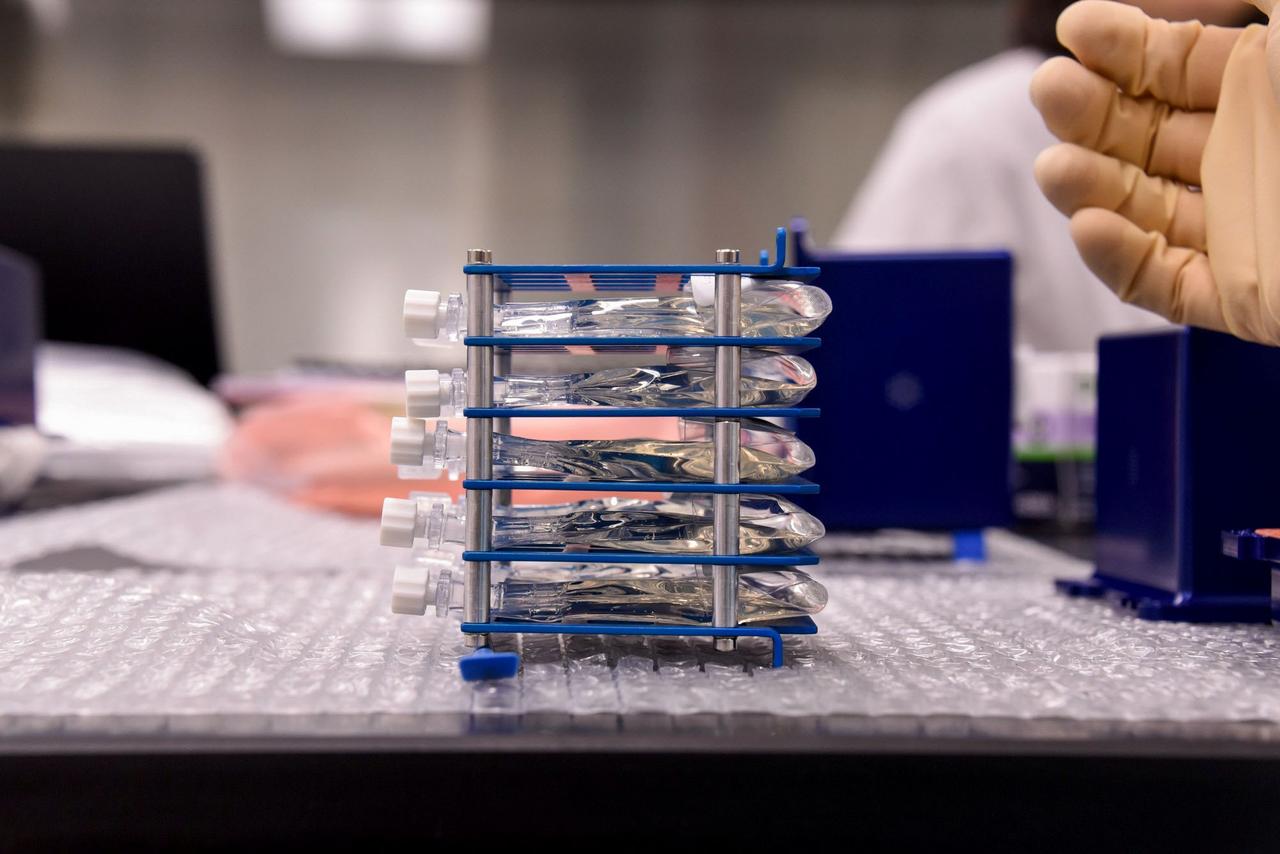
jsc2024e050833 (12/2/2019) --- Preflight image of the Rotifer-B2 experiment container. The Rotifer-B2 investigation aims to explore the effects that spaceflight has on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) repair mechanisms of the bdelloid rotifer Adineta vaga. This is achieved by pre-exposing rotifers to high levels of radiation on Earth and then culturing them in Kubik, an on-orbit incubator facility. After exposing rotifers to space conditions inside the International Space Station, the samples are frozen and returned to Earth for postflight analyses. Image courtesy of the University of Namur.

Comet Hyakutake C/1996 B2
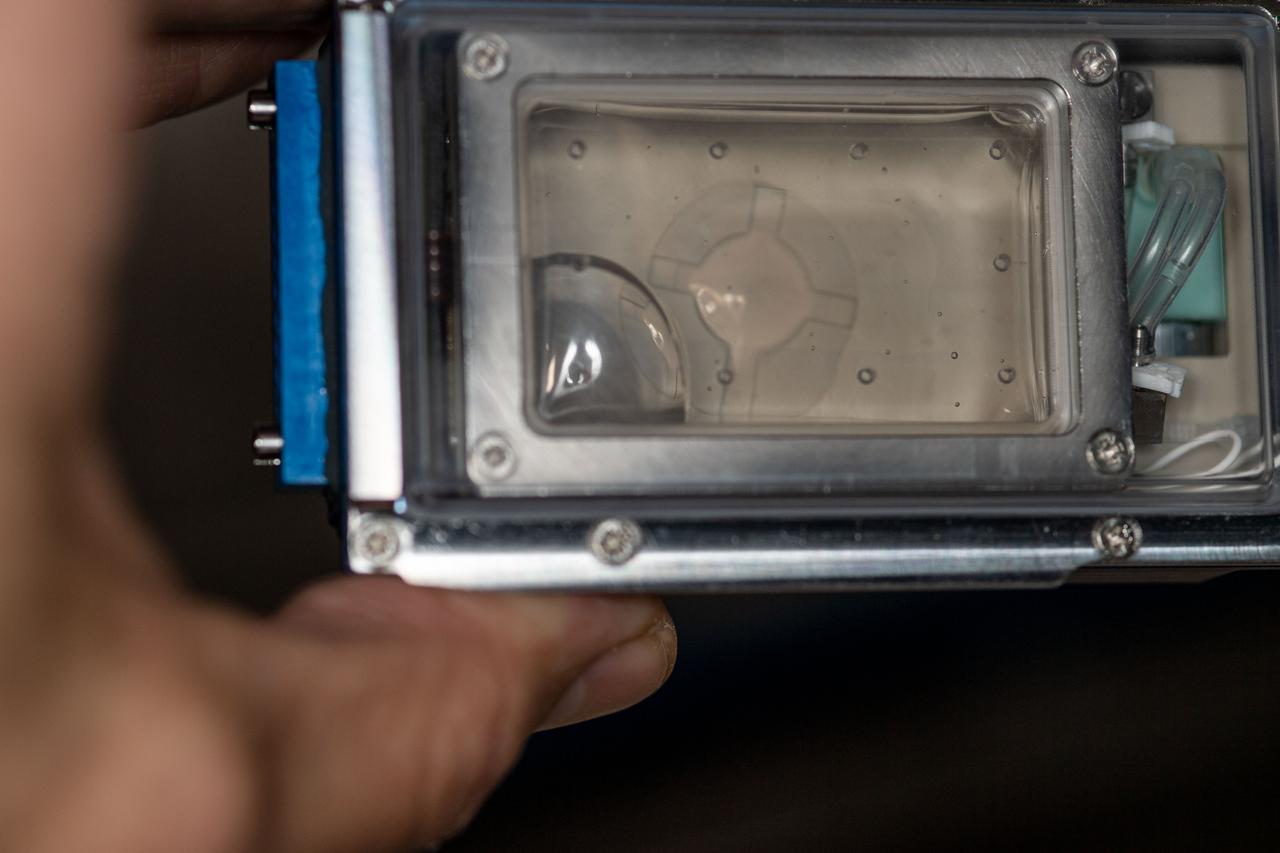

iss064e011243 (12/8/2020) --- A view of the Rotifer-B2 experiment container aboard the Internationals Space Station (ISS). The Rotifer-B2 investigation aims to explore the effects that spaceflight has on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) repair mechanisms of the bdelloid rotifer Adineta vaga.
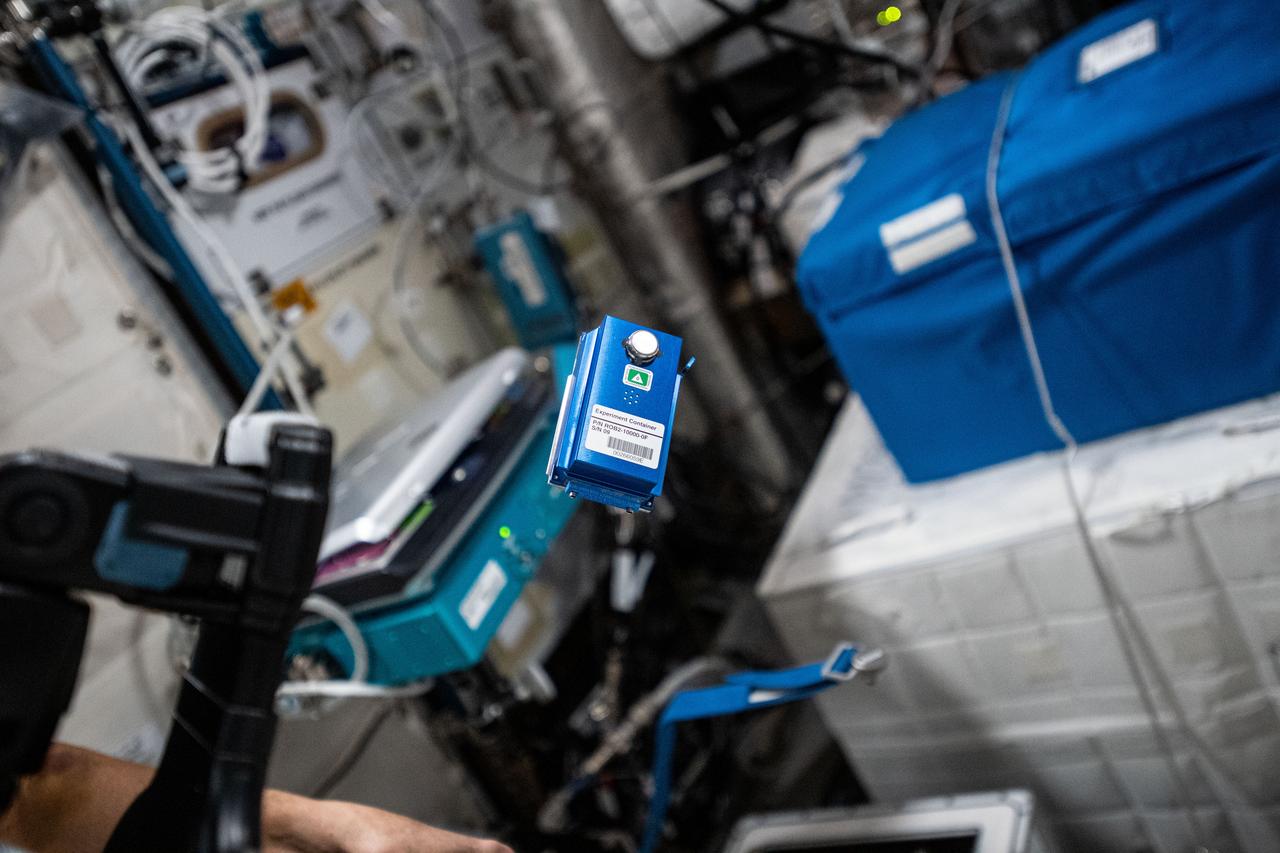

iss064e011398 (12/8/2020) --- A view of the Rotifer-B2 experiment container aboard the Internationals Space Station (ISS). The Rotifer-B2 investigation aims to explore the effects that spaceflight has on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) repair mechanisms of the bdelloid rotifer Adineta vaga.

jsc2025e007253 (2/14/2025) --- The logo for Polaris Bioremediation Science Experiment - Genetic Exchange in Microgravity for Biofilm Bioremediation (GEM-B2).
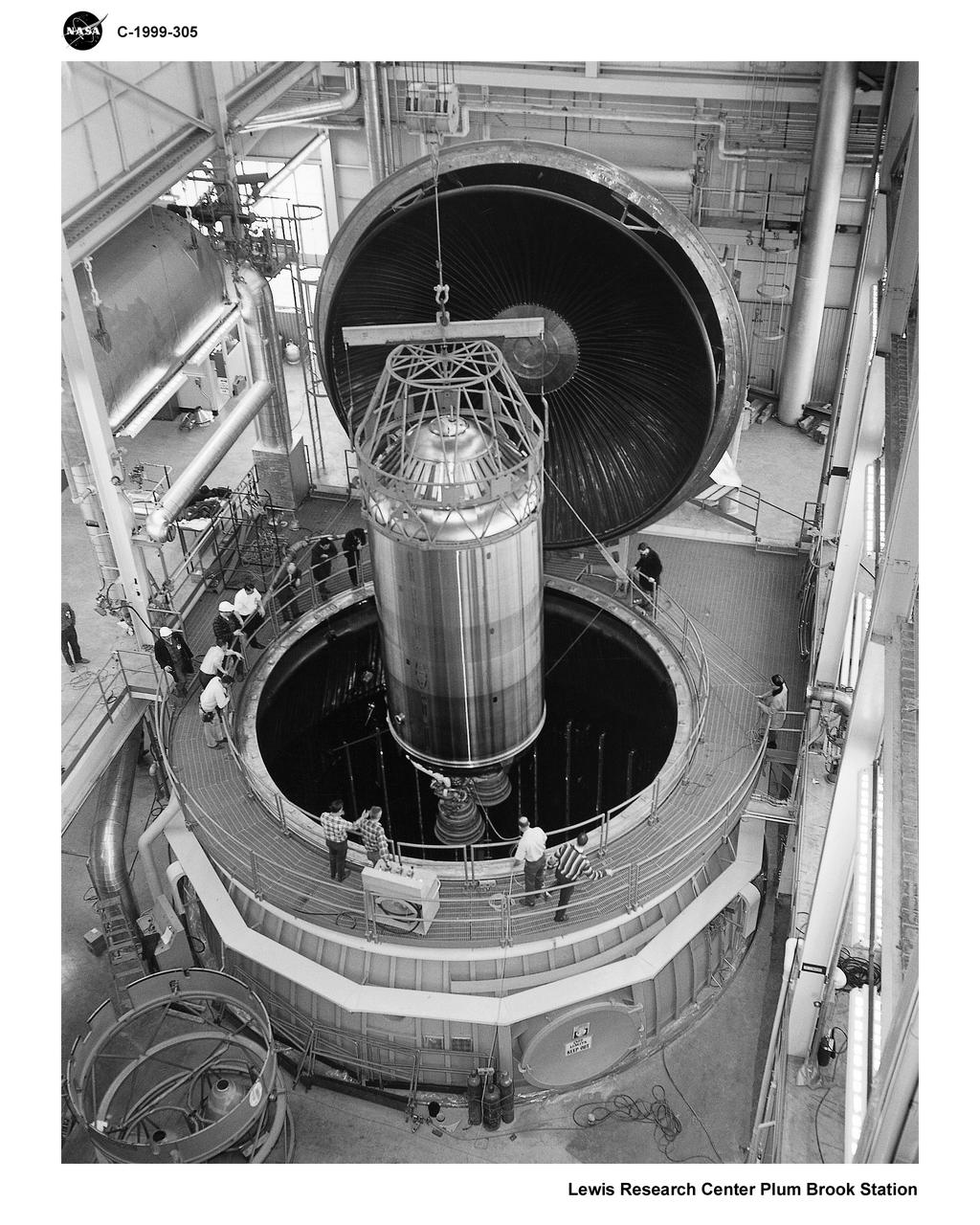

CENTAUR CENTER STAGE BEING LOWERED INTO THE CHAMBER IN THE B2 FACILITY AT PLUM BROOK STATION SANDUSKY OHIO
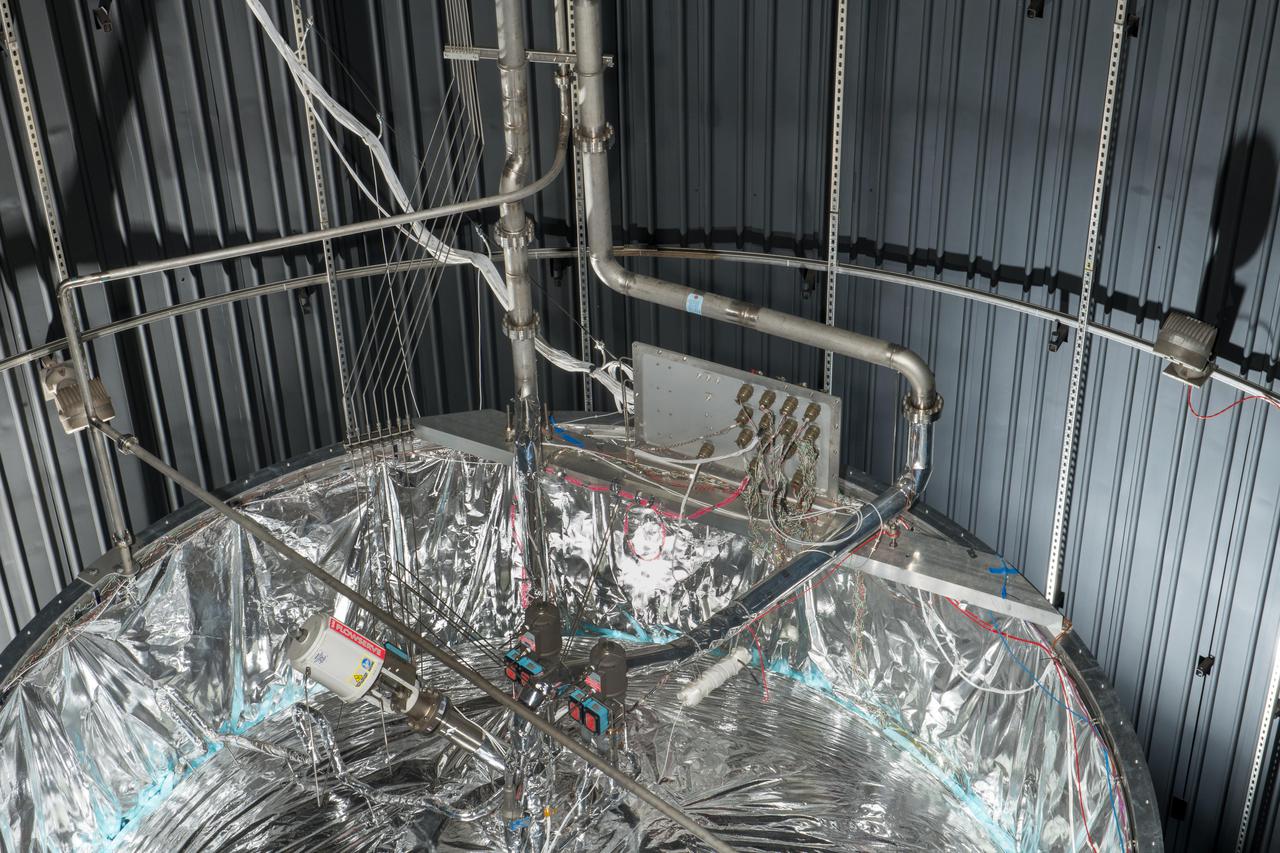

Structural Heat Intercept-Insulation-Vibration Evaluation Rig, SHIVER
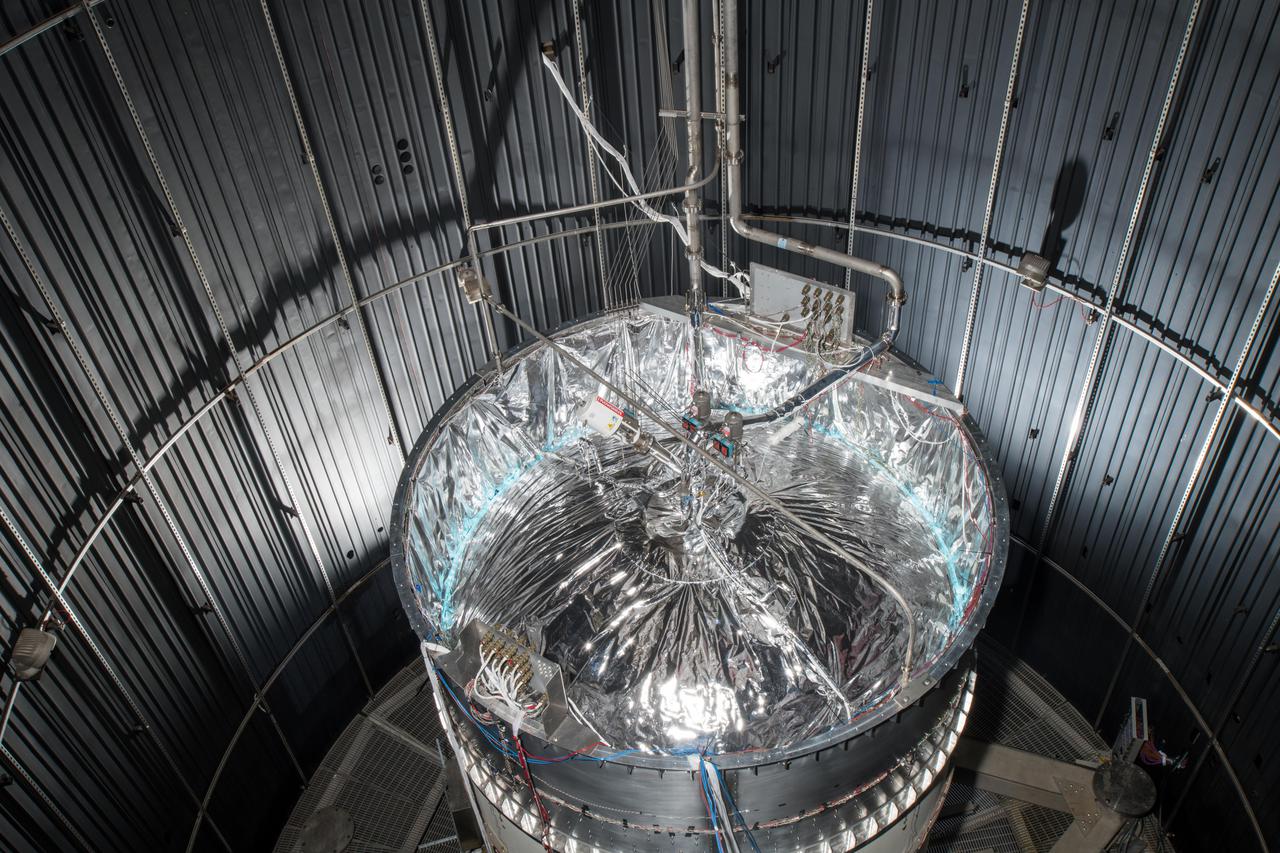

Structural Heat Intercept-Insulation-Vibration Evaluation Rig, SHIVER

Structural Heat Intercept-Insulation-Vibration Evaluation Rig, SHIVER
Structural Heat Intercept-Insulation-Vibration Evaluation Rig, SHIVER
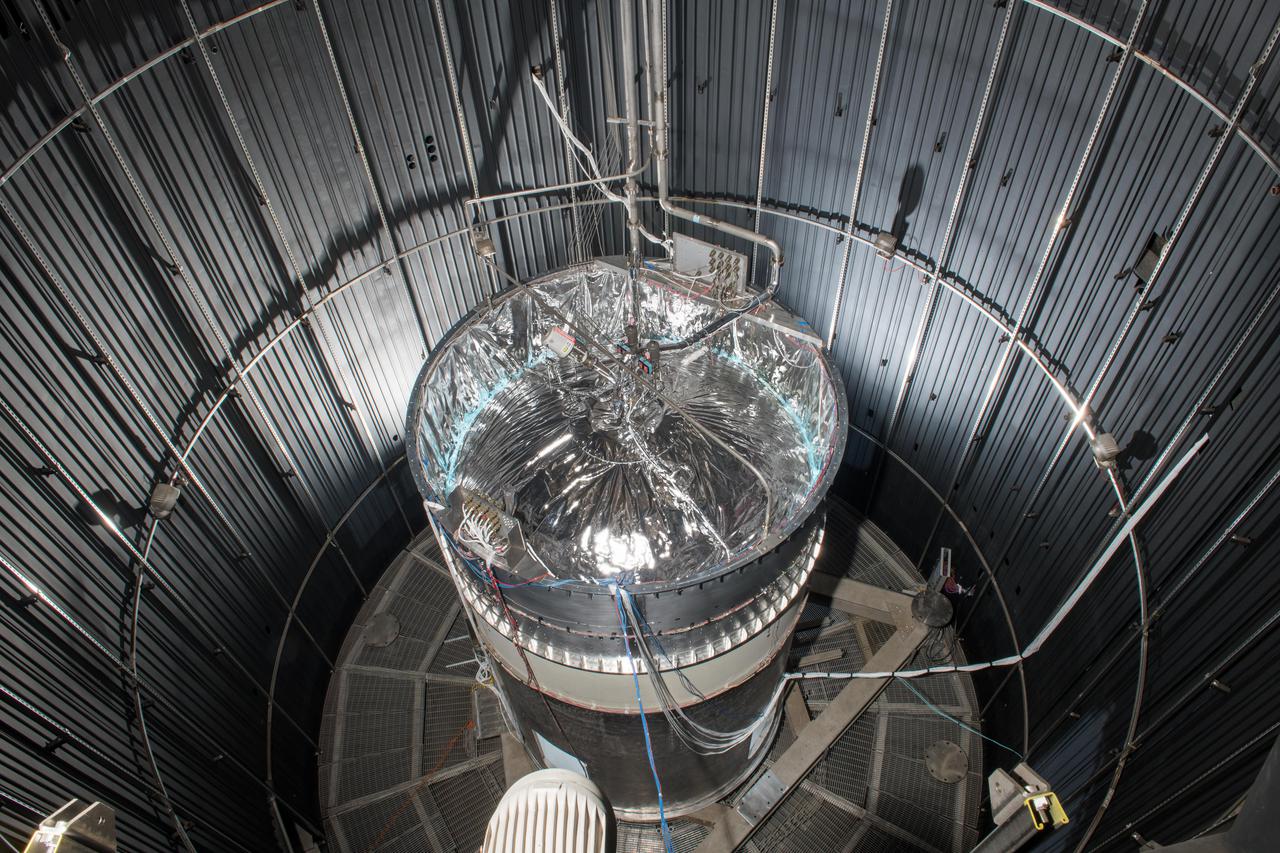

Structural Heat Intercept-Insulation-Vibration Evaluation Rig, SHIVER
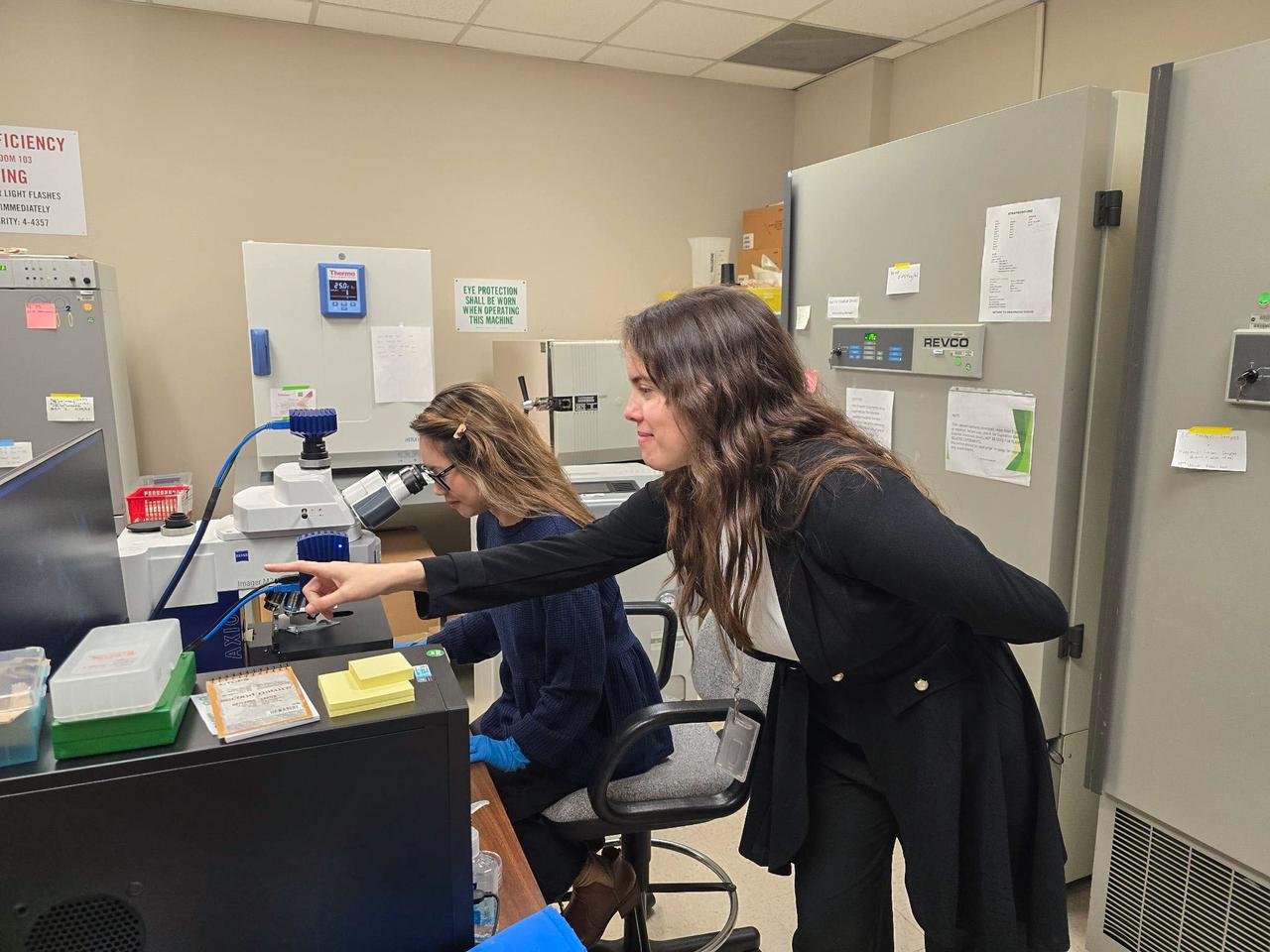

jsc2025e007252 (2/14/2025) --- Dr. Yo-Ann Velez performs microscopy in support of Polaris Bioremediation Science Experiment - Genetic Exchange in Microgravity for Biofilm Bioremediation (GEM-B2).
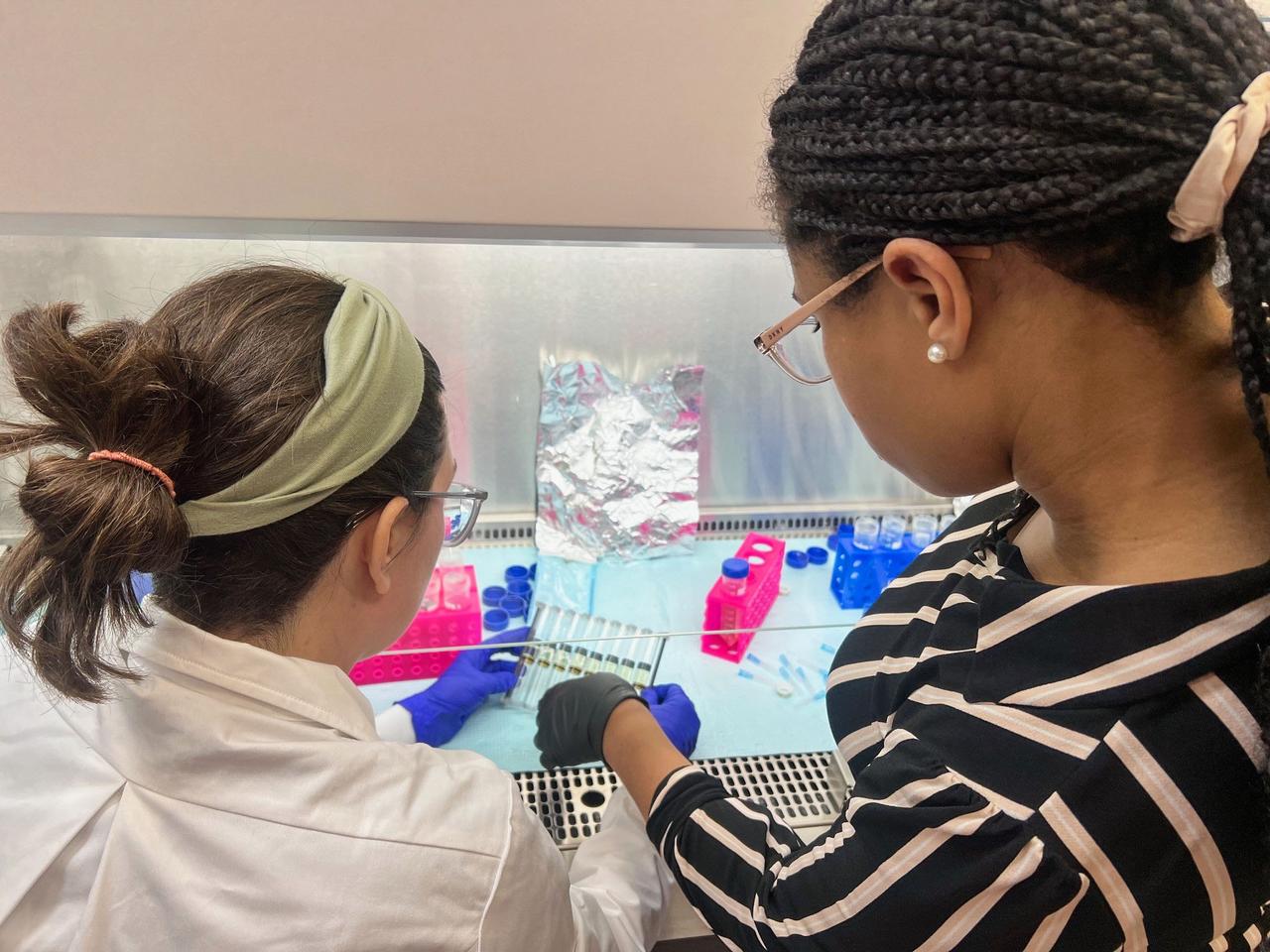

jsc2025e007257 (2/14/2025) --- A view of the Fluid Processing Apparatus (FPAs) used in the Polaris Bioremediation Science Experiment - Genetic Exchange in Microgravity for Biofilm Bioremediation (GEM-B2) investigation. Image courtesy of BioServe.
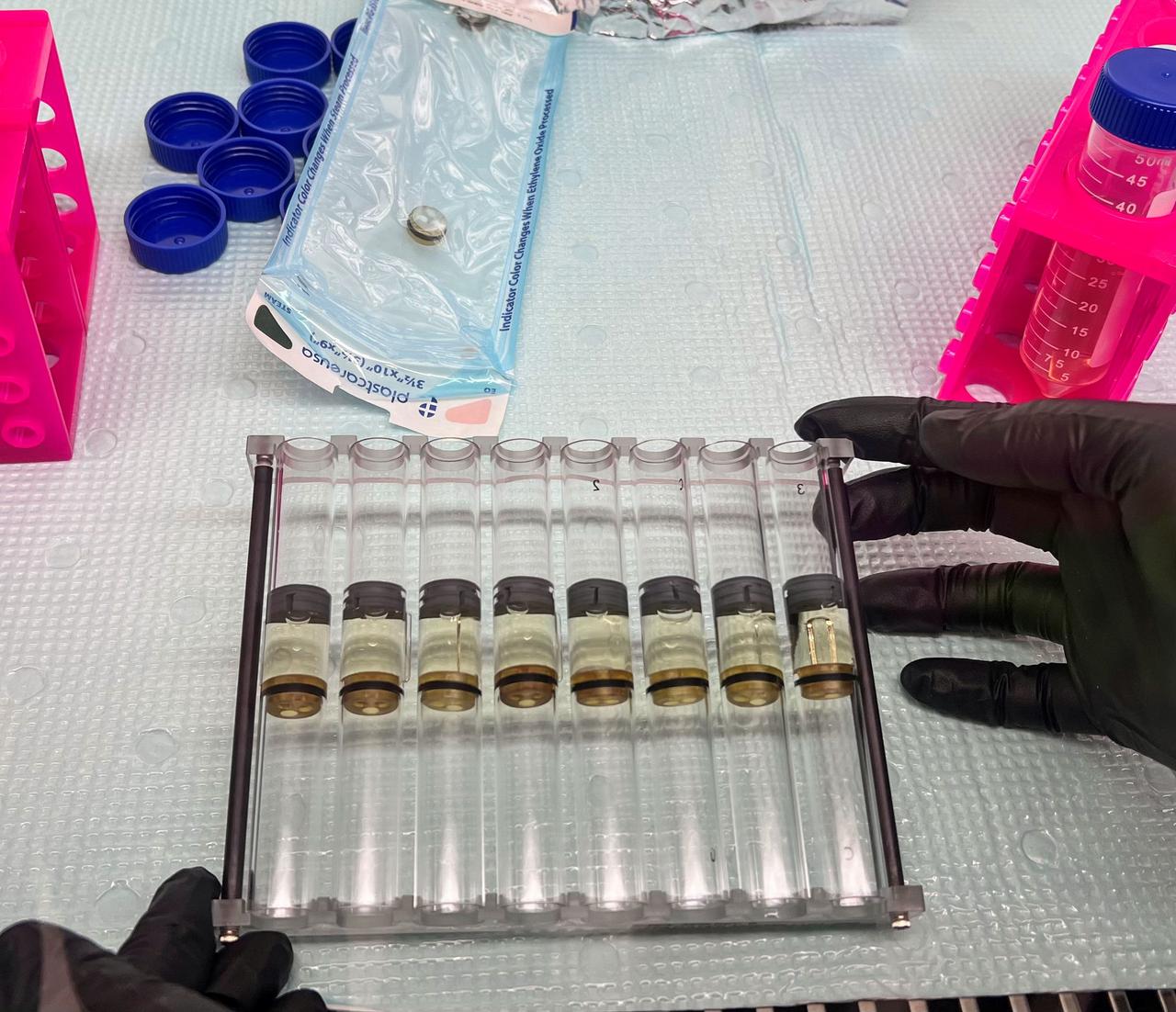
jsc2025e007256 (2/14/2025) --- Another view of the eight Fluid Processing Apparatus (FPAs) used in the Polaris Bioremediation Science Experiment - Genetic Exchange in Microgravity for Biofilm Bioremediation (GEM-B2) investigation. Image courtesy of BioServe.
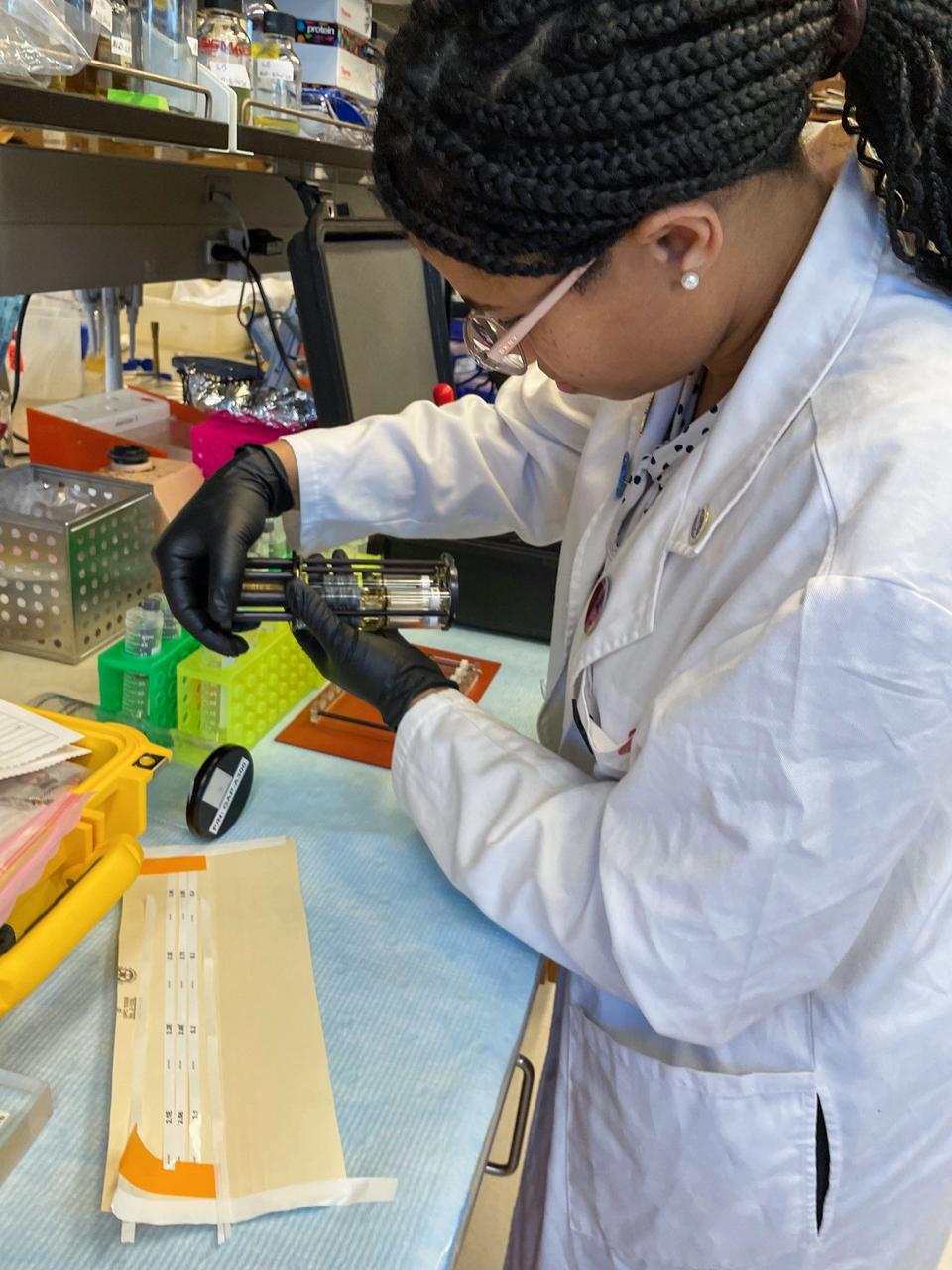

jsc2025e007254 (2/14/2025) --- Graduate student Lanie Briggs loads a Group Activation Pack (GAP) for the Polaris Bioremediation Science Experiment - Genetic Exchange in Microgravity for Biofilm Bioremediation (GEM-B2).
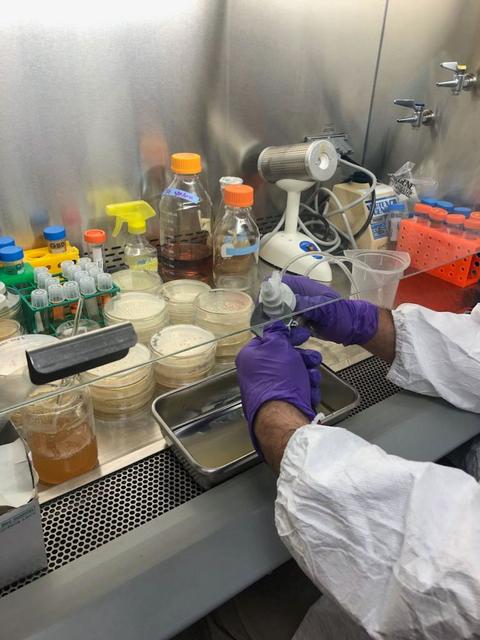

jsc2025e007251 (2/14/2025) --- Biofilm testing is shown in the early stages of the Polaris Bioremediation Science Experiment - Genetic Exchange in Microgravity for Biofilm Bioremediation (GEM-B2) project.

jsc2025e076266 (09/22/2025) --- NASA 2025 Astronaut Candidate (ASCAN) Announcement Ceremony Photo Date: 09/22/2025 Location: JSC B2 - Teague Auditorium Photo Credit: NASA - Helen Arase Vargas

jsc2025e076269 (09/22/2025) --- NASA 2025 Astronaut Candidate (ASCAN) Announcement Ceremony Photo Date: 09/22/2025 Location: JSC B2 - Teague Auditorium Photo Credit: NASA - Helen Arase Vargas
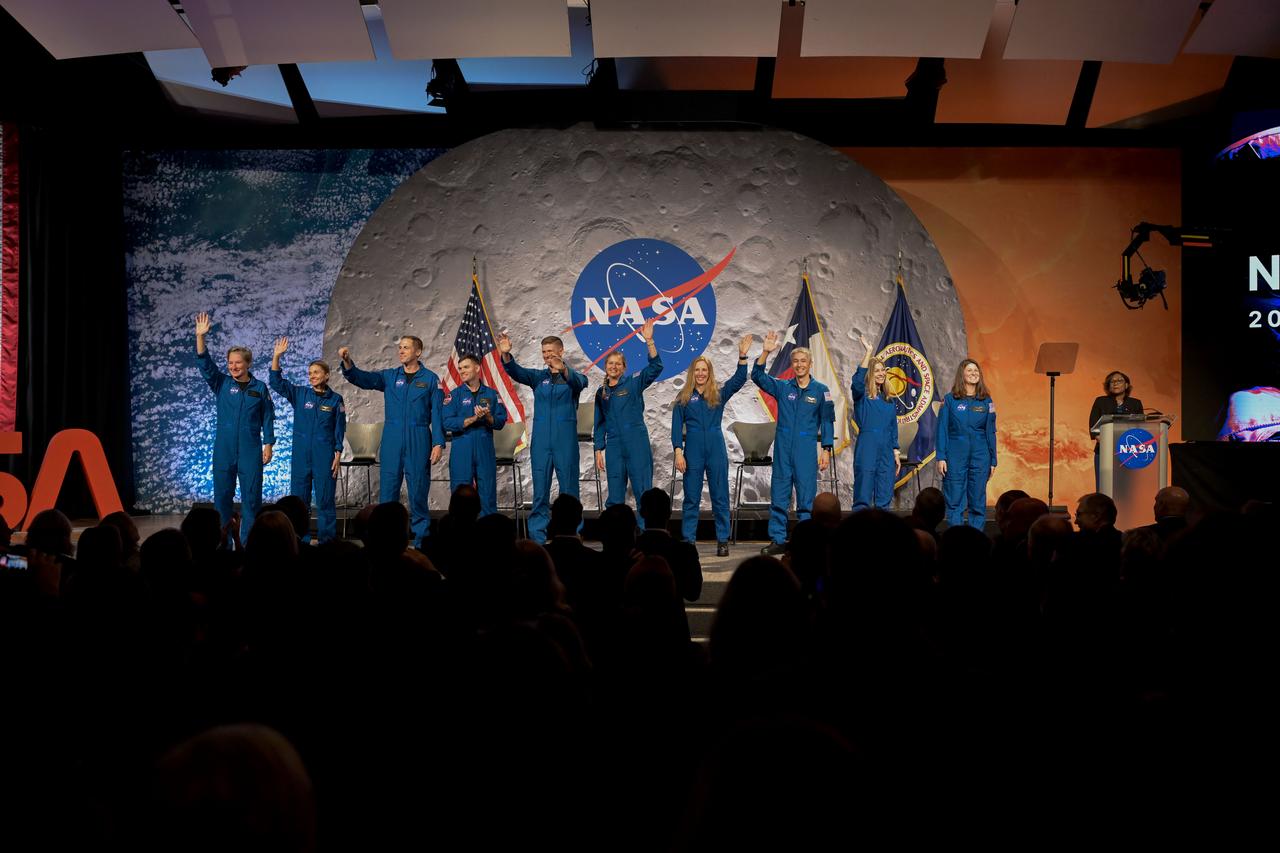

jsc2025e076292 (09/22/2025) --- NASA 2025 Astronaut Candidate (ASCAN) Announcement Ceremony Photo Date: 09/22/2025 Location: JSC B2 - Teague Auditorium Photo Credit: NASA - Helen Arase Vargas
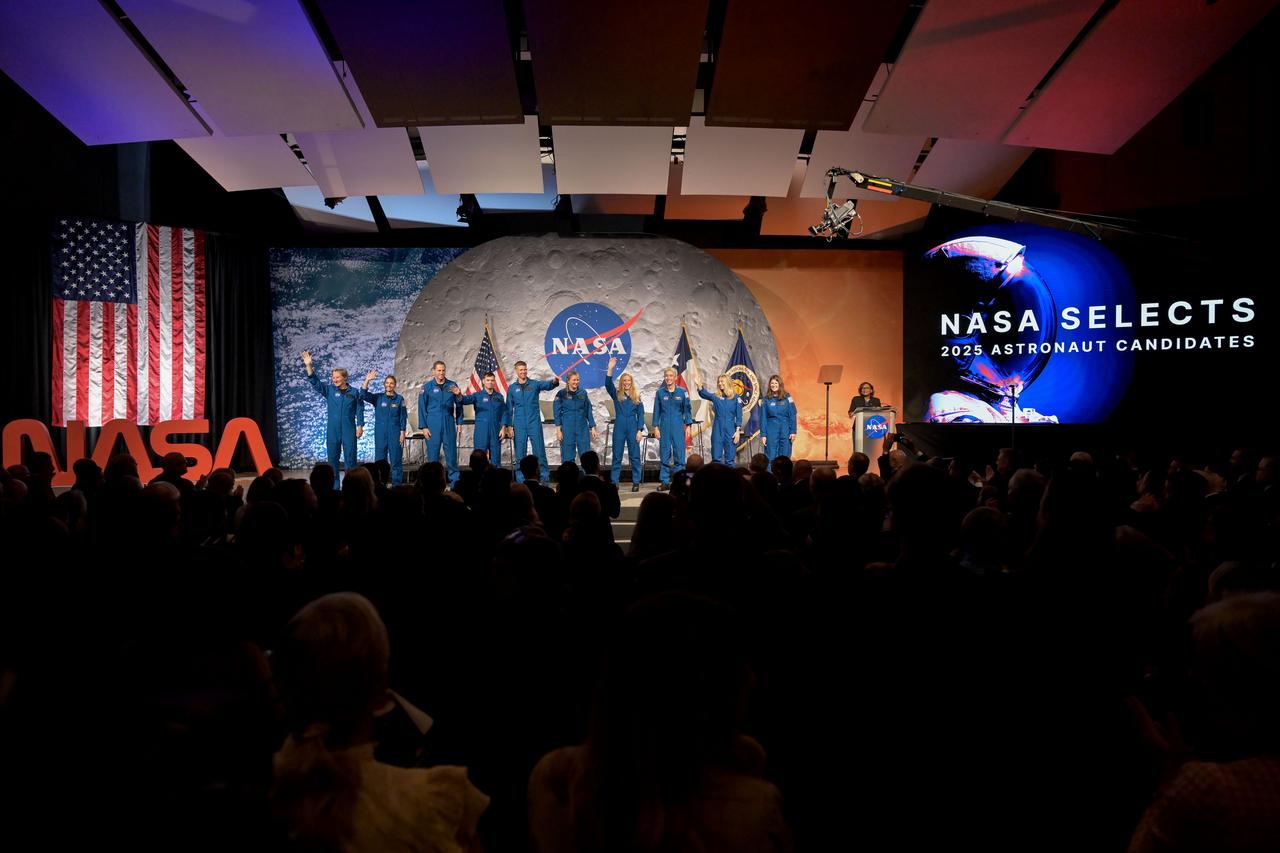

jsc2025e076293 (09/22/2025) --- NASA 2025 Astronaut Candidate (ASCAN) Announcement Ceremony Photo Date: 09/22/2025 Location: JSC B2 - Teague Auditorium Photo Credit: NASA - Helen Arase Vargas
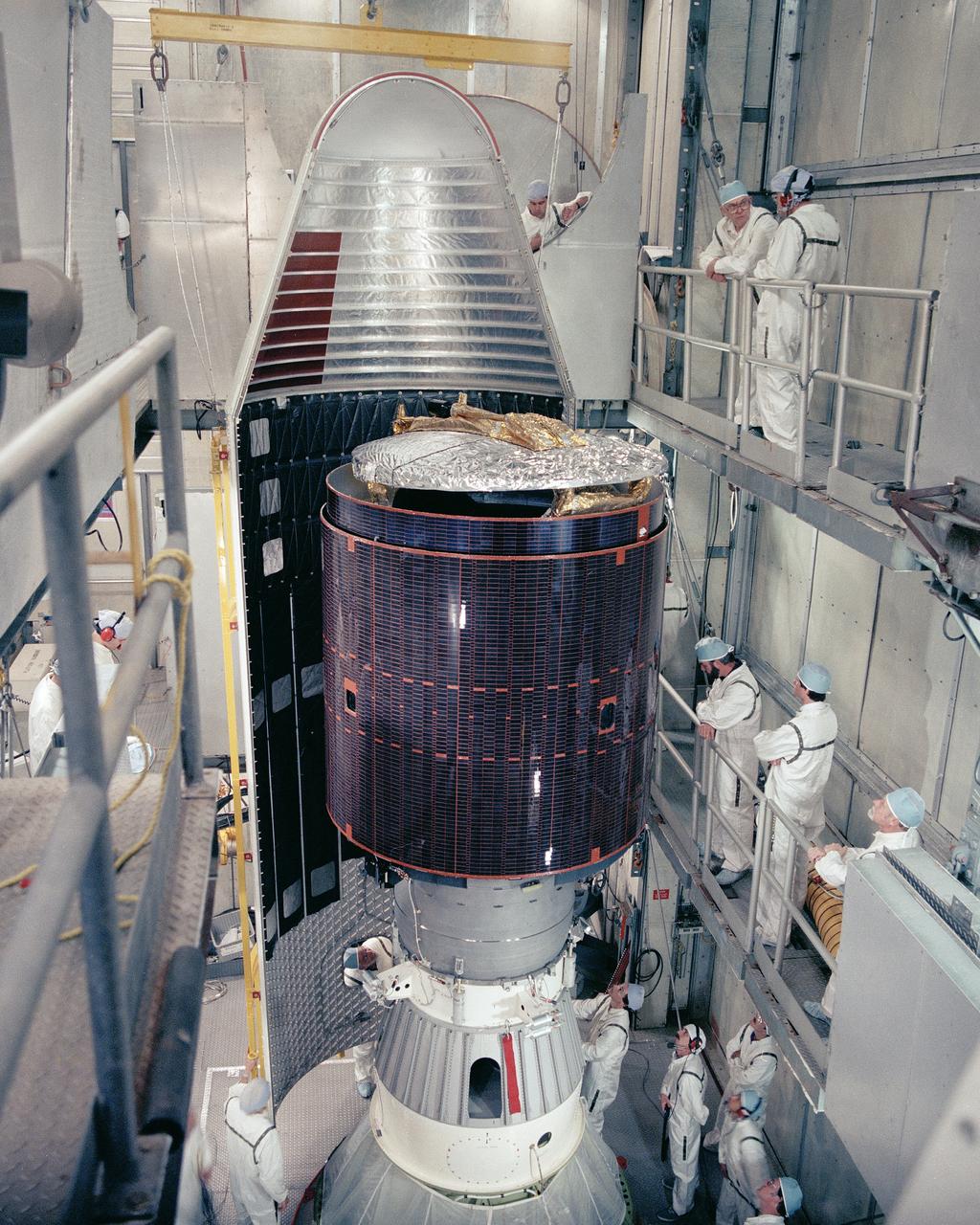
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the paylaod fairing of the Delta 182 launch vehicle is carefully moved into place as encapsulation procedures continue on the Palapa B2-P communications satellite at Launch Complex 17, Pad B. Palapa is scheduled for launch from Cape Canaveral for the government of Indonesia. Liftoff of Delta 182 and Palapa is scheduled for March 20. Photo Credit: NASA
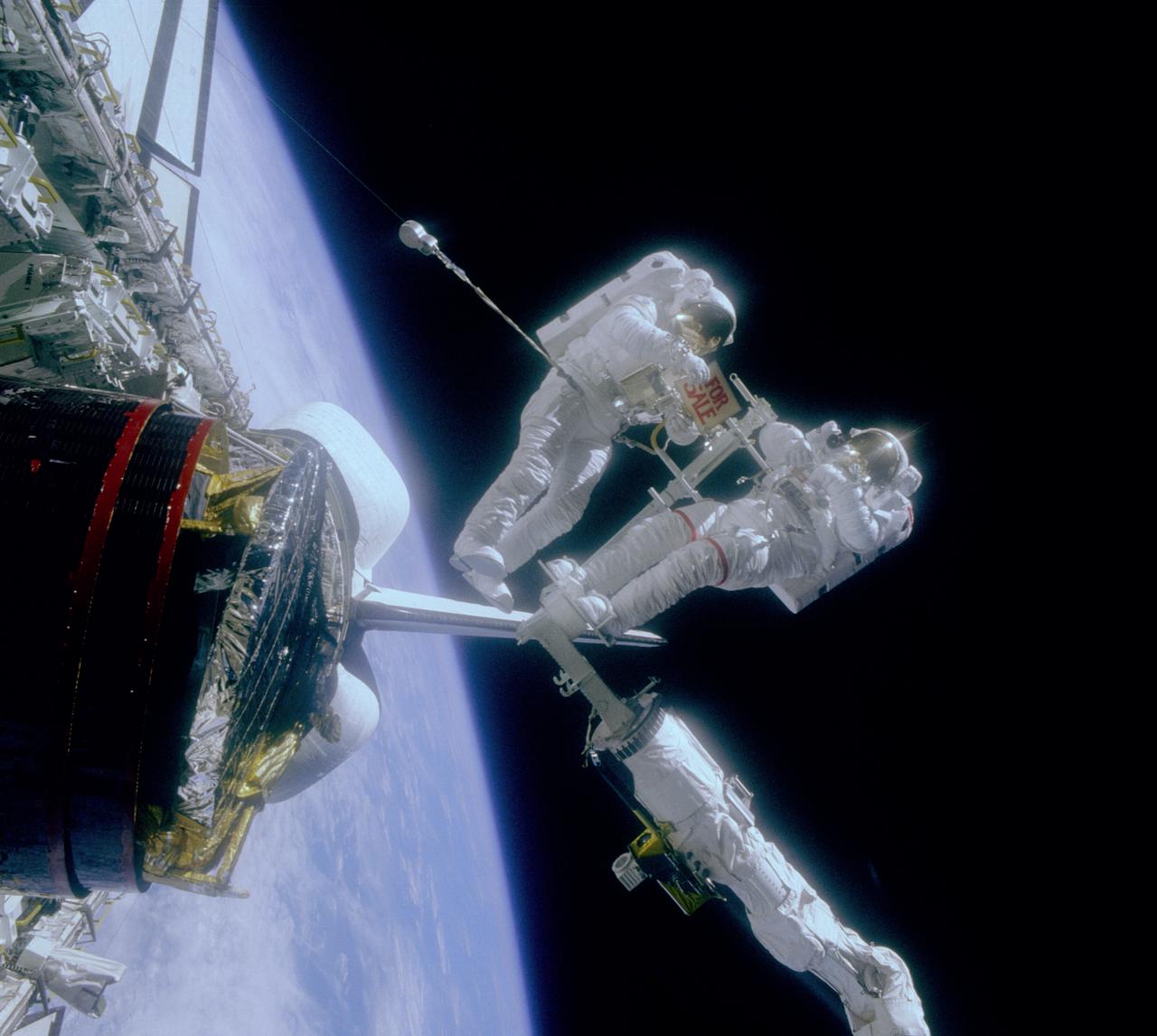

Astronauts are clowning around in space in this STS-51A onboard photo. Astronaut Gardner, holds a “For Sale” sign after the retrieval of two malfunctioning satellites; the Western Union Telegraph Communication Satellite (WESTAR VI); and the PALAPA-B2 Satellite. Astronaut Allen, who is standing on the RMS (Remote Manipulator System) is reflected in Gardner’s helmet visor. The 51A mission launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on November 8, 1984.
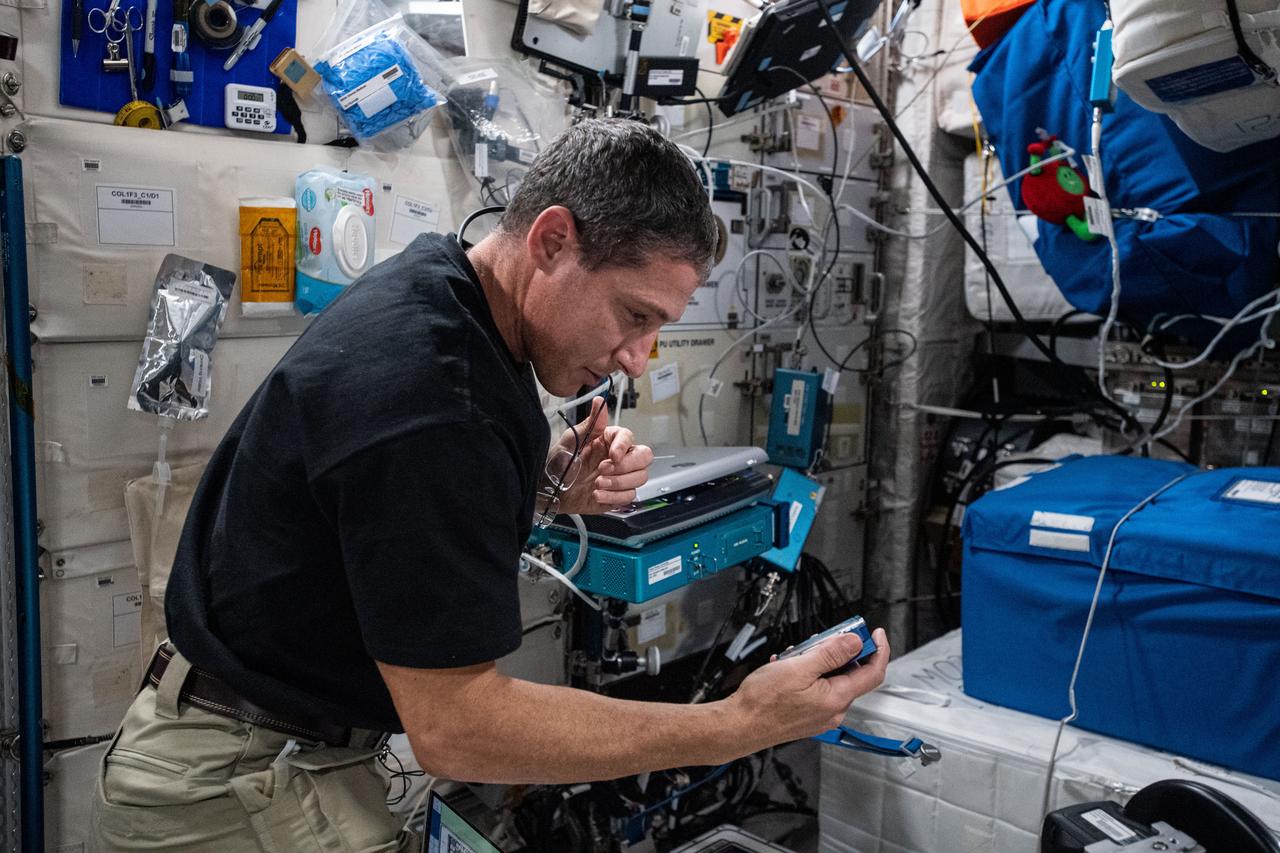

iss064e011391 (Dec. 8, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Michael Hopkins shakes an experiment container containing biological samples to displace bubbles before placing it into the Kubik incubator facility. Hopkins was servicing the samples for the Rotifer-B2 experiment that is exploring the effects spaceflight has on DNA repair mechanisms of the bdelloid rotifer Adineta vaga, a plankton-like microscopic organism.

Astronauts are clowning around in space in this STS-51A onboard photo. Astronaut Gardner, holds a “For Sale” sign after the retrieval of two malfunctioning satellites; the Western Union Telegraph Communication Satellite (WESTAR VI); and the PALAPA-B2 Satellite. Astronaut Allen, who is standing on the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) is reflected in Gardner’s helmet visor. The 51A mission launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on November 8, 1984.

The Rotifer-B2 investigation aims to explore the effects that spaceflight has on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) repair mechanisms of the bdelloid rotifer Adineta vaga. This is achieved by pre-exposing rotifers to high levels of radiation on Earth and then culturing them in Kubik, an on-orbit incubator facility. After exposing rotifers to space conditions inside the International Space Station, the samples are frozen and returned to Earth for postflight analyses. Image courtesy of the University of Namur.
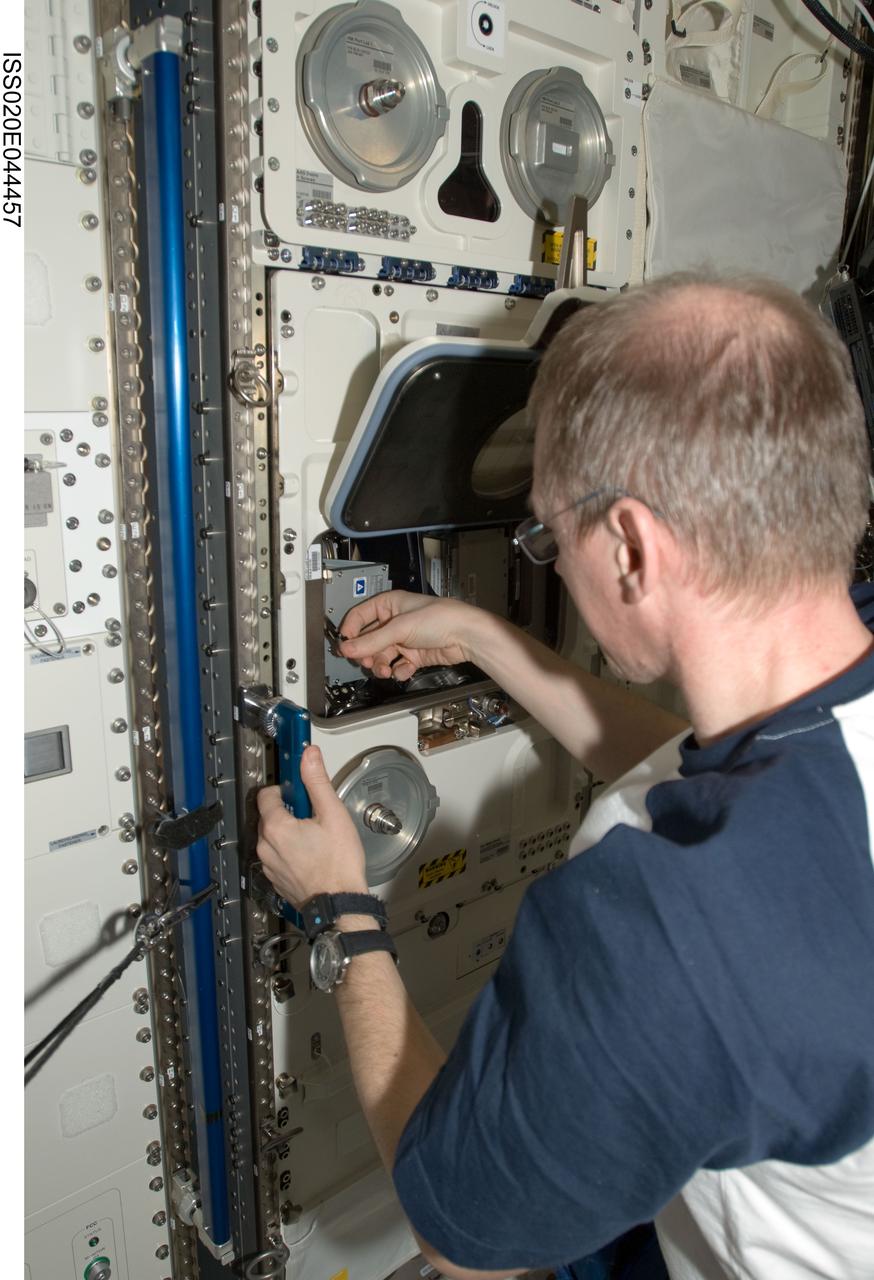

ISS020-E-044457 (2 Oct. 2009) --- European Space Agency astronaut Frank De Winne, Expedition 20 flight engineer and Expedition 21 commander, installs experiment containers in the Biolab incubator in the Columbus laboratory of the International Space Station.
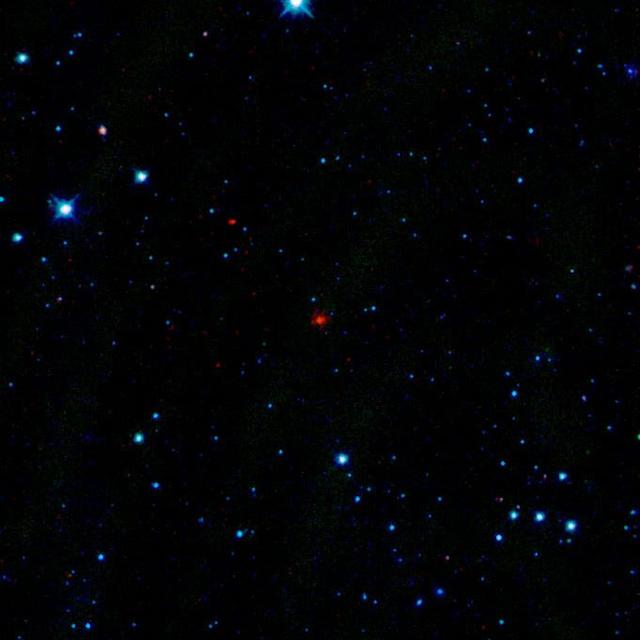

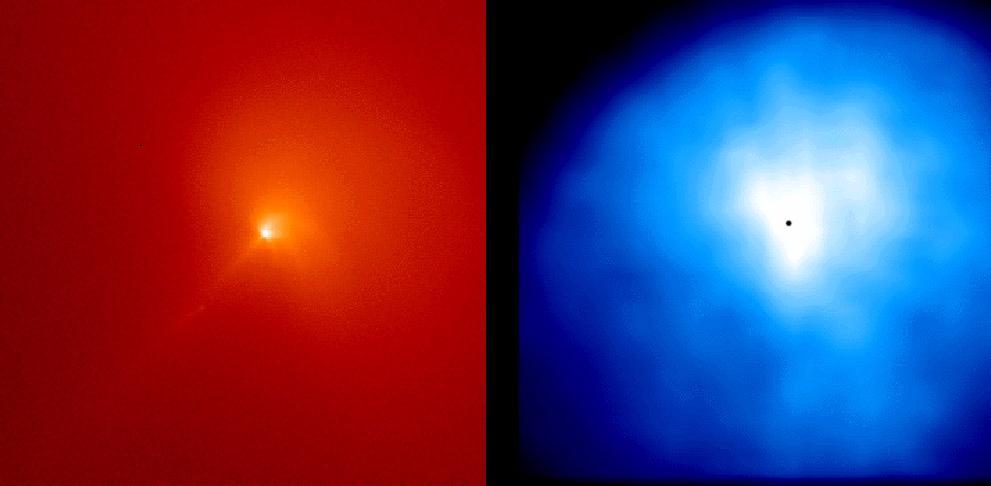
The red smudge at the center of this image is the first comet discovered by NASA Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE. The comet is a dusty mass of ice and parades around the sun every 4.7 years.
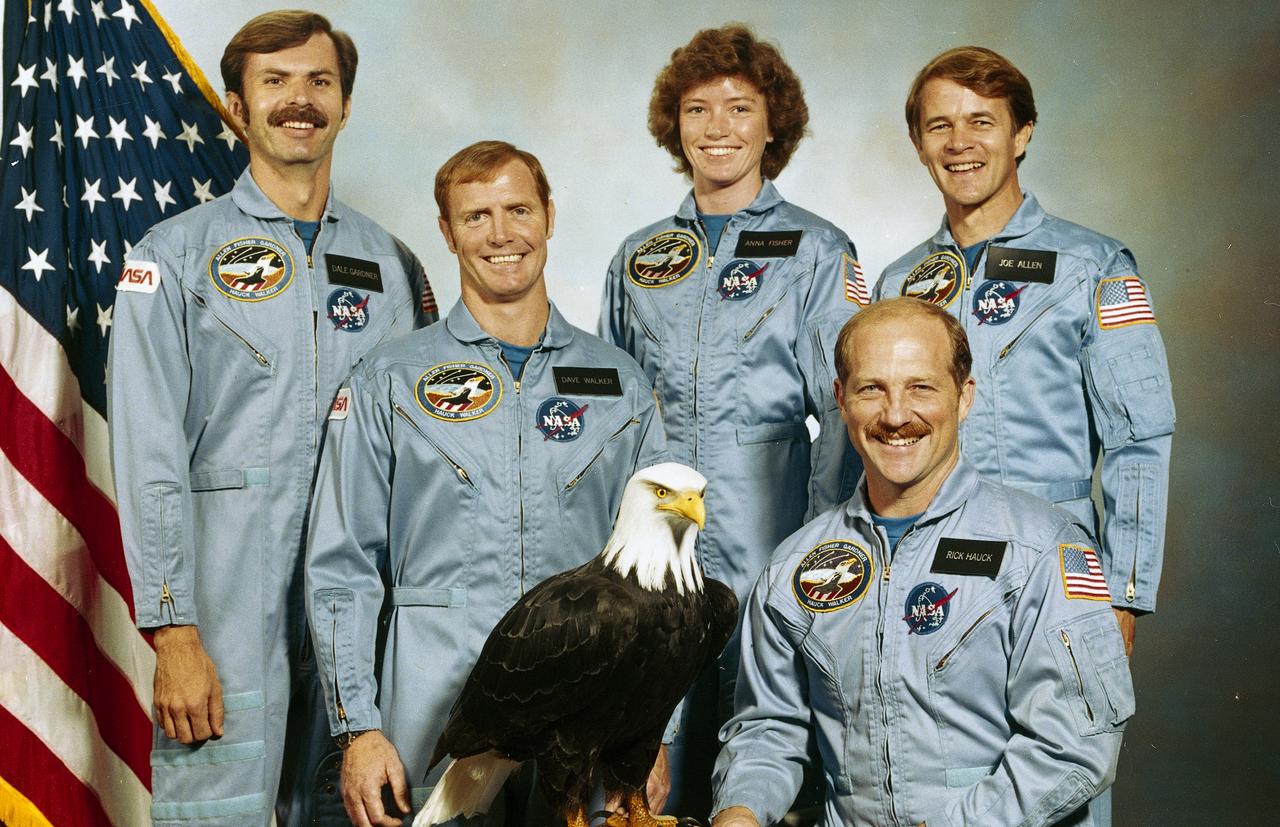

The crew assigned to the STS-51A mission included Frederick H. Hauck, commander,who is seated to the right. Standing, left to right, are Dale A. Gardner, mission specialist; David M. Walker, pilot; and mission specialists Anna L. Fisher, and Joseph P. Allen. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on November 8, 1984 at 7:15:00 am (EST), the STS-51A mission deployed the Canadian communications satellite TELLESAT-H (ANIK), and the defense communications satellite SYCOM IV-1 (also known as LEASAT-1). In addition, 2 malfunctioning satellites were retrieved: the PALAPA-B2 and the WESTAR-VI.
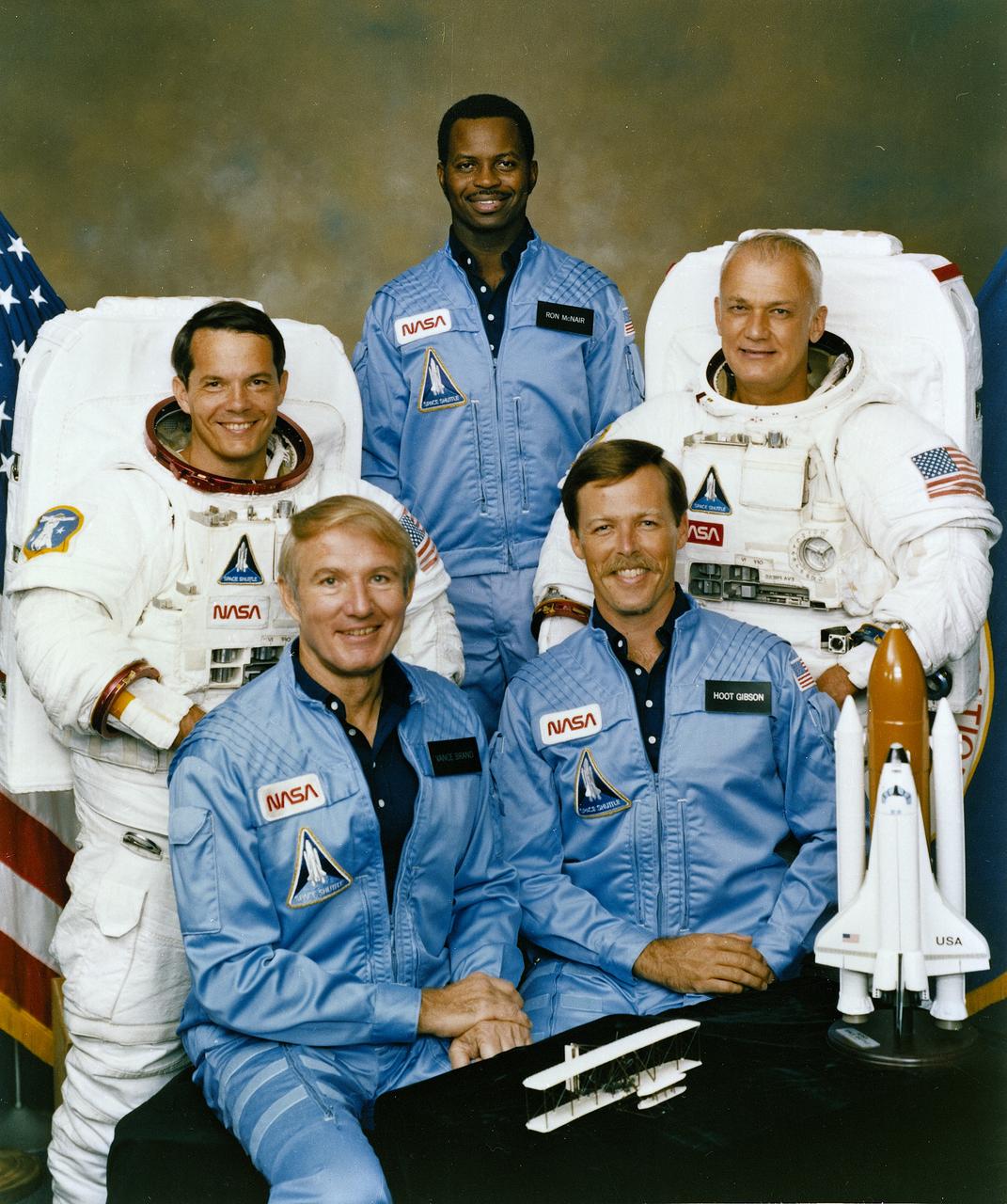

The crew assigned to the STS-41B (STS-11) mission included (seated left to right) Vance D. Brand, commander; and Robert L. Gibson, pilot. Standing left to right are mission specialists Robert L. Stewart, Ronald E. McNair, and Bruce McCandless. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Challenger on February 3, 1984 at 8:00:00 am (EST), the STS-41B mission marked the first untethered space walks which were performed by McCandless and Stewart. The crew deployed the WESTAR-VI and PALAPA-B2 satellites.
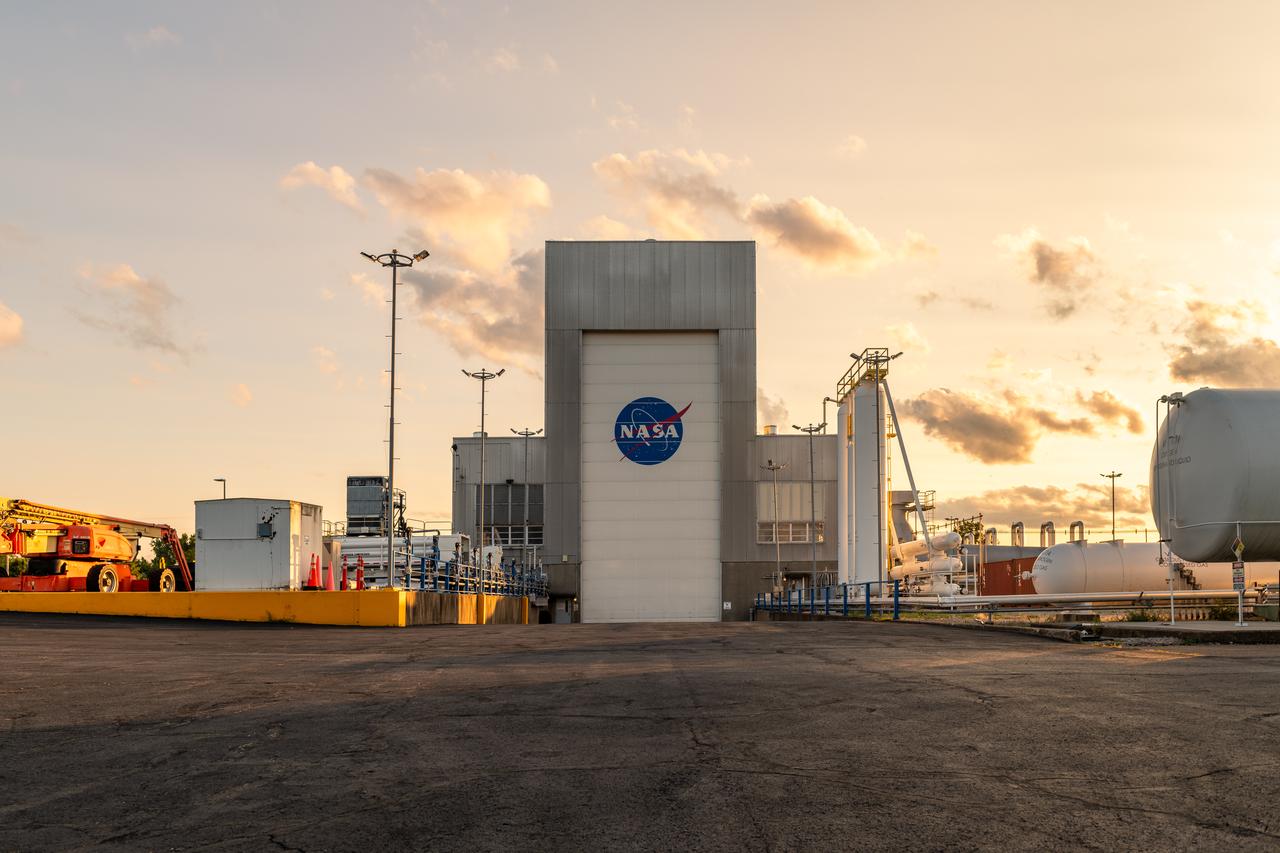

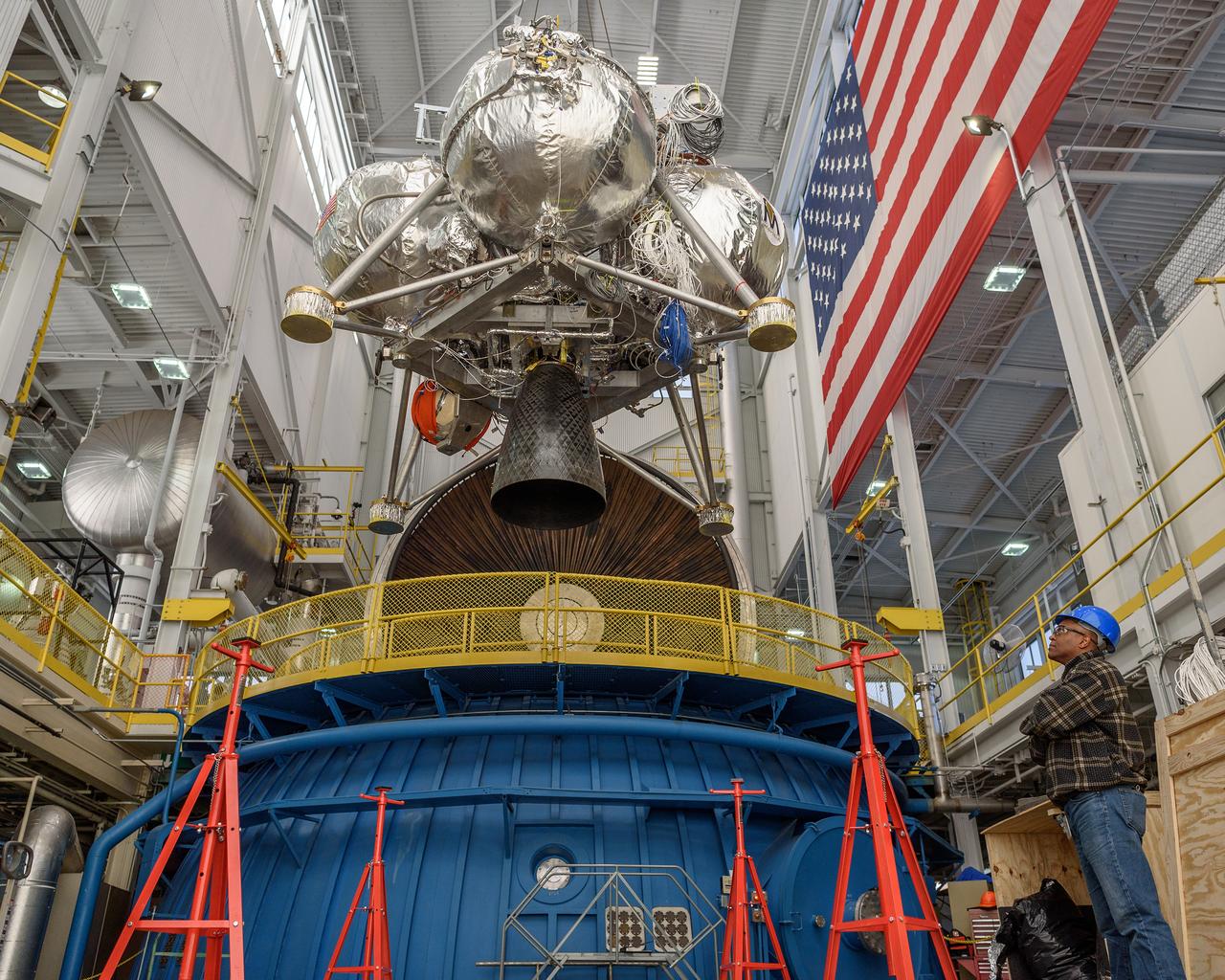
NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
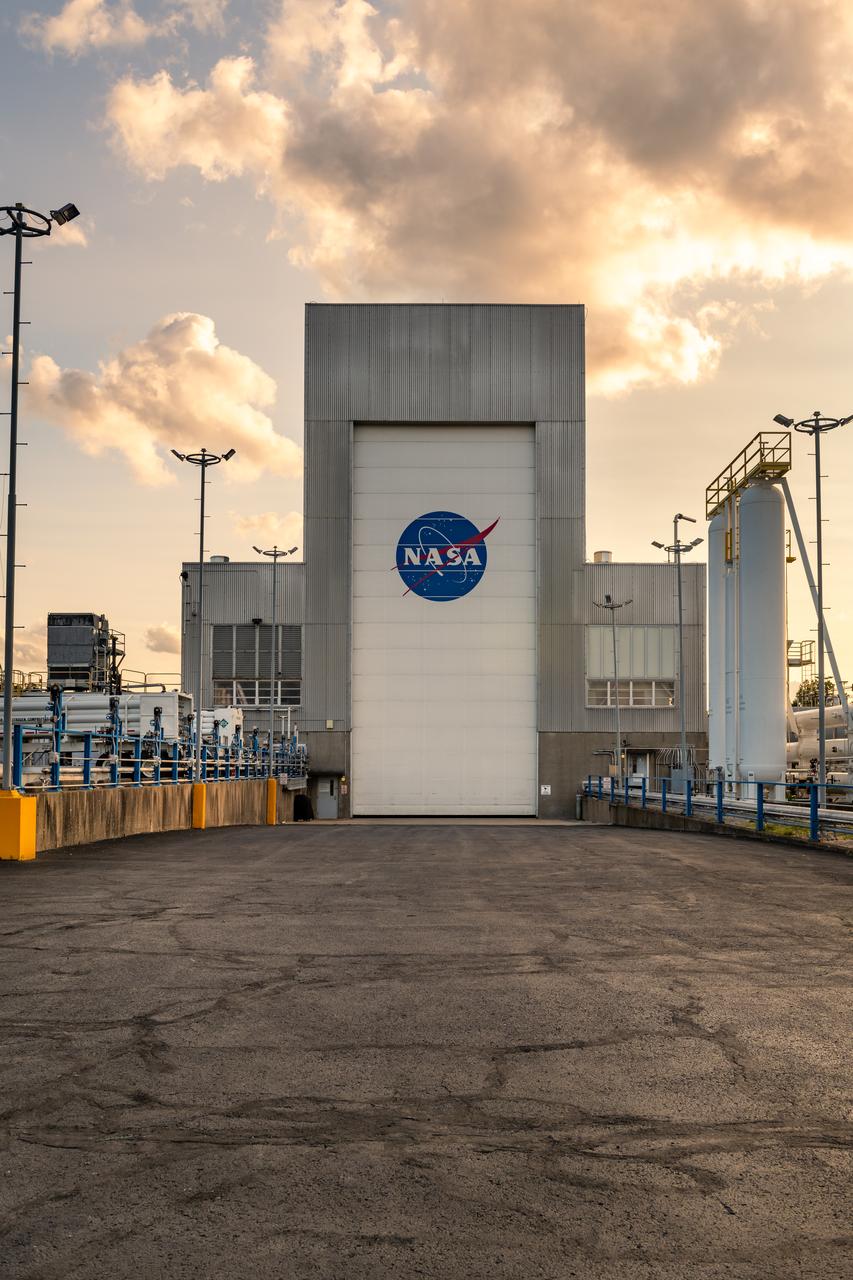

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
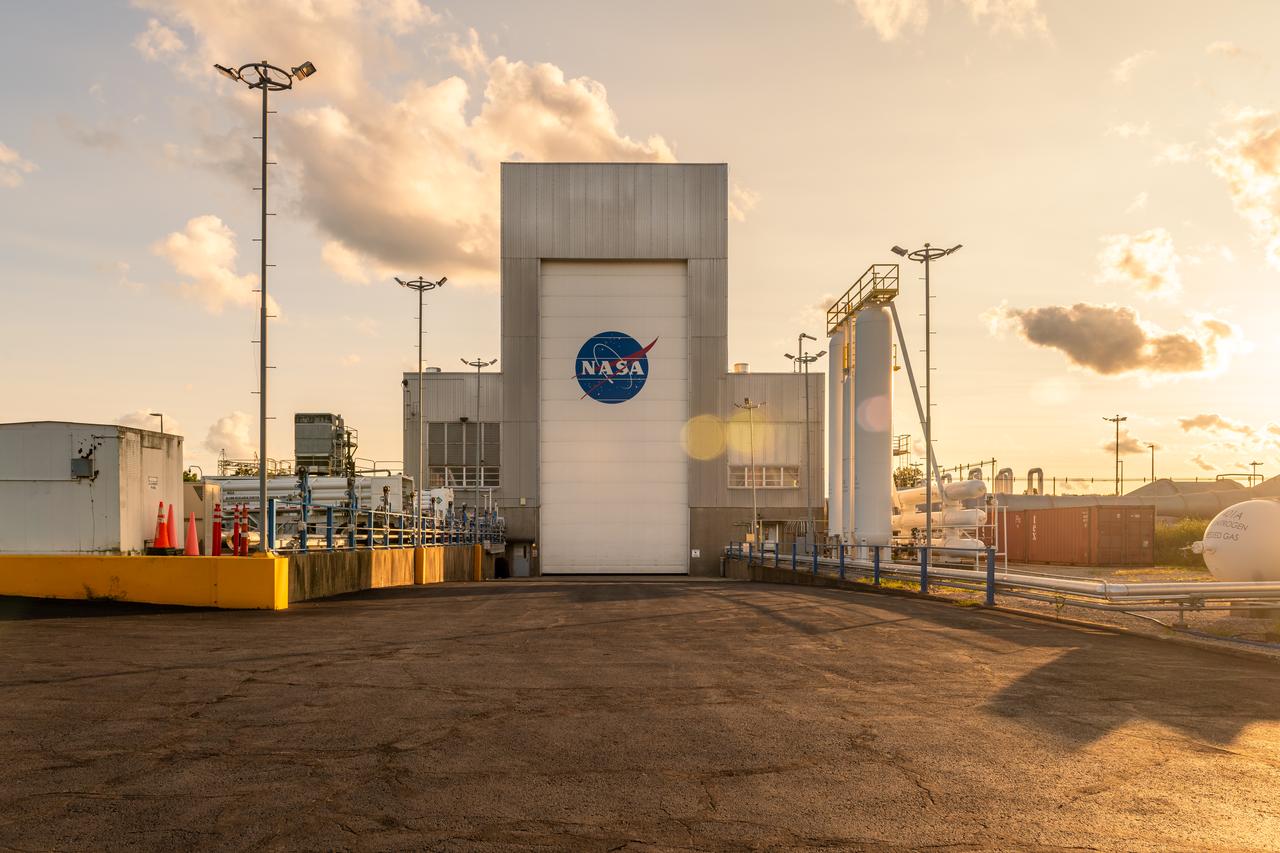

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
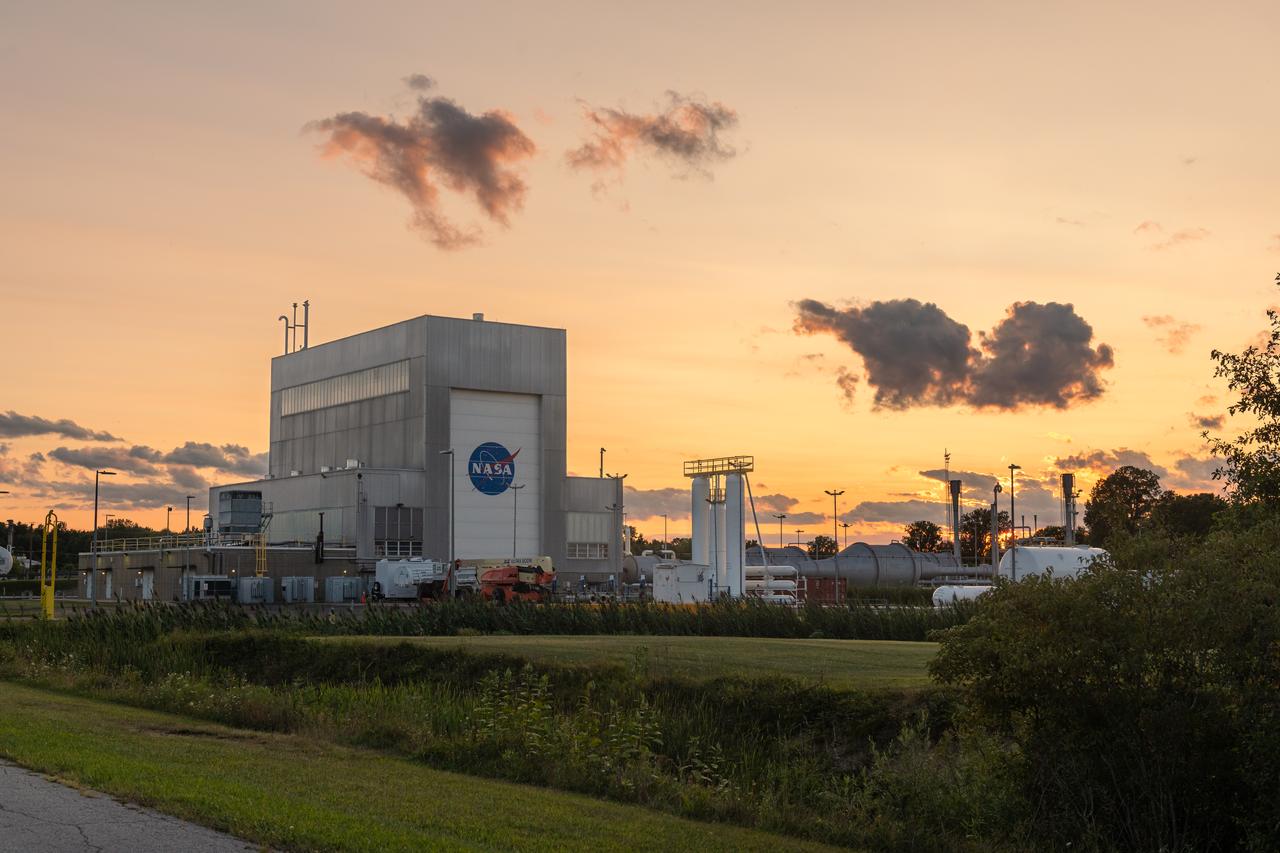

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
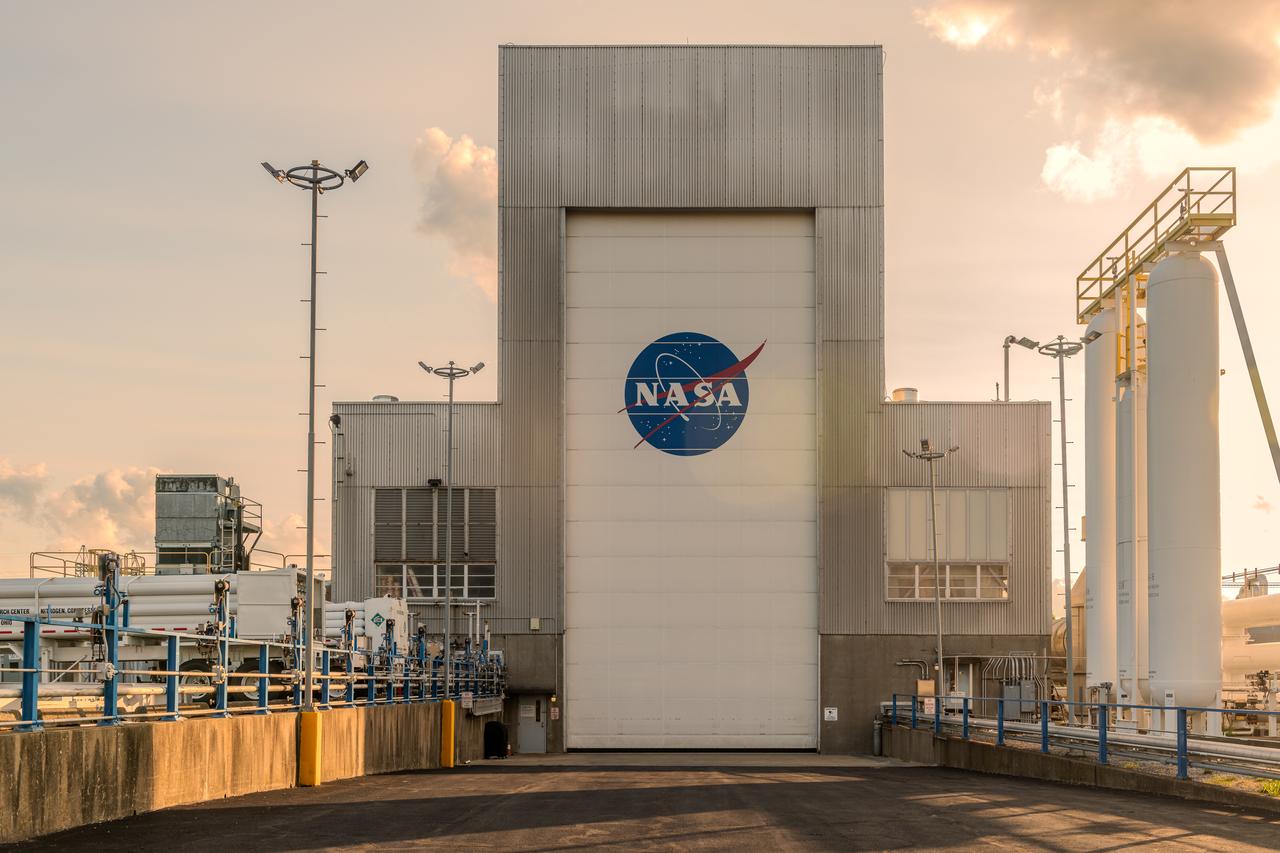

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
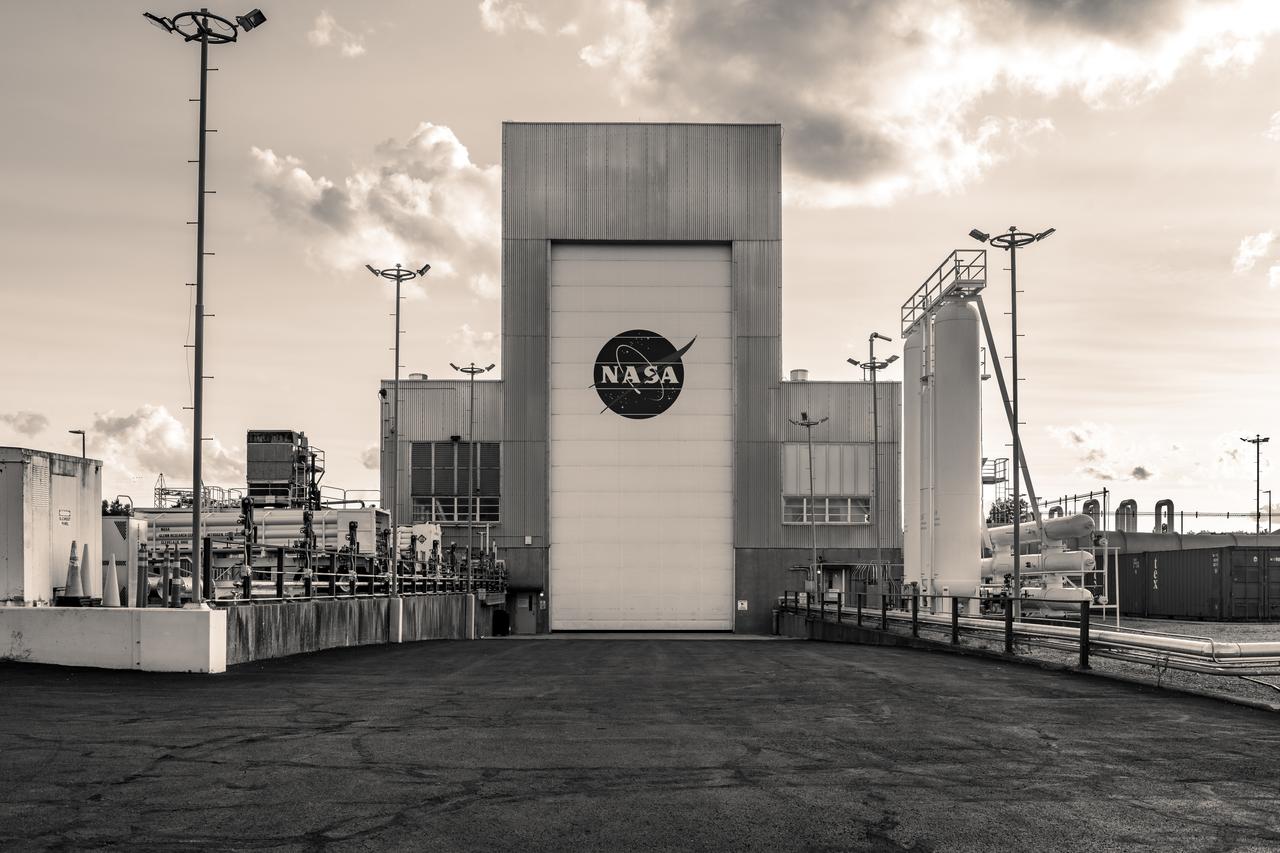

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
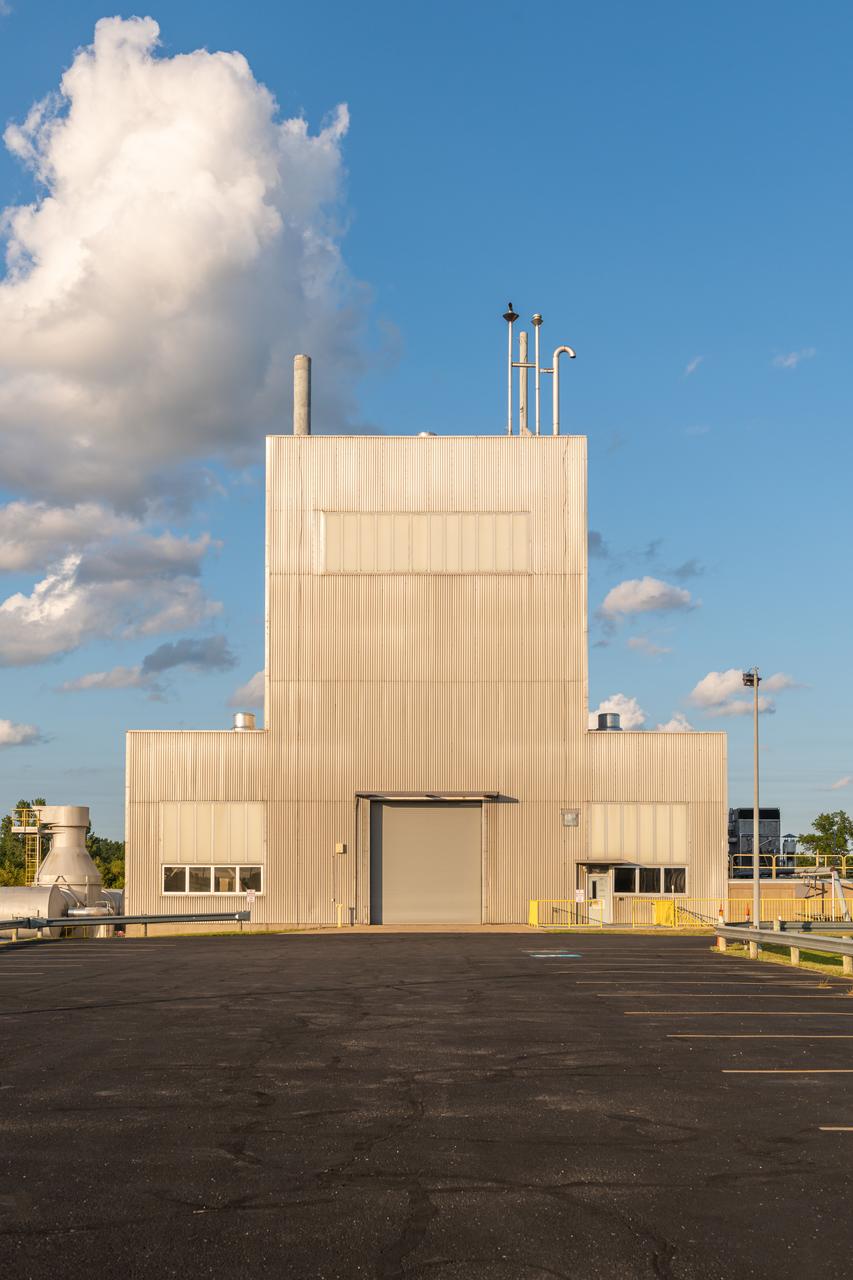

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
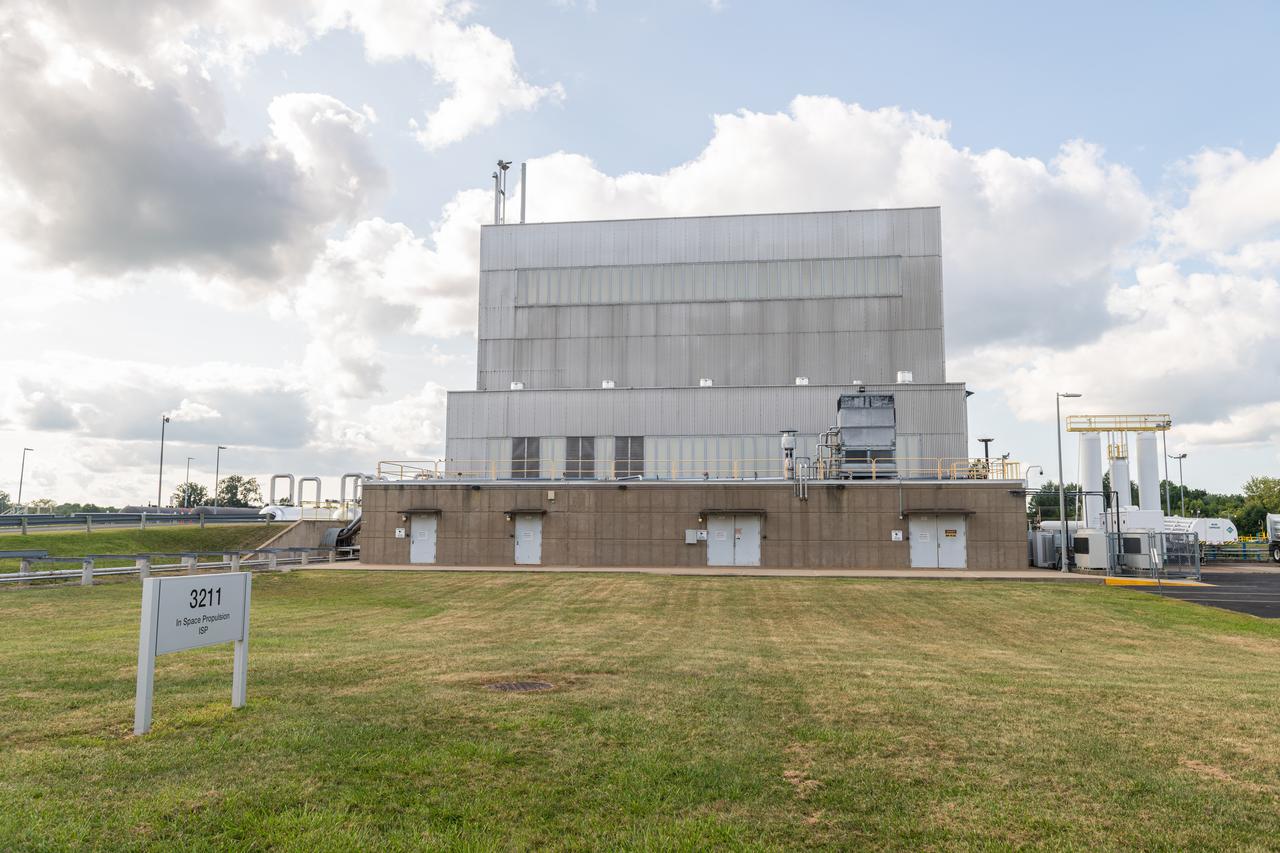

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
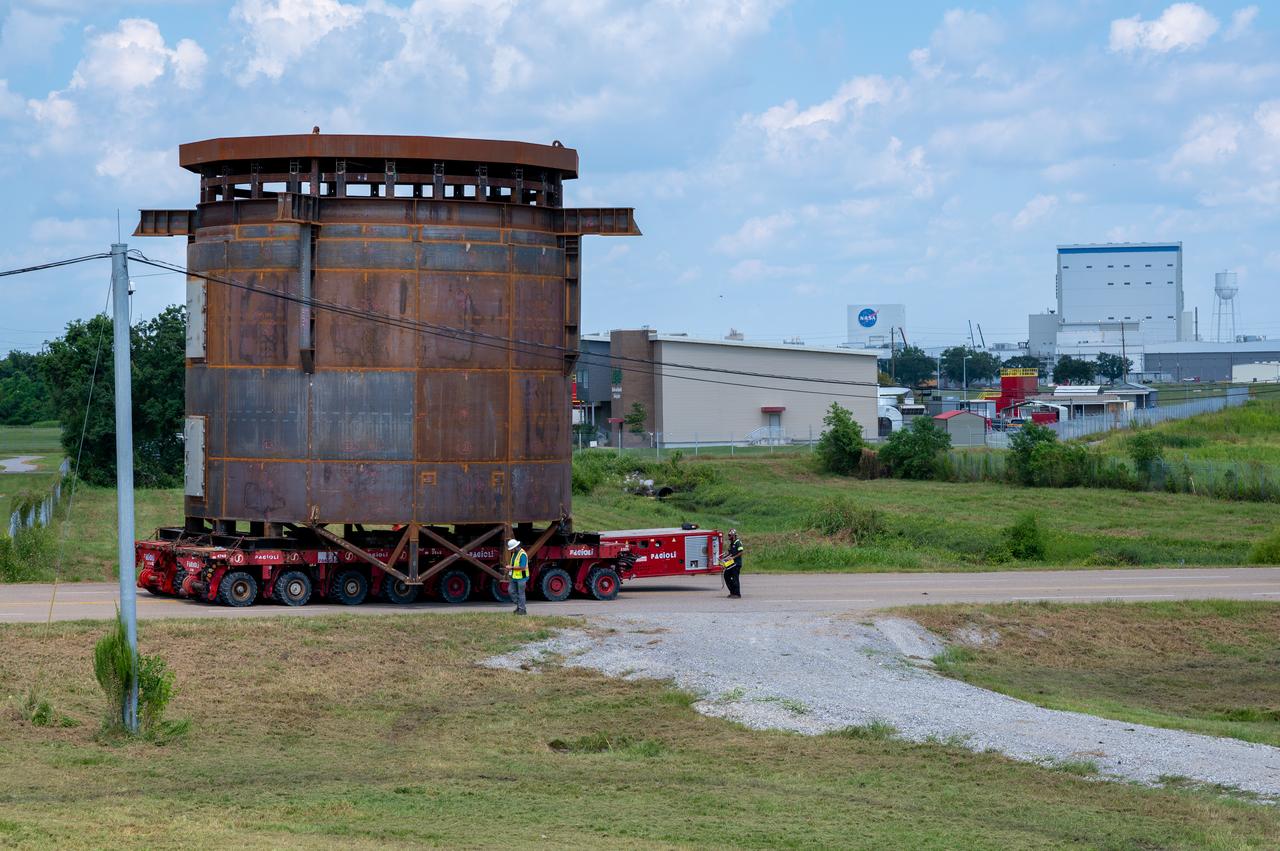

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.

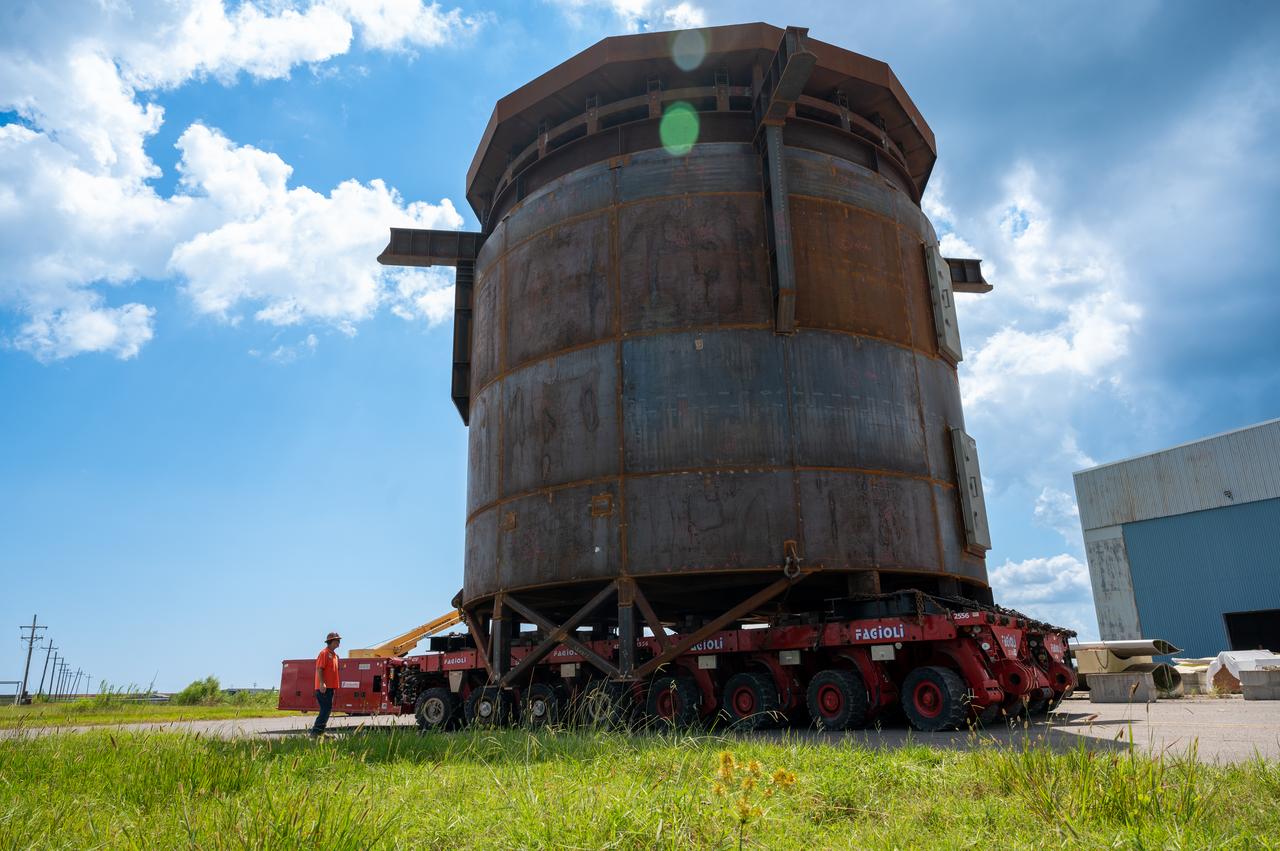
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Crews will lift the simulator into the B2 Test Stand at Stennis, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Crews will lift the simulator into the B2 Test Stand at Stennis, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.

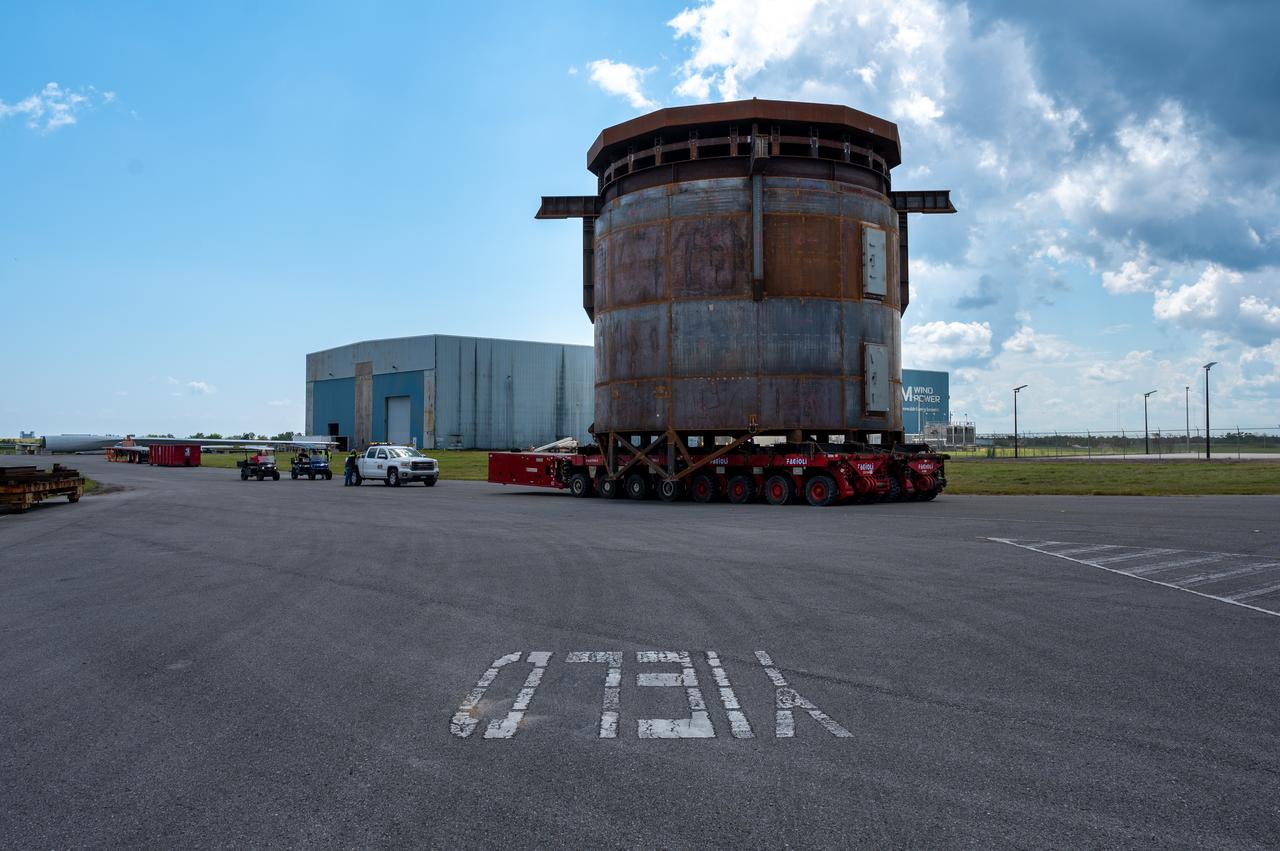
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
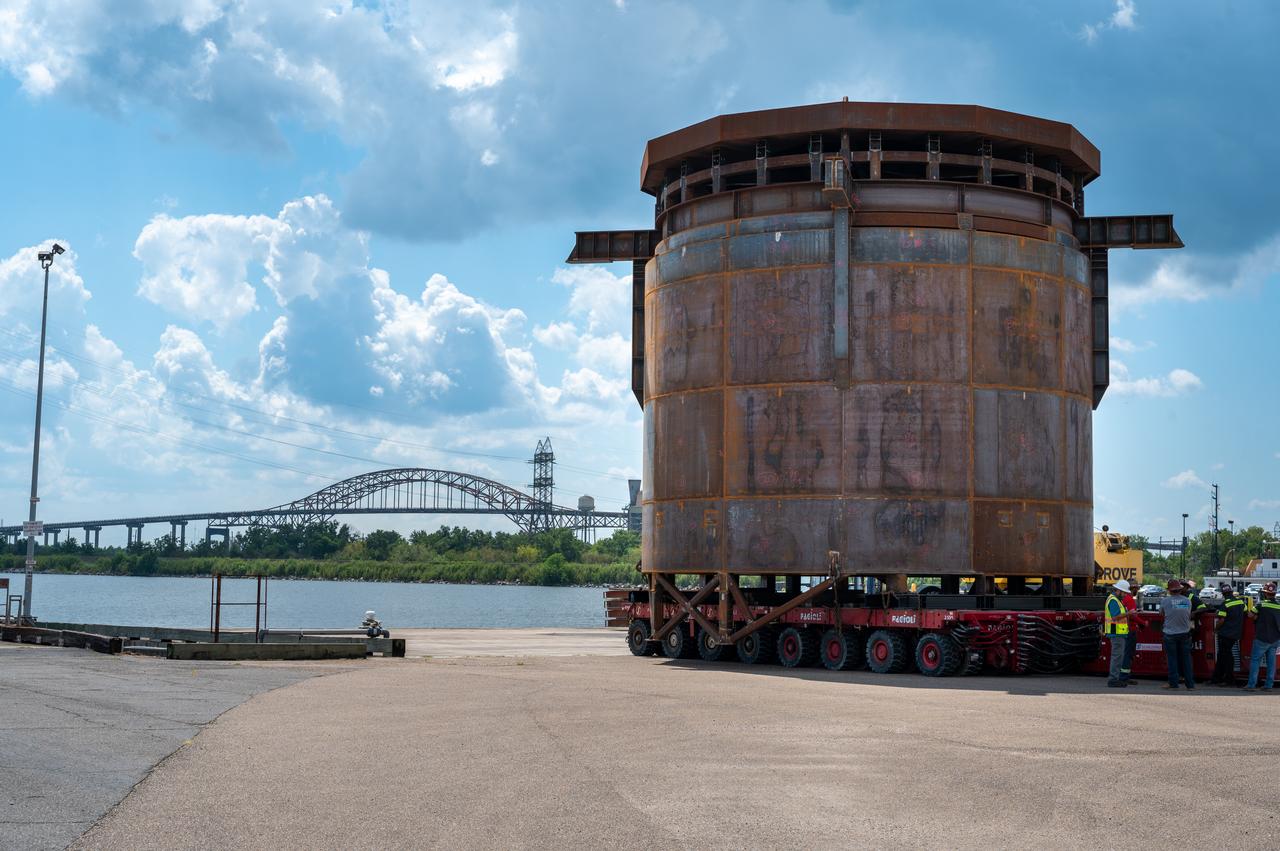

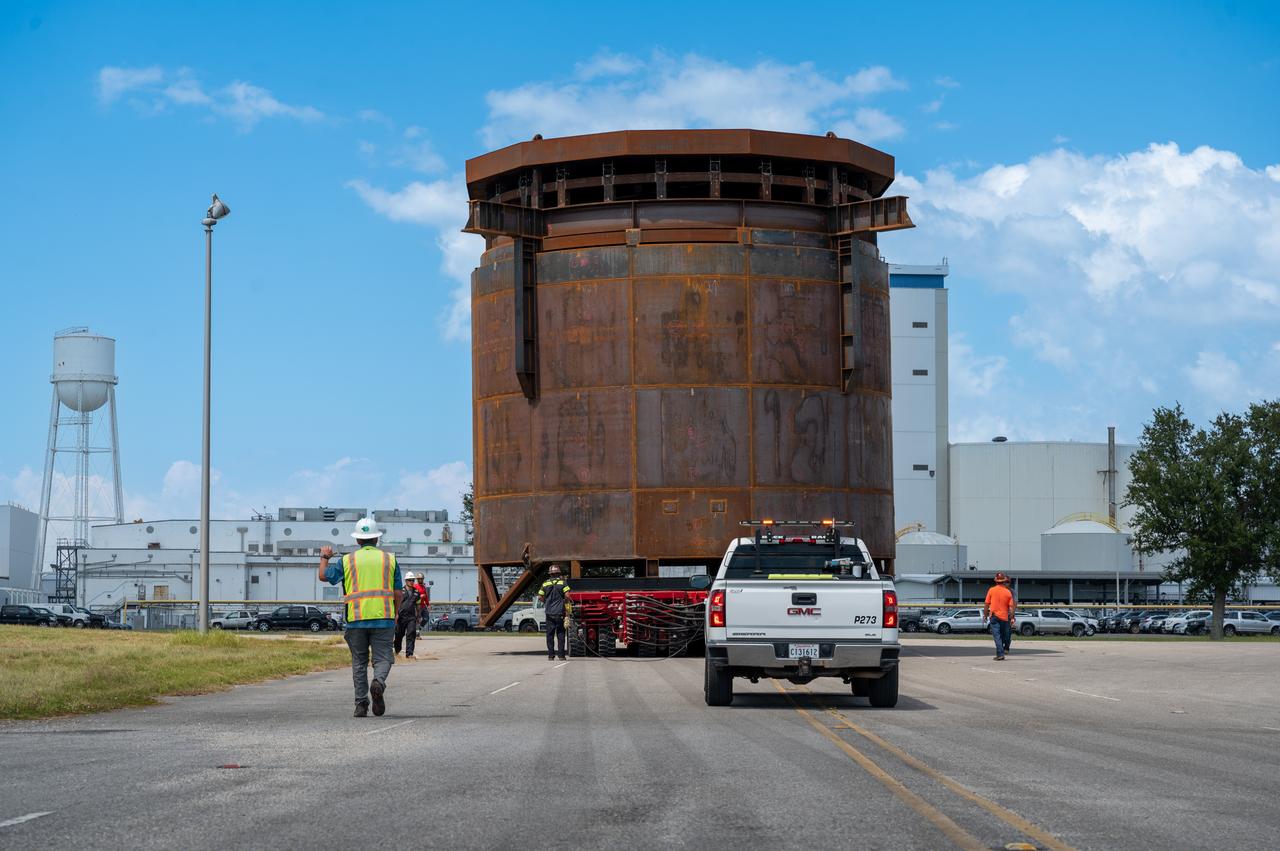
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Crews will lift the simulator into the B2 Test Stand at Stennis, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
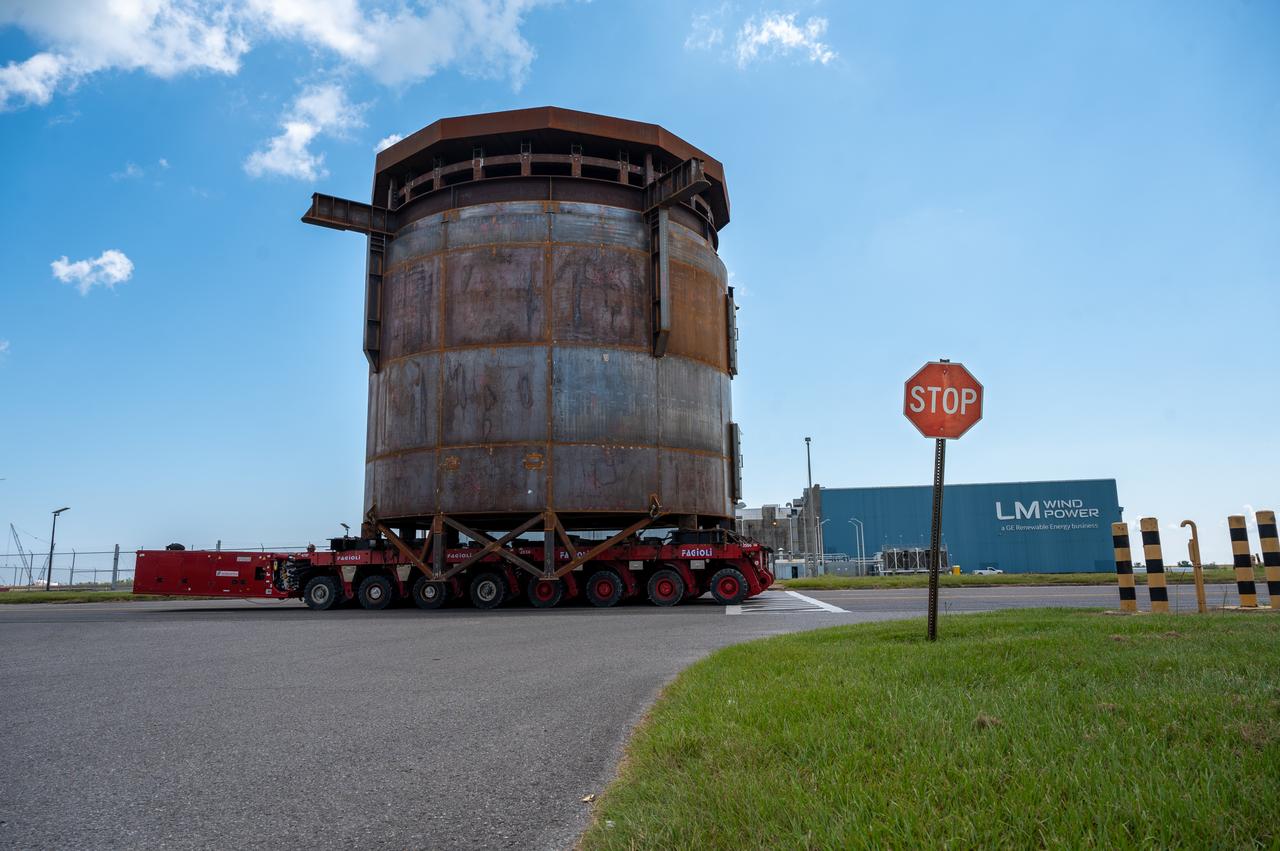

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
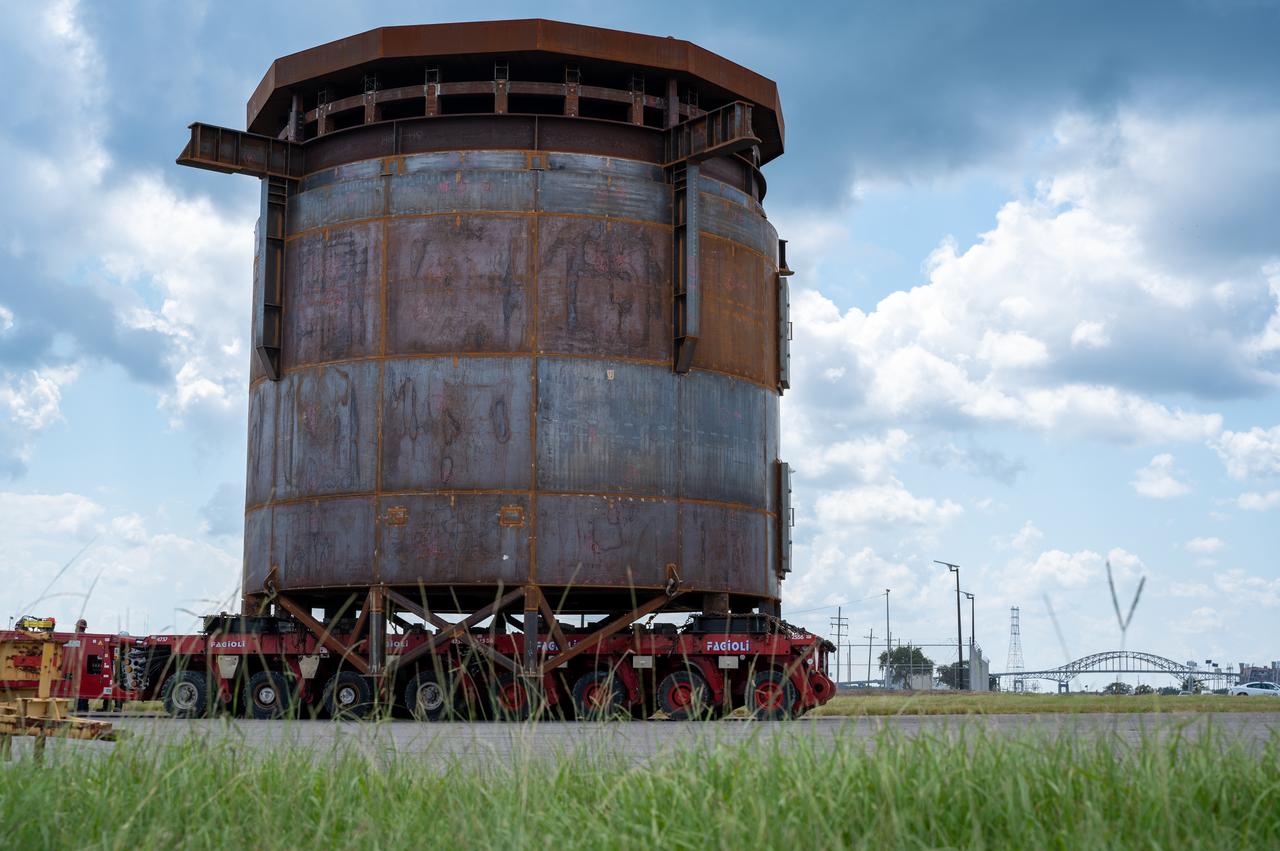

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
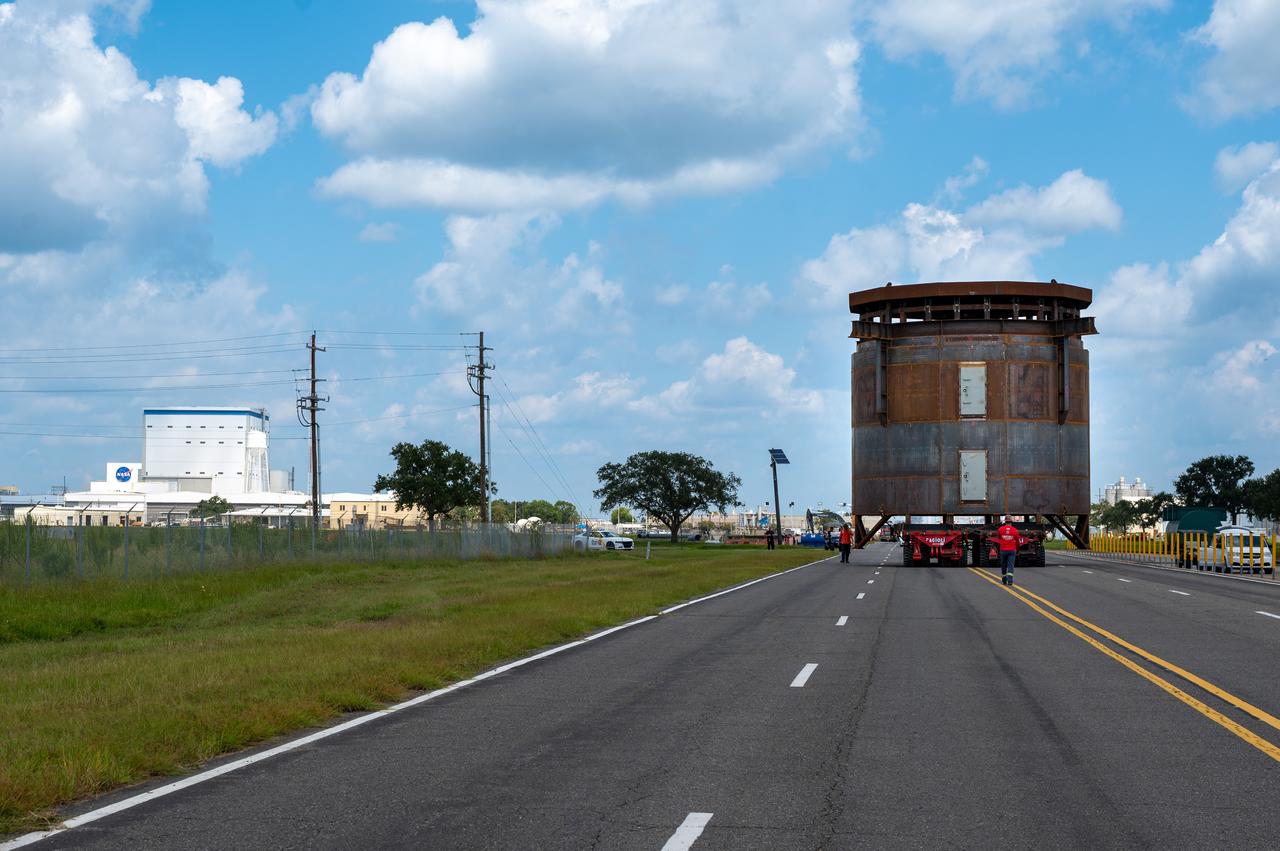

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Crews will lift the simulator into the B2 Test Stand at Stennis, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
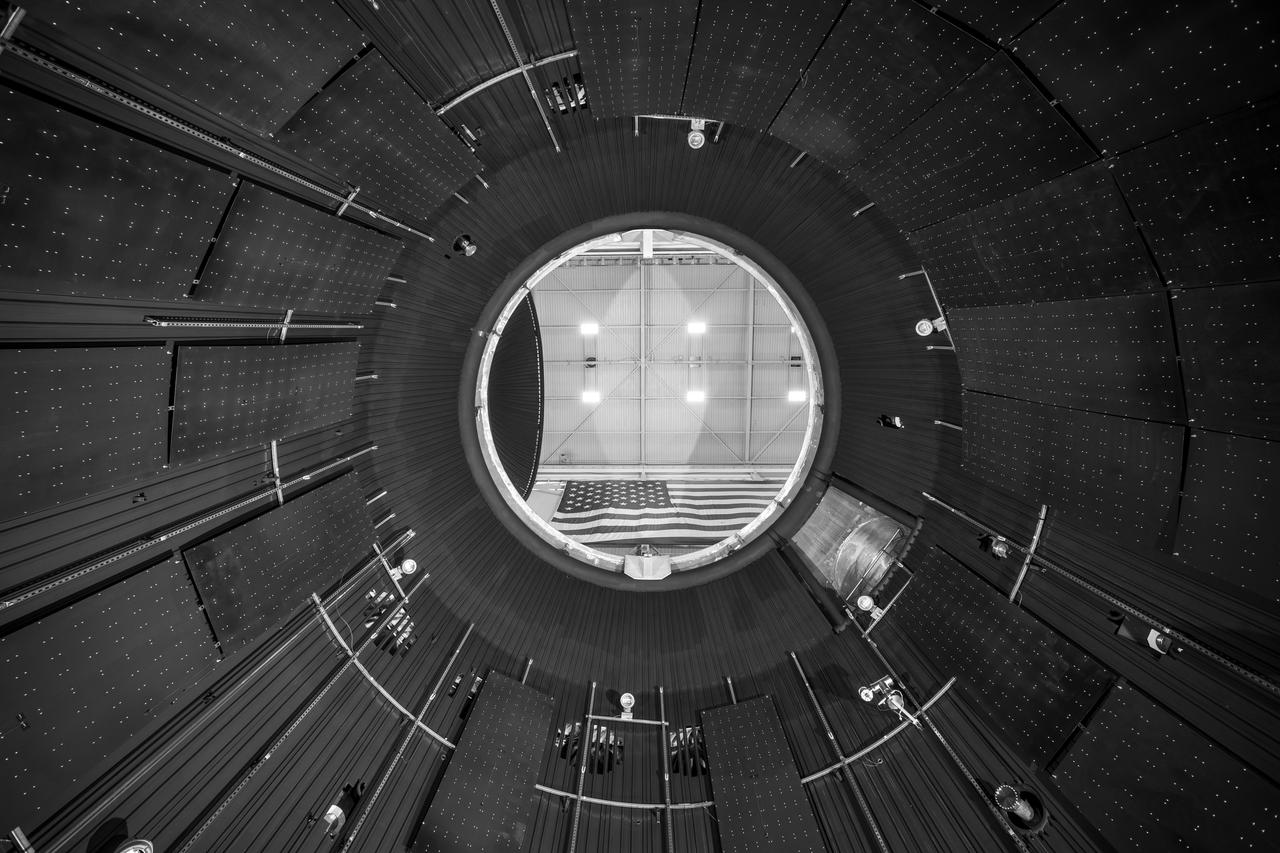

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. This is a view from inside the chamber looking up toward the American flag. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
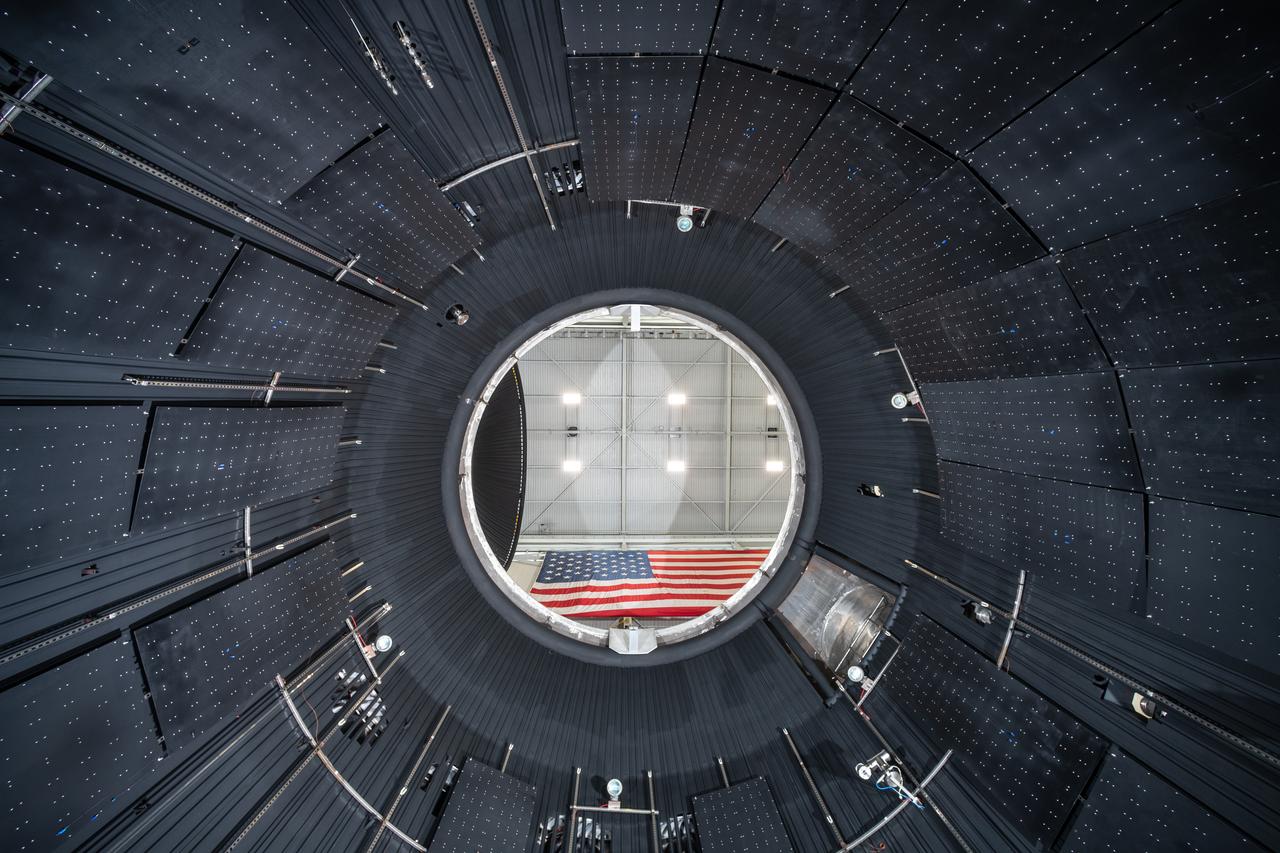

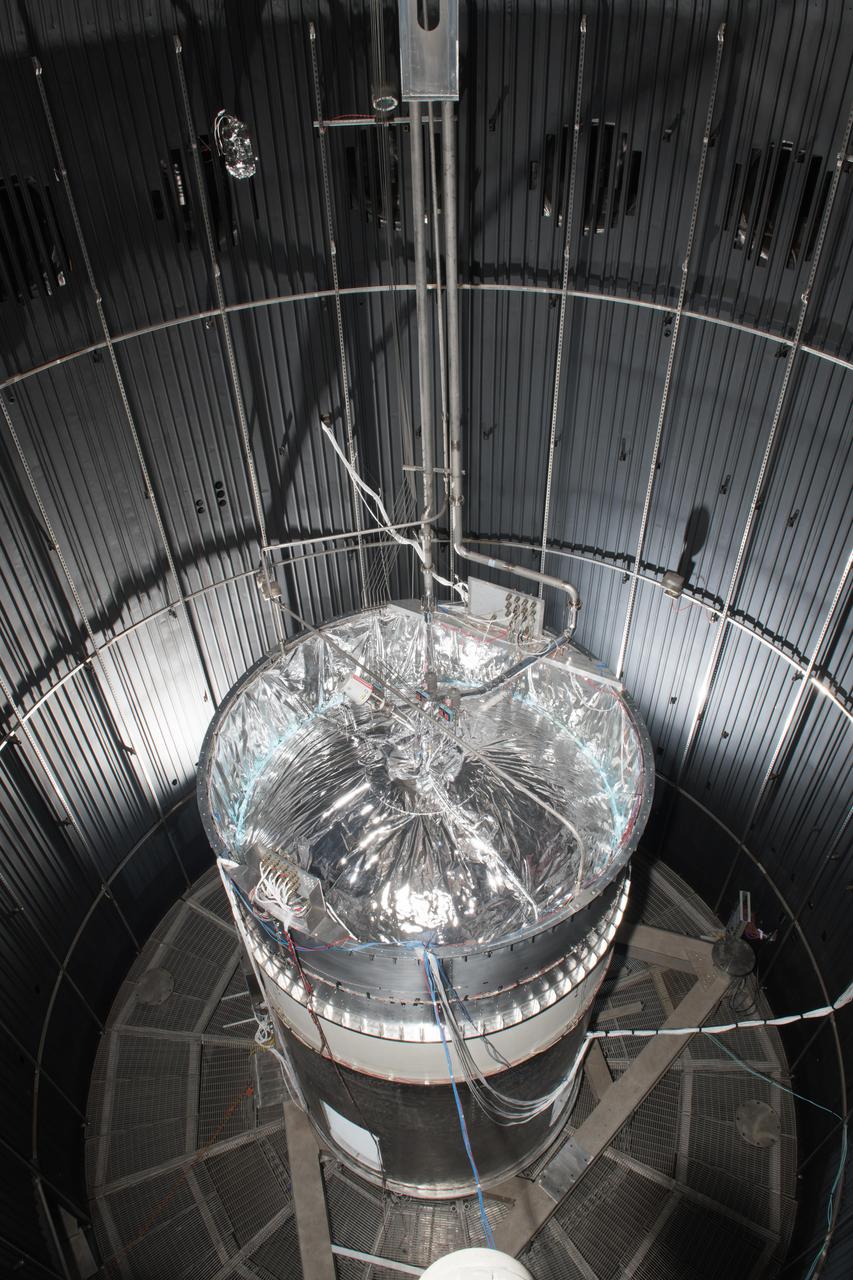
The vacuum chamber of the In-Space Propulsion (ISP) facility at the Neil Armstrong Test Facility spans 38ft in diameter and is 62ft tall. ISP is the world’s only facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. ISP also has a vacuum range of up to 100 statute miles in altitude. This is a view from inside the chamber. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
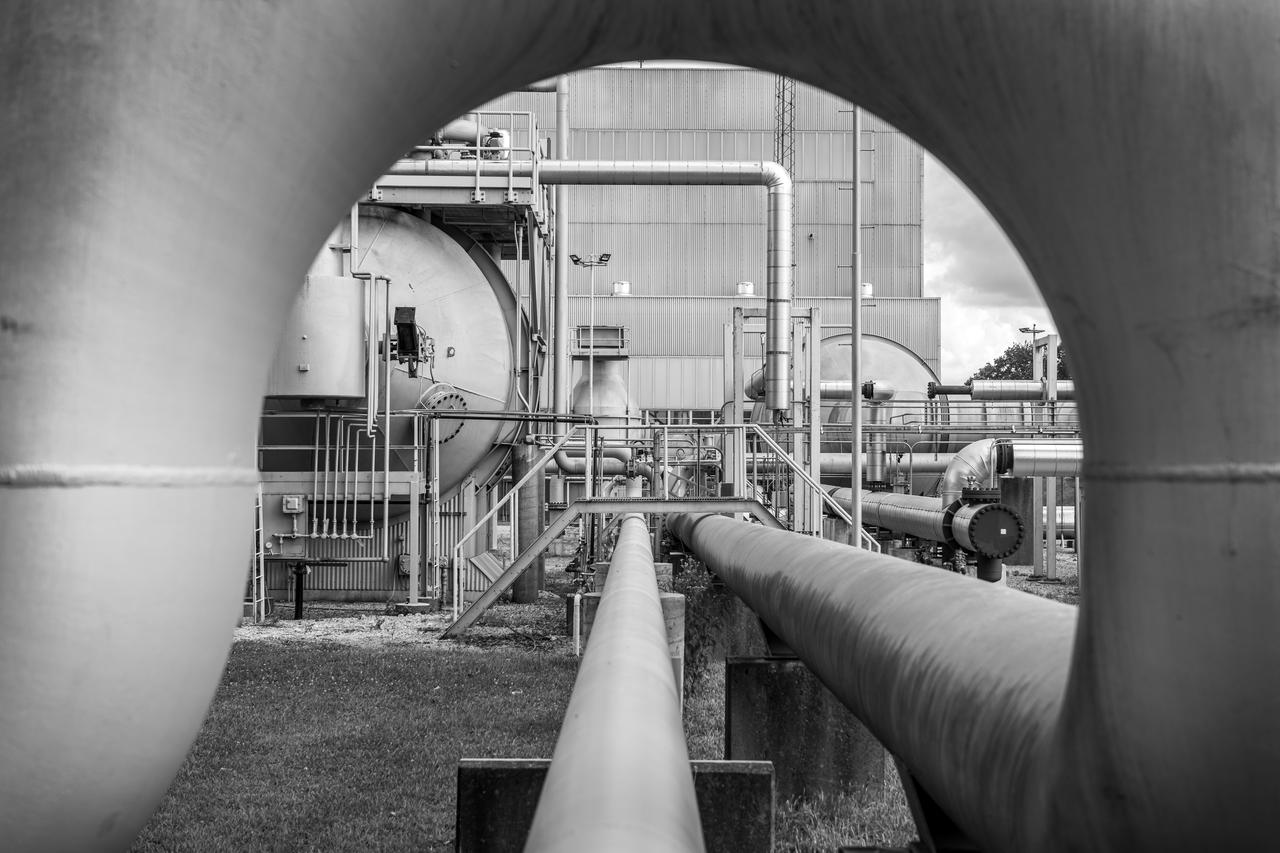

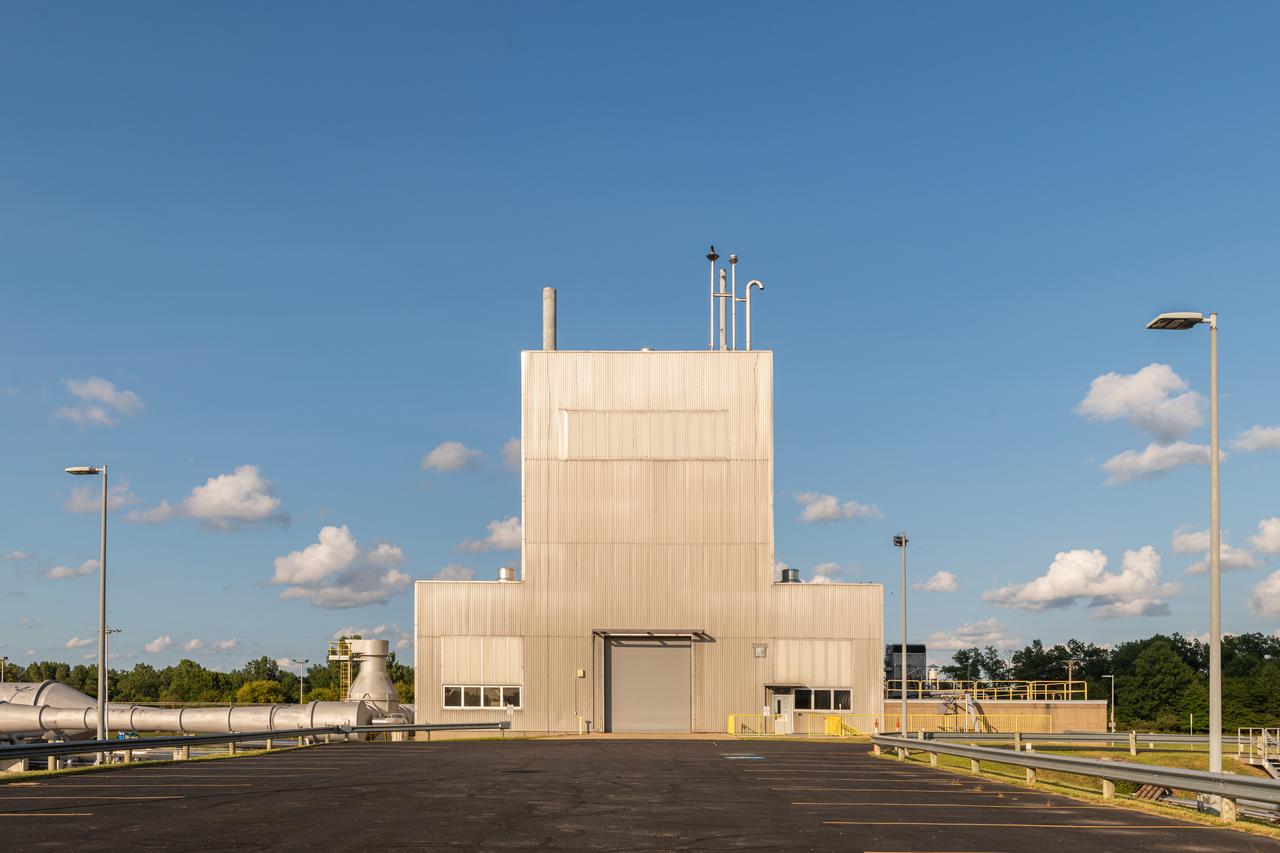
The In-Space Propulsion Facility (ISP) is shown at NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio. ISP is the world’s only facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
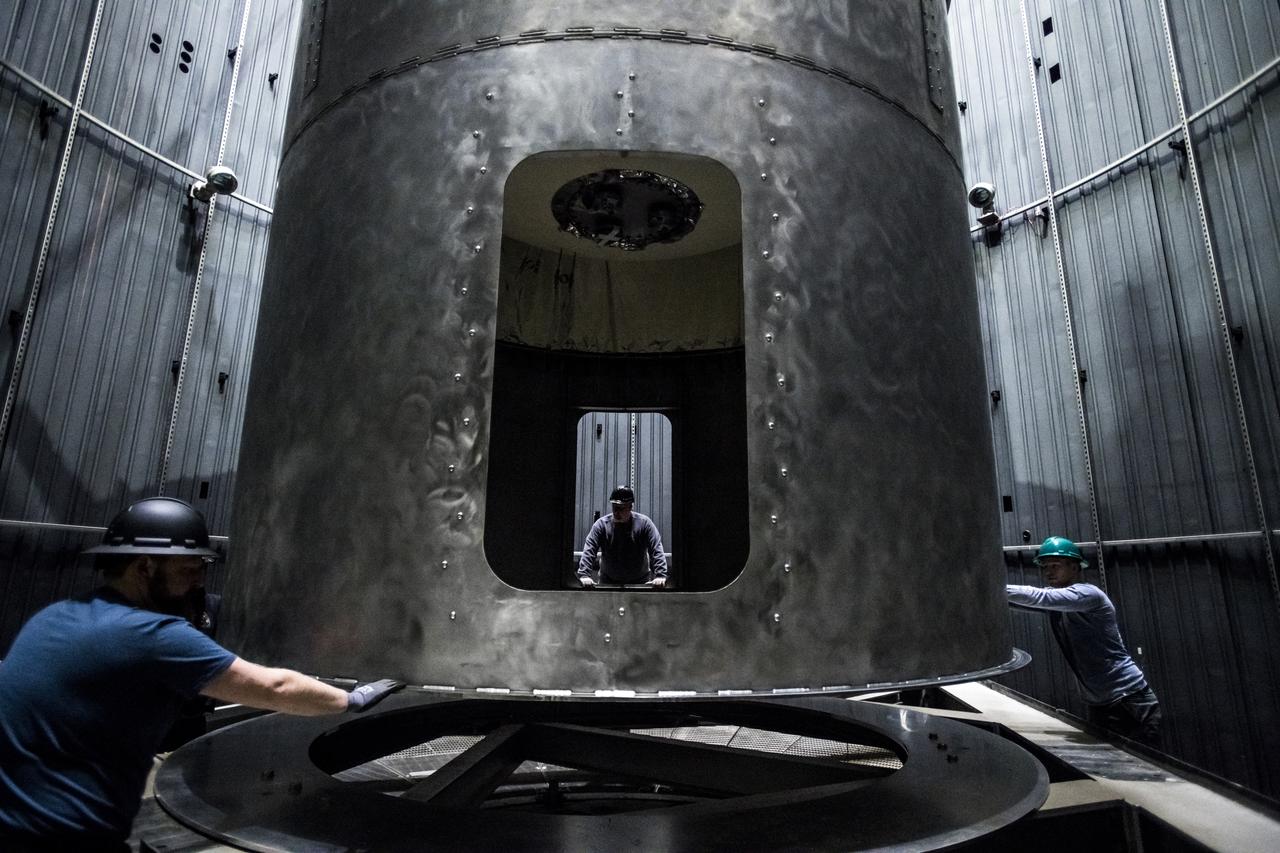

Structural Heat Intercept, Insulation and Vibration Evaluation Rig, SHIIVER is installed in the In-Space Propulsion Chamber at NASA Glenn, Plum Brook Station