
NASA’s Artemis III core stage boat-tail and RS-25 engines are shown inside the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. Used during the assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) core stage for Artemis III, the boat tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage. NASA’s Pegasus barge delivered the boat-tail, along with other hardware for future Artemis campaigns to NASA Kennedy on Thursday, Sept. 5, 2024.

NASA’s Artemis III core stage boat-tail and RS-25 engines are shown inside the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. Used during the assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) core stage for Artemis III, the boat tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage. NASA’s Pegasus barge delivered the boat-tail, along with other hardware for future Artemis campaigns to NASA Kennedy on Thursday, Sept. 5, 2024.
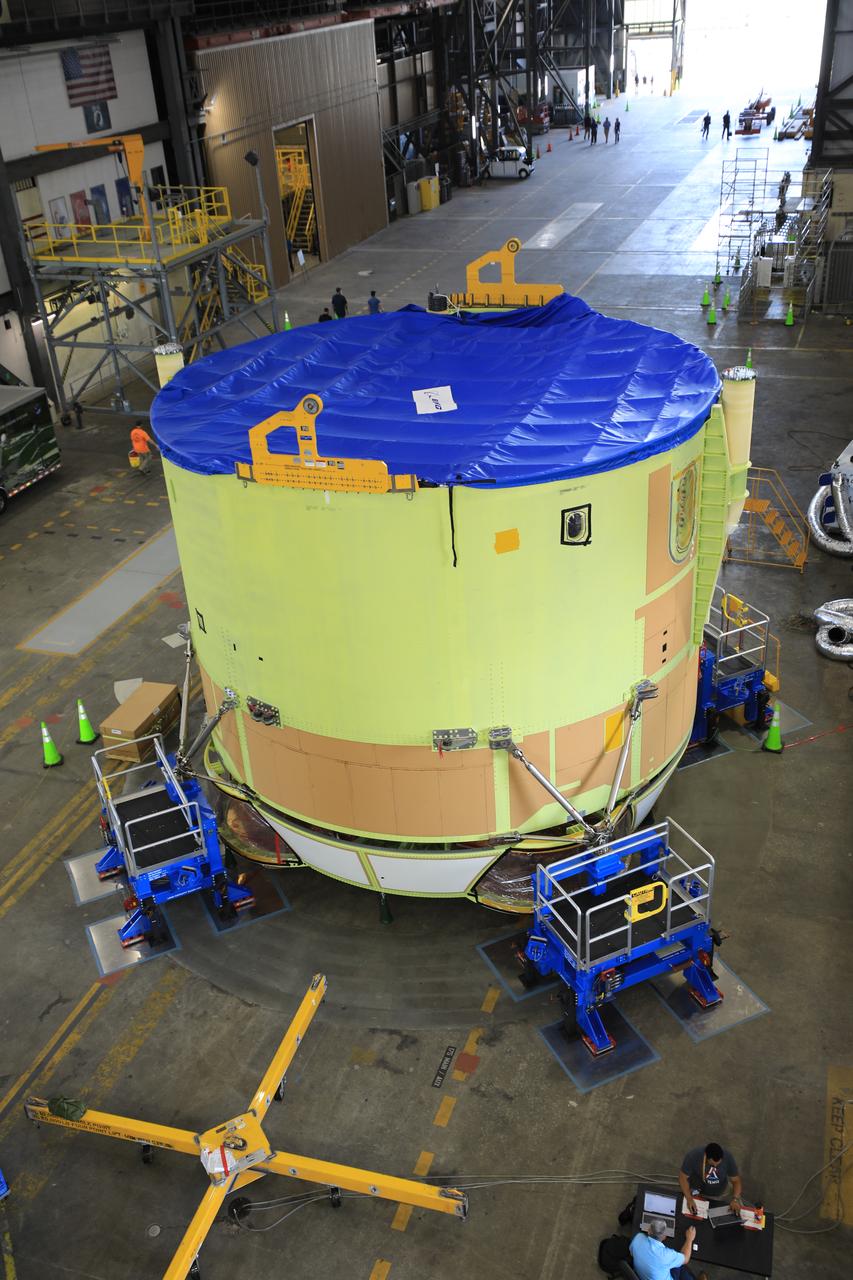

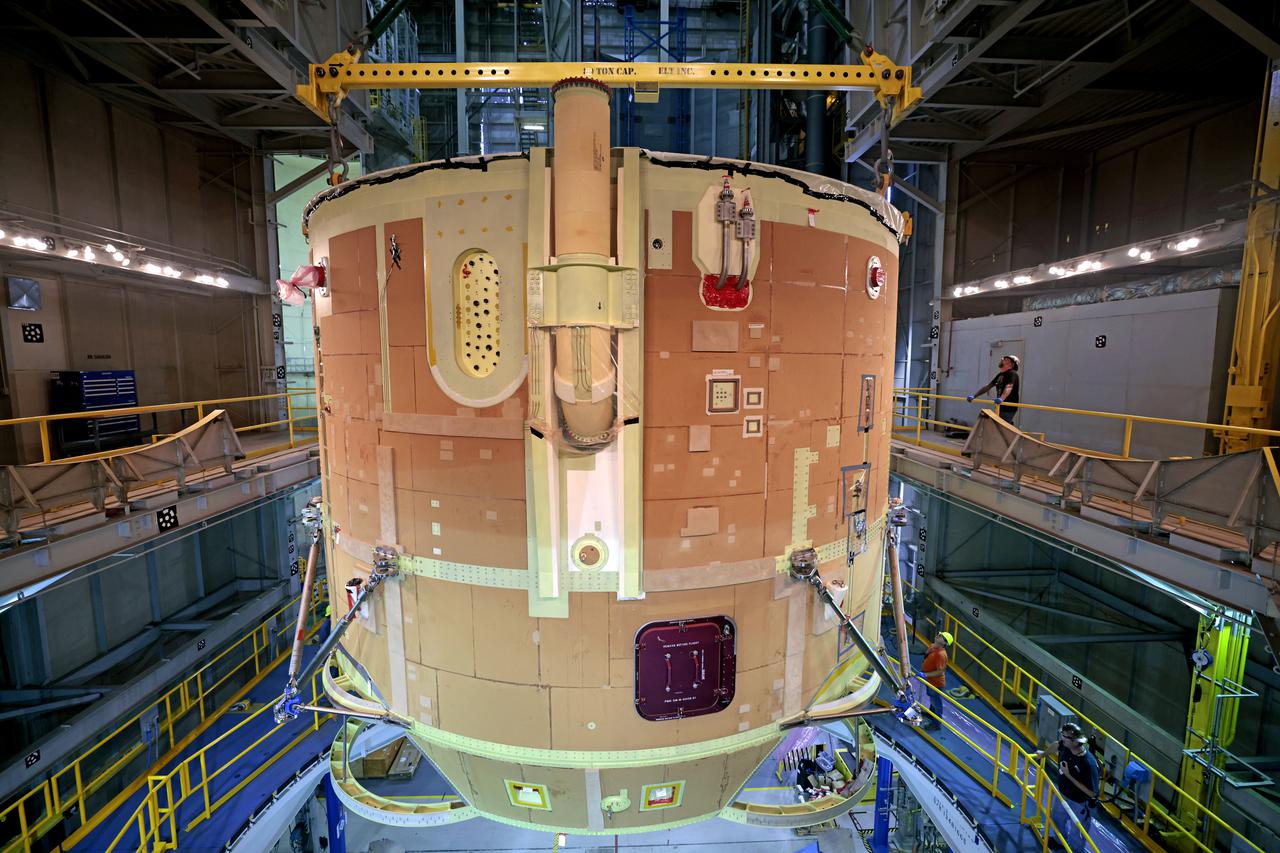
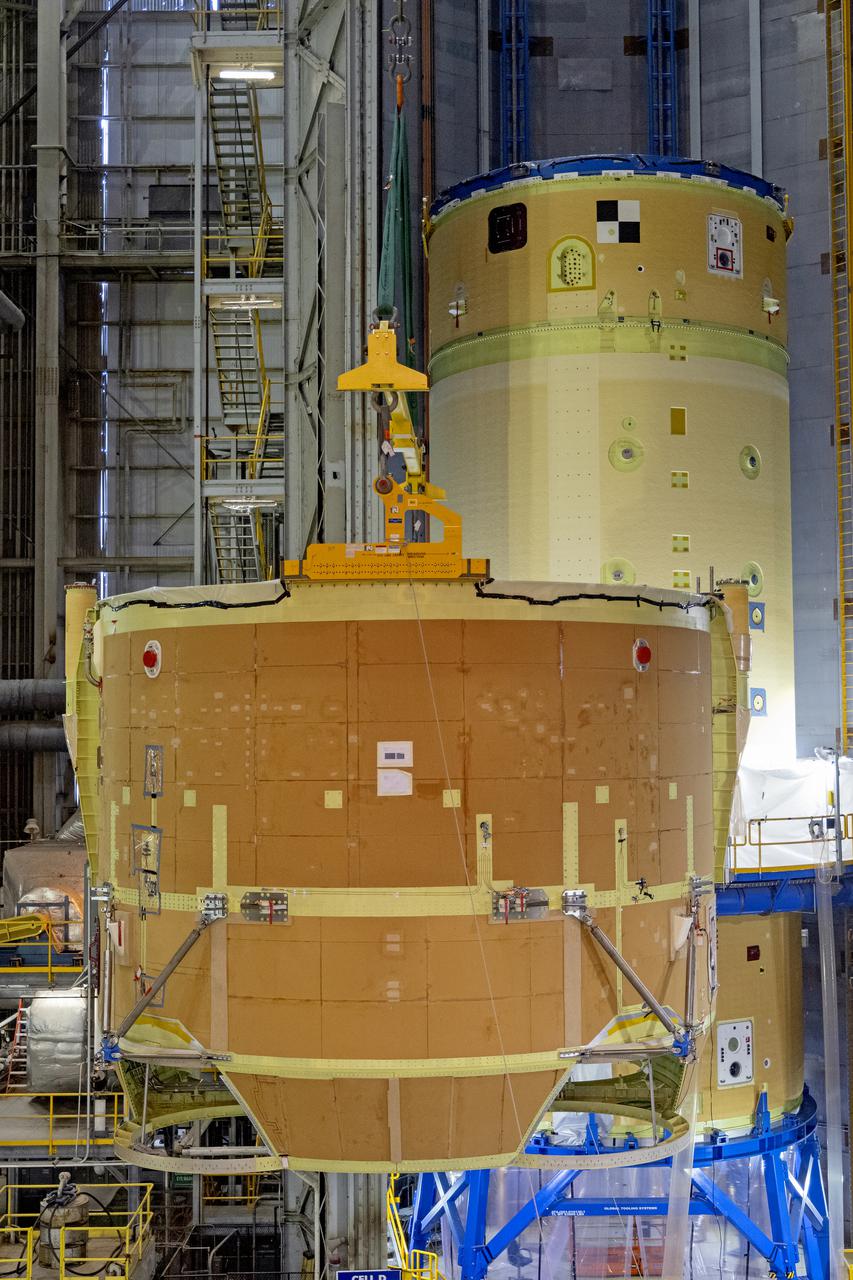
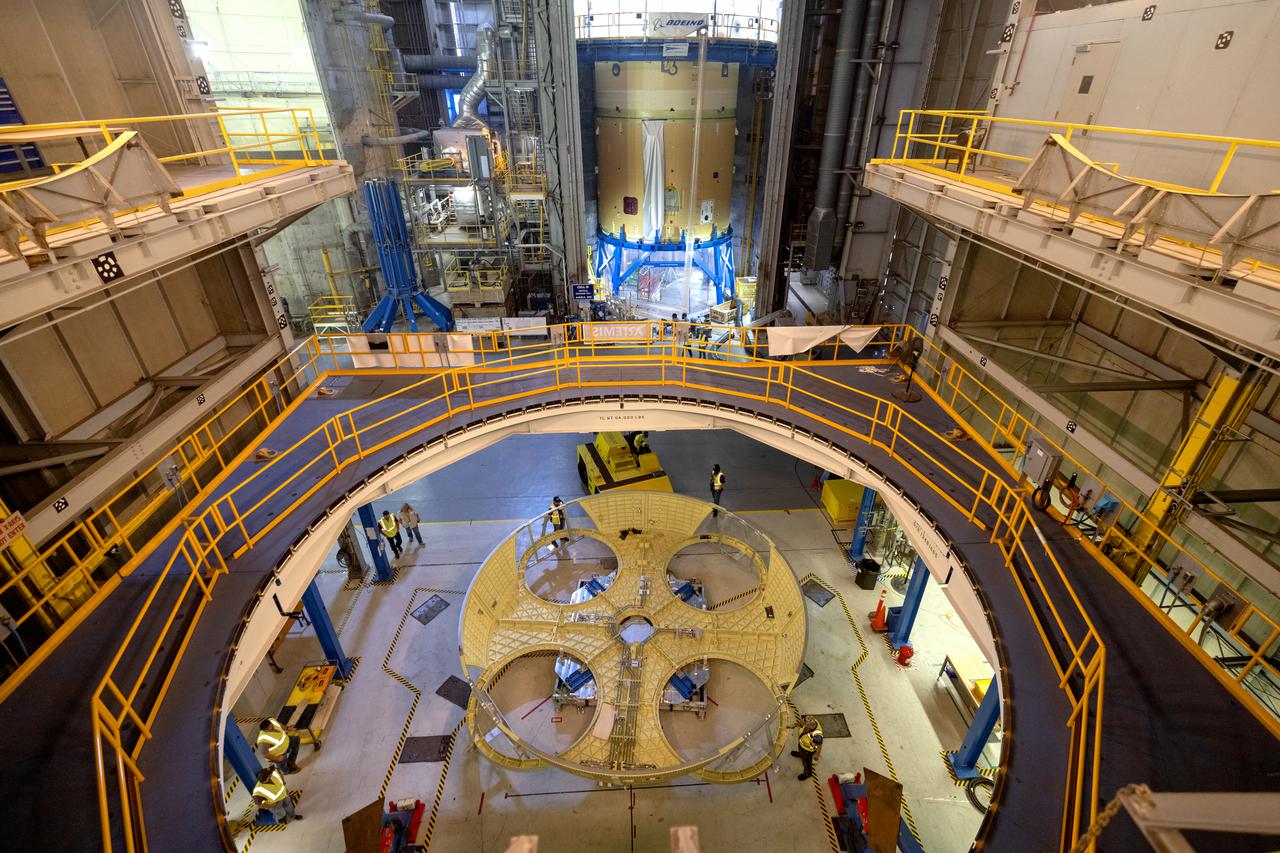
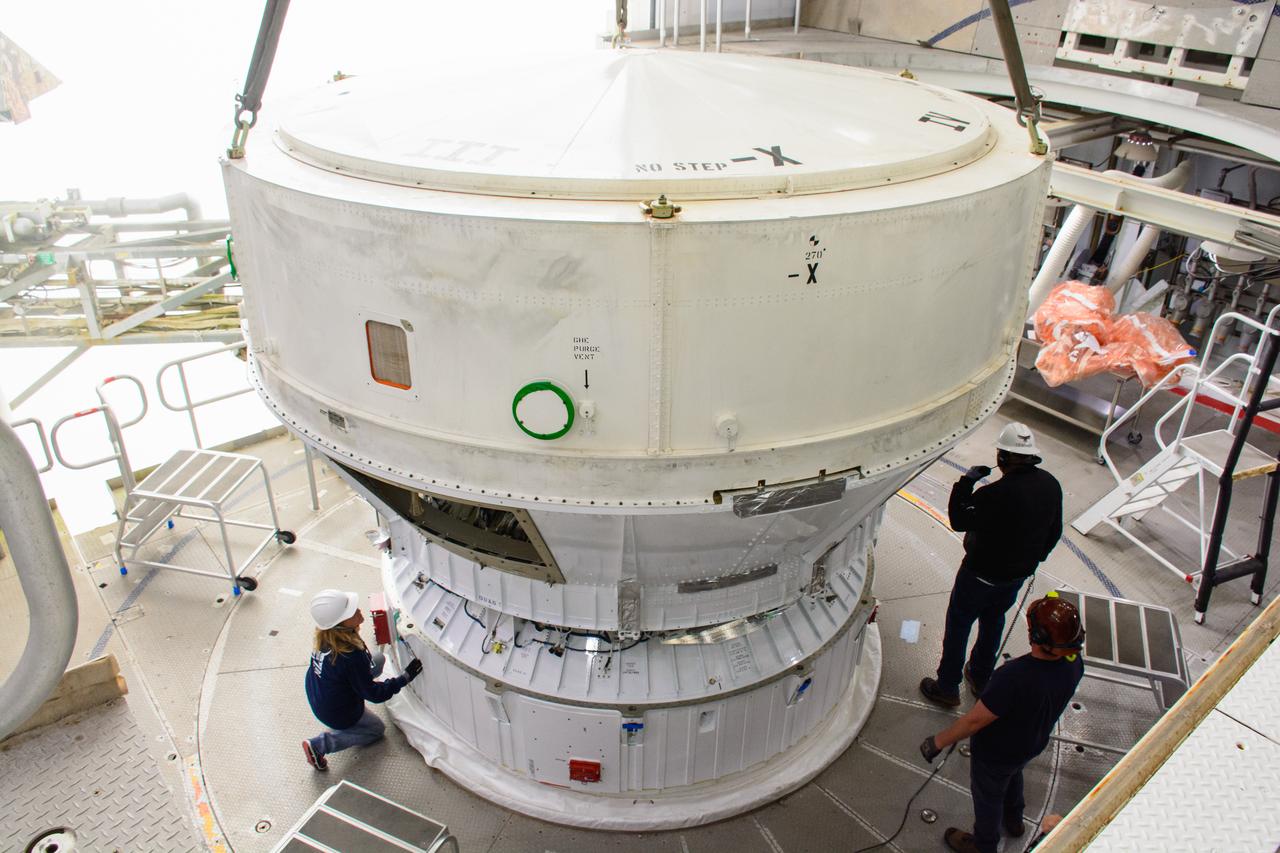
Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.

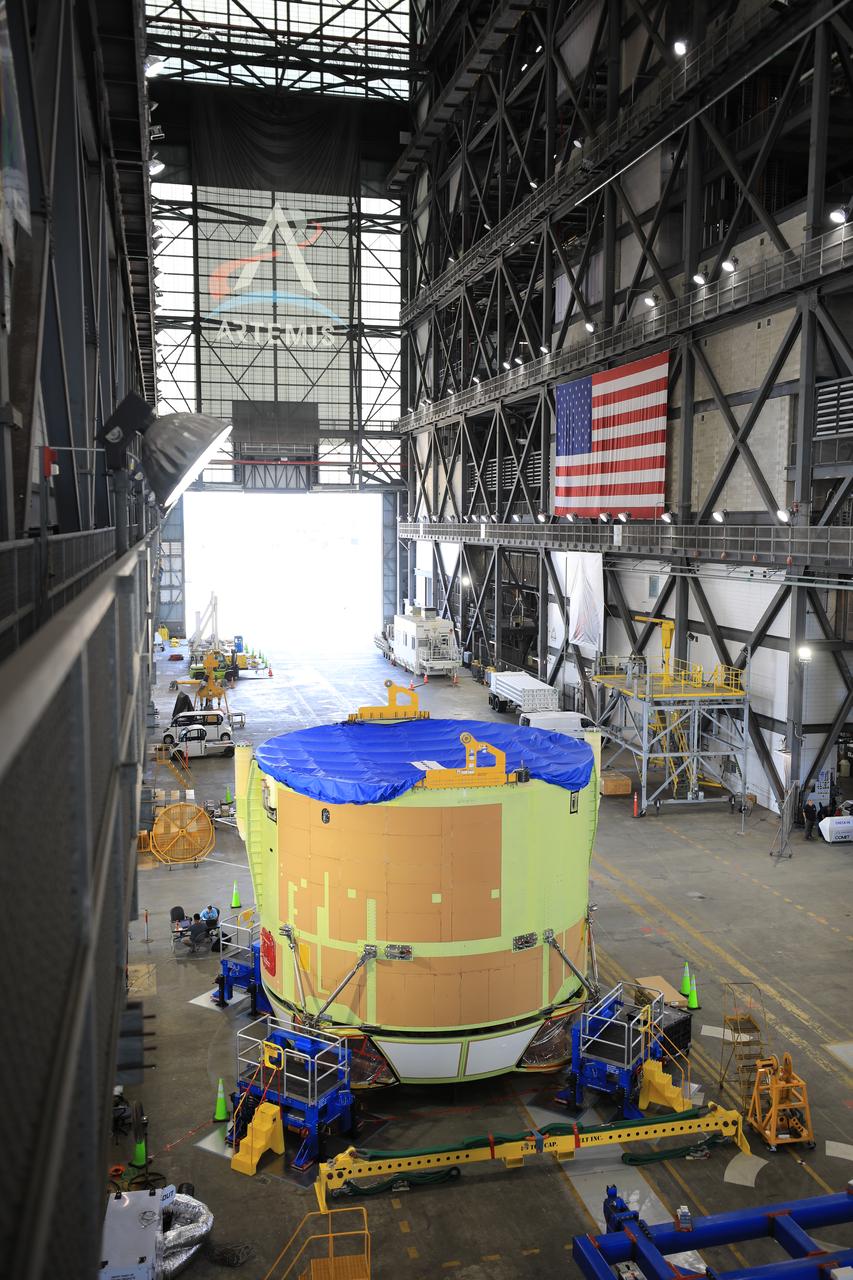
Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.

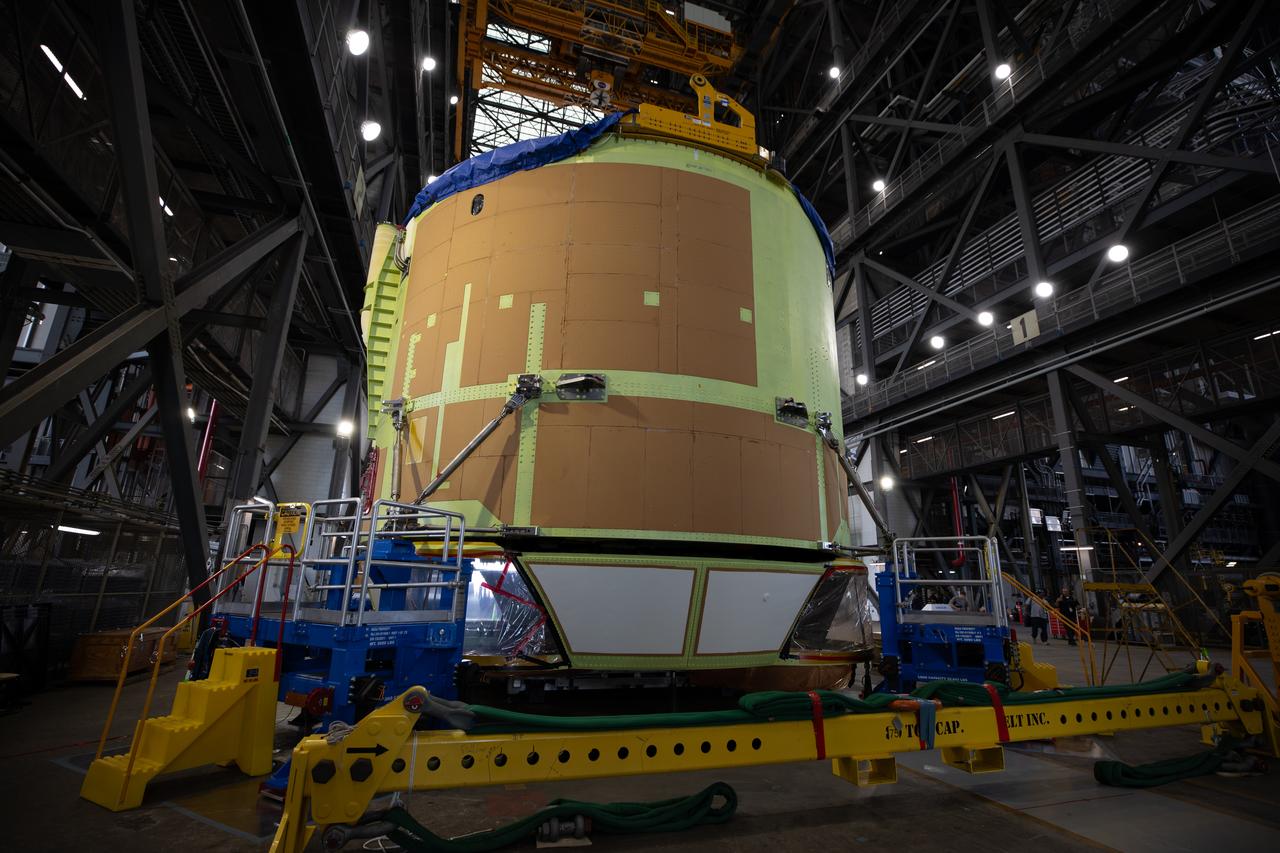
Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
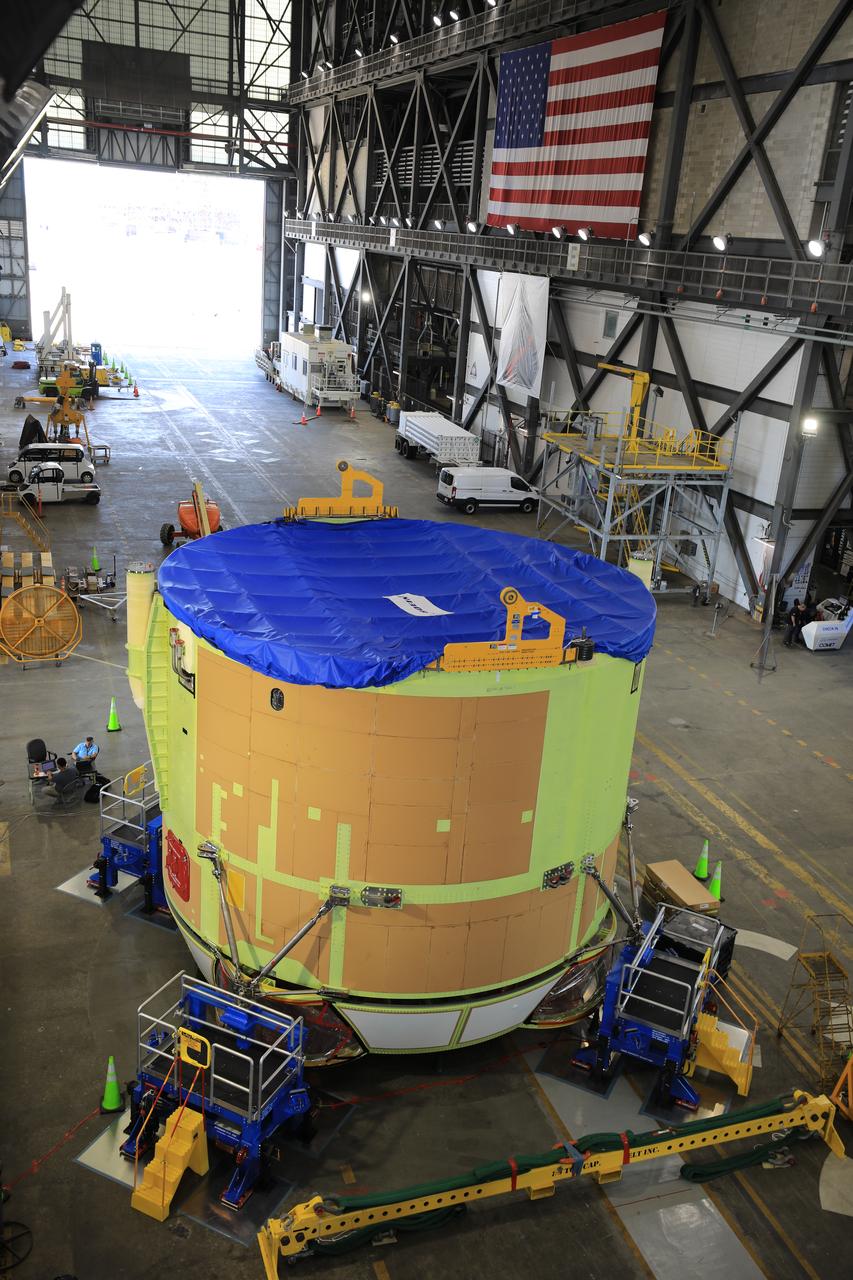

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida integrate NASA’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 30, 2025. The boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage, while the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
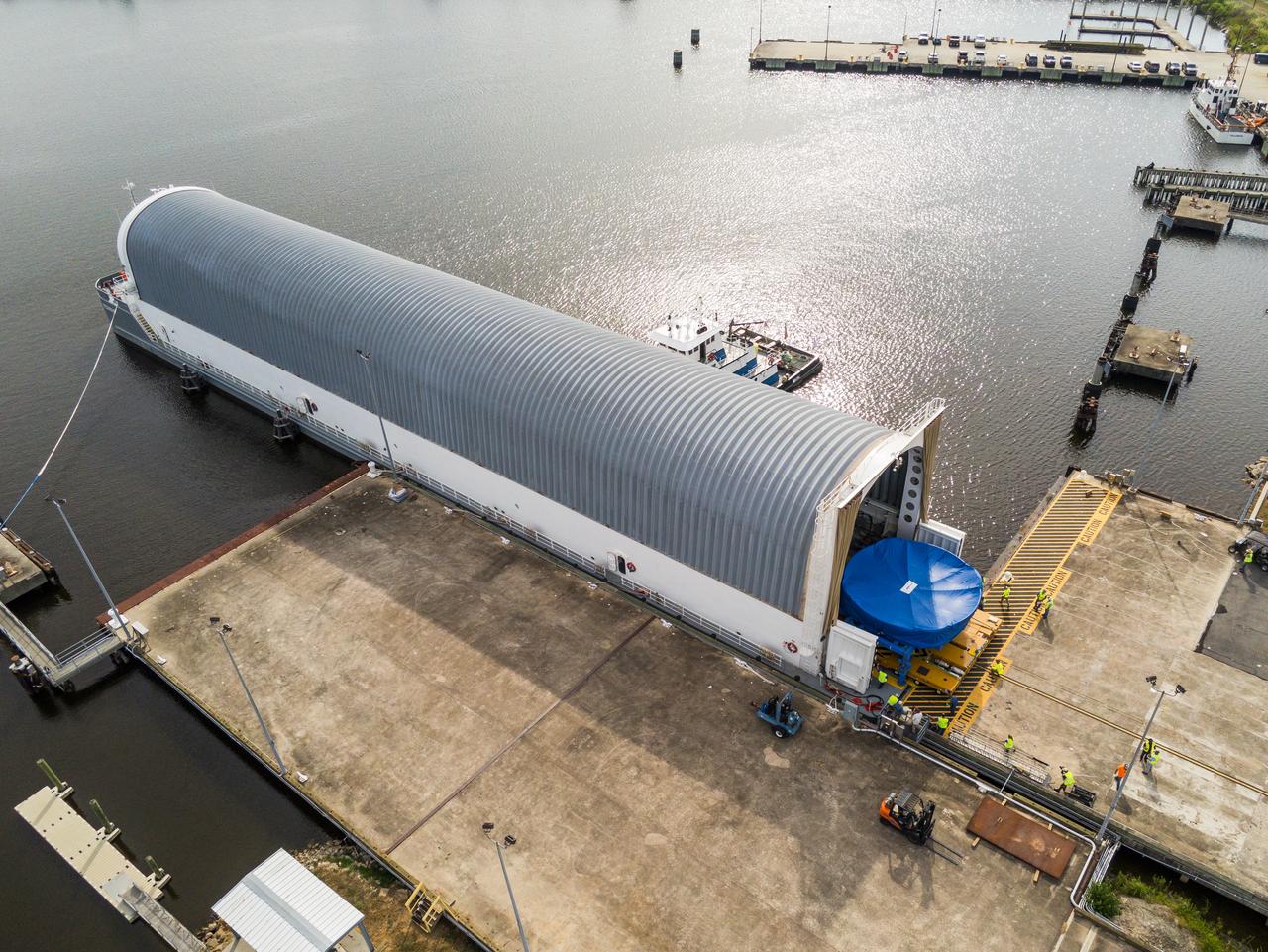

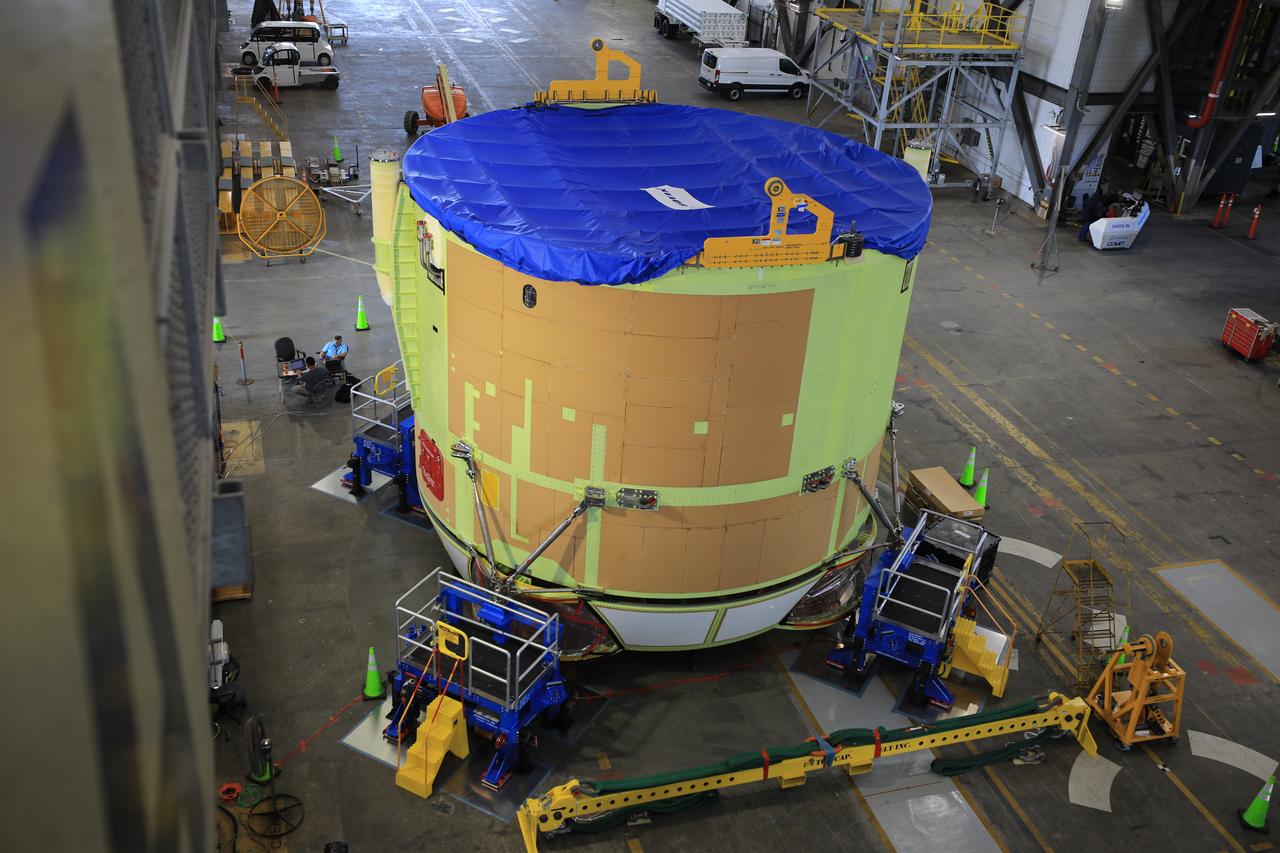
These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
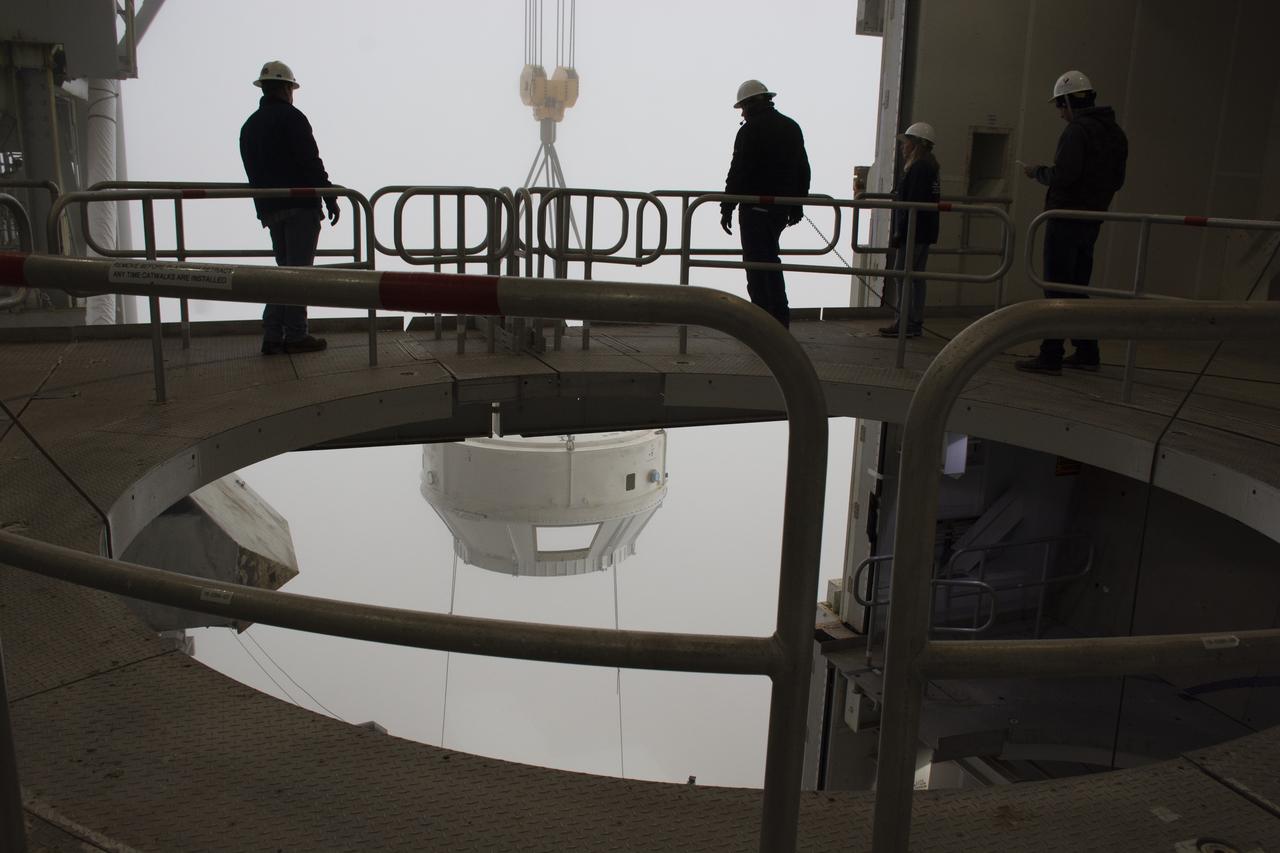

JPSS-2 Boat Tail transport and mate from HIF to SLC-3 and SLC-3, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
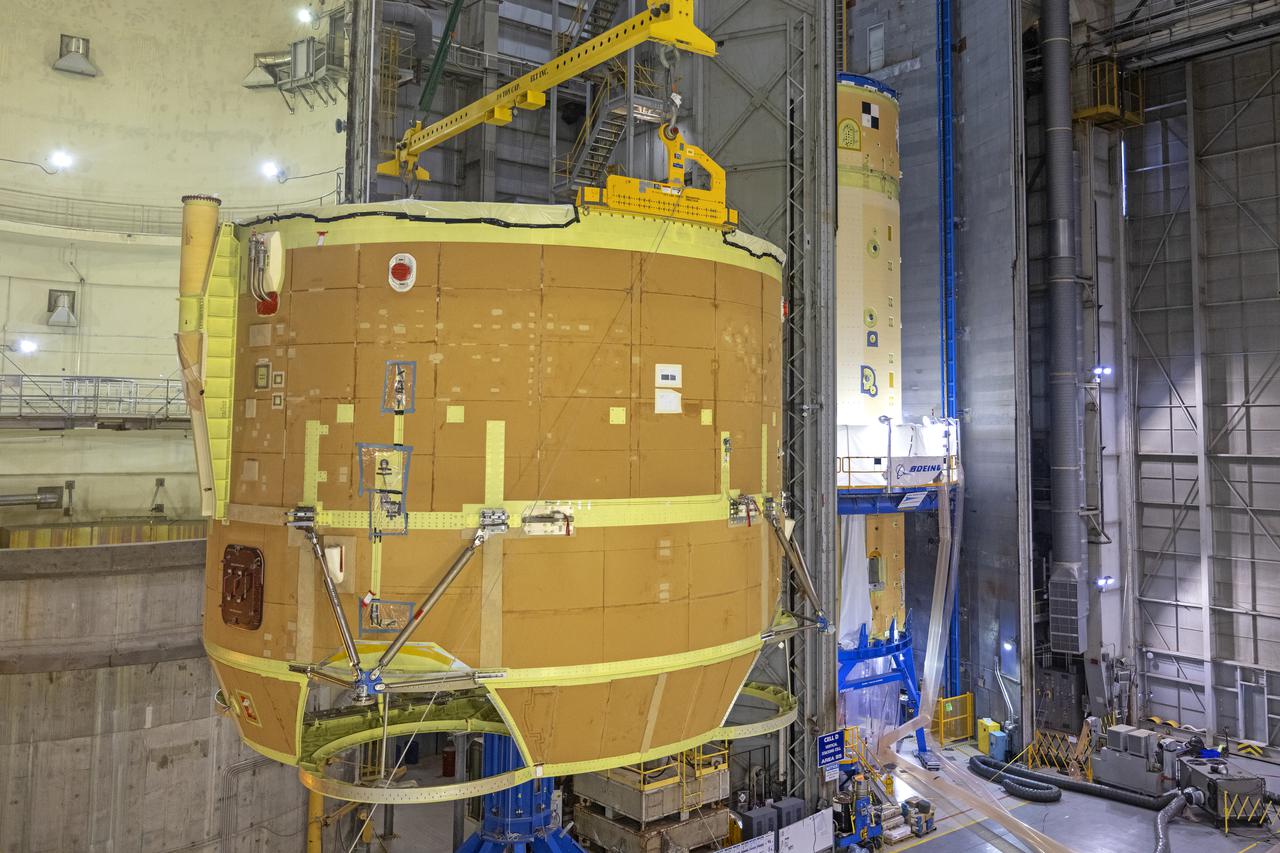

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility have joined the engine and boat-tail sections of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II in preparation for its next step in production. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines and was joined with the engine section to comprise the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility have joined the engine and boat-tail sections of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II in preparation for its next step in production. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines and was joined with the engine section to comprise the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility have joined the engine and boat-tail sections of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II in preparation for its next step in production. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines and was joined with the engine section to comprise the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

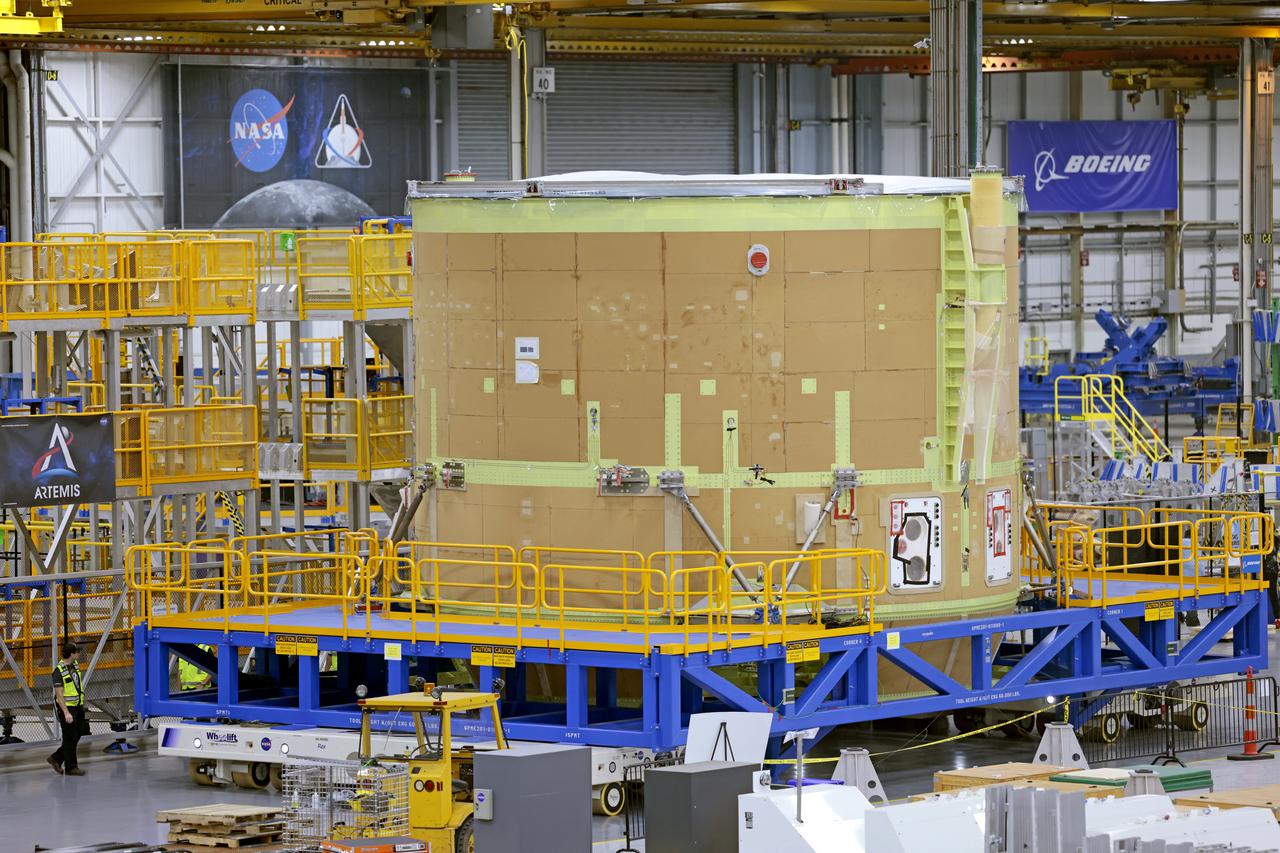
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility have joined the engine and boat-tail sections of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II in preparation for its next step in production. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines and was joined with the engine section to comprise the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

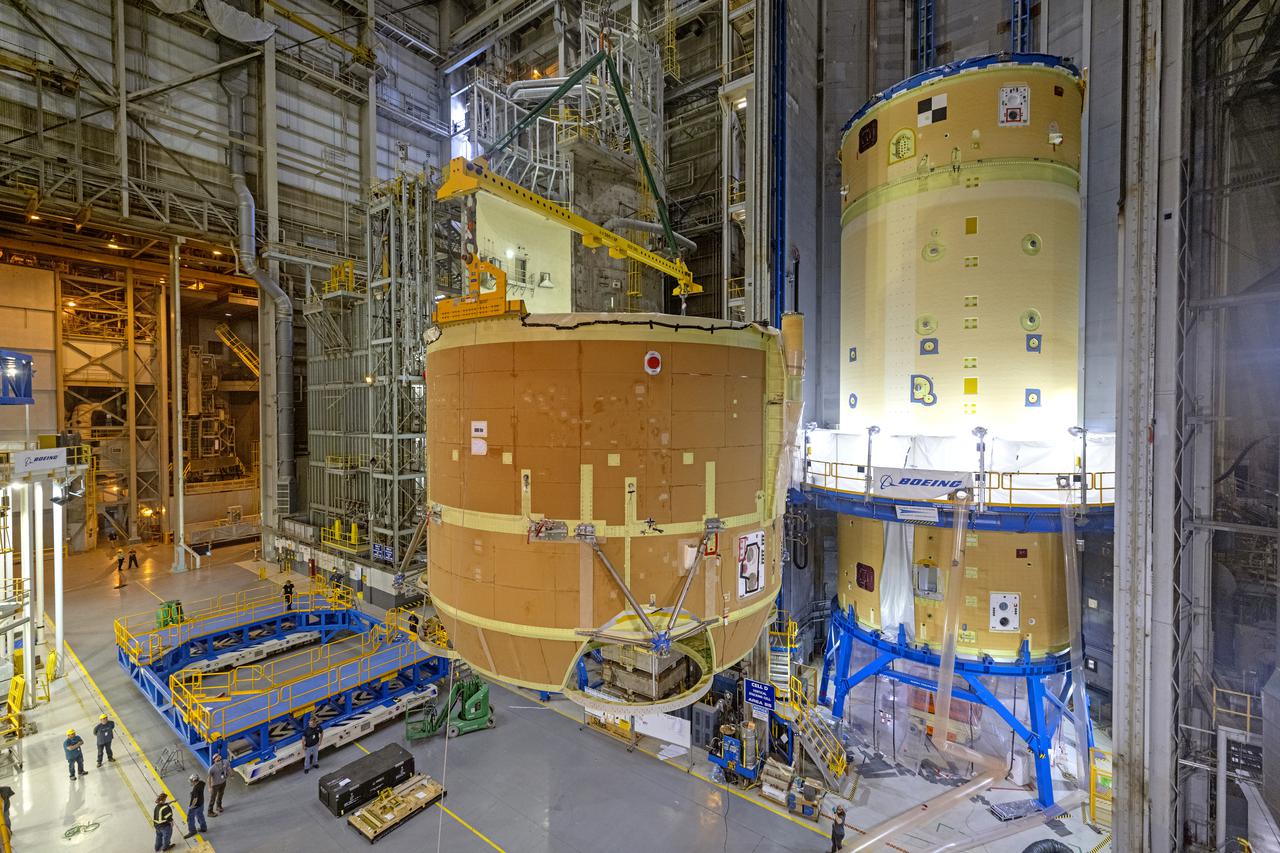
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility have joined the engine and boat-tail sections of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II in preparation for its next step in production. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines and was joined with the engine section to comprise the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility have joined the engine and boat-tail sections of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II in preparation for its next step in production. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines and was joined with the engine section to comprise the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

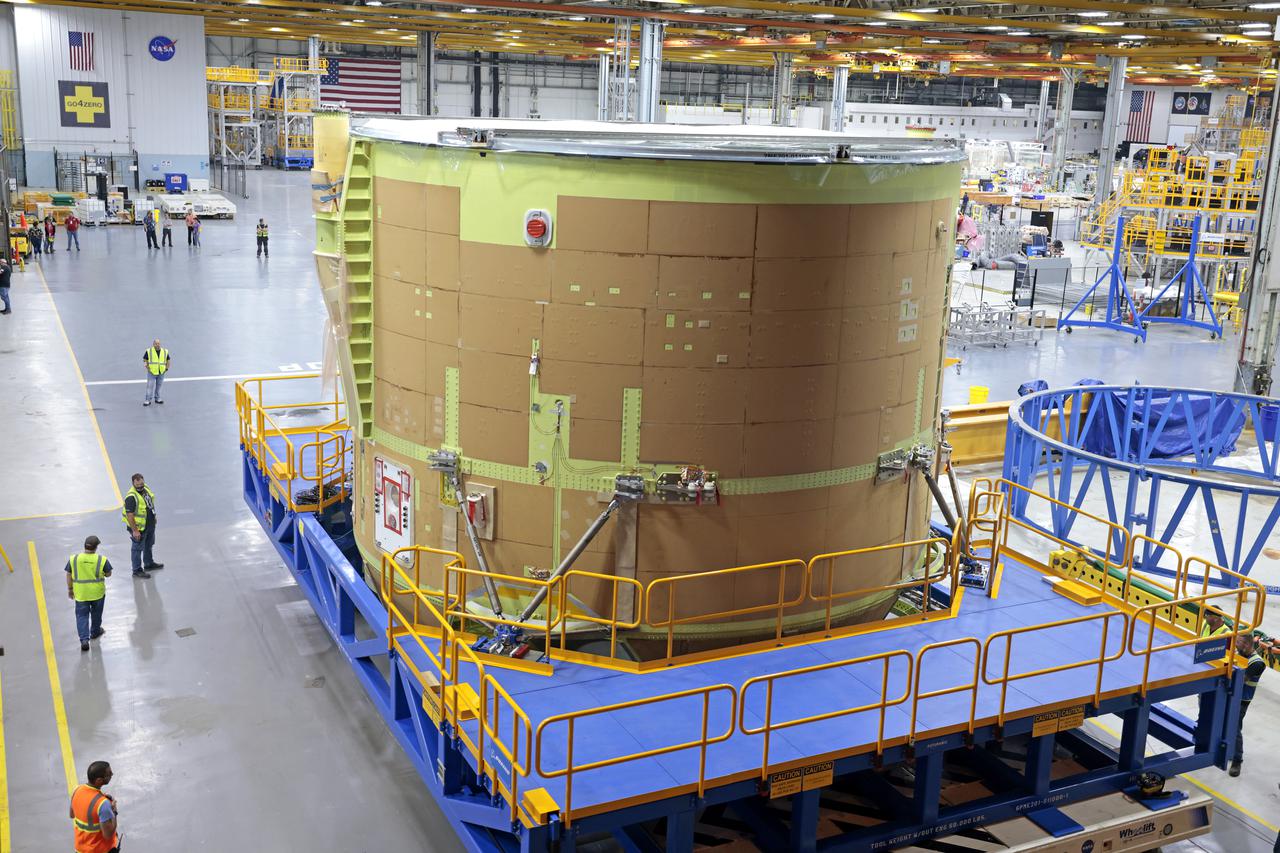
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility have joined the engine and boat-tail sections of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II in preparation for its next step in production. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines and was joined with the engine section to comprise the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility have joined the engine and boat-tail sections of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II in preparation for its next step in production. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines and was joined with the engine section to comprise the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility have joined the engine and boat-tail sections of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II in preparation for its next step in production. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines and was joined with the engine section to comprise the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility have joined the engine and boat-tail sections of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II in preparation for its next step in production. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines and was joined with the engine section to comprise the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility have joined the engine and boat-tail sections of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II in preparation for its next step in production. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines and was joined with the engine section to comprise the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
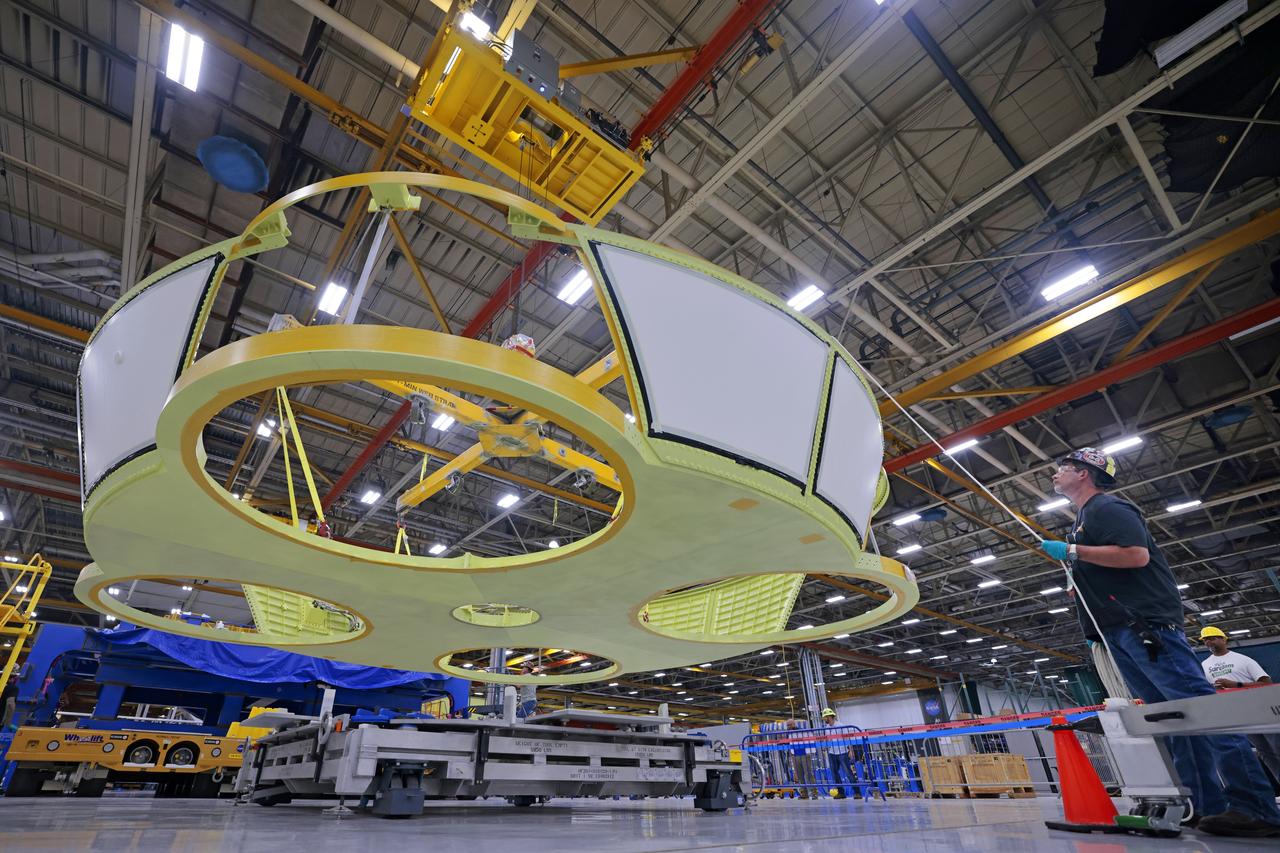

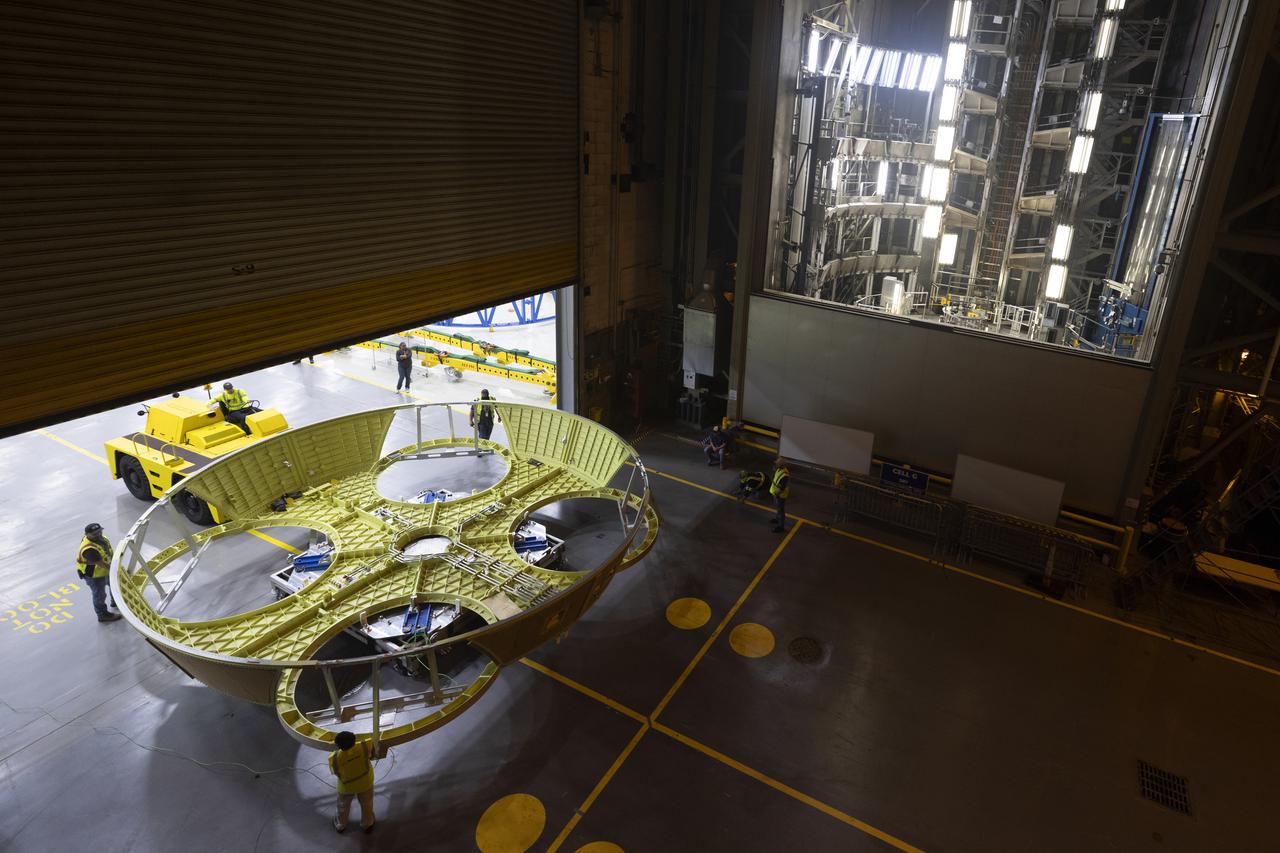
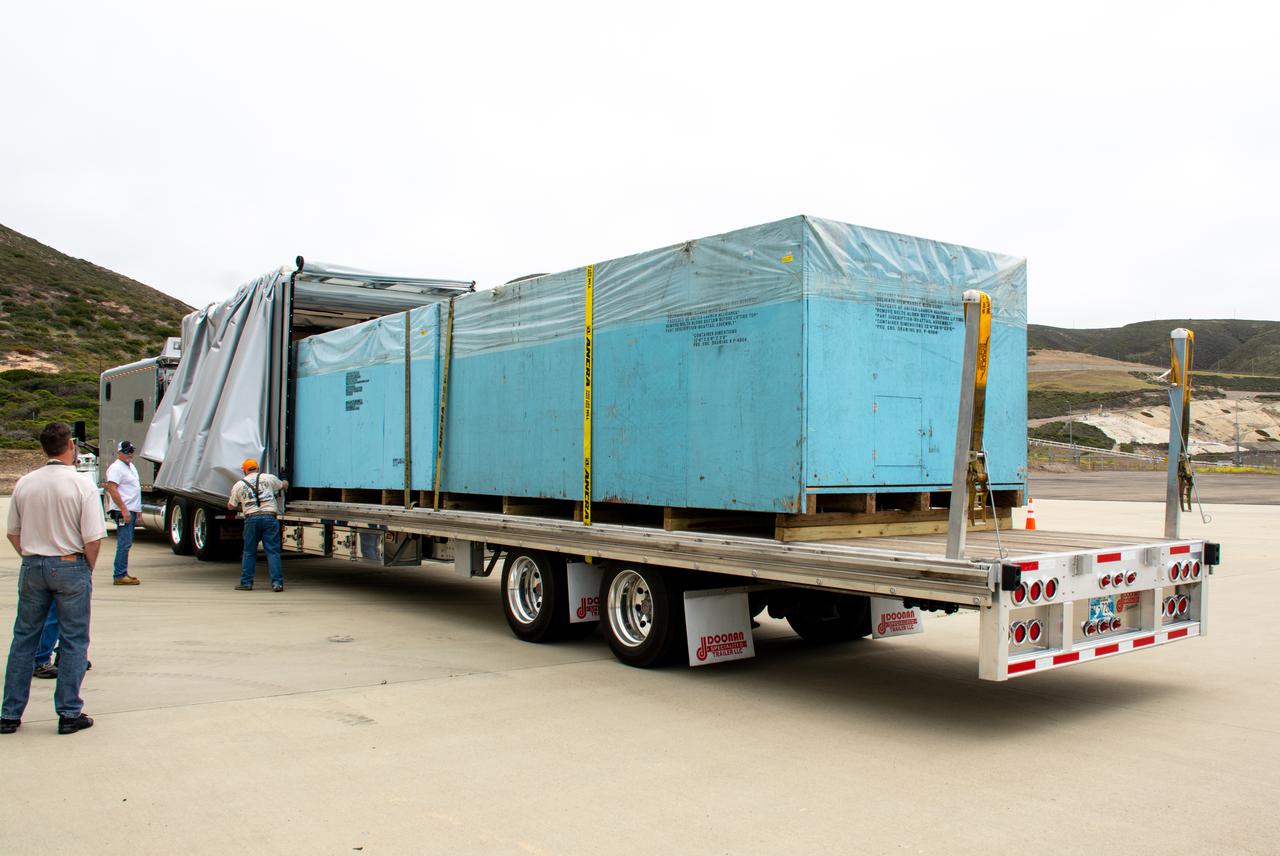
These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
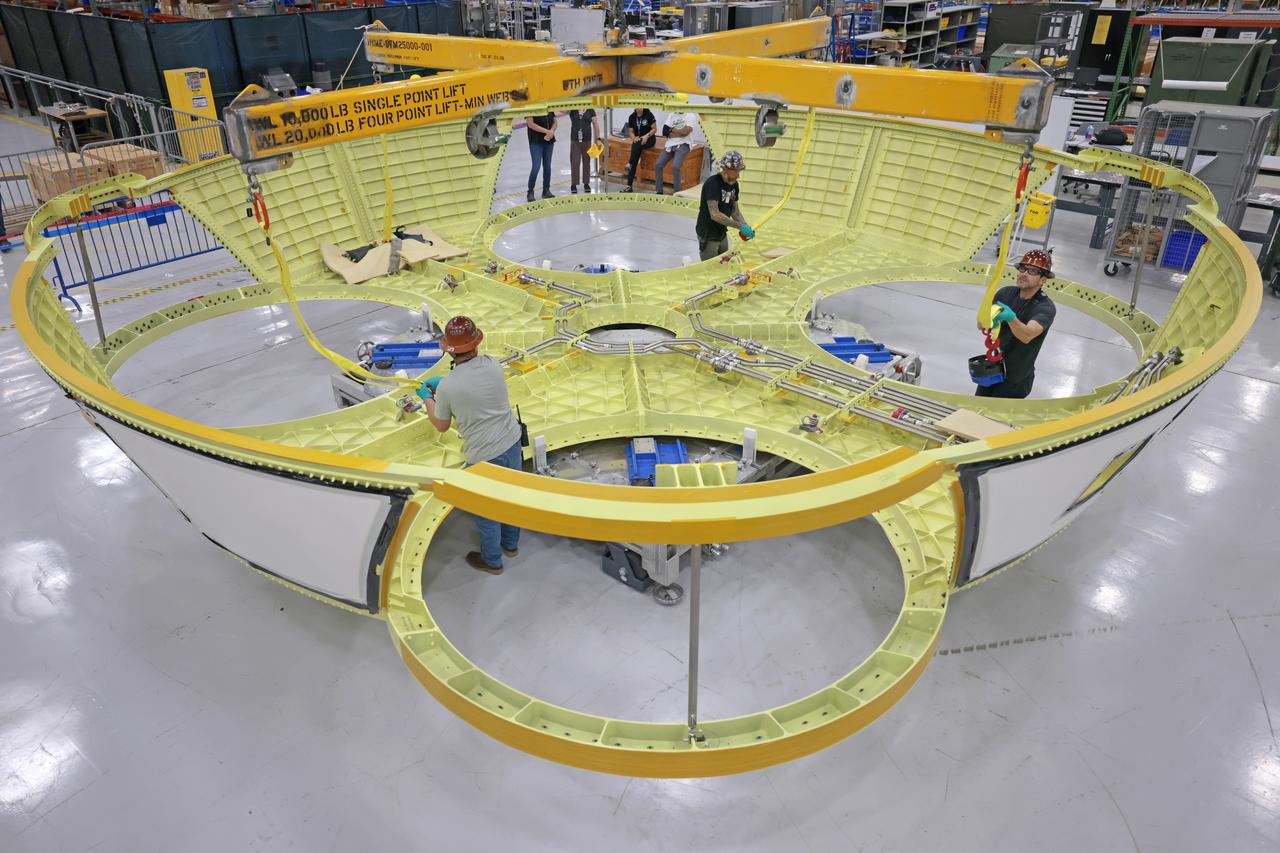

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
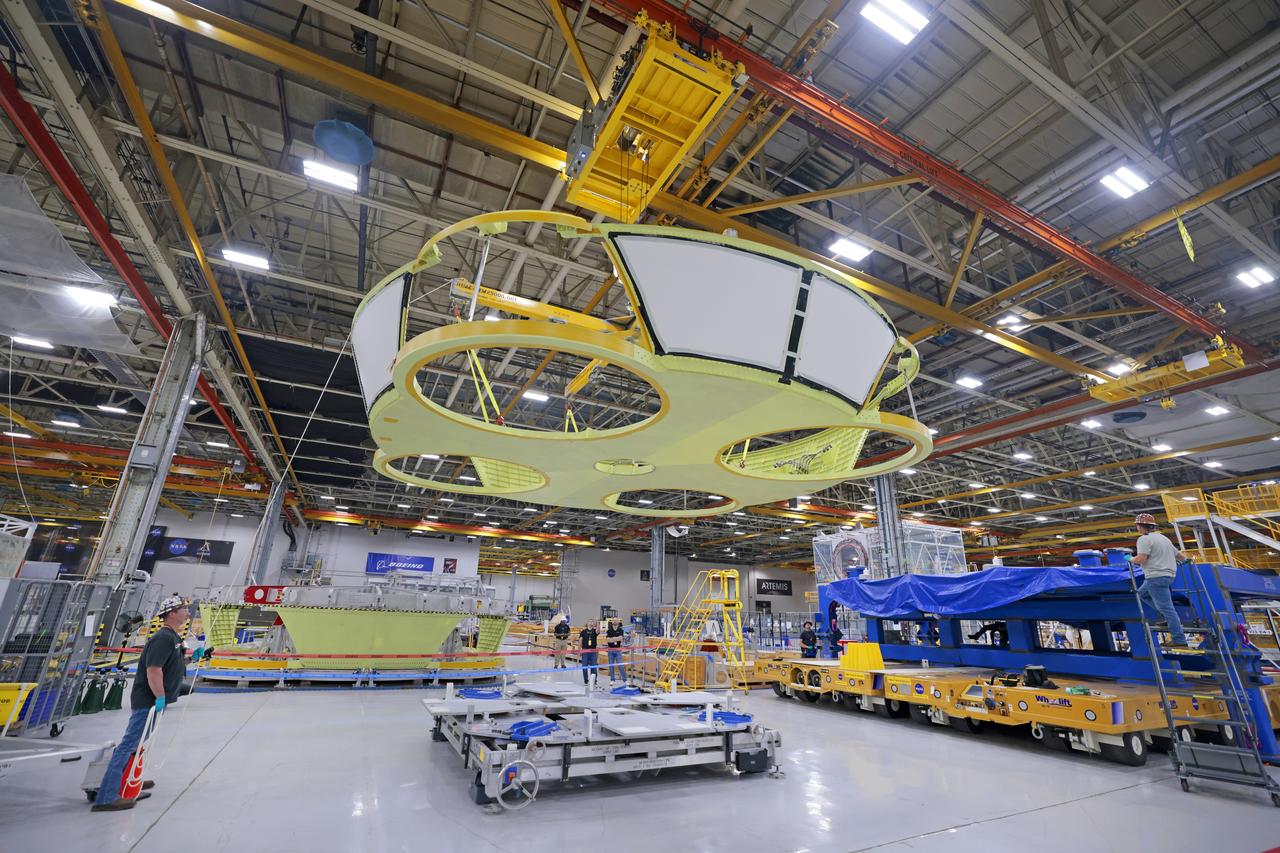

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
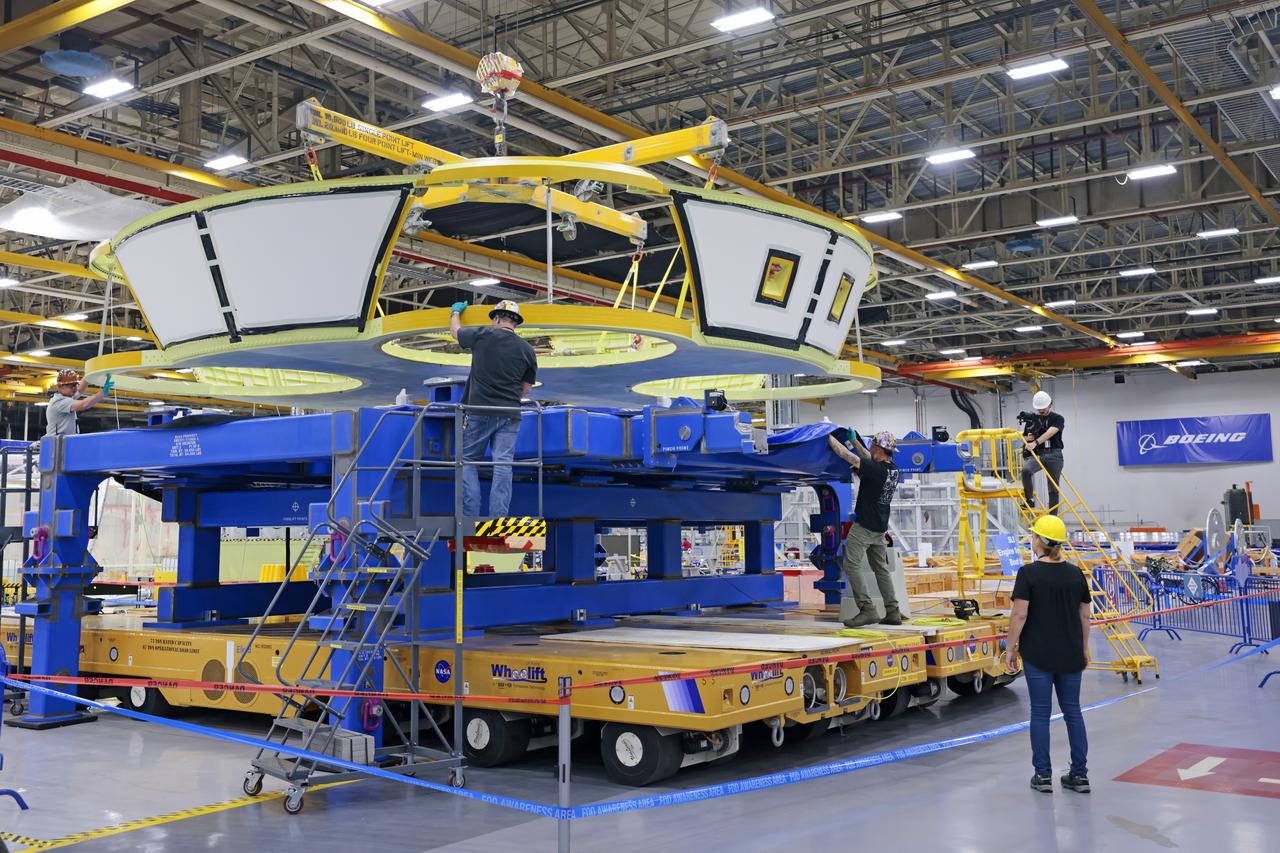

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
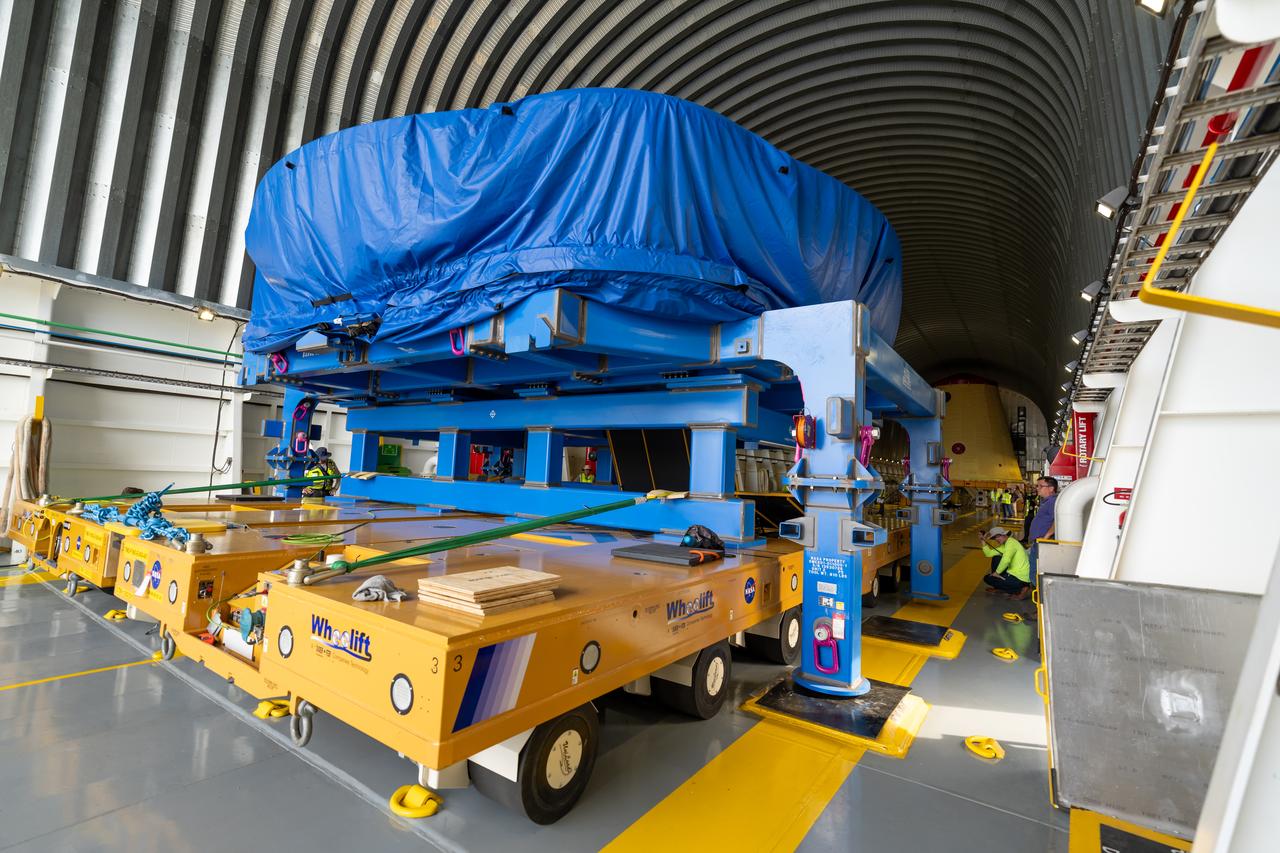

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
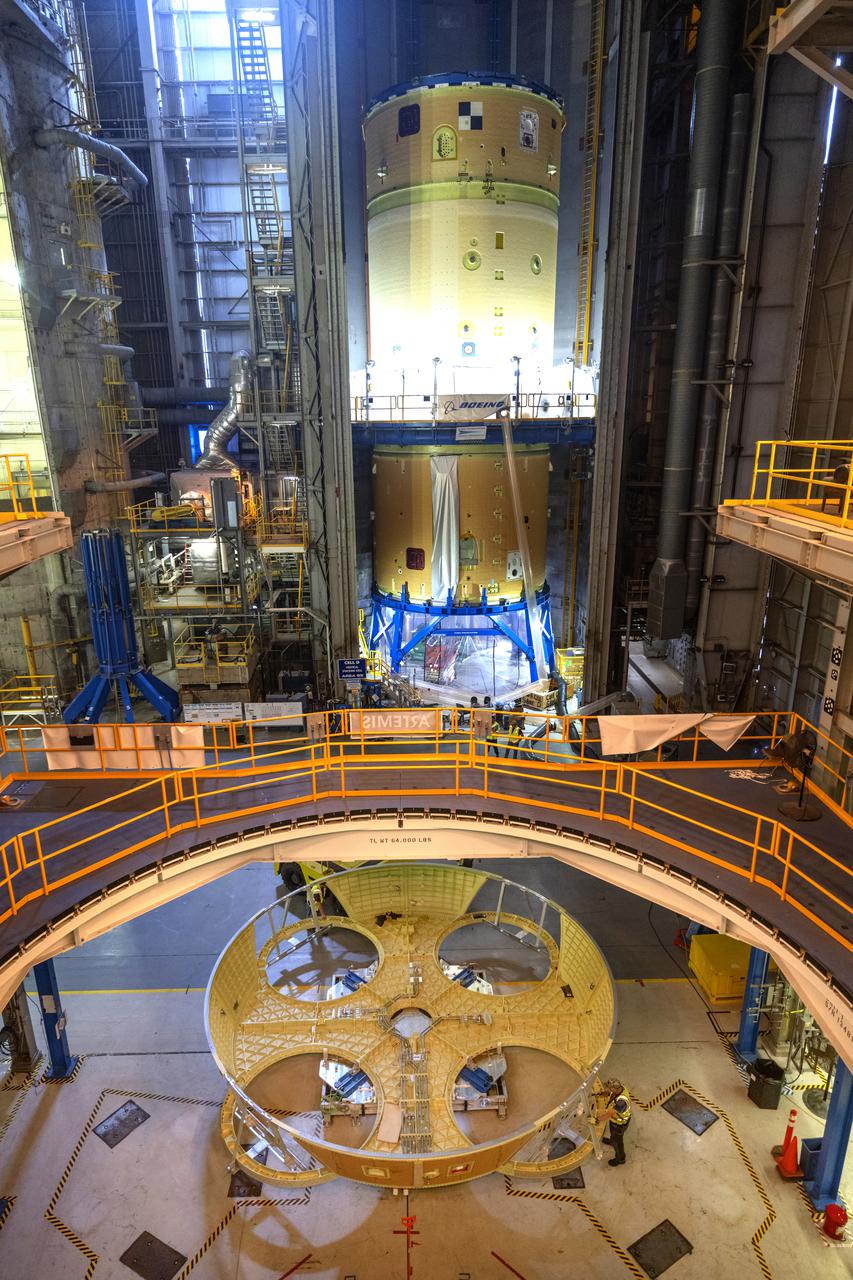

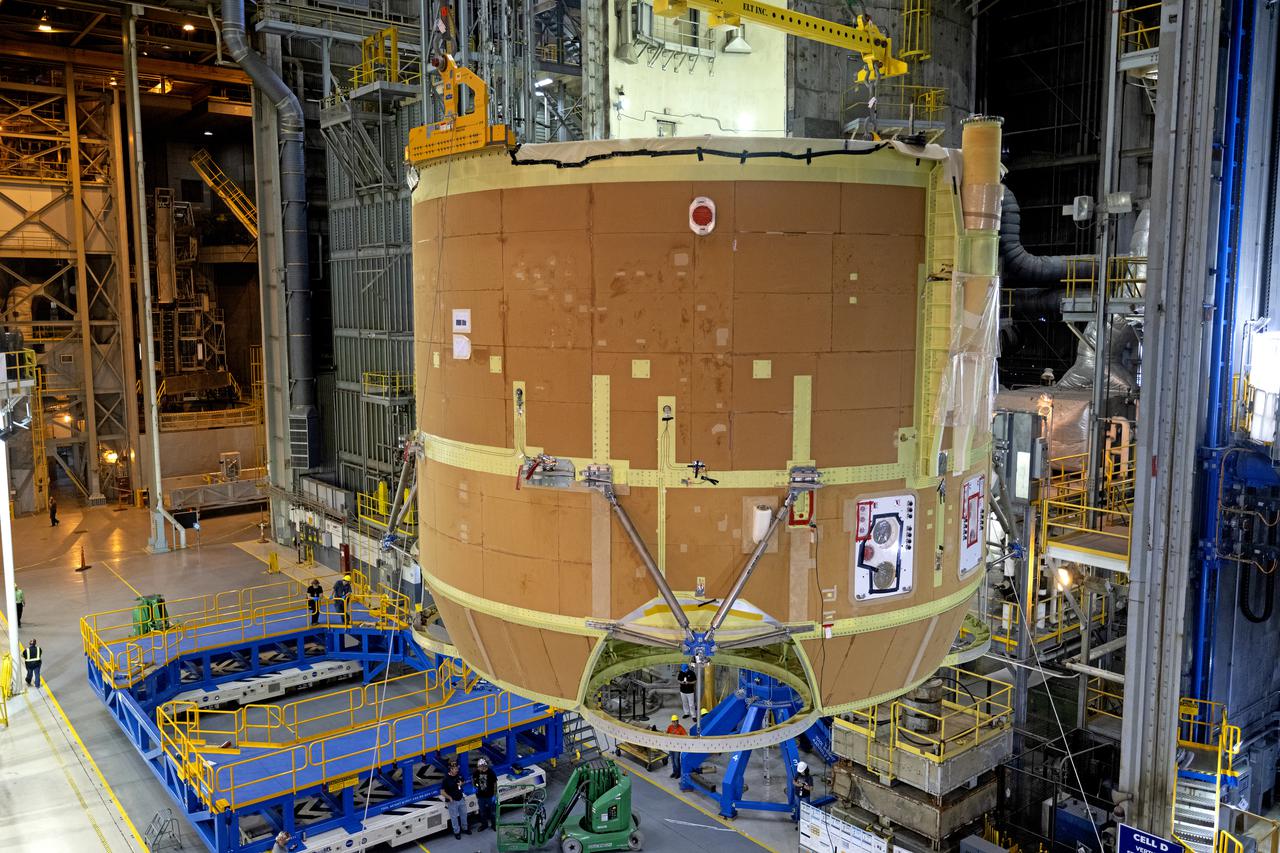
Technicians and engineers move the boat-tail structure for the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System’s (SLS) rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The boat-tail, a fairing-like cover that attaches to the engine section on the bottom of the core stage, protects and covers most of the four RS-25 engines’ critical systems. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Wednesday, June 9, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
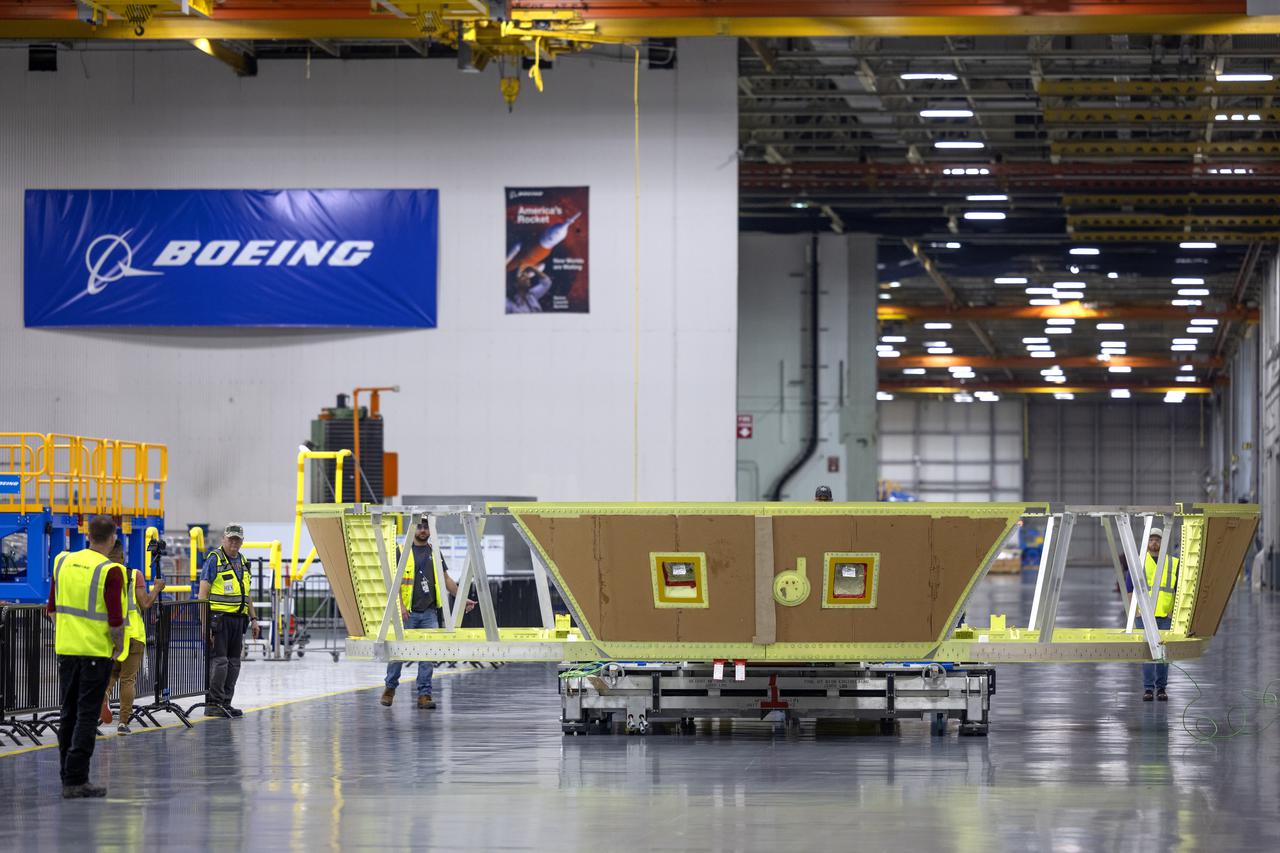

Technicians and engineers move the boat-tail structure for the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System’s (SLS) rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The boat-tail, a fairing-like cover that attaches to the engine section on the bottom of the core stage, protects and covers most of the four RS-25 engines’ critical systems. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Wednesday, June 9, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians and engineers move the boat-tail structure for the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System’s (SLS) rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The boat-tail, a fairing-like cover that attaches to the engine section on the bottom of the core stage, protects and covers most of the four RS-25 engines’ critical systems. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Wednesday, June 9, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
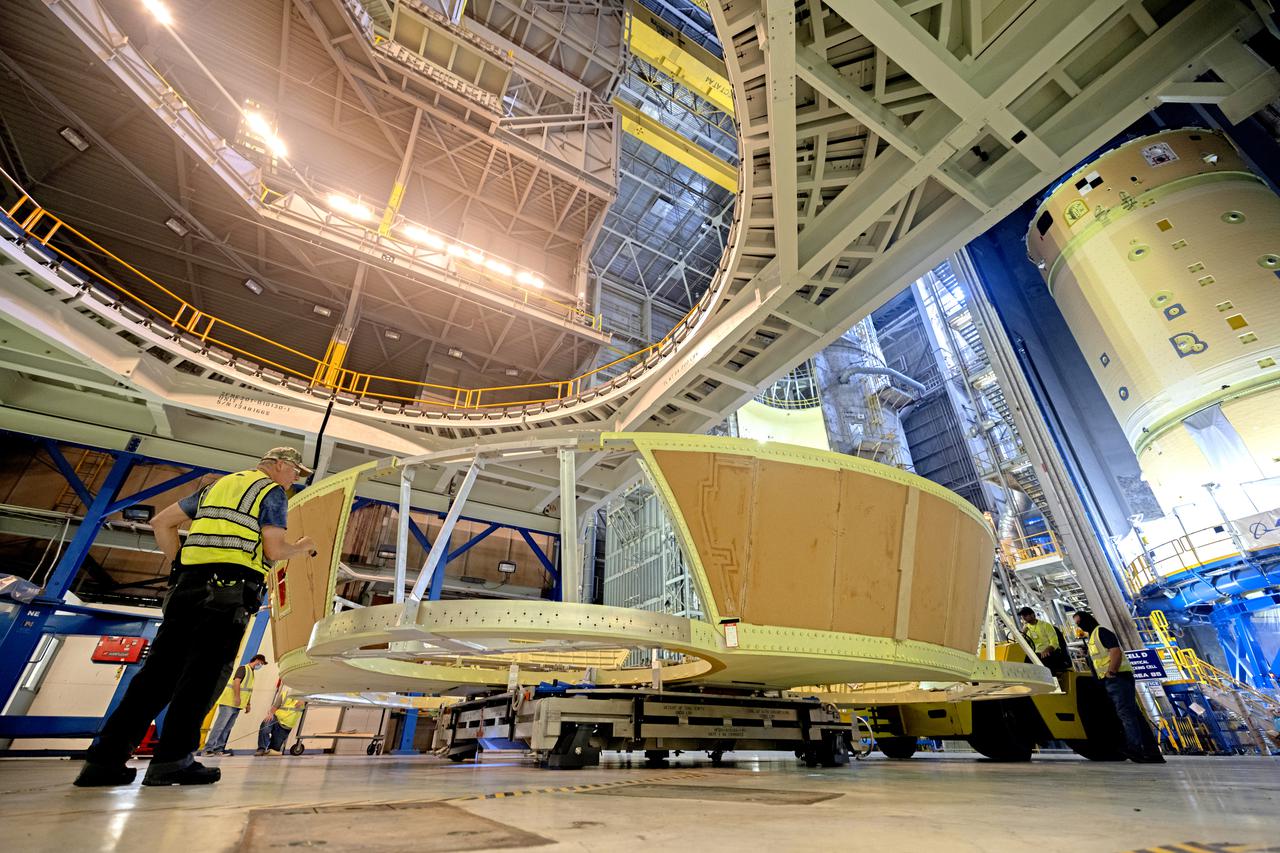

Technicians and engineers move the boat-tail structure for the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System’s (SLS) rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The boat-tail, a fairing-like cover that attaches to the engine section on the bottom of the core stage, protects and covers most of the four RS-25 engines’ critical systems. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Wednesday, June 9, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians and engineers move the boat-tail structure for the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System’s (SLS) rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The boat-tail, a fairing-like cover that attaches to the engine section on the bottom of the core stage, protects and covers most of the four RS-25 engines’ critical systems. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Wednesday, June 9, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
Technicians and engineers move the boat-tail structure for the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System’s (SLS) rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The boat-tail, a fairing-like cover that attaches to the engine section on the bottom of the core stage, protects and covers most of the four RS-25 engines’ critical systems. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Wednesday, June 9, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians and engineers move the boat-tail structure for the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System’s (SLS) rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The boat-tail, a fairing-like cover that attaches to the engine section on the bottom of the core stage, protects and covers most of the four RS-25 engines’ critical systems. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Wednesday, June 9, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians and engineers move the boat-tail structure for the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System’s (SLS) rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The boat-tail, a fairing-like cover that attaches to the engine section on the bottom of the core stage, protects and covers most of the four RS-25 engines’ critical systems. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Wednesday, June 9, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

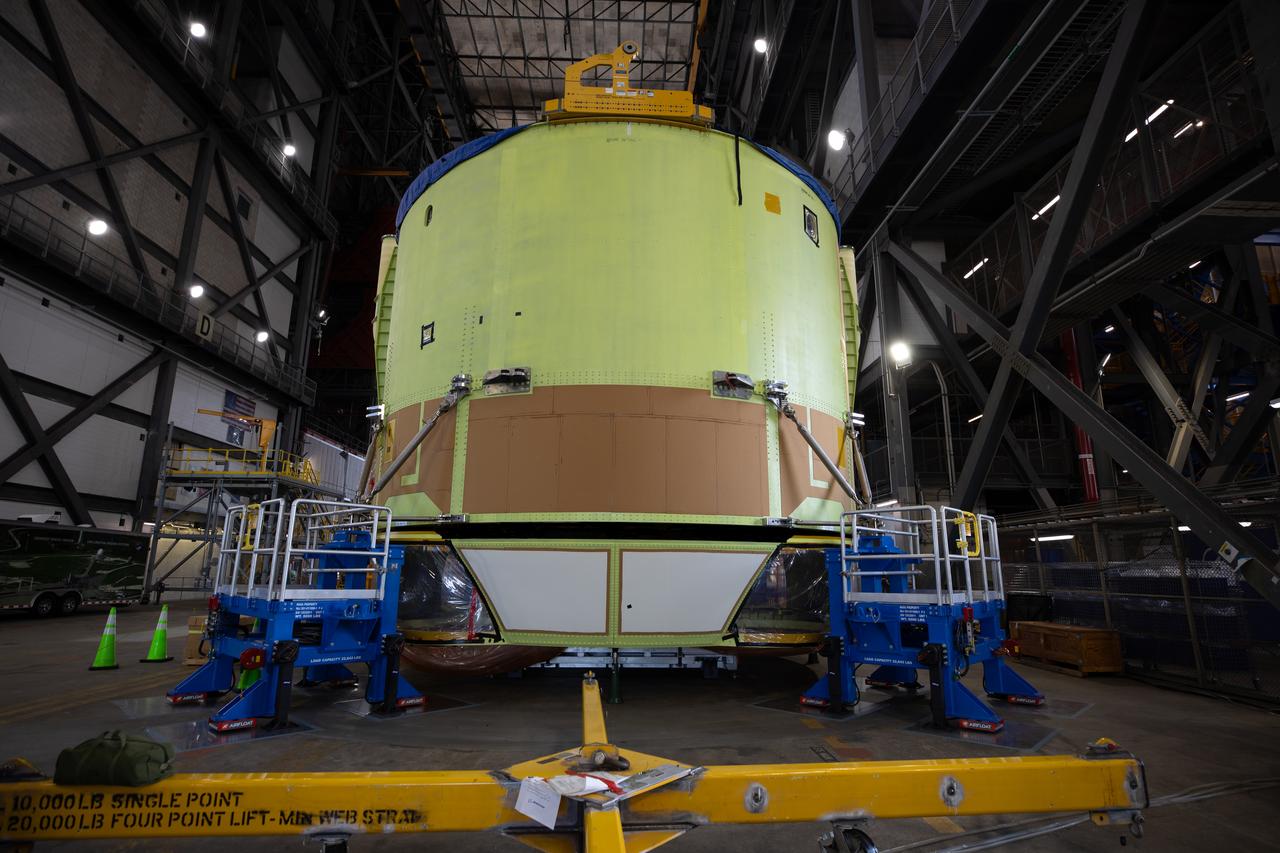
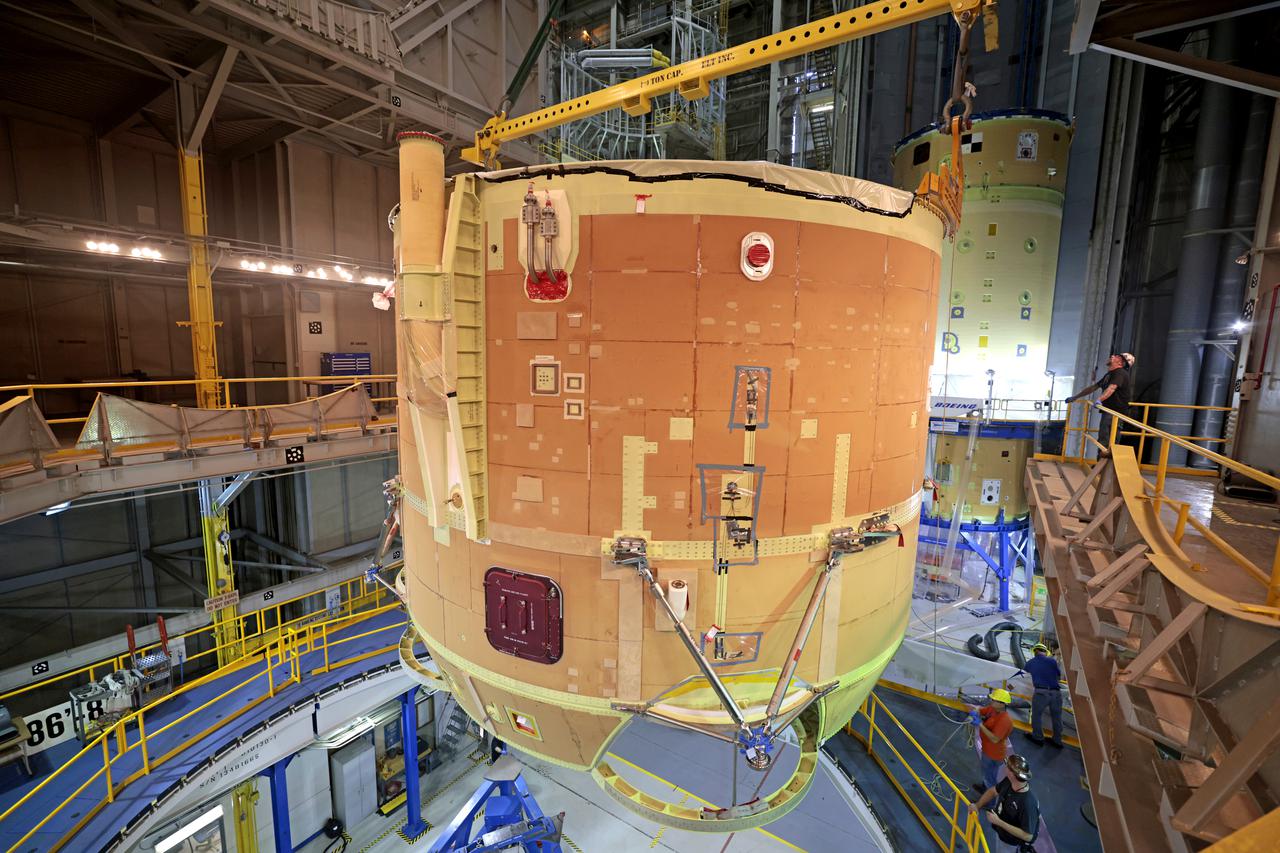
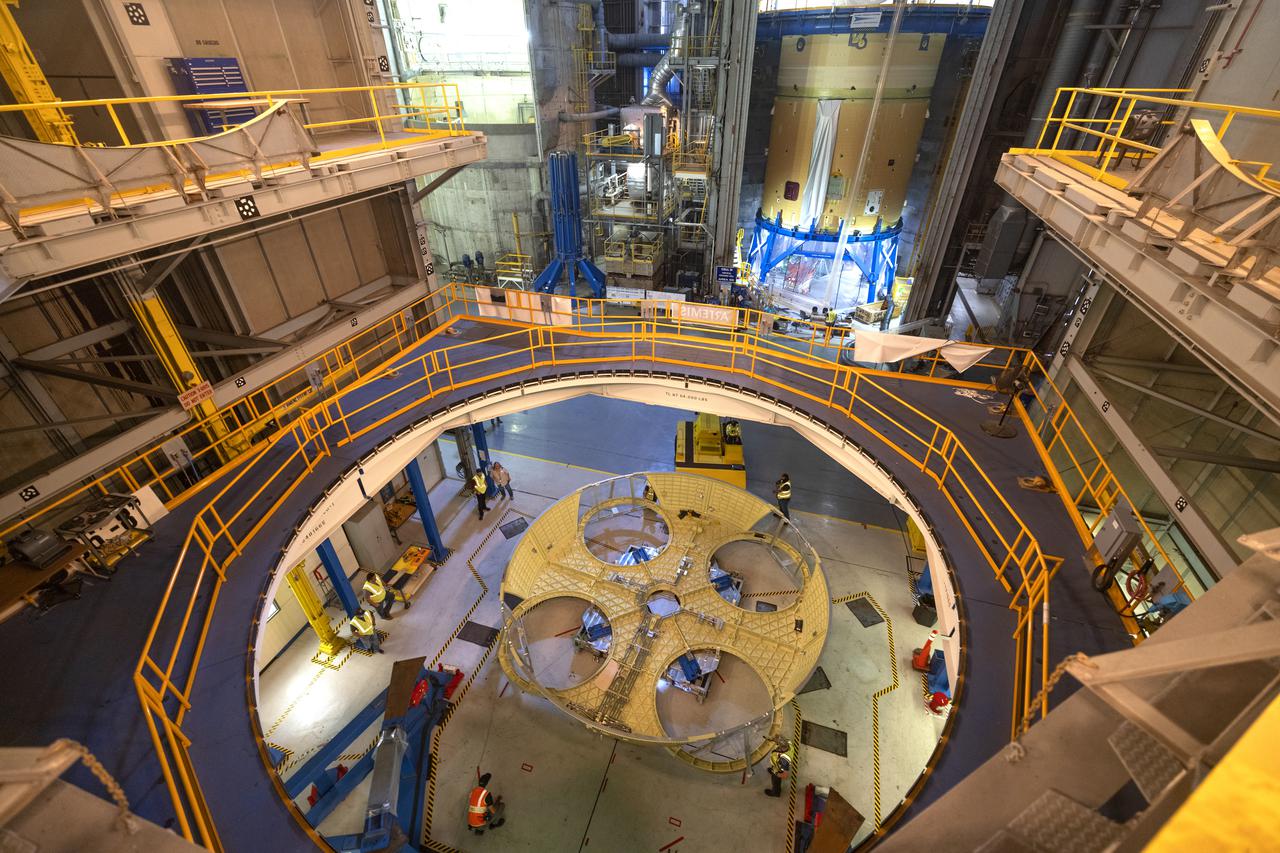
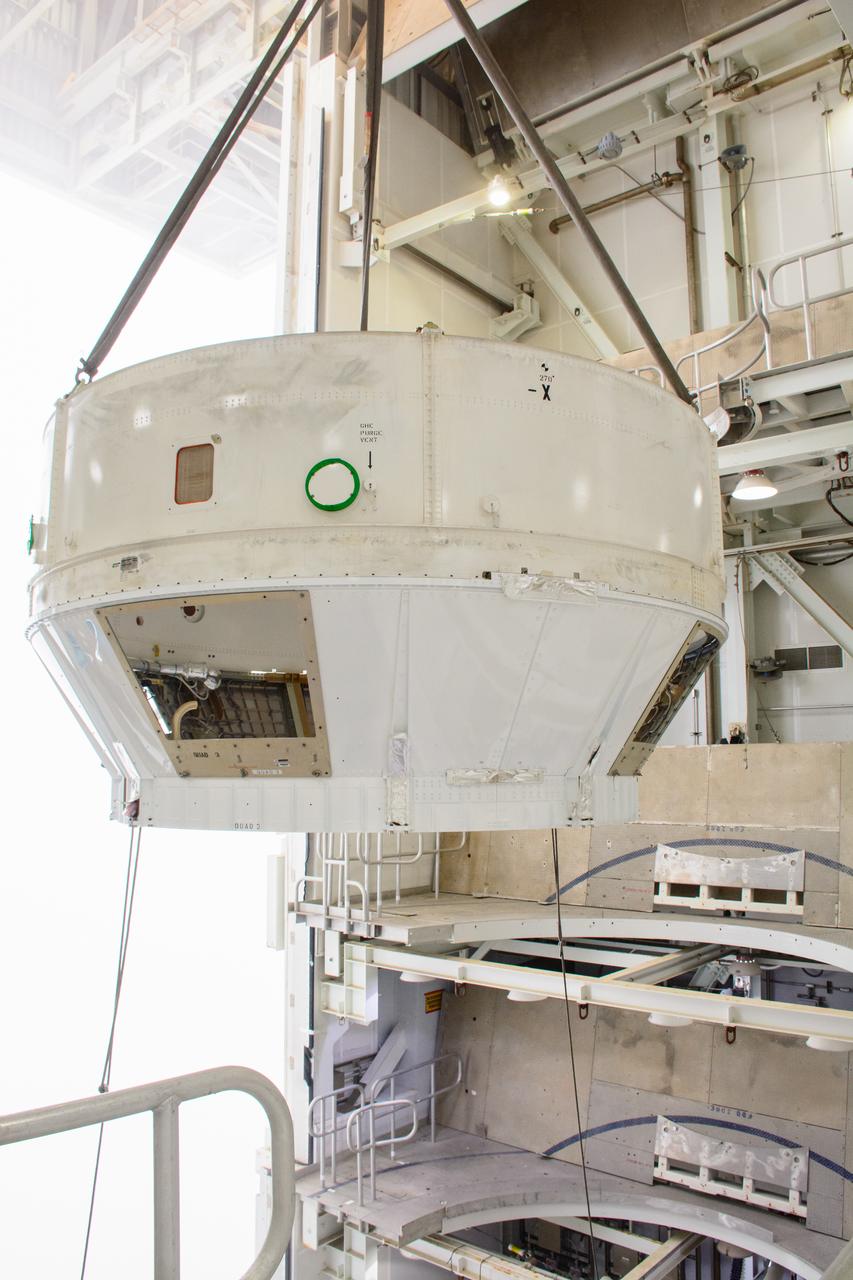
Teams from Kennedy lift NASA’s integrated Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the center’s Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 13, 2025. Shown inside the facility’s High Bay 2 for processing, the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.

Teams from Kennedy lift NASA’s integrated Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the center’s Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 13, 2025. Shown inside the facility’s High Bay 2 for processing, the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.

Teams from Kennedy lift NASA’s integrated Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the center’s Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 13, 2025. Shown inside the facility’s High Bay 2 for processing, the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
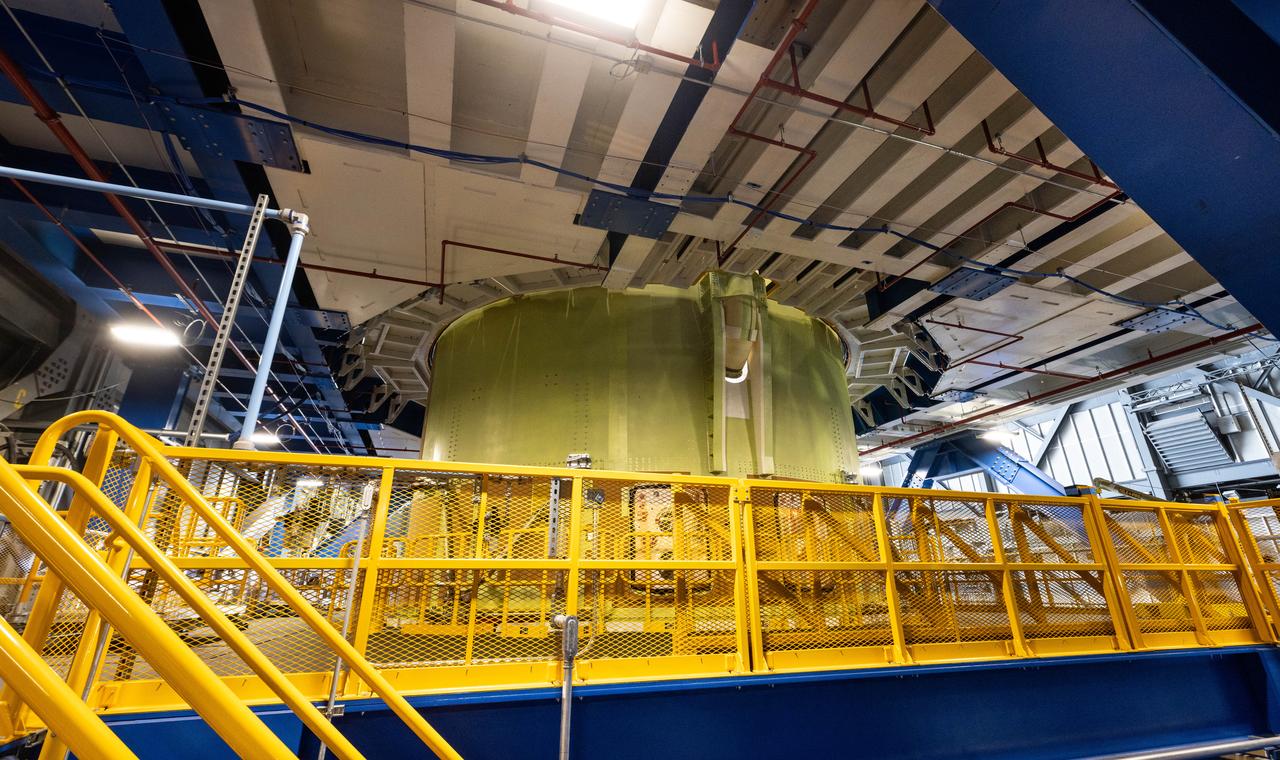

Teams from Kennedy lift NASA’s integrated Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage engine section with its boat-tail inside the center’s Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 13, 2025. Shown inside the facility’s High Bay 2 for processing, the engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying several pieces of the agency’s Artemis campaign hardware, including Artemis II’s launch vehicle stage adapter, Artemis III’s core stage boat tail, and Artemis IV’s core stage engine section arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Thursday, Sept. 5, 2024.

The Atlas V boat tail for the Landsat 9 mission is lifted and mated at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Space Launch Complex 3 in California on July 17, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission launch, which is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 27, 2021. Landsat 9 will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
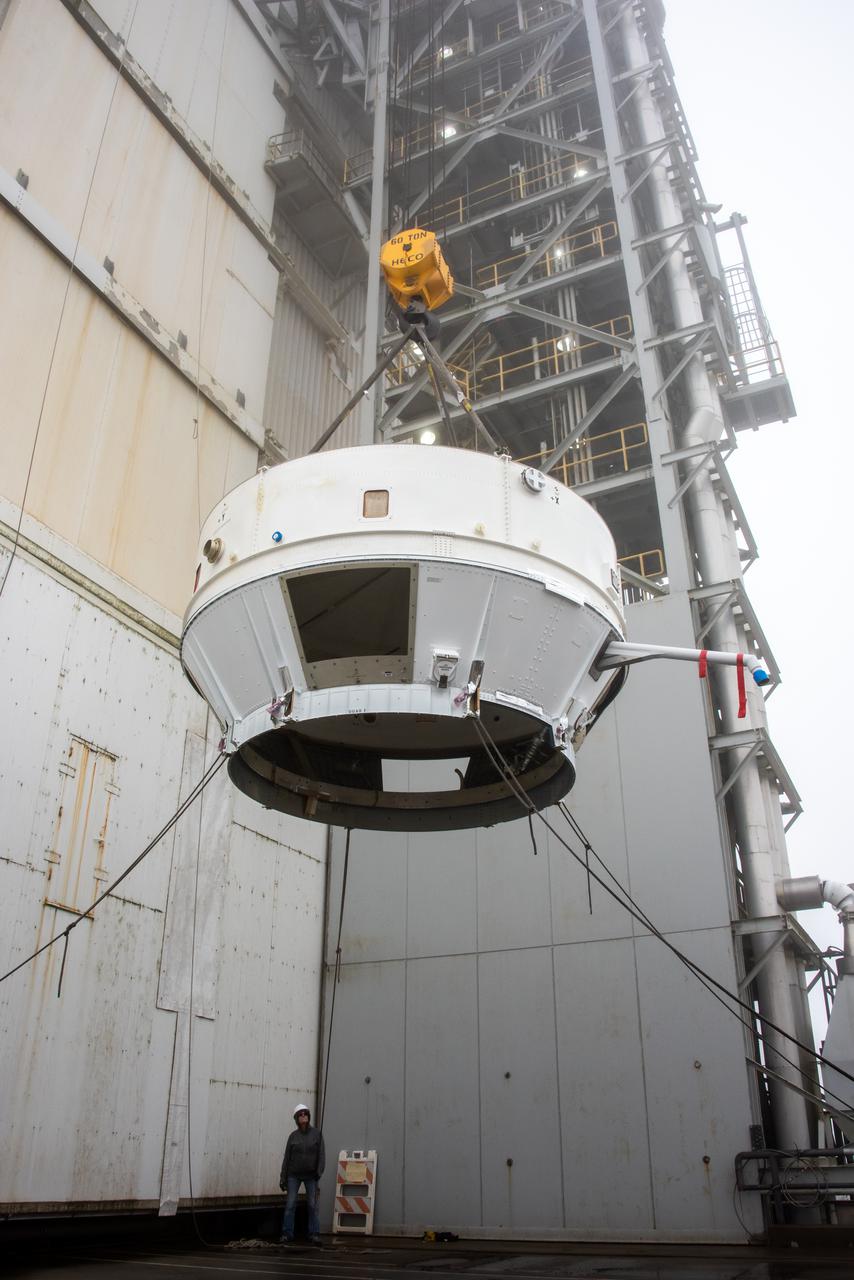

The Atlas V boat tail for the Landsat 9 mission is lifted and mated at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Space Launch Complex 3 in California on July 17, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission launch, which is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 27, 2021. Landsat 9 will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

The Atlas V boat tail for the Landsat 9 mission is lifted and mated at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Space Launch Complex 3 in California on July 17, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission launch, which is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 27, 2021. Landsat 9 will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
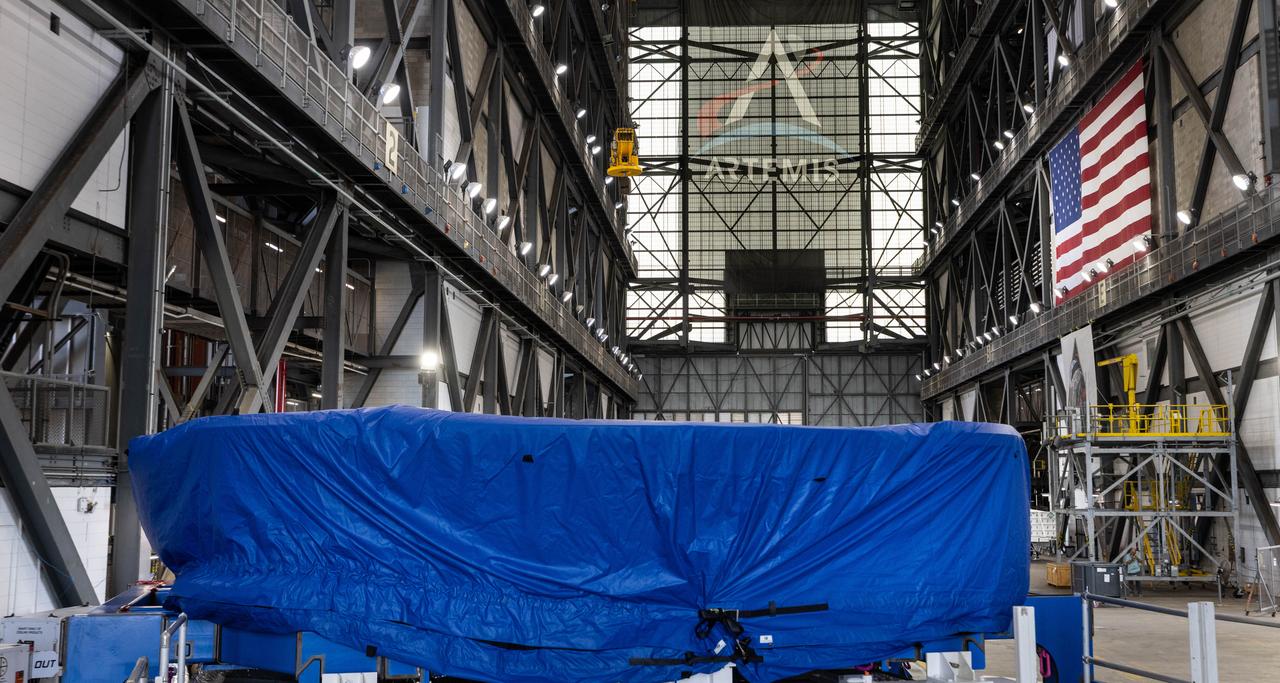

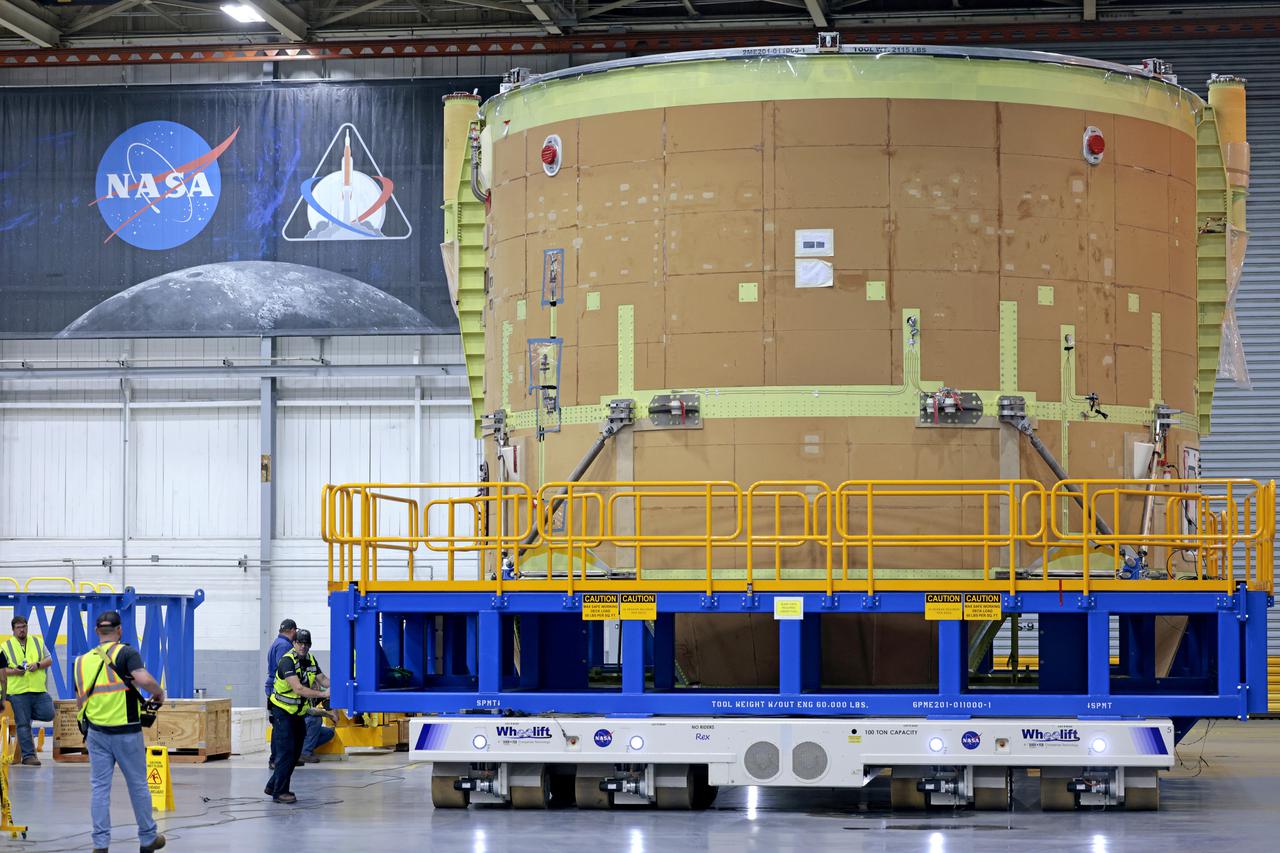
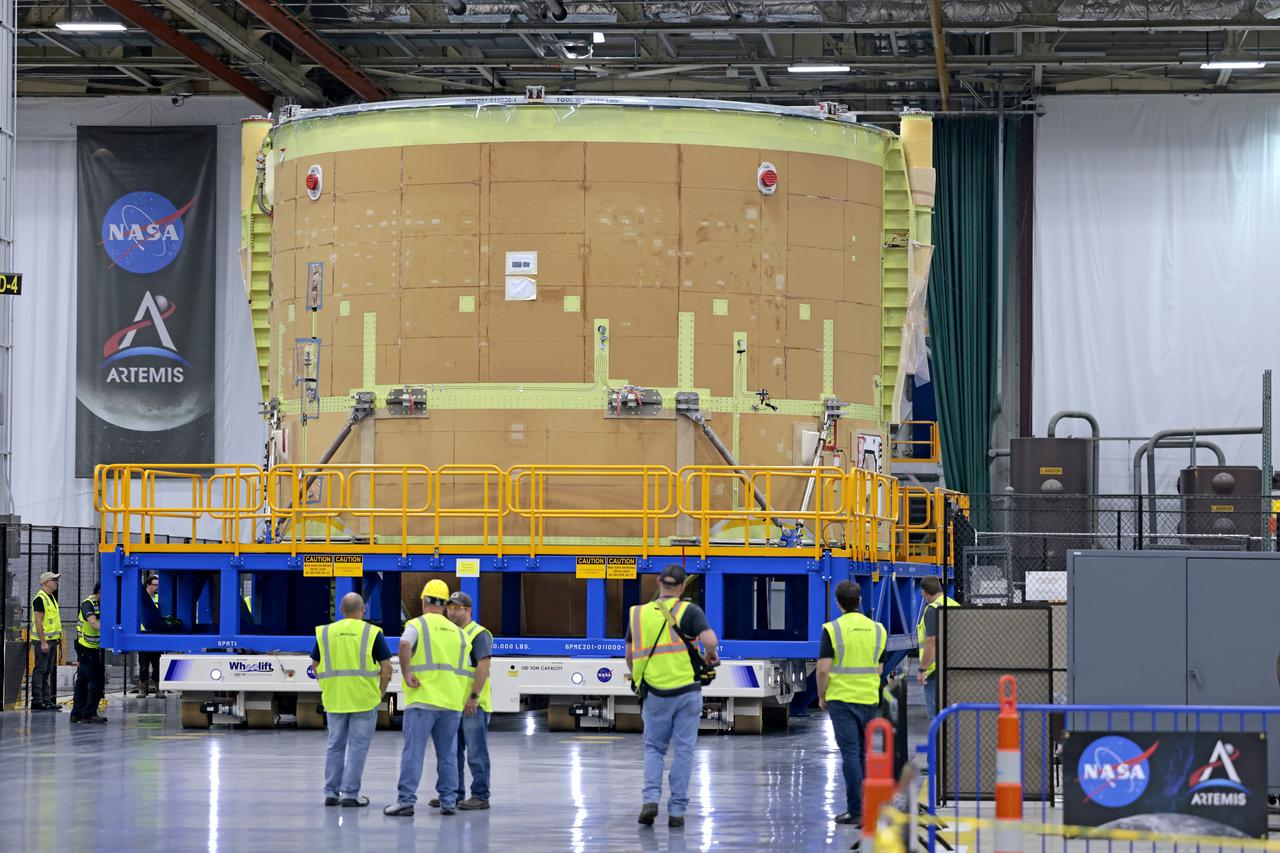
Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida transport the agency’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage boat-tail from the spaceport's Space Systems Processing Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building on Thursday, July 24. Used during the assembly of the SLS core stage, the boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage.
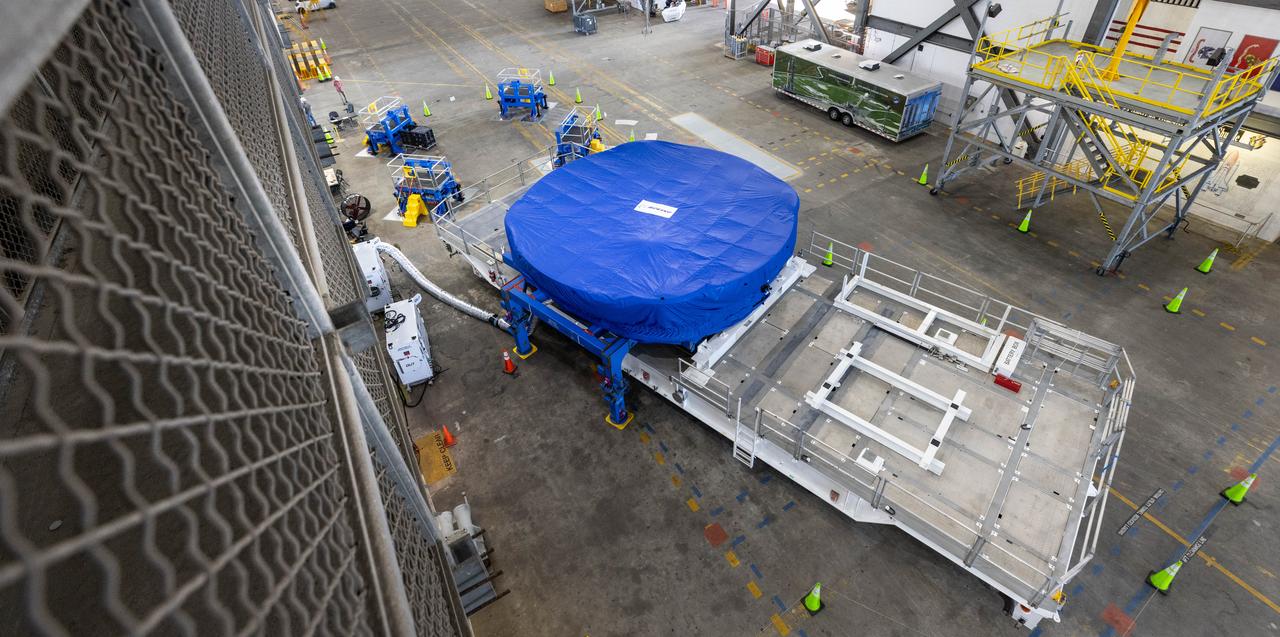

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida transport the agency’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage boat-tail from the spaceport's Space Systems Processing Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building on Thursday, July 24. Used during the assembly of the SLS core stage, the boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage.
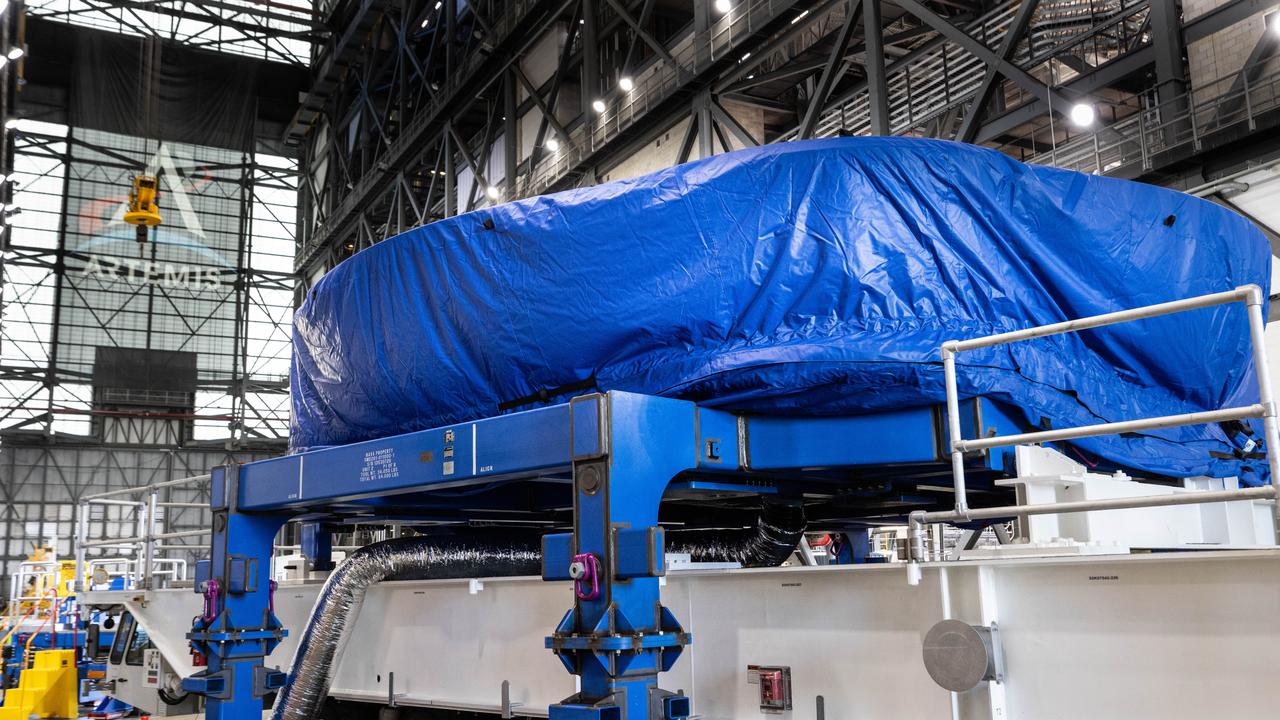

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida transport the agency’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage boat-tail from the spaceport's Space Systems Processing Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building on Thursday, July 24. Used during the assembly of the SLS core stage, the boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage.
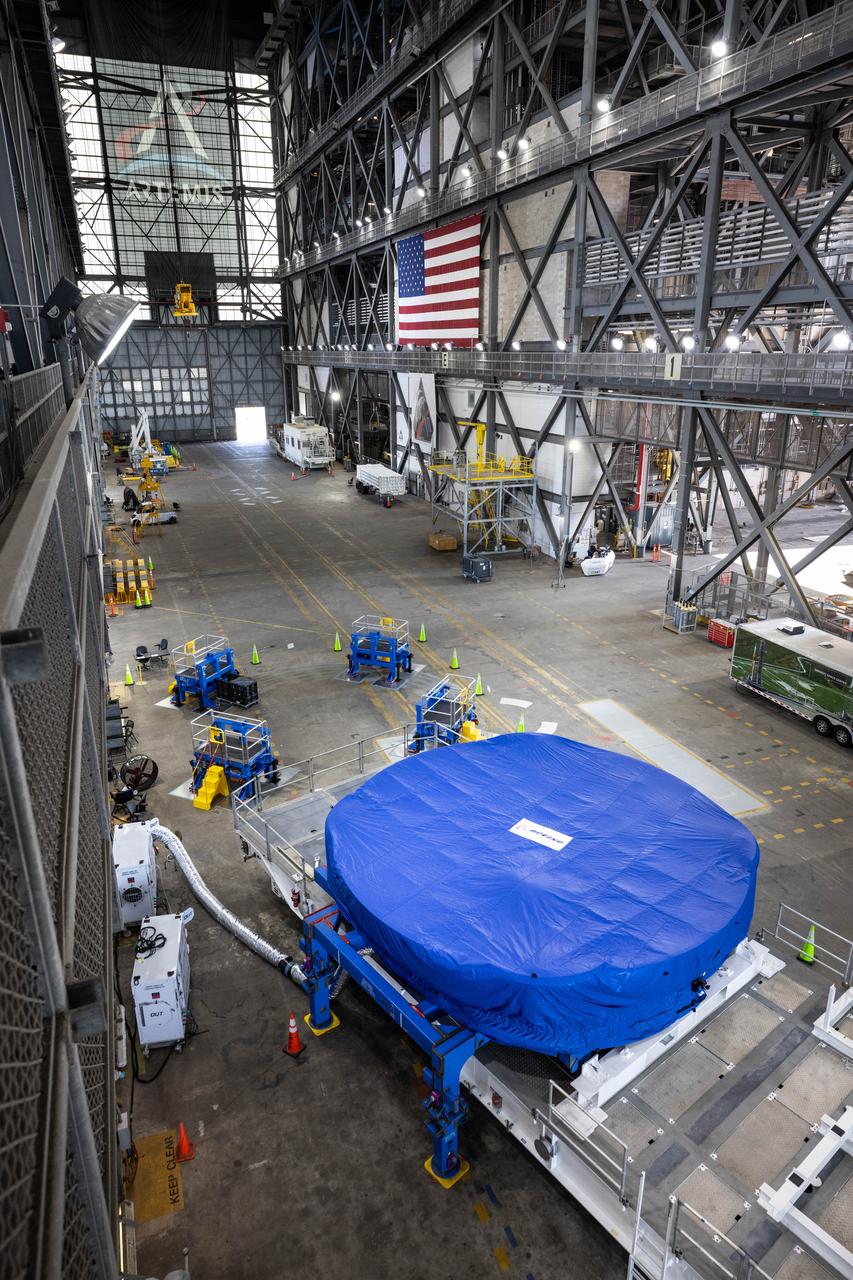

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida transport the agency’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage boat-tail from the spaceport's Space Systems Processing Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building on Thursday, July 24. Used during the assembly of the SLS core stage, the boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage.
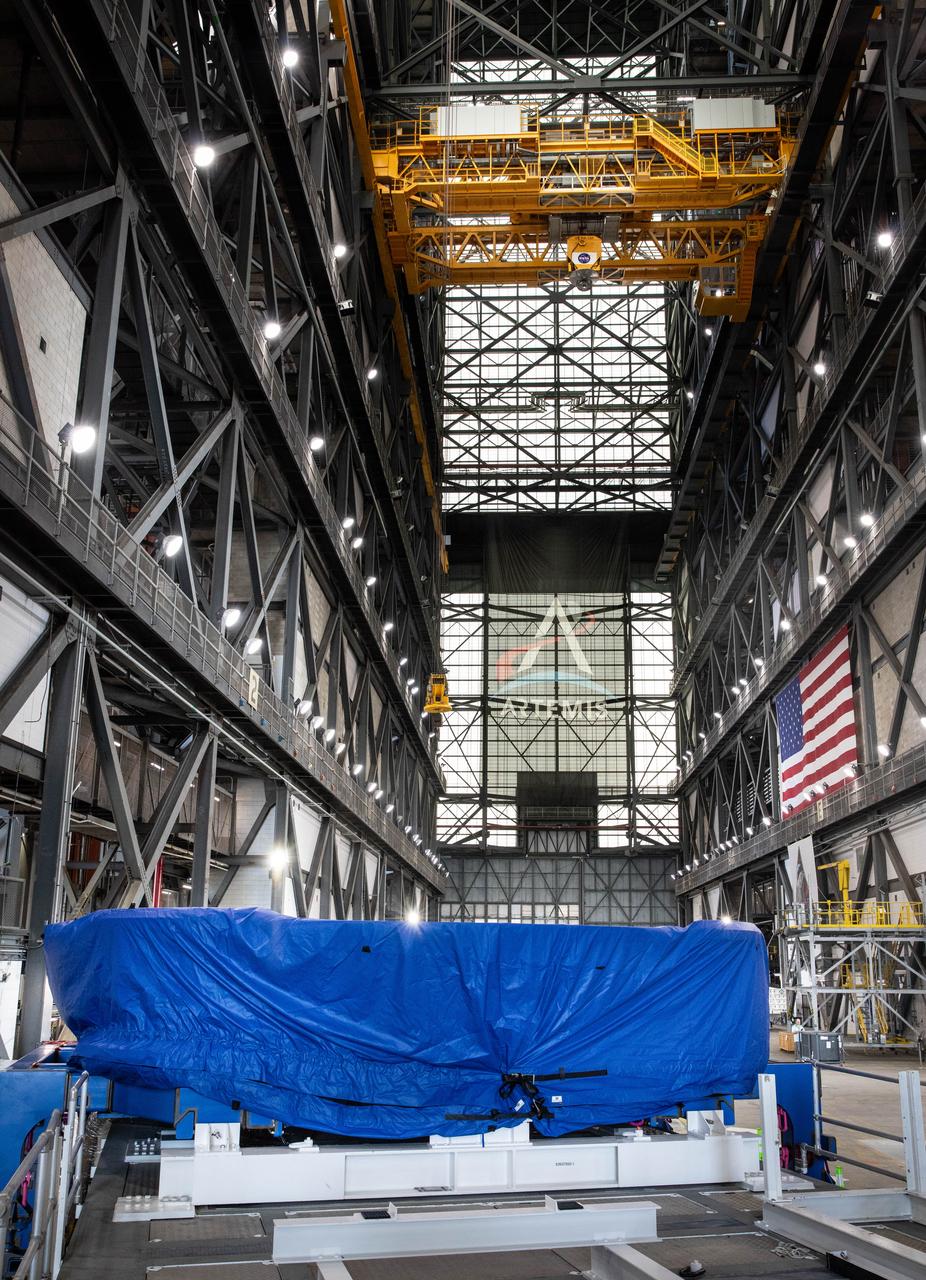

Teams from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida transport the agency’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) core stage boat-tail from the spaceport's Space Systems Processing Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building on Thursday, July 24. Used during the assembly of the SLS core stage, the boat-tail is a fairing-like structure that protects the bottom end of the core stage.
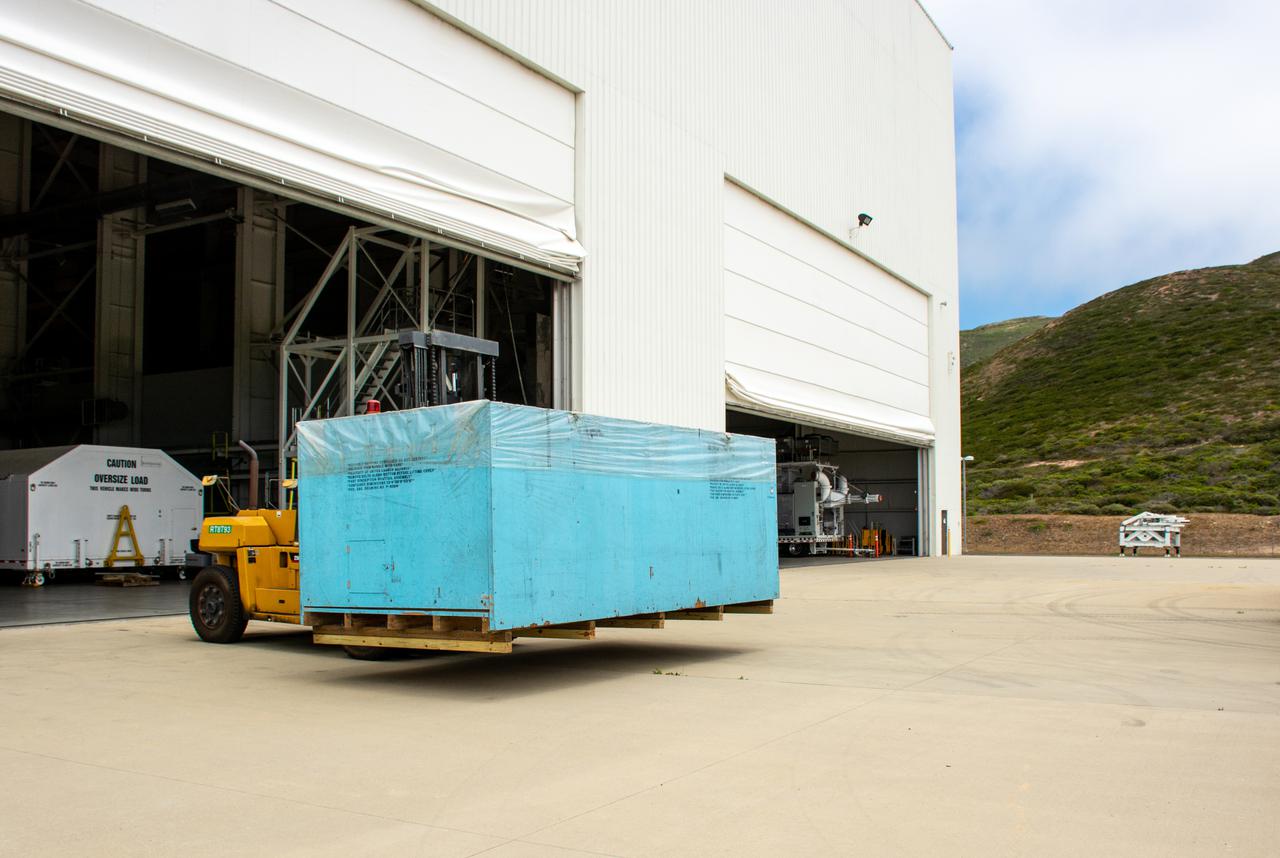

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V payload fairing boattail for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on June 21, 2021. The boattail will shield the spacecraft from particles in the retrorocket plume during separation from the payload fairing. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop a ULA Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V payload fairing boattail for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission is transported by flatbed truck to the Horizontal Integration Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on June 21, 2021. The boattail will shield the spacecraft from particles in the retrorocket plume during separation from the payload fairing. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop a ULA Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
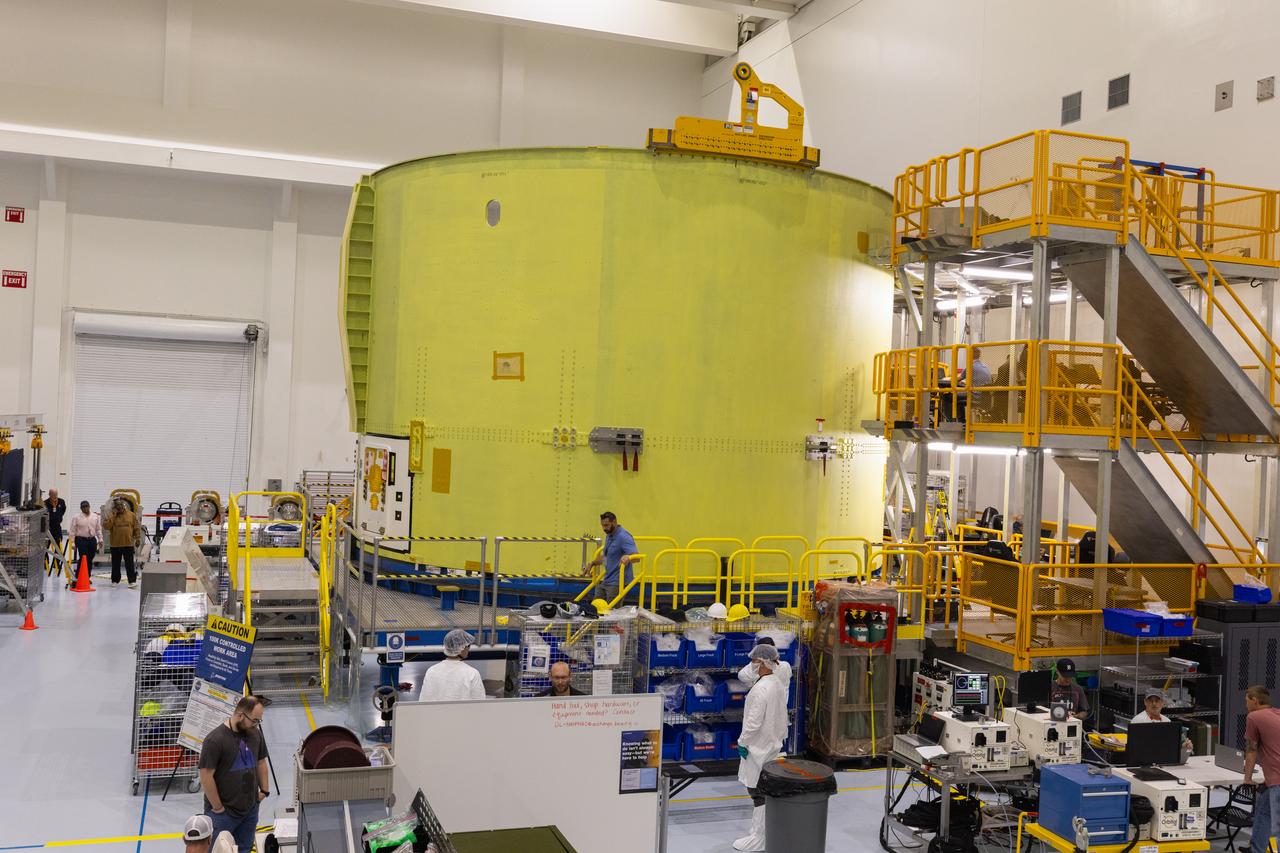

Technicians with NASA and Boeing complete attaching the engine section to the boat-tail for the agency’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the high bay of the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 30, 2024. The engine section is one of five major elements that makes up the SLS rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, which house the rocket’s four RS-25 engines and vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the stage’s two massive liquid propellant tanks to the engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines.

Technicians with NASA and Boeing complete attaching the engine section to the boat-tail for the agency’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the high bay of the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 30, 2024. The engine section is one of five major elements that makes up the SLS rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, which house the rocket’s four RS-25 engines and vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the stage’s two massive liquid propellant tanks to the engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines.

Technicians with NASA and Boeing complete attaching the engine section to the boat-tail for the agency’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the high bay of the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 30, 2024. The engine section is one of five major elements that makes up the SLS rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, which house the rocket’s four RS-25 engines and vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the stage’s two massive liquid propellant tanks to the engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines.

Technicians lower the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V boattail onto the rocket’s Centaur upper stage inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 4, 2022, for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) and NASA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) mission. The boattail is the connecting piece of flight hardware that joins that Atlas V upper stage with the payload fairing – the protective casing surrounding the JPSS-2 satellite. Once the payload fairing arrives at the VIF, teams will lower it onto the boattail to complete the Atlas V stack. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series and will scan the Earth as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day. Operating from 512 miles above Earth, JPSS-2 will capture data to improve weather forecasts, in turn helping scientists predict and prepare for extreme weather events and climate change. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a technology demonstration of an inflatable heat shield that could one day help land humans on Mars. Liftoff is targeted for 2:25 a.m. Pacific time (5:25 a.m. Eastern time) on Nov. 1, 2022, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex-3E.

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians secure the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V boattail onto the rocket’s Centaur upper stage on Oct. 4, 2022, for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) and NASA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) mission. The boattail is the connecting piece of flight hardware that joins that Atlas V upper stage with the payload fairing – the protective casing surrounding the JPSS-2 satellite. Once the payload fairing arrives at the VIF, teams will lower it onto the boattail to complete the Atlas V stack. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series and will scan the Earth as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day. Operating from 512 miles above Earth, JPSS-2 will capture data to improve weather forecasts, in turn helping scientists predict and prepare for extreme weather events and climate change. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a technology demonstration of an inflatable heat shield that could one day help land humans on Mars. Liftoff is targeted for 2:25 a.m. Pacific time (5:25 a.m. Eastern time) on Nov. 1, 2022, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex-3E.
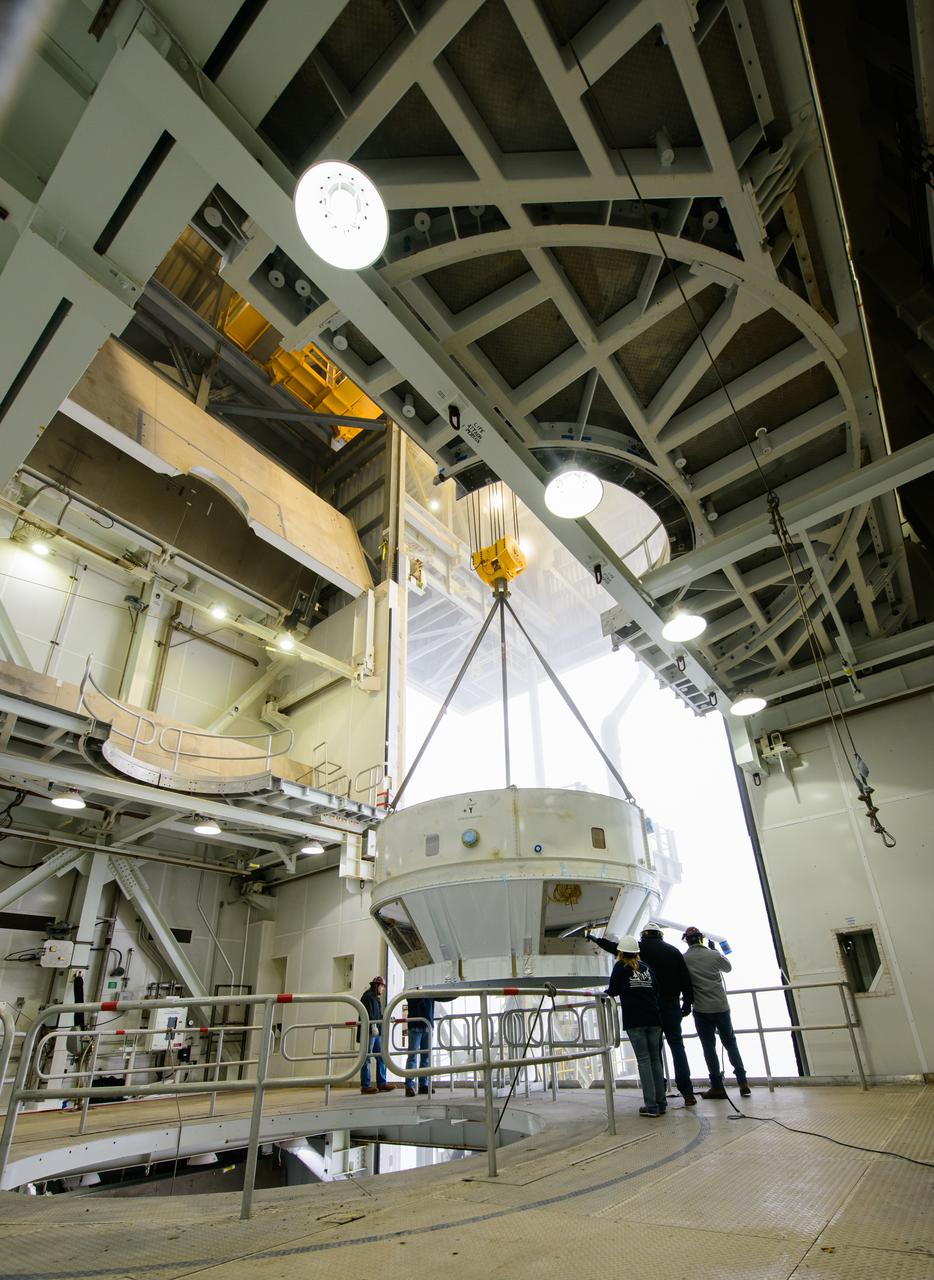

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians monitor the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V boattail as it’s lowered by crane onto the rocket’s Centaur upper stage on Oct. 4, 2022, for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) and NASA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) mission. The boattail is the connecting piece of flight hardware that joins that Atlas V upper stage with the payload fairing – the protective casing surrounding the JPSS-2 satellite. Once the payload fairing arrives at the VIF, teams will lower it onto the boattail to complete the Atlas V stack. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series and will scan the Earth as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day. Operating from 512 miles above Earth, JPSS-2 will capture data to improve weather forecasts, in turn helping scientists predict and prepare for extreme weather events and climate change. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a technology demonstration of an inflatable heat shield that could one day help land humans on Mars. Liftoff is targeted for 2:25 a.m. Pacific time (5:25 a.m. Eastern time) on Nov. 1, 2022, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex-3E.
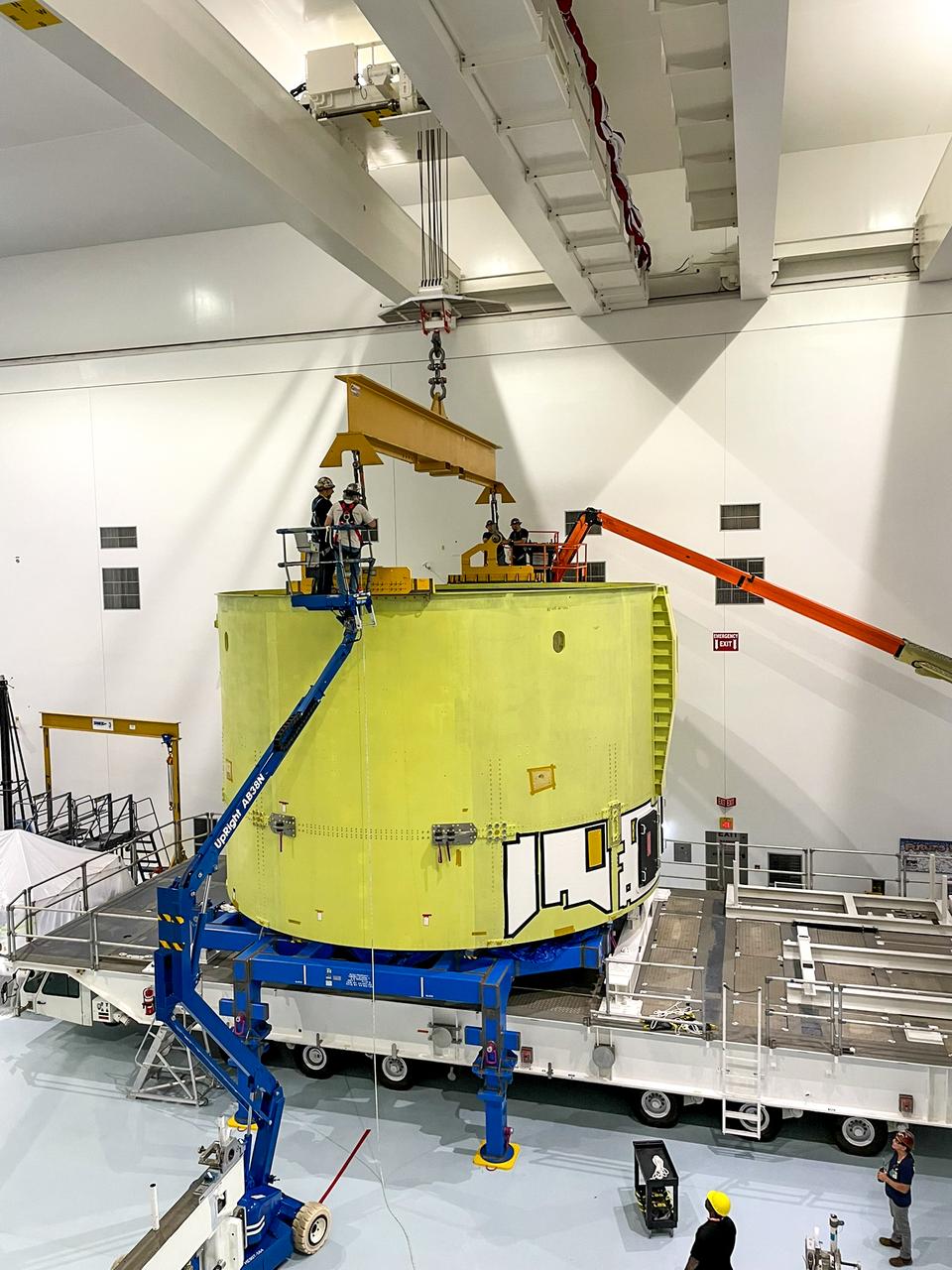

Technicians lift the engine section for NASA’s Artemis IV SLS (Space Launch System) rocket ahead of further processing inside the high bay of the Space Systems Processing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Oct. 21, 2024. The engine section is one of five major elements that makes up the SLS rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, which house the rocket’s four RS-25 engines and vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the stage’s two massive liquid propellant tanks to the engines.

Technicians lift the engine section for NASA’s Artemis IV SLS (Space Launch System) rocket ahead of further processing inside the high bay of the Space Systems Processing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Oct. 21, 2024. The engine section is one of five major elements that makes up the SLS rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, which house the rocket’s four RS-25 engines and vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the stage’s two massive liquid propellant tanks to the engines.
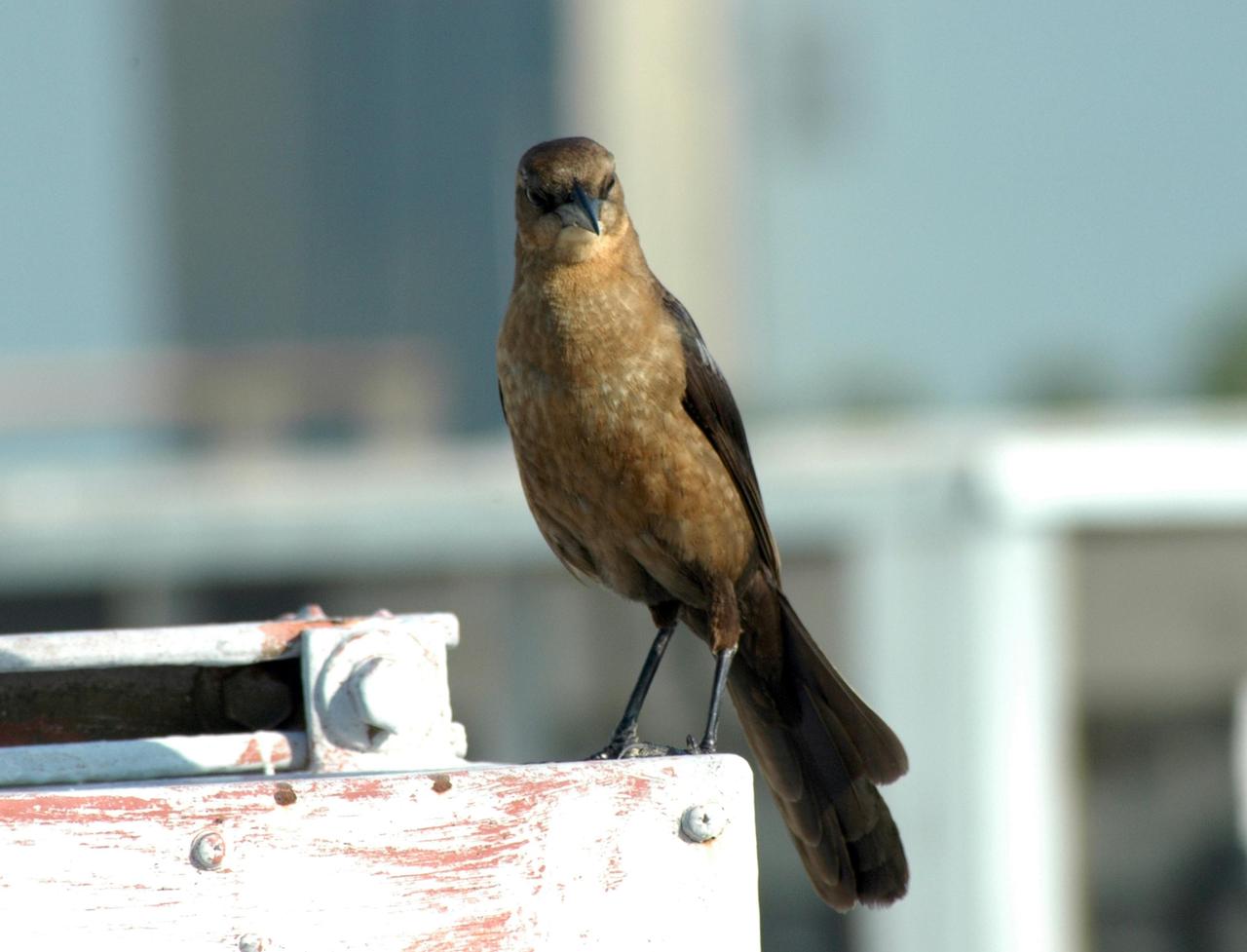

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This is a female boat-tailed grackle, which is prominently seen around NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Males are an iridescent, purple-black color. Boat-tailed grackles are resident along the eastern and Gulf coasts of the United States, from New York to southeastern Texas, and throughout much of Florida. Primarily a coastal species of the salt and brackish marsh, in Florida it is also found near lakes, rivers, and freshwater marshes. It is commonly found in urban environments. The Center shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which is a habitat for more than 310 species of birds, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles. In addition, the Refuge supports 19 endangered or threatened wildlife species on Federal or State lists, more than any other single refuge in the U.S. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
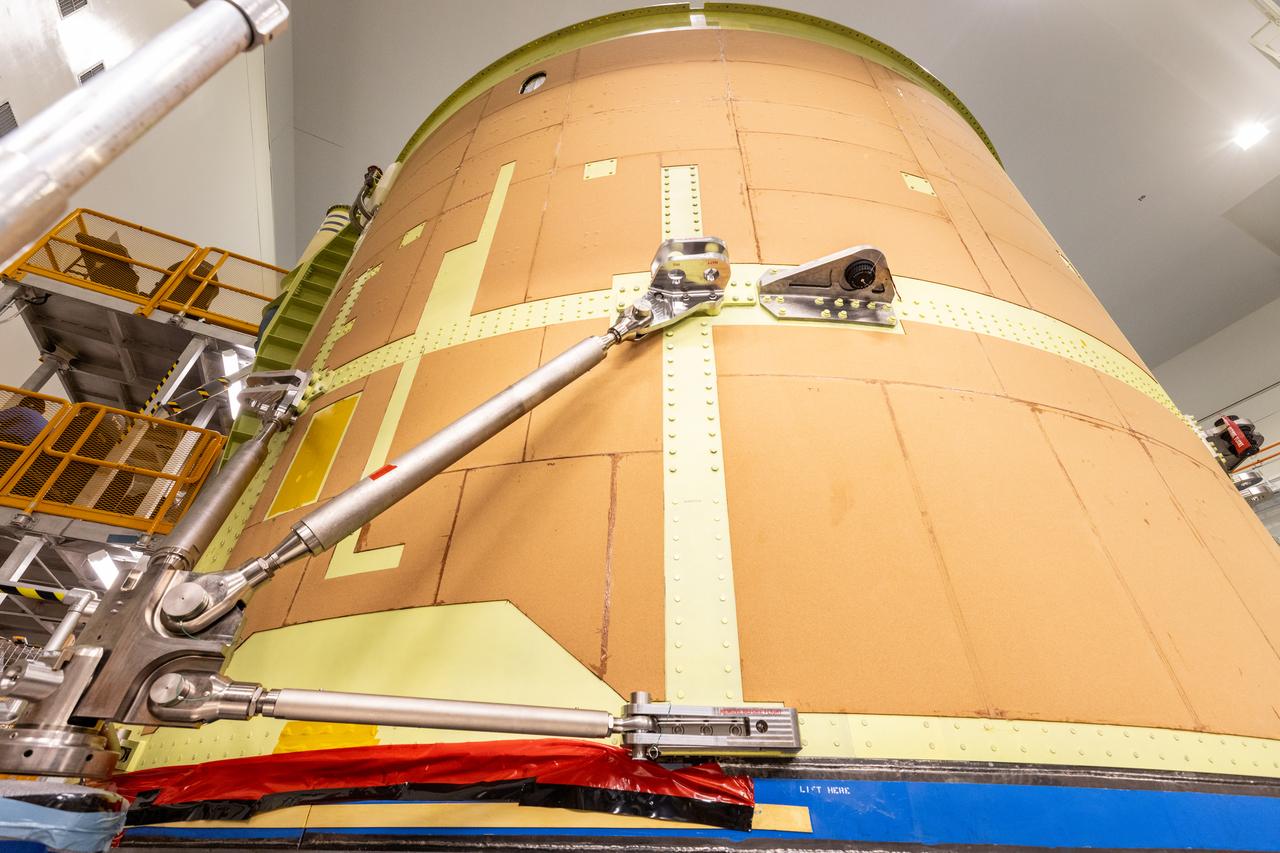

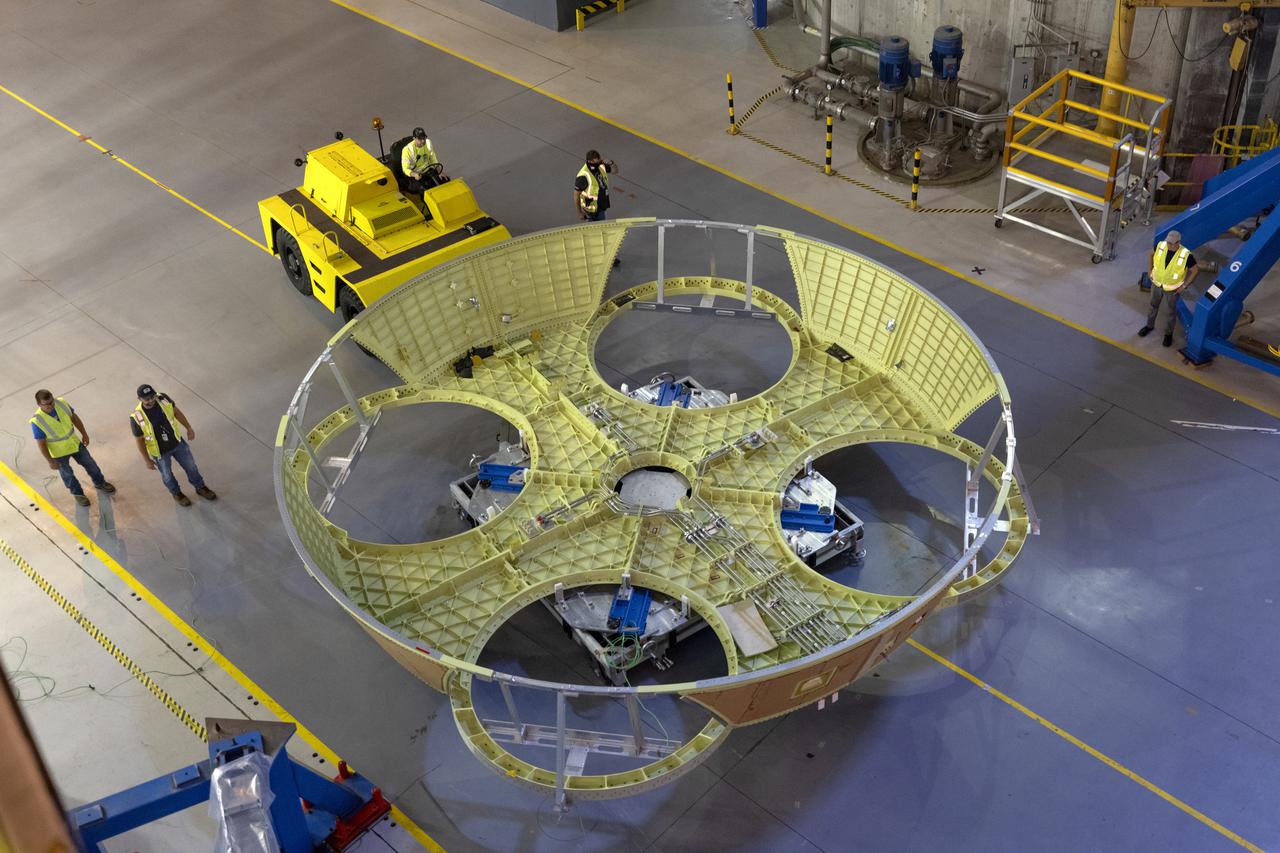
Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida installed four “quad pods” around the Artemis III core stage engine section inside the spaceport’s Space Systems Processing Facility on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. These structures are used to support the engine assembly during operations. The engine section will be transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building for final integration.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida installed four “quad pods” around the Artemis III core stage engine section inside the spaceport’s Space Systems Processing Facility on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. These structures are used to support the engine assembly during operations. The engine section will be transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building for final integration.