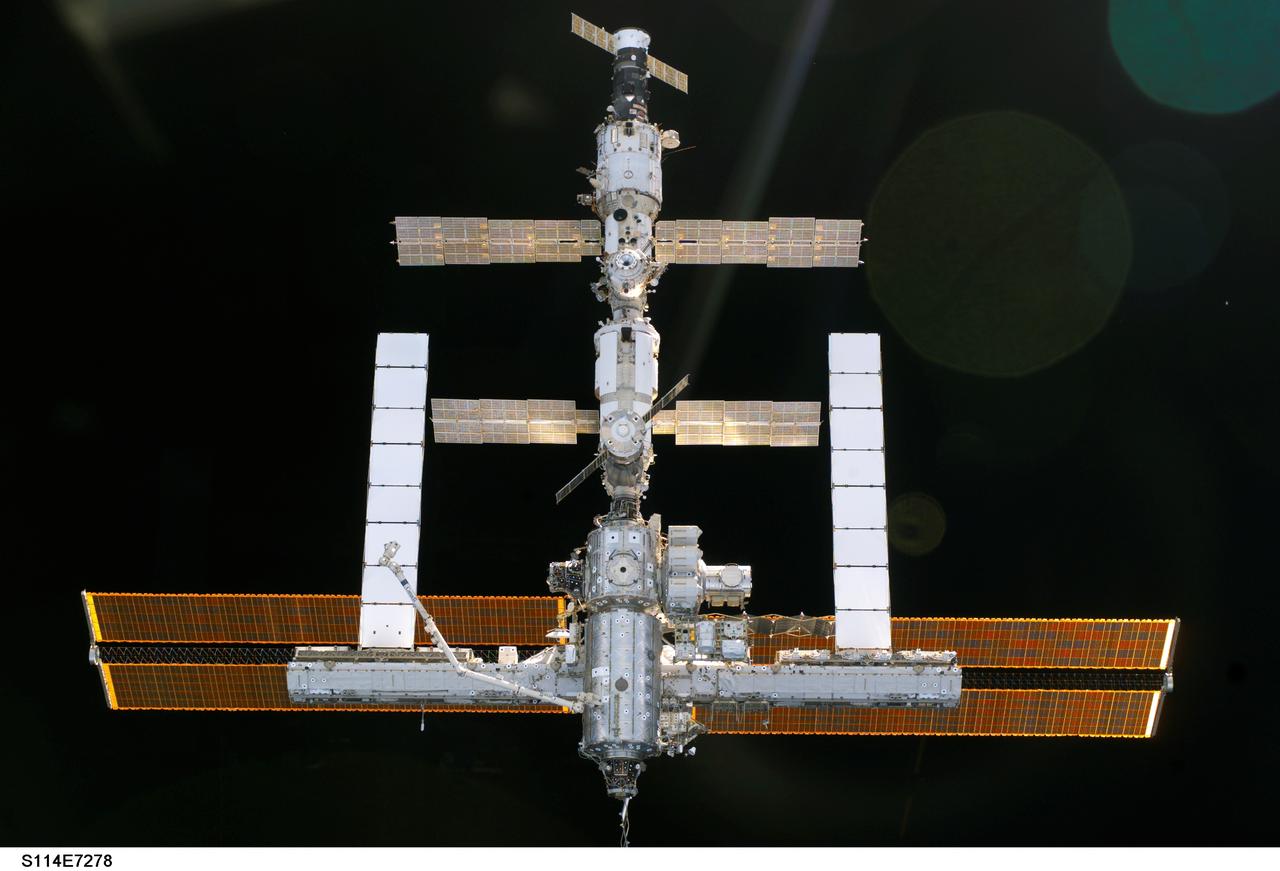
S114-E-7278 (6 August 2005) --- The International Space Station is backdropped against the blackness of space as the orbital outpost moves away from the Space Shuttle Discovery. Earlier, the crews of the two spacecraft concluded nine days of cooperative work. As the Shuttle moved away to a distance of about 400 feet, astronaut James M. Kelly, pilot, began a slow fly-around of the Station, as cameras on each spacecraft captured video and still images of the other. Undocking occurred at 2:24 a.m. (CDT), August 6, 2005.

STS065-214-037 (8-23 July 1994) --- Ready to begin one of her busy twelve hour shifts, payload specialist Dr. Chiaki Naito-Mukai enters the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) science module in the cargo bay via the tunnel connecting it to the Space Shuttle Columbia's cabin. Dr. Mukai joined six NASA astronauts for more than two weeks of experimenting in Earth orbit. This photo was among the first released by NASA following IML-2. Also onboard were NASA astronauts Robert D. Cabana, James D. Halsell, Jr., Richard J. Hieb, Carl E. Walz, Donald A. Thomas and Leroy Chiao. Dr. Mukai represented the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan.
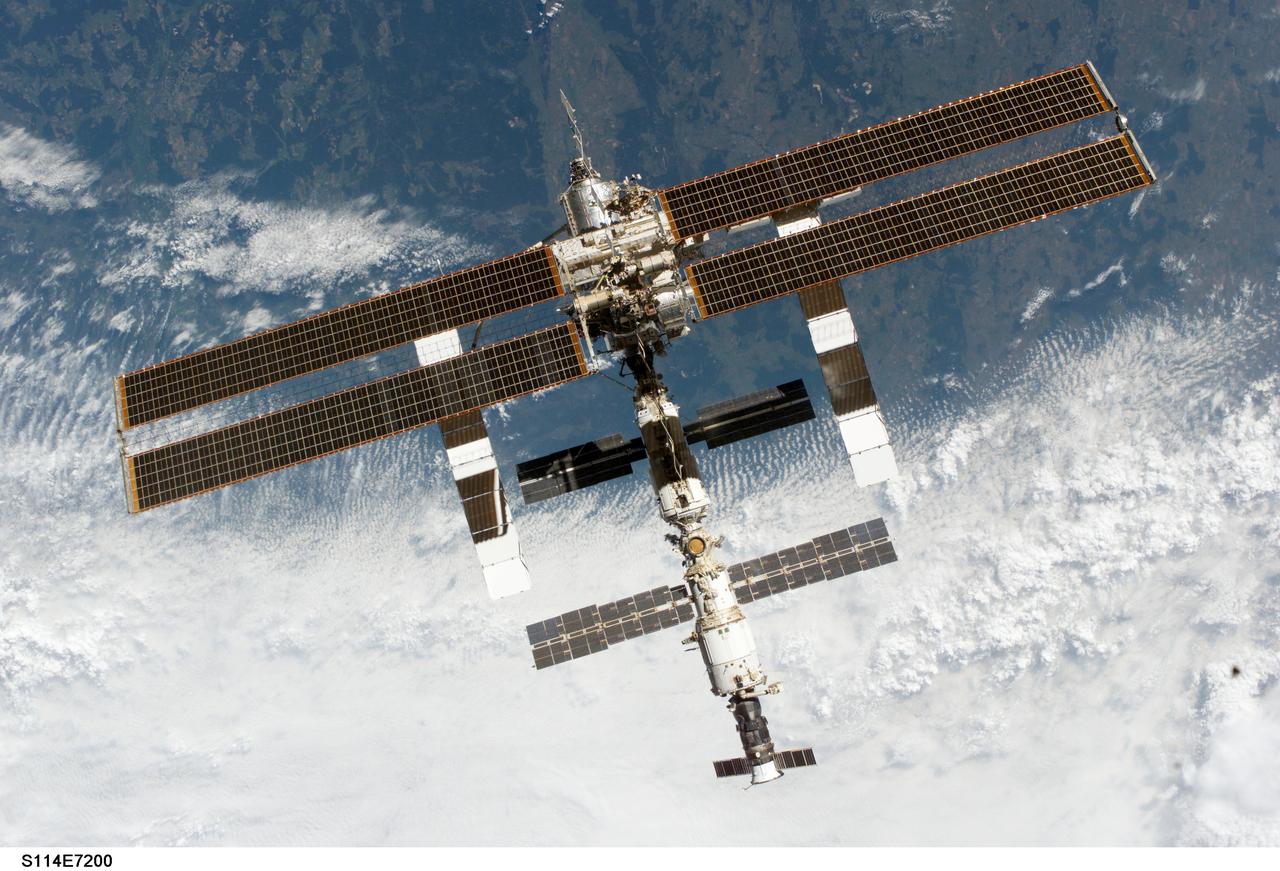

S114-E-7200 (6 August 2005) --- The International Space Station is backdropped against a heavily cloud-covered part of Earth as the orbital outpost moves away from the Space Shuttle Discovery. Earlier, the crews of the two spacecraft concluded nine days of cooperative work. As the Shuttle moved away to a distance of about 400 feet, astronaut James M. Kelly, pilot, began a slow fly-around of the Station, while cameras on each spacecraft captured video and still images of the other. Undocking occurred at 2:24 a.m. (CDT), August 6, 2005.
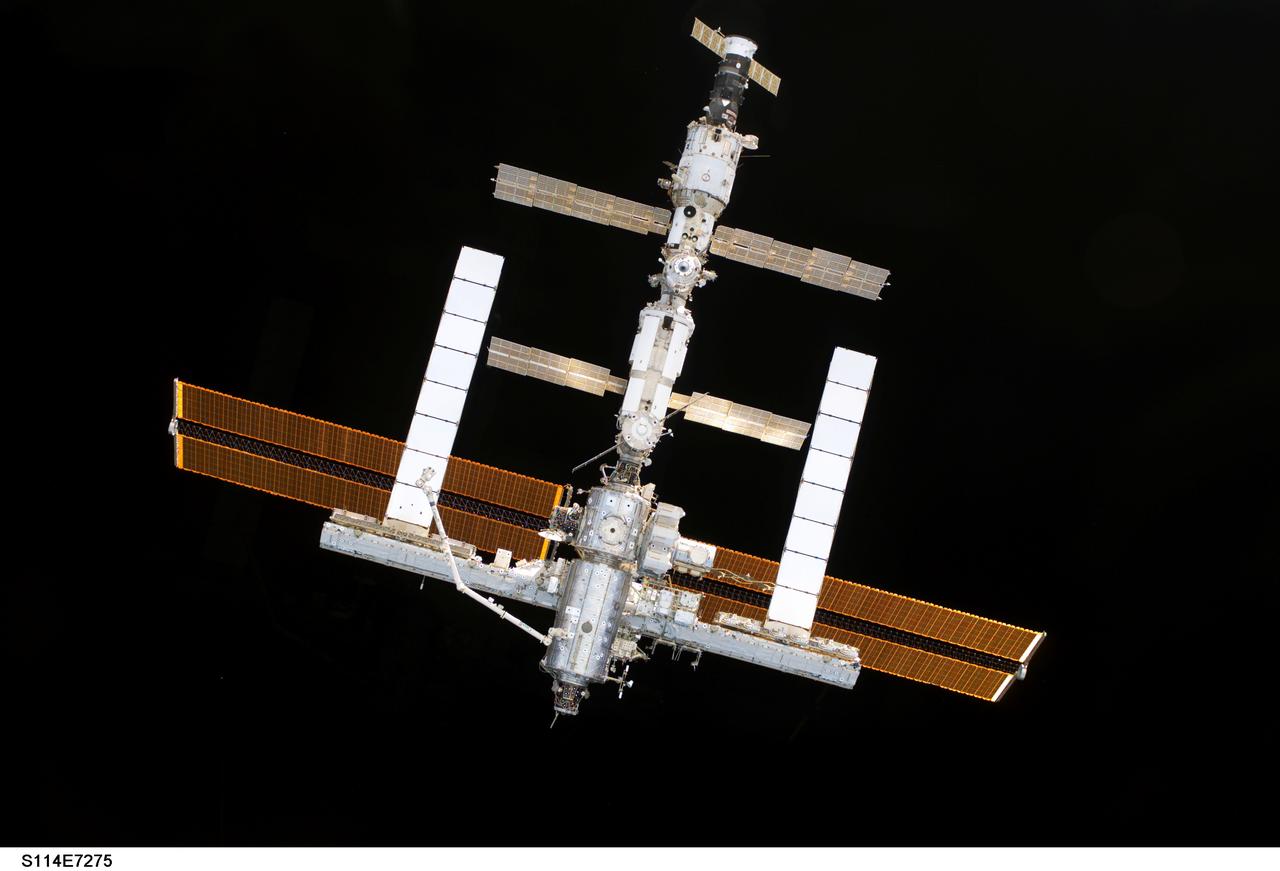

S114-E-7275 (6 August 2005) --- The International Space Station is backdropped against blackness of space as the orbital outpost moves away from the Space Shuttle Discovery. Earlier, the crews of the two spacecraft concluded nine days of cooperative work. As the Shuttle moved away to a distance of about 400 feet, astronaut James M. Kelly, pilot, began a slow fly-around of the Station, while cameras on each spacecraft captured video and still images of the other. Undocking occurred at 2:24 a.m. (CDT), August 6, 2005.
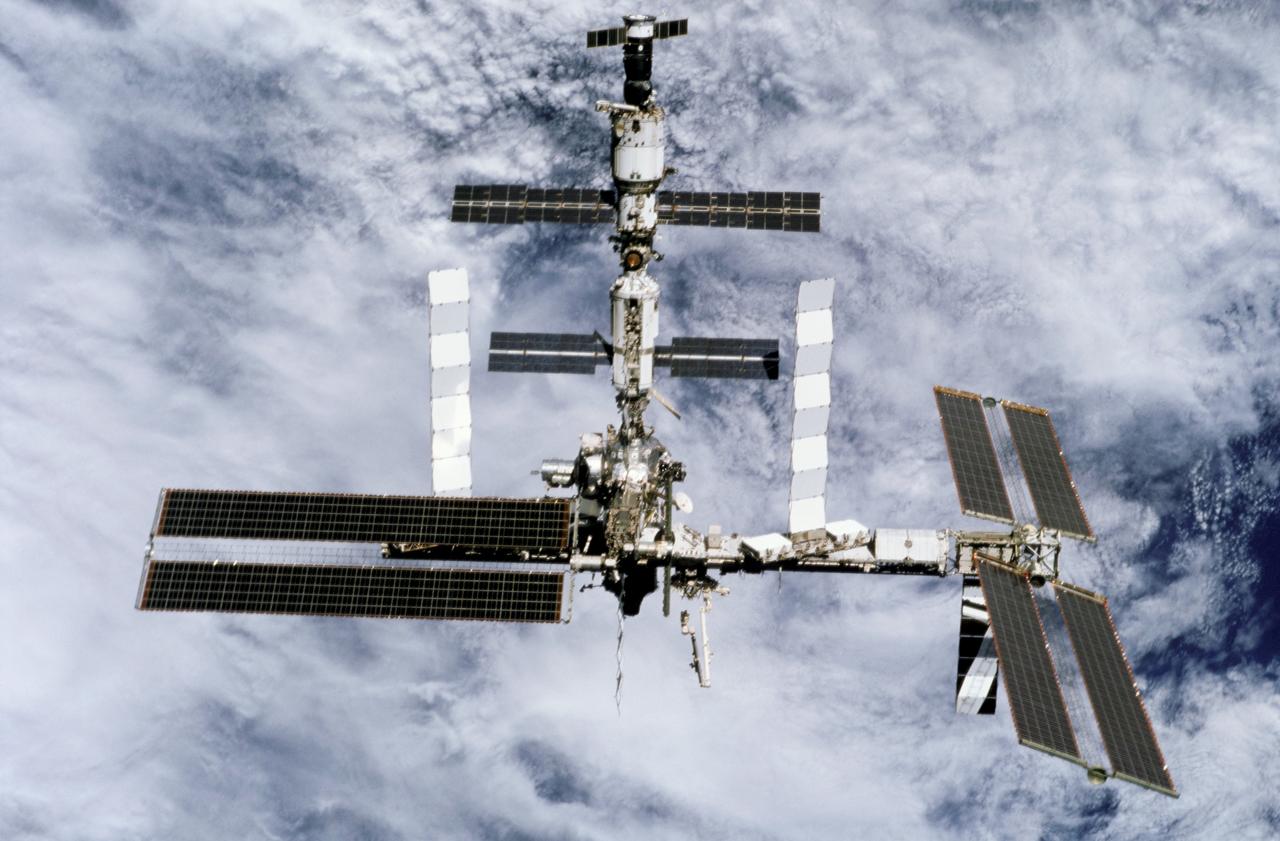

STS116-303-031 (19 Dec. 2006) --- Backdropped by a cloud-covered Earth, the International Space Station moves away from Space Shuttle Discovery. Earlier the STS-116 and Expedition 14 crews concluded eight days of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 4:10 p.m. (CST) on Dec. 19, 2006. Astronaut William A. (Bill) Oefelein, STS-116 pilot, was at the controls during the fly-around, which gave Discovery's crew a look at its handiwork, a new P5 spacer truss segment and a fully retracted P6 solar array wing. During their stay on orbital outpost, the combined crew installed the newest piece of the station's backbone and completely rewired the power grid over the course of four spacewalks. This image was recorded with a 35mm film-equipped camera.
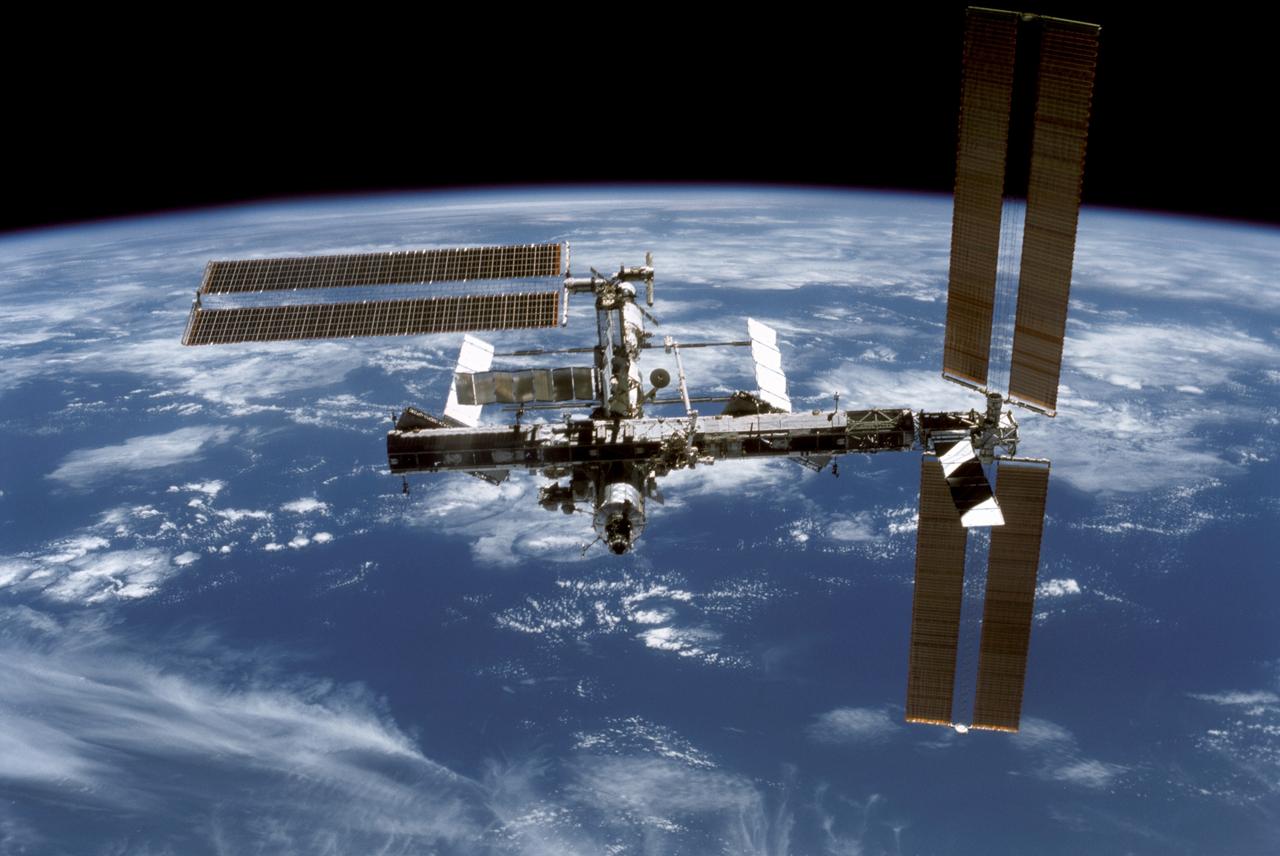

STS116-301-028 (19 Dec. 2006) --- Backdropped by the blackness of space and Earth's horizon, the International Space Station moves away from Space Shuttle Discovery. Earlier the STS-116 and Expedition 14 crews concluded eight days of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 4:10 p.m. (CST) on Dec. 19, 2006. Astronaut William A. (Bill) Oefelein, STS-116 pilot, was at the controls during the fly-around, which gave Discovery's crew a look at its handiwork, a new P5 spacer truss segment and a fully retracted P6 solar array wing. During their stay on orbital outpost, the combined crew installed the newest piece of the station's backbone and completely rewired the power grid over the course of four spacewalks. This image was recorded with a 35mm film-equipped camera.
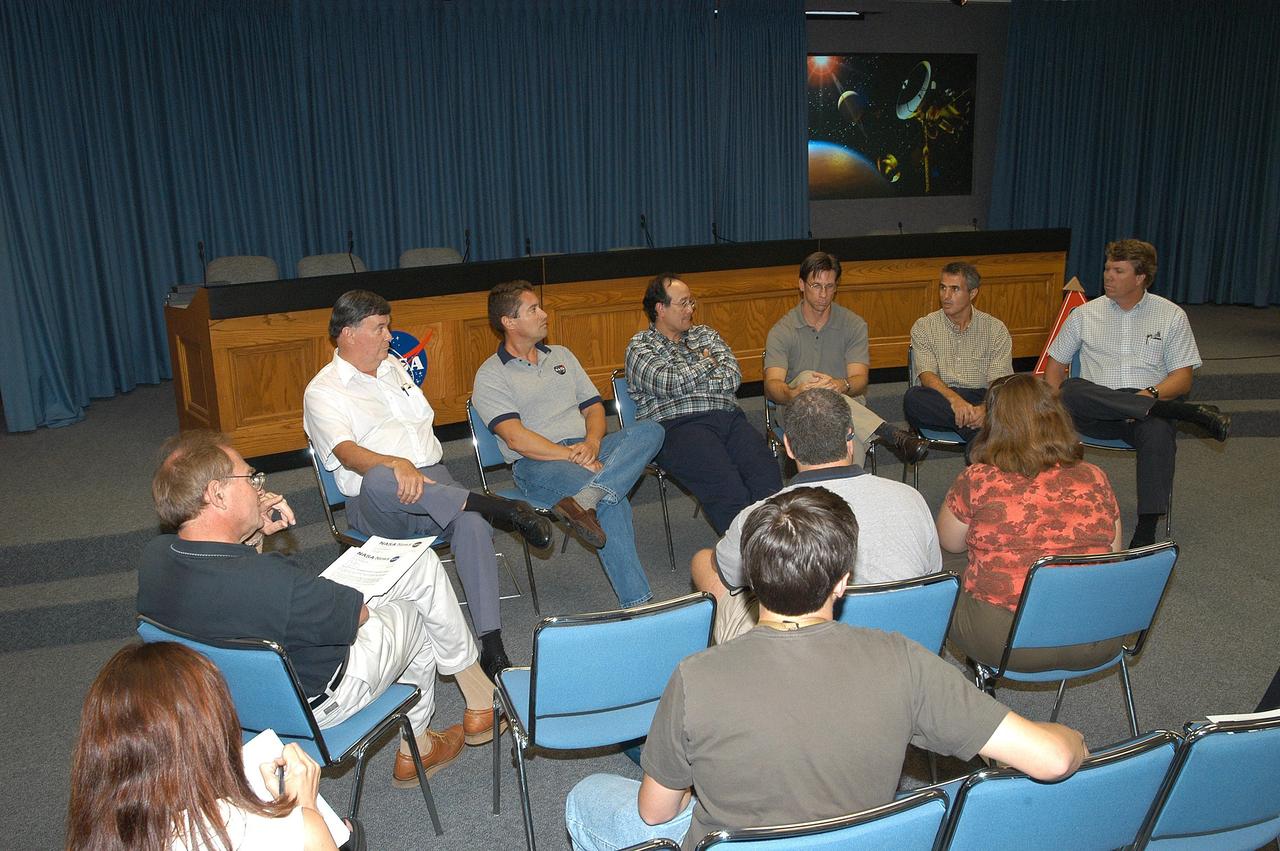

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Reporters (bottom) take notes during an informal briefing concerning NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, launched aboard an Air Force Titan IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Oct. 15, 1997. Cassini launch team members seen here discussed the challenge and experience of preparing Cassini for launch, integrating it with the Titan IV rocket and the countdown events of launch day. Facing the camera (from left) are Ron Gillett, NASA Safety and Lead Federal Agency official; Omar Baez, mechanical and propulsion systems engineer; Ray Lugo, NASA launch manager; Chuck Dovale, chief, Avionics Branch; George Haddad, Integration and Ground Systems mechanical engineer; and Ken Carr, Cassini assistant launch site support manager. Approximately 10:36 p.m. EDT, June 30, the Cassini-Huygens spacecraft will arrive at Saturn. After nearly a seven-year journey, it will be the first mission to orbit Saturn. The international cooperative mission plans a four-year tour of Saturn, its rings, icy moons, magnetosphere, and Titan, the planet’s largest moon.
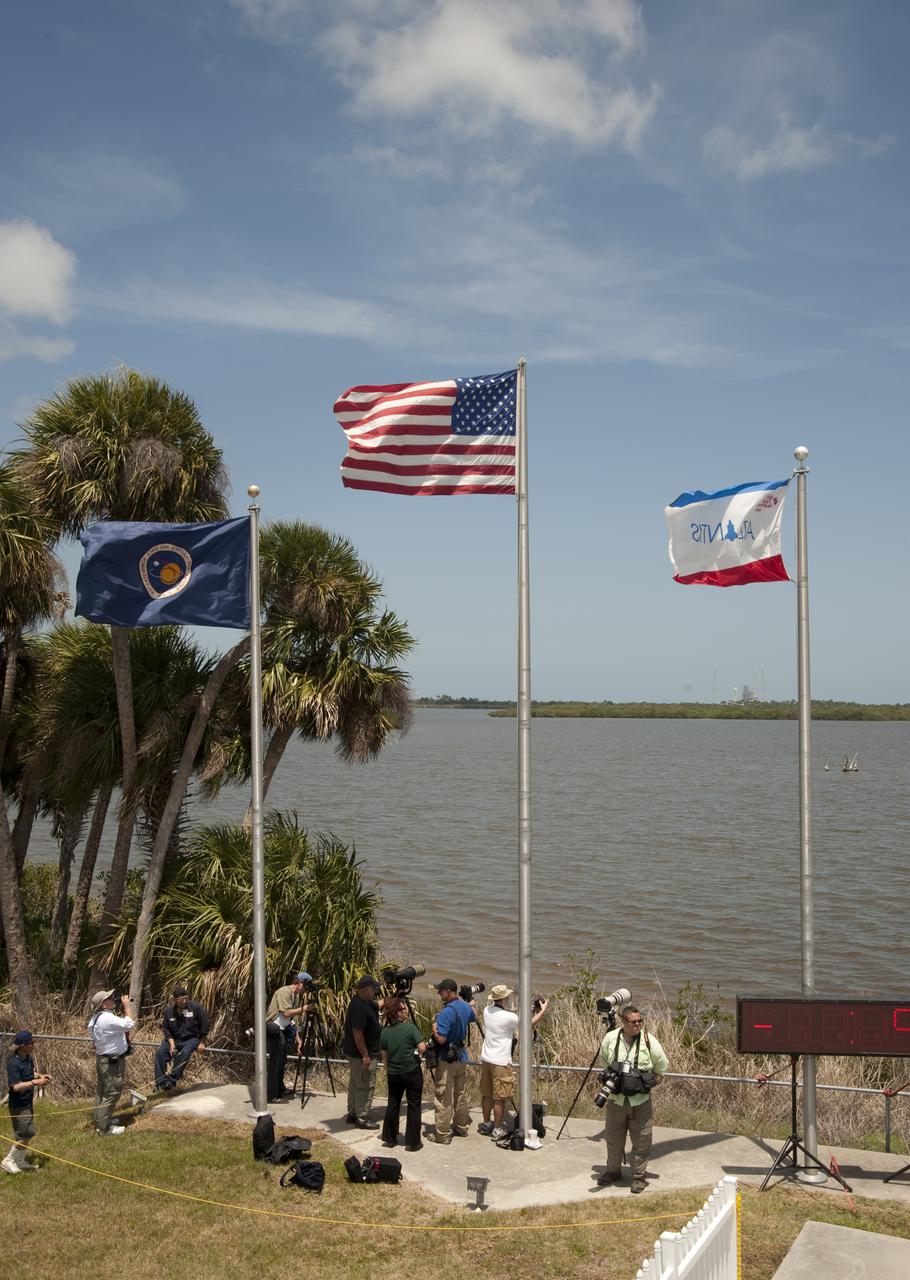

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida set their cameras up for the launch of space shuttle Atlantis from Launch Pad 39A. Liftoff of the STS-132 mission to the International Space Station occurred on time at 2:20 p.m. EDT on May 14. The Russian-built Mini Research Module-1 known as Rassvet, or 'dawn,' is inside the shuttle's cargo bay. It will provide additional storage space and a new docking port for Russian Soyuz and Progress spacecraft. The laboratory will be attached to the bottom port of the station's Zarya module. The mission's three spacewalks will focus on storing spare components outside the station, including six batteries, a communications antenna and parts for the Canadian Dextre robotic arm. STS-132 is the 132nd shuttle flight, the 32nd for Atlantis and the 34th shuttle mission dedicated to station assembly and maintenance. For more information on the STS-132 mission objectives, payload and crew, visit www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts132_index.html. Photo Credit: NASA_Ben Cooper
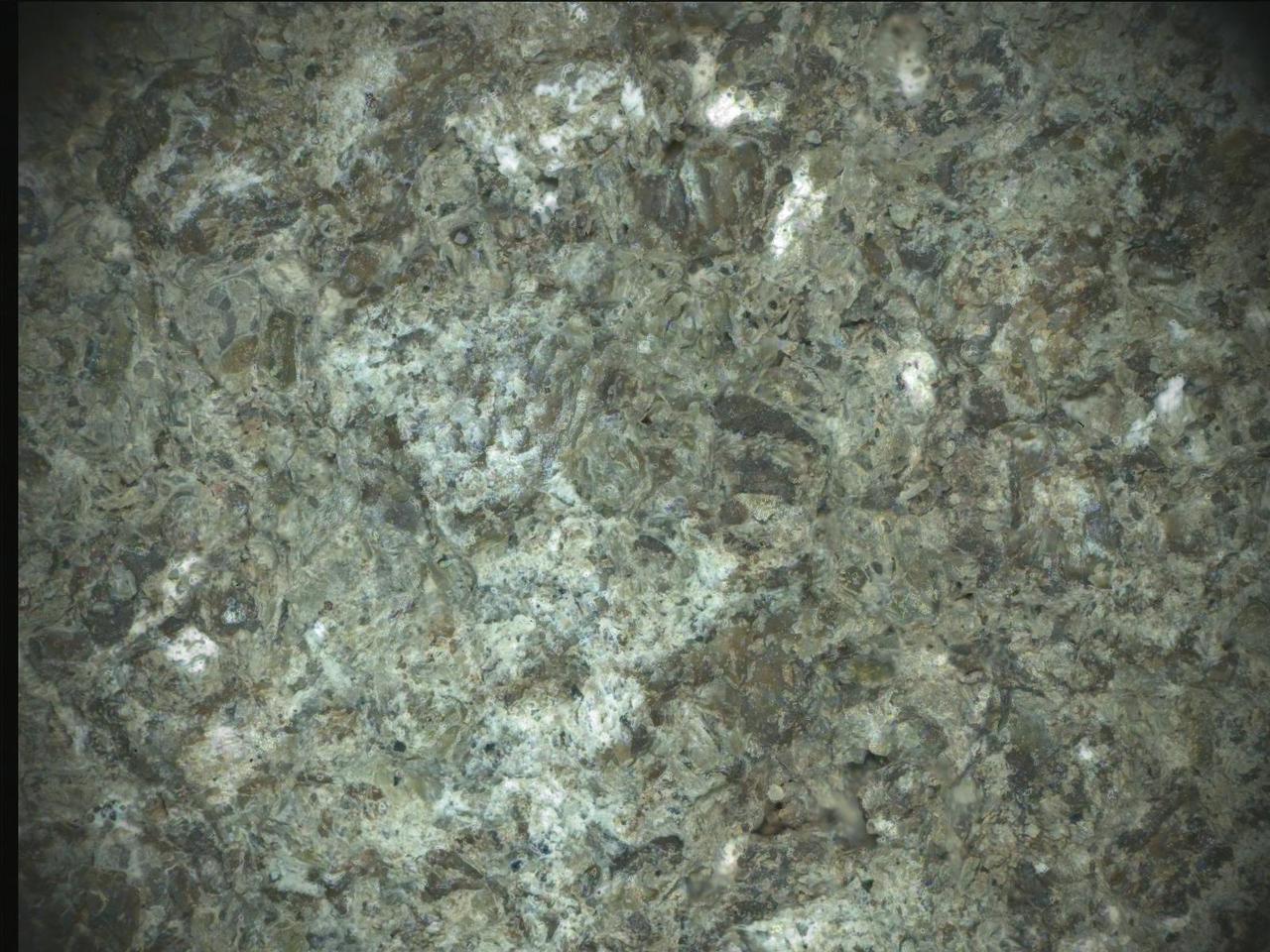

Before collecting a rock sample at a spot nicknamed "Lefroy Bay," NASA's Perseverance Mars rover employed an abrasion tool to wear down the rock surface and then used the Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry, or PIXL, to study the rock's internal chemistry. This image is composed of multiple shots of the abrasion patch, dubbed "Bills Bay," that were taken on Oct. 7 and Oct. 11, 2023, the 935th and 939th Martian days, or sols, of the mission. The image was taken by PIXL's camera, the Autofocus and Context Imager, or ACI. Color was added by overlaying data from WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering), a pair of cameras that are part of an instrument called Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals, or SHERLOC. On Earth, both silica and carbonates are good at preserving materials left behind by ancient life. Sand grains made of iron-rich carbonate are also mostly found in places on Earth that are good at protecting carbon-based materials known as organics. Organics can be made from both geological and biological sources; the Lefroy Bay sample does not necessarily show signs of ancient microbial life. Samples like Lefroy Bay would have to be brought back to Earth and studied with complex instruments in laboratories for scientists to confirm signs of ancient life, if indeed they are present. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26205
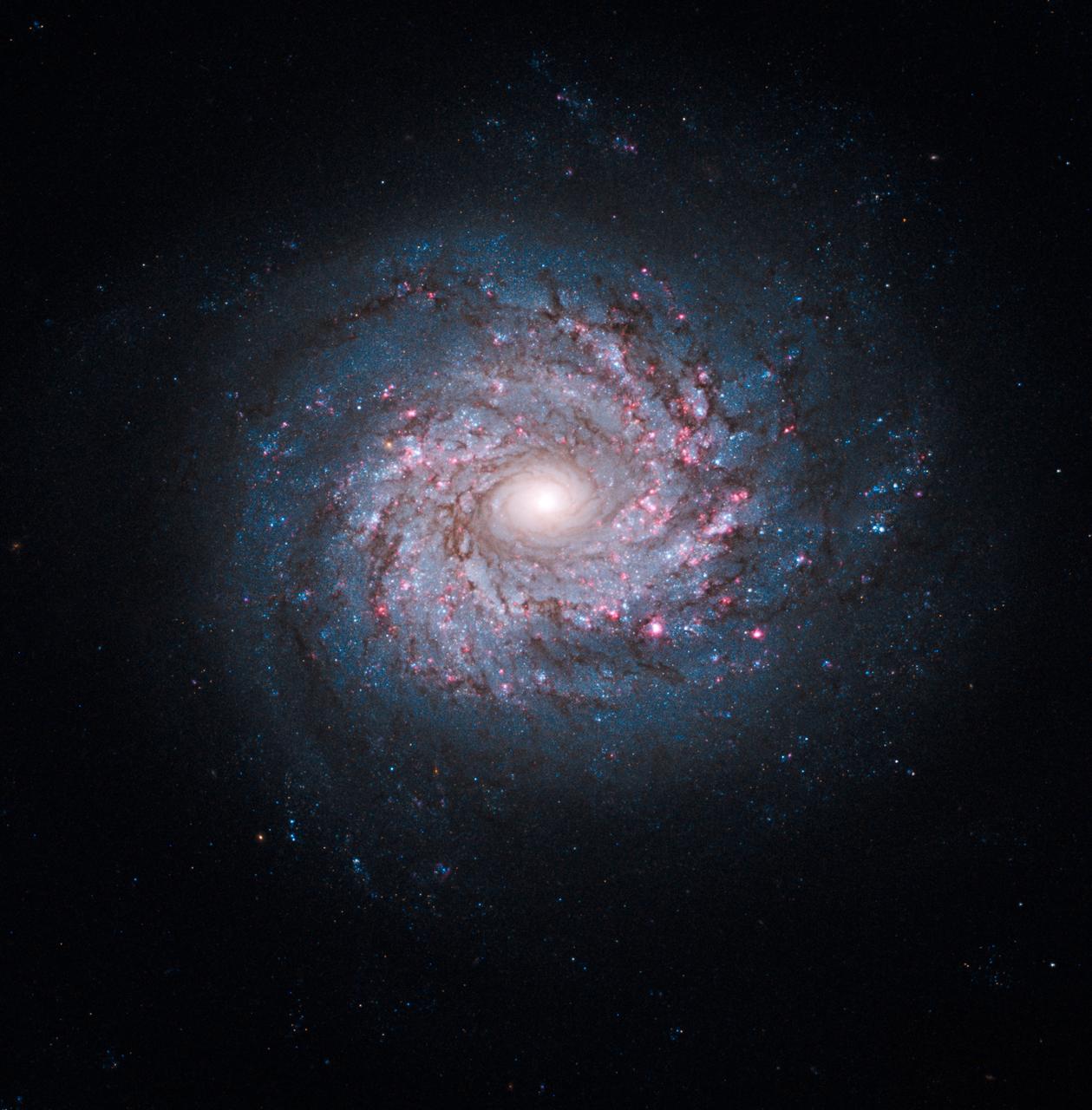

NASA image release October 19, 2010 Though the universe is chock full of spiral-shaped galaxies, no two look exactly the same. This face-on spiral galaxy, called NGC 3982, is striking for its rich tapestry of star birth, along with its winding arms. The arms are lined with pink star-forming regions of glowing hydrogen, newborn blue star clusters, and obscuring dust lanes that provide the raw material for future generations of stars. The bright nucleus is home to an older population of stars, which grow ever more densely packed toward the center. NGC 3982 is located about 68 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major. The galaxy spans about 30,000 light-years, one-third of the size of our Milky Way galaxy. This color image is composed of exposures taken by the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2), the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), and the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3). The observations were taken between March 2000 and August 2009. The rich color range comes from the fact that the galaxy was photographed invisible and near-infrared light. Also used was a filter that isolates hydrogen emission that emanates from bright star-forming regions dotting the spiral arms. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: A. Riess (STScI) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
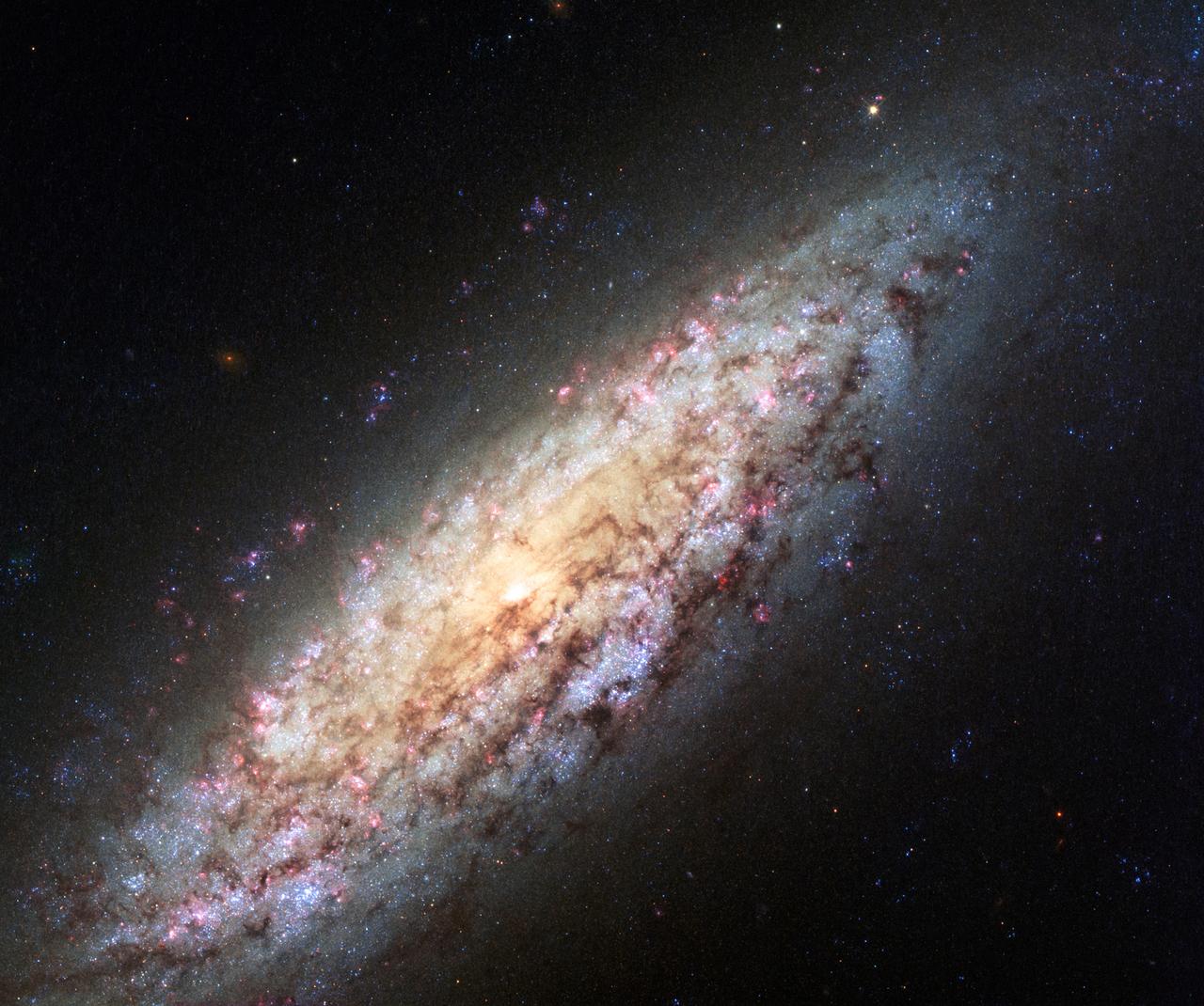

Most galaxies are clumped together in groups or clusters. A neighboring galaxy is never far away. But this galaxy, known as NGC 6503, has found itself in a lonely position, at the edge of a strangely empty patch of space called the Local Void. The Local Void is a huge stretch of space that is at least 150 million light-years across. It seems completely empty of stars or galaxies. The galaxy’s odd location on the edge of this never-land led stargazer Stephen James O’Meara to dub it the “Lost-In-Space galaxy” in his 2007 book, Hidden Treasures. NGC 6503 is 18 million light-years away from us in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco. NGC 6503 spans some 30,000 light-years, about a third of the size of the Milky Way. This Hubble Space Telescope image shows NGC 6503 in striking detail and with a rich set of colors. Bright red patches of gas can be seen scattered through its swirling spiral arms, mixed with bright blue regions that contain newly forming stars. Dark brown dust lanes snake across the galaxy’s bright arms and center, giving it a mottled appearance. The Hubble Advanced Camera for Surveys data for NGC 6503 were taken in April 2003, and the Wide Field Camera 3 data were taken in August 2013. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. Photo Credit: NASA, ESA, D. Calzetti (University of Massachusetts), H. Ford (Johns Hopkins University), and the Hubble Heritage Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
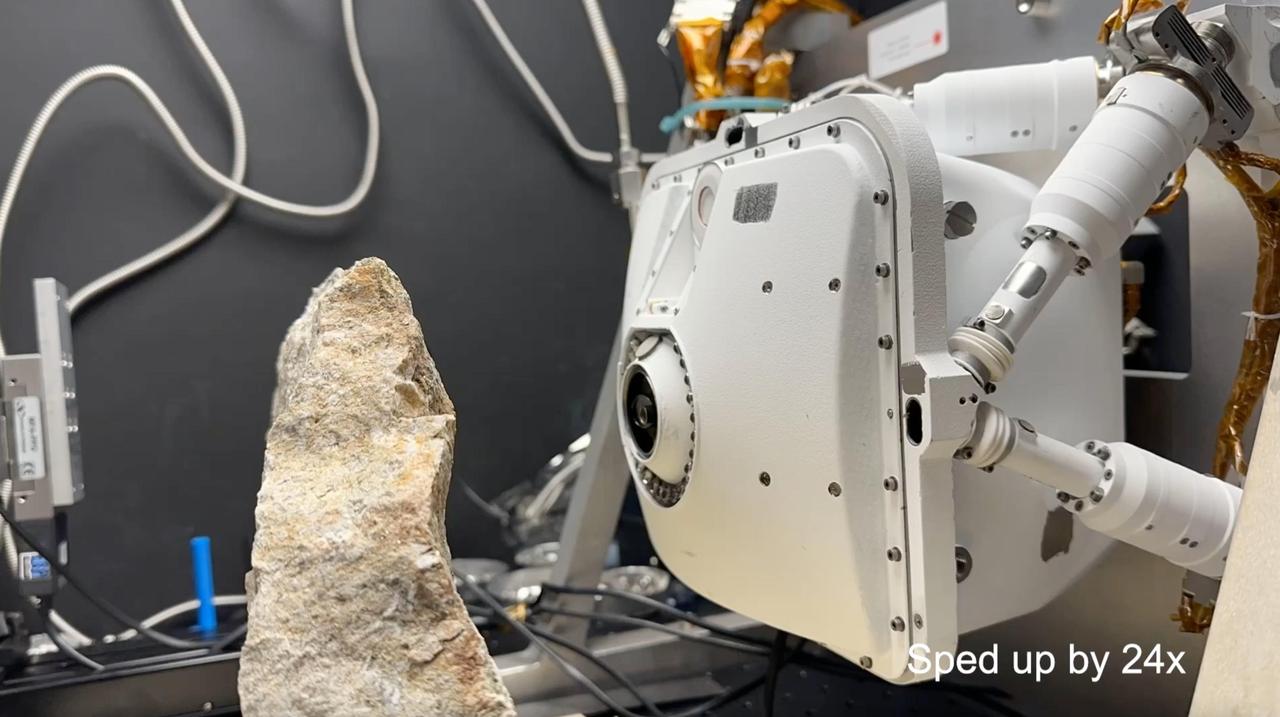

This time-lapse video, which has been sped up by 24 times, uses an engineering model of one of the instruments aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover to show how the instrument evaluates safe placement against a rock. If it's determined to be safe, the rover places the instrument, called the Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry (PIXL), close to the targeted rock for science observations. This test occurred at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on June 8, 2023. Located on the end of Perseverance's robotic arm, PIXL scans postage stamp-size areas on rocks with an X-ray beam the width of a human hair, determining which elements are present. Scientists use this information to infer what minerals and chemicals are in a rock and help decide whether Perseverance should collect a rock core using its drill. The X-ray beam exits the circular opening at the center of PIXL; colored LED lights around that circle can light up a surface, allowing an internal camera to take images. Those images allow PIXL to autonomously place itself – very slowly and precisely – as little as 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) away from a surface to collect its data. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26204

NASA image release September 16, 2010 Enjoying a frozen treat on a hot summer day can leave a sticky mess as it melts in the Sun and deforms. In the cold vacuum of space, there is no edible ice cream, but there is radiation from massive stars that is carving away at cold molecular clouds, creating bizarre, fantasy-like structures. These one-light-year-tall pillars of cold hydrogen and dust, imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope, are located in the Carina Nebula. Violent stellar winds and powerful radiation from massive stars are sculpting the surrounding nebula. Inside the dense structures, new stars may be born. This image of dust pillars in the Carina Nebula is a composite of 2005 observations taken of the region in hydrogen light (light emitted by hydrogen atoms) along with 2010 observations taken in oxygen light (light emitted by oxygen atoms), both times with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys. The immense Carina Nebula is an estimated 7,500 light-years away in the southern constellation Carina. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. in Washington, D.C. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
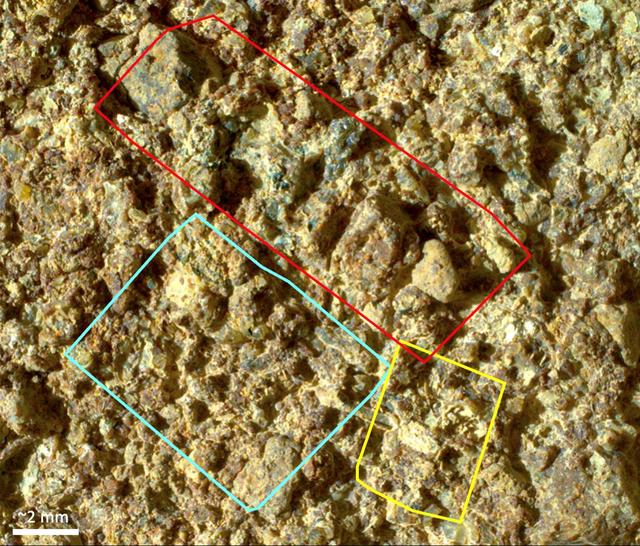

Before collecting a rock sample at a spot nicknamed "Otis Peak," NASA's Perseverance Mars rover employed an abrasion tool to wear down the rock surface and then used the Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry, or PIXL, to study the rock's internal chemistry. This image of the abrasion patch, dubbed "Ouzel Falls," was taken in May 2023 by WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering), a camera that is part of an instrument called Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals, or SHERLOC, on the end of the rover's robotic arm. Data from PIXL is laid over the image. Colored squares show different areas where PIXL's X-ray beam scanned the rock's surface. The instrument's data found the rock was rich in phosphate, a material found in the DNA and cell membranes of all known life, and which also serves as a way to store and transfer energy within living things. The Ouzel Falls scan areas contain a rich diversity of other mineral grains, including igneous minerals transported as sand and pebbles, such as olivine and spinel, and minerals crystallized from water, such as carbonates, clays, and sulfates. Each of these record unique aspects of the magmatic, climatic, and paleoenvironmental history of the ancient lake within Jezero Crater and the surrounding region. This diversity will make the Otis Peak sample a treasure trove for scientists on Earth who may study it in the future. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26206

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
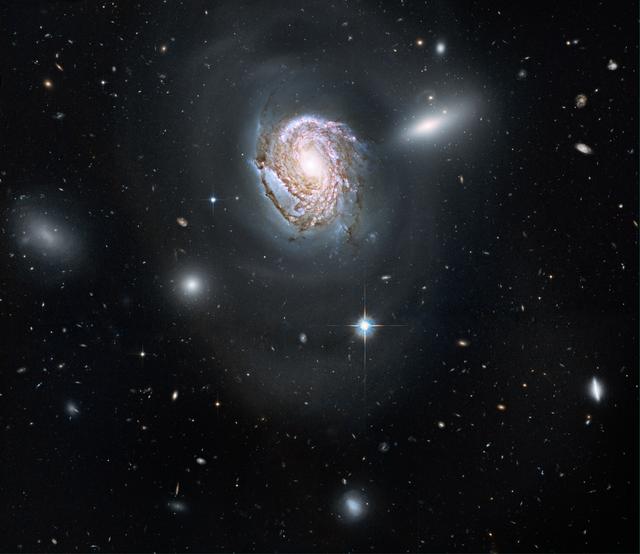

NASA image release August 10, 2010 A long-exposure Hubble Space Telescope image shows a majestic face-on spiral galaxy located deep within the Coma Cluster of galaxies, which lies 320 million light-years away in the northern constellation Coma Berenices. The galaxy, known as NGC 4911, contains rich lanes of dust and gas near its center. These are silhouetted against glowing newborn star clusters and iridescent pink clouds of hydrogen, the existence of which indicates ongoing star formation. Hubble has also captured the outer spiral arms of NGC 4911, along with thousands of other galaxies of varying sizes. The high resolution of Hubble's cameras, paired with considerably long exposures, made it possible to observe these faint details. NGC 4911 and other spirals near the center of the cluster are being transformed by the gravitational tug of their neighbors. In the case of NGC 4911, wispy arcs of the galaxy's outer spiral arms are being pulled and distorted by forces from a companion galaxy (NGC 4911A), to the upper right. The resultant stripped material will eventually be dispersed throughout the core of the Coma Cluster, where it will fuel the intergalactic populations of stars and star clusters. The Coma Cluster is home to almost 1,000 galaxies, making it one of the densest collections of galaxies in the nearby universe. It continues to transform galaxies at the present epoch, due to the interactions of close-proximity galaxy systems within the dense cluster. Vigorous star formation is triggered in such collisions. Galaxies in this cluster are so densely packed that they undergo frequent interactions and collisions. When galaxies of nearly equal masses merge, they form elliptical galaxies. Merging is more likely to occur in the center of the cluster where the density of galaxies is higher, giving rise to more elliptical galaxies. This natural-color Hubble image, which combines data obtained in 2006, 2007, and 2009 from the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 and the Advanced Camera for Surveys, required 28 hours of exposure time. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: K. Cook (Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory) To learn more about Hubble go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b></b></b>
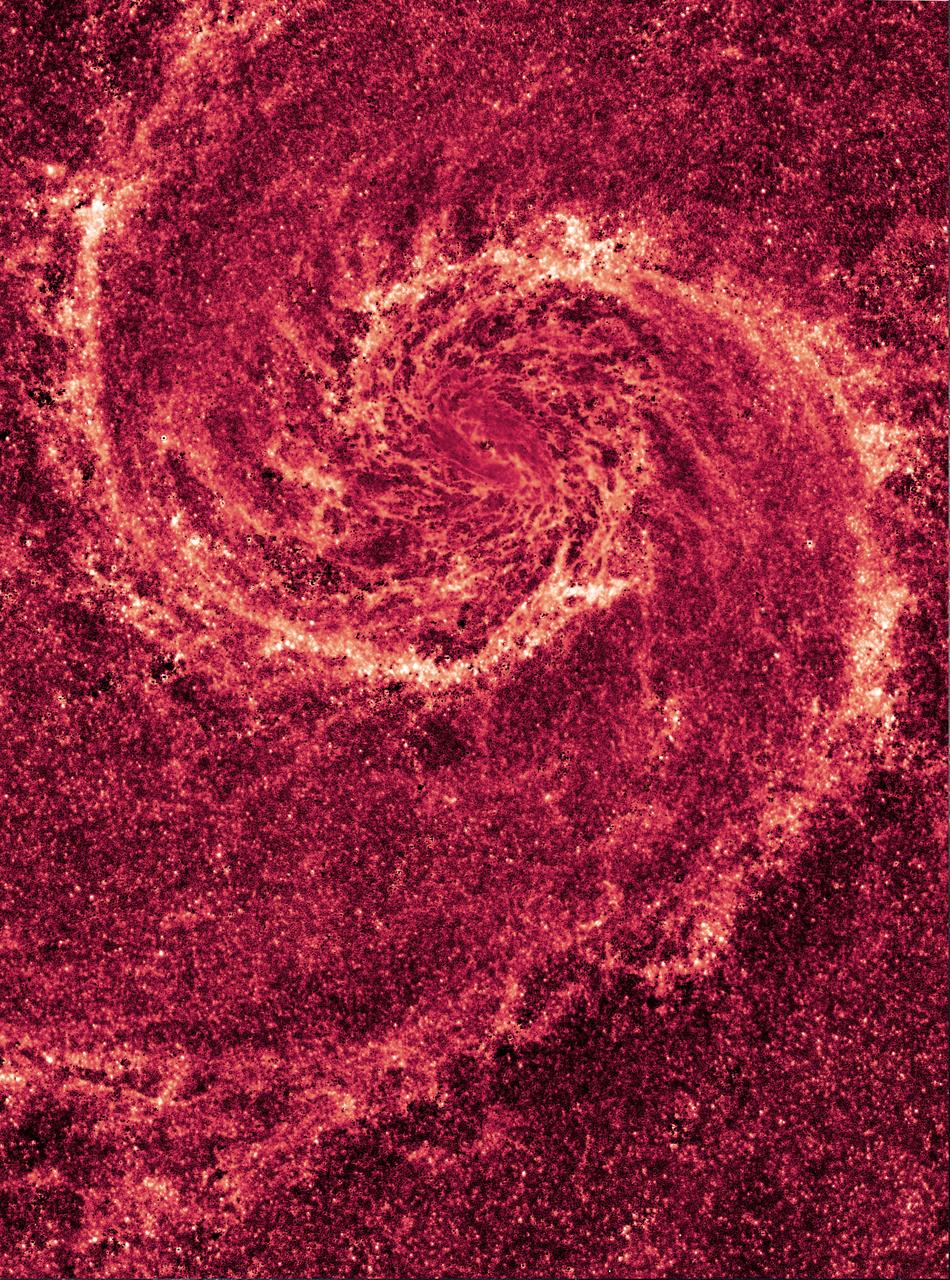
NASA image release January 13, 2011 <b><a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5352962836">These images</a></b> by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope show off two dramatically different face-on views of the spiral galaxy M51, dubbed the Whirlpool Galaxy. <b><a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5352955200/">The image here,</a></b> taken in visible light, highlights the attributes of a typical spiral galaxy, including graceful, curving arms, pink star-forming regions, and brilliant blue strands of star clusters. <b>In the image above,</b> most of the starlight has been removed, revealing the Whirlpool's skeletal dust structure, as seen in near-infrared light. This new image is the sharpest view of the dense dust in M51. The narrow lanes of dust revealed by Hubble reflect the galaxy's moniker, the Whirlpool Galaxy, as if they were swirling toward the galaxy's core. To map the galaxy's dust structure, researchers collected the galaxy's starlight by combining images taken in visible and near-infrared light. The visible-light image captured only some of the light; the rest was obscured by dust. The near-infrared view, however, revealed more starlight because near-infrared light penetrates dust. The researchers then subtracted the total amount of starlight from both images to see the galaxy's dust structure. The red color in the near-infrared image traces the dust, which is punctuated by hundreds of tiny clumps of stars, each about 65 light-years wide. These stars have never been seen before. The star clusters cannot be seen in visible light because dense dust enshrouds them. The image reveals details as small as 35 light-years across. Astronomers expected to see large dust clouds, ranging from about 100 light-years to more than 300 light-years wide. Instead, most of the dust is tied up in smooth and diffuse dust lanes. An encounter with another galaxy may have prevented giant clouds from forming. Probing a galaxy's dust structure serves as an important diagnostic tool for astronomers, providing invaluable information on how the gas and dust collapse to form stars. Although Hubble is providing incisive views of the internal structure of galaxies such as M51, the planned James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is expected to produce even crisper images. Researchers constructed the image by combining visible-light exposures from Jan. 18 to 22, 2005, with the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), and near-infrared light pictures taken in December 2005 with the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS). The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> Credit: NASA, ESA, M. Regan and B. Whitmore (STScI), and R. Chandar (University of Toledo)

NASA image release January 13, 2011 <b><a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5352962836">These images</a></b> by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope show off two dramatically different face-on views of the spiral galaxy M51, dubbed the Whirlpool Galaxy. <b>The image above,</b> taken in visible light, highlights the attributes of a typical spiral galaxy, including graceful, curving arms, pink star-forming regions, and brilliant blue strands of star clusters. <b><a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5352344517">In the image here,</a></b> most of the starlight has been removed, revealing the Whirlpool's skeletal dust structure, as seen in near-infrared light. This new image is the sharpest view of the dense dust in M51. The narrow lanes of dust revealed by Hubble reflect the galaxy's moniker, the Whirlpool Galaxy, as if they were swirling toward the galaxy's core. To map the galaxy's dust structure, researchers collected the galaxy's starlight by combining images taken in visible and near-infrared light. The visible-light image captured only some of the light; the rest was obscured by dust. The near-infrared view, however, revealed more starlight because near-infrared light penetrates dust. The researchers then subtracted the total amount of starlight from both images to see the galaxy's dust structure. The red color in the near-infrared image traces the dust, which is punctuated by hundreds of tiny clumps of stars, each about 65 light-years wide. These stars have never been seen before. The star clusters cannot be seen in visible light because dense dust enshrouds them. The image reveals details as small as 35 light-years across. Astronomers expected to see large dust clouds, ranging from about 100 light-years to more than 300 light-years wide. Instead, most of the dust is tied up in smooth and diffuse dust lanes. An encounter with another galaxy may have prevented giant clouds from forming. Probing a galaxy's dust structure serves as an important diagnostic tool for astronomers, providing invaluable information on how the gas and dust collapse to form stars. Although Hubble is providing incisive views of the internal structure of galaxies such as M51, the planned James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is expected to produce even crisper images. Researchers constructed the image by combining visible-light exposures from Jan. 18 to 22, 2005, with the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), and near-infrared light pictures taken in December 2005 with the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS). Credit: NASA, ESA, S. Beckwith (STScI), and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
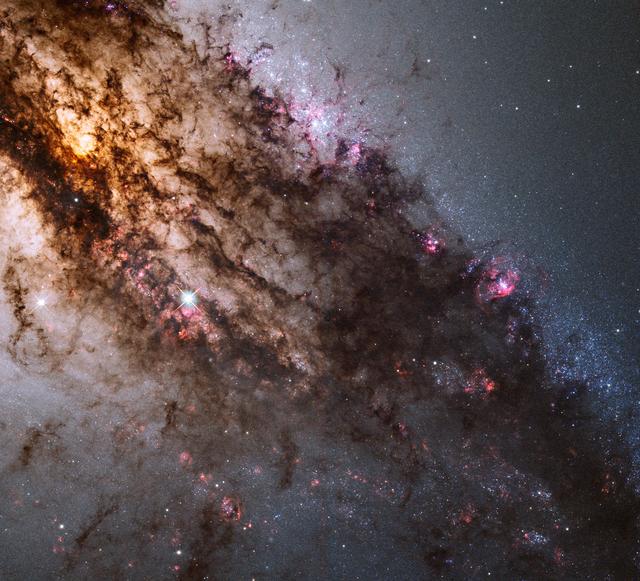

NASA image release June 16, 2011 Resembling looming rain clouds on a stormy day, dark lanes of dust crisscross the giant elliptical galaxy Centaurus A. Hubble's panchromatic vision, stretching from ultraviolet through near-infrared wavelengths, reveals the vibrant glow of young, blue star clusters and a glimpse into regions normally obscured by the dust. The warped shape of Centaurus A's disk of gas and dust is evidence for a past collision and merger with another galaxy. The resulting shockwaves cause hydrogen gas clouds to compress, triggering a firestorm of new star formation. These are visible in the red patches in this Hubble close-up. At a distance of just over 11 million light-years, Centaurus A contains the closest active galactic nucleus to Earth. The center is home for a supermassive black hole that ejects jets of high-speed gas into space, but neither the supermassive or the jets are visible in this image. This image was taken in July 2010 with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. For images and more information about the findings, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> and <a href="http://www.hubblesite.org/news/2011/18" rel="nofollow">www.hubblesite.org/news/2011/18</a> Cheryl Gundy, STSCI <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
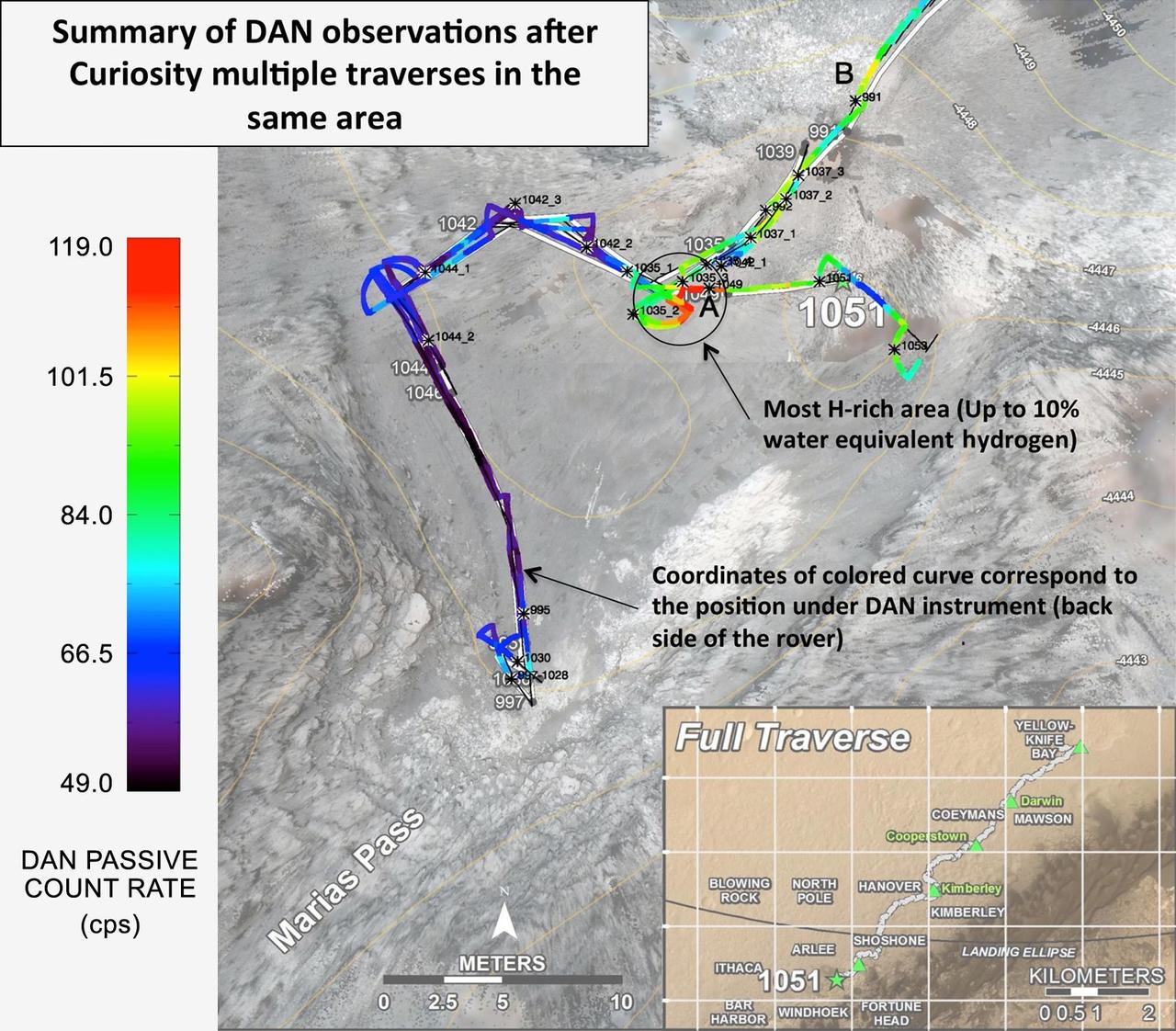
Curiosity's Russian-made instrument for checking hydration levels in the ground beneath the rover detected an unusually high amount at a site near "Marias Pass," prompting repeated passes over the area to map the hydrogen amounts. The instrument is named Dynamic Albedo of Neutrons, or DAN. It detects hydrogen by the effect of hydrogen atoms on neutrons entering the ground either from cosmic rays and Curiosity's power source (DAN's passive mode) or from the instrument's neutron pulse generator (DAN's active mode). DAN recognizes which neutrons have bounced off hydrogen from their rerduced energy level. This map, covering an area about 130 feet (40 meters) across, shows results from DAN's multiple traverses over the area, with color coding for levels of hydrogen detected. The red coding indicates amounts of hydrogen three to four times as high as the amounts detected anywhere previously along Curiosity's traverse of about 6.9 miles (11.1 kilometers) since landing in August 2012. The inset map at lower right shows the full traverse through Sol 1051 (July 21, 2015), with names assigned to rectangles within Gale Crater for geological mapping purposes. The vertical bar at left indicates the color coding according to counts per second in DAN's passive mode. The hydrogen detected by DAN is interpreted as water molecules or hydroxyl ions bound within minerals or water absorbed onto minerals in the rocks and soil, to a depth of about 3 feet (1 meter) beneath the rover. The amount of hydrogen is often expressed as "water equivalent hydrogen" based on two hydrogen atoms per molecule of water. In the same area where DAN detected an unusually high amount of hydration, Curiosity's Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) instrument detected an unusually high amount of silica in several rock targets. The DAN and ChemCam findings led to the rover's science team choosing a rock target called "Buckskin" for collection of a drilled sample to be analyzed by the rover's internal laboratory instruments. Russia's Space Research Institute developed DAN in close cooperation with the N.L. Dukhov All-Russia Research Institute of Automatics, Moscow, and the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna. The neutron generator development was supervised by the late technical designer German A. Smirnov of the All-Russia Institute of Automatics. Moscow. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19809

NASA image release June 6, 2010 Like a July 4 fireworks display a young, glittering collection of stars looks like an aerial burst. The cluster is surrounded by clouds of interstellar gas and dust - the raw material for new star formation. The nebula, located 20,000 light-years away in the constellation Carina, contains a central cluster of huge, hot stars, called NGC 3603. This environment is not as peaceful as it looks. Ultraviolet radiation and violent stellar winds have blown out an enormous cavity in the gas and dust enveloping the cluster, providing an unobstructed view of the cluster. Most of the stars in the cluster were born around the same time but differ in size, mass, temperature, and color. The course of a star's life is determined by its mass, so a cluster of a given age will contain stars in various stages of their lives, giving an opportunity for detailed analyses of stellar life cycles. NGC 3603 also contains some of the most massive stars known. These huge stars live fast and die young, burning through their hydrogen fuel quickly and ultimately ending their lives in supernova explosions. Star clusters like NGC 3603 provide important clues to understanding the origin of massive star formation in the early, distant universe. Astronomers also use massive clusters to study distant starbursts that occur when galaxies collide, igniting a flurry of star formation. The proximity of NGC 3603 makes it an excellent lab for studying such distant and momentous events. This Hubble Space Telescope image was captured in August 2009 and December 2009 with the Wide Field Camera 3 in both visible and infrared light, which trace the glow of sulfur, hydrogen, and iron. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, R. O'Connell (University of Virginia), F. Paresce (National Institute for Astrophysics, Bologna, Italy), E. Young (Universities Space Research Association/Ames Research Center), the WFC3 Science Oversight Committee, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
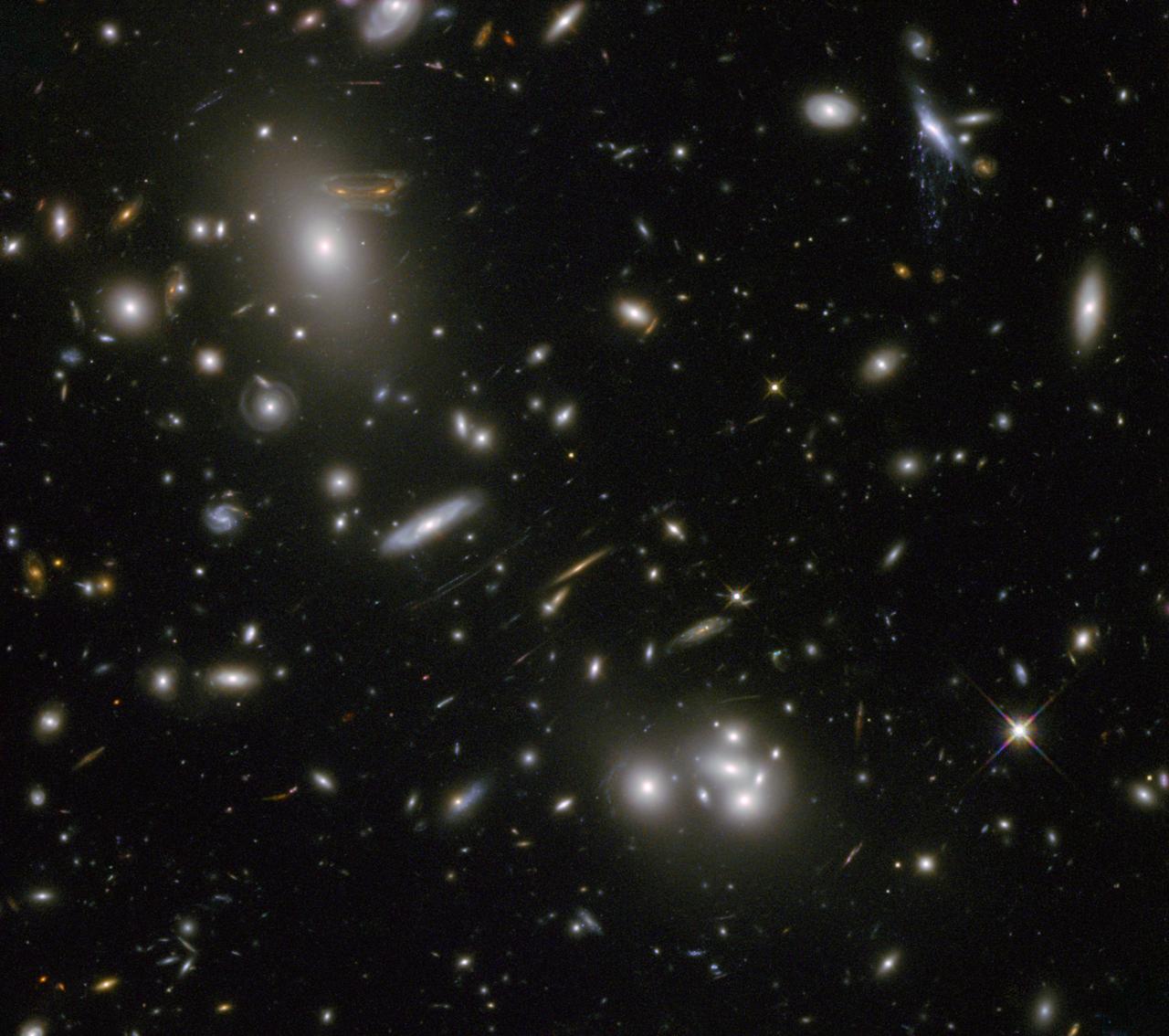

The gravitational field surrounding this massive cluster of galaxies, Abell 68, acts as a natural lens in space to brighten and magnify the light coming from very distant background galaxies. Like a fun house mirror, lensing creates a fantasy landscape of arc-like images and mirror images of background galaxies. The foreground cluster is 2 billion light-years away, and the lensed images come from galaxies far behind it. In this photo, the image of a spiral galaxy at upper left has been stretched and mirrored into a shape similar to that of a simulated alien from the classic 1970s computer game "Space Invaders!" A second, less distorted image of the same galaxy appears to the left of the large, bright elliptical galaxy. In the upper right of the photo is another striking feature of the image that is unrelated to gravitational lensing. What appears to be purple liquid dripping from a galaxy is a phenomenon called ram-pressure stripping. The gas clouds within the galaxy are being stripped out and heated up as the galaxy passes through a region of denser intergalactic gas. This image was taken in infrared light by Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3, and combined with near-infrared observations from Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. The image is based in part on data spotted by Nick Rose in the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures image processing competition. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md., conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington. Credit: NASA and ESA Acknowledgement: N. Rose For image files and more information about Abell 68, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2013/09" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2013/09</a> <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic04" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic04</a> <a href="http://heritage.stsci.edu/2013/09" rel="nofollow">heritage.stsci.edu/2013/09</a> <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/projects/hiddentreasures/" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/projects/hiddentreasures/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release December 14, 2010 A delicate sphere of gas, photographed by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, floats serenely in the depths of space. The pristine shell, or bubble, is the result of gas that is being shocked by the expanding blast wave from a supernova. Called SNR 0509-67.5 (or SNR 0509 for short), the bubble is the visible remnant of a powerful stellar explosion in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a small galaxy about 160,000 light-years from Earth. Ripples in the shell's surface may be caused by either subtle variations in the density of the ambient interstellar gas, or possibly driven from the interior by pieces of the ejecta. The bubble-shaped shroud of gas is 23 light-years across and is expanding at more than 11 million miles per hour (5,000 kilometers per second). Astronomers have concluded that the explosion was one of an especially energetic and bright variety of supernovae. Known as Type Ia, such supernova events are thought to result from a white dwarf star in a binary system that robs its partner of material, takes on much more mass than it is able to handle, and eventually explodes. Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys observed the supernova remnant on Oct. 28, 2006 with a filter that isolates light from glowing hydrogen seen in the expanding shell. These observations were then combined with visible-light images of the surrounding star field that were imaged with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 on Nov. 4, 2010. With an age of about 400 years as seen from Earth, the supernova might have been visible to southern hemisphere observers around the year 1600, however, there are no known records of a "new star" in the direction of the LMC near that time. A more recent supernova in the LMC, SN 1987A, did catch the eye of Earth viewers and continues to be studied with ground- and space-based telescopes, including Hubble. For images and more information about SNR 0509, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2010/27" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2010/27</a> <a href="http://heritage.stsci.edu/2010/27" rel="nofollow">heritage.stsci.edu/2010/27</a> <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. <b>Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: J. Hughes (Rutgers University)</b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
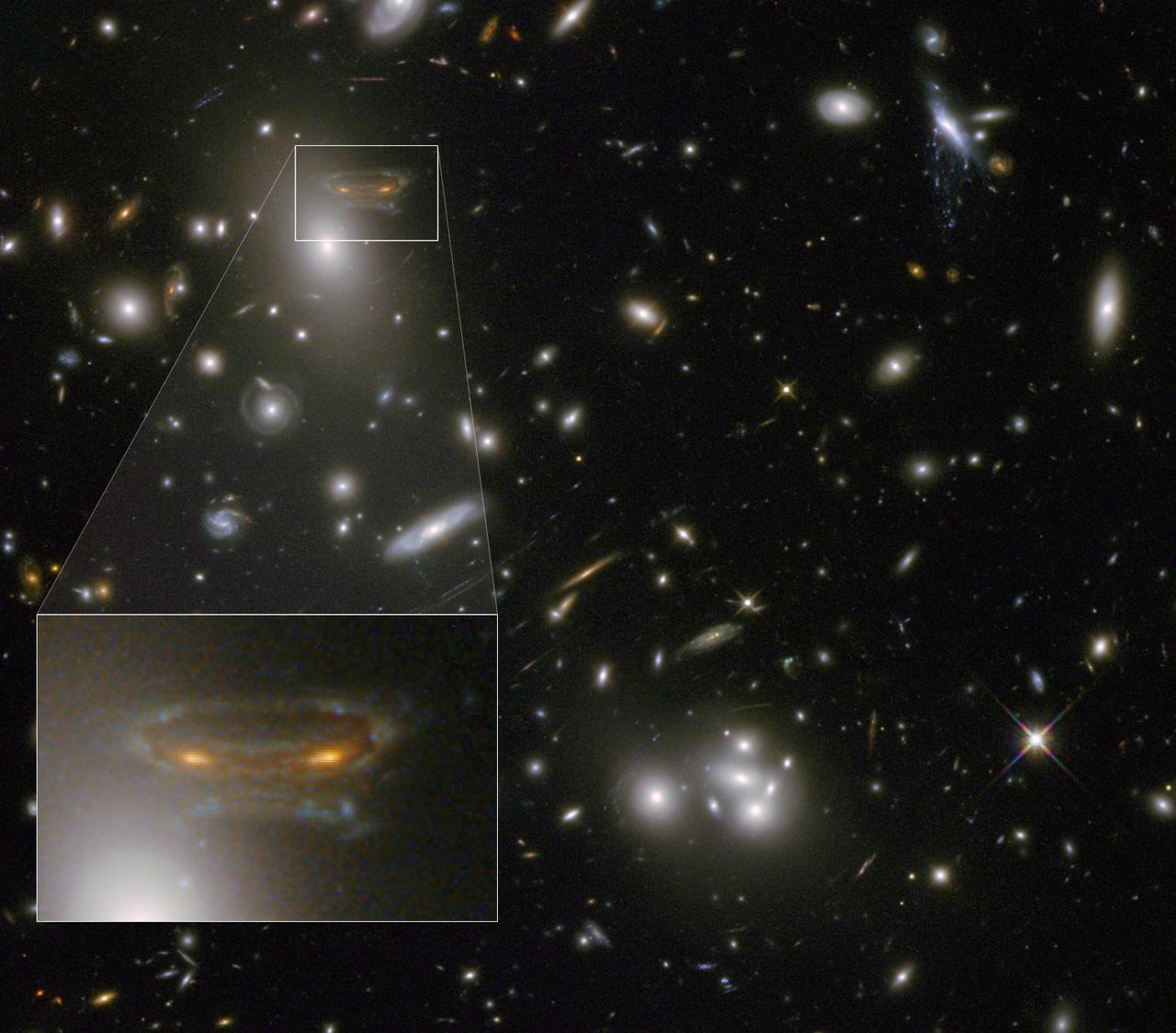

The gravitational field surrounding this massive cluster of galaxies, Abell 68, acts as a natural lens in space to brighten and magnify the light coming from very distant background galaxies. Like a fun house mirror, lensing creates a fantasy landscape of arc-like images and mirror images of background galaxies. The foreground cluster is 2 billion light-years away, and the lensed images come from galaxies far behind it. In this photo, the image of a spiral galaxy at upper left has been stretched and mirrored into a shape similar to that of a simulated alien from the classic 1970s computer game "Space Invaders!" A second, less distorted image of the same galaxy appears to the left of the large, bright elliptical galaxy. In the upper right of the photo is another striking feature of the image that is unrelated to gravitational lensing. What appears to be purple liquid dripping from a galaxy is a phenomenon called ram-pressure stripping. The gas clouds within the galaxy are being stripped out and heated up as the galaxy passes through a region of denser intergalactic gas. This image was taken in infrared light by Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3, and combined with near-infrared observations from Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. The image is based in part on data spotted by Nick Rose in the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures image processing competition. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md., conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/Z6uDUp" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/Z6uDUp</a> Credit: NASA and ESA Acknowledgement: N. Rose For image files and more information about Abell 68, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2013/09" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2013/09</a> <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic04" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic04</a> <a href="http://heritage.stsci.edu/2013/09" rel="nofollow">heritage.stsci.edu/2013/09</a> <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/projects/hiddentreasures/" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/projects/hiddentreasures/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Image release date September 22, 2010 To view a video of this image go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5014452203">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5014452203</a> Caption: A spectacular new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image reveals the heart of the Lagoon Nebula. Seen as a massive cloud of glowing dust and gas, bombarded by the energetic radiation of new stars, this placid name hides a dramatic reality. The Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) on the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has captured a dramatic view of gas and dust sculpted by intense radiation from hot young stars deep in the heart of the Lagoon Nebula (Messier 8). This spectacular object is named after the wide, lagoon-shaped dust lane that crosses the glowing gas of the nebula. This structure is prominent in wide-field images, but cannot be seen in this close-up. However the strange billowing shapes and sandy texture visible in this image make the Lagoon Nebula’s watery name eerily appropriate from this viewpoint too. Located four to five thousand light-years away, in the constellation of Sagittarius (the Archer), Messier 8 is a huge region of star birth that stretches across one hundred light-years. Clouds of hydrogen gas are slowly collapsing to form new stars, whose bright ultraviolet rays then light up the surrounding gas in a distinctive shade of red. The wispy tendrils and beach-like features of the nebula are not caused by the ebb and flow of tides, but rather by ultraviolet radiation’s ability to erode and disperse the gas and dust into the distinctive shapes that we see. In recent years astronomers probing the secrets of the Lagoon Nebula have found the first unambiguous proof that star formation by accretion of matter from the gas cloud is ongoing in this region. Young stars that are still surrounded by an accretion disc occasionally shoot out long tendrils of matter from their poles. Several examples of these jets, known as Herbig-Haro objects, have been found in this nebula in the last five years, providing strong support for astronomers’ theories about star formation in such hydrogen-rich regions. The Lagoon Nebula is faintly visible to the naked eye on dark nights as a small patch of grey in the heart of the Milky Way. Without a telescope, the nebula looks underwhelming because human eyes are unable to distinguish clearly between colours at low light levels. Charles Messier, the 18th century French astronomer, observed the nebula and included it in his famous astronomical catalogue, from which the nebula’s alternative name comes. But his relatively small refracting telescope would only have hinted at the dramatic structures and colours now visible thanks to Hubble. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. Image credit: NASA, ESA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b> To learn more about the Hubble Space Telescope go here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html</a>

The Cat's Eye Nebula, one of the first planetary nebulae discovered, also has one of the most complex forms known to this kind of nebula. Eleven rings, or shells, of gas make up the Cat's Eye. The full beauty of the Cat's Eye Nebula is revealed in this detailed view from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The image from Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) shows a bull's eye pattern of eleven or even more concentric rings, or shells, around the Cat's Eye. Each 'ring' is actually the edge of a spherical bubble seen projected onto the sky -- that's why it appears bright along its outer edge. Observations suggest the star ejected its mass in a series of pulses at 1,500-year intervals. These convulsions created dust shells, each of which contain as much mass as all of the planets in our solar system combined (still only one percent of the Sun's mass). These concentric shells make a layered, onion-skin structure around the dying star. The view from Hubble is like seeing an onion cut in half, where each skin layer is discernible. The bull's-eye patterns seen around planetary nebulae come as a surprise to astronomers because they had no expectation that episodes of mass loss at the end of stellar lives would repeat every 1,500 years. Several explanations have been proposed, including cycles of magnetic activity somewhat similar to our own Sun's sunspot cycle, the action of companion stars orbiting around the dying star, and stellar pulsations. Another school of thought is that the material is ejected smoothly from the star, and the rings are created later on due to formation of waves in the outflowing material. Credit: NASA, ESA, HEIC, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: R. Corradi (Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, Spain) and Z. Tsvetanov (NASA) The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute conducts Hubble science operations. Goddard is responsible for HST project management, including mission and science operations, servicing missions, and all associated development activities. To learn more about the Hubble Space Telescope go here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
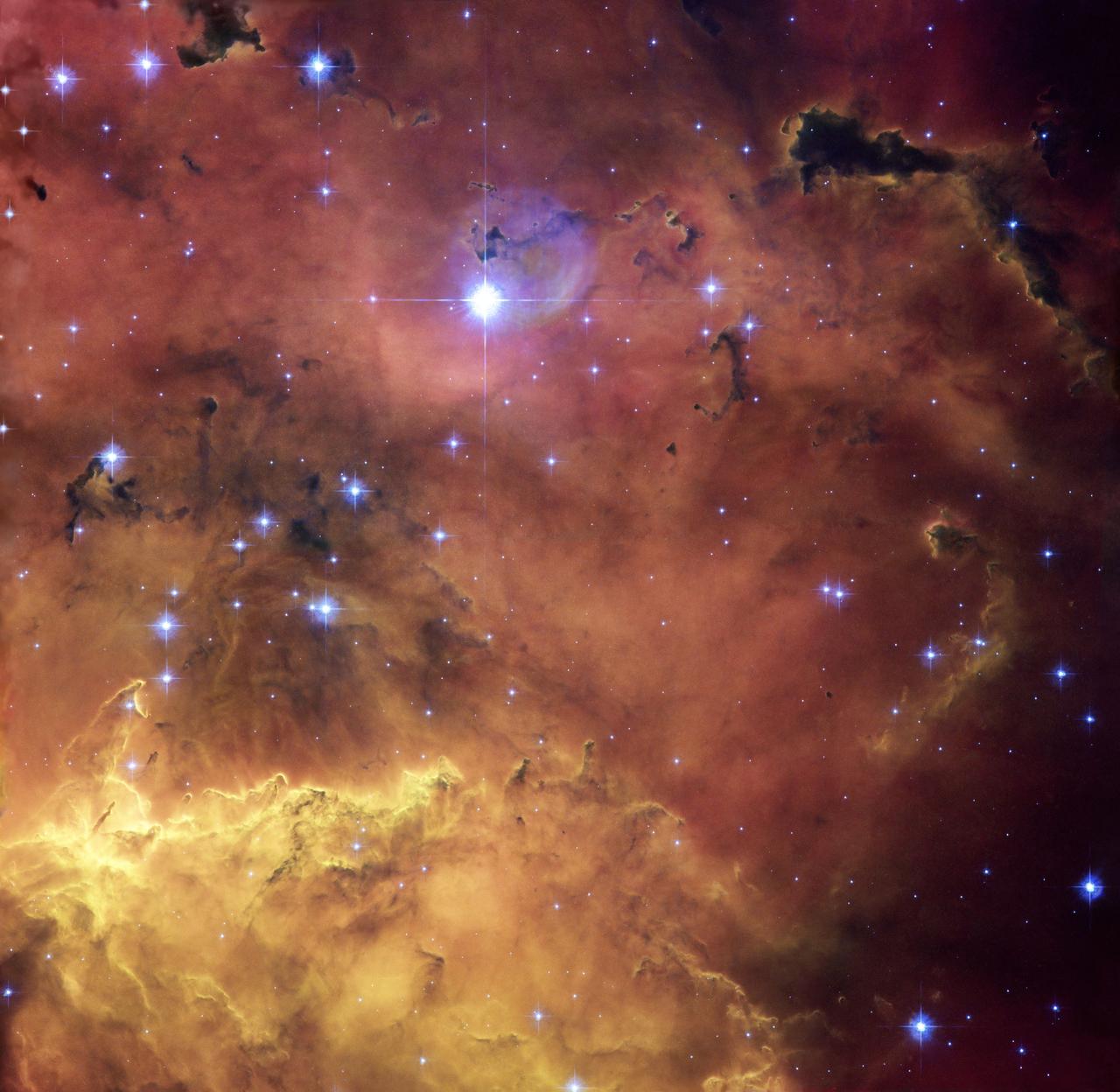

NASA image release July 13, 2010 To view a video of this image go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4790394066/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4790394066/</a> and here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4789786191/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4789786191/</a> A colourful star-forming region is featured in this stunning new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image of NGC 2467. Looking like a roiling cauldron of some exotic cosmic brew, huge clouds of gas and dust are sprinkled with bright blue hot young stars. Strangely shaped dust clouds, resembling spilled liquids, are silhouetted against a colourful background of glowing gas in this newly released Hubble image. The star-forming region NGC 2467 is a vast cloud of gas – mostly hydrogen – that serves as an incubator for new stars. Some of these youthful stars have emerged from the dense clouds where they were born and now shine brightly, hot and blue in this picture, but many others remain hidden. The full beauty of this object and hints of the astrophysical processes at work within it are revealed in this super-sharp image from Hubble. Hot young stars that recently formed from the cloud are emitting fierce ultraviolet radiation that is causing the whole scene to glow while also sculpting the environment and gradually eroding the gas clouds. Studies have shown that most of the radiation comes from the single hot and brilliant massive star just above the centre of the image. Its fierce radiation has cleared the surrounding region and some of the next generation of stars are forming in the denser regions around the edge. One of the most familiar star-forming regions is the Orion Nebula, which can be seen with the naked eye. NGC 2467 is a similar but more distant example. Such stellar nurseries can be seen out to considerable distances in the Universe, and their study is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Some galaxies contain huge star-forming regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Another dramatic example is the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud. NGC 2467 was discovered in the nineteenth century and lies in the southern constellation of Puppis, which represents the poop deck of Jason's fabled ship Argo from Greek mythology. NGC 2467 is thought to lie about 13 000 light-years from Earth. The picture was created from images taken with the Wide Field Channel of the Advanced Camera for Surveys through three different filters (F550M, F660N and F658N, shown in blue, green and red respectively). These data were taken in 2004. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. Credit: NASA, ESA and Orsola De Marco (Macquarie University) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

Fireworks shows are not just confined to Earth’s skies. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has captured a spectacular fireworks display in a small, nearby galaxy, which resembles a July 4th skyrocket. A firestorm of star birth is lighting up one end of the diminutive galaxy Kiso 5639. The dwarf galaxy is shaped like a flattened pancake, but because it is tilted edge-on, it resembles a skyrocket, with a brilliant blazing head and a long, star-studded tail. Kiso 5639 is a rare, nearby example of elongated galaxies that occur in abundance at larger distances, where we observe the universe during earlier epochs. Astronomers suggest that the frenzied star birth is sparked by intergalactic gas raining on one end of the galaxy as it drifts through space. “I think Kiso 5639 is a beautiful, up-close example of what must have been common long ago,” said lead researcher Debra Elmegreen of Vassar College, in Poughkeepsie, New York. “The current thinking is that galaxies in the early universe grow from accreting gas from the surrounding neighborhood. It’s a stage that galaxies, including our Milky Way, must go through as they are growing up.” Observations of the early universe, such as Hubble’s Ultra-Deep Field, reveal that about 10 percent of all galaxies have these elongated shapes, and are collectively called “tadpoles.” But studies of the nearby universe have turned up only a few of these unusual galaxies, including Kiso 5639. The development of the nearby star-making tadpole galaxies, however, has lagged behind that of their peers, which have spent billions of years building themselves up into many of the spiral galaxies seen today. Elmegreen used Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 to conduct a detailed imaging study of Kiso 5639. The images in different filters reveal information about an object by dissecting its light into its component colors. Hubble’s crisp resolution helped Elmegreen and her team analyze the giant star-forming clumps in Kiso 5639 and determine the masses and ages of the star clusters. The international team of researchers selected Kiso 5639 from a spectroscopic survey of 10 nearby tadpole galaxies, observed with the Grand Canary Telescope in La Palma, Spain, by Jorge Sanchez Almeida and collaborators at the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias. The observations revealed that in most of those galaxies, including Kiso 5639, the gas composition is not uniform. The bright gas in the galaxy’s head contains fewer heavier elements (collectively called “metals”), such as carbon and oxygen, than the rest of the galaxy. Stars consist mainly of hydrogen and helium, but cook up other “heavier” elements. When the stars die, they release their heavy elements and enrich the surrounding gas. “The metallicity suggests that there has to be rather pure gas, composed mostly of hydrogen, coming into the star-forming part of the galaxy, because intergalactic space contains more pristine hydrogen-rich gas,” Elmegreen explained. “Otherwise, the starburst region should be as rich in heavy elements as the rest of the galaxy.” Hubble offers a detailed view of the galaxy’s star-making frenzy. The telescope uncovered several dozen clusters of stars in the galaxy’s star-forming head, which spans 2,700 light-years across. These clusters have an average age of less than 1 million years and masses that are three to six times larger than those in the rest of the galaxy. Other star formation is taking place throughout the galaxy but on a much smaller scale. Star clusters in the rest of the galaxy are between several million to a few billion years old. “There is much more star formation going on in the head than what you would expect in such a tiny galaxy,” said team member Bruce Elmegreen of IBM’s Thomas J. Watson’s Research Center, in Yorktown Heights, New York. “And we think the star formation is triggered by the ongoing accretion of metal-poor gas onto a part of an otherwise quiescent dwarf galaxy.” Hubble also revealed giant holes peppered throughout the galaxy’s starburst head. These cavities give the galaxy’s head a Swiss-cheese appearance because numerous supernova detonations – like firework aerial bursts – have carved out holes of rarified superheated gas. The galaxy, located 82 million light-years away, has taken billions of years to develop because it has been drifting through an isolated “desert” in the universe, devoid of much gas. What triggered the starburst in such a backwater galaxy? Based on simulations by Daniel Ceverino of the Center for Astronomy at Heidelberg University in Germany, and other team members, the observations suggest that less than 1 million years ago, Kiso 5639’s leading edge encountered a filament of gas. The filament dropped a large clump of matter onto the galaxy, stoking the vigorous star birth. Debra Elmegreen expects that in the future other parts of the galaxy will join in the star-making fireworks show. “Galaxies rotate, and as Kiso 5639 continues to spin, another part of the galaxy may receive an infusion of new gas from this filament, instigating another round of star birth,” she said. The team’s results have been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. Other team members include Casiana Munoz-Tunon and Mercedes Filho (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Canary Islands), Jairo Mendez-Abreu (University of St. Andrews, United Kingdom), John Gallagher (University of Wisconsin-Madison), and Marc Rafelski (NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland). The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C.
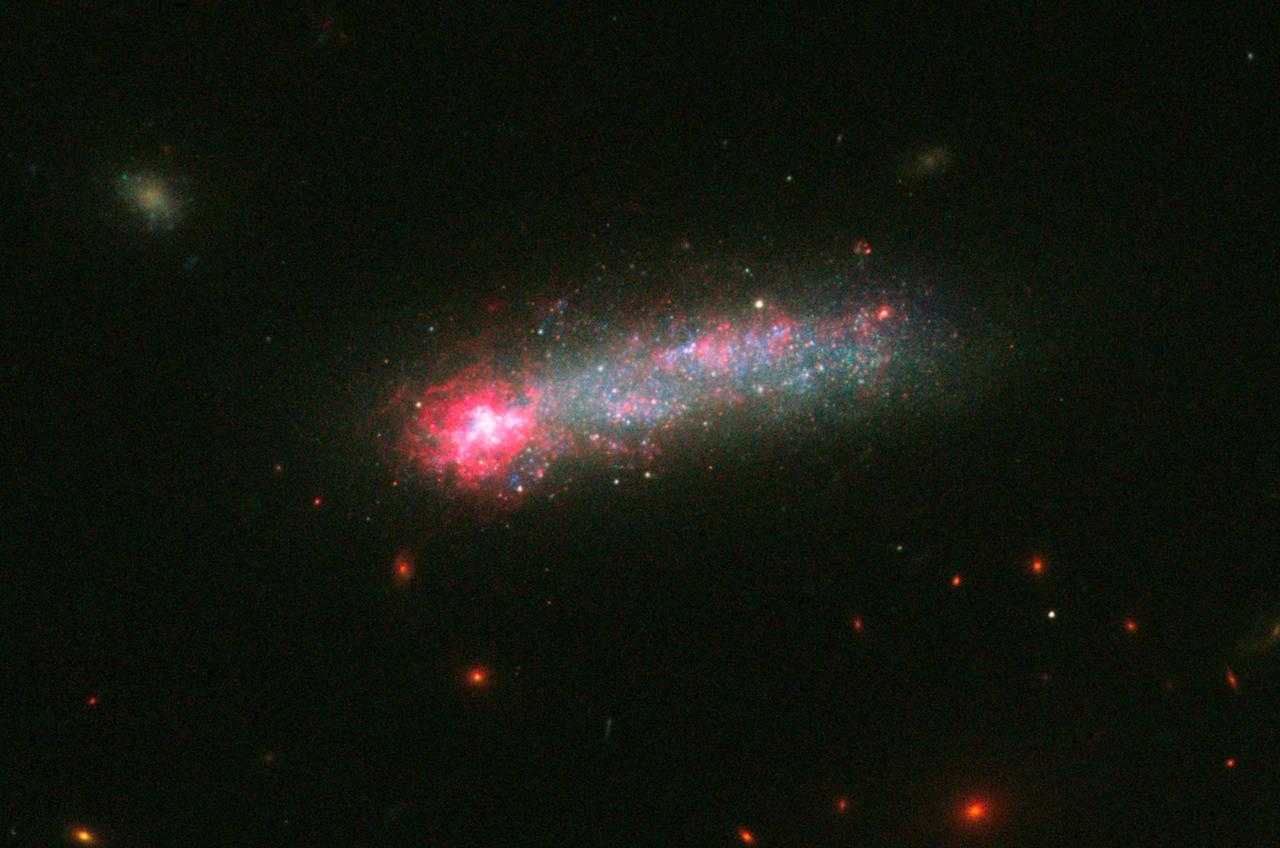

Fireworks shows are not just confined to Earth’s skies. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has captured a spectacular fireworks display in a small, nearby galaxy, which resembles a July 4th skyrocket. A firestorm of star birth is lighting up one end of the diminutive galaxy Kiso 5639. The dwarf galaxy is shaped like a flattened pancake, but because it is tilted edge-on, it resembles a skyrocket, with a brilliant blazing head and a long, star-studded tail. Kiso 5639 is a rare, nearby example of elongated galaxies that occur in abundance at larger distances, where we observe the universe during earlier epochs. Astronomers suggest that the frenzied star birth is sparked by intergalactic gas raining on one end of the galaxy as it drifts through space. “I think Kiso 5639 is a beautiful, up-close example of what must have been common long ago,” said lead researcher Debra Elmegreen of Vassar College, in Poughkeepsie, New York. “The current thinking is that galaxies in the early universe grow from accreting gas from the surrounding neighborhood. It’s a stage that galaxies, including our Milky Way, must go through as they are growing up.” Observations of the early universe, such as Hubble’s Ultra-Deep Field, reveal that about 10 percent of all galaxies have these elongated shapes, and are collectively called “tadpoles.” But studies of the nearby universe have turned up only a few of these unusual galaxies, including Kiso 5639. The development of the nearby star-making tadpole galaxies, however, has lagged behind that of their peers, which have spent billions of years building themselves up into many of the spiral galaxies seen today. Elmegreen used Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 to conduct a detailed imaging study of Kiso 5639. The images in different filters reveal information about an object by dissecting its light into its component colors. Hubble’s crisp resolution helped Elmegreen and her team analyze the giant star-forming clumps in Kiso 5639 and determine the masses and ages of the star clusters. The international team of researchers selected Kiso 5639 from a spectroscopic survey of 10 nearby tadpole galaxies, observed with the Grand Canary Telescope in La Palma, Spain, by Jorge Sanchez Almeida and collaborators at the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias. The observations revealed that in most of those galaxies, including Kiso 5639, the gas composition is not uniform. The bright gas in the galaxy’s head contains fewer heavier elements (collectively called “metals”), such as carbon and oxygen, than the rest of the galaxy. Stars consist mainly of hydrogen and helium, but cook up other “heavier” elements. When the stars die, they release their heavy elements and enrich the surrounding gas. “The metallicity suggests that there has to be rather pure gas, composed mostly of hydrogen, coming into the star-forming part of the galaxy, because intergalactic space contains more pristine hydrogen-rich gas,” Elmegreen explained. “Otherwise, the starburst region should be as rich in heavy elements as the rest of the galaxy.” Hubble offers a detailed view of the galaxy’s star-making frenzy. The telescope uncovered several dozen clusters of stars in the galaxy’s star-forming head, which spans 2,700 light-years across. These clusters have an average age of less than 1 million years and masses that are three to six times larger than those in the rest of the galaxy. Other star formation is taking place throughout the galaxy but on a much smaller scale. Star clusters in the rest of the galaxy are between several million to a few billion years old. “There is much more star formation going on in the head than what you would expect in such a tiny galaxy,” said team member Bruce Elmegreen of IBM’s Thomas J. Watson’s Research Center, in Yorktown Heights, New York. “And we think the star formation is triggered by the ongoing accretion of metal-poor gas onto a part of an otherwise quiescent dwarf galaxy.” Hubble also revealed giant holes peppered throughout the galaxy’s starburst head. These cavities give the galaxy’s head a Swiss-cheese appearance because numerous supernova detonations – like firework aerial bursts – have carved out holes of rarified superheated gas. The galaxy, located 82 million light-years away, has taken billions of years to develop because it has been drifting through an isolated “desert” in the universe, devoid of much gas. What triggered the starburst in such a backwater galaxy? Based on simulations by Daniel Ceverino of the Center for Astronomy at Heidelberg University in Germany, and other team members, the observations suggest that less than 1 million years ago, Kiso 5639’s leading edge encountered a filament of gas. The filament dropped a large clump of matter onto the galaxy, stoking the vigorous star birth. Debra Elmegreen expects that in the future other parts of the galaxy will join in the star-making fireworks show. “Galaxies rotate, and as Kiso 5639 continues to spin, another part of the galaxy may receive an infusion of new gas from this filament, instigating another round of star birth,” she said. The team’s results have been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. Other team members include Casiana Munoz-Tunon and Mercedes Filho (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Canary Islands), Jairo Mendez-Abreu (University of St. Andrews, United Kingdom), John Gallagher (University of Wisconsin-Madison), and Marc Rafelski (NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland). The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. For images and more information about Kiso 5639 and Hubble, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2016/23" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2016/23</a> <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> Image credit: NASA, ESA, and D. Elmegreen (Vassar College) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This image depicts a vast canyon of dust and gas in the Orion Nebula from a 3-D computer model based on observations by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and created by science visualization specialists at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md. A 3-D visualization of this model takes viewers on an amazing four-minute voyage through the 15-light-year-wide canyon. Credit: NASA, G. Bacon, L. Frattare, Z. Levay, and F. Summers (STScI/AURA) Go here to learn more about Hubble 3D: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/hubble_imax_premiere.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/hubble_imax_premier...</a> or <a href="http://www.imax.com/hubble/" rel="nofollow">www.imax.com/hubble/</a> Take an exhilarating ride through the Orion Nebula, a vast star-making factory 1,500 light-years away. Swoop through Orion's giant canyon of gas and dust. Fly past behemoth stars whose brilliant light illuminates and energizes the entire cloudy region. Zoom by dusty tadpole-shaped objects that are fledgling solar systems. This virtual space journey isn't the latest video game but one of several groundbreaking astronomy visualizations created by specialists at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, the science operations center for NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The cinematic space odysseys are part of the new Imax film "Hubble 3D," which opens today at select Imax theaters worldwide. The 43-minute movie chronicles the 20-year life of Hubble and includes highlights from the May 2009 servicing mission to the Earth-orbiting observatory, with footage taken by the astronauts. The giant-screen film showcases some of Hubble's breathtaking iconic pictures, such as the Eagle Nebula's "Pillars of Creation," as well as stunning views taken by the newly installed Wide Field Camera 3. While Hubble pictures of celestial objects are awe-inspiring, they are flat 2-D photographs. For this film, those 2-D images have been converted into 3-D environments, giving the audience the impression they are space travelers taking a tour of Hubble's most popular targets. "A large-format movie is a truly immersive experience," says Frank Summers, an STScI astronomer and science visualization specialist who led the team that developed the movie visualizations. The team labored for nine months, working on four visualization sequences that comprise about 12 minutes of the movie. "Seeing these Hubble images in 3-D, you feel like you are flying through space and not just looking at picture postcards," Summers continued. "The spacescapes are all based on Hubble images and data, though some artistic license is necessary to produce the full depth of field needed for 3-D." The most ambitious sequence is a four-minute voyage through the Orion Nebula's gas-and-dust canyon, about 15 light-years across. During the ride, viewers will see bright and dark, gaseous clouds; thousands of stars, including a grouping of bright, hefty stars called the Trapezium; and embryonic planetary systems. The tour ends with a detailed look at a young circumstellar disk, which is much like the structure from which our solar system formed 4.5 billion years ago. Based on a Hubble image of Orion released in 2006, the visualization was a collaborative effort between science visualization specialists at STScI, including Greg Bacon, who sculpted the Orion Nebula digital model, with input from STScI astronomer Massimo Roberto; the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign; and the Spitzer Science Center at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. For some of the sequences, STScI imaging specialists developed new techniques for transforming the 2-D Hubble images into 3-D. STScI image processing specialists Lisa Frattare and Zolt Levay, for example, created methods of splitting a giant gaseous pillar in the Carina Nebula into multiple layers to produce a 3-D effect, giving the structure depth. The Carina Nebula is a nursery for baby stars. Frattare painstakingly removed the thousands of stars in the image so that Levay could separate the gaseous layers on the isolated Carina pillar. Frattare then replaced the stars into both foreground and background layers to complete the 3-D model. For added effect, the same separation was done for both visible and infrared Hubble images, allowing the film to cross-fade between wavelength views in 3-D. In another sequence viewers fly into a field of 170,000 stars in the giant star cluster Omega Centauri. STScI astronomer Jay Anderson used his stellar database to create a synthetic star field in 3-D that matches recent razor-sharp Hubble photos. The film's final four-minute sequence takes viewers on a voyage from our Milky Way Galaxy past many of Hubble's best galaxy shots and deep into space. Some 15,000 galaxies from Hubble's deepest surveys stretch billions of light-years across the universe in a 3-D sequence created by STScI astronomers and visualizers. The view dissolves into a cobweb that traces the universe's large-scale structure, the backbone from which galaxies were born. In addition to creating visualizations, STScI's education group also provided guidance on the "Hubble 3D" Educator Guide, which includes standards-based lesson plans and activities about Hubble and its mission. Students will use the guide before or after seeing the movie. "The guide will enhance the movie experience for students and extend the movie into classrooms," says Bonnie Eisenhamer, STScI's Hubble Formal Education manager. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) and is managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in Greenbelt, Md. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. The institute is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., Washington, D.C.