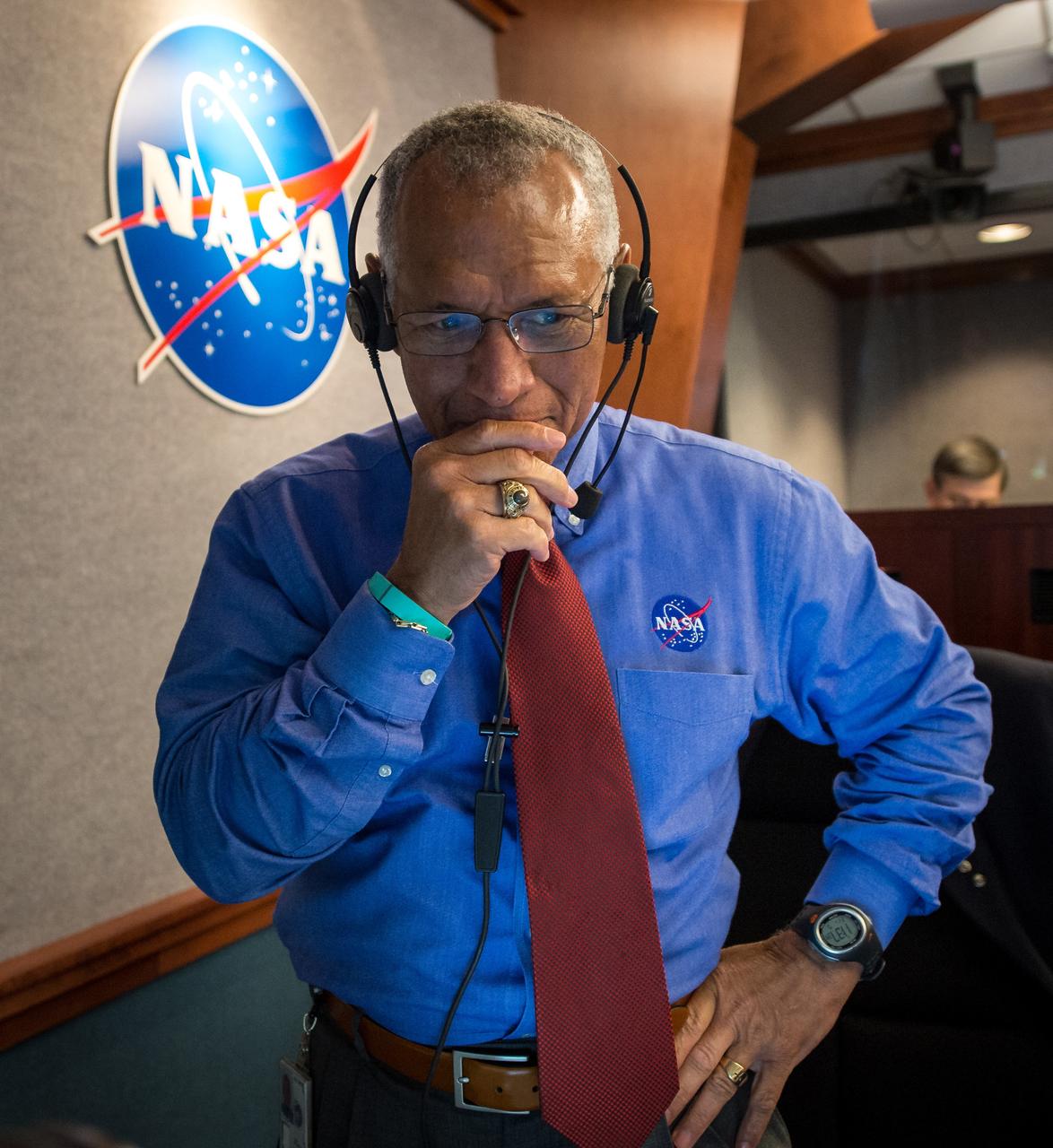

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden pauses for a moment in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station after having watched and celebrated the Orion spacecraft splash down in the Pacific Ocean more than three hours after the spacecraft launched onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 37, Friday, Dec. 5, 2014, Cape Canaveral, Florida. The Orion spacecraft orbited Earth twice, reaching an altitude of approximately 3,600 miles above Earth before landing. No one was aboard Orion for this flight test, but the spacecraft is designed to allow us to journey to destinations never before visited by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

Exterior View of Hangar AE

Interior View of Hangar AE

Interior View of Hangar AE
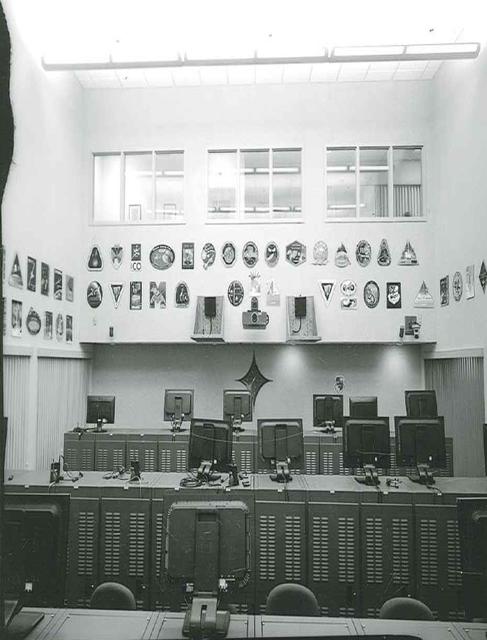

Interior View of Hangar AE
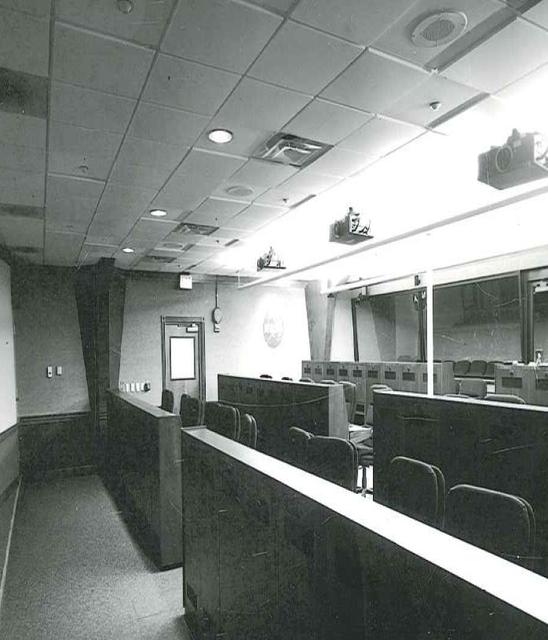

Interior View of Hangar AE
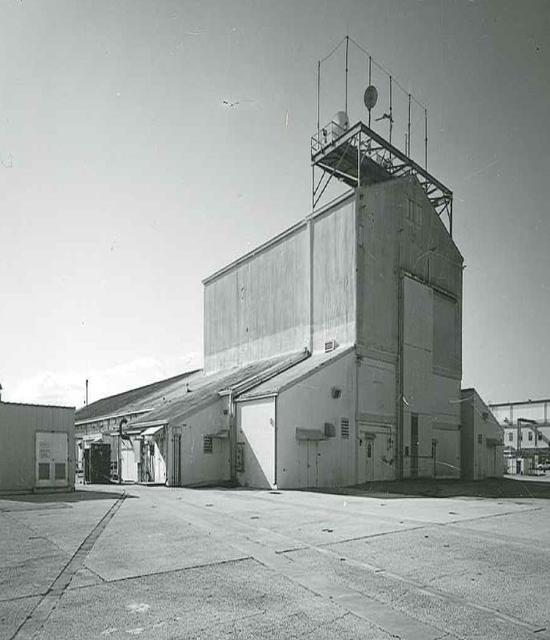

Exterior View of Hangar AE
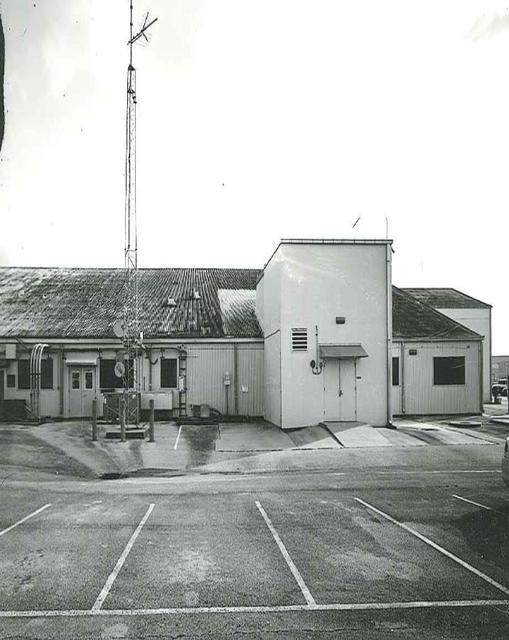

Exterior View of Hangar AE
Hangar AE
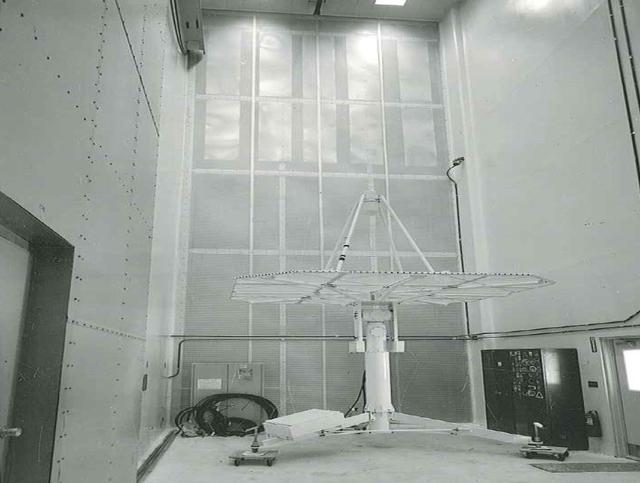

Hangar AE
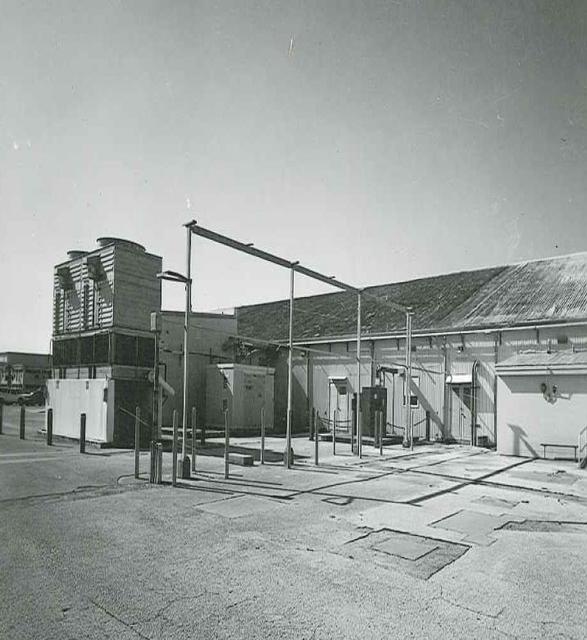

Exterior View of Hangar AE
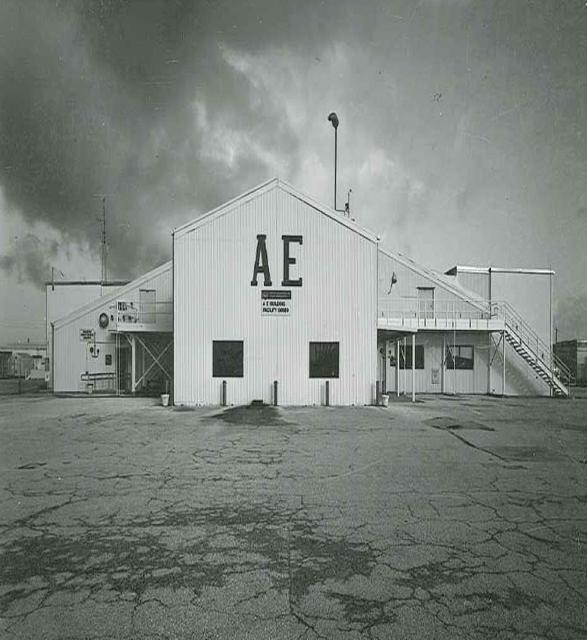

Exterior View of Hangar AE
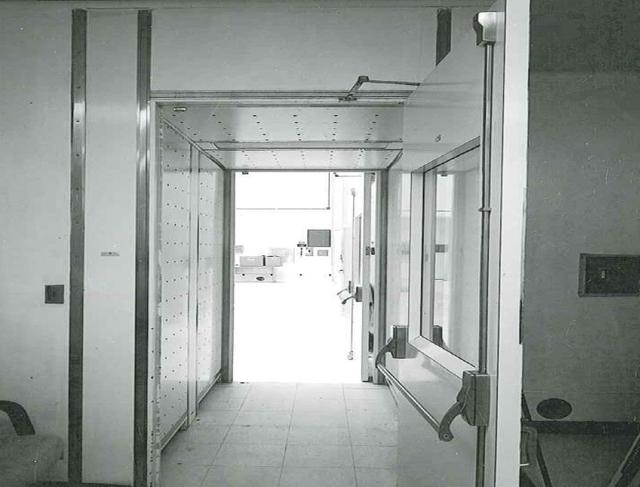

Hangar AE
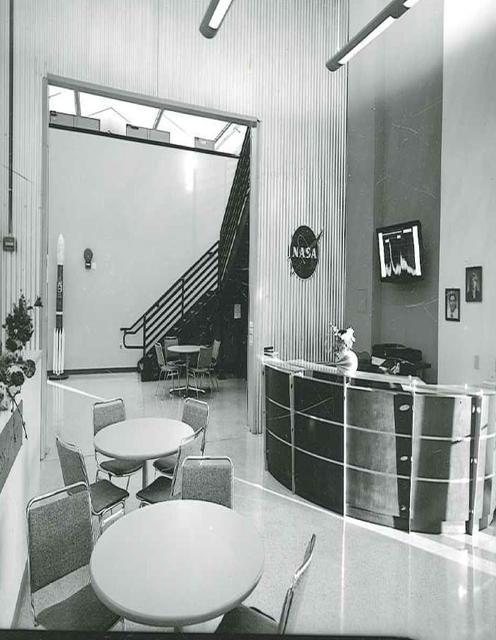

Interior View of Hangar AE

Hangar AE
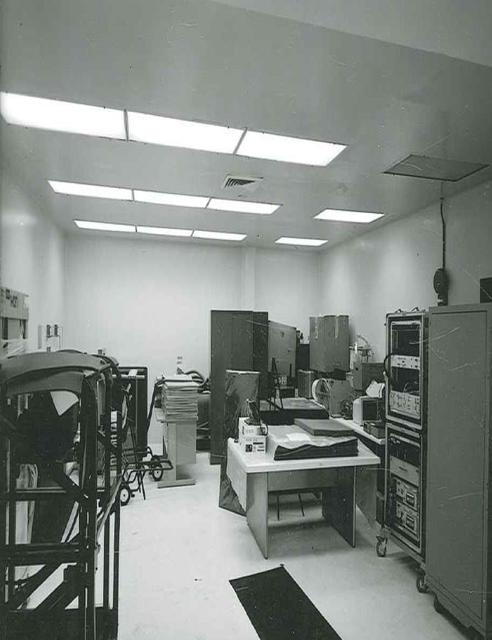

Hangar AE
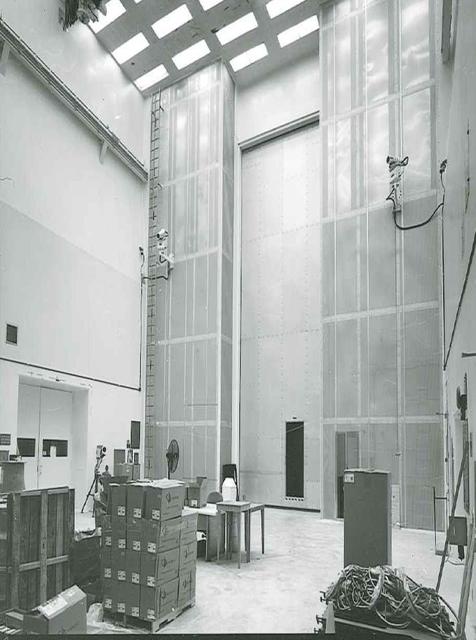

Hangar AE
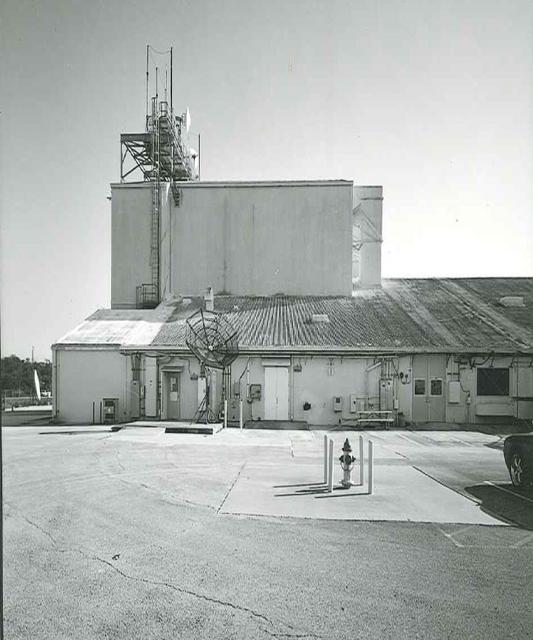

Exterior View of Hangar AE

Hangar AE

Exterior View of Hangar AE

Interior View of Hangar AE

Hangar AE
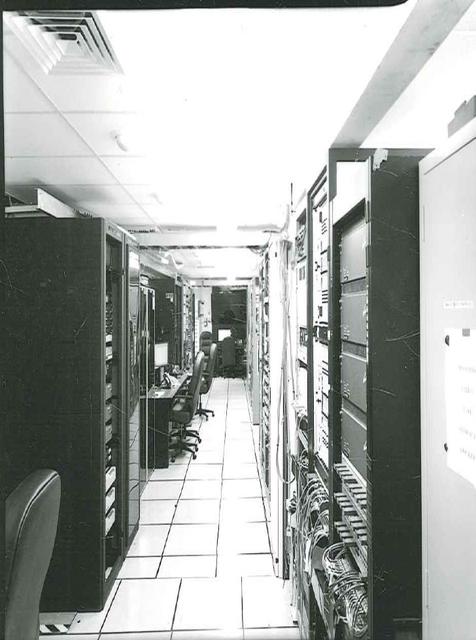

Interior View of Hangar AE
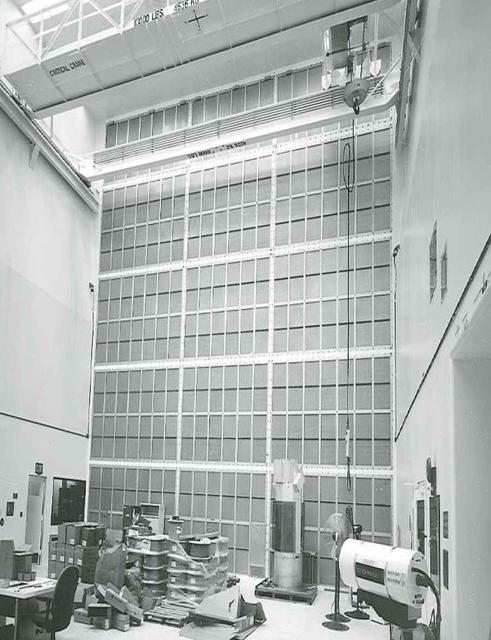

Hangar AE
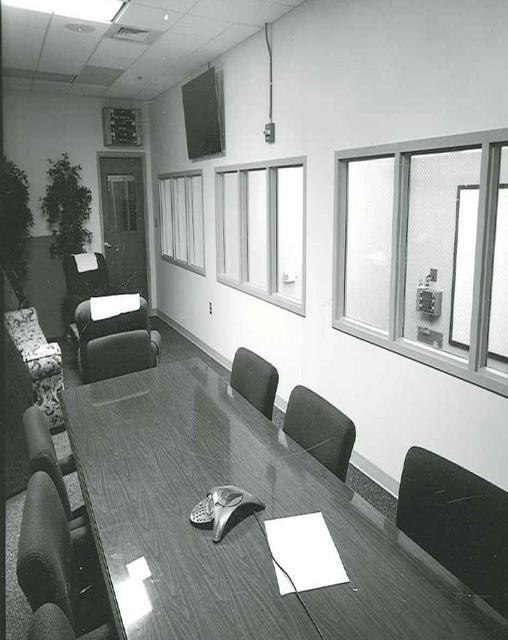

Hangar AE

Interior View of Hangar AE
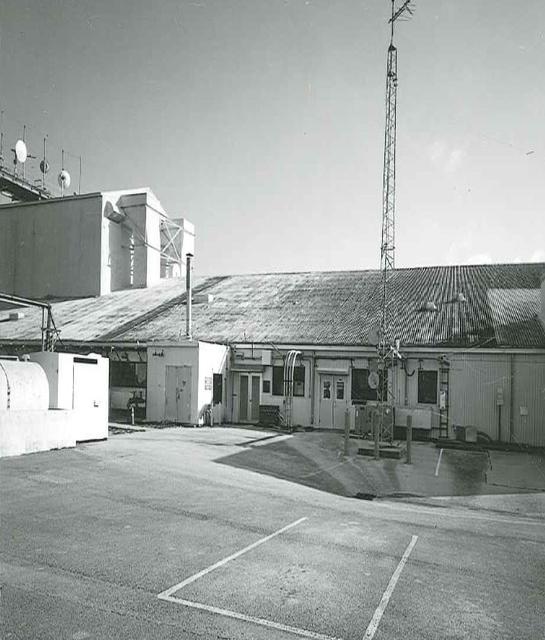

Exterior View of Hangar AE
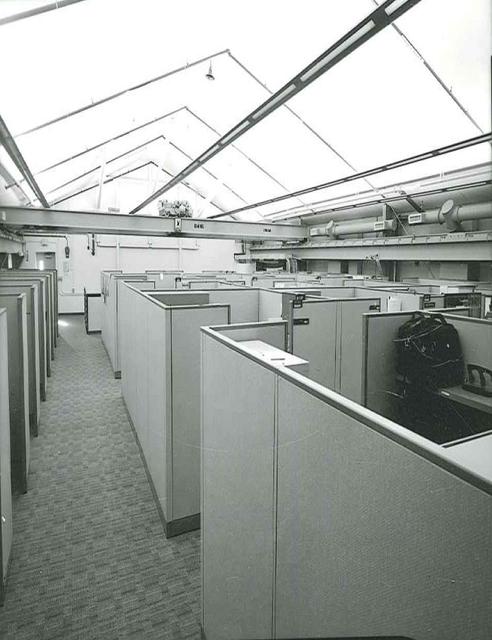

Hangar AE
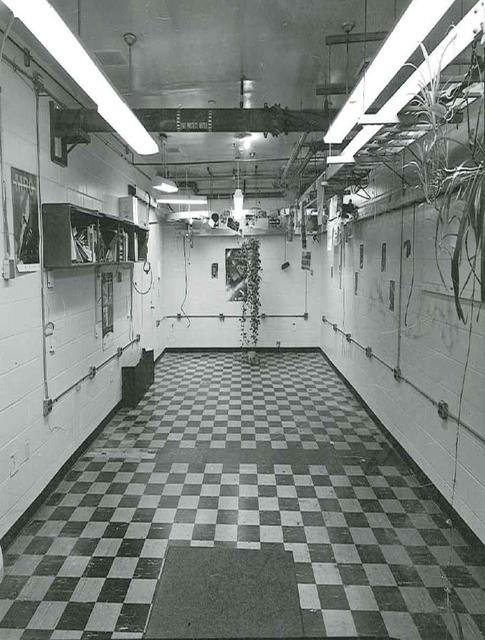

Interior View of Hangar AE
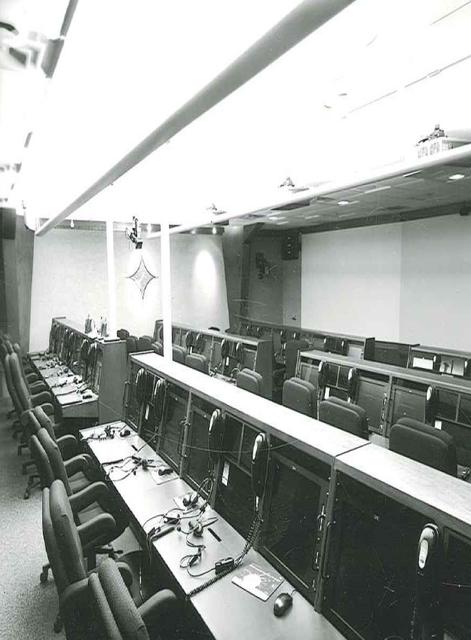

Interior View of Hangar AE
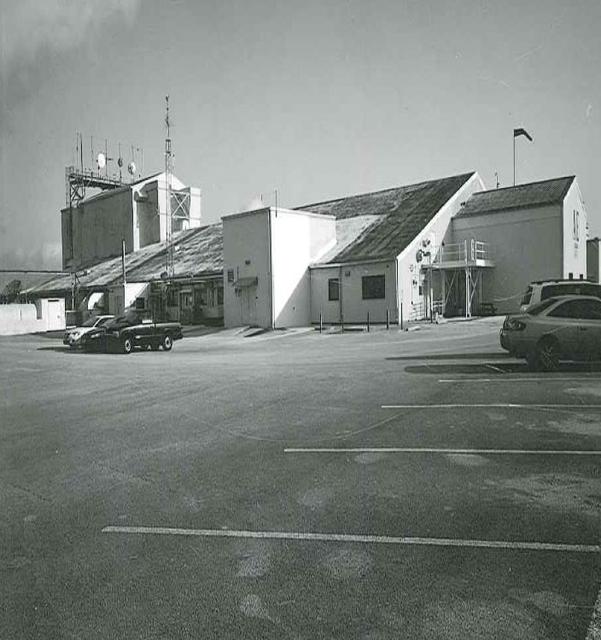

Exterior View of Hangar AE
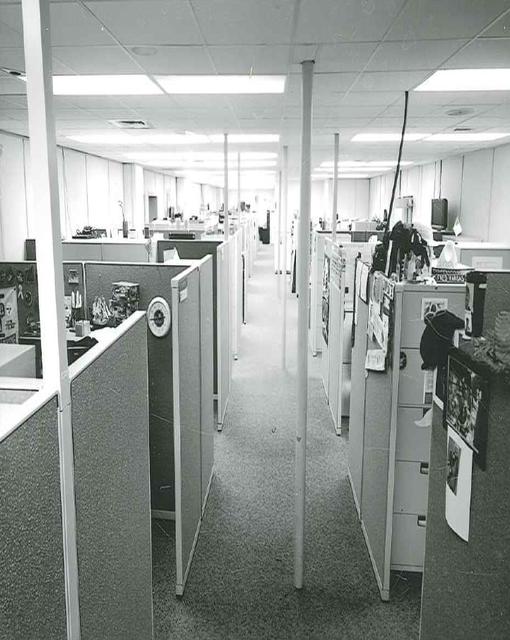

Interior View of Hangar AE
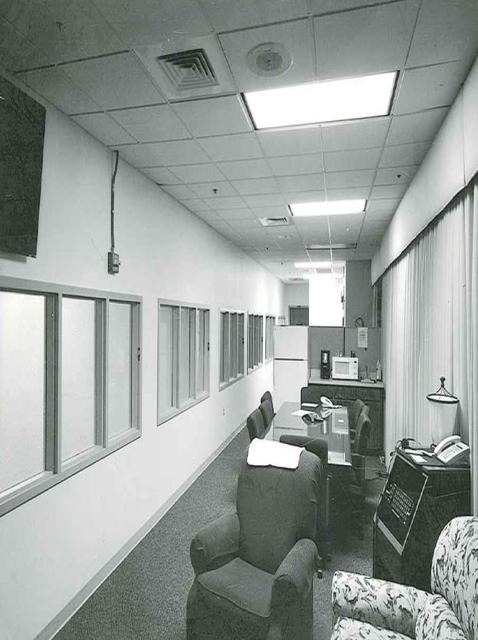

Hangar AE
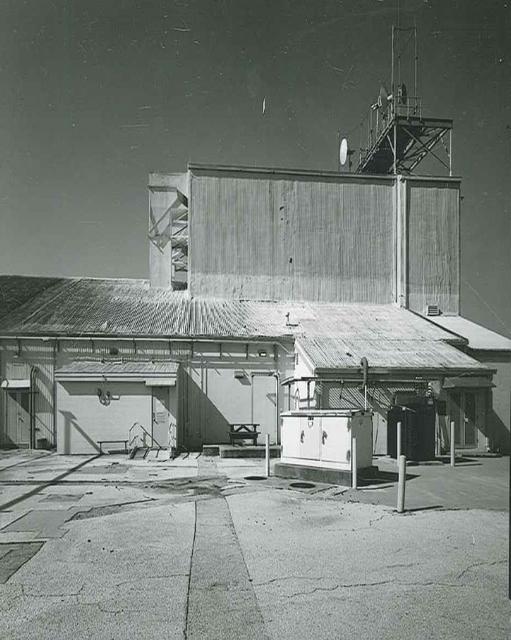

Exterior View of Hangar AE
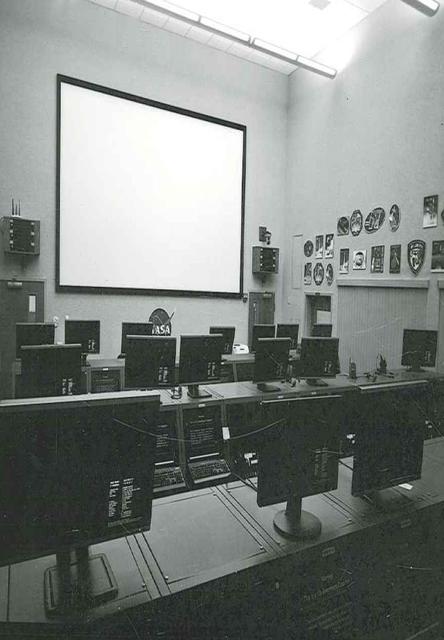

Interior View of Hangar AE
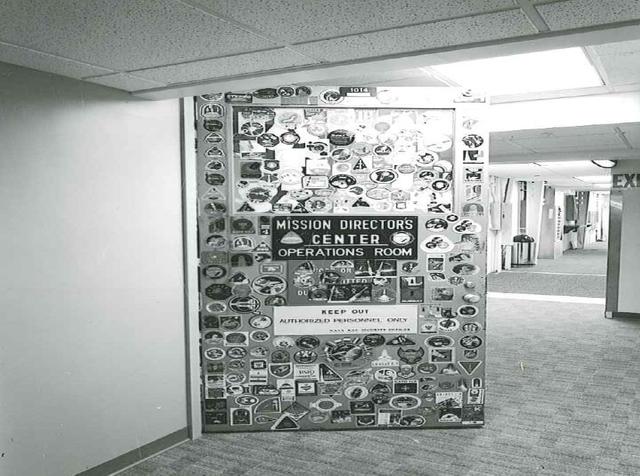

Interior View of Hangar AE

Hangar AE
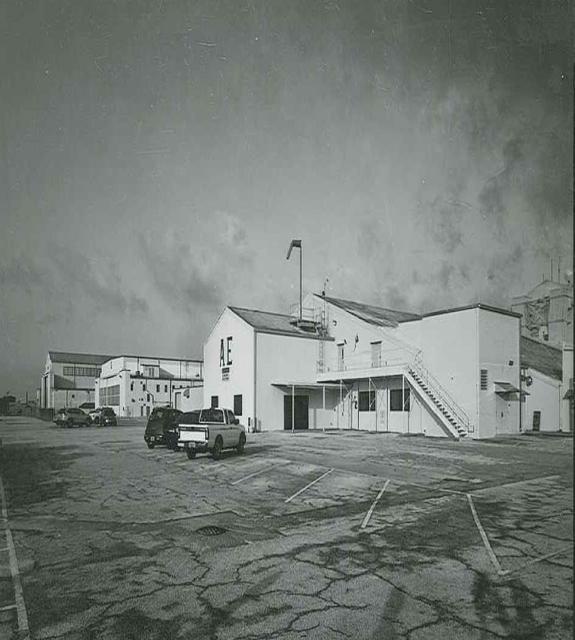

Exterior View of Hangar AE
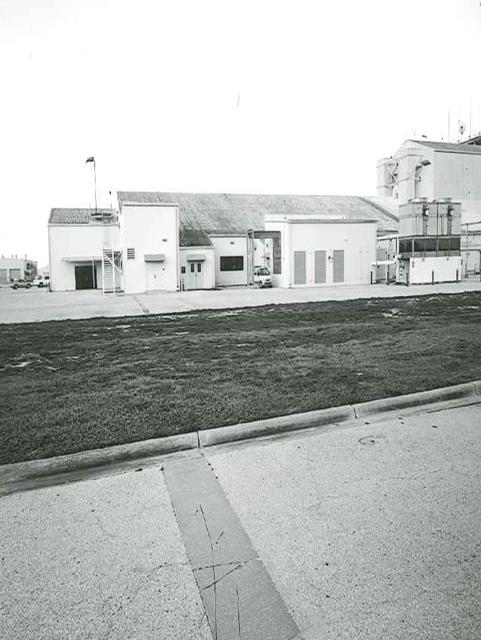

Exterior View of Hangar AE
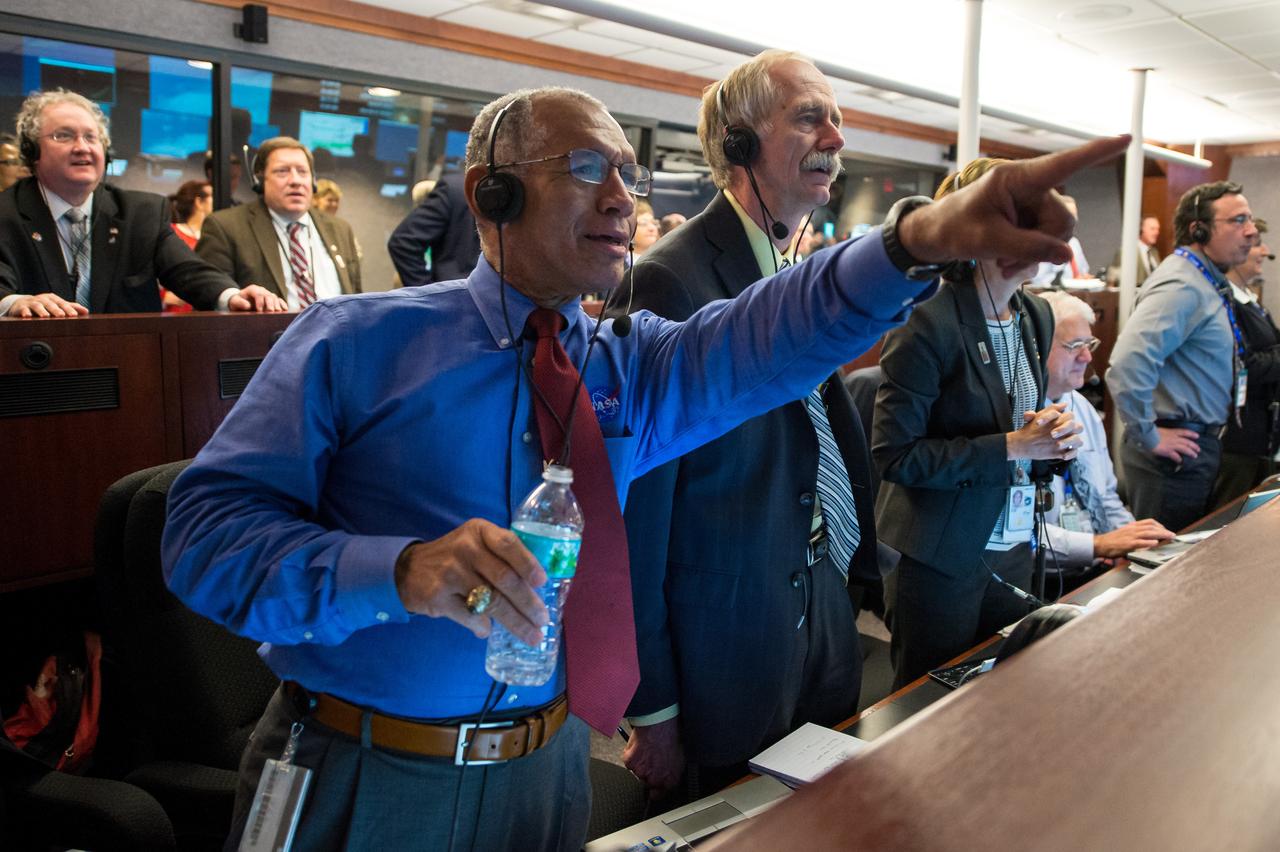

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Directorate William Gerstenmaier, and others in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, react as they watch the Orion spacecraft splash down in the Pacific Ocean a more than three hours after launching onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 37, Friday, Dec. 5, 2014, Cape Canaveral, Florida. The Orion spacecraft orbited Earth twice, reaching an altitude of approximately 3,600 miles above Earth before landing. No one was aboard Orion for this flight test, but the spacecraft is designed to allow us to journey to destinations never before visited by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
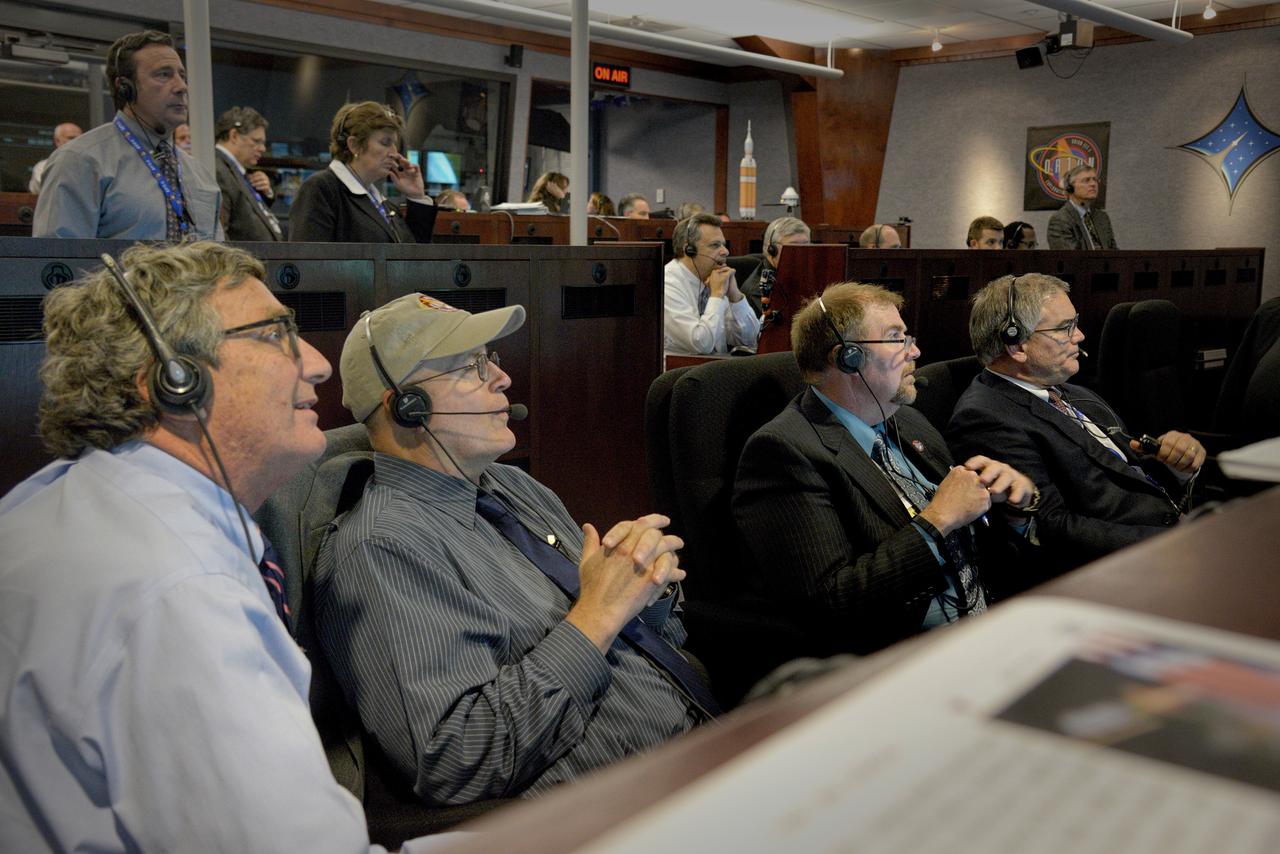

The Orion team watches the flight in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station during Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 5, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
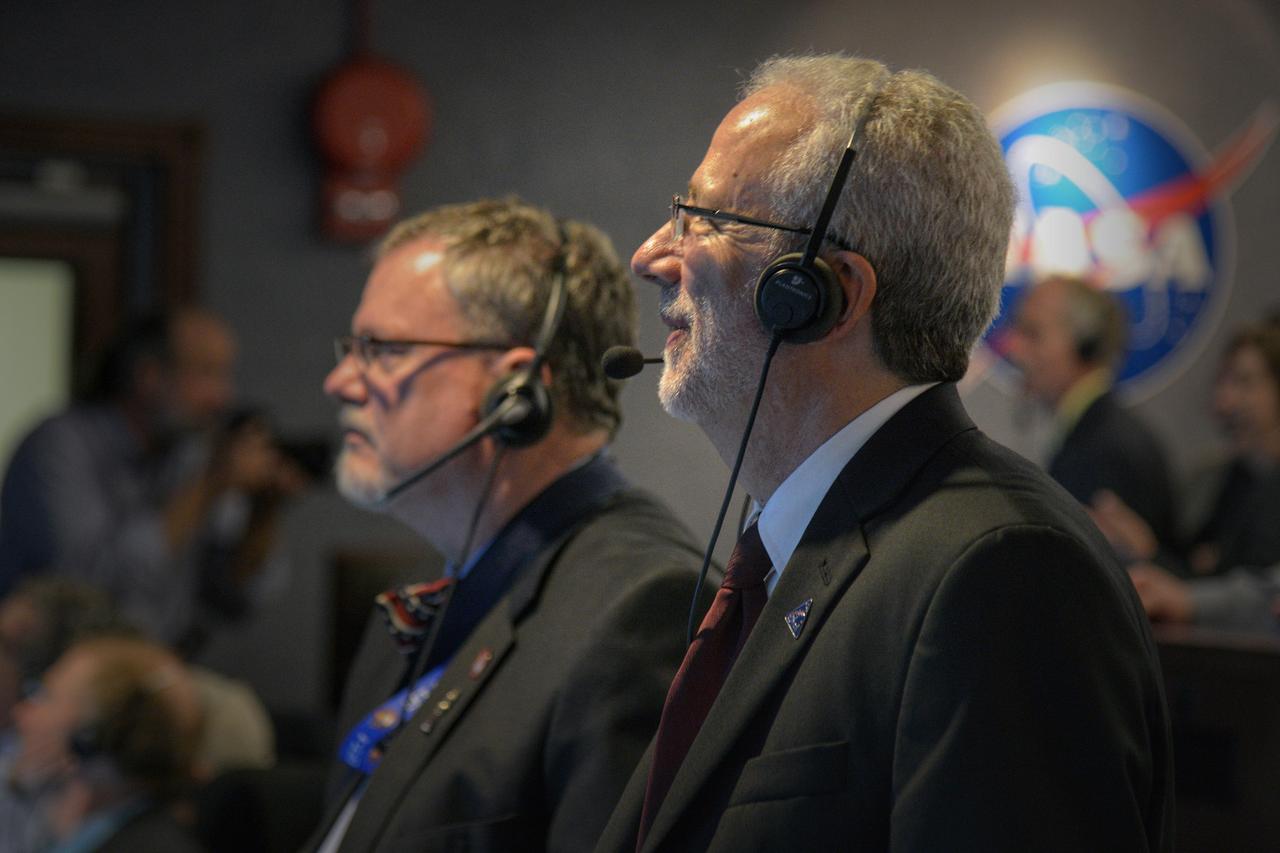

The Orion team watches the flight in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station during Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 5, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
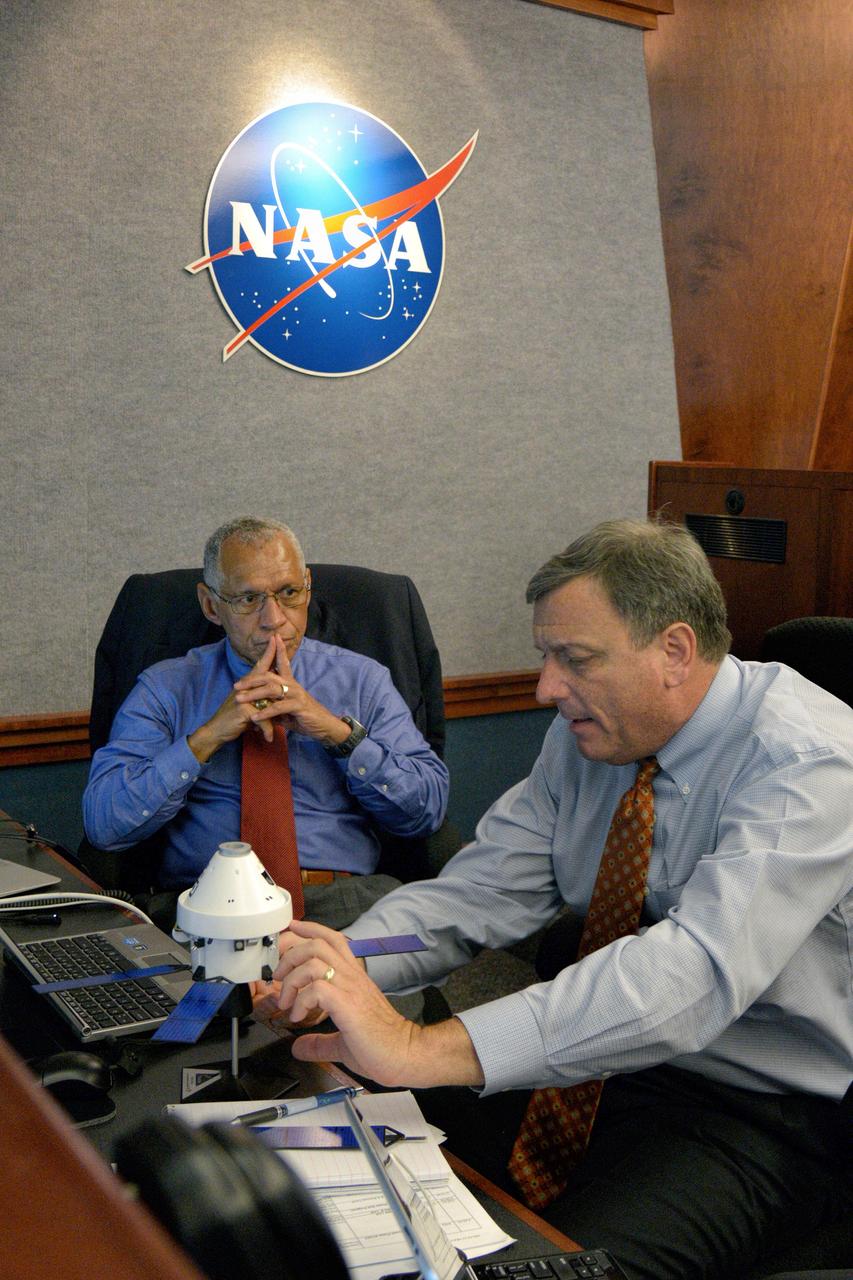

The Orion team discusses Orion operations in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station during Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 5, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
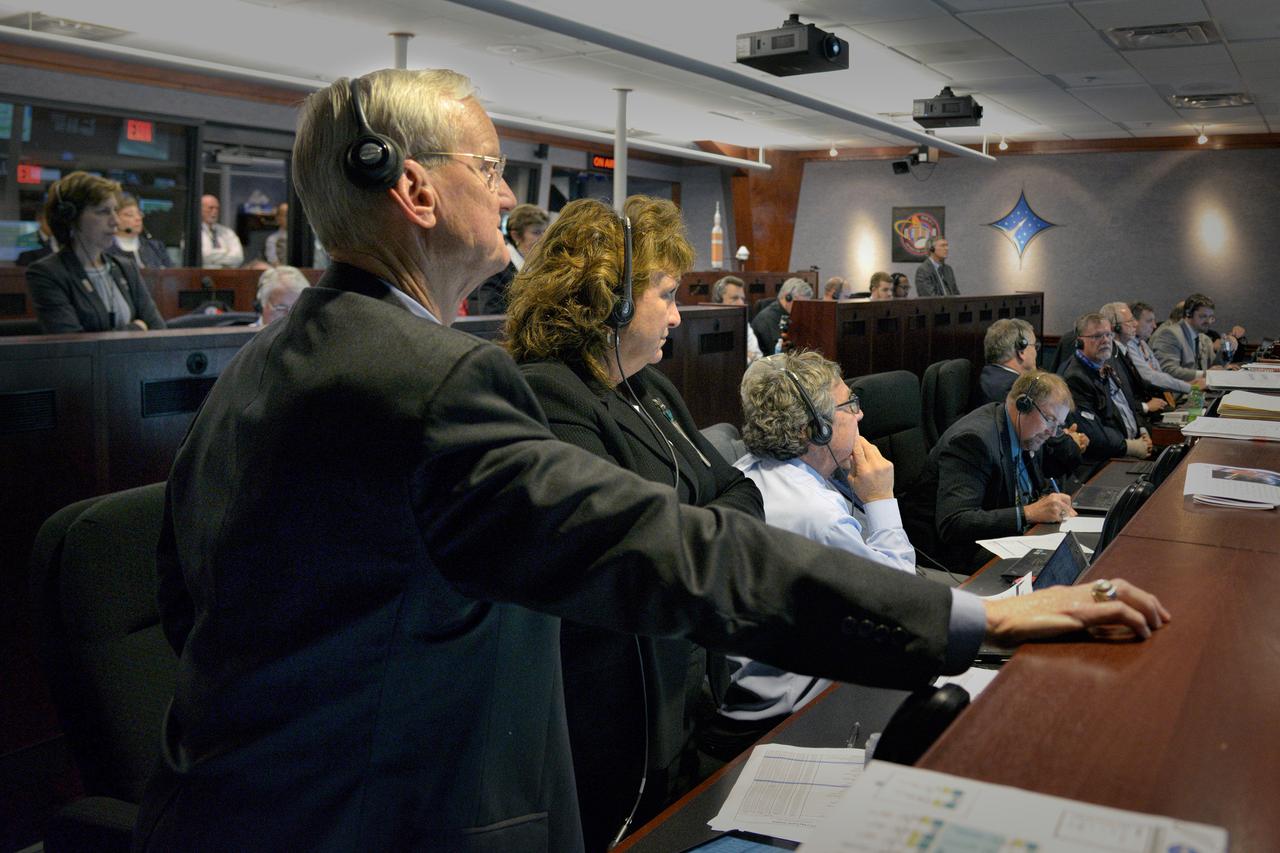

The Orion team watches the flight in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station during Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 5, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
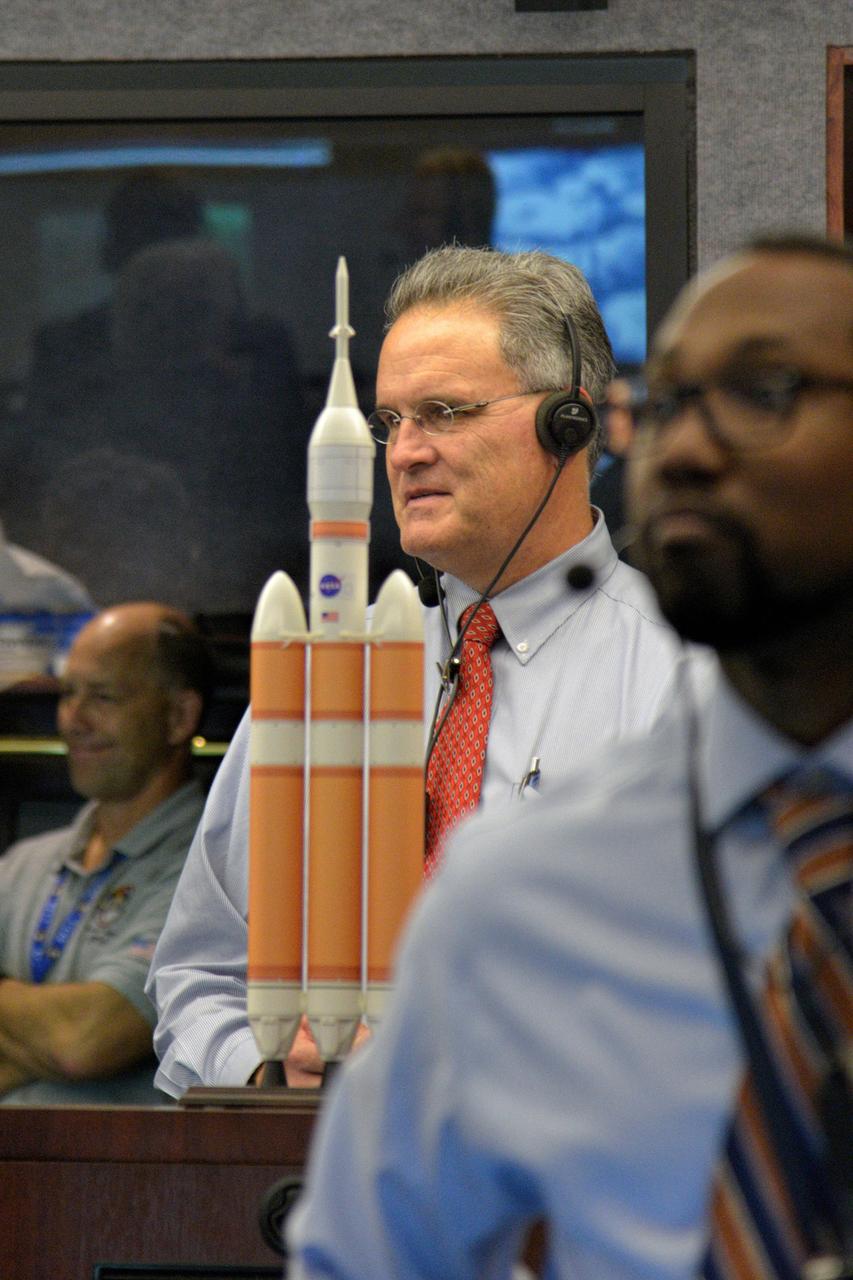

The Orion team watches the flight in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station during Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 5, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
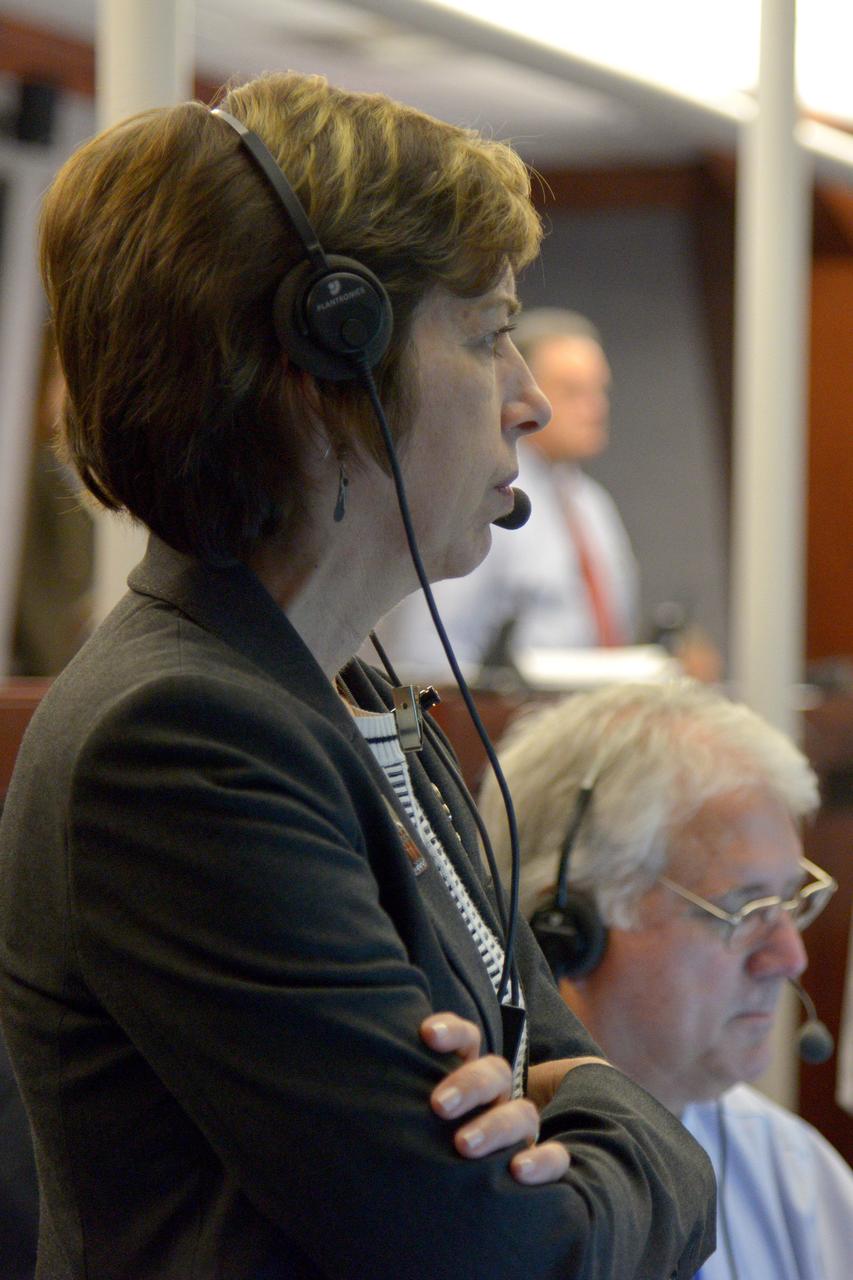

The Orion team watches the flight in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station during Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 5, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
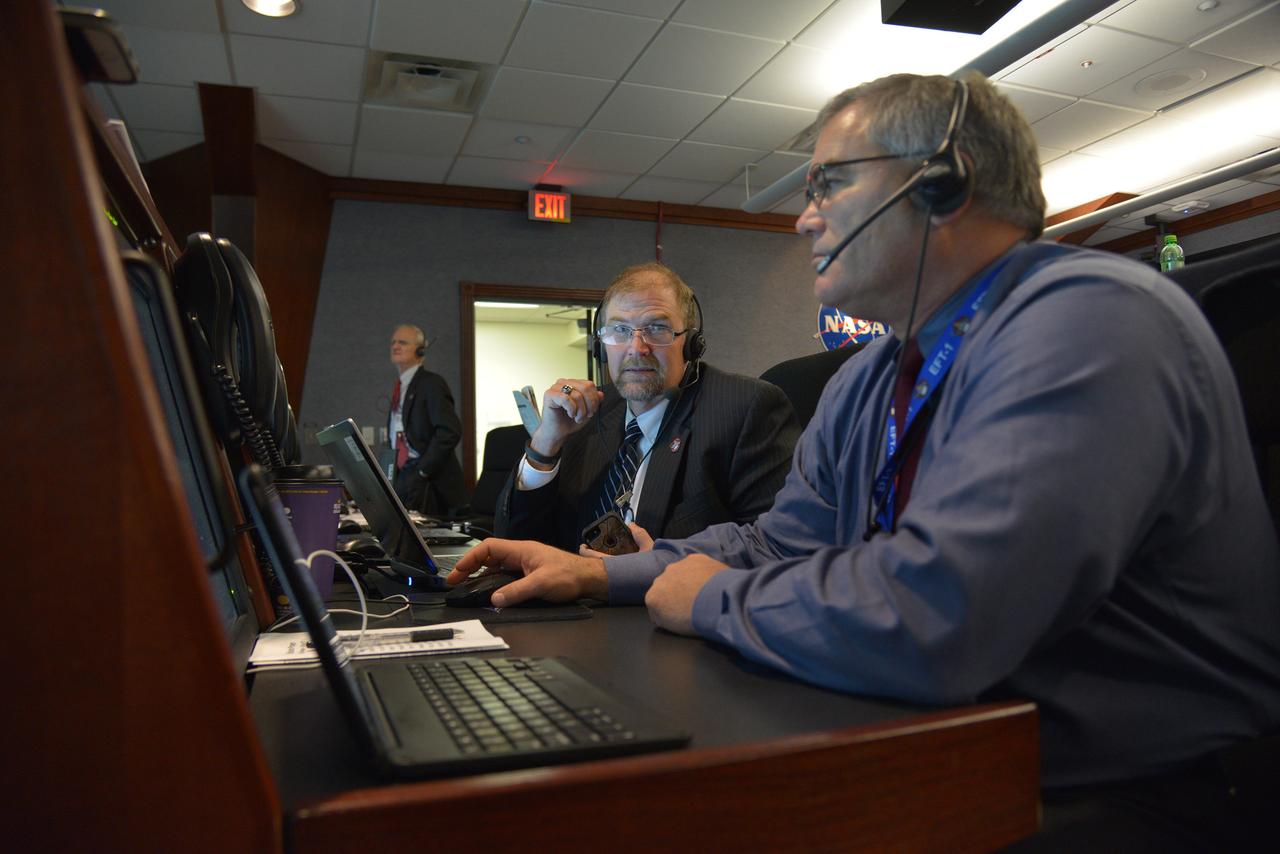

The Orion team reviews the launch procedure in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Stationahead of the launch of Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 4, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
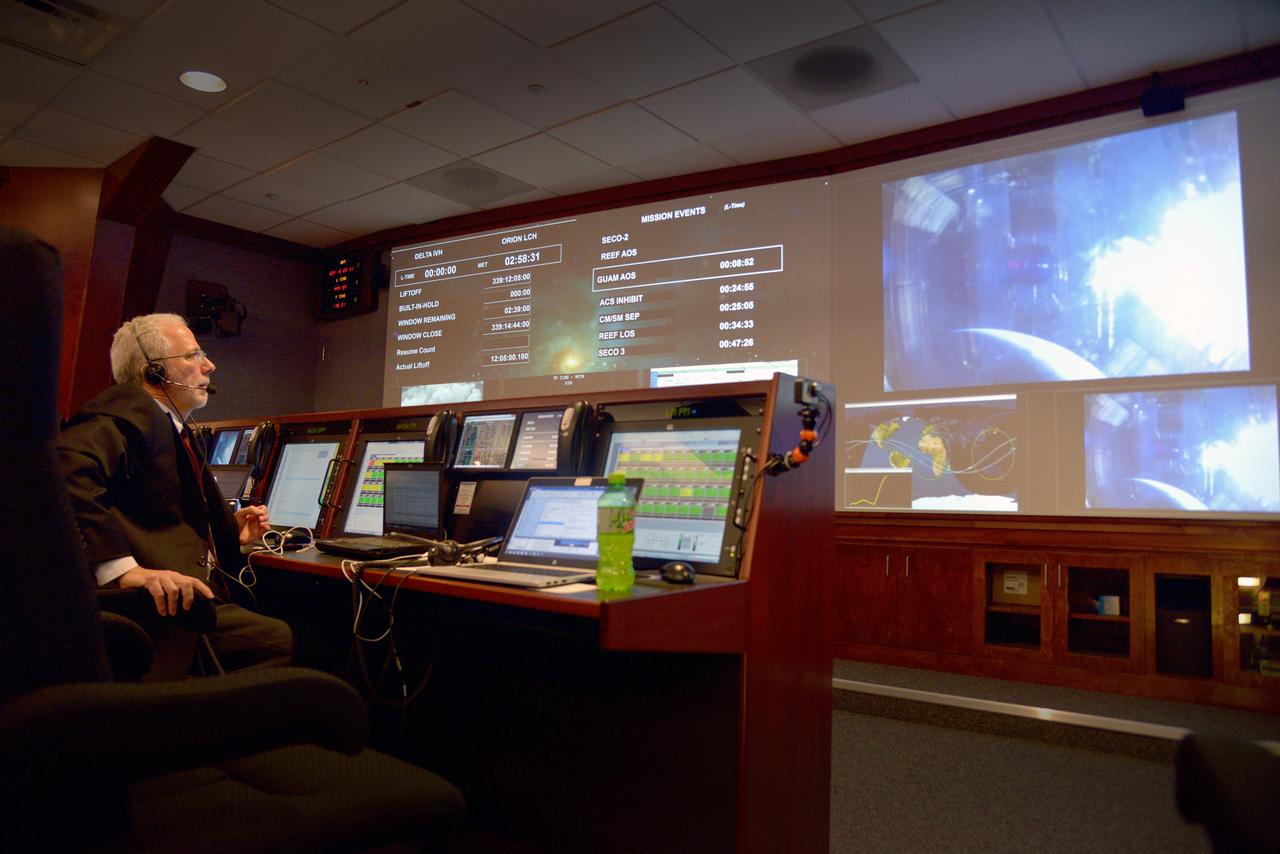

As Orion reaches an apogee of 3600 miles, Mark Geyer, Orion program manager, watches the view from Orion's windows in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Dec. 5, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
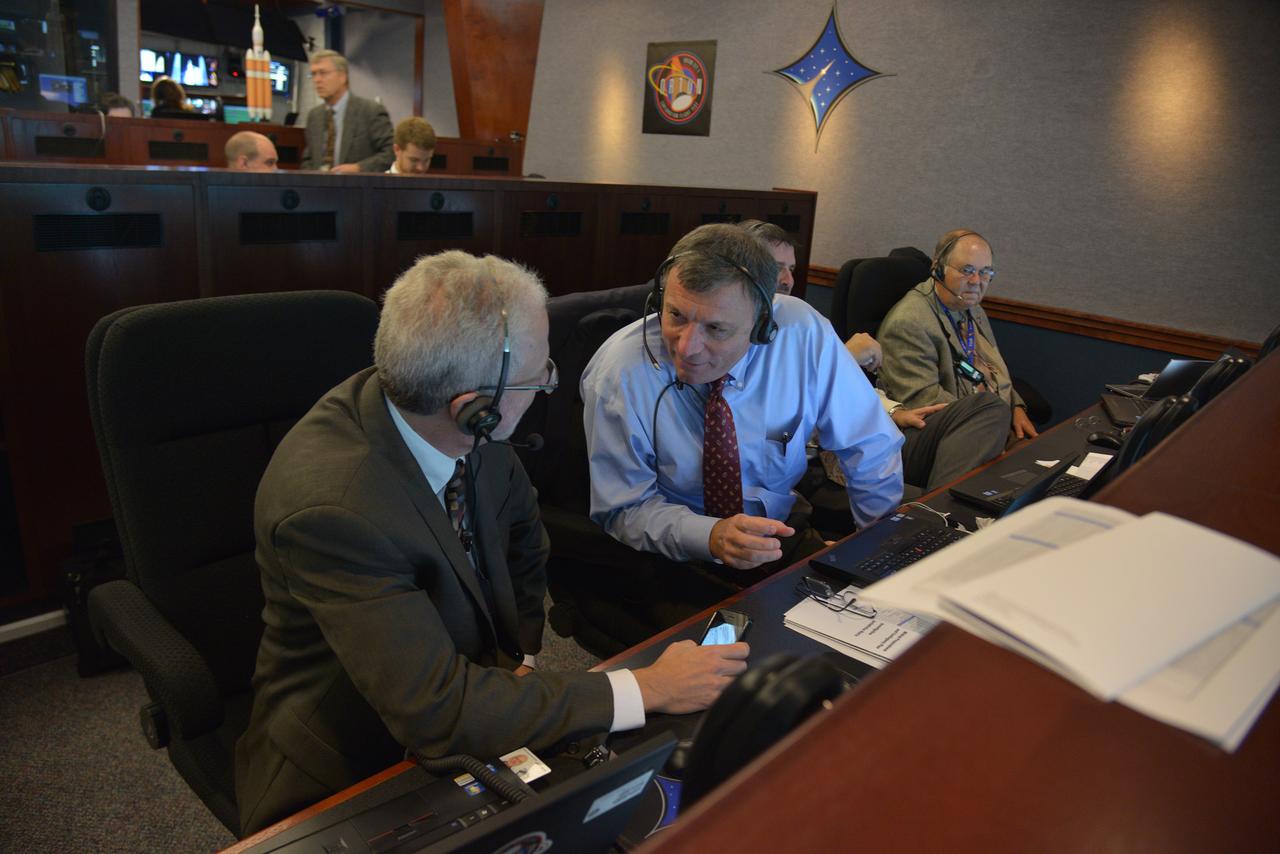

The Orion team reviews the launch procedure in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station ahead of the launch of Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 4, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
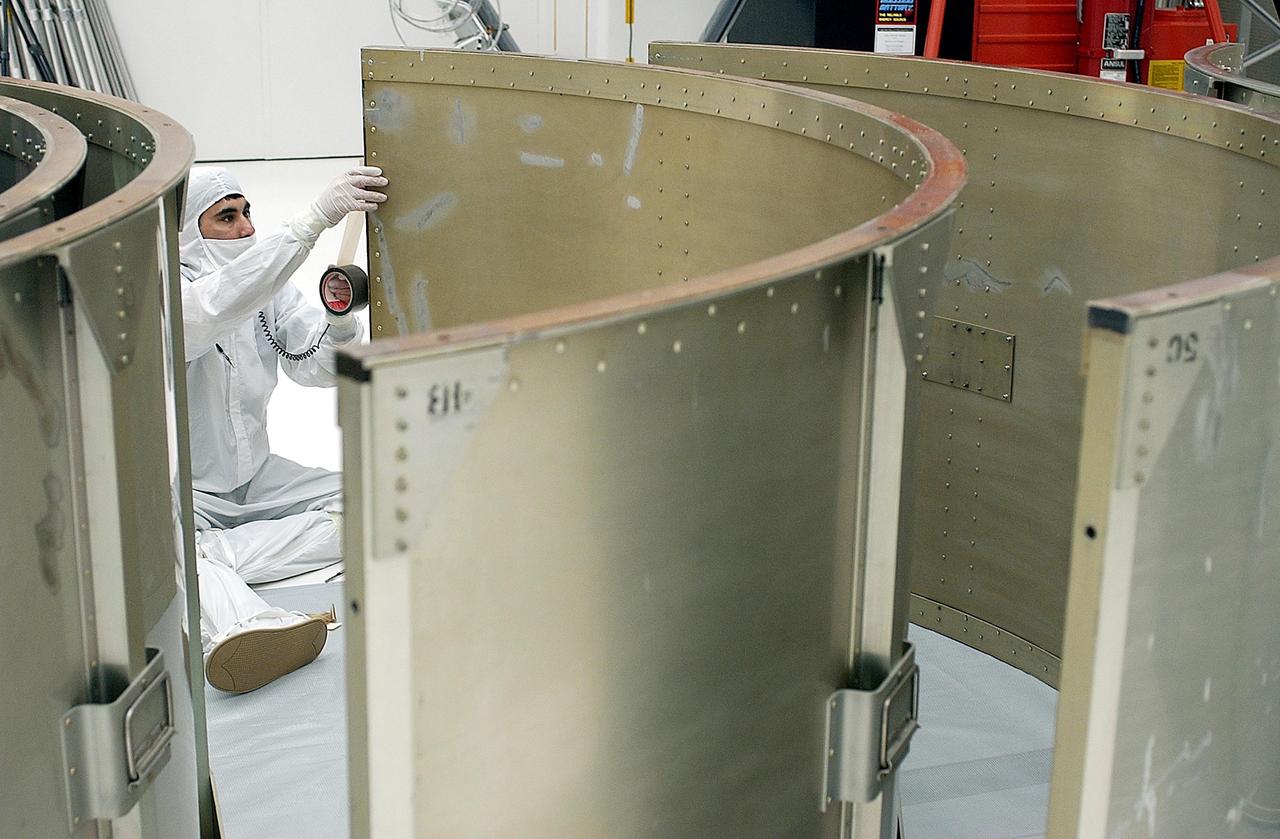

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker in Building AE prepares a segment of the payload canister for the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF). SIRTF is currently scheduled for transportation to Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and mating with the Delta II on or about April 4.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in Building AE are ready to assemble the payload canister around the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF). SIRTF is currently scheduled for transportation to Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and mating with the Delta II on or about April 4.
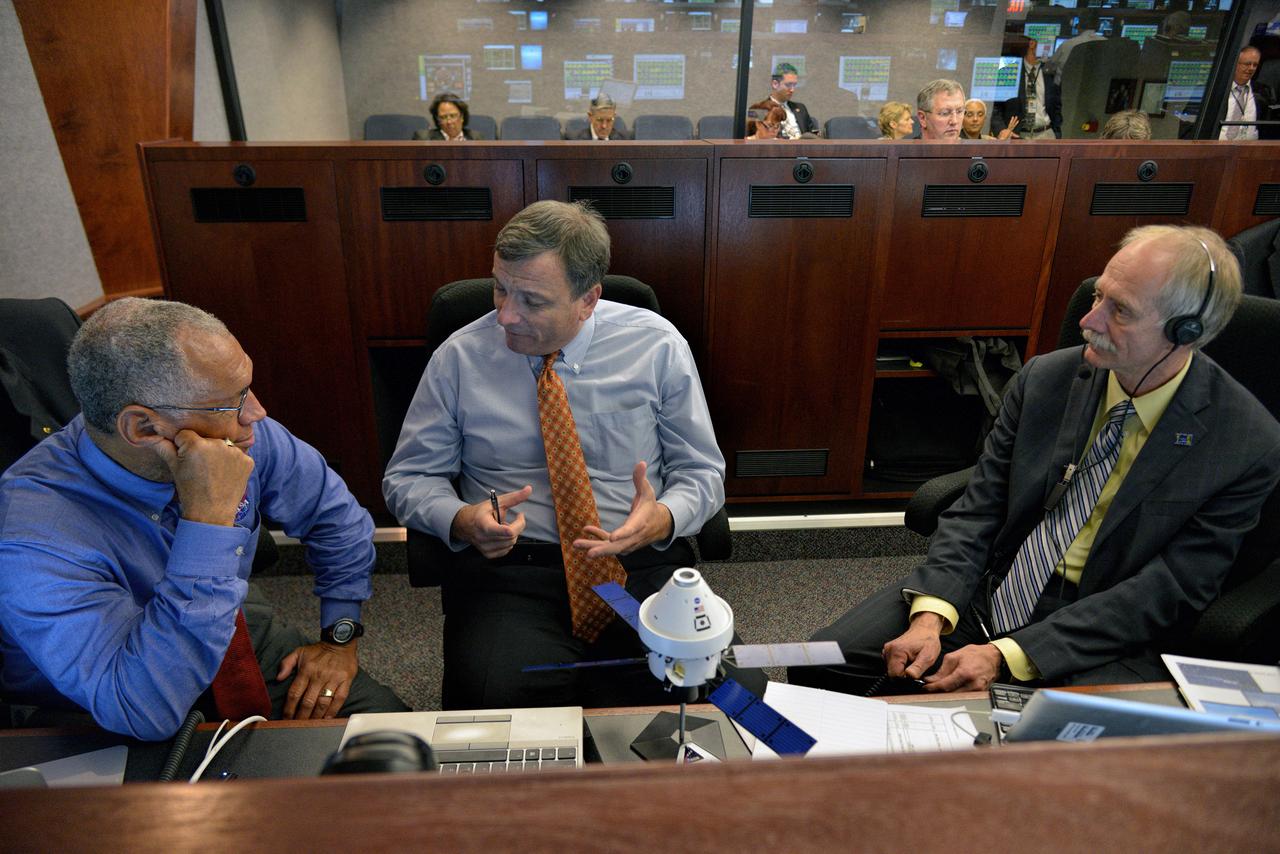

The Orion team (including NASA Administrator Charles Bolden and Operations Directorate William Gerstenmaier) discuss Orion operations in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station during Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 5, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
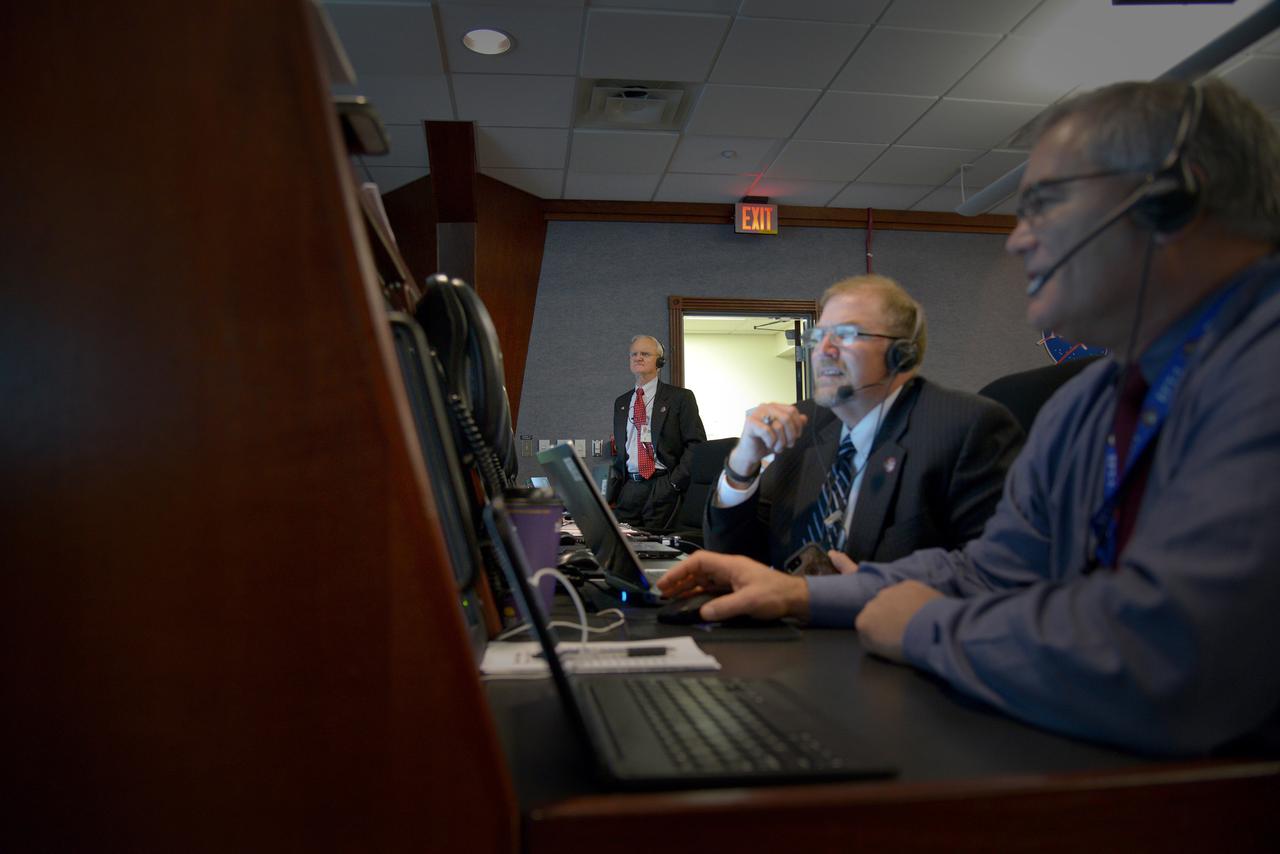

The Orion team reviews the launch procedure in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station ahead of the launch of Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 4, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
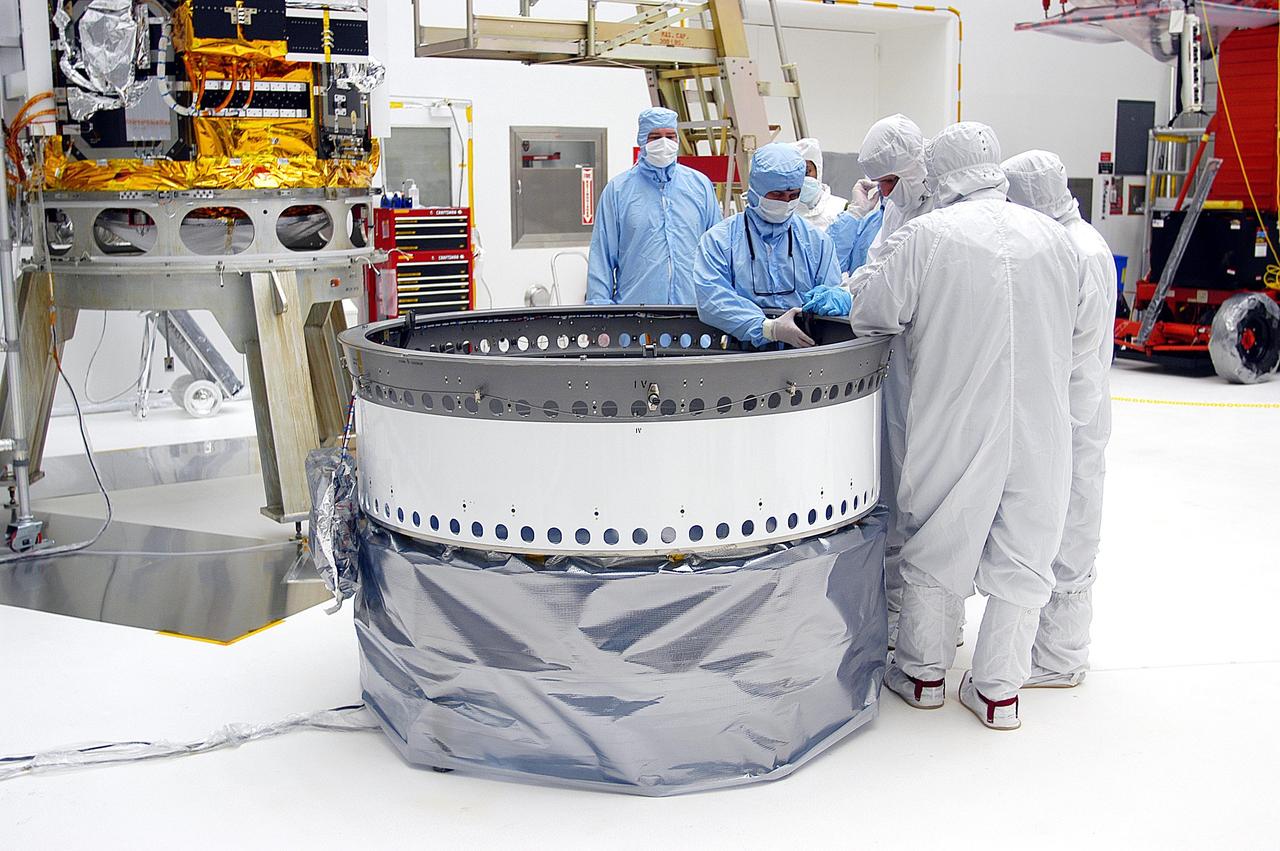

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in Building AE adjust the payload attach fitting for the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), in the background. SIRTF will be mated with the Delta II launch vehicle via the fitting. SIRTF is currently scheduled for transportation to Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and hoisting atop the Delta II on or about April 4.
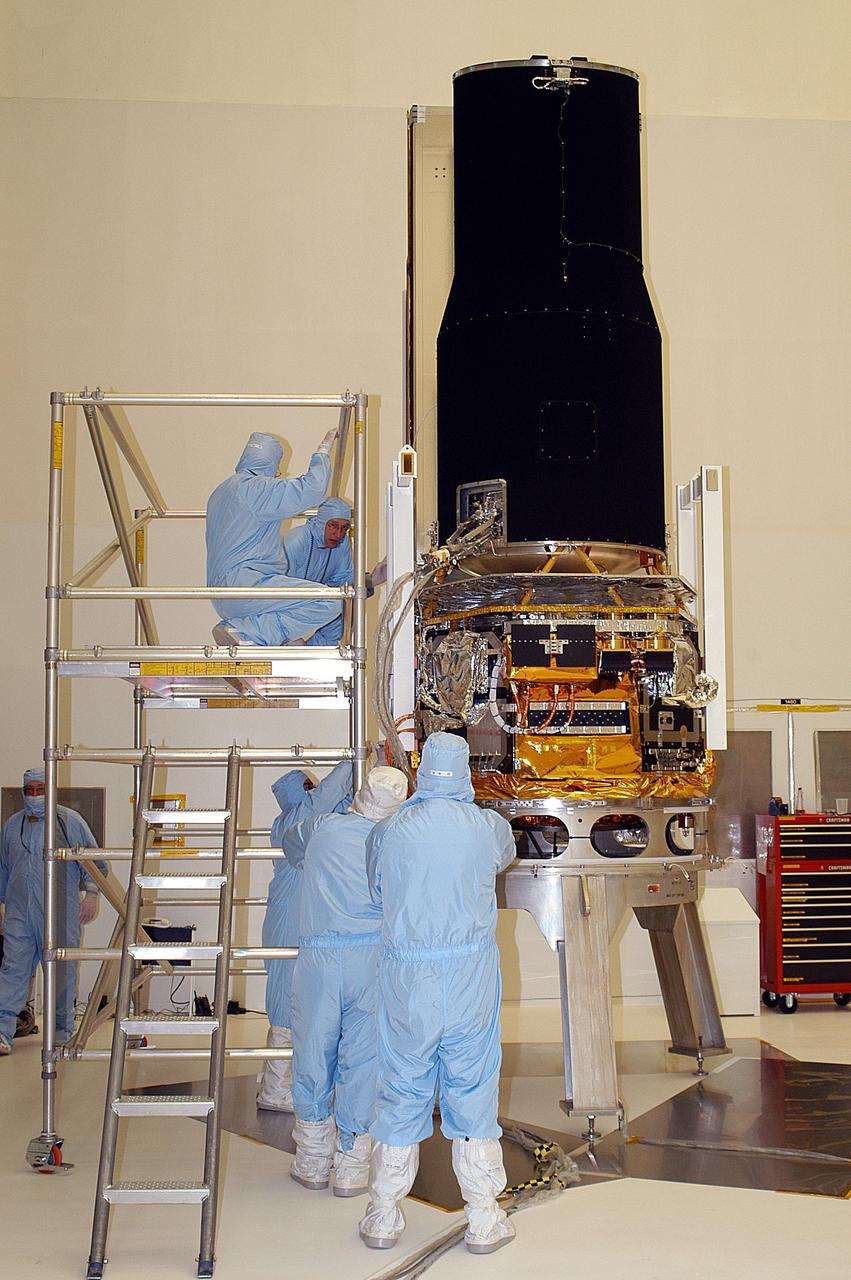

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- -- At Building AE, the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) is prepared for testing. SIRTF is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space.
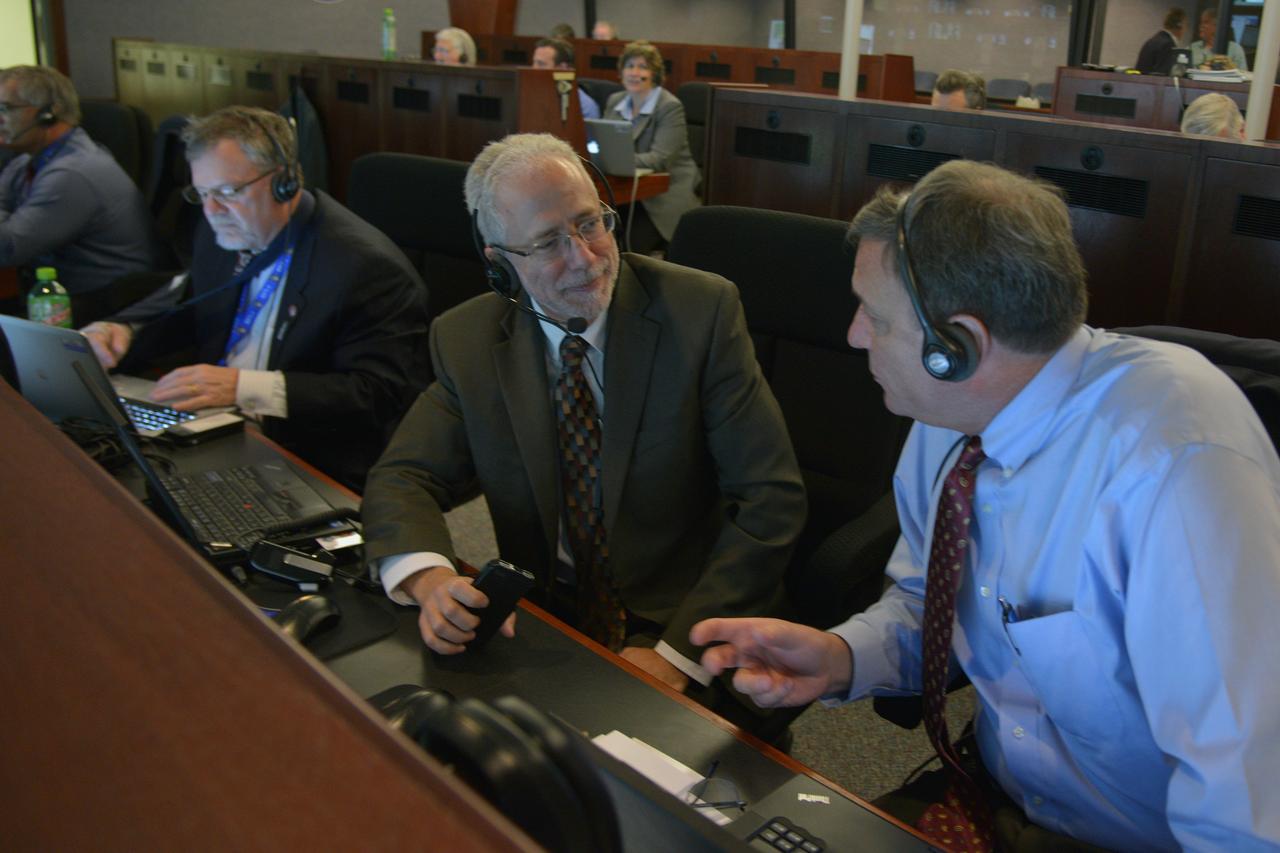

The Orion program management team reviews the launch procedure in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station ahead of the launch of Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 4, 2014. Pictured from left to right: Mike Hawes, Lockheed Martin Orion program manager, Mark Geyer, NASA Orion program manager, and Mark Kirasich, NASA Orion deputy program manager. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
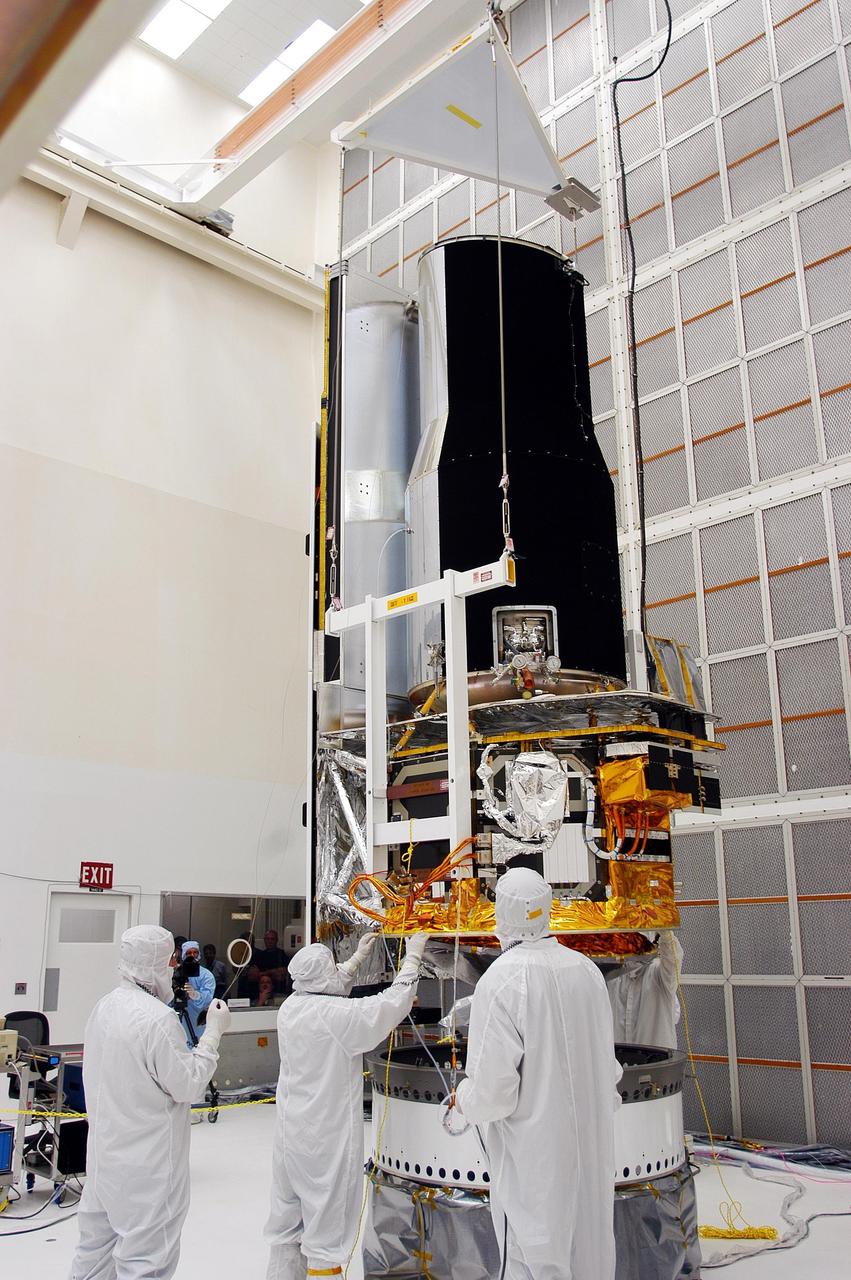

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers make additional adjustments on the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) in Building AE. The telescope will be mated with its Delta II launch vehicle via the payload attach fitting seen beneath it. SIRTF is currently scheduled for transportation to Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and hoisting atop the Delta II on or about April 4.
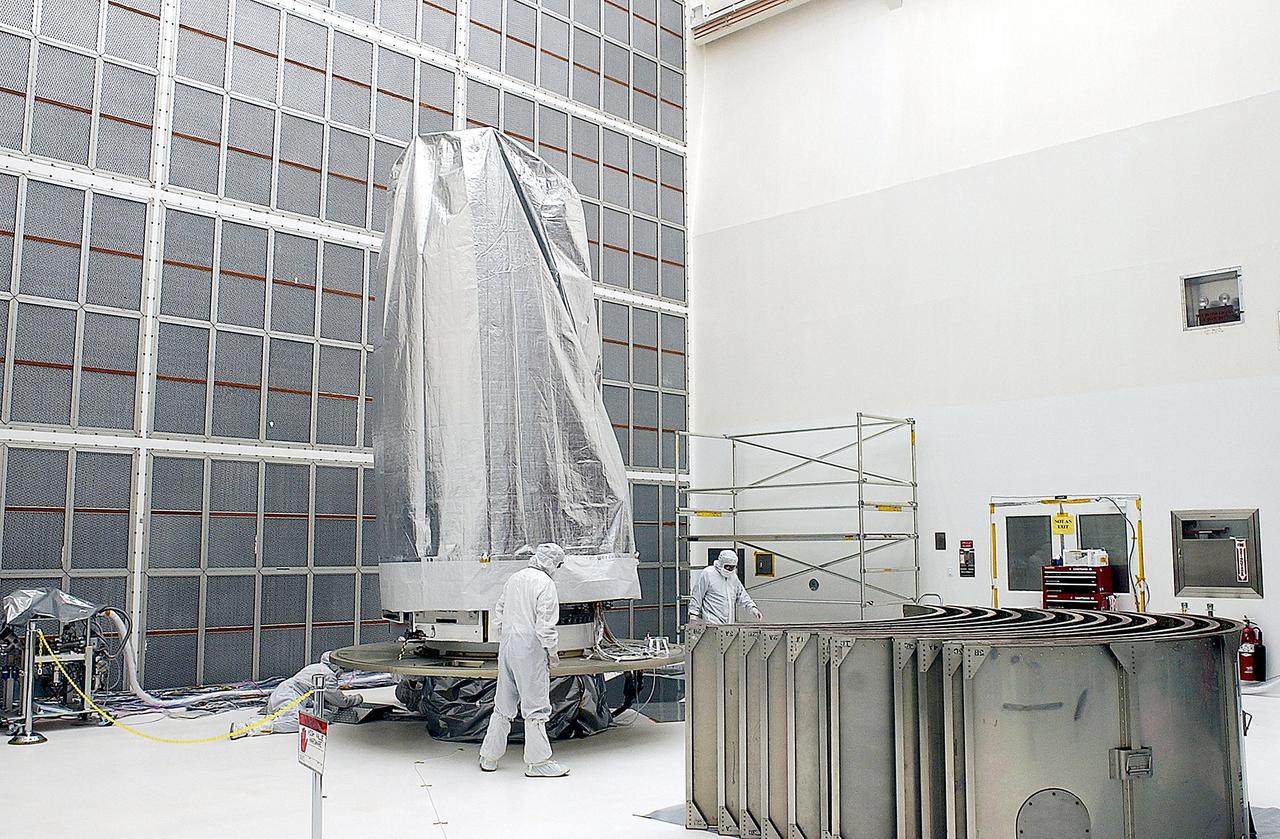

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in Building AE prepare the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), in the background, for buildup of the payload canister. SIRTF will be mated with the Delta II launch vehicle via the payload attach fitting at the bottom. SIRTF is currently scheduled for transportation to Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and hoisting atop the Delta II on or about April 4.
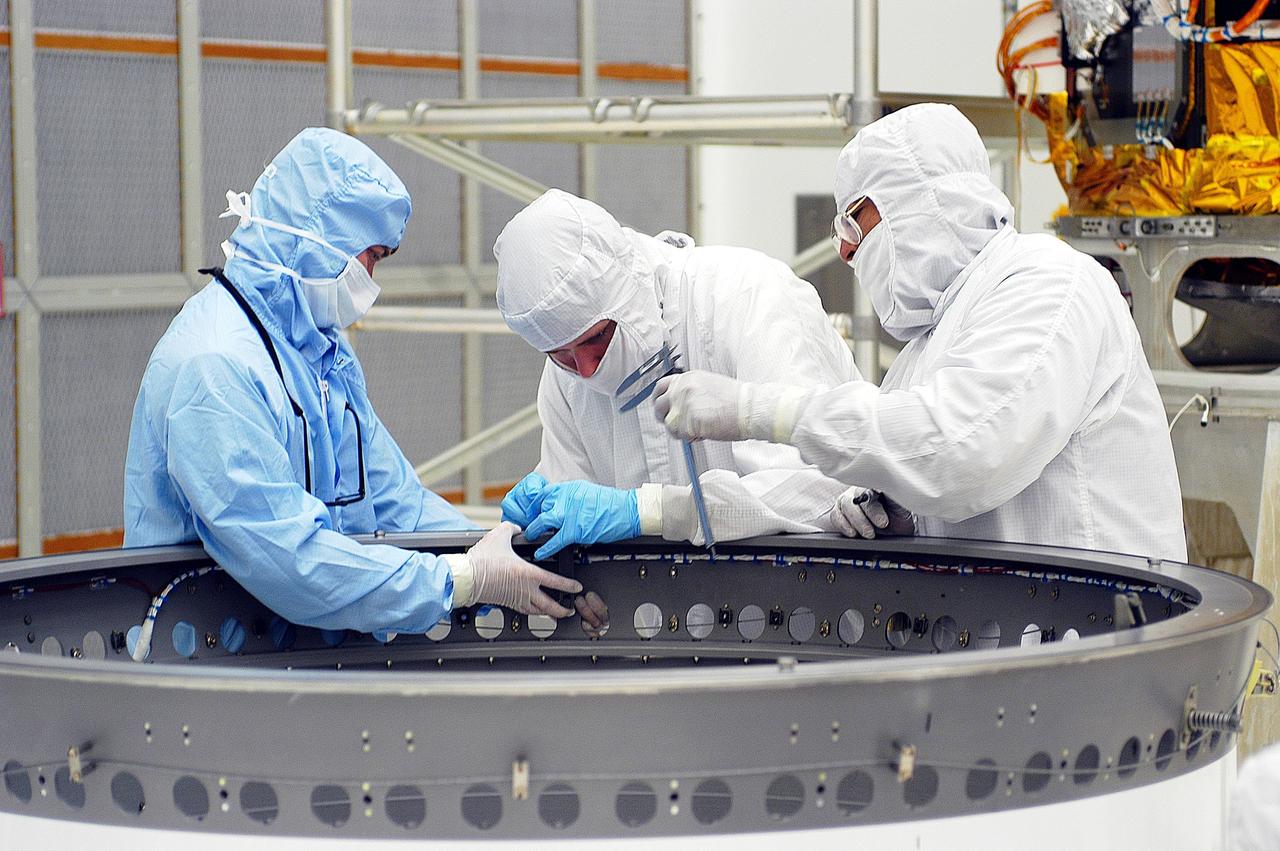

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in Building AE adjust the payload attach fitting for the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF). SIRTF will be mated with the Delta II launch vehicle via the fitting. SIRTF is currently scheduled for transportation to Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and hoisting atop the Delta II on or about April 4.
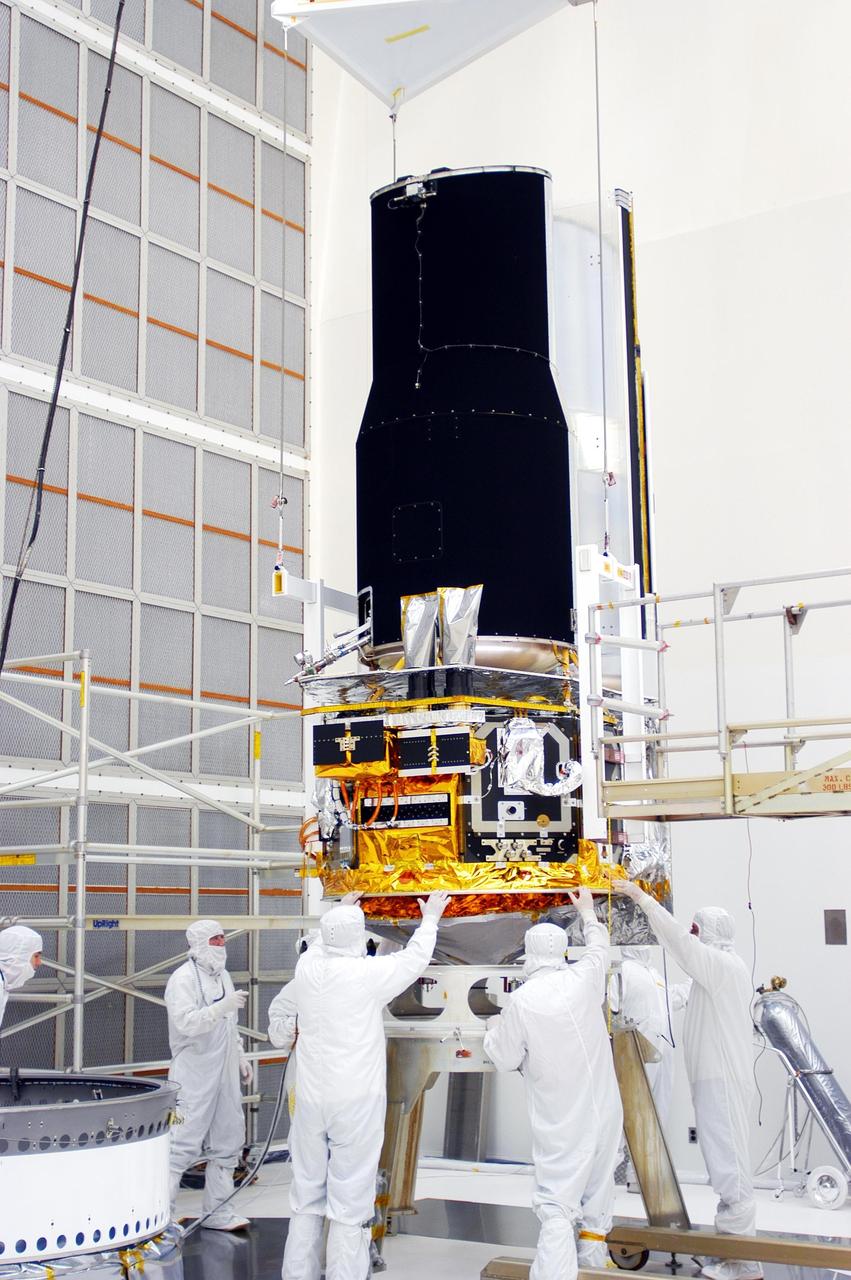

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in Building AE work on the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF). The telescope will be mated with its Delta II launch vehicle via the payload attach fitting seen at left. SIRTF is currently scheduled for transportation to Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and hoisting atop the Delta II on or about April 4.
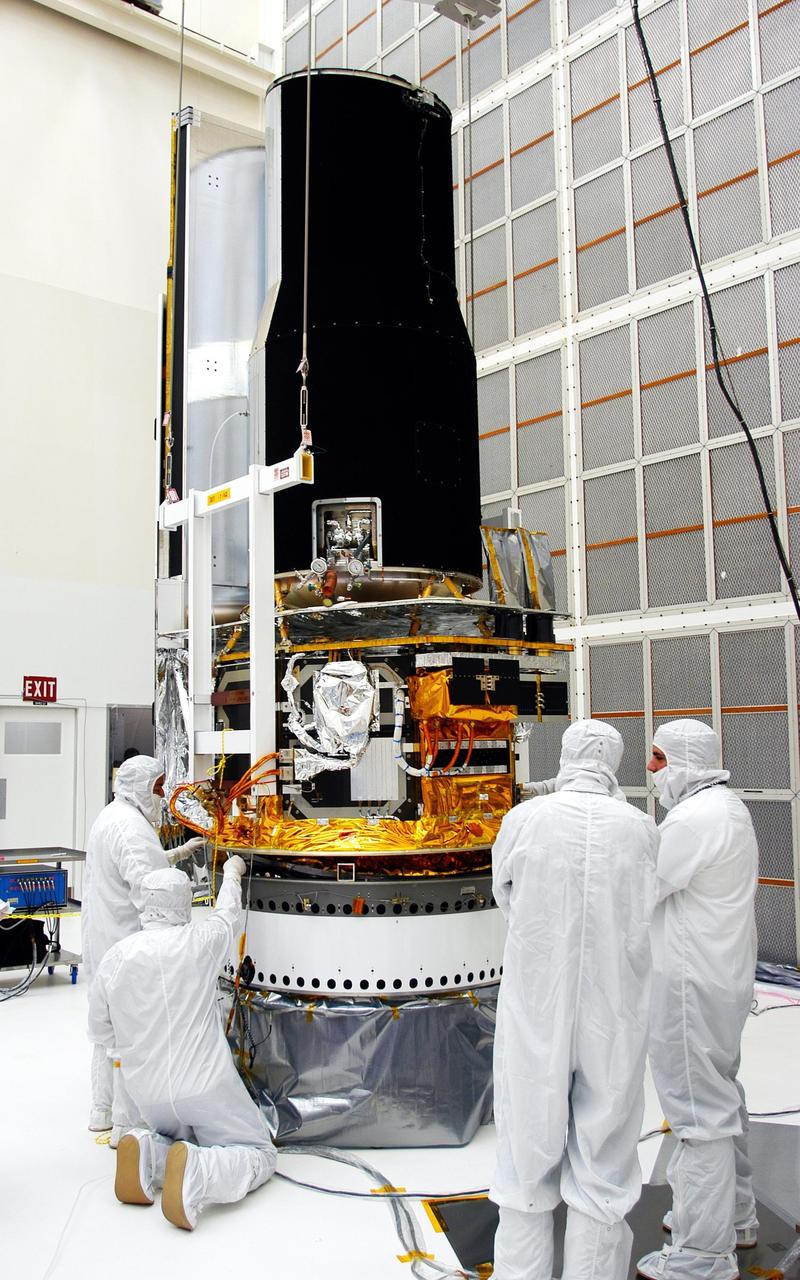

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in Building AE check the fitting of the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) with the payload attach fitting beneath. SIRTF will be mated with its Delta II launch vehicle via the fitting. SIRTF is currently scheduled for transportation to Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and hoisting atop the Delta II on or about April 4.
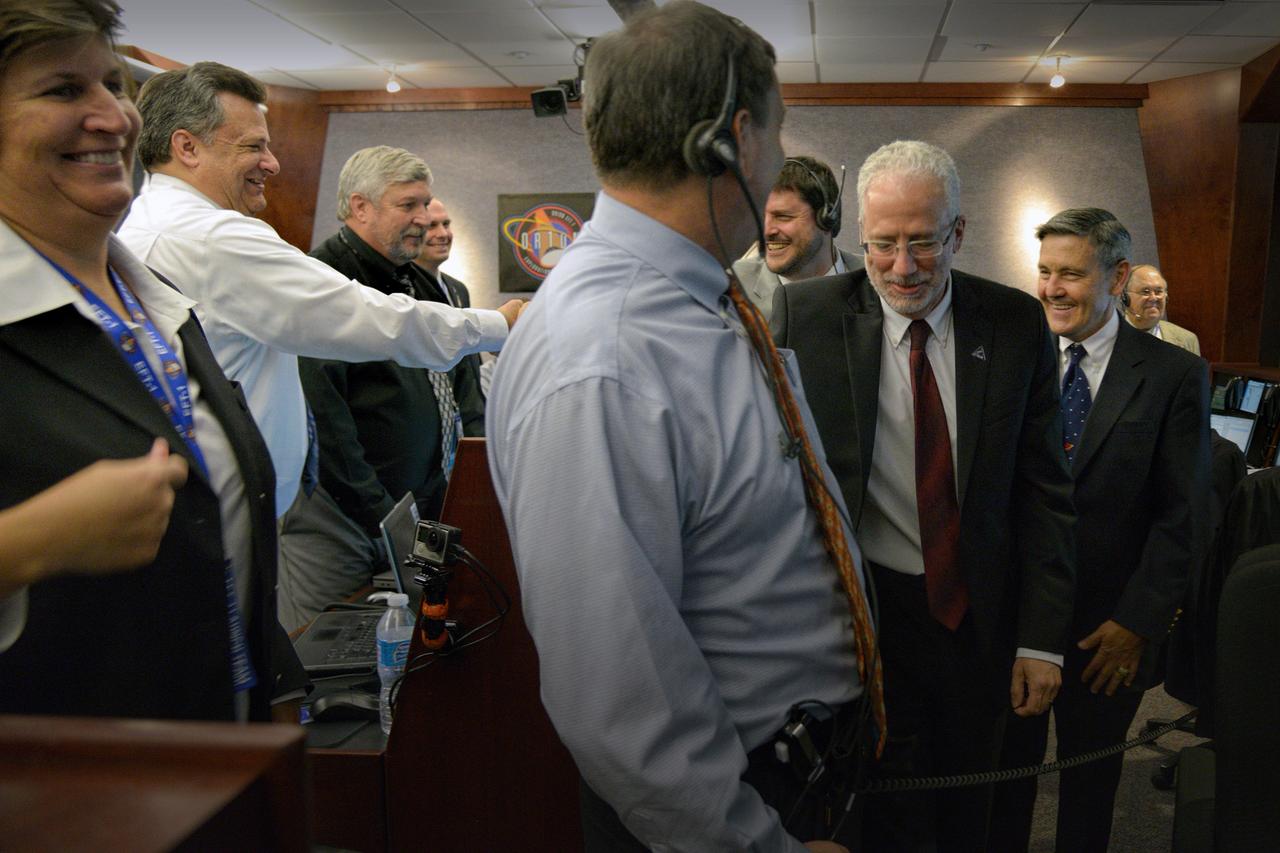

The Orion team celebrates Orion's successful Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) mission in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Dec. 5, 2014. The Orion spacecraft orbited Earth twice, reaching an altitude of approximately 3,600 miles above Earth before landing. No one was aboard Orion for this flight test, but the spacecraft is designed to allow us to journey to destinations never before visited by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
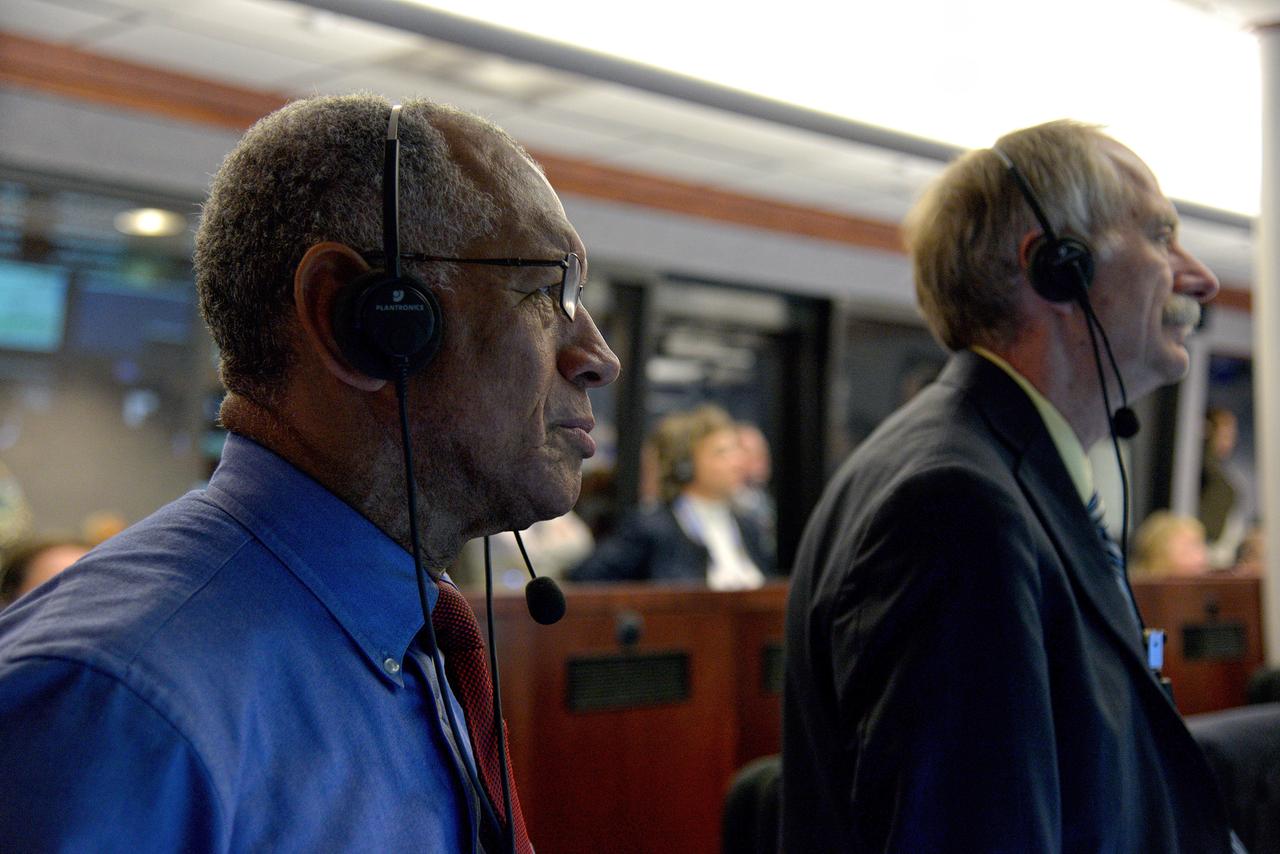

The Orion team watches the flight in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station during Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 5, 2014. NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Directorate William Gerstenmaier, are in frame. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
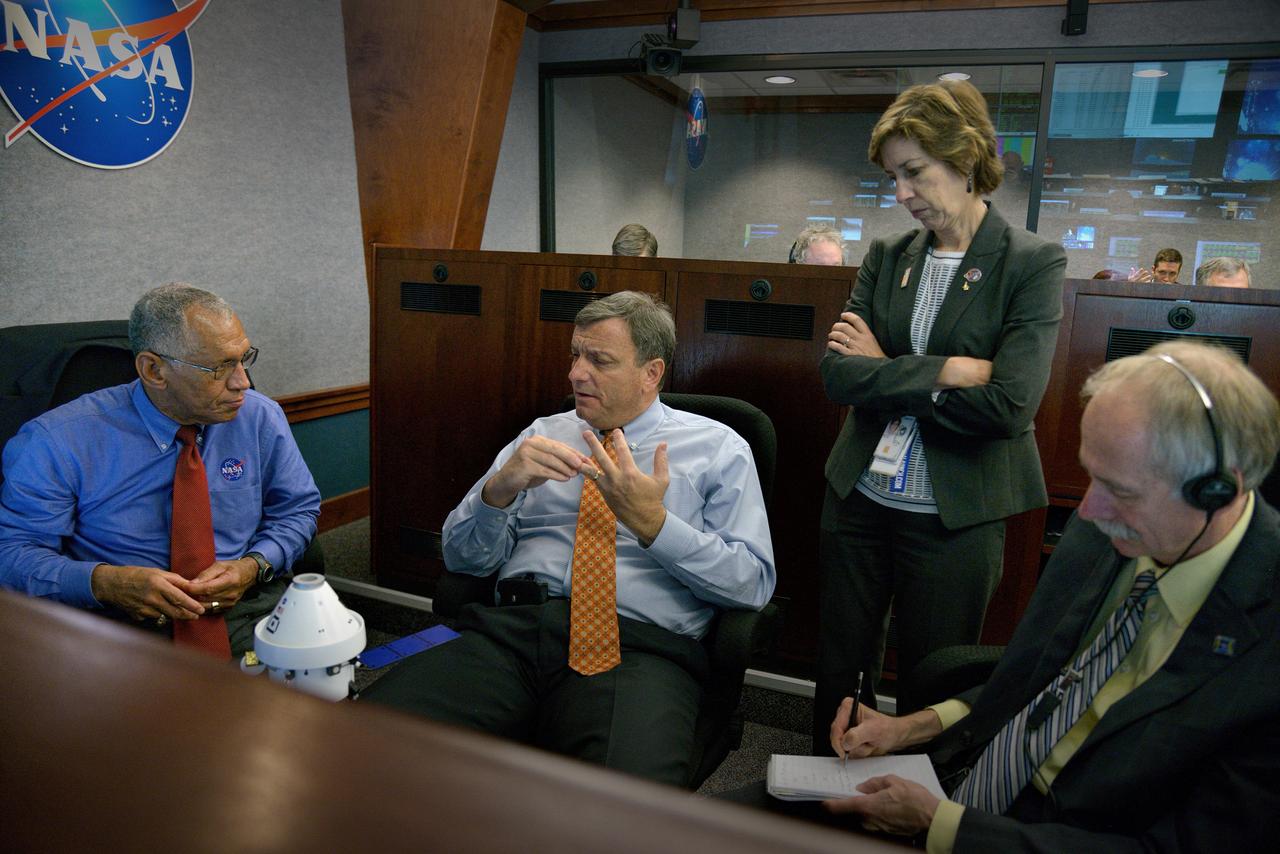

The Orion team (including JSC Director Ellen Ochoa, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden and Operations Directorate William Gerstenmaier) discuss Orion operations in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station during Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 5, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
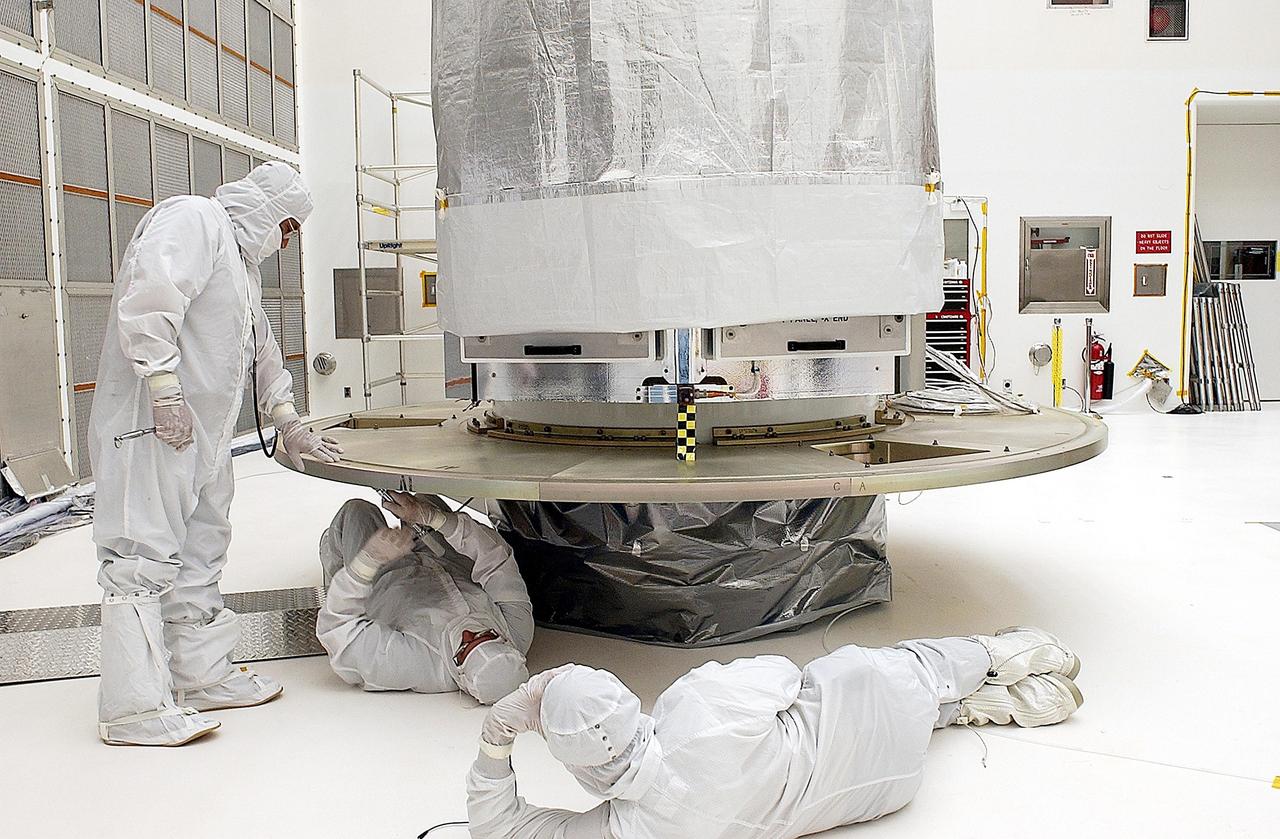

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in Building AE adjust the payload attach fitting on the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) before buildup of the payload canister. SIRTF will be mated with the Delta II launch vehicle via the fitting. SIRTF is currently scheduled for transportation to Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and hoisting atop the Delta II on or about April 4.
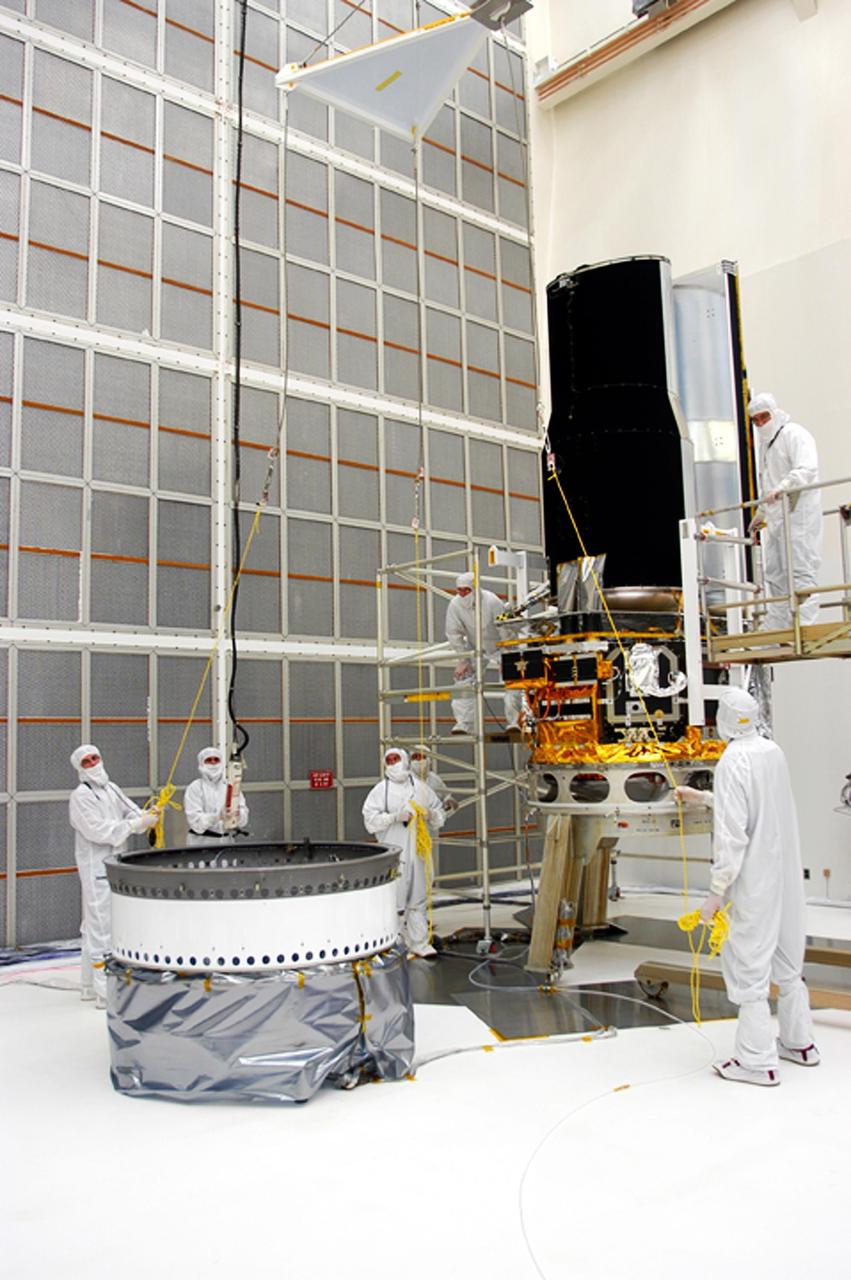

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in Building AE lower a part of the protective covering for the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), seen at right. SIRTF will be mated with its Delta II launch vehicle via the fitting seen at left. SIRTF is currently scheduled for transportation to Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and hoisting atop the Delta II on or about April 4.
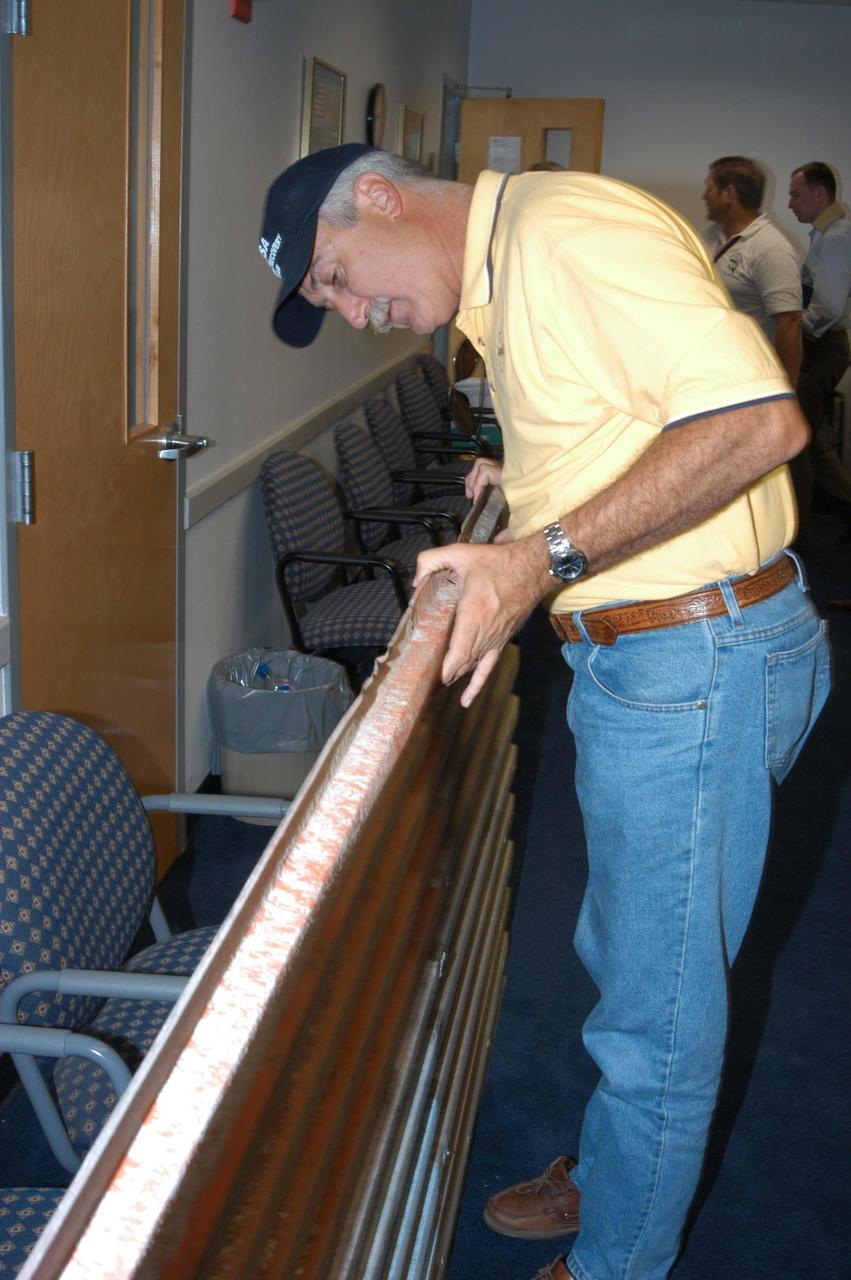

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe examines one of the panels that was blown off the Vehicle Assembly Building. O’Keefe is visiting KSC to survey the damage sustained by KSC facilities from Hurricane Frances over Labor Day weekend. The Vehicle Assembly Building, Thermal Protection System Facility, and Processing Control Center all received significant damage from the storm. Additionally, the Operations and Checkout Building, Vertical Processing Facility, Hangar AE, Hangar S and Hangar AF Small Parts Facility each received substantial damage. NASA’s three Space Shuttle orbiters -- Discovery, Atlantis and Endeavour - along with the Shuttle launch pads, all of the critical flight hardware for the orbiters and the International Space Station, and NASA’s Swift spacecraft, awaiting launch in October, were well protected and unharmed.
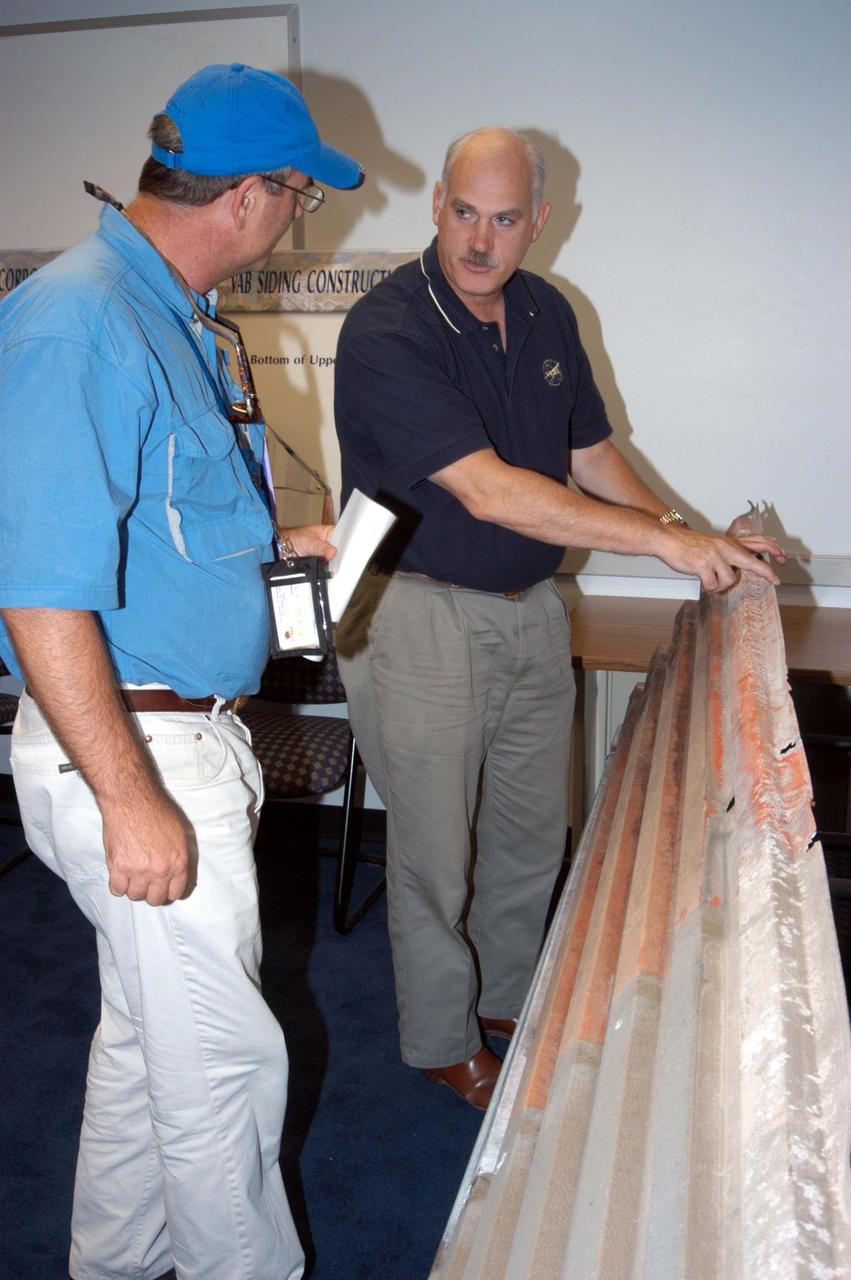

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - KSC Director of the Spaceport Services Scott Kerr (left) and NASA Associate Administrator of the Space Operations Mission Directorate William Readdy examine one of the panels that was blown off the Vehicle Assembly Building. NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe and Readdy are visiting KSC to survey the damage sustained by KSC facilities from Hurricane Frances over Labor Day weekend. The Vehicle Assembly Building, Thermal Protection System Facility, and Processing Control Center all received significant damage from the storm. Additionally, the Operations and Checkout Building, Vertical Processing Facility, Hangar AE, Hangar S and Hangar AF Small Parts Facility each received substantial damage. NASA’s three Space Shuttle orbiters -- Discovery, Atlantis and Endeavour - along with the Shuttle launch pads, all of the critical flight hardware for the orbiters and the International Space Station, and NASA’s Swift spacecraft, awaiting launch in October, were well protected and unharmed.
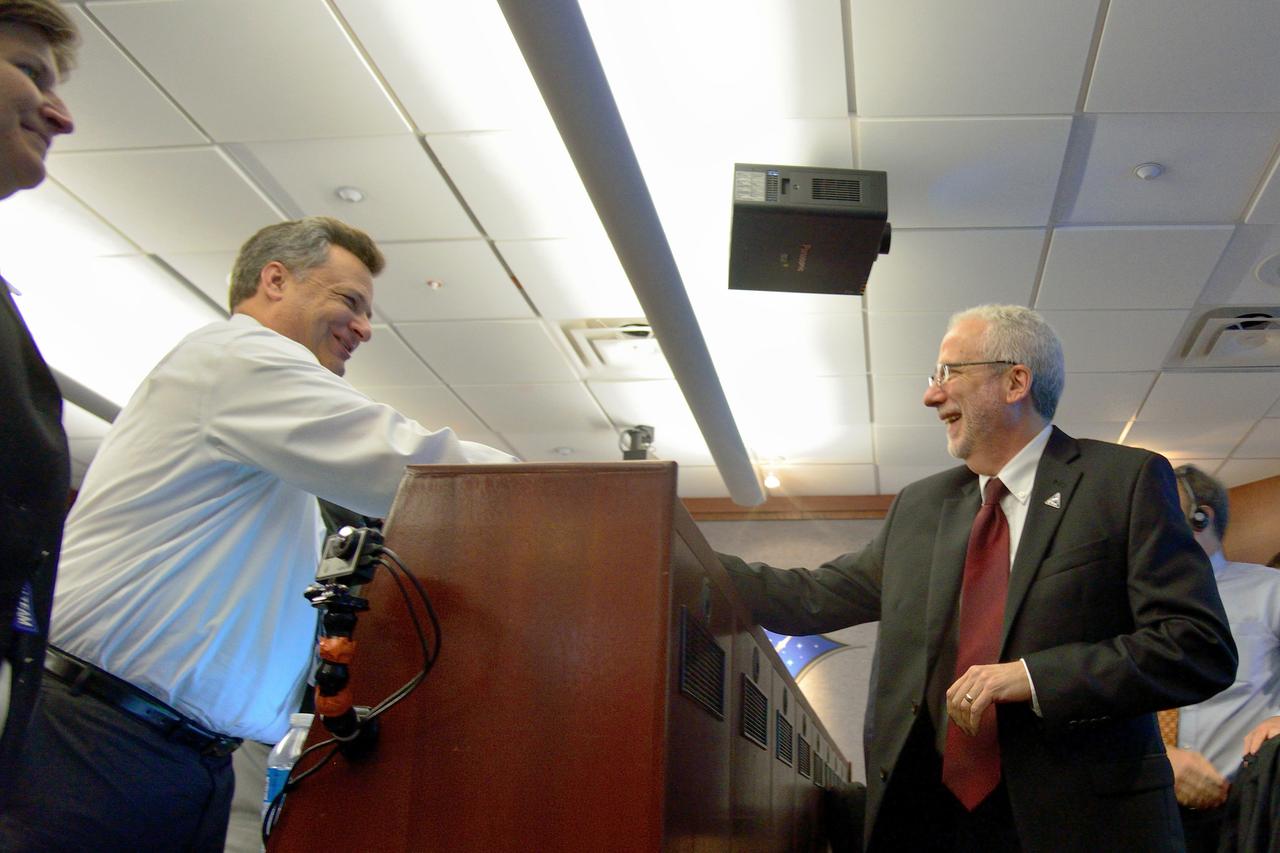

Orion Program Manager Mark Geyer congratulates the team after Orion's successful Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) mission in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Dec. 5, 2014. The Orion spacecraft orbited Earth twice, reaching an altitude of approximately 3,600 miles above Earth before landing. No one was aboard Orion for this flight test, but the spacecraft is designed to allow us to journey to destinations never before visited by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Building AE, the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) is unpacked after being shipped from the Lockheed Martin plant in Sunnyvale, Calif. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
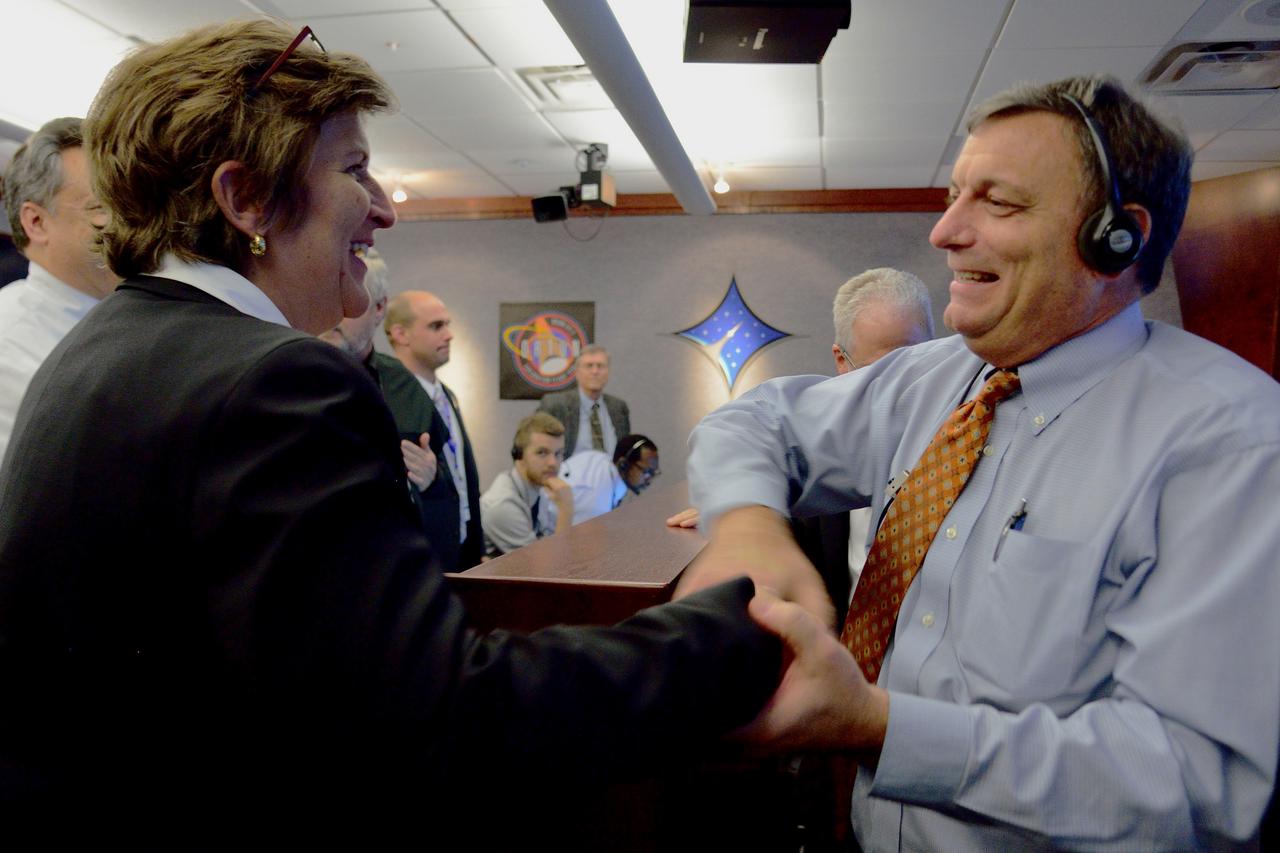

Orion Chief Engineer Julie and Deputy Program Manager Mark Kirasich celebrate Orion's successful Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) mission in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Dec. 5, 2014. The Orion spacecraft orbited Earth twice, reaching an altitude of approximately 3,600 miles above Earth before landing. No one was aboard Orion for this flight test, but the spacecraft is designed to allow us to journey to destinations never before visited by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
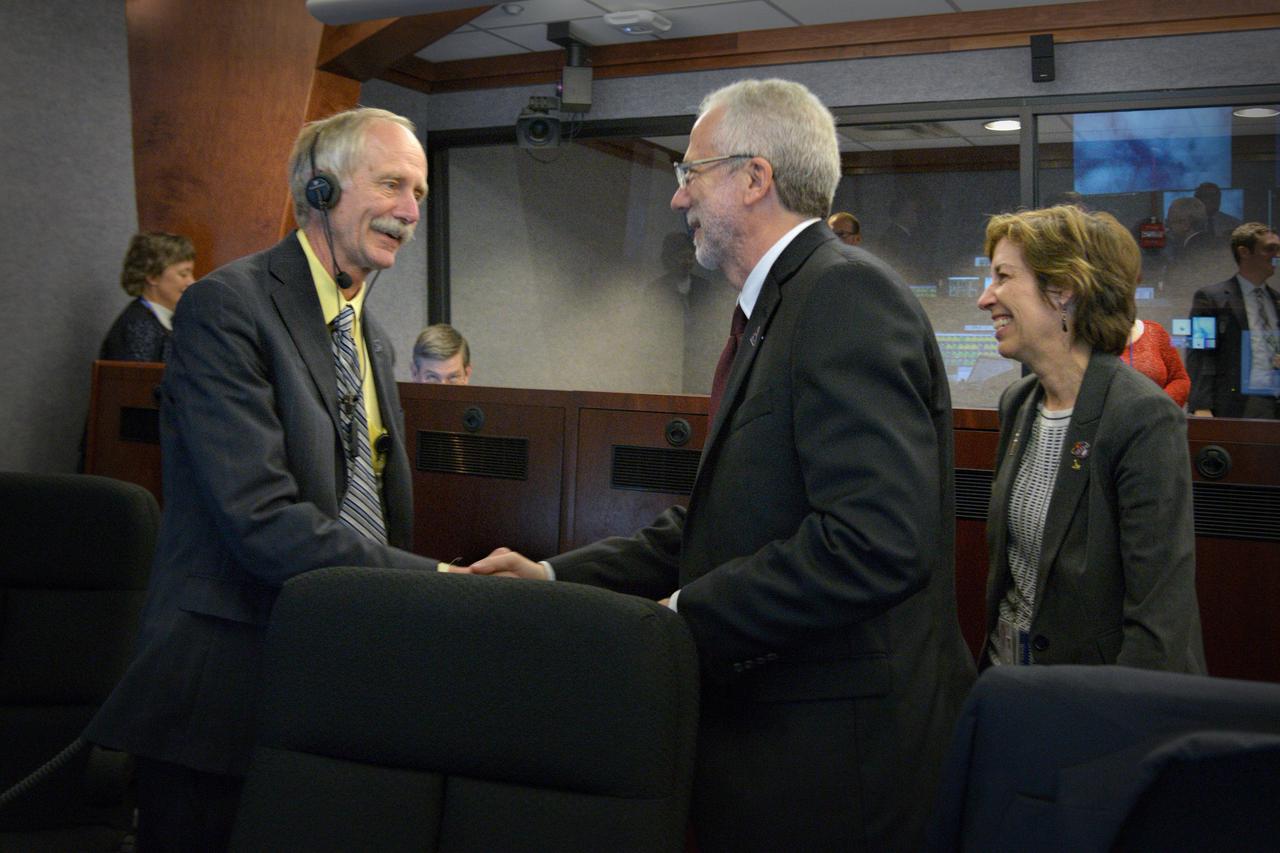

The Orion team celebrates Orion's successful Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) mission in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Dec. 5, 2014. Orion Program Manager Mark Geyer, NASA Director Ellen Ochoa and NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Directorate William Gerstenmaier are in frame. The Orion spacecraft orbited Earth twice, reaching an altitude of approximately 3,600 miles above Earth before landing. No one was aboard Orion for this flight test, but the spacecraft is designed to allow us to journey to destinations never before visited by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
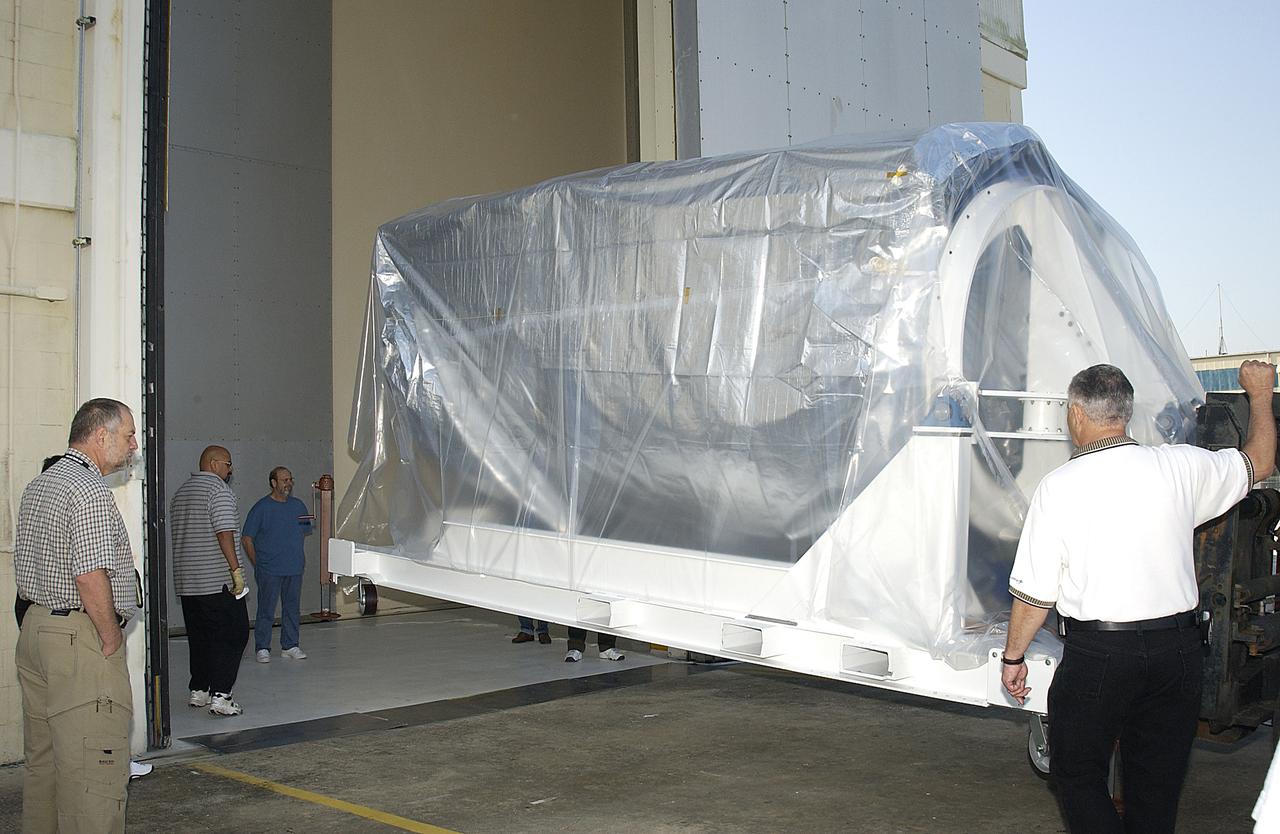

The Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) arrives at Building AE from the Lockheed Martin plant in Sunnyvale, Calif., to begin final preparations for its launch aboard a Delta II rocket. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is scheduled for launch April 15 at 4:34:07 a.m. EDT from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
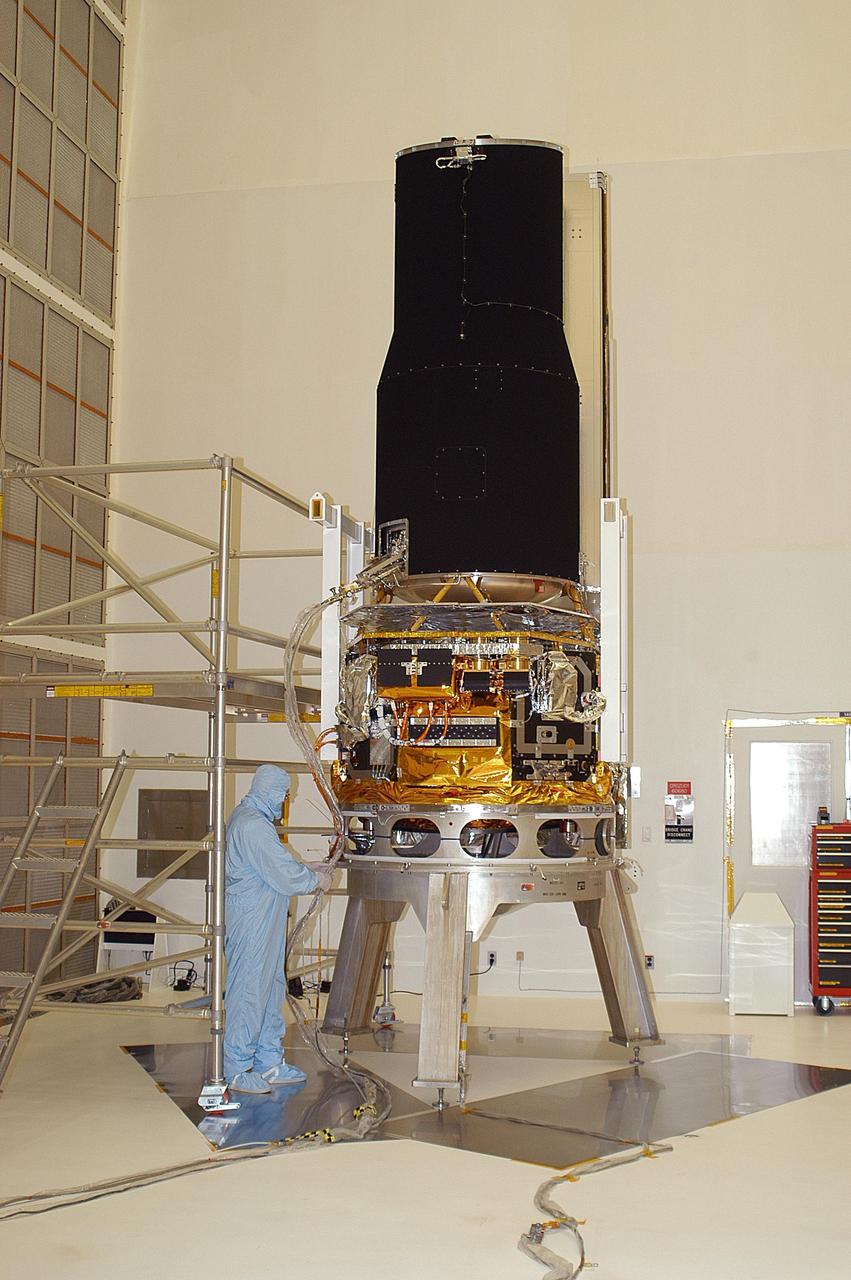

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Building AE, the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) is unpacked after being shipped from the Lockheed Martin plant in Sunnyvale, Calif. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
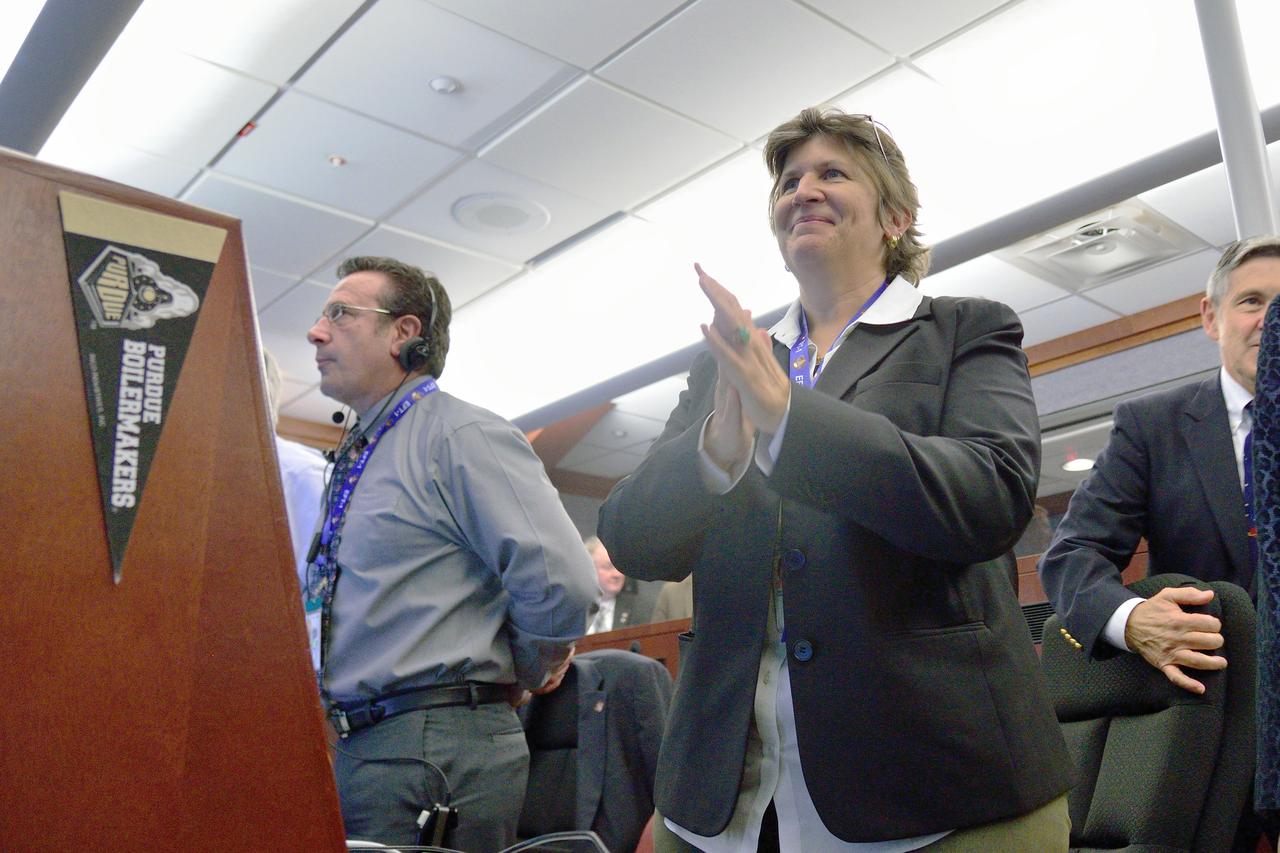

Orion Chief Engineer Julie Kramer celebrates Orion's successful splashdown in the Pacific Ocean after Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Dec. 5, 2014. The Orion spacecraft orbited Earth twice, reaching an altitude of approximately 3,600 miles above Earth before landing. No one was aboard Orion for this flight test, but the spacecraft is designed to allow us to journey to destinations never before visited by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

Orion Chief Engineer Julie Kramer waits for the parachute sequence to start after Orion reentered the atmosphere in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station during Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 5, 2014. The Orion spacecraft orbited Earth twice, reaching an altitude of approximately 3,600 miles above Earth before landing. No one was aboard Orion for this flight test, but the spacecraft is designed to allow us to journey to destinations never before visited by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Building AE, the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) is unpacked after being shipped from the Lockheed Martin plant in Sunnyvale, Calif. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

Lockheed Martin Program Manager Mike Hawes, Orion Program Manager Mark Geyer, and Orion Deputy Program Manager Mike Kirasich watch Orion's Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) reentry sequence in Building AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on a live stream from the Ikhana aircraft on Dec. 5, 2014. The Orion spacecraft orbited Earth twice, reaching an altitude of approximately 3,600 miles above Earth before landing. No one was aboard Orion for this flight test, but the spacecraft is designed to allow us to journey to destinations never before visited by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
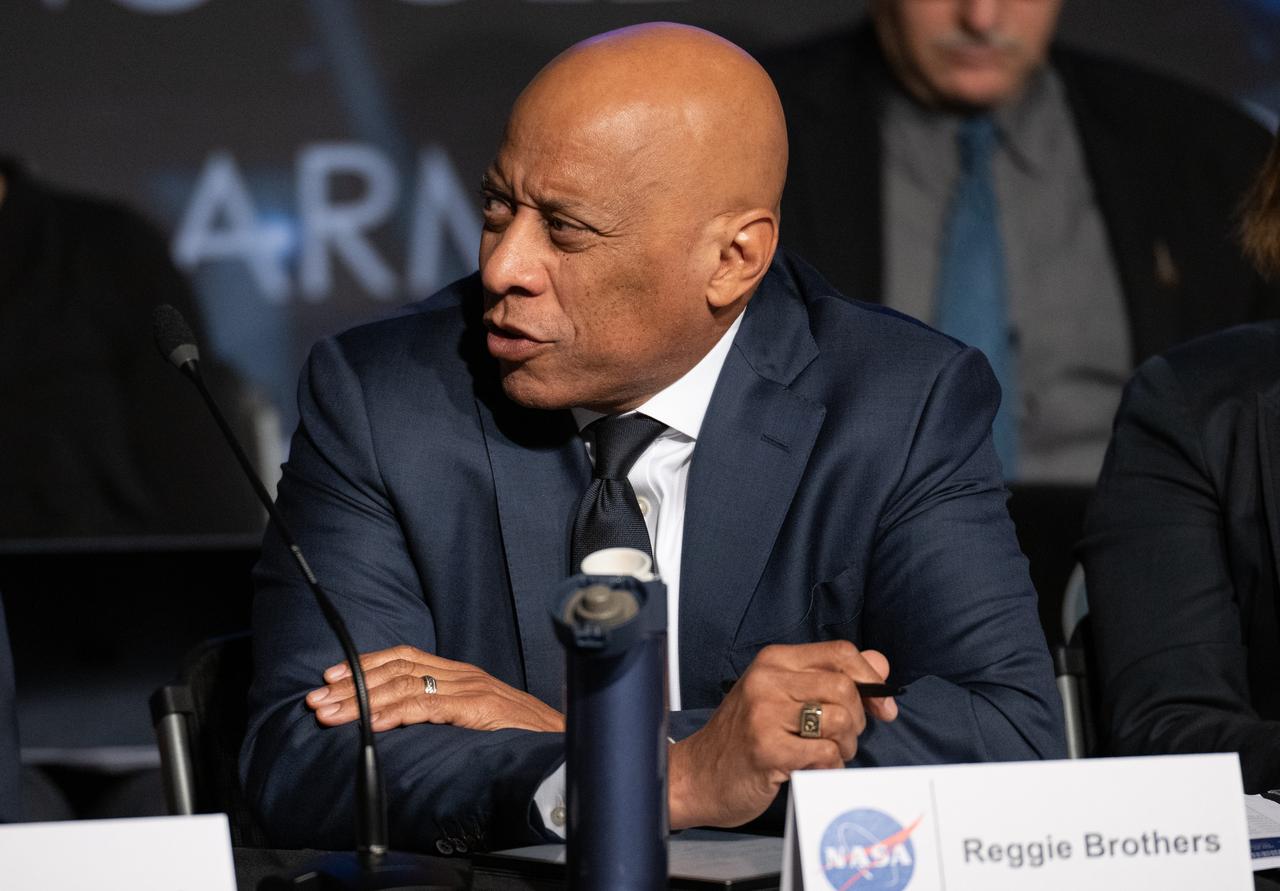

Reggie Brothers, operating partner at AE Industrial Partners, asks a question during a public meeting of NASA’s unidentified anomalous phenomena (UAP) independent study team, Wednesday, May 31, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The UAP independent study team is a counsel of 16 community experts across diverse areas on matters relevant to potential methods of study for unidentified anomalous phenomena. NASA commissioned the nine-month study to examine UAP from a scientific perspective and create a roadmap for how to use data and the tools of science to move our understanding of UAP forward. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
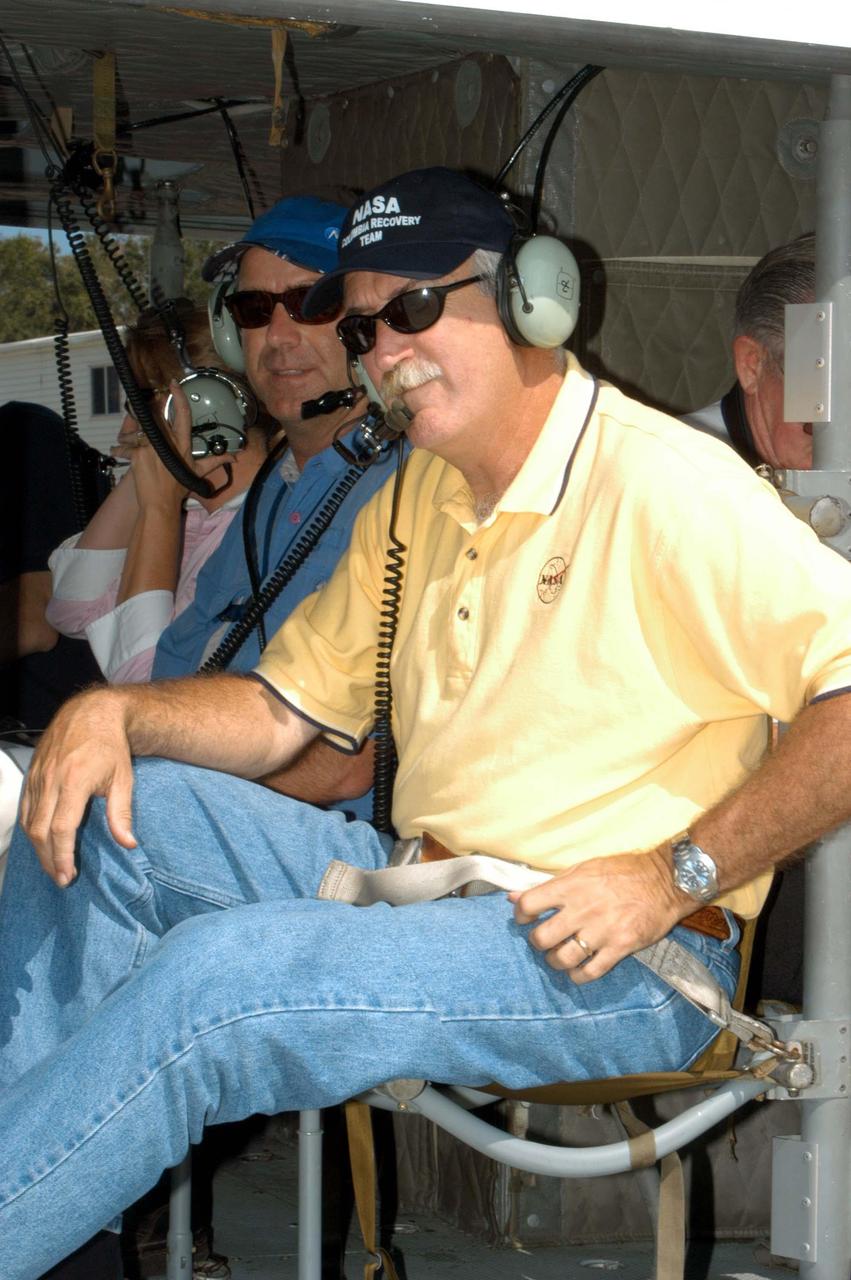

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe (right) sits next to KSC Director of Spaceport Services Scott Kerr in the helicopter from which they will observe overall damage at the Center from Hurricane Frances. O’Keefe and NASA Associate Administrator of Space Operations Mission Directorate William Readdy are visiting KSC to survey the damage sustained by KSC facilities from the hurricane. The Labor Day storm caused significant damage to the Vehicle Assembly Building, Thermal Protection System Facility, and Processing Control Center. Additionally, the Operations and Checkout Building, Vertical Processing Facility, Hangar AE, Hangar S and Hangar AF Small Parts Facility each received substantial damage. However, well-protected and unharmed were NASA’s three Space Shuttle orbiters -- Discovery, Atlantis and Endeavour - along with the Shuttle launch pads, all of the critical flight hardware for the orbiters and the International Space Station, and NASA’s Swift spacecraft that is awaiting launch in October.
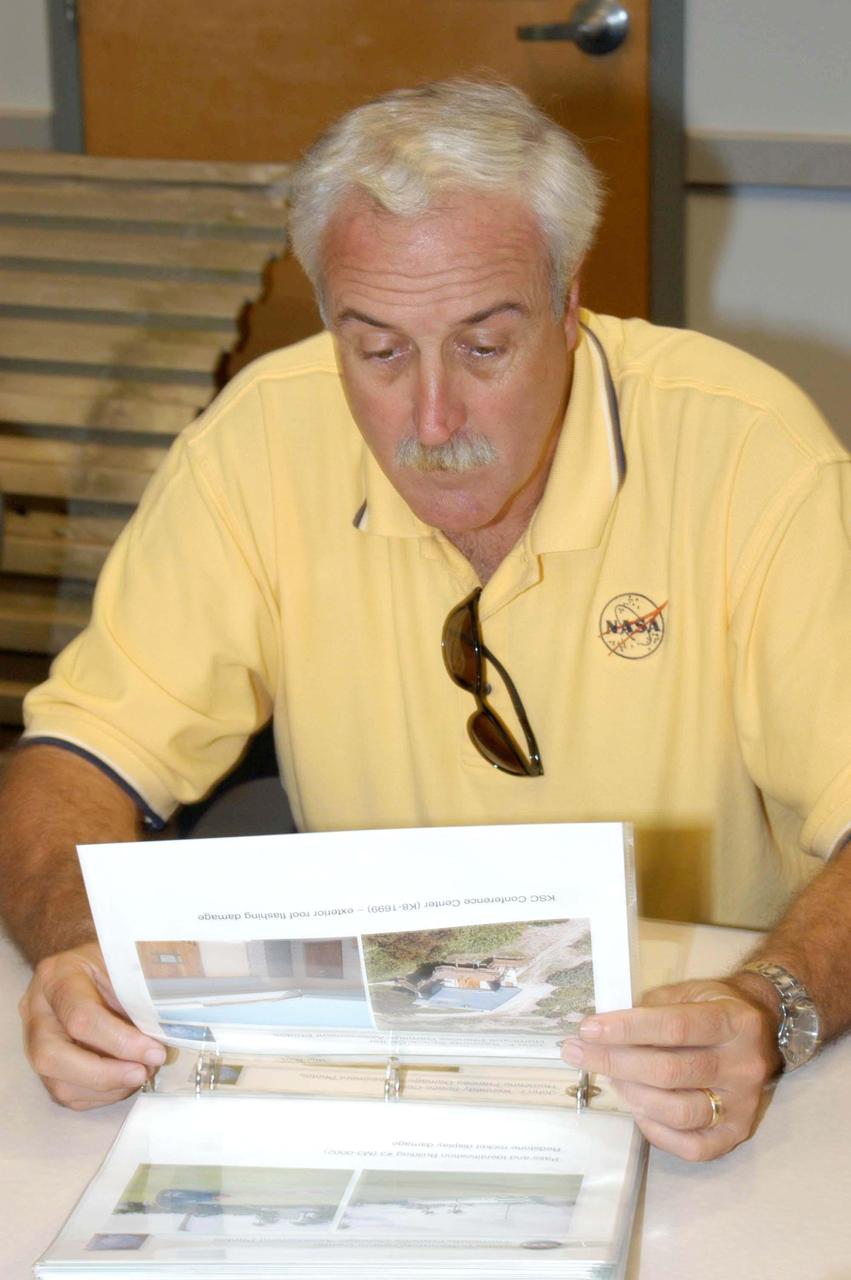

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe looks at images of damaged KSC facilities in the RLV Hangar before surveying the damage sustained by KSC facilities from Hurricane Frances over Labor Day weekend. The Vehicle Assembly Building, Thermal Protection System Facility, and Processing Control Center all received significant damage from the storm. Additionally, the Operations and Checkout Building, Vertical Processing Facility, Hangar AE, Hangar S and Hangar AF Small Parts Facility each received substantial damage. NASA’s three Space Shuttle orbiters -- Discovery, Atlantis and Endeavour - along with the Shuttle launch pads, all of the critical flight hardware for the orbiters and the International Space Station, and NASA’s Swift spacecraft, awaiting launch in October, were well protected and unharmed.
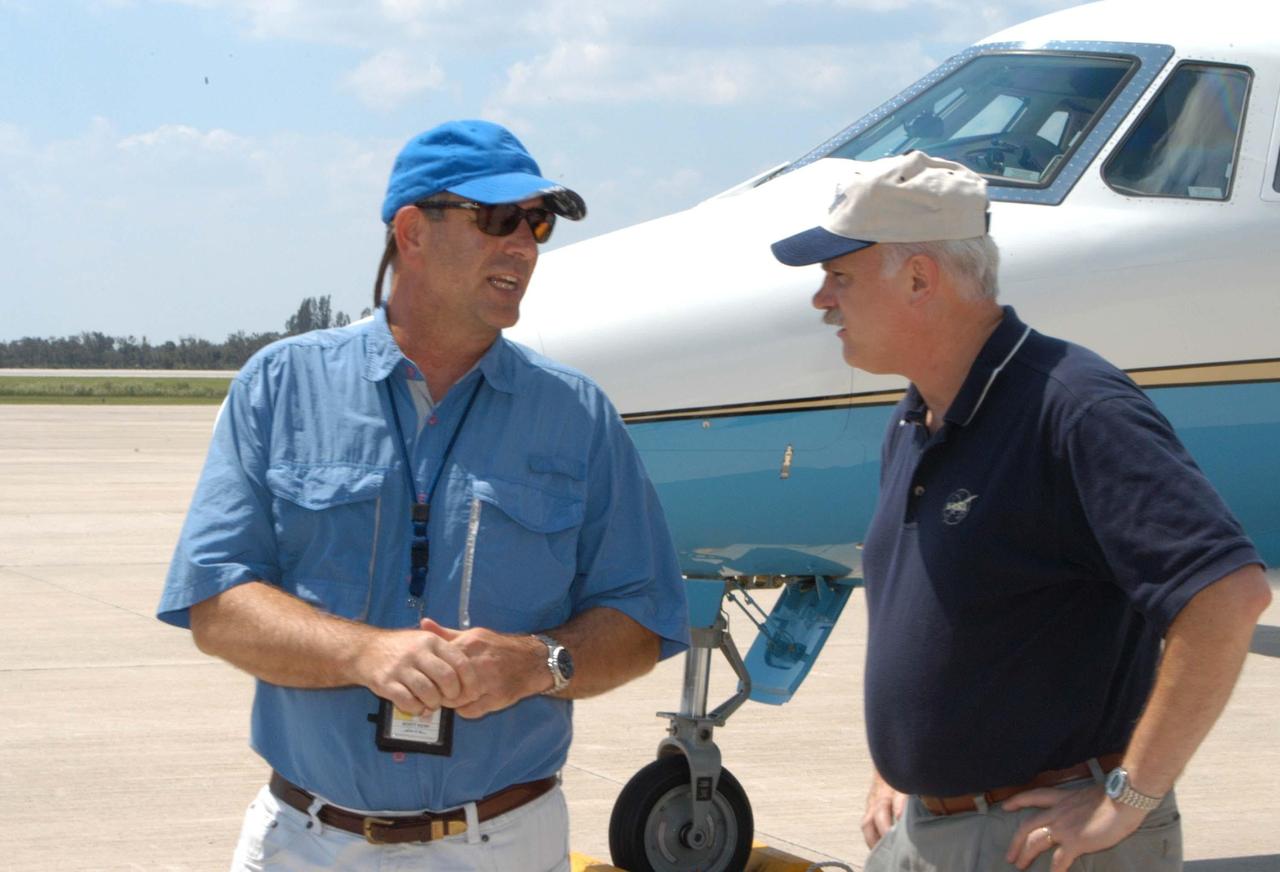

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - KSC Director of Spaceport Services Scott Kerr (left) talks to NASA Associate Administrator of the Space Operations Mission Directorate William Readdy at the Shuttle Landing Facility. NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe and Readdy are visiting KSC to survey the damage sustained by KSC facilities from Hurricane Frances over Labor Day weekend. The Vehicle Assembly Building, Thermal Protection System Facility, and Processing Control Center all received significant damage from the storm. Additionally, the Operations and Checkout Building, Vertical Processing Facility, Hangar AE, Hangar S and Hangar AF Small Parts Facility each received substantial damage. However, well-protected and unharmed were NASA’s three Space Shuttle orbiters -- Discovery, Atlantis and Endeavour - along with the Shuttle launch pads, all of the critical flight hardware for the orbiters and the International Space Station, and NASA’s Swift spacecraft that is awaiting launch in October.
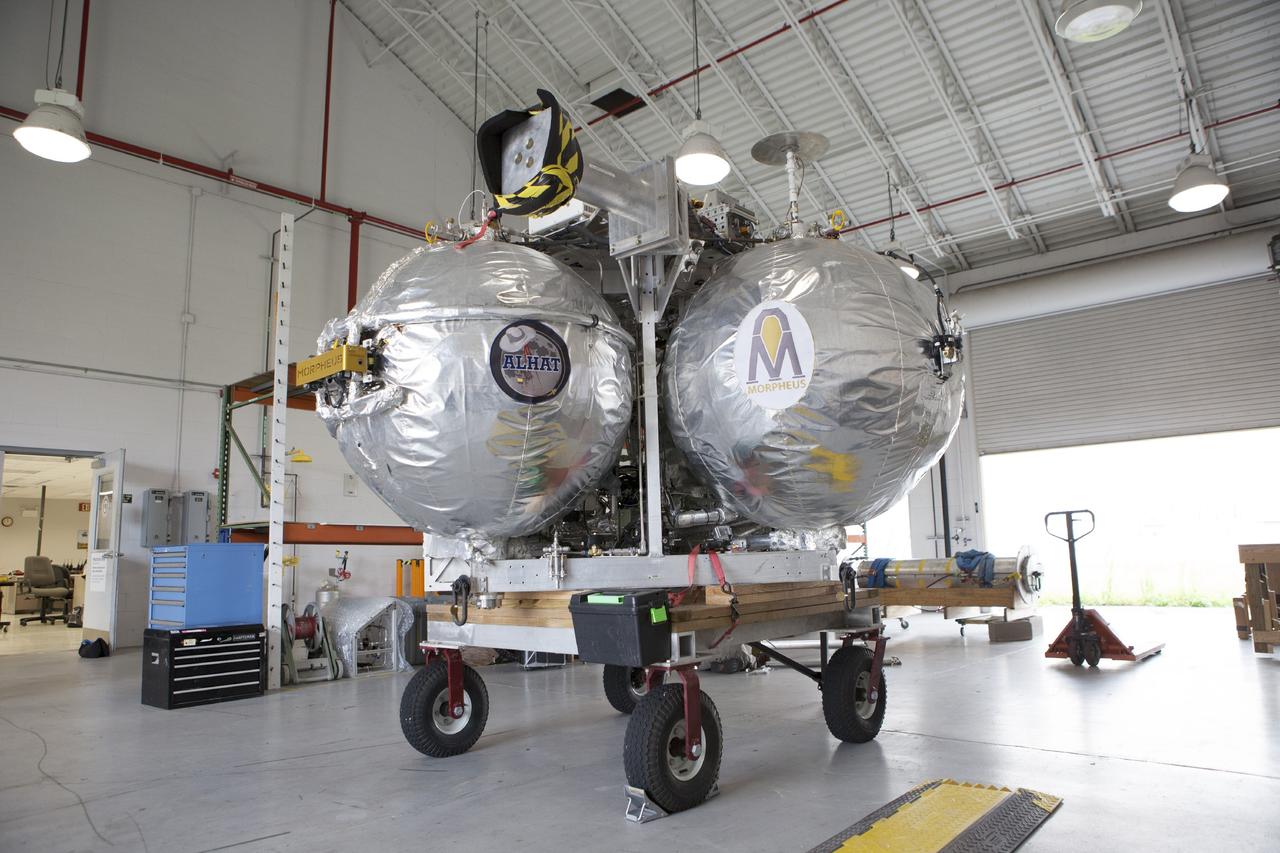

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Project Morpheus lander sits inside the bay of a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
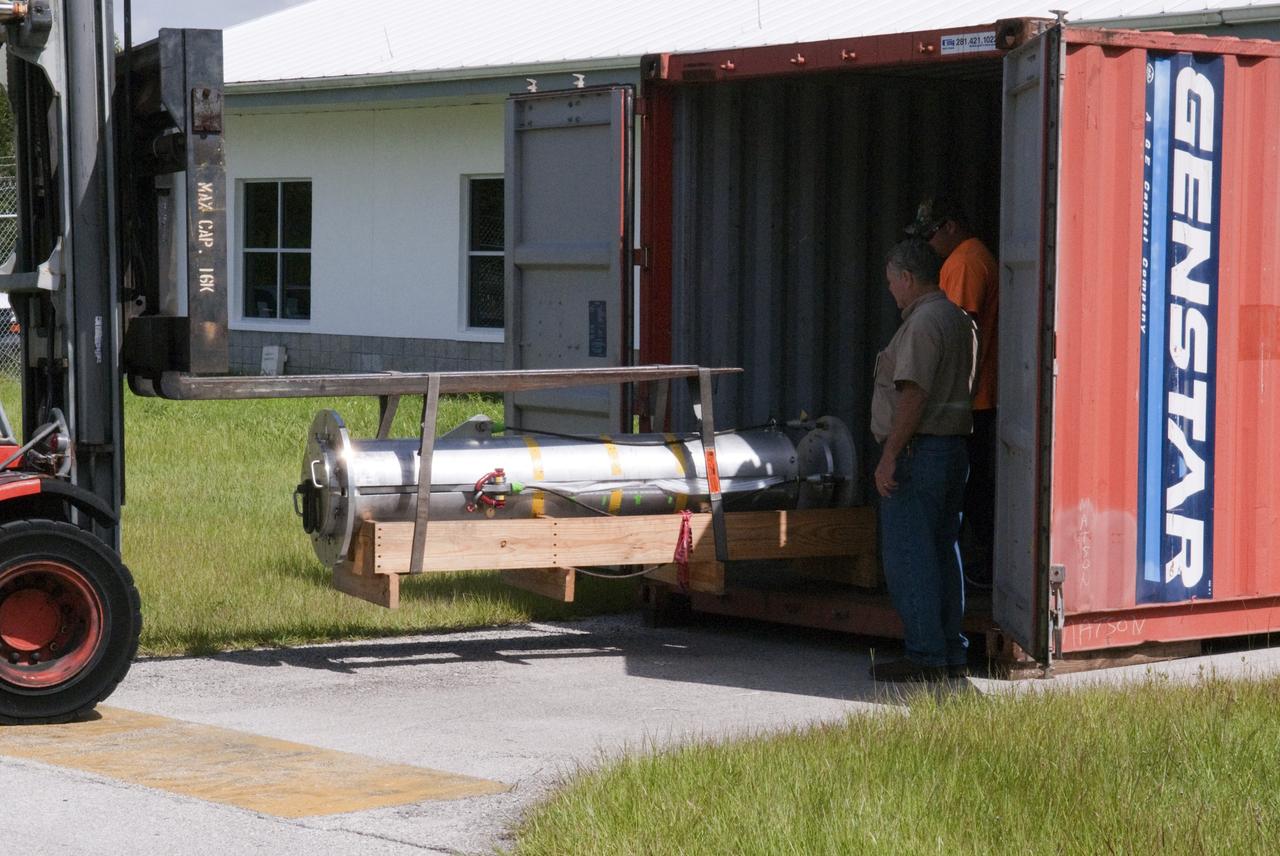

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Support equipment for NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
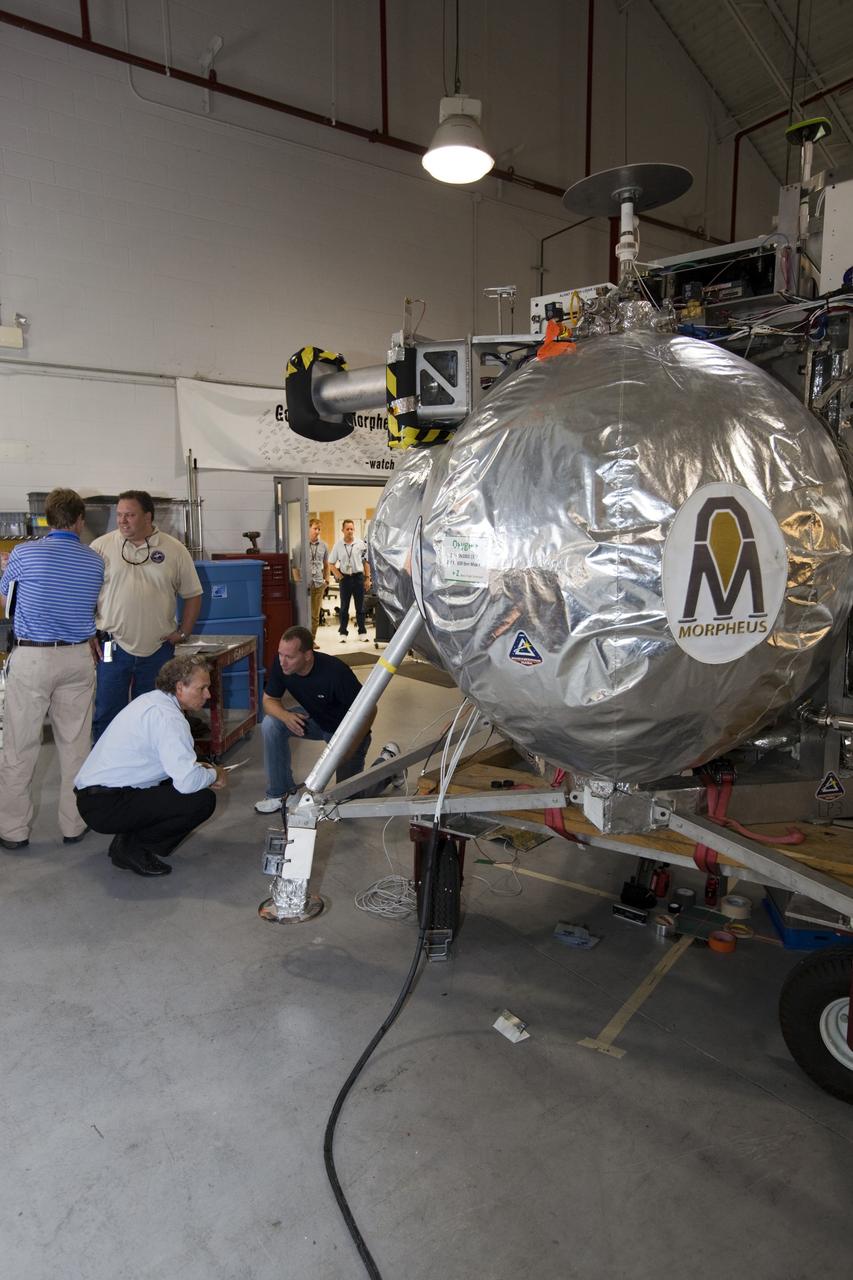

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Russell Romanella, director of Safety and Mission Assurance at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, kneeling on the left, is briefed on NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle. Morpheus is being checked out by technicians and engineers in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at Kennedy. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
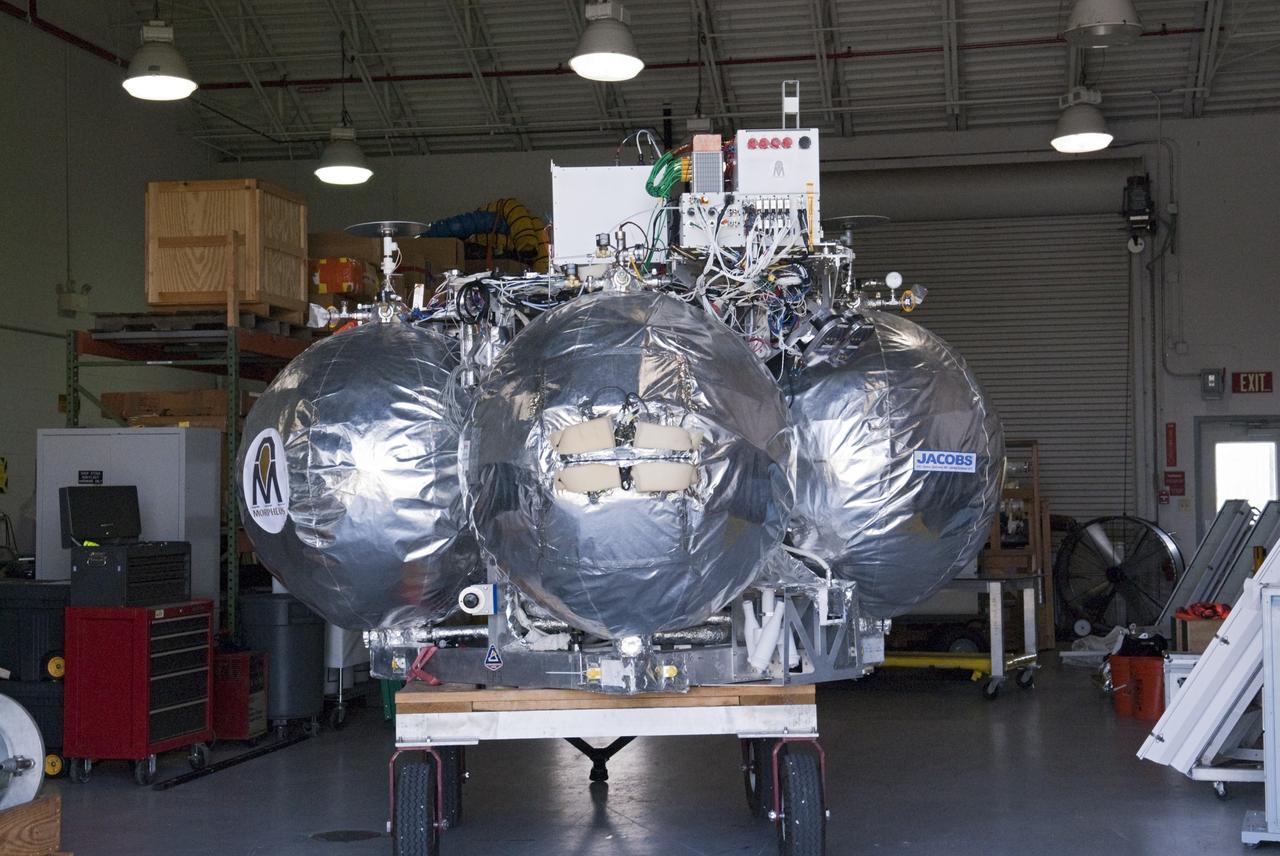

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, has been moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
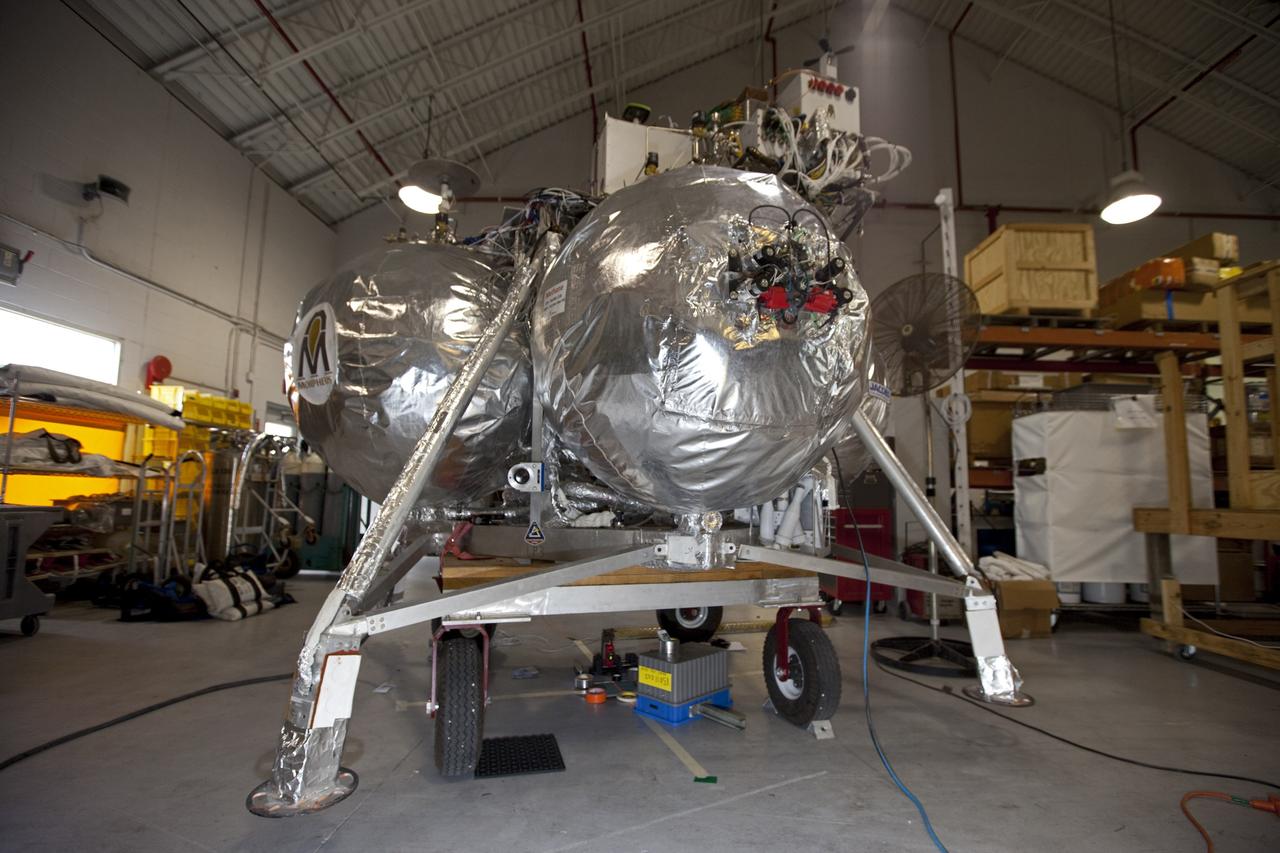

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being checked out in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
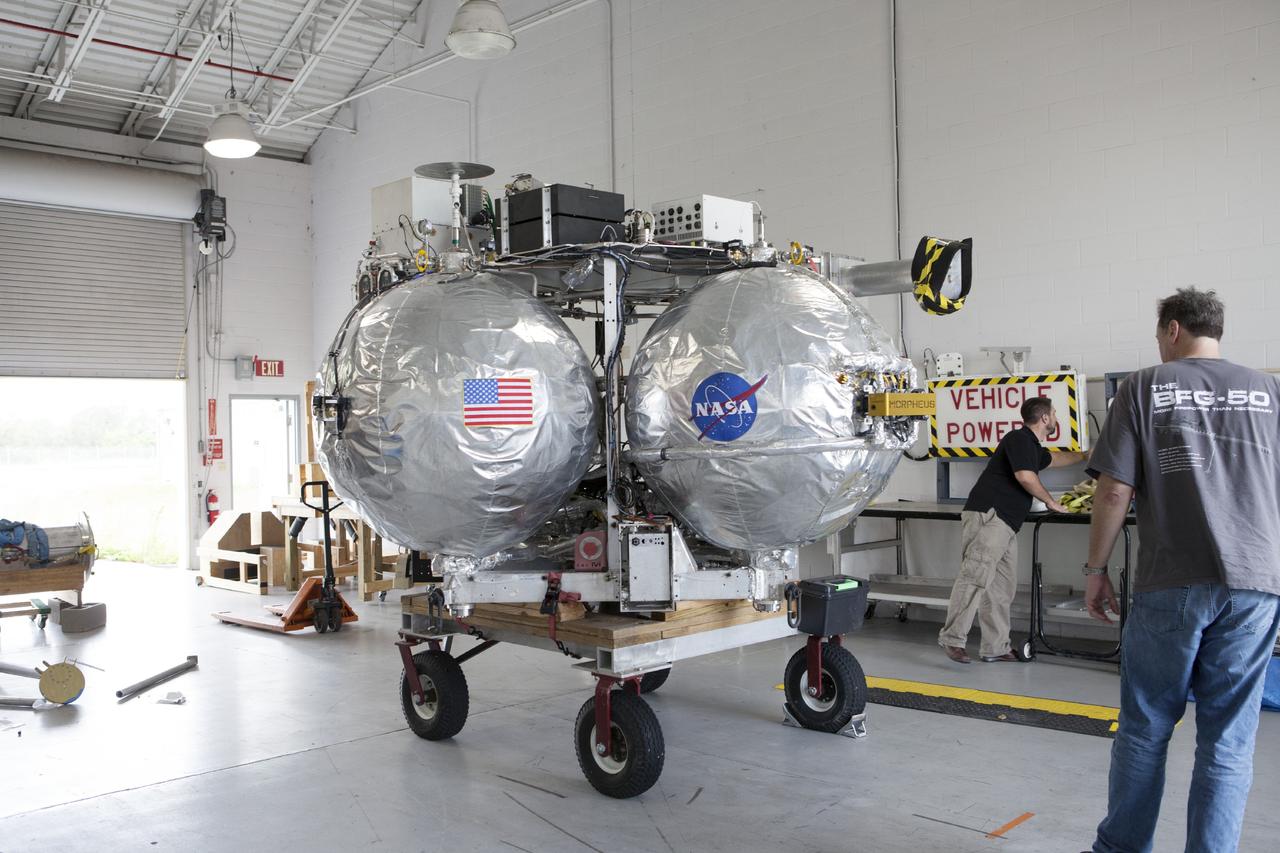

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Project Morpheus lander is moved into the bay of a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
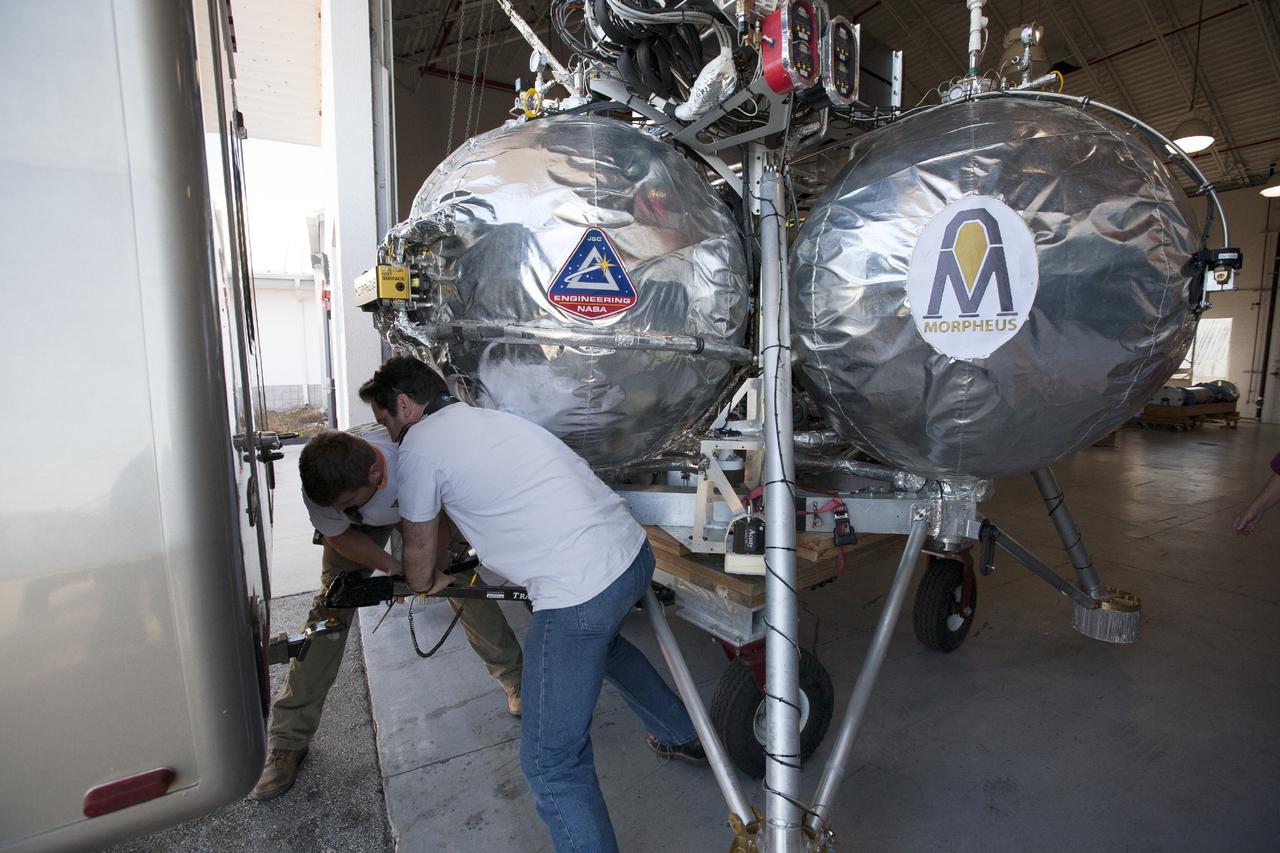

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare the Project Morpheus prototype lander to be transported from a support building to a launch platform at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility. Testing of the prototype lander was performed at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for tethered and free flight testing at Kennedy. The landing facility will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is being managed under the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, Division in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. The efforts in AES pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
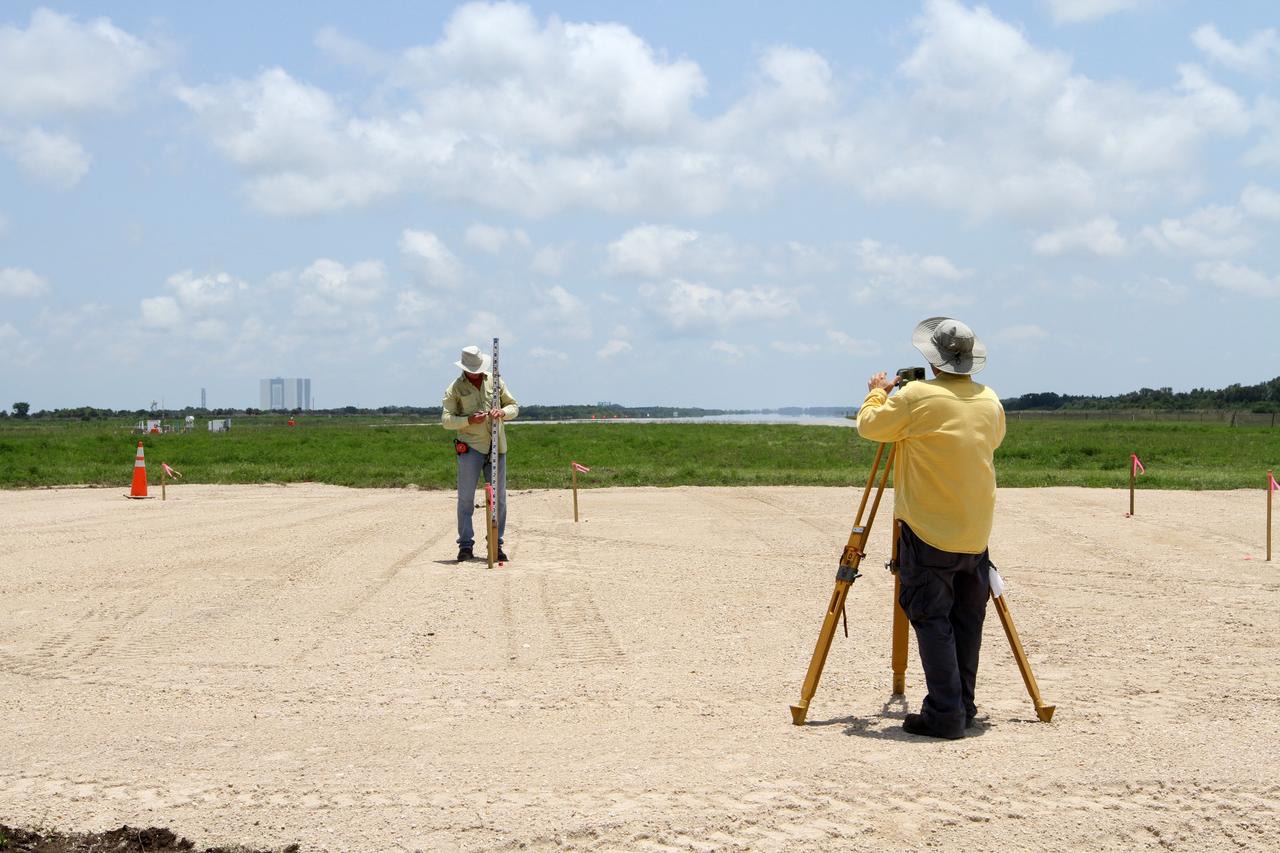

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Surveyors ensure the hazard field for the Project Morpheus lander is properly situated near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the distance is the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
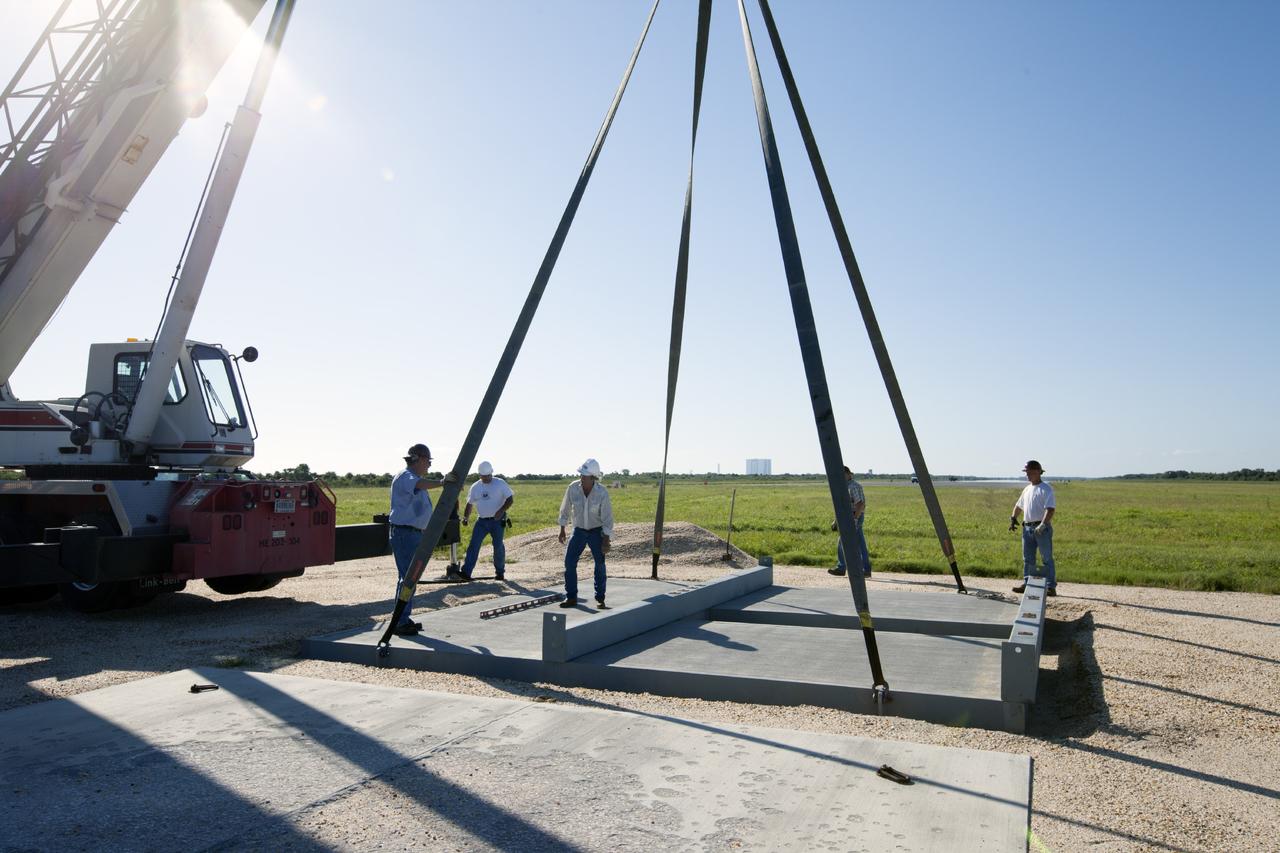

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers position the movable launch platform for the Project Morpheus lander in its new site adjacent to a hazard field created to support the project at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. In the distance is the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight. The lander is scheduled for delivery to Kennedy in October. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst obstacles during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
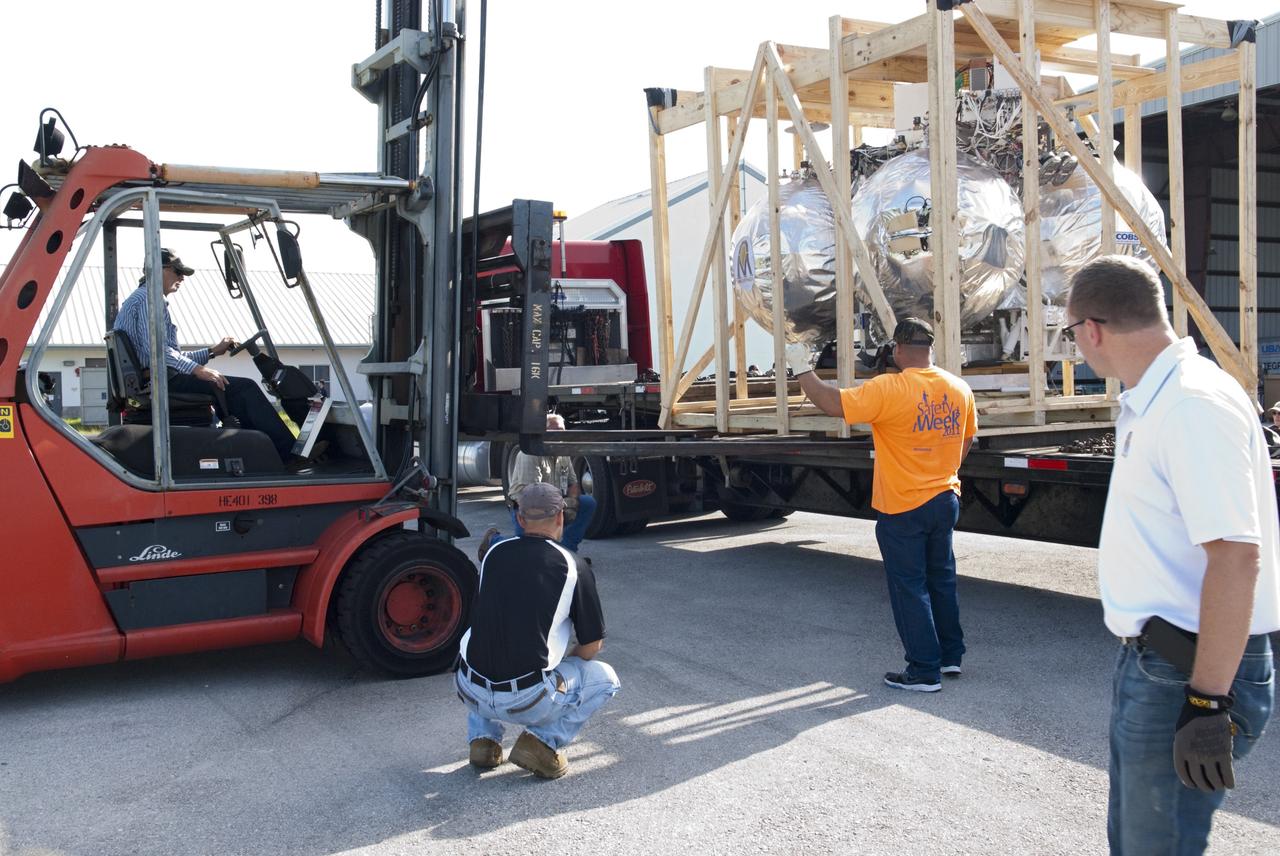

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
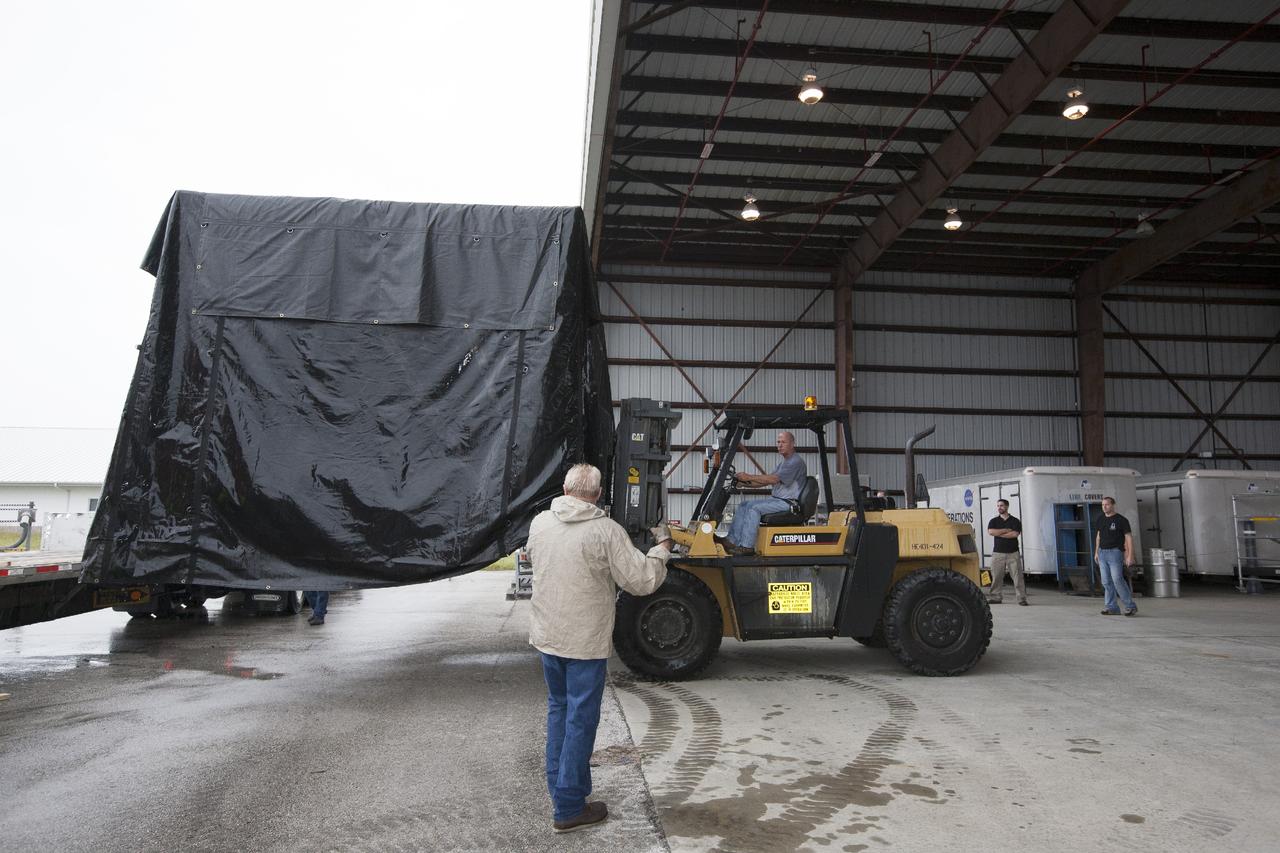

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Project Morpheus lander is moved into a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
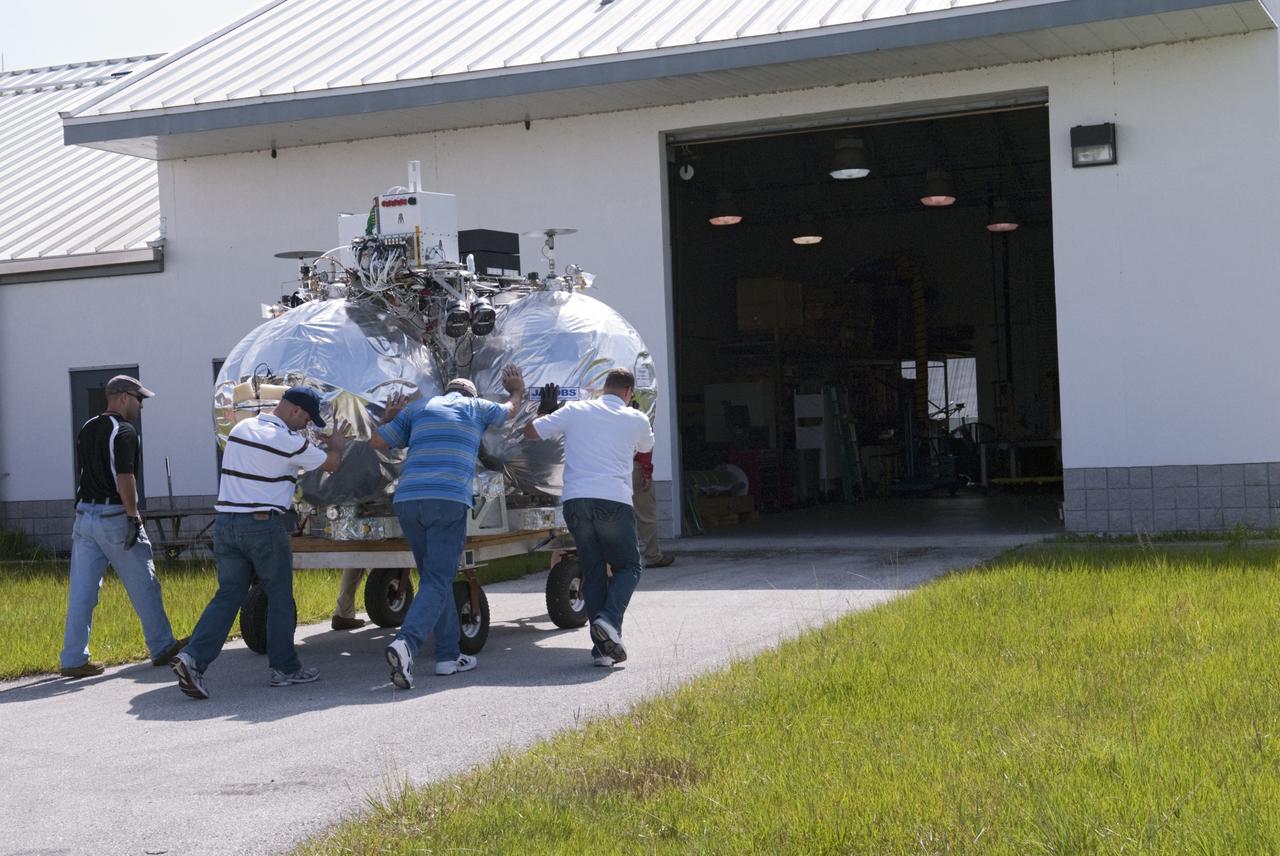

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
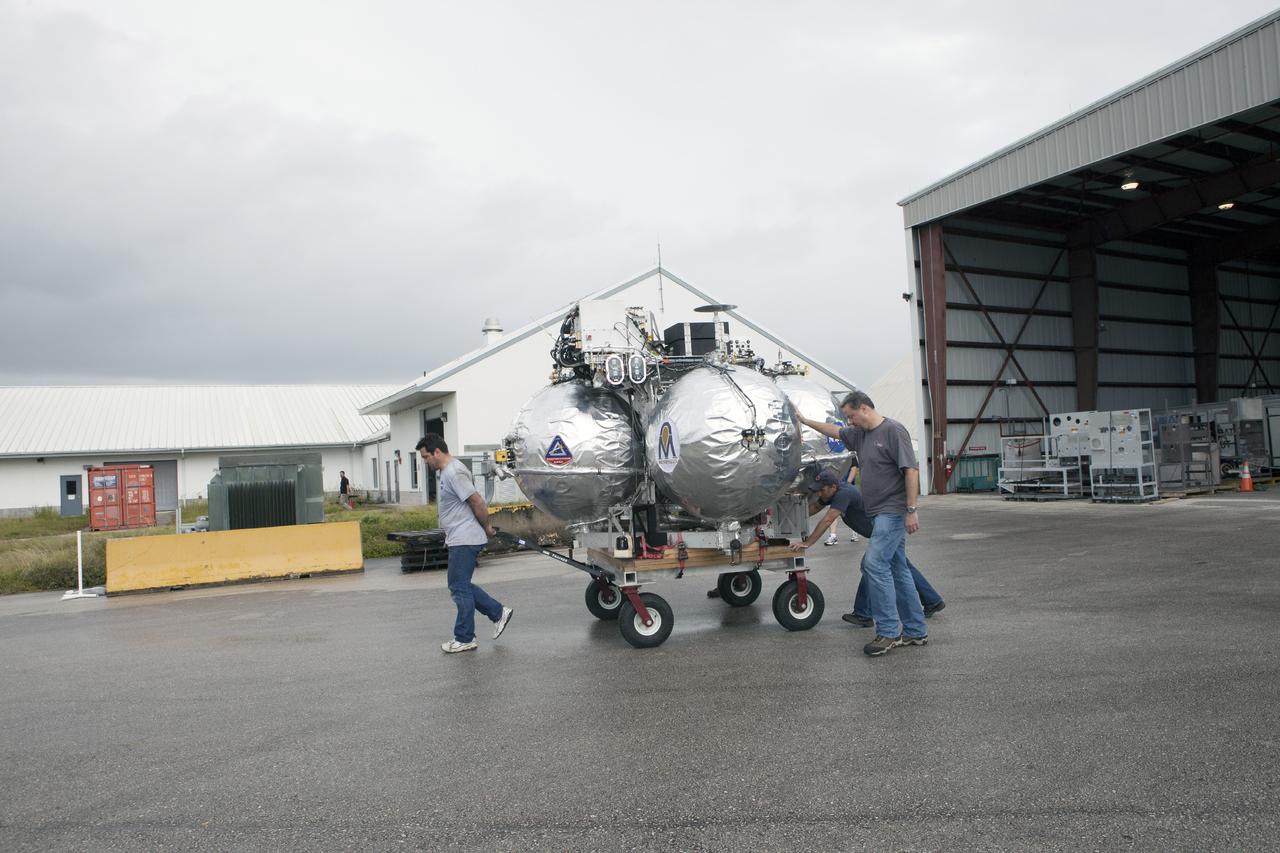

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians move the Project Morpheus lander on a small transporter to a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
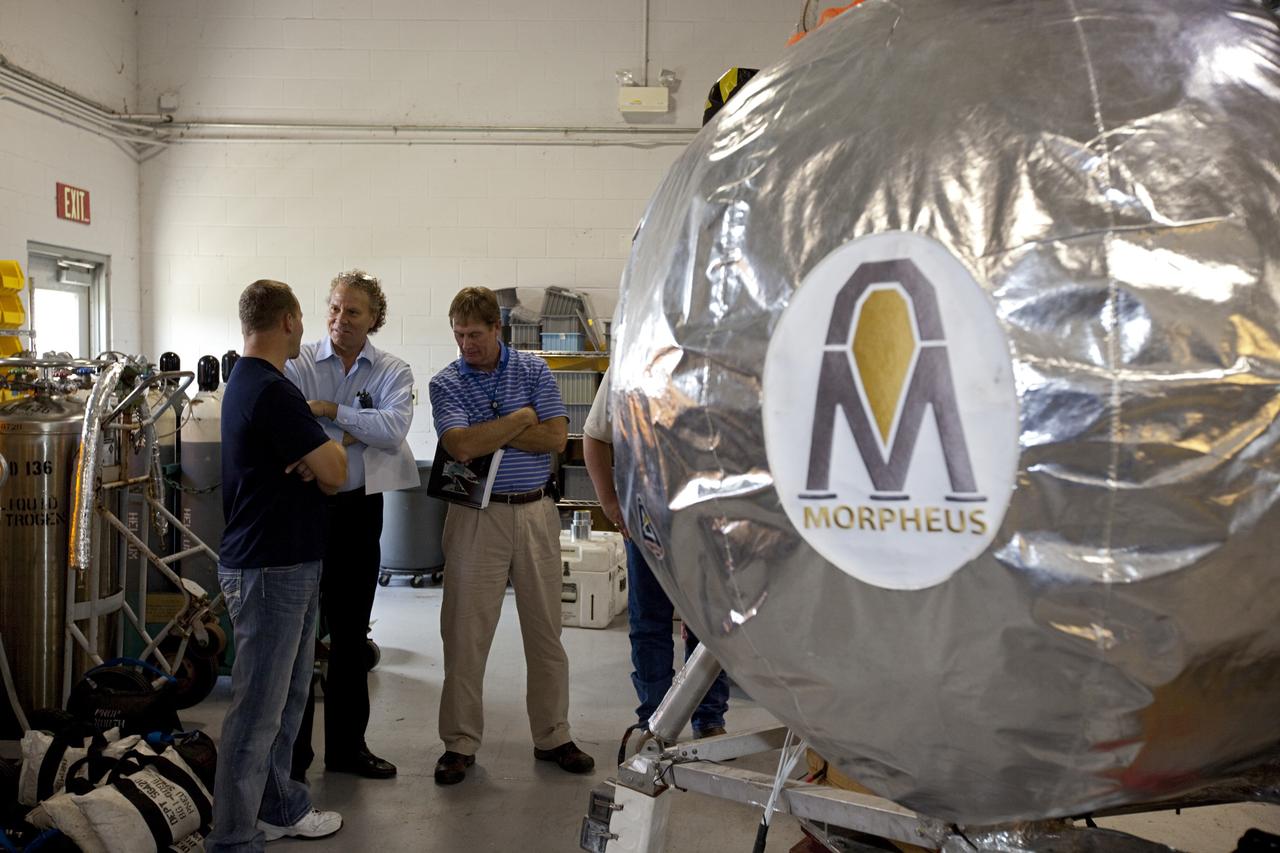

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Russell Romanella, director of Safety and Mission Assurance at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, center, is briefed on NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle. Morpheus is being checked out by technicians and engineers in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at Kennedy. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
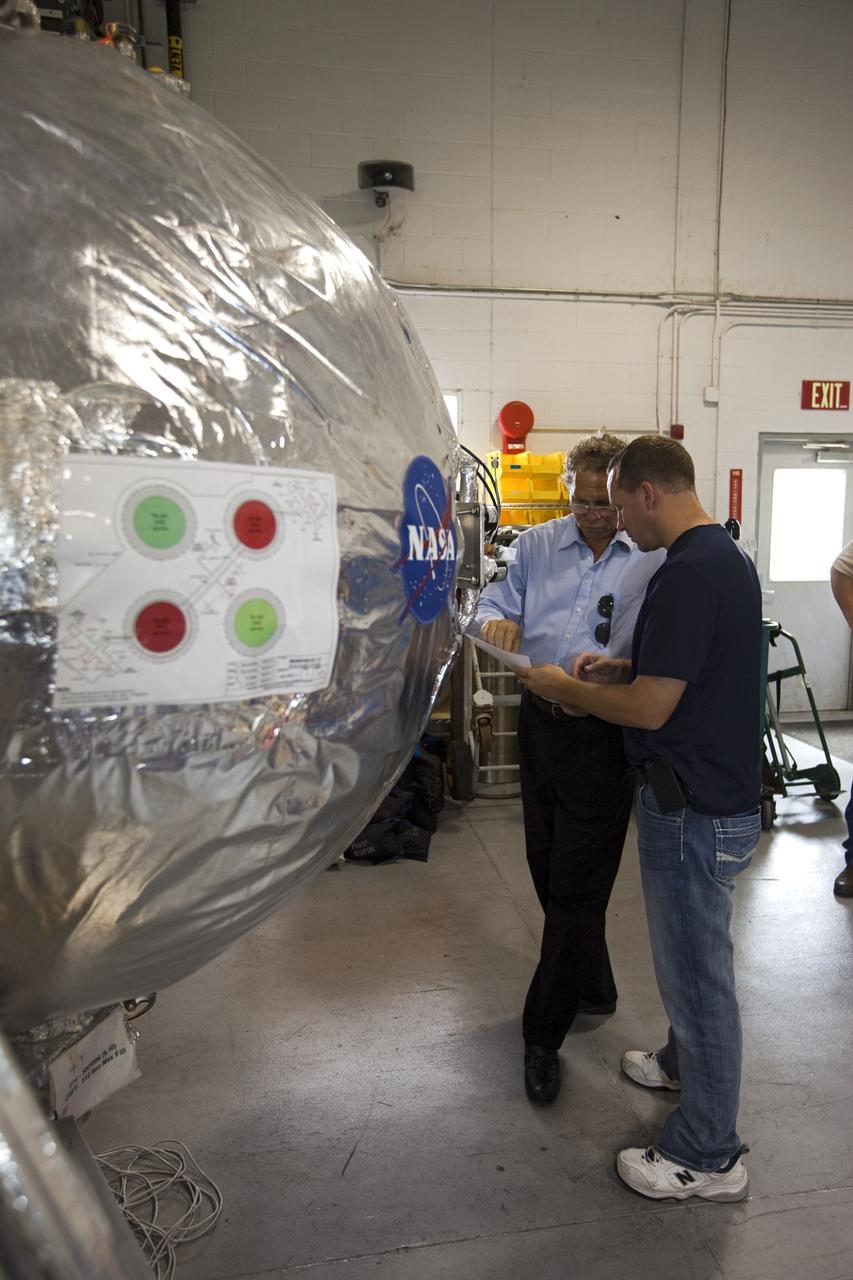

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Russell Romanella, director of Safety and Mission Assurance at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, left, is briefed on NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle. Morpheus is being checked out by technicians and engineers in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at Kennedy. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
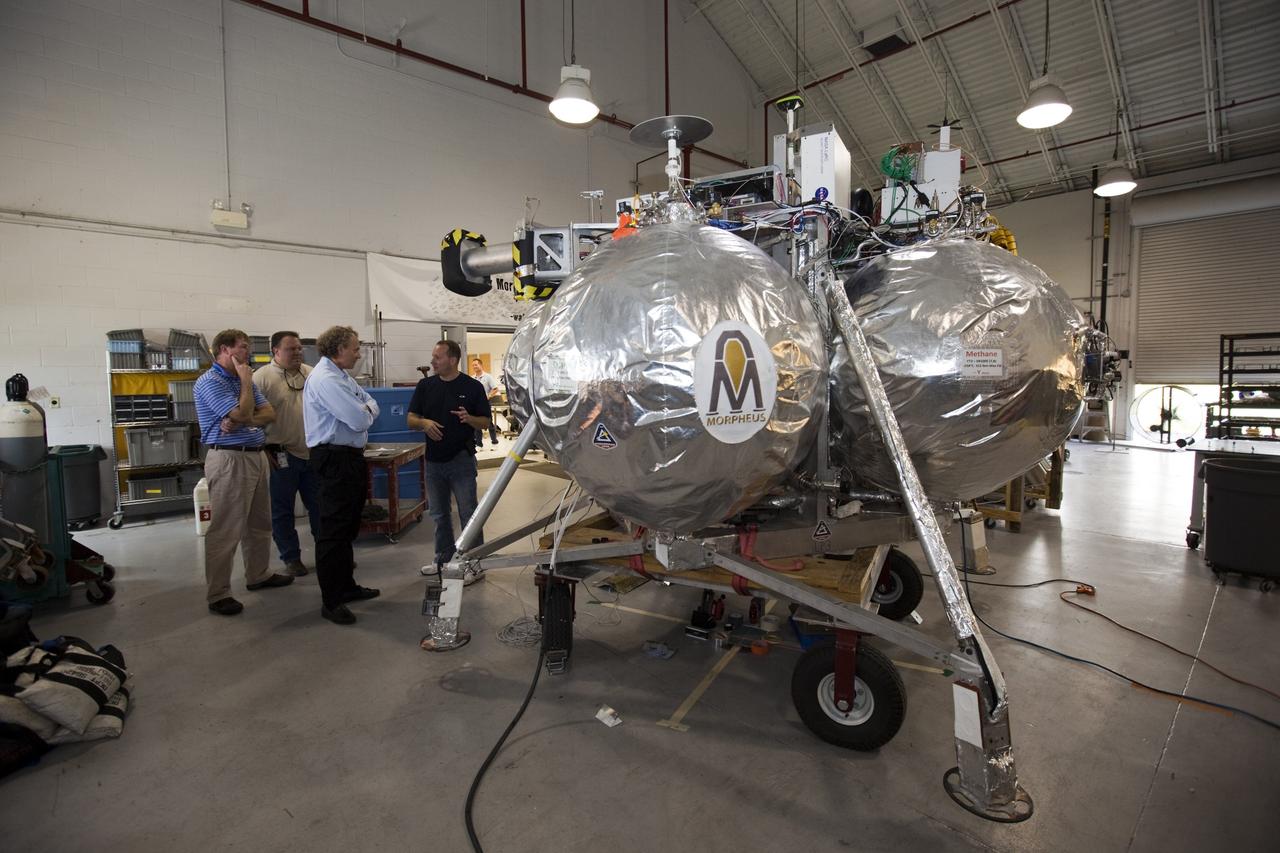

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Russell Romanella, director of Safety and Mission Assurance at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, right-center, is briefed on NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle. Morpheus is being checked out by technicians and engineers in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at Kennedy. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
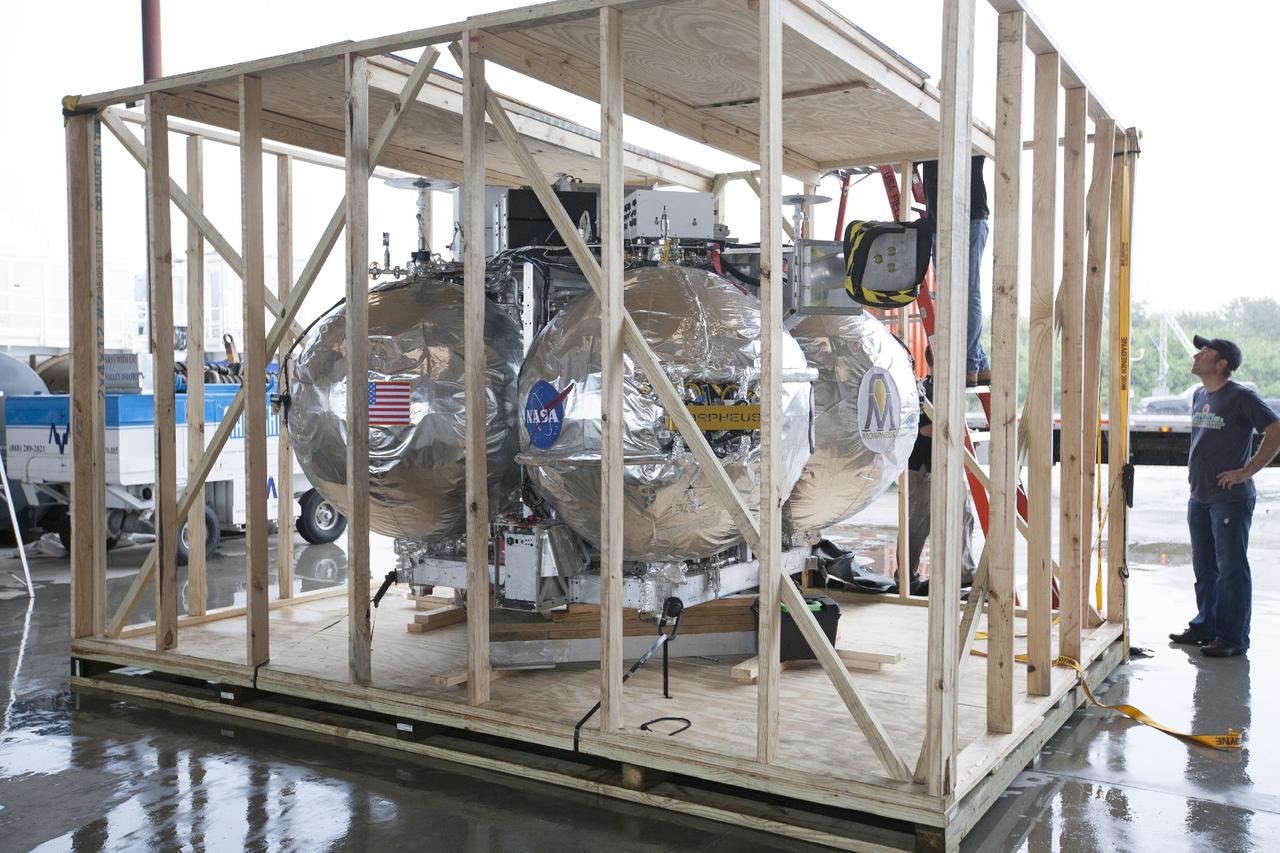
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Project Morpheus lander has been offloaded from a flatbed truck and sits inside a protective crate inside a support building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF. Testing of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for free flight testing at Kennedy. The SLF will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus utilizes an autonomous landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, payload that will allow it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
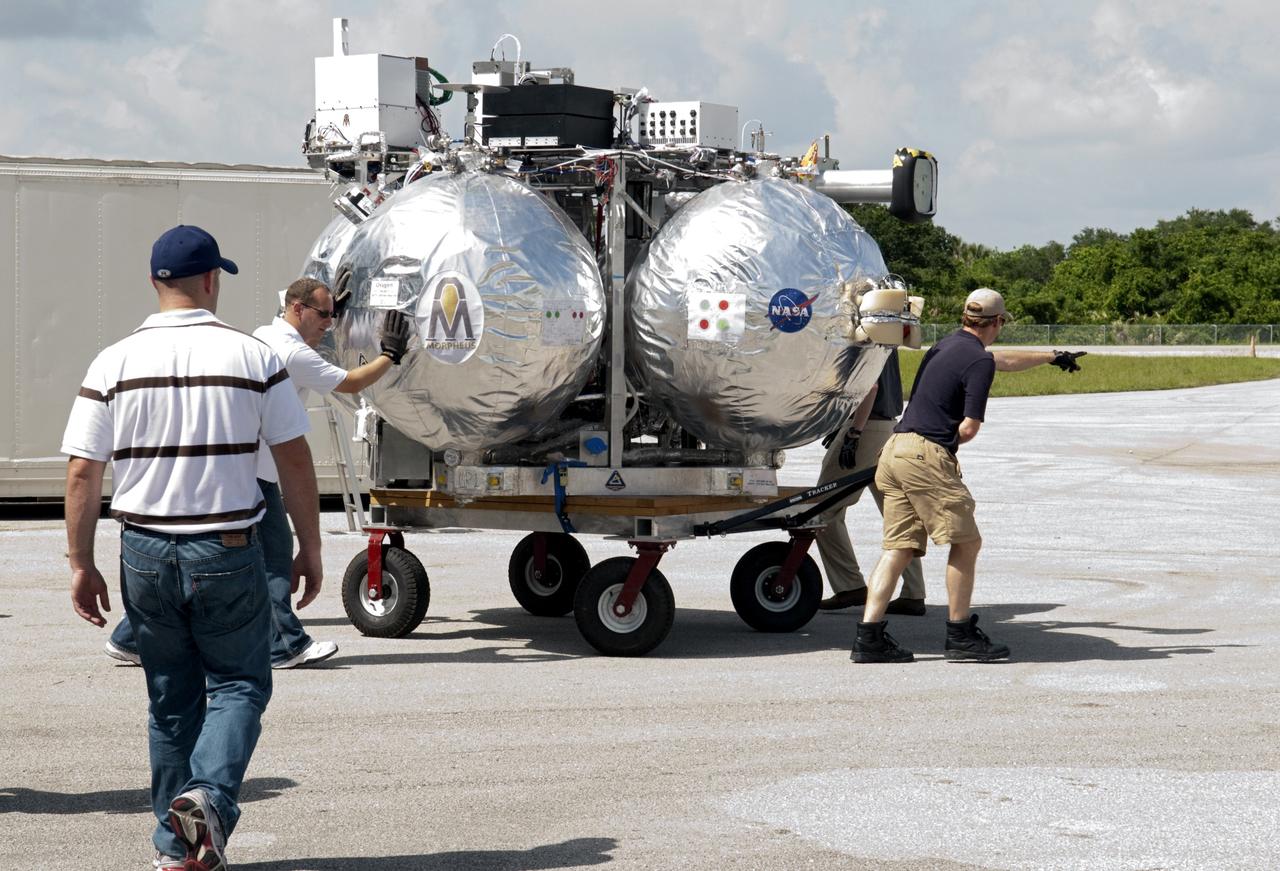

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser