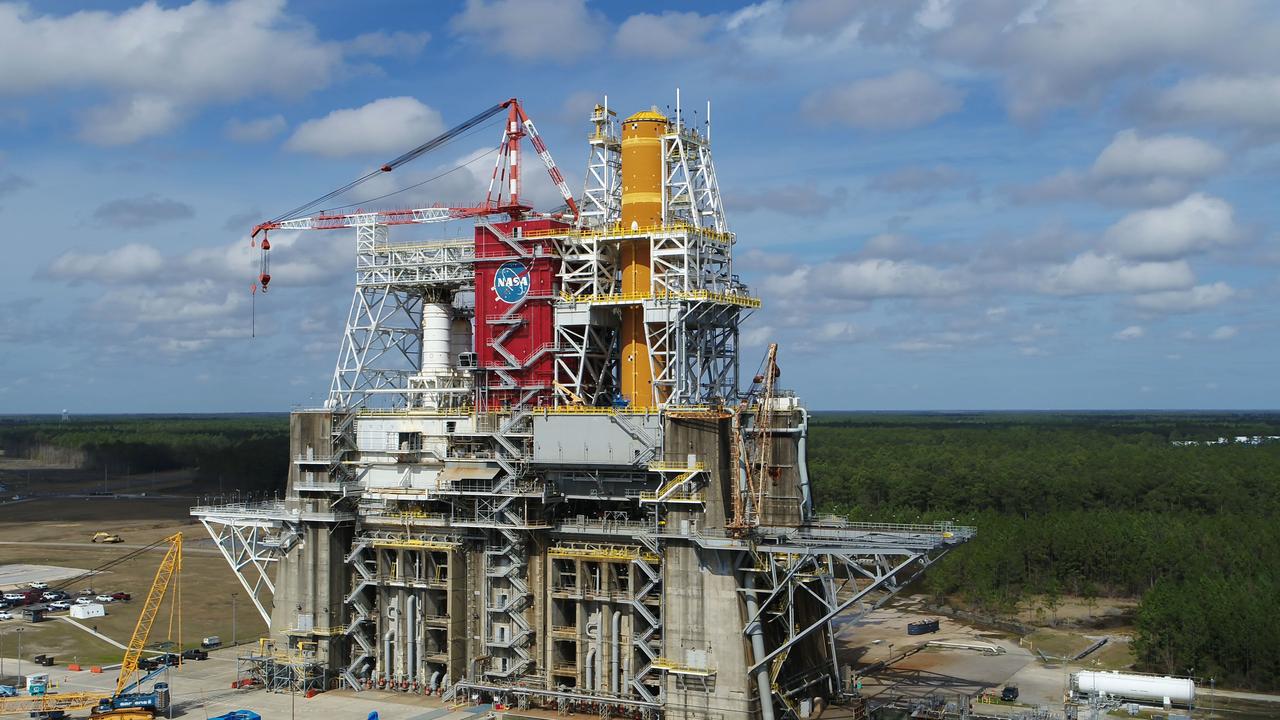

A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
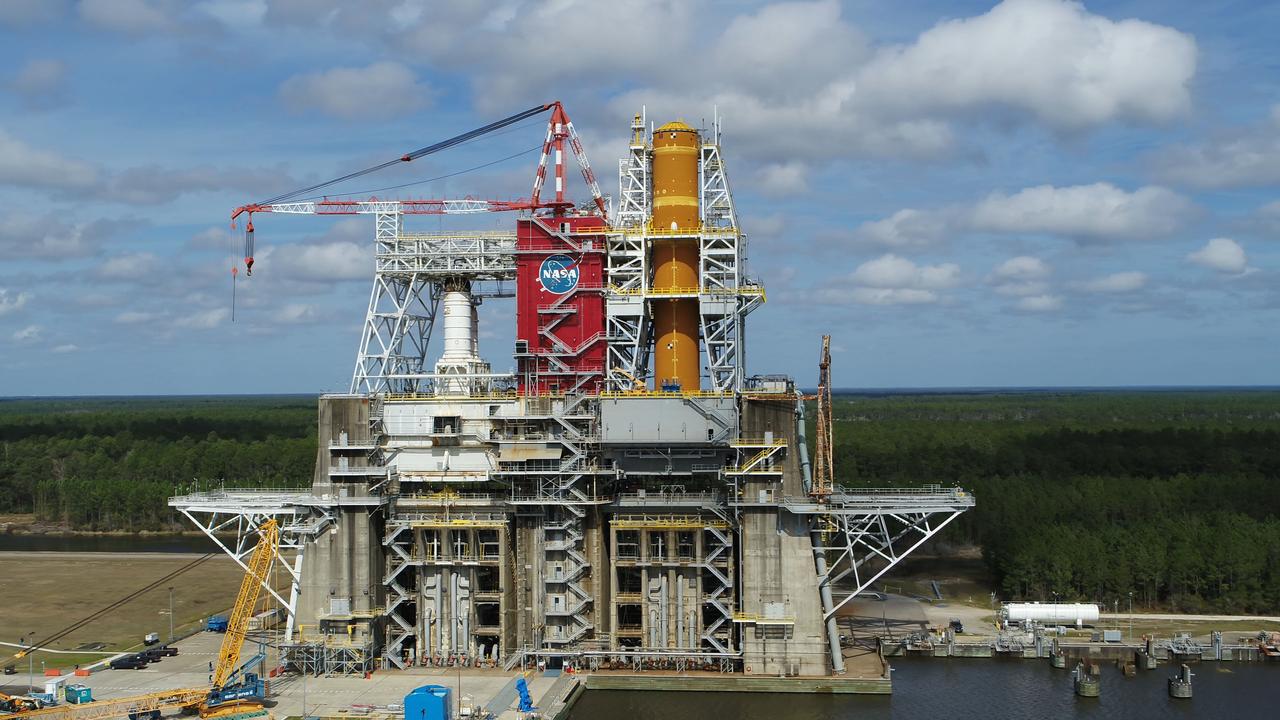
A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
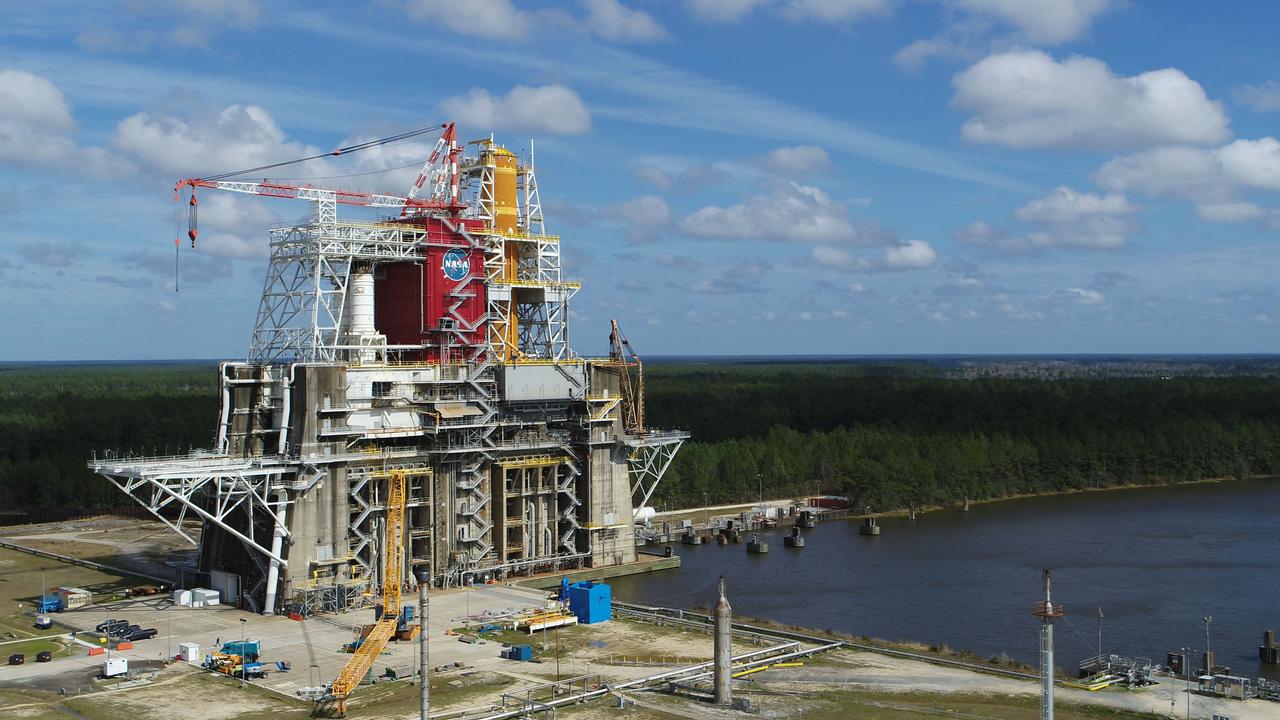

A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
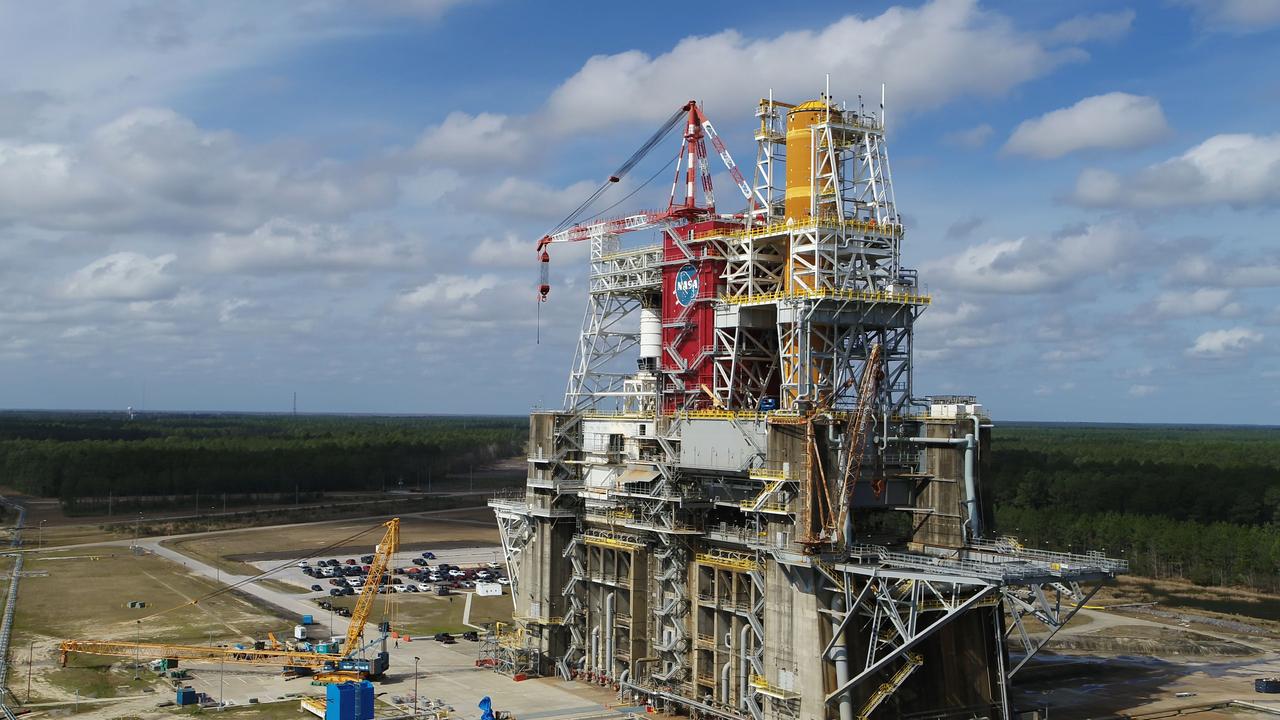

A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
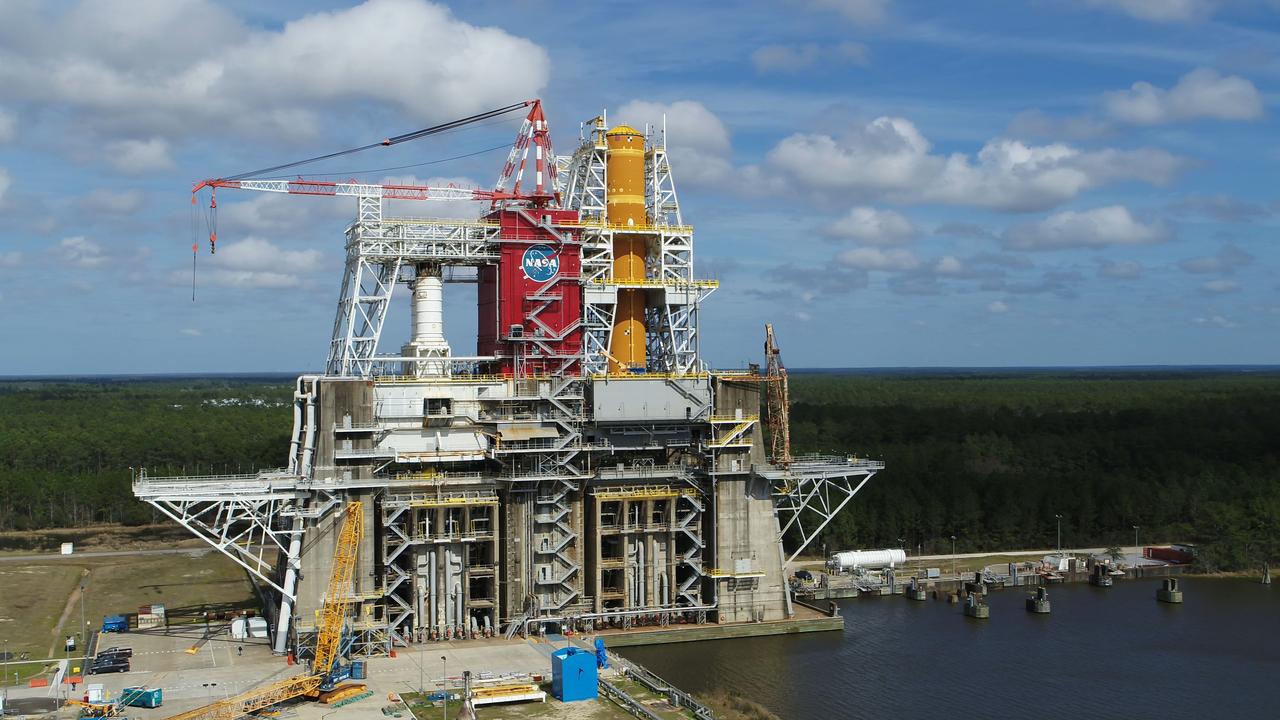

A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
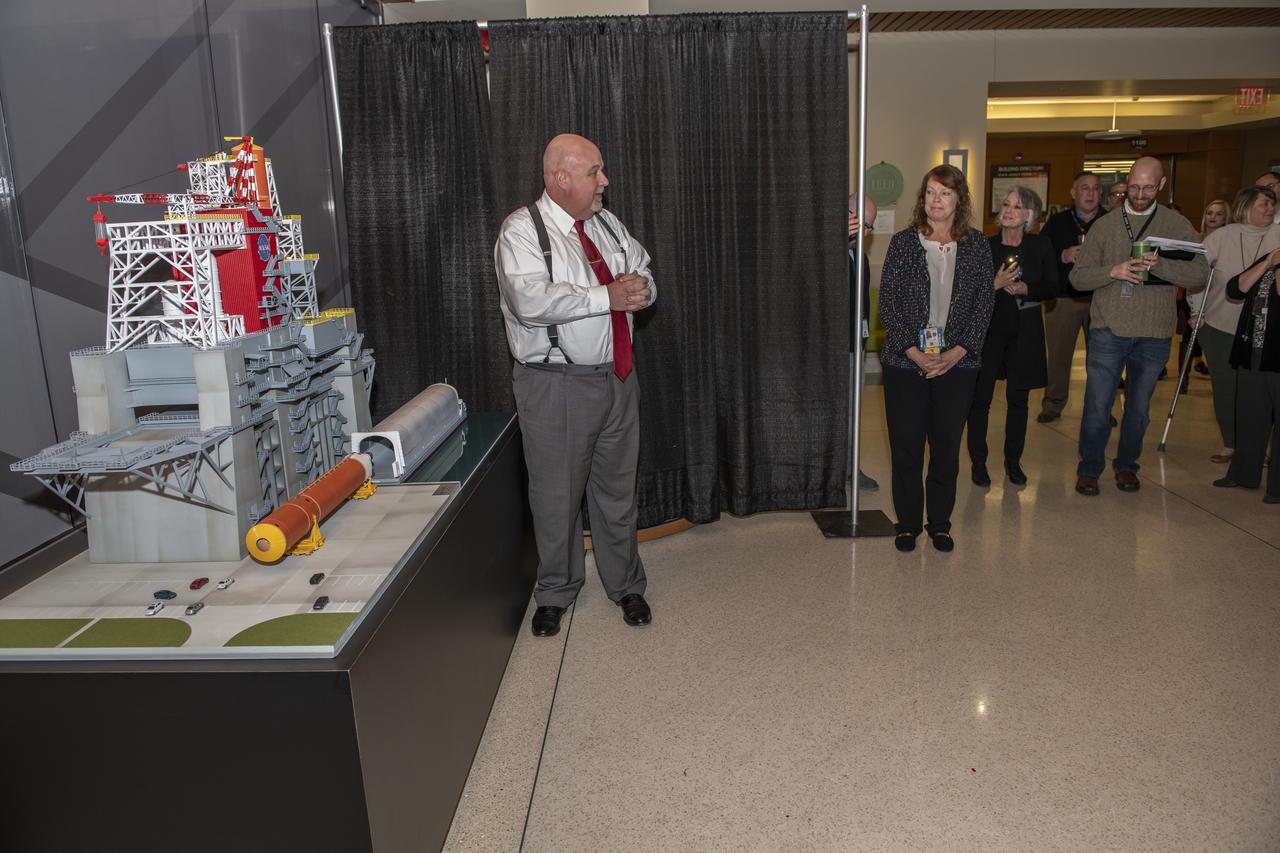

The unveiling of the B-2 Test Stand model for the SLS management team and employees in building 4220. Taking part was John Honeycutt and Julie Bassler.
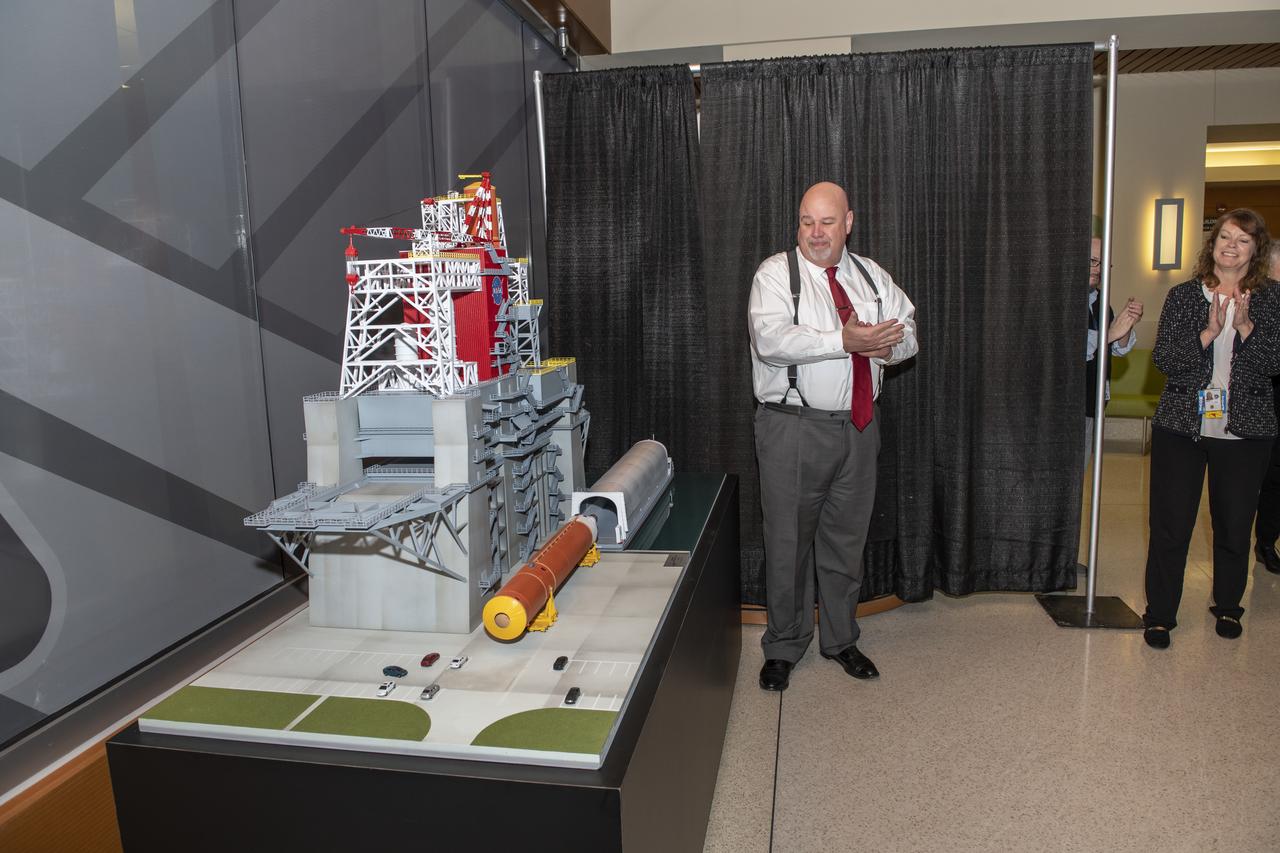

The unveiling of the B-2 Test Stand model for the SLS management team and employees in building 4220. Taking part was John Honeycutt and Julie Bassler.
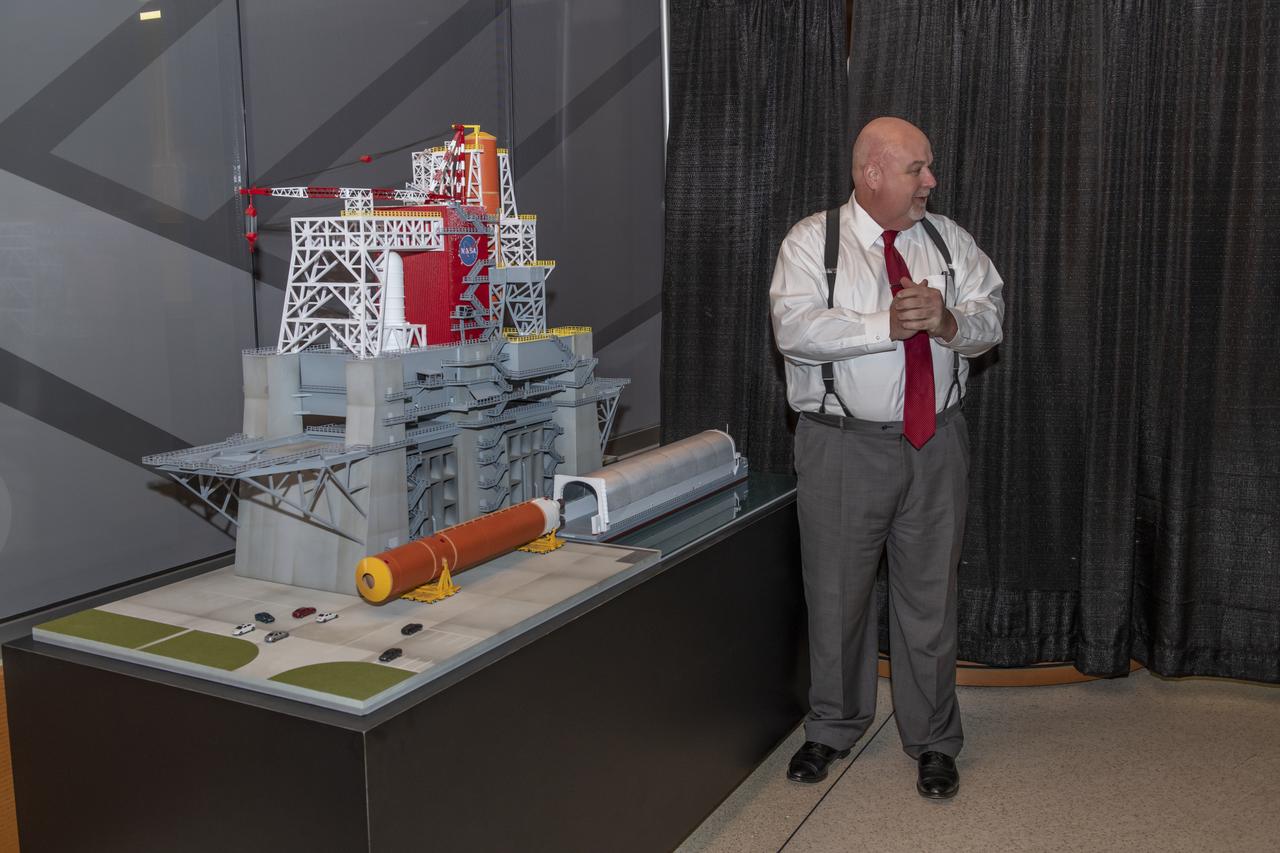

The unveiling of the B-2 Test Stand model for the SLS management team and employees in building 4220. Taking part was John Honeycutt and Julie Bassler.
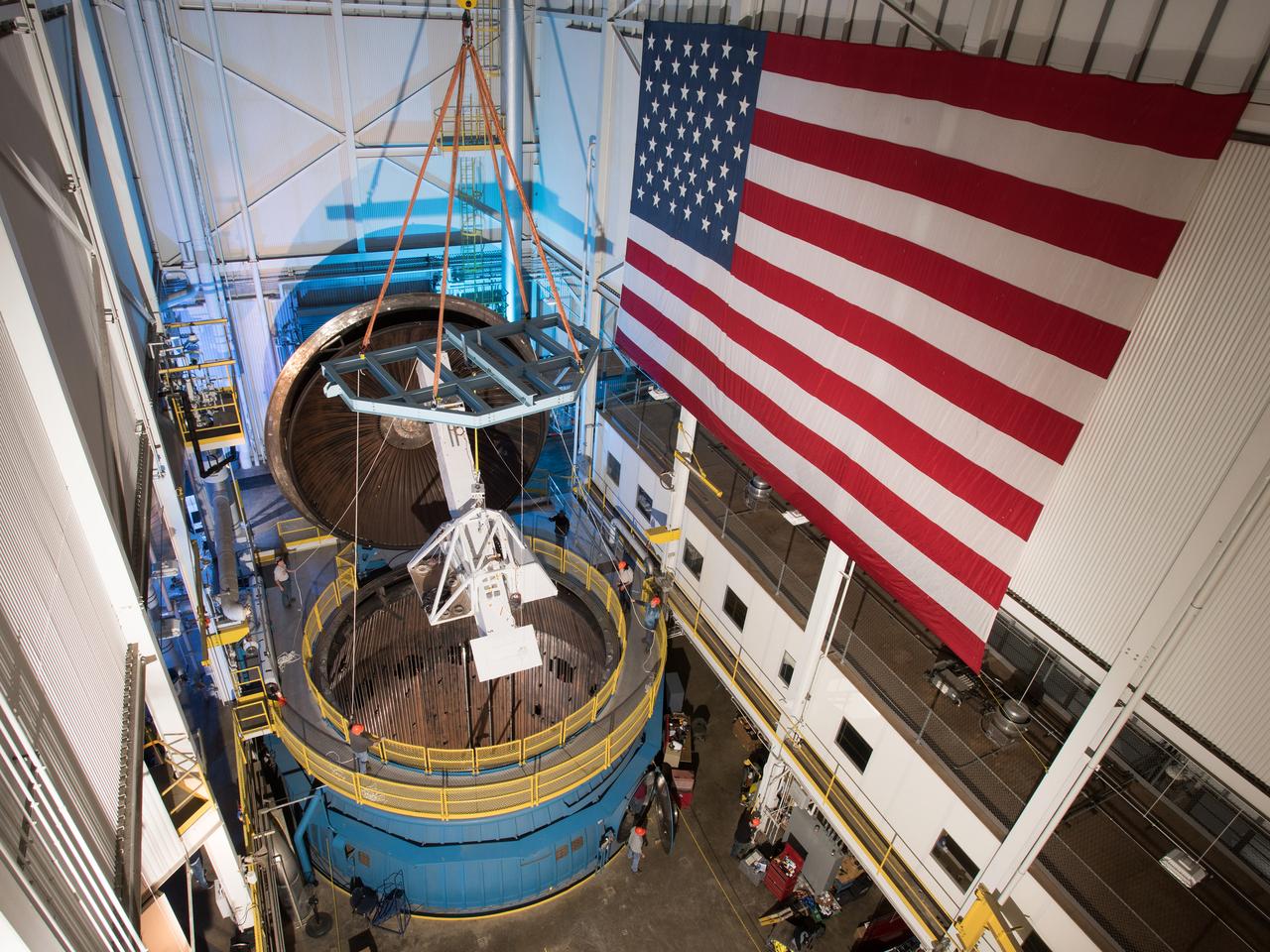
The Gamma-Ray Imager/Polarimeter for Solar flares (GRIPS) instrument is installed in the B-2 vacuum chamber for a full-instrument thermal-vacuum test in 2015. The GRIPS telescope was launched via balloon in January 2016 on a high-altitude flight over Antarctica to study the acceleration and transport of solar flare particles.
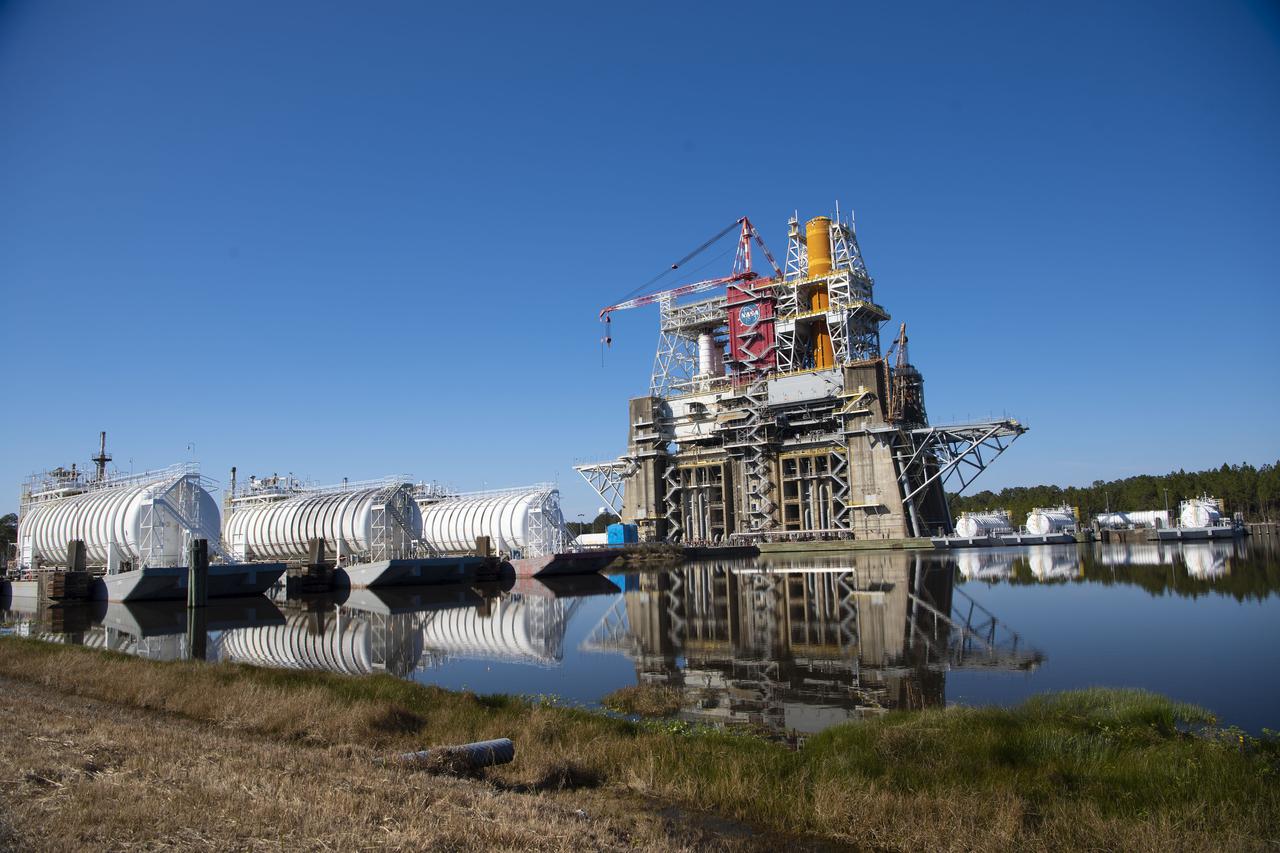

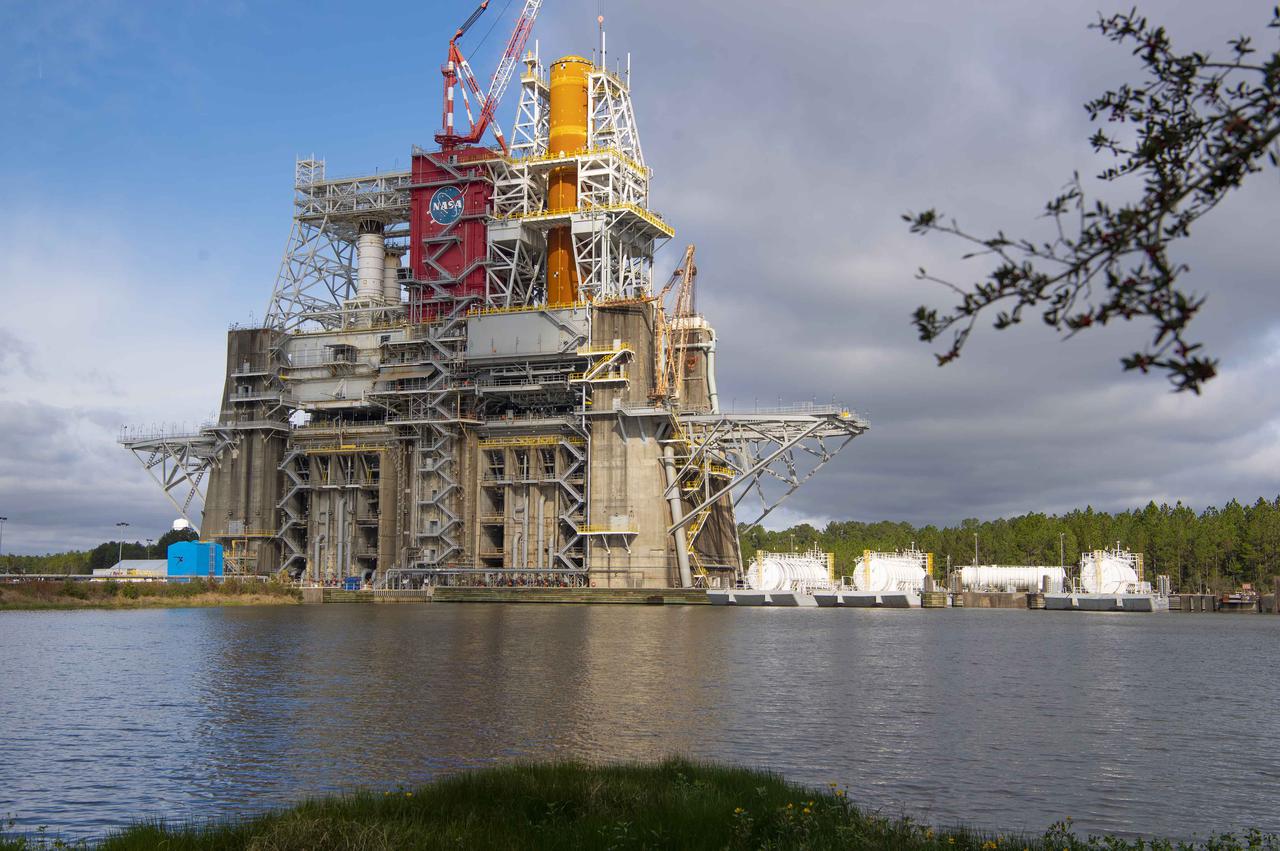
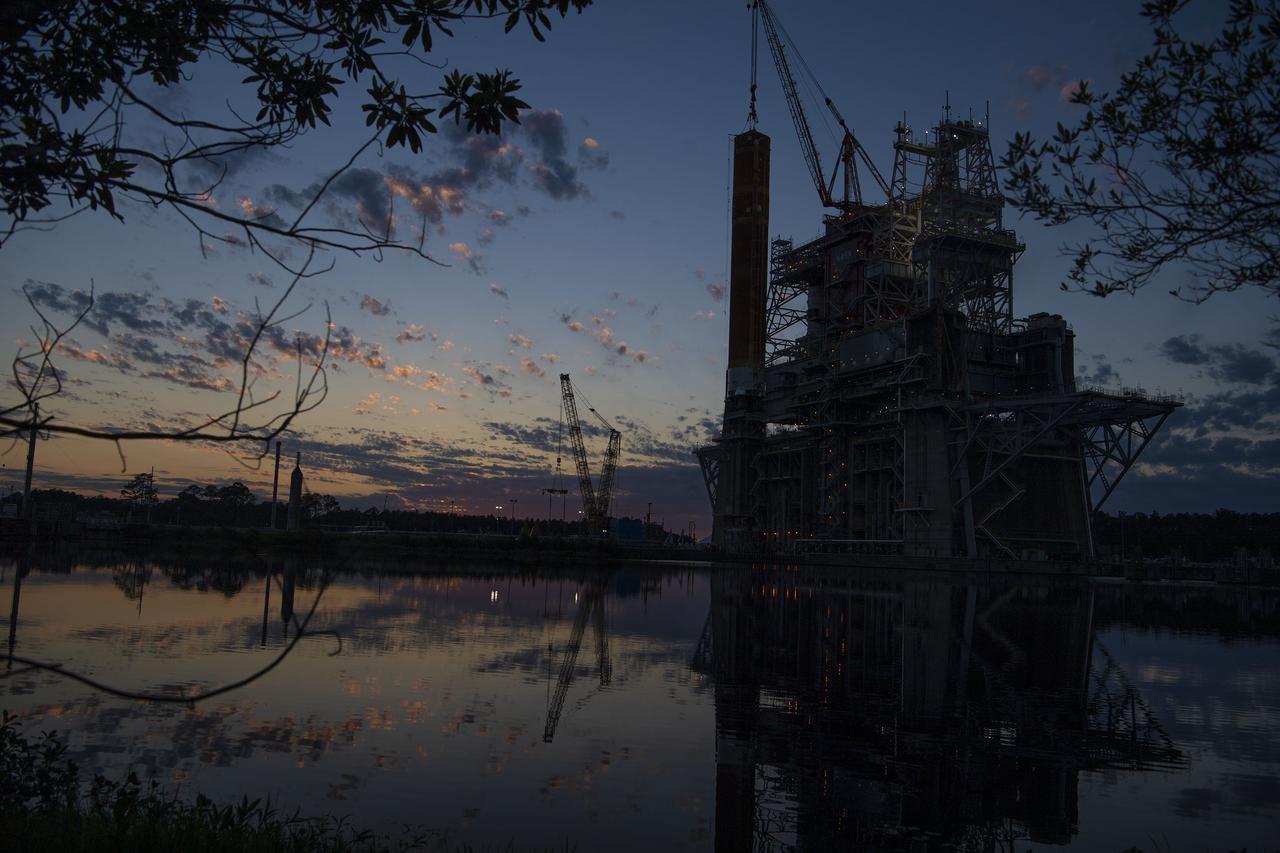
Propellant barges are docked at the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, prior the hot fire test of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket. The hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021 of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
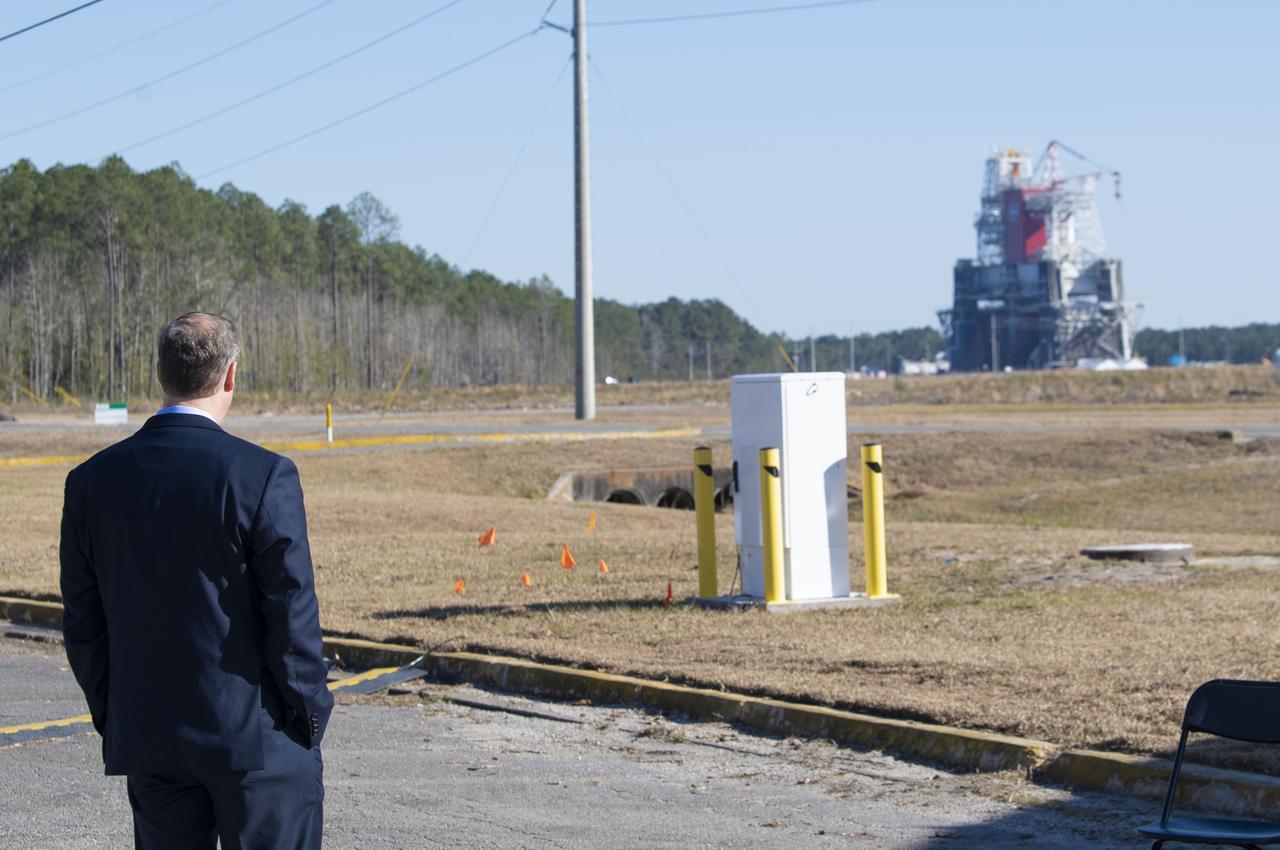

Outgoing NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine peers at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, prior to a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire at the B-2 Test Stand culminated a series of eight Green Run tests on the core stage and its integrated systems. The core stage now will be prepared and transported to Kennedy Space Center to be joined with the rest of the SLS rocket for launch on the Artemis I test mission.

Barges are docked at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Dec. 4, 2020, in preparation for upcoming Green Run test activities. Teams at the center have been performing Green Run tests of NASA’s Space Launch System core stage and its integrated systems throughout 2020. In mid-December, teams performed the seventh test of the Green Run series – a wet dress rehearsal of a countdown to hot fire. It marked the first time the stage tanks had been loaded with liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants supplied by the docked barges.

View of OPF High Bay No. 1 and Low Bay construction, 1976
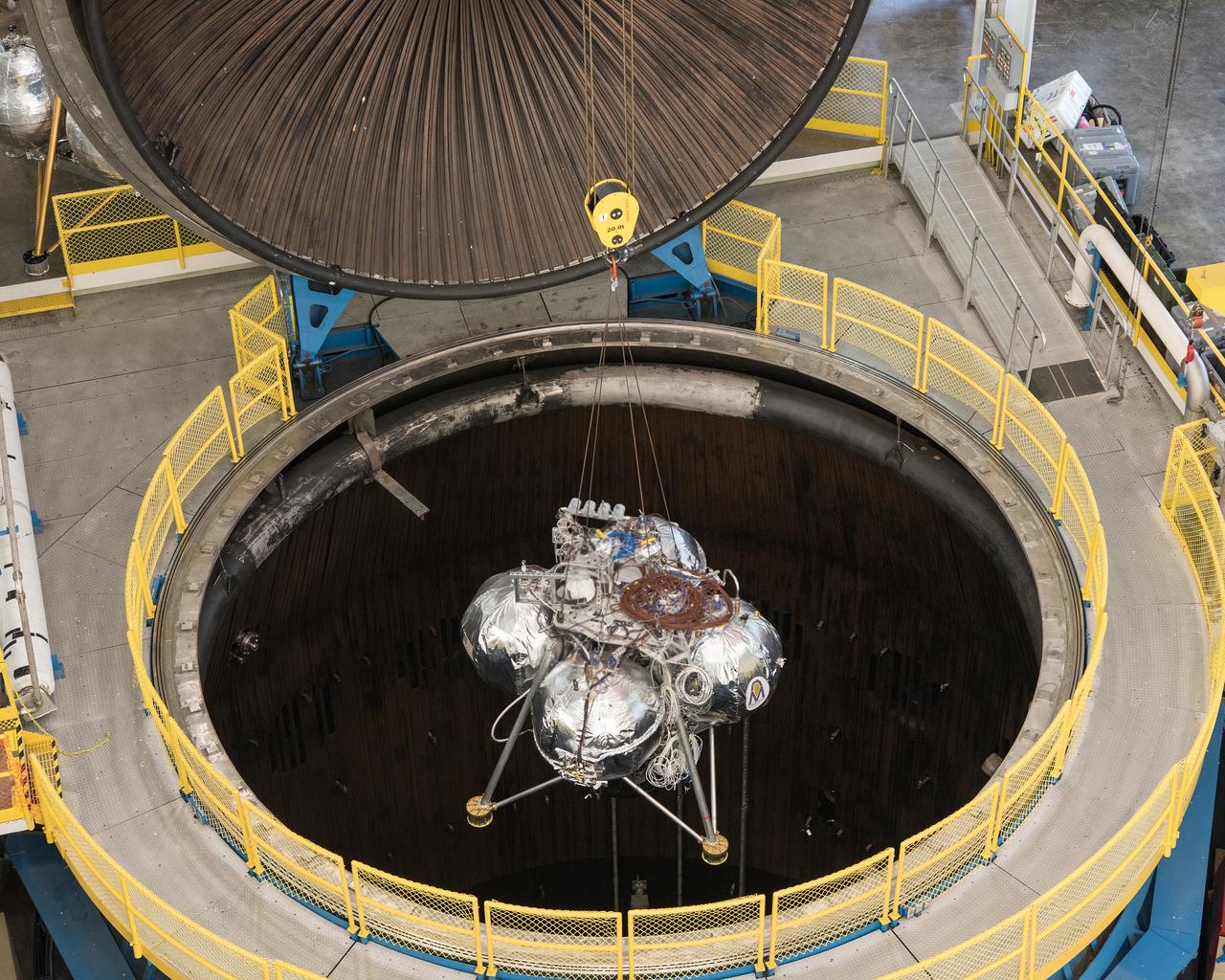

NASA's Morpheus Project has developed and tested a prototype planetary lander capable of vertical takeoff and landing. This is an image of the lander being installed in the B-2 facility for testing at Plum Brook Station.

This artist's concept depicts the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-2 in orbit. The HEAO-2, the first imaging and largest x-ray telescope built to date, was capable of producing actual photographs of x-ray objects. Shortly after launch, the HEAO-2 was nicknamed the Einstein Observatory by its scientific experimenters in honor of the centernial of the birth of Albert Einstein, whose concepts of relativity and gravitation have influenced much of modern astrophysics, particularly x-ray astronomy. The HEAO-2, designed and developed by TRW, Inc. under the project management of the Marshall Space Flight Center, was launched aboard an Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle on November 13, 1978. The HEAO-2 was originally identified as HEAO-B but the designation was changed once the spacecraft achieved orbit.
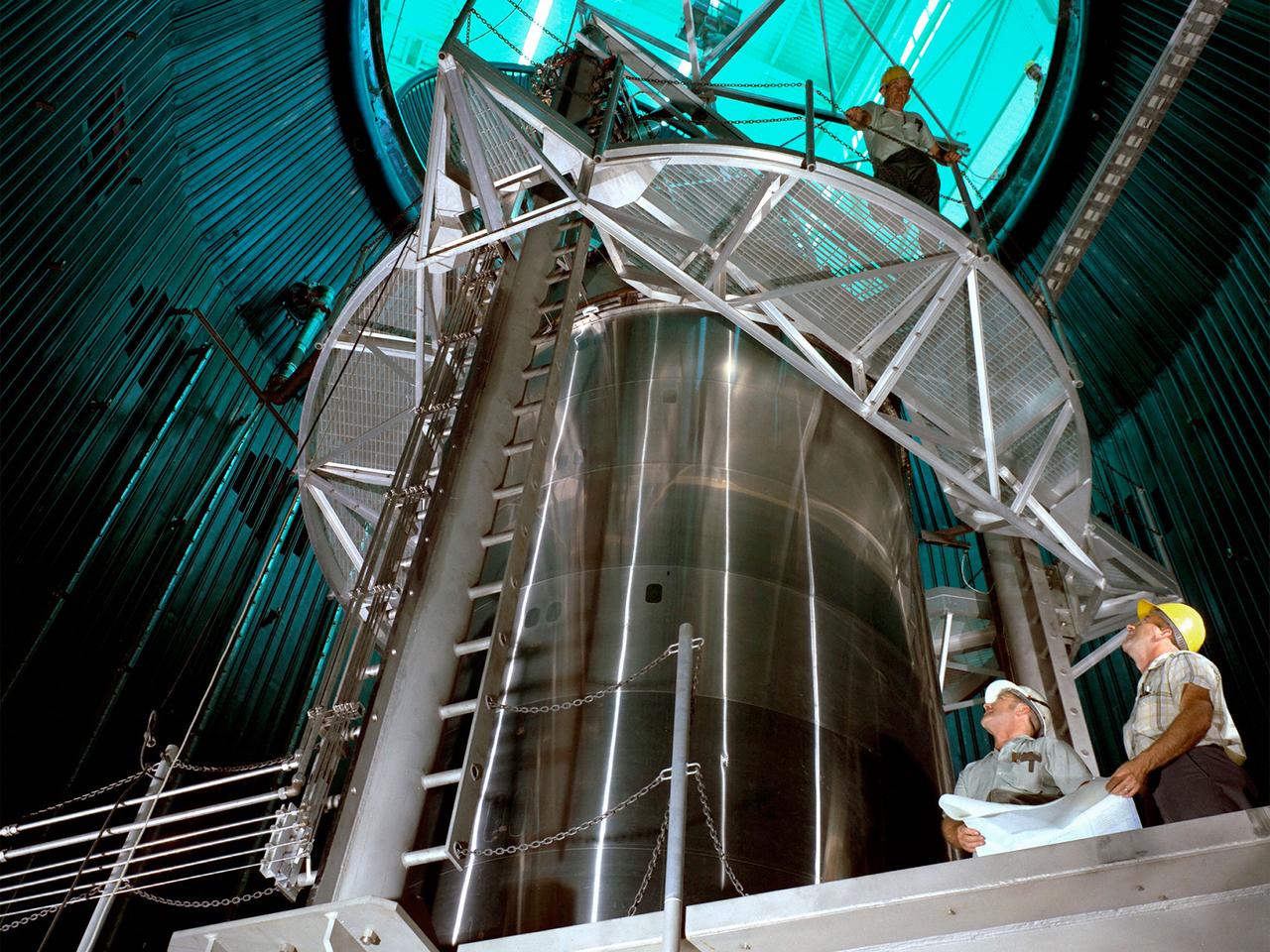

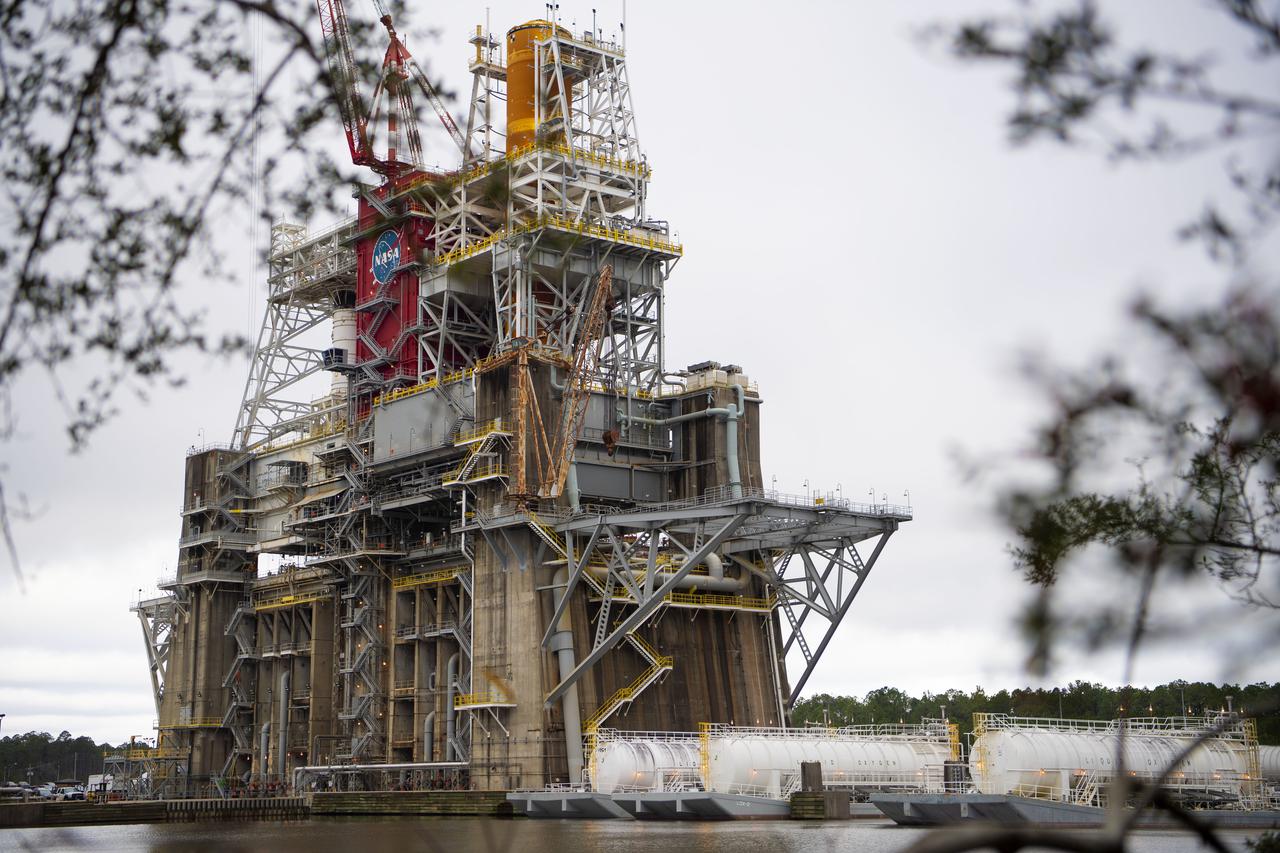
A Centaur second-stage rocket in the Space Propulsion Research Facility, better known as B‒2, operating at NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio. Centaur was designed to be used with an Atlas booster to send the Surveyor spacecraft to the moon in the mid-1960s. After those missions, the rocket was modified to launch a series of astronomical observation satellites into orbit and send space probes to other planets. Researchers conducted a series of systems tests at the Plum Brook test stands to improve the Centaur fuel pumping system. Follow up full-scale tests in the B-2 facility led to the eventual removal of the boost pumps from the design. This reduced the system’s complexity and significantly reduced the cost of a Centaur rocket. The Centaur tests were the first use of the new B-2 facility. B‒2 was the world's only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. It was created to test rocket propulsion systems with up to 100,000 pounds of thrust in a simulated space environment. The facility has the unique ability to maintain a vacuum at the rocket’s nozzle while the engine is firing. The rocket fires into a 120-foot deep spray chamber which cools the exhaust before it is ejected outside the facility. B‒2 simulated space using giant diffusion pumps to reduce chamber pressure 10-6 torr, nitrogen-filled cold walls create cryogenic temperatures, and quartz lamps replicate the radiation of the sun.
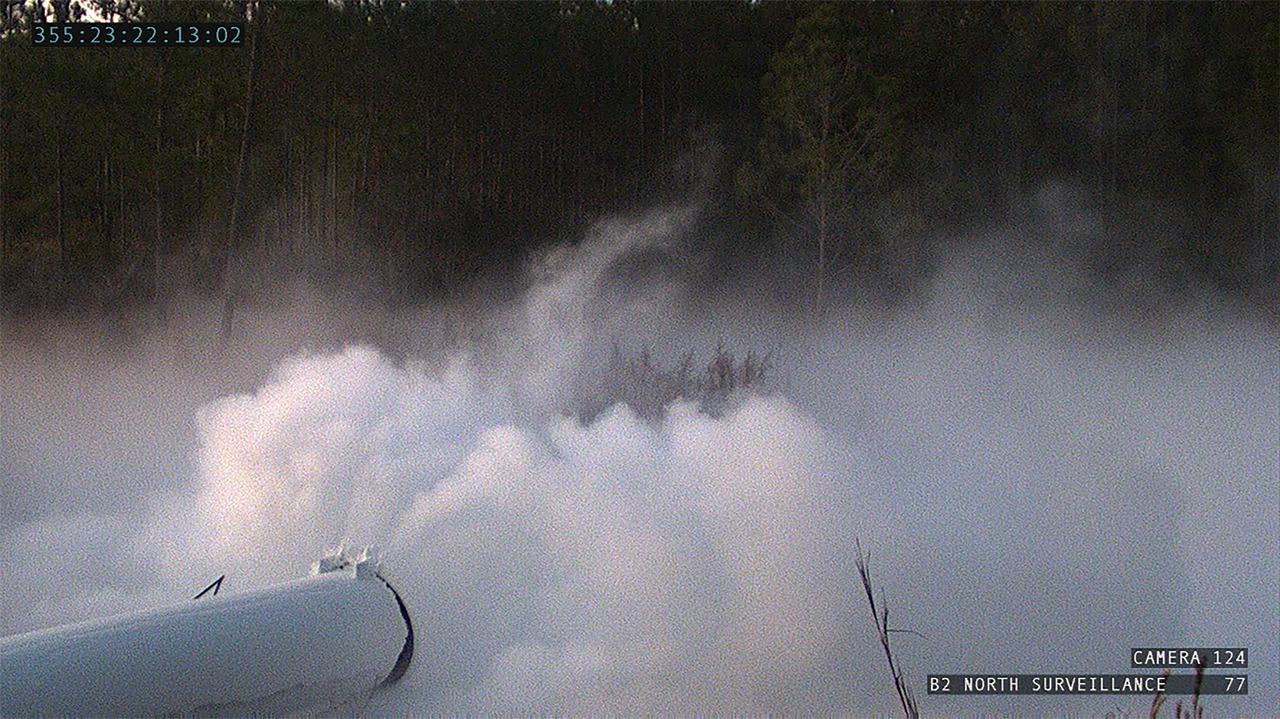

Operators at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, conducted a wet dress rehearsal for the hot fire test of the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System on Dec. 21, 2020. In this image, liquid oxygen can be seen venting from B-2 Test Stand piping. Following the wet dress rehearsal, operators will conduct a full hot fire test of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines. The hot fire will conclude a series of eight Green Run tests of all core stage systems before it is transported to Kennedy Space Center for launch on the Artemis I mission.
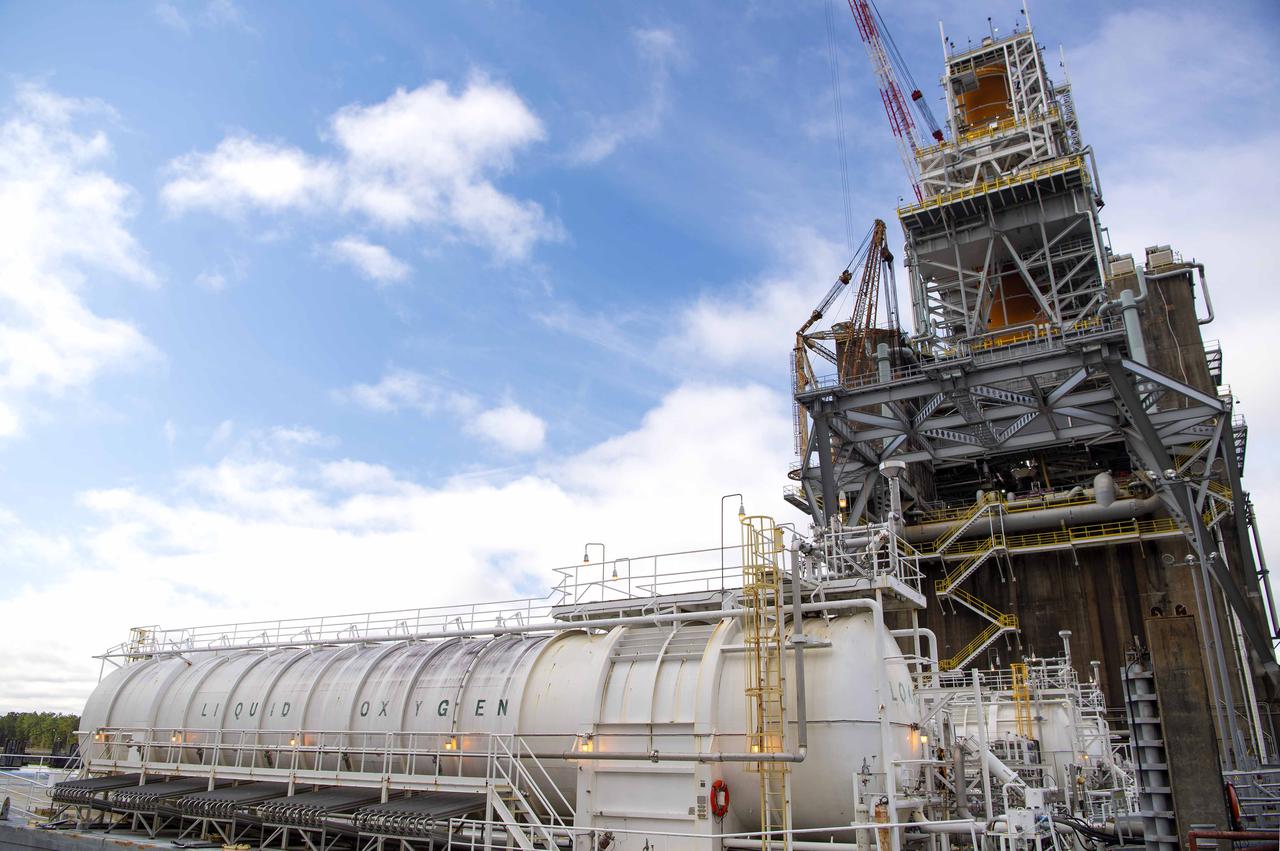

Barges are docked at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, during preparations for a wet dress rehearsal exercise with the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. During the wet dress rehearsal, operators will fully load the core stage’s propellant tanks for the first time and countdown just shy of engine ignition. The wet dress rehearsal is the seventh in a series of eight Green Run tests of the core stage’s integrated systems prior to its transport to Kennedy Space Center and launch on the Artemis I mission.
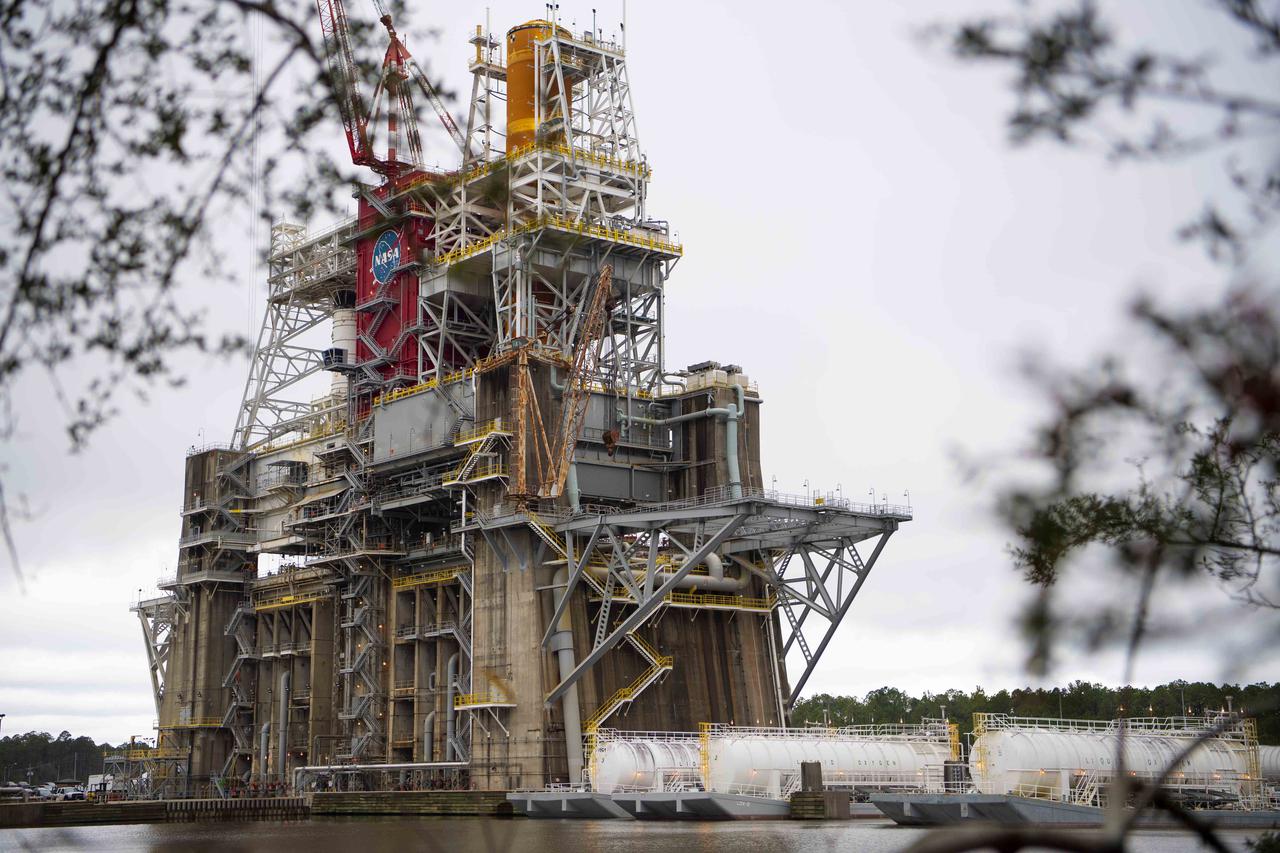

Barges are docked at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, during preparations for a wet dress rehearsal exercise with the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. During the wet dress rehearsal, operators will fully load the core stage’s propellant tanks for the first time and countdown just shy of engine ignition. The wet dress rehearsal is the seventh in a series of eight Green Run tests of the core stage’s integrated systems prior to its transport to Kennedy Space Center and launch on the Artemis I mission.

Barges are docked at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, during preparations for a wet dress rehearsal exercise with the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. During the wet dress rehearsal, operators will fully load the core stage’s propellant tanks for the first time and countdown just shy of engine ignition. The wet dress rehearsal is the seventh in a series of eight Green Run tests of the core stage’s integrated systems prior to its transport to Kennedy Space Center and launch on the Artemis I mission.
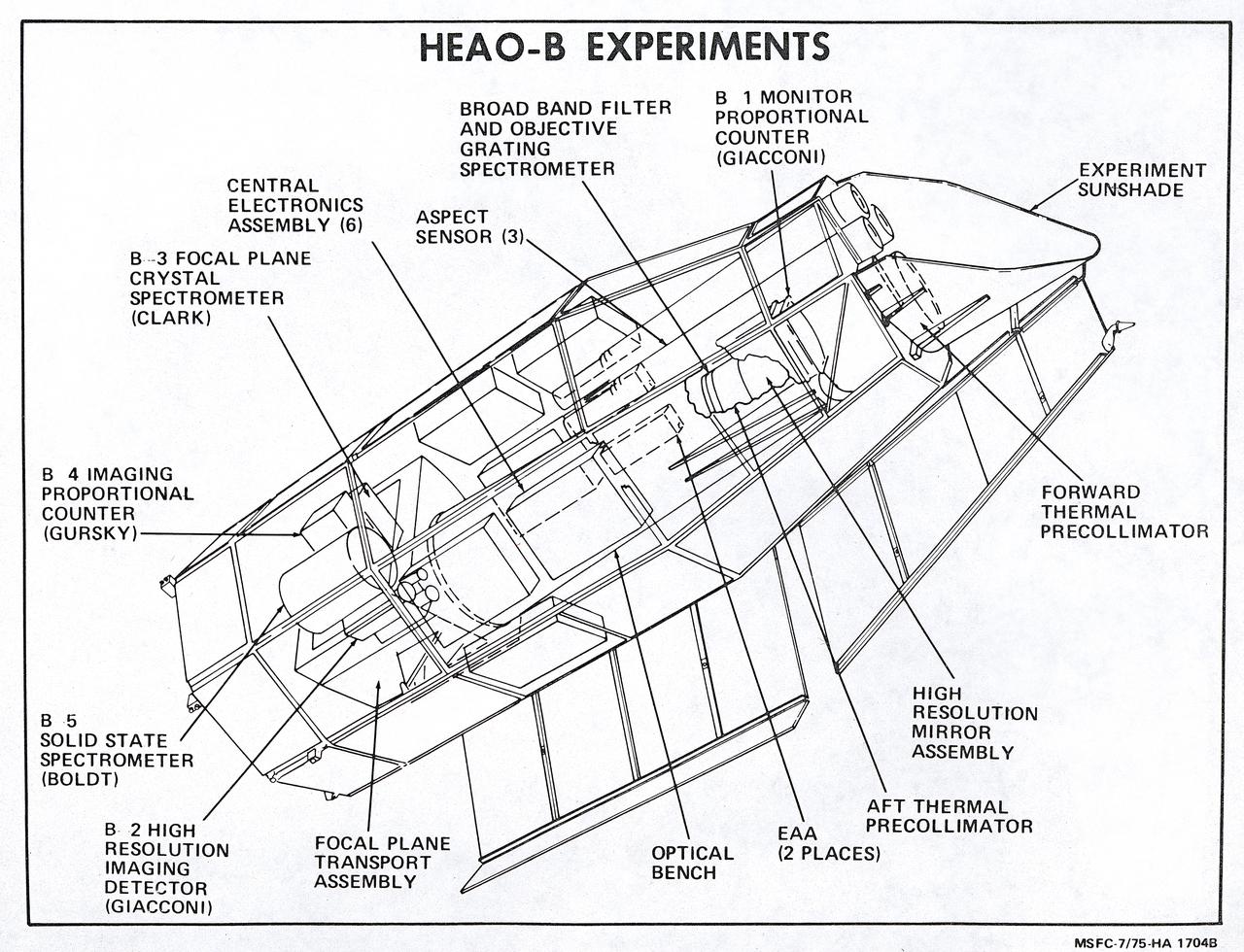
This illustration is a schematic of the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-2 and its experiments. It shows the focal plane instruments (at the right) plus the associated electronics for operating the telescope as it transmitted its observations to the ground. A fifth instrument, the Monitor Proportional Counter, is located near the front of the telescope. Four separate astronomical instruments are located at the focus of this telescope and they could be interchanged for different types of observations as the observatory pointed at interesting areas of the Sky. Two of these instruments produced images; a High Resolution Imaging Detector and an Imaging Proportional Counter. The other two instruments, the Solid State Spectrometer and the Crystal Spectrometer, measured the spectra of x-ray objects. A fifth instrument, the Monitor Proportional Counter, continuously viewed space independently to study a wider band of x-ray wavelengths and to examine the rapid time variations in the sources. The HEAO-2 was nicknamed the Einstein Observatory by its scientific experimenters in honor of the centernial of the birth of Albert Einstein, whose concepts of relativity and gravitation have influenced much of modern astrophysics, particularly x-ray astronomy. The HEAO-2, designed and developed by TRW, Inc. under the project management of the Marshall Space Flight Center, was launched aboard an Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle on November 13, 1978. The HEAO-2 was originally identified as HEAO-B but the designation was changed once the spacecraft achieved orbit.
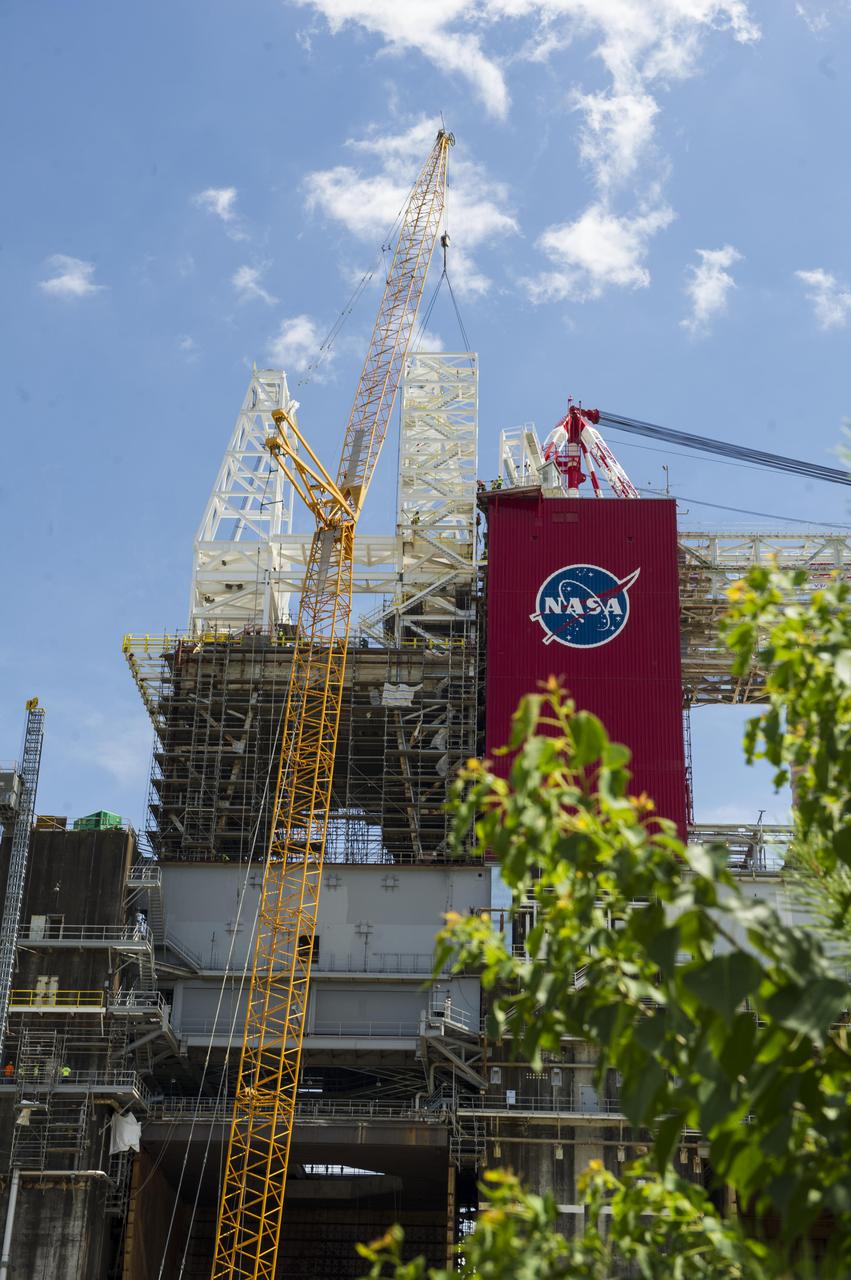

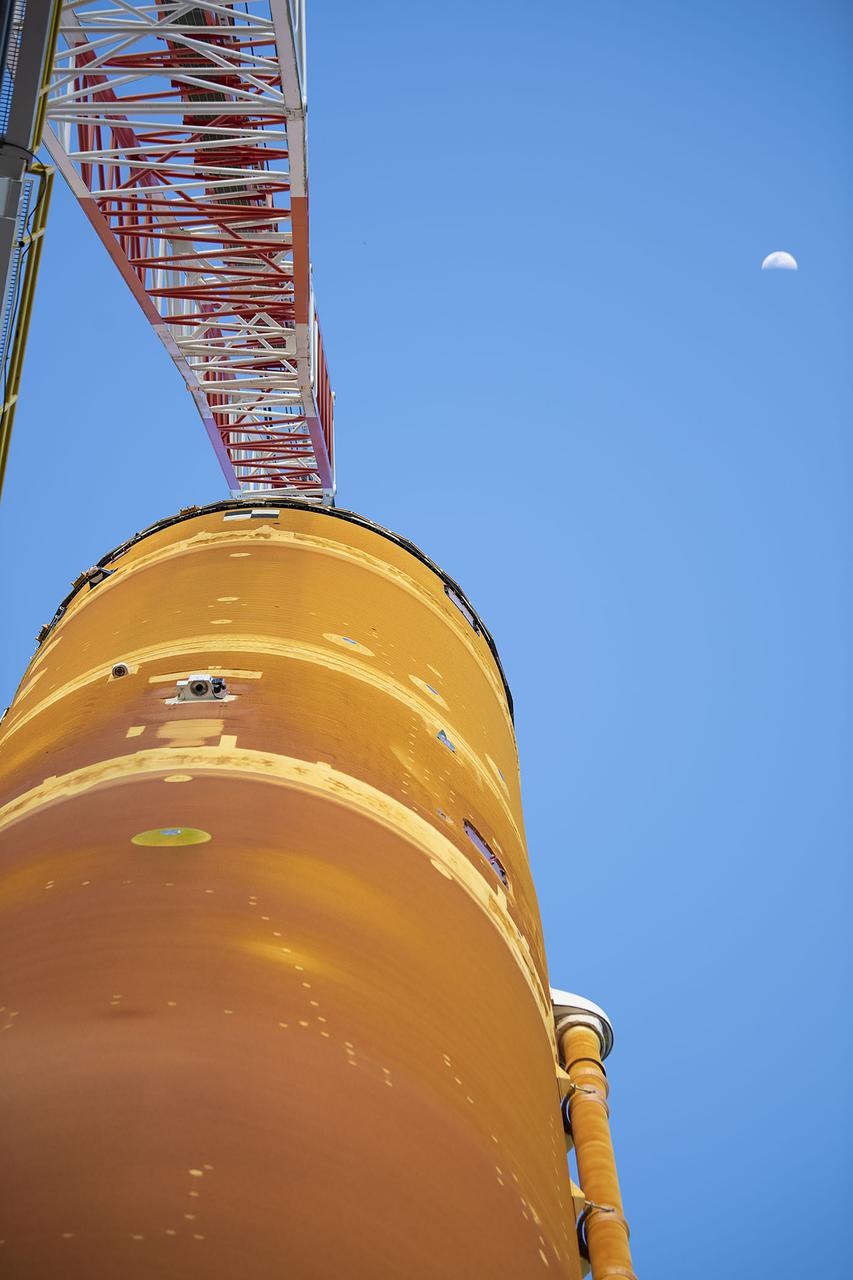
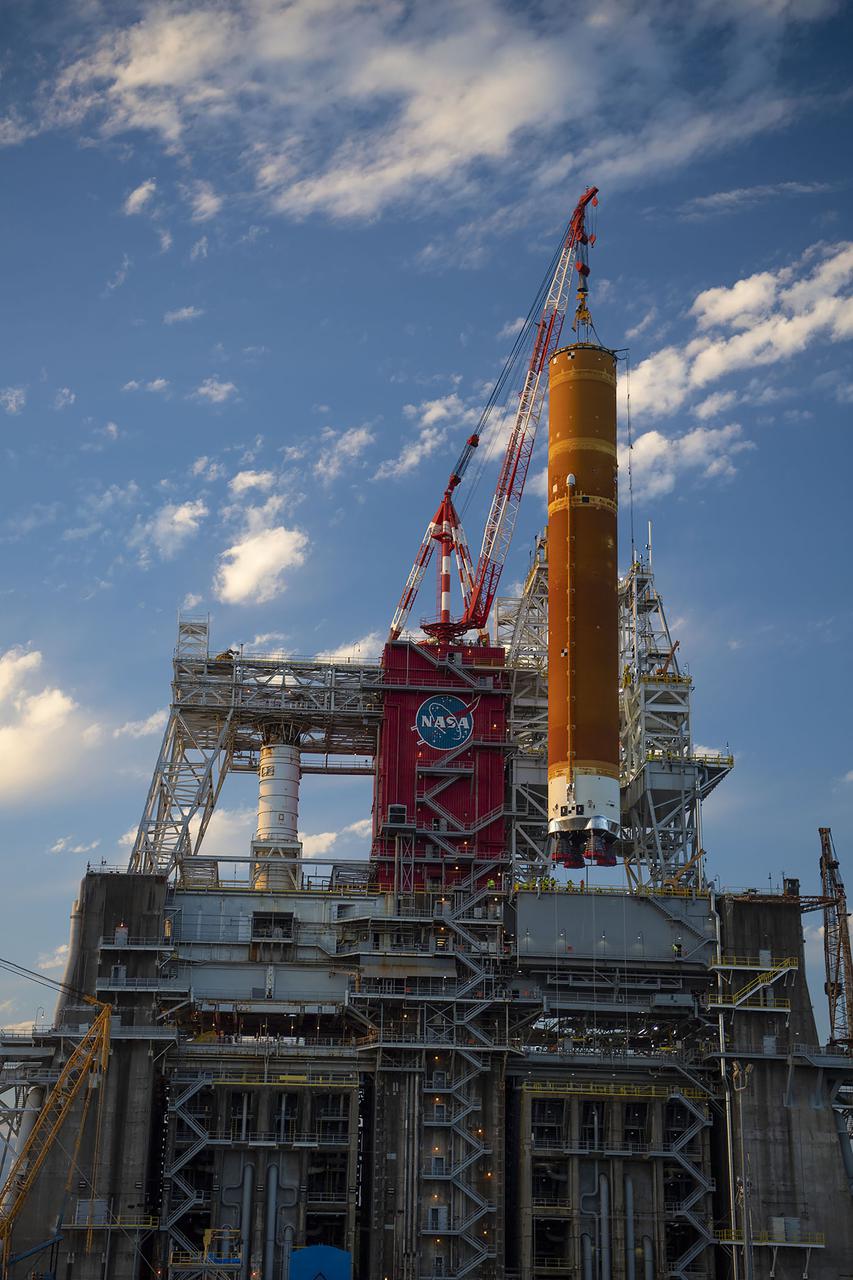
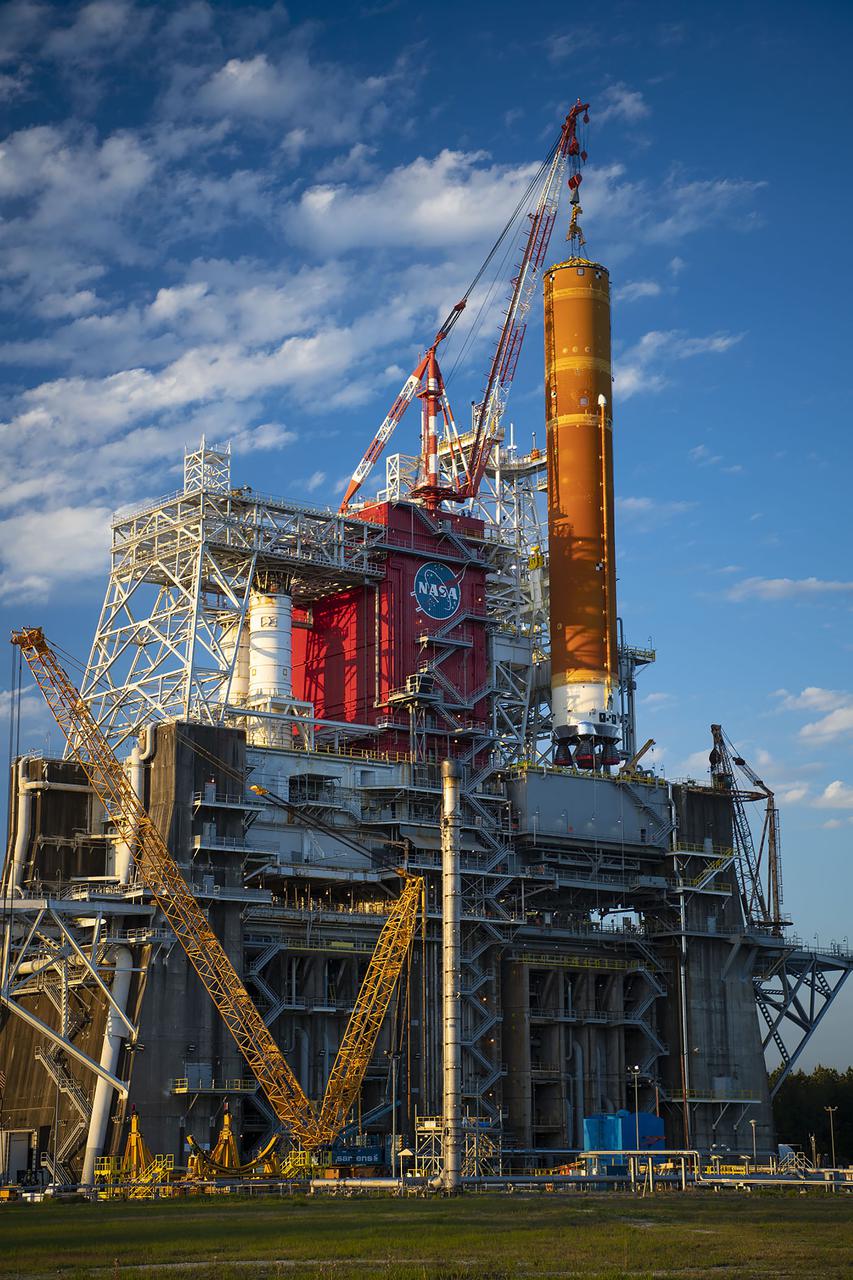
A structural steel section is lifted into place atop the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center as part of modification work to prepare for testing the core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System. The section is part of the Main Propulsion Test Article (MPTA) framework, which will support the SLS core stage for testing. The existing framework was installed on the stand in the late 1970s to test the shuttle MPTA. However, that framework had to be repositioned and modified to accommodate the larger SLS stage. About 1 million pounds of structural steel has been added, extending the framework about 100 feet higher and providing a new look to the Stennis skyline. Stennis will test the actual flight core stage for the first uncrewed SLS mission, Exploration Mission-1.
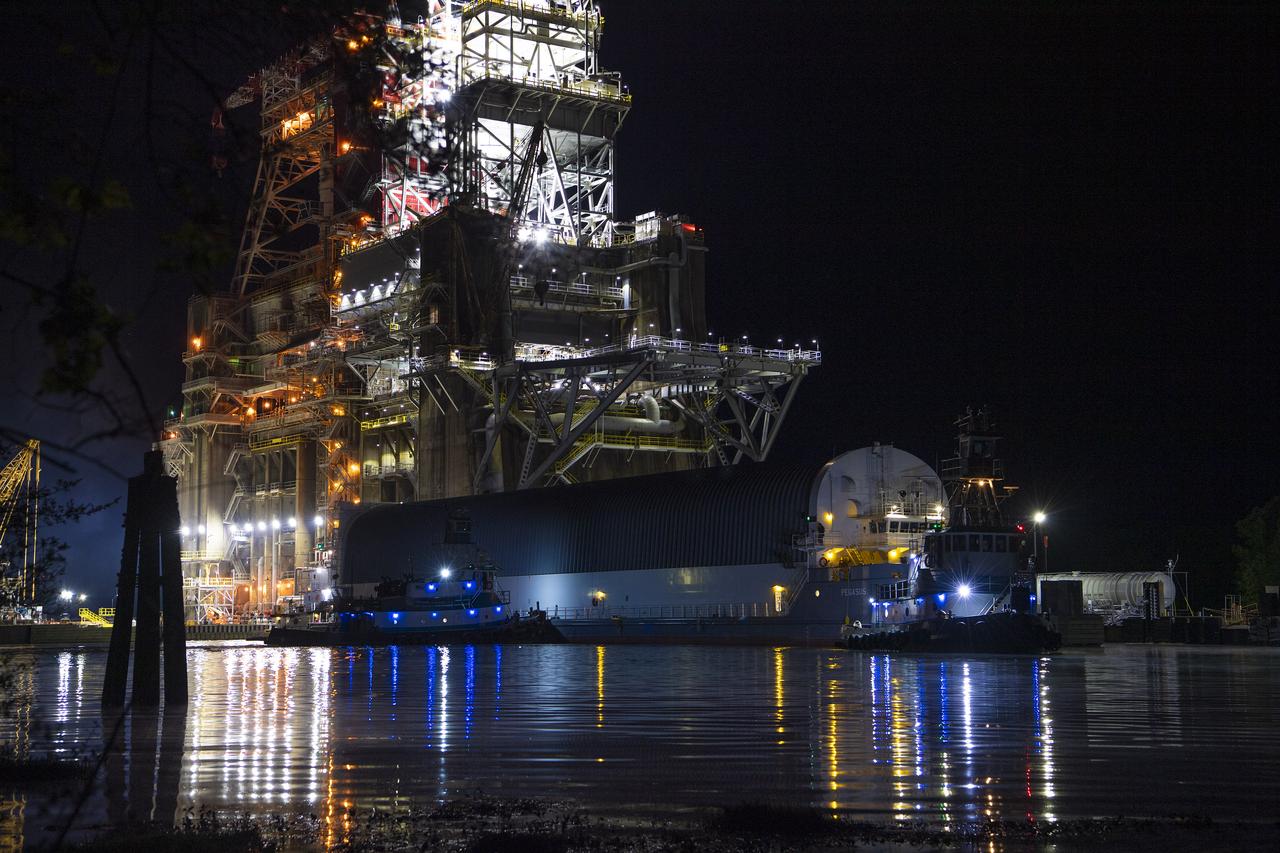

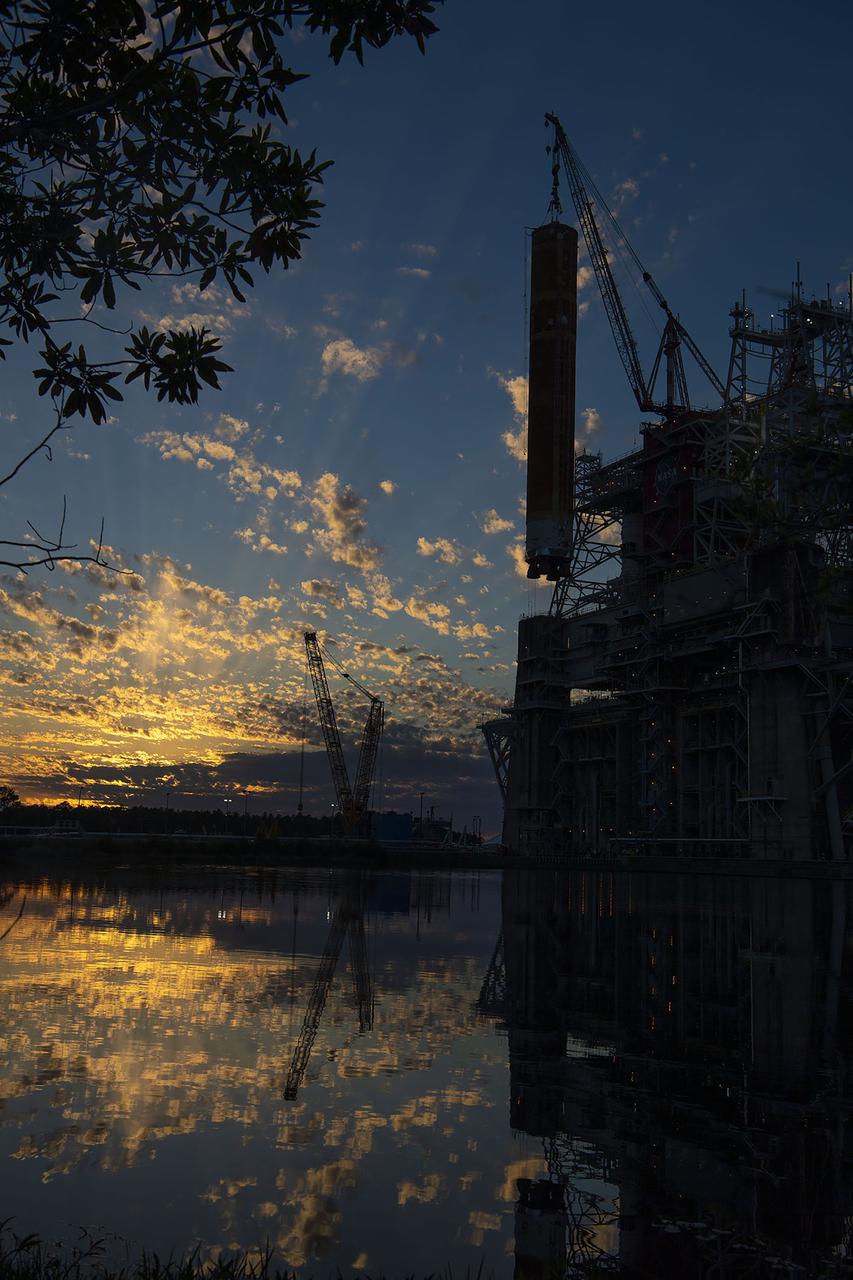
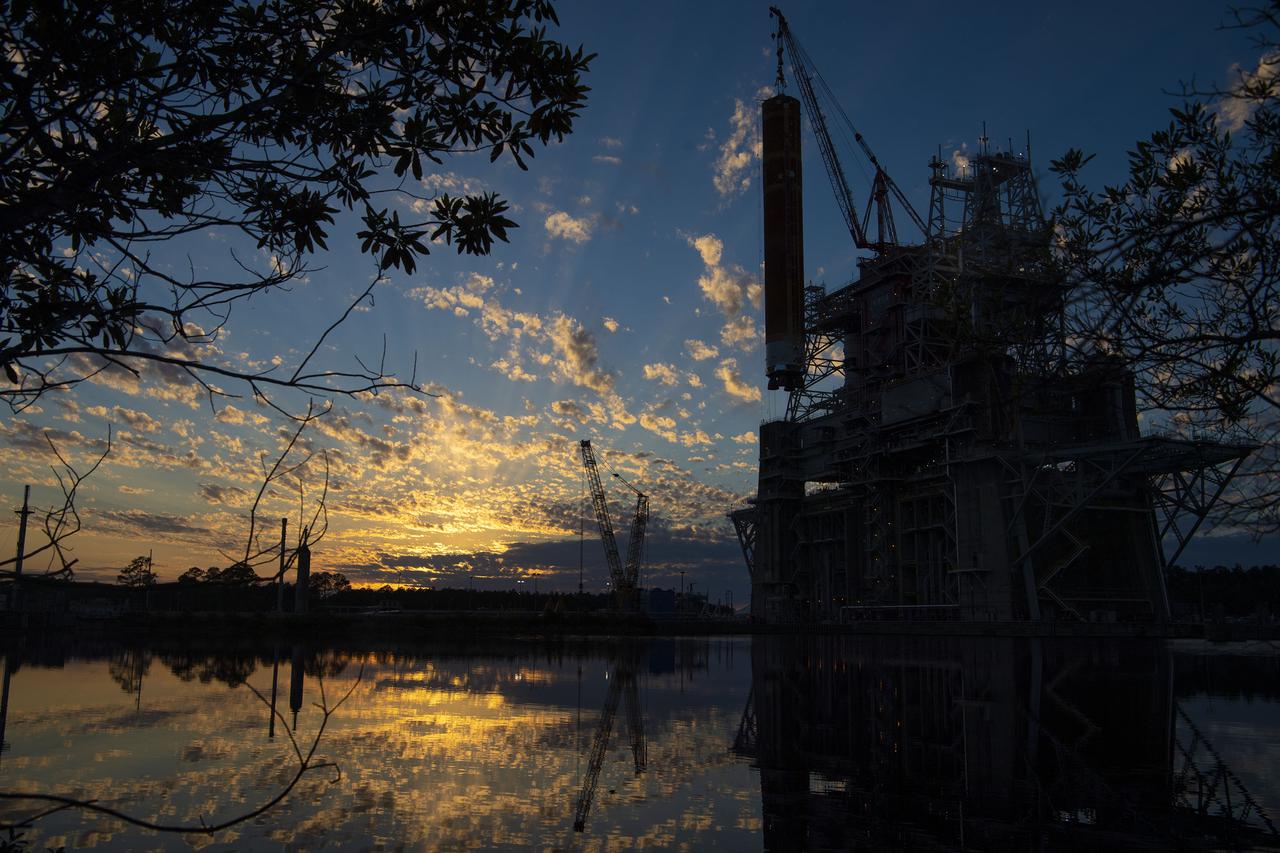
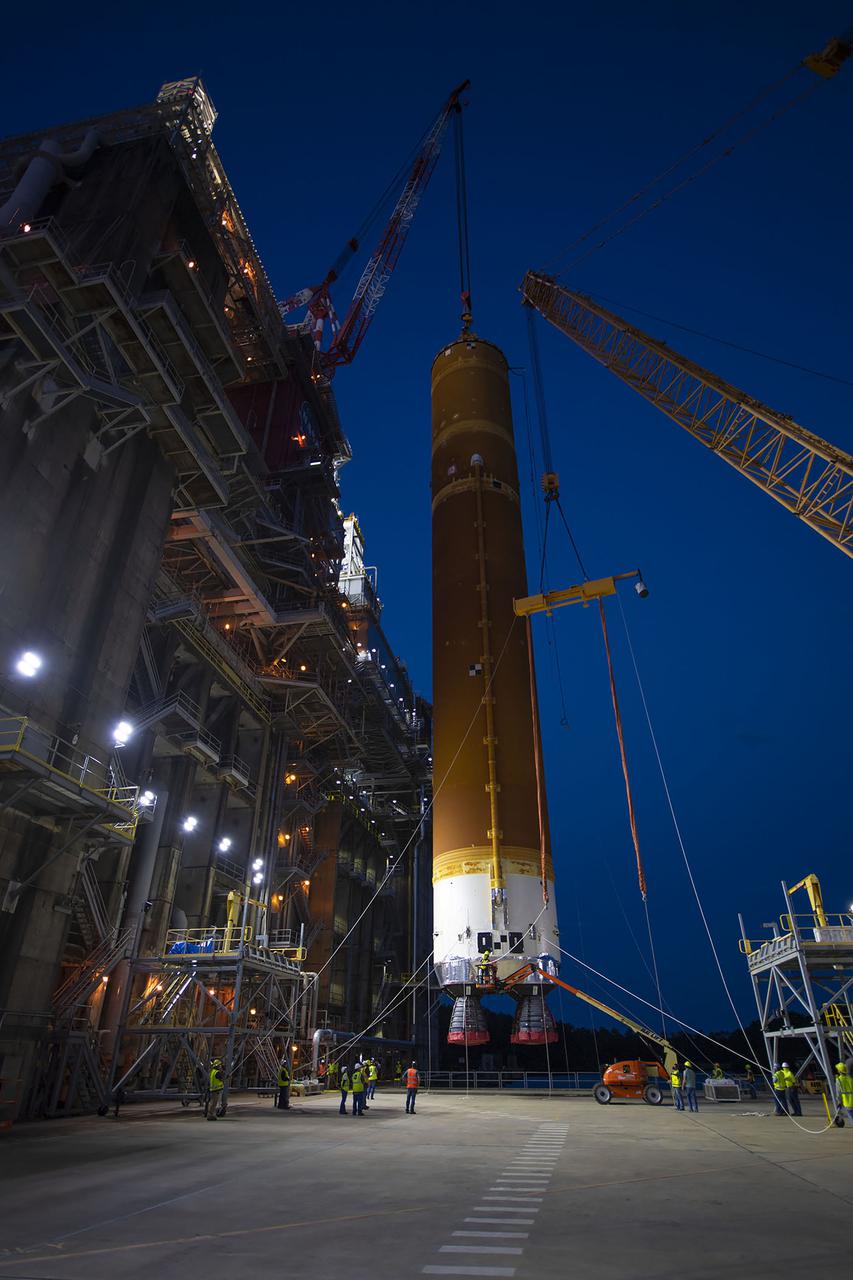
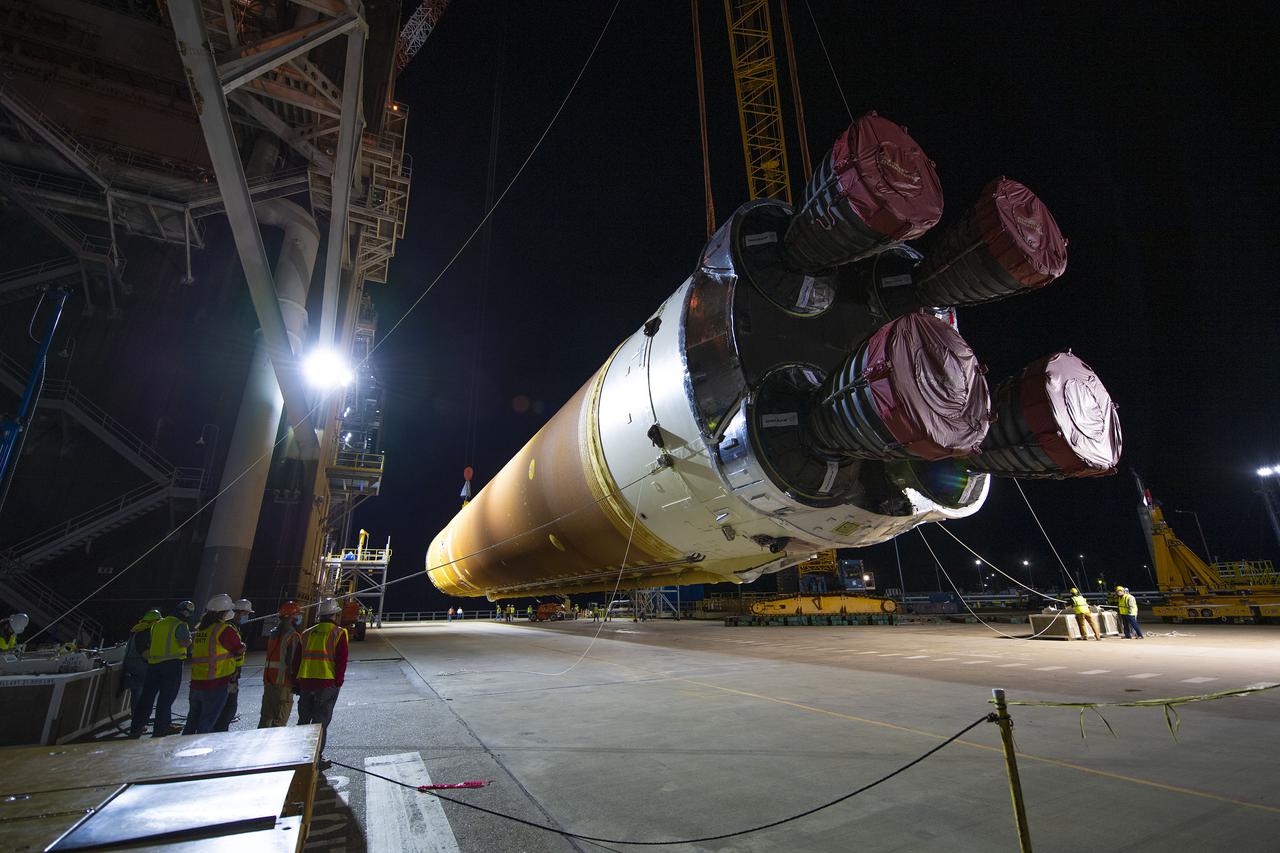
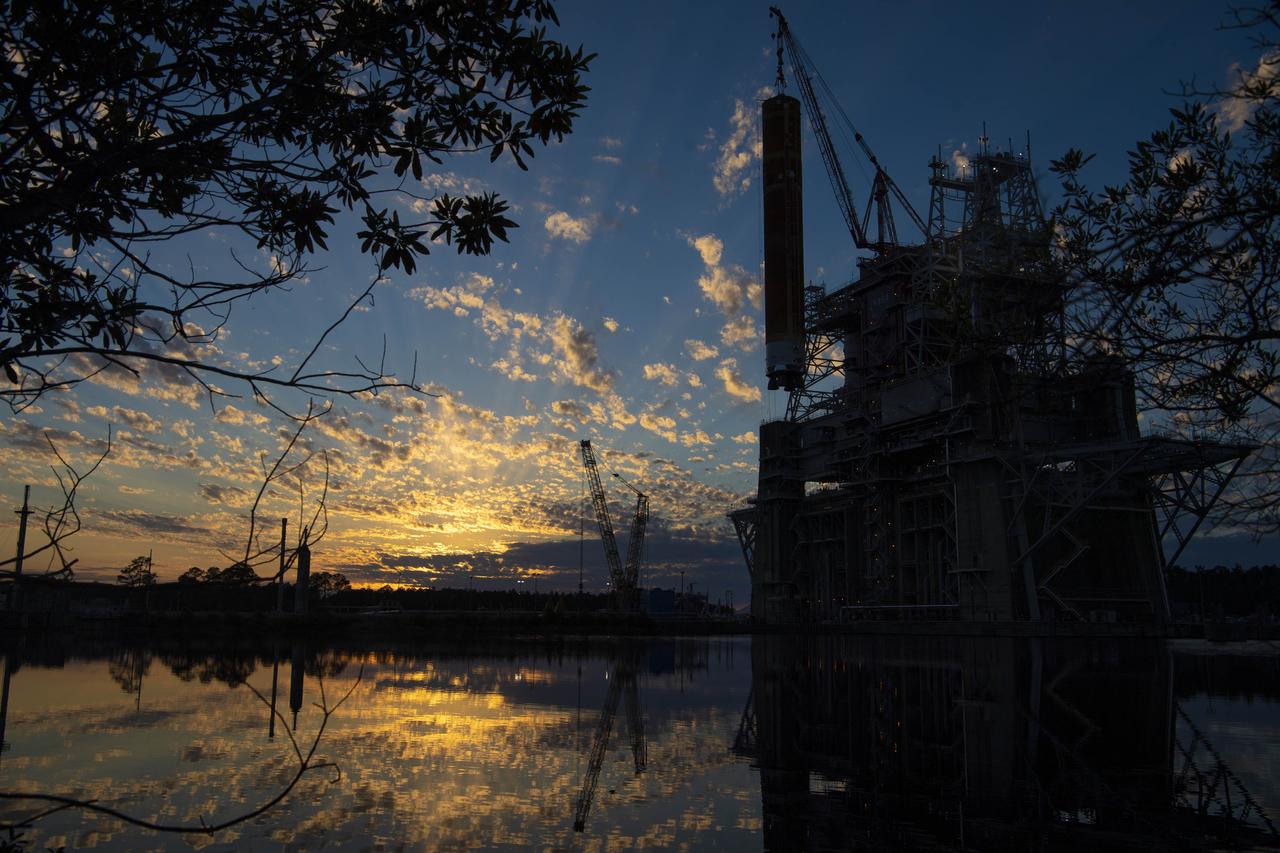
After a series of successful tests conducted the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center, NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage was loaded on the Pegasus barge and departed the test stand in the early morning hours of April 22, 2021, beginning its journey to Kennedy Space Center.
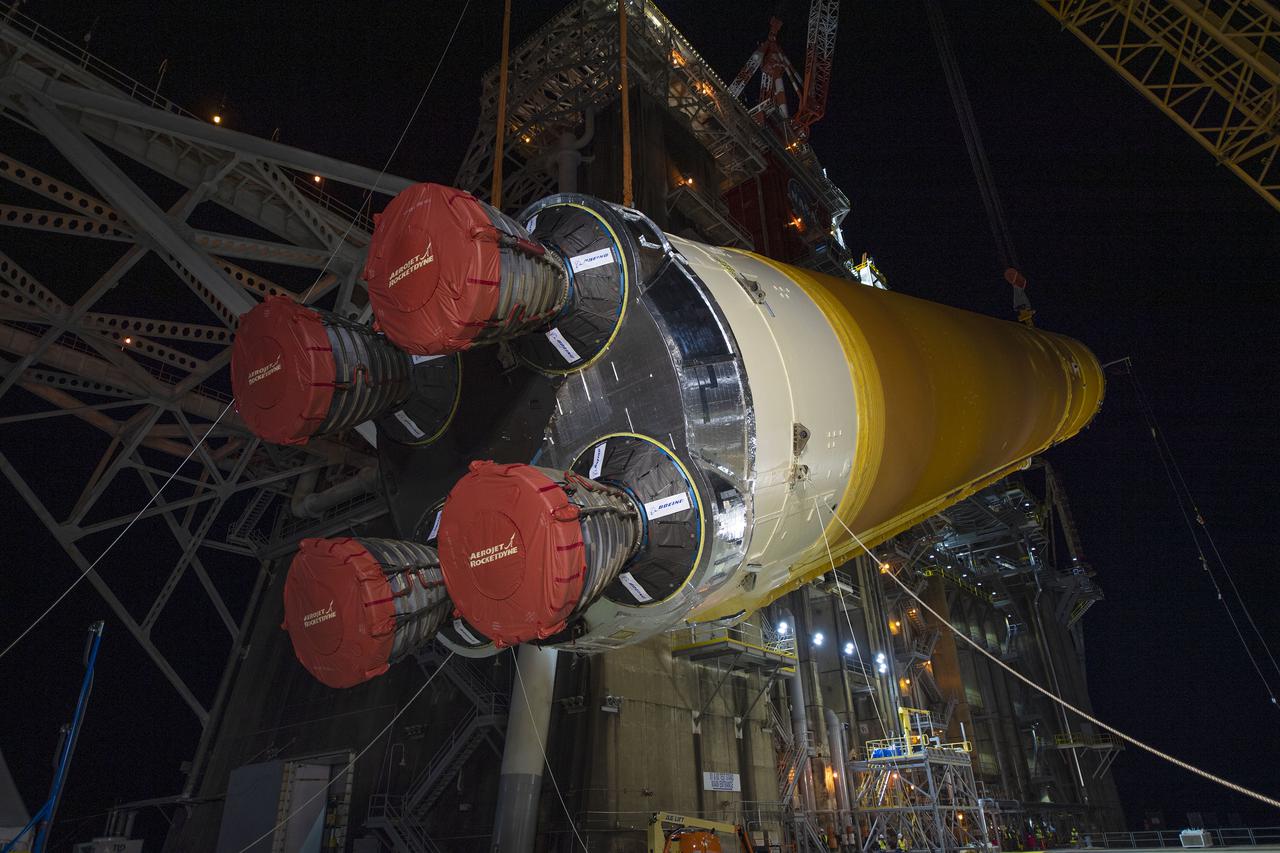
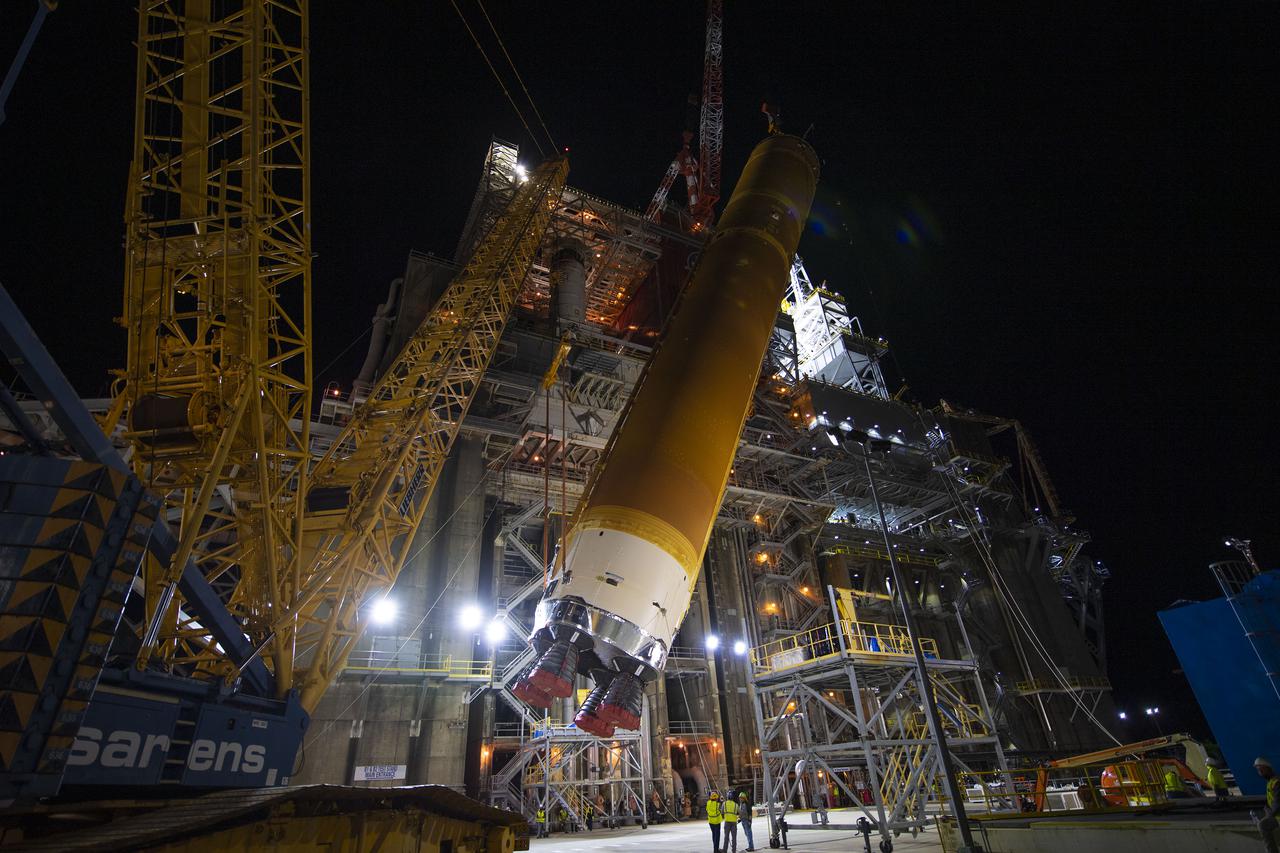
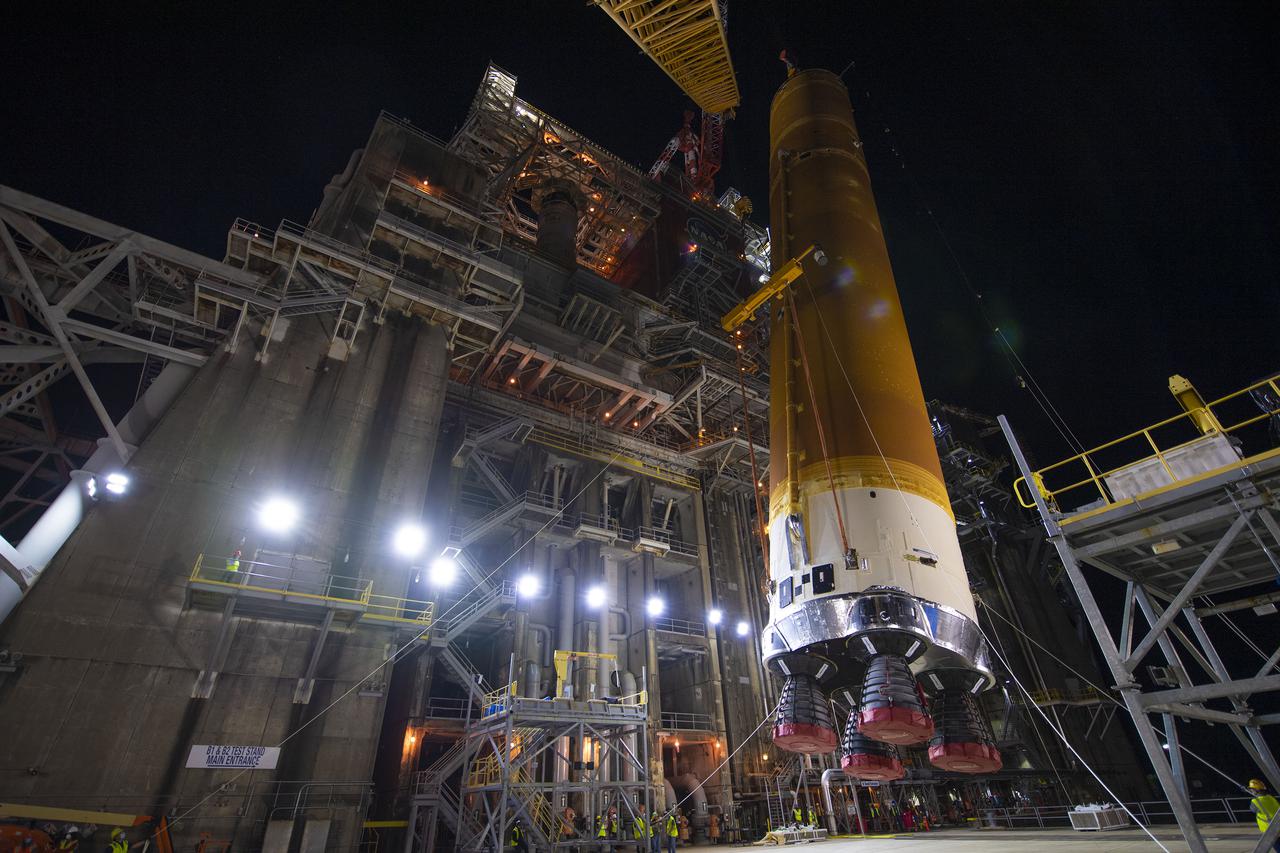
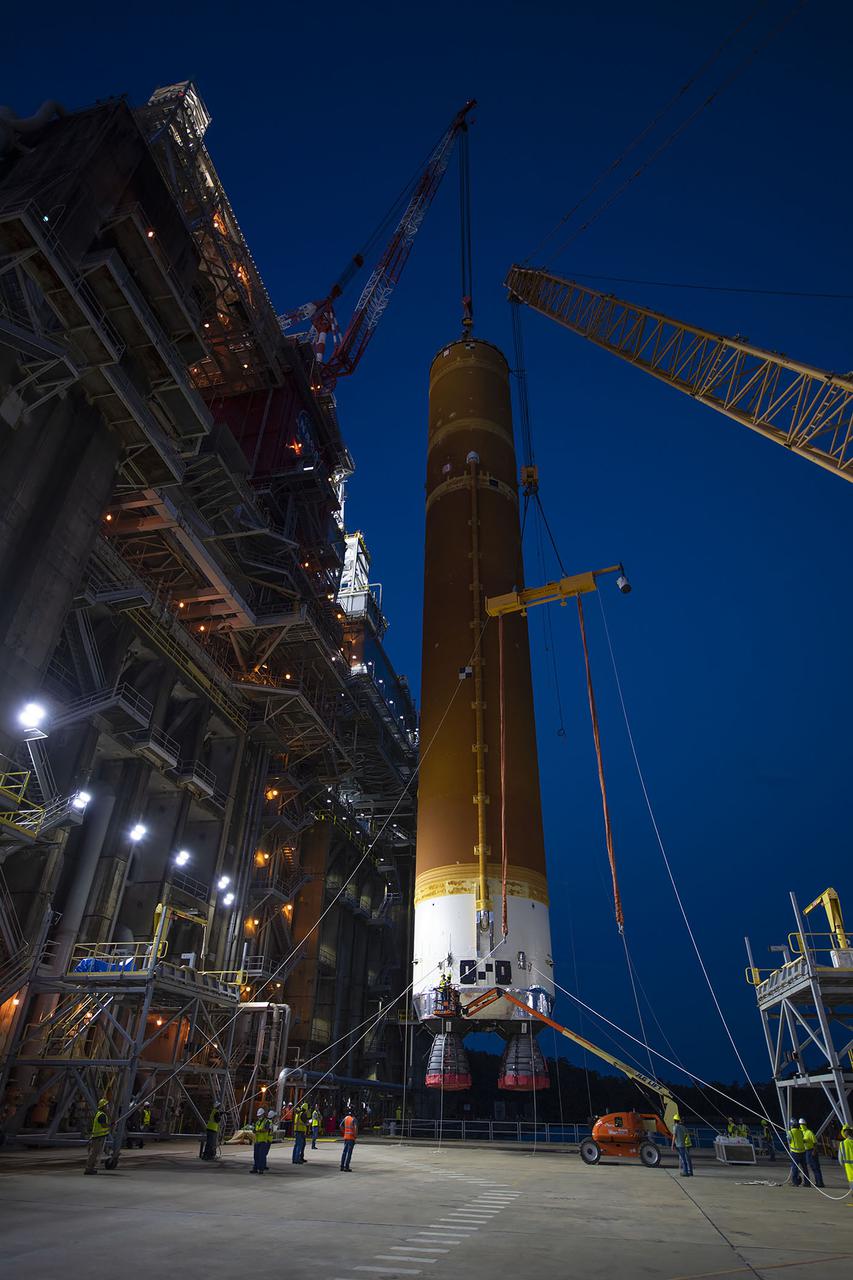
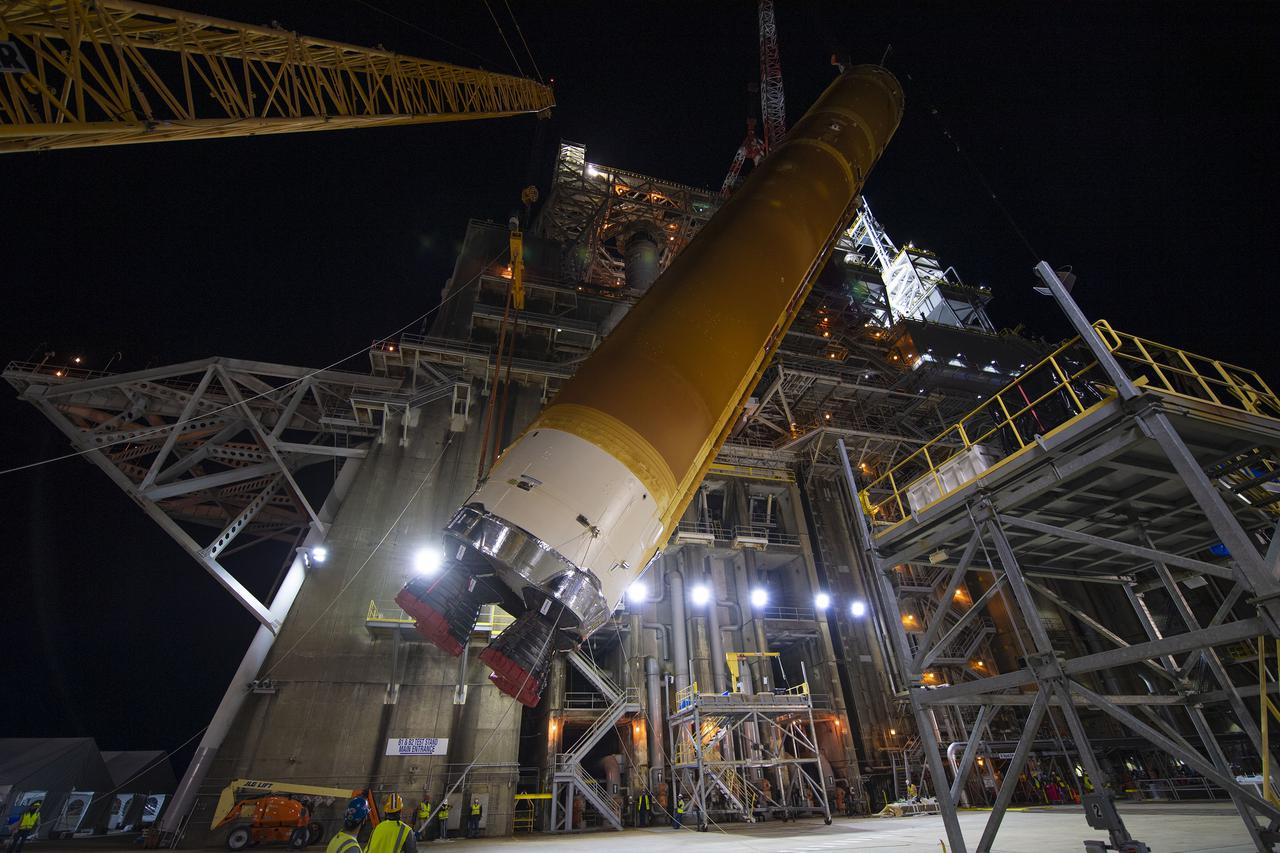
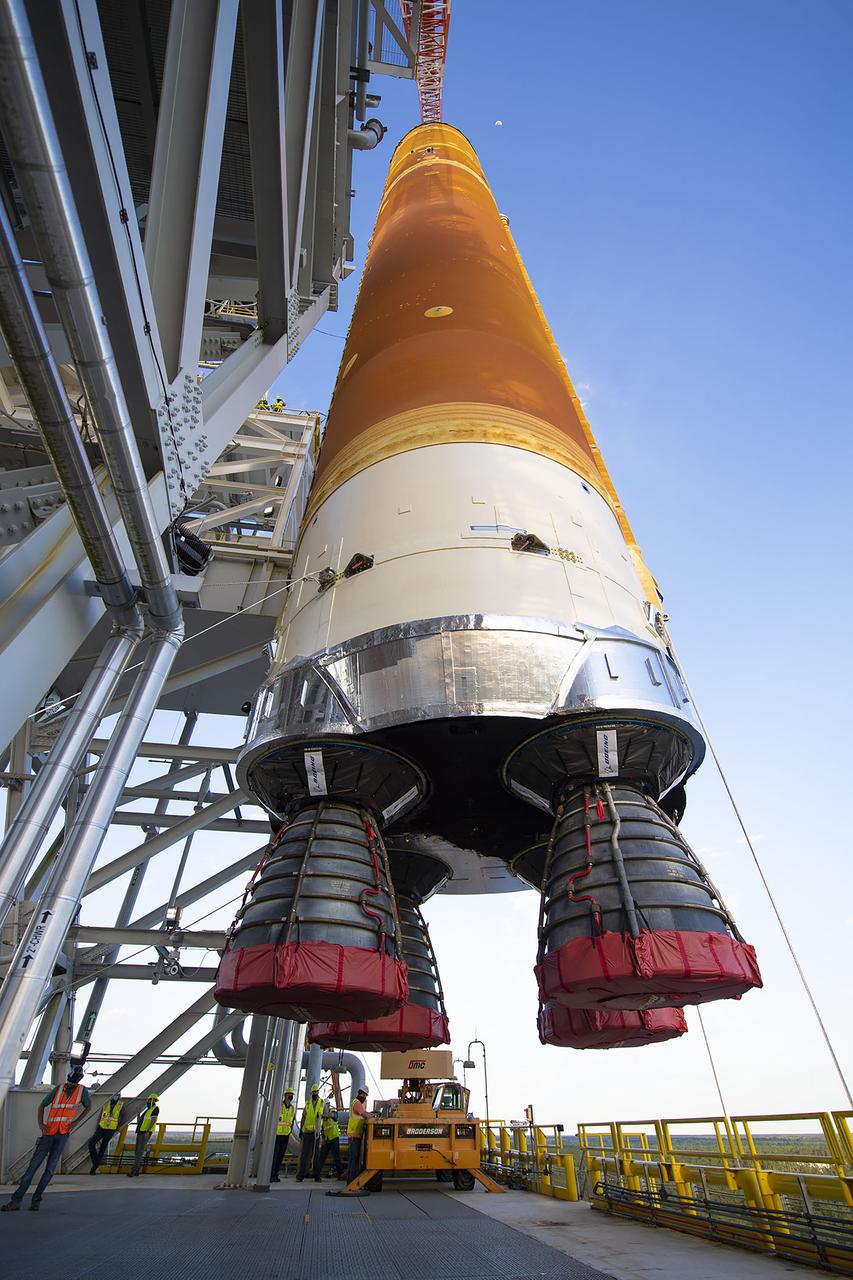
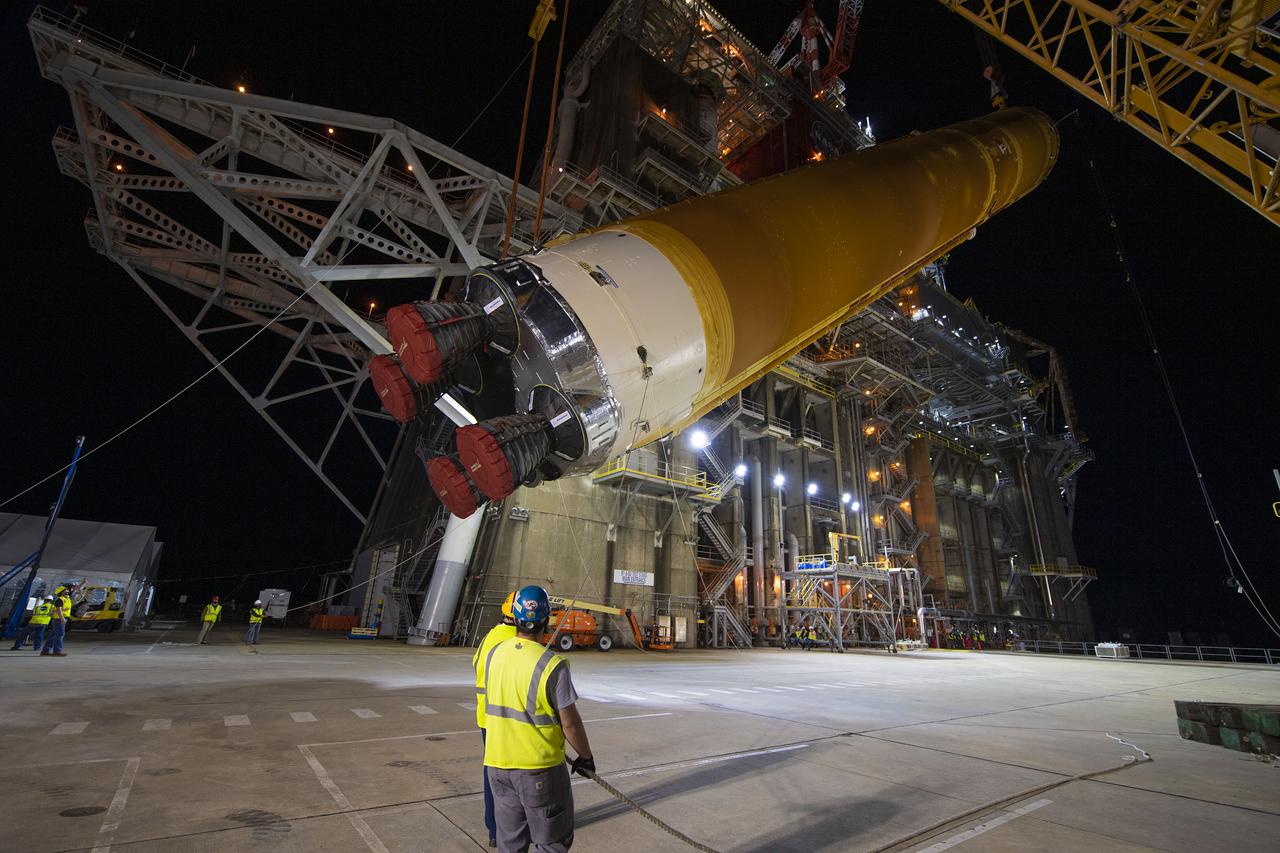
Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
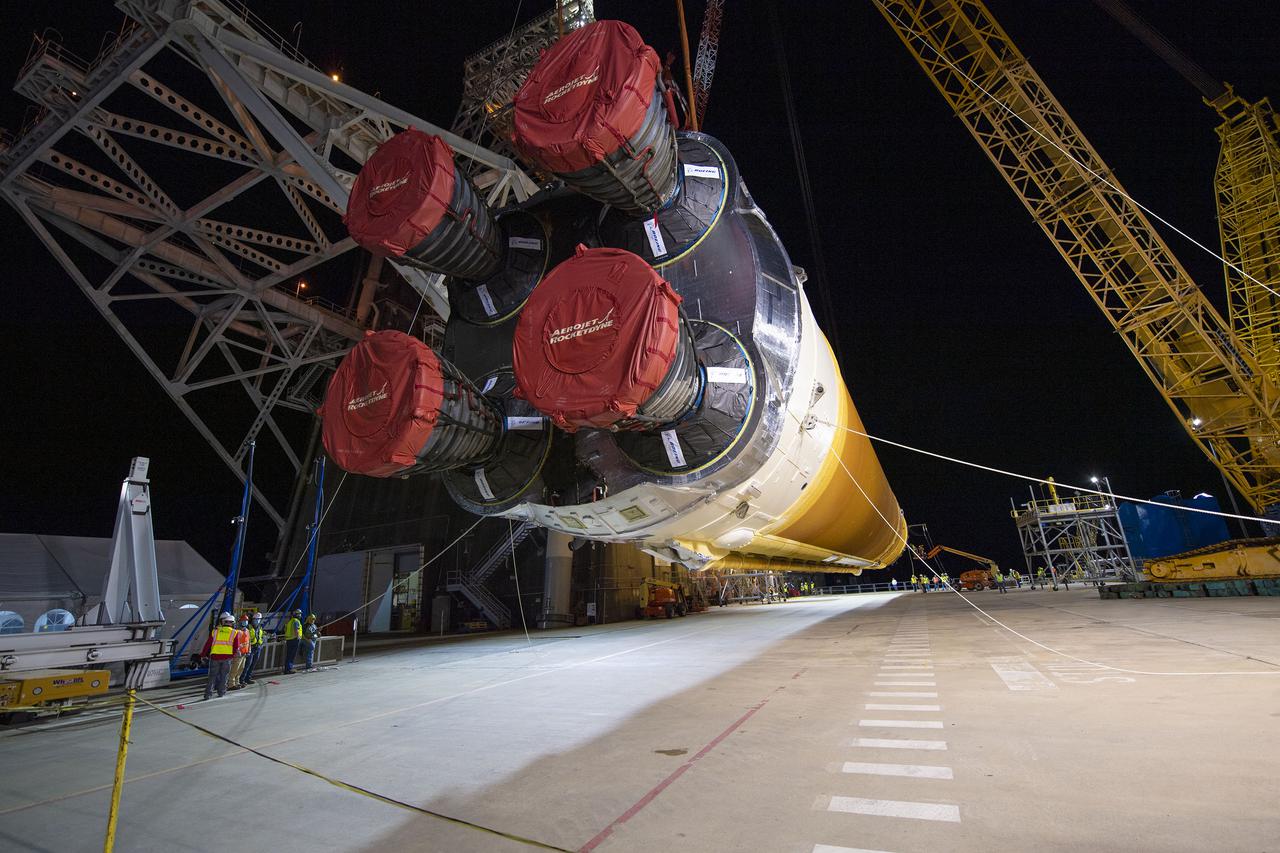

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
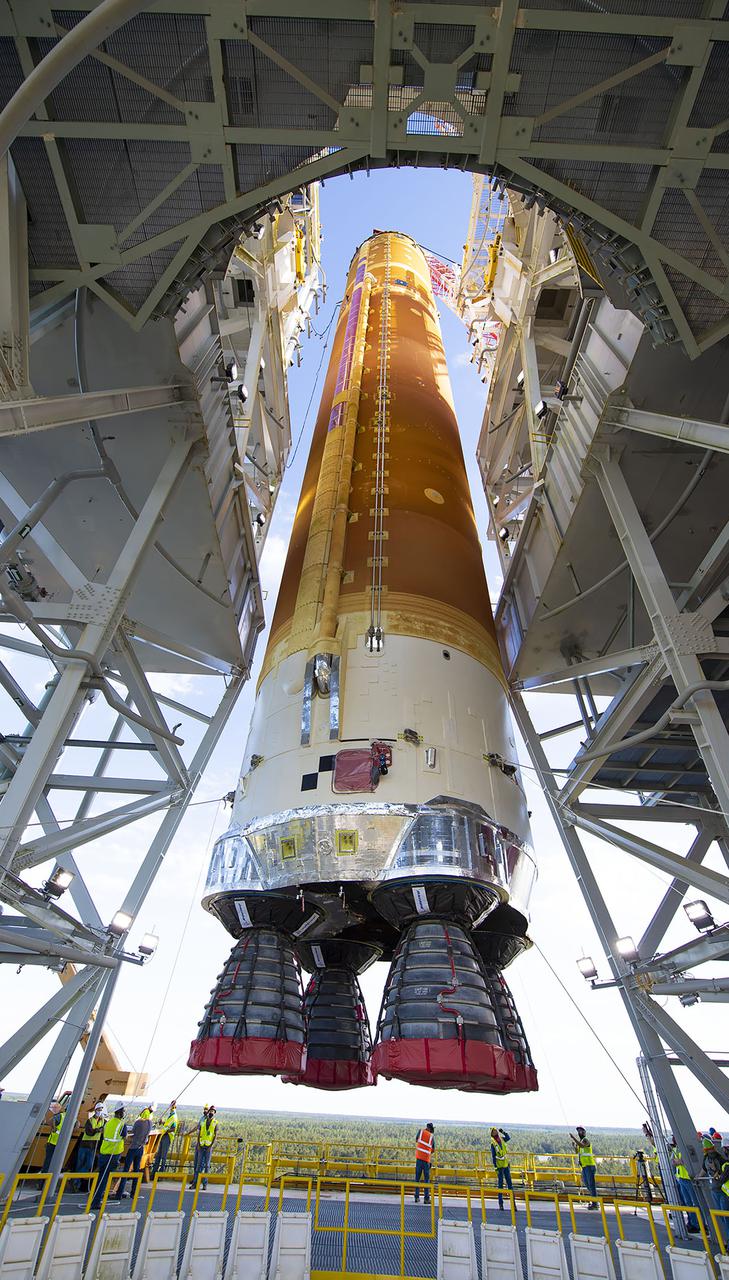

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
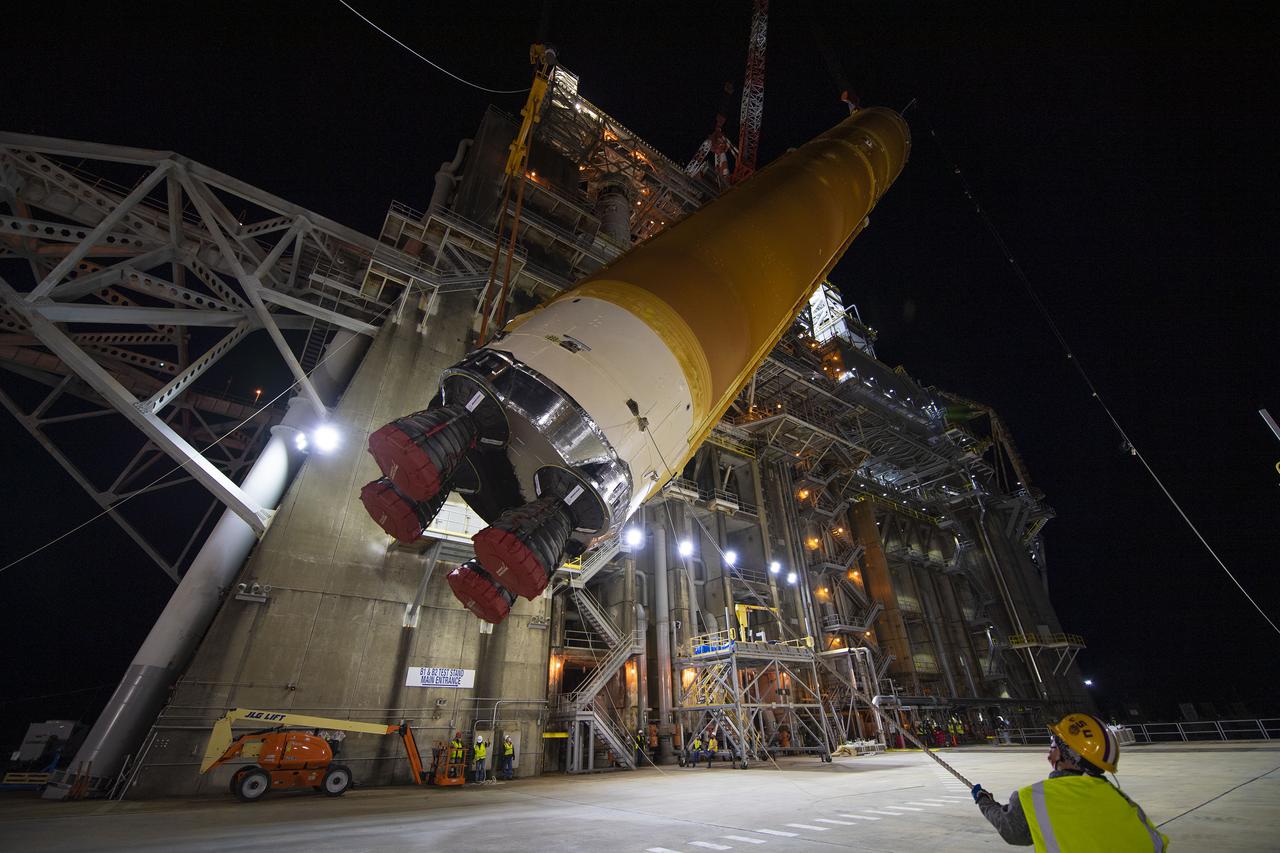

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
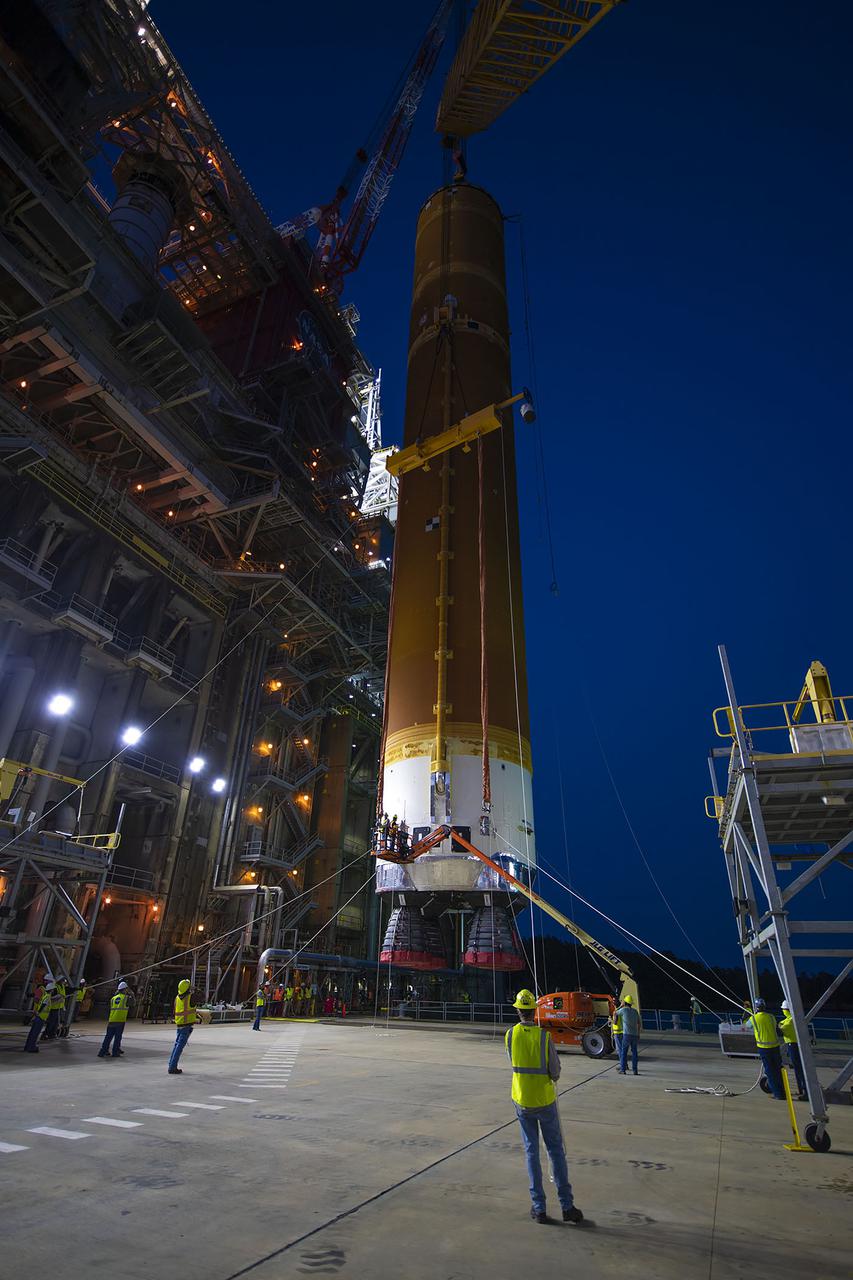

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
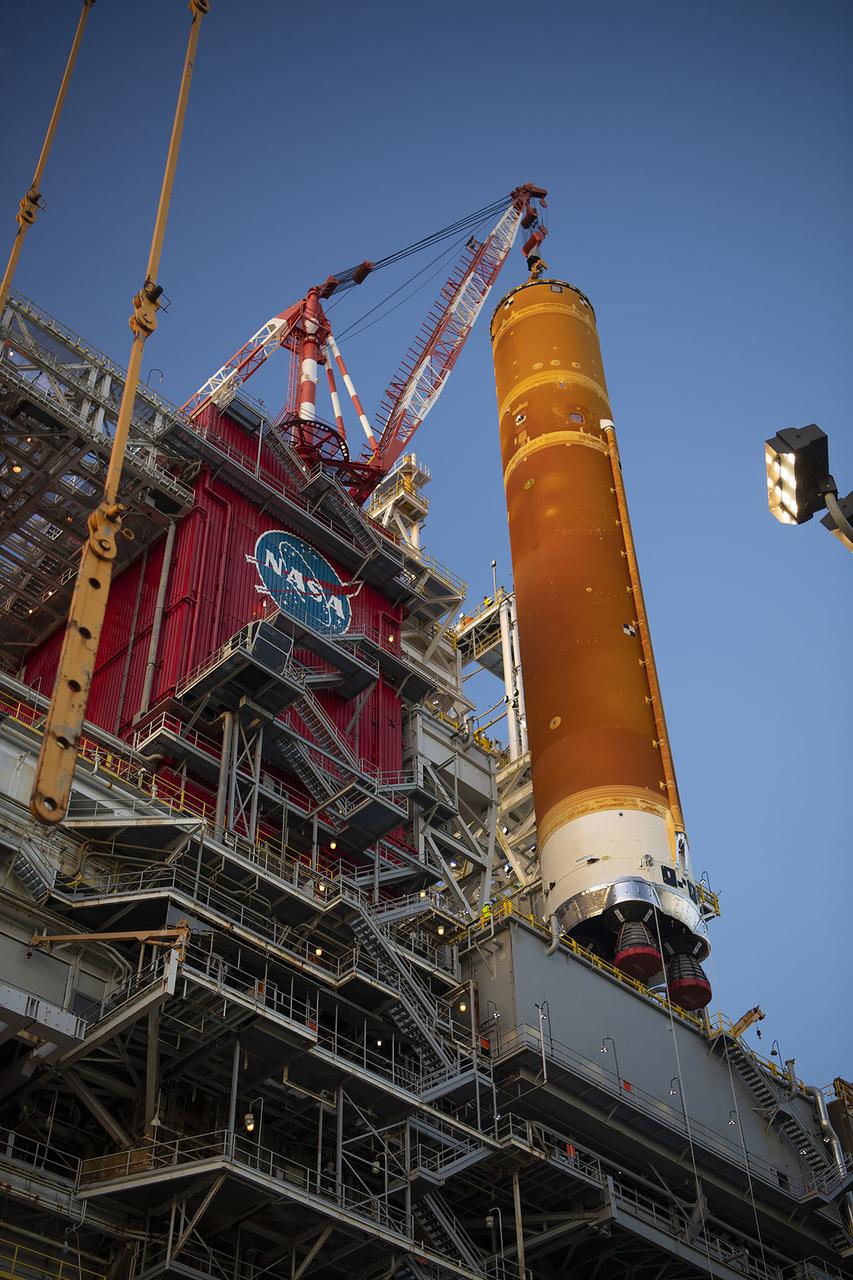

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
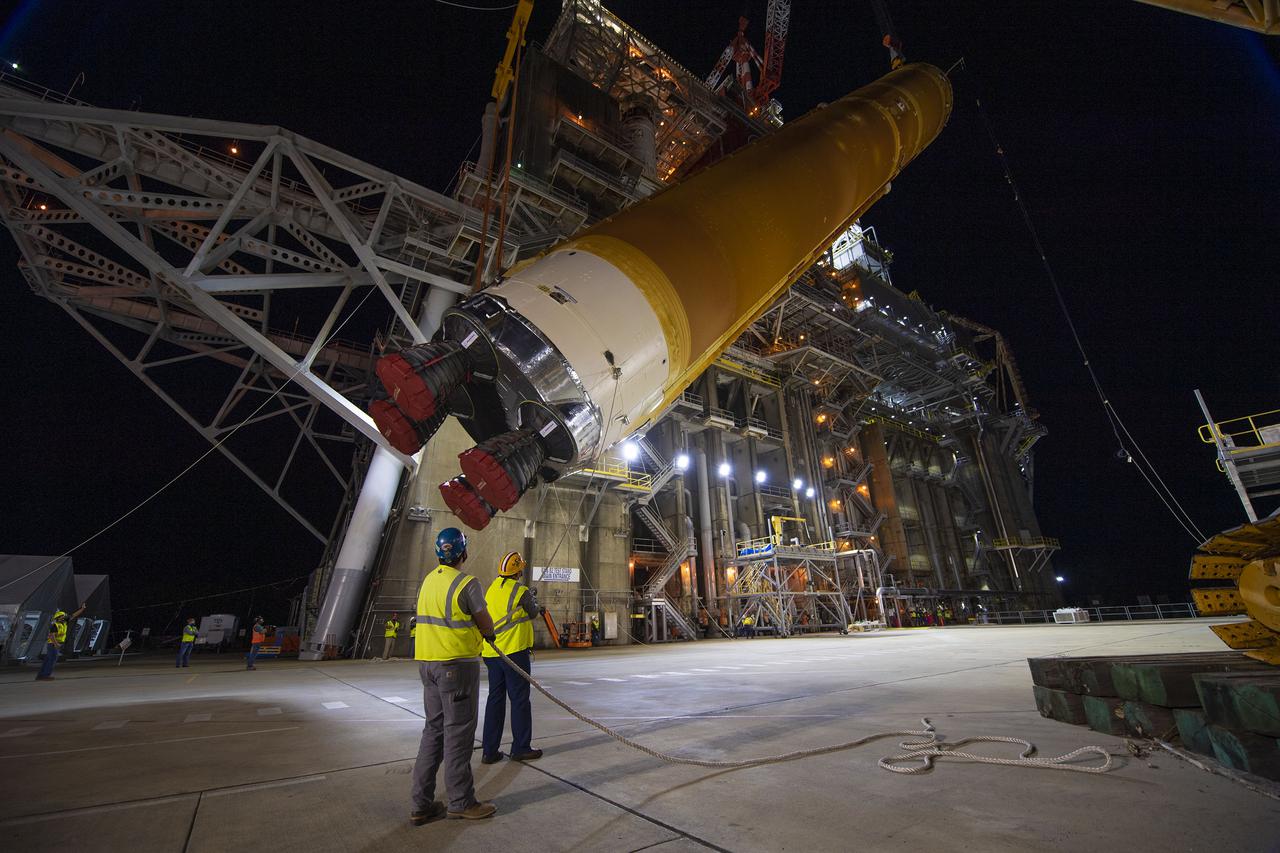

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
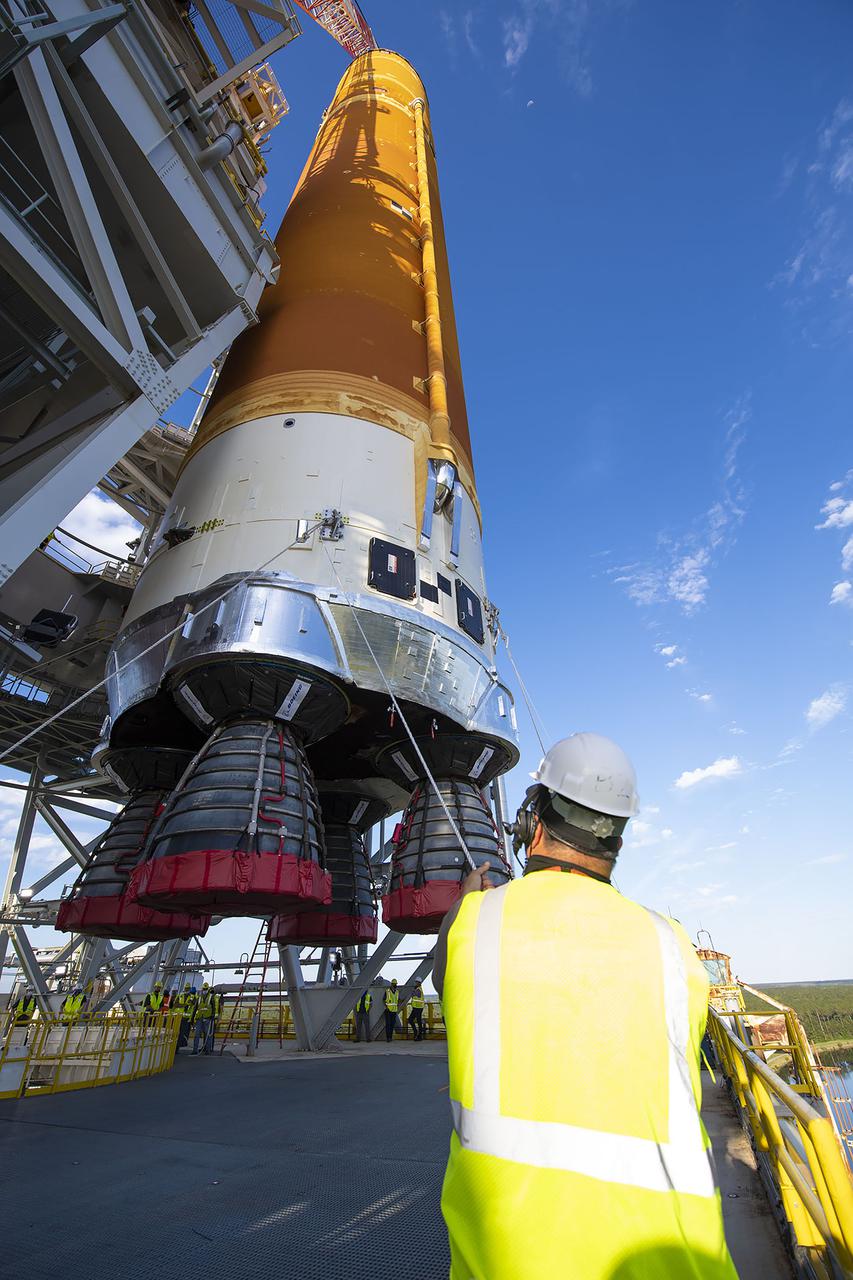

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
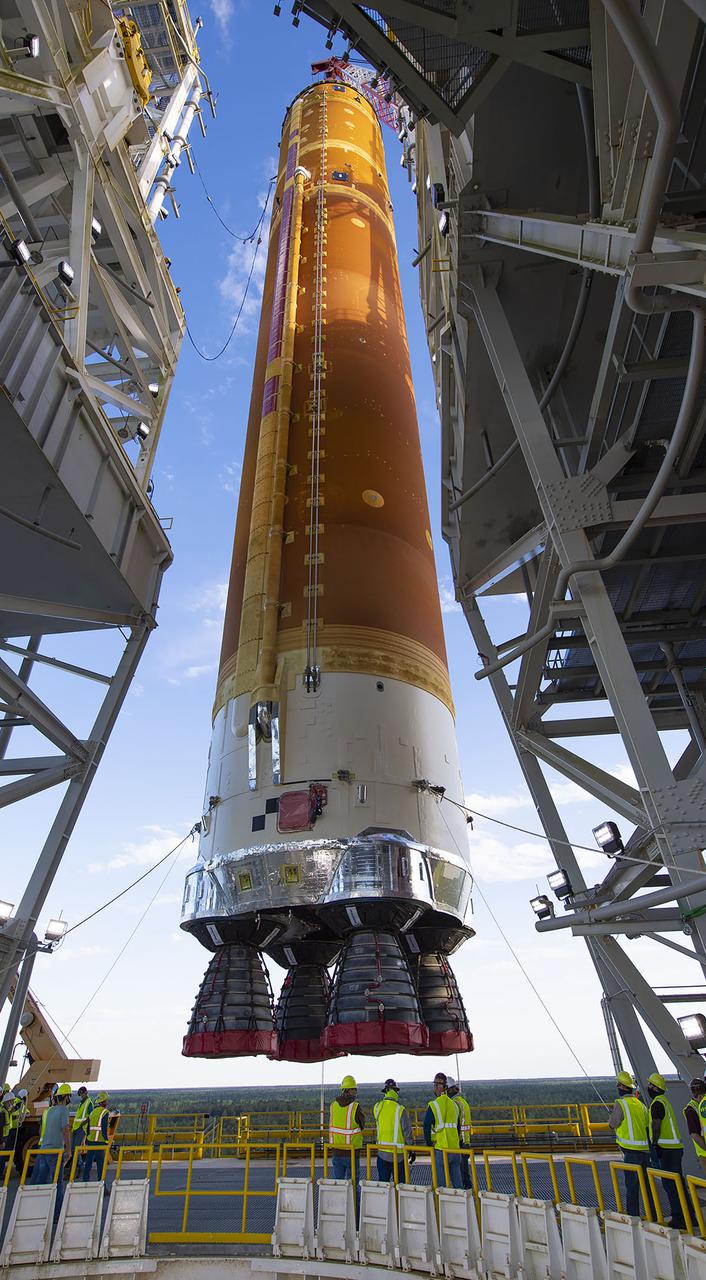

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
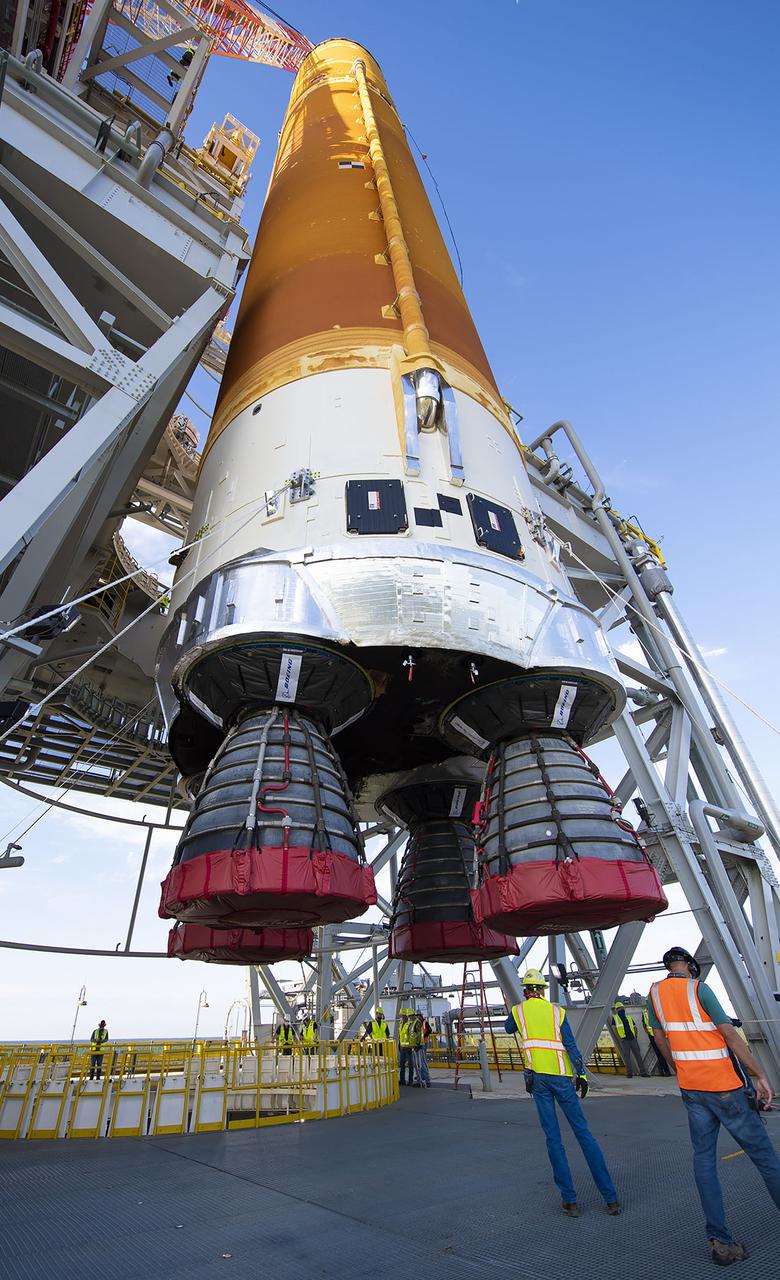

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
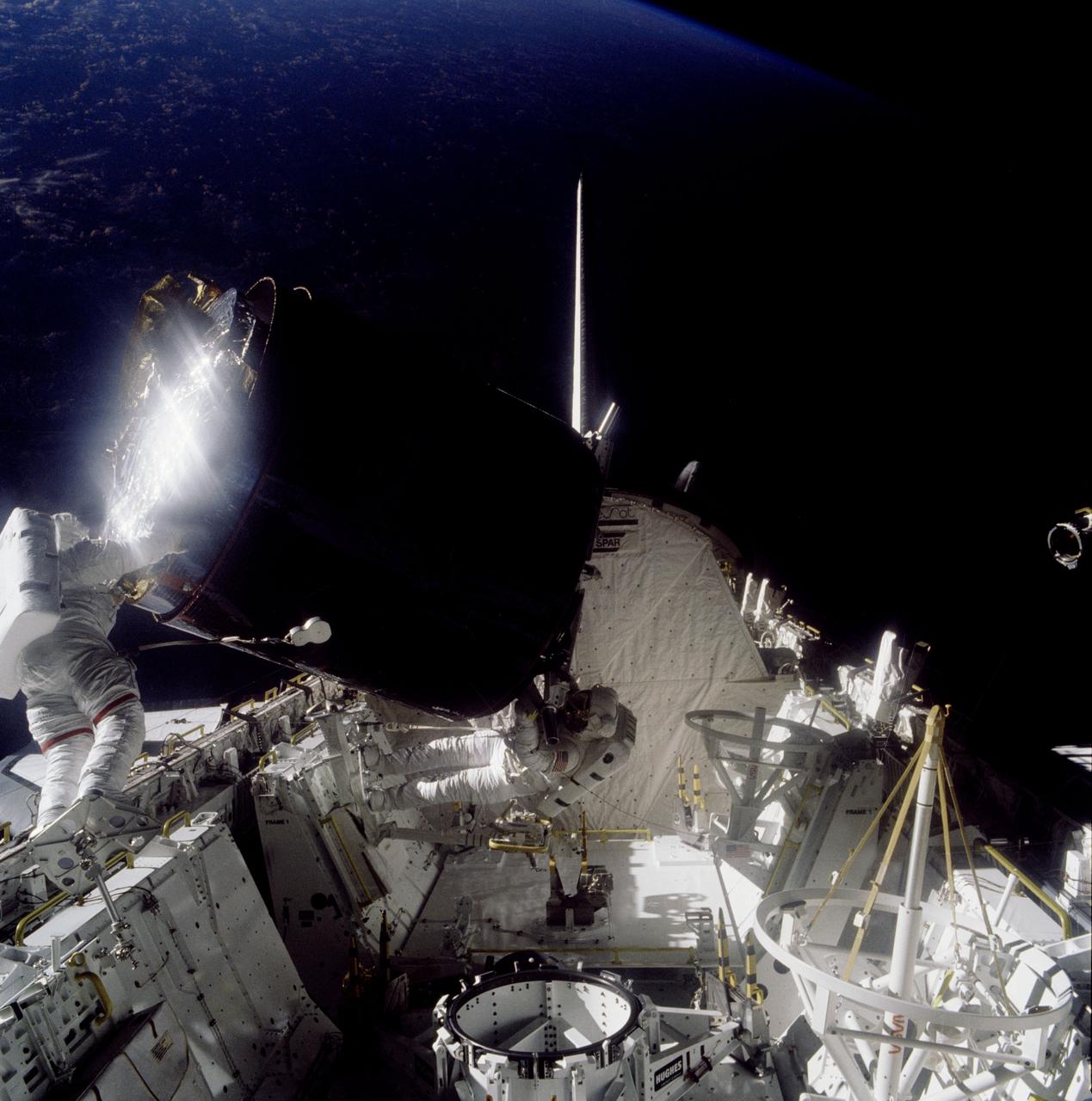

51A-41-058 (12 November 1984) --- Astronaut Joseph P. Allen IV appears to be lifting weights. Astronaut Dale A. Gardner holding on. Actually, Dr. Allen is the sole anchor for the top portion (and most of) the captured Palapa B-2 communications satellite during the Nov. 12 retrieval extravehicular activity (EVA) of the two mission specialists. This scene came near the end of the long-duration task. Gardner used a torque wrench to tighten clamps on an adapter used to secure the Palapa to its "parking place" in Discovery's cargo bay. Note the difference between the two stinger devices stowed on Challenger's port side (right side of frame). The one nearer the spacecraft's vertical stabilizer is spent, having been inserted by Allen earlier in the day to stabilize the communications satellite. The one nearer the camera awaited duty in two days when it would aid in the capture of the Westar VI satellite.

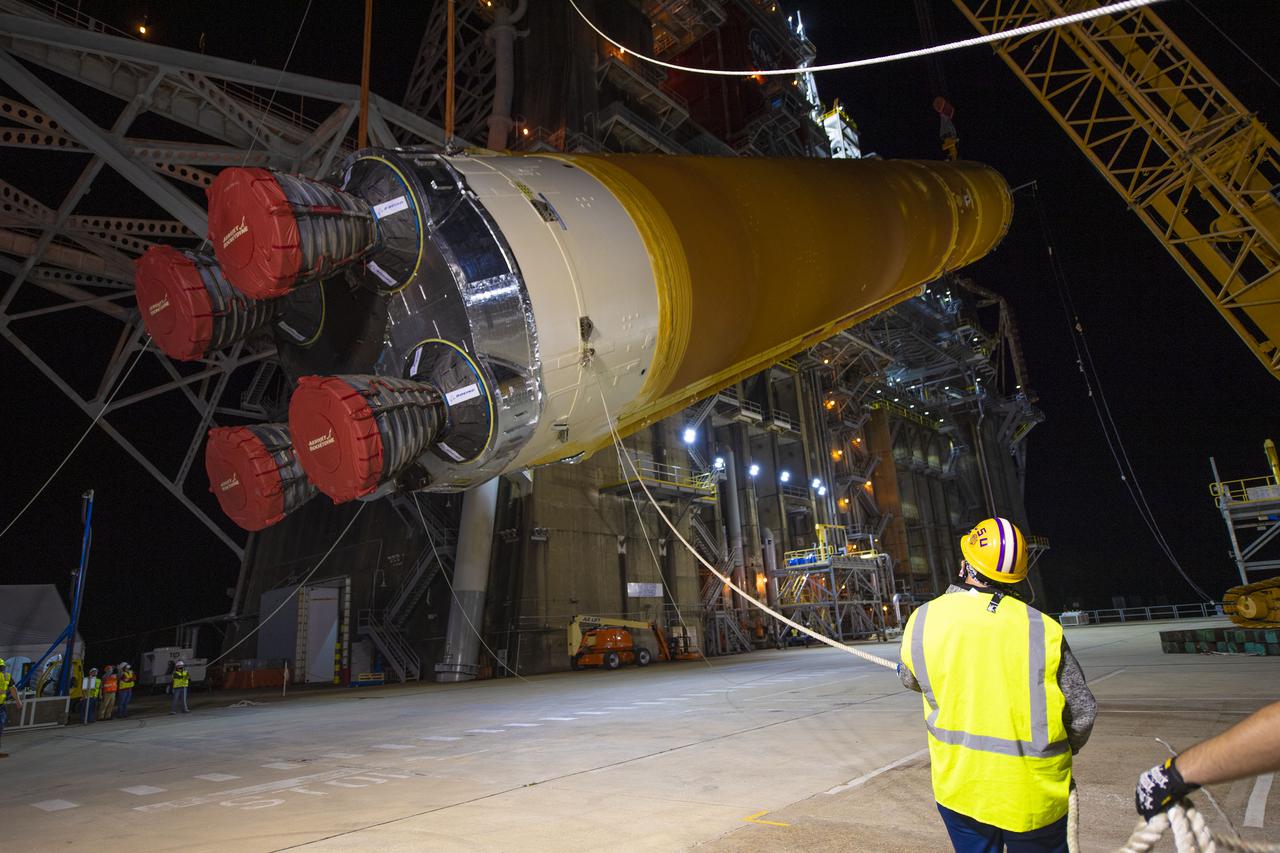
The first flight core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is removed from the B-2 Test Stand on April 19, 2021, following completion of a series of eight Green Run tests conducted at Stennis Space Center.
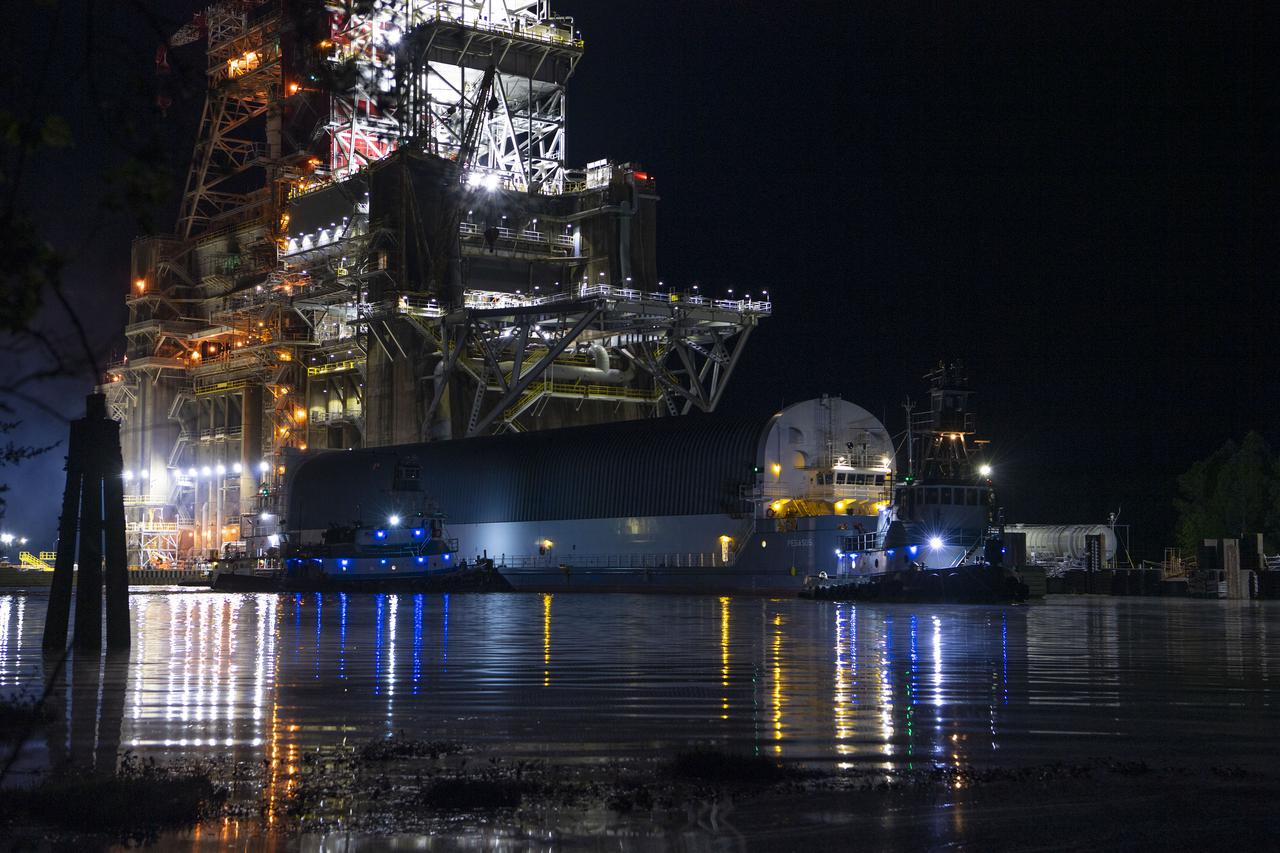

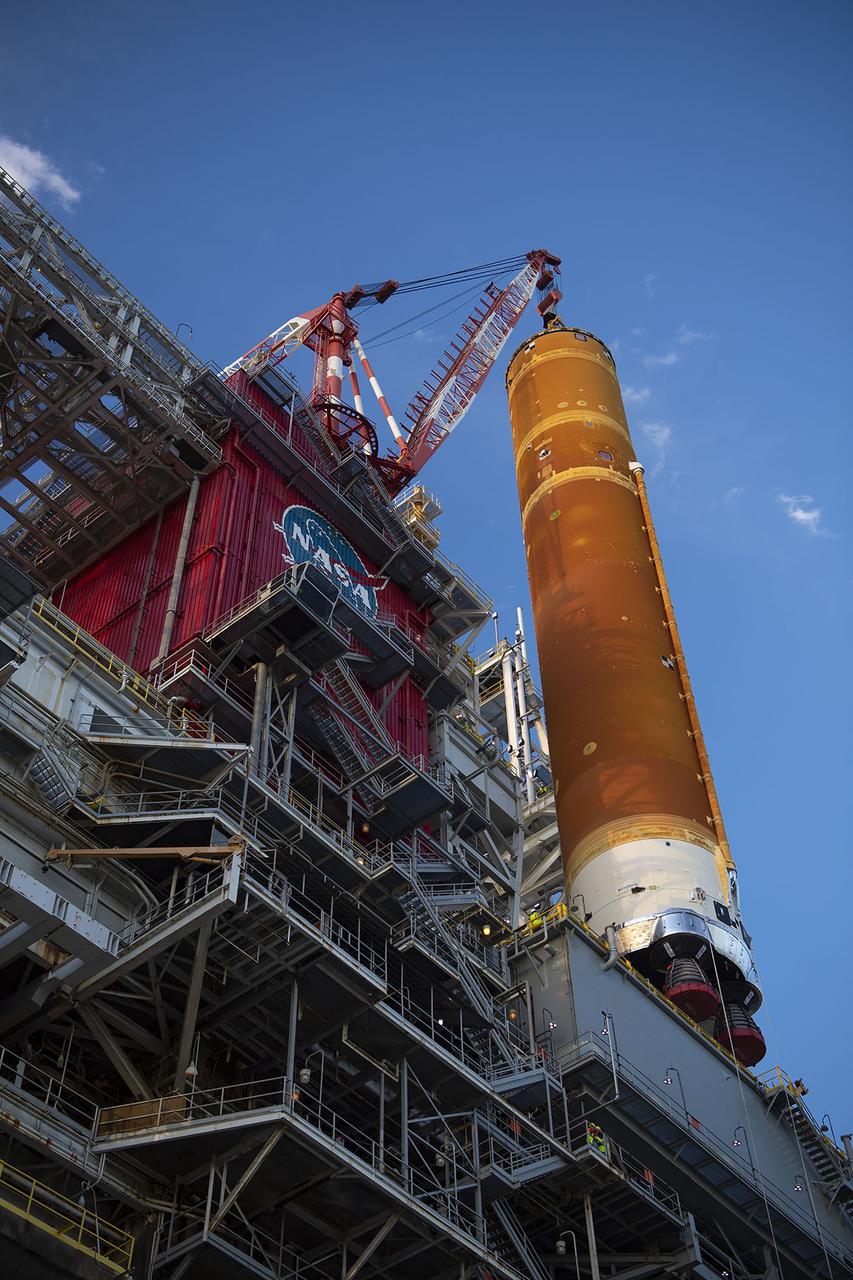
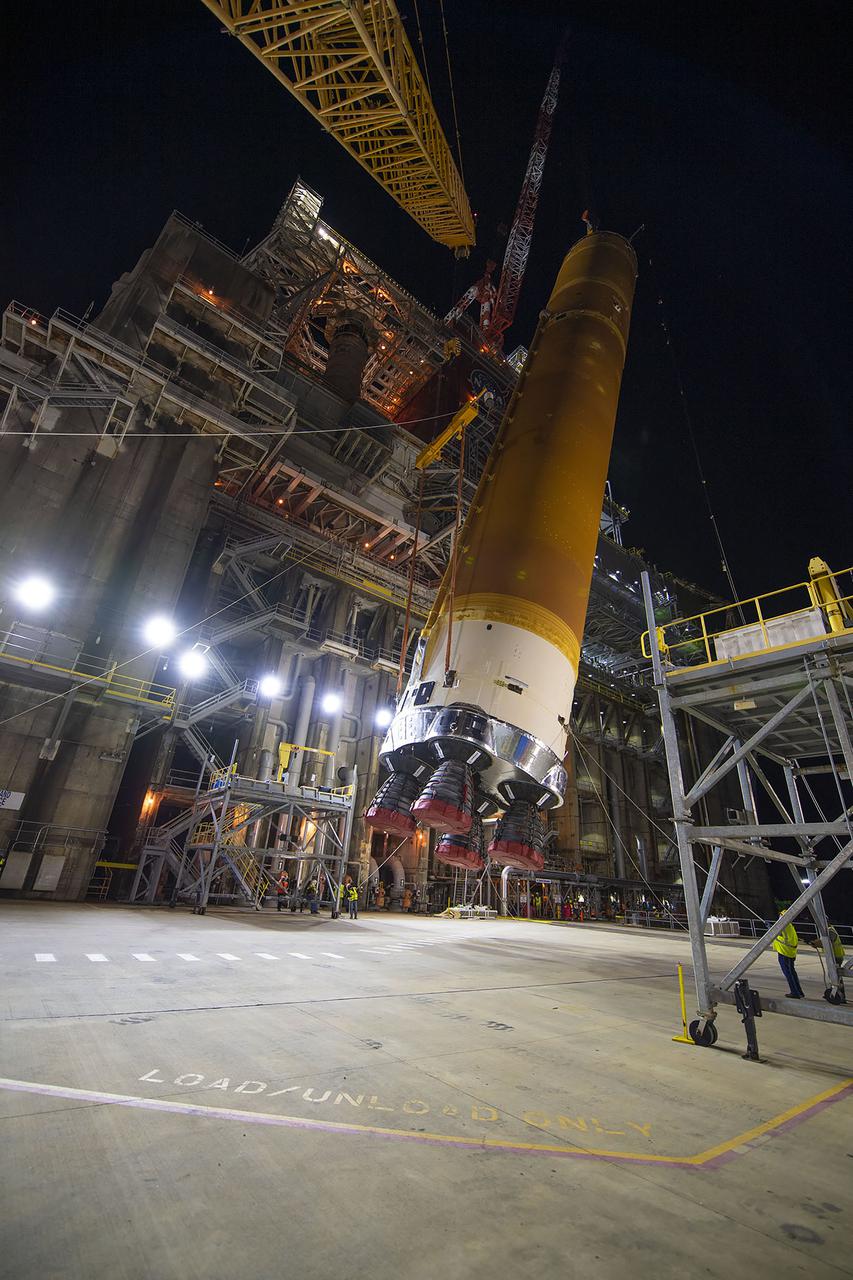
The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
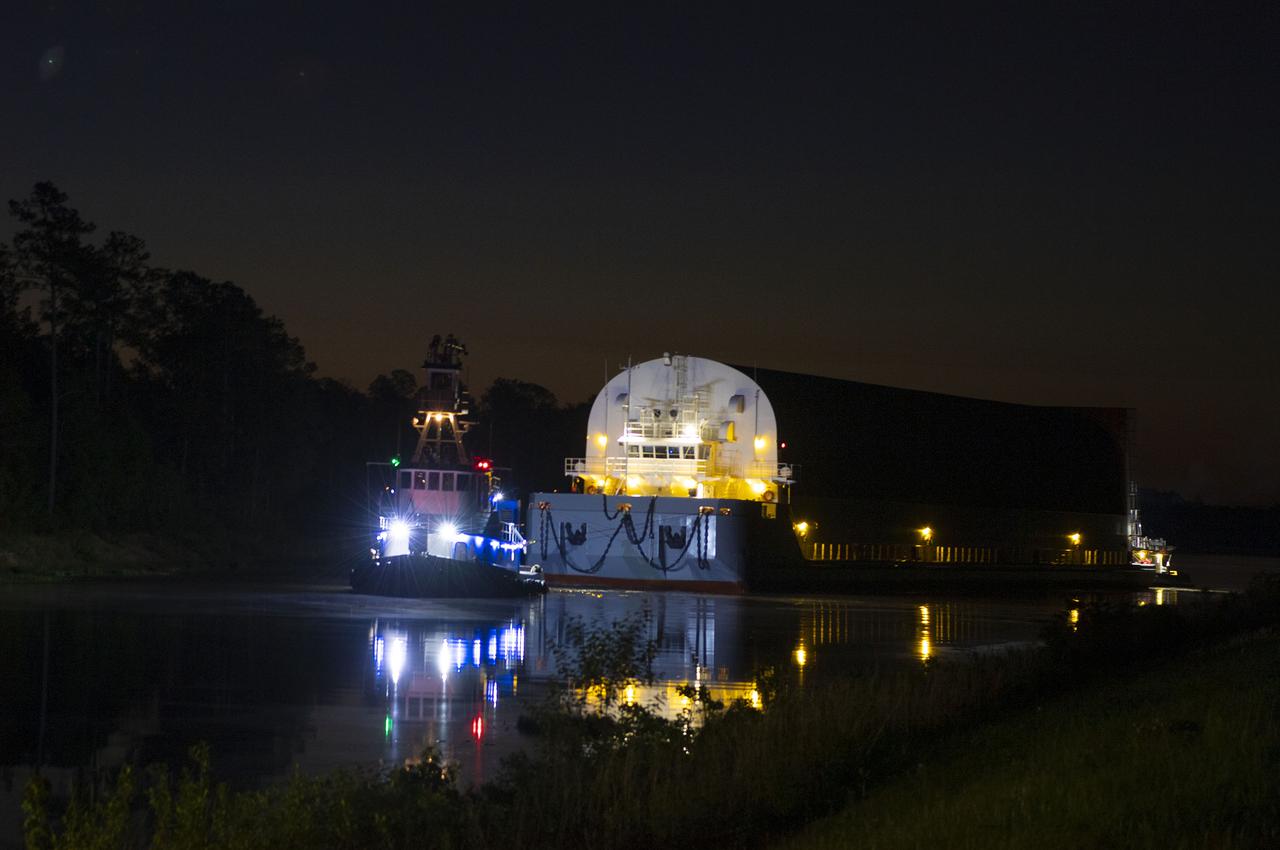

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
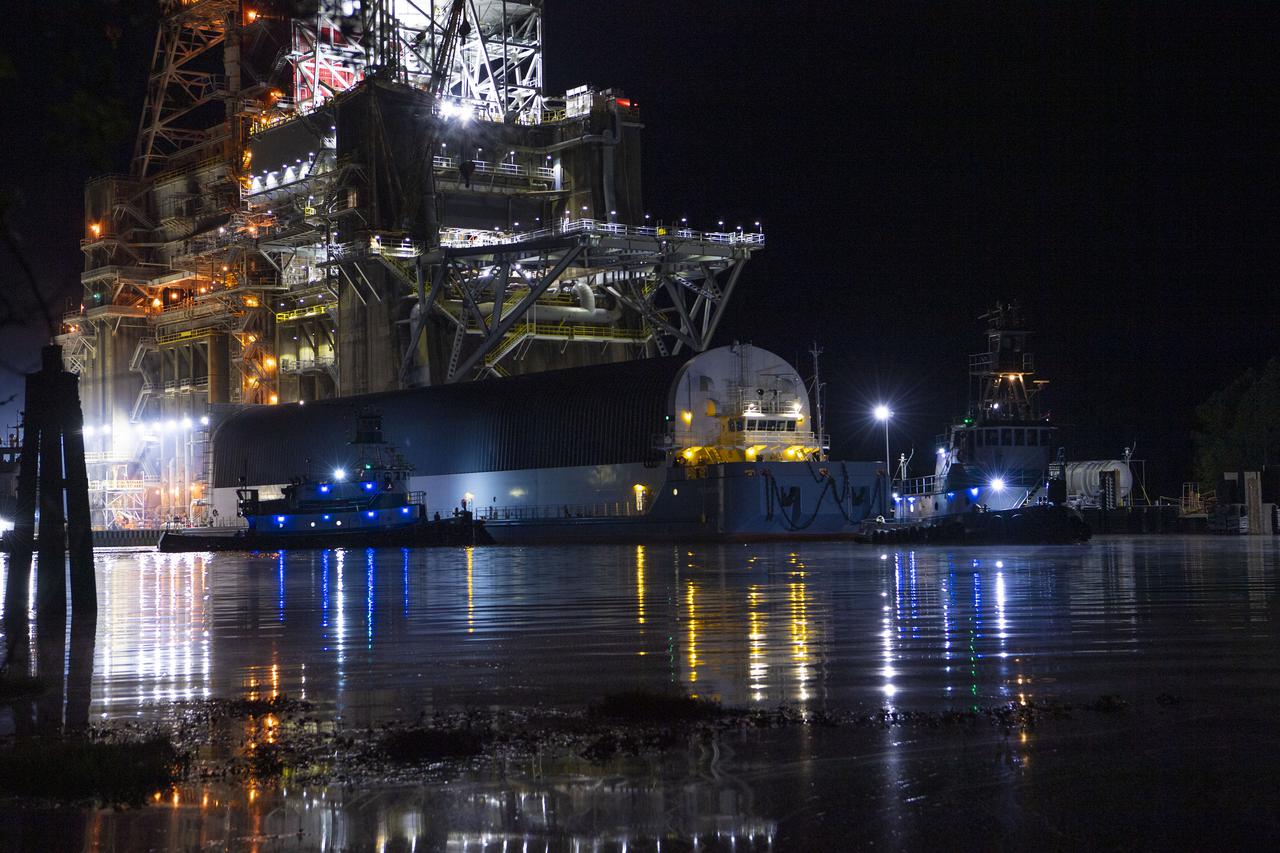

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
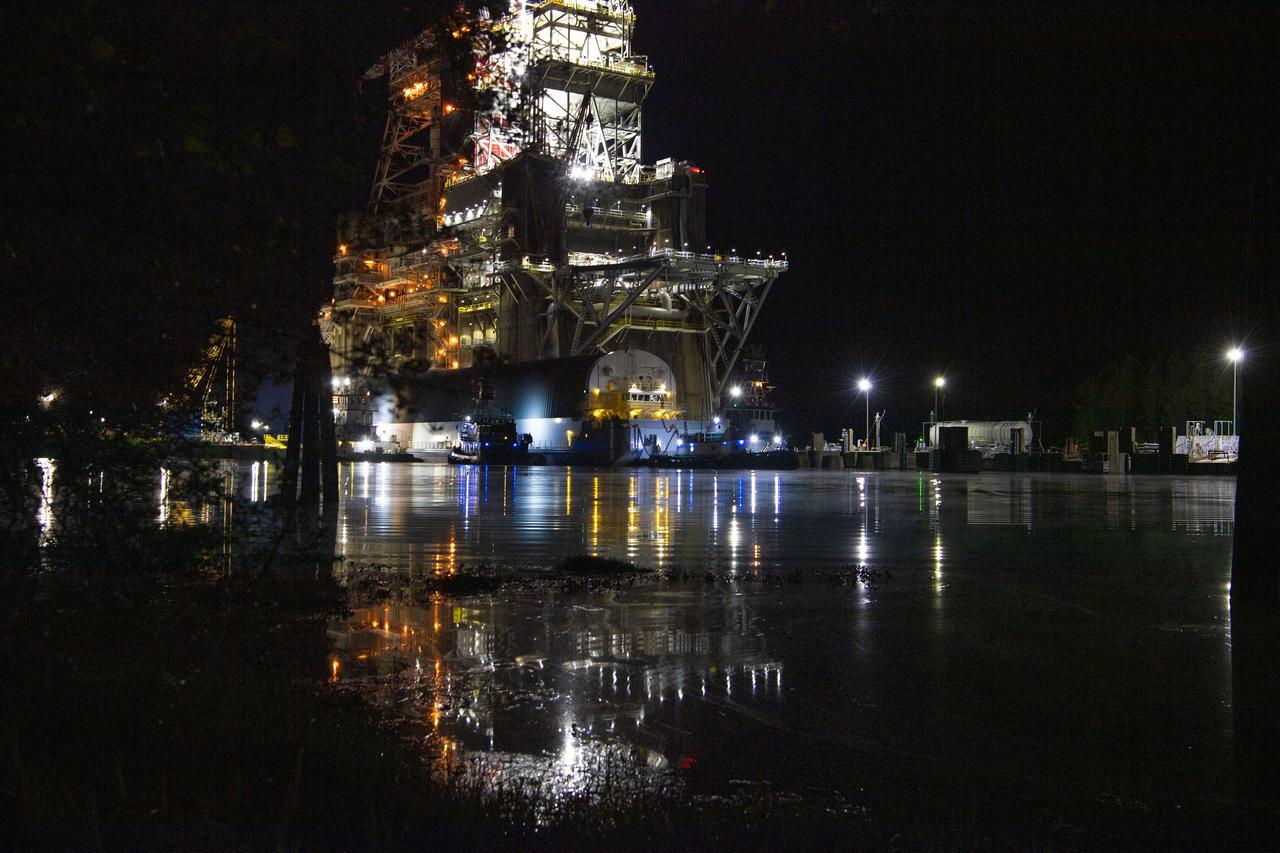

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
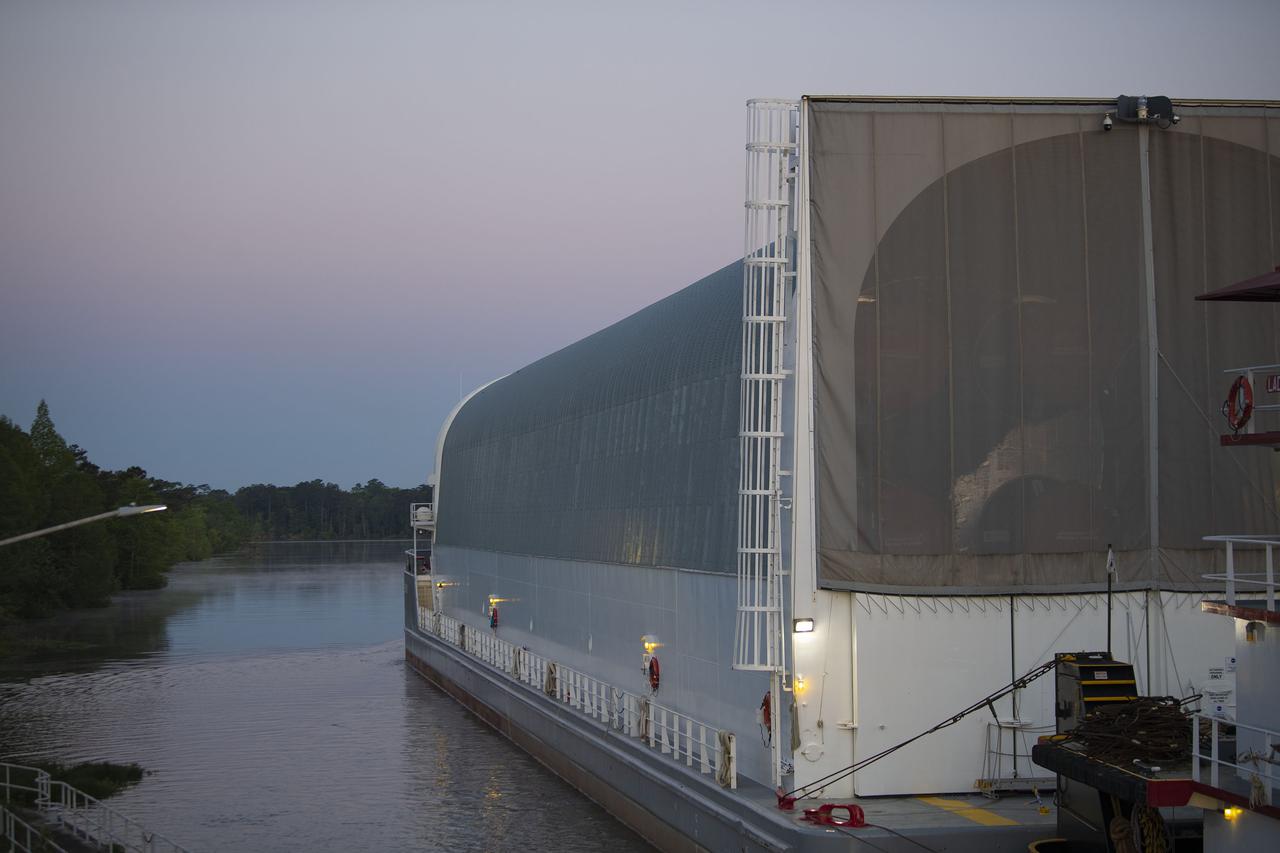

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
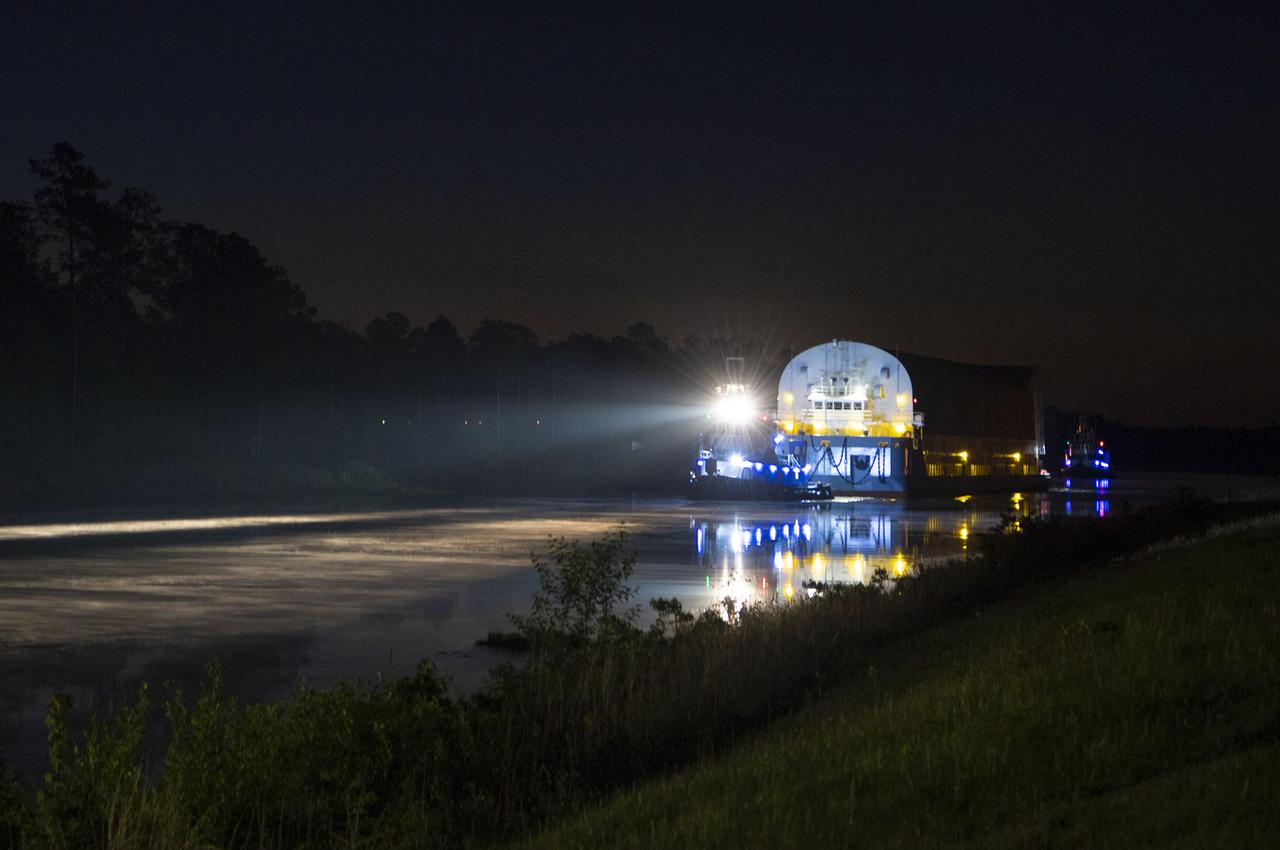

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
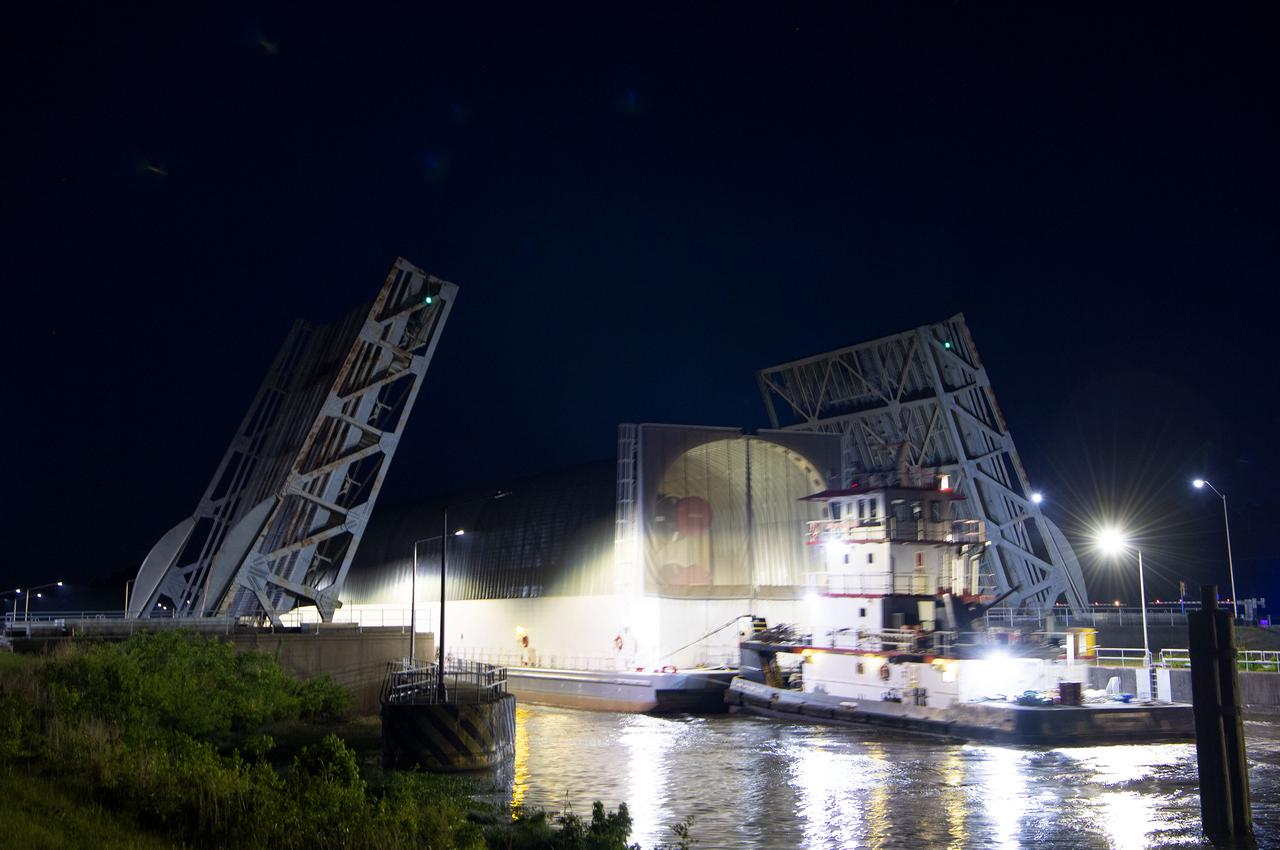

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
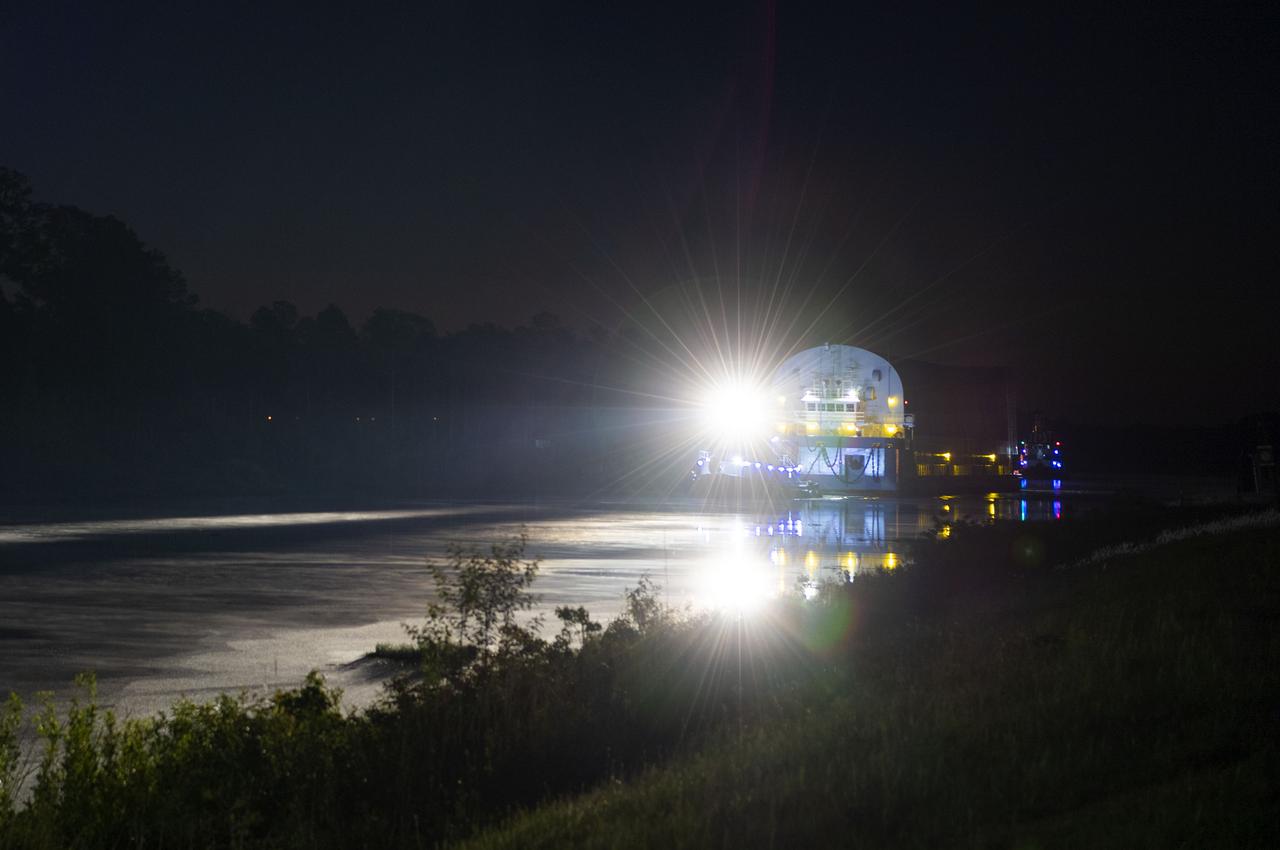

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
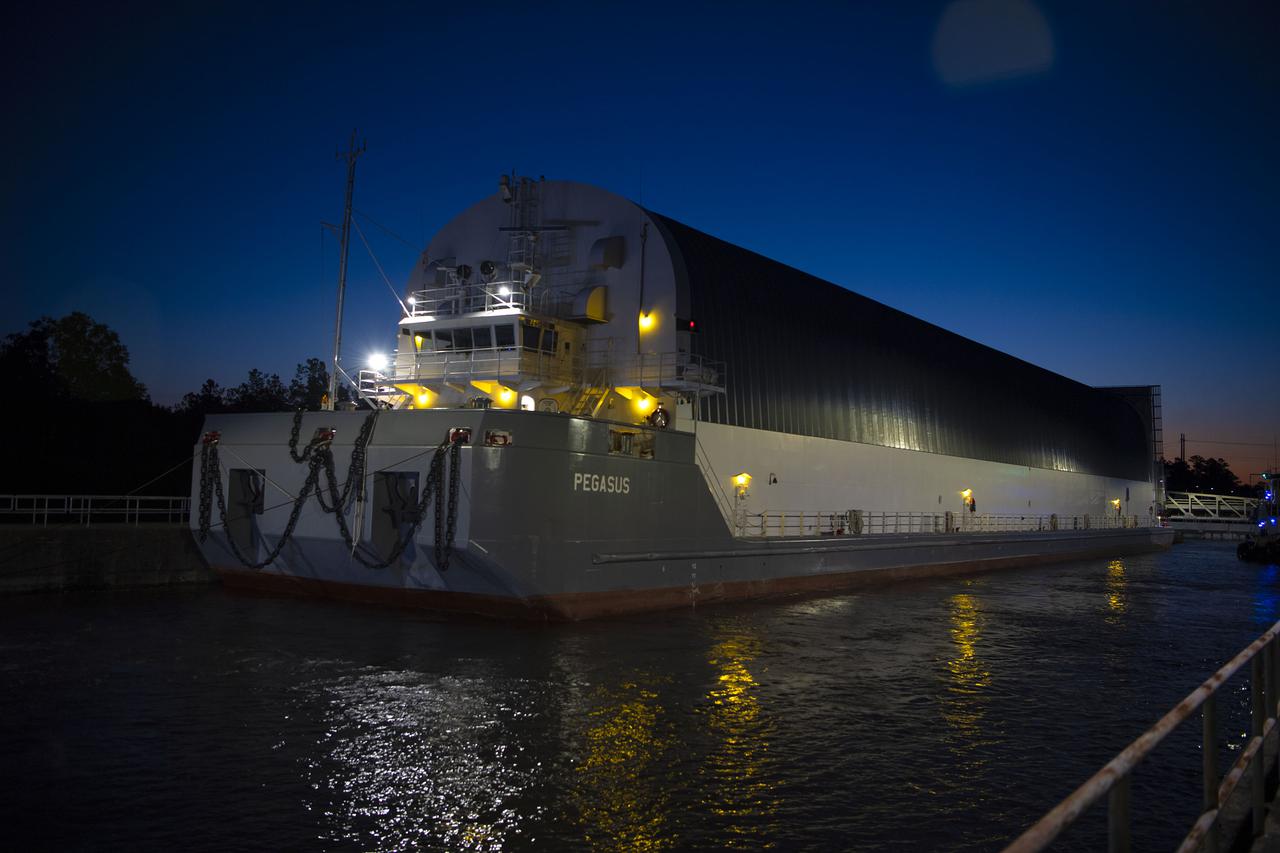

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA

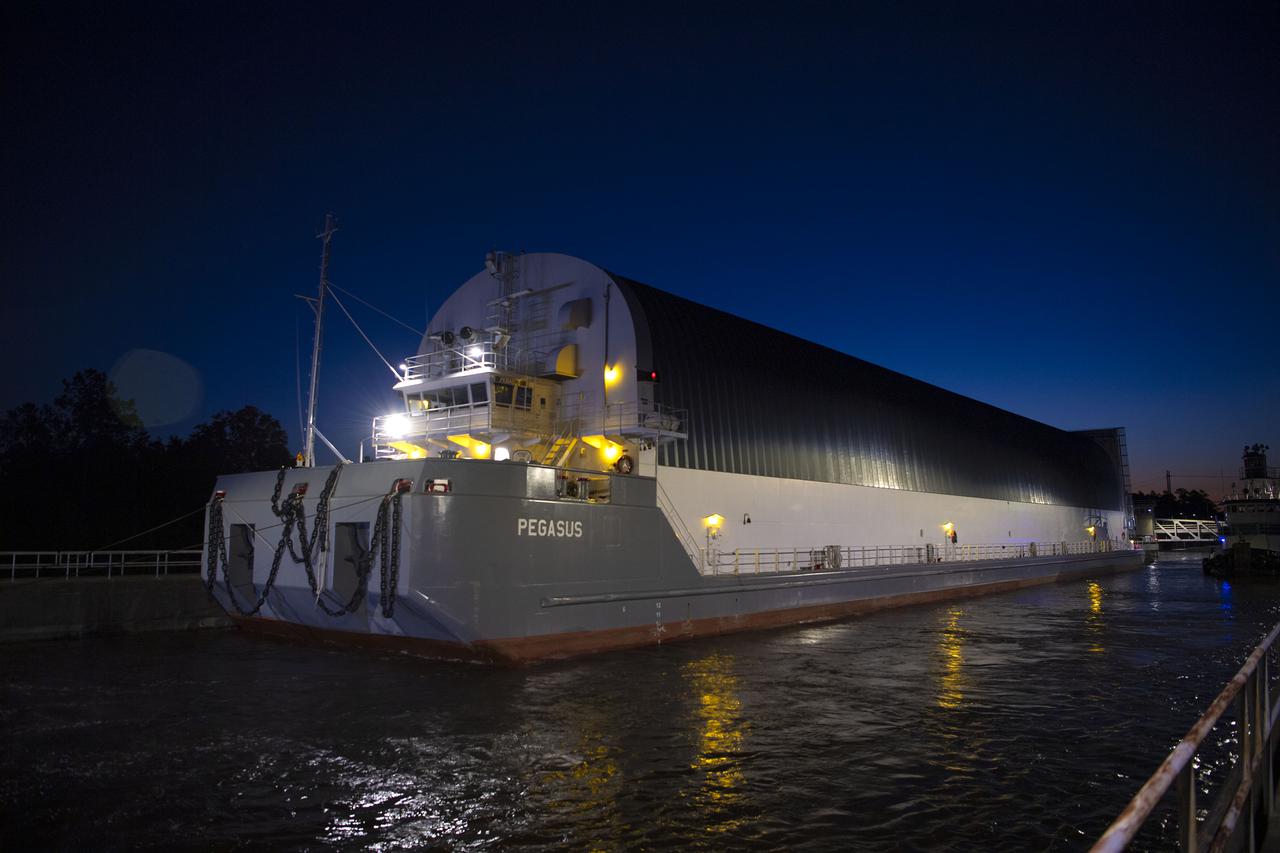
The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA

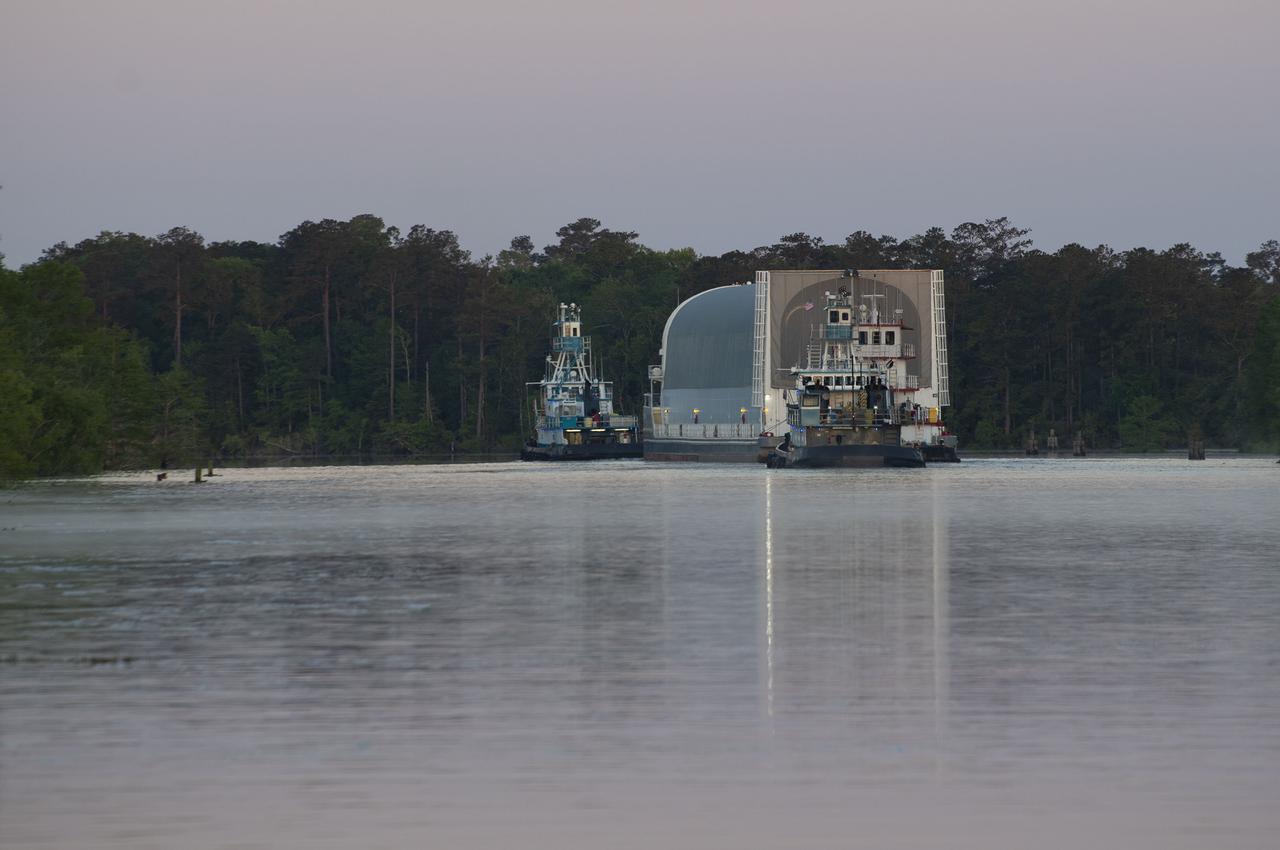
The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
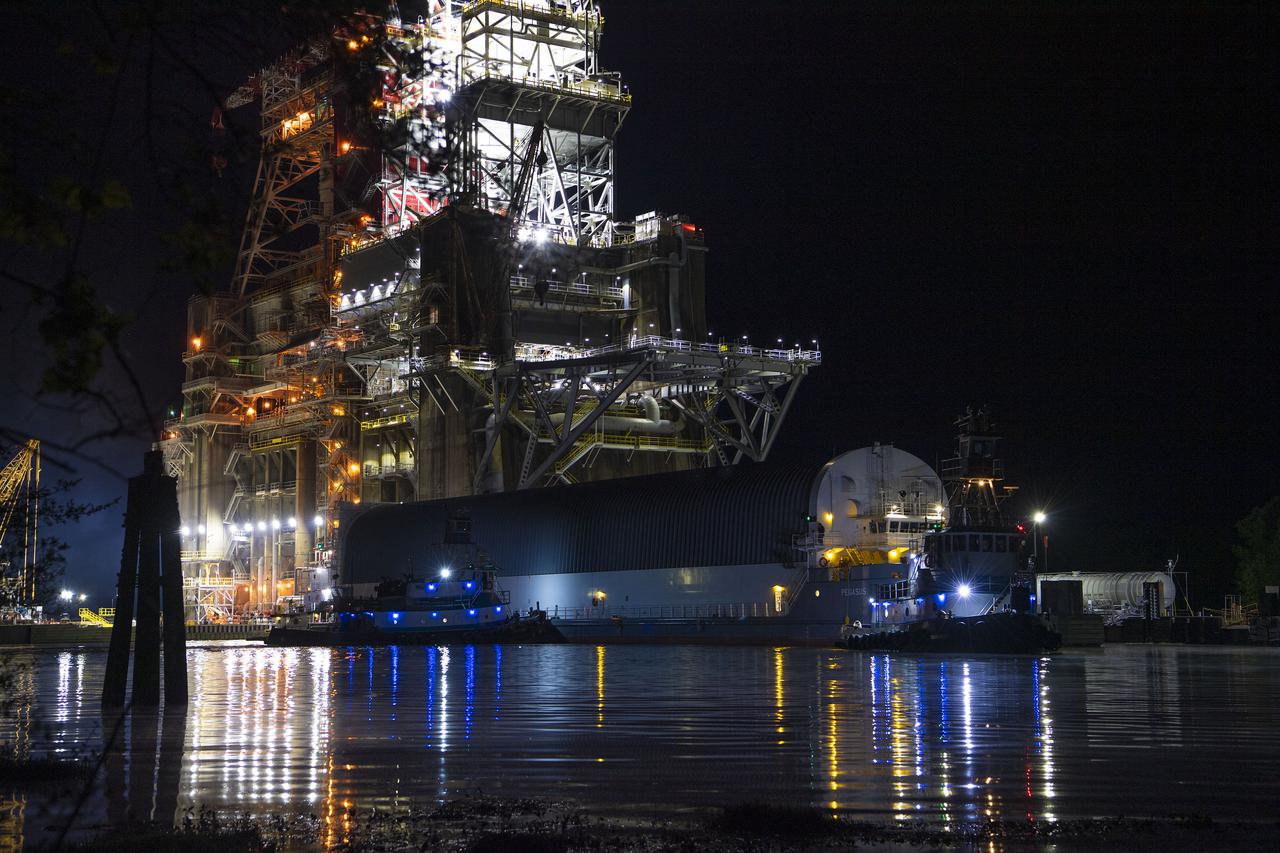

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
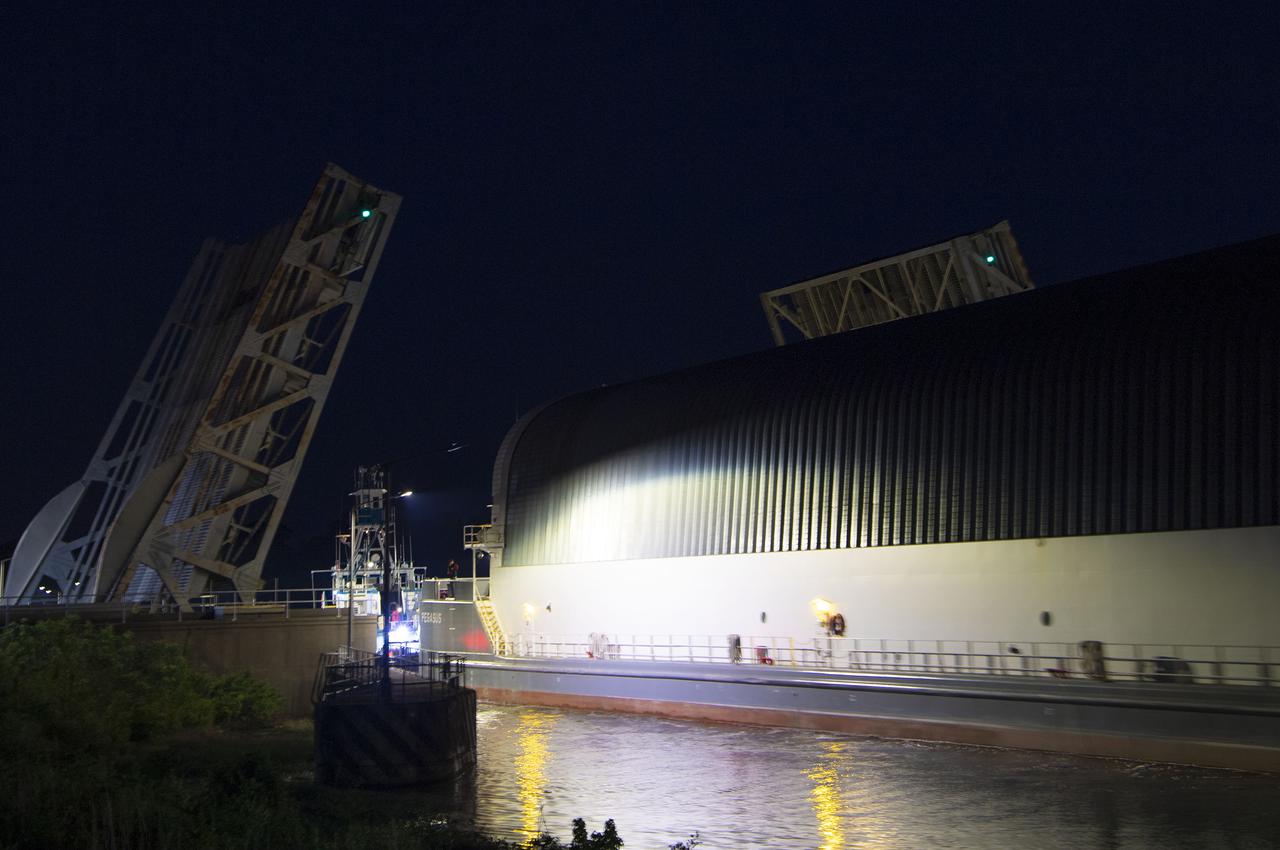

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
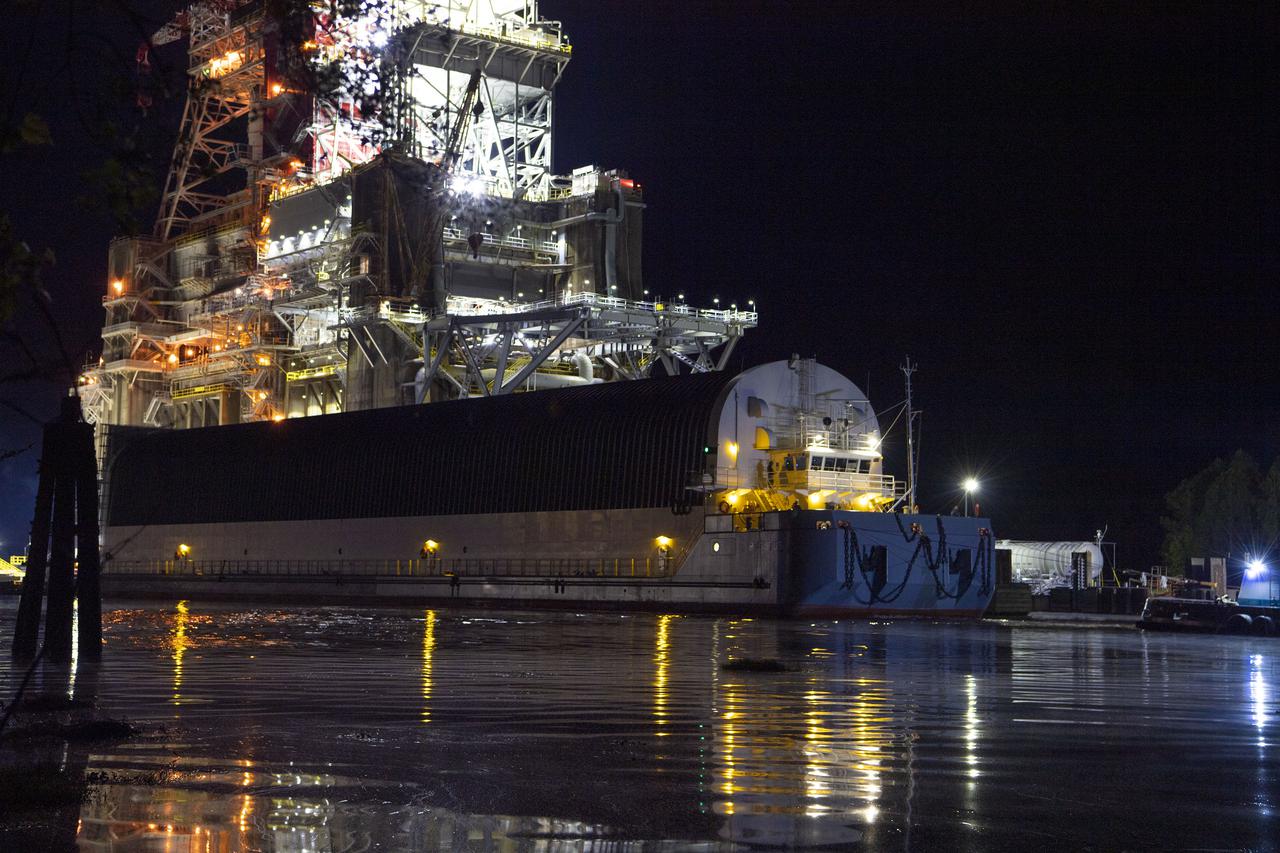

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
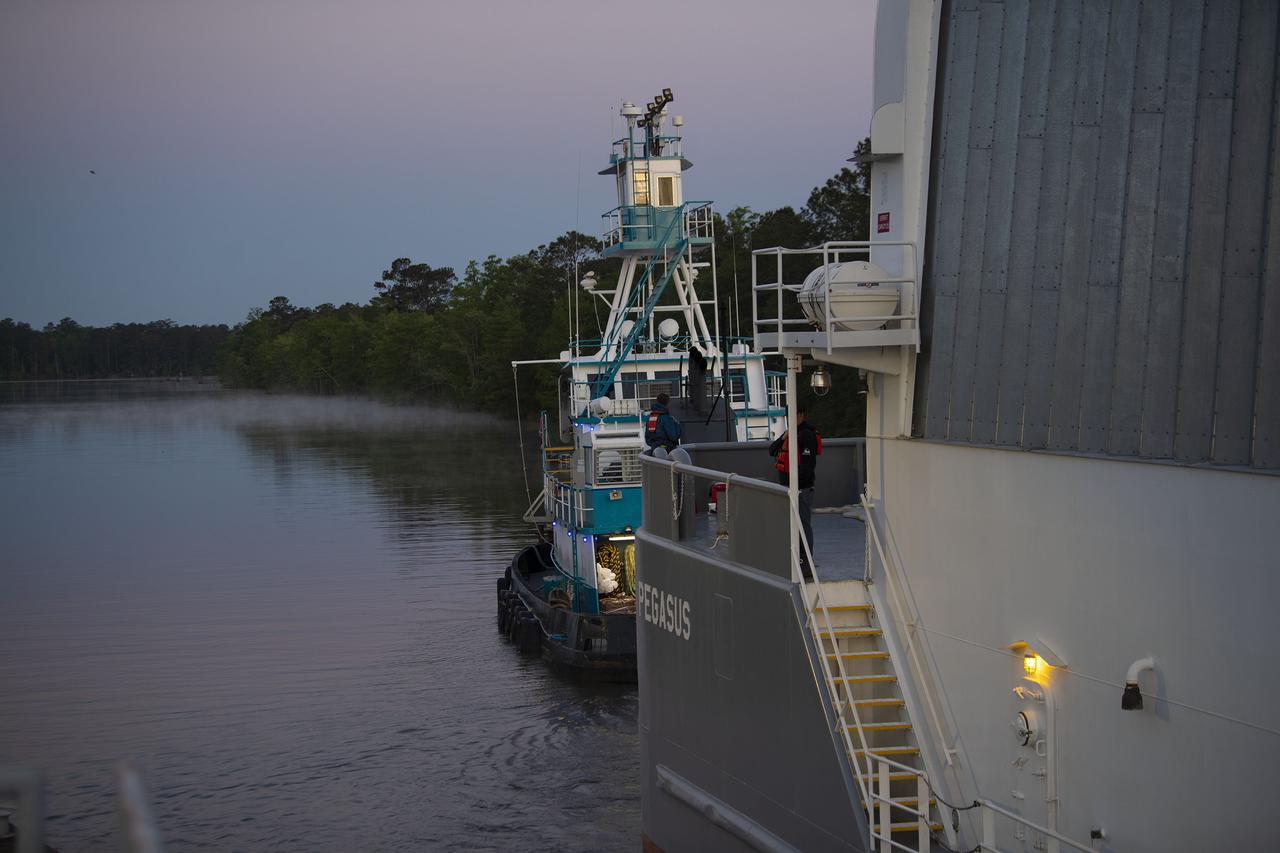

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
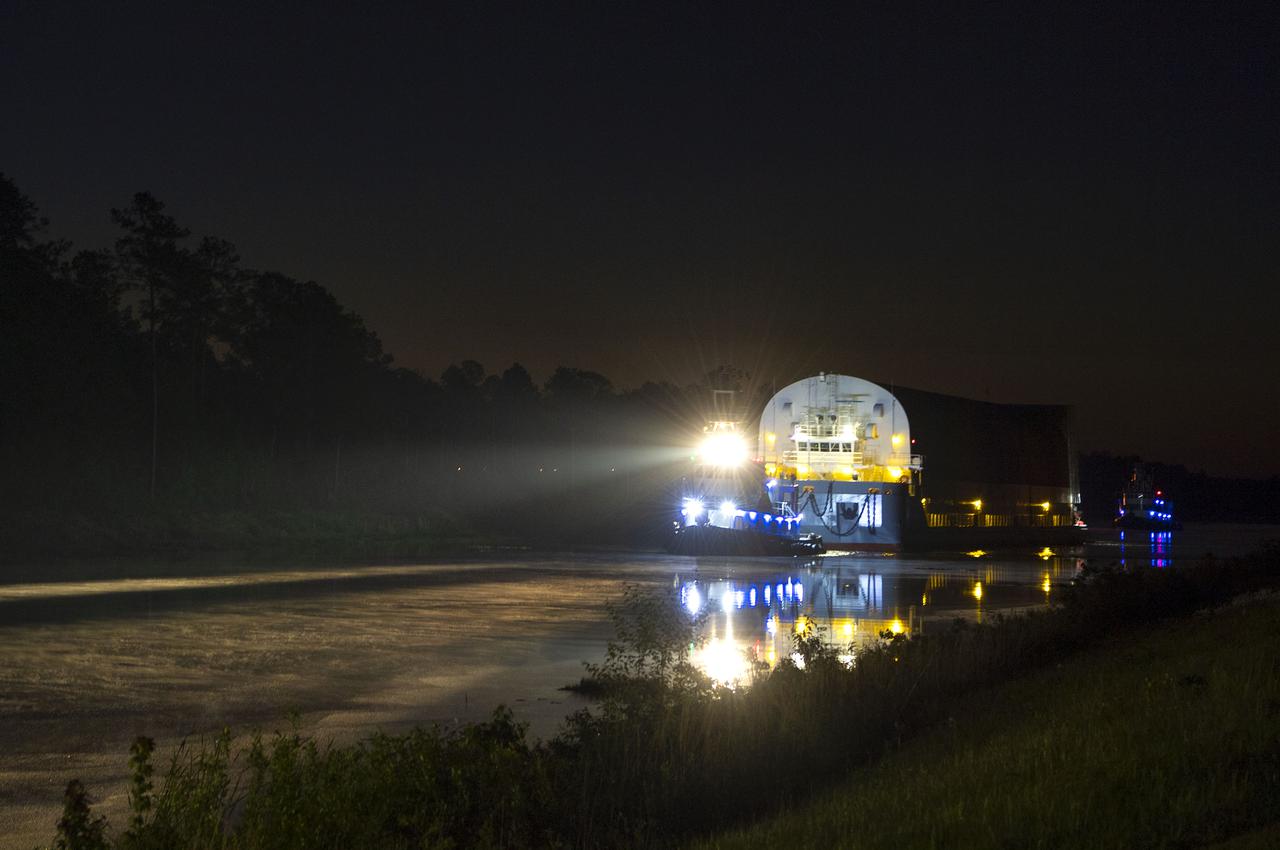

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
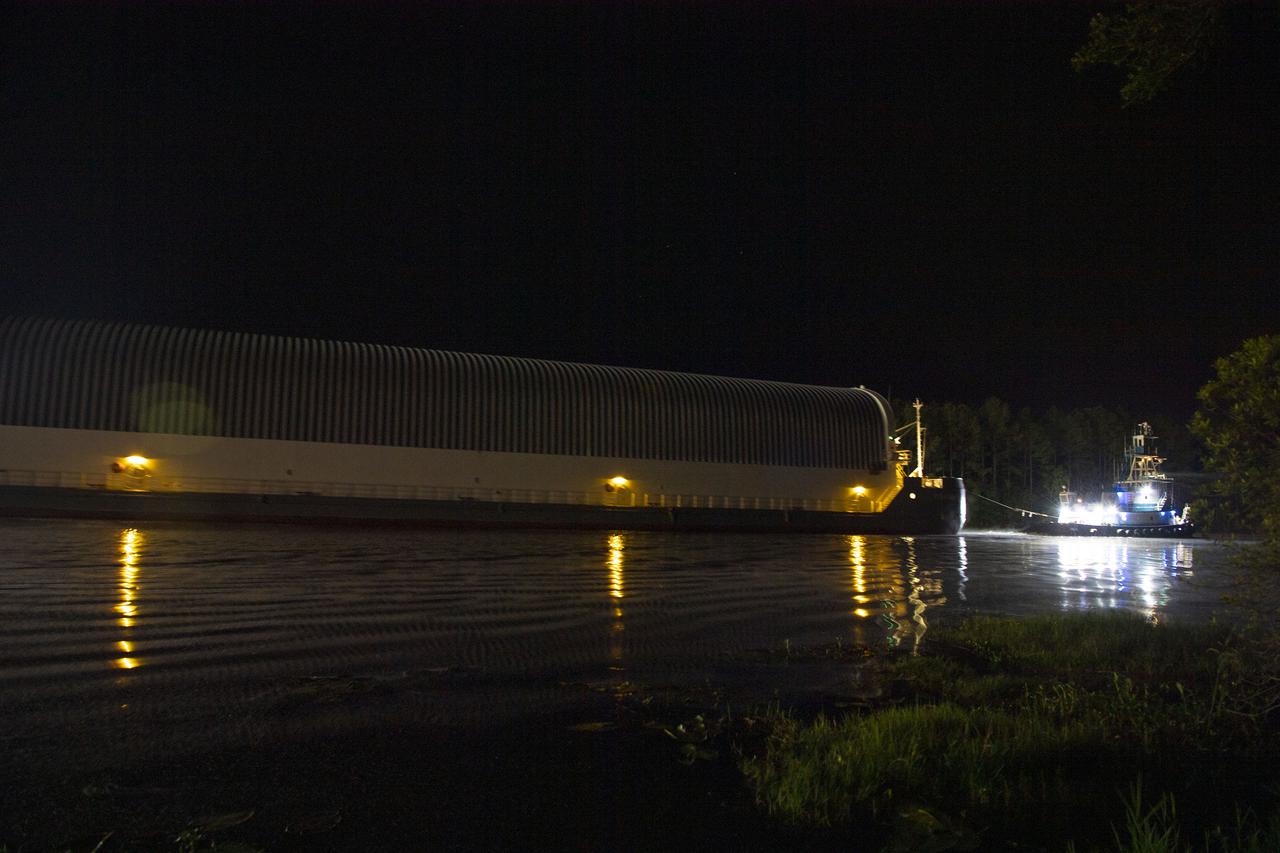

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
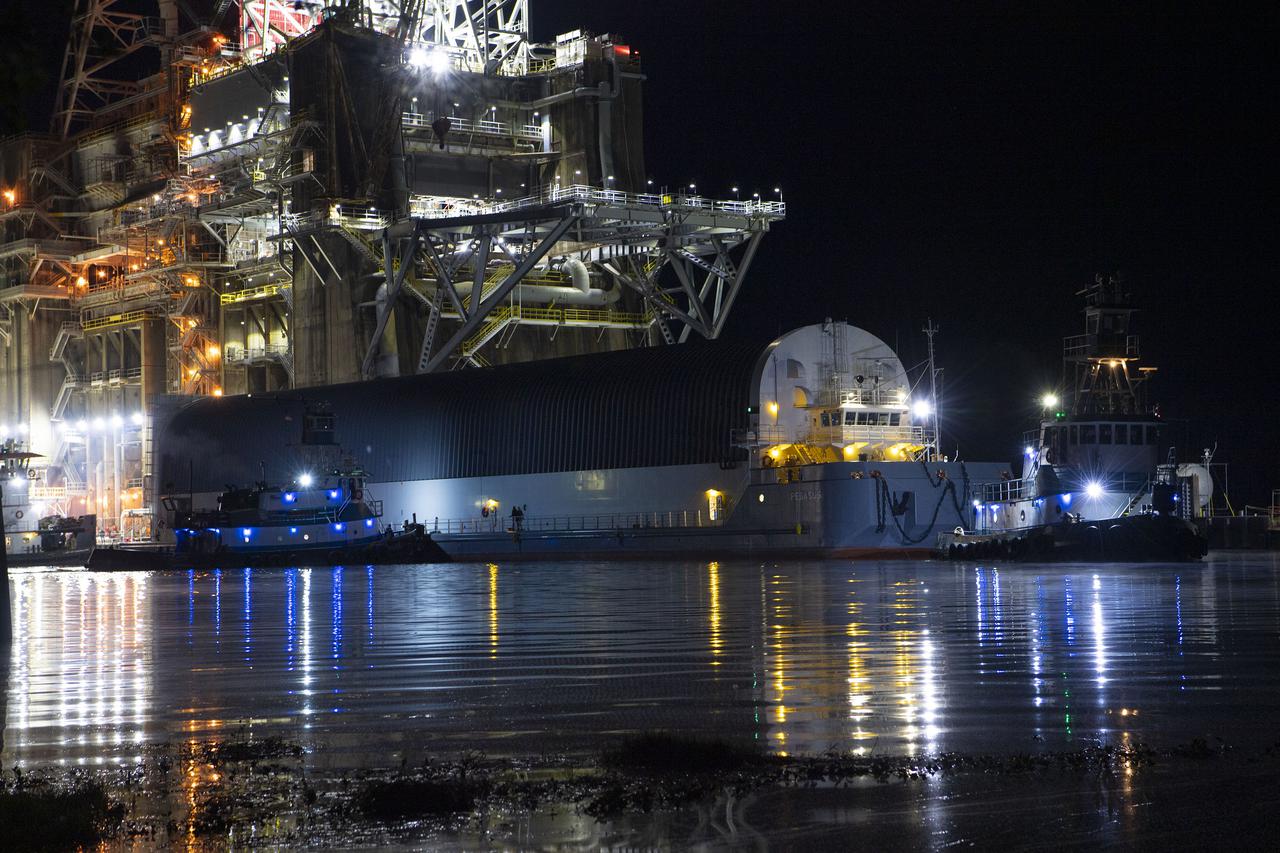

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
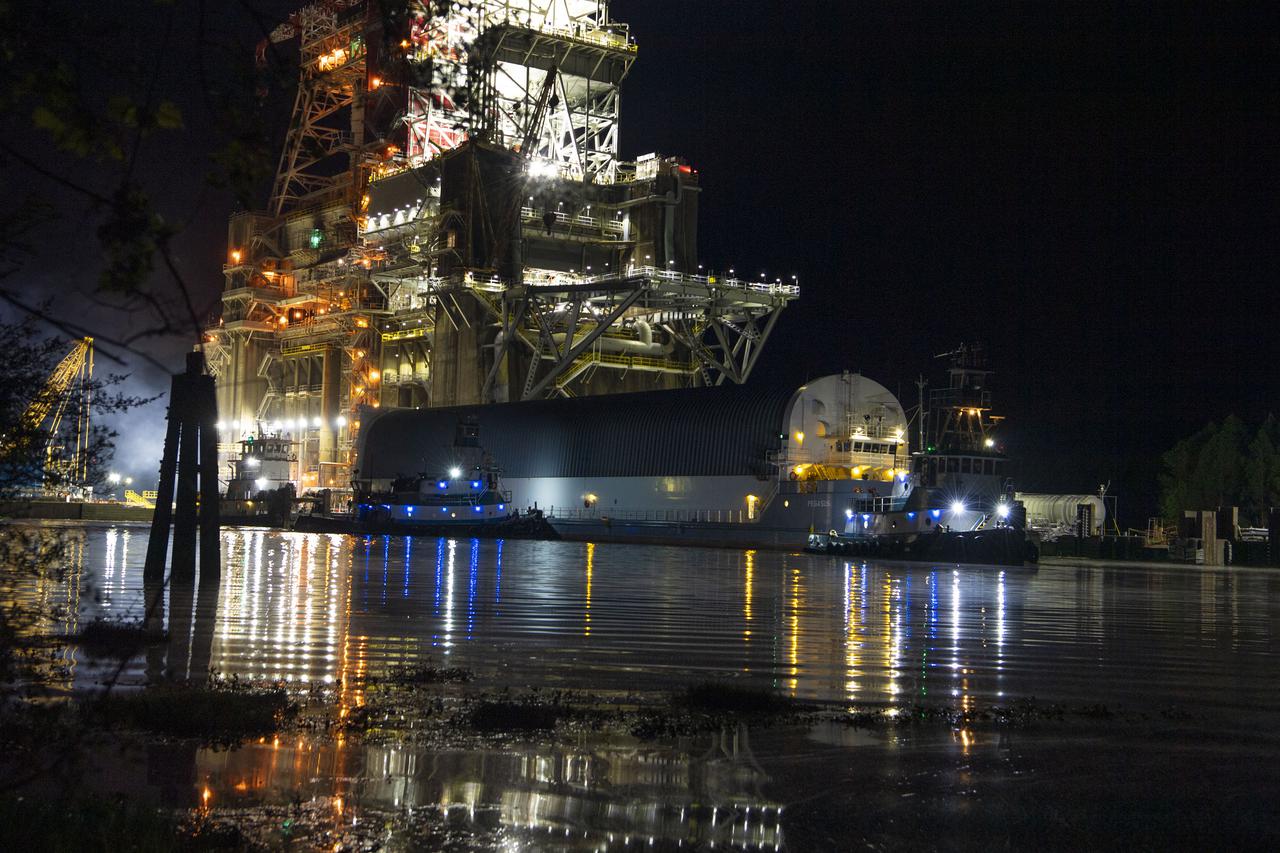

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
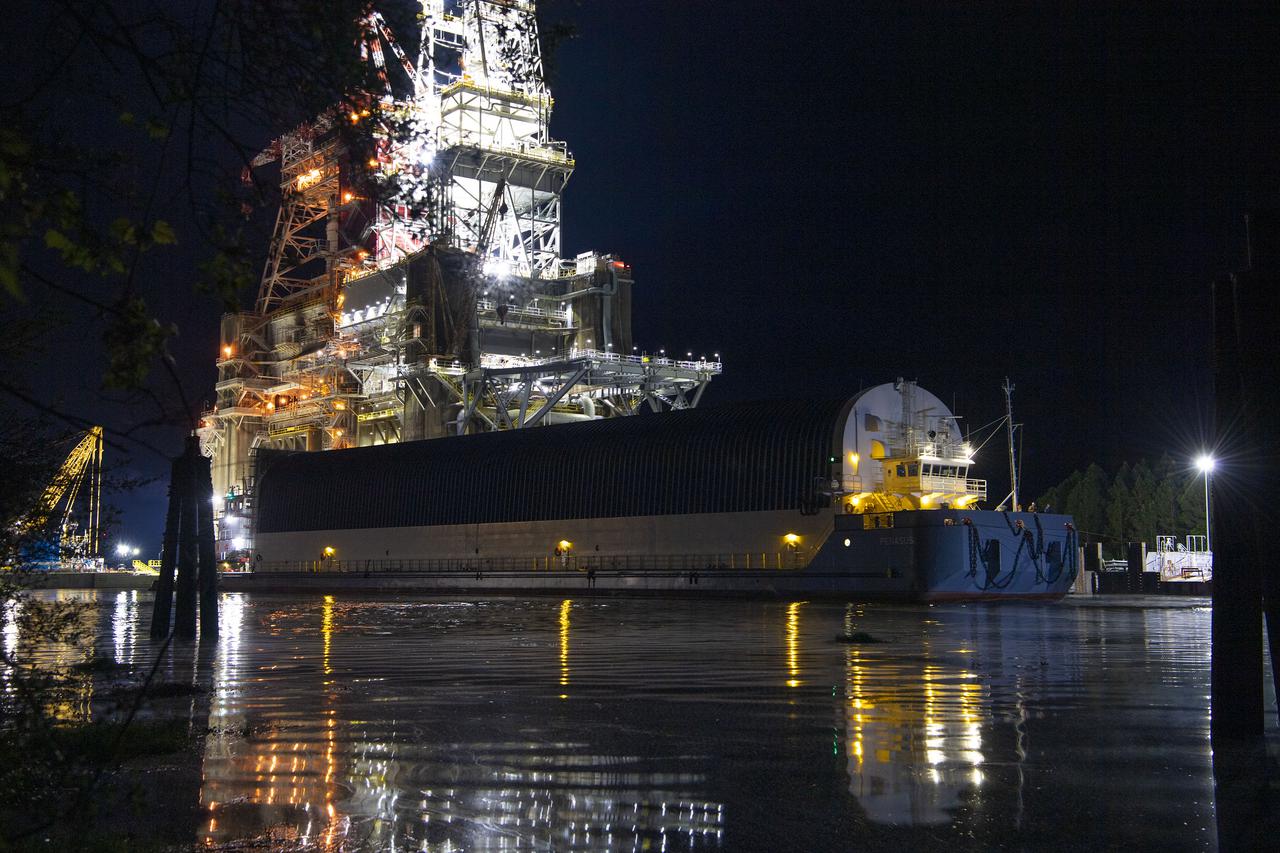

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
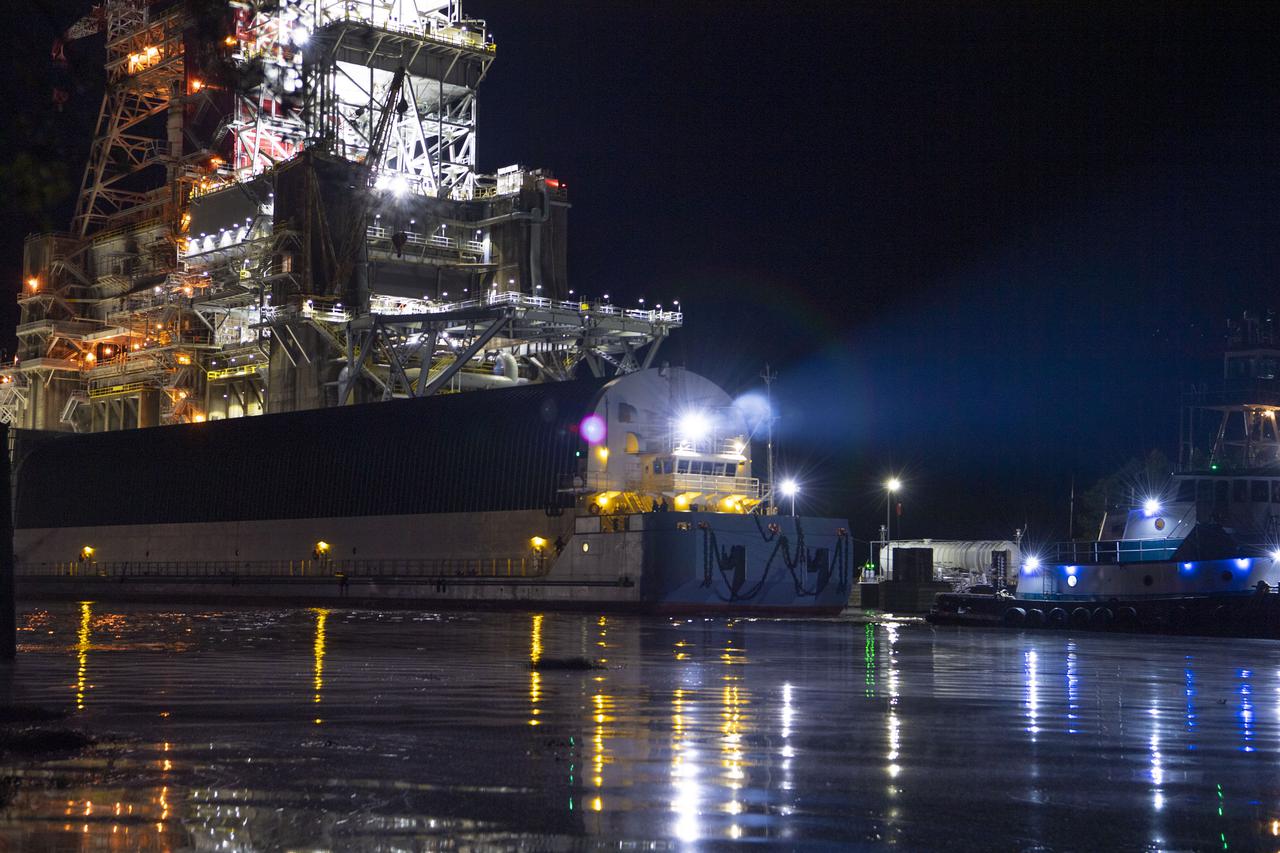

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
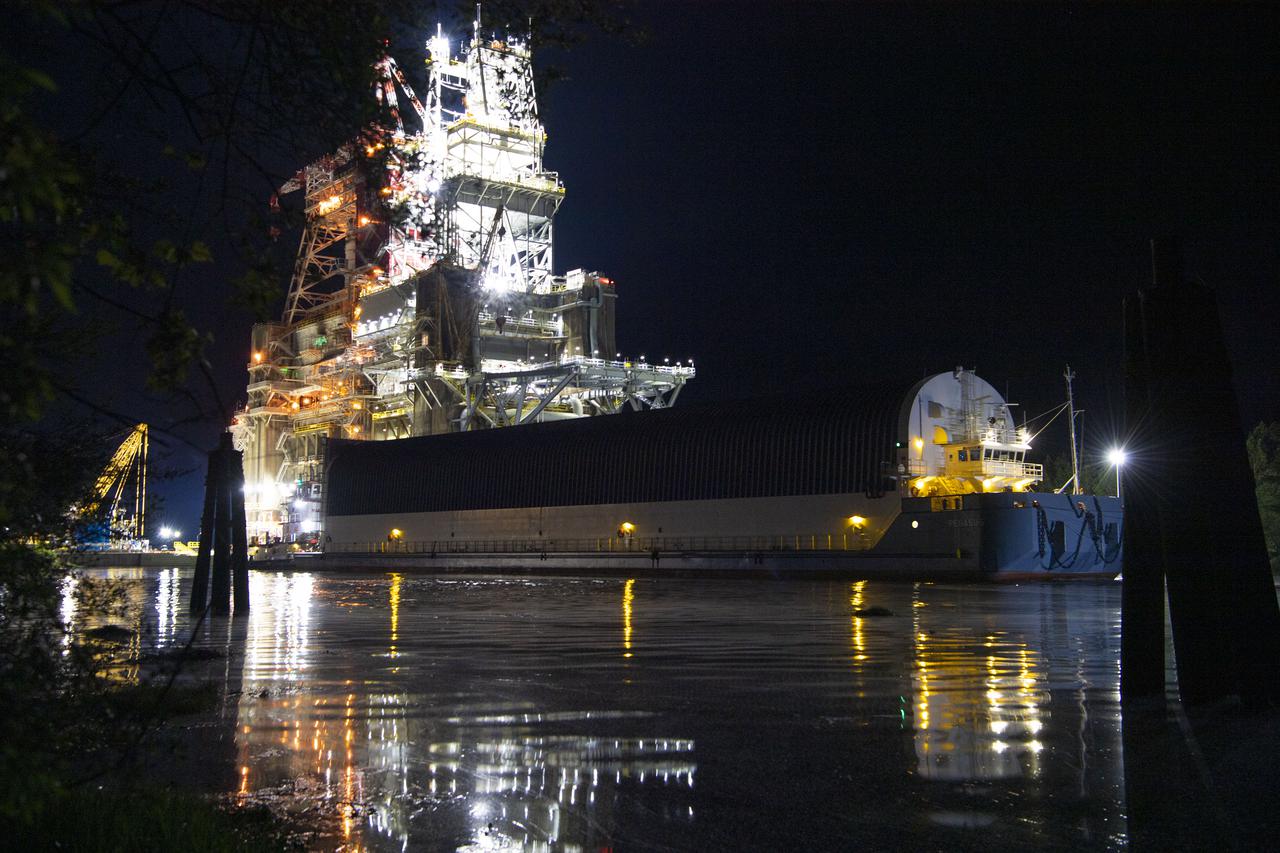

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
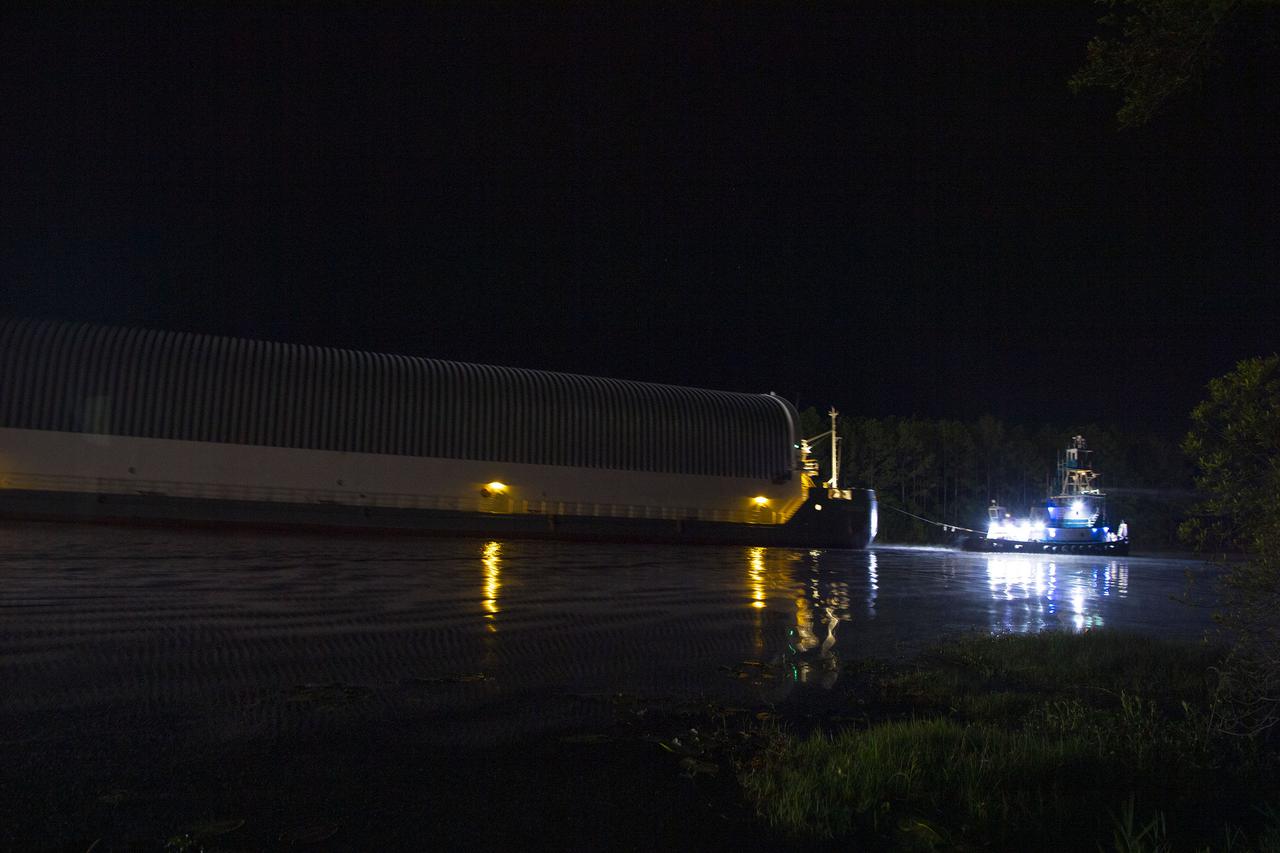

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
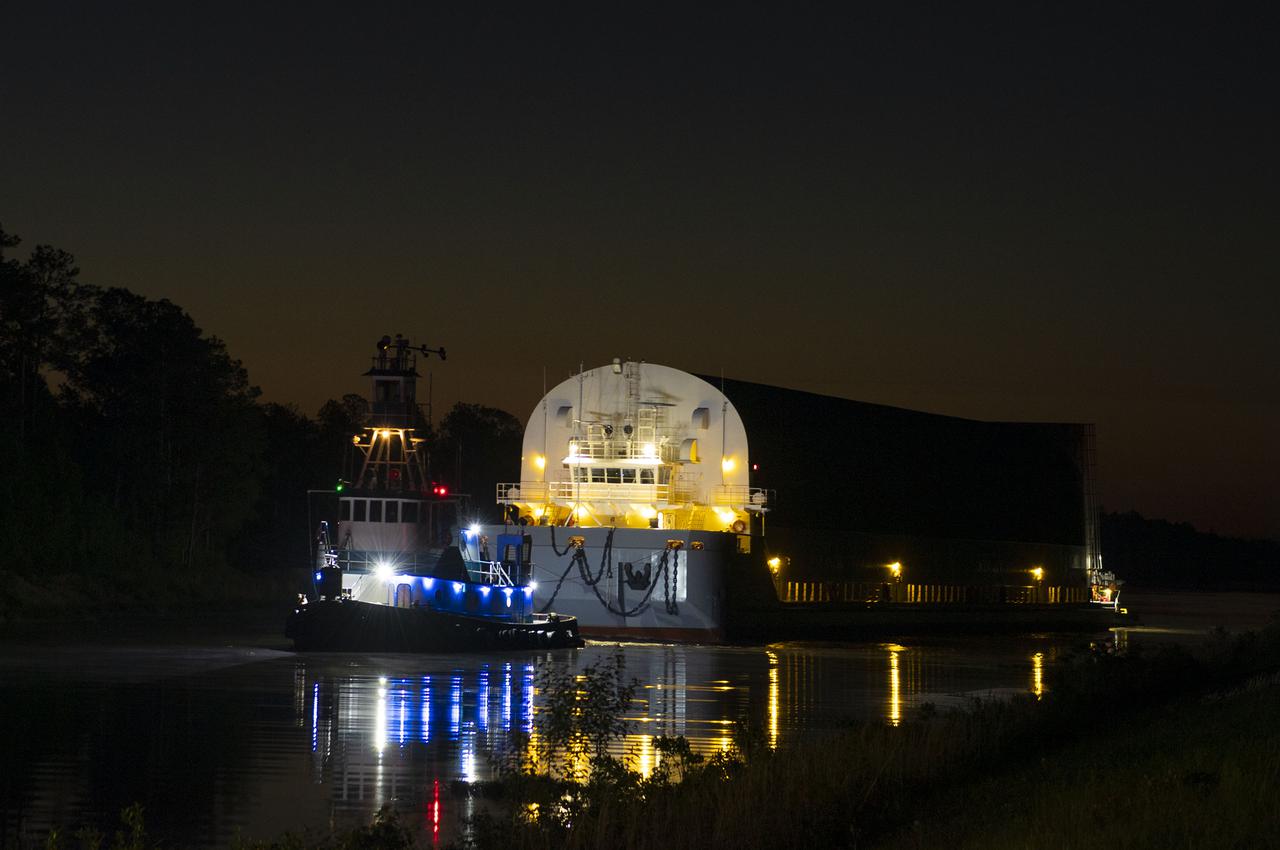

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
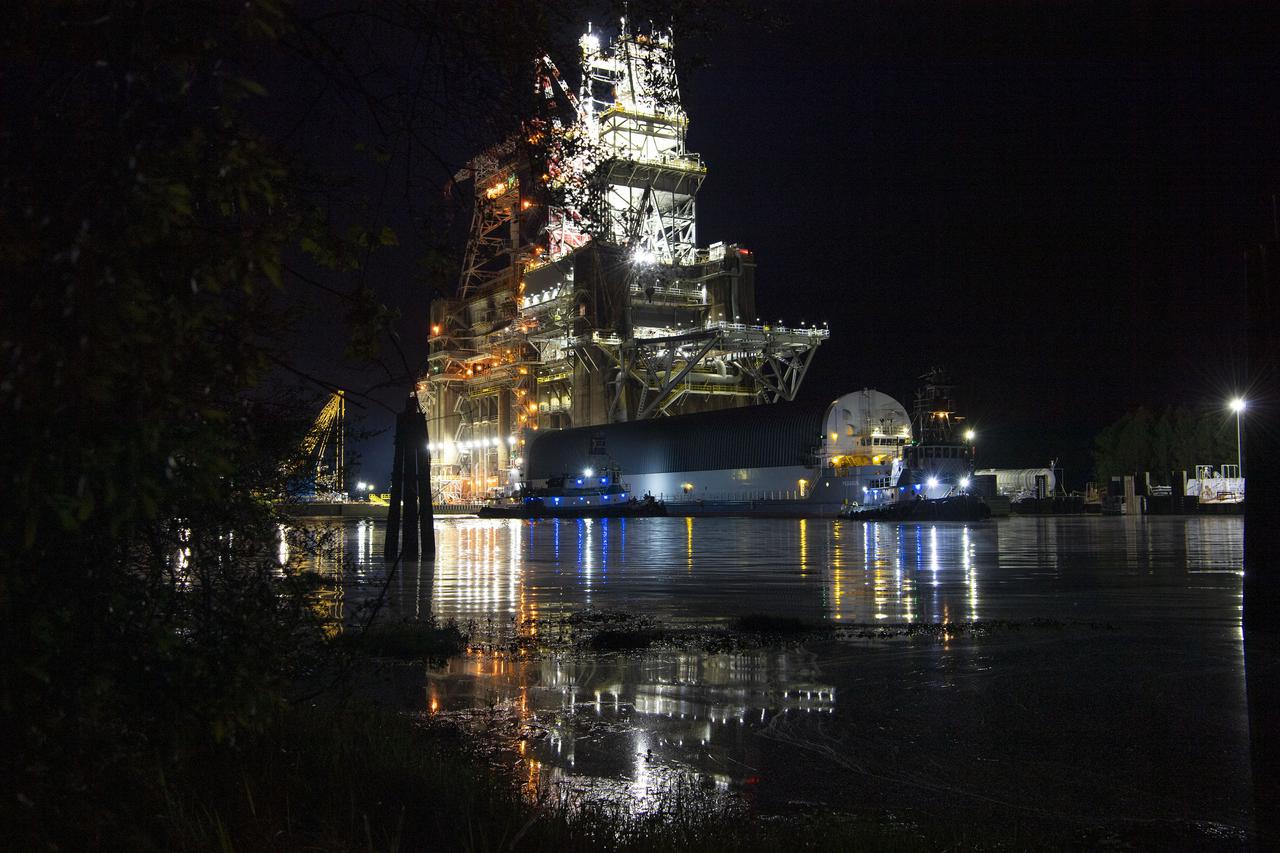

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
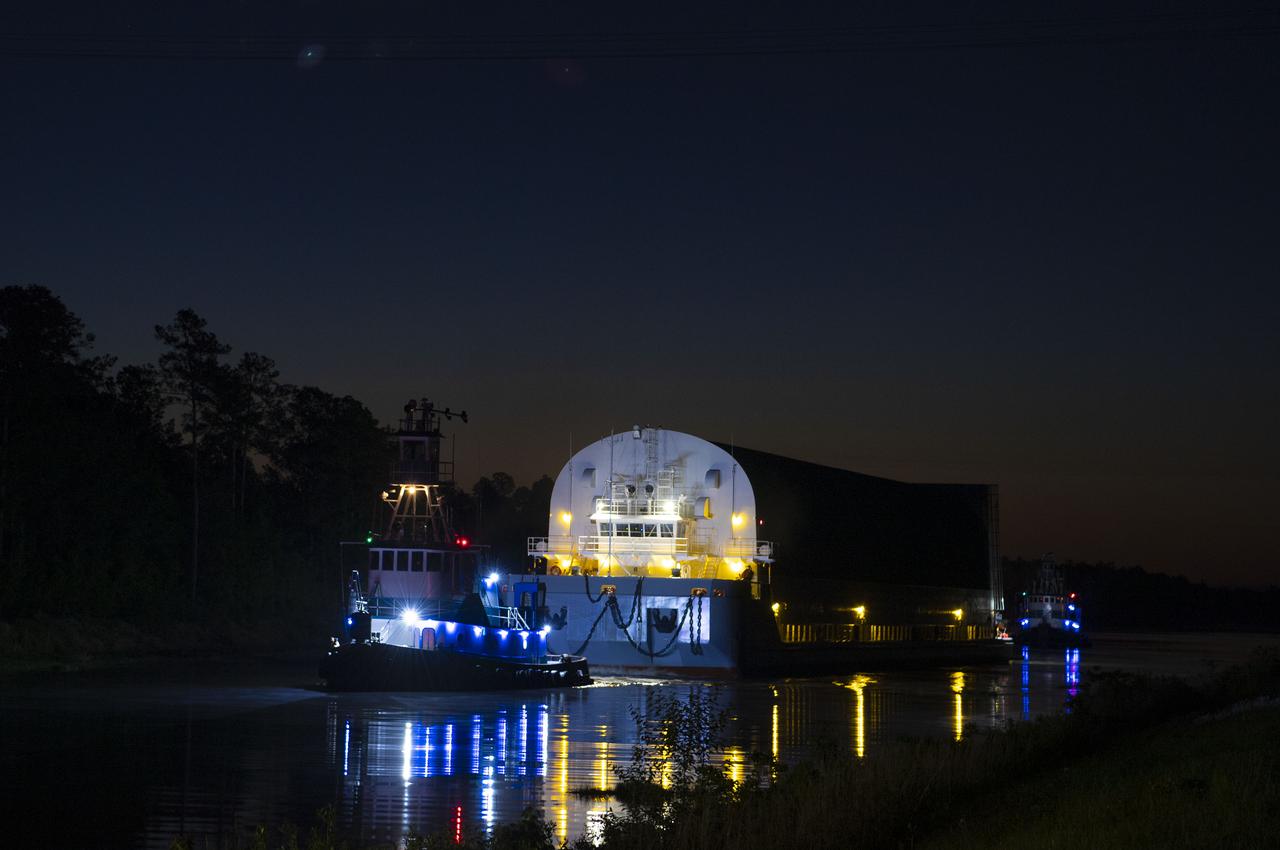

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
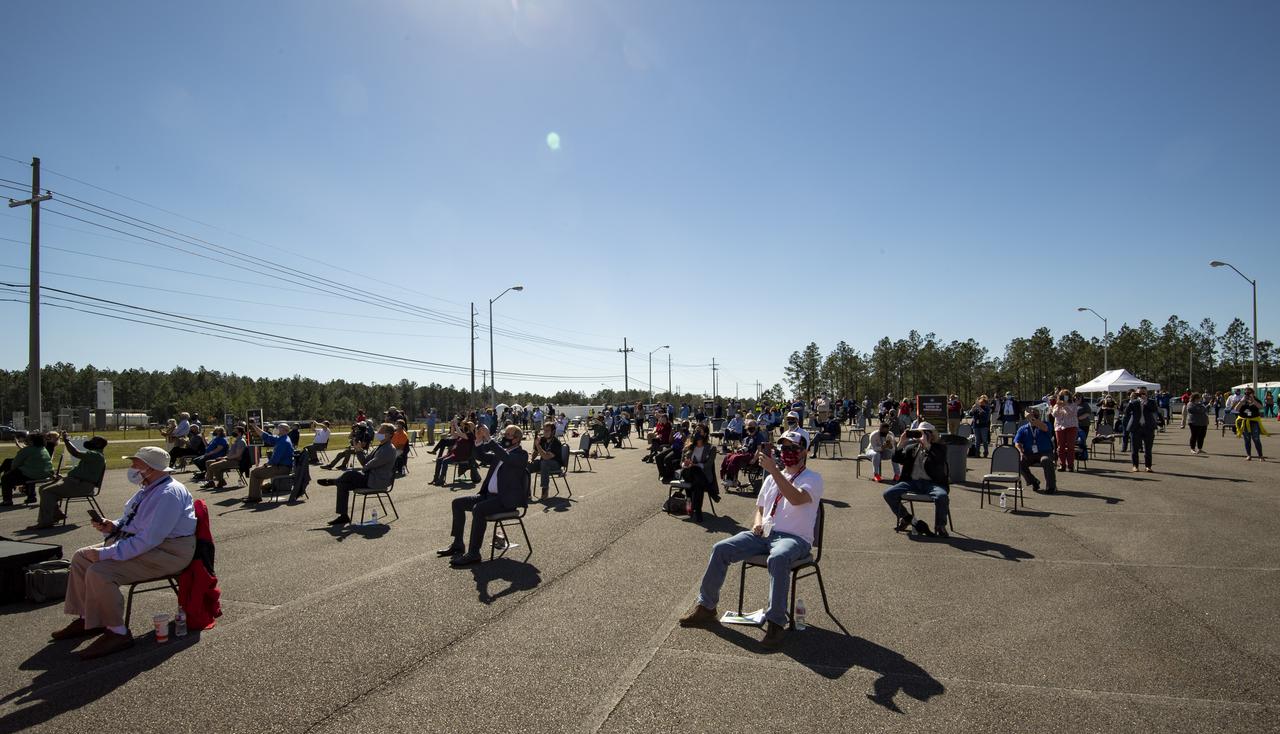

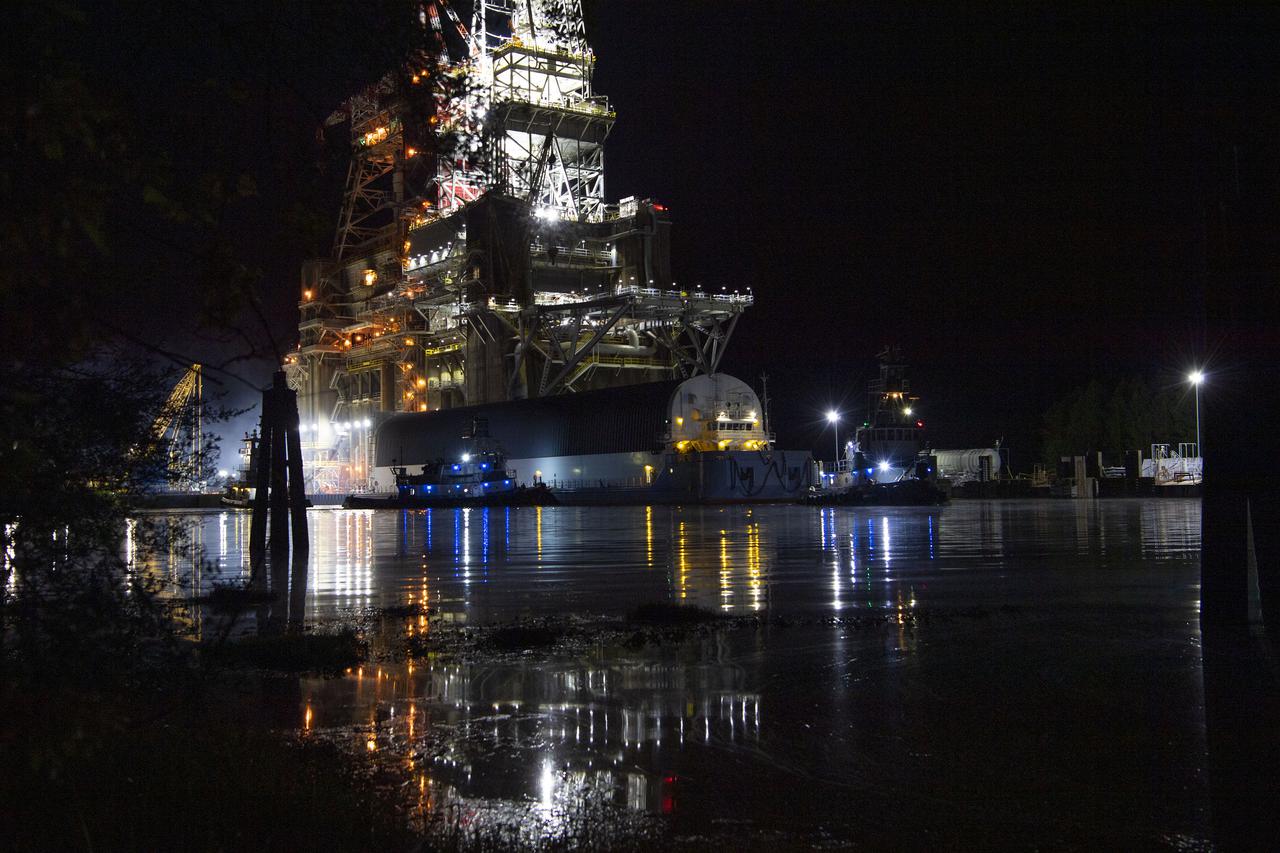
Invited guests watch as the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket undergoes a second hot fire test in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
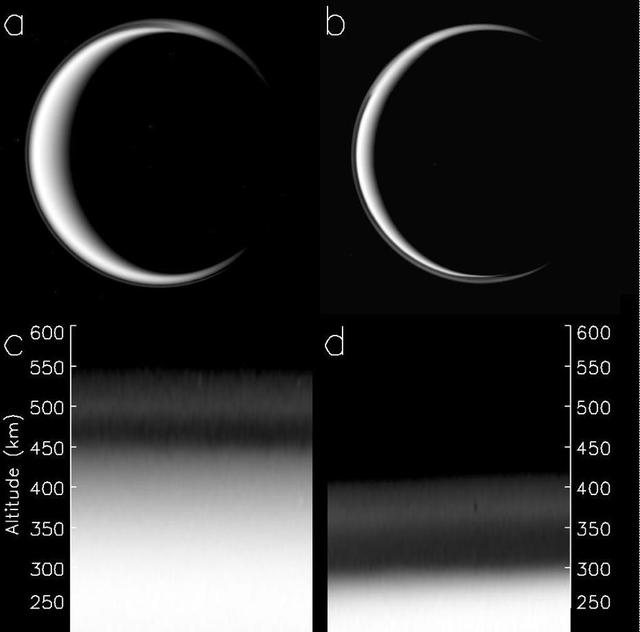
The change in Titan haze layer is illustrated in this figure, derived from data obtained by NASA Cassini spacecraft. The picture of Titan in panel a was taken on May 3, 2006, panel b was taken on April 2, 2010.
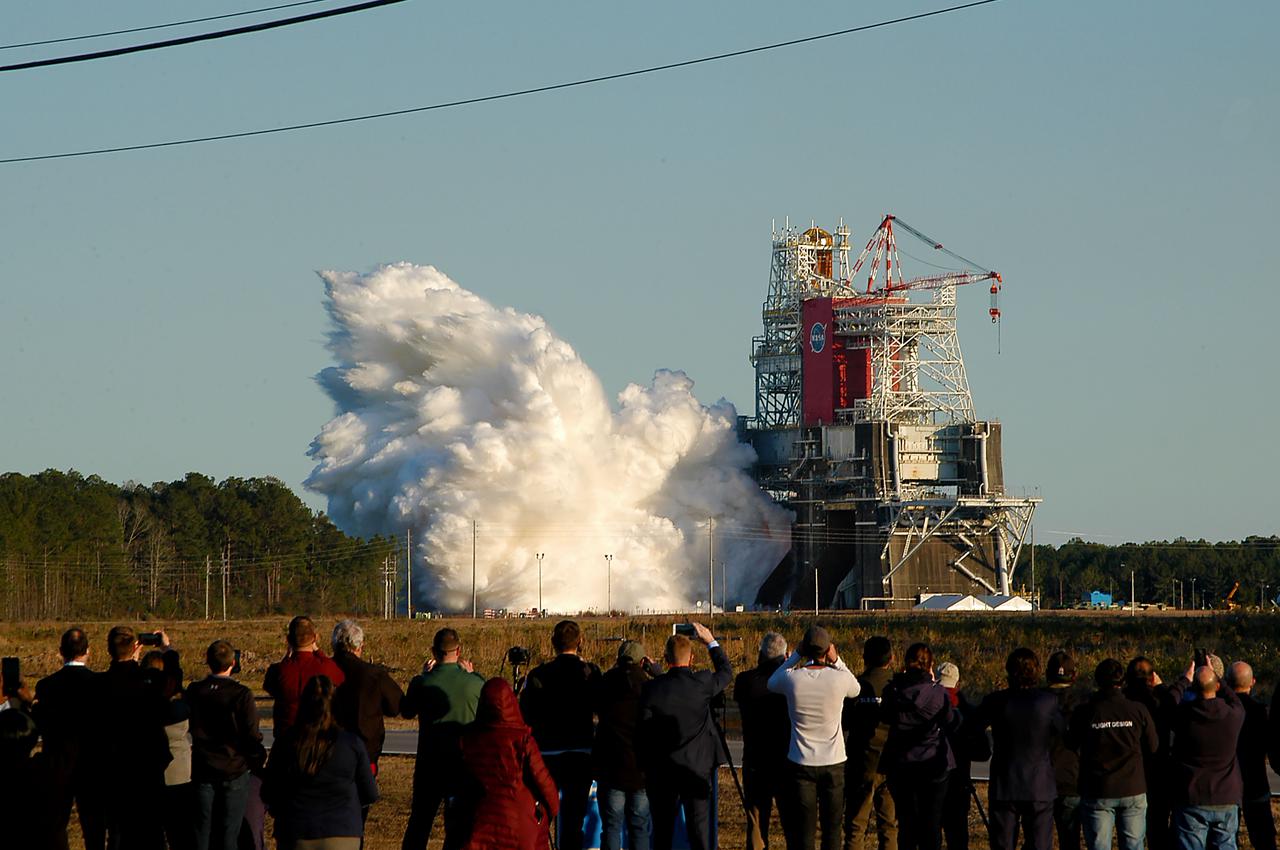

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand ahead of a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Friday, Jan. 15, 2021 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
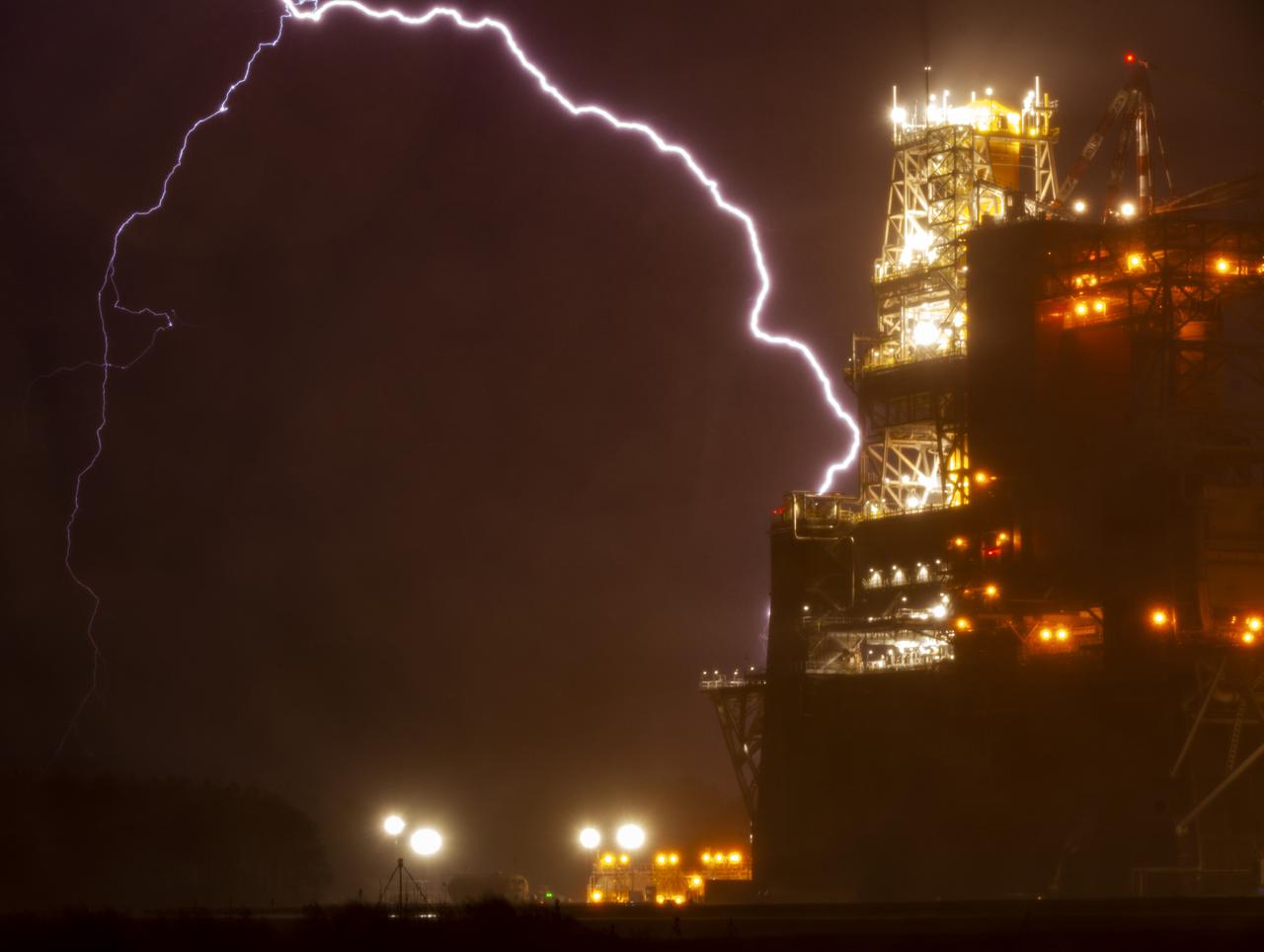

A bolt of lightning is seen near the B-2 Test Stand the night before a second hot fire test of the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket, Wednesday, March 17, 2021 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
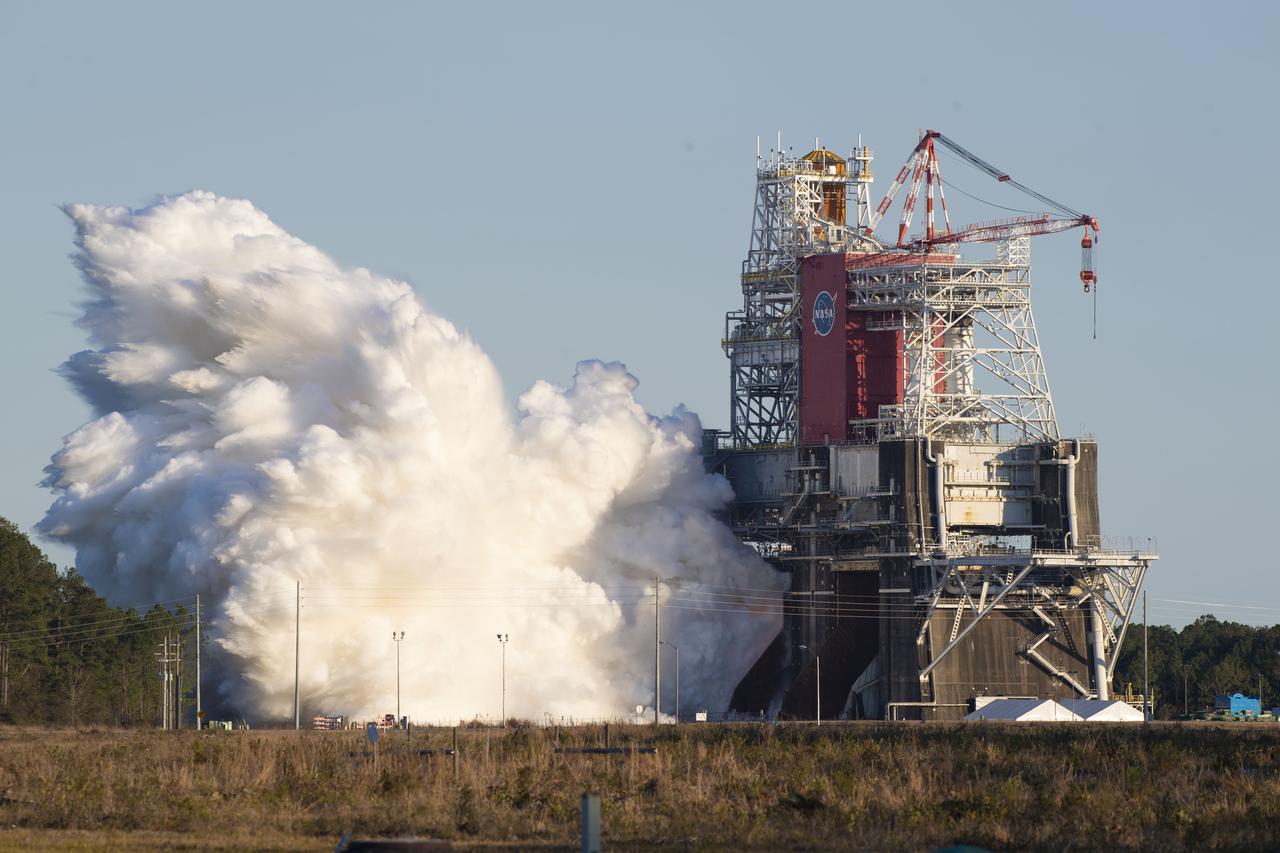

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
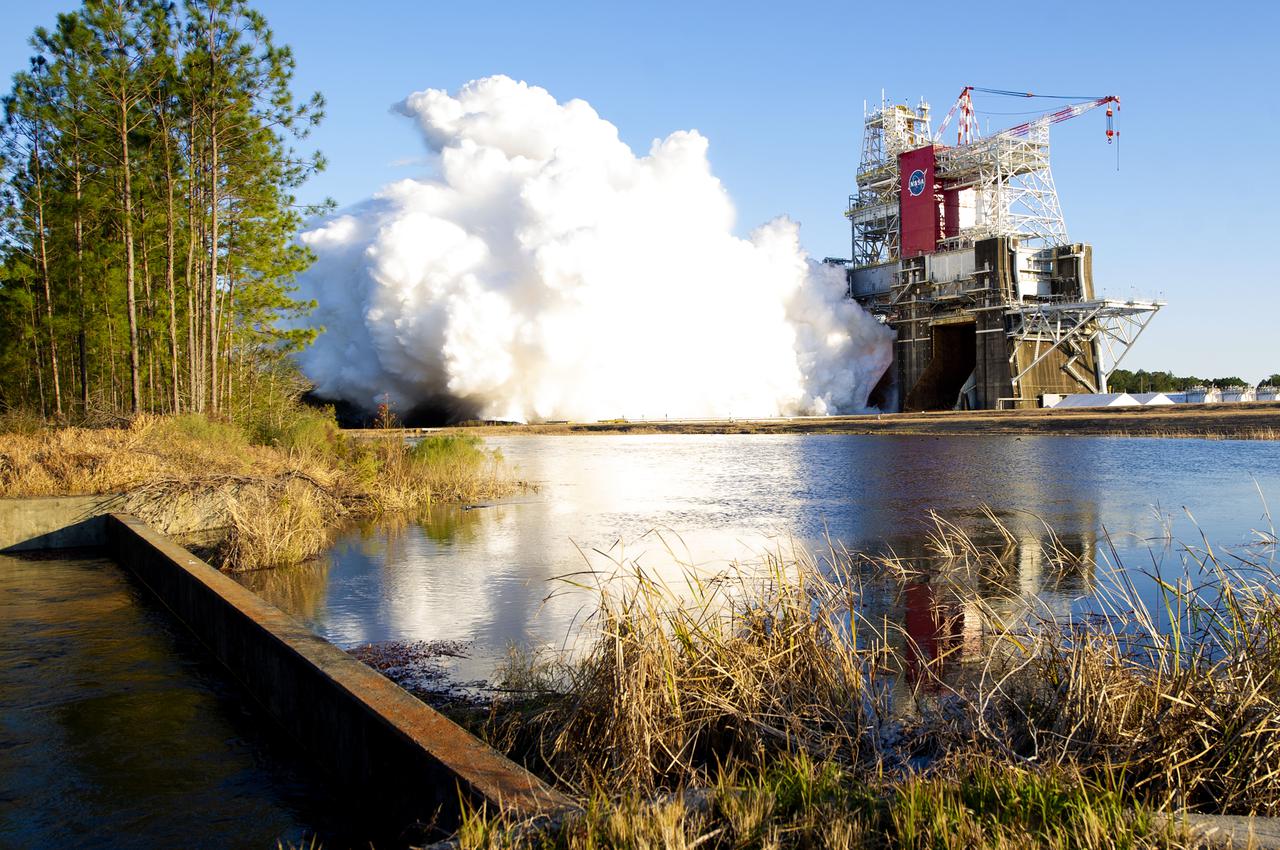

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
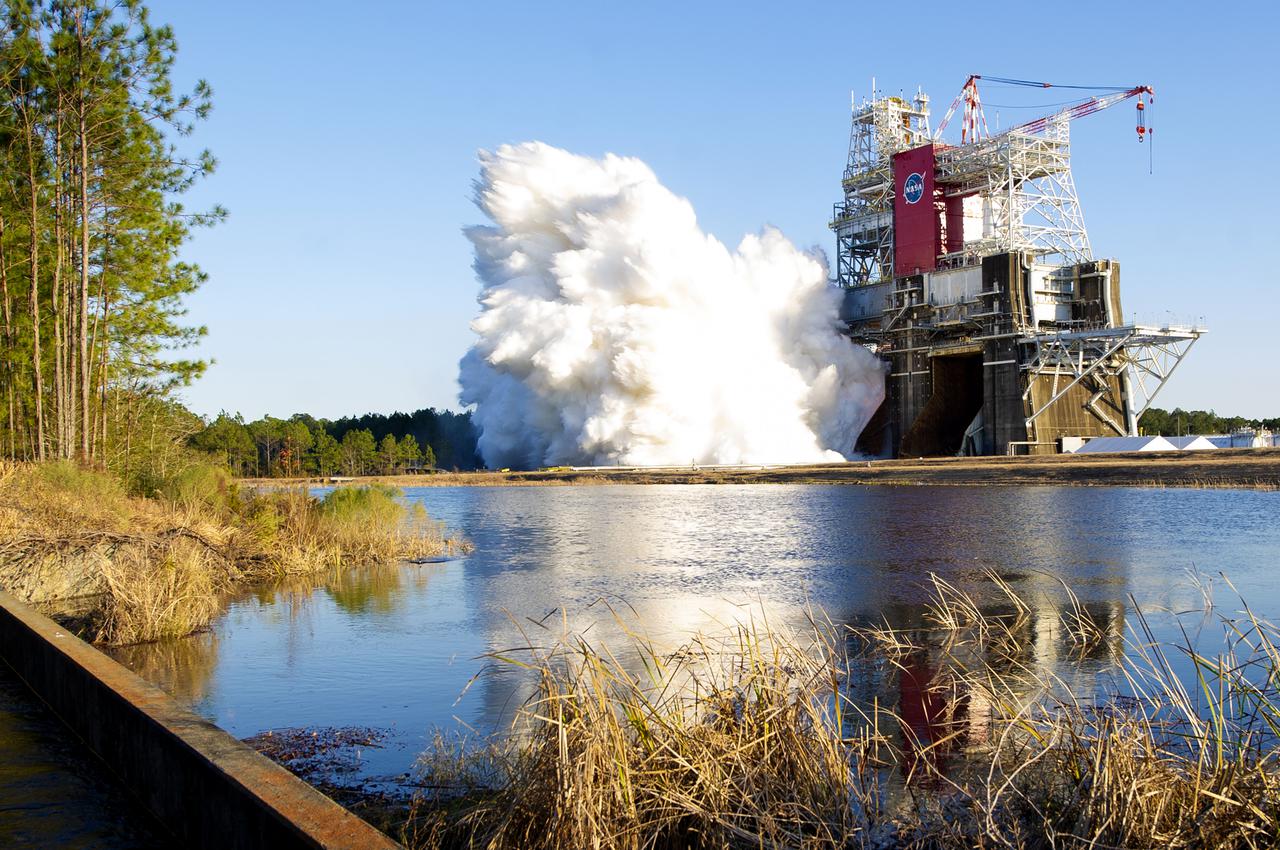

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
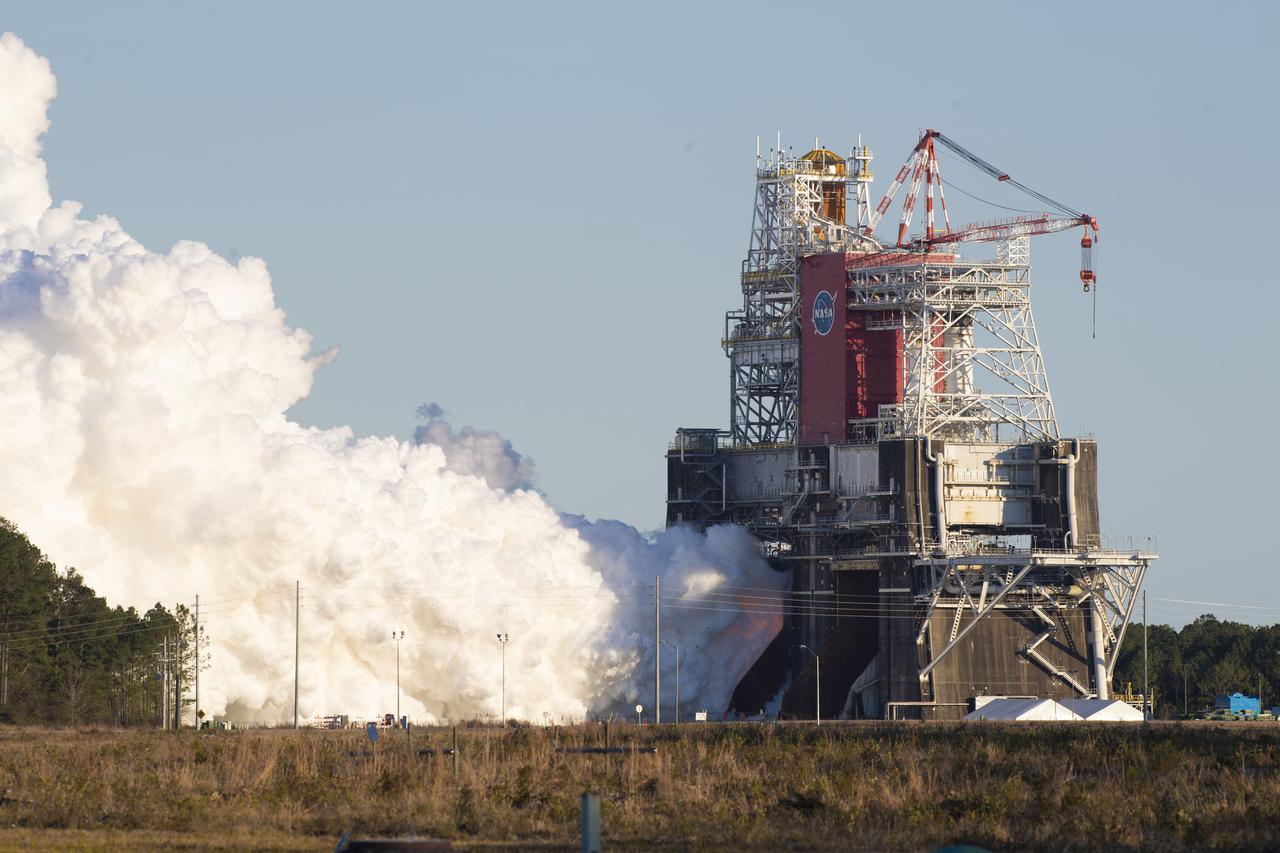

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
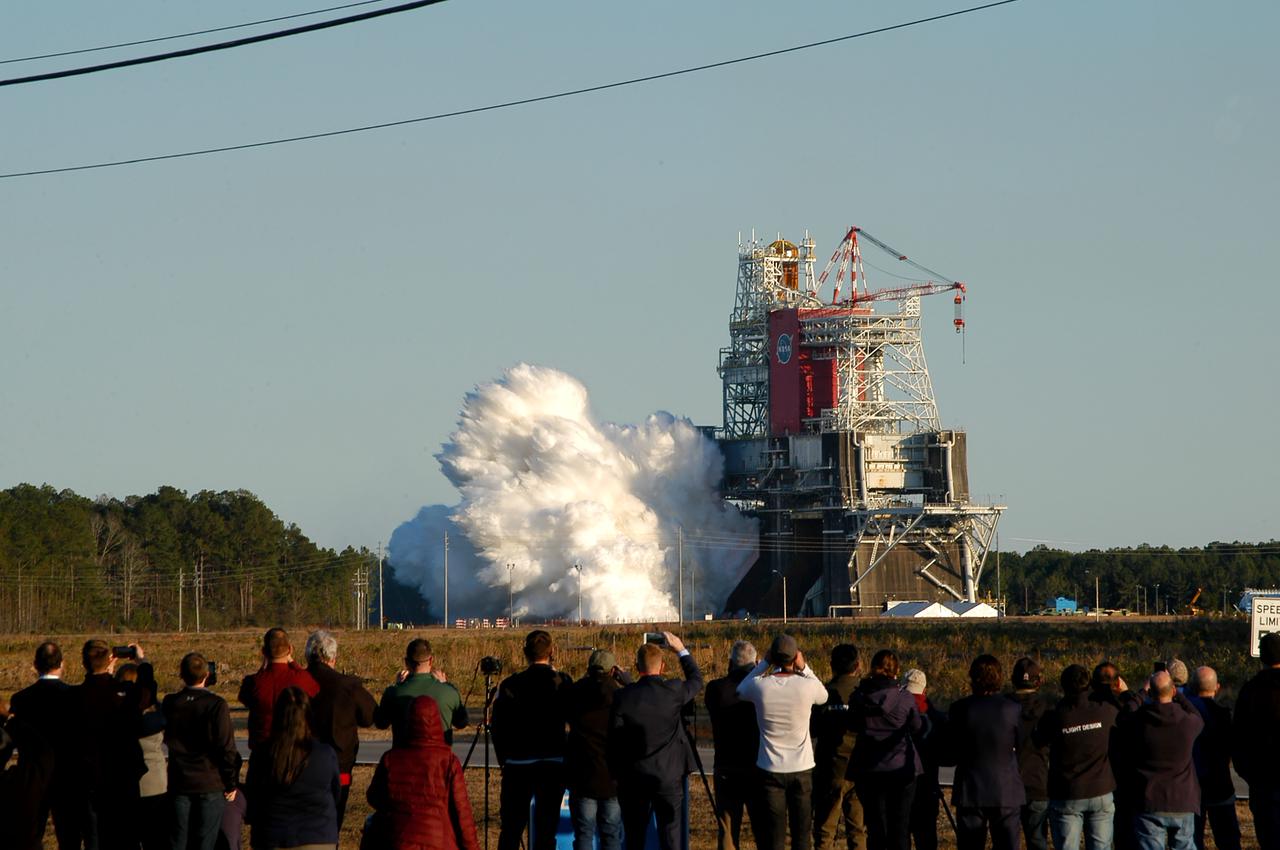

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
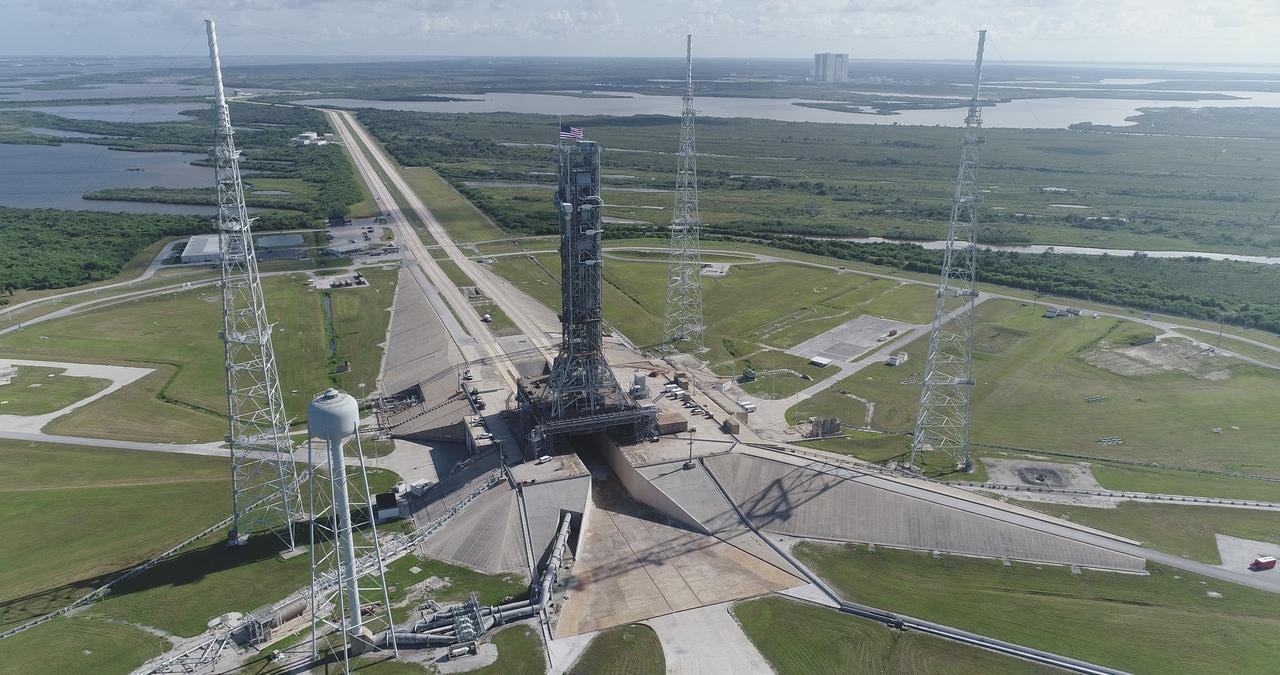

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 is at the top of Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars. Photo credit: NASA/Jamie Peer <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b>

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 is at the top of Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars. Photo credit: NASA/Jamie Peer <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b>
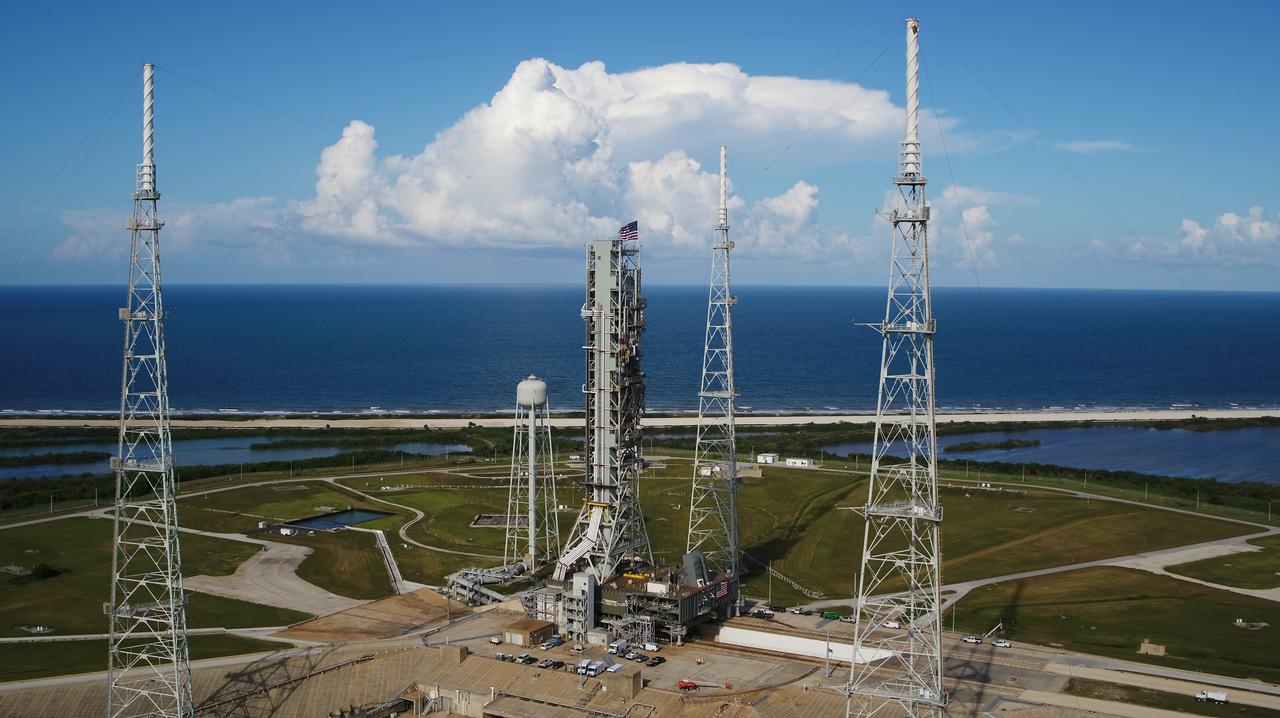

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 is at the top of Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars. Photo credit: NASA/Jamie Peer <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b>
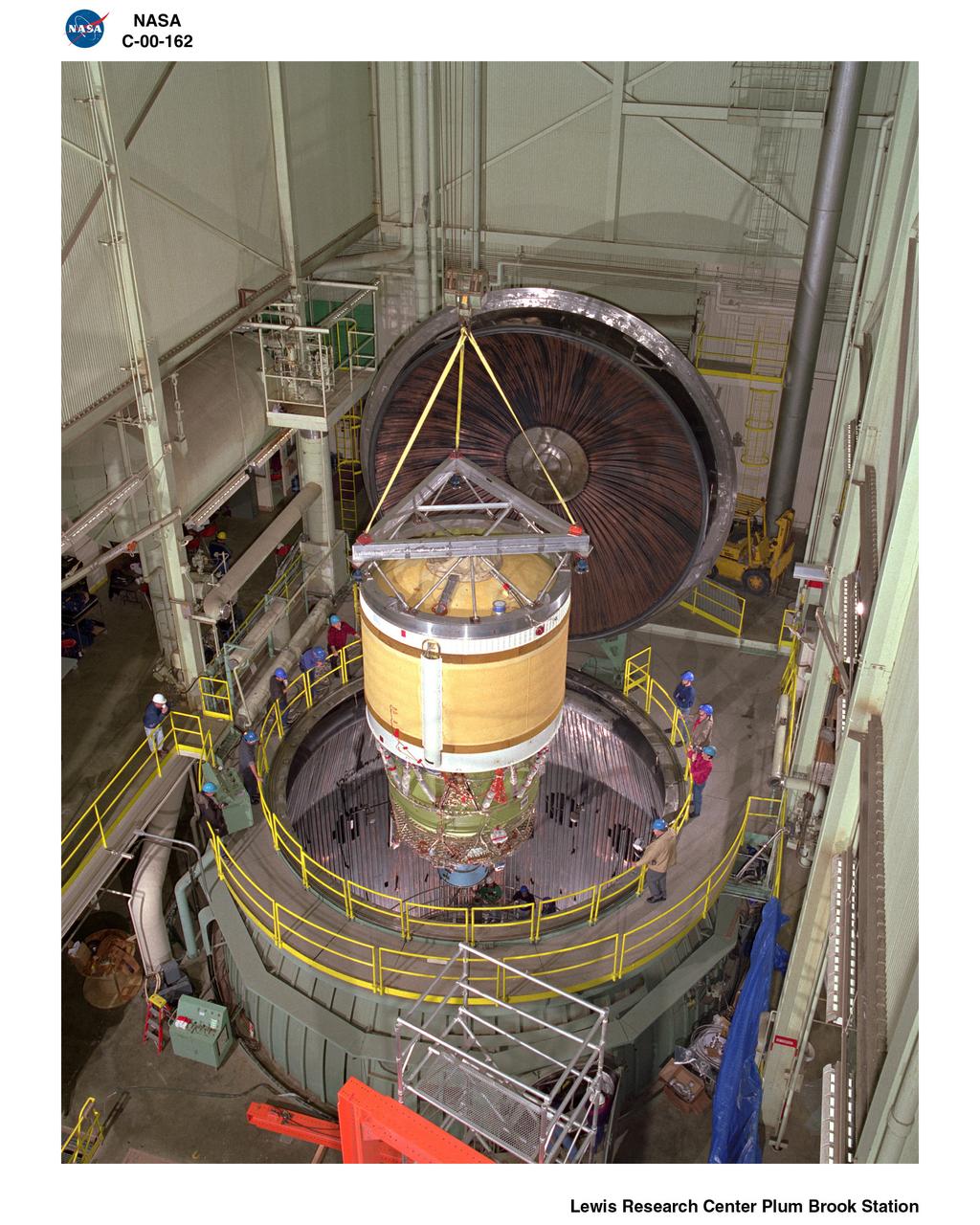

B-2 FACILITY WITH DELTA 111 2ND STAGE - B-2 DELTA 111 2ND STAGE GOING INTO CHAMBER AT NASA PLUM BROOK STATION
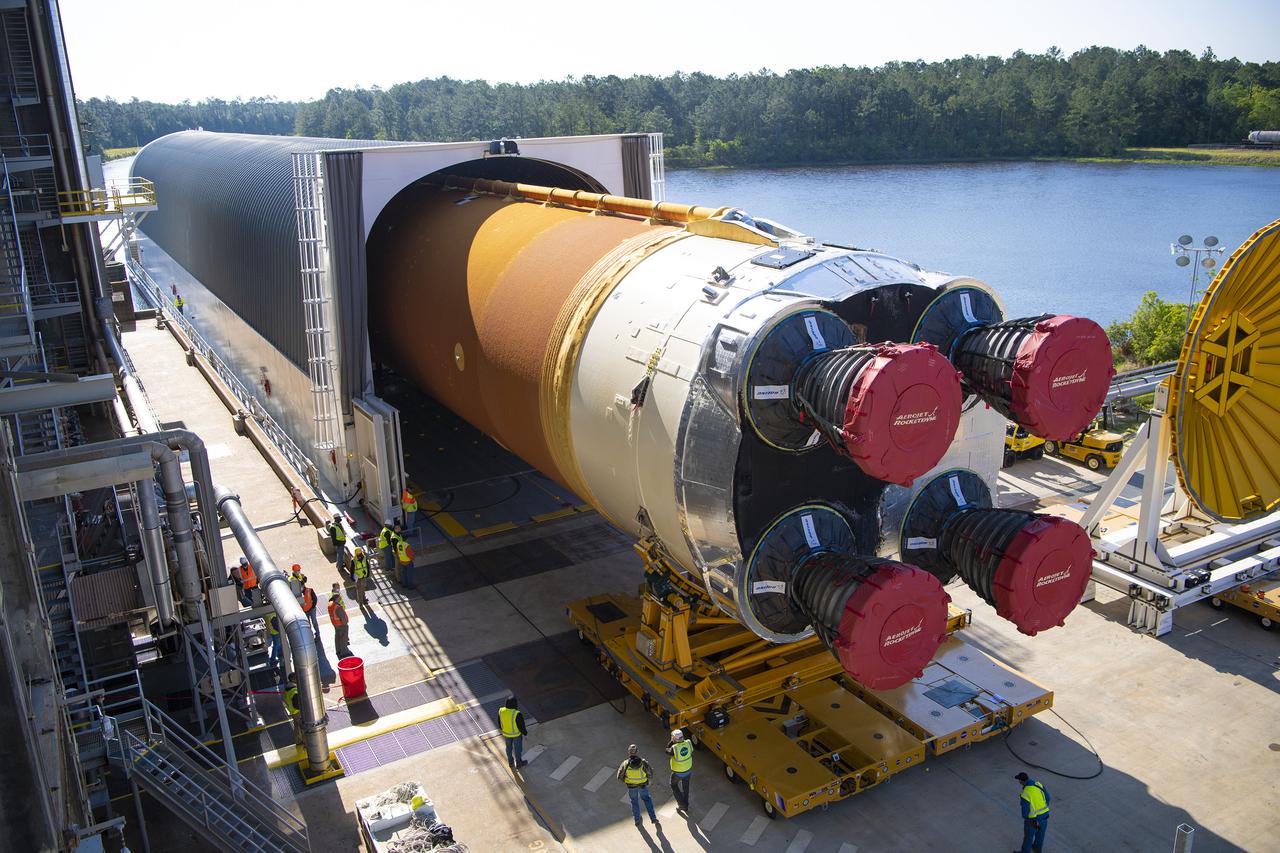

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, load the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on to the agency’s Pegasus barge in preparation for its transport to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The loading activity followed removal of the stage from the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis on April 19-20, 2021. It comes about a month after NASA conducted a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines on March 18 and after teams completed various refurbishment activities. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
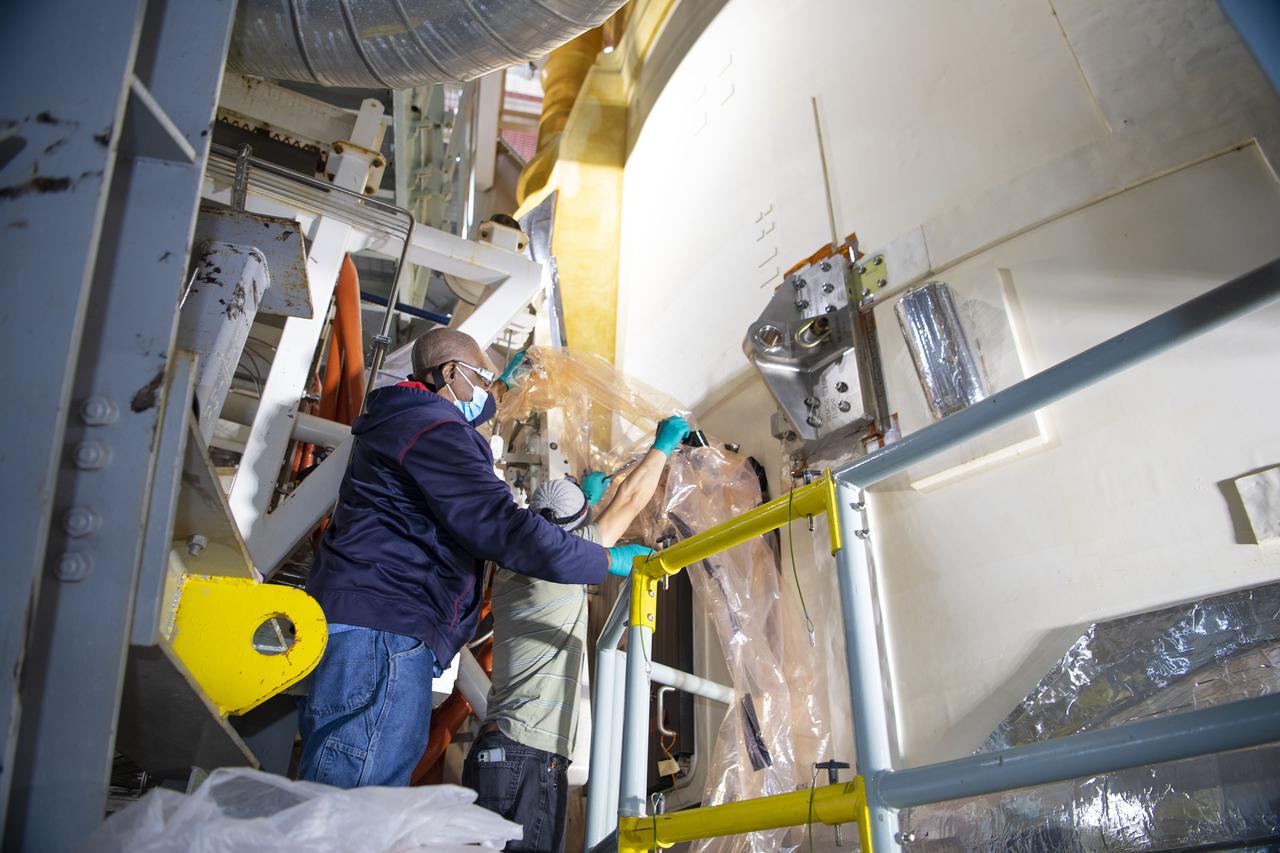

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, complete refurbishment work on the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The work followed a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines March 18. The hot fire marked the culmination of a yearlong Green Run series of tests of the stage and its integrated systems. Following refurbishment work, the core stage will be removed from the test stand and transported to Kennedy Space Center in Florida, aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge, shown delivering equipment to the B-2 Test Stand. At Kennedy, the core stage will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA