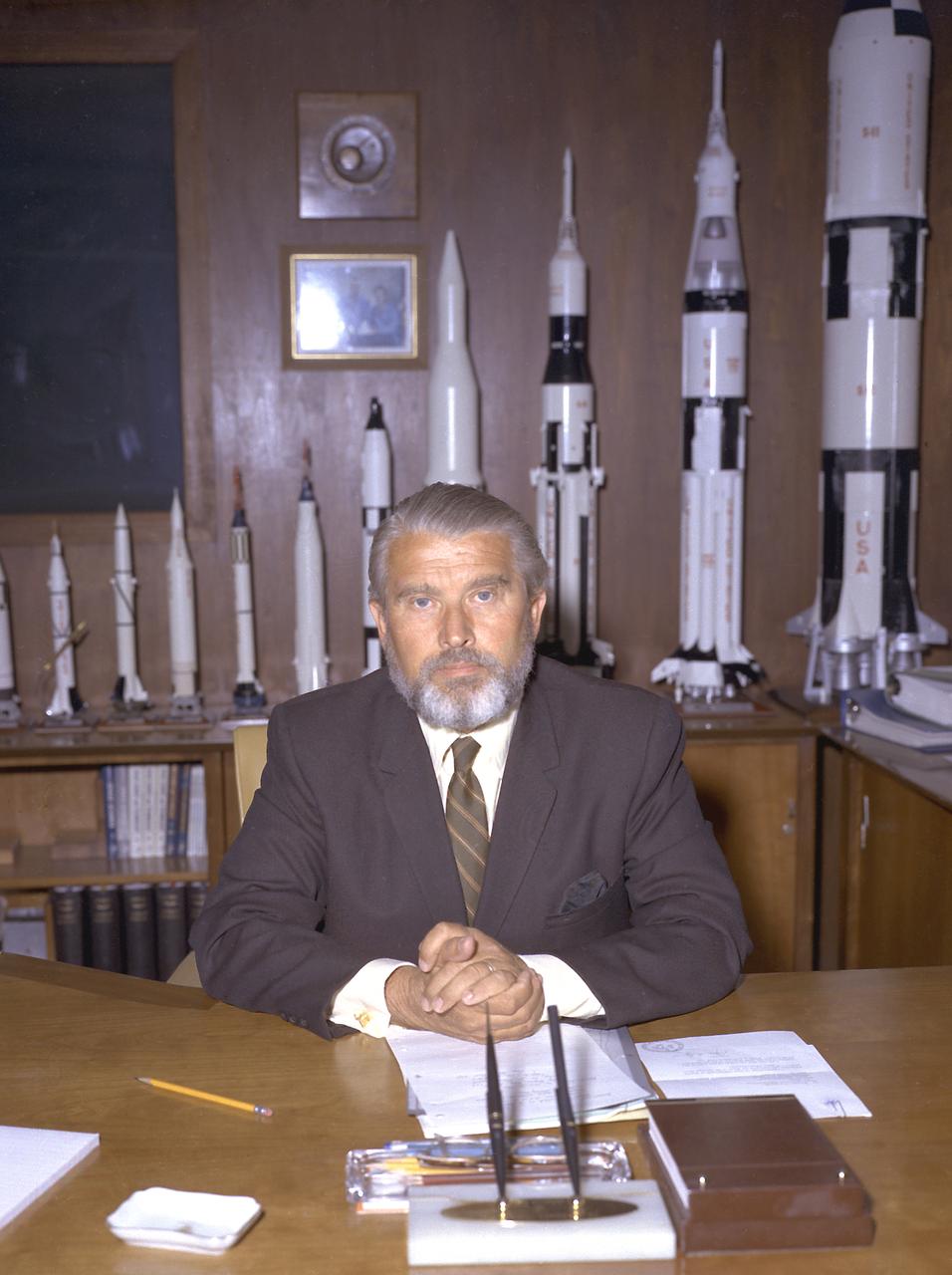

Upon return from a Bahamas vacation, Dr. von Braun pulled a practical joke upon his associates by sporting a beard.
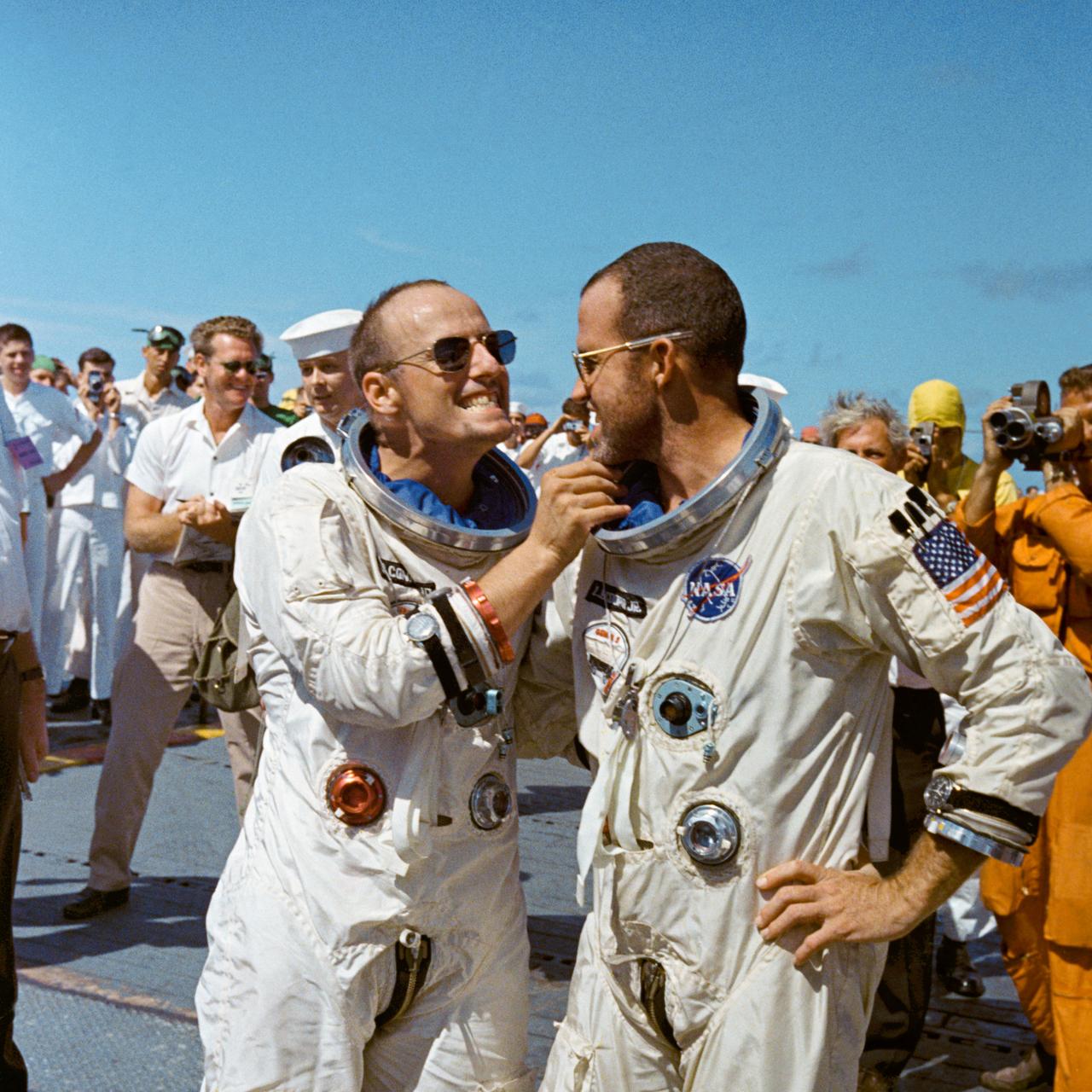

S65-46638 (29 Aug. 1965) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr. tweaks astronaut L. Gordon Cooper's eight-day growth of beard for the cameramen while onboard the prime recovery vessel after their Gemini-5 flight.
Back by popular demand: THEMIS ART IMAGE #72 Is this bearded wizard casting a martian spell?

Vertical Motion Simulator (VMS) control room with Steve Beard and Estela Hernandez-Buchmann
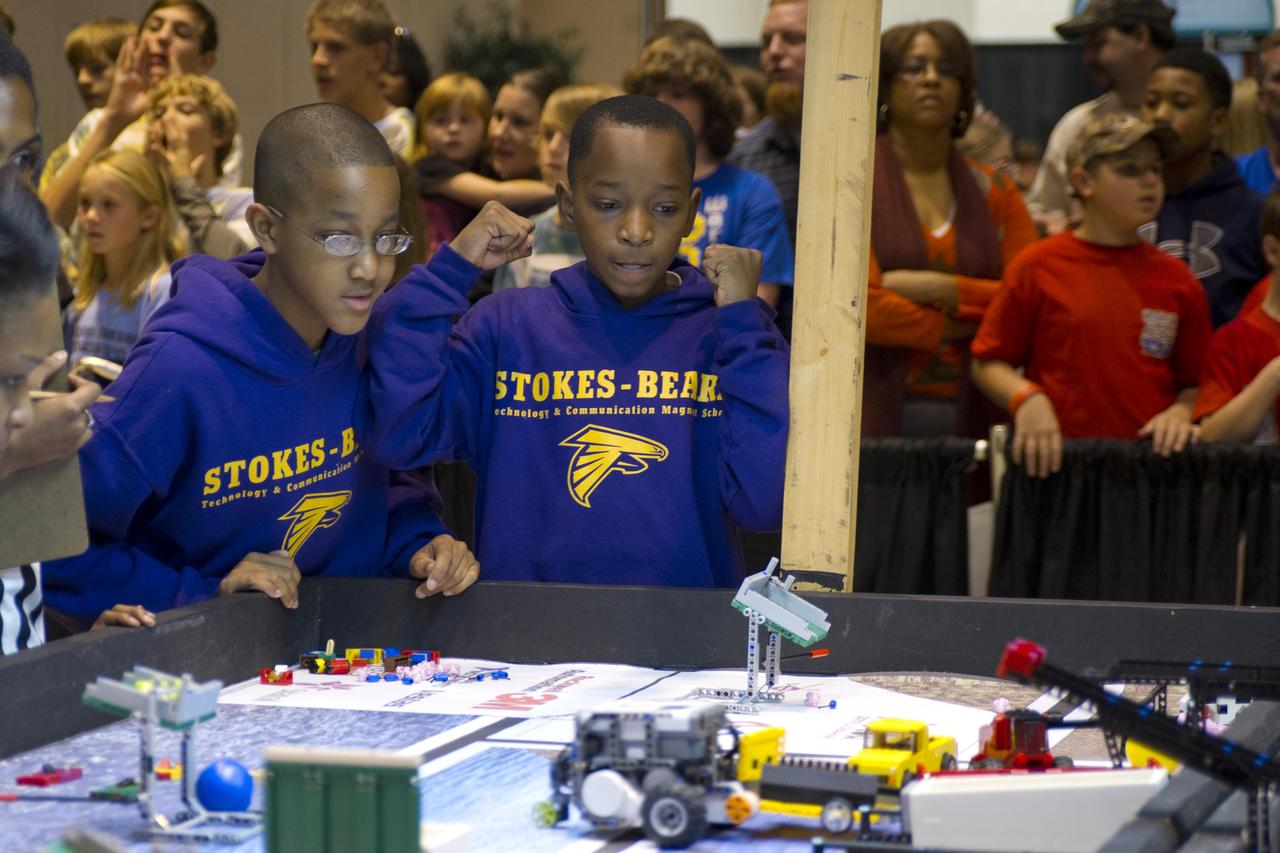

Two 2011 Mississippi FIRST LEGO League competitors from Stokes-Beard Magnet Elementary School in Columbus urge their robots on during the annual tournament Dec. 3. The competition attracted more than 1,000 participants and guests to the Lake Terrace Convention Center in Hattiesburg.

AS07-04-1600 (20 Oct. 1968) --- Astronaut Donn F. Eisele, Apollo 7 command module pilot, smiles through a heavy growth of beard as he is photographed during a momentary pause on the ninth day of the Apollo 7 mission.
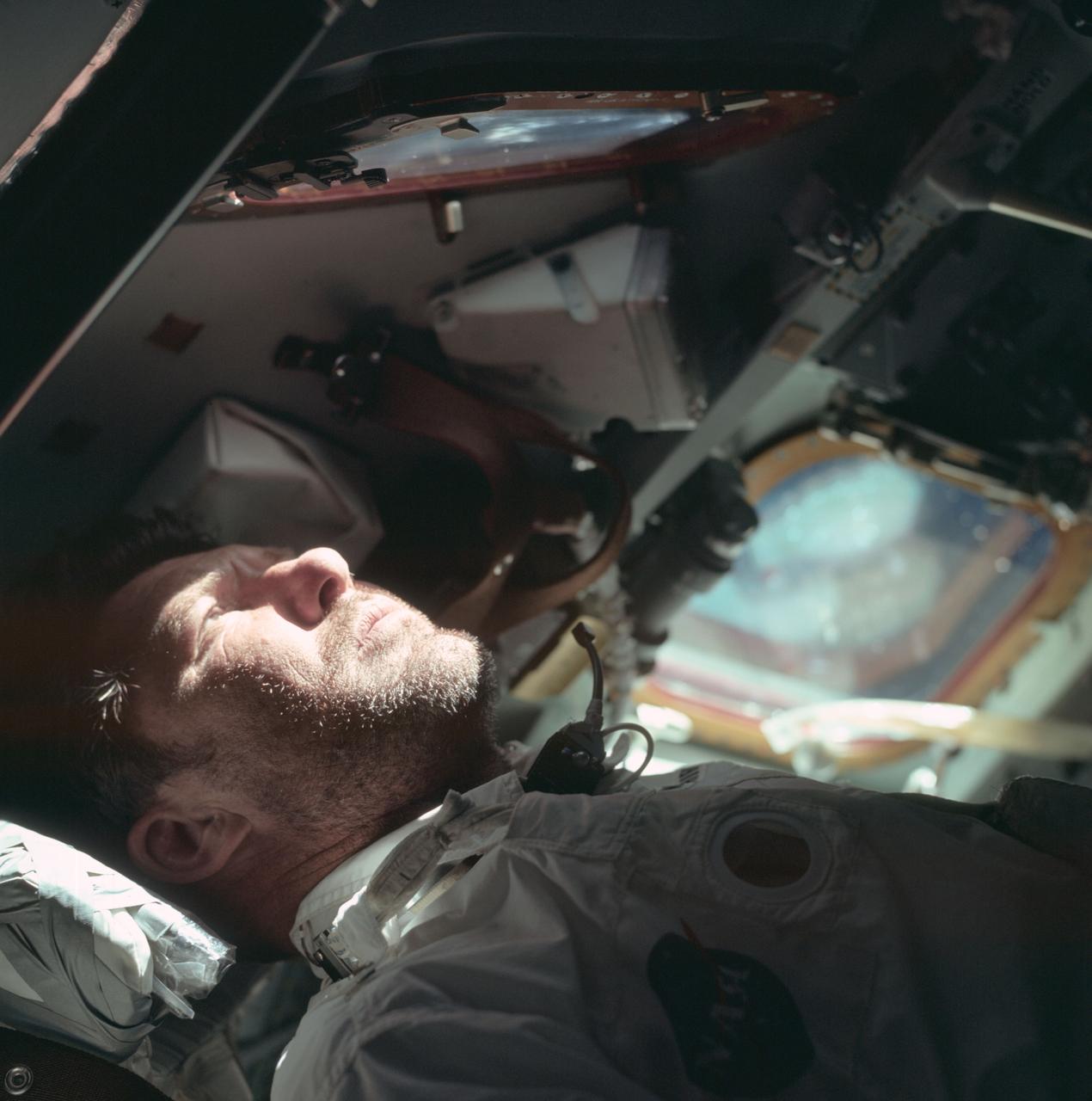

AS07-04-1596 (20 Oct. 1968) --- A heavy beard covers the face of astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr., Apollo 7 commander, as he looks out the rendezvous window in front of the commander's station on the ninth day of the Apollo 7 mission.
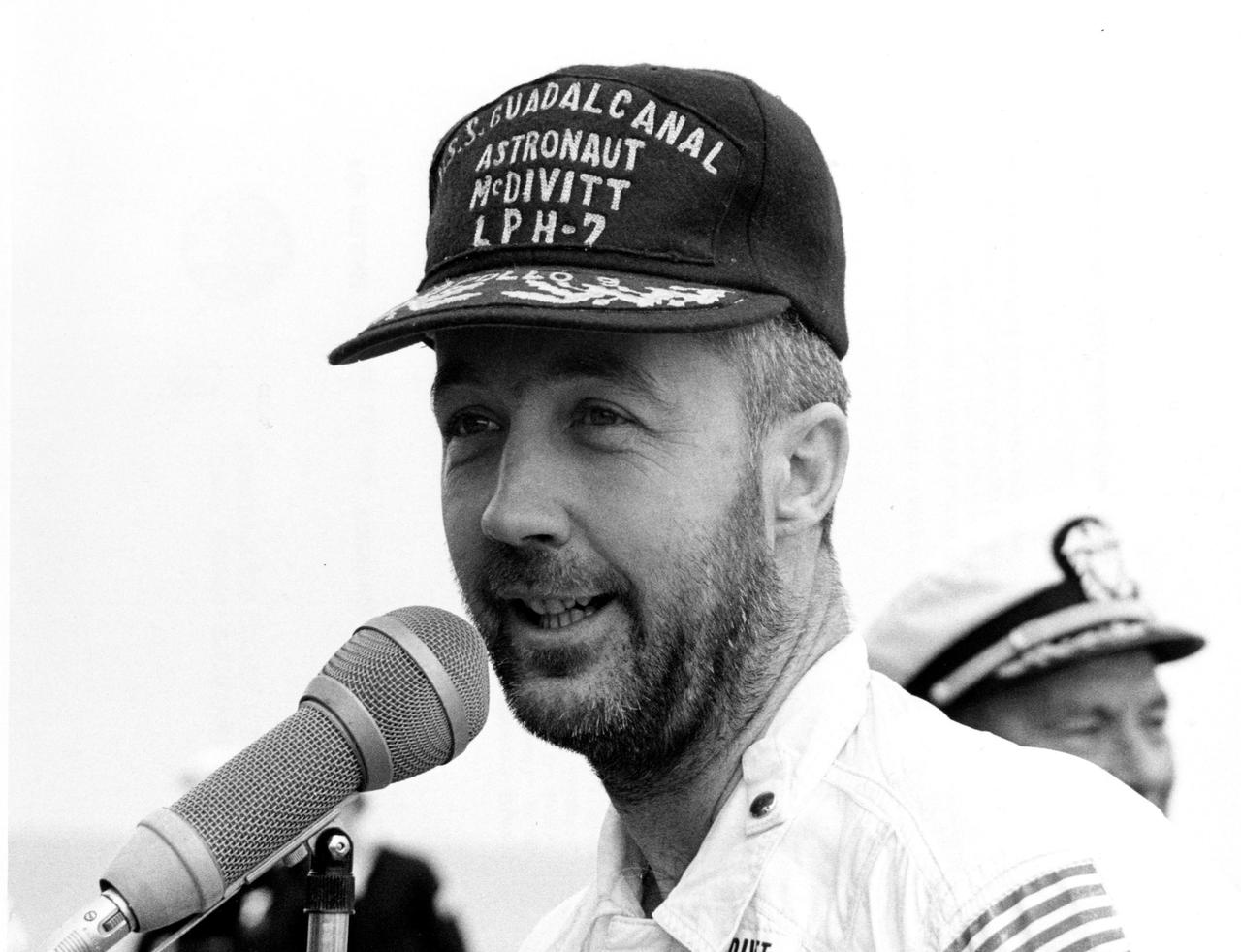

ABOARD THE USS GUADALCANAL -- Bearded Apollo 9 commander James A. McDivitt speaks to personnel aboard the USS Guadalcanal, prime recovery ship, an hour after he and astronauts David R. Scott and Russell L. Schweickart splashed down today in the Atlantic Ocean, 780 nautical miles southeast of Cape Kennedy. Their 10-day Earth orbital flight verified a lunar landing later this year. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration directs the Apollo program.
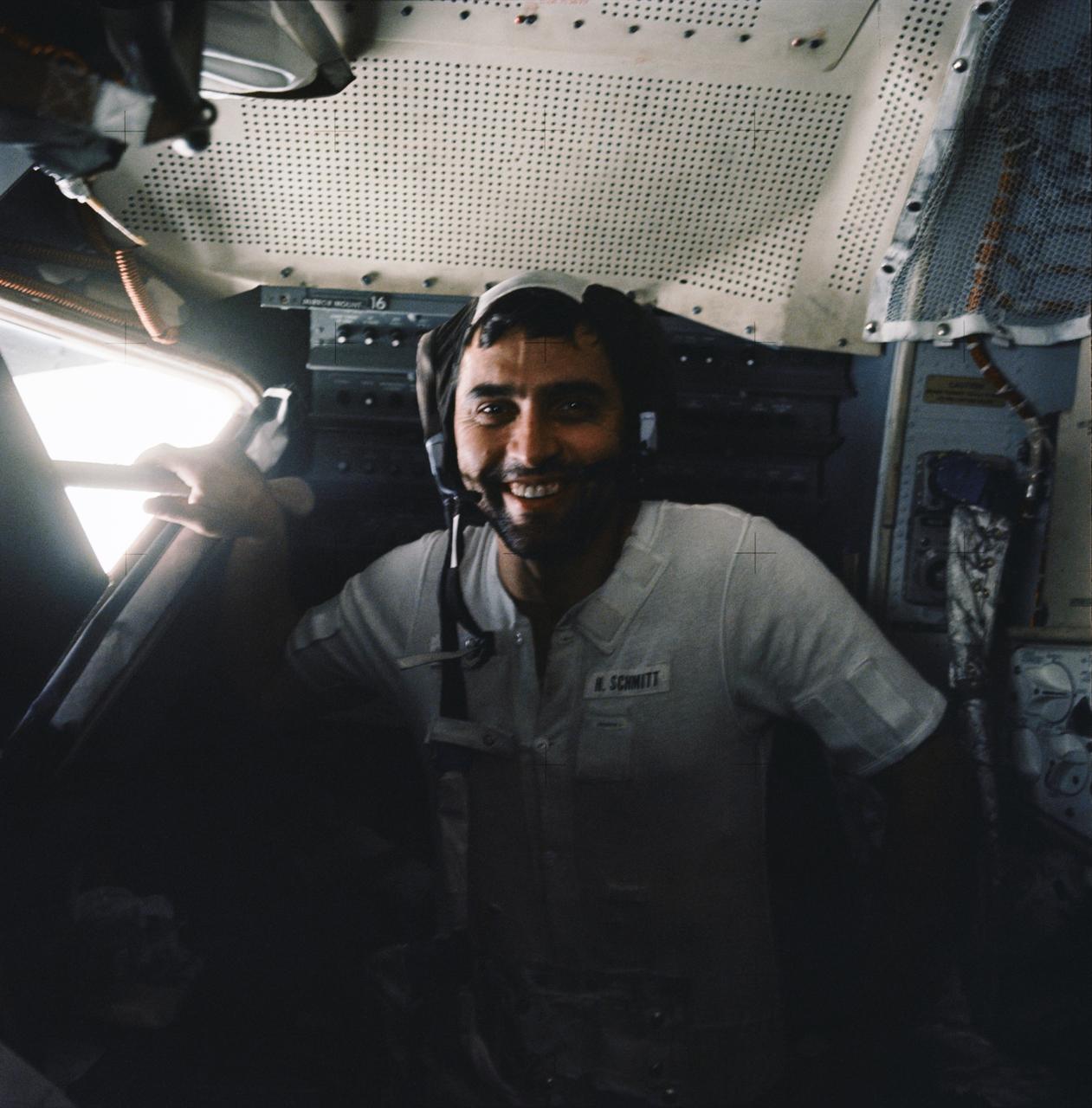

AS17-134-20530 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, displays several days of growth on his beard aboard the Lunar Module (LM) prior to its liftoff from the moon's surface. The photograph was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander. The two later re-joined astronaut Ronald E. Evans, who was orbiting the moon in the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM).
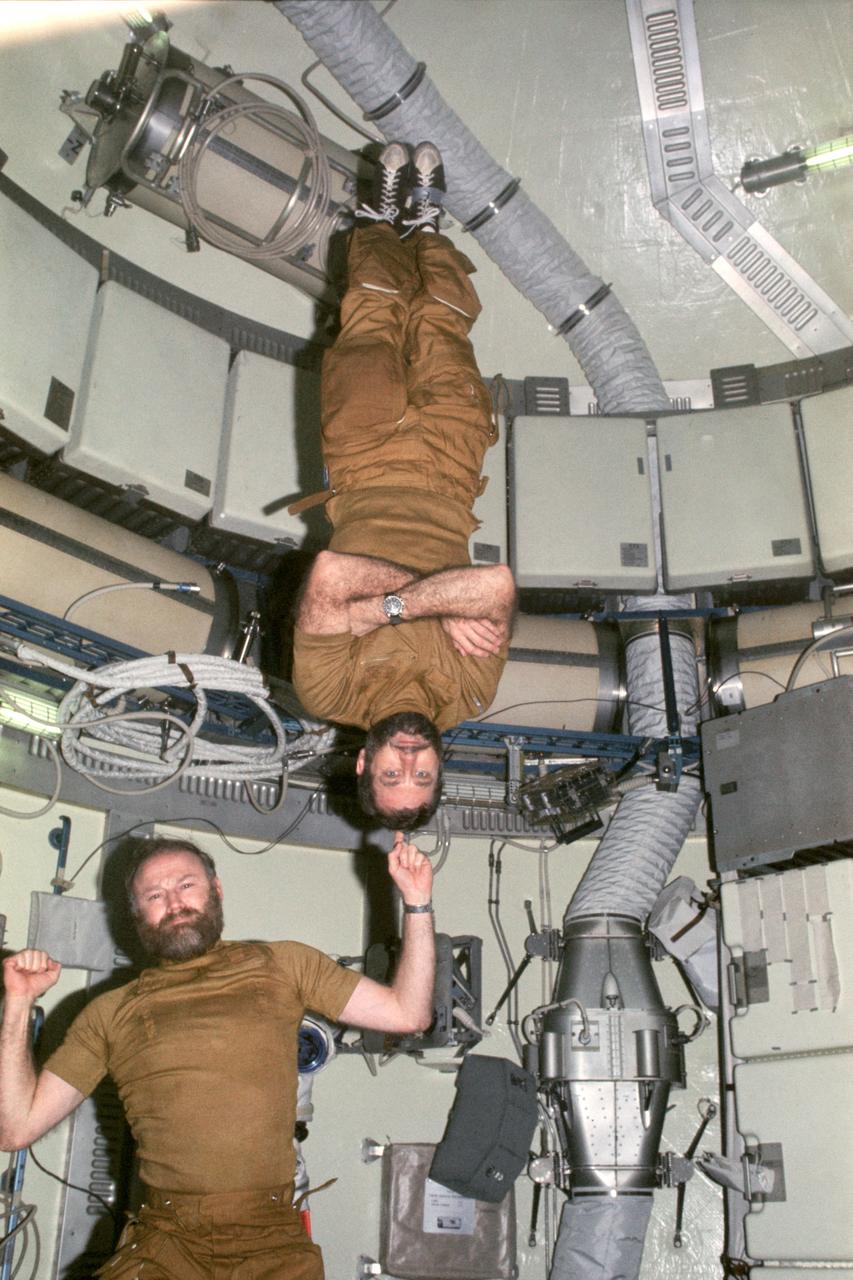

SL4-150-5080 (16 Nov. 1973-8 Feb. 1974) --- Two of the three Skylab 4 (third manning) astronauts exhibit the "magic" that can be accomplished in the weightlessness of space. Astronaut Gerald D. Carr, mission commander, uses his index finger to suspend astronaut William R. Pogue, pilot, in the Orbital Workshop (OWS). The two "wizards" completed almost three months aboard the Earth-orbiting Skylab space station, plenty of time to grow these full beards. The photograph was taken with a 35mm camera by astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot. Photo credit: NASA
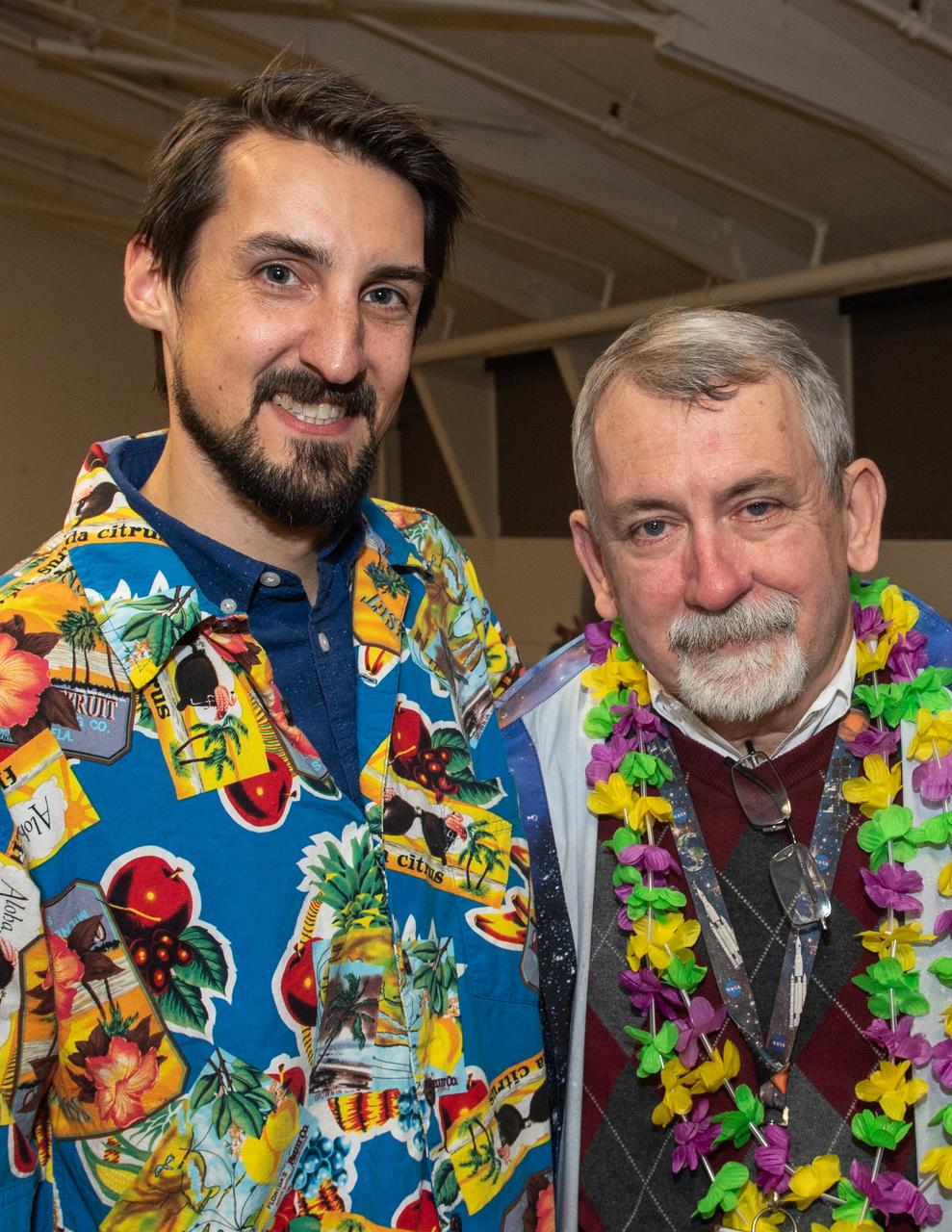

Rob Garner (left) and then-Goddard News Chief Ed Campion celebrating the latter's retirement in 2018. Aloha shirt Fridays were a mainstay of Campion's tenure.
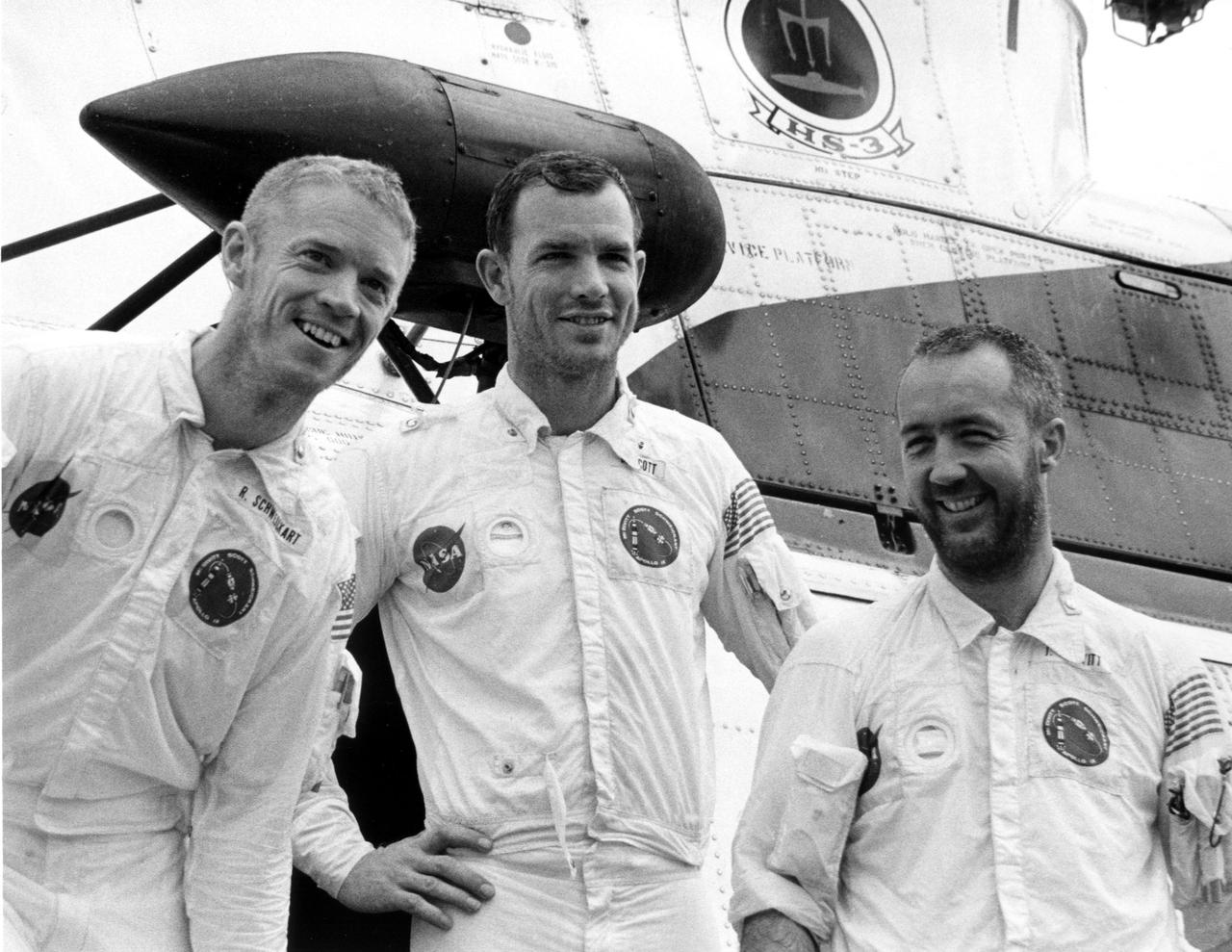

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Bearded and smiling, Apollo 9 astronauts, left to right, Russell L. Schweickart, David R. Scott and James A. McDivitt, pause in front of recovery helicopter, which carried them a short distance from their spacecraft's impact point to the USS Guadalcanal, prime recovery ship. They splashed down today less than five miles from the Guadalcanal, 780 nautical miles southeast of Cape Kennedy. The astronauts reentered at the beginning of their 152nd Earth orbit following a textbook flight that verified a lunar module spacecraft. It was similar to the one that is to land Americans on the Moon later this year. They were launched March 3, 1969, from the Kennedy Space Center aboard an Apollo_Saturn V space vehicle. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration directs the Apollo program.
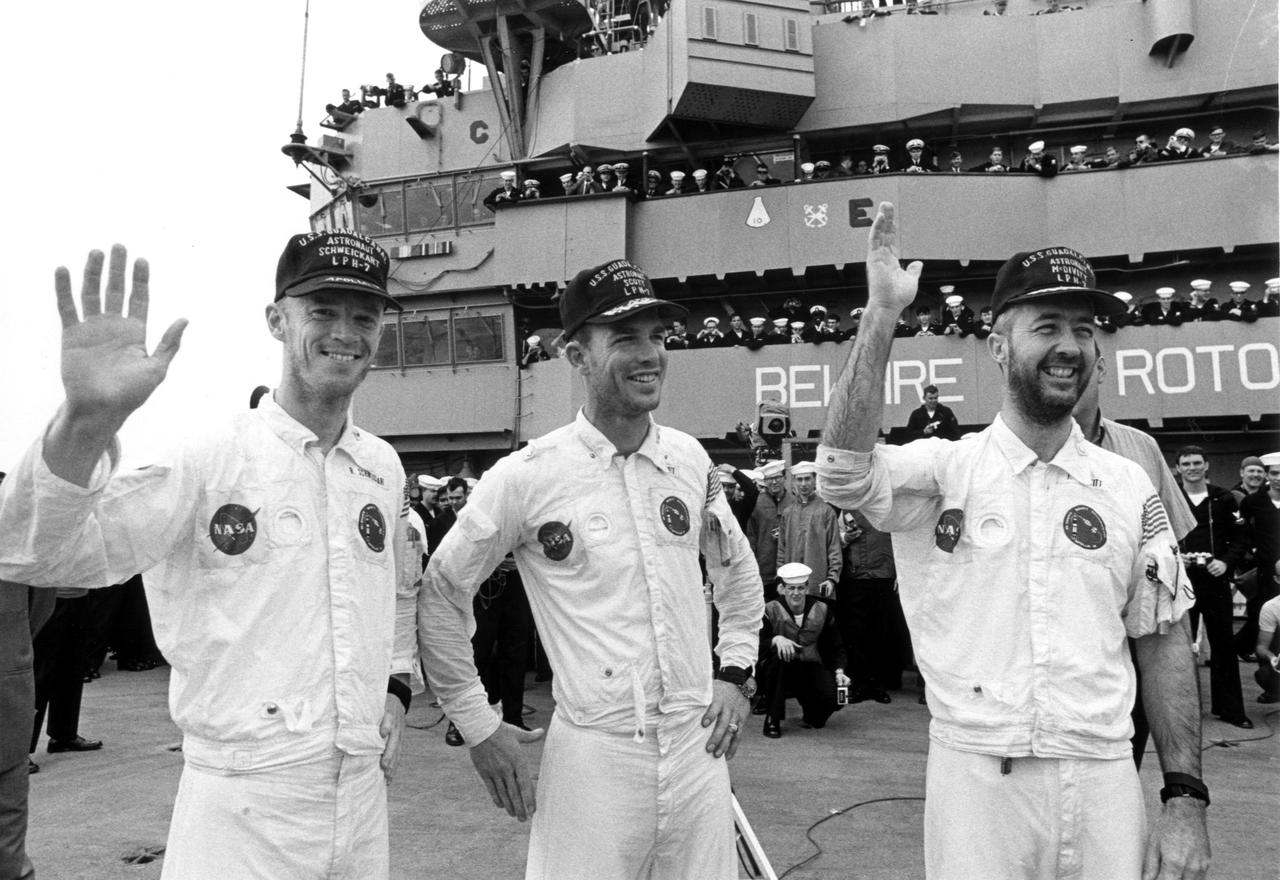

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Wearing flight caps presented to them by the crew of the USS Guadalcanal, bearded Apollo 9 astronauts (left to right) Russell L. Schweickart, David R. Scott and James A. McDivitt, wave to well-wishers aboard the recovery ship at the completion of their 10-day Earth orbital mission. Their spacecraft splashed down 780 nautical miles southeast of Cape Kennedy at 12:01 p.m. EST, March 13, 1969. During the textbook mission, the space pilots verified a lunar module spacecraft similar to the one that is to land Americans on the Moon later this year. Their flight began March 3 when they were launched by an Apollo_Saturn V rocket from the Kennedy Space Center. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration directs the Apollo program.
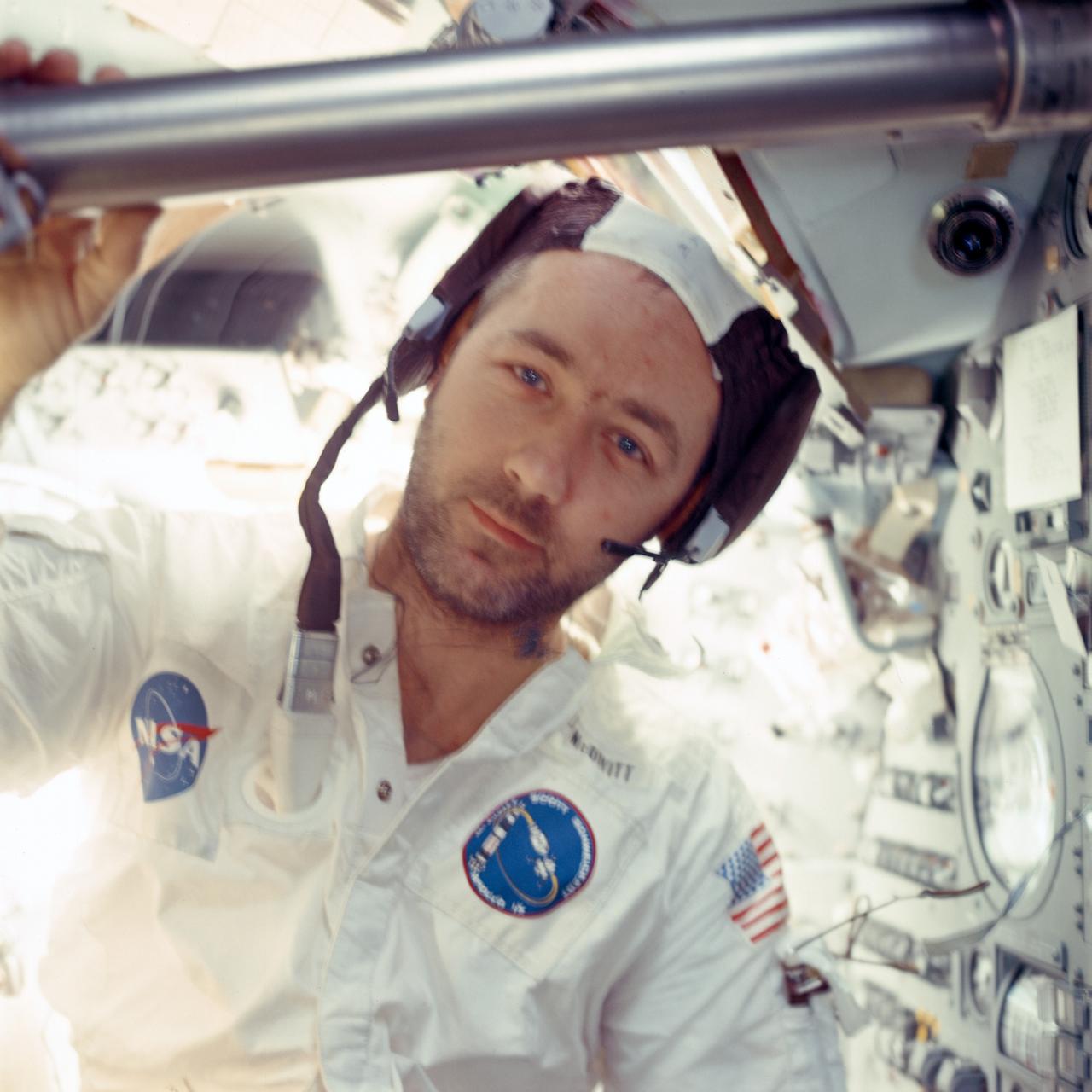

AS09-20-3154 (3-13 March 1969) --- This close-up view of astronaut James A. McDivitt shows several days' beard growth. The Apollo 9 mission commander was onboard the Lunar Module (LM) "Spider" in Earth orbit, near the end of the flight. He was joined on the mission by astronauts David R. Scott, command module pilot, and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Schweickart took this picture while Scott remained in the Command Module (CM) "Gumdrop." In Earth orbit, the three tested the transposition and docking systems of the lunar module and command module. On a scheduled lunar landing mission later this year, a team of three astronauts and ground controllers will use what this crew and its support staff have learned in handling the systems of the two spacecraft.
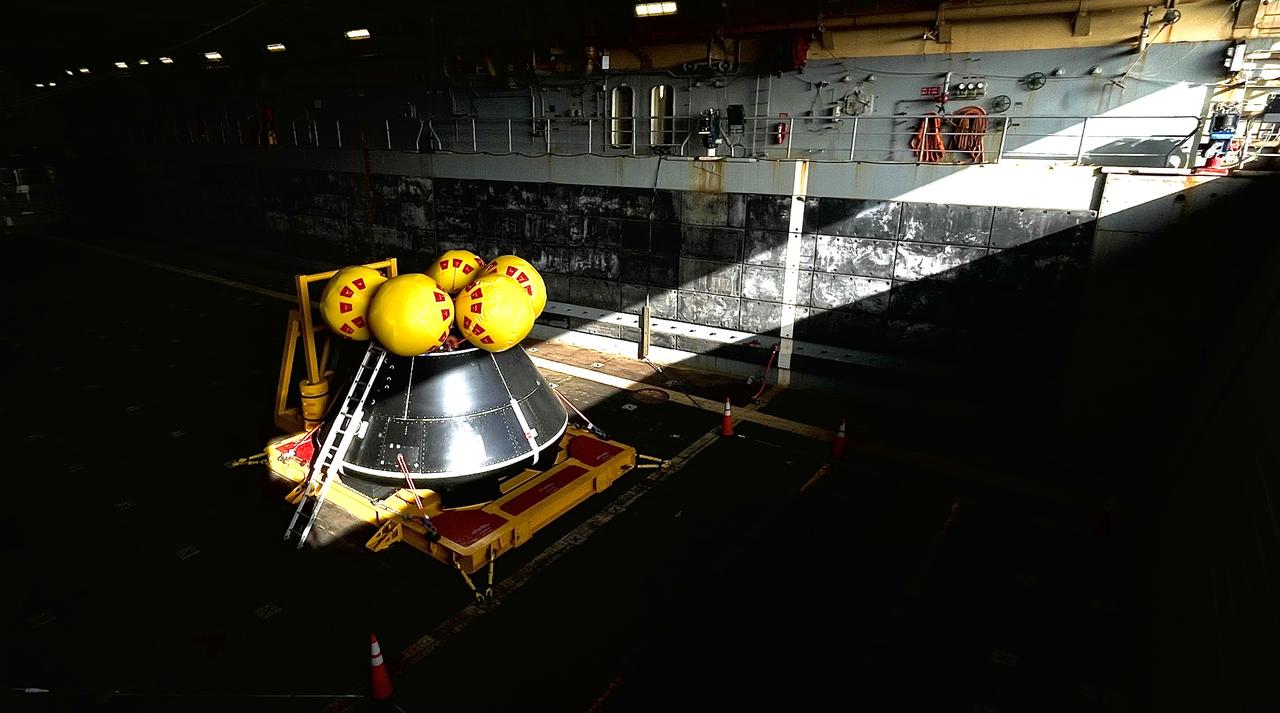

While onboard the USS John P. Murtha, NASA and the Department of Defense practice Artemis II recovery operations with the Crew Module Test Article (CMTA) in July of 2023. The CMTA is a full-scale mockup of the Orion spacecraft and is used to verify the recovery team is ready to support crew recovery after missions to the Moon.
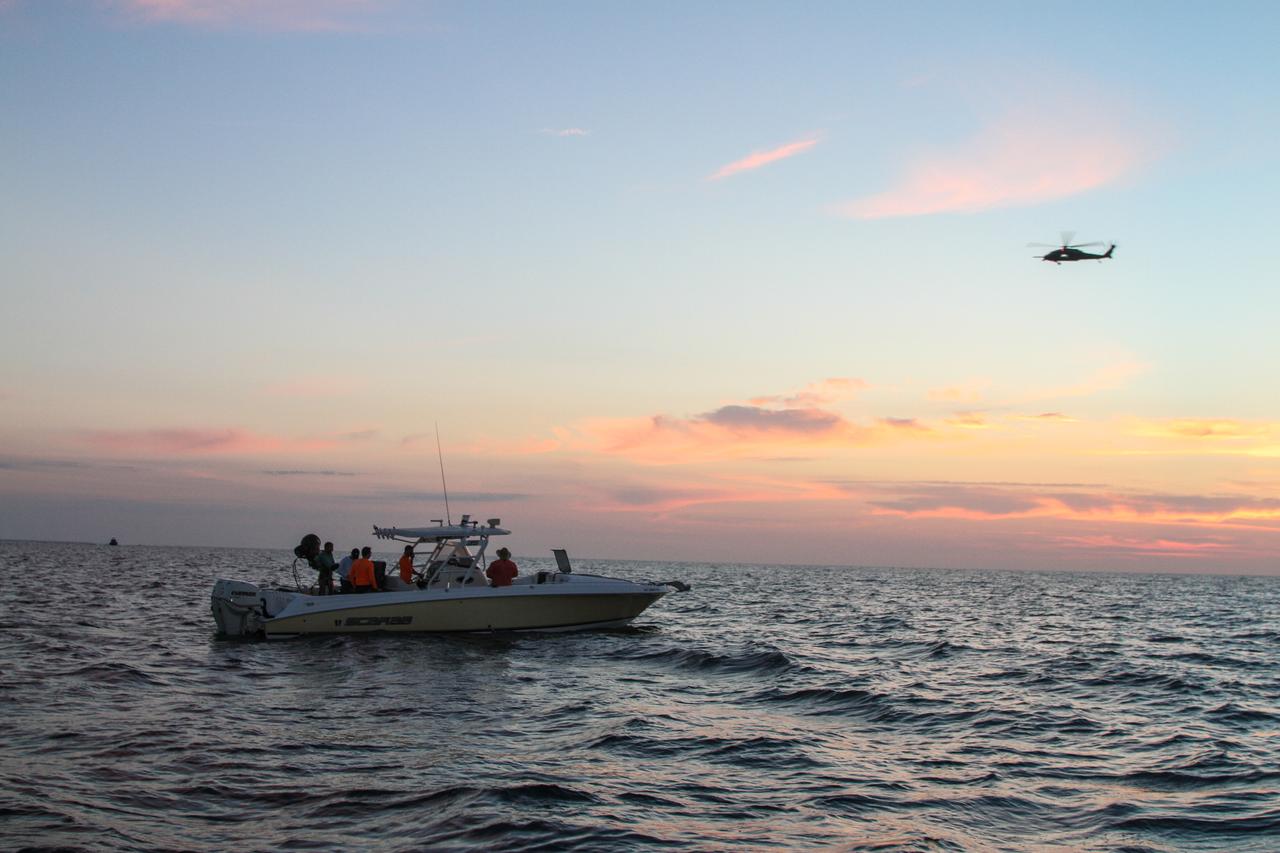

Members of the NASA Ejectable Data Recorder Recovery Team search for the ejectable data recorders in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida on July 2, 2019, after the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test. During AA-2, a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launched atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on July 2, 2019. Liftoff was at 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster sent the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors worked together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test proves that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent. Data from the recorders will be analyzed by engineers.
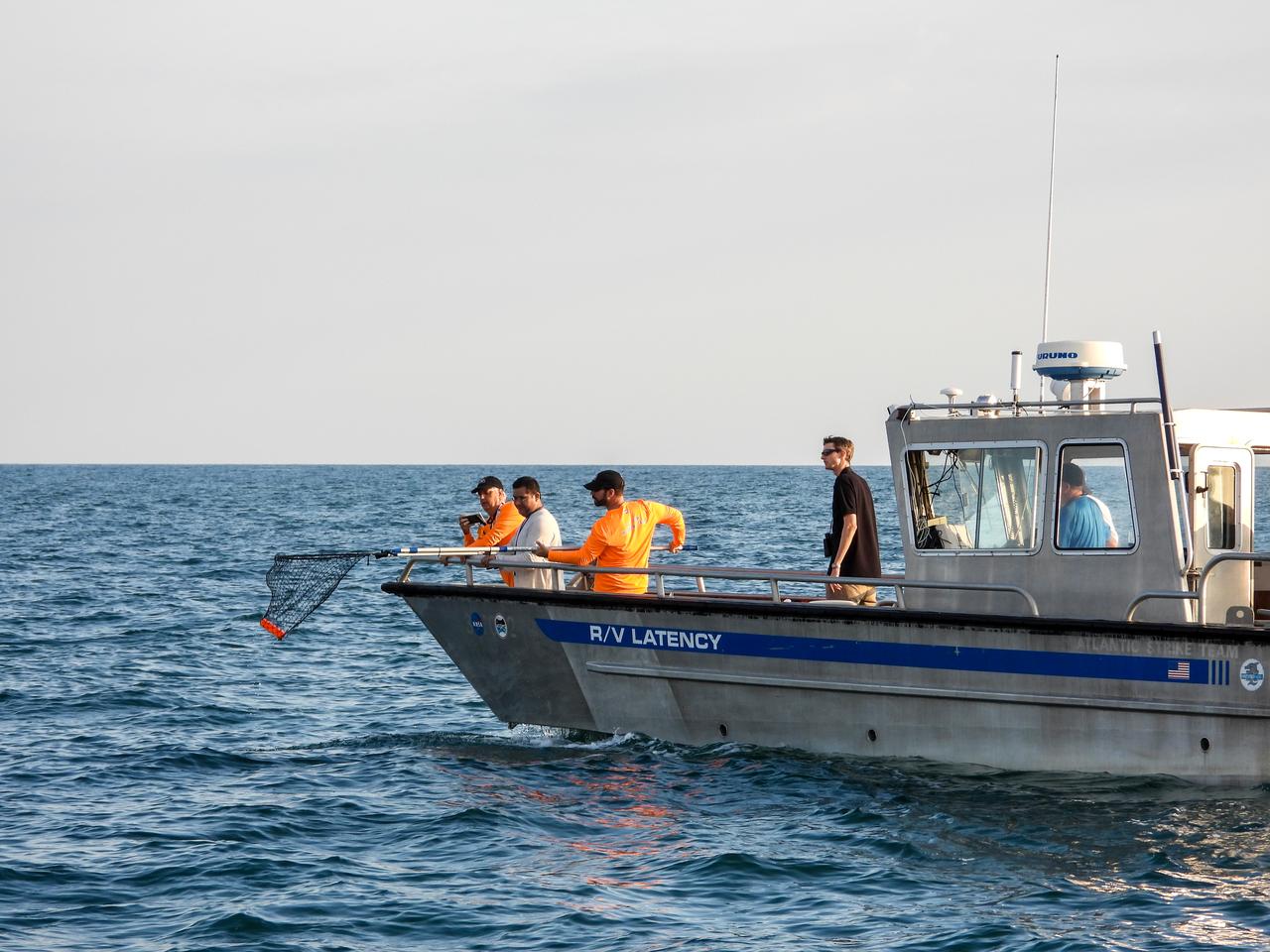

One of the 12 ejectable data recorders from NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test is retrieved from the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida by the NASA Ejectable Data Recorder Recovery Team on July 2, 2019. During AA-2, a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launched atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on July 2, 2019. Liftoff was at 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster sent the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors worked together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test proves that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent. Data from the recorders will be analyzed by engineers.
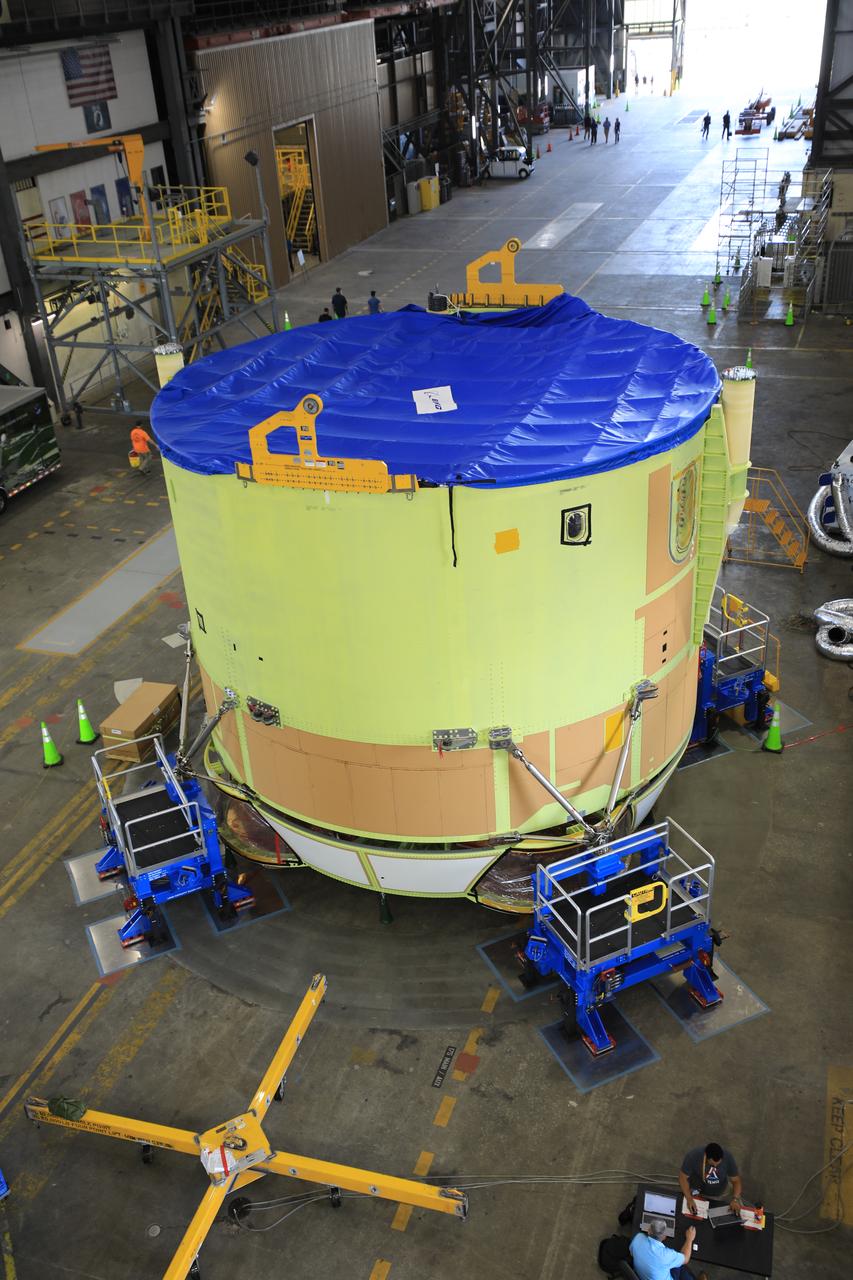

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
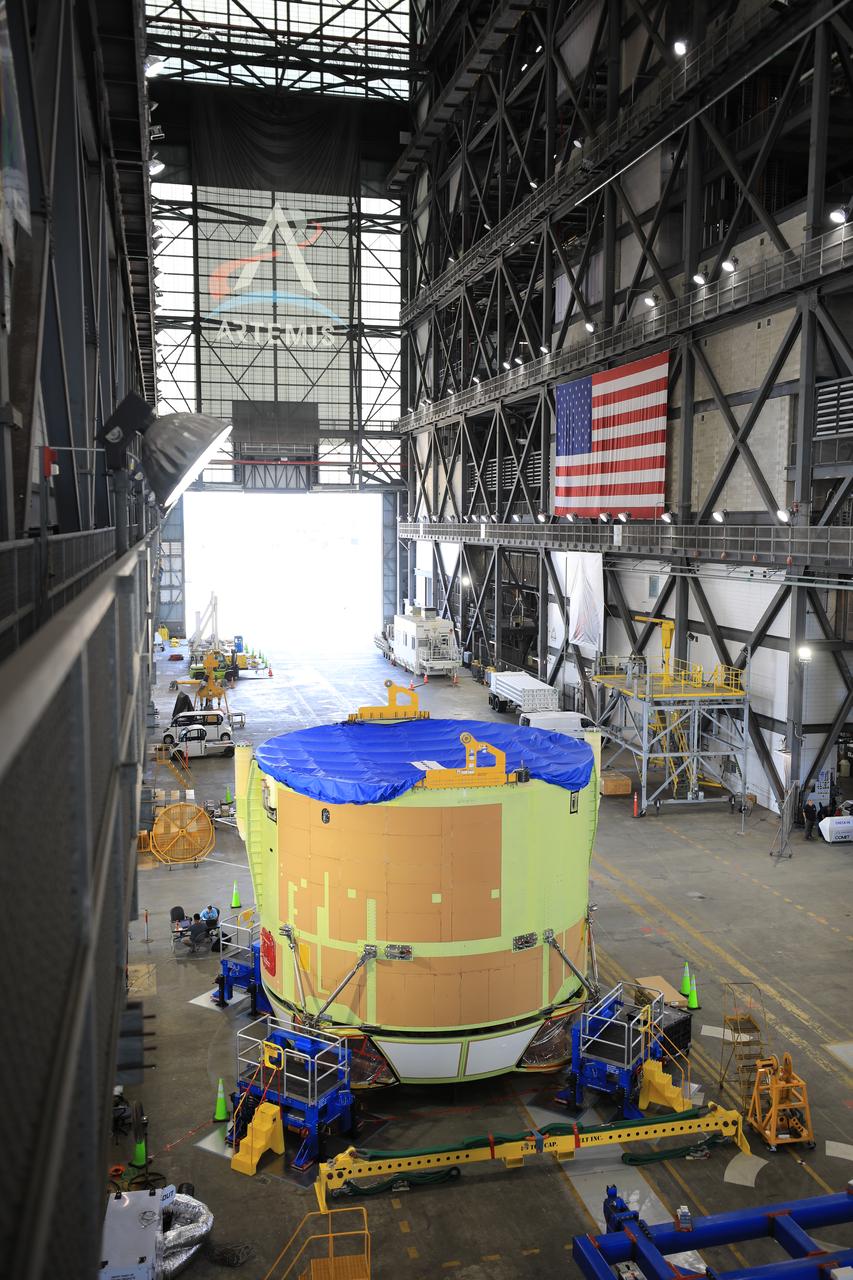

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
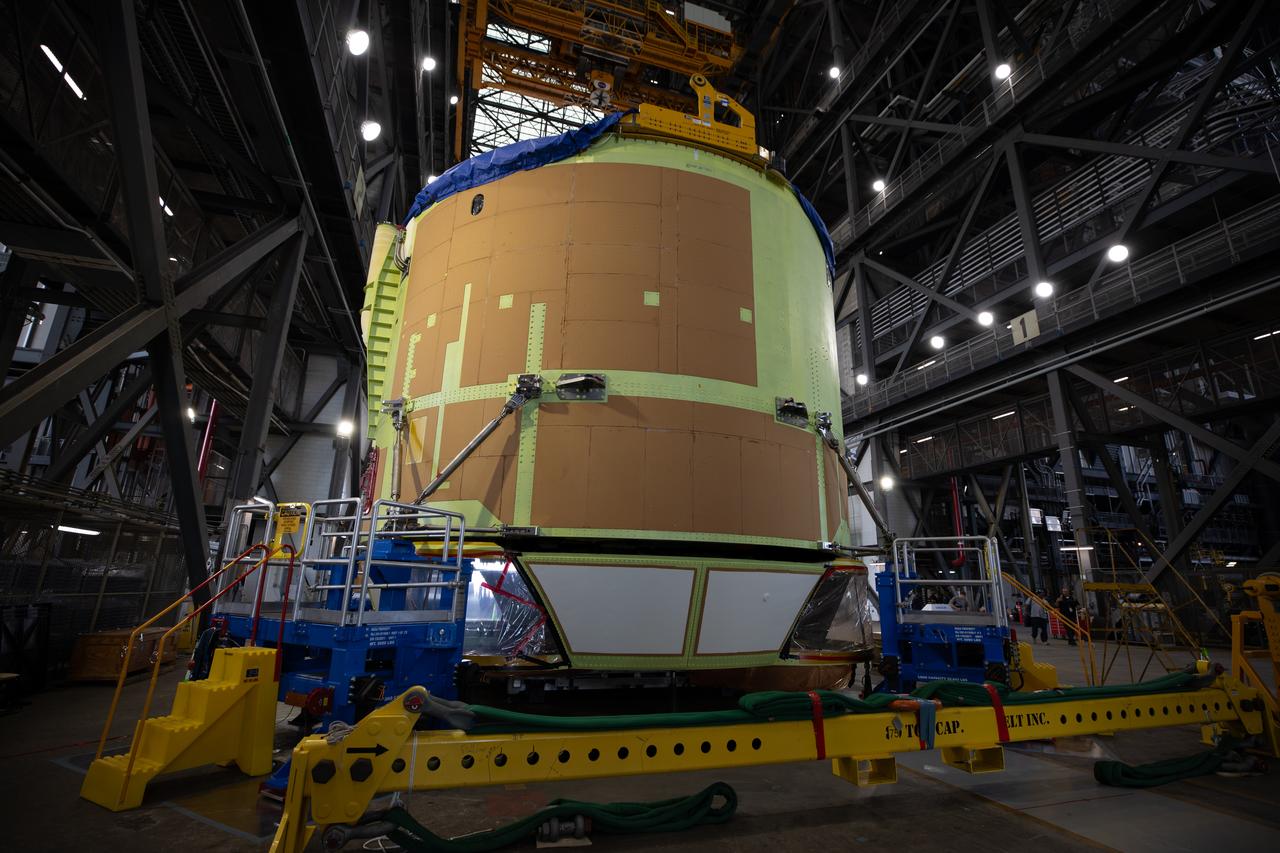

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
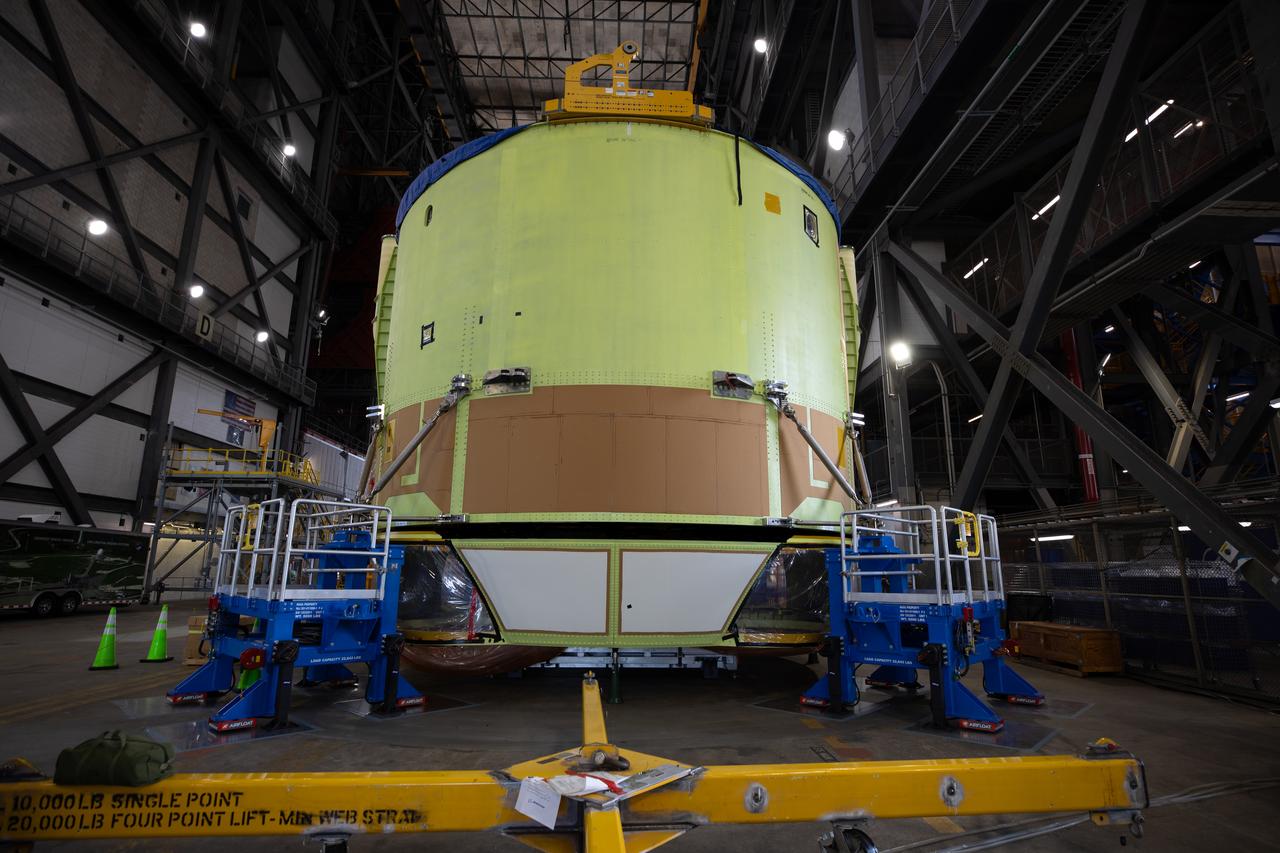

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
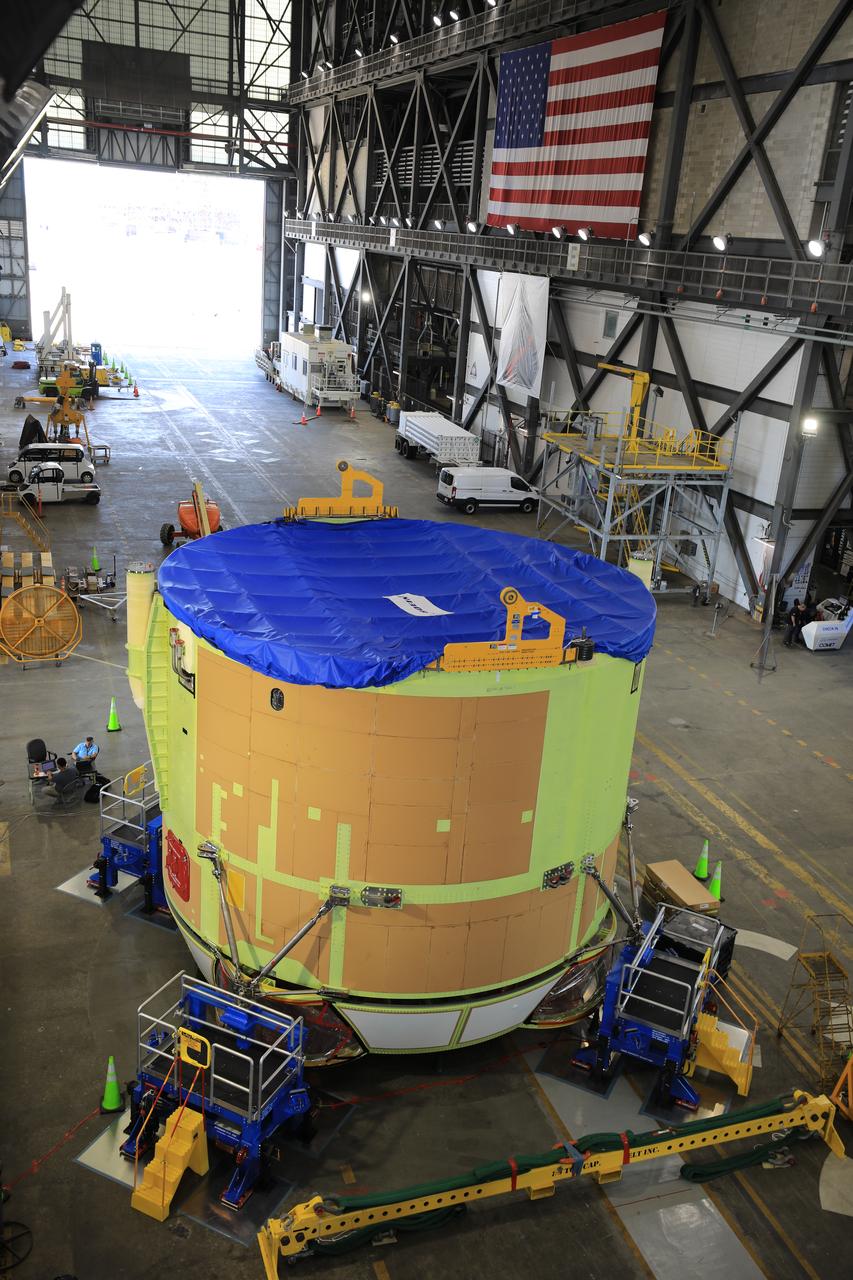

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
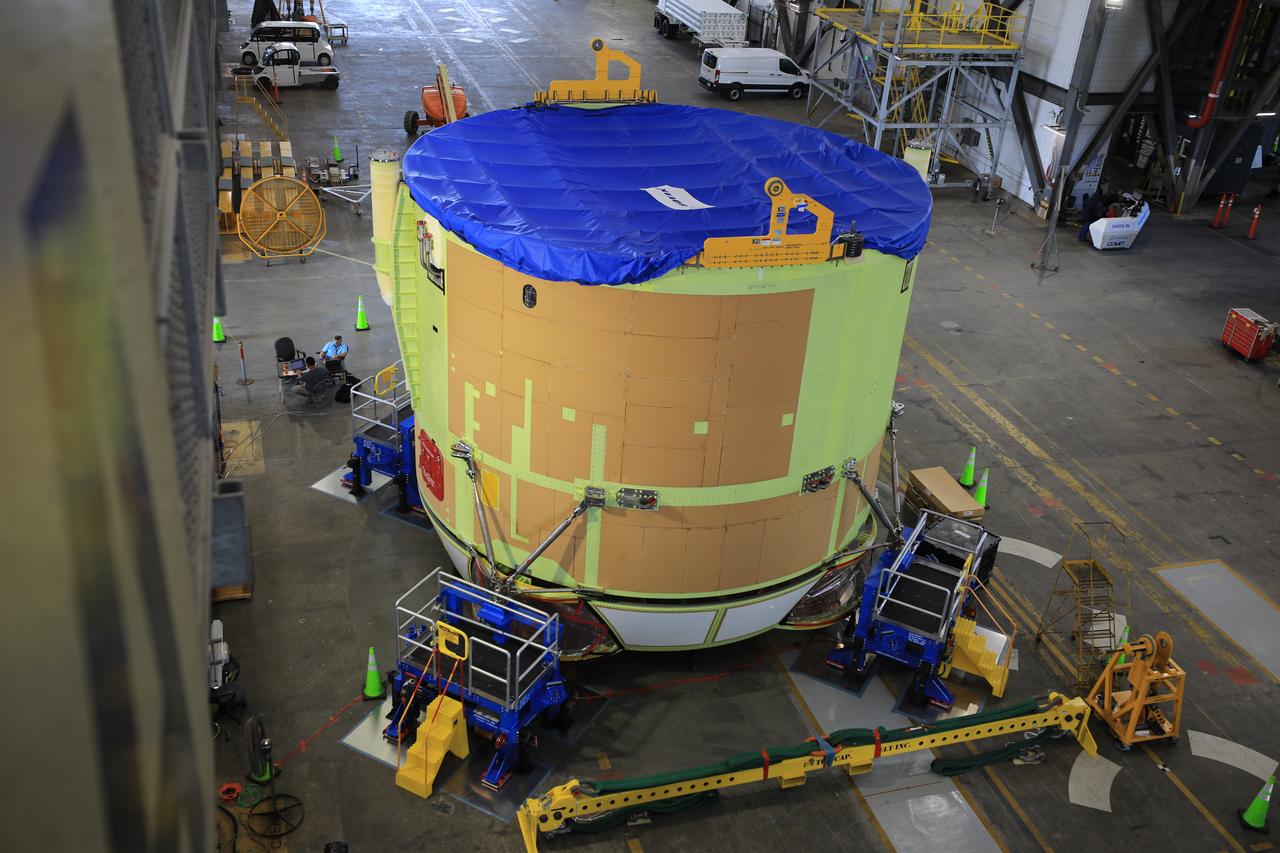
Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
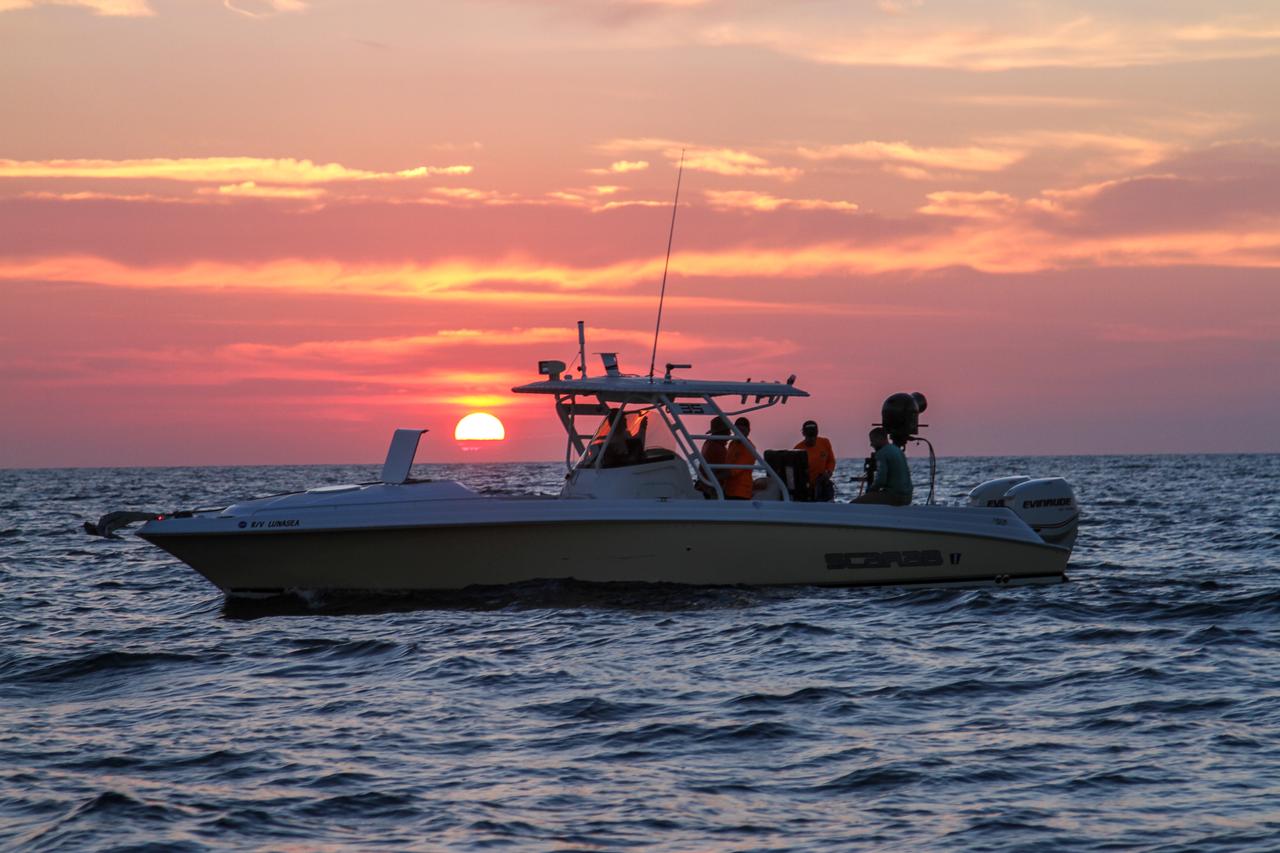

Members of the NASA Ejectable Data Recorder Recovery Team search for the ejectable data recorders in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida on July 2, 2019, after the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test. During AA-2, a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launched atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on July 2, 2019. Liftoff was at 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster sent the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors worked together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test proves that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent. Data from the recorders will be analyzed by engineers.
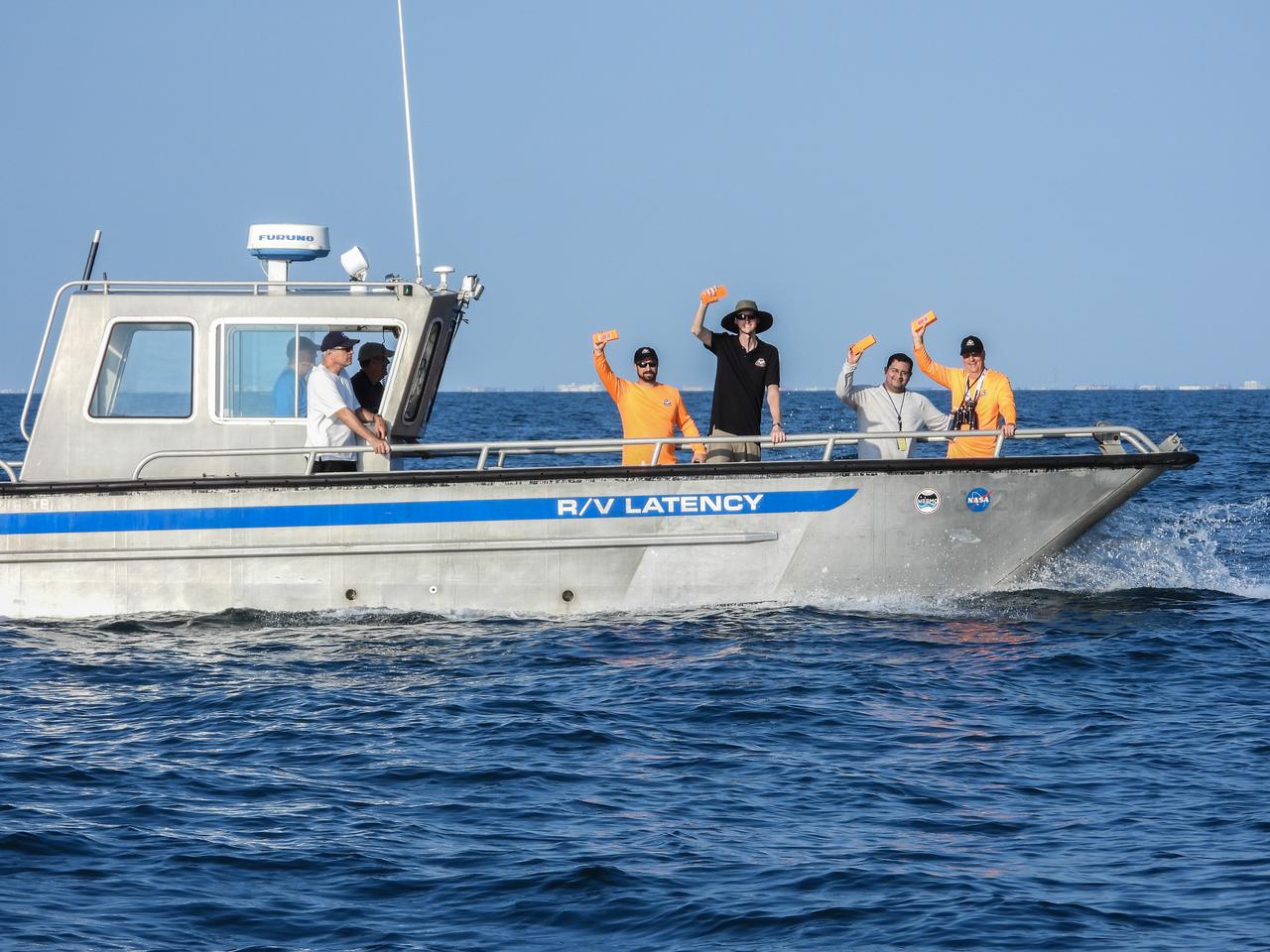

Members of the NASA Ejectable Data Recorder Recovery Team display some of the ejectable data recorders they recovered in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida on July 2, 2019, after the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test. During AA-2, a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launched atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on July 2, 2019. Liftoff was at 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster sent the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors worked together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test proves that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent. Data from the recorders will be analyzed by engineers.
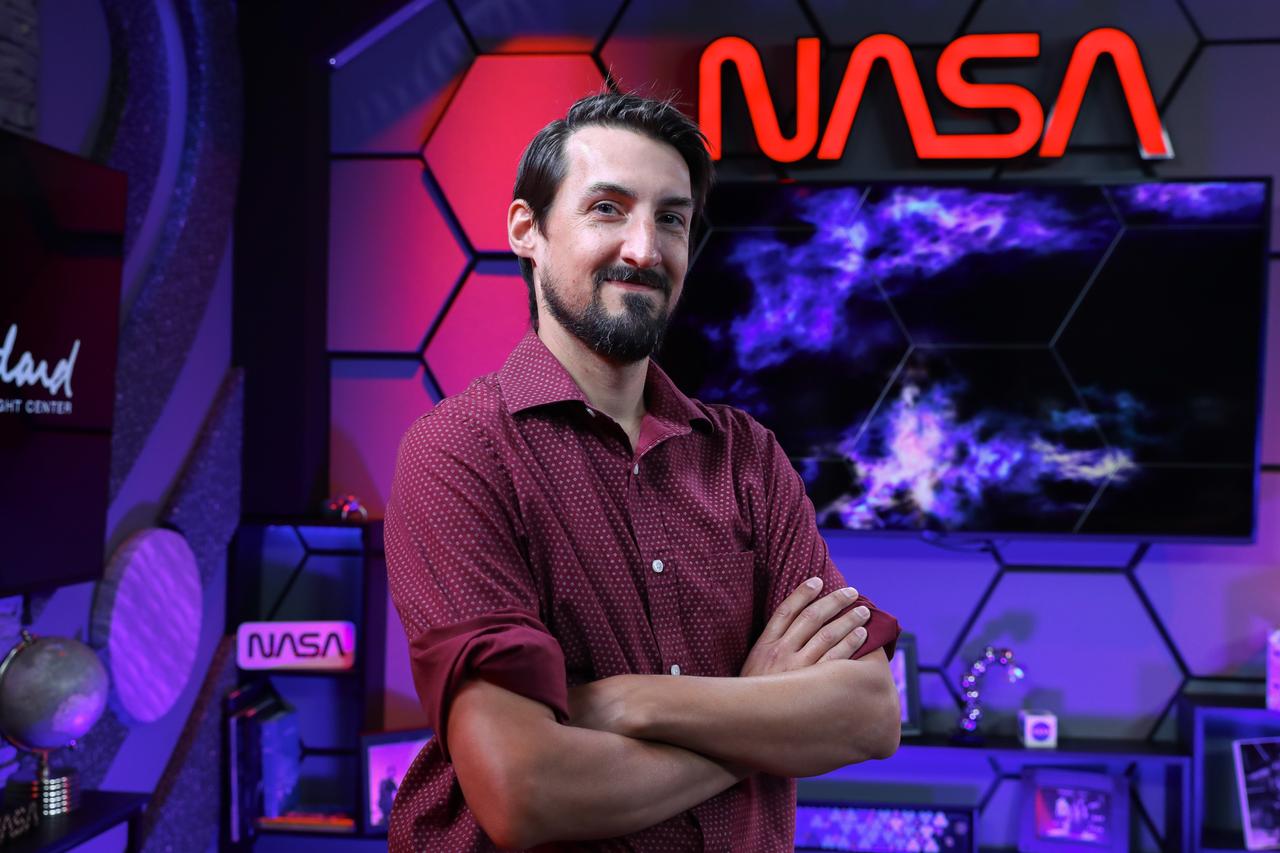

Rob Garner has worked in the Office of Communications at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., since 2007.
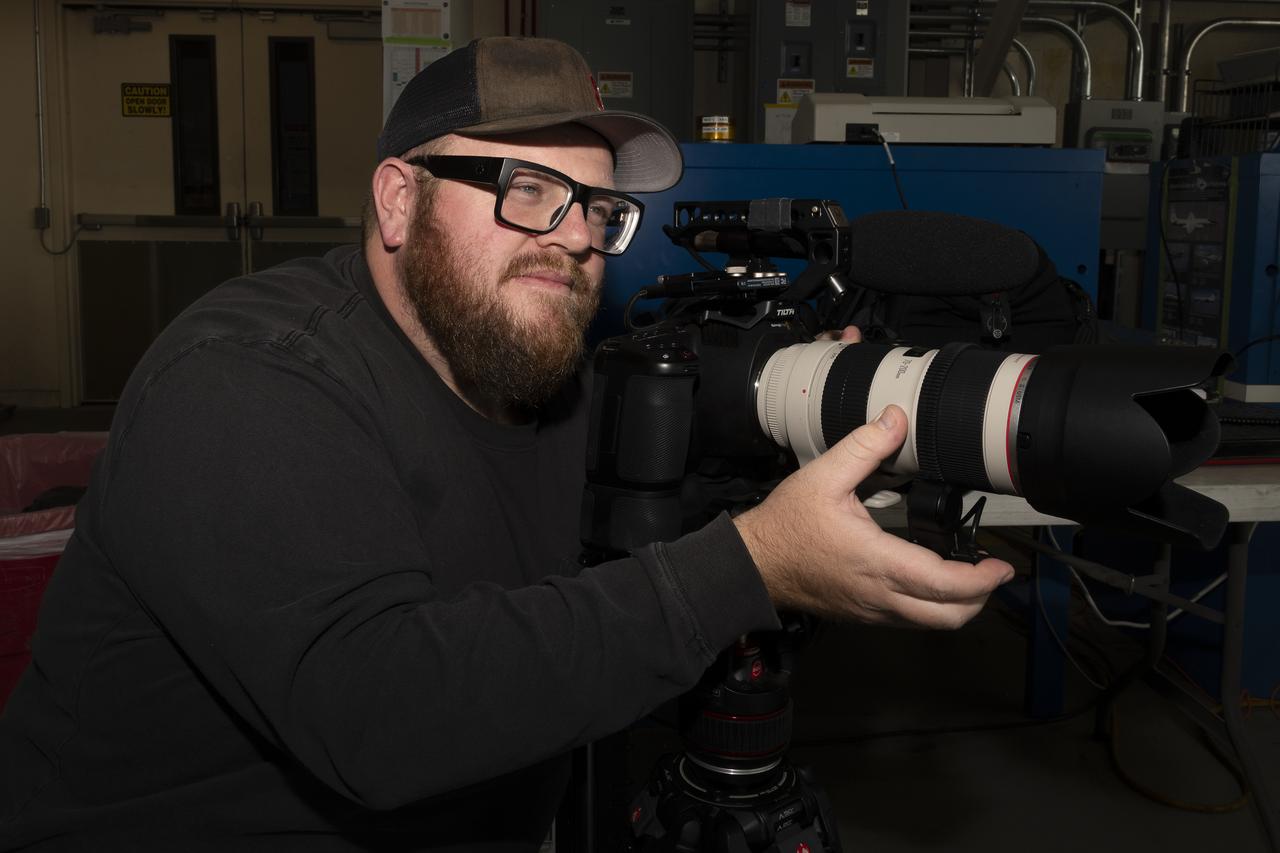

NASA videographer Jacob Shaw captures footage of the ER-2 aircraft inside a hangar at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, in December 2024. Shaw recently earned first place in NASA’s 2024 Videographer of the Year Awards – documentation category – for his film, “Reflections,” which chronicles the 2024 Airborne Science mission PACE-PAX – short for Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem Postlaunch Airborne eXperiment.
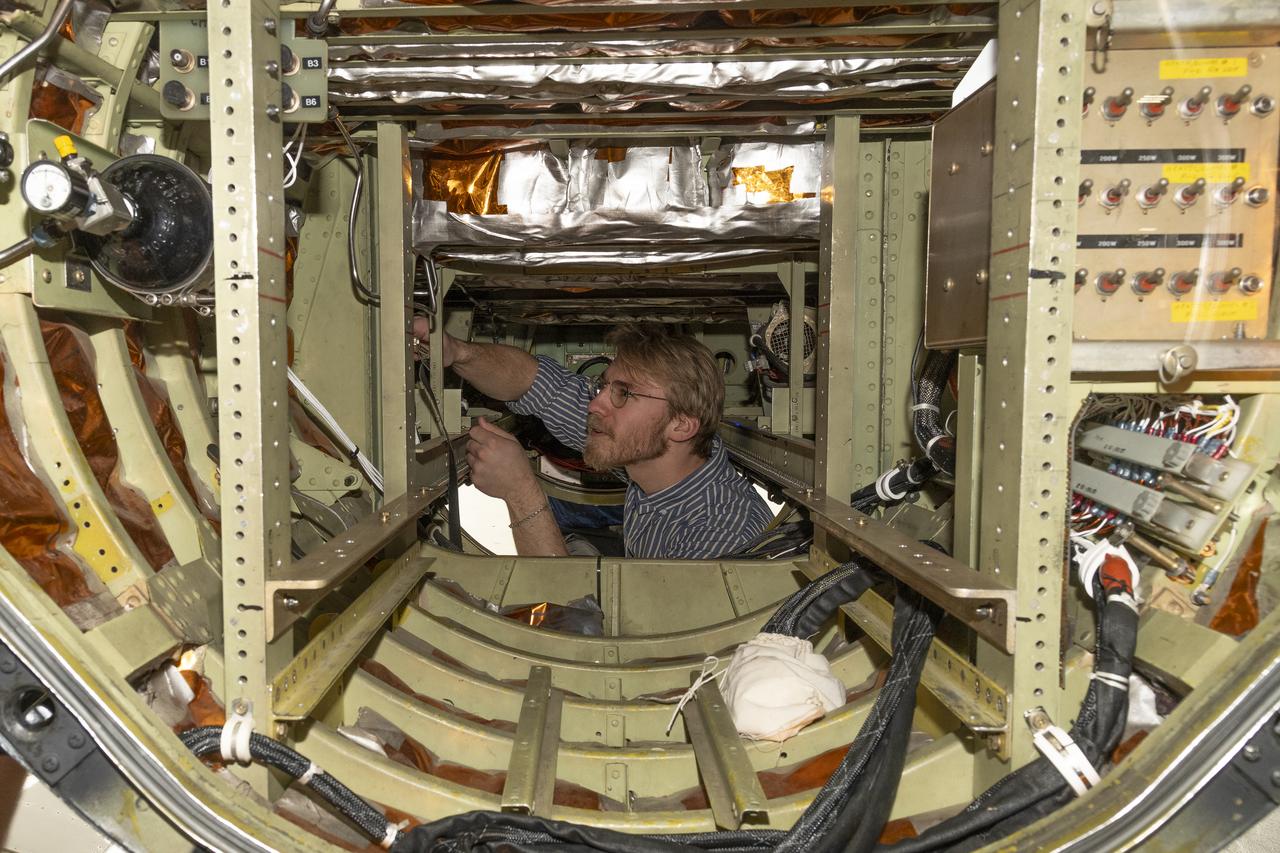

A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Researcher Jackson Begolka from the University of Iowa examines the instrument connectors in the ER-2 onboard the ER-2, which flies at high altitudes to validate satellite-borne data. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
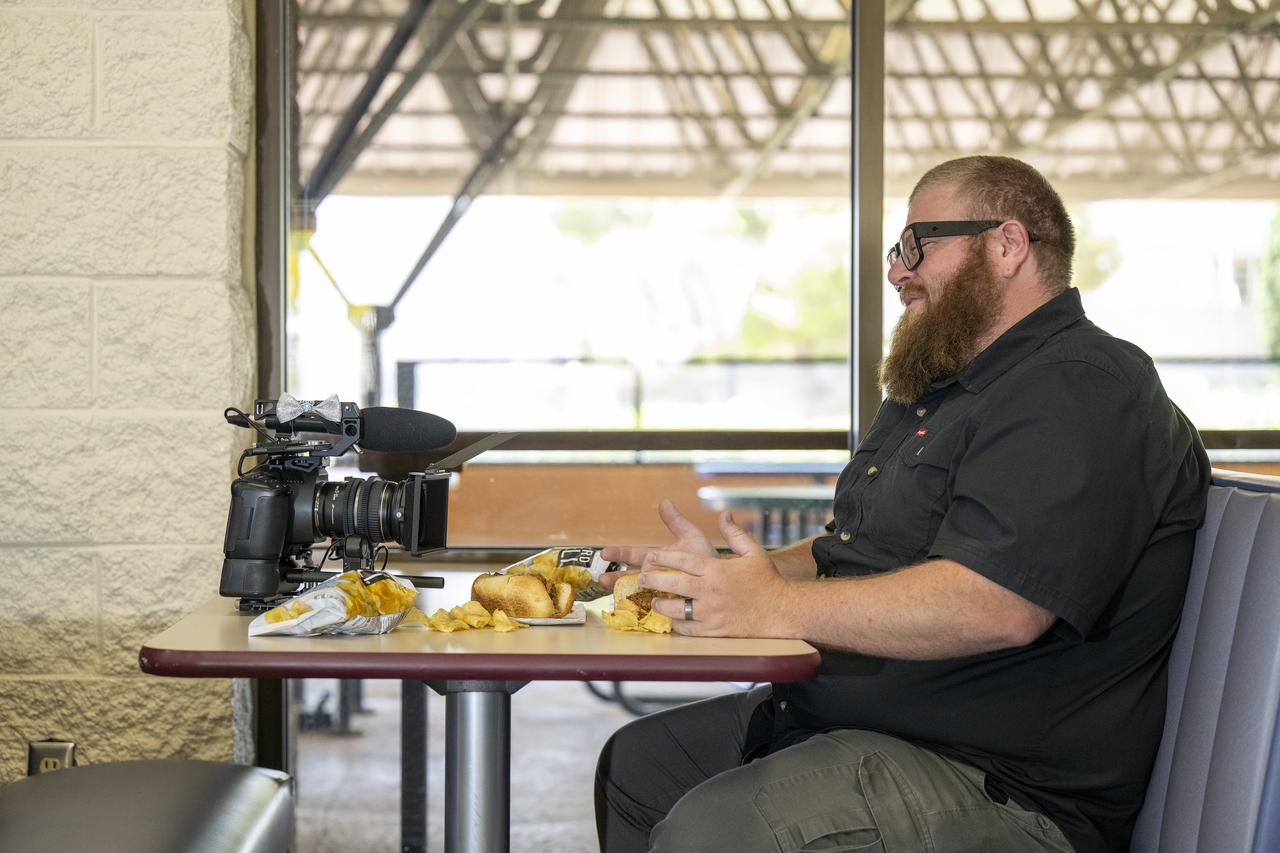

NASA videographer Jacob Shaw shares a moment with his constant companion during a break in the cafeteria at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, on May 21, 2025. Shaw recently earned first place in NASA’s 2024 Videographer of the Year Awards – documentation category – for his film, “Reflections,” which chronicles the 2024 Airborne Science mission PACE-PAX – short for Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem Postlaunch Airborne eXperiment.