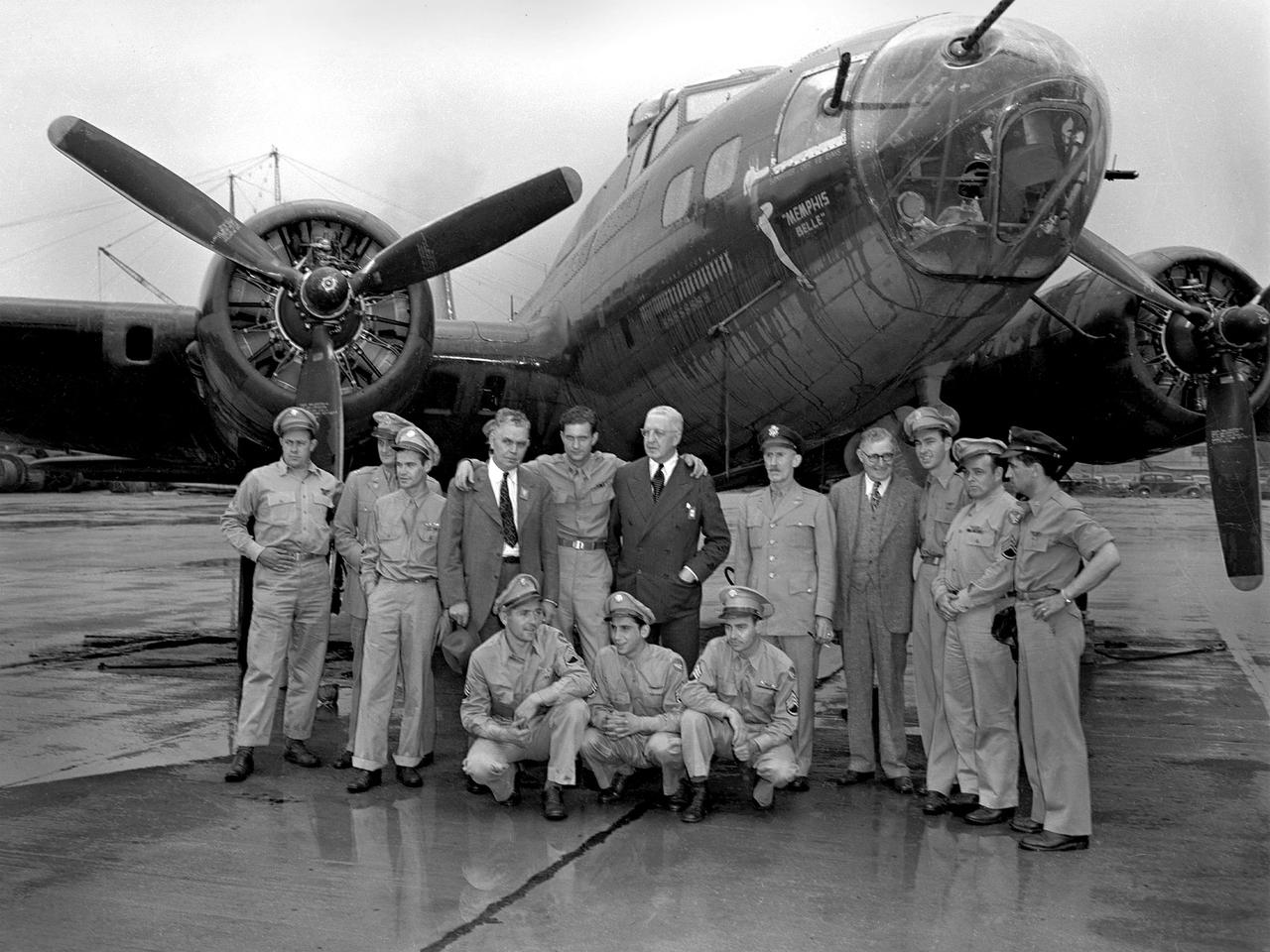

Captain Robert Morgan and the rest of the Memphis Belle crew arrive in Cleveland on a rainy July 7, 1943, for three-day publicity visit. This B–17 Flying Fortress had recently become the first U.S. bomber to complete 25 missions over Germany and France. The lack of long distance escort fighters made the feat even more remarkable. The Memphis Belle and its crew returned to the United States in June and were immediately thrown into a three-month-long war bond tour. While in Cleveland the crew toured the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory, the Cleveland Bomber Plant, and Thompson Products. In the evenings they were feted downtown by the Chamber of Commerce at the Hotel Cleveland. A local company brought Morgan’s family and his fiancé—the Memphis Belle’s inspiration—to Cleveland to participate in the activities. The bomber was on display to the public near the airport’s fenceline and stored in the NACA’s hangar overnight. Pictured in this photograph from left to right: Robert Hanson, Vincent Evans, Charles Leighton, NACA Manager Raymond Sharp, Robert Morgan, William Holliday of the Chamber of Commerce, Army Liaison Officer Colonel Edwin Page, Airport Commissioner Jack Berry, Cecil Scott, John Quinlan and James Verinis. Kneeling are Harold Loch, Casimer Nastal and Charles Wichell.
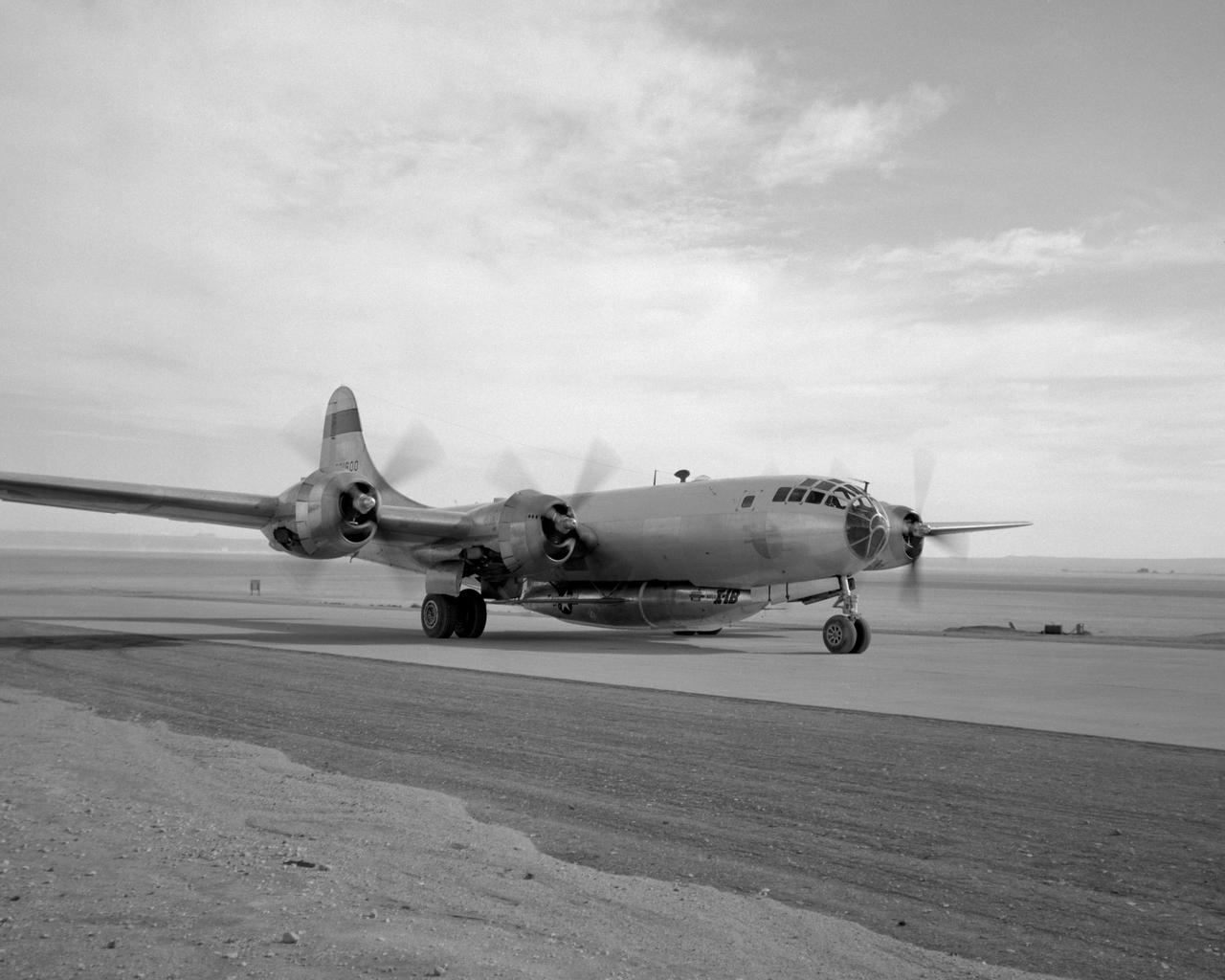

B-29 #800 with X-1B attached taxi's in off of the lakebed.
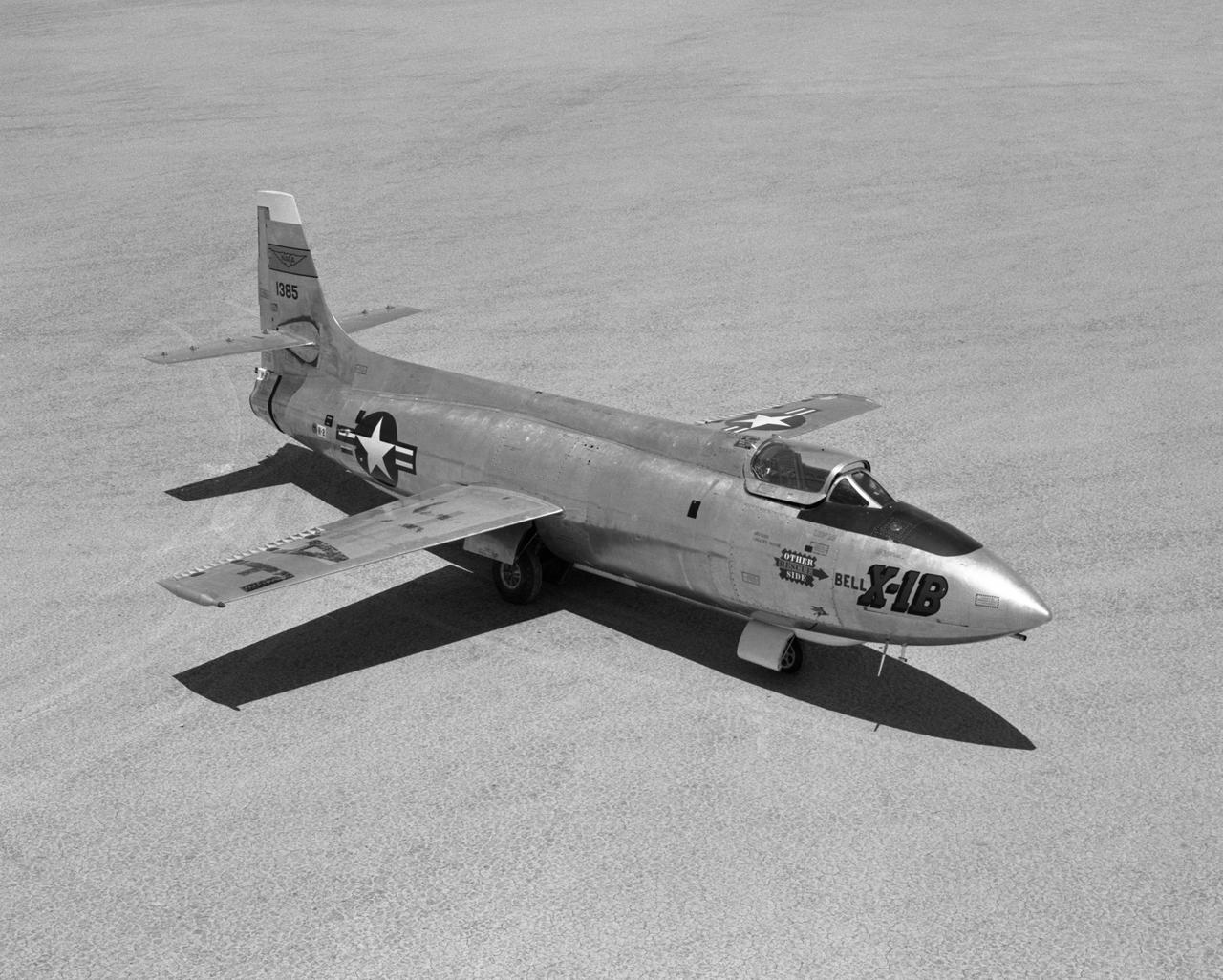

Bell X-1B fitted with a reaction control system on the lakebed
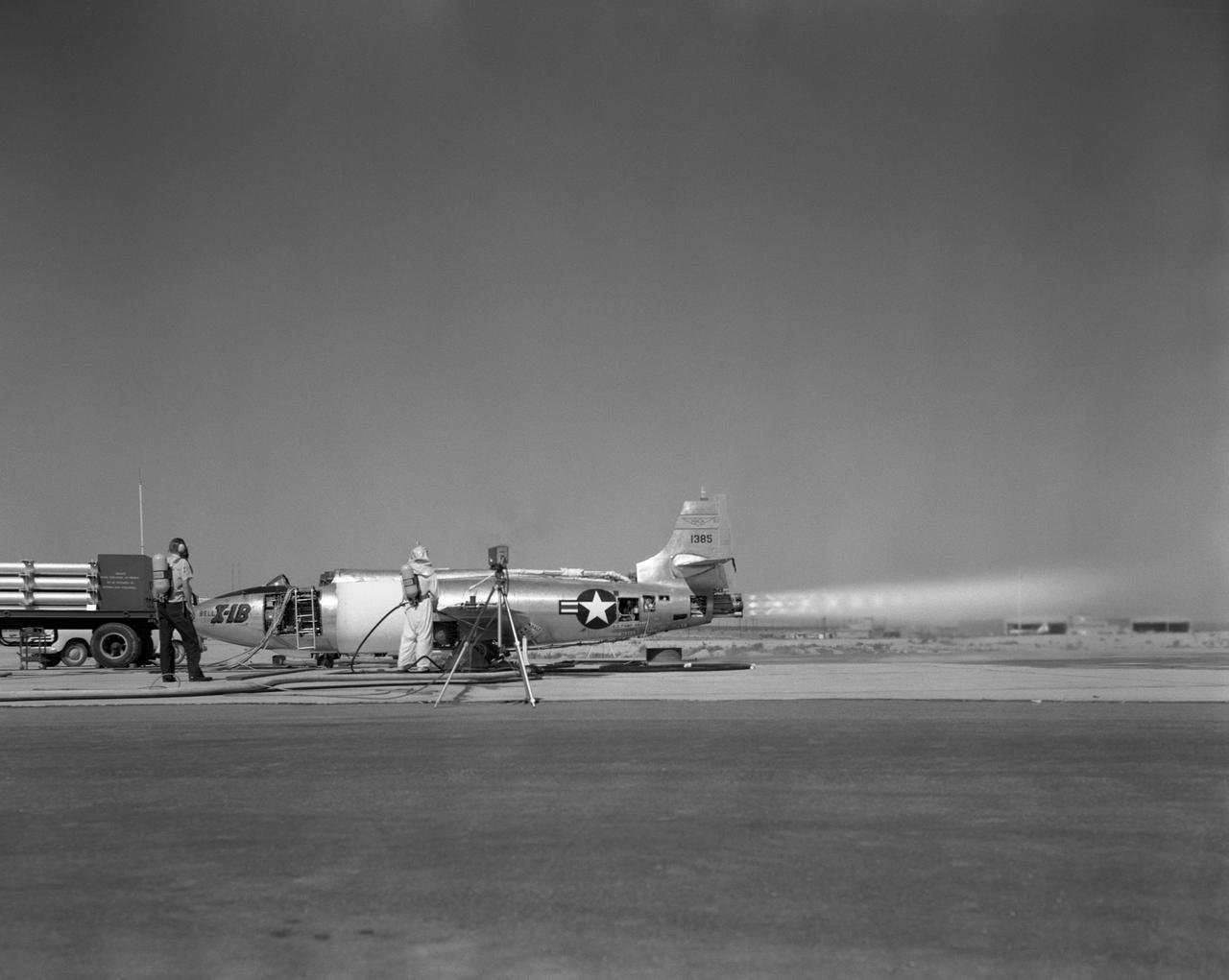

X-1B engine run on Air Force thrust stand.
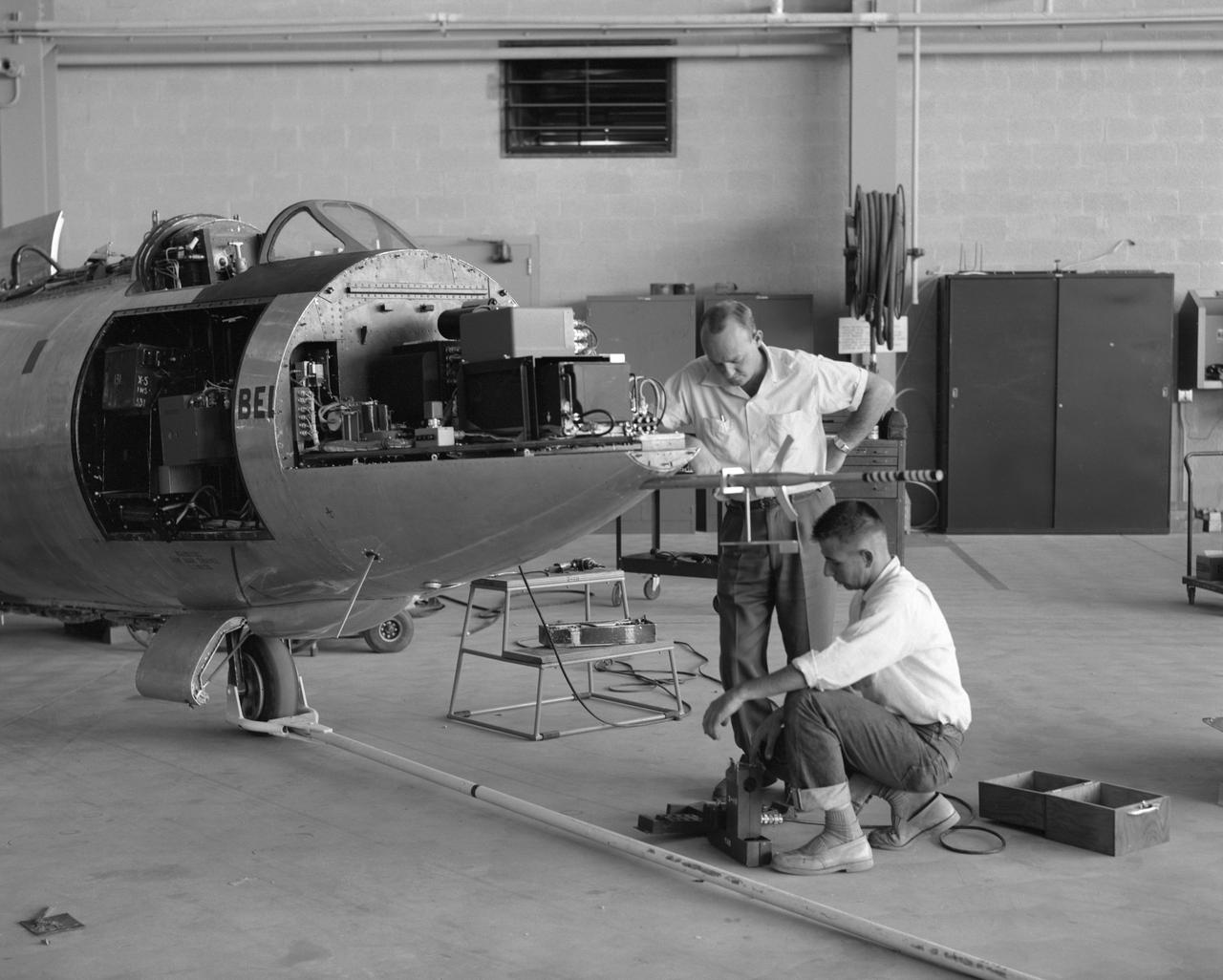

Lee Adelsbach and Bob Cook work on the instrumentation on the Bell X-1B.
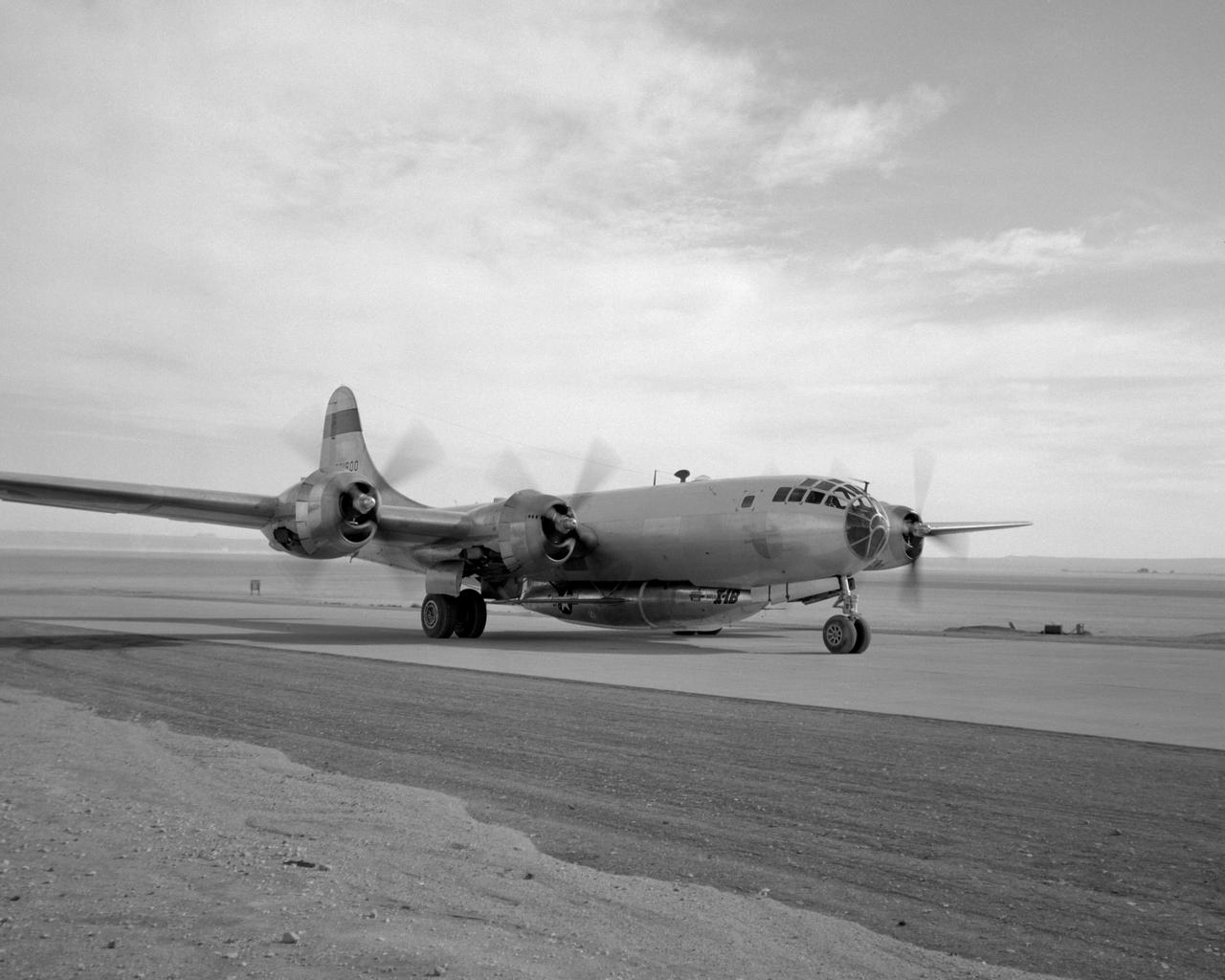

B-29 #800 with X-1B attached taxis in off of the lakebed.
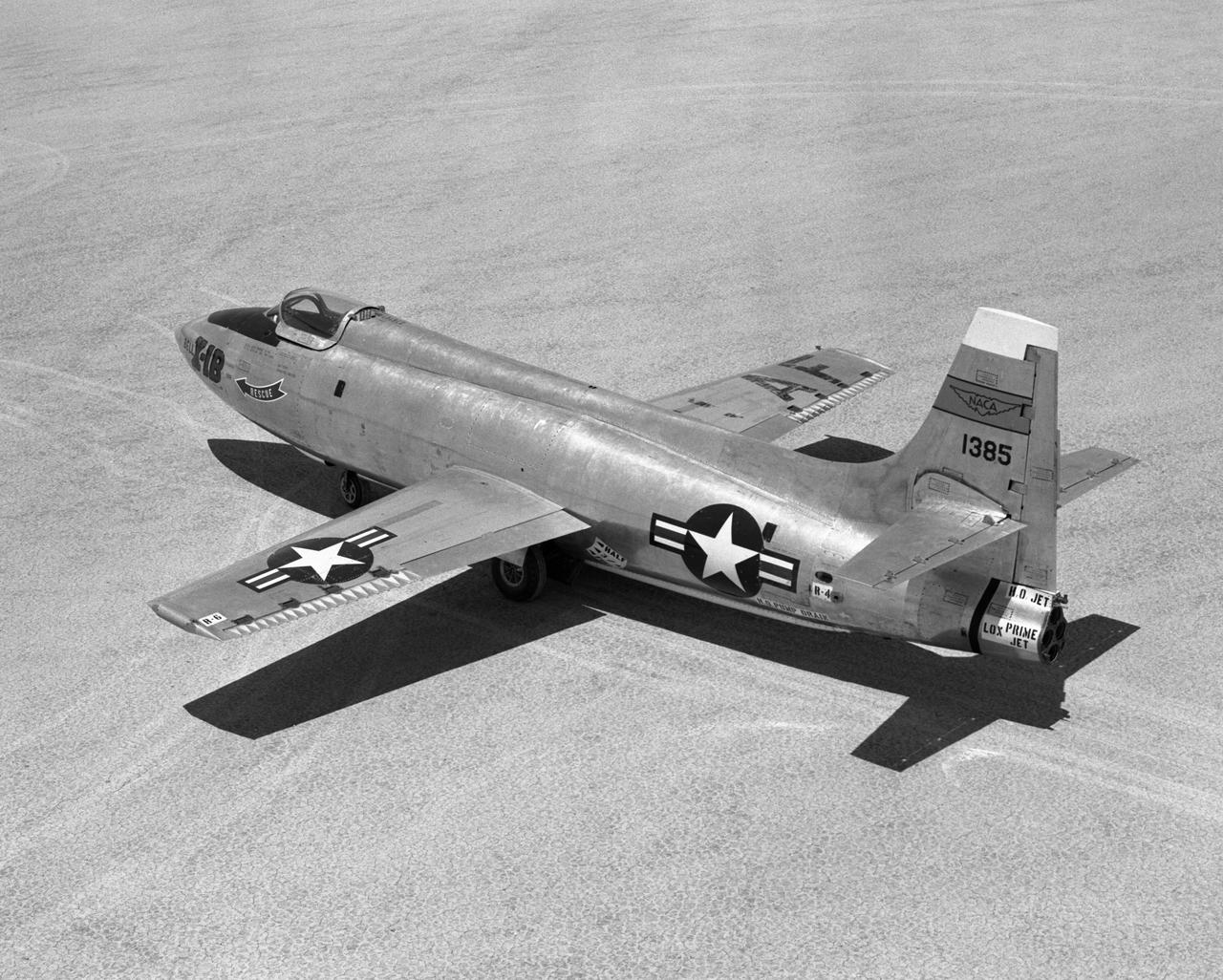

Bell X-1B fitted with a reaction control system on the lakebed.
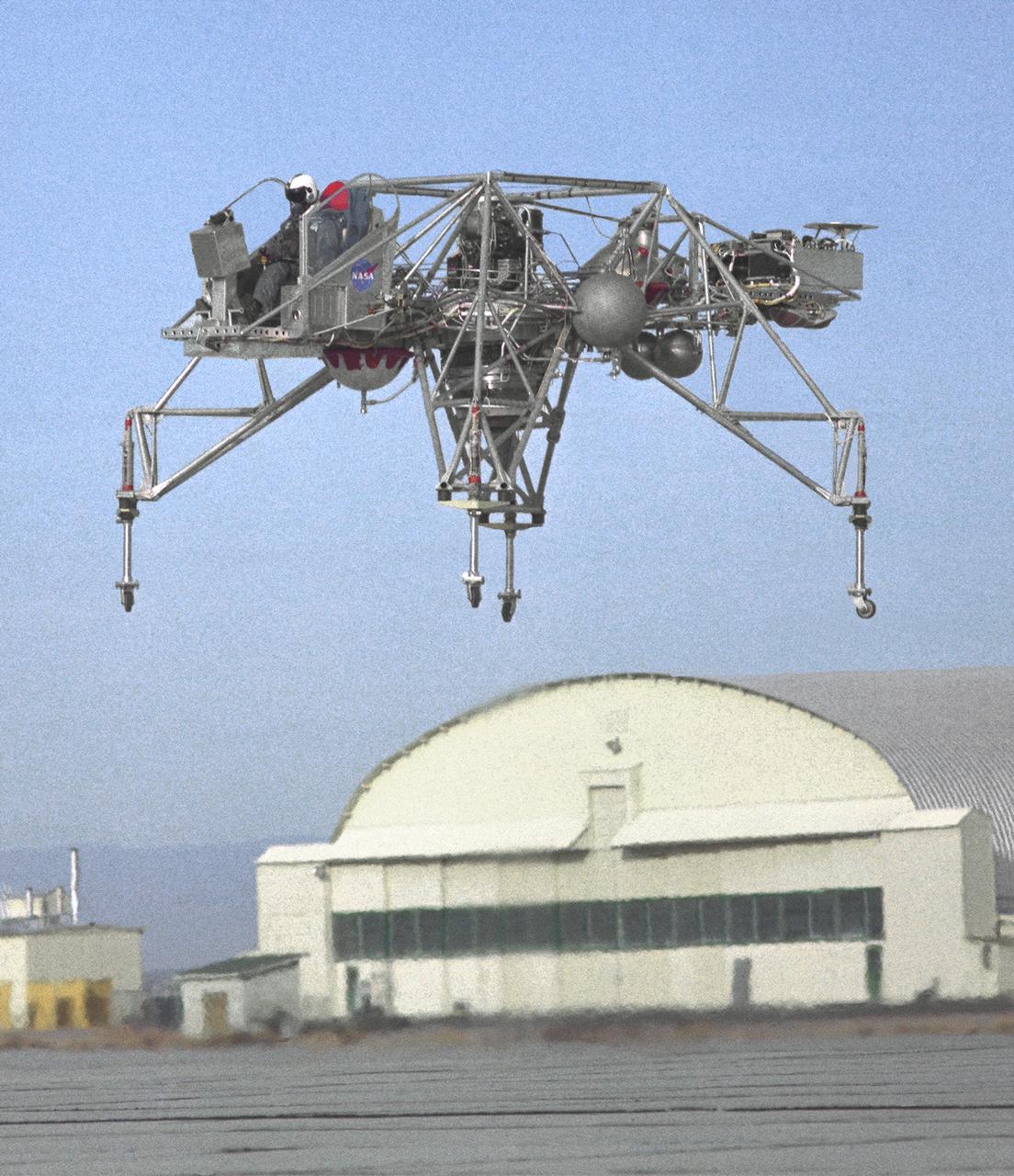

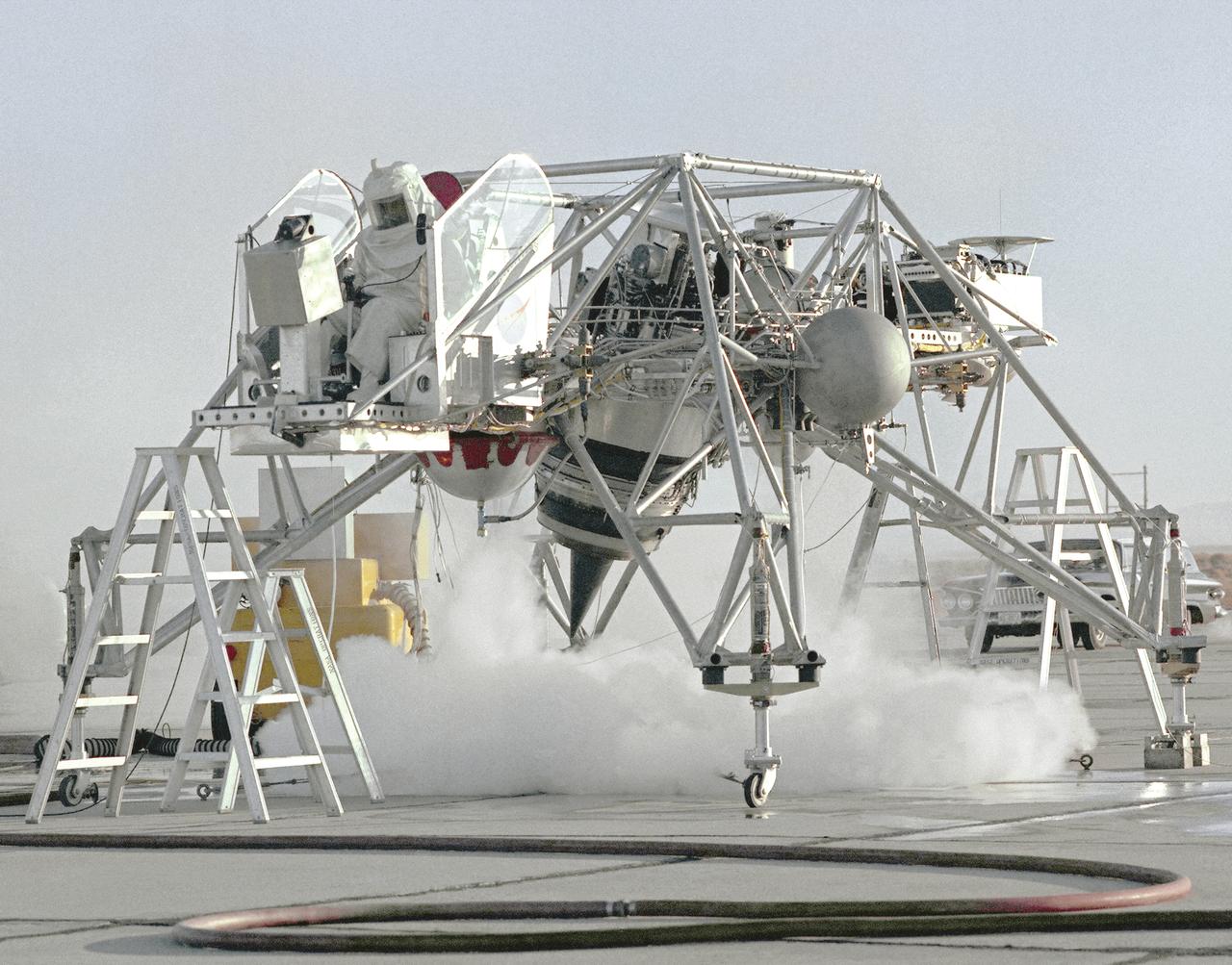
An inflight view from the left side of the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle, is shown in this 1964 NASA Flight Research Center photograph. The photograph was taken in front of the old NACA hangar located at the South Base, Edwards Air Force Base. When Apollo planning was underway in 1960, NASA was looking for a simulator to profile the descent to the Moon's surface. Three concepts surfaced: an electronic simulator, a tethered device, and the ambitious Dryden contribution, a free-flying vehicle. All three became serious projects, but eventually the NASA Flight Research Center's (FRC) Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) became the most significant one. Hubert M. Drake is credited with originating the idea, while Donald Bellman and Gene Matranga were senior engineers on the project, with Bellman, the project manager. Simultaneously, and independently, Bell Aerosystems Company, Buffalo, N.Y., a company with experience in vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft, had conceived a similar free-flying simulator and proposed their concept to NASA headquarters. NASA Headquarters put FRC and Bell together to collaborate. The challenge was; to allow a pilot to make a vertical landing on earth in a simulated Moon environment, one sixth of the earth's gravity and with totally transparent aerodynamic forces in a "free flight" vehicle with no tether forces acting on it. Built of tubular aluminum like a giant four-legged bedstead, the vehicle was to simulate a lunar landing profile from around 1500 feet to the Moon's surface. To do this, the LLRV had a General Electric CF-700-2V turbofan engine mounted vertically in gimbals, with 4200 pounds of thrust. The engine, using JP-4 fuel, got the vehicle up to the test altitude and was then throttled back to support five-sixths of the vehicle's weight, simulating the reduced gravity of the Moon. Two hydrogen-peroxide lift rockets with thrust that could be varied from 100 to 500 pounds handled the LLRV's rate of descent and horizontal transla
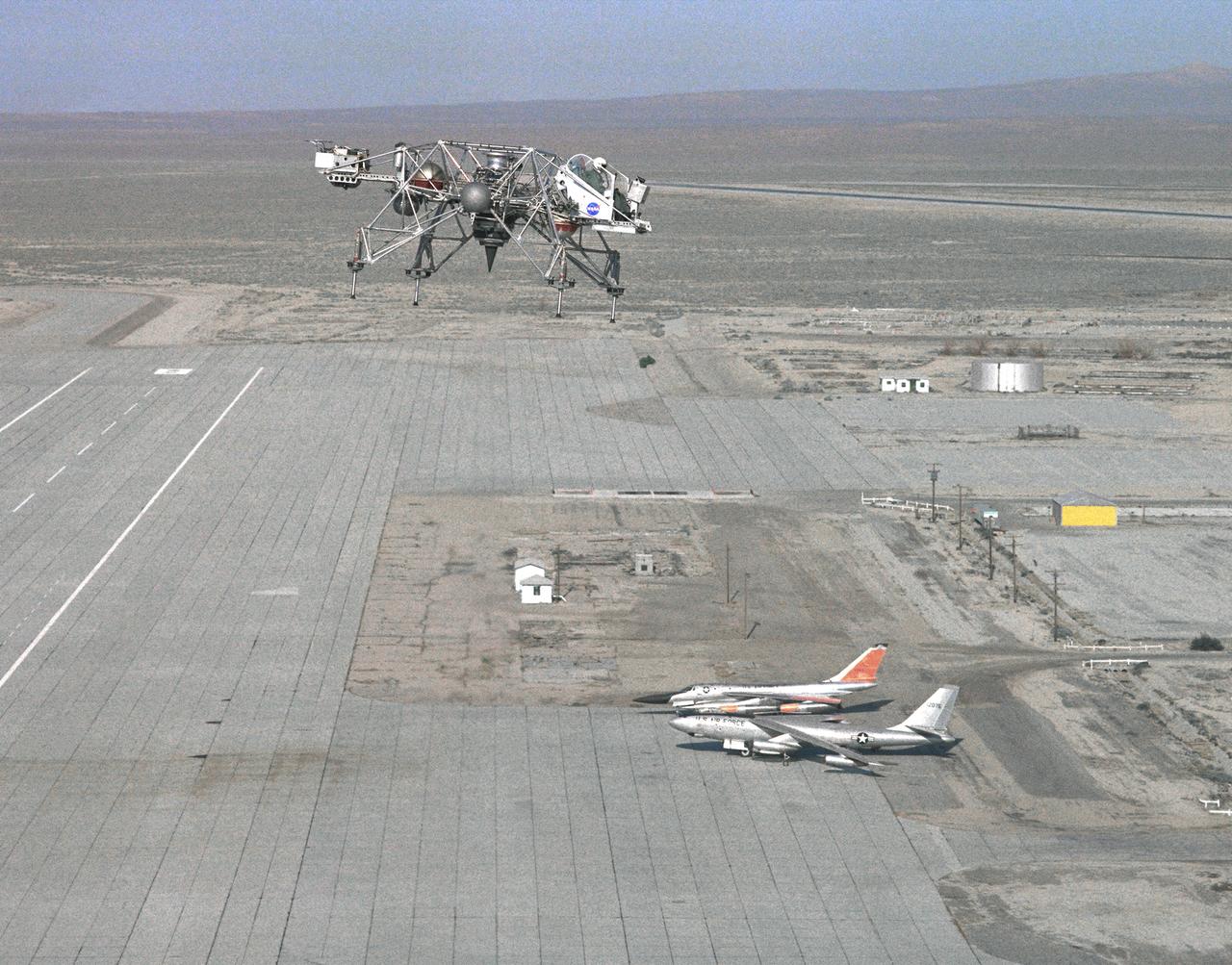

In this 1965 NASA Flight Reserch Center photograph the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) is shown at near maximum altitude over the south base at Edwards Air Force Base. When Apollo planning was underway in 1960, NASA was looking for a simulator to profile the descent to the moon's surface. Three concepts surfaced: an electronic simulator, a tethered device, and the ambitious Dryden contribution, a free-flying vehicle. All three became serious projects, but eventually the NASA Flight Research Center's (FRC) Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) became the most significant one. Hubert M. Drake is credited with originating the idea, while Donald Bellman and Gene Matranga were senior engineers on the project, with Bellman, the project manager. Simultaneously, and independently, Bell Aerosystems Company, Buffalo, N.Y., a company with experience in vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft, had conceived a similar free-flying simulator and proposed their concept to NASA headquarters. NASA Headquarters put FRC and Bell together to collaborate. The challenge was; to allow a pilot to make a vertical landing on Earth in a simulated moon environment, one sixth of the Earth's gravity and with totally transparent aerodynamic forces in a "free flight" vehicle with no tether forces acting on it. Built of tubular aluminum like a giant four-legged bedstead, the vehicle was to simulate a lunar landing profile from around 1500 feet to the moon's surface. To do this, the LLRV had a General Electric CF-700-2V turbofan engine mounted vertically in gimbals, with 4200 pounds of thrust. The engine, using JP-4 fuel, got the vehicle up to the test altitude and was then throttled back to support five-sixths of the vehicle's weight, simulating the reduced gravity of the moon. Two hydrogen-peroxide lift rockets with thrust that could be varied from 100 to 500 pounds handled the LLRV's rate of descent and horizontal translations. Sixteen smaller hydrogen-peroxide rockets, mounted in pairs, gav
This 1964 NASA Flight Reserch Center photograph shows a ground engine test underway on the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) number 1. When Apollo planning was underway in 1960, NASA was looking for a simulator to profile the descent to the Moon's surface. Three concepts surfaced: an electronic simulator, a tethered device, and the ambitious Dryden contribution, a free-flying vehicle. All three became serious projects, but eventually the NASA Flight Research Center's (FRC) Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) became the most significant one. Hubert M. Drake is credited with originating the idea, while Donald Bellman and Gene Matranga were senior engineers on the project, with Bellman, the project manager. Simultaneously, and independently, Bell Aerosystems Company, Buffalo, N.Y., a company with experience in vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft, had conceived a similar free-flying simulator and proposed their concept to NASA headquarters. NASA Headquarters put FRC and Bell together to collaborate. The challenge was; to allow a pilot to make a vertical landing on Earth in a simulated Moon environment, one sixth of the Earth's gravity and with totally transparent aerodynamic forces in a "free flight" vehicle with no tether forces acting on it. Built of tubular aluminum like a giant four-legged bedstead, the vehicle was to simulate a lunar landing profile from around 1500 feet to the Moon's surface. To do this, the LLRV had a General Electric CF-700-2V turbofan engine mounted vertically in gimbals, with 4200 pounds of thrust. The engine, using JP-4 fuel, got the vehicle up to the test altitude and was then throttled back to support five-sixths of the vehicle's weight, simulating the reduced gravity of the Moon. Two hydrogen-peroxide lift rockets with thrust that could be varied from 100 to 500 pounds handled the LLRV's rate of descent and horizontal translations. Sixteen smaller hydrogen-peroxide rockets, mounted in pairs, gave the pilot control in pitch, yaw,
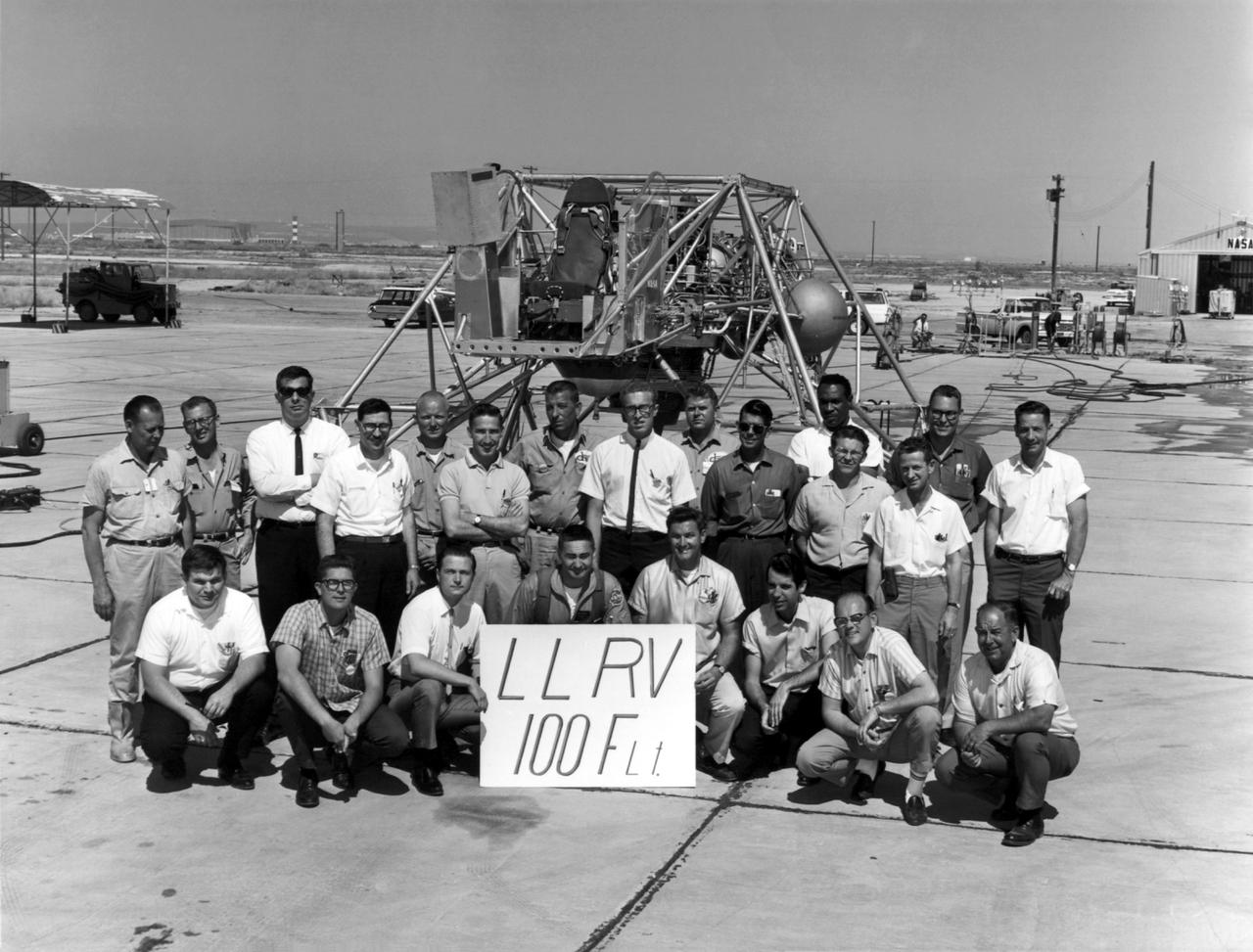

A group photo of the LLRV personnel following the program's 100th flight. The photo was taken at South Base, and was near the hangar first used by the original NACA group, at what was then called Muroc. When Apollo planning was underway in 1960, NASA was looking for a simulator to profile the descent to the moon's surface. Three concepts surfaced: an electronic simulator, a tethered device, and the ambitious Dryden contribution, a free-flying vehicle. All three became serious projects, but eventually the NASA Flight Research Center's (FRC) Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) became the most significant one. Hubert M. Drake is credited with originating the idea, while Donald Bellman and Gene Matranga were senior engineers on the project, with Bellman, the project manager. Simultaneously, and independently, Bell Aerosystems Company, Buffalo, N.Y., a company with experience in vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft, had conceived a similar free-flying simulator and proposed their concept to NASA headquarters. NASA Headquarters put FRC and Bell together to collaborate. The challenge was; to allow a pilot to make a vertical landing on Earth in a simulated moon environment, one sixth of the Earth's gravity and with totally transparent aerodynamic forces in a "free flight" vehicle with no tether forces acting on it. Built of tubular aluminum like a giant four-legged bedstead, the vehicle was to simulate a lunar landing profile from around 1500 feet to the moon's surface. To do this, the LLRV had a General Electric CF-700-2V turbofan engine mounted vertically in gimbals, with 4200 pounds of thrust. The engine, using JP-4 fuel, got the vehicle up to the test altitude and was then throttled back to support five-sixths of the vehicle's weight, simulating the reduced gravity of the moon. Two hydrogen-peroxide lift rockets with thrust that could be varied from 100 to 500 pounds handled the LLRV's rate of descent and horizontal translations. Sixteen smaller hydrogen-peroxide r
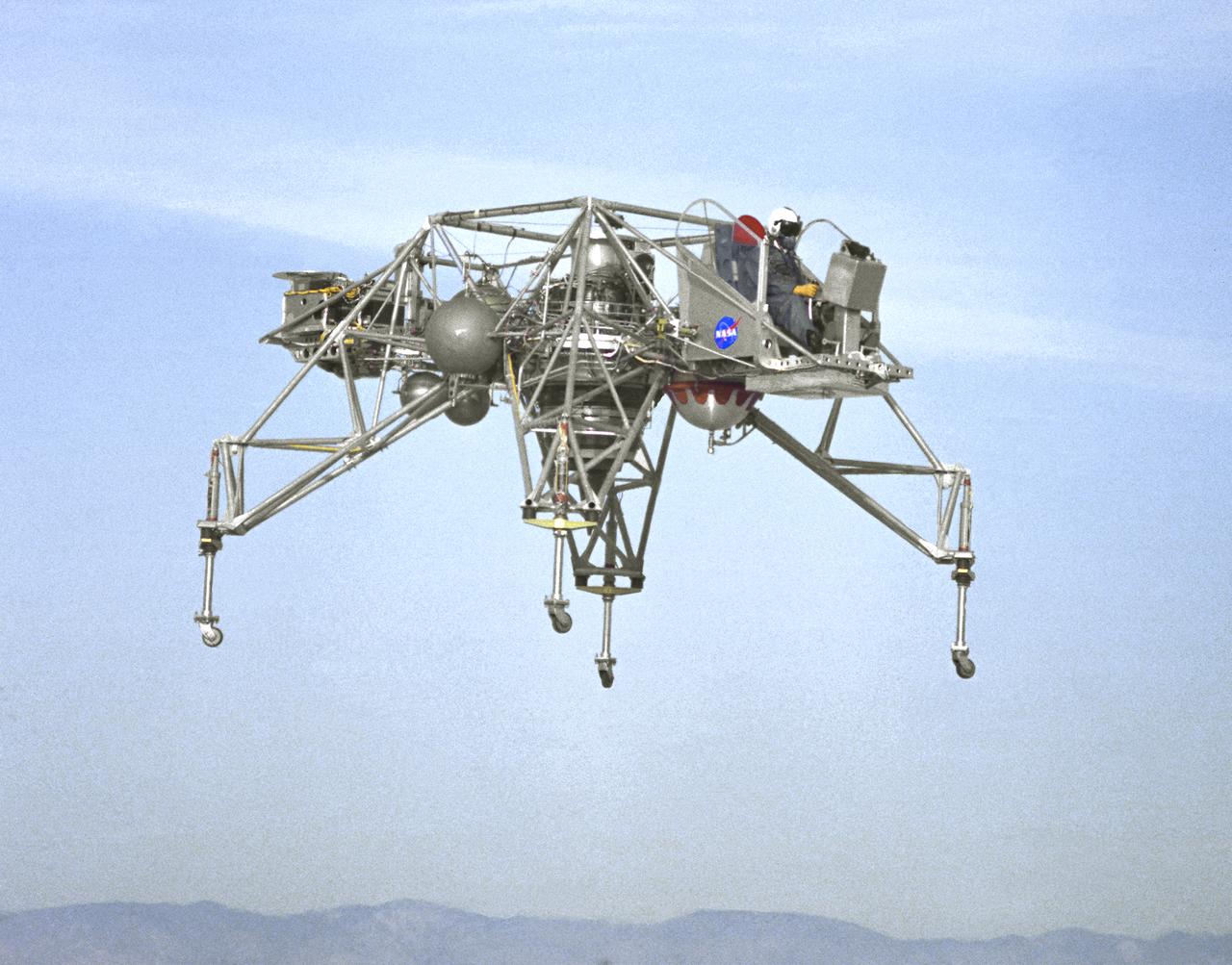

In this NASA Flight Reserch Center photograph the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) number 1 is shown in flight. When Apollo planning was underway in 1960, NASA was looking for a simulator to profile the descent to the Moon's surface. Three concepts surfaced: an electronic simulator, a tethered device, and the ambitious Dryden contribution, a free-flying vehicle. All three became serious projects, but eventually the NASA Flight Research Center's (FRC) Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) became the most significant one. Hubert M. Drake is credited with originating the idea, while Donald Bellman and Gene Matranga were senior engineers on the project, with Bellman, the project manager. Simultaneously, and independently, Bell Aerosystems Company, Buffalo, N.Y., a company with experience in vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft, had conceived a similar free-flying simulator and proposed their concept to NASA headquarters. NASA Headquarters put FRC and Bell together to collaborate. The challenge was; to allow a pilot to make a vertical landing on Earth in a simulated Moon environment, one sixth of the Earth's gravity and with totally transparent aerodynamic forces in a "free flight" vehicle with no tether forces acting on it. Built of tubular aluminum like a giant four-legged bedstead, the vehicle was to simulate a lunar landing profile from around 1500 feet to the Moon's surface. To do this, the LLRV had a General Electric CF-700-2V turbofan engine mounted vertically in gimbals, with 4200 pounds of thrust. The engine, using JP-4 fuel, got the vehicle up to the test altitude and was then throttled back to support five-sixths of the vehicle's weight, simulating the reduced gravity of the Moon. Two hydrogen-peroxide lift rockets with thrust that could be varied from 100 to 500 pounds handled the LLRV's rate of descent and horizontal translations. Sixteen smaller hydrogen-peroxide rockets, mounted in pairs, gave the pilot control in pitch, yaw, and roll. On the LLRV,
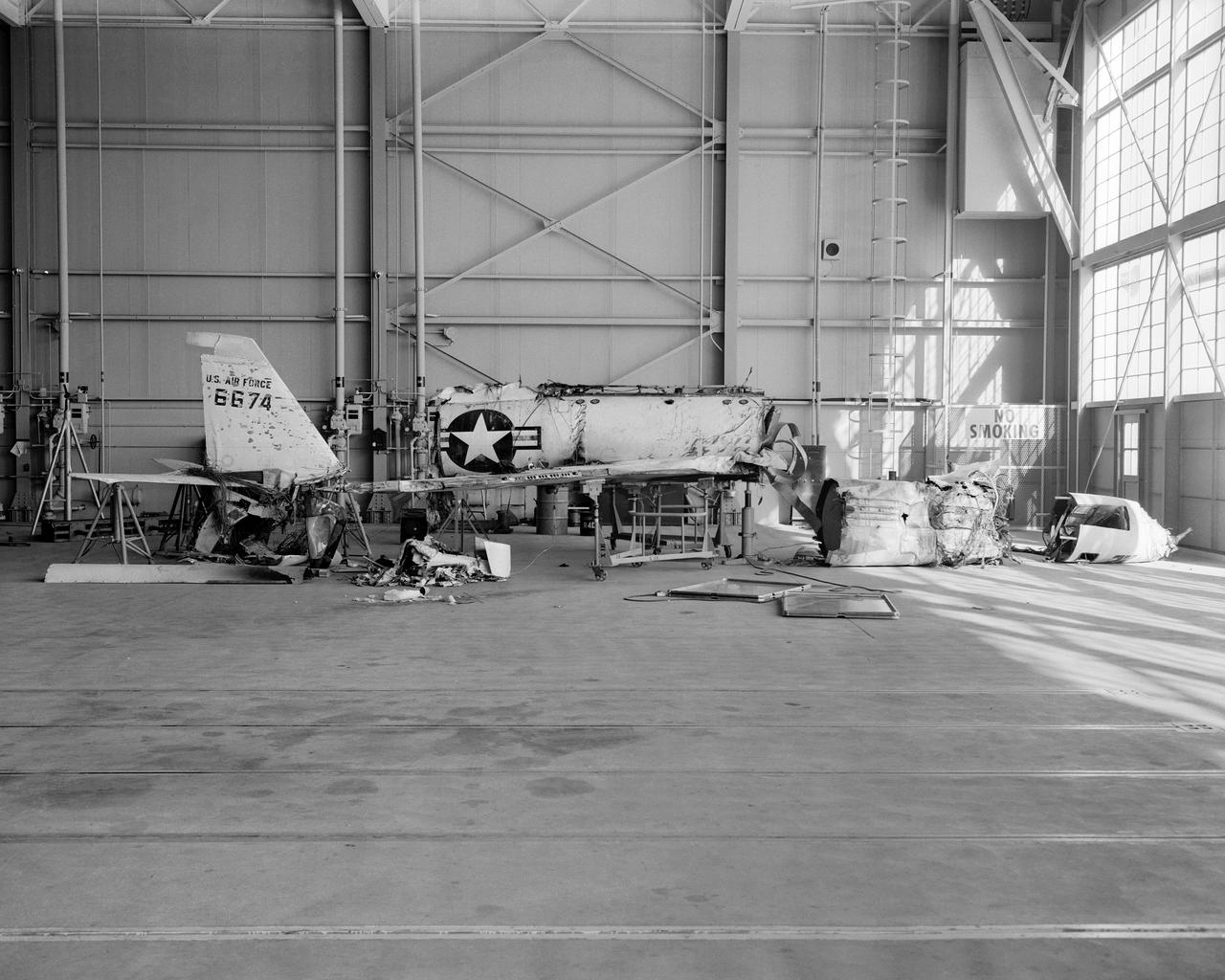

The X-2, initially an Air Force program, was scheduled to be transferred to the civilian National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) for scientific research. The Air Force delayed turning the aircraft over to the NACA in the hope of attaining Mach 3 in the airplane. The service requested and received a two-month extension to qualify another Air Force test pilot, Capt. Miburn "Mel" Apt, in the X-2 and attempt to exceed Mach 3. After several ground briefings in the simulator, Apt (with no previous rocket plane experience) made his flight on 27 September 1956. Apt raced away from the B-50 under full power, quickly outdistancing the F-100 chase planes. At high altitude, he nosed over, accelerating rapidly. The X-2 reached Mach 3.2 (2,094 mph) at 65,000 feet. Apt became the first man to fly more than three times the speed of sound. Still above Mach 3, he began an abrupt turn back to Edwards. This maneuver proved fatal as the X-2 began a series of diverging rolls and tumbled out of control. Apt tried to regain control of the aircraft. Unable to do so, Apt separated the escape capsule. Too late, he attempted to bail out and was killed when the capsule impacted on the Edwards bombing range. The rest of the X-2 crashed five miles away. The wreckage of the X-2 rocket plane was later taken to NACA's High Speed Flight Station for analysis following the crash.