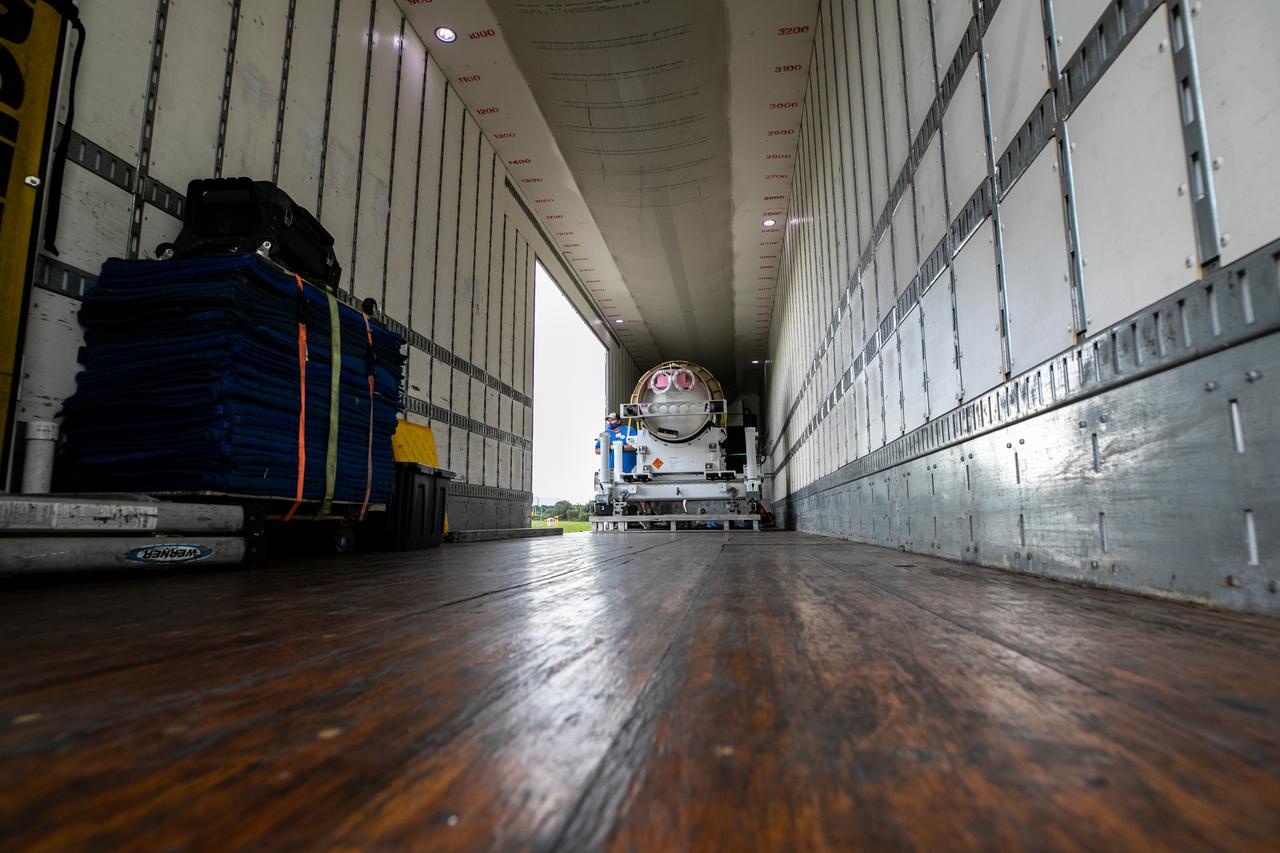

The last of three motors required to assemble the Launch Abort System for NASA’s Artemis II mission, the attitude control motor (ACM), arrives at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on August 28. The attitude control motor (ACM) was delivered by truck from Northrop Grumman’s manufacturing facility in Maryland, to the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy. During launch of Orion atop the agency’s Space Launch System rocket, the LAS motors work together to separate the spacecraft from the rocket in the unlikely event of an emergency during launch. The LAS includes three motors – the launch abort motor, the jettison motor, and the attitude control motor—that once activated, will steer the spacecraft carrying the astronauts to safety. The ACM operates to keep Orion’s crew module on a controlled flight path in the event it needs to jettison and steer away from the rocket. Artemis II is the first crewed flight in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will lay the foundation for exploration of Mars and beyond. Artemis II will confirm all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems operate as designed in the actual environment of deep space with astronauts aboard. As part of the Artemis program, NASA will send the first woman and next man to the Moon in 2024.
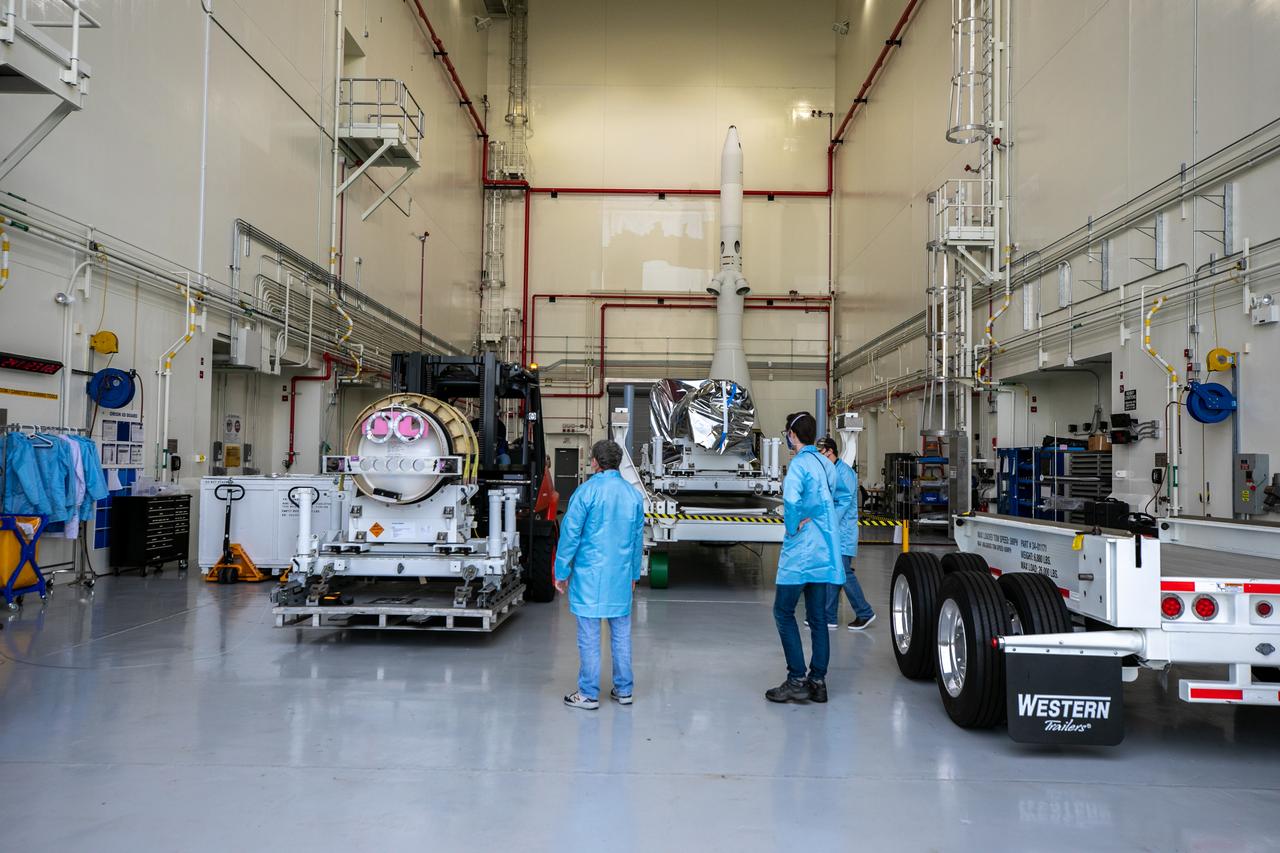

The last of three motors required to assemble the Launch Abort System for NASA’s Artemis II mission, the attitude control motor (ACM), arrives at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on August 28. The attitude control motor (ACM) was delivered by truck from Northrop Grumman’s manufacturing facility in Maryland, to the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy. During launch of Orion atop the agency’s Space Launch System rocket, the LAS motors work together to separate the spacecraft from the rocket in the unlikely event of an emergency during launch. The LAS includes three motors – the launch abort motor, the jettison motor, and the attitude control motor—that once activated, will steer the spacecraft carrying the astronauts to safety. The ACM operates to keep Orion’s crew module on a controlled flight path in the event it needs to jettison and steer away from the rocket. Artemis II is the first crewed flight in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will lay the foundation for exploration of Mars and beyond. Artemis II will confirm all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems operate as designed in the actual environment of deep space with astronauts aboard. As part of the Artemis program, NASA will send the first woman and next man to the Moon in 2024.
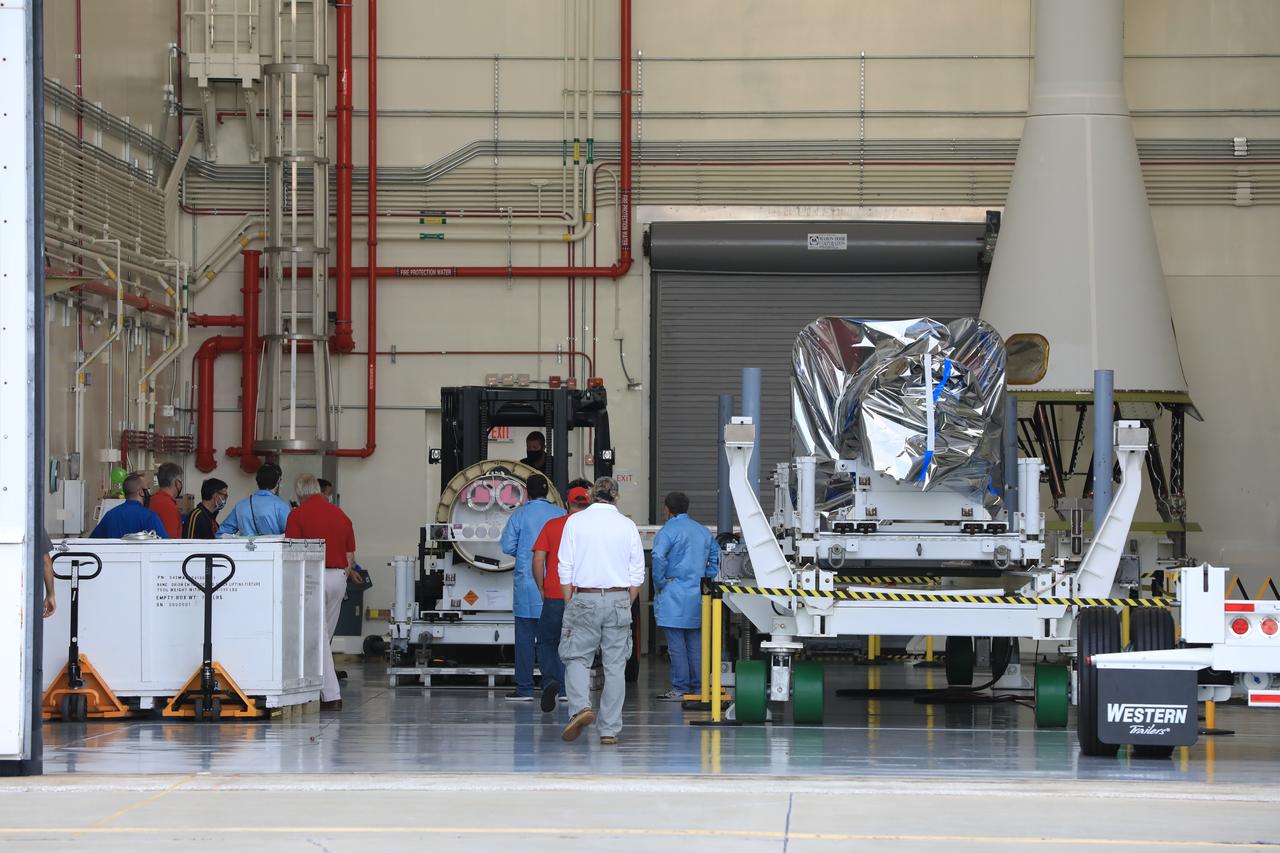

The last of three motors required to assemble the Launch Abort System for NASA’s Artemis II mission, the attitude control motor (ACM), arrives at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on August 28. The attitude control motor (ACM) was delivered by truck from Northrop Grumman’s manufacturing facility in Maryland, to the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy. During launch of Orion atop the agency’s Space Launch System rocket, the LAS motors work together to separate the spacecraft from the rocket in the unlikely event of an emergency during launch. The LAS includes three motors – the launch abort motor, the jettison motor, and the attitude control motor—that once activated, will steer the spacecraft carrying the astronauts to safety. The ACM operates to keep Orion’s crew module on a controlled flight path in the event it needs to jettison and steer away from the rocket. Artemis II is the first crewed flight in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will lay the foundation for exploration of Mars and beyond. Artemis II will confirm all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems operate as designed in the actual environment of deep space with astronauts aboard. As part of the Artemis program, NASA will send the first woman and next man to the Moon in 2024.
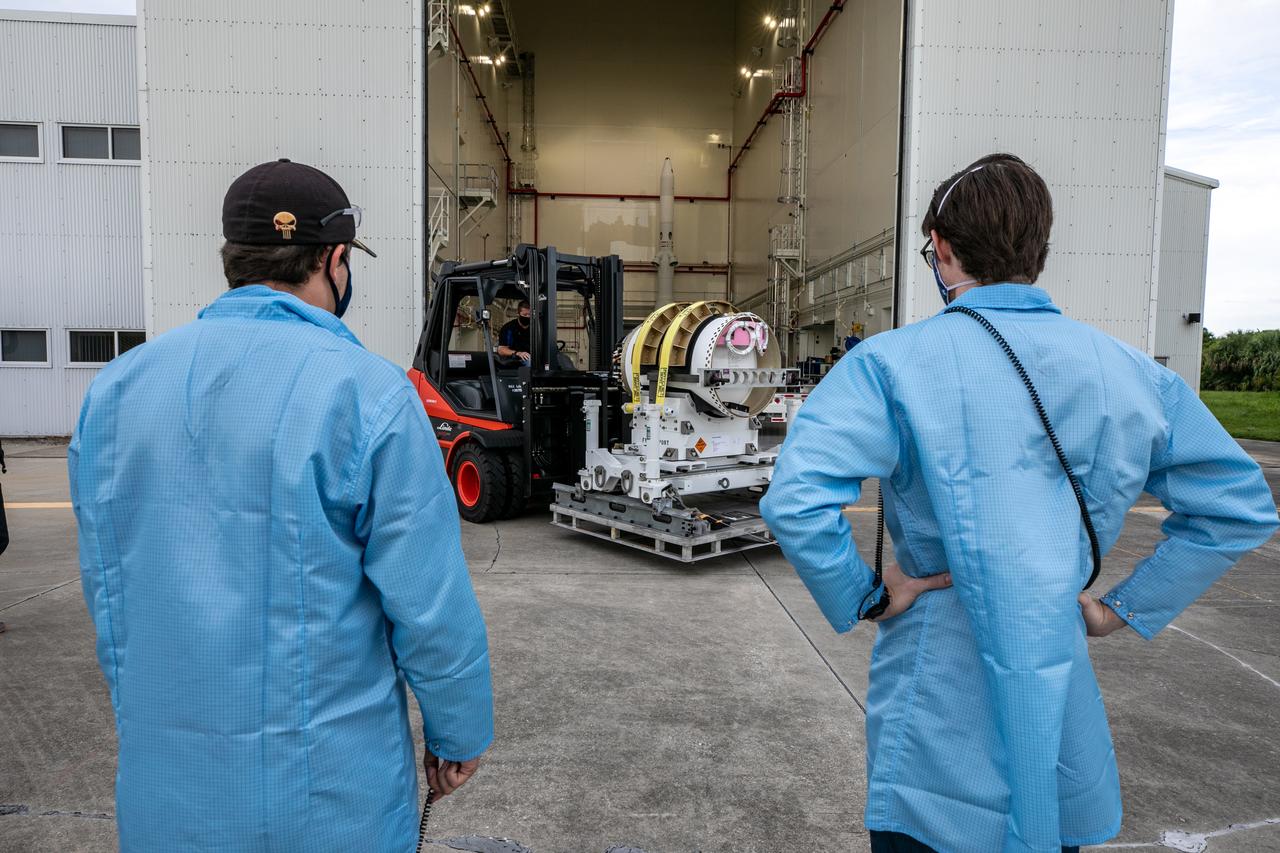

The last of three motors required to assemble the Launch Abort System for NASA’s Artemis II mission, the attitude control motor (ACM), arrives at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on August 28. The attitude control motor (ACM) was delivered by truck from Northrop Grumman’s manufacturing facility in Maryland, to the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy. During launch of Orion atop the agency’s Space Launch System rocket, the LAS motors work together to separate the spacecraft from the rocket in the unlikely event of an emergency during launch. The LAS includes three motors – the launch abort motor, the jettison motor, and the attitude control motor—that once activated, will steer the spacecraft carrying the astronauts to safety. The ACM operates to keep Orion’s crew module on a controlled flight path in the event it needs to jettison and steer away from the rocket. Artemis II is the first crewed flight in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will lay the foundation for exploration of Mars and beyond. Artemis II will confirm all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems operate as designed in the actual environment of deep space with astronauts aboard. As part of the Artemis program, NASA will send the first woman and next man to the Moon in 2024.

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
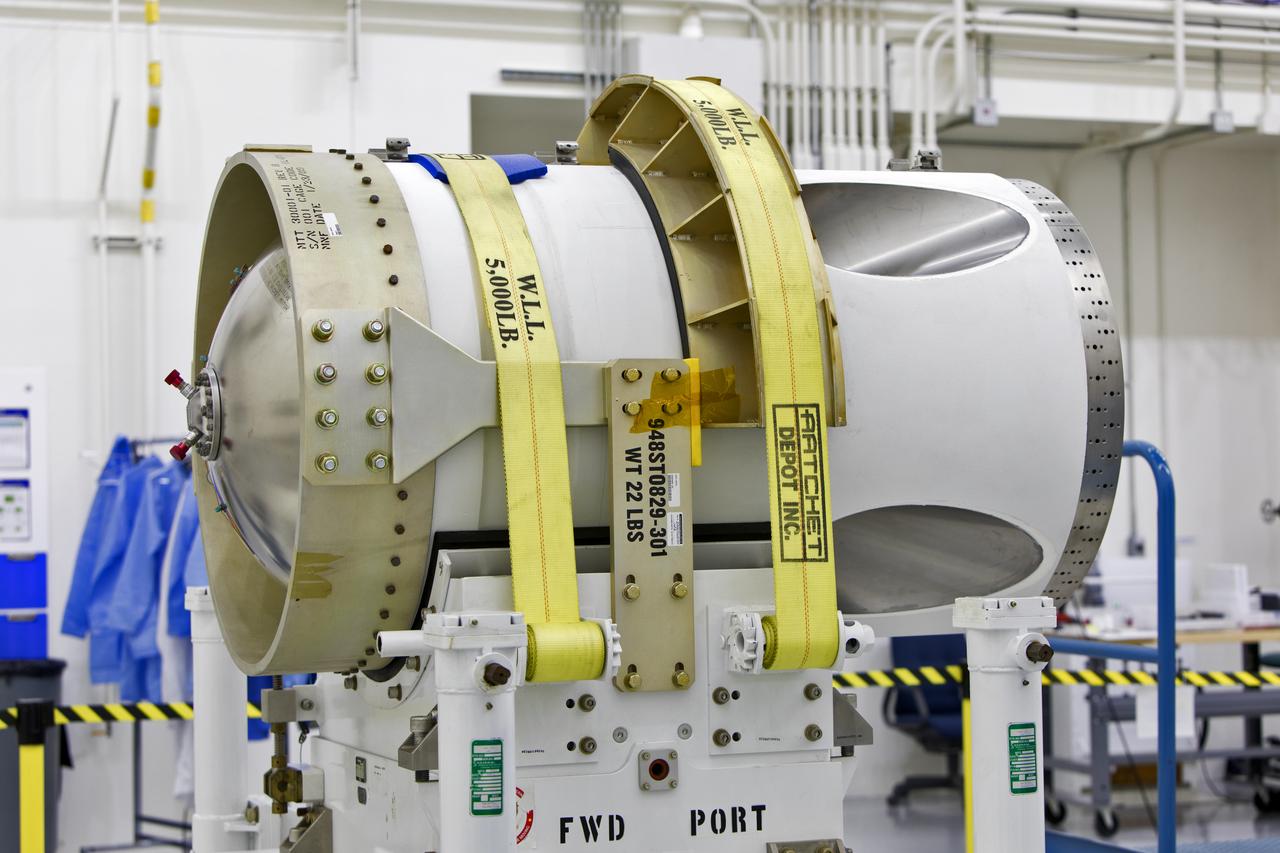
The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.

The jettison, abort, and attitude control motors for Artemis II are secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 17, 2021. The motors will continue undergoing inspections, testing, and assembly ahead of the first crewed Artemis mission. The launch abort system is designed to protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the Orion spacecraft away from a failing rocket. Artemis II will confirm all the Orion spacecraft’s systems operate as designed in the actual environment of deep space with astronauts aboard.

The jettison, abort, and attitude control motors for Artemis II are secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 17, 2021. The motors will continue undergoing inspections, testing, and assembly ahead of the first crewed Artemis mission. The launch abort system is designed to protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the Orion spacecraft away from a failing rocket. Artemis II will confirm all the Orion spacecraft’s systems operate as designed in the actual environment of deep space with astronauts aboard.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare the launch abort motor for connection to the attitude control motor. Both are segments of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician prepares the launch abort motor for connection to the attitude control motor. Both are segments of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the launch abort motor has been prepared for connection to the attitude control motor. Both are segments of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
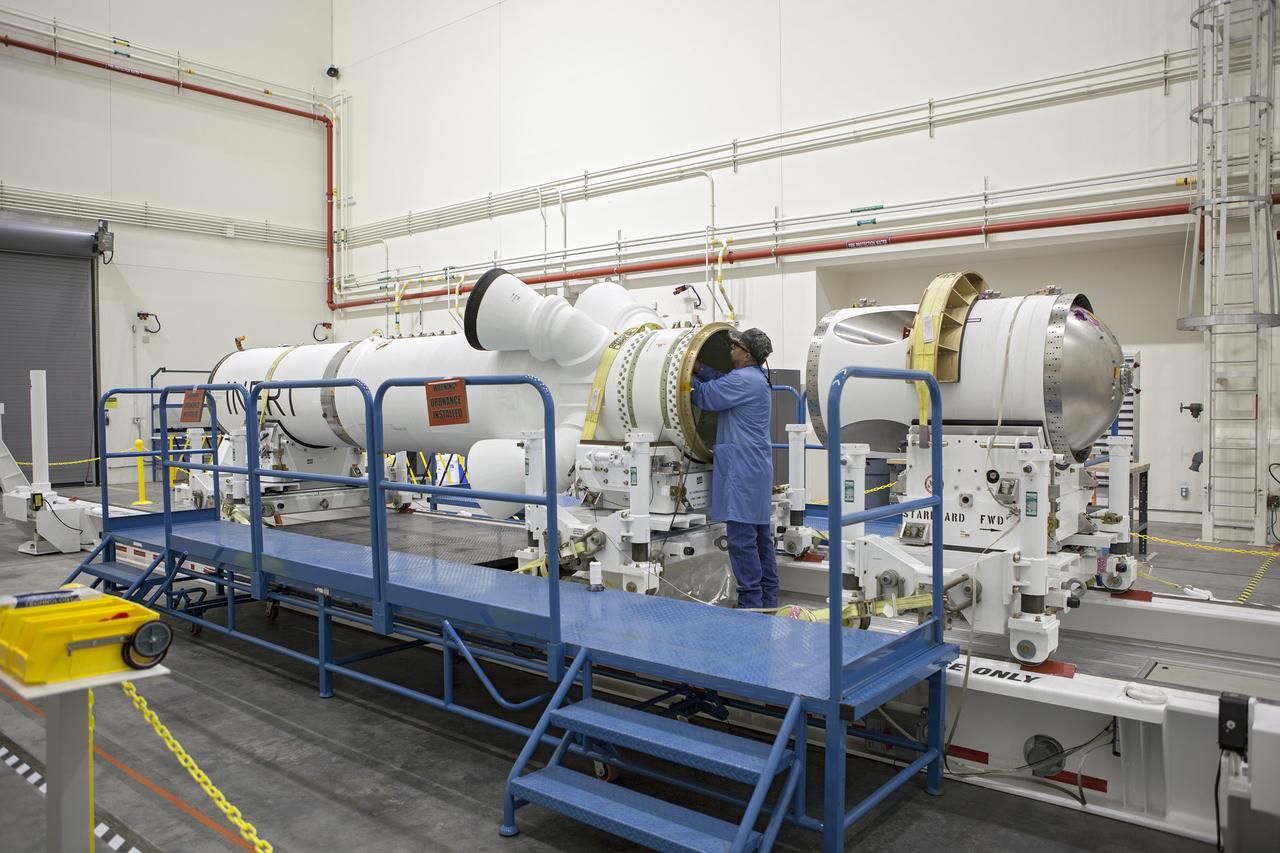

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician prepares the launch abort motor for connection to the attitude control motor. Both are segments of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
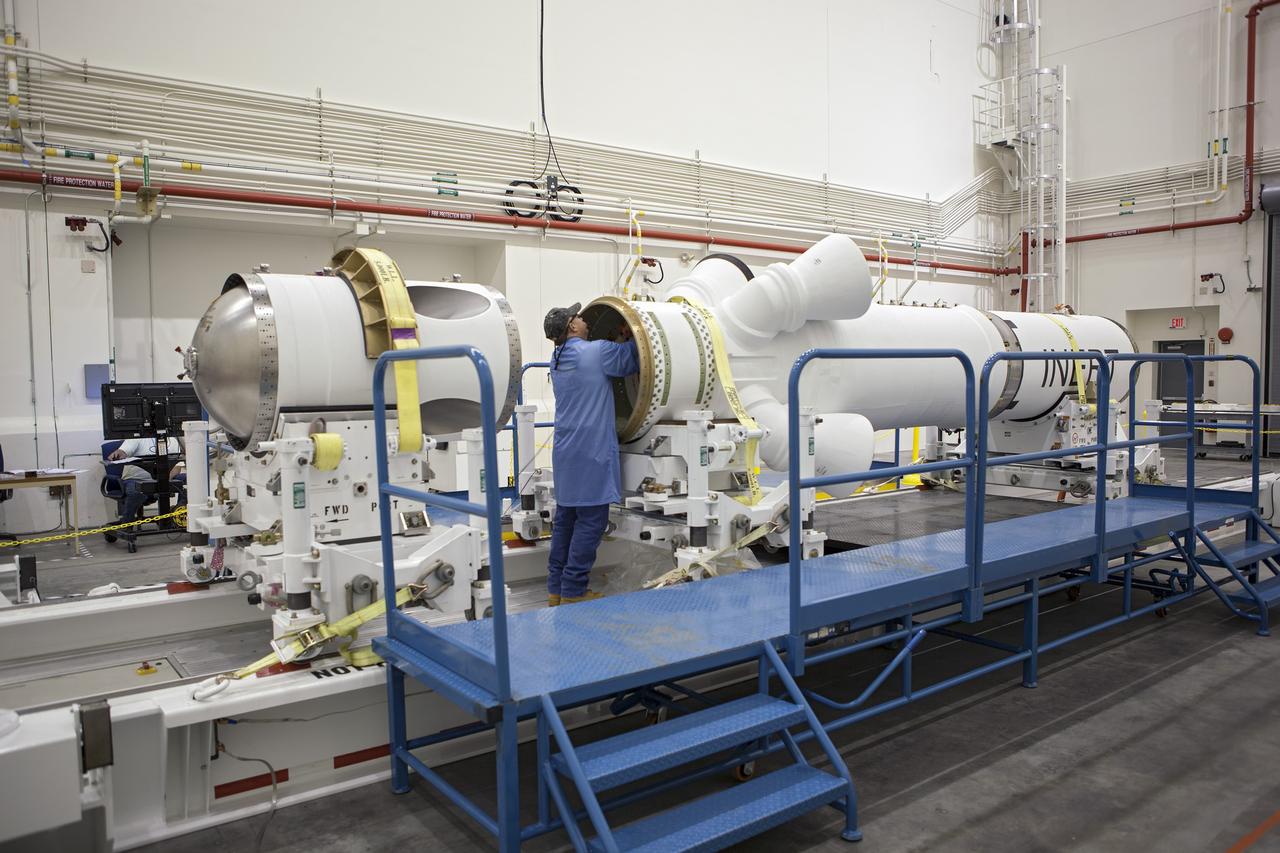

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician prepares the launch abort motor for connection to the attitude control motor. Both are segments of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
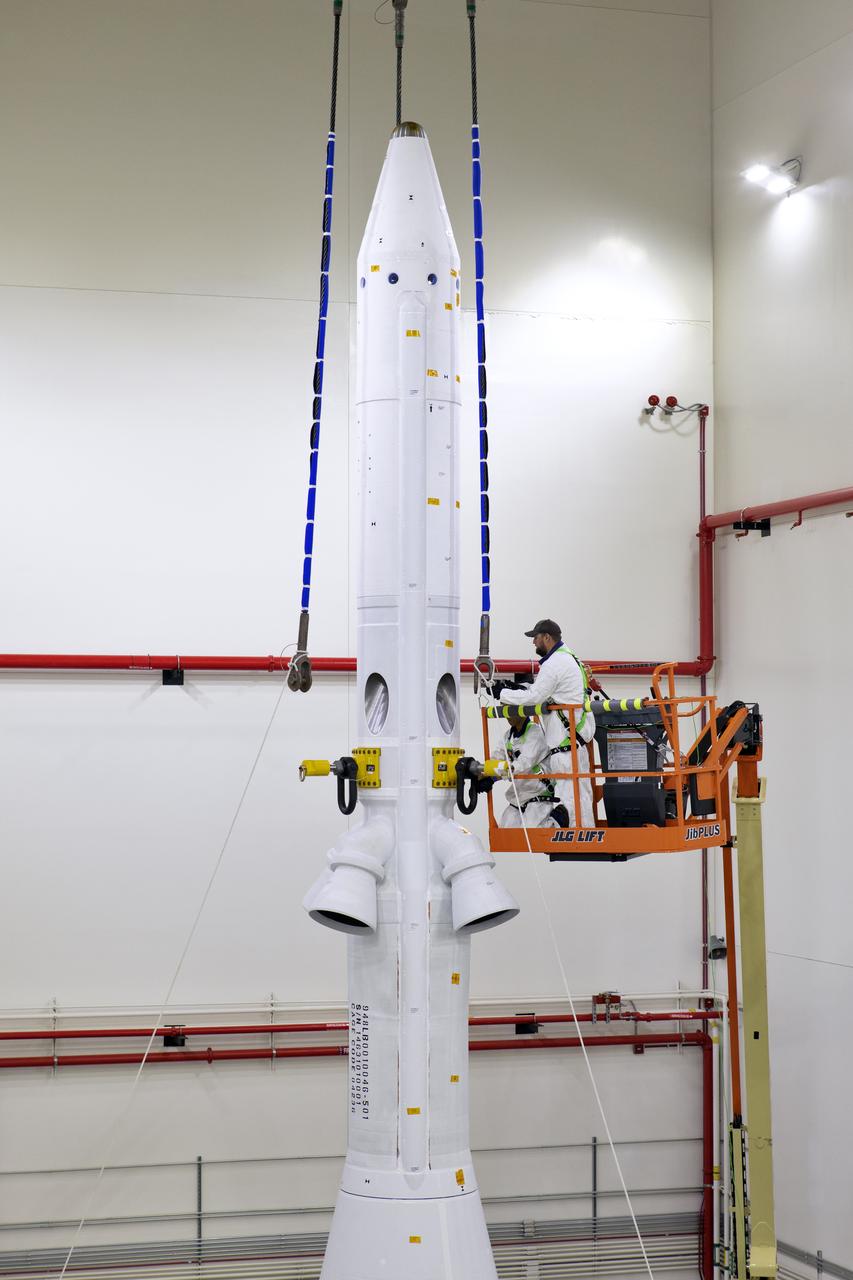

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are completing the integration of a test version of the Orion crew module with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. In view are the LAS attitude control motor, jettison motor and abort motor. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
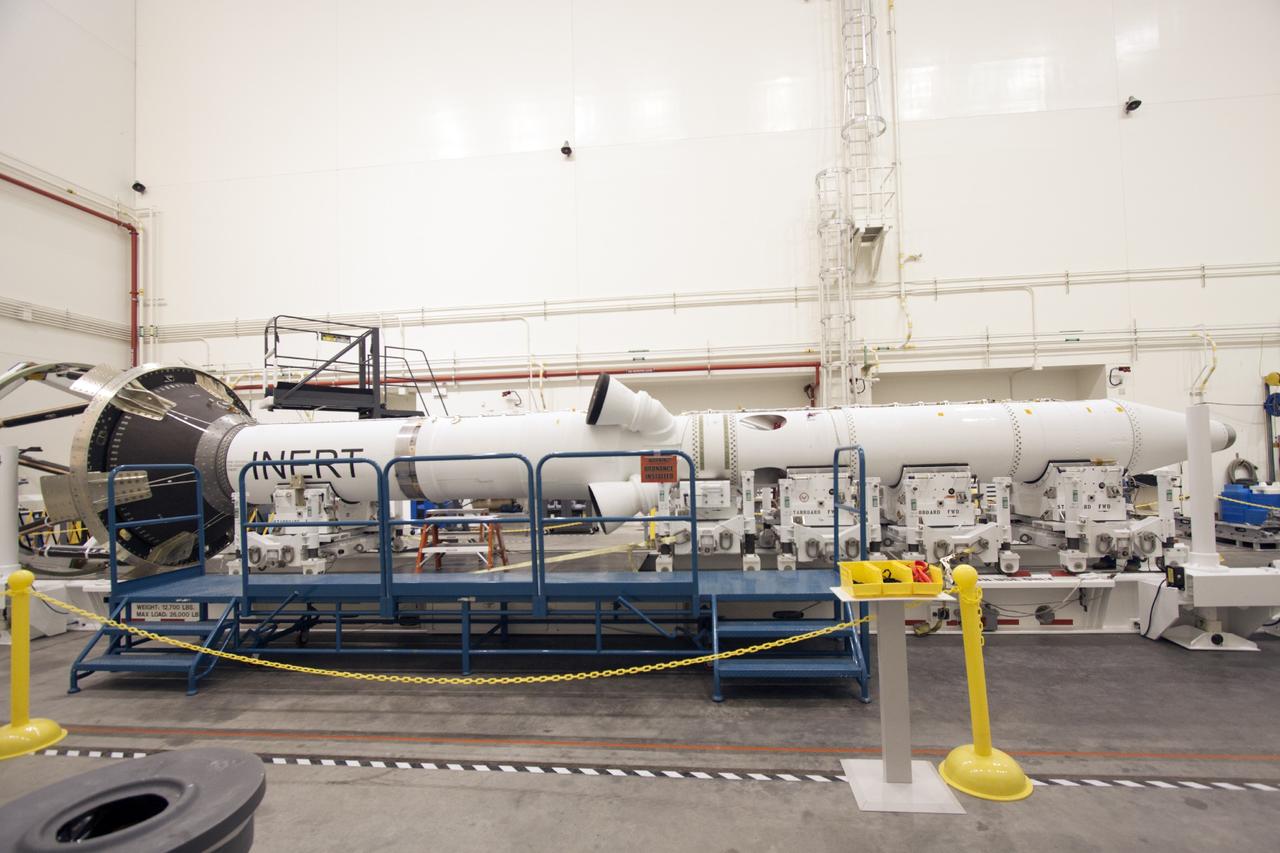

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the launch abort system, or LAS, components are horizontally stacked as processing continues for the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 mission. Components of the LAS are the launch abort motor, the attitude control motor, the jettison motor and the fairing. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The LAS is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to work on the launch abort system, or LAS, for the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 mission. Horizontally stacked together are the components of the LAS, the launch abort motor, the attitude control motor, the jettison motor and the fairing. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The LAS is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician works on the launch abort system, or LAS, for the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 mission. Horizontally stacked together are the components of the LAS, the launch abort motor, the attitude control motor, the jettison motor and the fairing. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The LAS is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
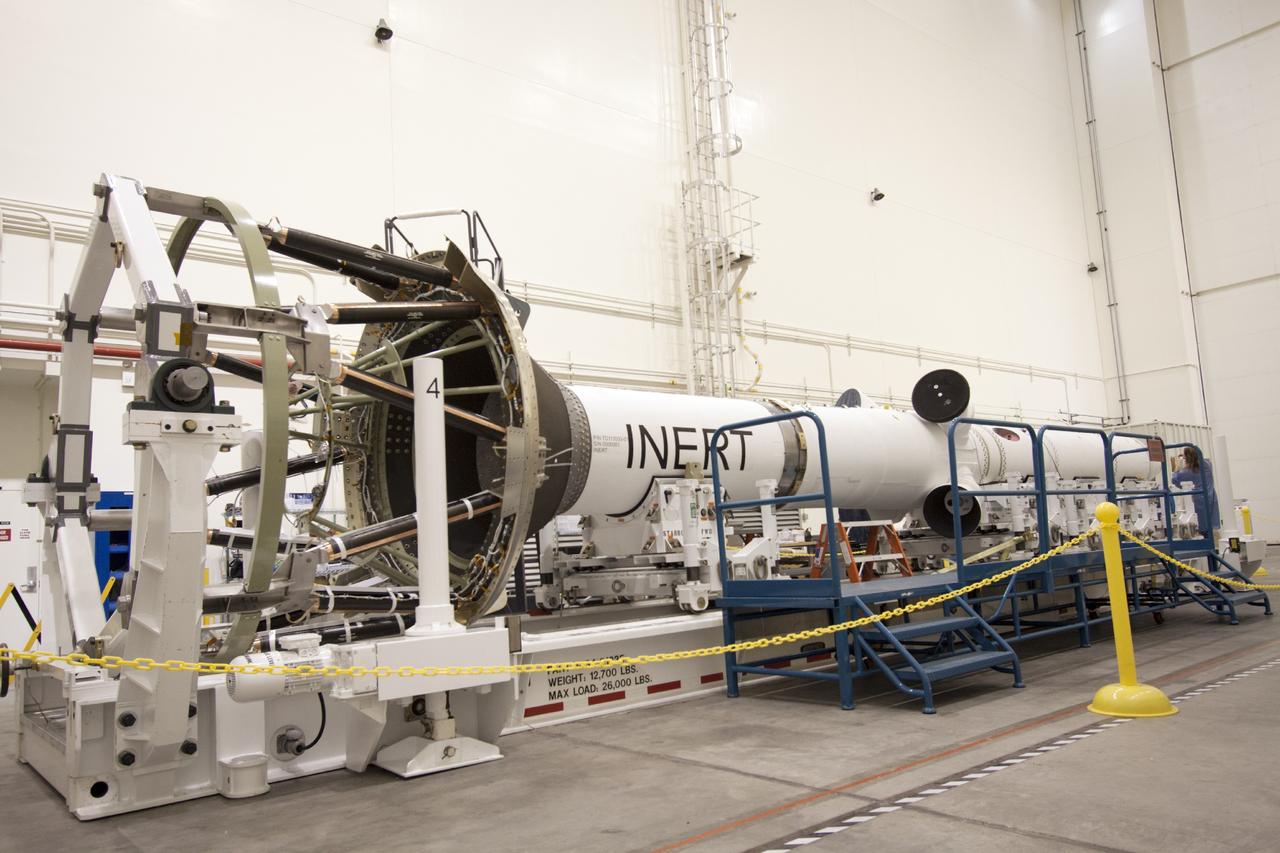

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the launch abort system, or LAS, components are horizontally stacked as processing continues for the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 mission. Components of the LAS are the launch abort motor, the attitude control motor, the jettison motor and the fairing. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The LAS is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
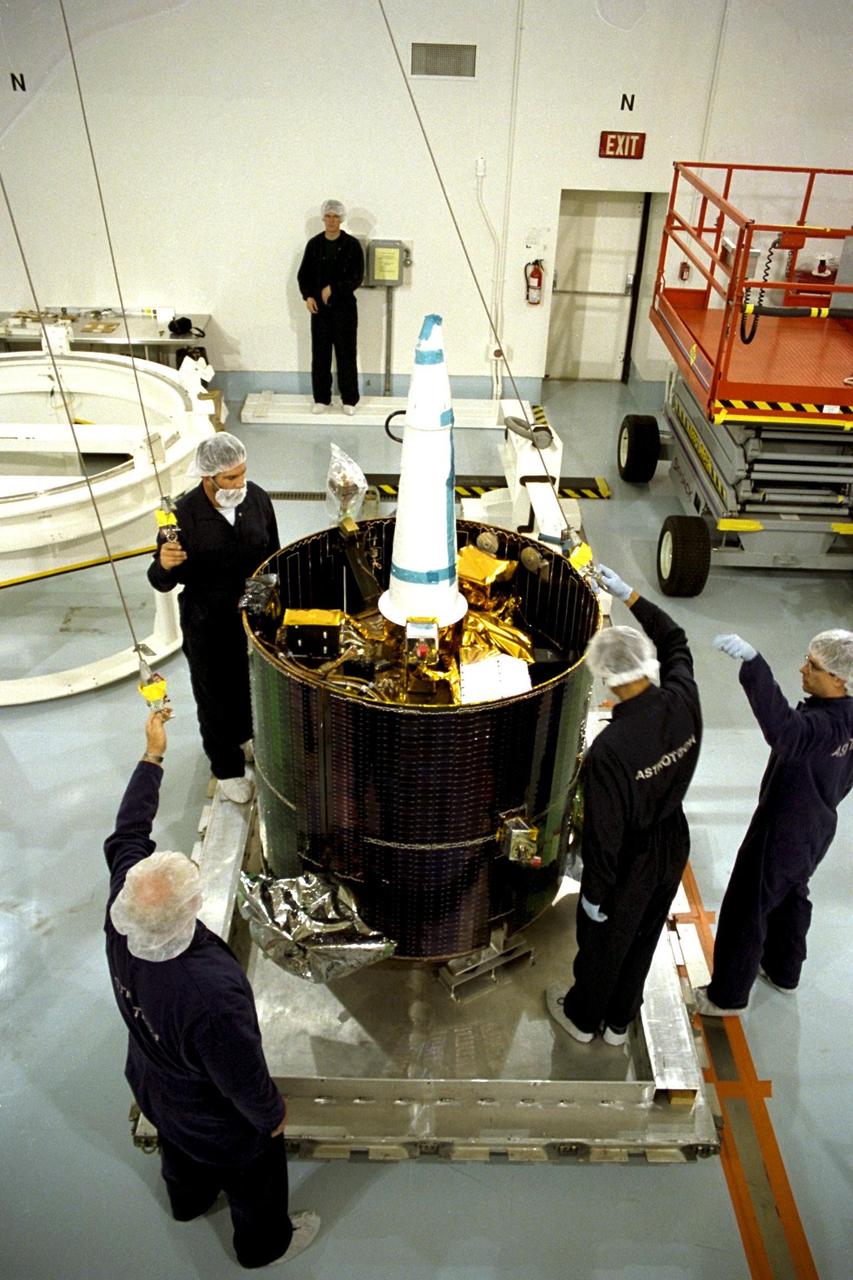

NASA's Lunar Prospector is taken out of its crate at Astrotech, a commercial payload processing facility, in Titusville, Fla. The small robotic spacecraft, to be launched for NASA on an Athena 2 rocket by Lockheed Martin, is designed to provide the first global maps of the Moon's surface compositional elements and its gravitational and magnetic fields. While at Astrotech, Lunar Prospector will be fueled with its attitude control propellant and then mated to a Trans-Lunar Injection Stage which is a solid propellant upper stage motor. The combination will next be spin tested to verify proper balance, then encapsulated into an Athena nose fairing. Then the Lunar Prospector will be transported from Astrotech to Cape Canaveral Air Station and mated to an Athena rocket. The launch of Lunar Prospector is scheduled for Jan. 5, 1998 at 8:31 p.m
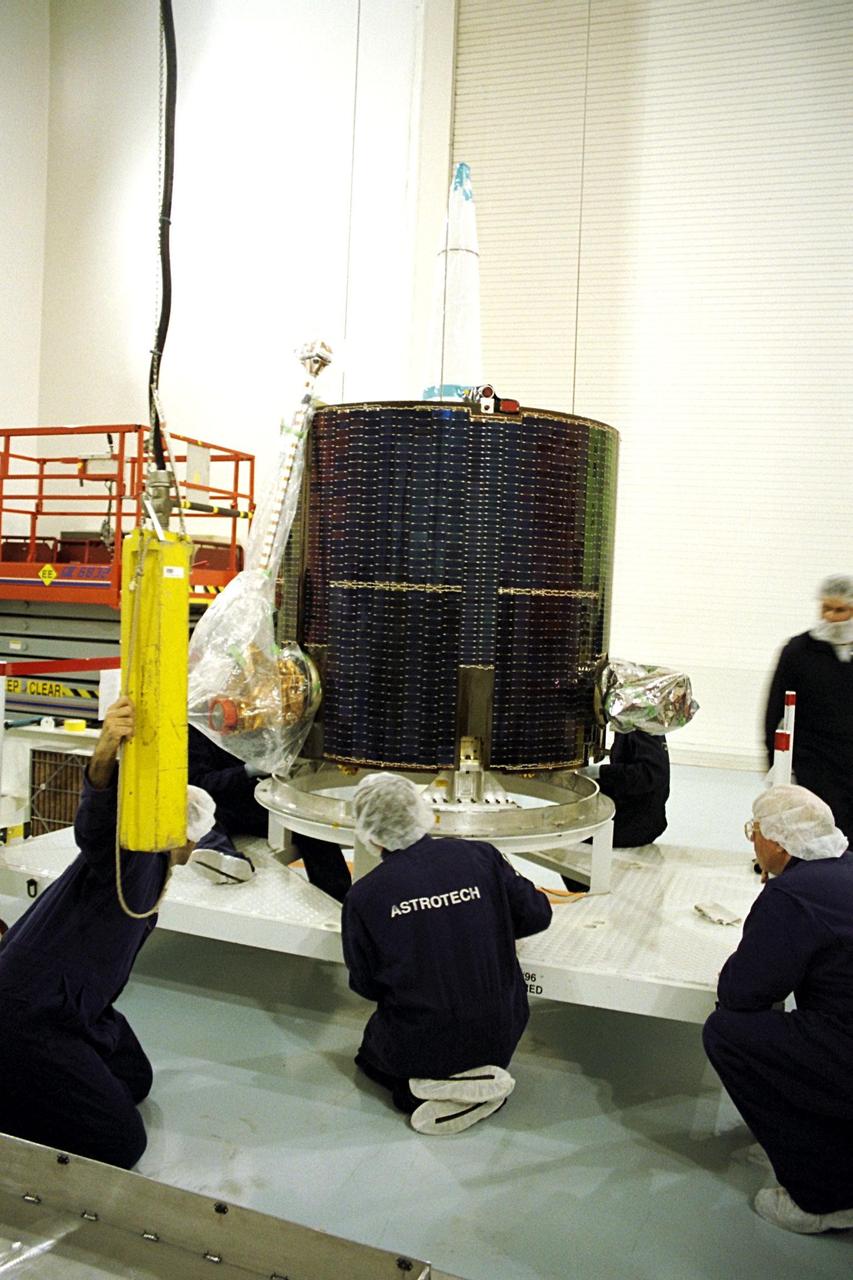

NASA's Lunar Prospector is taken out of its crate at Astrotech, a commercial payload processing facility, in Titusville, Fla. The small robotic spacecraft, to be launched for NASA on an Athena 2 rocket by Lockheed Martin, is designed to provide the first global maps of the Moon's surface compositional elements and its gravitational and magnetic fields. While at Astrotech, Lunar Prospector will be fueled with its attitude control propellant and then mated to a Trans-Lunar Injection Stage which is a solid propellant upper stage motor. The combination will next be spin tested to verify proper balance, then encapsulated into an Athena nose fairing. Then the Lunar Prospector will be transported from Astrotech to Cape Canaveral Air Station and mated to an Athena rocket. The launch of Lunar Prospector is scheduled for Jan. 5, 1998 at 8:31 p.m
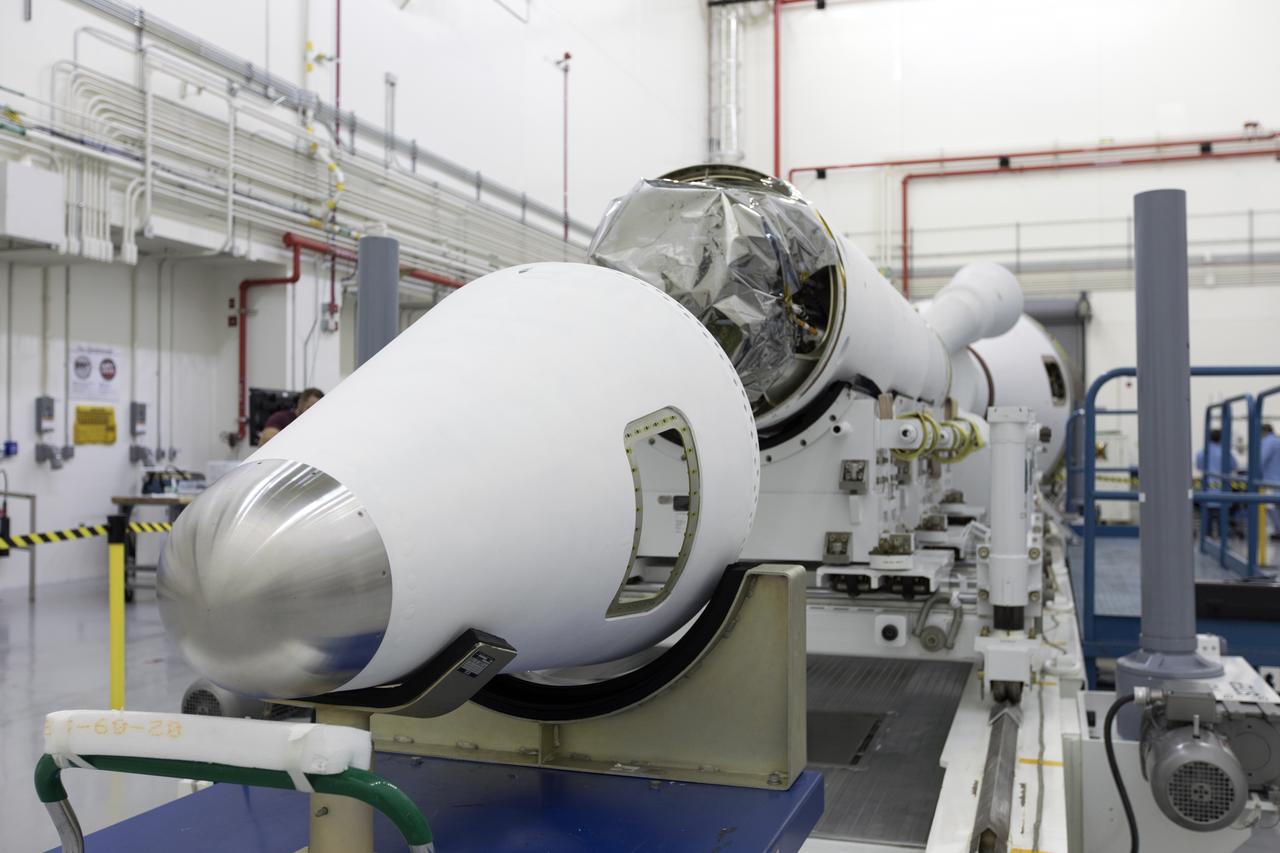

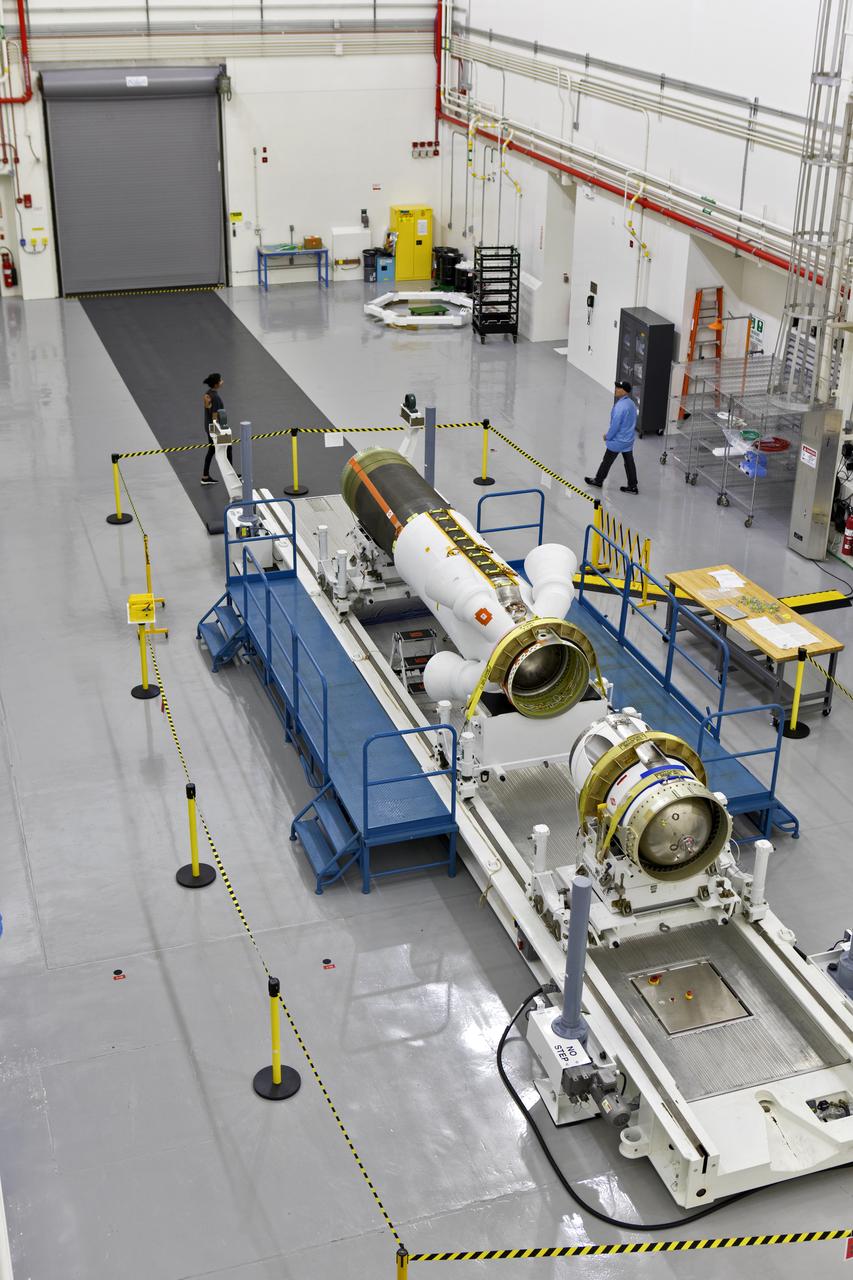
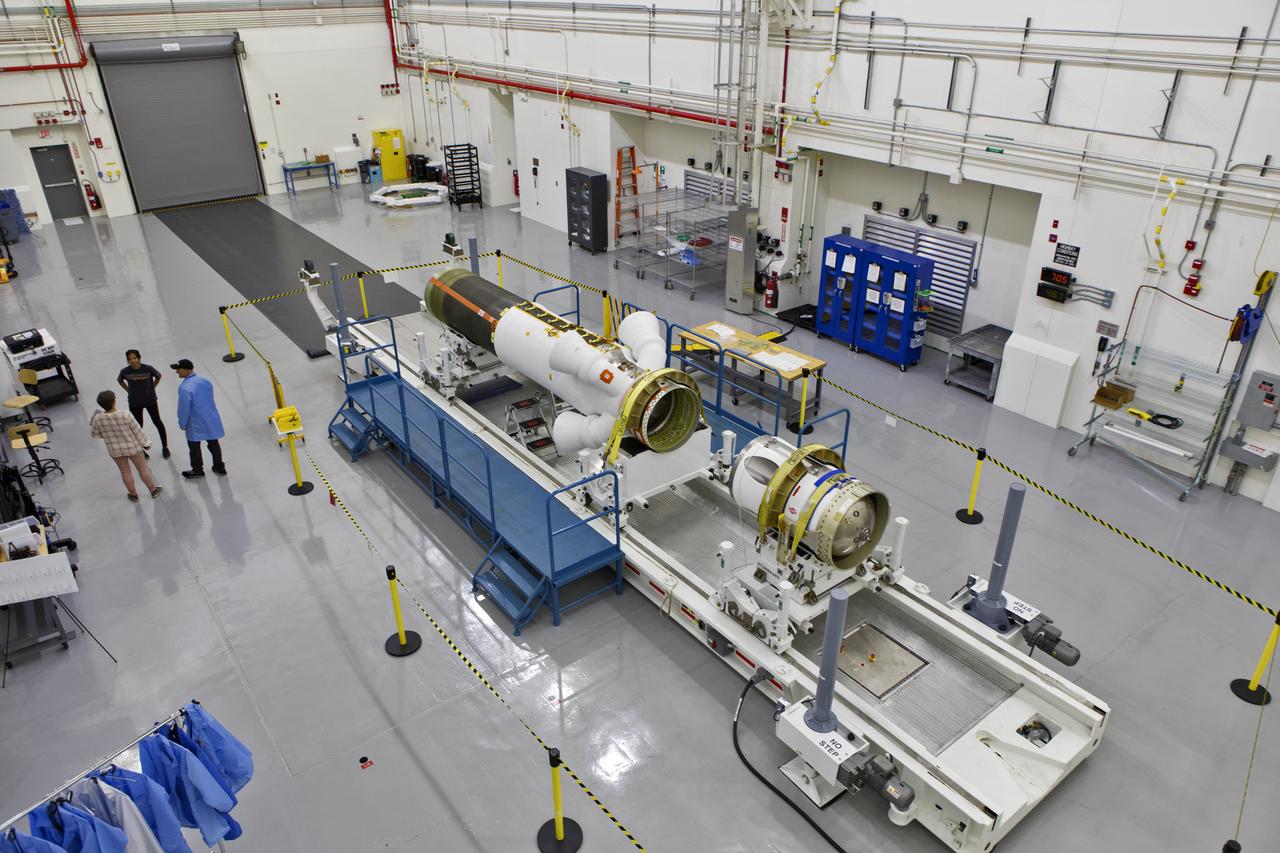
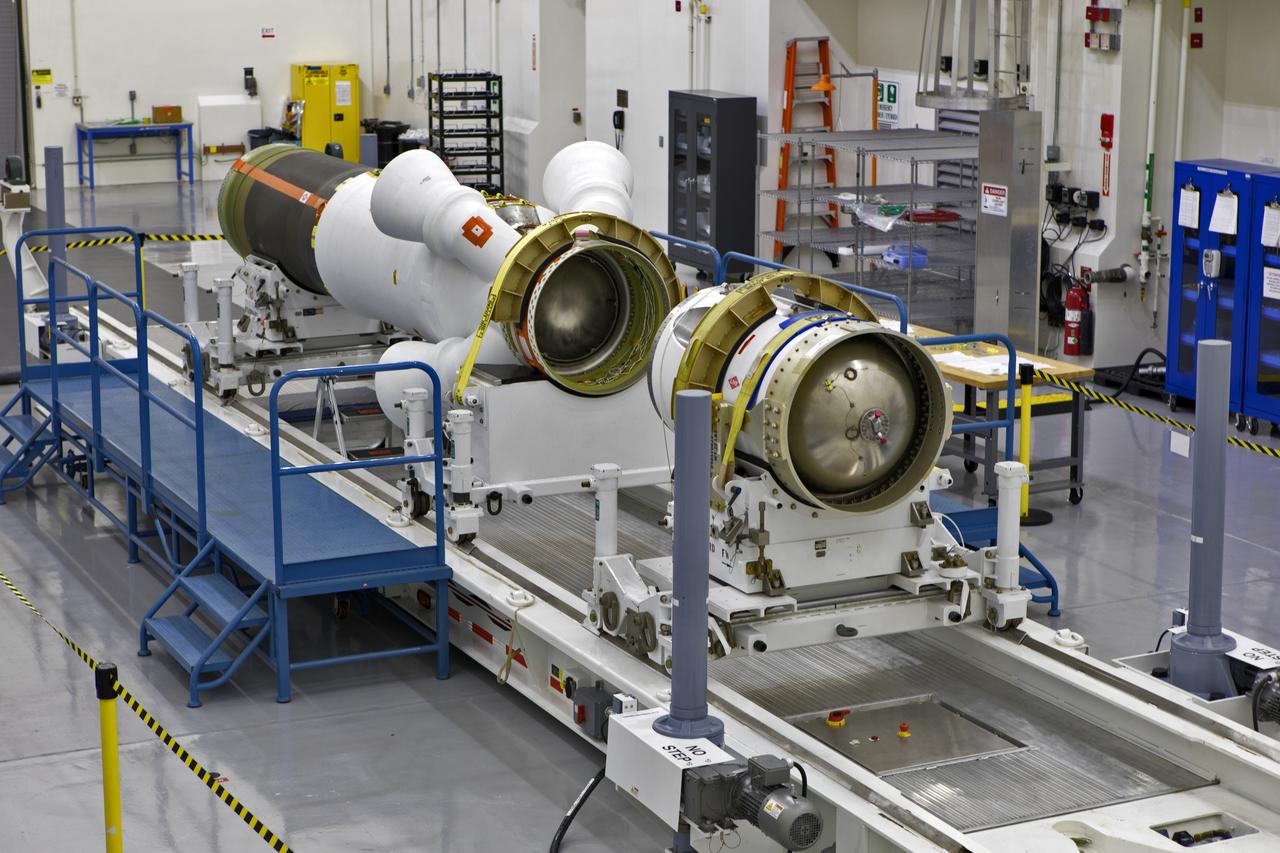
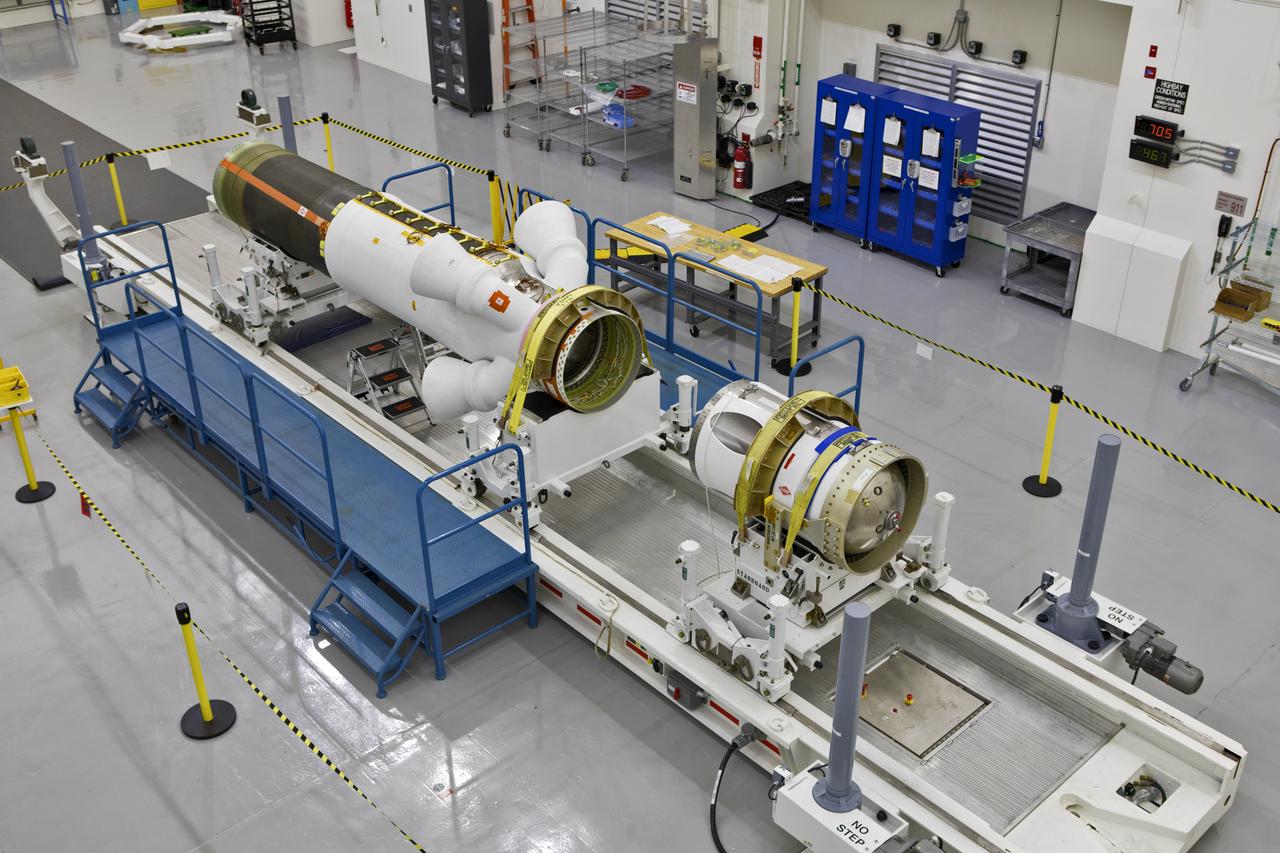
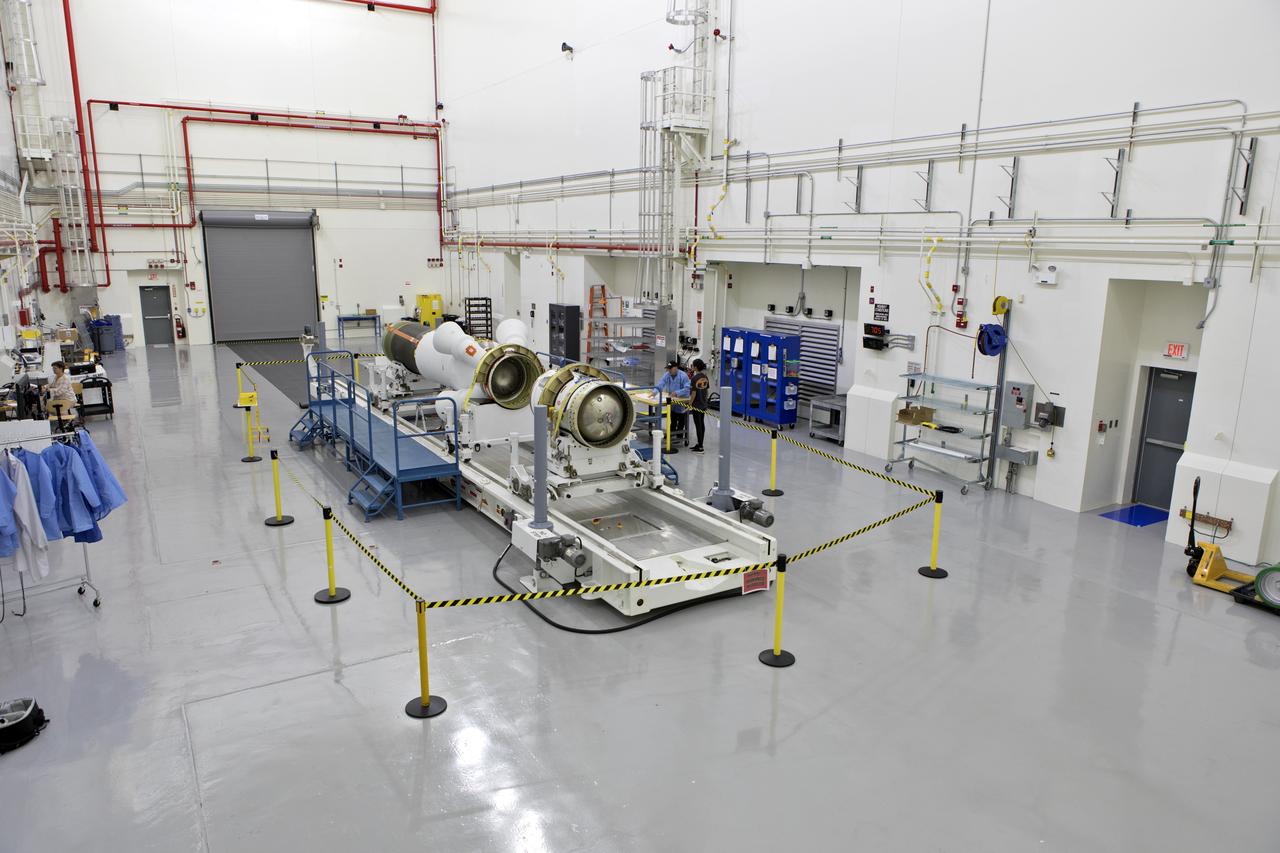
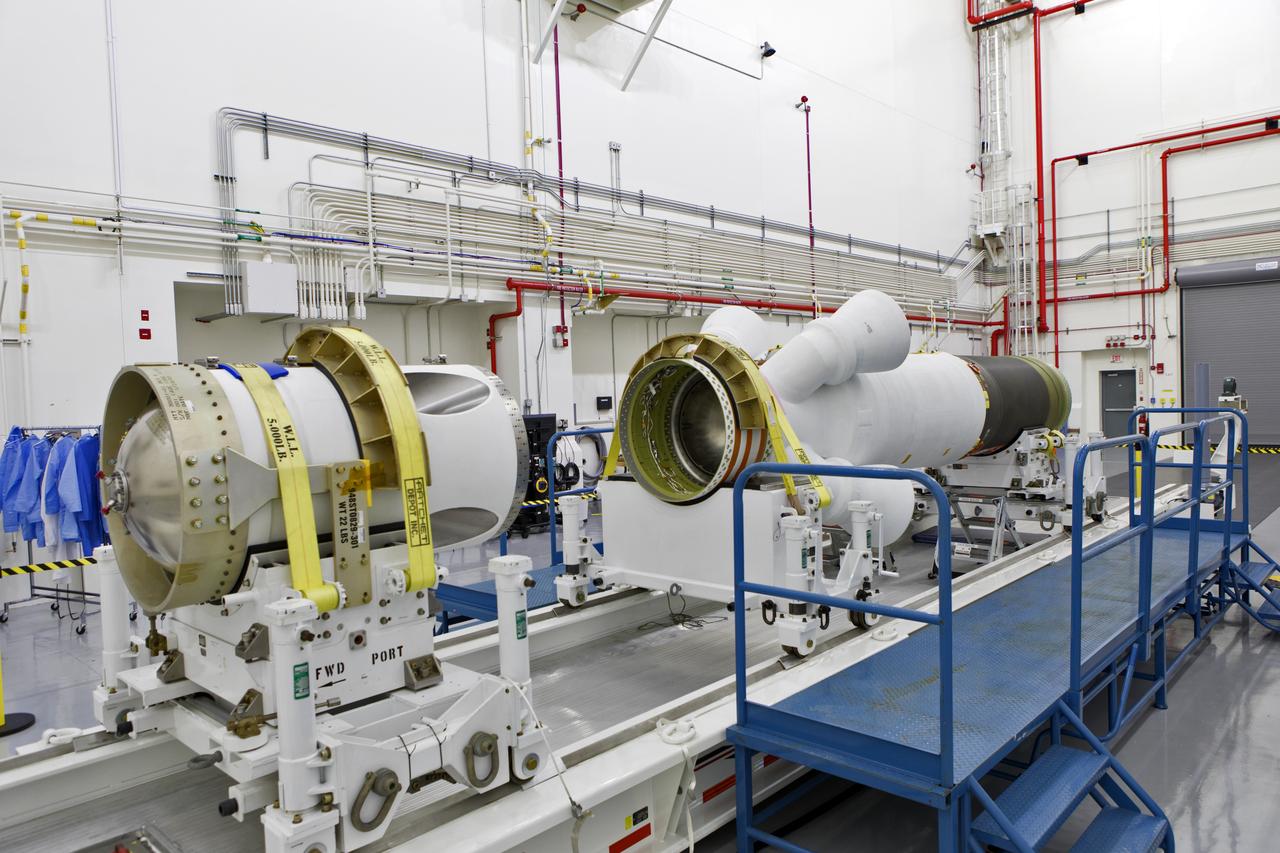
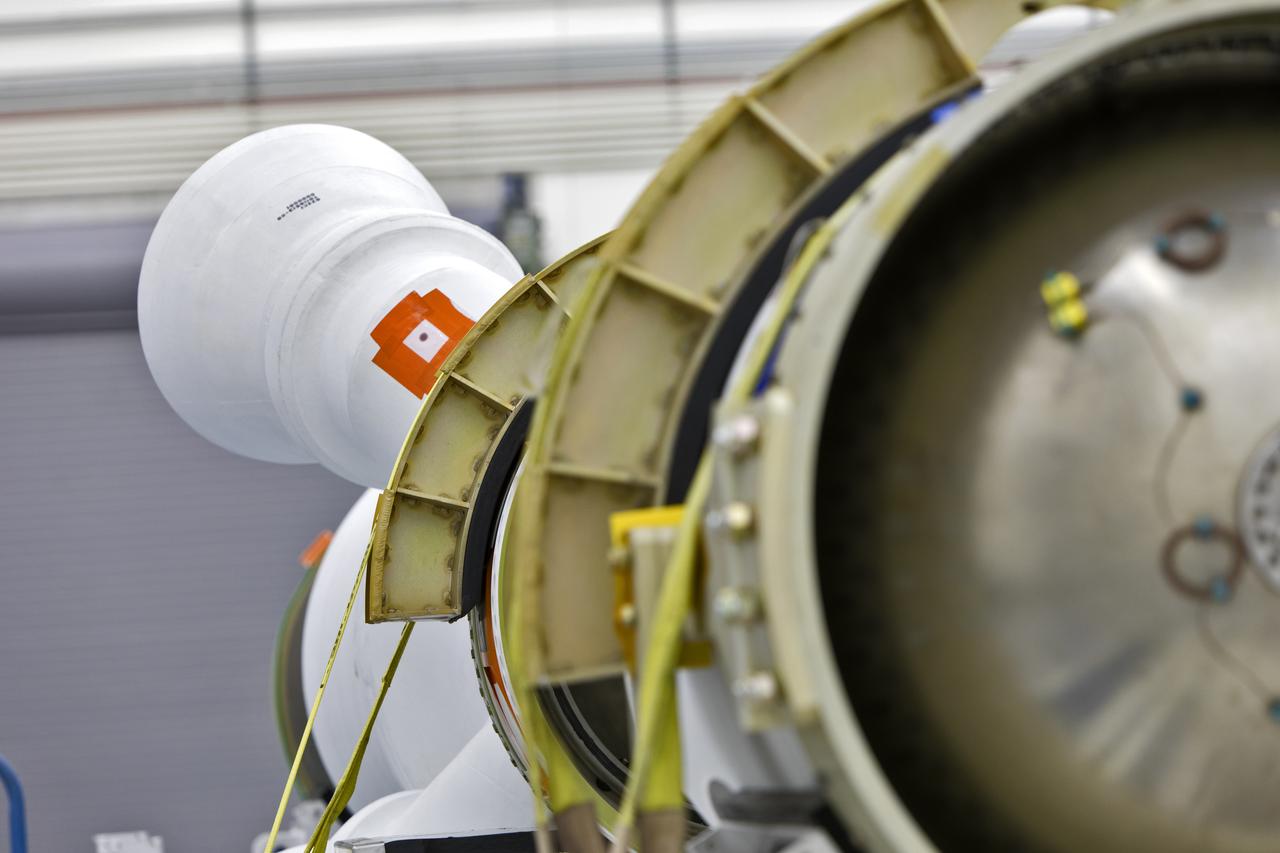
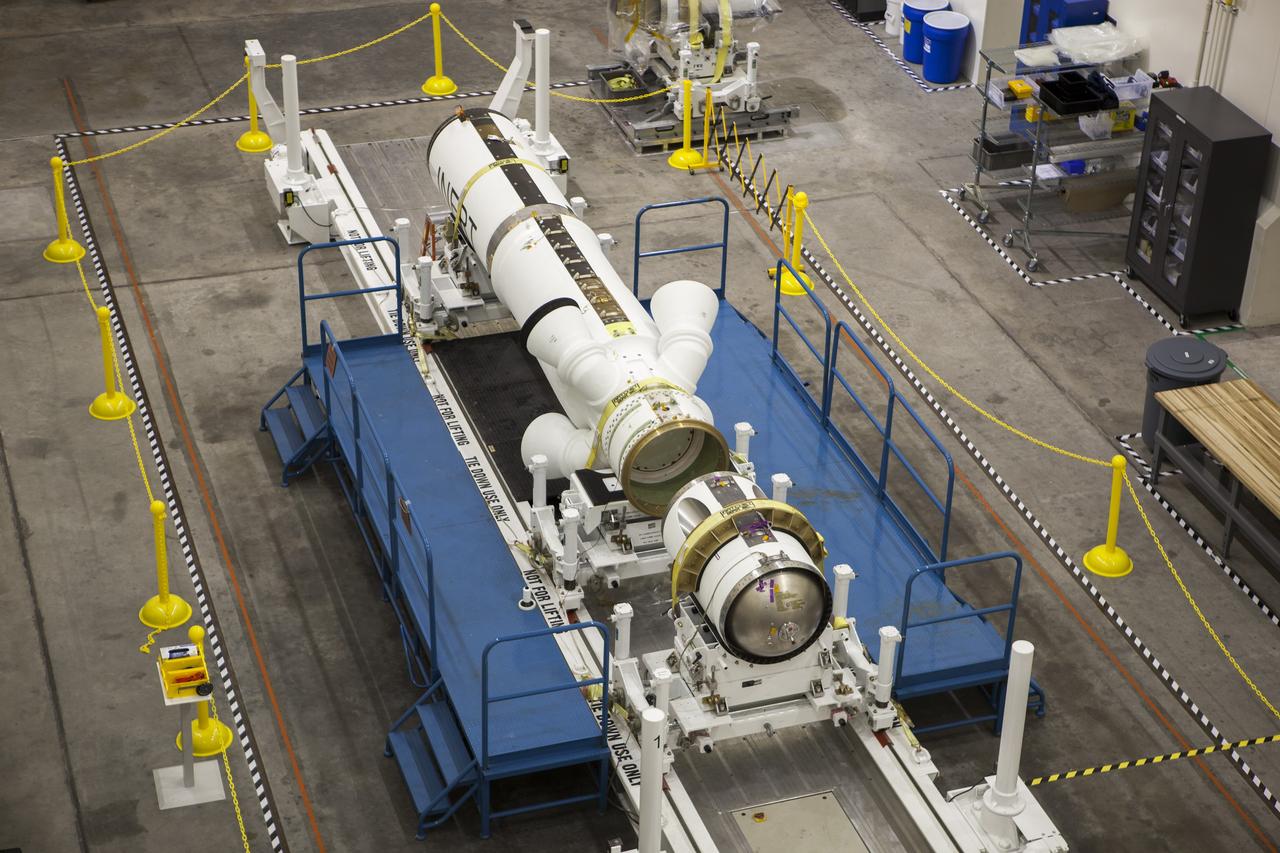
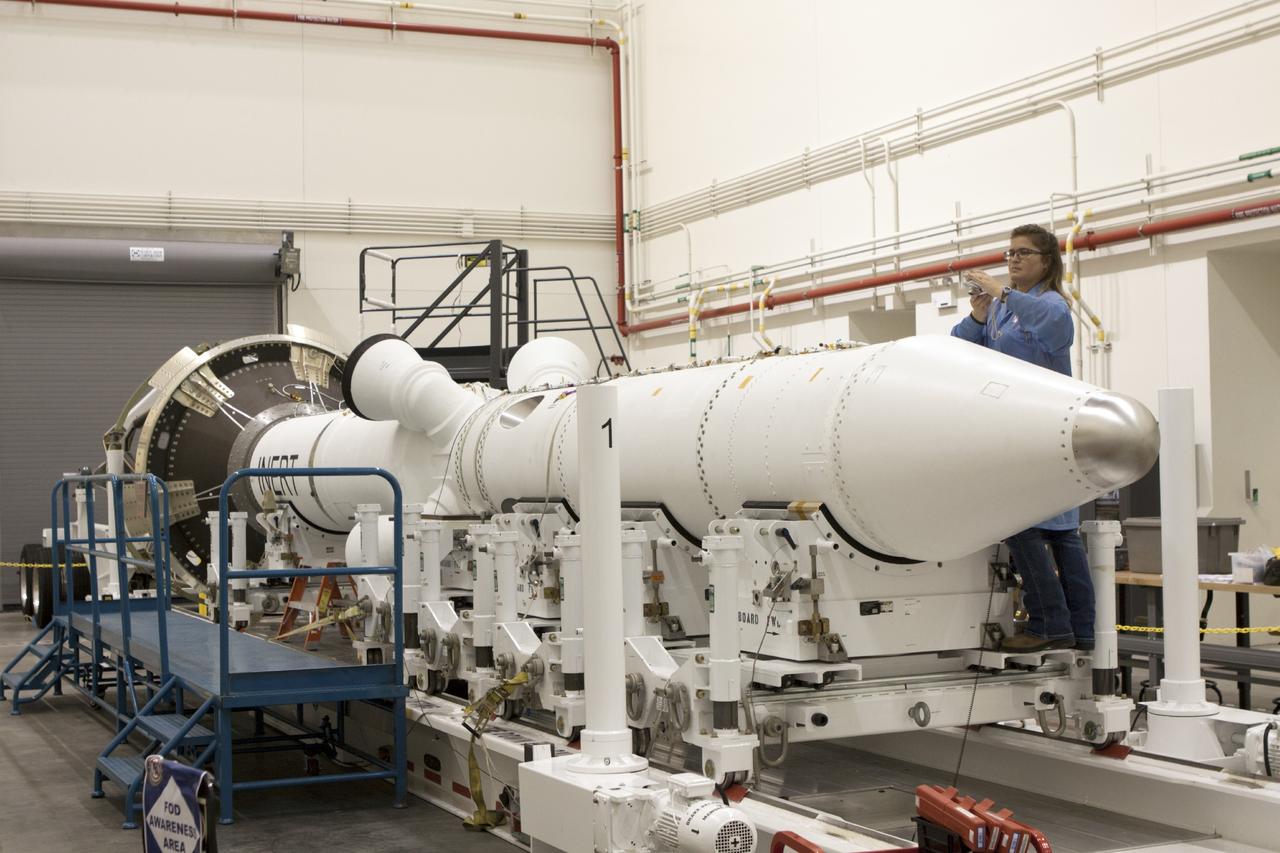
Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Launch Abort System (LAS) that will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is being assembled on Feb. 5, 2019. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for Spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
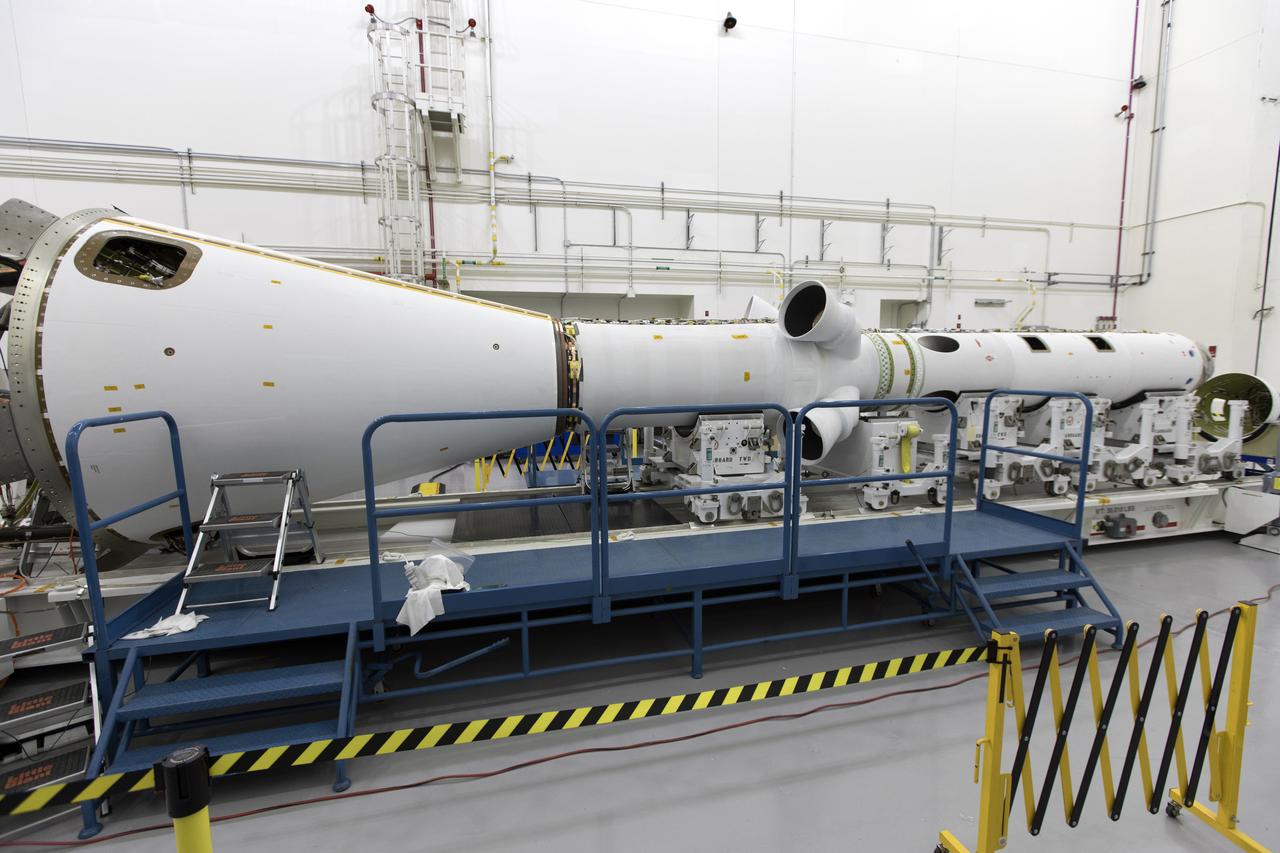

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Launch Abort System (LAS) that will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is being assembled on Feb. 5, 2019. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for Spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
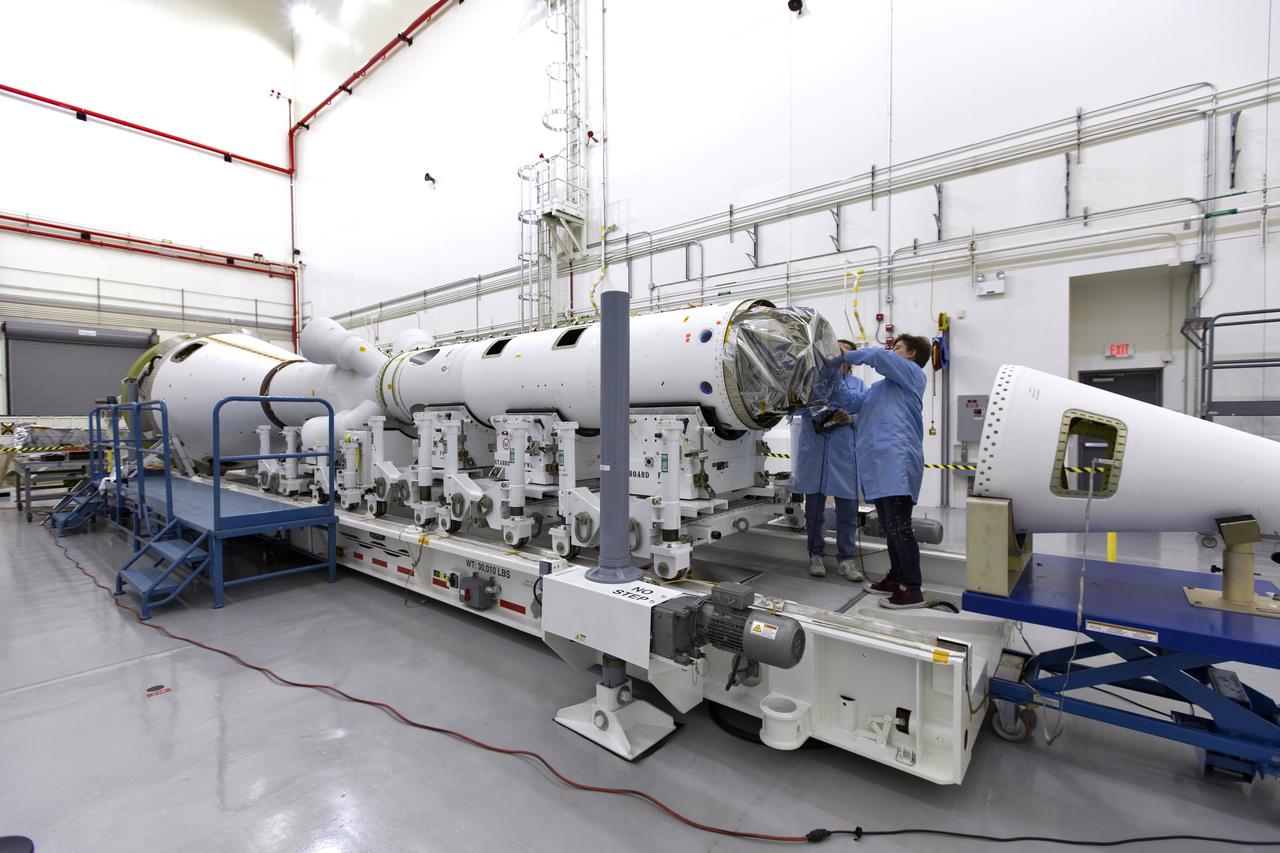

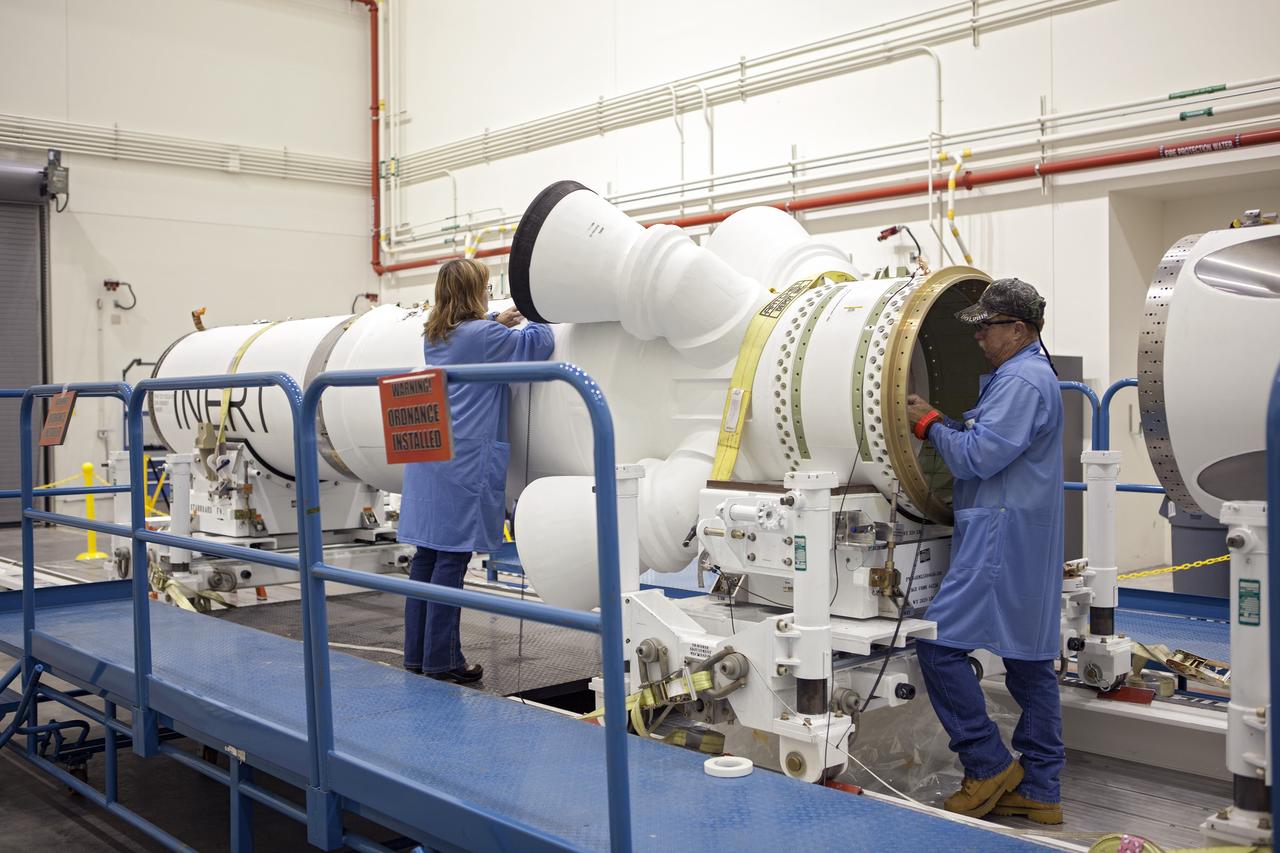
Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers assemble the Launch Abort System (LAS) on Feb. 5, 2019, that will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for Spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
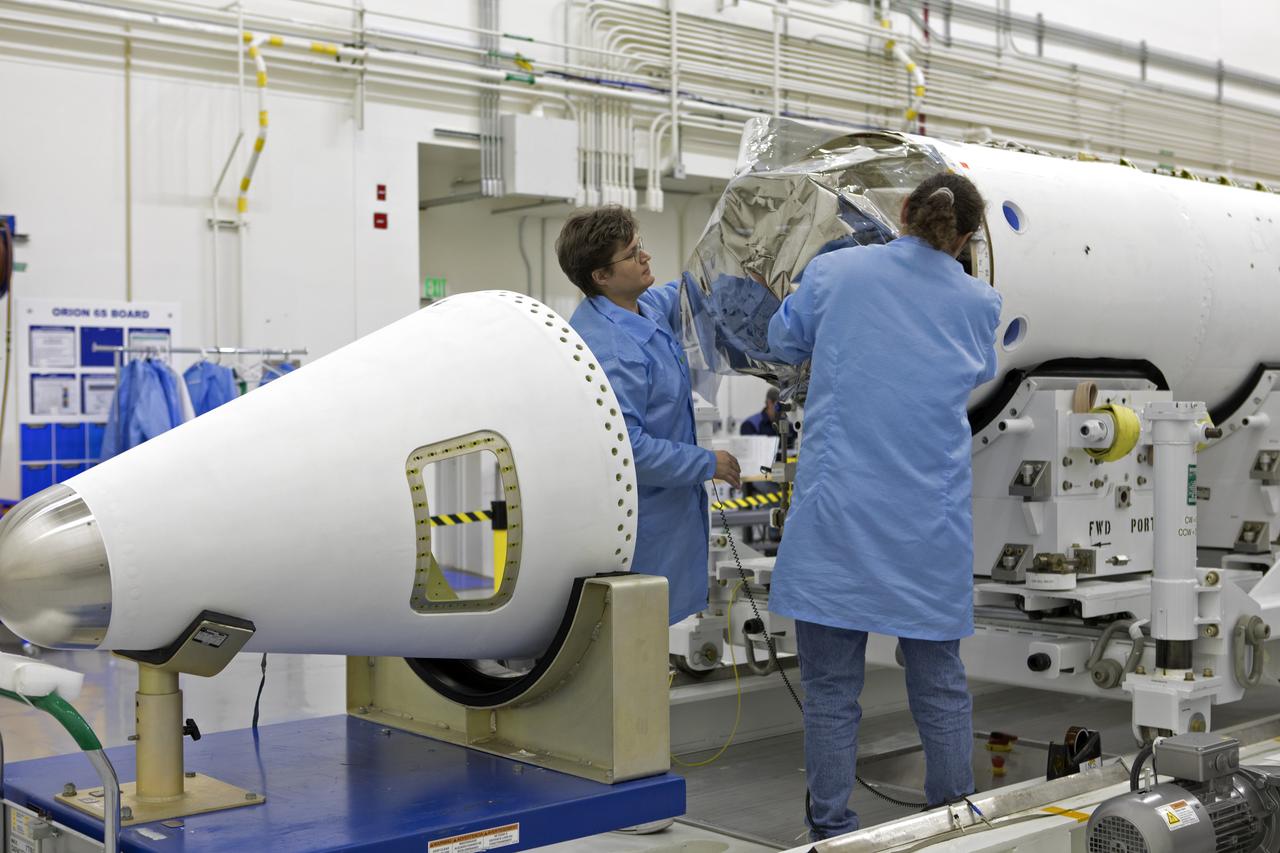

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers assemble the Launch Abort System (LAS) on Feb. 5, 2019, that will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for Spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
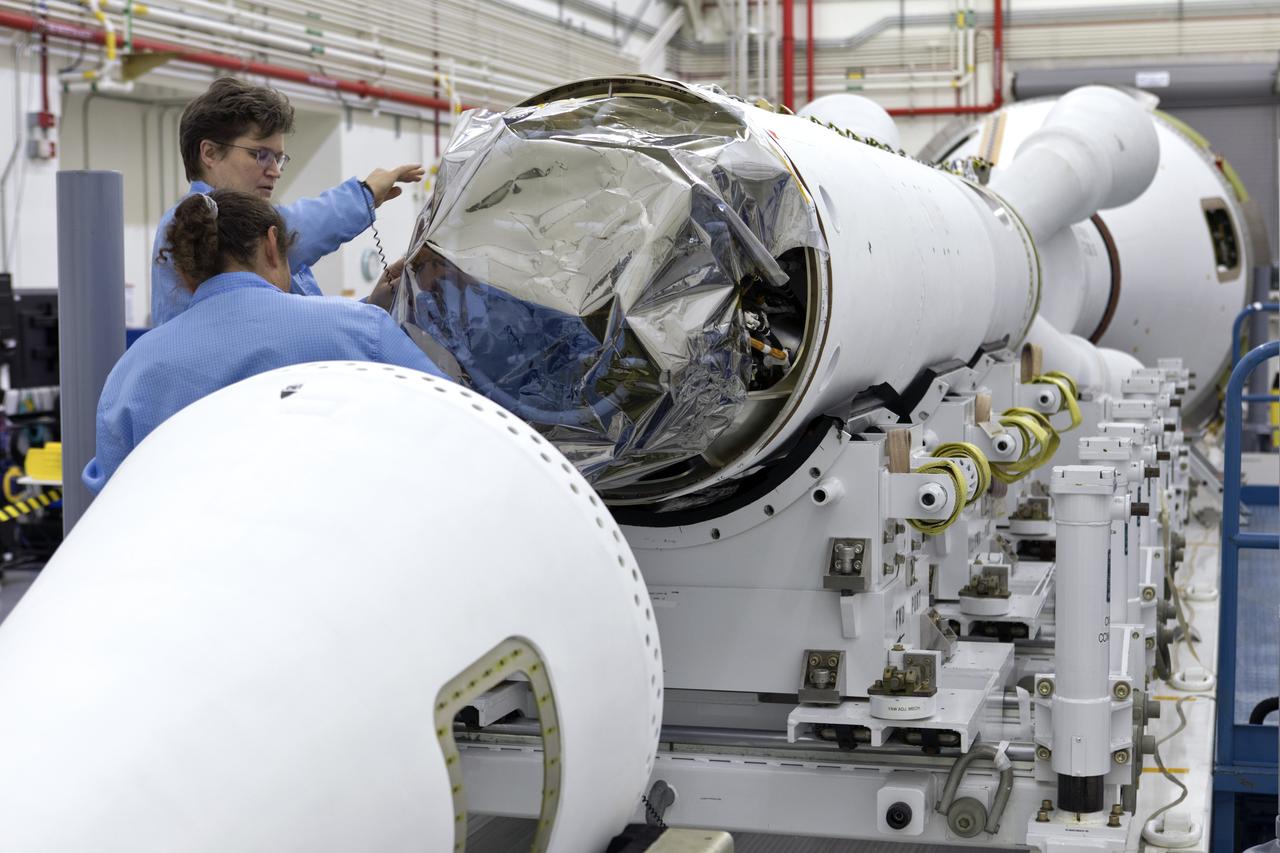

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers assemble the Launch Abort System (LAS) on Feb. 5, 2019, that will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for Spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
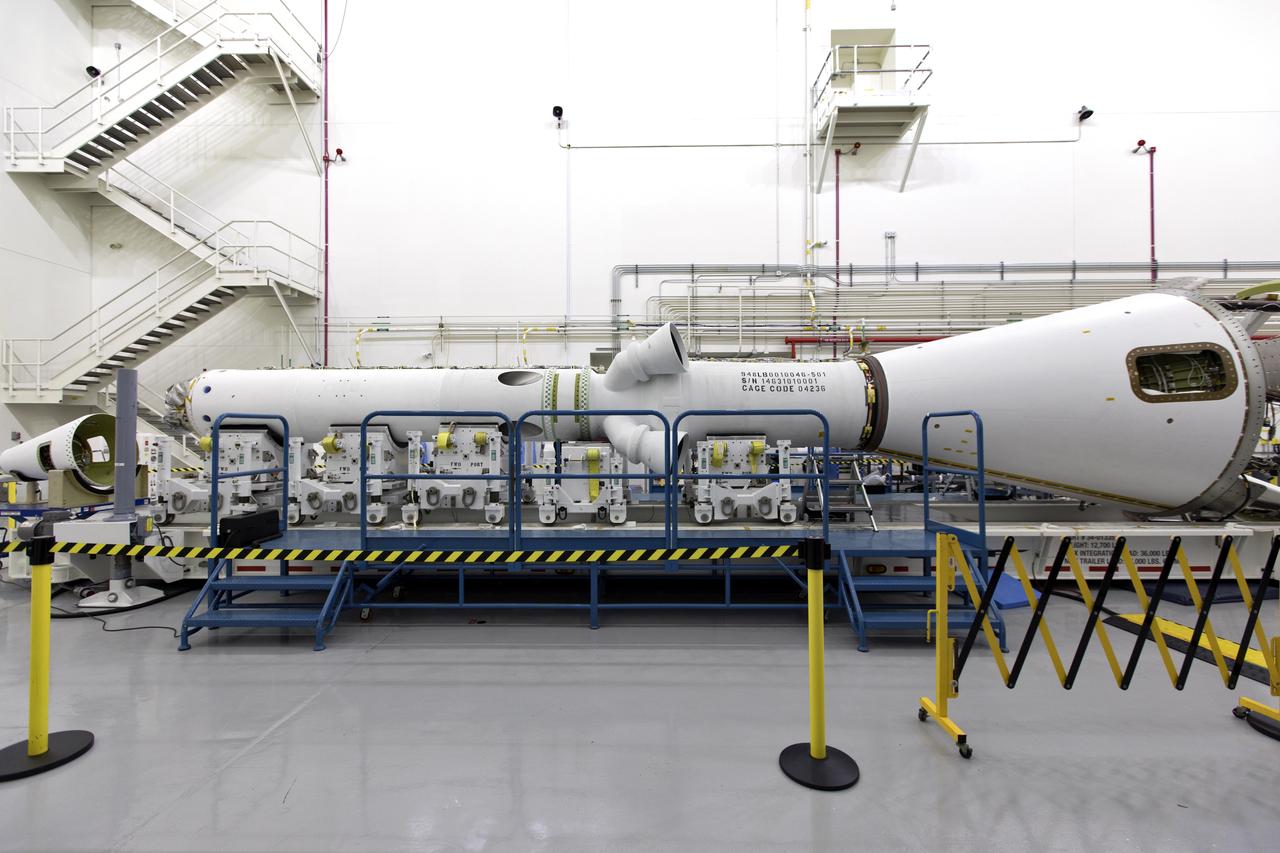

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Launch Abort System (LAS) that will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is being assembled on Feb. 5, 2019. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for Spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
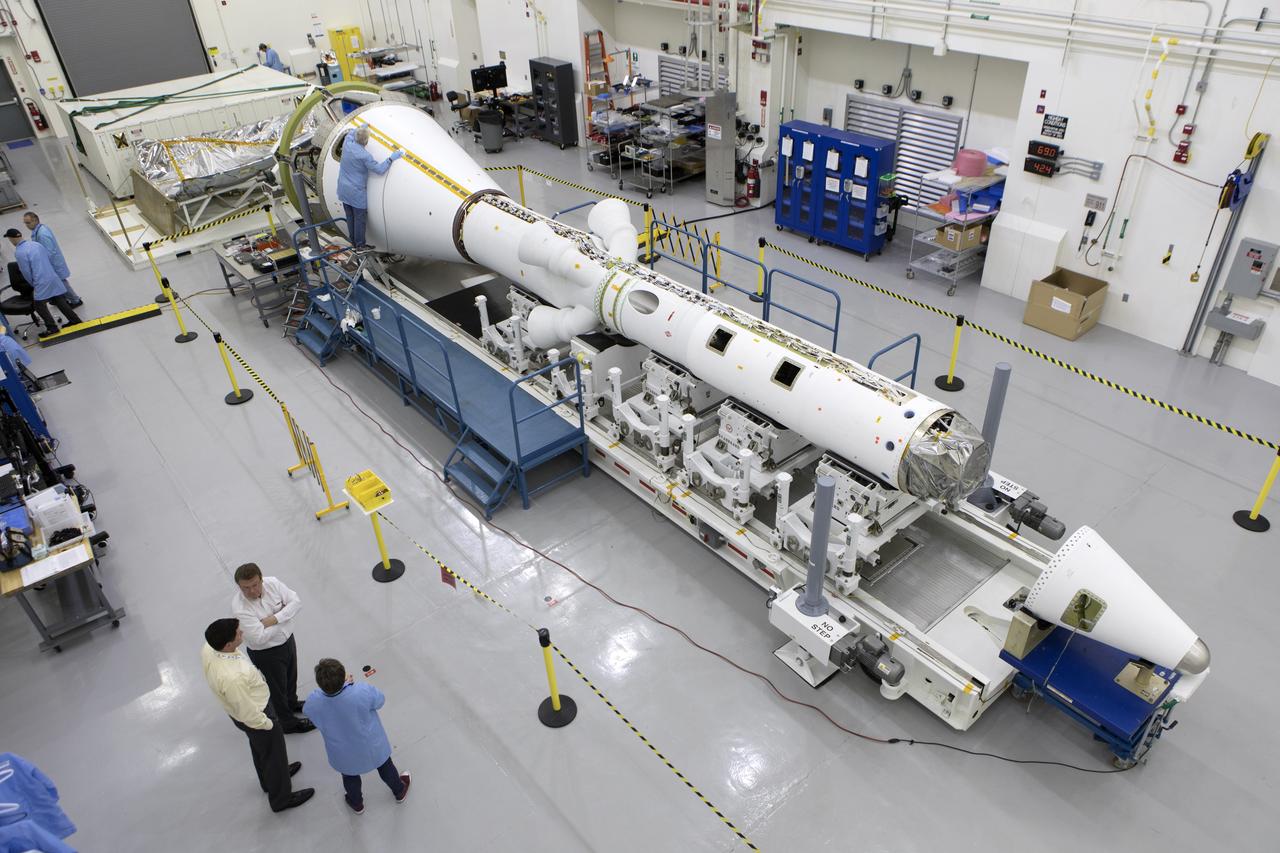

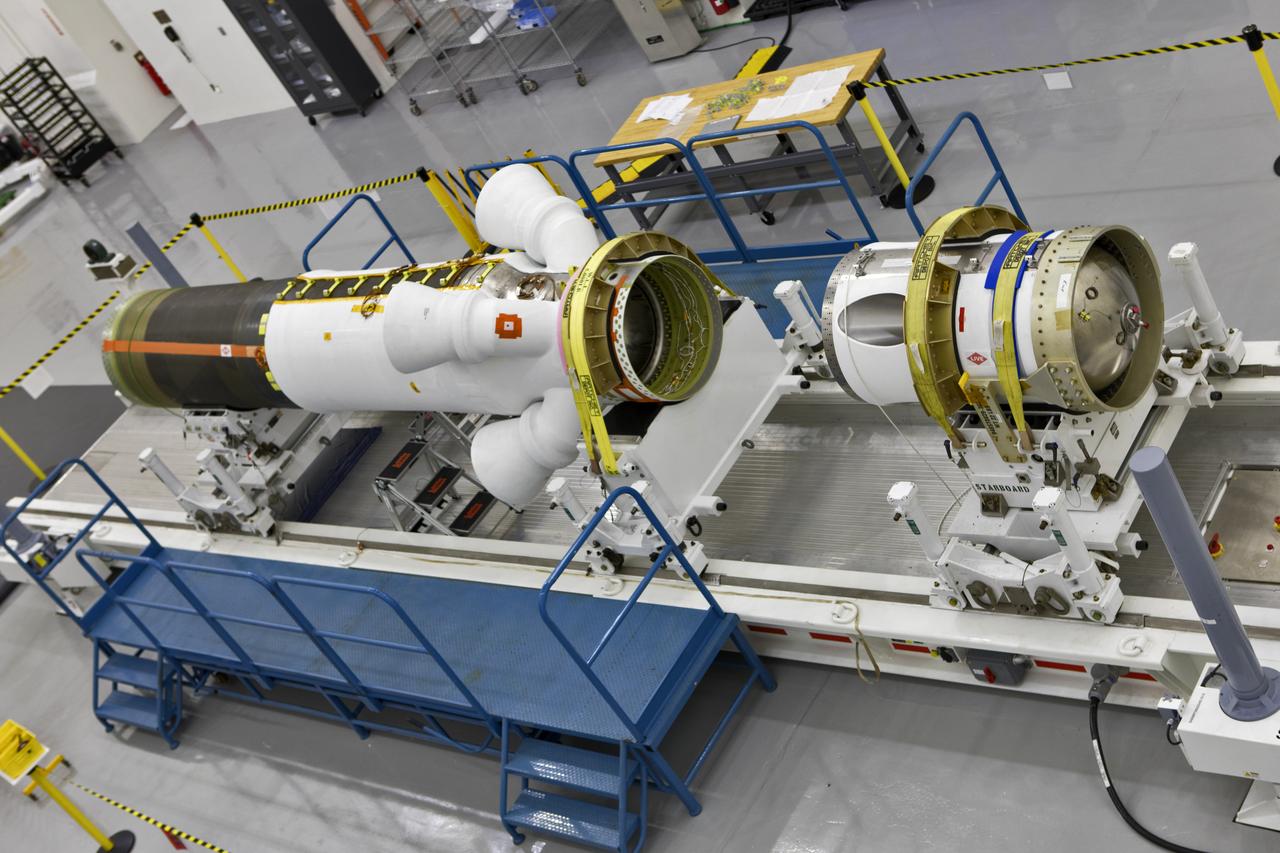
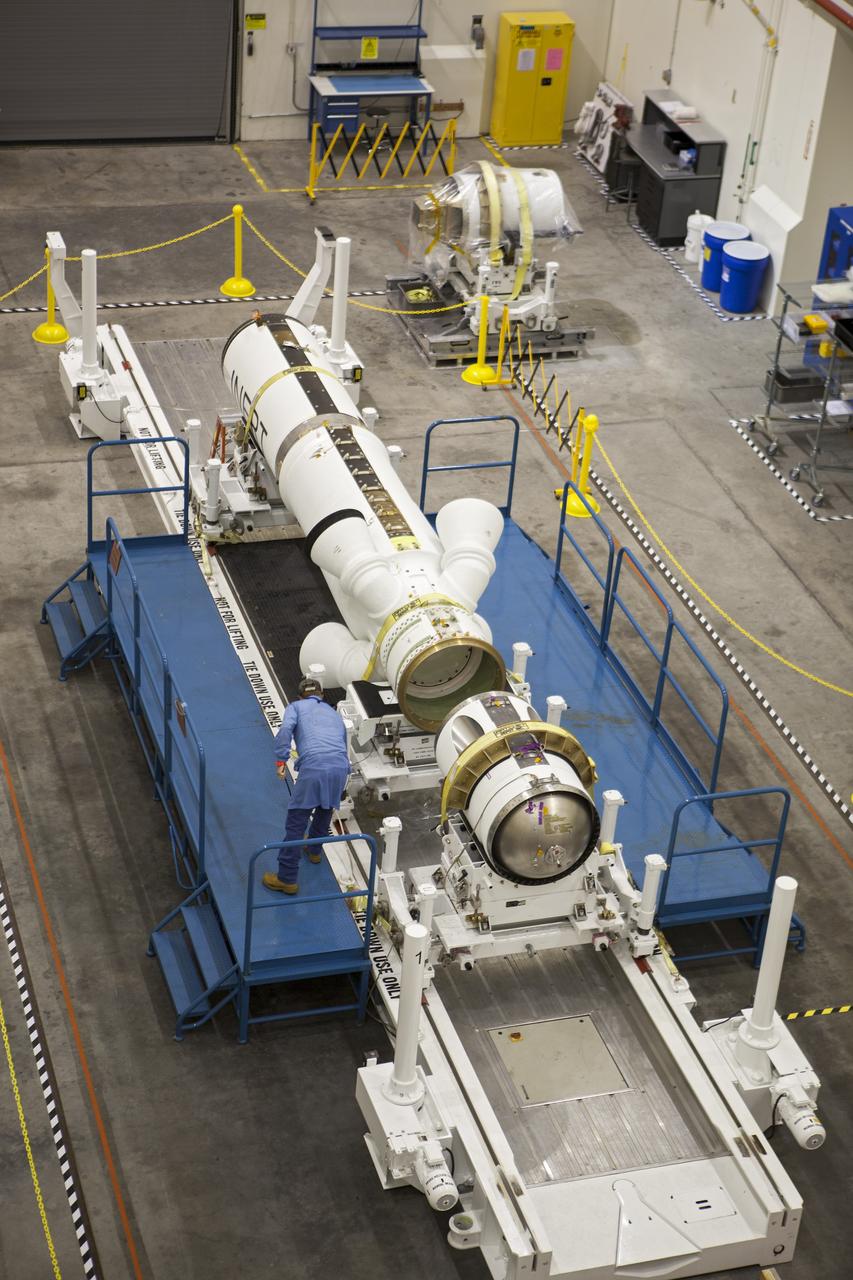
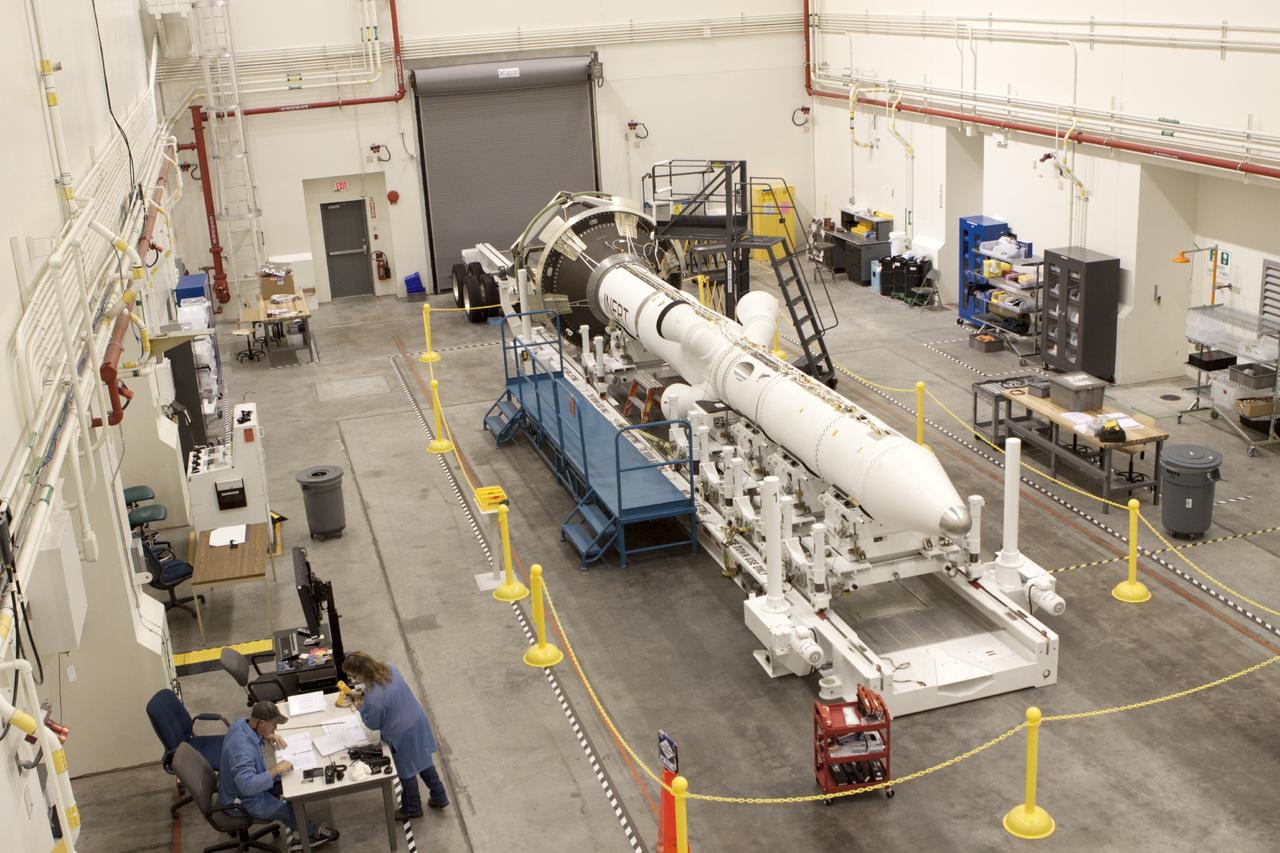
In this view from above inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Launch Abort System (LAS) that will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is being assembled on Feb. 5, 2019. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for Spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
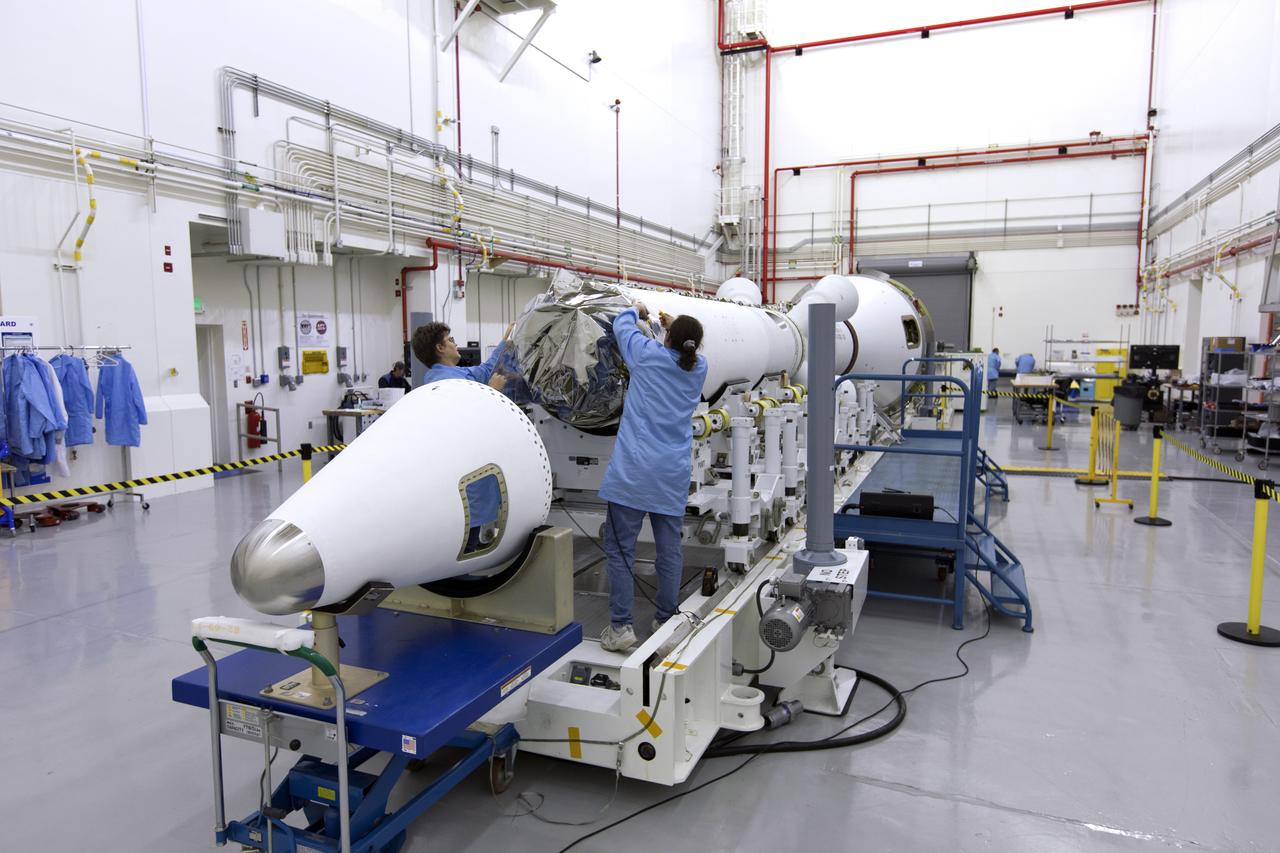

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers assemble the Launch Abort System (LAS) on Feb. 5, 2019, that will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for Spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
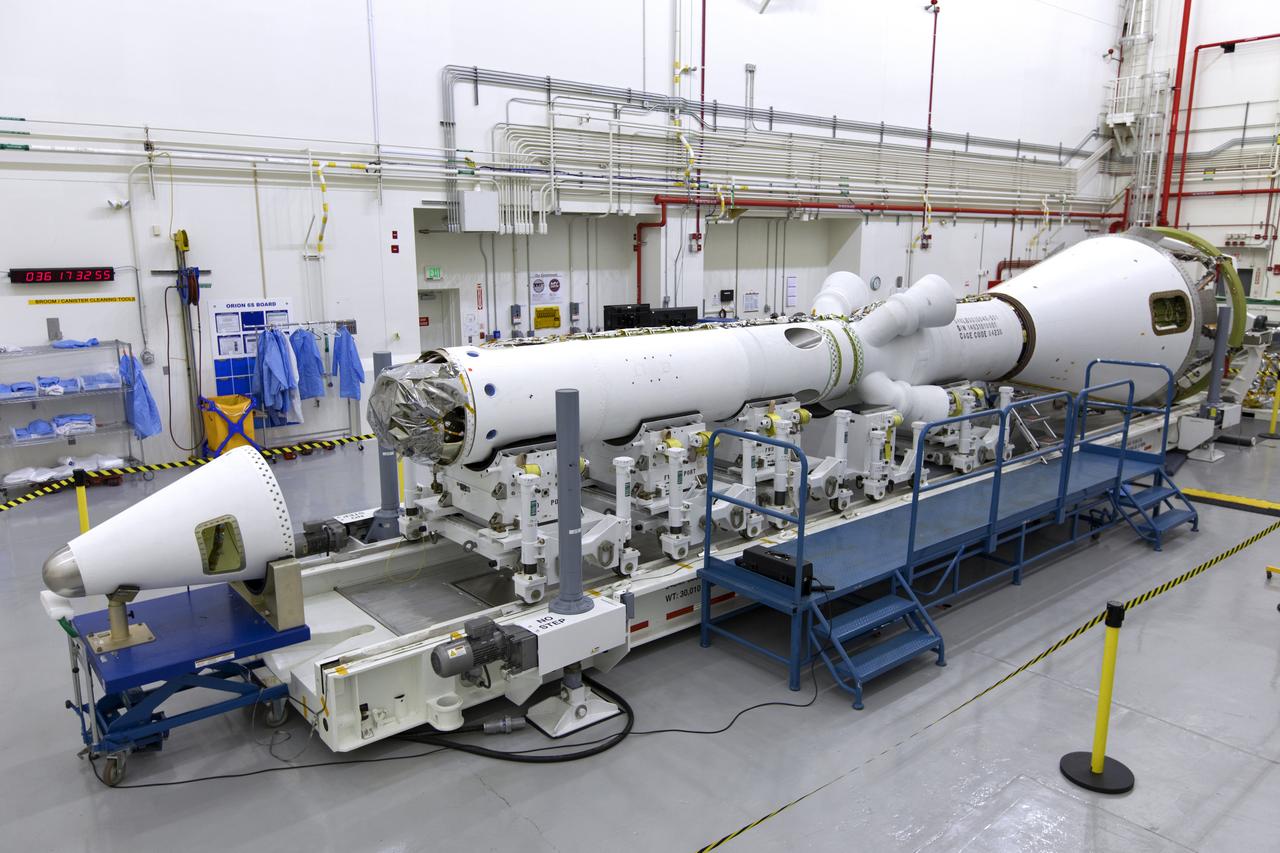

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Launch Abort System (LAS) that will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is being assembled on Feb. 5, 2019. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, scheduled for Spring 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrop Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.