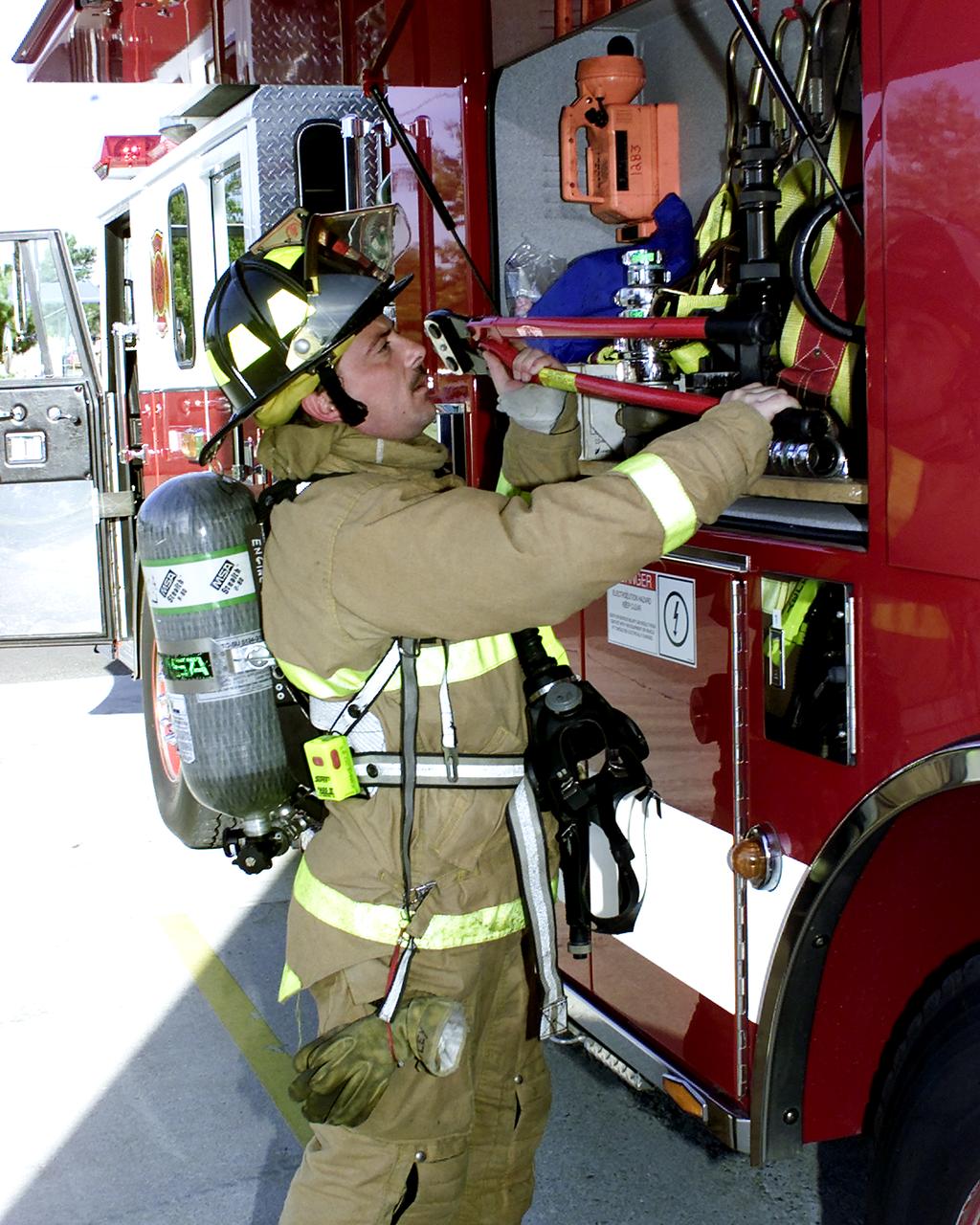

Technology used to provide thermal protection for Apollo astronauts and spacecraft components provides firefighters with better protective clothing and equipment. Spinoffs include a portable firefighting module, protective clothing for workers in hazardous environments, fire-retardant paints and forms, fireblocking coating for outdoor structures, and flame-resistant fabric. Perhaps the farthest reaching is the breathing apparatus worn by firefighters throughout the U.S. for protection against smoke inhalation injury. The breathing system weighs approximately 20 pounds, one-third less than past systems, and it enables the wearer to have improved mobility. It consists of a face mask, frame and harness, a warning device, and an air bottle. The basic air cylinder offers the same 30-minutes of operation time as its predecessor. The result is a drastic reduction in the number of inhalation injuries to firefighters. Though they have made many design modifications and refinements, manufacturers of breathing apparatus still incorporate the original NASA technology.
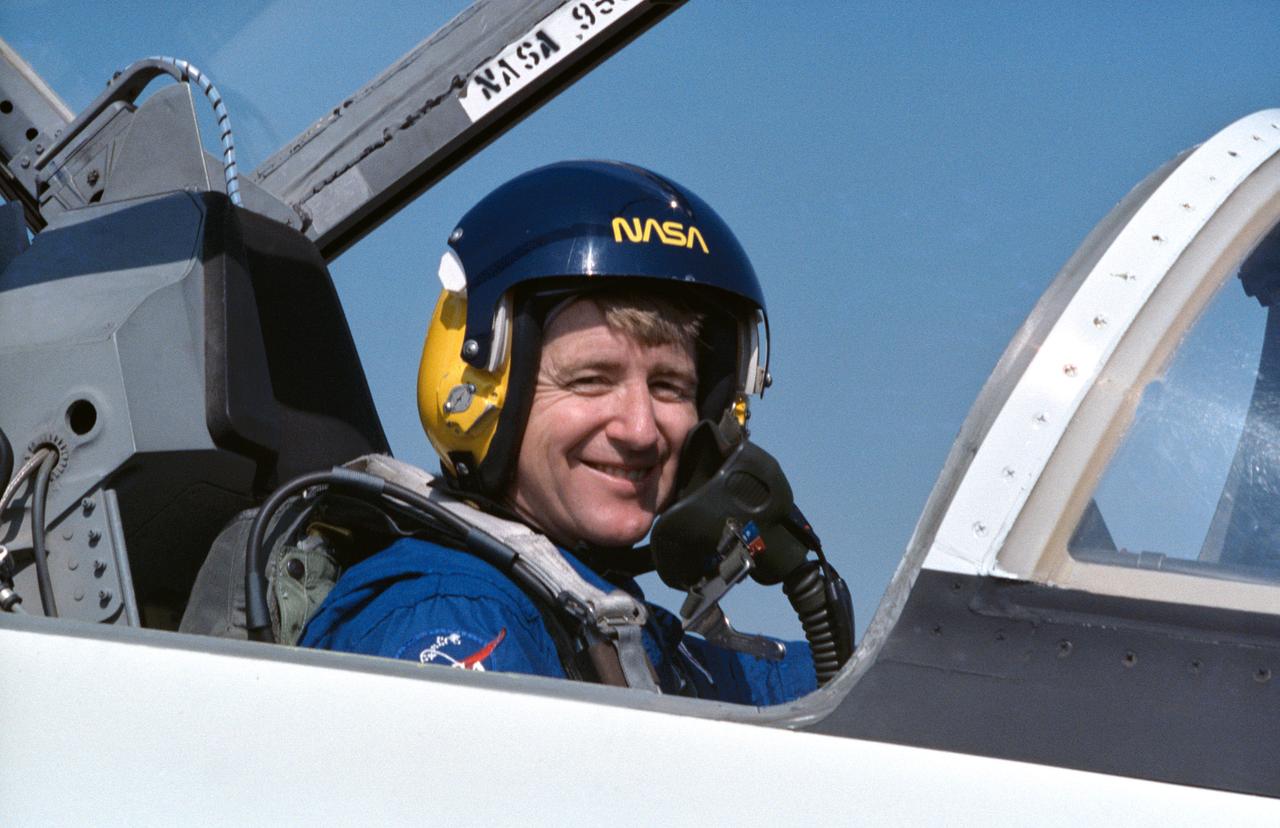

STS-38 Pilot Frank L. Culberston, smiling and wearing his helmet with breathing apparatus attached, sits in T-38A NASA 955 forward cockpit at Ellington Field and prepares for departure.
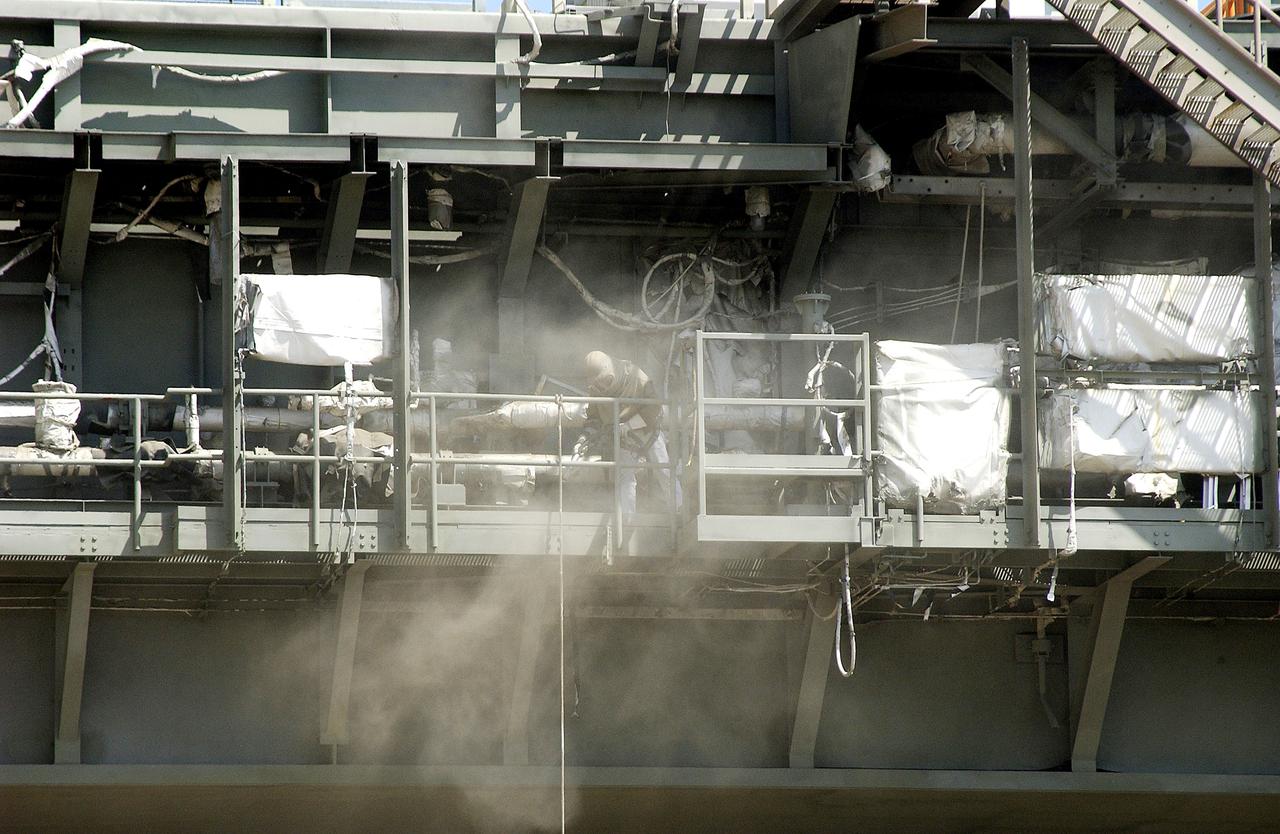

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers, covered in protective clothing and breathing apparatus, continue sandblasting on the Mobile Launcher Platform on Launch Pad 39A to remove corrosion before repainting. Routine maintenance includes sandblasting and repainting as preventive means to minimize corrosion.
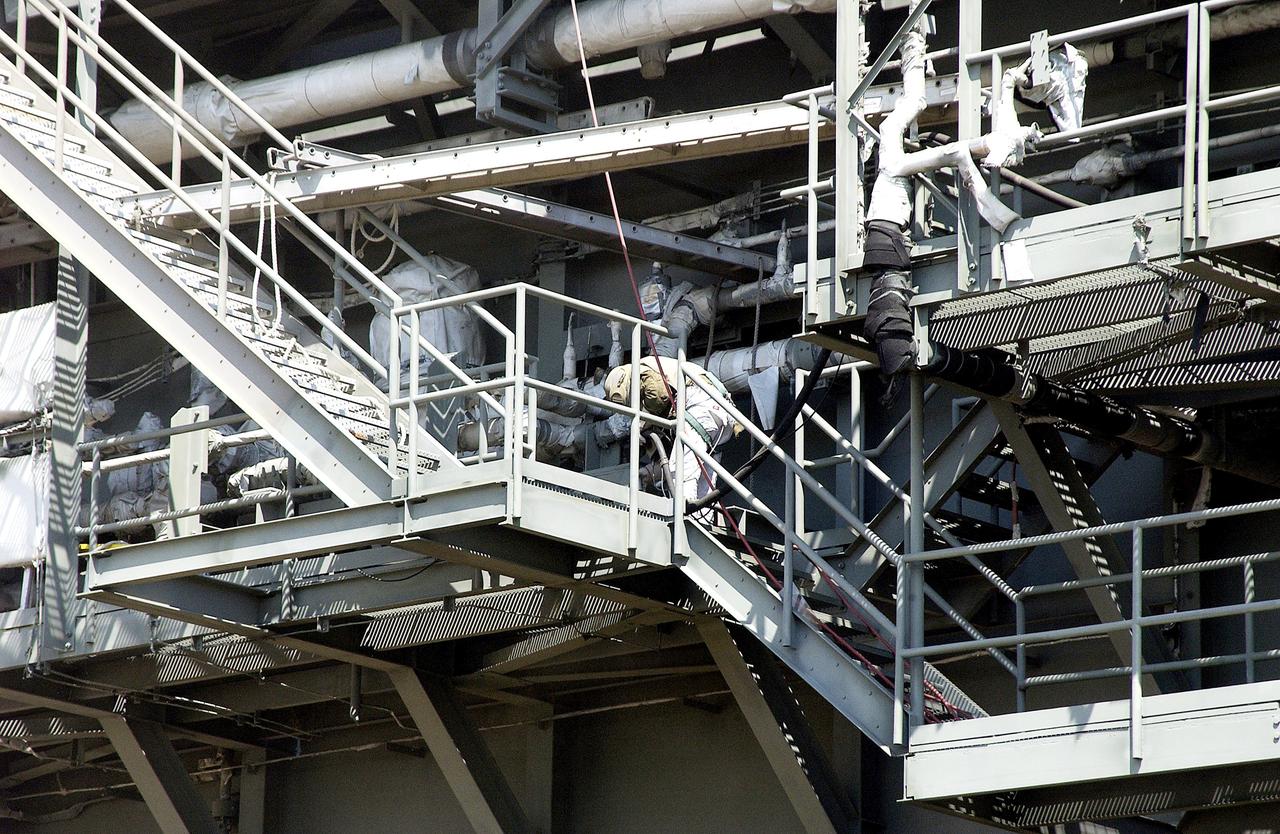

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers, covered in protective clothing and breathing apparatus, continue sandblasting on the Mobile Launcher Platform on Launch Pad 39A to remove corrosion before repainting. Routine maintenance includes sandblasting and repainting as preventive means to minimize corrosion.
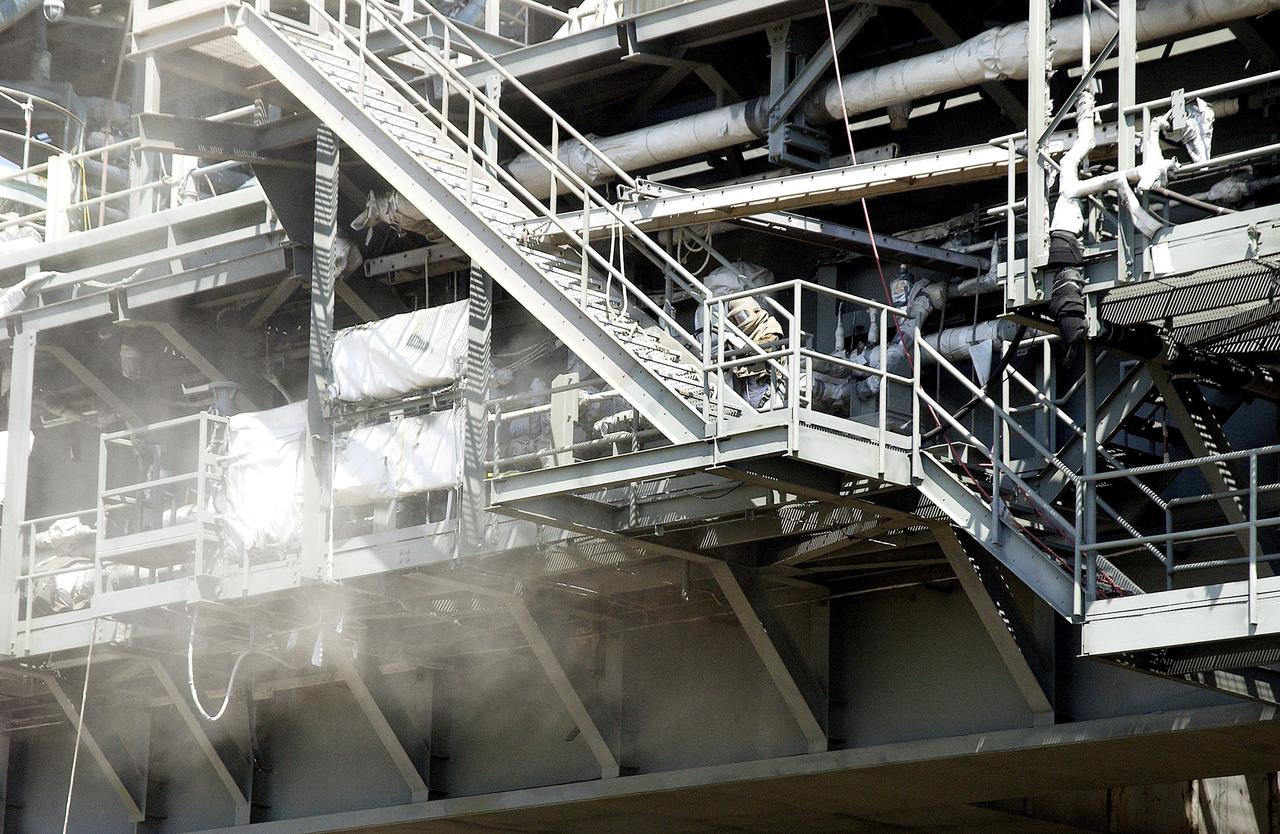

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers, covered in protective clothing and breathing apparatus, continue sandblasting on the Mobile Launcher Platform on Launch Pad 39A to remove corrosion before repainting. Routine maintenance includes sandblasting and repainting as preventive means to minimize corrosion.
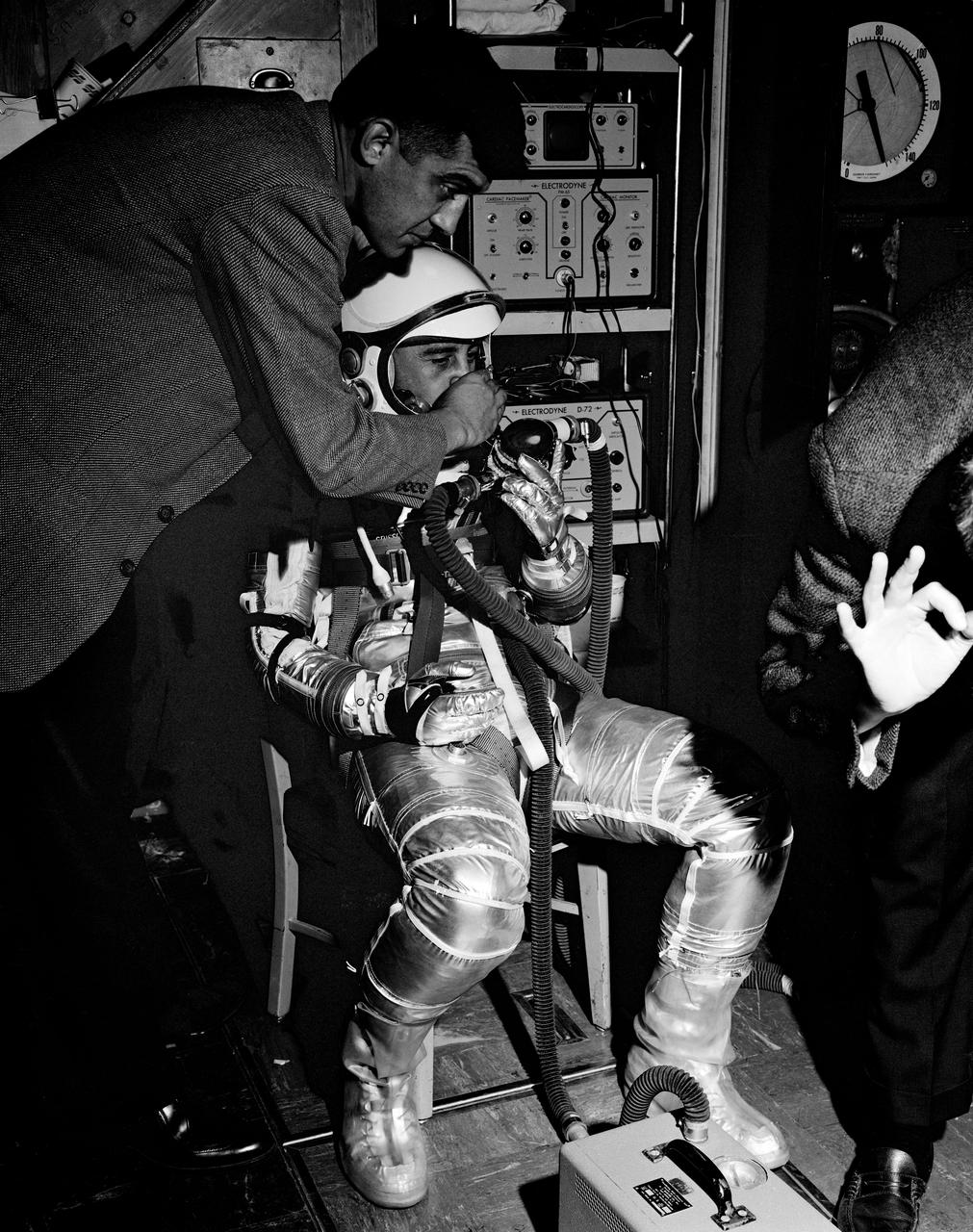

G61-00490 (1961) --- Astronaut Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom, wearing the new Mercury pressure suit, is preparing for centrifuge training. He is receiving assistance in adjusting the breathing apparatus which is attached to a data recording device at his feet. Assisting him is Dr. Jackson. Photo credit: NASA
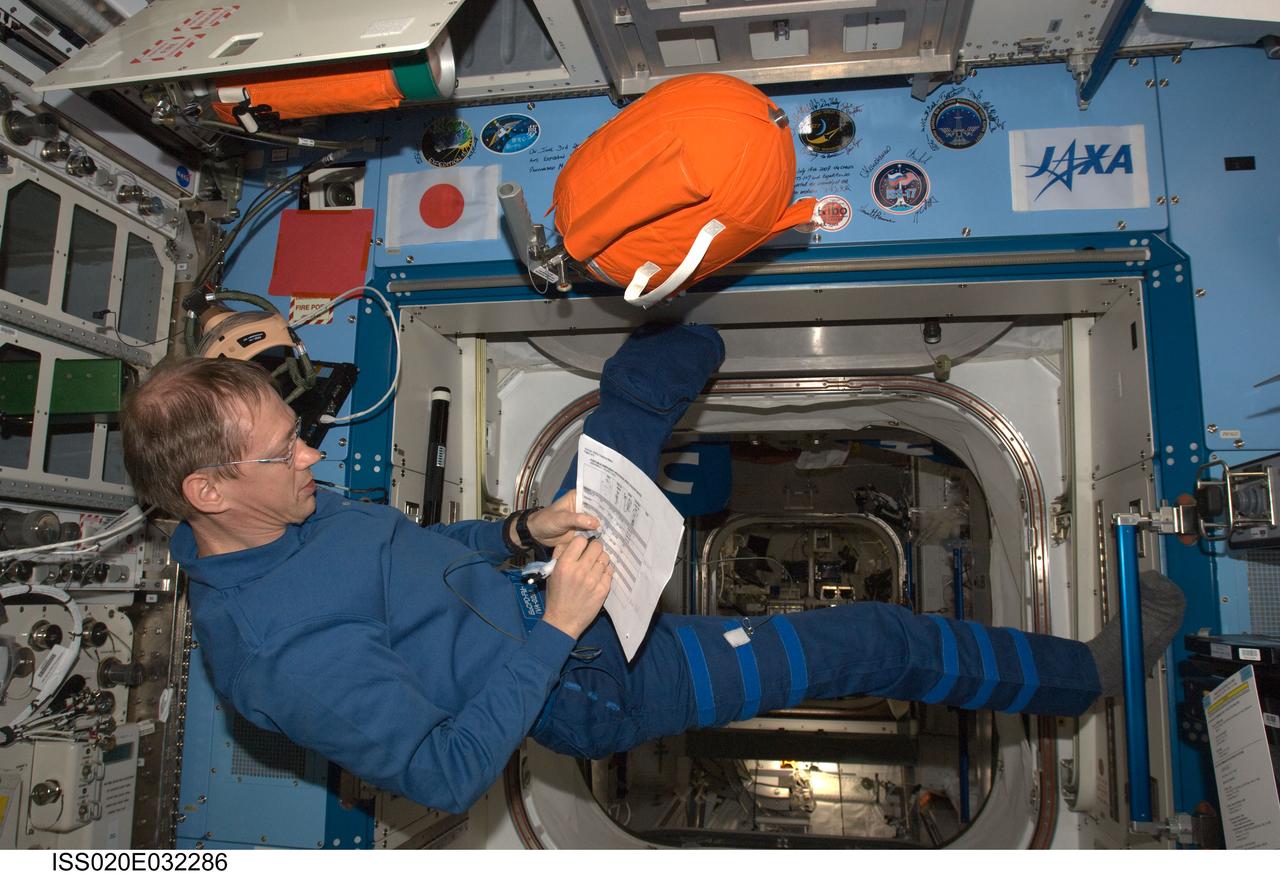

ISS020-E-032286 (19 Aug. 2009) --- European Space Agency astronaut Frank De Winne, Expedition 20 flight engineer, conducts the monthly inspection/audit on Portable Fire Extinguisher (PFE) and Portable Breathing Apparatus (PBA) equipment in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
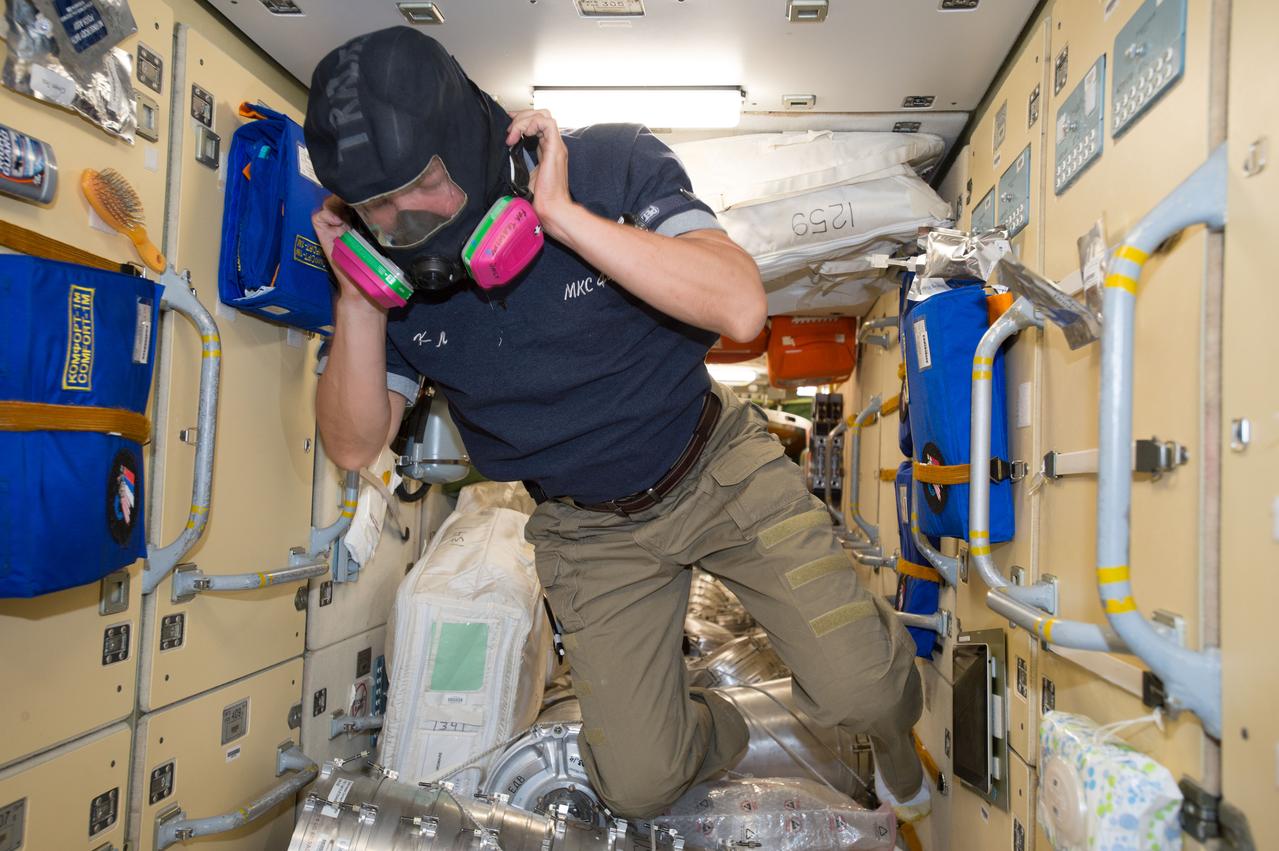

ISS044E025035 (07/29/2015) --- NASA astronaut Kjell Lindgren wears protective breathing apparatus that would be used in the unlikely event of a fire or hazardous chemical leak inside the pressurized air volume of the International Space Station. Familiarization of safety and emergency equipment is standard practice for all newly arrived crew members.
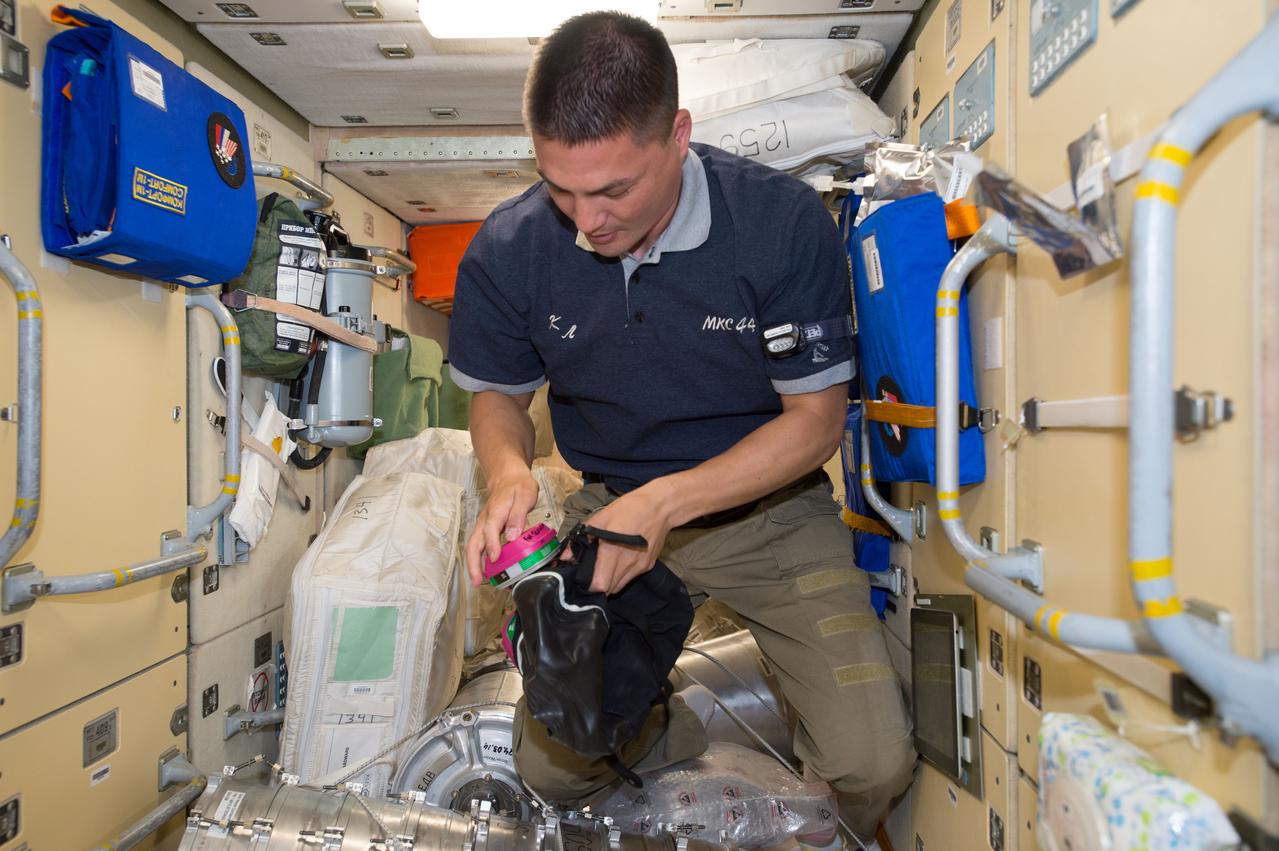

ISS044E025035 (07/29/2015) --- NASA astronaut Kjell Lindgren prepares to don protective breathing apparatus that would be used in the unlikely event of a fire or hazardous chemical leak inside the pressurized air volume of the International Space Station. Familiarization of safety and emergency equipment is standard practice for all newly arrived crew members.
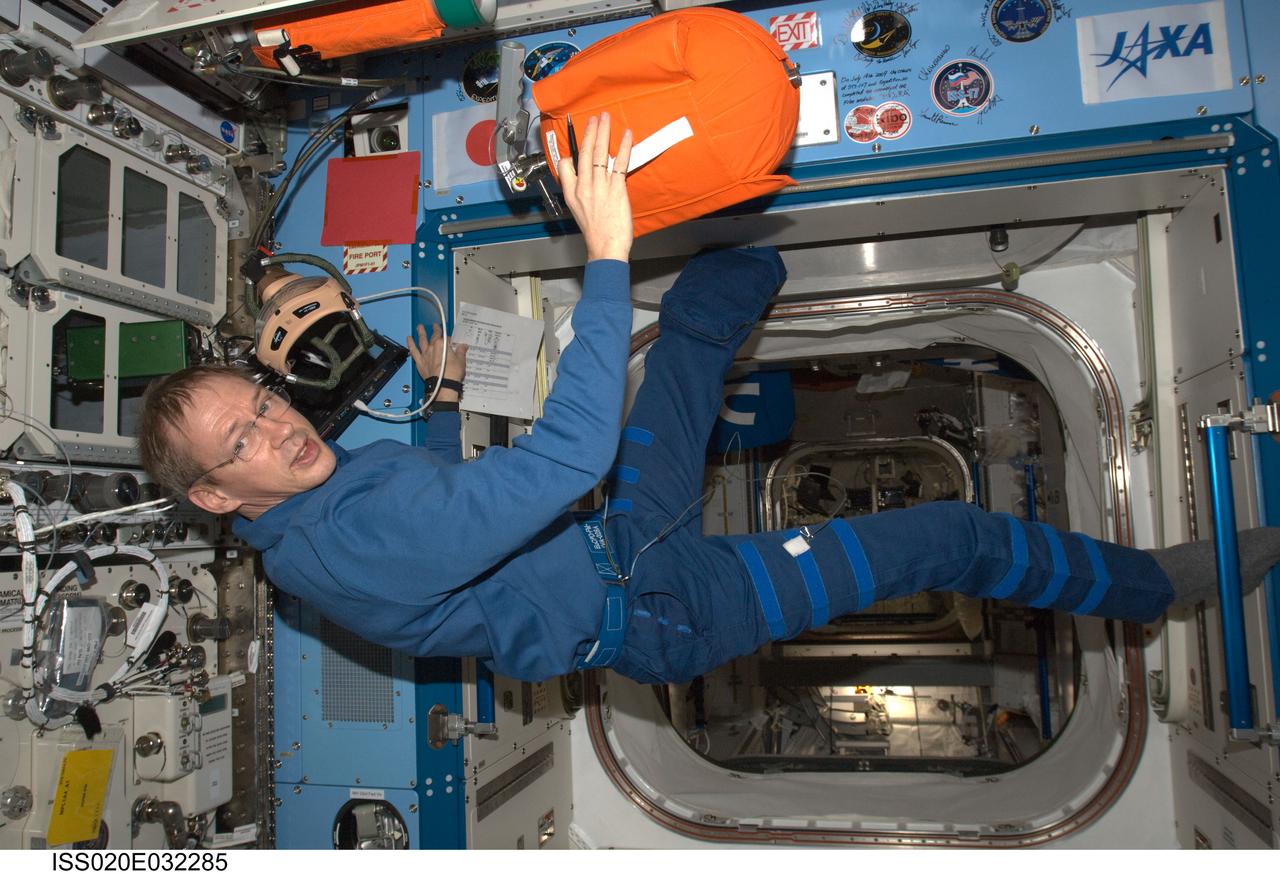

ISS020-E-032285 (19 Aug. 2009) --- European Space Agency astronaut Frank De Winne, Expedition 20 flight engineer, conducts the monthly inspection/audit on Portable Fire Extinguisher (PFE) and Portable Breathing Apparatus (PBA) equipment in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
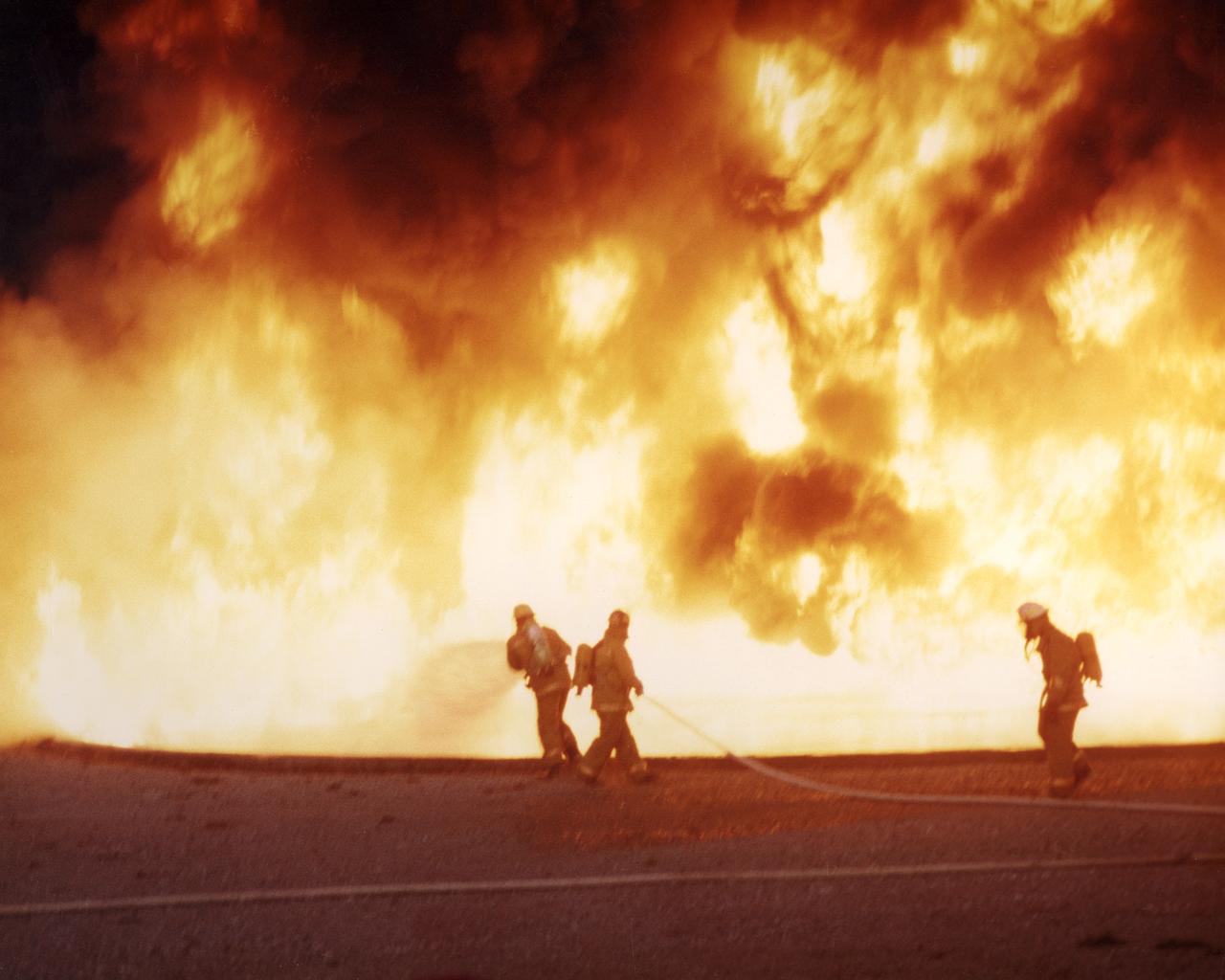

Firefighters are like astronauts. They both face dangerous, even hostile environments such as a building full of fire and the vacuum of space. They are both get breathing air from tanks on their backs. Early in the 1970's, NASA began working to improve firefighter breathing systems, which had hardly changed since the 1940s. NASA's Johnson Space Center conducted a 4-year program that applied technology from the portable life support systems used by Apollo astronauts on the moon. The new breathing system is made up of an air bottle, a frame and harness, a face mask, and a warning device. The new system weighs less than 20 pounds, one-third less than the old gear. The new air bottle provides 30 minutes of breathing air, as much as the old system. Like a good hiker's backpack, the new system puts the weight on the firefighter's hips rather than the shoulders. The face mask provides better visibility and the warning device lets the firefighter know when air in the bottle is low. Though they have made many design modifications and refinements, manufacturers of breathing apparatus still incorporate the original NASA technology.
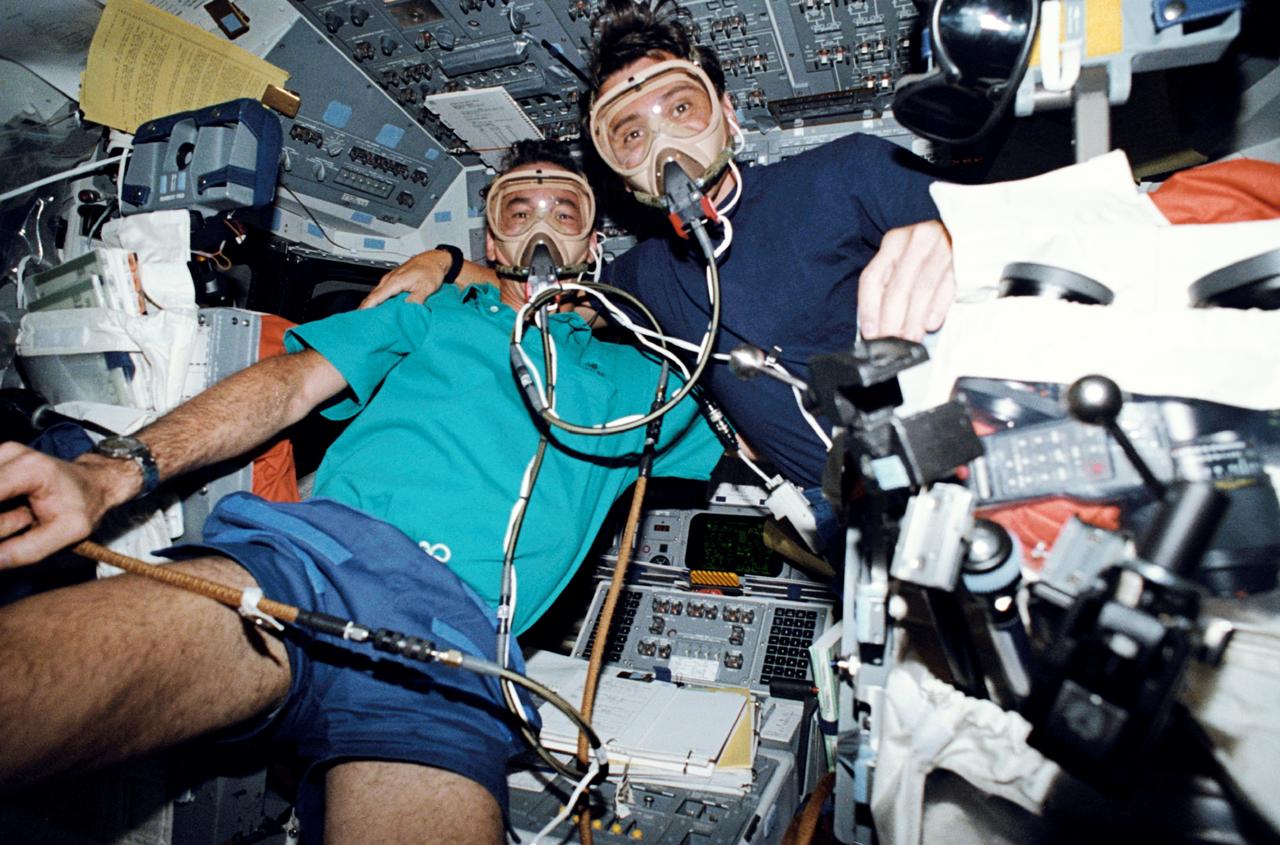

STS046-33-028 (4 Aug. 1992) --- With the possibility of an extravehicular activity (EVA) being added to the agenda, the two EVA-trained crew members begin their "pre-breathe" period on the space shuttle Atlantis' flight deck. Astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman (left), payload commander, and Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, mission specialist, reported to this station and began the "pre-breathe" process when problems developed during the extension of the Tethered Satellite System (TSS). When the human body is exposed to a sudden decrease in atmospheric pressure (for instance, from the 10.2 ppsi in the crew cabin to the 4.5 ppsi of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuit), nitrogen traces in the bloodstream will expand. This expansion can create tiny bubbles and potential for the "bends". In order to lessen the effect, an astronaut must "pre-breathe" pure oxygen (the same pure oxygen that he will breathe in the suit) to help "purge" nitrogen from his/her bloodstream before exerting him/herself in the low-pressure environment of the suit. The "pre-breathe" exercise and the EVA turned out to be not needed as the TSS operations were resumed by remote operations.

STS064-23-037 (16 Sept. 1994) --- Astronauts Mark C. Lee (left) and Carl J. Meade were photographed in the midst of 15-minute pre-breathe exercise in preparation for their Extravehicular Activity (EVA) of Sept. 16, 1994. On that day the two performed an in-space rehearsal or demonstration of a contingency rescue using the never-before flown Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue (SAFER) system some 130 nautical miles above Earth. During the EVA the two STS-64 mission specialists took turns using the SAFER hardware. The test was the first phase of a larger SAFER program leading finally to the development of a production version for future shuttle and space station applications. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
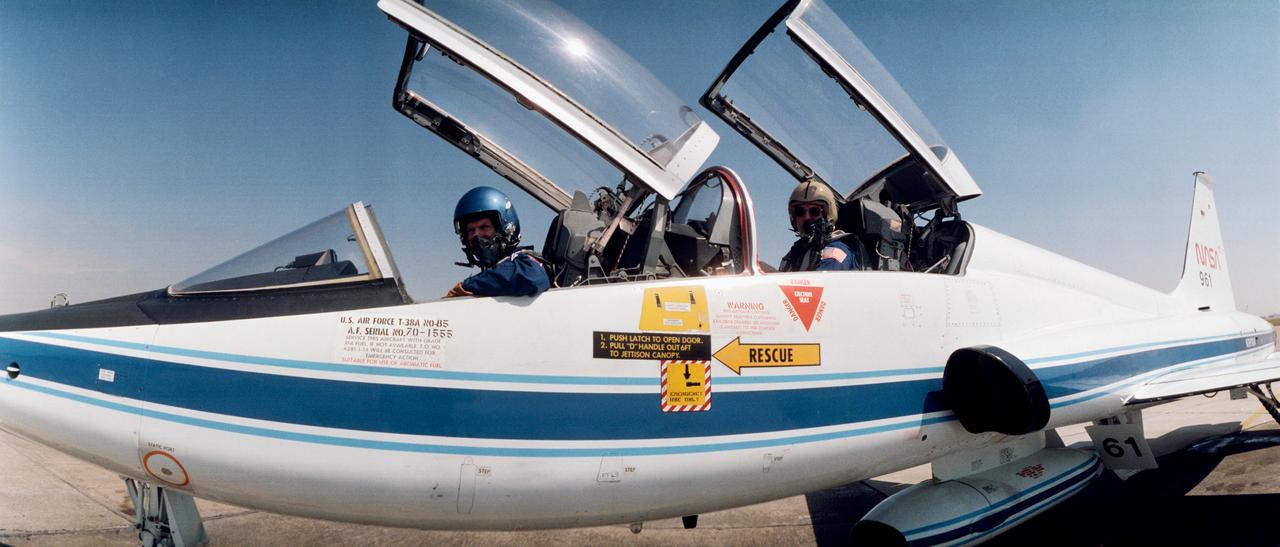

STS029-S-005 (10 March 1989) --- A wide angle view of a T-38 on the flight line at Ellington Field near the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Astronauts Michael L. Coats, mission commander; and James F. Buchli, STS-29 mission specialist, moments later were en route to Florida's Kennedy Space Center. In three days, they and three fellow STS-29 crew members are scheduled to lift off aboard the space shuttle Discovery from Launch Pad 39B. Photo credit: NASA

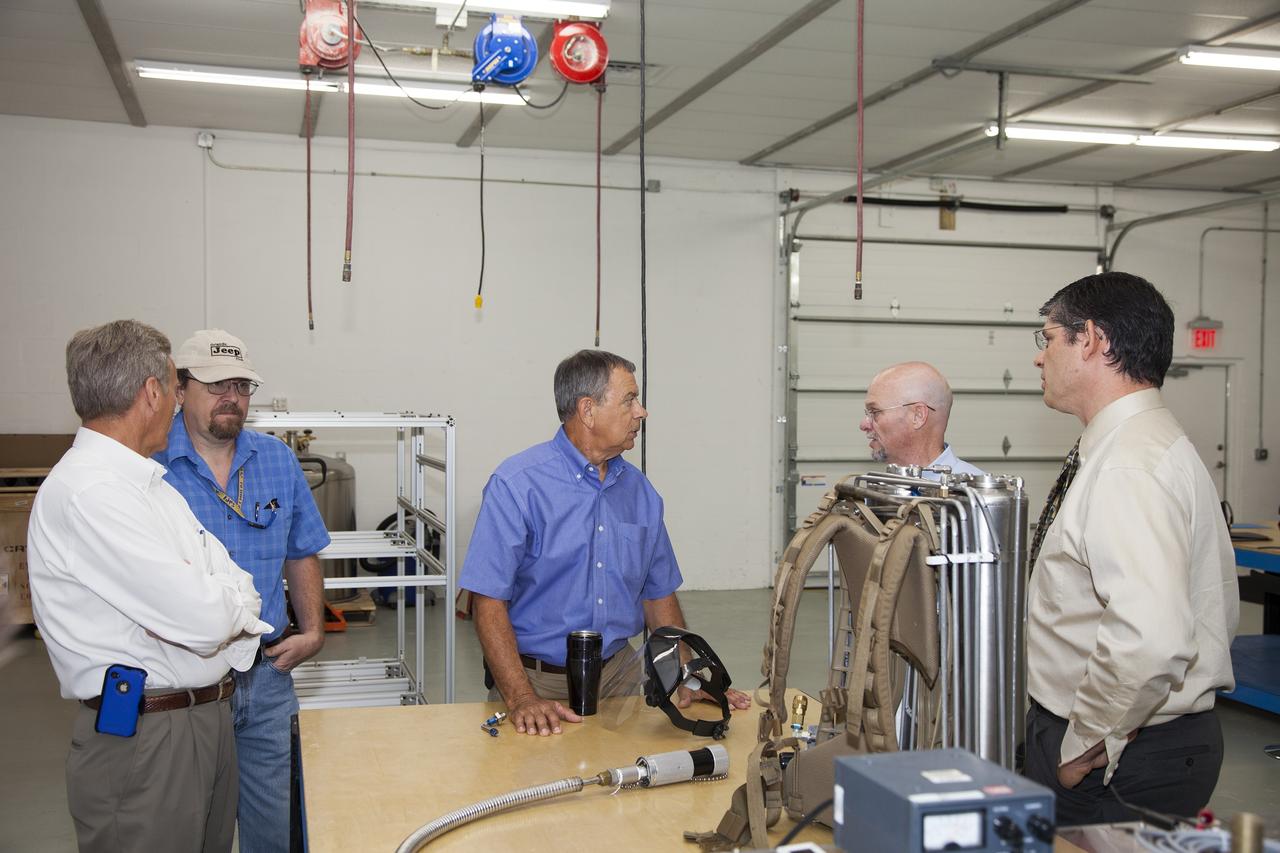
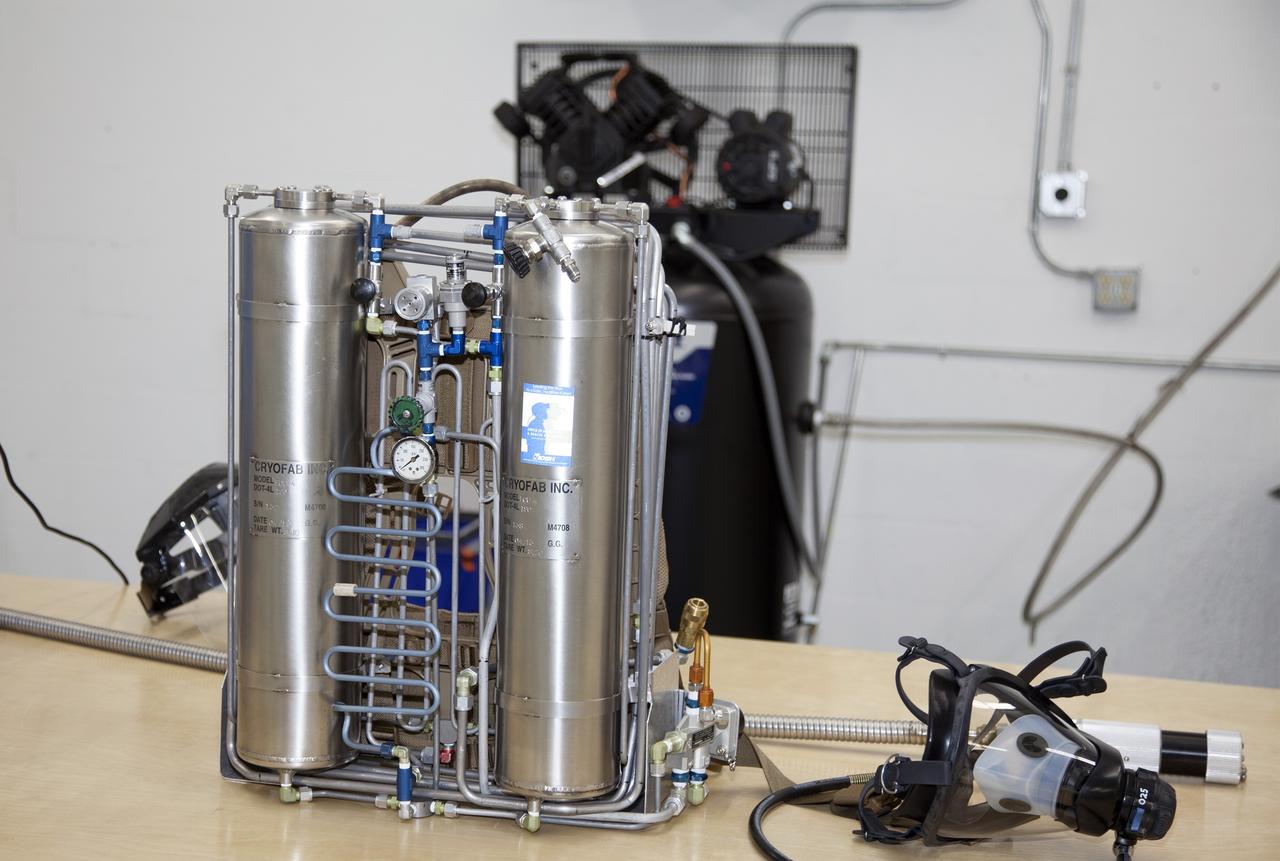
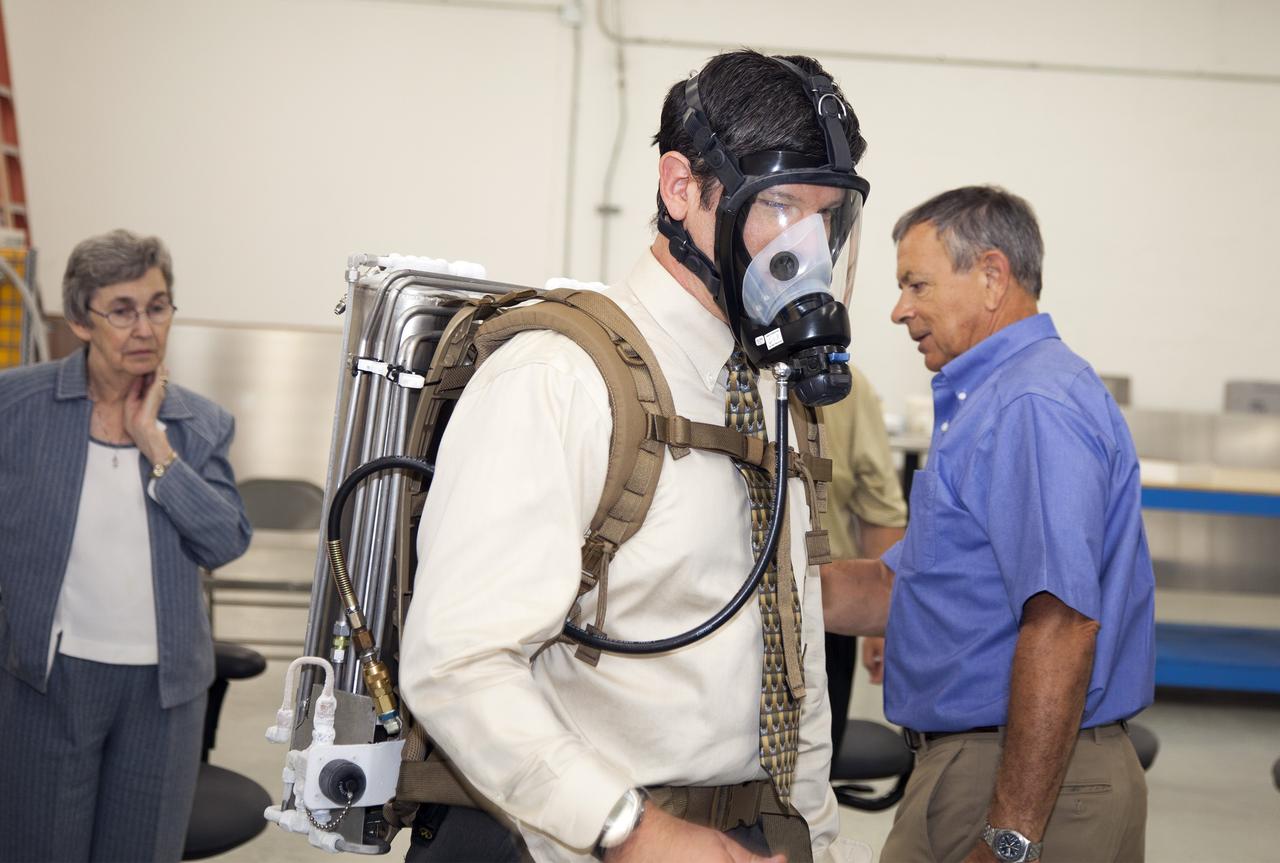
TITUSVILLE, Fla. - Representatives from NASA Kennedy Space Center, BCS Life Support, LabTech and URS prepare to demo a Cryogenic Refuge Alternative Supply System, or CryoRASS, and a smaller liquid-air filled backpack called CryoBA, short for Cryogenic Breathing Apparatus, in Titusville, Fla. The two systems are being developed by a Kennedy engineering team in collaboration with The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to provide miners with twice the amount of breathable and cooler air than traditional compressed systems. The technology also could be used for commercial applications, such as fire and military rescue operations, as well as NASA's future human spaceflight missions. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
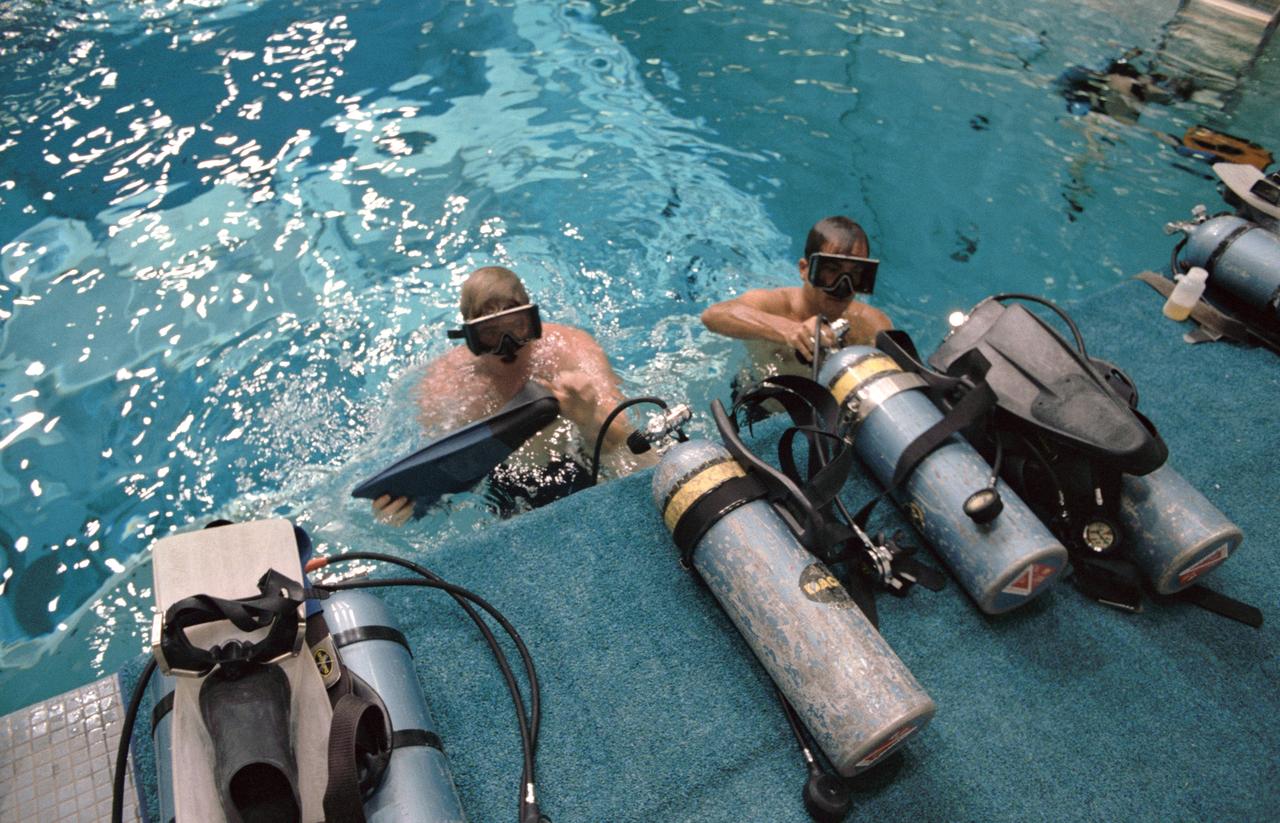

S84-36900 (29 June 1984) ---Astronauts Robert L. Crippen (right) and Jon A. McBride, crew commander and pilot, respectively, for NASA's 41-G Space Shuttle mission, don self contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA) gear prior to their underwater to observe a simulation of an extravehicular activity (EVA) to be performed on their mission. Astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan and David C. Leestma, two of three mission specialists on the seven-member crew, are scheduled for the EVA. The underwater training took place in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F).
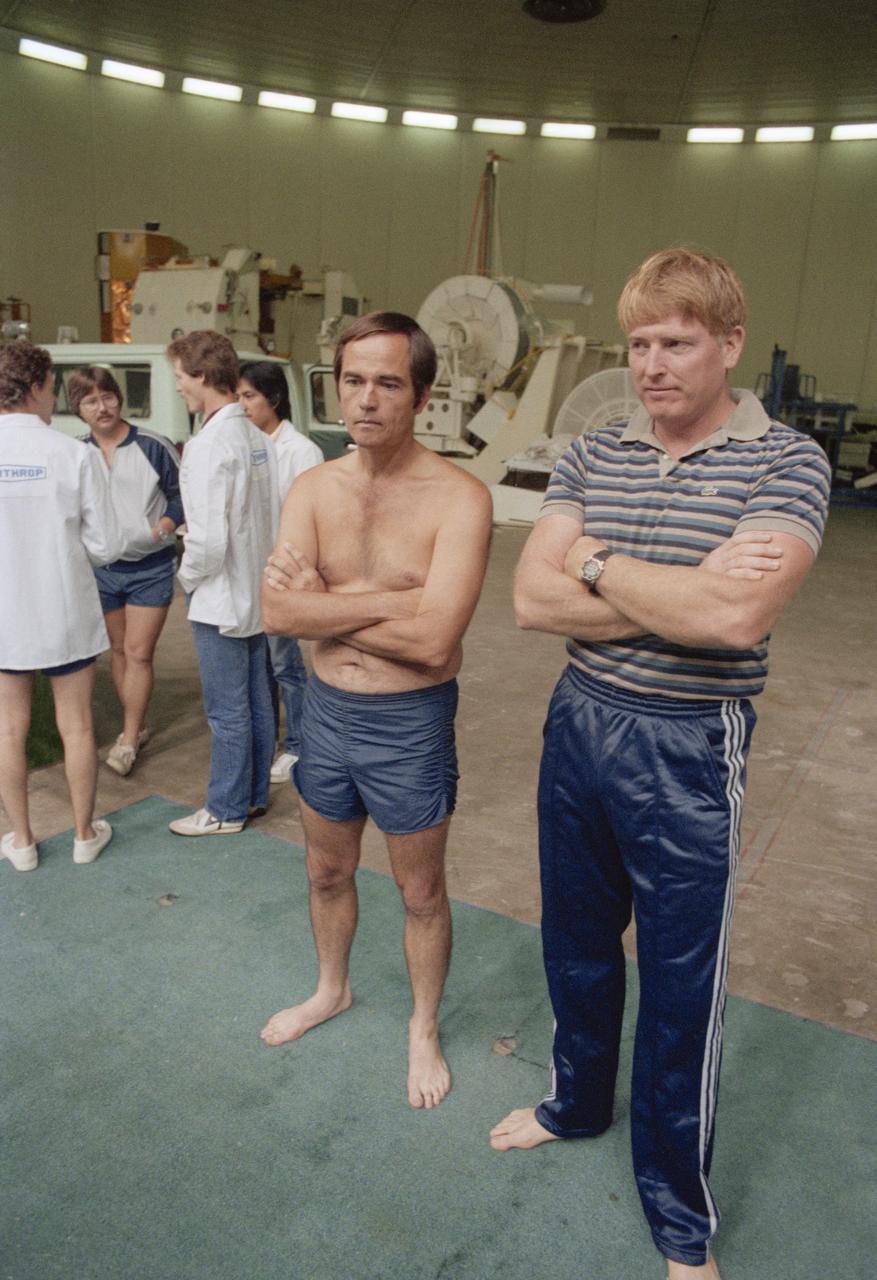

S84-36898 (29 June 1984) --- Astronauts Robert L. Crippen (left) and Jon A. McBride, crew commander and pilot, respectively for NASA's 41-G Space Shuttle mission, await the delivery of self contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA) gear prior to their going underwater to observe a simulation of an extravehicular activity (EVA) scheduled for their mission. The EVA will be performed by Astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan and David C. Leestma, two of three mission specialists named for the seven-member crew. The underwater training took place in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F).
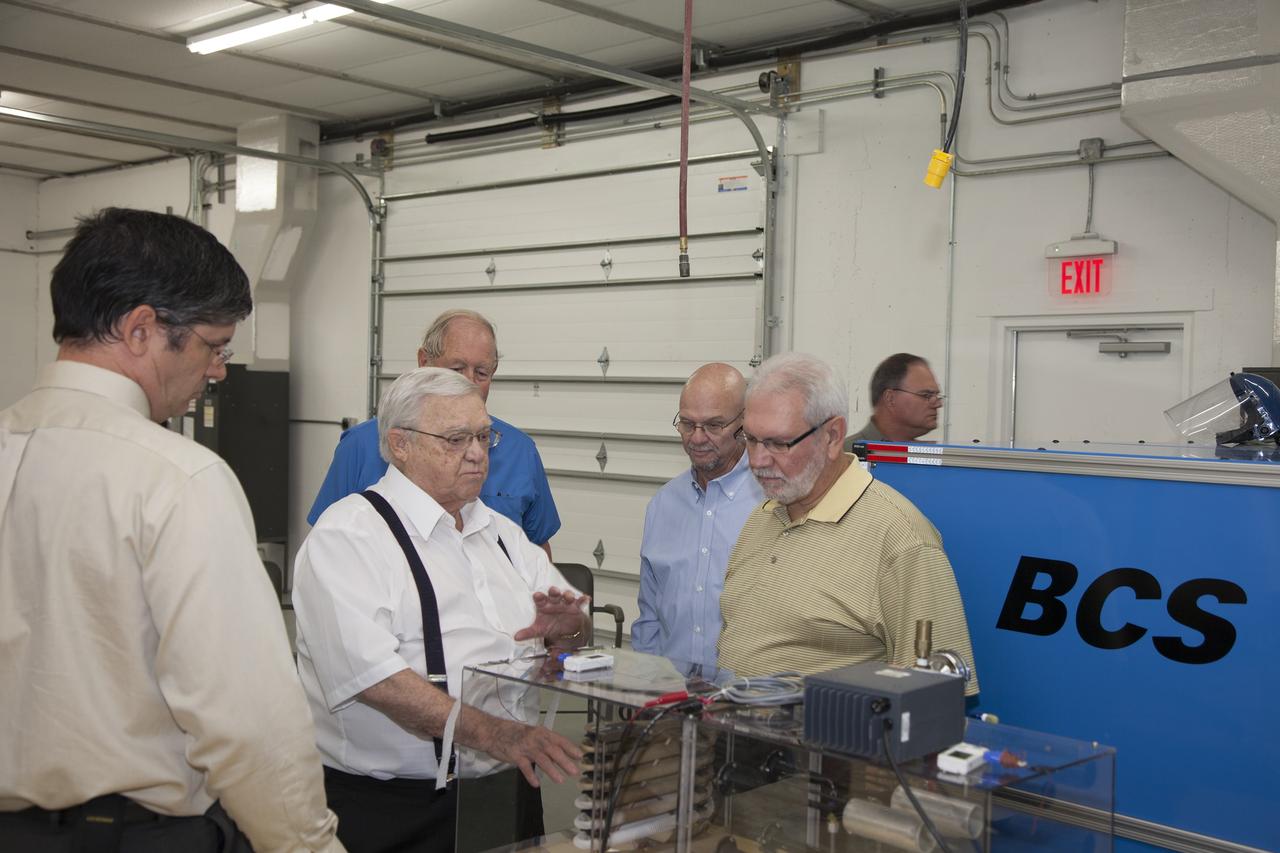

TITUSVILLE, Fla. - Representatives from NASA Kennedy Space Center, BCS Life Support, LabTech and URS demo a Cryogenic Refuge Alternative Supply System, or CryoRASS, and a smaller liquid-air filled backpack called CryoBA, short for Cryogenic Breathing Apparatus, in Titusville, Fla. The two systems are being developed by a Kennedy engineering team in collaboration with The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to provide miners with twice the amount of breathable and cooler air than traditional compressed systems. The technology also could be used for commercial applications, such as fire and military rescue operations, as well as NASA's future human spaceflight missions. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
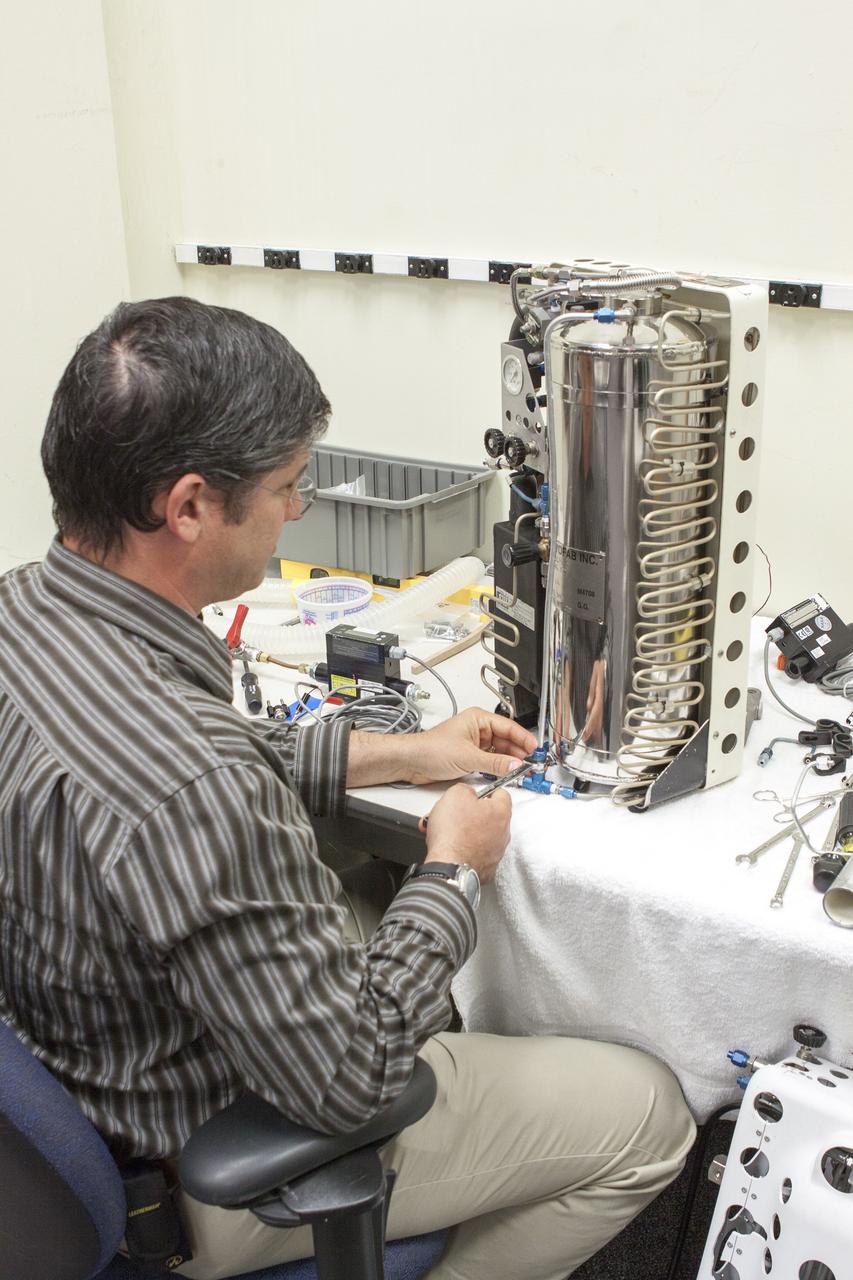

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA Kennedy Space Center Lead Engineer David Bush works on a prototype of a Cryogenic Refuge Alternative Supply System, or CryoRASS, in the Operations and Checkout Building. CryoRASS and a small liquid-air filled backpack called CryoBA, short for Cryogenic Breathing Apparatus, are being developed by a NASA Kennedy Space Center engineering team in collaboration with The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to provide miners with twice the amount of breathable and cooler air than traditional compressed systems. The technology also could be used for commercial applications, such as fire and military rescue operations, as well as NASA's future human spaceflight missions. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Gossmann
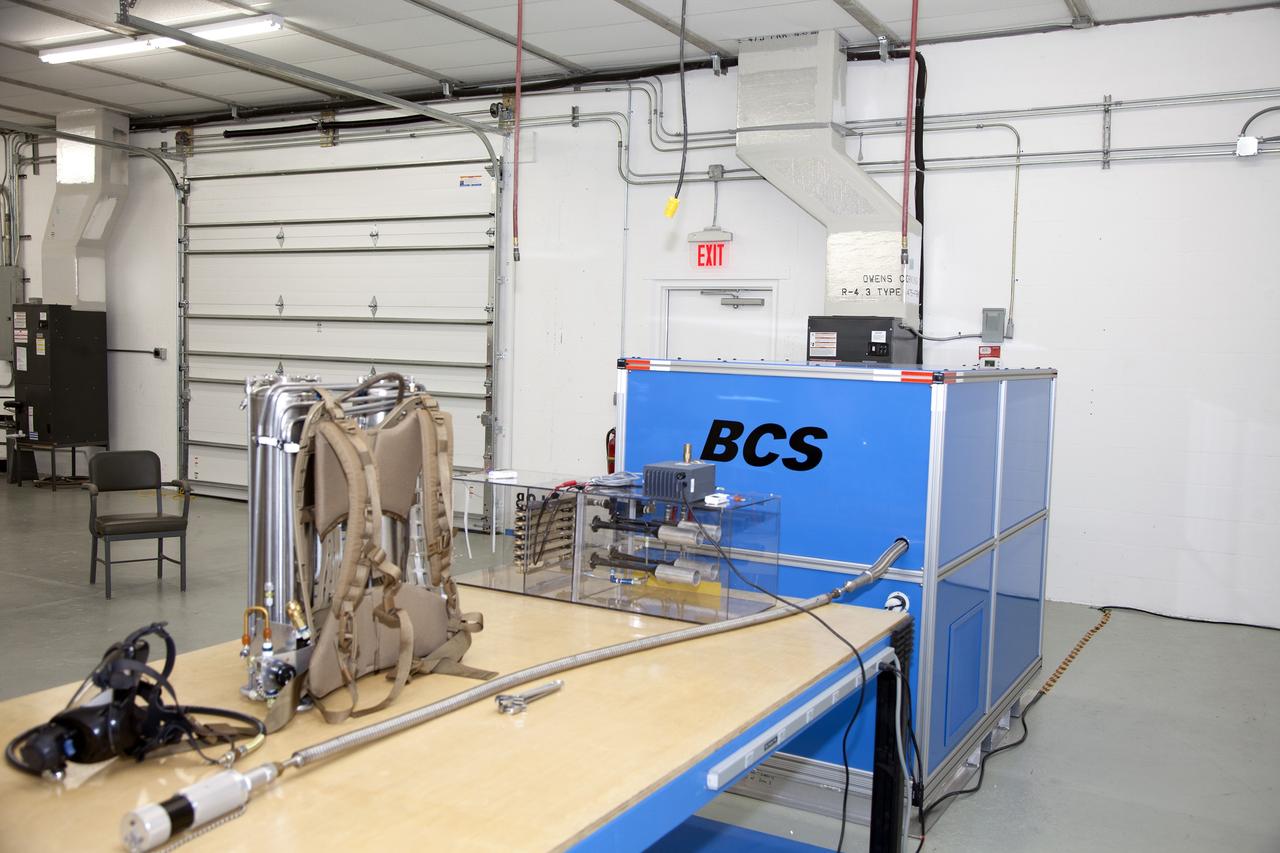

TITUSVILLE, Fla. - The Cryogenic Refuge Alternative Supply System, or CryoRASS, and a smaller liquid-air filled backpack called CryoBA, short for Cryogenic Breathing Apparatus, are on display at BCS Life Support in Titusville, Fla. The two systems are being developed by a NASA Kennedy Space Center engineering team in collaboration with The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to provide miners with twice the amount of breathable and cooler air than traditional compressed systems. The technology also could be used for commercial applications, such as fire and military rescue operations, as well as NASA's future human spaceflight missions. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
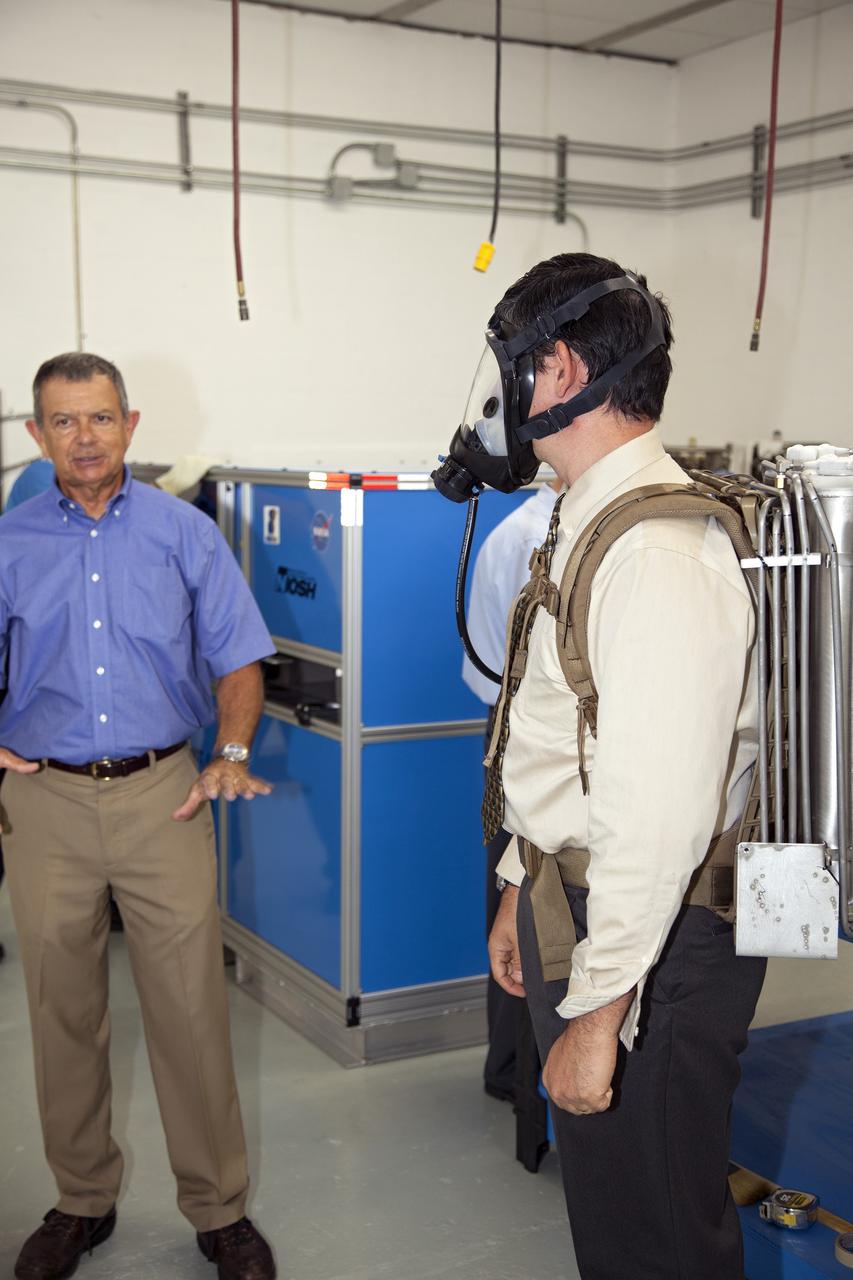

TITUSVILLE, Fla. - NASA Kennedy Space Center Lead Engineer David Bush, right, demos a small liquid-air filled backpack called CryoBA, short for Cryogenic Breathing Apparatus, at BCS Life Support in Titusville, Fla. The CryoBA and a larger Cryogenic Refuge Alternative Supply System, or CryoRASS, are being developed by a Kennedy engineering team in collaboration with The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to provide miners with twice the amount of breathable and cooler air than traditional compressed systems. The technology also could be used for commercial applications, such as fire and military rescue operations, as well as NASA's future human spaceflight missions. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

TITUSVILLE, Fla. - A small liquid-air filled backpack called CryoBA, short for Cryogenic Breathing Apparatus, is on display at BCS Life Support in Titusville, Fla. The CryoBA and a larger Cryogenic Refuge Alternative Supply System, or CryoRASS, are being developed by a NASA Kennedy Space Center engineering team in collaboration with The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to provide miners with twice the amount of breathable and cooler air than traditional compressed systems. The technology also could be used for commercial applications, such as fire and military rescue operations, as well as NASA's future human spaceflight missions. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
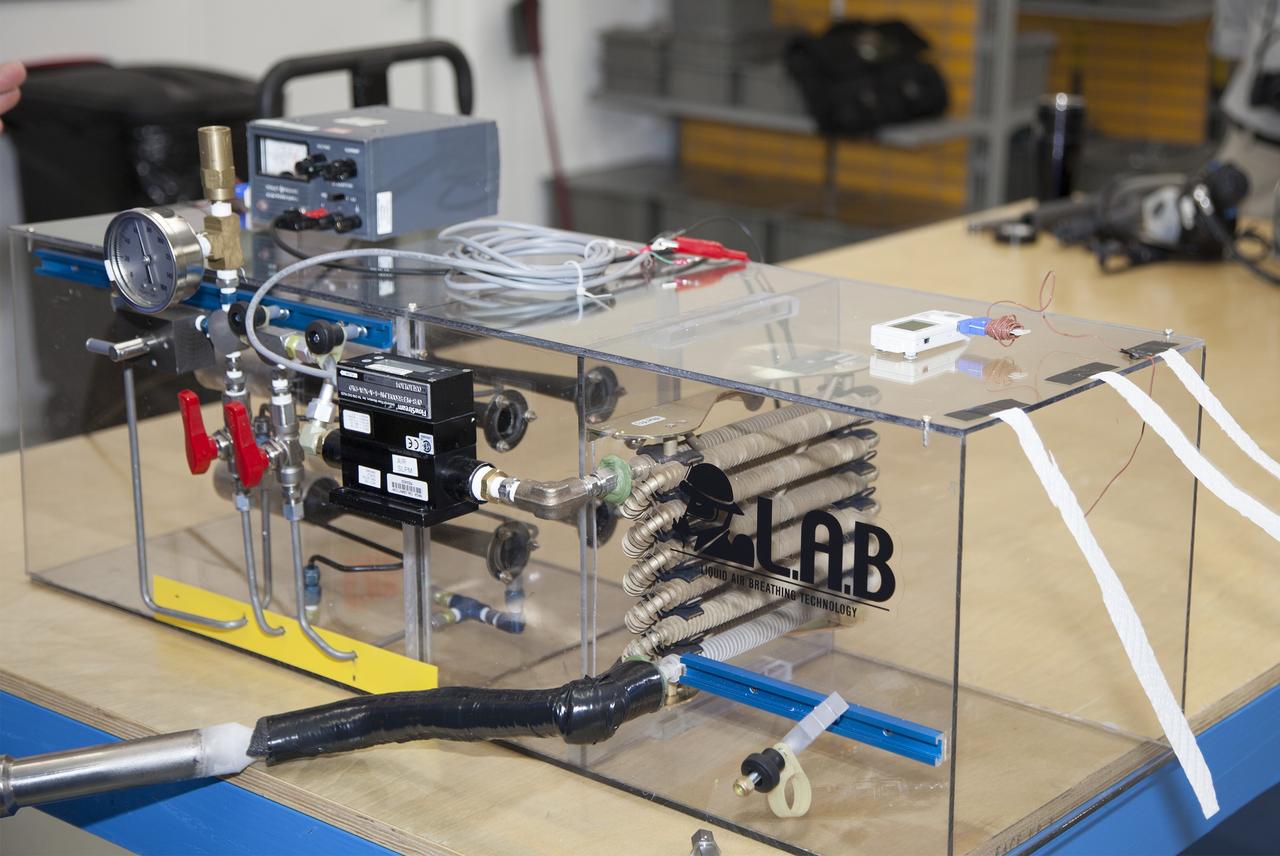
TITUSVILLE, Fla. - The Cryogenic Refuge Alternative Supply System, or CryoRASS, is on display at BCS Life Support in Titusville, Fla. CryoRASS and a small liquid-air filled backpack called CryoBA, short for Cryogenic Breathing Apparatus, are being developed by a NASA Kennedy Space Center engineering team in collaboration with The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to provide miners with twice the amount of breathable and cooler air than traditional compressed systems. The technology also could be used for commercial applications, such as fire and military rescue operations, as well as NASA's future human spaceflight missions. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

TITUSVILLE, Fla. - A small liquid-air filled backpack called CryoBA, short for Cryogenic Breathing Apparatus, is on display at BCS Life Support in Titusville, Fla. The CryoBA and a larger Cryogenic Refuge Alternative Supply System, or CryoRASS, are being developed by a NASA Kennedy Space Center engineering team in collaboration with The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to provide miners with twice the amount of breathable and cooler air than traditional compressed systems. The technology also could be used for commercial applications, such as fire and military rescue operations, as well as NASA's future human spaceflight missions. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

TITUSVILLE, Fla. - NASA Kennedy Space Center Lead Engineer David Bush, center, demos a small liquid-air filled backpack called CryoBA, short for Cryogenic Breathing Apparatus, at BCS Life Support in Titusville, Fla. The CryoBA and a larger Cryogenic Refuge Alternative Supply System, or CryoRASS, are being developed by a Kennedy engineering team in collaboration with The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to provide miners with twice the amount of breathable and cooler air than traditional compressed systems. The technology also could be used for commercial applications, such as fire and military rescue operations, as well as NASA's future human spaceflight missions. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
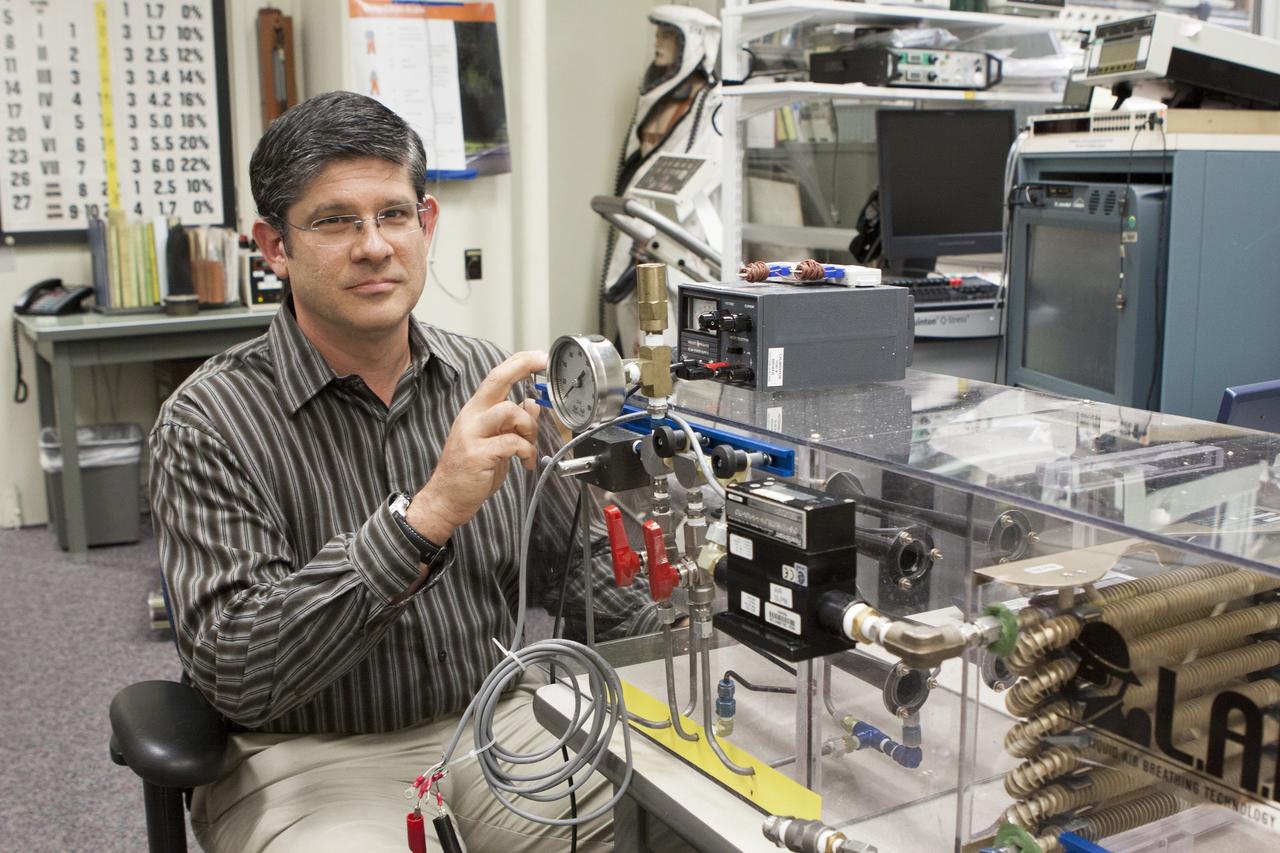
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA Kennedy Space Center Lead Engineer David Bush works on a prototype of a Cryogenic Refuge Alternative Supply System, or CryoRASS, in the Operations and Checkout Building. CryoRASS and a small liquid-air filled backpack called CryoBA, short for Cryogenic Breathing Apparatus, are being developed by a NASA Kennedy Space Center engineering team in collaboration with The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to provide miners with twice the amount of breathable and cooler air than traditional compressed systems. The technology also could be used for commercial applications, such as fire and military rescue operations, as well as NASA's future human spaceflight missions. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Gossmann
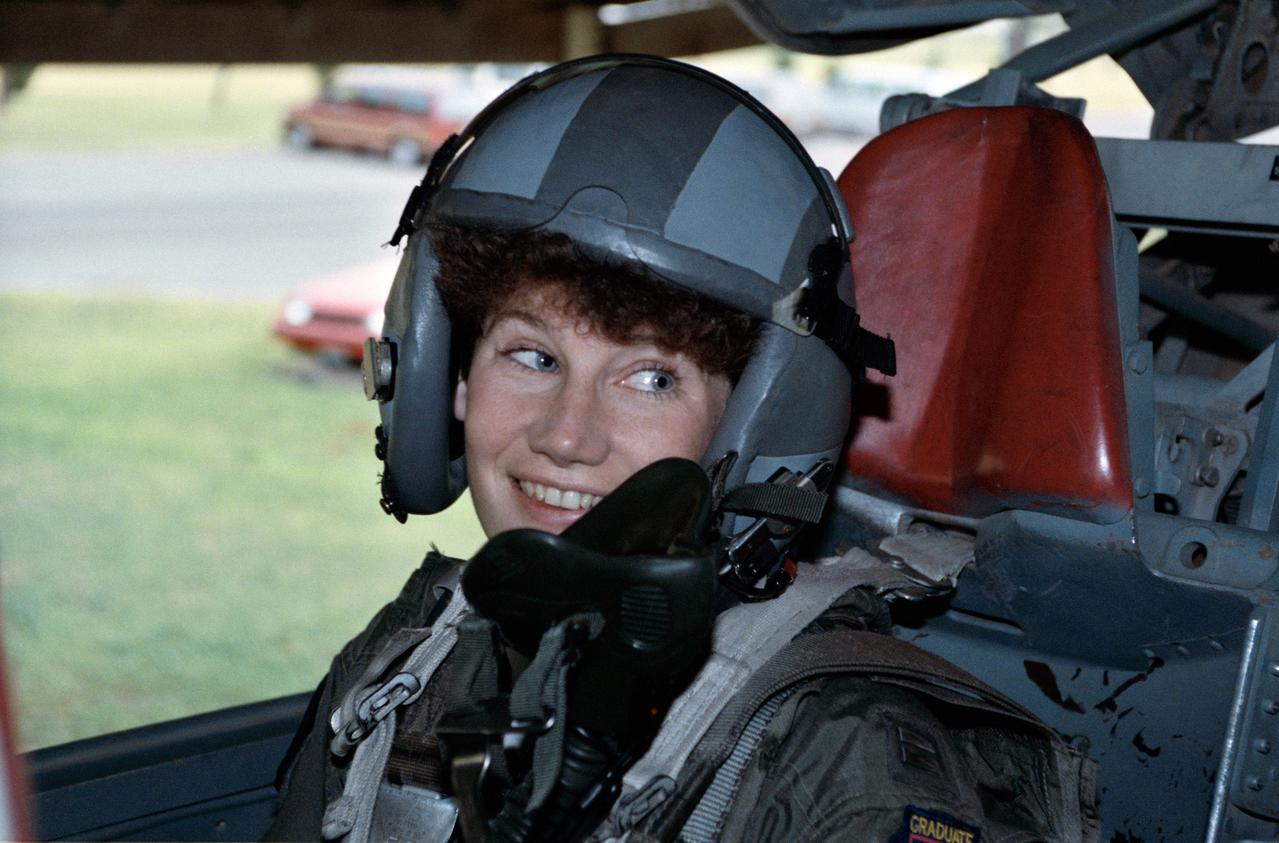

S90-45896 (29-31 July 1990) --- Susan J. Helms, one of the 23 astronaut candidates who began a year's training and evaluation program in July, participates in one of themany sessions at a survival training course at Vance Air Force Base. This portion of the course is designed to familiarize the trainee with procedures to follow in preparation for ejection from a jet aircraft.
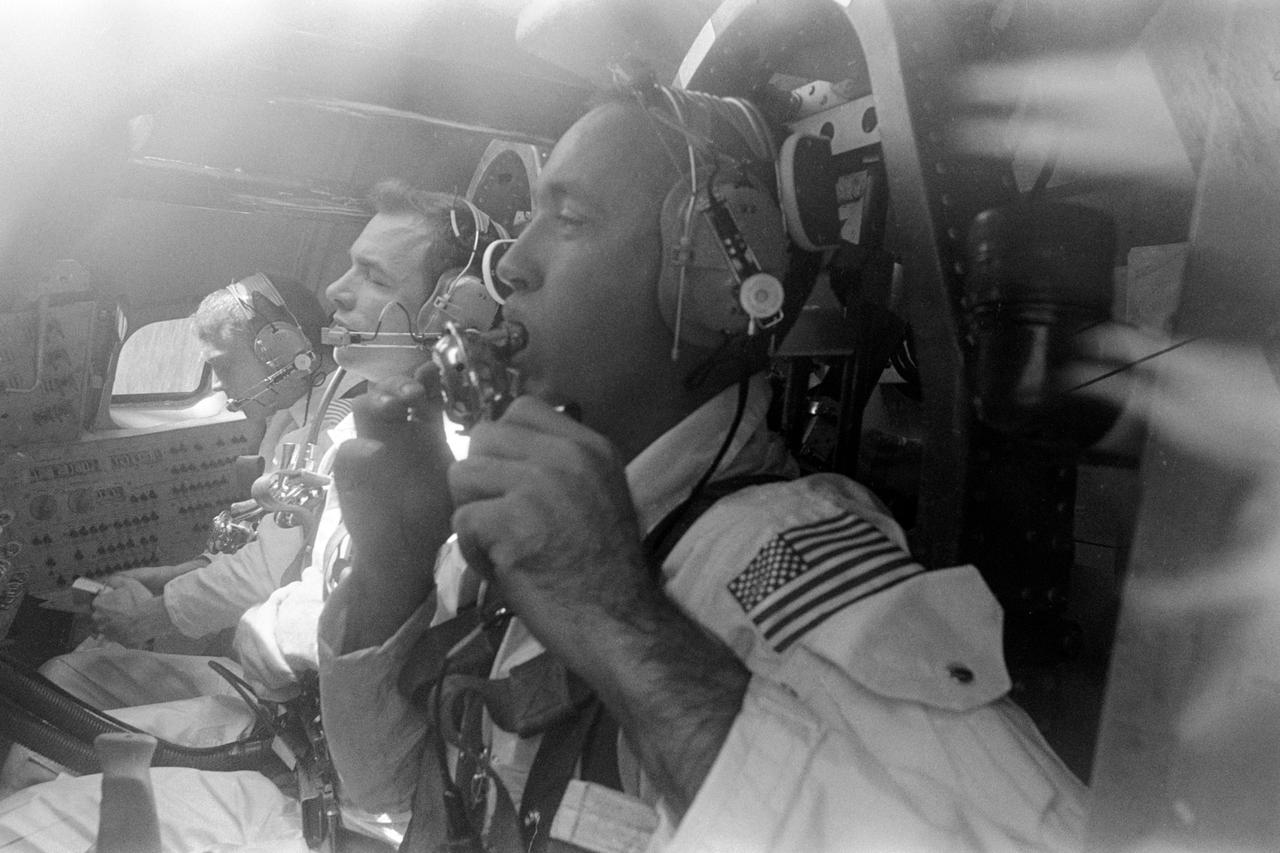

S68-54850 (5 Nov. 1968) --- The prime crew of the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/Saturn 504) space mission are seen inside an Apollo command module boilerplate during water egress training activity in the Gulf of Mexico. From foreground, are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot.
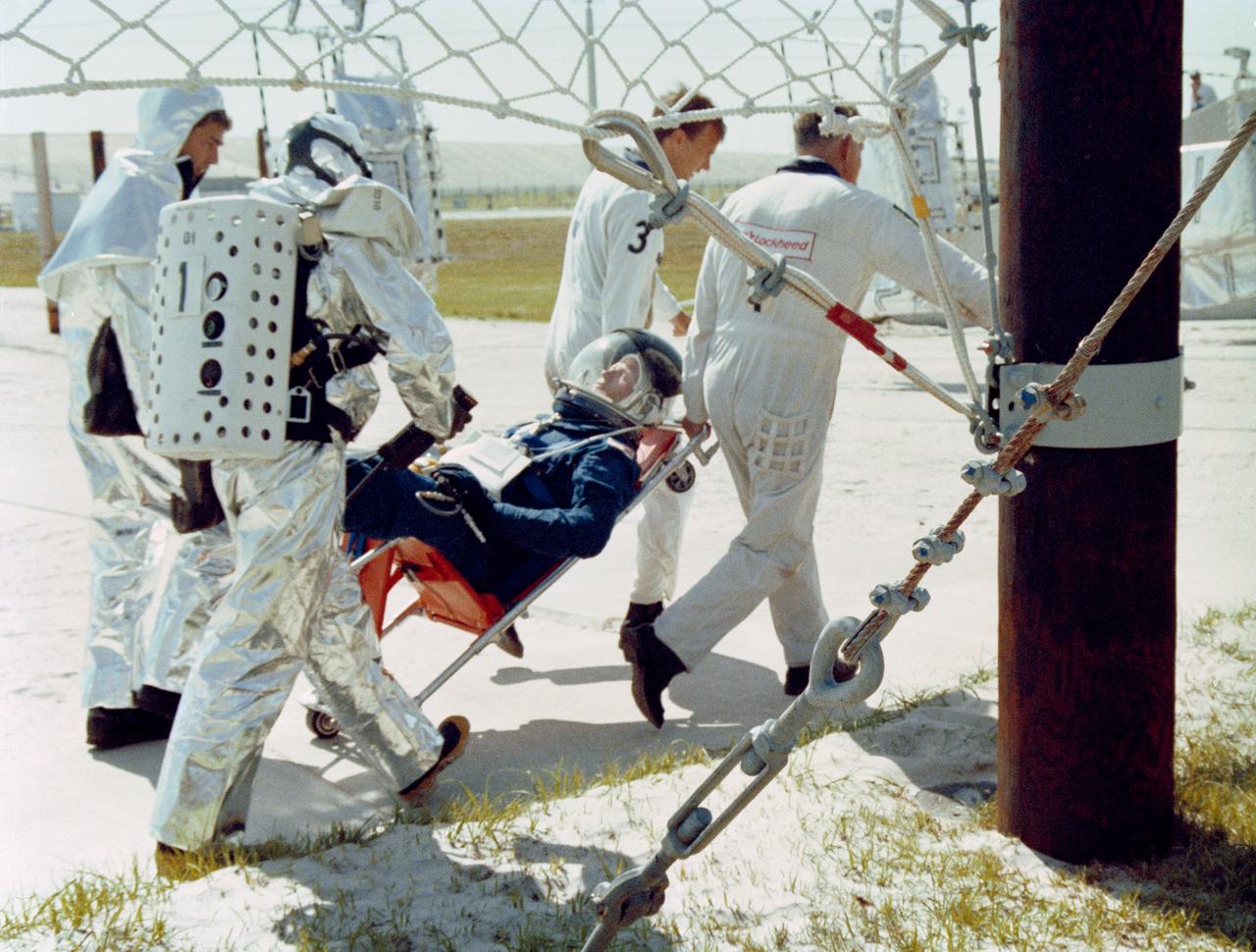

S88-40898 (4 May 1988) --- Astronauts, members of the orbiter close-out crew and fire and rescue personnel participate in a simulated emergency egress exercise near the slide wire termination point bunker at Launch Pad 39B. The simulated exercise was performed to familiarize personnel with evacuation routes as well as emergency equipment and procedures. Reasons for conducting the emergency exercises include the need to validate recent post-Challenger upgrades to the launch pad's emergency escape system and the new procedures developed in preparation for STS-26. (NOTE: The astronaut pictured and many of the others who participated in the exercises are not members of STS-26 prime crew).
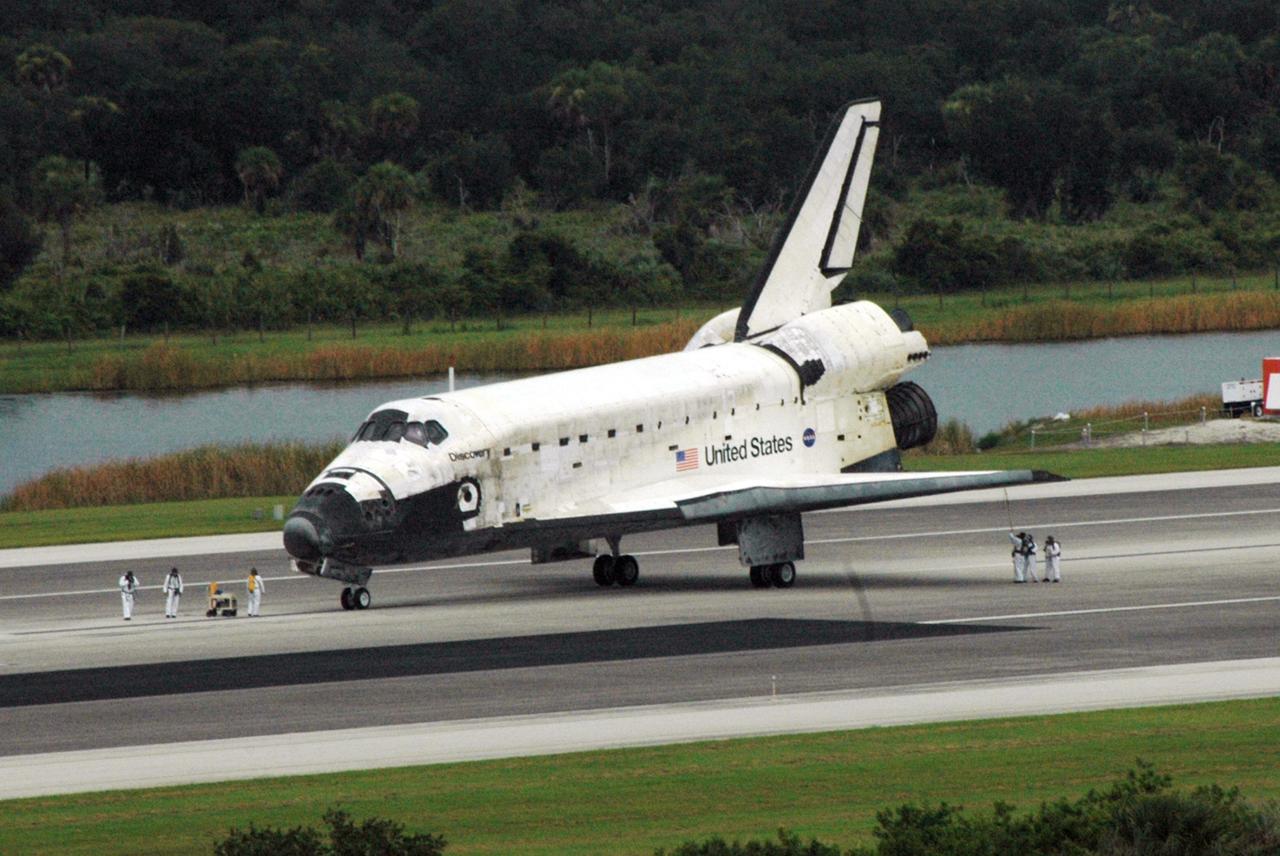

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After Discovery's safe landing on Runway 15 at NASA's Shuttle Landing Facility, safety assessment teams dressed in protective attire and with breathing apparatus obtain vapor level readings around the orbiter and test for possible explosive or toxic gases such as hydrogen, hydrazine, monomethyl-hydrazine, nitrogen tetroxide or ammonia . Completing mission STS-121 to the International Space Station, Discovery traveled 5.3 million miles, landing on orbit 202. Mission elapsed time was 12 days, 18 hours, 37 minutes and 54 seconds. Main gear touchdown occurred on time at 9:14:43 EDT. Wheel stop was at 9:15:49 EDT. The returning crew members are Commander Steven Lindsey, Pilot Mark Kelly and Mission Specialists Piers Sellers, Michael Fossum, Lisa Nowak and Stephanie Wilson. Mission Specialist Thomas Reiter, who launched with the crew on July 4, remained on the station to join the Expedition 13 crew there. The landing is the 62nd at Kennedy Space Center and the 32nd for Discovery. Discovery's landing was as exhilarating as its launch, the first to take place on America's Independence Day. During the mission, the STS-121 crew tested new equipment and procedures to improve shuttle safety, and delivered supplies and made repairs to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley