
You might see a DeLorean zipping around Greenbelt, Maryland, on Oct. 21, 2015, the day Marty McFly and Doc Brown arrive from 1985 in "Back to the Future, Part II," but don't look for flaming tread marks in its wake. The DeLorean DMC-12, commonly seen on the roads of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is better known for the version that starred as a plutonium-powered time machine in the “Back to the Future” trilogy. After some investigation, Goddard’s Office of Communications found the owner of the stainless steel, gull-winged, two-door coupe. Goddard software test engineer, Brendan Rebo bought the 1982 DeLorean off eBay about four and a half years ago. “The car attracts a lot more attention than I expected,” Rebo admitted. “I hear a lot of jokes about whether or not I’ve reached 88 miles per hour yet.” As “Back to the Future” fans around the world celebrate today, Rebo also celebrates his birthday. While the second film predicted technology, such as flying cars, that doesn’t yet exist, people can still marvel at the classic car and movie reference. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth

You might see a DeLorean zipping around Greenbelt, Maryland, on Oct. 21, 2015, the day Marty McFly and Doc Brown arrive from 1985 in "Back to the Future, Part II," but don't look for flaming tread marks in its wake. The DeLorean DMC-12, commonly seen on the roads of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is better known for the version that starred as a plutonium-powered time machine in the “Back to the Future” trilogy. After some investigation, Goddard’s Office of Communications found the owner of the stainless steel, gull-winged, two-door coupe. Goddard software test engineer, Brendan Rebo bought the 1982 DeLorean off eBay about four and a half years ago. “The car attracts a lot more attention than I expected,” Rebo admitted. “I hear a lot of jokes about whether or not I’ve reached 88 miles per hour yet.” As “Back to the Future” fans around the world celebrate today, Rebo also celebrates his birthday. While the second film predicted technology, such as flying cars, that doesn’t yet exist, people can still marvel at the classic car and movie reference. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth

You might see a DeLorean zipping around Greenbelt, Maryland, on Oct. 21, 2015, the day Marty McFly and Doc Brown arrive from 1985 in "Back to the Future, Part II," but don't look for flaming tread marks in its wake. The DeLorean DMC-12, commonly seen on the roads of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is better known for the version that starred as a plutonium-powered time machine in the “Back to the Future” trilogy. After some investigation, Goddard’s Office of Communications found the owner of the stainless steel, gull-winged, two-door coupe. Goddard software test engineer, Brendan Rebo bought the 1982 DeLorean off eBay about four and a half years ago. “The car attracts a lot more attention than I expected,” Rebo admitted. “I hear a lot of jokes about whether or not I’ve reached 88 miles per hour yet.” As “Back to the Future” fans around the world celebrate today, Rebo also celebrates his birthday. While the second film predicted technology, such as flying cars, that doesn’t yet exist, people can still marvel at the classic car and movie reference. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth

You might see a DeLorean zipping around Greenbelt, Maryland, on Oct. 21, 2015, the day Marty McFly and Doc Brown arrive from 1985 in "Back to the Future, Part II," but don't look for flaming tread marks in its wake. The DeLorean DMC-12, commonly seen on the roads of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is better known for the version that starred as a plutonium-powered time machine in the “Back to the Future” trilogy. After some investigation, Goddard’s Office of Communications found the owner of the stainless steel, gull-winged, two-door coupe. Goddard software test engineer, Brendan Rebo bought the 1982 DeLorean off eBay about four and a half years ago. “The car attracts a lot more attention than I expected,” Rebo admitted. “I hear a lot of jokes about whether or not I’ve reached 88 miles per hour yet.” As “Back to the Future” fans around the world celebrate today, Rebo also celebrates his birthday. While the second film predicted technology, such as flying cars, that doesn’t yet exist, people can still marvel at the classic car and movie reference. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth
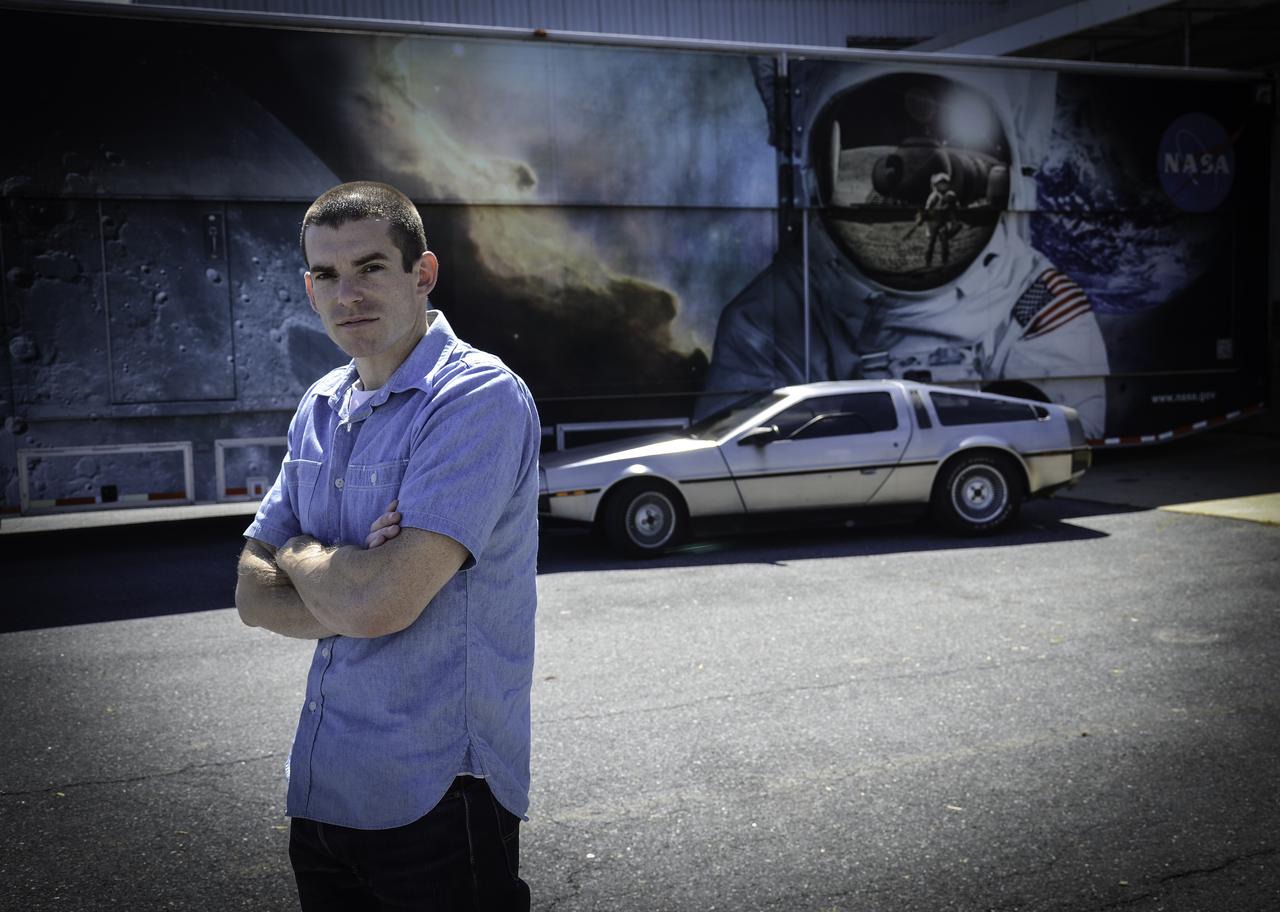

Great Scott, This is Heavy! You might see a DeLorean zipping around Greenbelt, Maryland, on Oct. 21, 2015, the day Marty McFly and Doc Brown arrive from 1985 in "Back to the Future, Part II," but don't look for flaming tread marks in its wake. The DeLorean DMC-12, commonly seen on the roads of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is better known for the version that starred as a plutonium-powered time machine in the “Back to the Future” trilogy. After some investigation, Goddard’s Office of Communications found the owner of the stainless steel, gull-winged, two-door coupe. Goddard software test engineer, Brendan Rebo bought the 1982 DeLorean off eBay about four and a half years ago. “The car attracts a lot more attention than I expected,” Rebo admitted. “I hear a lot of jokes about whether or not I’ve reached 88 miles per hour yet.” As “Back to the Future” fans around the world celebrate today, Rebo also celebrates his birthday. While the second film predicted technology, such as flying cars, that doesn’t yet exist, people can still marvel at the classic car and movie reference. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
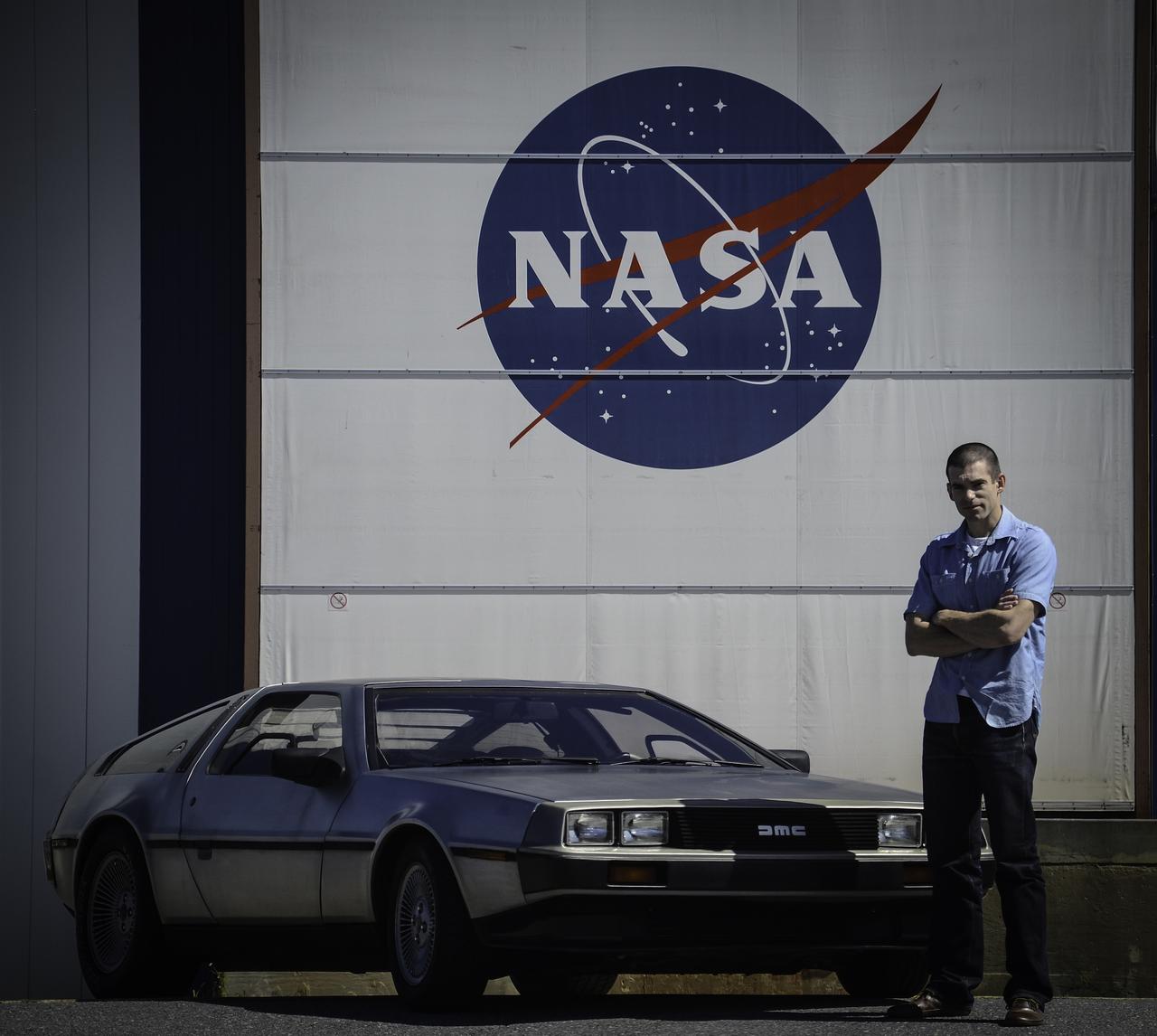

Great Scott, This is Heavy! You might see a DeLorean zipping around Greenbelt, Maryland, on Oct. 21, 2015, the day Marty McFly and Doc Brown arrive from 1985 in "Back to the Future, Part II," but don't look for flaming tread marks in its wake. The DeLorean DMC-12, commonly seen on the roads of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is better known for the version that starred as a plutonium-powered time machine in the “Back to the Future” trilogy. After some investigation, Goddard’s Office of Communications found the owner of the stainless steel, gull-winged, two-door coupe. Goddard software test engineer, Brendan Rebo bought the 1982 DeLorean off eBay about four and a half years ago. “The car attracts a lot more attention than I expected,” Rebo admitted. “I hear a lot of jokes about whether or not I’ve reached 88 miles per hour yet.” As “Back to the Future” fans around the world celebrate today, Rebo also celebrates his birthday. While the second film predicted technology, such as flying cars, that doesn’t yet exist, people can still marvel at the classic car and movie reference. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
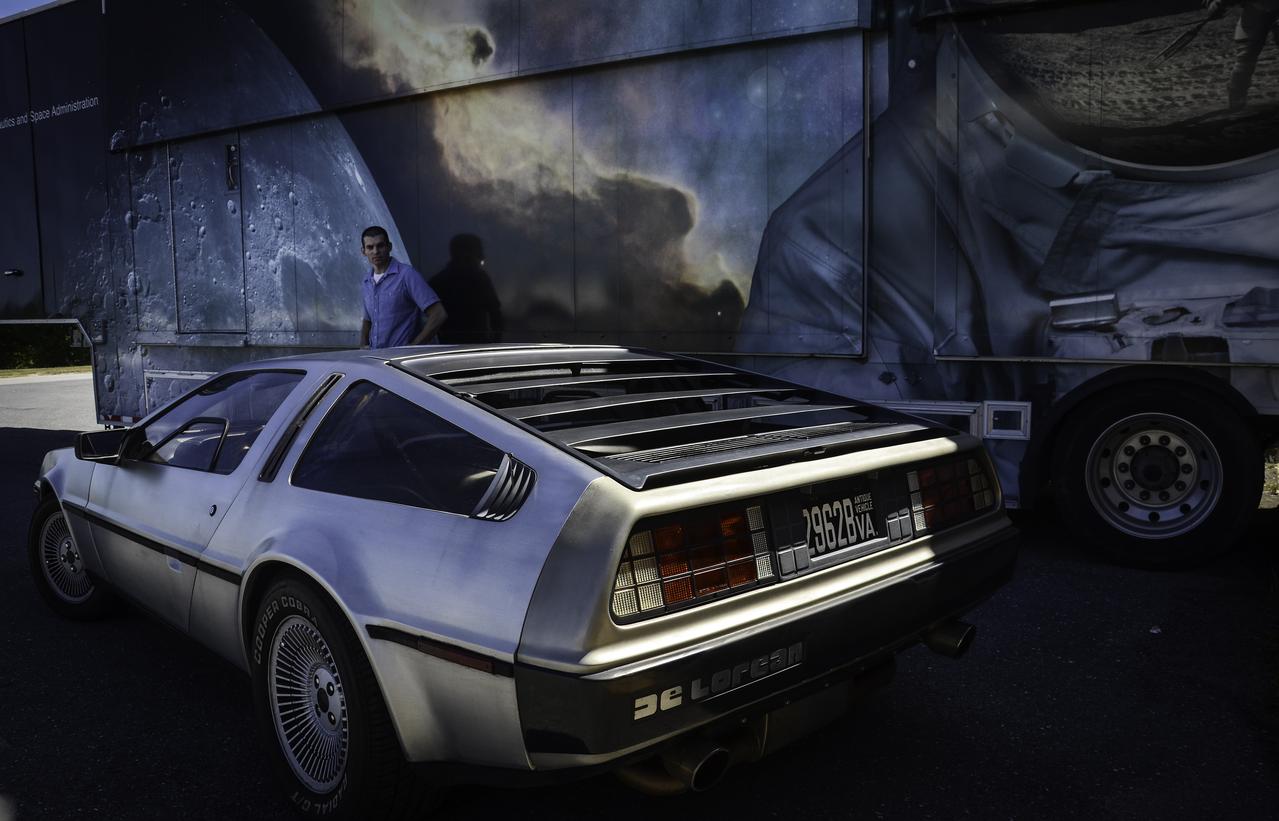

Great Scott, This is Heavy! You might see a DeLorean zipping around Greenbelt, Maryland, on Oct. 21, 2015, the day Marty McFly and Doc Brown arrive from 1985 in "Back to the Future, Part II," but don't look for flaming tread marks in its wake. The DeLorean DMC-12, commonly seen on the roads of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is better known for the version that starred as a plutonium-powered time machine in the “Back to the Future” trilogy. After some investigation, Goddard’s Office of Communications found the owner of the stainless steel, gull-winged, two-door coupe. Goddard software test engineer, Brendan Rebo bought the 1982 DeLorean off eBay about four and a half years ago. “The car attracts a lot more attention than I expected,” Rebo admitted. “I hear a lot of jokes about whether or not I’ve reached 88 miles per hour yet.” As “Back to the Future” fans around the world celebrate today, Rebo also celebrates his birthday. While the second film predicted technology, such as flying cars, that doesn’t yet exist, people can still marvel at the classic car and movie reference. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
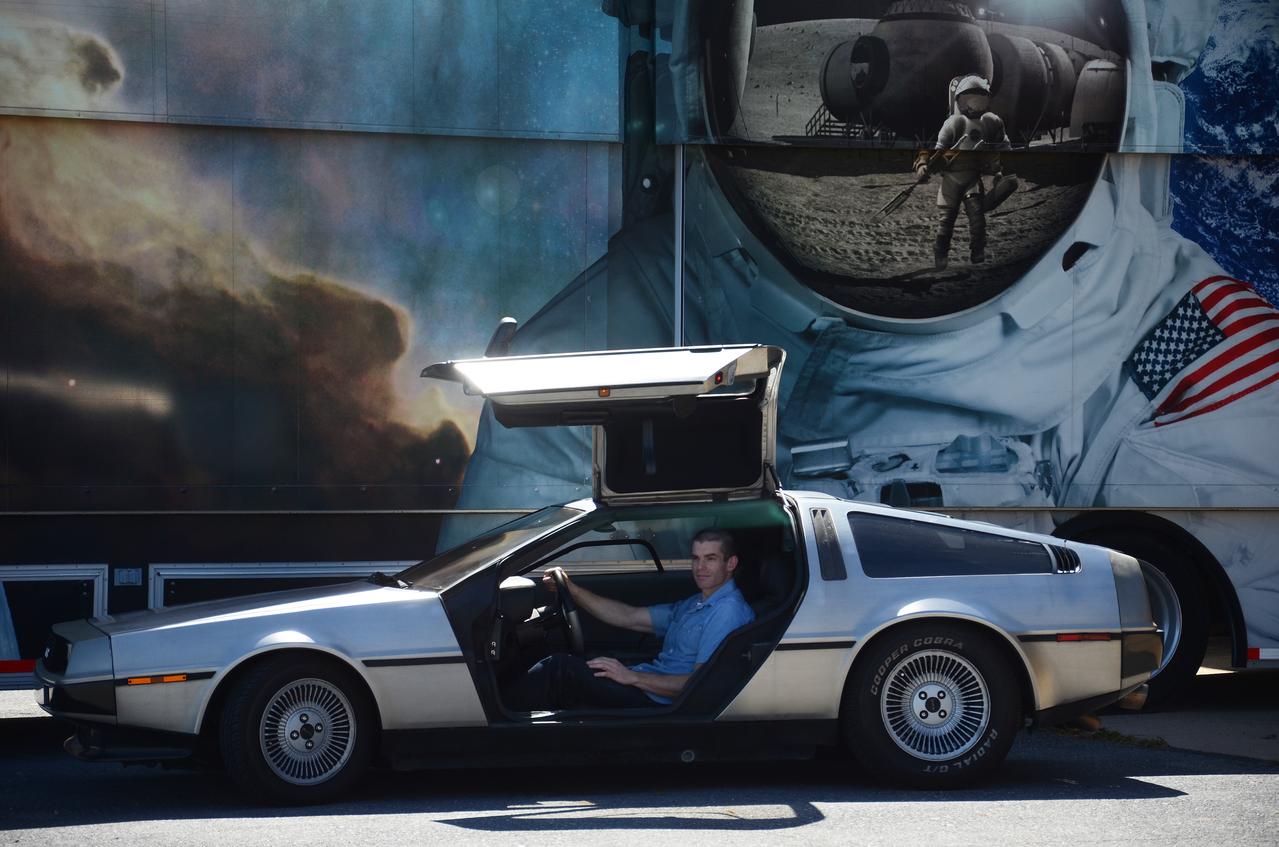

Great Scott, This is Heavy! You might see a DeLorean zipping around Greenbelt, Maryland, on Oct. 21, 2015, the day Marty McFly and Doc Brown arrive from 1985 in "Back to the Future, Part II," but don't look for flaming tread marks in its wake. The DeLorean DMC-12, commonly seen on the roads of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is better known for the version that starred as a plutonium-powered time machine in the “Back to the Future” trilogy. After some investigation, Goddard’s Office of Communications found the owner of the stainless steel, gull-winged, two-door coupe. Goddard software test engineer, Brendan Rebo bought the 1982 DeLorean off eBay about four and a half years ago. “The car attracts a lot more attention than I expected,” Rebo admitted. “I hear a lot of jokes about whether or not I’ve reached 88 miles per hour yet.” As “Back to the Future” fans around the world celebrate today, Rebo also celebrates his birthday. While the second film predicted technology, such as flying cars, that doesn’t yet exist, people can still marvel at the classic car and movie reference. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
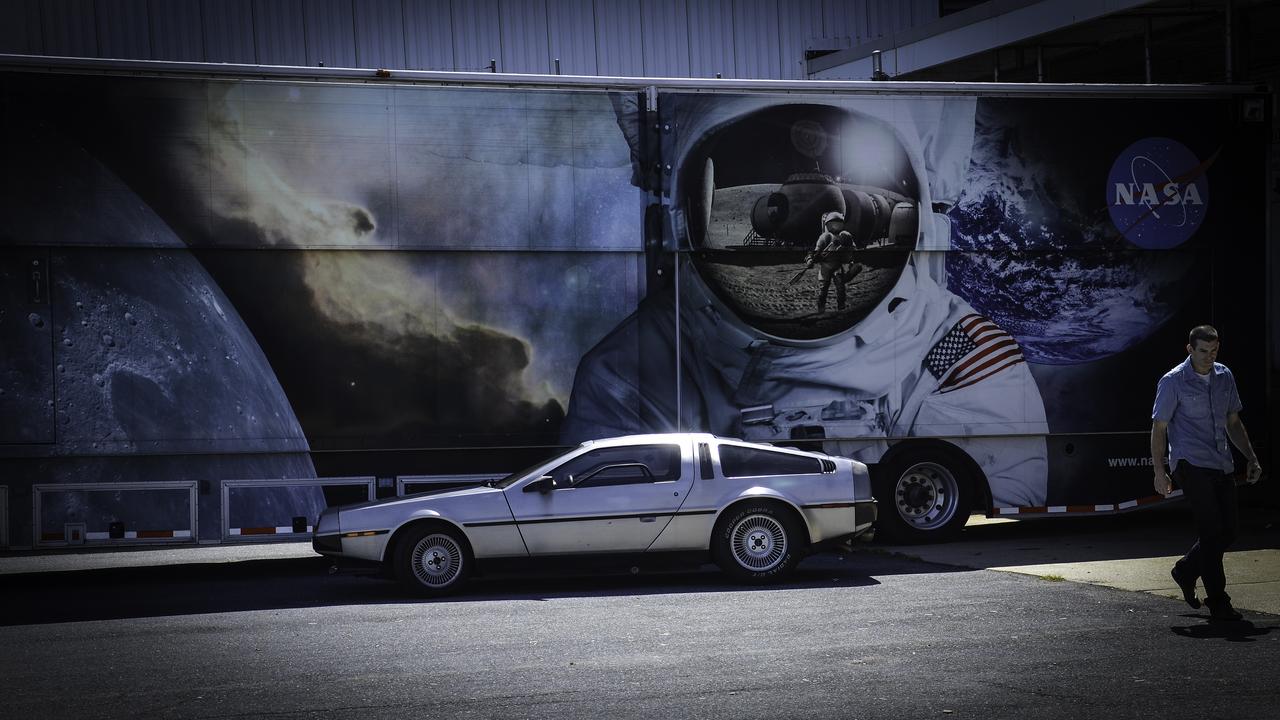

Great Scott, This is Heavy! You might see a DeLorean zipping around Greenbelt, Maryland, on Oct. 21, 2015, the day Marty McFly and Doc Brown arrive from 1985 in "Back to the Future, Part II," but don't look for flaming tread marks in its wake. The DeLorean DMC-12, commonly seen on the roads of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is better known for the version that starred as a plutonium-powered time machine in the “Back to the Future” trilogy. After some investigation, Goddard’s Office of Communications found the owner of the stainless steel, gull-winged, two-door coupe. Goddard software test engineer, Brendan Rebo bought the 1982 DeLorean off eBay about four and a half years ago. “The car attracts a lot more attention than I expected,” Rebo admitted. “I hear a lot of jokes about whether or not I’ve reached 88 miles per hour yet.” As “Back to the Future” fans around the world celebrate today, Rebo also celebrates his birthday. While the second film predicted technology, such as flying cars, that doesn’t yet exist, people can still marvel at the classic car and movie reference. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

You might see a DeLorean zipping around Greenbelt, Maryland, on Oct. 21, 2015, the day Marty McFly and Doc Brown arrive from 1985 in "Back to the Future, Part II," but don't look for flaming tread marks in its wake. The DeLorean DMC-12, commonly seen on the roads of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is better known for the version that starred as a plutonium-powered time machine in the “Back to the Future” trilogy. After some investigation, Goddard’s Office of Communications found the owner of the stainless steel, gull-winged, two-door coupe. Goddard software test engineer, Brendan Rebo bought the 1982 DeLorean off eBay about four and a half years ago. “The car attracts a lot more attention than I expected,” Rebo admitted. “I hear a lot of jokes about whether or not I’ve reached 88 miles per hour yet.” As “Back to the Future” fans around the world celebrate today, Rebo also celebrates his birthday. While the second film predicted technology, such as flying cars, that doesn’t yet exist, people can still marvel at the classic car and movie reference. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth
On July 21, 1969, only days after walking on the Moon's surface, Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin leave lunar orbit and begin the journey back to the space ship Columbia and its return to Earth. As they leave the Moon's orbit, a look back gives them a new perspective of where they were and where man's future lies. This was their final sight of the moon before they began docking procedures with Columbia.
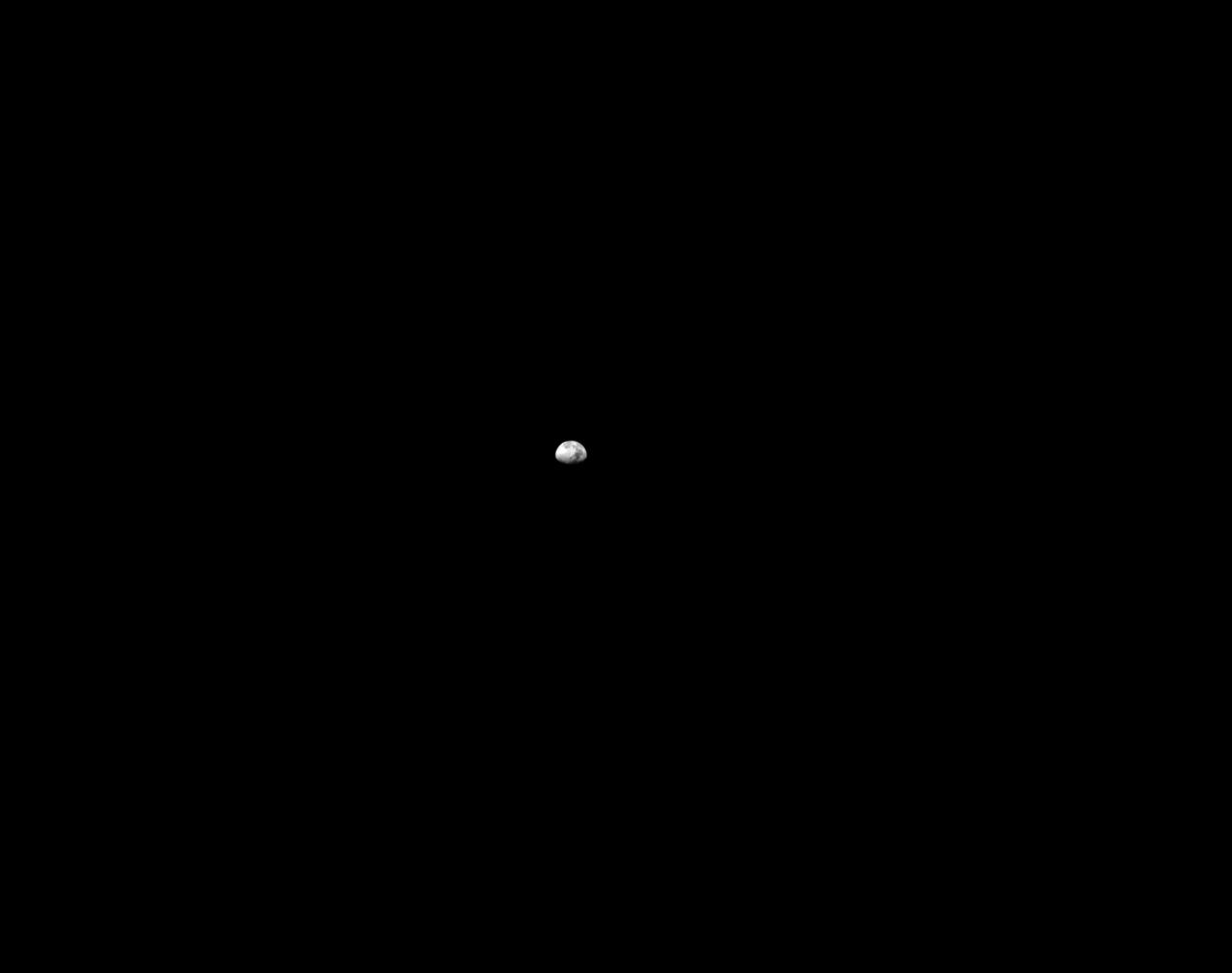

art001e003051 (Dec. 10, 2022) On flight day 25 of the 25.5-day Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera looked back at the Moon as the spacecraft continued its return journey to Earth. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
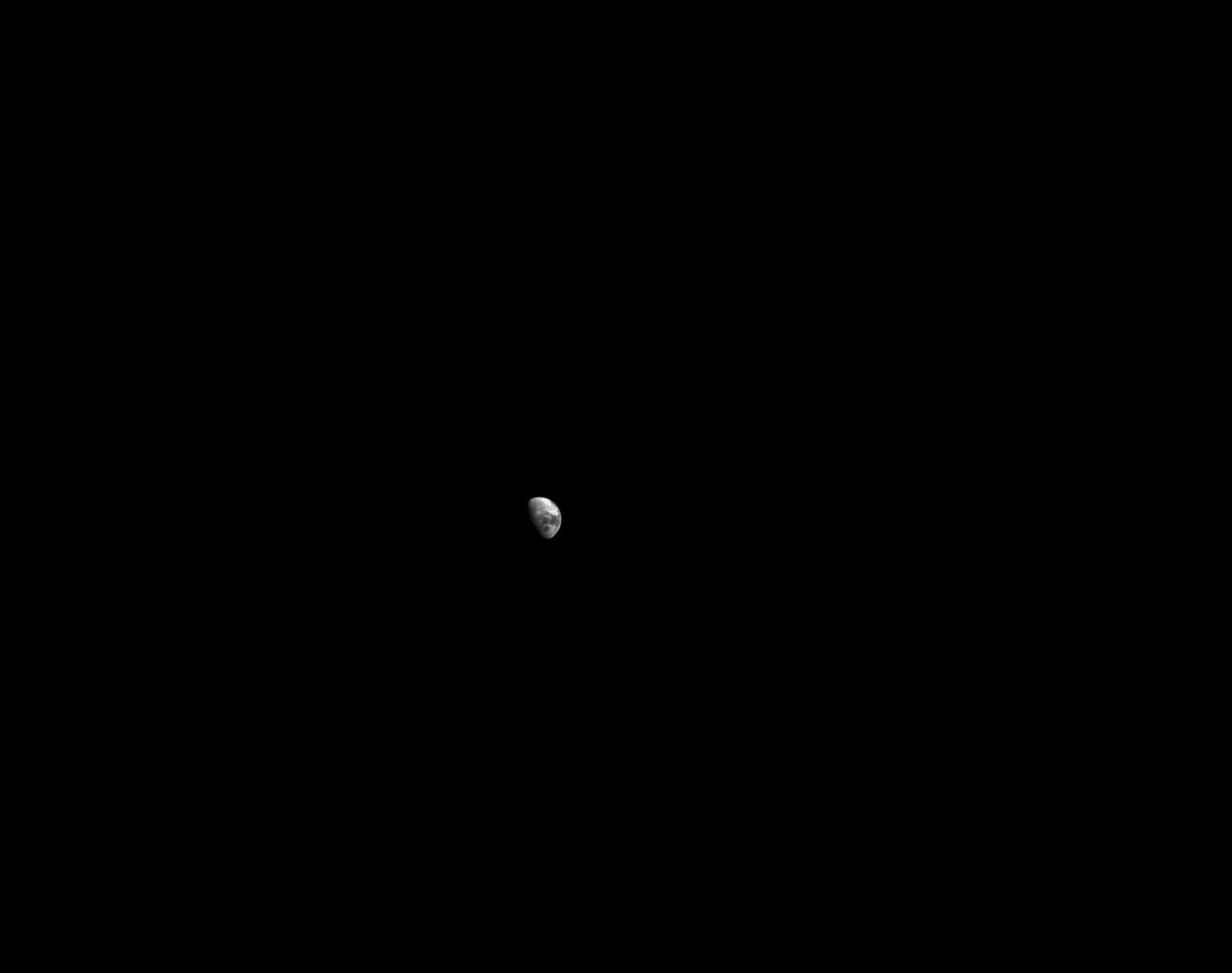

art001e002461 (Dec. 8, 2022) Orion looks back at the Moon on flight day 23 of the Artemis I mission, at the time over 180,000 miles away. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
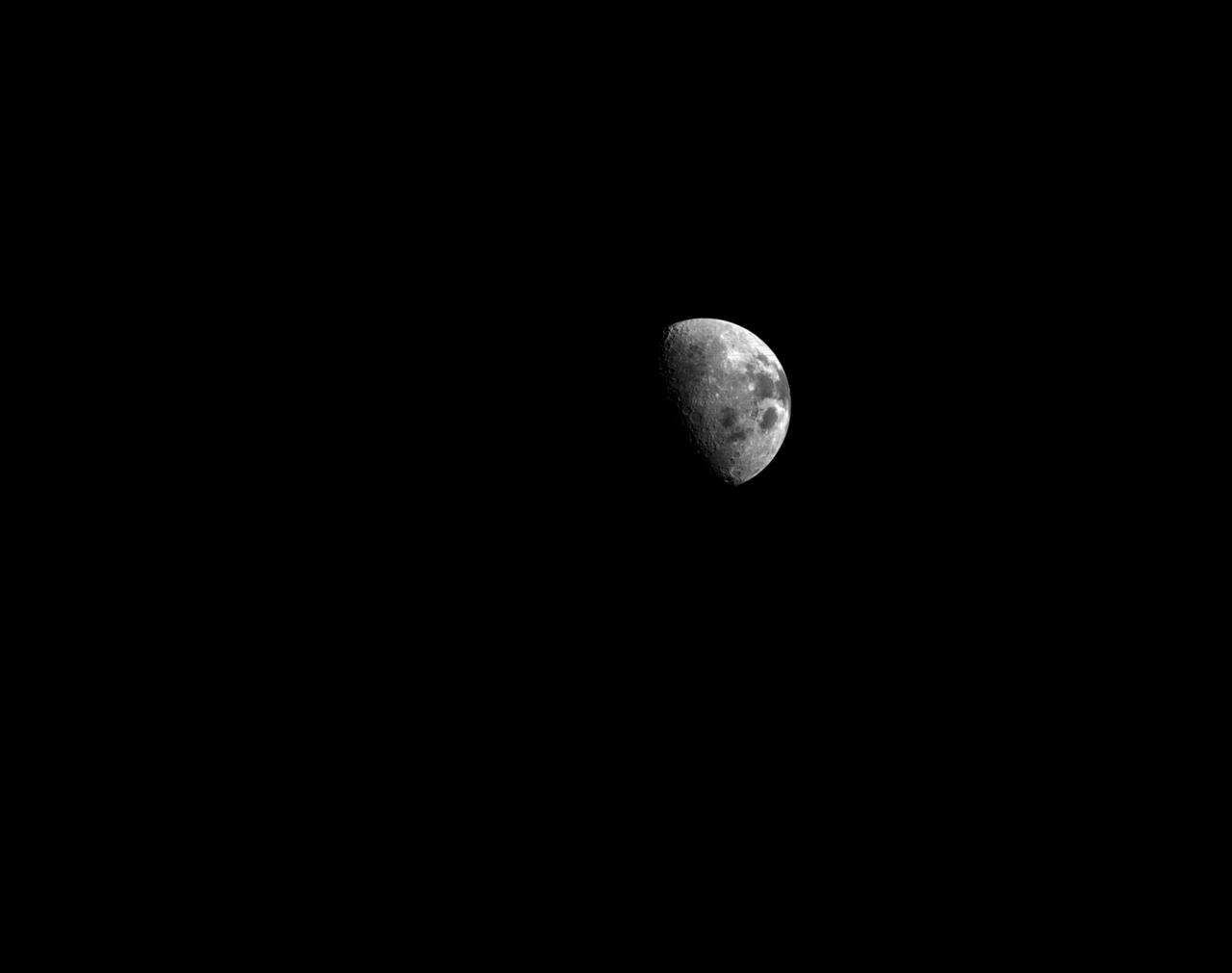

art001e002196 (Dec. 6, 2022) On flight day 21 of NASA’s Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera looked back at the Moon as the spacecraft continued its journey home. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
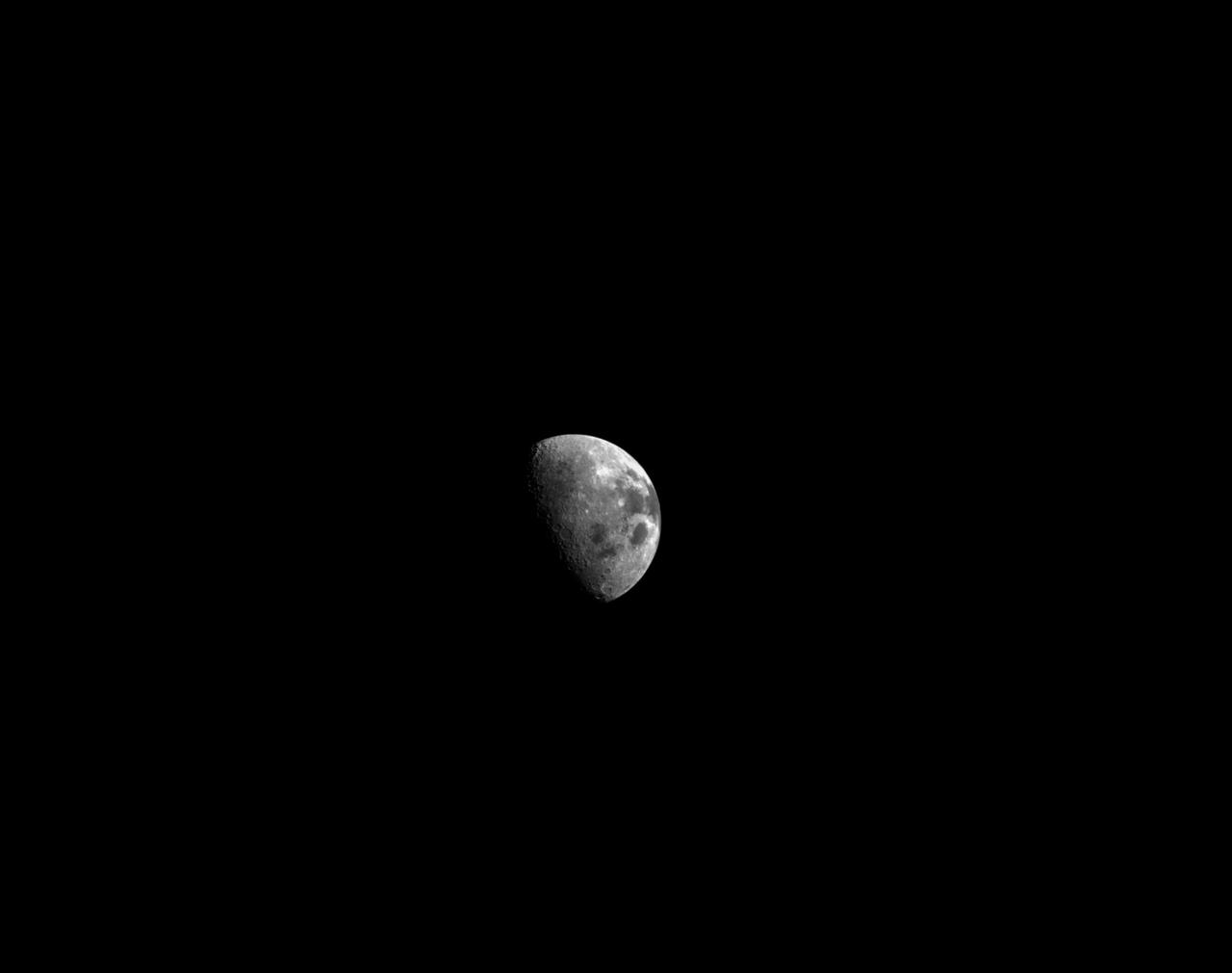

art001e002355 (Dec. 6, 2022) On flight day 21 of NASA’s Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera looked back at the Moon as the spacecraft continued its journey home. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
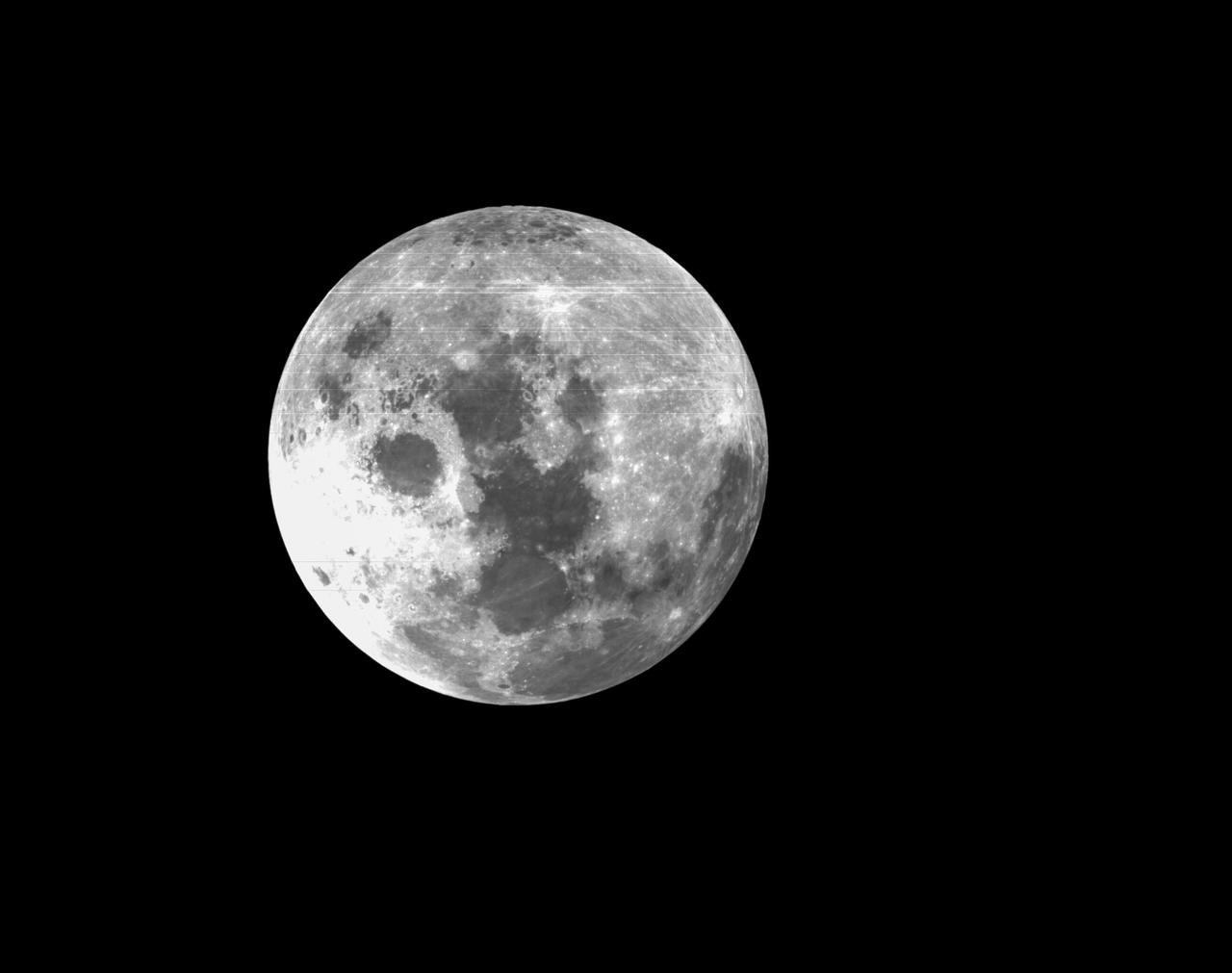

art001e002194 (Dec. 5, 2022) On flight day 20 of NASA’s Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera looked back at the Moon as the spacecraft began its journey home. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
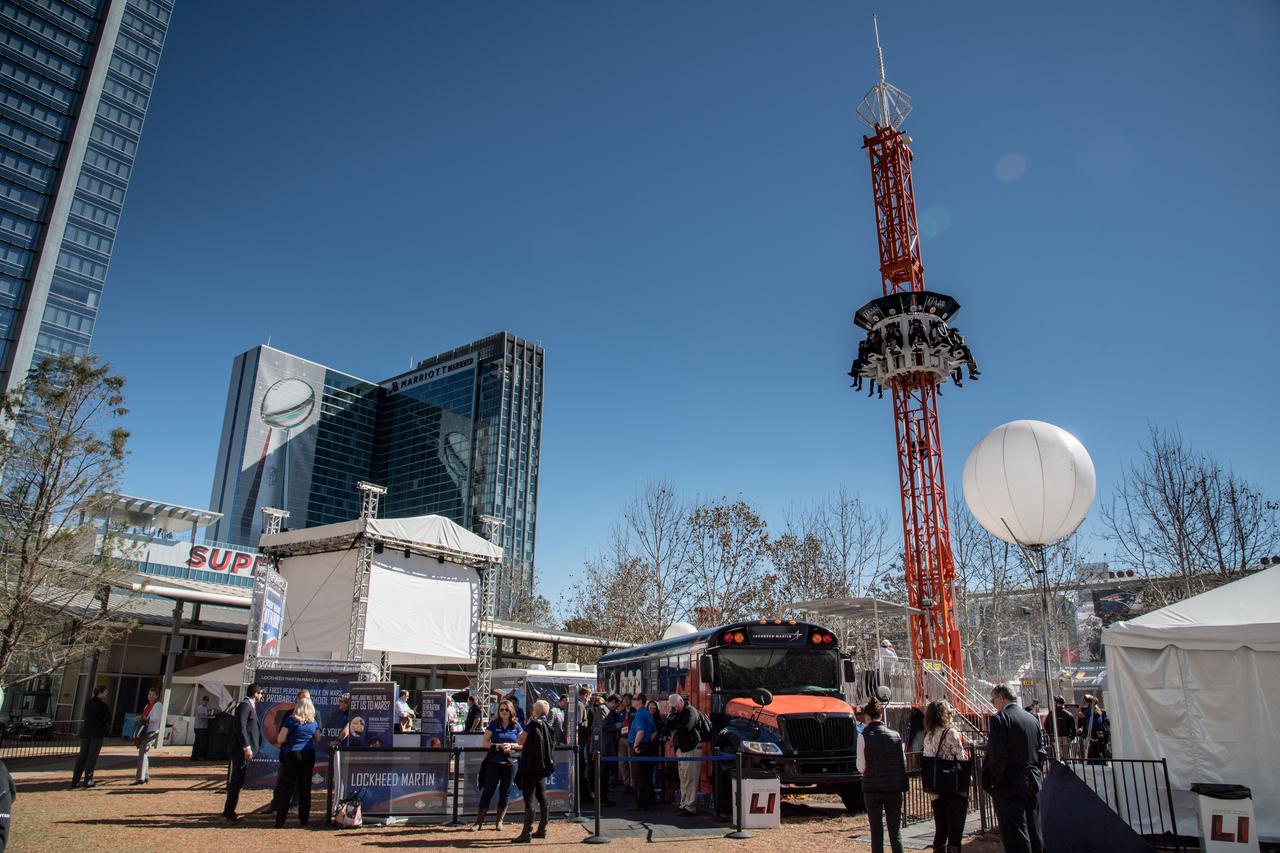

jsc2017e011393 (01/30/2017) --- Space exploration will feature prominently at Super Bowl LIVE, a nine-day fan festival running Jan. 28 through Feb. 5 on Discovery Green, Houston Texas where 100,000 visitors are expected each day. NASA is collaborating with the Houston Super Bowl Host Committee, which is the fan festival organizer, to share NASA’s contributions with the Houston community and to the nation. At NASA's Future Flight, the primary attraction at the free fan festival, riders will take a trip to Mars and back using virtual reality goggles on a 90-foot drop tower ride. Visitors also will get a chance to see several NASA assets that have been transported to downtown Houston for the activities. These assets include: the Orion mockup used for water recovery testing, Space Exploration Vehicle (SEV /Rover), the Driven to Explore mobile exhibit, Mars Science Laboratory – Curiosity Rover - replica, Robonaut 1 (Centaur configuration), EMU space suit presentation unit, Arctic meteorite and astromaterials display, and the Mark III advanced space suit photo-op. Several of NASA’s industry partners sponsoring Future Flight will also have assets on display, and a replica of the James Webb Space Telescope will be located near but not inside the activities on Discovery Green. NASA and industry partner volunteers will be staffing the Future Flight area. NASA PHOTOGRAPHER: Bill Stafford
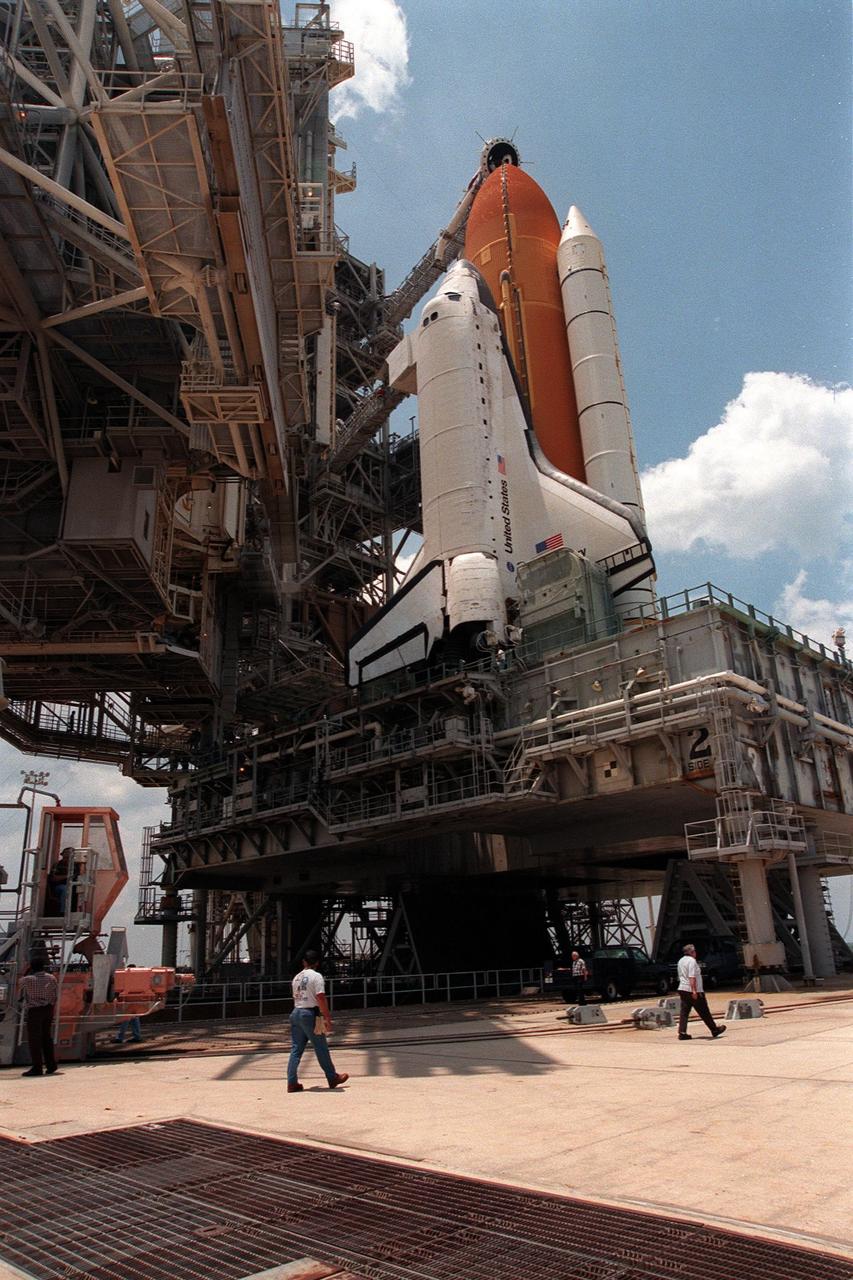

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Rotating Service Structure is rolled back at Launch Pad 39B to reveal the Space Shuttle Discovery, scheduled to launch on mission STS-96 at 6:49 a.m. EDT on May 27. STS-96 is a 10-day logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying about 4,000 pounds of supplies to be stored aboard the station, for use by future crews, including laptop computers, cameras, tools, spare parts, and clothing. The mission also includes such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-involved experiment. The mission will include a space walk to attach the cranes to the outside of the ISS for use in future construction. Space Shuttle Discovery is due to launch on May 27 at 6:49 a.m. EDT. Landing is expected at the SLF on June 6 about 1:58 a.m. EDT
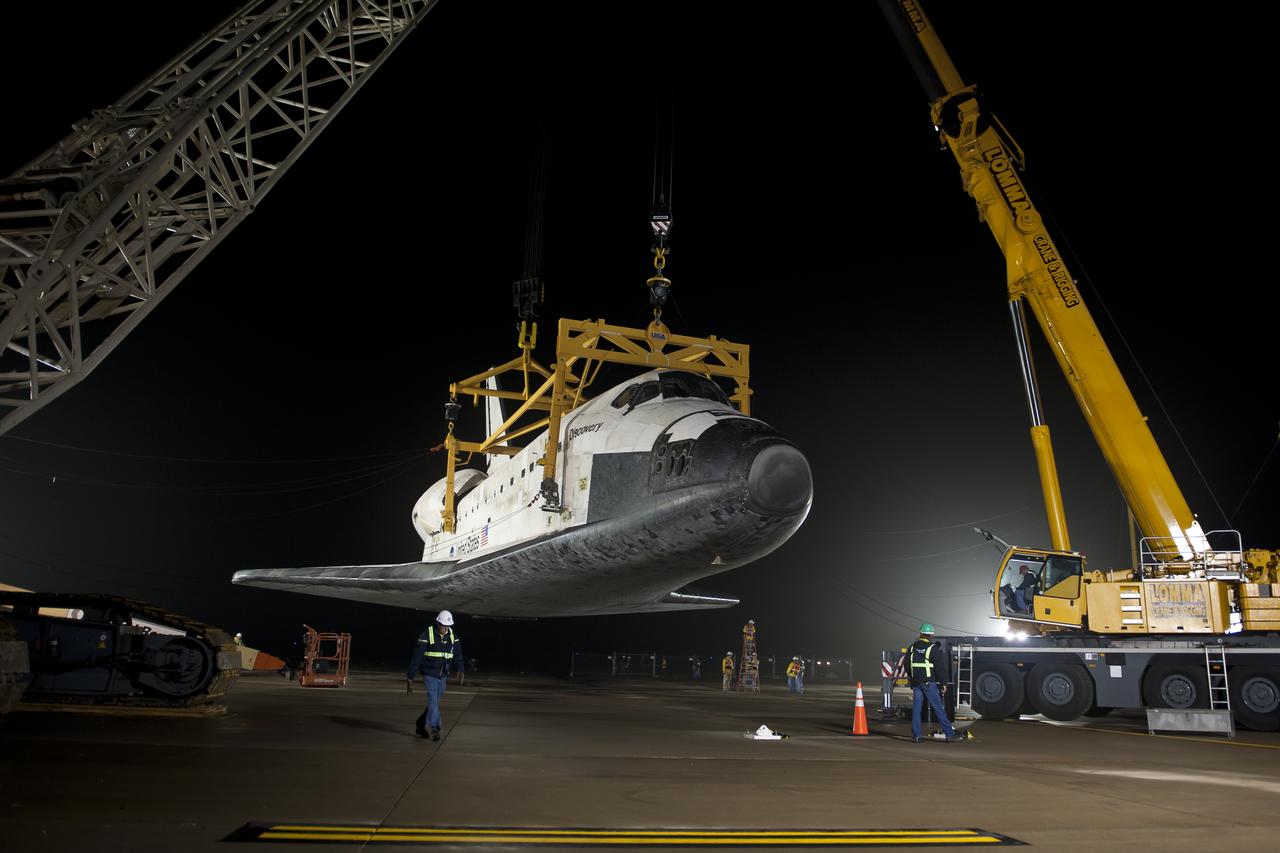

The space shuttle Discovery is suspended from a sling held by two cranes after the NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) was pushed back from underneath at Washington Dulles International Airport, Thursday, April 19, 2012, in Sterling, VA. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
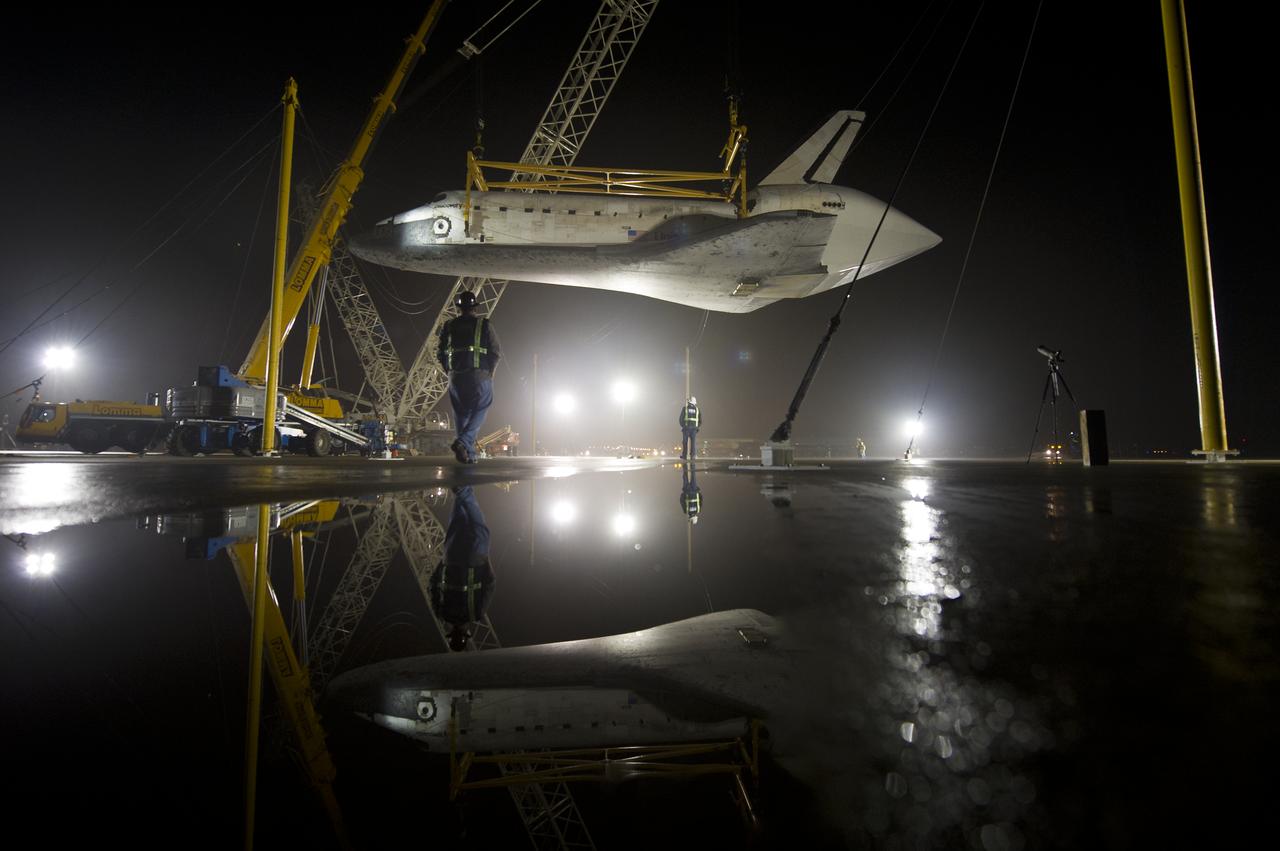

The space shuttle Discovery is suspended from a sling held by two cranes shortly after the NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) was pushed back from underneath at Washington Dulles International Airport, Thursday, April 19, 2012, in Sterling, VA. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
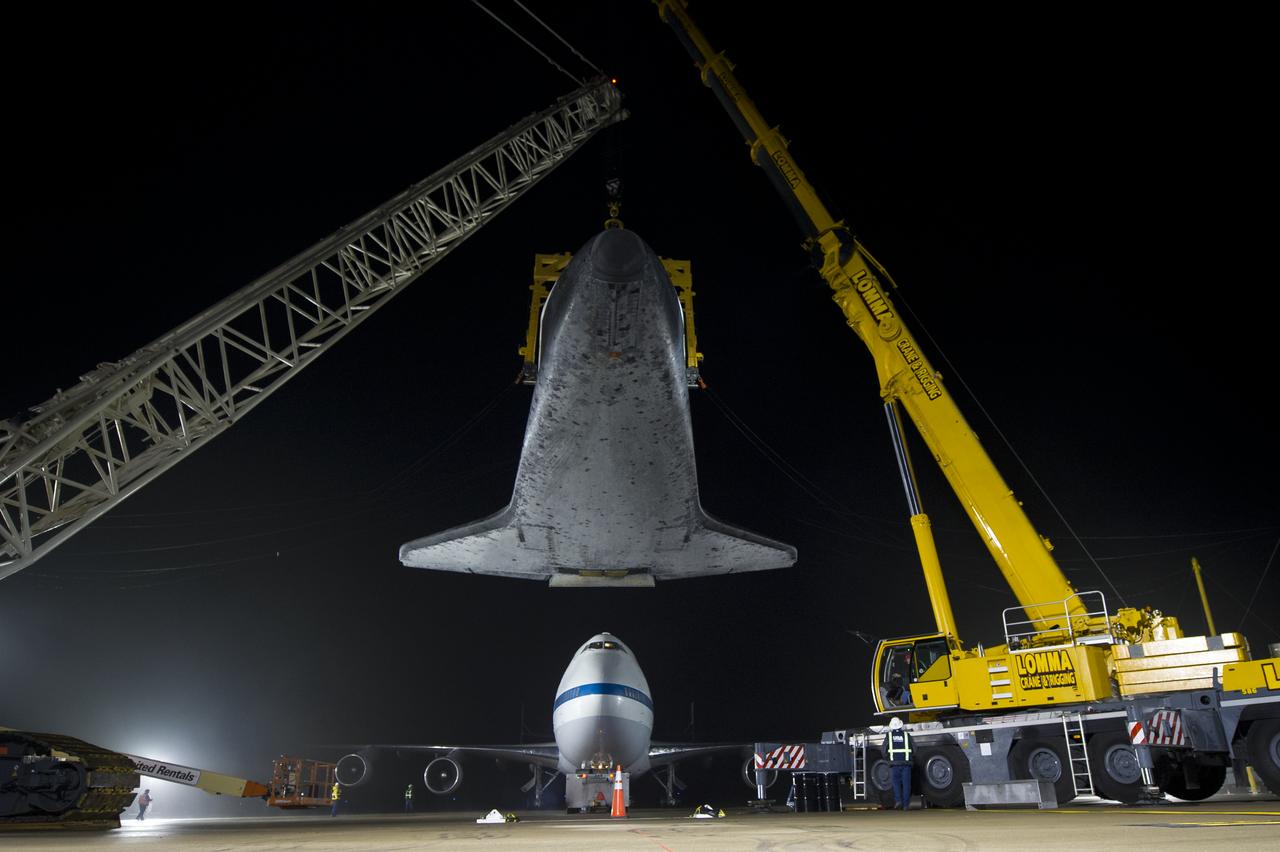

The space shuttle Discovery is suspended from a sling held by two cranes as the NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) is pushed back from underneath at Washington Dulles International Airport, Thursday, April 19, 2012, in Sterling, VA. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems unveil on Monday, Dec. 1, 2025, the America 250 logo on the twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen on a 10-day mission around the Moon and back in early 2026 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA Kennedy. America 250 commemorates the 250th anniversary of the signing of the Declaration of Independence with NASA celebrating the “Spirit of Innovation” theme to inspire future generations.

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems unveil on Monday, Dec. 1, 2025, the America 250 logo on the twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen on a 10-day mission around the Moon and back in early 2026 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA Kennedy. America 250 commemorates the 250th anniversary of the signing of the Declaration of Independence with NASA celebrating the “Spirit of Innovation” theme to inspire future generations.
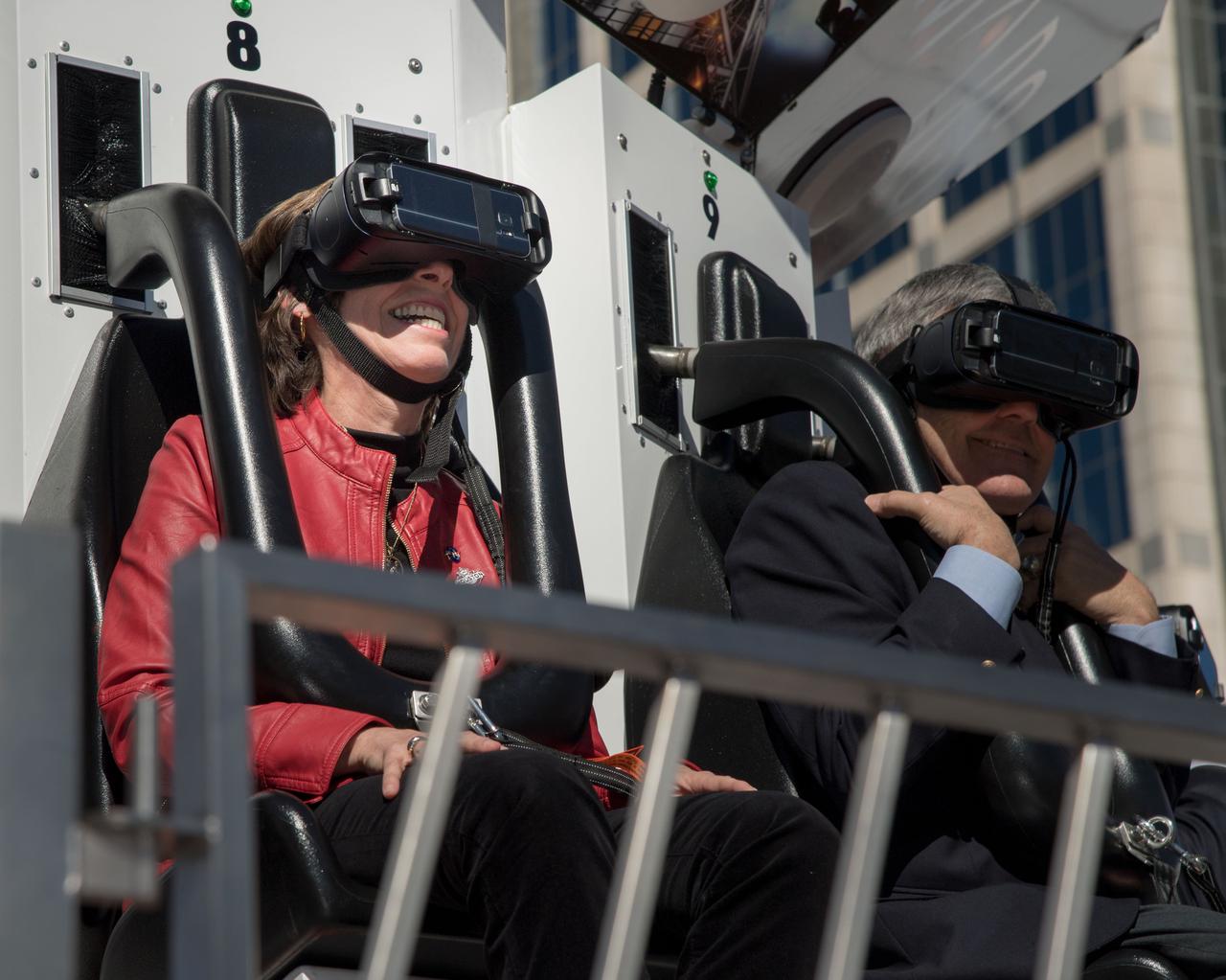

jsc2017e011384 (01/30/2017) --- With virtual reality googles in place, Johnson Space Center Director Ellen Ochoa and Kennedy Space Center Director Robert Cabana prepare for the Journey to Mars ride that will pull the Orion capsule up 90 feet and suddenly drop them, while they experience a virtual trip to Mars and back. The Houston Texas Super Bowl Live event at Discovery Green lasts through the 5th of February and has an estimated 100,000 visitors each day. The Mars ride is but one of the many attractions that NASA has provided in their Future Flight area. NASA PHOTOGRAPHER Bill Stafford

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-110 Mission Specialists Jerry Ross (left) and Steven Smith (right) are happy to be back on Earth after a successful mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis landed on KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility after 171 orbits, completing a 10-day, 19-hour, 4.5-million mile journey. Main gear touchdown was 12:26:57 p.m. EDT, nose gear touchdown was 12:27:09 p.m. and wheel stop was 12:28:07 p.m. The crew delivered and installed the S0 truss, which will support cooling and power systems essential for the addition of future international laboratories, on the Station
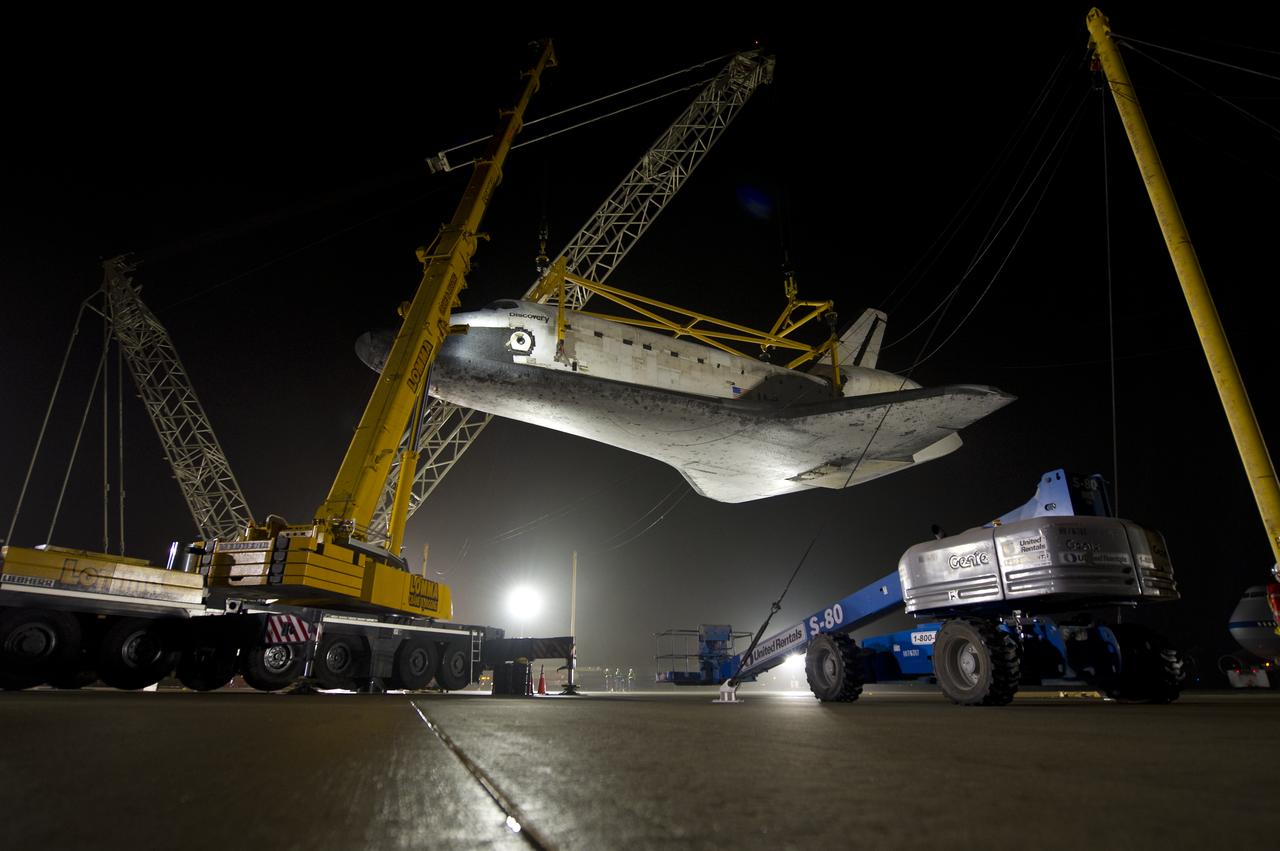

The space shuttle Discovery is suspended from a sling held by two cranes shortly after the NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) was pushed back from underneath at Washington Dulles International Airport, Thursday, April 19, 2012, in Sterling, VA. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
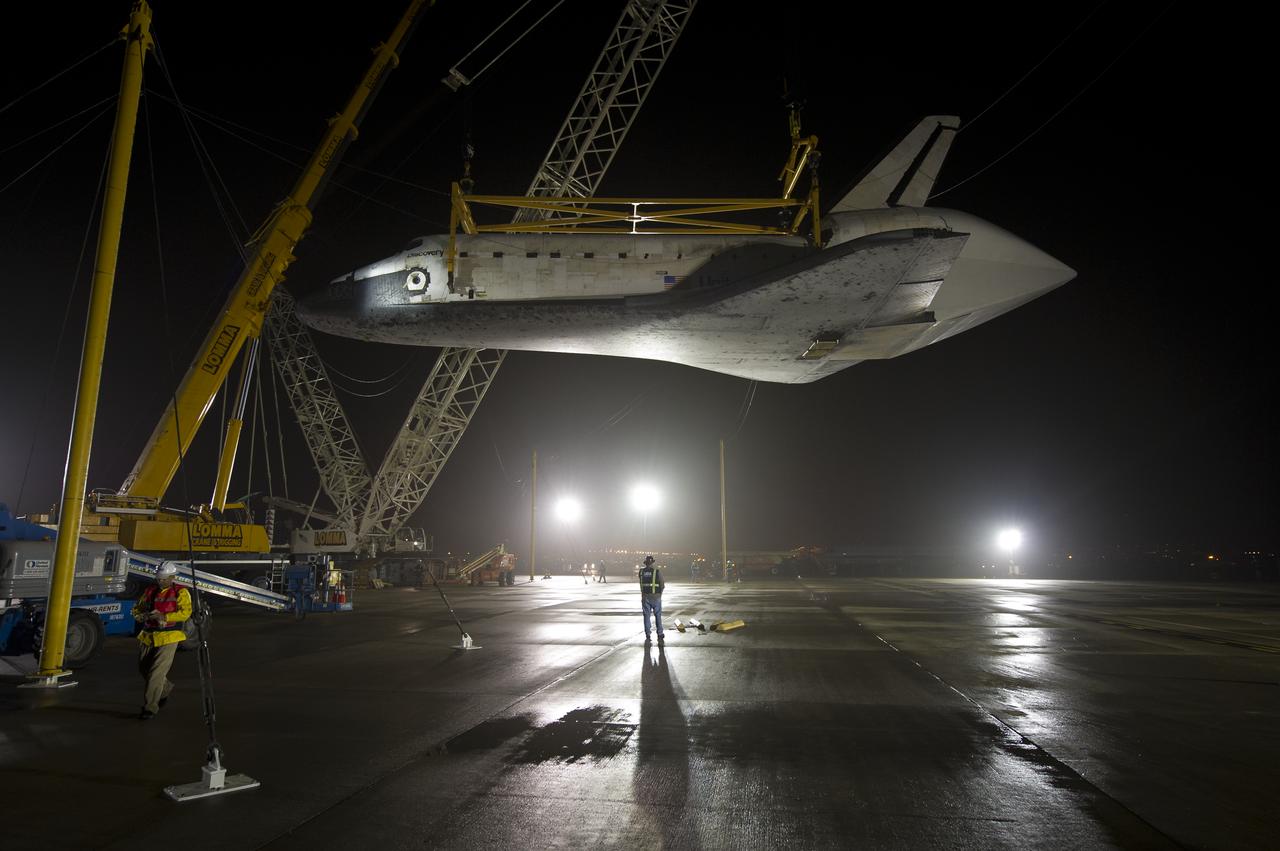

The space shuttle Discovery is suspended from a sling held by two cranes shortly after the NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) was pushed back from underneath at Washington Dulles International Airport, Thursday, April 19, 2012, in Sterling, VA. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
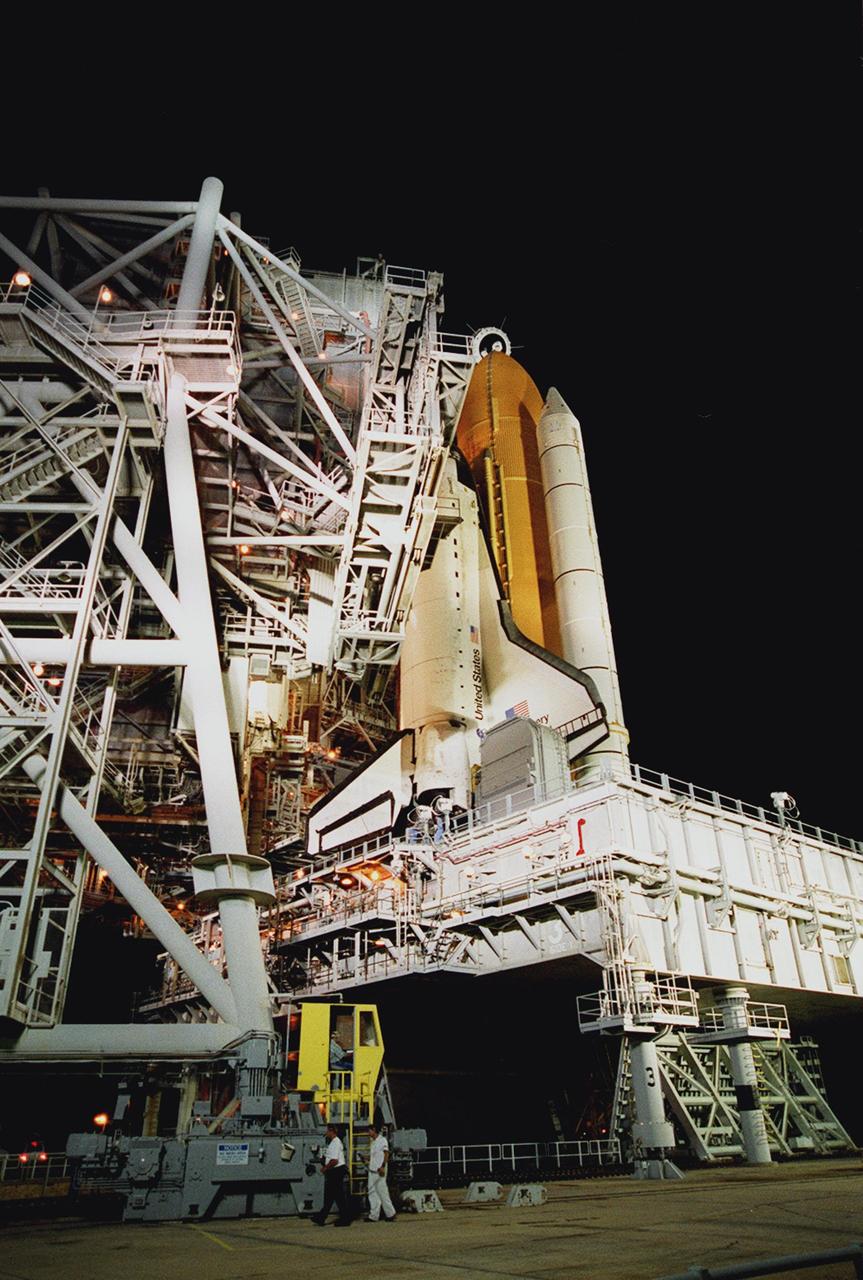

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Rotating Service Structure at Launch Pad 39A rolls back, revealing the Space Shuttle Discovery on the Mobile Launcher Platform. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). The mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT
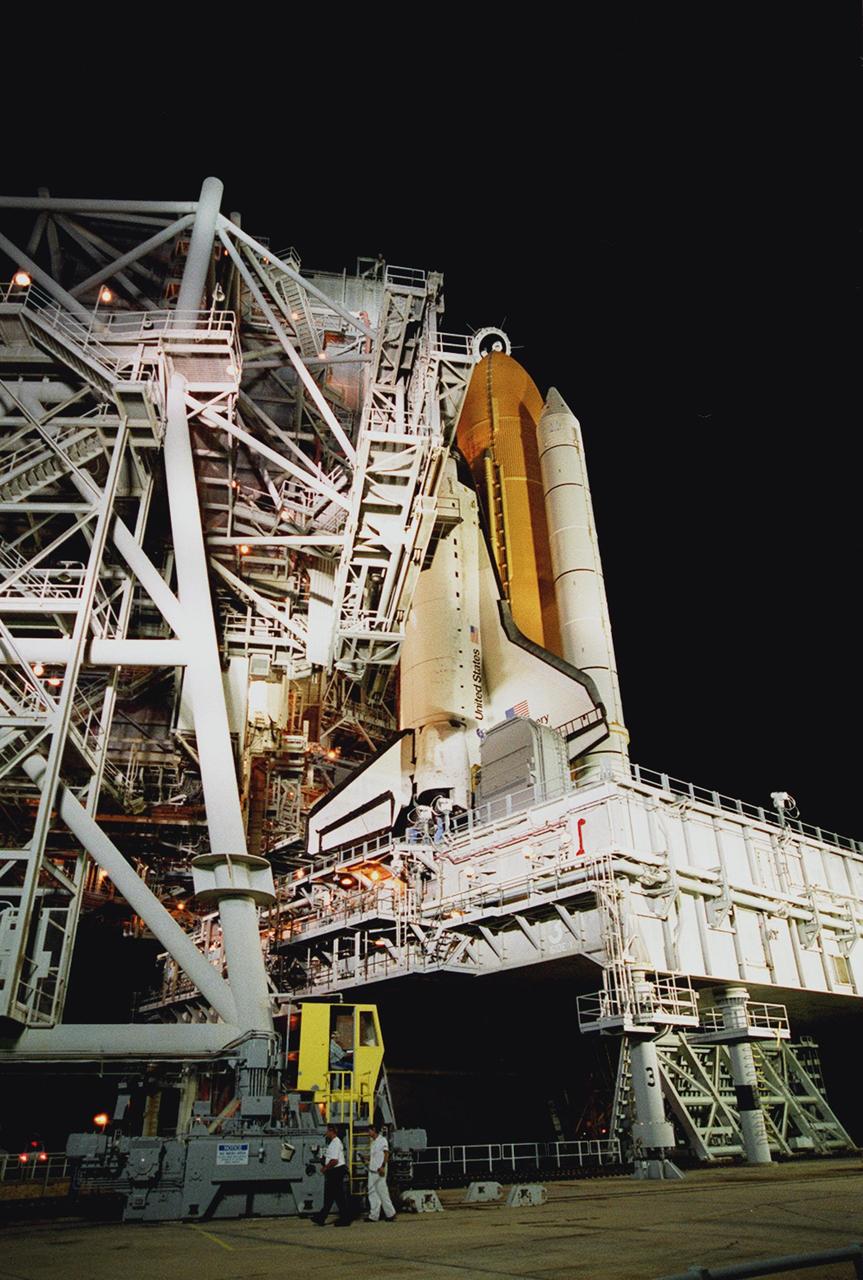

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Rotating Service Structure at Launch Pad 39A rolls back, revealing the Space Shuttle Discovery on the Mobile Launcher Platform. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). The mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT
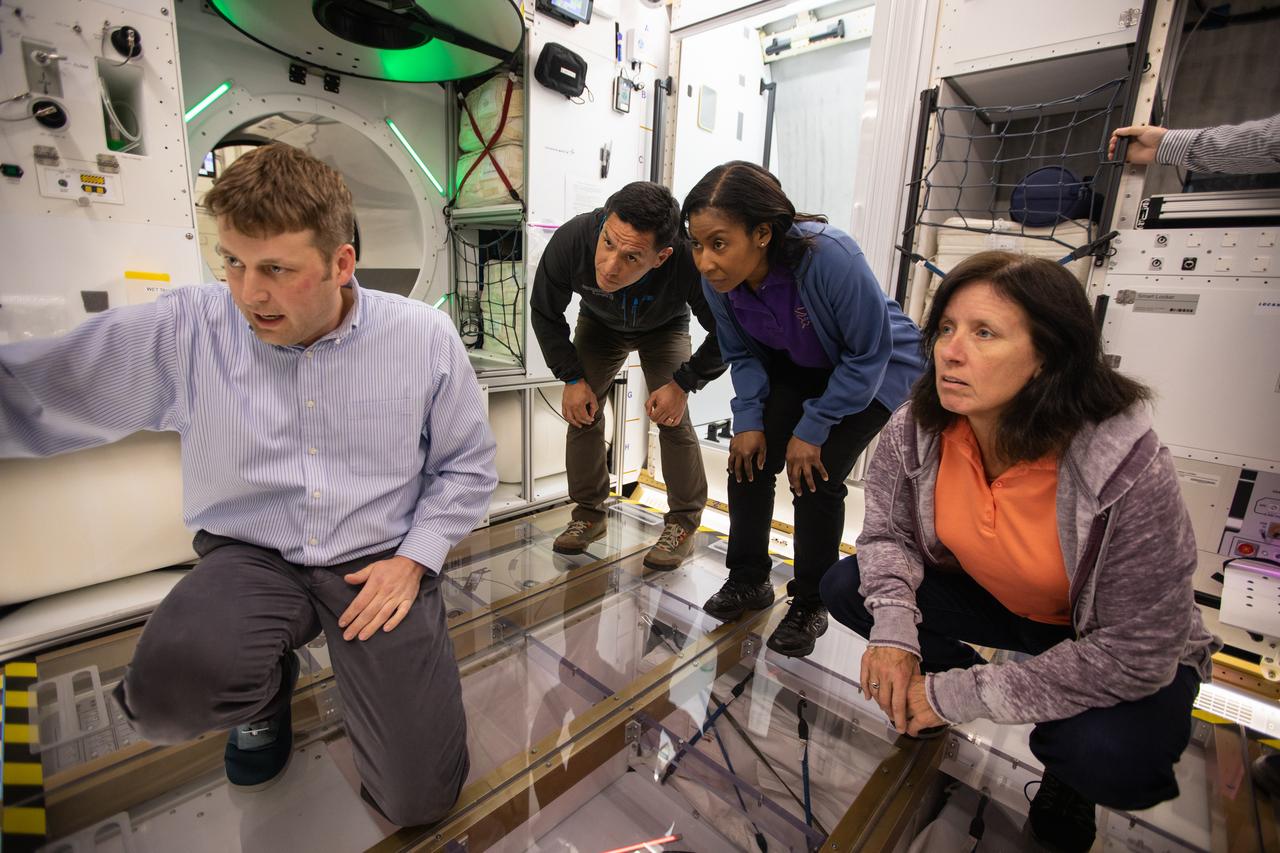

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, in back from left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Stephanie Wilson and Shannon Walker. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
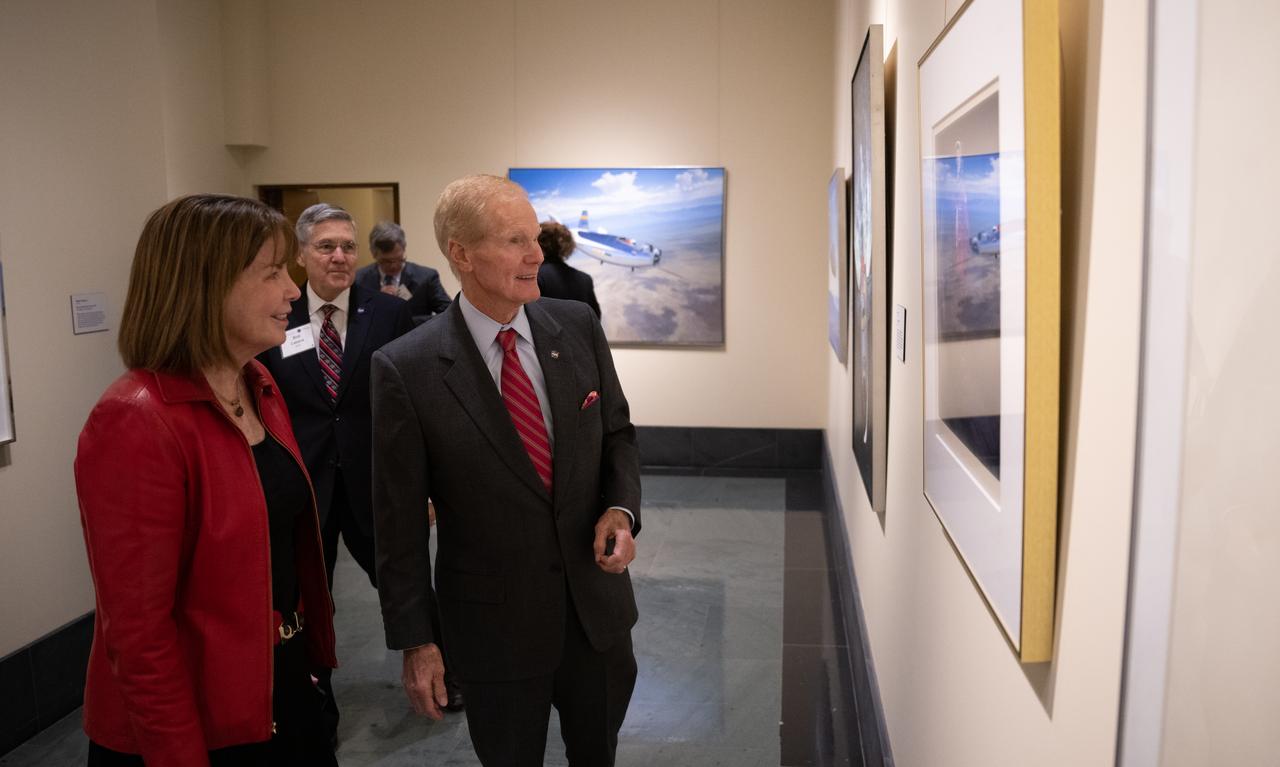

Colleen Hartman, director of physics, aeronautics, and space science at the National Academies of Science , left, and NASA Administrator Bill Nelson are seen as they view the NASA Art Program Exhibition “Launching the Future: Looking Back to Look Forward” during an event celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 17 mission, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at the National Academies of Science in Washington. The three-astronaut crew of Apollo 17 - commander Eugene Cernan, lunar module pilot Harrison Schmitt, and command module pilot Ronald Evans, embarked on the last mission of the Apollo program to land humans on the Moon in December of 1972. Cernan and Schmitt spent three days on the lunar surface collecting samples and performing scientific experiments before lifting off from the Taurus-Littrow Valley on December 14, 1972. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
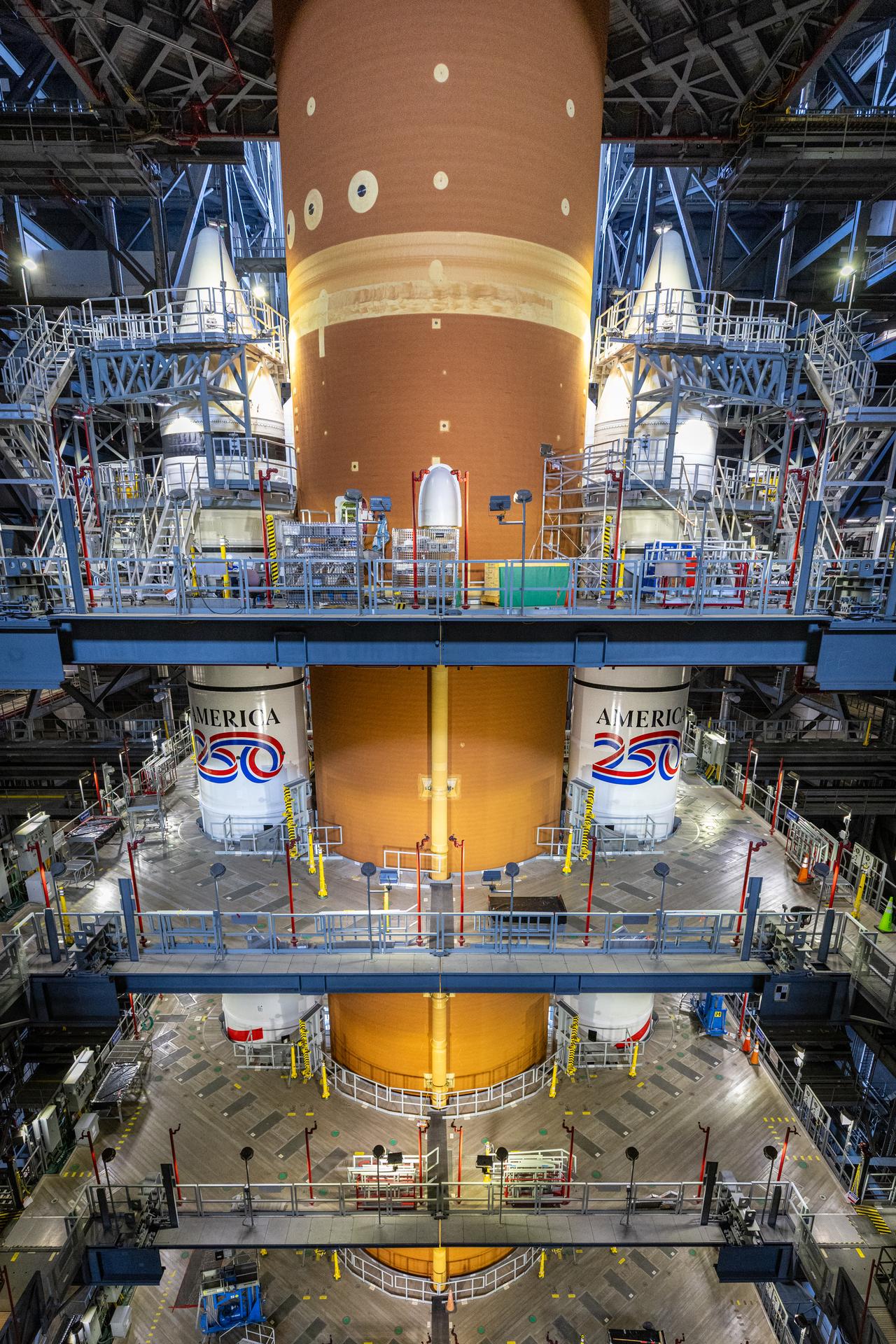

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program complete installation of the America 250 emblem on the twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Dec. 4, 2025. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen on a 10-day mission around the Moon and back in early 2026 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA Kennedy. America 250 commemorates the 250th anniversary of the signing of the Declaration of Independence with NASA celebrating the “Spirit of Innovation” theme to inspire future generations.
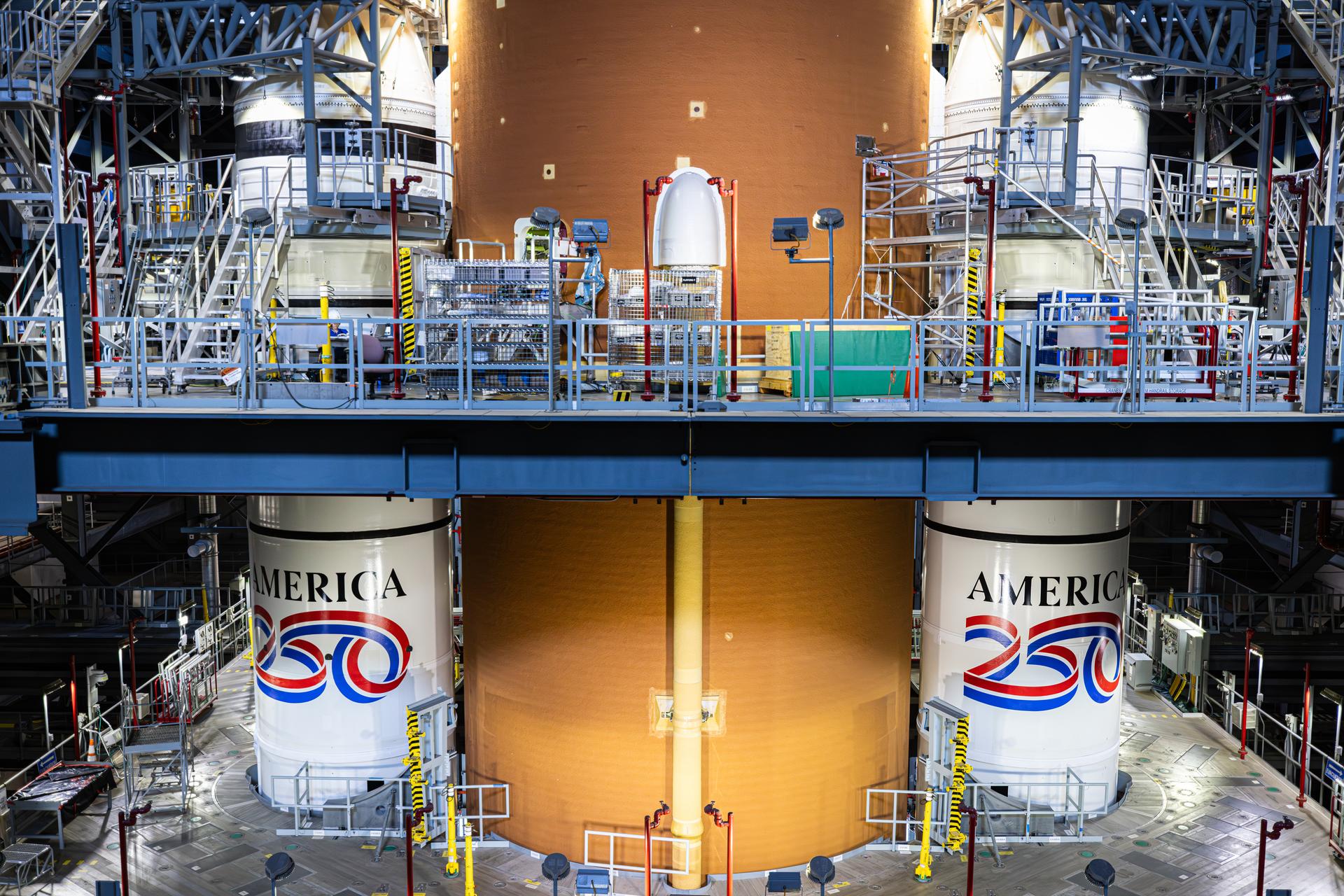

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program complete installation of the America 250 emblem on the twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Dec. 4, 2025. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen on a 10-day mission around the Moon and back in early 2026 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA Kennedy. America 250 commemorates the 250th anniversary of the signing of the Declaration of Independence with NASA celebrating the “Spirit of Innovation” theme to inspire future generations.
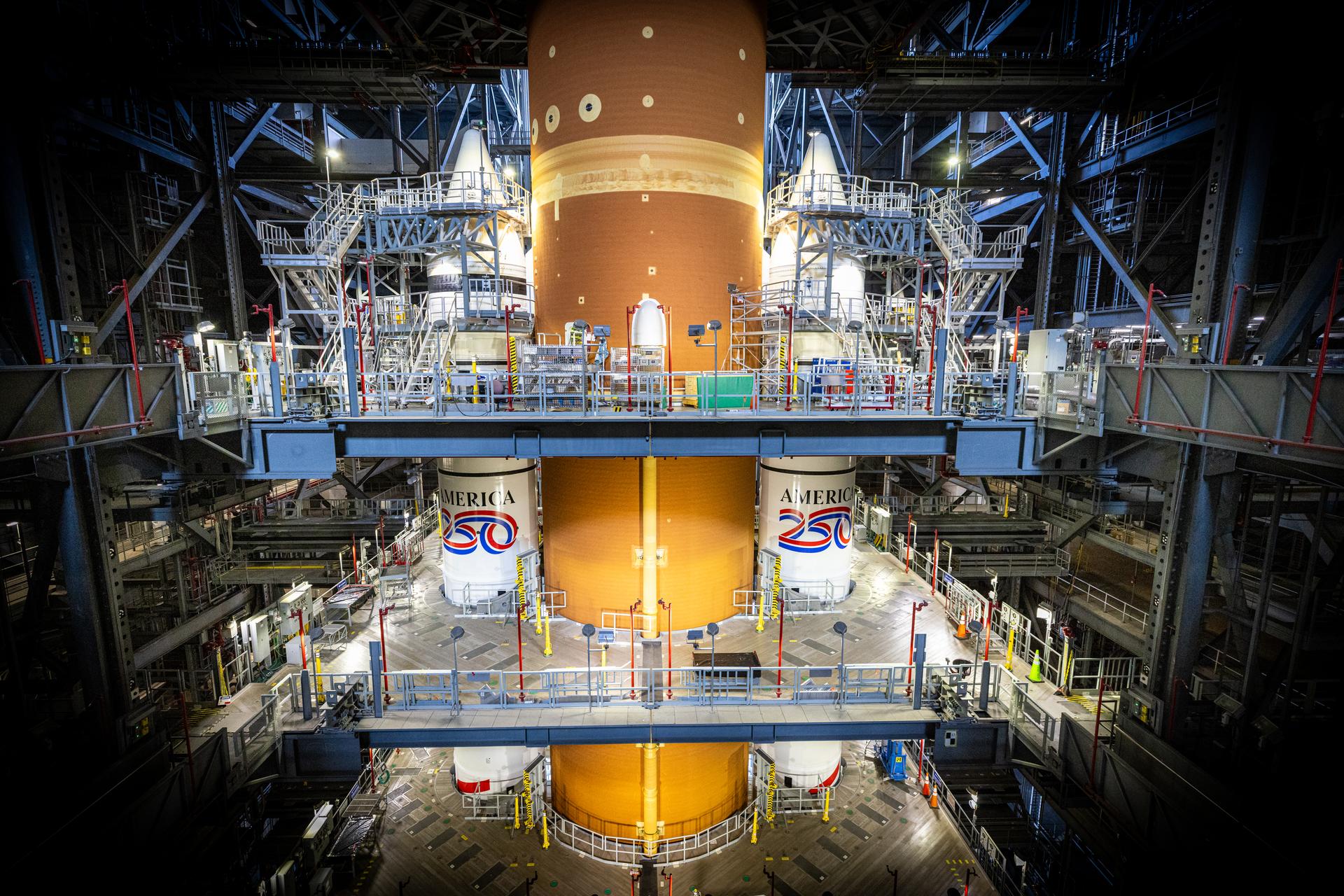

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program complete installation of the America 250 emblem on the twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Dec. 4, 2025. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen on a 10-day mission around the Moon and back in early 2026 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA Kennedy. America 250 commemorates the 250th anniversary of the signing of the Declaration of Independence with NASA celebrating the “Spirit of Innovation” theme to inspire future generations.
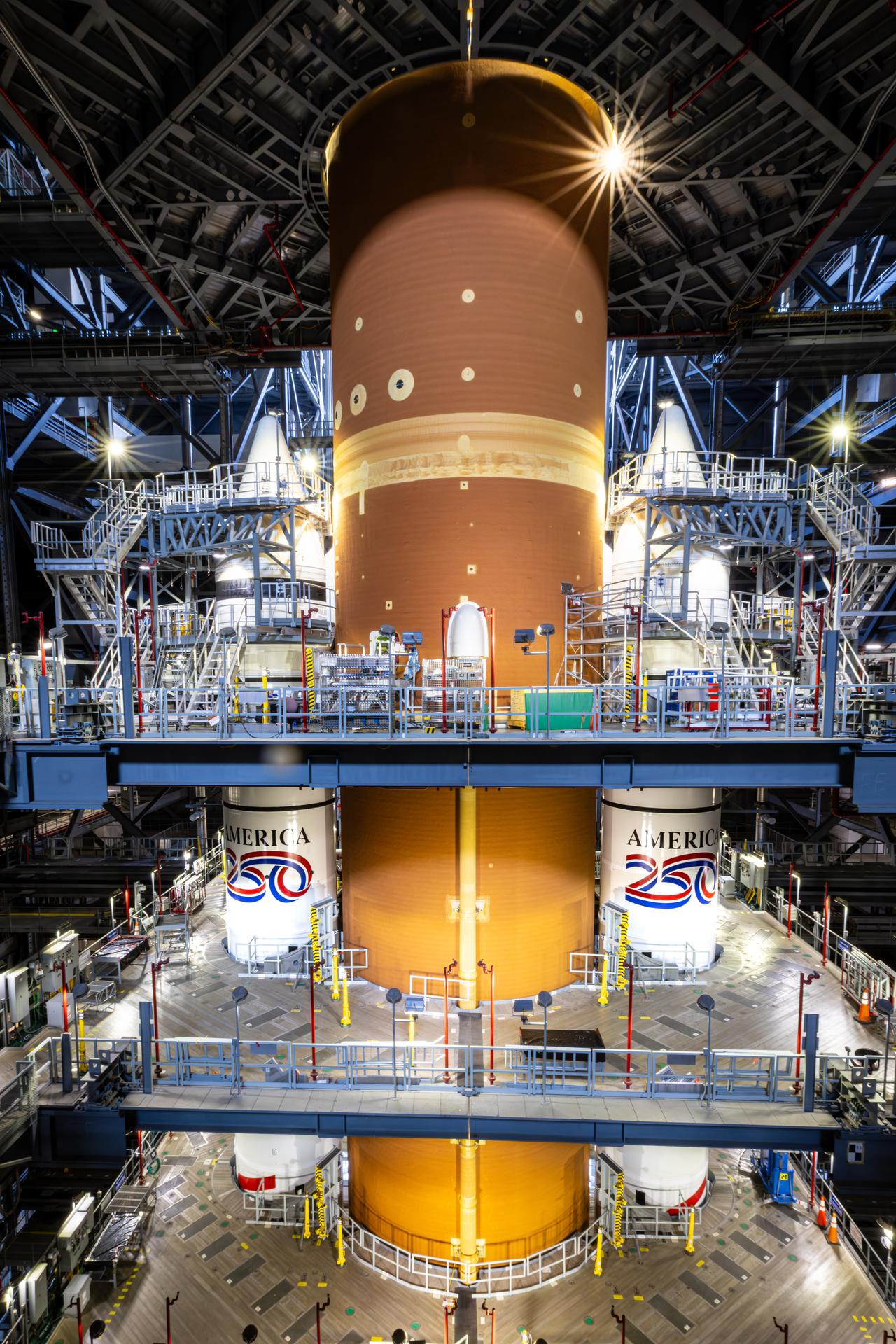

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program complete installation of the America 250 emblem on the twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Dec. 4, 2025. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen on a 10-day mission around the Moon and back in early 2026 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA Kennedy. America 250 commemorates the 250th anniversary of the signing of the Declaration of Independence with NASA celebrating the “Spirit of Innovation” theme to inspire future generations.
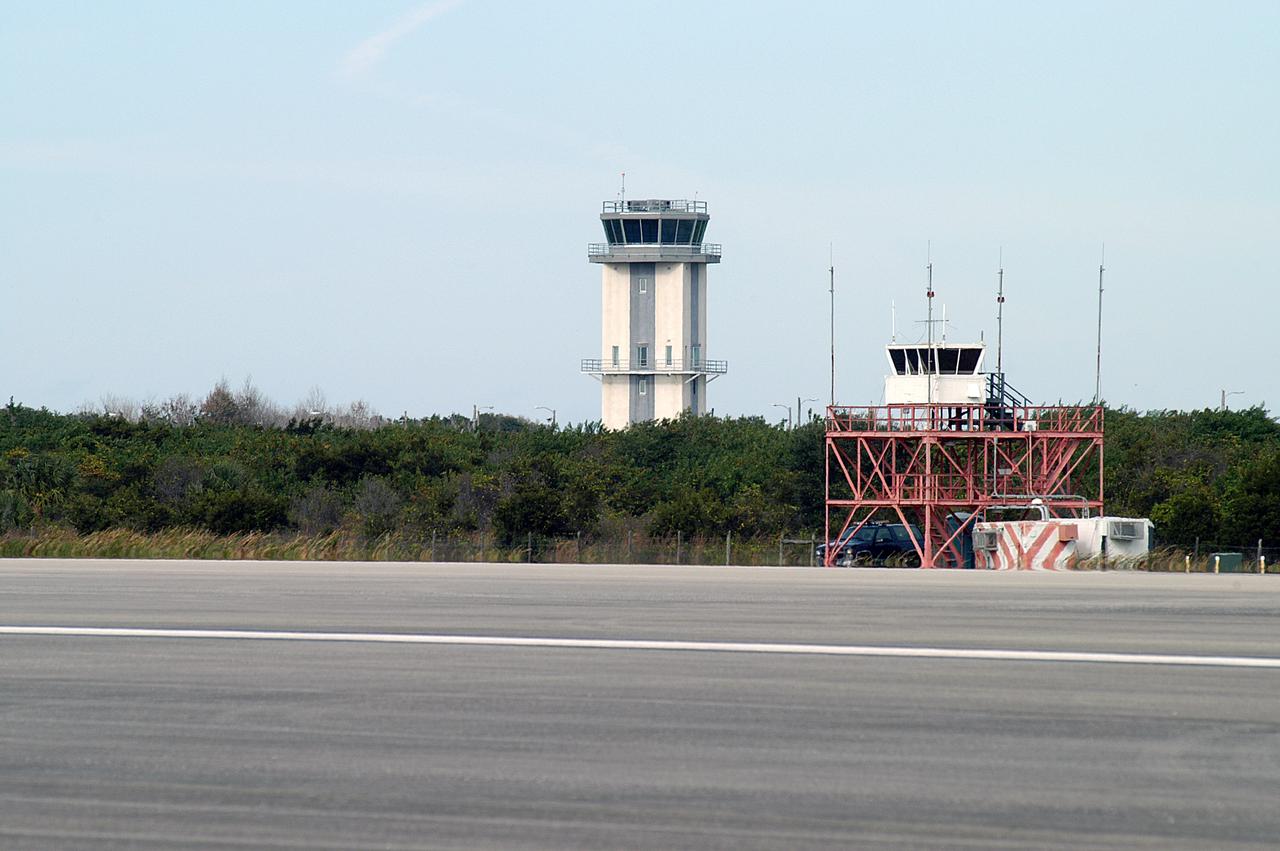

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Two control towers are seen at the edge of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, the old one in front and the nearly completed new tower in back. The old tower stands only 20 feet above the runway surface, too low to see the launch pads to the east. During nighttime landing operations, those inside the tower have been hindered by the eight-billion candlepower xenon lights that illuminate the runway. The new control tower is built atop an existing mound, rising nearly 100 feet over the midpoint of the runway. The height gives controllers a spectacular 360-degree view of NASA-KSC and northern Brevard County. The new facility will also replace the SLF Operations Building. The operations building is home to the Military Radar Unit that monitors NASA-KSC airspace 24 hours a day, as well as runway light controls, navigational aids, weather and wind speed instrumentation, and gate controls. In the new tower, the computer displays will be fully modernized to Federal Aviation Administration standards with touch-screen technology. Construction on the new facility began in February 2003 and is nearly ready for occupancy. Only some final inspections and approvals remain. A support building and Public Affairs viewing deck, to be used for observing future landing operations, will be added and are already in work.
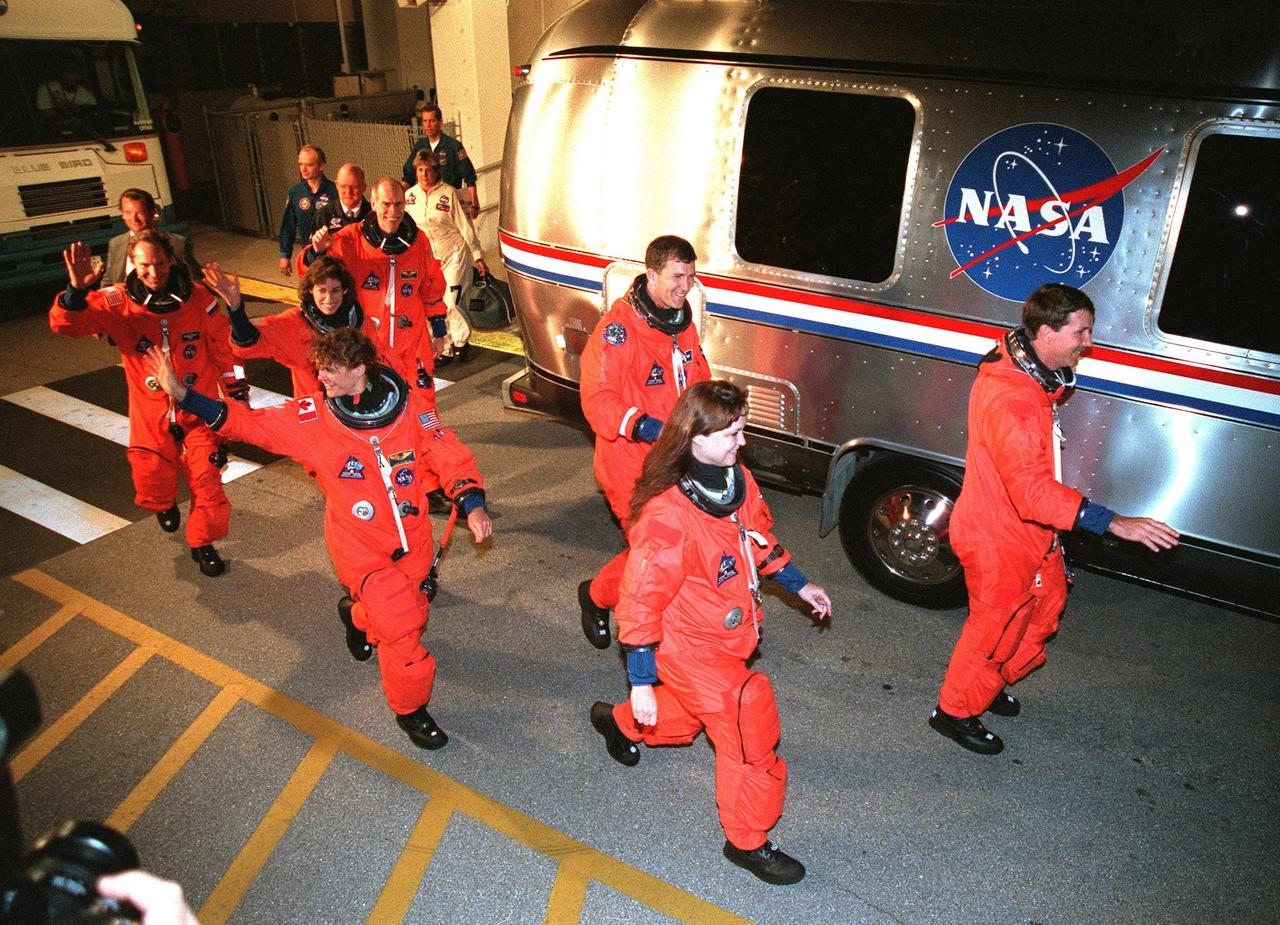

The STS-96 crew smile and wave at onlookers as they eagerly head for the bus that will take them to Launch Pad 39B for liftoff of Space Shuttle Discovery, targeted for 6:49 a.m. EDT. From left to right in front are Mission Specialists Valery Ivanovich Tokarev, Ellen Ochoa, Julie Payette and Tamara E. Jernigan; in back are Mission Specialist Daniel T. Barry, Pilot Rick D. Husband, and Commander Kent V. Rominger. Payette is with the Canadian Space Agency, and Tokarev is with the Russian Space Agency. STS-96 is a 10-day logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying about 4,000 pounds of supplies, to be stored aboard the station for use by future crews, including laptop computers, cameras, tools, spare parts, and clothing. The mission also includes such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-involved experiment. It will include a space walk to attach the cranes to the outside of the ISS for use in future construction. Landing is expected at the SLF on June 6 about 1:58 a.m. EDT
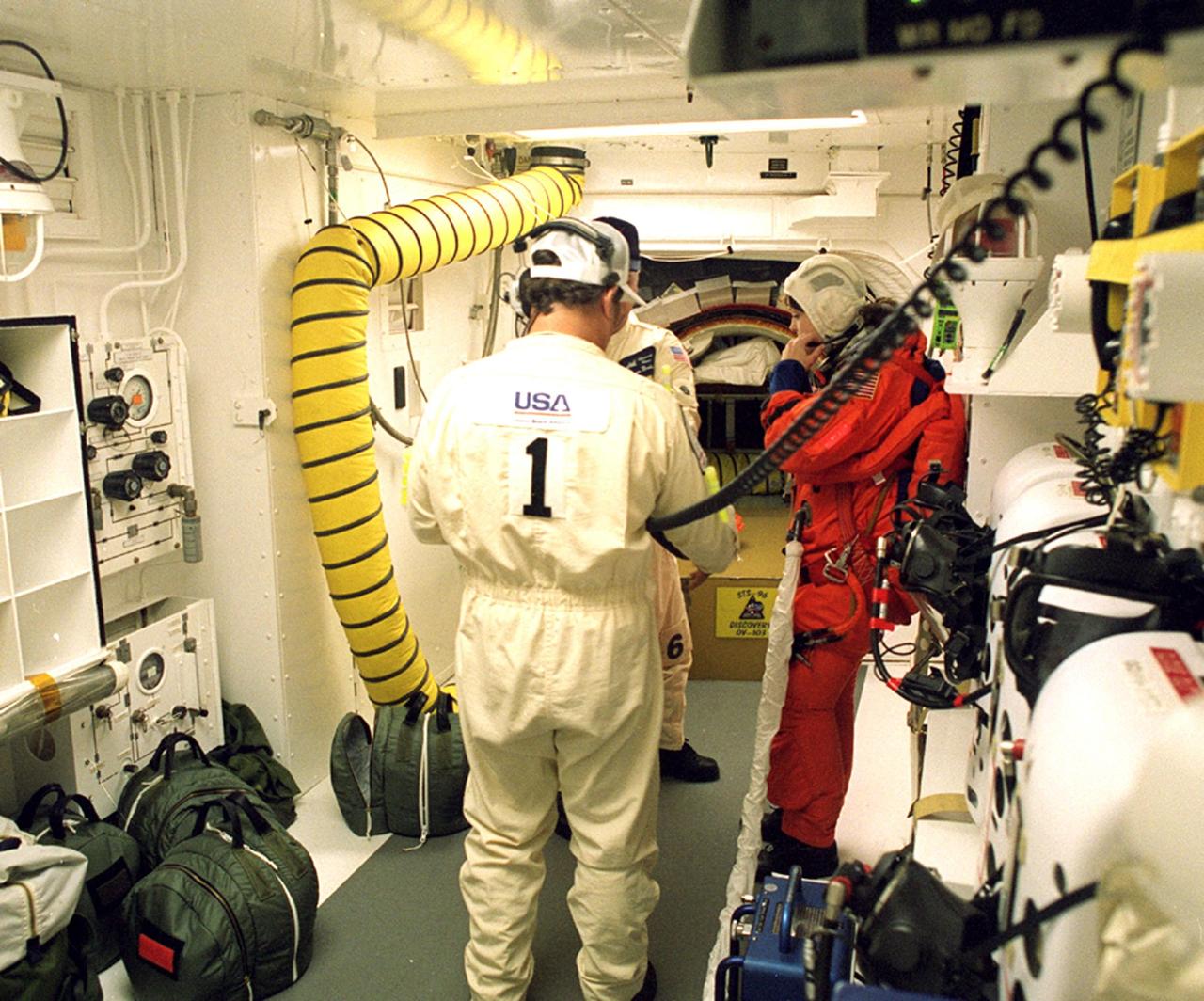

Before entering the orbiter Discovery, STS-96 Mission Specialist Tamara E. Jernigan is checked out in the white room by Closeout Crew Chief Travis Thompson (back to camera) and Quality Assurance Specialist James Davis. The white room is an environmental chamber at the end of the orbiter access arm that provides entry to the orbiter crew compartment. STS-96 is a 10-day logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying about 4,000 pounds of supplies, to be stored aboard the station for use by future crews, including laptop computers, cameras, tools, spare parts, and clothing. The mission also includes such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-involved experiment. It will include a space walk to attach the cranes to the outside of the ISS for use in future construction. Space Shuttle Discovery is due to launch today at 6:49 a.m. EDT. Landing is expected at the SLF on June 6 about 1:58 a.m. EDT
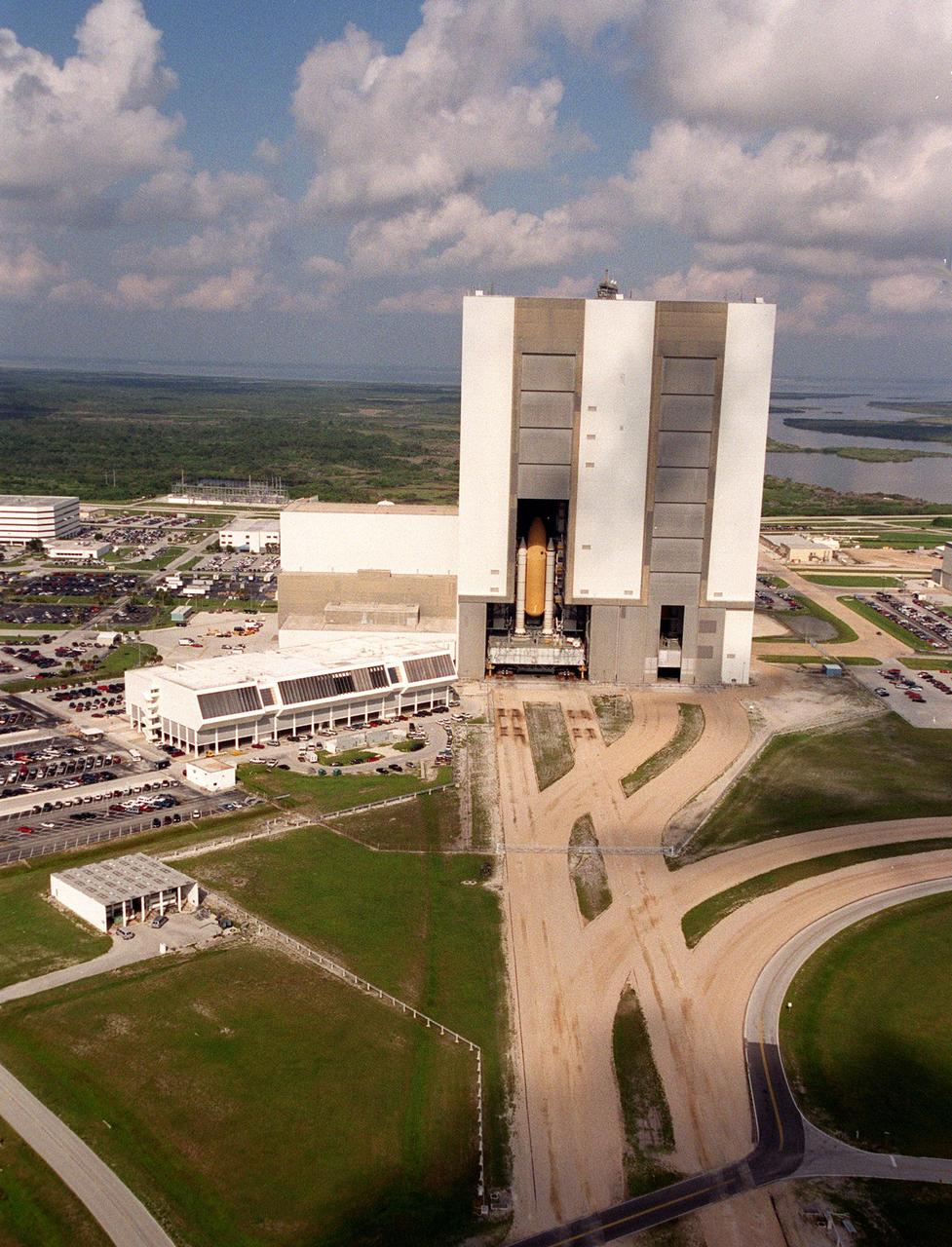

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Scattered clouds cast shadows as Space Shuttle Atlantis crawls back inside the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 1. After earlier starting its trek to Launch Pad 39B, Atlantis was returned to the VAB due to lightning in the area. To the left of the VAB is the Launch Control Center. The four-story building houses the firing rooms that are used to conduct Space Shuttle launches. Leading away from the VAB, in the foreground, is the crawlerway, the 130-foot-wide road specially constructed to transport the Shuttle, mobile launcher platform and crawler-transporter with a combined weight of about 17 million pounds. Space Shuttle Atlantis is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
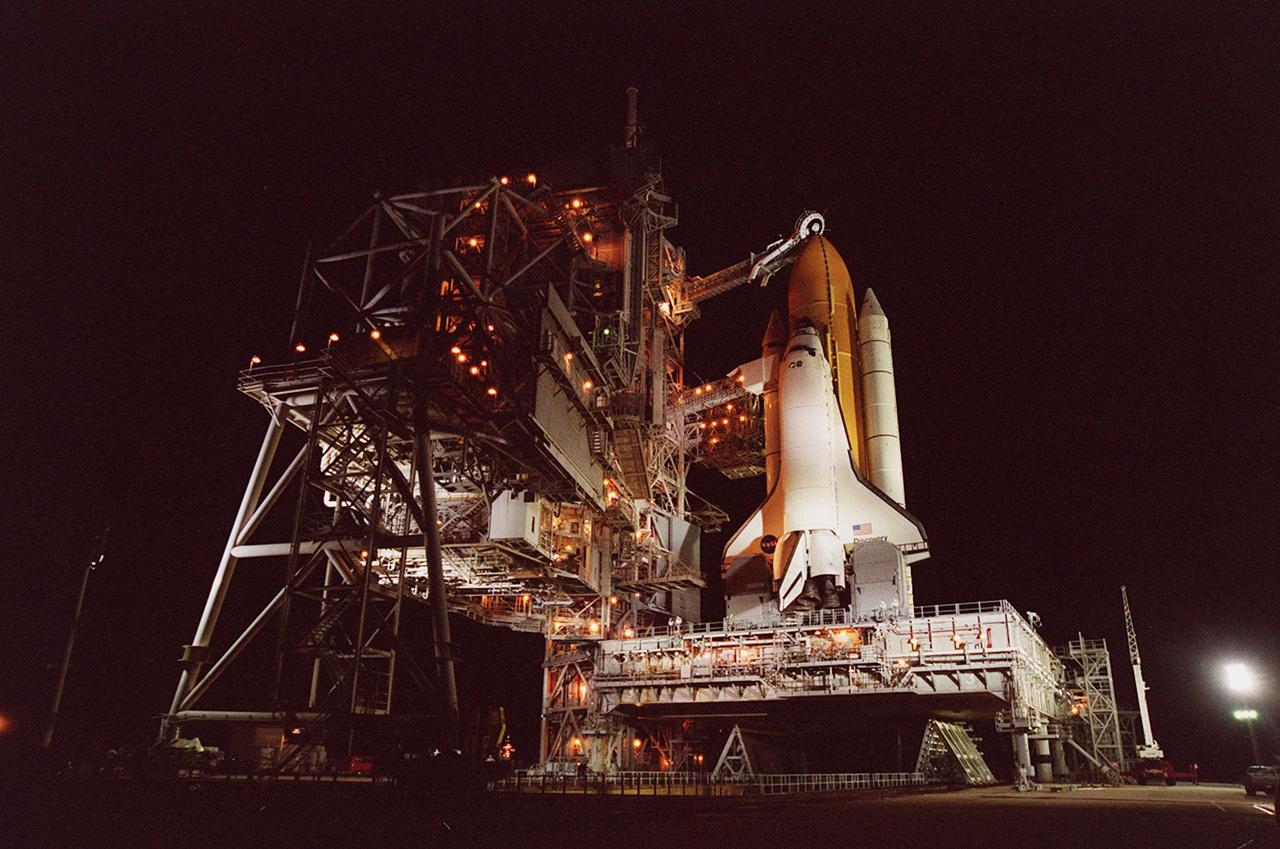

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- With the Rotating Service Structure rolled back, Space Shuttle Discovery is revealed on the Mobile Launcher Platform at Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). At the top is the 13-foot-wide “beanie cap,” at the end of the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm, designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Space Shuttle. Lower is the Orbiter Access Arm with the environmental chamber, known as the “white room,” extended to the orbiter. The chamber provides entry for the crew into the orbiter and also serves as emergency egress up to 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. The STS-92 mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT
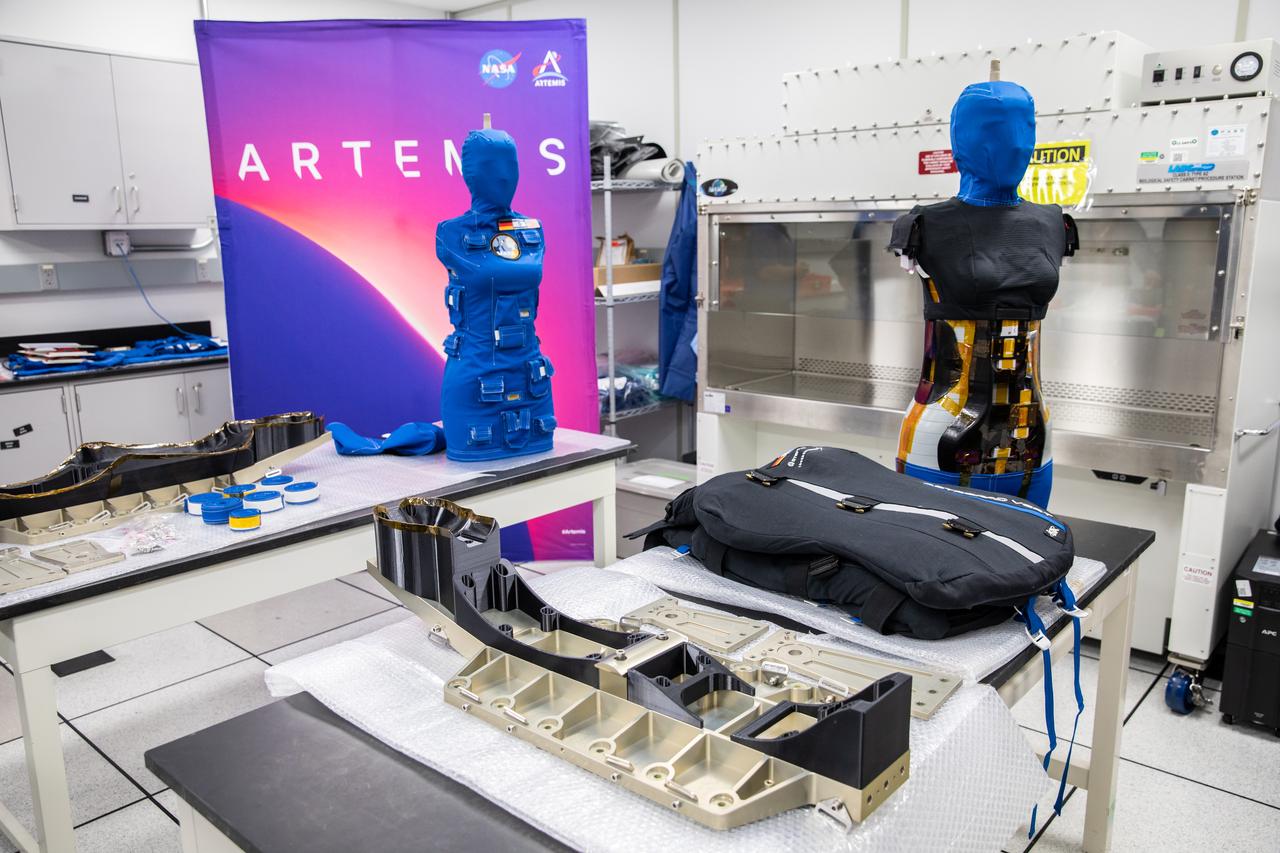

After a 25-day flight beyond the Moon and back inside the Artemis I Orion crew module, two manikins undergo post-flight payload inspections inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2023. As part of the Matroshka AstroRad Radiation Experiment (MARE) investigation, the two female manikins – Helga and Zohar – were equipped with radiation detectors. Zohar also wore a radiation protection vest, to determine the radiation risk during the Artemis I mission and potentially reduce exposure during future missions with astronauts. The detectors will be removed at Kennedy and the torsos will return to teams at the German Space Agency for further analysis. Artemis I Orion launched atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022, at 1:47 a.m. EST. During the flight, Orion flew farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown, paving the way for human deep space exploration and demonstrating NASA’s commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I was to thoroughly test the SLS and Orion spacecraft’s integrated systems before crewed missions. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
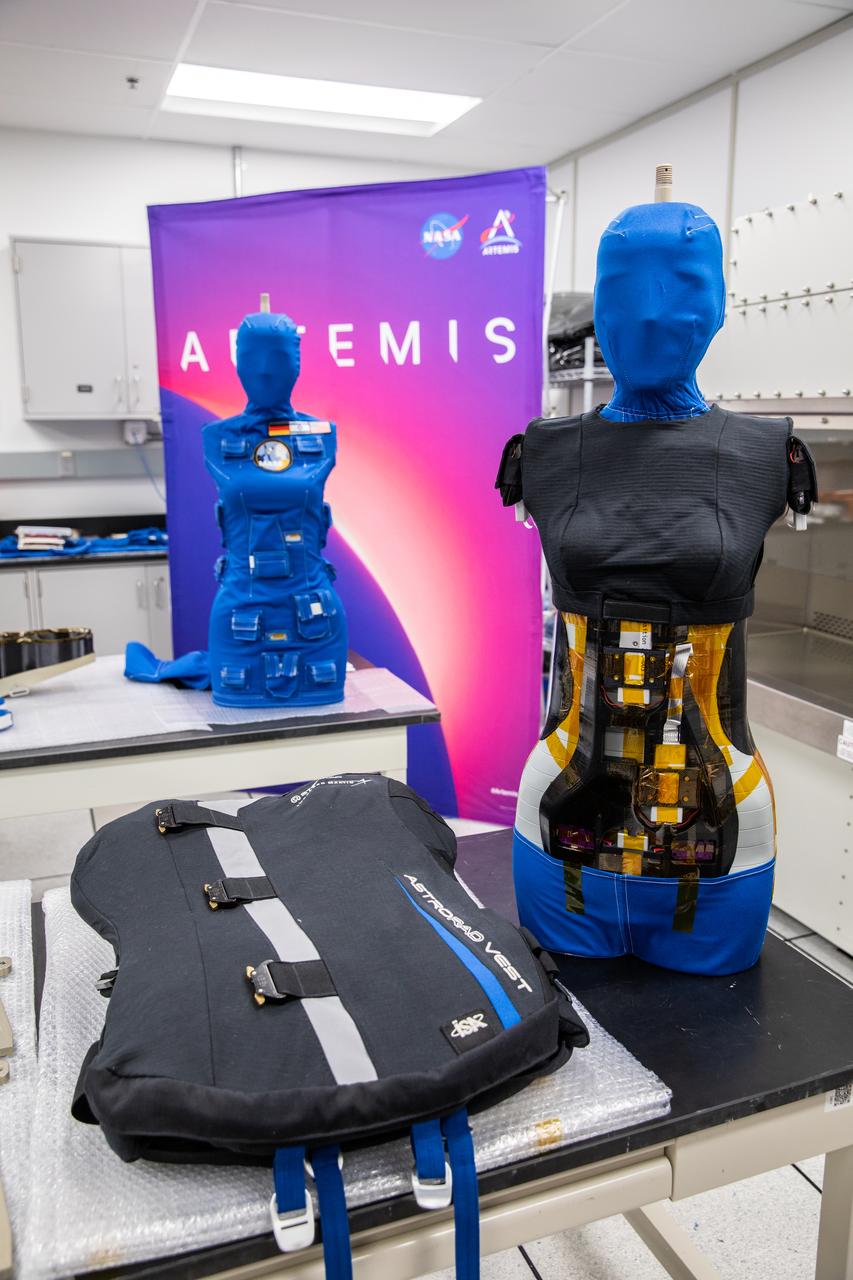

After a 25-day flight beyond the Moon and back inside the Artemis I Orion crew module, two manikins undergo post-flight payload inspections inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2023. As part of the Matroshka AstroRad Radiation Experiment (MARE) investigation, the two female manikins – Helga and Zohar – were equipped with radiation detectors. Zohar also wore a radiation protection vest, to determine the radiation risk during the Artemis I mission and potentially reduce exposure during future missions with astronauts. The detectors will be removed at Kennedy and the torsos will return to teams at the German Space Agency for further analysis. Artemis I Orion launched atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022, at 1:47 a.m. EST. During the flight, Orion flew farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown, paving the way for human deep space exploration and demonstrating NASA’s commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I was to thoroughly test the SLS and Orion spacecraft’s integrated systems before crewed missions. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
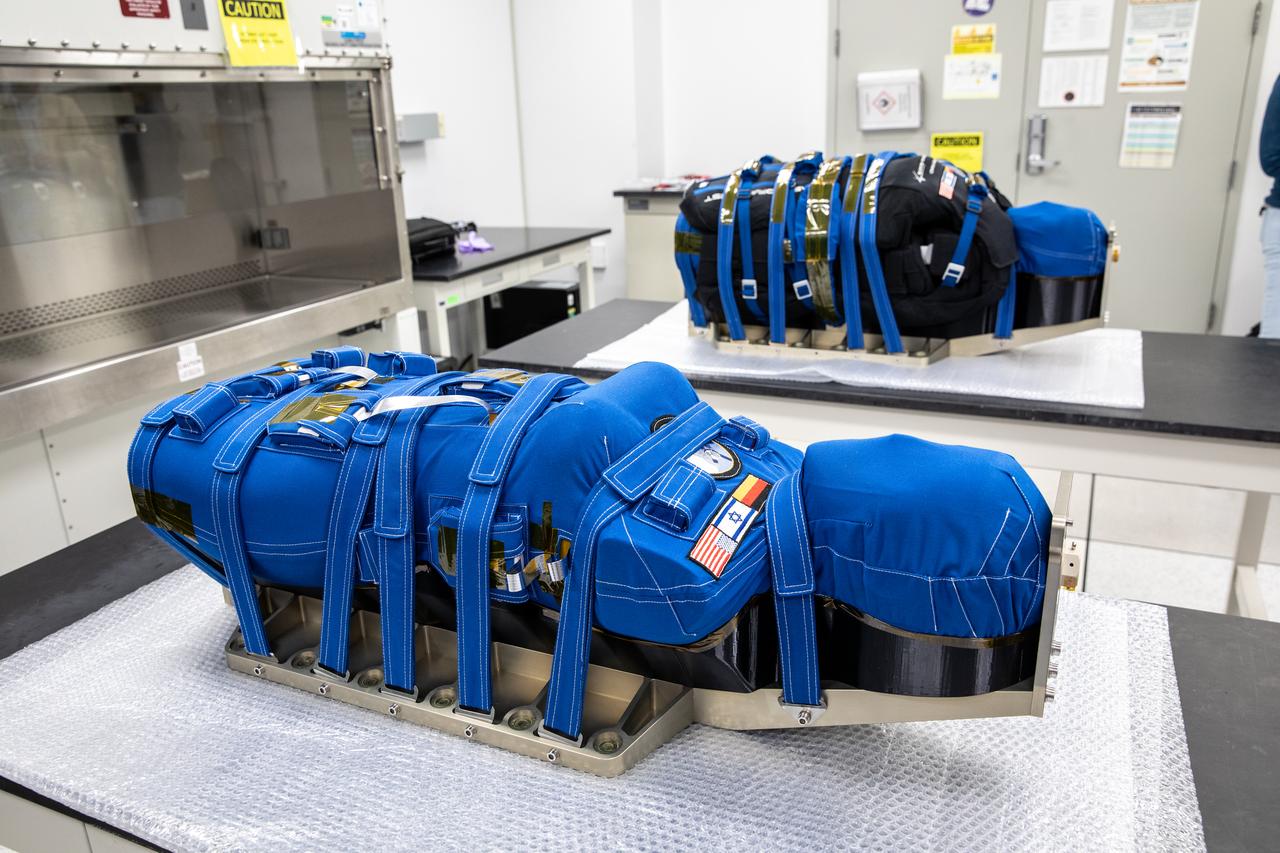

After a 25-day flight beyond the Moon and back inside the Artemis I Orion crew module, two manikins undergo post-flight payload inspections inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2023. As part of the Matroshka AstroRad Radiation Experiment (MARE) investigation, the two female manikins – Helga and Zohar – were equipped with radiation detectors. Zohar also wore a radiation protection vest, to determine the radiation risk during the Artemis I mission and potentially reduce exposure during future missions with astronauts. The detectors will be removed at Kennedy and the torsos will return to teams at the German Space Agency for further analysis. Artemis I Orion launched atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022, at 1:47 a.m. EST. During the flight, Orion flew farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown, paving the way for human deep space exploration and demonstrating NASA’s commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I was to thoroughly test the SLS and Orion spacecraft’s integrated systems before crewed missions. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
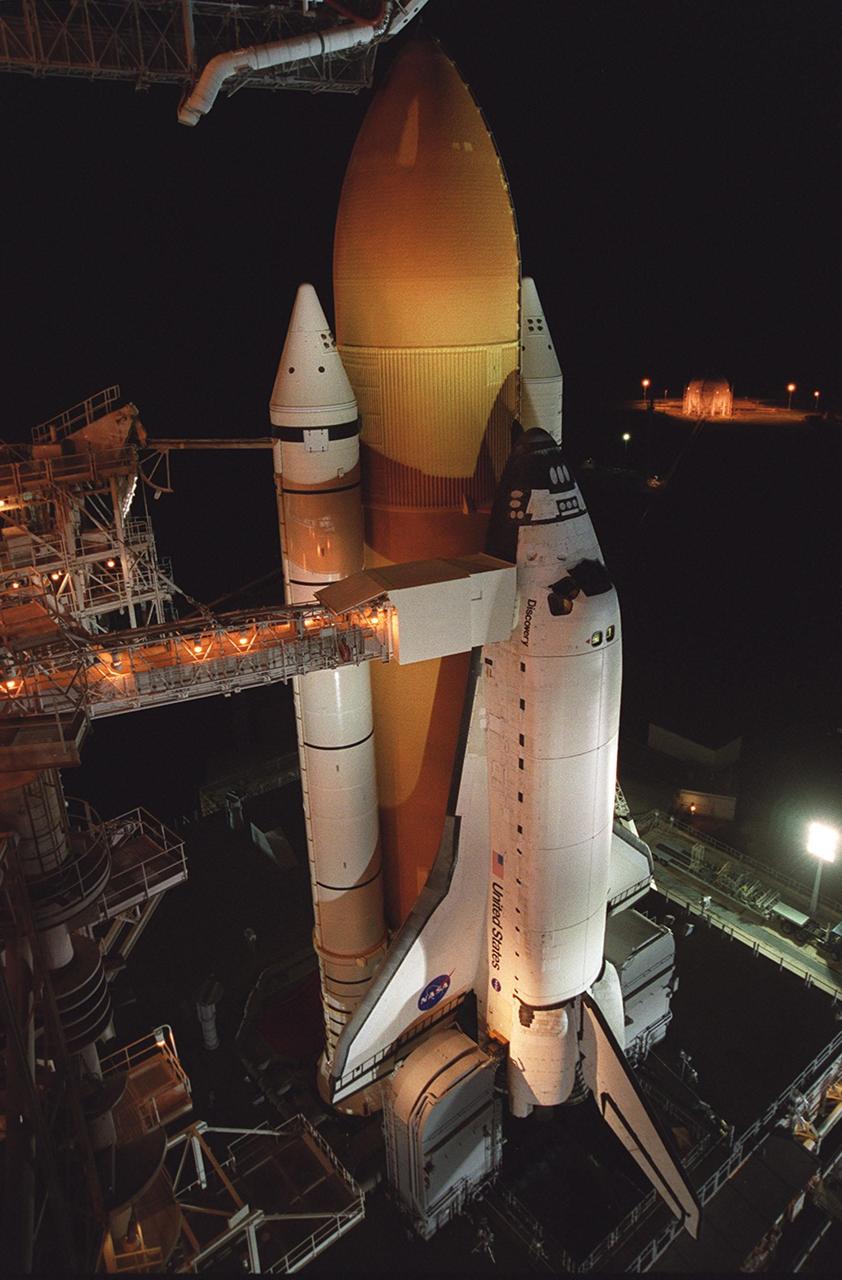

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- With the Rotating Service Structure rolled back, Space Shuttle Discovery is revealed on the Mobile Launcher Platform at Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). At the top is the 13-foot-wide “beanie cap,” at the end of the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm, designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Space Shuttle. Lower is the Orbiter Access Arm with the environmental chamber, known as the “white room,” extended to the orbiter. The chamber provides entry for the crew into the orbiter and also serves as emergency egress up to 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. The STS-92 mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT
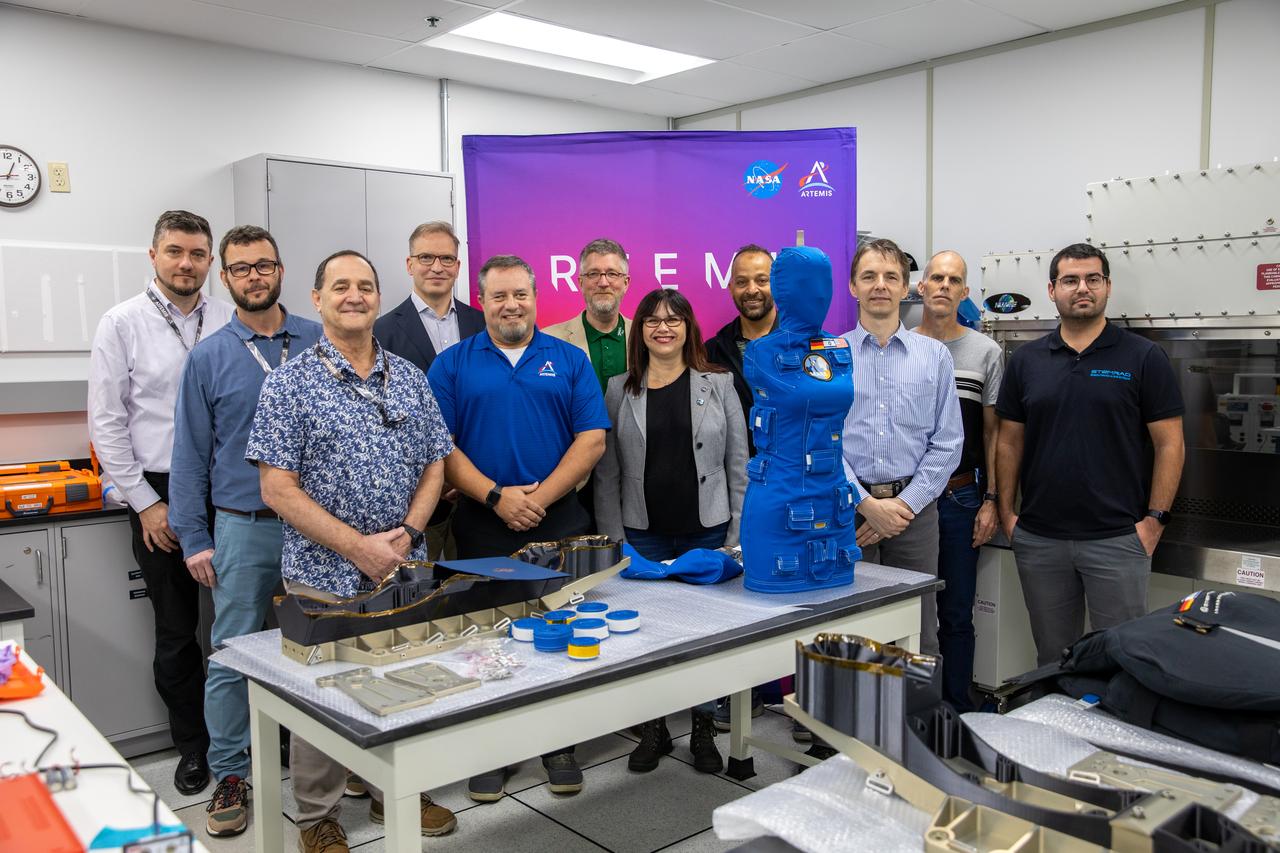

After a 25-day flight beyond the Moon and back inside the Artemis I Orion crew module, two manikins undergo post-flight payload inspections by teams from NASA, Lockheed Martin, AstroRad and the German Space Agency inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 17, 2023. As part of the Matroshka AstroRad Radiation Experiment (MARE) investigation, the two female manikins – Helga and Zohar – were equipped with radiation detectors. Zohar also wore a radiation protection vest, to determine the radiation risk during the Artemis I mission and potentially reduce exposure during future missions with astronauts. Artemis I Orion launched atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022, at 1:47 a.m. EST. During the flight, Orion flew farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown, paving the way for human deep space exploration and demonstrating NASA’s commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I was to thoroughly test the SLS and Orion spacecraft’s integrated systems before crewed missions. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-112 crew members share a few words after their arrival at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility to begin launch preparations. In the center are Commander Jeffrey Ashby (left) and Mission Specialist David Wolf (right). With their backs to the camera are Mission Specialists Piers Sellers (far left) and Sandra Magnus (far right). Not shown are Pilot Pamela Melroy and Mission Specialist Fyodor Yurchikhin, who is with the Russian Space Agency. STS-112, aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis, is the 15th assembly mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis will be carrying the S1 Integrated Truss Structure, the first starboard truss segment, to be attached to the central truss segment, S0, and the Crew and Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) Cart A. The CETA is the first of two human-powered carts that will ride along the ISS railway, providing mobile work platforms for future spacewalking astronauts. The 11-day mission includes three spacewalks. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 2 between 2 and 6 p.m.
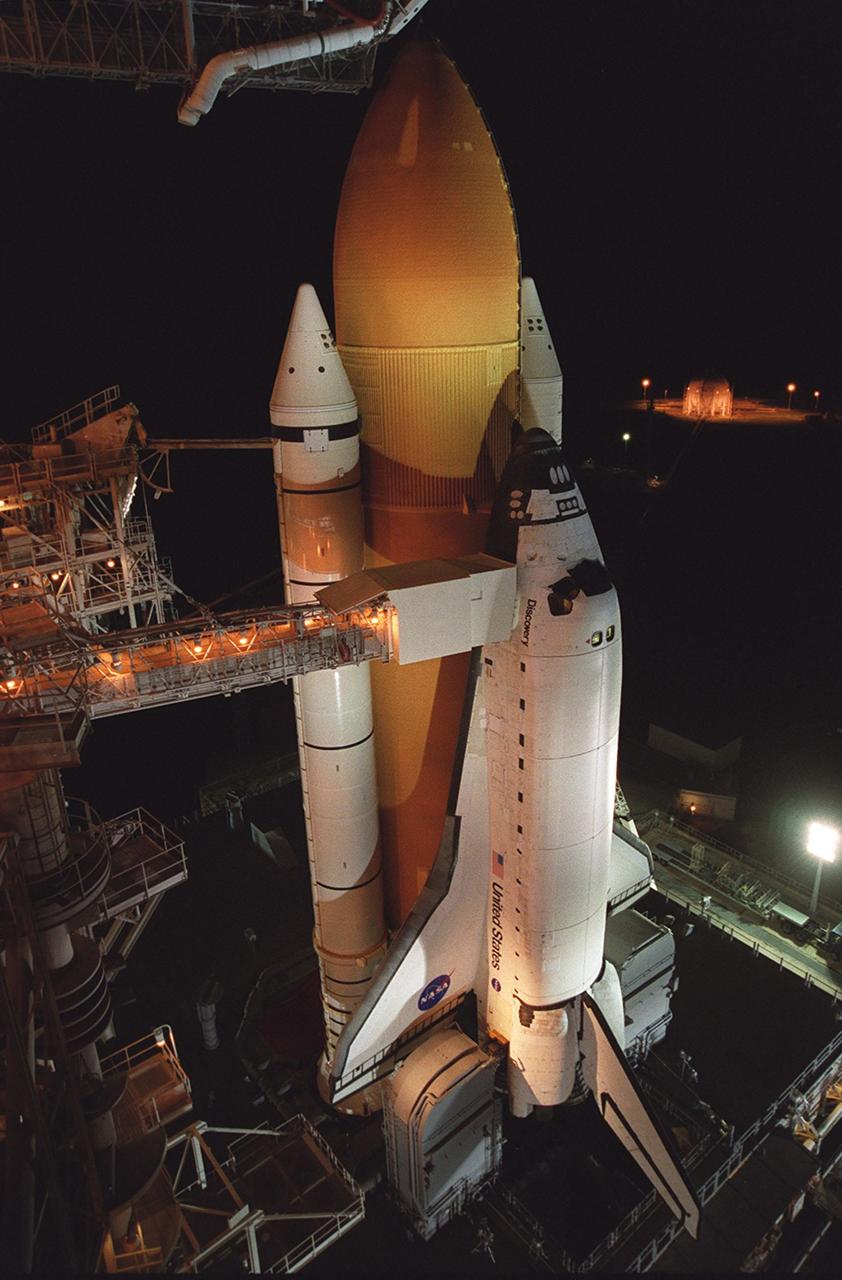

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- With the Rotating Service Structure rolled back, Space Shuttle Discovery is revealed on the Mobile Launcher Platform at Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). At the top is the 13-foot-wide “beanie cap,” at the end of the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm, designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Space Shuttle. Lower is the Orbiter Access Arm with the environmental chamber, known as the “white room,” extended to the orbiter. The chamber provides entry for the crew into the orbiter and also serves as emergency egress up to 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. The STS-92 mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT
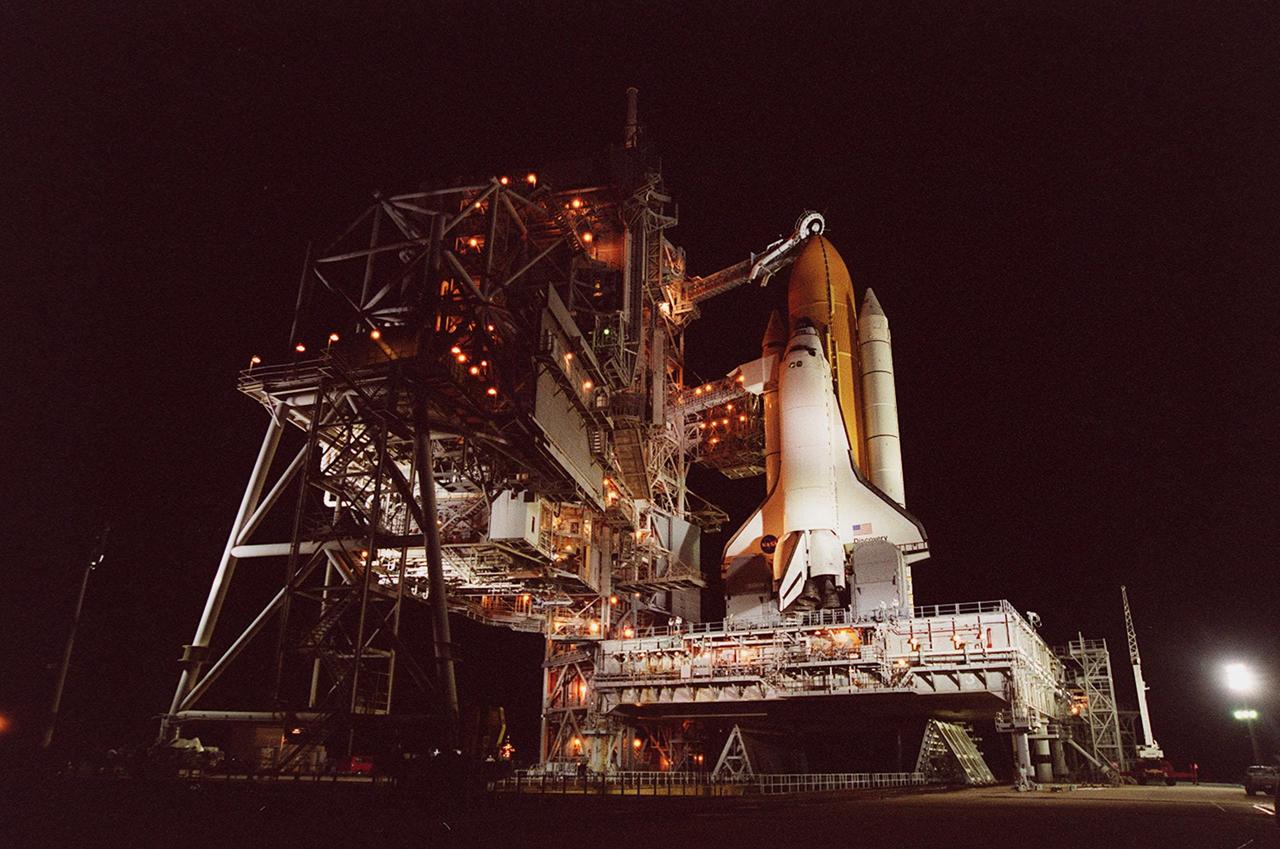

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- With the Rotating Service Structure rolled back, Space Shuttle Discovery is revealed on the Mobile Launcher Platform at Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). At the top is the 13-foot-wide “beanie cap,” at the end of the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm, designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Space Shuttle. Lower is the Orbiter Access Arm with the environmental chamber, known as the “white room,” extended to the orbiter. The chamber provides entry for the crew into the orbiter and also serves as emergency egress up to 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. The STS-92 mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT
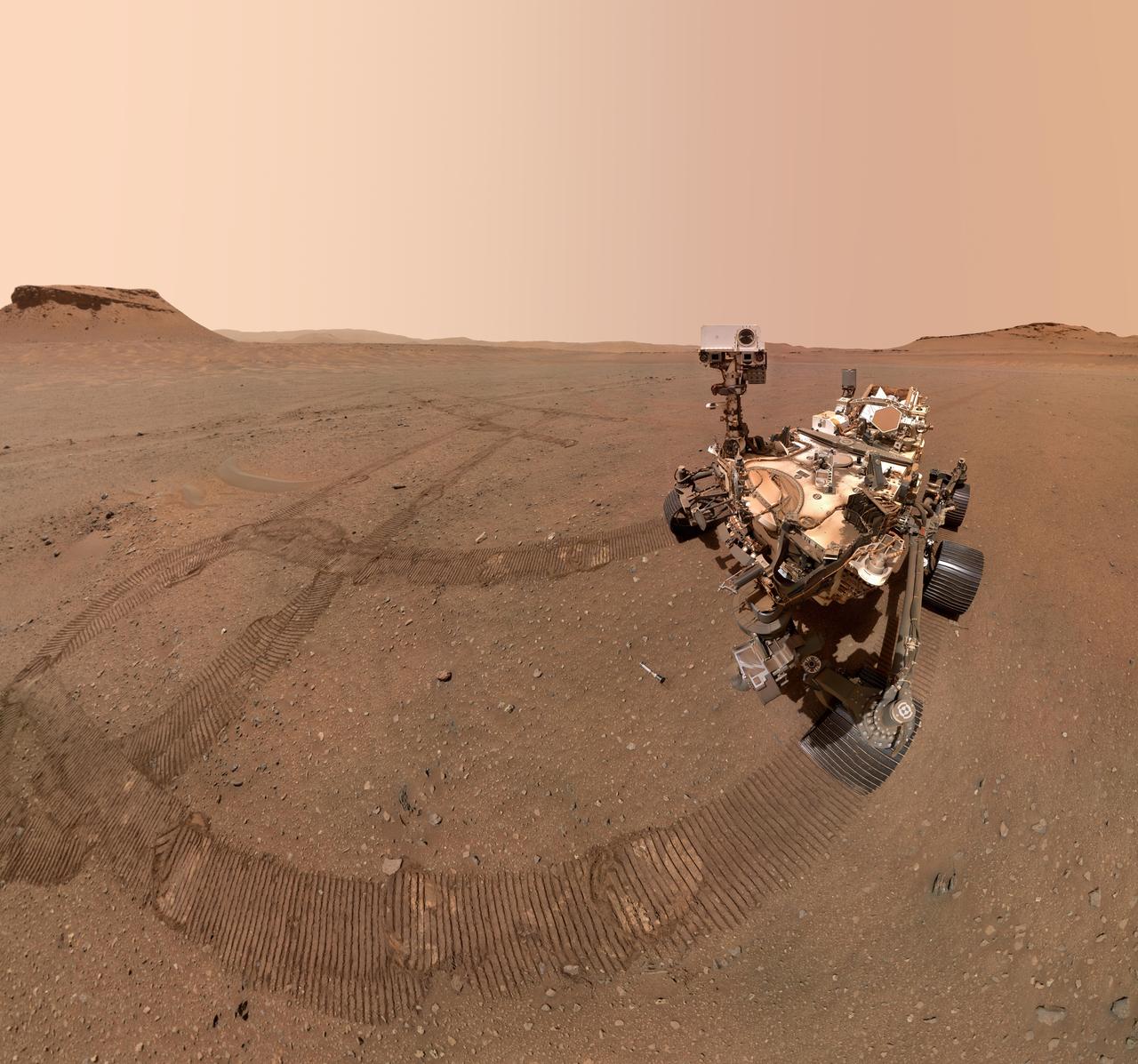

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover took a selfie with several of the 10 sample tubes it deposited at a sample depot it is creating within an area of Jezero Crater nicknamed "Three Forks." The image was taken by the WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) camera on the end of the rover's robotic arm on Jan. 22, 2023, the 684th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The ninth tube dropped during the construction of the depot, containing the sample the science team refers to as "Atsah," can be seen in front of the rover. Other sample tubes are visible in the background. In an animated GIF, the rover looks down at the "Atsah" sample then back at the camera. The selfie is composed of 59 individual WATSON images that were stitched together once they were sent back to Earth. The Curiosity rover takes similar selfies using a camera on its robotic arm; videos explaining how the rovers take their selfies can be found here. The depot marks a crucial milestone in the NASA-ESA (European Space Agency) Mars Sample Return campaign that aims to bring Mars samples to Earth for closer study. The depot will serve as a backup if Perseverance can't deliver its samples to a future robotic lander. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25681
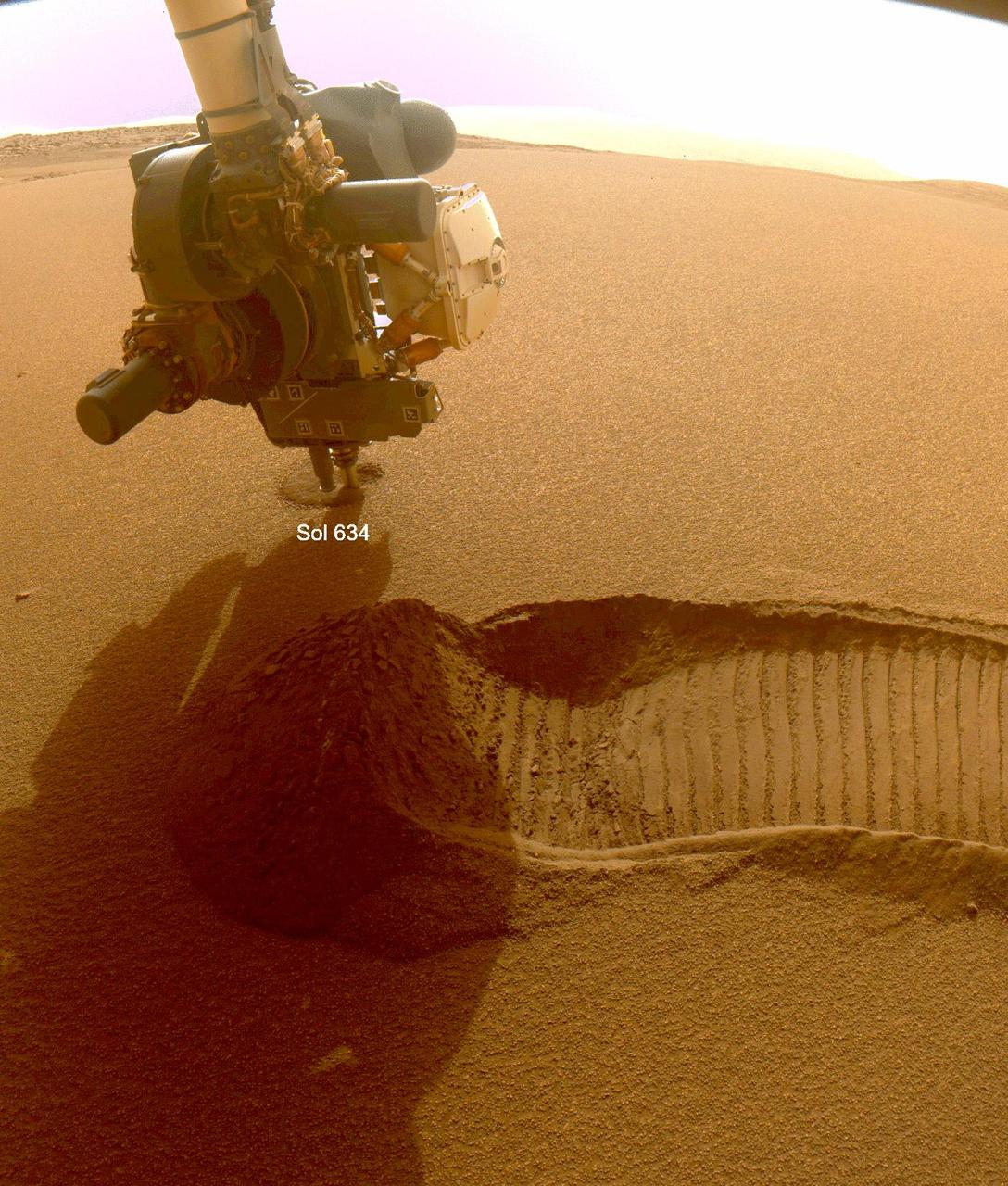

This GIF shows NASA's Perseverance Mars rover collecting two samples of regolith – broken rock and dust – with a regolith sampling bit on the end of its robotic arm. The samples were collected on Dec. 2 and 6, 2022, the 634th and 639th Martian days, or sols, of the mission. The images were taken by one of the rover's front hazard cameras. One of the two regolith samples will be considered for deposit on the Martian surface in coming weeks as part of the Mars Sample Return campaign. Studying regolith with powerful lab equipment back on Earth will allow scientists to better understand the processes that have shaped the surface of Mars and help engineers design future missions as well as equipment used by future Martian astronauts. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25654
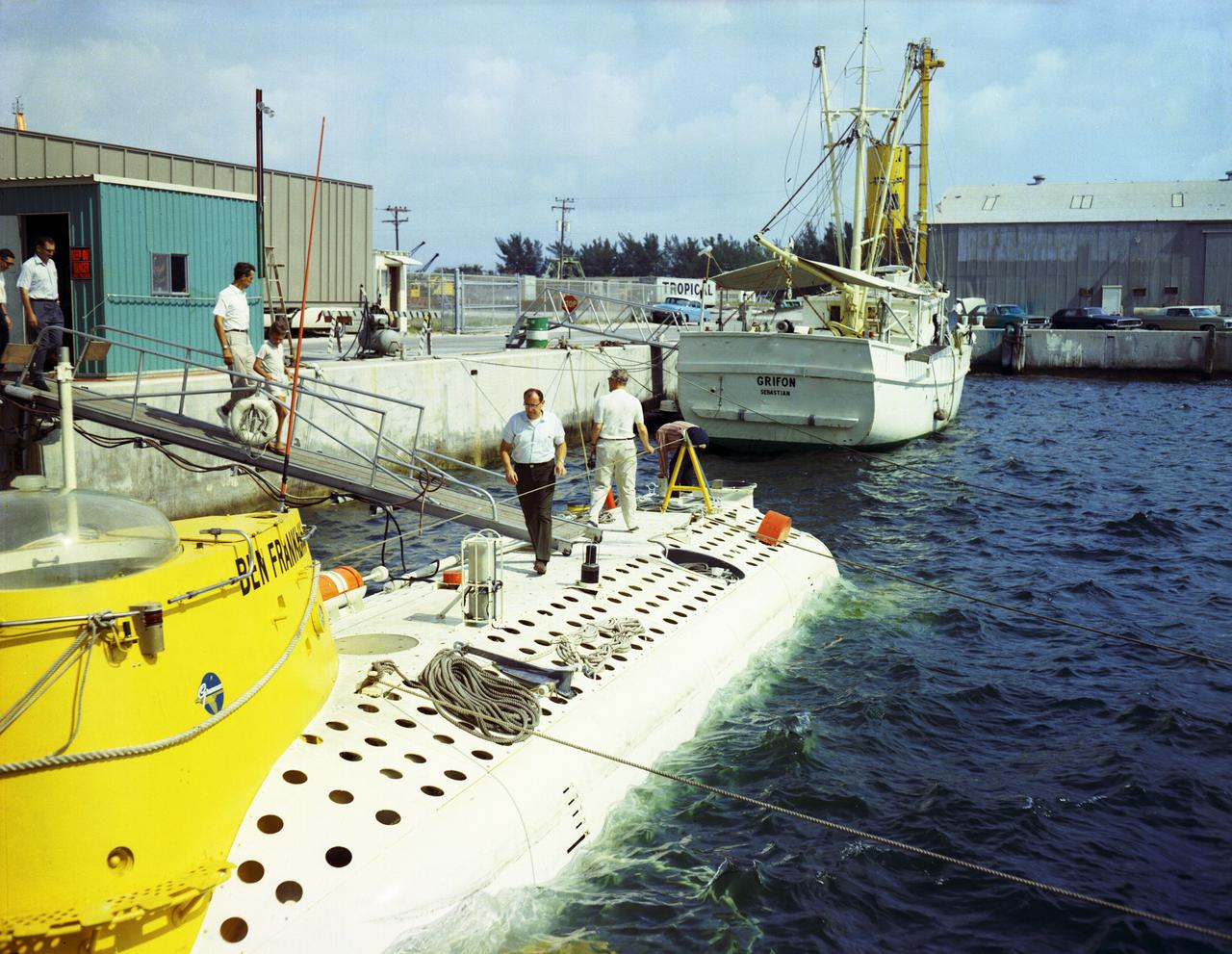

This photograph depicts Dr. von Braun (at right, showing his back) and other NASA officials surveying the deep-sea research submarine "Ben Franklin." Named for American patriot and inventor Ben Franklin, who discovered the Gulf Steam, the 50-foot Ben Franklin was built between 1966 and 1968 in Switzerland for deep-ocean explorer Jacques Piccard and the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. The submersible made a famous 30-day drift dive off the East Coast of the United States and Canada in 1969 mapping the Gulf Stream's currents and sea life, and also made space exploration history by studying the behavior of aquanauts in a sealed, self-contained, self-sufficient capsule for NASA. On July 14, 1969, the Ben Franklin was towed to the high-velocity center of the Stream off the coast of Palm Beach, Florida. With a NASA observer on board, the sub descended to 1,000 feet off of Riviera Beach, Florida and drifted 1,400 miles north with the current for more than four weeks, reemerging near Maine. During the course of the dive, NASA conducted exhaustive analyses of virtually every aspect of onboard life. They measured sleep quality and patterns, sense of humor and behavioral shifts, physical reflexes, and the effects of a long-term routine on the crew. The submarine's record-shattering dive influenced the design of Apollo and Skylab missions and continued to guide NASA scientists as they devised future marned space-flight missions.
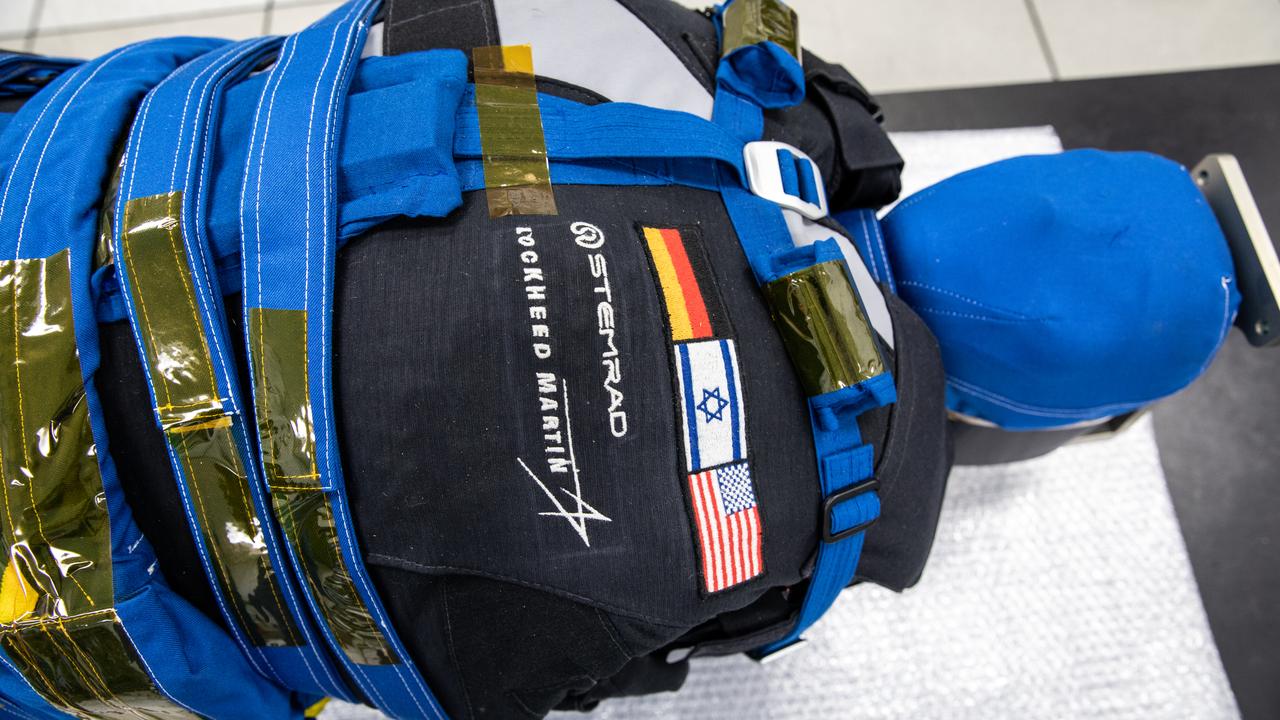

After a 25-day flight inside the Artemis I Orion crew module beyond the Moon and back, Helga, one of two identical phantom torsos, is shown without a radiation detection vest while undergoing post-flight payload inspections inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2023. The detectors will be removed at Kennedy and the torsos will return to teams at the German Space Agency for further analysis. As part of the Matroshka AstroRad Radiation Experiment (MARE) investigation, two female manikins – Helga and Zohar – were equipped with radiation detectors, while Zohar also wore a radiation protection vest, to determine the radiation risk during the Artemis I mission and potentially reduce exposure during future missions with astronauts. Artemis I Orion launched atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022, at 1:47 a.m. EST. During the flight, Orion flew farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown, paving the way for human deep space exploration and demonstrating NASA’s commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I was to thoroughly test the SLS and Orion spacecraft’s integrated systems before crewed missions. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.

Imagine a future spacecraft following New Horizons' trailblazing path to Pluto, but instead of flying past its target -- as New Horizons needed to do to explore Pluto and the Kuiper Belt beyond -- the next visitor touches down near the tall mountains on the frozen icy, plains of Pluto's heart. A video produced by New Horizons scientists that offers that very perspective. Made from more than 100 New Horizons images taken over six weeks of approach and close flyby, the video offers a trip in to Pluto -- starting with a distant spacecraft's-eye view of Pluto and its largest moon, Charon, to an eventual ride in for a "landing" on the shoreline of Pluto's informally named Sputnik Planum. The video shows what it would be like to ride aboard an approaching spacecraft and see Pluto grow from a "dot" to become a world, and then to swoop down over Pluto's spectacular terrains. New Horizons scientists had to interpolate some of the frames in the movie based on what they know Pluto looks like to make it as smooth and seamless as possible. After a 9.5-year voyage covering more than three billion miles, New Horizons flew through the Pluto system on July 14, 2015, coming within 7,800 miles (12,500 kilometers) of Pluto itself. Carrying powerful telescopic cameras that could spot features smaller than a football field, New Horizons has sent back hundreds of images of Pluto and its moons that show how dynamic and fascinating their surfaces are - and what great targets they'd make for follow-up mission one day. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20742

After a 25-day flight inside the Artemis I Orion crew module beyond the Moon and back, Helga, one of two identical phantom torsos, is shown without a radiation detection vest while undergoing post-flight payload inspections inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2023. The detectors will be removed at Kennedy and the torsos will return to teams at the German Space Agency for further analysis. As part of the Matroshka AstroRad Radiation Experiment (MARE) investigation, two female manikins – Helga and Zohar – were equipped with radiation detectors, while Zohar also wore a radiation protection vest, to determine the radiation risk during the Artemis I mission and potentially reduce exposure during future missions with astronauts. Artemis I Orion launched atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022, at 1:47 a.m. EST. During the flight, Orion flew farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown, paving the way for human deep space exploration and demonstrating NASA’s commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I was to thoroughly test the SLS and Orion spacecraft’s integrated systems before crewed missions. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
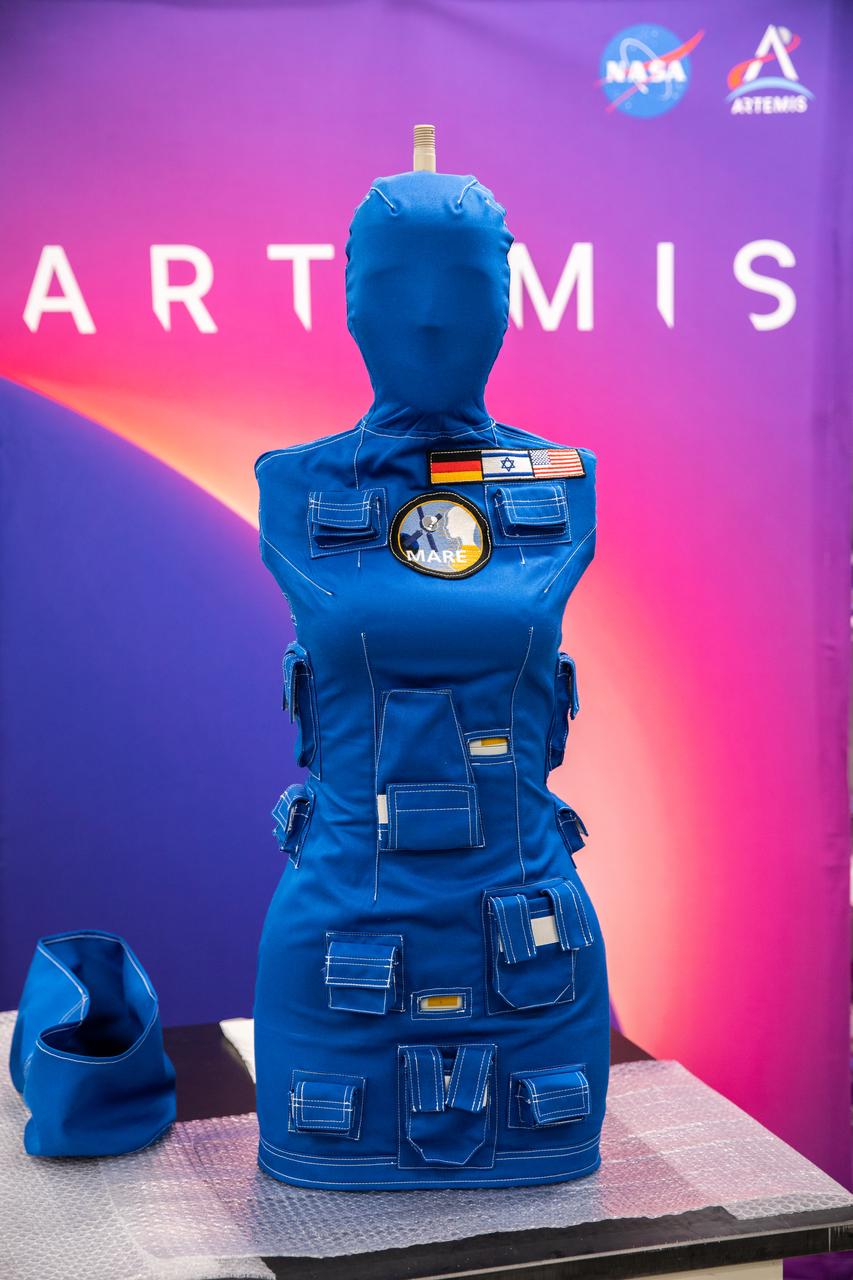

After a 25-day flight inside the Artemis I Orion crew module beyond the Moon and back, Helga, one of two identical phantom torsos, is shown without a radiation detection vest while undergoing post-flight payload inspections inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2023. The detectors will be removed at Kennedy and the torsos will return to teams at the German Space Agency for further analysis. As part of the Matroshka AstroRad Radiation Experiment (MARE) investigation, two female manikins – Helga and Zohar – were equipped with radiation detectors, while Zohar also wore a radiation protection vest, to determine the radiation risk during the Artemis I mission and potentially reduce exposure during future missions with astronauts. Artemis I Orion launched atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022, at 1:47 a.m. EST. During the flight, Orion flew farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown, paving the way for human deep space exploration and demonstrating NASA’s commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I was to thoroughly test the SLS and Orion spacecraft’s integrated systems before crewed missions. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
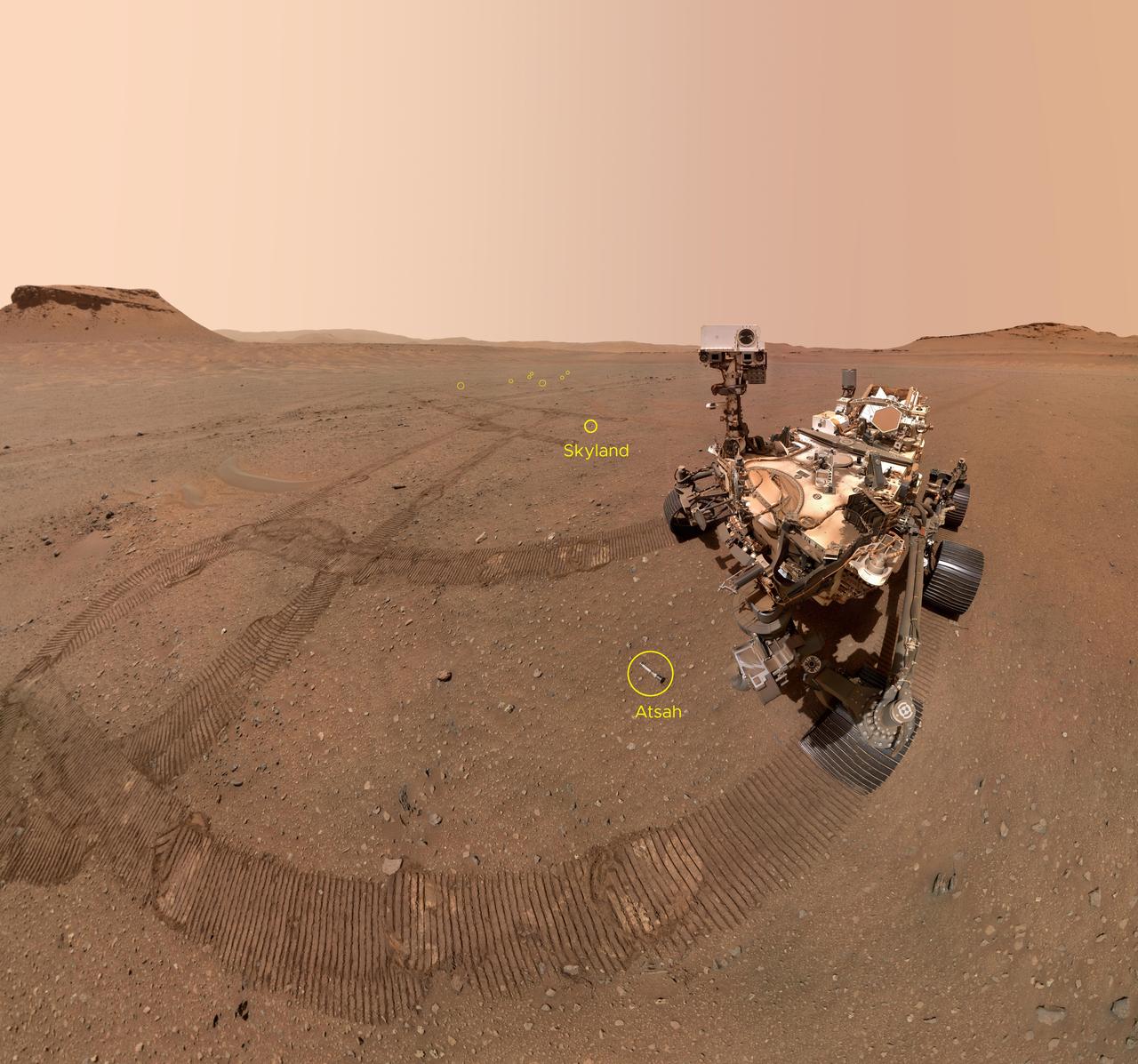

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover took a selfie with nine of the 10 sample tubes it deposited at a sample depot created within an area of Jezero Crater nicknamed "Three Forks." This annotated version of the selfie points out the estimated locations of those nine tubes. The ninth tube dropped during the construction of the depot, containing the sample the science team refers to as "Atsah," can be seen in front of the rover. Other sample tubes are visible in the background, including "Skyland," which is labeled. The image was taken by the WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) camera on the end of the rover's robotic arm on Jan. 22, 2023, the 684th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The selfie is composed of 59 individual WATSON images that were stitched together once they were sent back to Earth. The Curiosity rover takes similar selfies using a camera on its robotic arm; videos explaining how the rovers take their selfies can be found here. The depot marks a crucial milestone in the NASA-ESA (European Space Agency) Mars Sample Return campaign that aims to bring Mars samples to Earth for closer study. The depot – completed when the 10th tube was dropped on Jan. 29, 2023 – will serve as a backup if Perseverance can't deliver its samples to a future robotic lander. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25735

Intriguing Martian rocks surround NASA's Perseverance rover in this panorama showing an ancient river delta, made from images captured by the Mastcam-Z camera system. This 2.5-billion-pixel mosaic, which combines 1,118 individual frames, is the most detailed landscape panorama ever returned from Mars. The delta in Mars' Jezero Crater is an area where scientists surmise that, billions of years ago, a river once flowed into a lake and deposited rocks and sediments in a fan shape. Deltas are believed to be the best places on Mars to search for potential signs of ancient microbial life. Arrival at the Jezero delta has been a primary goal of the Perseverance mission since the rover landed in the crater in February 2021. The panorama shows sedimentary rocks of great interest to scientists. The Perseverance rover has abraded the surface of several rocks in this area and acquired compositional information. It also has collected rock samples that the Mars Sample Return campaign could bring back to Earth in the future, enabling detailed laboratory studies as part of a search for signs of ancient life. In this enhanced-color view, the color bands of the image have been processed to improve visual contrast and accentuate color differences. Figure A shows the same panorama using a natural-color view. A guided tour of the panorama is available at https://images.nasa.gov/details-JPL-20220906-Perseverance_Explores_Jezero_Crater_Delta_UHD. These images were taken in 2022 on June 12, 13, 16, 17, and 20 (the 466th, 467th, 470th, 471st, and 474th Martian days, or sols, of Perseverance's mission). A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24921
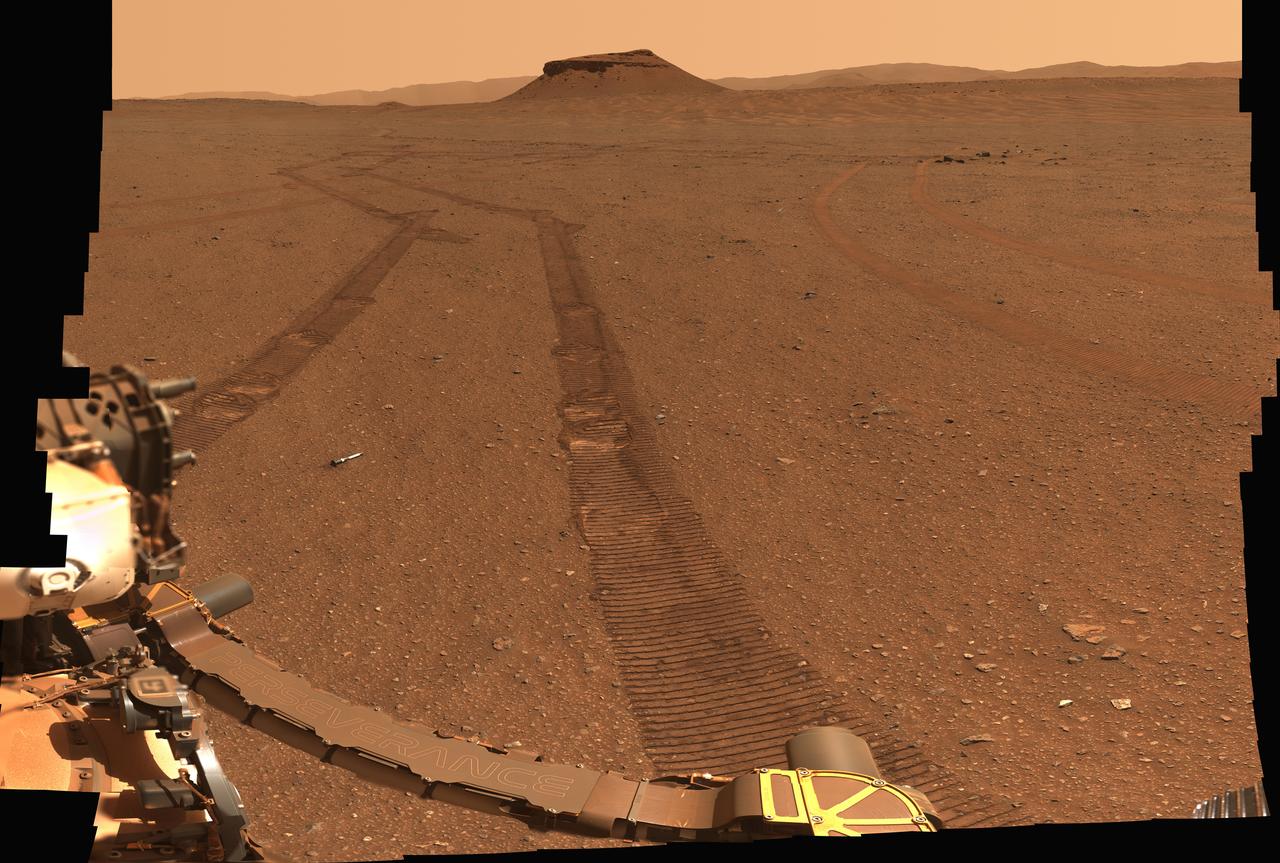

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this portrait of its recently completed sample depot using its Mastcam-Z camera on Jan. 31, 2023, the 693rd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This panorama is made up of 368 individual images that were stitched together after being sent back to Earth. The color in the scene has been adjusted to show the Martian surface as it would look to the human eye. Each sample tube is approximately 7 inches (18 centimeters) long and .8 inches (2 centimeters) in diameter. The "Amalik" sample closest to the rover was approximately 10 feet (3 meters) away from the camera at the time the image was taken. The "Atsah" and "Skyland" samples were approximately 66 feet (20 meters) away. "Bearwallow," "Coulettes," "Montdenier," "Crosswind Lake," and "Roubion" were approximately 115 to 164 feet (35 to 50 meters) away. "Mageik" and "Malay" were approximately 197 feet (60 meters) away. This is a natural-color view of the scene, showing the surface as it would appear to a human observer. Throughout its science campaigns, the rover has been taking a pair of samples from rocks the mission team deems scientifically significant. One sample from each pair taken so far now sits in the depot – along with one atmospheric sample and one "witness" tube – for a total of 10 tubes that were carefully arranged on the surface in a zigzag pattern. The depot is a crucial milestone in the NASA-ESA (European Space Agency) Mars Sample Return campaign, which aims to bring Mars samples to Earth for closer study. The Perseverance rover will be the primary means to hand off the collected samples to a future robotic lander as part of the campaign. The lander would, in turn, use a robotic arm to place the samples in a containment capsule aboard a small rocket that would blast off to Mars orbit, where another spacecraft would capture the sample container and return it safely to Earth. Hosting a duplicate set, the depot will serve as a backup if Perseverance can't deliver its samples. Perseverance built the depot at "Three Forks," a location within Mars' Jezero Crater. Billions of years ago, this crater was filled by a lake and delta. Sediment that built up in the delta formed a steep mound that Perseverance will be driving up in the months ahead to arrive at the top of the delta. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25736
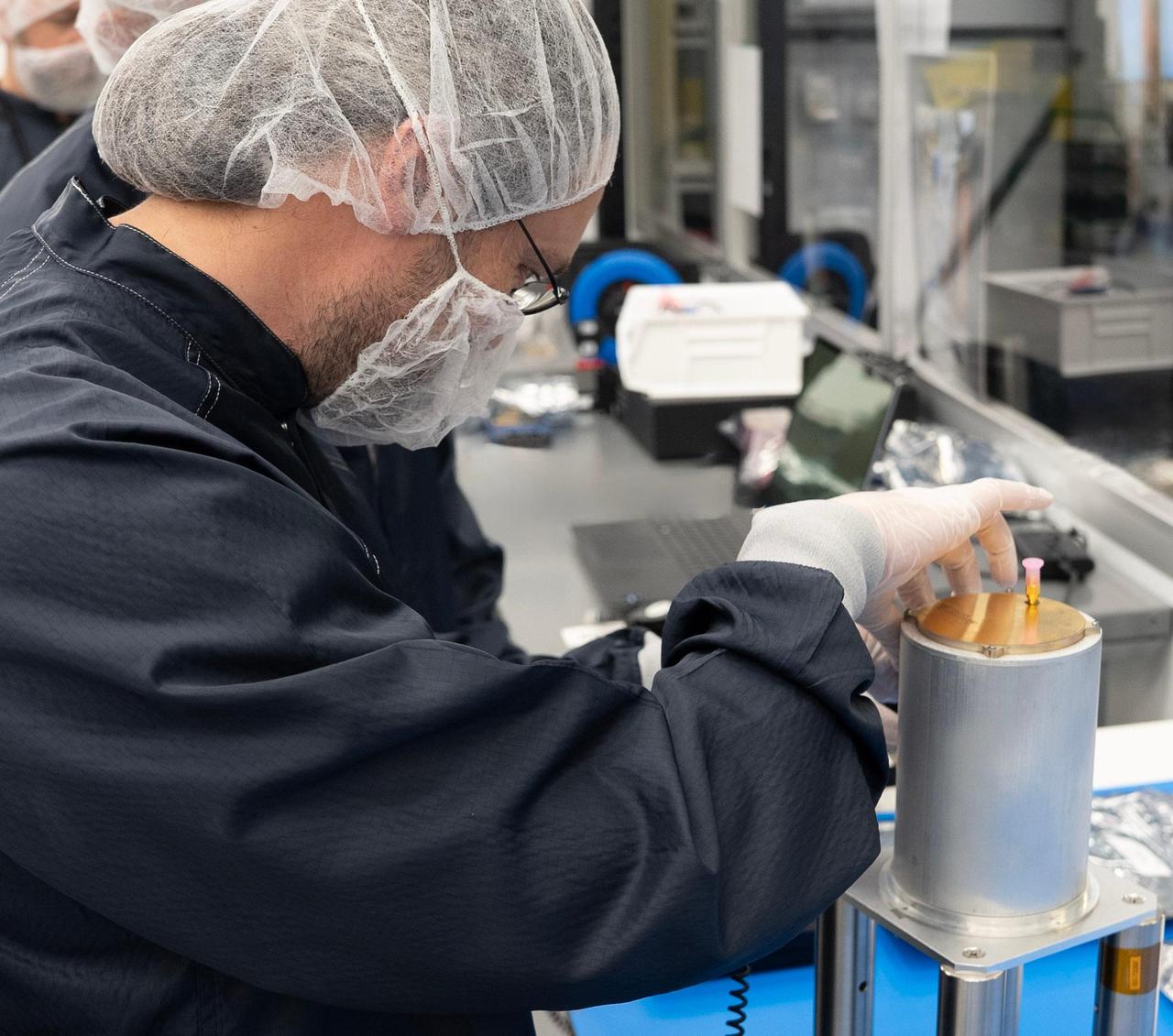

Engineer Emmanuel Decrossas of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California makes an adjustment to an antenna's connector, part of a NASA telecommunications payload called User Terminal, at Firefly Aerospace's facility in Cedar Park, Texas, in August 2025. Figure A (https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/figures/PIA26596_figA.jpg) shows members of the team from JPL and NASA (dark blue) and Firefly (white) with the User Terminal antenna, radio, and other components on the bench behind them. Managed by JPL, the User Terminal will test a new, low-cost lunar communications system that future missions to the Moon's far side could use to transfer data to and from Earth via lunar relay satellite. The User Terminal payload will be installed atop Firefly's Blue Ghost Mission 2 lunar lander, which is slated to launch to the Moon's far side in 2026 under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. NASA's Apollo missions brought large and powerful telecommunications systems to the lunar near-side surface to communicate directly with Earth. But spacecraft on the far side will not have that option because only the near side of the Moon is visible to Earth. Sending messages between the Moon and Earth via a relay orbiter enables communication with the lunar far side and improves it at the Moon's poles. The User Terminal will for the first time test such a setup for NASA by using a compact, lightweight software defined radio, antenna, and related hardware to communicate with a satellite that Blue Ghost Mission 2 is delivering to lunar orbit: ESA's (the European Space Agency's) Lunar Pathfinder. The User Terminal radio and antenna installed on the Blue Ghost lander will be used to commission Lunar Pathfinder, sending test data back and forth. After the lander ceases operations as planned at the end of a single lunar day (about 14 Earth days), a separate User Terminal radio and antenna installed on LuSEE-Night – another payload on the lander – will send LuSEE-Night's data to Lunar Pathfinder, which will relay the information to a commercial network of ground stations on Earth. LuSEE-Night is a radio telescope that expected to operate for at least 1½ years; it is a joint effort by NASA, the U.S. Department of Energy, and University of California, Berkeley's Space Sciences Laboratory. Additionally, User Terminal will be able to communicate with another satellite that's being delivered to lunar orbit by Blue Ghost Mission 2: Firefly's own Elytra Dark orbital vehicle. The hardware on the lander is only part of the User Terminal project, which was also designed to implement a new S-band two-way protocol, or standard, for short-range space communications between entities on the lunar surface (such as rovers and landers) and lunar orbiters, enabling reliable data transfer between them. The standard is a new version of a space communications protocol called Proximity-1 that was initially developed more than two decades ago for use at Mars by an international standard body called the Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems (CCSDS), of which NASA is a member agency. The User Terminal team made recommendations to CCSDS on the development of the new lunar S-band standard, which was specified in 2024. The new standard will enable lunar orbiters and surface spacecraft from various entities – NASA and other civil space agencies as well as industry and academia – to communicate with each other, a concept known as interoperability. At Mars, NASA rovers communicate with various Red Planet orbiters using the Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) radio band version of the Proximity-1 standard. On the Moon's far side, use of UHF is reserved for radio astronomy science; so a new lunar standard was needed using a different frequency range, S-band, as were more efficient modulation and coding schemes to better fit the available frequency spectrum specified by the new standard. User Terminal is funded by NASA's Exploration Science Strategy and Integration Office, part of the agency's Science Mission Directorate, which manages the CLPS initiative. JPL manages the project and supported development of the new S-band radio standard and the payload in coordination with Vulcan Wireless in Carlsbad, California, which built the radio. Caltech in Pasadena manages JPL for NASA. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26596

NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) recently captured a unique view of Earth from the spacecraft's vantage point in orbit around the moon. "The image is simply stunning," said Noah Petro, Deputy Project Scientist for LRO at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. "The image of the Earth evokes the famous 'Blue Marble' image taken by Astronaut Harrison Schmitt during Apollo 17, 43 years ago, which also showed Africa prominently in the picture." In this composite image we see Earth appear to rise over the lunar horizon from the viewpoint of the spacecraft, with the center of the Earth just off the coast of Liberia (at 4.04 degrees North, 12.44 degrees West). The large tan area in the upper right is the Sahara Desert, and just beyond is Saudi Arabia. The Atlantic and Pacific coasts of South America are visible to the left. On the moon, we get a glimpse of the crater Compton, which is located just beyond the eastern limb of the moon, on the lunar farside. LRO was launched on June 18, 2009, and has collected a treasure trove of data with its seven powerful instruments, making an invaluable contribution to our knowledge about the moon. LRO experiences 12 earthrises every day; however the spacecraft is almost always busy imaging the lunar surface so only rarely does an opportunity arise such that its camera instrument can capture a view of Earth. Occasionally LRO points off into space to acquire observations of the extremely thin lunar atmosphere and perform instrument calibration measurements. During these movements sometimes Earth (and other planets) pass through the camera's field of view and dramatic images such as the one shown here are acquired. This image was composed from a series of images taken Oct. 12, when LRO was about 83 miles (134 kilometers) above the moon's farside crater Compton. Capturing an image of the Earth and moon with LRO's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) instrument is a complicated task. First the spacecraft must be rolled to the side (in this case 67 degrees), then the spacecraft slews with the direction of travel to maximize the width of the lunar horizon in LROC's Narrow Angle Camera image. All this takes place while LRO is traveling faster than 3,580 miles per hour (over 1,600 meters per second) relative to the lunar surface below the spacecraft! The high-resolution Narrow Angle Camera (NAC) on LRO takes black-and-white images, while the lower resolution Wide Angle Camera (WAC) takes color images, so you might wonder how we got a high-resolution picture of the Earth in color. Since the spacecraft, Earth, and moon are all in motion, we had to do some special processing to create an image that represents the view of the Earth and moon at one particular time. The final Earth image contains both WAC and NAC information. WAC provides the color, and the NAC provides high-resolution detail. "From the Earth, the daily moonrise and moonset are always inspiring moments," said Mark Robinson of Arizona State University in Tempe, principal investigator for LROC. "However, lunar astronauts will see something very different: viewed from the lunar surface, the Earth never rises or sets. Since the moon is tidally locked, Earth is always in the same spot above the horizon, varying only a small amount with the slight wobble of the moon. The Earth may not move across the 'sky', but the view is not static. Future astronauts will see the continents rotate in and out of view and the ever-changing pattern of clouds will always catch one's eye, at least on the nearside. The Earth is never visible from the farside; imagine a sky with no Earth or moon - what will farside explorers think with no Earth overhead?" NASA's first Earthrise image was taken with the Lunar Orbiter 1 spacecraft in 1966. Perhaps NASA's most iconic Earthrise photo was taken by the crew of the Apollo 8 mission as the spacecraft entered lunar orbit on Christmas Eve Dec. 24, 1968. That evening, the astronauts -- Commander Frank Borman, Command Module Pilot Jim Lovell, and Lunar Module Pilot William Anders -- held a live broadcast from lunar orbit, in which they showed pictures of the Earth and moon as seen from their spacecraft. Said Lovell, "The vast loneliness is awe-inspiring and it makes you realize just what you have back there on Earth." Credit: NASA/Goddard/Arizona State University <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>