
Fundamental Study of a boundary layer ingesting (BLI) propulsion model
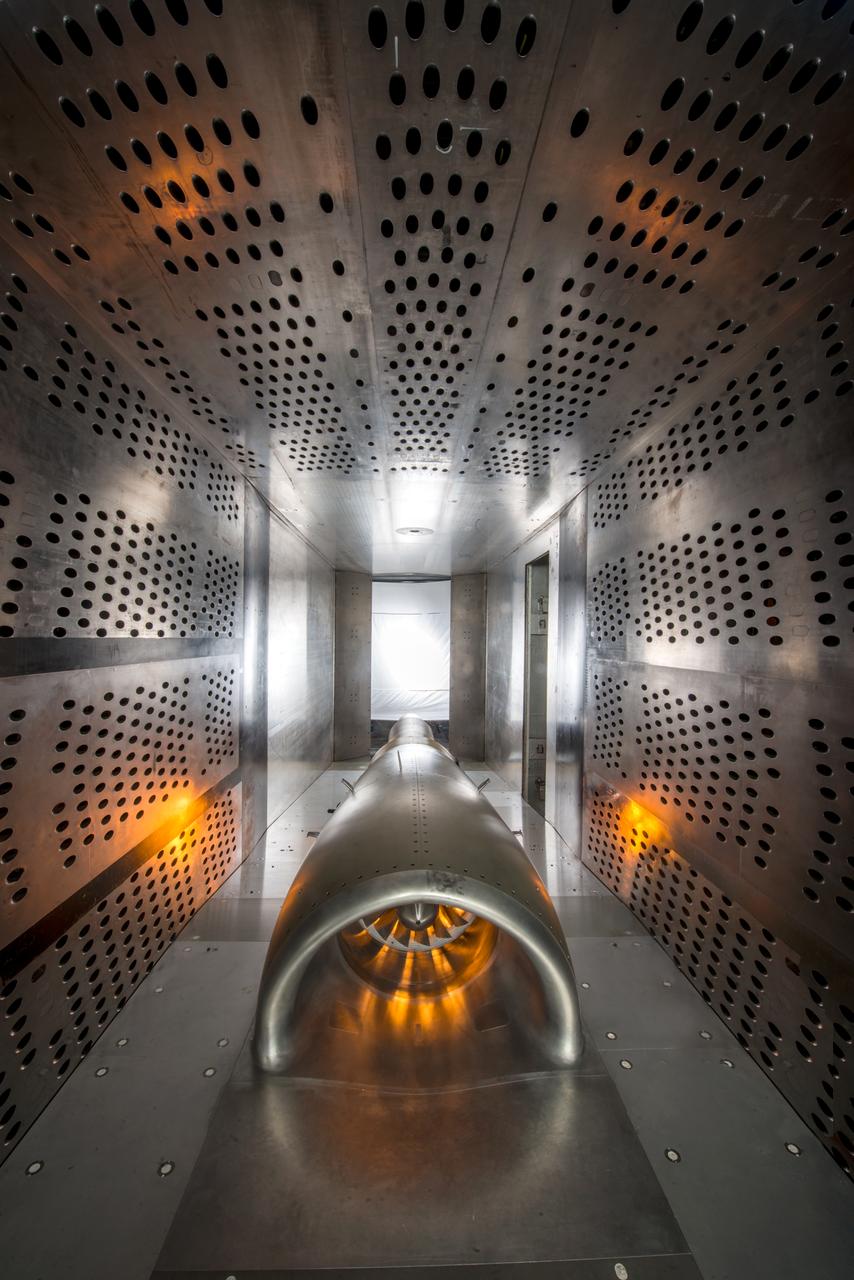

In an effort to improve fuel efficiency, NASA and the aircraft industry are rethinking aircraft design. Inside the 8' x 6' wind tunnel at NASA Glenn, engineers recently tested a fan and inlet design, commonly called a propulsor, which could use four to eight percent less fuel than today's advanced aircraft.
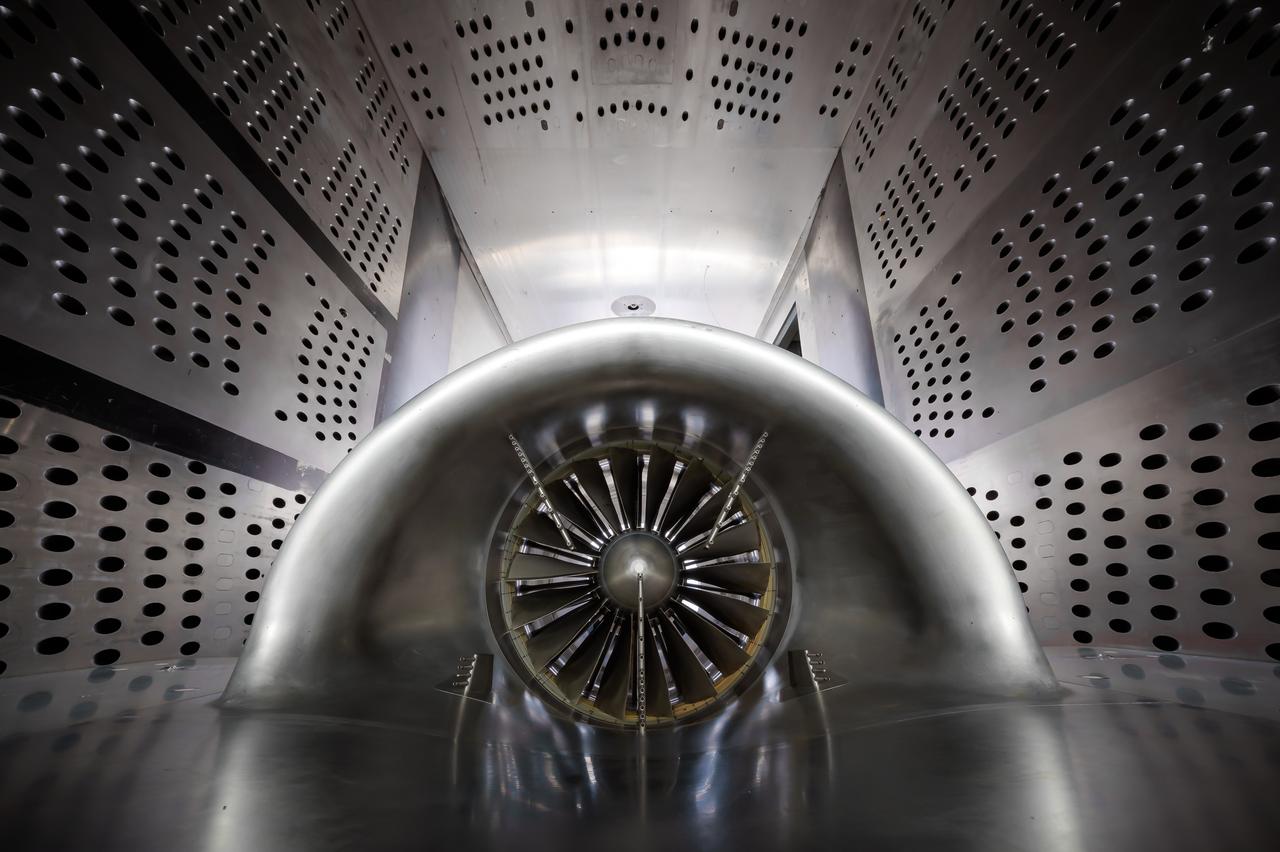

In an effort to improve fuel efficiency, NASA and the aircraft industry are rethinking aircraft design. Inside the 8' x 6' wind tunnel at NASA Glenn, engineers recently tested a fan and inlet design, commonly called a propulsor, which could use four to eight percent less fuel than today's advanced aircraft.
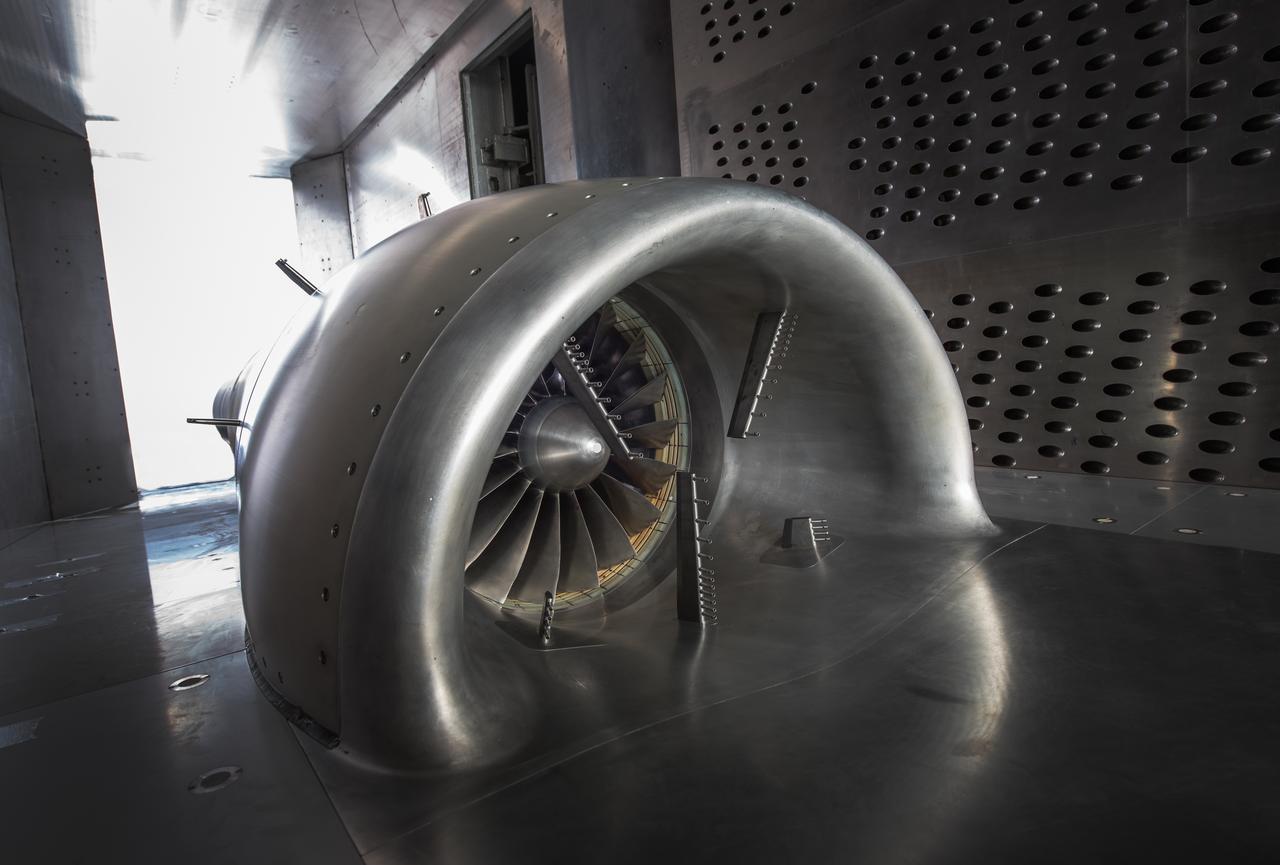

In an effort to improve fuel efficiency, NASA and the aircraft industry are rethinking aircraft design. Inside the 8' x 6' wind tunnel at NASA Glenn, engineers recently tested a fan and inlet design, commonly called a propulsor, which could use four to eight percent less fuel than today's advanced aircraft.
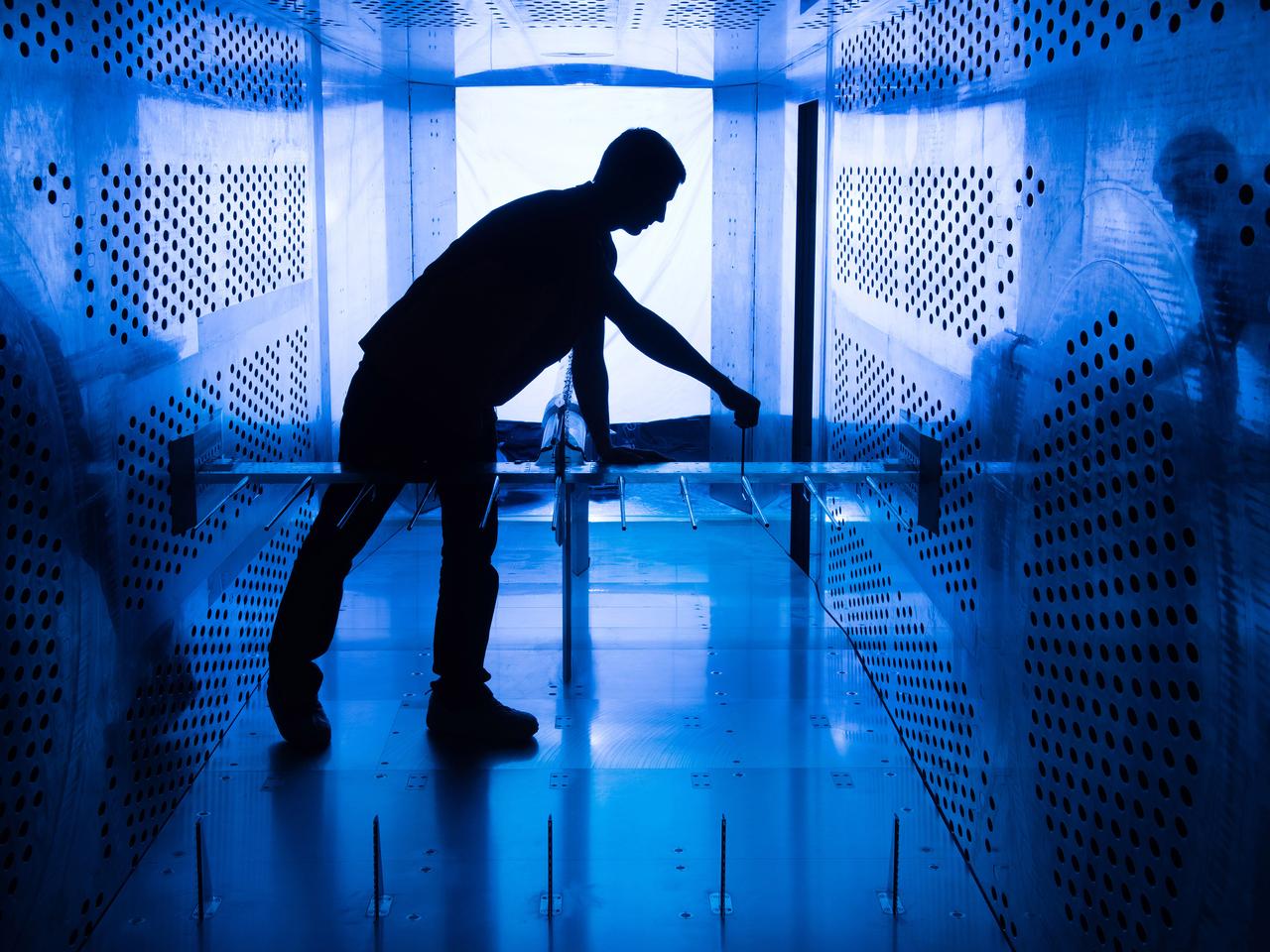

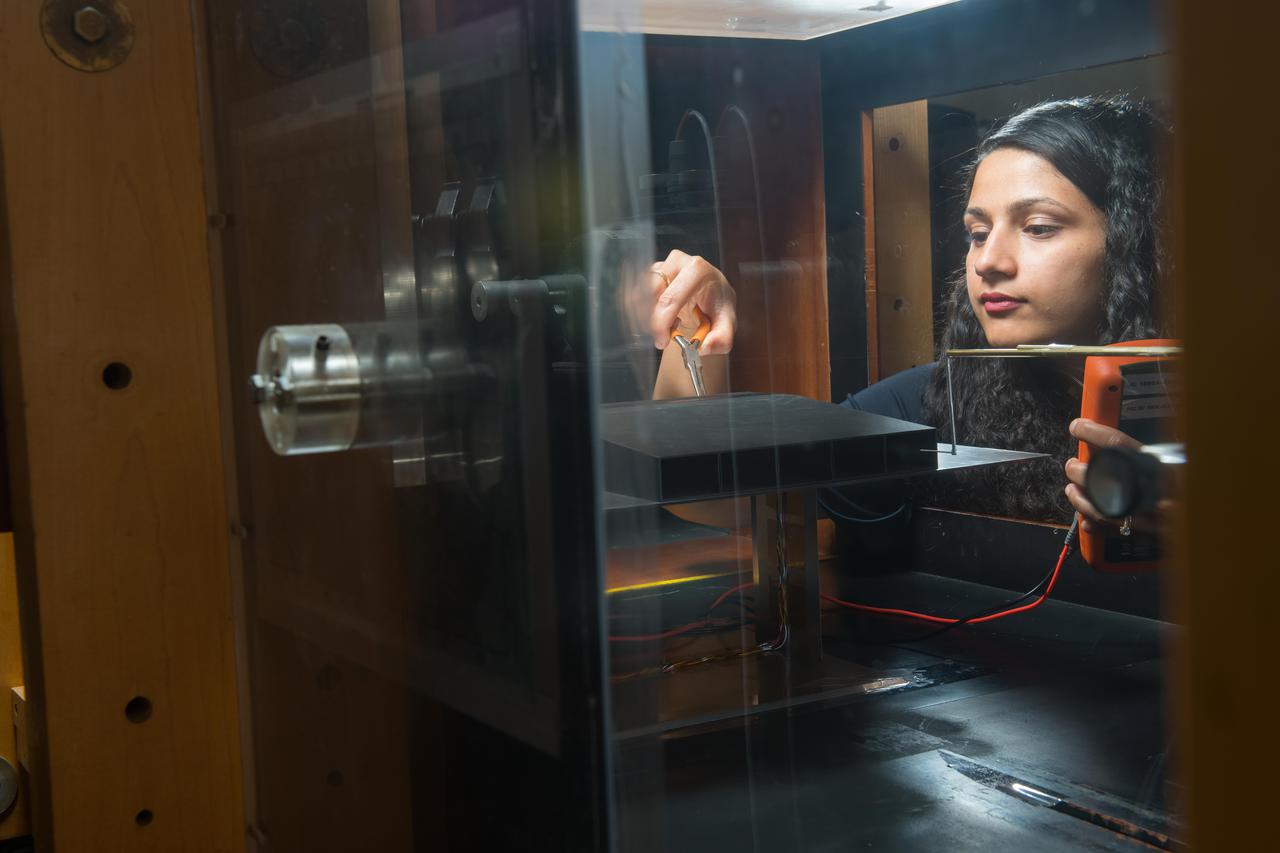
Raised Floor Calibration Hardware for the Boundary Layer Ingesting Inlet Distortion Tolerant Fan tests to be performed in the 8' x 6' Supersonic Wind Tunnel at NASA Glenn Research Center.
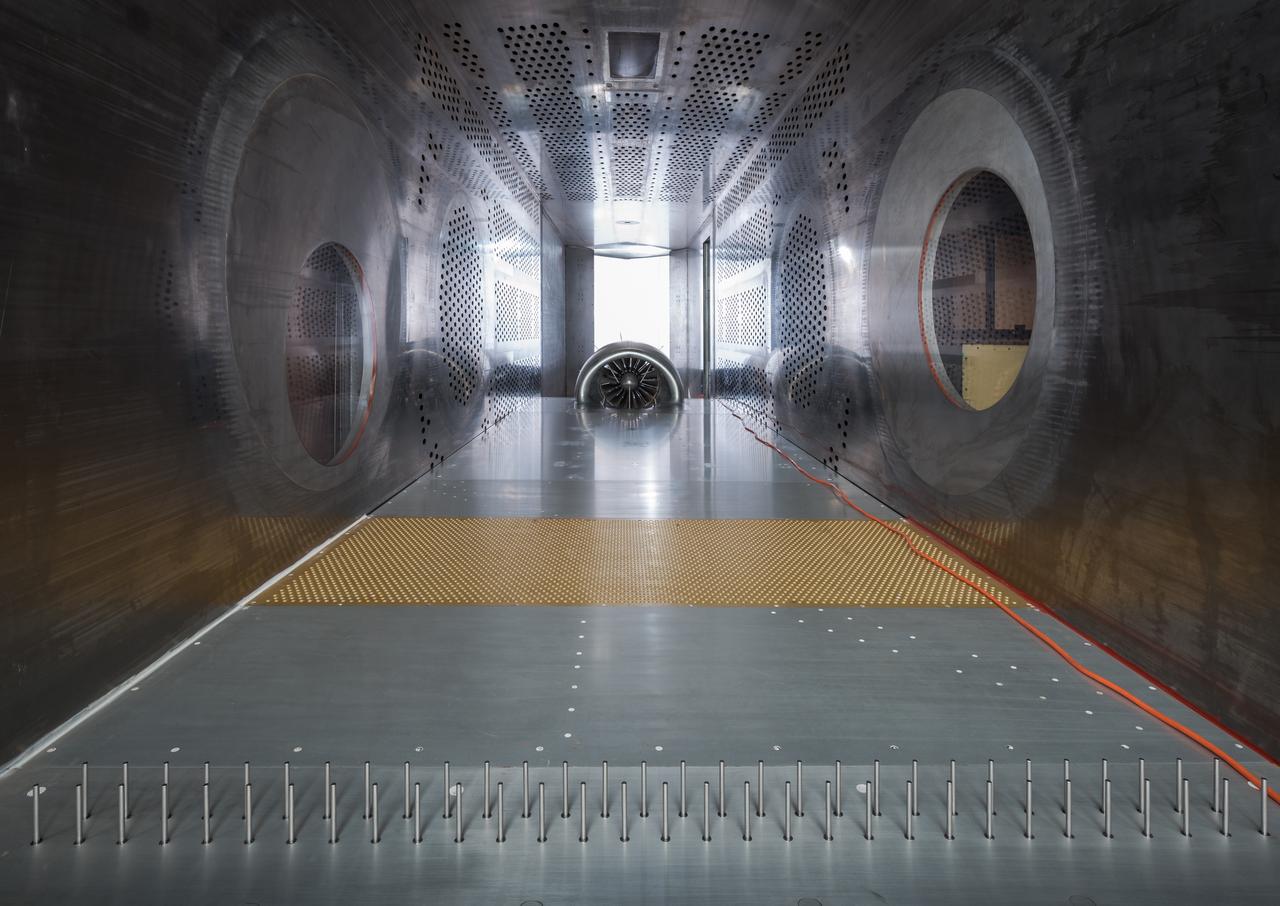

In an effort to improve fuel efficiency, NASA and the aircraft industry are rethinking aircraft design. Inside the 8' x 6' wind tunnel at NASA Glenn, engineers recently tested a fan and inlet design, commonly called a propulsor, which could use four to eight percent less fuel than today's advanced aircraft.
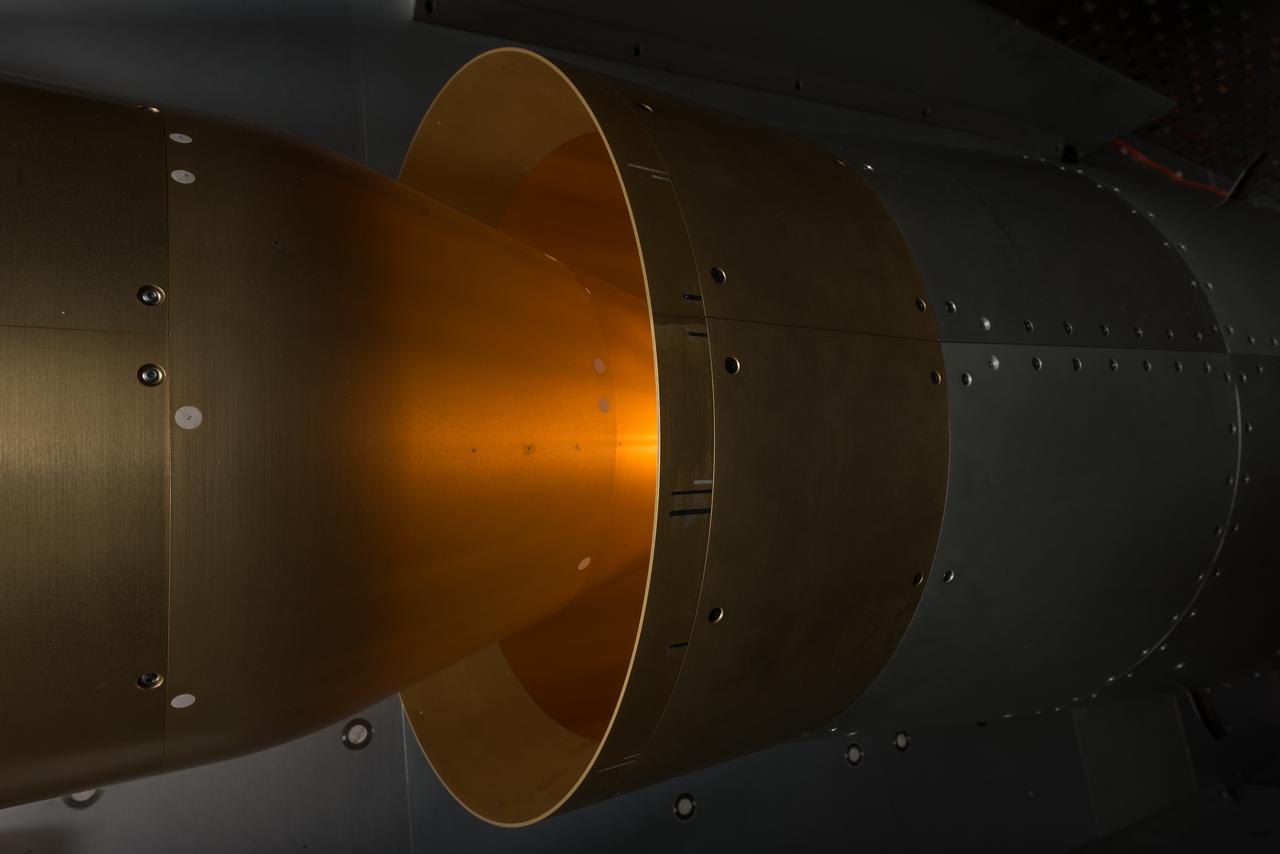
In an effort to improve fuel efficiency, NASA and the aircraft industry are rethinking aircraft design. Inside the 8' x 6' wind tunnel at NASA Glenn, engineers recently tested a fan and inlet design, commonly called a propulsor, which could use four to eight percent less fuel than today's advanced aircraft.
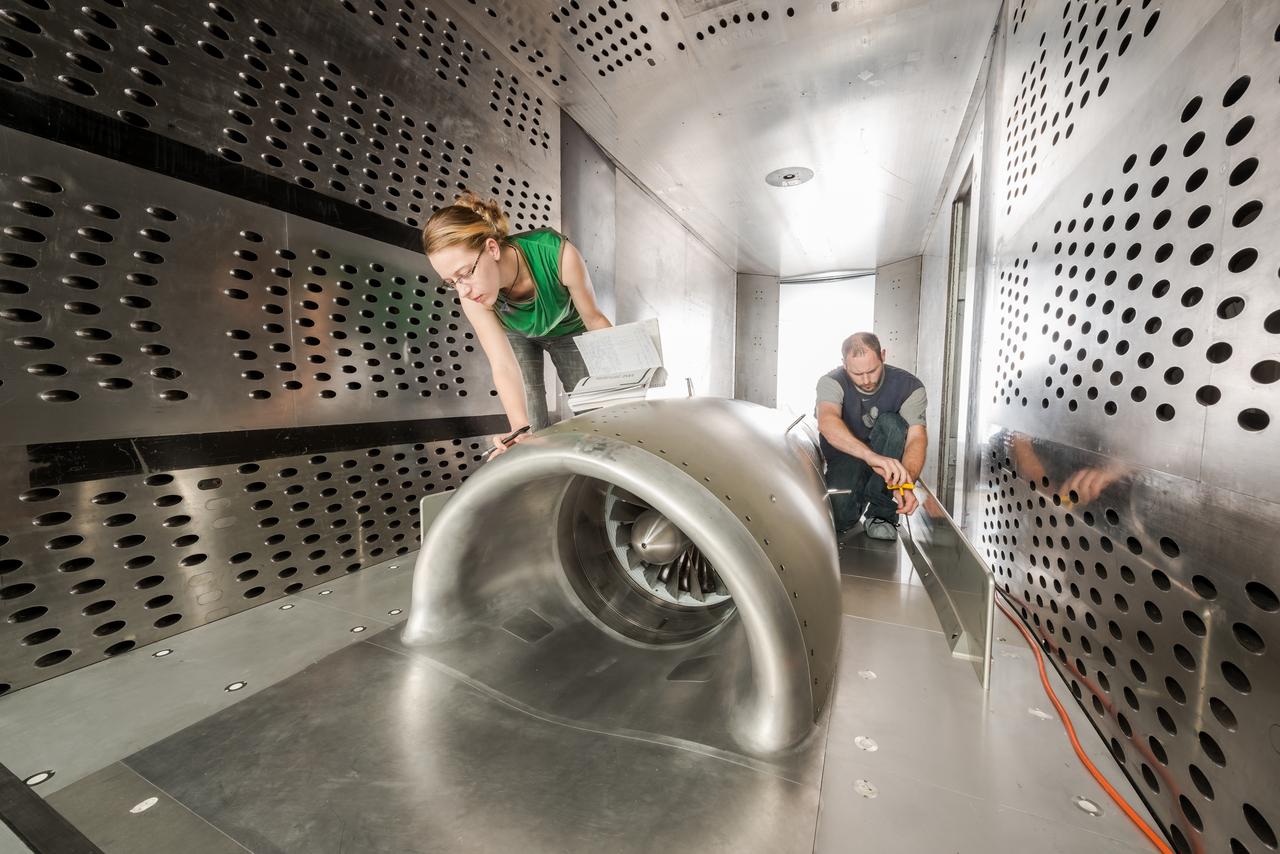

In an effort to improve fuel efficiency, NASA and the aircraft industry are rethinking aircraft design. Inside the 8' x 6' wind tunnel at NASA Glenn, engineers recently tested a fan and inlet design, commonly called a propulsor, which could use four to eight percent less fuel than today's advanced aircraft.
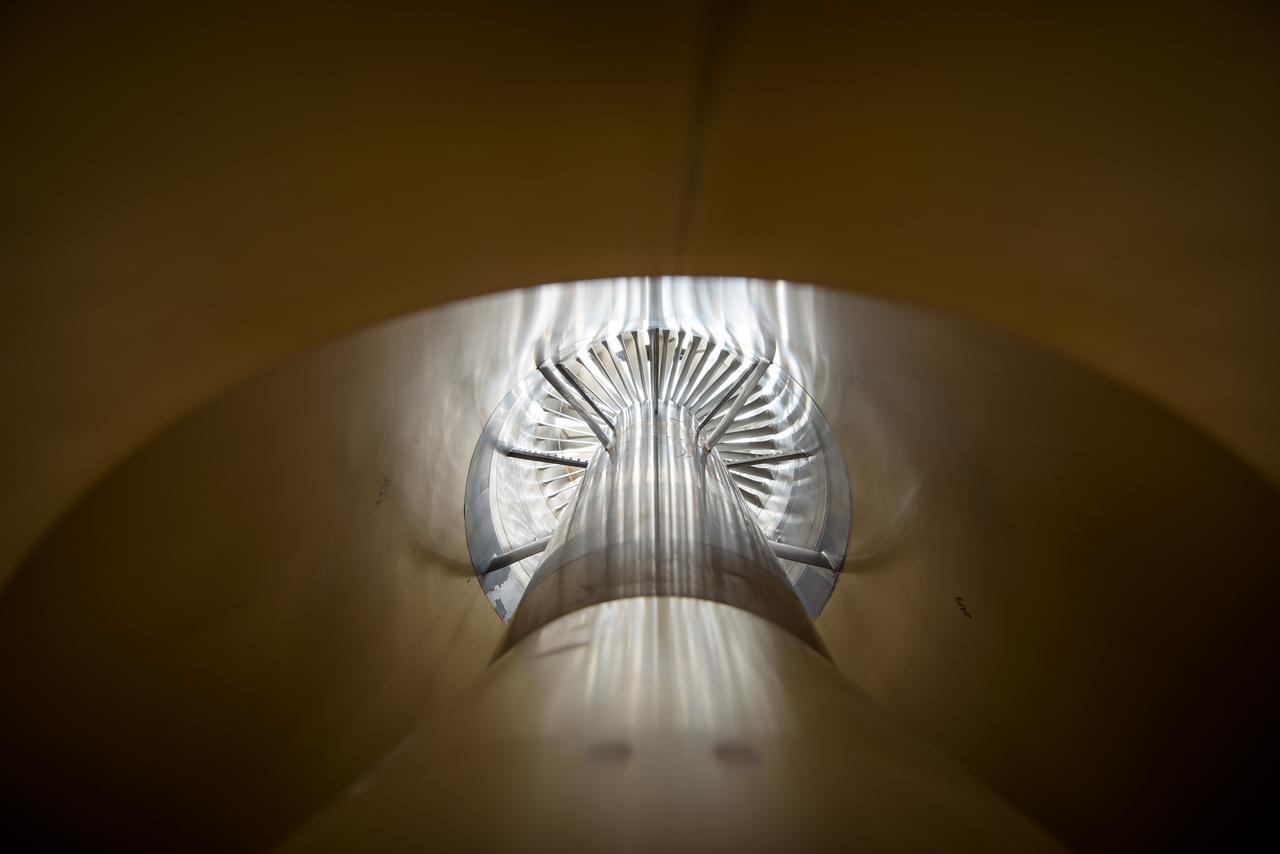

In an effort to improve fuel efficiency, NASA and the aircraft industry are rethinking aircraft design. Inside the 8' x 6' wind tunnel at NASA Glenn, engineers recently tested a fan and inlet design, commonly called a propulsor, which could use four to eight percent less fuel than today's advanced aircraft.
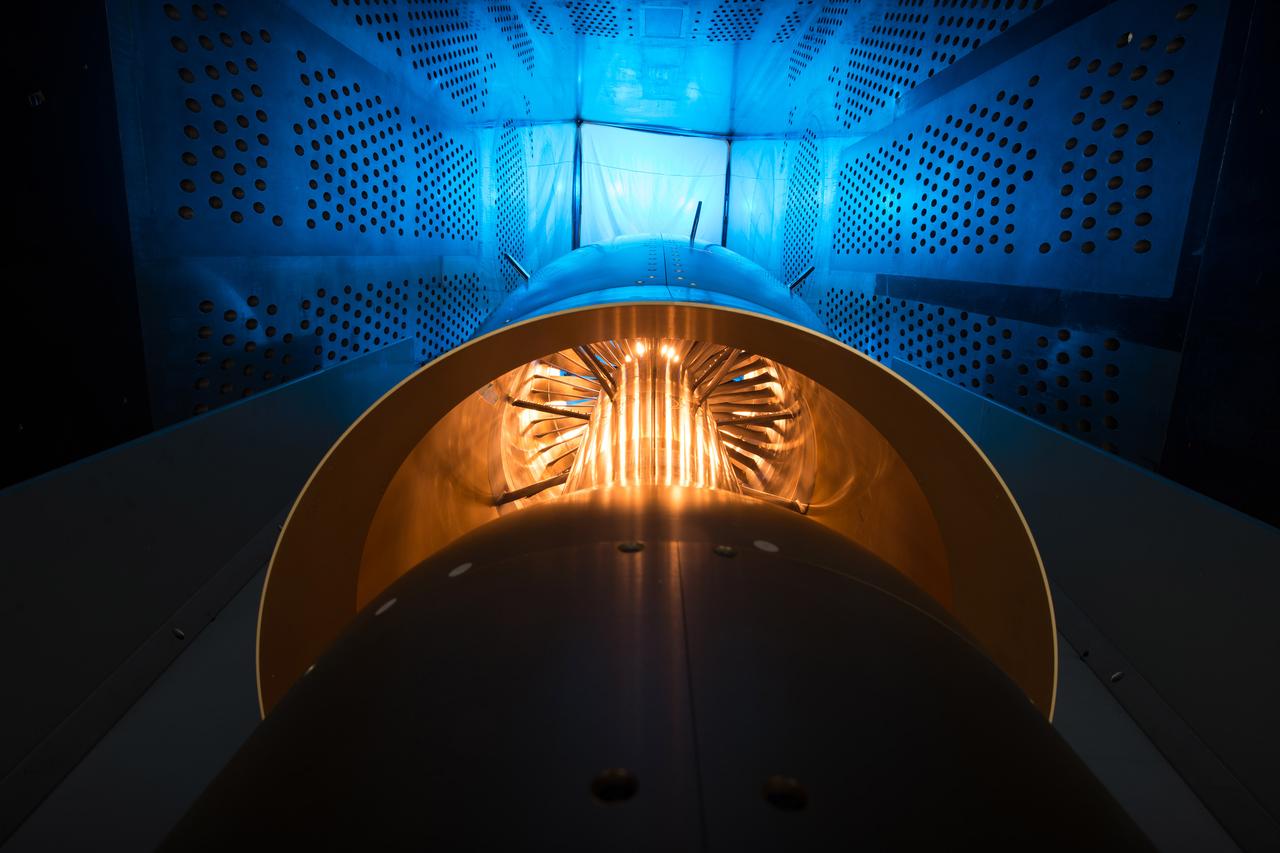

In an effort to improve fuel efficiency, NASA and the aircraft industry are rethinking aircraft design. Inside the 8' x 6' wind tunnel at NASA Glenn, engineers recently tested a fan and inlet design, commonly called a propulsor, which could use four to eight percent less fuel than today's advanced aircraft.
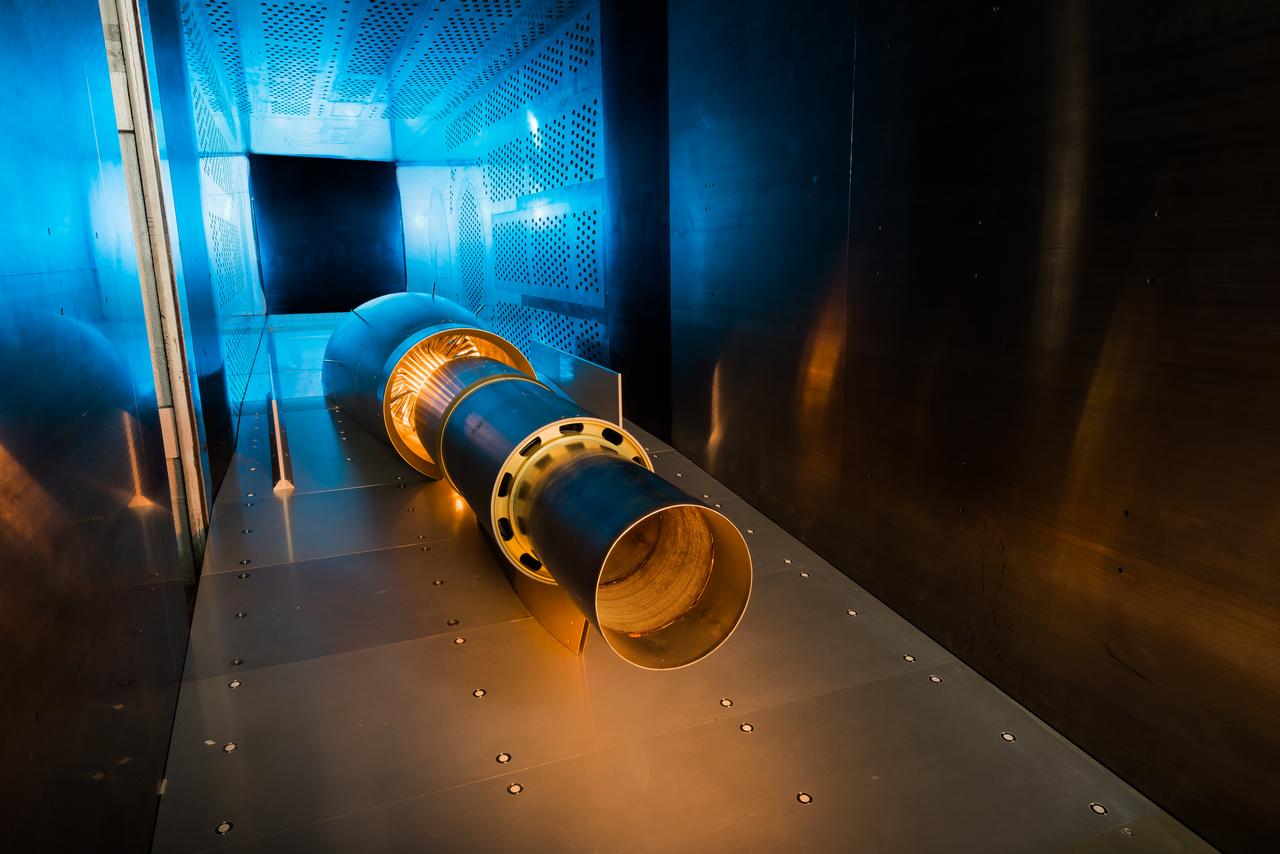
In an effort to improve fuel efficiency, NASA and the aircraft industry are rethinking aircraft design. Inside the 8' x 6' wind tunnel at NASA Glenn, engineers recently tested a fan and inlet design, commonly called a propulsor, which could use four to eight percent less fuel than today's advanced aircraft.