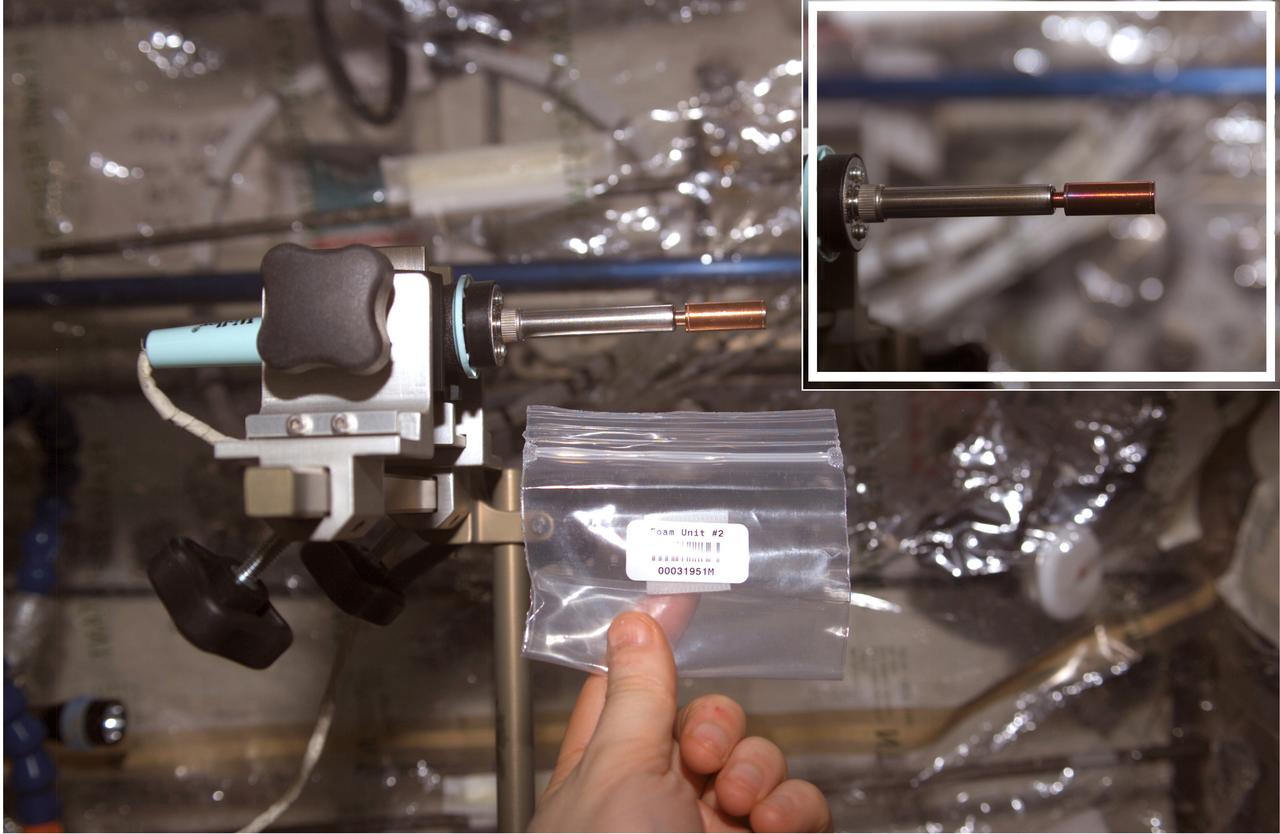
This soldering iron has an evacuated copper capsule at the tip that contains a pellet of Bulk Metallic Glass (BMG) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Prior to flight, researchers sealed a pellet of bulk metallic glass mixed with microscopic gas-generating particles into the copper ampoule under vacuum. Once heated in space, such as in this photograph, the particles generated gas and the BMG becomes a viscous liquid. The released gas made the sample foam within the capsule where each microscopic particle formed a gas-filled pore within the foam. The inset image shows the oxidation of the sample after several minutes of applying heat. Although hidden within the brass sleeve, the sample retained the foam shape when cooled, because the viscosity increased during cooling until it was solid.
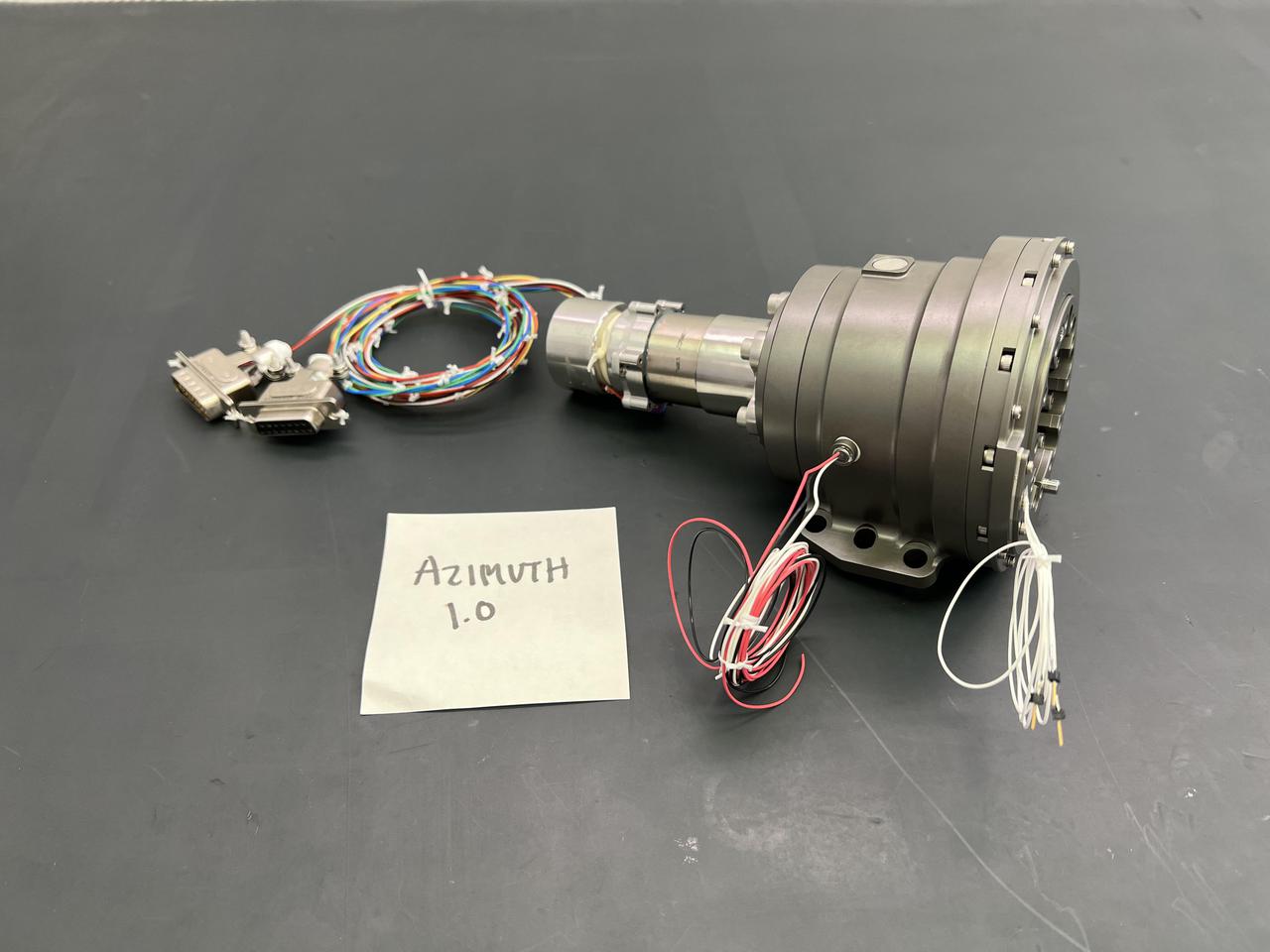

In early 2022, the Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) project – led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California – successfully integrated special gears into pieces of a robotic arm that is planned to perform a robot-controlled lunar surface experiment with imagery in the coming years. These bulk metallic glass (BMG) gears, integrated into COLDArm's joints and actuators, were developed through the Game Changing Development bulk metallic glass gears project to operate at extreme temperatures below minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). The gear alloys have a disordered atomic-scale structure, making them both strong and elastic enough to withstand these exceptionally low temperatures. Typical gearboxes require heating to operate at such cryogenic temperatures. The BMG gear motors have been tested and successfully operated at roughly minus 279 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius) without heating assistance. This gear motor is one of the key technologies to enable the robotic arm to operate in extremely cold environments, such as during lunar night. Each of the four joints containing BMG gears will be tested once the arm is fully assembled, which is scheduled for spring of 2022. Robotic joint testing will include dynamometer testing to measure torque/rotational speed, as well as cryogenic thermal vacuum testing to understand how the equipment would perform in an environment similar to space. Once proven, the BMG gears and COLDArm capabilities will enable future missions to work in extreme environments on the Moon, Mars, and ocean worlds. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24567