
EXPLODING WIRE GUN, BLDG 4205, WITH BACKING BLOCK, BARREL, COPPER RIBBON WITH WIRE

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows one of millions of small (10s of meters in diameter) craters and their ejecta material that dot the Elysium Planitia region of Mars. The small craters were likely formed when high-speed blocks of rock were thrown out by a much larger impact (about 10-kilometers in diameter) and fell back to the ground. Some of these blocks may actually escape Mars, which is how we get samples in the form of meteorites that fall to Earth. Other ejected blocks have insufficient velocity, or the wrong trajectory, to escape the Red Planet. As such, when one of these high-speed blocks impacts the surface, it makes what is called a "secondary" crater. These secondaries can form dense "chains" or "rays," which are radial to the crater that formed them. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21769
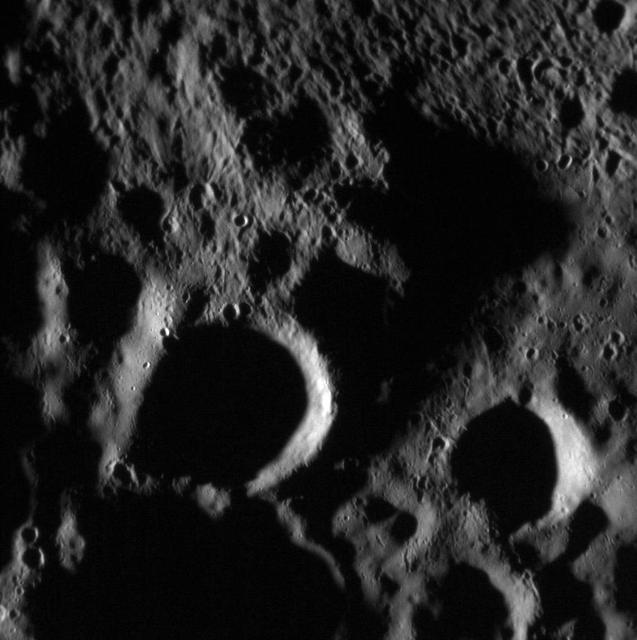

NASA MESSENGER is again sending images back to Earth after the spacecraft emerged from superior solar conjunction, when communication is largely blocked by the Sun. These will be some of our last views of Mercury from MESSENGER. Featured here is the ejecta blanket of a fresh impact crater located just outside the scene. Ejecta scoured the surface leaving behind beautiful patterns of secondary craters. Date acquired: April 16, 2015 Image Mission Elapsed Time (MET): 71544702 Image ID: 8343072 Instrument: Narrow Angle Camera (NAC) of the Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS) Center Latitude: 55.67° Center Longitude: 97.37° E Resolution: 19.9 meters/pixel Scale: This scene is approximately 20 km (12 miles) across http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19424
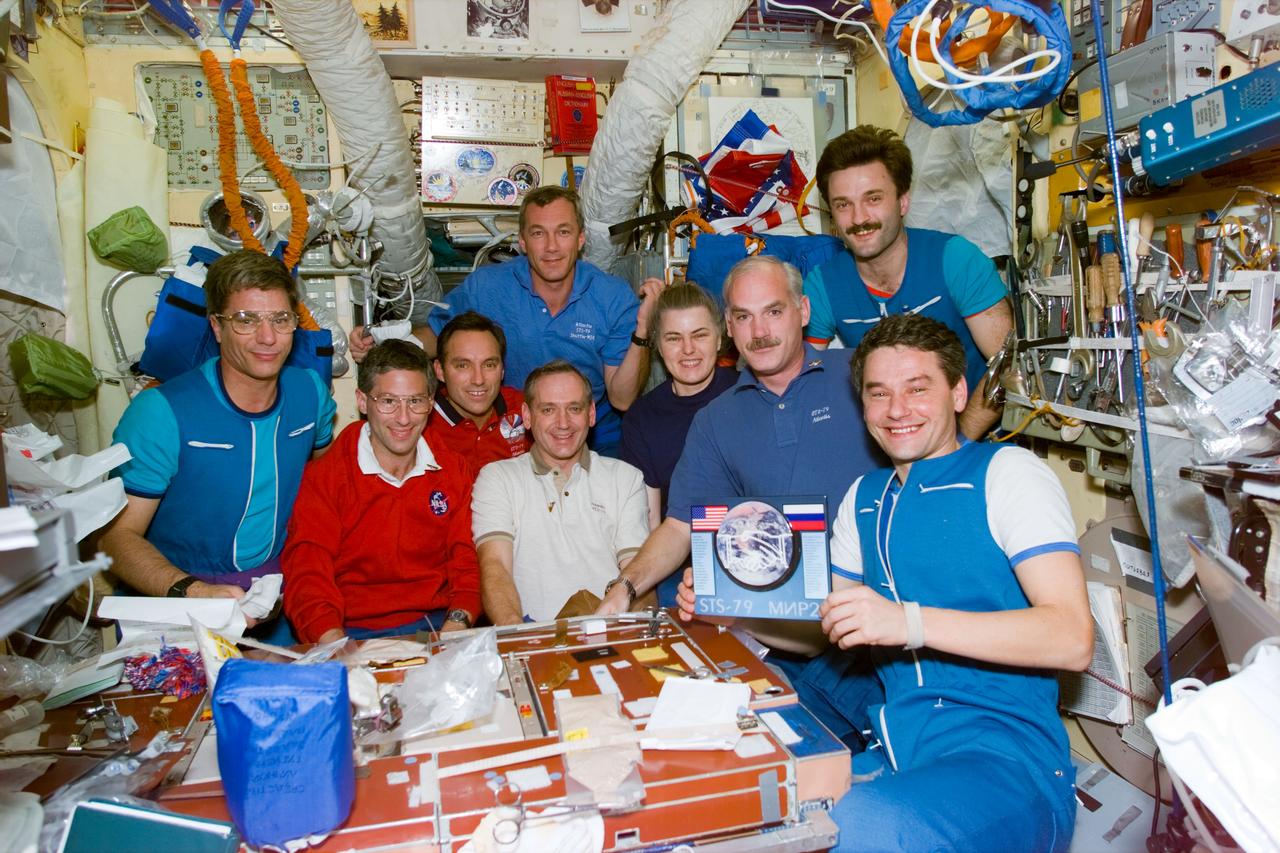

STS79-E-5180 (20 September 1996) --- The entire crews of STS-79 and Mir-22 are shown during a gift exchange ceremony aboard Russia's Mir Space Station's Base Block, during Flight Day 5. Front row, from the left, John E. Blaha, Jerome (Jay) Apt, Carl E. Walz, Thomas D. Akers, Shannon W. Lucid, William F. Readdy and Valeri G. Korzun. Back row: Terrence W. Wilcutt and Aleksandr Y. Kaleri.
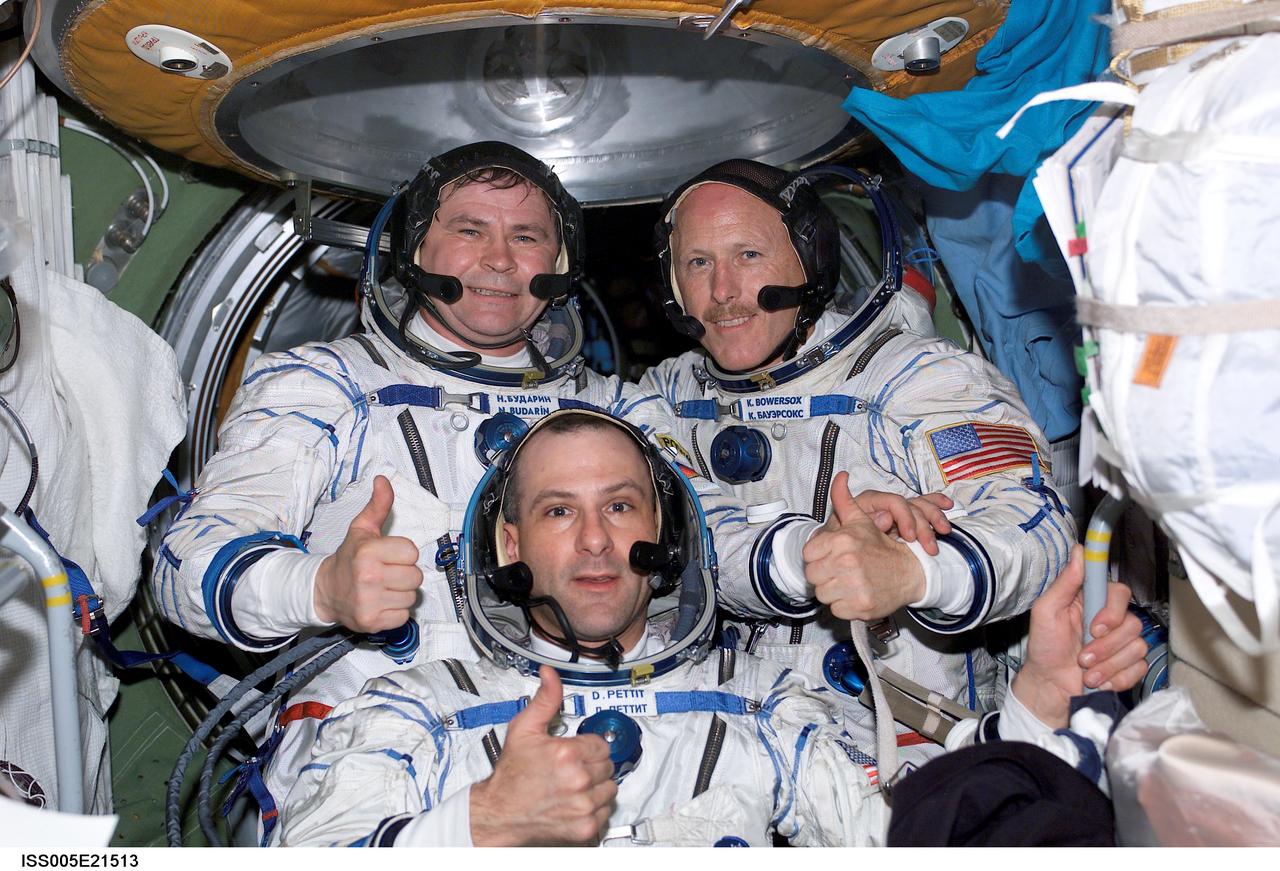

ISS005-E-21513 (26 November 2002) --- The Expedition Six crewmembers, wearing Russian Sokol suits, pose for a crew photo in the functional cargo block (FGB), or Zarya, on the International Space Station (ISS). Pictured are astronaut Donald R. Pettit (front), NASA ISS science officer; cosmonaut Nikolai M. Budarin (left back), flight engineer; and astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, mission commander. Budarin represents Rosaviakosmos.
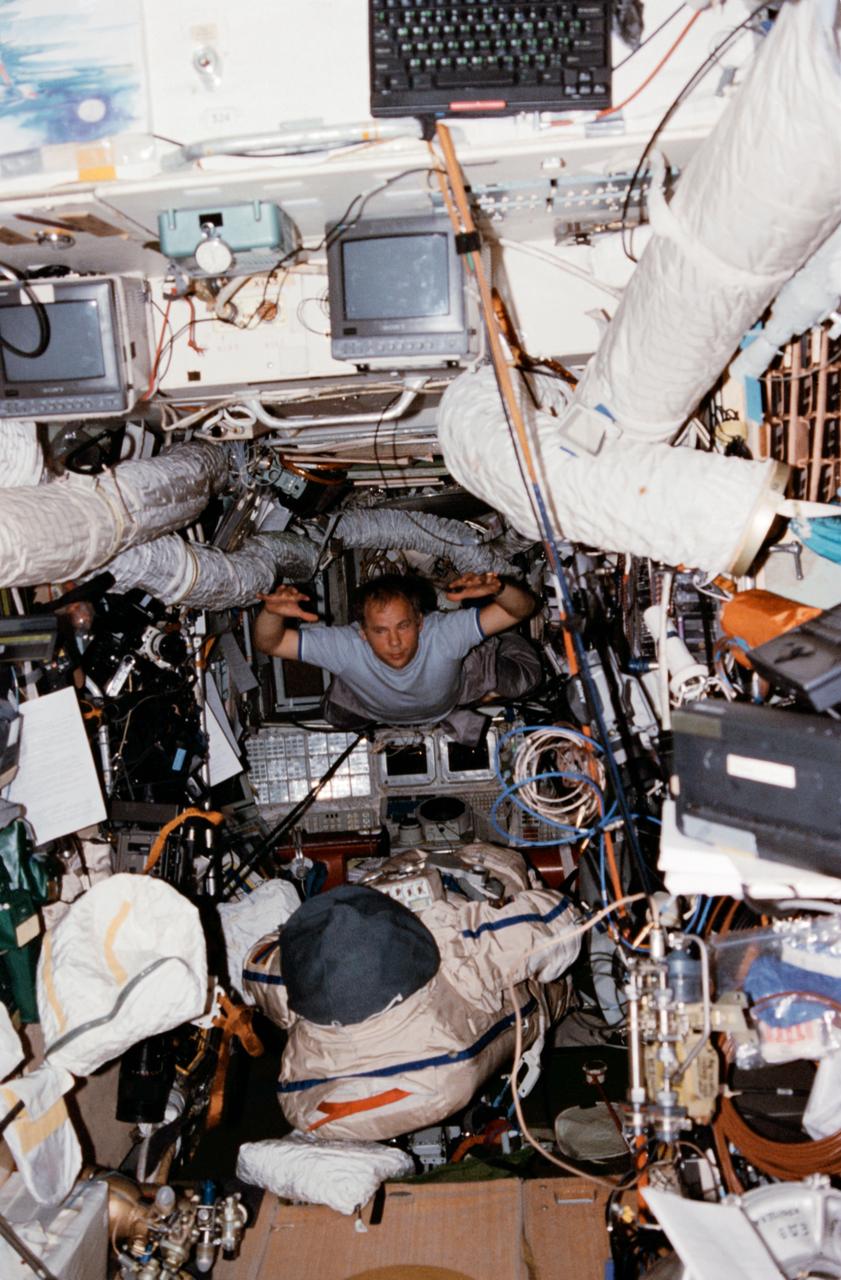

Various views of activities surrounding the Mir 24 crew's preparation for an intravehicular activity (IVA) in the Mir space station. Views include: Mir 24 crew in the Orlan suits in the Soyuz spacecraft (012-3,016). Commander Anatoly Solovyev climbs out of his suit in the Soyuz (014-5). Solovyev floats into the Base Block module (017). Underexposed views of Solovyev (left) and flight engineer Pavel Vinogradov in the Soyuz (018-20). Interior views of the airlock with IVA hardware (oxygen for suits) in view (021-2). Mir 24 crewmember climbing into his suit with his back to the camera (023). View 024 is blank. View 025 is of a Mir viewing portal. Portrait of Vinogradov in his suit, wearing his helmet (026). Guest researcher Michael Foale in the Soyuz, wearing his pressure suit (027-8). Interior views of the Soyuz (029-32). Solovyev and Vinogradov in the Base Block (033).
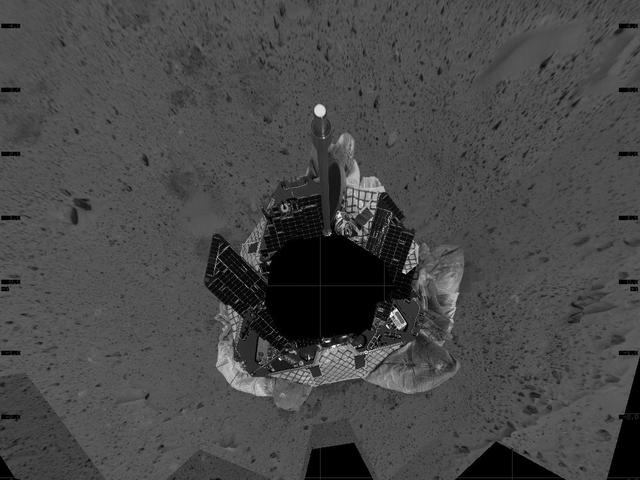

This mosaic image taken by the navigation camera on the Mars Exploration Rover Spirit represents an overhead view of the rover as it prepares to roll off the lander and onto the martian surface. The yellow arrow illustrates the direction the rover may take to roll safely off the lander. The rover was originally positioned to roll straight forward off the lander (south side of image). However, an airbag is blocking its path. To take this northeastern route, the rover must back up and perform what is likened to a 3-point turn in a cramped parking lot. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05044
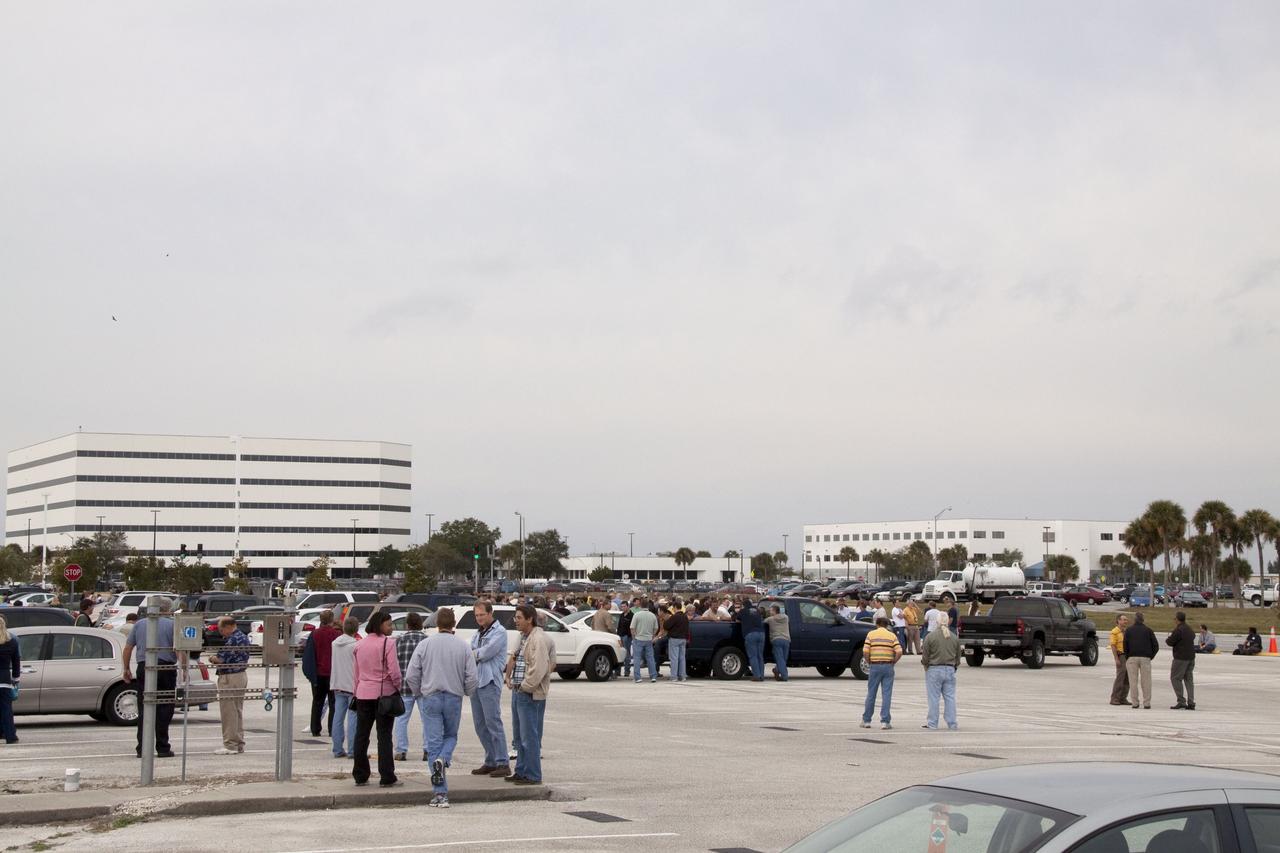

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers wait to return to their buildings at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line at around 8:40 a.m. EST in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF). As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
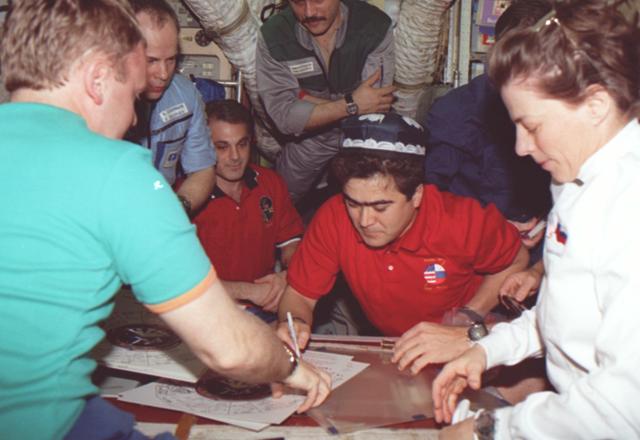

STS089-335-016 (22-31 Jan. 1998) --- Salizhan S. Sharipov (center) signs his name on a long-lived Mir roster on the Base Block of Russia's Mir Space Station, while Mir and shuttle crew members look on. From the left are Andrew S. W. Thomas (back to camera), Anatoliy Y. Solovyev, David A. Wolf, Pavel V. Vinogradov, Joe F. Edwards Jr., (partially obscured) and Bonnie J. Dunbar. Sharipov, representing the Russian Space Agency (RSA), is a mission specialist on the STS-89 crew. Photo credit: NASA
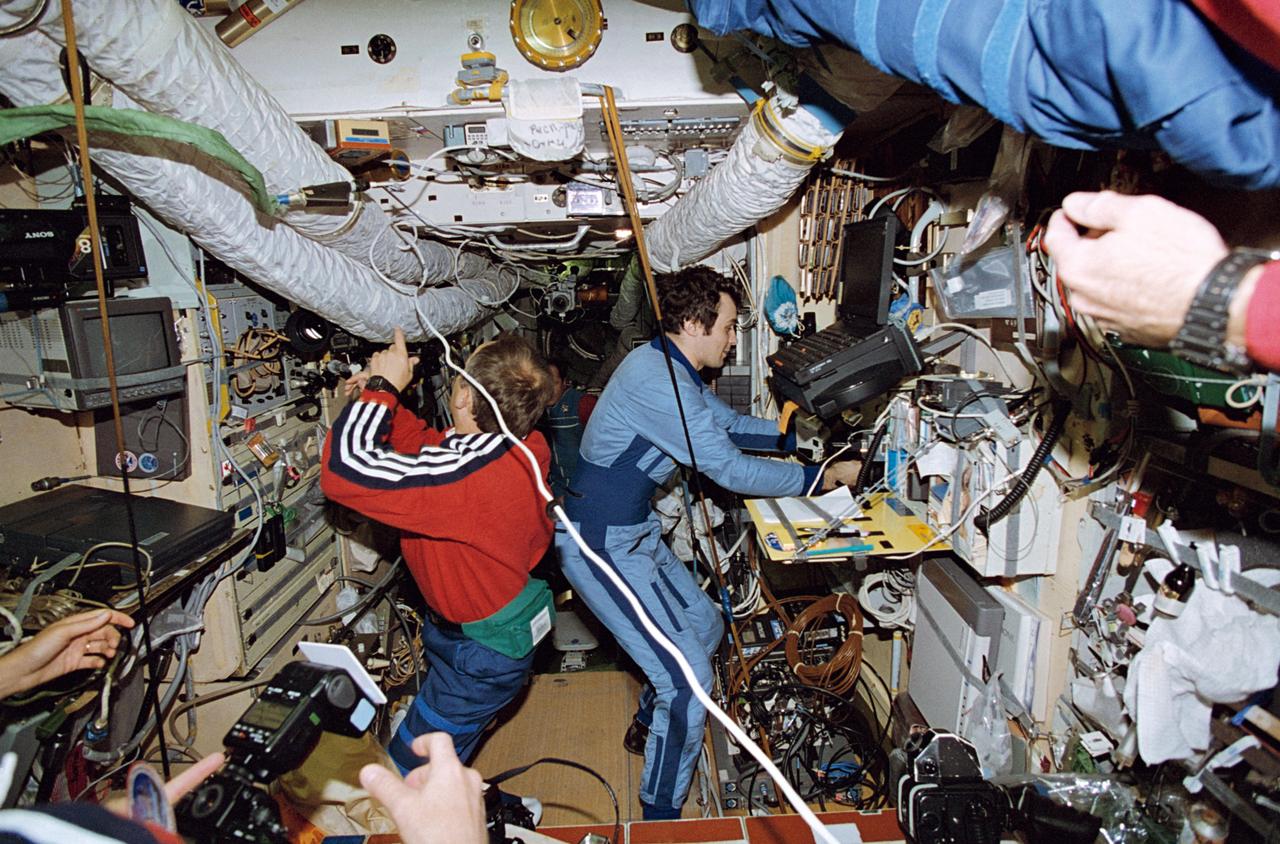

STS071-118-007 (27 June - 7 July 1995) --- Onboard the Russia?s Mir Space Station Mir Base Block, cosmonauts Anatoly Y. Solovyev (left) and Vladimir N. Dezhurov, Mir 19 and 18 commanders, respectively, exchange information about their research tasks. The two represent a change of guard aboard Mir, as Dezhurov prepares to come back to Earth with the STS-71 crew aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis. Nikolai M. Budarin and Gennadiy M. Strekalov - cosmonaut/flight engineers making the same exchange -- are out of frame.
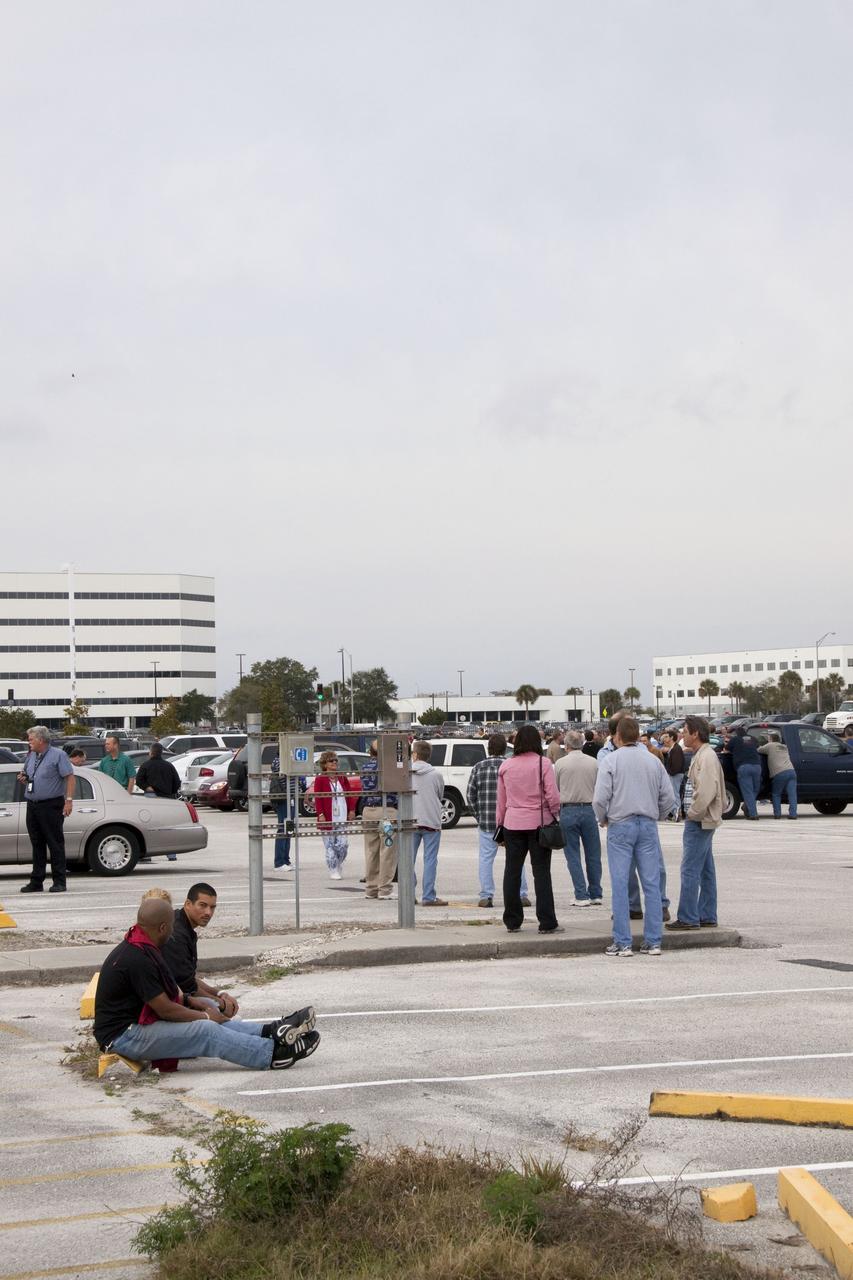

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers wait to return to their buildings at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line at around 8:40 a.m. EST in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF). As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
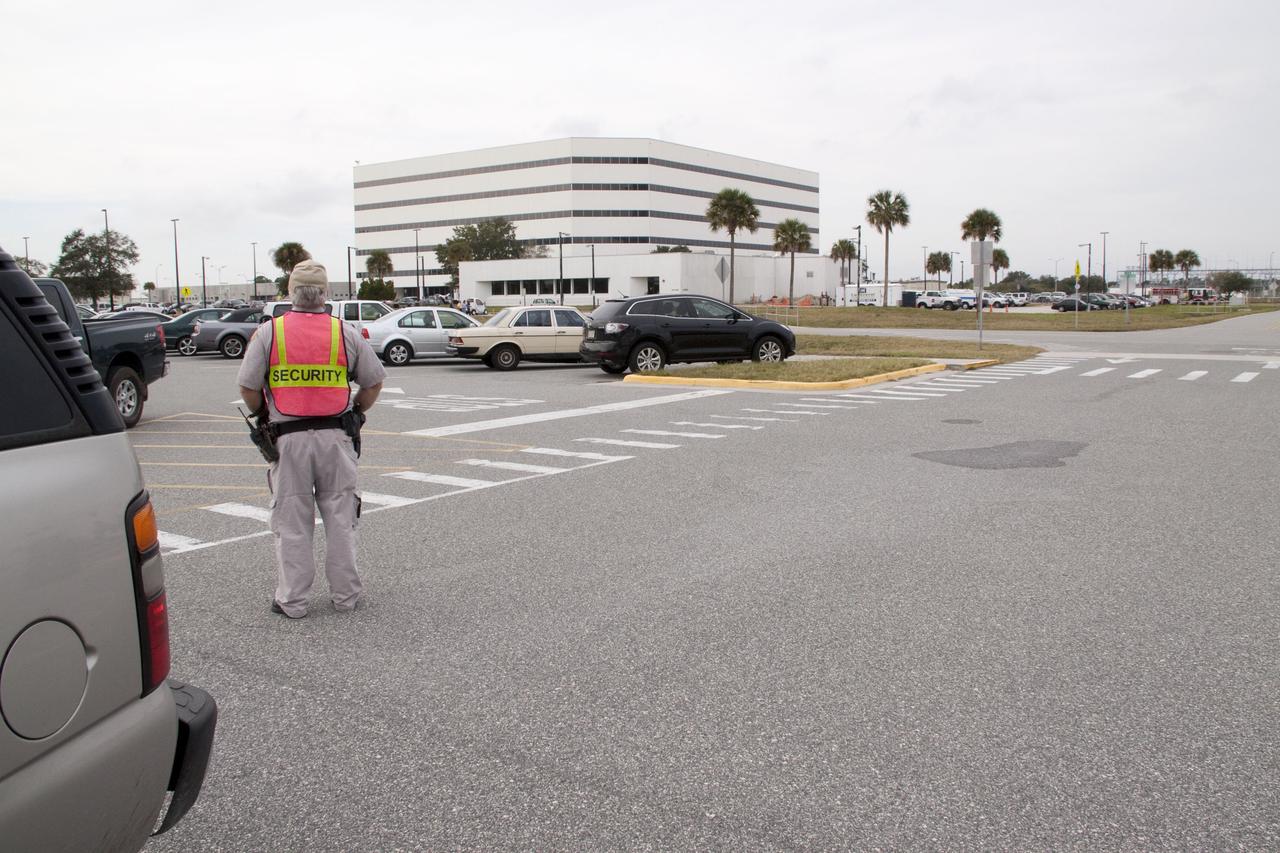

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a security officer monitors the area after a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line at around 8:40 a.m. EST in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF). As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
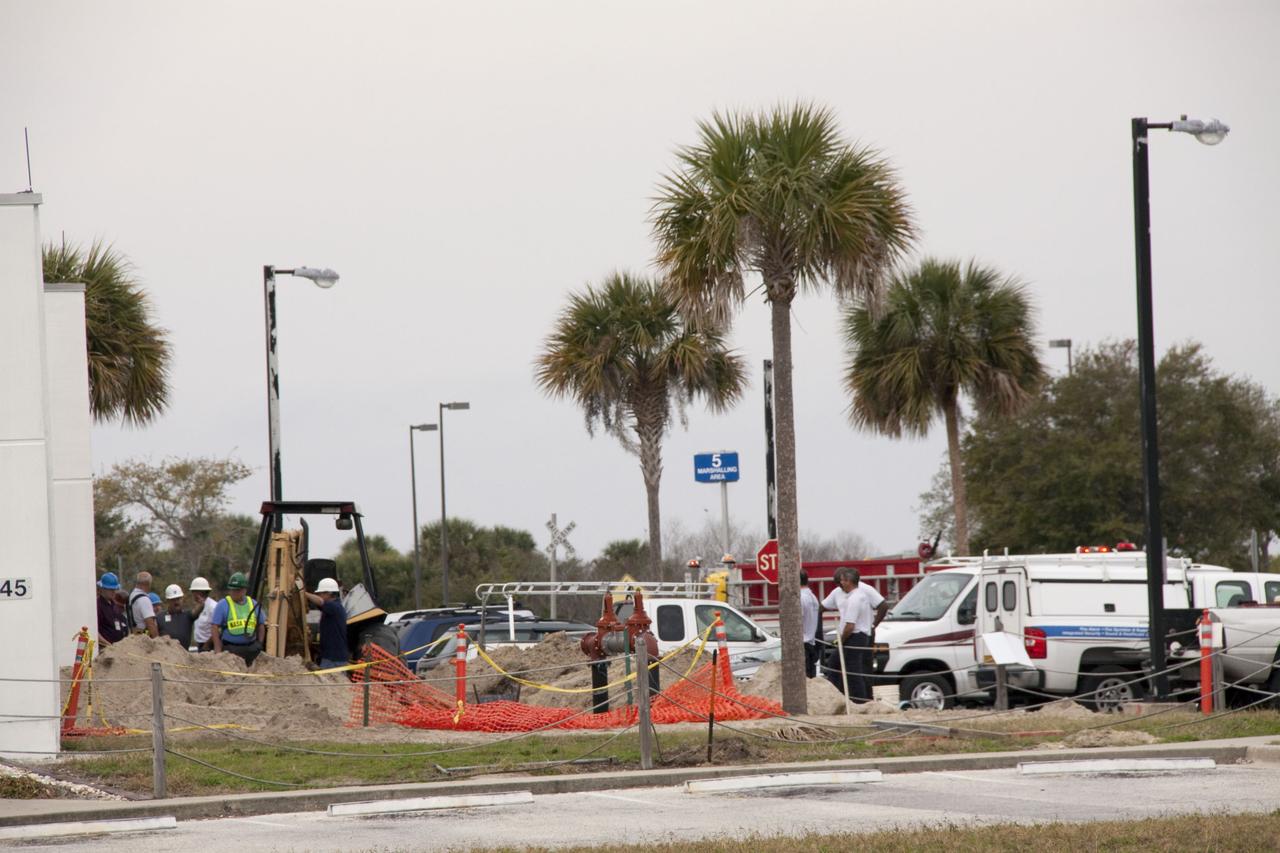

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF), at around 8:40 a.m. EST. As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and the Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. With the backhoe idle, workers assess the area where the break in the gas line occurred. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
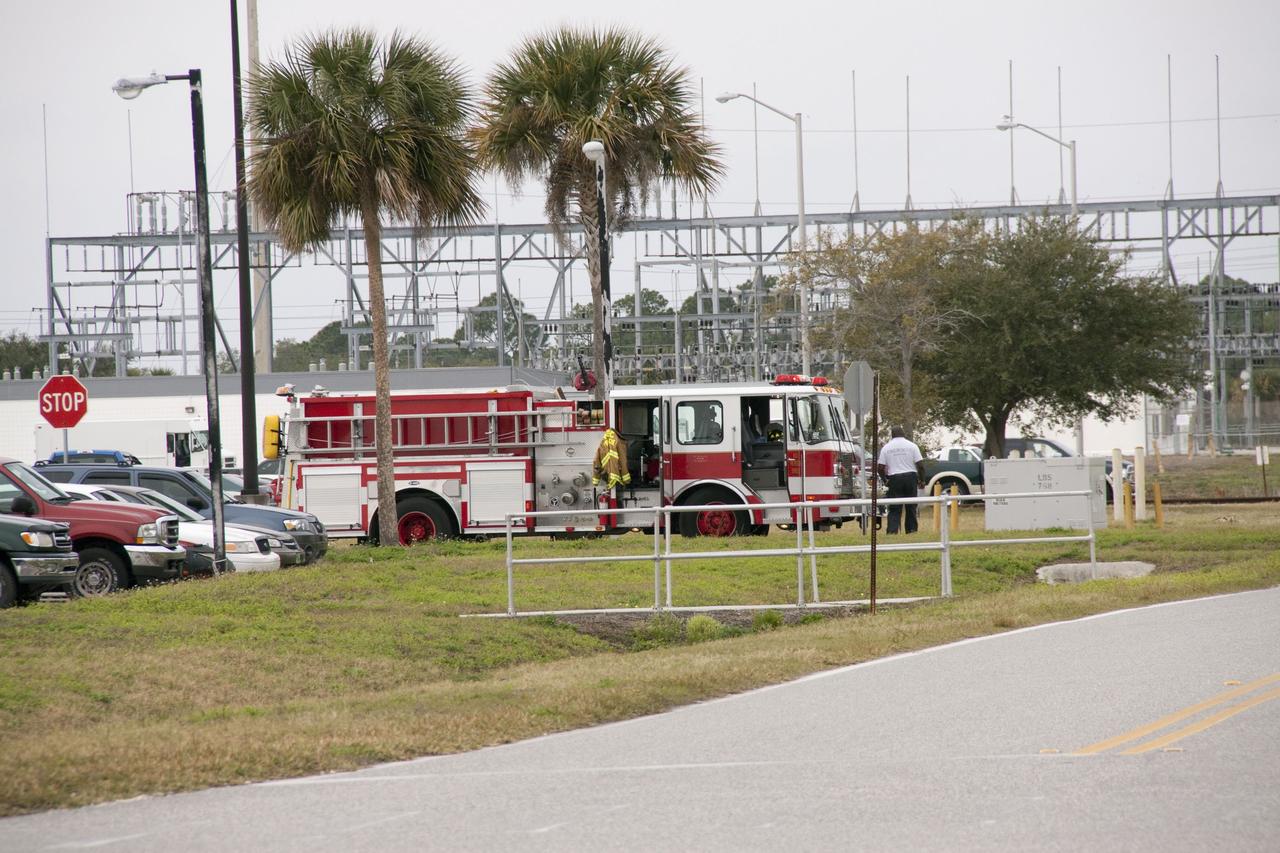

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, KSC firefighters were on the scene after a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line at around 8:40 a.m. EST in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF). As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
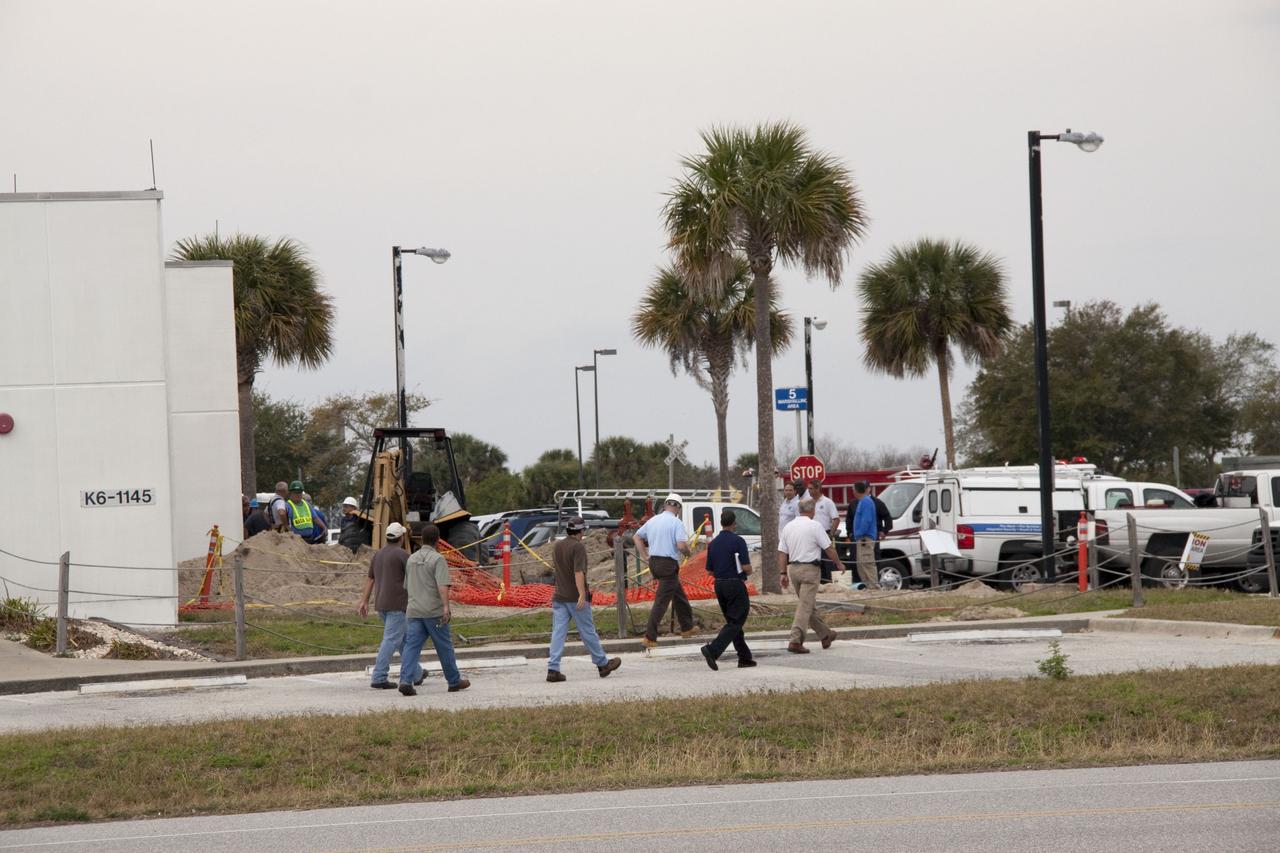

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF), at around 8:40 a.m. EST. As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and the Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. With the backhoe idle, workers assess the area where the break in the gas line occurred. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
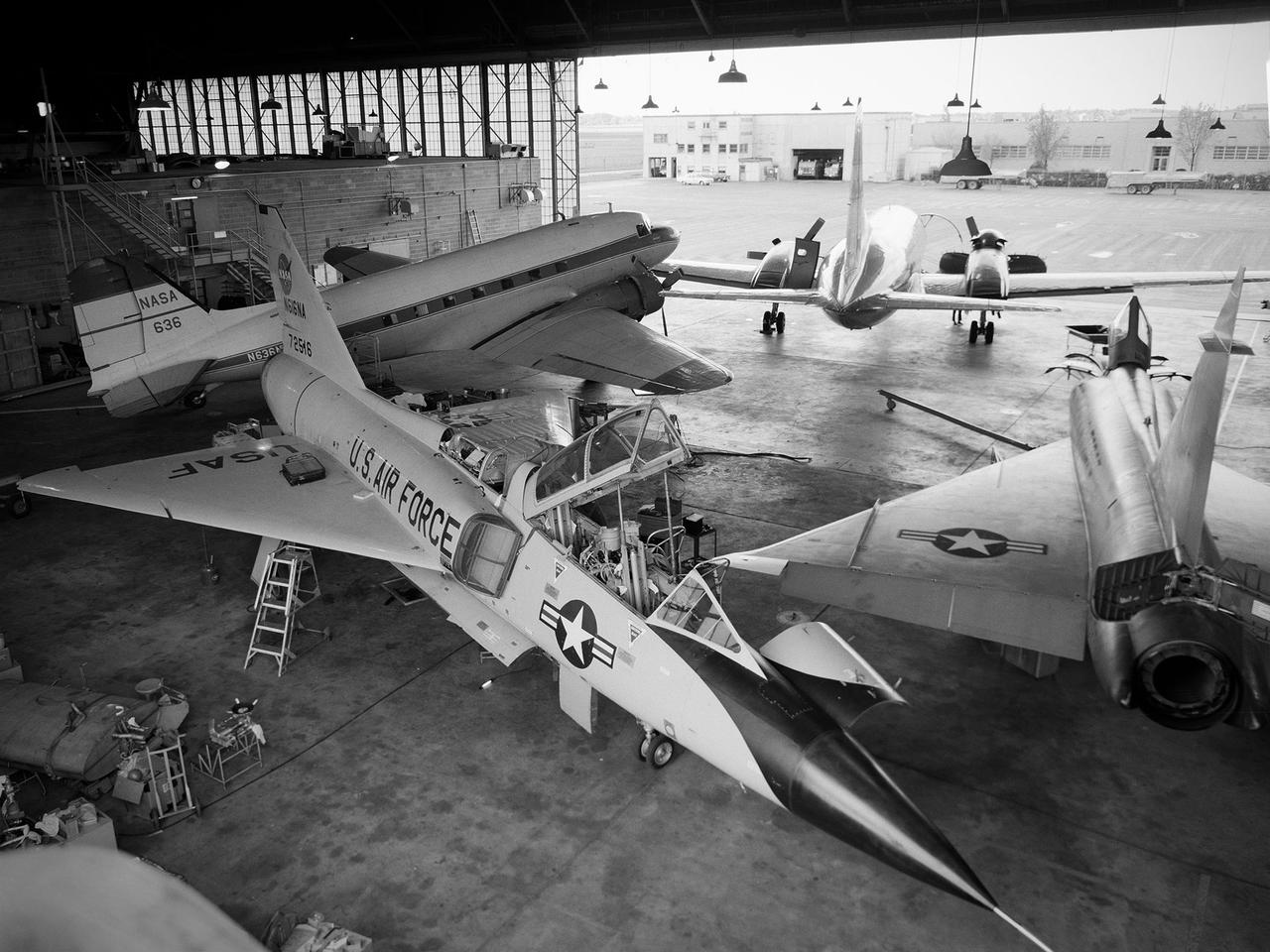

Several aircraft parked inside the Flight Research Building, or hangar, at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. A Convair F-106B Delta Dart is in the foreground, a Convair F-102A Delta Dagger is to the right, a Douglas DC-3 is in the back to left, and a Convair T-29 is in background. Lewis’ Martin B-57B Canberra is not seen in this photograph. The F-102A had just been acquired by Lewis to serve as a chase plane for the F-106B. The Lewis team removed the weapons system and 700 pounds of wire from the F-106B when it was acquired on October 20, 1966. The staff cut holes in the wings and modified the elevons to mount the test nacelles. A 228-gallon fuel tank was installed in the missile bay, and the existing wing tanks were used for instrumentation. This photograph contains a rare view of the Block House, seen to the left of the aircraft. Lewis acquired three large developmental programs in 1962—the Centaur and Agena rockets and the M-1 engine. The center was short on office space at the time, and its flight research program was temporarily on the wane. Lewis management decided to construct a large cinderblock structure inside one half of the hangar to house the new personnel. This structure was used until 1965 when the new Developmental Engineering Building was built. The Block House was eventually torn down in 1973.

A close-up view of the treads on crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) as the behemoth vehicle moves along the crawlerway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 22, 2021. Teams are working to ensure the crawlerway, the path the CT-2, mobile launcher, and Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop will take from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Complex 39B, is strong enough to withstand the weight and provide stability for the Artemis I mission. CT-2 carrying mobile launcher platform 1, used during the shuttle program, was driven back and forth on the crawlerway with several cement blocks, each weighing about 40,000 pounds to strengthen the crawlerway for launch. Artemis I will be the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA aims to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 and establish sustainable lunar exploration by the end of the decade.
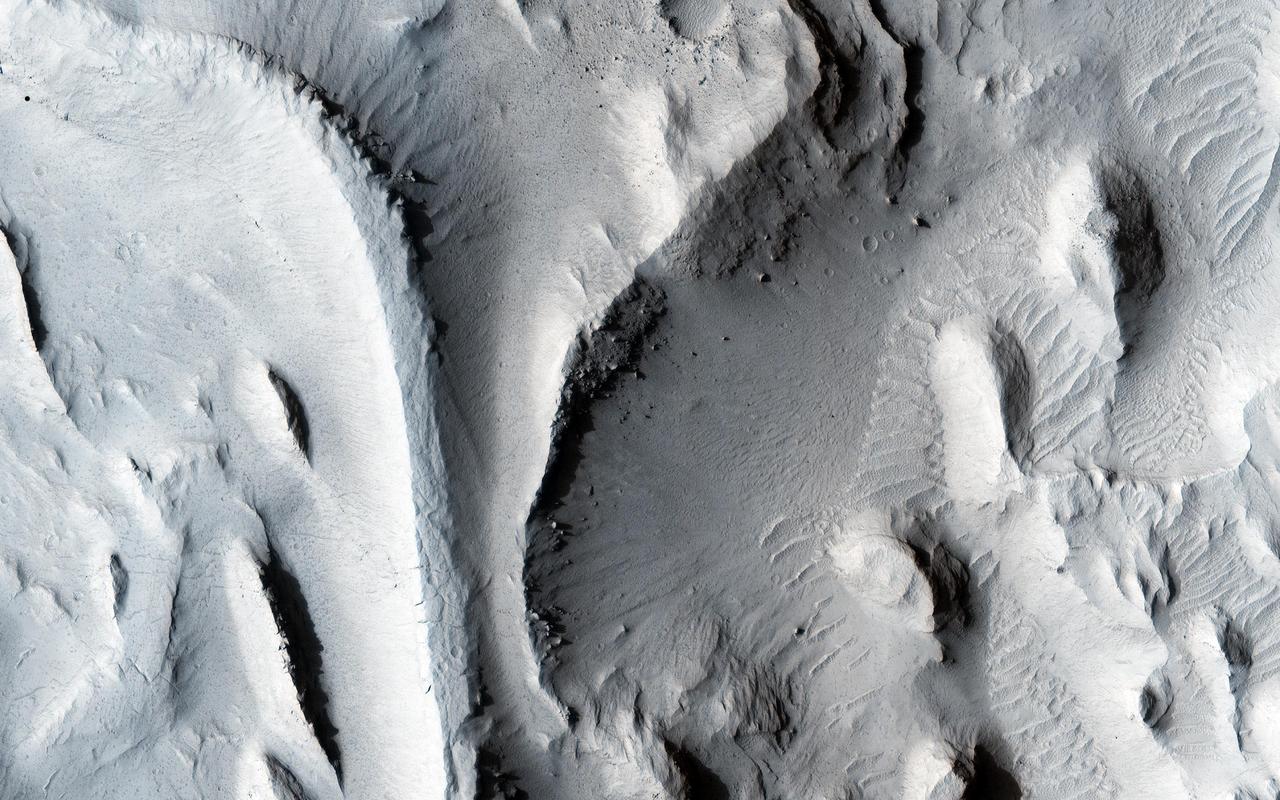

The sinuous ridges in this image display strong characteristics of ancient meandering riverbeds that are preserved as inverted topography (blue). The ancient river sediments that make up the ridges might have allowed fluids to produce cements (e.g., calcite or iron oxides) to make the channel lithology resistant to weathering and erosion. Later, physical and/or chemical processes removed the weaker surrounding flood plain material and left inverted river channels, or "positive relief." On closer inspection, degradation along sections of some inverted channels display large blocks of cemented sediment that were transported downslope by mass wasting. The sinuous character of the ridges resembles multi-thread river branches, implying that the ancient river flowed down a gentle to nearly horizontal slope (i.e., a moderate to low stream gradient). This ancient river was a mature meandering system, with flow from south to north. Multiple branches that diverted from the main flow later converged back with it. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20210
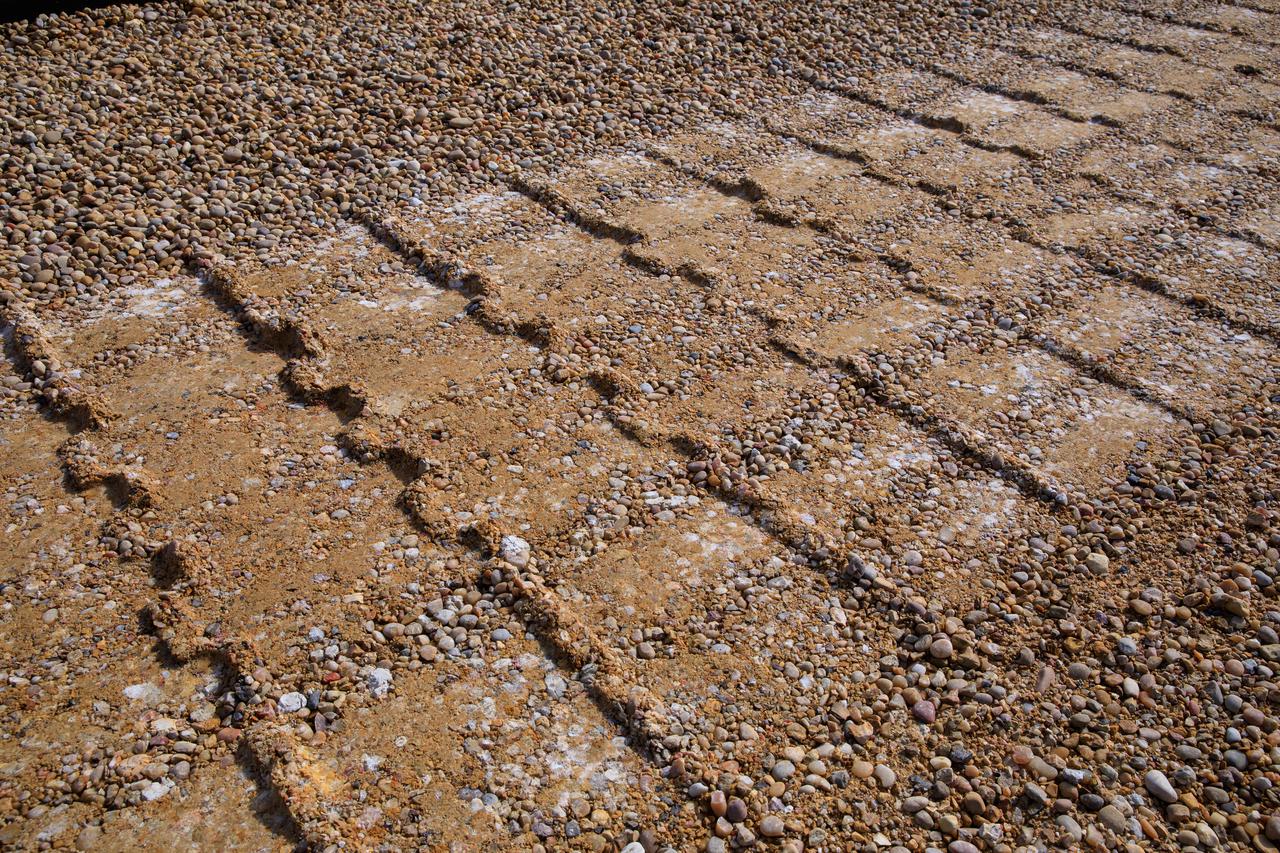

A close-up view of tread marks from crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) as the behemoth vehicle moves along the crawlerway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 22, 2021. Teams are working to ensure the crawlerway, the path the CT-2, mobile launcher, and Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop will take from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Complex 39B, is strong enough to withstand the weight and provide stability for the Artemis I mission. CT-2 carrying mobile launcher platform 1, used during the shuttle program, was driven back and forth on the crawlerway with several cement blocks, each weighing about 40,000 pounds to strengthen the crawlerway for launch. Artemis I will be the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA aims to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 and establish sustainable lunar exploration by the end of the decade.
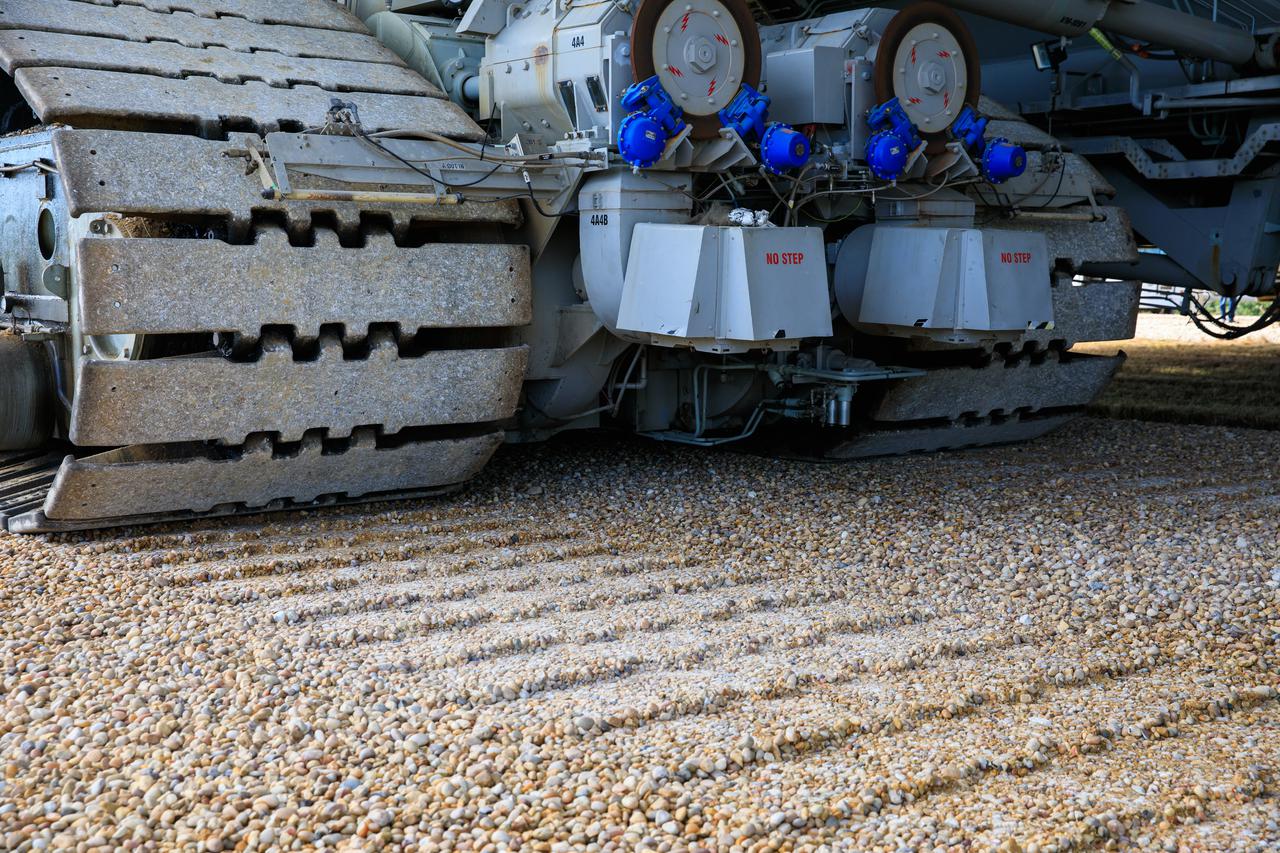

A close-up view of the treads on crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) as the behemoth vehicle moves along the crawlerway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 22, 2021. Teams are working to ensure the crawlerway, the path the CT-2, mobile launcher, and Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop will take from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Complex 39B, is strong enough to withstand the weight and provide stability for the Artemis I mission. CT-2 carrying mobile launcher platform 1, used during the shuttle program, was driven back and forth on the crawlerway with several cement blocks, each weighing about 40,000 pounds to strengthen the crawlerway for launch. Artemis I will be the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA aims to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 and establish sustainable lunar exploration by the end of the decade.

A close-up view of one of the treads on crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) as the behemoth vehicle moves along the crawlerway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 22, 2021. Teams are working to ensure the crawlerway, the path the CT-2, mobile launcher, and Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop will take from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Complex 39B, is strong enough to withstand the weight and provide stability for the Artemis I mission. CT-2 carrying mobile launcher platform 1, used during the shuttle program, was driven back and forth on the crawlerway with several cement blocks, each weighing about 40,000 pounds to strengthen the crawlerway for launch. Artemis I will be the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA aims to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 and establish sustainable lunar exploration by the end of the decade.
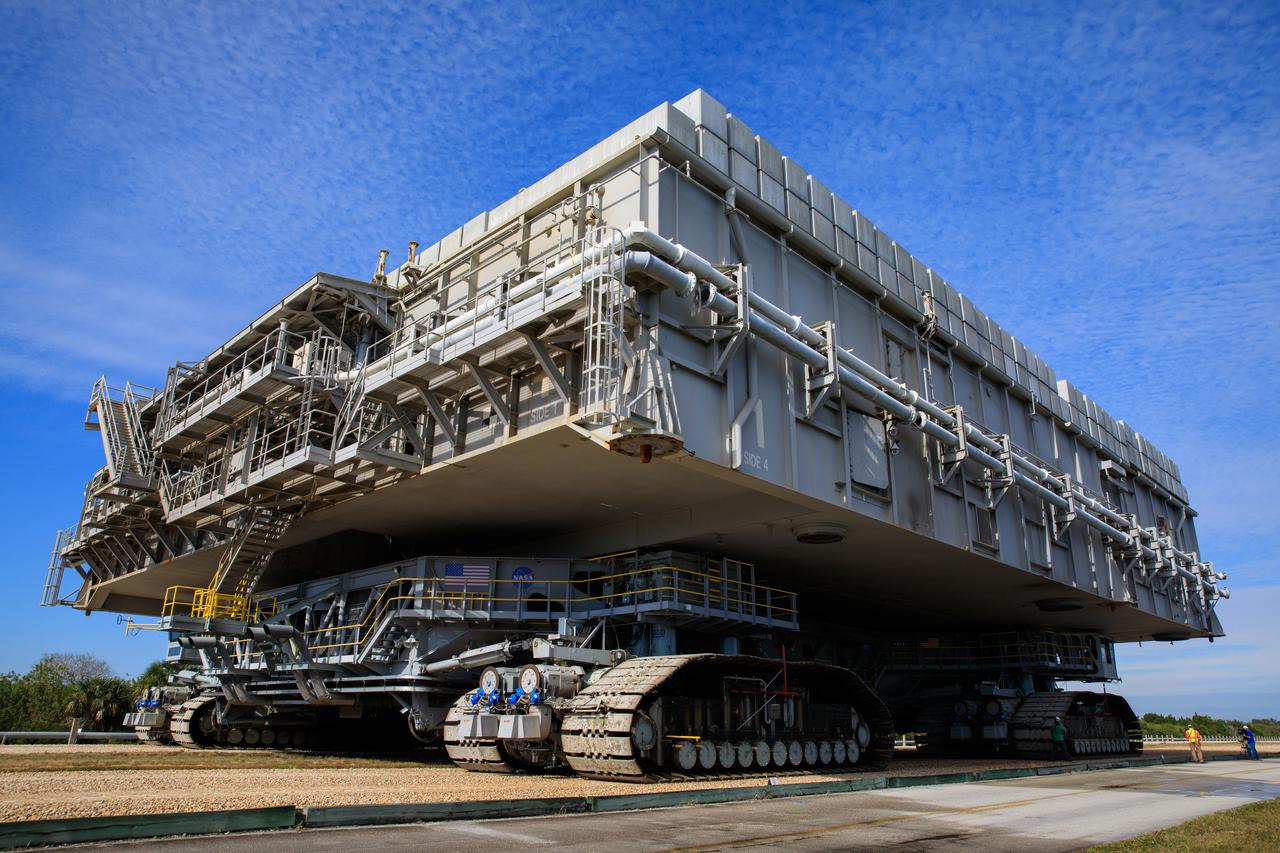

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida are working to ensure the crawlerway, the path the crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2), mobile launcher, and Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop will take from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Complex 39B, is strong enough to withstand the weight and provide stability for the Artemis I mission. In this view on Jan. 22, 2021, CT-2 carrying mobile launcher platform 1 that was used during the shuttle program was driven back and forth on the crawlerway with several cement blocks, each weighing about 40,000 pounds to strengthen the crawlerway for launch. Artemis I will be the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA aims to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 and establish sustainable lunar exploration by the end of the decade.
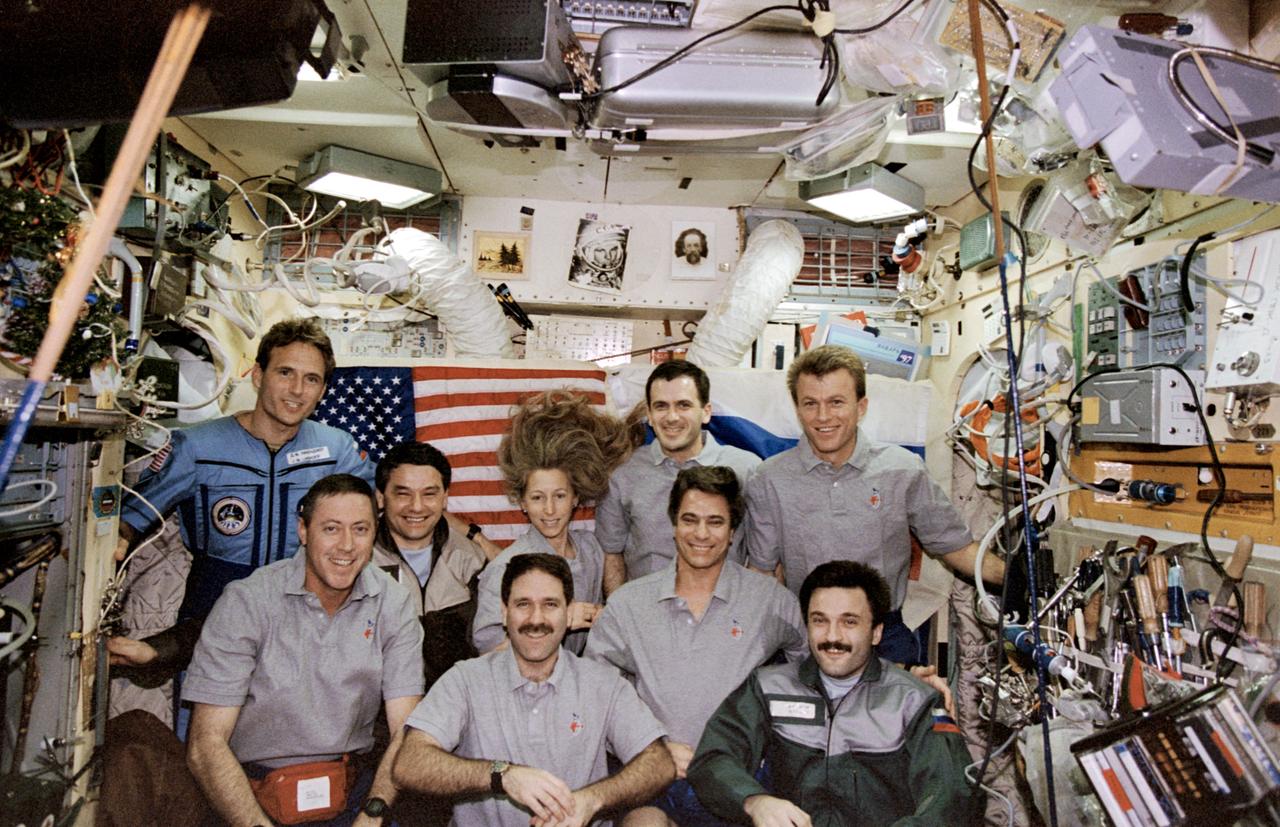

STS081-369-003 (12-22 Jan. 1997) --- Traditional inflight crew portrait of the combined Mir-22 and STS-81 crews in the Base Block Module aboard Russia's Mir Space Station. Front row: left to right, Michael A. Baker, commander; John M. Grunsfeld, mission specialist; and cosmonaut Aleksandr Y. Kaleri, Mir-22 flight engineer. Middle row: cosmonaut Valeri G. Korzun, Mir-22 commander; Marsha S. Ivins, mission specialist; and John E. Blaha, former cosmonaut guest researcher. Back row: Jerry M. Linenger, cosmonaut guest researcher; Peter J. K. (Jeff) Wisoff, mission specialist; and Brent W. Jett, Jr., pilot. Linenger is seen in a Russian jump suit, and Blaha now wears a Space Shuttle inflight garment as the two exchanged cosmonaut guest researcher roles on January 14, 1997, following the docking of the Atlantis and the Mir complex.
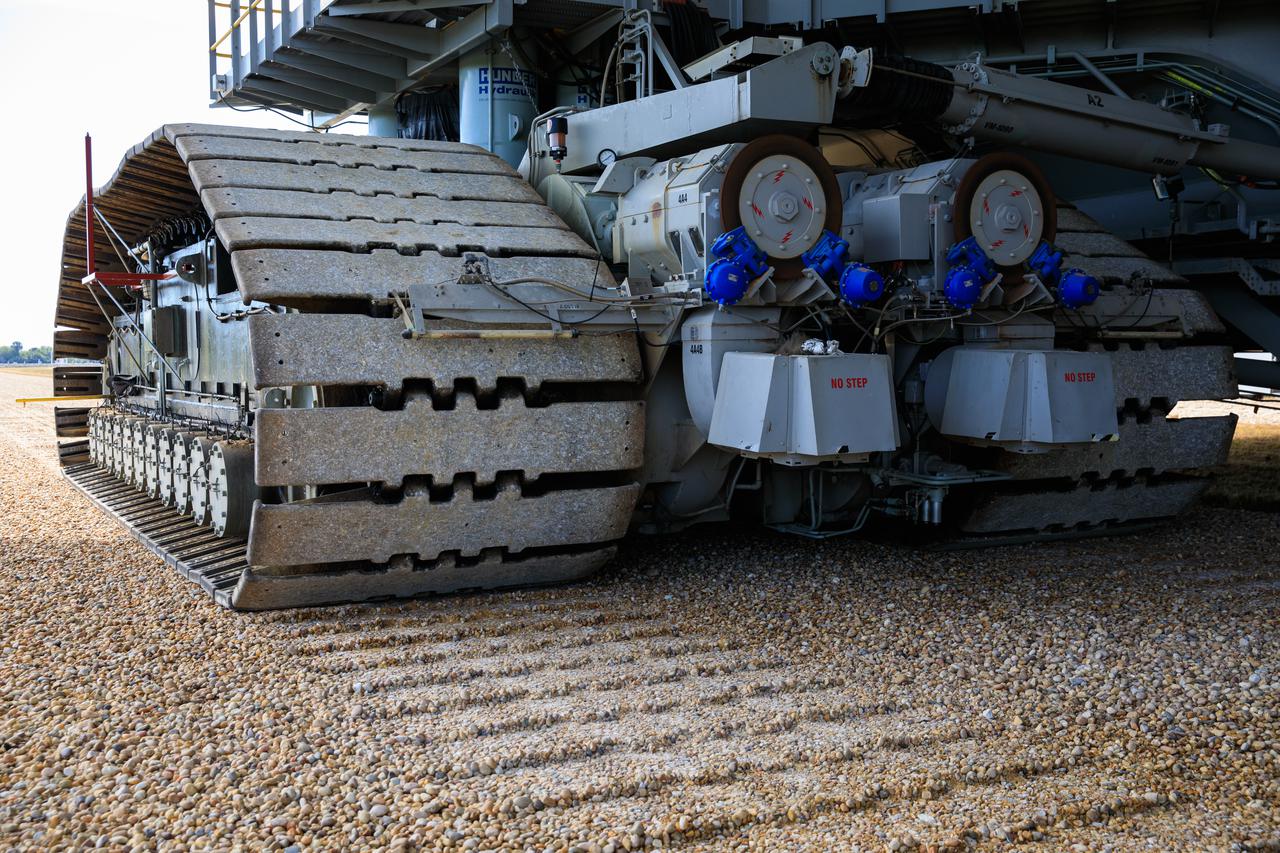

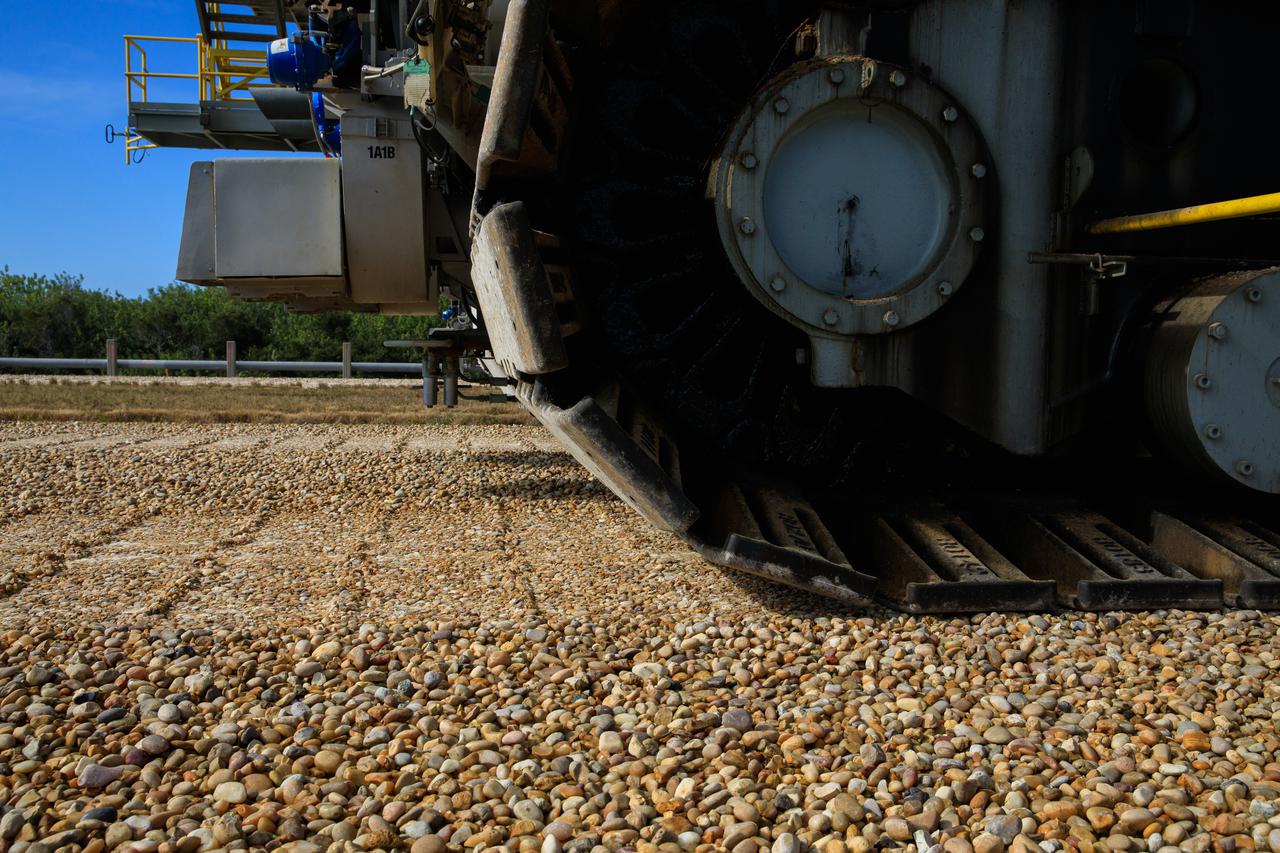
A close-up view of the treads on crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) as the behemoth vehicle moves along the crawlerway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 22, 2021. Teams are working to ensure the crawlerway, the path the CT-2, mobile launcher, and Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop will take from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Complex 39B, is strong enough to withstand the weight and provide stability for the Artemis I mission. CT-2 carrying mobile launcher platform 1, used during the shuttle program, was driven back and forth on the crawlerway with several cement blocks, each weighing about 40,000 pounds to strengthen the crawlerway for launch. Artemis I will be the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA aims to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 and establish sustainable lunar exploration by the end of the decade.
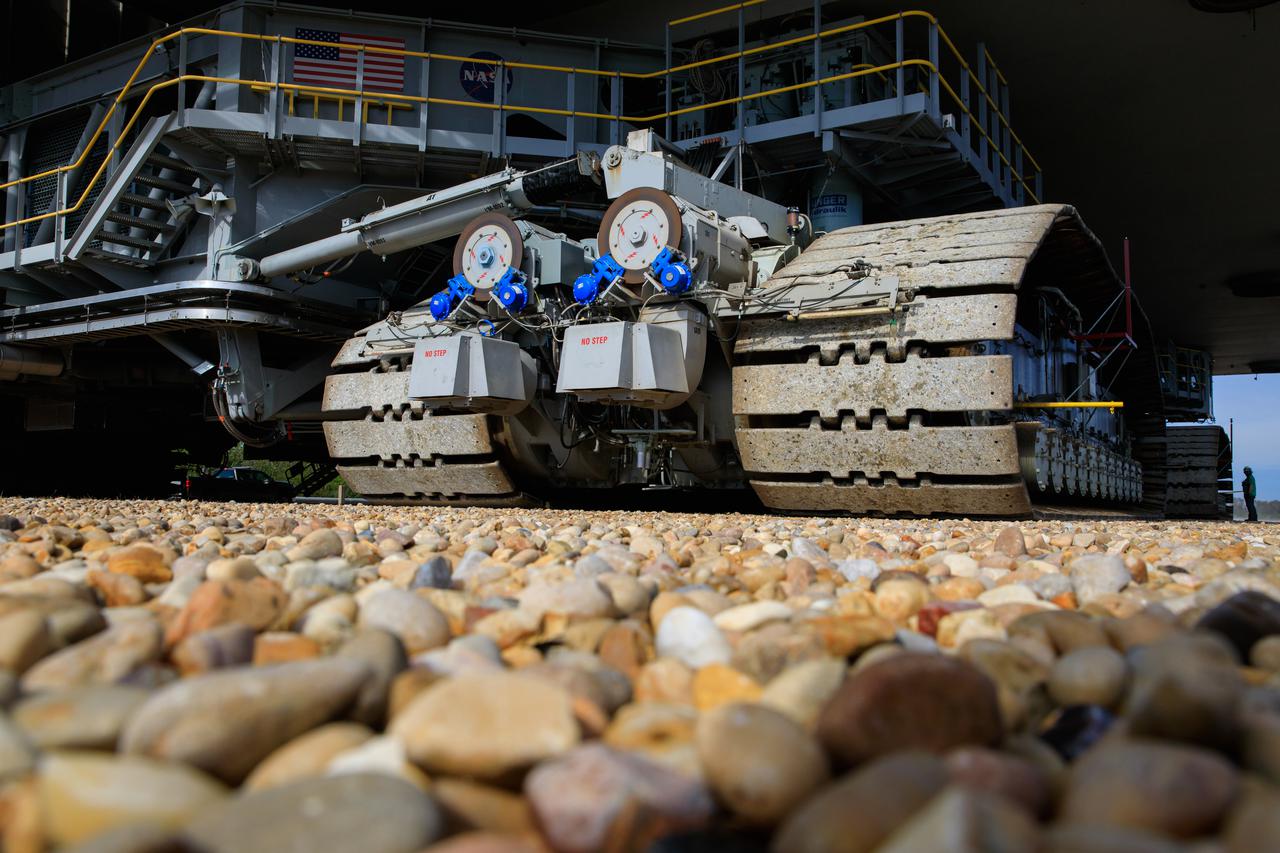

A close-up view of some of the treads on crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) as the behemoth vehicle moves along the crawlerway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 22, 2021. Teams are working to ensure the crawlerway, the path the CT-2, mobile launcher, and Space Launch System rocket with Orion atop will take from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Complex 39B, is strong enough to withstand the weight and provide stability for the Artemis I mission. CT-2 carrying mobile launcher platform 1, used during the shuttle program, was driven back and forth on the crawlerway with several cement blocks, each weighing about 40,000 pounds to strengthen the crawlerway for launch. Artemis I will be the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA aims to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 and establish sustainable lunar exploration by the end of the decade.

S74-15583 (July 1973) --- A huge solar eruption can be seen in this Spectroheliogram obtained during the Skylab 3 mission by the Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrograph/Spectroheliograph SO82A Experiment aboard the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. SO82 is one of the Apollo Telescope Mount experiments. The SO82 "A" instrument covers the wavelength region from 150-650 angstroms (EUV regions). The magnitude of the eruption can be visualized by comparing it with the small white dot that represents the size of Earth. This photograph reveals for the first time that helium erupting from the sun can stay together to altitudes of up to 500,000 miles. After being ejected from the sun, the gas clouds seem to have come to a standstill, as though blocked by an unseen wall. Some materials appear to have been directed back toward the sun as a rain, distinguished by fine threads. At present it is a challenge to explain this mystery--what forces expelled these huge clouds, then blocked its further progress, yet allowed the cloud to maintain its threads. Both magnetic fields and gravity must play a part, but these curious forms seem to defy explanation based on magnetic and gravitational fields alone. The EUV spectroheliograph was designed and constructed by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory and the Ball Brothers Research Corporation under the direction of Dr. R. Tousey, the principal investigator for this NASA experiment. On the left may be seen the sun's image in emission from iron atoms which have lost 14 electrons by collision in the sun's million-degree coronal plasma gas. Photo credit: NASA
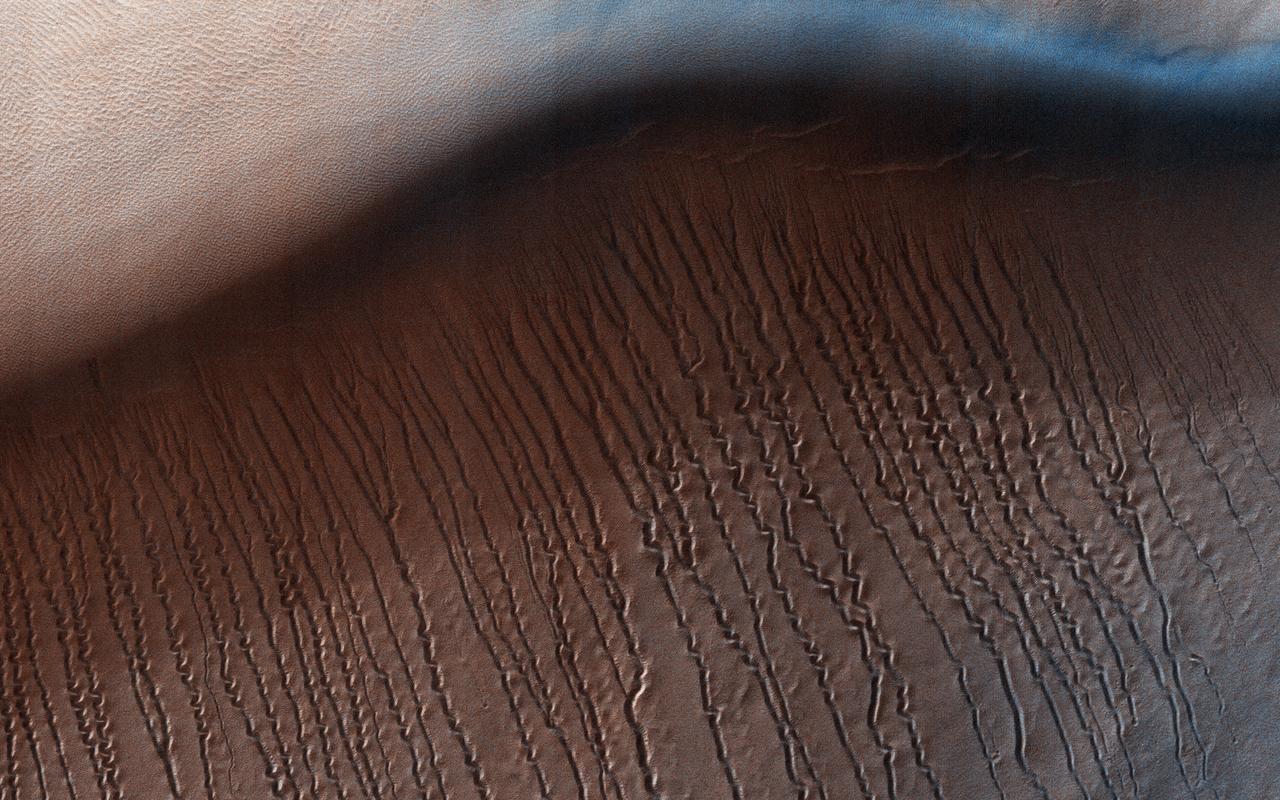

At around 2,200 kilometers in diameter, Hellas Planitia is the largest visible impact basin in the Solar System, and hosts the lowest elevations on Mars' surface as well as a variety of landscapes. This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaisance Orbiter (MRO) covers a small central portion of the basin and shows a dune field with lots of dust devil trails. In the middle, we see what appears to be long and straight "scratch marks" running down the southeast (bottom-right) facing dune slopes. If we look closer, we can see these scratch marks actually squiggle back and forth on their way down the dune. These scratch marks are linear gullies. Just like on Earth, high-latitude regions on Mars are covered with frost in the winter. However, the winter frost on Mars is made of carbon dioxide ice (dry ice) instead of water ice. We believe linear gullies are the result of this dry ice breaking apart into blocks, which then slide or roll down warmer sandy slopes, sublimating and carving as they go. The linear gullies exhibit exceptional sinuosity (the squiggle pattern) and we believe this to be the result of repeated movement of dry ice blocks in the same path, possibly in combination with different hardness or flow resistance of the sand within the dune slopes. Determining the specific process that causes the formation and evolution of sinuosity in linear gullies is a question scientists are still trying to answer. What do you think causes the squiggles? https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22052

The Roman Coronagraph Instrument on NASA's upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will test new tools that block starlight, revealing planets hidden by the glare of their parent stars. This graphic shows a test of what engineers call "digging the dark hole." The image shows three computer readouts of real data from the coronagraph's camera. Engineers used lasers and special optics to replicate the light from a star as it would look when observed by the Roman telescope. The image at left shows the amount of starlight that leaks into the coronagraph's field of view when only fixed components called masks are used to block the star at the center of the circle. Using moveable components such as deformable mirrors, the coronagraph can remove more and more of this starlight. The middle and right images show the progression of this process, where red indicates less starlight, and black indicates most or all starlight has been removed. The deformable mirrors are each only 2 inches (5 centimeters) in diameter and backed by more than 2,000 tiny pistons that move up and down. The pistons work together to change the shape of the mirrors to compensate for the unwanted stray light that spills around the edges of the masks. Though they are too small to affect Roman's other highly precise measurements, the imperfections can send stray starlight into the dark hole. In space, this technique will enable astronomers to observe light directly from planets around other stars, or exoplanets. Once demonstrated on Roman, similar technologies on a future mission could enable astronomers to use that light to identify chemicals in an exoplanet's atmosphere, potentially indicating the presence of life. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26279
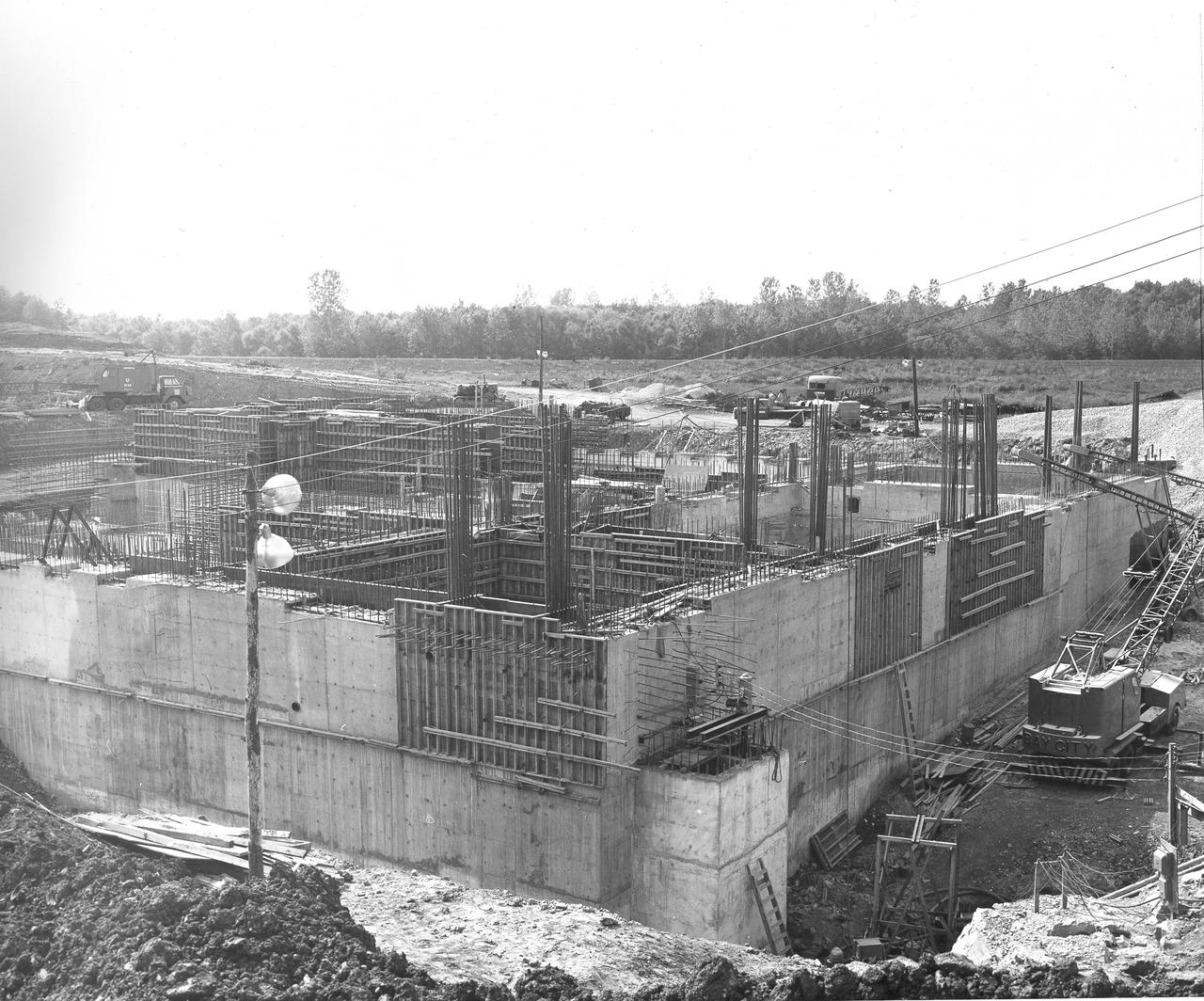

At its founding, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) inherited the Army’s Jupiter and Redstone test stands, but much larger facilities were needed for the giant stages of the Saturn V. From 1960 to 1964, the existing stands were remodeled and a sizable new test area was developed. The new comprehensive test complex for propulsion and structural dynamics was unique within the nation and the free world, and they remain so today because they were constructed with foresight to meet the future as well as on going needs. Construction of the S-IC Static test stand complex began in 1961 in the west test area of MSFC, and was completed in 1964. The S-IC static test stand was designed to develop and test the 138-ft long and 33-ft diameter Saturn V S-IC first stage, or booster stage, weighing in at 280,000 pounds. Required to hold down the brute force of a 7,500,000-pound thrust produced by 5 F-1 engines, the S-IC static test stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and 12,000,000 pounds of cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level. The foundation walls, constructed with concrete and steel, are 4 feet thick. The base structure consists of four towers with 40-foot-thick walls extending upward 144 feet above ground level. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the upright position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. In addition to the stand itself, related facilities were constructed during this time. Built directly east of the test stand was the Block House, which served as the control center for the test stand. The two were connected by a narrow access tunnel which housed the cables for the controls. This construction photo taken August 17, 1962 depicts a back side view of the Block House.
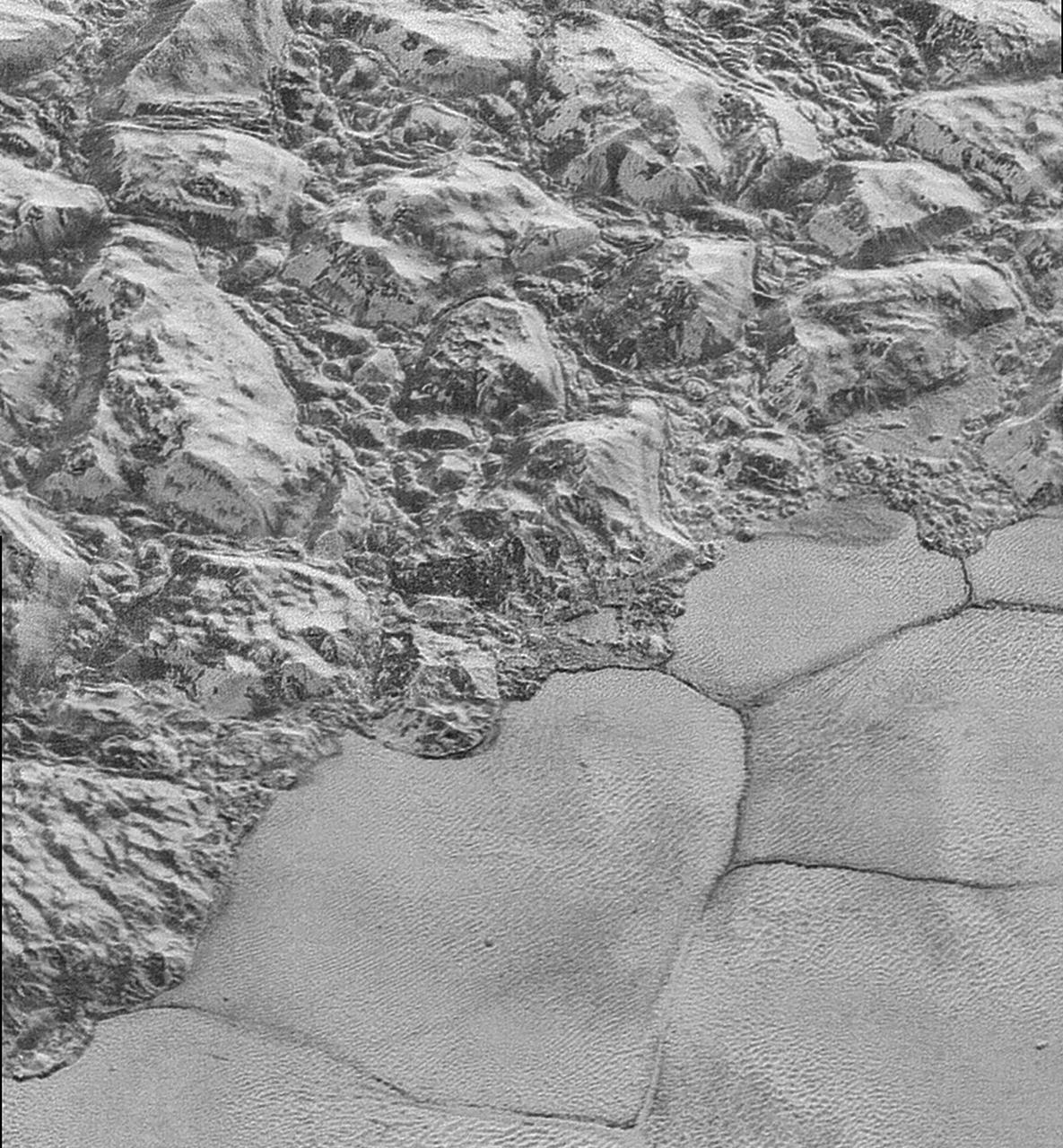

In this highest-resolution image from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft, great blocks of Pluto's water-ice crust appear jammed together in the informally named al-Idrisi mountains. Some mountain sides appear coated in dark material, while other sides are bright. Several sheer faces appear to show crustal layering, perhaps related to the layers seen in some of Pluto's crater walls. Other materials appear crushed between the mountains, as if these great blocks of water ice, some standing as much as 1.5 miles high, were jostled back and forth. The mountains end abruptly at the shoreline of the informally named Sputnik Planum, where the soft, nitrogen-rich ices of the plain form a nearly level surface, broken only by the fine trace work of striking, cellular boundaries and the textured surface of the plain's ices (which is possibly related to sunlight-driven ice sublimation). This view is about 50 miles wide. The top of the image is to Pluto's northwest. These images were made with the telescopic Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard New Horizons, in a timespan of about a minute centered on 11:36 UT on July 14 -- just about 15 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto -- from a range of just 10,000 miles (17,000 kilometers). They were obtained with an unusual observing mode; instead of working in the usual "point and shoot," LORRI snapped pictures every three seconds while the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC) aboard New Horizons was scanning the surface. This mode requires unusually short exposures to avoid blurring the images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20198
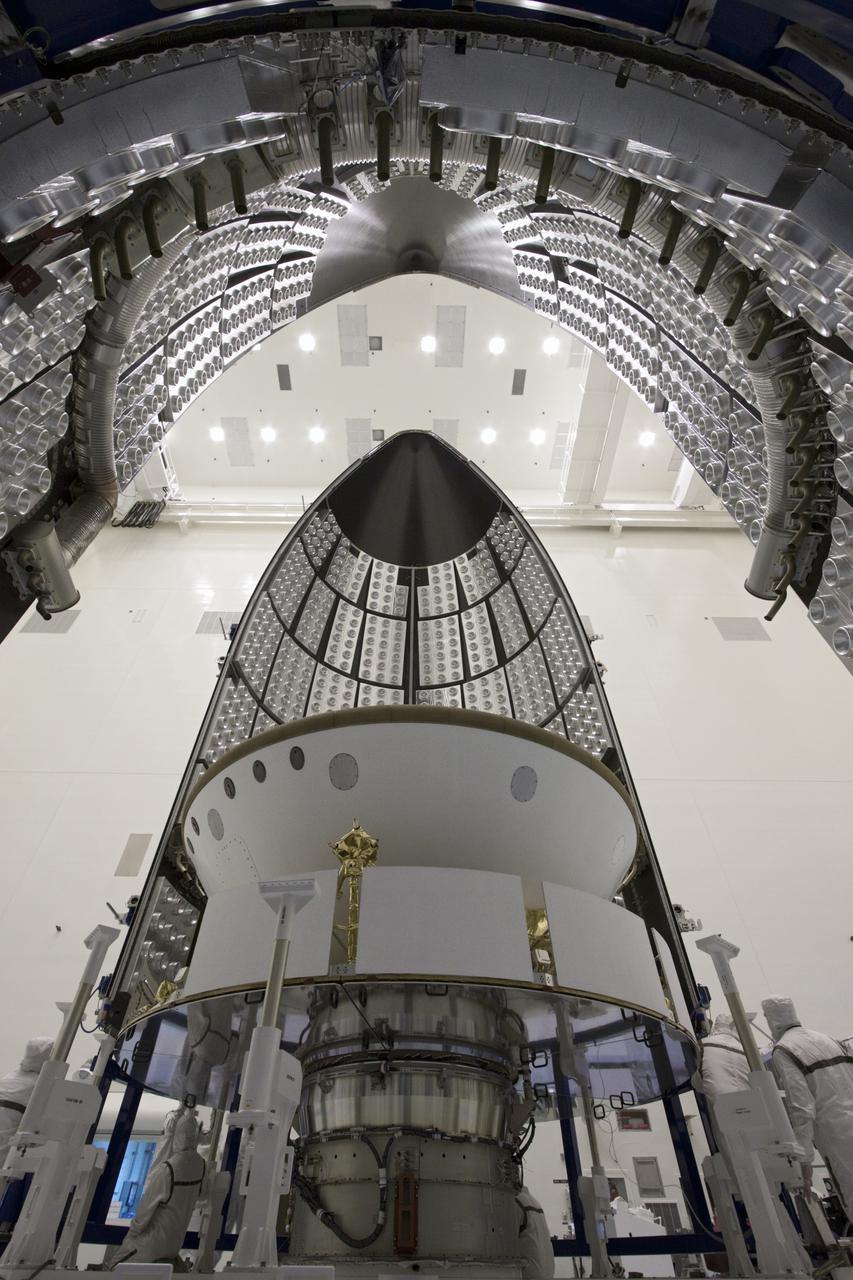

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, sections of an Atlas V rocket payload fairing engulf NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) as they close in around it. The blocks on the interior of the fairing are components of the fairing acoustic protection (FAP) system, designed to protect the payload by dampening the sound created by the rocket during liftoff. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including the chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
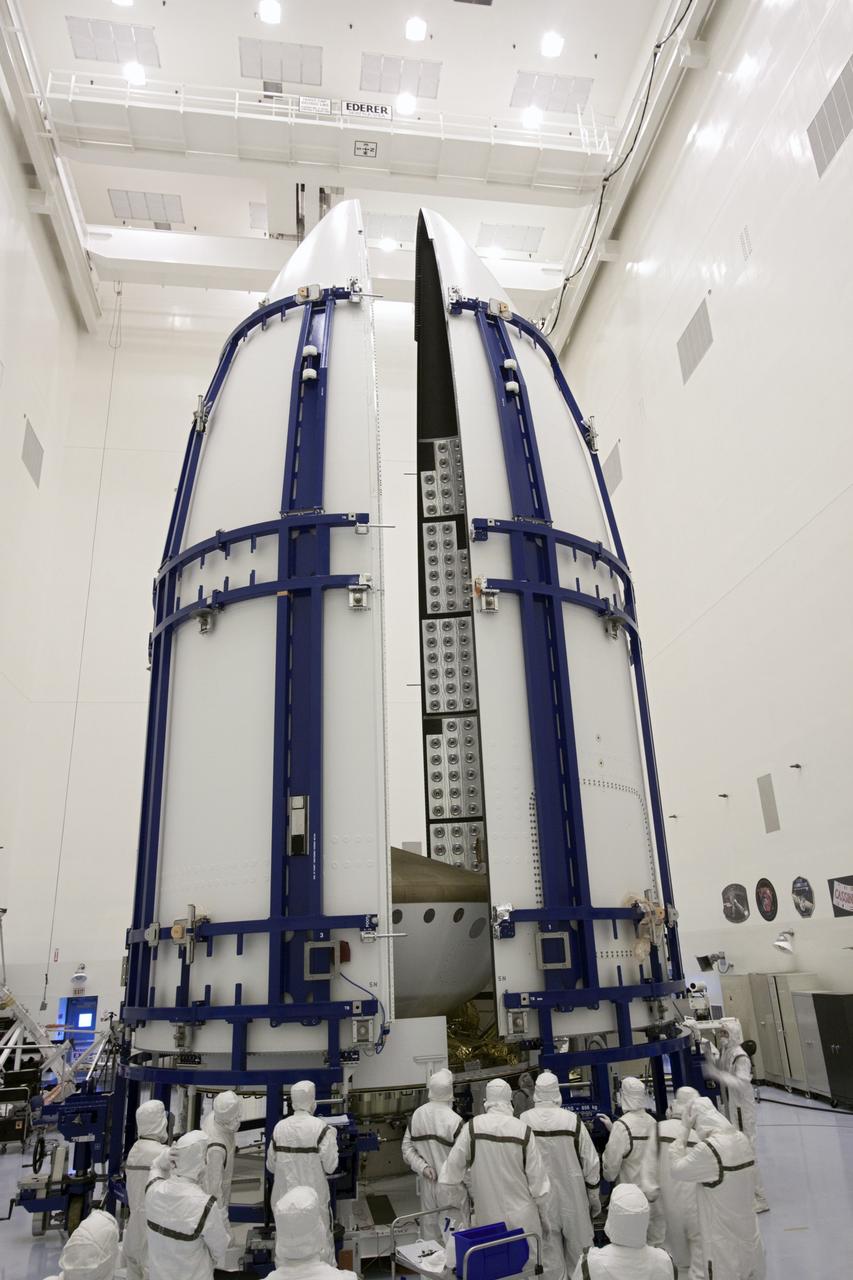

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, sections of an Atlas V rocket payload fairing obscure NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) from view as they close in around it. The blocks on the interior of the fairing are components of the fairing acoustic protection (FAP) system, designed to protect the payload by dampening the sound created by the rocket during liftoff. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including the chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
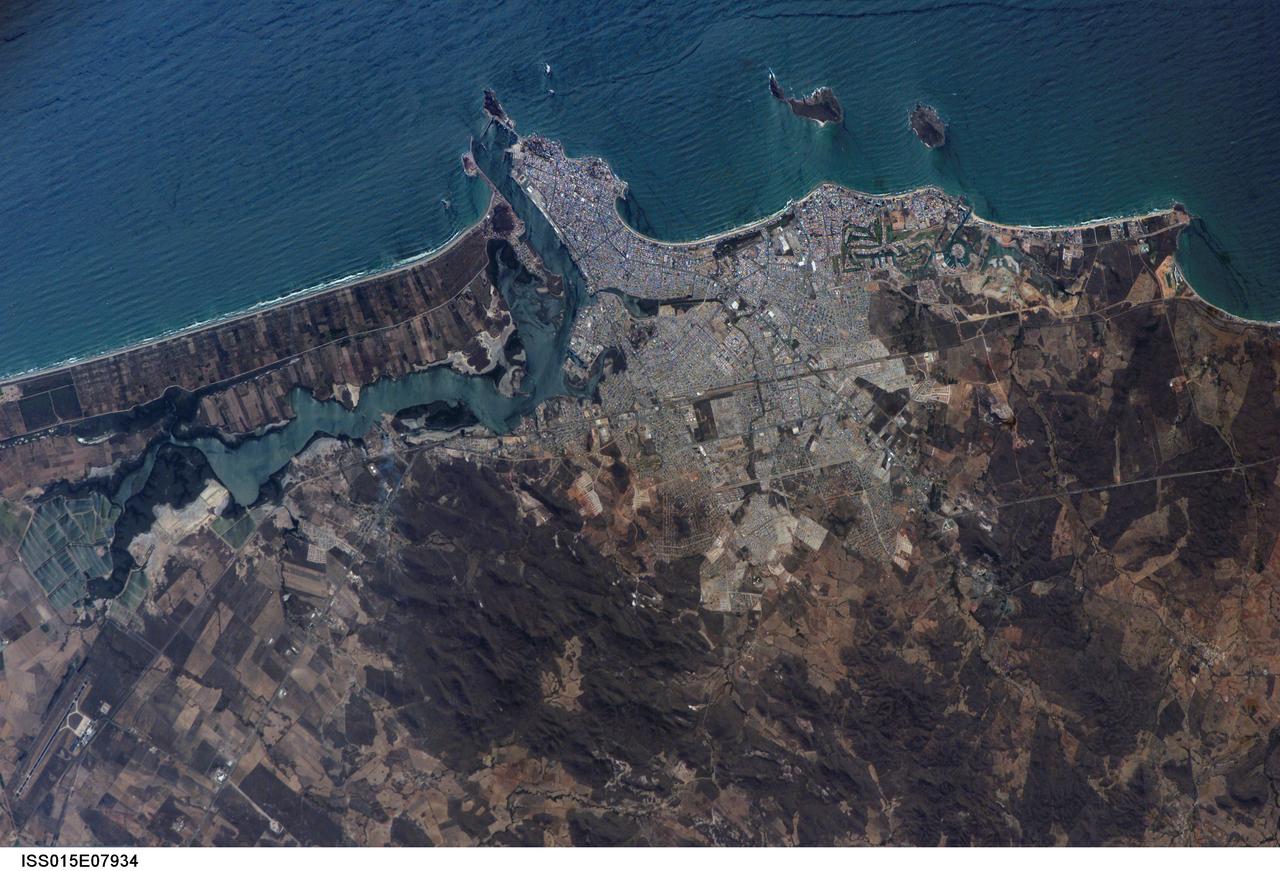

ISS015-E-07934 (13 May 2007) --- Mazatlan, Mexico is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crewmember on the International Space Station. Mazatlan is Mexico's largest port, situated on one of the best estuaries on Mexico's Pacific coast, illustrated well in this image. Docks and naval yards line the north side of the estuary. The city itself appears as a series of light-toned city blocks covering the center of the image. Mazatlan (population of 352,000 in 2005) is growing northward from the downtown peninsula, with tourist beaches backed by hotels, and a marina and golf courses just beyond. No city growth yet appears on the south side the estuary where farm lands can be seen. The famous Faro Lighthouse occupies the top of a steep island--now connected by a bridge to the mainland--at the mouth of the estuary (top center). The Faro Lighthouse is the second tallest in the world behind Gibraltar's. The wide, straight, almost vertical line of the railroad appears to bisect the picture. This image shows sea features well, primarily ocean swells coming in from the southwest, which appear as a series of parallel lines covering the entire sea surface in this view. An oil slick offshore of the tourist beaches appears as a dark line along the left side of the image.
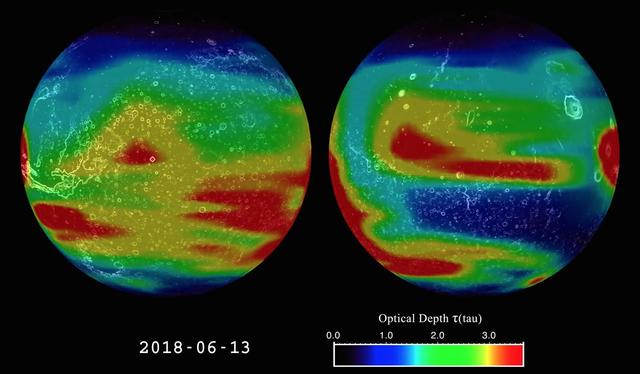
This image is from an animation that shows the evolution of the 2018 Mars global dust storm from late May to September. The animation shows the optical depth tau -- a measure of how much light is being blocked by atmospheric dust as measured by the Mars Climate Sounder instrument onboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. NASA's Opportunity rover is marked with a red dot. The dust is mapped to two opposite hemispheres of Mars, giving a view of the full globe. Certain features of the Martian terrain, including Olympus Mons, the three volcanoes in the equatorial region, and Vallis Marineris, are also visible. The data shows the daily global column of dust, illustrating how the dust behaves over the course of the storm. The storm has a complex growth affecting most of Mars over the first month. It then remains near the peak for three weeks. Finally, the storm starts a multi-month decay back to regular weather. A color scale in the lower right-hand corner of the animation explains the colors in relation to approximate tau values. A tau of three indicates that only about 5 percent of the sunlight entering the atmosphere directly reaches the surface. Animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22737
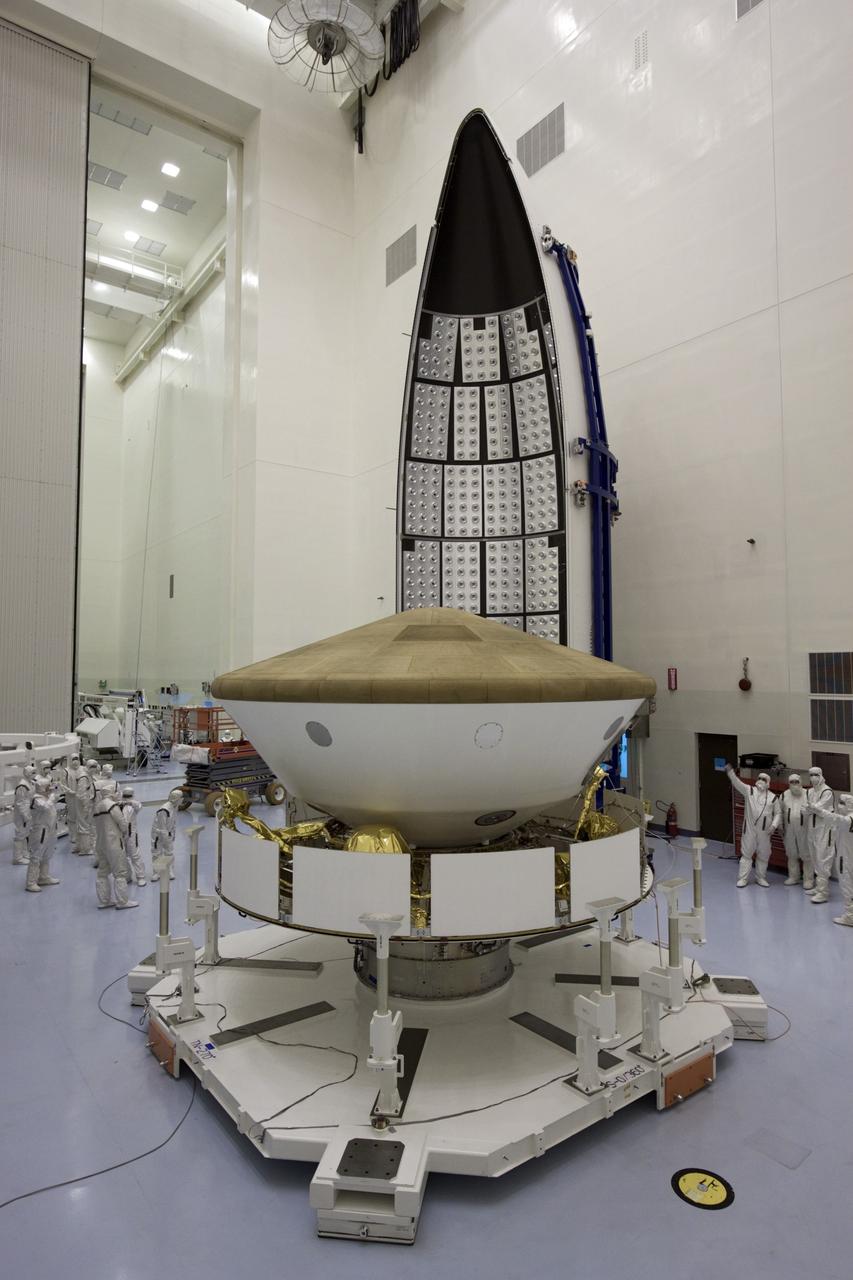

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians prepare to enclose NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) in an Atlas V rocket payload fairing. The blocks on the interior of the fairing are components of the fairing acoustic protection (FAP) system, designed to protect the payload by dampening the sound created by the rocket during liftoff. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including the chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) is ready to be enclosed in the Atlas V rocket payload fairing in the background. The blocks on the interior of the fairing are components of the fairing acoustic protection (FAP) system, designed to protect the payload by dampening the sound created by the rocket during liftoff. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including the chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
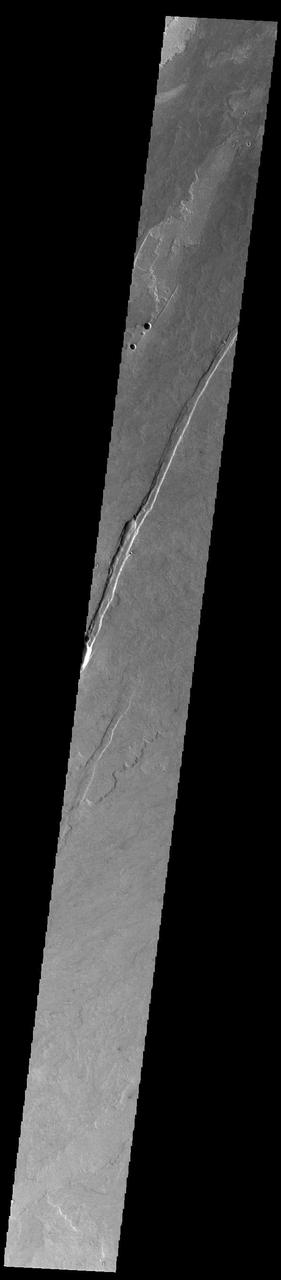
Today's VIS image shows a small portion of the immense lava flows that originated from Arsia Mons. Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the three large aligned volcanoes in the Tharsis region. Arsia Mons' last eruption was 10s of million years ago. The different surface textures are created by differences in the lava viscosity and cooling rates. The lobate margins of each flow can be traced back to the start of each flow — or to the point where they are covered by younger flows. Flows in Daedalia Planum can be as long as 180 km (111 miles). For comparison the longest Hawaiian lava flow is only 51 km (˜31 miles) long. The long linear feature in the image is a tectonic graben, formed when a block of material slides downward between paired faults. It is very common to have both tectonic and volcanic processes affecting the same region. The total area of Daedalia Planum is 2.9 million square km – more than four times the size of Texas. Orbit Number: 91653 Latitude: -22.9324 Longitude: 236.47 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-08-12 23:29 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25615
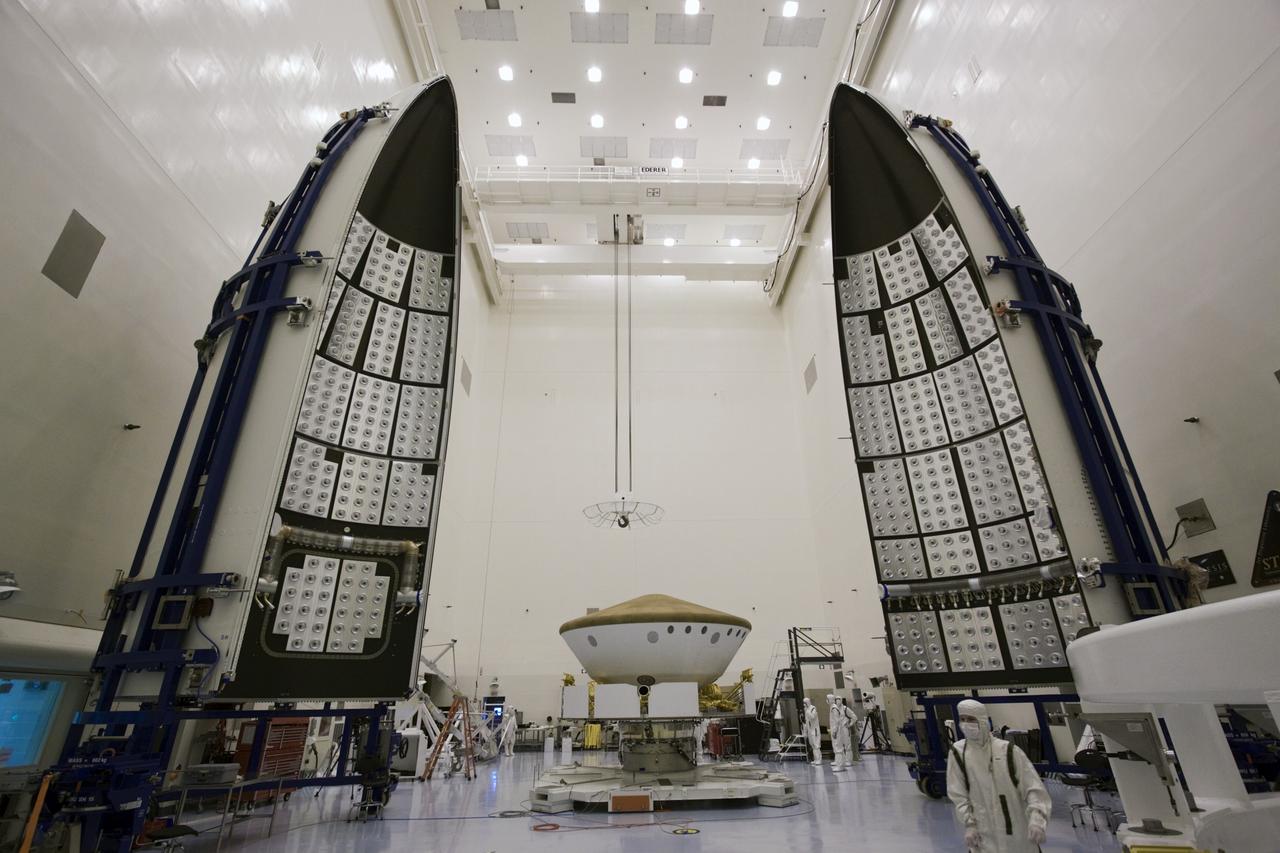

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are under way to enclose NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) in an Atlas V rocket payload fairing. The blocks on the interior of the fairing are components of the fairing acoustic protection (FAP) system, designed to protect the payload by dampening the sound created by the rocket during liftoff. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including the chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
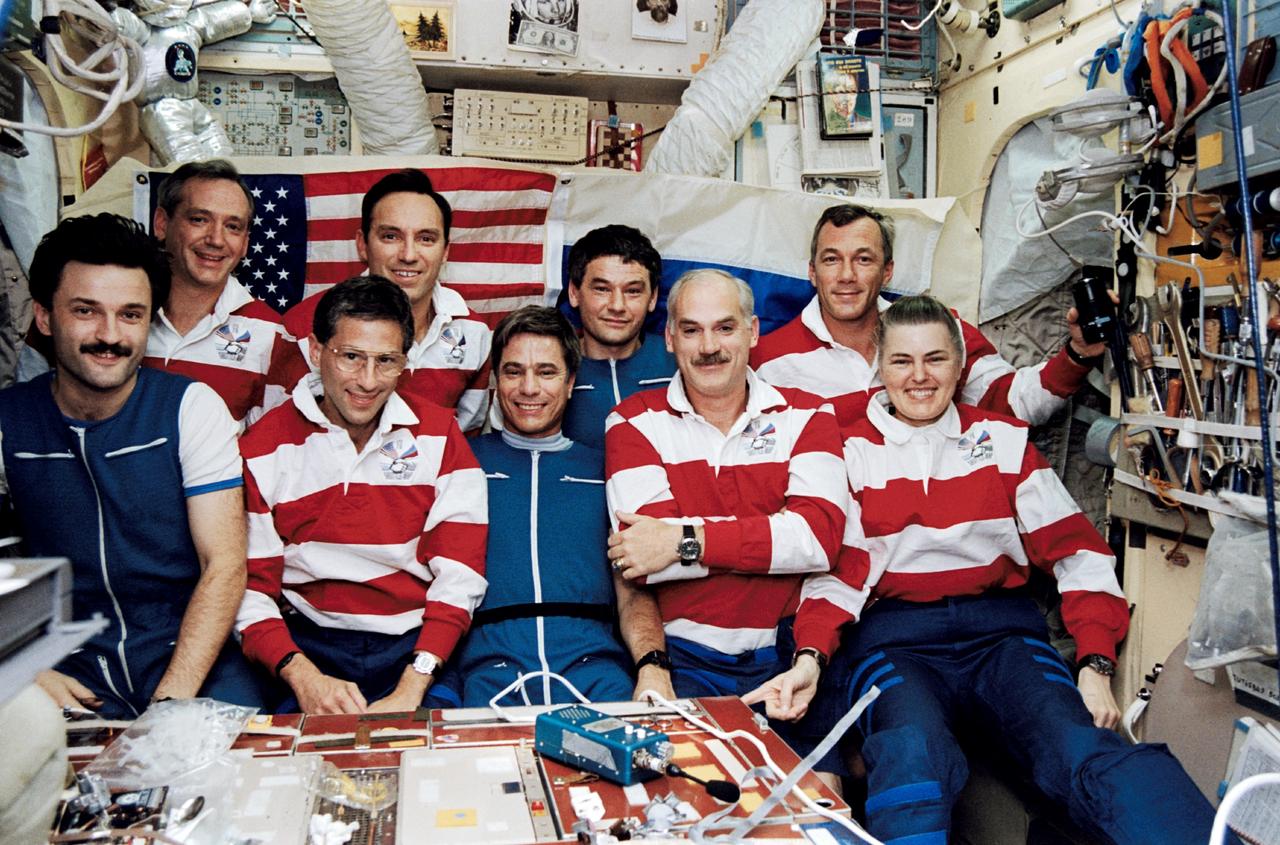

STS079-349-022 (16-26 Sept. 1996) --- The traditional inflight crew portrait, taken in Russia's Mir Space Station base block. Front row, left to right, Aleksandr Y. Kaleri, Jerome (Jay) Apt, John E. Blaha, William F. Readdy and Shannon W. Lucid. Back row, left to right, Thomas D. Akers, Carl E. Walz, Valeri G. Korzun and Terrence W. Wilcutt. This photograph is one of fifteen 35mm frames (along with four 70mm frames) of still photography documenting the activities of NASA's STS-79 mission, which began with a September 16, 1996, liftoff from Launch Pad 39A the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) and ended with a landing at KSC on September 26, 1996. Onboard for the launch were astronauts Readdy, commander; Wilcutt, pilot; Blaha, Apt, Akers and Walz, all mission specialists. On flight day 4, the crew docked with the Mir Space Station. Lucid, who had spent six months aboard Mir, switched cosmonaut guest researcher roles with Blaha. The latter joined fellow Mir-22 crewmembers Korzun, commander, and Kaleri, flight engineer.

This perspective view shows the Strait of Gibraltar, which is the entrance to the Mediterranean Sea from the Atlantic Ocean. Europe (Spain) is on the left. Africa (Morocco) is on the right. The Rock of Gibraltar, administered by Great Britain, is the peninsula in the back left. The Strait of Gibraltar is the only natural gap in the topographic barriers that separate the Mediterranean Sea from the world's oceans. The Sea is about 3700 kilometers (2300 miles) long and covers about 2.5 million square kilometers (one million square miles), while the Strait is only about 13 kilometers (8 miles) wide. Sediment samples from the bottom of the Mediterranean Sea that include evaporite minerals, soils, and fossil plants show that about five million years ago the Strait was topographically blocked and the Sea had evaporated into a deep basin far lower in elevation than the oceans. Consequent changes in the world's hydrologic cycle, including effects upon ocean salinity, likely led to more ice formation in polar regions and more reflection of sunlight back to space, resulting in a cooler global climate at that time. Today, topography plays a key role in our regional climate patterns. But through Earth history, topographic change, even perhaps over areas as small as 13 kilometers across, has also affected the global climate. This image was generated from a Landsat satellite image draped over an elevation model produced by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). The view is eastward with a 3-times vertical exaggeration to enhance topographic expression. Natural colors of the scene (green vegetation, blue water, brown soil, white beaches) are enhanced by image processing, inclusion of some infrared reflectance (as green) to highlight the vegetation pattern, and inclusion of shading of the elevation model to further highlight the topographic features. Landsat has been providing visible and infrared views of the Earth since 1972. SRTM elevation data matches the 30-meter (99-feet) resolution of most Landsat images and will substantially help in analyses of the large Landsat image archive. Elevation data used in this image was acquired by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour, launched on February 11, 2000. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03397
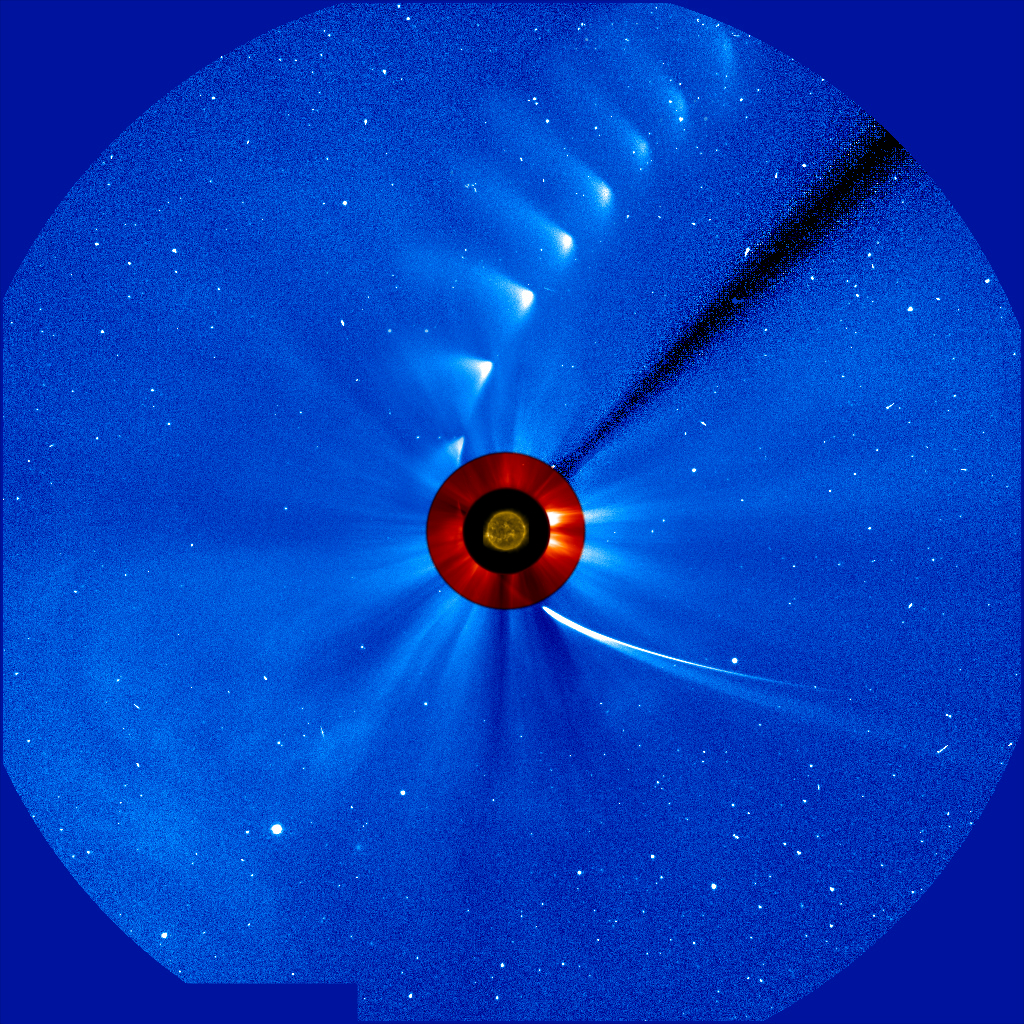
Comet ISON comes in from the bottom right and moves out toward the upper right, growing more faint, in this time-lapse image from the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory. The image of the sun at the center is from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. Credit: ESA/NASA/SOHO/SDO/GSFC After several days of fading, scientists continue to work to determine and to understand the fate of Comet ISON: There's no doubt that the comet shrank in size considerably as it rounded the sun and there's no doubt that something made it out on the other side to shoot back into space. The question remains as to whether the bright spot seen moving away from the sun was simply debris, or whether a small nucleus of the original ball of ice was still there. Regardless, it is likely that it is now only dust. Comet ISON, which began its journey from the Oort Cloud some 3 million years ago, made its closest approach to the sun on Nov. 28, 2013. The comet was visible in instruments on NASA's Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, and the joint European Space Agency/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO, via images called coronagraphs. Coronagraphs block out the sun and a considerable distance around it, in order to better observe the dim structures in the sun's atmosphere, the corona. As such, there was a period of several hours when the comet was obscured in these images, blocked from view along with the sun. During this period of time, NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory could not see the comet, leading many scientists to surmise that the comet had disintegrated completely. However, something did reappear in SOHO and STEREO coronagraphs some time later – though it was significantly less bright. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/18hGYag" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/18hGYag</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
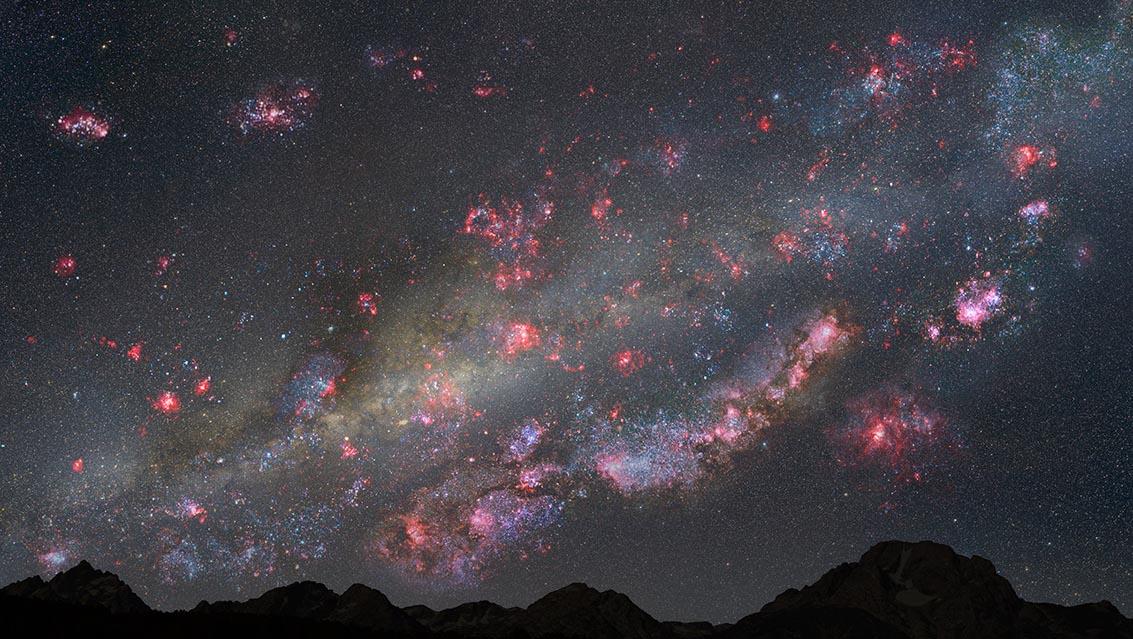

Caption: Artist's view of night sky from a hypothetical planet within a young Milky Way-like galaxy 10 billion years ago, the sky are ablaze with star birth. Pink clouds of gas harbor newborn stars, and bluish-white, young star clusters litter the landscape. Image Credit: NASA/ESA/Z. Levay (STScI) More info: In one of the most comprehensive multi-observatory galaxy surveys yet, astronomers find that galaxies like our Milky Way underwent a stellar “baby boom,” churning out stars at a prodigious rate, about 30 times faster than today. Our sun, however, is a late “boomer.” The Milky Way’s star-birthing frenzy peaked 10 billion years ago, but our sun was late for the party, not forming until roughly 5 billion years ago. By that time the star formation rate in our galaxy had plunged to a trickle. Missing the party, however, may not have been so bad. The sun’s late appearance may actually have fostered the growth of our solar system’s planets. Elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were more abundant later in the star-forming boom as more massive stars ended their lives early and enriched the galaxy with material that served as the building blocks of planets and even life on Earth. Astronomers don’t have baby pictures of our Milky Way’s formative years to trace the history of stellar growth so they studied galaxies similar in mass to our Milky Way, found in deep surveys of the universe. The farther into the universe astronomers look, the further back in time they are seeing, because starlight from long ago is just arriving at Earth now. From those surveys, stretching back in time more than 10 billion years, researchers assembled an album of images containing nearly 2,000 snapshots of Milky Way-like galaxies. The new census provides the most complete picture yet of how galaxies like the Milky Way grew over the past 10 billion years into today’s majestic spiral galaxies. The multi-wavelength study spans ultraviolet to far-infrared light, combining observations from NASA’s Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, the European Space Agency’s Herschel Space Observatory, and ground-based telescopes, including the Magellan Baade Telescope at the Las Campanas Observatory in Chile. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/our-sun-came-late-to-the-milky-way-s-star-birth-party/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/our-sun-came-late-to-the-mil...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The primary mirror of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope consisting of 18 hexagonal mirrors looks like a giant puzzle piece standing in the massive clean room of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Appropriately, combined with the rest of the observatory, the mirrors will help piece together puzzles scientists have been trying to solve throughout the cosmos. Webb's primary mirror will collect light for the observatory in the scientific quest to better understand our solar system and beyond. Using these mirrors and Webb's infrared vision scientists will peer back over 13.5 billion years to see the first stars and galaxies forming out of the darkness of the early universe. Unprecedented infrared sensitivity will help astronomers to compare the faintest, earliest galaxies to today's grand spirals and ellipticals, helping us to understand how galaxies assemble over billions of years. Webb will see behind cosmic dust clouds to see where stars and planetary systems are being born. It will also help reveal information about atmospheres of planets outside our solar system, and perhaps even find signs of the building blocks of life elsewhere in the universe. The Webb telescope was mounted upright after a "center of curvature" test conducted at Goddard. This initial center of curvature test ensures the integrity and accuracy, and test will be repeated later to verify those same properties after the structure undergoes launch environment testing. In the photo, two technicians stand before the giant primary mirror. For information on the Webb's Center of Curvature test, visit: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2fidD9S" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2fidD9S</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Photographs documenting International Space Station (ISS) Phase One activities at the Russian Space Agency's (RSA) Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center, Korolov Mission Control Center and Zvezda; and ISS and Soyuz manufacturing at RSA's Khrunichev Design Center and RSC Energiya in Moscow, Russia, the French Space Agency's (CNES) INTESPACE facility in Toulouse, France, and the Italian Space Agency's (ASI) Alenia Spazio facility in Torino, Italy. Photographs were taken by Johnson Space Center Imagery and Publications Office contractors travelling from October 7 to November 4, 1996. Includes: VIEWS FROM RSC ENERGIYA'S SPACE MUSEUM: Room with a Buran model and photographic displays (17372-374). Salyut Space Station mock-up (17376). Russian propulsion engines on display (17377-378). Russian spacecraft on display (17375, 17387-398). Graphic displays (17399-405). VIEWS FROM RSC ENERGIYA MANUFACTURING FACILITIES: Unidentified facility (17379). Mir 24 crew member Michael C. Foale, suited in a Soyuz pressure suit, ingresses the Soyuz TM-26 flight article at RSC Energiya for a fit check (17380-381). Closeups of Foale inside the Soyuz during the fit check (17382-383, 17466-467). Overhead views of RSC Energiya's Building 444 manufacturing floor where docking modules and Soyuz TM spacecraft are built (17495-498). Technicians on the Building 444 manufacturing floor assembling probe and drogue docking modules (17499-500, 17504). Technicians assembling Soyuz spacecraft (17437-439). Views of other Soyuz spacecraft (17440-441). Androgynous Peripheral Docking System (APDS) mock-up (17501-503). Closeups of a control panel, possibly for the APDS mock-up (17519-528). VIEWS FROM ZVEZDA, RSA CONTRACTOR FOR SUIT DESIGN AND SOYUZ SEAT LINERS: Mir 24 crew member Foale dons a "penguin" flight suit for a fit check (17454-456). Zvezda personnel adjust Foale's Soyuz seat and seat liner (17442). Closeup of Foale, suited in a Soyuz pressure suit, sitting on a chair (17444). Zvezda personnel strap pressure-suited Foale into his Soyuz seat (17443, 17445, 17450). Views of Foale in his Soyuz seat during a pressurized pressure suit fit check (17451-453). Views looking into a vacuum chamber where Foale, wearing pressure suit, is strapped into his Soyuz seat (17466-467). Views of Zvezda personnel working at the vacuum chamber control station during the vacuum chamber suit test (17468-471). VIEWS FROM KHRUNICHEV DESIGN CENTER: Views of a green ISS Functional Cargo Block (FGB) test article on the manufacturing floor (17529, 17532-536, 17540-544). Views of an ISS Service Module (SM) test article on the manufacturing floor (17530-531, 17537, 17539). Closeup of the SM test article docking sphere (17538). Views of the FGB flight article on the manufacturing floor during systems tests (17545-548, 17550-567). Views of technicians conducting the FGB systems tests (17549, 17557). VIEWS FROM GAGARIN COSMONAUT TRAINING CENTER: NASA astronauts work out in the cosmonaut gym at Gagarin: Closeup of ISS 2R Expedition Commander William Shepherd on a weight machine (17384). Shepherd and an unidentified man with back to camera work out with dumbbells (17386). Shepherd does pull-ups (17447). Closeup of Foale on an exercise machine (17385). Closeups of Foale exercising arms on a cycle ergometer and a weight machine (17415, 17448-449). Foale exercises on a Nordic Track (17416). Closeup of Mir 23 crew member Jerry Linenger exercising arms (17417). Wendy Lawrence exercises with dumbbells (17418). Closeup of Lawrence in a handstand position (17419). David Wolf works out on a leg press machine (17446). Views of the Mir Space Station mock-up at Gagarin: Interior views of the Mir Base Module mock-up looking toward the transfer compartment (17421-425). Mir Base Module living area mock-up (17420). Overall views of the Base Module mock-up central control station (17426-427, 17505). Closeups of switch panels on the central control station (17428-436, 17506-518). Other views from Gagarin: Personnel work at an unidentified test/trainer control station (17472-473). Linenger sits at a table next to an RSA trainer during a Mir 23 meeting (17475-476). Out-of-focus view of two subjects in the Soyuz trainer (17474). Foale examines a Mir Complex EVA Suit (Orlan) with RSA trainers during an EVA suit training class (17492-494). VIEWS FROM KOROLOV MISSION CONTROL CENTER: Various views of personnel working in the NASA Consulting Room and/or PAO Consulting Room at Korolov Mission Control Center (17457-463). VIEWS FROM INTESPACE: Exterior views of an ISS Mini Pressurized Logistics Module (MPLM) structural test article (STA) during testing at INTESPACE (17406-409, 17477, 17482-484). Technicians install hatch on the MPLM STA (17410-414). Interior views of the MPLM STA (17478-481). VIEWS FROM ALENIA SPAZIO: Closeups of MPLM flight article #1 side panels during milling and refining at Alenia Spazio (17485-488). Workers process MPLM parts at milling machines (17489-491).
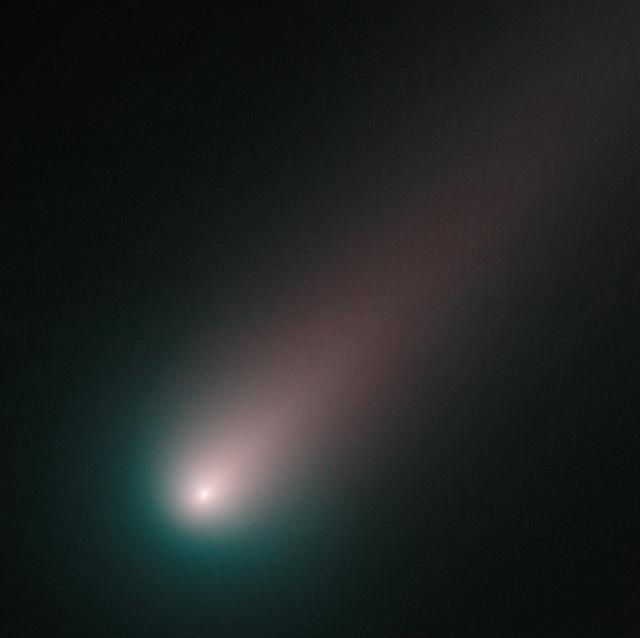

As of mid-November, ISON is officially upon us. Using Hubble, we've taken our closest look yet at the innermost region of the comet, where geysers of sublimating ice are fueling a spectacular tail. Made from observations on November 2nd, the image combines pictures of ISON taken through blue and red filters. As we expect, the round coma around ISON's nucleus is blue and the tail has a redder hue. Ice and gas in the coma reflect blue light from the Sun, while dust grains in the tail reflect more red light than blue light. This is the most color separation we've seen so far in ISON -- that's because the comet, nearer than ever to the Sun, is brighter and more structured than ever before. We've certainly come a long way since Hubble started observing Comet ISON, way back in April. Of course, our eight-month retrospective pales in comparison with ISON's own journey, which started some 10,000 years ago in the Oort cloud. ISON will come closest to the Sun on November 28, a point in its orbit known as perihelion. What's remarkable here is that the entire ISON, this awesome, shimmery space tadpole, is being produced from a dusty ball of ice estimated to be a few kilometers in diameter. Compared to ISON's full extent, Hubble's latest image is tiny. It only shows the very base of the tail. Yet even in this closest closeup we've ever had, a single pixel spans 24 km across the comet. Now that Comet ISON is close, amateur astromers rule the day. But Hubble observations, including this latest image, are still providing key insights into the science and spectacle of a comet we hope will continue to impress. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is