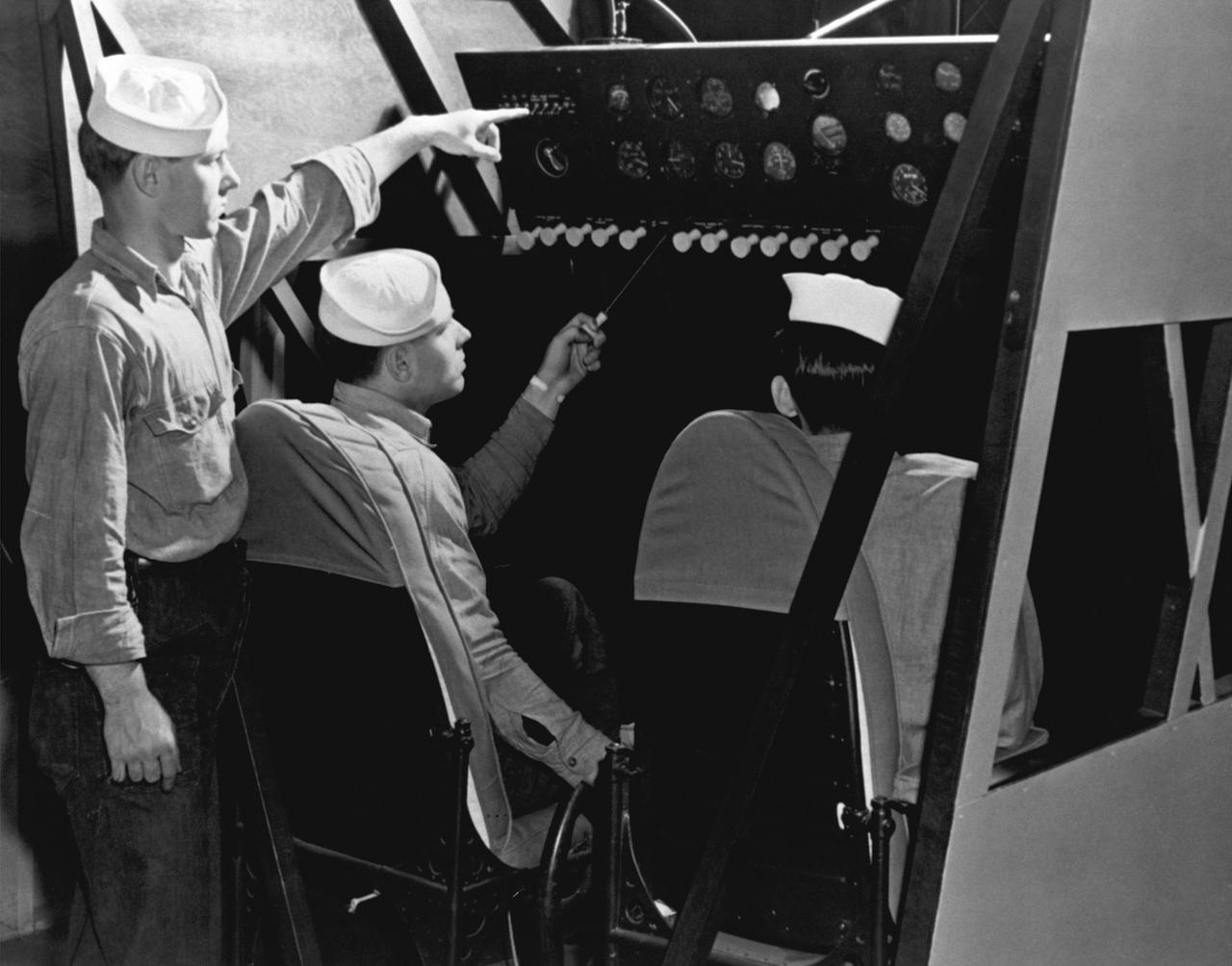

Blimp Synthetic Training of Navy personnel
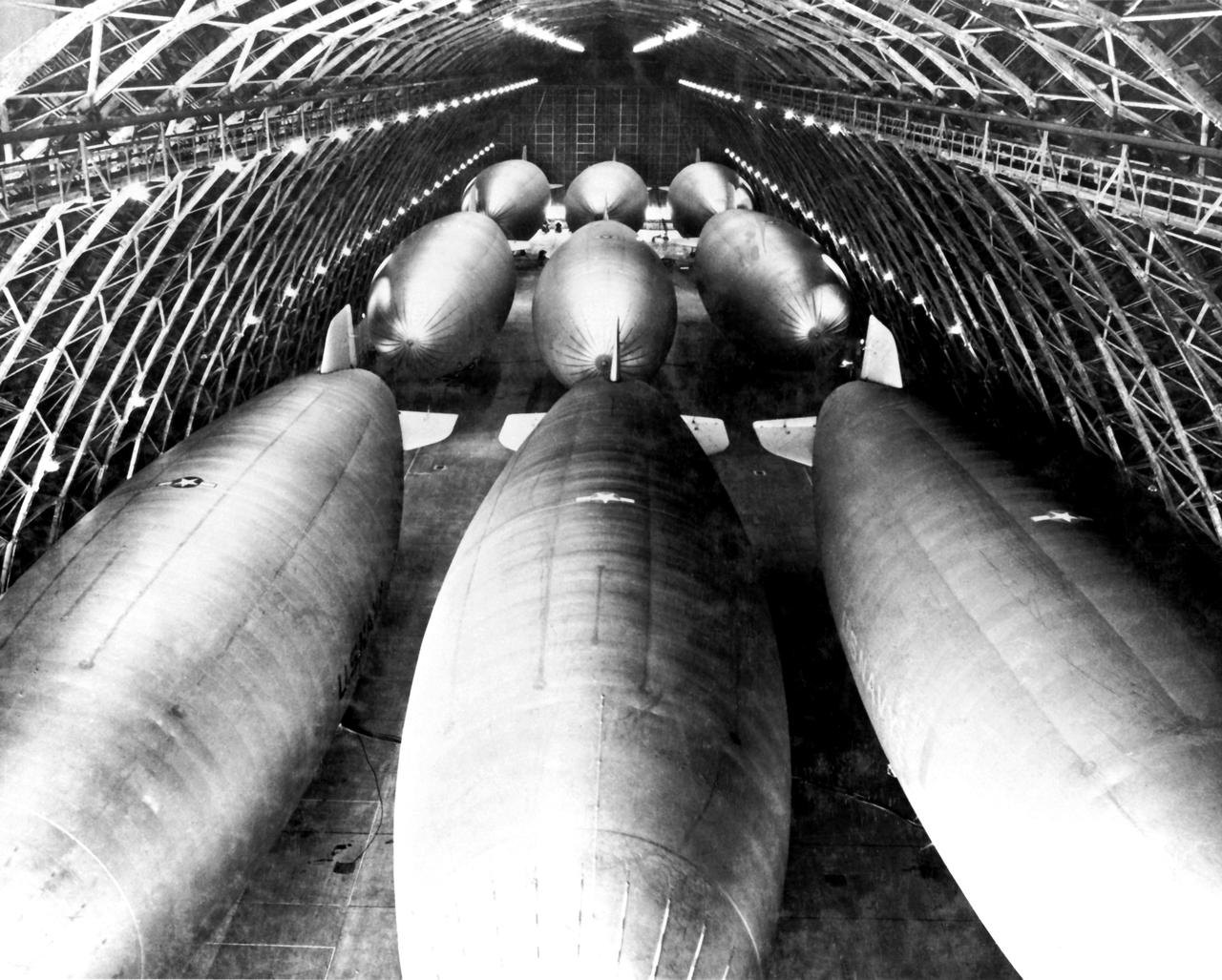

Navy Nine Blimps inflated in Hangar, NAS Sunnyvale, CA
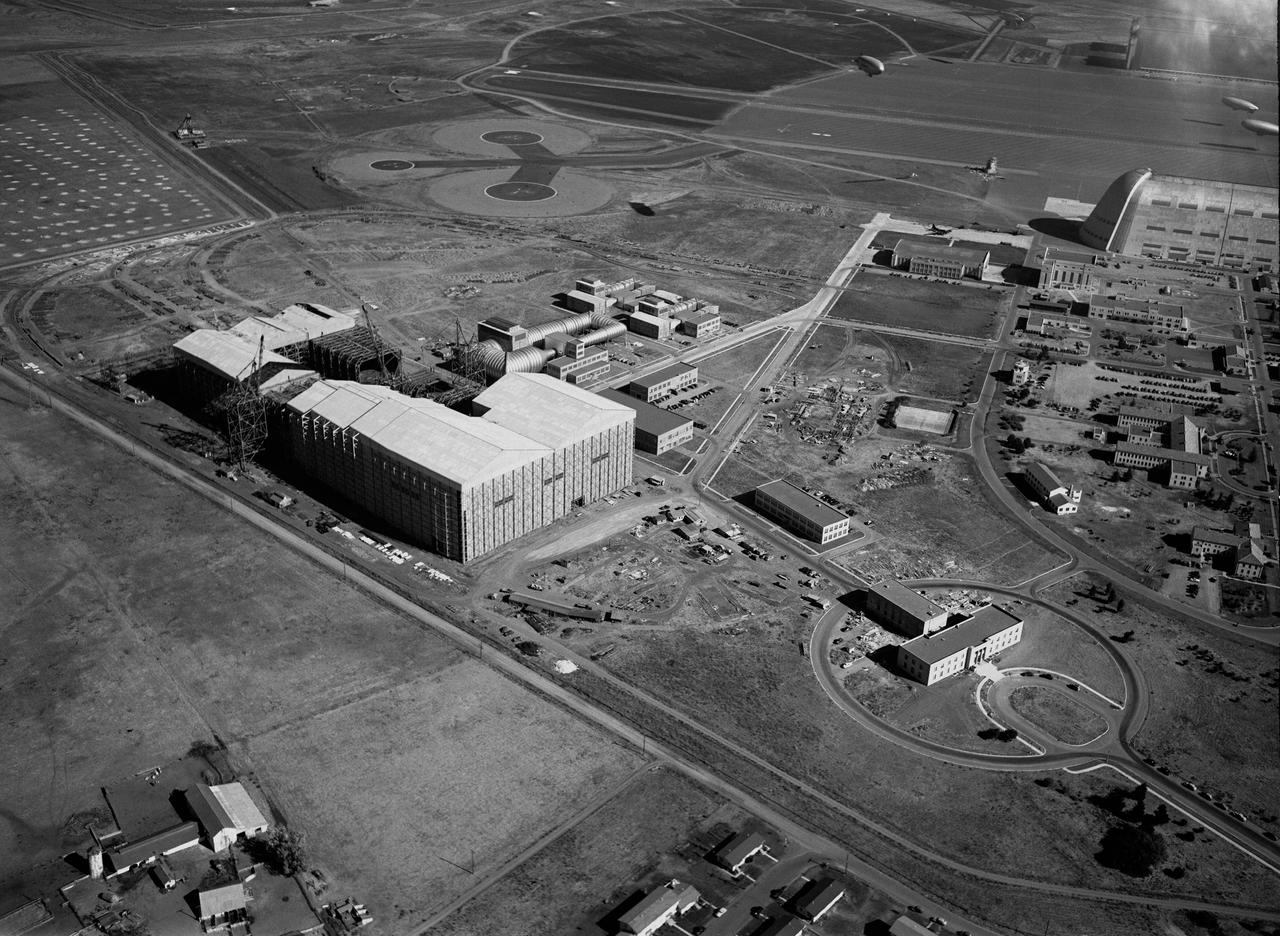

Aerial view of Ames Aeronautical Laboratory (with blimps in flight over Moffett runway)
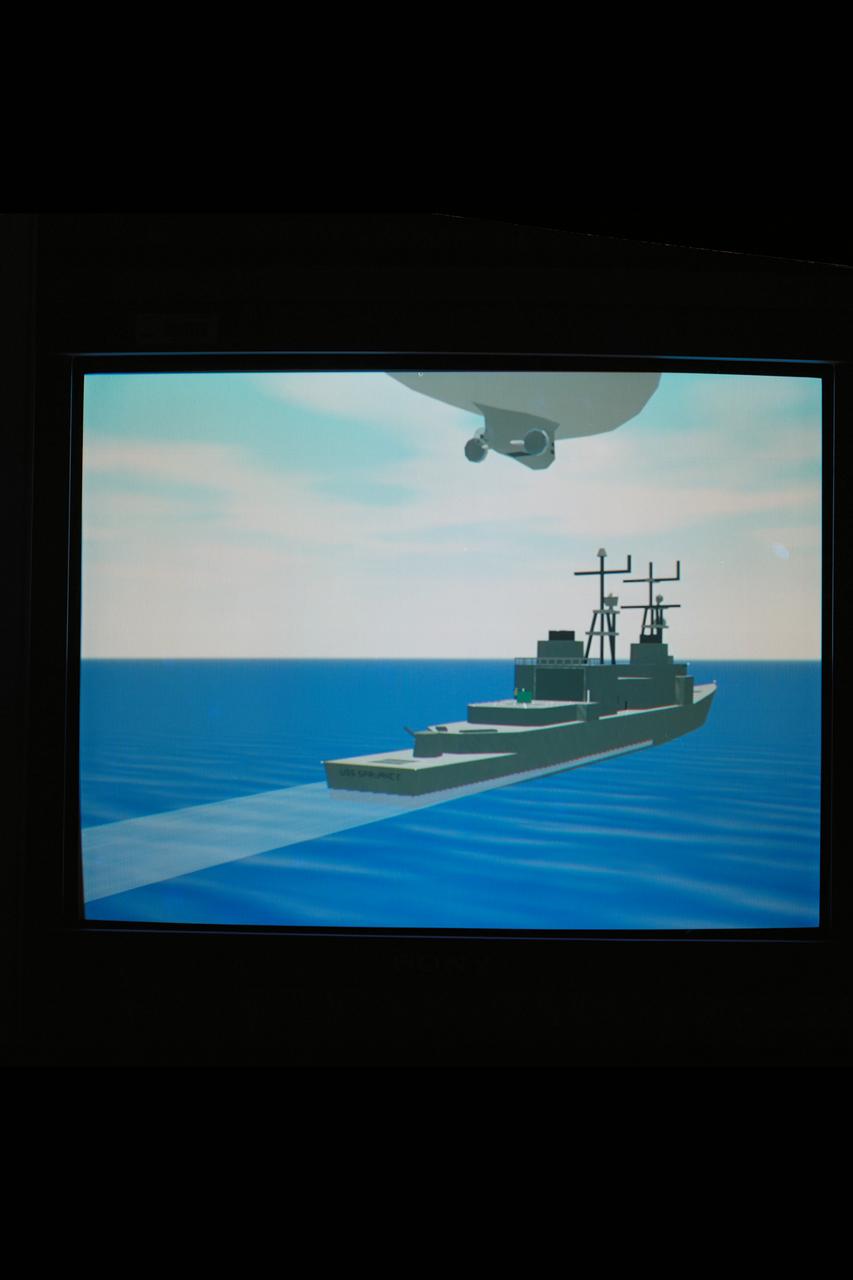

N-243 VMS: Blimp Simulation (GODS Point of View) WAI (Westinghouse Airship Inc.)
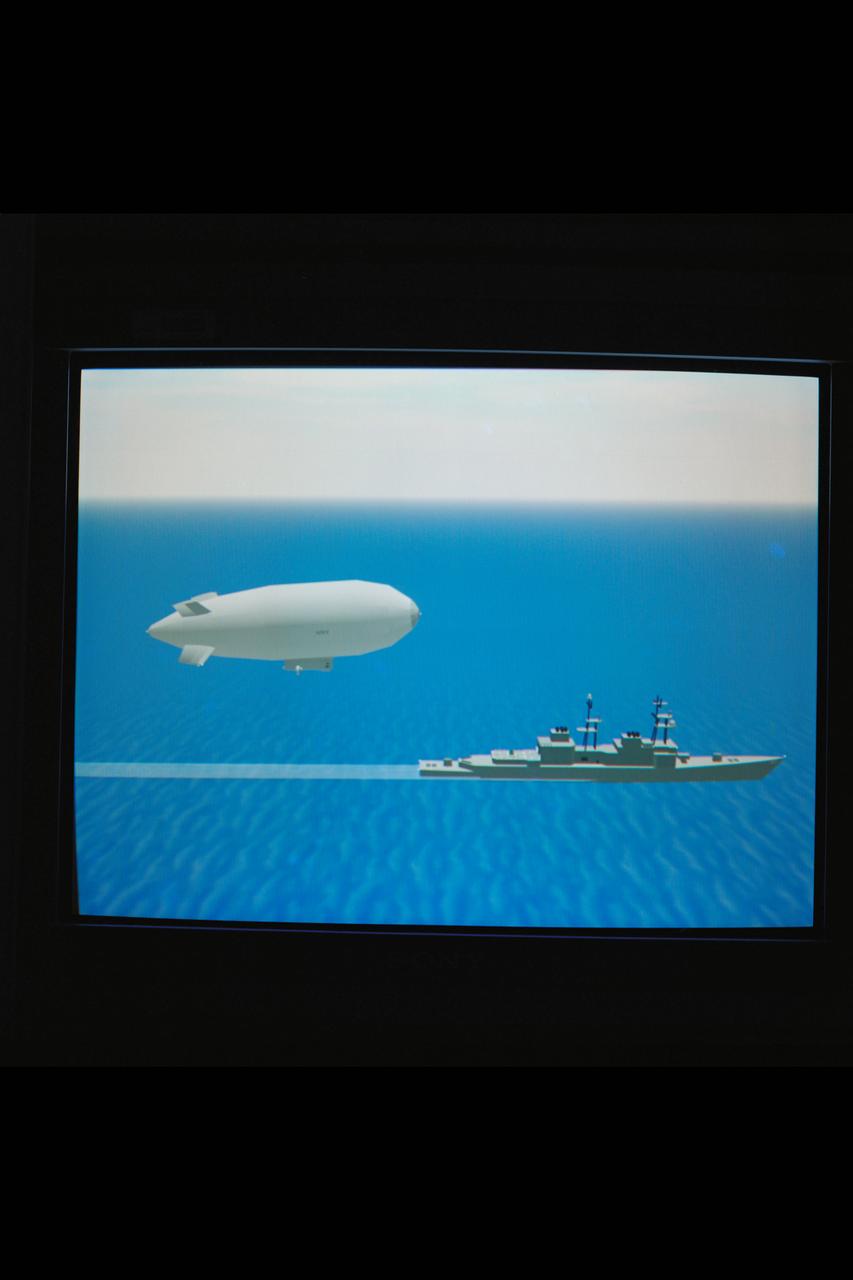

N-243 VMS: Blimp Simulation (GODS Point of View) WAI (Westinghouse Airship Inc.)
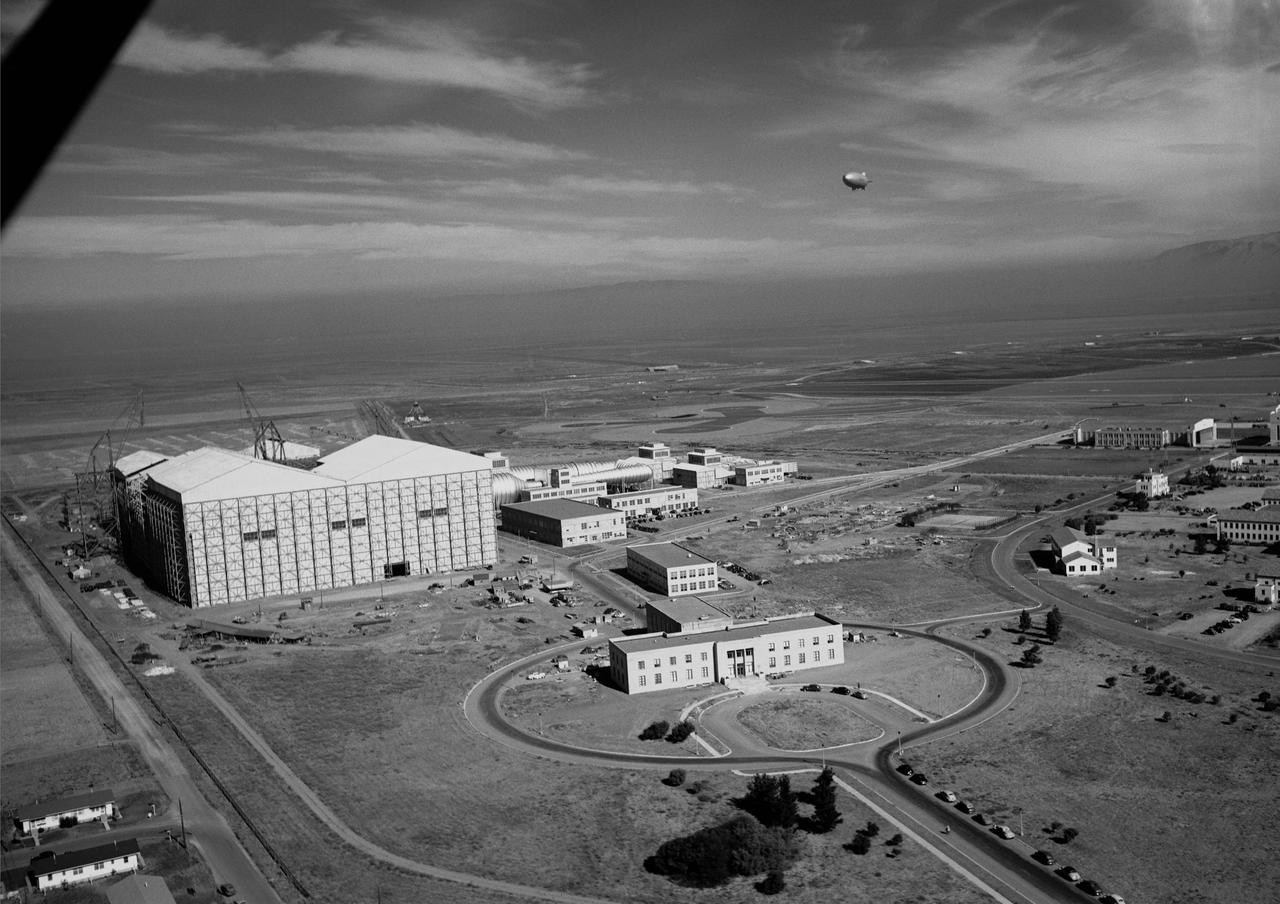

Ames aerial view of Ames Aeronautical Laboratory plot looking northeast with blimp in flight over Moffett Naval airstation.
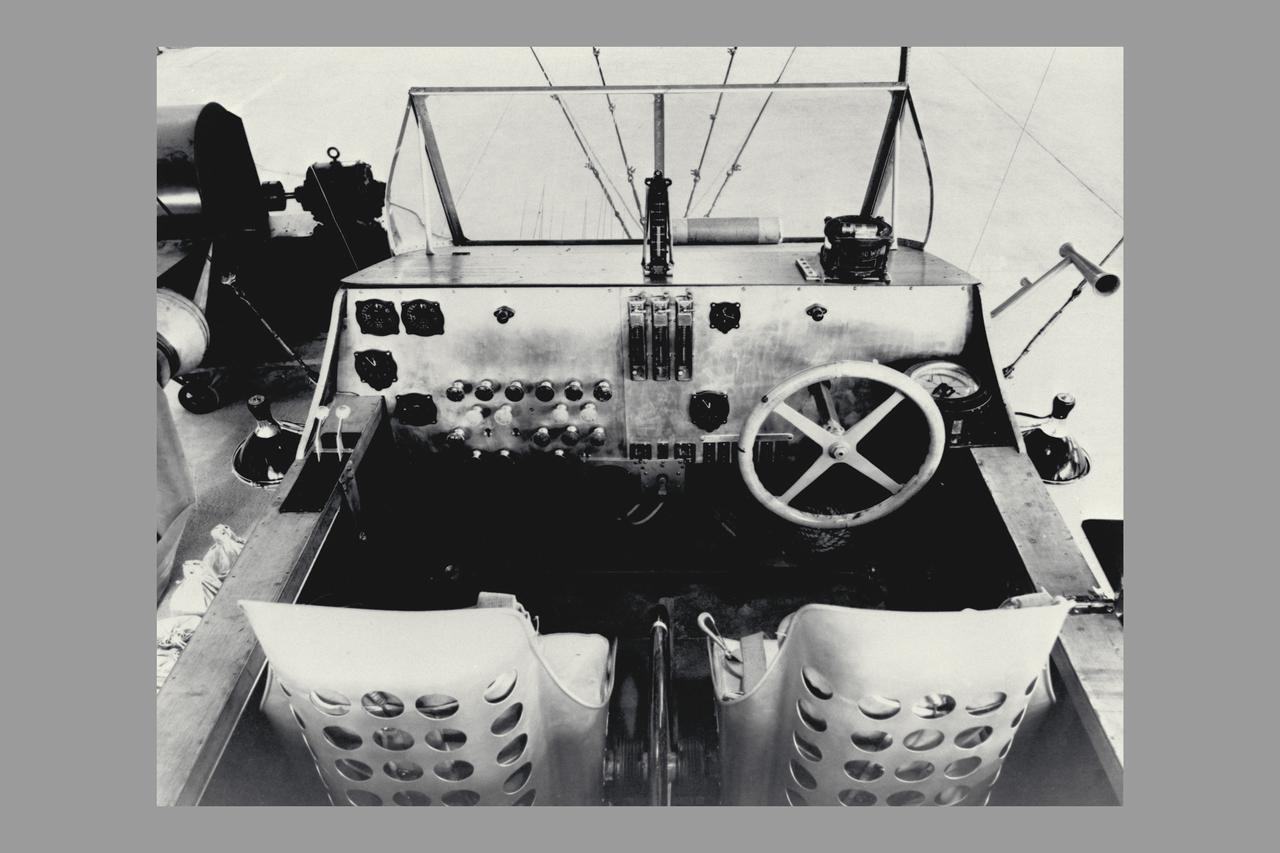
Blimp J-4 Car instrument panel (non-rigid air ship)
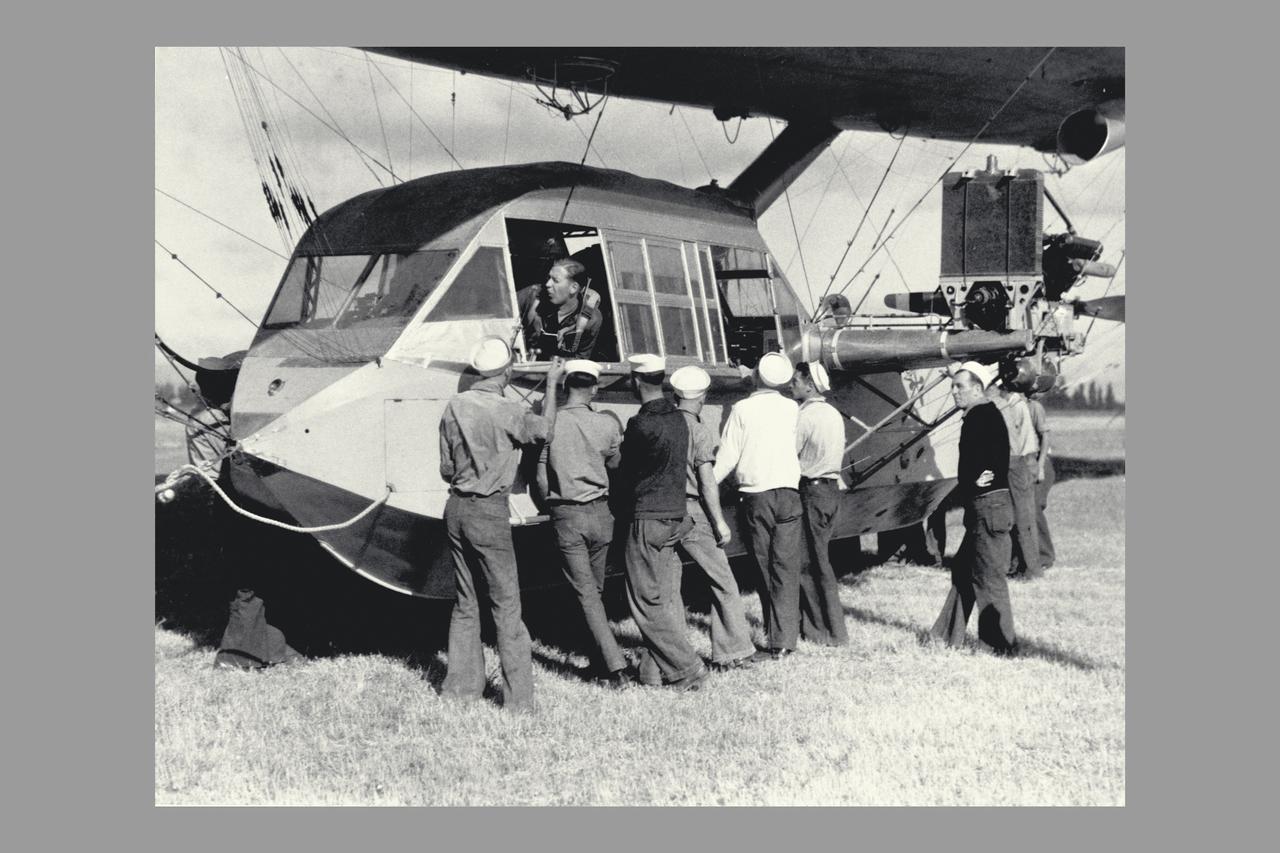

Blimp J-4 Gondola (non-rigid air ship)

Blimp J-4 tether (non-rigid air ship)
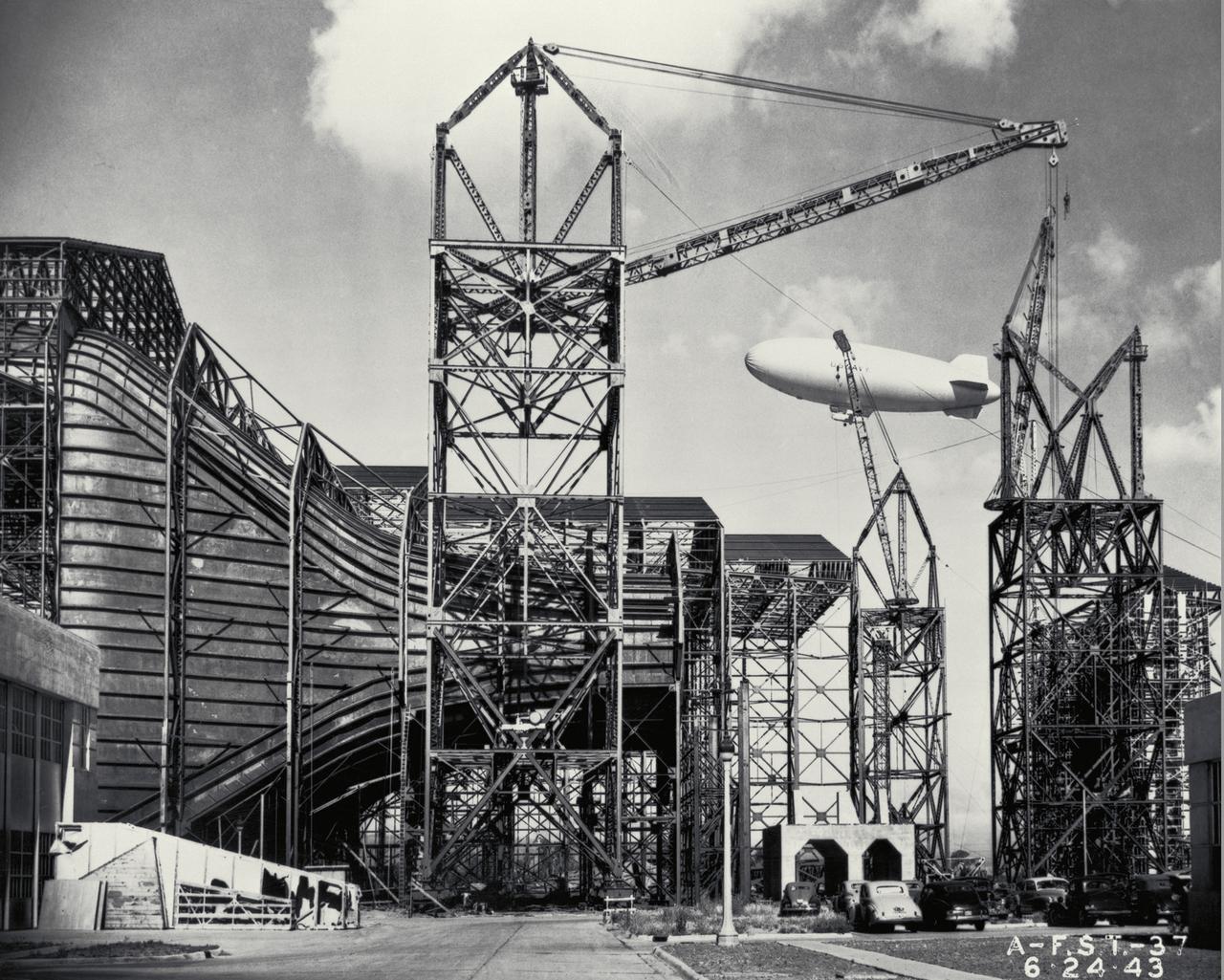

Construction of the Ames Full-Scale 40x80ft Wind tunnel. - side view of entrance cone, blimp in background
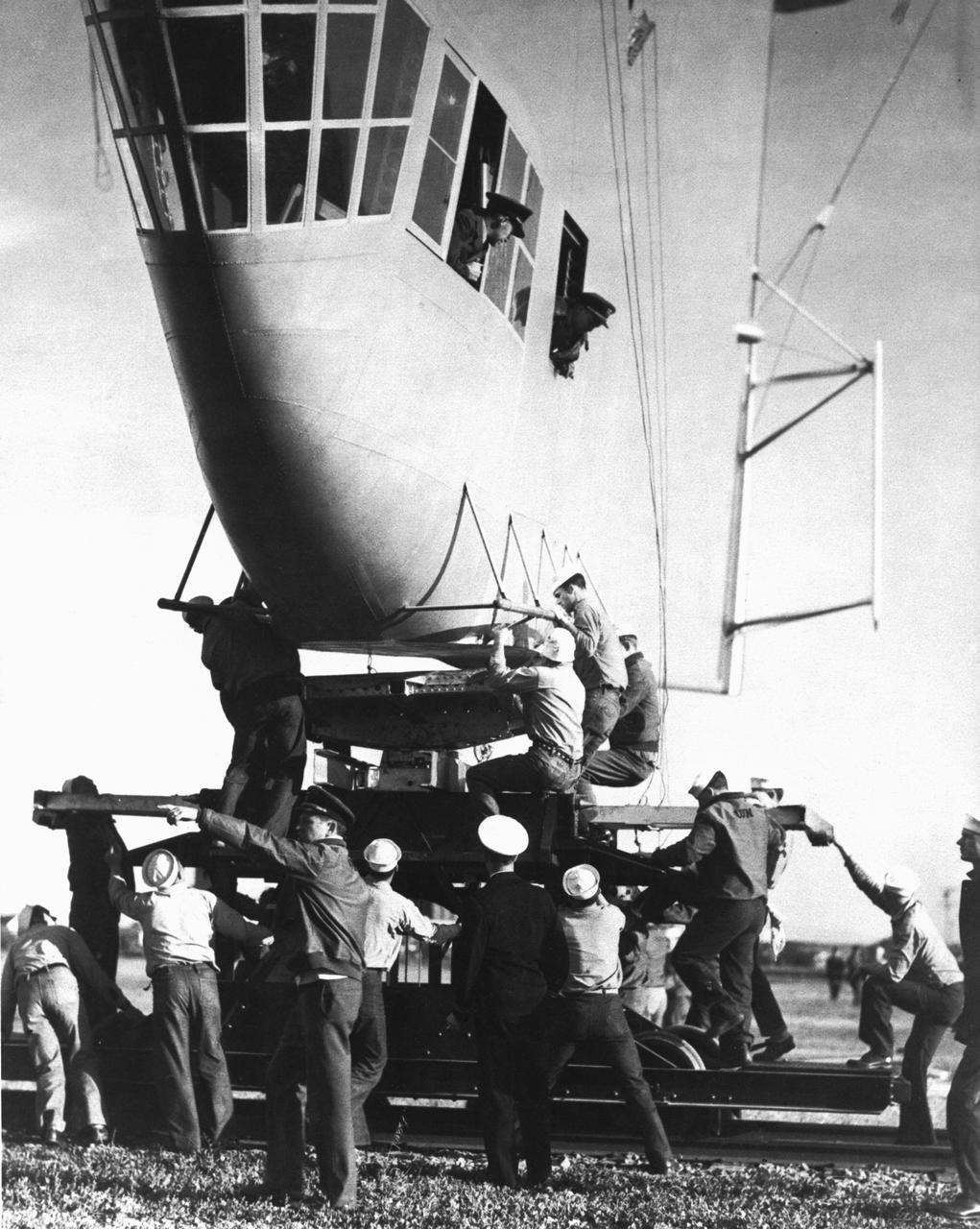

Circa 1935 History of Cockpits - Macon Dirigible cabin housing viewed as sailors moor the blimp at Moffett Field (@ 1935)
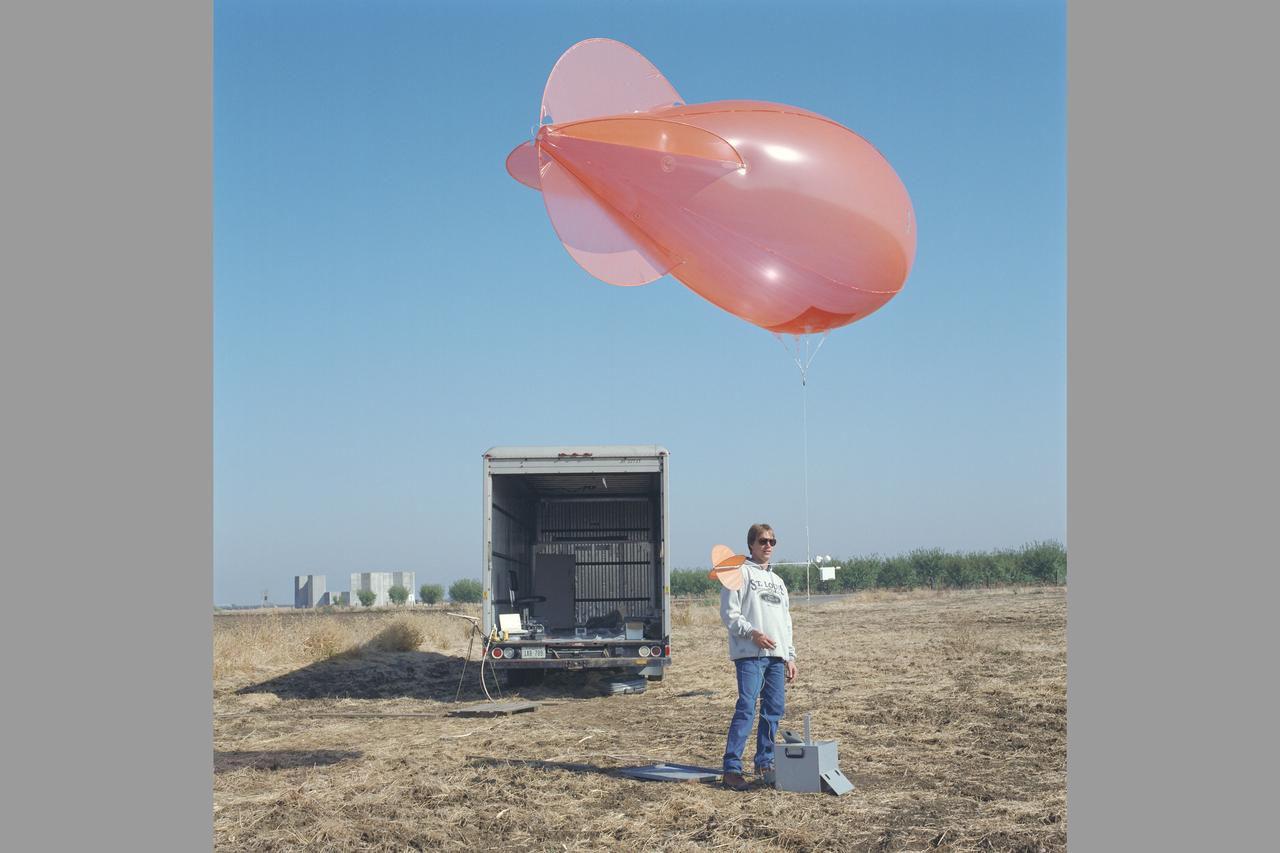

MD-900 (N900MH) Helicopter Noise Abatement Test - Crows Landing, Microphones, Van and balloon blimp (wind indicator)
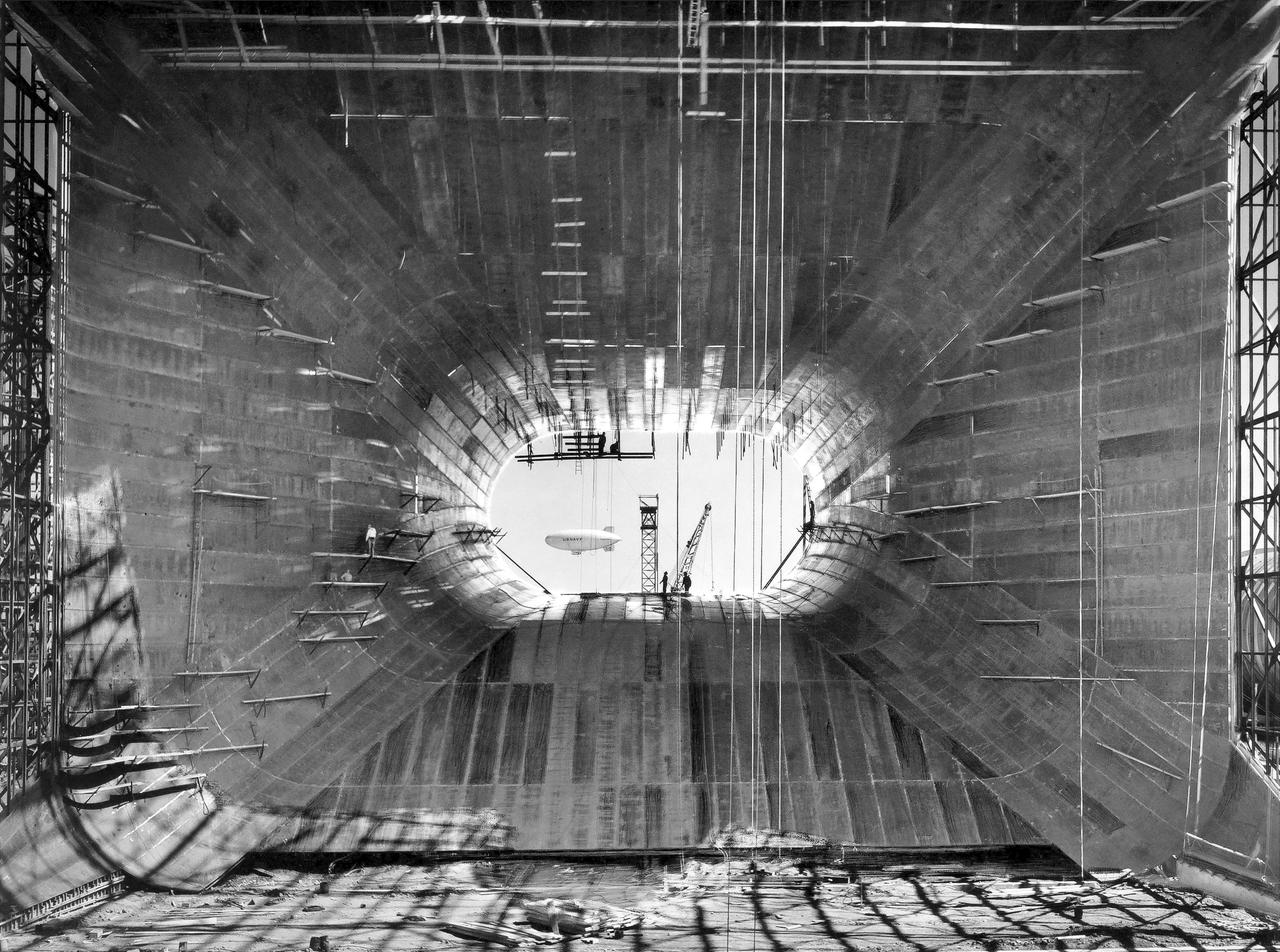
(07/07/1943) Construction view from inside the contraction framing of the 40x80 foot wind tunnel with a blimp flying in the background.
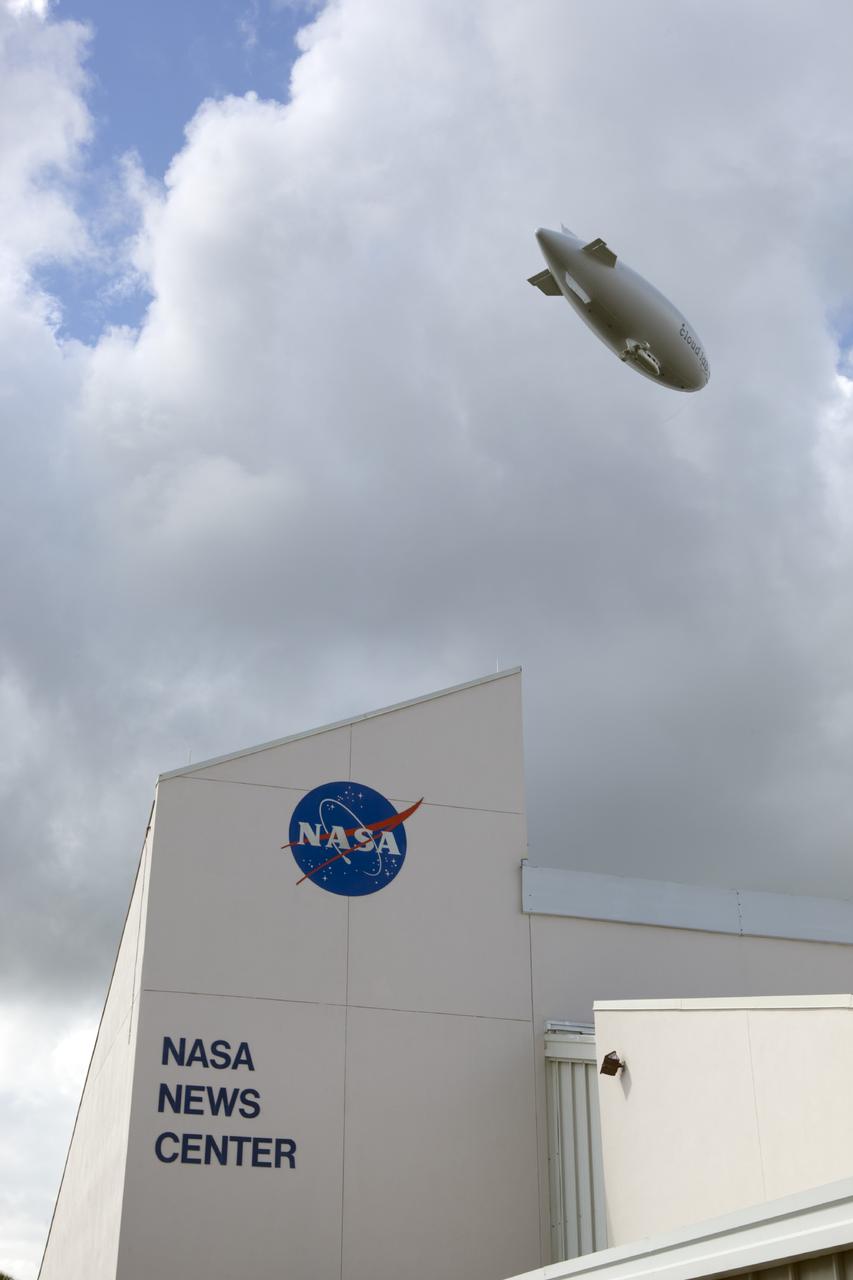

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An airship from the British Broadcasting Corp., or BBC, flies over Launch Complex 39 past the NASA News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A team of scientists from the BBC's television project "Cloud Lab" are conducting a number of experiments aboard the airship as it flies across the U.S., exploring all aspects of the Earth's atmosphere. One of the experiments is NASA's Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, which is designed to measure the microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

The first of three Prandtl-M prototype aircraft was air launched Aug. 16, 2019, from an Aerostat blimp at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. Three different prototypes of varying size, two still in development, eventually will be air launched from a weather balloon at 100,000 feet to simulate the atmosphere on Mars. The validated Prandtl-M could give scientists options to fly sensors in the Martian atmosphere to collect weather and landing site information for future human exploration of Mars.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Mars Simulation Chamber is being prepared for the Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, mission support. The chamber allows MIST scientists and engineers to simulate the stratosphere prior to high altitude flight experiments. The MIST mission will fly a small biological payload in low altitudes aboard a blimp in July to measure microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Later in the year, the MIST mission will deploy samples at even high altitudes in the stratosphere using scientific balloons. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
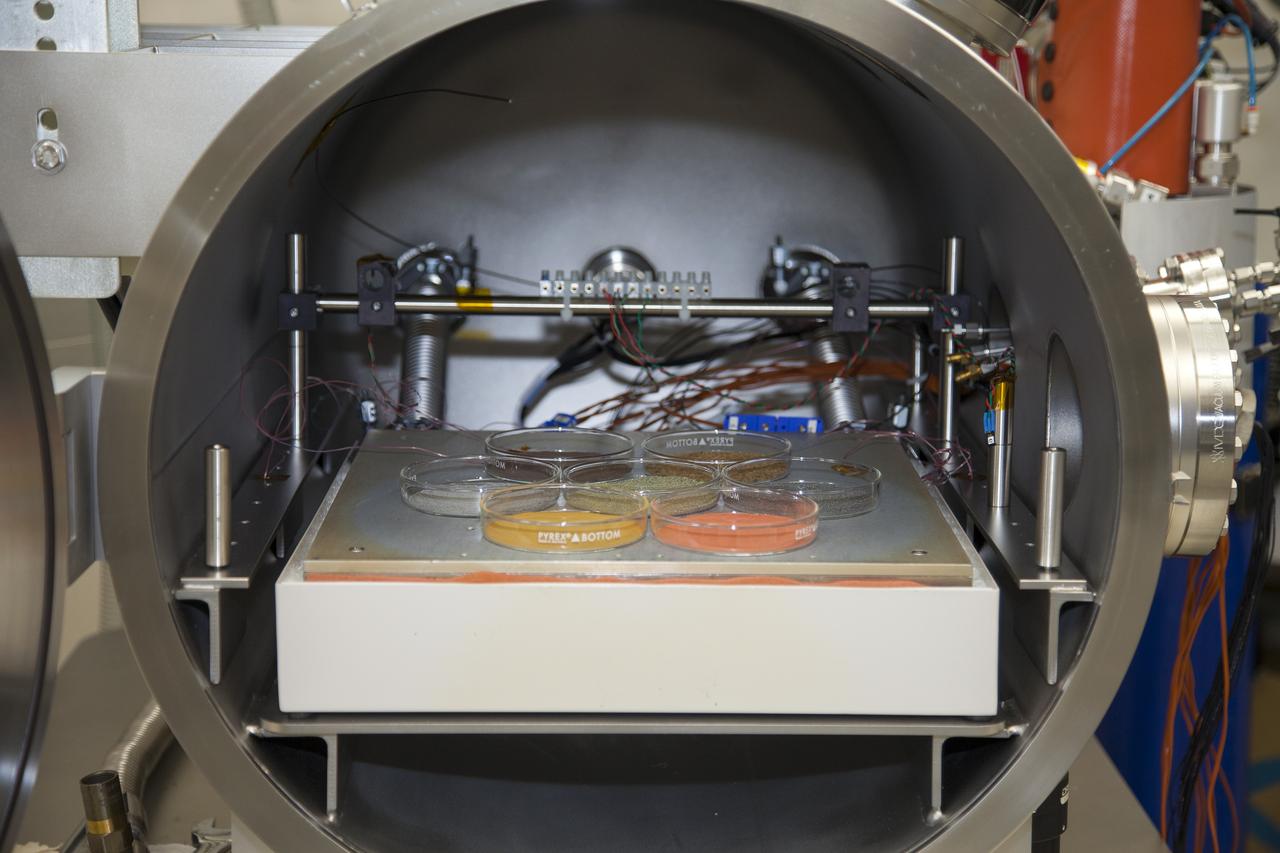

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Mars Simulation Chamber is being prepared for the Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, mission support. The chamber allows MIST scientists and engineers to simulate the stratosphere prior to high altitude flight experiments. The MIST mission will fly a small biological payload aboard a blimp in July to measure microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Later in the year, the MIST mission will deploy samples at even higher altitudes in the stratosphere using scientific balloons. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
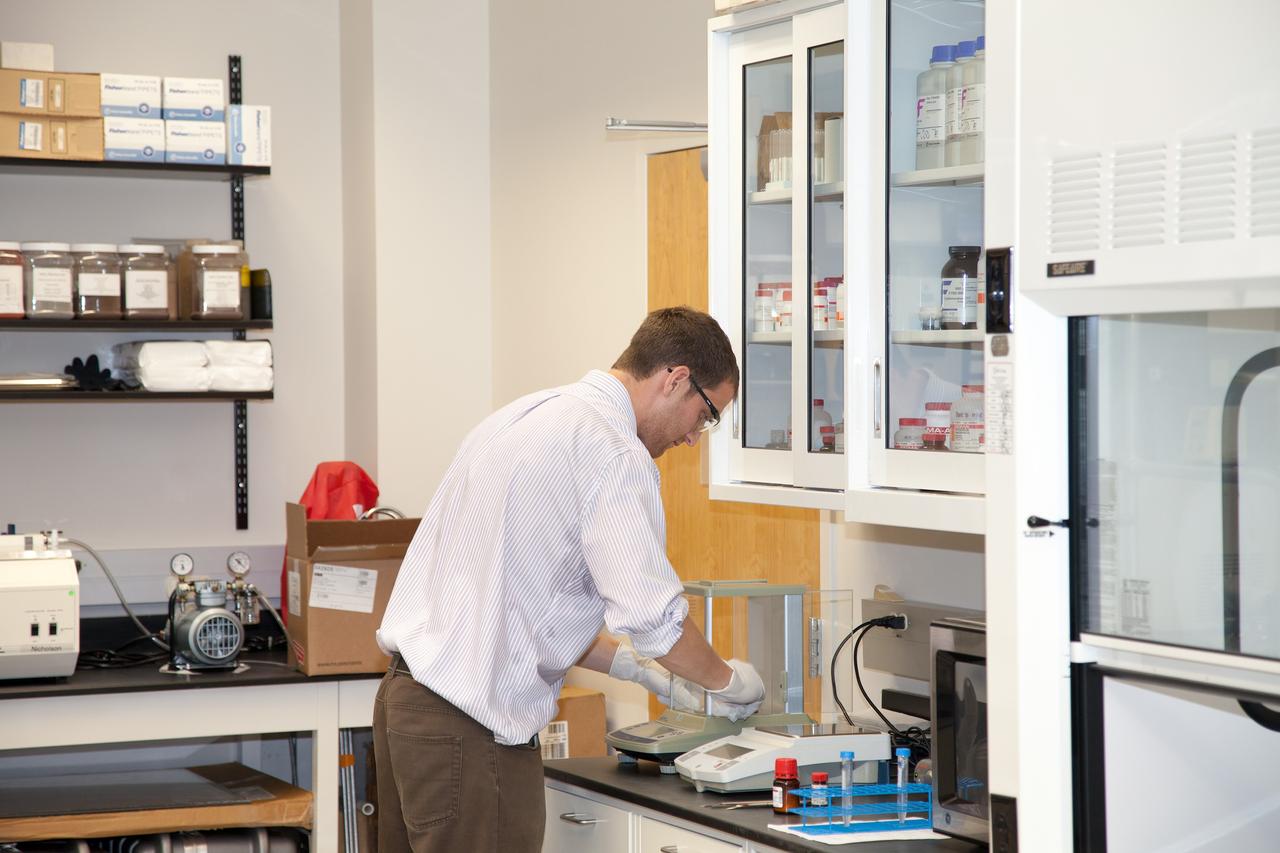

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Dr. David J. Smith, a microbiologist in the Surface Systems Office, prepares microbes that will be deployed for the Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, mission. High altitudes exert a unique combination of stresses on microbes, outside the range of conditions normally encountered on the Earth's surface. Results from MIST may improve our understanding of the physical limits and habitable environments for life. The MIST mission will fly a small biological payload aboard a blimp in July to measure microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmoshere. Later in the year, the MIST mission will deploy samples at even higher altitudes in the stratosphere using scientific balloons. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
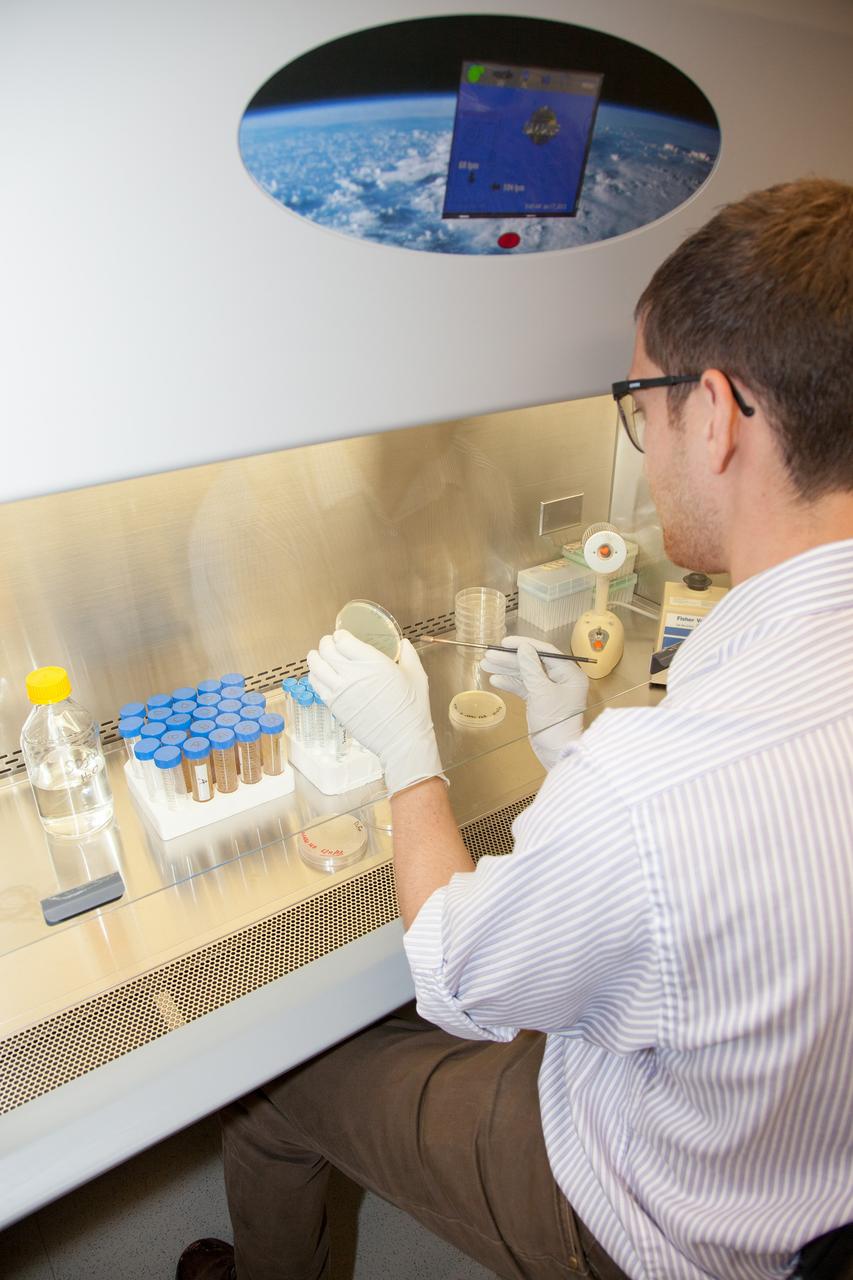

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Dr. David J. Smith, a microbiologist in the Surface Systems Office, prepares microbes that will be deployed for the Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, mission. High altitudes exert a unique combination of stresses on microbes, outside the range of conditions normally encountered on the Earth's surface. Results from MIST may improve our understanding of physical limits and habitable environments for life. The MIST mission will fly a small biological payload aboard a blimp in July to measure microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Later in the year, the MIST mission will deploy samples at even higher altitudes in the stratosphere using scientific balloons. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
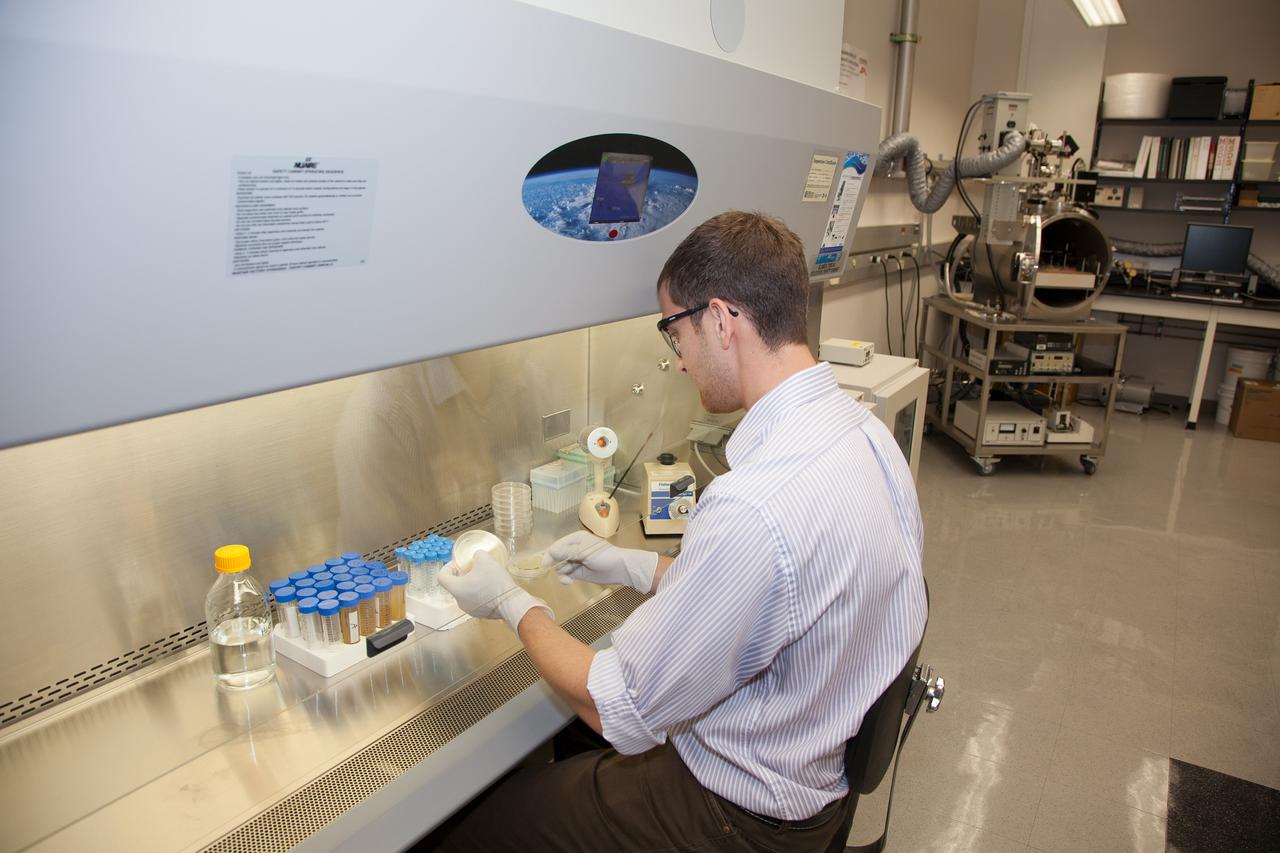

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Dr. David J. Smith, a microbiologist in the Surface Systems Office, prepares microbes that will be deployed for the Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, mission. High altitudes exert a unique combination of stresses on microbes, outside the range of conditions normally encountered on the Earth's surface. Results from MIST may improve our understanding of the physical limits and habitable environments for life. The MIST mission will fly a small biological payload aboard a blimp in July to measure the microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Later in the year, the MIST mission will deploy samples at even higher altitudes in the stratosphere using scientific balloons. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
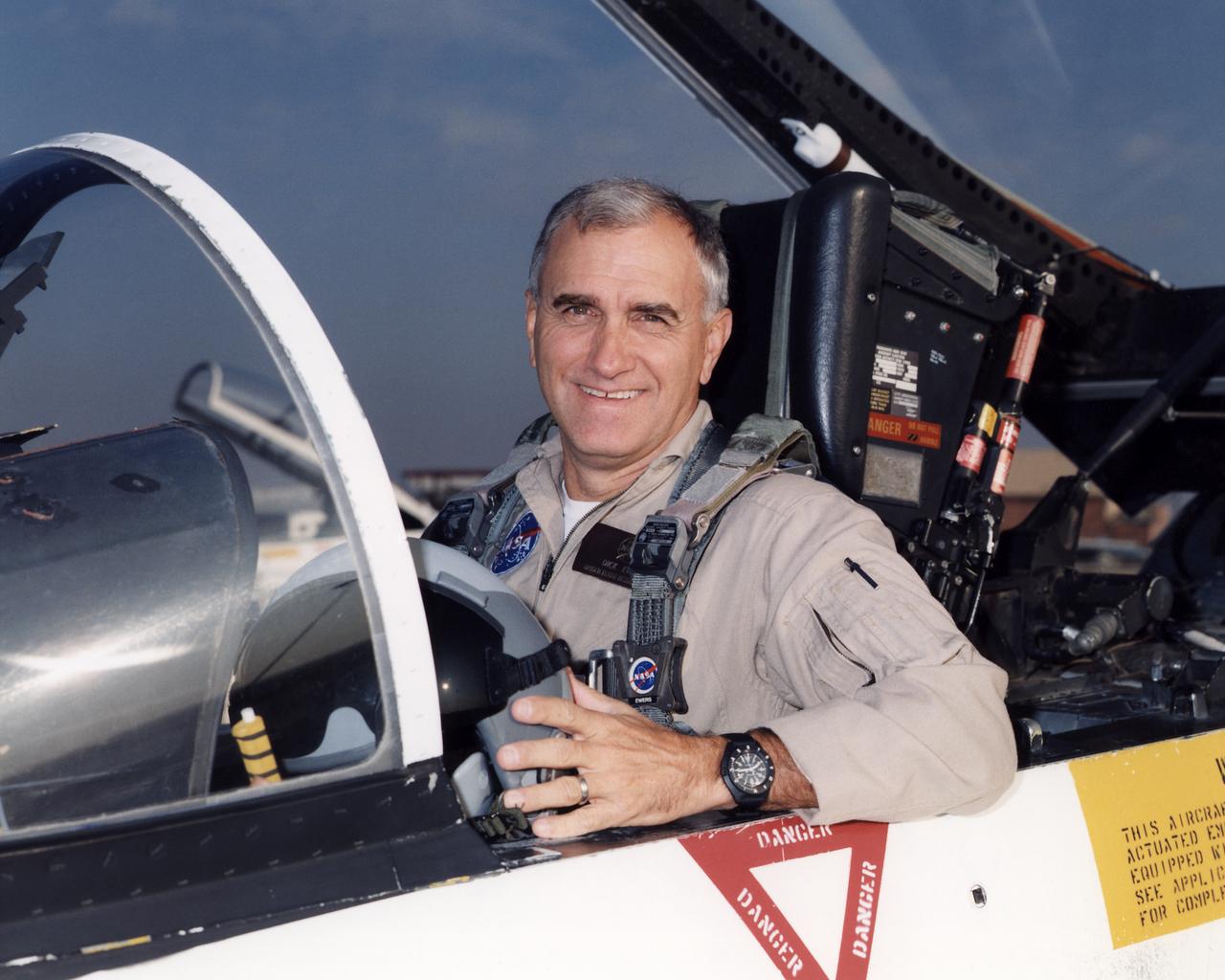

Richard G. (Dick) Ewers became a pilot in the Flight Crew Branch of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, in May 1998. His flying duties focus on operation of the Airborne Science DC-8 and Systems Research F/A-18 aircraft, but he also maintains qualifications in the King Air and T-34C. He has more than 32 years and nearly 9,000 hours of military and civilian flight experience in all types of aircraft from jet fighters to blimps. Ewers came to NASA Dryden from a position as an engineering test pilot with Northrop Grumman's Electronic Sensors and Systems Division (formerly Westinghouse's Electronic Systems Group). He spent eight and a half years with Westinghouse flight testing radar and forward looking infrared systems under development for military and civilian use. Before going to work for Westinghouse, Ewers served for more than 21 years as a U.S. Marine Corps fighter and test pilot, flying F-4, A-4, and F/A-18 aircraft. He underwent flight training at Naval Air Station Pensacola, Fla., in 1969-70. He was subsequently assigned to both fighter/attack and reconnaissance squadrons before ultimately commanding an F-4S squadron for two years. Additionally, his flying included combat service in Vietnam and operational exchange tours with both U.S. Navy and U.S. Air Force squadrons flying F-4s around the world, including off aircraft carriers. Ewers graduated from the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School in 1981 and subsequently served two tours as a test pilot at the Naval Air Test Center, Patuxent River, Md. Most of his flight test experience was with the F/A-18 Hornet. He retired from the Marine Corps in 1989 with the rank of lieutenant colonel. Ewers graduated from the U.S. Air Force Academy in 1968 with a bachelor of science degree in engineering mechanics. He earned a master of science degree in aeronautical systems from the University of West Florida in 1970.

Caption: A NASA Super Pressure Balloon with the COSI payload is ready for launch from McMurdo, Antarctica. Credit: NASA More info: NASA’s globetrotting Balloon Program Office is wrapping up its 2014-2015 Antarctic campaign while prepping for an around-the-world flight launching out of Wanaka, New Zealand, in March. After 16 days, 12 hours, and 56 minutes of flight, operators successfully conducted a planned flight termination of the Suborbital Polarimeter for Inflation Dust and the Epoch of Reionization (SPIDER) mission Saturday, Jan. 18, the final mission of the campaign. Other flights in the 2014-2015 Antarctic campaign included the Antarctic Impulsive Transient Antenna (ANITA-III) mission as well as the Compton Spectrometer and Imager (COSI) payload flown on the developmental Super Pressure Balloon (SPB). ANITA-III successfully wrapped up Jan. 9 after 22 days, 9 hours, and 14 minutes of flight. Flight controllers terminated the COSI flight 43 hours into the mission after detecting a small gas leak in the balloon. Crews are now working to recover all three instruments from different locations across the continent. The 6,480-pound SPIDER payload is stationary at a position about 290 miles from the United Kingdom’s Sky Blu Logistics Facility in Antarctica. The 4,601 pound ANITA-III payload, located about 100 miles from Australia’s Davis Station, and the 2,866 pound COSI payload, located about 340 miles from the United States McMurdo Station both had numerous key components recovered in the past few days. Beginning in late January, the Balloon Program Office will deploy a team to Wanaka, New Zealand, to begin preparations for an SPB flight, scheduled to launch in March. The Program Office seeks to fly the SPB more than 100 days, which would shatter the current flight duration record of 55 days, 1 hour, and 34 minutes for a large scientific balloon. “We’re looking forward to the New Zealand campaign and hopefully a history-making flight with the Super Pressure Balloon,” said Debbie Fairbrother, NASA’s Balloon Program Office Chief. Most scientific balloons see altitude variances based on temperature changes in the atmosphere at night and during the day. The SPB is capable of missions on the order of 100 days or more at constant float altitudes due to the pressurization of the balloon. “Stable, long-duration flights at near-space altitudes above more than 99 percent of the atmosphere are highly desirable in the science community, and we’re ready to deliver,” said Fairbrother. In addition to the SPB flight in March, the Balloon Program Office has 10 more balloon missions planned through September 2015 to include scheduled test flights of the Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator, which is testing new technologies for landing larger, heavier payloads on Mars. NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility manages the agency’s Scientific Balloon Program with 10 to 15 flights each year from launch sites worldwide. The balloons are massive in volume; the average-sized balloon could hold the volume of nearly 200 blimps. Previous work on balloons have contributed to confirming the Big Bang Theory. For more information on NASA’s Scientific Balloon Program, see: <a href="http://sites.wff.nasa.gov/code820/index.html" rel="nofollow">sites.wff.nasa.gov/code820/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>