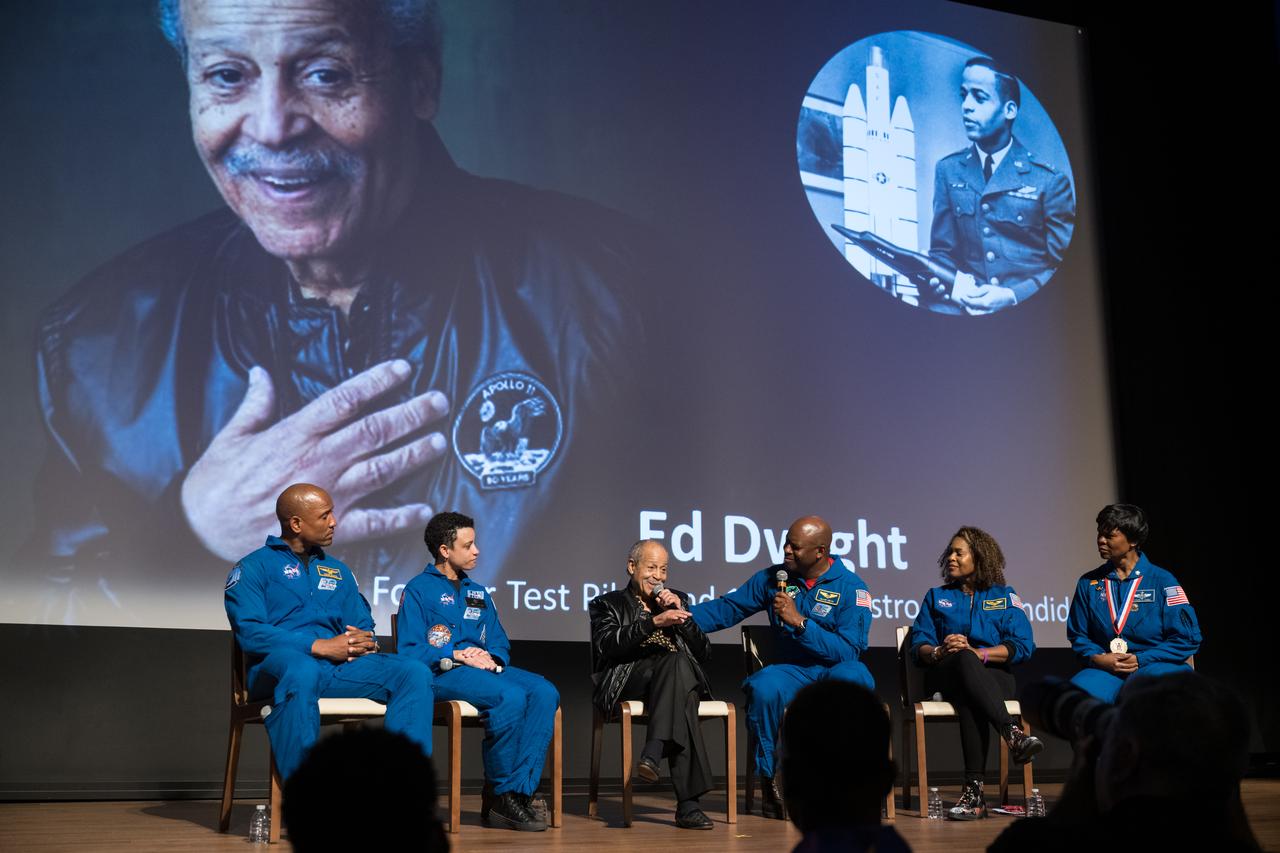

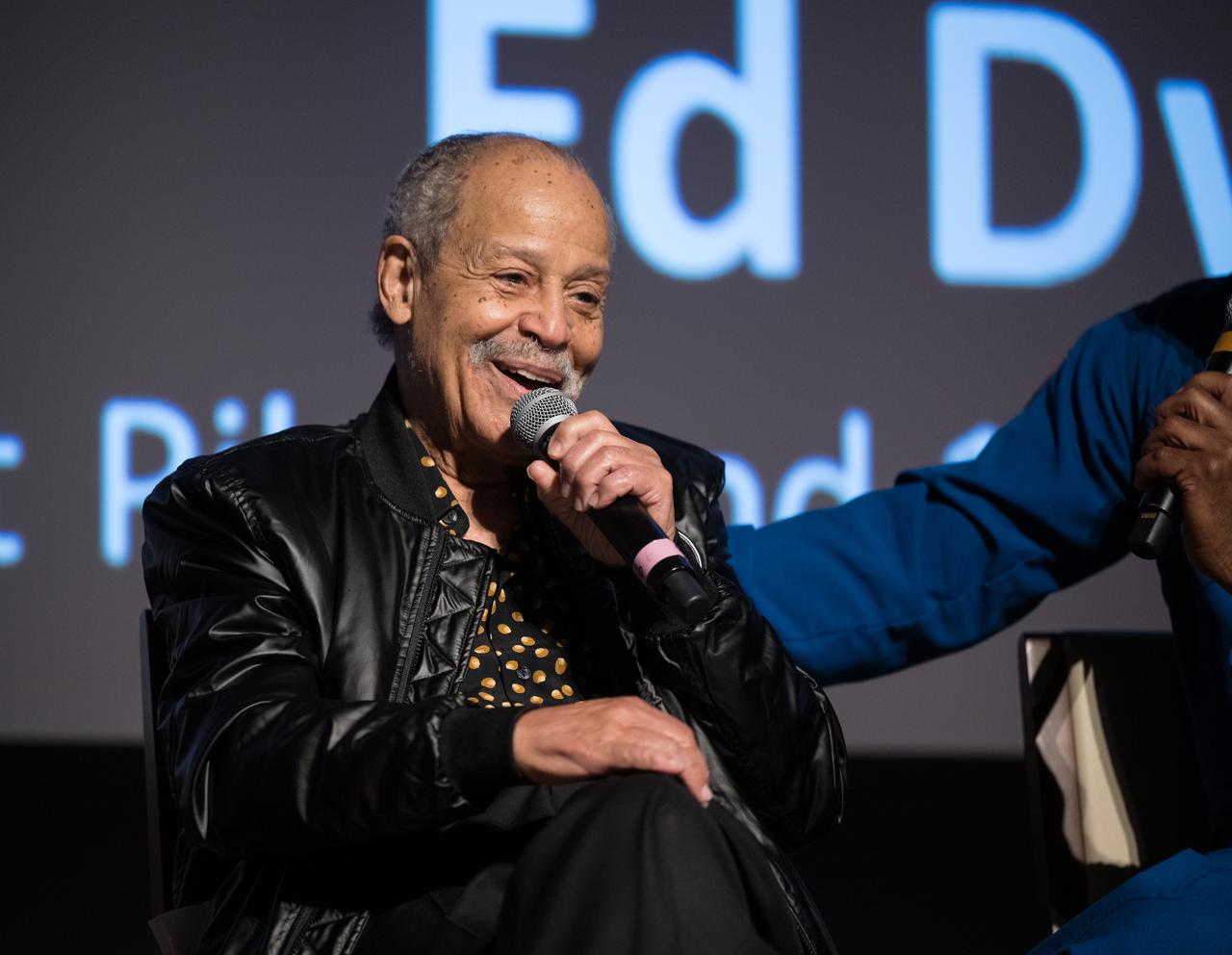
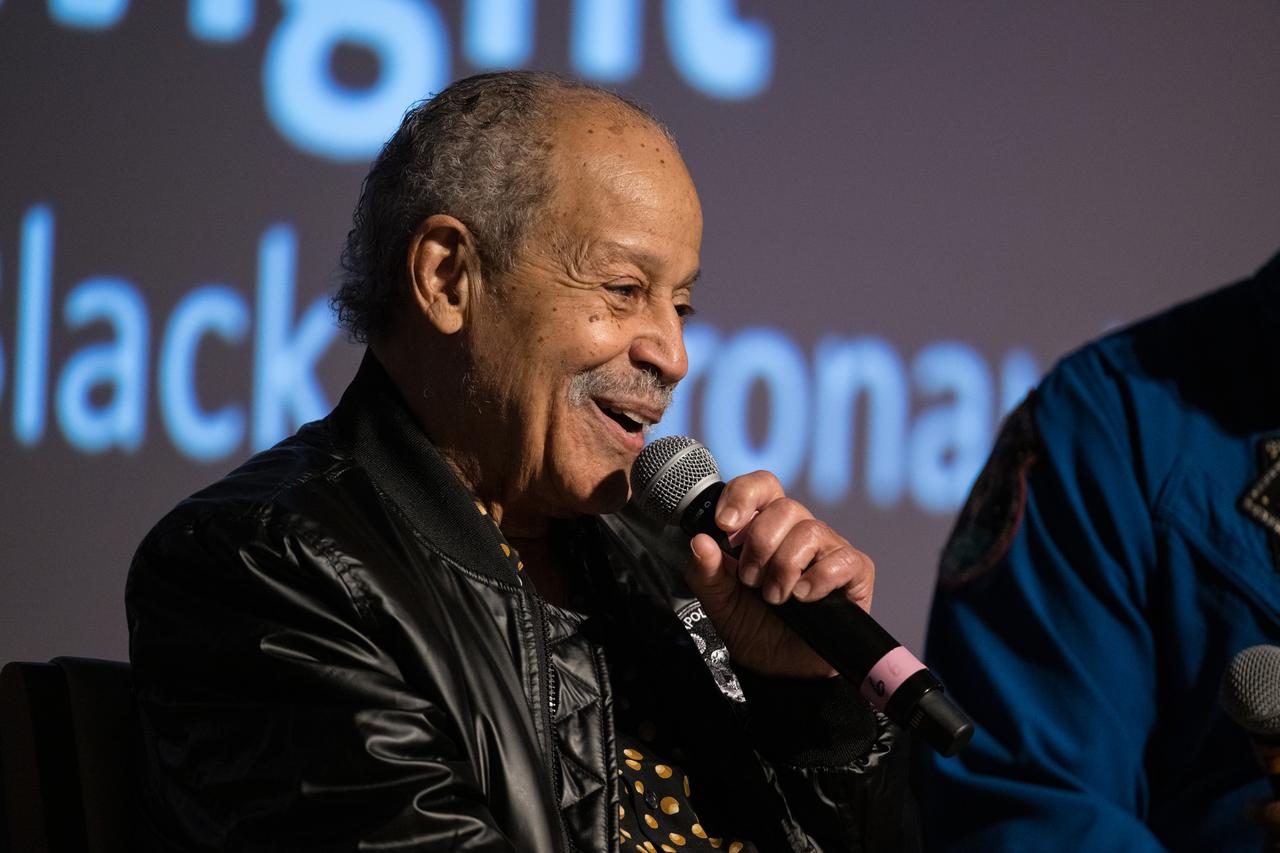
Ed Dwight, America's first African American astronaut candidate, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Dr. Kevin Strait, curator of history, National Museum of African American History and Culture (NMAAHC), speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Audience members are seen as Don Graves, deputy secretary, U.S. Department of Commerce, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Ed Dwight, America's first African American astronaut candidate, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Ed Dwight, America's first African American astronaut candidate, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
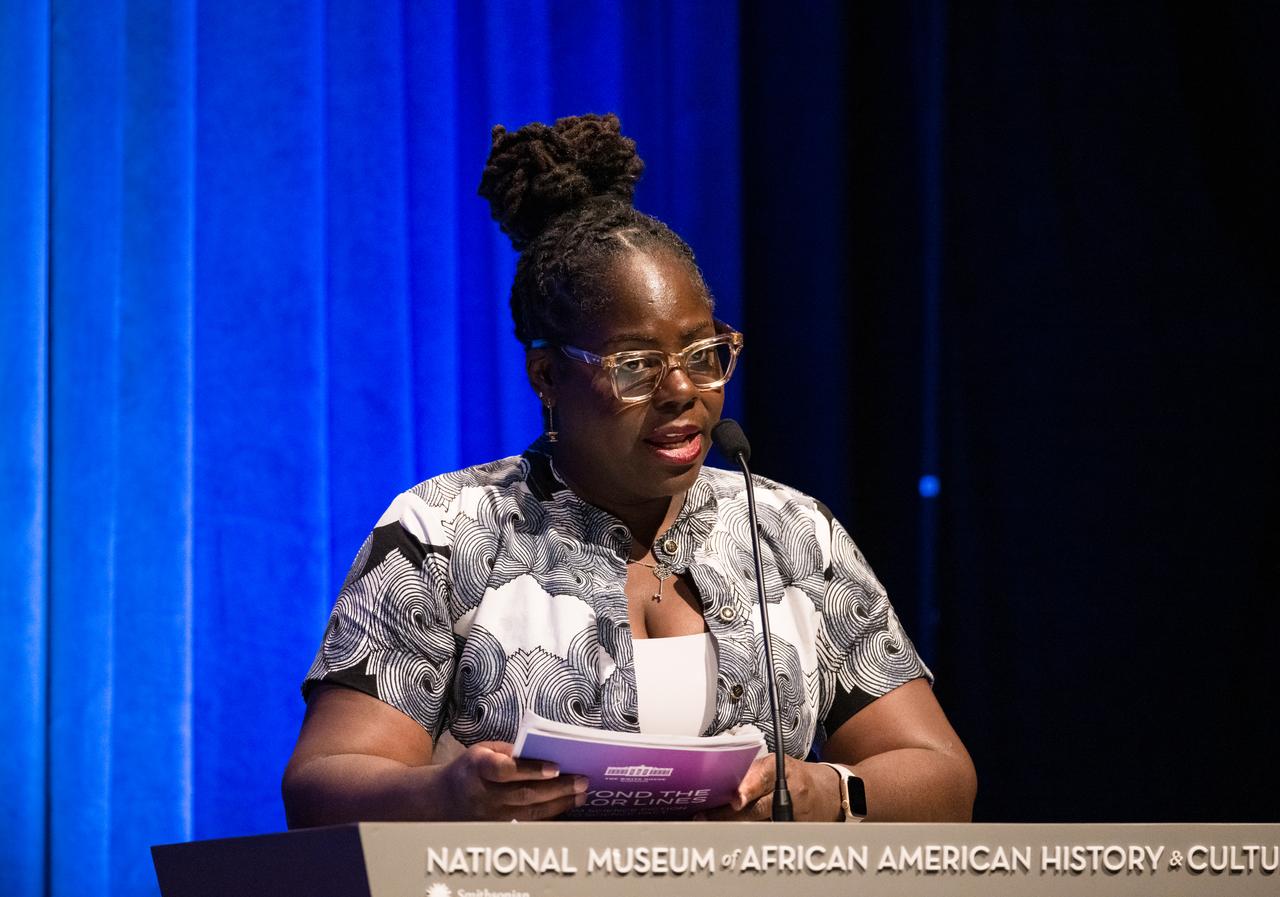

Dr. Quincy Brown, director of space STEM and workforce policy for the White House National Space Council, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
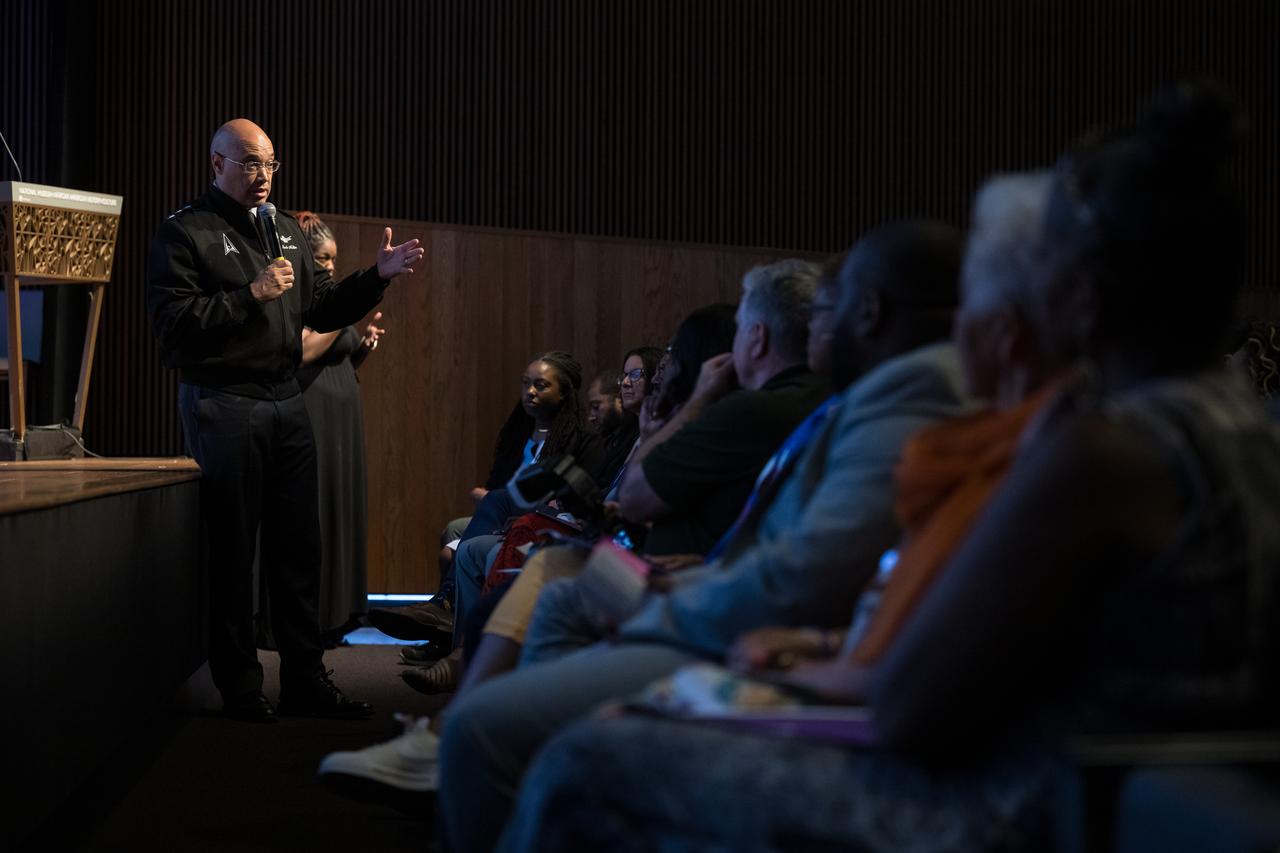

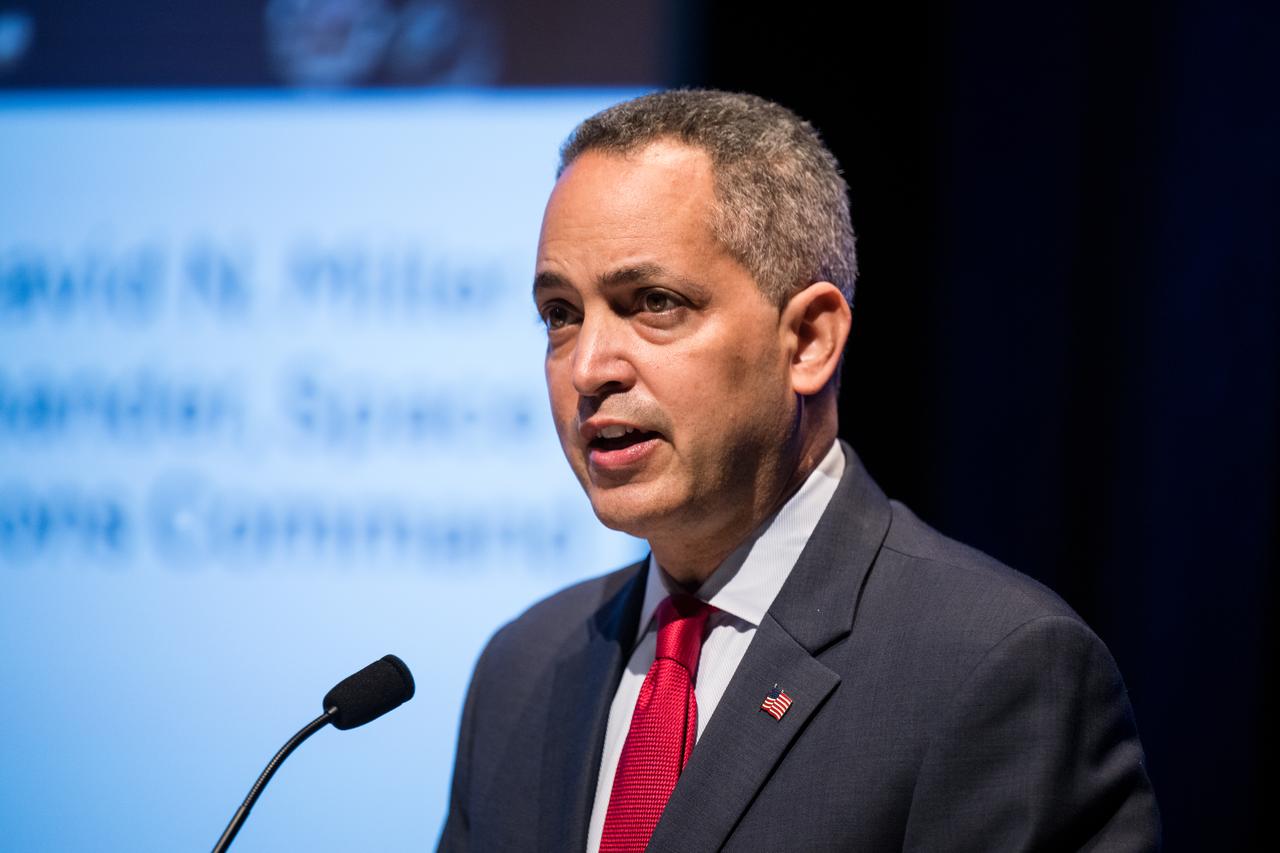
Lt. General David Miller Jr., commander, Space Operations Command, answers a question at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
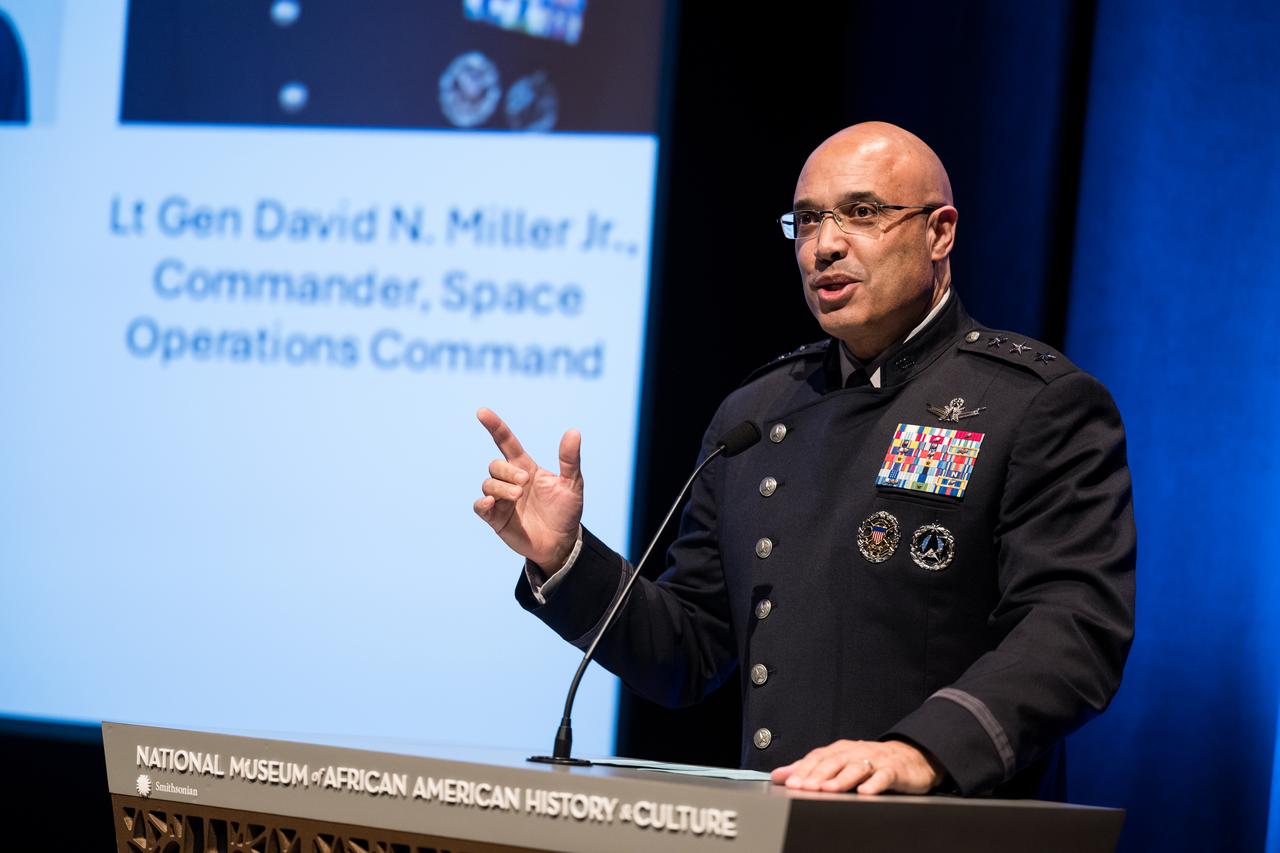

Lt. General David Miller Jr., commander, Space Operations Command, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Lt. General David Miller Jr., commander, Space Operations Command, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
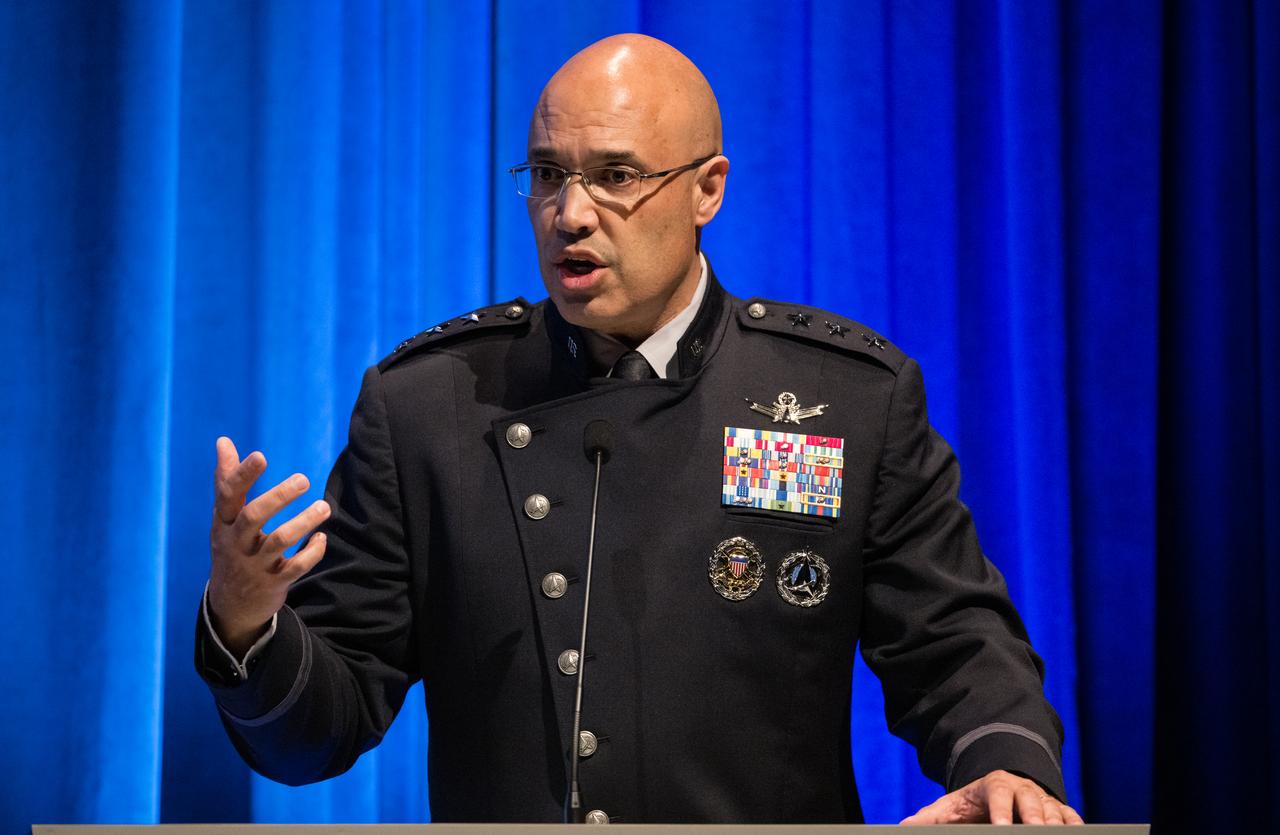

Lt. General David Miller Jr., commander, Space Operations Command, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
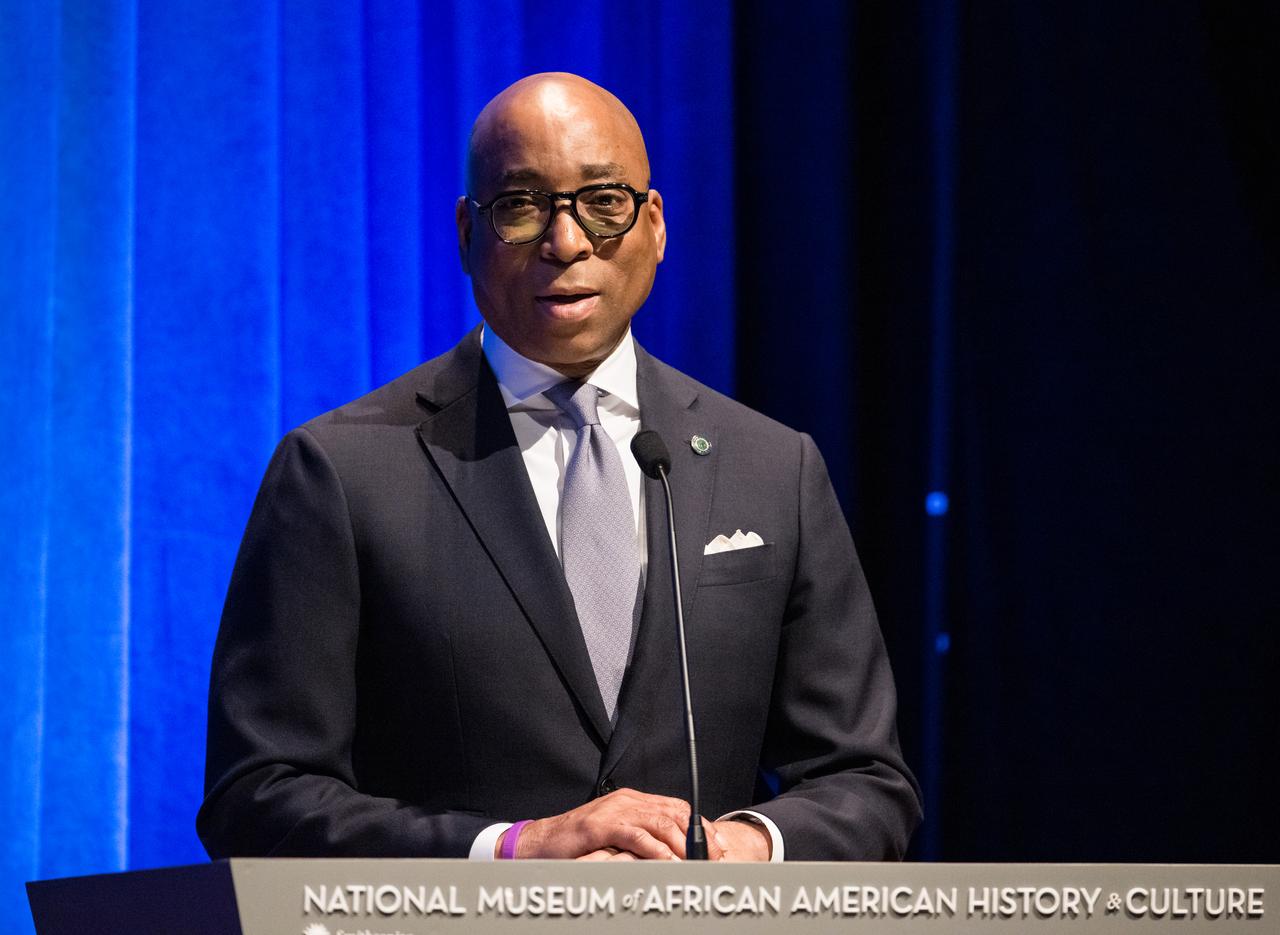

Kelvin Coleman, associate administrator, Office of Commercial Space Transportation, Federal Aviation Administration, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
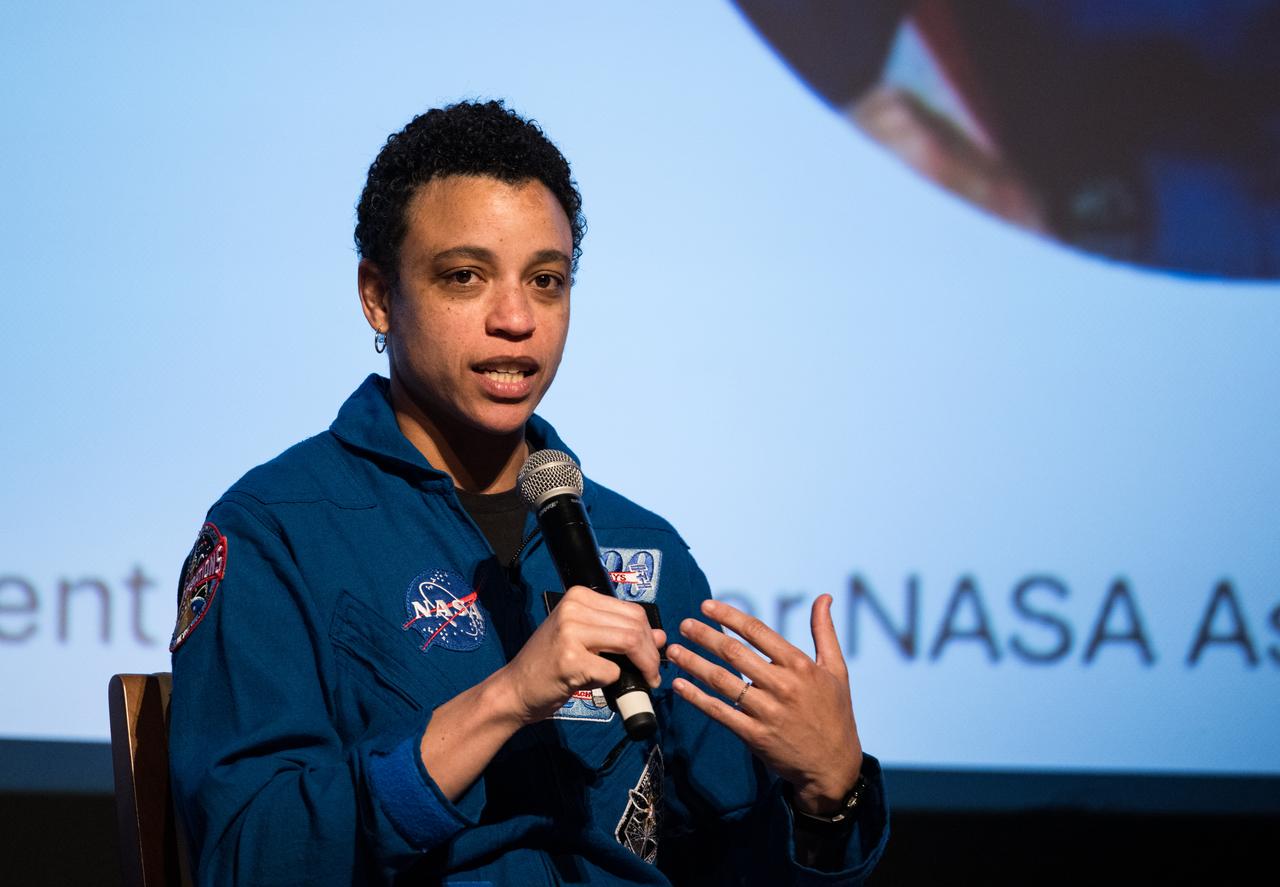

Jessica Watkins, NASA astronaut, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
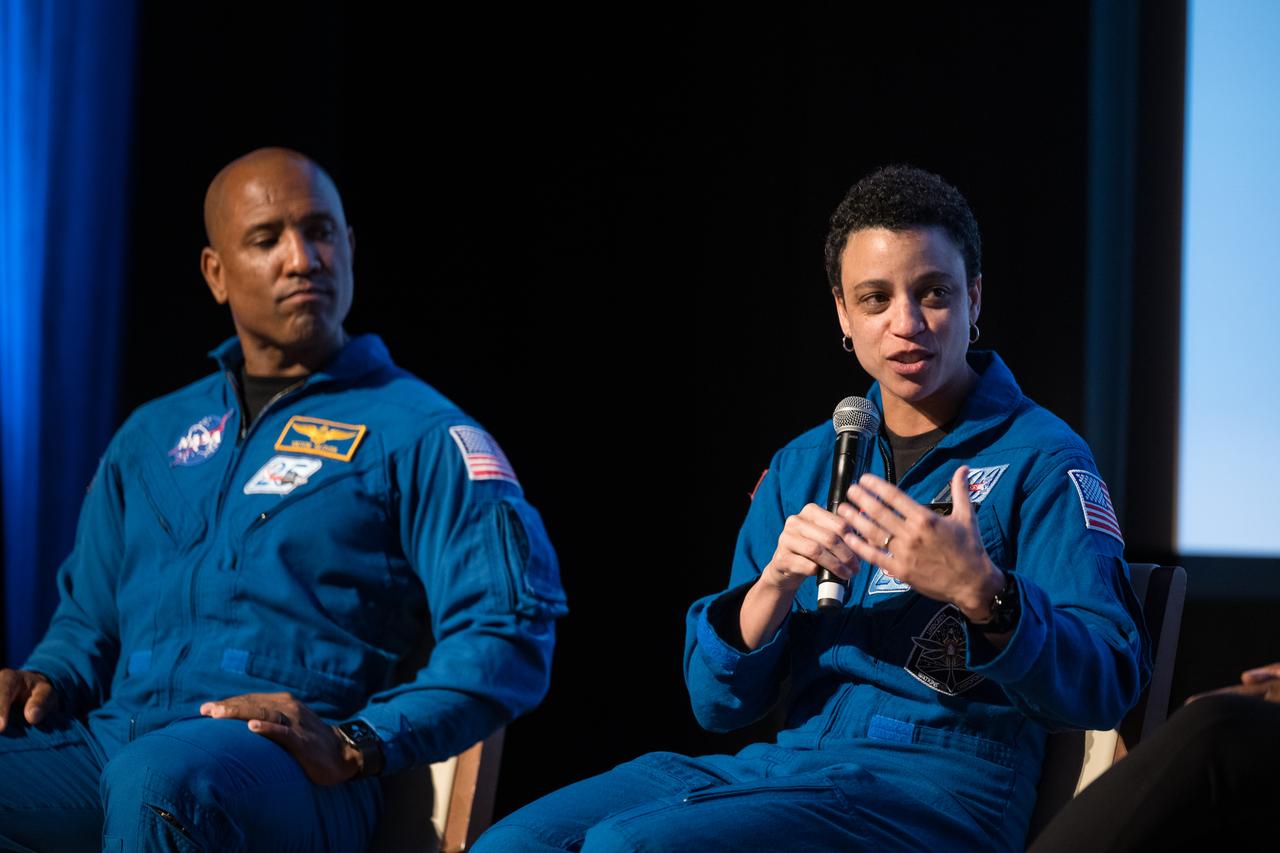

Jessica Watkins, NASA astronaut, speaks on a panel at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
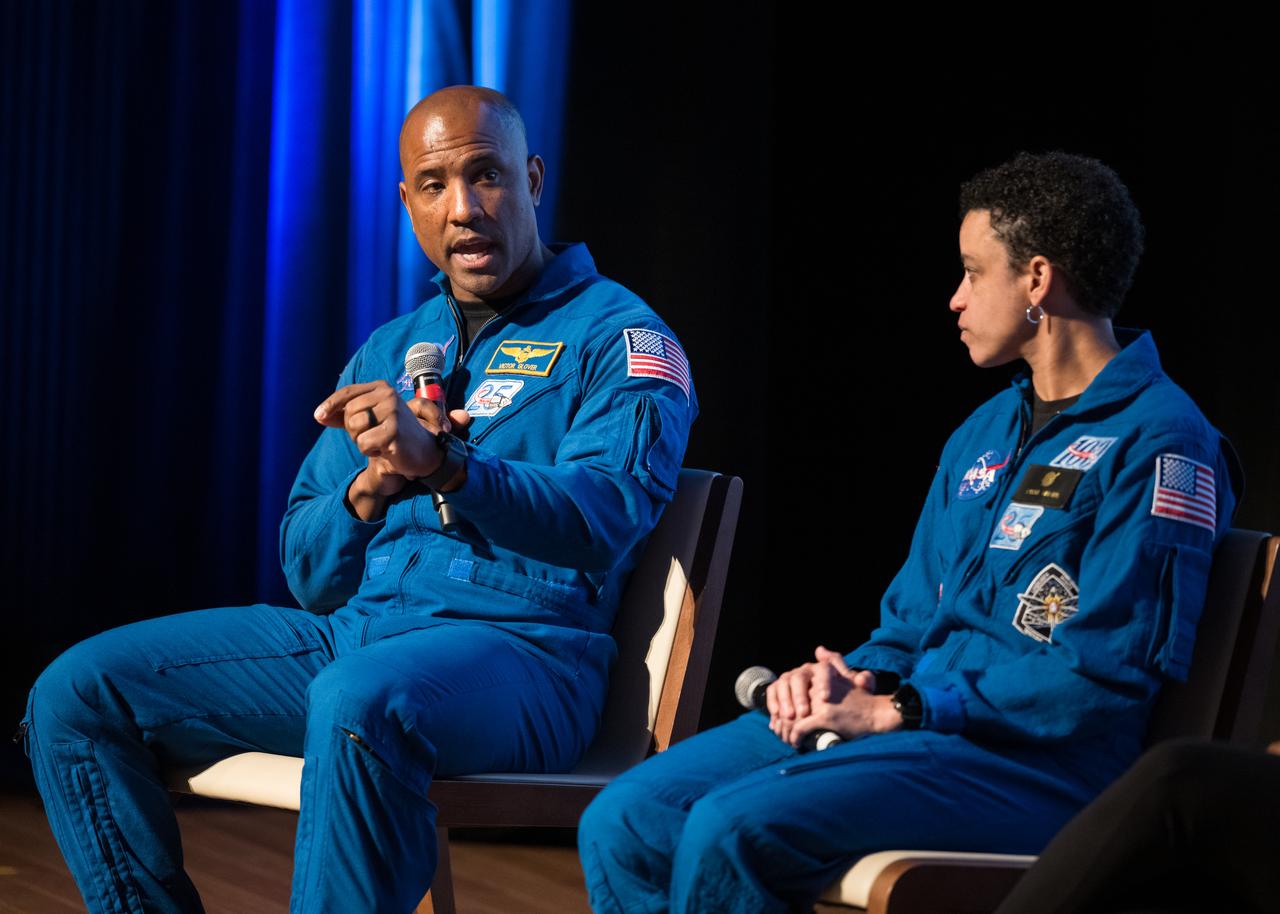

Victor Glover, NASA astronaut, speaks on a panel at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Joan Higginbotham, retired NASA astronaut, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
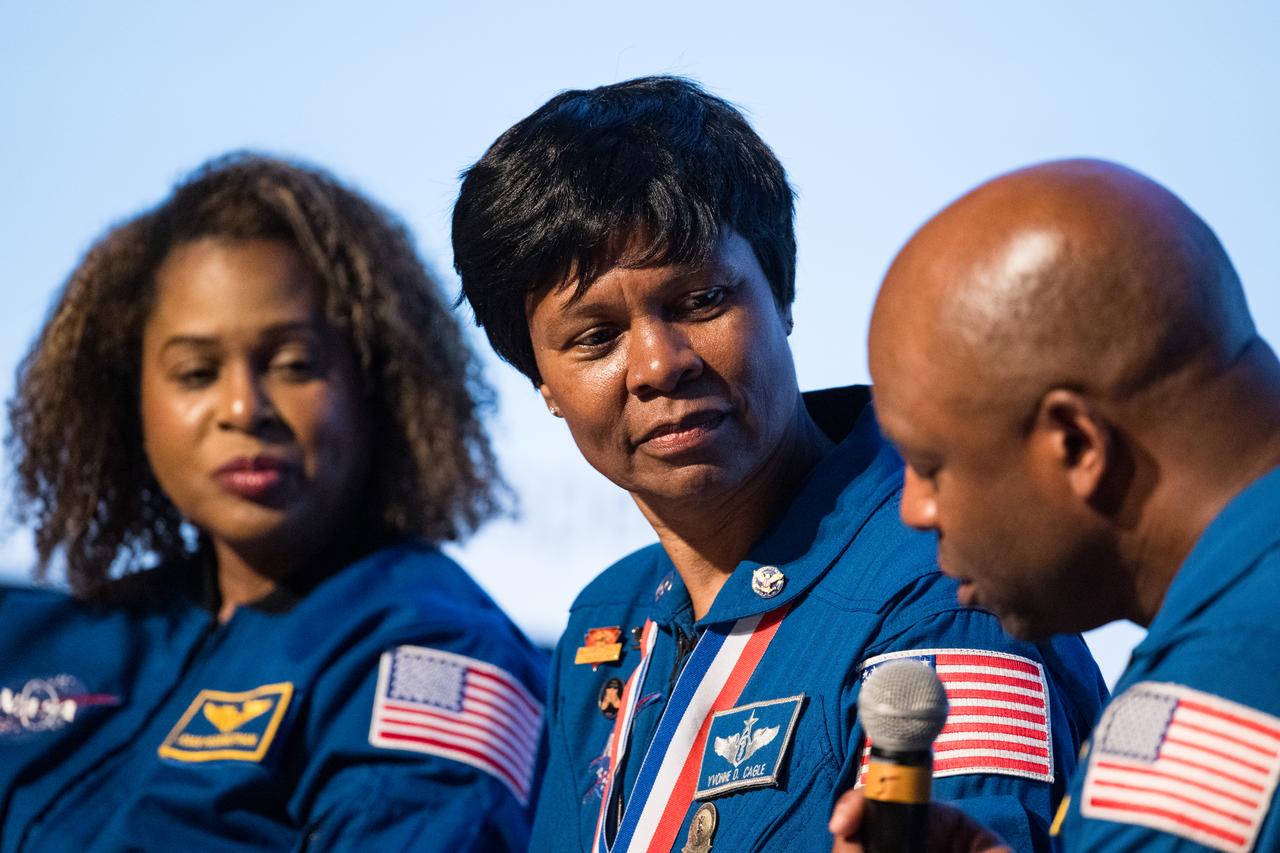

Dr. Yvonne Cagle, NASA astronaut is seen while participating in a panel discussion at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Don Graves, deputy secretary, U.S. Department of Commerce, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
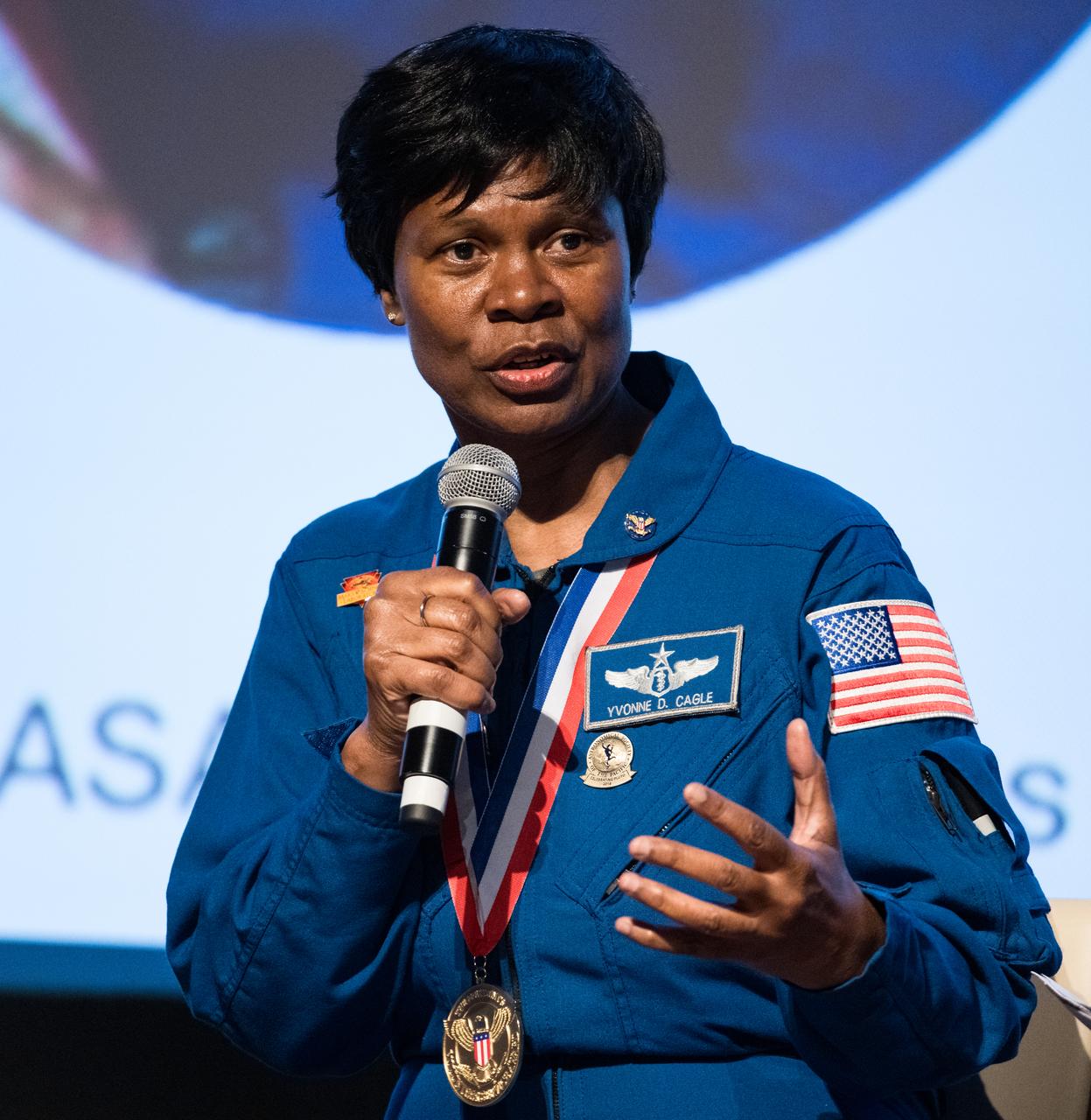

Dr. Yvonne Cagle, NASA astronaut, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
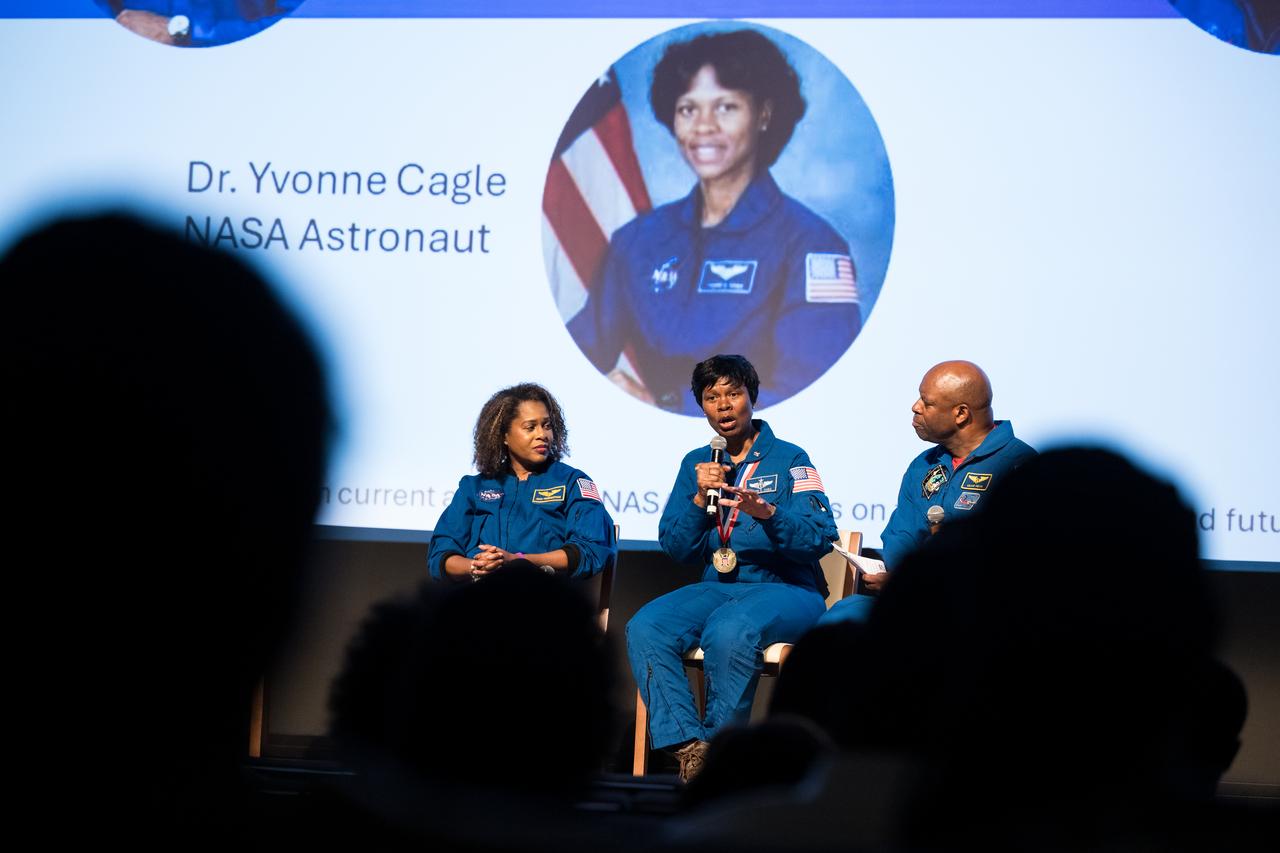

Dr. Yvonne Cagle, NASA astronaut, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
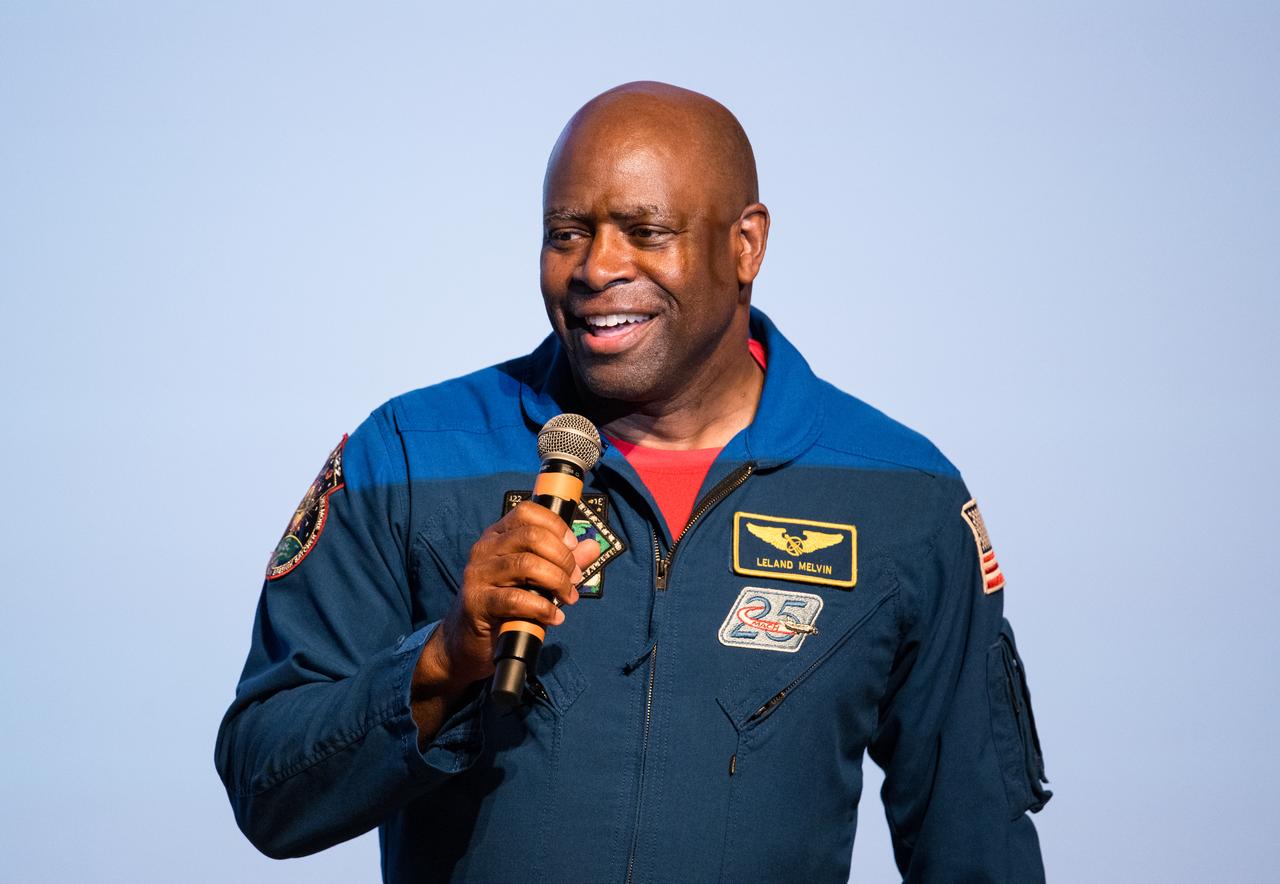

Leland Melvin, retired NASA astronaut, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
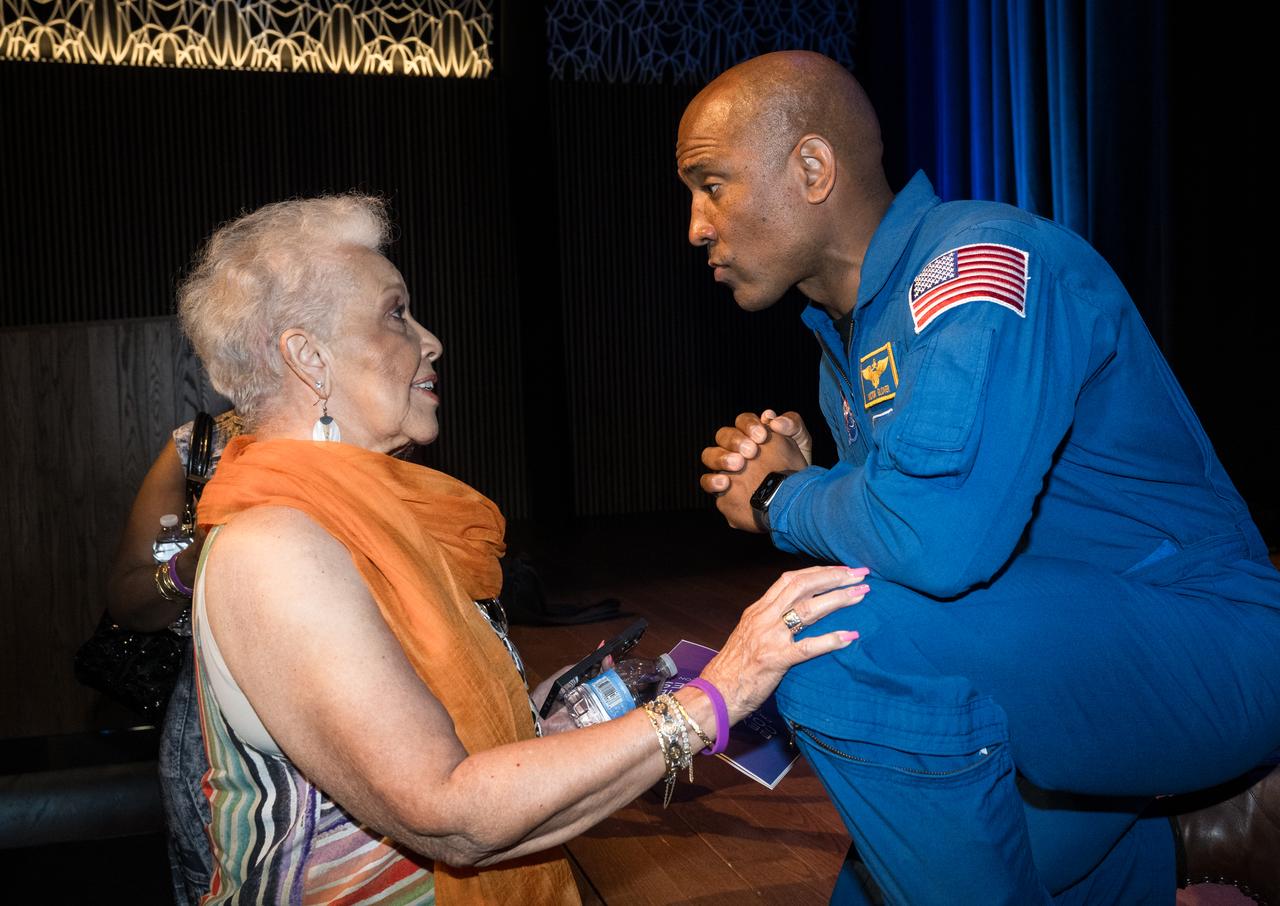

Joylette Goble Hylick, daughter of Katherine Johnson, speaks to NASA astronaut Victor Glover at the conclusion of an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
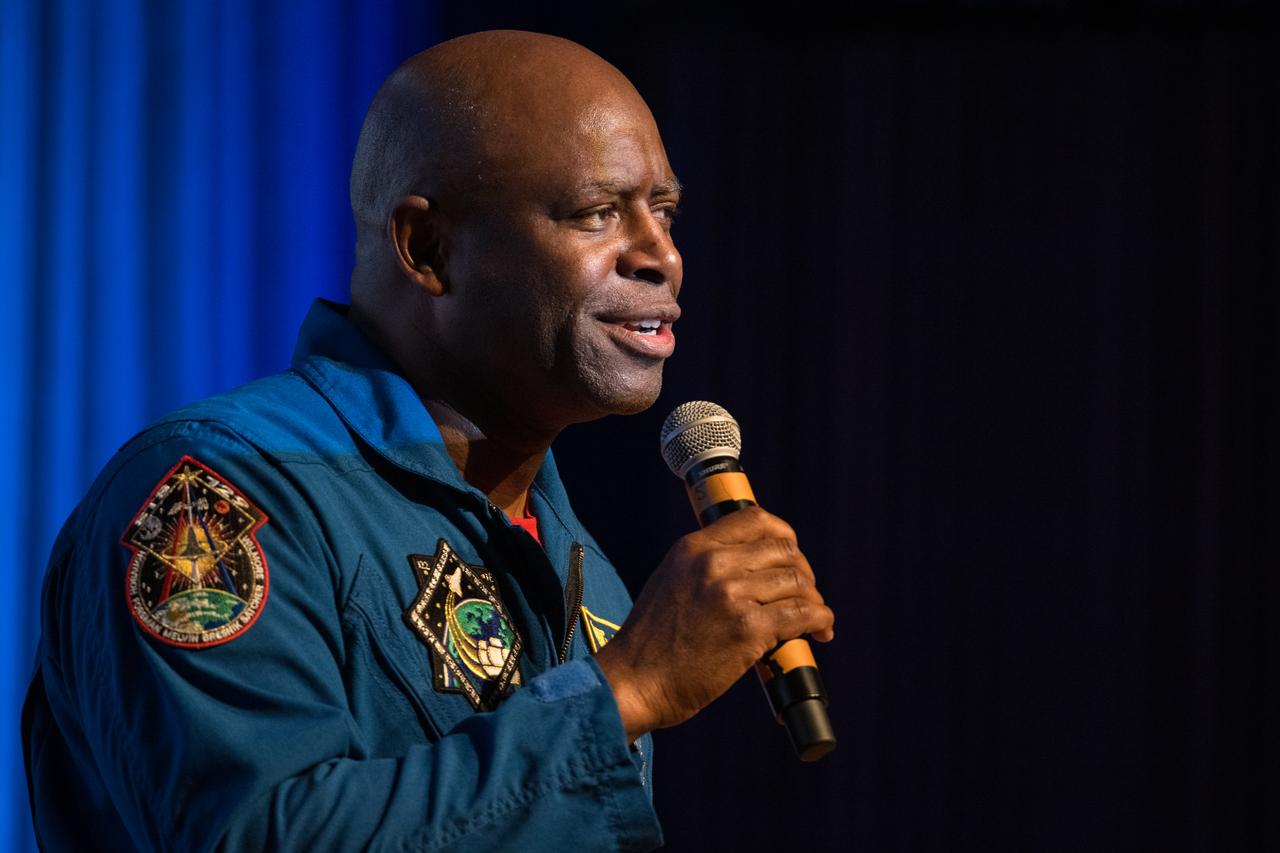

Leland Melvin, retired NASA astronaut, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
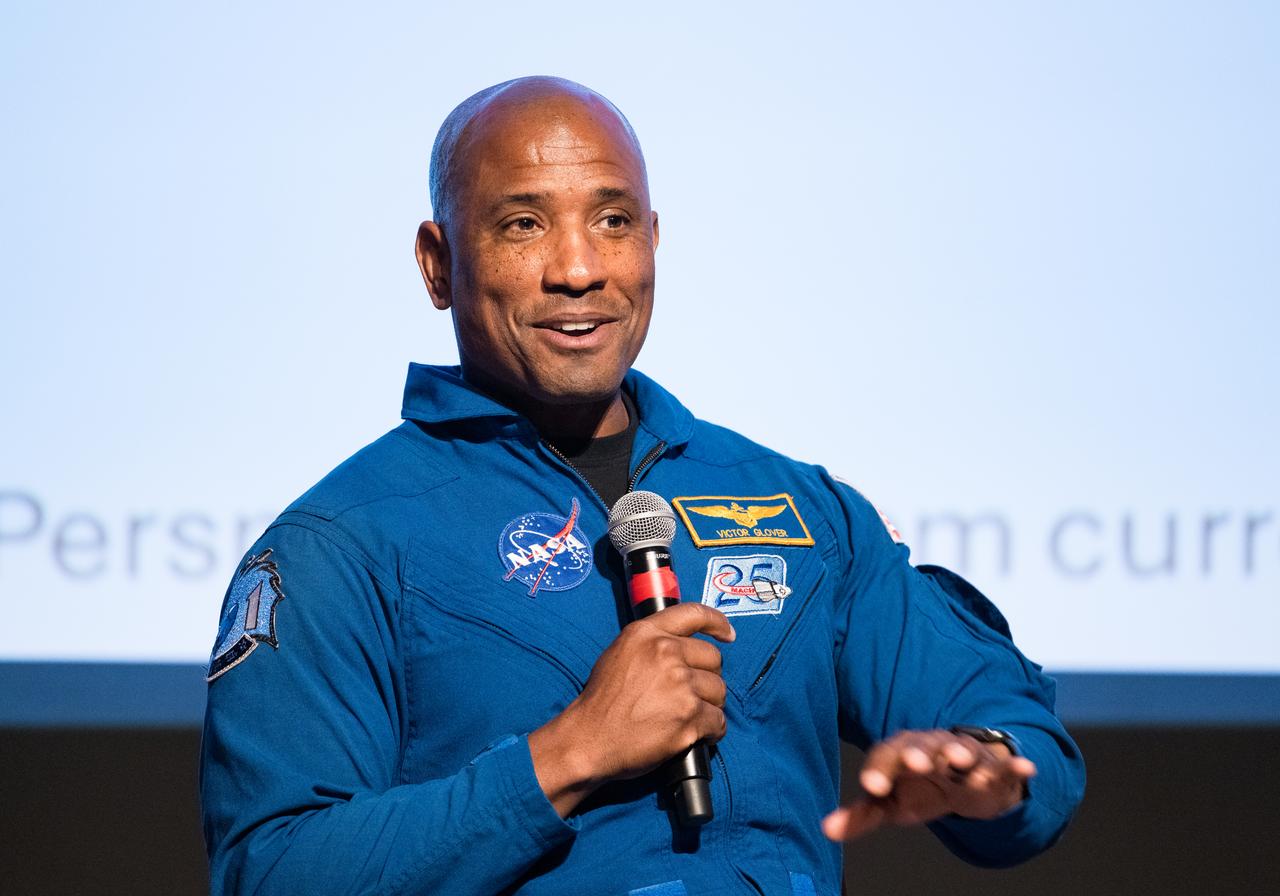

Victor Glover, NASA astronaut, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
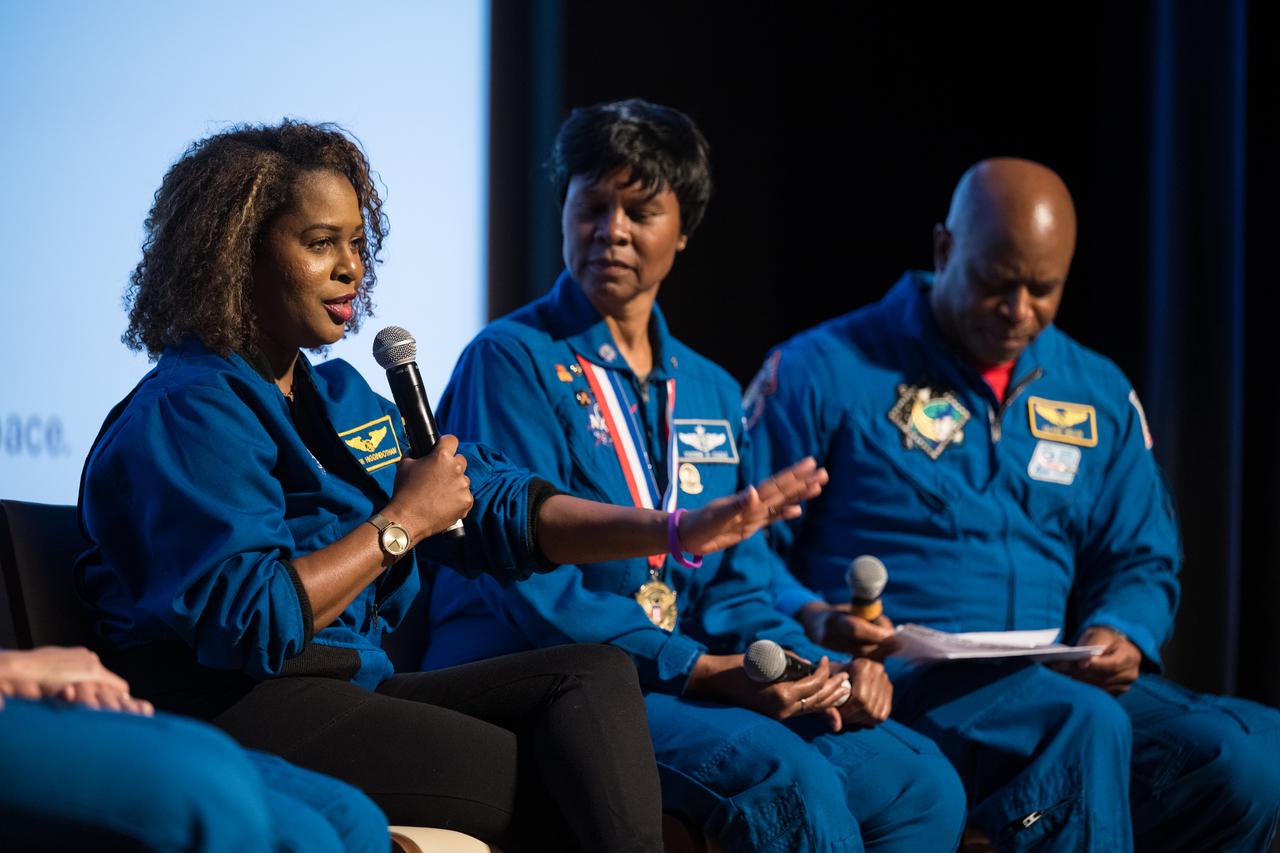

Joan Higginbotham, retired NASA astronaut, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
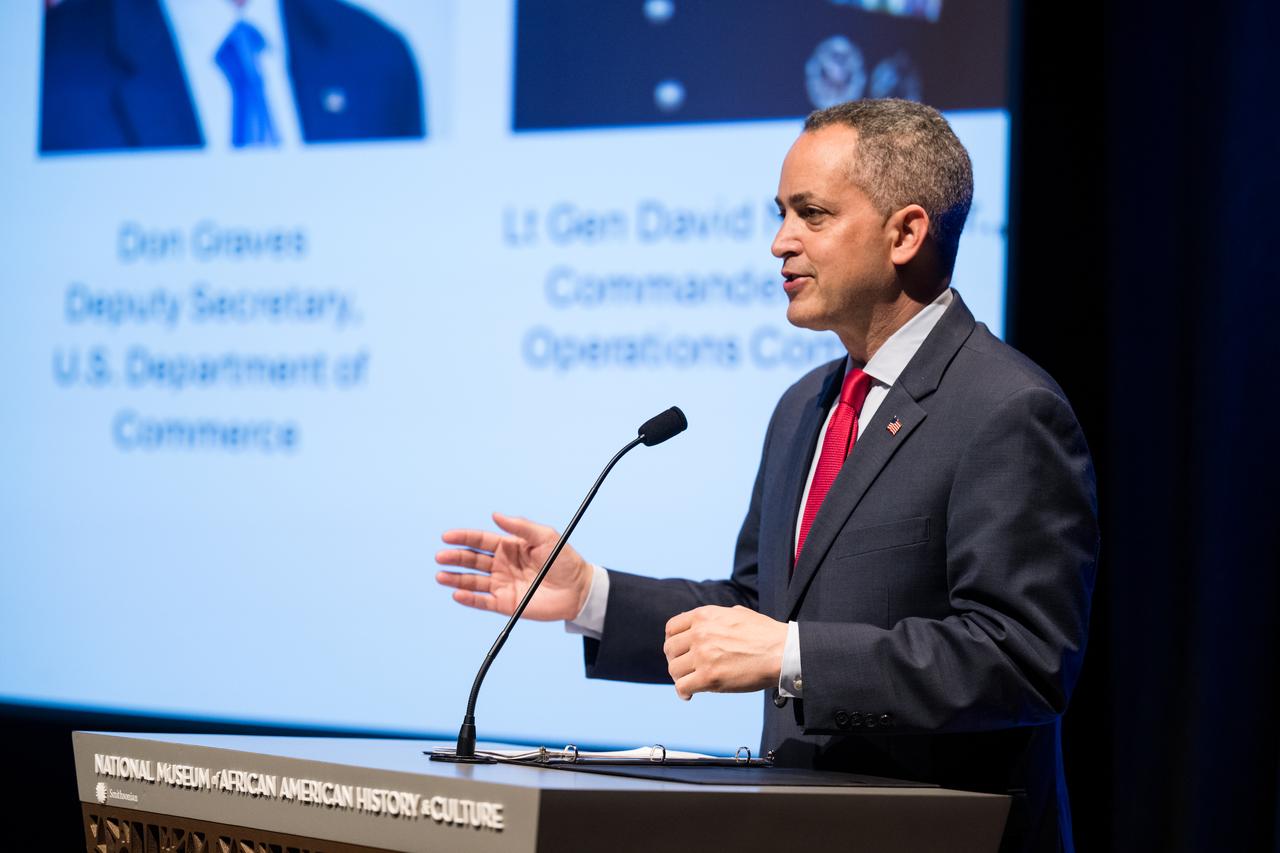

Don Graves, deputy secretary, U.S. Department of Commerce, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
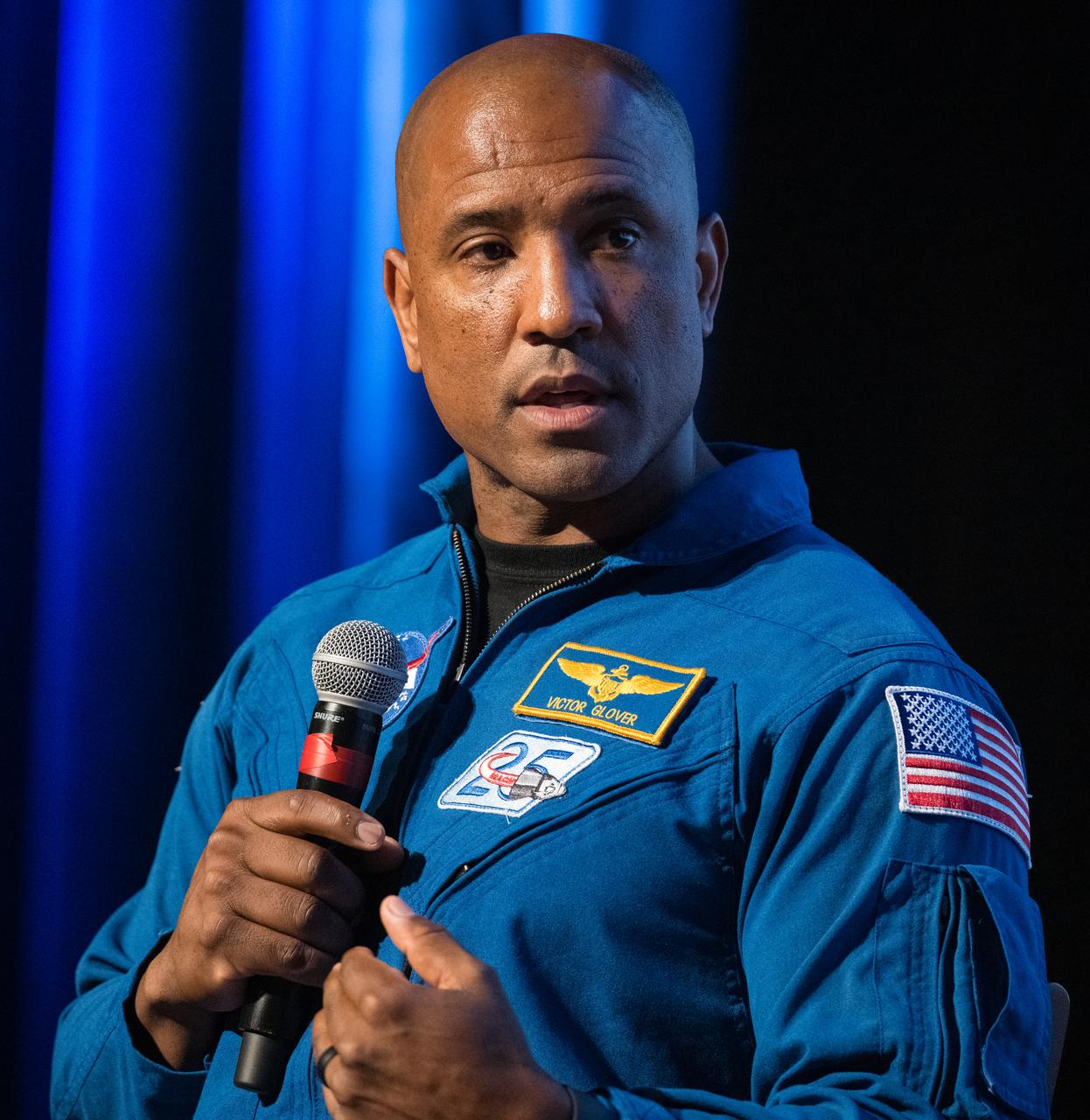

Victor Glover, NASA astronaut, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
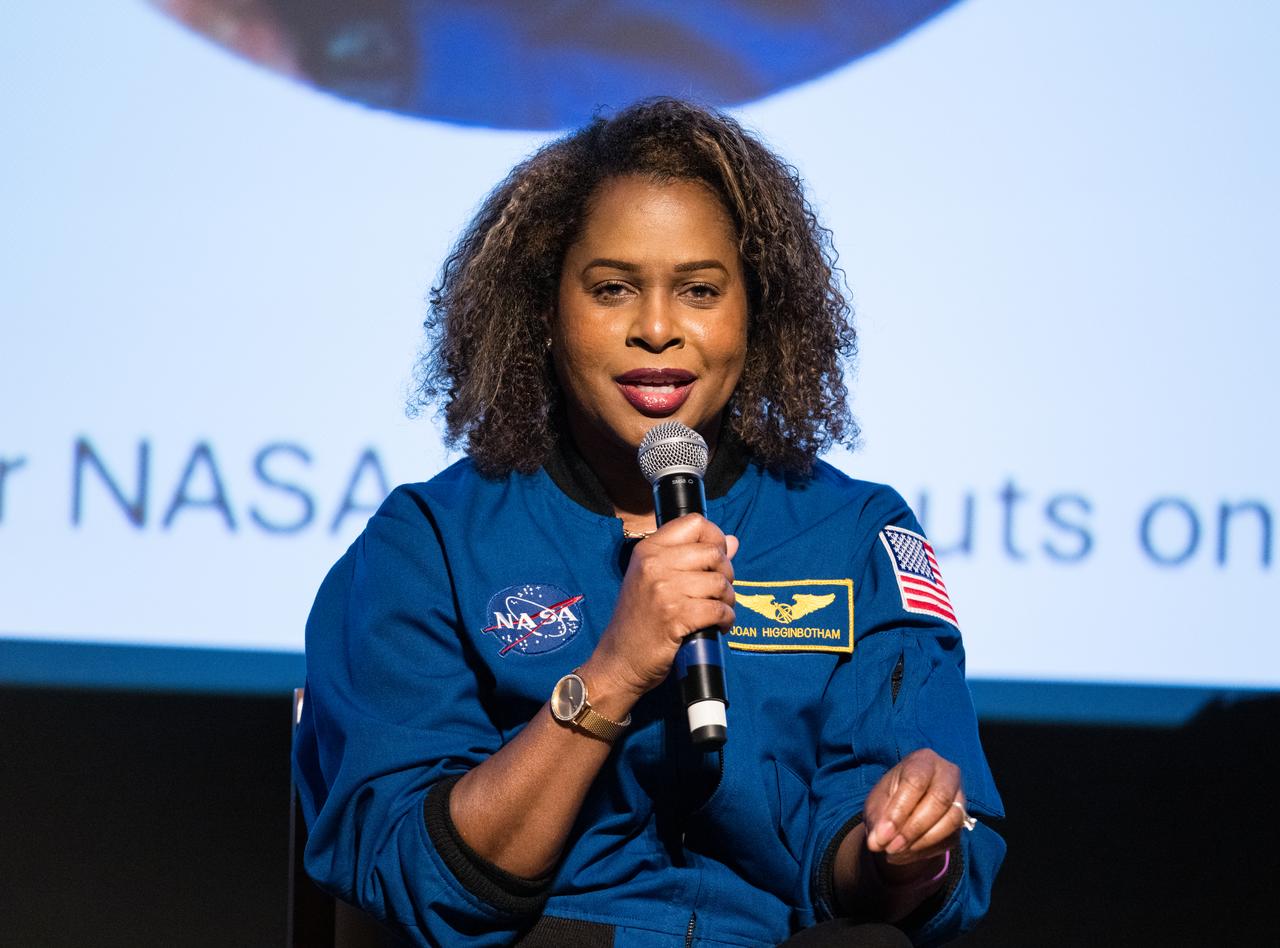

Joan Higginbotham, retired NASA astronaut, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Leland Melvin, retired NASA astronaut, speaks at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

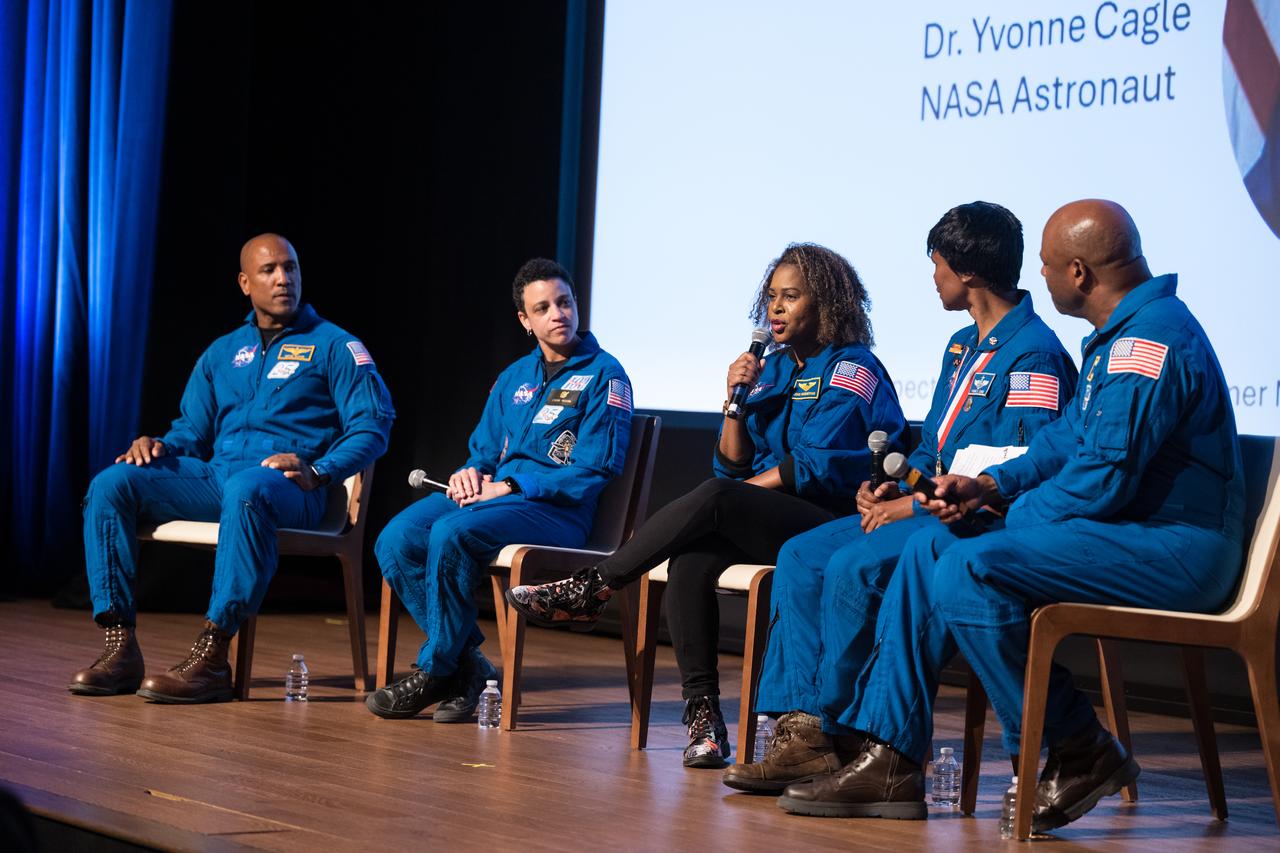
NASA astronaut Jessica Watkins speaks on a panel with NASA astronauts Victor Glover, Joan Higginbotham (retired), Dr. Yvonne Cagle, and Leland Melvin (retired), at an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
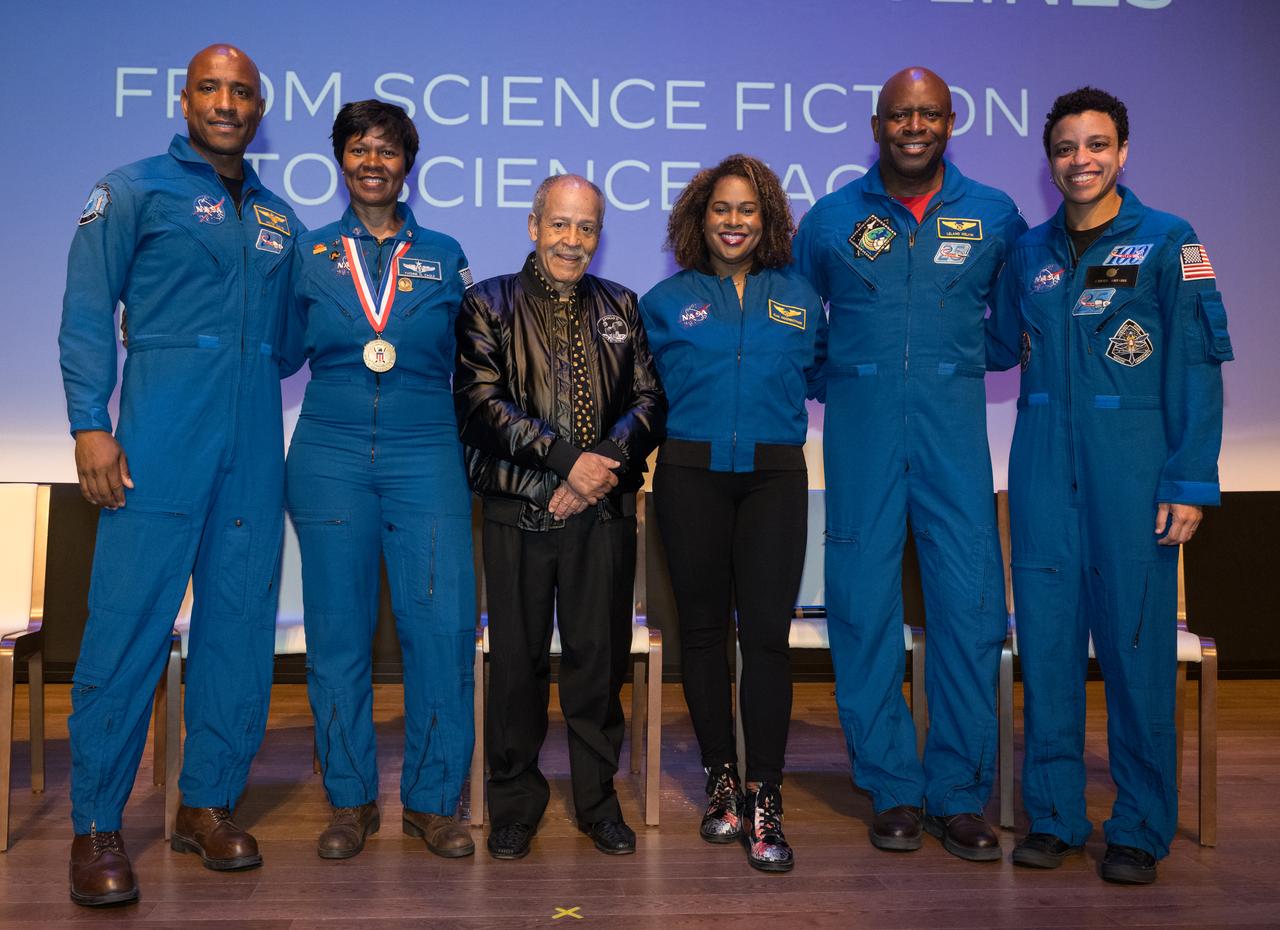

From left to right, NASA astronauts Victor Glover, Dr. Yvonne Cagle, America's first African American astronaut candidate, Ed Dwight, Joan Higginbotham (retired), Leland Melvin (retired) and Jessica Watkins pose for a photo at the conclusion of an event to commemorate Black Space Week (BSW) 2024 titled, "Beyond the Color Lines From Science Fiction to Science Fact," in the Oprah Winfrey Theater at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, Monday, June 17, 2024 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
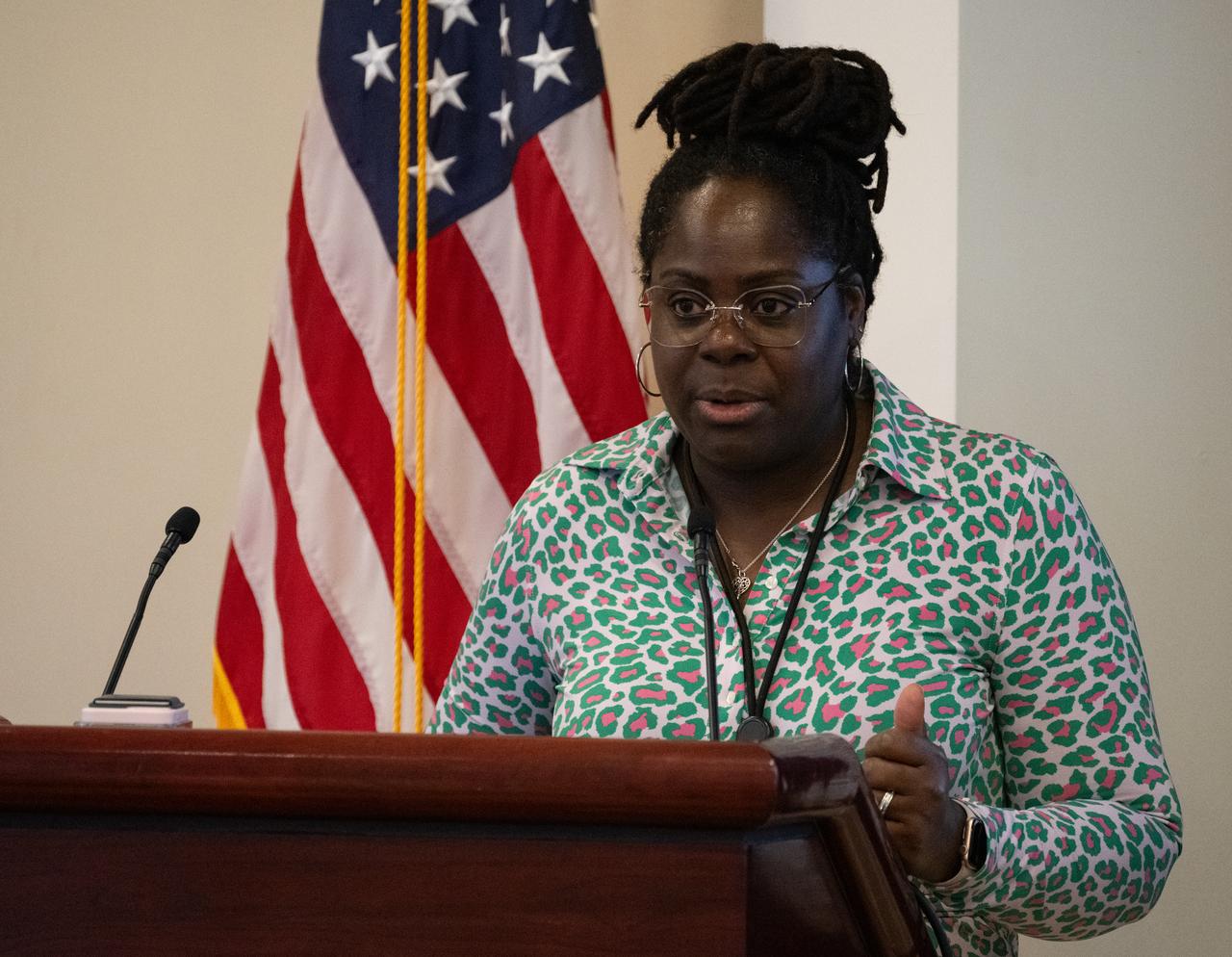

Quincy Brown, Director of Space STEM and Workforce Policy for the National Space Council speaks during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
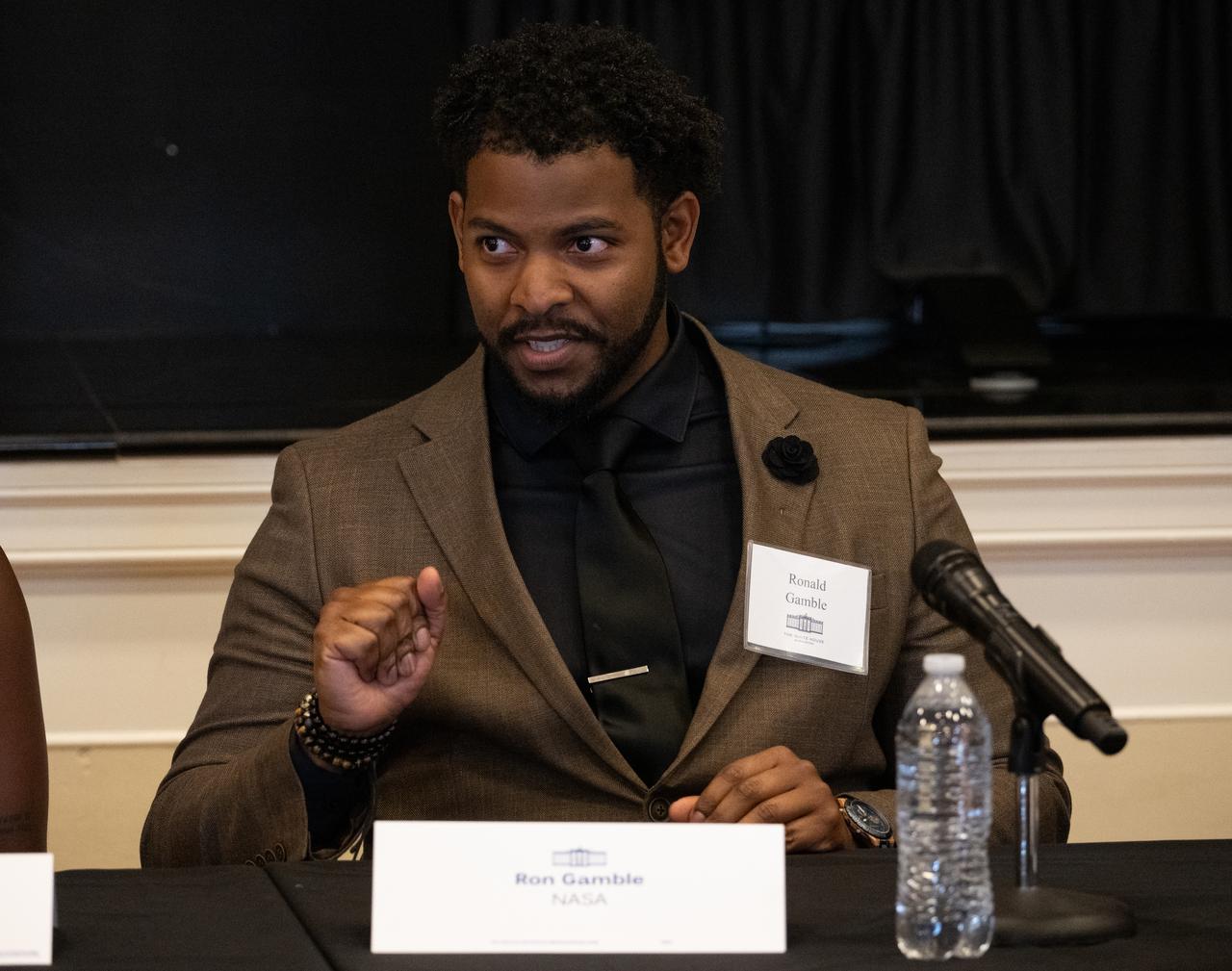

Ronald Gamble, a Theoretical Astrophysicist at NASA”s Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
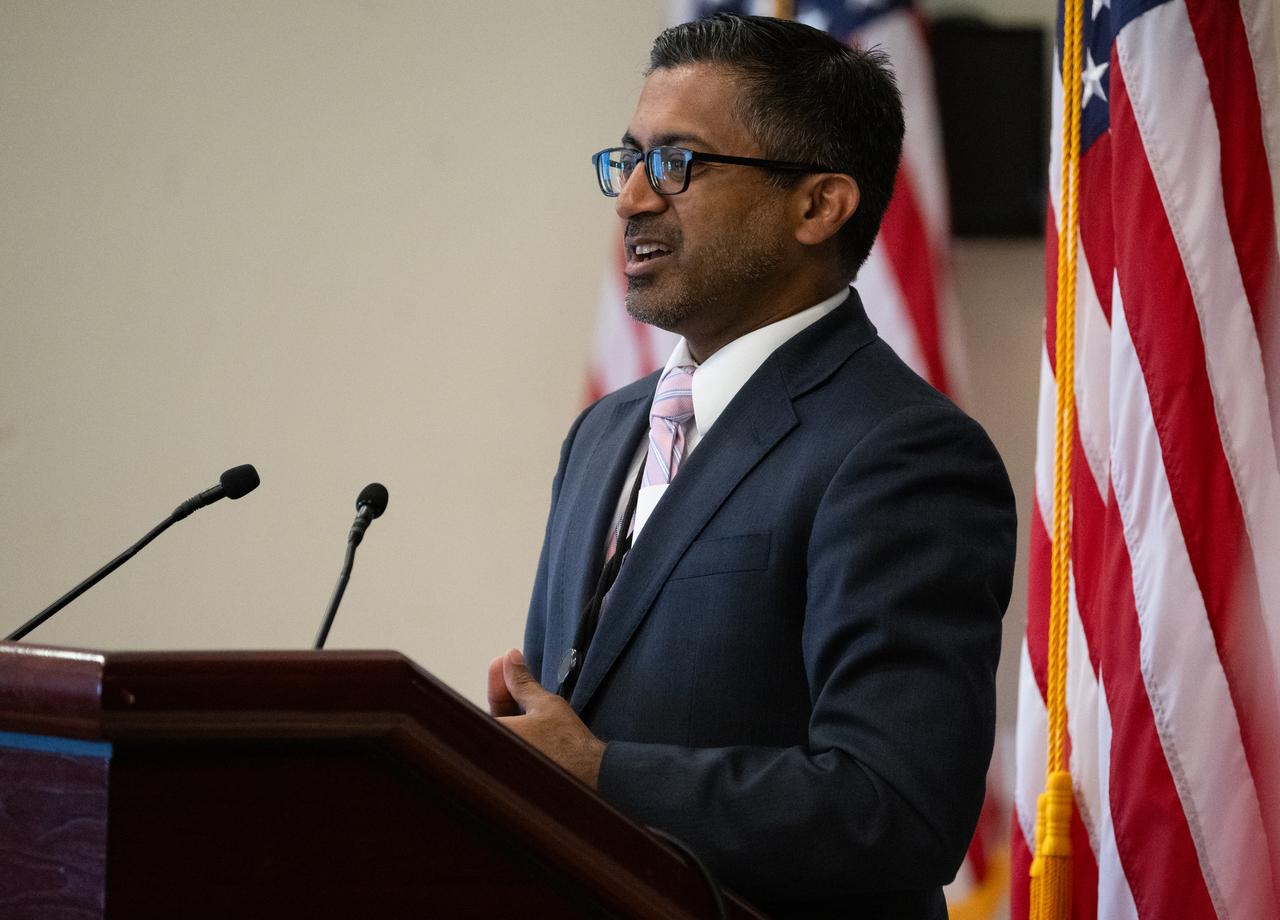

Chirag Parikh, Executive Secretary of the National Space Council, speaks during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Tahara Dawkins, Chief of Staff for the National Space Council speaks during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
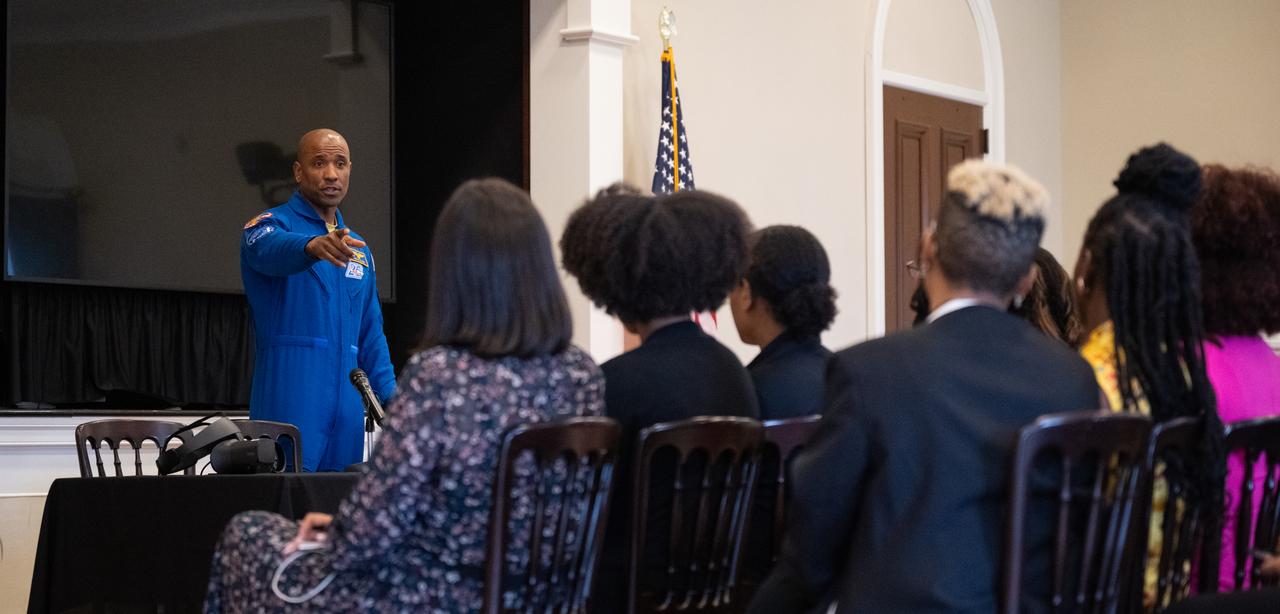

NASA astronaut Victor Glover speaks during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
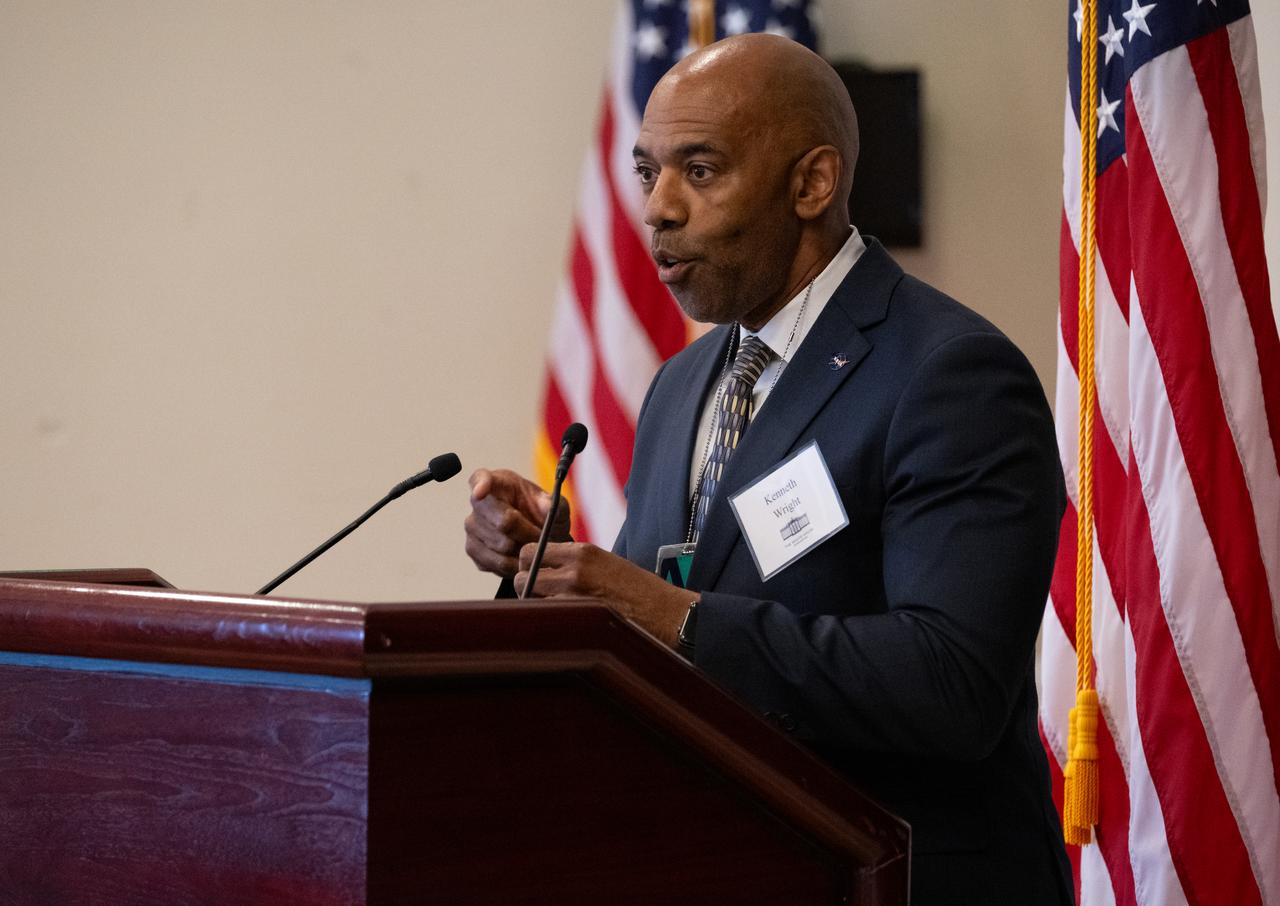

Kenneth Wright, Senior Policy Analyst and Innovation Lead in NASA’s Office of Technology, Policy, and Strategy, speaks during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
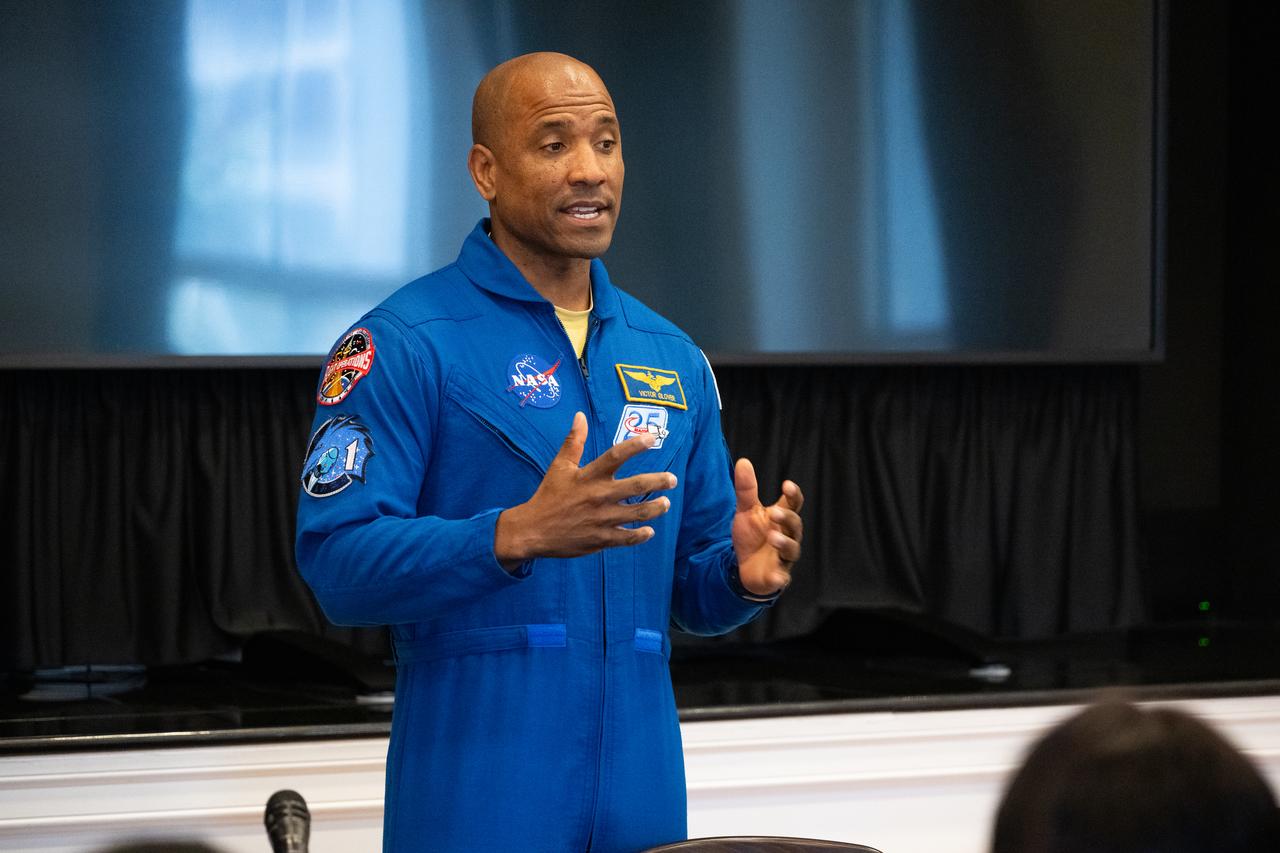

NASA astronaut Victor Glover speaks during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
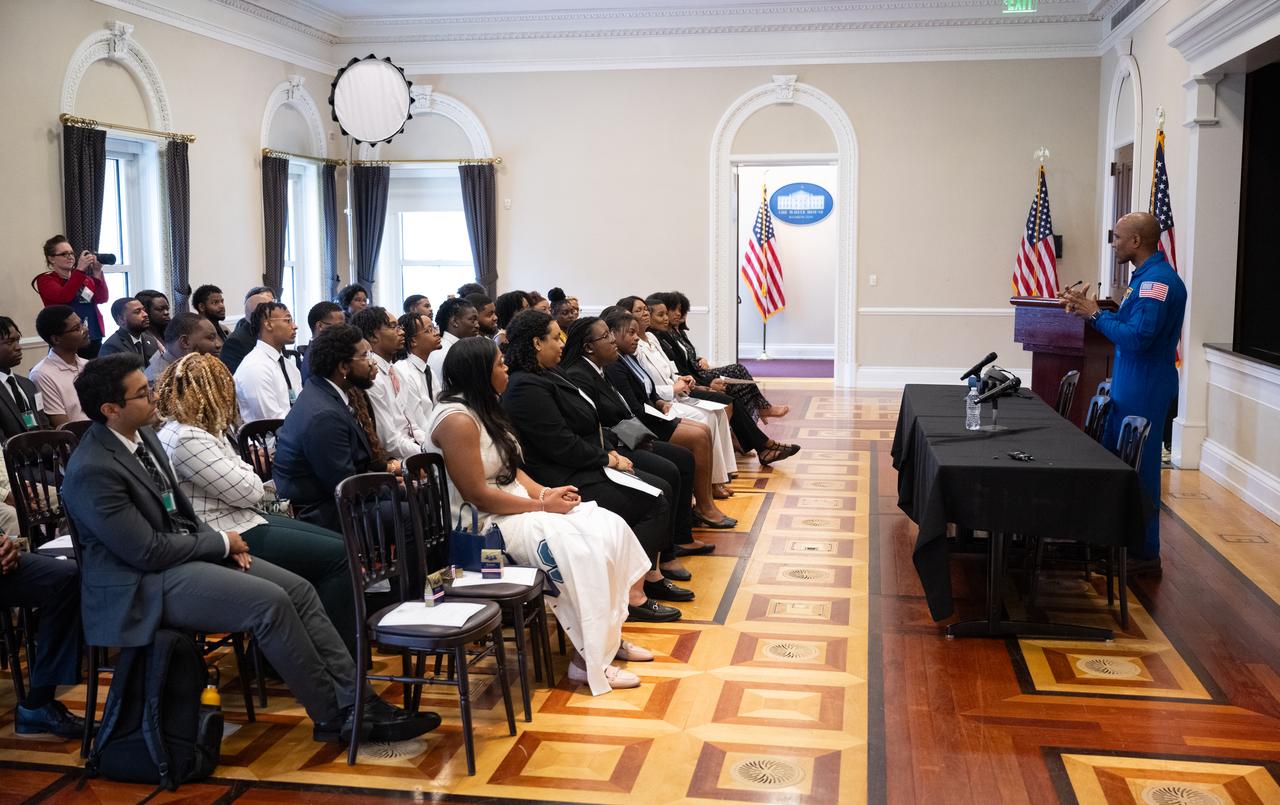

NASA astronaut Victor Glover speaks during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
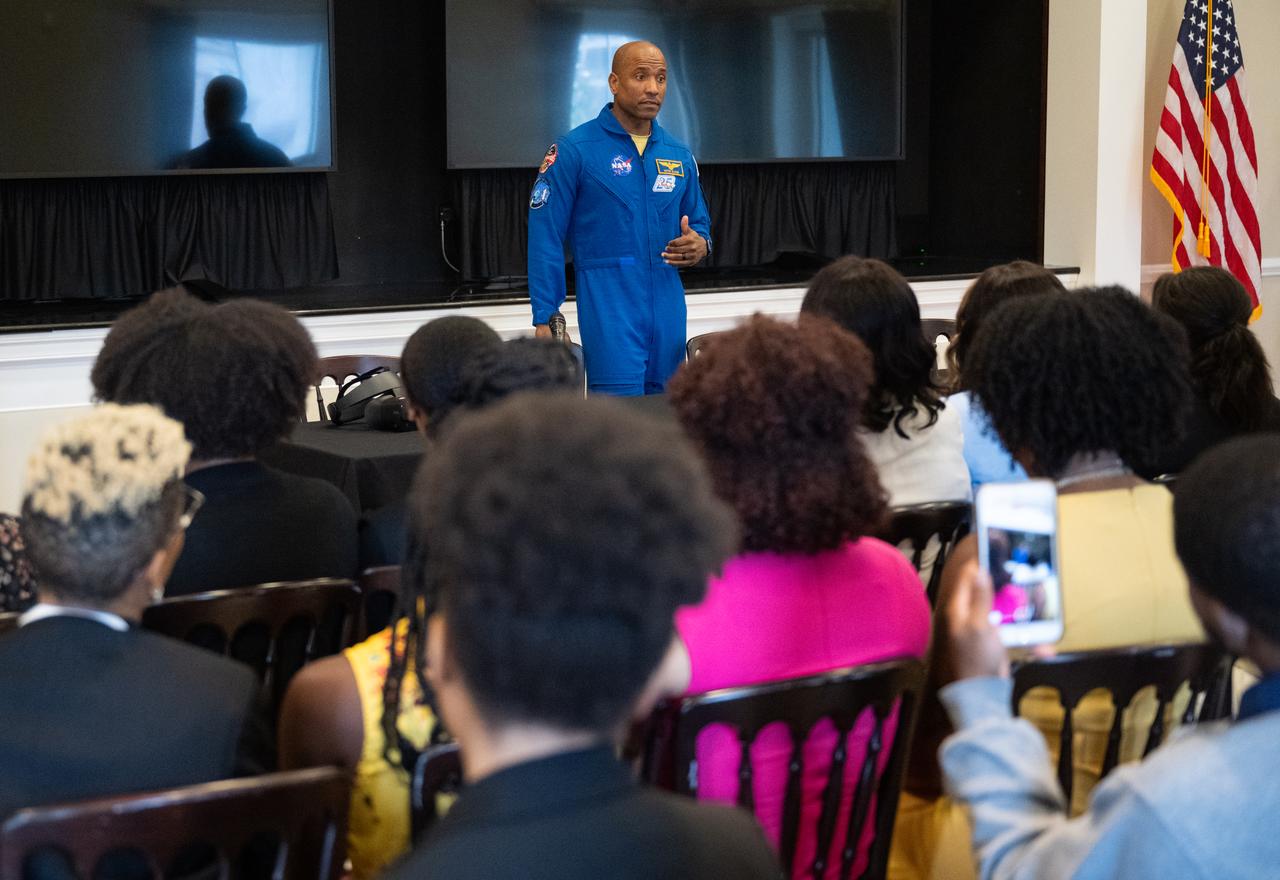

NASA astronaut Victor Glover speaks during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
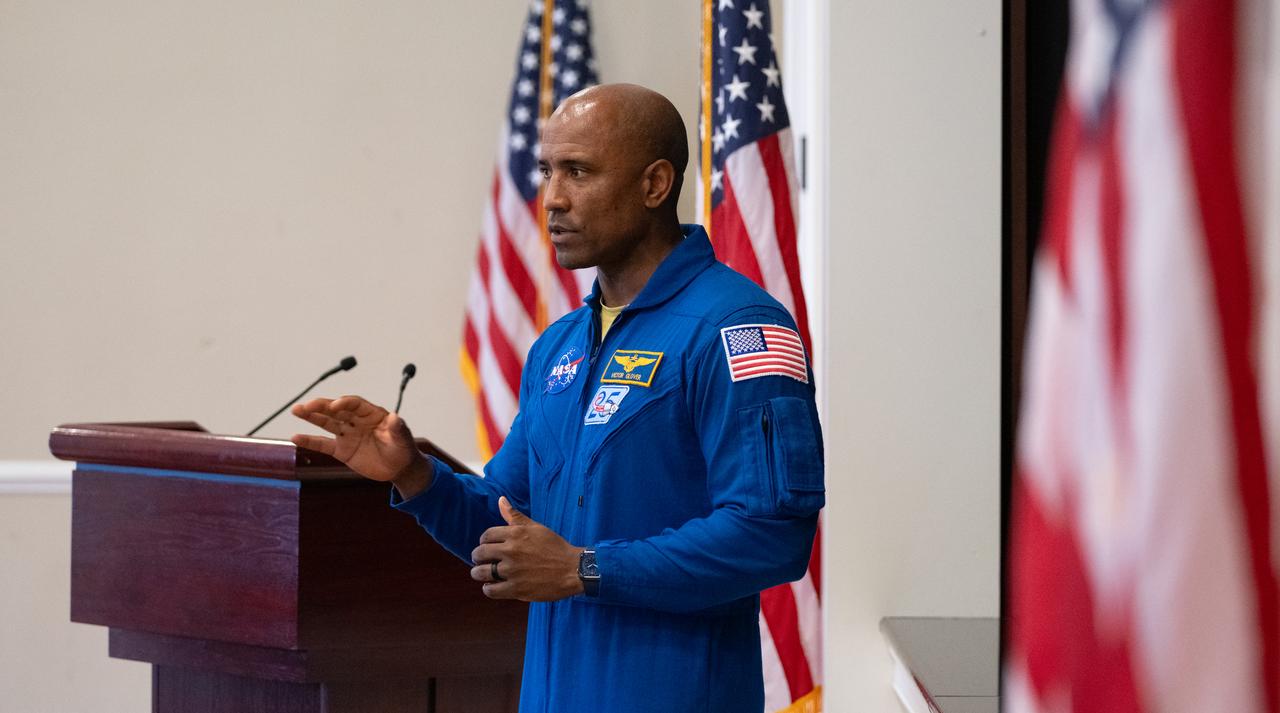

NASA astronaut Victor Glover speaks during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
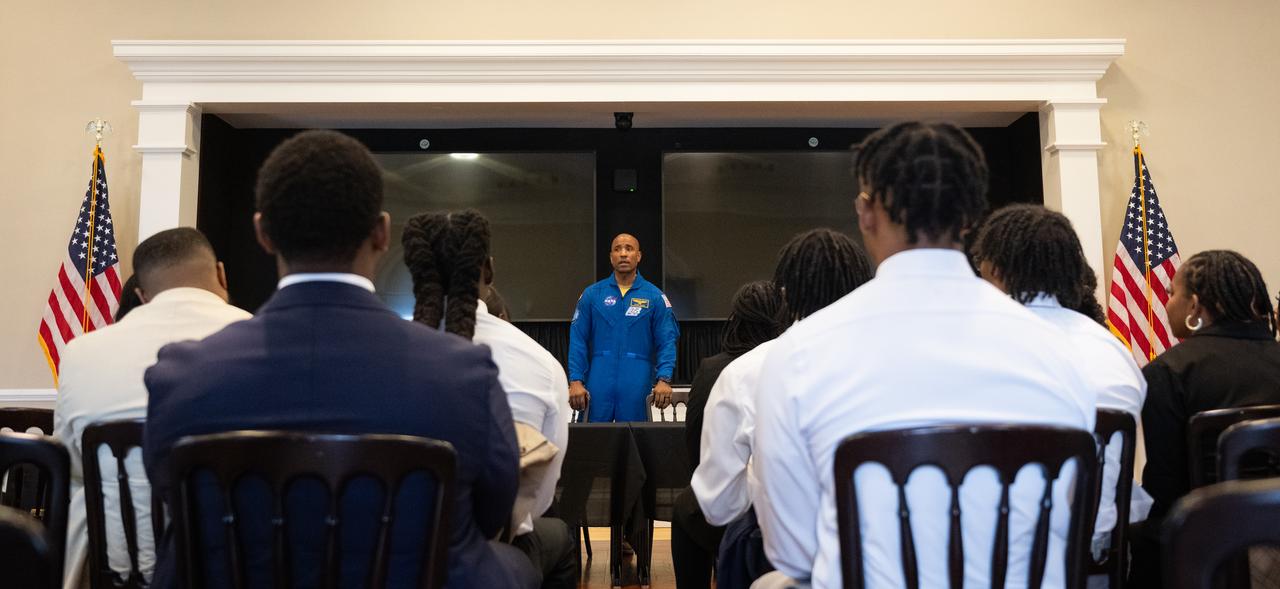

NASA astronaut Victor Glover speaks during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
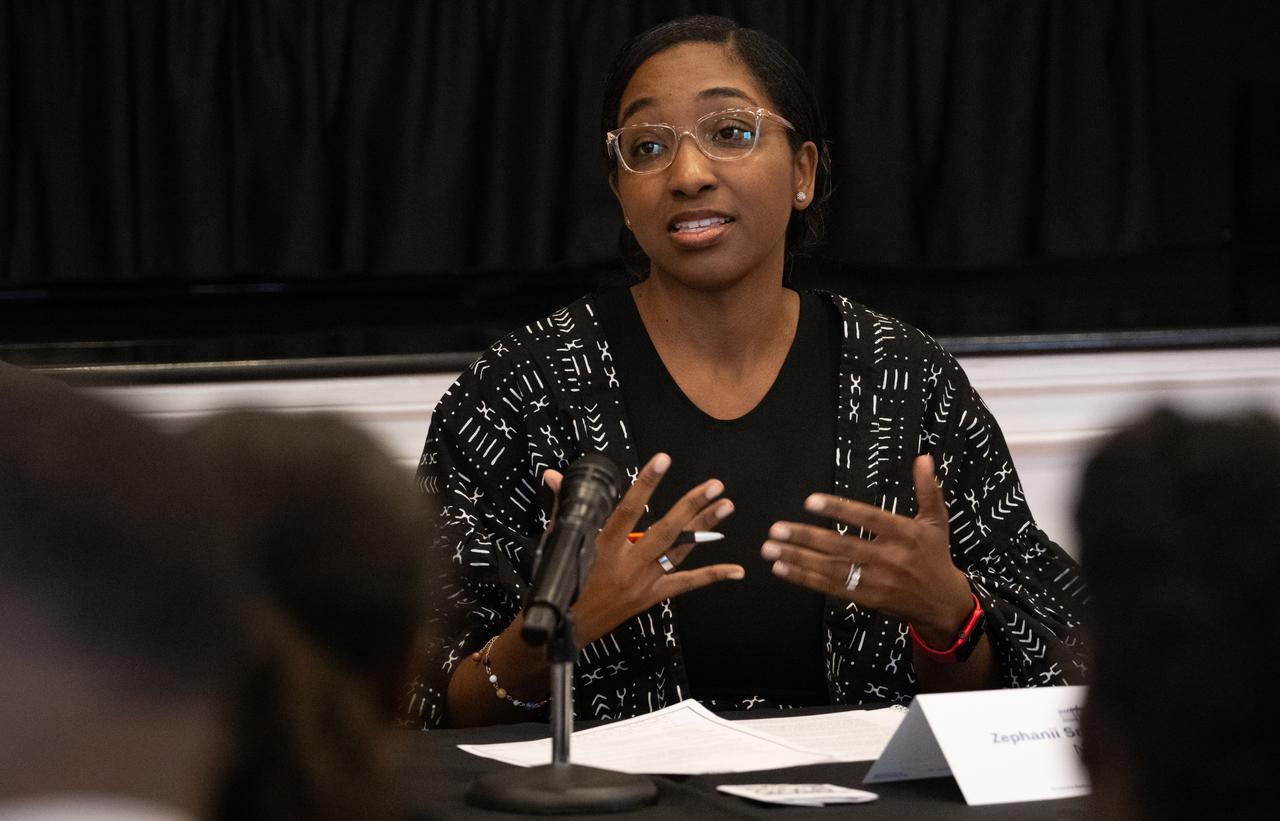

Zephanii Eisenstat, Space and Social Justice Advocate at the NAACP, speaks during a panel discussion moderated by Amber McIntyre, Interagency and International Relations Advisor at NASA with Kim Macharia, Executive Director at Space Prize, and Ronald Gamble, a theoretical astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
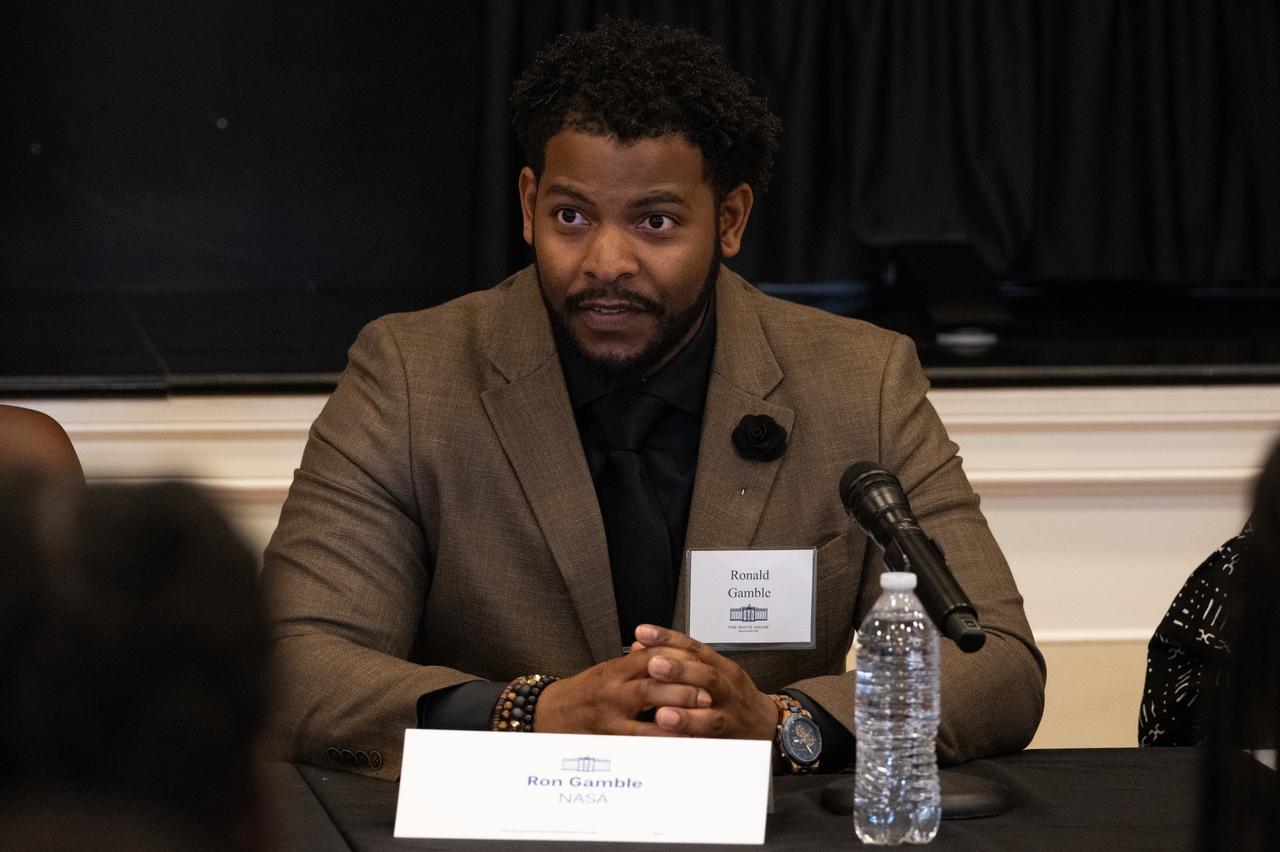

Ronald Gamble, a theoretical astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks during a panel discussion moderated by Amber McIntyre, Interagency and International Relations Advisor at NASA with Kim Macharia, Executive Director at Space Prize, and Zephanii Eisenstat, Space and Social Justice Advocate at the NAACP, during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
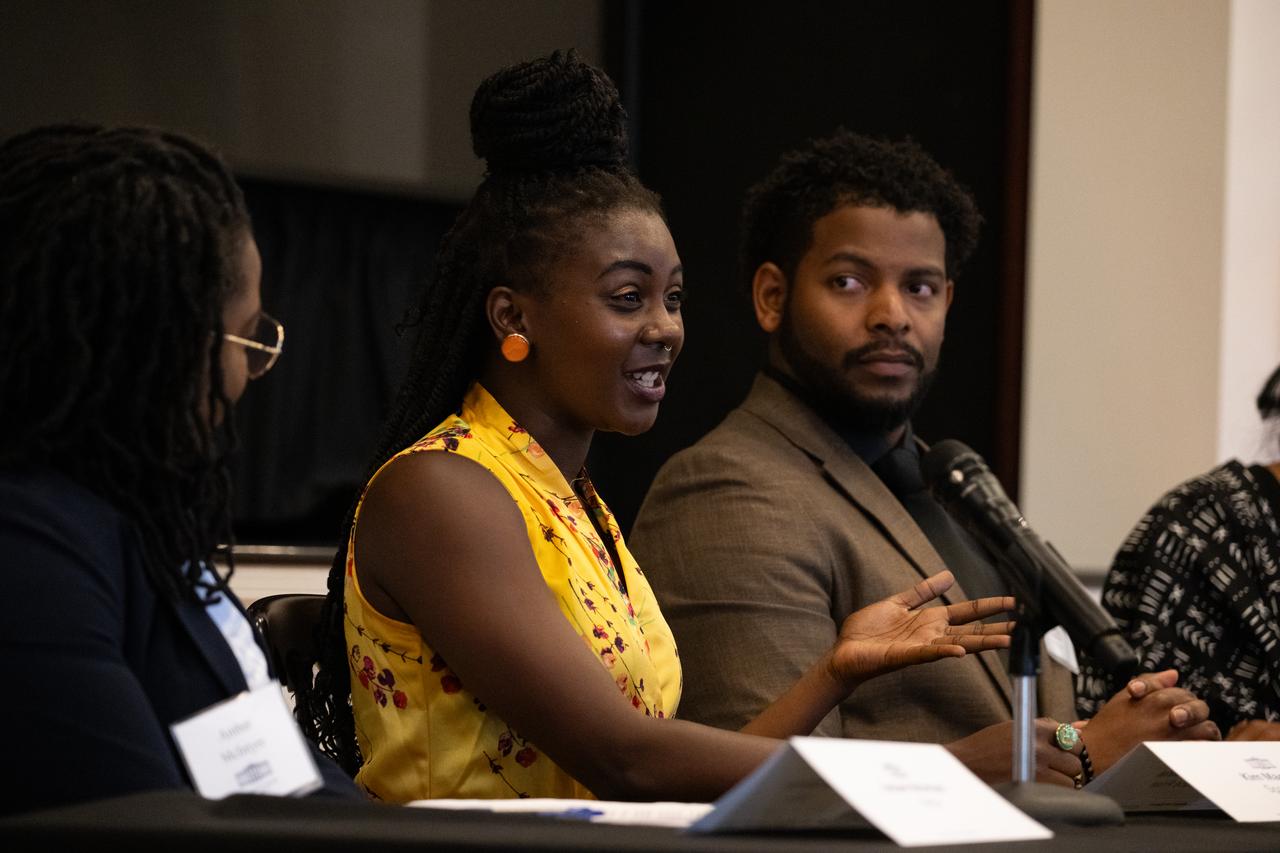

Kim Macharia, Executive Director at Space Prize, speaks during a panel discussion moderated by Amber McIntyre, Interagency and International Relations Advisor at NASA with Ronald Gamble, a theoretical astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and Zephanii Eisenstat, Space and Social Justice Advocate at the NAACP, during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
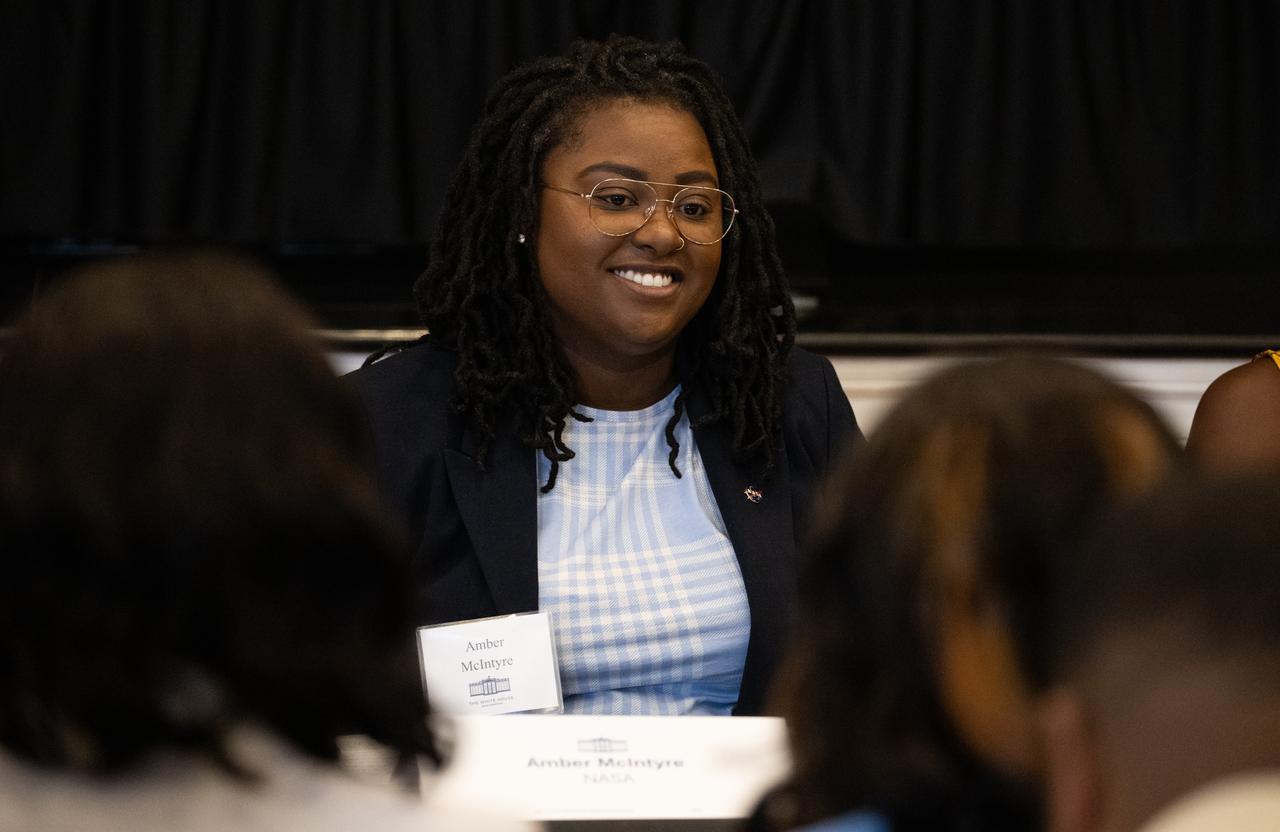

Amber McIntyre, Interagency and International Relations Advisor at NASA, is seen during a panel discussion with Kim Macharia, Executive Director at Space Prize, Ronald Gamble, a theoretical astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and Zephanii Eisenstat, Space and Social Justice Advocate at the NAACP, during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
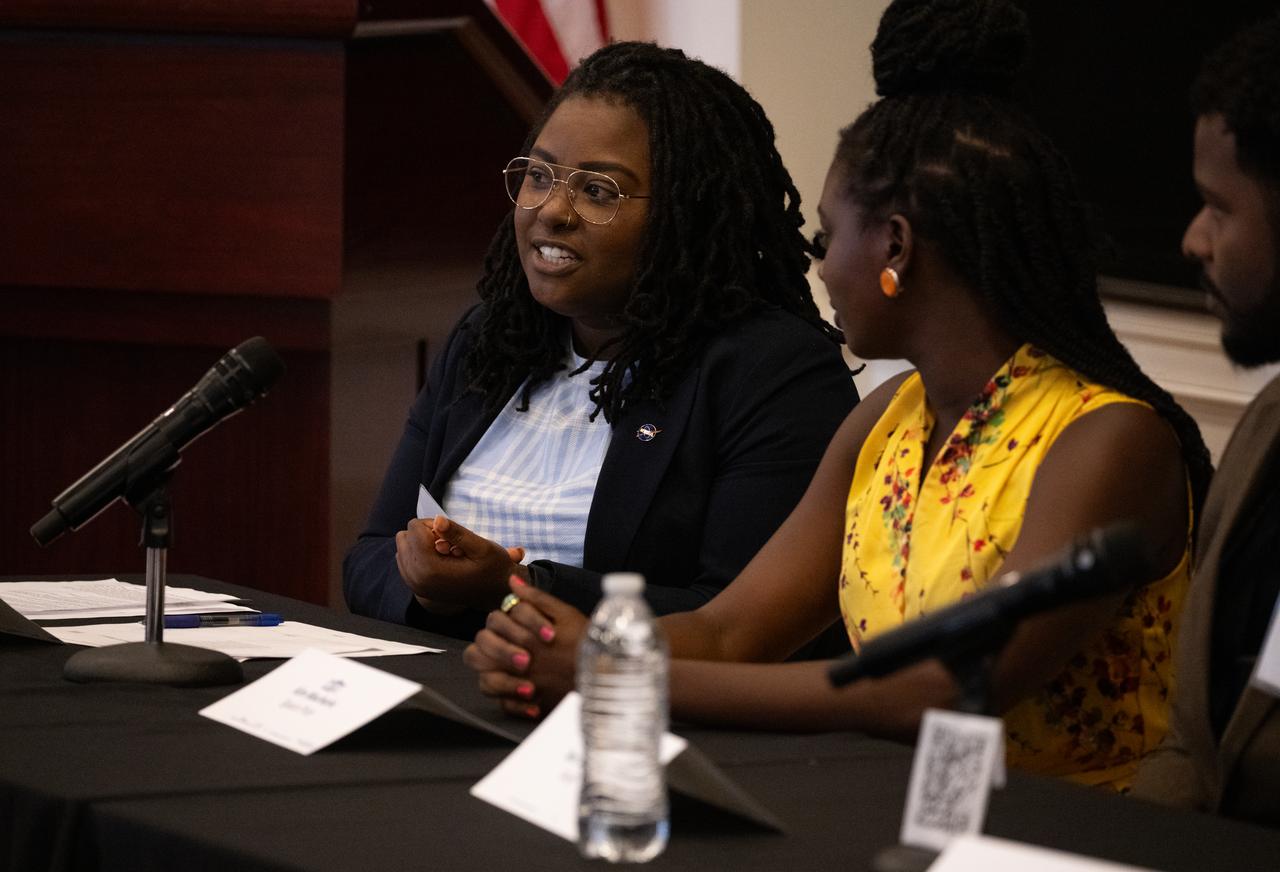

Amber McIntyre, Interagency and International Relations Advisor at NASA, speaks during a panel discussion with Kim Macharia, Executive Director at Space Prize, Ronald Gamble, a theoretical astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and Zephanii Eisenstat, Space and Social Justice Advocate at the NAACP, during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Sydney Hamilton, structures manager for transonic truss braced wing at The Boeing Company, left, and Tony Castilleja Jr., senior manager for space at The Boeing Company, are seen during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Amber McIntyre, Interagency and International Relations Advisor at NASA, left, moderates a panel discussion with Kim Macharia, Executive Director at Space Prize, second from left, Ronald Gamble, a theoretical astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, second from right, and Zephanii Eisenstat, Space and Social Justice Advocate at the NAACP, right, during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Amber McIntyre, Interagency and International Relations Advisor at NASA, left, moderates a panel discussion with Kim Macharia, Executive Director at Space Prize, second from left, Ronald Gamble, a theoretical astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, second from right, and Zephanii Eisenstat, Space and Social Justice Advocate at the NAACP, right, during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Amber McIntyre, Interagency and International Relations Advisor at NASA, left, moderates a panel discussion with Kim Macharia, Executive Director at Space Prize, second from left, Ronald Gamble, a theoretical astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, second from right, and Zephanii Eisenstat, Space and Social Justice Advocate at the NAACP, right, during an Artemis Generation Roundtable for Black Space Week, Tuesday, June 20, 2023, at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building in Washington. As part of Black Space Week, the National Space Council and NASA collaborated with Black In Astro to host students for a discussion on the future of space exploration and equity. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A disk of hot gas swirls around a black hole in this illustration. Some of the gas came from a star that was pulled apart by the black hole, forming the long stream of hot gas on the right, feeding into the disk. These events are formally known as tidal disruption events, or TDEs. It can take just a matter or weeks or months from the destruction of the star to the formation of the disk. The gas gets hotter the closer it gets to the black hole, but the hottest material can be found above the black hole. This hottest material is cloud of plasma (gas atoms with their electrons stripped away) known as a corona. Most TDEs that result in the formation of a corona also produce jets of material that spew into space away from the black hole at its poles. A TDE called AT2021ehb is the first confirmed example of a corona forming without jets in a tidal disruption event. The observation of AT2021ehb makes it possible for scientists to study the formation of jets and coronae separately. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25440

ISS034-E-062471 (3 March 2013) --- This is one of a series of photos taken by the Expedition 34 crew members aboard the International Space Station during the March 3 approach, capture and docking of the SpaceX Dragon. Earth's horizon and the blackness of space form the backdrop for this image, featuring Dragon, framed by one of the Cupola's windows, and being docked to the orbital outpost with the aid of the Space Station Remote Manipulator System or Canadarm2. The spacecraft begins its scheduled three-week-long stay at the orbiting space station.

ISS034-E-062490 (3 March 2013) --- This is one of a series of photos taken by the Expedition 34 crew members aboard the International Space Station during the March 3 approach, capture and docking of the SpaceX Dragon. A blue and white Earth and the blackness of space share the background for this image, featuring Dragon in the grasp of the Space Station Remote Manipulator System or Canadarm2. The spacecraft begins a scheduled three-week-long stay at the orbiting space station.
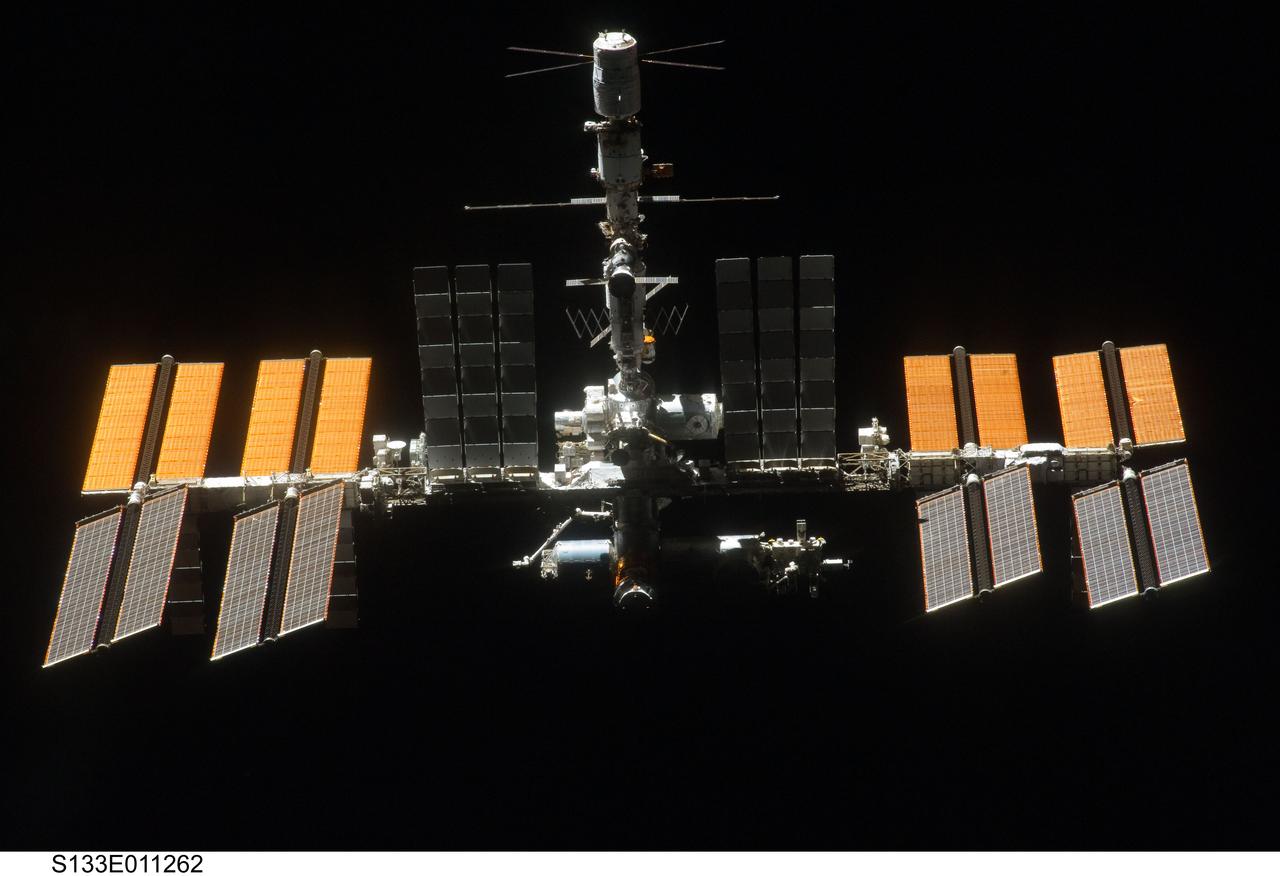

S133-E-011262 (7 March 2011) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, the International Space Station is seen from Discovery as the two orbital spacecraft accomplish their relative separation on March 7 after an aggregate of 12 astronauts and cosmonauts worked together for over a week. During a post undocking fly-around, the crew members aboard the two spacecraft collected a series of photos of each other?s vehicle. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
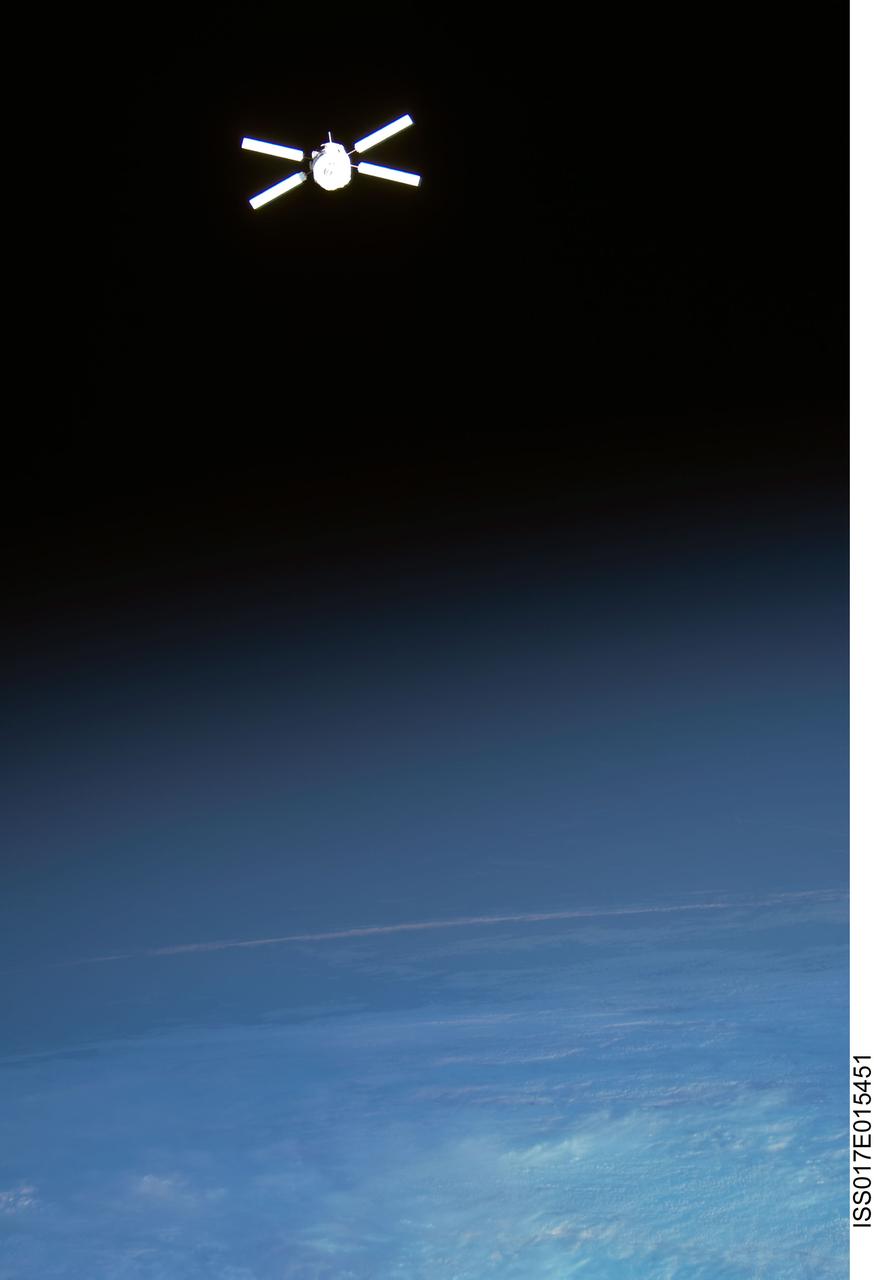

ISS017-E-015451 (5 Sept. 2008) --- Backdropped by Earth's horizon and the blackness of space, European Space Agency's (ESA) "Jules Verne" Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) begins its relative separation from the International Space Station. The ATV undocked from the aft port of the Zvezda Service Module at 4:29 p.m. (CDT) on Sept. 5, 2008 and was placed in a parking orbit for three weeks, scheduled to be deorbited on Sept. 29 when lighting conditions are correct for an ESA imagery experiment of reentry.
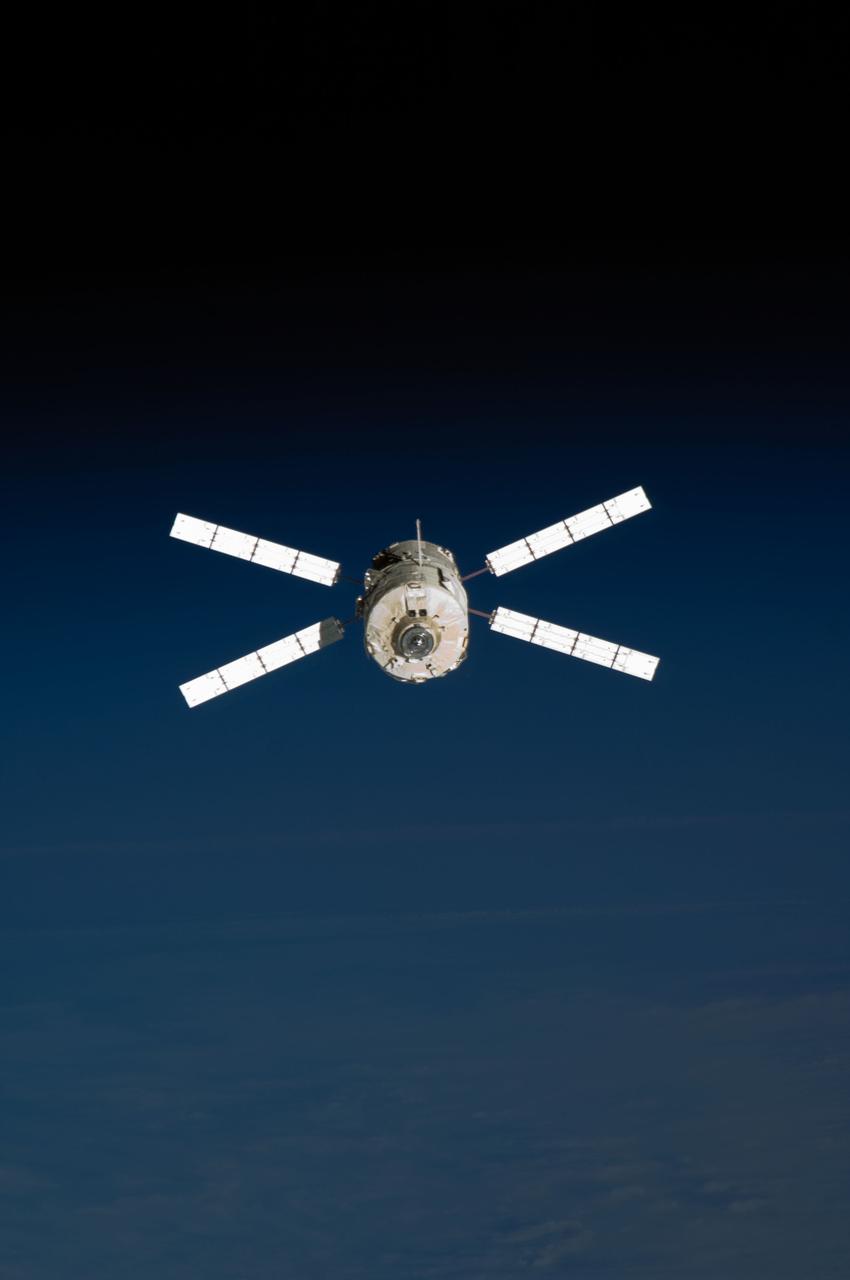
ISS017-E-015468 (5 Sept. 2008) --- Backdropped by the blackness of space, European Space Agency's (ESA) "Jules Verne" Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) begins its relative separation from the International Space Station. The ATV undocked from the aft port of the Zvezda Service Module at 4:29 p.m. (CDT) on Sept. 5, 2008 and was placed in a parking orbit for three weeks, scheduled to be deorbited on Sept. 29 when lighting conditions are correct for an ESA imagery experiment of reentry.

ISS034-E-062482 (3 March 2013) --- This is one of a series of photos taken by the Expedition 34 crew members aboard the International Space Station during the March 3 approach, capture and docking of the SpaceX Dragon. A blue and white Earth and the blackness of space share the background for this image, featuring Dragon in the grasp of the Space Station Remote Manipulator System or Canadarm2. The spacecraft begins a scheduled three-week-long stay at the orbital outpost.
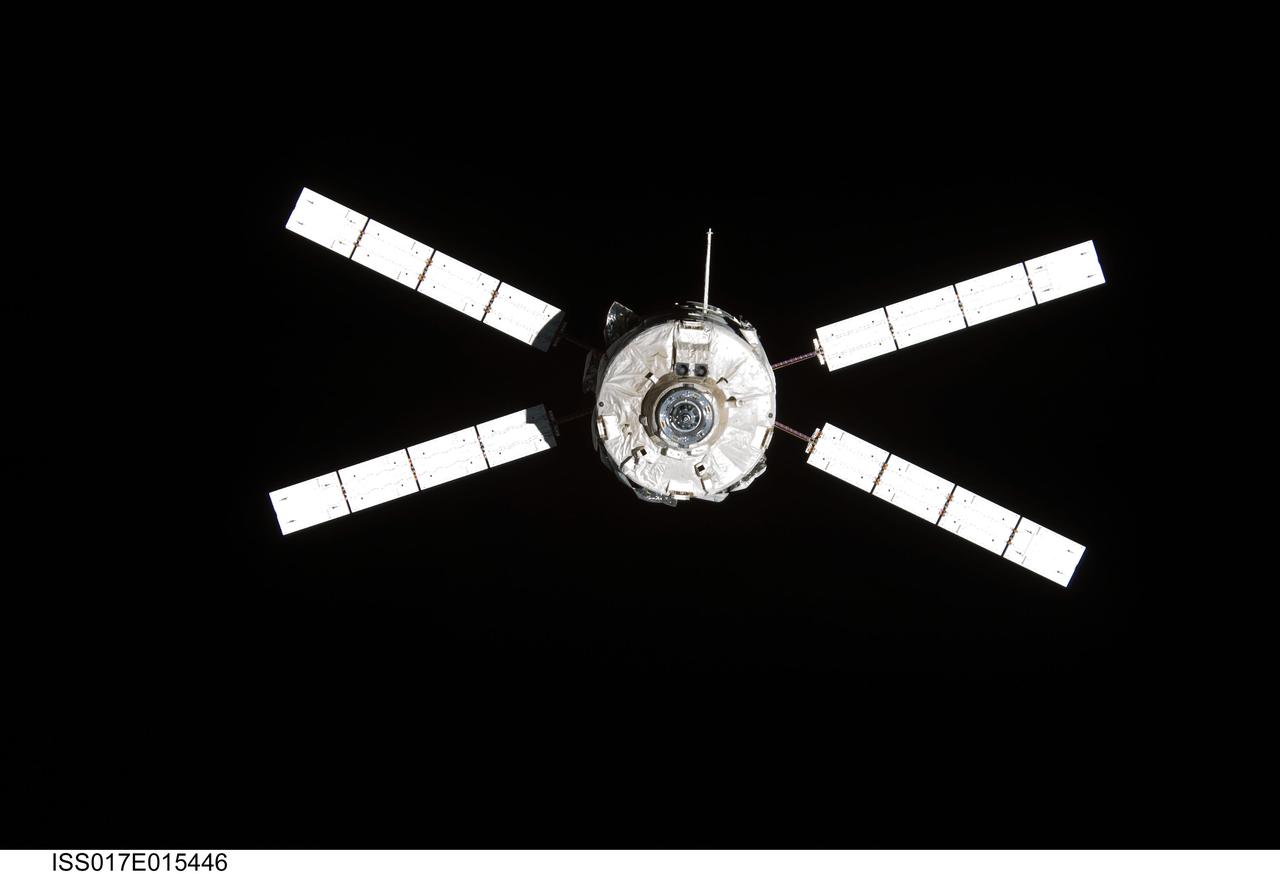

ISS017-E-015446 (5 Sept. 2008) --- Backdropped by the blackness of space, European Space Agency's (ESA) "Jules Verne" Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) begins its relative separation from the International Space Station. The ATV undocked from the aft port of the Zvezda Service Module at 4:29 p.m. (CDT) on Sept. 5, 2008 and was placed in a parking orbit for three weeks, scheduled to be deorbited on Sept. 29 when lighting conditions are correct for an ESA imagery experiment of reentry.
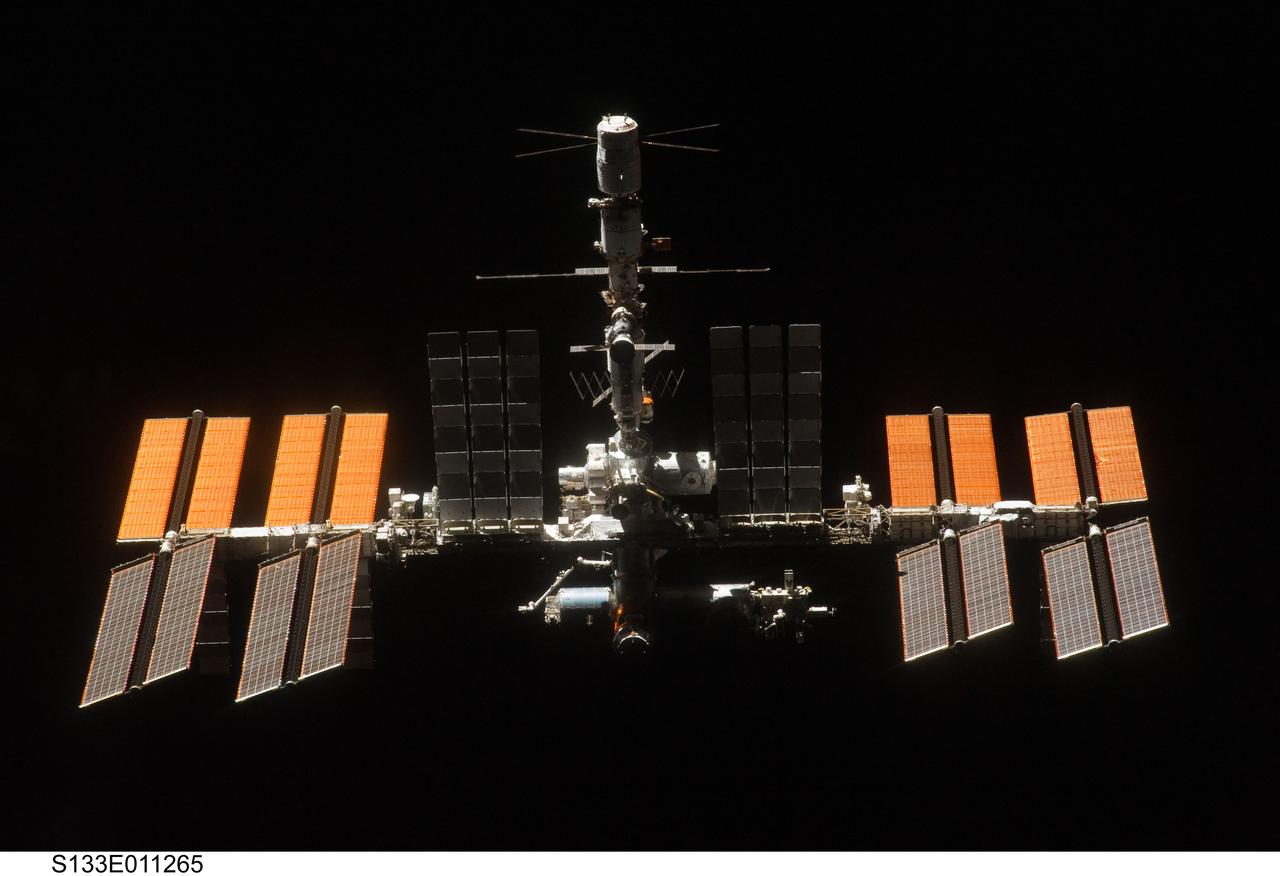

S133-E-011265 (7 March 2011) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, the International Space Station is seen from Discovery as the two orbital spacecraft accomplish their relative separation on March 7 after an aggregate of 12 astronauts and cosmonauts worked together for over a week. During a post undocking fly-around, the crew members aboard the two spacecraft collected a series of photos of each other?s vehicle. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
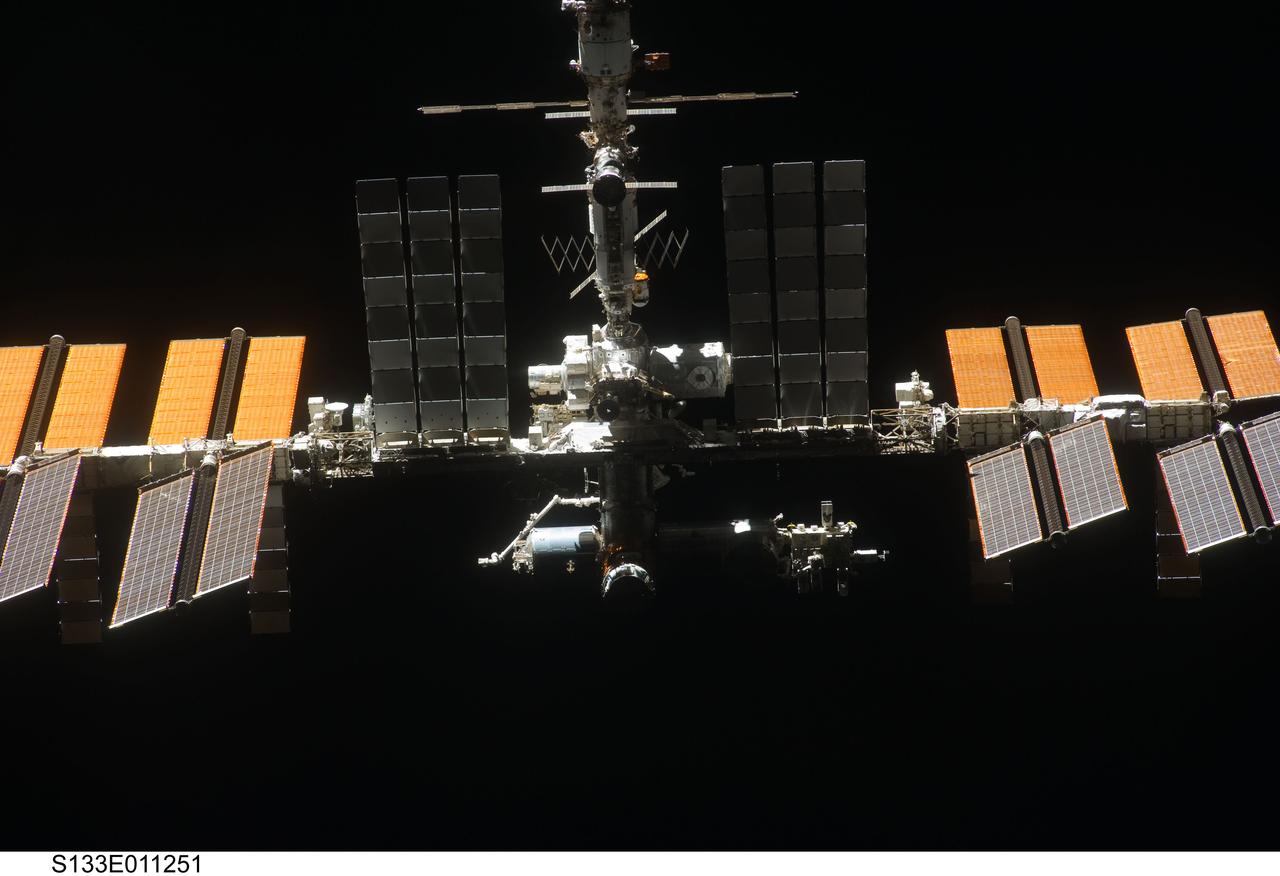

S133-E-011251 (7 March 2011) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, the International Space Station is seen from Discovery as the two orbital spacecraft accomplish their relative separation on March 7 after an aggregate of 12 astronauts and cosmonauts worked together for over a week. During a post undocking fly-around, the crew members aboard the two spacecraft collected a series of photos of each other?s vehicle. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
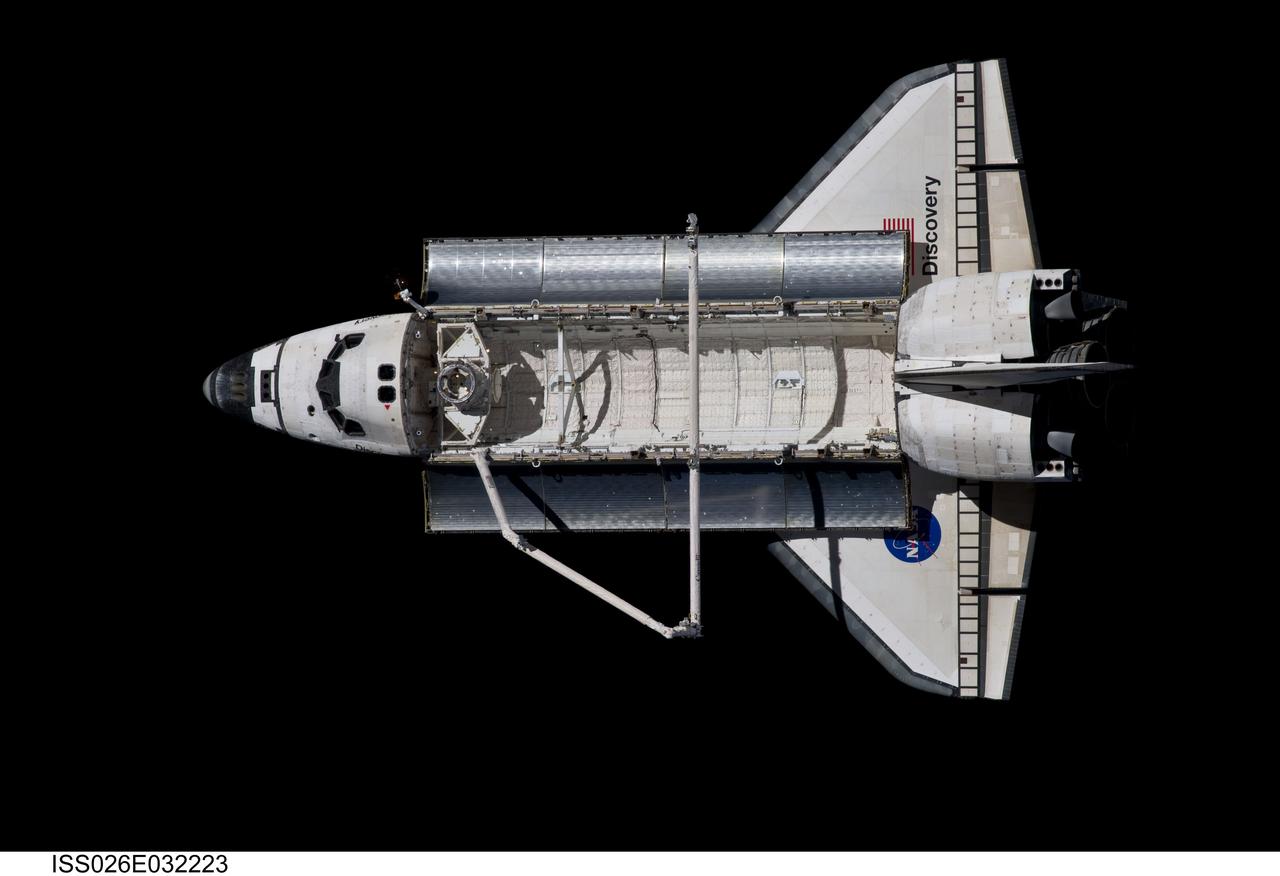

ISS026-E-032223 (7 March 2011) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, Discovery is seen from the International Space Station as the two orbital spacecraft accomplish their relative separation on March 7 after an aggregate of 12 astronauts and cosmonauts worked together for over a week. During a post undocking fly-around, the crew members aboard the two spacecraft collected a series of photos of each other’s vehicle.
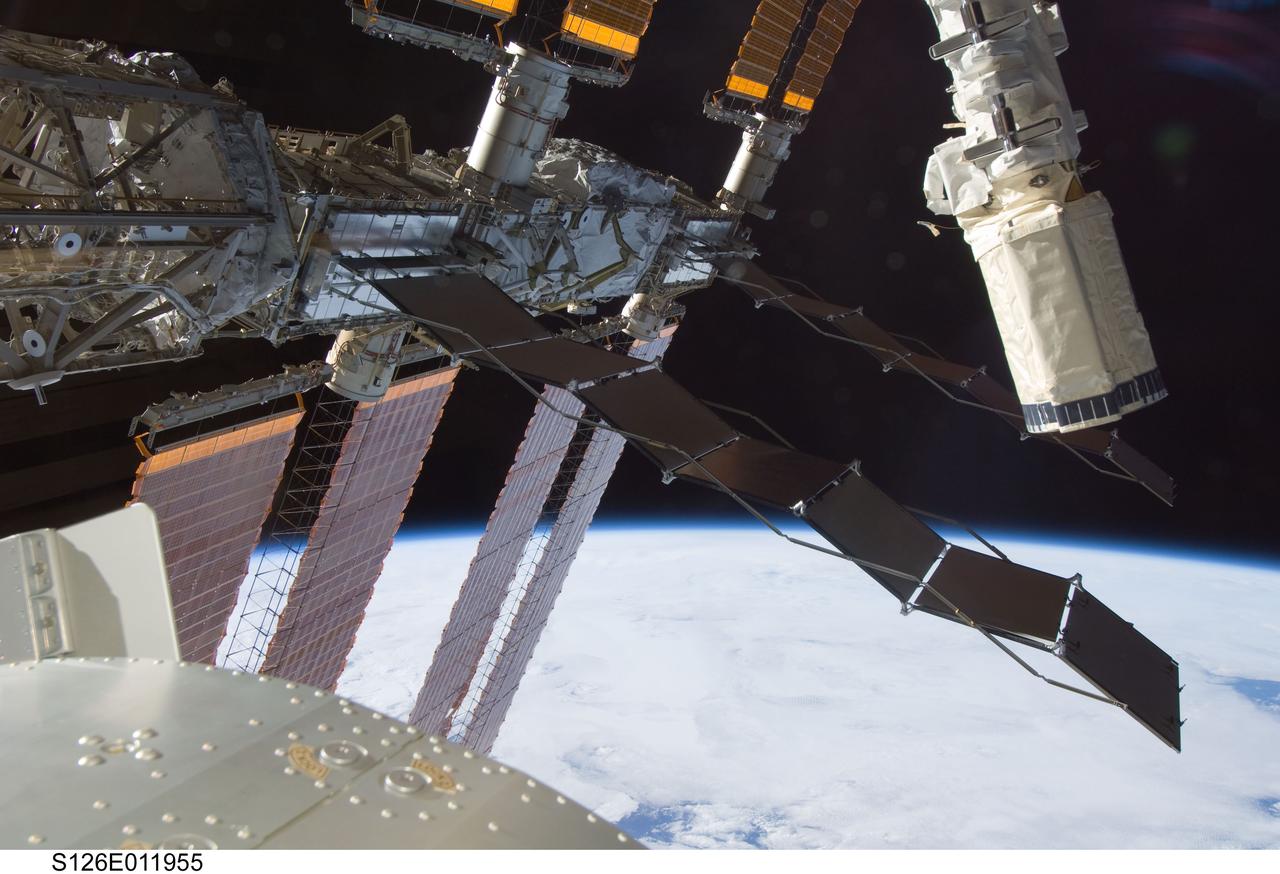

S126-E-11955 (26 Nov. 2008) --- Backdropped against Earth's horizon and the blackness of space, the end effector of Endeavour's Canadian-built robot arm appears amidst elements of the International Space Station. Endeavour and the orbital outpost have been docked for almost two weeks while their crews have joined efforts in home improvement on the station and other work
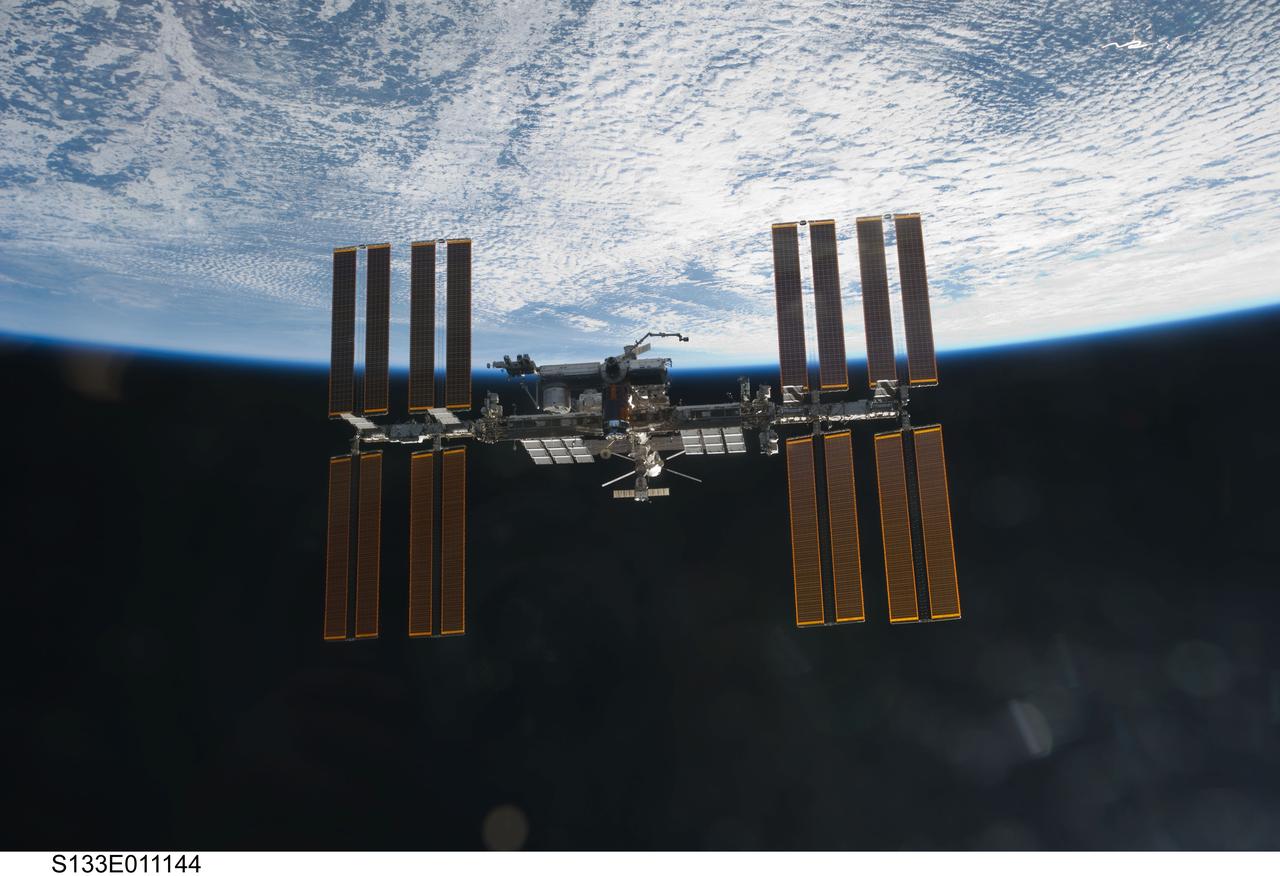

S133-E-011144 (7 March 2011) --- Backdropped against the blackness of spaec and clouds over Earth, the International Space Station is seen from Discovery as the two orbital spacecraft accomplish their relative separation on March 7 after an aggregate of 12 astronauts and cosmonauts worked together for over a week. During a post undocking fly-around, the crew members aboard the two spacecraft collected a series of photos of each other’s vehicle. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
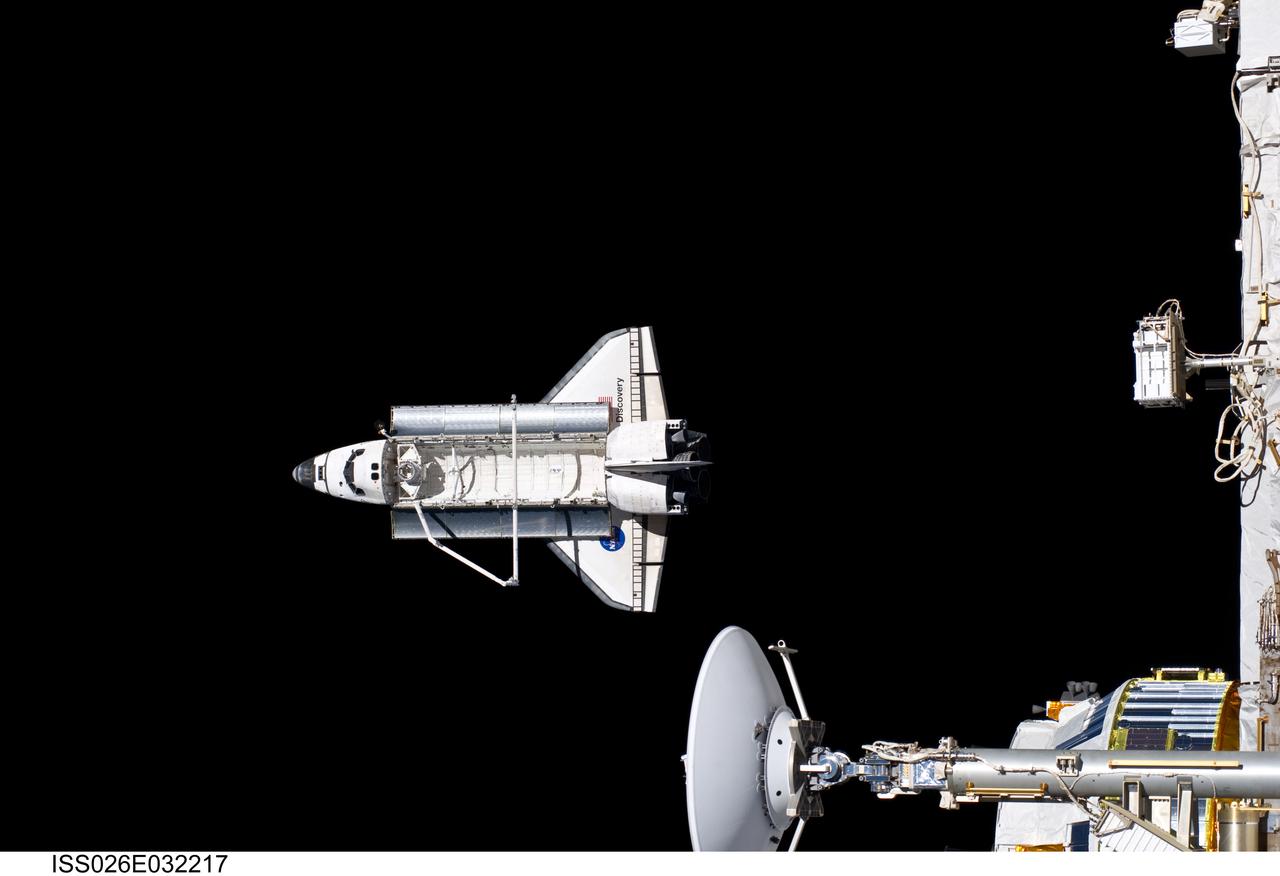

ISS026-E-032217 (7 March 2011) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, Discovery is seen from the International Space Station as the two orbital spacecraft accomplish their relative separation on March 7 after an aggregate of 12 astronauts and cosmonauts worked together for over a week. During a post undocking fly-around, the crew members aboard the two spacecraft collected a series of photos of each other’s vehicle.
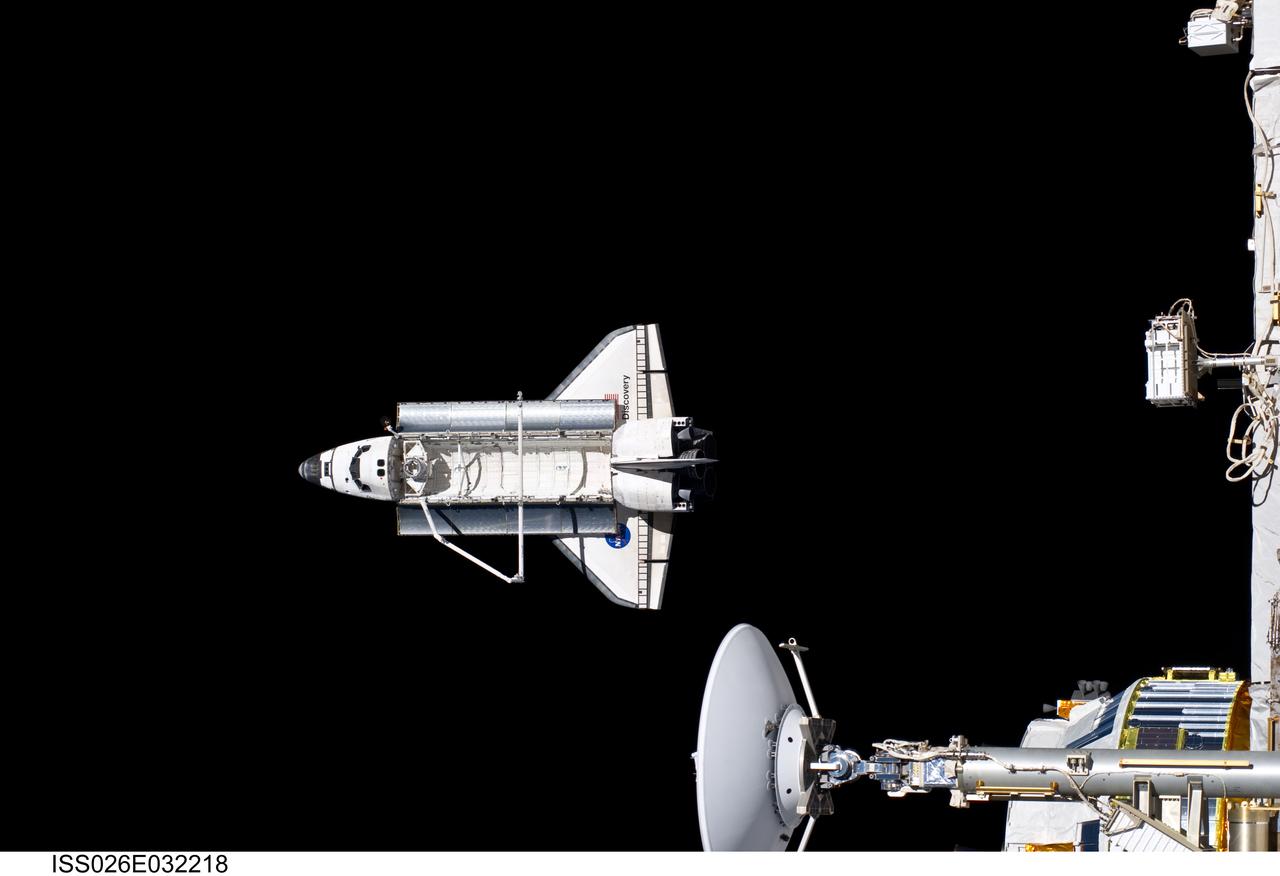

ISS026-E-032218 (7 March 2011) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, Discovery is seen from the International Space Station as the two orbital spacecraft accomplish their relative separation on March 7 after an aggregate of 12 astronauts and cosmonauts worked together for over a week. During a post undocking fly-around, the crew members aboard the two spacecraft collected a series of photos of each other’s vehicle.
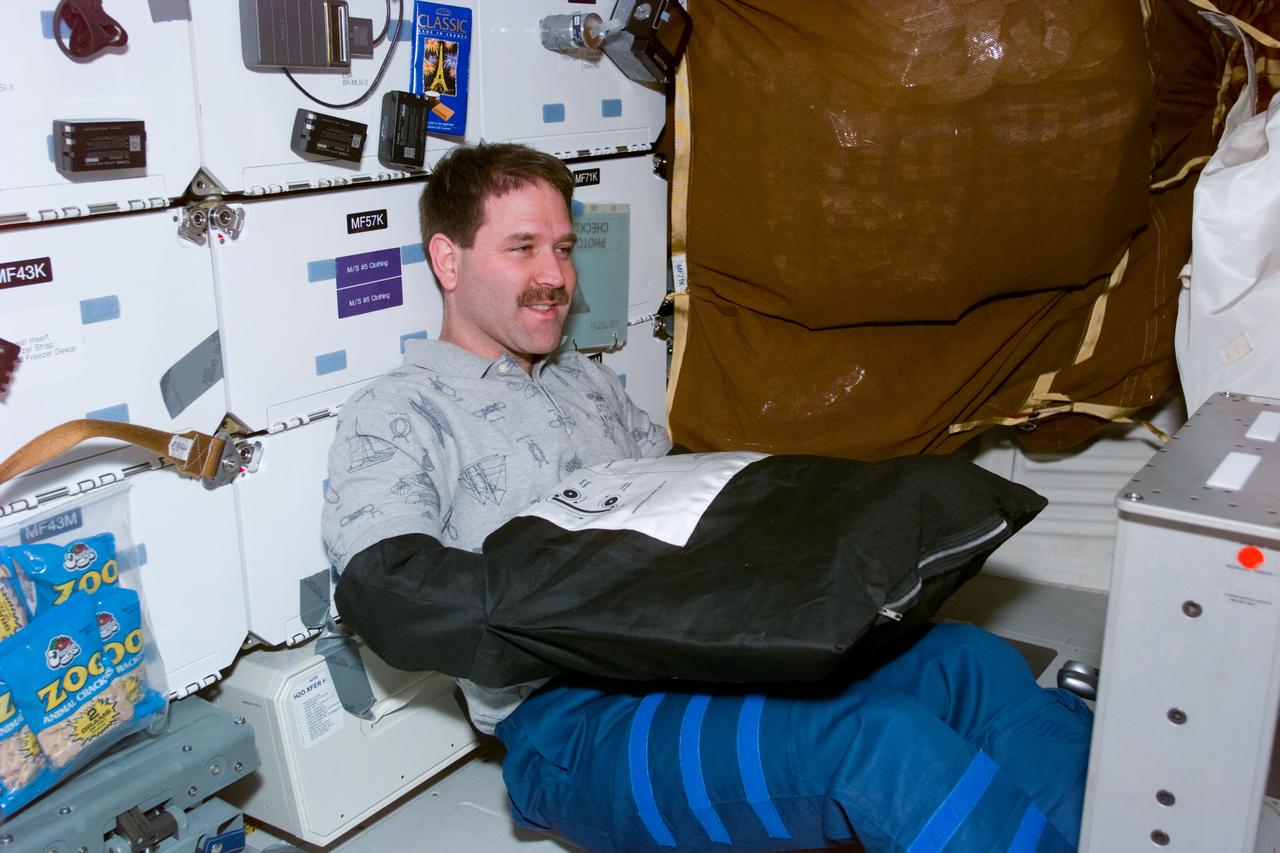

S81-E-05468 (16 Jan. 1997) --- To protect it from exposure to light, astronaut John M. Grunsfeld, mission specialist, uses a black bag to change out a film magazine on a 70mm handheld camera during mid-week activity aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The photograph was recorded with an Electronic Still Camera (ESC) and later was downlinked to flight controllers in Houston, Texas.
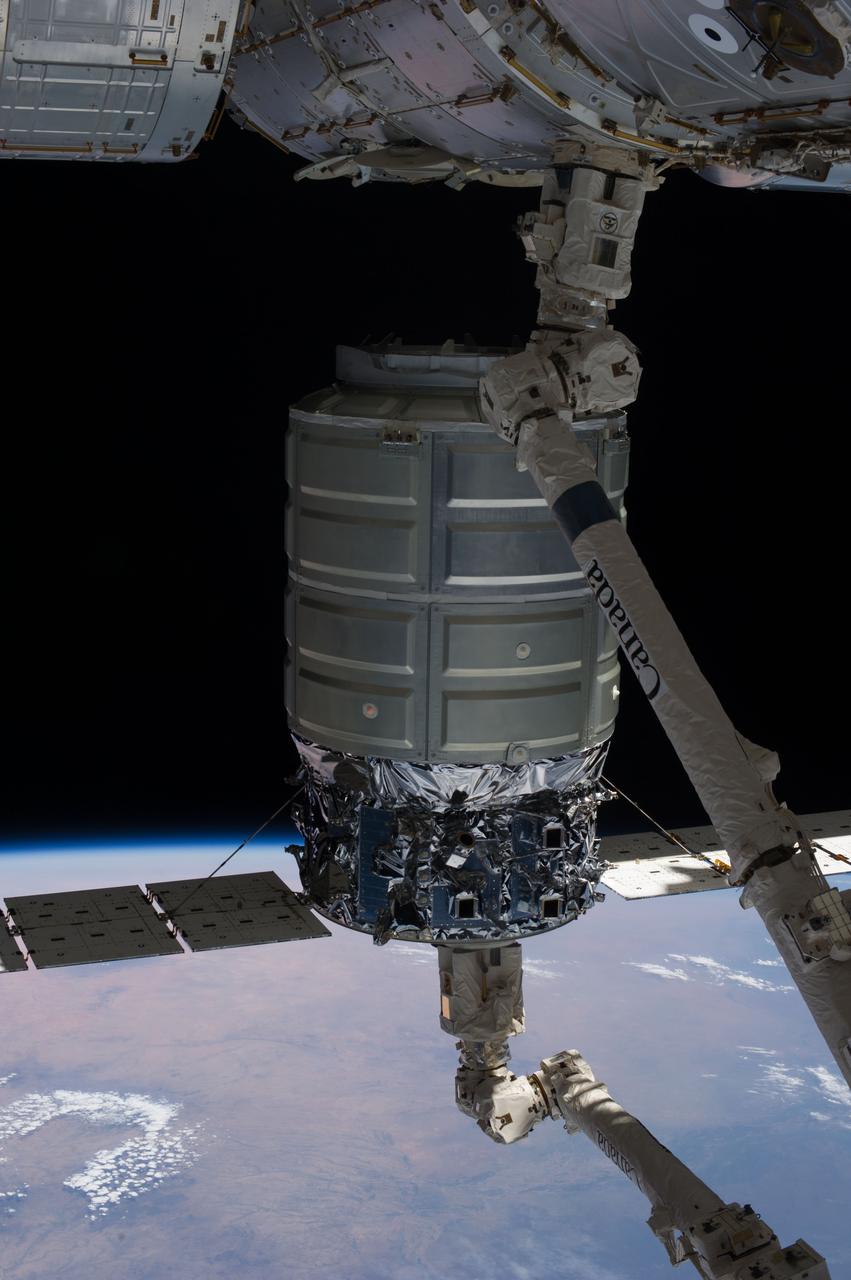

ISS037-E-018505 (22 Oct. 2013) --- The International Space Station’s Canadarm2 unberths the Orbital Sciences’ Cygnus commercial craft after three weeks at the space station. European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano and NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, both Expedition 37 flight engineers, were at the controls of the robotics workstation removing Cygnus from the Harmony node then safely releasing it at 7:31 a.m. (EDT) Oct. 22, 2013. On Oct. 23, the Cygnus will fire its engines for the last time at 1:41 p.m. and re-enter Earth’s atmosphere for destruction over the Pacific Ocean. Earth’s horizon and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
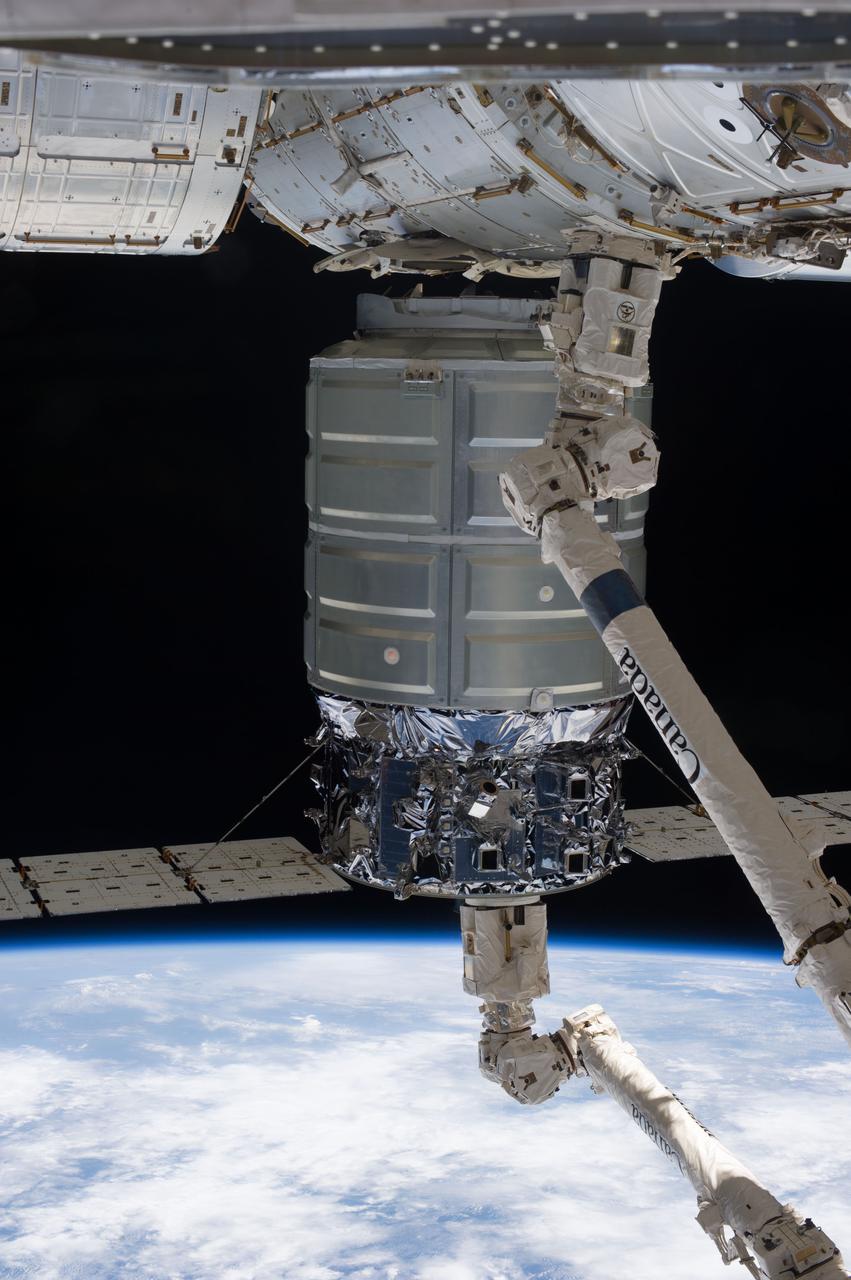

ISS037-E-018502 (22 Oct. 2013) --- The International Space Station’s Canadarm2 unberths the Orbital Sciences’ Cygnus commercial craft after three weeks at the space station. European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano and NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, both Expedition 37 flight engineers, were at the controls of the robotics workstation removing Cygnus from the Harmony node then safely releasing it at 7:31 a.m. (EDT) Oct. 22, 2013. On Oct. 23, the Cygnus will fire its engines for the last time at 1:41 p.m. and re-enter Earth’s atmosphere for destruction over the Pacific Ocean. Earth’s horizon and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
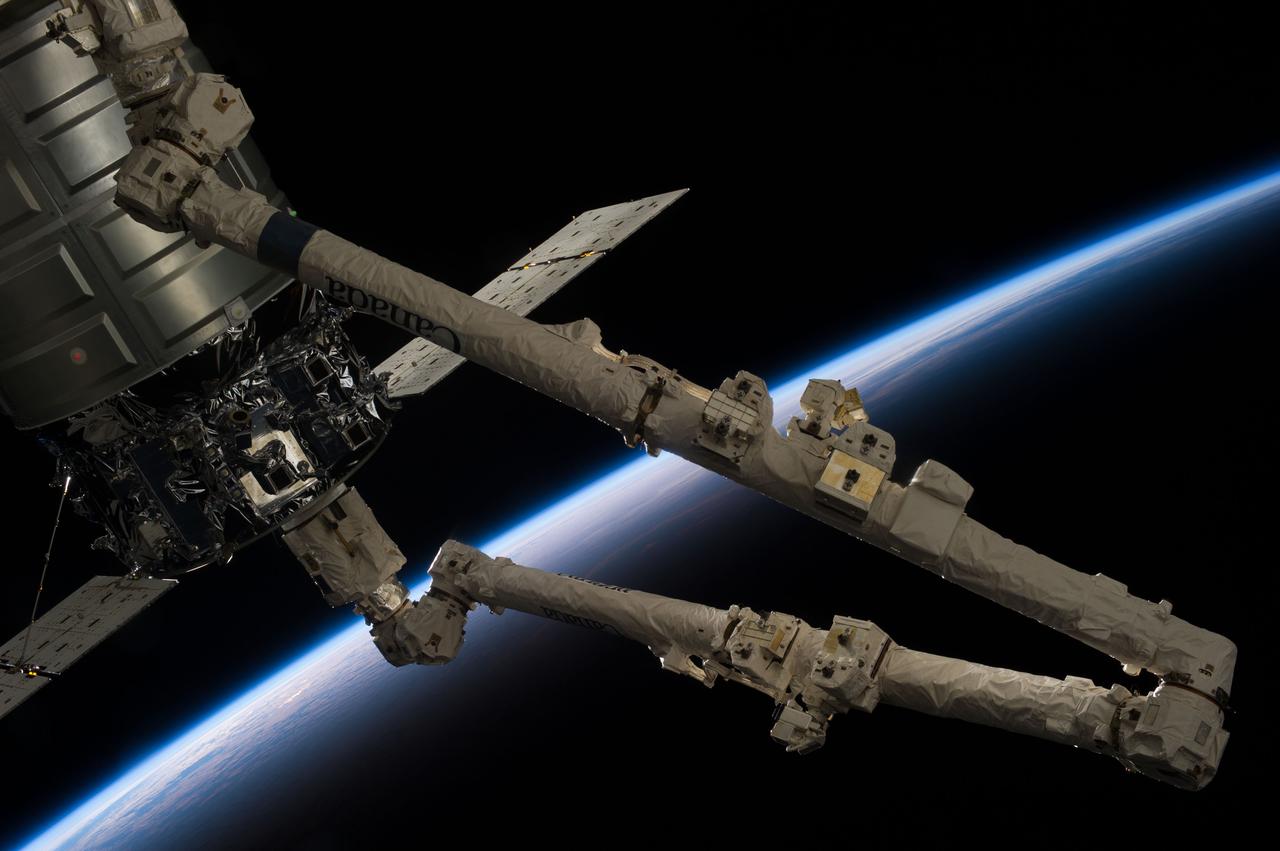

ISS037-E-018500 (22 Oct. 2013) --- The International Space Station’s Canadarm2 prepares to release the Orbital Sciences’ Cygnus commercial craft after three weeks at the space station. European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano and NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, both Expedition 37 flight engineers, were at the controls of the robotics workstation removing Cygnus from the Harmony node then safely releasing it at 7:31 a.m. (EDT) Oct. 22, 2013. On Oct. 23, the Cygnus will fire its engines for the last time at 1:41 p.m. and re-enter Earth’s atmosphere for destruction over the Pacific Ocean. Earth’s horizon and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
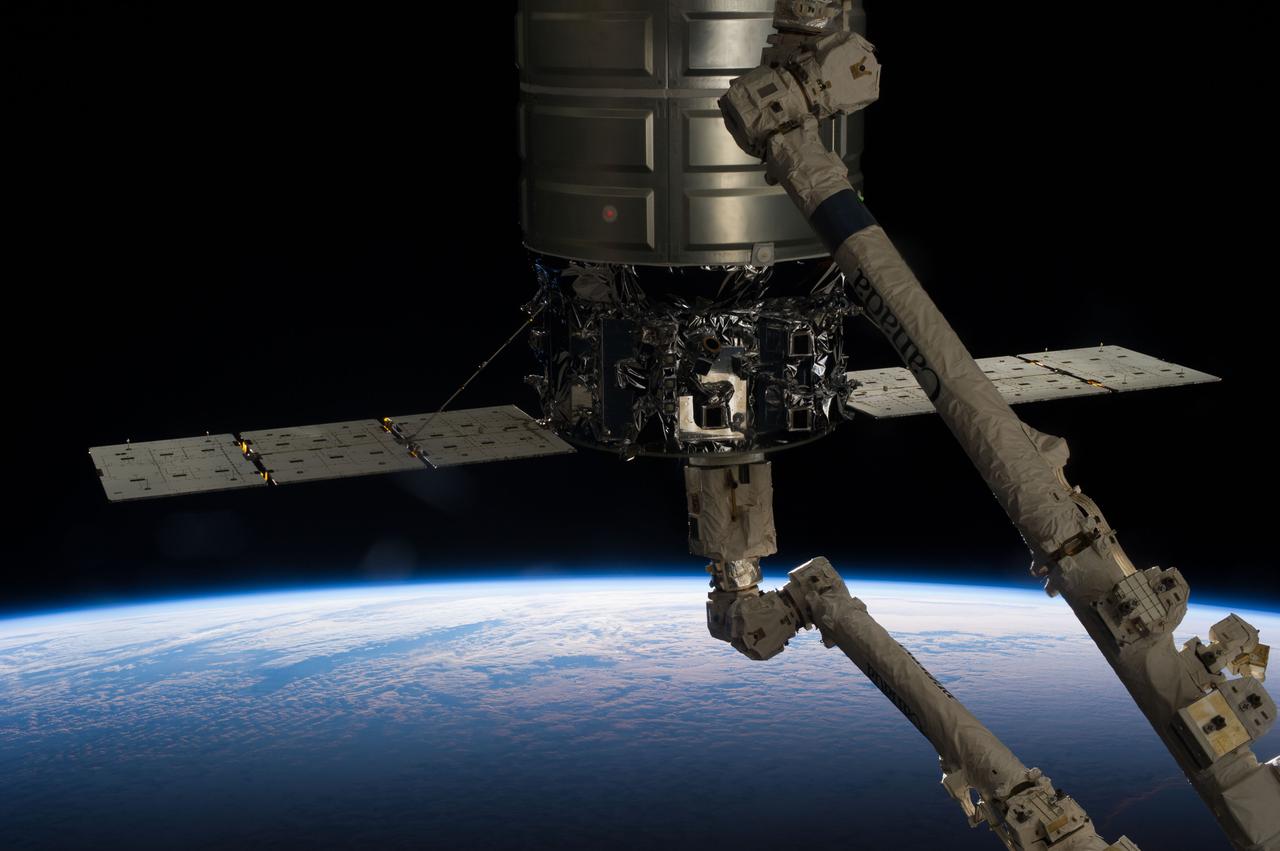

ISS037-E-018501 (22 Oct. 2013) --- The International Space Station’s Canadarm2 prepares to release the Orbital Sciences’ Cygnus commercial craft after three weeks at the space station. European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano and NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, both Expedition 37 flight engineers, were at the controls of the robotics workstation removing Cygnus from the Harmony node then safely releasing it at 7:31 a.m. (EDT) Oct. 22, 2013. On Oct. 23, the Cygnus will fire its engines for the last time at 1:41 p.m. and re-enter Earth’s atmosphere for destruction over the Pacific Ocean. Earth’s horizon and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
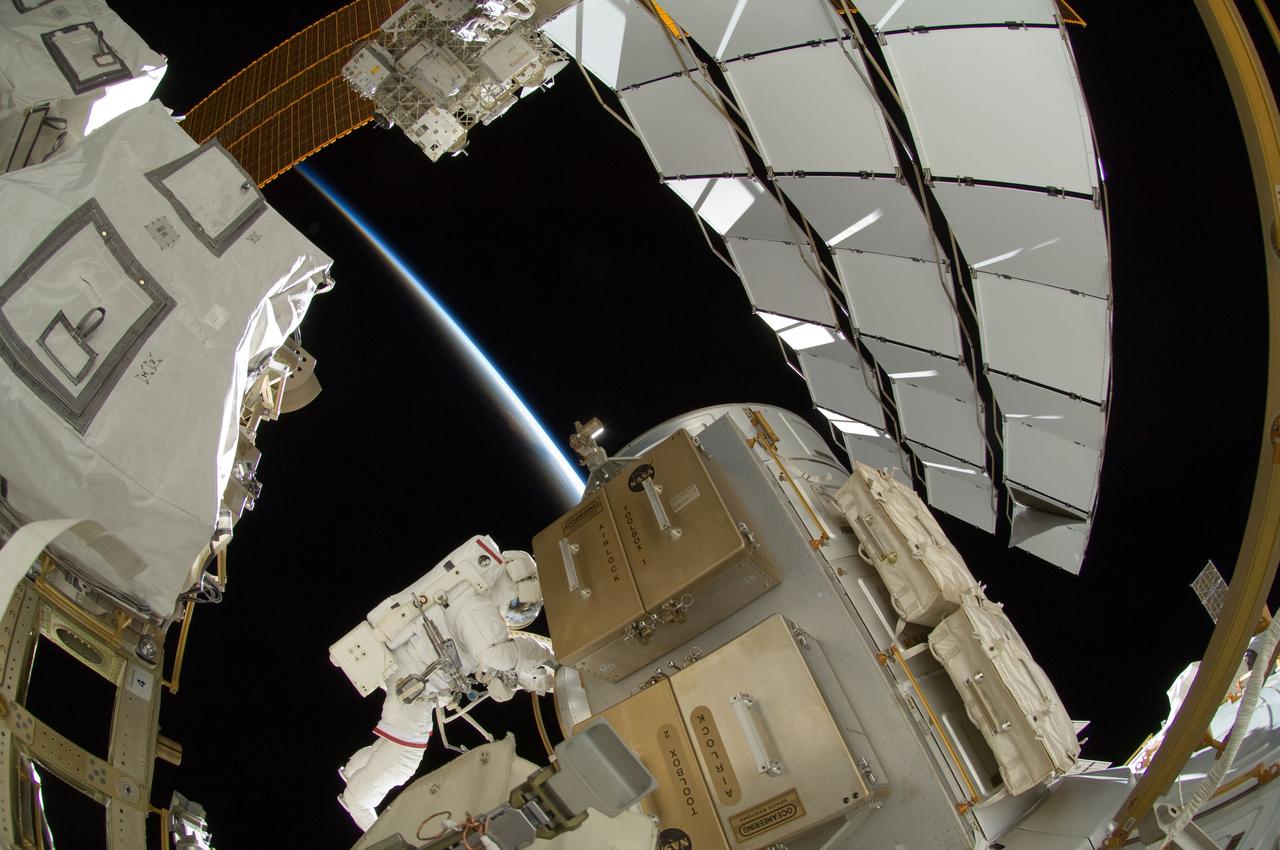

ISS032-E-025280 (5 Sept. 2012) --- NASA astronaut Sunita Williams, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in the mission?s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA). During the six-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Williams and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Aki Hoshide (out of frame), flight engineer, completed the installation of a Main Bus Switching Unit (MBSU) that was hampered last week by a possible misalignment and damaged threads where a bolt must be placed. They also installed a camera on the International Space Station?s robotic arm, Canadarm2. The thin blue line of Earth?s atmosphere and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.

ISS012-E-16907 (3 Feb. 2006) --- Backdropped by the blackness of space and Earth’s horizon, a spacesuit-turned-satellite called SuitSat began its orbit around the Earth after it was released by the Expedition 12 crewmembers during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on Feb. 3, 2006. SuitSat, an unneeded Russian Orlan spacesuit, was outfitted by the crew with three batteries, internal sensors and a radio transmitter, which faintly transmitted recorded voices of school children to amateur radio operators worldwide. The suit will enter the atmosphere and burn up in a few weeks.
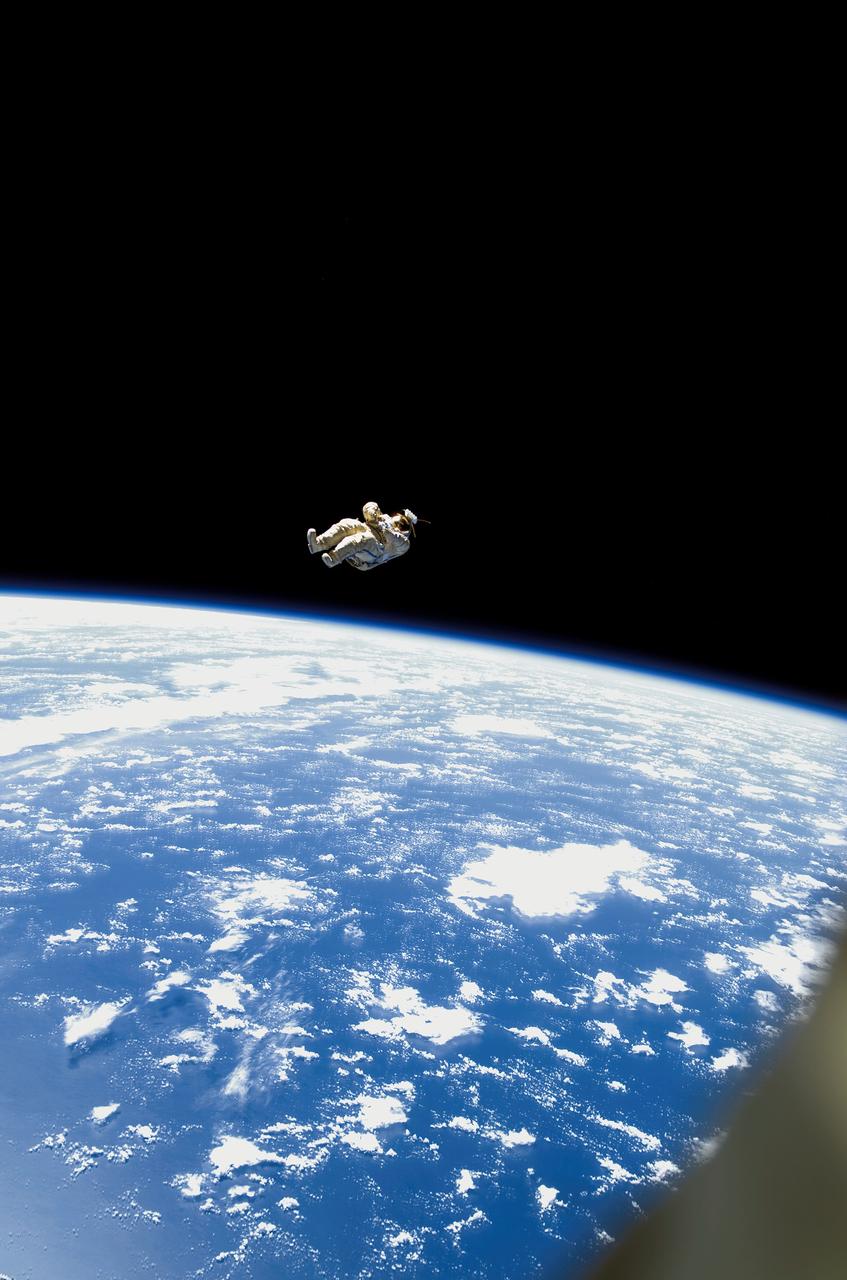

ISS012-E-16908 (3 Feb. 2006) --- Backdropped by the blackness of space and Earth’s horizon, a spacesuit-turned-satellite called SuitSat began its orbit around the Earth after it was released by the Expedition 12 crewmembers during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on Feb. 3, 2006. SuitSat, an unneeded Russian Orlan spacesuit, was outfitted by the crew with three batteries, internal sensors and a radio transmitter, which faintly transmitted recorded voices of school children to amateur radio operators worldwide. The suit will enter the atmosphere and burn up in a few weeks.
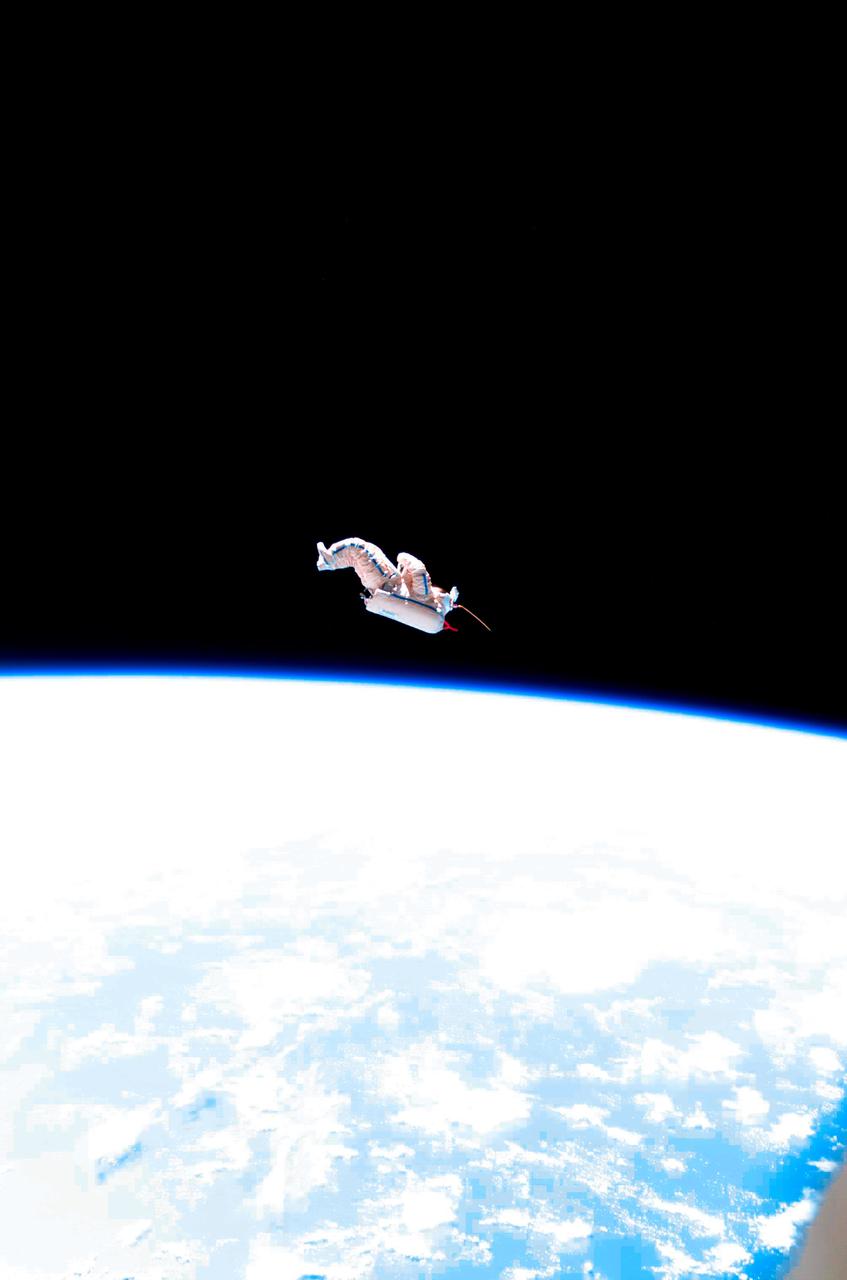

ISS012-E-24449 (3 Feb. 2006) --- Backdropped by the blackness of space and Earth's horizon, a spacesuit-turned-satellite called SuitSat began its orbit around the Earth after being released by the Expedition 12 crewmembers during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on Feb. 3, 2006. SuitSat, an unneeded Russian Orlan spacesuit, was outfitted by the crew with three batteries, internal sensors and a radio transmitter, which faintly transmitted recorded voices of school children to amateur radio operators worldwide. The suit will enter the atmosphere and burn up in a few weeks.

ISS012-E-16905 (3 Feb. 2006) --- Backdropped by the blackness of space and Earth’s horizon, a spacesuit-turned-satellite called SuitSat began its orbit around the Earth after it was released by the Expedition 12 crewmembers during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on Feb. 3, 2006. SuitSat, an unneeded Russian Orlan spacesuit, was outfitted by the crew with three batteries, internal sensors and a radio transmitter, which faintly transmitted recorded voices of school children to amateur radio operators worldwide. The suit will enter the atmosphere and burn up in a few weeks.
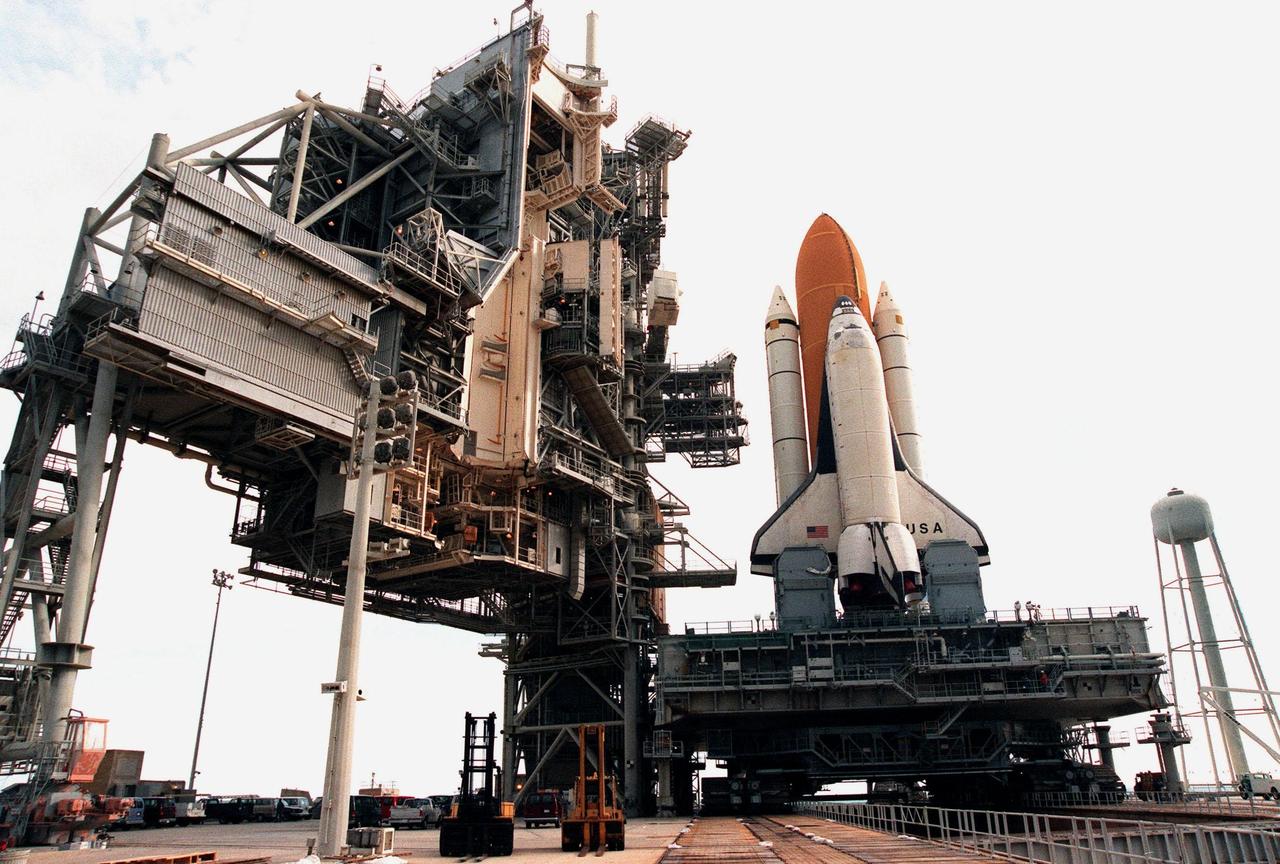

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This closeup of Space Shuttle Columbia on Launch Pad 39B shows the Rotating Service Structure, at left, which will be moved into place on Tuesday, June 8. Columbia was rolled out June 7, less than two weeks after the liftoff of Discovery on mission STS-96, in preparation for the launch of STS-93. The mission payload is the Chandra X-ray Observatory, the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, which will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Columbia (OV-102) is the first of NASA's orbiter fleet, delivered to Kennedy Space Center in March 1979. Columbia initiated the Space Shuttle flight program at KSC when it lifted off Launch Pad 39A on April 12, 1981
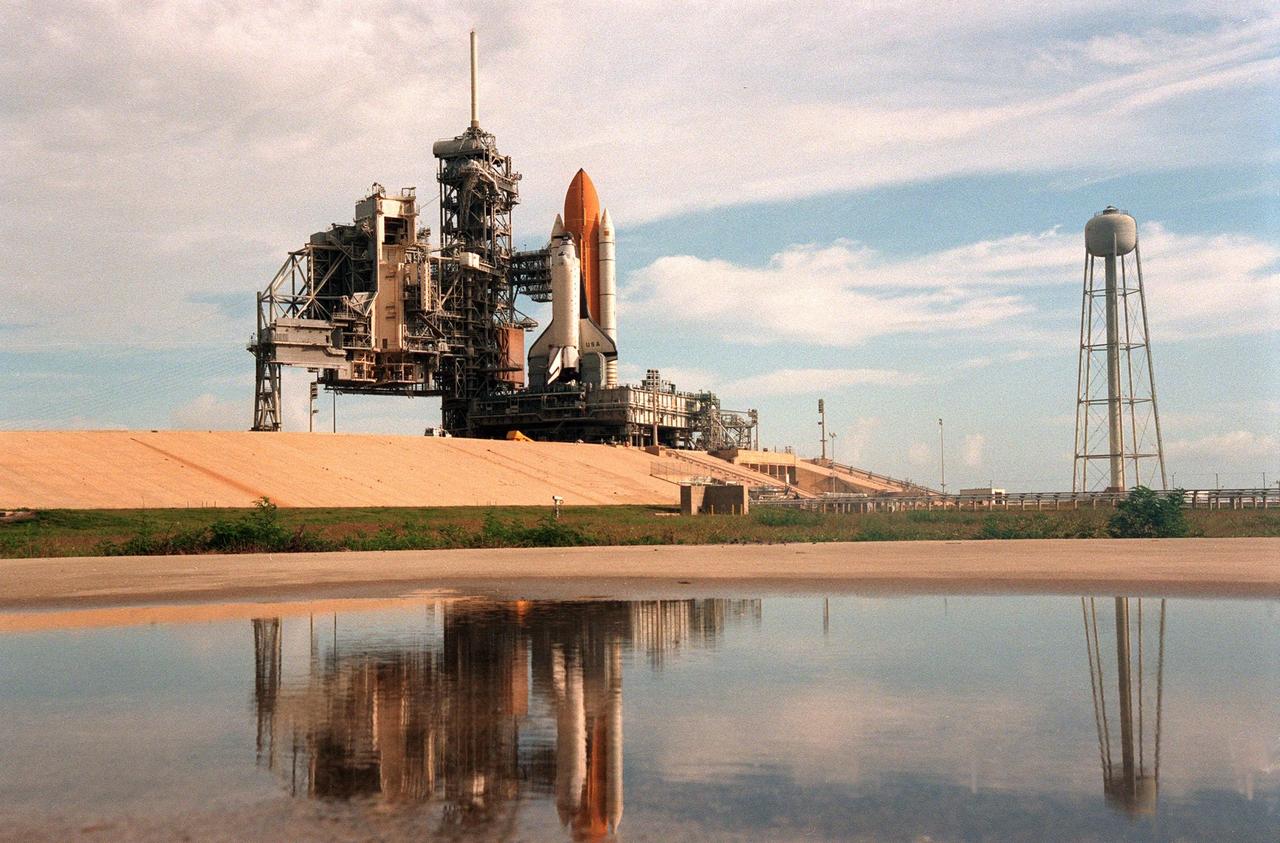

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Columbia sits on Launch Pad 39B less than two weeks after liftoff of Discovery on mission STS-96. Columbia was rolled out June 7 in preparation for the launch of STS-93 with its payload of the Chandra X-ray Observatory. The Rotating Service Structure, at left, will be moved into place on Tuesday, June 8. With the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Columbia (OV-102) is the first of NASA's orbiter fleet, delivered to Kennedy Space Center in March 1979. Columbia initiated the Space Shuttle flight program at KSC when it lifted off Launch Pad 39A on April 12, 1981
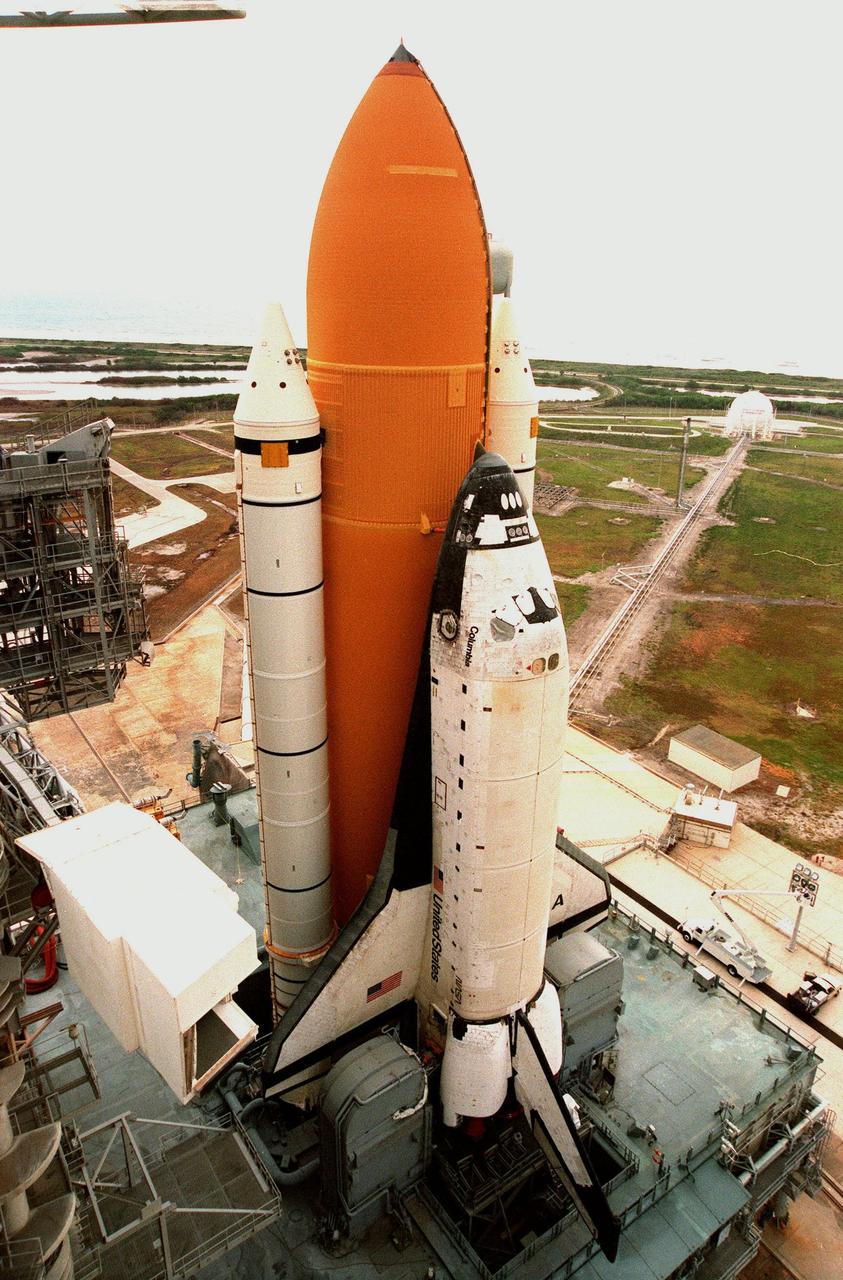

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Columbia sits on Launch Pad 39B less than two weeks after liftoff of Discovery on mission STS-96. Columbia was rolled out June 7 in preparation for the launch of STS-93 with its payload of the Chandra X-ray Observatory. The Rotating Service Structure will be moved into place around it on Tuesday, June 8. With the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Columbia (OV-102) is the first of NASA's orbiter fleet, delivered to Kennedy Space Center in March 1979. Columbia initiated the Space Shuttle flight program at KSC when it lifted off Launch Pad 39A on April 12, 1981
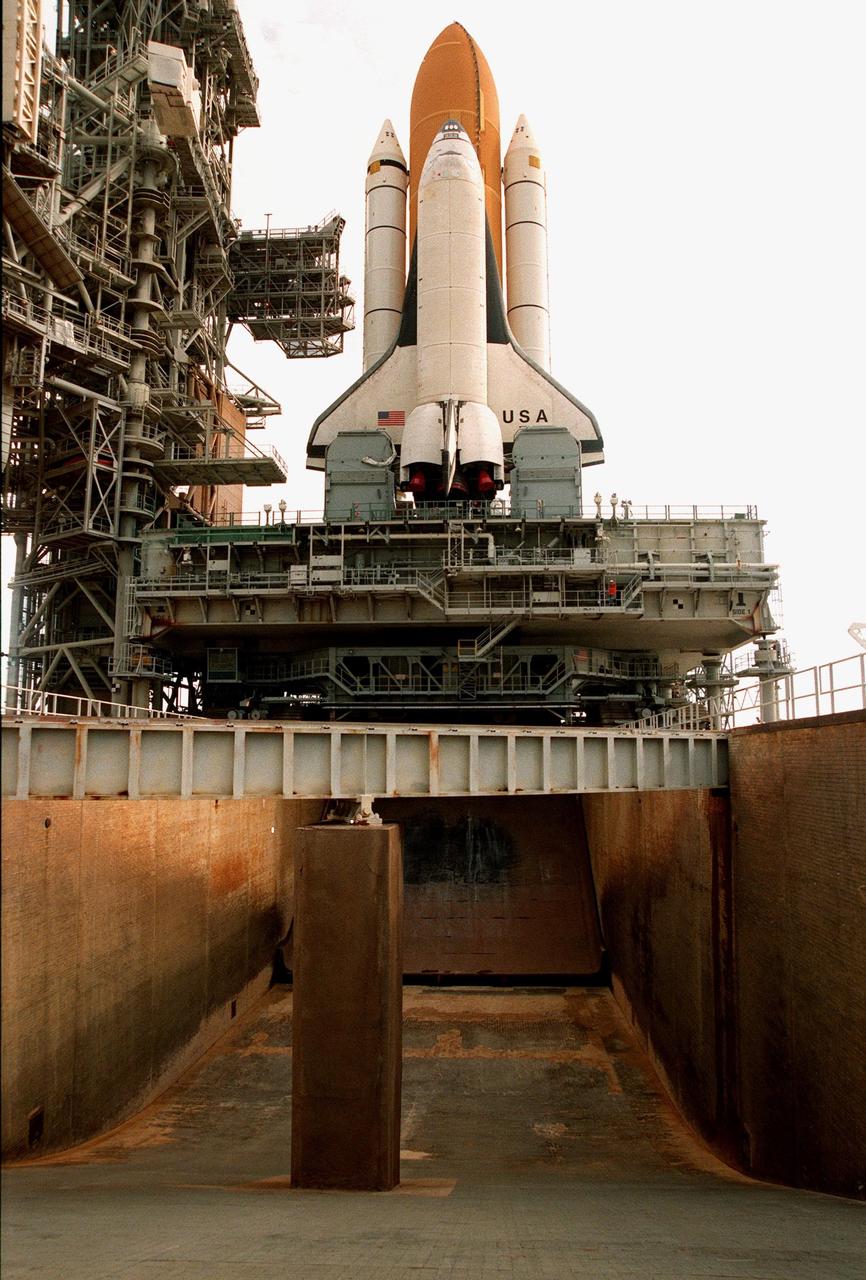

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Columbia sits on Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the launch of STS-93. This view shows the flame trench, 490 feet long and 40 feet high, which helps contain the intense heat that occurs at launch. Columbia was rolled out June 7, less than two weeks after the liftoff of Discovery on mission STS-96. The STS-93 payload is the Chandra X-ray Observatory, the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, which will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Columbia (OV-102) is the first of NASA's orbiter fleet, delivered to Kennedy Space Center in March 1979. Columbia initiated the Space Shuttle flight program at KSC when it lifted off Launch Pad 39A on April 12, 1981
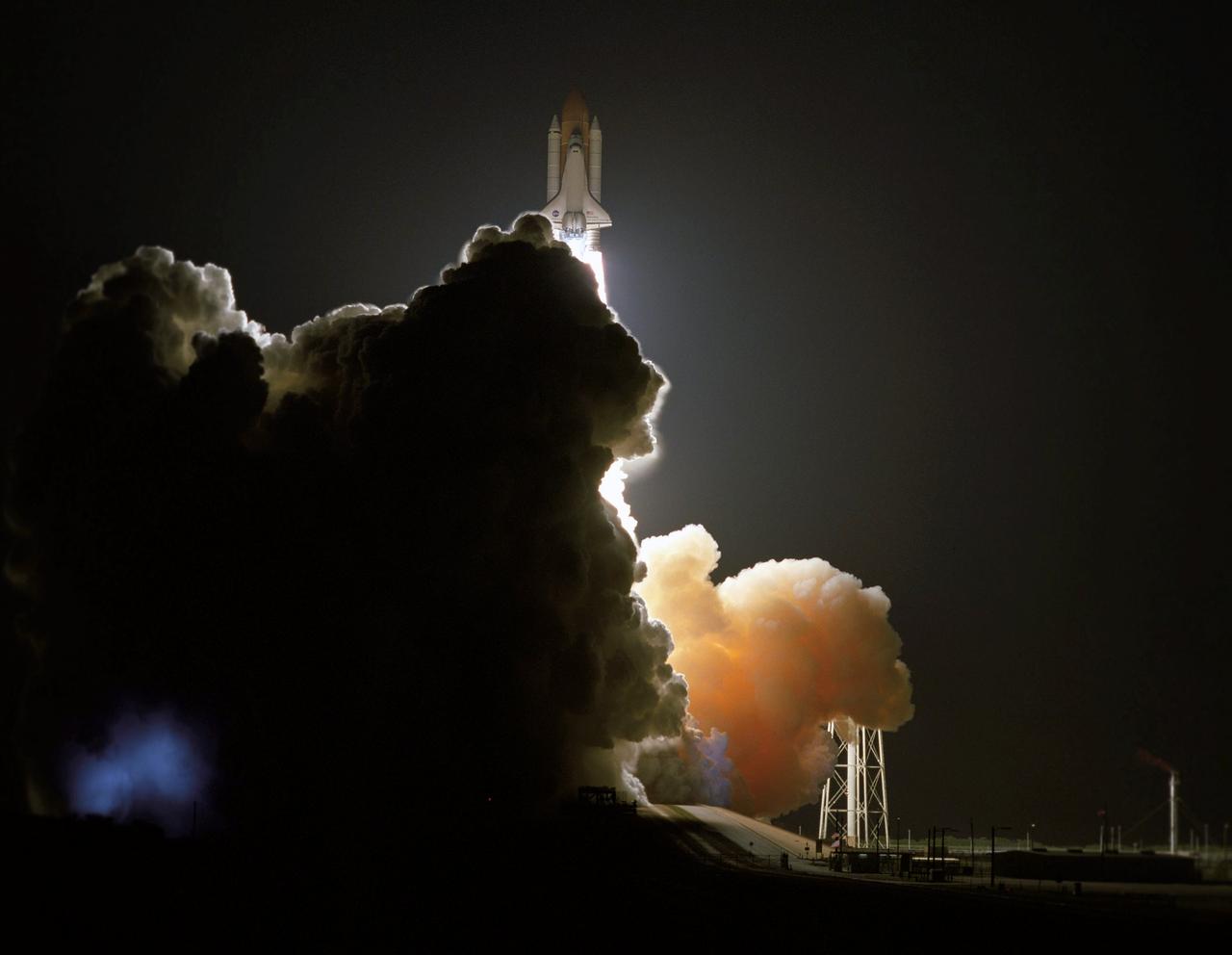

STS116-S-021 (9 Dec. 2006) --- Against a black night sky, the Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B occurred at 8:47 p.m. (EST) on Dec. 9, 2006 in what was the first evening shuttle launch since 2002. The STS-116 crew will link up with the station on Monday, Dec. 11, to begin a complex, week-long stay that will rewire the outpost and increase its power supply. During three spacewalks and intricate choreography with ground controllers, the astronauts will bring electrical power on line generated by a giant solar array wing delivered to the station in September.
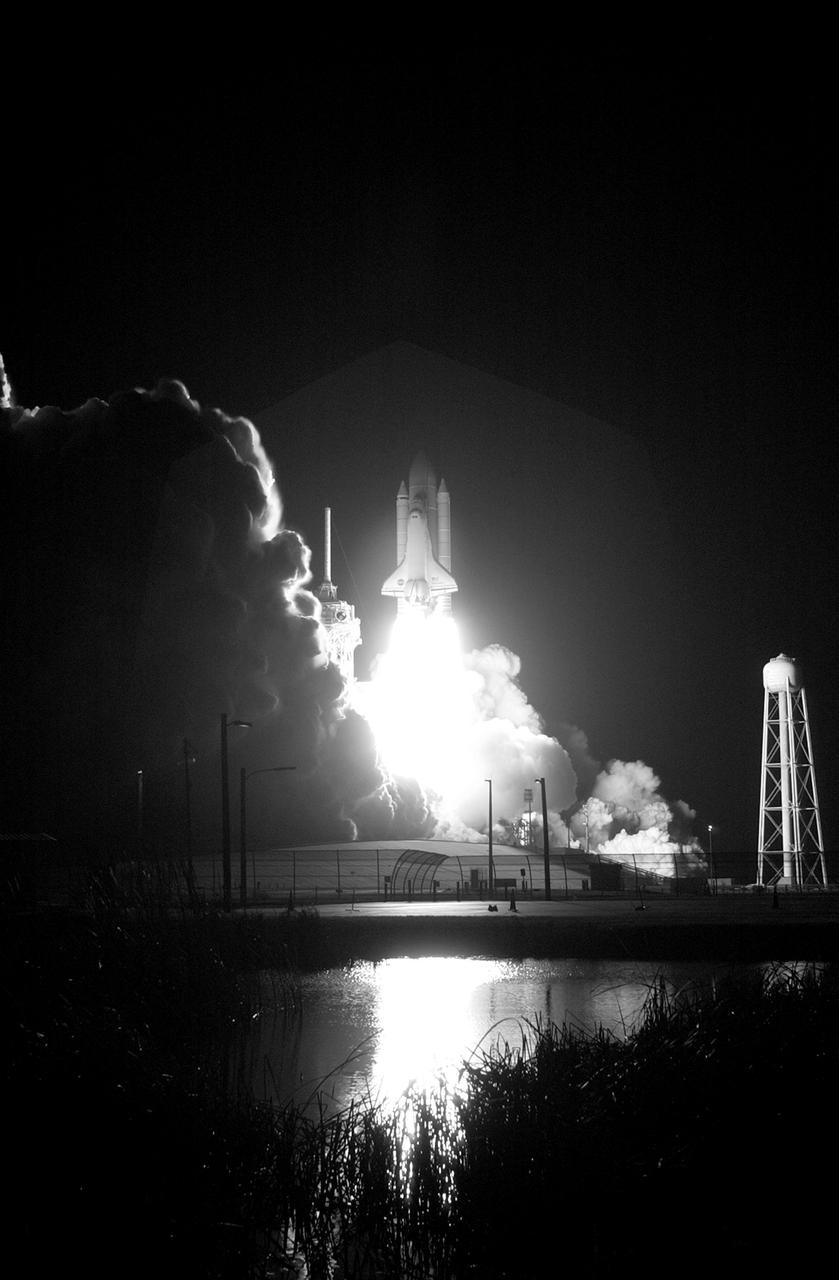

STS116-S-016 (9 Dec. 2006) --- Against a black night sky, the Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B occurred at 8:47 p.m. (EST) on Dec. 9, 2006 in what was the first evening shuttle launch since 2002. The STS-116 crew will link up with the station on Monday, Dec. 11, to begin a complex, week-long stay that will rewire the outpost and increase its power supply. During three spacewalks and intricate choreography with ground controllers, the astronauts will bring electrical power on line generated by a giant solar array wing delivered to the station in September.

STS116-S-008 (9 Dec. 2006) --- Against a black night sky, the Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B occurred at 8:47 p.m. (EST) on Dec. 9, 2006 in what was the first evening shuttle launch since 2002. The STS-116 crew will link up with the station on Monday, Dec. 11, to begin a complex, week-long stay that will rewire the outpost and increase its power supply. During three spacewalks and intricate choreography with ground controllers, the astronauts will bring electrical power on line generated by a giant solar array wing delivered to the station in September.
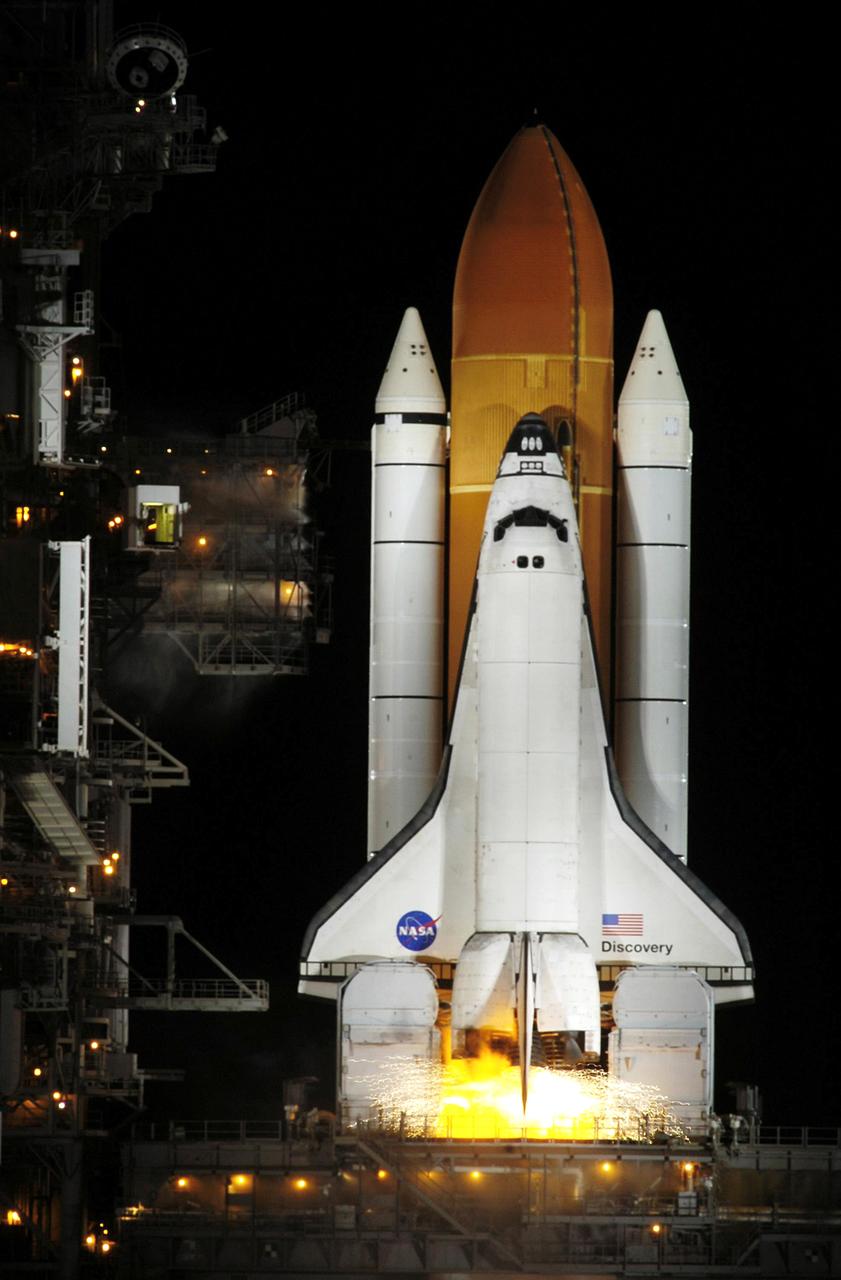

STS116-S-024 (9 Dec. 2006) --- Against a black night sky, the Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B occurred at 8:47 p.m. (EST) on Dec. 9, 2006 in what was the first evening shuttle launch since 2002. The STS-116 crew will link up with the station on Monday, Dec. 11, to begin a complex, week-long stay that will rewire the outpost and increase its power supply. During three spacewalks and intricate choreography with ground controllers, the astronauts will bring electrical power on line generated by a giant solar array wing delivered to the station in September.
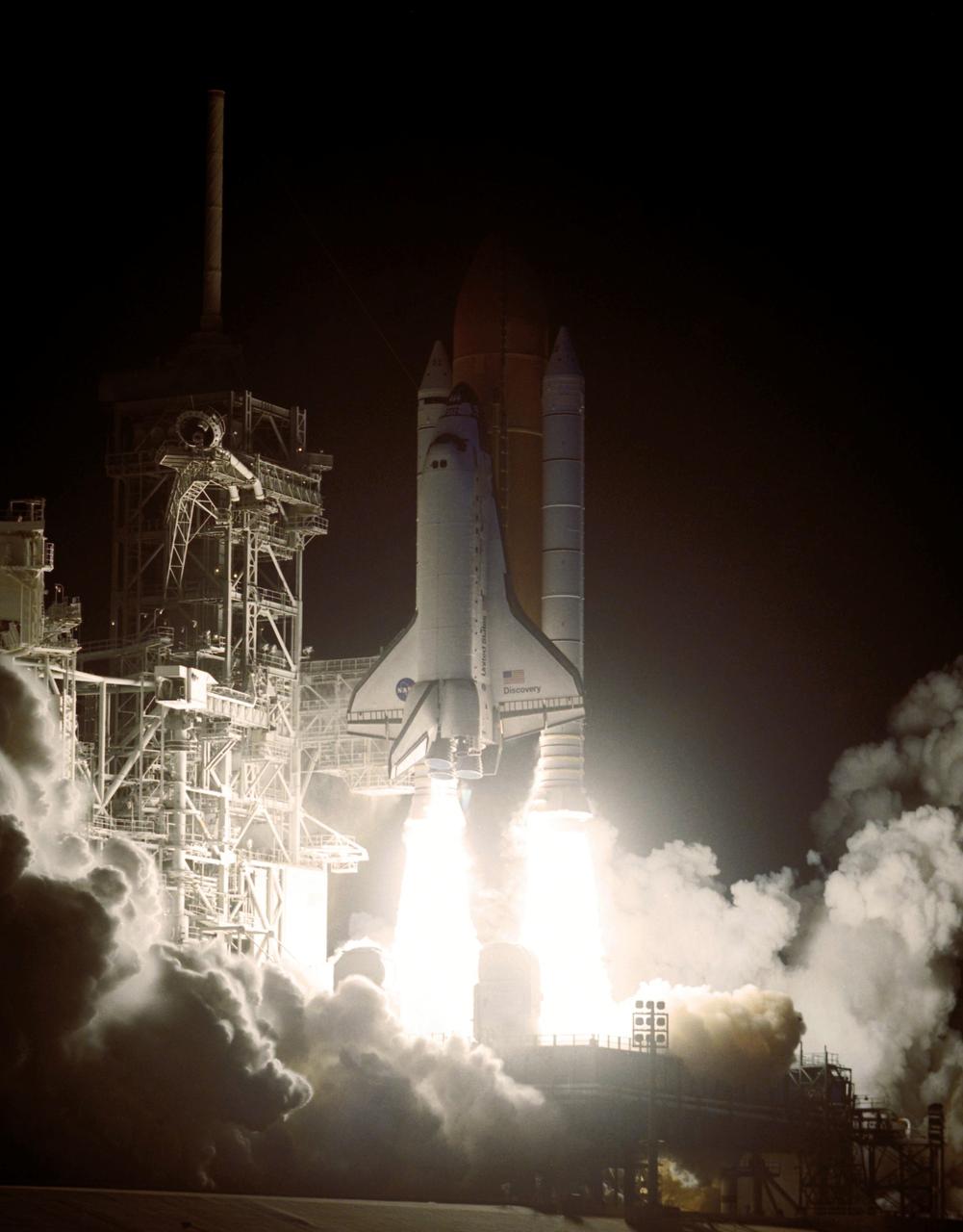

STS116-S-023 (9 Dec. 2006) --- Against a black night sky, the Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B occurred at 8:47 p.m. (EST) on Dec. 9, 2006 in what was the first evening shuttle launch since 2002. The STS-116 crew will link up with the station on Monday, Dec. 11, to begin a complex, week-long stay that will rewire the outpost and increase its power supply. During three spacewalks and intricate choreography with ground controllers, the astronauts will bring electrical power on line generated by a giant solar array wing delivered to the station in September.
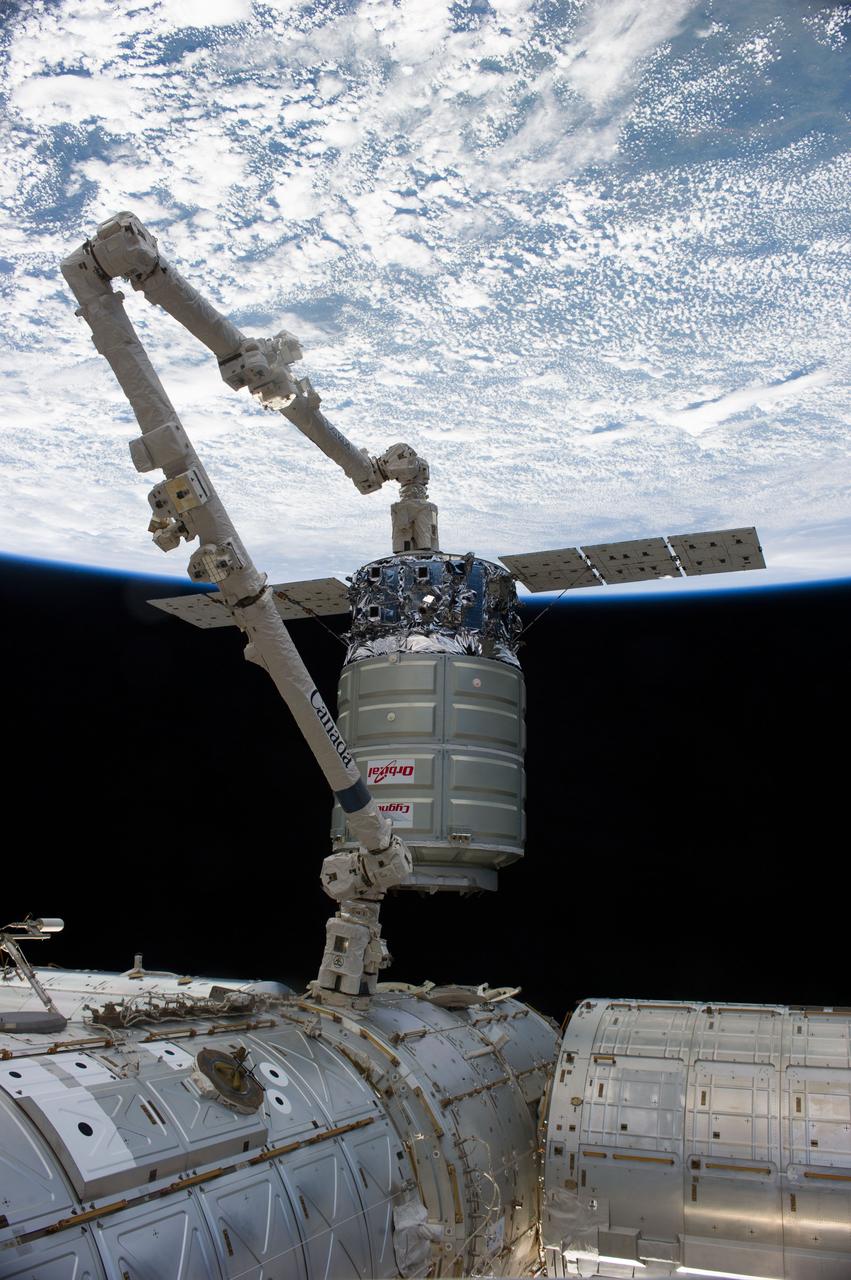

ISS038-E-050734 (18 Feb. 2014) --- The International Space Station's Canadarm2 unberths the Orbital Sciences Corporation's Cygnus spacecraft after several weeks at the space station. NASA astronaut Mike Hopkins, with assistance from Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Koichi Wakata, both Expedition 38 flight engineers, used the station's 57-foot Canadarm2 robotic arm to detach Cygnus from the Earth-facing port of the Harmony node at 5:15 a.m. (EST) on Feb. 18, 2014. While Wakata monitored data and kept in contact with the team at Houston's Mission Control Center, Hopkins released Cygnus from the robotic arm at 6:41 a.m. Earth's horizon and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
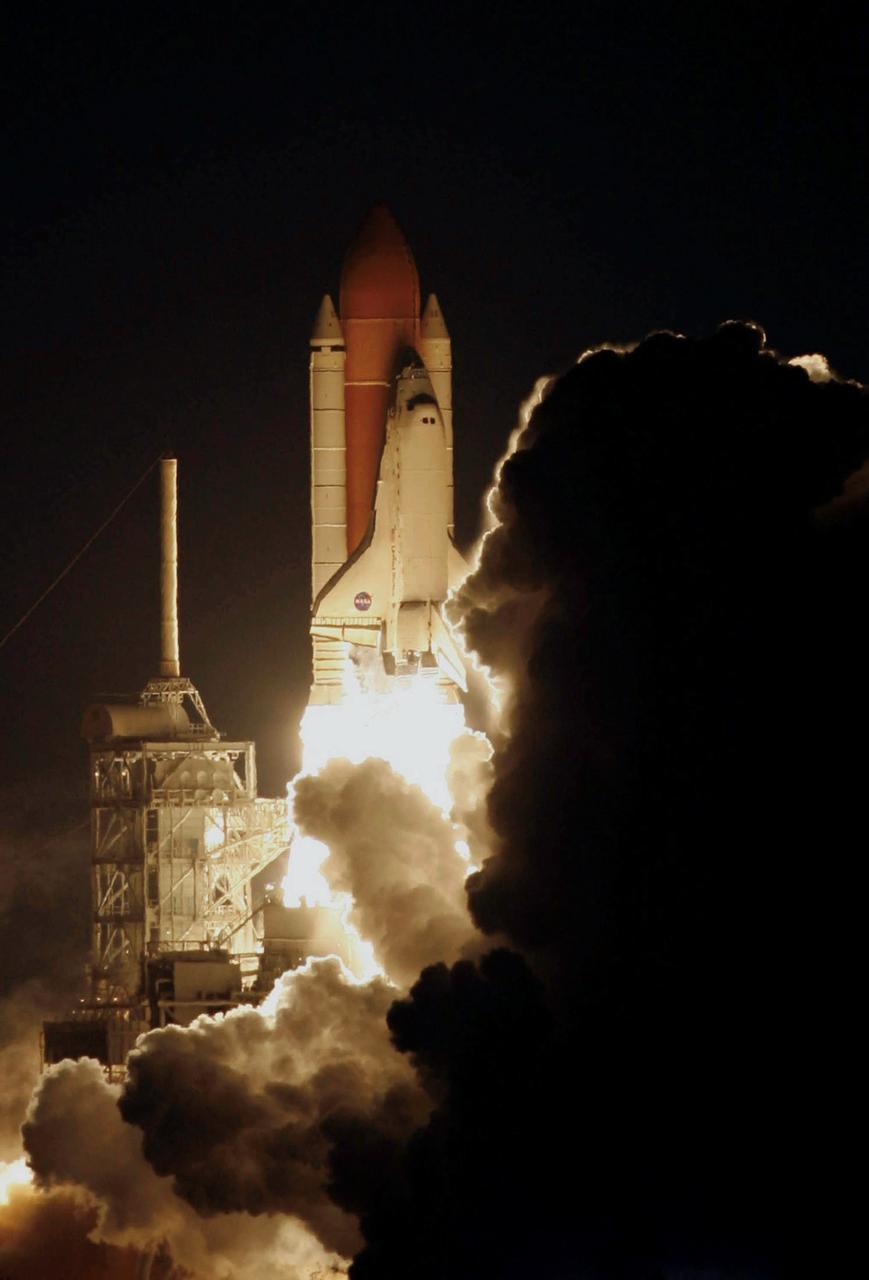

STS116-S-011 (9 Dec. 2006) --- Against a black night sky, the Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B occurred at 8:47 p.m. (EST) on Dec. 9, 2006 in what was the first evening shuttle launch since 2002. The STS-116 crew will link up with the station on Monday, Dec. 11, to begin a complex, week-long stay that will rewire the outpost and increase its power supply. During three spacewalks and intricate choreography with ground controllers, the astronauts will bring electrical power on line generated by a giant solar array wing delivered to the station in September.

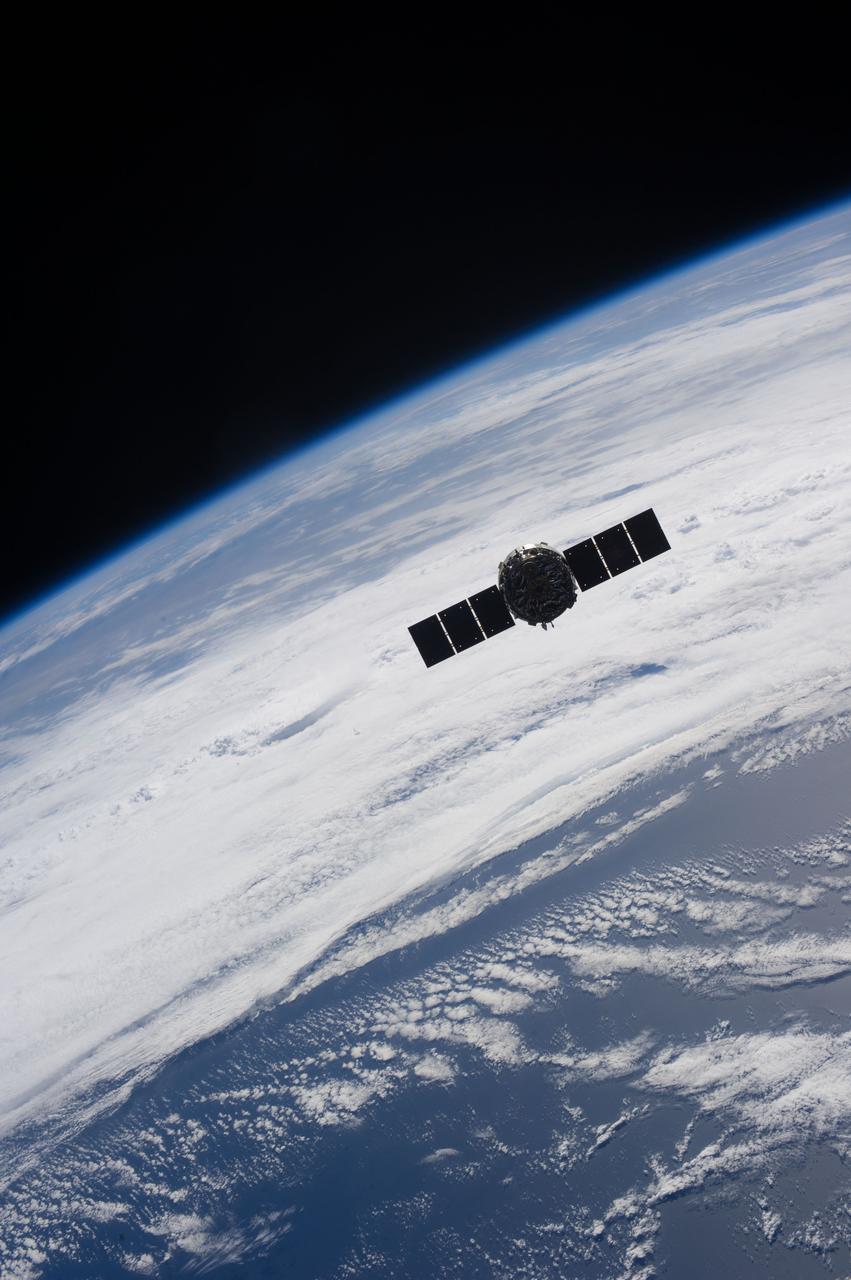
ISS031-E-071203 (25 May 2012) --- With the blackness of space and clouds over Earth forming a backdrop, the SpaceX Dragon commercial cargo craft is grappled by the Canadarm2 robotic arm at the International Space Station. Expedition 31 Flight Engineers Don Pettit and Andre Kuipers grappled Dragon at 9:56 a.m. (EDT) and used the robotic arm to berth Dragon to the Earth-facing side of the station's Harmony node at 12:02 p.m. May 25, 2012. Dragon became the first commercially developed space vehicle to be launched to the station to join Russian, European and Japanese resupply craft that service the complex while restoring a U.S. capability to deliver cargo to the orbital laboratory. Dragon is scheduled to spend about a week docked with the station before returning to Earth on May 31 for retrieval.

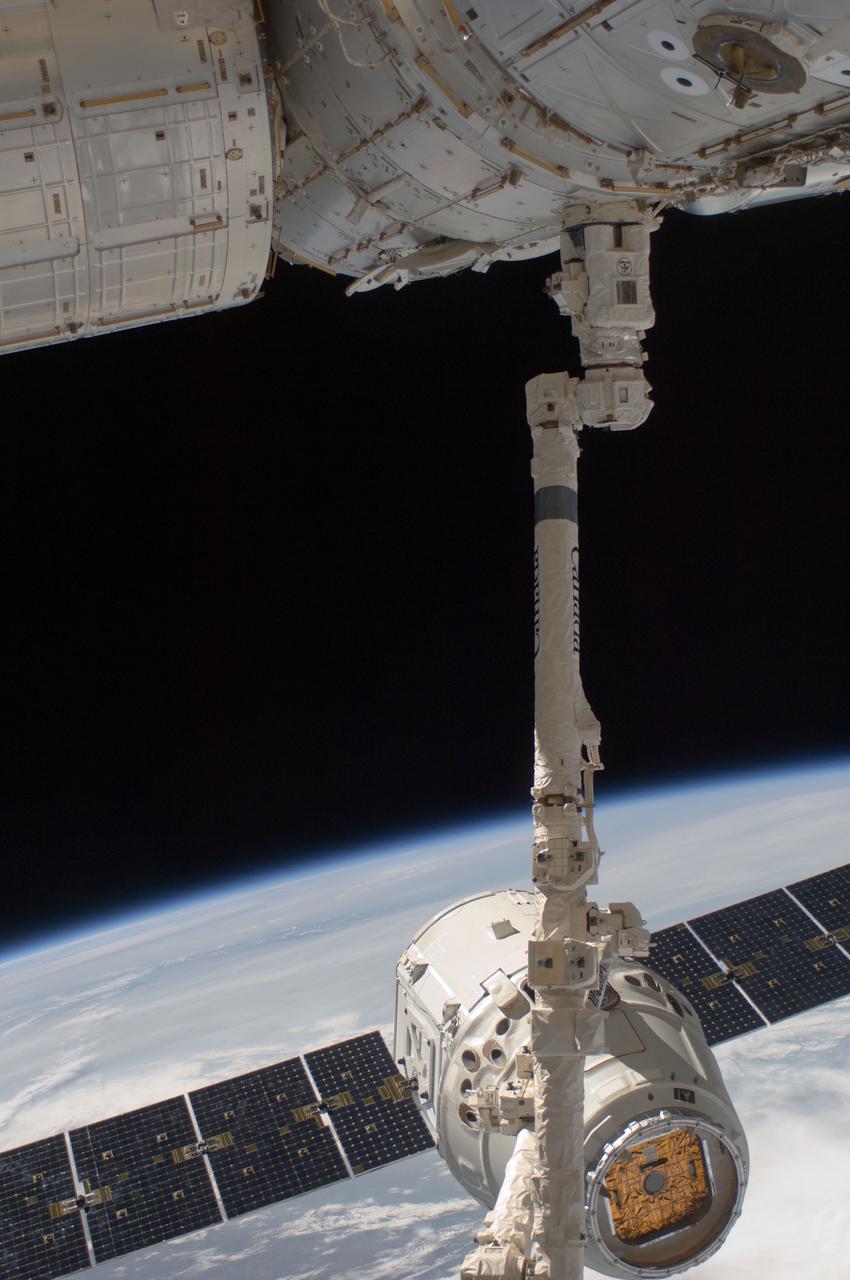
ISS037-E-018572 (22 Oct. 2013) --- The Orbital Sciences’ Cygnus commercial craft begins its relative separation from the International Space Station after three weeks at the station. European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano and NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, both Expedition 37 flight engineers, were at the controls of the robotics workstation removing Cygnus from the Harmony node then safely releasing it at 7:31 a.m. (EDT) Oct. 22, 2013. On Oct. 23, the Cygnus will fire its engines for the last time at 1:41 p.m. and re-enter Earth’s atmosphere for destruction over the Pacific Ocean. A blue and white part of Earth and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
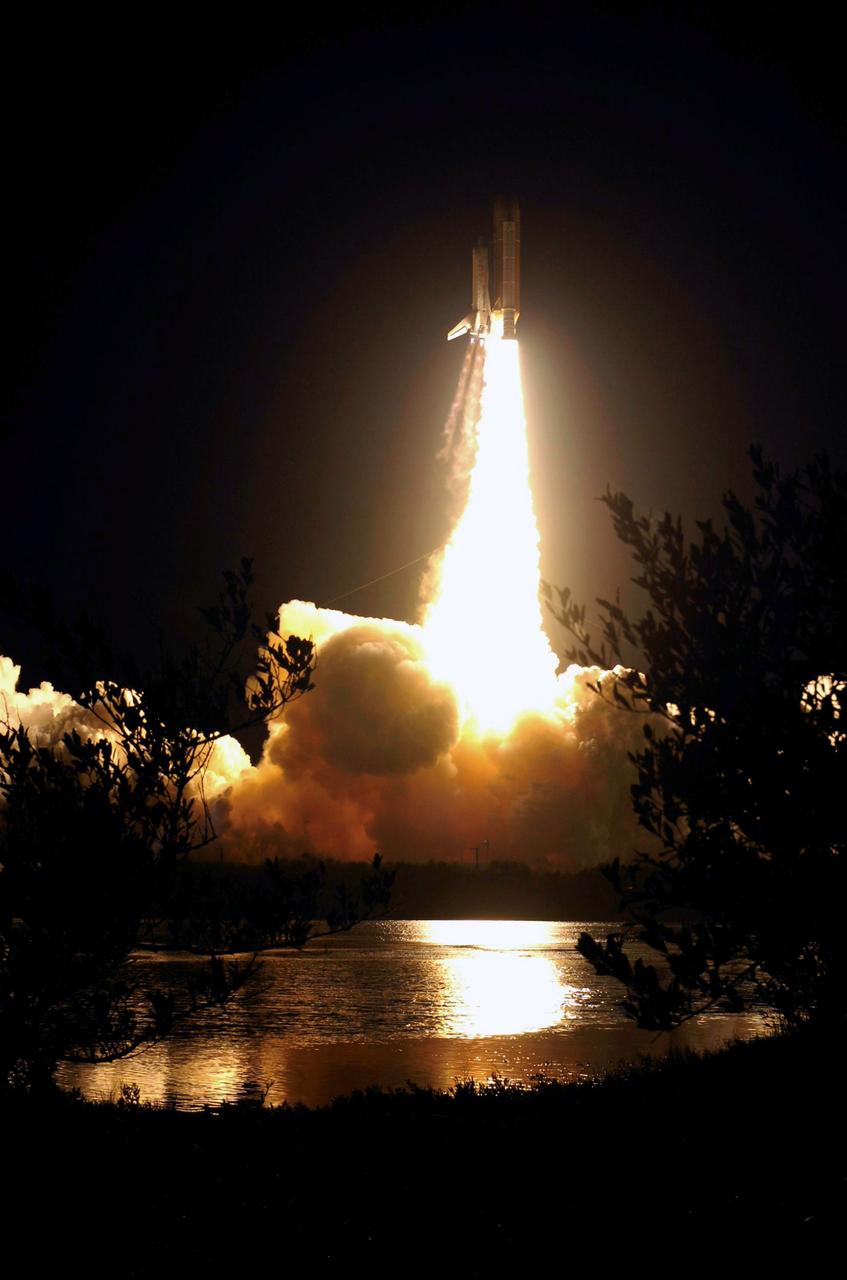

STS116-S-018 (9 Dec. 2006) --- Against a black night sky, the Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B occurred at 8:47 p.m. (EST) on Dec. 9, 2006 in what was the first evening shuttle launch since 2002. The STS-116 crew will link up with the station on Monday, Dec. 11, to begin a complex, week-long stay that will rewire the outpost and increase its power supply. During three spacewalks and intricate choreography with ground controllers, the astronauts will bring electrical power on line generated by a giant solar array wing delivered to the station in September.
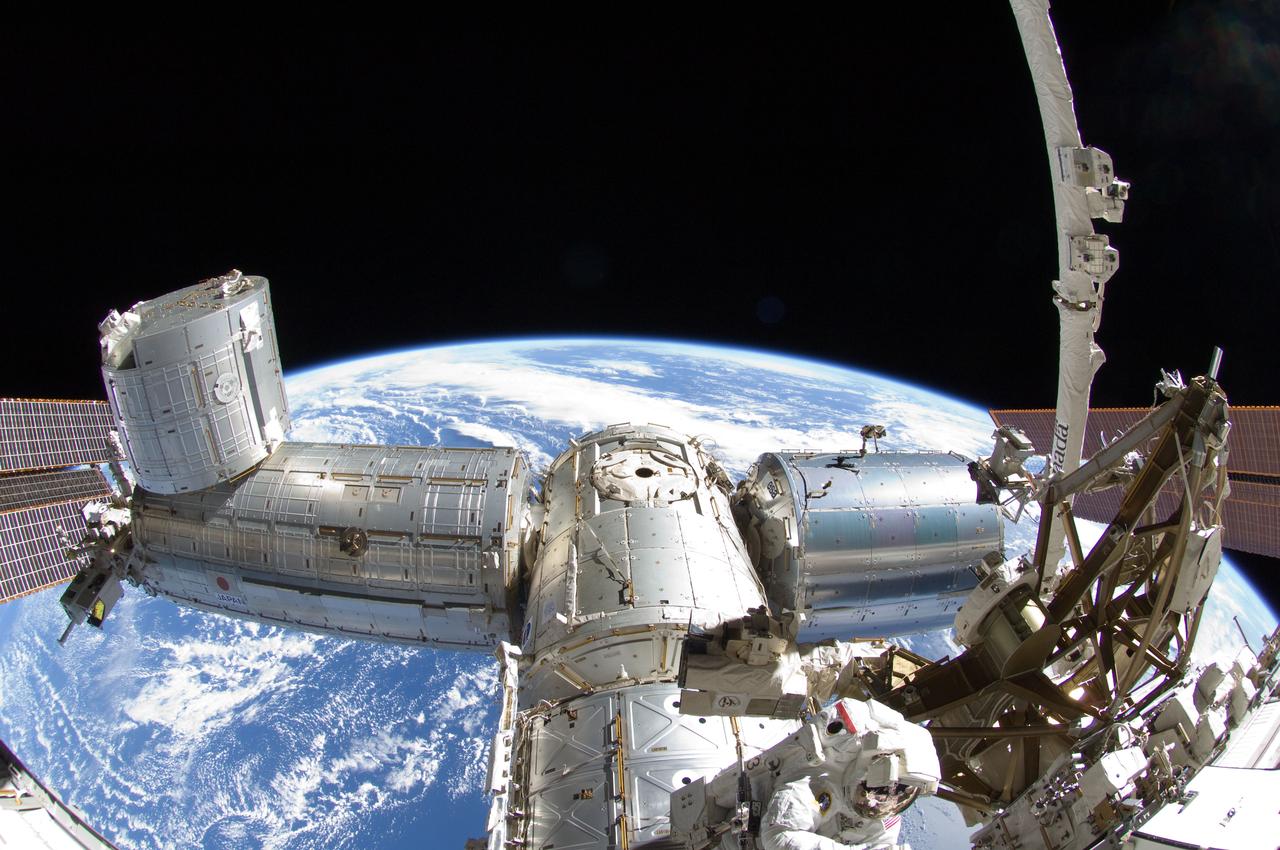

ISS032-E-025255 (5 Sept. 2012) --- A fisheye lens attached to an electronic still camera was used to capture this image of NASA astronaut Sunita Williams, Expedition 32 flight engineer, during the mission?s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA). During the six-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Williams and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Aki Hoshide (out of frame), flight engineer, completed the installation of a Main Bus Switching Unit (MBSU) that was hampered last week by a possible misalignment and damaged threads where a bolt must be placed. They also installed a camera on the International Space Station?s robotic arm, Canadarm2. A portion of the space station, Earth?s horizon and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
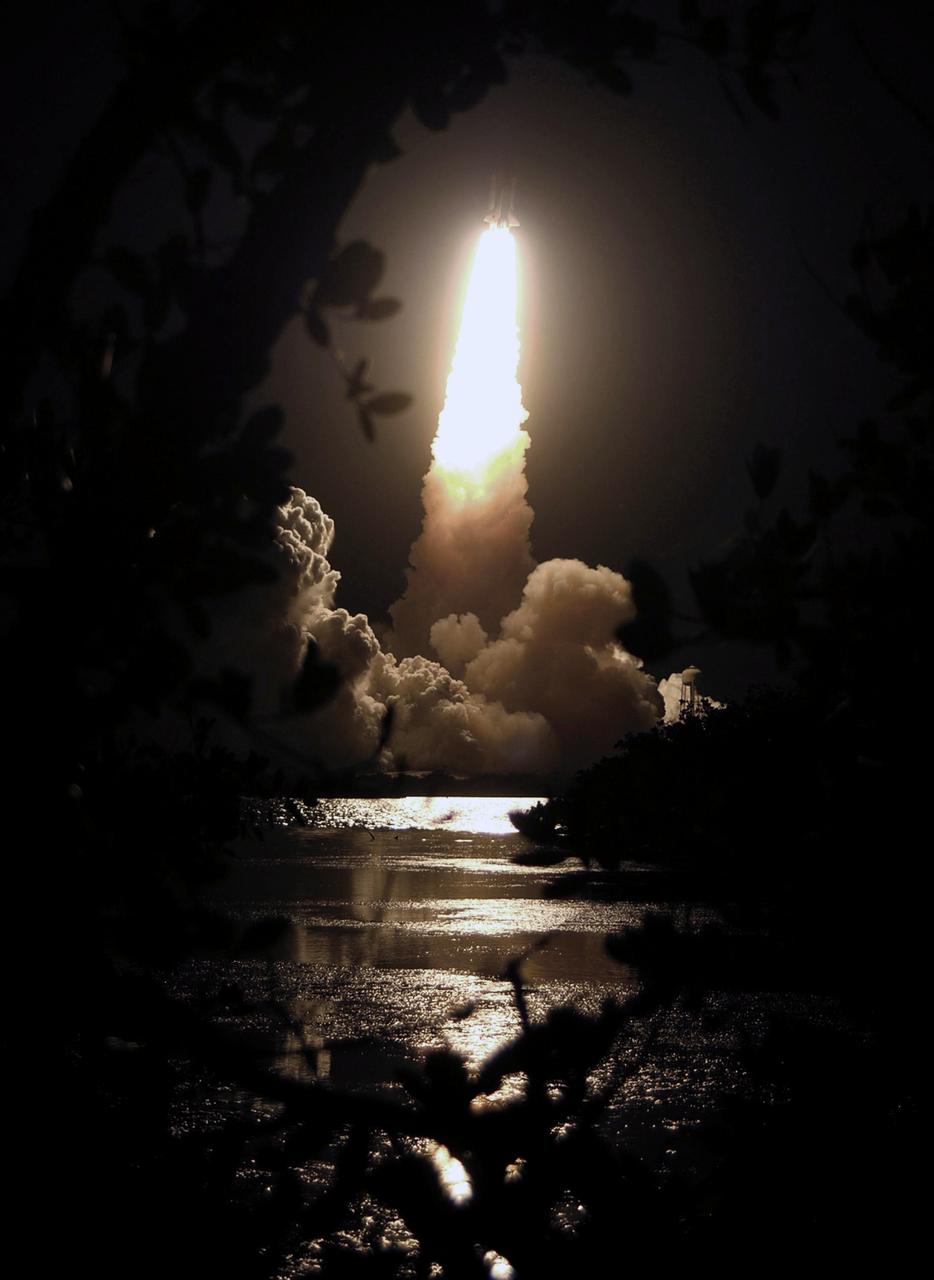

STS116-S-025 (9 Dec. 2006) --- Against a black night sky, the Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B occurred at 8:47 p.m. (EST) on Dec. 9, 2006 in what was the first evening shuttle launch since 2002. The STS-116 crew will link up with the station on Monday, Dec. 11, to begin a complex, week-long stay that will rewire the outpost and increase its power supply. During three spacewalks and intricate choreography with ground controllers, the astronauts will bring electrical power on line generated by a giant solar array wing delivered to the station in September.
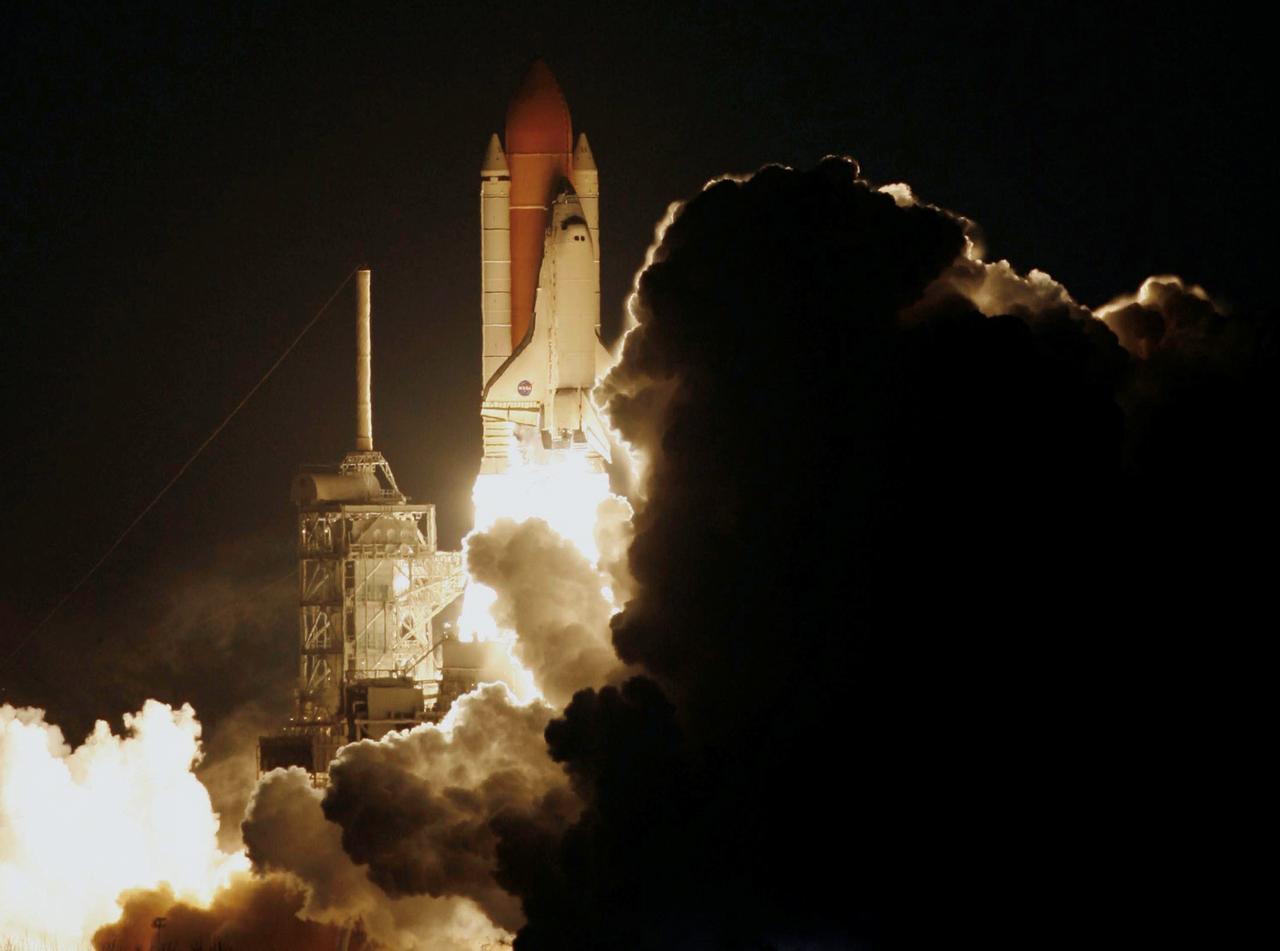

STS116-S-010 (9 Dec. 2006) --- Against a black night sky, the Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B occurred at 8:47 p.m. (EST) on Dec. 9, 2006 in what was the first evening shuttle launch since 2002. The STS-116 crew will link up with the station on Monday, Dec. 11, to begin a complex, week-long stay that will rewire the outpost and increase its power supply. During three spacewalks and intricate choreography with ground controllers, the astronauts will bring electrical power on line generated by a giant solar array wing delivered to the station in September.
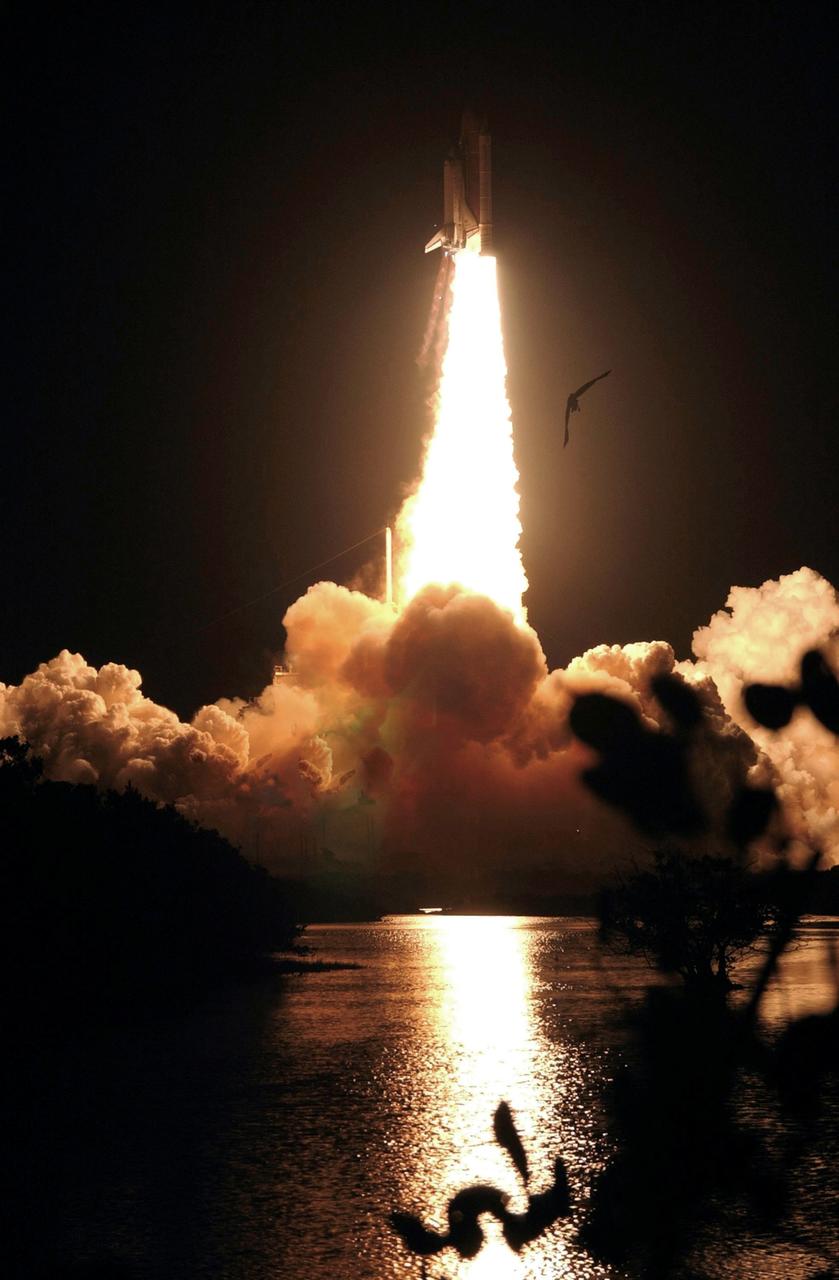

STS116-S-014 (9 Dec. 2006) --- Against a black night sky, the Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B occurred at 8:47 p.m. (EST) on Dec. 9, 2006 in what was the first evening shuttle launch since 2002. The STS-116 crew will link up with the station on Monday, Dec. 11, to begin a complex, week-long stay that will rewire the outpost and increase its power supply. During three spacewalks and intricate choreography with ground controllers, the astronauts will bring electrical power on line generated by a giant solar array wing delivered to the station in September.
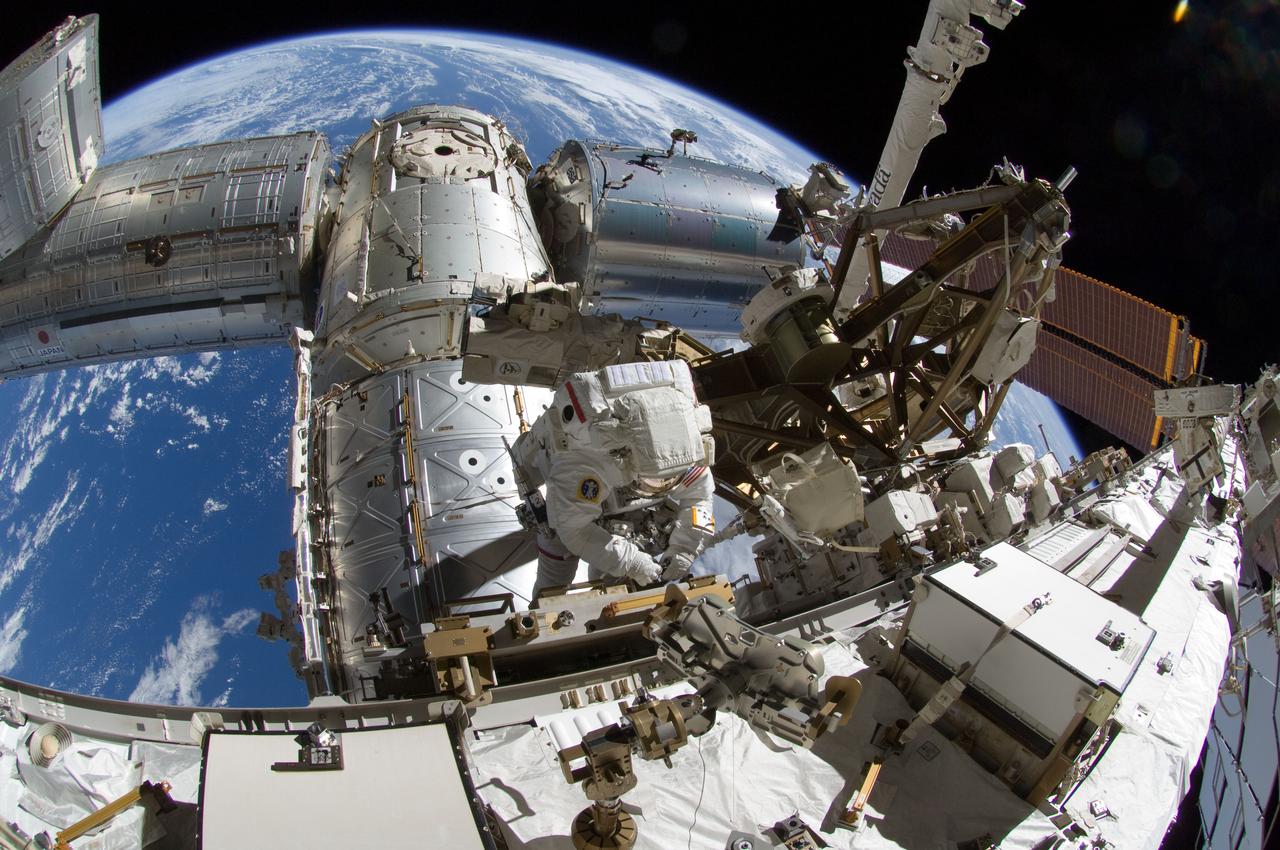

ISS032-E-025249 (5 Sept. 2012) --- A fisheye lens attached to an electronic still camera was used to capture this image of NASA astronaut Sunita Williams, Expedition 32 flight engineer, during the mission?s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA). During the six-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Williams and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Aki Hoshide (out of frame), flight engineer, completed the installation of a Main Bus Switching Unit (MBSU) that was hampered last week by a possible misalignment and damaged threads where a bolt must be placed. They also installed a camera on the International Space Station?s robotic arm, Canadarm2. A portion of the space station, Earth?s horizon and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
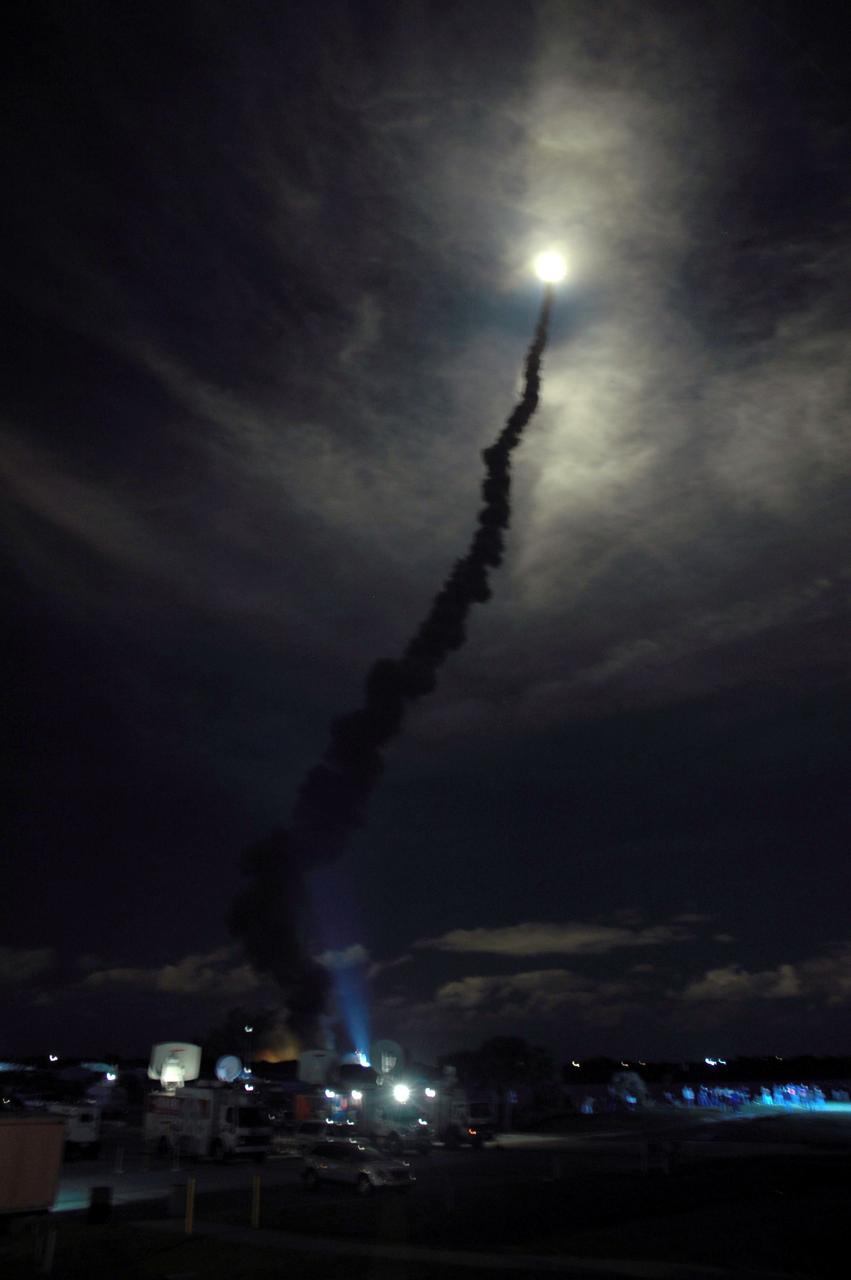

STS116-S-009 (9 Dec. 2006) --- Against a black night sky, the Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B occurred at 8:47 p.m. (EST) on Dec. 9, 2006 in what was the first evening shuttle launch since 2002. The STS-116 crew will link up with the station on Monday, Dec. 11, to begin a complex, week-long stay that will rewire the outpost and increase its power supply. During three spacewalks and intricate choreography with ground controllers, the astronauts will bring electrical power on line generated by a giant solar array wing delivered to the station in September.
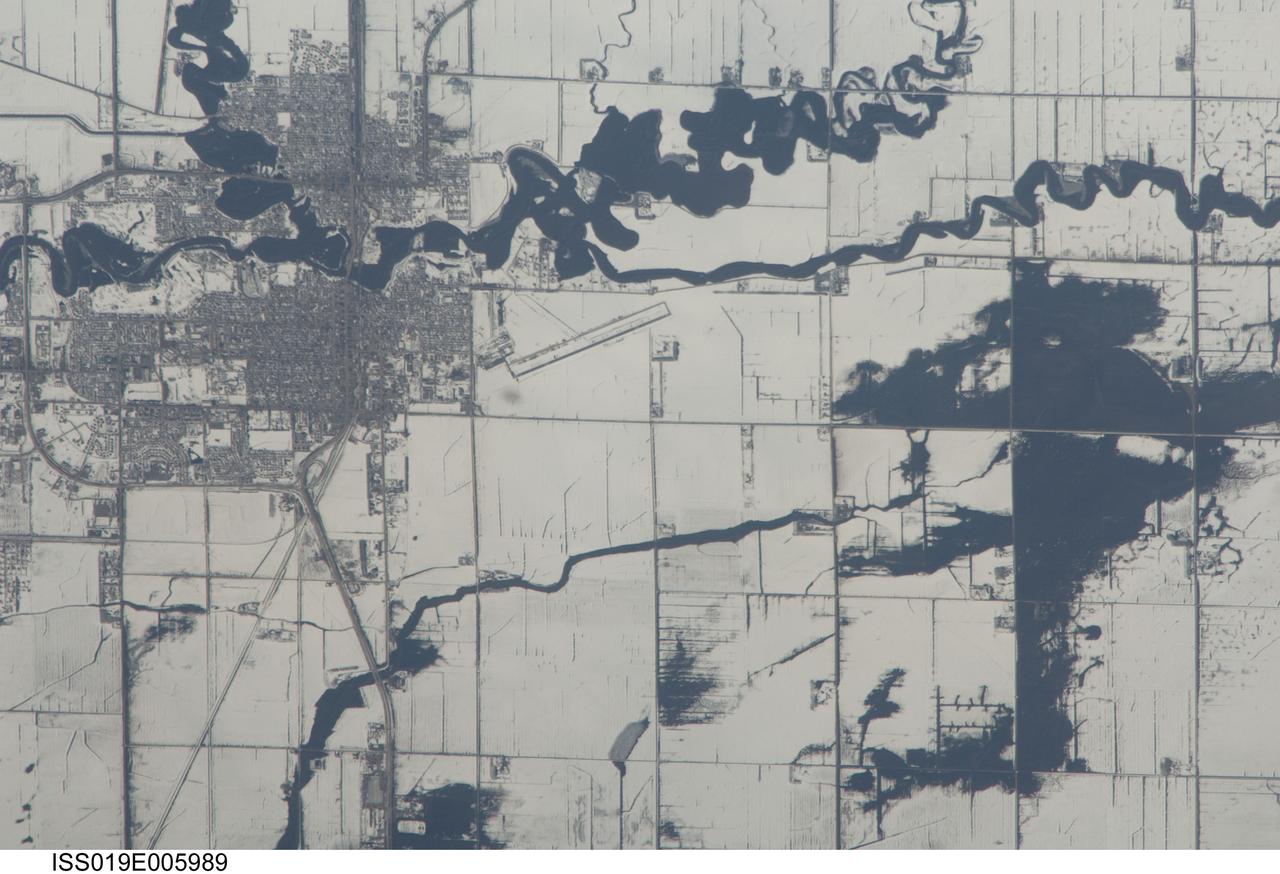

ISS019-E-005989 (9 April 2009) --- Red River floods in North Dakota and Minnesota are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 19 crewmember on the International Space Station. The Red River, which flows north between North Dakota and Minnesota, flooded for a second time on the day this image was taken (9 April 2009). Two weeks earlier the river had crested at very high levels. The new floodwaters in the Red River, and especially in the less well-drained meandering tributaries east of the river, appear as black shapes against a snowy agricultural landscape defined by rectangular fields. The largest irregular black patches are the flooded low parts of fields along a canalized western tributary of the Red River (right). The city-block patterns of Wahpeton ND and Breckenridge MN, opposite one another on the banks of the Red River, stand out as dark gray patches against the snow at image top left. The main runway of the Henry Stern Airport lies angled northwest directly south of Wahpeton, and its 1.3 kilometers runway length gives scale to the view. Access roads to the agricultural fields tend to follow an orthogonal pattern, while larger roads leading to the cities cut across this pattern (lower left, near Wahpeton). A subtle pattern of drainage ditches and plow lines appear as thin parallel lines throughout fields in the scene.
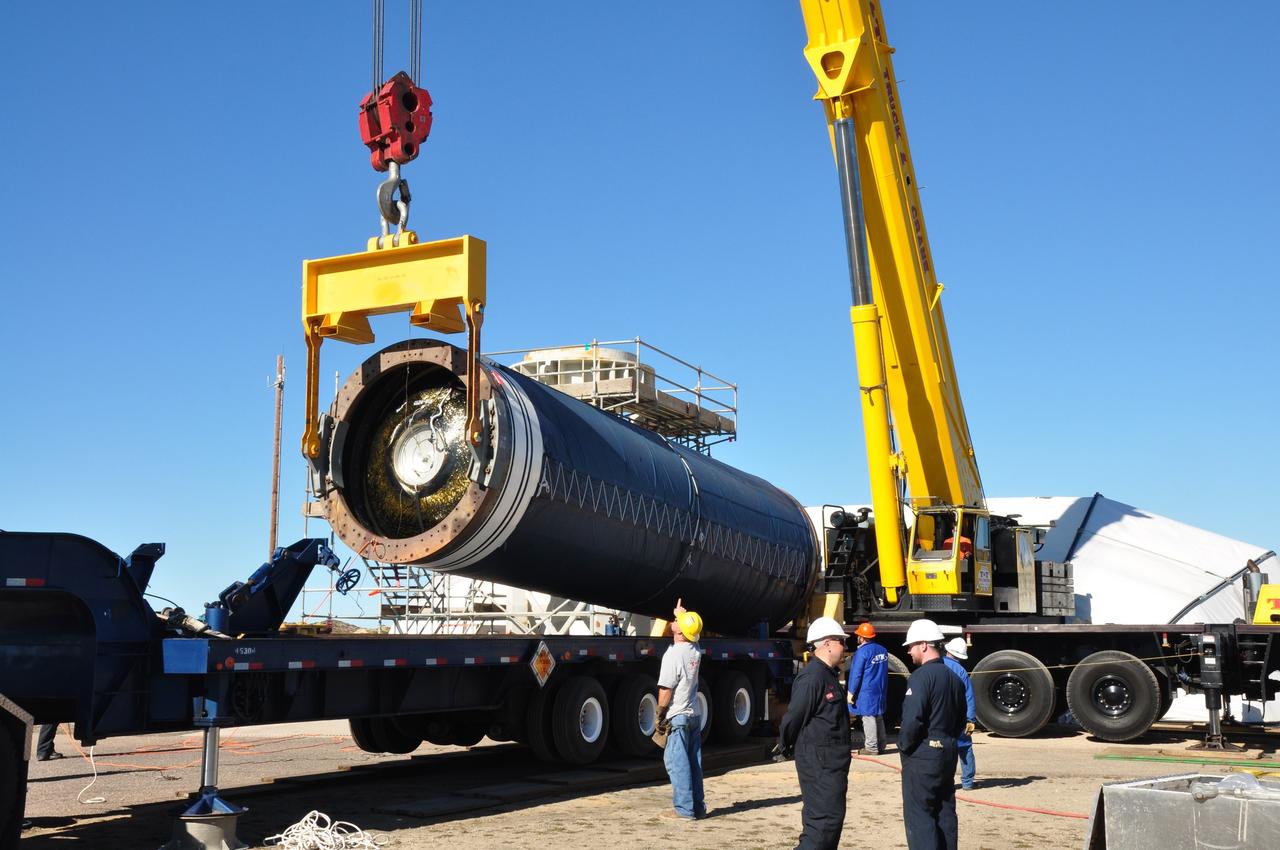

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The Stage 0 motor of the Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL is hoisted into launch position by crane at Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. As part of the four-stage Taurus XL rocket that will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit, stages 1, 2 and 3 will join Stage 0 at the launch pad about a week later. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
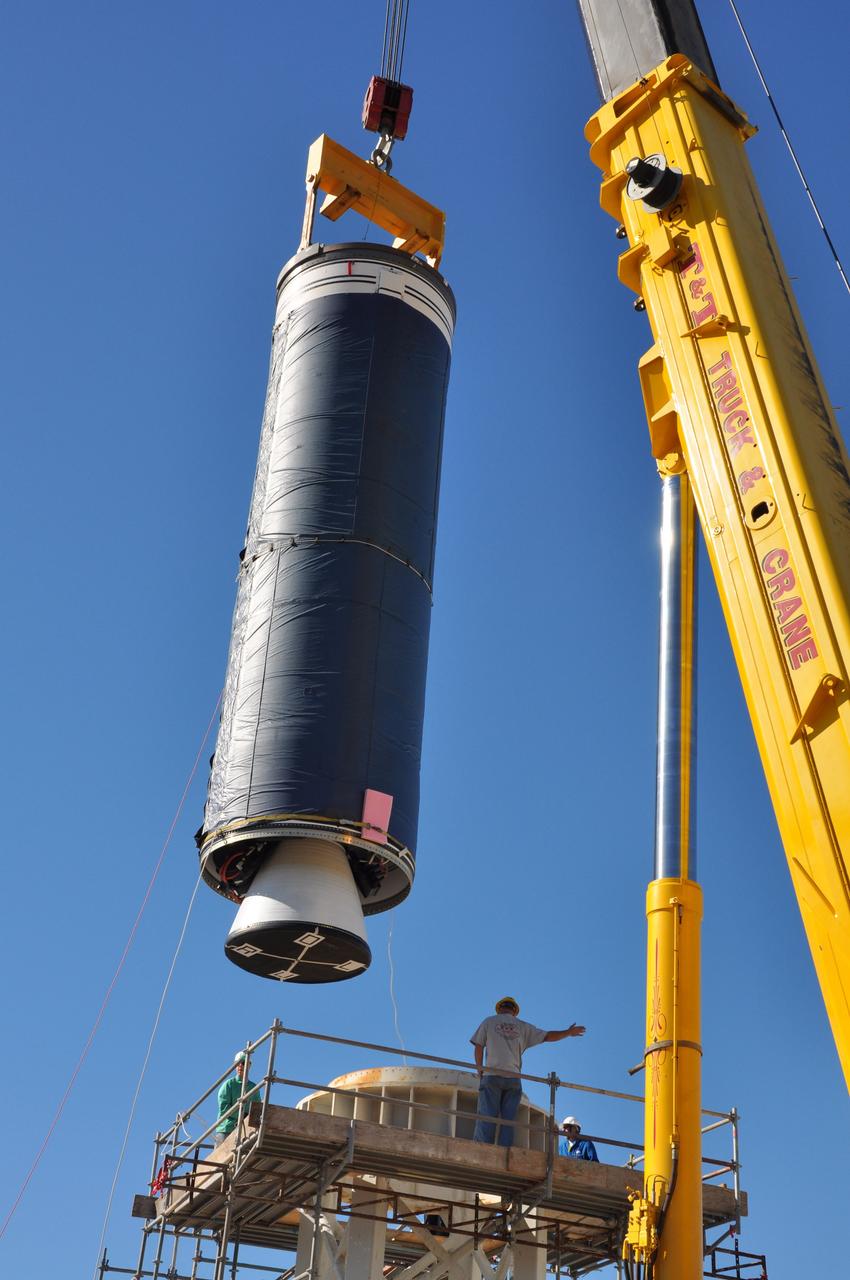

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The Stage 0 motor of the Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL is moved into launch position on Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. As part of the four-stage Taurus XL rocket that will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit, stages 1, 2 and 3 will join Stage 0 at the launch pad about a week later. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
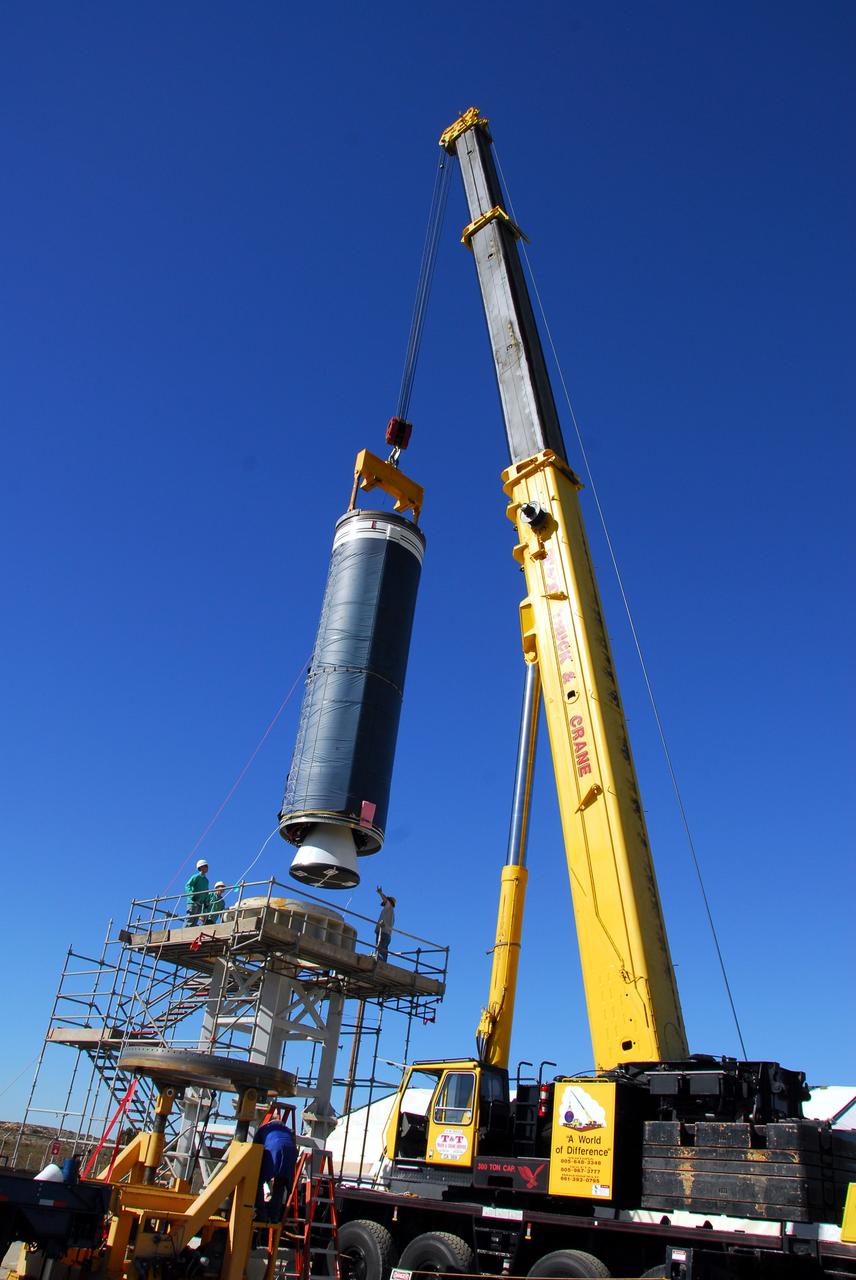

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The Stage 0 motor of the Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL is moved into launch position on Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. As part of the four-stage Taurus XL rocket that will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit, stages 1, 2 and 3 will join Stage 0 at the launch pad about a week later. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Don Kosoksa, VAFB
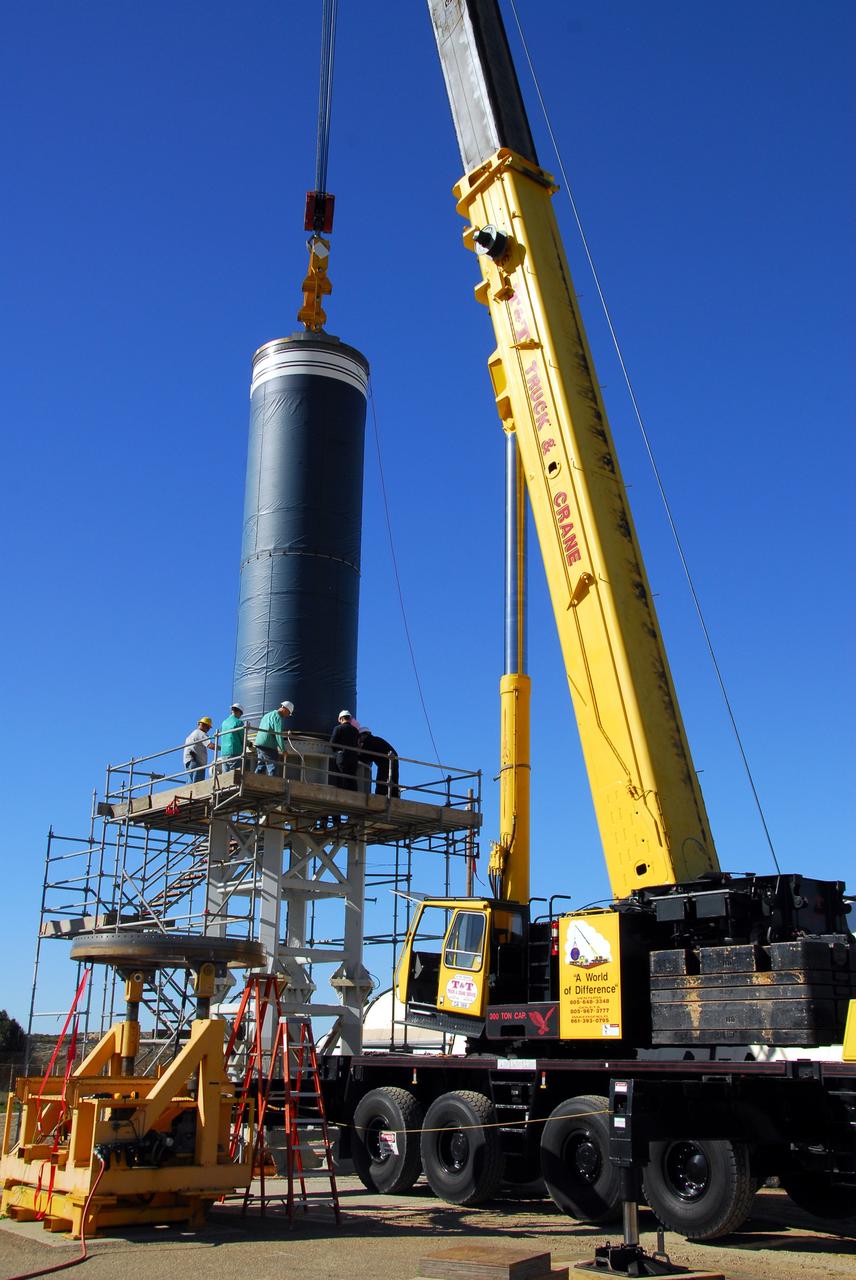

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers move the Stage 0 motor of the Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL into launch position on Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. As part of the four-stage Taurus XL rocket that will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit, stages 1, 2 and 3 will join Stage 0 at the launch pad about a week later. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Don Kosoksa, VAFB