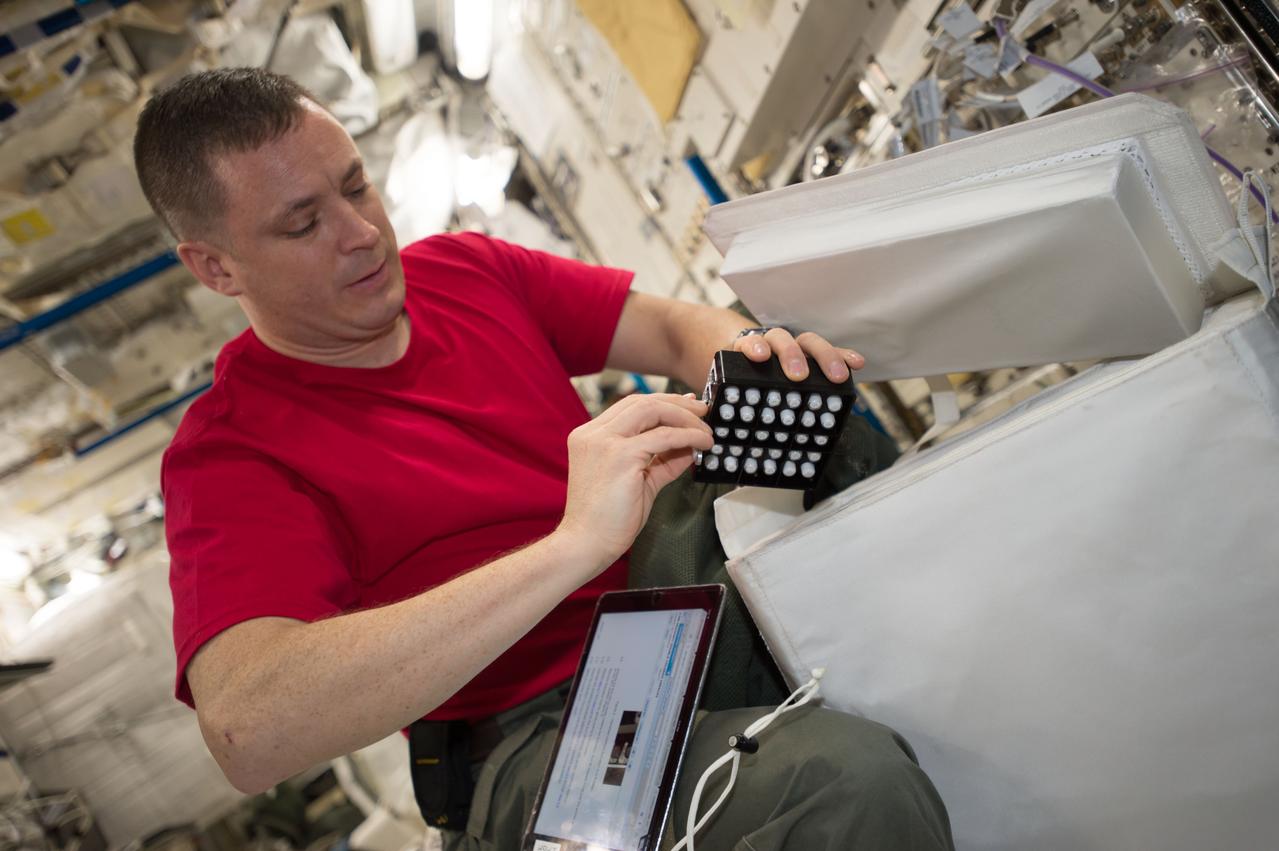

iss052e000508 (June 6, 2017) --- View of astronaut Jack Fischer working with the Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 6) experiment in the Japanese Experiment Module
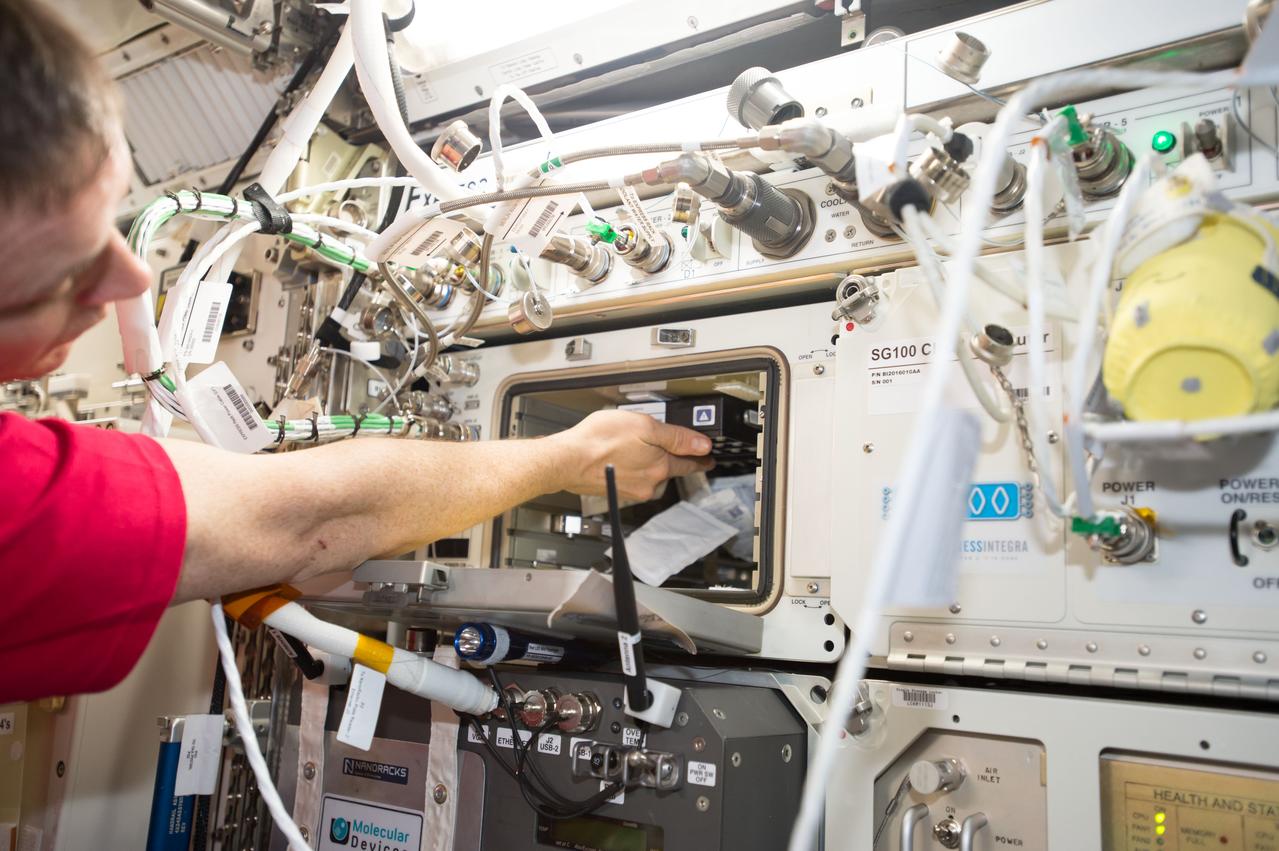

iss052e000515 (June 6, 2017) --- View of astronaut Jack Fischer working with the Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 6) experiment in the Japanese Experiment Module.
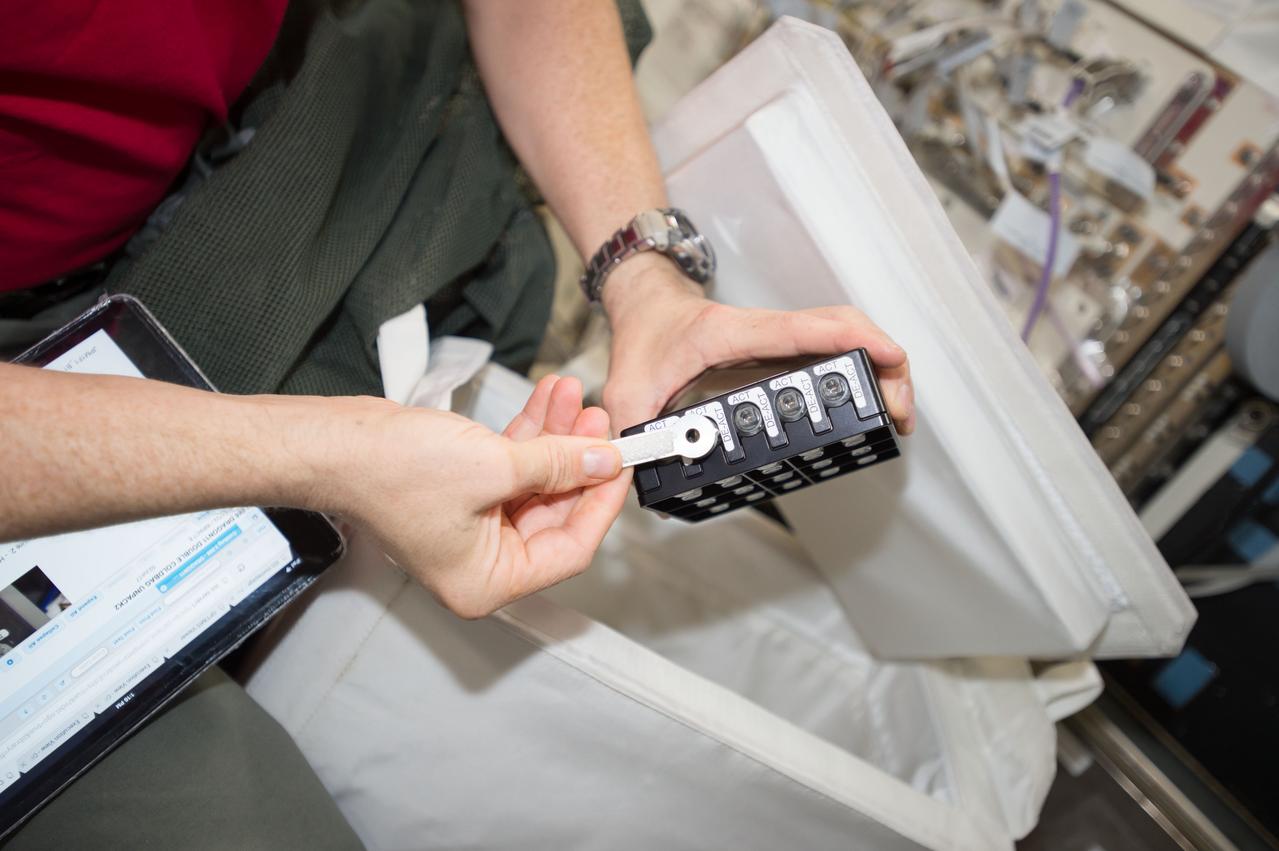

iss052e000503 (June 6, 2017) --- View of astronaut Jack Fischer working with the Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 6) experiment in the Japanese Experiment Module.
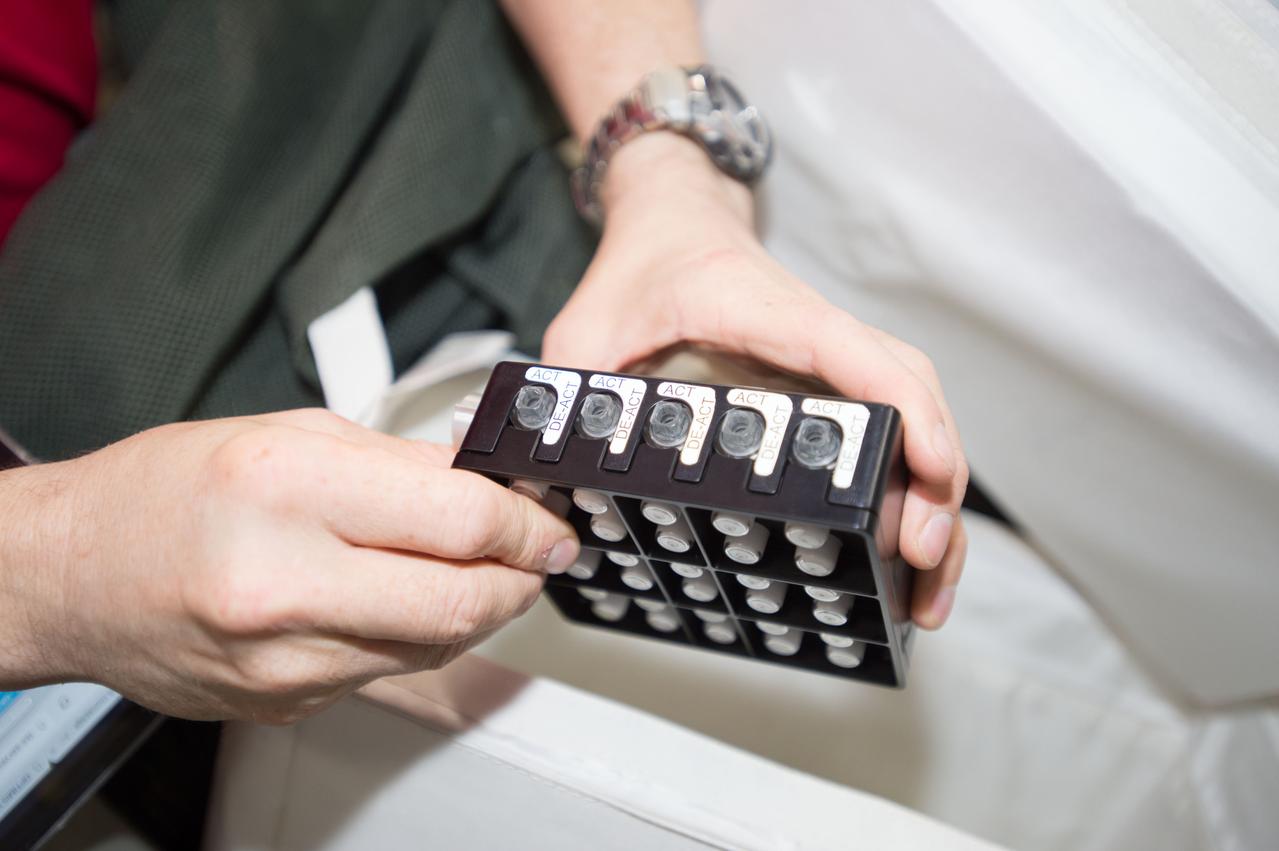

iss052e000504 (June 6, 2017) --- View of astronaut Jack Fischer working with the Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 6) experiment in the Japanese Experiment Module.
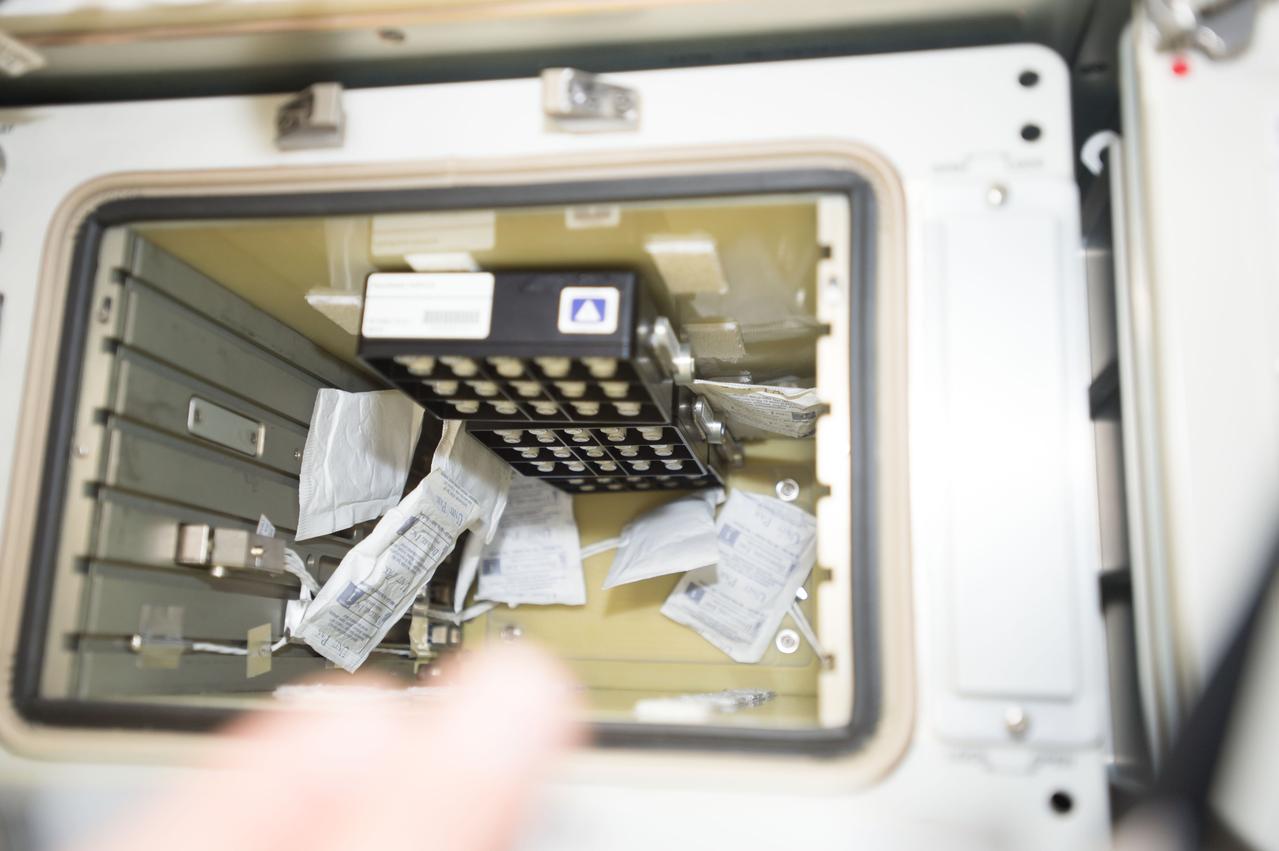

iss052e000516 (6/6/2017) --- View of the Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 6) experiment in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM).
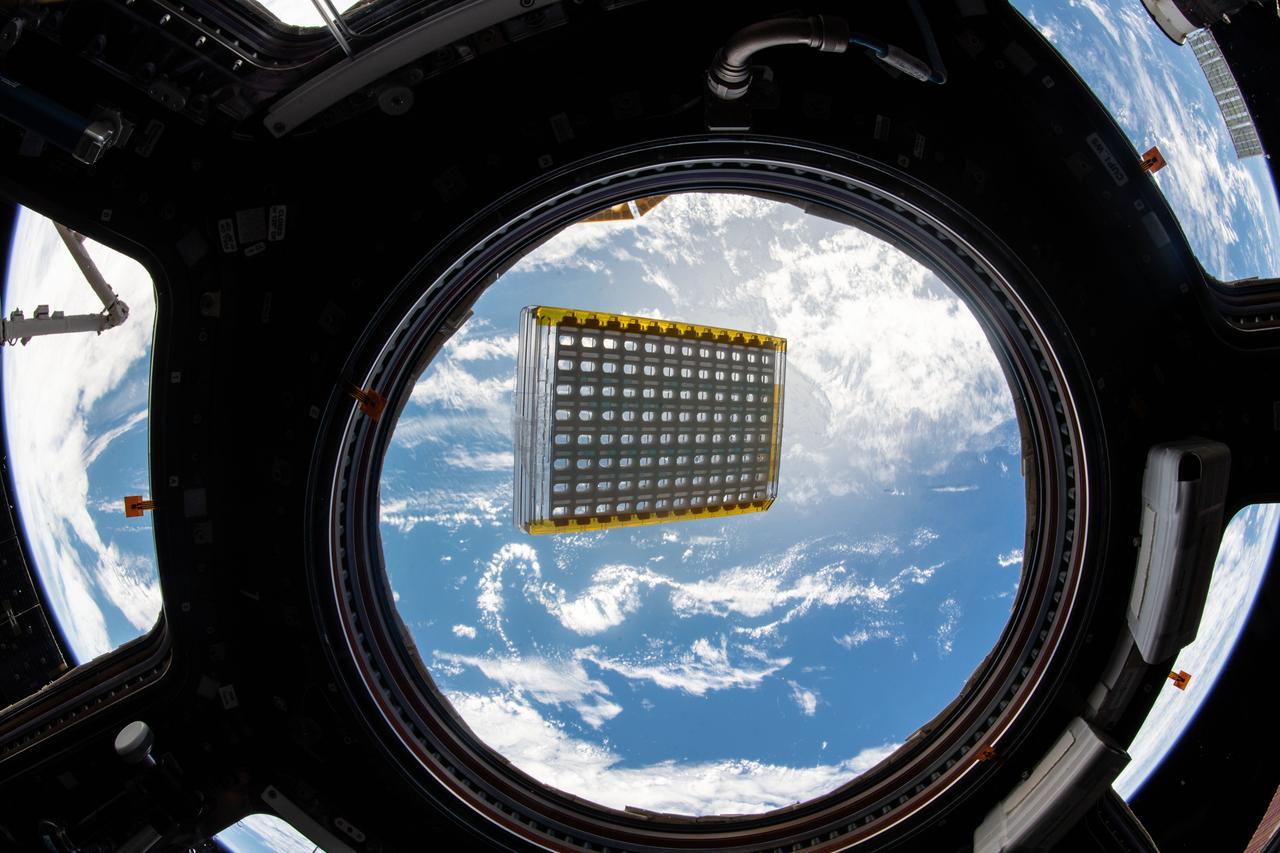
iss058e002064 (1/6/2019) --- CASIS PCG 16 floating in front of Window 7 in the Cupola module. Earth is in the background. Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) evaluates growth of Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein crystals in microgravity. LRRK2 is implicated in Parkinson’s disease, but crystals of the protein grown on Earth are too small and compact to study. Detailed analysis of larger, space-grown crystals can define the protein’s exact shape and morphology and help scientists better understand the disease’s pathology.
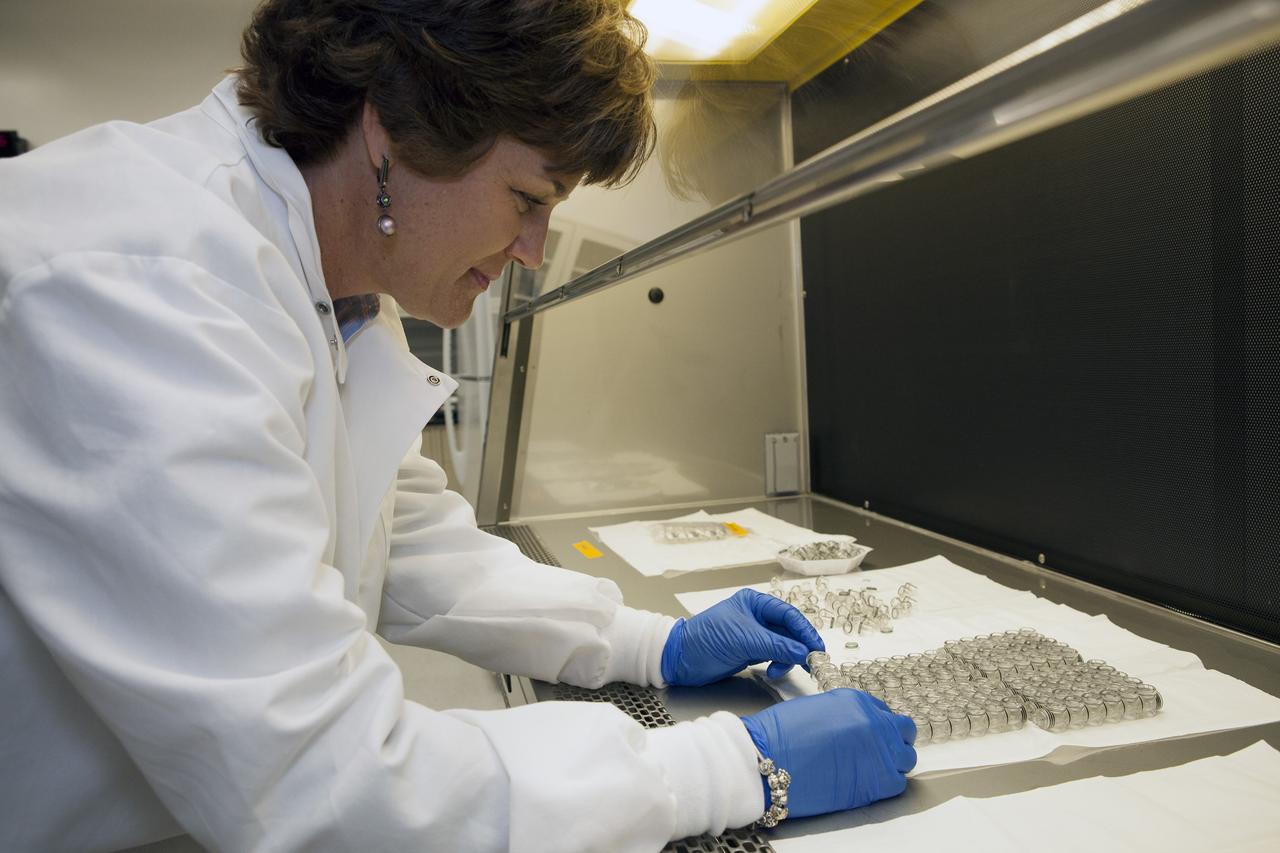

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, April Spinale, a payload integration specialist with Bionetics, cleans the vials that will hold the Protein Crystal Growth 2 samples for the Center for Advancement of Science in Space, or CASIS. The experiment is one of many that will be delivered to the International Space Station on the SpaceX-4 commercial cargo resupply mission. The CASIS experiment will be used in the National Laboratory on the space station. Kennedy's ISS Ground Processing and Research Project Office is providing the necessary laboratories, equipment, supplies and consumables for 61 principal investigators, including 17 from other countries, as they prepare their science experiments for flight. The SpaceX-4 flight is targeted to launch in September 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, April Spinale, a payload integration specialist with Bionetics, fills vials with clear water during an acceptance leak test on the hardware for the Protein Crystal Growth 2 experiment. To her left is Ray Polniak, a quality assurance specialist with Dynamac. They are both consultants for the Center for Advancement of Science in Space, or CASIS. The experiment is one of many that will be delivered to the International Space Station on the SpaceX-4 commercial cargo resupply mission. Kennedy's ISS Ground Processing and Research Project Office is providing the necessary laboratories, equipment, supplies and consumables for 61 principal investigators, including 17 from other countries, as they prepare their science experiments for flight. The SpaceX-4 flight is targeted to launch in September 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
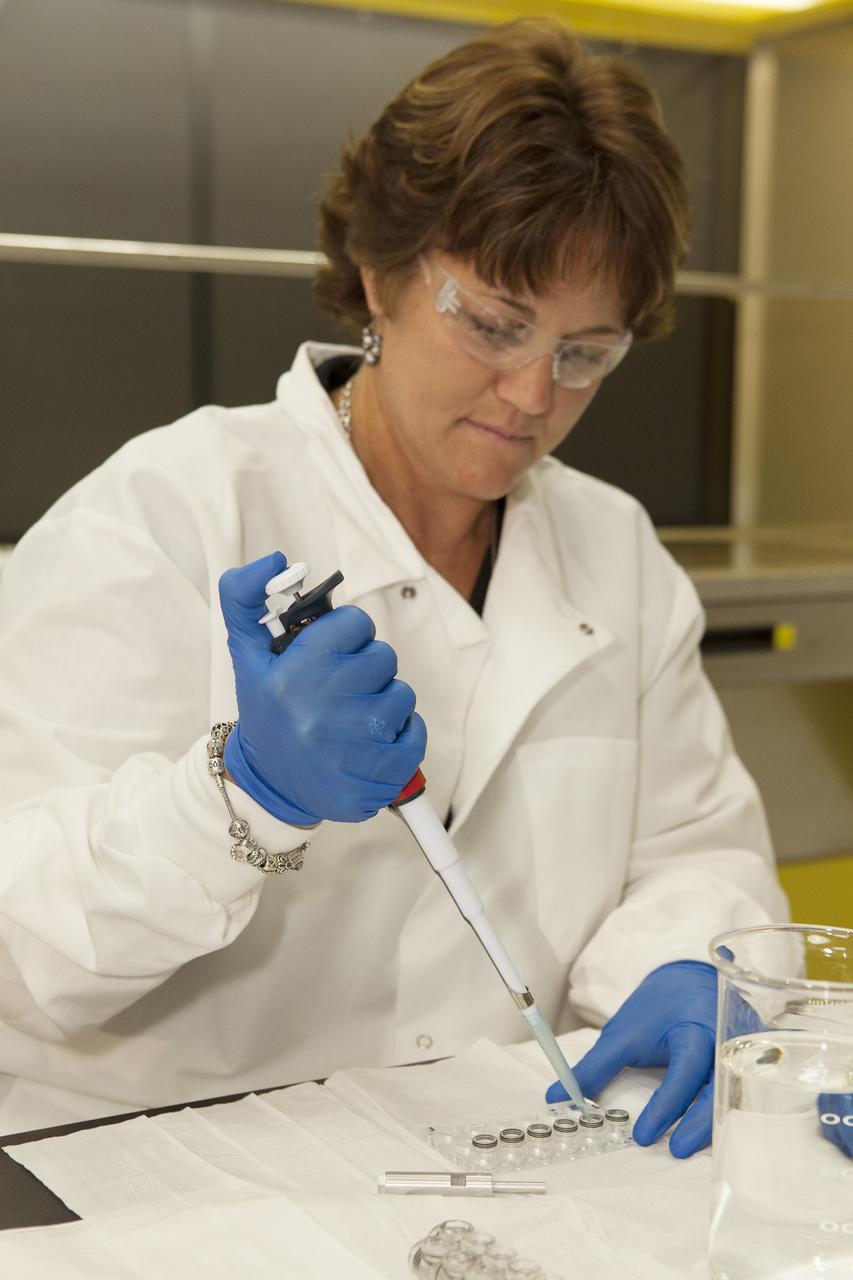

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, April Spinale, a payload integration specialist with Bionetics, fills vials with clear water during an acceptance leak test on the hardware for the Protein Crystal Growth 2 experiment. Spinale is a consultant for the Center for Advancement of Science in Space, or CASIS. The experiment is one of many that will be delivered to the International Space Station on the SpaceX-4 commercial cargo resupply mission. Kennedy's ISS Ground Processing and Research Project Office is providing the necessary laboratories, equipment, supplies and consumables for 61 principal investigators, including 17 from other countries, as they prepare their science experiments for flight. The SpaceX-4 flight is targeted to launch in September 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
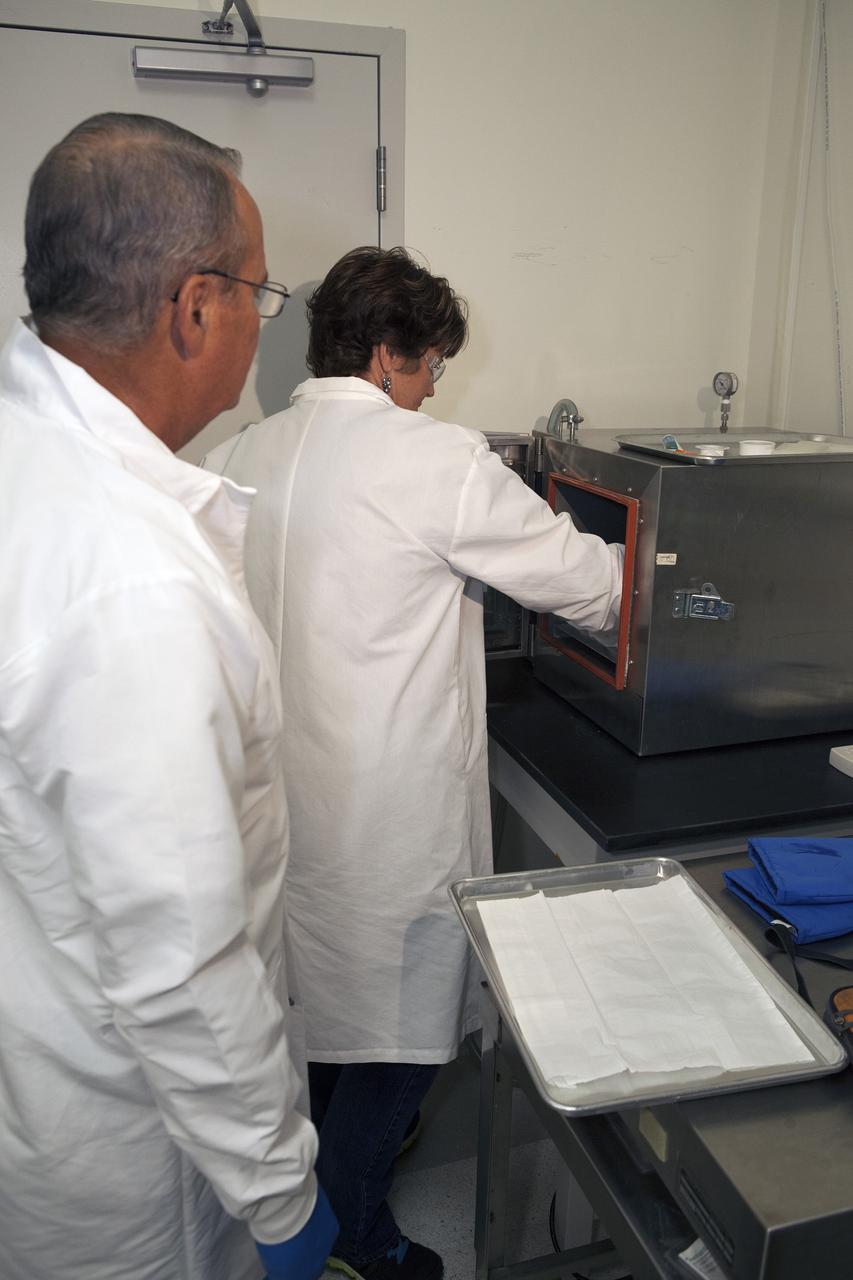

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, April Spinale, a payload integration specialist with Bionetics, and Ray Polniak, a quality assurance specialist with Dynamac, place a set of vials for the Protein Crystal Growth 2 experiment into a vacuum chamber for an acceptance leak test. The vials have been filled with clear water. The test will verify that the hardware is providing adequate containment for the liquids. Both are consultants for the Center for Advancement of Science in Space, or CASIS. The experiment is one of many that will be delivered to the International Space Station on the SpaceX-4 commercial cargo resupply mission. Kennedy's ISS Ground Processing and Research Project Office is providing the necessary laboratories, equipment, supplies and consumables for 61 principal investigators, including 17 from other countries, as they prepare their science experiments for flight. The SpaceX-4 flight is targeted to launch in September 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
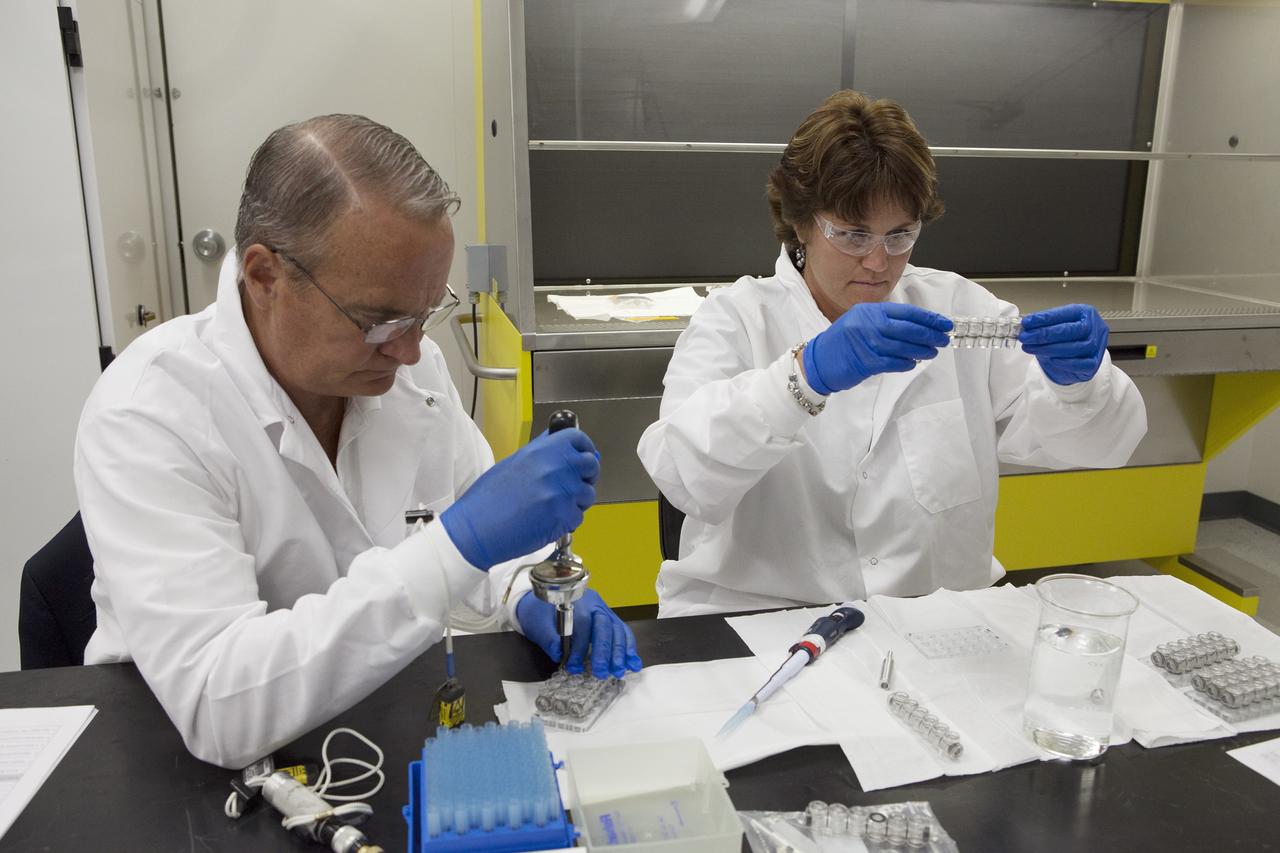

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, April Spinale, a payload integration specialist with Bionetics, and Ray Polniak, a quality assurance specialist with Dynamac, fill vials with clear water during an acceptance leak test on the hardware for the Protein Crystal Growth 2 experiment. They are both consultants for the Center for Advancement of Science in Space, or CASIS. The experiment is one of many that will be delivered to the International Space Station on the SpaceX-4 commercial cargo resupply mission. Kennedy's ISS Ground Processing and Research Project Office is providing the necessary laboratories, equipment, supplies and consumables for 61 principal investigators, including 17 from other countries, as they prepare their science experiments for flight. The SpaceX-4 flight is targeted to launch in September 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
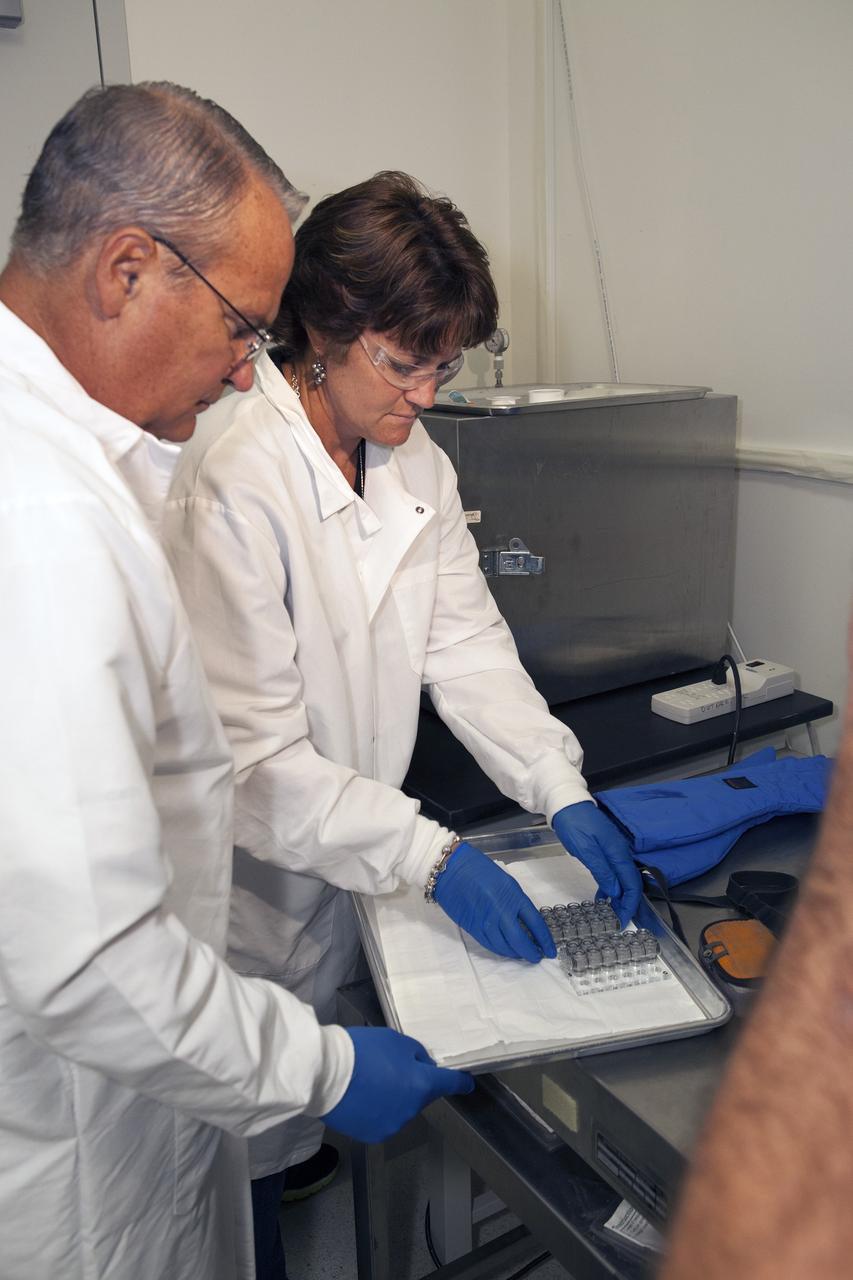

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, April Spinale, a payload integration specialist with Bionetics, and Ray Polniak, a quality assurance specialist with Dynamac, prepare vials for the Protein Crystal Growth 2 experiment for an acceptance leak test. The vials have been filled with clear water and will be put into a vacuum chamber to verify that the hardware is providing adequate containment for the liquids. Both are consultants for the Center for Advancement of Science in Space, or CASIS. The experiment is one of many that will be delivered to the International Space Station on the SpaceX-4 commercial cargo resupply mission. Kennedy's ISS Ground Processing and Research Project Office is providing the necessary laboratories, equipment, supplies and consumables for 61 principal investigators, including 17 from other countries, as they prepare their science experiments for flight. The SpaceX-4 flight is targeted to launch in September 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
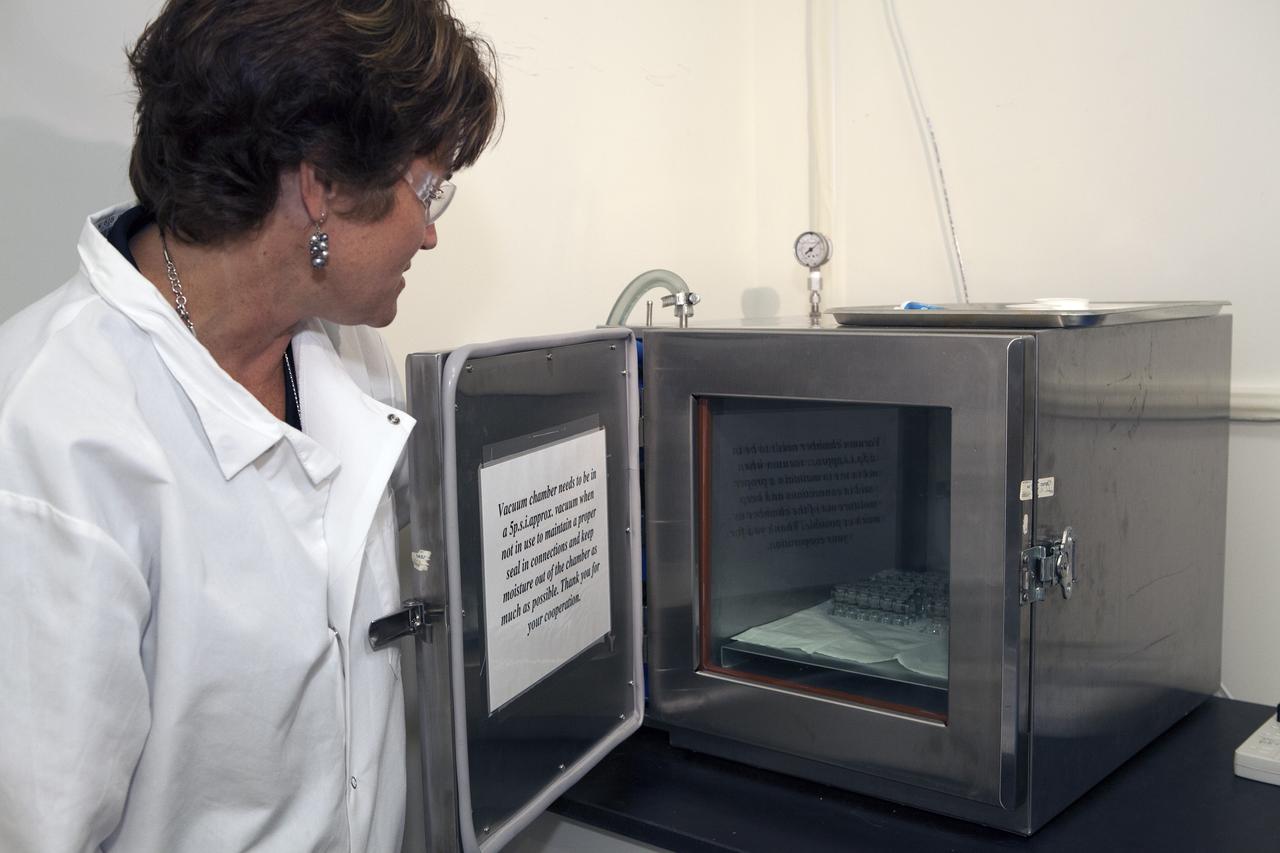

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, April Spinale, a payload integration specialist with Bionetics, places a set of vials for the Protein Crystal Growth 2 experiment into a vacuum chamber for an acceptance leak test. The vials have been filled with clear water and the test will verify that the hardware is providing adequate containment for the liquids. Spinale is a consultants for the Center for Advancement of Science in Space, or CASIS. The experiment is one of many that will be delivered to the International Space Station on the SpaceX-4 commercial cargo resupply mission. Kennedy's ISS Ground Processing and Research Project Office is providing the necessary laboratories, equipment, supplies and consumables for 61 principal investigators, including 17 from other countries, as they prepare their science experiments for flight. The SpaceX-4 flight is targeted to launch in September 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
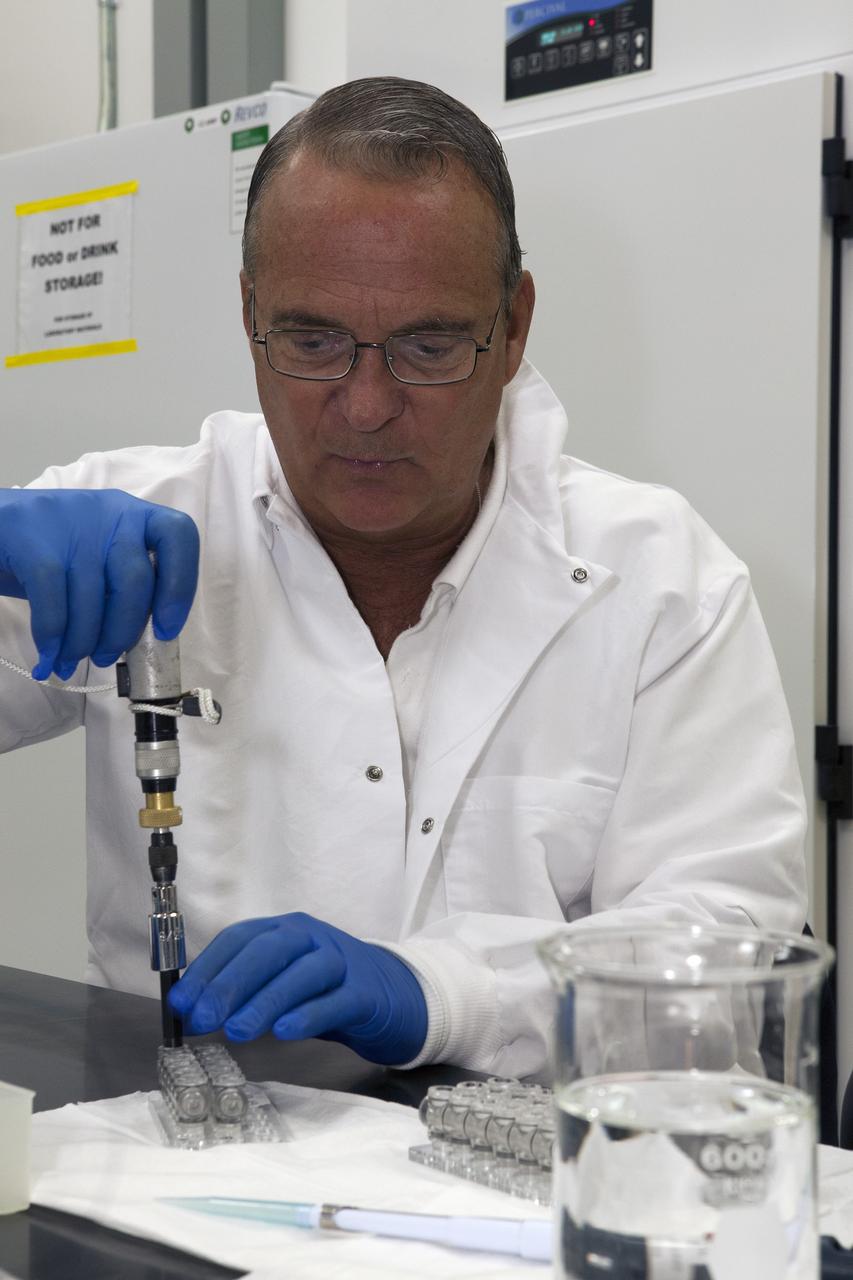

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Ray Polniak, a quality assurance specialist with Dynamac, prepares vials for the Crystal Protein Growth 2 experiment for an acceptance leak test. Polniak is a consultant for the Center for Advancement of Science is Space, or CASIS. The experiment is one of many that will be delivered to the International Space Station on the SpaceX-4 commercial cargo resupply mission. Kennedy's ISS Ground Processing and Research Project Office is providing the necessary laboratories, equipment, supplies and consumables for 61 principal investigators, including 17 from other countries, as they prepare their science experiments for flight. The SpaceX-4 flight is targeted to launch in September 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
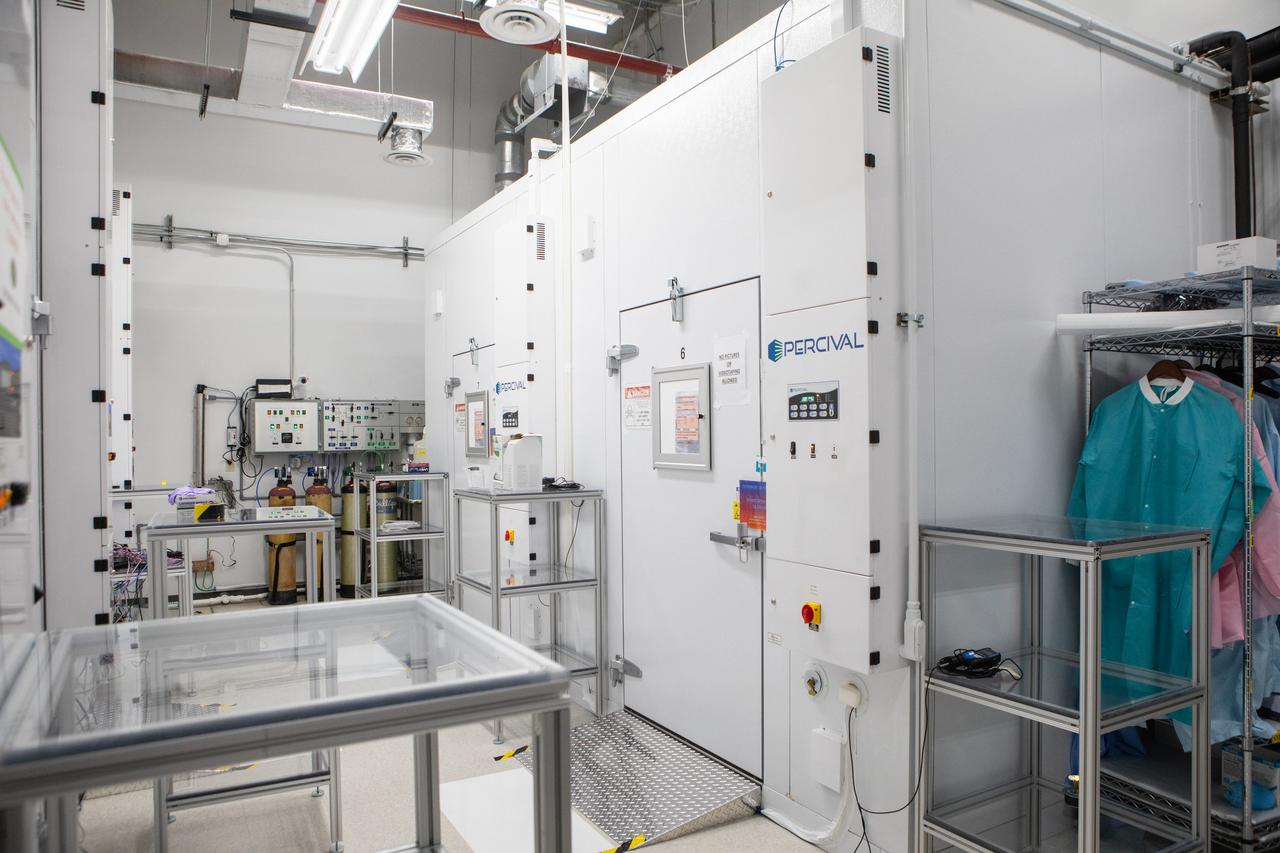

A walk-in experiment chamber for the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS) is in view inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on May 16, 2019. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
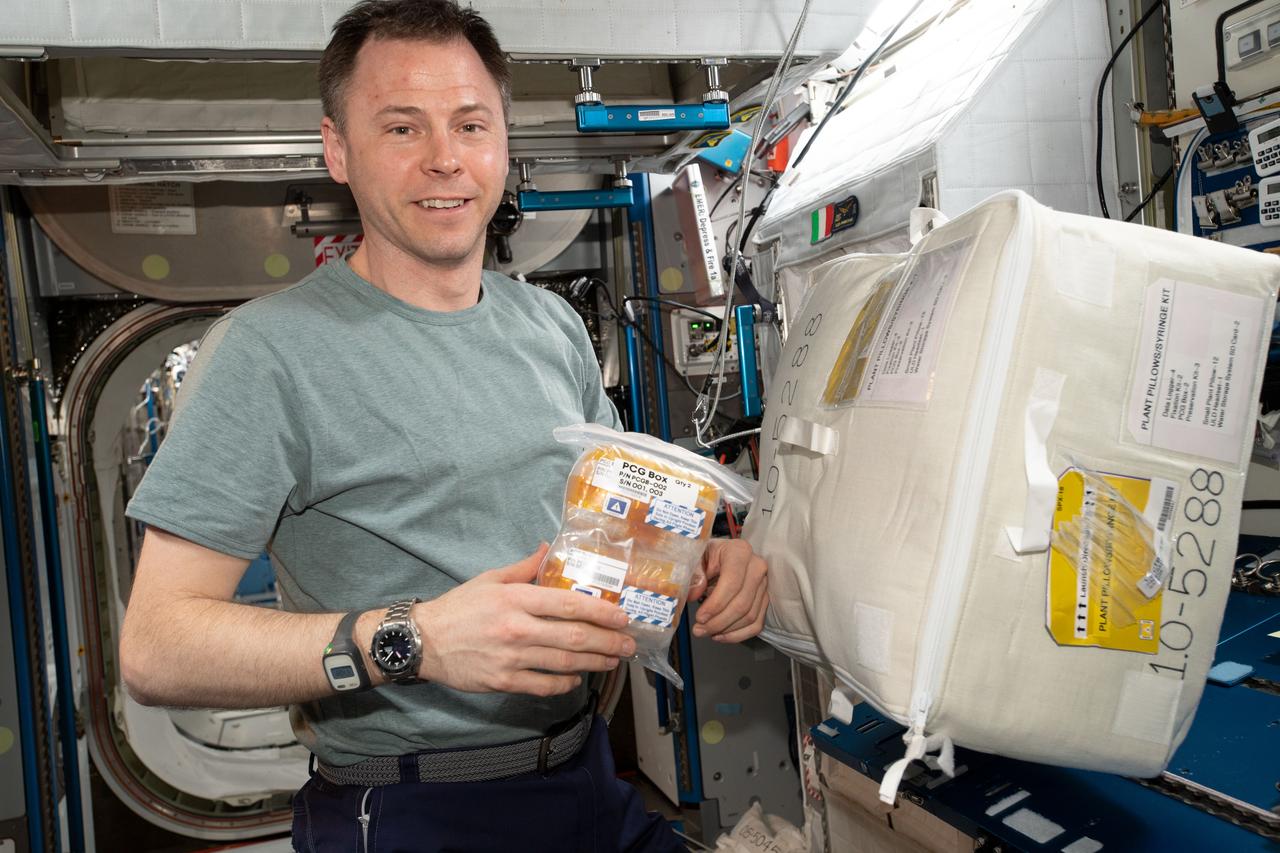

iss060e015014 (7/28/2019) — NASA astronaut Nick Hague is shown holding the CASIS Protein Crystal Growth 15 (CASIS PCG 15) investigation samples aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Microgravity Crystal Growth for Improvement in Neutron Diffraction and the Analysis of Protein Complexes (CASIS PCG 15) seeks a better understanding of enzyme catalysis by examining crystals from two model Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) dependent enzymes and from a bacteriophage transient deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) repair complex. Analysis of the crystals may reveal catalyst mechanisms and structures and visualize the interaction between the repair proteins. Results could contribute to identification of biomarkers for diagnosis of disease and to development of better antimicrobials.
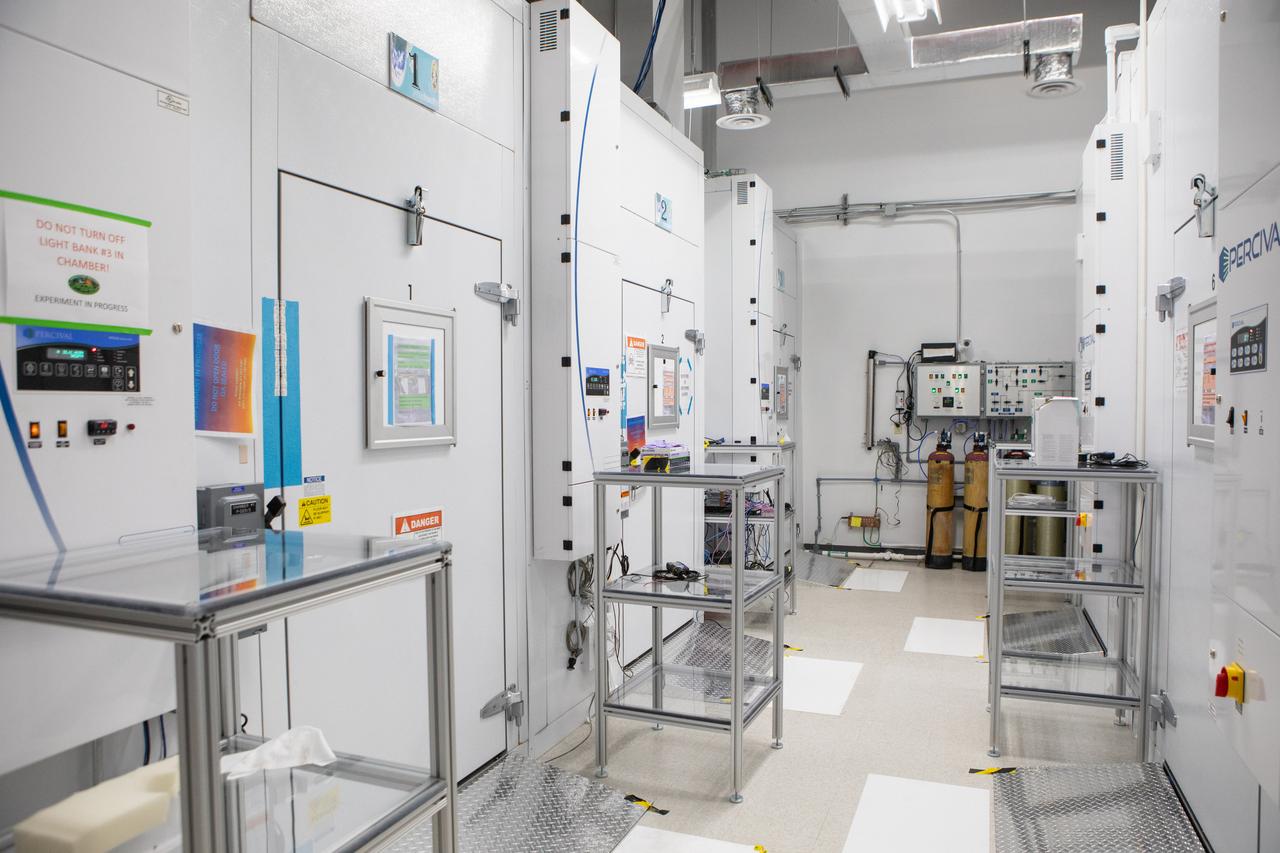

A walk-in experiment chamber for the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS) is in view in the foreground inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on May 16, 2019. Further back is an experiment chamber for ground test flight experiments. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
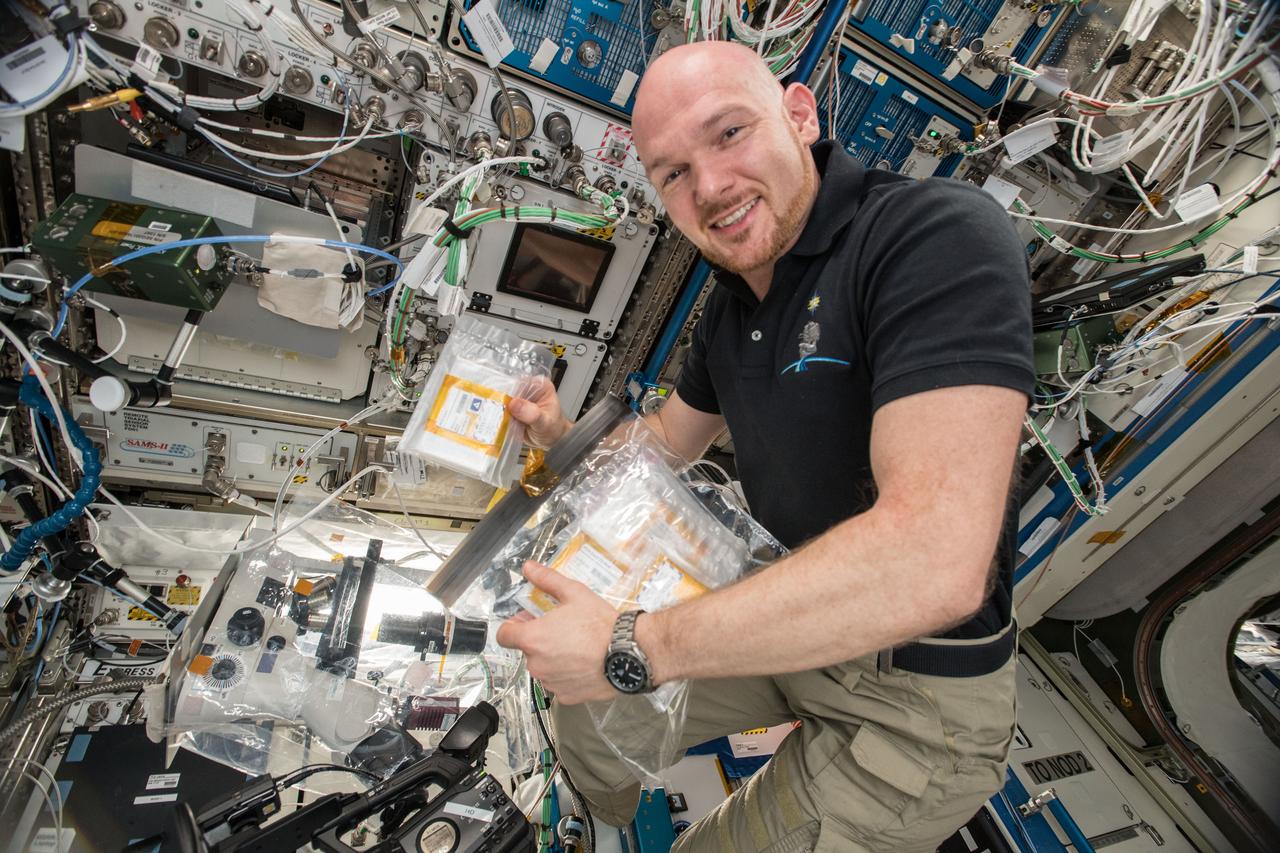

iss057e114766 (12/9/2018) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Alex Gerst is photographed with the Crystallization of RAS in Space (CASIS PCG 17) investigation. CASIS PCG 17grows crystals of KRAS proteins, which have a pivotal role in cell growth and death. Mutations in KRAS proteins are responsible for a third of all cancers and identifying the structure of these proteins is critical to developing therapeutics and treatments. Protein crystals grow larger and more perfectly in microgravity, allowing for detailed laboratory analysis of their structure back on Earth.
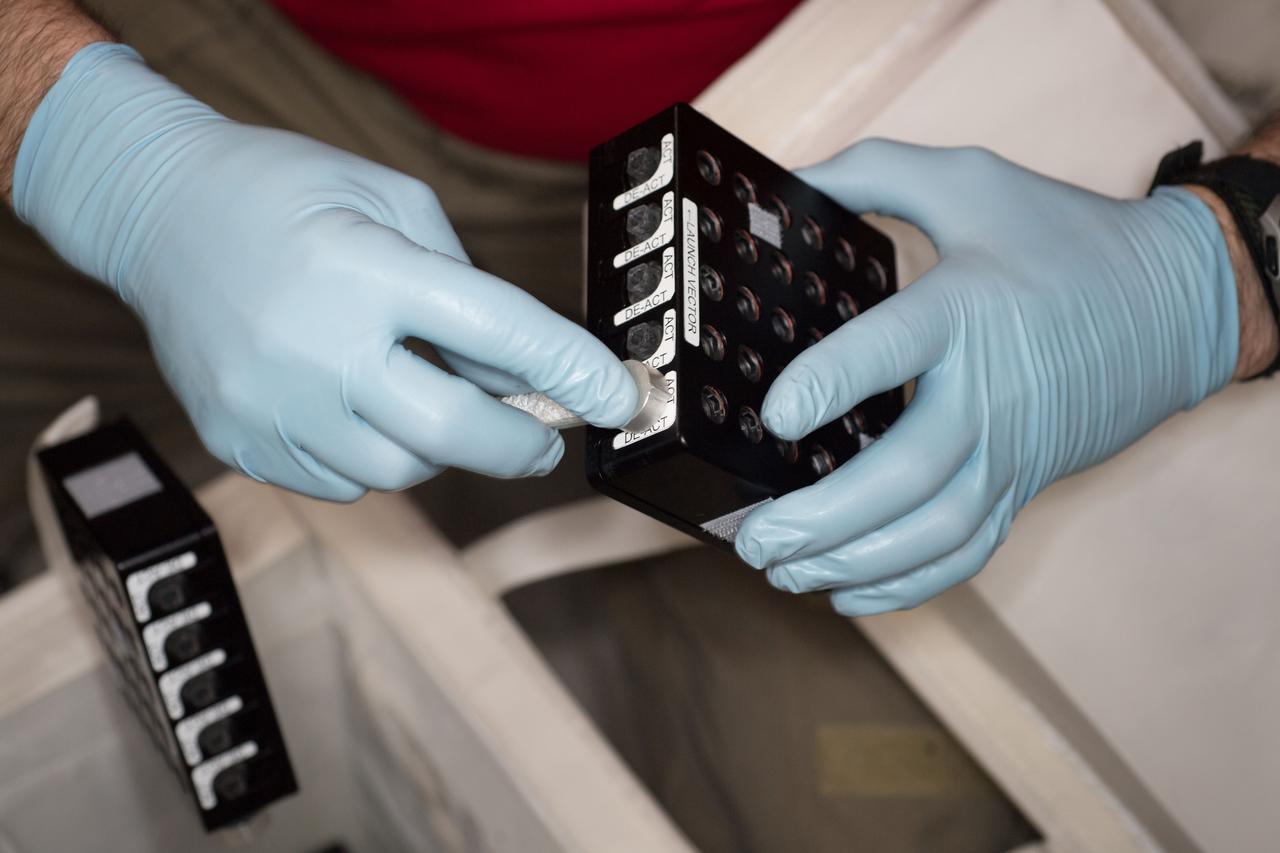

iss055e010761 (4/5/2018) --- Photographic documentation of CASIS Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -11 hardware during CS-DCB-Unpack2 activity aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 11) produces acetylcholinesterase crystals, a neurotransmitter enzyme. Crystals grown in microgravity are larger, of higher-quality and can be used for a technique called macromolecular neutron crystallography (MNC) to locate hydrogen atoms in the crystal’s structure.
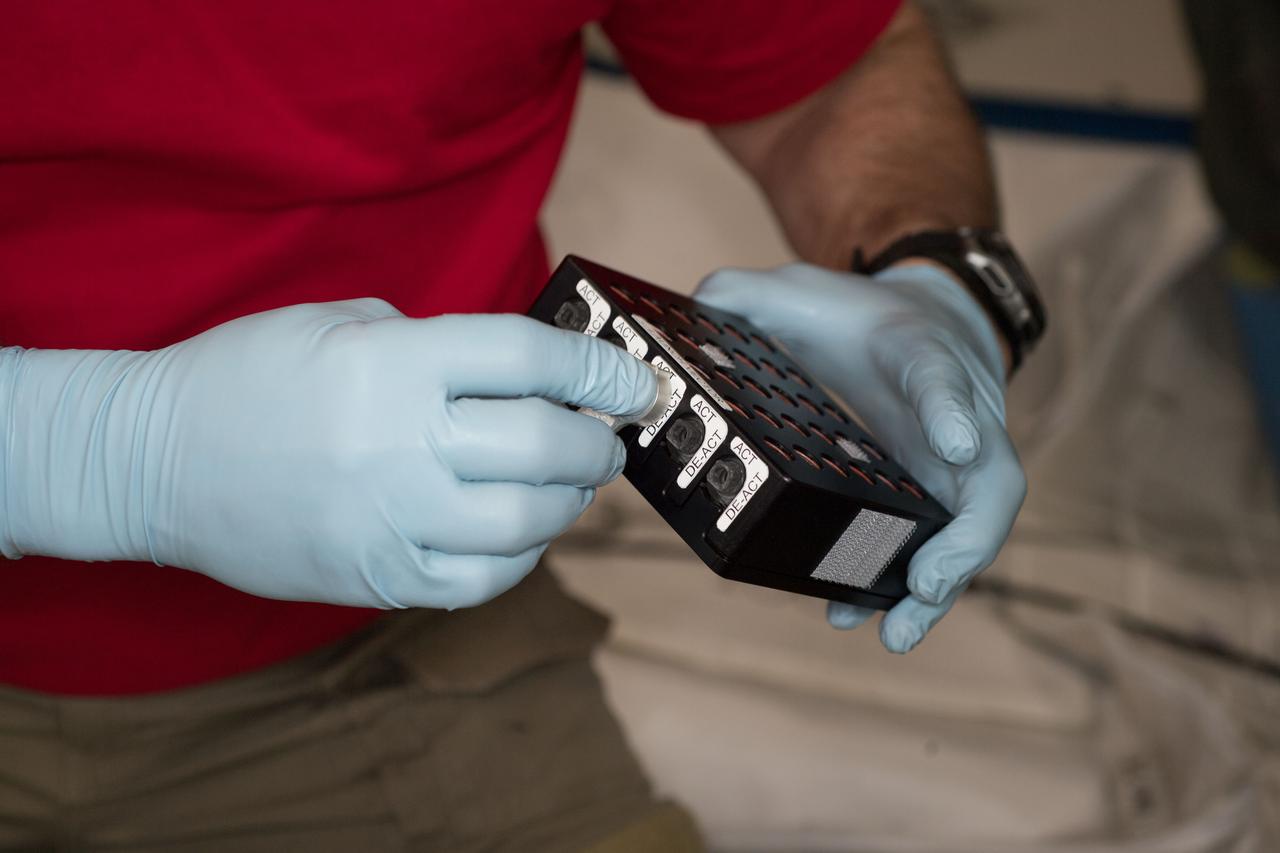

iss055e010753 (4/5/2018) --- Photographic documentation of CASIS Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -11 hardware during CS-DCB-Unpack2 activity aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 11) produces acetylcholinesterase crystals, a neurotransmitter enzyme. Crystals grown in microgravity are larger, of higher-quality and can be used for a technique called macromolecular neutron crystallography (MNC) to locate hydrogen atoms in the crystal’s structure.
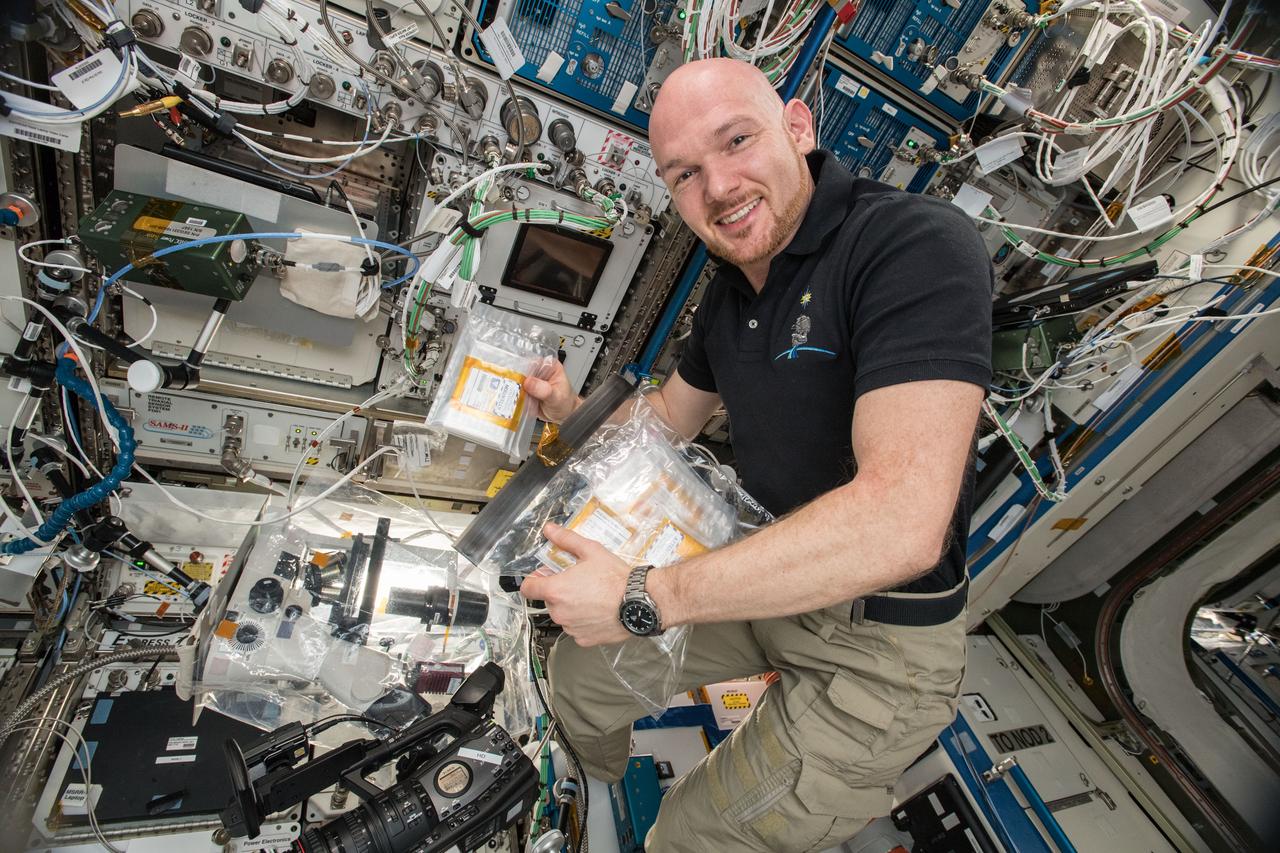

iss057e114765 (12/9/2018) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Alex Gerst is photographed with the Crystallization of RAS in Space (CASIS PCG 17) investigation. CASIS PCG 17grows crystals of KRAS proteins, which have a pivotal role in cell growth and death. Mutations in KRAS proteins are responsible for a third of all cancers and identifying the structure of these proteins is critical to developing therapeutics and treatments. Protein crystals grow larger and more perfectly in microgravity, allowing for detailed laboratory analysis of their structure back on Earth.
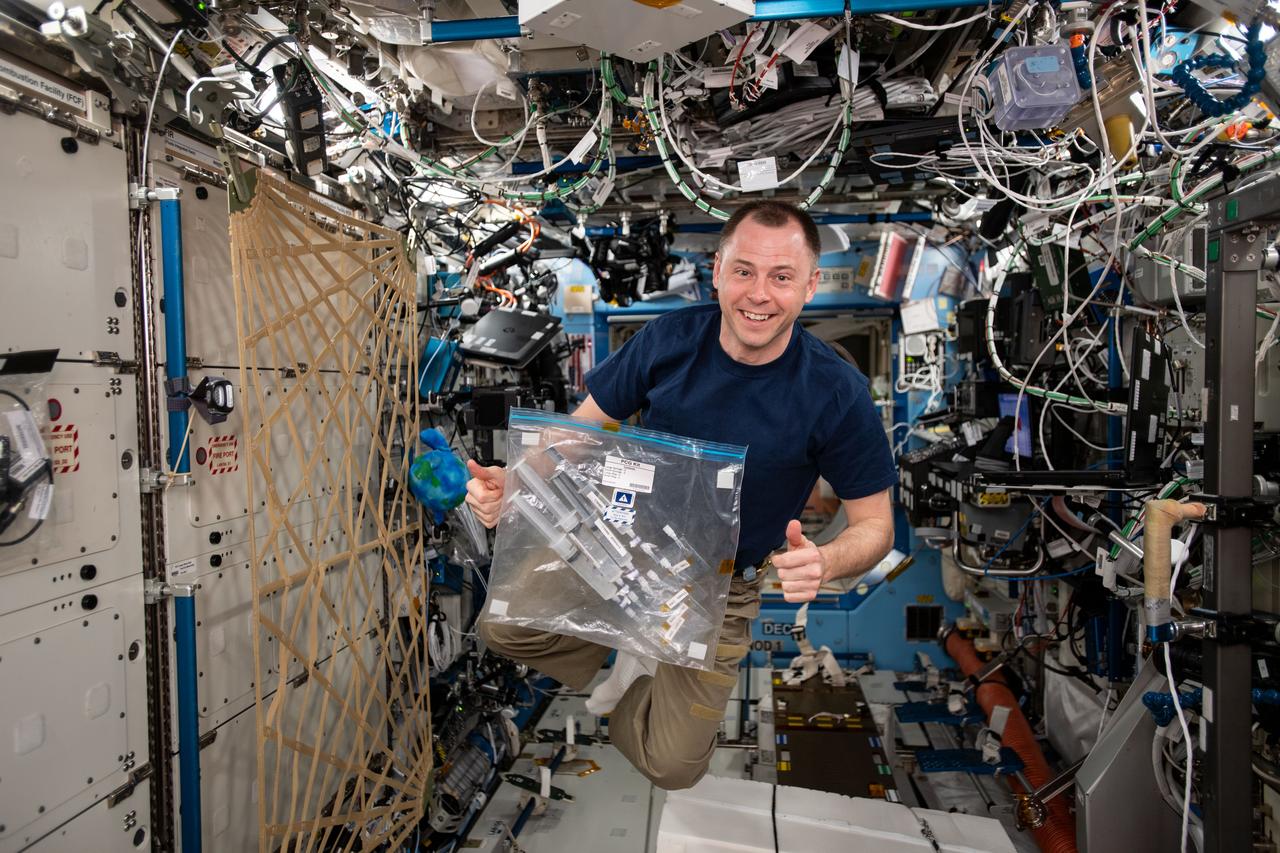

iss059e068212 (5/20/2019) --- NASA astronaut Nick Hague is photographed with the CASIS PCG-14 investigation in the Destiny module of the International Space Station (ISS). The Wisconsin Crystal Growing Contest-Wisconsin Space Crystals (CASIS PCG 14) teaches middle and high school students the unique engineering research and operations of the space program. The investigation allows students to understand the capabilities and constraints of conducting an experiment in microgravity.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Panelists conduct a question and answer session with news media after NASA awards a cooperative agreement with the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS) to manage the portion of the International Space Station that operates as a U.S. national laboratory. From left are: Waleed Abdalati, NASA chief scientist; Mark Uhran, NASA assistant associate administrator for the International Space Station; and Jeanne Becker, CASIS executive director. CASIS will be located at the Space Life Sciences Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The organization will increase station use to maximize the public’s return on its investment by managing its diversified research and development portfolio based on needs for basic and applied research in a variety of fields. CASIS will identify opportunities for non-NASA uses linking scientific review and economic value, and will match potential research and development opportunities with funding sources. The organization also will increase awareness among schools and students about using the station as a learning platform. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
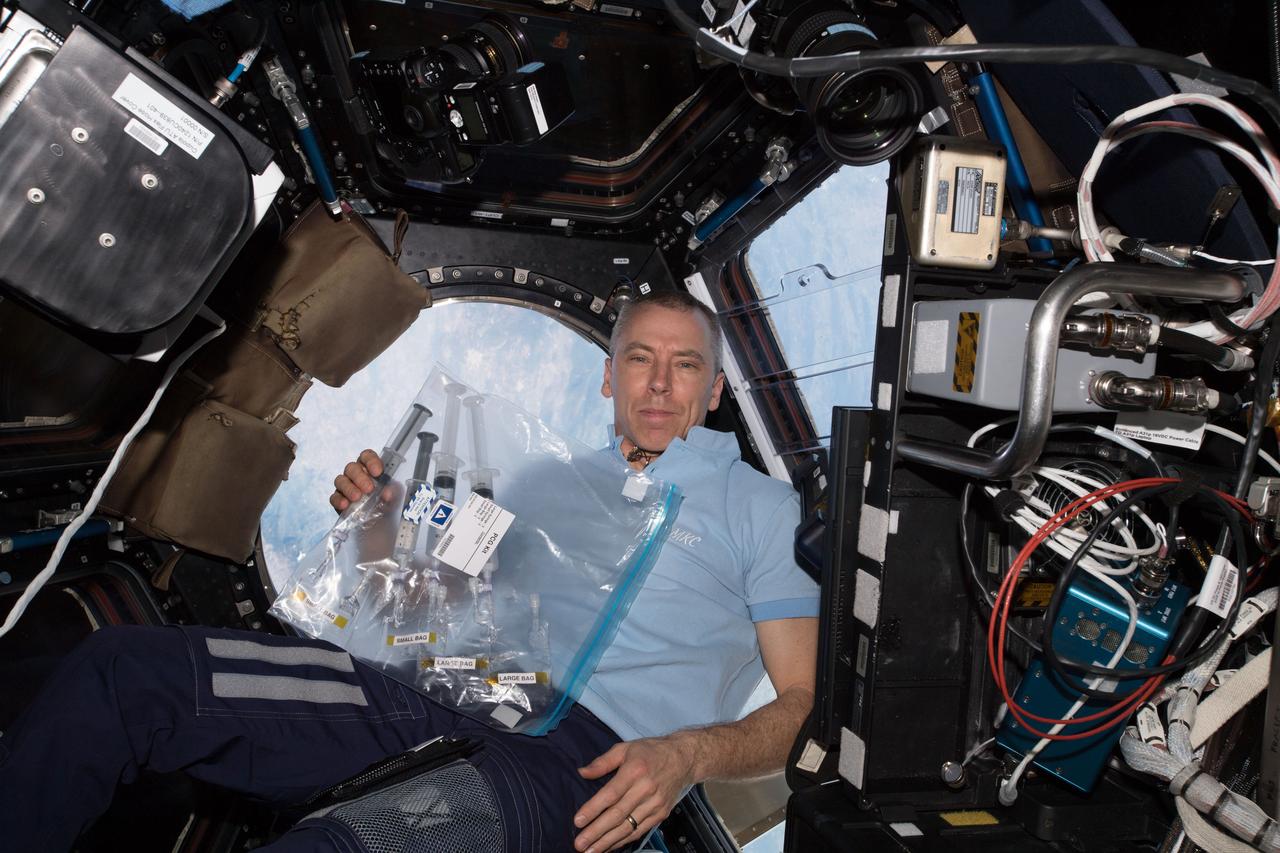

iss055e024523 (Apr. 18, 2018) --- NASA astronaut Andrew Feustel is seen in the Cupola, holding sample bags of crystals grown under experimental conditions controlled by middle and high school students as part of the CASIS PCG-9 investigation
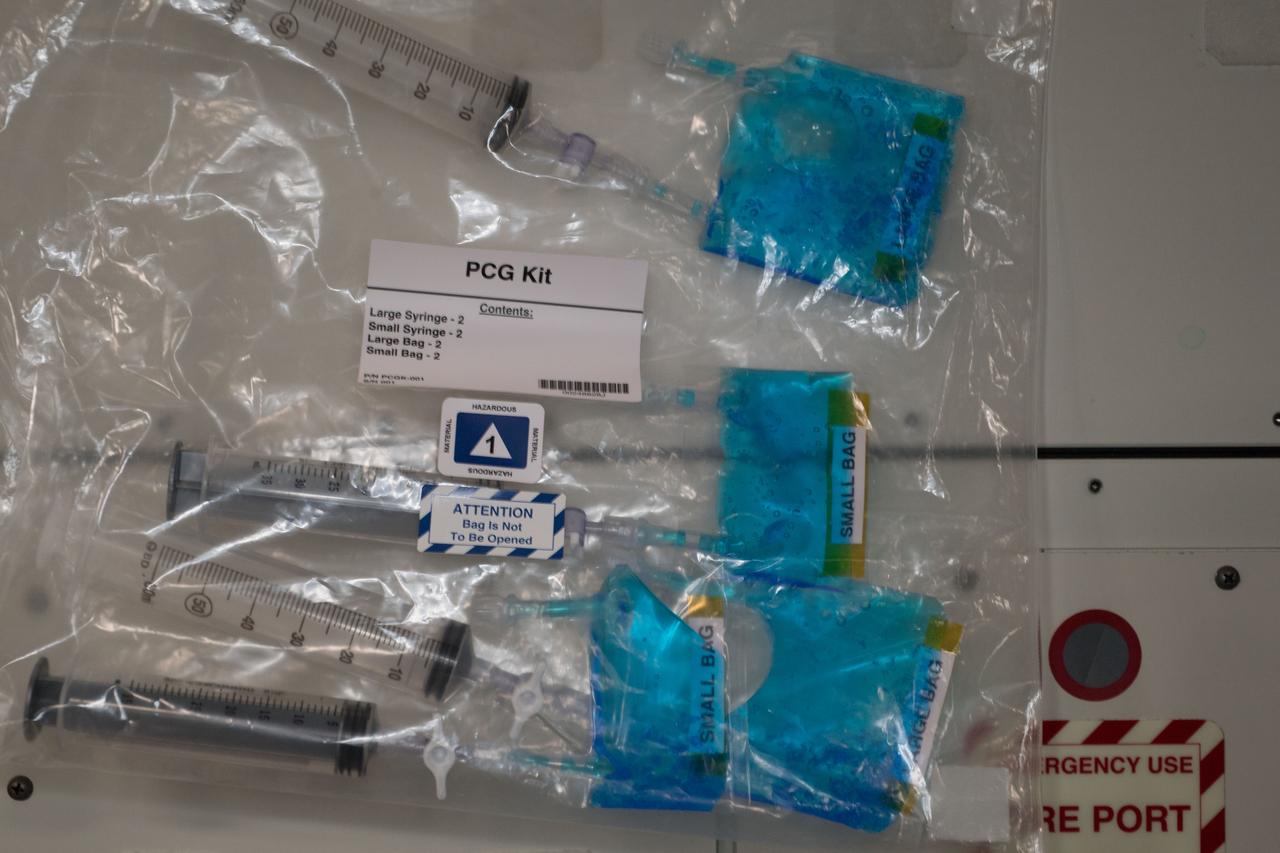
iss055e043705 (Apr. 30, 2018) --- Sample bags of crystals grown under experimental conditions controlled by middle and high school students as part of the CASIS PCG-9 investigation.
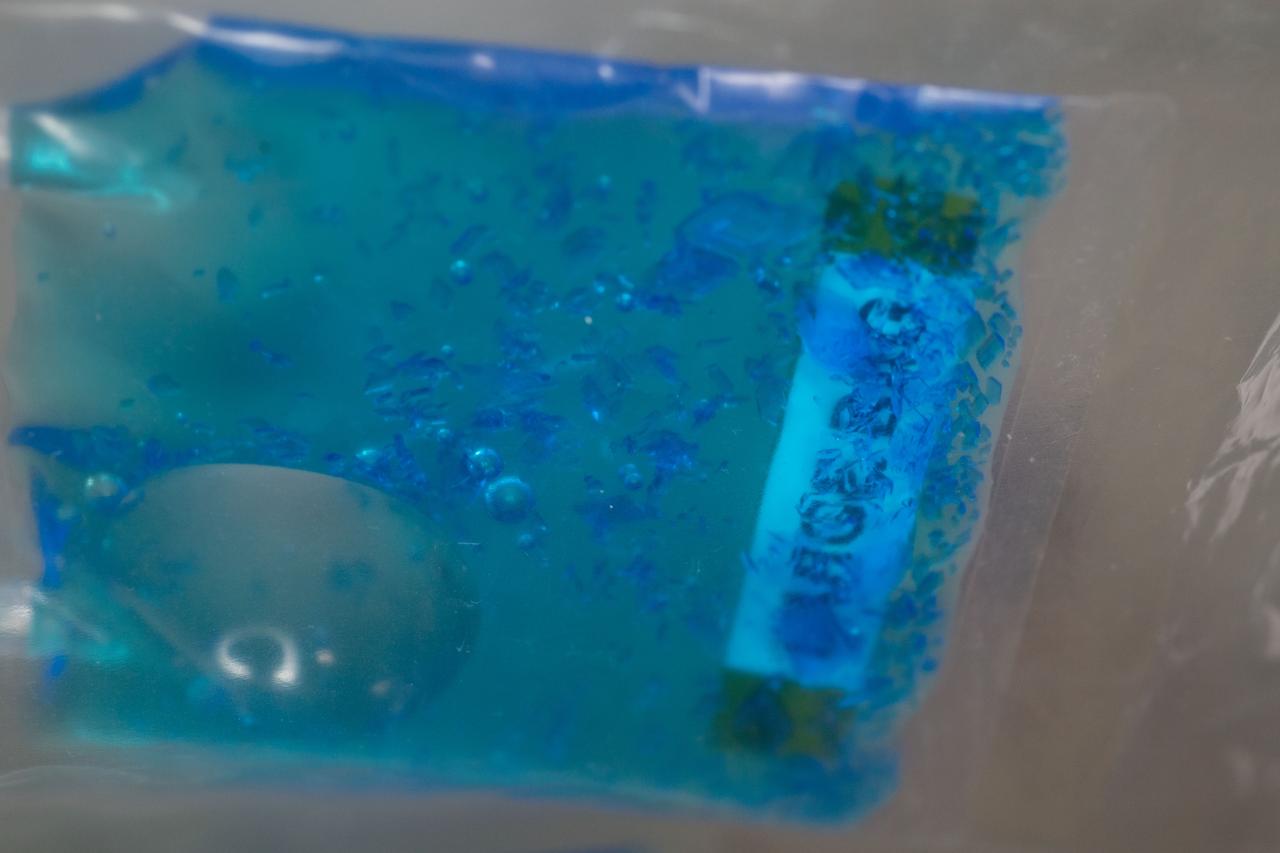

iss055e043707 (Apr. 30, 2018) --- A close look at crystals grown under experimental conditions controlled by middle and high school students as part of the CASIS PCG-9 investigation to examine the effects of microgravity on crystal growth.
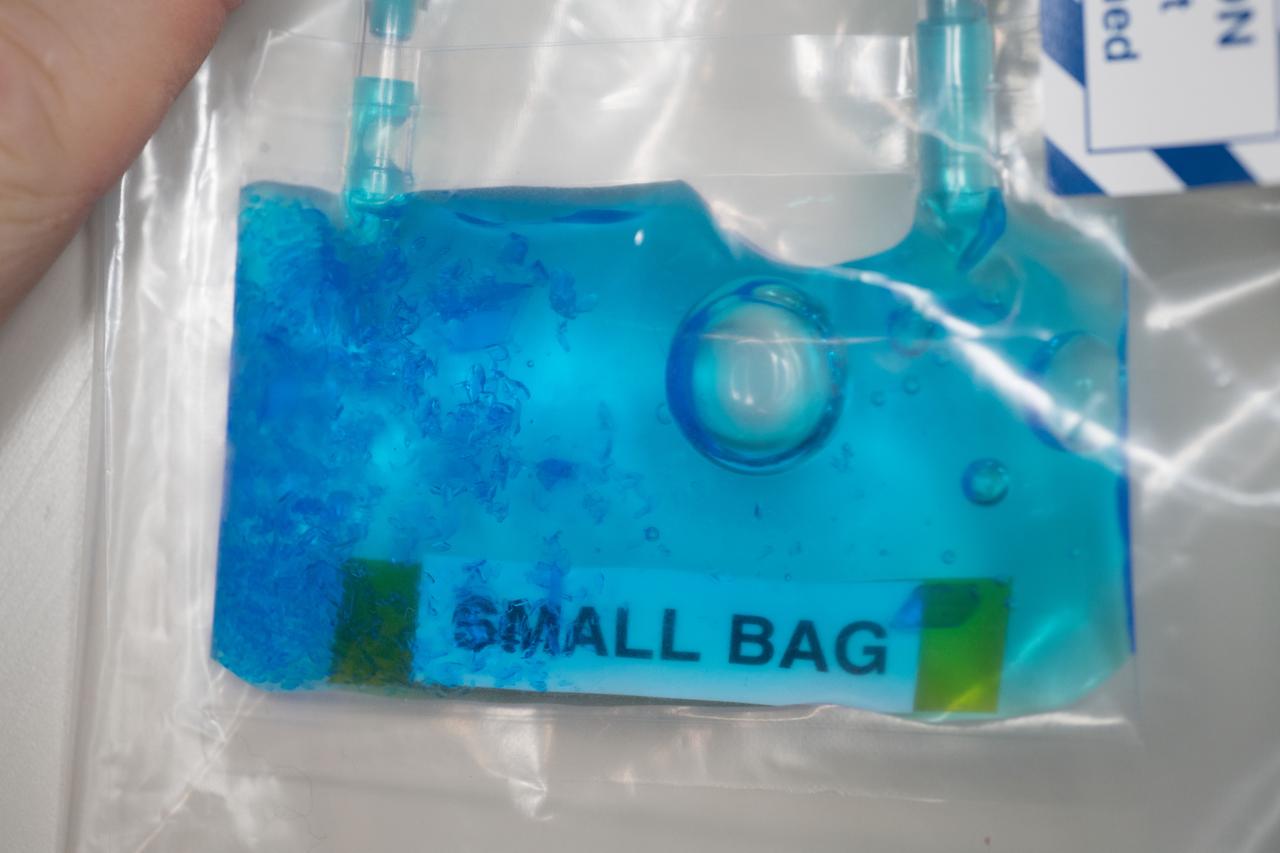
iss055e043718 (Apr. 30, 2018) --- A close look at crystals grown under experimental conditions controlled by middle and high school students as part of the CASIS PCG-9 investigation to examine the effects of microgravity on crystal growth.
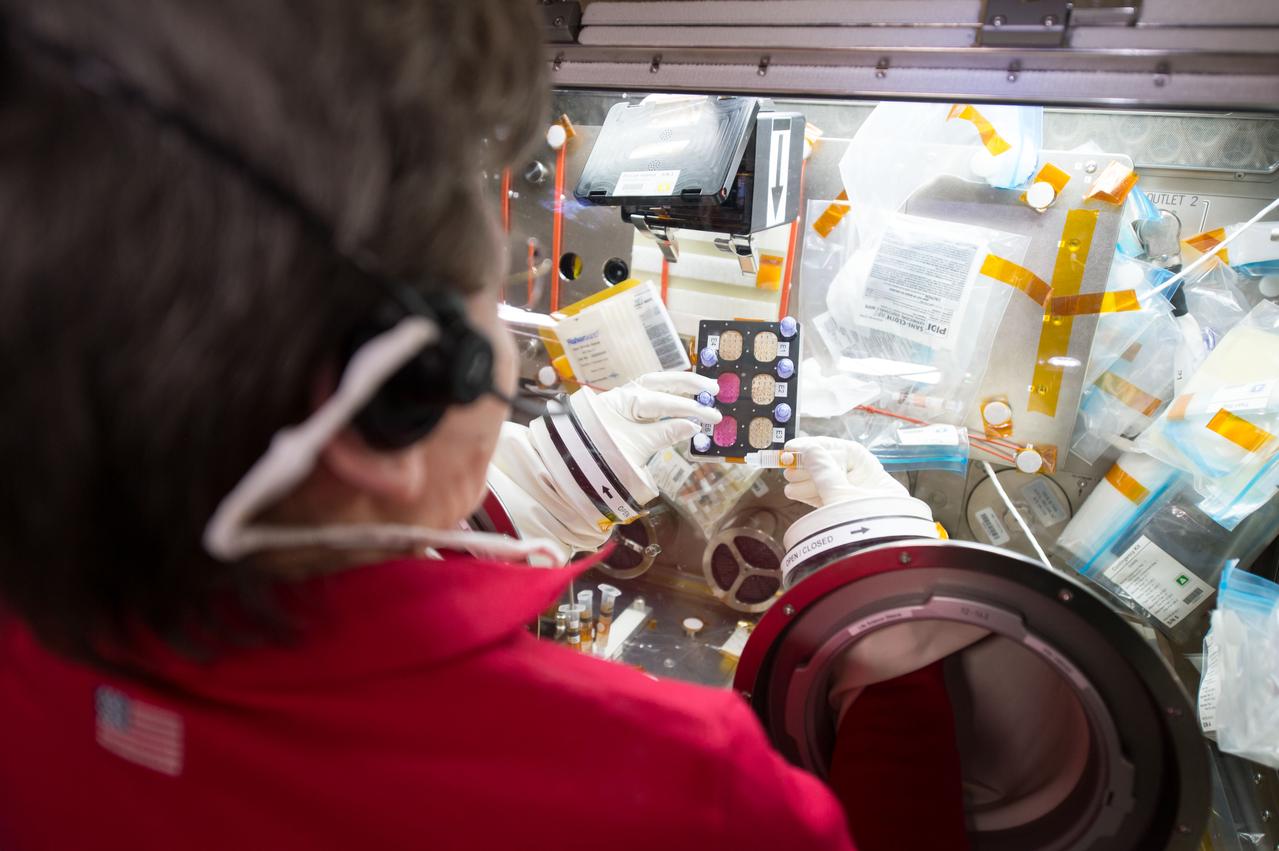

iss052e018939 (7/24/2017) --- NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson working with the Efficacy and Metabolism of Azonafide Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Microgravity (ADCs in Microgravity). The ADCs in Microgravity investigation evaluates new antibody-drug conjugates that combine an immune-activating drug with antibodies in order to target only cancer cells, increasing the effectiveness of chemotherapy and reducing its side effects. In microgravity, cancer cells grow in three-dimensional, spheroid structures that closely resemble their form in the human body, allowing for better drug testing. This investigation may accelerate development of targeted therapies for cancer patients.
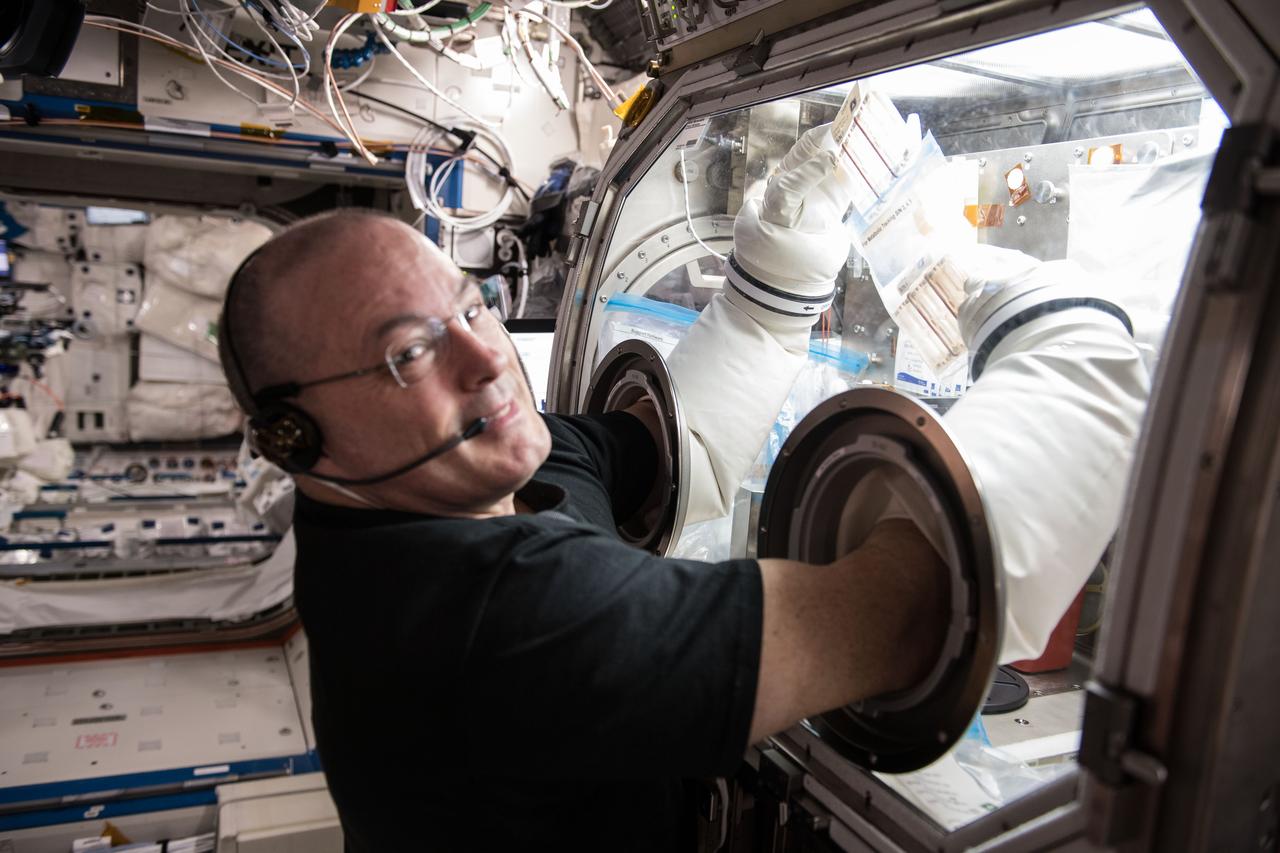

iss055e035338 (April 13, 2018) --- NASA astronaut Scott Tingle performs research operations with the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module. Tingle was working on the Metabolic Tracking experiment that looks at a particular type of medicine and how it interacts with human tissue cultures. Results could improve therapies in space and lead to better, cheaper drugs on Earth.
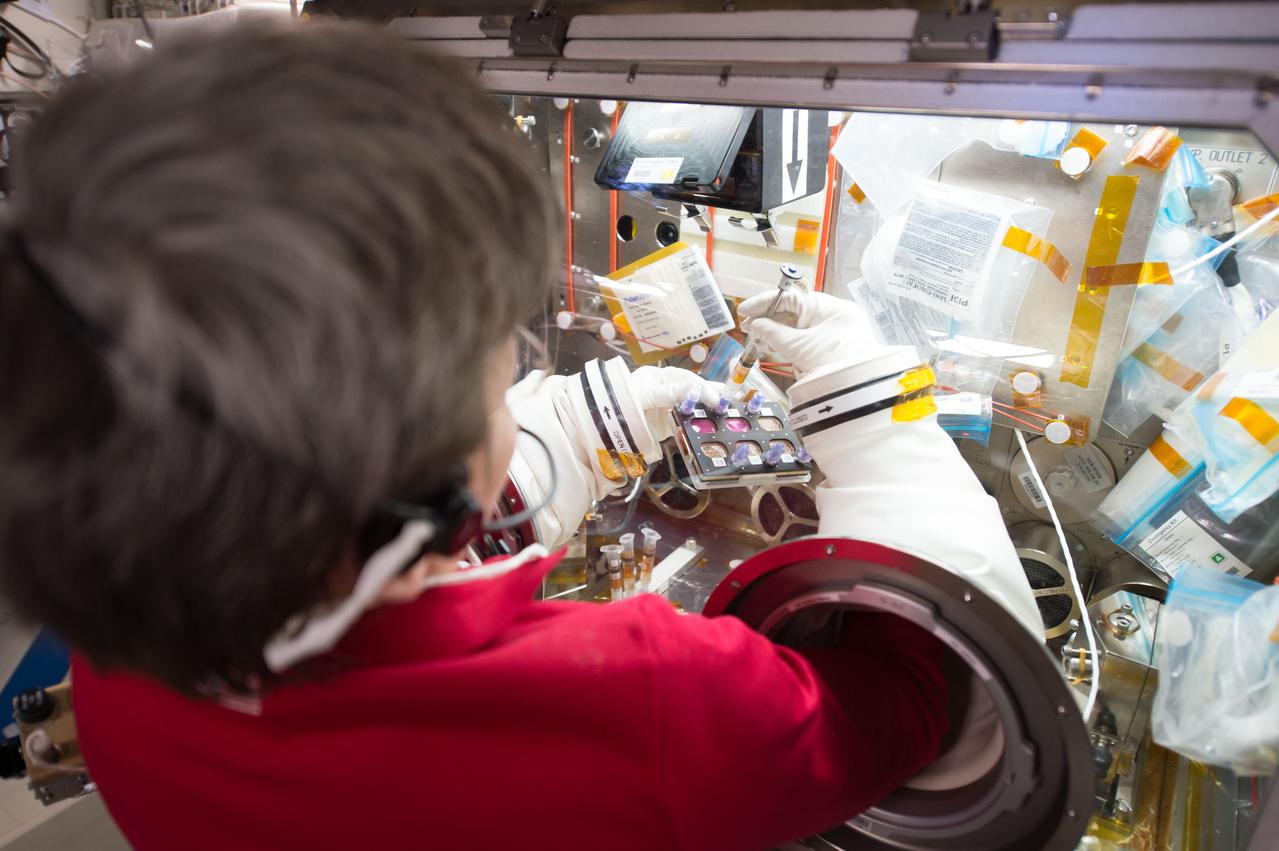

iss052e018944 (7/24/2017) --- NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson working with the Efficacy and Metabolism of Azonafide Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Microgravity (ADCs in Microgravity). The ADCs in Microgravity investigation evaluates new antibody-drug conjugates that combine an immune-activating drug with antibodies in order to target only cancer cells, increasing the effectiveness of chemotherapy and reducing its side effects. In microgravity, cancer cells grow in three-dimensional, spheroid structures that closely resemble their form in the human body, allowing for better drug testing. This investigation may accelerate development of targeted therapies for cancer patients.
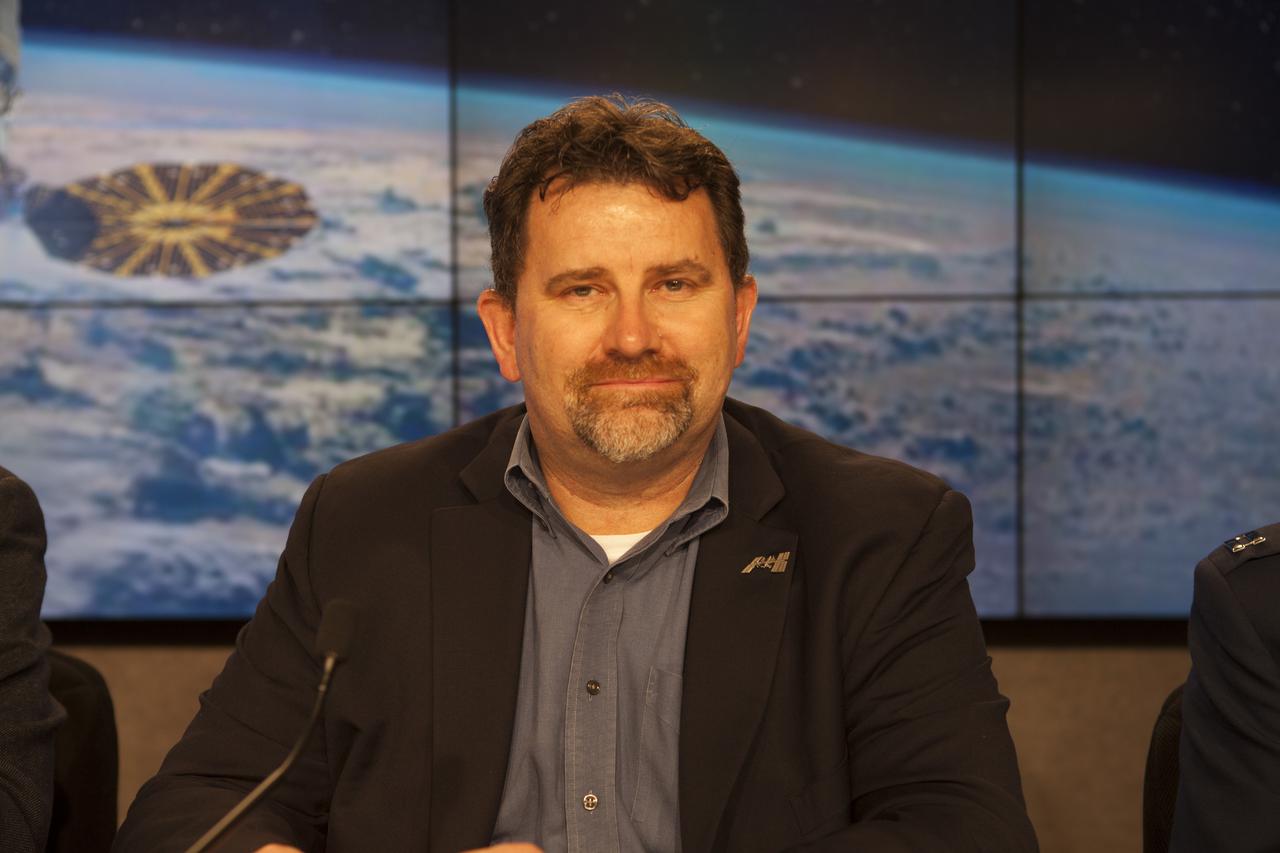

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, Dr. Michael Roberts deputy chief scientist for the Center for the Advancement for Science in Space, or CASIS, speaks to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference for Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station.
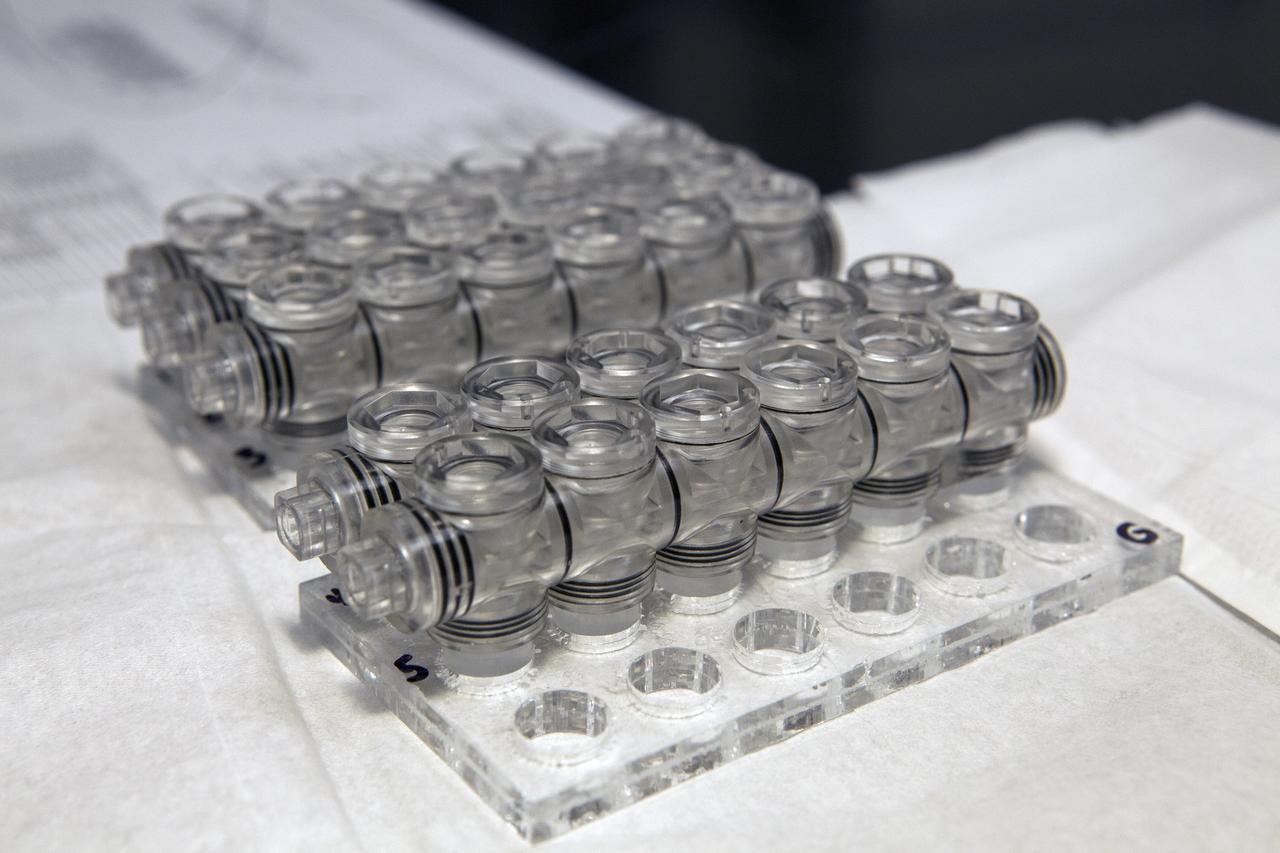

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, vials for the Protein Crystal Growth 2 experiment are being prepared for an acceptance leak test. The vials will be filled with clear water and then put in a vacuum chamber to verify that they are providing adequate containment for liquids. The experiment is one of many that will be delivered to the International Space Station on the SpaceX-4 commercial cargo resupply mission. Kennedy's ISS Ground Processing and Research Project Office is providing the necessary laboratories, equipment, supplies and consumables for 61 principal investigators, including 17 from other countries, as they prepare their science experiments for flight. The SpaceX-4 flight is targeted to launch in September 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
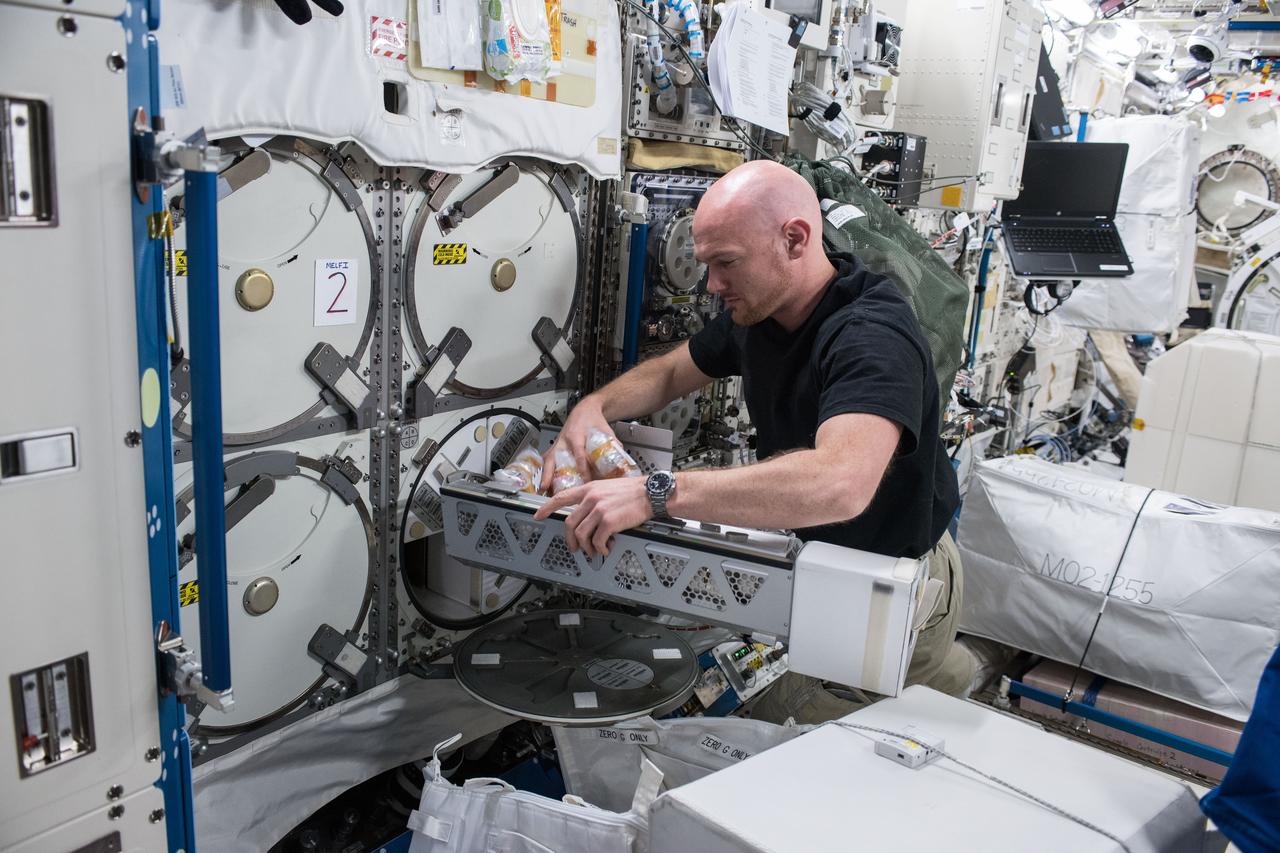

iss056e075950 (July 3, 2018) --- Astronaut Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency) works inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module retrieving Protein Crystal Growth samples from a science freezer, also known as the Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI).

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, members of the media participate in a briefing on science research and technology work planned for the International Space Station, or ISS. NASA is preparing for the launch of a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission to the ISS. From left are: Pete Hasbrook, NASA associate program scientist for the ISS Program at the Johnson Space Center in Houston, and Dr. Michael Roberts, deputy chief scientist for the Center for the Advancement for Science in Space, or CASIS.
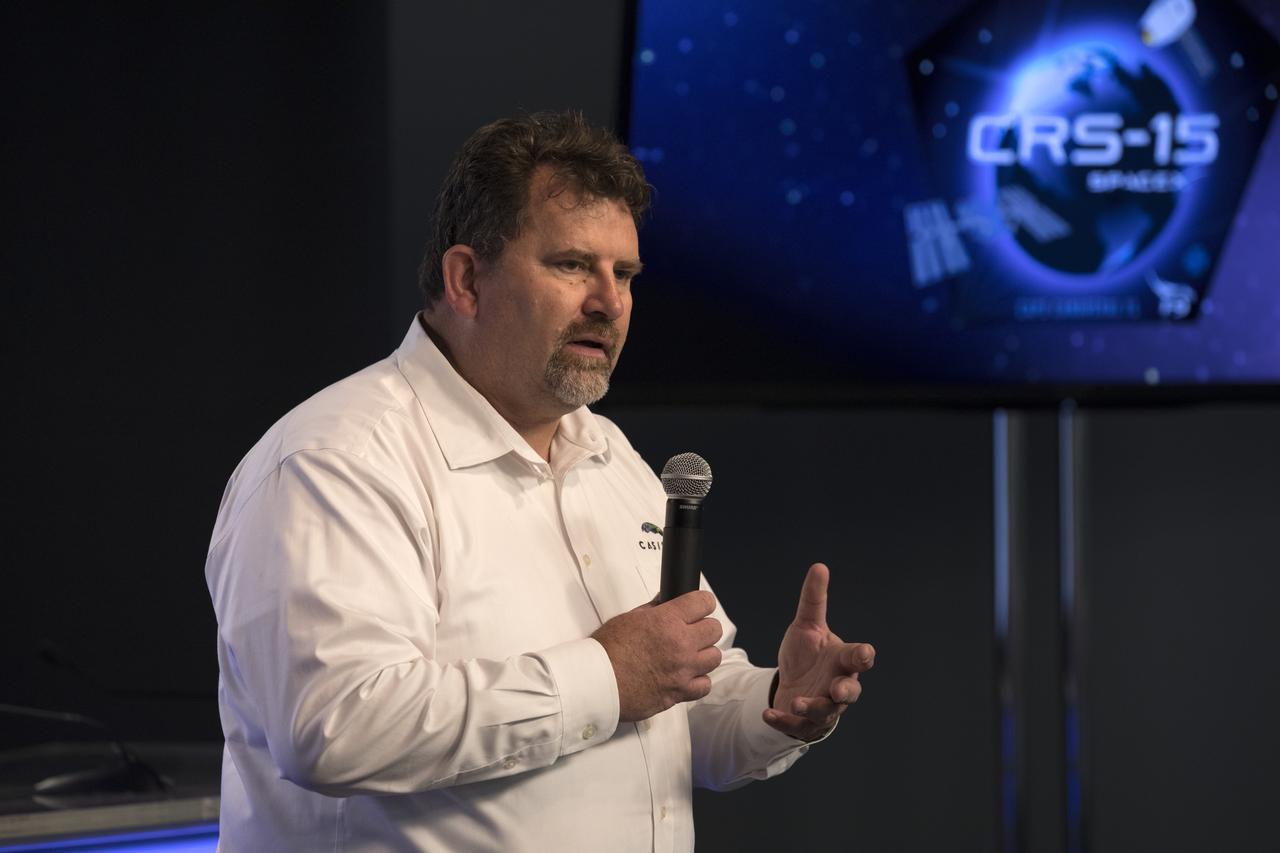

Mike Roberts, deputy chief scientist, Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS), speaks to members of the media during a briefing in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 15th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.

Greg “Box” Johnson, executive director of Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS) and former astronaut, foreground, and NASA Acting Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier watch as attendees of the Boy Scouts of America National Jamboree launch a weather balloon, Tuesday, July 25, 2017 at the Summit Bechtel Reserve in Glen Jean, West Virginia. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
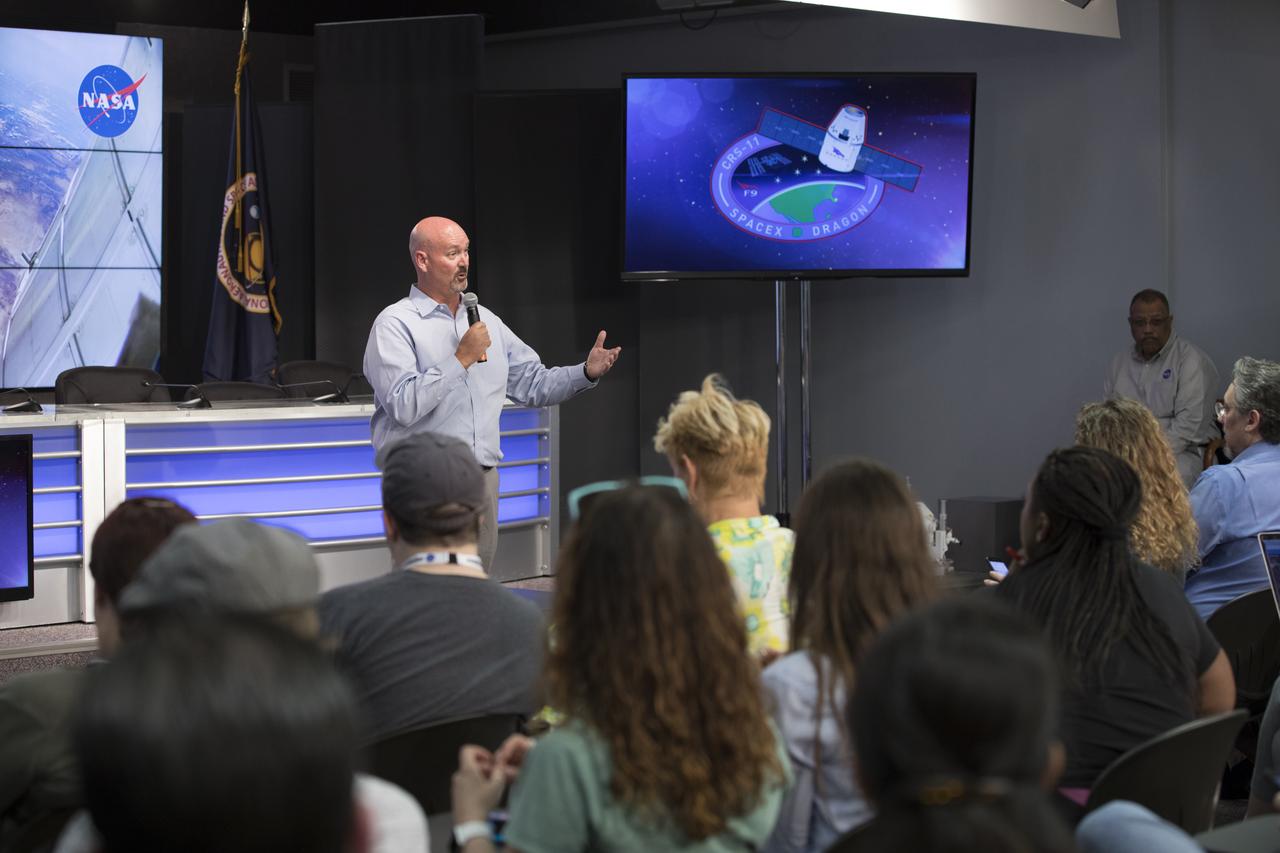

Ken Shields, director of Operations for the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS)/ISS National Lab, speaks to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for launch from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on June 1 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on the company's 11th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
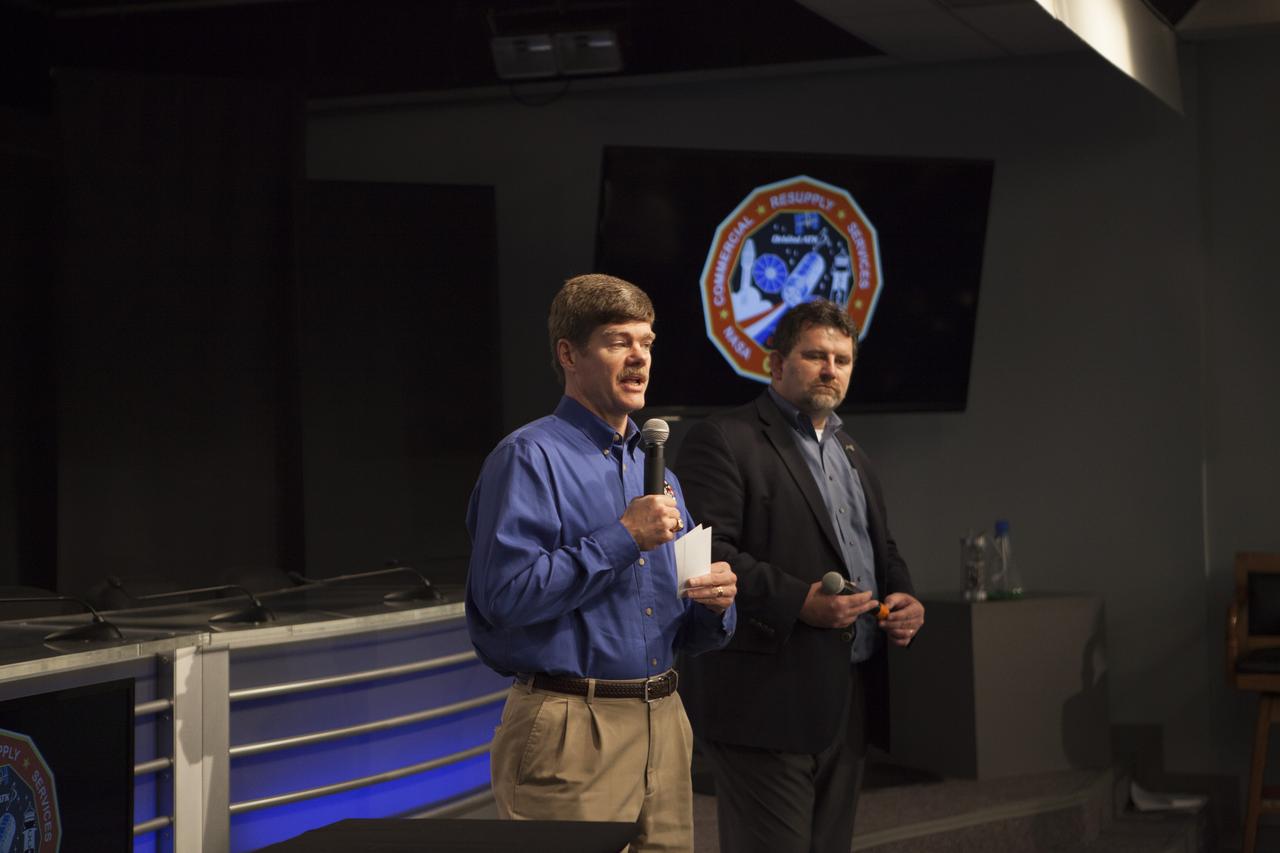

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, members of the media participate in a briefing on science research and technology work planned for the International Space Station, or ISS. NASA is preparing for the launch of a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission to the ISS. From left are: Pete Hasbrook, NASA associate program scientist for the ISS Program at the Johnson Space Center in Houston, and Dr. Michael Roberts, deputy chief scientist for the Center for the Advancement for Science in Space, or CASIS.
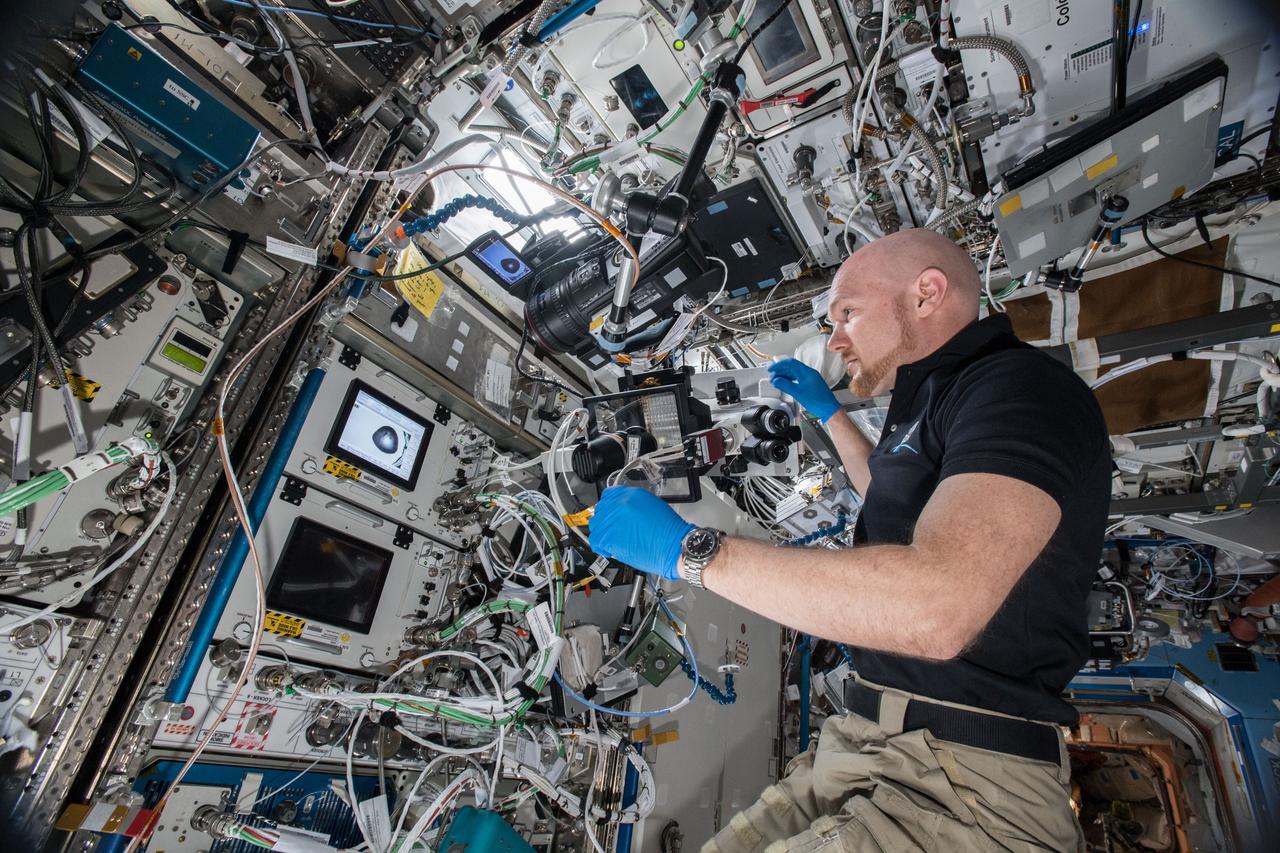

ISS057E106426 - European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Alex Gerst uses a microscope with the Space Automated Bioproduct Laboratory (SABL) Camera attached to document a Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) MicroG Card. The photo was taken in the Destiny U.S. Laboratory aboard the International Space Station (ISS) for the Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) investigation.
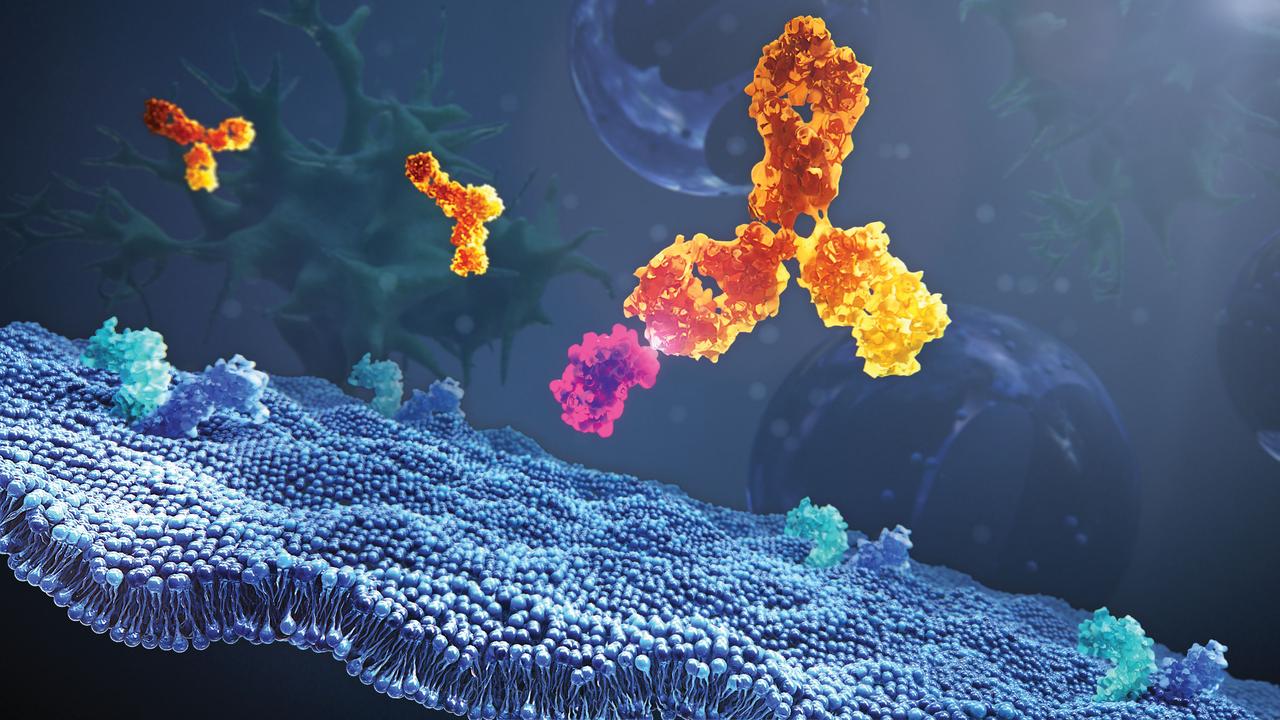
jsc2019e039826 (7/27/2017) --- This preflight image shows a monoclonal antibody binding to a ligand in the inter-cellular space. Monocronal antibodies can fight a wide range of diseases by very selectively binding to their targets, thus leaving healthy tissues and cells intact. Monoclonal Antibody Production and Stability in Microgravity-Formulation Study (CASIS PCG 19) compares the impact of microgravity on antibody formulation stability to stability trends observed on Earth. The study may broaden an understanding of the routes of antibody degradation and, as space travel becomes more common, it may improve knowledge of monoclonal antibody therapeutic stability for treating patients in space environments.
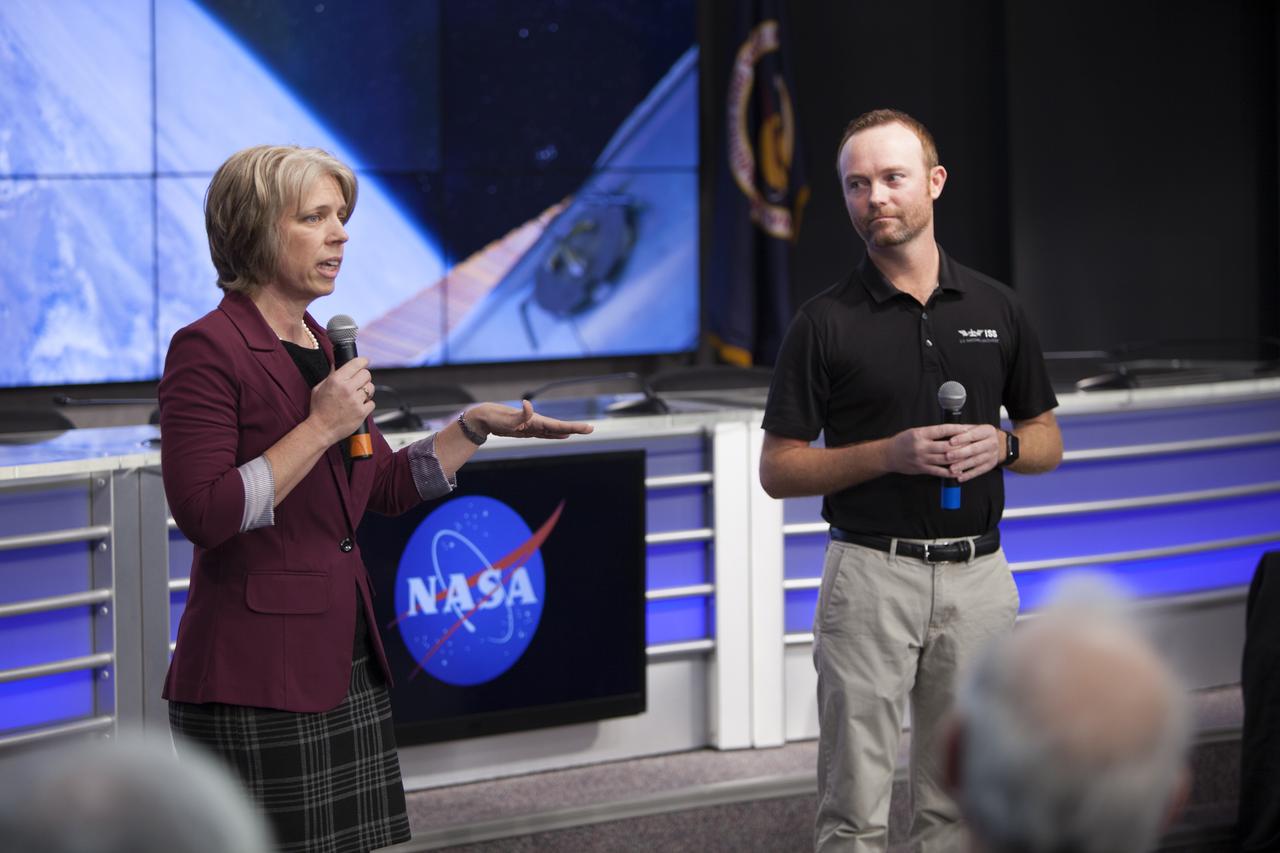

Tara Ruttley, NASA associate scientist for the International Space Station Program, left, and Patrick O'Nell, Marketing and Communications manager for the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS), speak to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for launch from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on Feb. 18 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on the company's 10th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
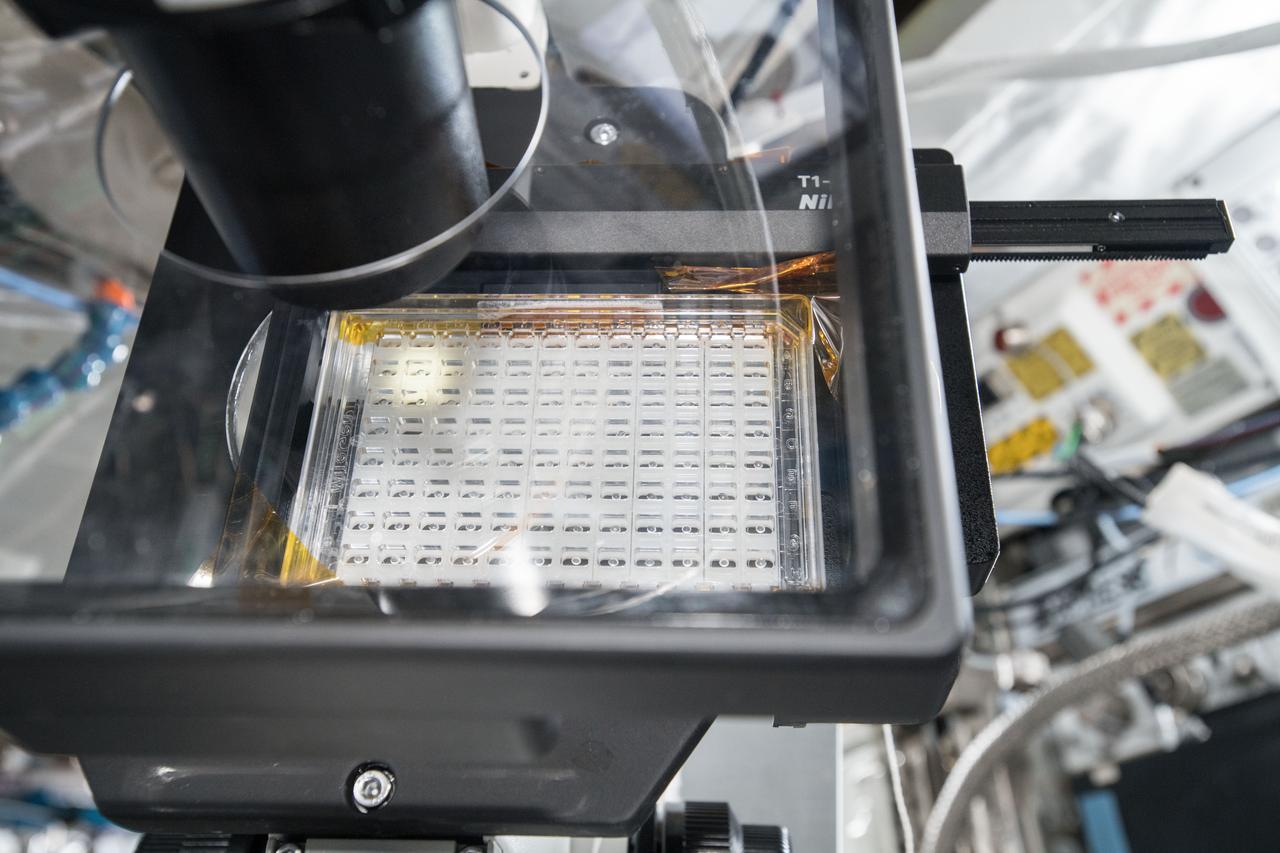
iss057e106419 (Nov. 30, 2018) --- Samples from the Protein Crystal Growth Card are examined using a microscope for an experiment observing protein crystals associated with Parkinson’s disease to potentially improve treatments on Earth. Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) evaluates growth of Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein crystals in microgravity. LRRK2 is implicated in Parkinson’s disease, but crystals of the protein grown on Earth are too small and compact to study. Detailed analysis of larger, space-grown crystals can define the protein’s exact shape and morphology and help scientists better understand the disease’s pathology.
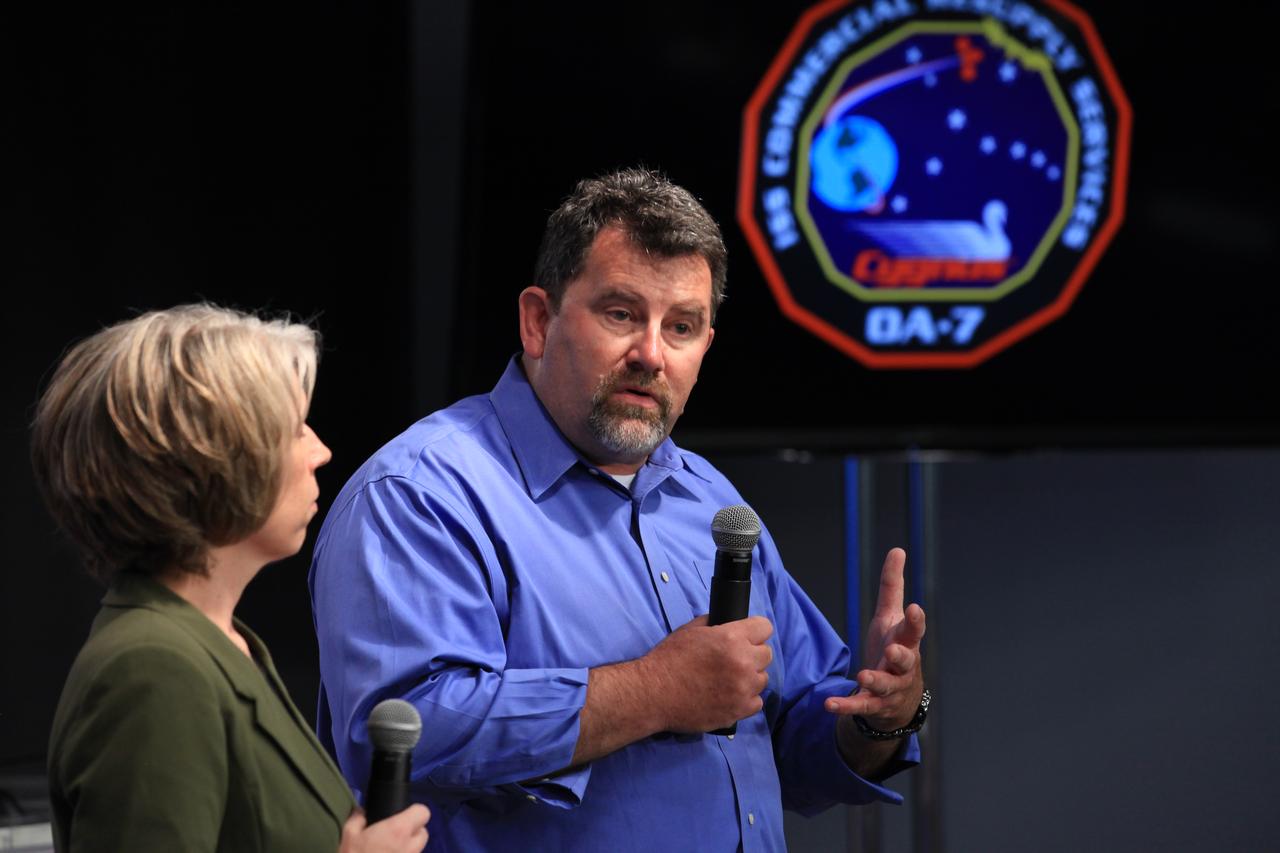

Tara Ruttley, left, associate program scientist with NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, and Dr. Mike Roberts, with the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS), speak to NASA Social participants during a "What's on Board" science briefing at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The briefing is for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply services mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's Cygnus pressurized cargo module is set to launch on the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 18. Liftoff is scheduled for 11:11 a.m. EDT.
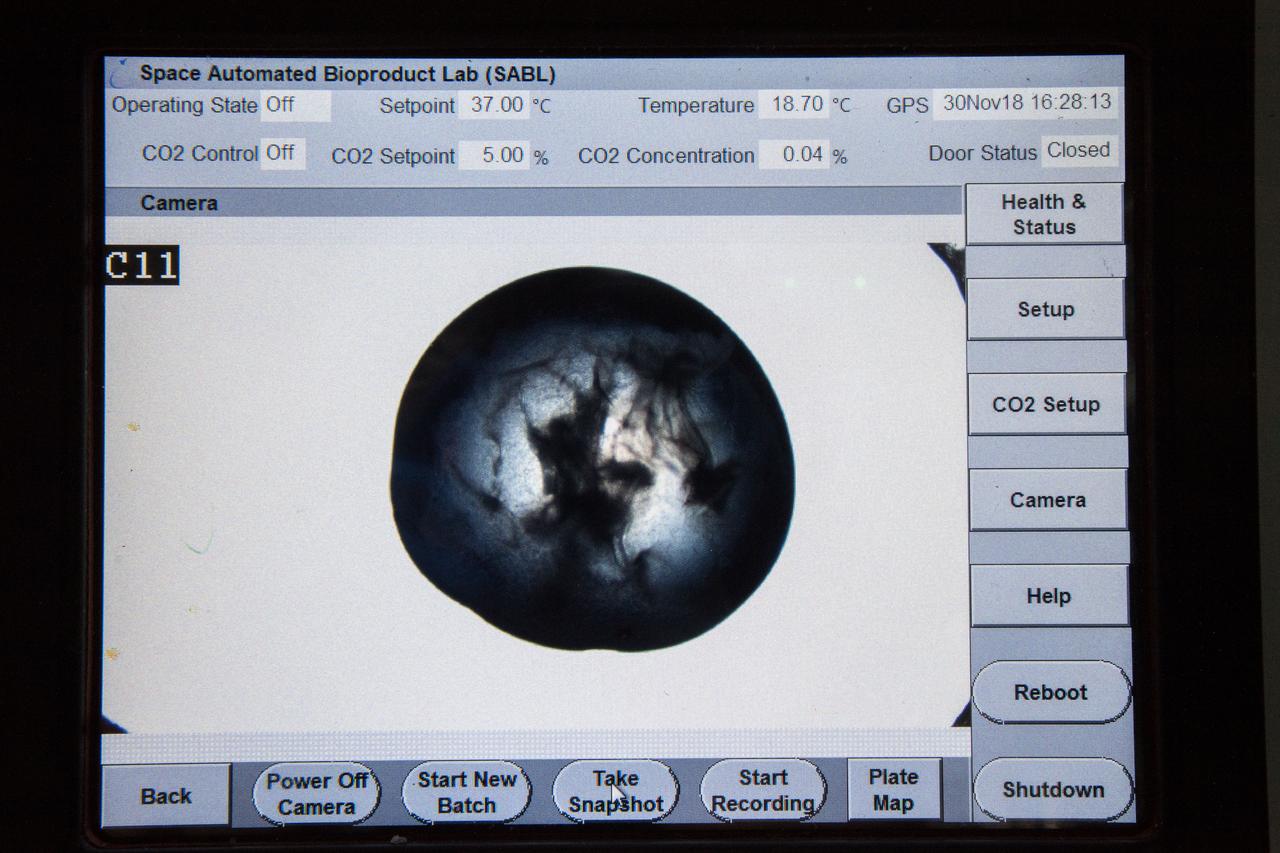
iss057e106417 (Nov. 30, 2018) --- Samples from the Protein Crystal Growth Card are examined using a microscope for an experiment observing protein crystals associated with Parkinson’s disease to potentially improve treatments on Earth. Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) evaluates growth of Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein crystals in microgravity. LRRK2 is implicated in Parkinson’s disease, but crystals of the protein grown on Earth are too small and compact to study. Detailed analysis of larger, space-grown crystals can define the protein’s exact shape and morphology and help scientists better understand the disease’s pathology.
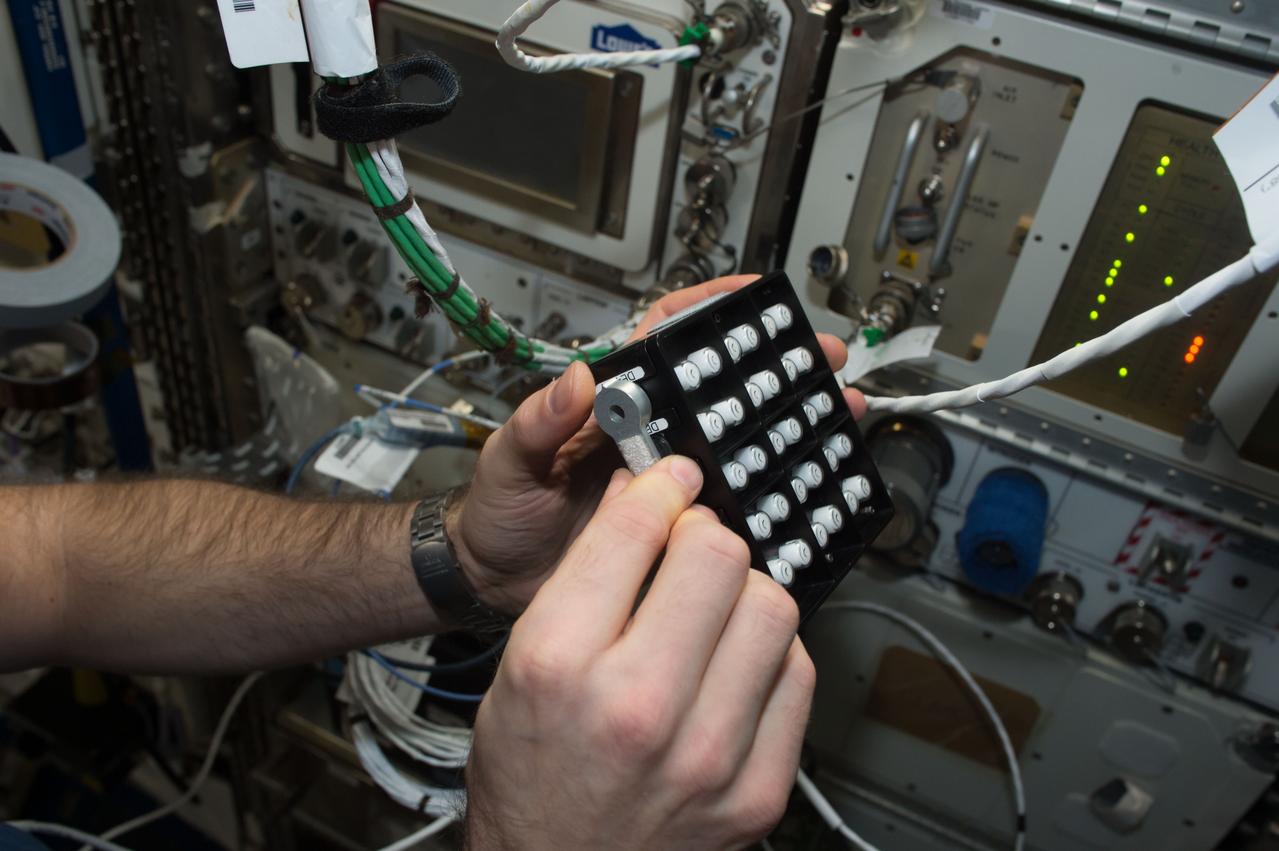

iss050e058807 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
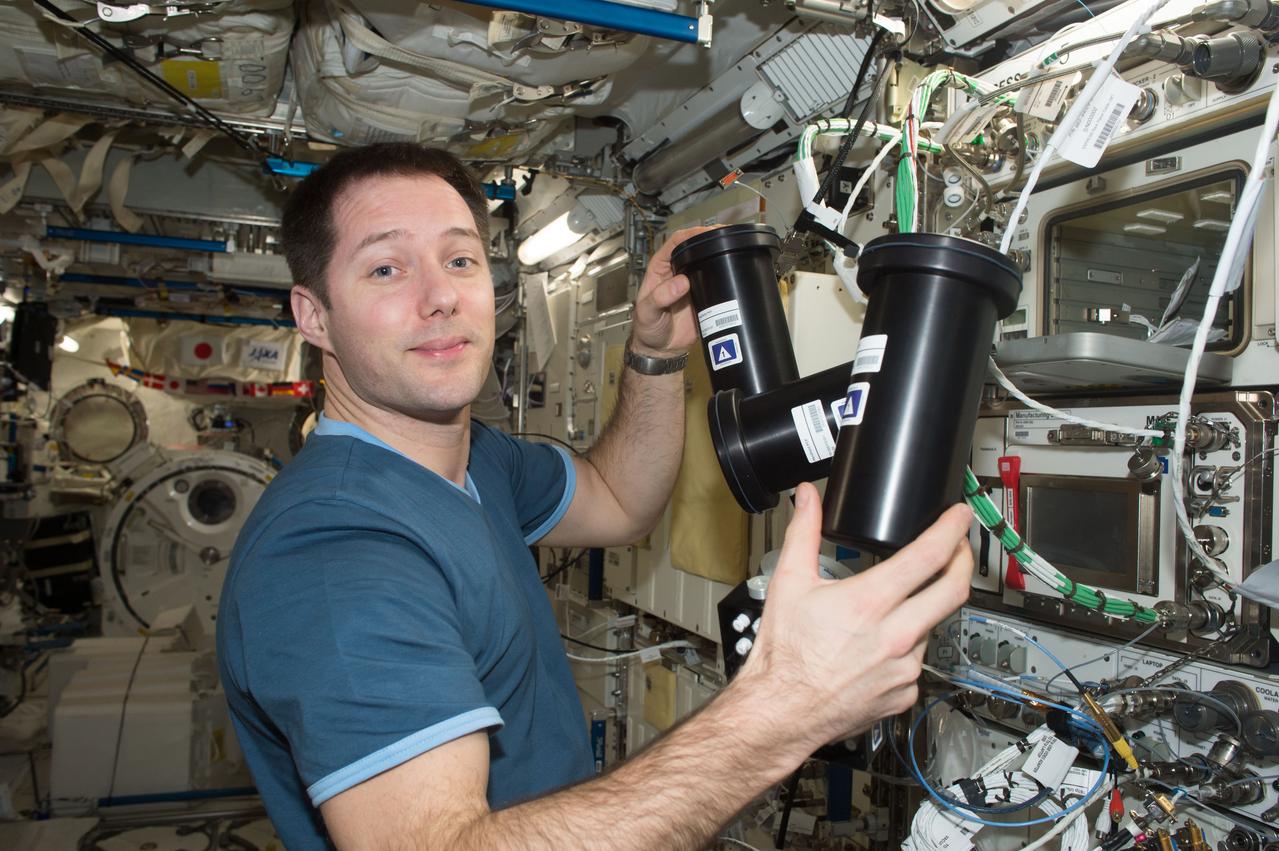

iss050e058812 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
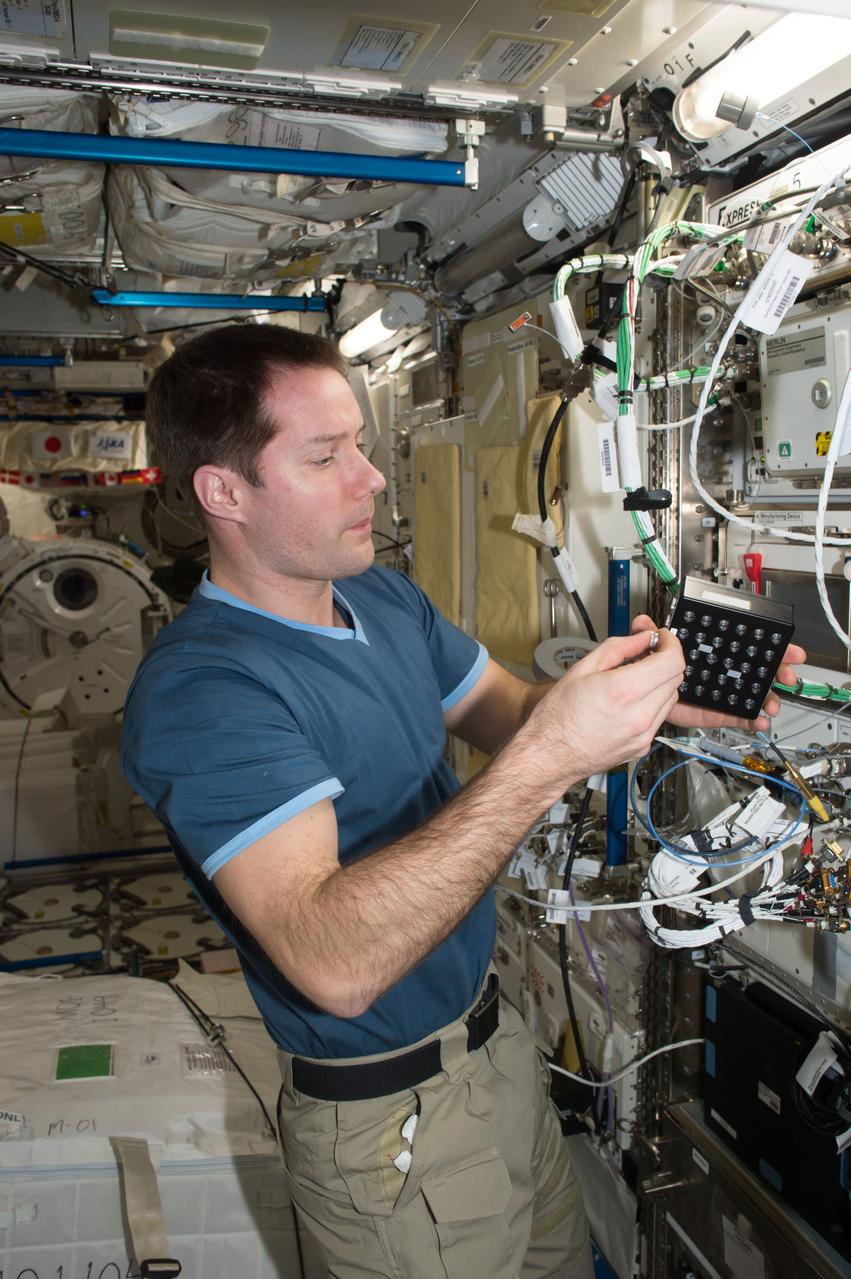

iss050e058802 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
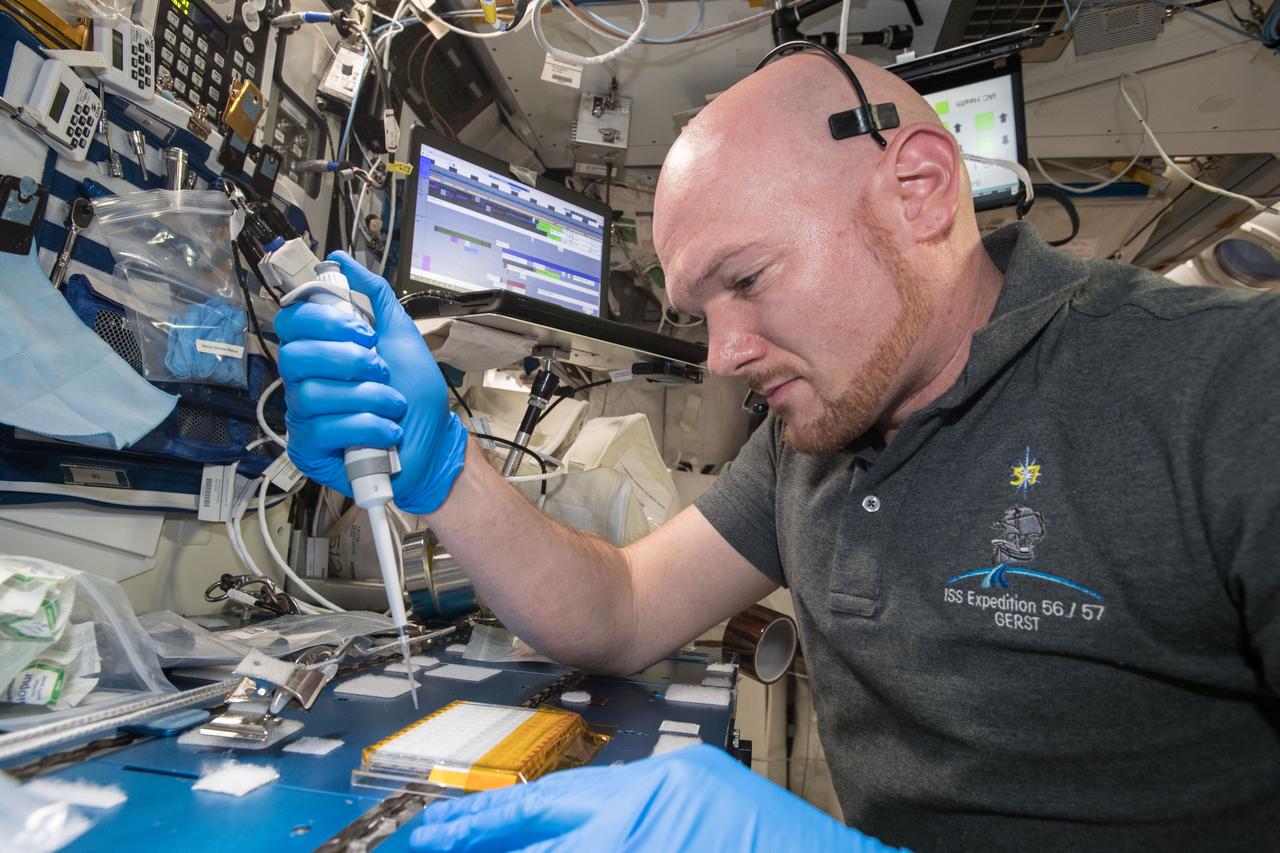

iss057e106231 (Nov. 26, 2018) --- European Space Agency (ESA) asrtonaut Alexander Gerst uses a uses a pipette to transfer a protein solution into the Protein Crystal Growth Card for an experiment observing protein crystals associated with Parkinson’s disease to potentially improve treatments on Earth. Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) evaluates growth of Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein crystals in microgravity. LRRK2 is implicated in Parkinson’s disease, but crystals of the protein grown on Earth are too small and compact to study. Detailed analysis of larger, space-grown crystals can define the protein’s exact shape and morphology and help scientists better understand the disease’s pathology.
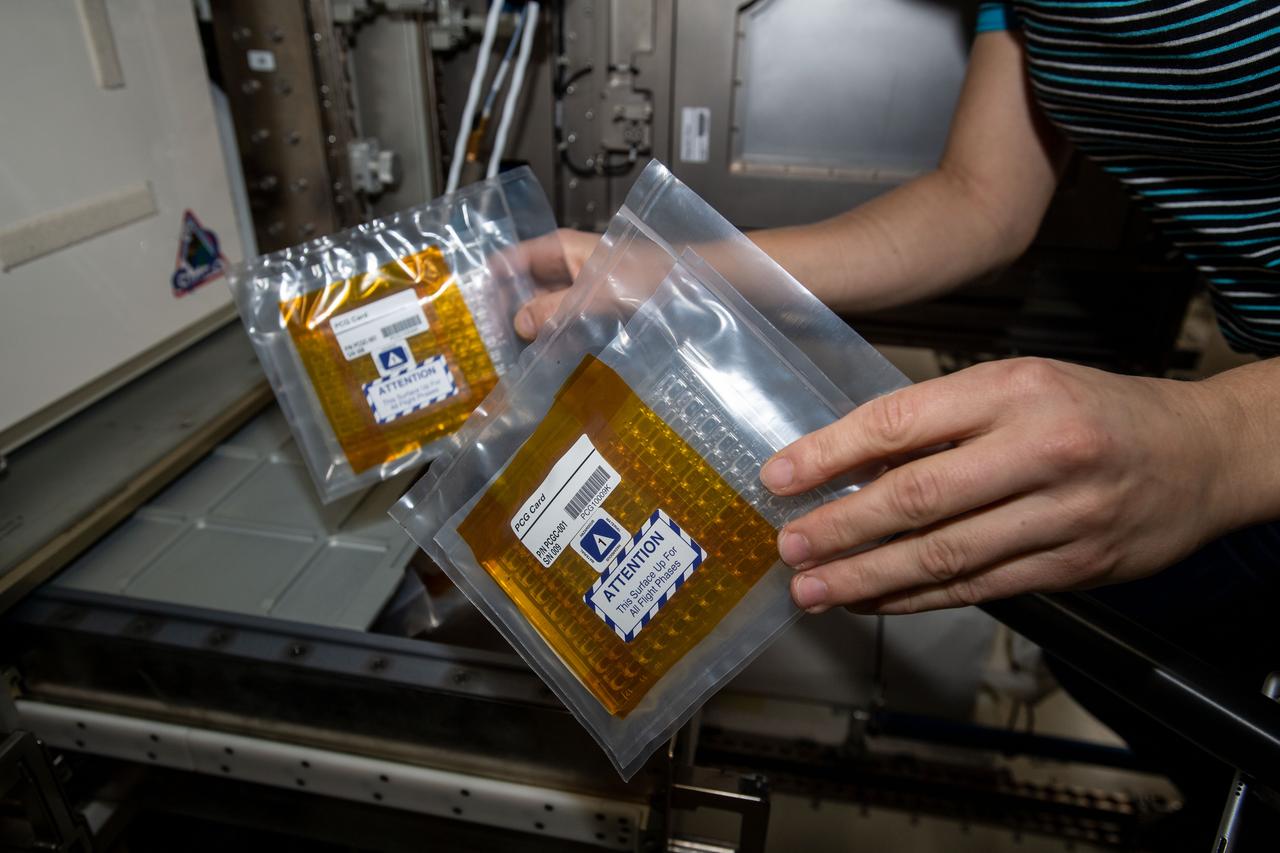

iss062e087808 (3/11/2020) --- A view of Protein Crystal Growth-10 experiment hardware inside JAXA's (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Kibo laboratory module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Microgravity Crystallization of Glycogen Synthase-Glycogenin Protein Complex (CASIS PCG 10) crystallizes human glycogen synthase proteins on the space station. Determining the structure of the human glycogen synthase and full-length glycogenin protein complex could facilitate the development of treatments on Earth for metabolic disorders such as Type 2 diabetes, obesity, rare genetic disorders, and some forms of cancer.
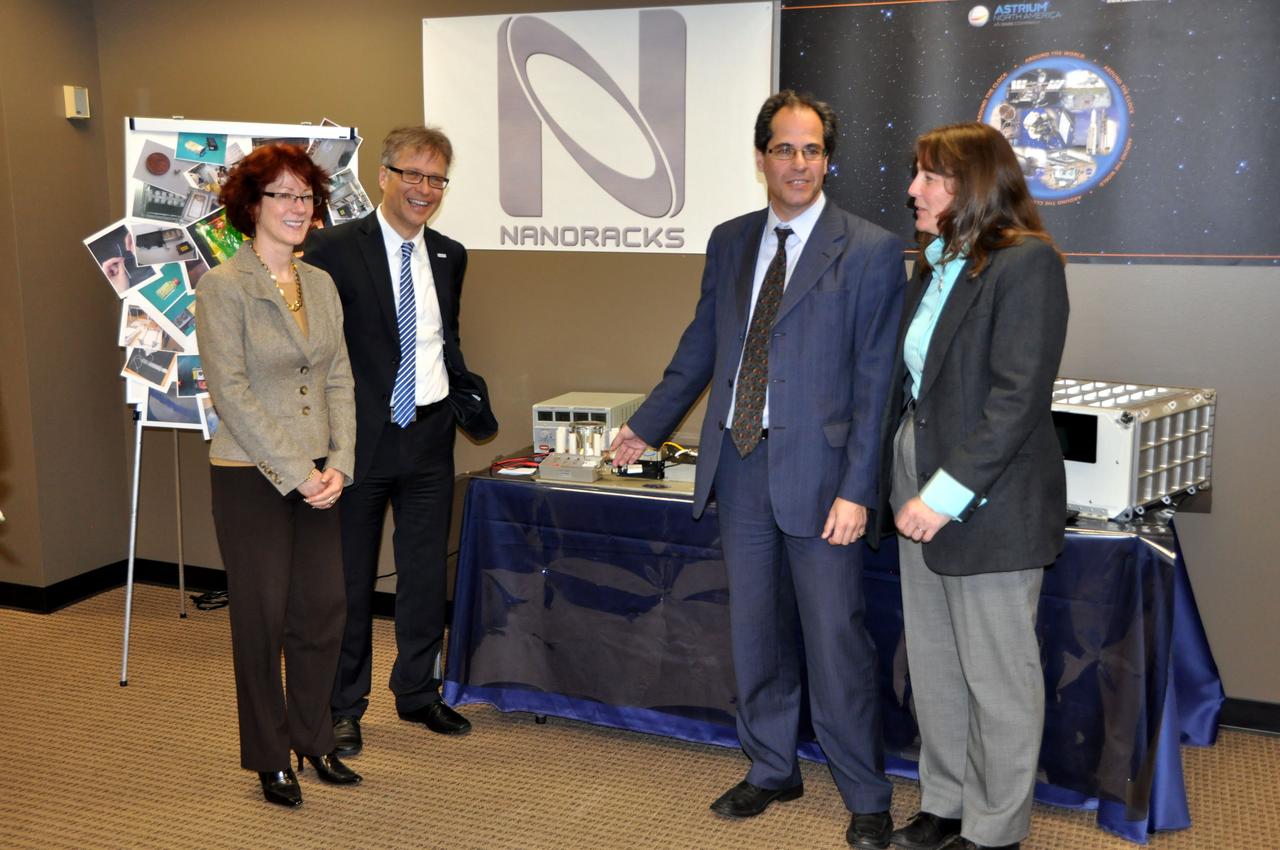

JSC2012-E-029877 (14 Feb. 2012) --- During a ceremony on Feb. 14, at the Astrium North America facility in Houston, some of the principal participants stand near a gravitational research centrifuge which Astrium ST handed over to NanoRacks LLC representatives. From the left are Jeanne Becker, President, CEO and Executive Director of the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS); Ulrich Kuebler of Astrium ST ; Jeff Manber, managing director of NanoRacks; and Marybeth Edeen, U.S. National Lab manager at NASA?s Johnson Space Center. NASA Photo courtesy Astrium North America
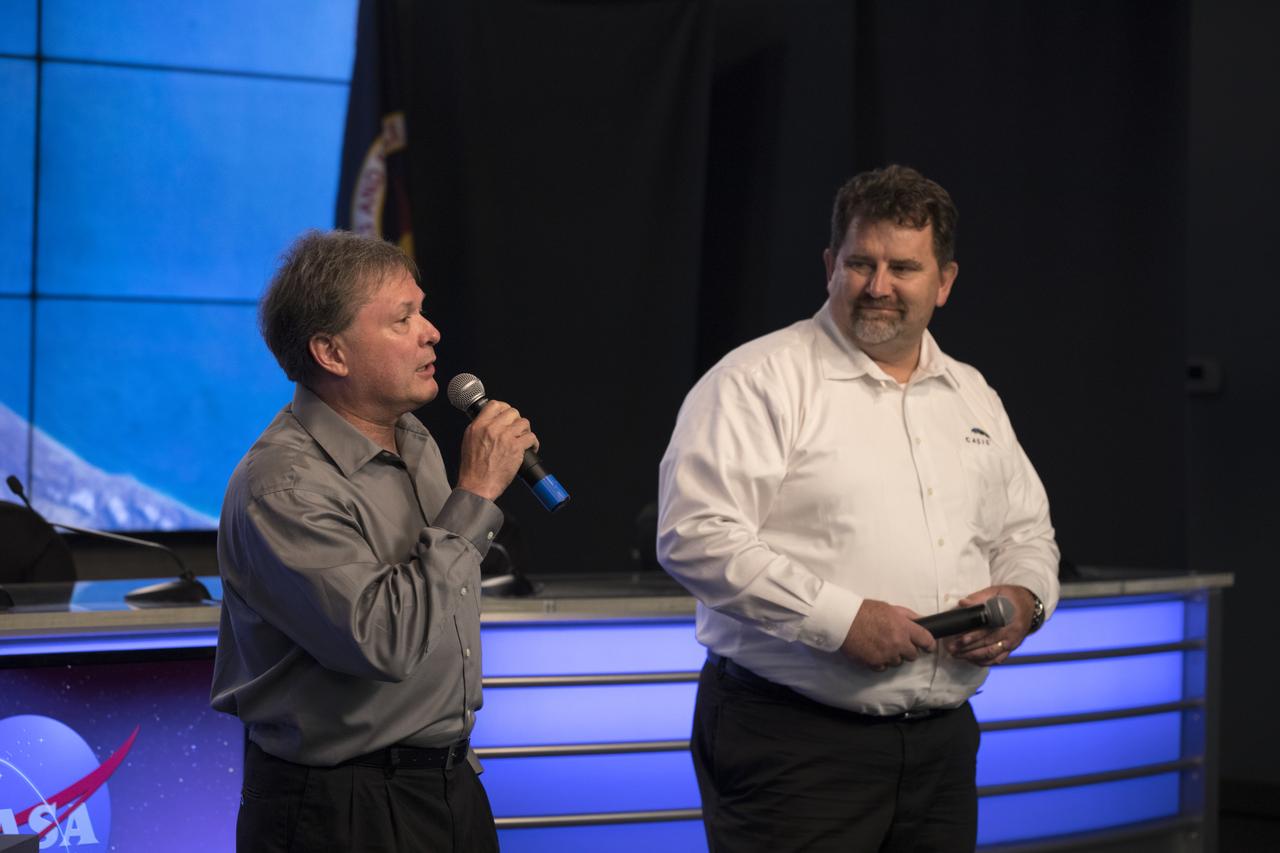

David Brady, assistant program scientist for the International Space Station Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center left, speaks to members of the media during a briefing in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. At right is Mike Roberts, deputy chief scientist, Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS). The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 15th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
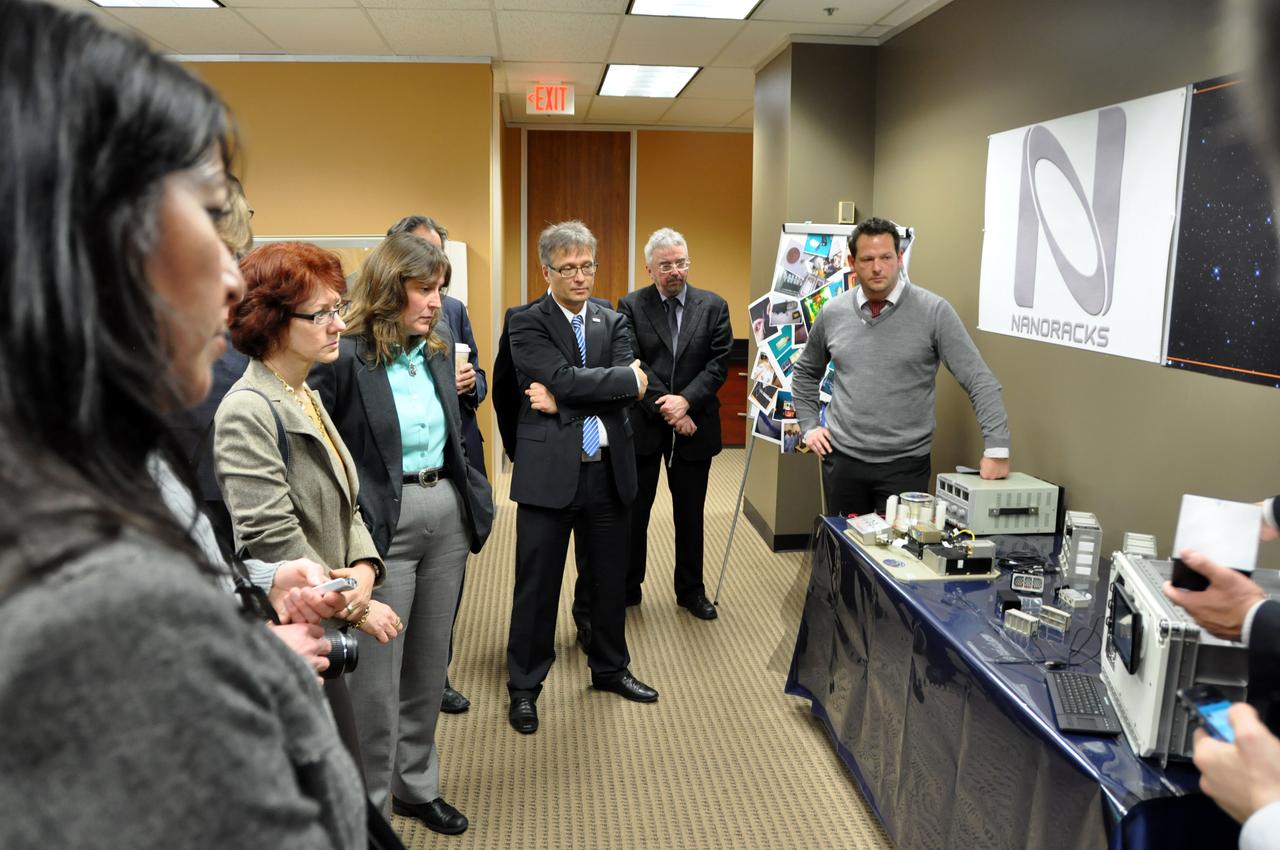

JSC2012-E-029876 (14 Feb. 2012) --- During a ceremony on Feb. 14, at the Astrium North America facility in Houston, the group of participants monitors a demonstration of the gravitational research centrifuge which Astrium ST handed over to NanoRacks LLC representatives. From the left are Jeanne Kranz of the staff of U.S. Rep. Pete Olson; Jeanne Becker, President, CEO and Executive Director of the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS); Marybeth Edeen, U.S. National Lab manager at NASA?s Johnson Space Center; Ulrich Kuebler, Uwe Pape, and Achim Schwarzwaelder, all with Astrium ST . Astrium ST and NanoRacks are teaming up to cooperate with NASA to deliver a commercial centrifuge facility to the International Space Station. NASA Photo courtesy Astrium North America

Cheryl Warner of NASA Communications, left, Kirt Costello, deputy chief scientist for the International Space Station Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, center, and Patrick O'Neill, Marketing and Communications manager at the Center of Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS), speak to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40 at 11:46 a.m. EST, on Dec. 12, 2017. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 13th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
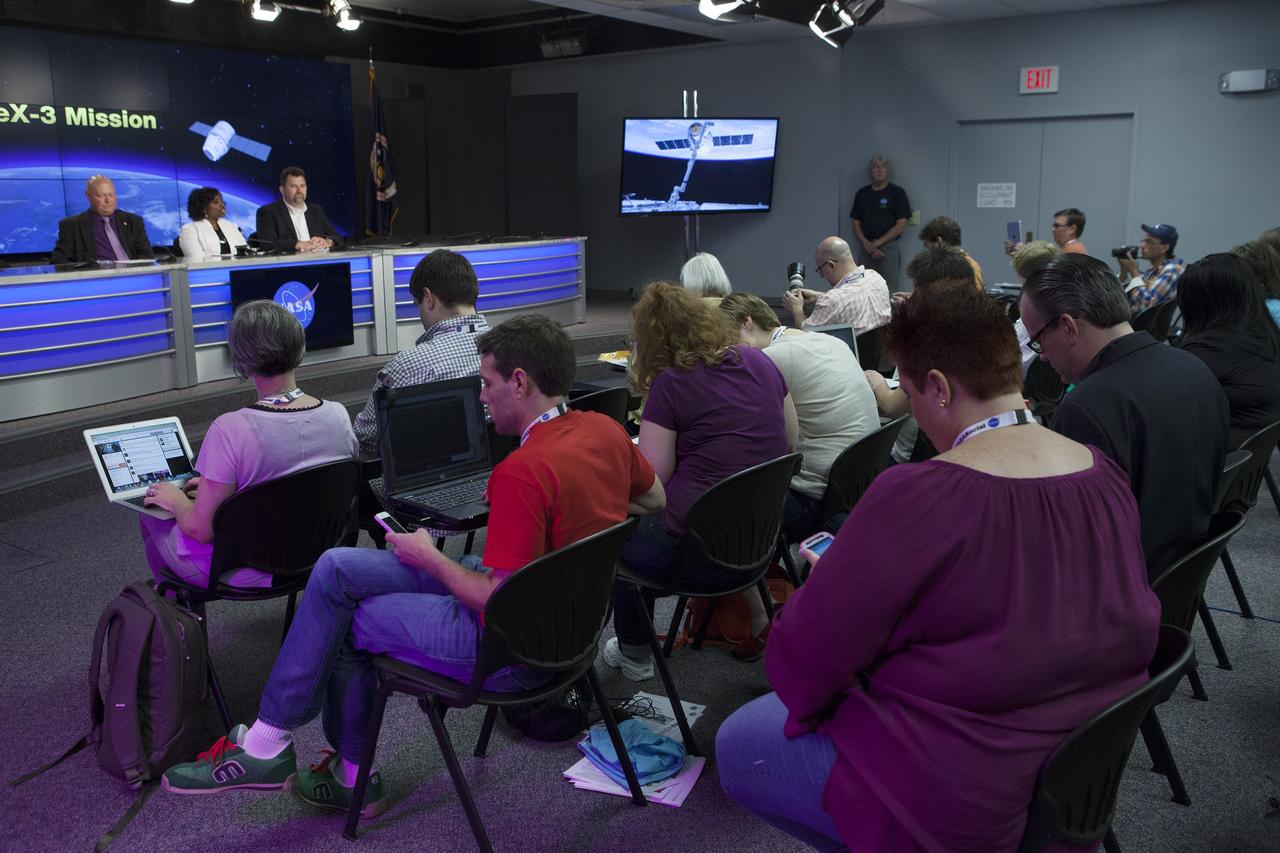

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a news conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, agency and contractor officials discussed science and technology experiment payloads being transported to the International Space Station by the SpaceX-3 Commercial Resupply Services mission. Participating in the briefing, from the left, are Mike Curie of NASA Public Affairs, Camille Alleyne, assistant program scientist in the NASA ISS Program Science Office, and Michael Roberts, senior research pathway manager with the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space CASIS. Scheduled for launch on April 14, 2014 atop a Falcon 9 rocket, the Dragon spacecraft will be marking its fourth trip to the space station. The SpaceX-3 mission carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments is the third of 12 flights contracted by NASA to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Kim Shiflett
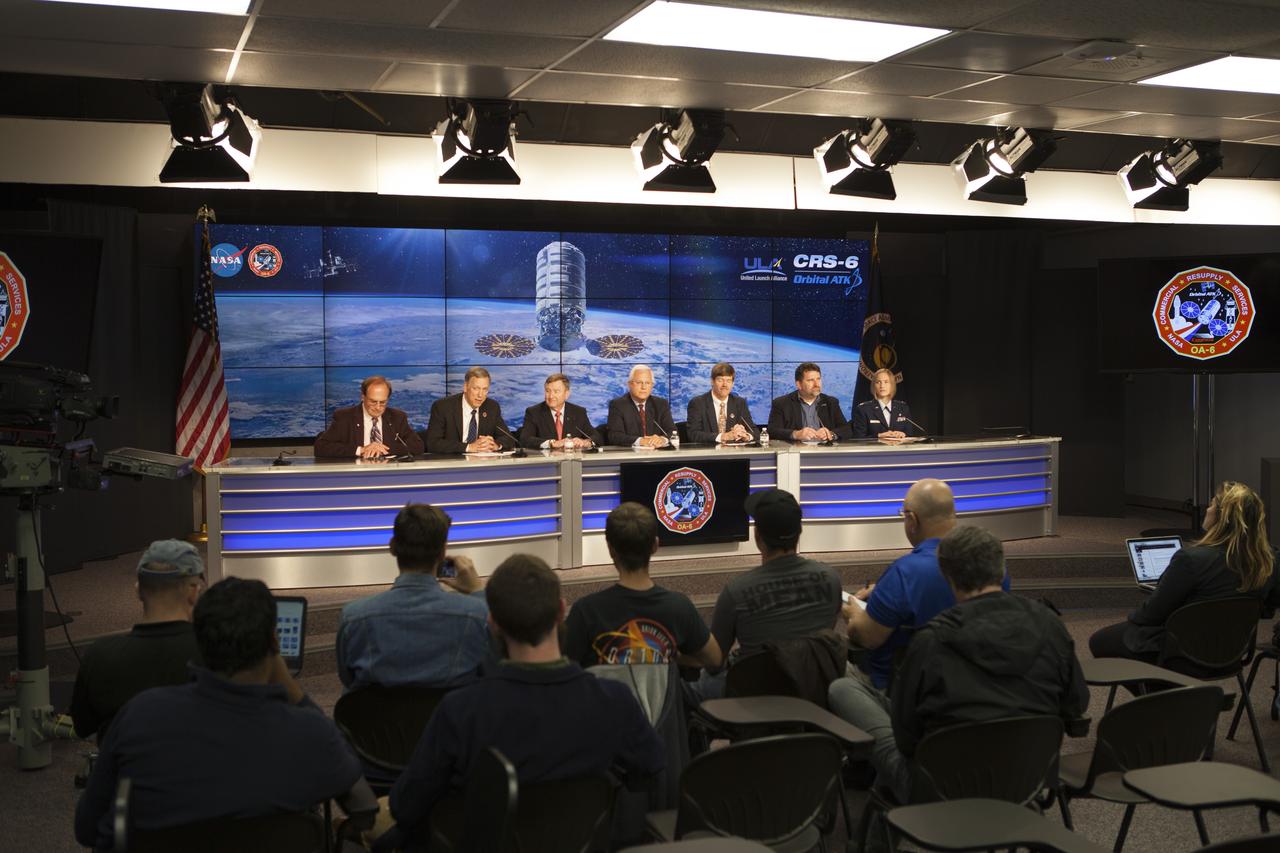

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, agency and industry leaders speak to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference for Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. From left are: George Diller of NASA Communications; Kenneth Todd, NASA ISS Operations Integration manager; Frank Culbertson, president of Orbital ATK's Space System Group; Vern Thorp, United Space Alliance's program manager for NASA missions; Pete Hasbrook, NASA associate program scientist for the ISS Program at the Johnson Space Center in Houston; Dr. Michael Roberts deputy chief scientist for the Center for the Advancement for Science in Space, or CASIS; and Capt. Laura Godoy, launch weather officer of the U.S. Air Force 45th Weather Squadron.
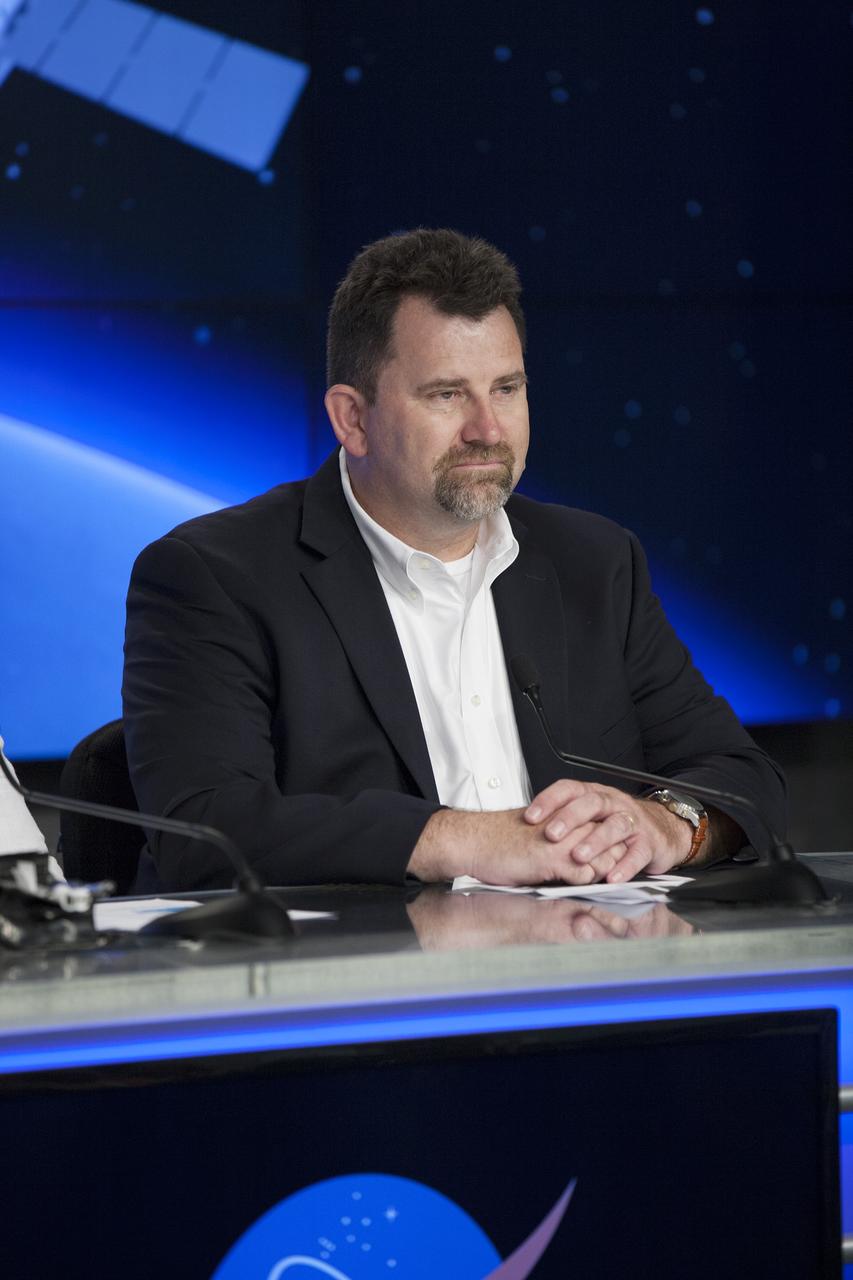

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a news conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, agency and contractor officials discussed science and technology experiment payloads being transported to the International Space Station by the SpaceX-3 Commercial Resupply Services mission. Participating in the briefing is Michael Roberts, senior research pathway manager with the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space CASIS. Scheduled for launch on April 14, 2014 atop a Falcon 9 rocket, the Dragon spacecraft will be marking its fourth trip to the space station. The SpaceX-3 mission carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments is the third of 12 flights contracted by NASA to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a news conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, agency and contractor officials discussed science and technology experiment payloads being transported to the International Space Station by the SpaceX-3 Commercial Resupply Services mission. Participating in the briefing, from the left, are Camille Alleyne, assistant program scientist in the NASA ISS Program Science Office, and Michael Roberts, senior research pathway manager with the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space CASIS. Scheduled for launch on April 14, 2014 atop a Falcon 9 rocket, the Dragon spacecraft will be marking its fourth trip to the space station. The SpaceX-3 mission carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments is the third of 12 flights contracted by NASA to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Kim Shiflett
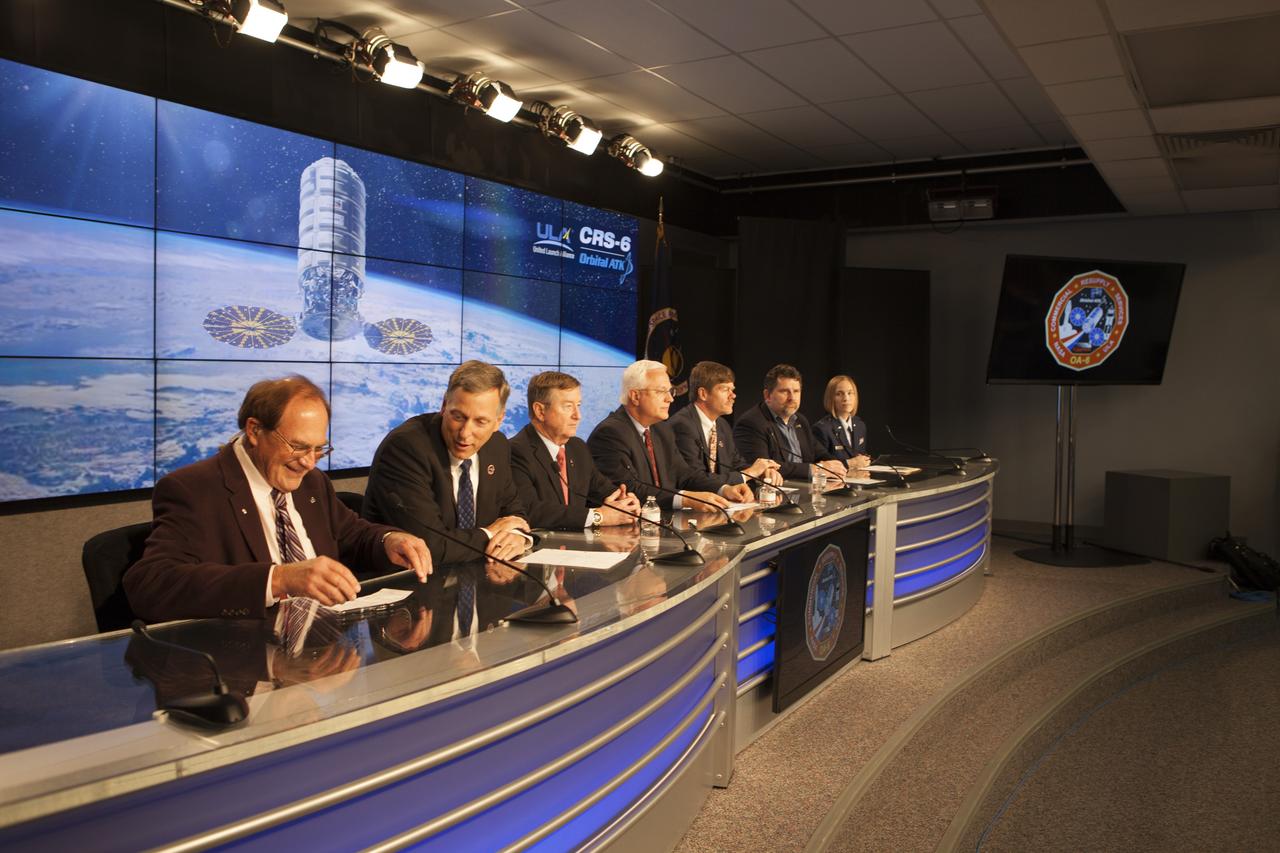

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, agency and industry leaders speak to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference for Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. From left are: George Diller of NASA Communications; Kenneth Todd, NASA ISS Operations Integration manager; Frank Culbertson, president of Orbital ATK's Space System Group; Vern Thorp, United Space Alliance's program manager for NASA missions; Pete Hasbrook, NASA associate program scientist for the ISS Program at the Johnson Space Center in Houston; Dr. Michael Roberts deputy chief scientist for the Center for the Advancement for Science in Space, or CASIS; and Capt. Laura Godoy, launch weather officer of the U.S. Air Force 45th Weather Squadron.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a news conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, agency and contractor officials discussed science and technology experiment payloads being transported to the International Space Station by the SpaceX-3 Commercial Resupply Services mission. Participating in the briefing, from the left, are Mike Curie of NASA Public Affairs, Camille Alleyne, assistant program scientist in the NASA ISS Program Science Office, and Michael Roberts, senior research pathway manager with the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space CASIS. Andy Petro of the agency's Space Technology Mission Directorate participated in the briefing by telephone from NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C. Scheduled for launch on April 14, 2014 atop a Falcon 9 rocket, the Dragon spacecraft will be marking its fourth trip to the space station. The SpaceX-3 mission carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments is the third of 12 flights contracted by NASA to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Media representatives ask questions of the ISS Research and Technology Panel in Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium in preparation for the launch of the SpaceX CRS-4 mission to resupply the International Space Station. On the dais from left are Michael Curie, NASA Public Affairs, Duane Ratliff, chief operating officer, CASIS, Mike Yagley, COBRA PUMA Golf, director of Research and Testing, Dr. Eugene Boland, Techshot chief scientist, Jason Gilbert, scientific associate, Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research, and Niki Werkheiser, 3D Printing in Zero-G project manager. The mission is the fourth of 12 SpaceX flights NASA contracted with the company to resupply the space station. It will be the fifth trip by a Dragon spacecraft to the orbiting laboratory. The spacecraft’s 2.5 tons of supplies, science experiments, and technology demonstrations include critical materials to support 255 science and research investigations that will occur during the station's Expeditions 41 and 42. Liftoff is targeted for an instantaneous window at 2:14 a.m. EDT. To learn more about the mission, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/launch/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Members of an ISS Research and Technology Panel brief media representatives in Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium in preparation for the launch of the SpaceX CRS-4 mission to resupply the International Space Station. From left are Duane Ratliff, chief operating officer, CASIS, Mike Yagley, COBRA PUMA Golf, director of Research and Testing, Dr. Eugene Boland, Techshot chief scientist, Jason Gilbert, scientific associate, Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research, and Niki Werkheiser, 3D Printing in Zero-G project manager. The mission is the fourth of 12 SpaceX flights NASA contracted with the company to resupply the space station. It will be the fifth trip by a Dragon spacecraft to the orbiting laboratory. The spacecraft’s 2.5 tons of supplies, science experiments, and technology demonstrations include critical materials to support 255 science and research investigations that will occur during the station's Expeditions 41 and 42. Liftoff is targeted for an instantaneous window at 2:14 a.m. EDT. To learn more about the mission, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/launch/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
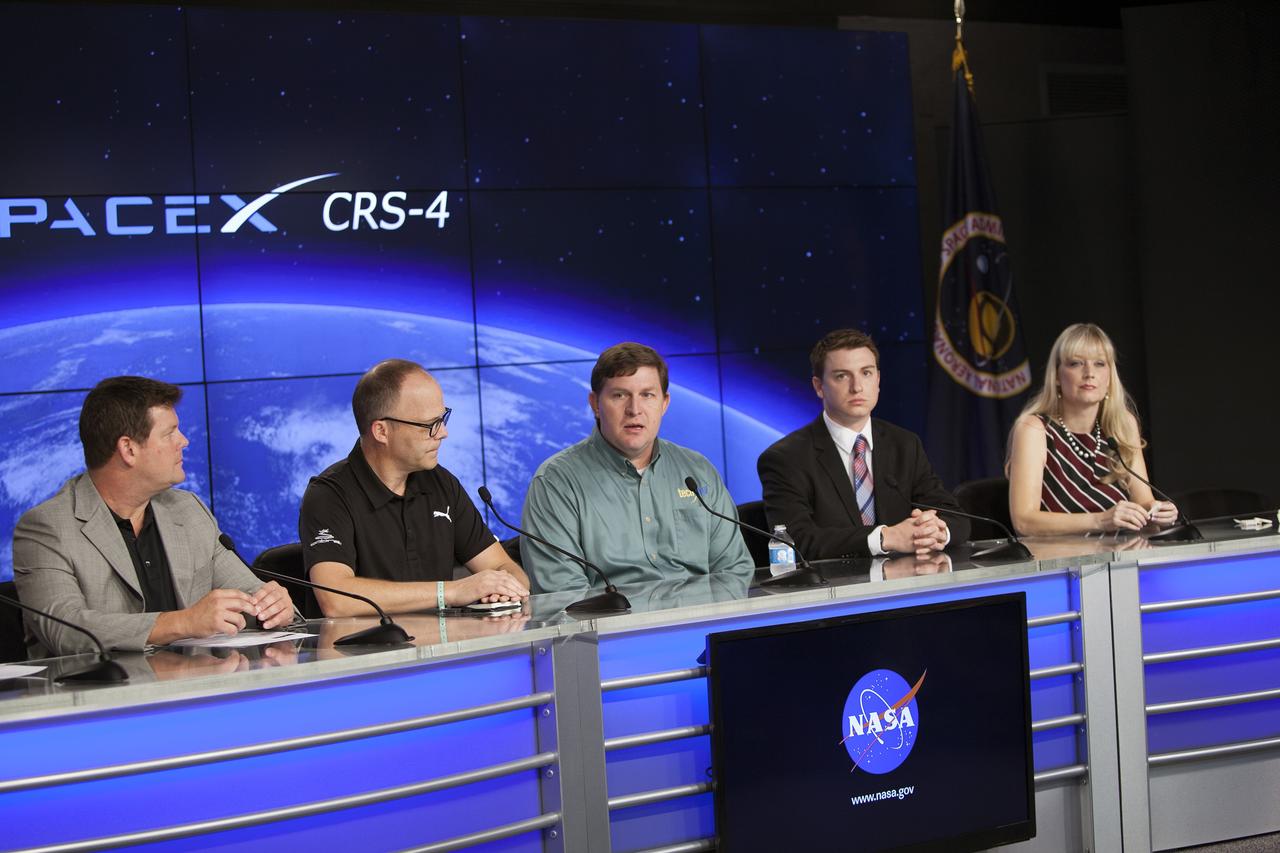

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Members of an ISS Research and Technology Panel brief media representatives in Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium in preparation for the launch of the SpaceX CRS-4 mission to resupply the International Space Station. From left are Duane Ratliff, chief operating officer, CASIS, Mike Yagley, COBRA PUMA Golf, director of Research and Testing, Dr. Eugene Boland, Techshot chief scientist, Jason Gilbert, scientific associate, Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research, and Niki Werkheiser, 3D Printing in Zero-G project manager. The mission is the fourth of 12 SpaceX flights NASA contracted with the company to resupply the space station. It will be the fifth trip by a Dragon spacecraft to the orbiting laboratory. The spacecraft’s 2.5 tons of supplies, science experiments, and technology demonstrations include critical materials to support 255 science and research investigations that will occur during the station's Expeditions 41 and 42. Liftoff is targeted for an instantaneous window at 2:14 a.m. EDT. To learn more about the mission, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/launch/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann