The Bubble Crater
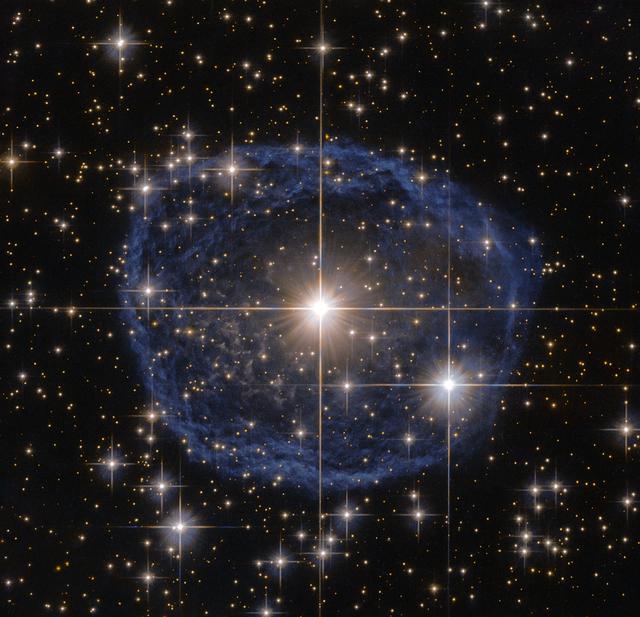

A large blue bubble with a bright star in the center on a black background filled with stars Sparkling at the center of this beautiful NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image is a Wolf–Rayet star known as WR 31a, located about 30,000 light-years away in the constellation of Carina (The Keel). The distinctive blue bubble appearing to encircle WR 31a is a Wolf–Rayet nebula — an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, helium and other gases. Created when speedy stellar winds interact with the outer layers of hydrogen ejected by Wolf–Rayet stars, these nebulae are frequently ring-shaped or spherical. The bubble — estimated to have formed around 20,000 years ago — is expanding at a rate of around 220,000 kilometers (136,700 miles) per hour! Unfortunately, the lifecycle of a Wolf–Rayet star is only a few hundred thousand years — the blink of an eye in cosmic terms. Despite beginning life with a mass at least 20 times that of the sun, Wolf–Rayet stars typically lose half their mass in less than 100,000 years. And WR 31a is no exception to this case. It will, therefore, eventually end its life as a spectacular supernova, and the stellar material expelled from its explosion will later nourish a new generation of stars and planets. Image credi: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt

This entrancing image shows a few of the tenuous threads that comprise Sh2-308, a faint and wispy shell of gas located 5,200 light-years away in the constellation of Canis Major (The Great Dog). Sh2-308 is a large bubble-like structure wrapped around an extremely large, bright type of star known as a Wolf-Rayet Star — this particular star is called EZ Canis Majoris. These type of stars are among the brightest and most massive stars in the Universe, tens of times more massive than our own sun, and they represent the extremes of stellar evolution. Thick winds continually poured off the progenitors of such stars, flooding their surroundings and draining the outer layers of the Wolf-Rayet stars. The fast wind of a Wolf-Rayet star therefore sweeps up the surrounding material to form bubbles of gas. EZ Canis Majoris is responsible for creating the bubble of Sh2-308 — the star threw off its outer layers to create the strands visible here. The intense and ongoing radiation from the star pushes the bubble out farther and farther, blowing it bigger and bigger. Currently the edges of Sh2-308 are some 60 light-years apart! Beautiful as these cosmic bubbles are, they are fleeting. The same stars that form them will also cause their death, eclipsing and subsuming them in violent supernova explosions. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
Entering the Magnetic Bubble
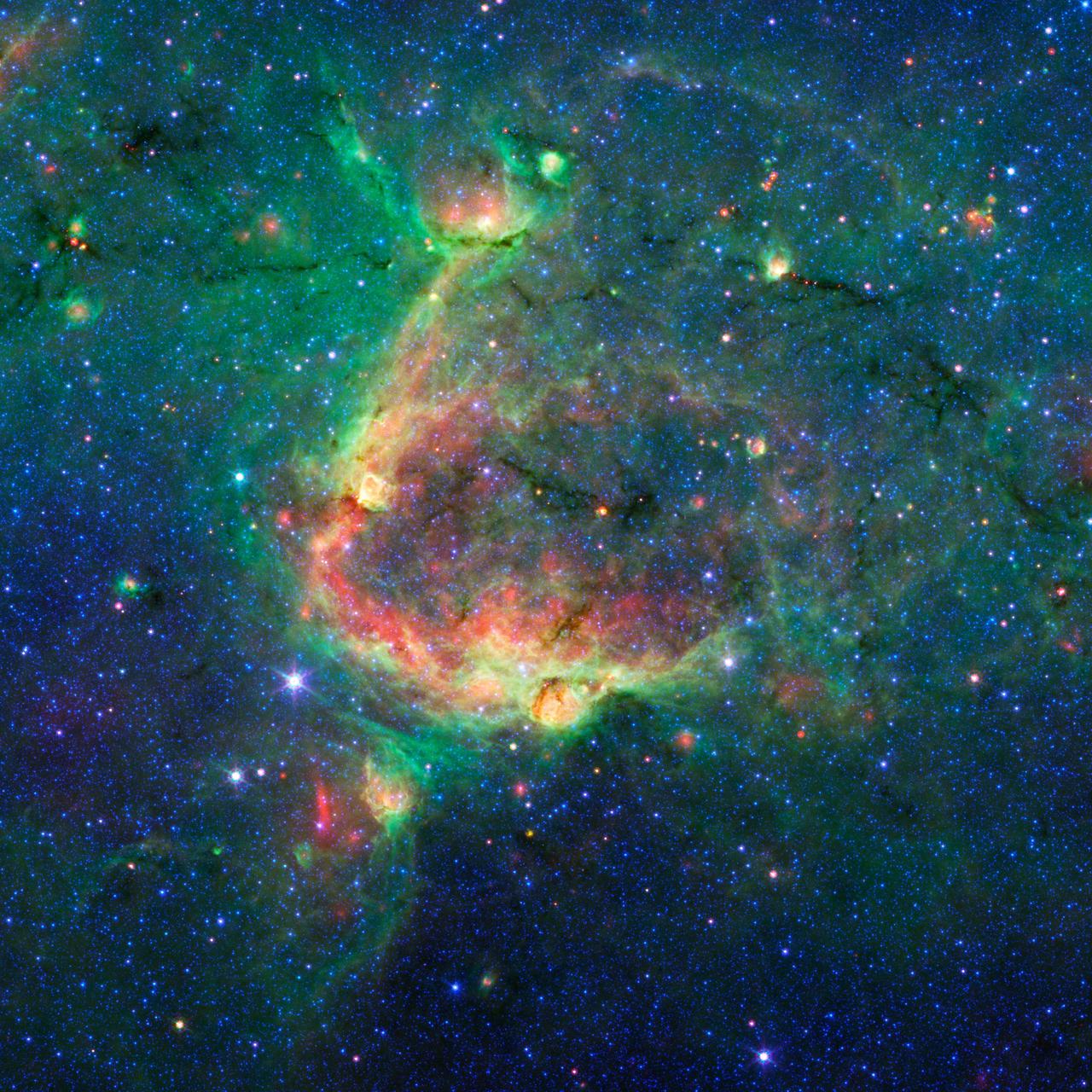

This infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows a striking example of what is called a hierarchical bubble structure, in which one giant bubble, carved into the dust of space by massive stars, has triggered the formation of smaller bubbles.
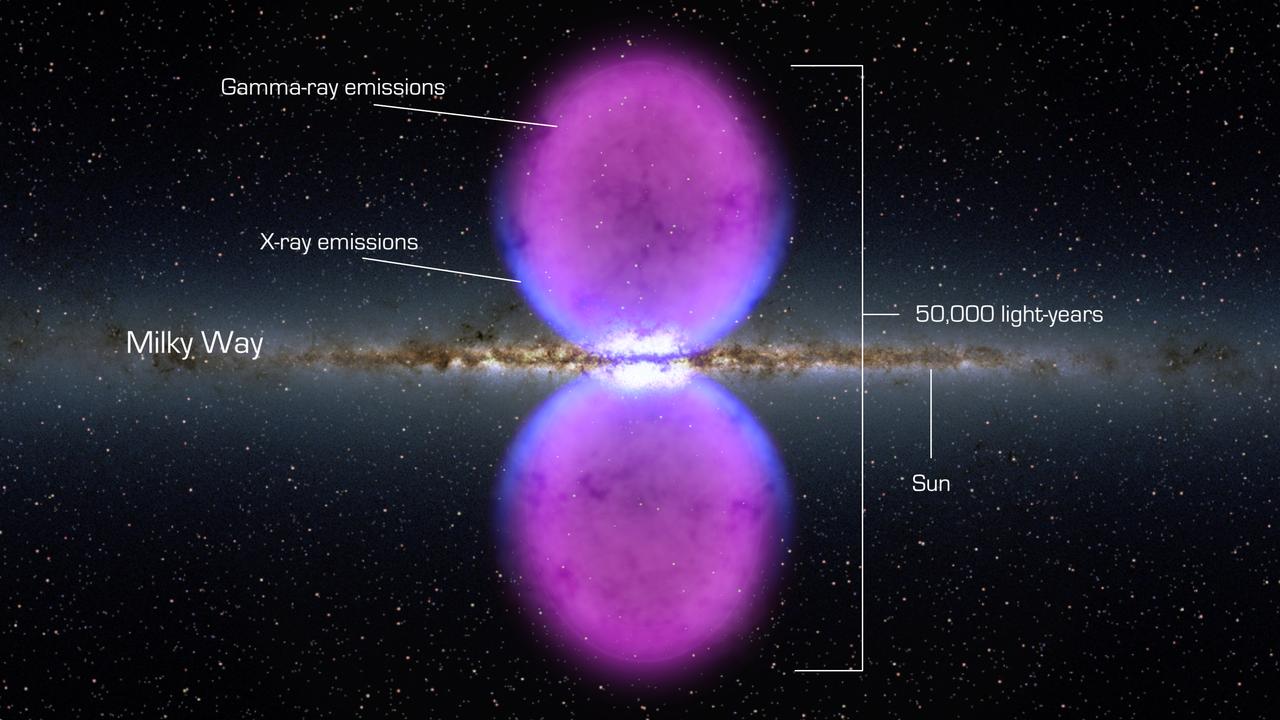
NASA image release November 9, 2010 To view a video about this story go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5162413062">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5162413062</a> From end to end, the gamma-ray bubbles extend 50,000 light-years, or roughly half of the Milky Way's diameter, as shown in this illustration. The bubbles stretch across 100 degrees, spanning the sky from the constellation Virgo to the constellation Grus. If the structure were rotated into the galaxy's plane, it would extend beyond our solar system. Hints of the bubbles' edges were first observed in X-rays (blue) by ROSAT (Röntgen Satellite), a Germany-led mission operating in the 1990s. The gamma rays mapped by Fermi (magenta) extend much farther from the galaxy's plane. To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/new-structure.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/new-structure.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a>

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
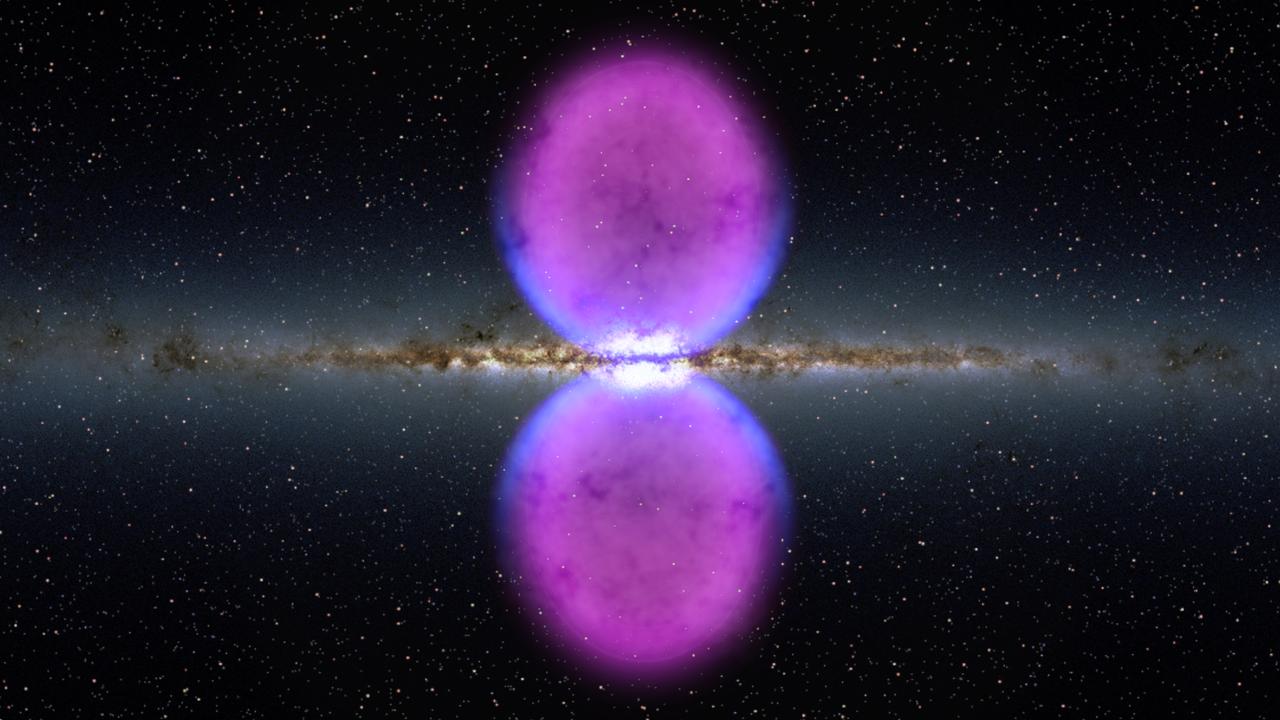

NASA image release November 9, 2010 To view a video about this story go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5162413062">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5162413062</a> From end to end, the newly discovered gamma-ray bubbles extend 50,000 light-years, or roughly half of the Milky Way's diameter, as shown in this illustration. Hints of the bubbles' edges were first observed in X-rays (blue) by ROSAT, a Germany-led mission operating in the 1990s. The gamma rays mapped by Fermi (magenta) extend much farther from the galaxy's plane. To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/new-structure.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/new-structure.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a>

The large bubble is an embryonic star that looks set to turn into one of the brightest stars in our Milky Way galaxy in this infrared image from the Herschel Space Telescope.

Aboard the International Space Station (ISS), European Space Agency astronaut Pedro Duque of Spain watches a water bubble float between a camera and himself. The bubble shows his reflection (reversed). Duque was launched aboard a Russian Soyuz TMA-3 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan on October 18th, along with expedition-8 crew members Michael C. Foale, Mission Commander and NASA ISS Science Officer, and Cosmonaut Alexander Y. Kaleri, Soyuz Commander and flight engineer.

ISS034-E-031694 (21 Jan. 2013) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut Chris Hadfield, Expedition 34 flight engineer, watches a water bubble float freely between him and the camera, showing his image refracted, in the Unity node of the International Space Station.

NASA image release December 14, 2010 A delicate sphere of gas, photographed by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, floats serenely in the depths of space. The pristine shell, or bubble, is the result of gas that is being shocked by the expanding blast wave from a supernova. Called SNR 0509-67.5 (or SNR 0509 for short), the bubble is the visible remnant of a powerful stellar explosion in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a small galaxy about 160,000 light-years from Earth. Ripples in the shell's surface may be caused by either subtle variations in the density of the ambient interstellar gas, or possibly driven from the interior by pieces of the ejecta. The bubble-shaped shroud of gas is 23 light-years across and is expanding at more than 11 million miles per hour (5,000 kilometers per second). Astronomers have concluded that the explosion was one of an especially energetic and bright variety of supernovae. Known as Type Ia, such supernova events are thought to result from a white dwarf star in a binary system that robs its partner of material, takes on much more mass than it is able to handle, and eventually explodes. Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys observed the supernova remnant on Oct. 28, 2006 with a filter that isolates light from glowing hydrogen seen in the expanding shell. These observations were then combined with visible-light images of the surrounding star field that were imaged with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 on Nov. 4, 2010. With an age of about 400 years as seen from Earth, the supernova might have been visible to southern hemisphere observers around the year 1600, however, there are no known records of a "new star" in the direction of the LMC near that time. A more recent supernova in the LMC, SN 1987A, did catch the eye of Earth viewers and continues to be studied with ground- and space-based telescopes, including Hubble. For images and more information about SNR 0509, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2010/27" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2010/27</a> <a href="http://heritage.stsci.edu/2010/27" rel="nofollow">heritage.stsci.edu/2010/27</a> <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. <b>Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: J. Hughes (Rutgers University)</b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

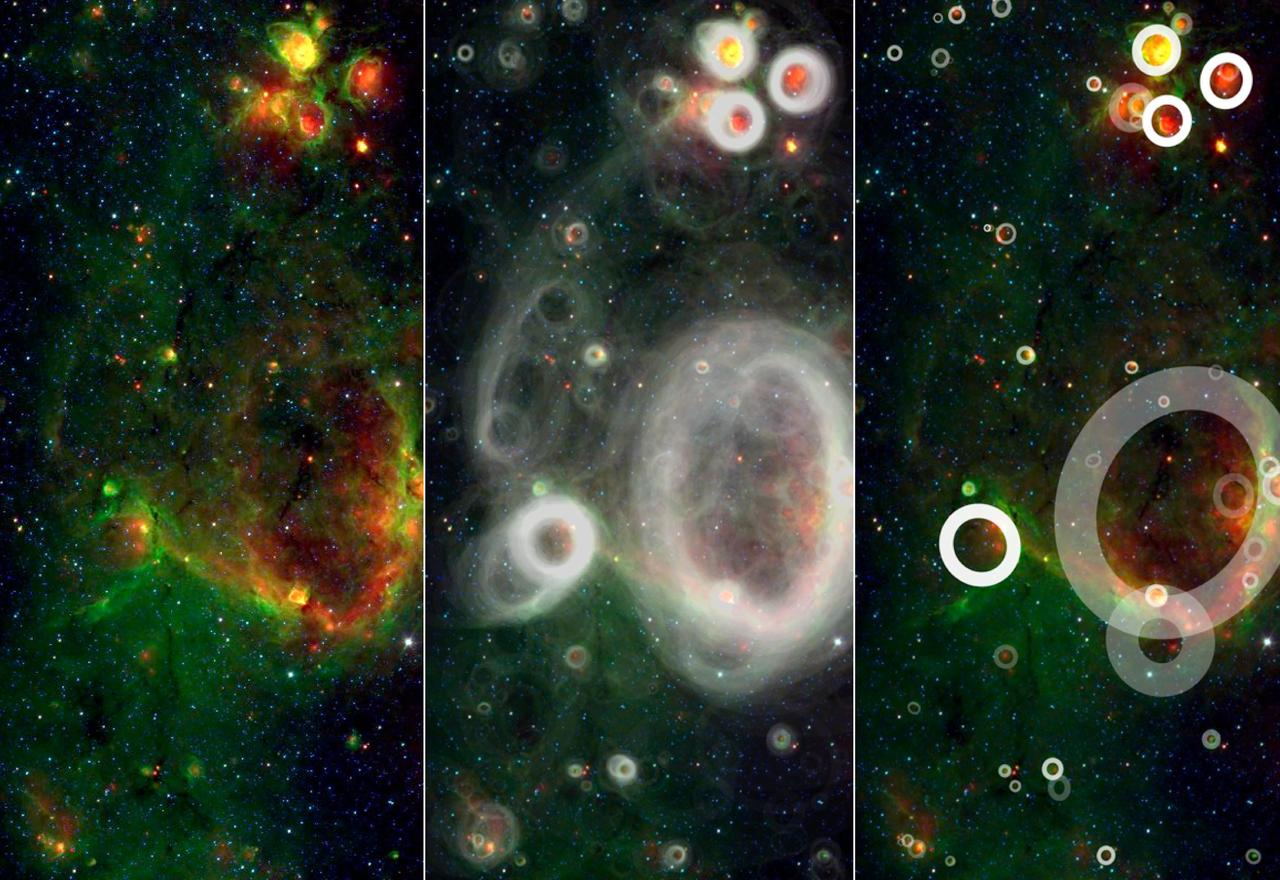
This infrared image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows a cloud of gas and dust full of bubbles, which are inflated by wind and radiation from massive young stars. Each bubble is filled with hundreds to thousands of stars, which form from dense clouds of gas and dust. The bubbles are estimated to be 10 to 30 light-years across, based on what astronomers know about them and other cosmic bubbles. However, determining the exact sizes of individual bubbles can be difficult, because their distance from Earth is challenging to measure and objects appear smaller the farther away they are. Flows of particles called stellar winds emitted by the stars, as well as the pressure of the light those winds produce, can push the surrounding material outward, sometimes creating a distinct perimeter. In Figure 1, the yellow circles and ovals outline more than 30 bubbles. This active region of star formation is located inside the Milky Way galaxy, in the constellation Aquila (also known as the Eagle). Black veins running throughout the cloud are regions of especially dense cold dust and gas where even more new stars are likely to form. The colors in this image represent different wavelengths of infrared light. Blue represents a wavelength of light primarily emitted by stars; dust and organic molecules called hydrocarbons appear green, and warm dust that's been heated by stars appears red. Also visible are four bow shocks — red arcs of warm dust formed as winds from fast-moving stars push aside dust grains scattered sparsely through most of the nebula. The locations of the bow shocks are indicated by squares in Figure 1. Figure 2 shows zoomed-in views of the four bow shocks. The bubbles and bow shocks in this image were identified as part of The Milky Way Project, a citizen science initiative on Zooniverse.org that seeks to map star formation throughout the galaxy. Participating citizen scientists looked through images from Spitzer's public data archive and identified as many bubbles as they could. More than 78,000 unique user accounts contributed. Astronomers running this program recently published a catalog of the bubble candidates that multiple citizen scientists had identified. The full Milky Way Project catalogs, which list a total of 2,600 bubbles and 599 bow shocks, are described in a paper published recently in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23402

S82-28914 (26 March 1982) --- Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, STS-3 commander, spins a package of colored liquid in zero-gravity aboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Columbia. He was actually creating a centrifuge to conduct a test involving the separation of bubbles from the liquid rehydrated strawberry powder for visible clarity. The gas from liquid experiment is a test devised by scientist-astronaut William E. Thornton. The gun-like device at center of left edge is a water-dispenser which the astronauts use in rehydrating food packets, many of which can be seen in the background of this middeck area of the Columbia. Astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton, pilot, exposed this frame with a 35mm camera. Photo credit: NASA
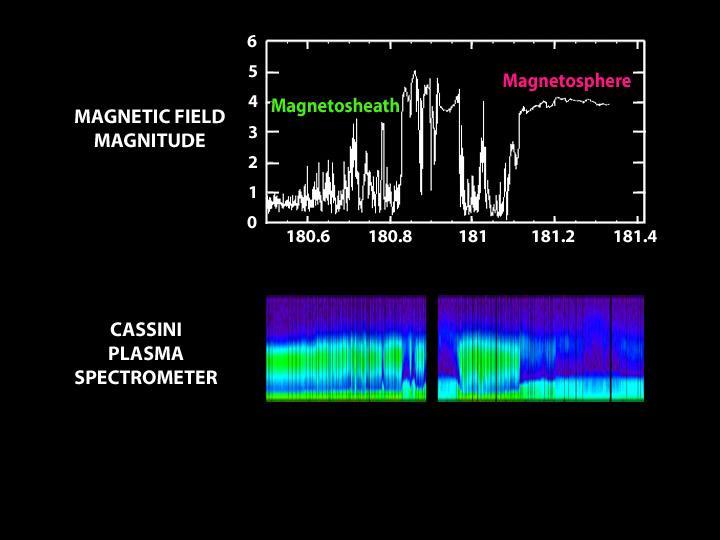
New data from NASA Cassini spacecraft suggest that the shape of our solar system moving through the local Milky Way galaxy looks like a bubble -- or a rat -- traveling through a boa constrictor belly.
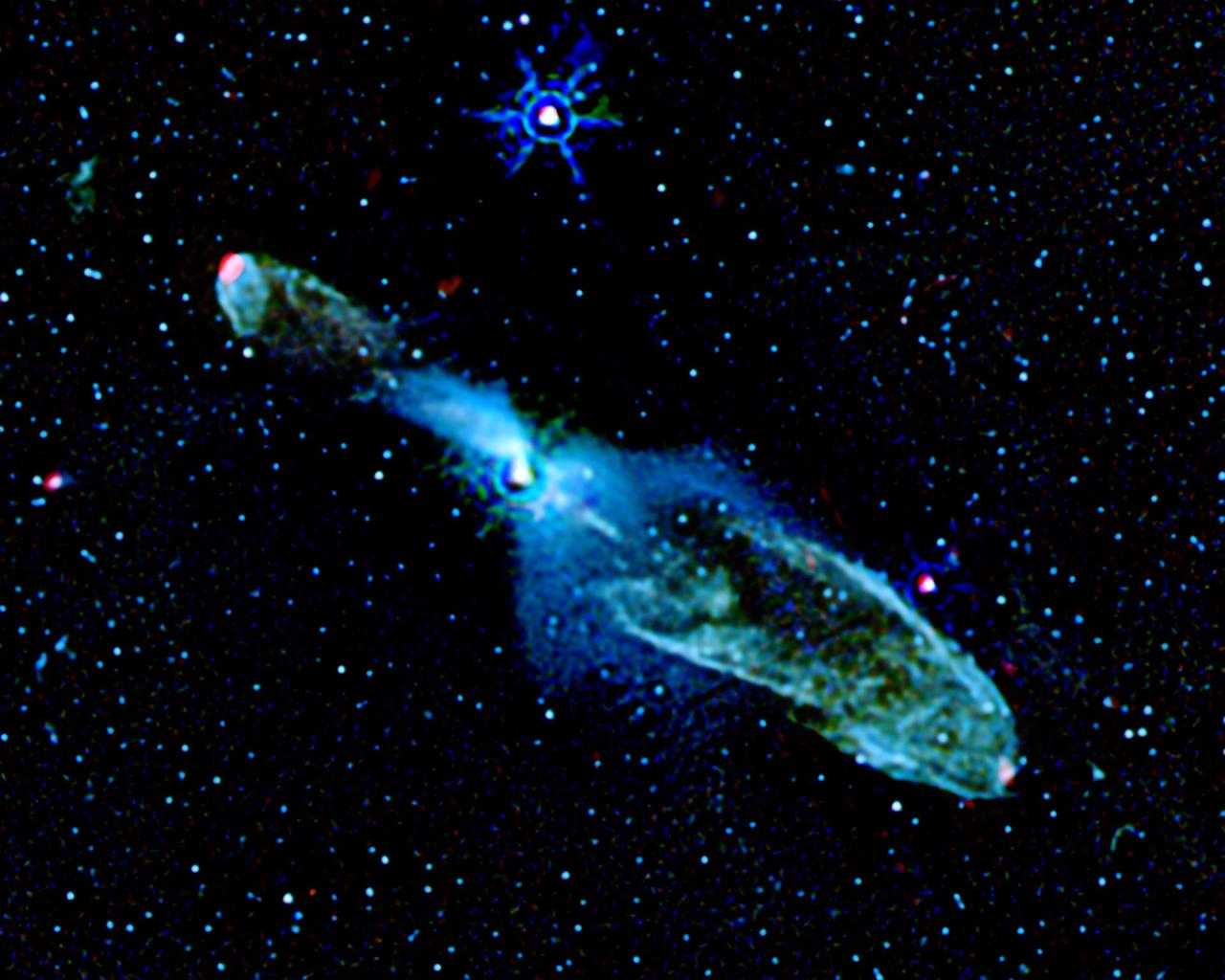

In this processed Spitzer Space Telescope image, baby star HH 46/47 can be seen blowing two massive bubbles. The star is 1,140 light-years away from Earth.

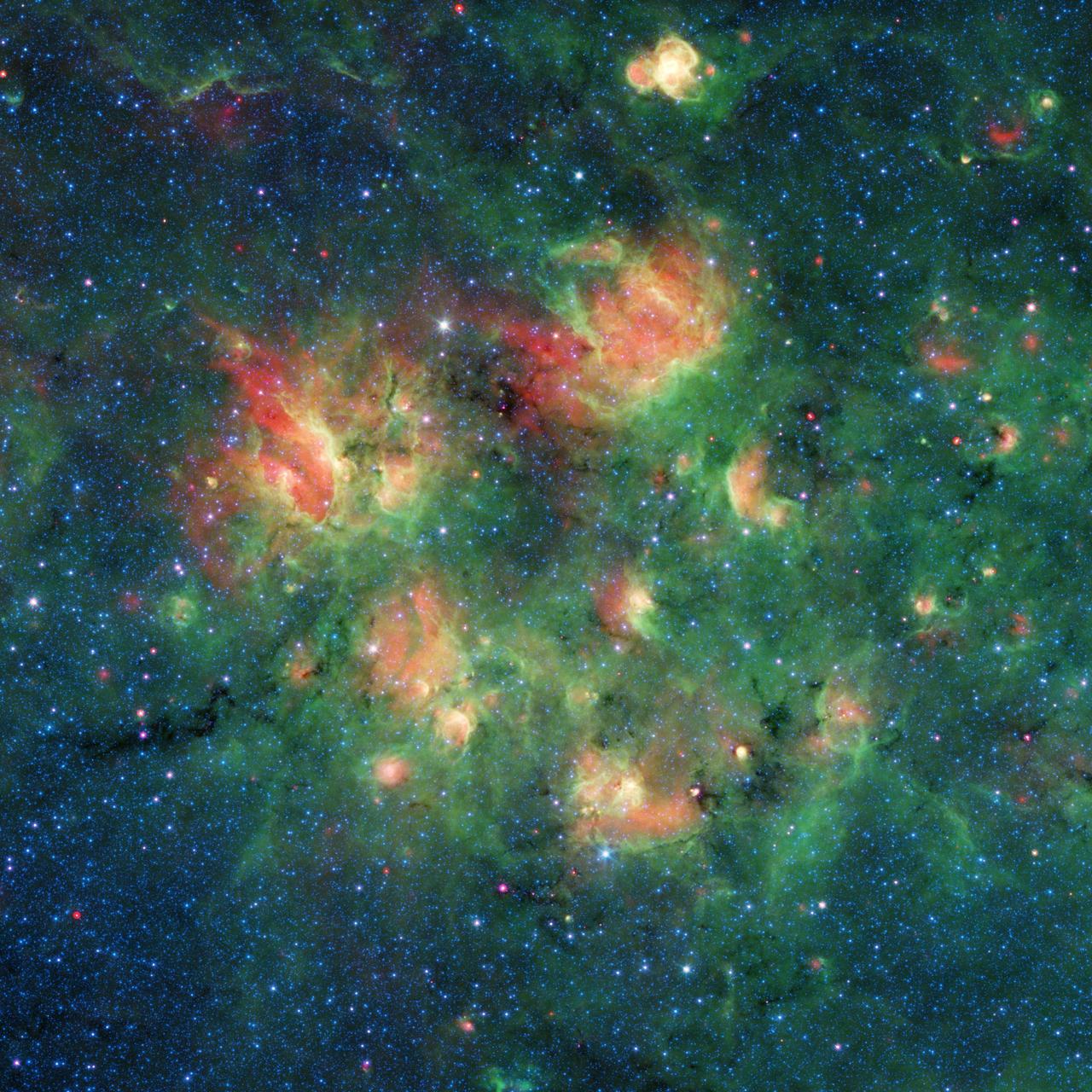
A team of volunteers from the general public has pored over observations from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope and discovered more than 5,000 bubbles in the disk of our Milky Way galaxy.
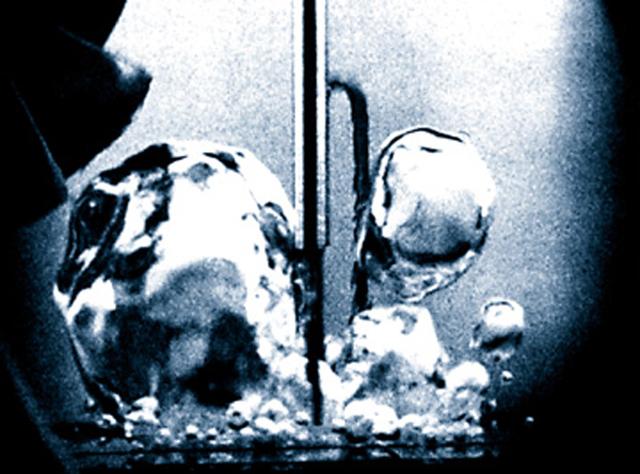
Fluid Physics is study of the motion of fluids and the effects of such motion. When a liquid is heated from the bottom to the boiling point in Earth's microgravity, small bubbles of heated gas form near the bottom of the container and are carried to the top of the liquid by gravity-driven convective flows. In the same setup in microgravity, the lack of convection and buoyancy allows the heated gas bubbles to grow larger and remain attached to the container's bottom for a significantly longer period.

NASA image release November 9, 2010 To view a video about this story go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5162413062">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5162413062</a> Using data from NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, scientists have recently discovered a gigantic, mysterious structure in our galaxy. This never-before-seen feature looks like a pair of bubbles extending above and below our galaxy's center. But these enormous gamma-ray emitting lobes aren't immediately visible in the Fermi all-sky map. However, by processing the data, a group of scientists was able to bring these unexpected structures into sharp relief. Each lobe is 25,000 light-years tall and the whole structure may be only a few million years old. Within the bubbles, extremely energetic electrons are interacting with lower-energy light to create gamma rays, but right now, no one knows the source of these electrons. Are the bubbles remnants of a massive burst of star formation? Leftovers from an eruption by the supermassive black hole at our galaxy's center? Or or did these forces work in tandem to produce them? Scientists aren't sure yet, but the more they learn about this amazing structure, the better we'll understand the Milky Way. To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/new-structure.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/new-structure.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a>
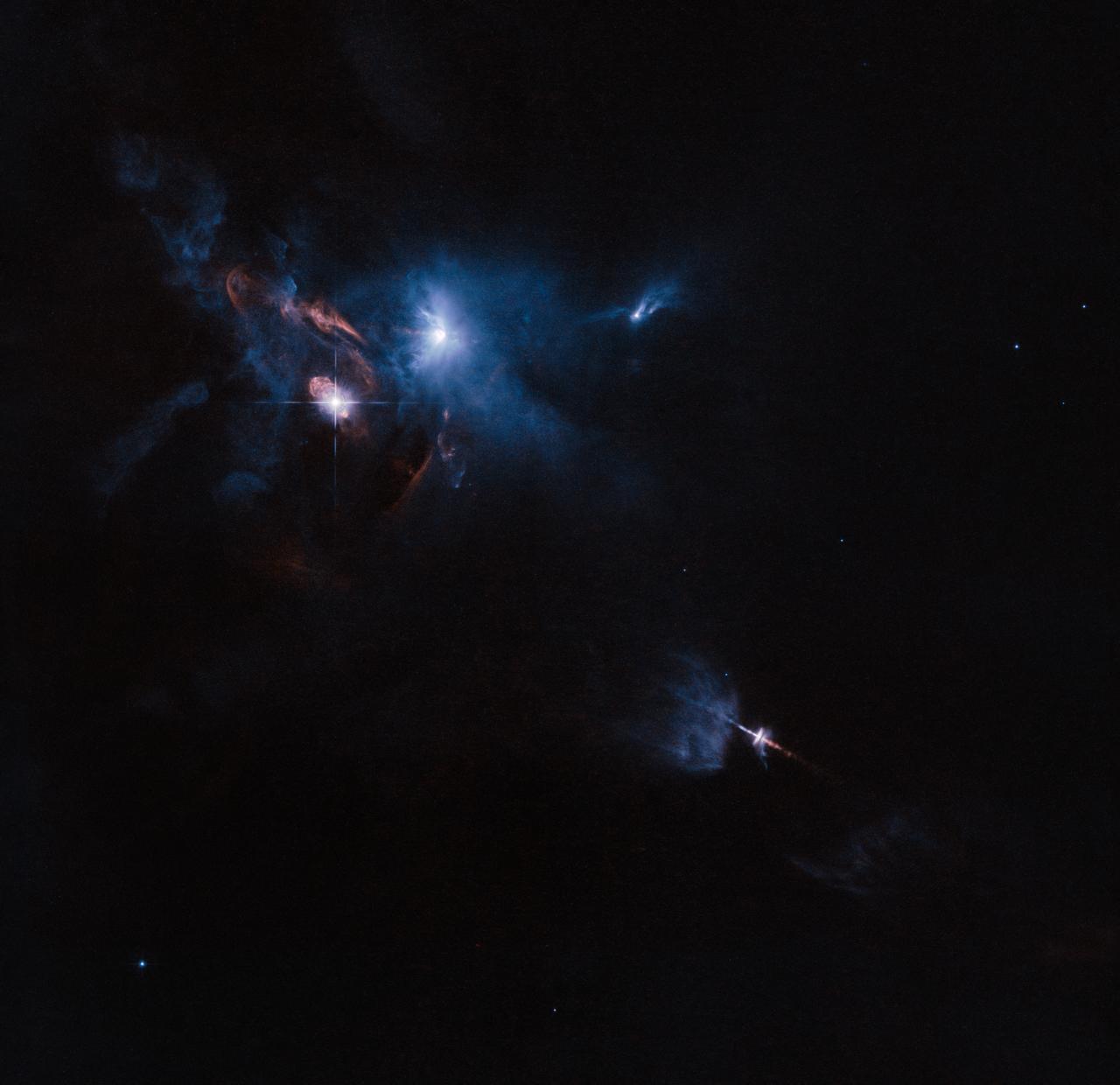

The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has snapped a striking view of a multiple star system called XZ Tauri, its neighbor HL Tauri, and several nearby young stellar objects. XZ Tauri is blowing a hot bubble of gas into the surrounding space, which is filled with bright and beautiful clumps that are emitting strong winds and jets. These objects illuminate the region, creating a truly dramatic scene. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1Guj3aQ" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1Guj3aQ</a> Credit: ESA/Hubble and NASA; acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
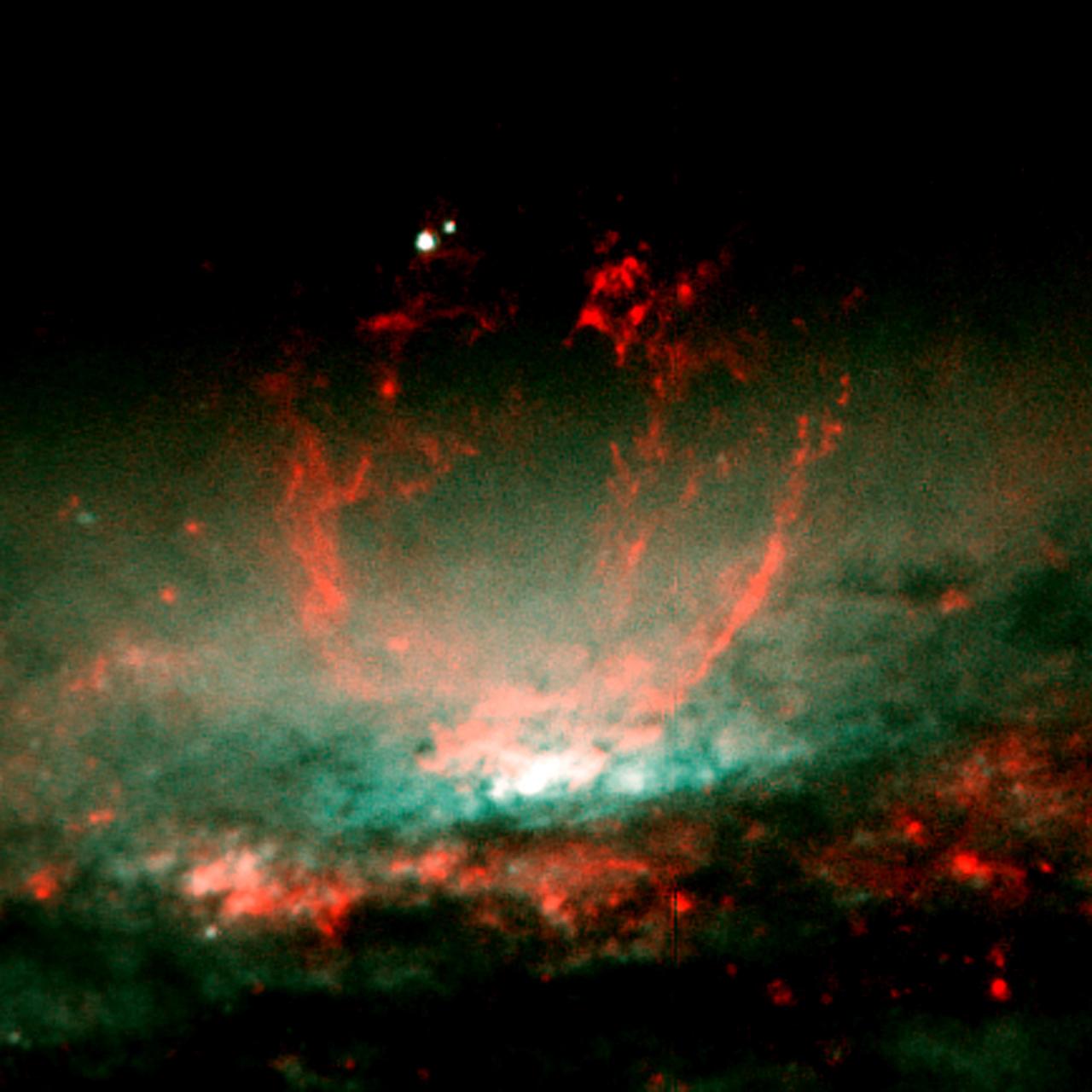
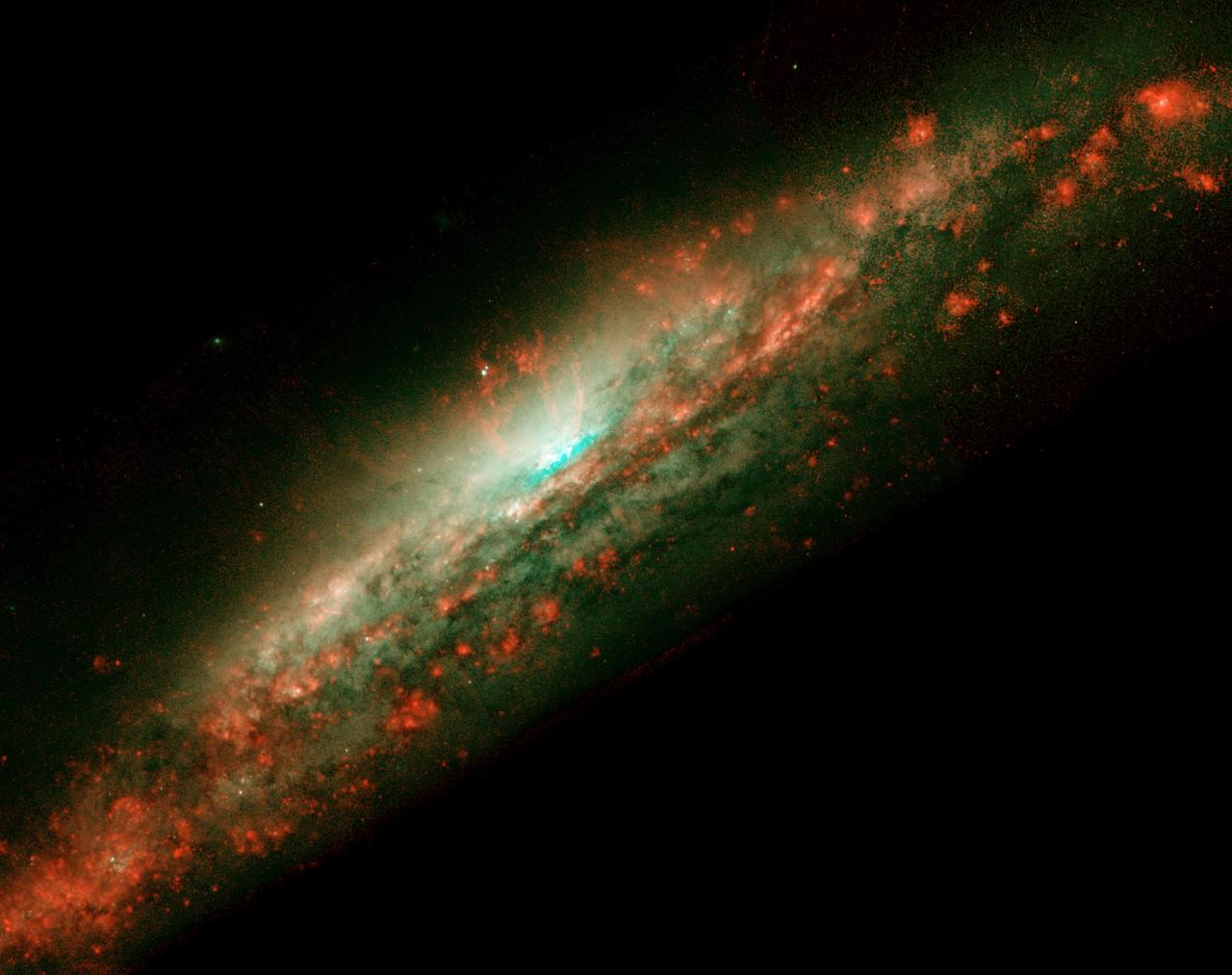
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (HST) captures a lumpy bubble of hot gas rising from a cauldron of glowing matter in Galaxy NGC 3079, located 50 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Ursa Major. Astronomers suspect the bubble is being blown by "winds" or high speed streams of particles, released during a burst of star formation. The bubble's lumpy surface has four columns of gaseous filaments towering above the galaxy's disc that whirl around in a vortex and are expelled into space. Eventually, this gas will rain down on the disc and may collide with gas clouds, compress them, and form a new generation of stars.
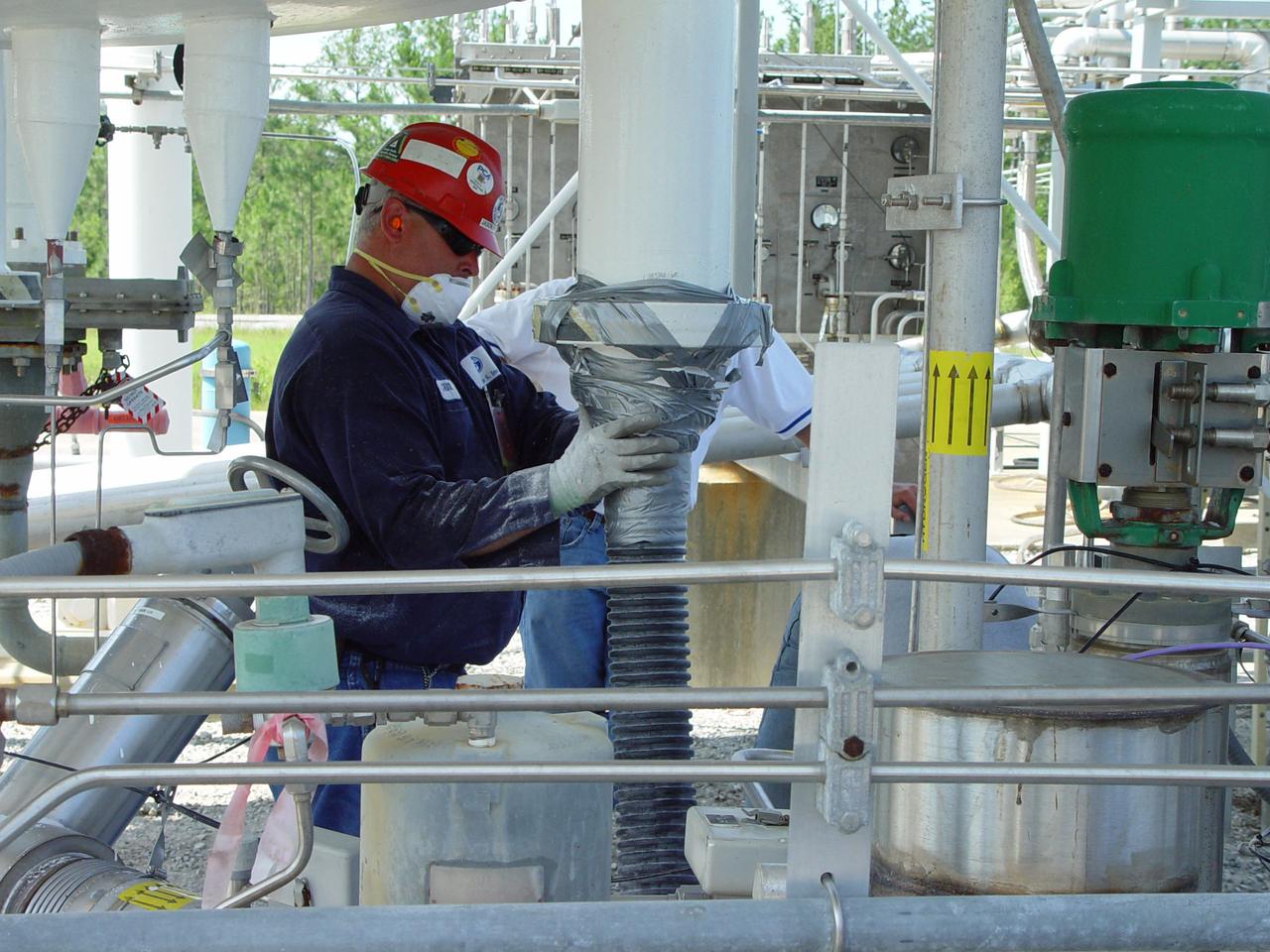

A worker removes Perlite insulation from a liquid hydrogen storage tank to replace it with glass bubble insulation.

NASA astronaut Karen Nyberger, Expedition 36 flight engineer, watches a water bubble float freely between her and the camera, showing her image refracted in the droplet, while in the Node 1Unity module of the International Space Station.
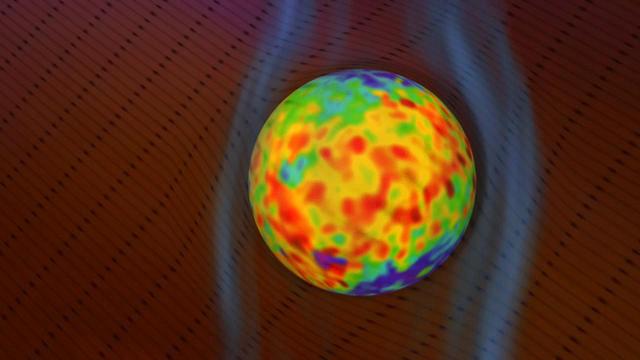
As the solar wind flows from the sun, it creates a bubble in space known as the heliosphere around our solar system. The heliosphere is the region of space under the influence of our sun.

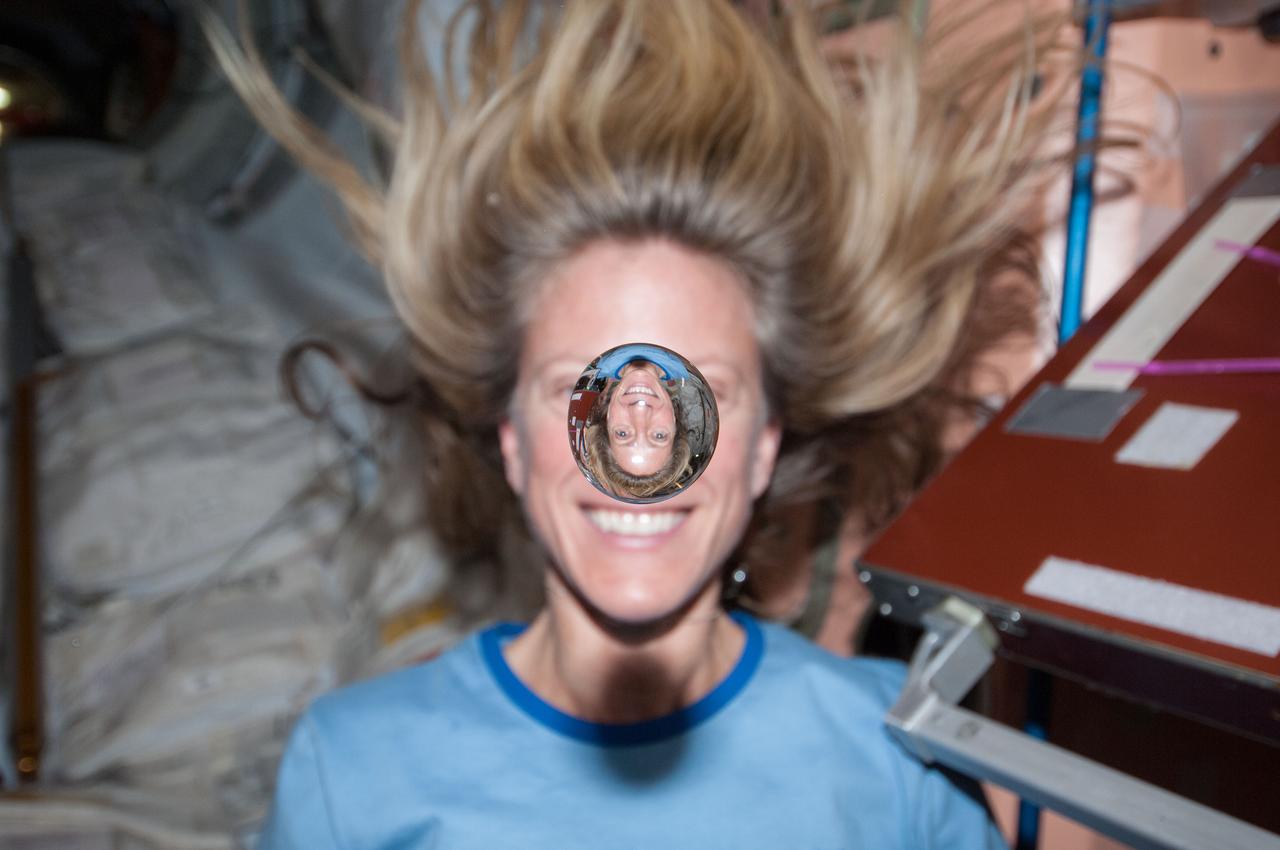
S131-E-009277 (12 April 2010) --- NASA astronaut Clayton Anderson, STS-131 mission specialist, watches a water bubble float freely between him and the camera, showing his image refracted, on the middeck of space shuttle Discovery while docked with the International Space Station.
S131-E-009282 (12 April 2010) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Naoko Yamazaki, STS-131 mission specialist, squeezes a water bubble out of her beverage container, showing her image refracted, on the middeck of space shuttle Discovery while docked with the International Space Station.
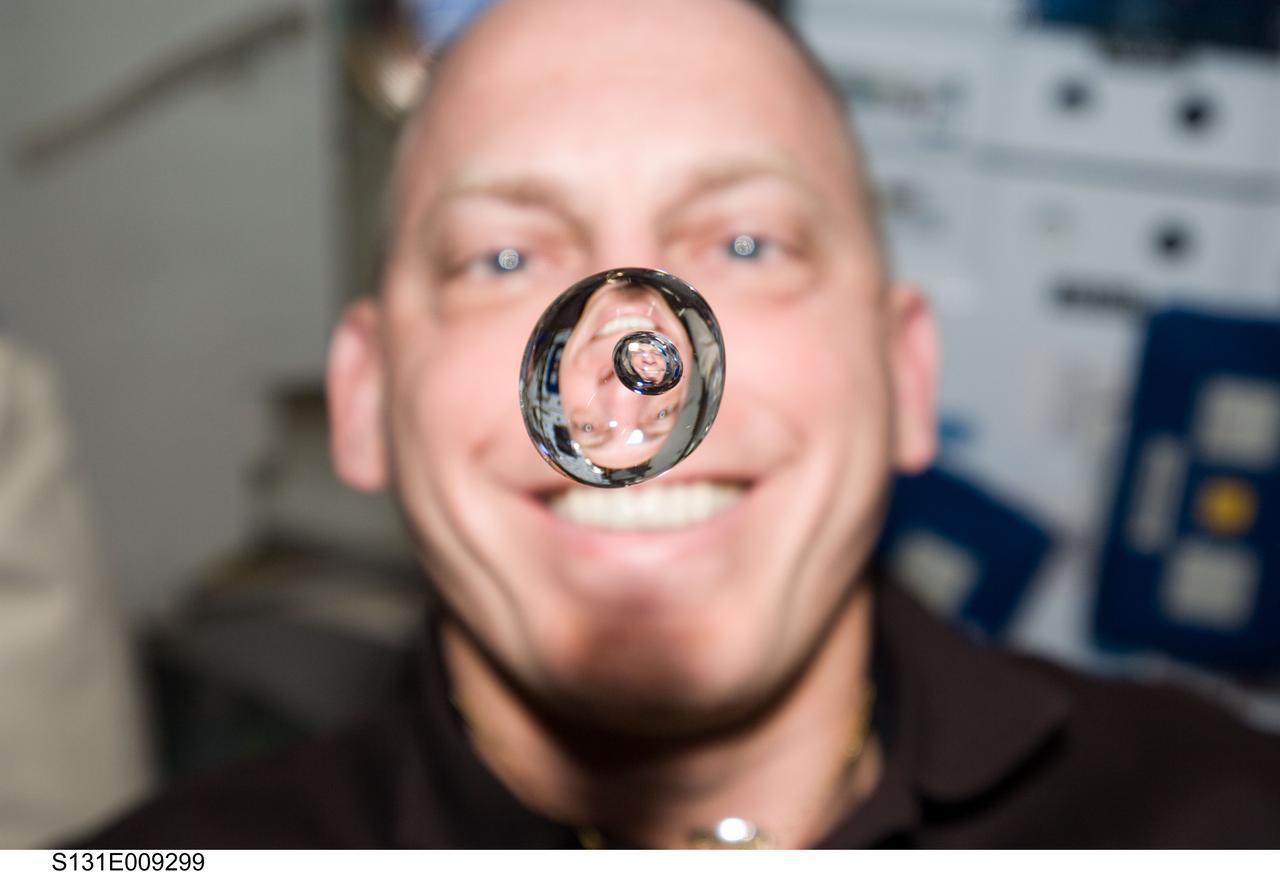

S131-E-009299 (12 April 2010) --- NASA astronaut Clayton Anderson, STS-131 mission specialist, watches a water bubble float freely between him and the camera, showing his image refracted, on the middeck of space shuttle Discovery while docked with the International Space Station.
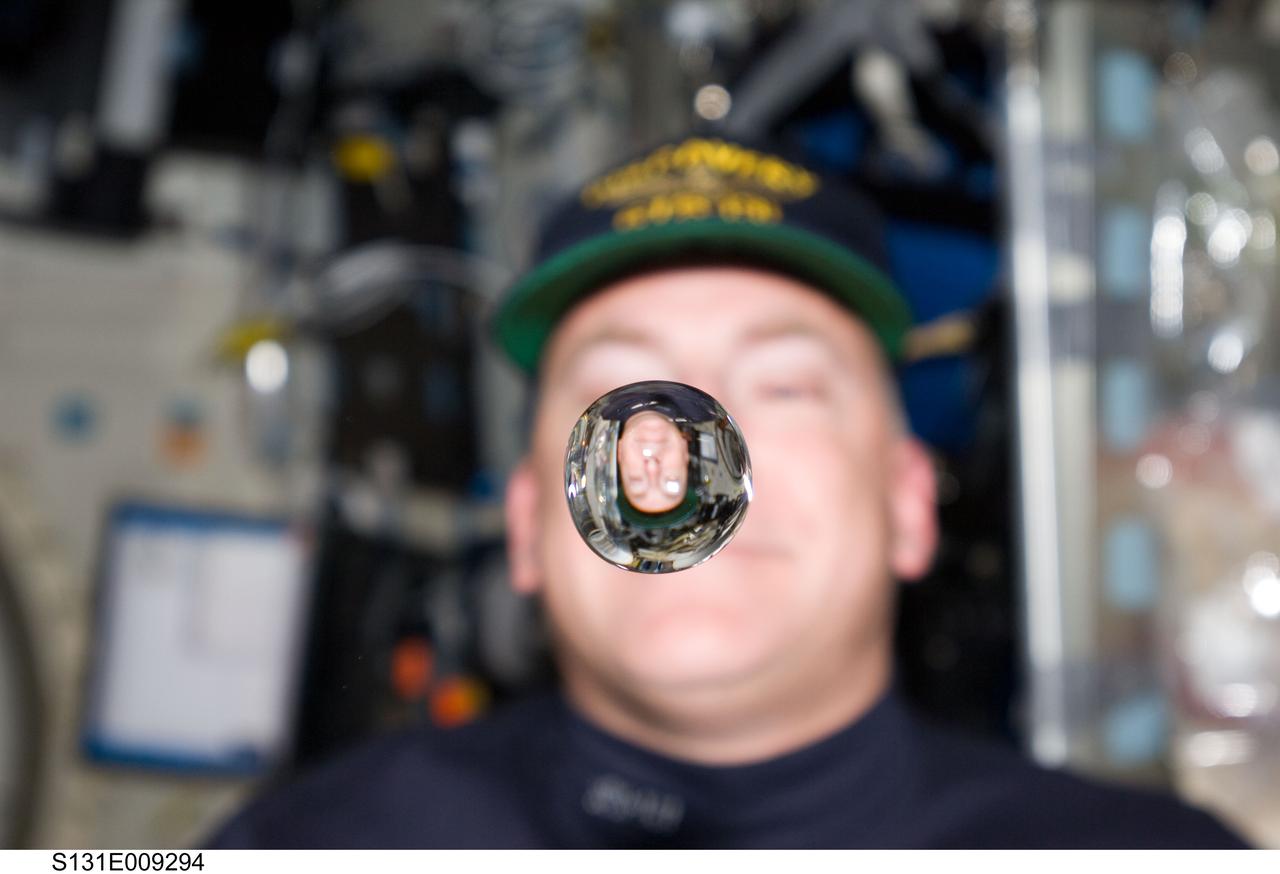

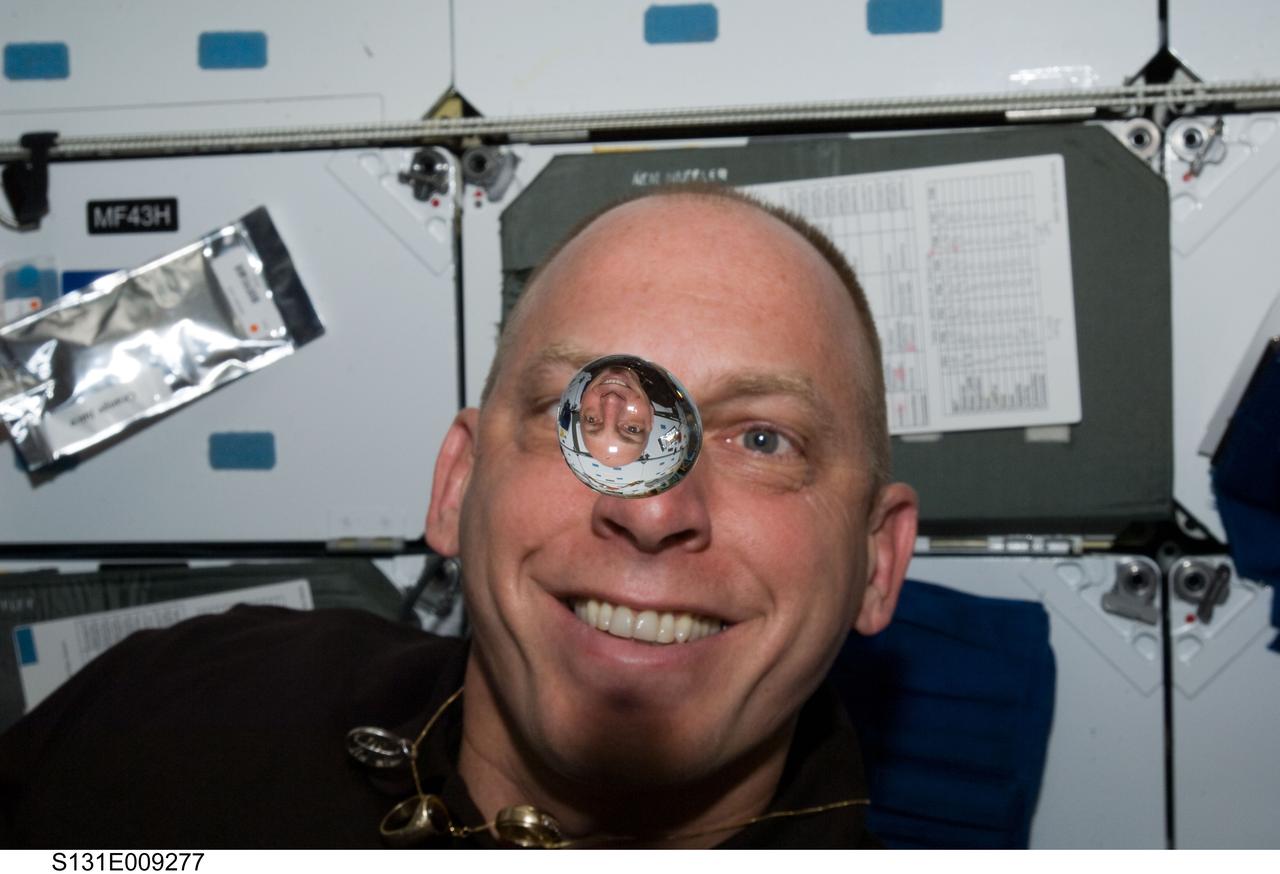
S131-E-009294 (12 April 2010) --- NASA astronaut Alan Poindexter, STS-131 commander, watches a water bubble float freely between him and the camera, showing his image refracted, on the middeck of space shuttle Discovery while docked with the International Space Station.
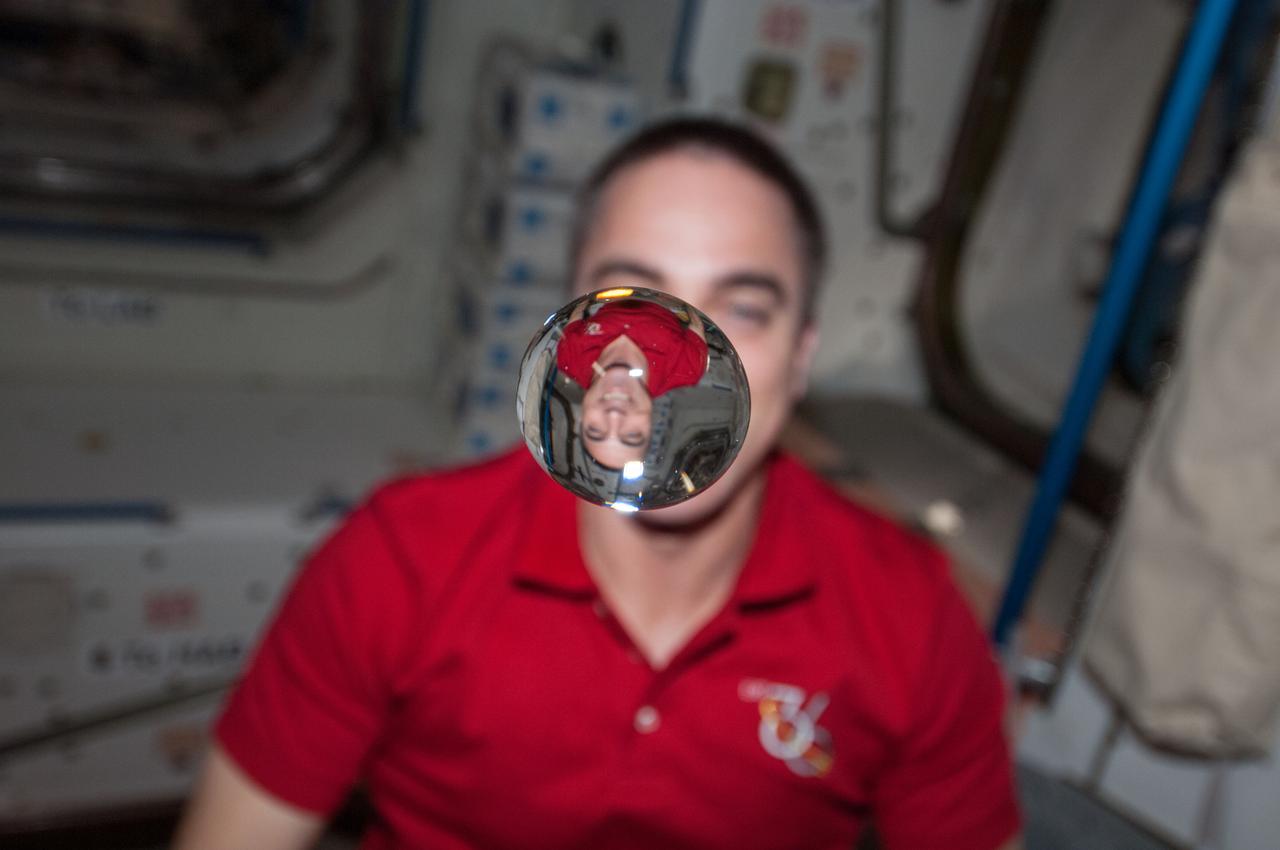

ISS036-E-018302 (12 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, Expedition 36 flight engineer, watches a water bubble float freely between him and the camera, showing his image refracted, in the Unity node of the International Space Station.
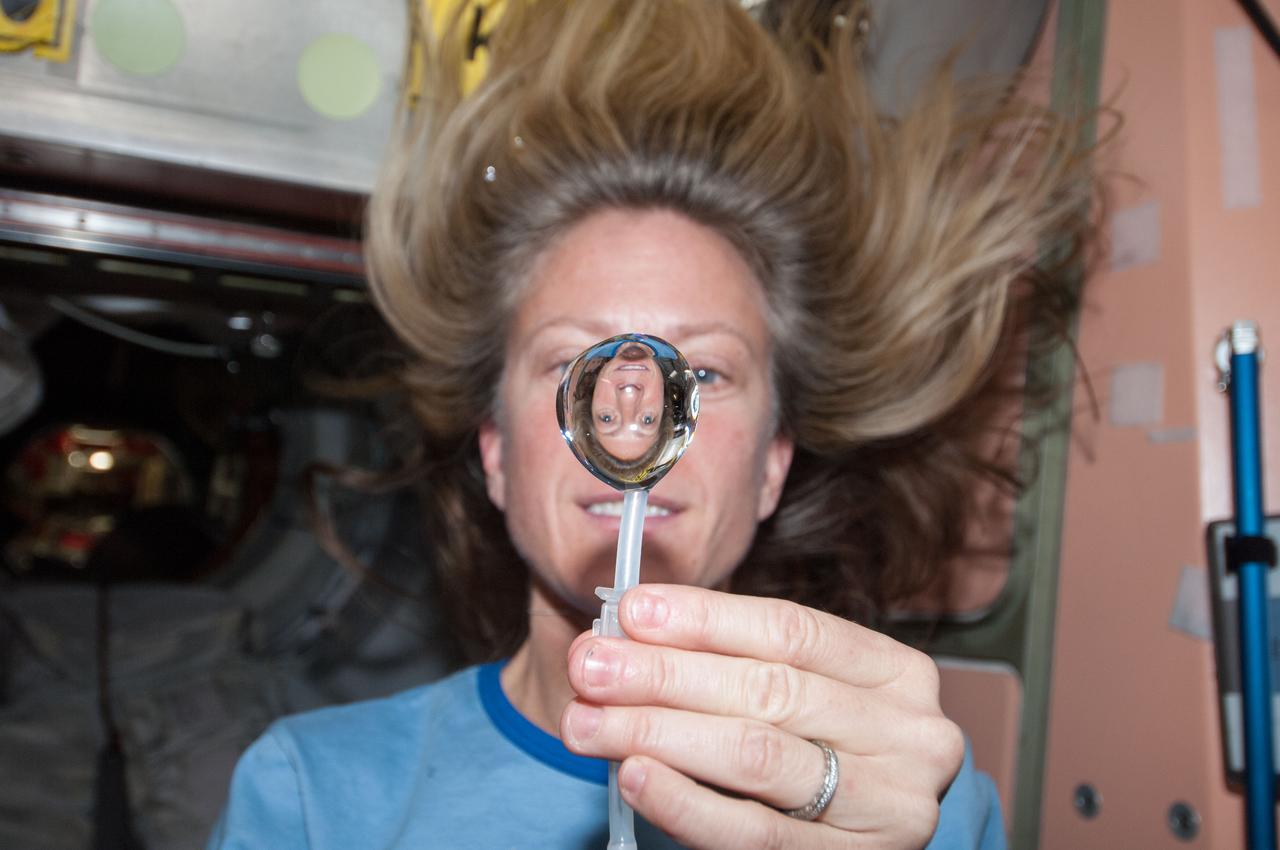

ISS036-E-018290 (12 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 36 flight engineer, squeezes a water bubble out of her beverage container, showing her image refracted, in the Unity node of the International Space Station.
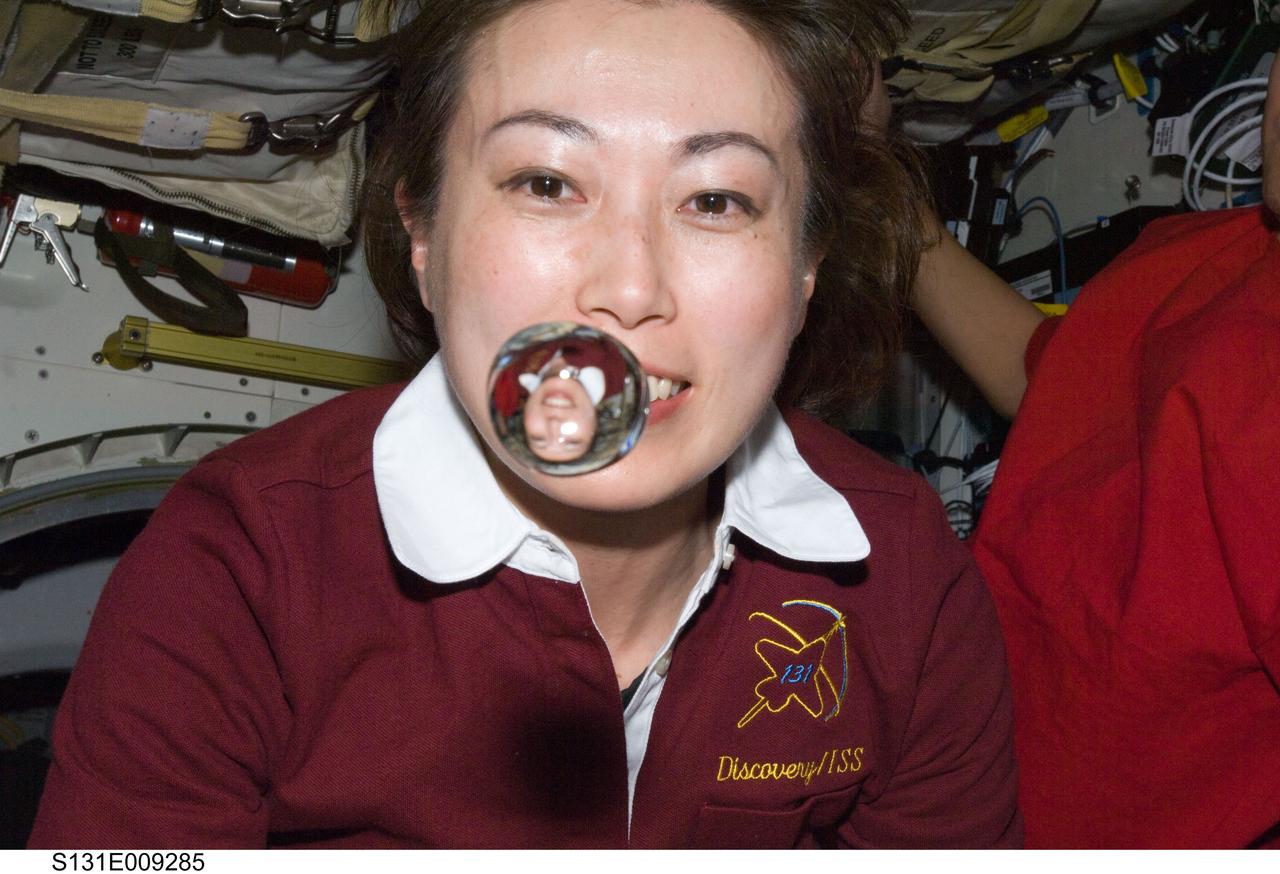

S131-E-009285 (12 April 2010) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Naoko Yamazaki, STS-131 mission specialist, watches a water bubble float freely between her and the camera, showing her image refracted, on the middeck of space shuttle Discovery while docked with the International Space Station.
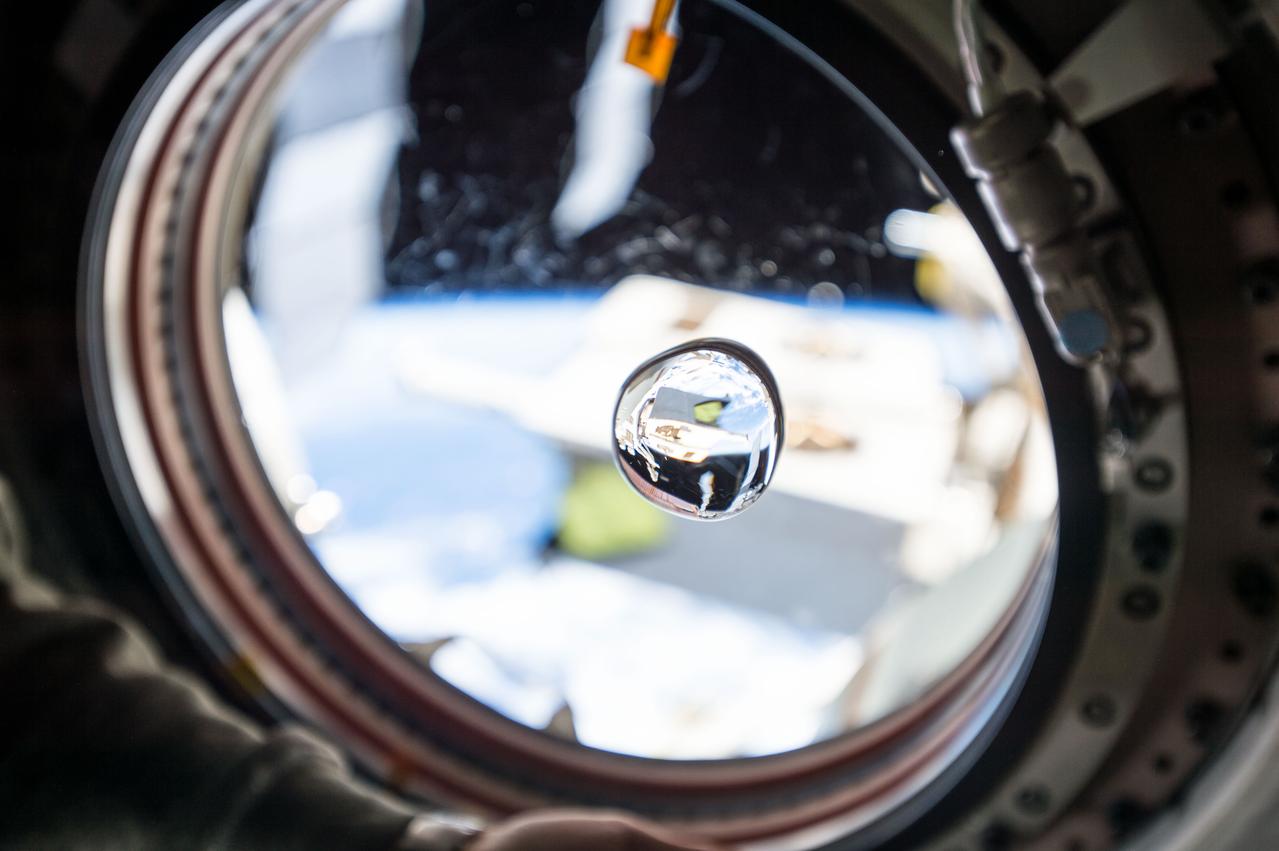

View of water bubble formed in front of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) window. The JEM Exposed Facility (JEF) is visible in the background through the window and reflected in the water. Scratches visible on the window.
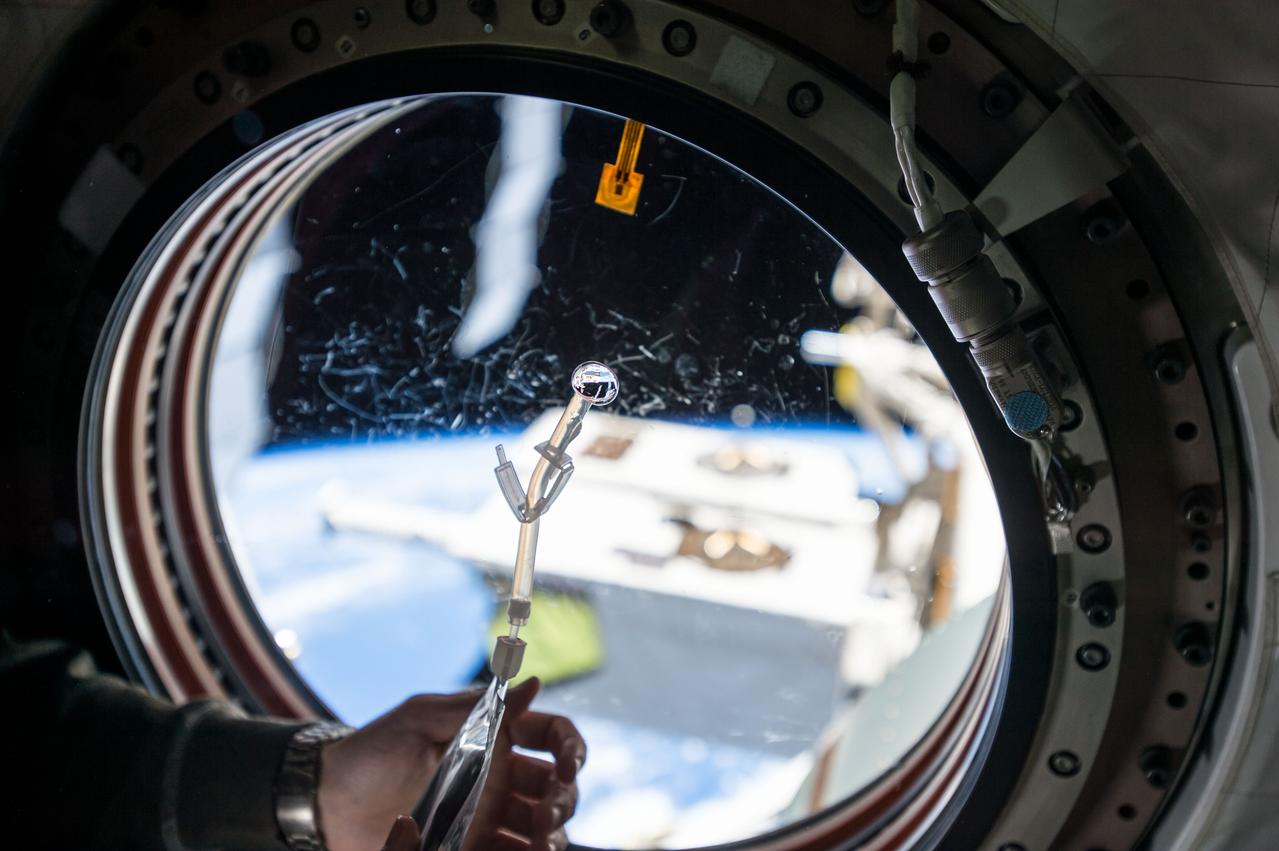

View of water bubble formed in front of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) window. The JEM Exposed Facility (JEF) is visible in the background through the window and reflected in the water. Scratches visible on the window.

Image release June 22, 2010 A spectacular new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image — one of the largest ever released of a star-forming region — highlights N11, part of a complex network of gas clouds and star clusters within our neighbouring galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud. This region of energetic star formation is one of the most active in the nearby Universe. The Large Magellanic Cloud contains many bright bubbles of glowing gas. One of the largest and most spectacular has the name LHA 120-N 11, from its listing in a catalogue compiled by the American astronomer and astronaut Karl Henize in 1956, and is informally known as N11. Close up, the billowing pink clouds of glowing gas make N11 resemble a puffy swirl of fairground candy floss. From further away, its distinctive overall shape led some observers to nickname it the Bean Nebula. The dramatic and colourful features visible in the nebula are the telltale signs of star formation. N11 is a well-studied region that extends over 1000 light-years. It is the second largest star-forming region within the Large Magellanic Cloud and has produced some of the most massive stars known. It is the process of star formation that gives N11 its distinctive look. Three successive generations of stars, each of which formed further away from the centre of the nebula than the last, have created shells of gas and dust. These shells were blown away from the newborn stars in the turmoil of their energetic birth and early life, creating the ring shapes so prominent in this image. Beans are not the only terrestrial shapes to be found in this spectacular high resolution image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. In the upper left is the red bloom of nebula LHA 120-N 11A. Its rose-like petals of gas and dust are illuminated from within, thanks to the radiation from the massive hot stars at its centre. N11A is relatively compact and dense and is the site of the most recent burst of star development in the region. Other star clusters abound in N11, including NGC 1761 at the bottom of the image, which is a group of massive hot young stars busily pouring intense ultraviolet radiation out into space. Although it is much smaller than our own galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud is a very vigorous region of star formation. Studying these stellar nurseries helps astronomers understand a lot more about how stars are born and their ultimate development and lifespan. Both the Large Magellanic Cloud and its small companion, the Small Magellanic Cloud, are easily seen with the unaided eye and have always been familiar to people living in the southern hemisphere. The credit for bringing these galaxies to the attention of Europeans is usually given to Portuguese explorer Fernando de Magellan and his crew, who viewed it on their 1519 sea voyage. However, the Persian astronomer Abd Al-Rahman Al Sufi and the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci recorded the Large Magellanic Cloud in 964 and 1503 respectively. Credit: NASA, ESA and Jesús Maíz Apellániz (Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía, Spain) To learn more about Hubble go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
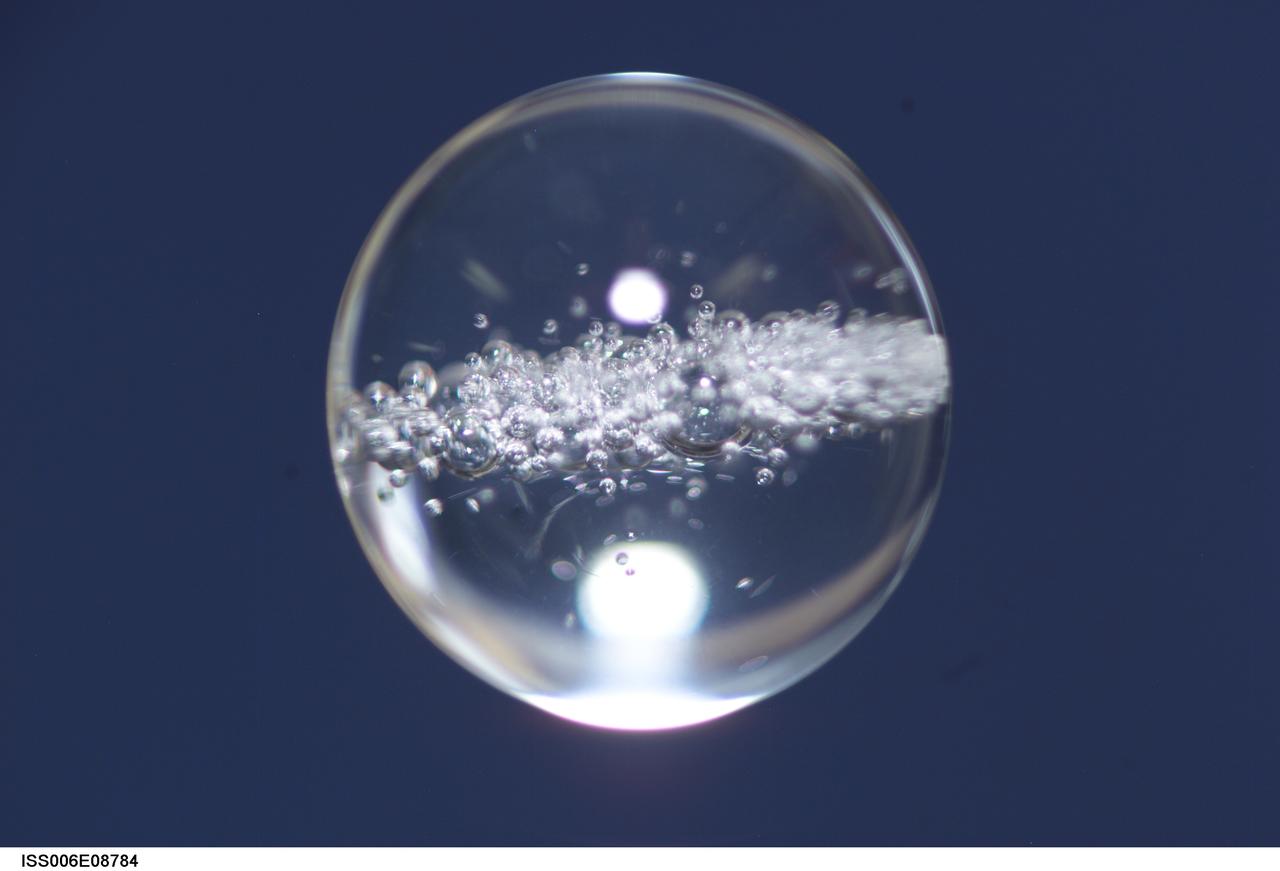

ISS006-E-08784 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
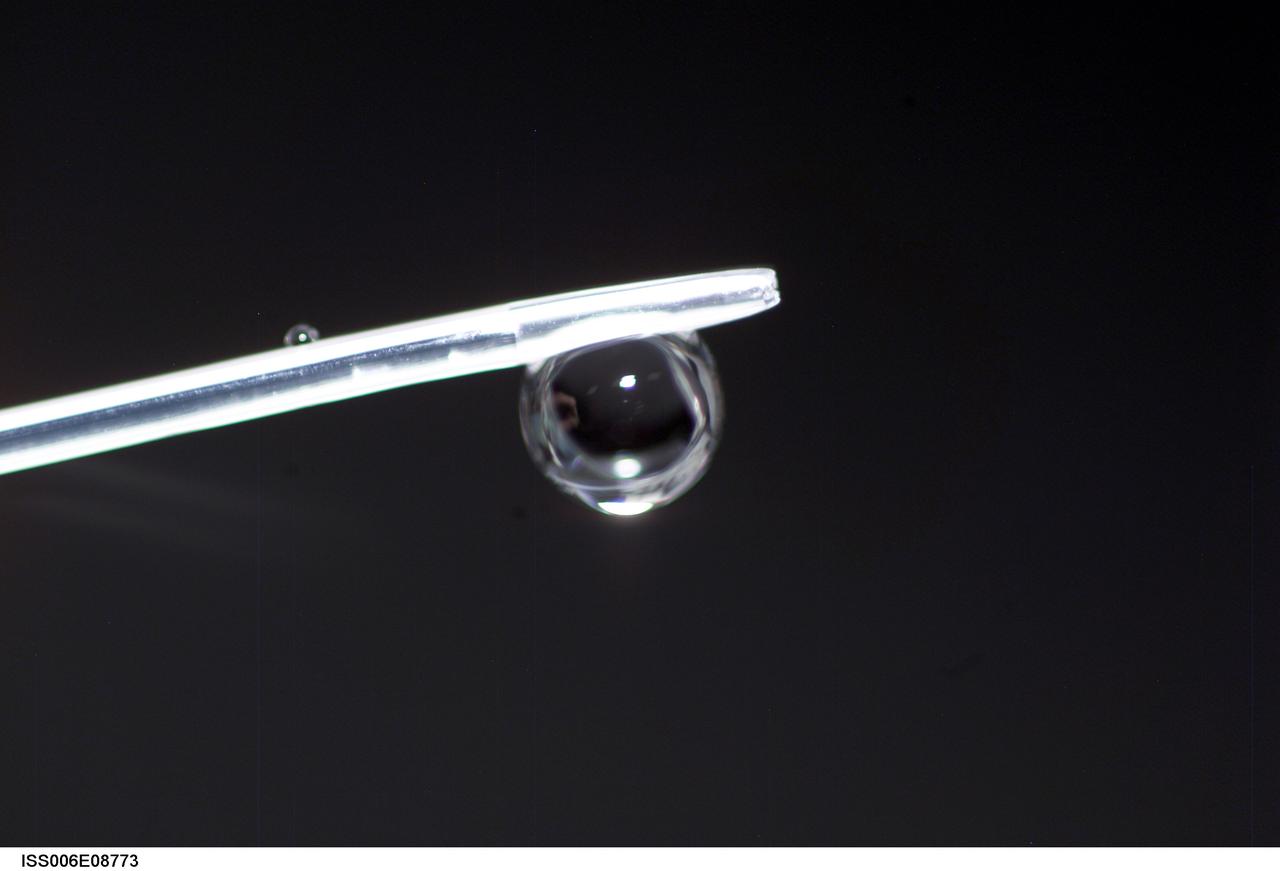

ISS006-E-08773 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
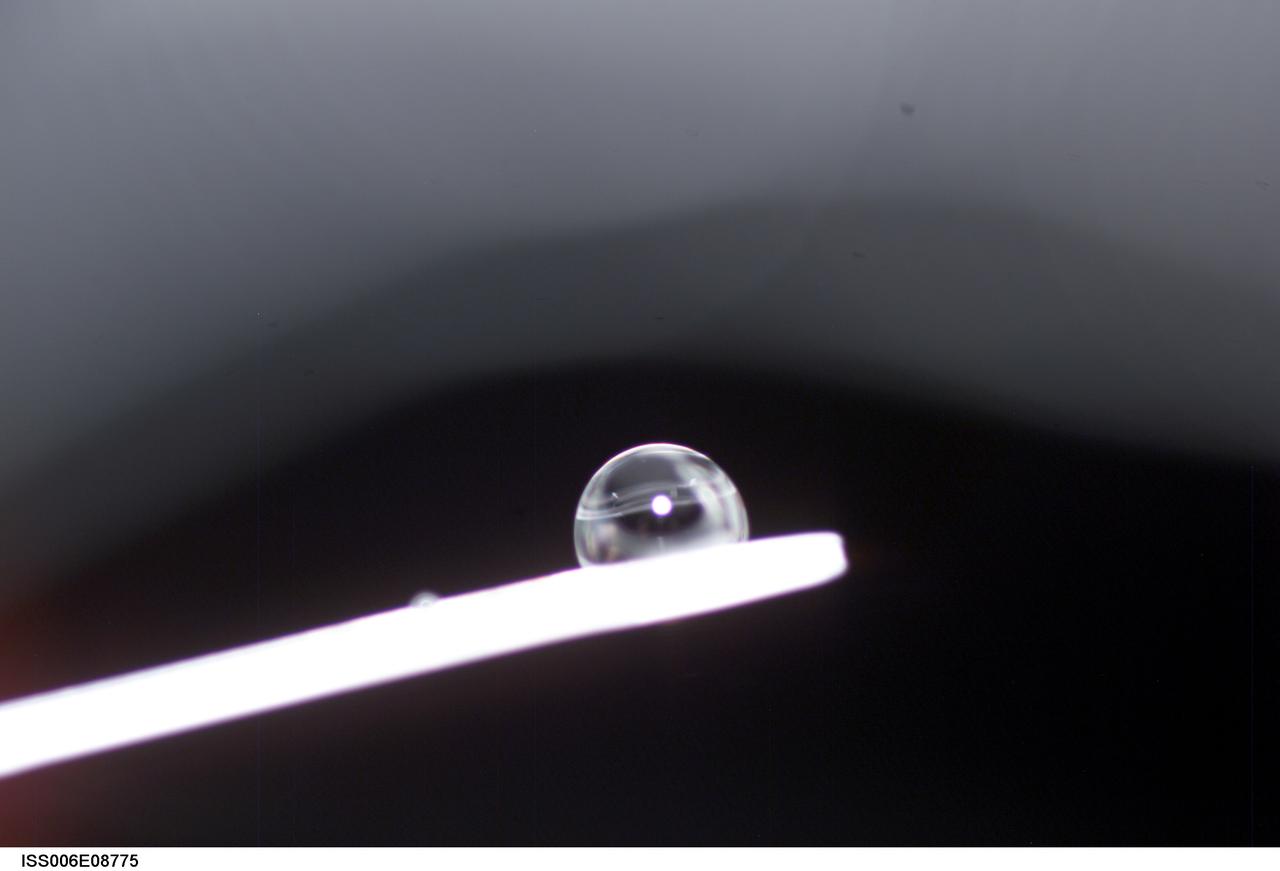

ISS006-E-08775 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.

ISS006-E-08799 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
ISS006-E-08805 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
ISS006-E-08822 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
ISS006-E-08836 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.

ISS006-E-08831 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
ISS006-E-08778 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.

ISS006-E-08835 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
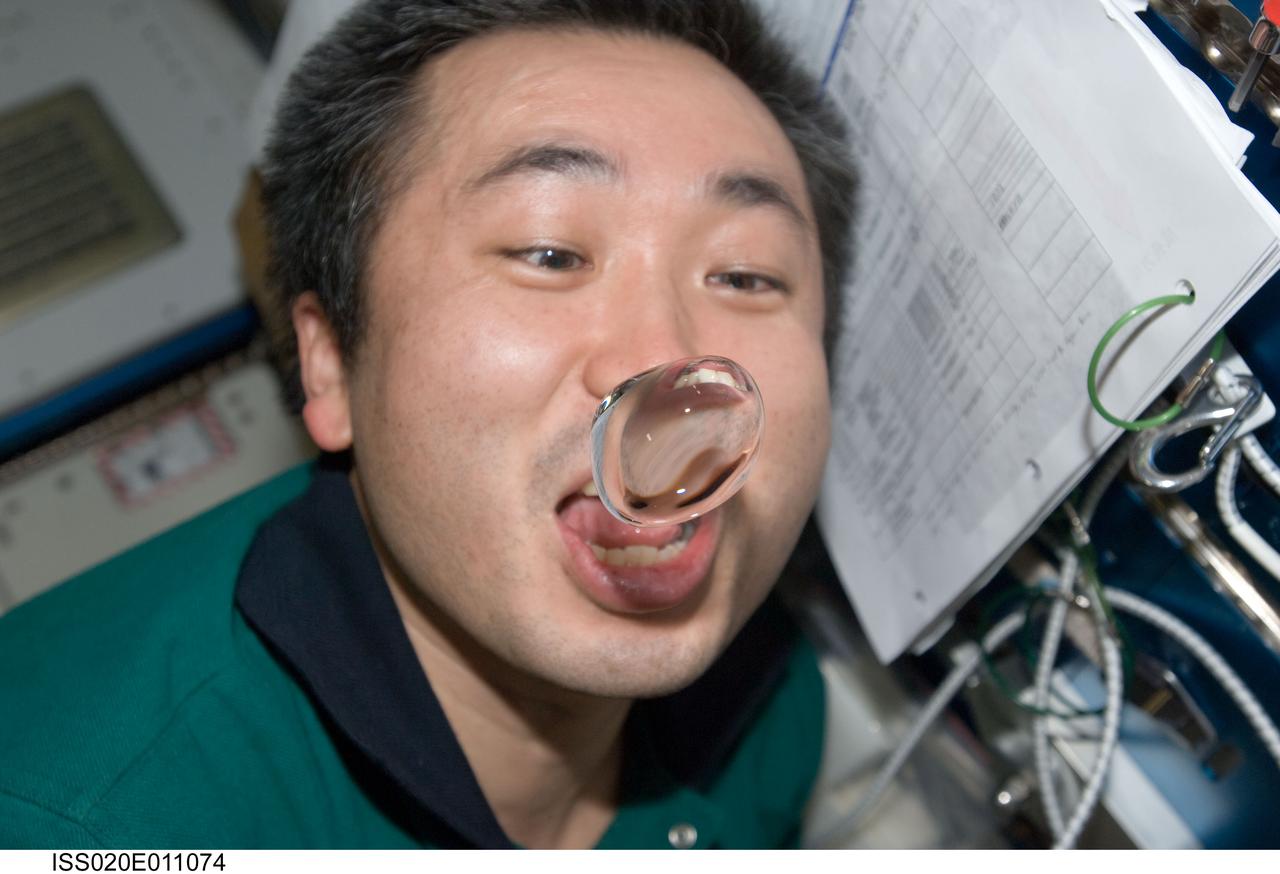
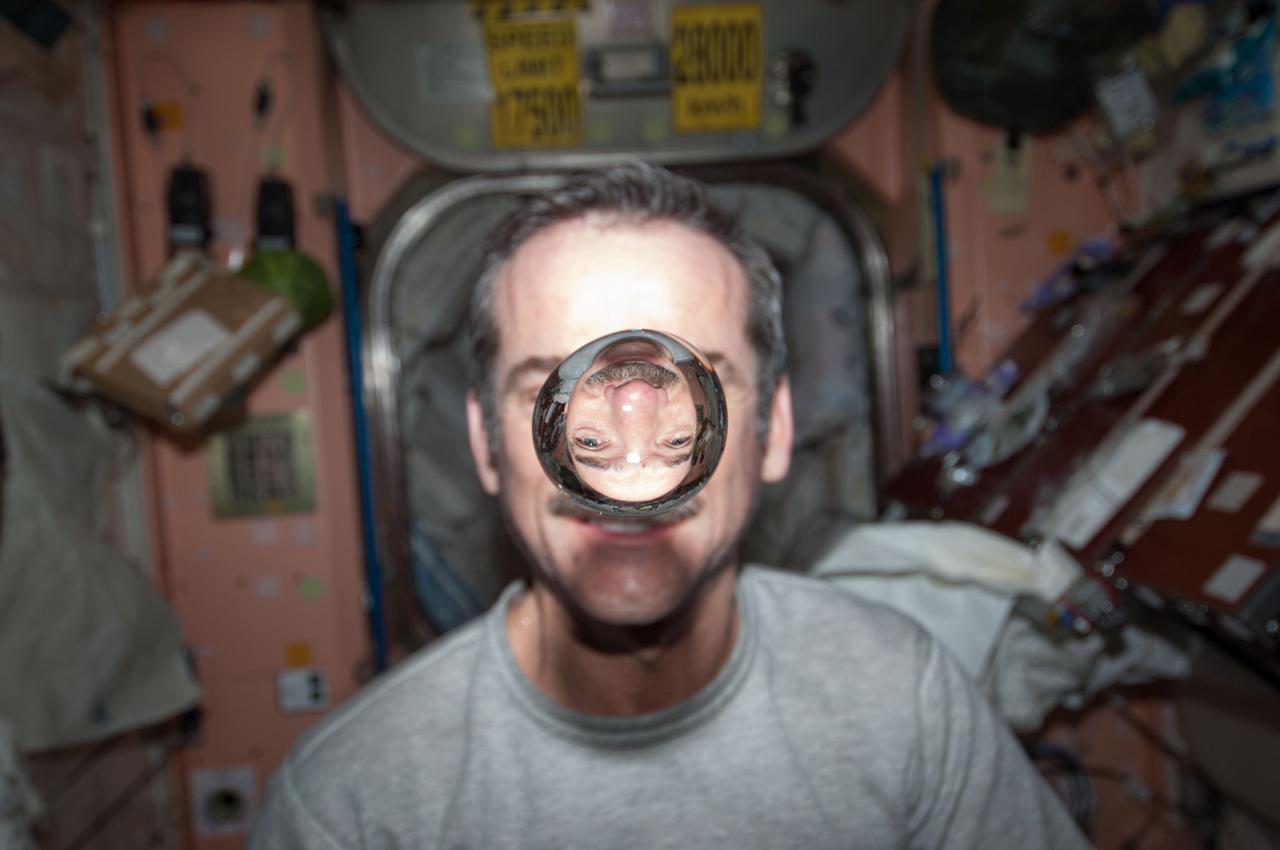
ISS020-E-011074 (16 June 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 20 flight engineer, attempts to catch a water bubble with his mouth in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
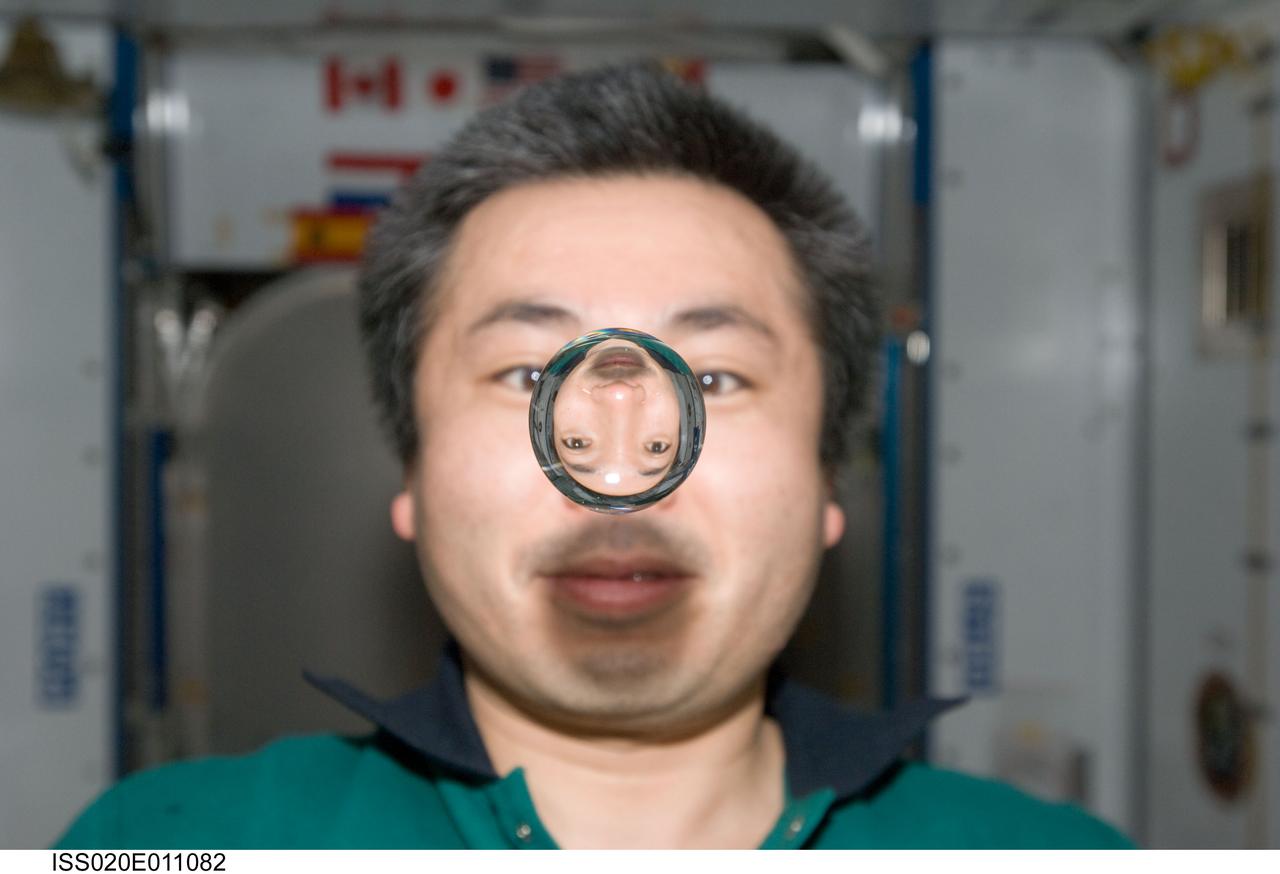
ISS020-E-011082 (16 June 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 20 flight engineer, watches a water bubble float freely between him and the camera, showing his image refracted, in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
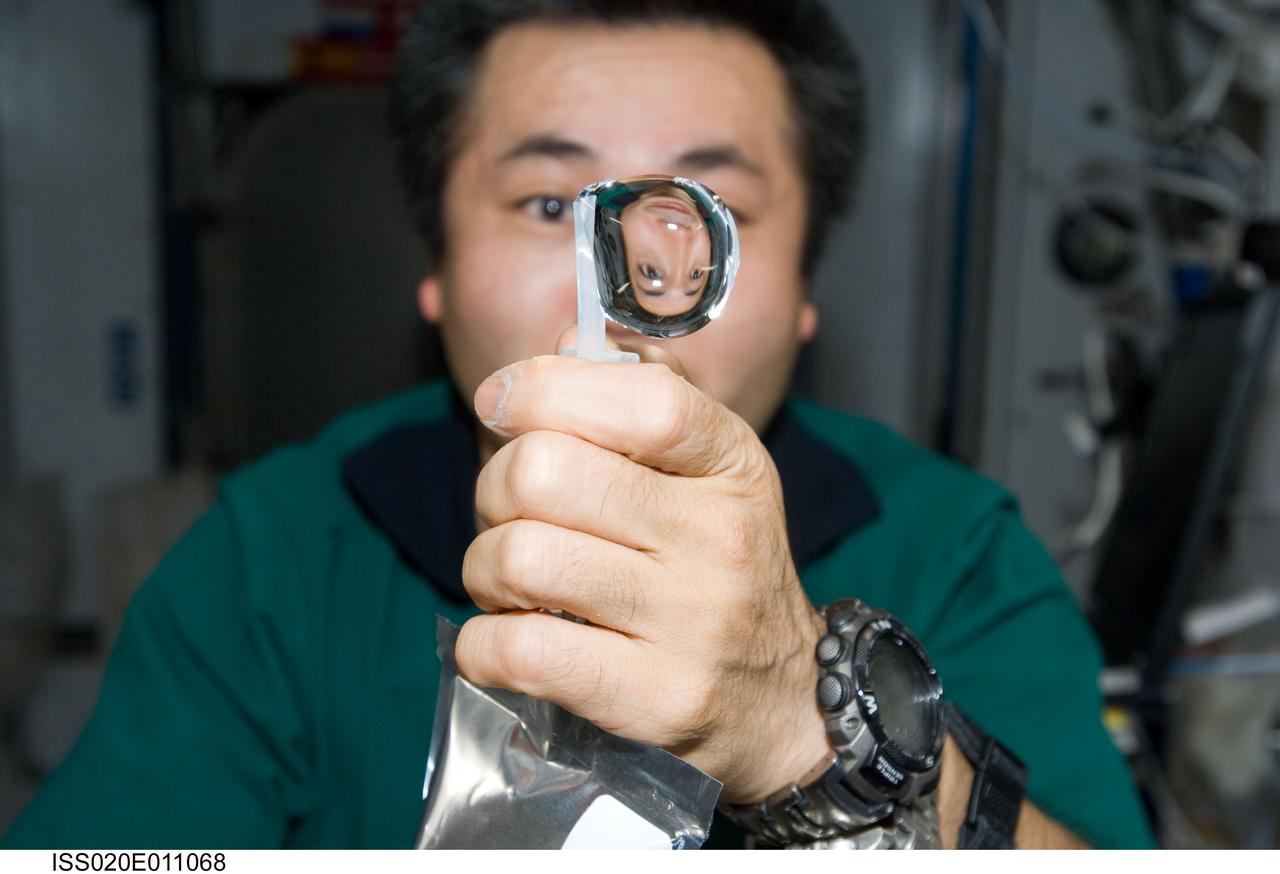
ISS020-E-011068 (16 June 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 20 flight engineer, squeezes a water bubble out of his beverage container, showing his image refracted, in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
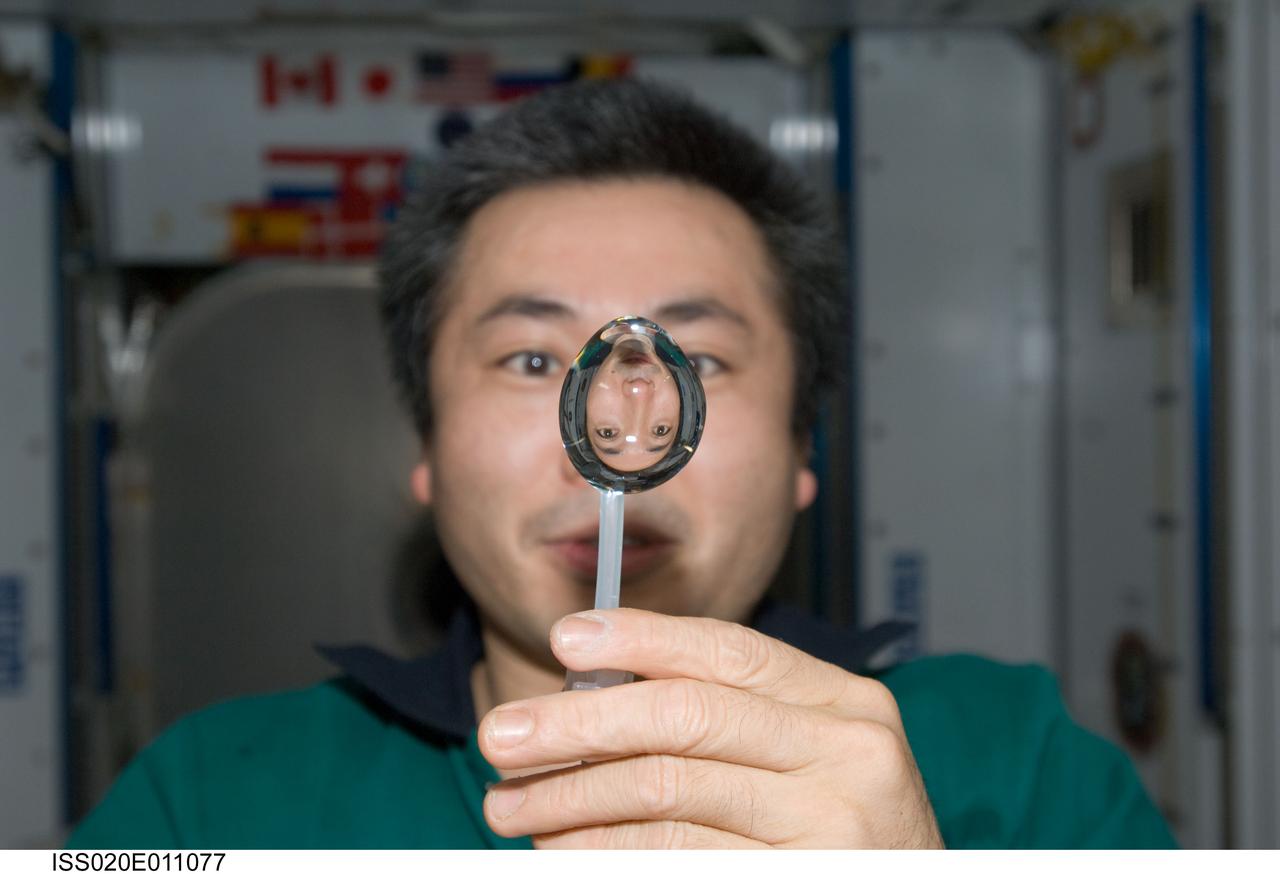

ISS020-E-011077 (16 June 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 20 flight engineer, squeezes a water bubble out of his beverage container, showing his image refracted, in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
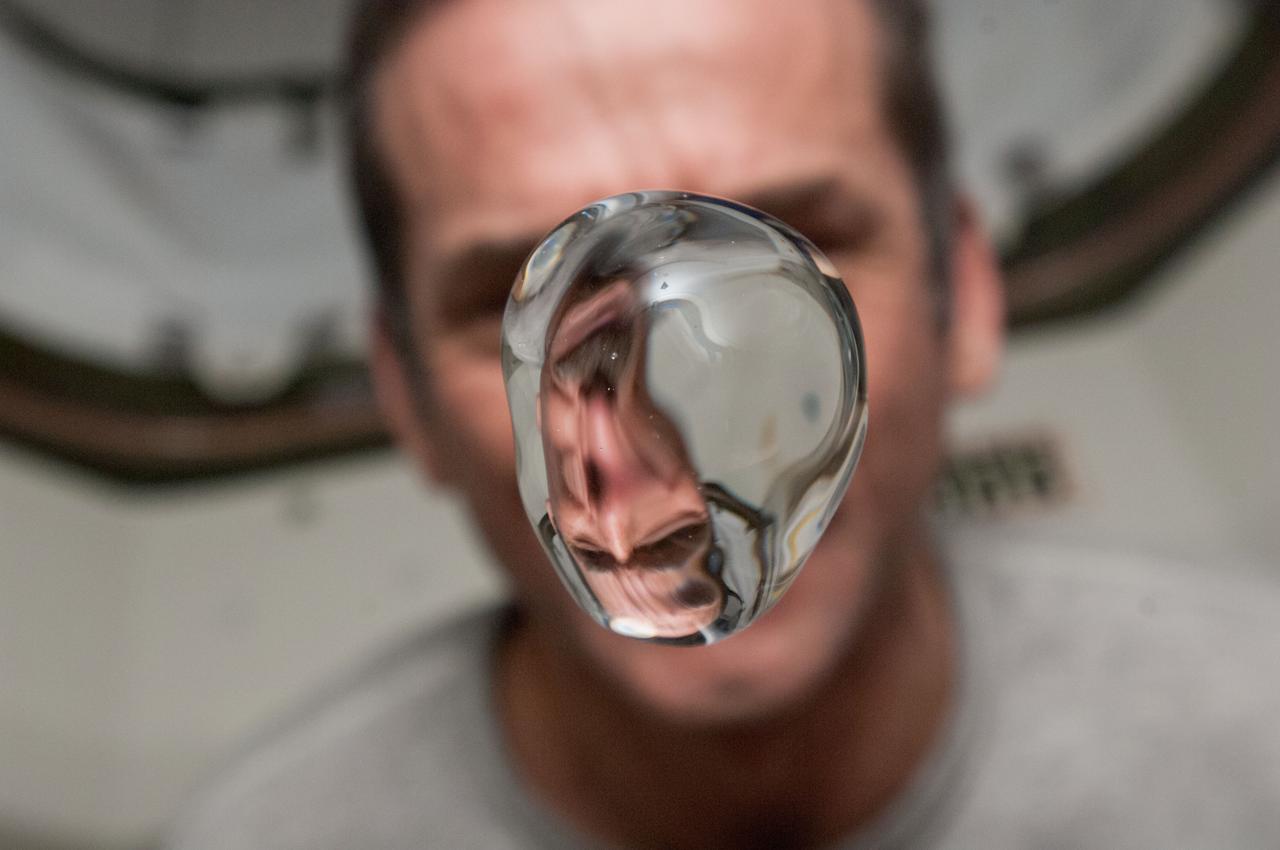

View of Canadian Space Agency (CSA) Chris Hadfield,Expedition 34 Flight Engineer (FE),watching a water bubble float freely,showing his image refracted,in the Node 1. Photo was taken during Expedition 34.
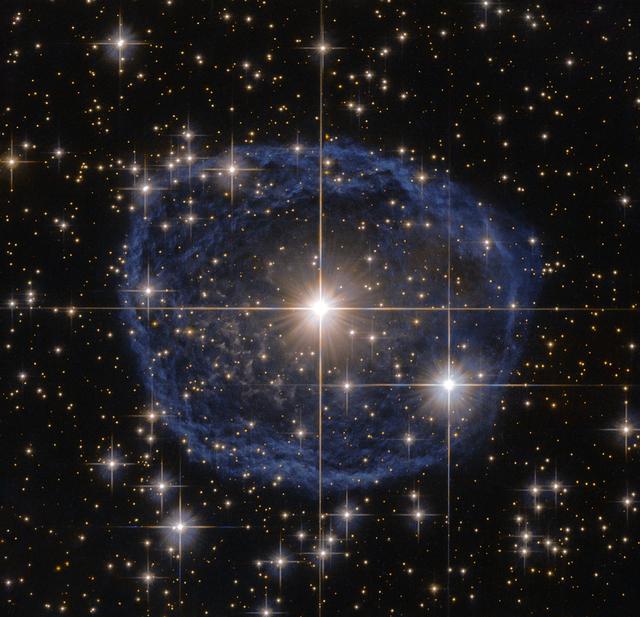

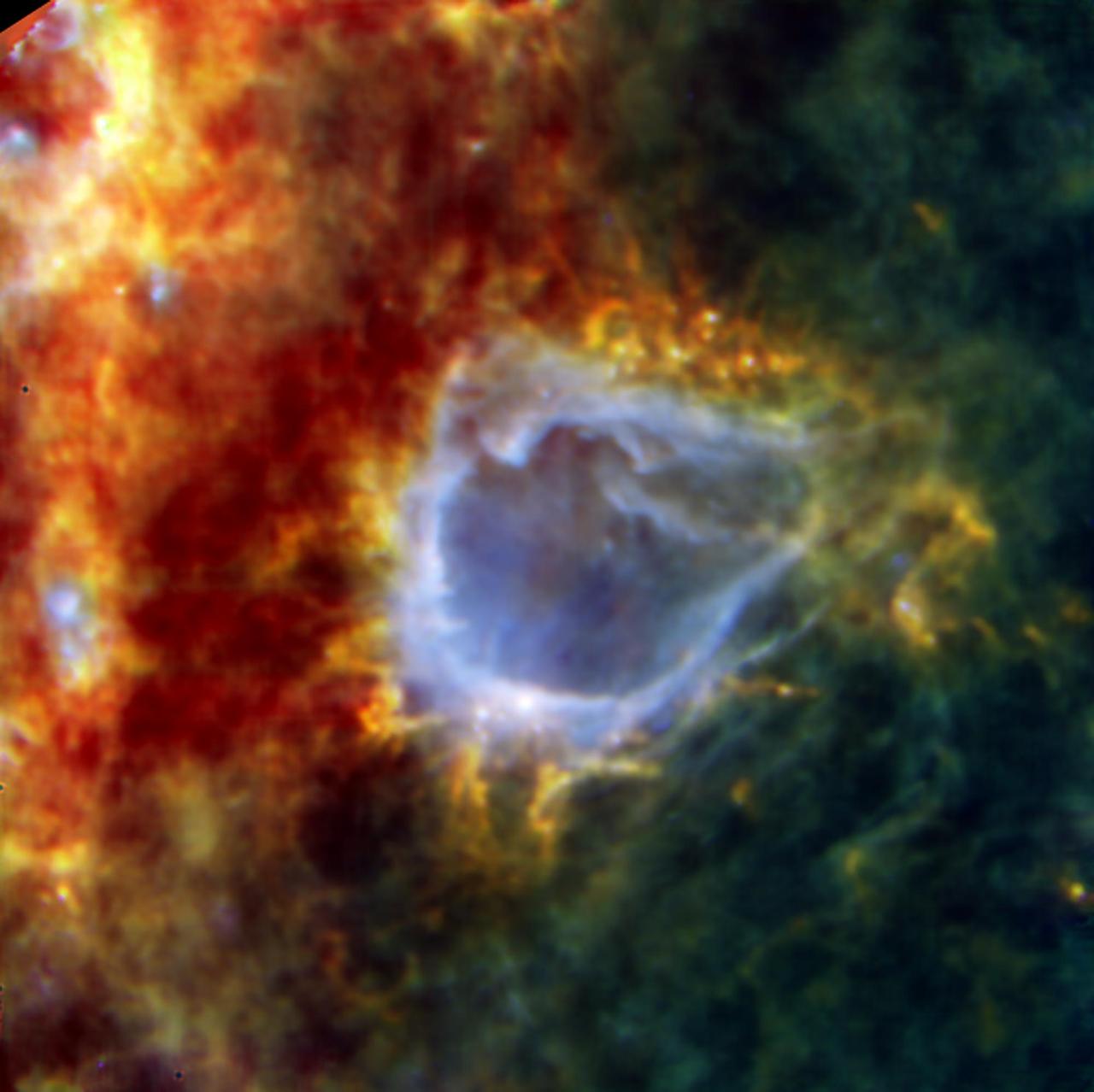
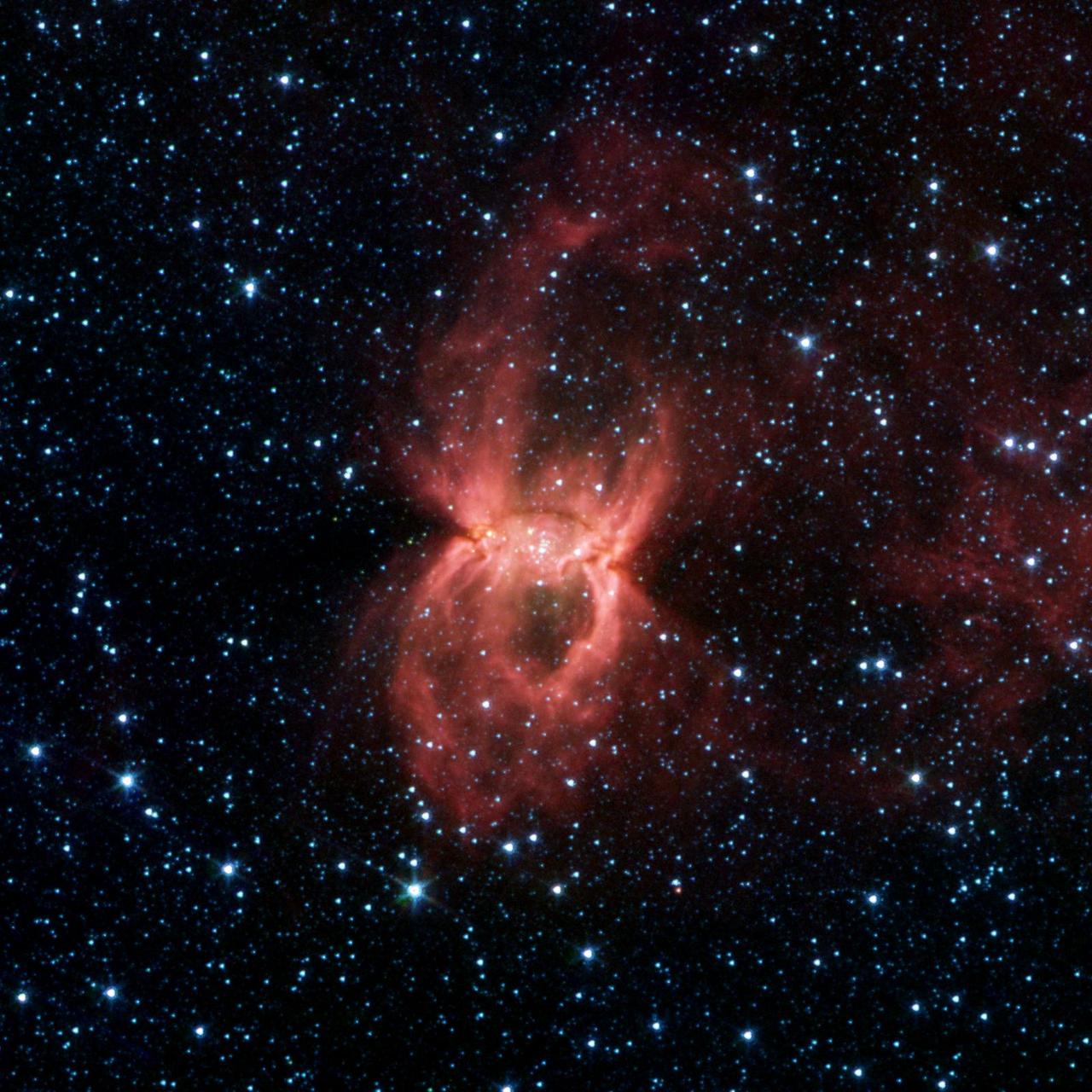
Sparkling at the centre of this beautiful NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image is a Wolf–Rayet star known as WR 31a, located about 30 000 light-years away in the constellation of Carina (The Keel). The distinctive blue bubble appearing to encircle WR 31a, and its uncatalogued stellar sidekick, is a Wolf–Rayet nebula — an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, helium and other gases. Created when speedy stellar winds interact with the outer layers of hydrogen ejected by Wolf–Rayet stars, these nebulae are frequently ring-shaped or spherical. The bubble — estimated to have formed around 20 000 years ago — is expanding at a rate of around 220 000 kilometres per hour! Unfortunately, the lifecycle of a Wolf–Rayet star is only a few hundred thousand years — the blink of an eye in cosmic terms. Despite beginning life with a mass at least 20 times that of the Sun, Wolf–Rayet stars typically lose half their mass in less than 100 000 years. And WR 31a is no exception to this case. It will, therefore, eventually end its life as a spectacular supernova, and the stellar material expelled from its explosion will later nourish a new generation of stars and planets.
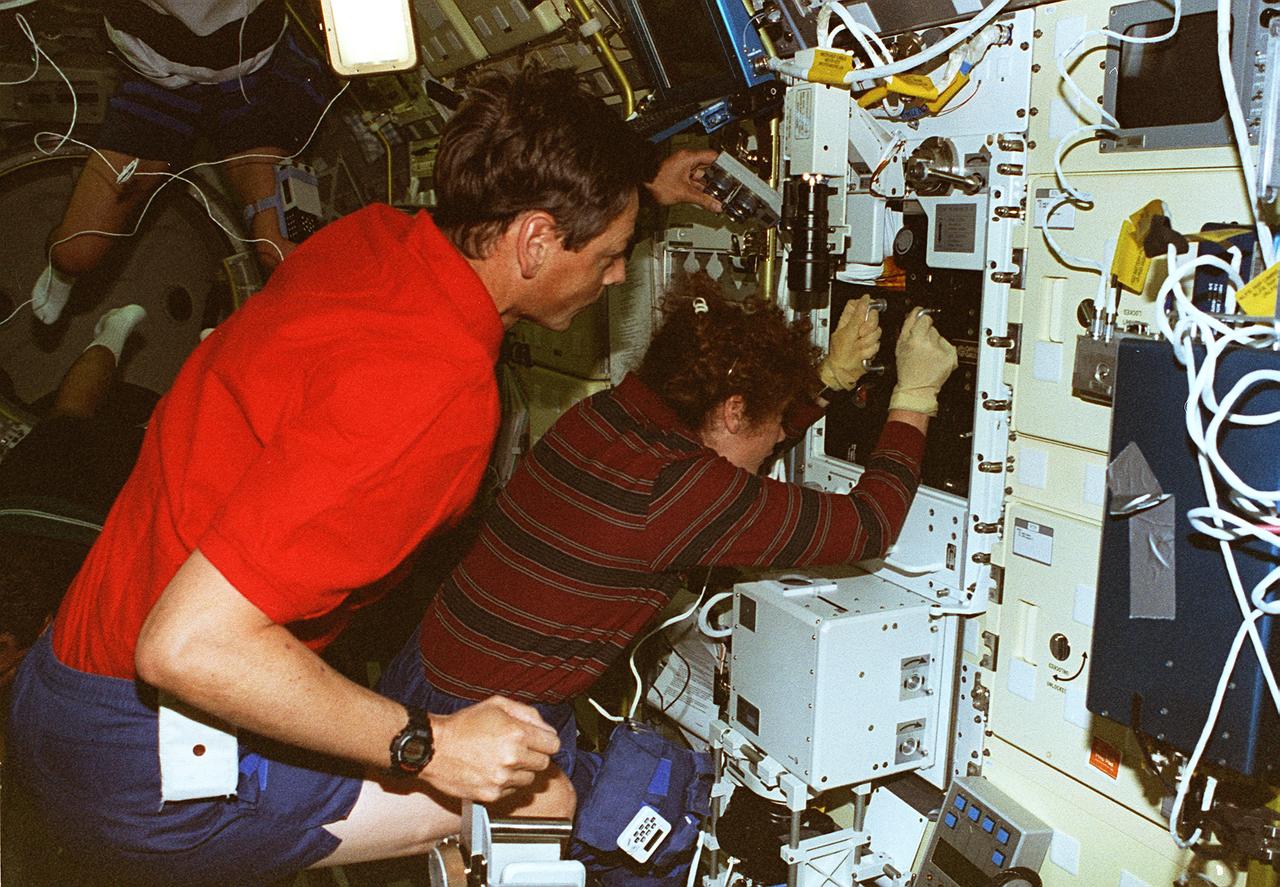

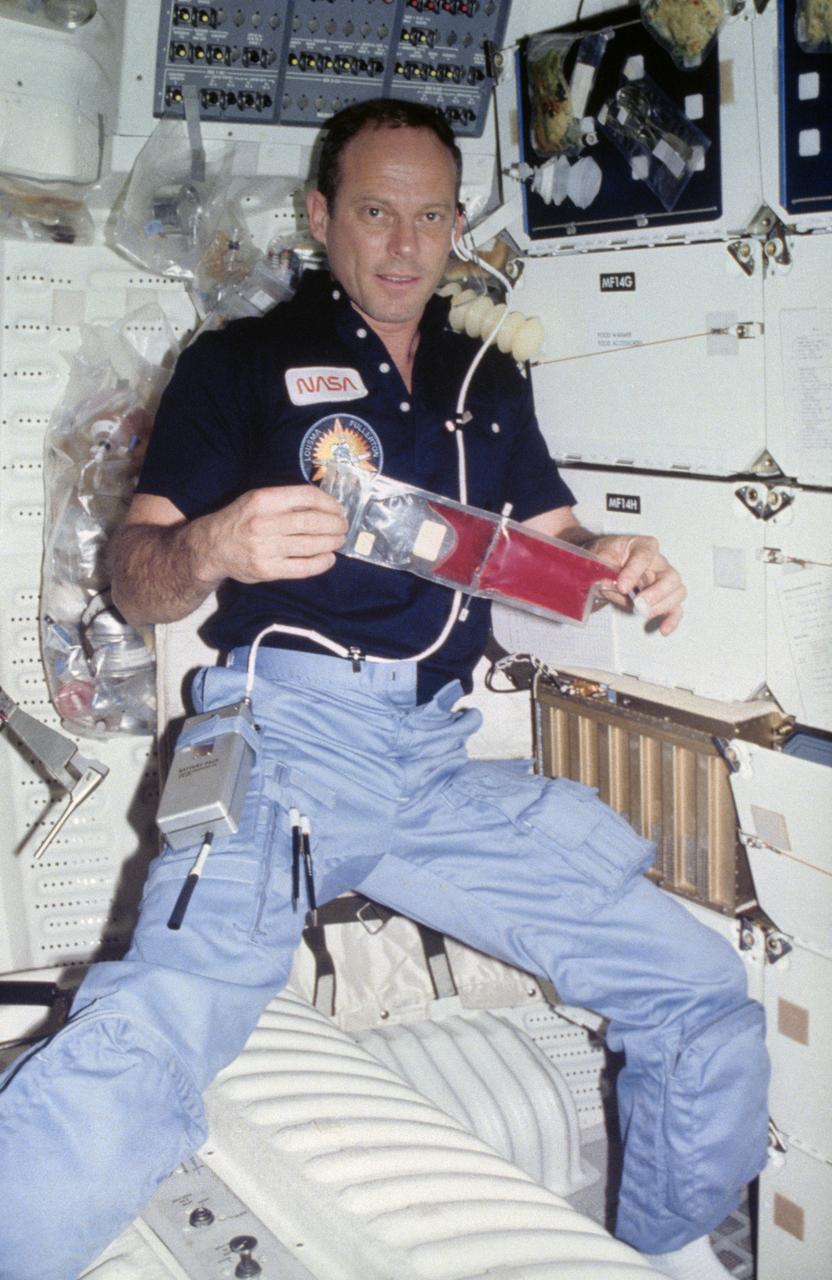
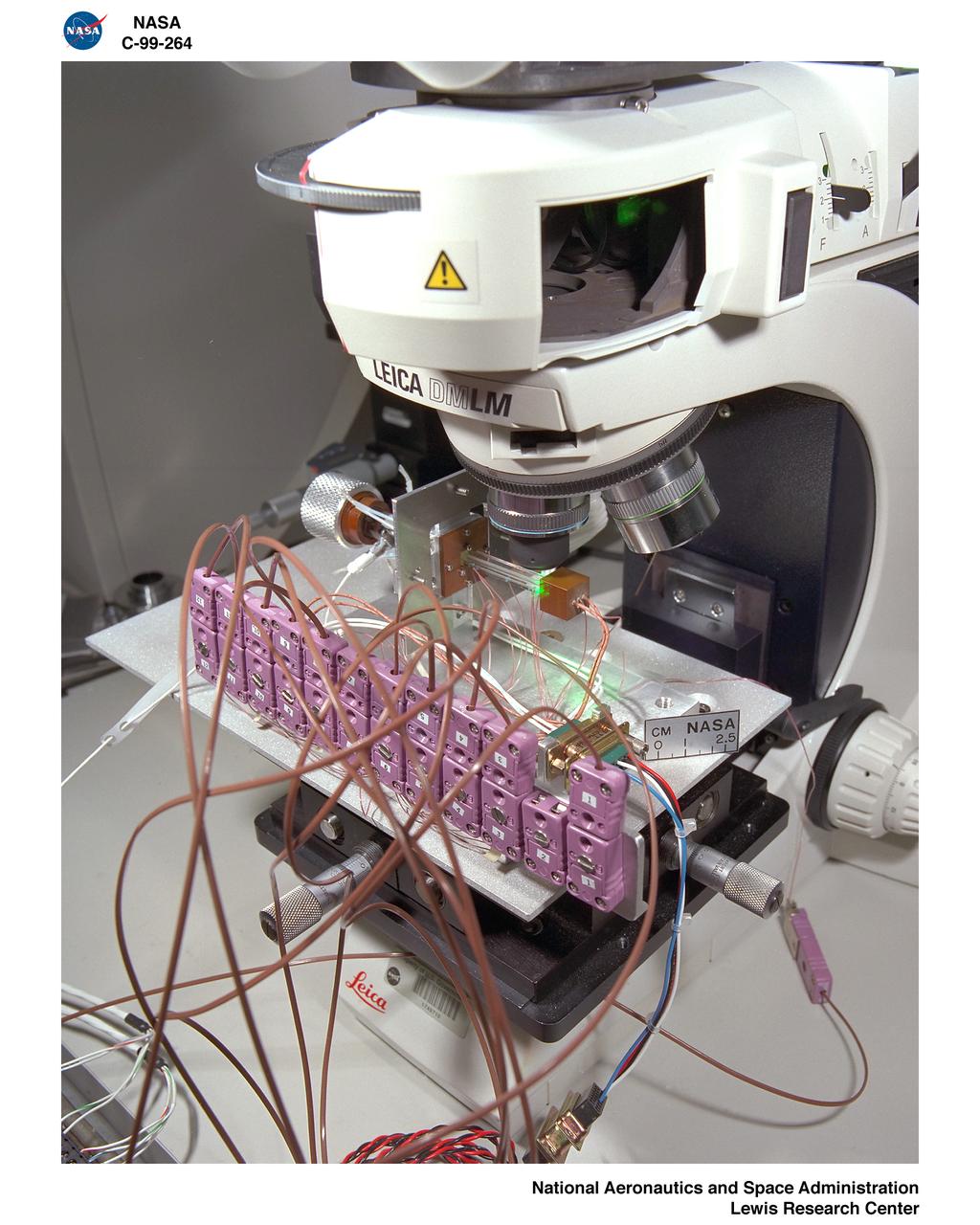
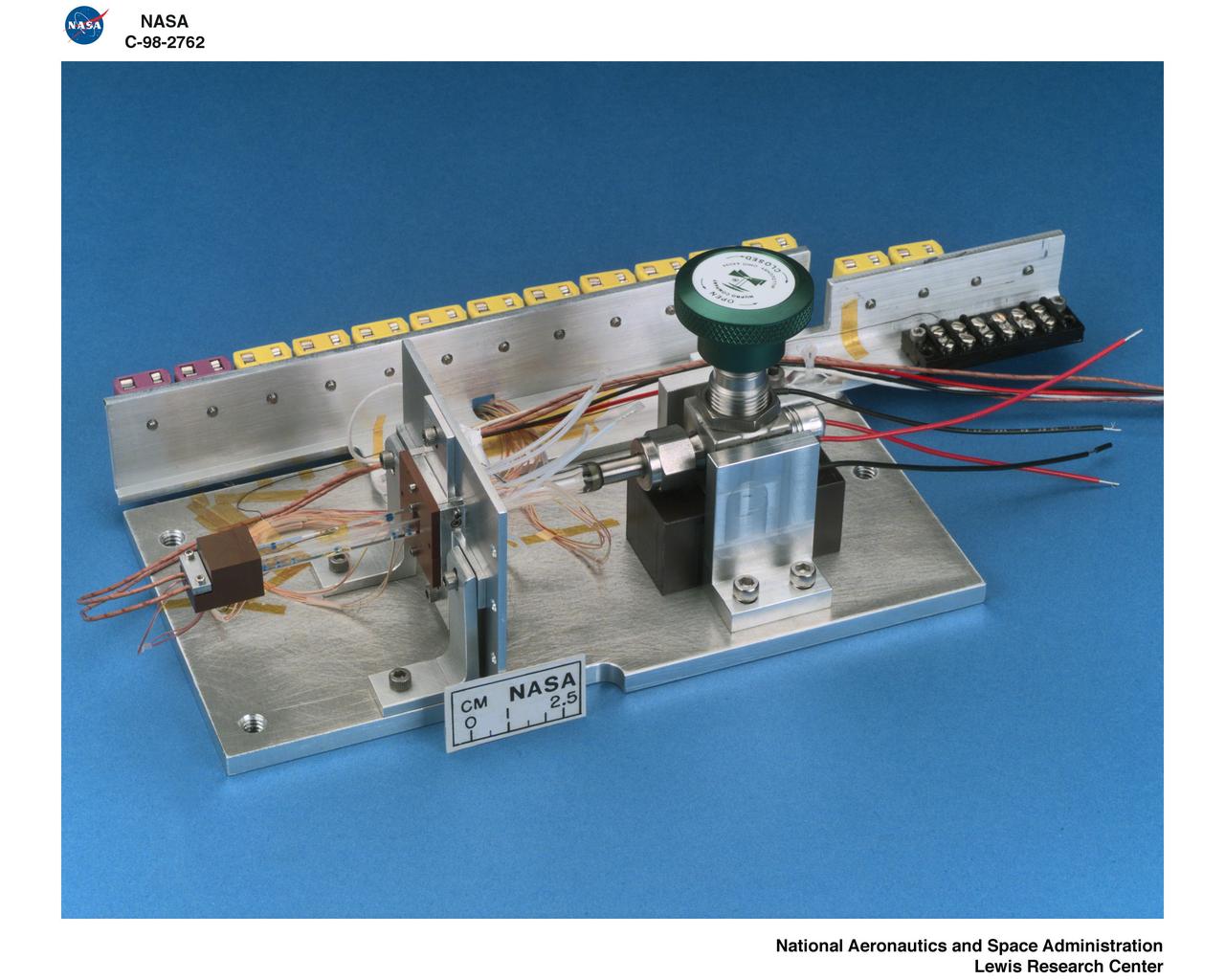
STS078-306-035 (20 June - 7 July 1996) --- Astronaut Susan J. Helms, payload commander, and payload specialist Jean-Jacques Favier, representing the French Space Agency (CNES), insert a test container into the Bubble Drop Particle Unit (BDPU) in the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS-1) Science Module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. The fluid in the chamber is heated and the fluid processes are observed by use of three internal cameras mounted inside the BDPU. Investigations in this facility will help characterize interfacial processes involving either bubbles, drops, liquid columns or liquid layers.
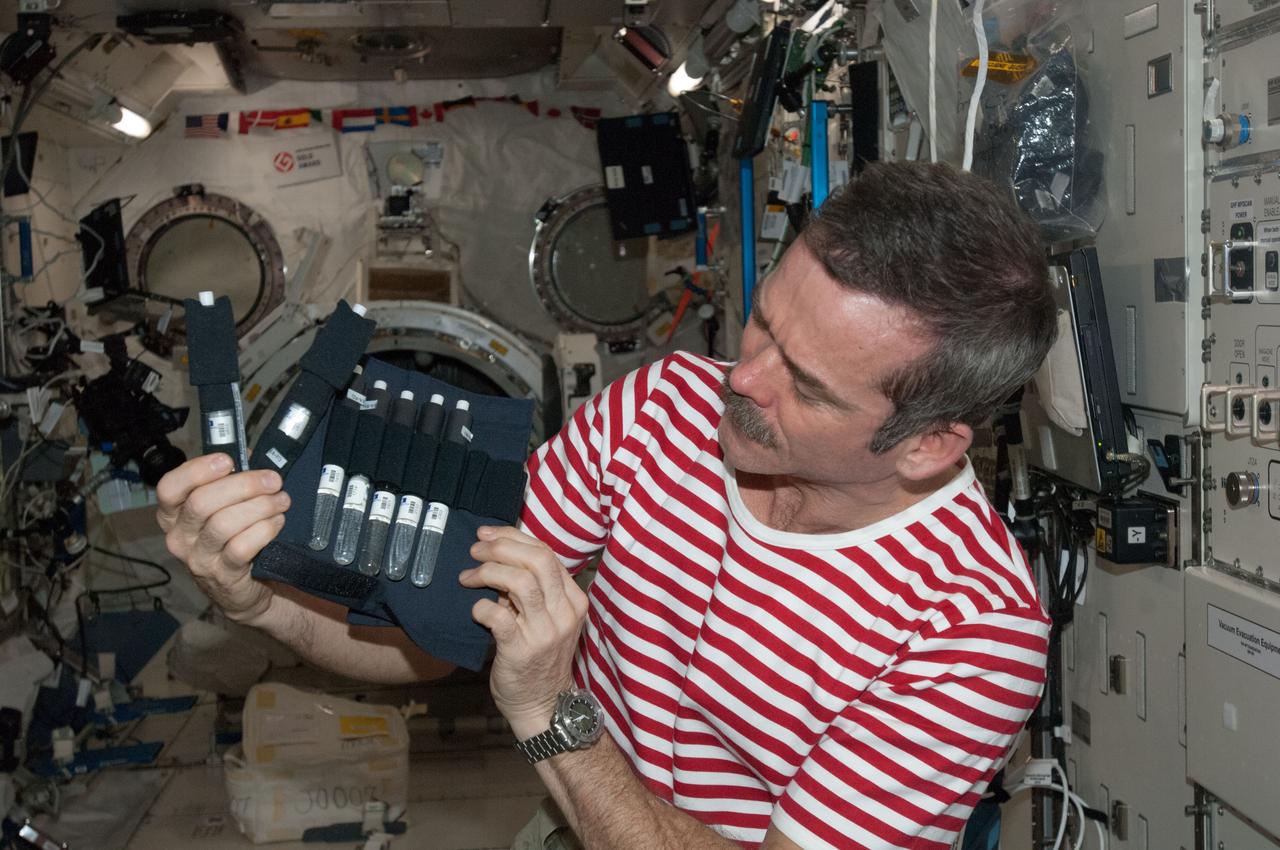

ISS034-E-034506 (25 Jan. 2013) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut Chris Hadfield, Expedition 34 flight engineer, holds bubble detectors for the RaDI-N experiment in the International Space Station?s Kibo laboratory. RaDI-N measures neutron radiation levels onboard the space station. RaDI-N uses bubble detectors as neutron monitors which have been designed to only detect neutrons and ignore all other radiation.
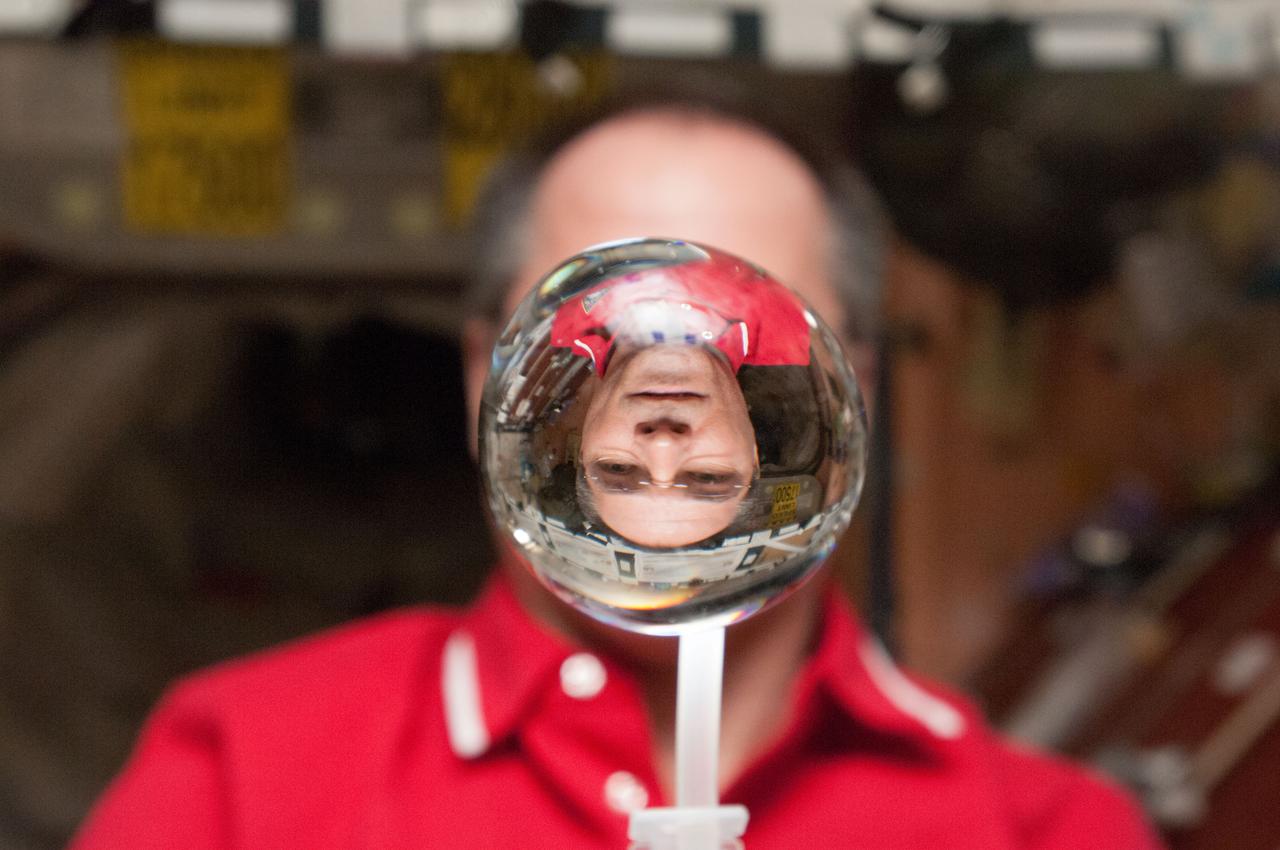

ISS034-E-031855 (21 Jan. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Kevin Ford, Expedition 34 commander, watches a water bubble float freely between him and the camera, showing his image refracted, in the Unity node of the International Space Station.
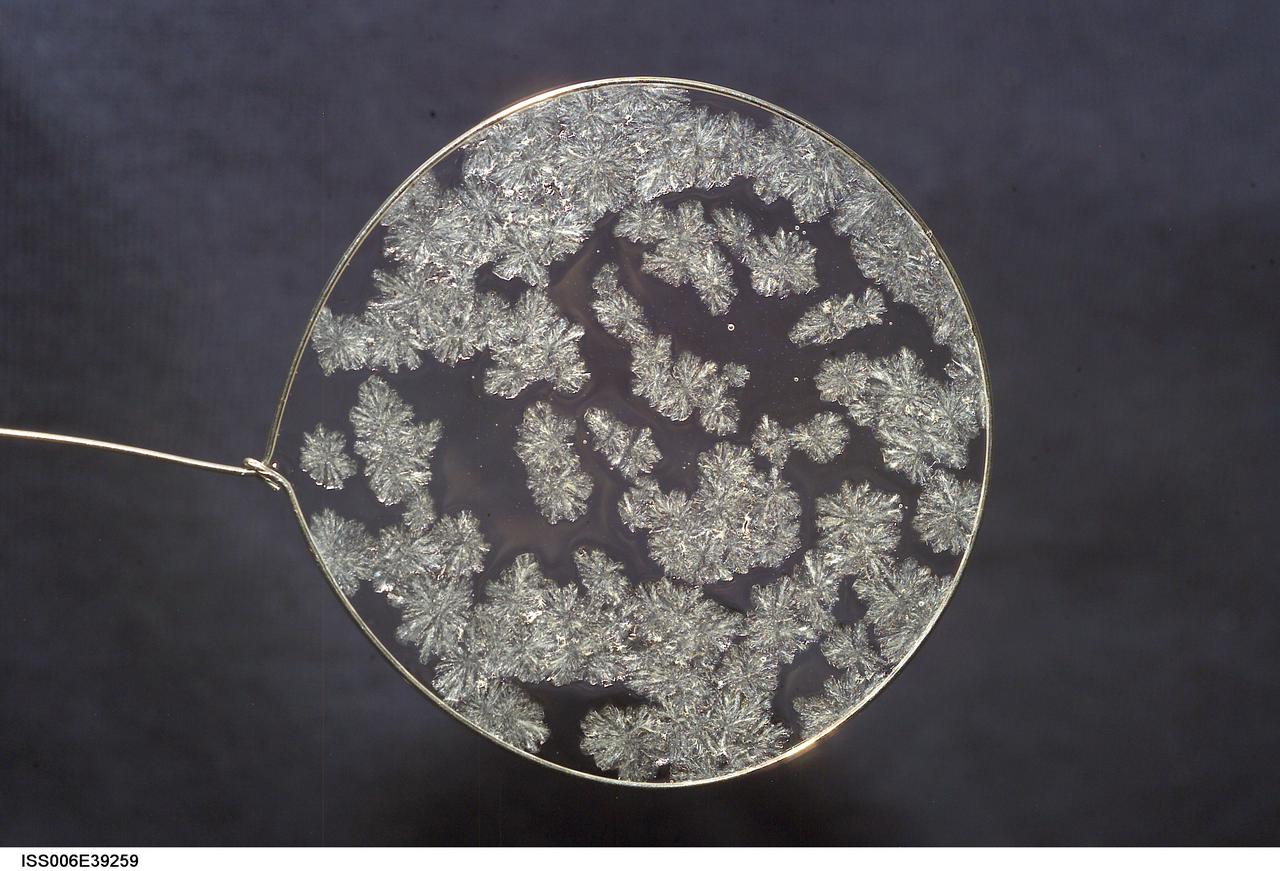

ISS006-E-39259 (14 March 2003) --- A view of sugar crystals in a water bubble within a 50-millimeter (mm) metal loop was photographed by an Expedition Six crewmember. The experiment took place in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
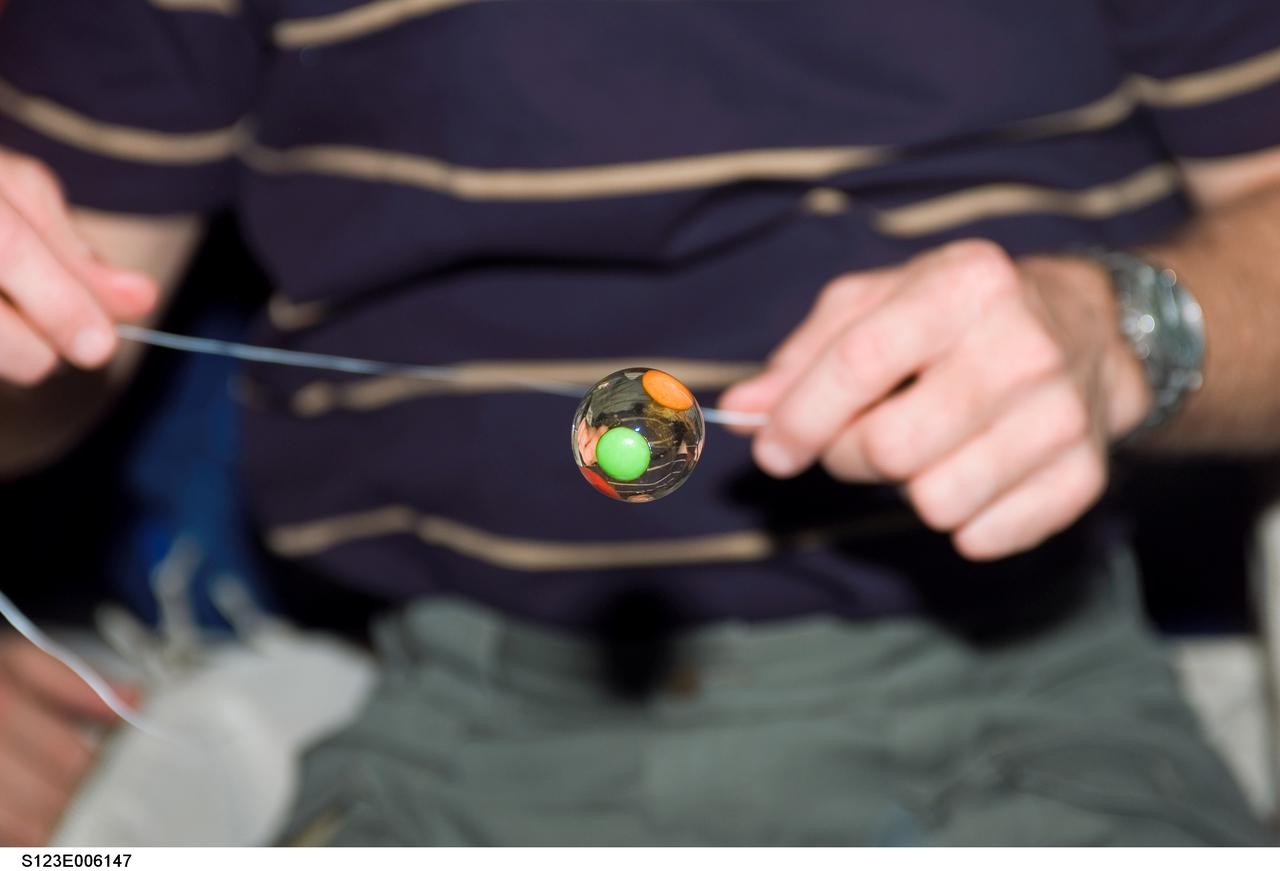

S123-E-006147 (14 March 2008) --- A water bubble with candy trapped inside floats freely on the middeck of Space Shuttle Endeavour while docked with the International Space Station. Astronaut Dominic Gorie (partially out of frame), STS-123 commander, holds a string near the bubble.
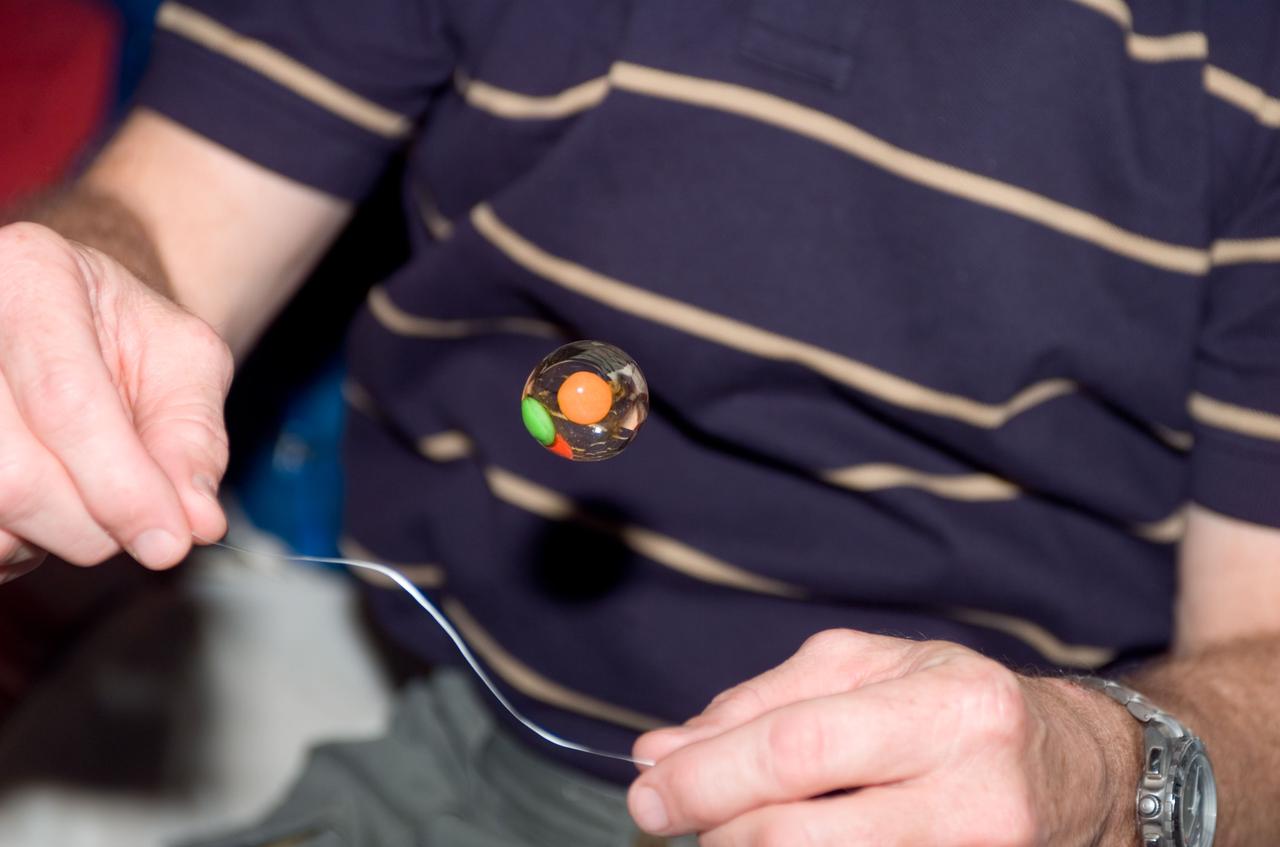

S123-E-006145 (14 March 2008) --- A water bubble with candy trapped inside floats freely on the middeck of Space Shuttle Endeavour while docked with the International Space Station. Astronaut Dominic Gorie (partially out of frame), STS-123 commander, holds a string near the bubble.
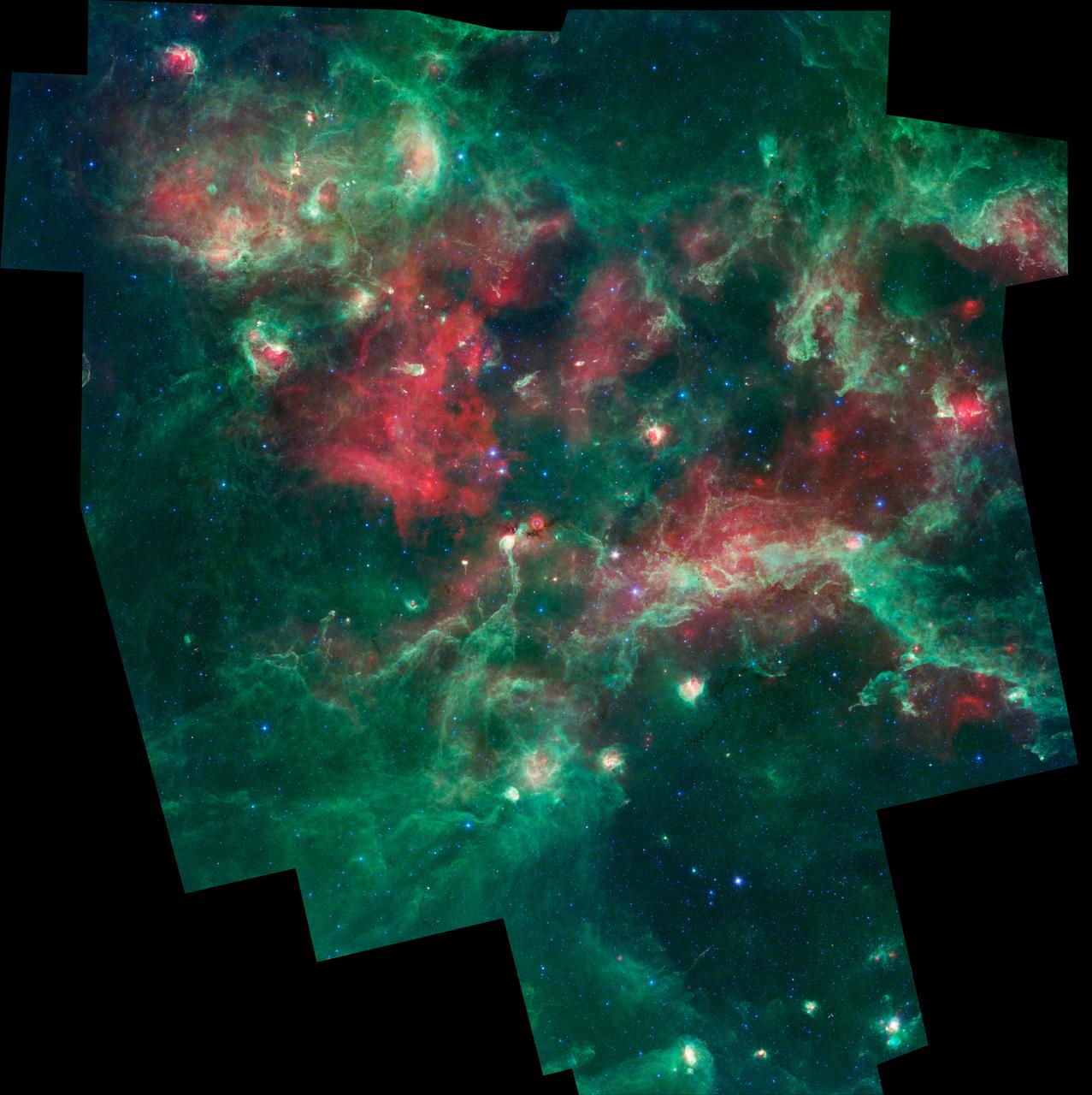

A bubbling cauldron of star birth is highlighted in this image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. Massive stars have blown bubbles, or cavities, in the dust and gas -- a violent process that triggers both the death and birth of stars.

STS078-301-021 (20 June - 7 July 1996) --- Payload specialist Jean-Jacques Favier, representing the French Space Agency (CNES), holds up a test container to a Spacelab camera. The test involves the Bubble Drop Particle Unit (BDPU), which Favier is showing to ground controllers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in order to check the condition of the unit prior to heating in the BDPU facility. The test container holds experimental fluid and allows experiment observation through optical windows. BDPU contains three internal cameras that are used to continuously downlink BDPU activity so that behavior of the bubbles can be monitored. Astronaut Richard M. Linnehan, mission specialist, conducts biomedical testing in the background.
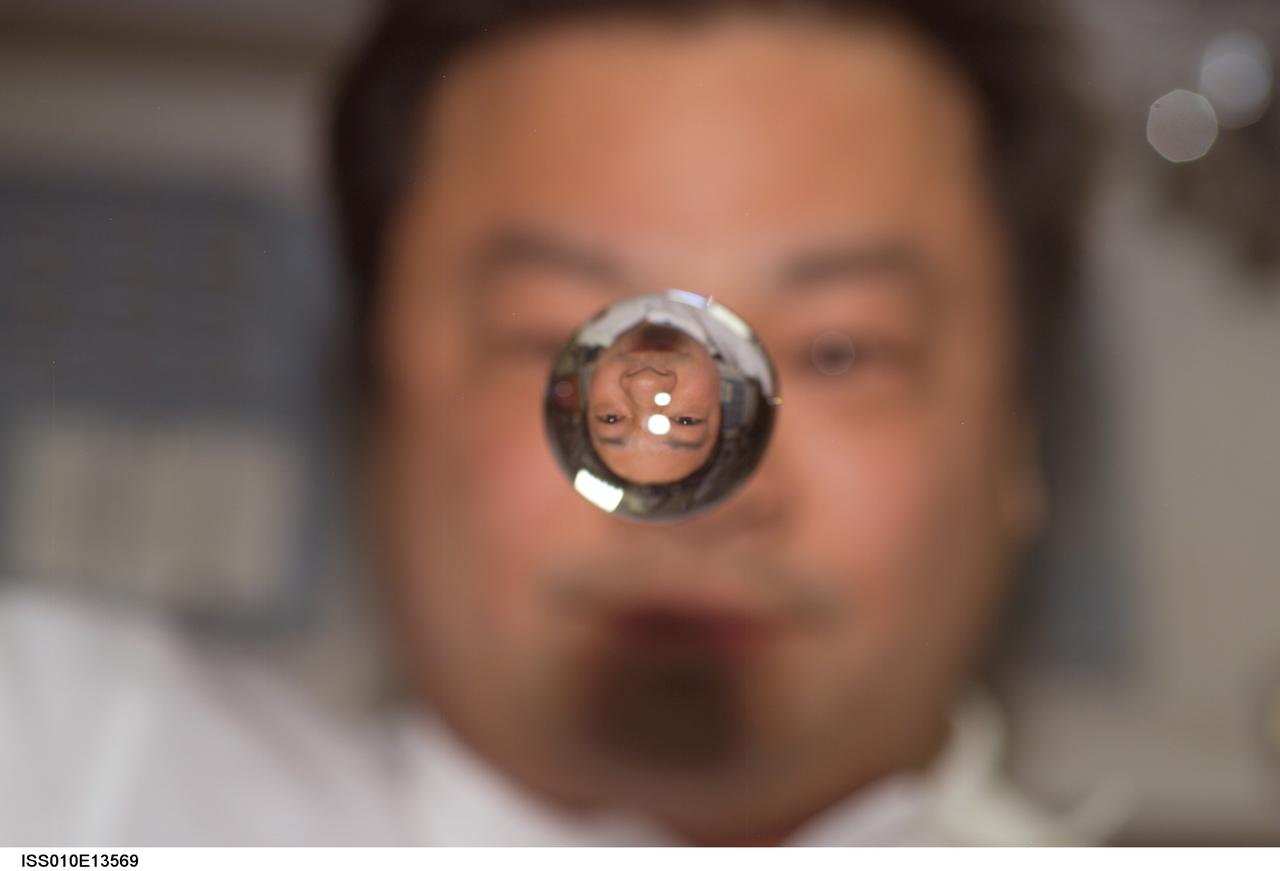
ISS010-E-13569 (15 January 2005) --- Astronaut Leroy Chiao, Expedition 10 commander and NASA ISS science officer, watches a water bubble float between him and the camera, showing his image refracted, on the International Space Station (ISS).
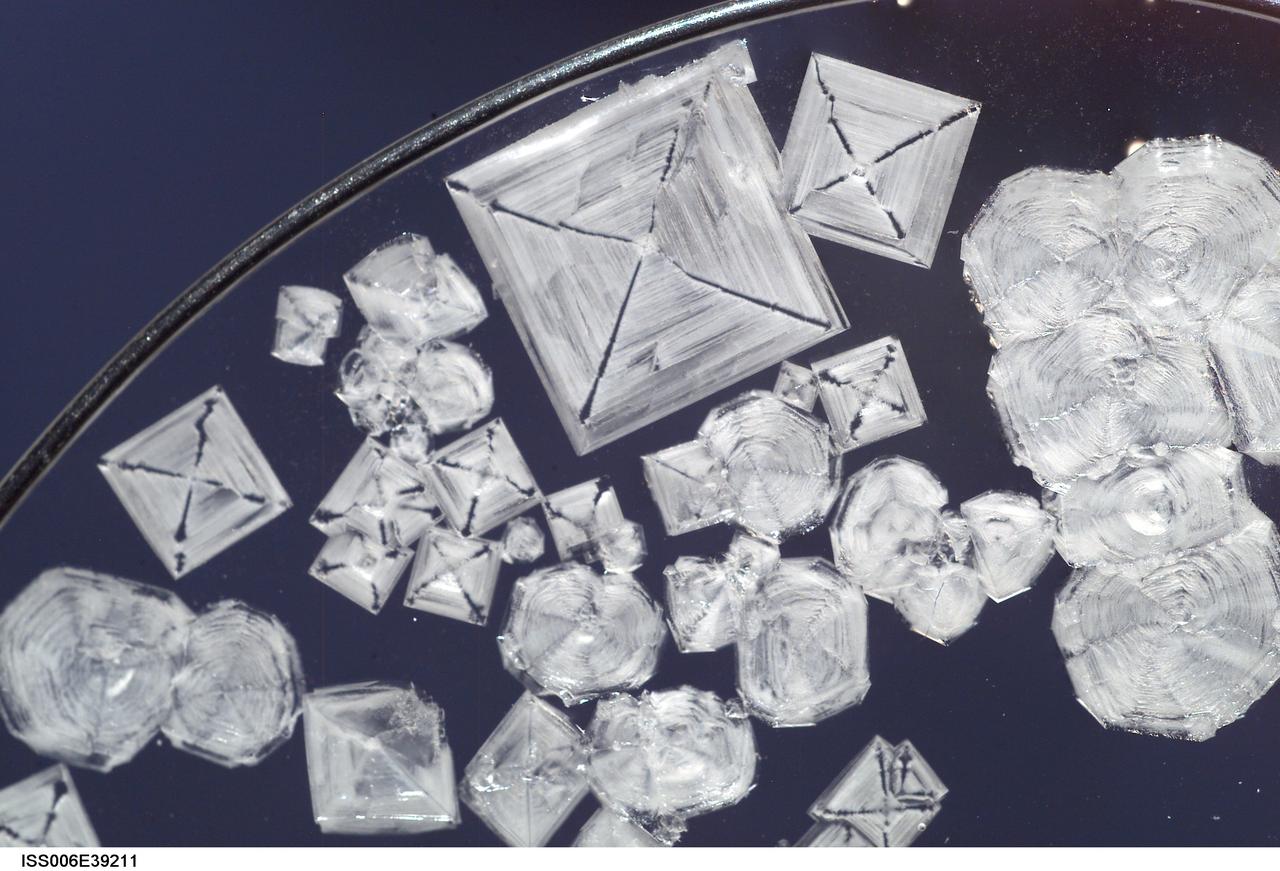

ISS006-E-39211 (13 March 2003) --- A close up view of sodium chloride crystals in a water bubble within a 50-millimeter metal loop was photographed by an Expedition Six crewmember. The experiment took place in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).

ISS013-E-38348 (18 June 2006) --- Astronaut Jeffrey N. Williams, Expedition 13 NASA space station science officer and flight engineer, watches a water bubble float freely while holding a container of water in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
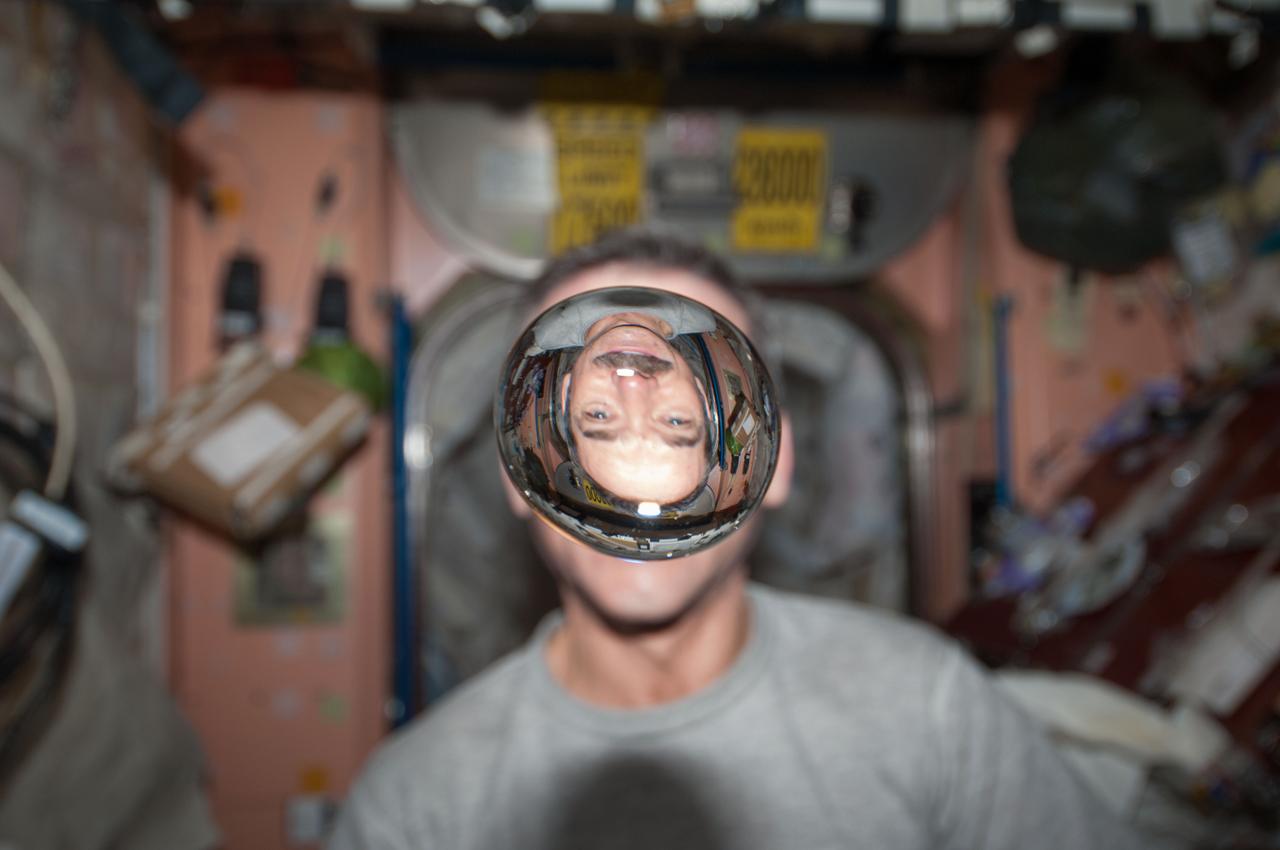

ISS034-E-031695 (21 Jan. 2013) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut Chris Hadfield, Expedition 34 flight engineer, watches a water bubble float freely between him and the camera, showing his image refracted, in the Unity node of the International Space Station.
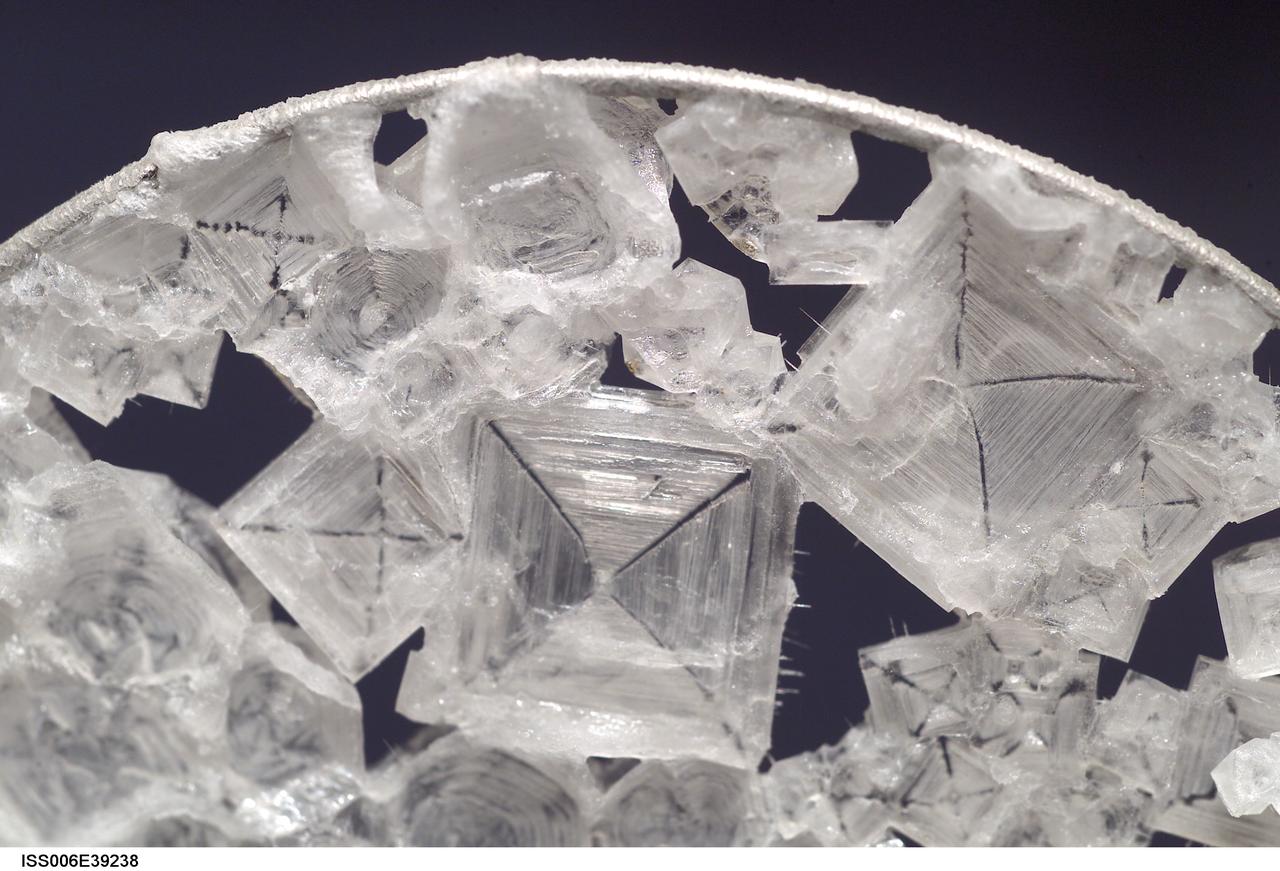

ISS006-E-39238 (14 March 2003) --- A close up view of sodium chloride crystals in a water bubble within a 50-millimeter metal loop was photographed by an Expedition Six crewmember. The experiment took place in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
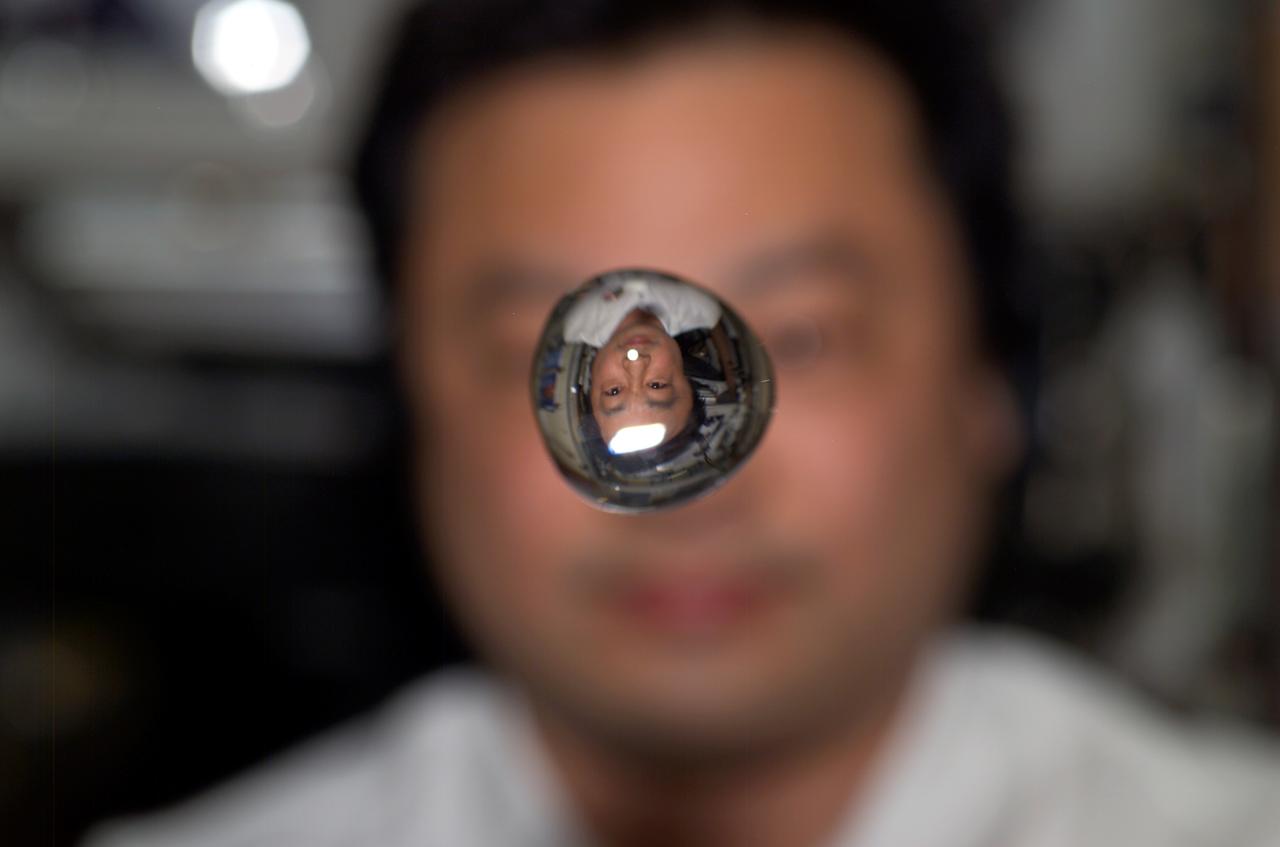

ISS010-E-13562 (15 January 2005) --- Astronaut Leroy Chiao, Expedition 10 commander and NASA Space Station science officer, watches a water bubble float between himself and the camera in the Zvezda Service Module, showing his image refracted.
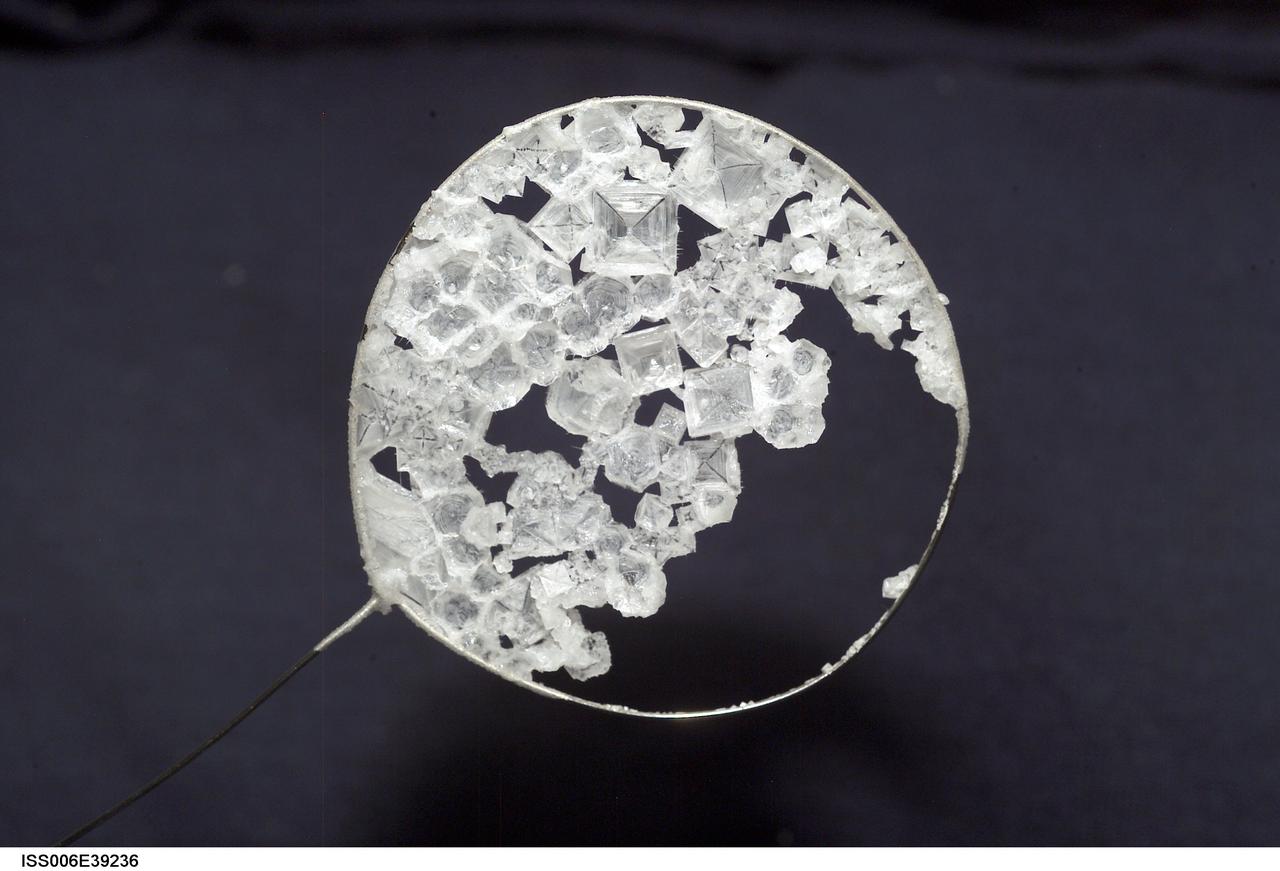

ISS006-E-39236 (14 March 2003) --- A view of sodium chloride crystals in a water bubble within a 50-millimeter metal loop was photographed by an Expedition Six crewmember. The experiment took place in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).

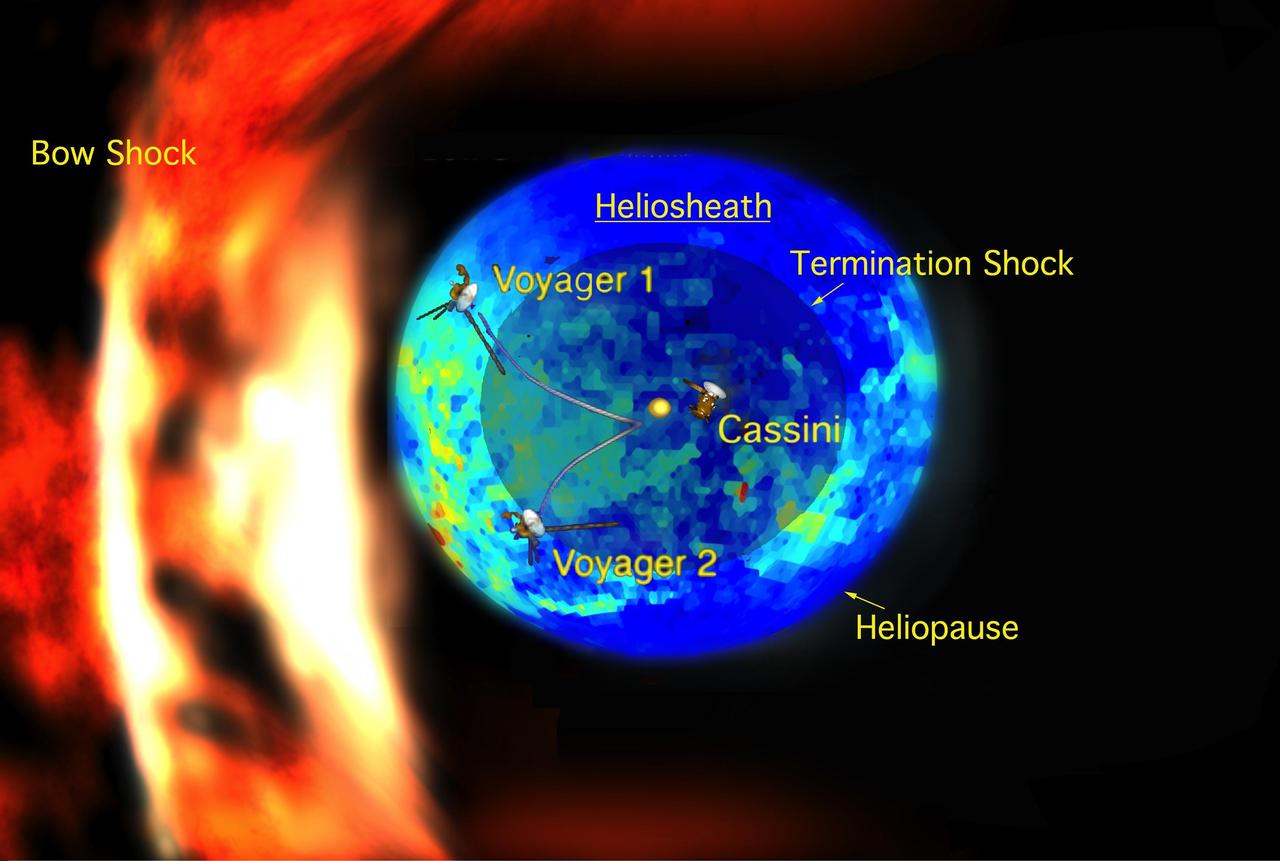
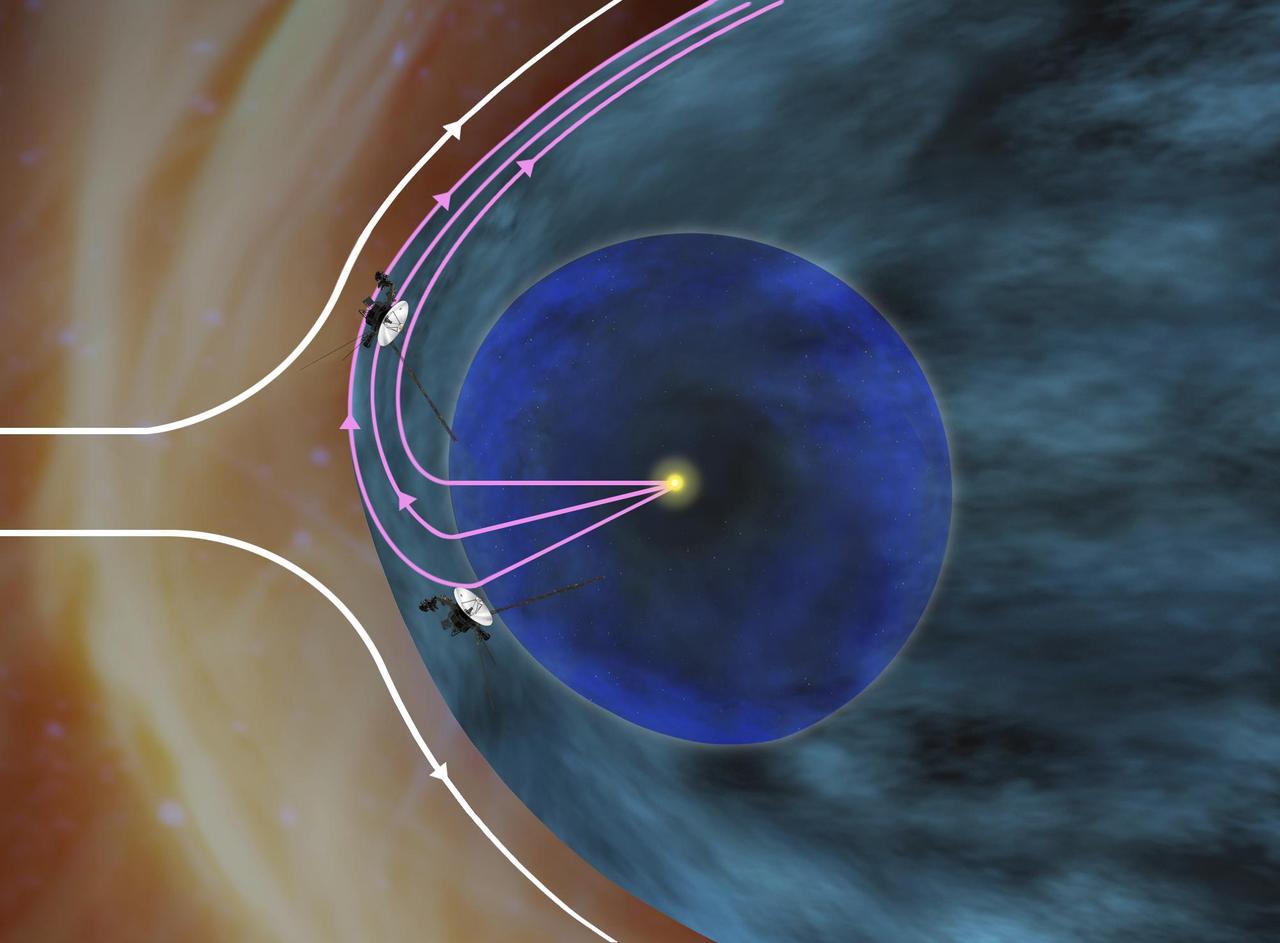
This artist concept shows the general locations of NASA two Voyager spacecraft. Voyager 1 top has sailed beyond our solar bubble into interstellar space. Voyager 2 bottom is still exploring the outer layer of the solar bubble.

NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows two opposing bubbles being formed in opposite directions by the powerful outflows from massive groups of forming stars. The baby stars can be seen as specks of yellow where the two bubbles overlap.

A lumpy bubble of hot gas rises from a cauldron of glowing matter in a distant galaxy, as seen by NASA Hubble Space Telescope.
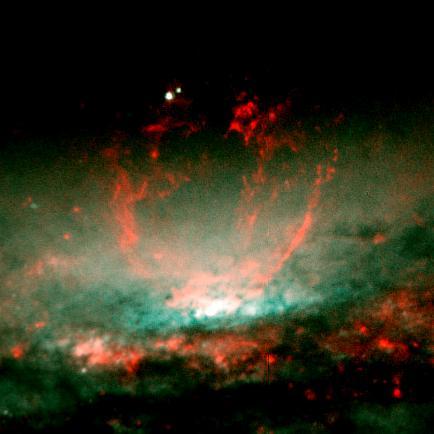
A lumpy bubble of hot gas rises from a cauldron of glowing matter in a distant galaxy, as seen by NASA Hubble Space Telescope.
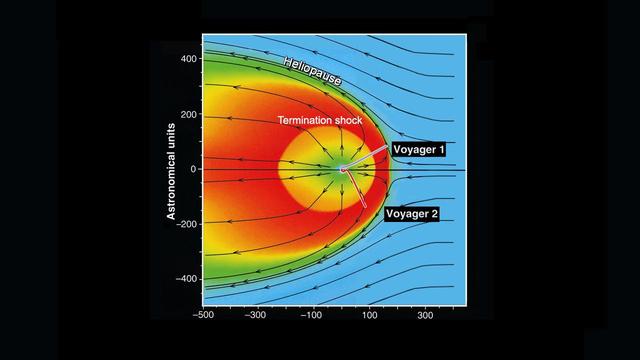
This schematic shows our solar bubble moving through nearby interstellar space, or the space between stars.
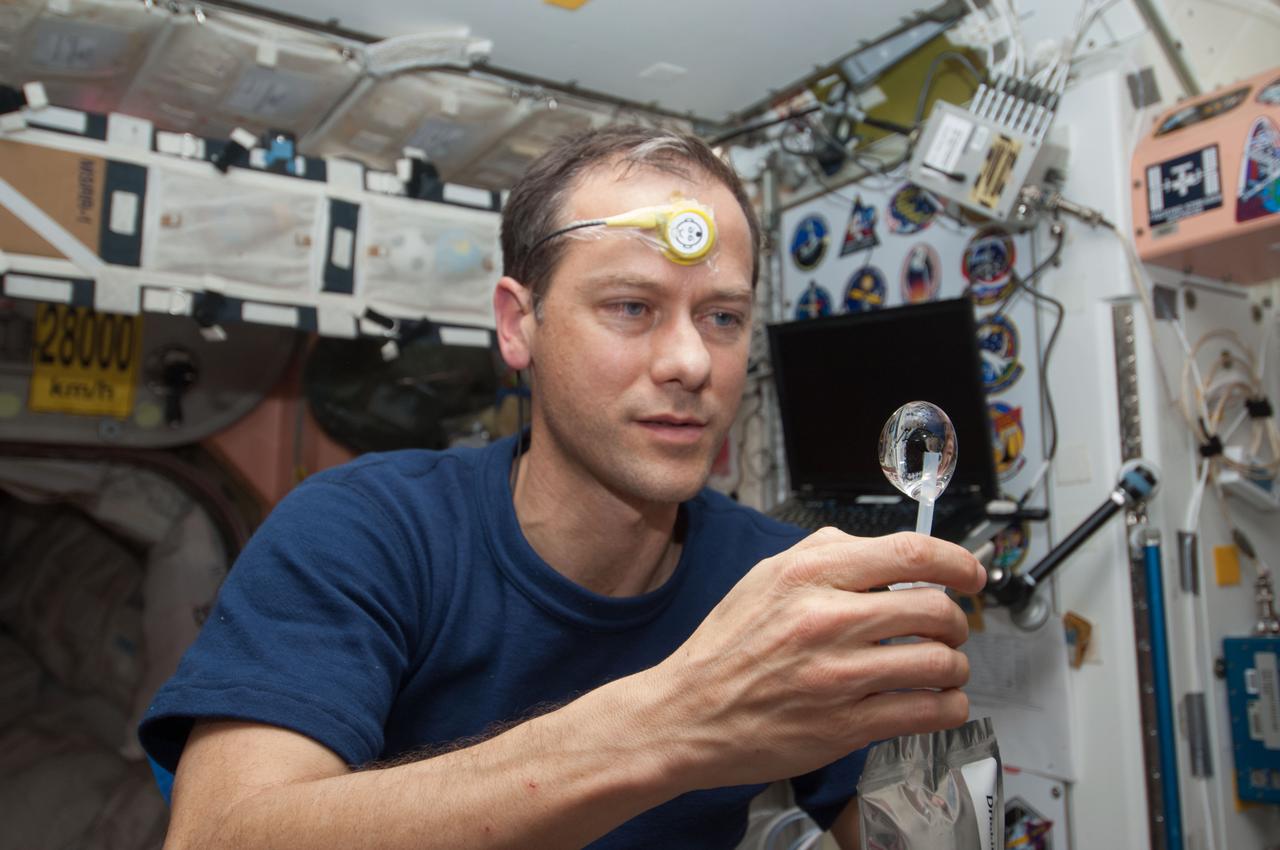

ISS034-E-031709 (21 Jan. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Tom Marshburn, Expedition 34 flight engineer, squeezes a water bubble out of his beverage container in the Unity node of the International Space Station. He is wearing a Drager Double Sensor on his forehead which is used on the Circadian Rhythms Experiment. This experiment examines the hypothesis that long-term spaceflights significantly affect the synchronization of the circadian rhythms in humans due to changes of a non-24 hour light-dark cycle.
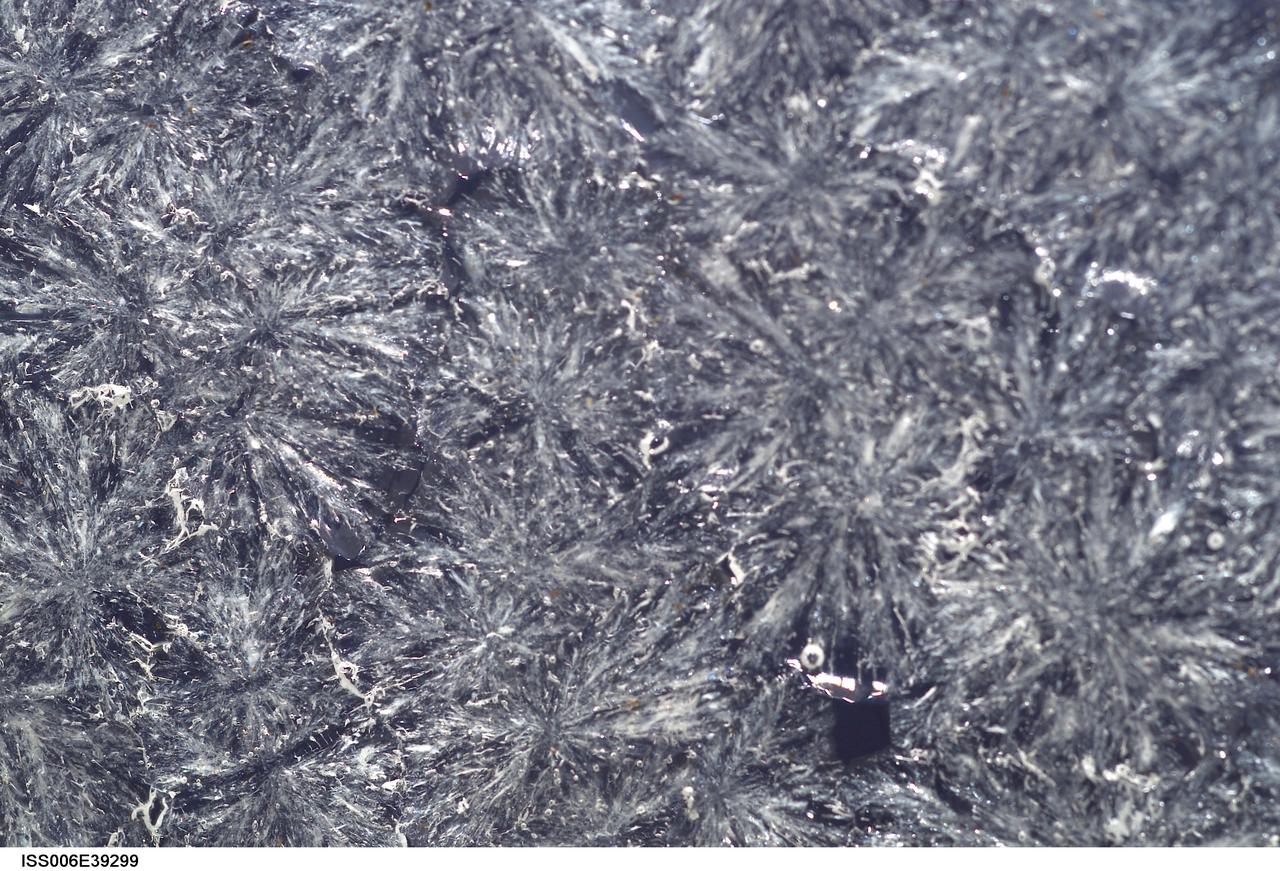

ISS006-E-39299 (15 March 2003) --- A close up view of sugar crystals in a water bubble within a 50-millimeter (mm) metal loop was photographed by an Expedition Six crewmember. The experiment took place in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
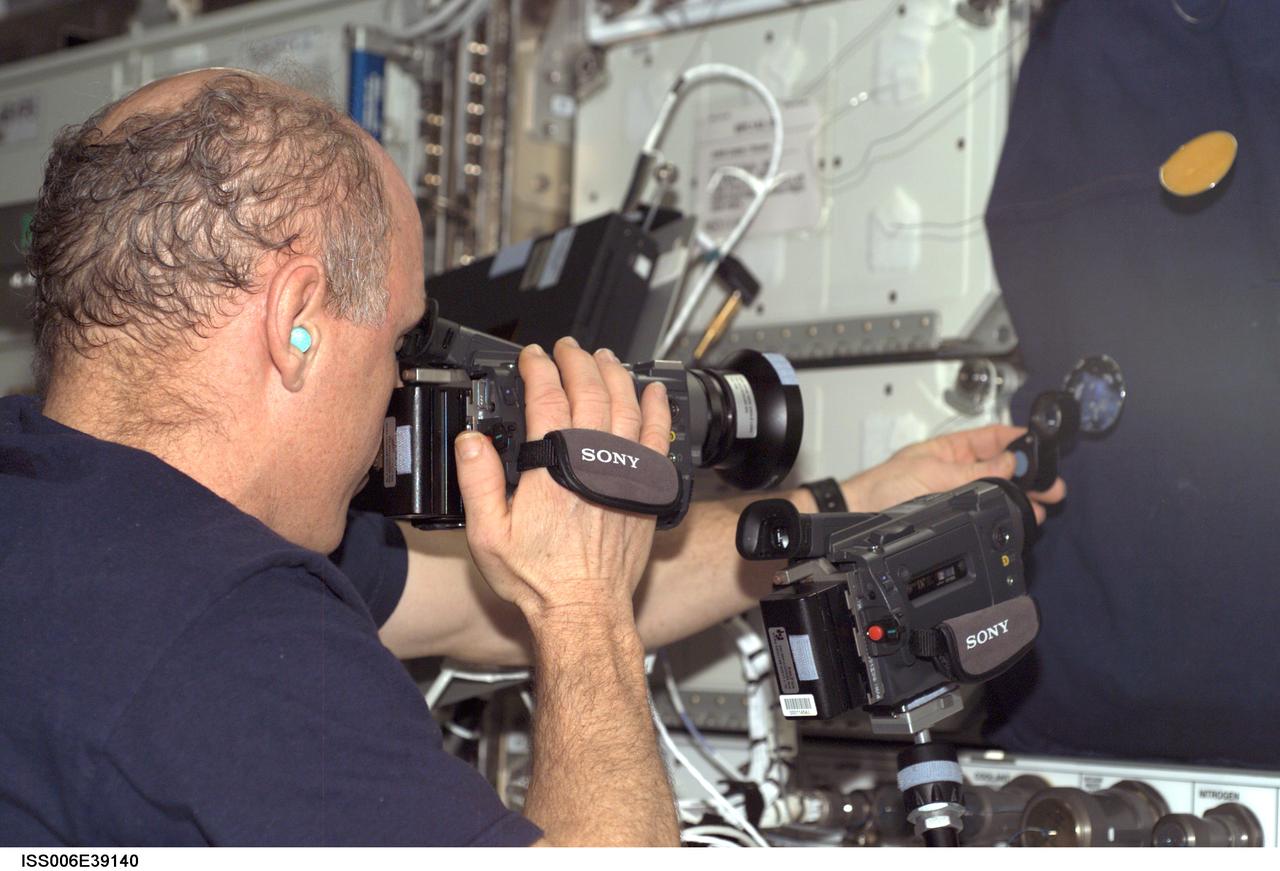

ISS006-E-39140 (12 March 2003) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, Expedition Six mission commander, photographs a water bubble within a 50-millimeter metal loop. The experiment took place in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
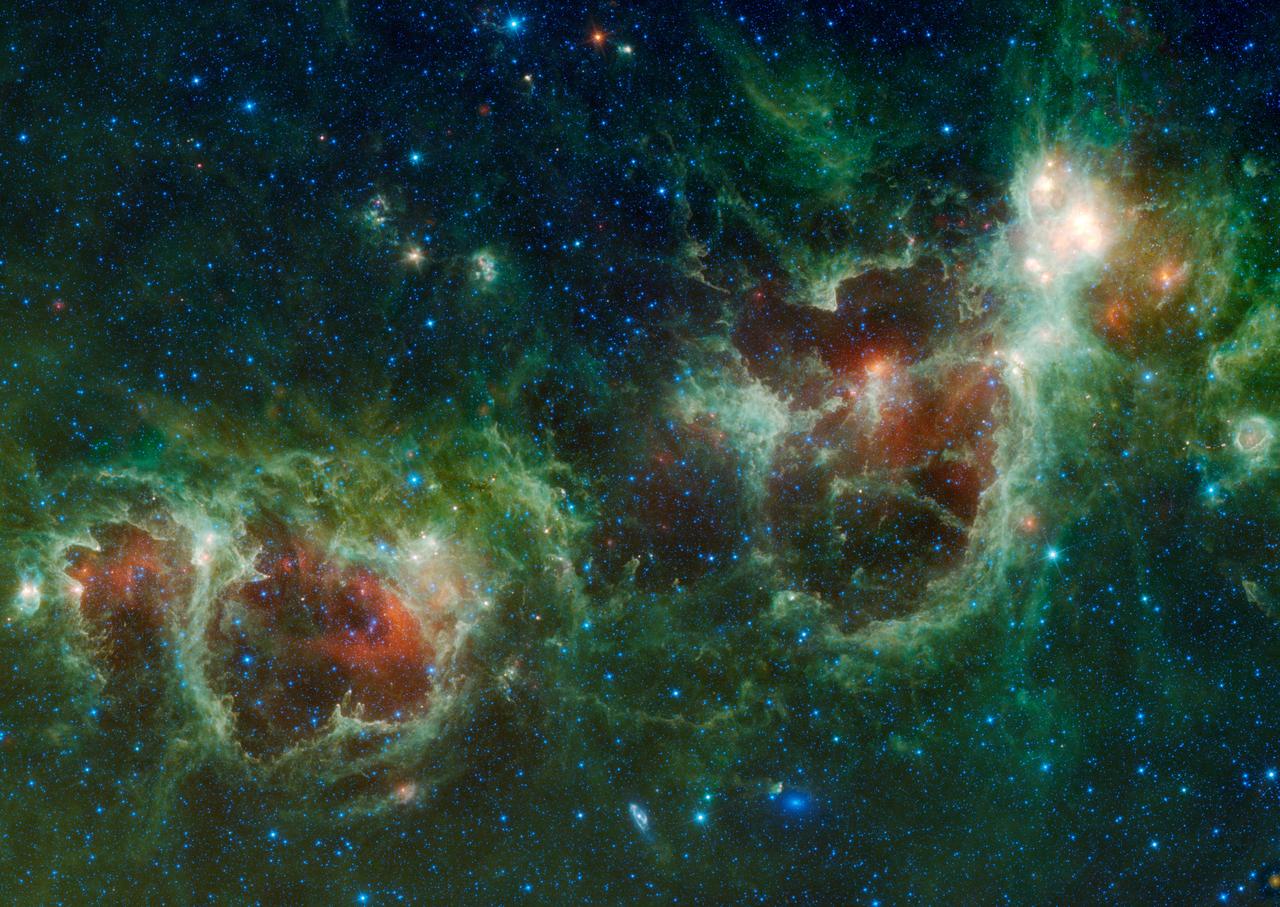

NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer has captured a huge mosaic of two bubbling clouds in space, known as the Heart and Soul nebulae.
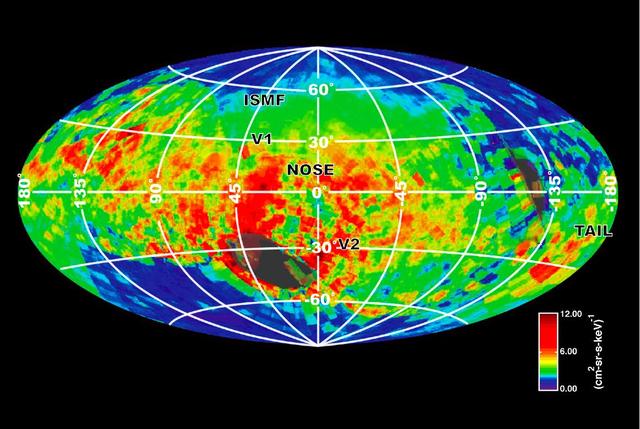
NASA Cassini spacecraft created this image of the bubble around our solar system based on emissions of particles known as energetic neutral atoms.
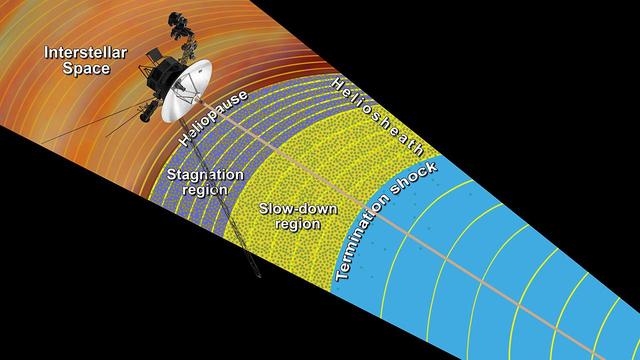
This artist concept shows the outer layers of our solar bubble, or heliosphere, and nearby interstellar space. NASA Voyager 1 is currently exploring a region of interstellar space.
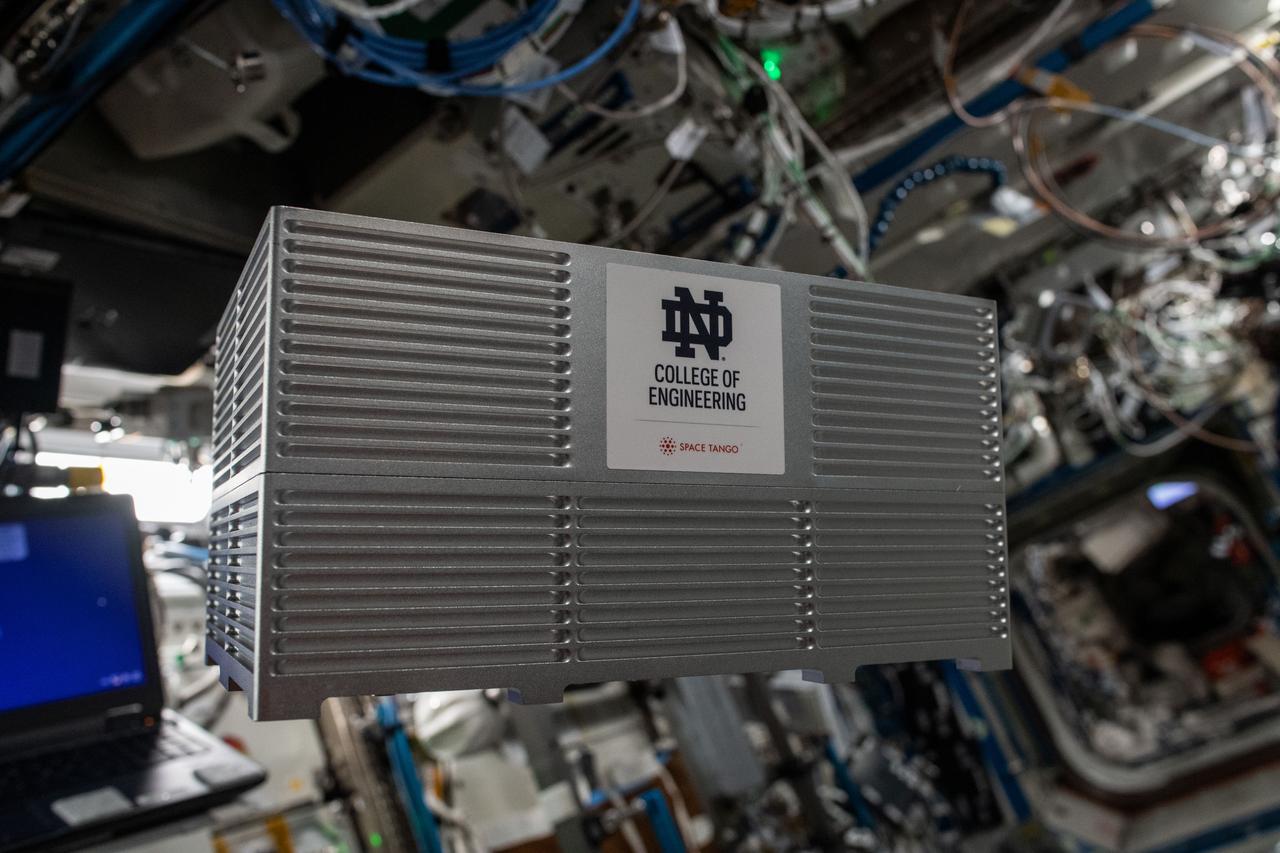

iss067e000391 (3/31/2022) --- A Nona Cube containing Optical Imaging of Bubble Dynamics on Nanostructured Surfaces, part of TangoLab Mission-25. The Optical Imaging of Bubble Dynamics on Nanostructured Surfaces investigation observes thermal bubbles in a microgravity environment with the use of an optical imaging system.
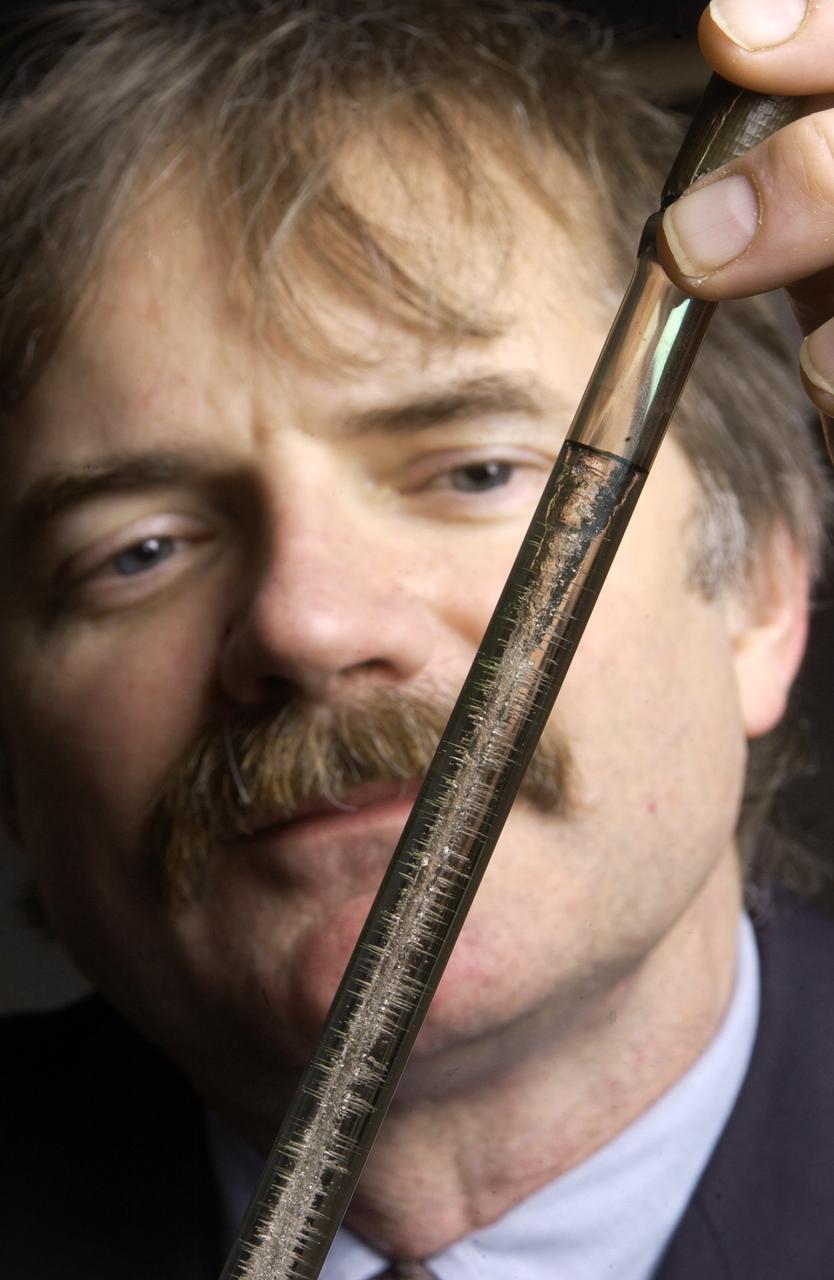

On Earth when scientists melt metals, bubbles that form in the molten material can rise to the surface, pop and disappear. In microgravity -- the near-weightless environment created as the International Space Station orbits Earth -- the lighter bubbles do not rise and disappear. Prior space experiments have shown that bubbles often become trapped in the final metal or crystal sample -similar to the bubbles trapped in this sample. In the solid, these bubbles, or porosity, are defects that diminish both the material's strength and usefulness. The Pore Formation and Mobility Investigation will melt samples of a transparent modeling material, succinonitrile and succinonitrile water mixtures, shown here in an ampoule being examined by Dr. Richard Grugel, the principal investigator for the experiment at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. As the samples are processed in space, Grugel will be able to observe how bubbles form in the samples and study their movements and interactions.
CONSTRAINED VAPOR BUBBLE
The lack of normal convection in microgravity is demonstrated by a carbonated soft drink floating in the middeck of the Space Shuttle. While the droplet is oscillating slightly and starting to assume a spherical shape, it is filled with carbon dioxide bubbles in a range of sizes. On Earth, the bubbles would quickly foat up to form a head. In space, they are suspended. They may drift with time and eventually the surface tension between individual bubbles breaks, allowing larger bubbles to form. This image was taken during STS-51F mission (Spacelab 2) which carried test models of dispensers from two pupular soft drink manufacturers. Photo credit: NASA/Johnson Space Center (JSC)
CONSTRAINED VAPOR BUBBLE CVB SAMPLE
This artist concept shows how NASA Voyager 1 spacecraft is bathed in solar wind from the southern hemisphere flowing northward. This phenomenon creates a layer of giant bubble of solar ions just inside the outer boundary of the heliosphere.
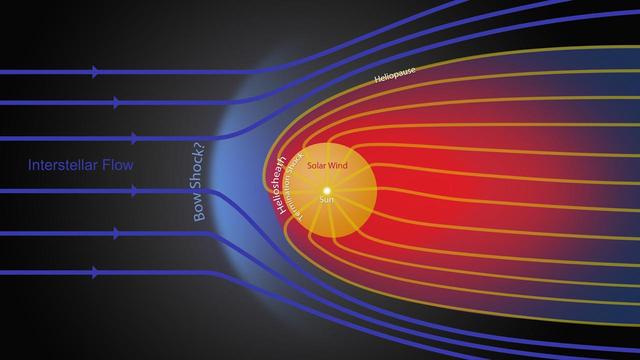
This graphic shows the different streams of charged particles inside the bubble around our sun and outside, in the unexplored territory of interstellar space. The heliosheath, where NASA two Voyager spacecraft are now traveling, is shown in red.

This visible-light view from from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope highlights the bright M17 nebula, as well as the glowing hot gas filling the bubble to its left.
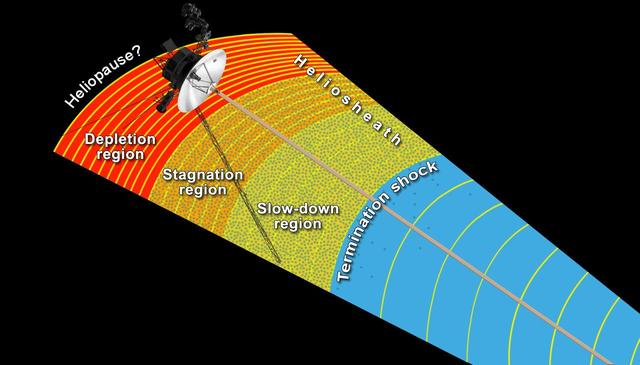
This artist concept shows NASA Voyager 1 spacecraft exploring a region called the depletion region or magnetic highway at the outer limits of our heliosphere, the bubble the sun blows around itself.
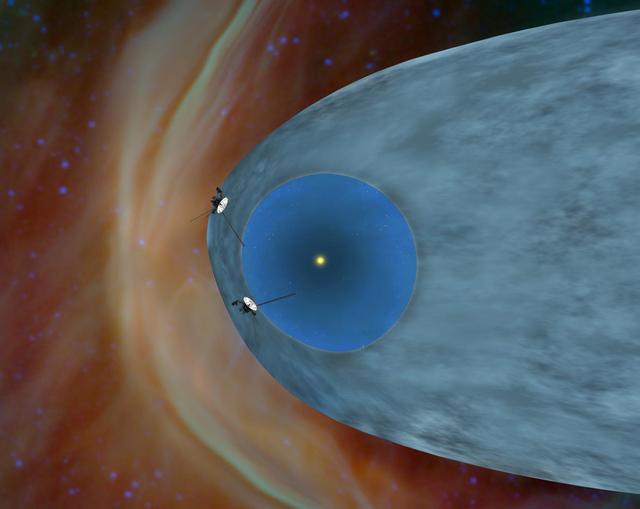

This artist concept shows NASA two Voyager spacecraft exploring a turbulent region of space known as the heliosheath, the outer shell of the bubble of charged particles around our sun.
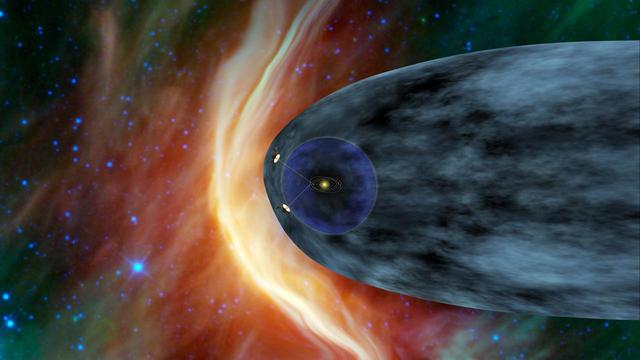
This artist concept shows NASA two Voyager spacecraft exploring a turbulent region of space known as the heliosheath, the outer shell of the bubble of charged particles around our sun. The Voyagers have been in space 33 years.

The nearby dwarf galaxy NGC 1569 is a hotbed of vigorous star birth activity, which blows huge bubbles that riddle the galaxy main body. The image was taken by the WPF2 camera, designed and built by JPL, on NASA Hubble.

This image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows a wispy, vast structure in the constellation Perseus with a small bubble right in its center puffed out by spasms of fresh-formed, heavyweight stars.
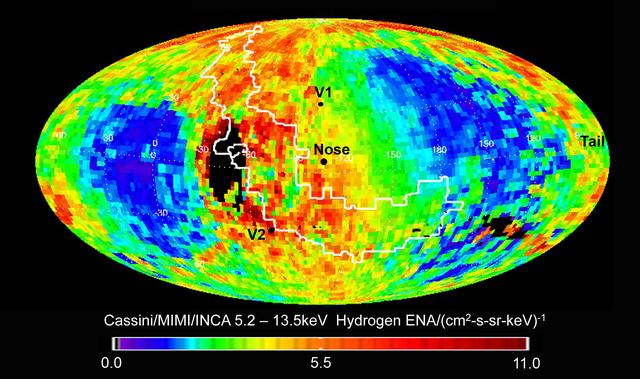
Data from NASA Cassini spacecraft have enabled scientists to create this map of the heliosphere, the bubble of charged particles around our sun. Charged particles stream out from our sun in a phenomenon known as solar wind.

This graphic shows the position of the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes, relative to the heliosphere, a protective bubble created by the Sun that extends well past the orbit of Pluto. Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause, or the edge of the heliosphere, in 2012. Voyager 2 is still in the heliosheath, or the outermost part of the heliosphere. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22566

NASA Spitzer Space Telescope sees RCW 79 in the southern Milky Way, 17,200 light-years from Earth in the constellation Centaurus.
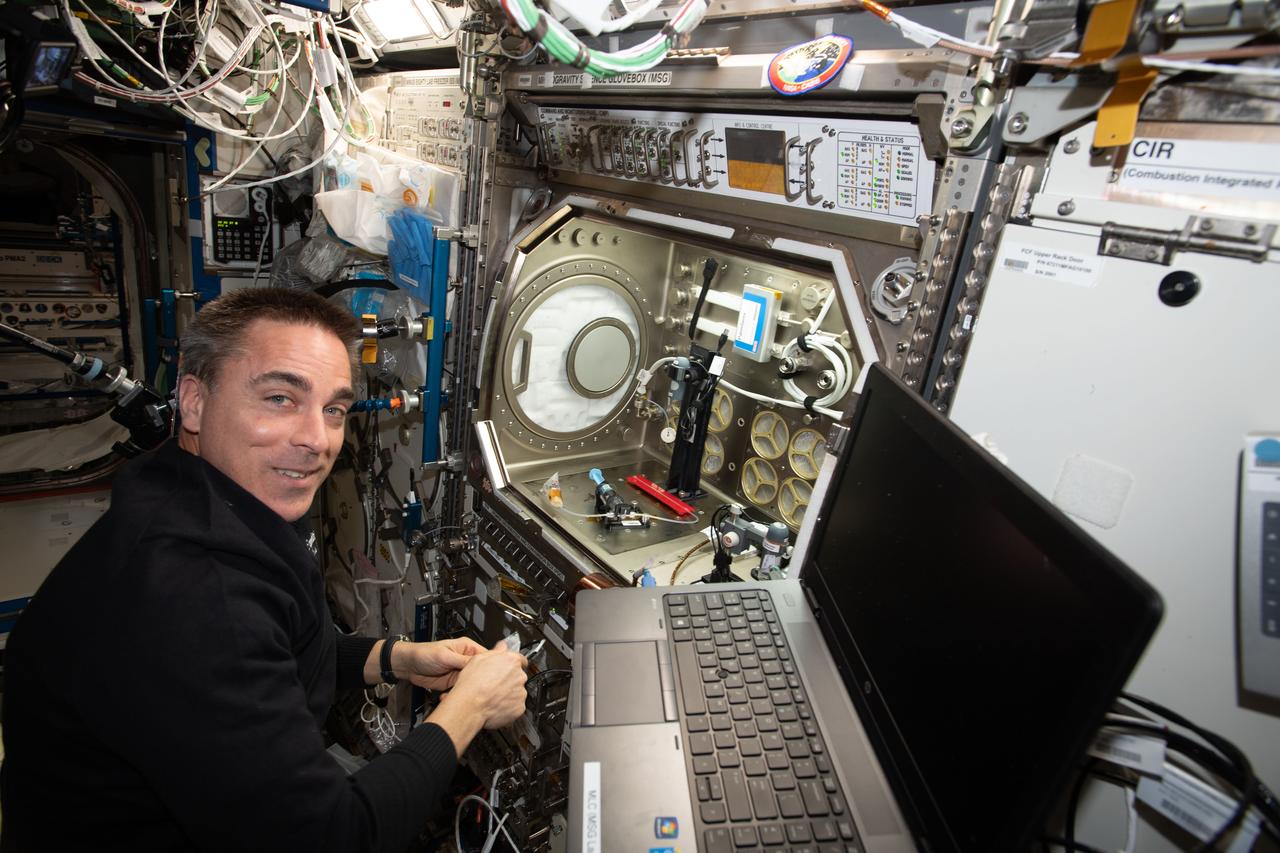

iss063e022562 (June 3, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 63 Commander Chris Cassidy sets up the Microgravity Science Glovebox for a space bubbles experiment. The Electrolysis Measurement study is observing how bubbles inside microfluid systems may help produce oxygen on a spacecraft and deliver drugs though skin patches.

EuCropis Power Cells built by Micronics and showing bubbles in manufacturing
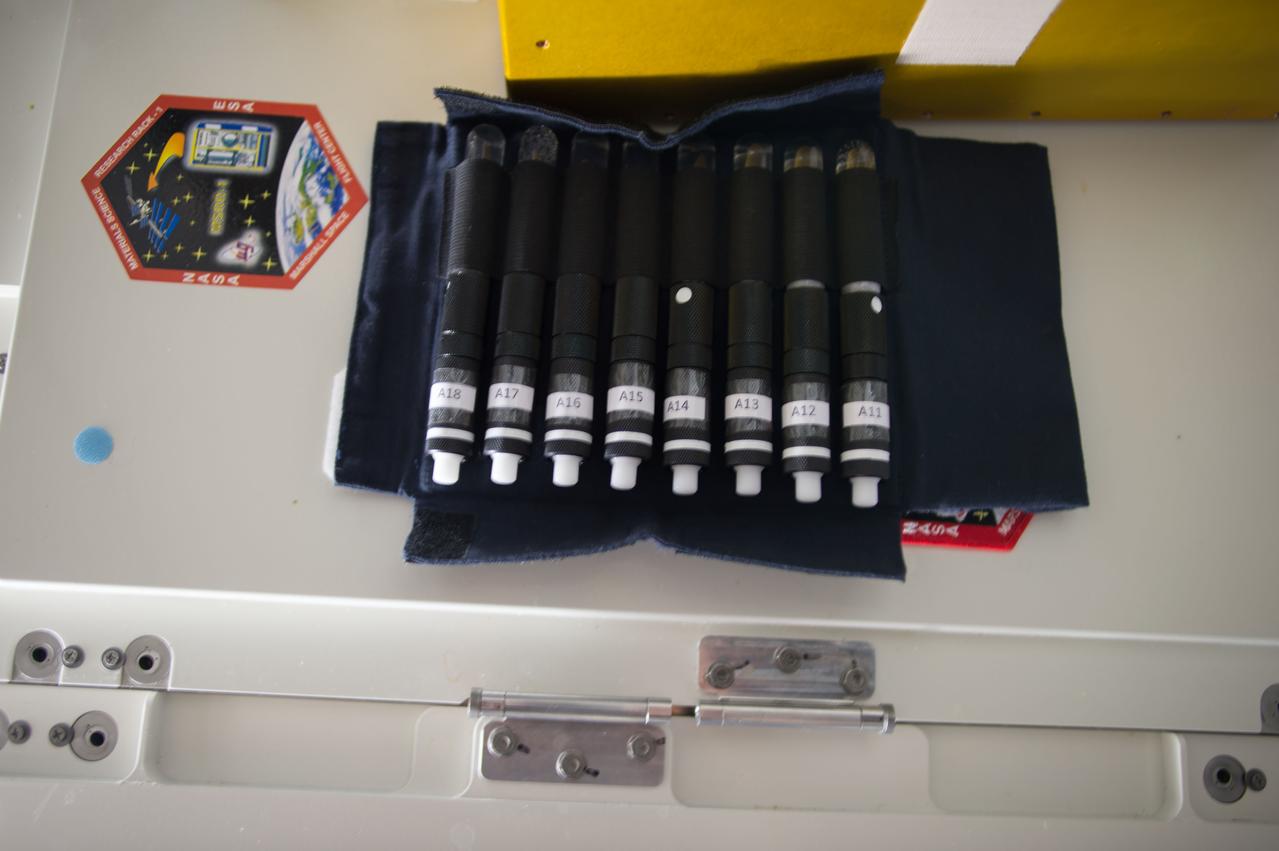

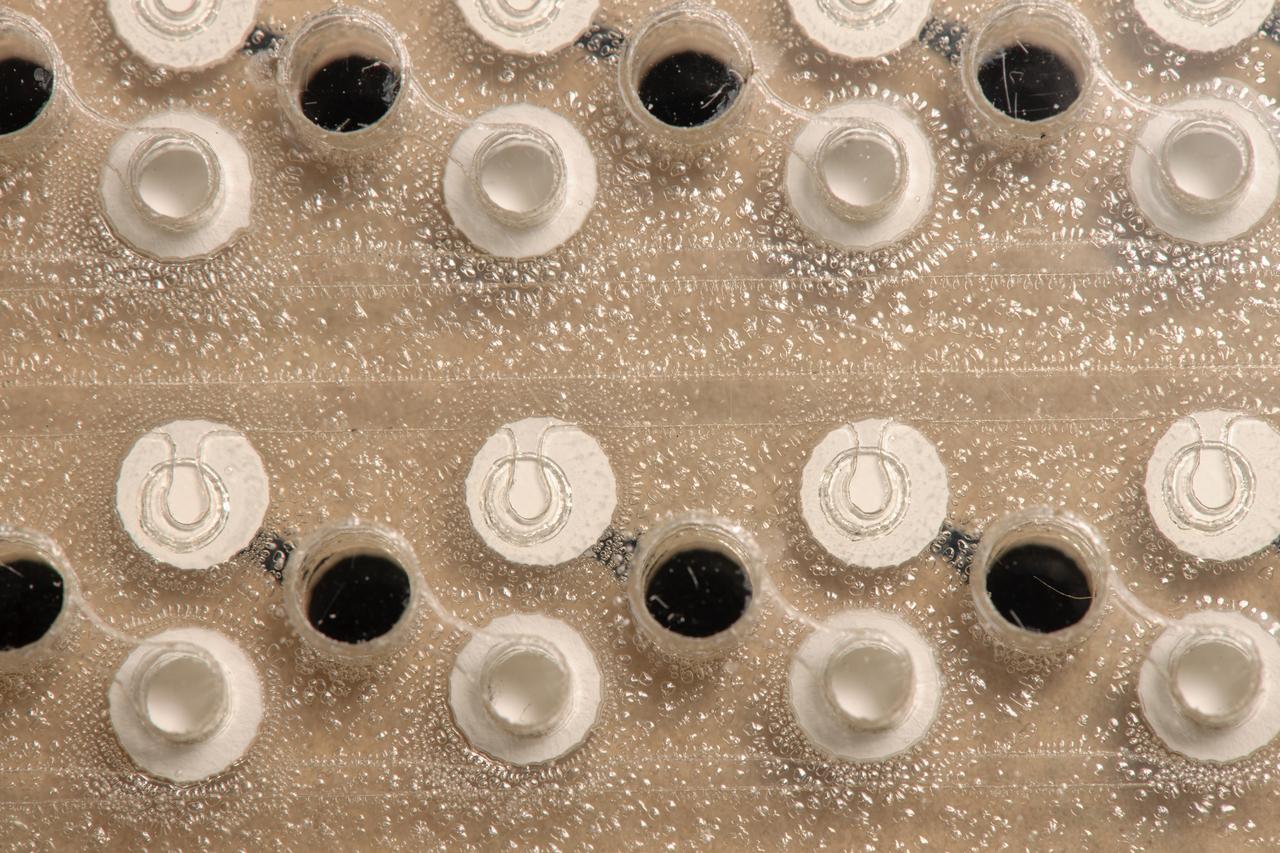
iss050e000936 (11/7/2016) --- View of eight bubble detectors in pack during Radi-N2 deployment in the U.S. Laboratory for RADI-N2 experiment. Radi-N2 Neutron Field Study (Radi-N2) is a follow on investigation designed to characterize the neutron radiation environment aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Eight neutron “bubble detectors” produced by the Canadian company Bubble Technology Industries are attached to fixed locations inside the ISS, including one carried by a crew member. The objective of this investigation is to better characterize the ISS neutron environment and define the risk posed to the crew members’ health and provide the data necessary to develop advanced protective measures for future spaceflight.
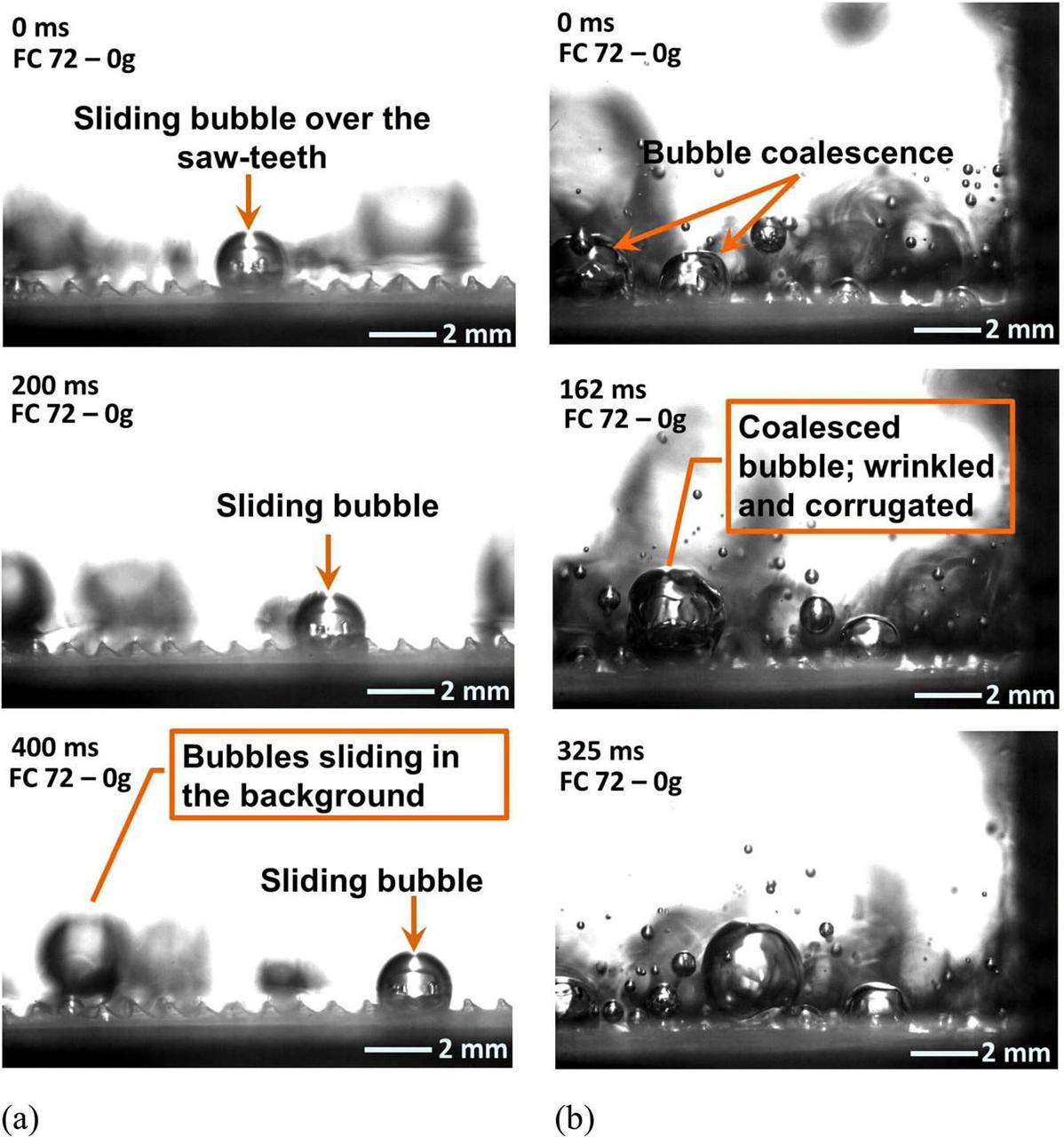
jsc2020e030483 (4/20/2020) --- A preflight image sequence from parabolic flight experiments indicating motion of vapor bubble on heated ratchet surface. Asymmetric Sawtooth and Cavity-Enhanced Nucleation-Driven Transport (PFMI-ASCENT) demonstrates a passive cooling system for electronic devices in microgravity using a microstructured surface. When fluids boil over flat heated surfaces in microgravity, vapor bubbles grow larger in size, causing poor heat transfer that can lead to damage of devices. Adding microscopic rachets on the surface may passively enable mobility of vapor bubbles and prevent this damage. (Image courtesy of: Techshot, Inc.)

This image represents a view of NASA Kepler supernova remnant taken in X-rays, visible light, and infrared radiation, indicating that the bubble of gas that makes up the supernova remnant appears different in various types of light. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06909
![The images indicate that the bubble of gas that makes up the supernova remnant appears different in various types of light. Chandra reveals the hottest gas [colored blue and colored green], which radiates in X-rays. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06908](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA06908/PIA06908~medium.jpg)
The images indicate that the bubble of gas that makes up the supernova remnant appears different in various types of light. Chandra reveals the hottest gas [colored blue and colored green], which radiates in X-rays. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06908
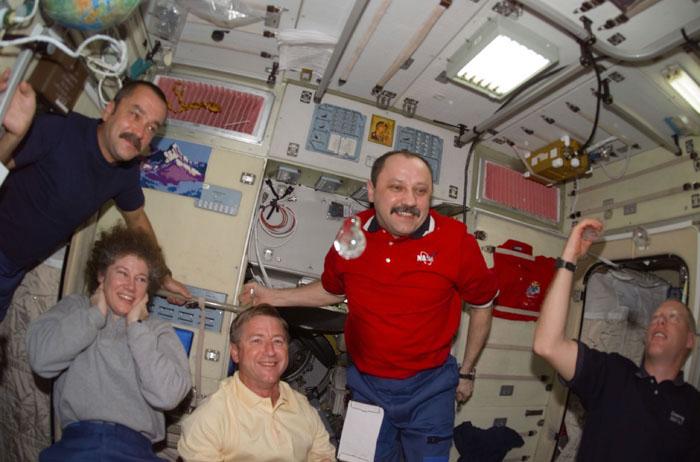

STS105-E-5205 (15 August 2001) --- The astronauts and cosmonauts of STS-105 and Expedition Two and Expedition Three share some time in the Zvezda Service Module aboard the International Space Station. From left to right are cosmonaut Mikhail Tyurin, Expedition Three flight engineer; astronaut Susan J. Helms, Expedition Two flight engineer; astronaut Frank L. Culbertson, Jr., Expedition Three commander; cosmonaut Yury V. Usachev, Expedition Two commander; and Patrick G. Forrester, STS-105 mission specialist. Taking a brief break from busy moving chores, the astronauts and cosmonauts fashioned some liquid bubbles, which always perform interestingly in zero gravity. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.