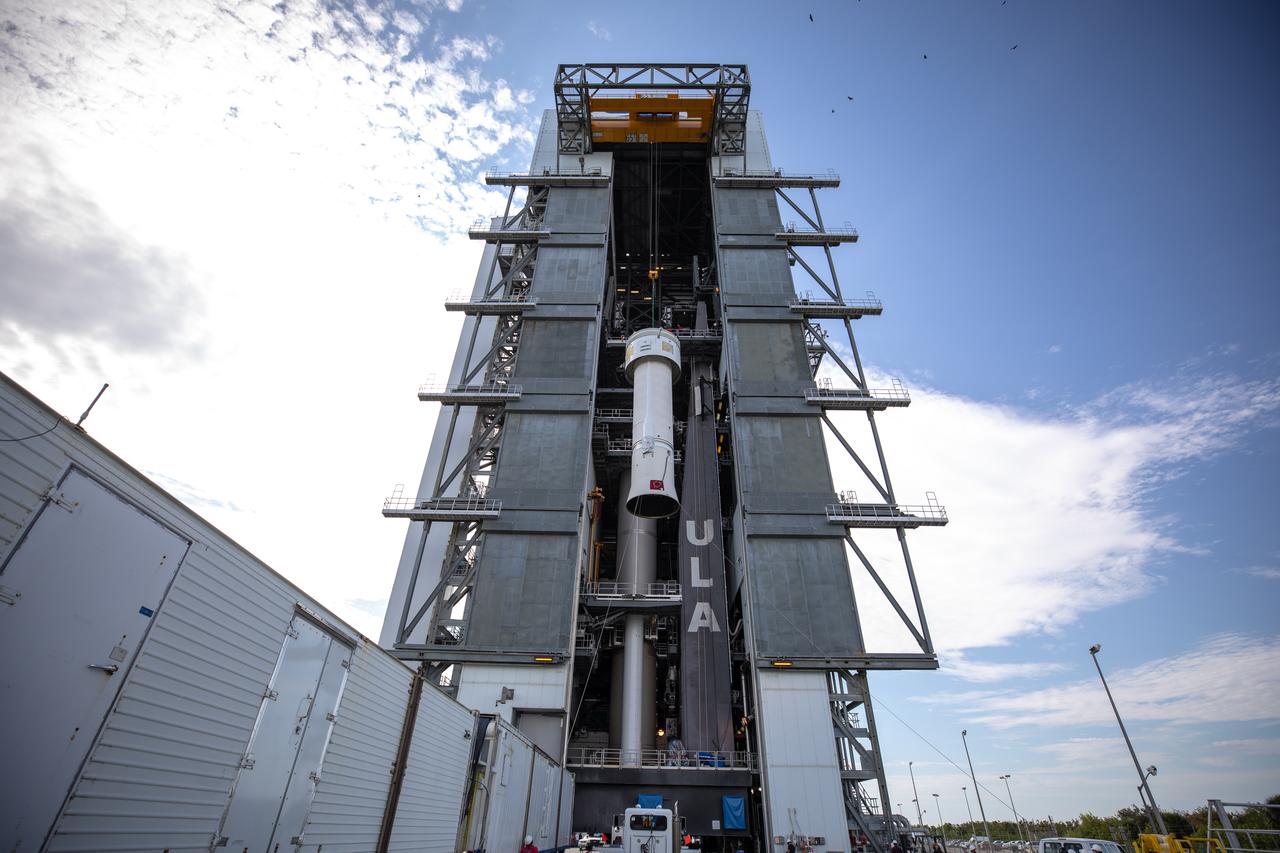

A Centaur upper stage is lifted at the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 8, 2019, for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
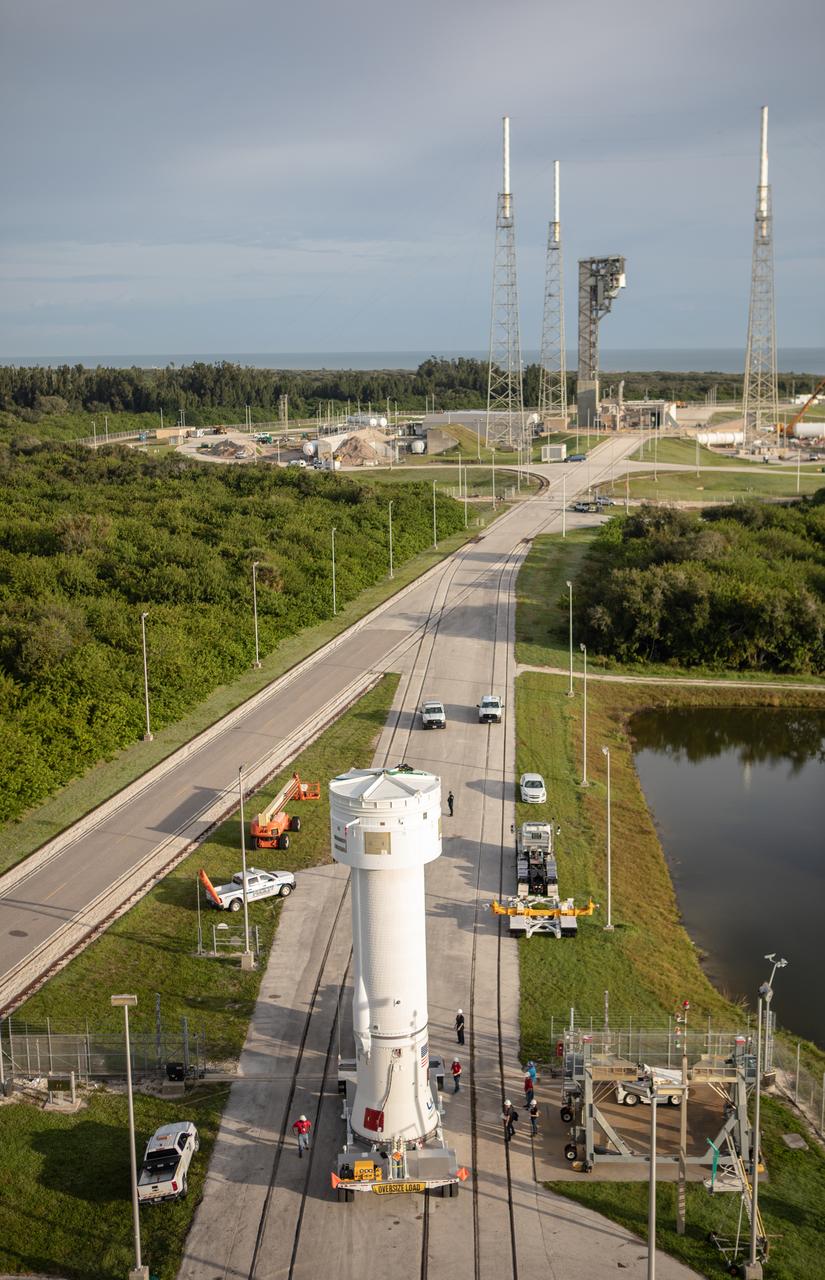

A Centaur upper stage approaches the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 8, 2019, for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
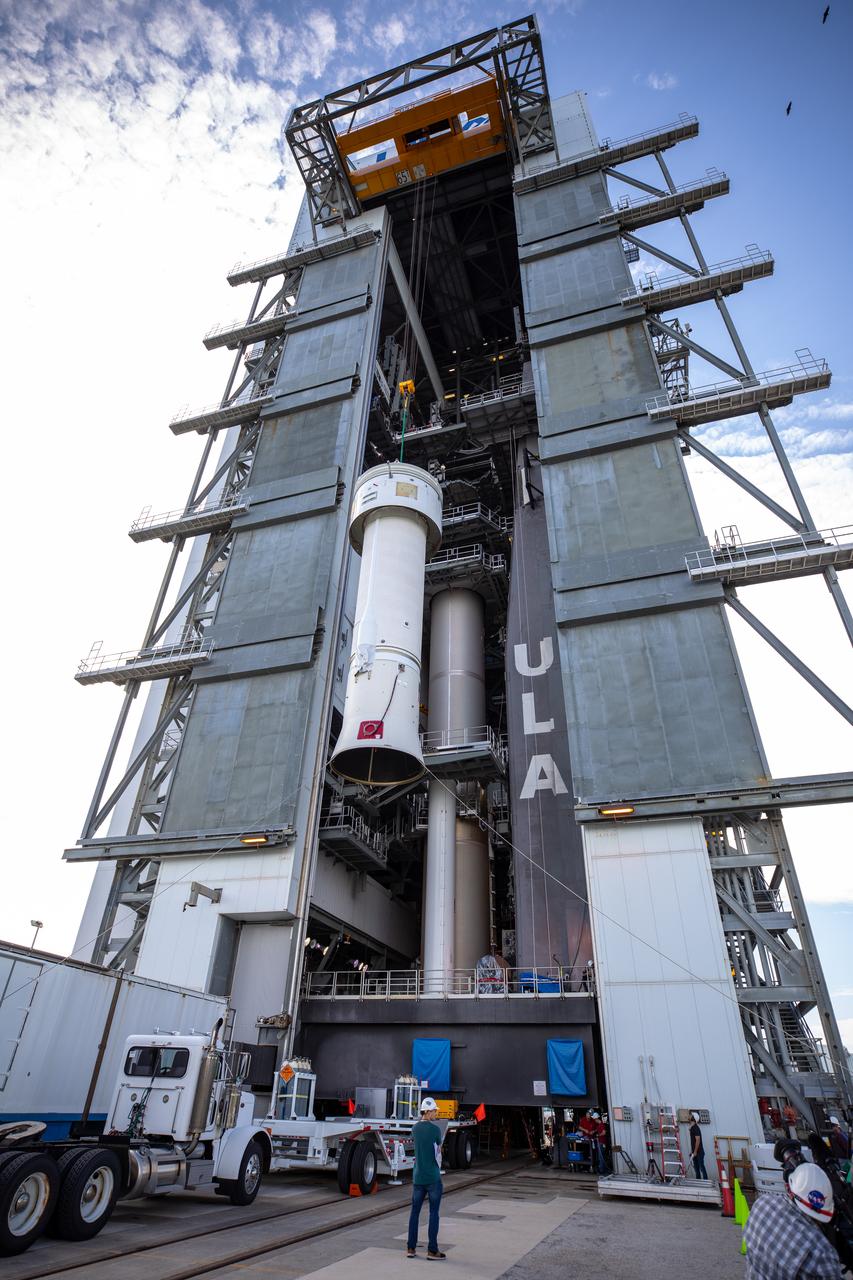

A Centaur upper stage is lifted at the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 8, 2019, for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
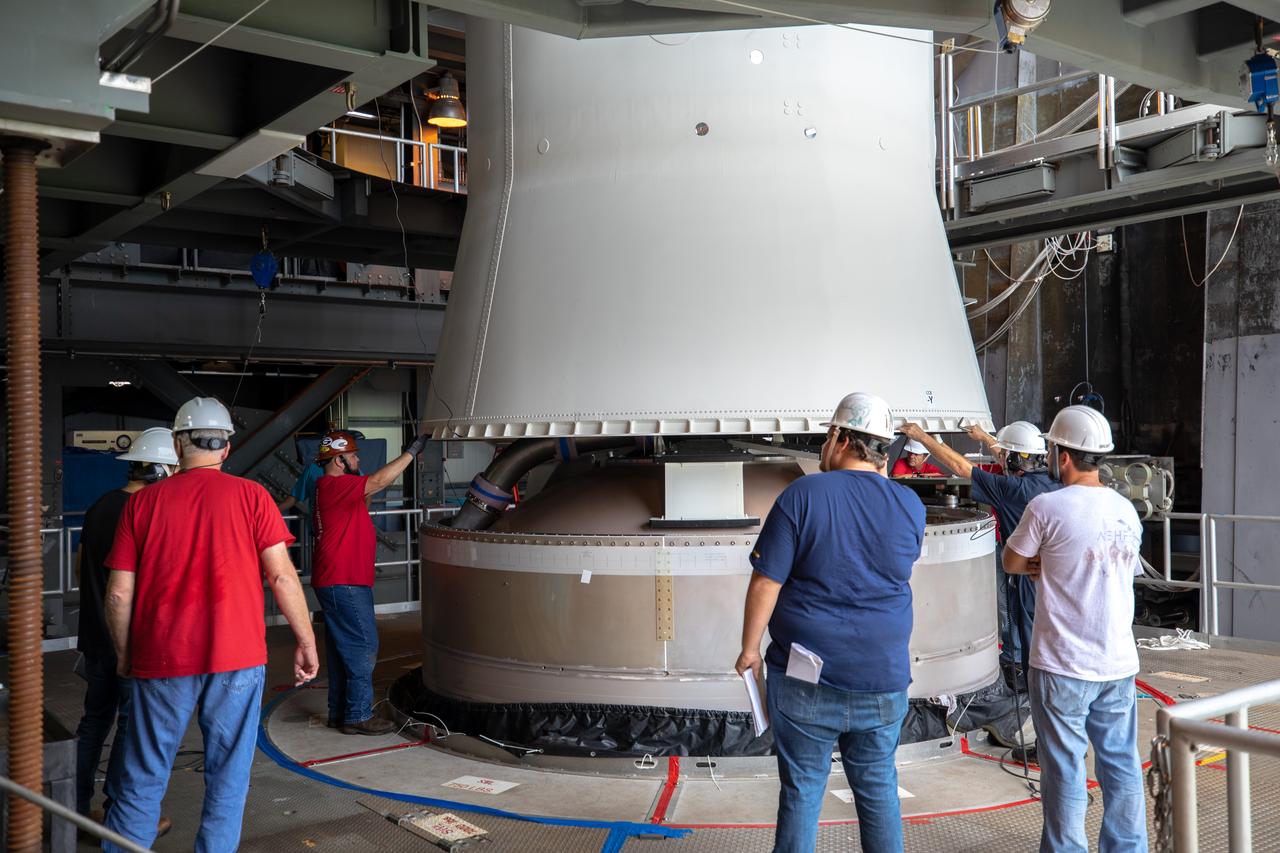

A Centaur upper stage is mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 8, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
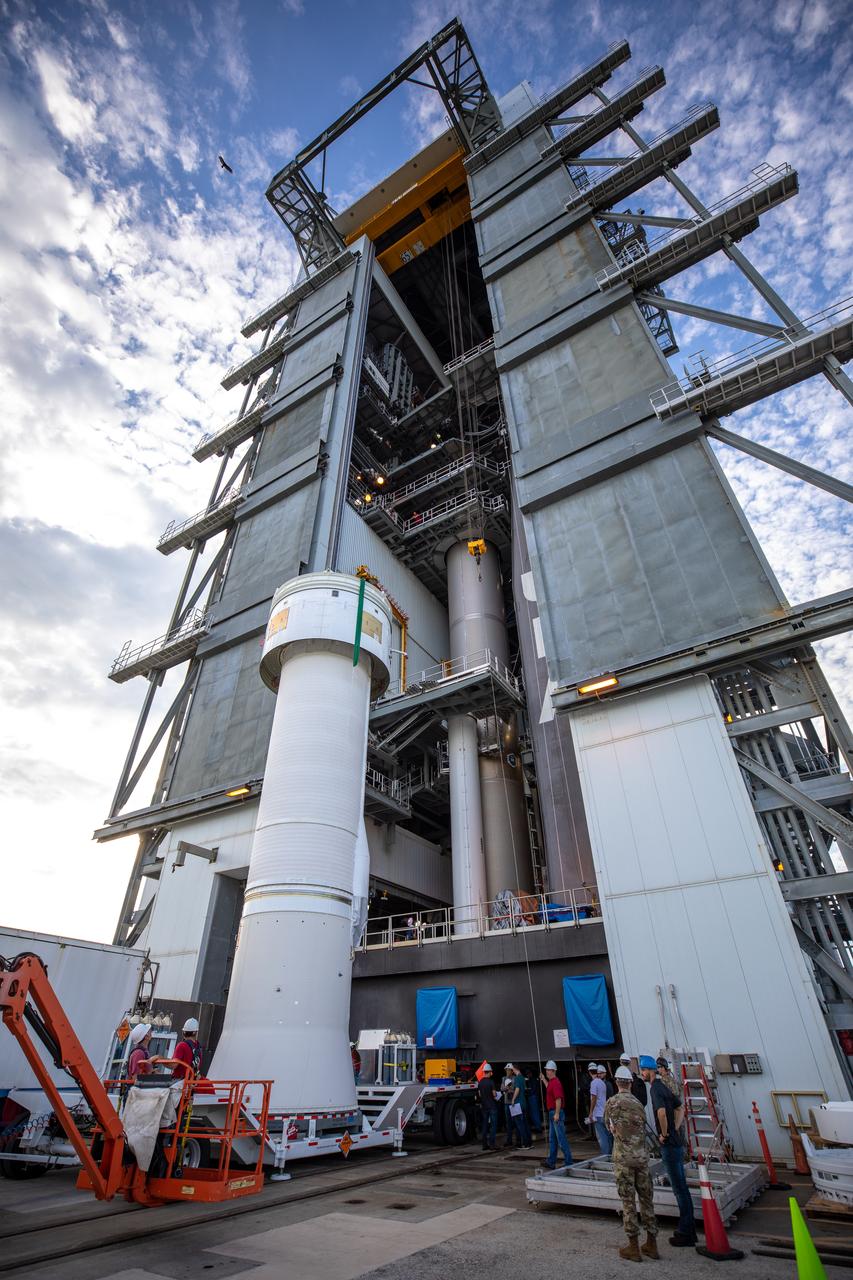

A Centaur upper stage arrives at the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 8, 2019, for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
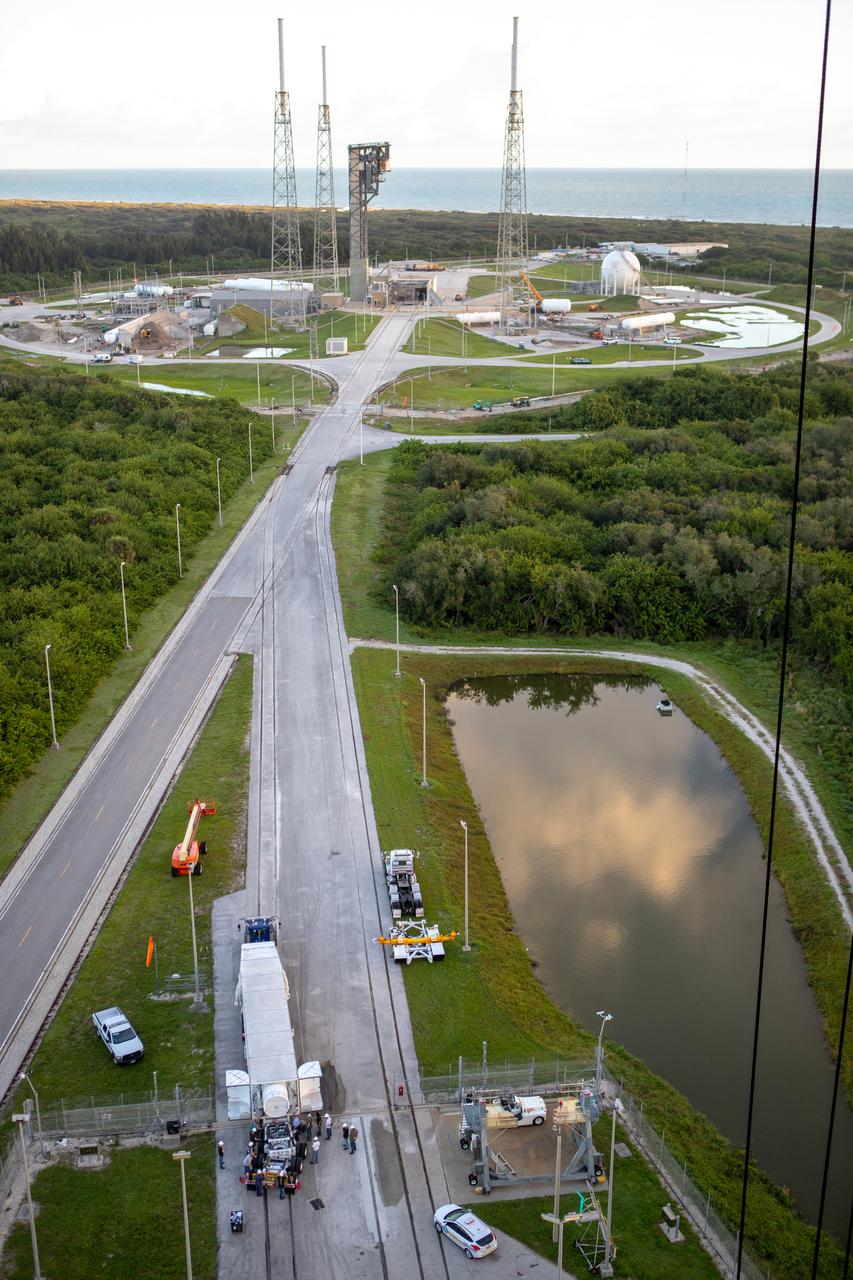

Two solid rocket boosters are delivered to the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2019. The boosters were then mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
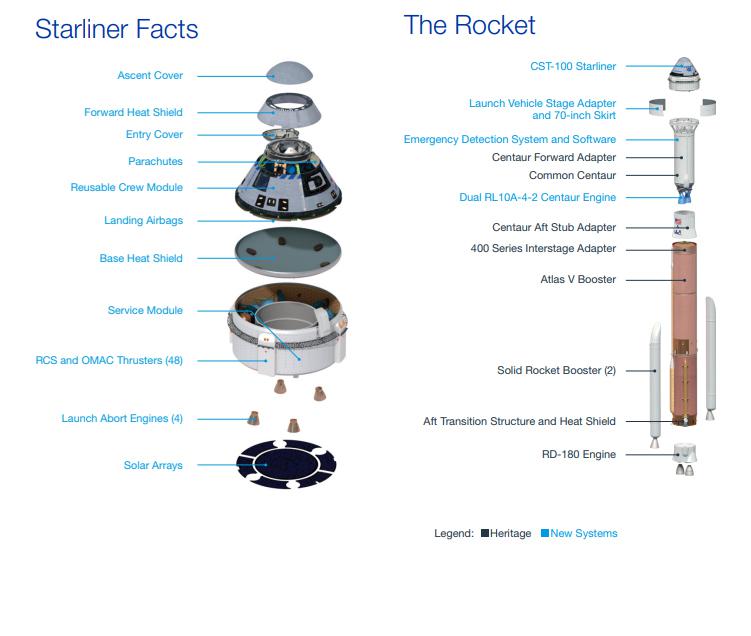
This graphic provides a detailed overview of the makeup of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft, as well as the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
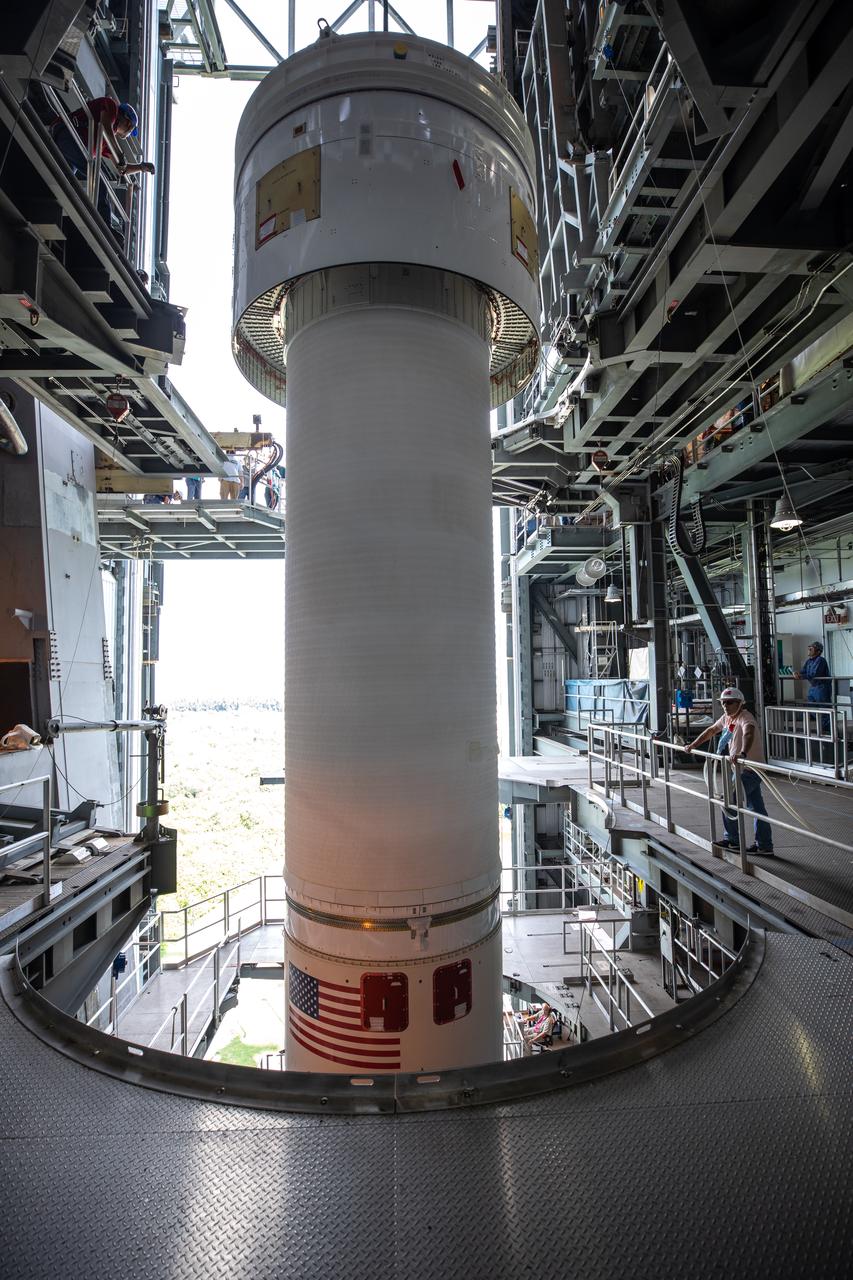

A Centaur upper stage is moved into position above the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 8, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
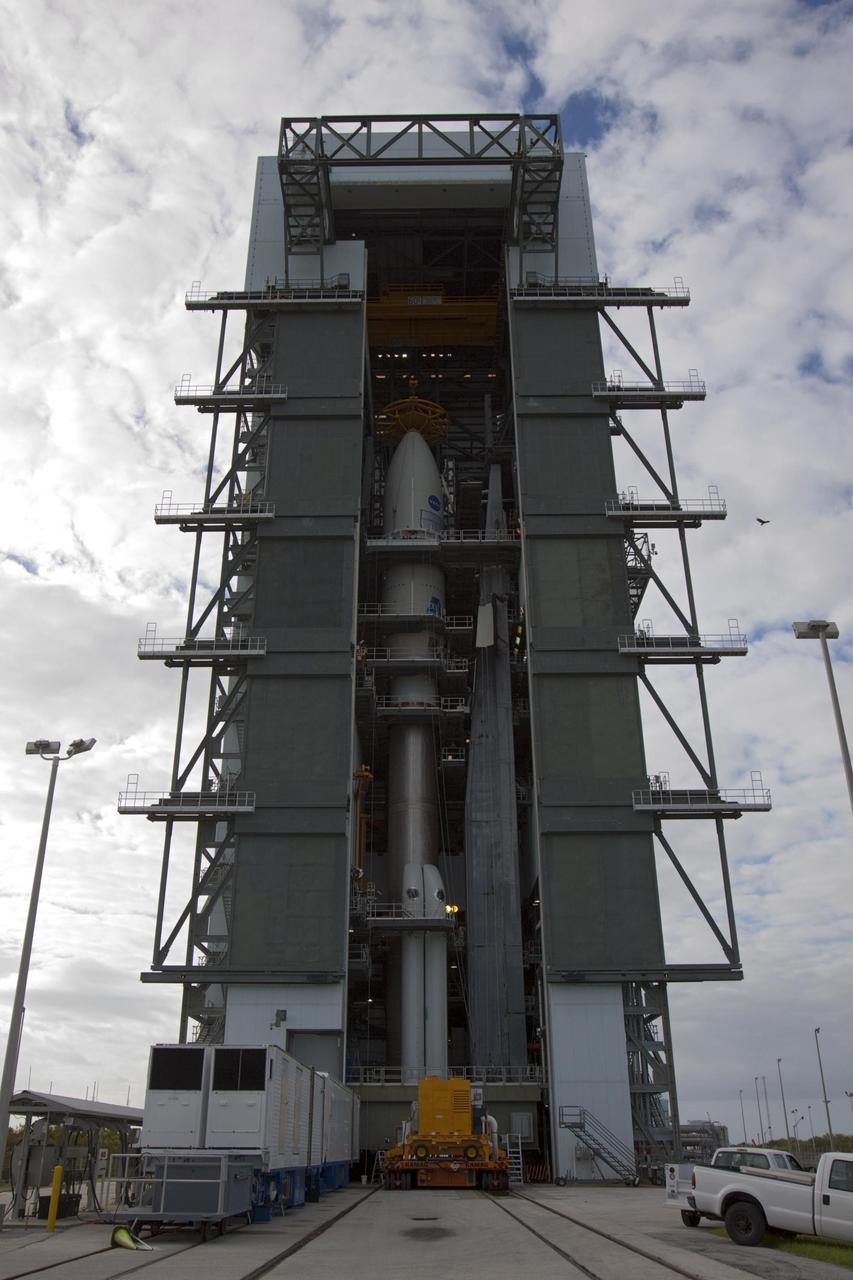

In the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41, the payload fairing containing NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft was attached to its Atlas V rocket on Nov. 3, 2011.
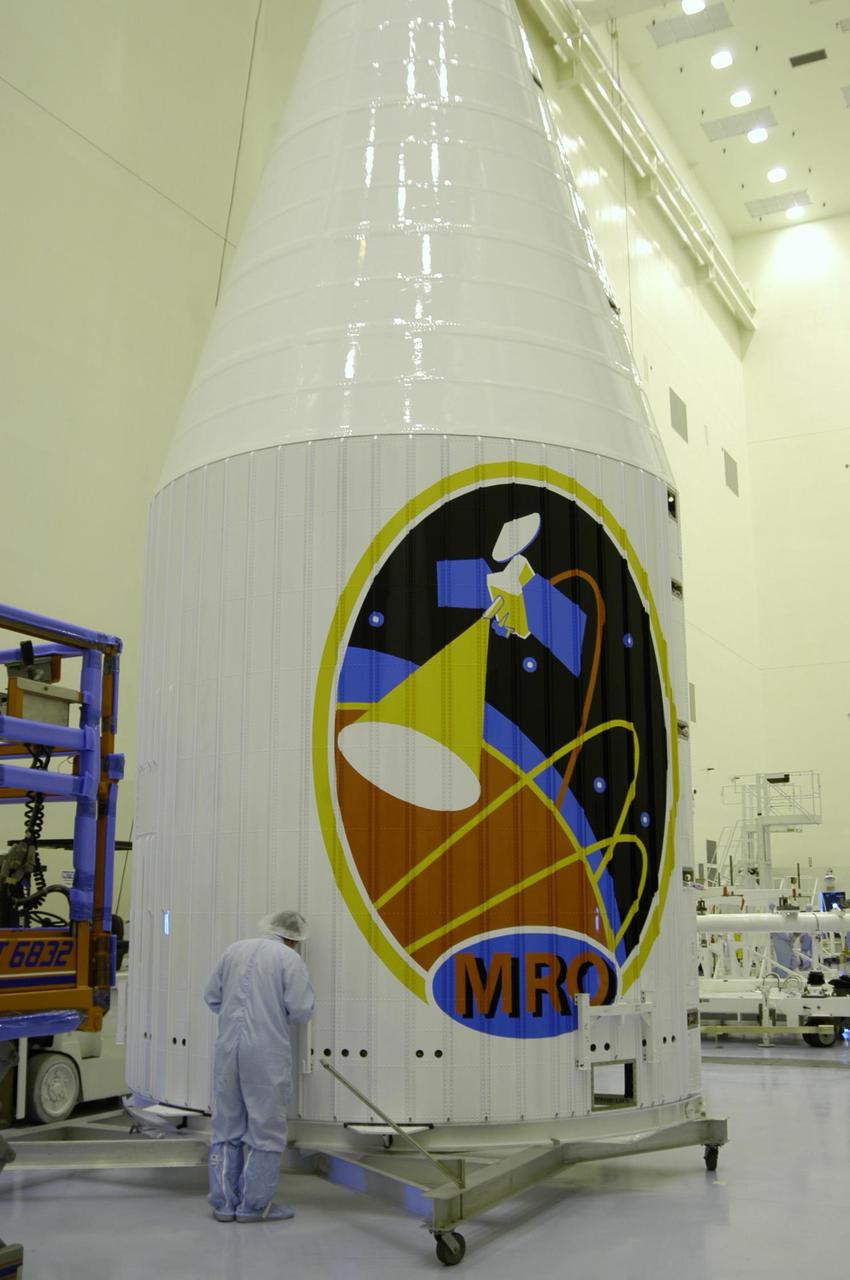

This image features the protective fairing that encapsulated NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter atop an Atlas V rocket. The lively logo celebrates the intense science mission ahead of the orbiter.
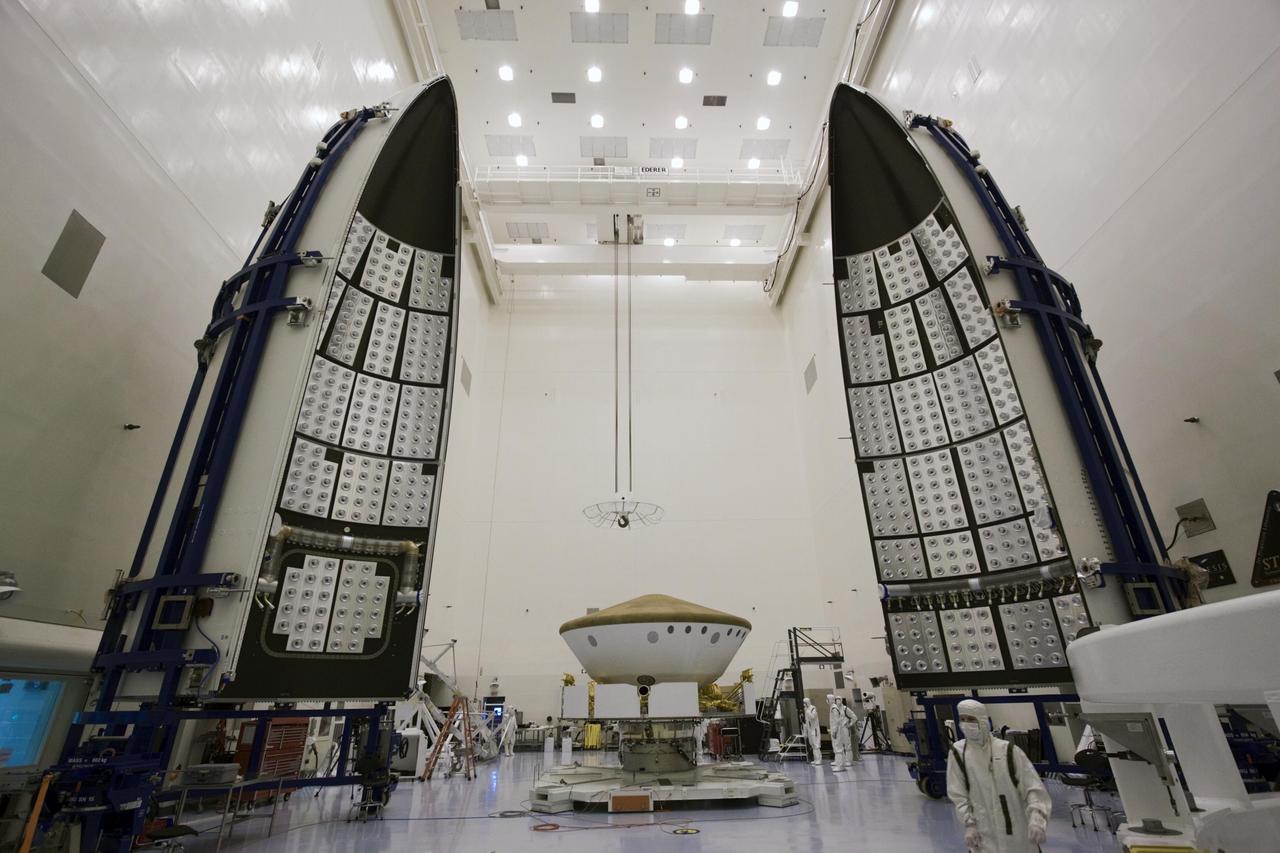

Preparations are under way to enclose NASA Mars Science Laboratory in an Atlas V rocket payload fairing. The fairing protects the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent.
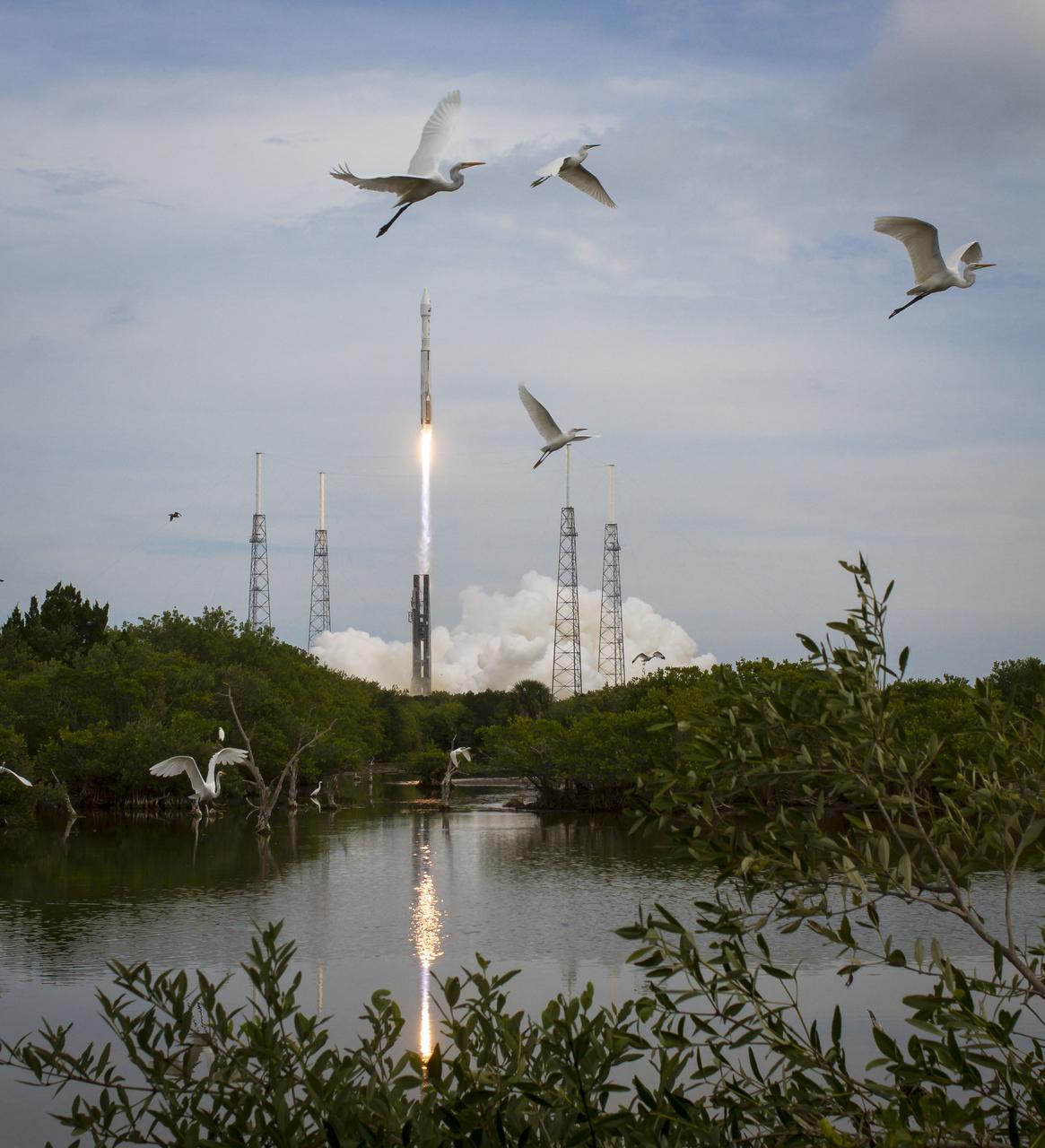

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 41, Monday, Nov. 18, 2013, Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Mars-bound spacecraft, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, is the first spacecraft devoted to exploring and understanding the Martian upper atmosphere. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 41, Monday, Nov. 18, 2013, Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Mars-bound spacecraft, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, is the first spacecraft devoted to exploring and understanding the Martian upper atmosphere. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
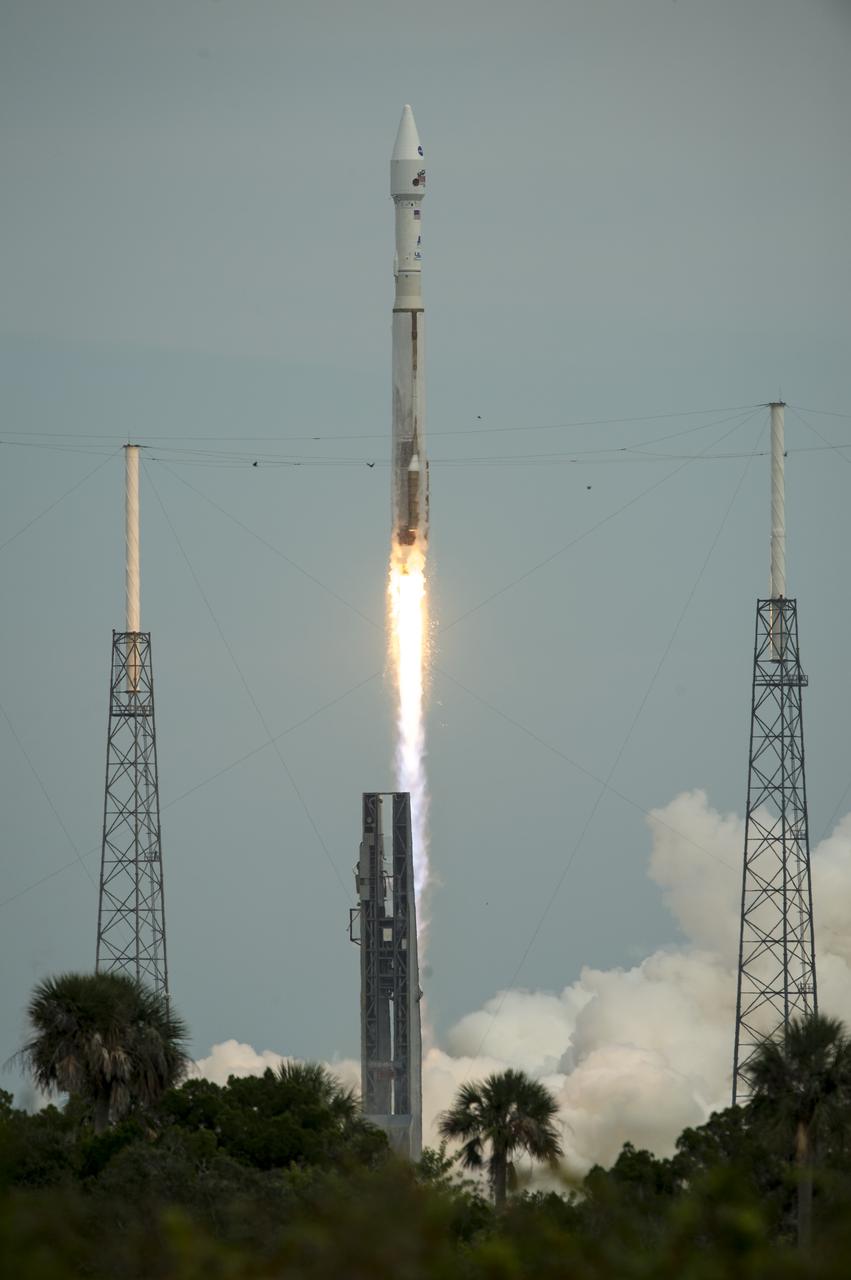

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 41, Monday, Nov. 18, 2013, Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Mars-bound spacecraft, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, is the first spacecraft devoted to exploring and understanding the Martian upper atmosphere. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
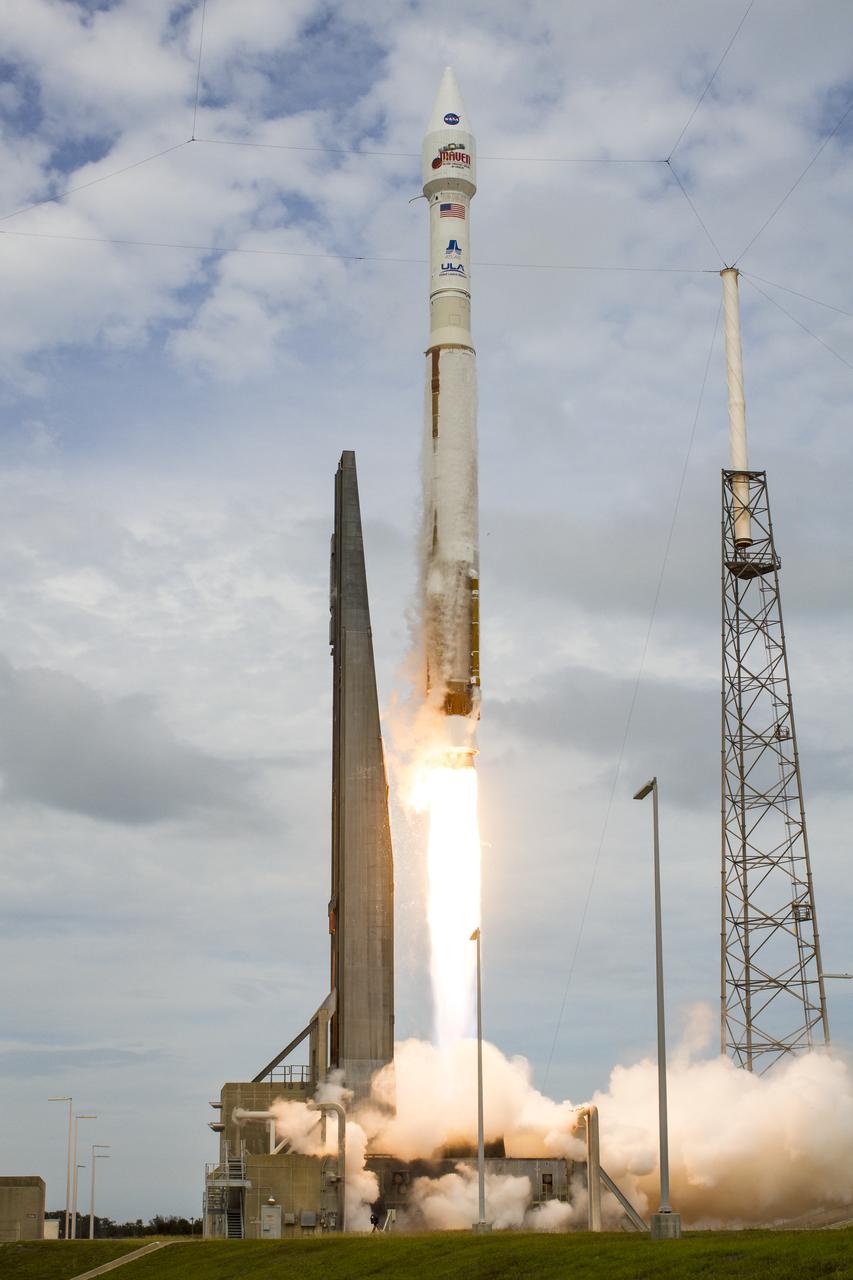

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) spacecraft launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 41, Monday, Nov. 18, 2013, Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Mars-bound spacecraft, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutionN, or MAVEN, is the first spacecraft devoted to exploring and understanding the Martian upper atmosphere. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
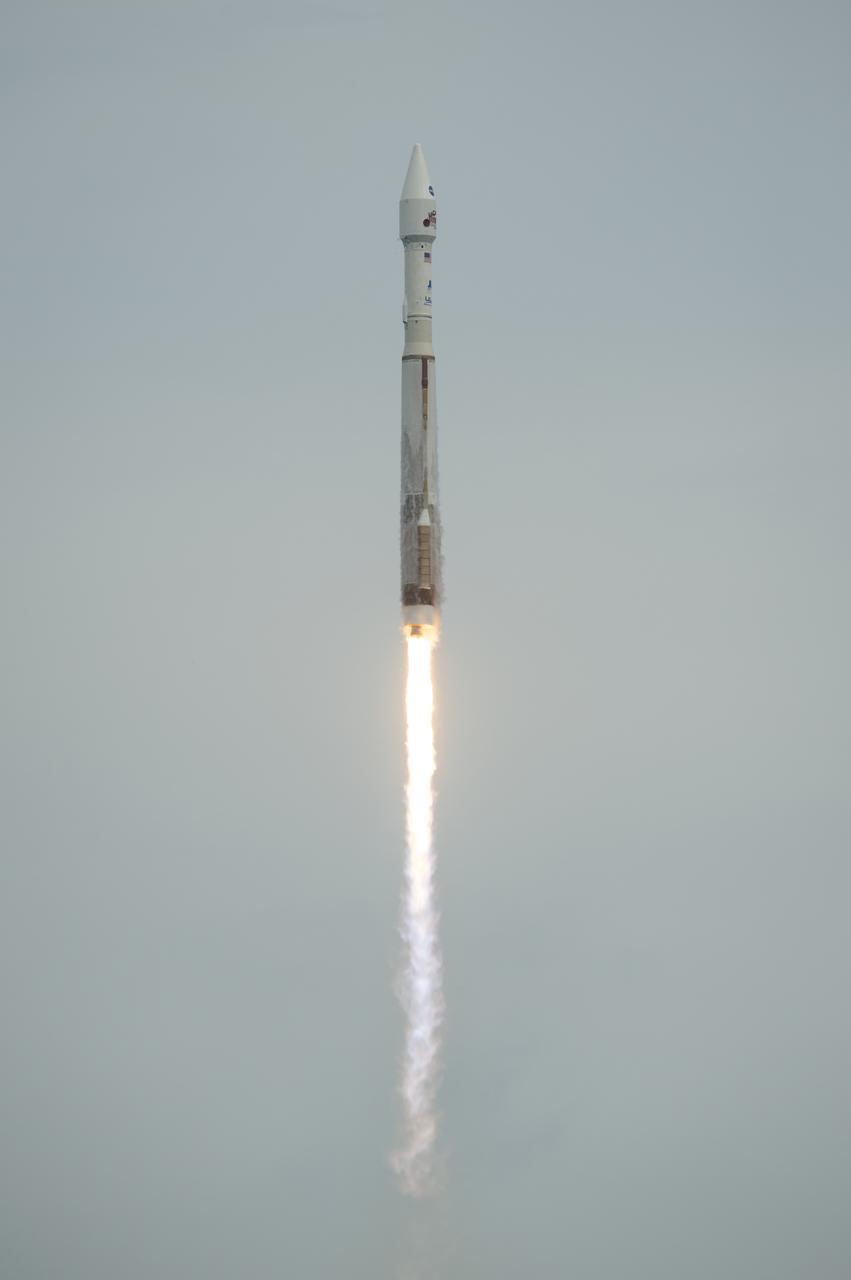

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 41, Monday, Nov. 18, 2013, Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Mars-bound spacecraft, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, is the first spacecraft devoted to exploring and understanding the Martian upper atmosphere. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
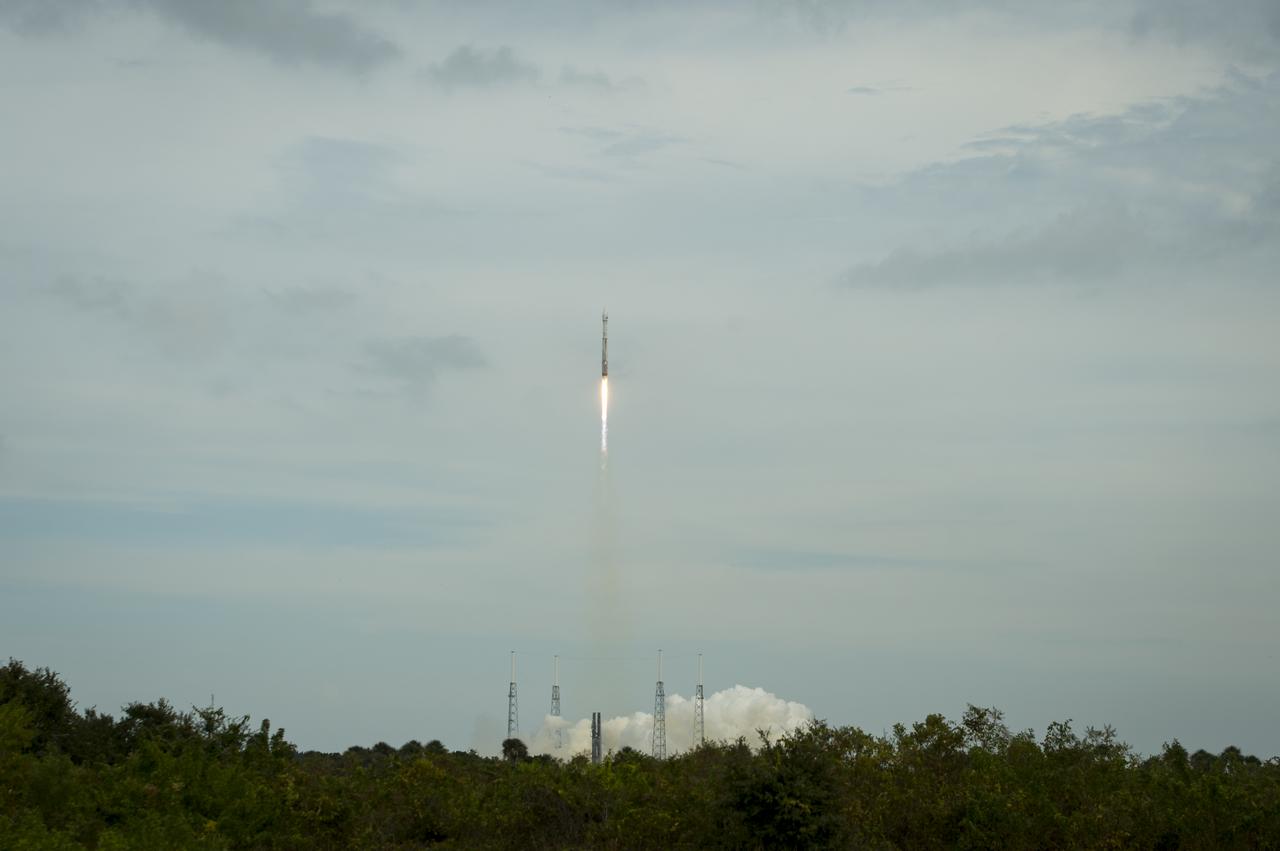

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 41, Monday, Nov. 18, 2013, Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Mars-bound spacecraft, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, is the first spacecraft devoted to exploring and understanding the Martian upper atmosphere. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
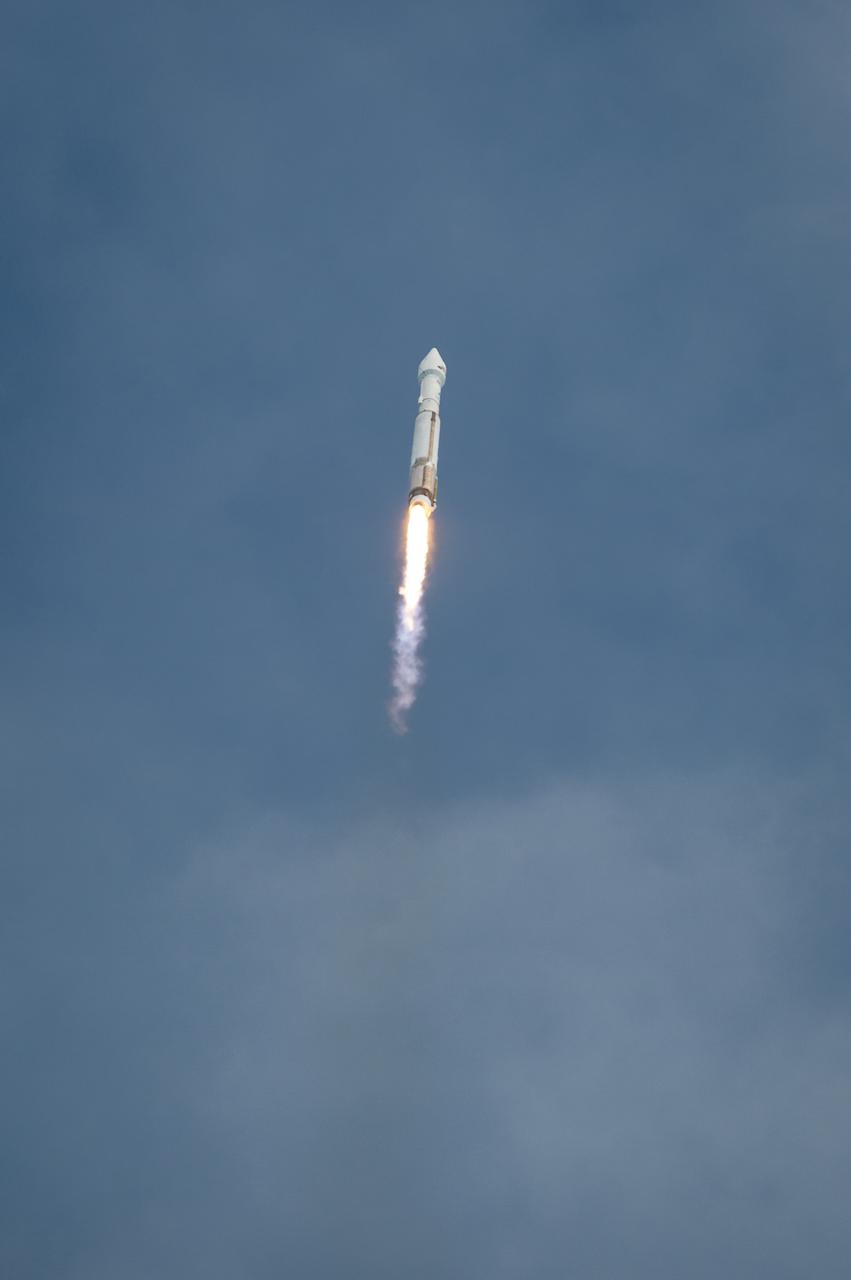

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 41, Monday, Nov. 18, 2013, Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Mars-bound spacecraft, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, is the first spacecraft devoted to exploring and understanding the Martian upper atmosphere. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
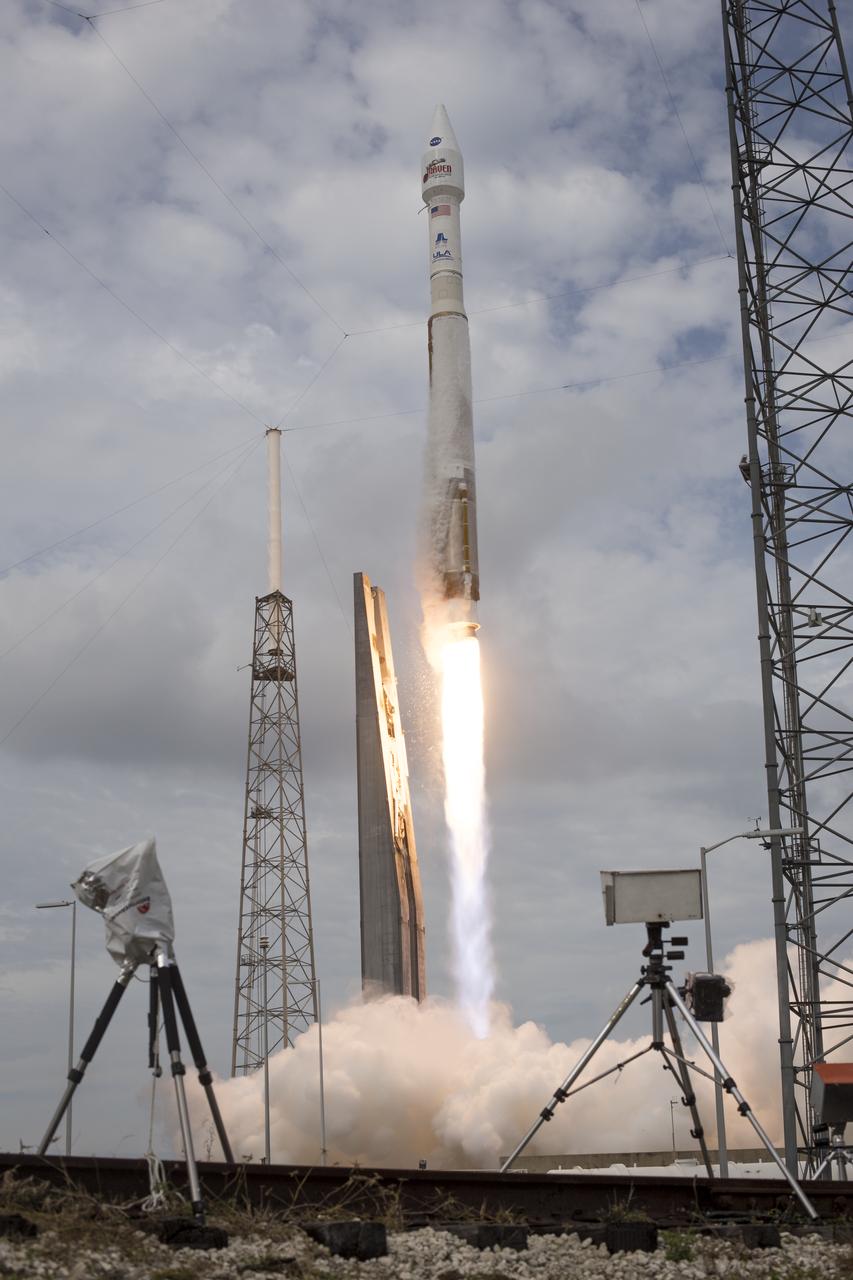

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 41, Monday, Nov. 18, 2013, Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Mars-bound spacecraft, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, is the first spacecraft devoted to exploring and understanding the Martian upper atmosphere. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
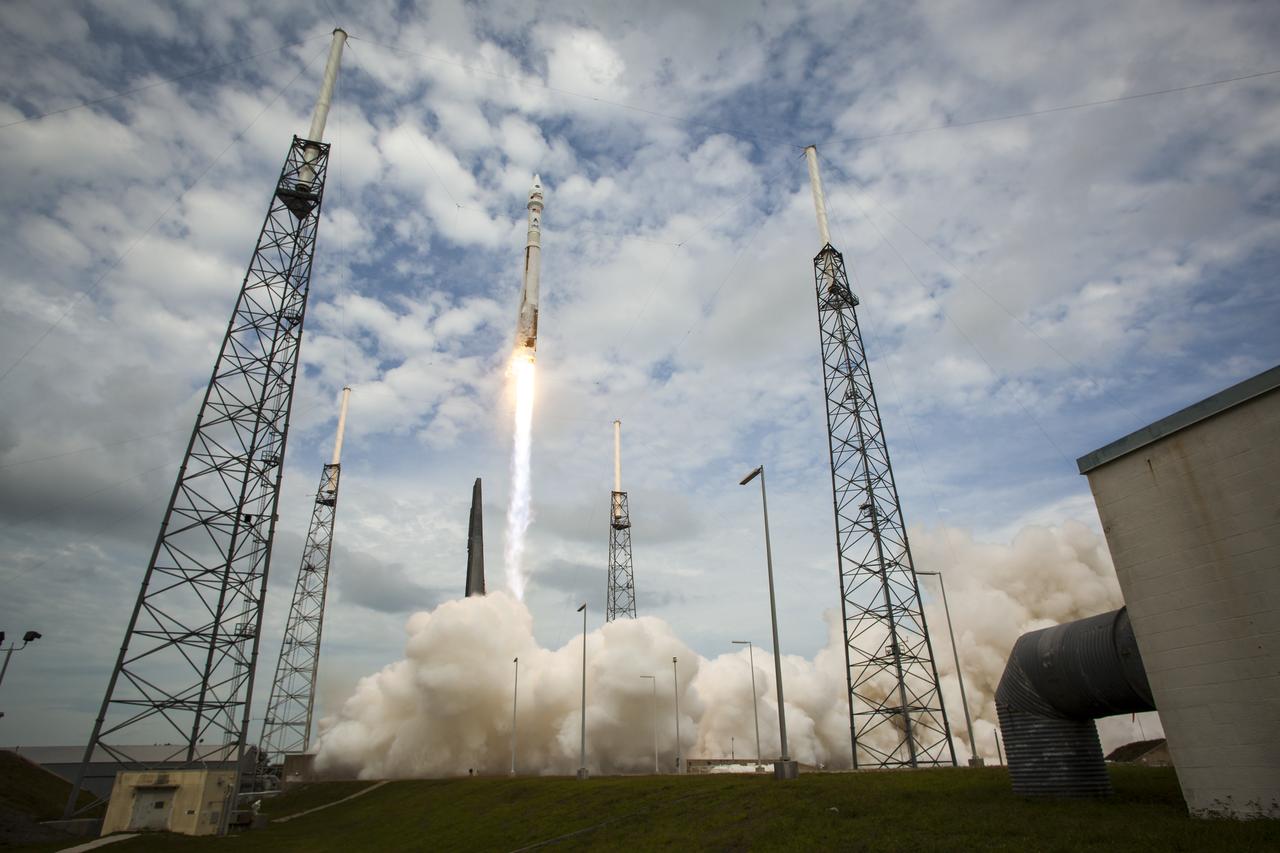

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 41, Monday, Nov. 18, 2013, Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Mars-bound spacecraft, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, is the first spacecraft devoted to exploring and understanding the Martian upper atmosphere. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
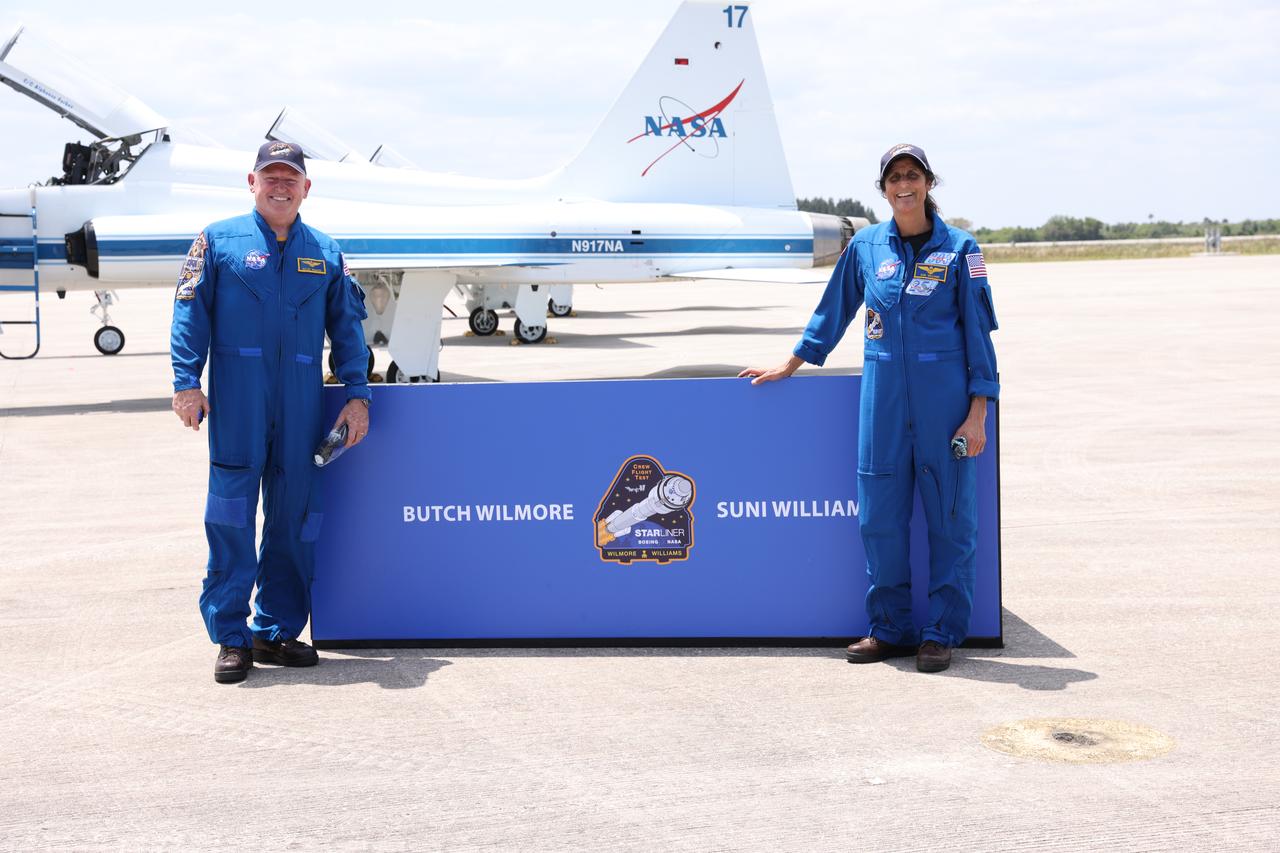

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Associate Director Jennifer Kunz and NASA Commercial Crew Program Deputy Manager Dana Hutcherson participate in a media event at the Florida spaceport on Thursday, April 25, 2024, upon the arrival of NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams for the agency’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station. As part of the NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 10:34 p.m. EDT on Monday, May 6. The Atlas V will lift off from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
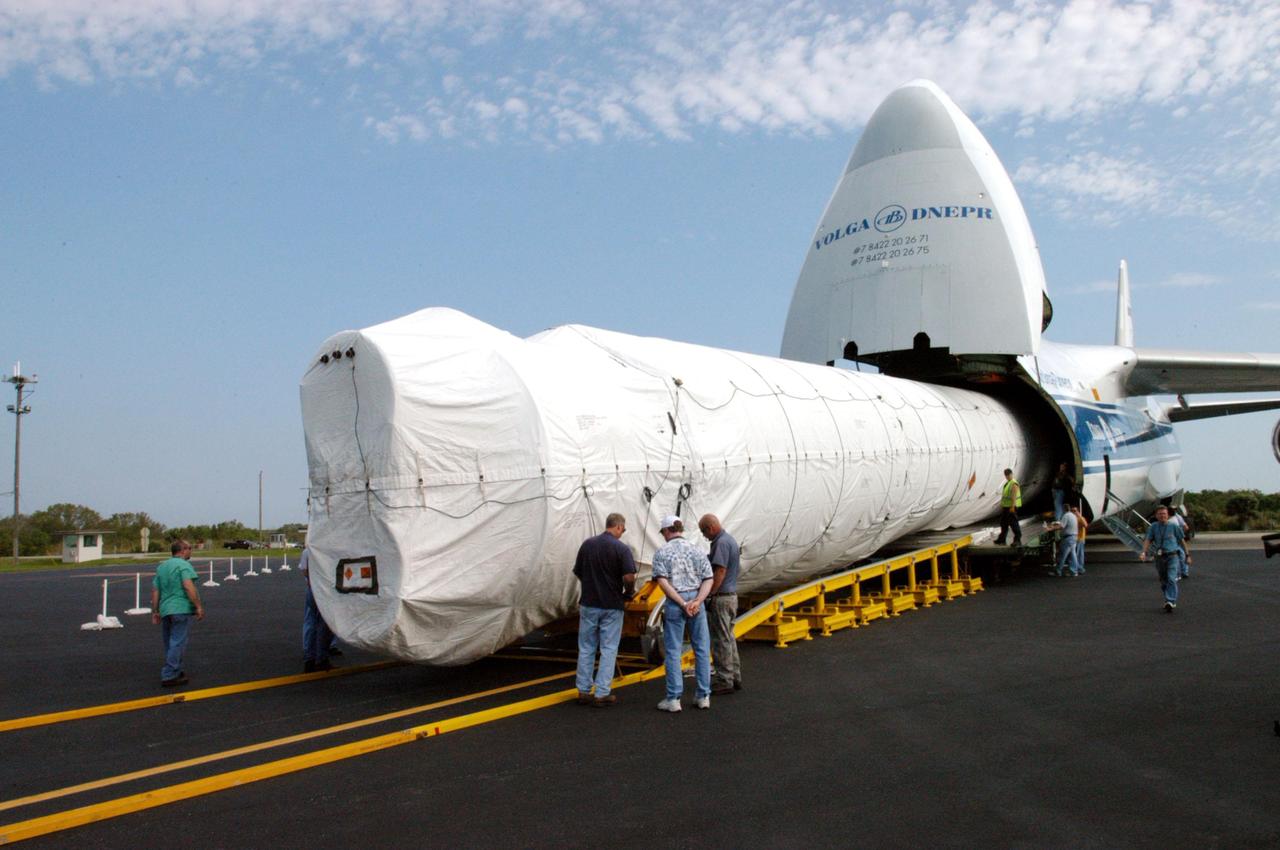

Lockheed Martin delivering the Atlas V rocket to Cape Canaveral in July of 2005. After going through a series of tests to ensure its readiness to send Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to the red planet, lift-off occurred on August 12, 2005.
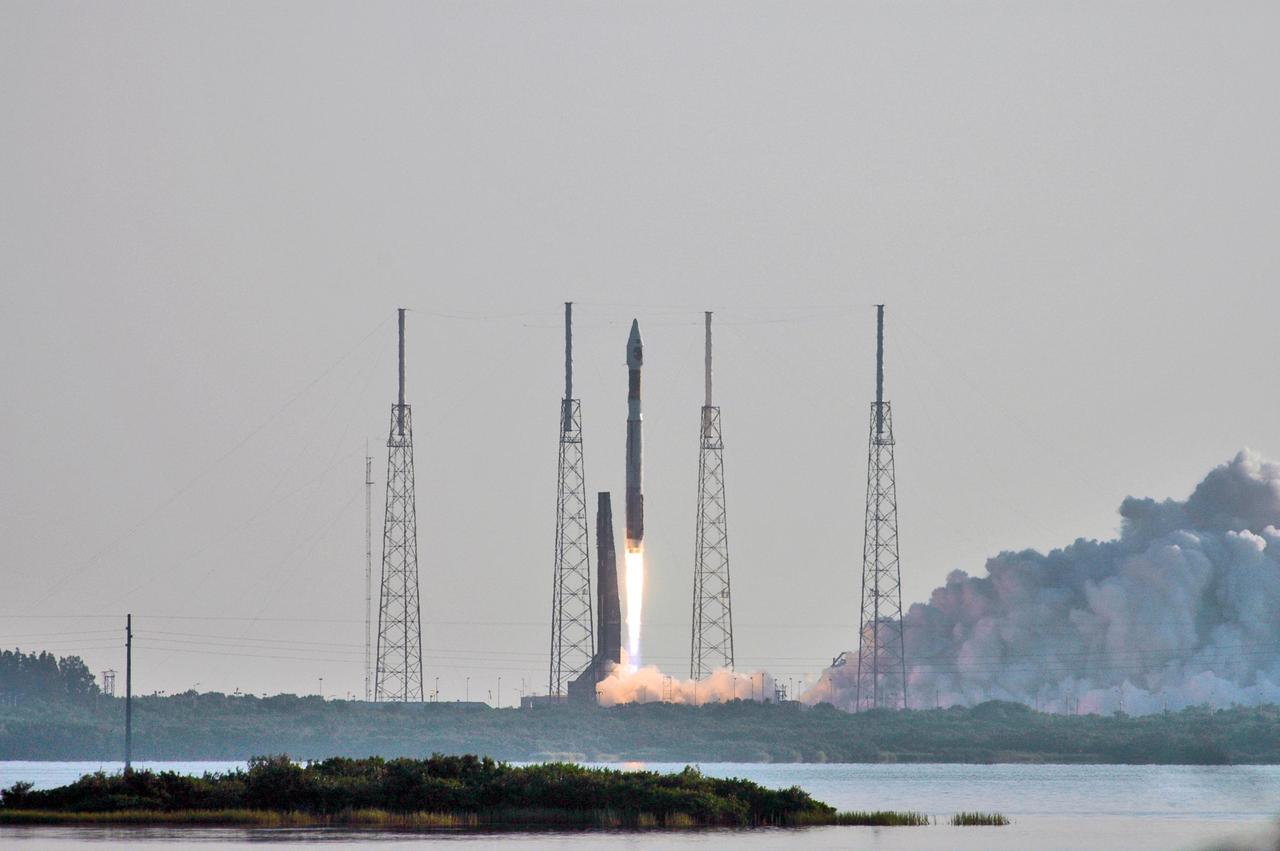

NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO launched at 7:43 a.m. EDT atop a Lockheed Martin Atlas V rocket from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Aug. 12, 2005.
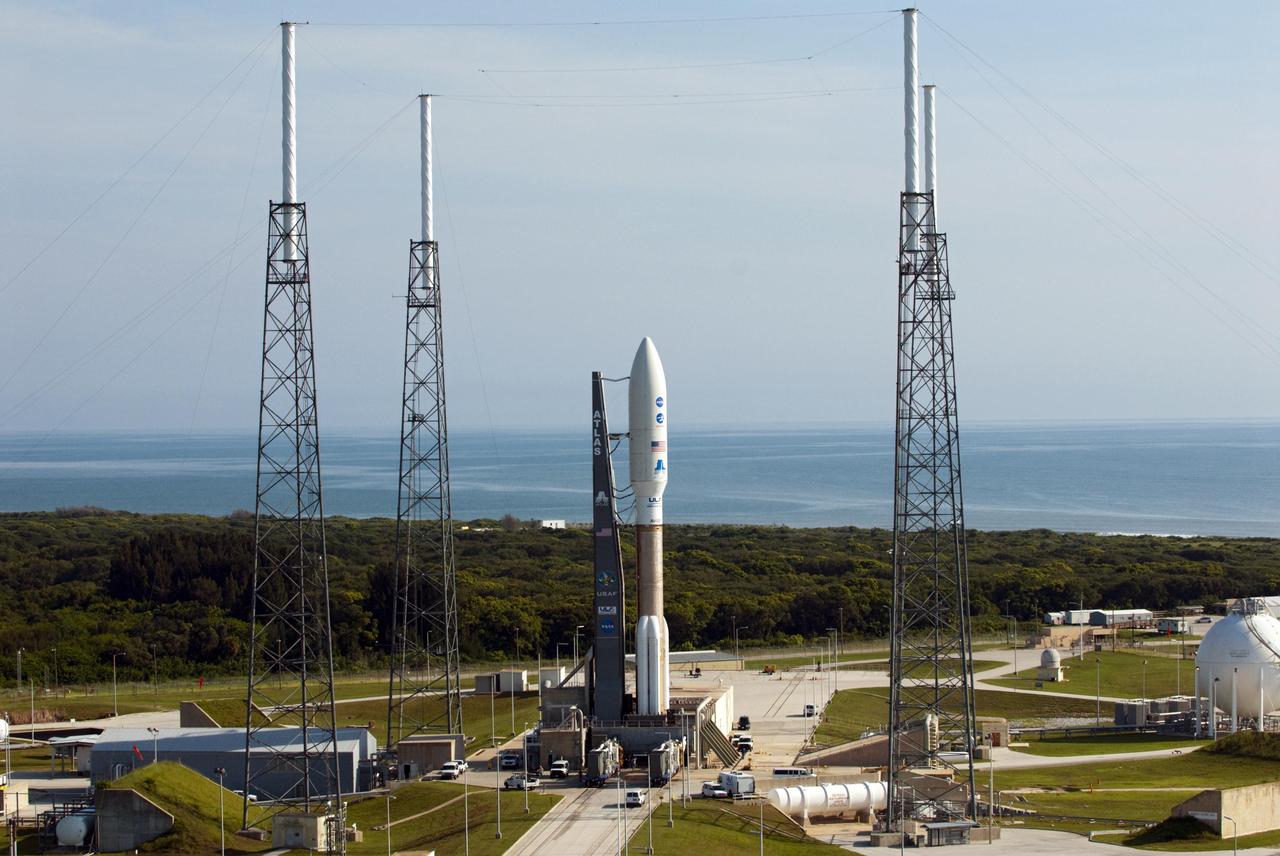

NASA Juno spacecraft awaits launch from inside the payload fairing atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V-551 launch vehicle. Juno and its rocket are at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
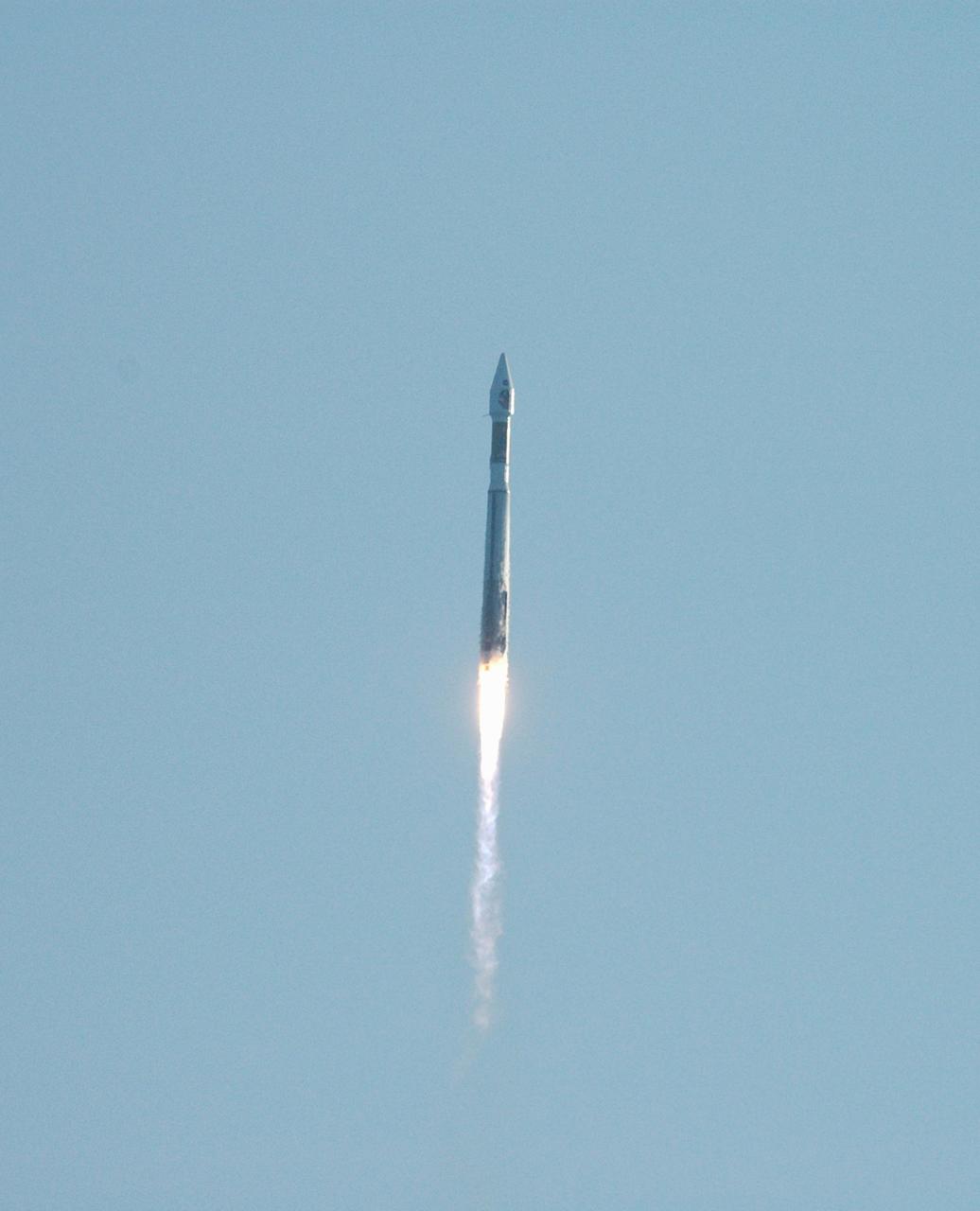

NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO launched at 7:43 a.m. EDT atop a Lockheed Martin Atlas V rocket from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Aug. 12, 2005.
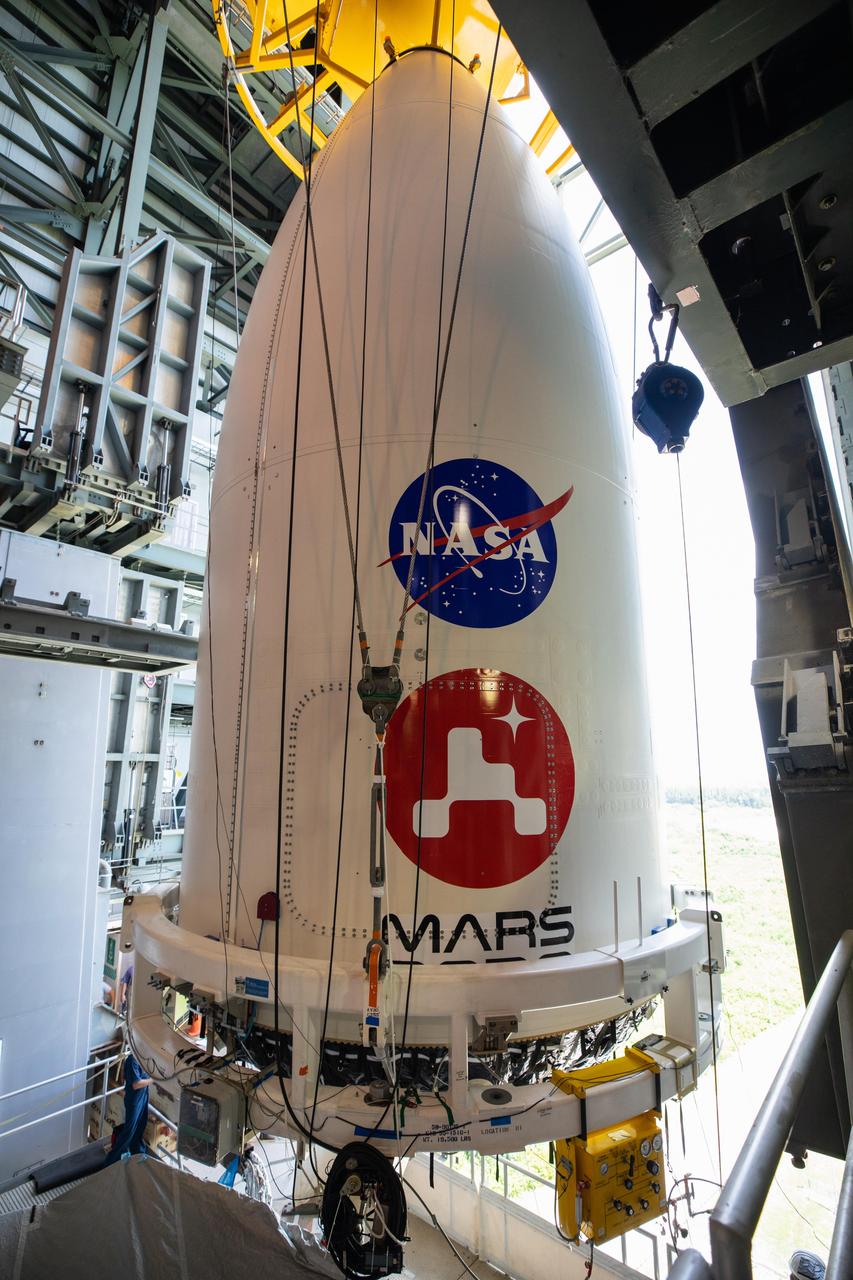

The payload fairing, or nose cone, containing NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover is maneuvered into place atop the Atlas V rocket that will hurl it toward Mars. The image was taken on July 7, 2020, inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23986
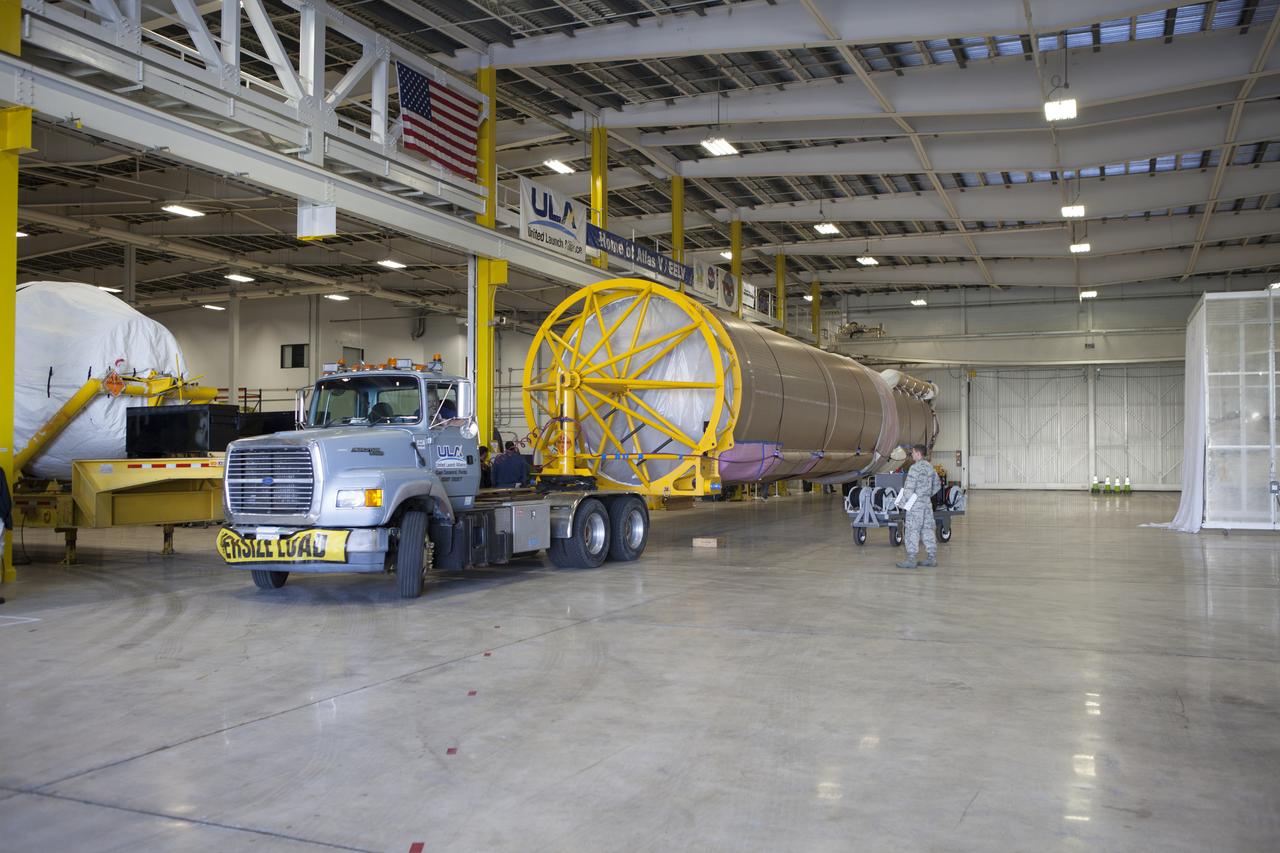

A truck positions an Atlas V booster stage inside the hangar at the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.
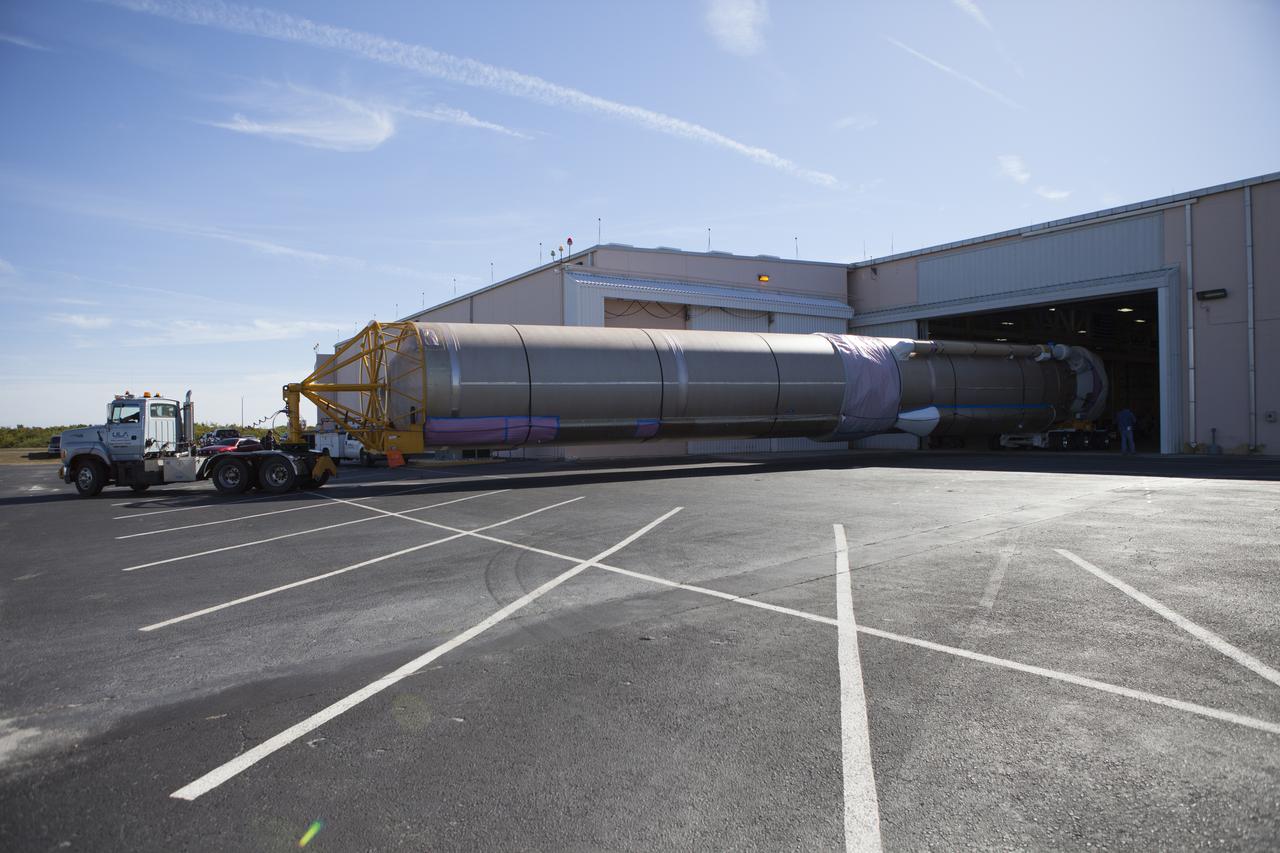

A truck positions an Atlas V booster stage inside the hangar at the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.
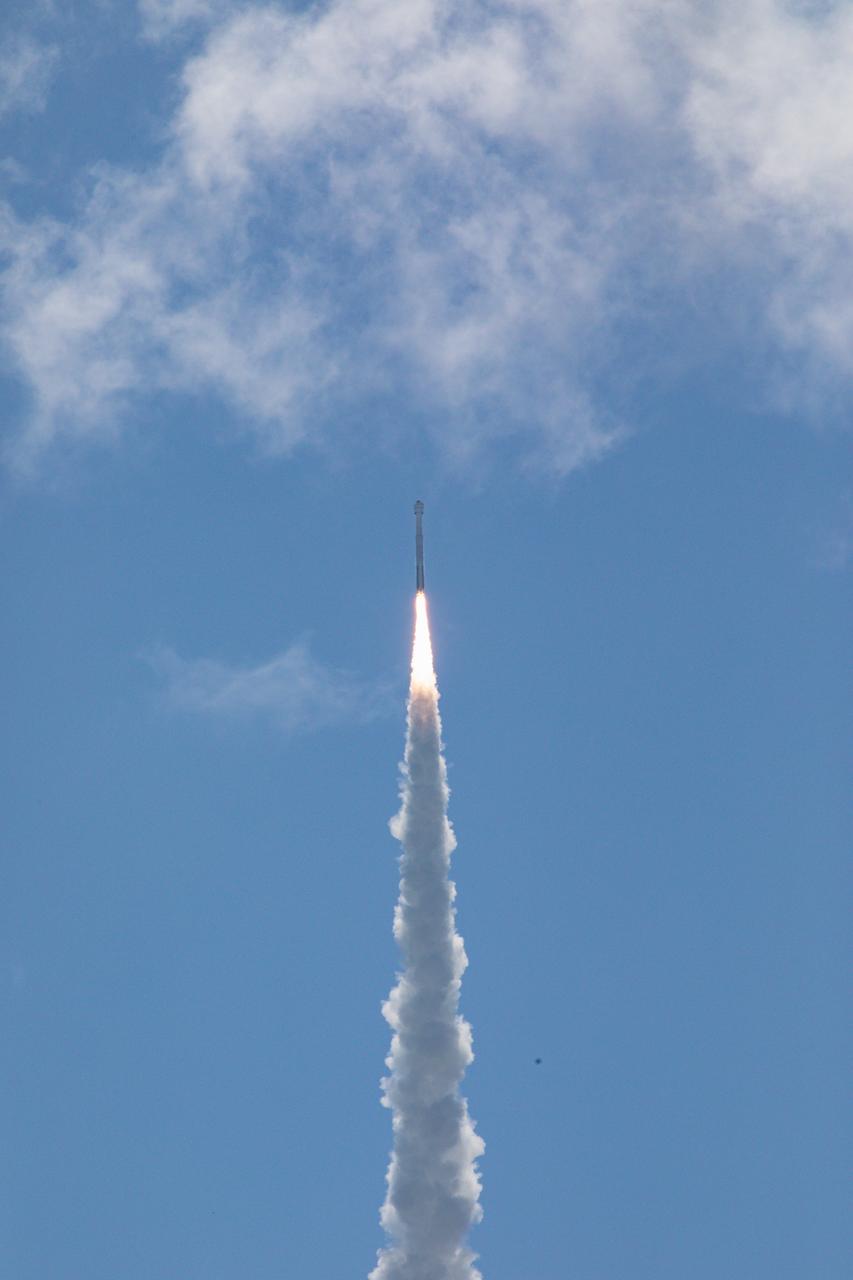

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket soars upward from the pad at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station. Aboard Starliner are NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams on the first crewed flight of the spacecraft as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
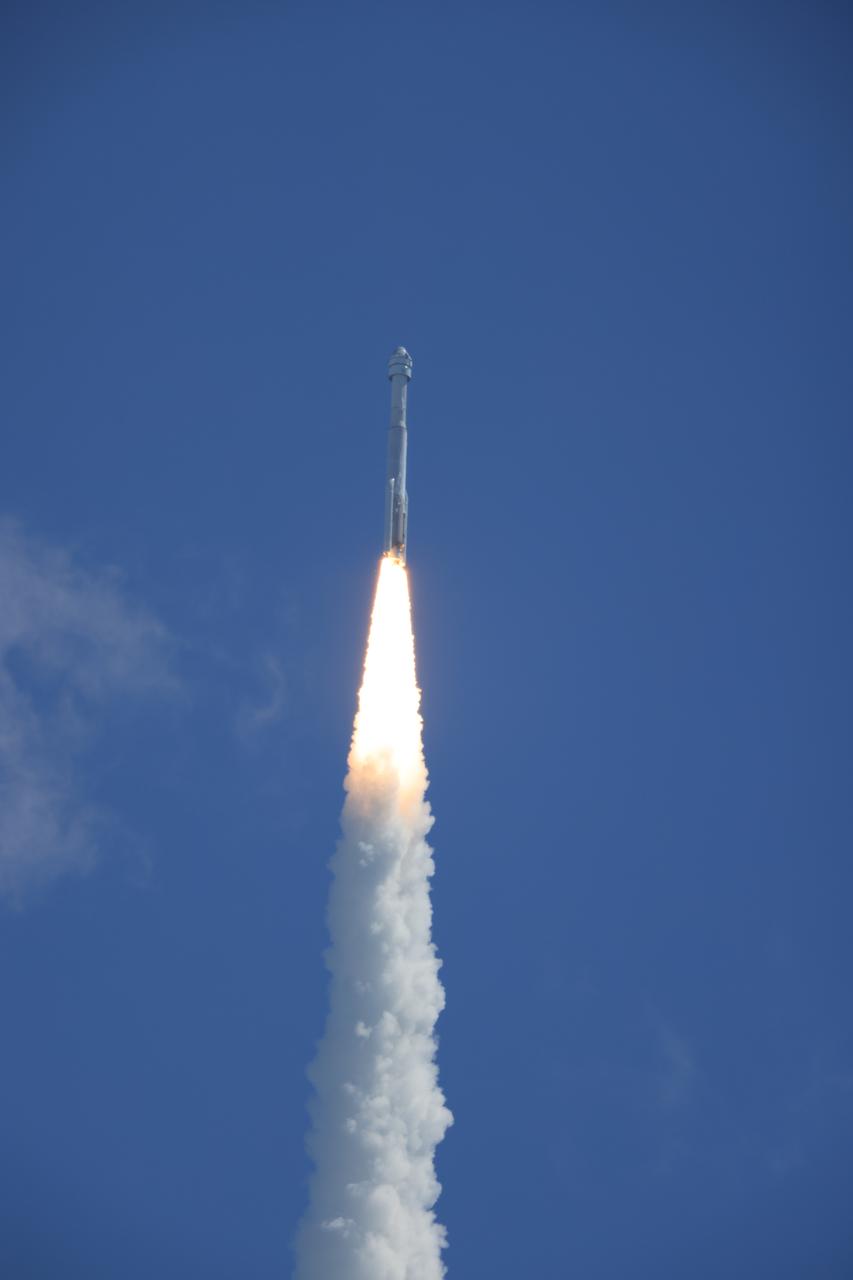

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket soars upward from the pad at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station. Aboard Starliner are NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams on the first crewed flight of the spacecraft as part of the agency’s Commercial crew Program.
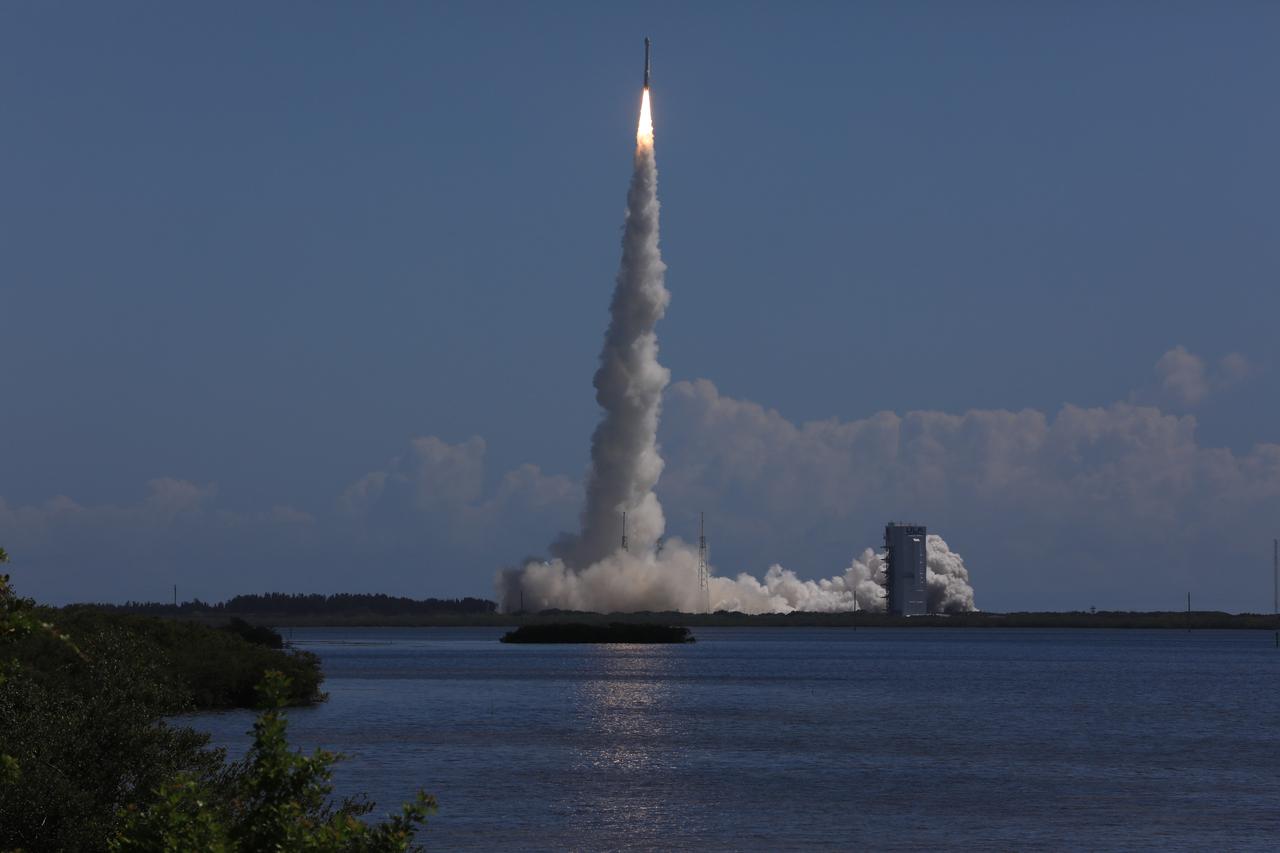

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
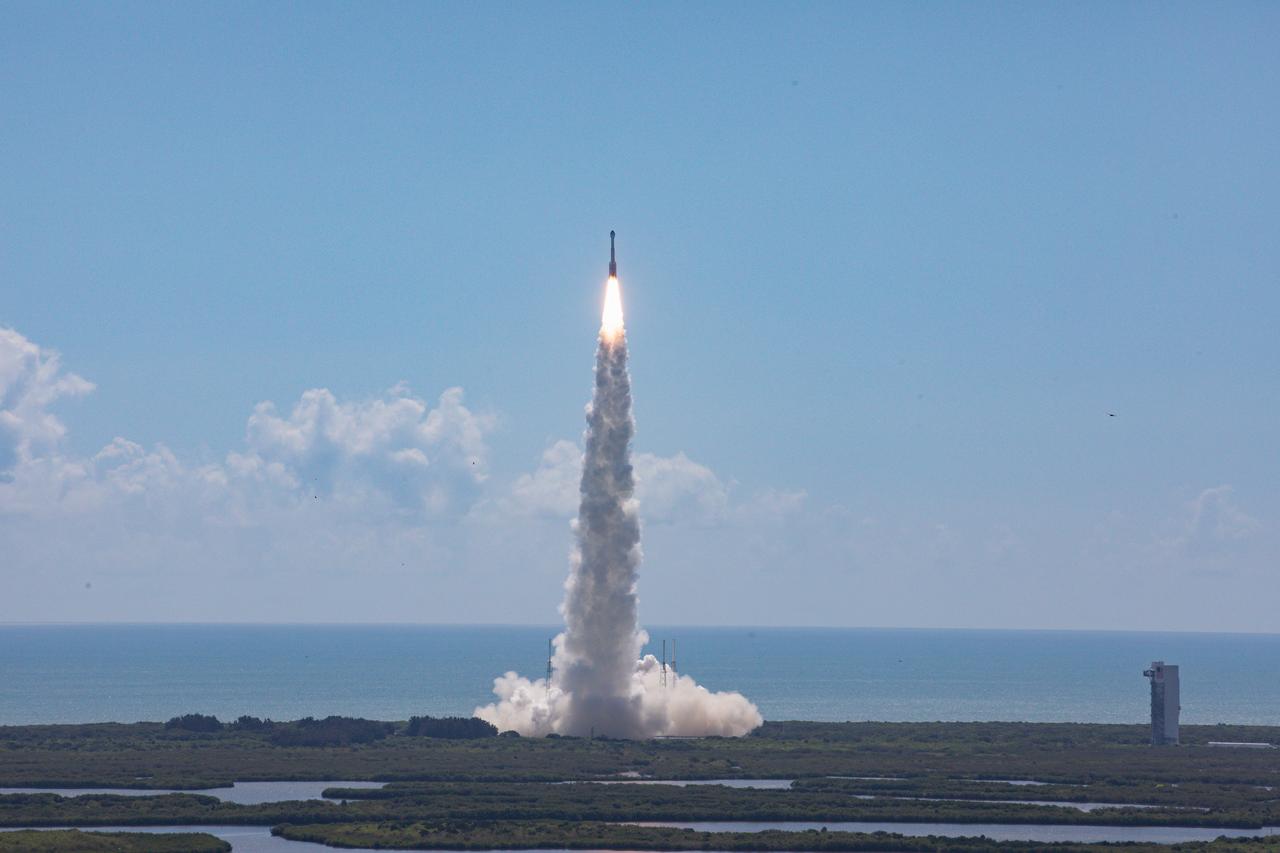

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
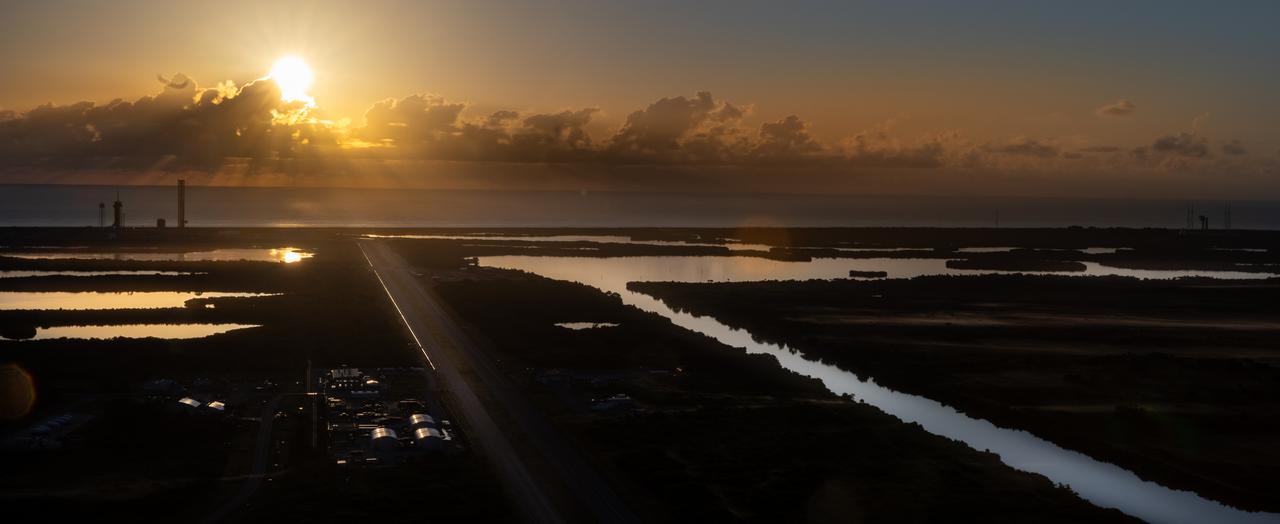

Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is seen during sunrise on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Wednesday, June 5, 2024, ahead of NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test. As part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are the first to launch to the International Space Station aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft 10:52 a.m. EDT.
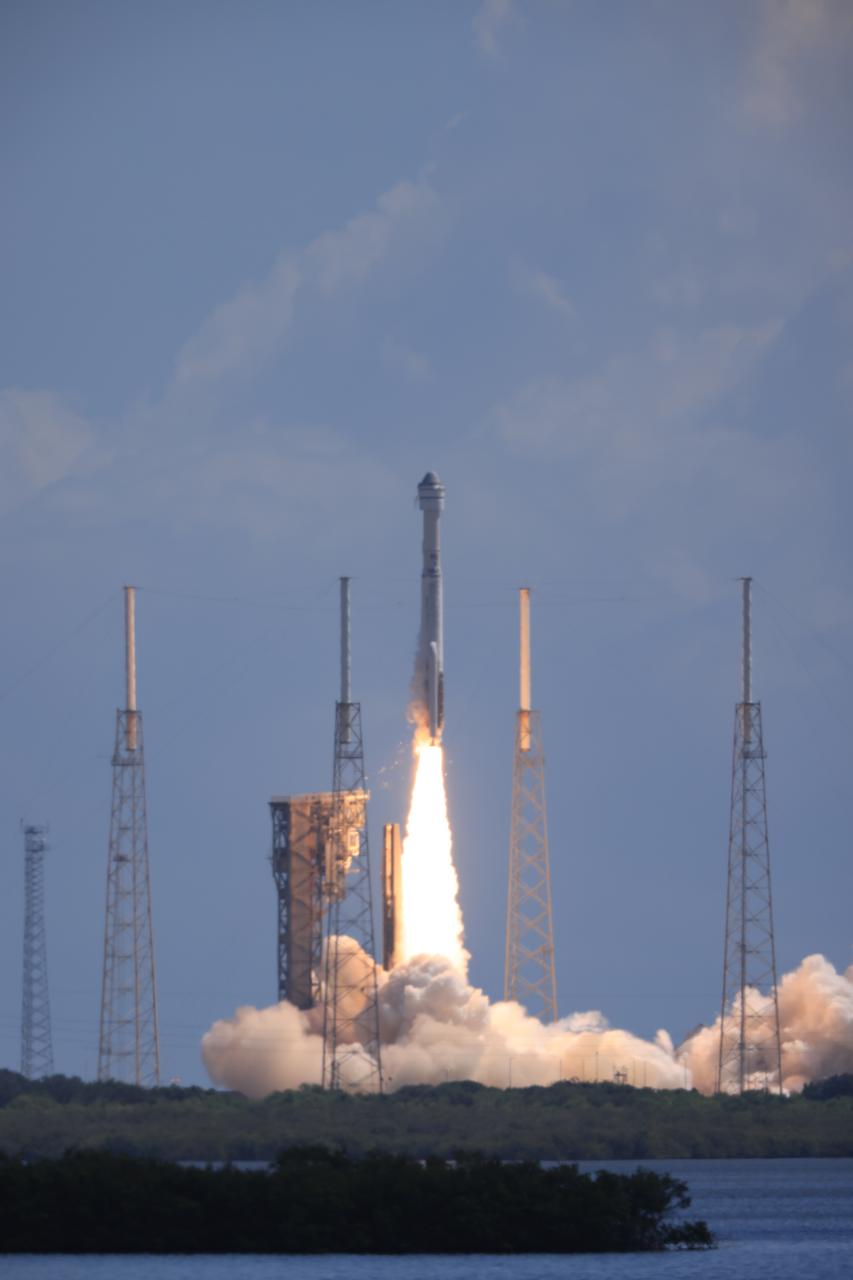

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
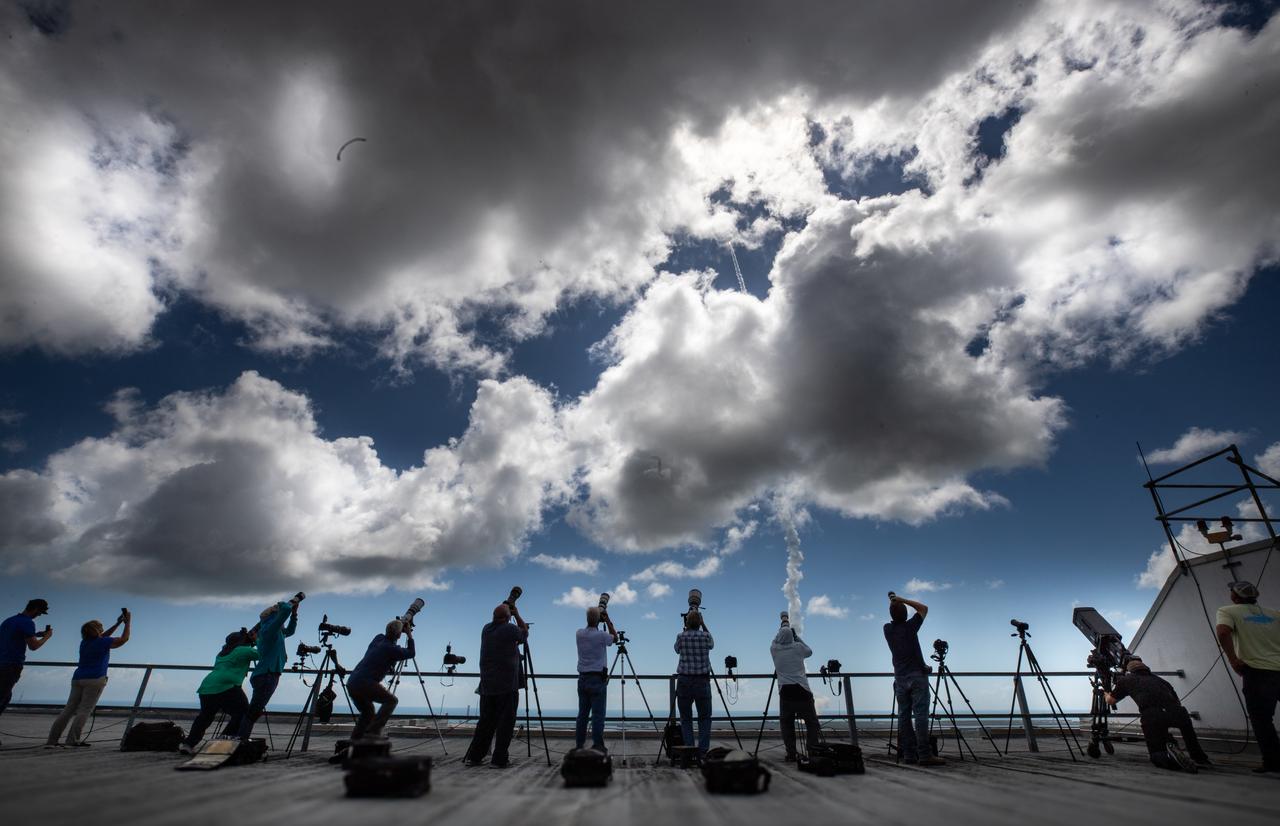

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
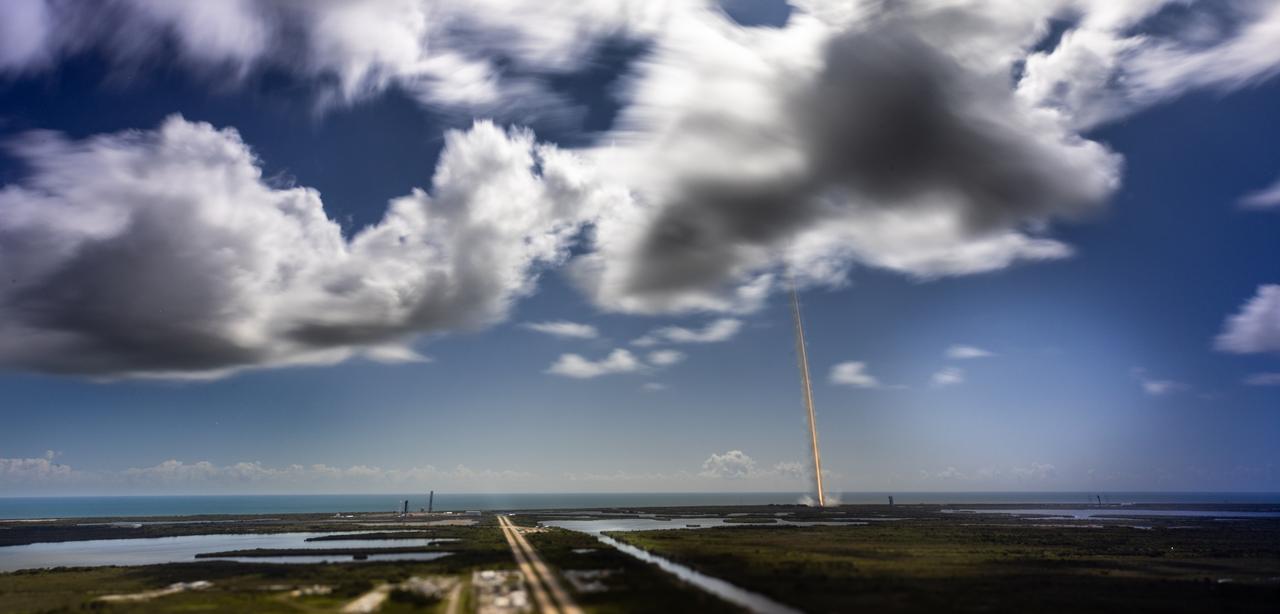

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
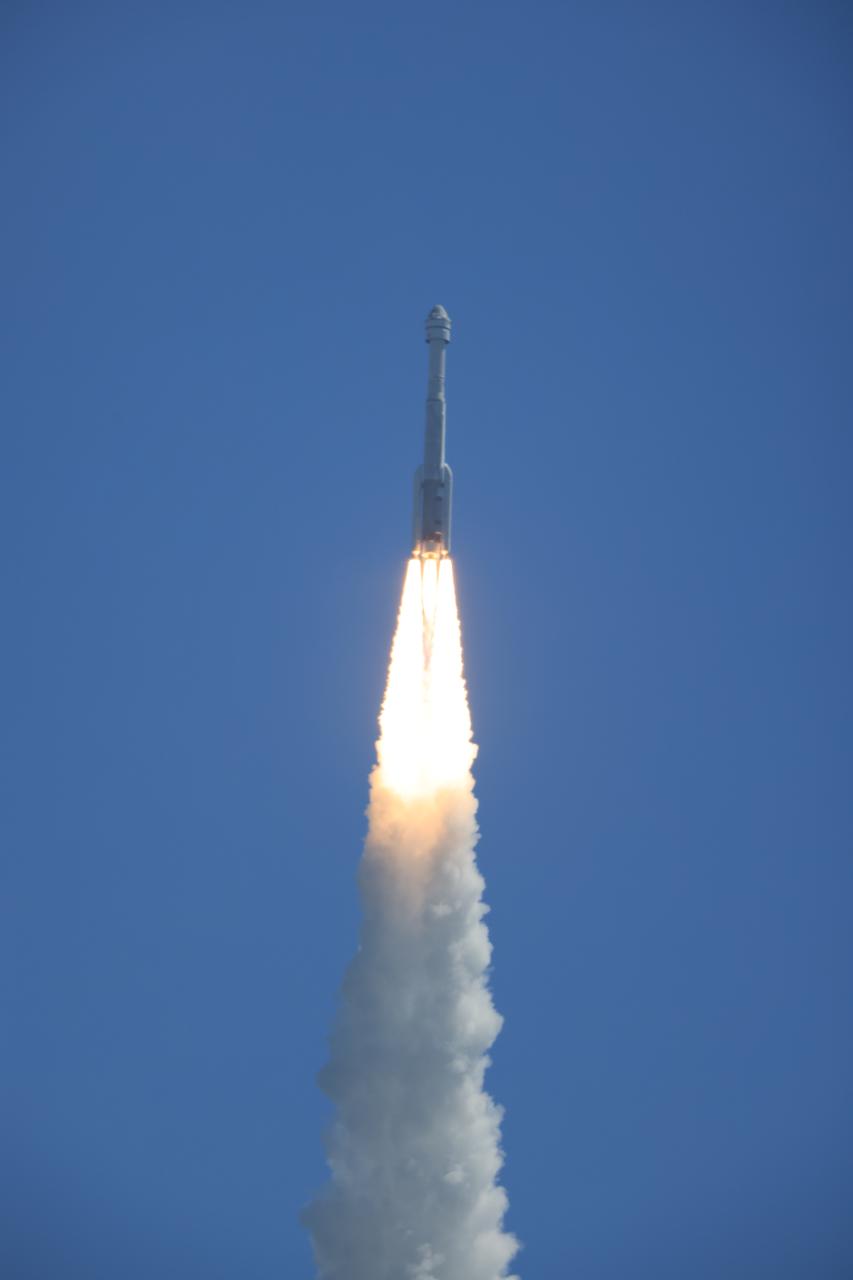

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket soars upward from the pad at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station. Aboard Starliner are NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams on the first crewed flight of the spacecraft as part of the agency’s Commercial crew Program.
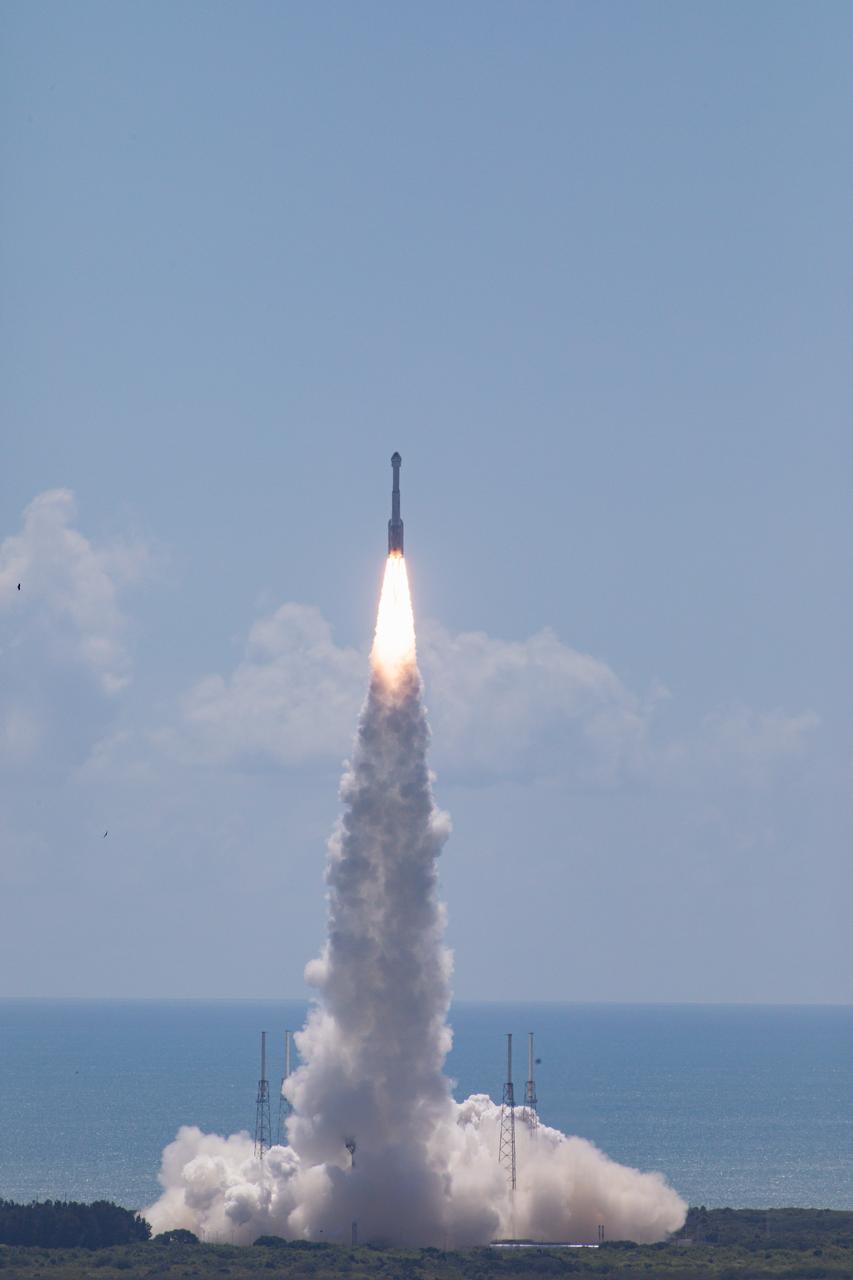

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
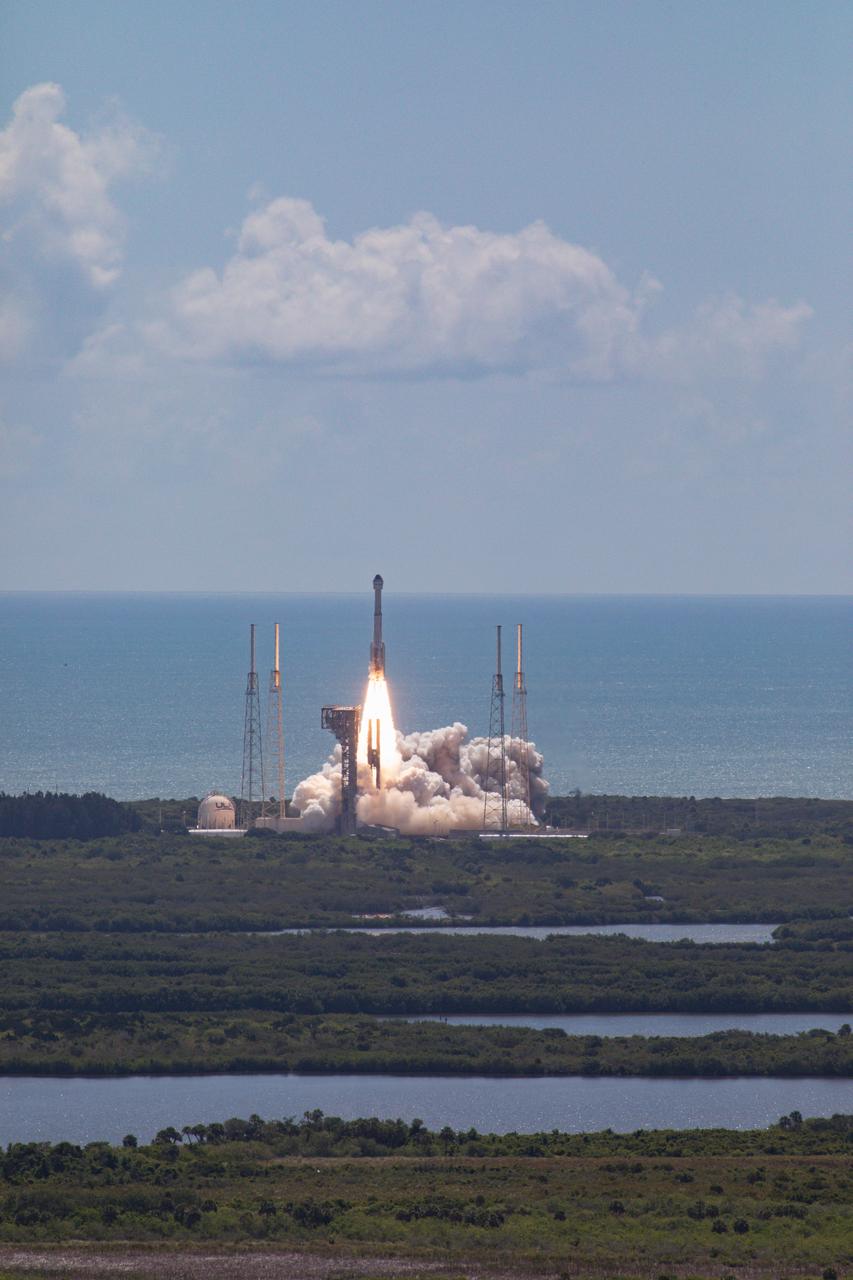

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
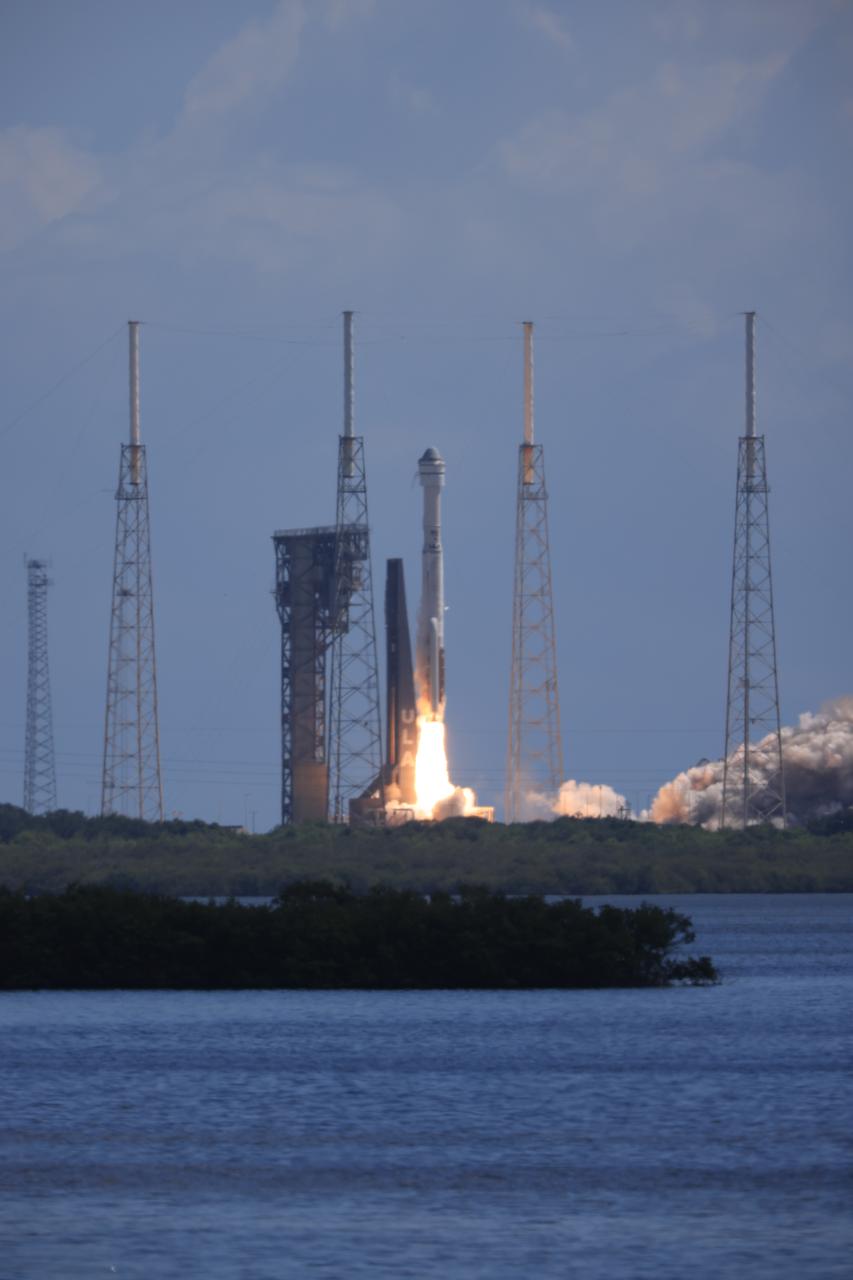

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
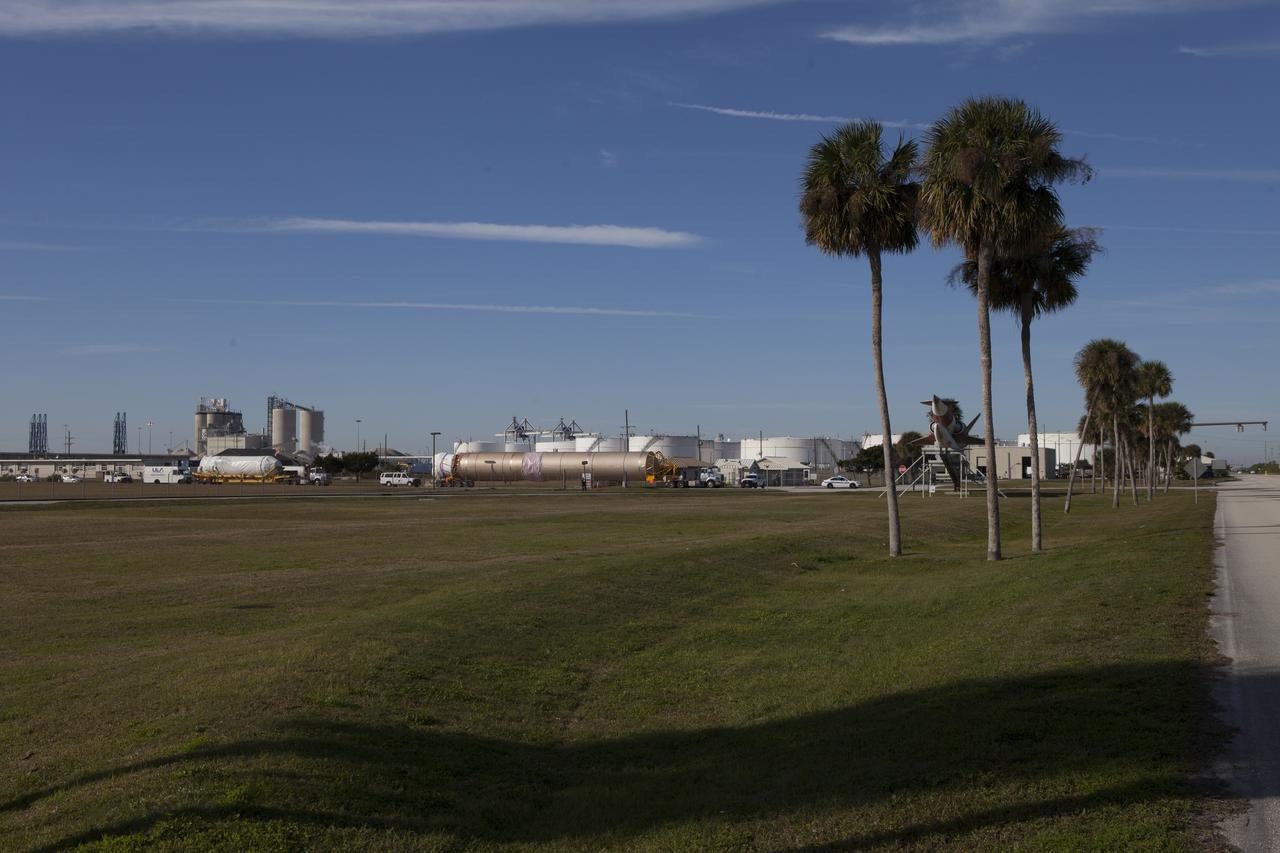

Trucks transport the Atlas V rocket and Centaur upper stage from the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner to the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.
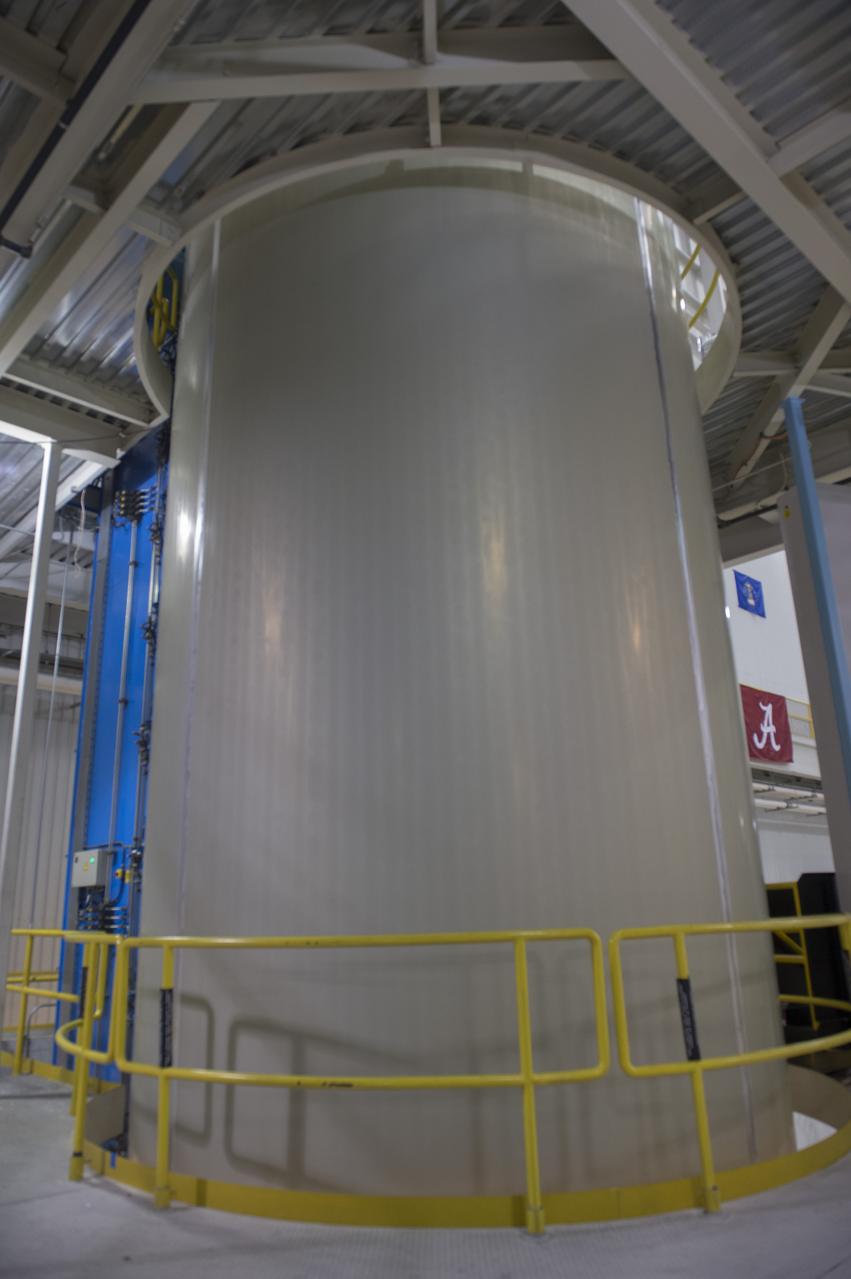

The Atlas V rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is coming together inside a United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, Alabama. Boeing’s Starliner will launch on the Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
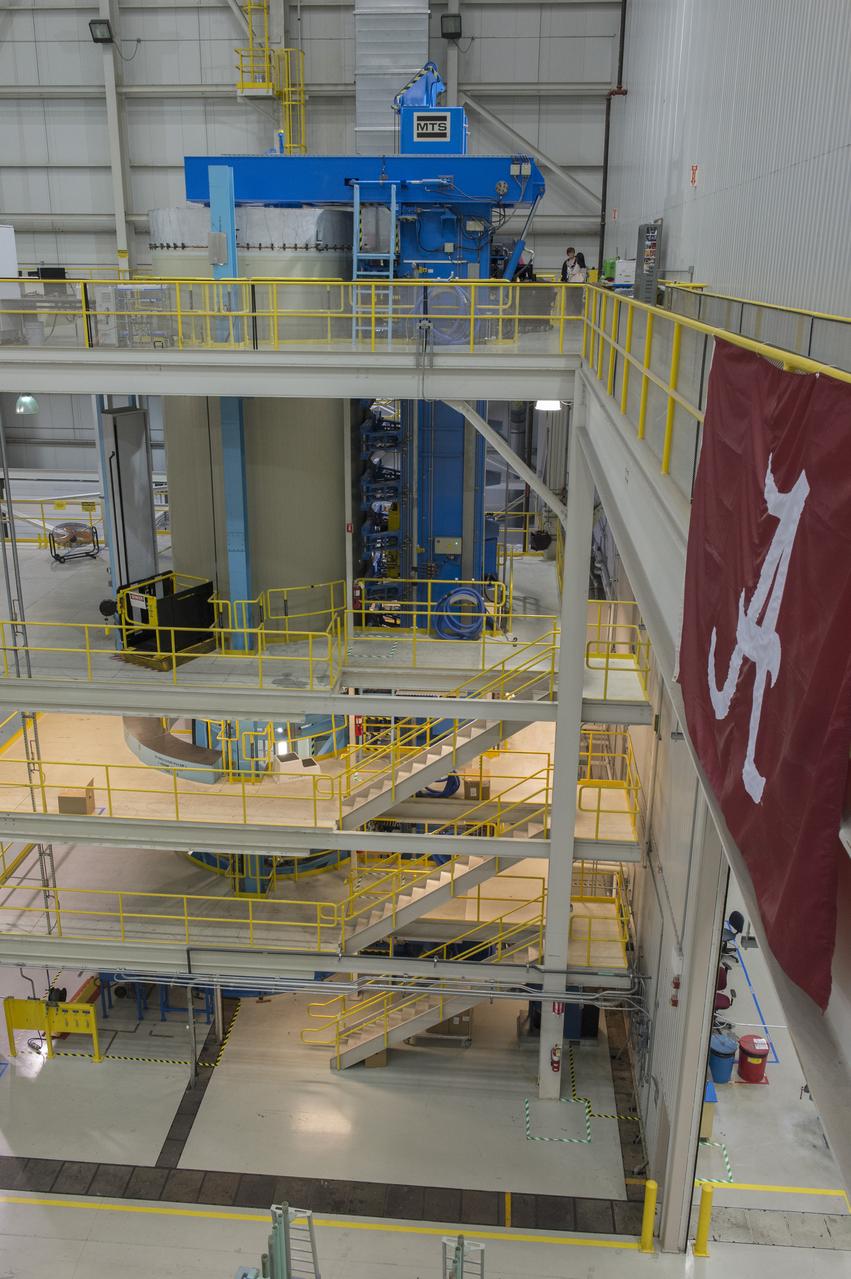

The Atlas V rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is coming together inside a United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, Alabama. Boeing’s Starliner will launch on the Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
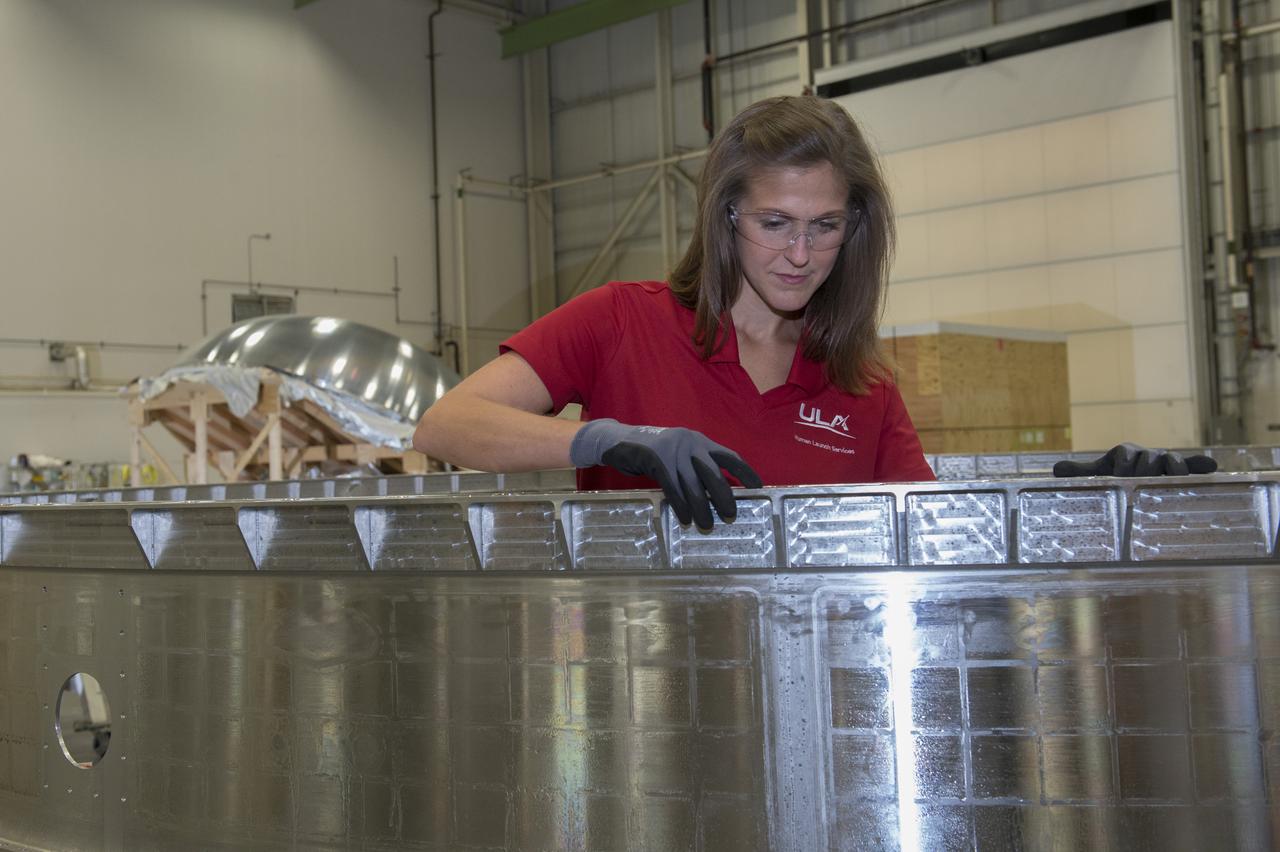

The Atlas V rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is coming together inside a United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, Alabama. Boeing’s Starliner will launch on the Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
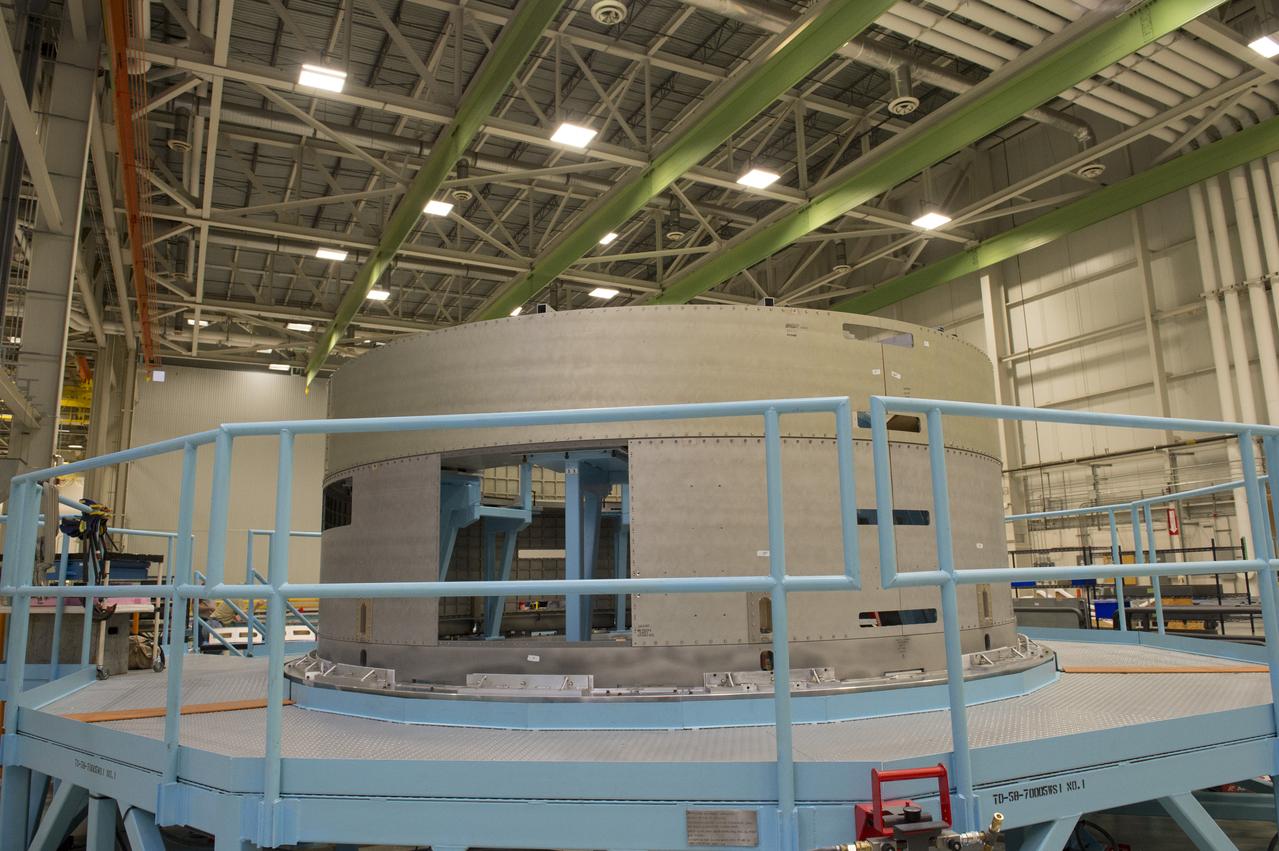

The Atlas V rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is coming together inside a United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, Alabama. Boeing’s Starliner will launch on the Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.

Trucks transport the Atlas V rocket and Centaur upper stage from the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner to the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.
The Atlas V rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is coming together inside a United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, Alabama. Boeing’s Starliner will launch on the Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
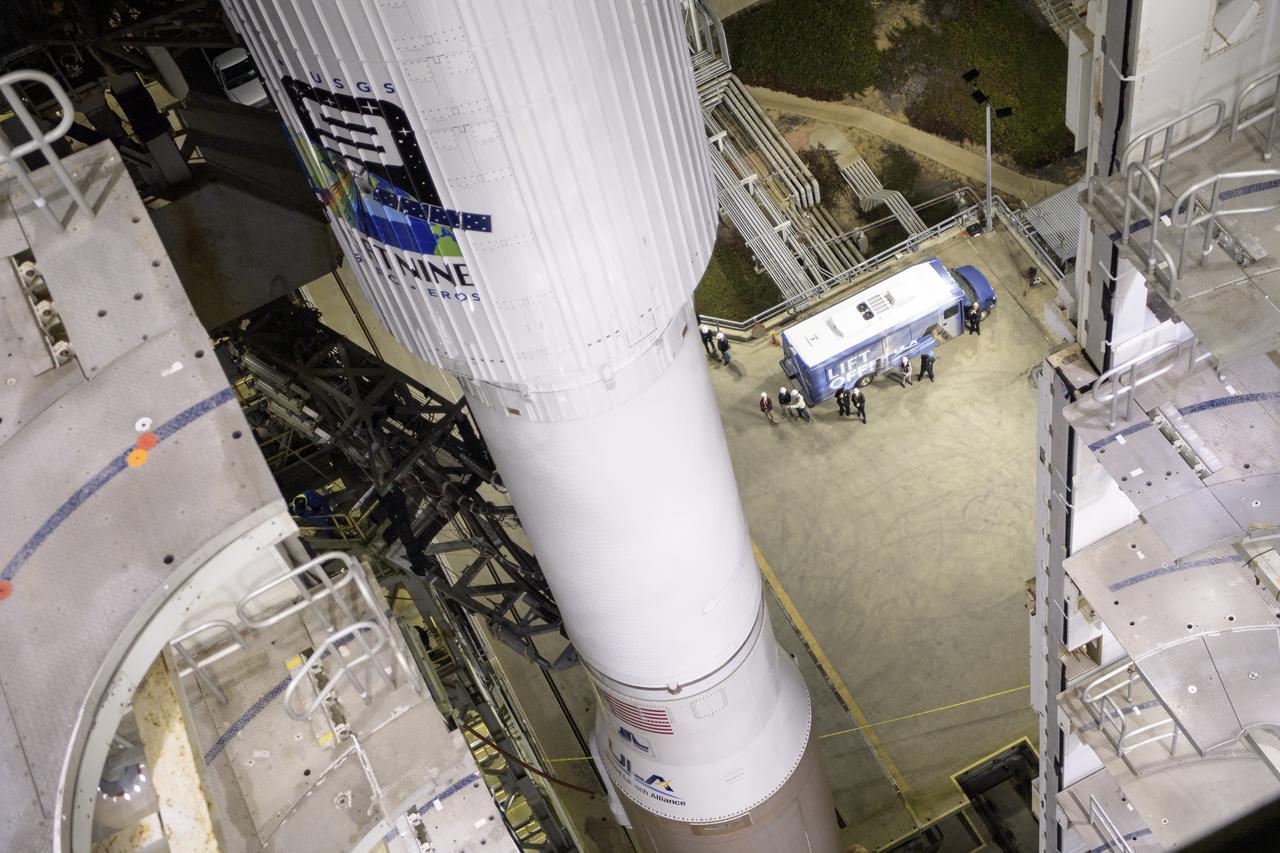

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket with the Landsat 9 satellite onboard is seen, Monday, Sept. 27, 2021, as the mobile launcher platform (MLP) is rolled back at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The Landsat 9 satellite is a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
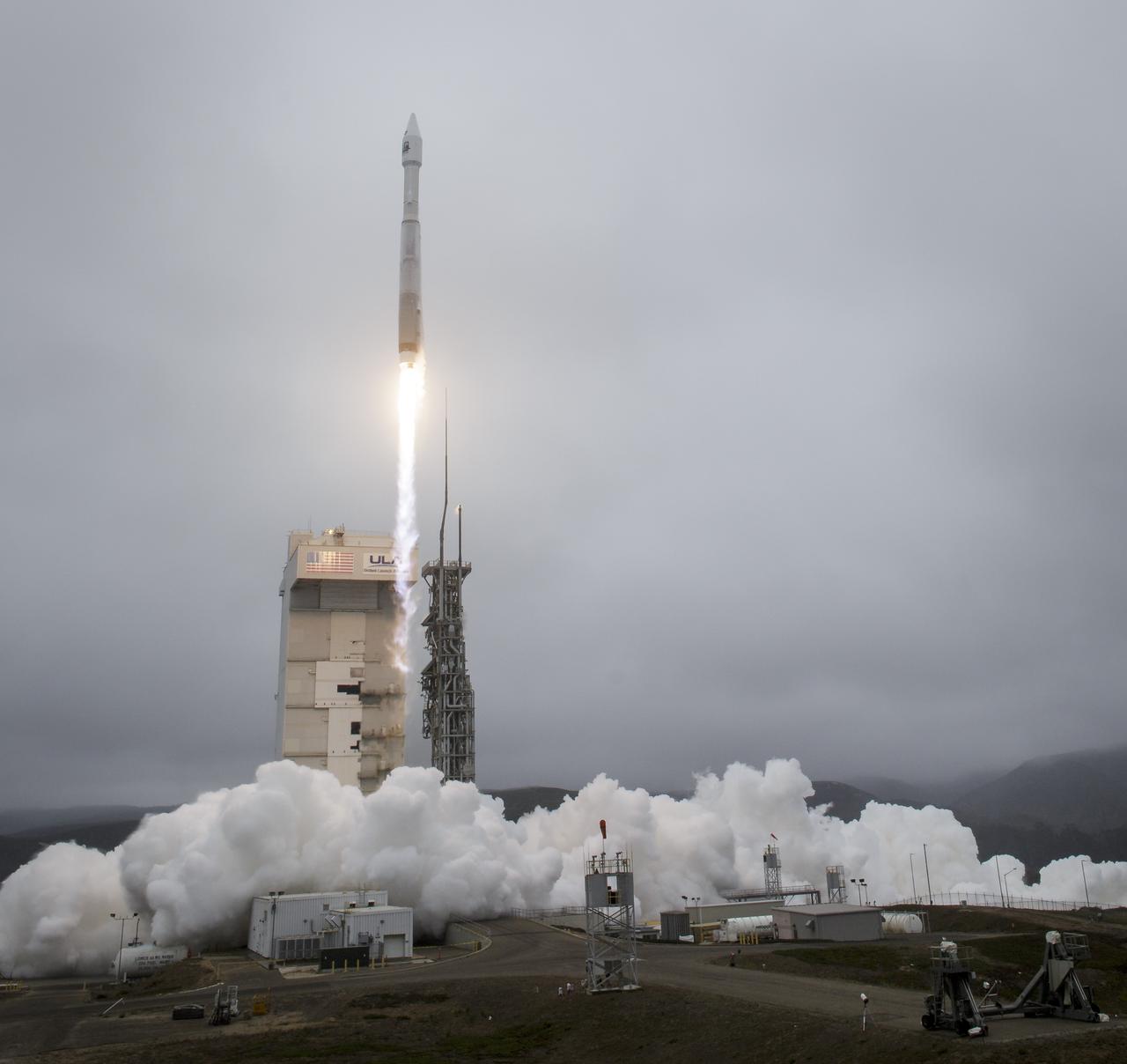

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket with the Landsat 9 satellite onboard launches, Monday, Sept. 27, 2021, from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The Landsat 9 satellite is a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
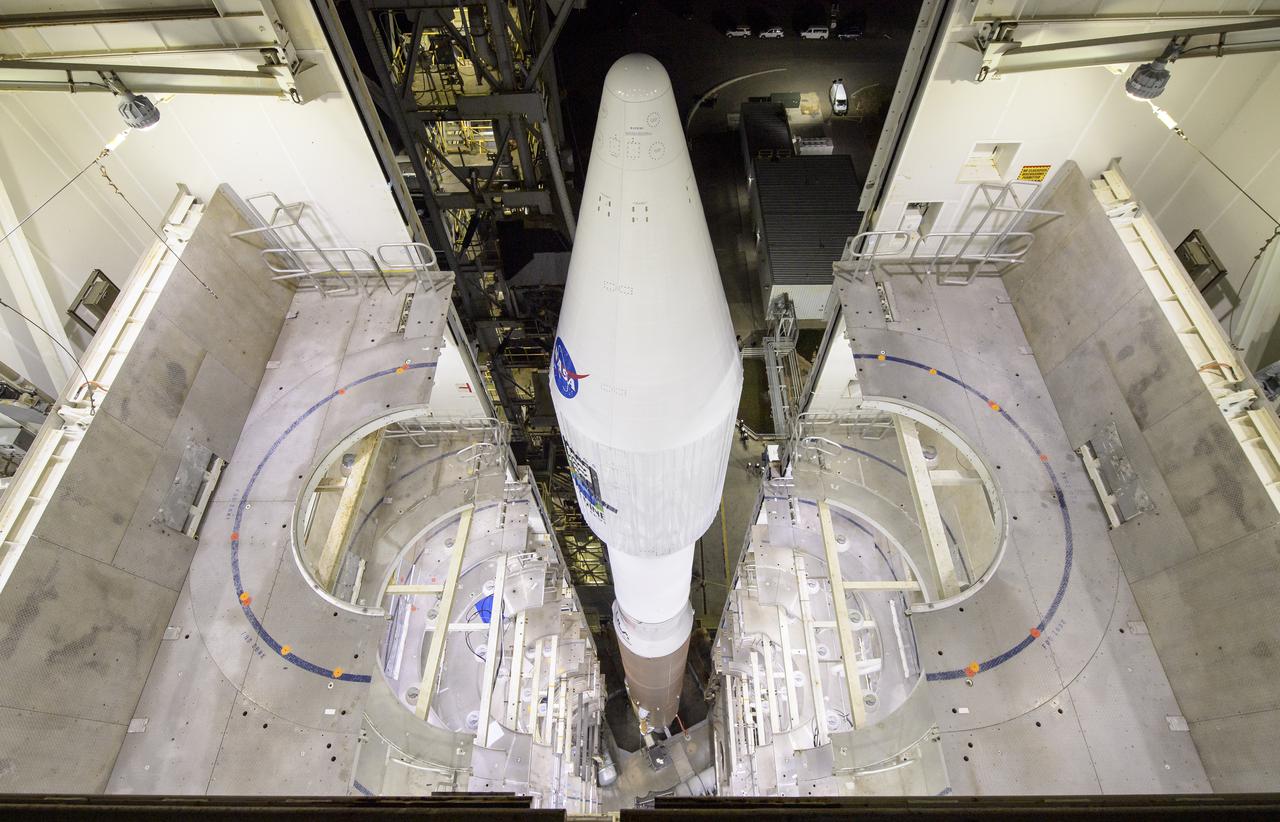

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket with the Landsat 9 satellite onboard is seen, Monday, Sept. 27, 2021, as the mobile launcher platform (MLP) is rolled back at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The Landsat 9 satellite is a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
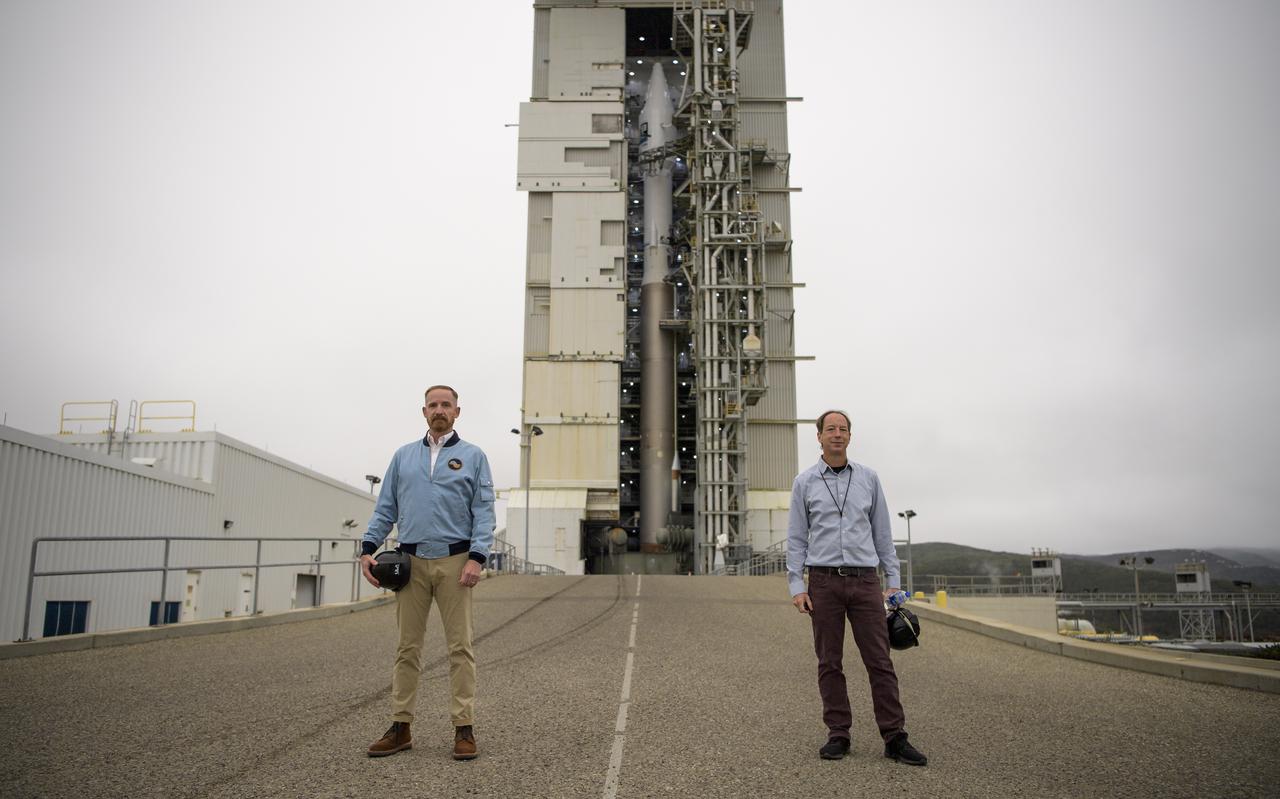

Actor Marc Evan Jackson, left, and NASA Landsat 9 Project Scientist Jeff Masek pose for a photograph by the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket with the Landsat 9 satellite onboard, Sunday, Sept. 26, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The Landsat 9 satellite, a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions, is scheduled for liftoff Monday, Sept. 27. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
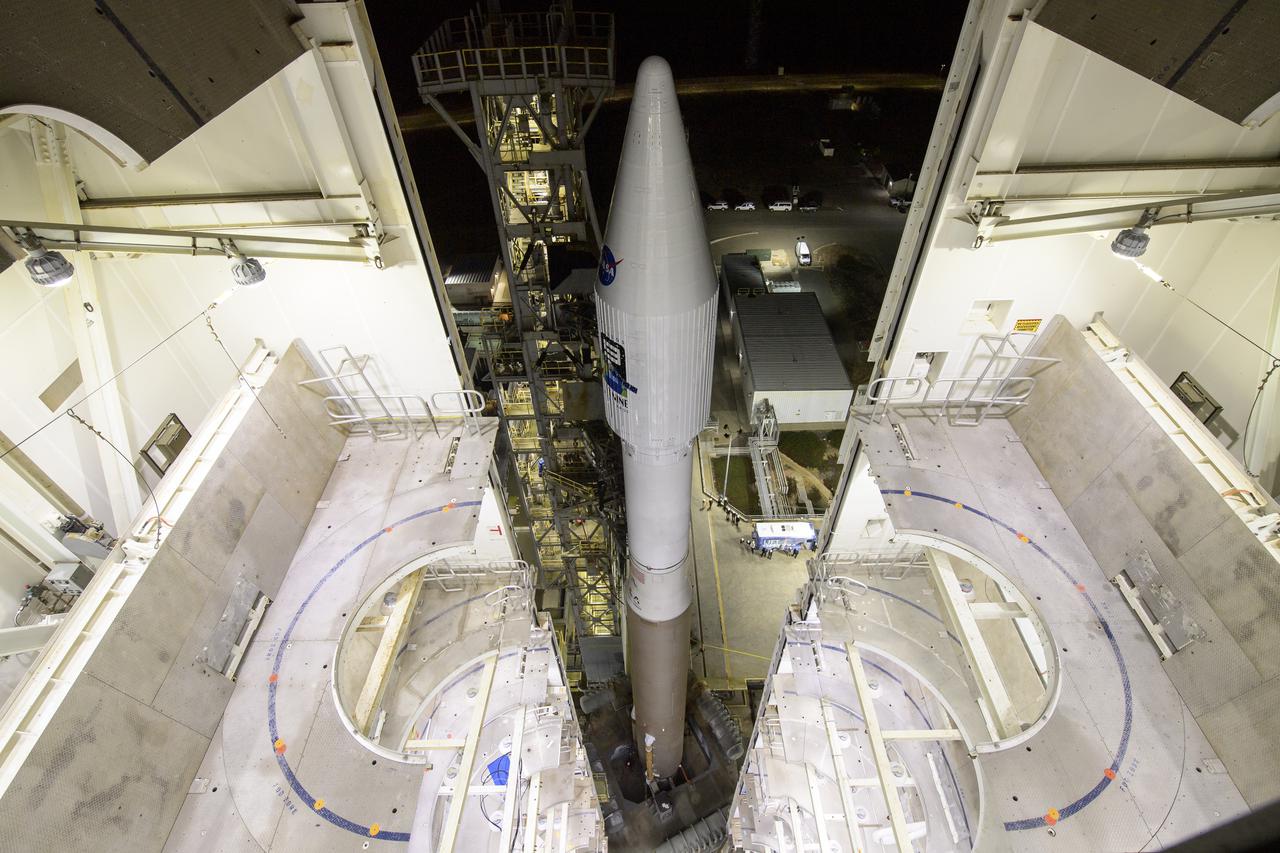

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket with the Landsat 9 satellite onboard is seen, Monday, Sept. 27, 2021, as the mobile launcher platform (MLP) is rolled back at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The Landsat 9 satellite is a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
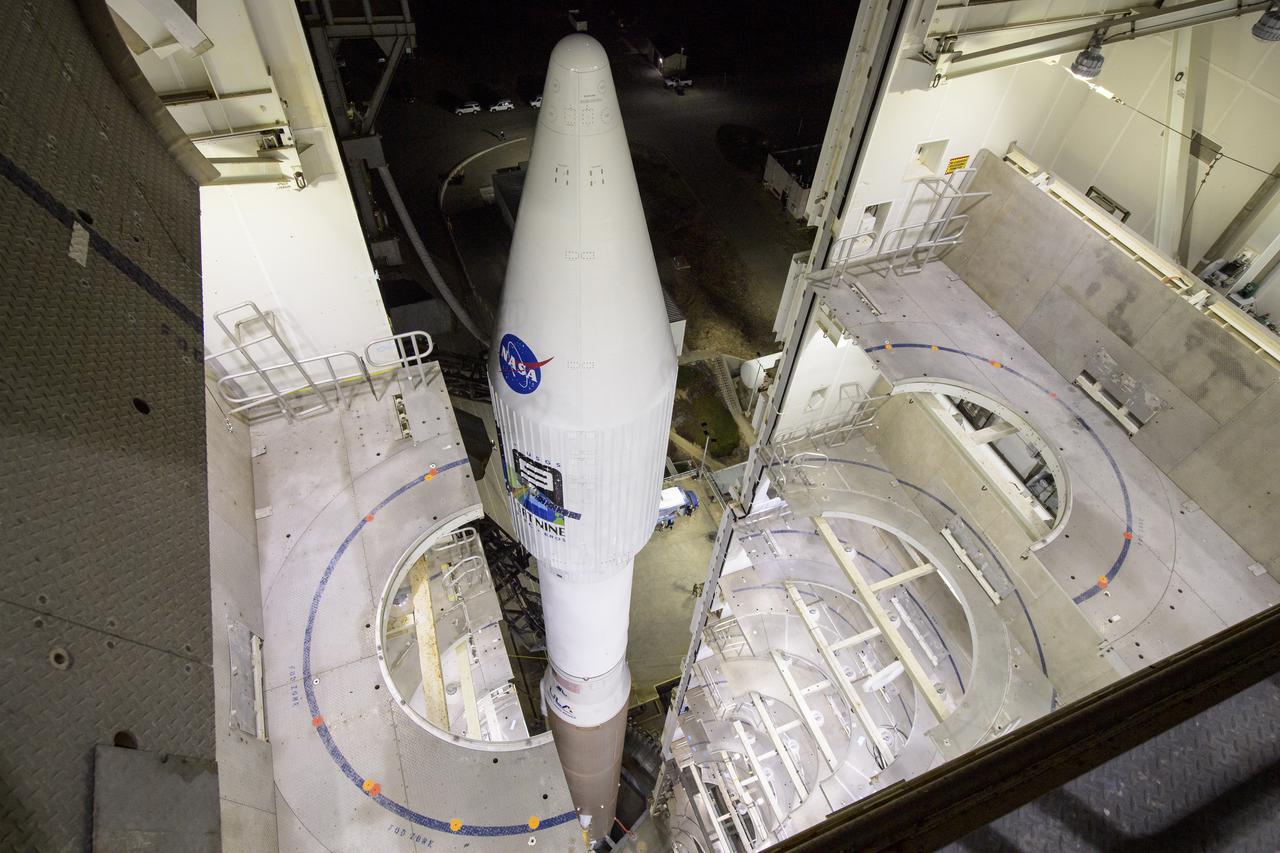

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket with the Landsat 9 satellite onboard is seen, Monday, Sept. 27, 2021, as the mobile launcher platform (MLP) is rolled back at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The Landsat 9 satellite is a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)