
ICUBATE PROCESSOR WITH CASSETTE

ICUBATE PROCESSOR WITH CASSETTE
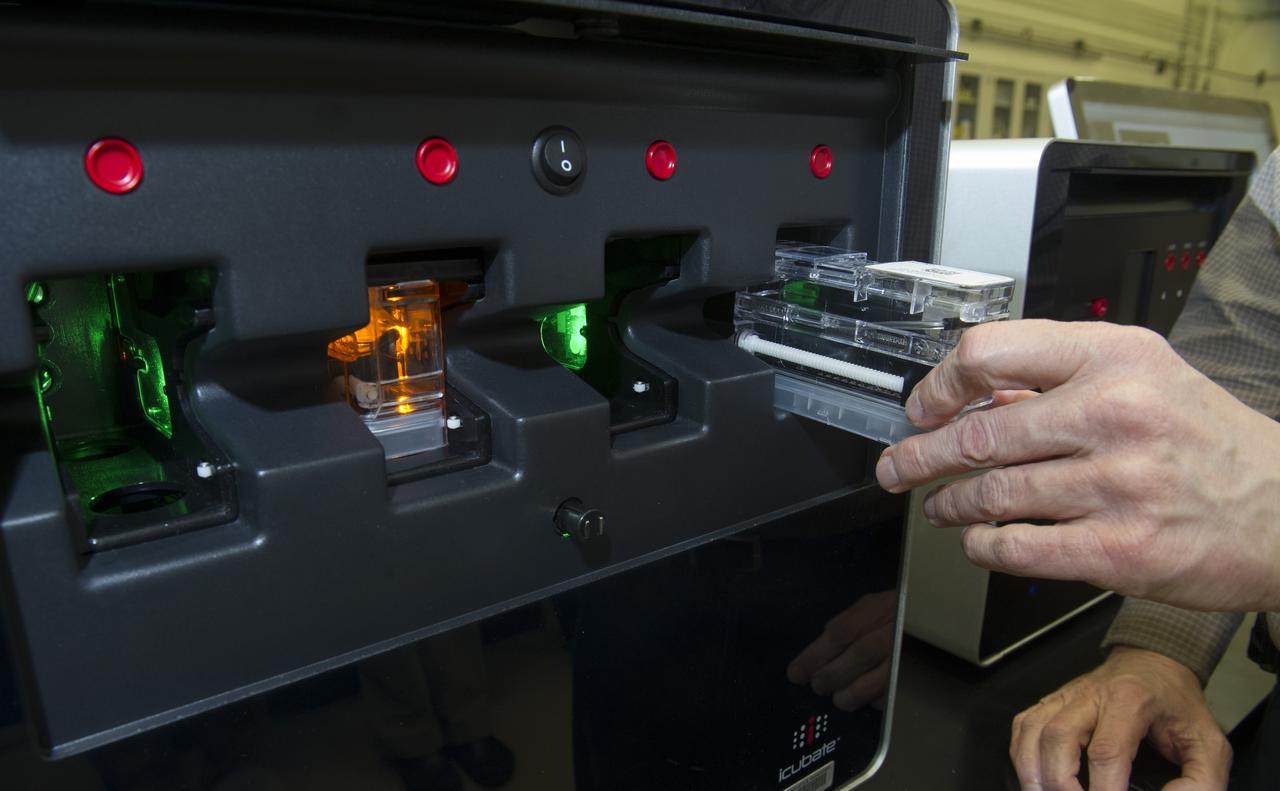

ICUBATE PROCESSOR WITH CASSETTE
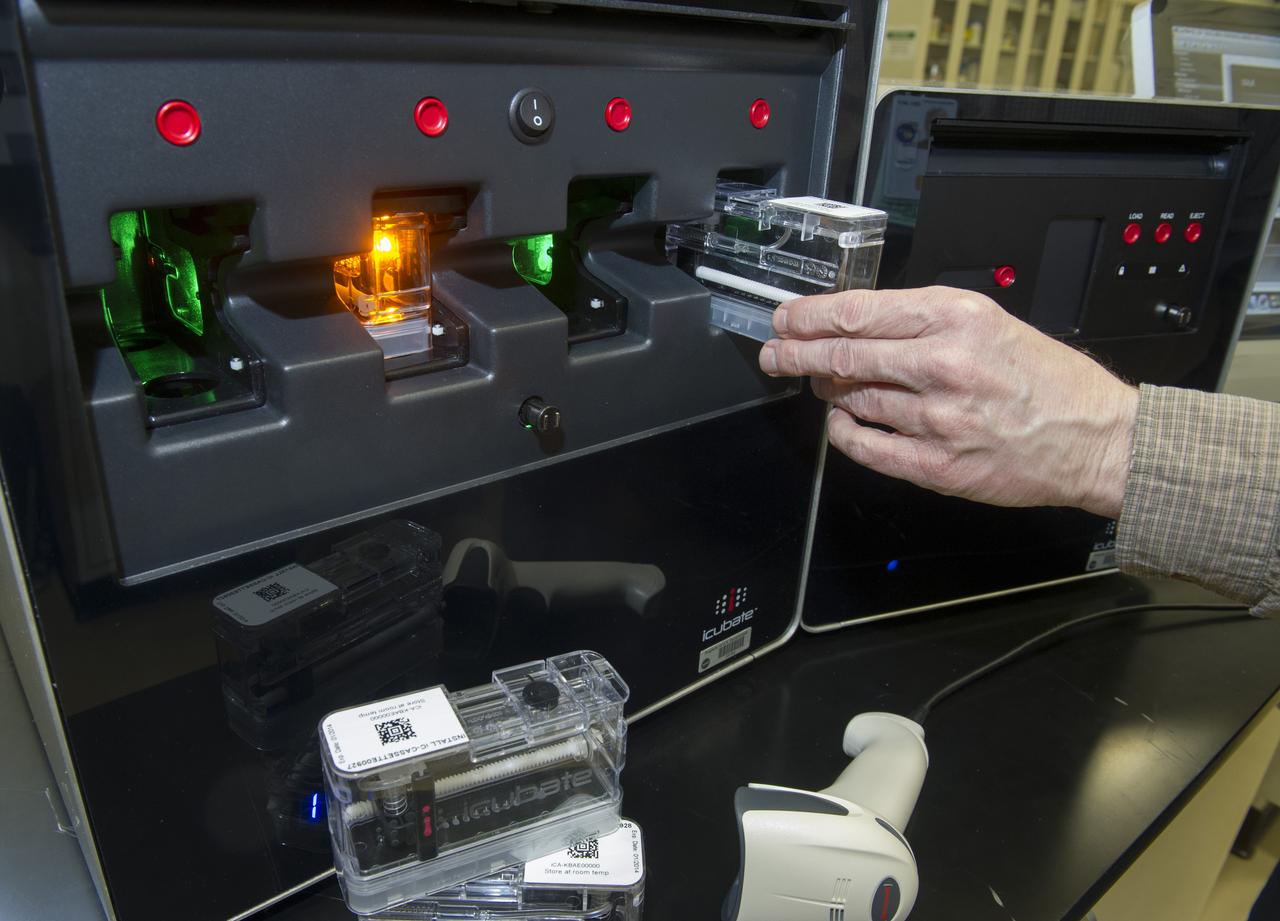

ICUBATE PROCESSOR WITH CASSETTE, SCANNER, AND READER
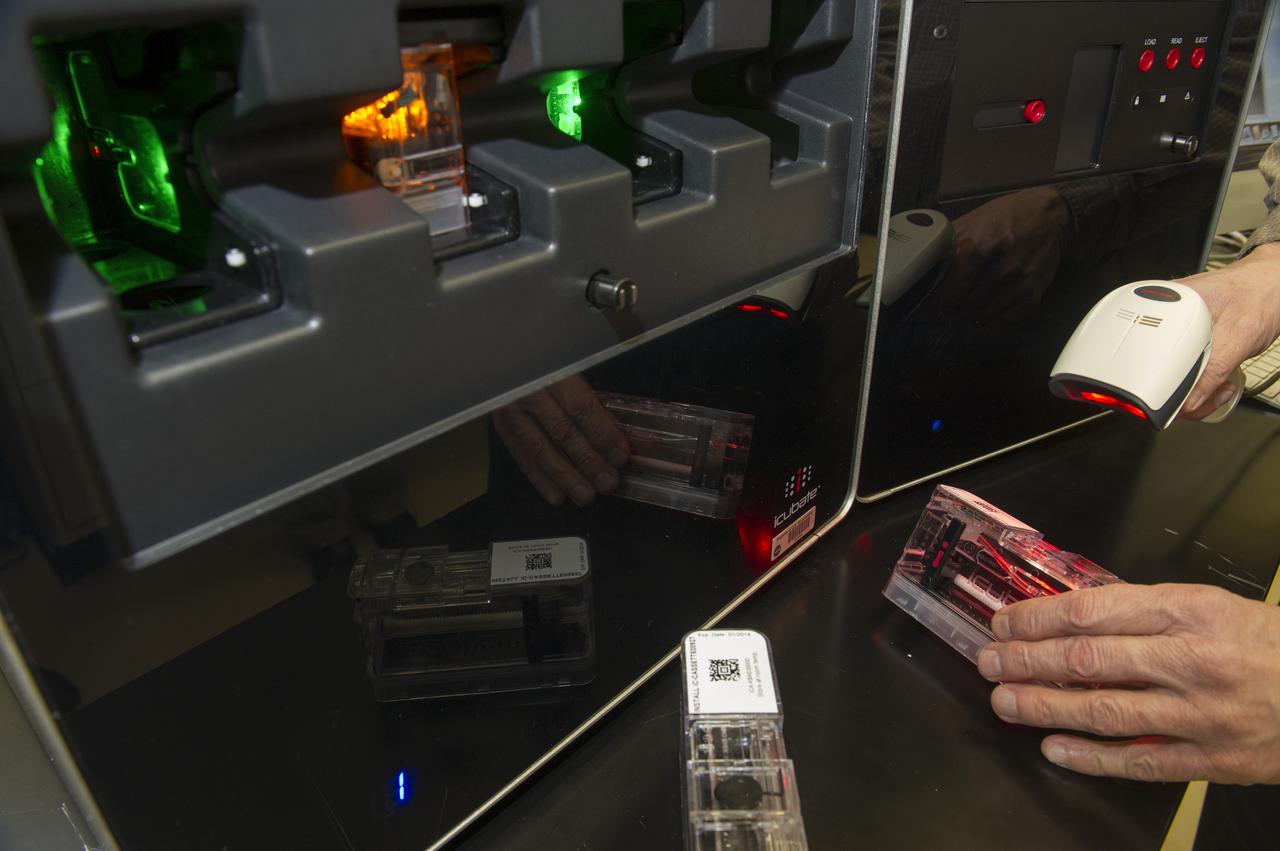

ICUBATE PROCESSOR WITH CASSETTE, SCANNER, AND READER
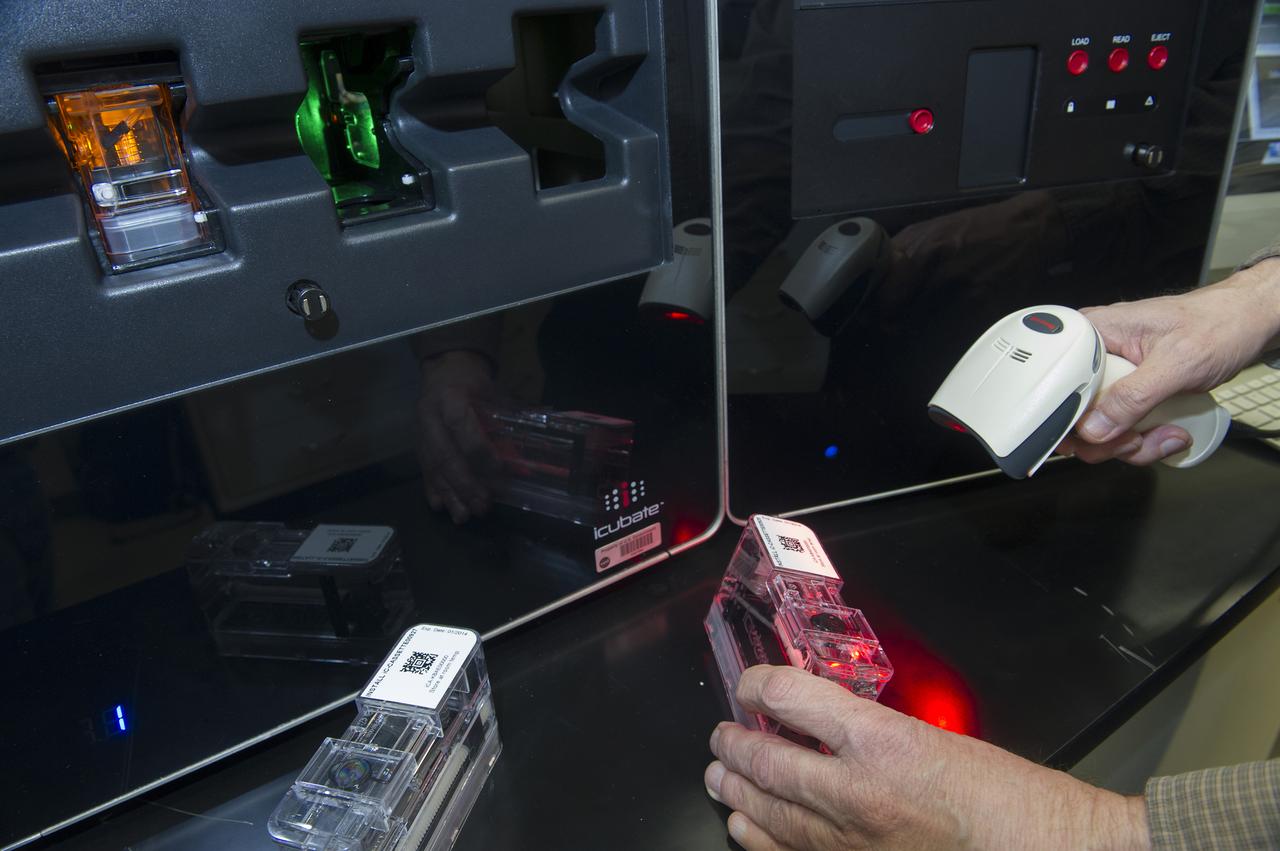

ICUBATE PROCESSOR WITH CASSETTE, SCANNER, AND READER
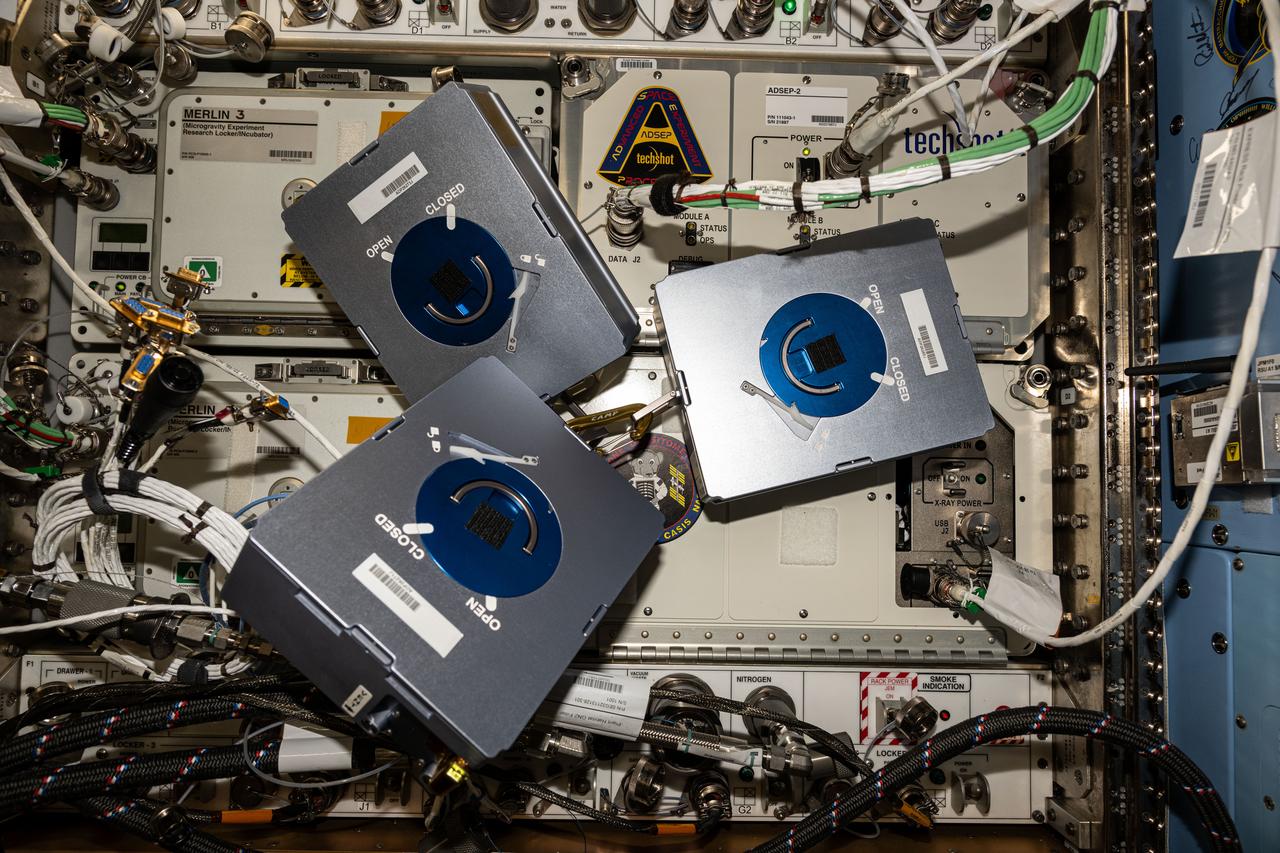

Documentation of three cassettes for the In-Space Production Application – Pharmaceutical In-space Laboratory – 02 (InSPA-PIL-02 or ADSEP-PIL-02) experiment removed from the ADSEP-2 (ADvanced Space Experiment Processor) for Fluid Loop replacement. Photo was taken in the Harmony Node 2.

jsc2025e036383 (4/4/2025) --- The blue box is The Redwire Industrial Crystallization Cassette (ICC), a facility capable of large quantities of crystal growth. The white cylindrical growth chamber below the ICC is capable of holding 200mL in volume, compared to <1mL held by the PIL-BOX cassettes. The ADSEP Industrial Crystallization Cassette Technology Demonstration (ADSEP-ICC) investigation validates the ICC’s capability to grow large quantities of crystals in its high-volume crystal growth chambers aboard the International Space Station. Image courtesy of Redwire.

iss069e000087 (March 29, 2023) --- UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Sultan Alneyadi services tissue sample cassettes inside the Columbus laboratory Module's BioFabrication Facility (BFF). The BFF-Meniscus study investigates bioprinting tissues to heal musculoskeletal injuries both in space and on Earth,
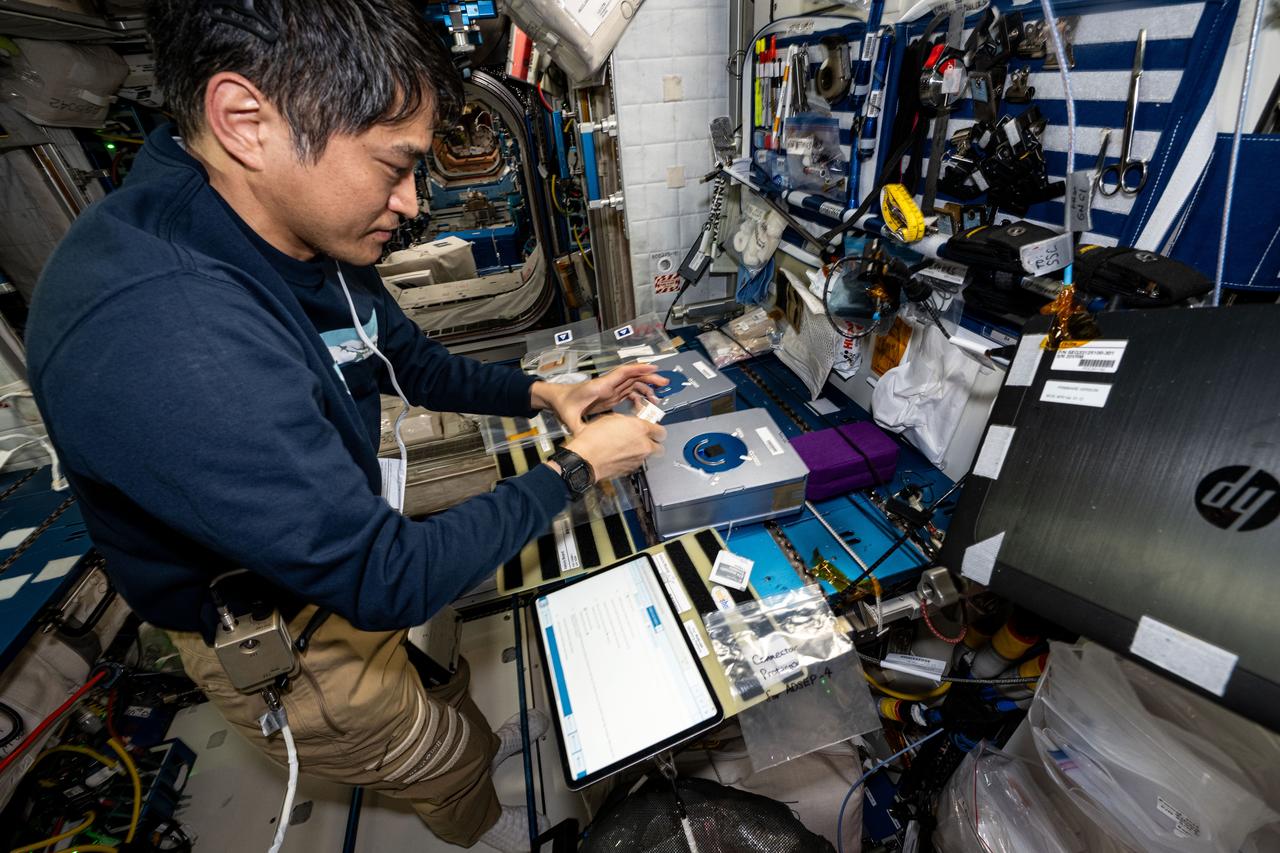

iss073e0002477_alt (April 28, 2025) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 73 Commander Takuya Onishi processes cassettes containing biological fluid samples for installation inside the Advanced Space Experiment Processor-4, a research facility that can be shipped back and forth from Earth to space, for a biotechnology study.
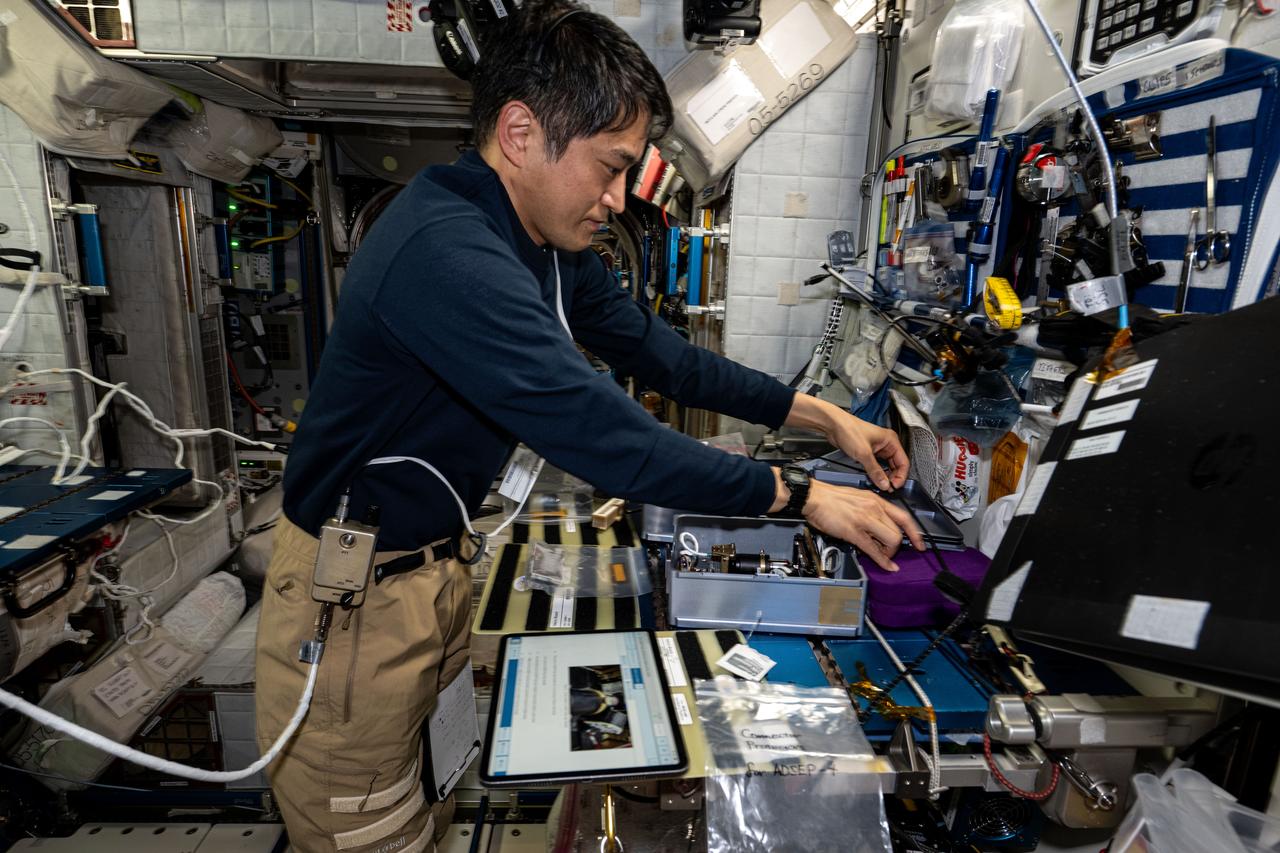

iss073e0002467 (April 28, 2025) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 73 Commander Takuya Onishi processes cassettes containing biological fluid samples for installation inside the Advanced Space Experiment Processor-4, a research facility that can be shipped back and forth from Earth to space, for a biotechnology study.
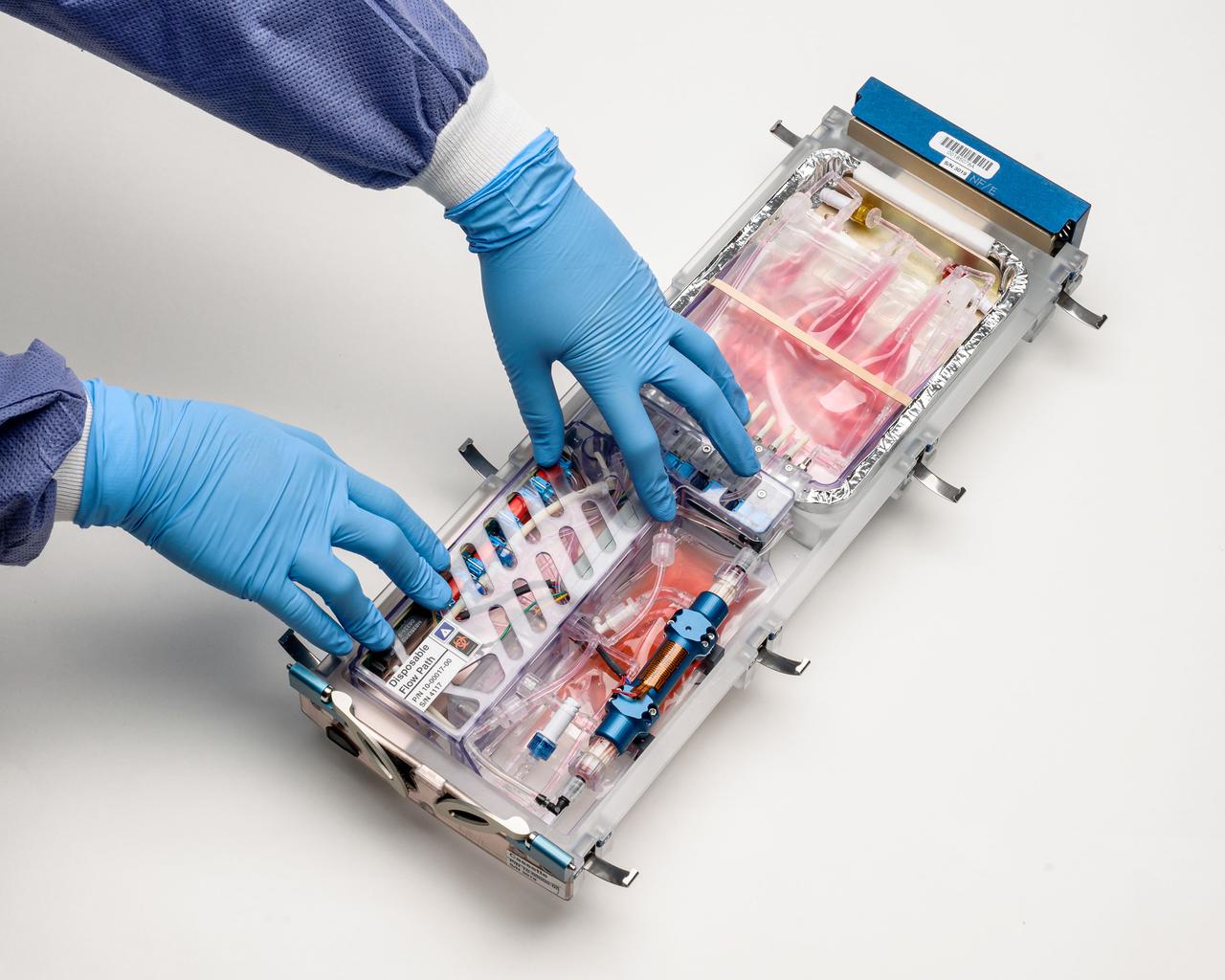

jsc2020e031189 (8/8/2015) --- A preflight interior view of the incubator cassette from the Bioculture System. The Bioculture System is a biological science incubator for use on the International Space Station (ISS) with the capability of transporting active and stored investigations to ISS. This incubator supports a wide diversity of tissue, cell, and microbiological cultures and experiment methods to meet any spaceflight research investigation goals and objectives. The facility enables variable duration and long-duration cellular and microbiological investigations on ISS to meet the scientific needs of academic and biotechnology interests. Credits: NASA photo by Dominic Hart
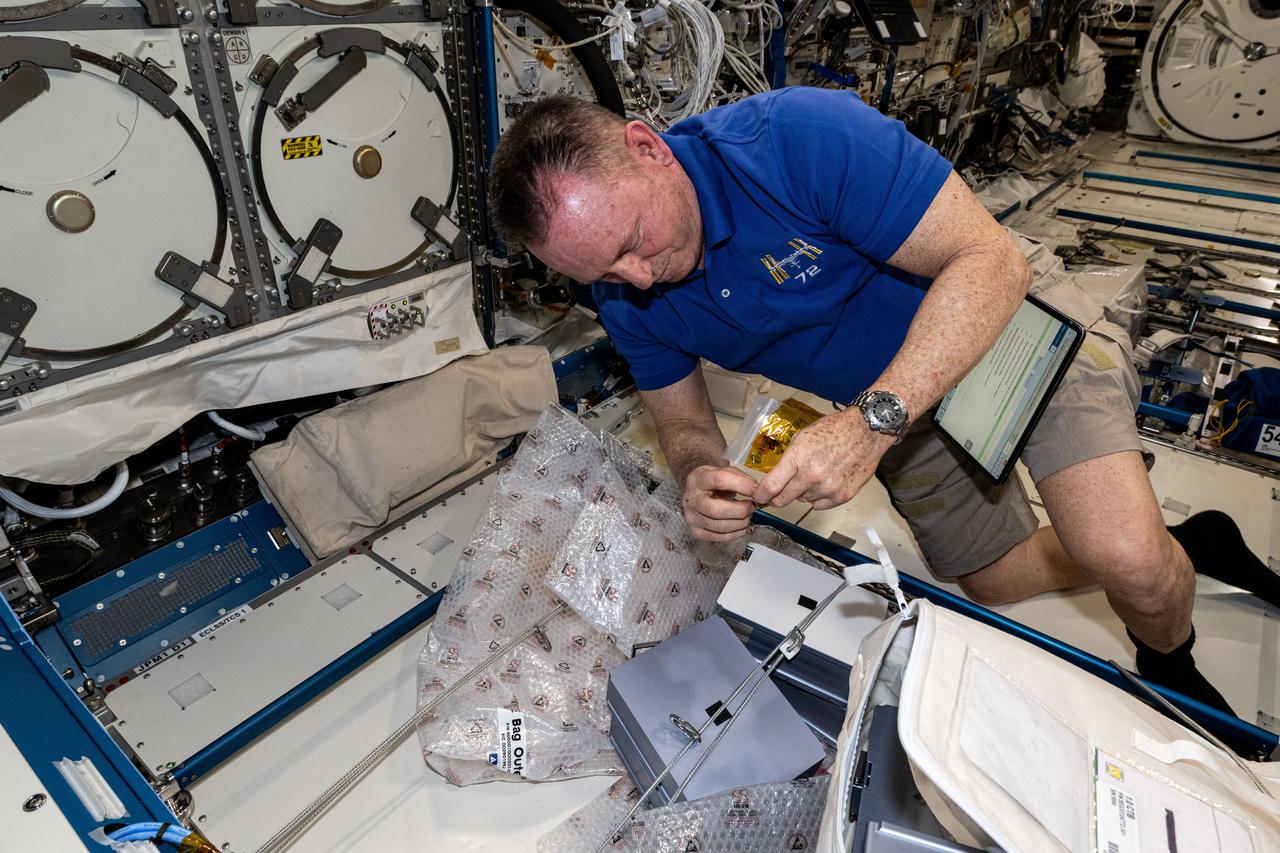

iss072e217983 (Nov. 18, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Butch Wilmore swaps sample cassettes inside the Advanced Space Experiment Processor-4 (ADSEP-4) located aboard the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. The ADSEP-4 is a portable research facility that supports multiple types of science experiments on the orbital outpost and also interfaces with the SpaceX Dragon and Northrop Grumman Cygnus cargo spacecraft.
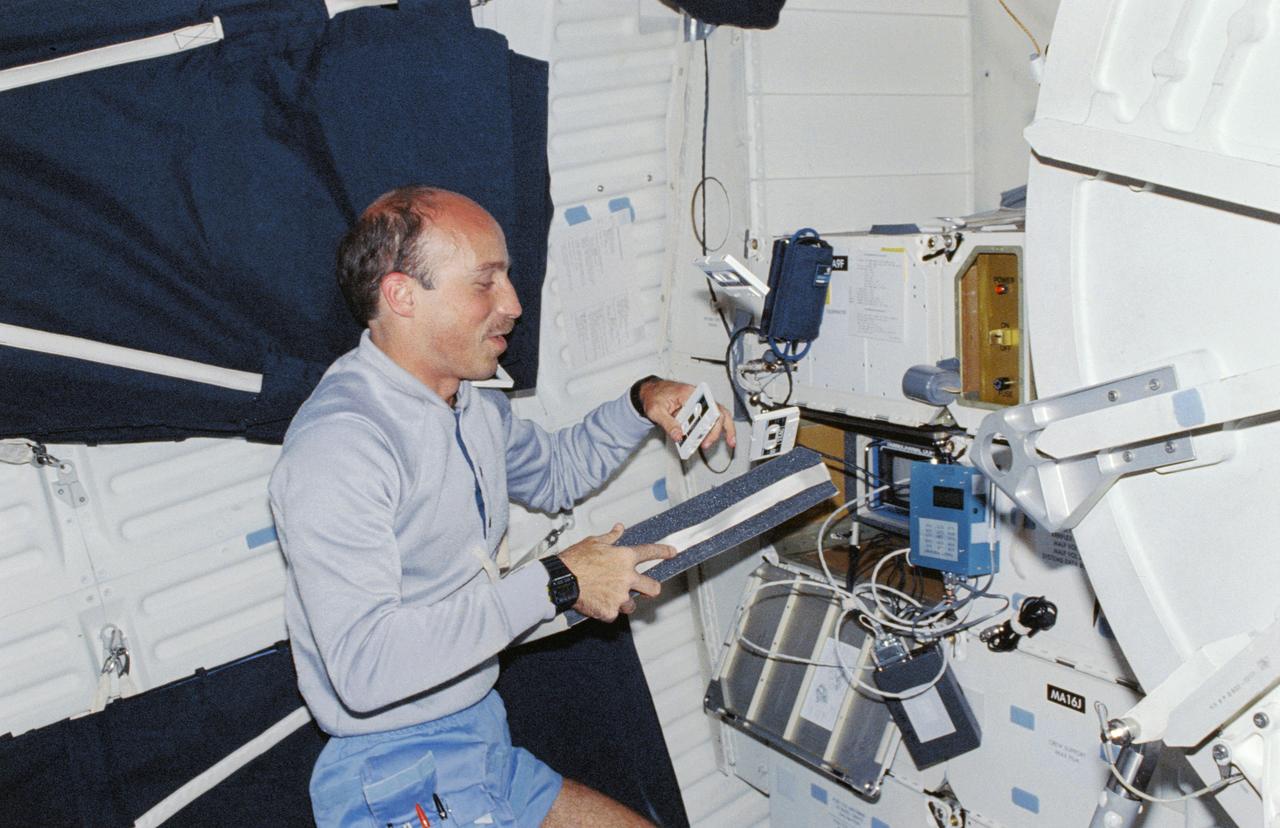

STS29-02-033 (3-18 March 1989) --- In what appears to be a juggling act in the microgravity of space, James P. Bagian, a physician, is actually attempting to organize audio cassettes. Other frames taken during the flight document Bagian's medical testing of his fellow crewmembers. This photographic frame was among NASA's third STS-29 photo release. Monday, March 20, 1989. Crewmembers were Astronauts Michael L. Coats, John E. Blaha, James F. Buchli, Robert C. Springer and James P. Bagian.
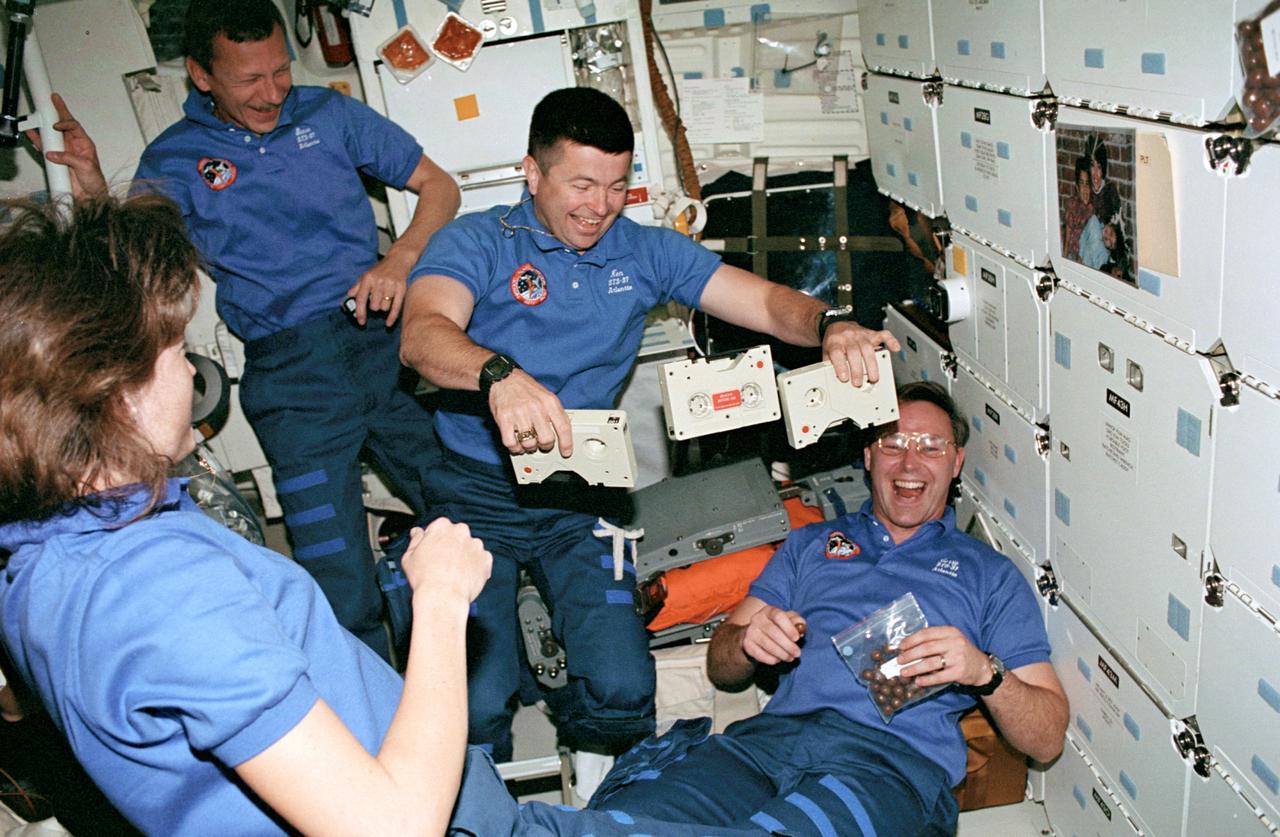

STS037-54-004 (5-11 April 1991) --- Four crew members have fun with weightlessness on the Space Shuttle Atlantis' middeck. Astronaut Kenneth D. Cameron, pilot, performs a "quick hands" feat with three tape cassettes -- obviously a feat much more difficult on Earth. Looking on, left to right, are astronauts Linda M. Godwin, mission specialist; Steven R. Nagel, mission commander; and Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist. Ross later used the microgravity environment to have some fun with the bag of malted milk balls in his hands. This 35mm frame was exposed by astronaut Jerome (Jay) Apt, mission specialist. This was one of the visuals used by the crew members during their April 19 Post Flight Press Conference (PFPC) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC).
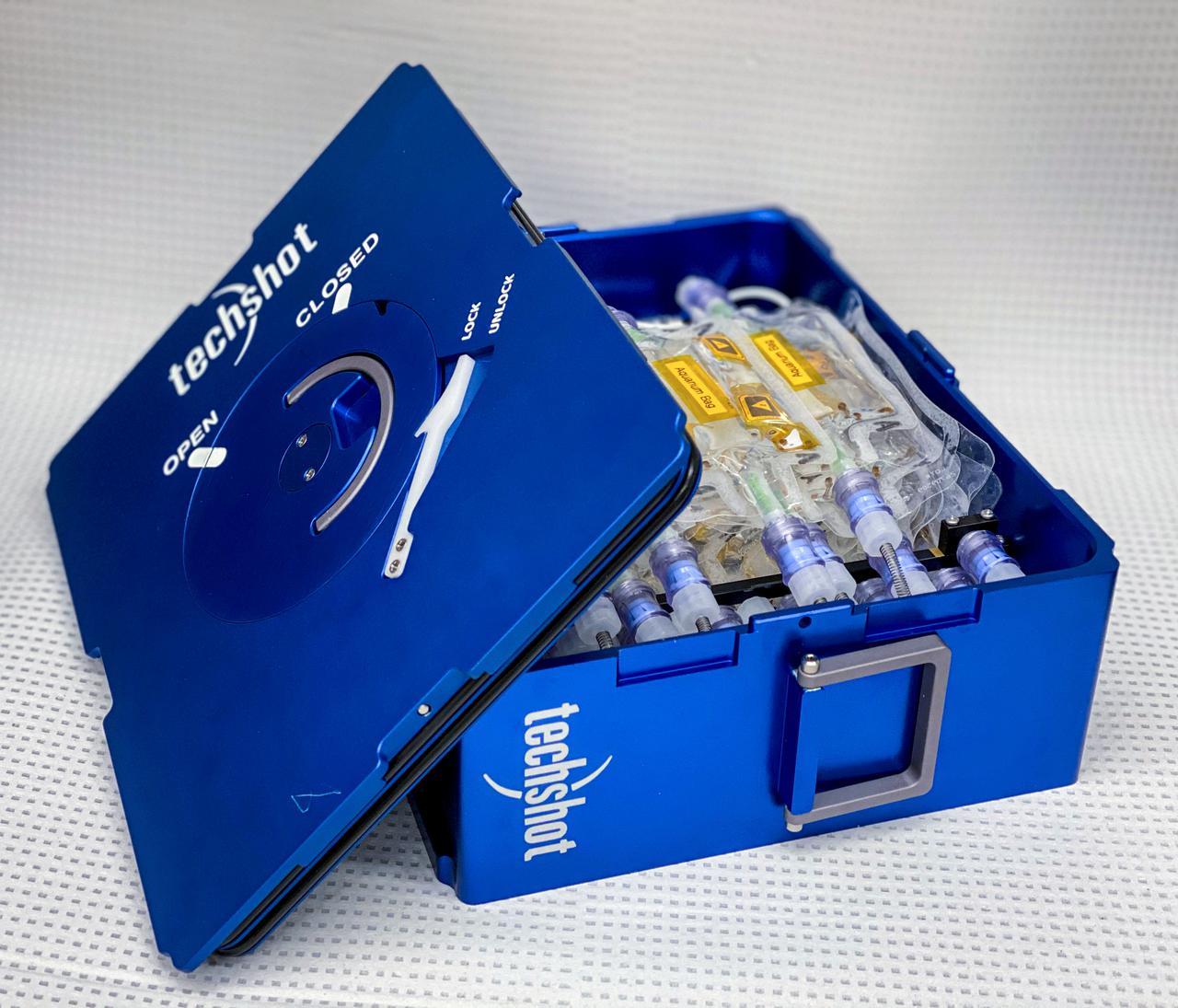

jsc2021e019403 (1/29/2021) --- A Techshot Fluid Processing Cassette that is part of Techshot’s ADSEP fleet of spaceflight hardware facilities. The flight hardware cassette is loaded with small aquarium bags containing the juvenile bobtail squid. Once launched into space, the aquarium bags will inoculated with luminescent bacterium to start the normal symbiosis with the squid. Understanding of Microgravity on Animal-Microbe Interactions (UMAMI) examines the effects of spaceflight on the molecular and chemical interactions between beneficial microbes and their animal hosts. Image courtesy of Rachel Ormsby.
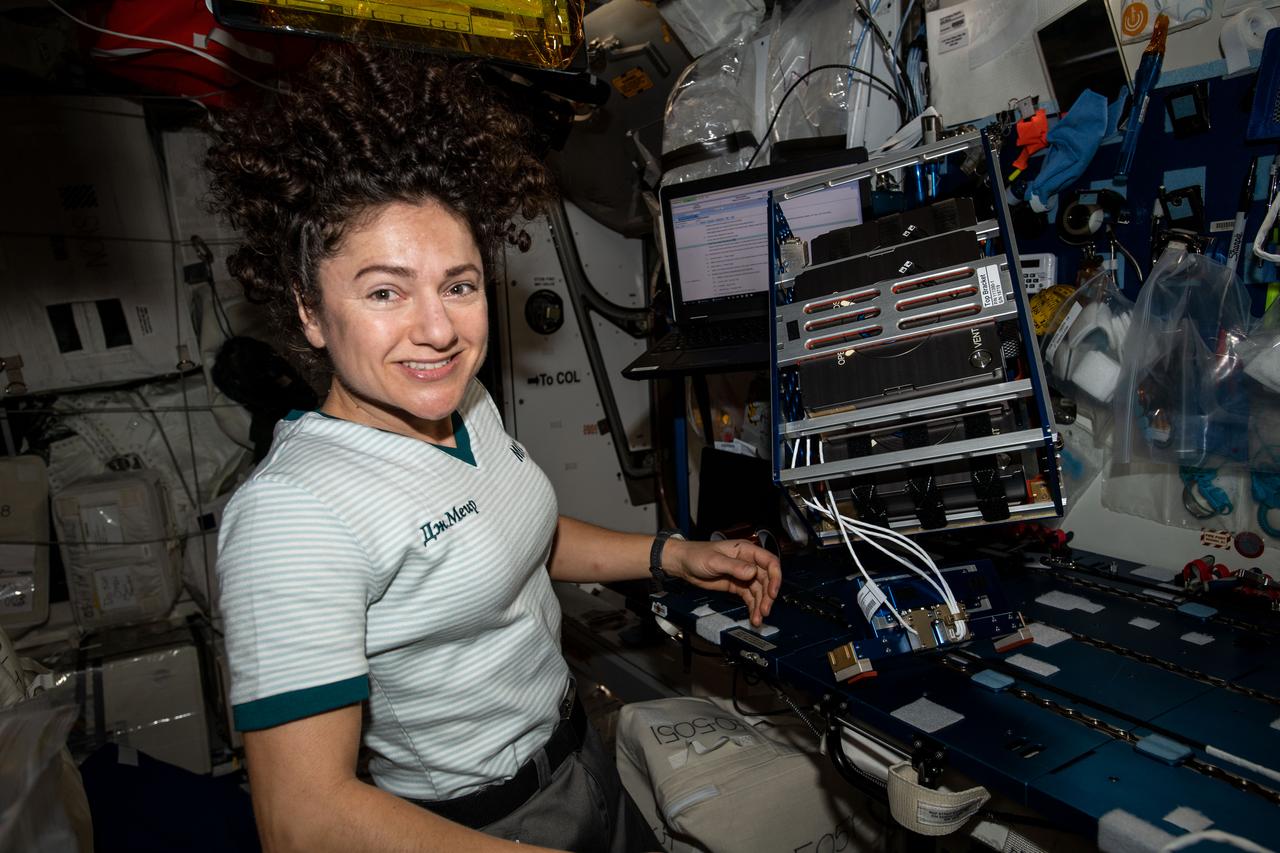

iss061e113336 (Jan. 2, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 61 Flight Engineer Jessica Meir inserts Techshot Tissue Cassettes into racks that allow them to be installed in a Microgravity Experiment Research Locker/Incubator (MERLIN) for sample return to Earth. These particular tissue cassettes were used in the 3D printing of tissue-like constructs as part of the initiation of Techshot’s BioFabrication Facility (BFF) aboard the International Space Station.
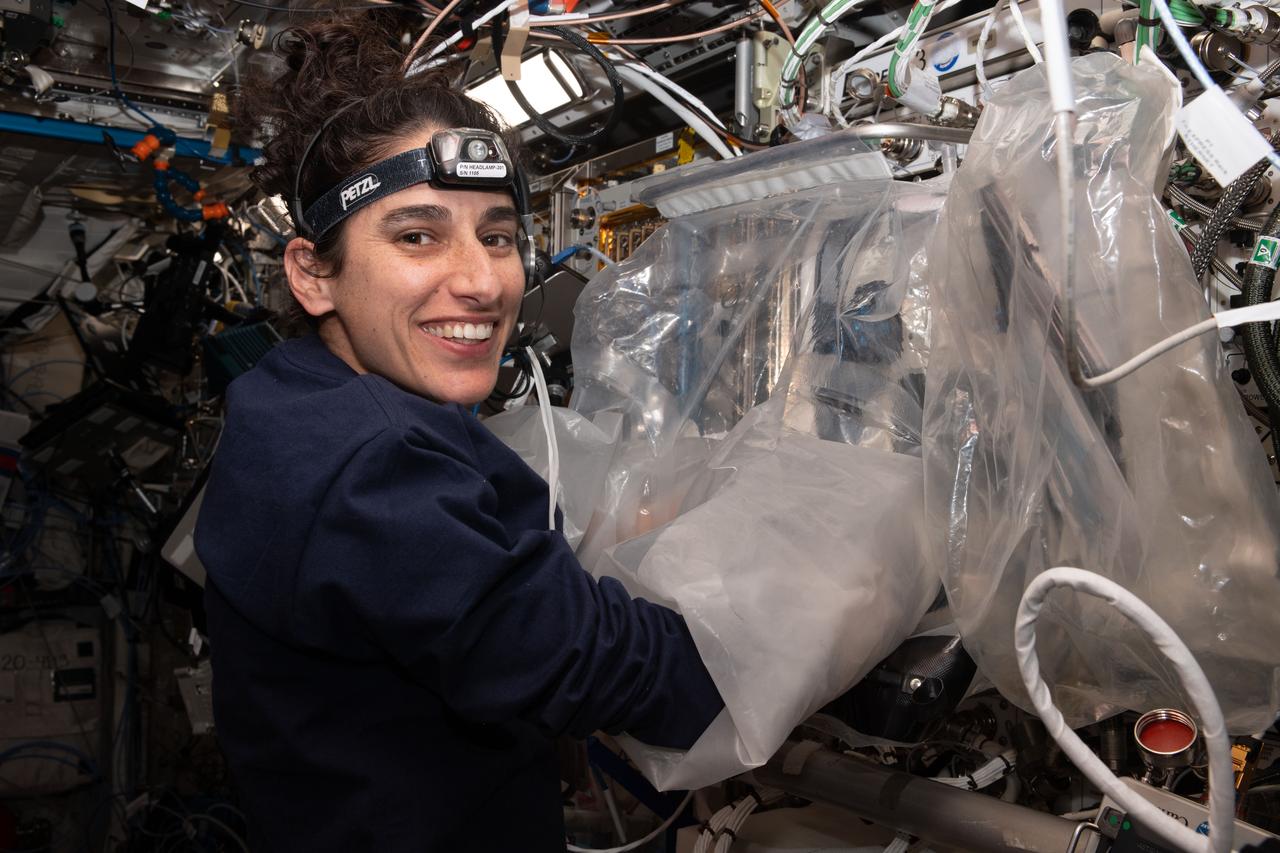

iss070e035114 (Dec. 1, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flight Engineer Jasmin Moghbeli uses a portable glovebag and removes a tissue cassette containing printed cardiac tissue samples from the BioFabrication Facility that is demonstrating printing organ-like tissues in microgravity. The cassette was then installed into an advanced sample processor that can be configured for a variety of biological and physics investigations.
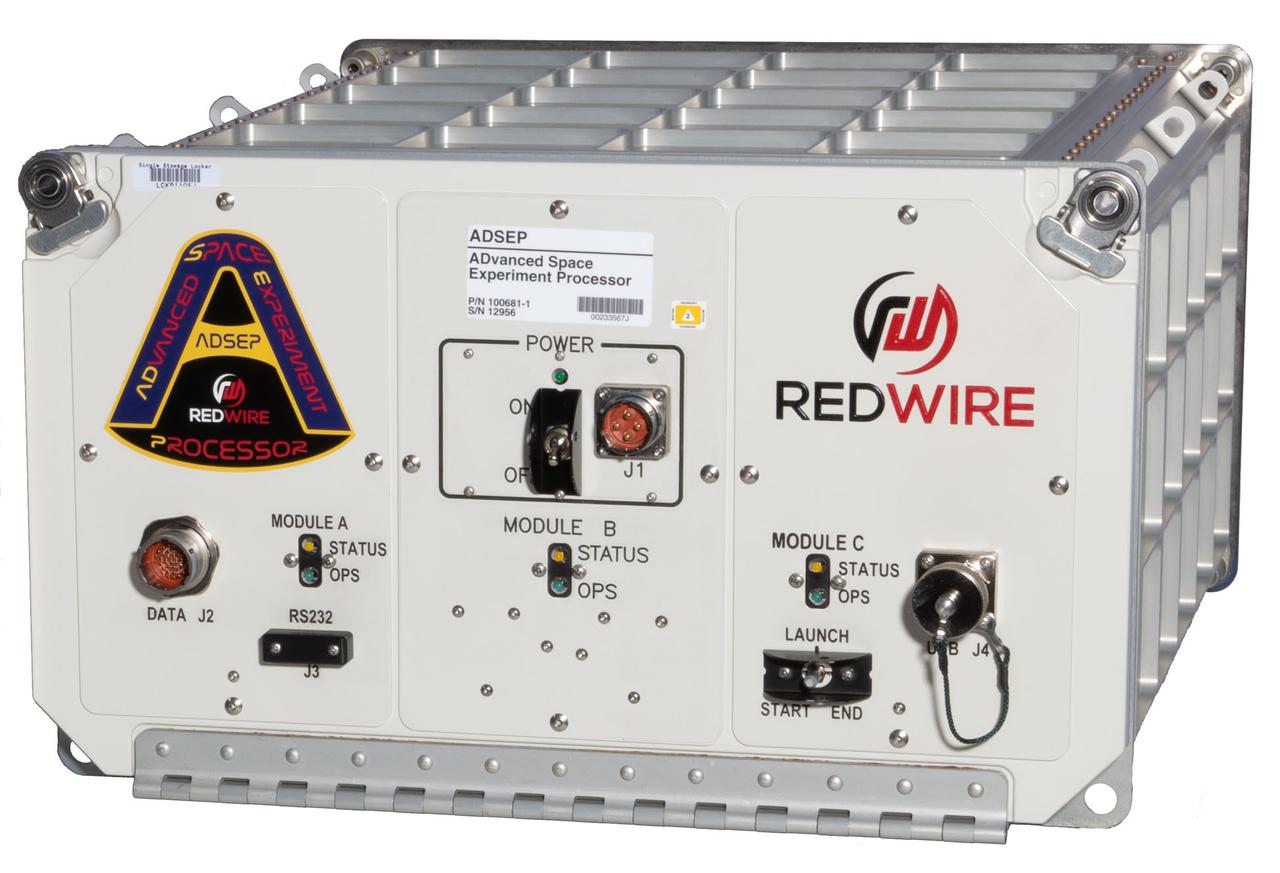

jsc2024e043200 (10/9/2020) --- The Redwire Space ADvanced Space Experiment Processor (ADSEP) is a fully automated, multi-use single middeck locker processing facility used to conduct a variety of life and physical-science research as well as small-batch production. The ADSEP facility contains three independent thermal zones, each accommodates one “mini-laboratory” cassette and an internal computer that controls the processing of all three cassettes. Image courtesy of Redwire. Original Filename
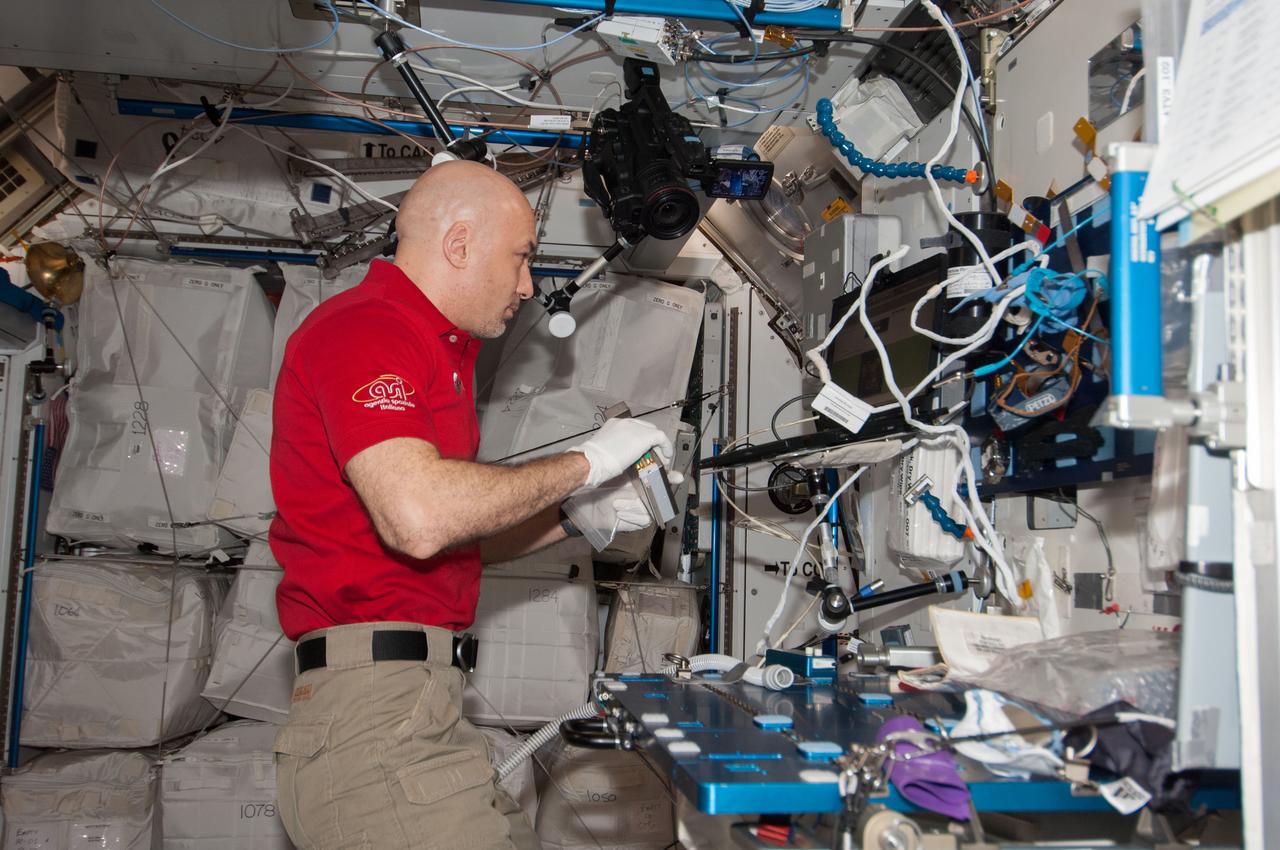

ISS037-E-026923 (5 Nov. 2013) --- European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano, Expedition 37 flight engineer, works with hardware at a workstation in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
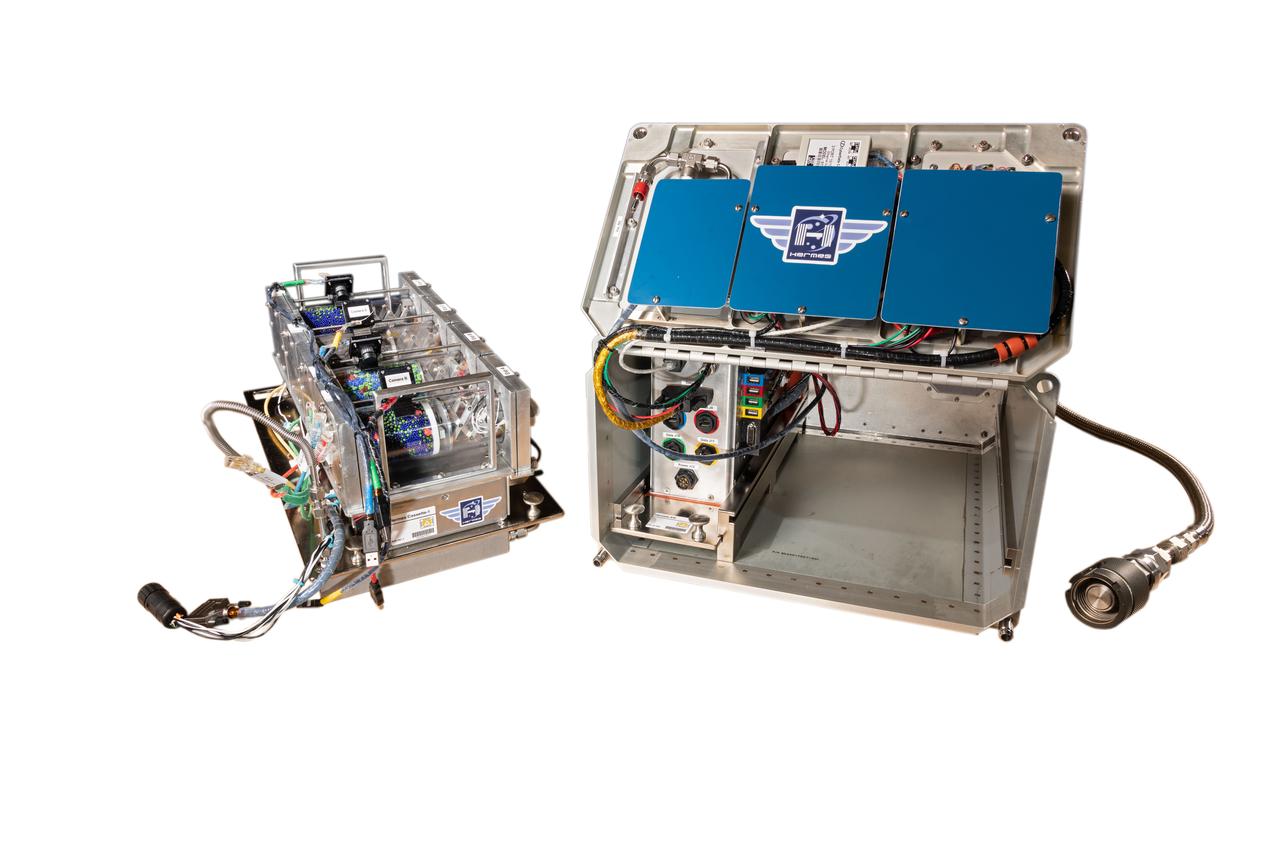
jsc2019e014139_alt (3/8/2019) --- Photo documentation of the Hermes facility. Hermes is a research facility on the ISS aimed at regolith and granular material investigations with applications to asteroids, planetary science, and exploration. It is a reconfigurable on-orbit facility capable of accommodating up to four user-configurable experiment volumes at a time. The facility provides long duration exposure to microgravity, vacuum, power, lighting, cameras and customizable experiment tools with ground commanding capability.
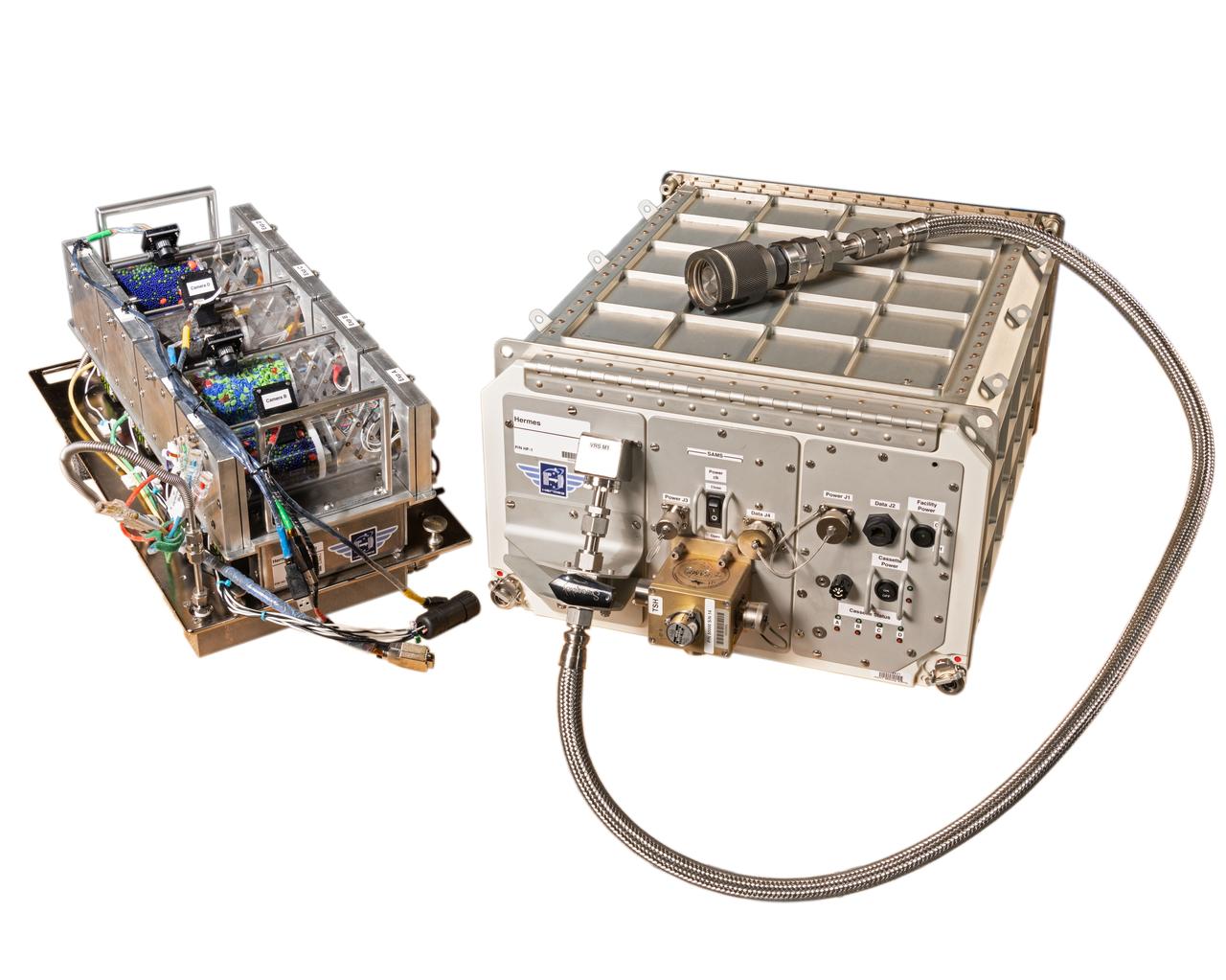

jsc2019e014137_alt (3/8/20419) --- Photo documentation of the Hermes facility. Hermes is a research facility on the ISS aimed at regolith and granular material investigations with applications to asteroids, planetary science, and exploration. It is a reconfigurable on-orbit facility capable of accommodating up to four user-configurable experiment volumes at a time. The facility provides long duration exposure to microgravity, vacuum, power, lighting, cameras and customizable experiment tools with ground commanding capability.
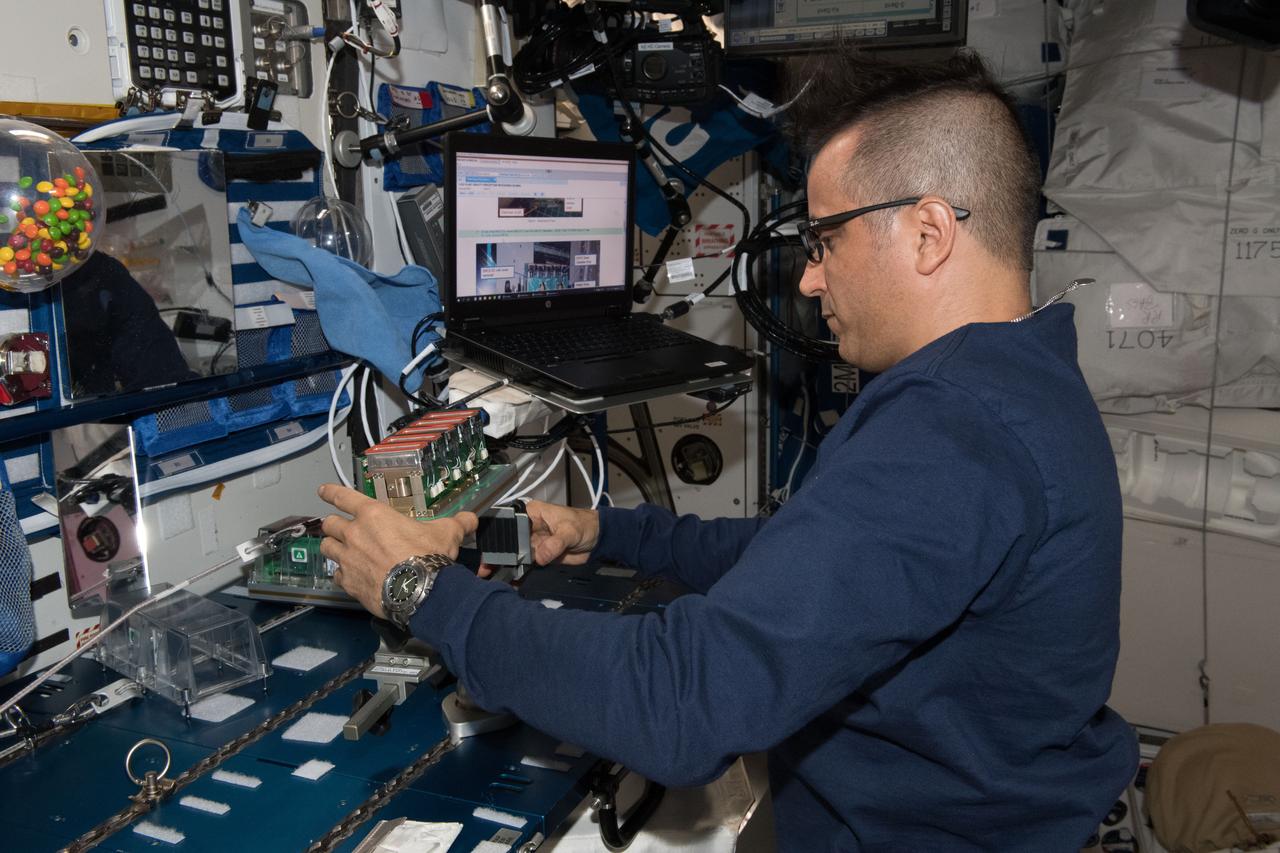

iss054e052250 (Feb. 20, 2018) --- NASA astronaut Joe Acaba removes Seed Cassettes for the Plant Gravity Perception experiment, which tests the gravity sensing ability of plants in microgravity.

iss060e008906 (7/17/2019) --- Photo documentation of the Hermes Cassette-1 investigation aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Hermes Cassette-1 is the the first set of experiments in the Hermes Facility, it explores the dynamics and properties of material on the surface of small asteroids, including regolith. Regolith creates a loosely aggregated surface on airless bodies and researchers expect it is dominated by interactions between individual grains of the material. Results improve understanding of asteroid and small body dynamics and validate and improve small body models, essential for future crewed and robotic missions to these small bodies.
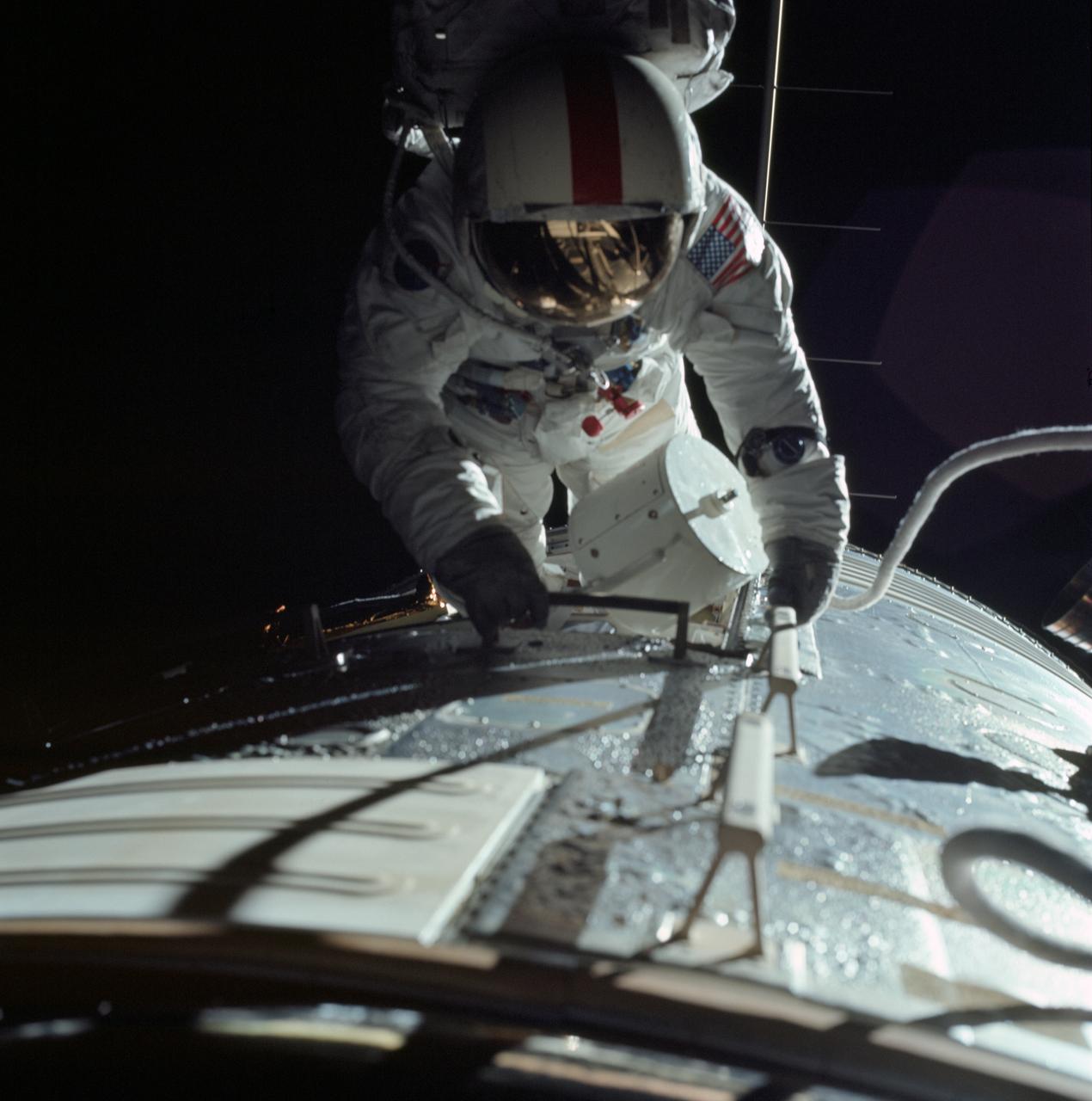

AS17-152-23393 (17 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Ronald E. Evans is photographed performing extravehicular activity during the Apollo 17 spacecraft's trans-Earth coast. During his EVA, command module pilot Evans retrieved film cassettes from the Lunar Sounder, Mapping Camera, and Panoramic Camera. The cylindrical object at Evans' left side is the Mapping Camera cassette. The total time for the trans-Earth EVA was one hour seven minutes 18 seconds, starting at ground elapsed time of 257:25 (2:28 p.m.) and ending at ground elapsed timed of 258:42 (3:35 p.m.) on Sunday, Dec. 17, 1972.
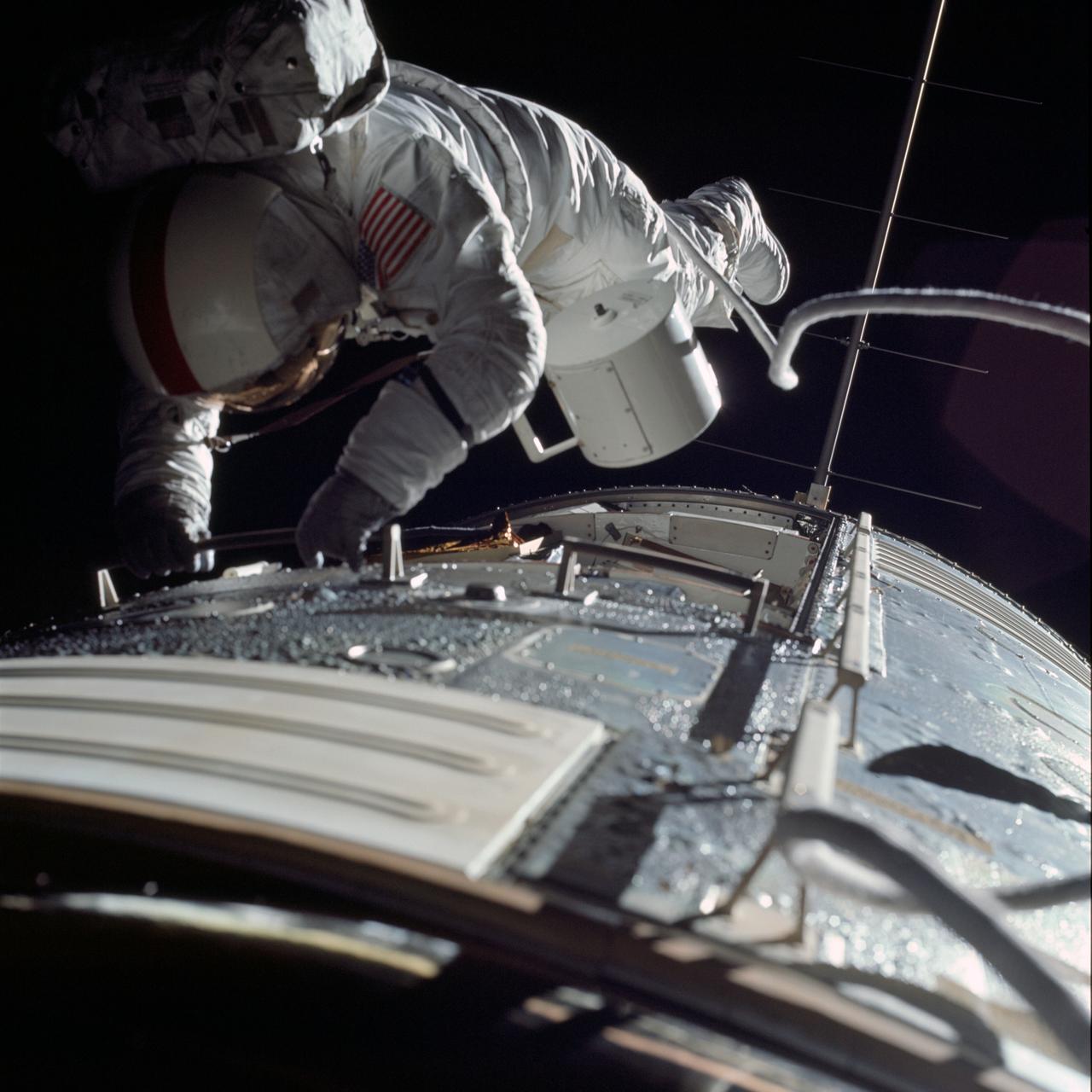

AS17-152-23391 (17 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Ronald E. Evans is photographed performing extravehicular activity during the Apollo 17 spacecraft's trans-Earth coast. During his EVA, Evans, command module pilot, retrieved film cassettes from the lunar sounder, mapping camera and panoramic camera. The cylindrical object at Evans' left side is the mapping camera cassette. The total time for the trans-Earth EVA was one hour, seven minutes, 18 seconds, starting at ground elapsed time of 257:25 (2:28 p.m.) and ending at G.E.T. of 258:42 (3:35 p.m.) on Sunday, Dec. 17, 1972.
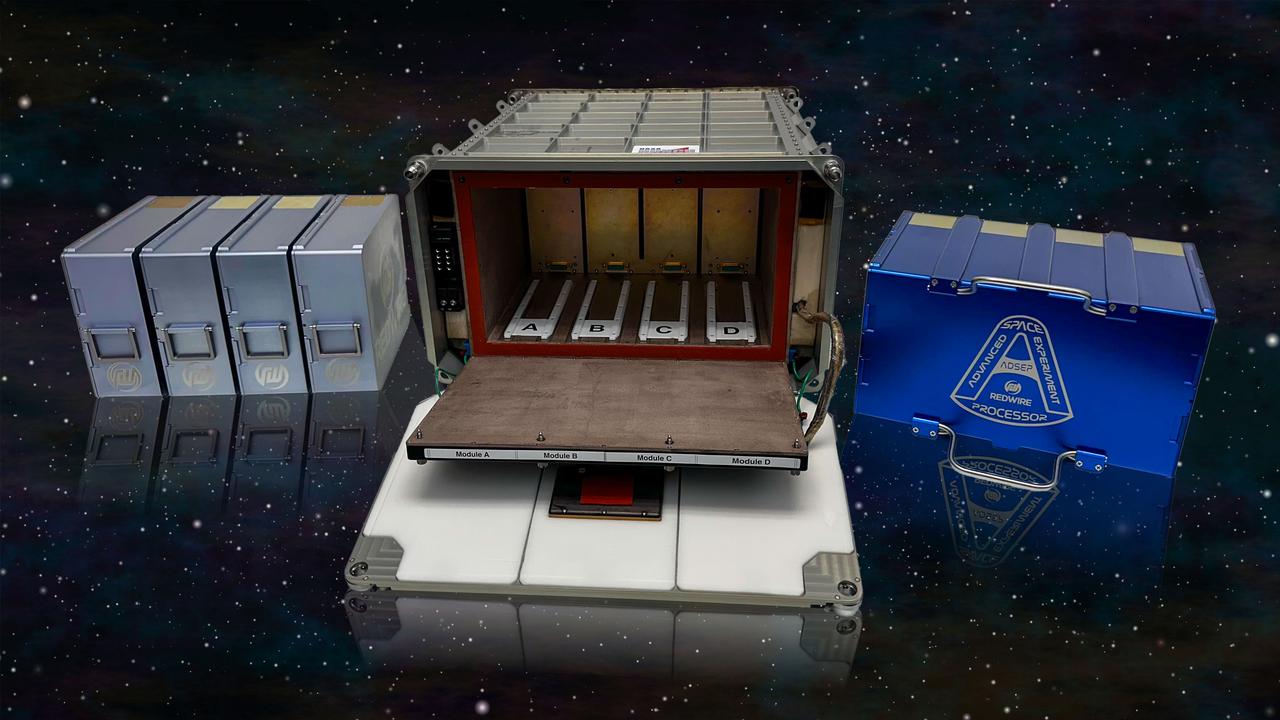

jsc2025e036385 (4/4/2025) --- A lineup of Redwire hardware. Left: Redwire’s in-space pharmaceutical manufacturing system (PIL-BOX) system are chambers that allow crystal growth in small batches. Middle: The Redwire Advanced Space Experiment Processor (ADSEP) in an open configuration onto which either the PIL-BOX or ICC can be installed. Right: The Redwire Industrial Crystallization Cassette (ICC), a facility capable of larger quantities of crystal growth than the PIL-BOX. The ADSEP Industrial Crystallization Cassette Technology Demonstration (ADSEP-ICC) investigation validates the ICC’s capability to grow large quantities of crystals in its high-volume crystal growth chambers aboard the International Space Station. Image courtesy of Redwire.
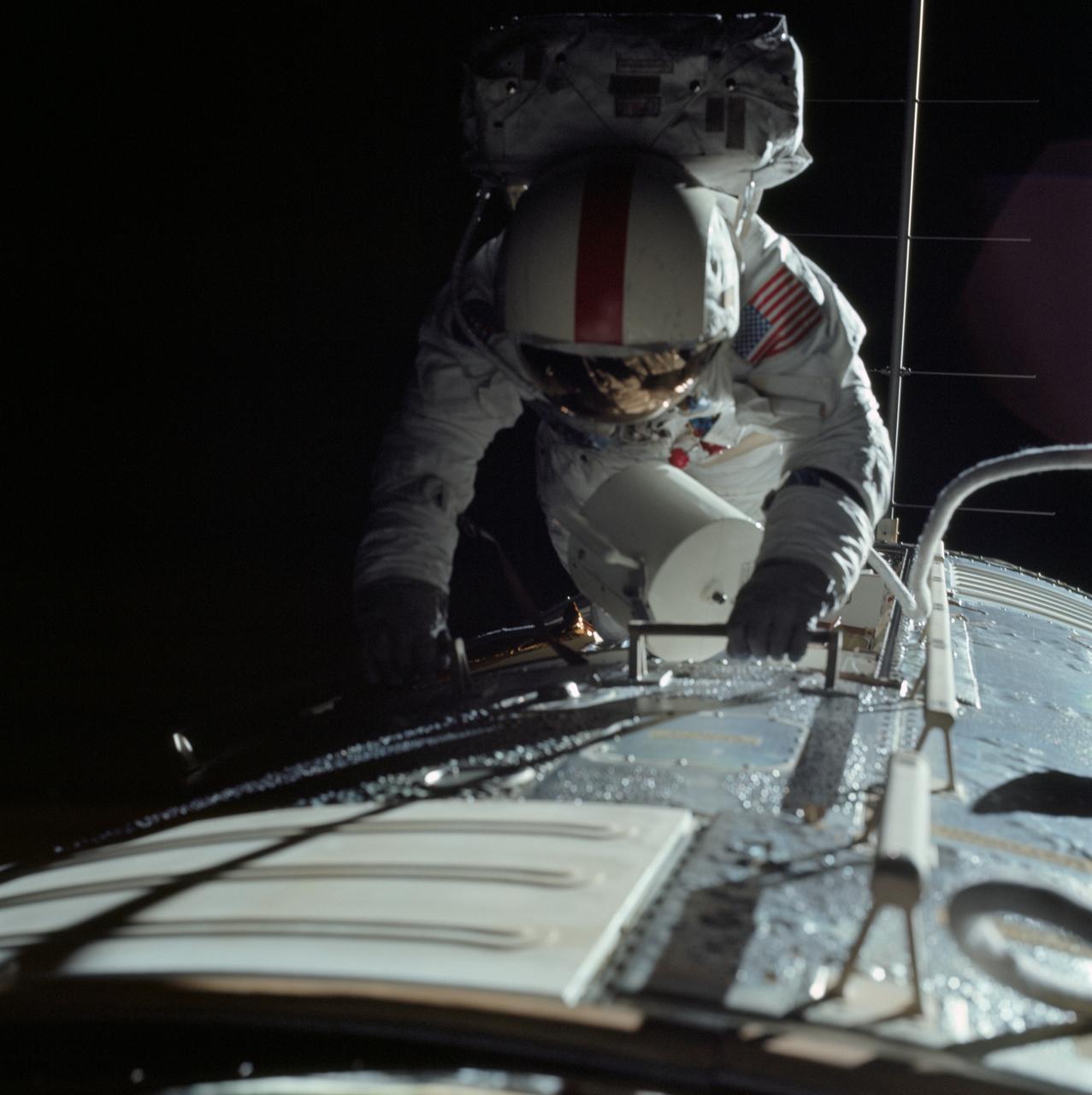

AS17-152-23392 (17 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Ronald E. Evans is photographed performing extravehicular activity during the Apollo 17 spacecraft's trans-Earth coast. During his EVA, command module pilot Evans retrieved film cassettes from the Lunar Sounder, Mapping Camera, and Panoramic Camera. The cylindrical object at Evans' left side is the Mapping Camera cassette. The total time for the trans-Earth EVA was one hour seven minutes 18 seconds, starting at ground elapsed time of 257:25 (2:28 p.m.) and ending at ground elapsed timed of 258:42 (3:35 p.m.) on Sunday, Dec. 17, 1972.
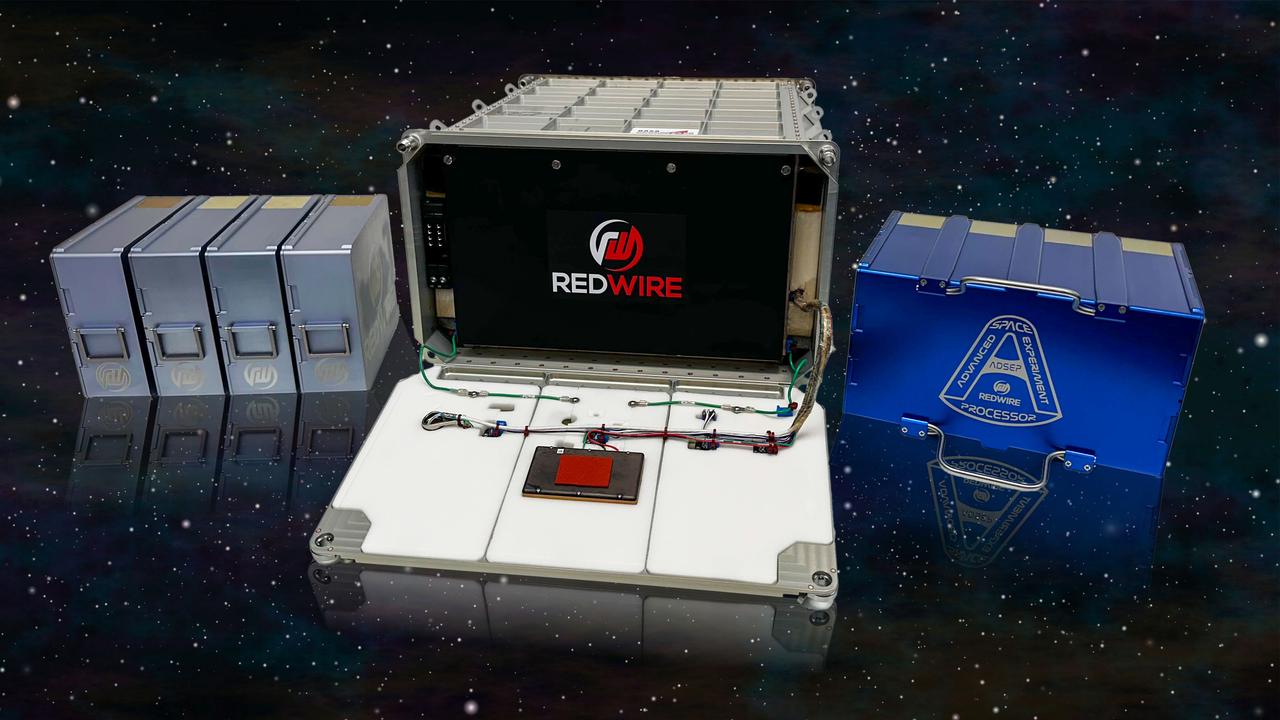

jsc2025e036384 (4/4/2025) --- A lineup of Redwire hardware. Left: Redwire’s in-space pharmaceutical manufacturing system (PIL-BOX) system are chambers that allow crystal growth in small batches. Middle: The Redwire Advanced Space Experiment Processor (ADSEP) in a close configuration onto which either the PIL-BOX or ICC can be installed. Right: The Redwire Industrial Crystallization Cassette (ICC), a facility capable of larger quantities of crystal growth than the PIL-BOX. The ADSEP Industrial Crystallization Cassette Technology Demonstration (ADSEP-ICC) investigation validates the ICC’s capability to grow large quantities of crystals in its high-volume crystal growth chambers aboard the International Space Station. Image courtesy of Redwire.
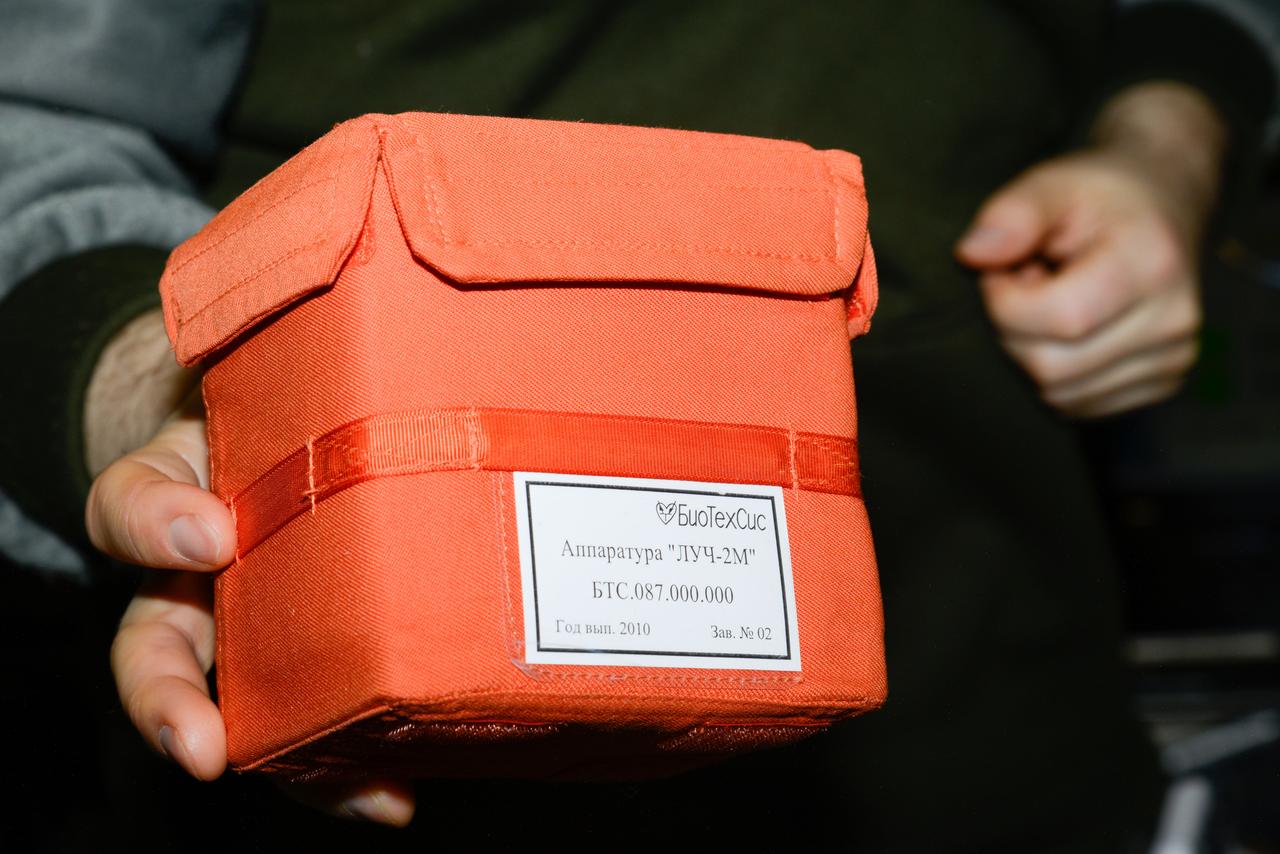

iss047e154711 (6/17/2016) --- Photographic documentation of Luch-2M Multipurpose Crystallization Cassette (УБК) within orange case. Struktura is a study of protein crystallization processes and growth of single crystals which are suitable for X-ray structural analysis and structural decoding.
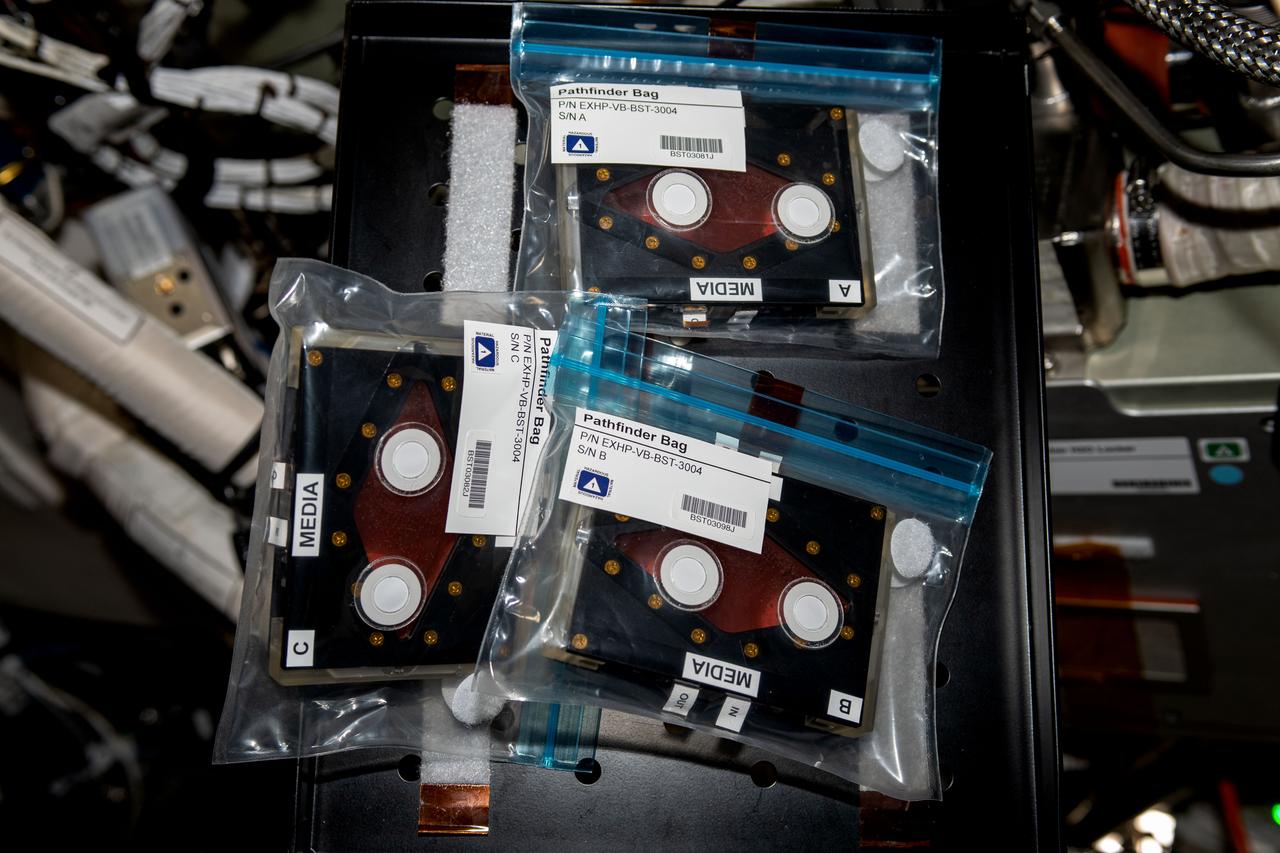

iss069e054973 (8/8/2023) --- A view of the StemCellEX-H Pathfinder sample cassettes aboard the International space Station (ISS). Hematopoietic Stem Cell Expansion in Space: Pathfinder Investigation (StemCellEX-H Pathfinder) tests methods for producing human hematopoietic stem cells in space.
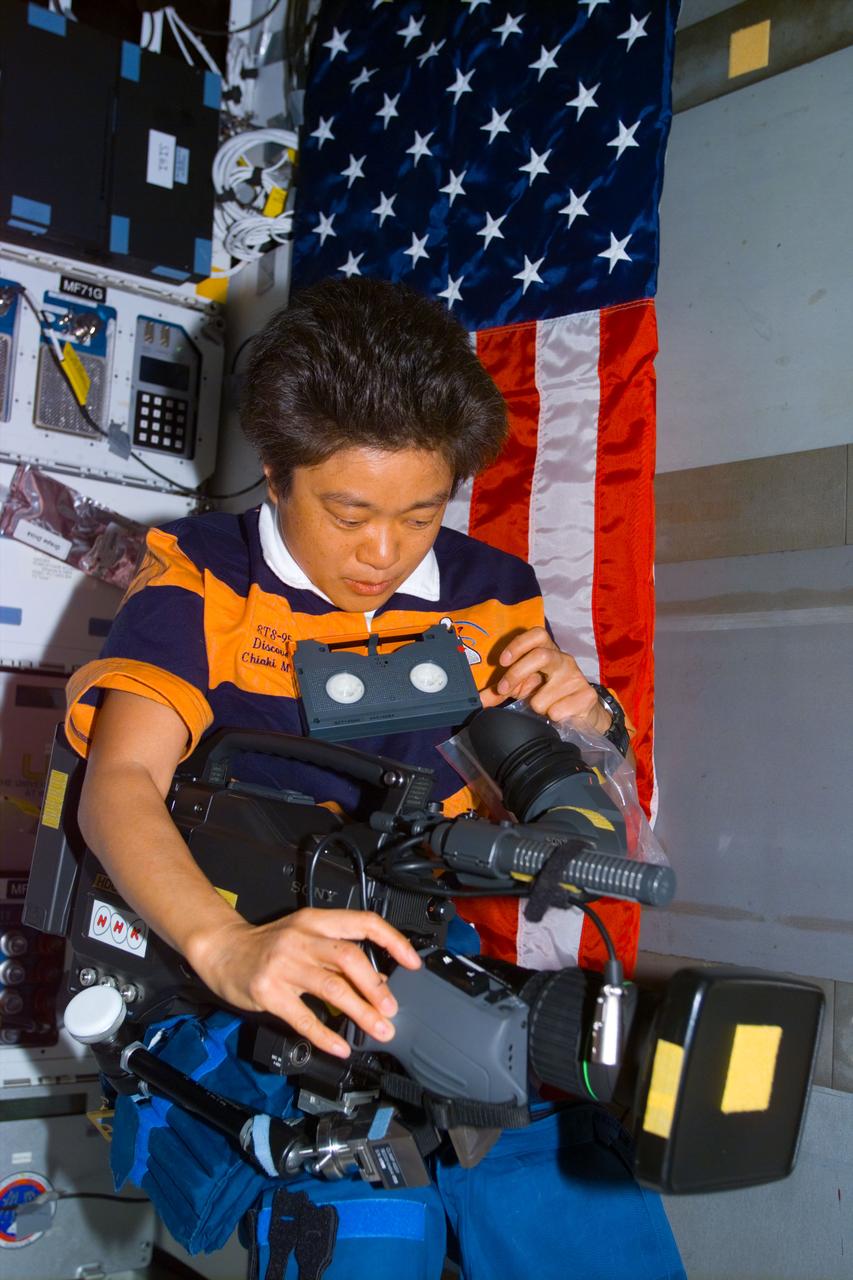

STS095-E-5229 (4 Nov. 1998)--- STS-95 payload specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA), changes out cassette on camera. The scene was recorded with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 03:09:07 GMT, Nov. 4.
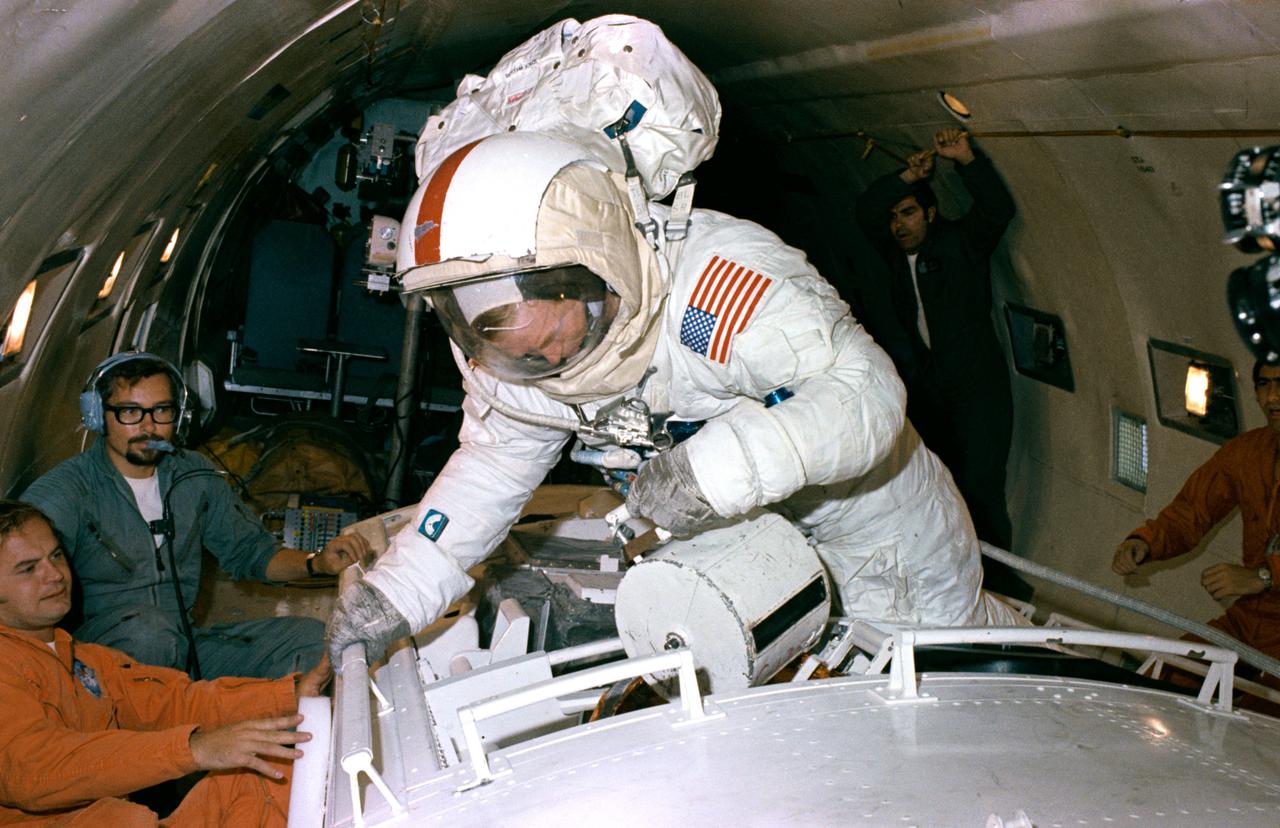

S72-50271 (September 1972) --- Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, backup crew command module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission, participates in extravehicular activity simulation training under zero-gravity conditions aboard a U. S. Air Force KC-135 aircraft. A mock-up of the Scientific Instrument Module (SIM) bay of the Apollo 17 Service Module is used in the exercise. Here, Roosa simulates retrieving the film cassette of the Mapping Camera from the SIM bay. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, Apollo 17 prime crew command module pilot, is scheduled to receive film cassettes from the Mapping Camera, Panoramic Camera, and Lunar Sounder during Apollo 17 trans-Earth extravehicular activity.
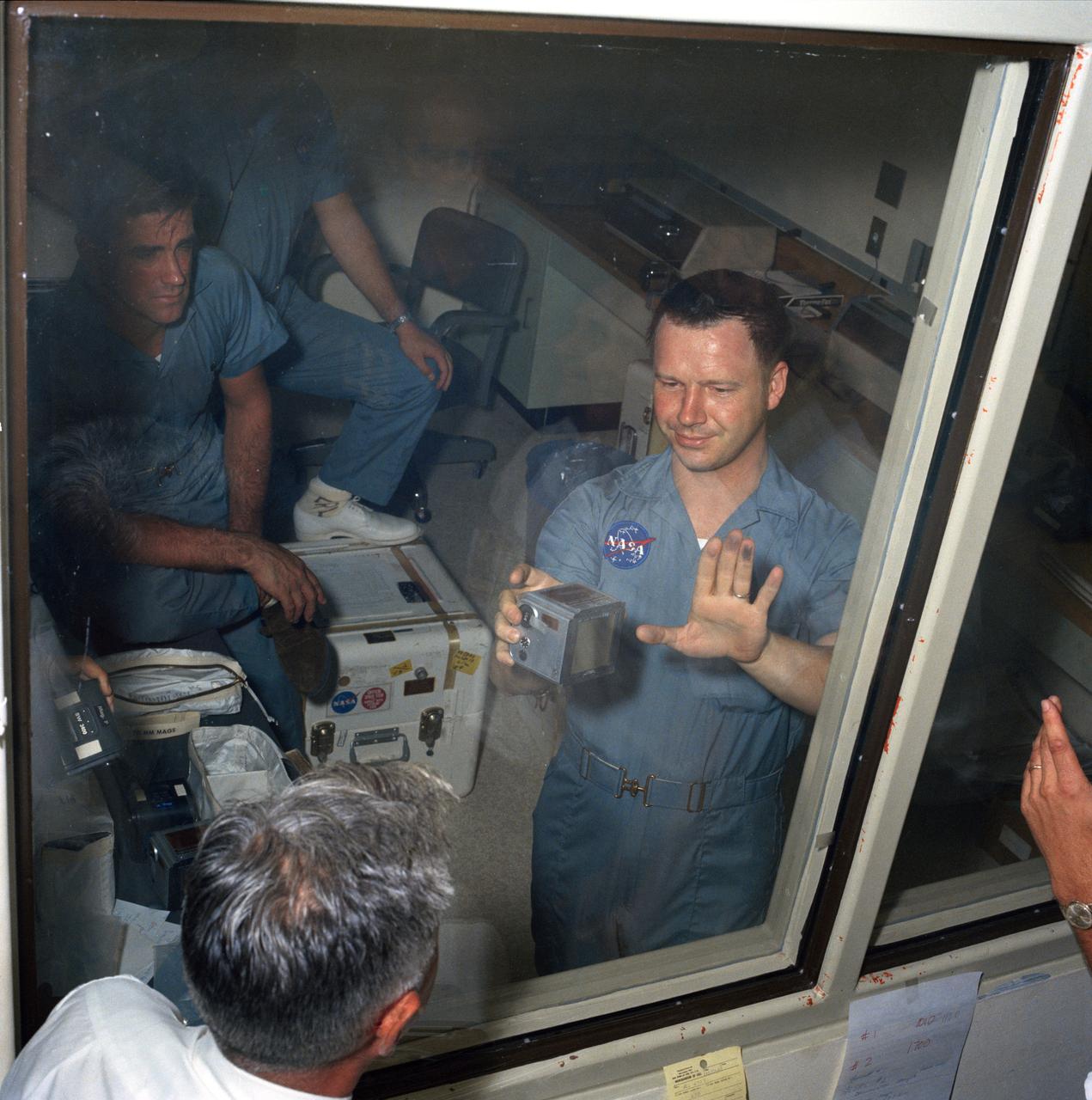

The first direct exposure to Lunar material for Crew Reception Personnel probably happened late Friday, 07/25/1969. Terry Slezak (displaying Moon dust on his left hand fingers), MSC photographic technician, was removing film magazines from the first of two (2) containers when the incident occurred. As he removed the plastic seal from Magazine "S", one of the 70mm magazines taken during Apollo XI Extravehicular Activity (EVA), it was apparent that the exterior of the cassette displayed traces of a black powdery substance. Apollo XI Commander Neil Armstrong reported during the mission that he had retrieved a 70mm cassette which had dropped to the Lunar surface. Seen in the backgound is John H. Boynton. ( S69-40054 ) MSC, Houston, TX
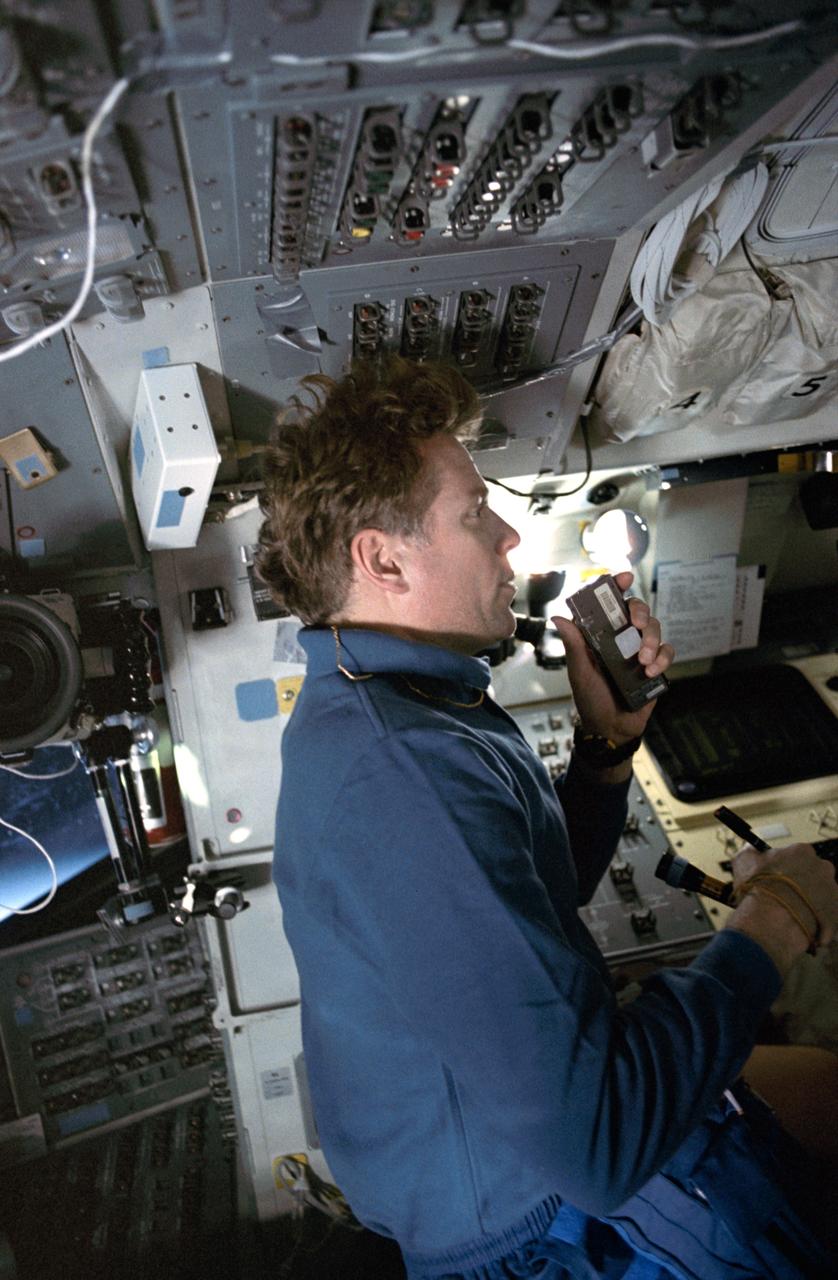

STS045-20-018 (2 April 1992) --- STS-45 Payload Specialist Byron K. Lichtenberg talks into a cassette tape recorder to note observations following a science run of the Atmospheric Emissions Photometric Imaging (AEPI) experiment. Lichtenberg is on the aft flight deck of Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104. At Lichtenberg's left is the mission station, the forward flight deck and window W6 appear behind him, and overhead control panels appear above his head.
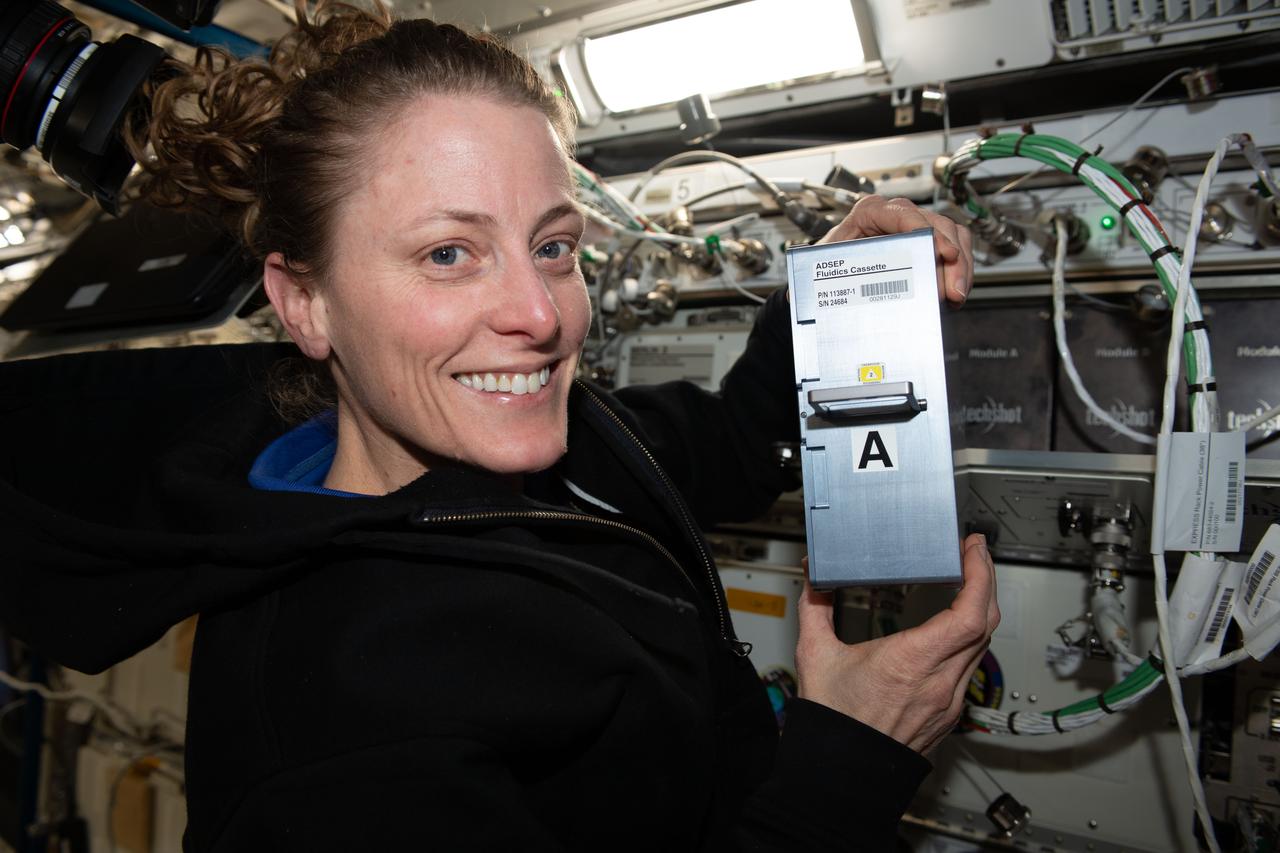

iss070e037585 (Dec. 11, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flught Engineer Loral O'Hara shows off research hardware supporting the UMAMI, or Understanding of Microgravity on Animal-Microbe Interaction, space biology experiment. O'Hara is holdng the Avanced Space Experiment Processor (ADSEP) Fluid Processing Cassette (FPC) that supports the observation of the effects of spaceflight on the molecular and chemical interactions between beneficial microbes and their animal hosts.
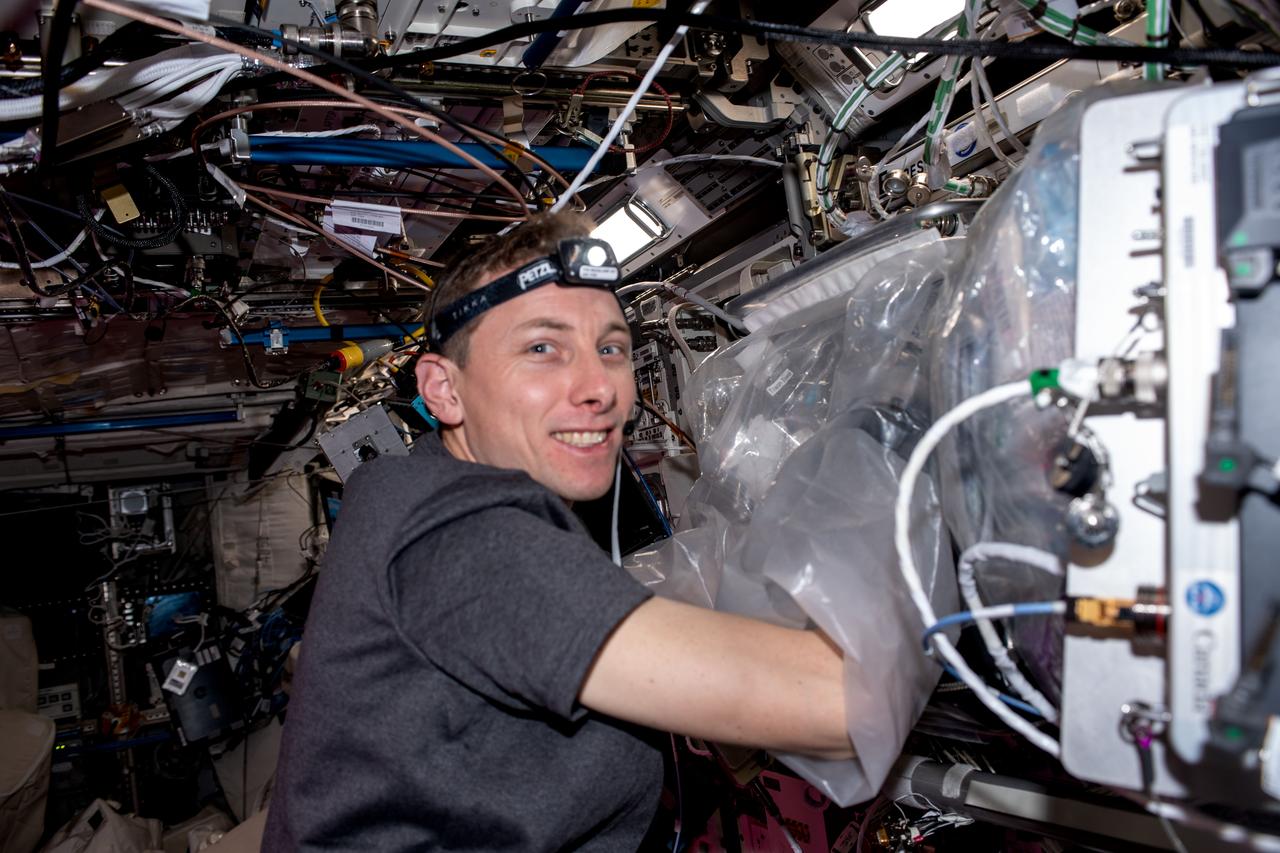

iss068e076275 (March 24, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Woody Hoburg works in a glove bag attached to the BioFabrication Facility (BFF). Hoburg installed a tissue cassette in the BFF to evaluate using bio-inks and cells for a study exploring printing knee cartilage tissue to treat injuries in space and in remote environments on Earth.
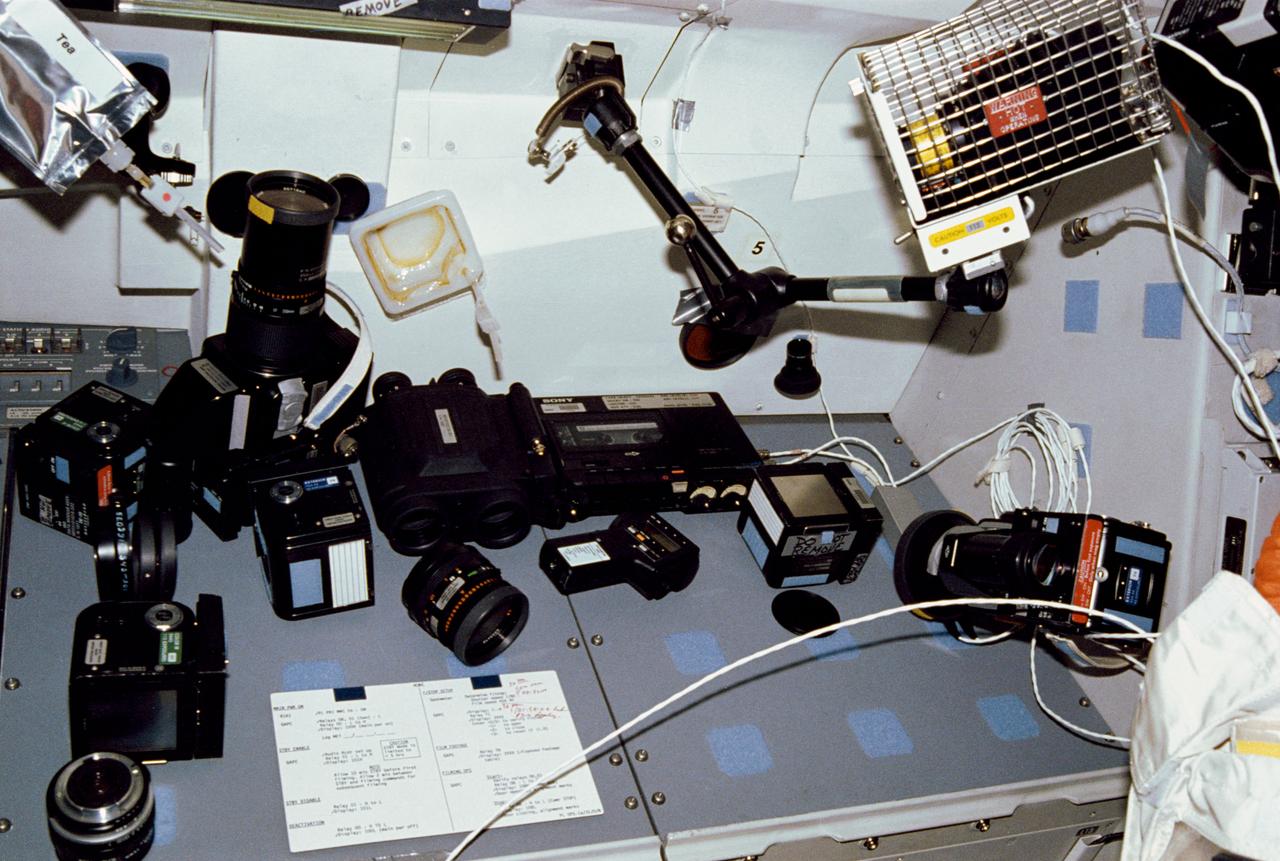

This array of photographic equipment, displayed on the aft flight deck payload station, represents just a part of the imaging and recording hardware which was carried aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, for STS-31's five day mission. Lenses, film magazines, cassettes, recorders, camera chassis, a pair of binoculars, spot meter, tape recorder, and a bracket-mounted light fixture are included among the array.
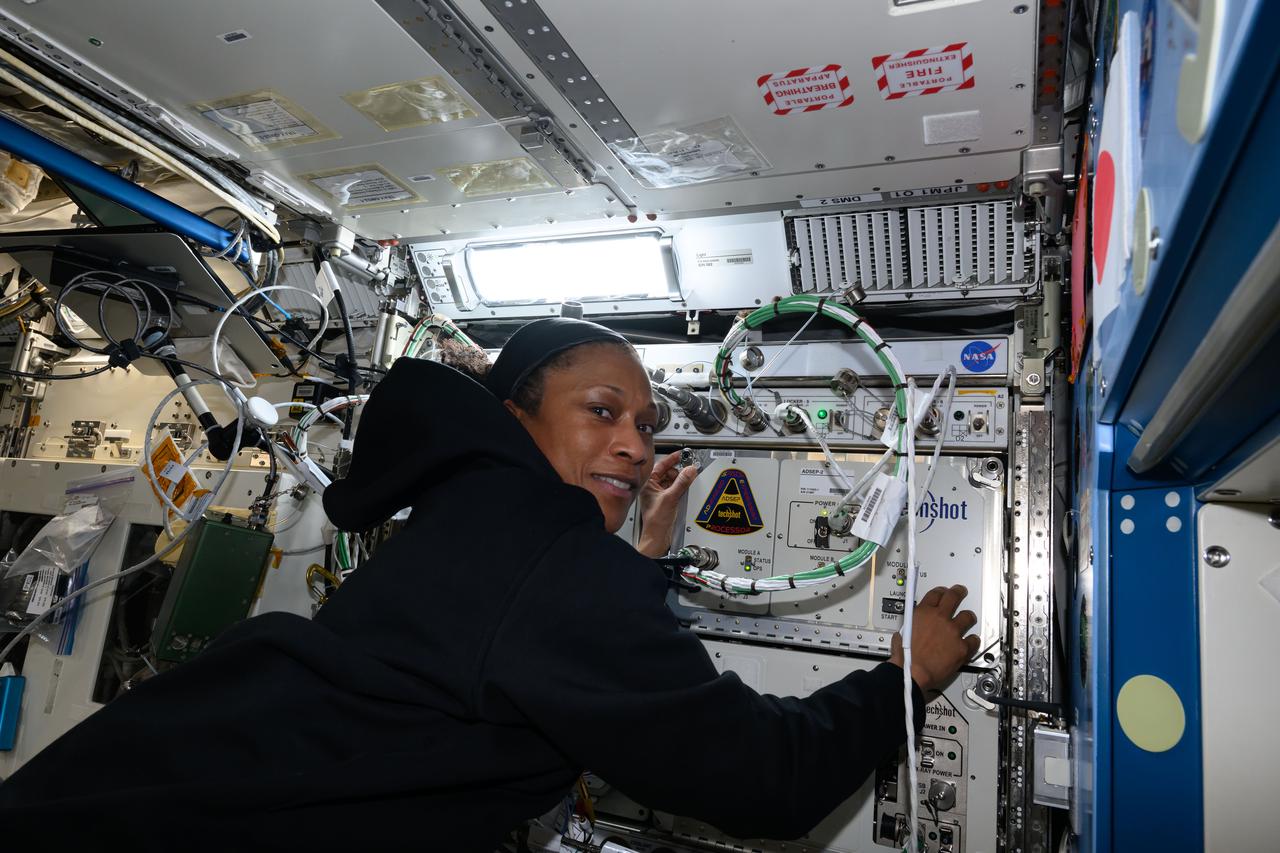

iss070e129706 (March 25, 2024) --- Expedition 70 Flight Engineer and NASA astronaut Jeanette Epps installs the Advanced Space Experiment Processor-2, or ADSEP-2. The scientific device can interface with the Dragon and Cygnus cargo craft and houses cassettes that process samples for biology and physics research including cell and tissue culturing, protein crystal growth, microorganism and bacteria studies, and materials science research.

iss073e0025371 (5/7/2025) --- NASA astronaut Nichole Ayers prepares to swap sample cassettes inside the Advanced Space Experiment Processor-4 (ADSEP-4). The research device enables the automated processing of samples in microgravity, is configurable for space biology and space physics investigations, and can be launched to the International Space Station and returned to Earth inside the SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft for further processing and analysis.
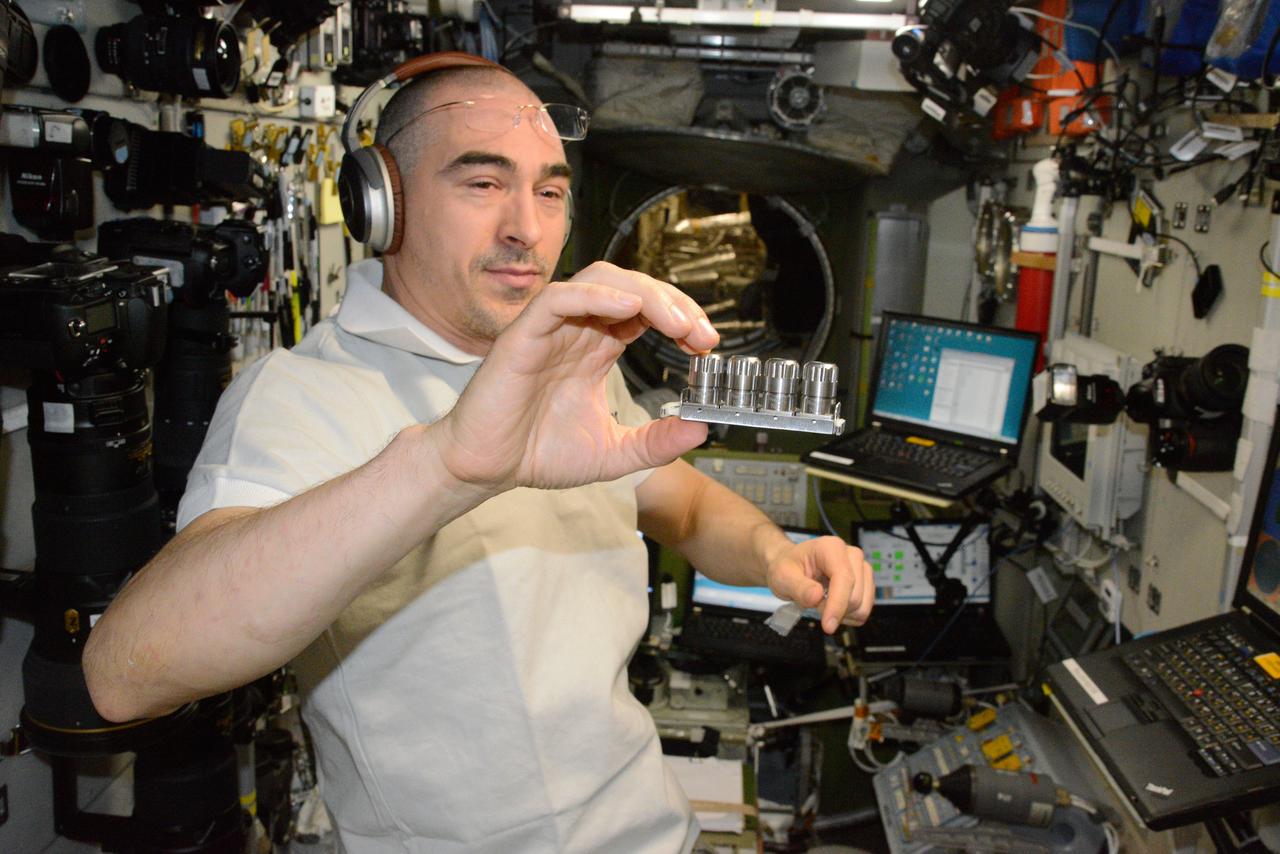

iss048e038163 (7/17/2016) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut Anatoly Ivanishin displays Luch-2M Multipurpose Crystallization Cassette (УБК) No. 3 during Struktura-Luch-2M (Structure-Beam-2M) experiment hardware activation and deployment. Image was taken in the Zvezda Service Module (SM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Struktura is a study of protein crystallization processes and growth of single crystals which are suitable for X-ray structural analysis and structural decoding.
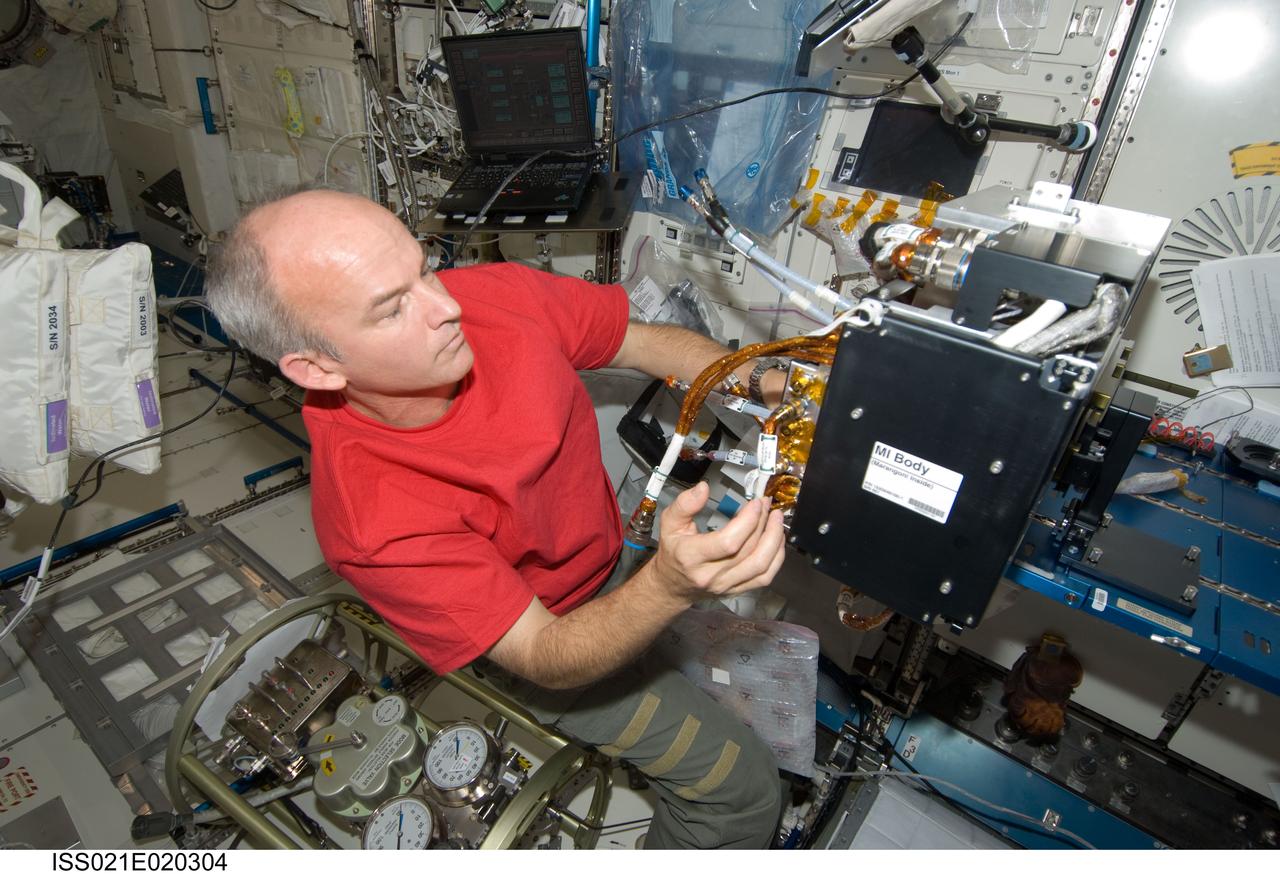

ISS021-E-020304 (5 Nov. 2009) --- NASA astronaut Jeffrey Williams, Expedition 21 flight engineer, works with Fluid Physics Experiment Facility/Marangoni Surface (FPEF MS) Core hardware in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. Williams first inserted the Marangoni Inside (MI) cassette in the MI Core for a leak check, and then installed the MI Core into the FPEF MI Body. The Marangoni convection experiment in the FPEF examines fluid tension flow in micro-G.
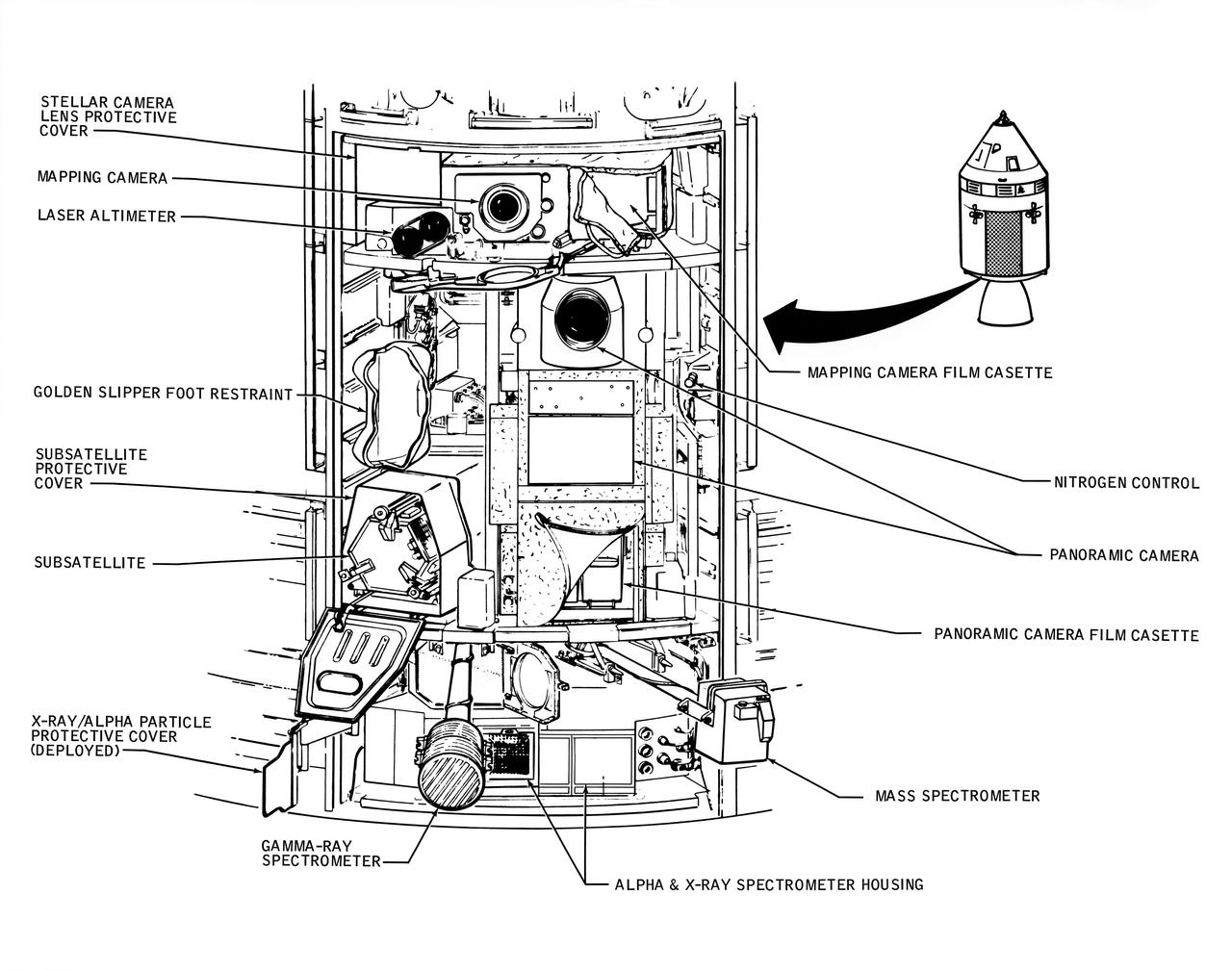
A line drawing illustrating the layout of the Scietific Instrument Module (SIM) of the Apollo 16 Service Module. Shown here is the location in the SIM bay of the equipment for each orbital experiment. Arrows point to various components of the SIM bay. The sensors for the gamma ray spectrometer and the mas spectrometer both extend outward on a boom about 25 feet when the instruments are in use. The subsatellite is launched while the Service Module is in orbit around the moon. The film cassettes must be retrieved prior to Command Module/Service Module separation.
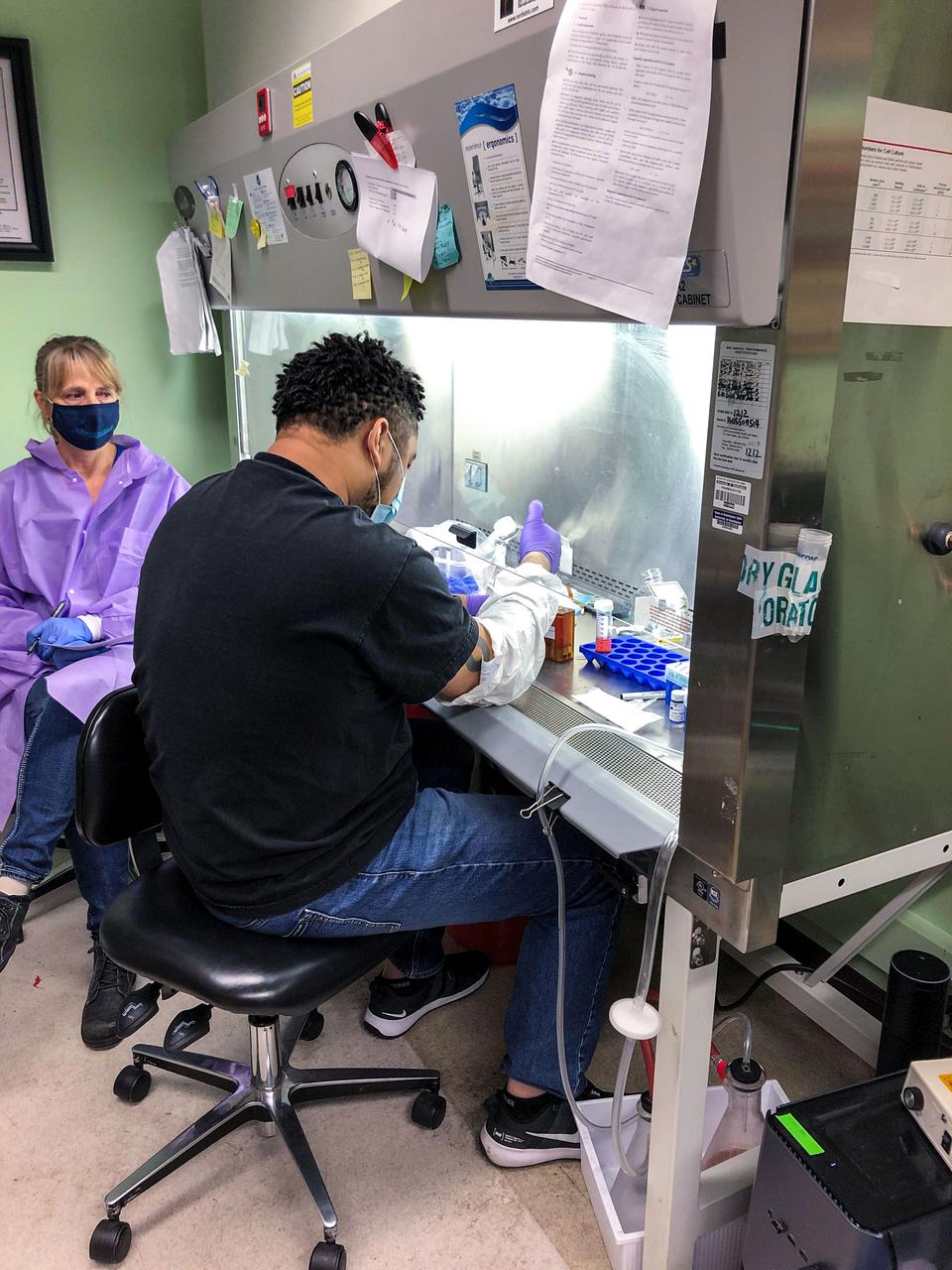

jsc2021e019395 (5/19/2021) --- Stefanie Countryman (Director, Bioserve), and Kendan Jones (UW) prepare media cassettes during system testing. Effects of Microgravity on the Structure and Function of Proximal and Distal Tubule MPS (Kidney Cells-02) uses a 3D kidney cell model or chip to study the effects of microgravity on formation of microcrystals in kidney tubules. Image courtesy of Cathy Yeung (UW School of Pharmacy).
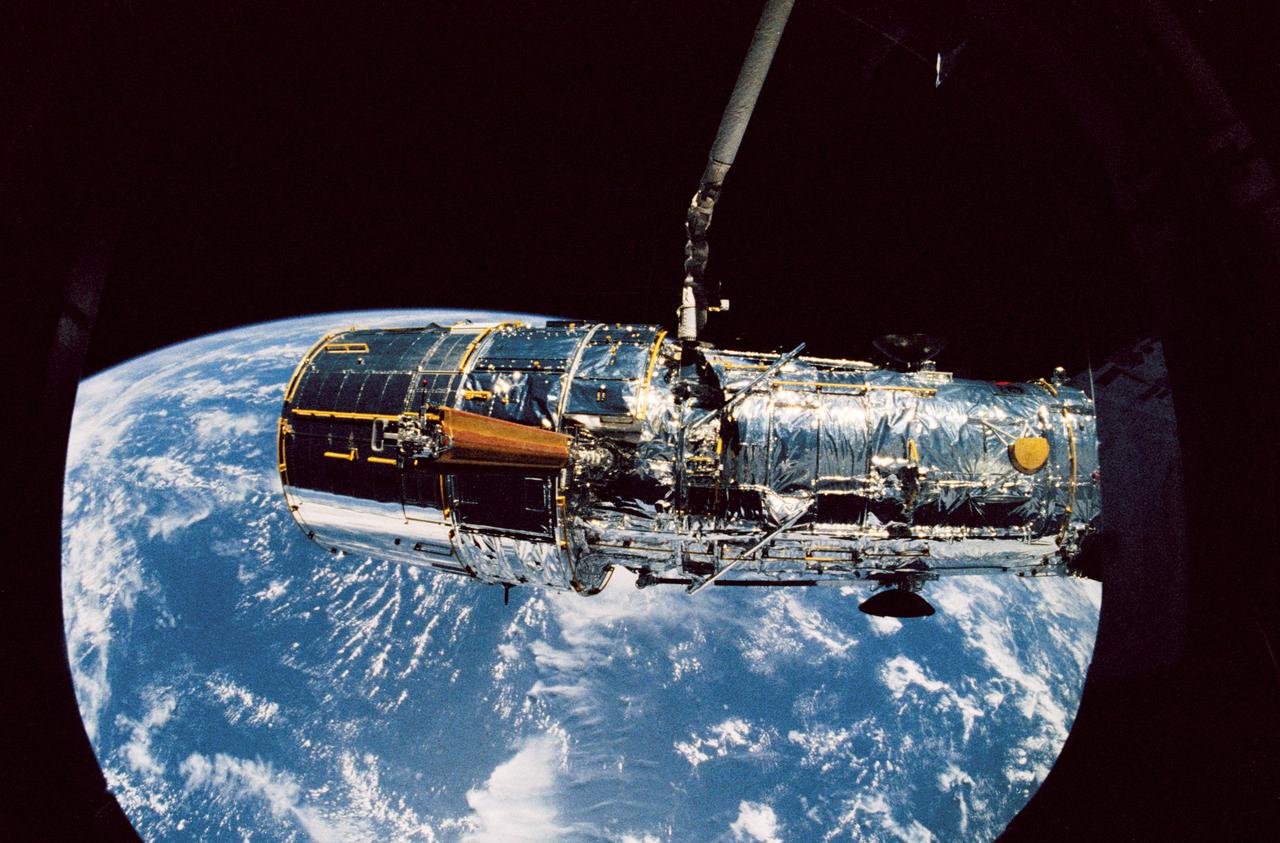

Held in appendage deploy position by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS), the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) starboard solar array (SA) bistem cassette is released from its stowed position on the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. The spreader bar & bistem begin to unfurl the SA wing. View was taken by an STS-31 crewmember through an overhead window & is backdropped against the surface of the Earth.
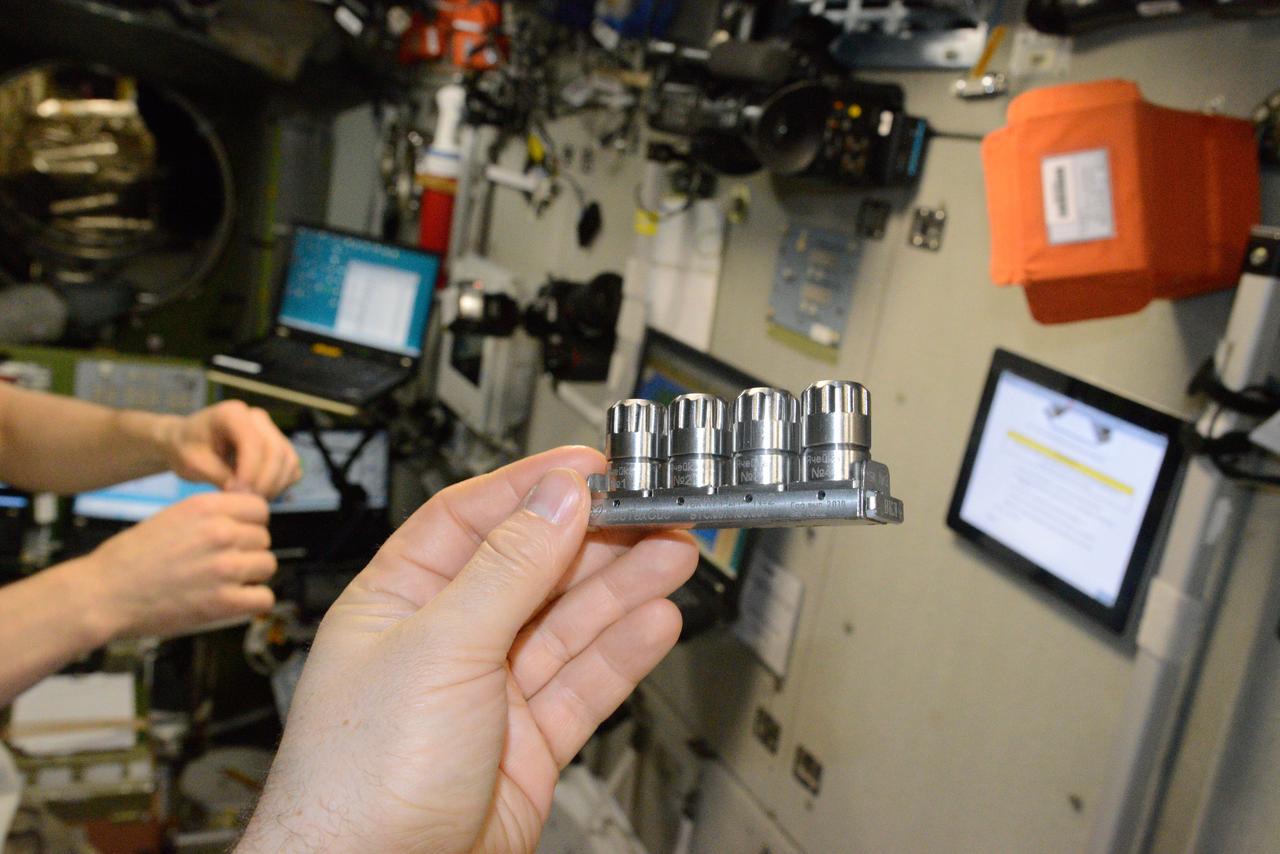
iss048e038162 (7/19/2016) --- The hand of a crewmember displays Luch-2M Multipurpose Crystallization Cassette (УБК) No. 2 during Struktura-Luch-2M (Structure-Beam-2M) experiment hardware activation and deployment. Image was taken in the Zvezda Service Module (SM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Struktura is a study of protein crystallization processes and growth of single crystals which are suitable for X-ray structural analysis and structural decoding.

iss072e217998 (Nov. 18, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Butch Wilmore swaps sample cassettes inside the Advanced Space Experiment Processor-4 (ADSEP-4) located aboard the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. The ADSEP-4 is a portable research facility that supports multiple types of science experiments on the orbital outpost and also interfaces with the SpaceX Dragon and Northrop Grumman Cygnus cargo spacecraft.
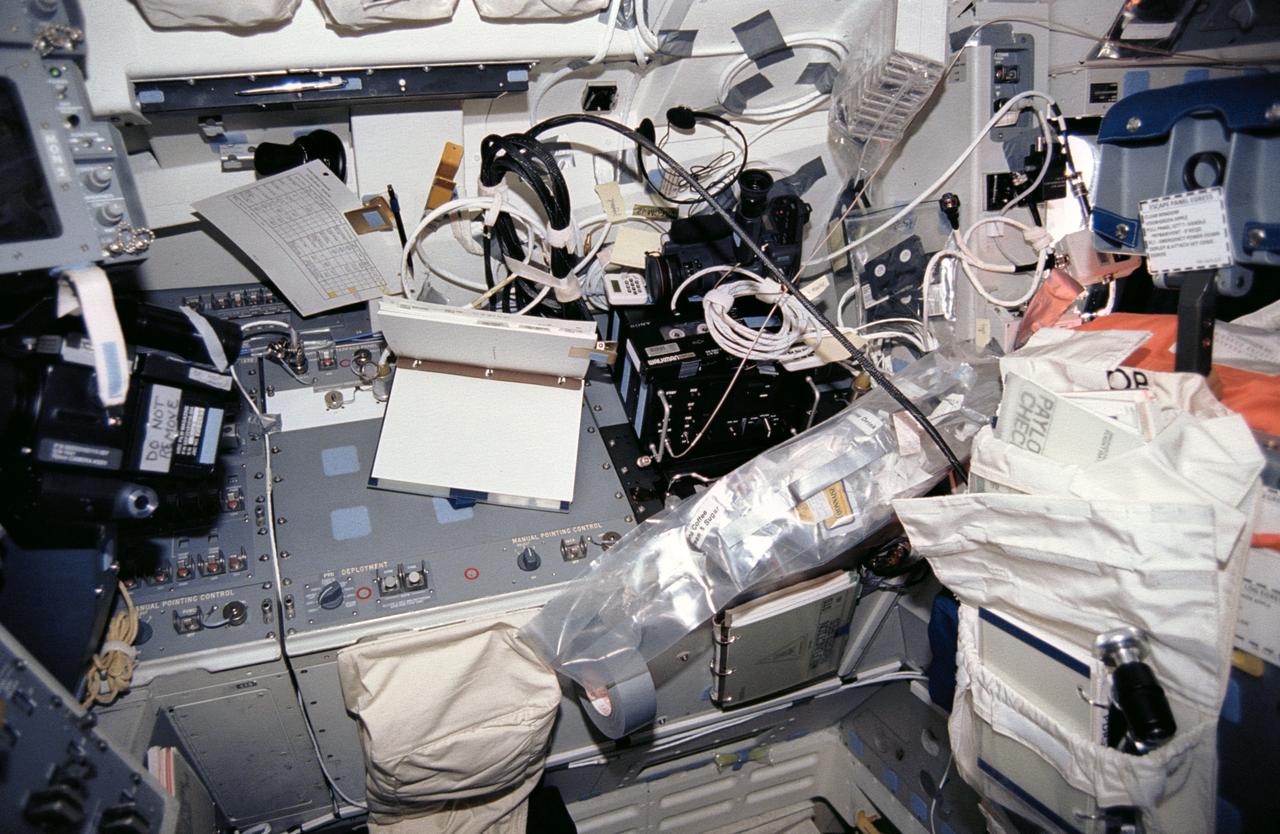

STS046-01-024 (31 July-8 Aug 1992) --- This area on the Space Shuttle Atlantis' flight deck forward port side was referred to as "Marsha's (Ivins) work station" by fellow crew members who good-naturedly kidded the mission specialist and who usually added various descriptive modifiers such as "messy" or "cluttered". Food, cameras, camera gear, cassettes, cable, flight text material and other paraphernalia can be seen in the area, just behind the commander's station.
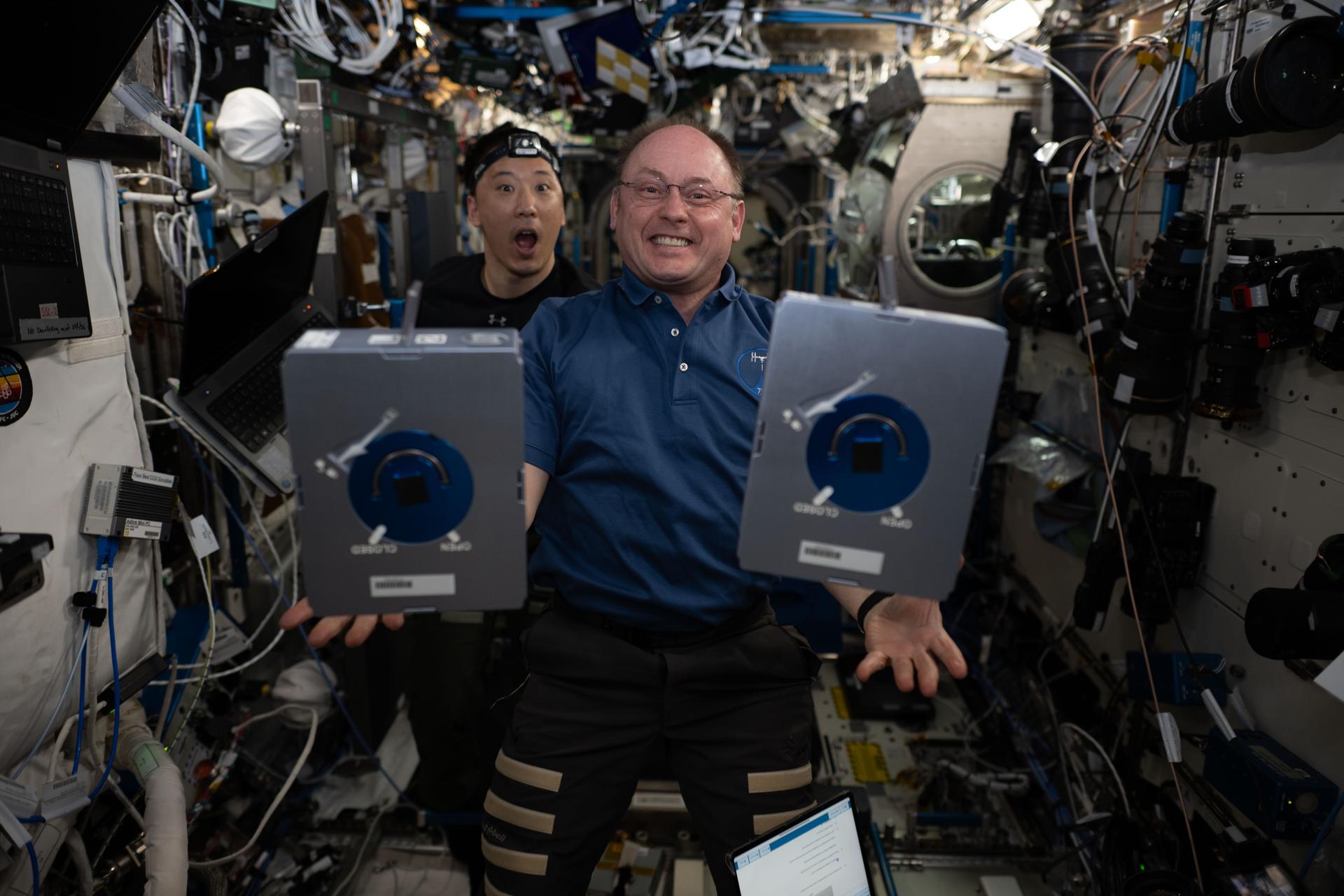

iss073e0886423 (Oct. 17, 2025) --- NASA astronauts (from left) Jonny Kim and Mike Fincke, both Expedition 73 flight engineers, pose for a fun portrait during research and maintenance activities inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. Fincke shows off a pair of research cassettes housing samples for the Pharmaceutical In-space Laboratory experiment that explores growing protein crystals in microgravity. Results may promote the development of new pharmaceuticals and advanced therapies in weightlessness.
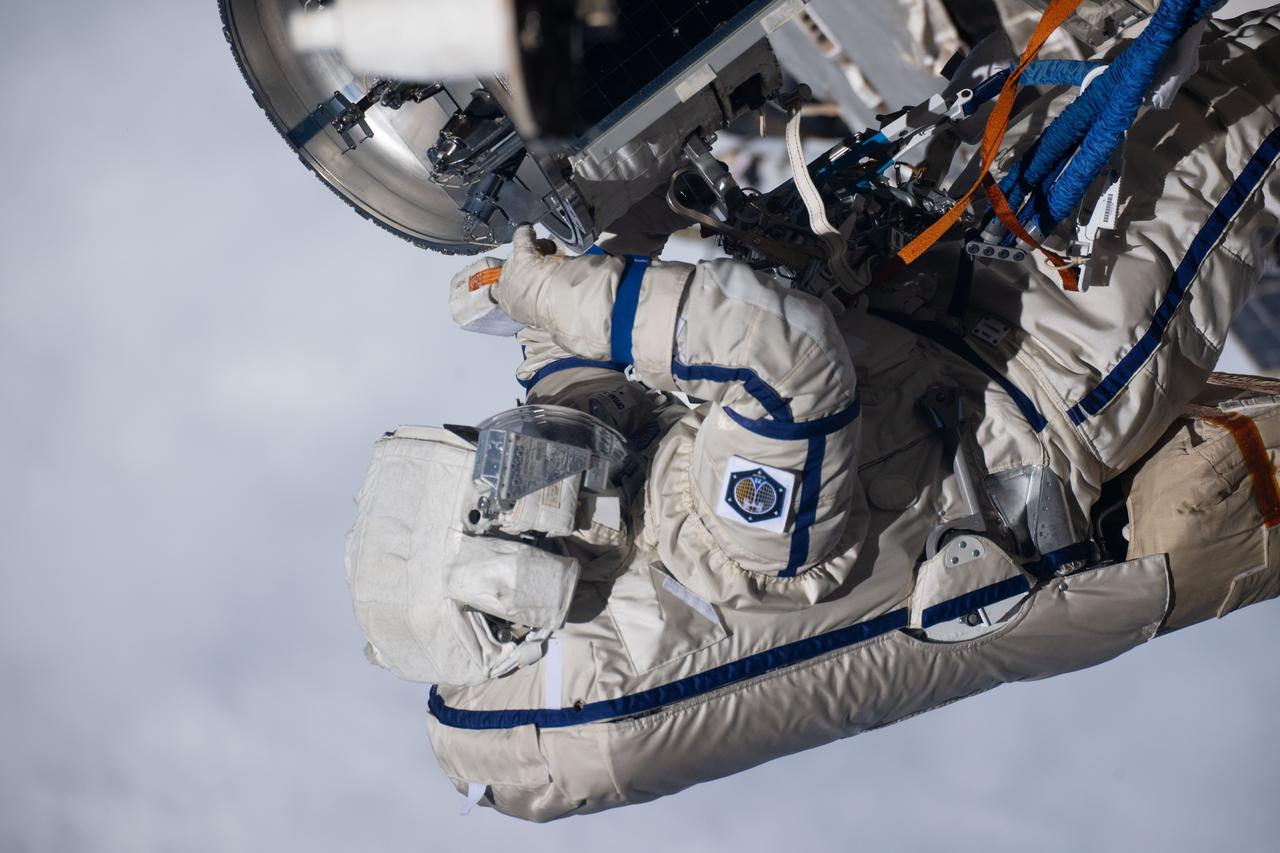

iss073e0988196 (Oct. 28, 2025) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Alexey Zubritsky is pictured in his Orlan spacesuit conducting a spacewalk 269 miles above Earth. During the spacewalk, Zubritsky installed a pulse plasma injector, cleaned a window on the Nauka science module, replaced a materials science cassette on Nauka, and moved a controller interface for the European robotic arm.
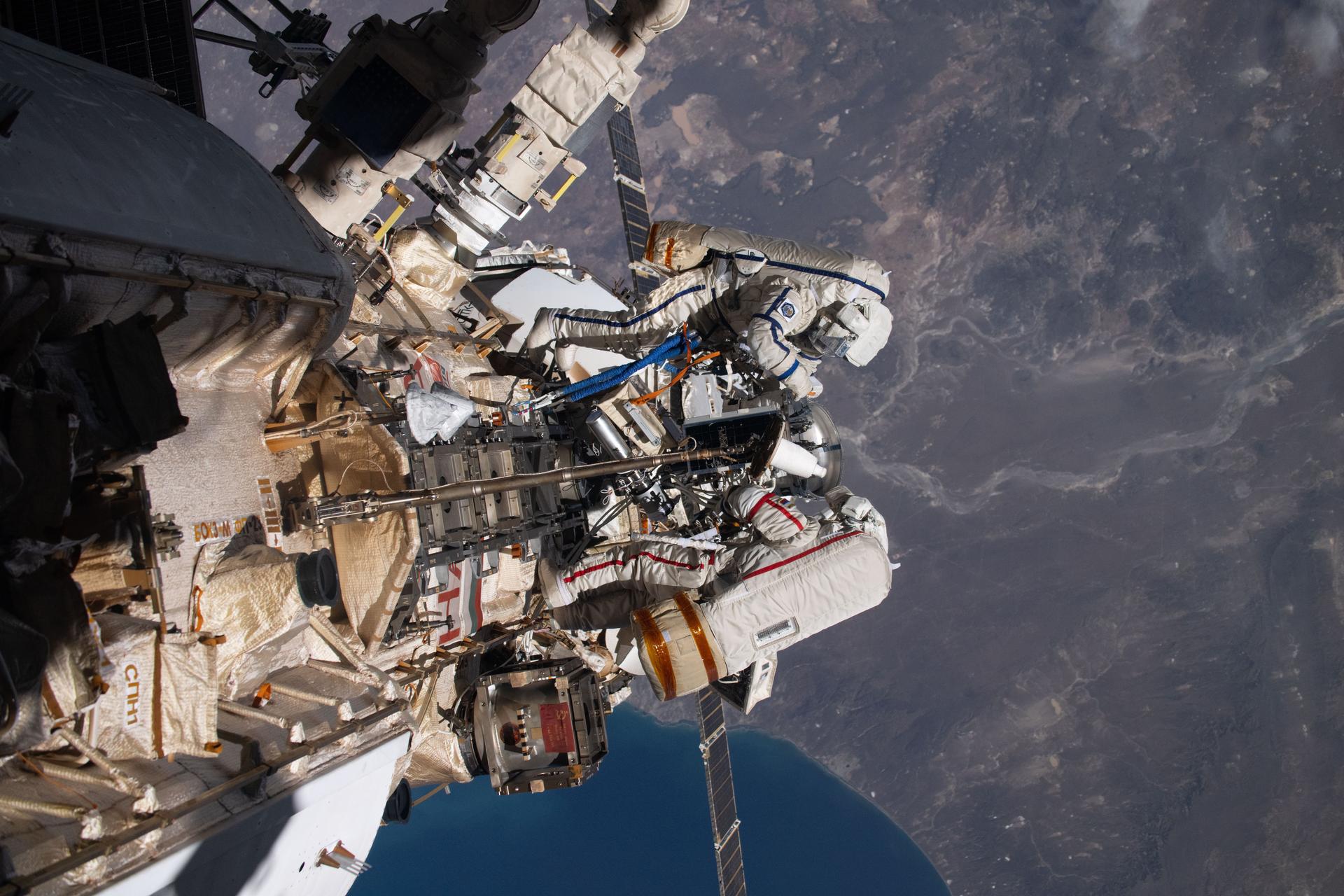

iss073e0988203 (Oct. 28, 2025) --- Roscosmos cosmonauts (top to bottom) Alexey Zubritsky and Sergey Ryzhikov are pictured in their Orlan spacesuits conducting a spacewalk 270 miles above southern Argentina. During the spacewalk, the duo installed a pulse plasma injector, cleaned a window on the Nauka science module, replaced a materials science cassette on Nauka, and moved a controller interface for the European robotic arm.
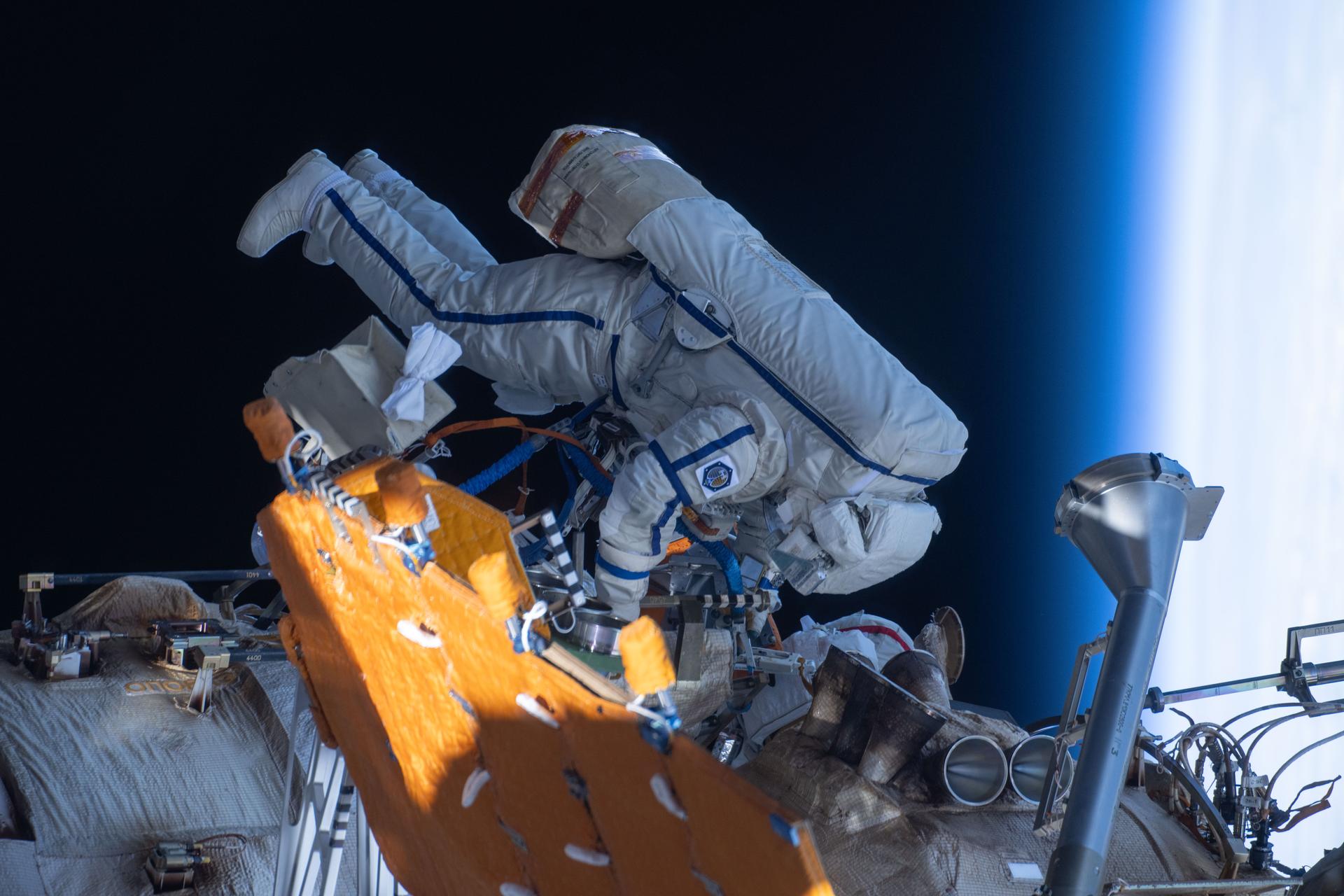

iss073e0988184 (Oct. 28, 2025) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Alexey Zubritsky is pictured in his Orlan spacesuit conducting a spacewalk 262 miles above Earth. During the spacewalk, Zubritsky installed a pulse plasma injector, cleaned a window on the Nauka science module, replaced a materials science cassette on Nauka, and moved a controller interface for the European robotic arm.
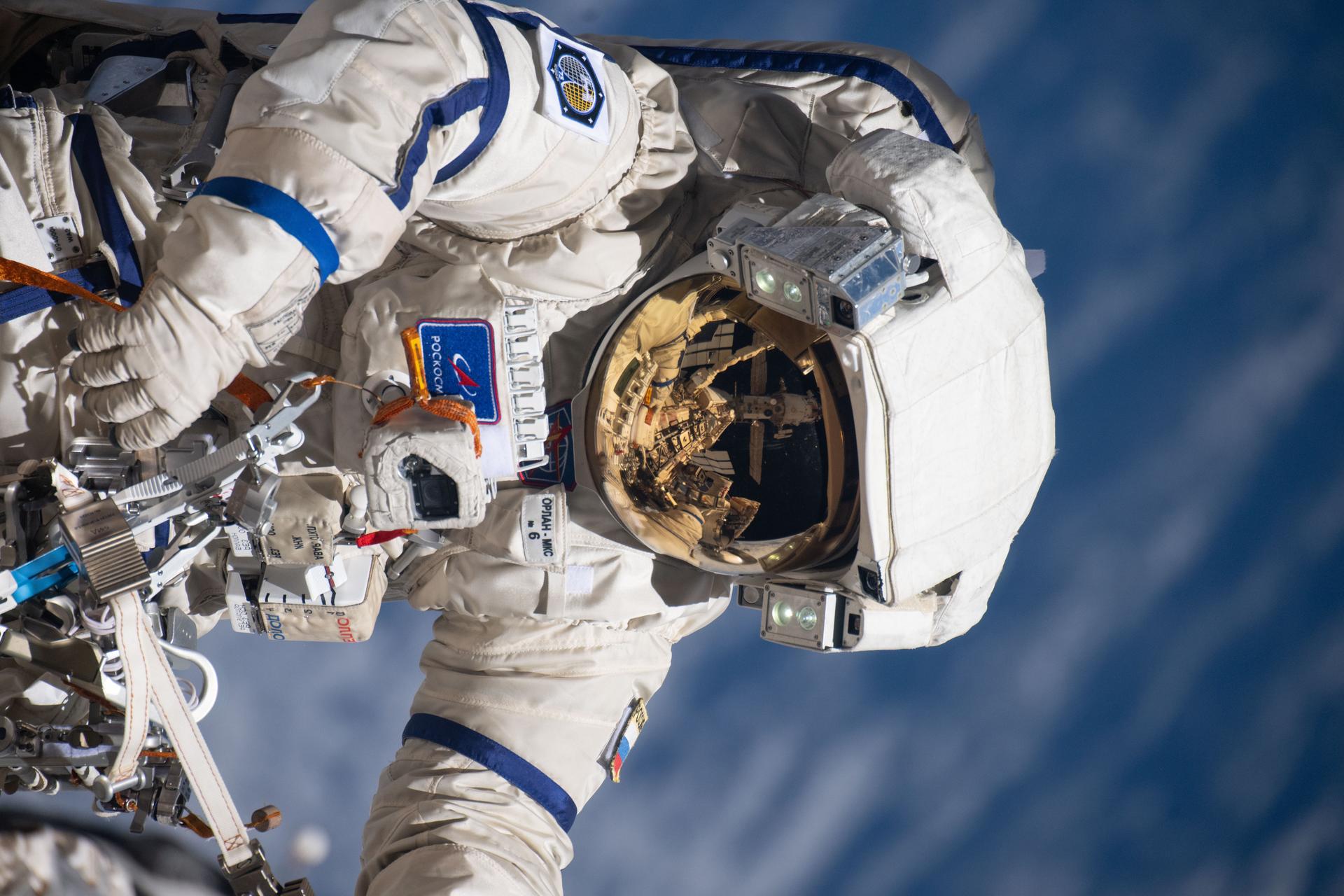

iss073e0988292 (Oct. 28, 2025) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Alexey Zubritsky is pictured in his Orlan spacesuit conducting a spacewalk 271 miles above Earth. During the the spacewalk, Zubritsky installed a pulse plasma injector, cleaned a window on the Nauka science module, replaced a materials science cassette on Nauka, and moved a controller interface for the European robotic arm.
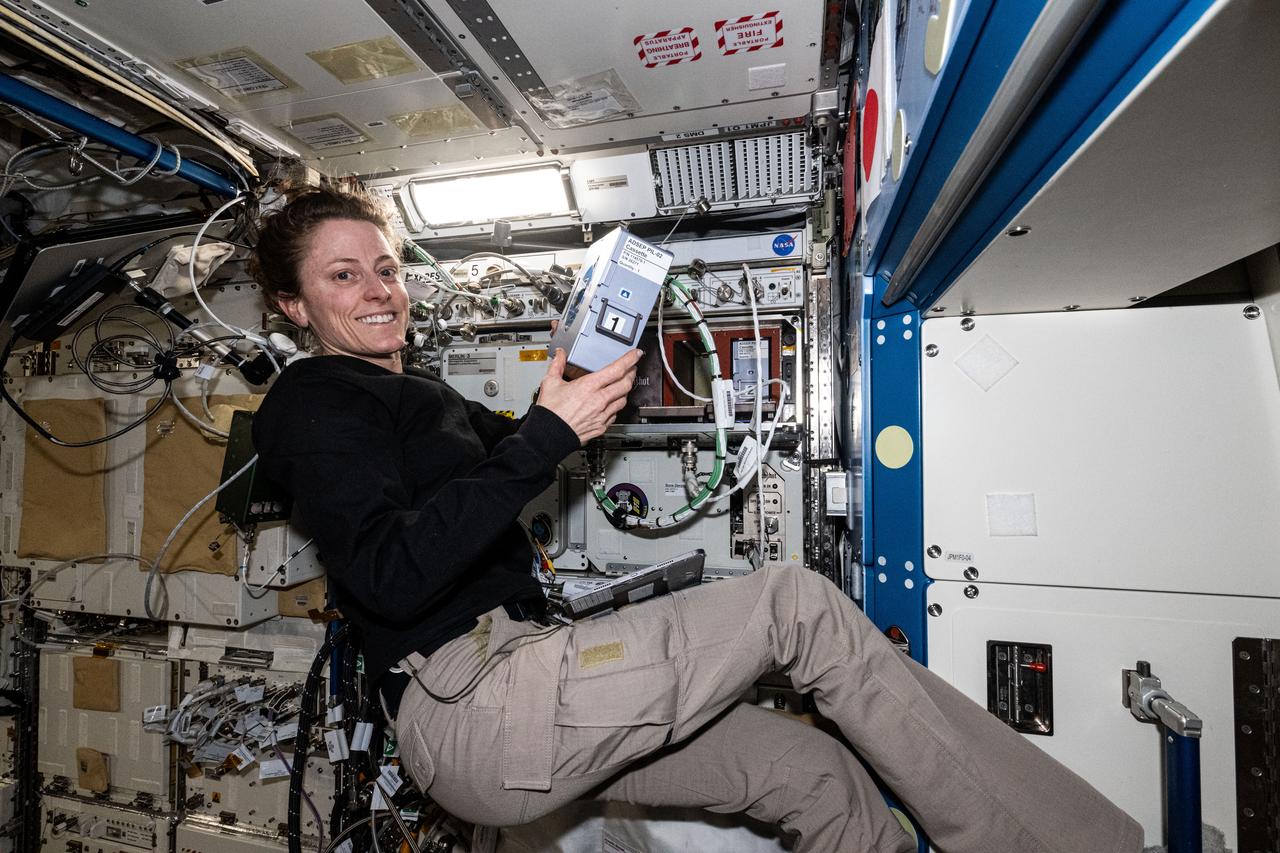

iss070e129524 (March 25, 2024) --- Expedition 70 Flight Engineer and NASA astronaut Loral O'Hara shows off the Advanced Space Experiment Processor-2, or ADSEP-2. The scientific device can interface with the Dragon and Cygnus cargo craft and houses cassettes that process samples for biology and physics research including cell and tissue culturing, protein crystal growth, microorganism and bacteria studies, and materials science research.
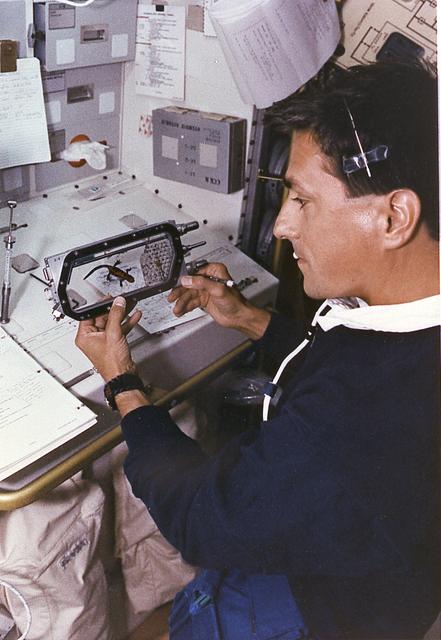

Astronaut Donald Thomas conducts the Fertilization and Embryonic Development of Japanese Newt in Space (AstroNewt) experiment at the Aquatic Animal Experiment Unit (AAEU) inside the International Microgravity Laboratory-2 (IML-2) science module. The AstroNewt experiment aims to know the effects of gravity on the early developmental process of fertilized eggs using a unique aquatic animal, the Japanese red-bellied newt. The newt egg is a large single cell at the begirning of development. The Japanese newt mates in spring and autumn. In late autumn, female newts enter hibernation with sperm in their body cavity and in spring lay eggs and fertilized them with the stored sperm. The experiment takes advantage of this feature of the newt. Groups of newts were sent to the Kennedy Space Center and kept in hibernation until the mission. The AAEU cassettes carried four newts aboard the Space Shuttle. Two newts in one cassette are treated by hormone injection on the ground to simulate egg laying. The other two newts are treated on orbit by the crew. The former group started maturization of eggs before launch. The effects of gravity on that early process were differentiated by comparison of the two groups. The IML-2 was the second in a series of Spacelab flights designed to conduct research by the international science community in a microgravity environment. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the IML-2 was launch on July 8, 1994 aboard the STS-65 Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia mission.
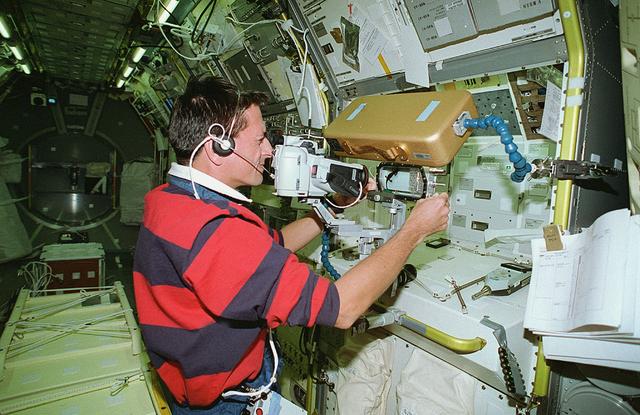

Astronaut Donald Thomas conducts the Fertilization and Embryonic Development of Japanese Newt in Space (AstroNewt) experiment at the Aquatic Animal Experiment Unit (AAEU) inside the International Microgravity Laboratory-2 (IML-2) science module. The AstroNewt experiment aims to know the effects of gravity on the early developmental process of fertilized eggs using a unique aquatic animal, the Japanese red-bellied newt. The newt egg is a large single cell at the begirning of development. The Japanese newt mates in spring and autumn. In late autumn, female newts enter hibernation with sperm in their body cavity and in spring lay eggs and fertilize them with the stored sperm. The experiment takes advantage of this feature of the newt. Groups of newts were sent to the Kennedy Space Center and kept in hibernation until the mission. The AAEU cassettes carried four newts aboard the Space Shuttle. Two newts in one cassette are treated by hormone injection on the ground to simulate egg laying. The other two newts are treated on orbit by the crew. The former group started maturization of eggs before launch. The effects of gravity on that early process were differentiated by comparison of the two groups. The IML-2 was the second in a series of Spacelab flights designed to conduct research by the international science community in a microgravity environment. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the IML-2 was launched on July 8, 1994 aboard the STS-65 Space Shuttle mission, Orbiter Columbia.
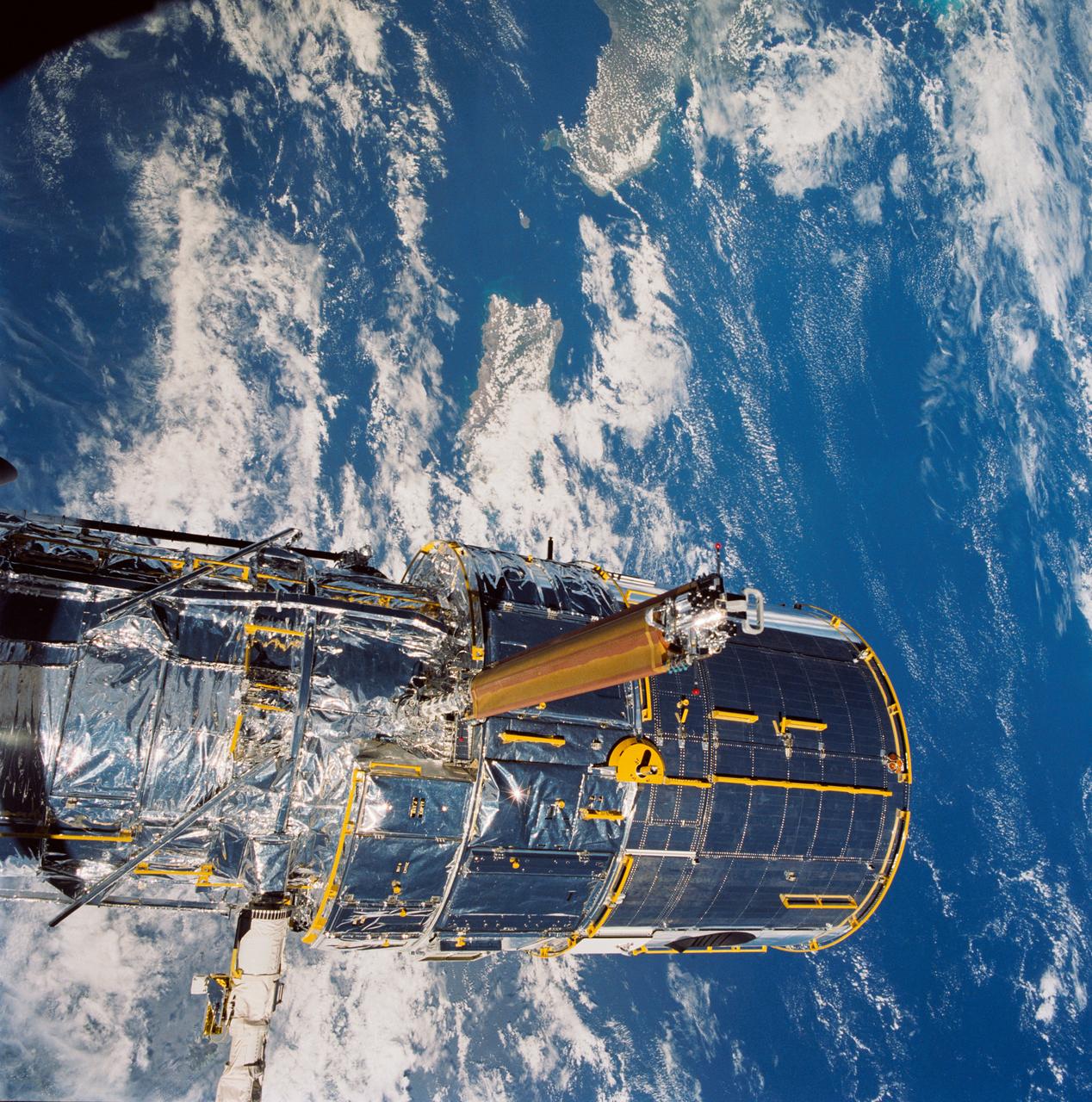

During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector is held in appendage deploy position above Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. The solar array (SA) bistem cassette has been released from its latch fittings. The bistem spreader bars begin to unfurl the SA wing. The secondary deployment mechanism (SDM) handle is visible at the SA end. Stowed against either side of the HST System Support Module (SSM) forward shell are the high-gain antennae (HGA). Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic are recognizable at the left of the frame.
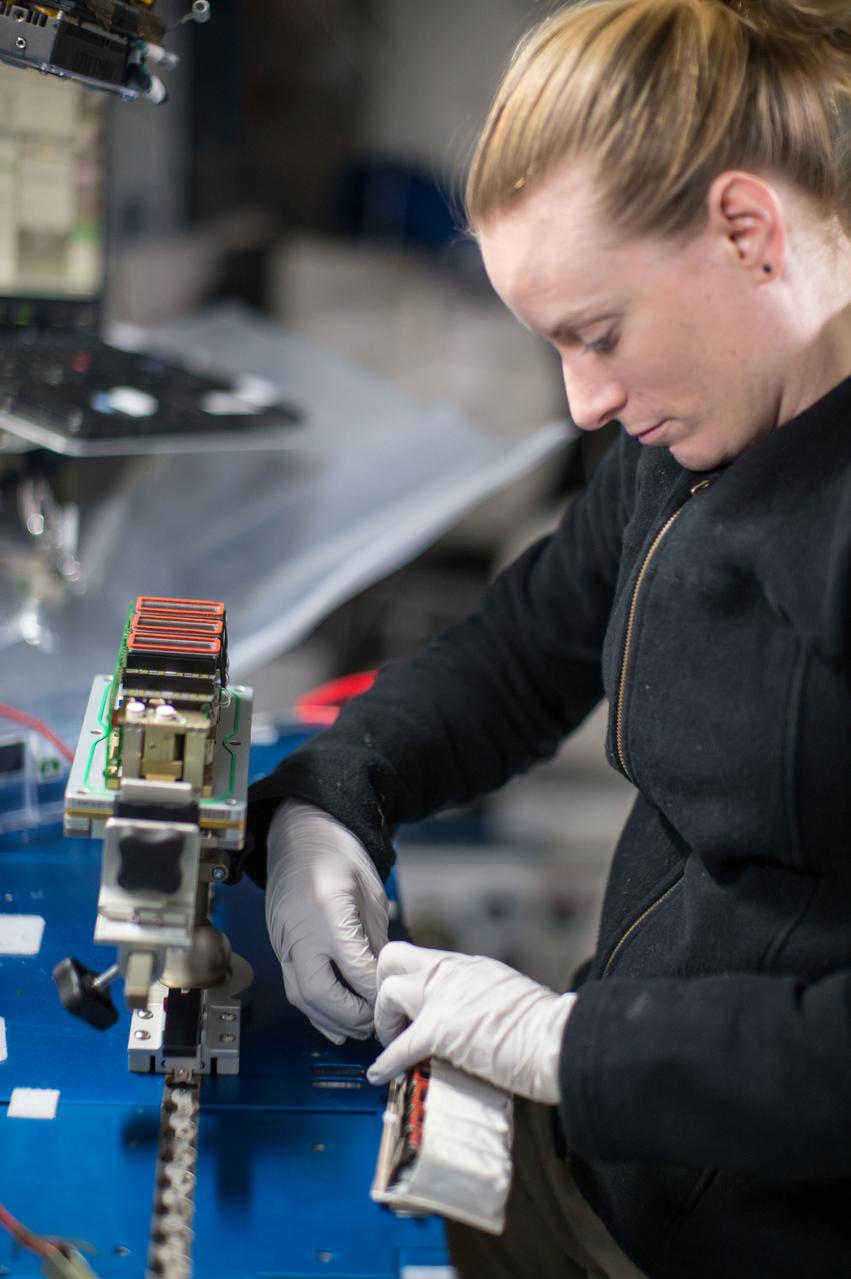

iss049e008866 (9/23/2016) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins is photographed performing the second harvest of the Plant RNA Regulation experiment by removing the European Modular Cultivation System (EMCS) Seed Cassettes from EMCS Rotors A and B stowing them in an EMCS Cold Stowage Pouch. The Plant RNA Regulation investigation studies the first steps of gene expression involved in development of roots and shoots. Scientists expect to find new molecules that play a role in how plants adapt and respond to the microgravity environment of space, which provides new insight into growing plants for food and oxygen supplies on long-duration missions.
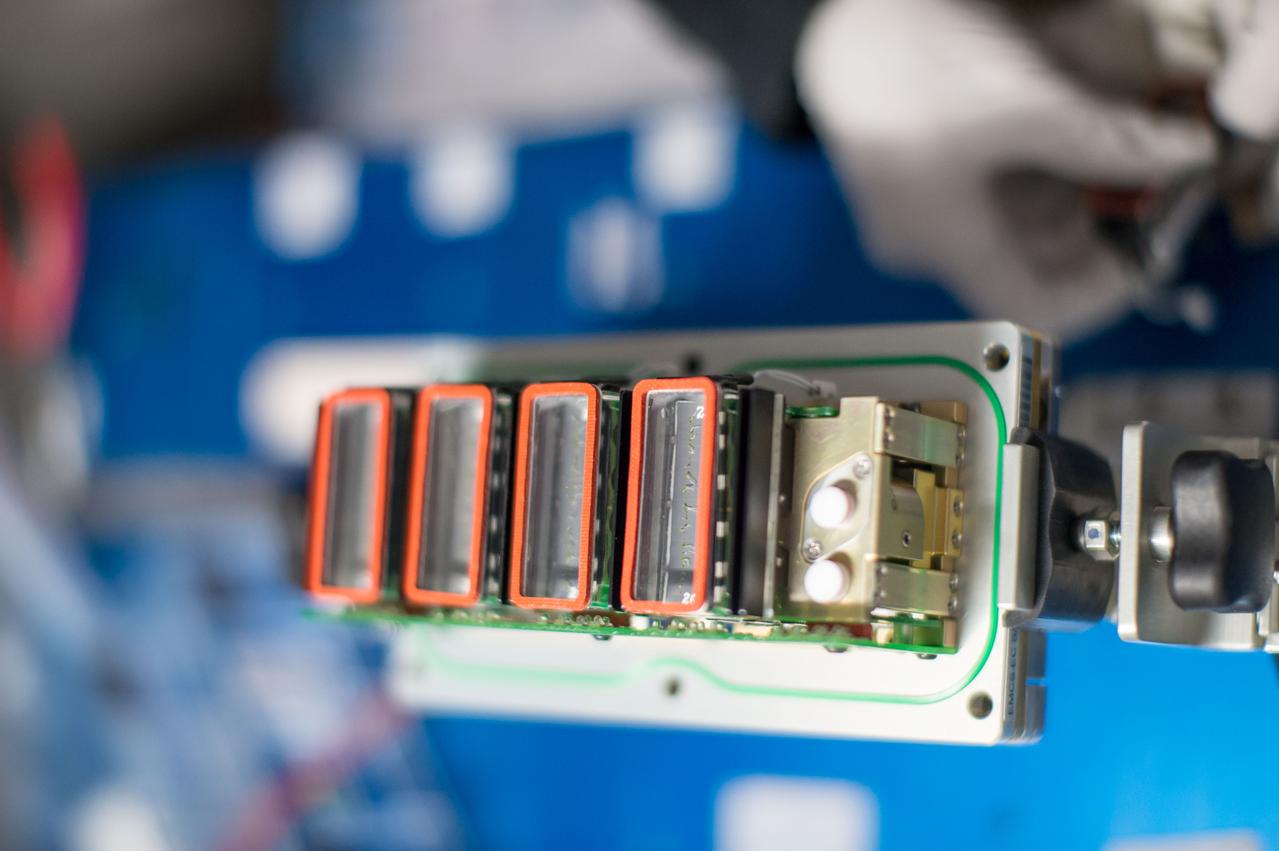
iss049e008864 (9/23/2016) --- Photo taken aboard the International Space Station (ISS) during the second harvest of the Plant RNA Regulation experiment performed by removing the European Modular Cultivation System (EMCS) Seed Cassettes from EMCS Rotors A and B. The Plant RNA Regulation investigation studies the first steps of gene expression involved in development of roots and shoots. Scientists expect to find new molecules that play a role in how plants adapt and respond to the microgravity environment of space, which provides new insight into growing plants for food and oxygen supplies on long-duration missions.
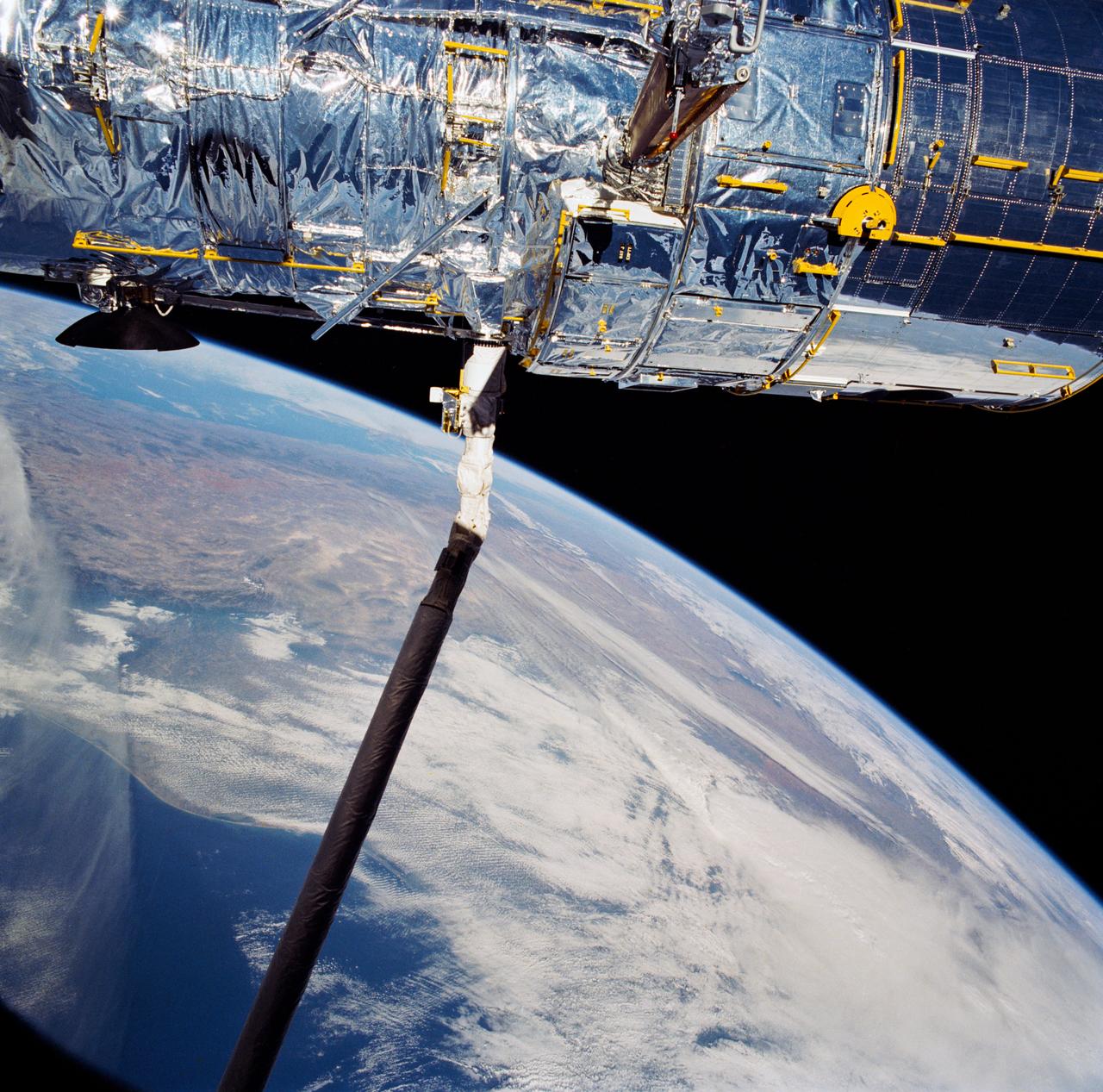

During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is held in appendage deploy position by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS) above the payload bay (PLB) and crew compartment cabin. While in this position the solar array (SA) wing bistem cassette (HST center) is deployed from its stowed location along side the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. A high gain antenna (HGA) remains stowed along the SSM. The Earth's surface and the Earth limb creates a dramatic backdrop.
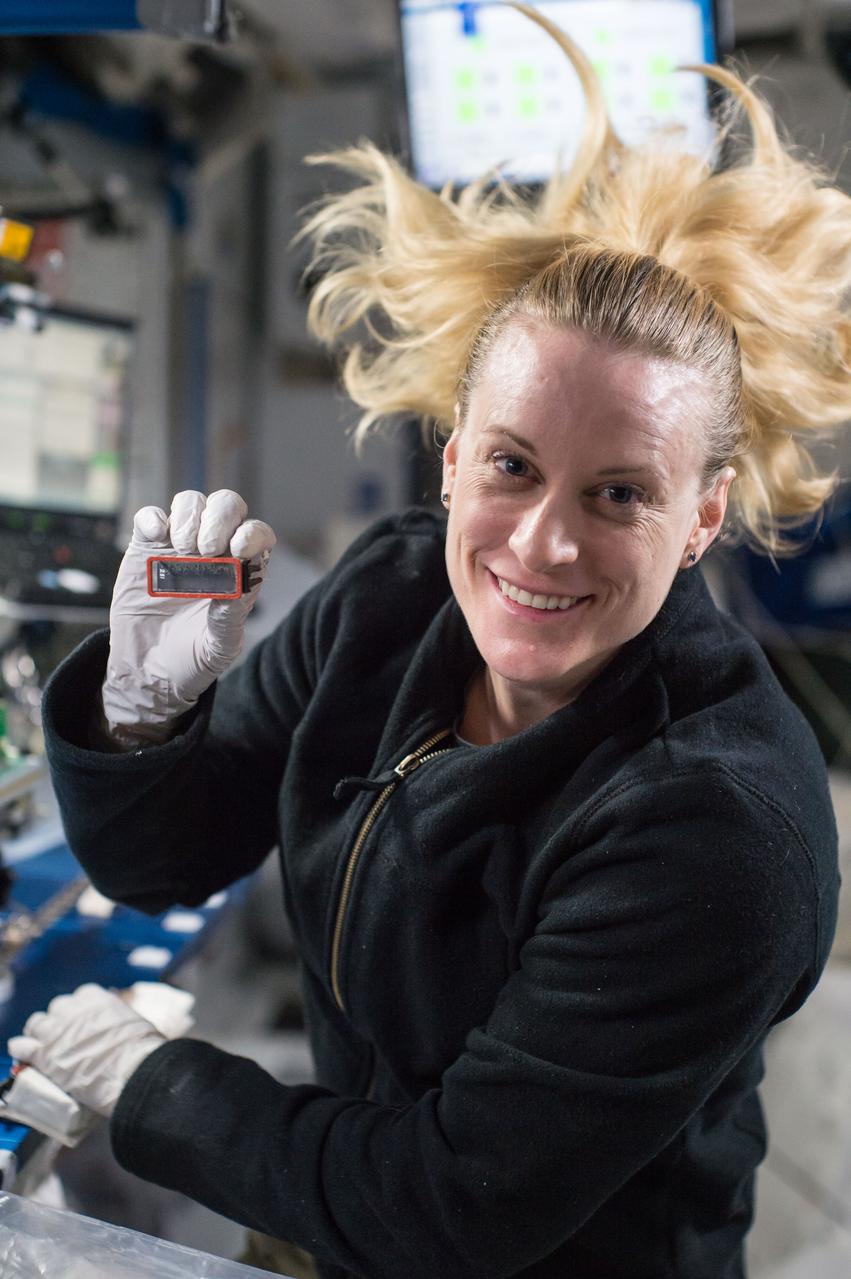

iss049e008853 (9/23/2016) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins is photographed performing the second harvest of the Plant RNA Regulation experiment by removing the European Modular Cultivation System (EMCS) Seed Cassettes from EMCS Rotors A and B stowing them in an EMCS Cold Stowage Pouch. The Plant RNA Regulation investigation studies the first steps of gene expression involved in development of roots and shoots. Scientists expect to find new molecules that play a role in how plants adapt and respond to the microgravity environment of space, which provides new insight into growing plants for food and oxygen supplies on long-duration missions.
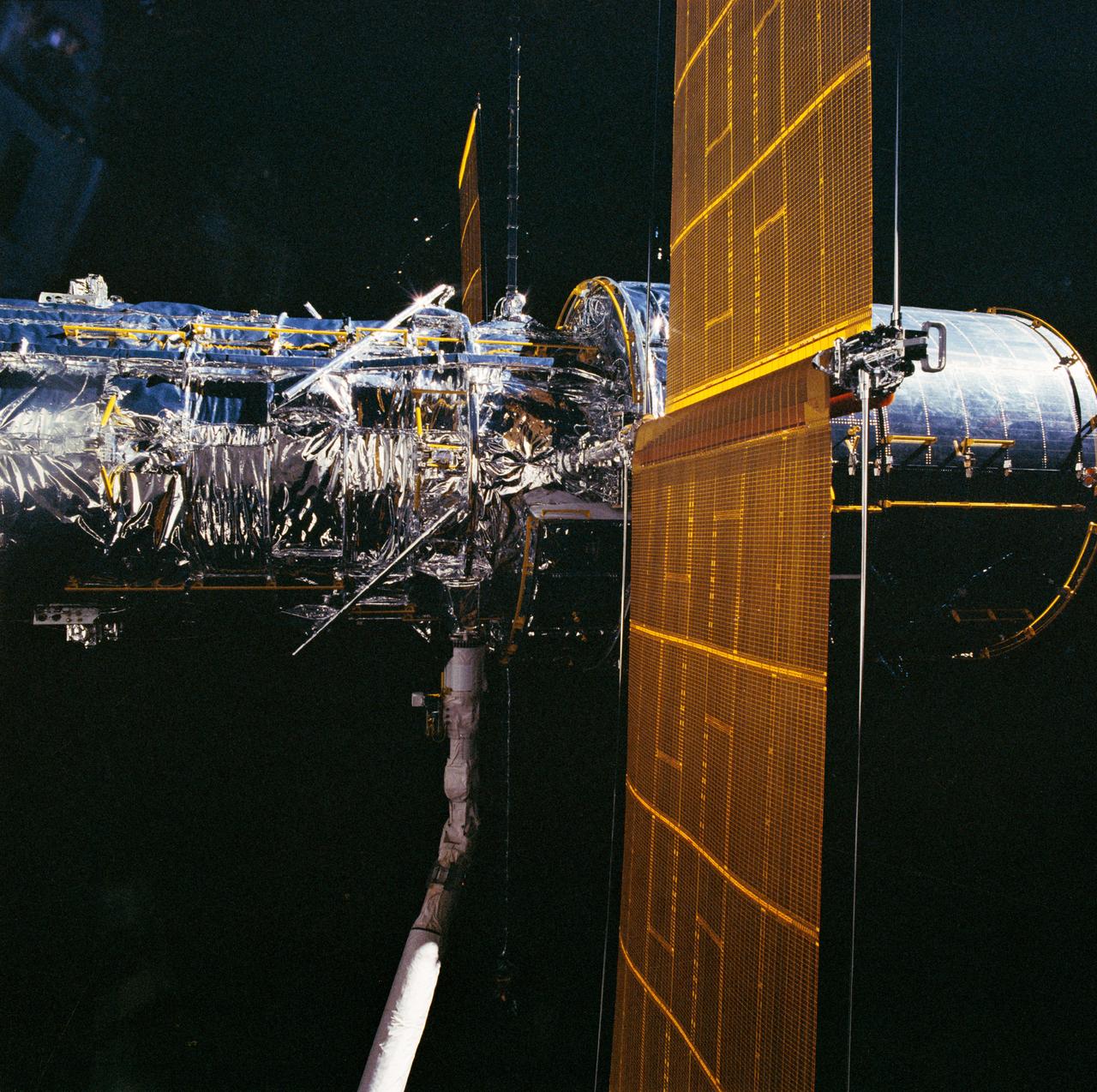
During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector, is held against the blackness of space. The two solar array (SA) wings (large gold panels) are fully extended with bistem cassette and secondary deployment mechanism (SDM) handle clearly visible. The two deployed high gain antennae (HGA) masts are parallel to the SA panels. RMS end effector is positioned on the starboard fixture during the predeployment checkout operations above Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, payload bay (PLB).

iss070e129992 (March 29, 2024) --- Expedition 70 Flight Engineer and NASA astronaut Mike Barratt works aboard the International Space Station's Harmony module processing protein crystal samples inside a portable glovebag to learn how to generate personalized medicines in space for astronauts.
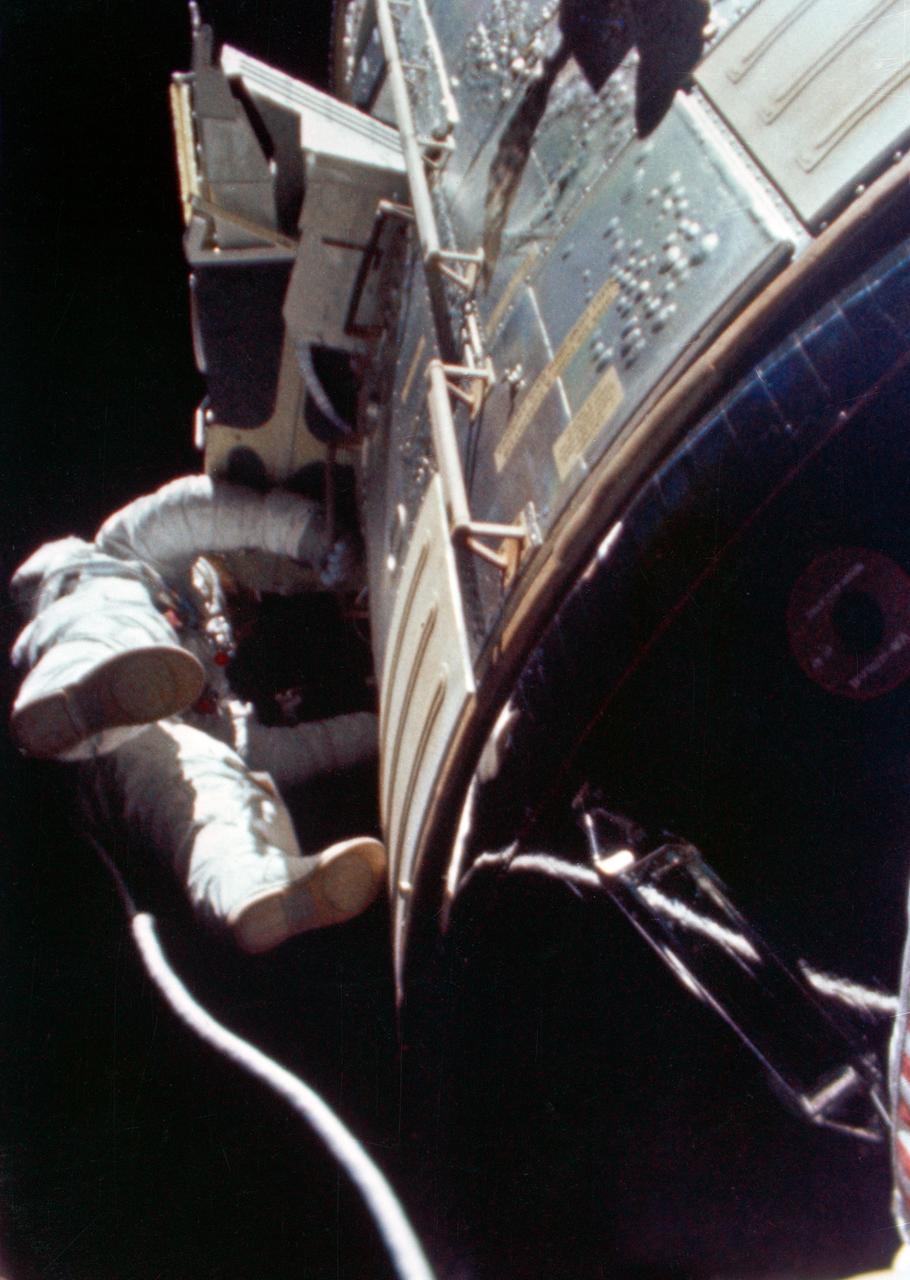

S71-43202 (5 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission, floats in space outside the spacecraft during his trans-Earth extravehicular activity (EVA). This photograph was taken from a frame of motion picture film exposed by the 16mm Maurer camera mounted in the hatch of the Command Module (CM). During his EVA, Worden made an inspection of the Service Module's (SM) Scientific Instrument Module (SIM) bay and retrieved the film cassettes from the Panoramic Camera and the Mapping Camera. The SIM bay holds eight orbital science experiments. The EVA occurred when the spacecraft was homeward bound approximately 171,000 nautical miles from Earth.
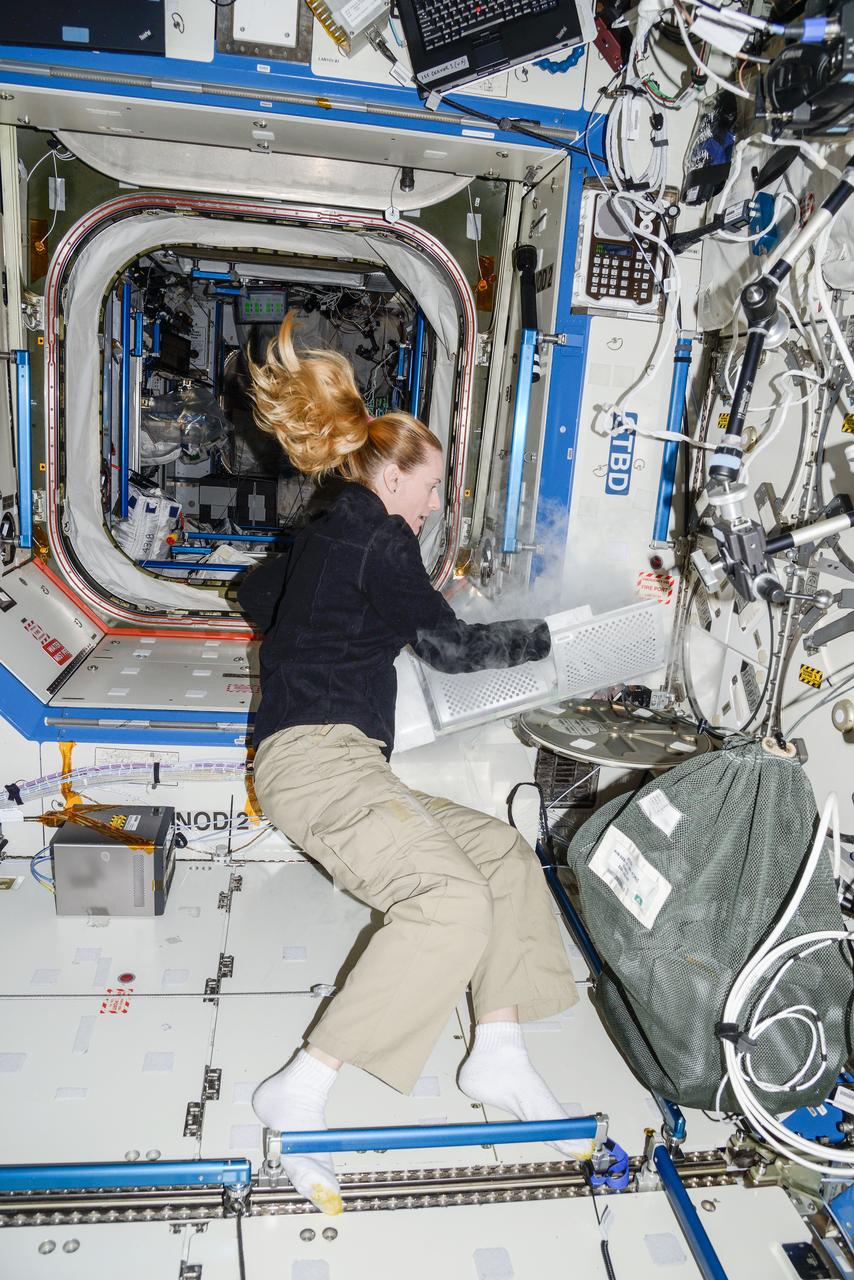

iss049e053079 (9/23/2016) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins is photographed in U.S. lab aboard the International Space Station (ISS) performing the second harvest of the Plant RNA Regulation experiment by stowing the European Modular Cultivation System (EMCS) Seed Cassettes from EMCS Rotors A and B in an EMCS Cold Stowage Pouch and placing them in Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI). The Plant RNA Regulation investigation studies the first steps of gene expression involved in development of roots and shoots. Scientists expect to find new molecules that play a role in how plants adapt and respond to the microgravity environment of space, which provides new insight into growing plants for food and oxygen supplies on long-duration missions. Sent as part of Russian Return imagery on 47S.

S72-35901 (25 April 1972) --- Astronaut Thomas K. (Ken) Mattingly II, command module pilot of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, floats in space outside the spacecraft during his trans-Earth extravehicular activity (EVA), as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a color TV camera mounted on the Command Module (CM) hatch. Mattingly used hand-holds and a foot restraint to hold himself in position, and he was secured to the spacecraft by an umbilical tether line. During his EVA, Mattingly made an inspection of the Service Module's (SM) Scientific Instrument Module (SIM) bay, and retrieved film cassettes from the Panoramic Camera and the Mapping Camera. The trans-Earth EVA occurred at ground elapsed time of 242:55, and 2:49 p.m. (CST), Tuesday, April 25, 1972.

S72-35900 (25 April 1972) --- Astronaut Thomas K. (Ken) Mattingly II, command module pilot of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, floats in space outside the spacecraft during his trans-Earth extravehicular activity (EVA), as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a color TV camera mounted on the Command Module (CM) hatch. Mattingly used hand-holds and a foot restraint to hold himself in position, and he was secured to the spacecraft by an umbilical tether line. During his EVA, Mattingly made an inspection of the Service Module's (SM) Scientific Instrument Module (SIM) bay, and retrieved film cassettes from the Panoramic Camera and the Mapping Camera. The trans-Earth EVA occurred at ground elapsed time of 242:55, and 2:49 p.m. (CST), Tuesday, April 25, 1972.