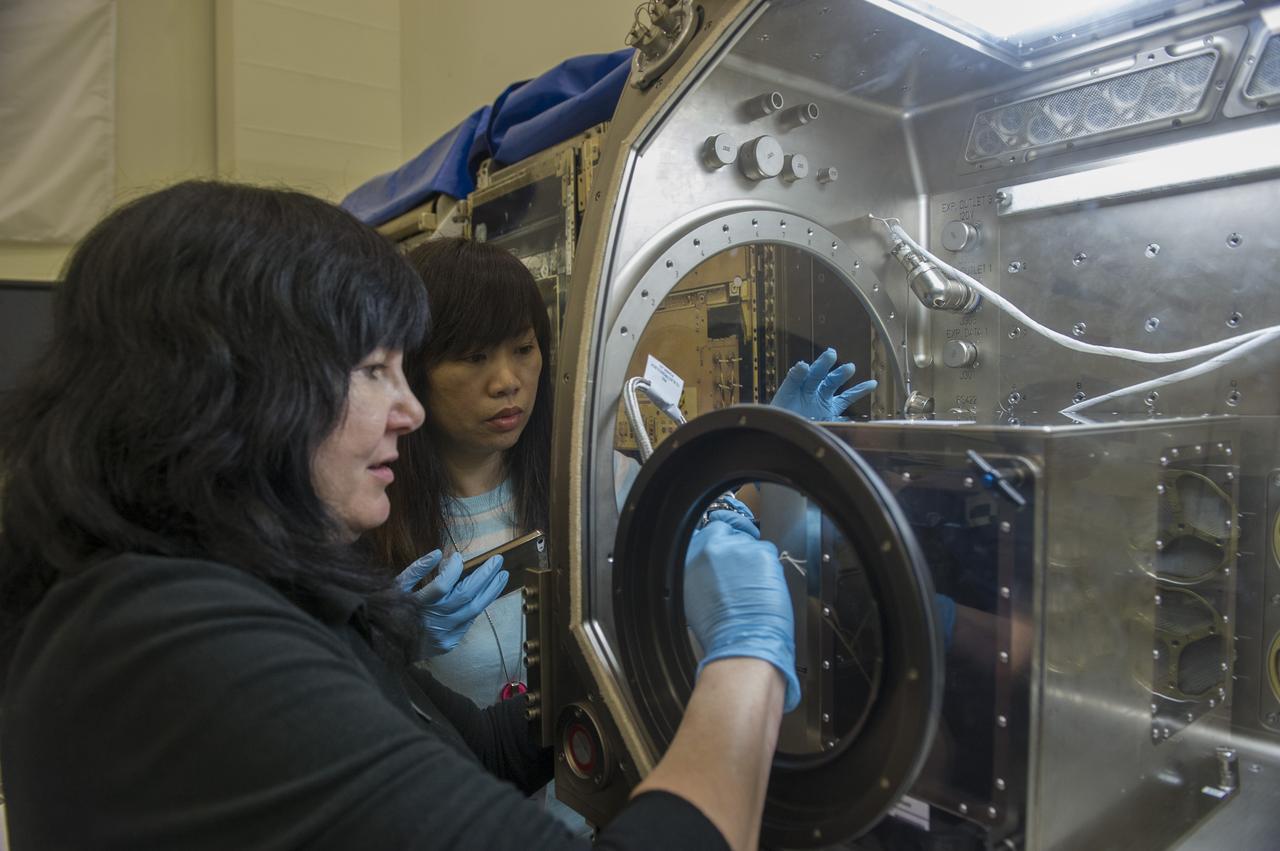

CINDY AZZARITA,(L), JSC WORKS FOR UNITED SPACE ALLIANCE IN THE HUMAN FACTORS INTEGRATION TEAM (HFIT) AND CHEN DENG,(R), BOEING CO JSC, ALSO HFIT, REVIEW HARDWARE TO HFIT REQUIREMENTS
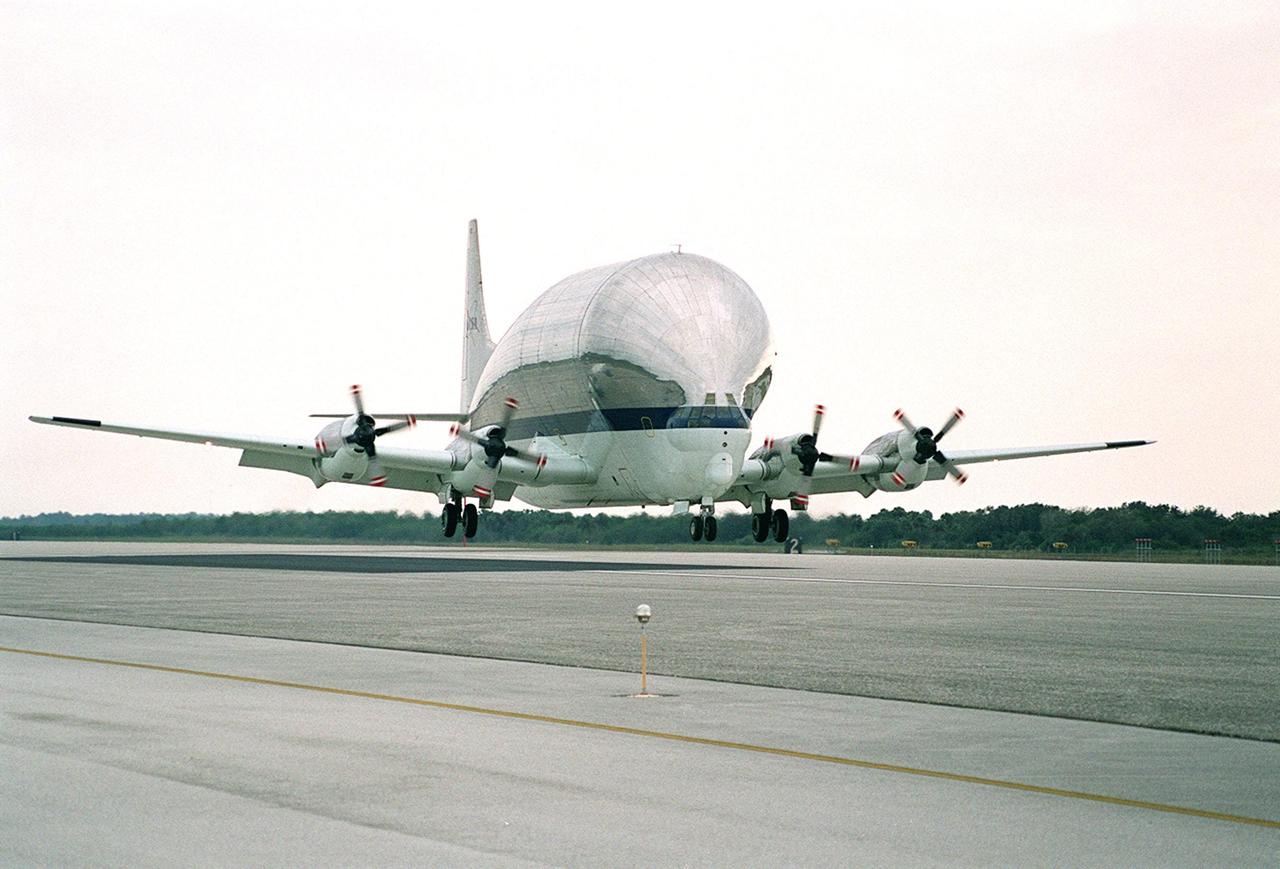

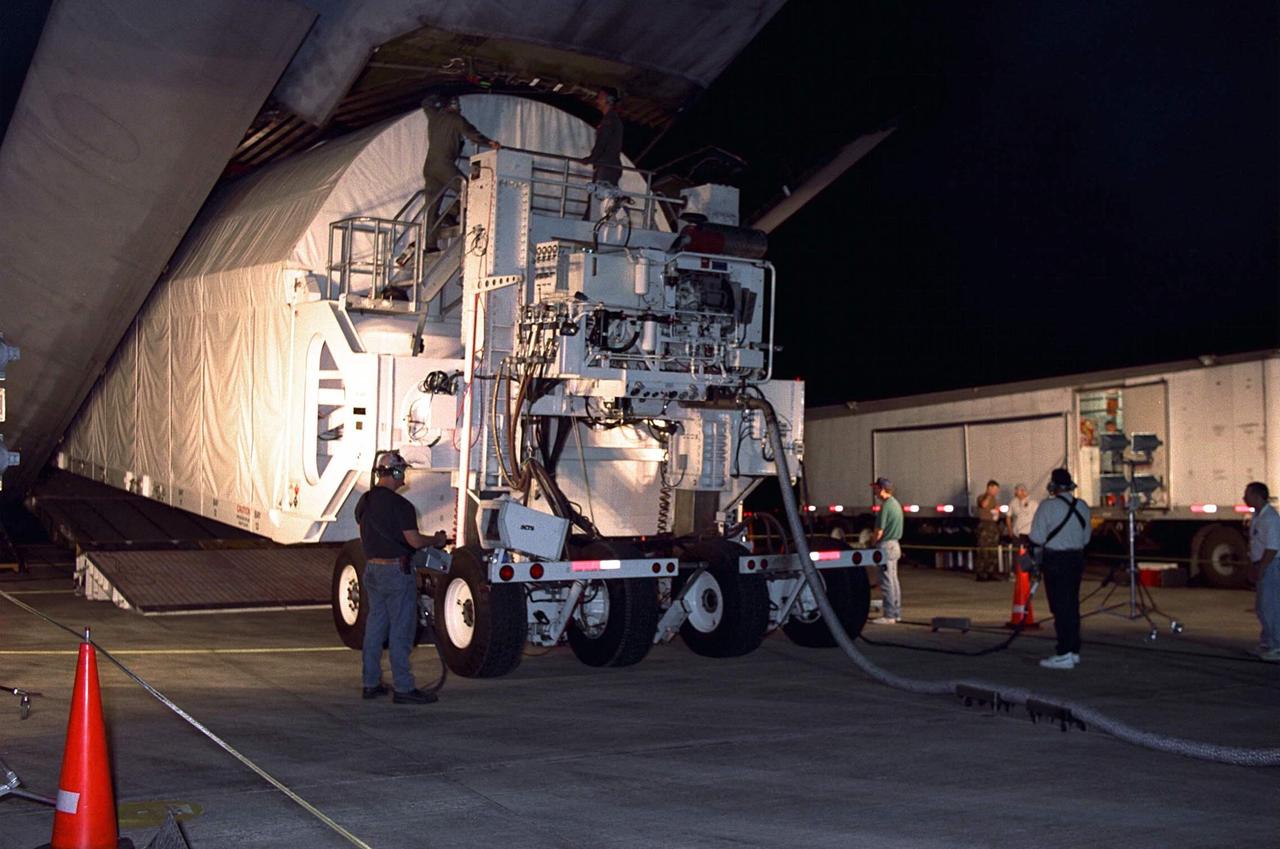
A Super Guppy aircraft arrives at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility with its cargo of Integrated Truss Structure S3, built by The Boeing Co. After offloading, the S3 will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
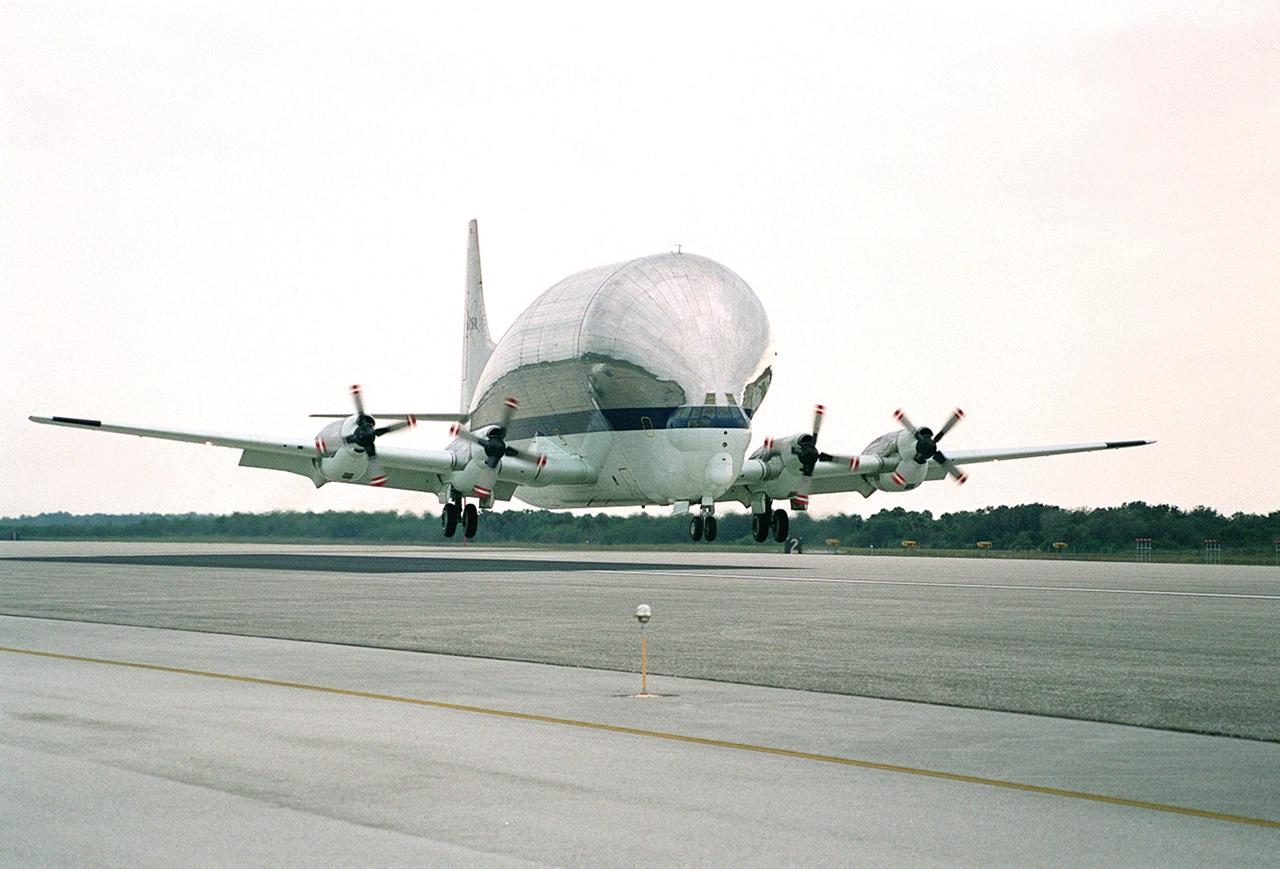

A Super Guppy aircraft arrives at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility with its cargo of Integrated Truss Structure S3, built by The Boeing Co. After offloading, the S3 will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
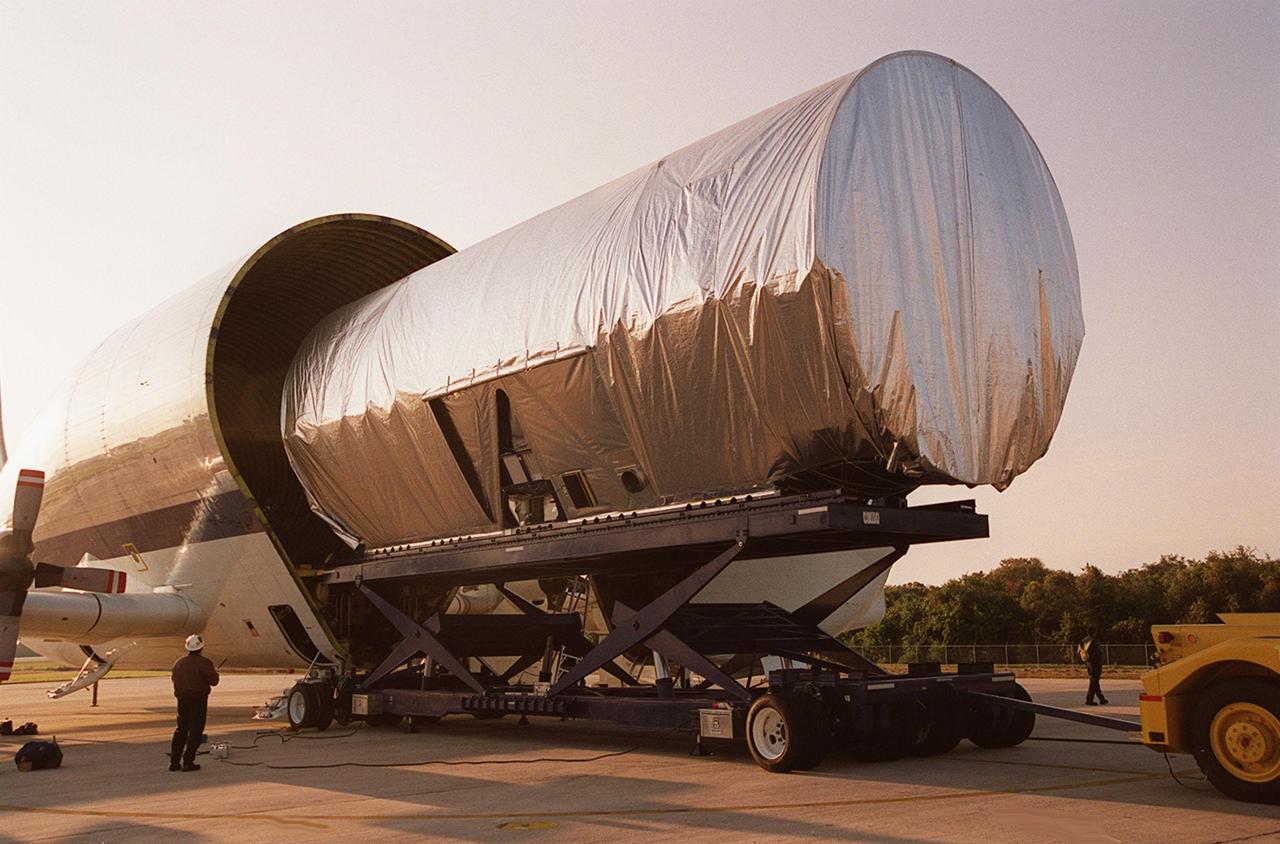

The Integrated Truss Structure S3 is offloaded from the Super Guppy aircraft that brought it to KSC from Tulsa, Okla. The S3 is built by The Boeing Co. The truss will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
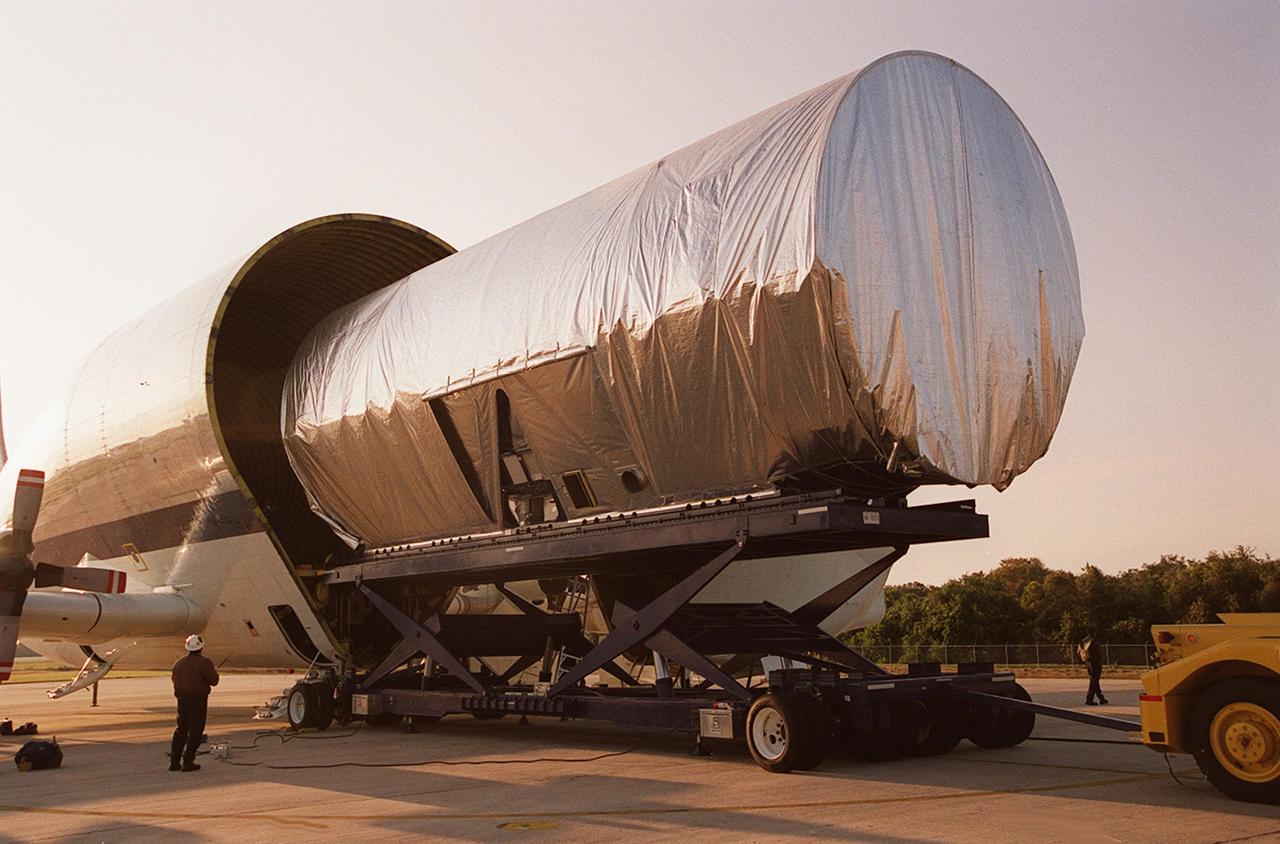

The Integrated Truss Structure S3 is offloaded from the Super Guppy aircraft that brought it to KSC from Tulsa, Okla. The S3 is built by The Boeing Co. The truss will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
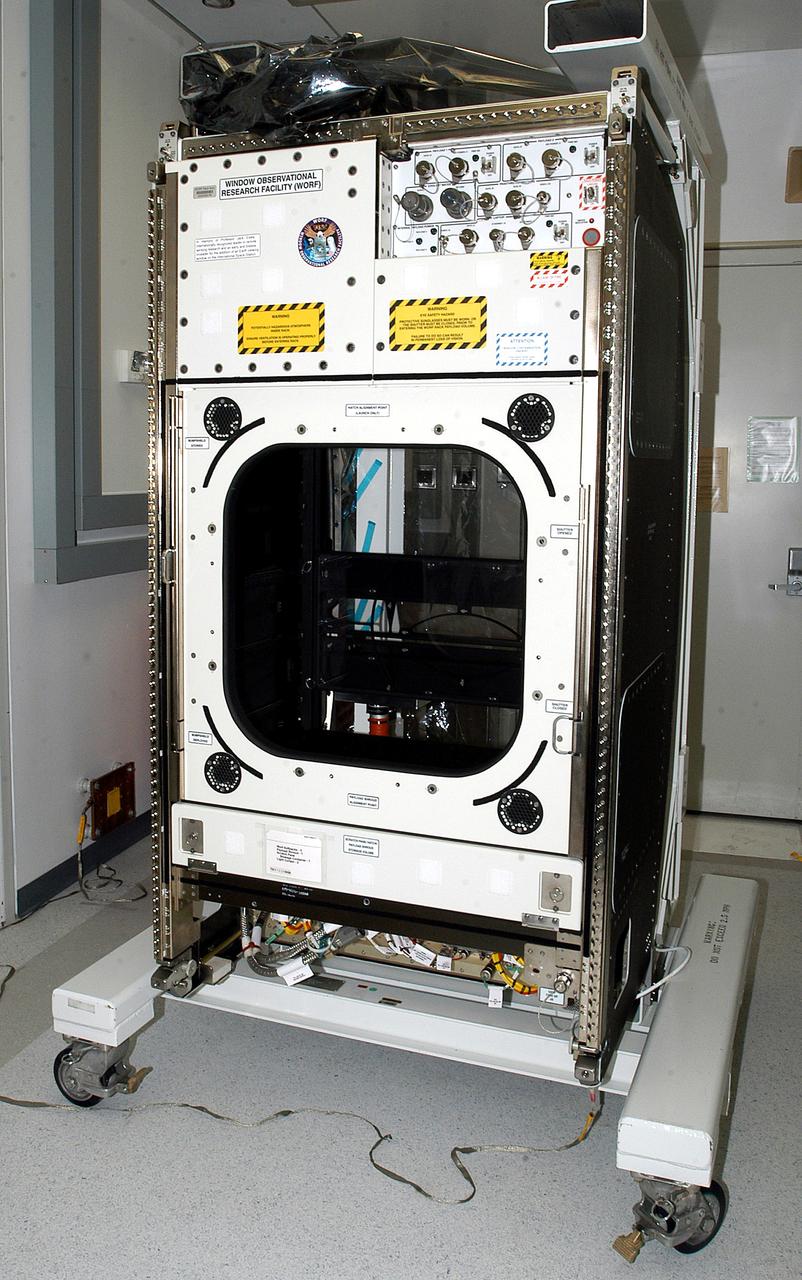

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Window Observational Research Facility (WORF), seen in the Space Station Processing Facility, was designed and built by the Boeing Co. at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. WORF will be delivered to the International Space Station and placed in the rack position in front of the Destiny lab window, providing locations for attaching cameras, multi-spectral scanners and other instruments. WORF will support a variety of scientific and commercial experiments in areas of Earth systems and processes, global ecological changes in Earth’s biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere and climate system, Earth resources, natural hazards, and education. After installation, it will become a permanent focal point for Earth Science research aboard the space station.
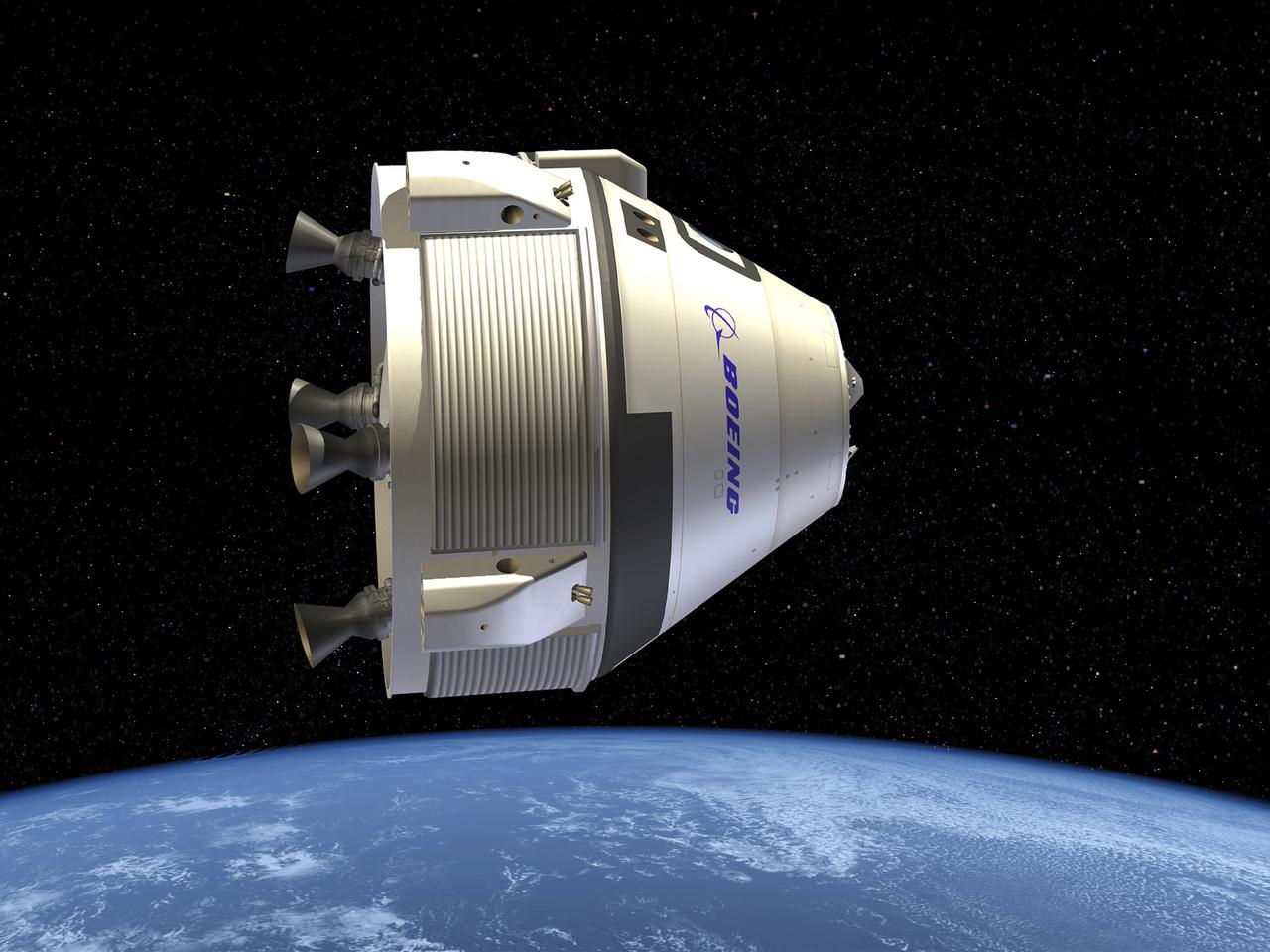

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is an artist's conception of the CST-100 under development by The Boeing Co. of Houston for NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP). In 2011, NASA selected Boeing during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 (CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. (ATK), Blue Origin, Excalibur Almaz Inc., Sierra Nevada Corp., Space Exploration Technologies (SpaceX), and United Launch Alliance (ULA). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: The Boeing Co.
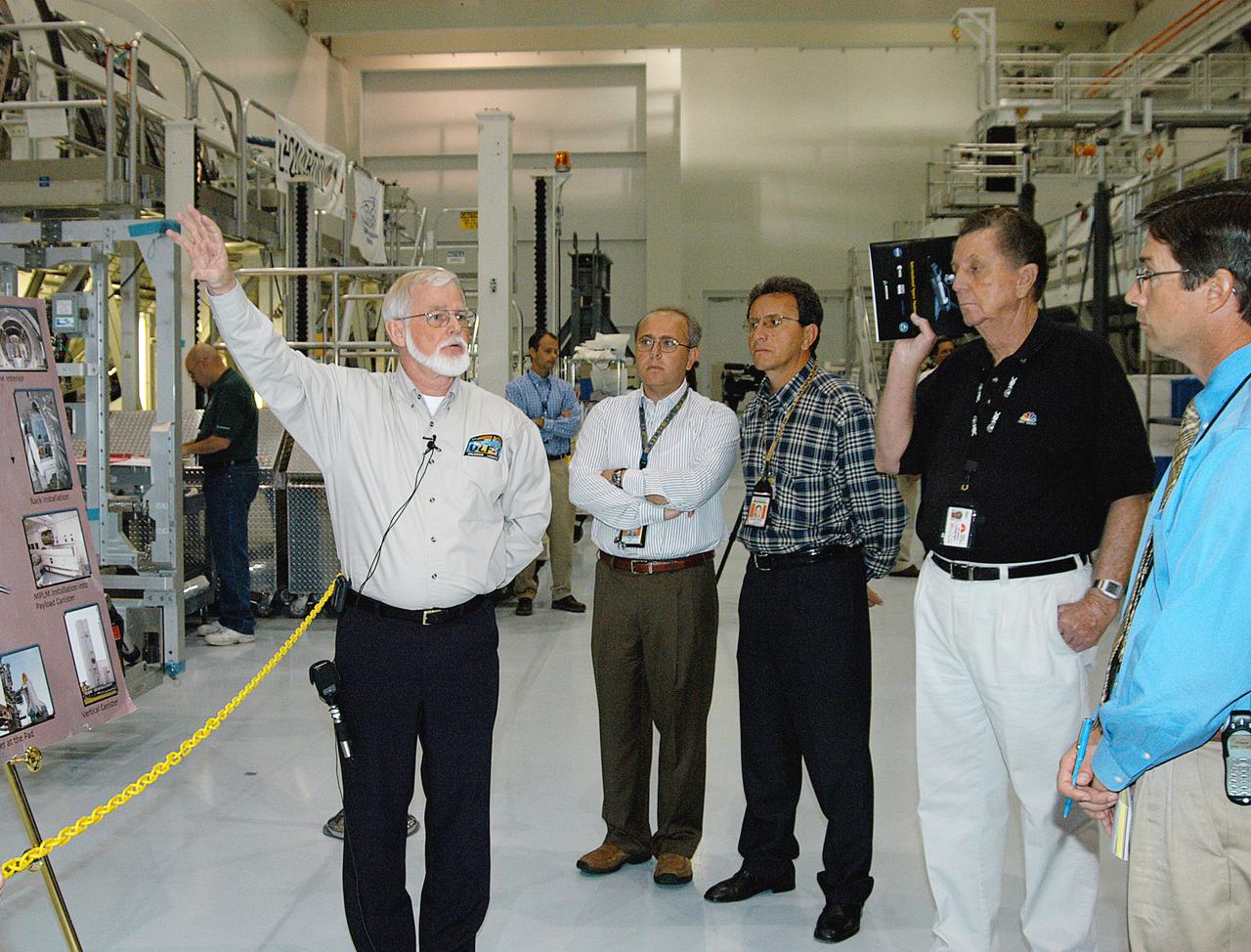

In the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF), Jeff Traylor, with The Boeing Co., talks to the media about the Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules, reusable logistics carriers used on missions to the International Space Station. To commemorate the fifth anniversary of the launch of the first element of the International Space Station, the media were invited to tour the SSPF at KSC. Reporters had the opportunity to see Space Station hardware that is being processed for deployment once the Space Shuttles return to flight as well as talk with NASA and Boeing mission managers about the various hardware elements currently being processed for flight.
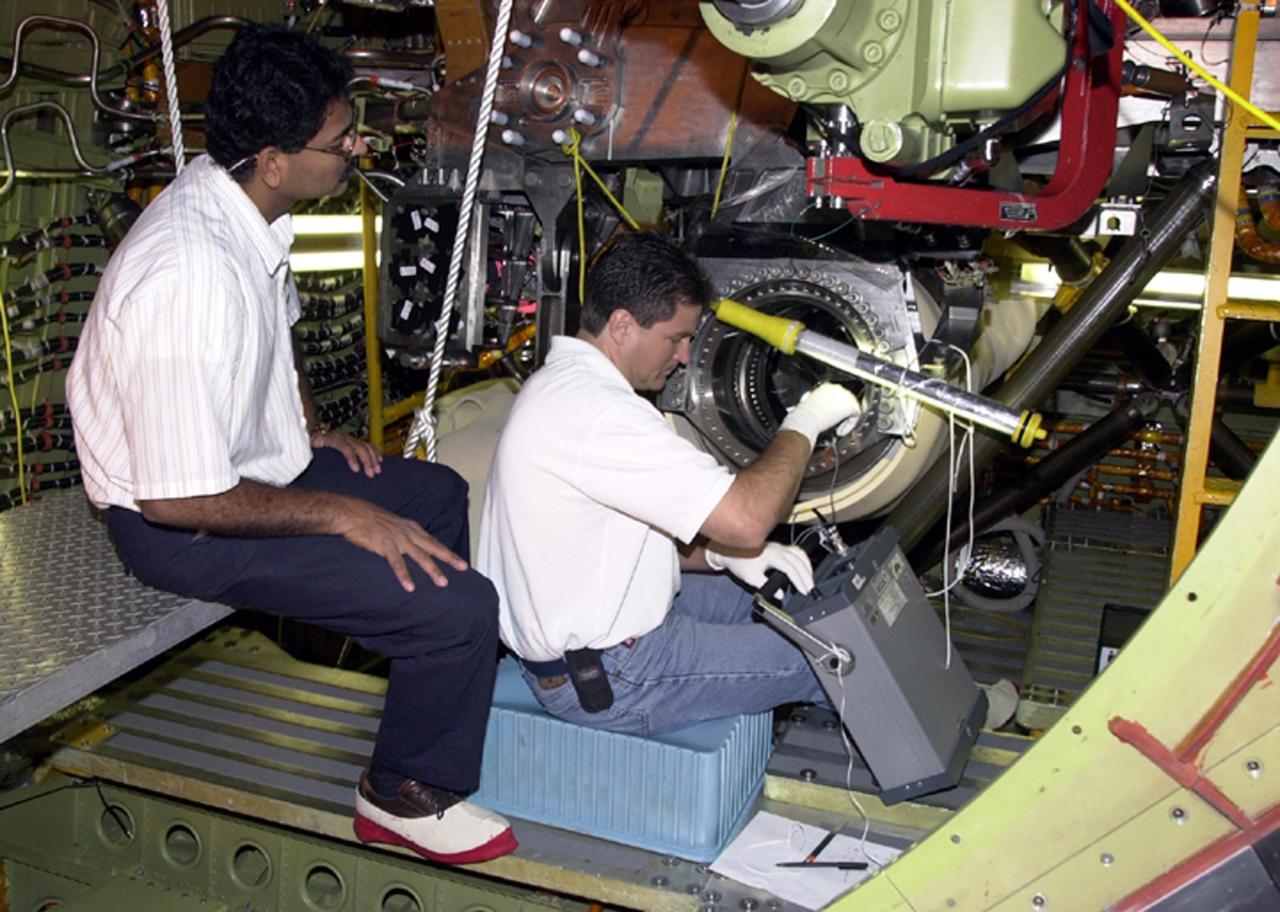

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After engine removal on Columbia, the flow line is being inspected by (left) A.J. Koshti, with The Boeing Co., and (right) Ken Tauer, with United Space Alliance. The inspection is the result of small cracks being discovered on the LH2 Main Propulsion System (MPS) flow liners in two other orbiters. Program managers decided to conduct inspections on Columbia before clearing it for flight on STS-107. The July 19 launch of Columbia on STS-107 has been delayed a few weeks
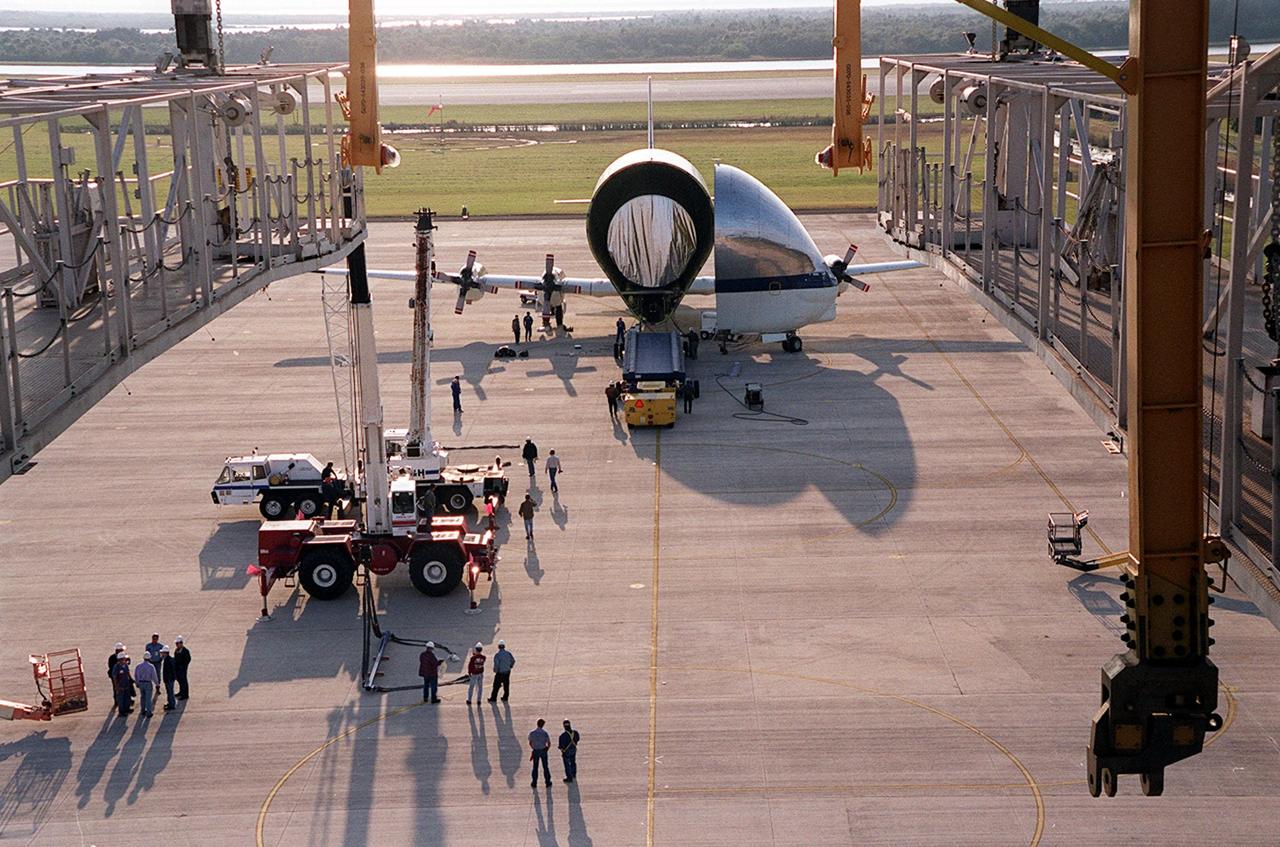

On the parking apron of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, near the Mate/Demate device (seen in the foreground), the opened nose of the Super Guppy aircraft reveals its cargo, the Integrated Truss Structure S3. It was built by The Boeing Co. After offloading, the S3 will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
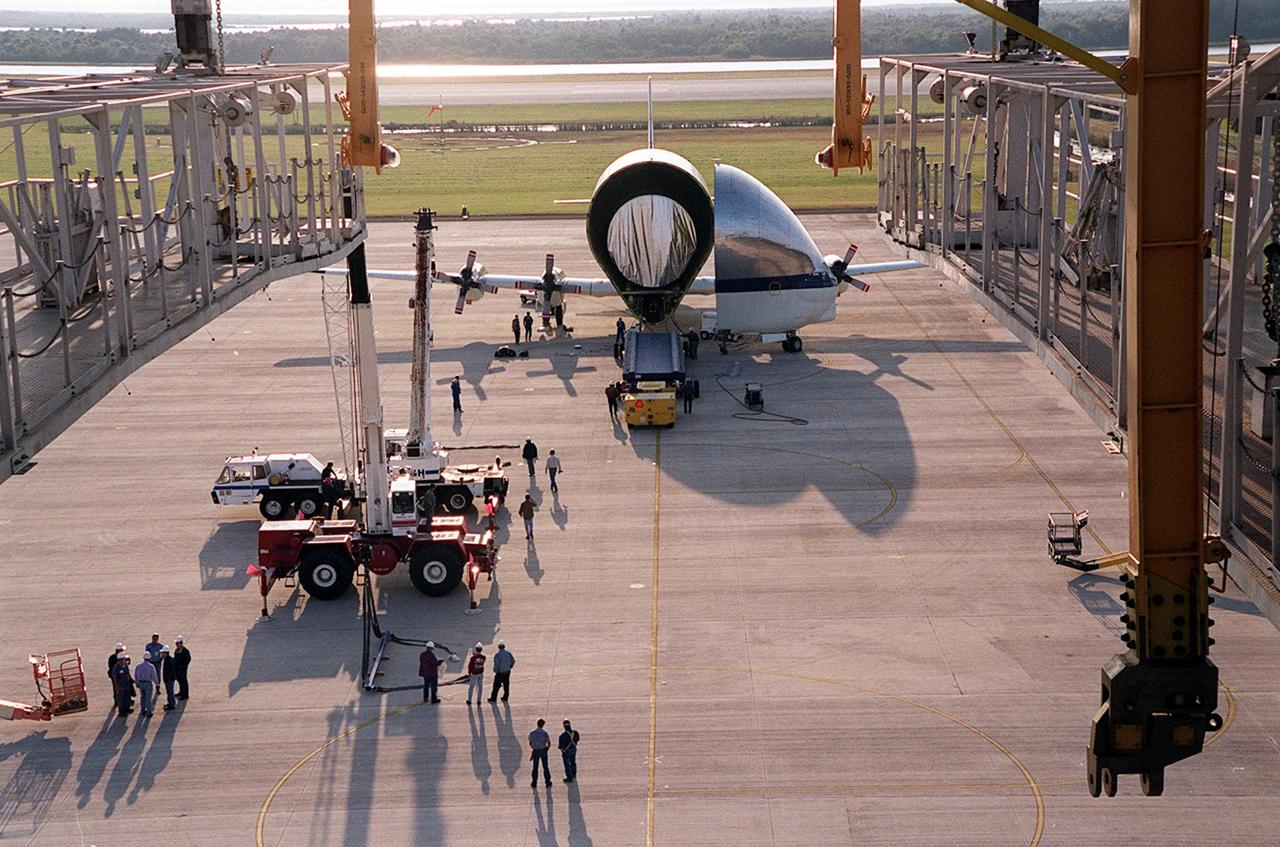

On the parking apron of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, near the Mate/Demate device (seen in the foreground), the opened nose of the Super Guppy aircraft reveals its cargo, the Integrated Truss Structure S3. It was built by The Boeing Co. After offloading, the S3 will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – International Space Station employees based at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida participate in the "ISS Is Alive" employee recognition barbecue celebration at Kars Park II. NASA and The Boeing Co. hosted the celebration to thank the employees based at the Kennedy Space Center who were involved in building the largest, most complex international scientific project in history and the largest venture in space to date. The station has hosted human life, work and research in space for more than 10 years. Boeing is the prime contractor to NASA for the space station. In addition to designing and building all the major U.S. elements, Boeing also is responsible for ensuring the successful integration of new hardware and software -- including components from international partners -- as well as for providing sustaining engineering work. For more information on the International Space Station, visit http://www.nasa.gov/station. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
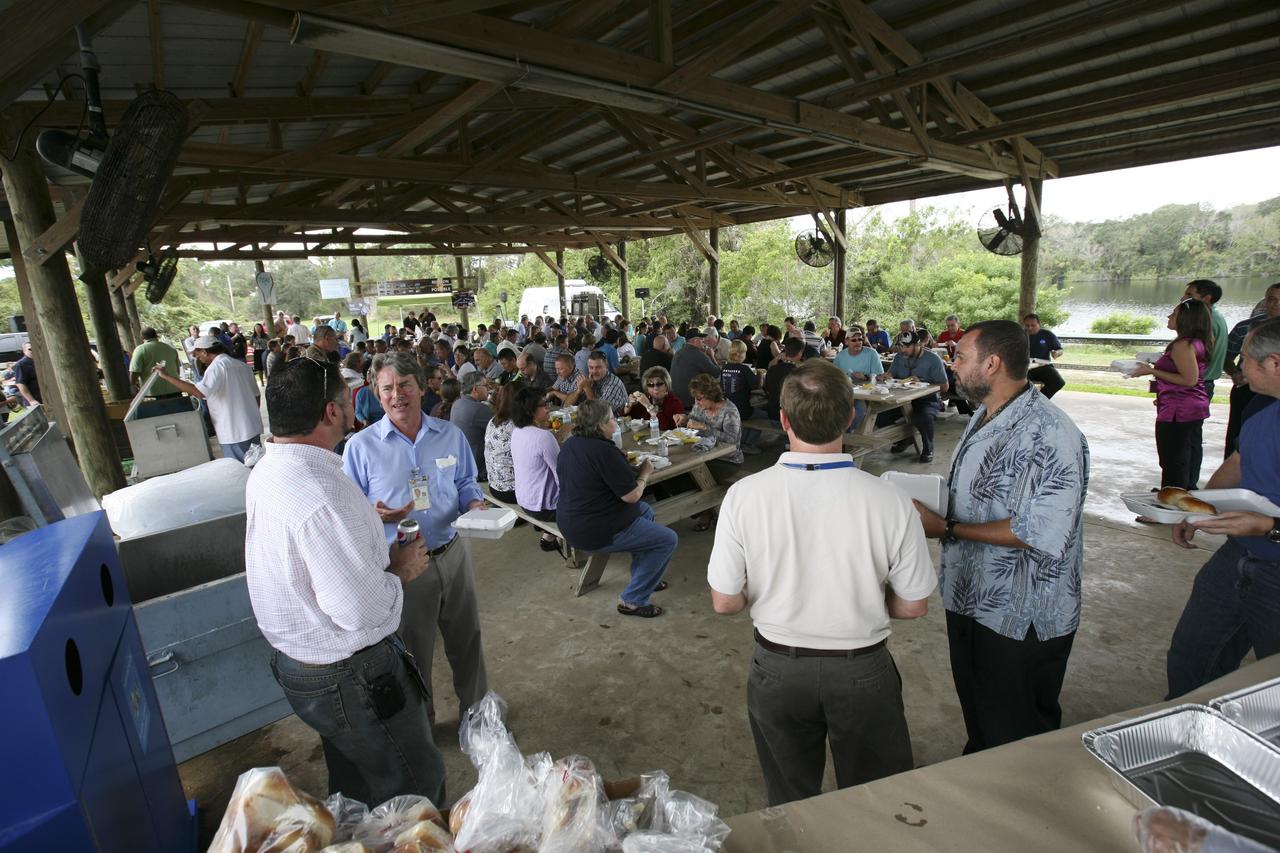

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – International Space Station employees based at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida participate in the "ISS Is Alive" employee recognition barbecue celebration at Kars Park II. The Boeing Co. and NASA hosted the celebration to thank the employees based at the Kennedy Space Center who were involved in building the largest, most complex international scientific project in history and the largest venture in space to date. The station has hosted human life, work and research in space for more than 10 years. Boeing is the prime contractor to NASA for the space station. In addition to designing and building all the major U.S. elements, Boeing also is responsible for ensuring the successful integration of new hardware and software -- including components from international partners -- as well as for providing sustaining engineering work. For more information on the International Space Station, visit http://www.nasa.gov/station. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
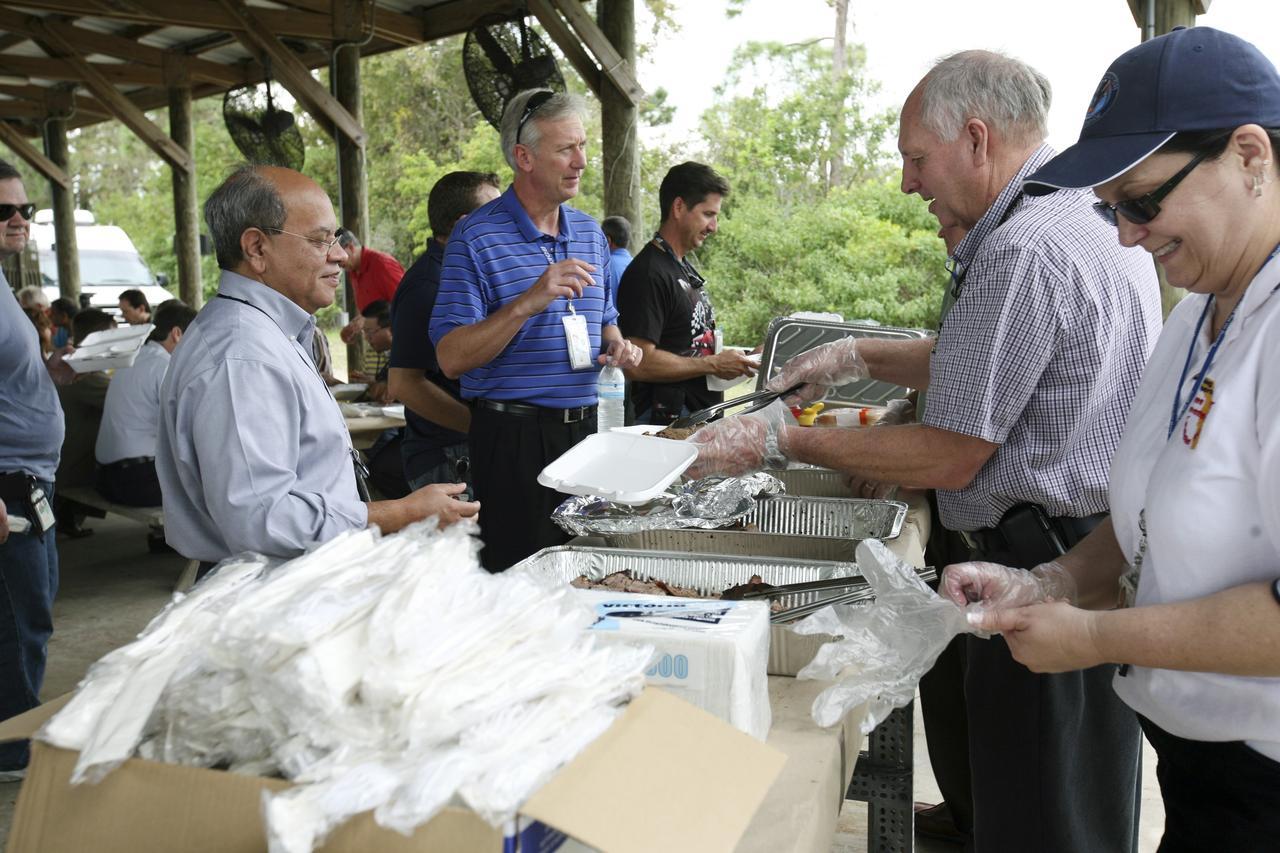

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – International Space Station employees based at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida participate in the "ISS Is Alive" employee recognition barbecue celebration at Kars Park II. The Boeing Co. and NASA hosted the celebration to thank the employees based at the Kennedy Space Center who were involved in building the largest, most complex international scientific project in history and the largest venture in space to date. The station has hosted human life, work and research in space for more than 10 years. Boeing is the prime contractor to NASA for the space station. In addition to designing and building all the major U.S. elements, Boeing also is responsible for ensuring the successful integration of new hardware and software -- including components from international partners -- as well as for providing sustaining engineering work. For more information on the International Space Station, visit http://www.nasa.gov/station. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
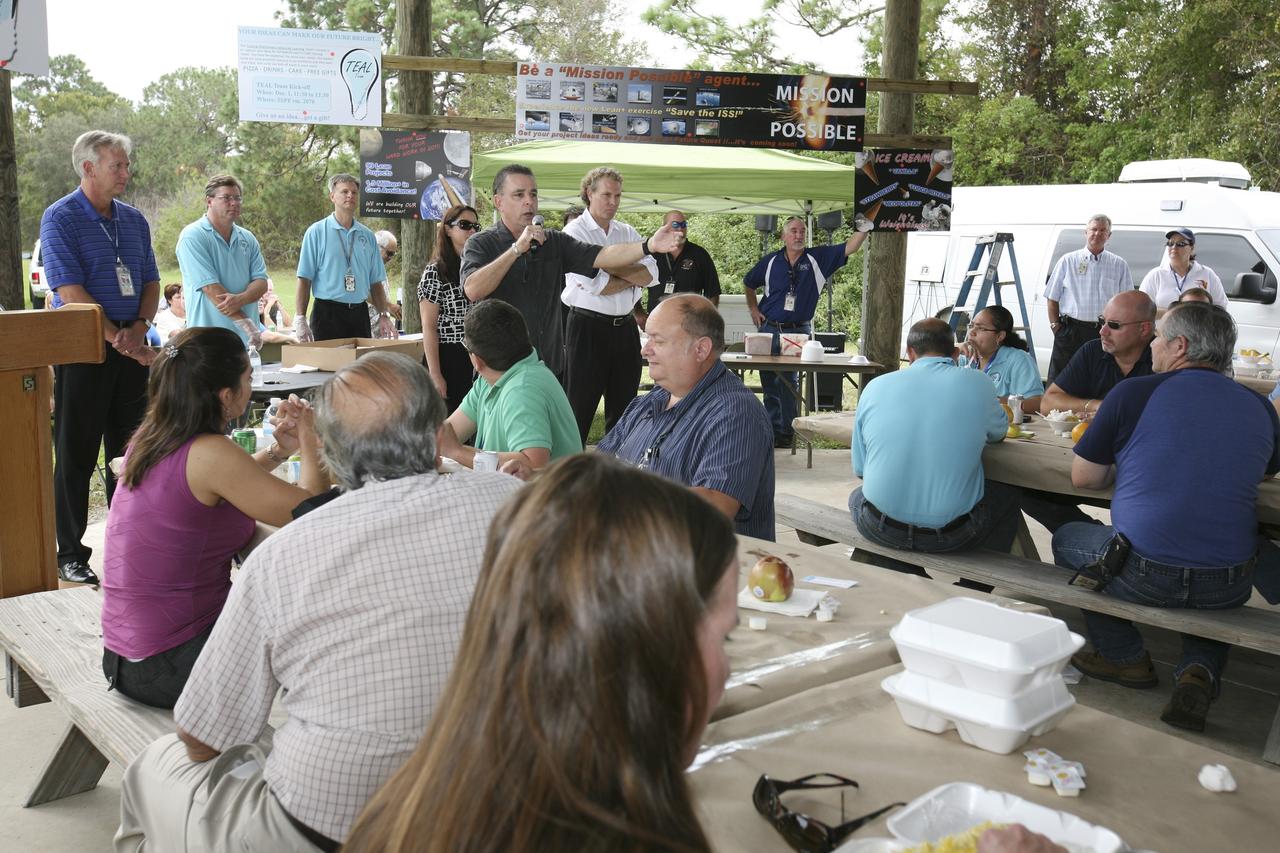

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Director Bill Dowdell talks to station employees based at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida during the "ISS Is Alive" employee recognition barbecue celebration at Kars Park II. NASA and The Boeing Co. hosted the celebration to thank the employees based at the Kennedy Space Center who were involved in building the largest, most complex international scientific project in history and the largest venture in space to date. The station has hosted human life, work and research in space for more than 10 years. Boeing is the prime contractor to NASA for the space station. In addition to designing and building all the major U.S. elements, Boeing also is responsible for ensuring the successful integration of new hardware and software -- including components from international partners -- as well as for providing sustaining engineering work. For more information on the International Space Station, visit http://www.nasa.gov/station. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
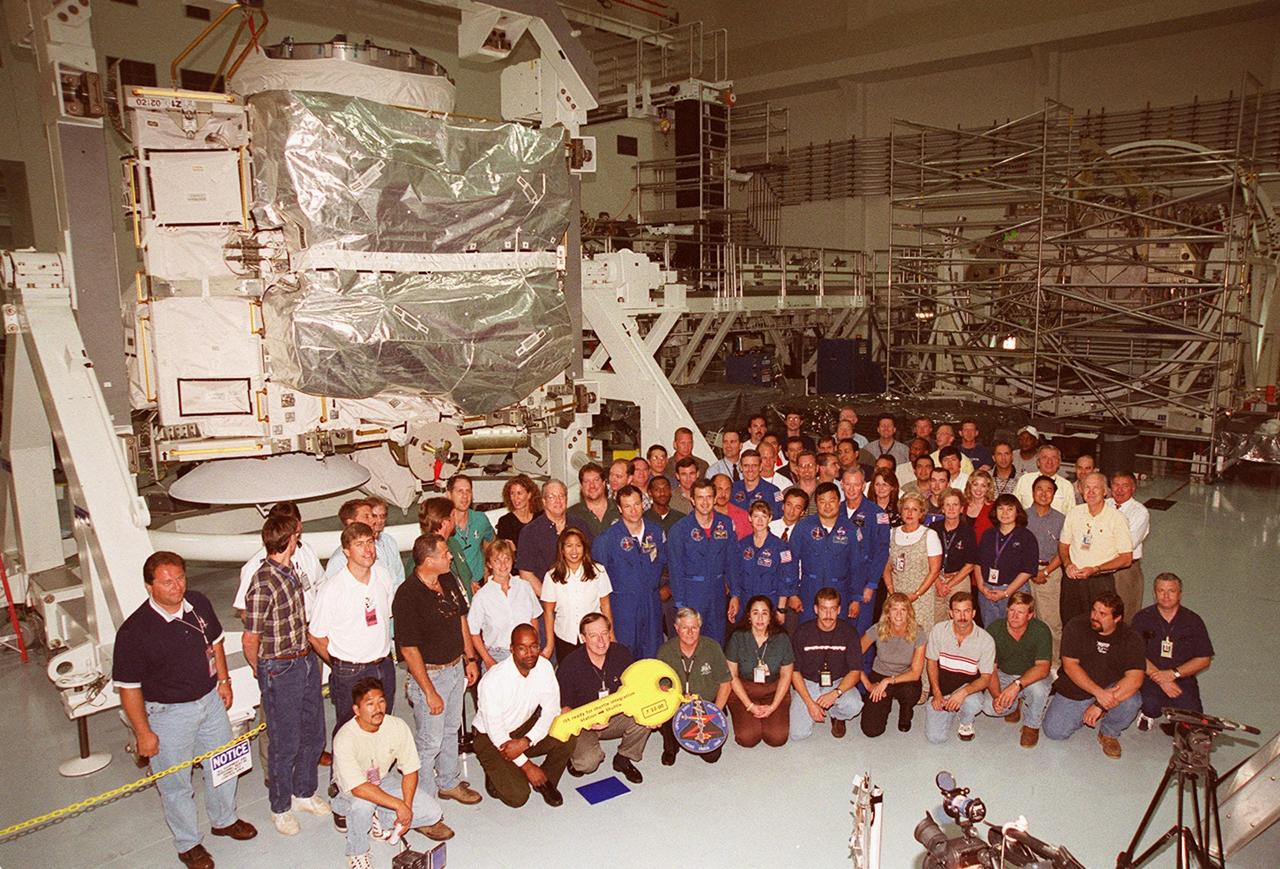
The Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss is officially presented to NASA by The Boeing Co. on the Space Station Processing Facility floor on July 31. STS-92 Commander Col. Brian Duffy, comments on the presentation. Pictured are The Boeing Co. processing team and STS-92 astronauts. The Z-1 Truss is the cornerstone truss of the International Space Station and is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998
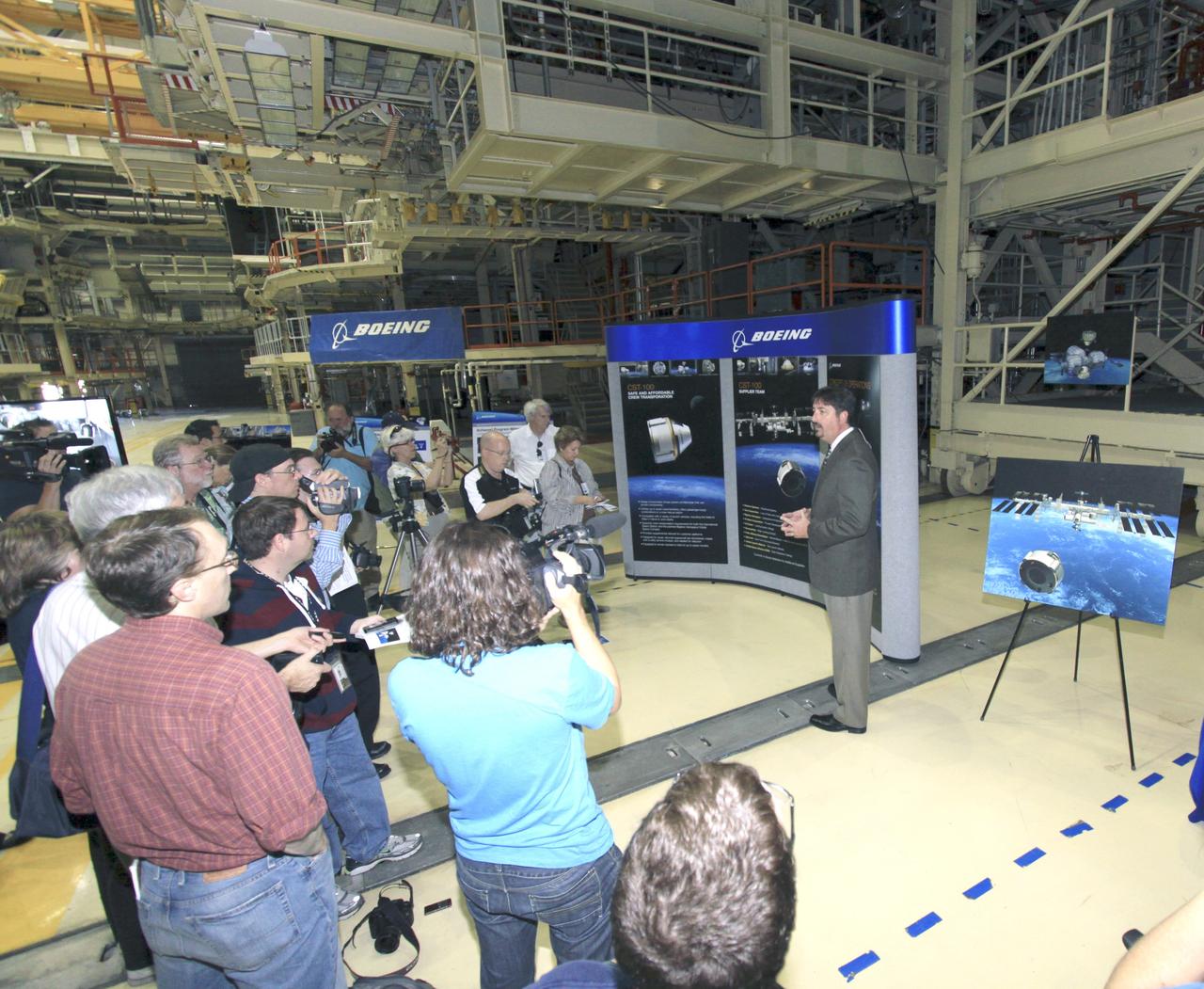

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chuck Hardison, the production and ground operations manager of The Boeing Co.'s Commercial Crew Transportation System, talks to media about plans to take NASA astronauts to the International Space Station in Orbiter Processing Facility-3 (OPF-3) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Boeing is maturing its CST-100 spacecraft design for NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP) under the Commercial Crew Development Round 2 (CCDev2) activities. Boeing's current design shows the CST-100 taking up to seven astronauts and cargo to the space station or other low Earth orbit destinations by the middle of the decade. Through an agreement with NASA and Space Florida, Boeing is leasing OPF-3, the Processing Control Facility (PCC) and Space Shuttle Main Engine Shop at Kennedy to design, manufacture, process and integrate the CST-100. This work is expected to generate up to 550 engineering and technical jobs for Florida's Space Coast. Hardison explained that the CST-100 will be manufactured using a spin-form technology, which is expected to bring down the cost and safety concerns of a traditional welded spacecraft. It's innovations such as this that CCP hopes will drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before. Seven aerospace companies are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. (ATK) of Promontory, Utah, Blue Origin of Kent, Wash., The Boeing Co., of Houston, Excalibur Almaz Inc. of Houston, Sierra Nevada Corp. of Louisville, Colo., Space Exploration Technologies (SpaceX) of Hawthorne, Calif., and United Launch Alliance (ULA) of Centennial, Colo. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/exploration/commercial Photo credit: Jim Grossmann
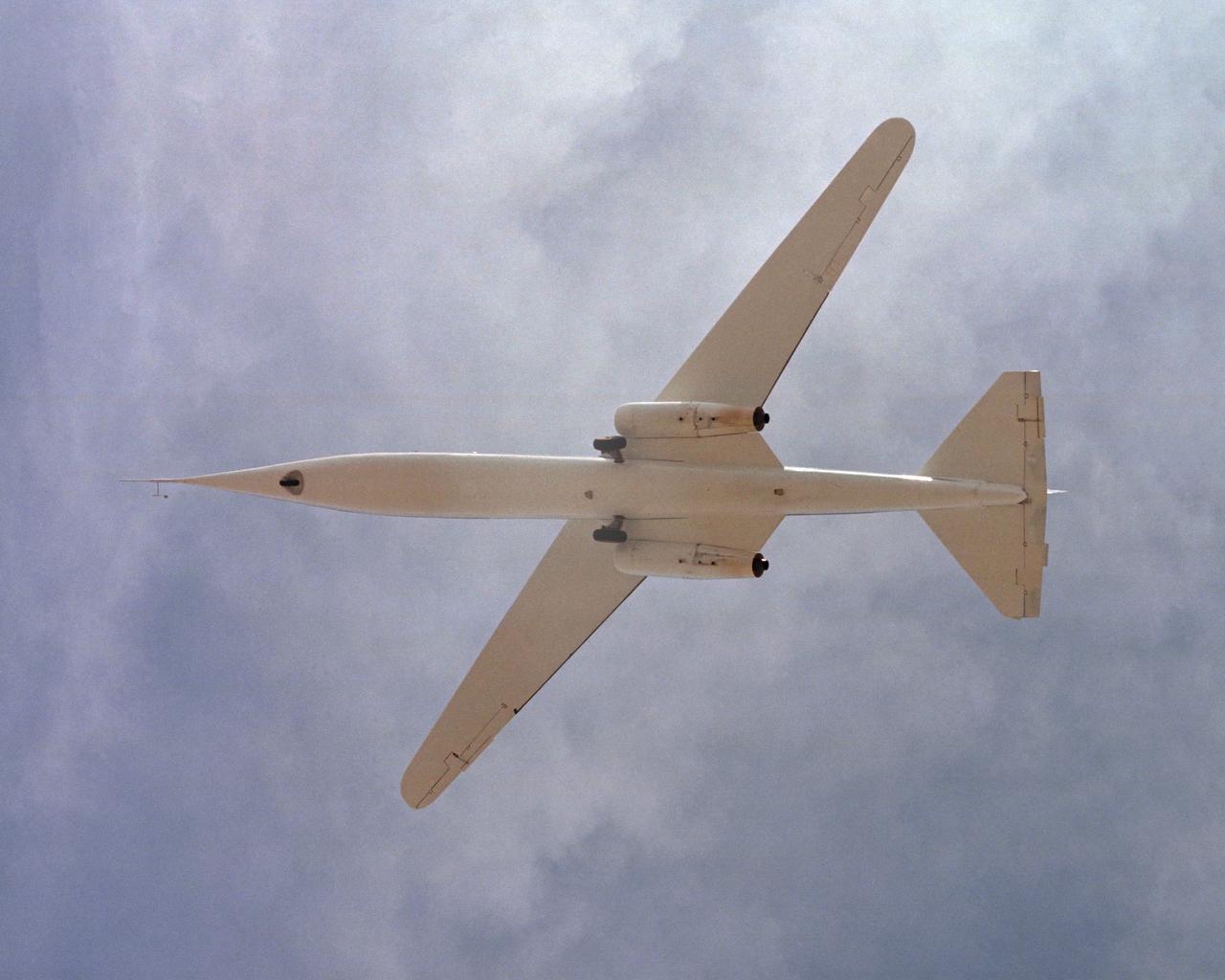

The AD-1 aircraft with its wing swept. Visible are the twin jet engines that powered the aircraft and the fixed landing gear.
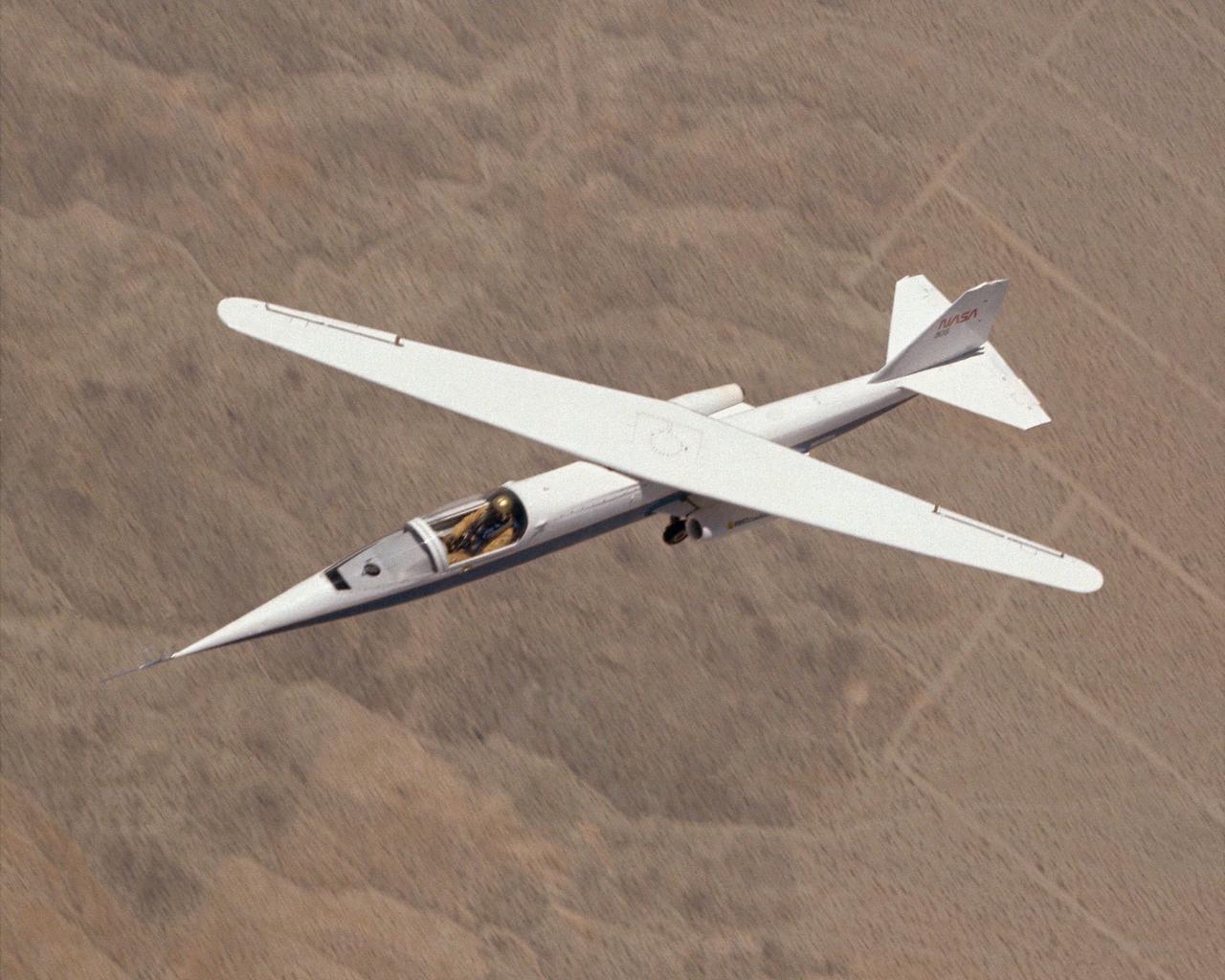

AD-1 in flight. Flight #30. The AD-1 aircraft in flight with its wing swept at 60 degrees, the maximum sweep angle.
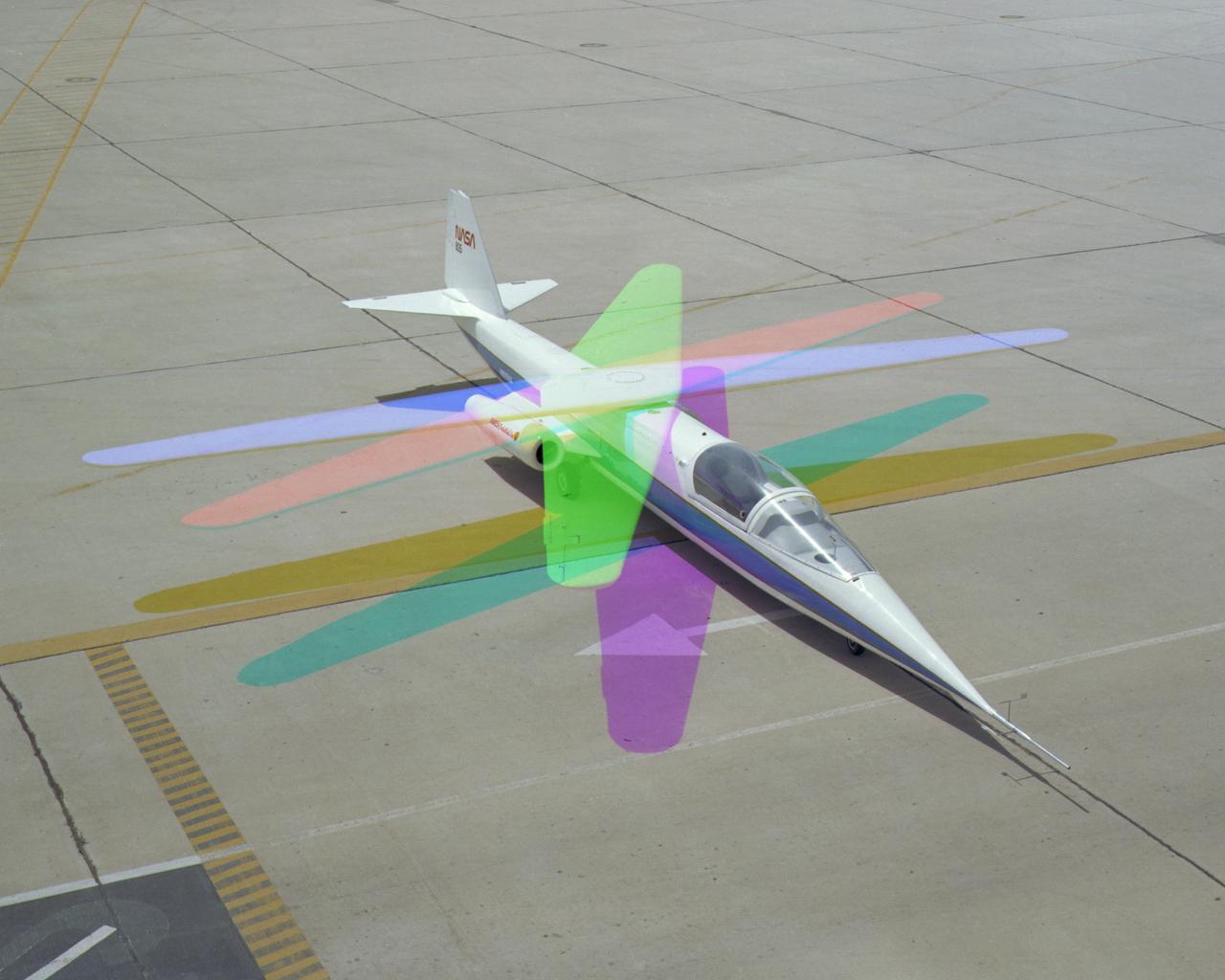
Multiple exposure image showing wing movement on AD-1.
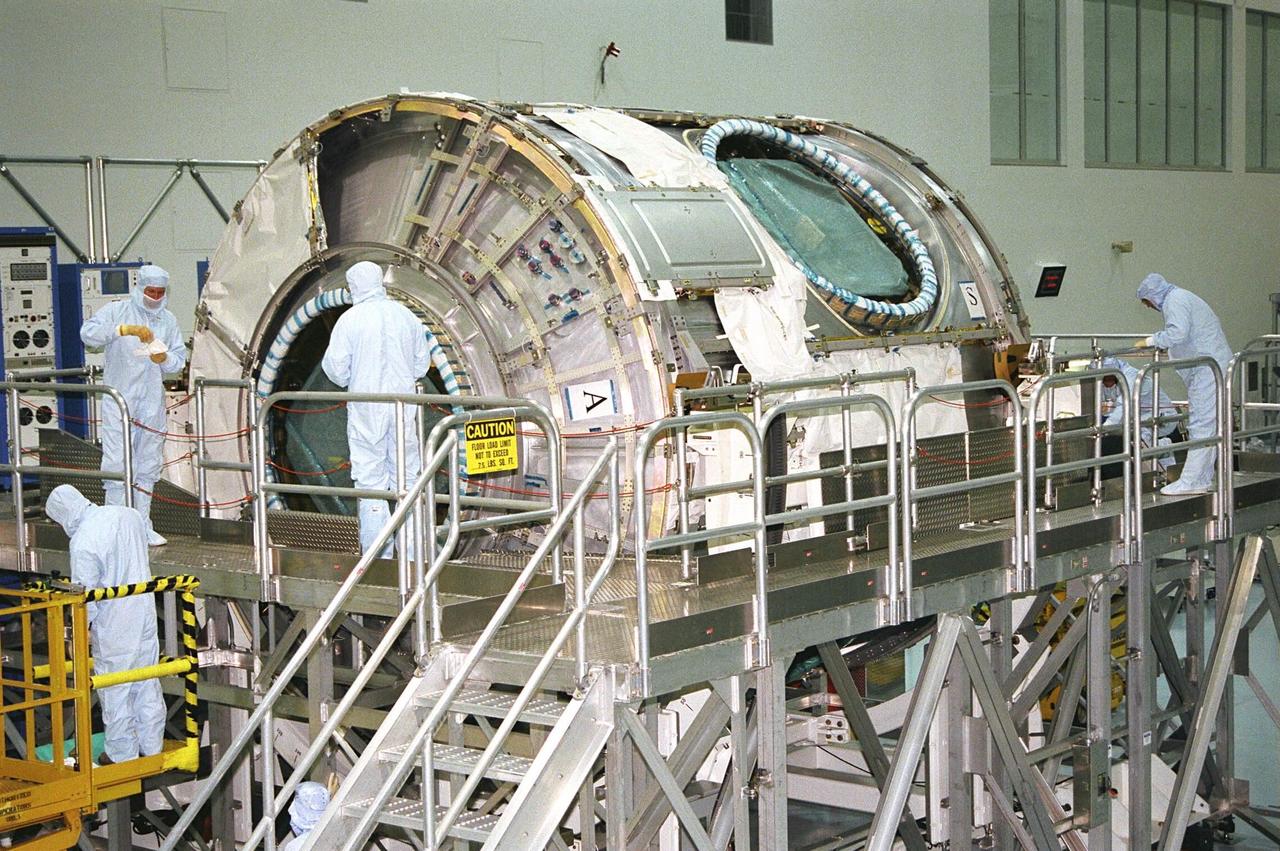
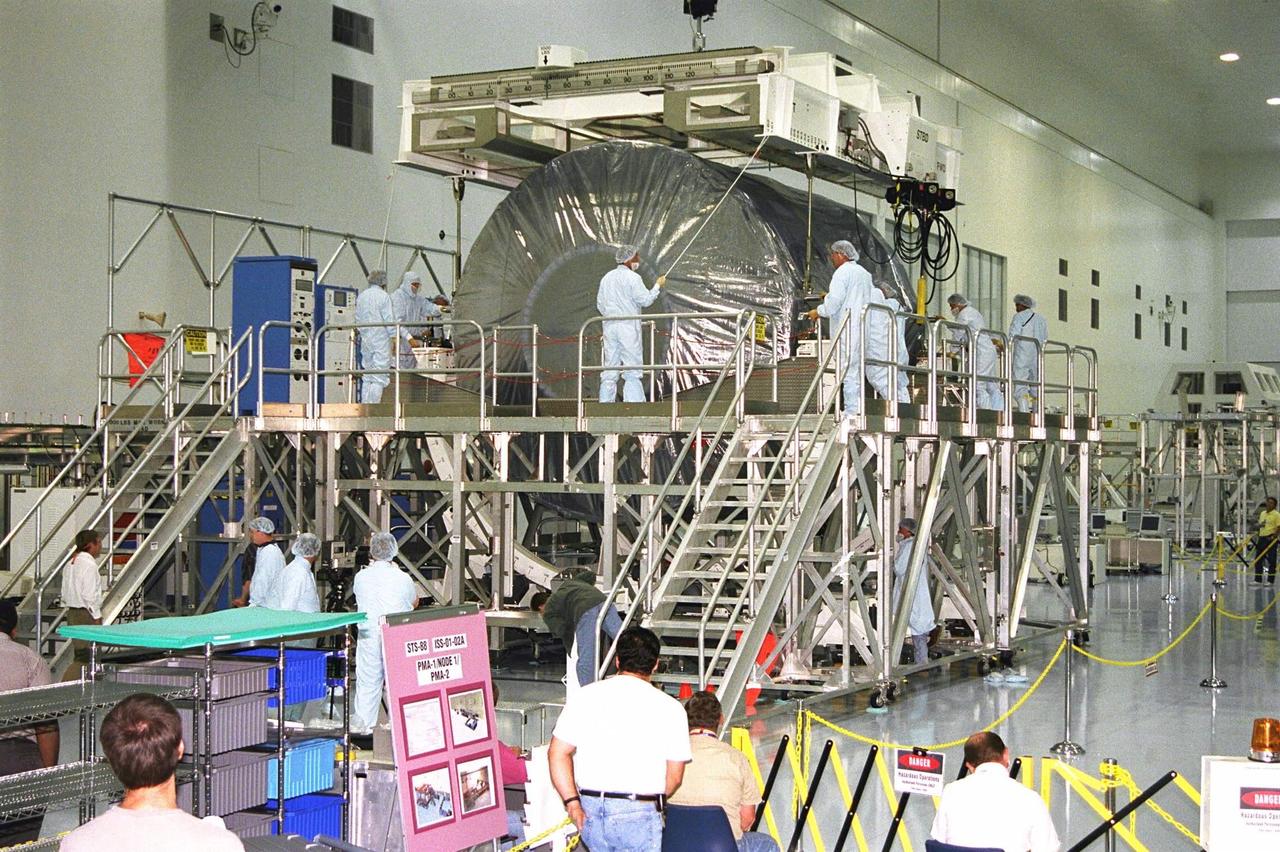
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Boeing technicians move a piece of hardware into position on Node 1 of the International Space Station (ISS) in KSC's Space Station Processing Facility in preparation for mating with Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA)-2. The node is the first element of the ISS to be manufactured in the United States and is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on STS-88 later this year, along with PMAs 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the ISS. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
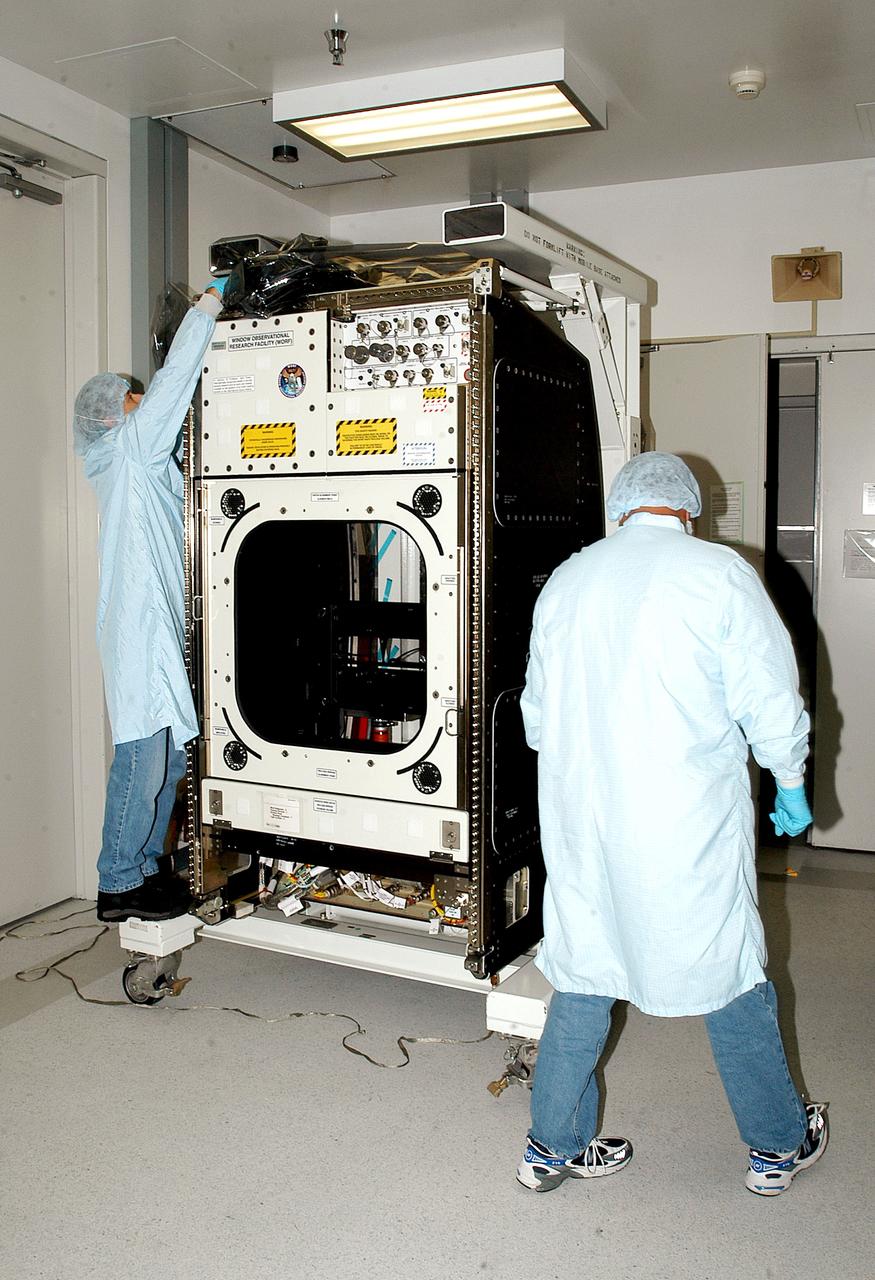

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility check out the Window Observational Research Facility (WORF), designed and built by the Boeing Co. at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. WORF will be delivered to the International Space Station and placed in the rack position in front of the Destiny lab window, providing locations for attaching cameras, multi-spectral scanners and other instruments. WORF will support a variety of scientific and commercial experiments in areas of Earth systems and processes, global ecological changes in Earth’s biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere and climate system, Earth resources, natural hazards, and education. After installation, it will become a permanent focal point for Earth Science research aboard the space station.
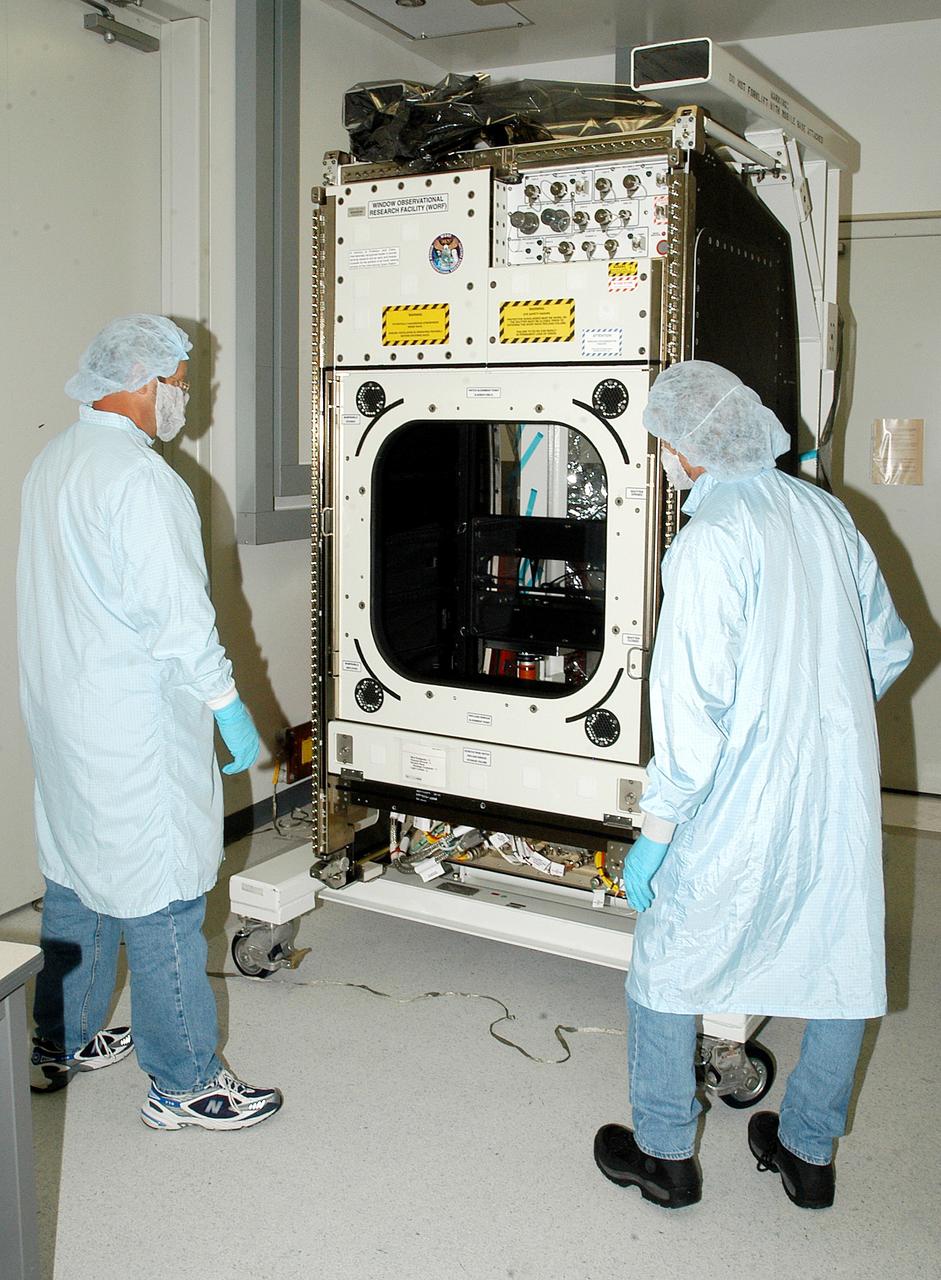

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility check out the Window Observational Research Facility (WORF), designed and built by the Boeing Co. at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. WORF will be delivered to the International Space Station and placed in the rack position in front of the Destiny lab window, providing locations for attaching cameras, multi-spectral scanners and other instruments. WORF will support a variety of scientific and commercial experiments in areas of Earth systems and processes, global ecological changes in Earth’s biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere and climate system, Earth resources, natural hazards, and education. After installation, it will become a permanent focal point for Earth Science research aboard the space station.
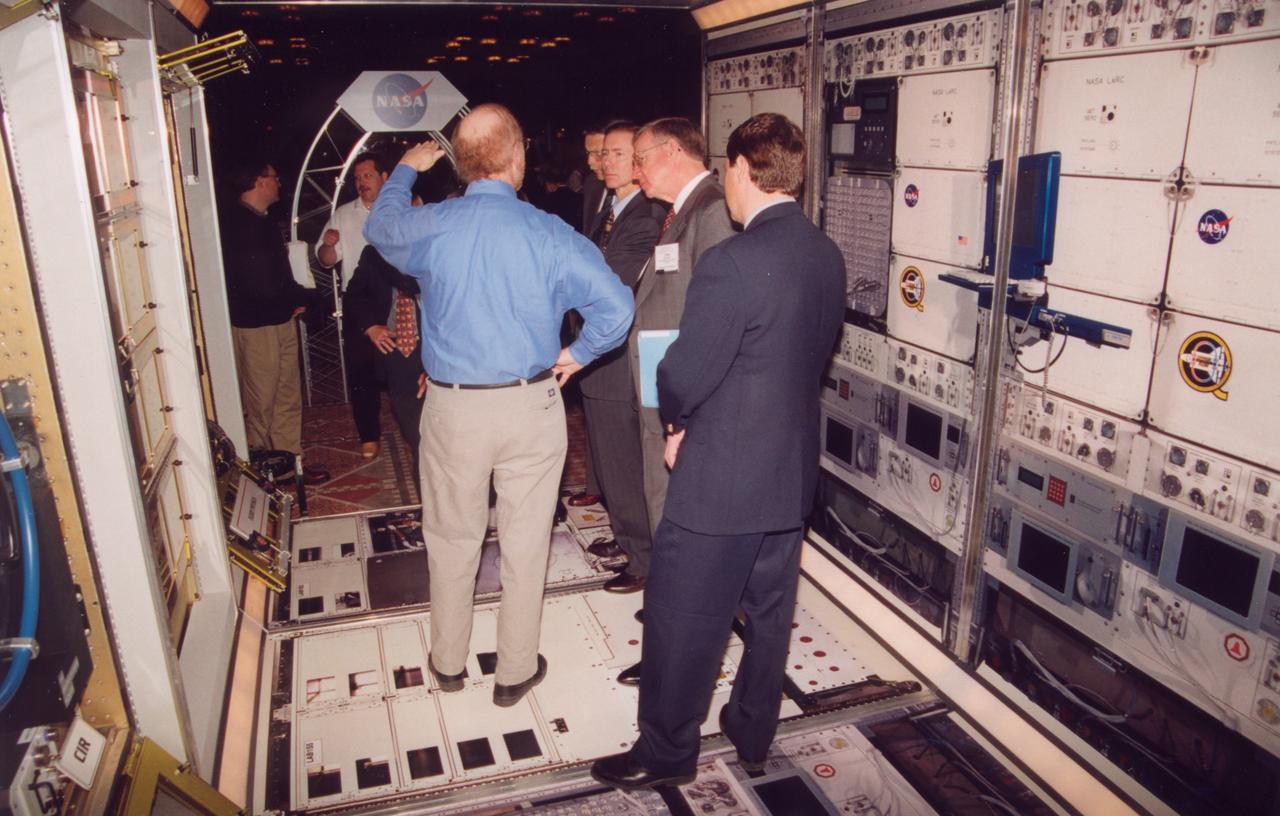

Engineers from NASA's Glenn Research Center demonstrate the access to one of the experiment racks planned for the U.S. Destiny laboratory module on the International Space Station (ISS). This mockup has the full diameter, full corridor width, and half the length of the module. The mockup includes engineering mockups of the Fluids and Combustion Facility being developed by NASA's Glenn Research Center. (The full module will be six racks long; the mockup is three racks long). Listening at center is former astronaut Brewster Shaw (center), now a program official with the Boeing Co., the ISS prime contractor. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
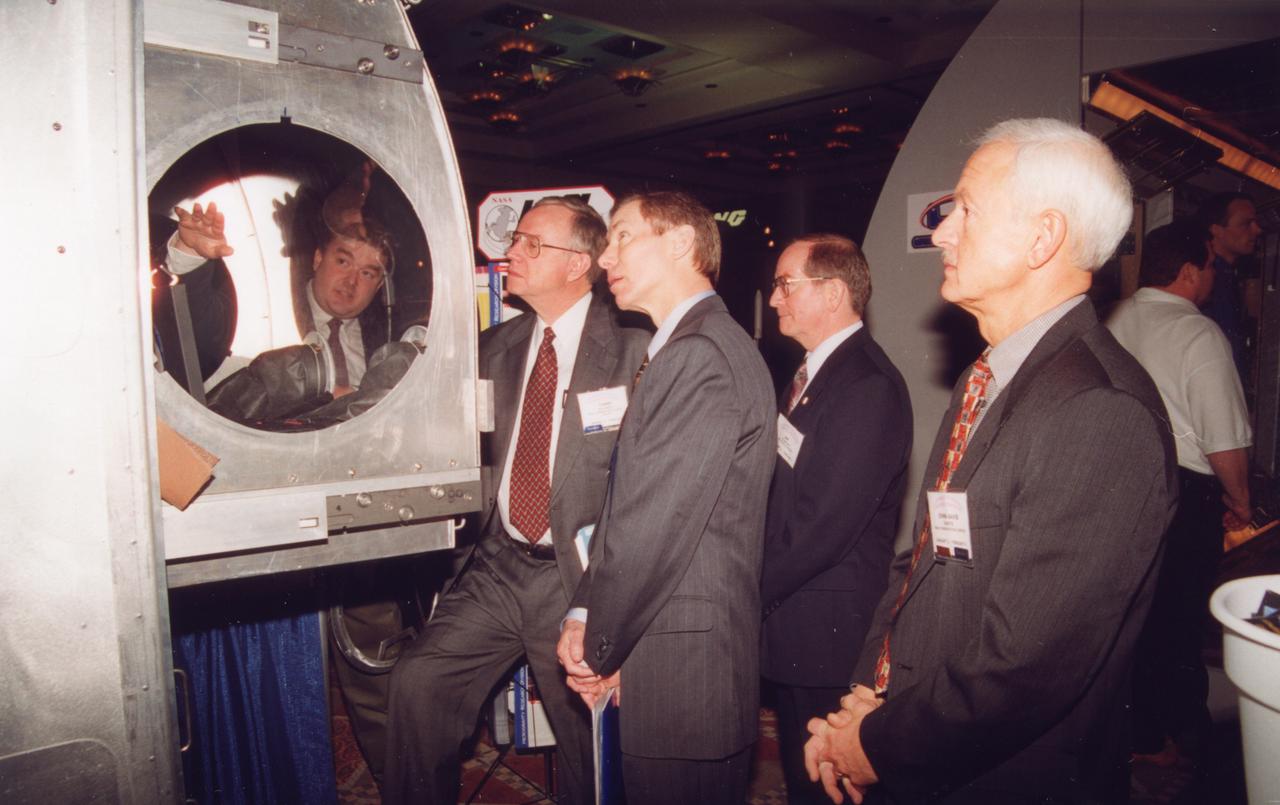

Tim Broach (seen through window) of NASA/Marshall Spce Flight Center (MSFC), demonstrates the working volume inside the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox being developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) for use aboard the U.S. Destiny laboratory module on the International Space Station (ISS). This mockup is the same size as the flight hardware. Observing are Tommy Holloway and Brewster Shaw of The Boeing Co. (center) and John-David Bartoe, ISS research manager at NASA/John Space Center and a payload specialist on Spacelab-2 mission (1985). Photo crdit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
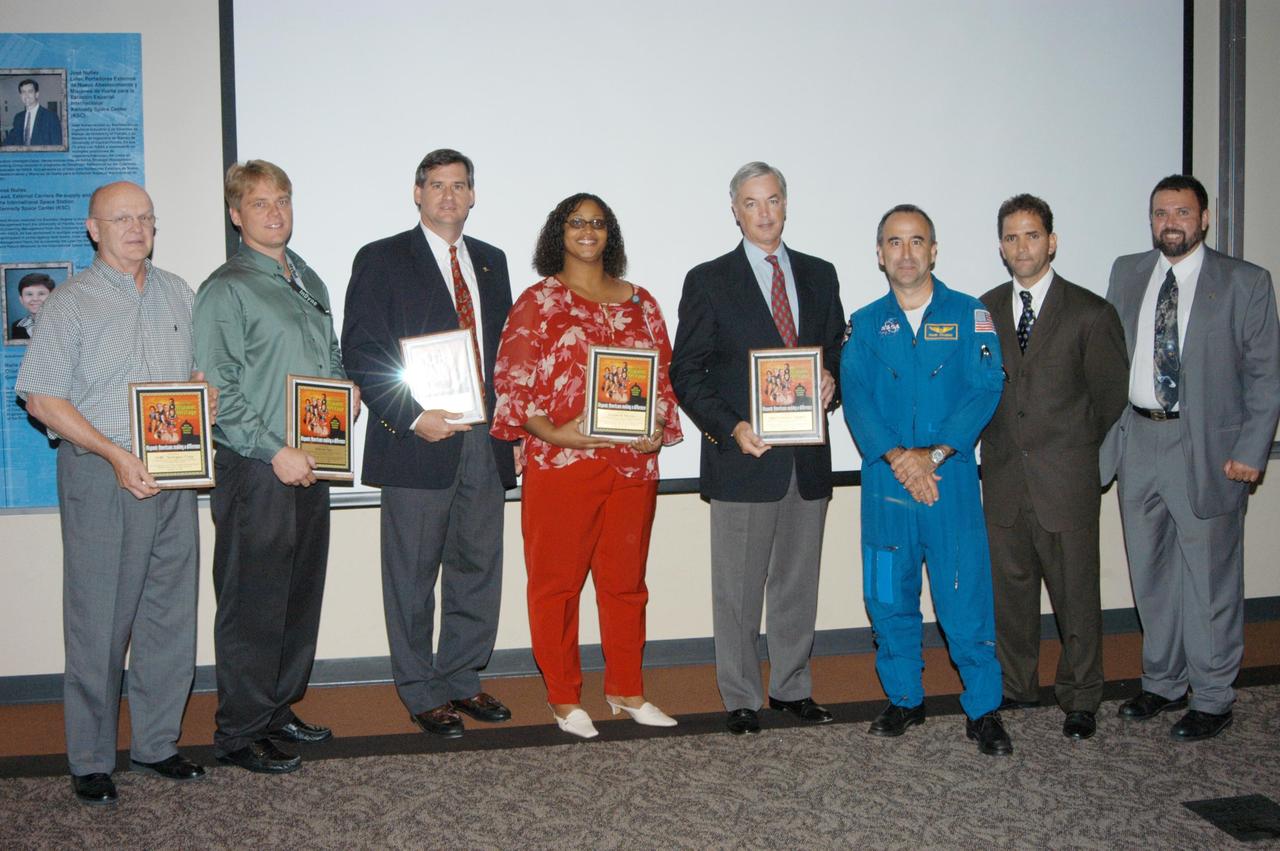

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At KSC’s annual Hispanic American Heritage luncheon, contractor sponsors were presented certificates of appreciation. Accepting were (from left) Dick Lyons, with ASRC Aerospace Corp.; Tom Niemeyer, with InDyne Corp.; Kevin Hoshstrasser (with Boeing); Vera Pettis, with Lockheed Martin; and Bill Sample, with SGS. Next to them are astronaut Fernando Caldeiro, Felix A. Soto Toro and Joseph Tellado. Soto Toro and Tellado were co-chairs of the event hosted by the Hispanic Employment Program Working Group. The annual event helps employees reflect on the extensive contributions Hispanics have made to KSC, NASA and the nation.
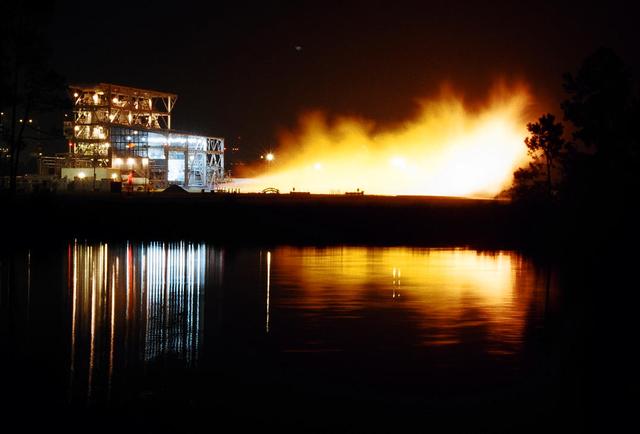

Gaseous hydrogen is burned off at the E1 Test Stand the night of Oct. 7 during a cold-flow test of the fuel turbopump of the Integrated Powerhead Demonstrator (IPD) at NASA Stennis Space Center (SSC). The gaseous hydrogen spins the pump's turbine during the test, which was conducted to verify the pump's performance. Engineers plan one more test before sending the pump to The Boeing Co. for inspection. It will then be returned to SSC for engine system assembly. The IPD is the first reusable hydrogen-fueled advanced engine in development since the Space Shuttle Main Engine.
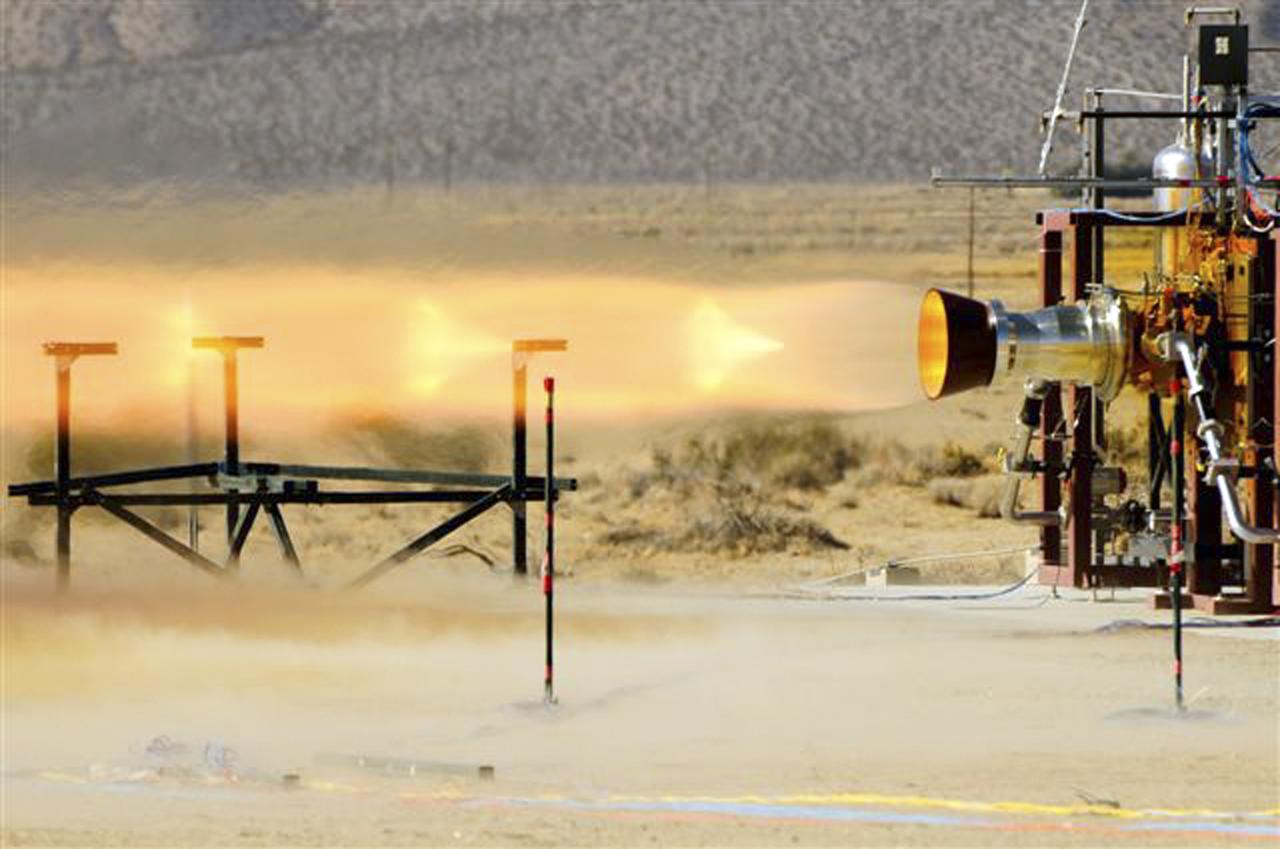

CANOGA PARK, Calif. -- Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne hot-fires a launch abort engine for The Boeing Co., which is developing its CST-100 spacecraft for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Under its fixed-price contract with Boeing, Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne is combining its Attitude Control Propulsion System thrusters from heritage spaceflight programs, Bantam abort engine design and storable propellant engineering capabilities. In 2011, NASA selected Boeing of Houston during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, Blue Origin, Excalibur Almaz Inc., Sierra Nevada Corp., Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne
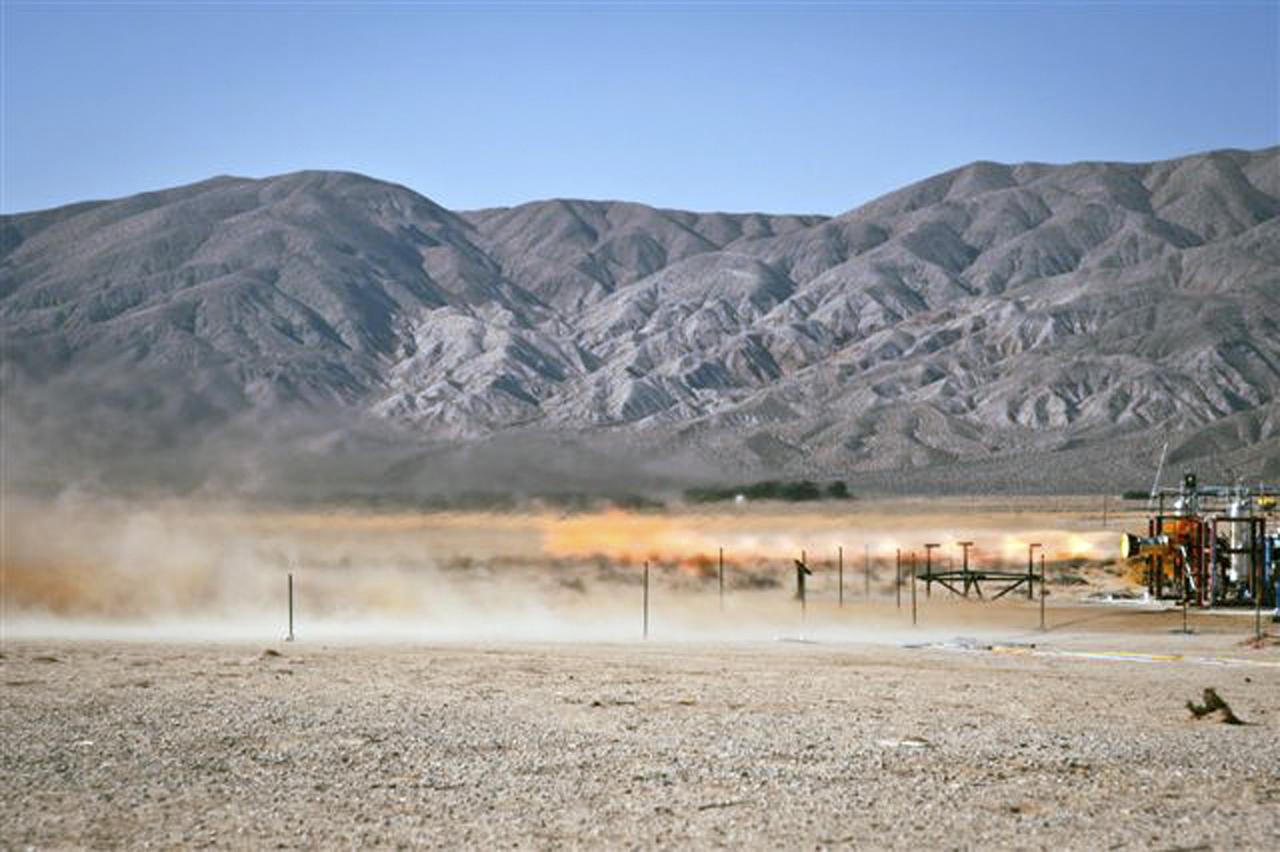

CANOGA PARK, Calif. -- Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne hot-fires a launch abort engine for The Boeing Co., which is developing its CST-100 spacecraft for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Under its fixed-price contract with Boeing, Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne is combining its Attitude Control Propulsion System thrusters from heritage spaceflight programs, Bantam abort engine design and storable propellant engineering capabilities. In 2011, NASA selected Boeing of Houston during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, Blue Origin, Excalibur Almaz Inc., Sierra Nevada Corp., Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne
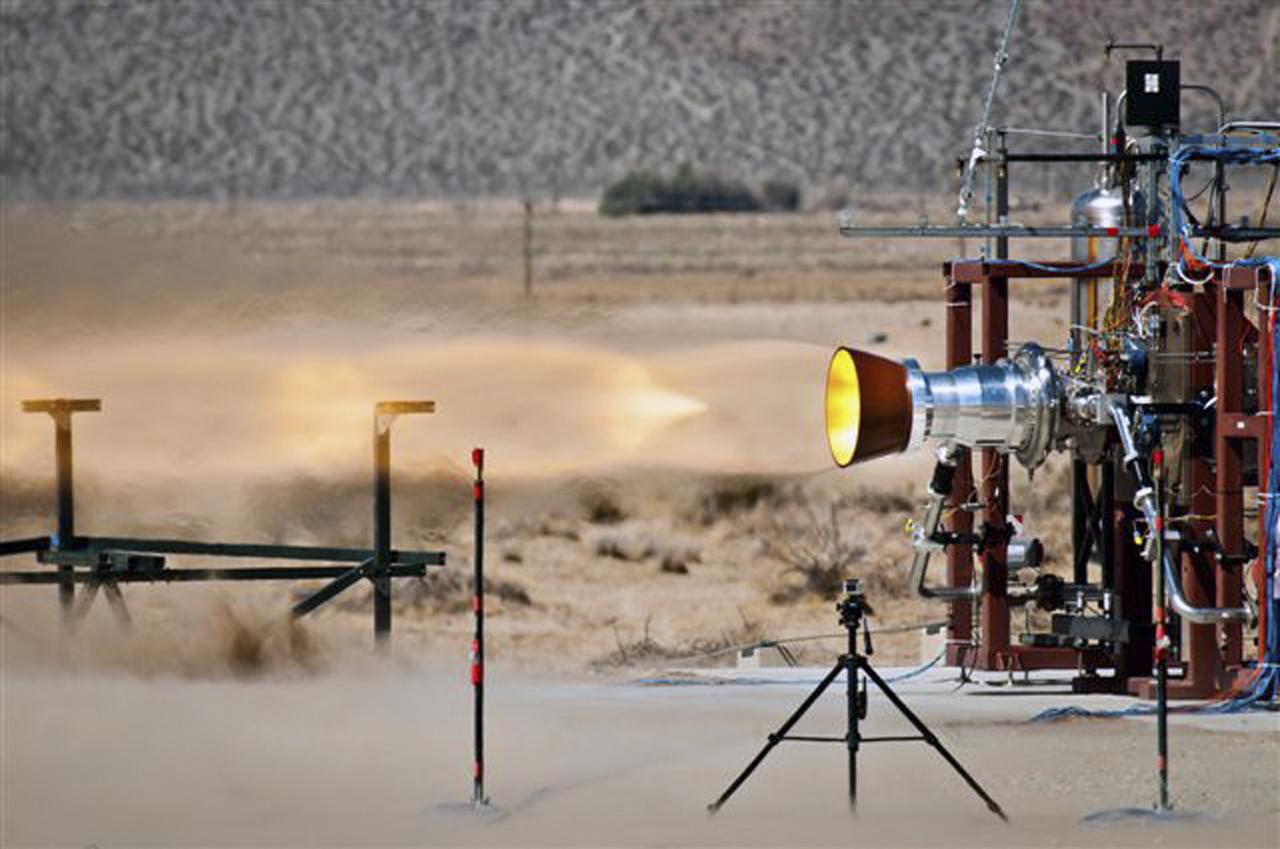

CANOGA PARK, Calif. -- Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne hot-fires a launch abort engine for The Boeing Co., which is developing its CST-100 spacecraft for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Under its fixed-price contract with Boeing, Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne is combining its Attitude Control Propulsion System thrusters from heritage spaceflight programs, Bantam abort engine design and storable propellant engineering capabilities. In 2011, NASA selected Boeing of Houston during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, Blue Origin, Excalibur Almaz Inc., Sierra Nevada Corp., Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne
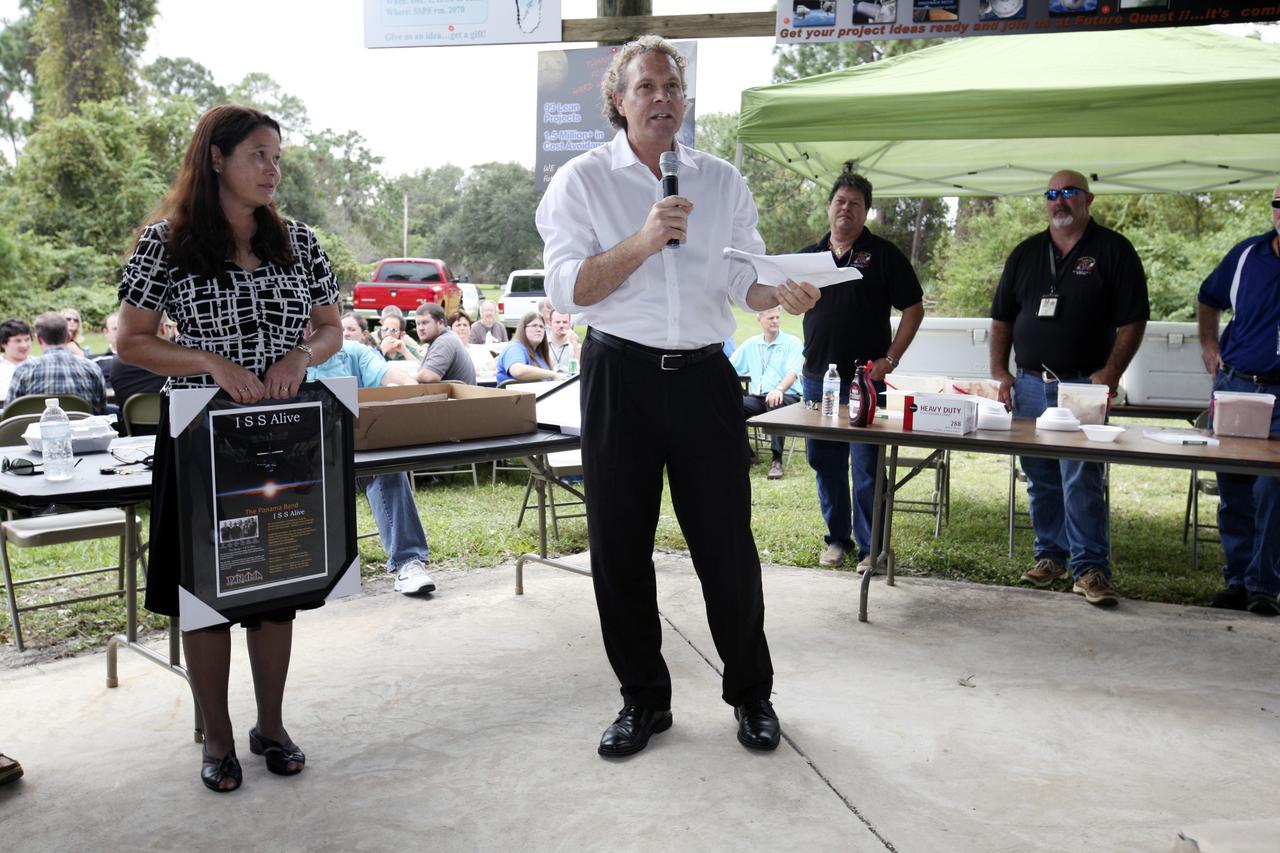

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Associate Director for Engineering and Technical Operations Russell Romanella talks to International Space Station employees based at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida during the "ISS Is Alive" employee recognition barbecue celebration at Kars Park II while International Space Station Ground Processing and Research Project Office Director Josie Burnett, left, looks on. NASA and The Boeing Co. hosted the celebration to thank the employees based at the Kennedy Space Center who were involved in building the largest, most complex international scientific project in history and the largest venture in space to date. The station has hosted human life, work and research in space for more than 10 years. Boeing is the prime contractor to NASA for the space station. In addition to designing and building all the major U.S. elements, Boeing also is responsible for ensuring the successful integration of new hardware and software -- including components from international partners -- as well as for providing sustaining engineering work. For more information on the International Space Station, visit http://www.nasa.gov/station. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
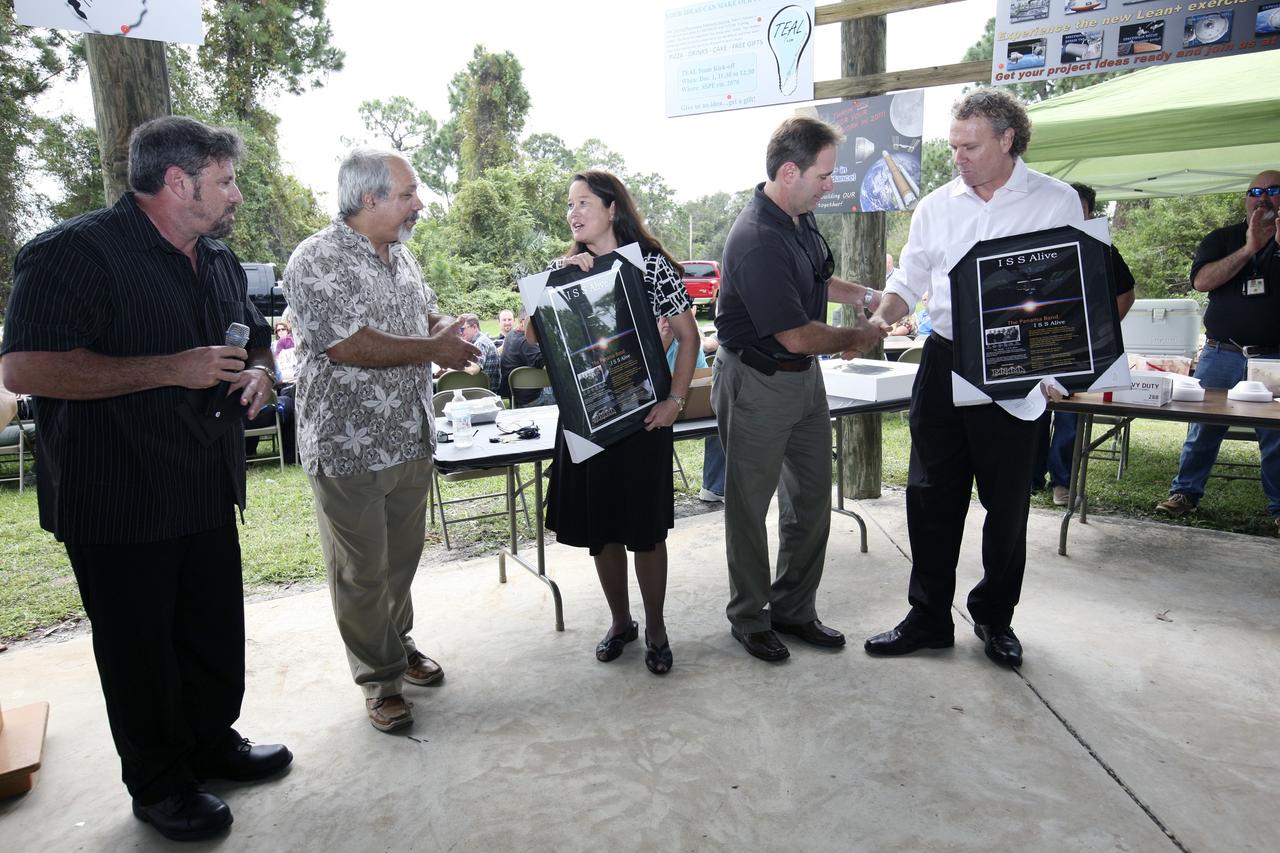

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – International Space Station Ground Processing and Research Project Office Director Josie Burnett, third from left, and Associate Director for Engineering and Technical Operations Russell Romanella, right, are presented plaques and CDs of the song “ISS Alive,” written and recorded by the Panama Band, during the "ISS Is Alive" employee recognition barbecue celebration at Kars Park II at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are also band members Lew Ingelido, who composed the song, Tom Hadoulias and Norm Tokarz. NASA and The Boeing Co. hosted the celebration to thank the employees based at the Kennedy Space Center who were involved in building the largest, most complex international scientific project in history and the largest venture in space to date. The station has hosted human life, work and research in space for more than 10 years. Boeing is the prime contractor to NASA for the space station. In addition to designing and building all the major U.S. elements, Boeing also is responsible for ensuring the successful integration of new hardware and software -- including components from international partners -- as well as for providing sustaining engineering work. For more information on the International Space Station, visit http://www.nasa.gov/station. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is an artist's conception of NASA's Commercial Crew Program or CCP, logo and low Earth orbit. The program is entering its third phase of development, called Commercial Crew integrated Capability, or CCiCap, to propel America's next human space transportation system to low Earth orbit forward. Operating under funded Space Act Agreements, or SAAs, The Boeing Co. of Houston, Sierra Nevada Corp., or SNC, Space Systems of Louisville, Colo., and Space Exploration Technologies, or SpaceX, of Hawthorne, Calif., will spend the next 21 months completing their designs, conducting critical risk reduction testing on their spacecraft and launch vehicles, and showcasing how they would operate and manage missions from launch through orbit and landing, setting the stage for future demonstration missions. To learn more about CCP, which is based at Kennedy and supported by NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Matthew Young
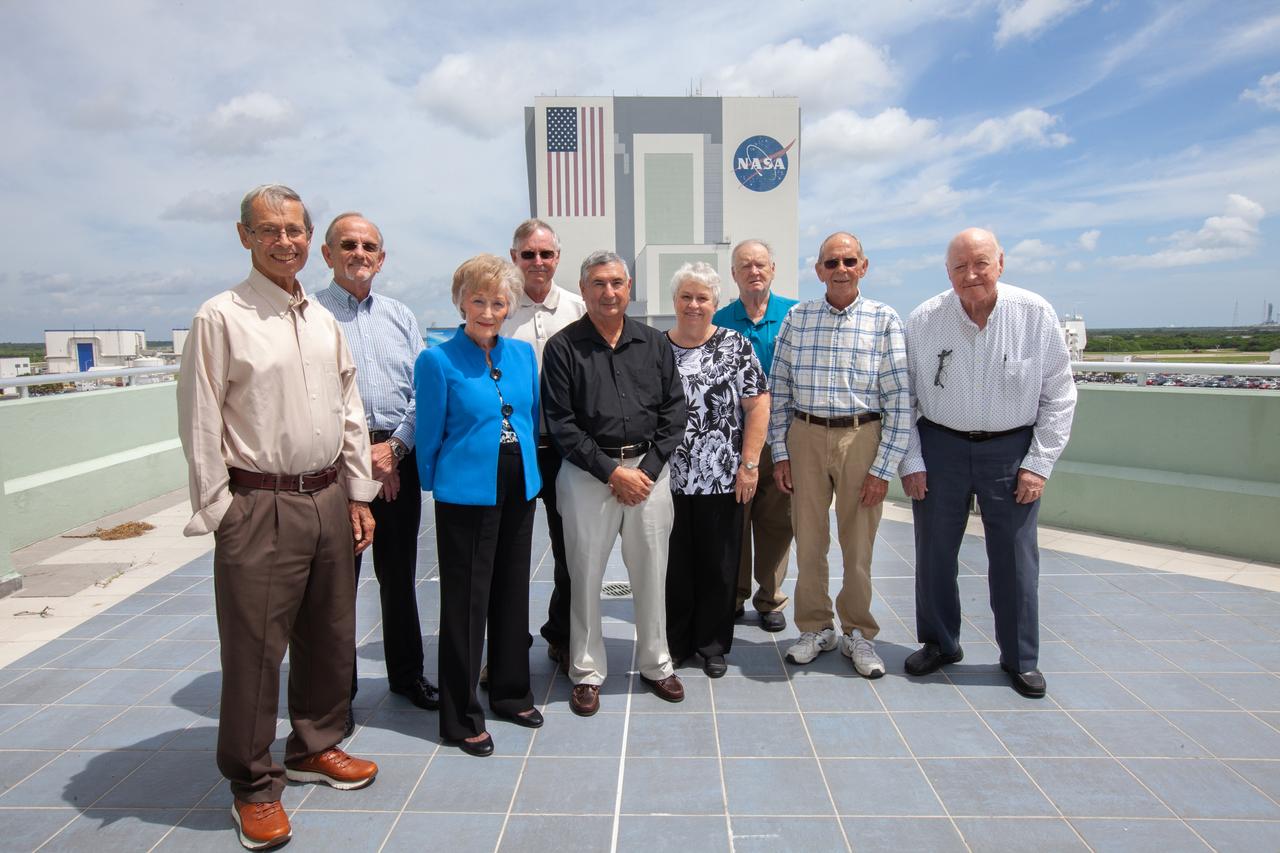

NASA and contractor employees who were working at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during the Apollo 11 launch gathered for a group photo on the observation deck of Operations and Support Building II on July 11, 2019. From left, along with their titles from 50 years ago, are Richard Sharum, NASA civil servant; Edward Wilson, security officer for Wackenhut Corporation; Sue Gross, secretary to the deputy procurement officer; Emery Lamar, NASA Kennedy co-op student in Apollo Spacecraft Electrical Division; James Scotti, material clerk with Bendix Corporation; Suzanne Stuckey, secretary for telemetry; Andrew Pritchard, contractor with McGregor-Warner; Ken Poimboeuf, Design Engineering Directorate; and Grady McCorquodale, Launch Control Center engineer with Boeing. Not pictured are Richard Cota, civil servant in the Engineering Directorate; and Victor Kurjack, data courier.
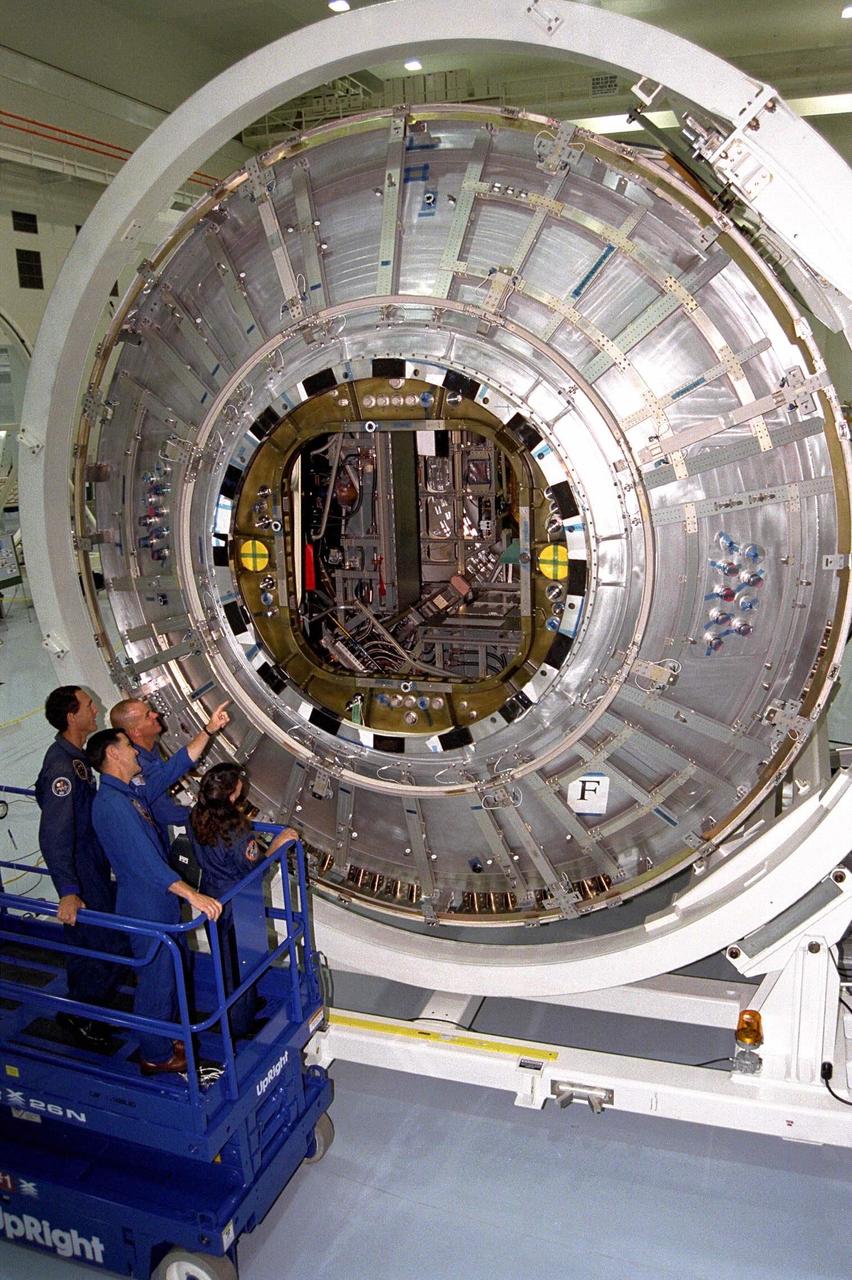
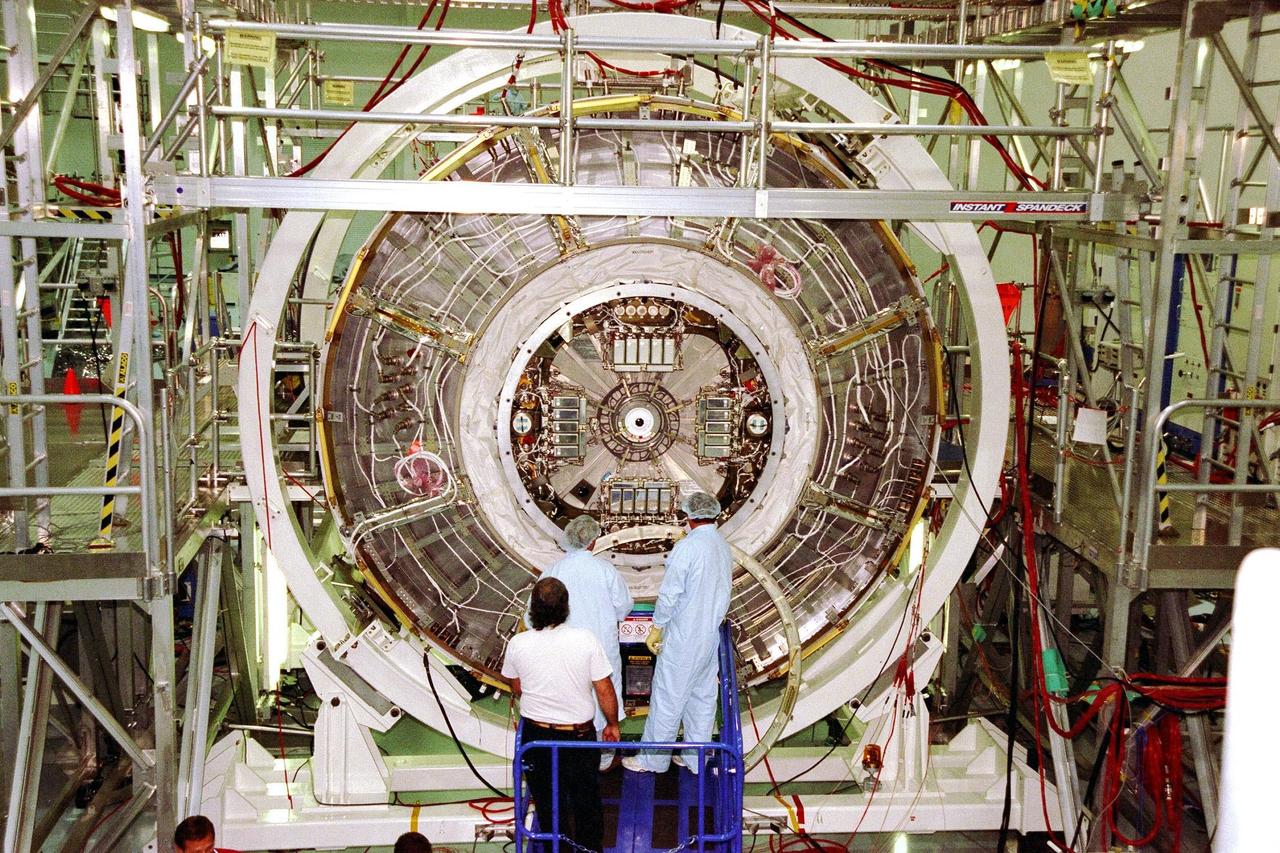
Members of the STS-88 crew examine the Node 1 of the Internation Space Station in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. The six hatches on the Node 1 will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements

The Node 1, the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first to be launched on the Space Shuttle, rests in its container in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay after its arrival at KSC from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Node 1 module is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998 along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot in diameter, 22- foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at MSFC. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
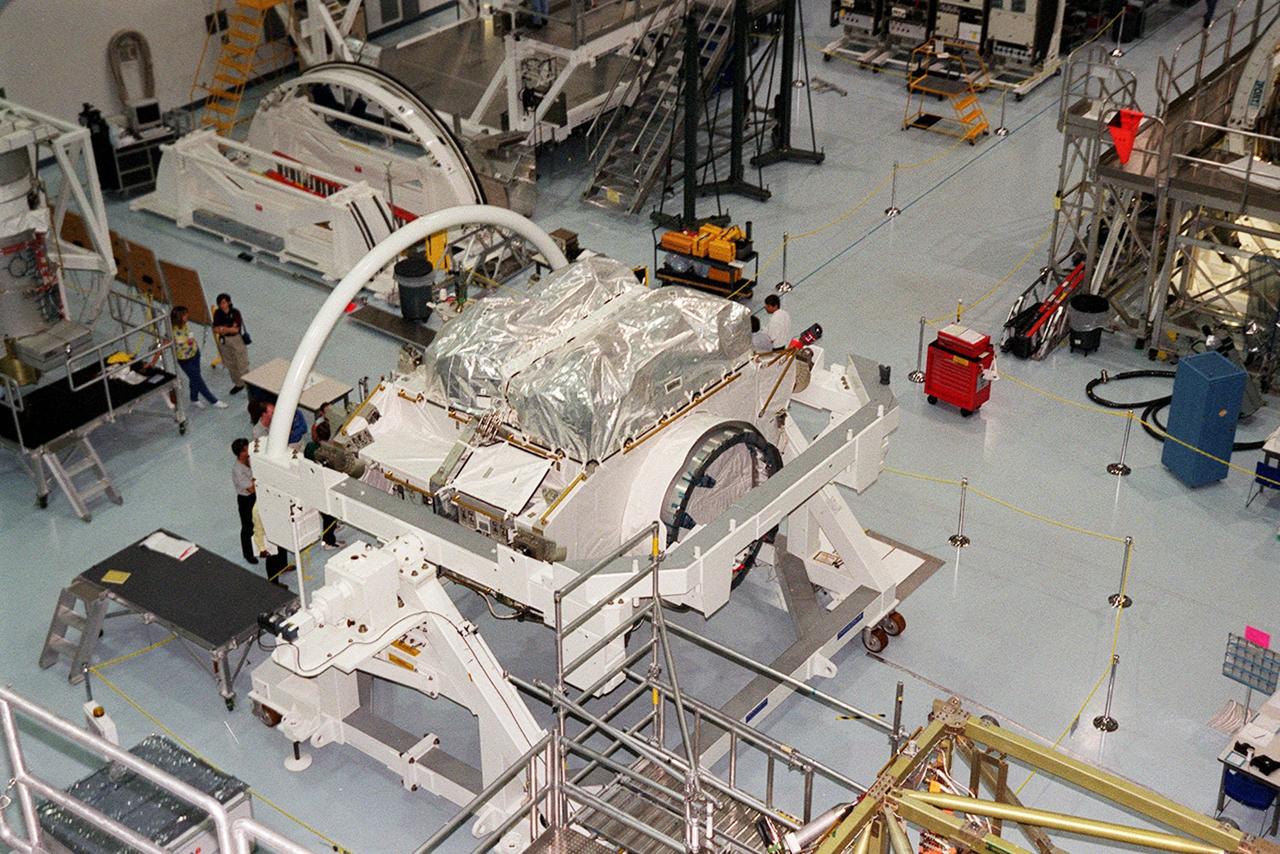
The Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss, the cornerstone truss of the Space Station, is shown on the floor of the Space Station Processing Facility. The Z-1 Truss was officially turned over to NASA from The Boeing Co. on July 31. It is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, employees from The Boeing Co., Huntington Beach, Calif., install a strain gauge on a test panel prior to installation of Thermal Protection System tile on the panel. The test panel and sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF), Paul King, an employee of The Boeing Co., Huntington Beach, Calif., installs a strain gauge on a simulated orbiter wing in preparation for Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile installation. The wing, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.

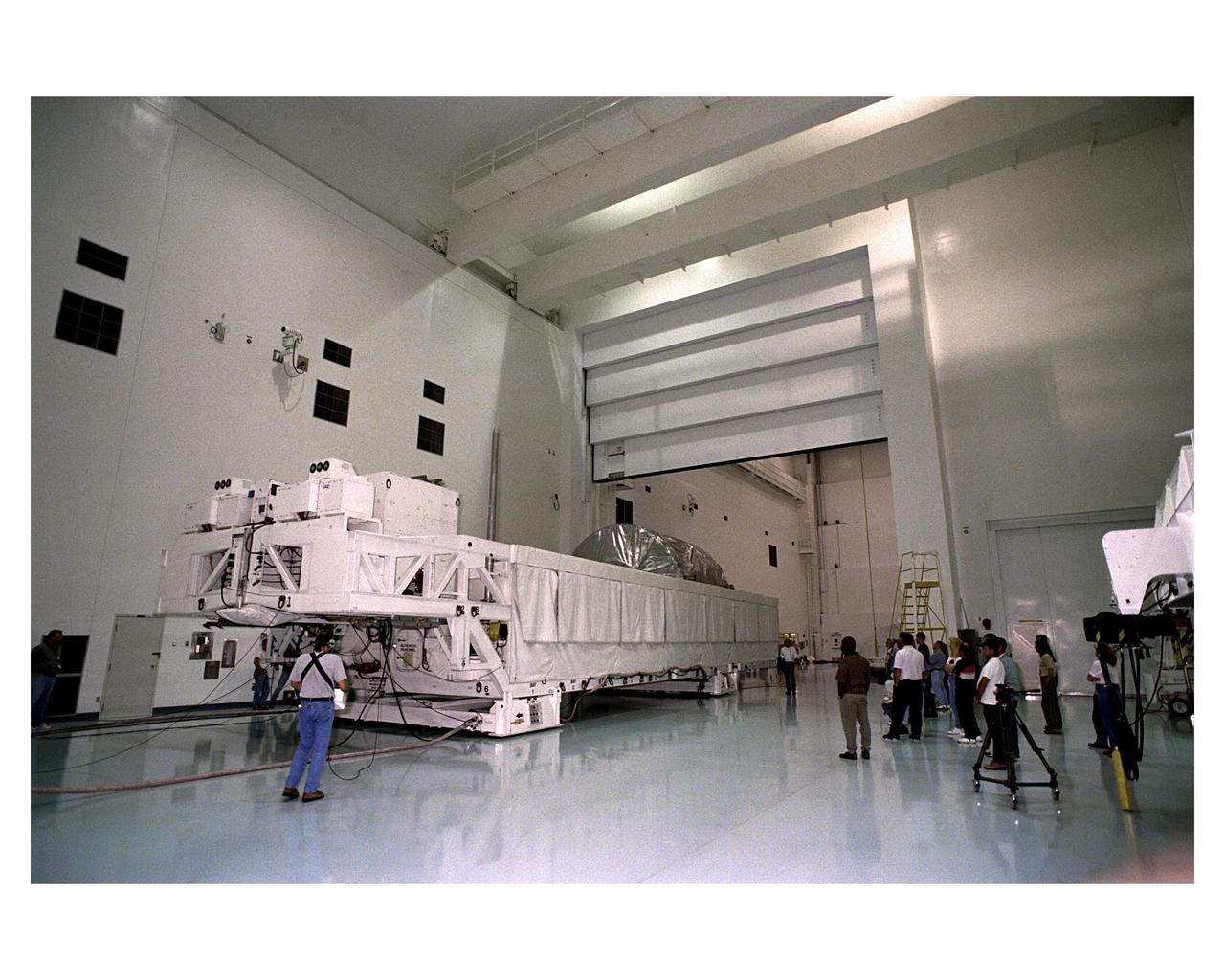
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Operations and Checkout Building, a strongback lifts the S1 truss from the Guppy cargo carrier that protected it during flight and transfer. Manufactured by the Boeing Co. in Huntington Beach, Calif., this component of the International Space Station is the first starboard (right-side) truss segment, whose main job is providing structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels that cool the Space Station's complex power system. The S1 truss segment also will house communications systems, external experiment positions and other subsystems. Primarily constructed of aluminum, the truss segment is 45 feet long, 15 feet wide and 6 feet tall. When fully outfitted, it will weigh 31,137 pounds. The truss is slated for flight in 2001
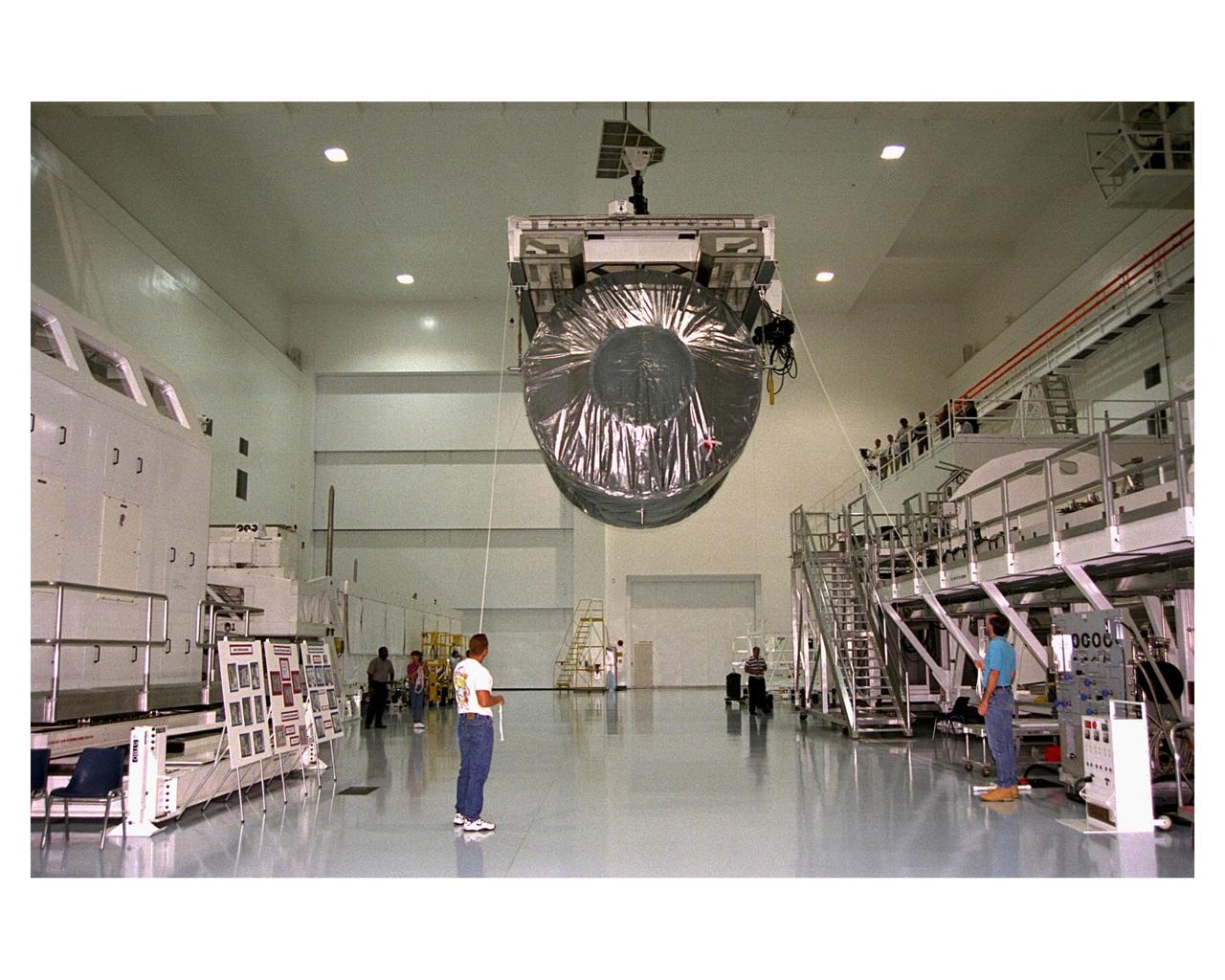

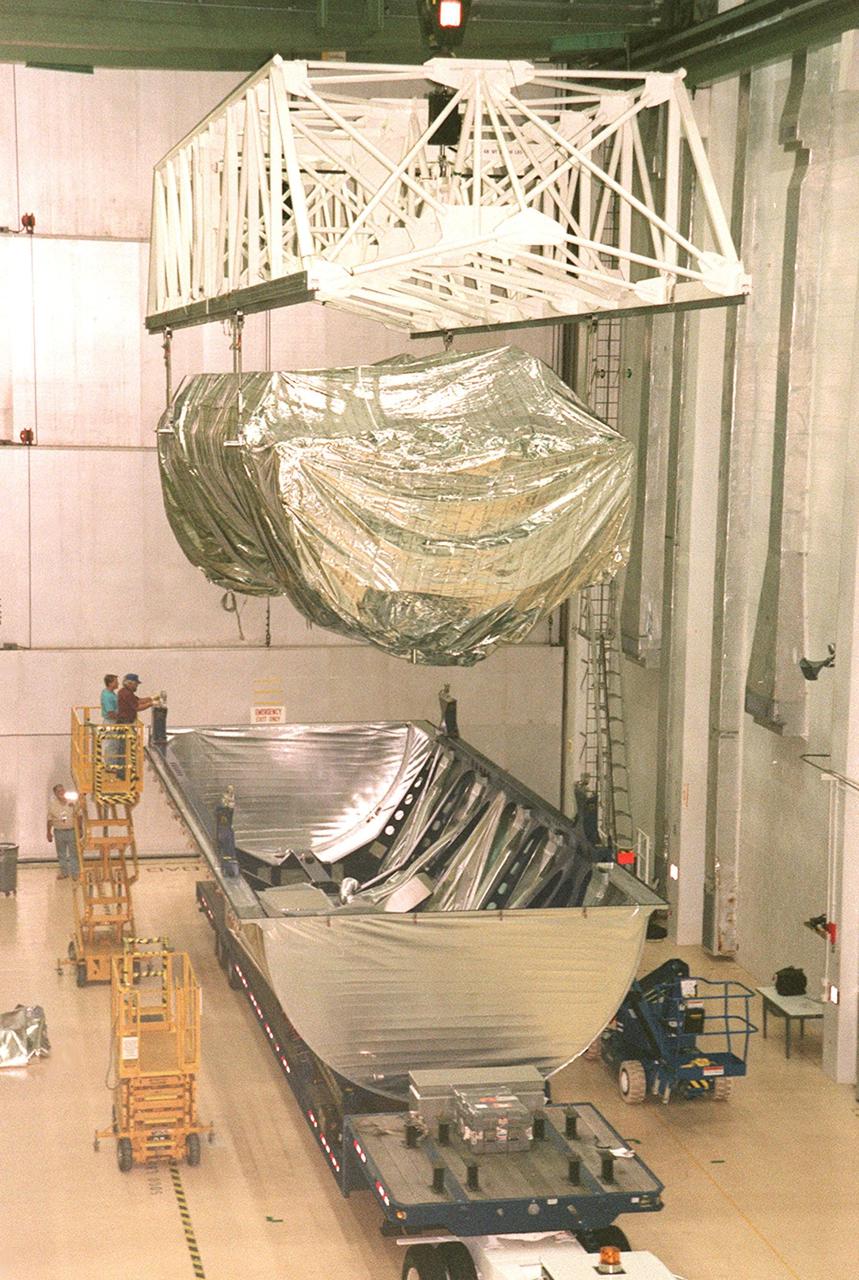
Covered in a protective sheath, International Space Station Node 1 is hoisted for installation in its work stand in the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A KSC transporter moves the Guppy cargo carrier encasing the S1 truss into the Operations and Checkout Building. Manufactured by the Boeing Co. in Huntington Beach, Calif., this component of the International Space Station is the first starboard (right-side) truss segment, whose main job is providing structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels that cool the Space Station's complex power system. The S1 truss segment also will house communications systems, external experiment positions and other subsystems. Primarily constructed of aluminum, the truss segment is 45 feet long, 15 feet wide and 6 feet tall. When fully outfitted, it will weigh 31,137 pounds. The truss is slated for flight in 2001
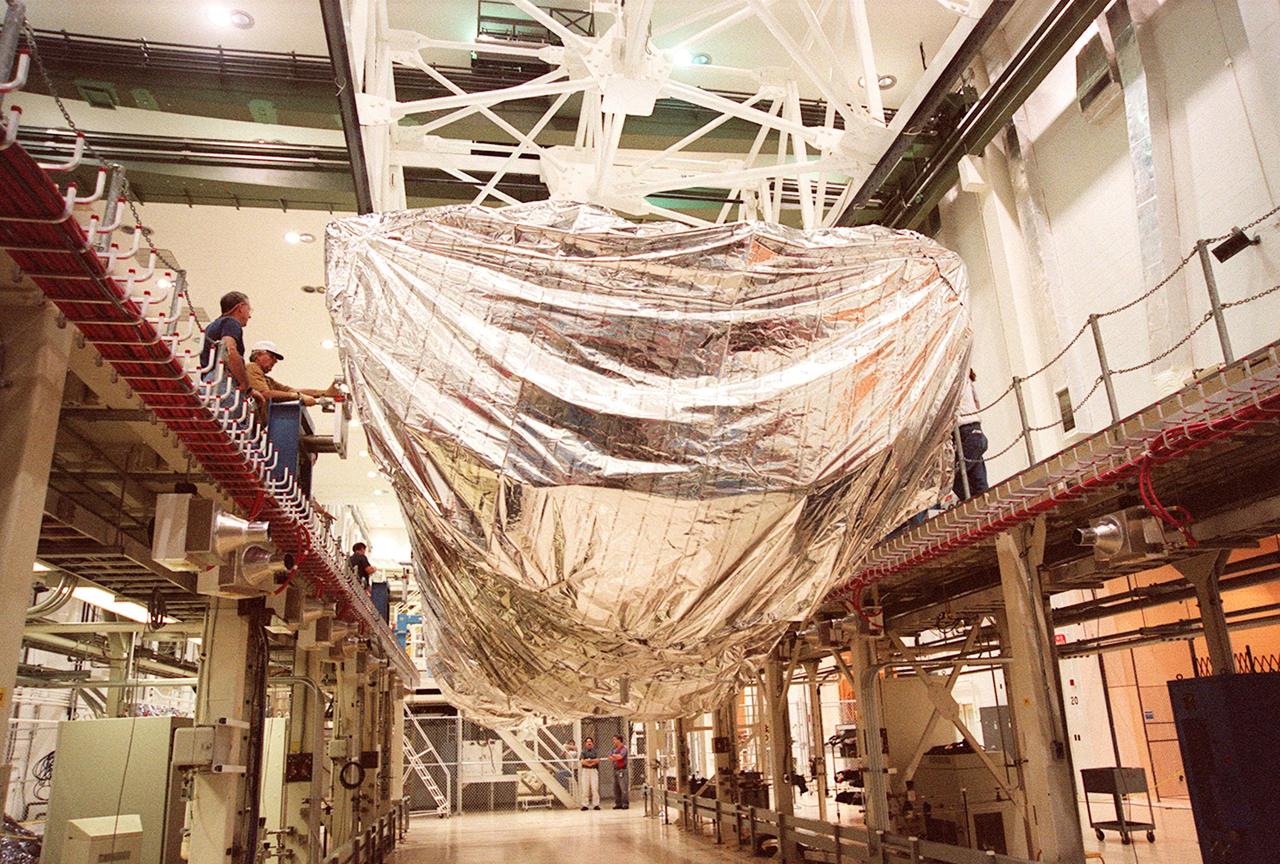

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Operations and Checkout Building, the S1 truss, a segment of the International Space Station, is lowered toward workstand number three. Manufactured by the Boeing Co. in Huntington Beach, Calif., this component of the International Space Station is the first starboard (right-side) truss segment, whose main job is providing structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels that cool the Space Station's complex power system. The S1 truss segment also will house communications systems, external experiment positions and other subsystems. Primarily constructed of aluminum, the truss segment is 45 feet long, 15 feet wide and 6 feet tall. When fully outfitted, it will weigh 31,137 pounds. The truss is slated for flight in 2001
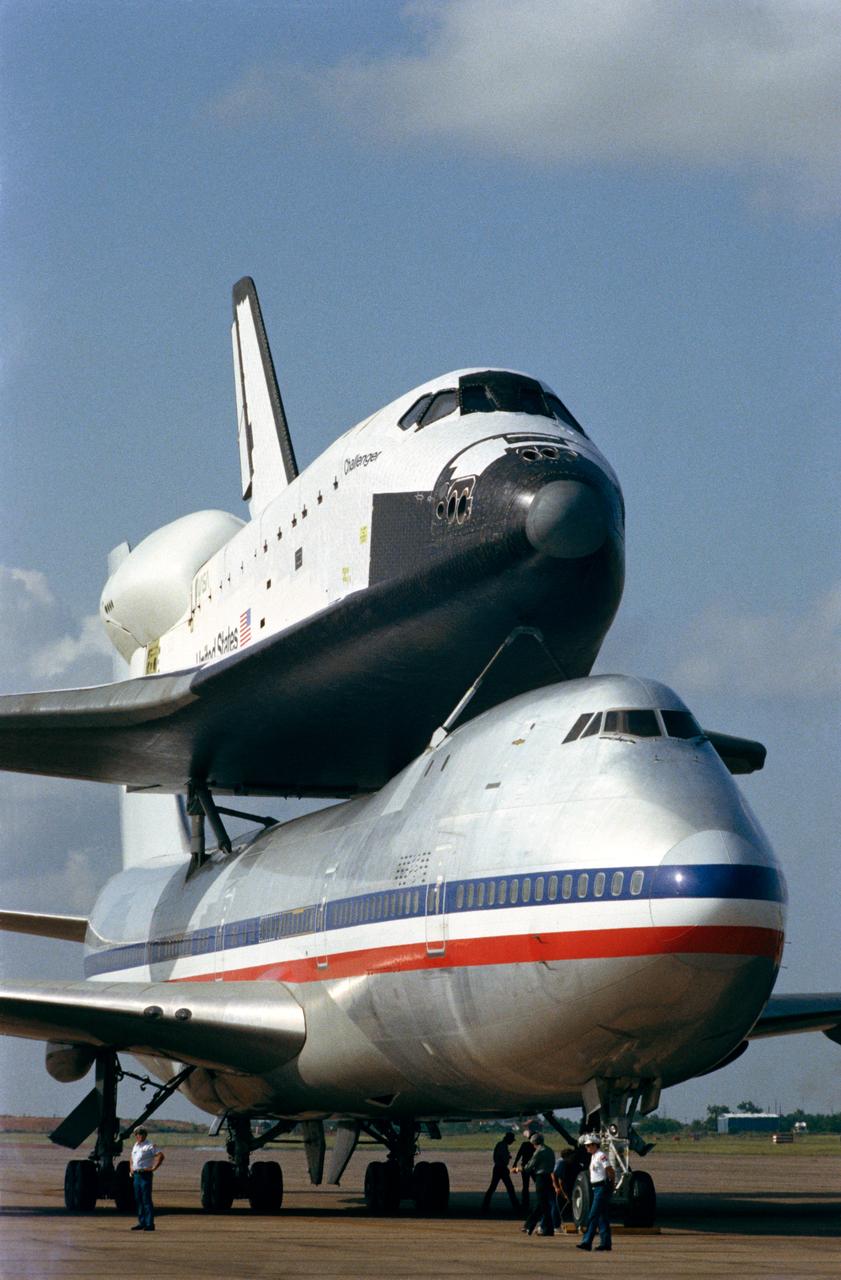

S82-33394 (5 July 1982) --- A rare sight in Houston is the appearance of the spacecraft whose flights are monitored from that city, but with the brief stopover of NASA's new space shuttle Challenger, thousands of area residents were afforded that opportunity yesterday as part of a nationwide special July 4 celebration. Here, the Challenger and its NASA 905 (a modified Boeing 747 aircraft) transport vehicle are readied for the completion of the journey from California to Florida. The Columbia landed in California yesterday and the Enterprise was already there, so three shuttlecraft were together as appropriate backdrops for a space-oriented July 4 speech by President Ronald Reagan. Crew for the NASA 905 for Challenger's Florida trip from Houston were Pilot Joseph S. Algranti, Co-Pilot Francis R. (Dick) Scobee. Photo credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a printable banner of the aerospace companies NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP) entered into Space Act Agreements with during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 (CCDev2) activities in 2011 in order to mature the design and development of crew transportation systems with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. CCDev2 companies are Alliant Techsystems (ATK), Blue Origin, The Boeing Co., Excalibur Almaz Inc., Sierra Nevada Corp., Space Exploration Technologies (SpaceX), and United Launch Alliance (ULA). The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew
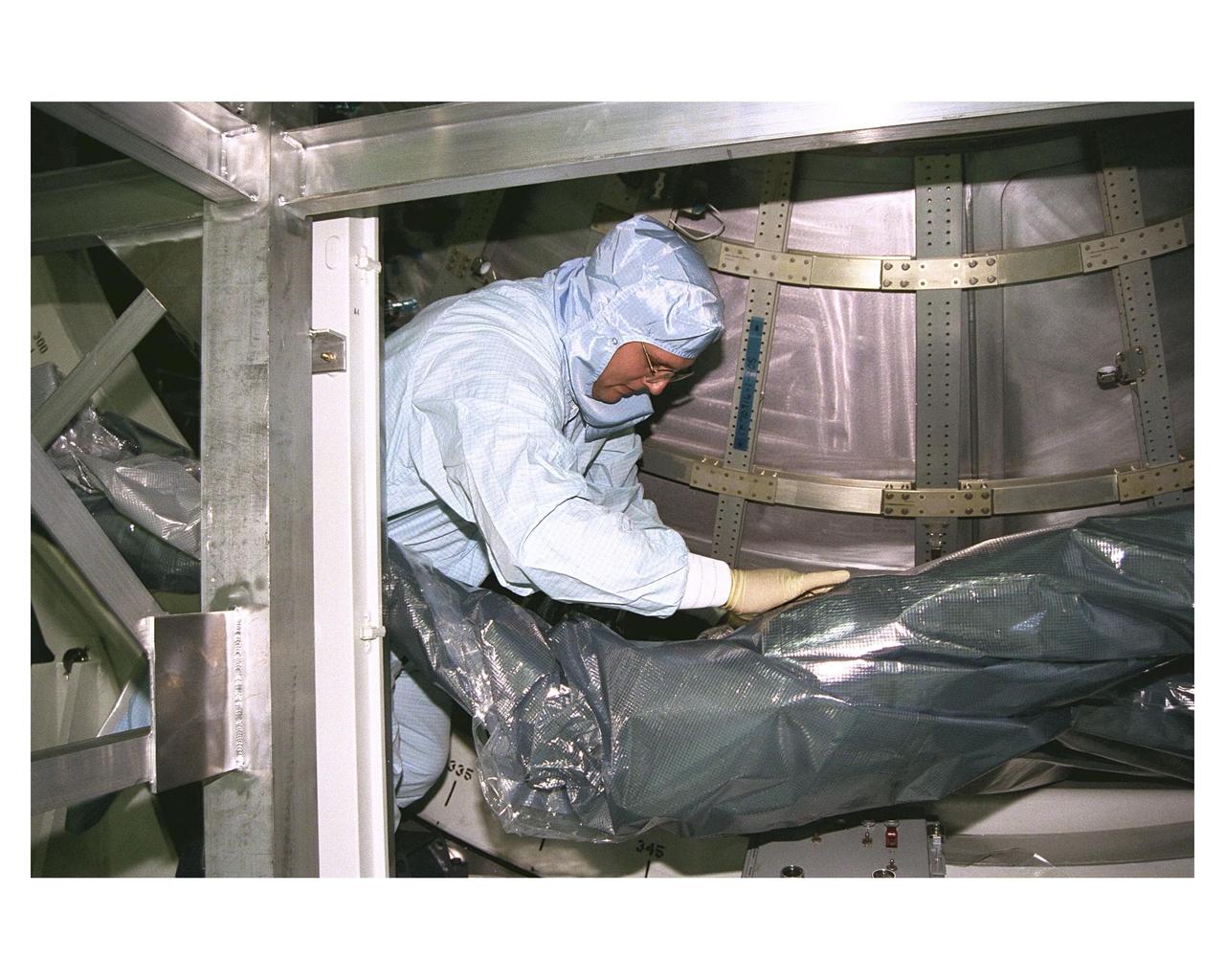

A KSC payloads processing employee removes a protective sheath part of the Node 1 in its work stand in the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
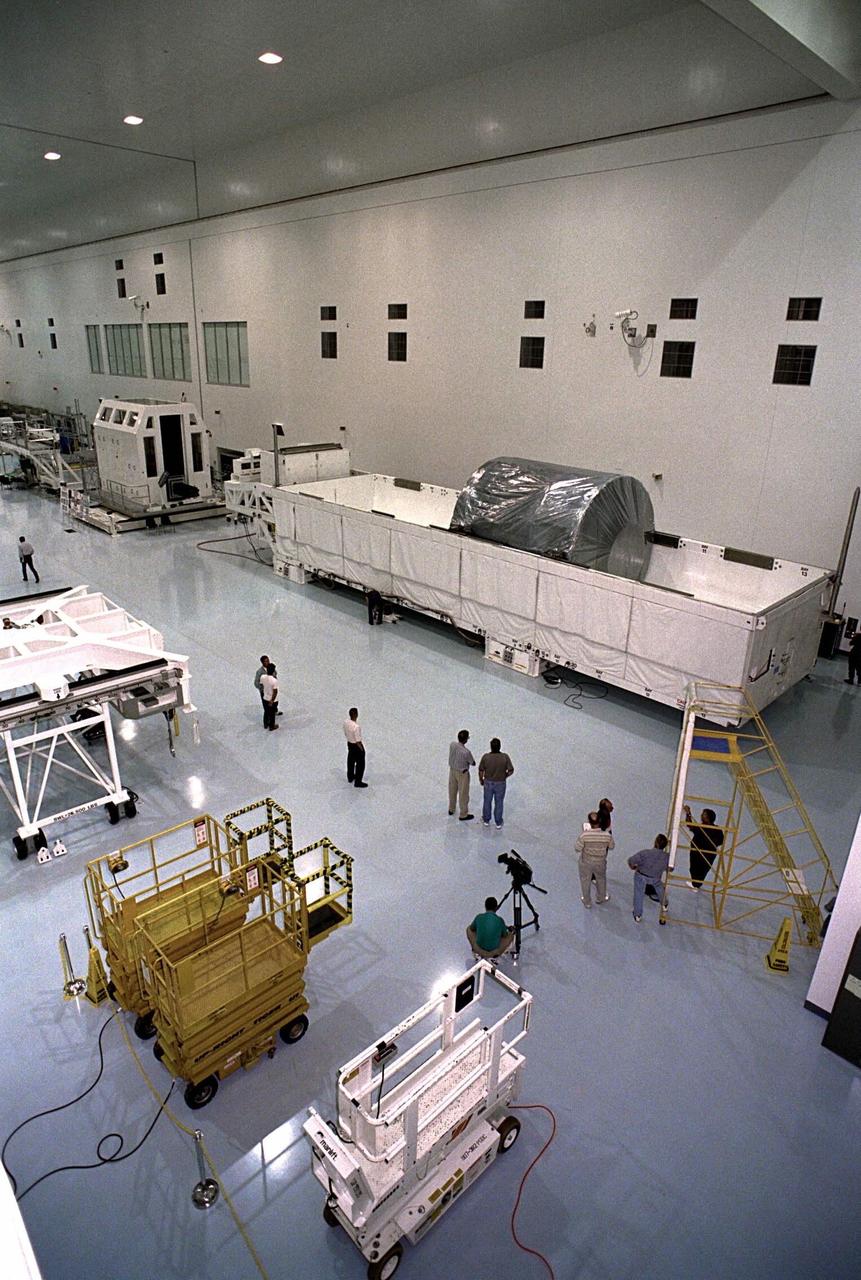

The Node 1, the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first to be launched on the Space Shuttle, rests in its container in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay after its arrival at KSC from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Node 1 module is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998 along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22- foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at MSFC. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
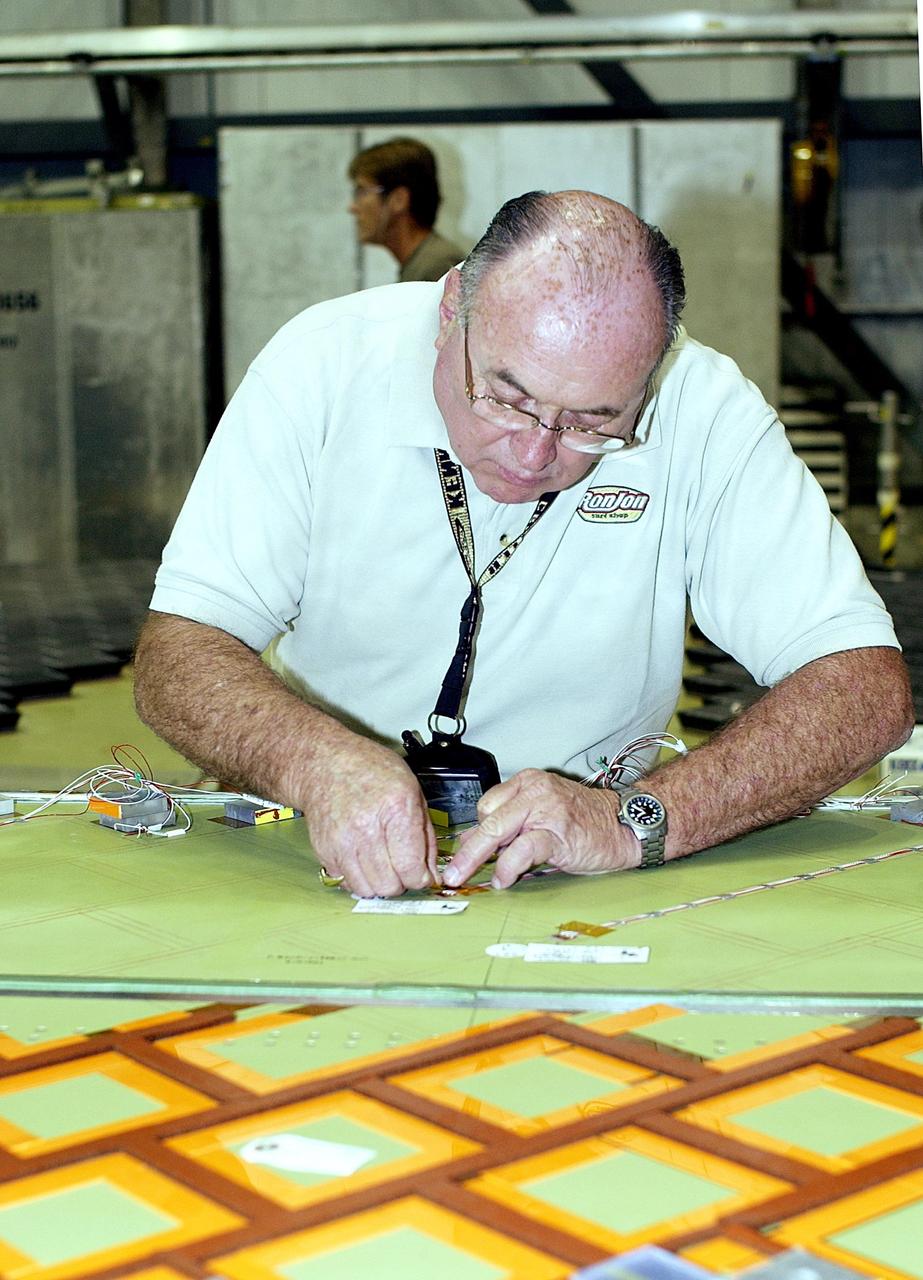

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, an employee from The Boeing Co., Huntington Beach, Calif., installs a strain gauge on a test panel prior to installation of Thermal Protection System tile on the panel. The test panel and sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
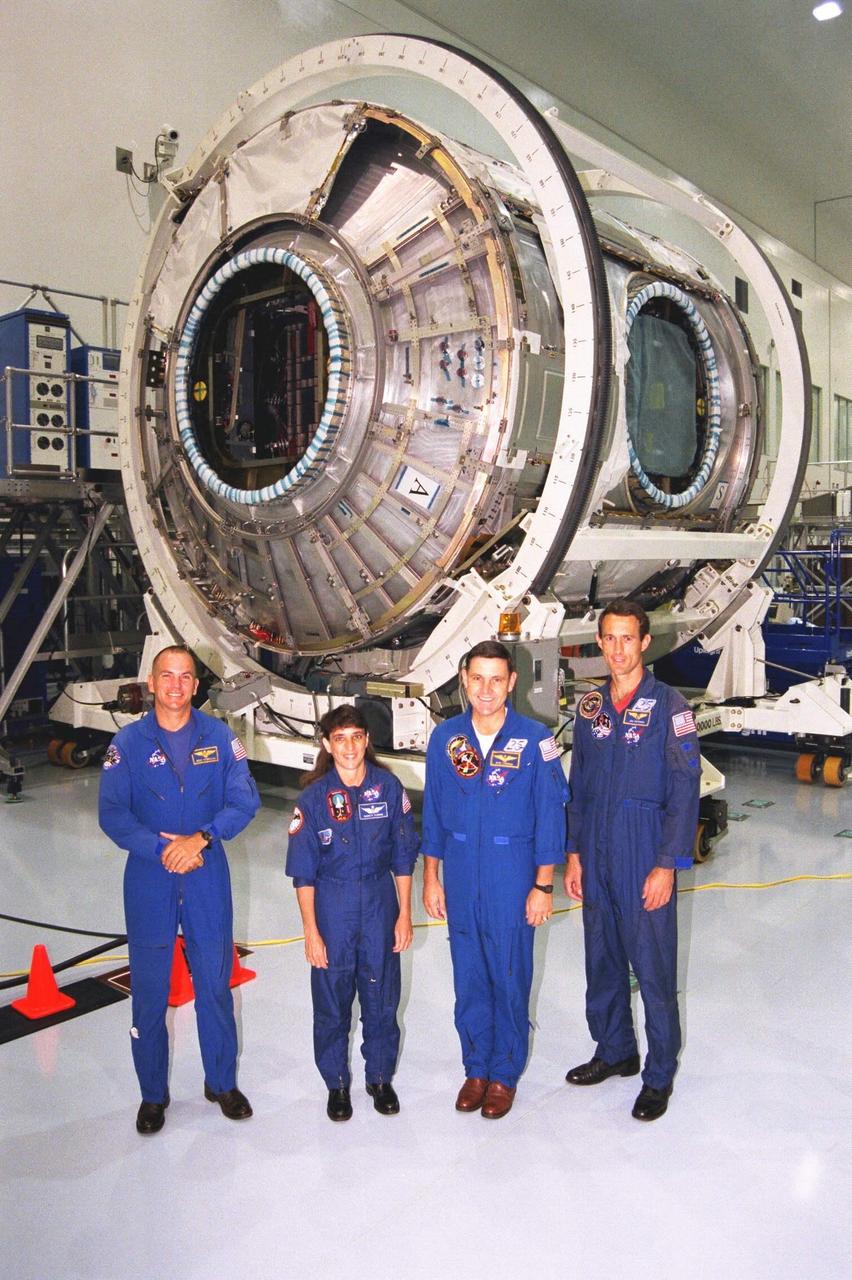

Members of the STS-88 crew pose with the Node 1 of the Internation Space Station in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. The six hatches on the Node 1 will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements

A close-up view of the Node 1 in its work stand in the Space Station Processing Facility shows two of its six hatches that will serve as docking ports. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. The six hatches on the Node 1 will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Operations and Checkout Building, the top of the Guppy cargo carrier is lifted off the S1 truss (background). Manufactured by the Boeing Co. in Huntington Beach, Calif., this component of the International Space Station is the first starboard (right-side) truss segment, whose main job is providing structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels that cool the Space Station's complex power system. The S1 truss segment also will house communications systems, external experiment positions and other subsystems. Primarily constructed of aluminum, the truss segment is 45 feet long, 15 feet wide and 6 feet tall. When fully outfitted, it will weigh 31,137 pounds. The truss is slated for flight in 2001

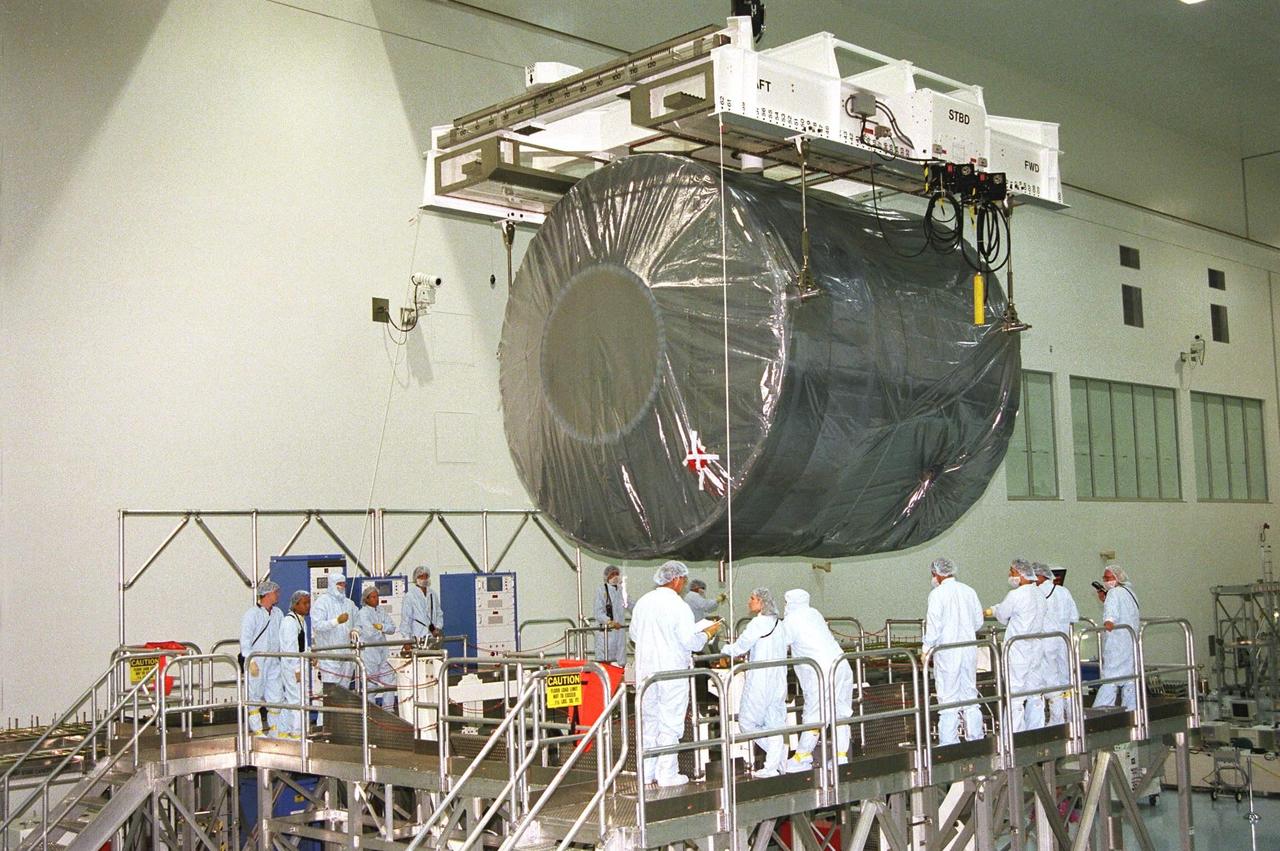
Node 1, the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first to be launched on the Space Shuttle, is unloaded in its container from an Air Force C-5 jet cargo transport at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway on June 23 after its arrival from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The module was then transported to the Space Station Processing Facility. The Node 1 module is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998 along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at MSFC. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other Space Station elements
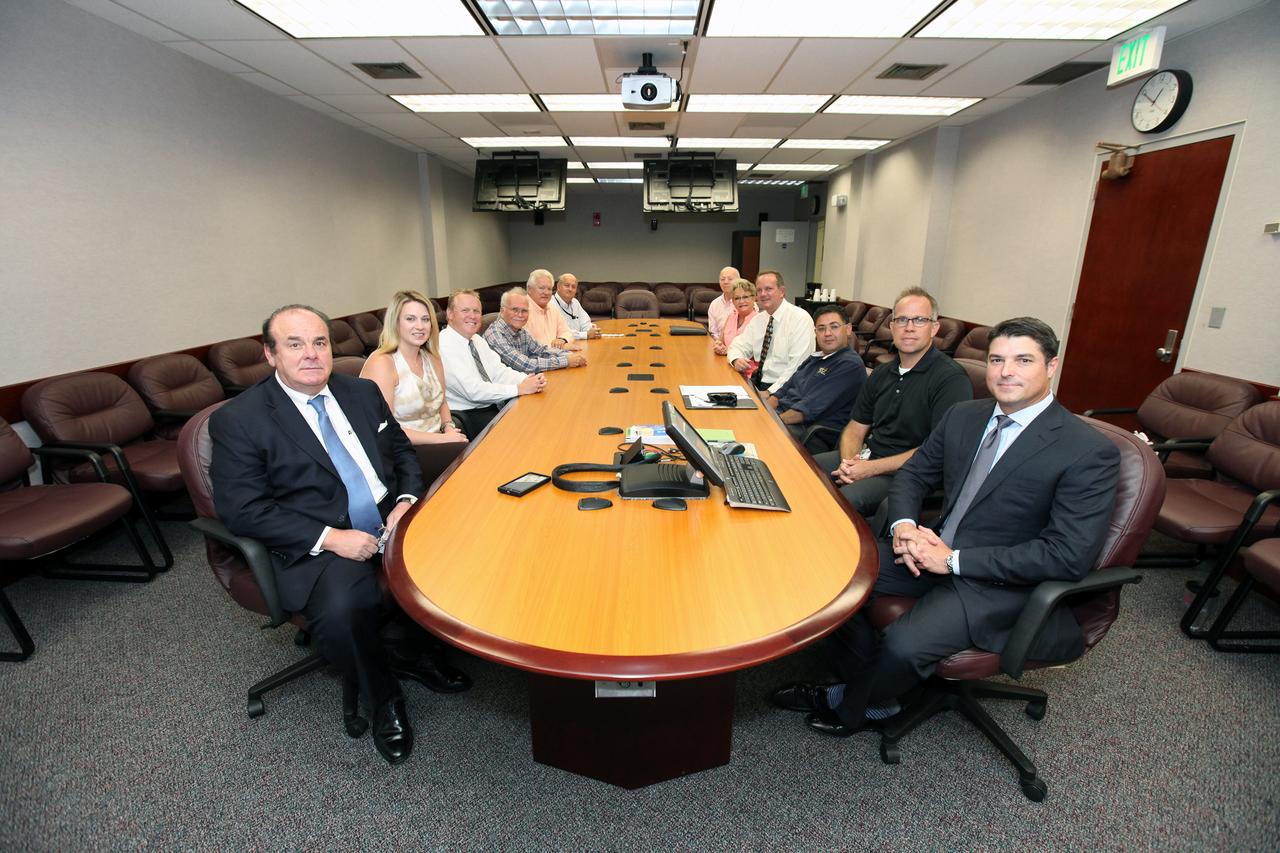

NASA, local and state officials met at Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the sixth KSC Roundtable, in which participants exchanged ideas about the center’s current plans. The meeting was hosted by Kennedy’s Center Planning and Development Directorate (CPD). Seated from left to right are Greg Weiner of the Economic Development Commission of Florida’s Space Coast; Ashley Guinn, legislative assistant to Steve Crisafulli, speaker of the Florida House of Representatives; Todd Pokrywa of The Viera Co.; Charles Lee of the Florida Audubon Society; Rich Biter, former assistant secretary of Intermodal Systems Development, Florida Department of Transportation (FDOT); David Pierce of CPD; Marshall Heard, retired Boeing senior executive; Nancy Potts of CPD; Tom Engler, acting director of CPD; Moataz Hassan of FDOT District 5; Trey Carlson of CPD; and Rep. Crisafulli.

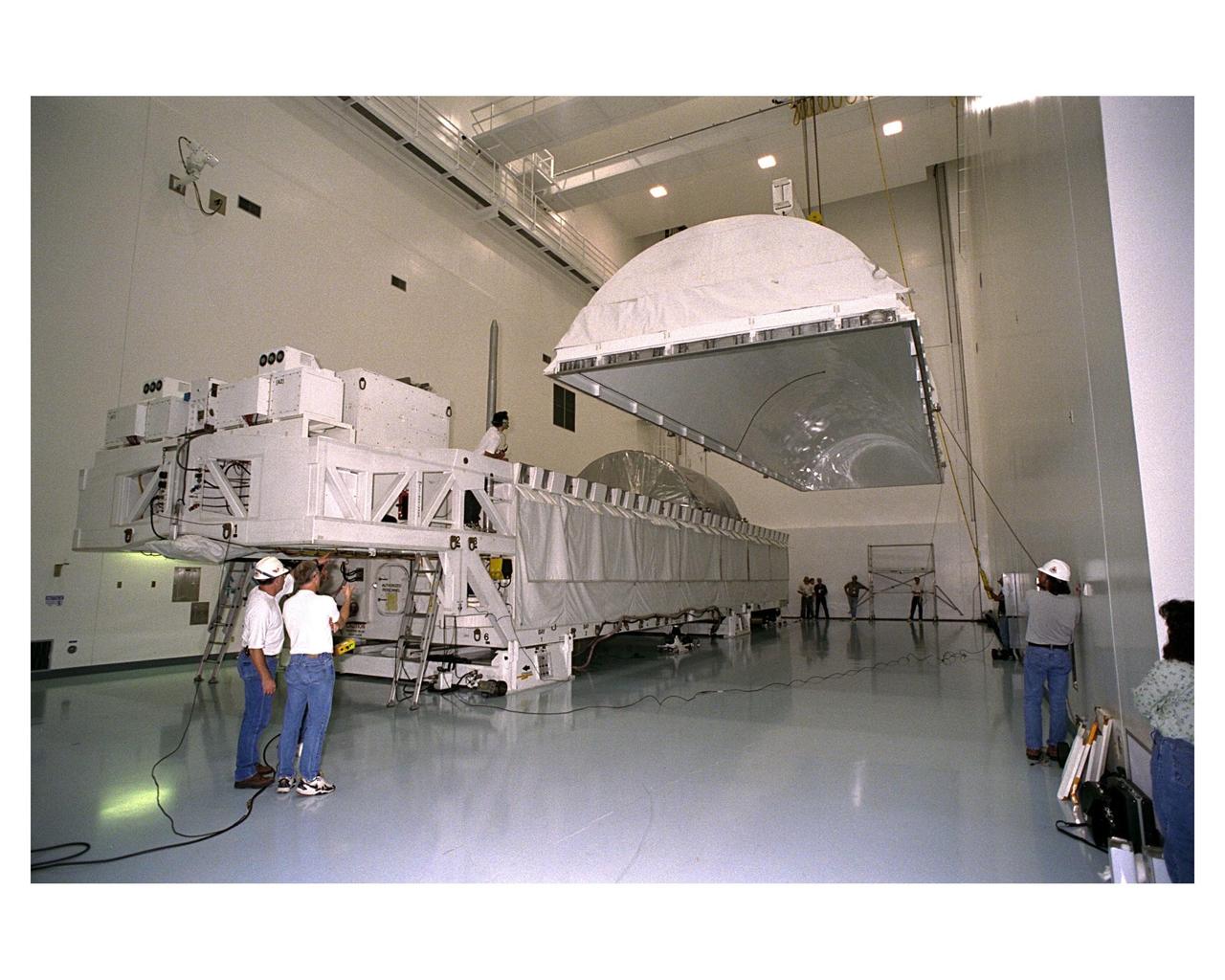
Covered in a protective sheath, International Space Station Node 1 is hoisted for installation in its work stand in the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
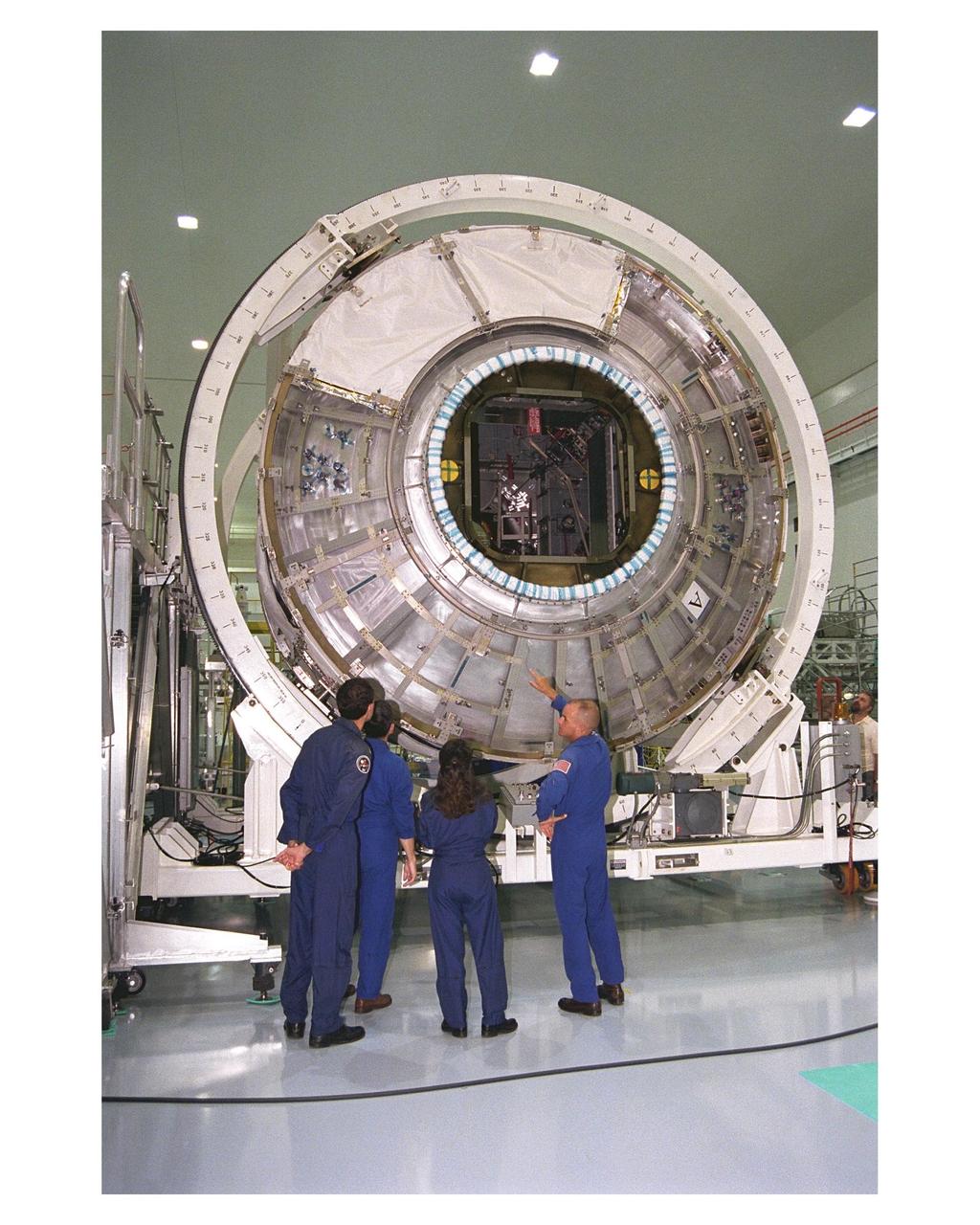
Members of the STS-88 crew examine the Node 1 of the Internation Space Station in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. The six hatches on the Node 1 will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements

The Node 1, the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first to be launched on the Space Shuttle, rests in its container in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay after its arrival at KSC from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Node 1 module is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998 along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot in diameter, 22- foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at MSFC. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
The STS-92 astronaut team study the the Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss during the Crew Equipment Interface Test. The Z-1 Truss was officially presented to NASA by The Boeing Co. on the Space Station Processing Facility floor on July 31. The truss is the cornerstone truss of the International Space Station and is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998

NASA and contractor employees who were working at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during the Apollo 11 launch gathered for a group photo on the observation deck of Operations and Support Building II on July 11, 2019. From left, along with their titles from 50 years ago, are Richard Sharum, NASA civil servant; Edward Wilson, security officer for Wackenhut Corporation; Sue Gross, secretary to the deputy procurement officer; Emery Lamar, NASA Kennedy co-op student in Apollo Spacecraft Electrical Division; James Scotti, material clerk with Bendix Corporation; Suzanne Stuckey, secretary for telemetry; Andrew Pritchard, contractor with McGregor-Warner; Ken Poimboeuf, Design Engineering Directorate; and Grady McCorquodale, Launch Control Center engineer with Boeing. Not pictured are Richard Cota, civil servant in the Engineering Directorate; and Victor Kurjack, data courier.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a printable poster of the aerospace companies NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP) entered into Space Act Agreements with during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 (CCDev2) activities in 2011 in order to mature the design and development of crew transportation systems with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. CCDev2 companies are Alliant Techsystems (ATK), Blue Origin, The Boeing Co., Excalibur Almaz Inc., Sierra Nevada Corp., Space Exploration Technologies (SpaceX), and United Launch Alliance (ULA). The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew
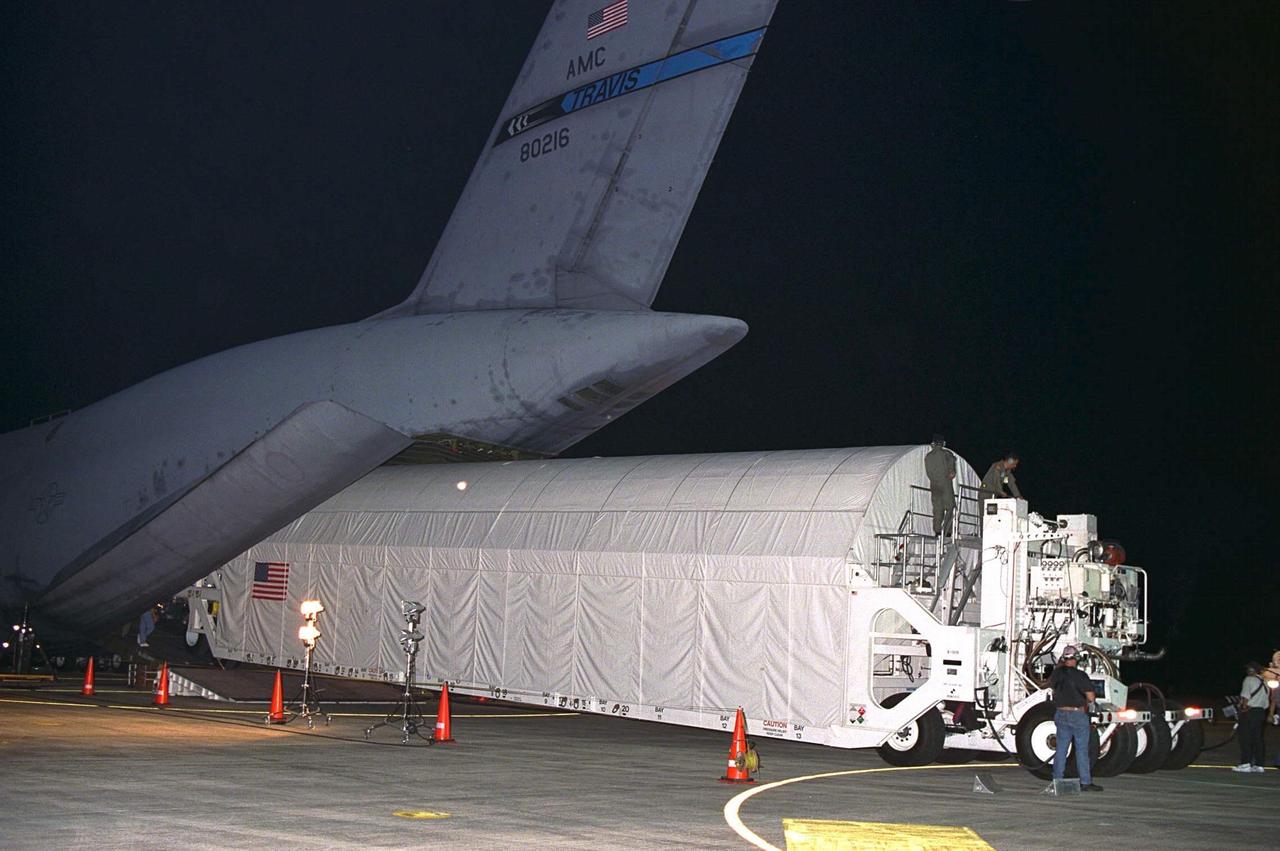

Node 1, the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first to be launched on the Space Shuttle, is unloaded in its container from an Air Force C-5 jet cargo transport at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway on June 23 after its arrival from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The module was then transported to the Space Station Processing Facility. The Node 1 module is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998 along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot in diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at MSFC. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other Space Station elements
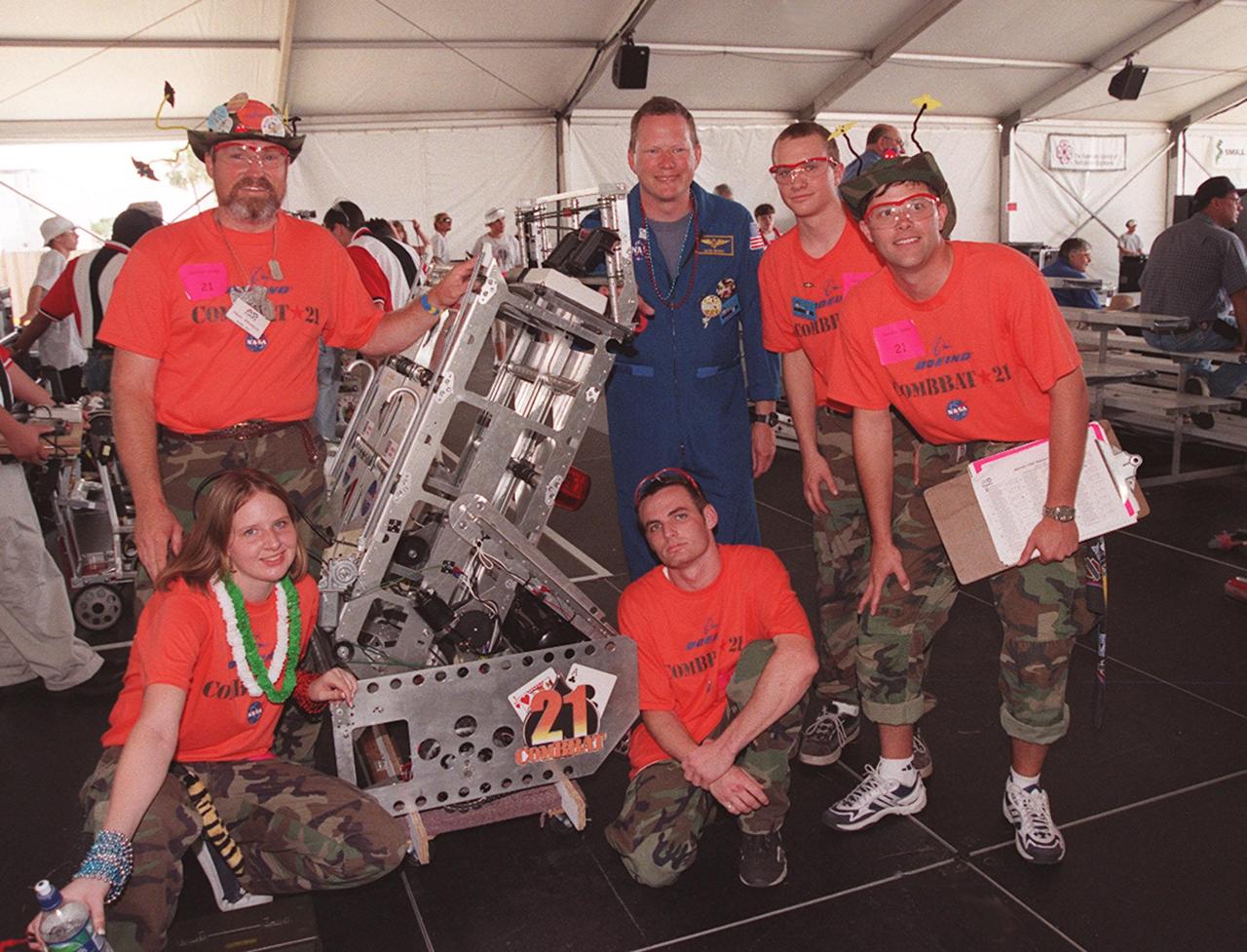

Astronaut David Brown poses with members of the team known as ComBBat, representing Central Florida's Astronaut and Titusville high schools. ComBBat was teamed with Boeing at KSC and Brevard Community College. Students from all over the country are at the KSC Visitor Complex for the FIRST (For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology) Southeast Regional competition being held March 9-11 in the Rocket Garden. Teams of high school students are testing the limits of their imagination using robots they have designed, with the support of business and engineering professionals and corporate sponsors, to compete in a technological battle against other schools' robots. Of the 30 high school teams competing, 16 are Florida teams co-sponsored by NASA and KSC contractors. Local high schools participating are Astronaut, Bayside, Cocoa Beach, Eau Gallie, Melbourne, Melbourne Central Catholic, Palm Bay, Rockledge, Satellite, and Titusville
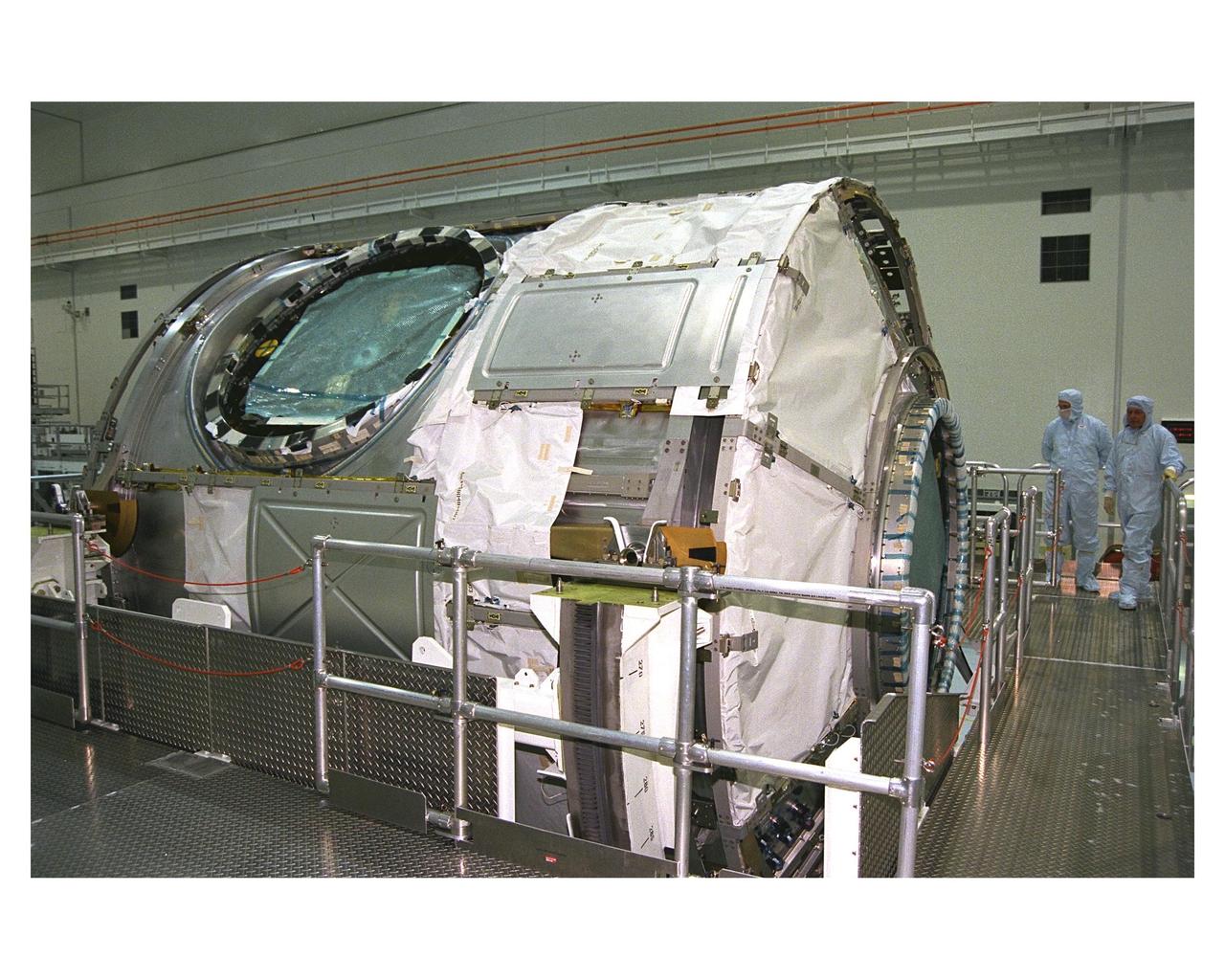

A close-up view of the Node 1 in its work stand in the Space Station Processing Facility shows one of its six hatches that will serve as docking ports. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. The six hatches on the Node 1 will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
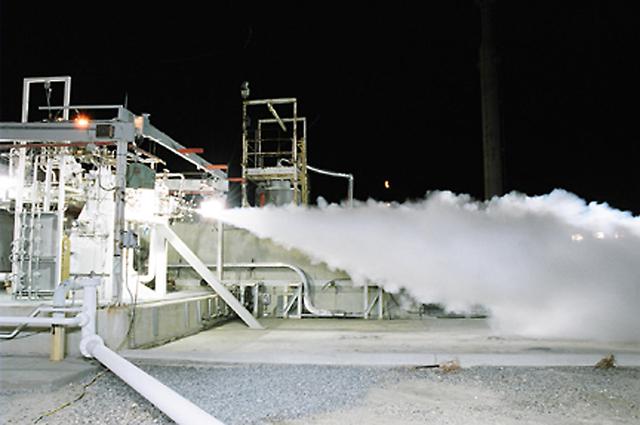

NASA Stennis Space Center engineers conducted a successful cold-flow test of an RS-84 engine component Sept. 24. The RS-84 is a reusable engine fueled by rocket propellant - a special blend of kerosene - designed to power future flight vehicles. Liquid oxygen was blown through the RS-84 subscale preburner to characterize the test facility's performance and the hardware's resistance. Engineers are now moving into the next phase, hot-fire testing, which is expected to continue into February 2004. The RS-84 engine prototype, developed by the Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. of Canoga Park, Calif., is one of two competing Rocket Engine Prototype technologies - a key element of NASA's Next Generation Launch Technology program.
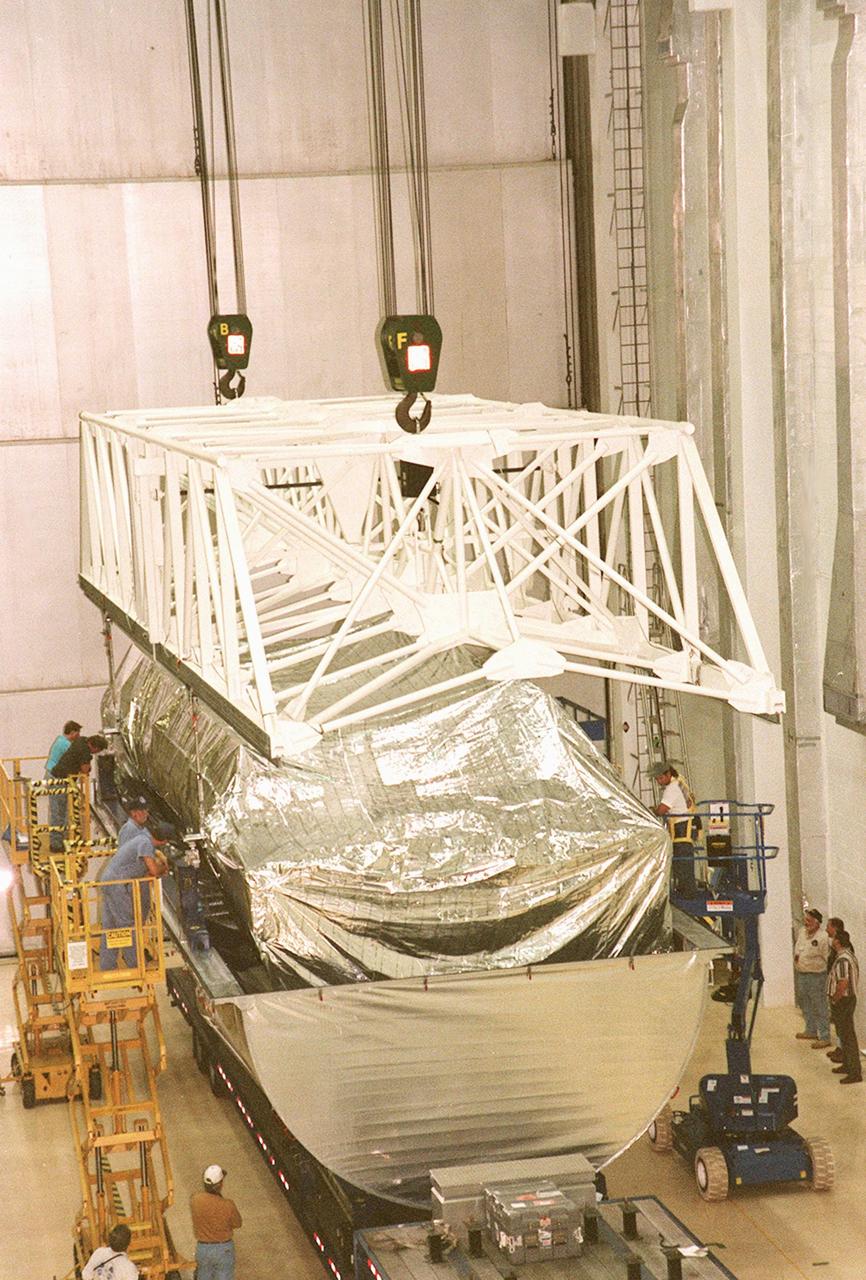

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Operations and Checkout Building, a strongback is lowered toward the S1 truss below it in order to lift the truss from the Guppy cargo carrier that protected it during flight and transfer. Manufactured by the Boeing Co. in Huntington Beach, Calif., this component of the International Space Station is the first starboard (right-side) truss segment, whose main job is providing structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels that cool the Space Station's complex power system. The S1 truss segment also will house communications systems, external experiment positions and other subsystems. Primarily constructed of aluminum, the truss segment is 45 feet long, 15 feet wide and 6 feet tall. When fully outfitted, it will weigh 31,137 pounds. The truss is slated for flight in 2001
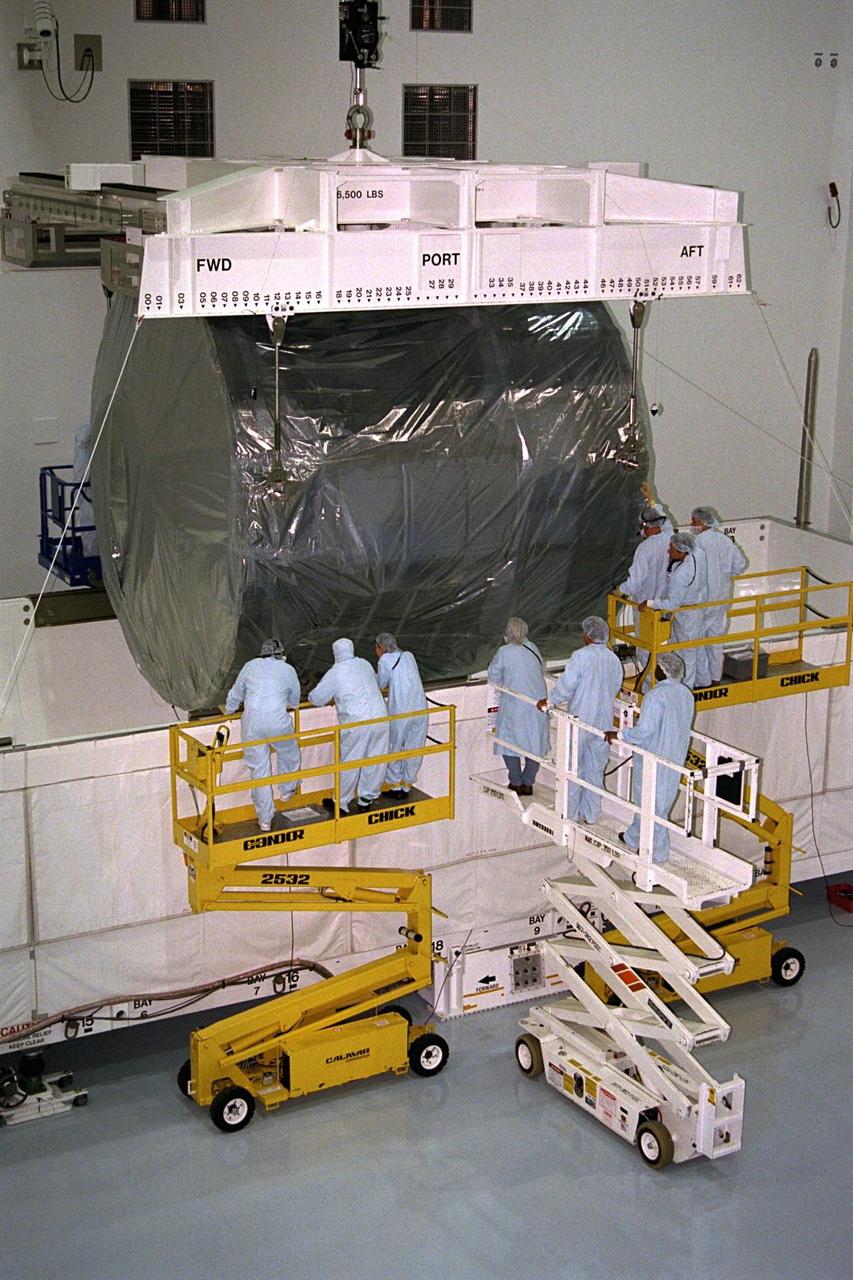

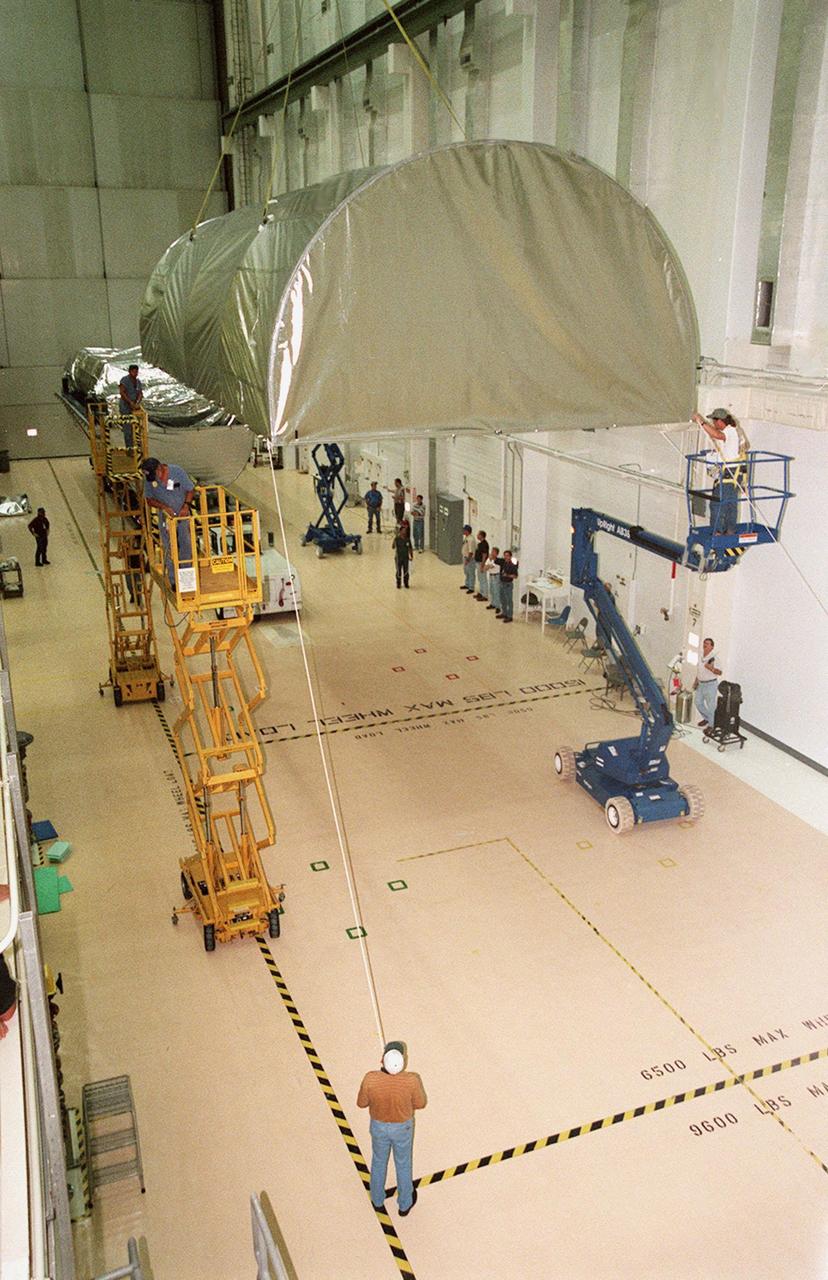
Covered in a protective sheath, International Space Station Node 1 is hoisted from its transporting container for installation in its work stand in the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
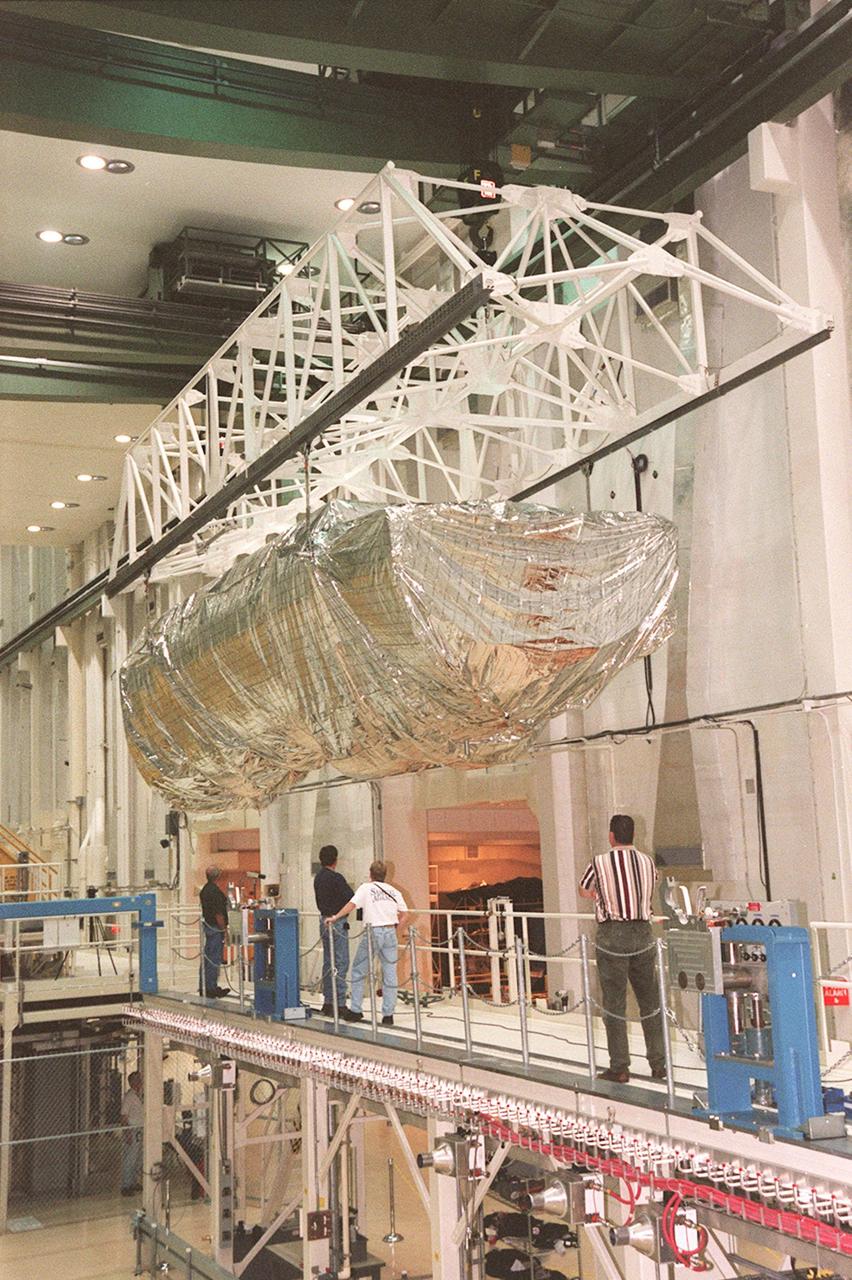

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Operations and Checkout Building, the S1 truss, a segment of the International Space Station, is moved toward workstand number three. Manufactured by the Boeing Co. in Huntington Beach, Calif., this component of the International Space Station is the first starboard (right-side) truss segment, whose main job is providing structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels that cool the Space Station's complex power system. The S1 truss segment also will house communications systems, external experiment positions and other subsystems. Primarily constructed of aluminum, the truss segment is 45 feet long, 15 feet wide and 6 feet tall. When fully outfitted, it will weigh 31,137 pounds. The truss is slated for flight in 2001

Covered in a protective sheath, International Space Station Node 1 is installed in its work stand in the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
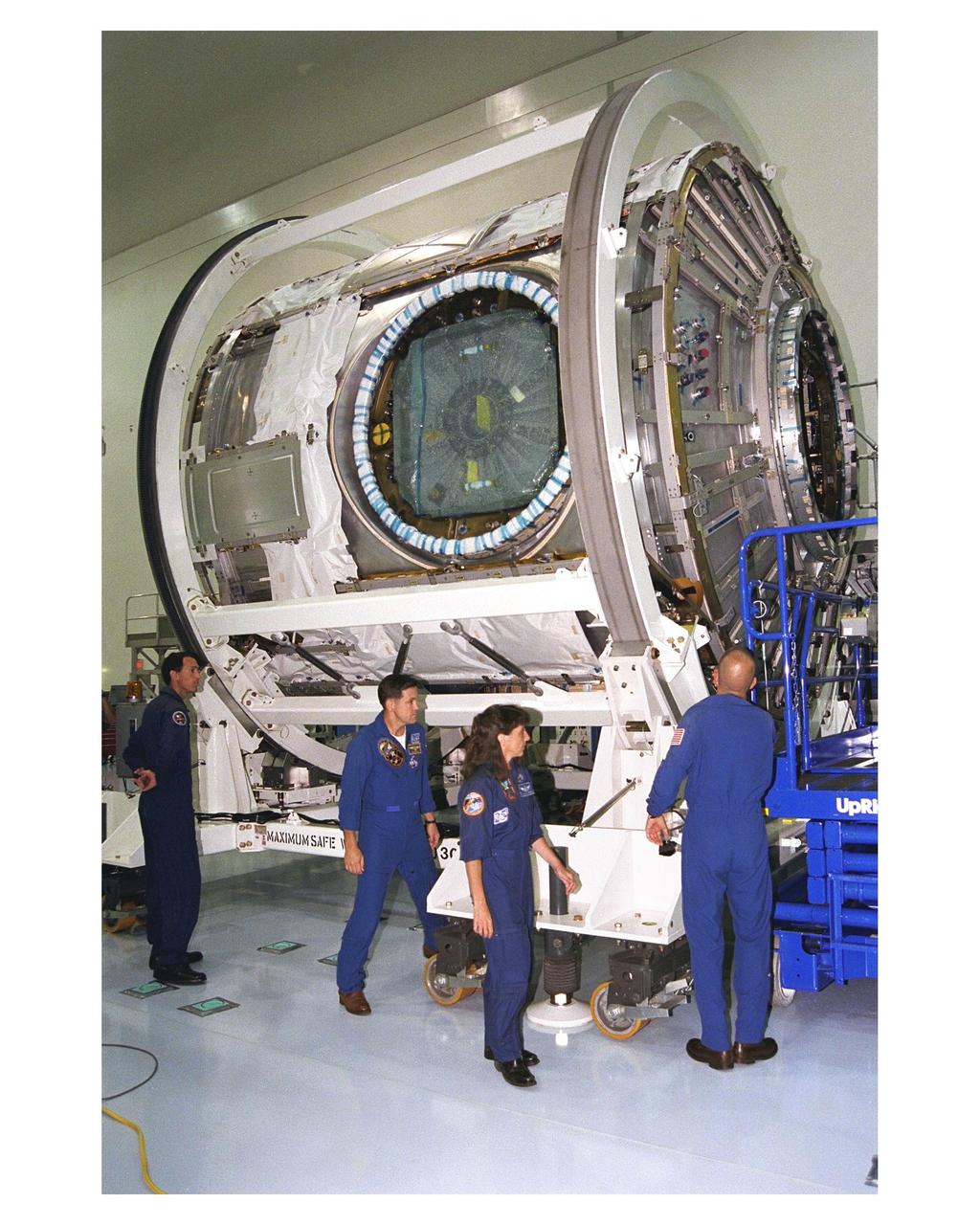

Members of the STS-88 crew examine the Node 1 of the International Space Station in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is the first element of the ISS to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the ISS. The six hatches on the Node 1 will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other Space Station elements

Covered in a protective sheath, International Space Station Node 1 is hoisted for installation in its work stand in the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
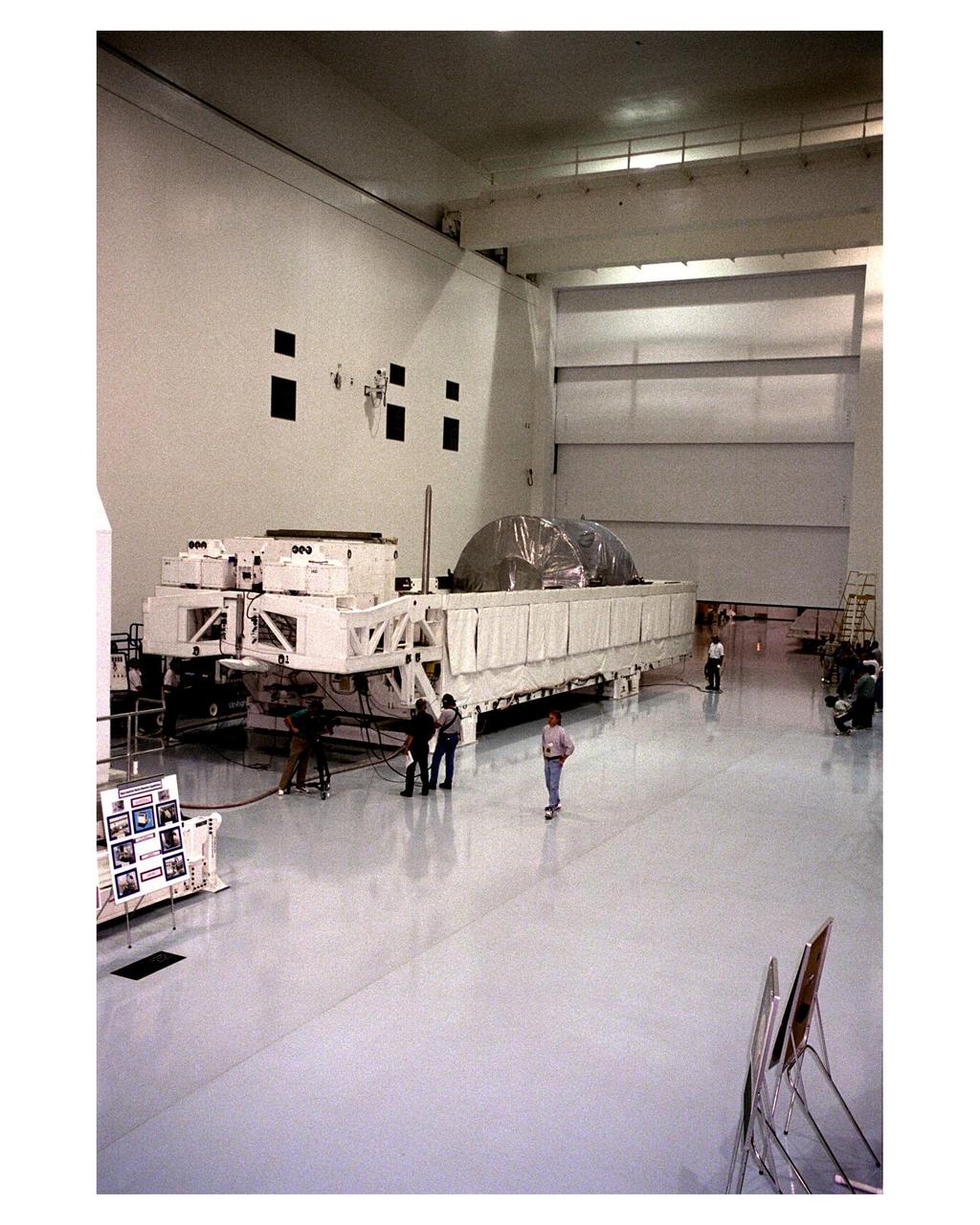
The Node 1, the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first to be launched on the Space Shuttle, rests in its container in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay after its arrival at KSC from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Node 1 module is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998 along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot in diameter, 22- foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at MSFC. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
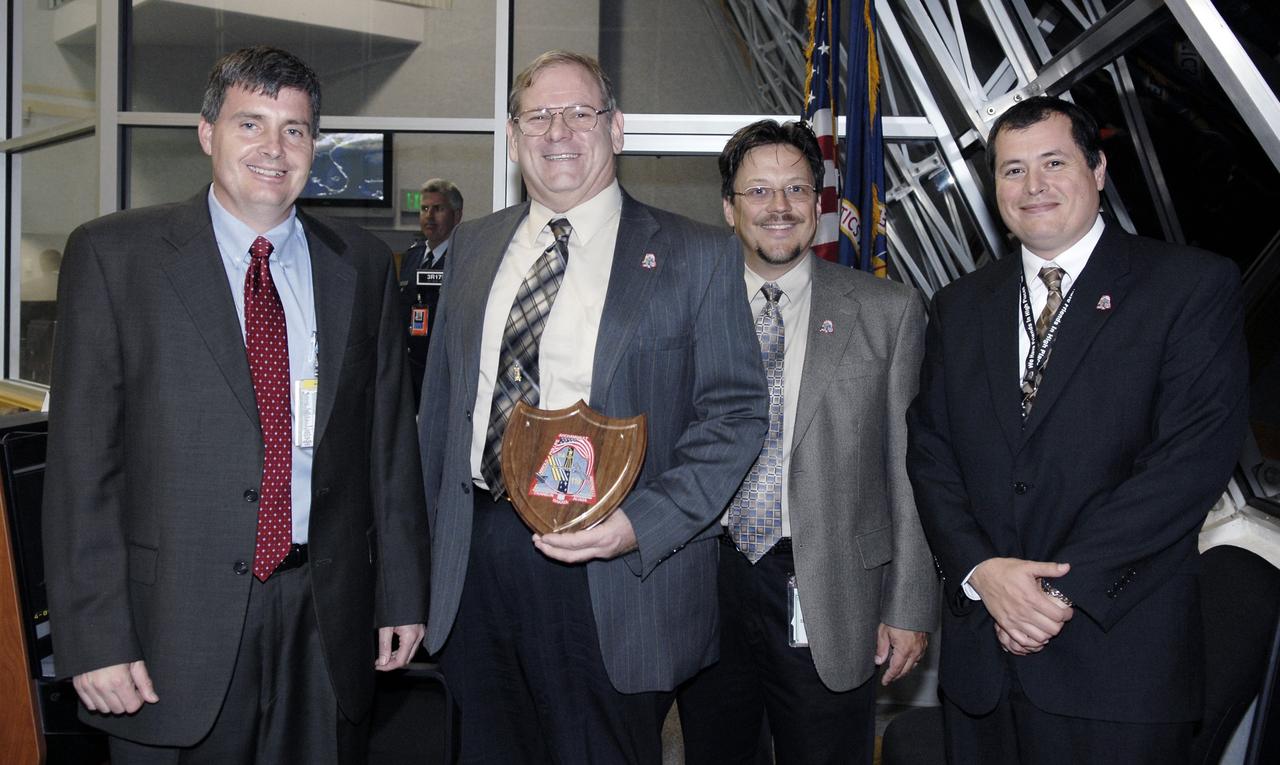

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, from left, Steve Stich, manager of the Kennedy Orbiter Project Office; John Fraser, with Boeing Co. at the Marshall Space Flight Center; Rick Russell, with the NASA Orbiter Sustaining Engineering Office; and Rene Ortega with Marshall Space Flight Center's Shuttle Propulsion Office, are presented with a plaque for their work on the fuel control valve problem on space shuttle Discovery. The award was presented after the successful launch of Discovery on the STS-119 mission. Liftoff was on time at 7:43 p. m. EDT. The STS-119 mission is the 28th to the space station and Discovery's 36th flight. Discovery will deliver the final pair of power-generating solar array wings and the S6 truss segment. Installation of S6 will signal the station's readiness to house a six-member crew for conducting increased science. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
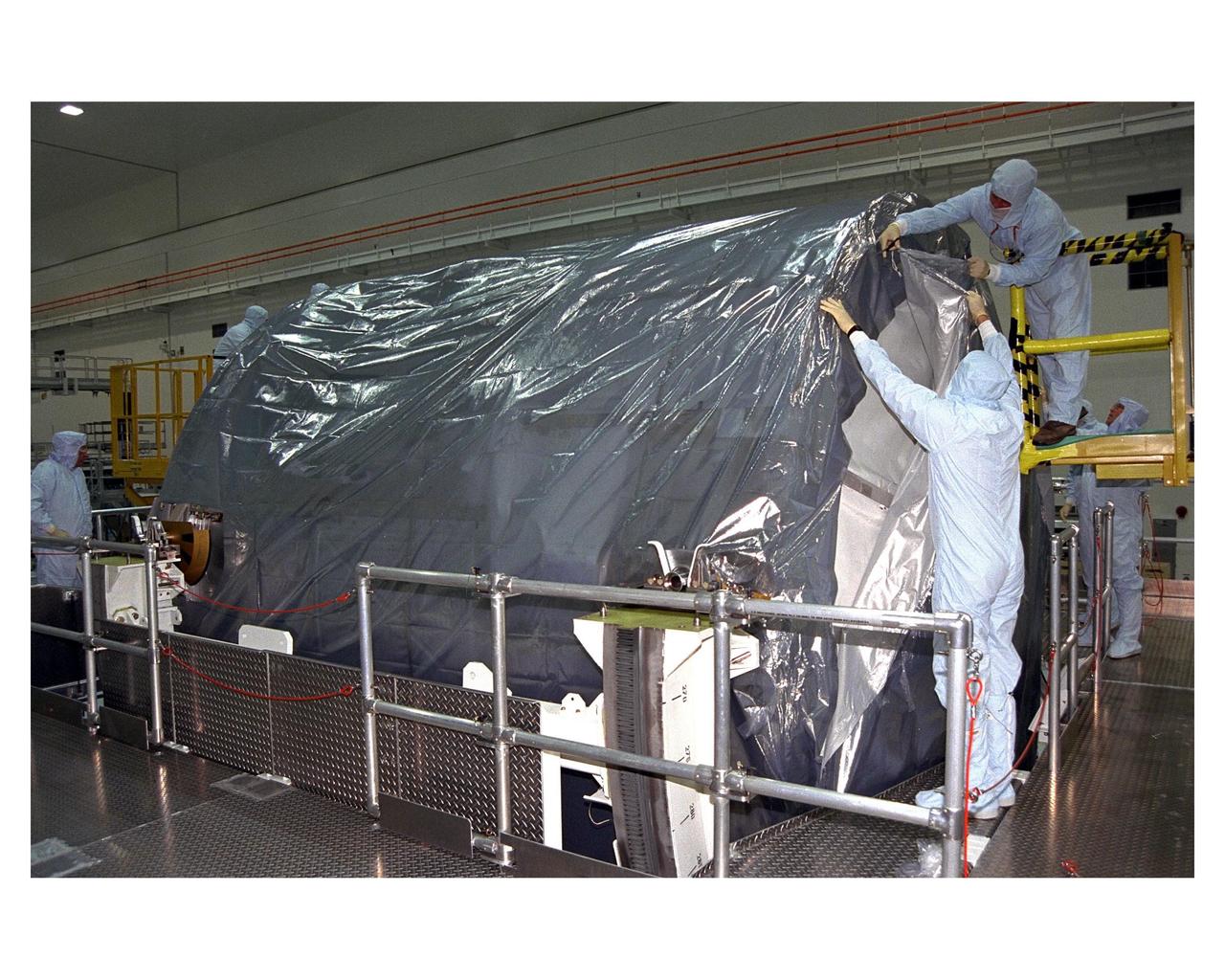

KSC workers begin to remove a protective sheath from the Node 1 in its work stand in the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first scheduled to be launched on the Space Shuttle. The Node 1 is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998, along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot-in-diameter, 22-foot- long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at Marshall Space Flight Center. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
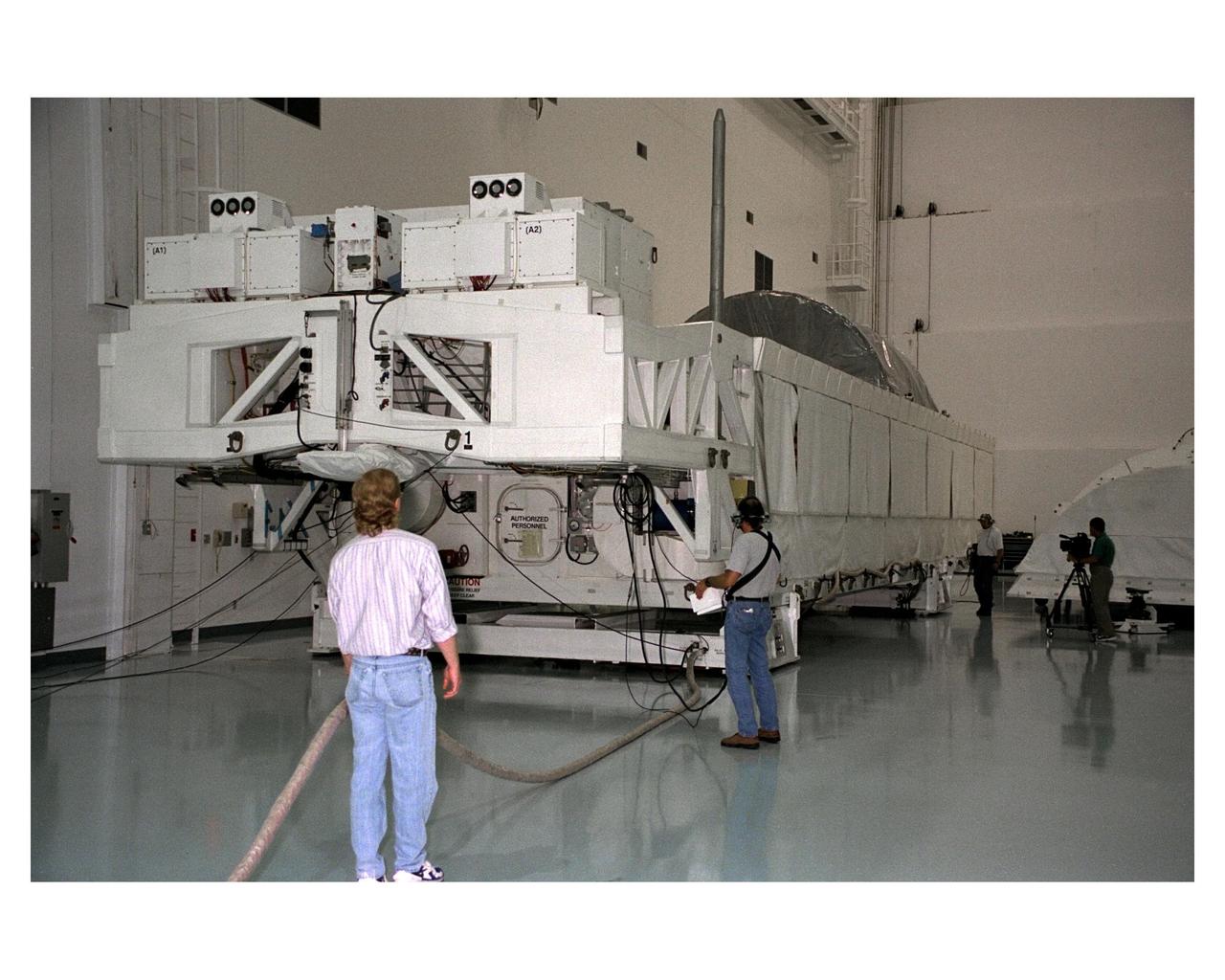

The Node 1, the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first to be launched on the Space Shuttle, rests in its container in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay after its arrival at KSC from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Node 1 module is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998 along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot in diameter, 22- foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at MSFC. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
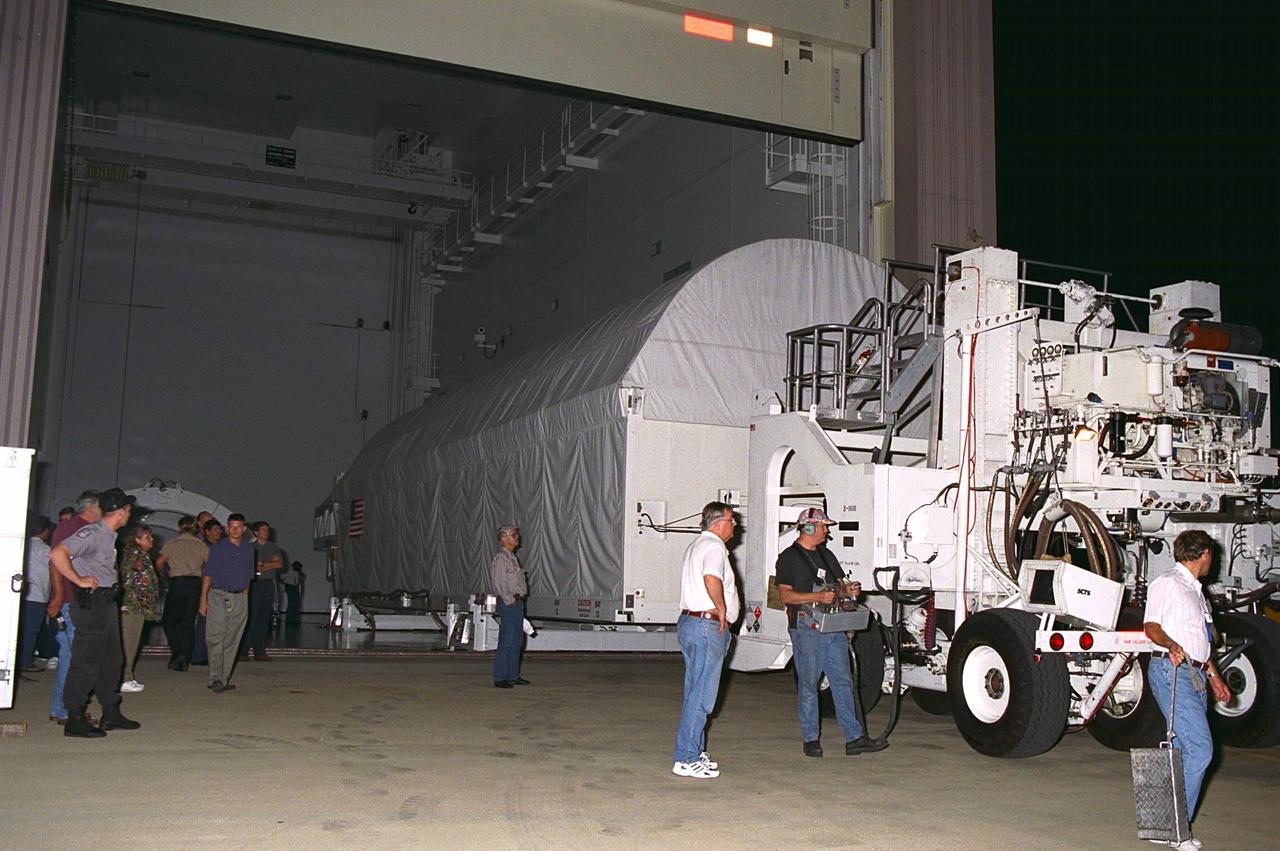

The container transporting the Node 1, the first element of the International Space Station to be manufactured in the United States and the first to be launched on the Space Shuttle, is moved into the Space Station Processing Facility high bay June 23 after its arrival from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Node 1 module is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in July 1998 along with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) 1 and 2. The 18-foot in diameter, 22-foot-long aluminum module was manufactured by the Boeing Co. at MSFC. Once in space, the Node 1 will function as a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the International Space Station. It has six hatches that will serve as docking ports to the U.S. laboratory module, U.S. habitation module, an airlock and other space station elements
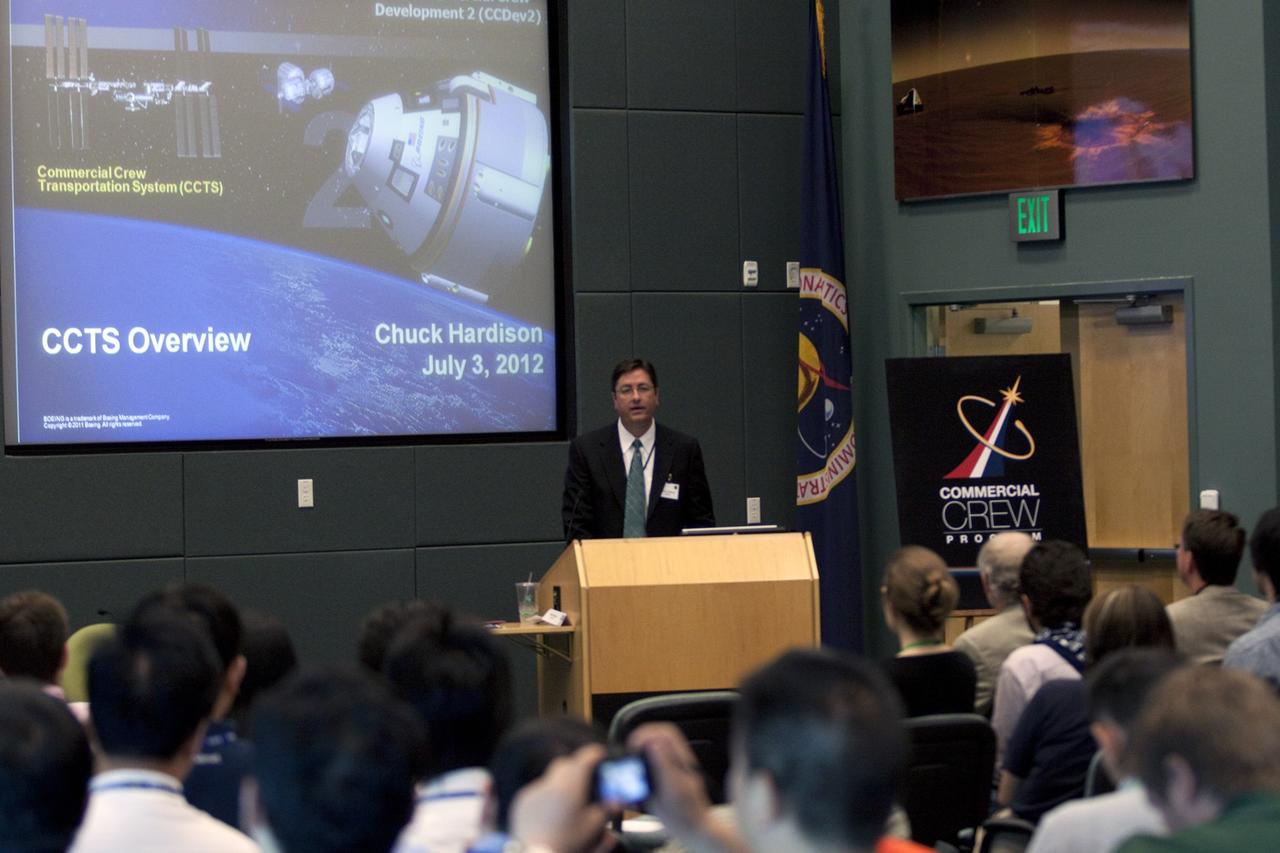

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Chuck Hardison of Boeing provides a Commercial Crew Transportation System overview for participants of the International Space University session on July 3 in Operations Support Building II at the Kennedy Space Center, Fla. The International Space University is a nine-week intensive course designed for post-graduate university students and professionals during the summer. The program is hosted by a different country each year, providing a unique educational experience for participants from around the world. NASA Kennedy Space Center and the Florida Institute of Technology are co-hosting this year's event which runs from June 4 to Aug. 3. There are about 125 participants representing 31 countries. For more information, visit http://www.isunet.edu Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
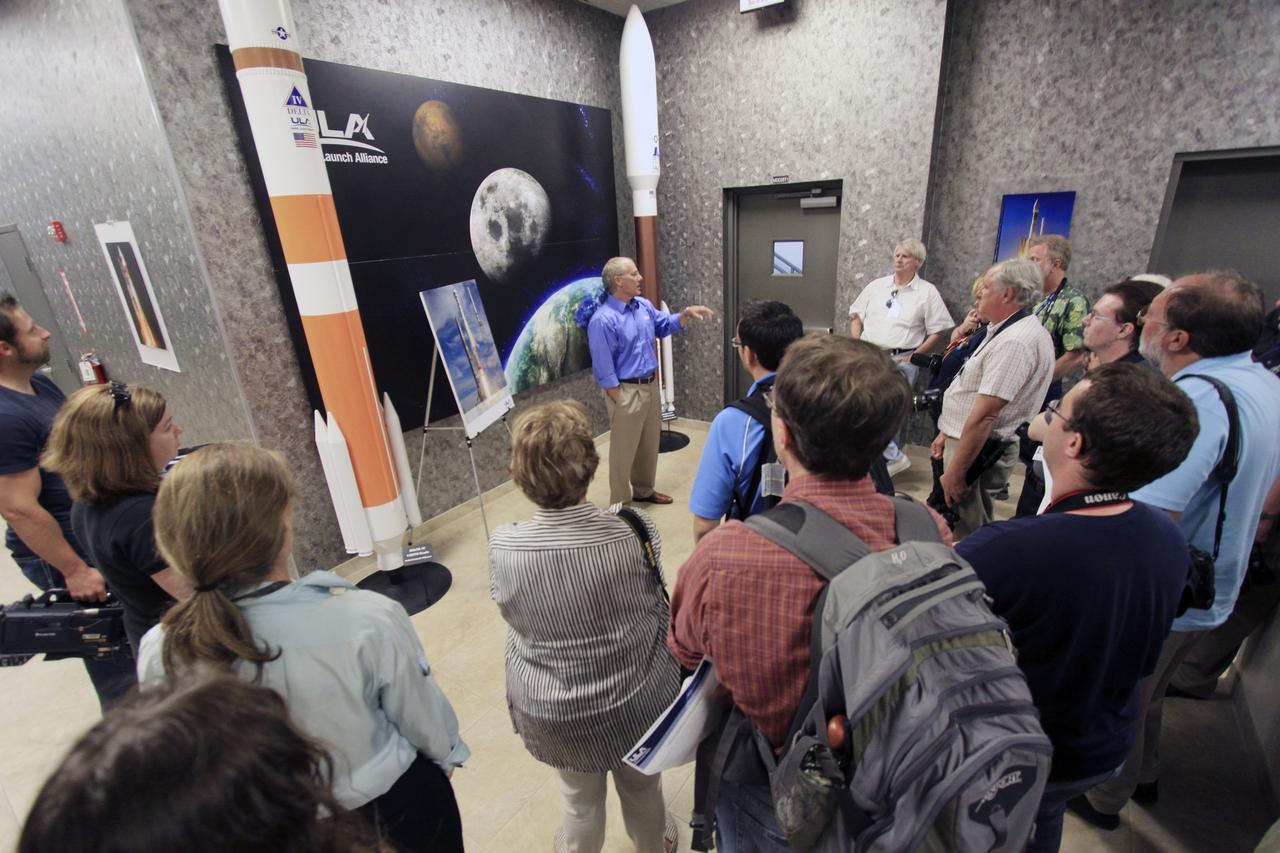

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Andy Aldrin, director of business development for United Launch Alliance (ULA), talks to media about plans to launch NASA astronauts to the International Space Station in the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ULA is working to make its Atlas V rocket safe for humans for NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP) under the Commercial Crew Development Round 2 (CCDev2) activities. Part of those plans will be to design and test an emergency detection system and crew access capabilities. ULA also is working with other aerospace system providers developing spacecraft that would launch atop the company's Atlas V rocket, such as Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada and The Boeing Co. CCP, which is based at the adjacent NASA's Kennedy Space Center, is partnering with industry to take crews to the station or other low Earth orbit destinations. Aldrin explained that the goal of ULA will be to develop a human spaceflight capability without altering rocket's proven design and successful track record. It's the freedom to develop innovative solutions such as this that CCP hopes will drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before. Seven aerospace companies are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. (ATK) of Promontory, Utah, Blue Origin of Kent, Wash., The Boeing Co., of Houston, Excalibur Almaz Inc. of Houston, Sierra Nevada Corp. of Louisville, Colo., Space Exploration Technologies (SpaceX) of Hawthorne, Calif., and United Launch Alliance (ULA) of Centennial, Colo. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/exploration/commercial Photo credit: Jim Grossmann
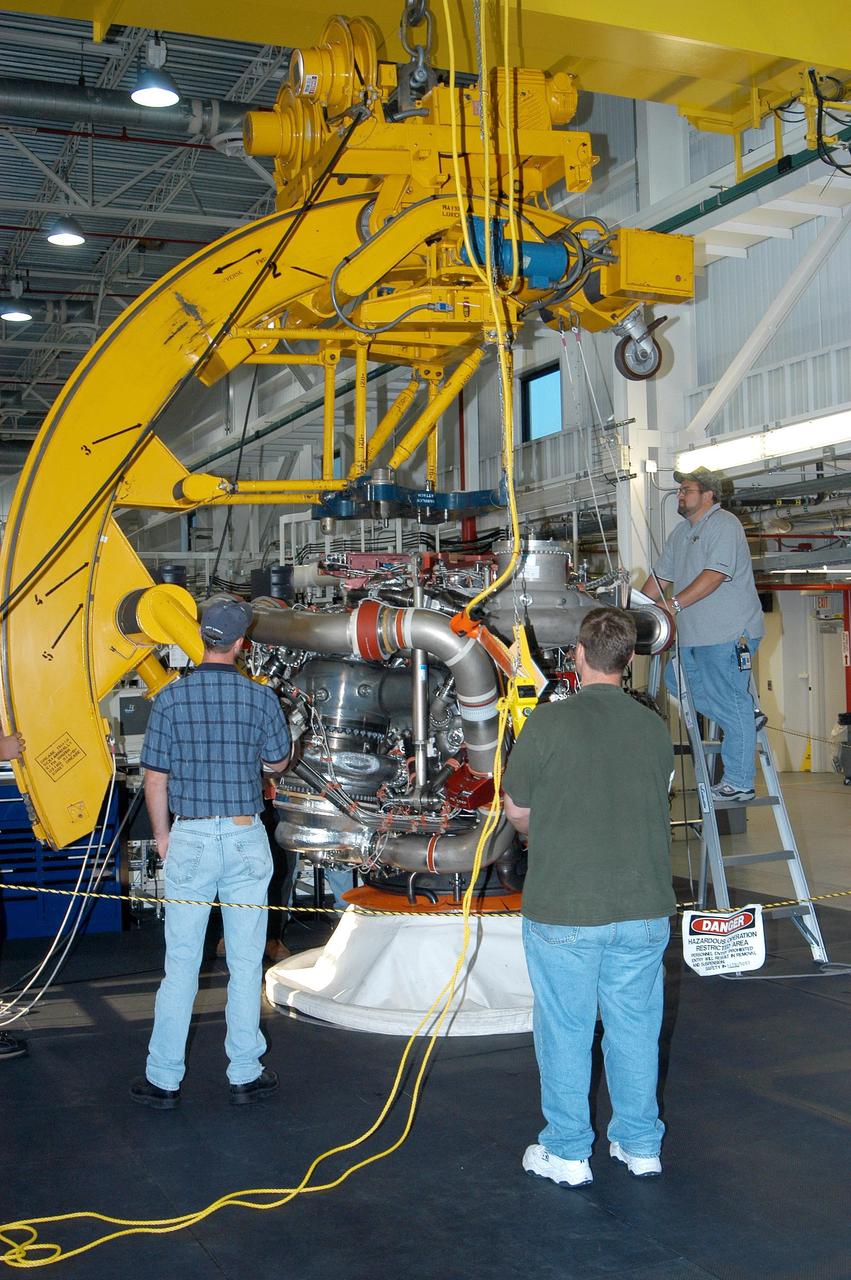

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Processing Facility, Boeing-Rocketdyne technicians prepare to move SSME 2058, the first SSME fully assembled at KSC. Move conductor Bob Brackett (on ladder) supervises the placement of a sling around the engine with the assistance of crane operator Joe Ferrante (center) and a technician. The engine will be lifted from its vertical work stand into a horizontal position in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi to undergo a hot fire acceptance test. It is the first of five engines to be fully assembled on site to reach the desired number of 15 engines ready for launch at any given time in the Space Shuttle program. A Space Shuttle has three reusable main engines. Each is 14 feet long, weighs about 7,800 pounds, is seven-and-a-half feet in diameter at the end of its nozzle, and generates almost 400,000 pounds of thrust. Historically, SSMEs were assembled in Canoga Park, Calif., with post-flight inspections performed at KSC. Both functions were consolidated in February 2002. The Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. manufactures the engines for NASA.
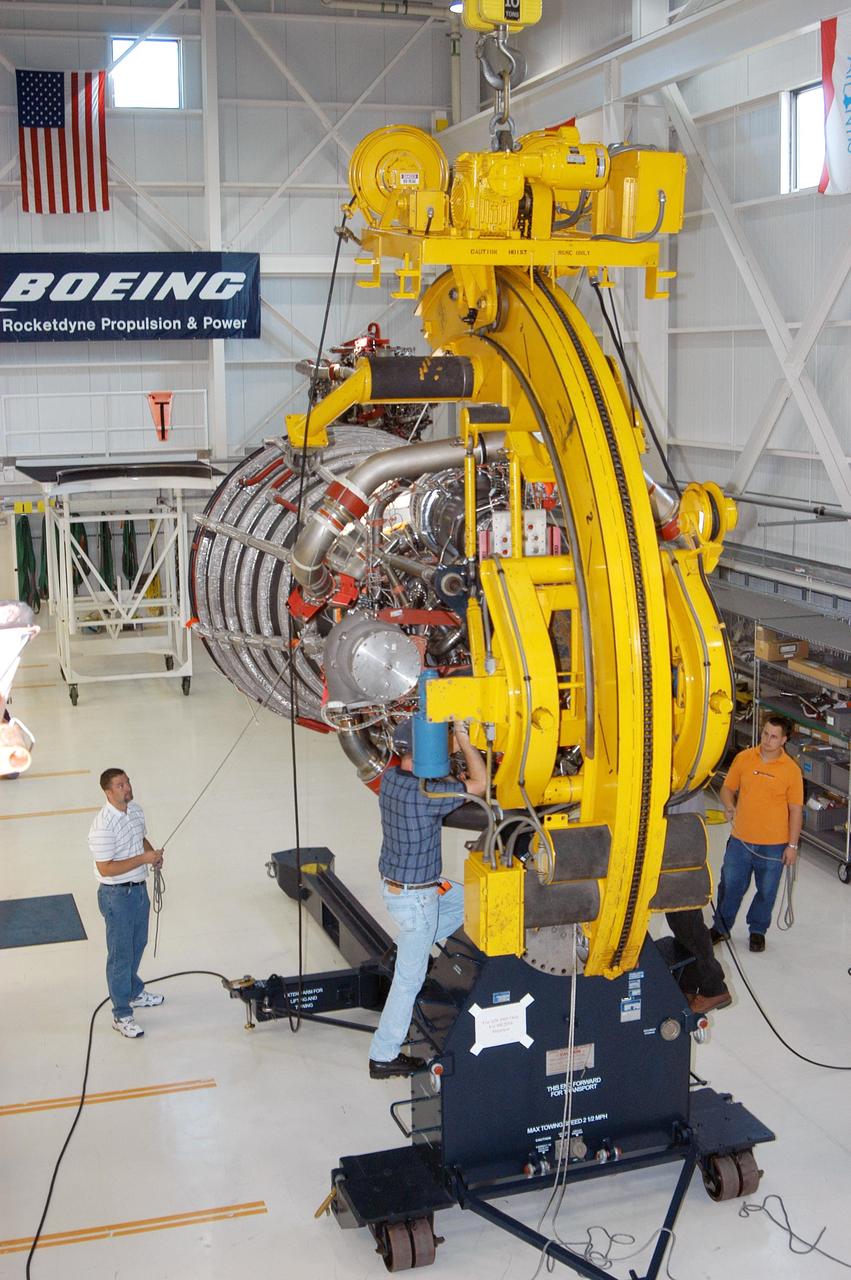

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Processing Facility, Boeing-Rocketdyne technicians lower SSME 2058, the first SSME fully assembled at KSC, onto an engine stand. The engine is being moved from its vertical work stand into a horizontal position in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi to undergo a hot fire acceptance test. It is the first of five engines to be fully assembled on site to reach the desired number of 15 engines ready for launch at any given time in the Space Shuttle program. A Space Shuttle has three reusable main engines. Each is 14 feet long, weighs about 7,800 pounds, is seven-and-a-half feet in diameter at the end of its nozzle, and generates almost 400,000 pounds of thrust. Historically, SSMEs were assembled in Canoga Park, Calif., with post-flight inspections performed at KSC. Both functions were consolidated in February 2002. The Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. manufactures the engines for NASA.
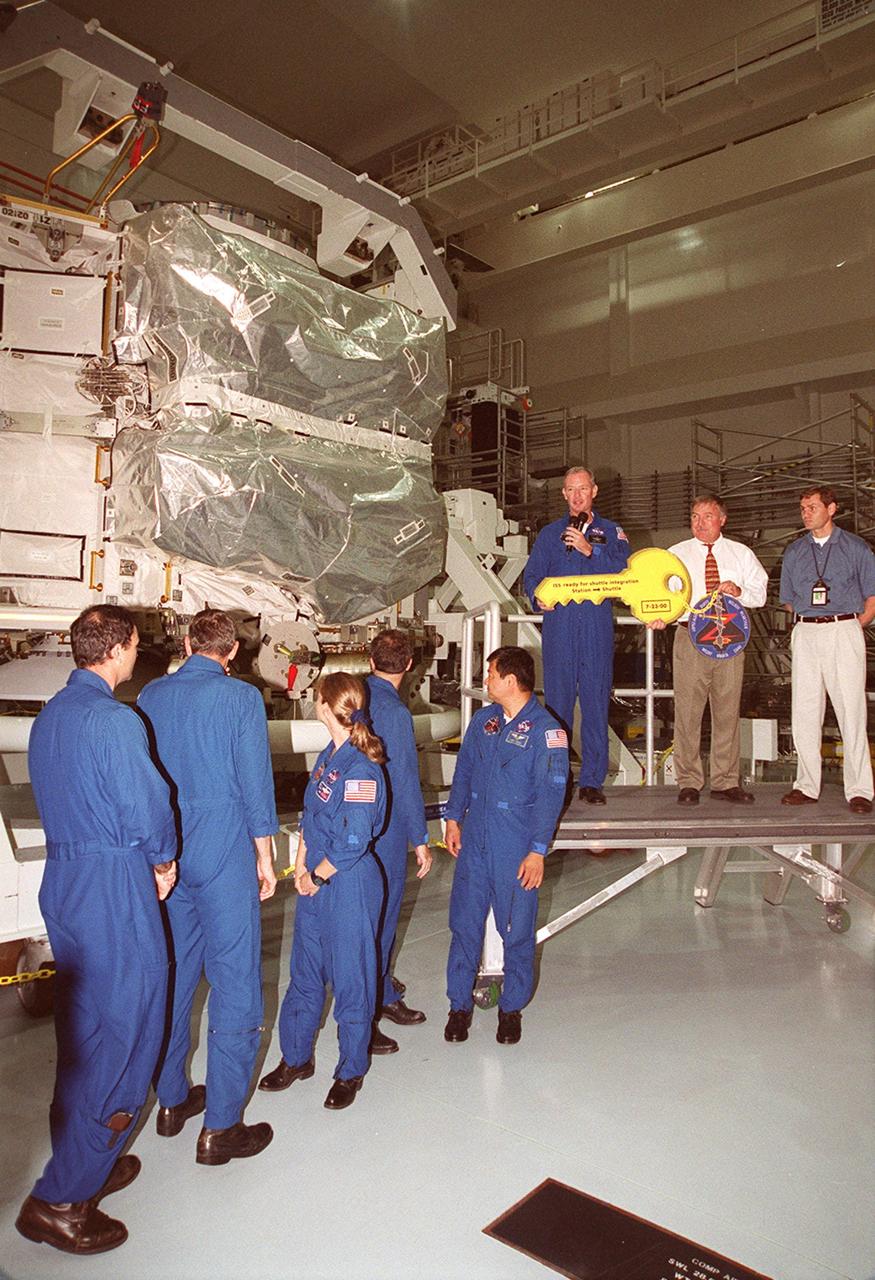
The Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss is officially presented to NASA by The Boeing Co. on the Space Station Processing Facility floor on July 31. STS-92 Commander Col. Brian Duffy, comments on the presentation. At his side is Tip Talone, NASA director of International Space Station and Payload Processing at KSC. Talone and Col. Duffy received a symbolic key for the truss from John Elbon, Boeing director of ISS ground operations. The Z-1 Truss is the cornerstone truss of the International Space Station and is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998
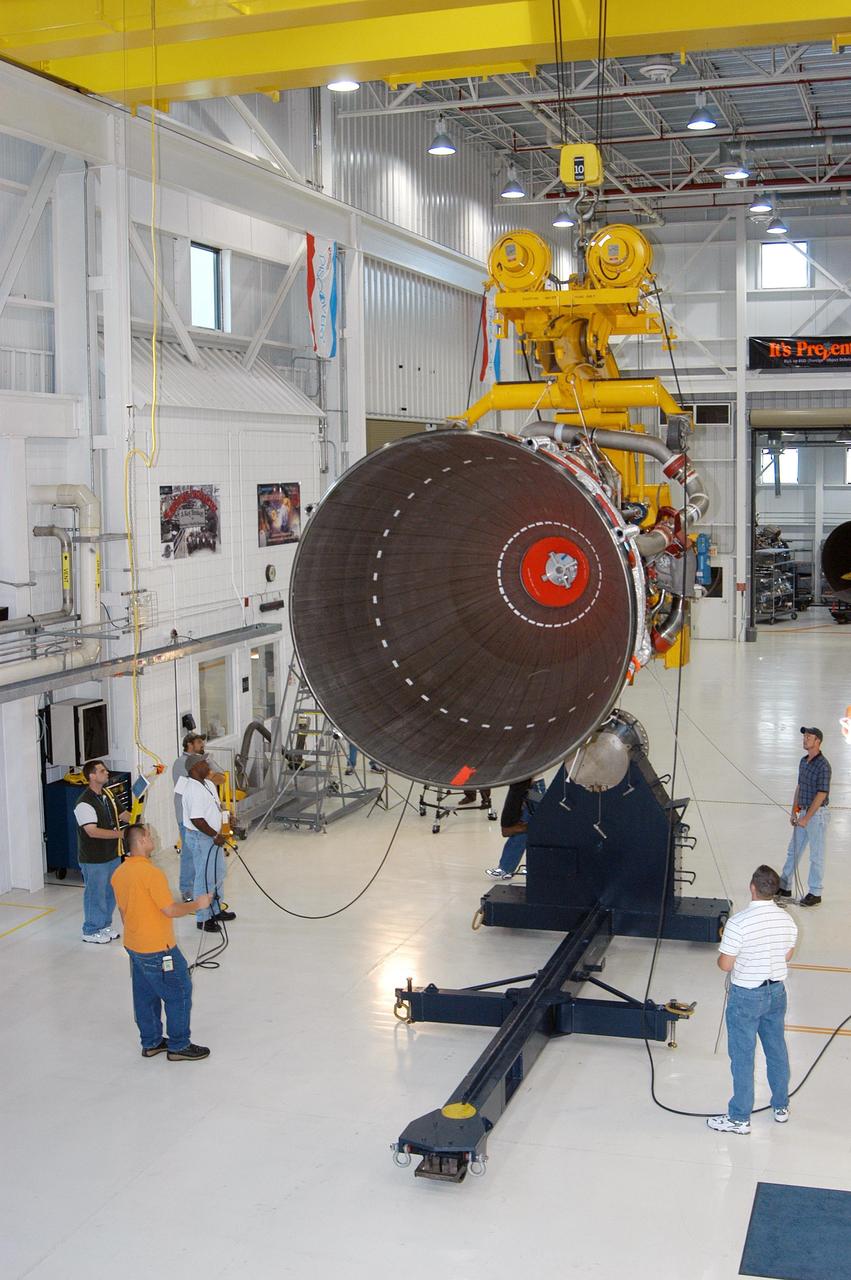

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Processing Facility, Boeing-Rocketdyne crane operator Joe Ferrante (left) lowers SSME 2058, the first SSME fully assembled at KSC, onto an engine stand with the assistance of other technicians on his team. The engine is being moved from its vertical work stand into a horizontal position in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi to undergo a hot fire acceptance test. It is the first of five engines to be fully assembled on site to reach the desired number of 15 engines ready for launch at any given time in the Space Shuttle program. A Space Shuttle has three reusable main engines. Each is 14 feet long, weighs about 7,800 pounds, is seven-and-a-half feet in diameter at the end of its nozzle, and generates almost 400,000 pounds of thrust. Historically, SSMEs were assembled in Canoga Park, Calif., with post-flight inspections performed at KSC. Both functions were consolidated in February 2002. The Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. manufactures the engines for NASA.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Processing Facility, Boeing-Rocketdyne technicians lift SSME 2058, the first SSME fully assembled at KSC. The engine is being lifted from its vertical work stand into a horizontal position in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi to undergo a hot fire acceptance test. It is the first of five engines to be fully assembled on site to reach the desired number of 15 engines ready for launch at any given time in the Space Shuttle program. A Space Shuttle has three reusable main engines. Each is 14 feet long, weighs about 7,800 pounds, is seven-and-a-half feet in diameter at the end of its nozzle, and generates almost 400,000 pounds of thrust. Historically, SSMEs were assembled in Canoga Park, Calif., with post-flight inspections performed at KSC. Both functions were consolidated in February 2002. The Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. manufactures the engines for NASA.
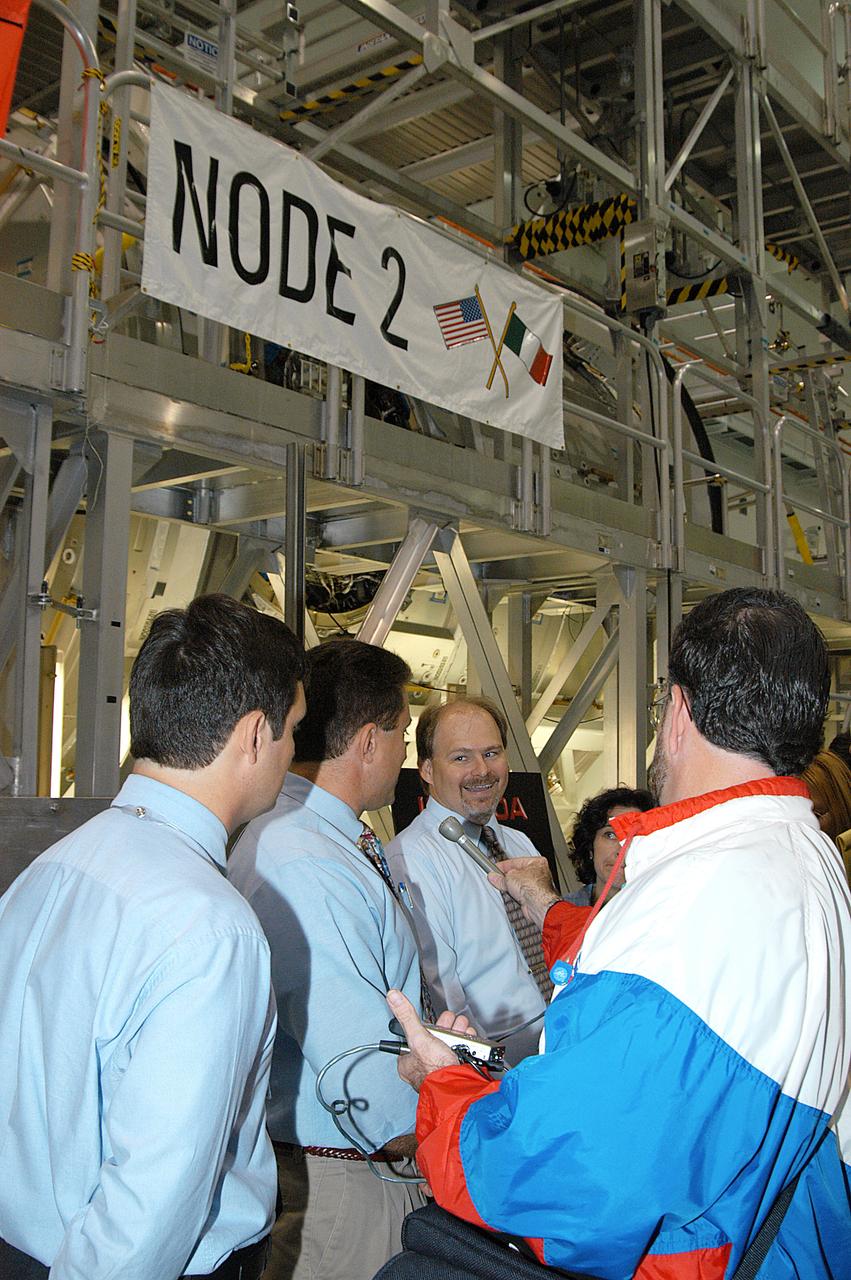

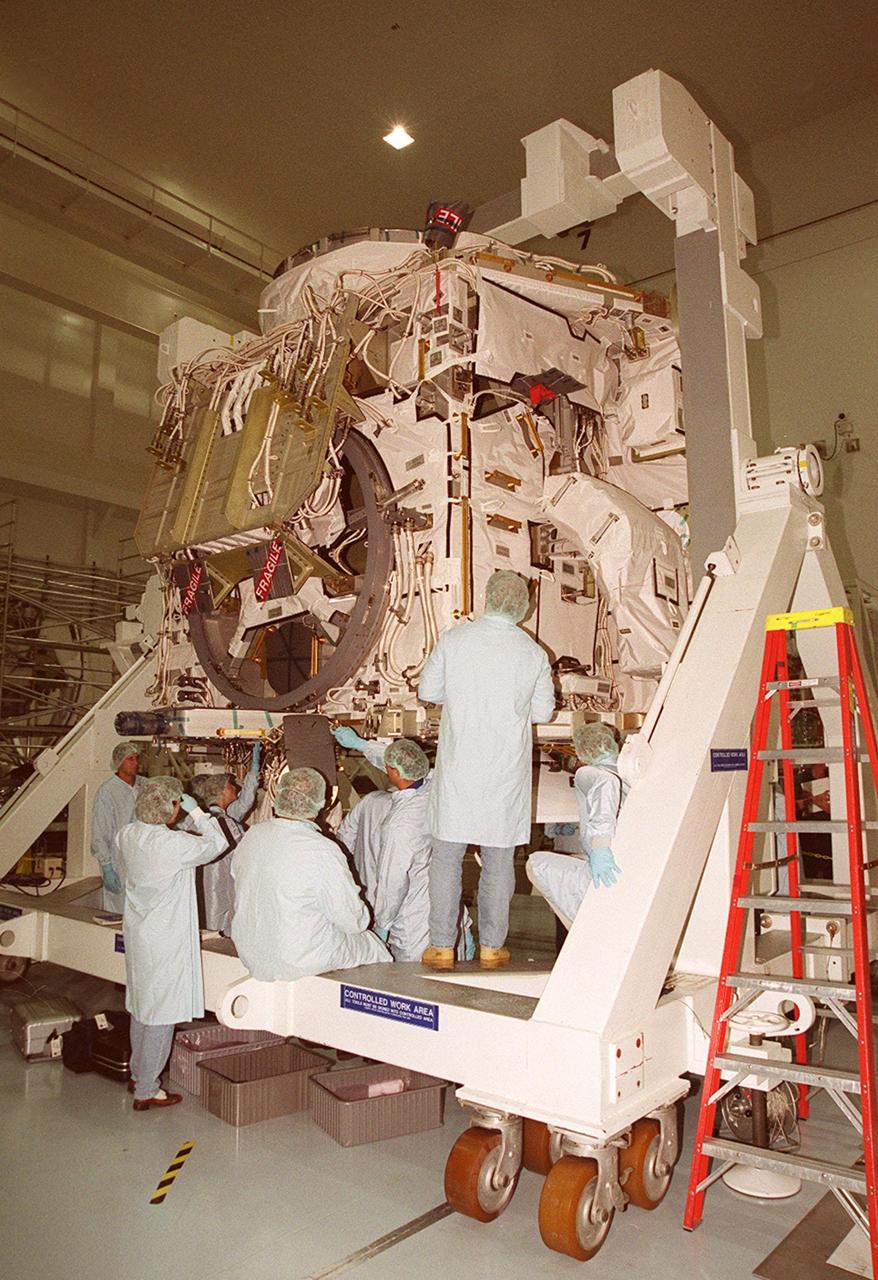
In the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF), Richard Kuhns, NASA Node 2/10A Mission Integration Engineer, International Space Station and Payload Processing, discusses the Node 2 with members of the media. From left are Stefano Masiello, Alenia Spazio; Steve Shannon, Node 2 Mission Manager, The Boeing Co.; and Kuhns. The installation of NASA's Node 2 denotes the U.S. Core Complete stage of International Space Station assembly and, among other functions, will provide a passageway between four Station science experiment facilities: the U.S. Destiny Laboratory, the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module, the European Columbus Laboratory and the Centrifuge Accommodation Module. Reporters were invited to commemorate the fifth anniversary of the launch of the first element of the Station with a tour of the SSPF and had the opportunity to see Space Station hardware that is being processed for deployment once the Space Shuttles return to flight. NASA and Boeing mission managers were on hand to talk about the various hardware elements currently being processed for flight.
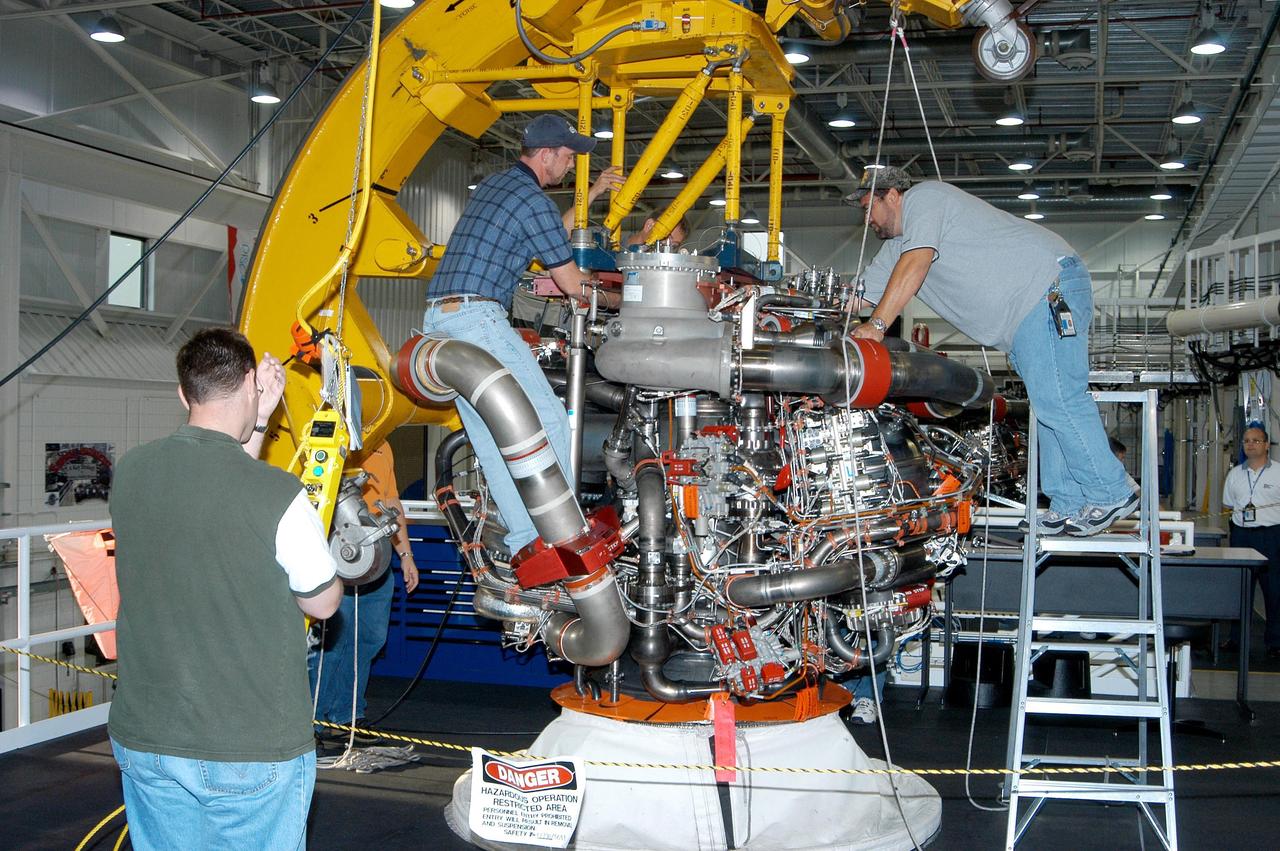

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Processing Facility, Boeing-Rocketdyne technicians prepare to move SSME 2058, the first SSME fully assembled at KSC. Move conductor Bob Brackett (on ladder) and technicians secure a sling around the engine under the direction of crane operator Joe Ferrante (left). The engine will be lifted from its vertical work stand into a horizontal position in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi to undergo a hot fire acceptance test. It is the first of five engines to be fully assembled on site to reach the desired number of 15 engines ready for launch at any given time in the Space Shuttle program. A Space Shuttle has three reusable main engines. Each is 14 feet long, weighs about 7,800 pounds, is seven-and-a-half feet in diameter at the end of its nozzle, and generates almost 400,000 pounds of thrust. Historically, SSMEs were assembled in Canoga Park, Calif., with post-flight inspections performed at KSC. Both functions were consolidated in February 2002. The Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. manufactures the engines for NASA.
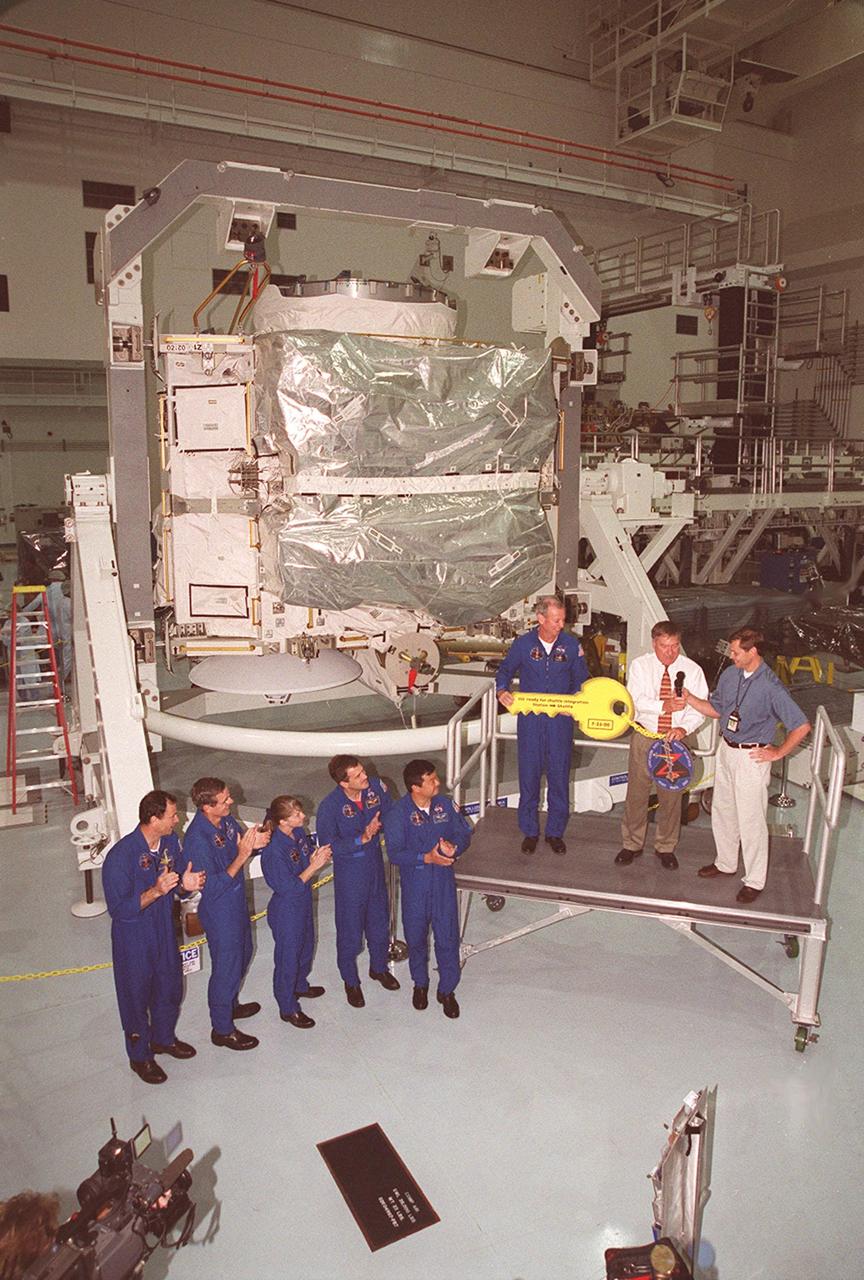
The Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss is officially presented to NASA by The Boeing Co. on the Space Station Processing Facility floor on July 31. Astronauts from the STS-92 crew look on while their commander, Col. Brian Duffy, and Tip Talone, NASA director of International Space Station and Payload Processing at KSC, receive a symbolic key from John Elbon, Boeing director of ISS ground operations. The Z-1 Truss is the cornerstone truss of the International Space Station and is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998
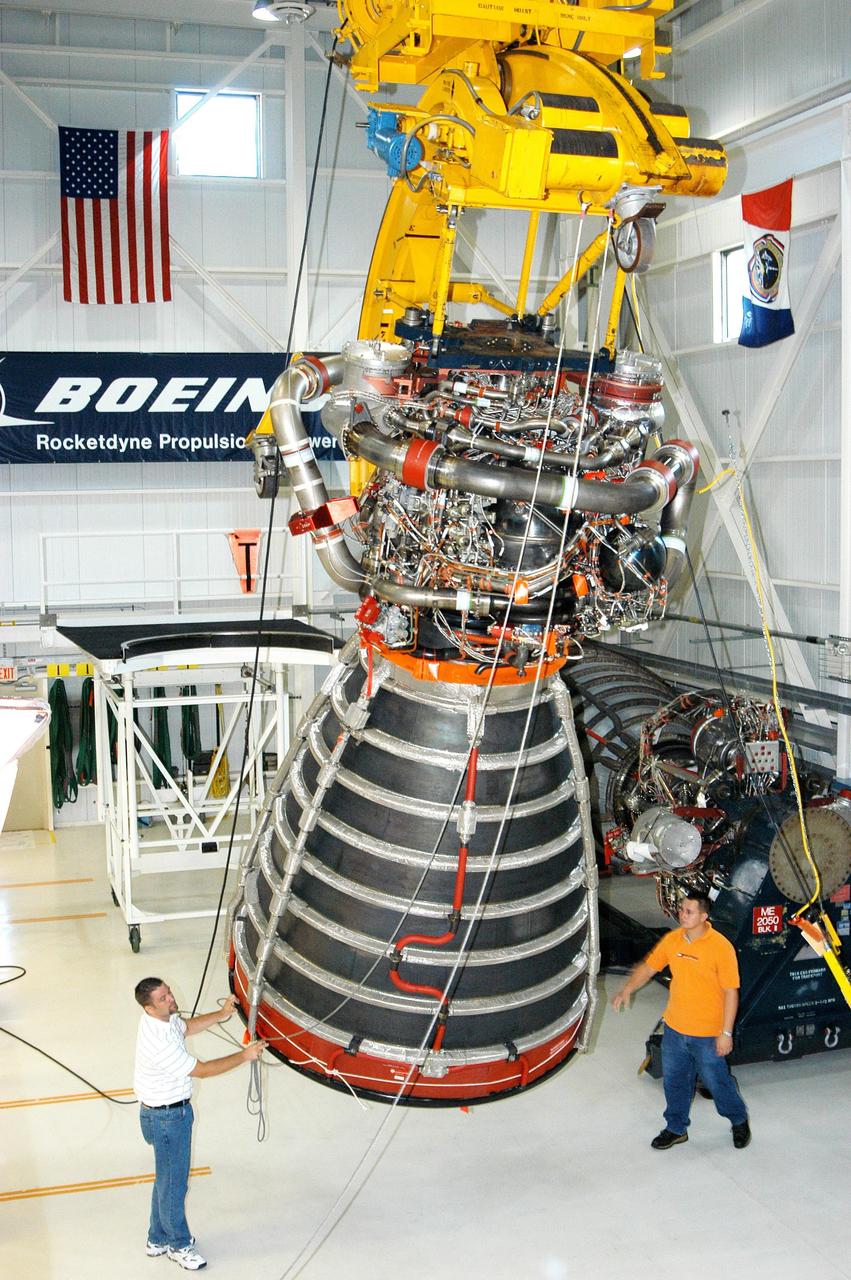

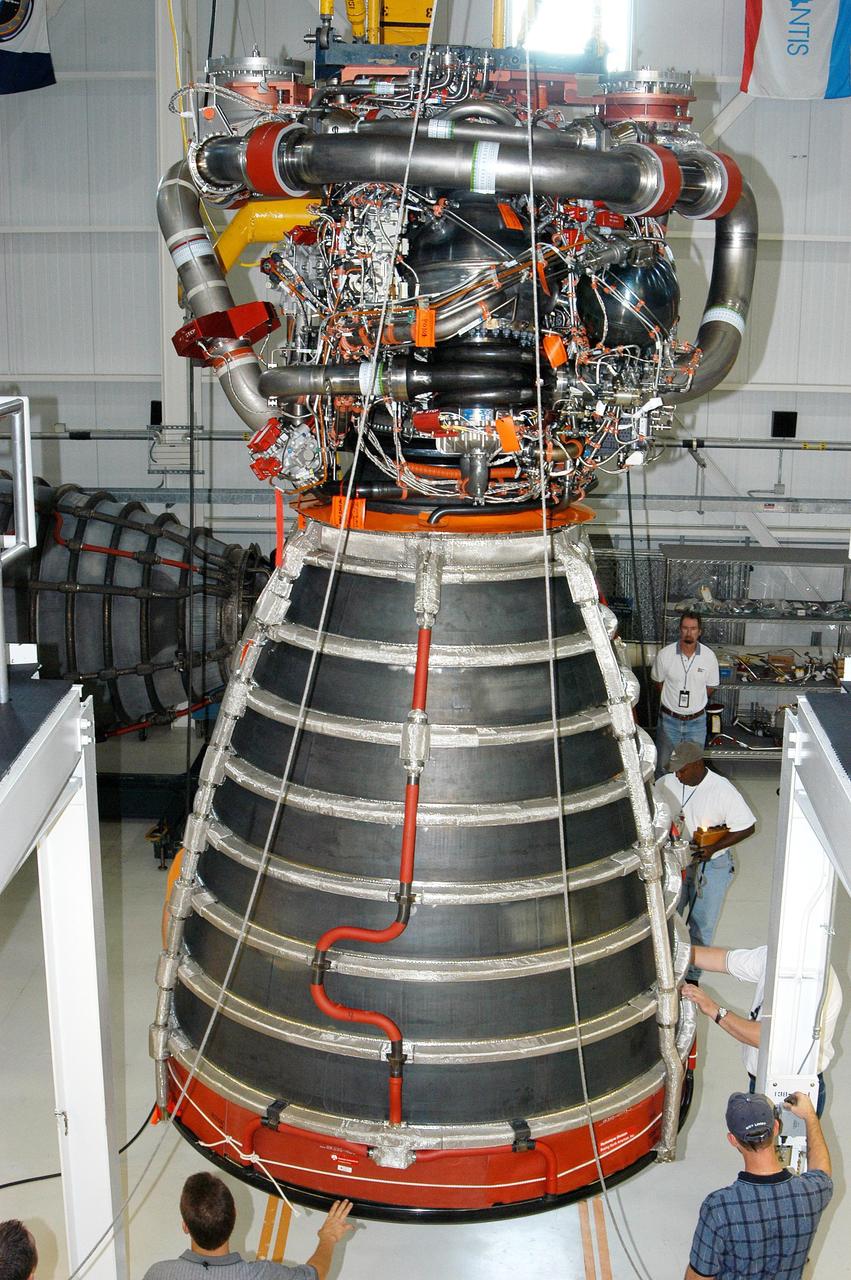
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Processing Facility, Boeing-Rocketdyne technicians steady SSME 2058, the first SSME fully assembled at KSC. The engine is being lifted from its vertical work stand into a horizontal position in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi to undergo a hot fire acceptance test. It is the first of five engines to be fully assembled on site to reach the desired number of 15 engines ready for launch at any given time in the Space Shuttle program. A Space Shuttle has three reusable main engines. Each is 14 feet long, weighs about 7,800 pounds, is seven-and-a-half feet in diameter at the end of its nozzle, and generates almost 400,000 pounds of thrust. Historically, SSMEs were assembled in Canoga Park, Calif., with post-flight inspections performed at KSC. Both functions were consolidated in February 2002. The Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. manufactures the engines for NASA.
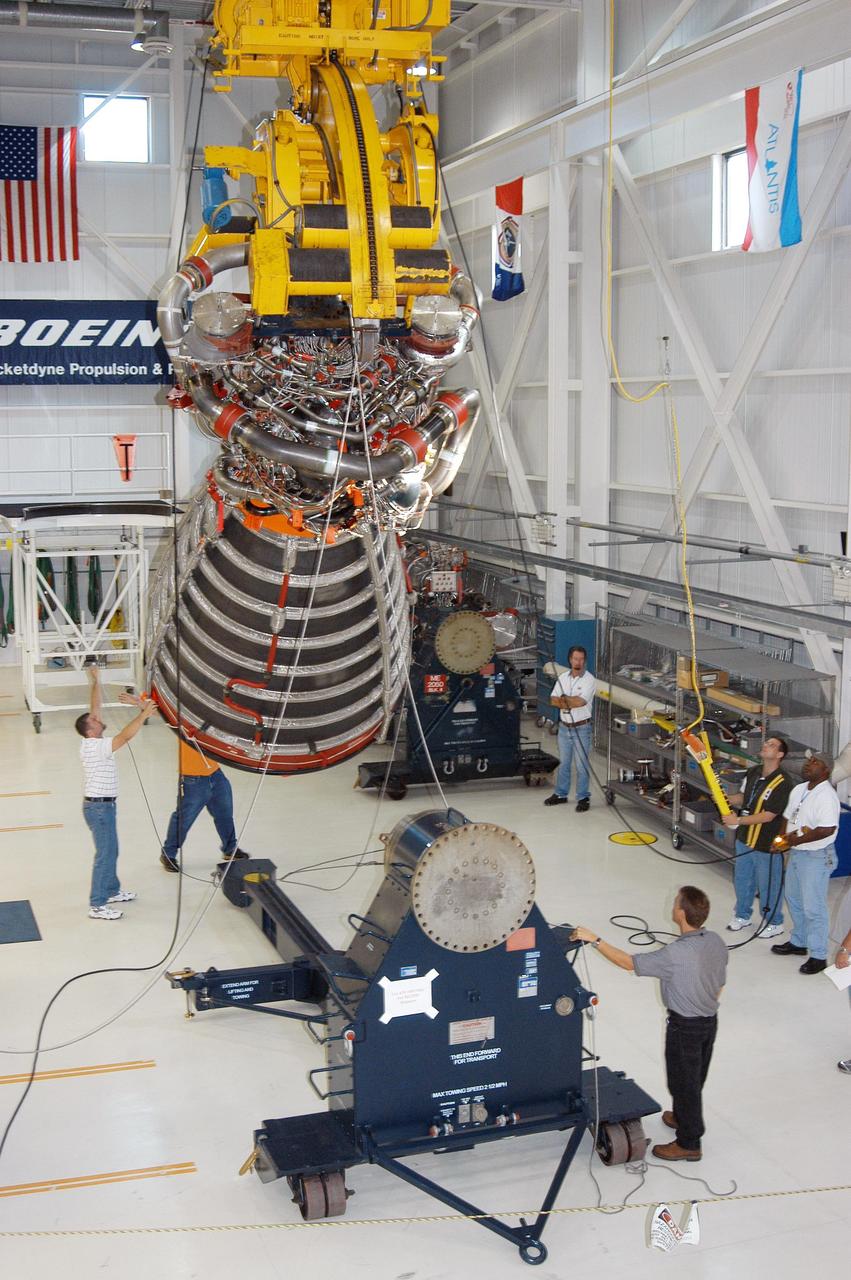

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Processing Facility, Boeing-Rocketdyne crane operator Joe Ferrante (second from right) lifts SSME 2058, the first SSME fully assembled at KSC, with the assistance of other technicians on his team. The engine is being lifted from its vertical work stand into a horizontal position in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi to undergo a hot fire acceptance test. It is the first of five engines to be fully assembled on site to reach the desired number of 15 engines ready for launch at any given time in the Space Shuttle program. A Space Shuttle has three reusable main engines. Each is 14 feet long, weighs about 7,800 pounds, is seven-and-a-half feet in diameter at the end of its nozzle, and generates almost 400,000 pounds of thrust. Historically, SSMEs were assembled in Canoga Park, Calif., with post-flight inspections performed at KSC. Both functions were consolidated in February 2002. The Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. manufactures the engines for NASA.
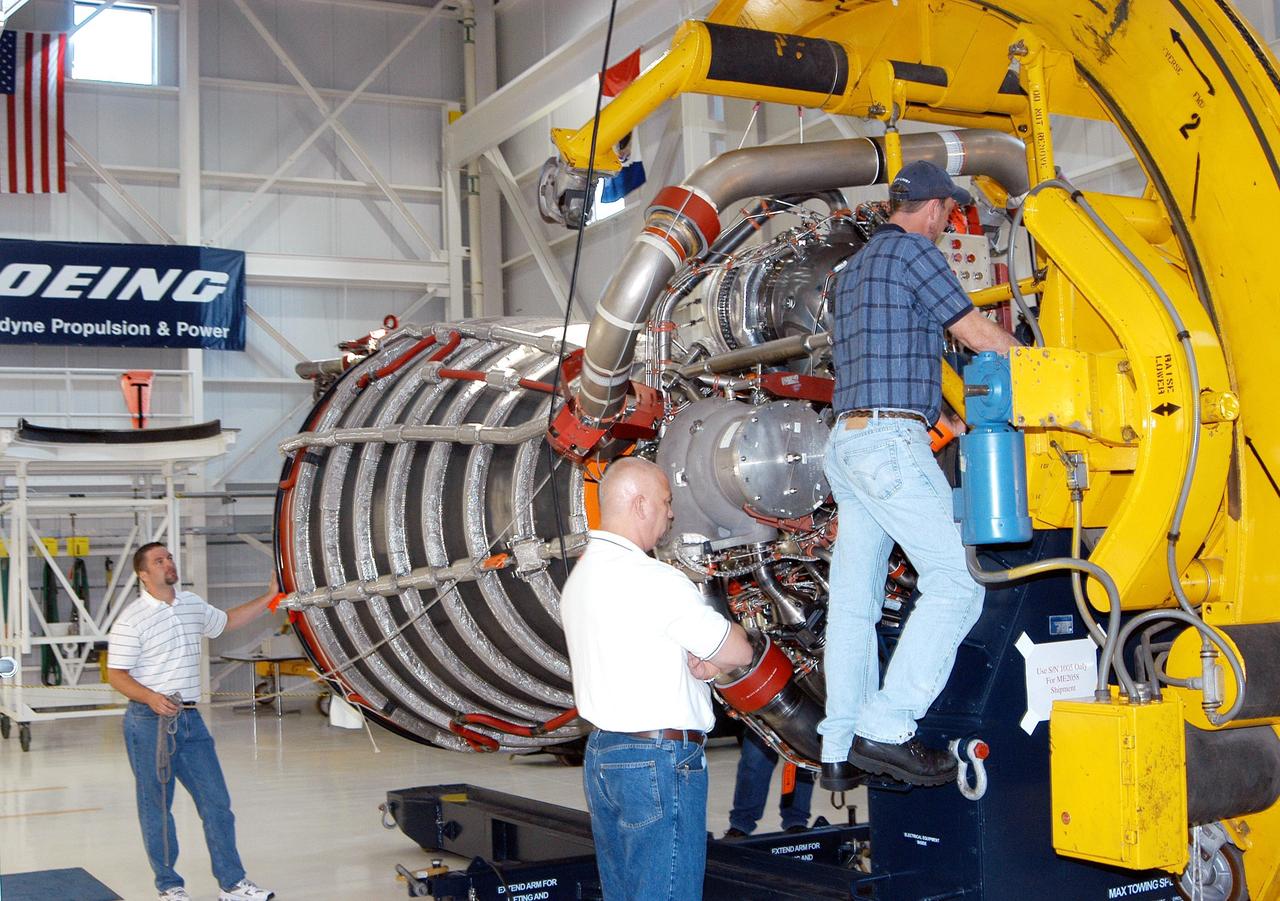

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Processing Facility, Boeing-Rocketdyne quality inspector Nick Grimm (center) monitors the work of technicians on his team as they lower SSME 2058, the first SSME fully assembled at KSC, onto an engine stand. The engine is being placed into a horizontal position in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi to undergo a hot fire acceptance test. It is the first of five engines to be fully assembled on site to reach the desired number of 15 engines ready for launch at any given time in the Space Shuttle program. A Space Shuttle has three reusable main engines. Each is 14 feet long, weighs about 7,800 pounds, is seven-and-a-half feet in diameter at the end of its nozzle, and generates almost 400,000 pounds of thrust. Historically, SSMEs were assembled in Canoga Park, Calif., with post-flight inspections performed at KSC. Both functions were consolidated in February 2002. The Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. manufactures the engines for NASA.
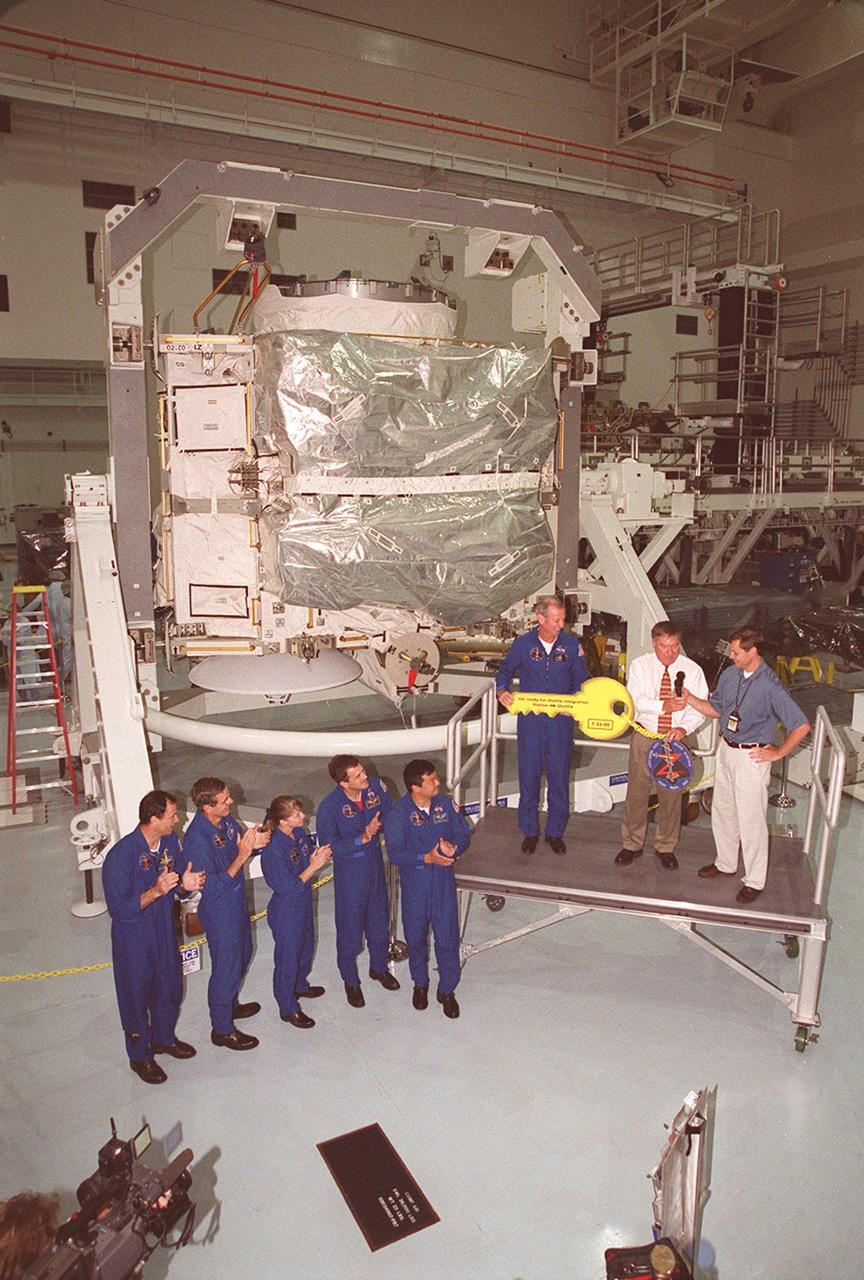
The Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss is officially presented to NASA by The Boeing Co. on the Space Station Processing Facility floor on July 31. Astronauts from the STS-92 crew look on while their commander, Col. Brian Duffy, and Tip Talone, NASA director of International Space Station and Payload Processing at KSC, receive a symbolic key from John Elbon, Boeing director of ISS ground operations. The Z-1 Truss is the cornerstone truss of the International Space Station and is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998
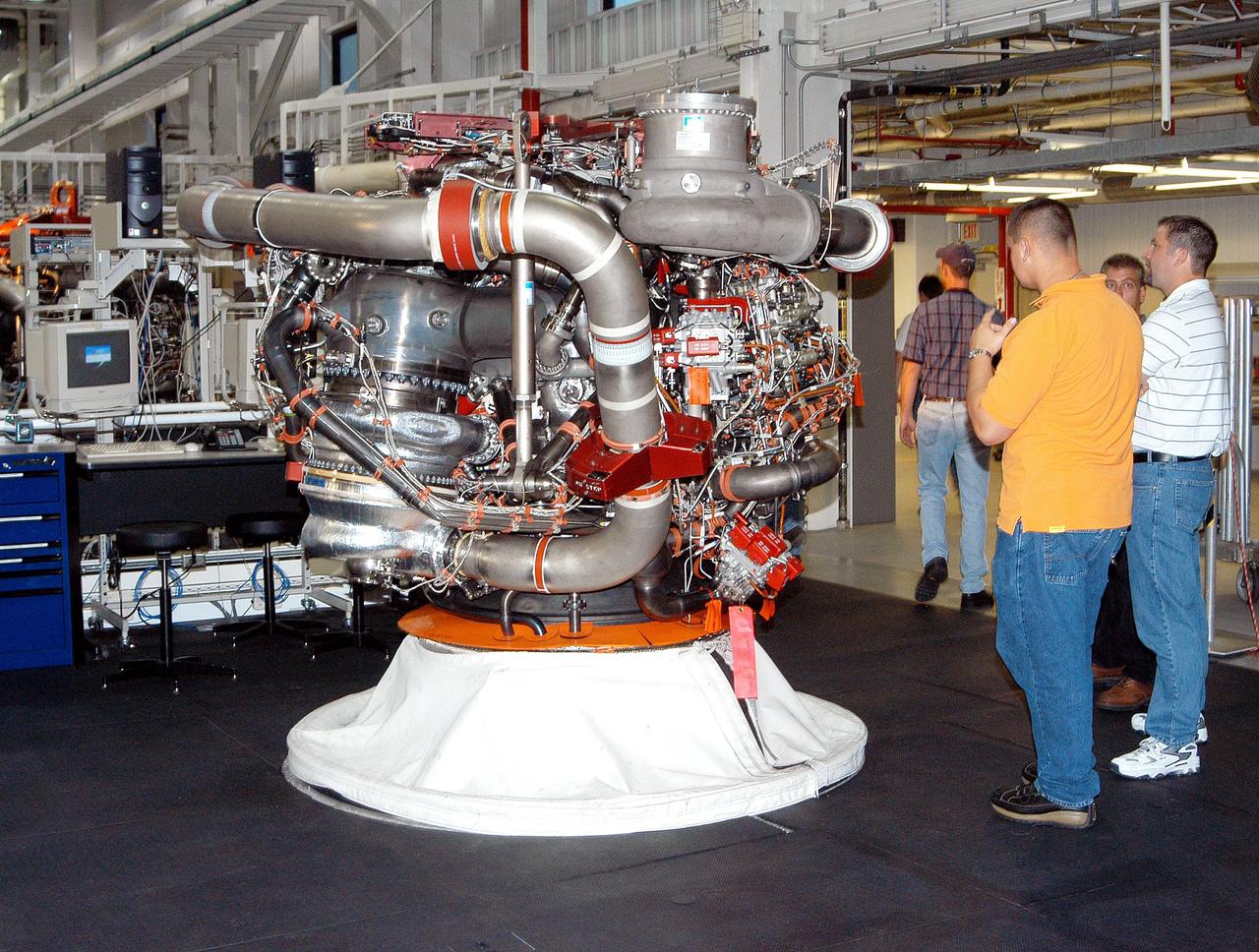

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Processing Facility, Boeing-Rocketdyne technicians prepare to move SSME 2058, the first SSME fully assembled at KSC. The engine will be lifted from its vertical work stand into a horizontal position in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi to undergo a hot fire acceptance test. It is the first of five engines to be fully assembled on site to reach the desired number of 15 engines ready for launch at any given time in the Space Shuttle program. A Space Shuttle has three reusable main engines. Each is 14 feet long, weighs about 7,800 pounds, is seven-and-a-half feet in diameter at the end of its nozzle, and generates almost 400,000 pounds of thrust. Historically, SSMEs were assembled in Canoga Park, Calif., with post-flight inspections performed at KSC. Both functions were consolidated in February 2002. The Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. manufactures the engines for NASA.
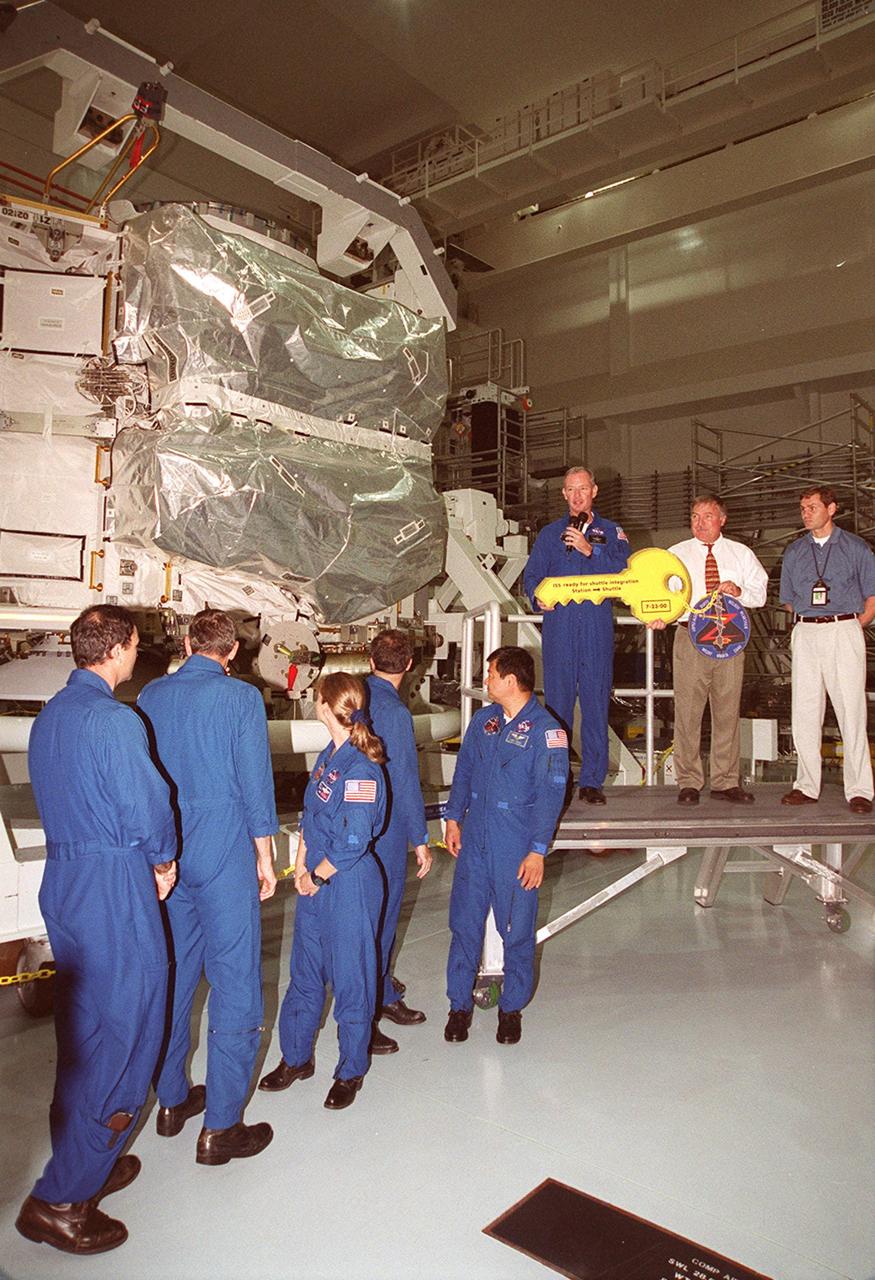
The Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss is officially presented to NASA by The Boeing Co. on the Space Station Processing Facility floor on July 31. STS-92 Commander Col. Brian Duffy, comments on the presentation. At his side is Tip Talone, NASA director of International Space Station and Payload Processing at KSC. Talone and Col. Duffy received a symbolic key for the truss from John Elbon, Boeing director of ISS ground operations. The Z-1 Truss is the cornerstone truss of the International Space Station and is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998
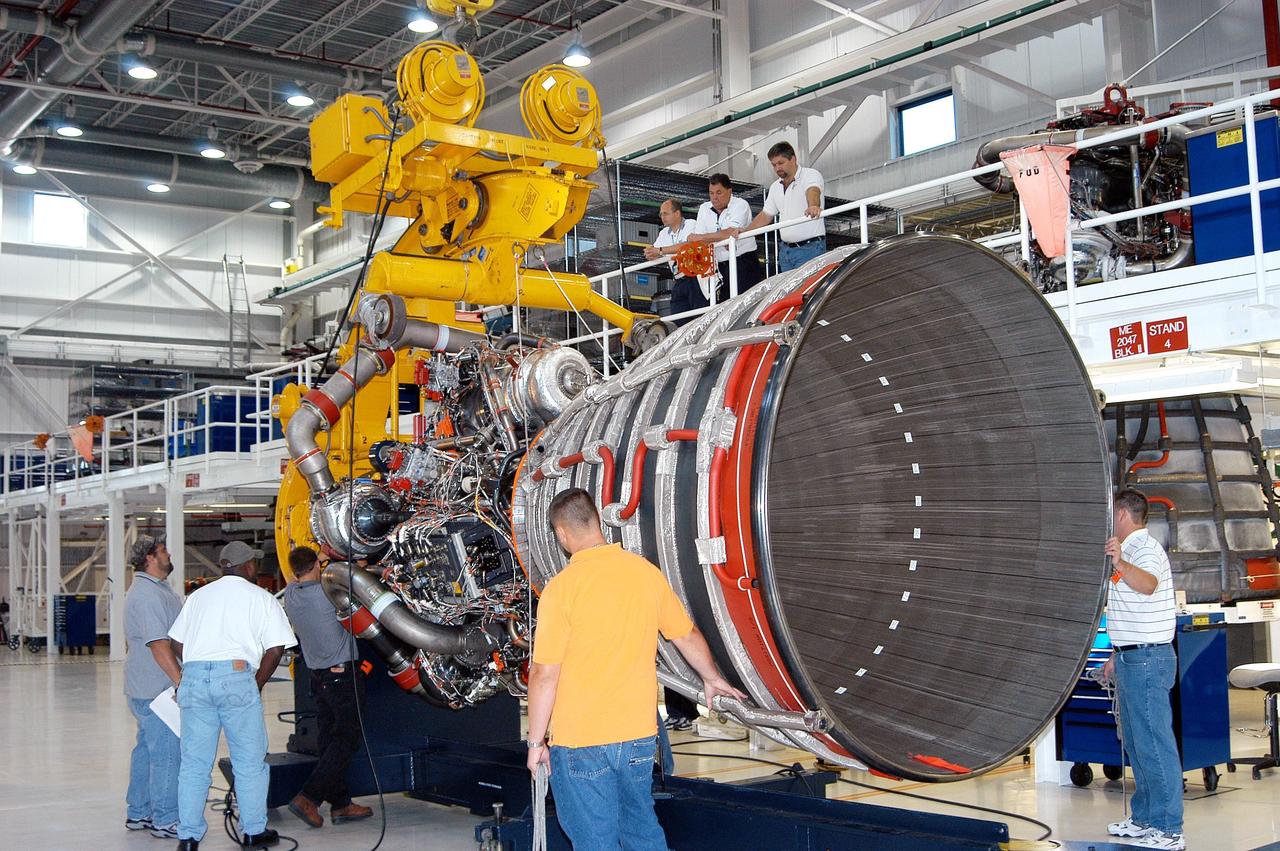

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Processing Facility, Boeing-Rocketdyne move conductor Bob Brackett (left) oversees the work of technicians on his team as they secure SSME 2058, the first SSME fully assembled at KSC, onto an engine stand. The engine is being placed into a horizontal position in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi to undergo a hot fire acceptance test. It is the first of five engines to be fully assembled on site to reach the desired number of 15 engines ready for launch at any given time in the Space Shuttle program. A Space Shuttle has three reusable main engines. Each is 14 feet long, weighs about 7,800 pounds, is seven-and-a-half feet in diameter at the end of its nozzle, and generates almost 400,000 pounds of thrust. Historically, SSMEs were assembled in Canoga Park, Calif., with post-flight inspections performed at KSC. Both functions were consolidated in February 2002. The Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. manufactures the engines for NASA.
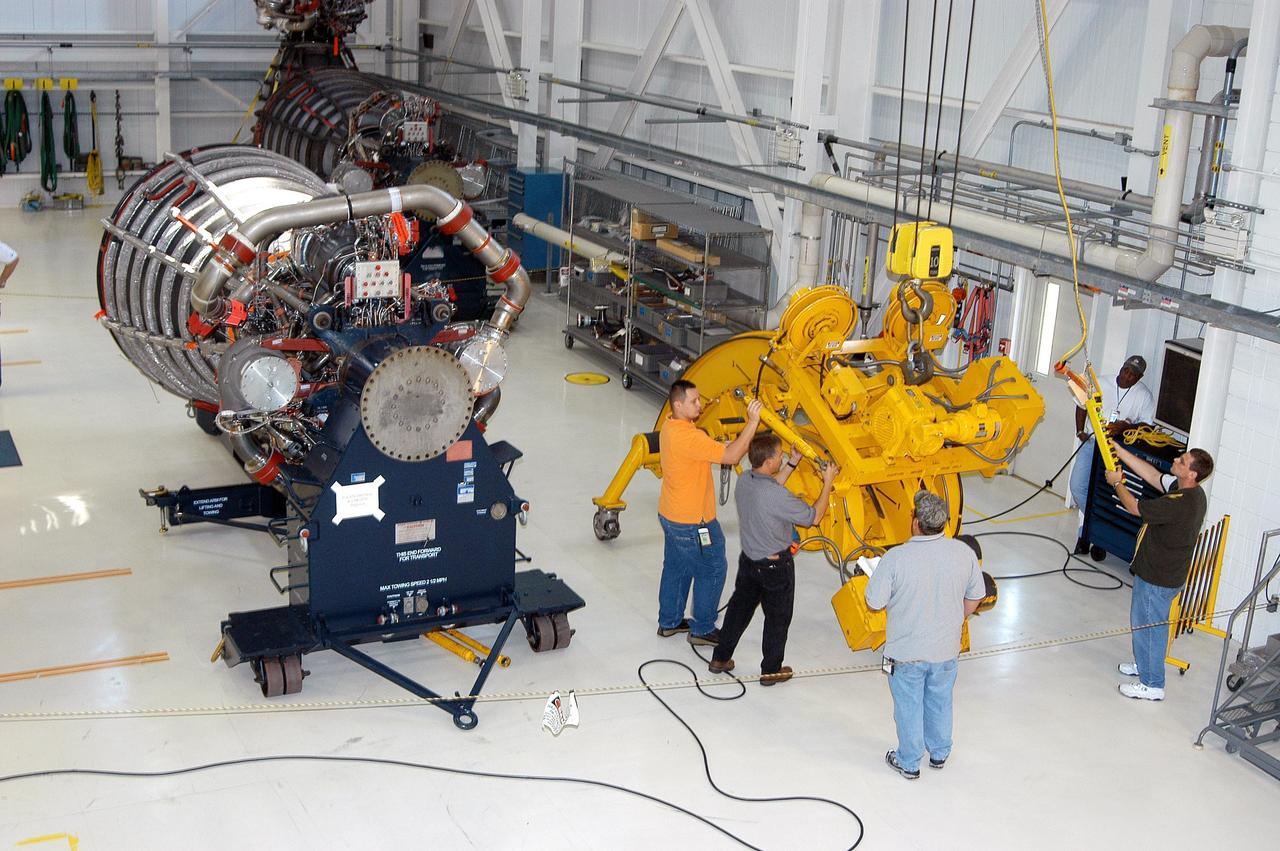

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Processing Facility, Boeing-Rocketdyne move conductor Bob Brackett (center) oversees the work of technicians on his team as they remove the crane used to lift SSME 2058, the first SSME fully assembled at KSC, from its vertical work stand. The engine has been placed into a horizontal position in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi to undergo a hot fire acceptance test. It is the first of five engines to be fully assembled on site to reach the desired number of 15 engines ready for launch at any given time in the Space Shuttle program. A Space Shuttle has three reusable main engines. Each is 14 feet long, weighs about 7,800 pounds, is seven-and-a-half feet in diameter at the end of its nozzle, and generates almost 400,000 pounds of thrust. Historically, SSMEs were assembled in Canoga Park, Calif., with post-flight inspections performed at KSC. Both functions were consolidated in February 2002. The Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. manufactures the engines for NASA.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The manager of NASA's Commercial Crew Program CCP, Ed Mango, hosts a virtual conversation, called a Tweet Chat, with Twitter followers from around the world. Those who follow www.twitter.com/commercial_crew had an hour-long opportunity to ask Mango questions about NASA’s efforts to get astronauts to low Earth orbit and the International Space Station aboard American rockets and spacecraft. Mango stuck to the social networking service's 140 character limit and answered dozens of questions. At left, is Brittani Sims, a member of the CCP team. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Seven aerospace companies are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under the program’s second round of development, called Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2), including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, The Boeing Co., Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada, Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Gianni Woods
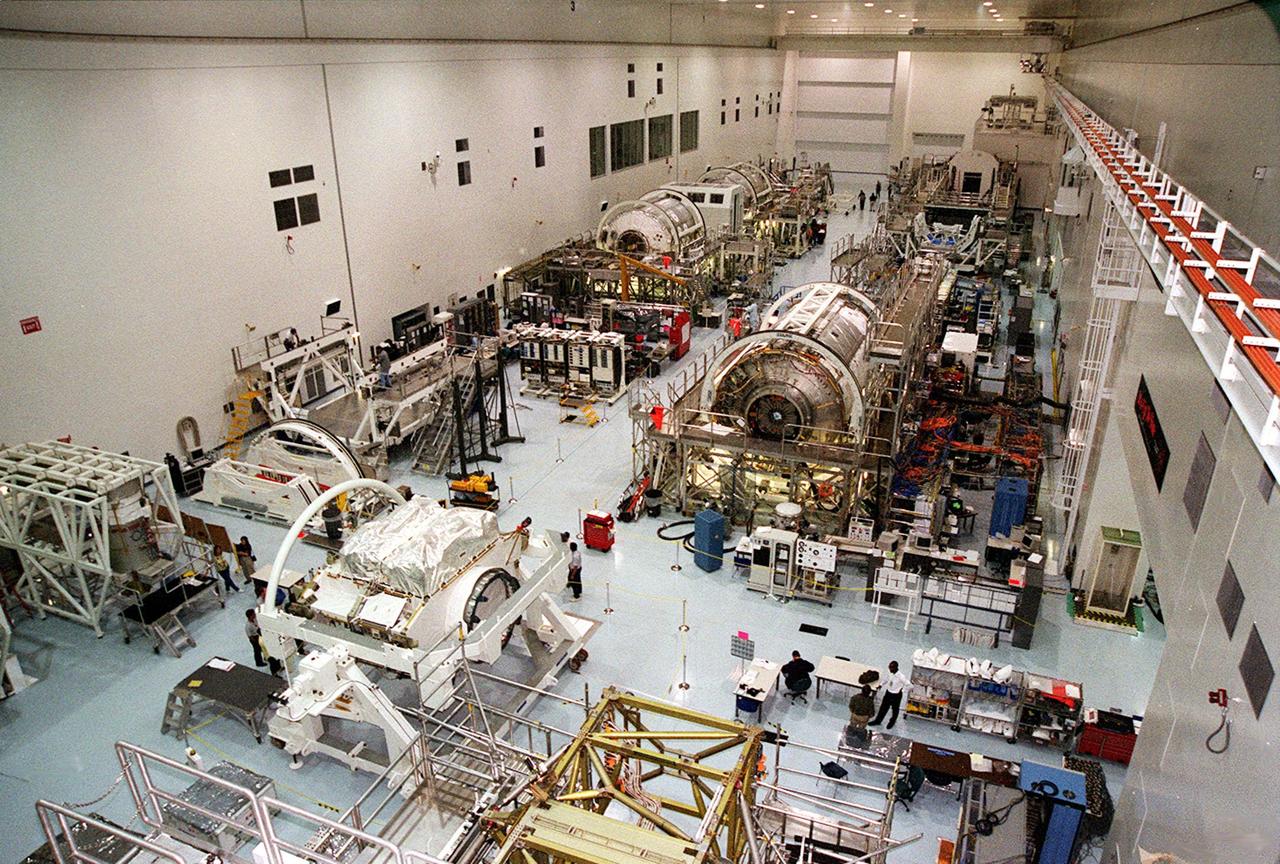
A wide-angle view of the floor of the Space Station Processing Facility. The floor is filled with racks and hardware for processing and testing the various components of the International Space Station (ISS). At the bottom left is the Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss, the cornerstone truss of the Space Station. The Z-1 Truss was officially turned over to NASA from The Boeing Co. on July 31. The truss is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998. The large module in the center of the floor is the U.S. Lab, Destiny. Expected to be a major feature in future research, Destiny will provide facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research. It is scheduled to be launched on mission STS-98 (no date determined yet for launch)
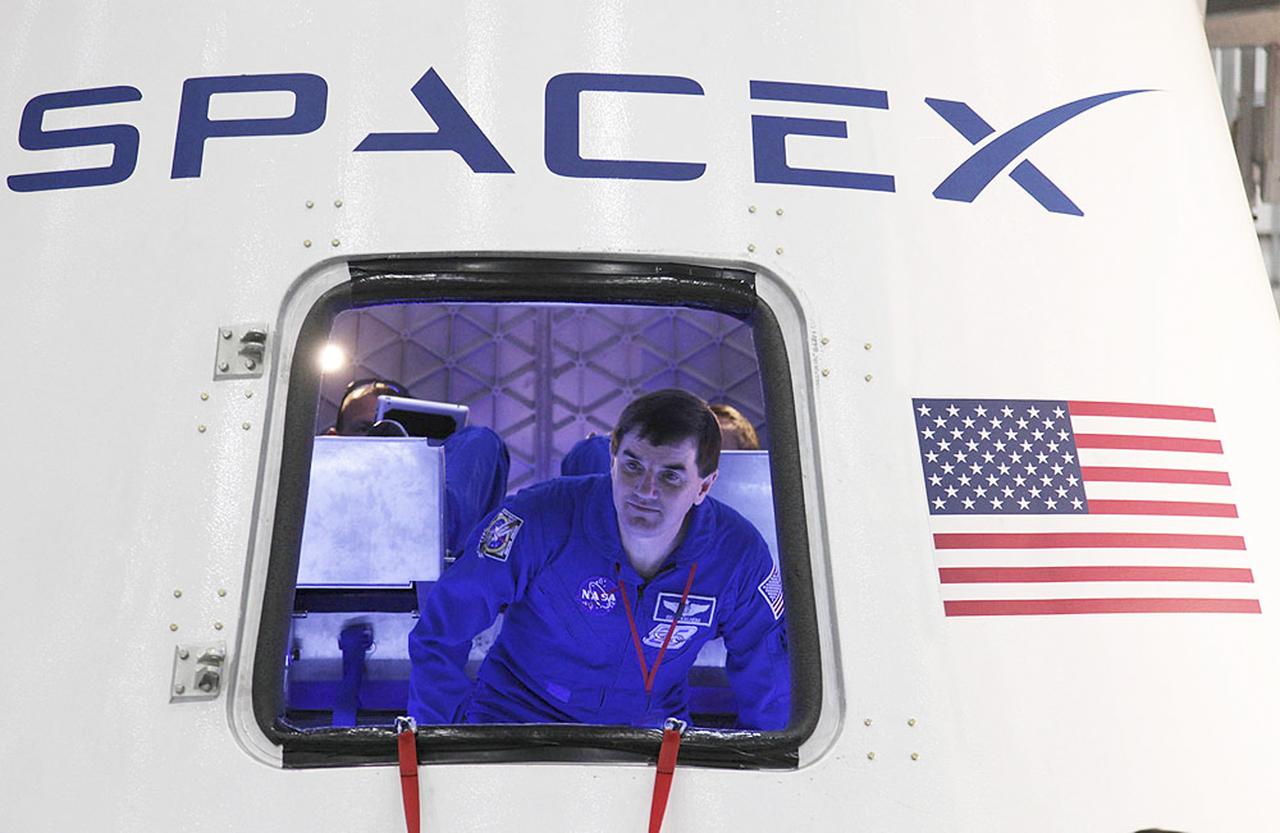

HAWTHORNE, Calif. -- NASA astronaut Rex Walheim checks out the Dragon spacecraft under development by Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX of Hawthorne, Calif., for the agency's Commercial Crew Program. In 2011, NASA selected SpaceX during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, The Boeing Co., Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Space Exploration Technologies
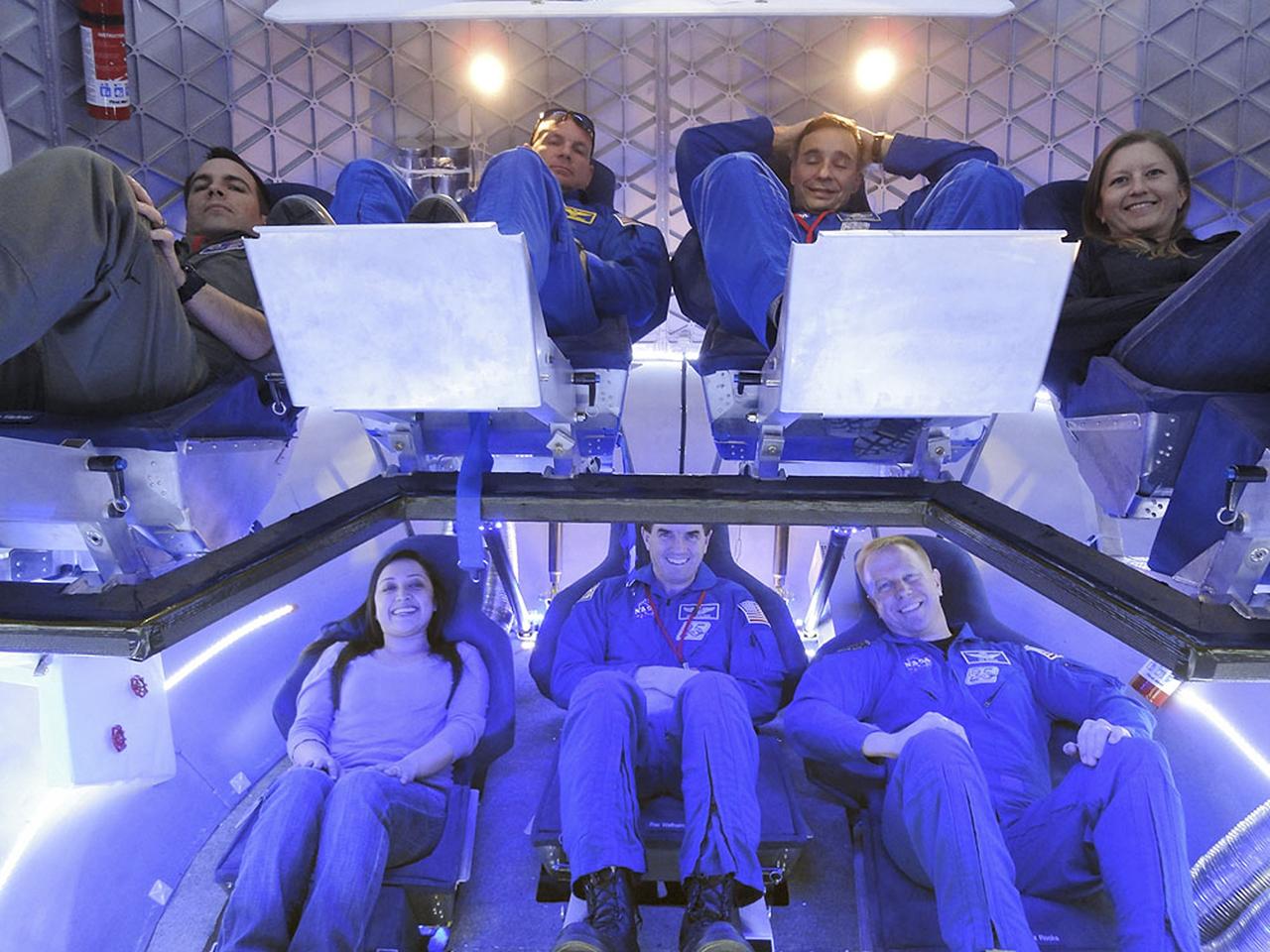

HAWTHORNE, Calif. -- NASA astronauts and industry experts check out the crew accommodations in the Dragon spacecraft under development by Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX of Hawthorne, Calif., for the agency's Commercial Crew Program. On top, from left, are NASA Crew Survival Engineering Team Lead Dustin Gohmert, NASA astronauts Tony Antonelli and Lee Archambault, and SpaceX Mission Operations Engineer Laura Crabtree. On bottom, from left, are SpaceX Thermal Engineer Brenda Hernandez and NASA astronauts Rex Walheim and Tim Kopra. In 2011, NASA selected SpaceX during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, The Boeing Co., Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Space Exploration Technologies
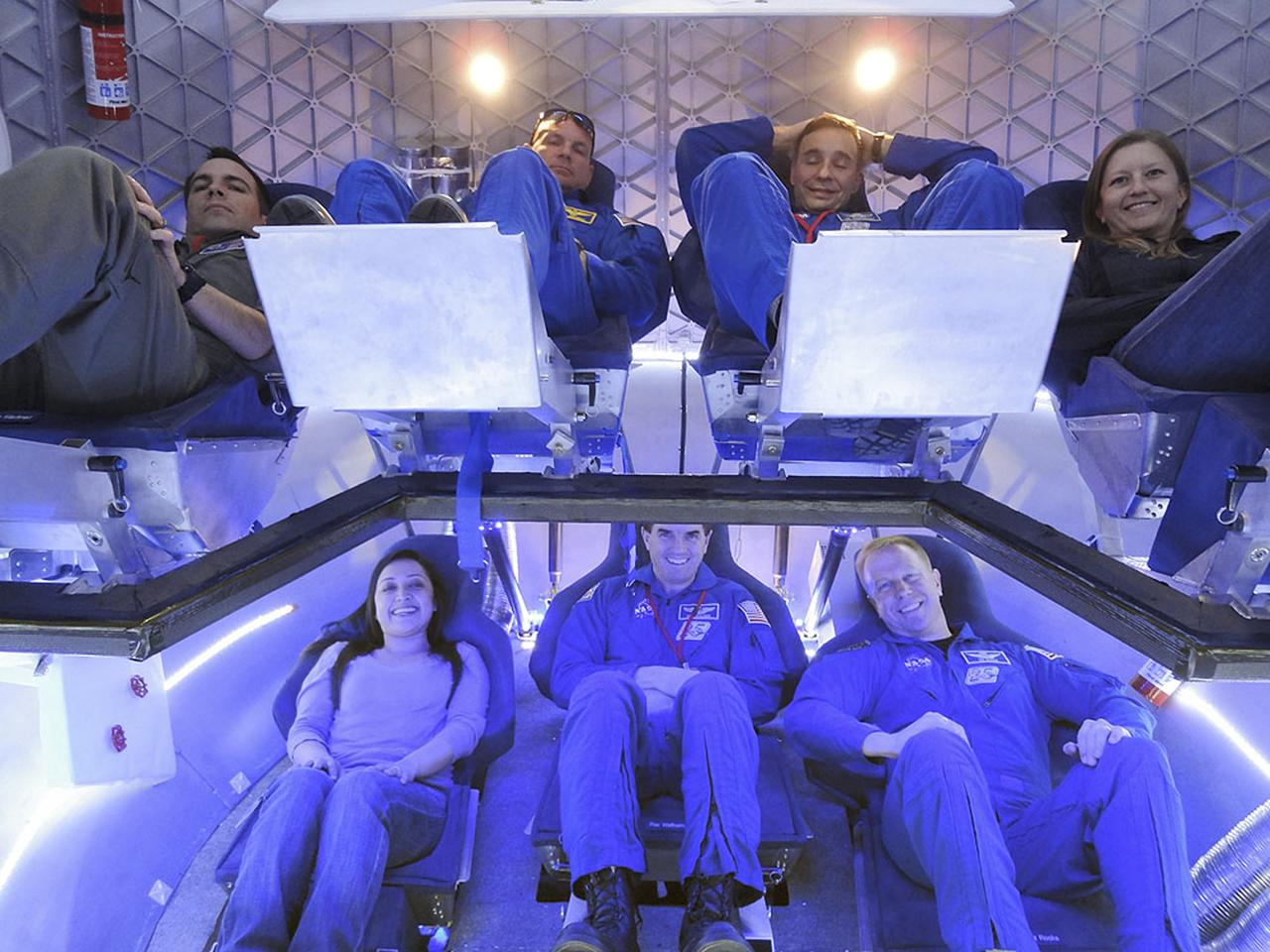

HAWTHORNE, Calif. -- NASA astronauts and industry experts check out the crew accommodations in the Dragon spacecraft under development by Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX of Hawthorne, Calif., for the agency's Commercial Crew Program. On top, from left, are NASA Crew Survival Engineering Team Lead Dustin Gohmert, NASA astronauts Tony Antonelli and Lee Archambault, and SpaceX Mission Operations Engineer Laura Crabtree. On bottom, from left, are SpaceX Thermal Engineer Brenda Hernandez and NASA astronauts Rex Walheim and Tim Kopra. In 2011, NASA selected SpaceX during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, The Boeing Co., Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Space Exploration Technologies

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is an artist's conception of the Human Spacecraft being considered for NASA's Commercial Crew Program CCP. In 2011, NASA and Excalibur Almaz Inc. of Houston entered into an unfunded Space Act Agreement during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, Blue Origin, The Boeing Co., Sierra Nevada Corp., Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/exploration/commercialcrew Image credit: Excalibur Almaz Inc.
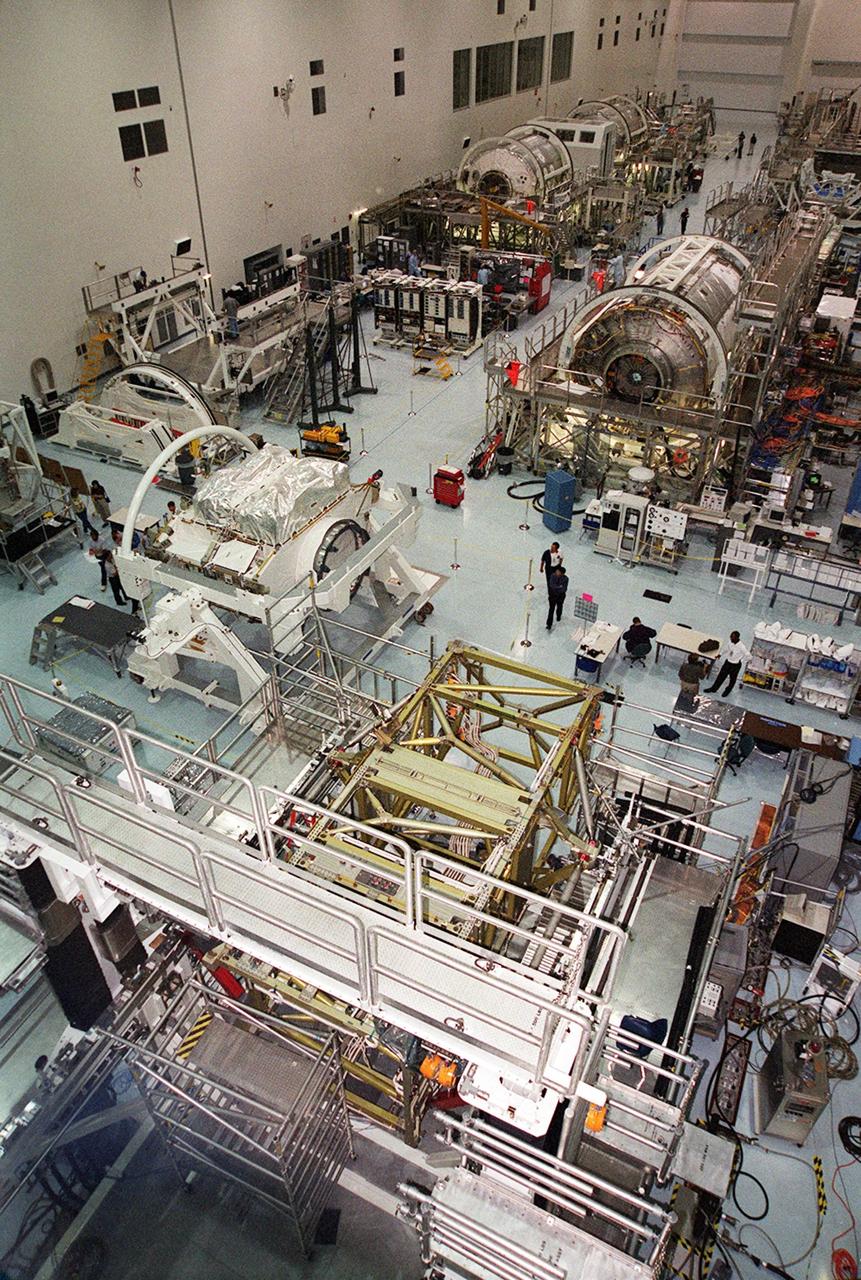
A wide-angle view of the floor of the Space Station Processing Facility. The floor is filled with racks and hardware for processing and testing the various components of the International Space Station (ISS). At center left is the Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss, the cornerstone truss of the Space Station. The Z-1 Truss was officially turned over to NASA from The Boeing Co. on July 31. It is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998. The large module in the upper right hand corner of the floor is the U.S. Lab, Destiny. Expected to be a major feature in future research, Destiny will provide facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research. It is scheduled to be launched on mission STS-98 (no date determined yet for launch)

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- NASA Commercial Crew Program CCP Manager Ed Mango discusses the program's newest partnerships from the Operations Support Building 2 OSB II at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left, are Kennedy Space Center Director Robert Cabana and NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden. Three integrated systems were selected for CCP's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability CCiCap initiative to propel America's next human space transportation system to low Earth orbit forward. Operating under funded Space Act Agreements SAAs, The Boeing Co. of Houston, Sierra Nevada Corp. SNC Space Systems of Louisville, Colo., and Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX of Hawthorne, Calif., will spend the next 21 months completing their designs, conducting critical risk reduction testing on their spacecraft and launch vehicles, and showcasing how they would operate and manage missions from launch through orbit and landing, setting the stage for future demonstration missions. To learn more about CCP, which is based at Kennedy and supported by NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett