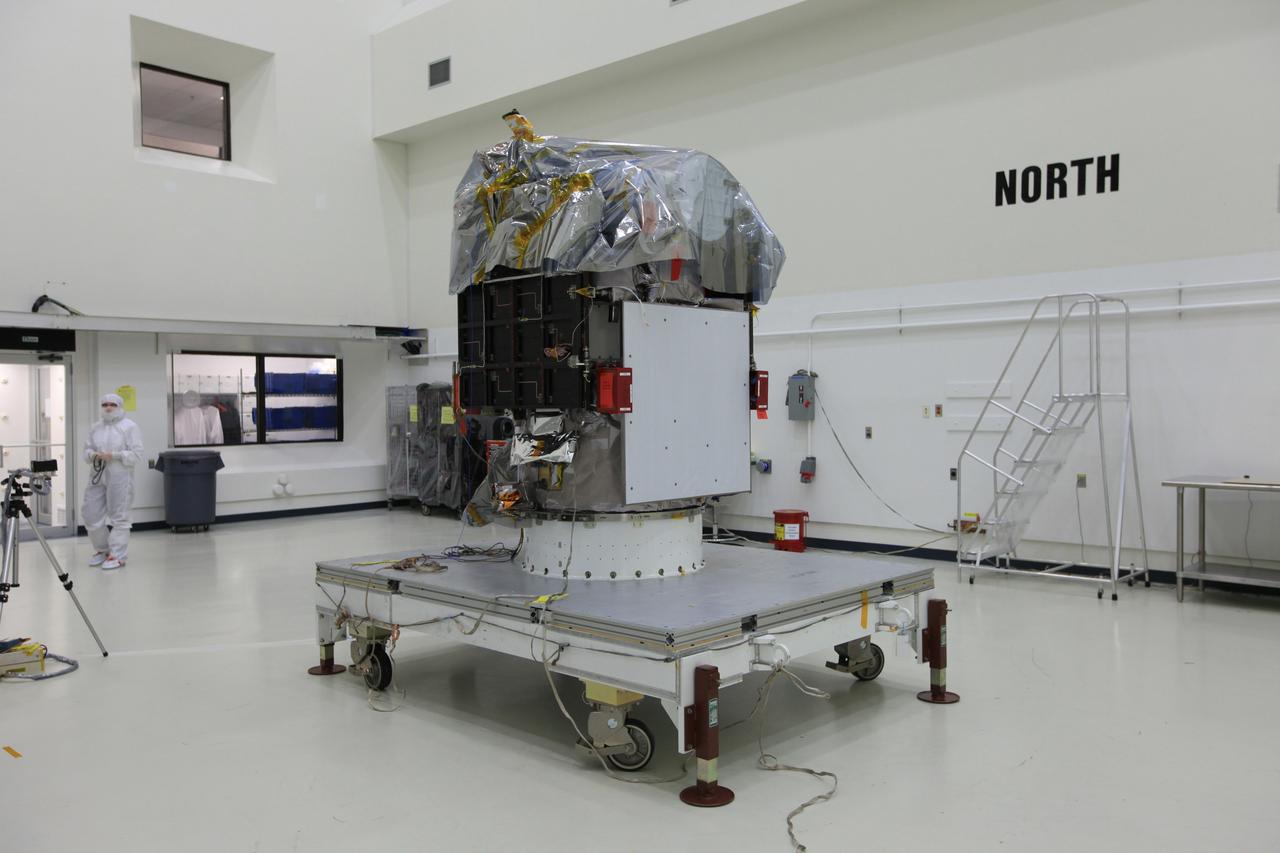

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, has been uncovered and is ready for processing in the high bay of Building 1 at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is currently scheduled for January 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. To learn more about DSCOVR, visit http://www.nesdis.noaa.gov/DSCOVR. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, has been uncovered and is ready for processing in the high bay of Building 1 at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is currently scheduled for January 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. To learn more about DSCOVR, visit http://www.nesdis.noaa.gov/DSCOVR. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

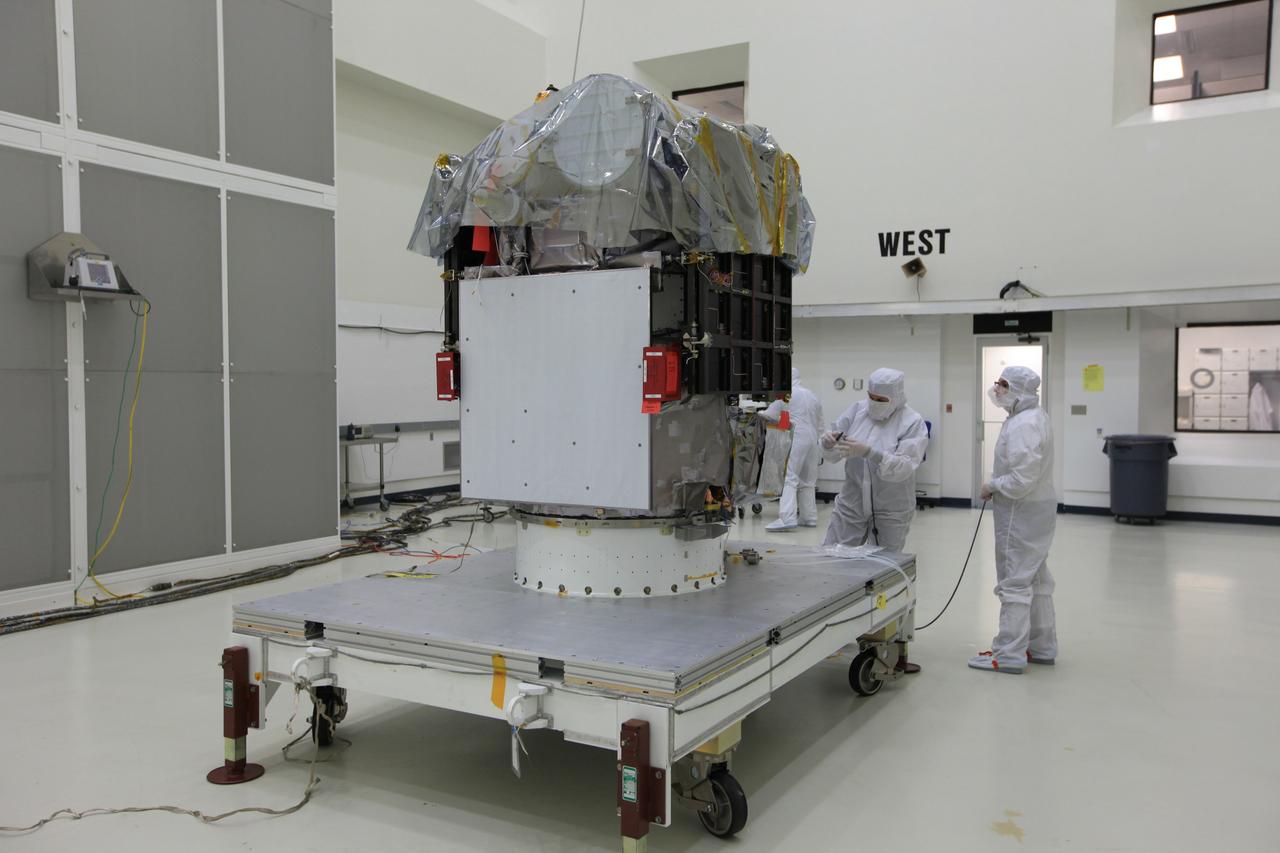
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers remove the plastic cover from NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, in the high bay of Building 1 at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is currently scheduled for January 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. To learn more about DSCOVR, visit http://www.nesdis.noaa.gov/DSCOVR. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers remove the plastic cover from NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, in the high bay of Building 1 at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is currently scheduled for January 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. To learn more about DSCOVR, visit http://www.nesdis.noaa.gov/DSCOVR. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
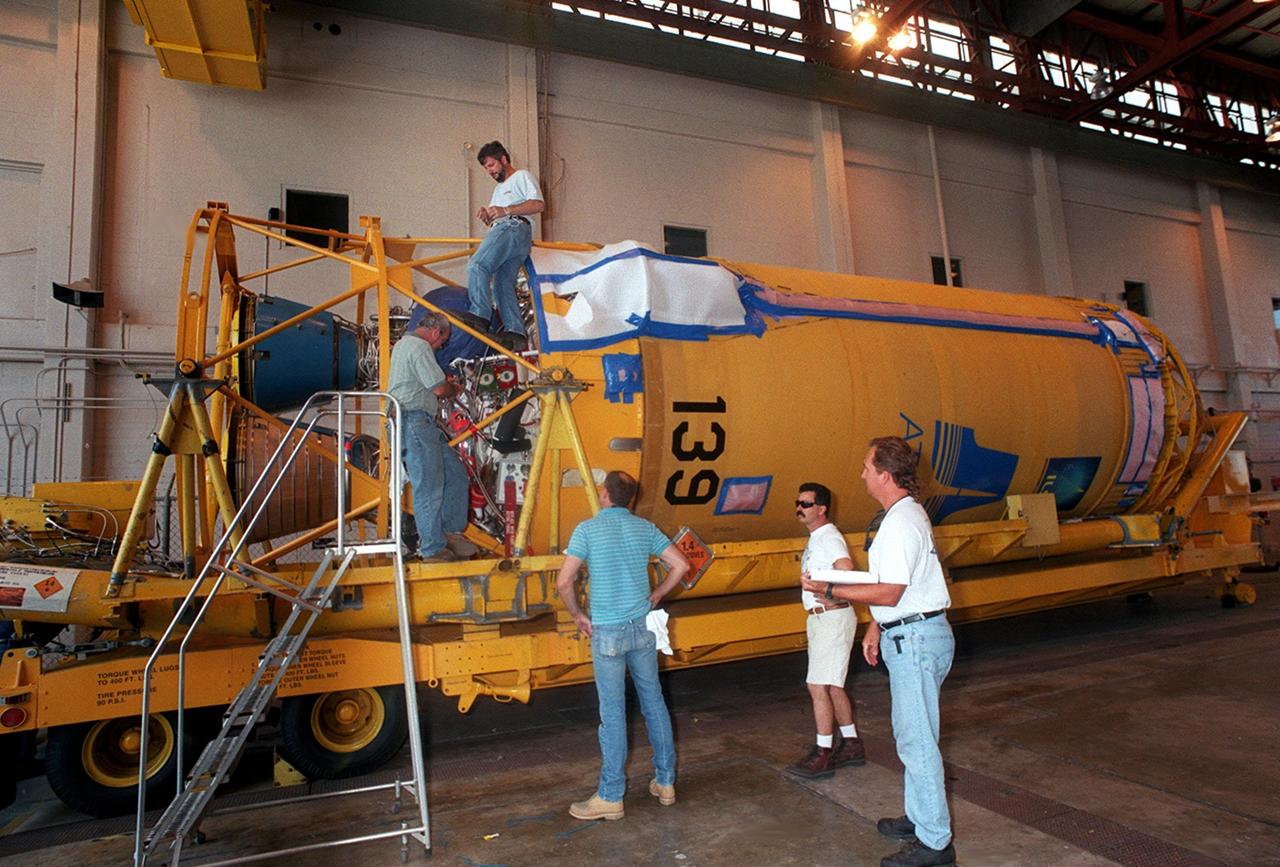

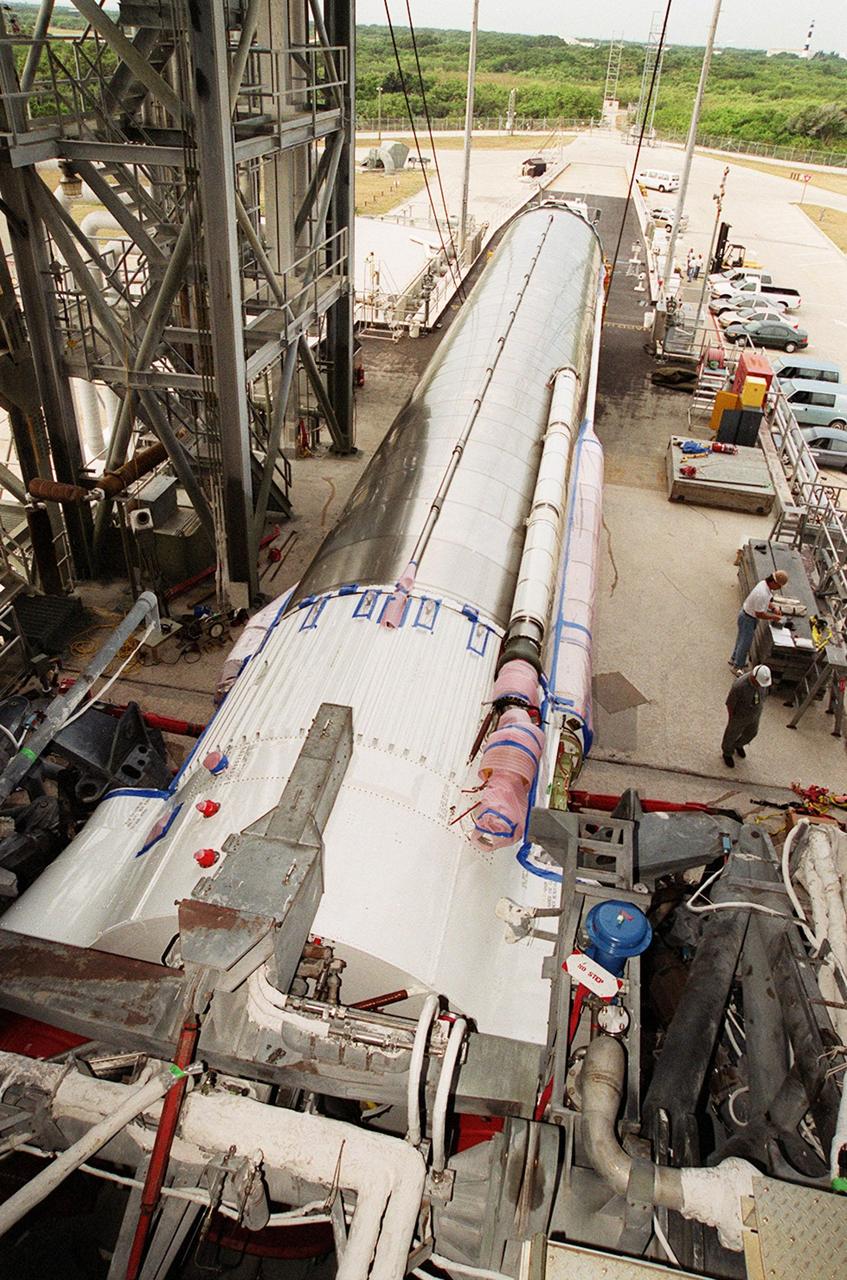
At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
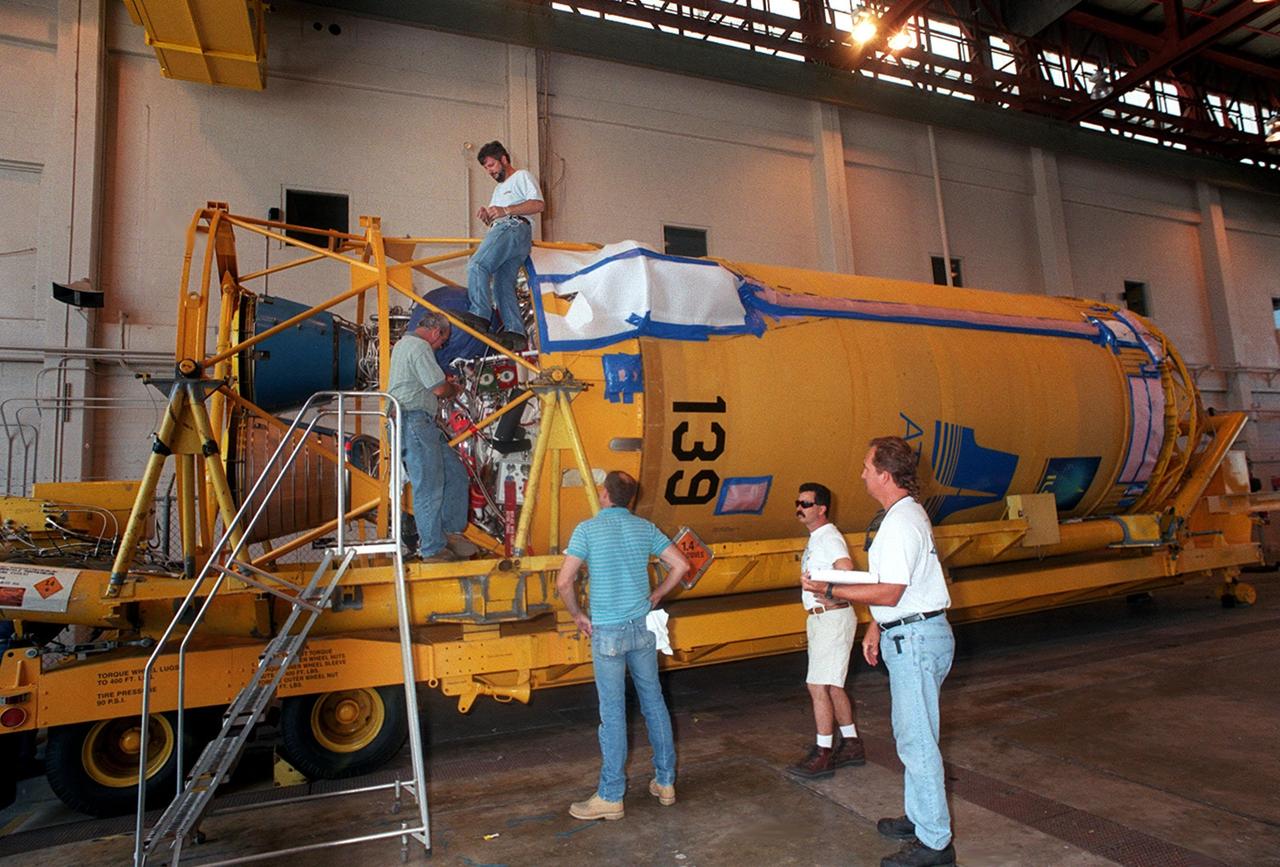

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
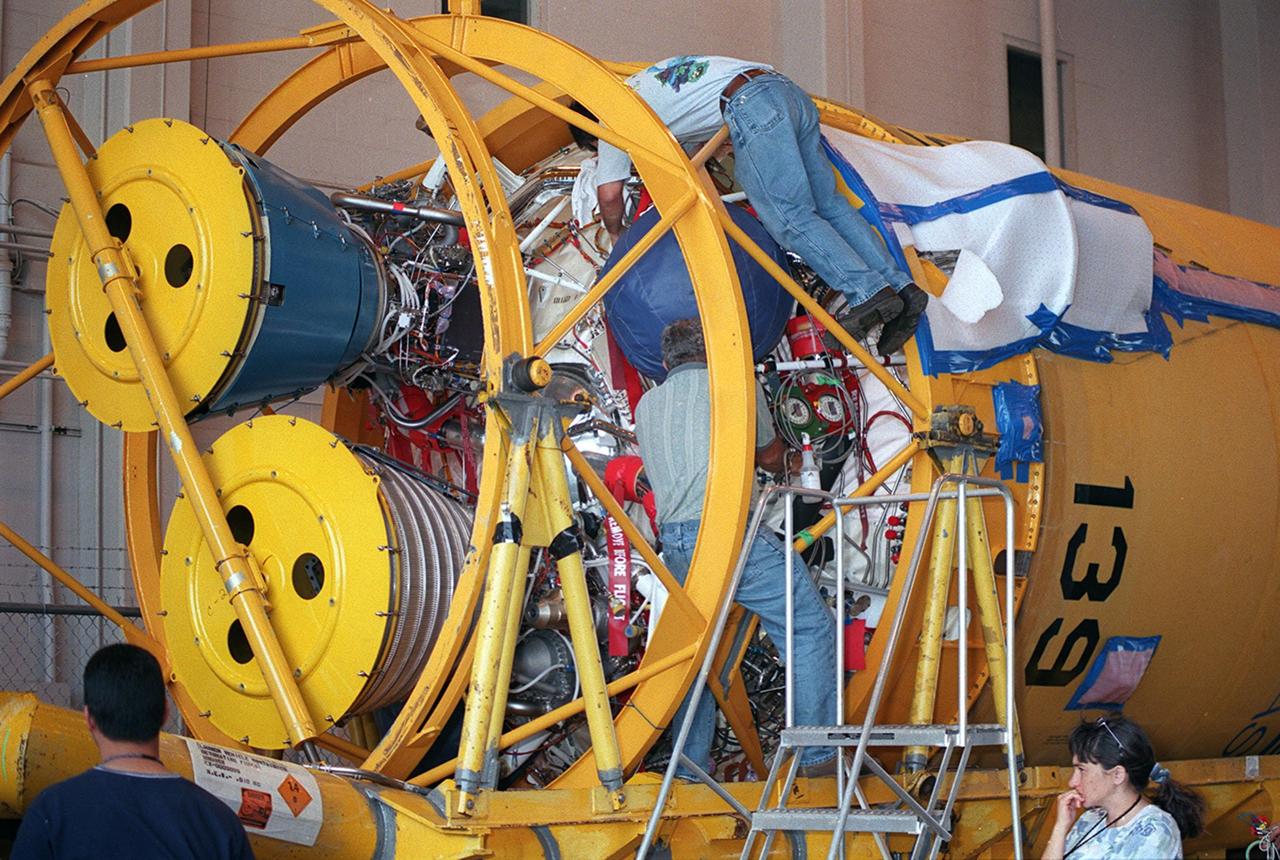

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
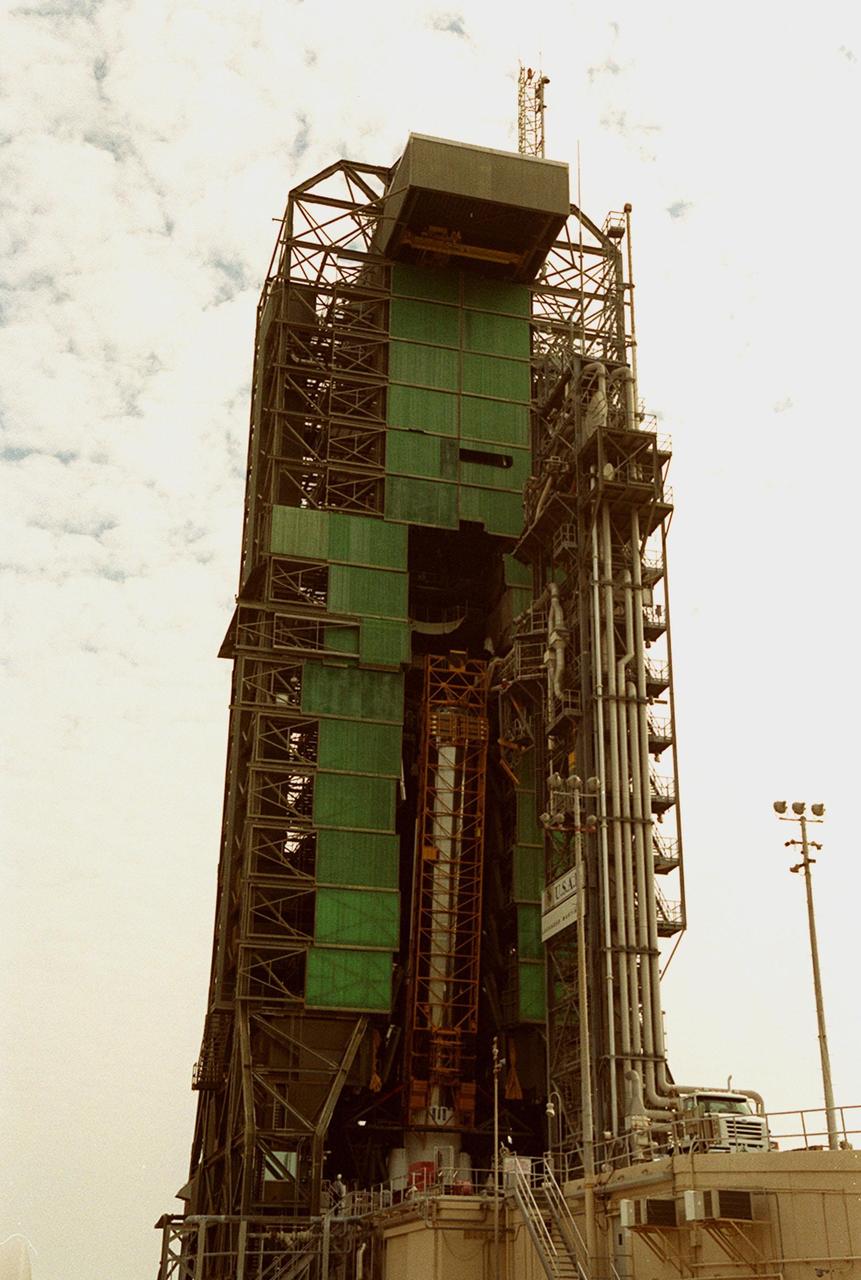

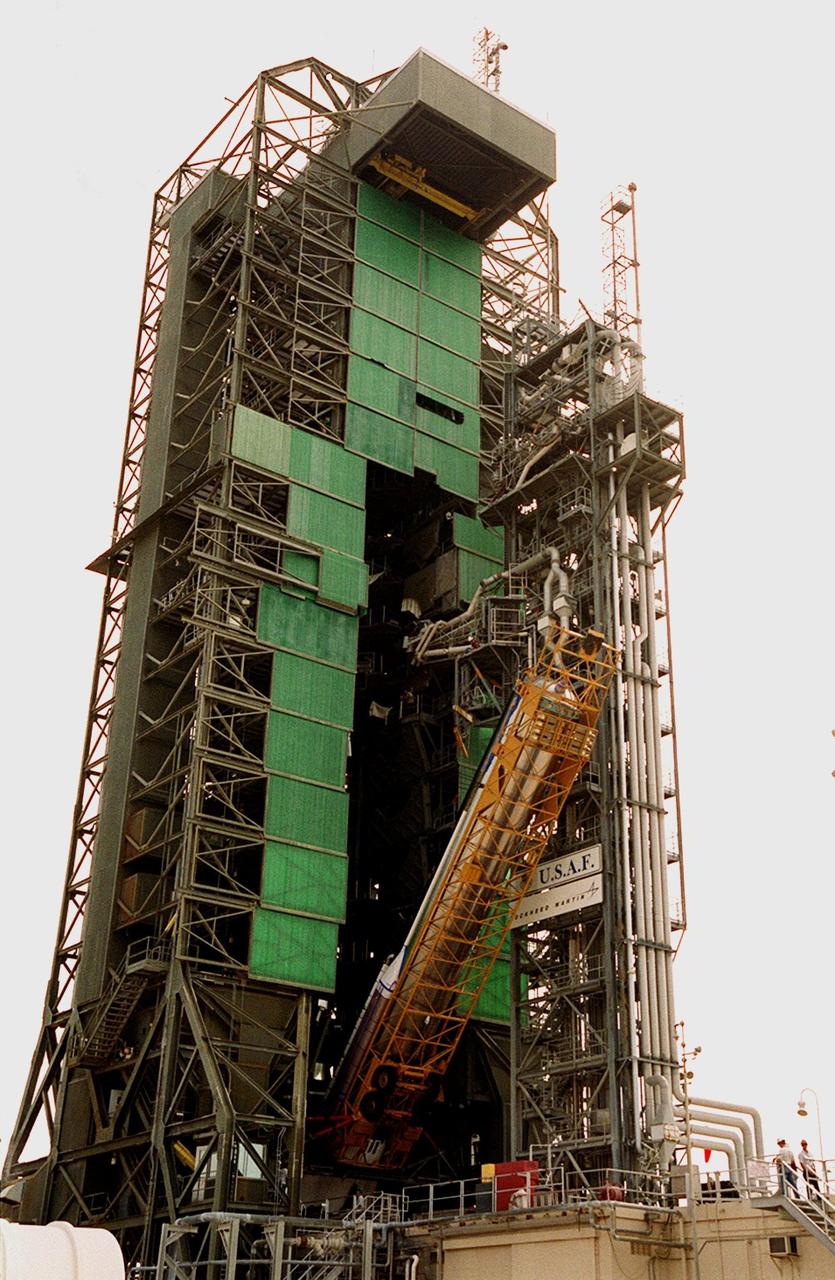
The Atlas IIA rocket is close to its vertical position in the launch tower at Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). It will be mated with a Centaur upper stage to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
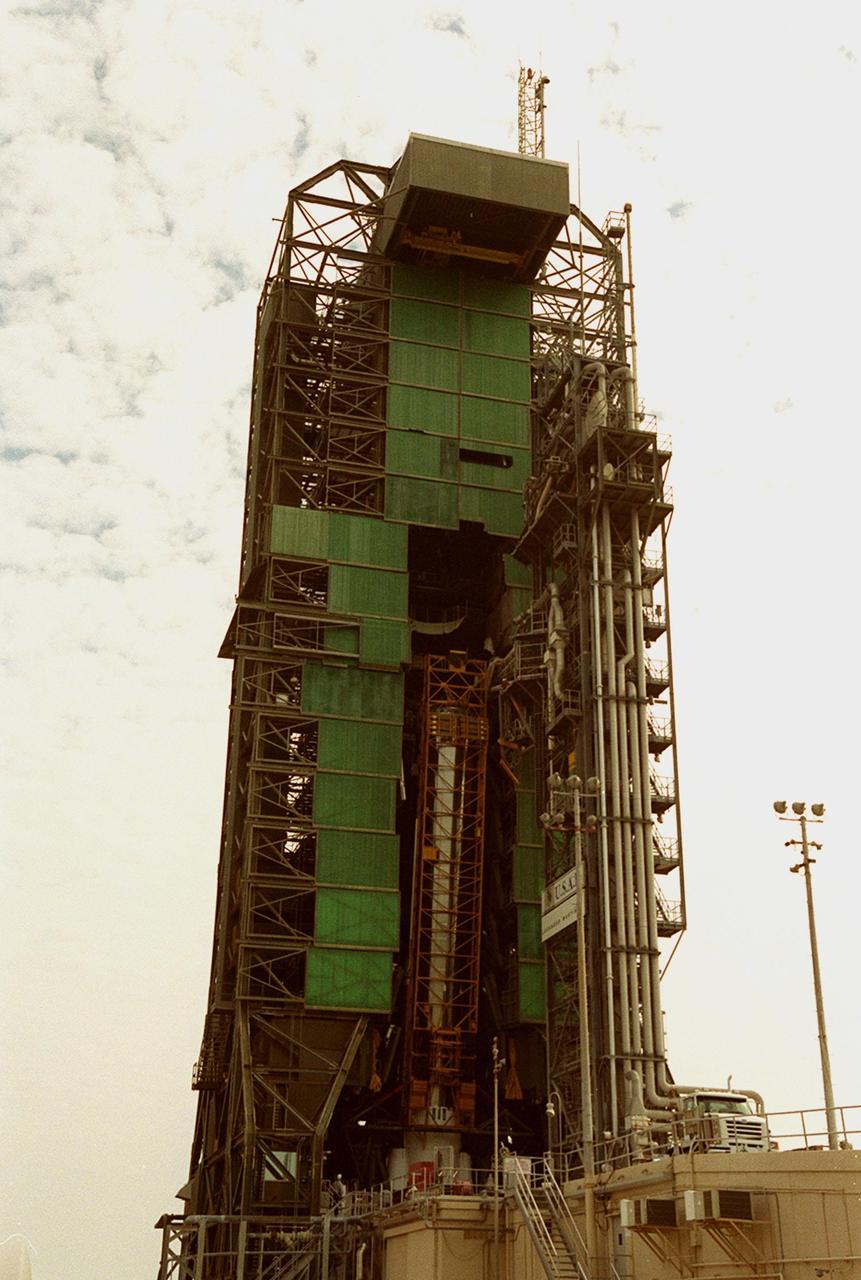

The Atlas IIA rocket is close to its vertical position in the launch tower at Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). It will be mated with a Centaur upper stage to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
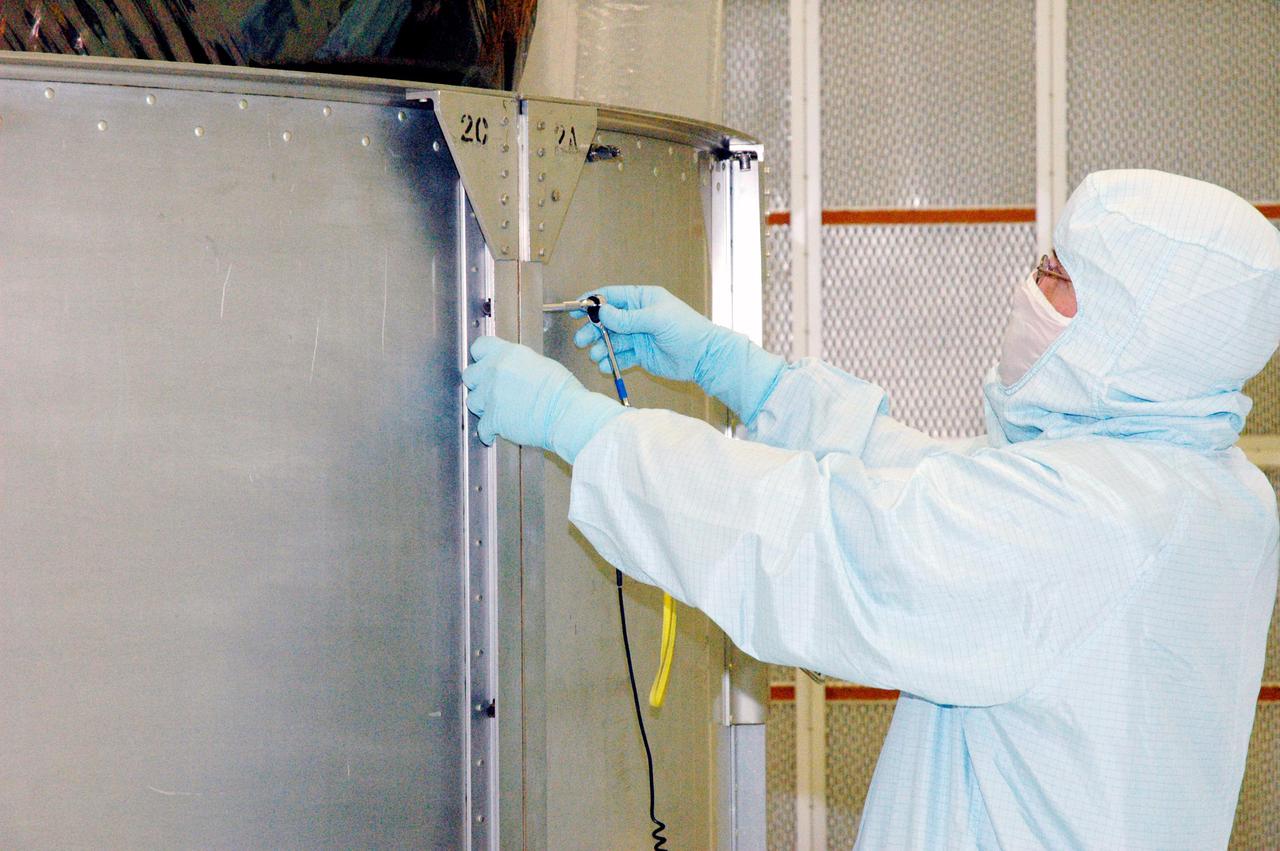

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Boeing technician in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida attaches two of the lower segments of the payload transfer canister being installed around the plastic-wrapped Swift spacecraft. The launch of the Swift observatory, a NASA spacecraft to pinpoint the location of gamma-ray bursts, is scheduled for Nov. 17 from Pad 17-A on CCAFS. Liftoff aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is targeted at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. They are the most powerful explosions known in the universe, emitting more than 100 billion times the energy that the Sun emits in a year. Yet they last only from a few milliseconds to a few minutes, never to appear in the same spot again.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Boeing technicians in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida install a second ring of segments of the payload transfer canister around the plastic-wrapped Swift spacecraft. The launch of the Swift observatory, a NASA spacecraft to pinpoint the location of gamma-ray bursts, is scheduled for Nov. 17 from Pad 17-A on CCAFS. Liftoff aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is targeted at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. They are the most powerful explosions known in the universe, emitting more than 100 billion times the energy that the Sun emits in a year. Yet they last only from a few milliseconds to a few minutes, never to appear in the same spot again.
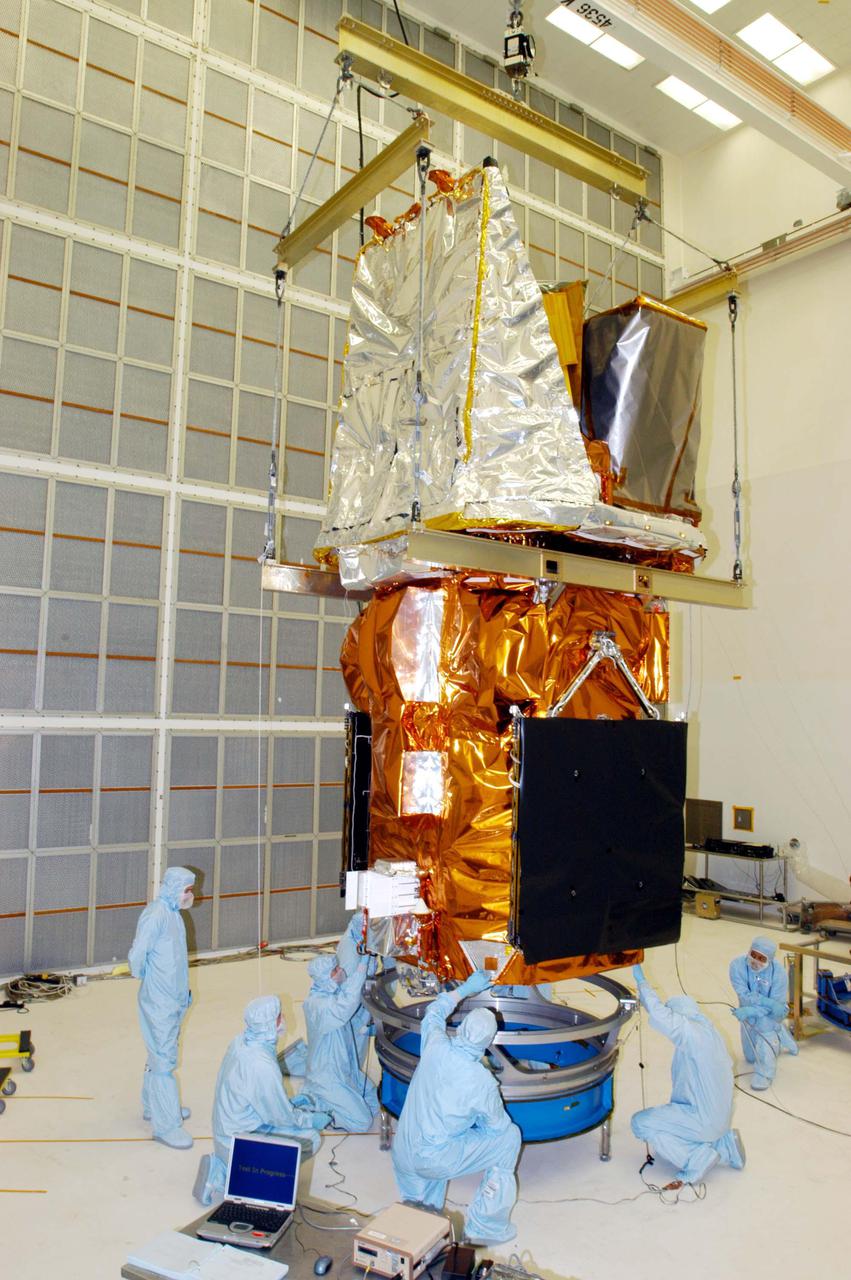

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians at NASA’s Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), help guide the Swift spacecraft being lowered onto a payload attach fitting, the interface between the spacecraft and the second stage of the Boeing Delta II rocket. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Swift is scheduled to launch in November from Launch Pad 17-A at CCAFS.
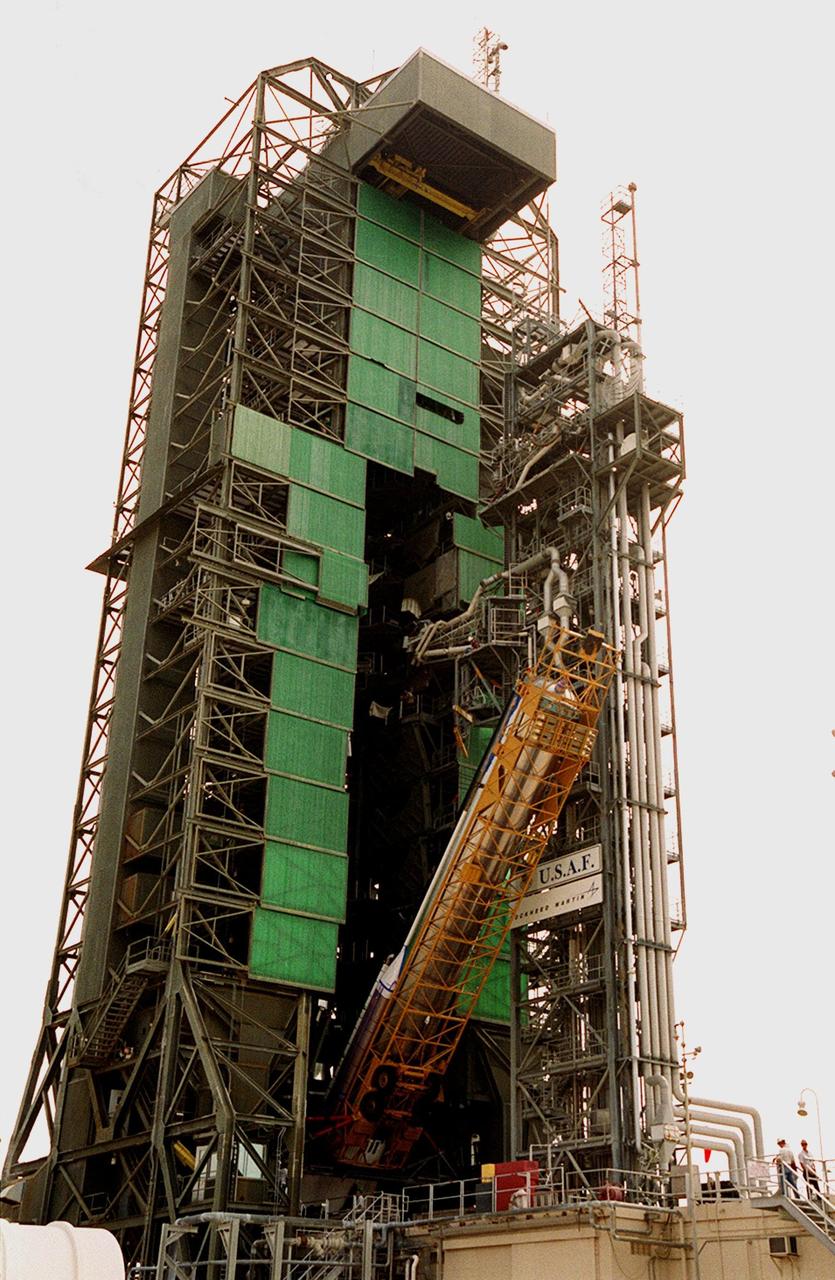

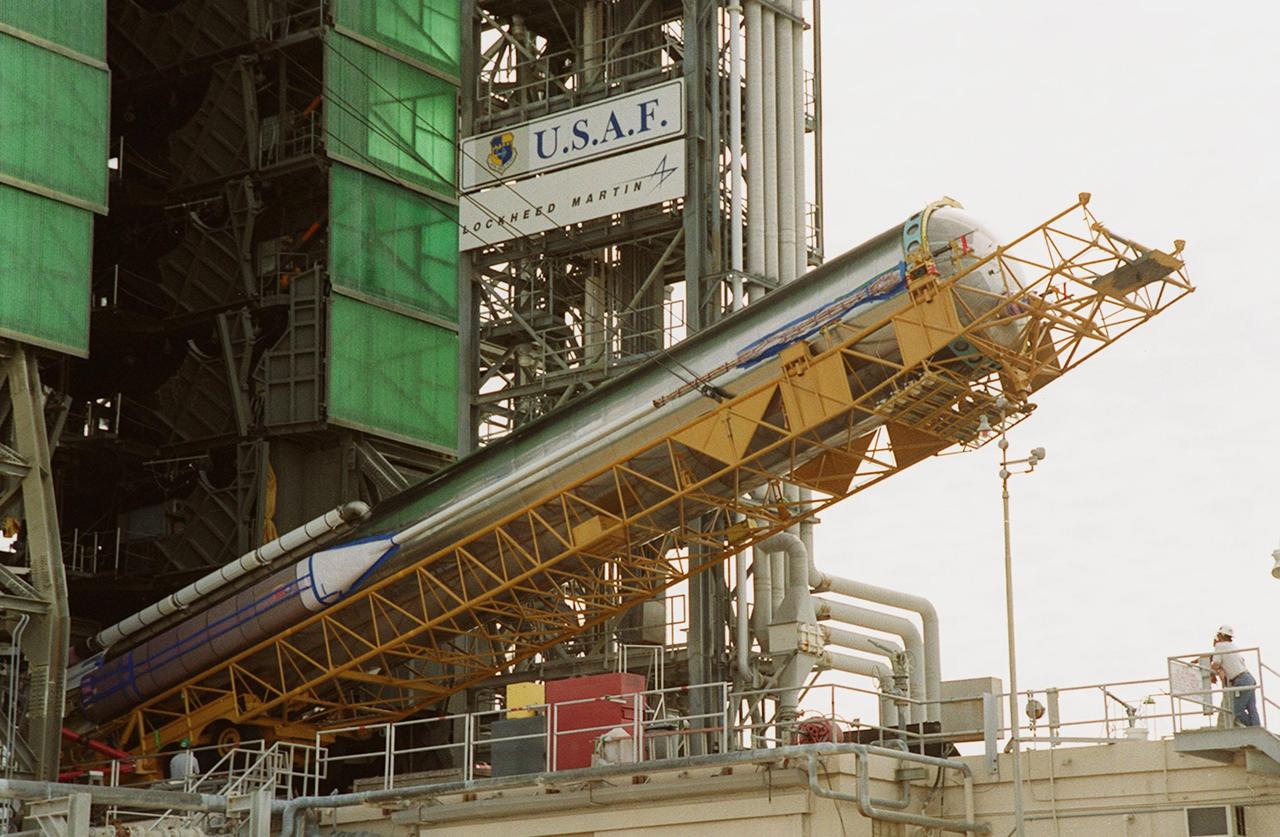
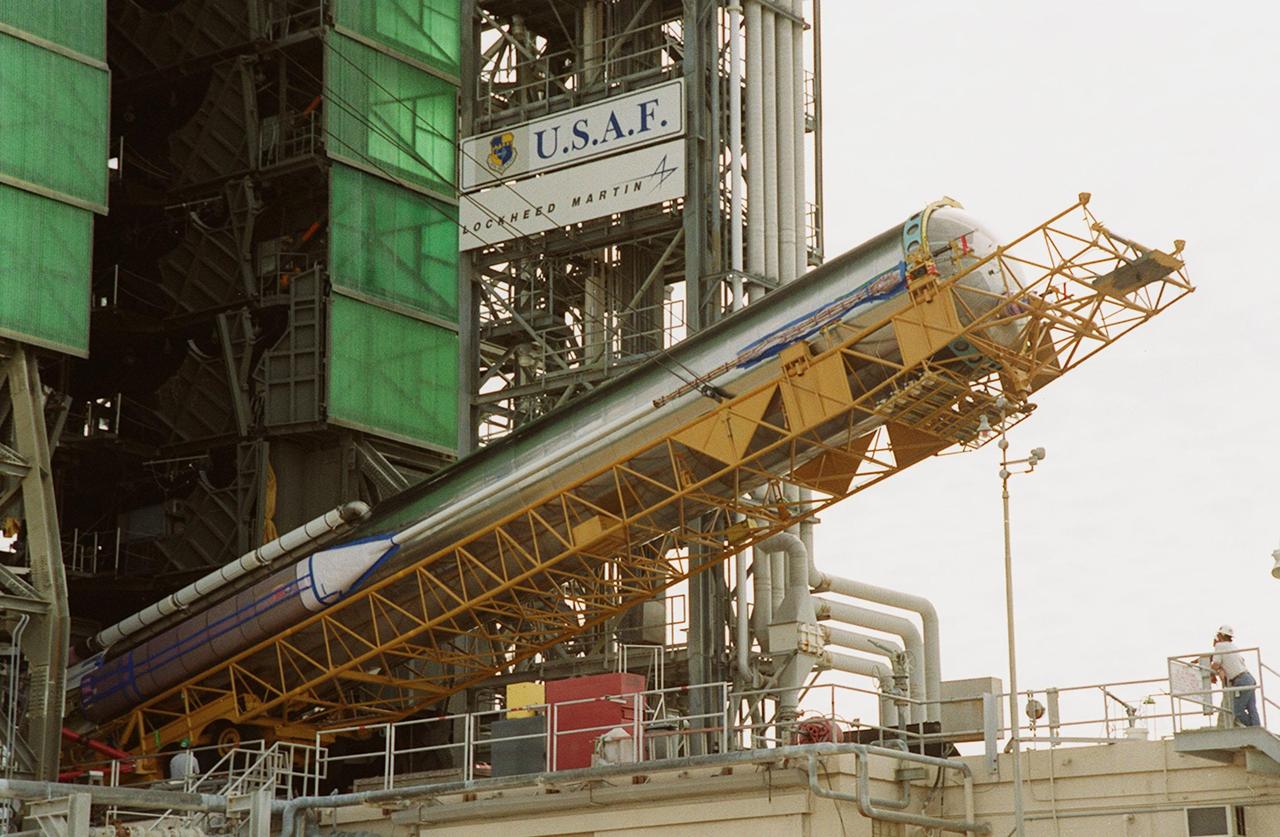
At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), the Atlas IIA rocket is halfway to a vertical position at the launch tower where it will be mated with the Centaur upper stage. The Atlas IIA/Centaur will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
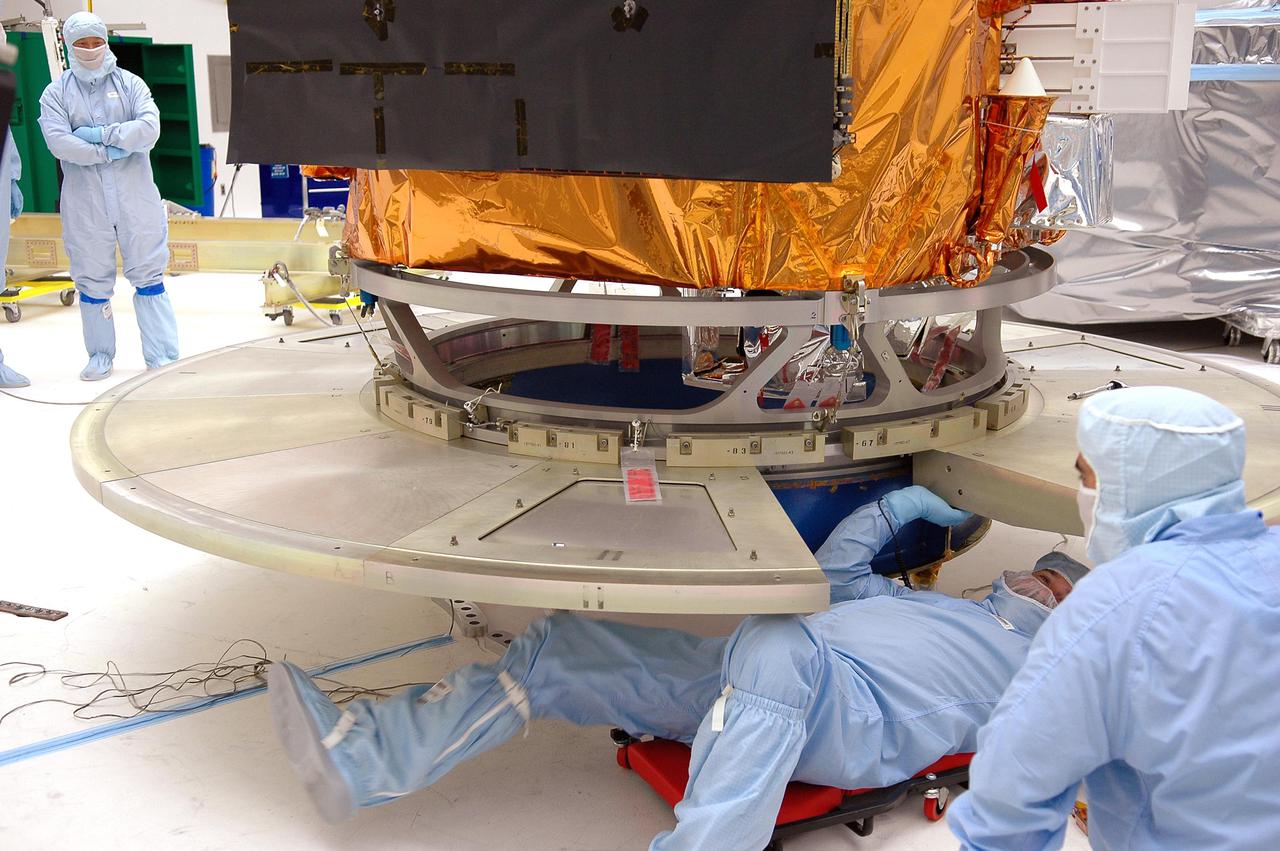

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA’s Hangar AE on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Fla., technicians check the attachment of the base petals of a transportation canister around the bottom of the payload attach fitting on the Swift spacecraft. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Swift is scheduled to launch in mid-November from Launch Pad 17-A at CCAFS.
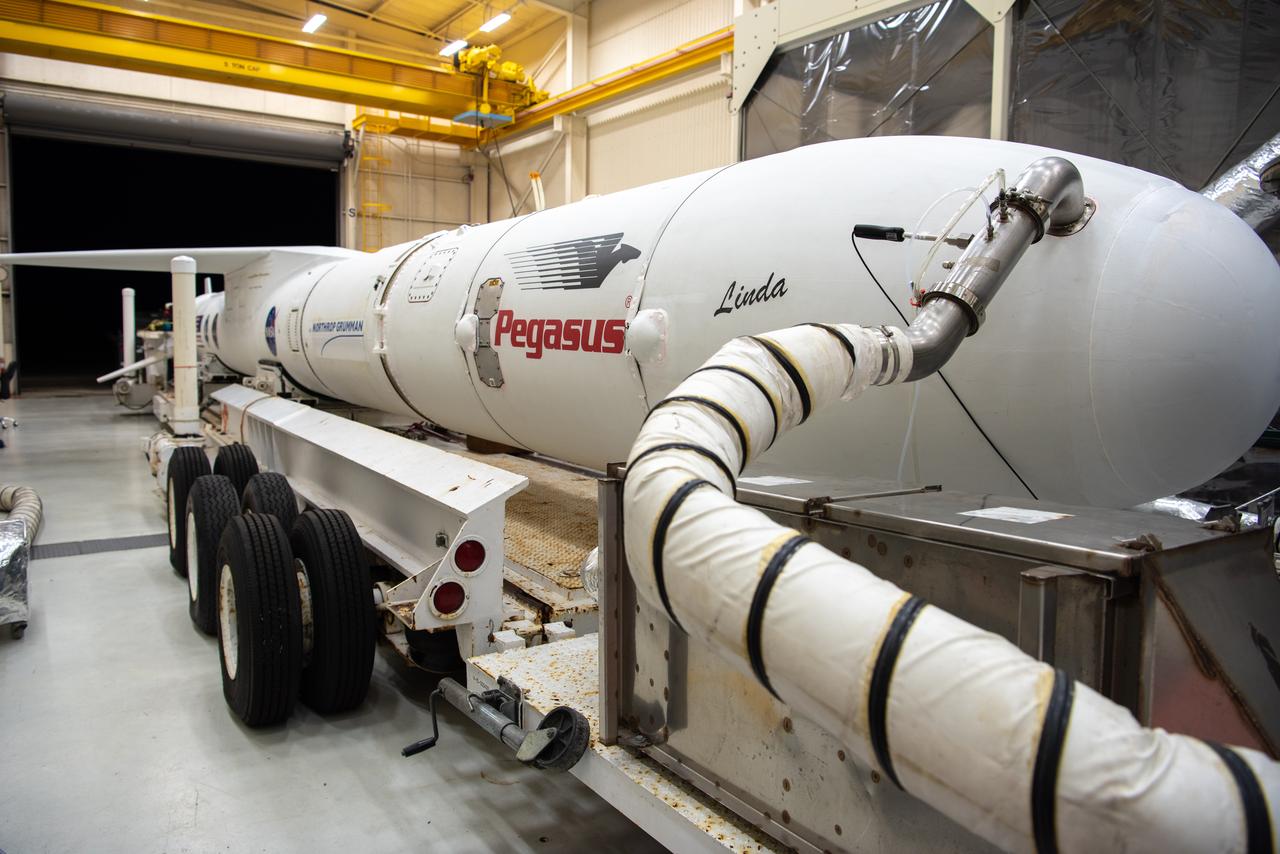

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, begins rollout from Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
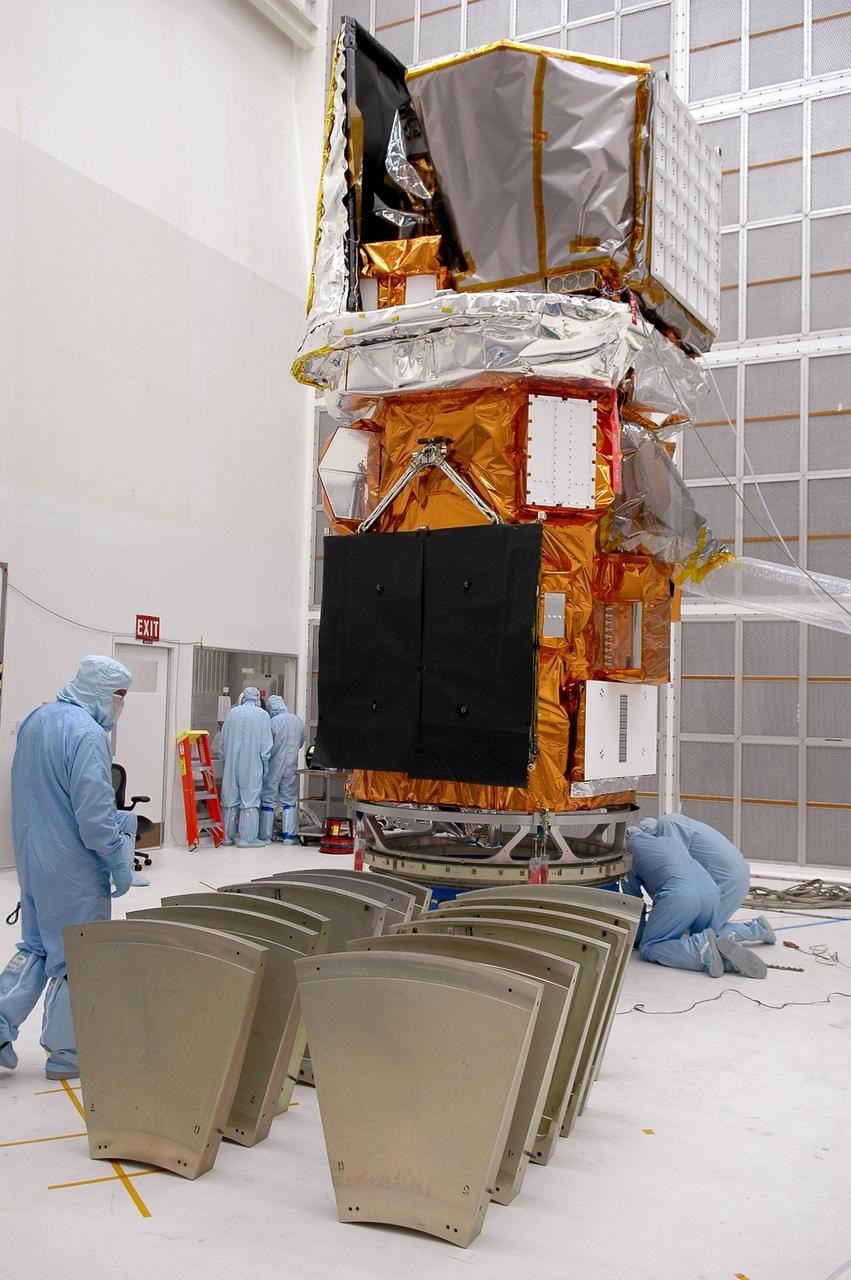

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA’s Hangar AE on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Fla., preparations are underway to enclose the Swift spacecraft in a canister before moving it to the launch pad. The base petals are lined up around the work stand before attaching them to the payload attach fitting on the Swift spacecraft. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Swift is scheduled to launch in mid-November from Launch Pad 17-A at CCAFS.
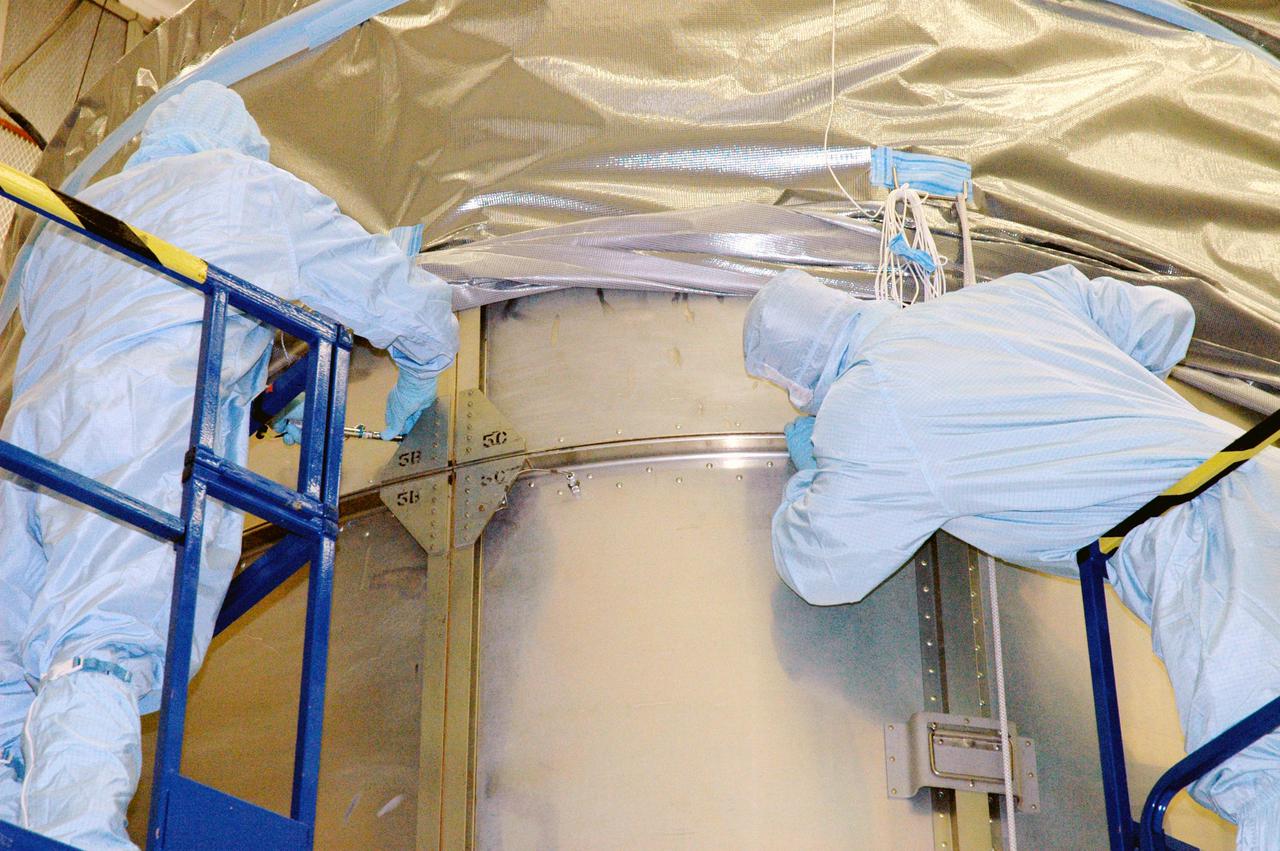

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Boeing technicians in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida attach the top of the payload transfer canister to the lower segments that surround the plastic-wrapped Swift spacecraft. The top holds an additional cover that will be lowered into place over the canister. The launch of the Swift observatory, a NASA spacecraft to pinpoint the location of gamma-ray bursts, is scheduled for Nov. 17 from Pad 17-A on CCAFS. Liftoff aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is targeted at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. They are the most powerful explosions known in the universe, emitting more than 100 billion times the energy that the Sun emits in a year. Yet they last only from a few milliseconds to a few minutes, never to appear in the same spot again.
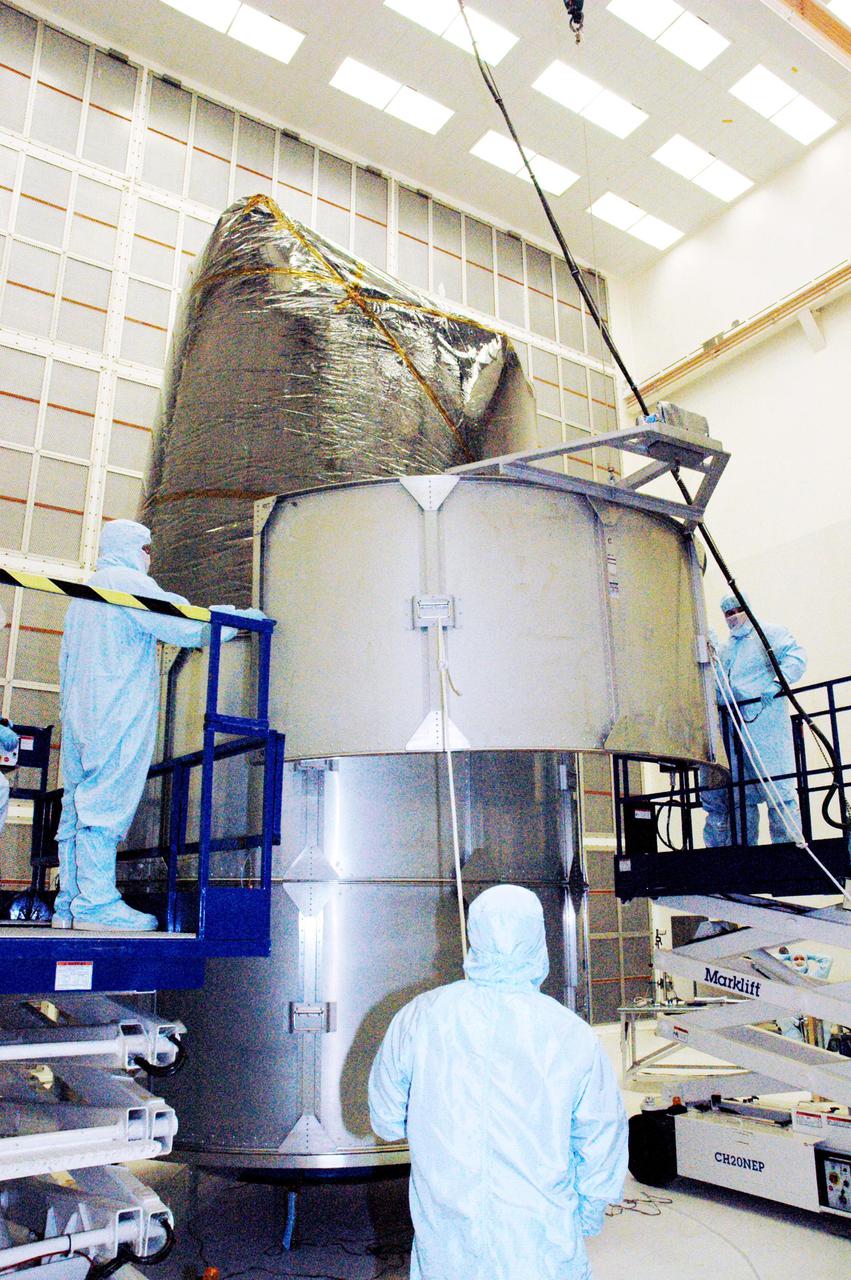

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Boeing technicians in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida maneuver a segment of the payload transfer canister into place around the plastic-wrapped Swift spacecraft. The launch of the Swift observatory, a NASA spacecraft to pinpoint the location of gamma-ray bursts, is scheduled for Nov. 17 from Pad 17-A on CCAFS. Liftoff aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is targeted at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. They are the most powerful explosions known in the universe, emitting more than 100 billion times the energy that the Sun emits in a year. Yet they last only from a few milliseconds to a few minutes, never to appear in the same spot again.
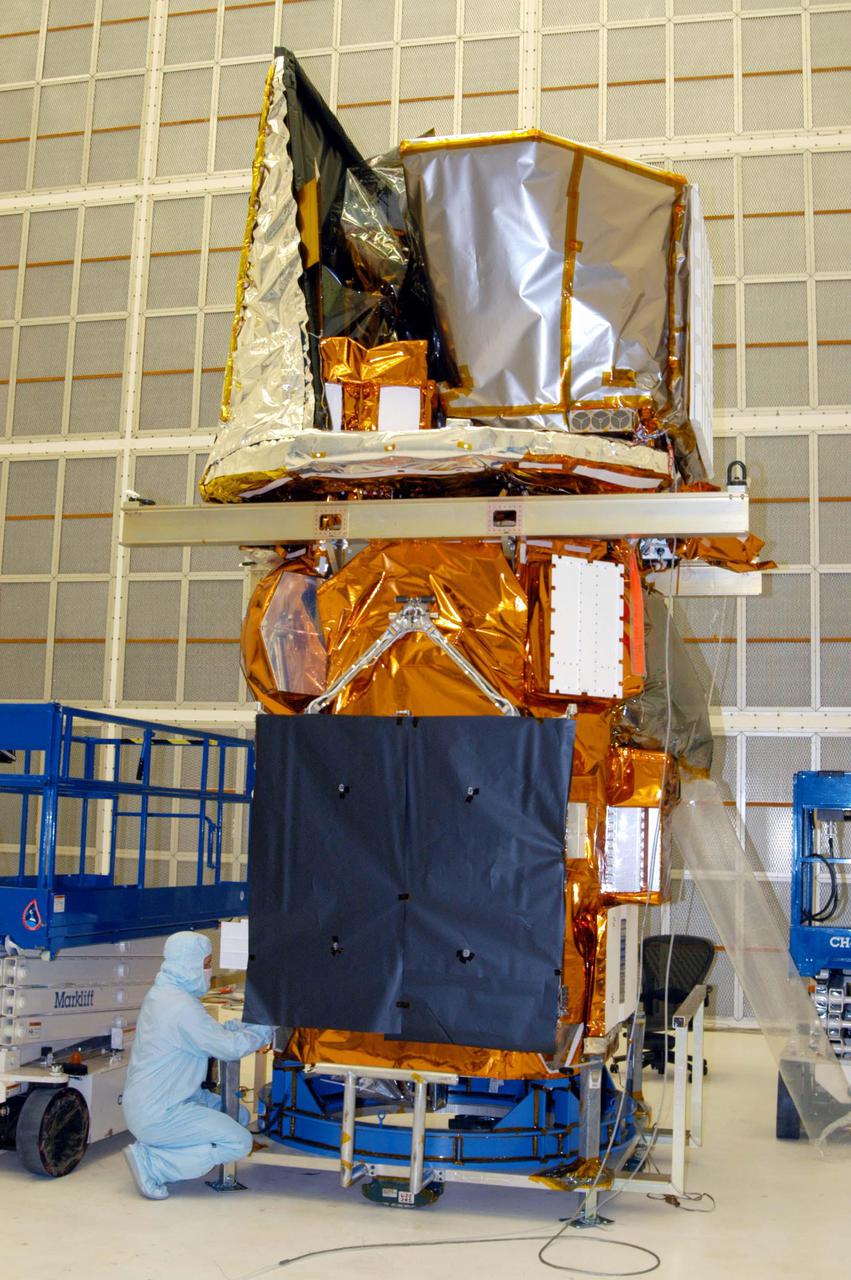

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A technician at NASA’s Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), prepares the Swift spacecraft to be lifted off its workstand. The spacecraft will be mated to a payload attach fitting, the interface between the spacecraft and the second stage of the Boeing Delta II rocket. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Swift is scheduled to launch in November from Launch Pad 17-A at CCAFS.
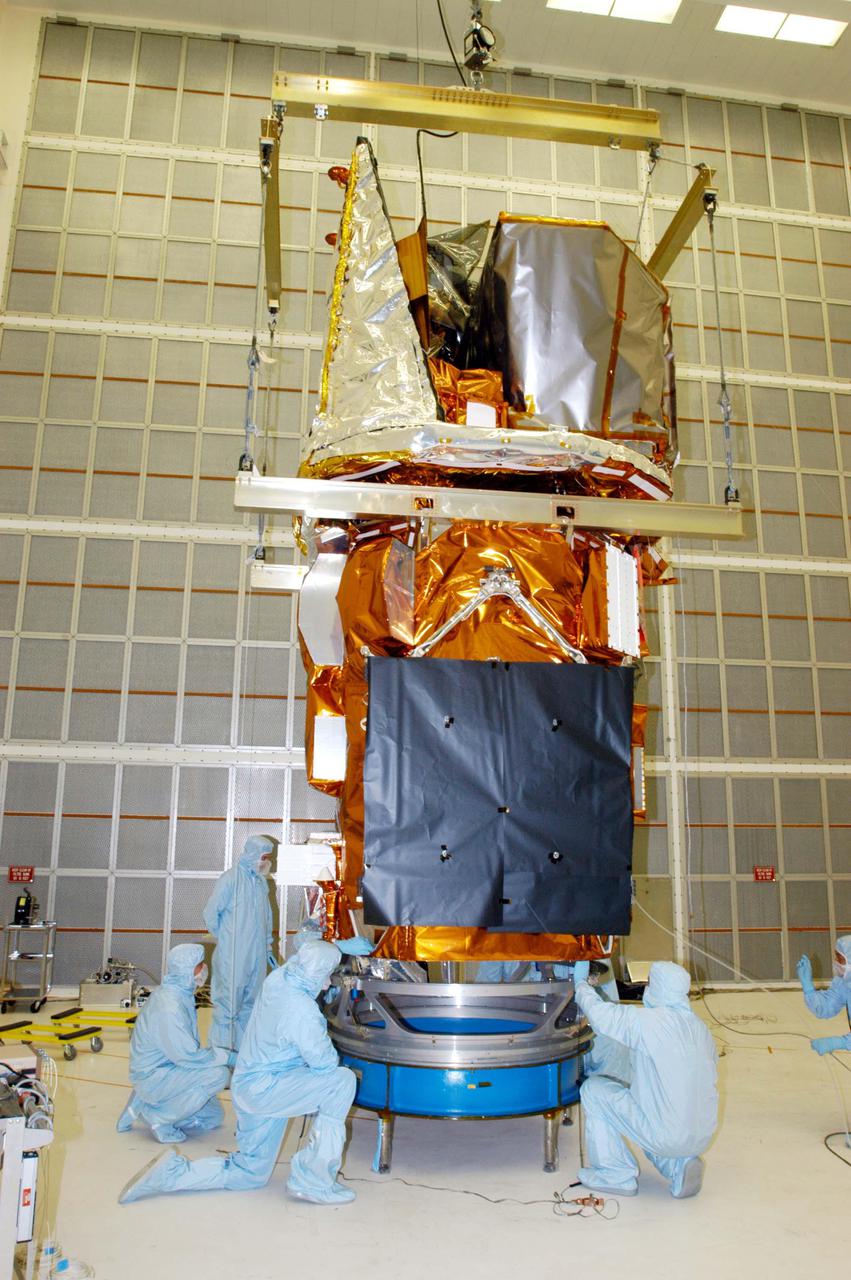

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians at NASA’s Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), help guide the Swift spacecraft being lowered onto a payload attach fitting, the interface between the spacecraft and the second stage of the Boeing Delta II rocket. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Swift is scheduled to launch in November from Launch Pad 17-A at CCAFS.
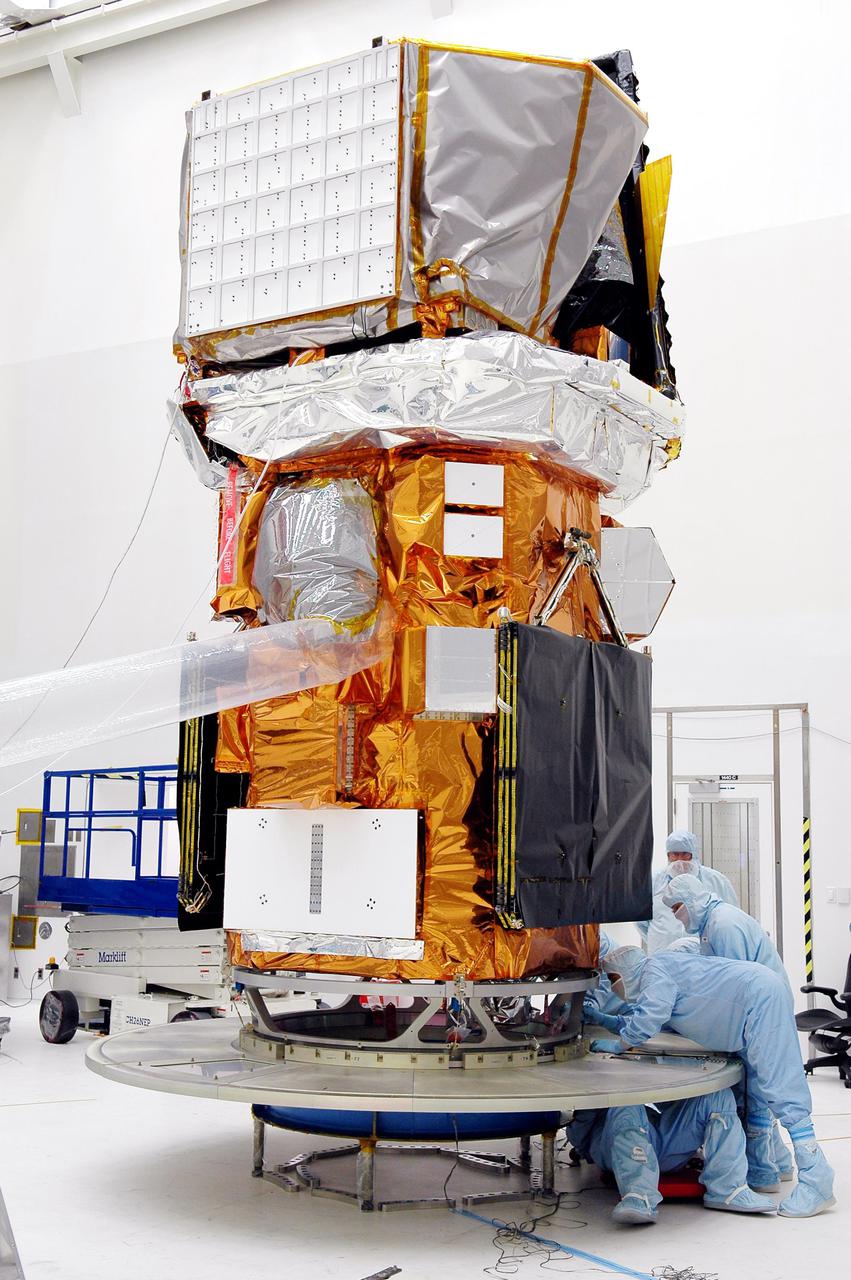

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA’s Hangar AE on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Fla., technicians check the attachment of the base petals of a transportation canister around the bottom of the payload attach fitting on the Swift spacecraft. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Swift is scheduled to launch in mid-November from Launch Pad 17-A at CCAFS.
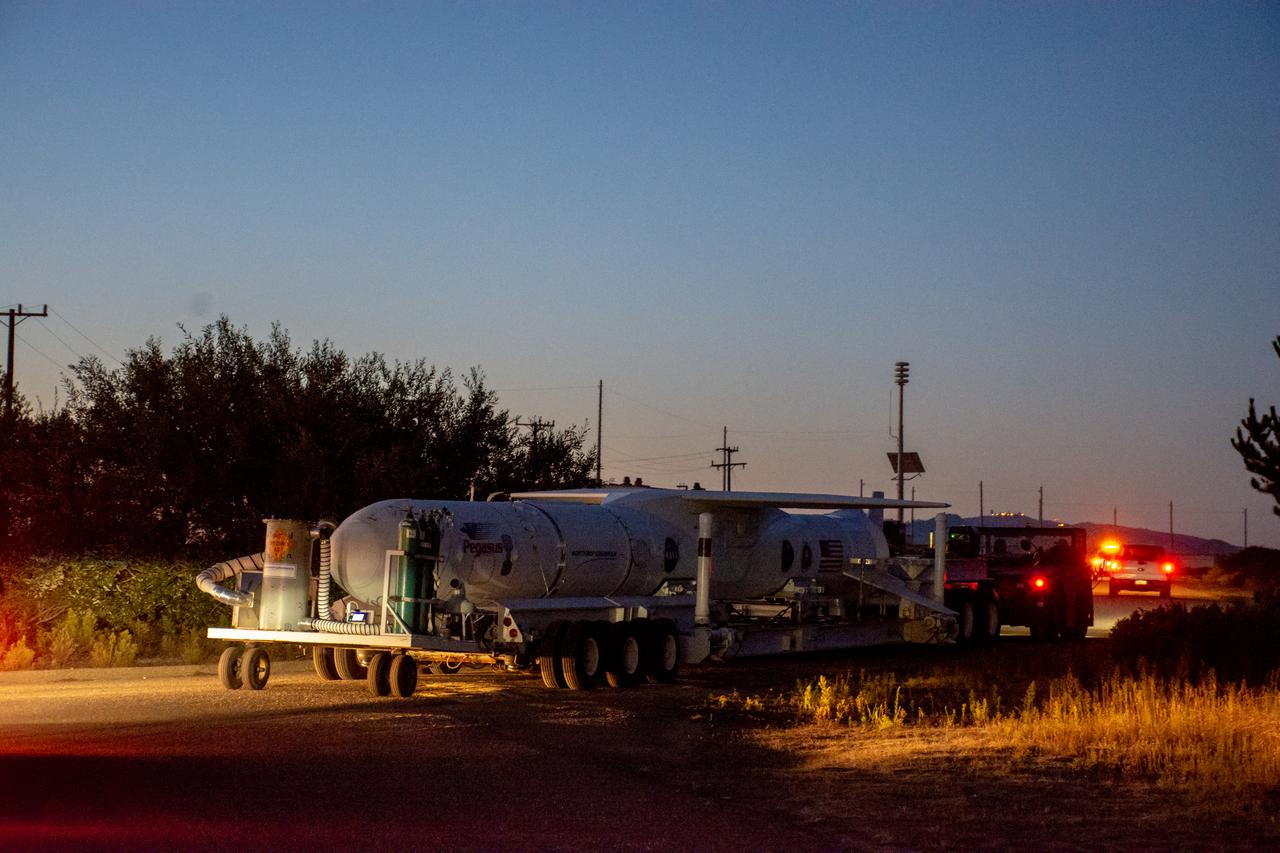

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, rolls out to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
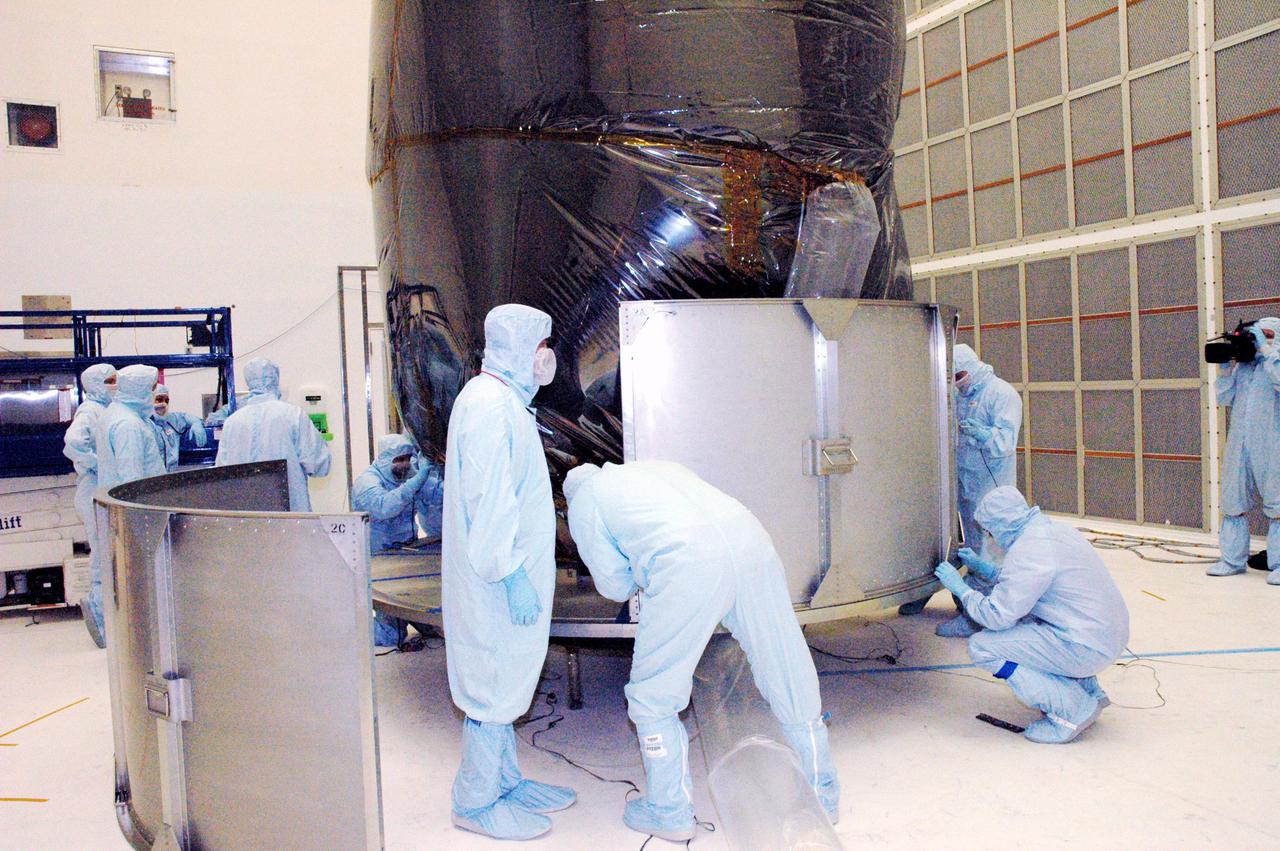

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Boeing technicians in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida install the lower part of the payload transfer canister around the plastic-wrapped Swift spacecraft. The launch of the Swift observatory, a NASA spacecraft to pinpoint the location of gamma-ray bursts, is scheduled for Nov. 17 from Pad 17-A on CCAFS. Liftoff aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is targeted at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. They are the most powerful explosions known in the universe, emitting more than 100 billion times the energy that the Sun emits in a year. Yet they last only from a few milliseconds to a few minutes, never to appear in the same spot again.
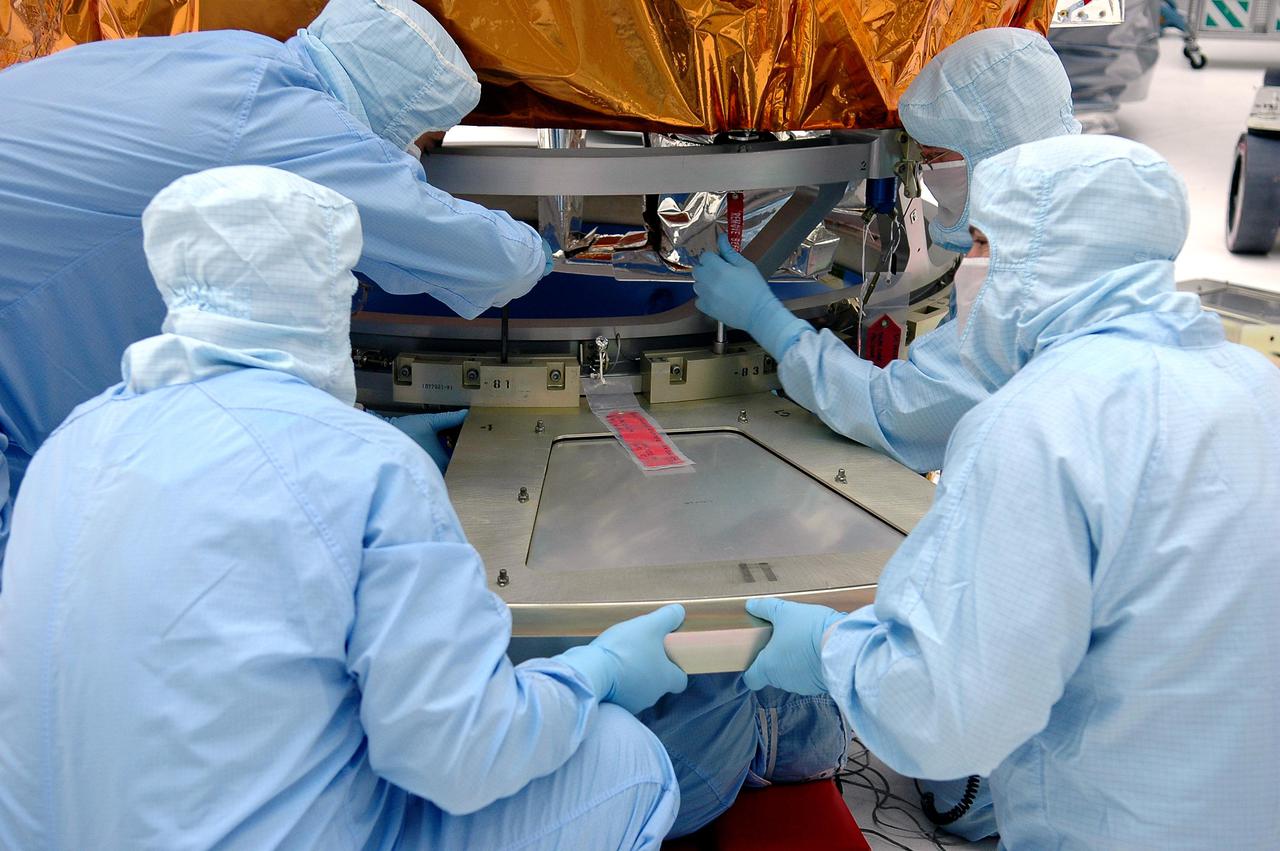

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA’s Hangar AE on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Fla., technicians attach the base petals of a transportation canister around the bottom of the payload attach fitting on the Swift spacecraft. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Swift is scheduled to launch in mid-November from Launch Pad 17-A at CCAFS.
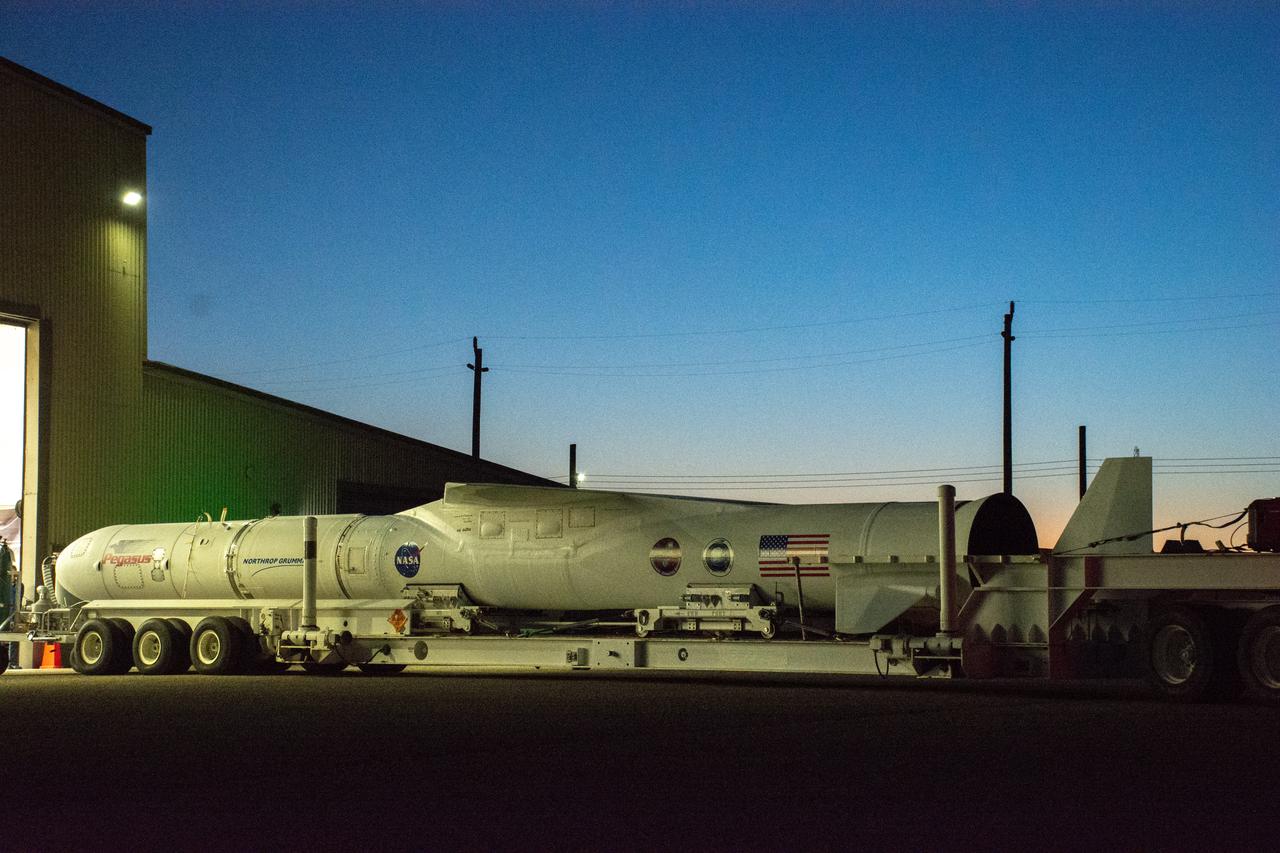

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, begins rollout from Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Boeing technicians in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida secure bands around the payload transfer canister to hold the plastic cover in place. The launch of the Swift observatory, a NASA spacecraft to pinpoint the location of gamma-ray bursts, is scheduled for Nov. 17 from Pad 17-A on CCAFS. Liftoff aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is targeted at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. They are the most powerful explosions known in the universe, emitting more than 100 billion times the energy that the Sun emits in a year. Yet they last only from a few milliseconds to a few minutes, never to appear in the same spot again.
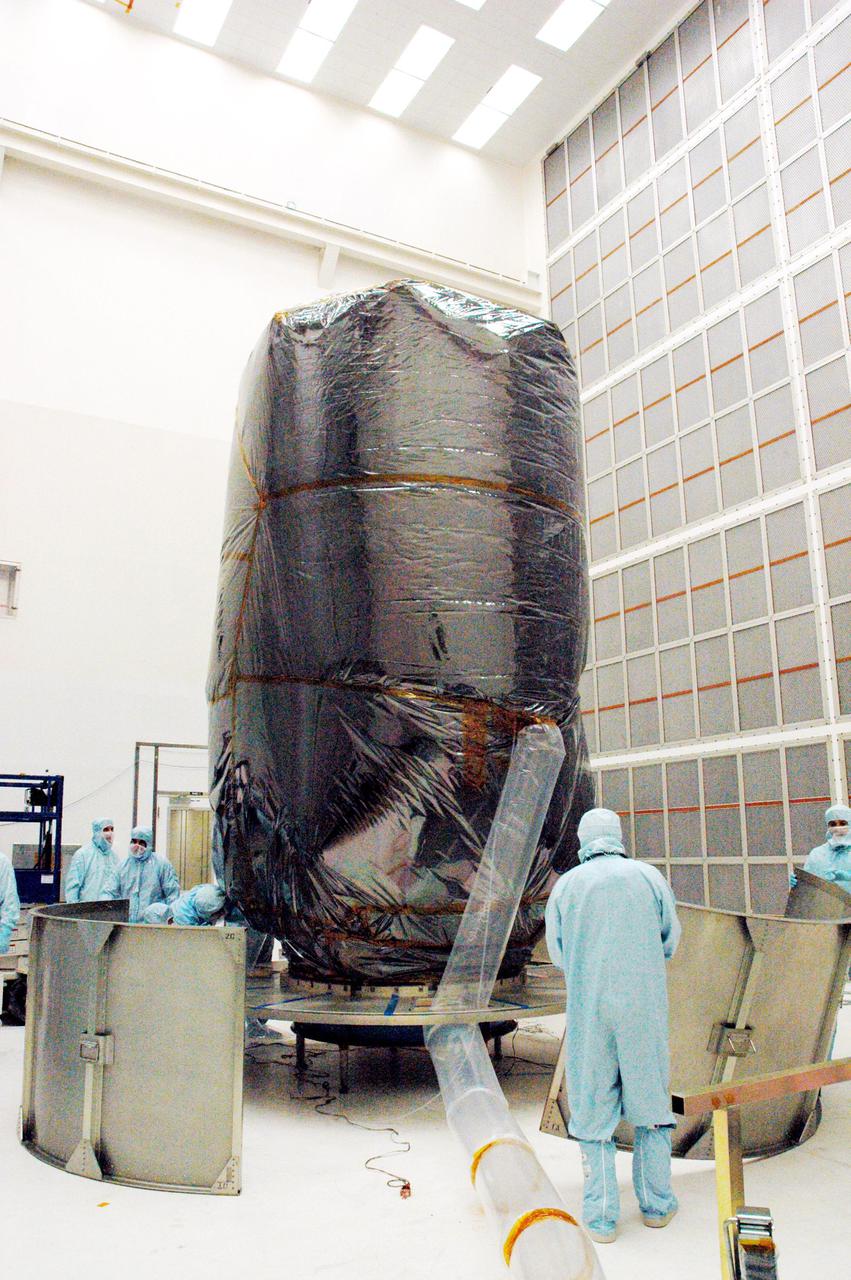

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Boeing technicians in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida set up segments of the payload transfer canister that will be installed around the plastic-wrapped Swift spacecraft. The launch of the Swift observatory, a NASA spacecraft to pinpoint the location of gamma-ray bursts, is scheduled for Nov. 17 from Pad 17-A on CCAFS. Liftoff aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is targeted at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. They are the most powerful explosions known in the universe, emitting more than 100 billion times the energy that the Sun emits in a year. Yet they last only from a few milliseconds to a few minutes, never to appear in the same spot again.
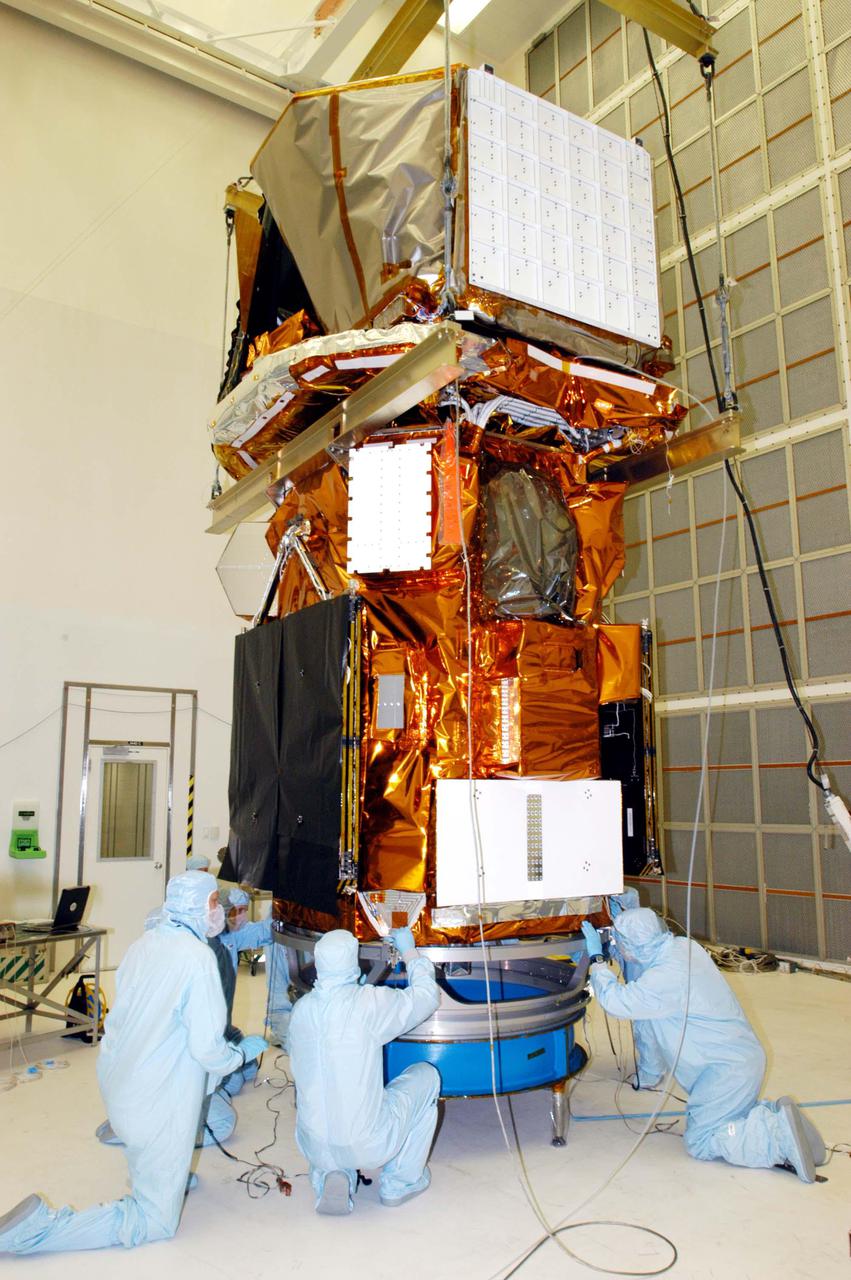

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians at NASA’s Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), check the attachment of the Swift spacecraft to the payload attach fitting, the interface between the spacecraft and the second stage of the Boeing Delta II rocket. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Swift is scheduled to launch in November from Launch Pad 17-A at CCAFS.
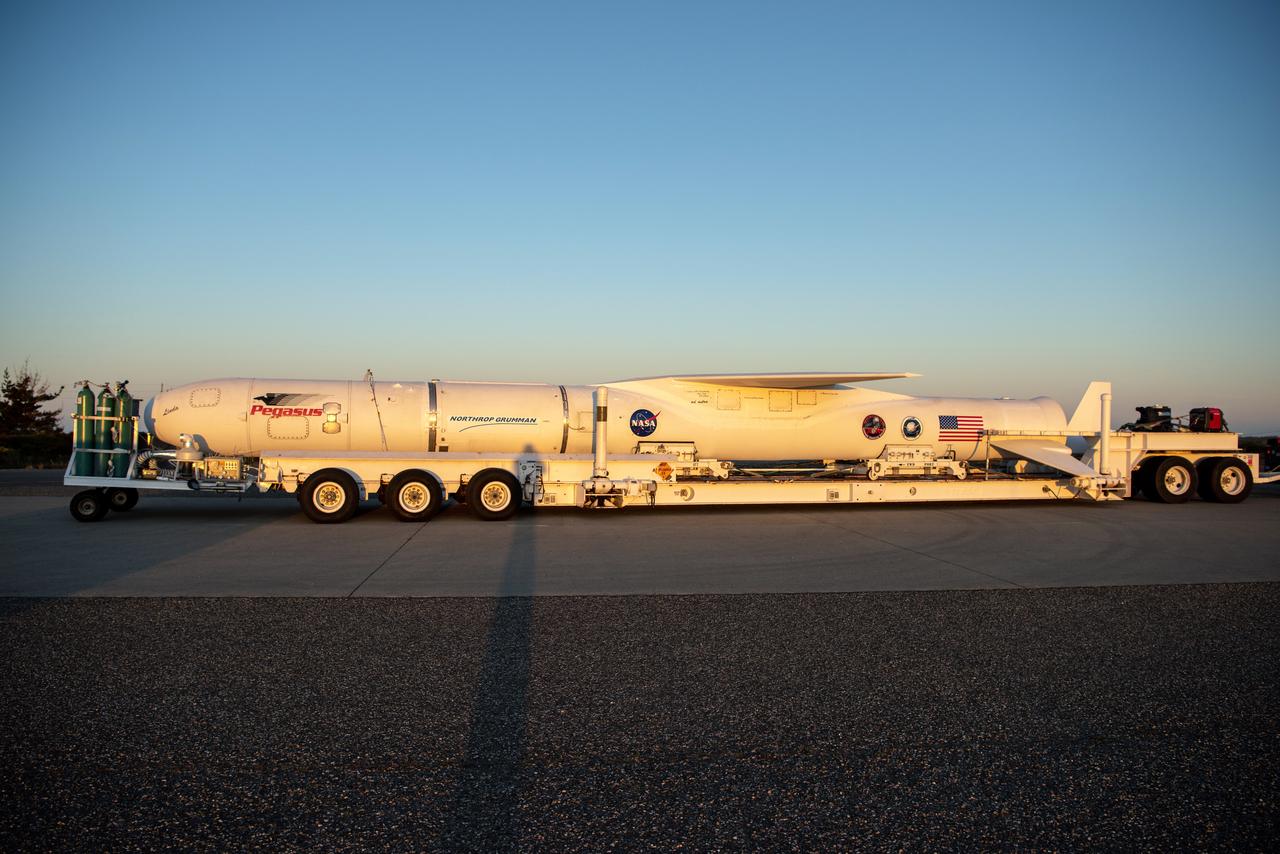

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, rolls out to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
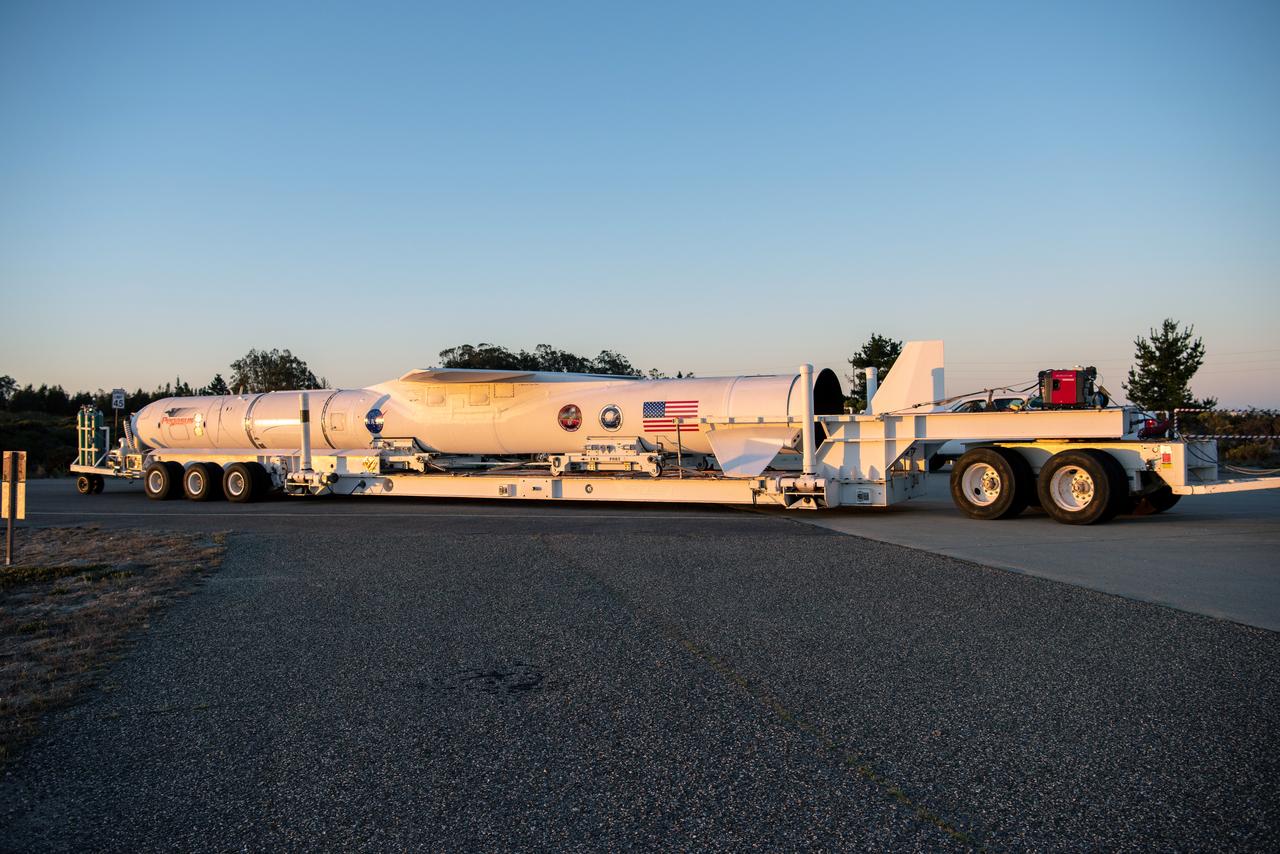

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, rolls out from Building 1555 to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
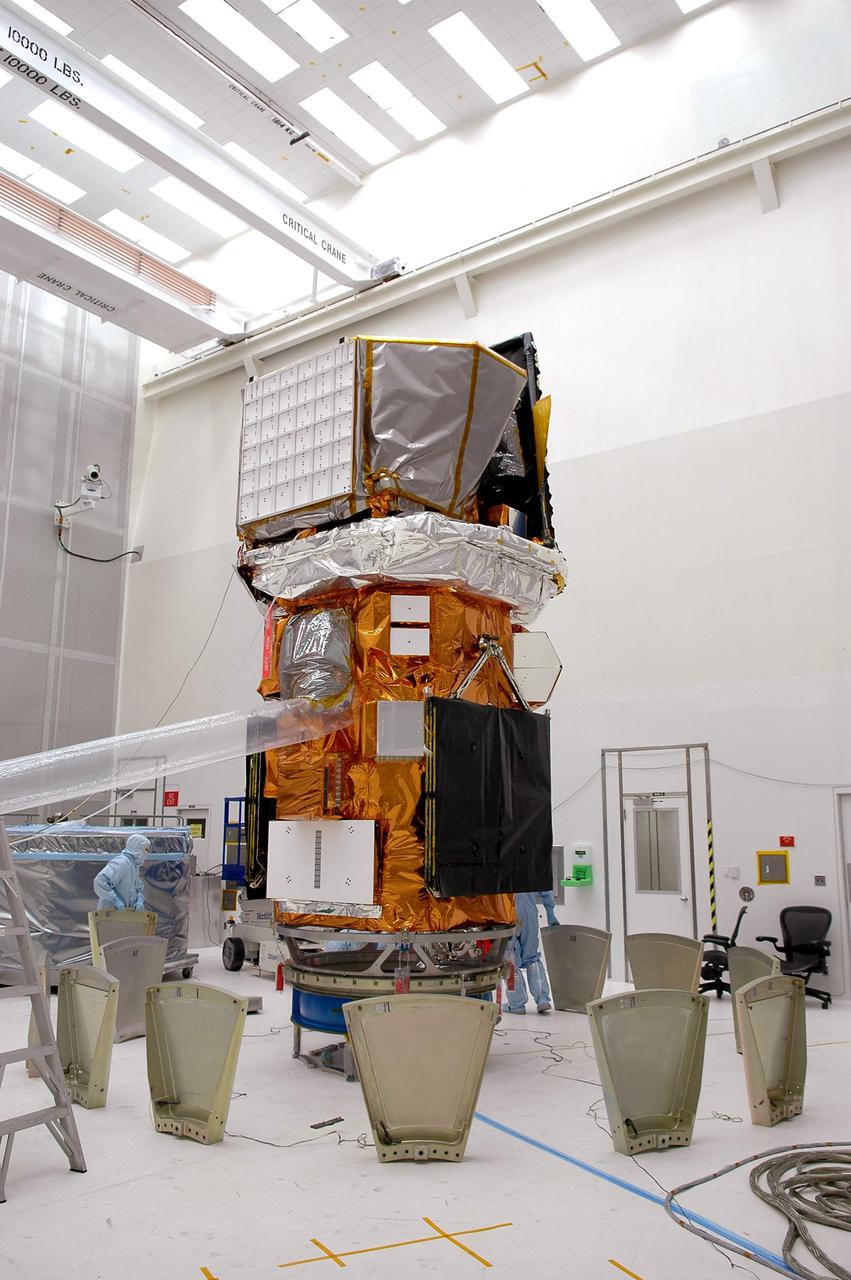

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA’s Hangar AE on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Fla., preparations are underway to enclose the Swift spacecraft in a canister before moving it to the launch pad. The base petals are lined up around the work stand before attaching them to the payload attach fitting on the Swift spacecraft. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Swift is scheduled to launch in mid-November from Launch Pad 17-A at CCAFS.
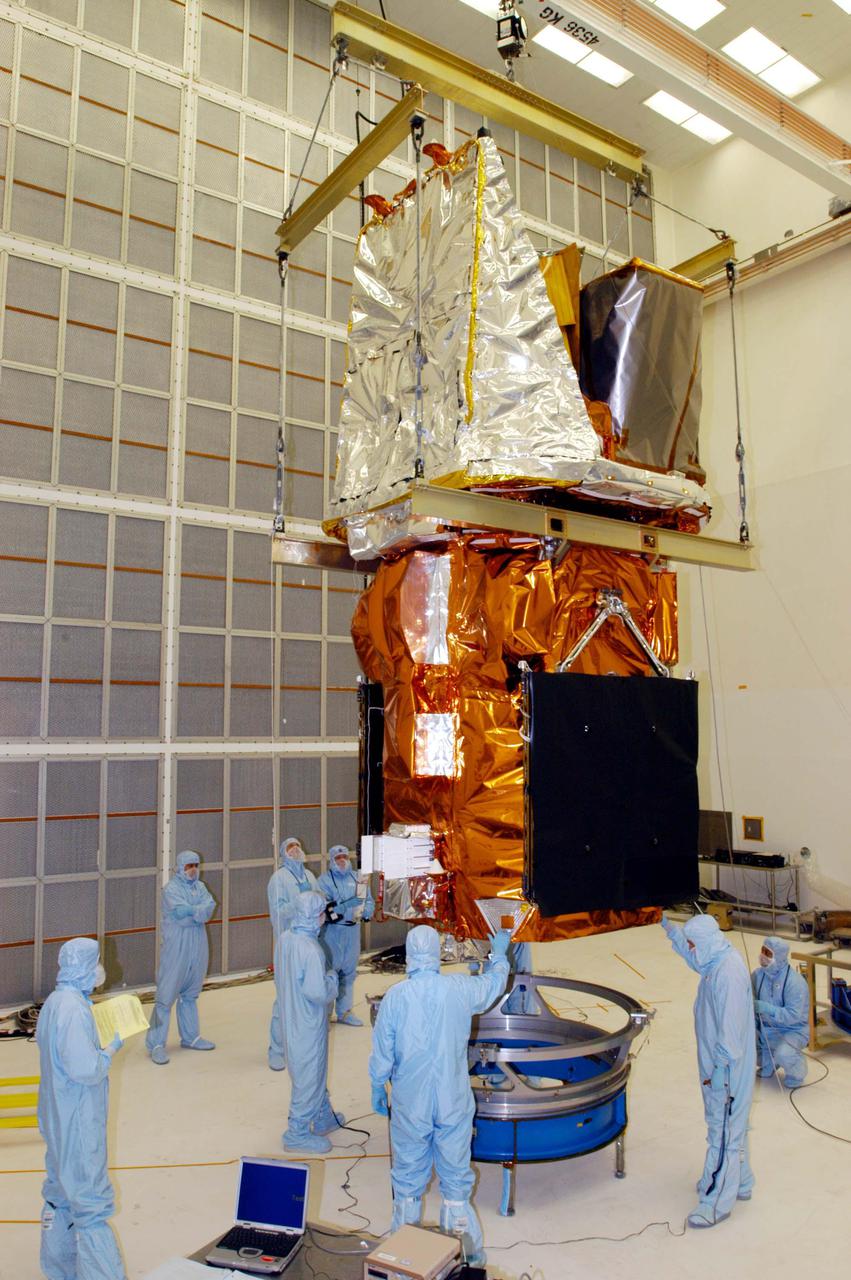

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians at NASA’s Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), stand by while the Swift spacecraft is lowered toward a payload attach fitting, the interface between the spacecraft and the second stage of the Boeing Delta II rocket. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Swift is scheduled to launch in November from Launch Pad 17-A at CCAFS.

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), the Atlas IIA rocket is halfway to a vertical position at the launch tower where it will be mated with the Centaur upper stage. The Atlas IIA/Centaur will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket is ready to be lifted to vertical in the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket begins to be lifted to a vertical position at the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket begins to be lifted to a vertical position at the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
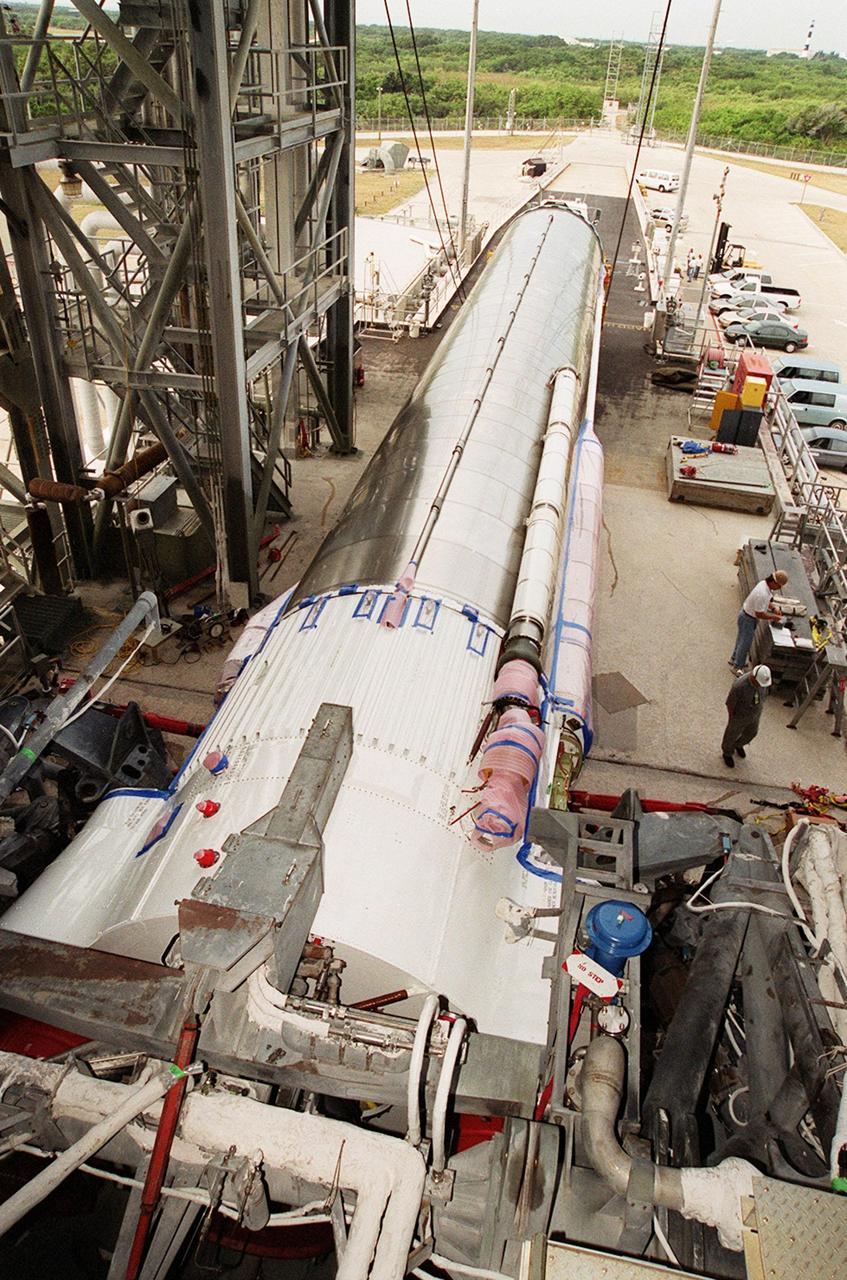

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket is ready to be lifted to vertical in the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
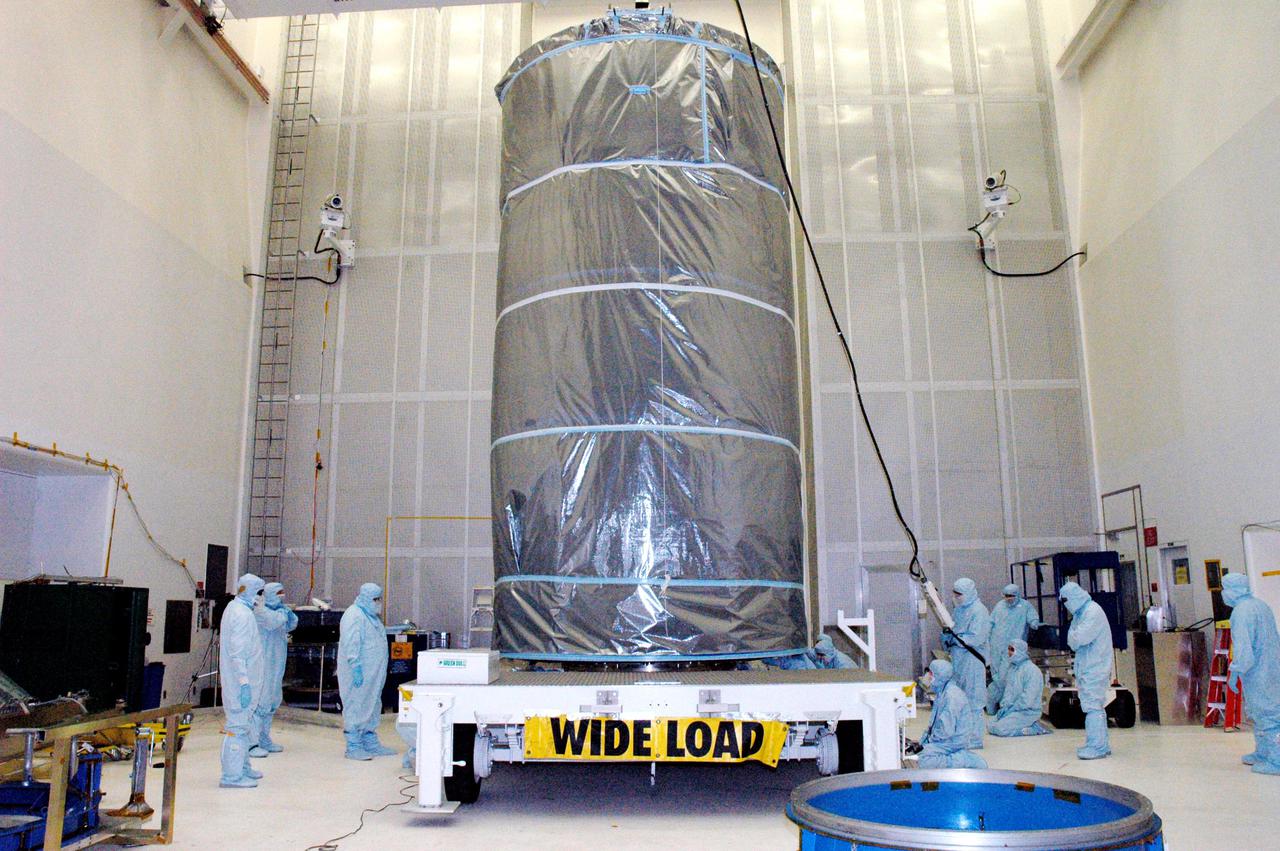

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Swift spacecraft, fully encased inside the payload transfer canister, is secured on a transport vehicle for a trip to the launch pad. The launch of the Swift observatory, a NASA spacecraft to pinpoint the location of gamma-ray bursts, is scheduled for Nov. 17 from Pad 17-A on CCAFS. Liftoff aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is targeted at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. They are the most powerful explosions known in the universe, emitting more than 100 billion times the energy that the Sun emits in a year. Yet they last only from a few milliseconds to a few minutes, never to appear in the same spot again.
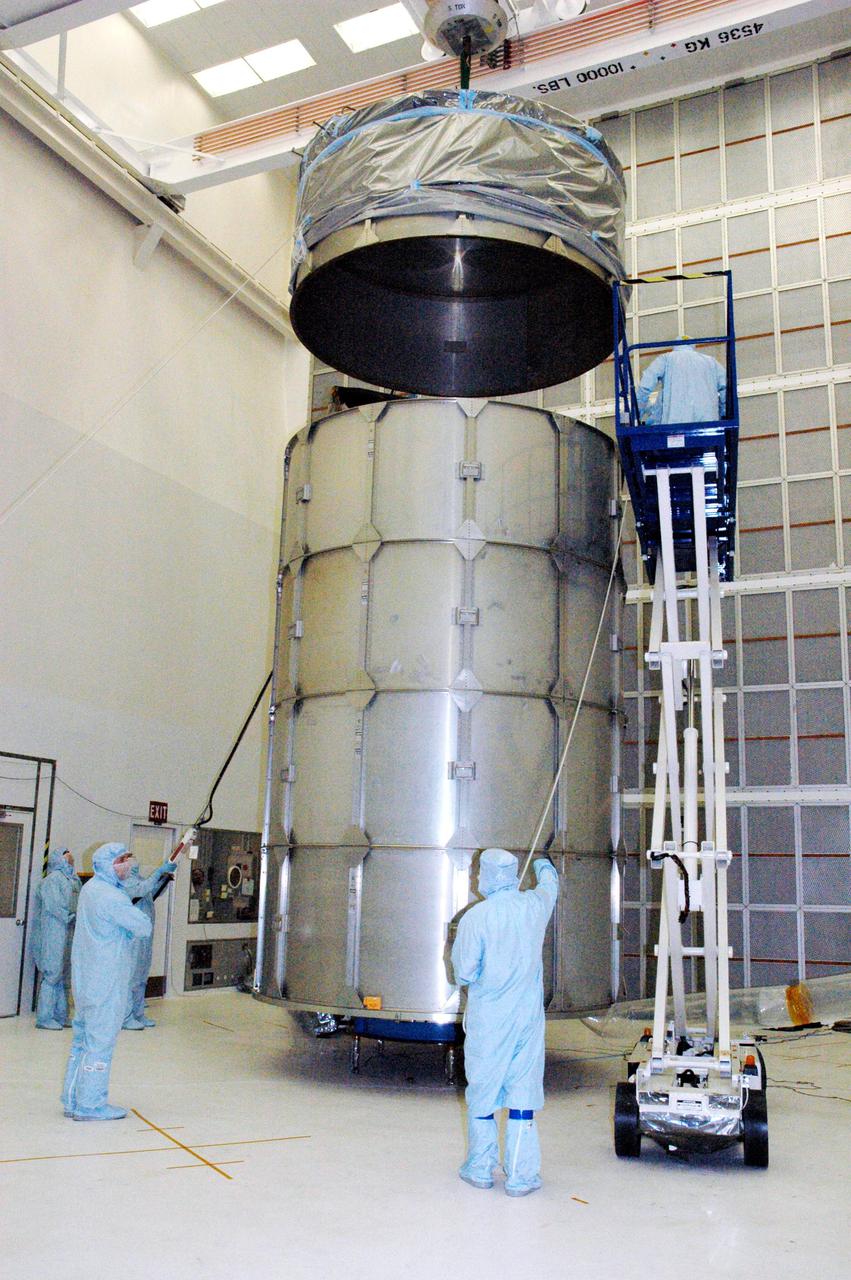

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - With four rows of payload transfer canister segments in place around the plastic-wrapped Swift spacecraft, Boeing technicians lower the top into place. The top holds an additional cover that will be lowered into place over the canister. The launch of the Swift observatory, a NASA spacecraft to pinpoint the location of gamma-ray bursts, is scheduled for Nov. 17 from Pad 17-A on CCAFS. Liftoff aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is targeted at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. They are the most powerful explosions known in the universe, emitting more than 100 billion times the energy that the Sun emits in a year. Yet they last only from a few milliseconds to a few minutes, never to appear in the same spot again.
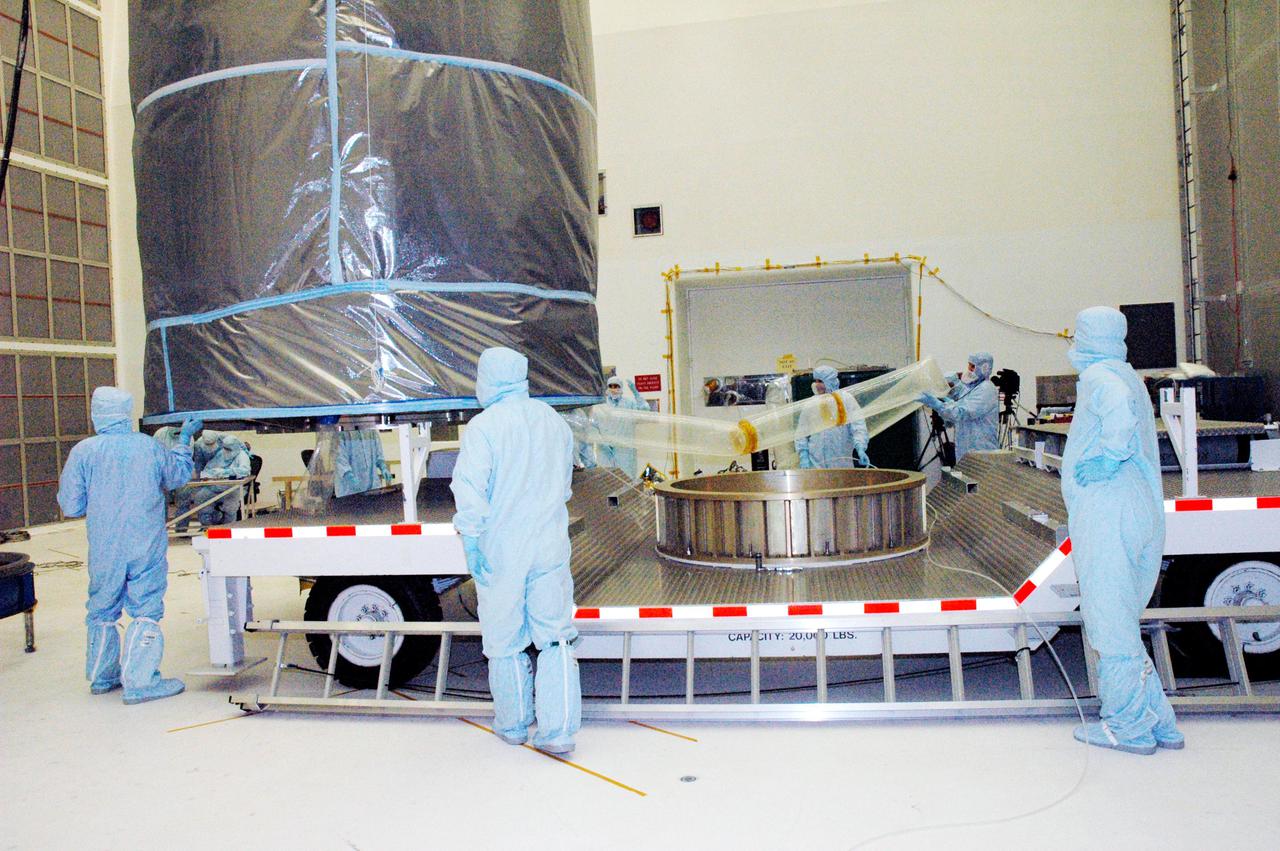

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Swift spacecraft, fully encased inside the payload transfer canister, is lifted onto a transport vehicle for a trip to the launch pad. The launch of the Swift observatory, a NASA spacecraft to pinpoint the location of gamma-ray bursts, is scheduled for Nov. 17 from Pad 17-A on CCAFS. Liftoff aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is targeted at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. They are the most powerful explosions known in the universe, emitting more than 100 billion times the energy that the Sun emits in a year. Yet they last only from a few milliseconds to a few minutes, never to appear in the same spot again.
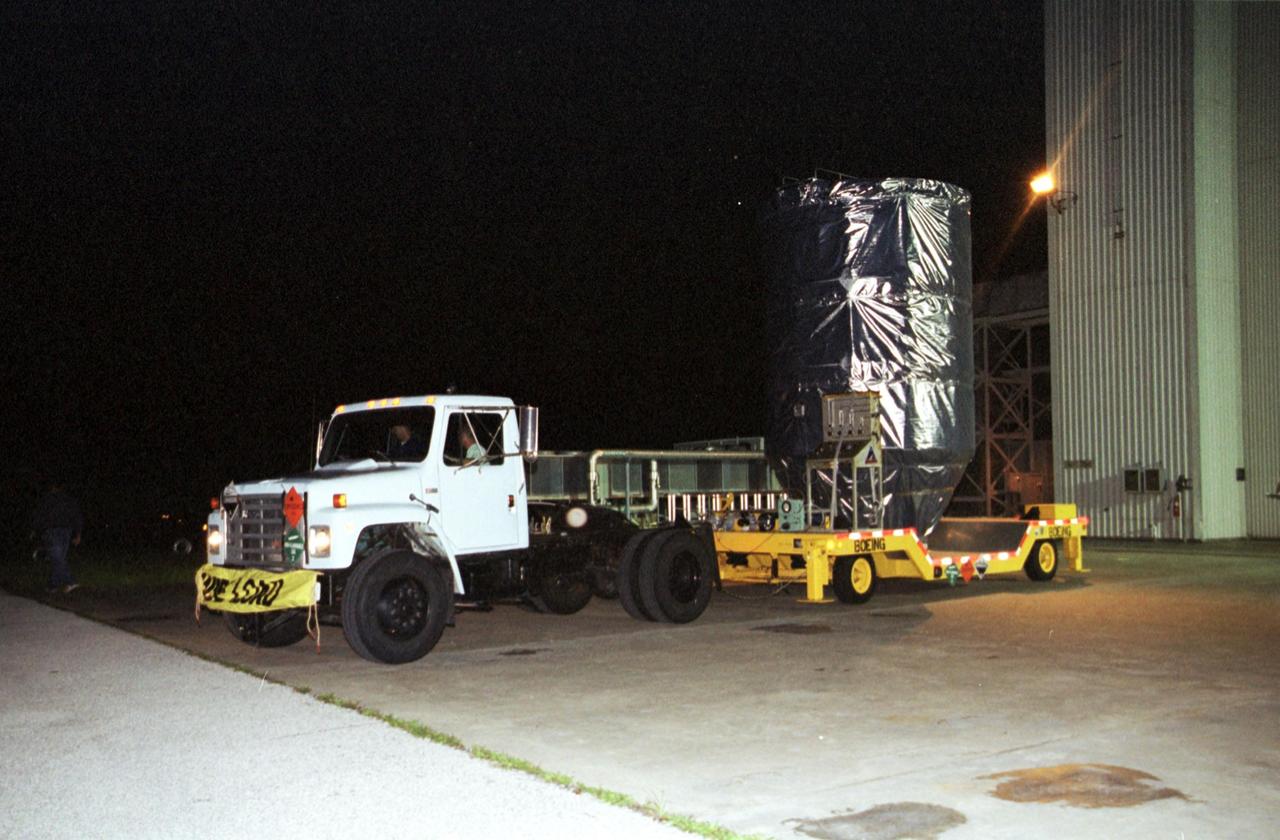

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Genesis spacecraft, enclosed in its protective cover, is transported from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on its way to Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Genesis is 7.5 feet (2.3 meters) long and 6.6 feet (2 meters) wide, with a wingspan of solar array 26 feet (7.9 meters) tip to tip. Genesis will be on a robotic NASA space mission to catch a wisp of the raw material of the Sun and return it to Earth with a spectacular mid-air helicopter capture. The sample return capsule is 4.9 feet (1.5 meters) in diameter and 52 inches (1.31 meters) tall. The mission’s goal is to collect and return to Earth just 10 to 20 micrograms -- or the weight of a few grains of salt -- of solar wind, invisible charged particles that flow outward from the Sun. This treasured smidgen of the Sun will be preserved in a special laboratory for study by scientists over the next century in search of answers to fundamental questions about the exact composition of our star and the birth of our solar system. The Genesis launch is scheduled for 12:36 p.m. EDT on July 30 from CCAFS
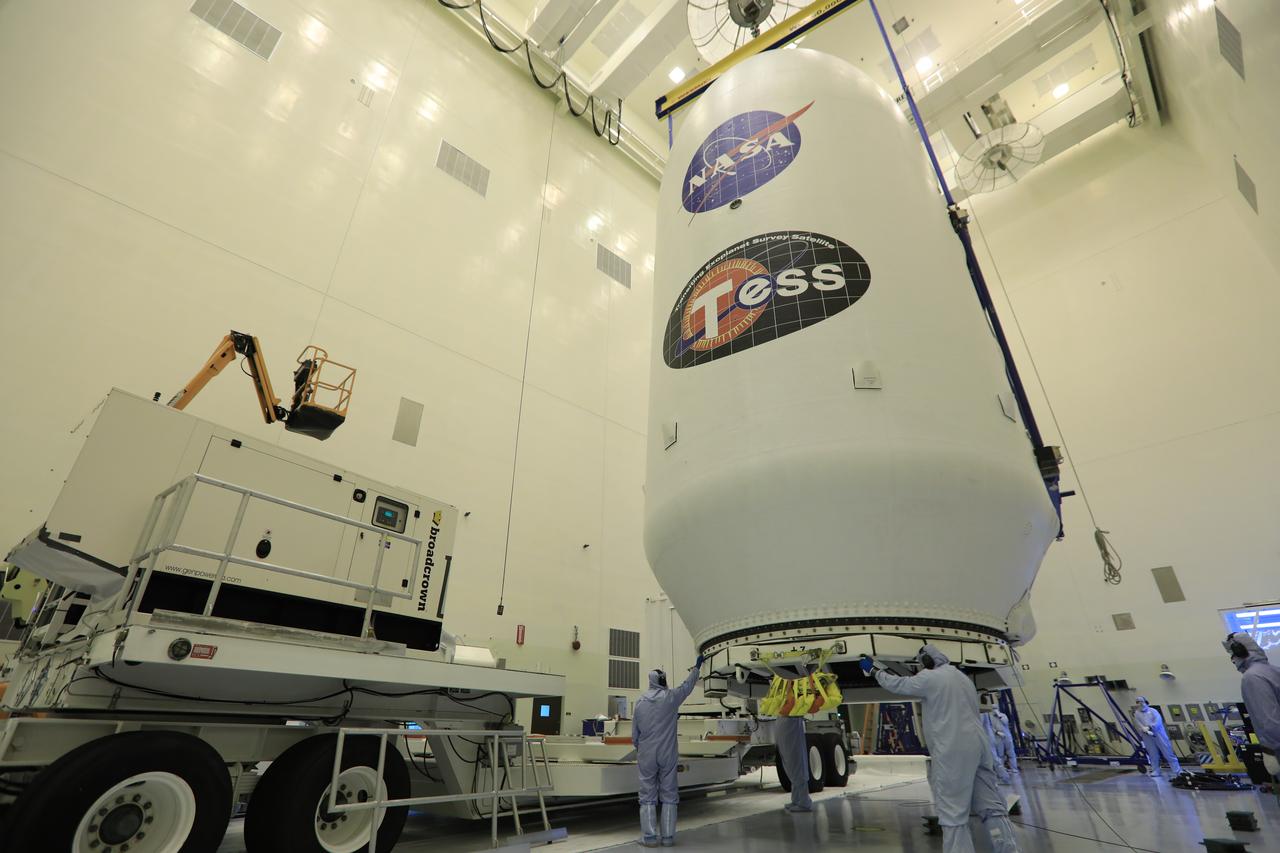

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as the SpaceX payload fairing containing the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is moved by crane to a transporter. The fairing will be moved to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is scheduled to launch on the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.

Technicians prepare NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) for encapsulation in the SpaceX payload fairing inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
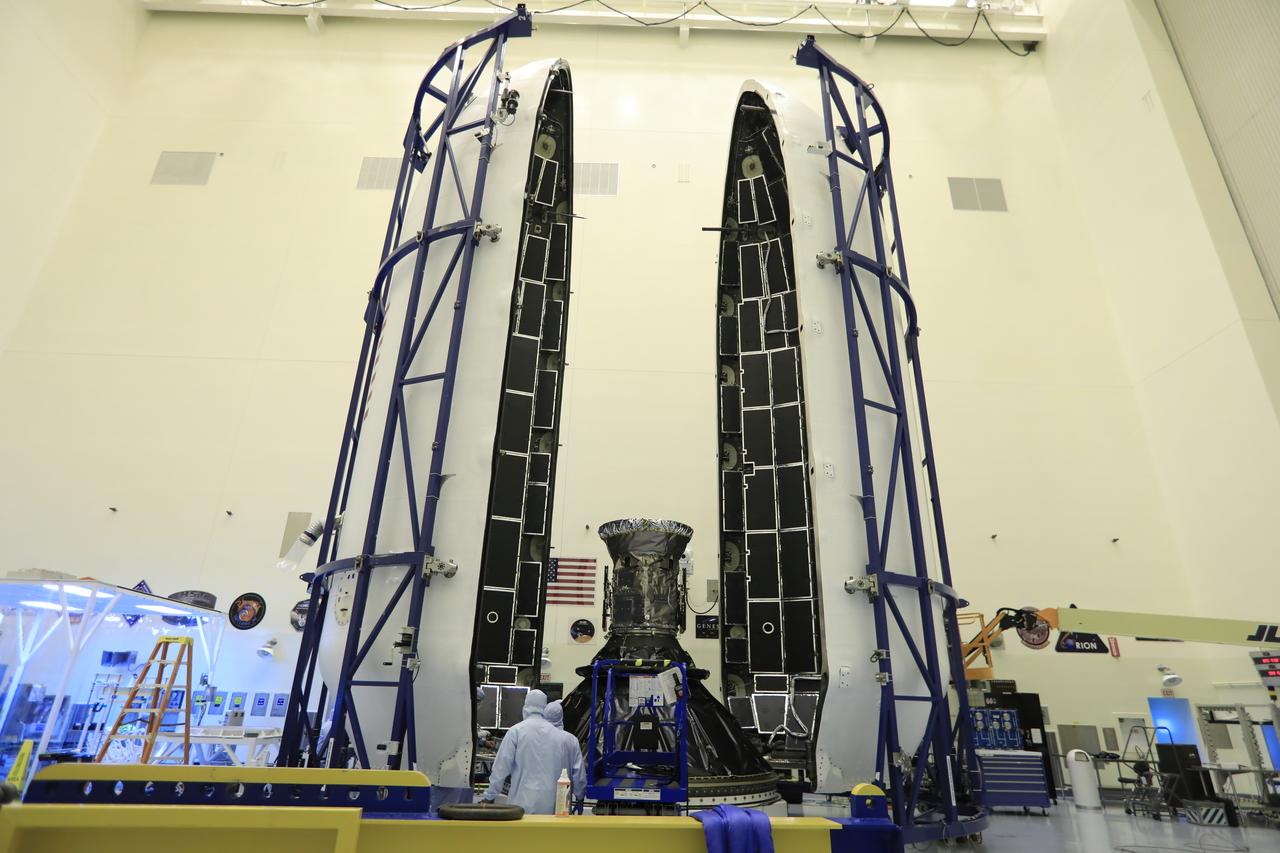

Technicians prepare NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) for encapsulation in the SpaceX payload fairing inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
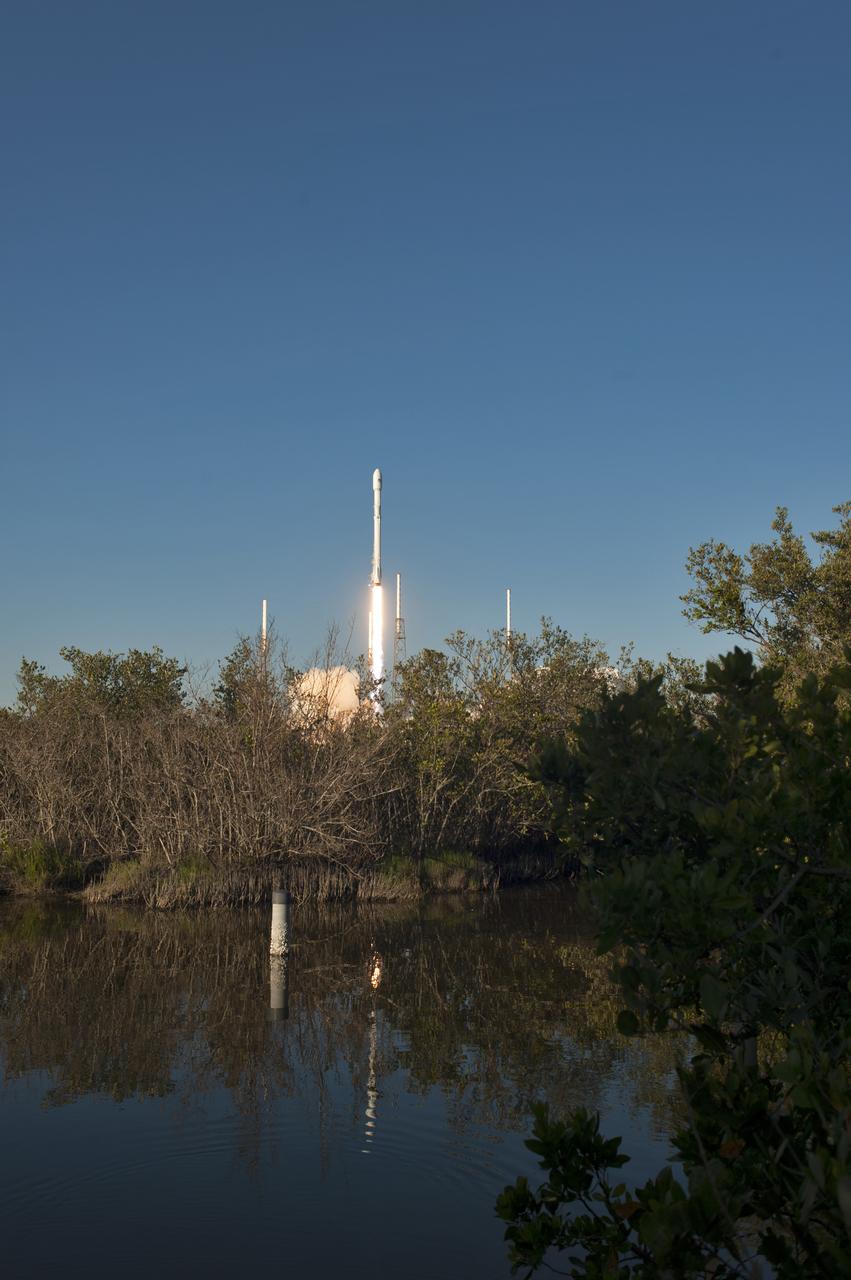

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
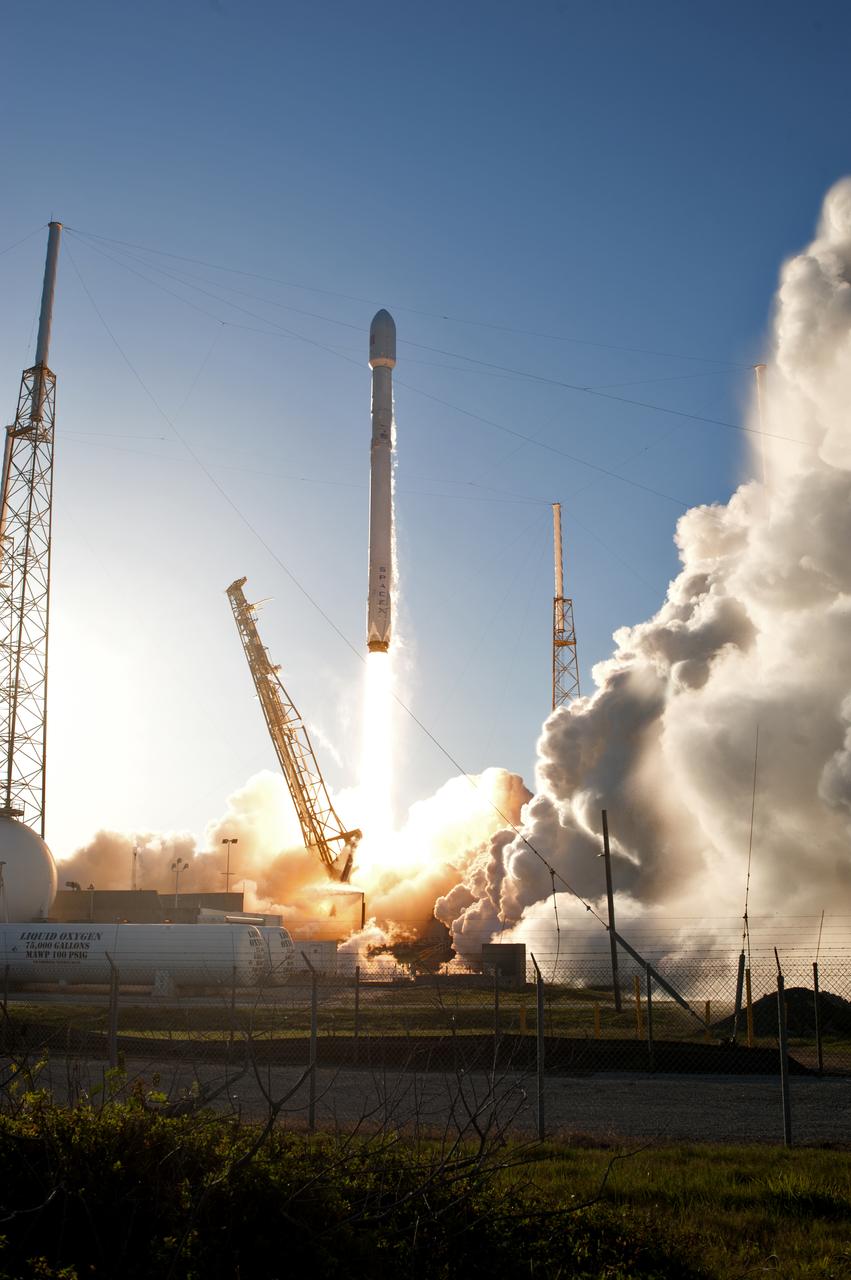

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
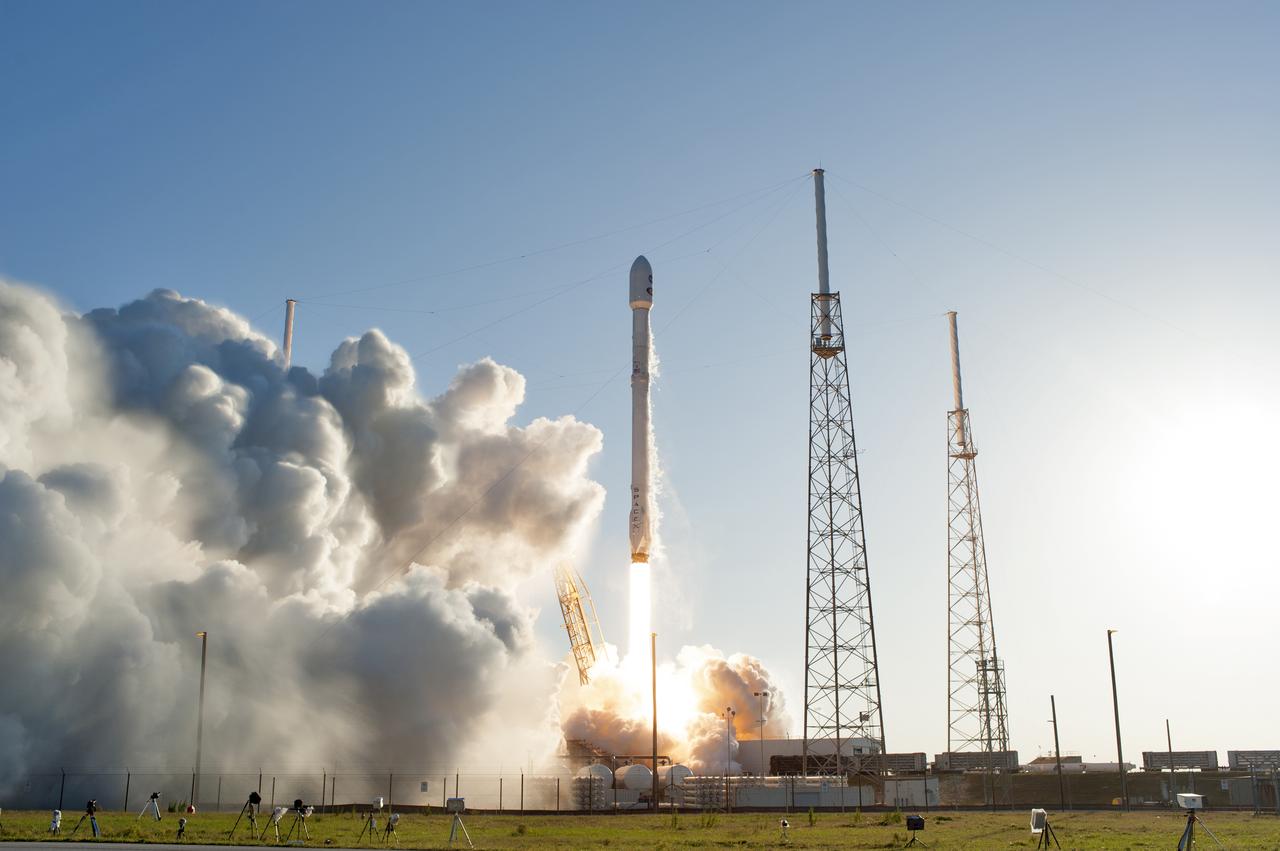

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
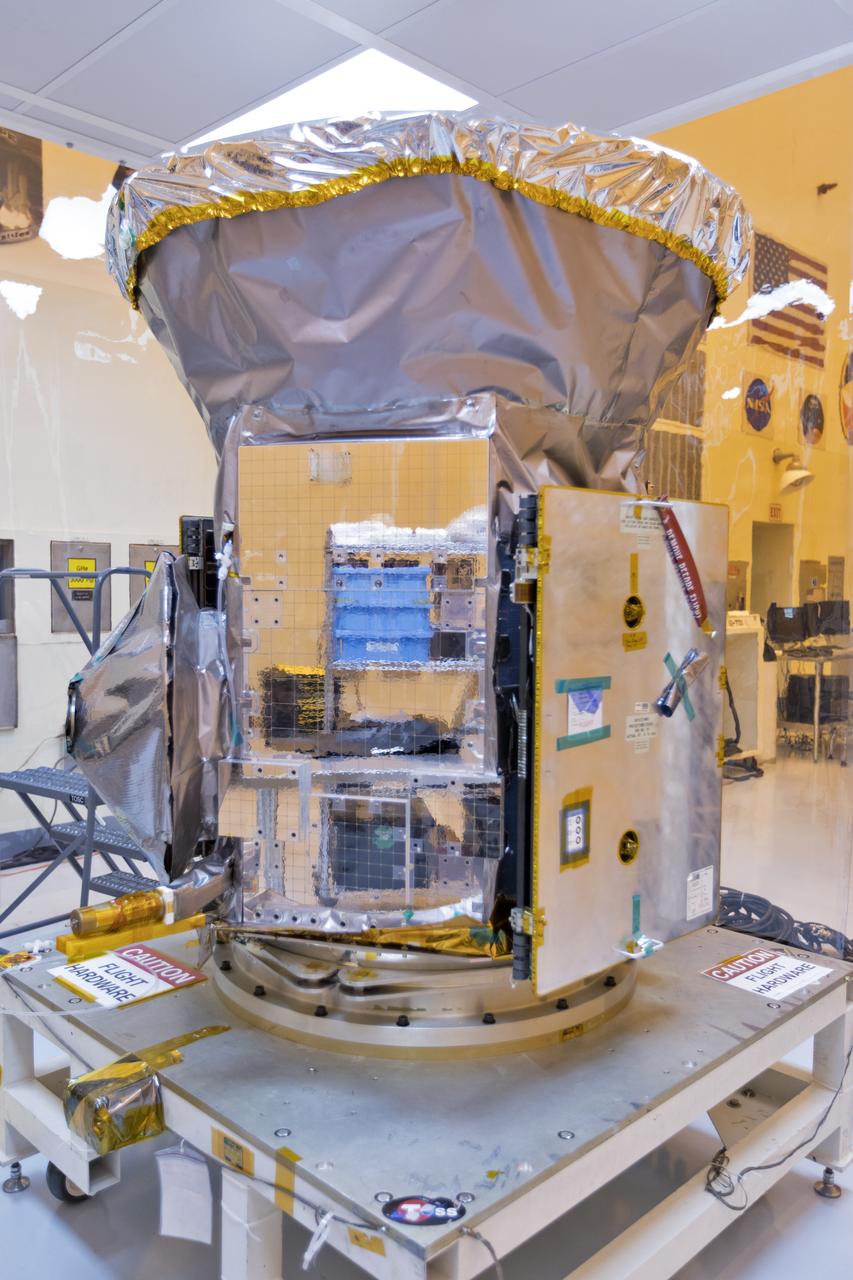

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, or TESS, has been uncreated from its shipping container for inspections and preflight processing. The satellite is NASA's next step in the search for planets outside of the solar system also known as "exoplanets." TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, and the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management. SpaceX of Hawthorne, California, is the provider of the Falcon 9 launch service. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket no earlier than April 16, 2018 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

The SpaceX payload fairing containing NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is prepared for the move from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. TESS is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
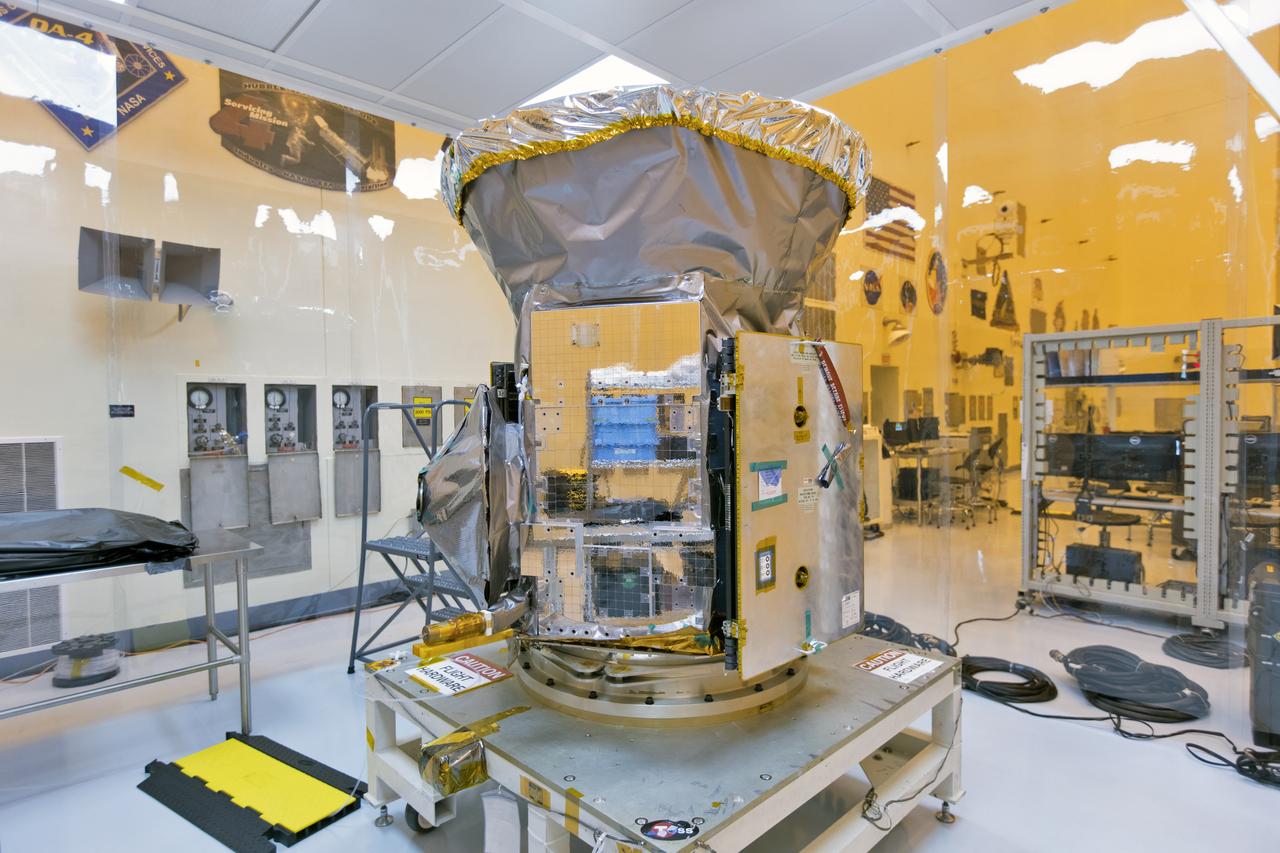

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, or TESS, has been uncreated from its shipping container for inspections and preflight processing. The satellite is NASA's next step in the search for planets outside of the solar system also known as "exoplanets." TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, and the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management. SpaceX of Hawthorne, California, is the provider of the Falcon 9 launch service. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket no earlier than April 16, 2018 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
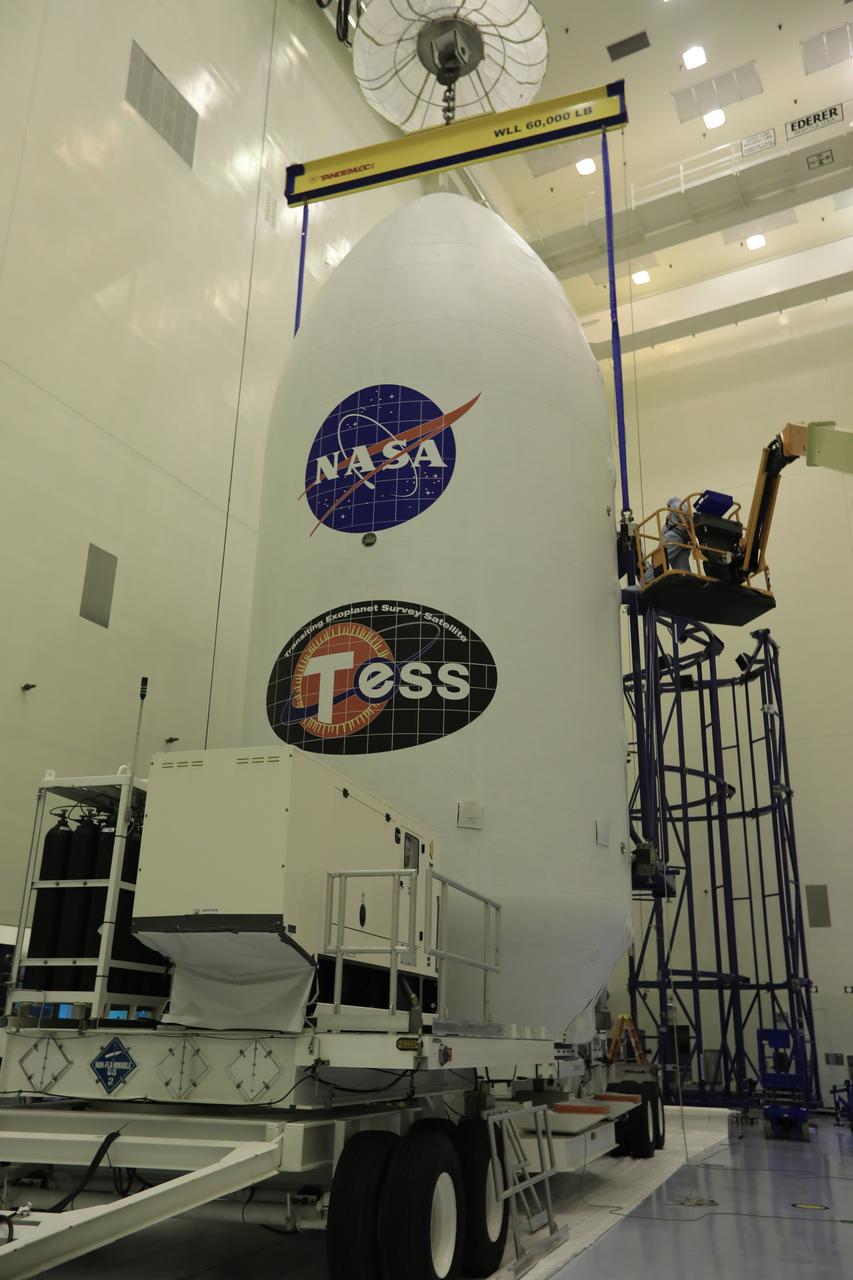

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the SpaceX payload fairing containing the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is secured onto a transporter. The fairing will be moved to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is scheduled to launch on the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
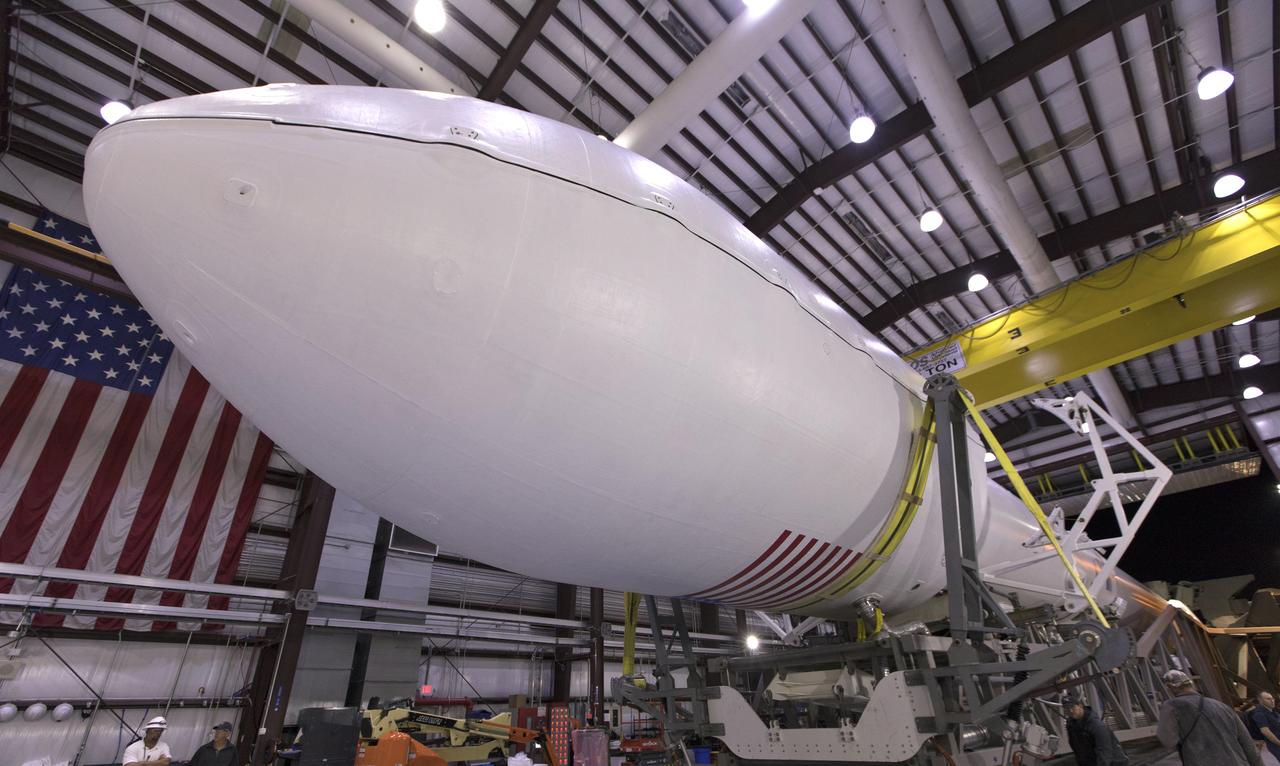

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is ready to roll out to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, with NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) secured in its payload fairing. TESS will launch on the Falcon 9 no earlier than 6:51 p.m. EDT on April 18. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
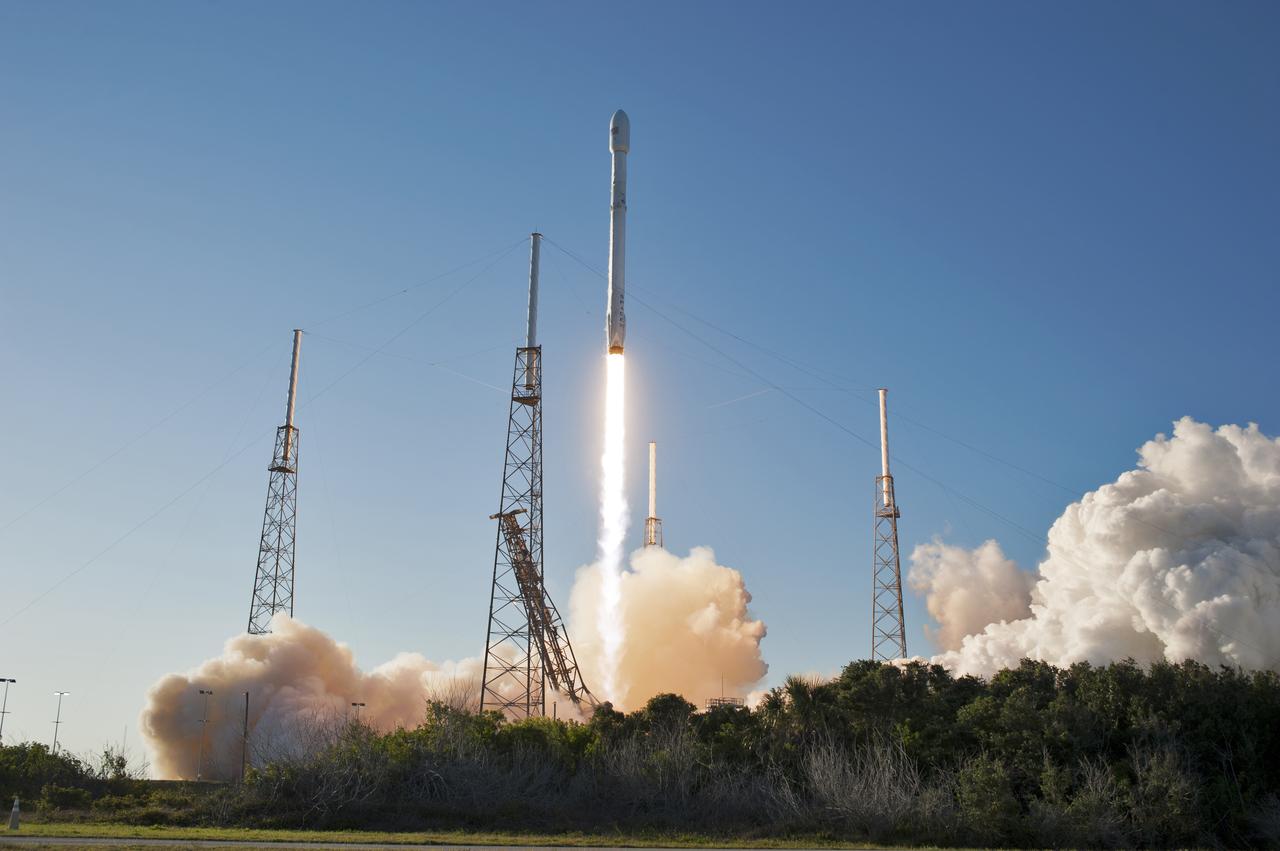

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
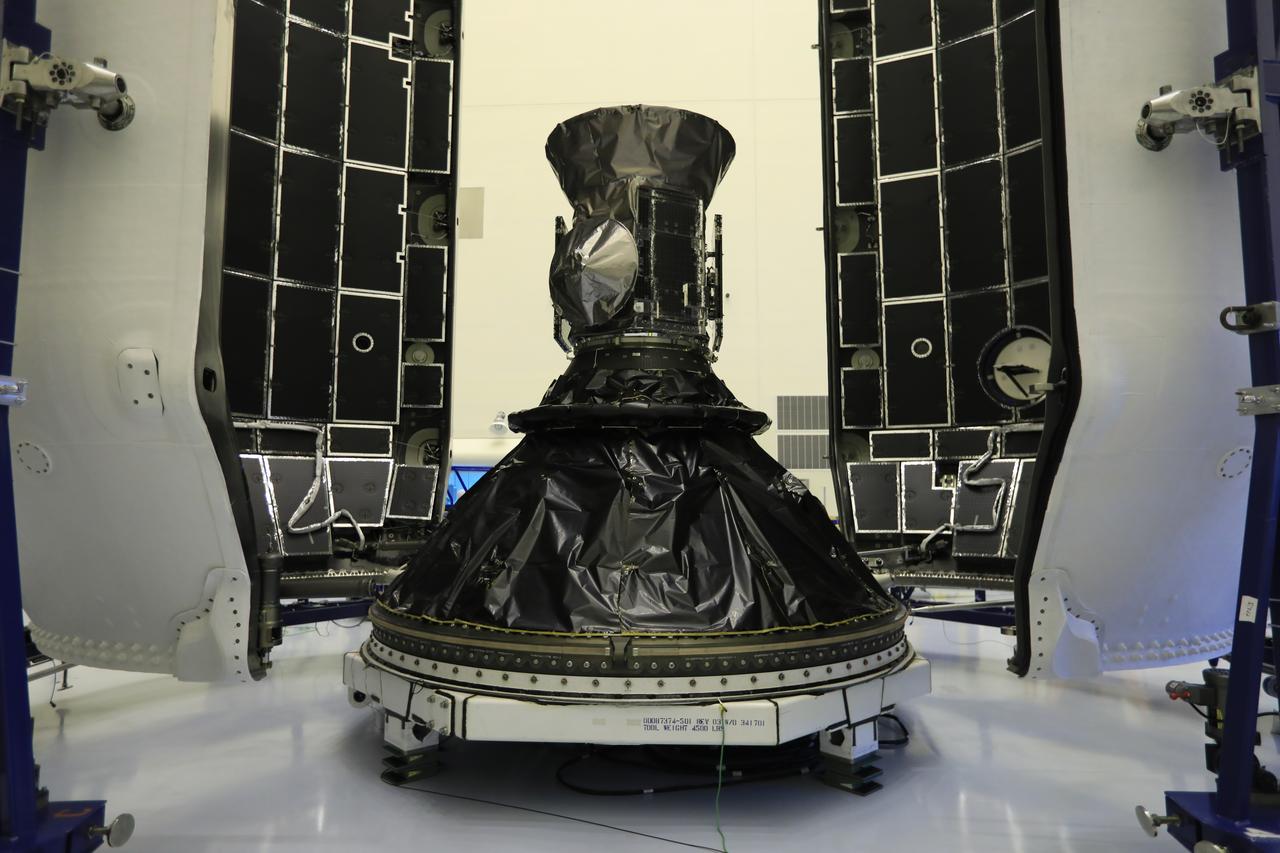
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is being prepared for encapsulation in the SpaceX payload fairing. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
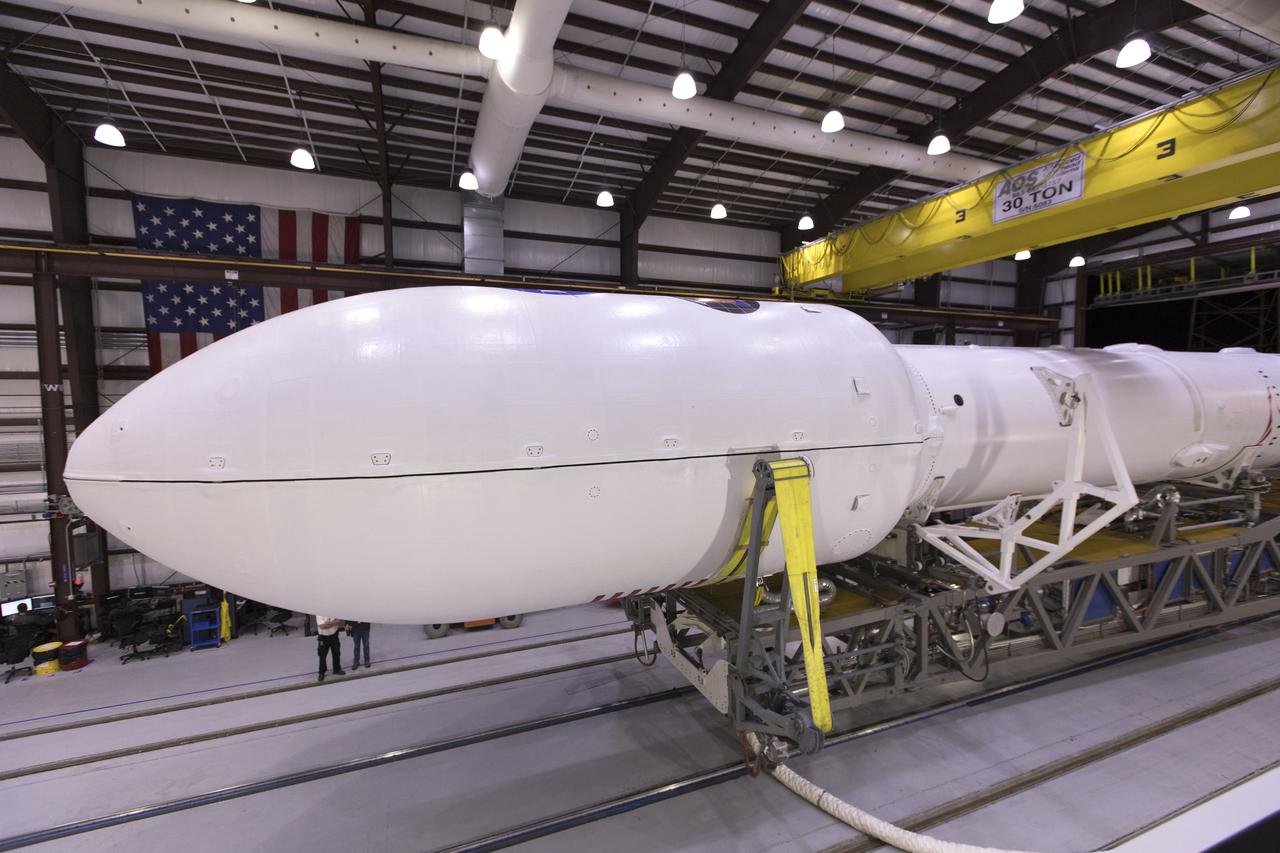

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is ready to roll out to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, with NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) secured in its payload fairing. TESS will launch on the Falcon 9 no earlier than 6:51 p.m. EDT on April 18. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
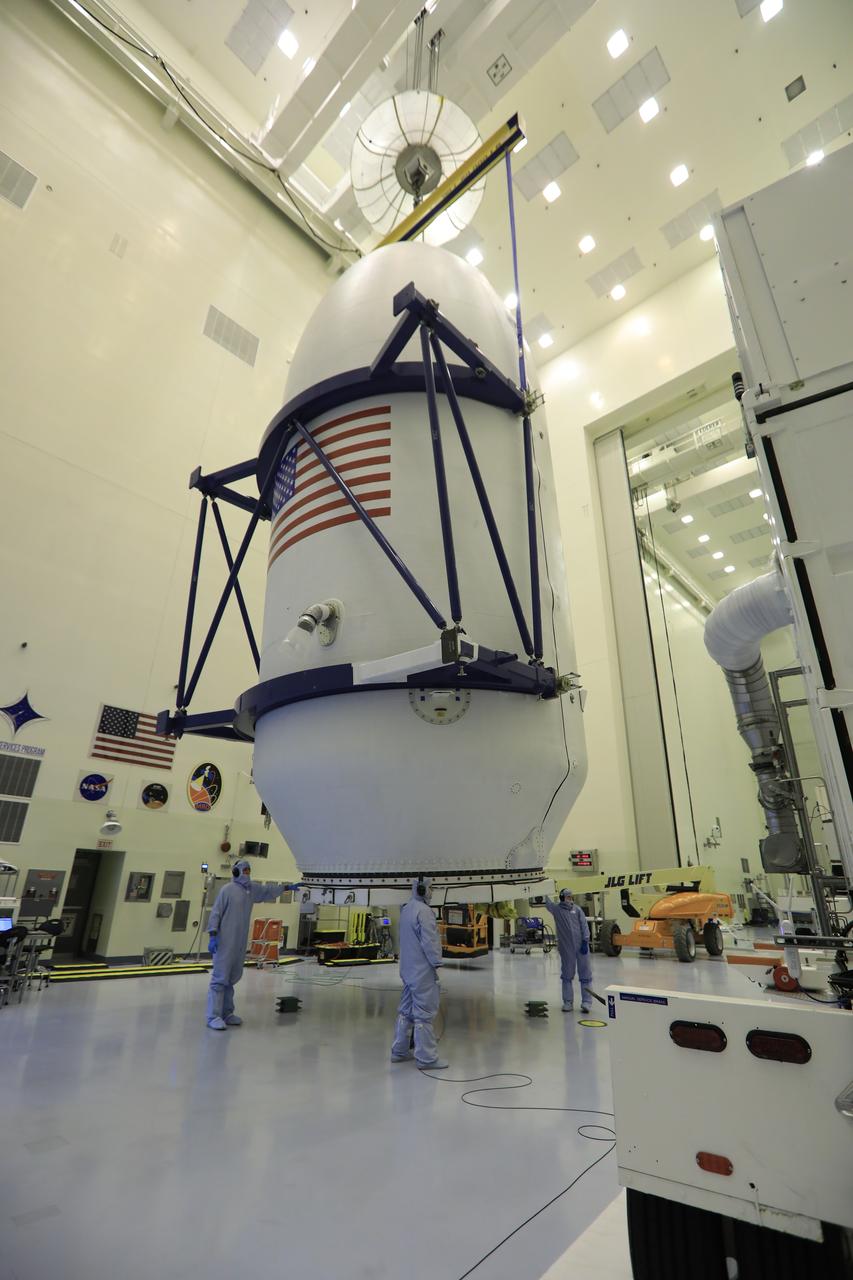

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as the SpaceX payload fairing containing the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is lifted for the move to a transporter. The fairing will be moved to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. TESS is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
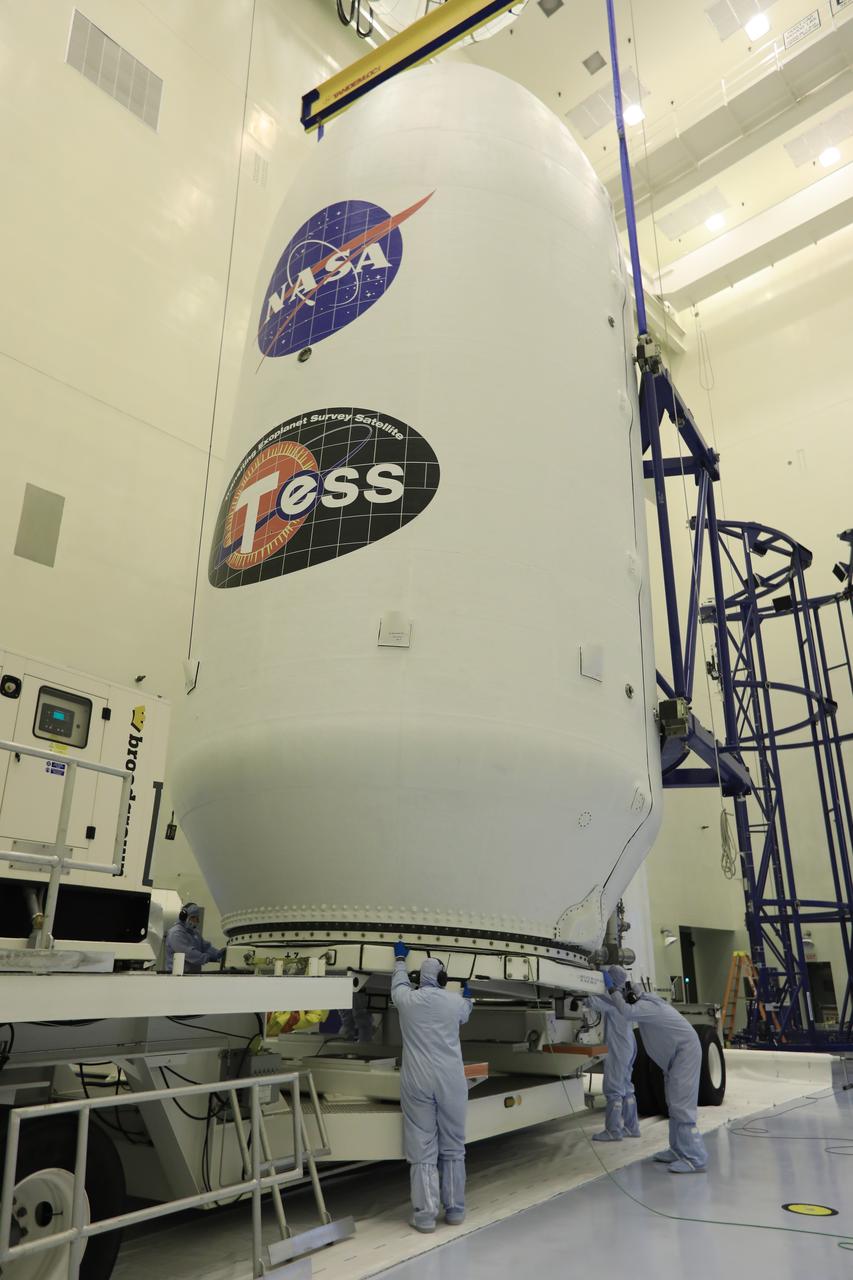

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as the SpaceX payload fairing containing the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is lowered by crane onto a transporter. The fairing will be moved to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is scheduled to launch on the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
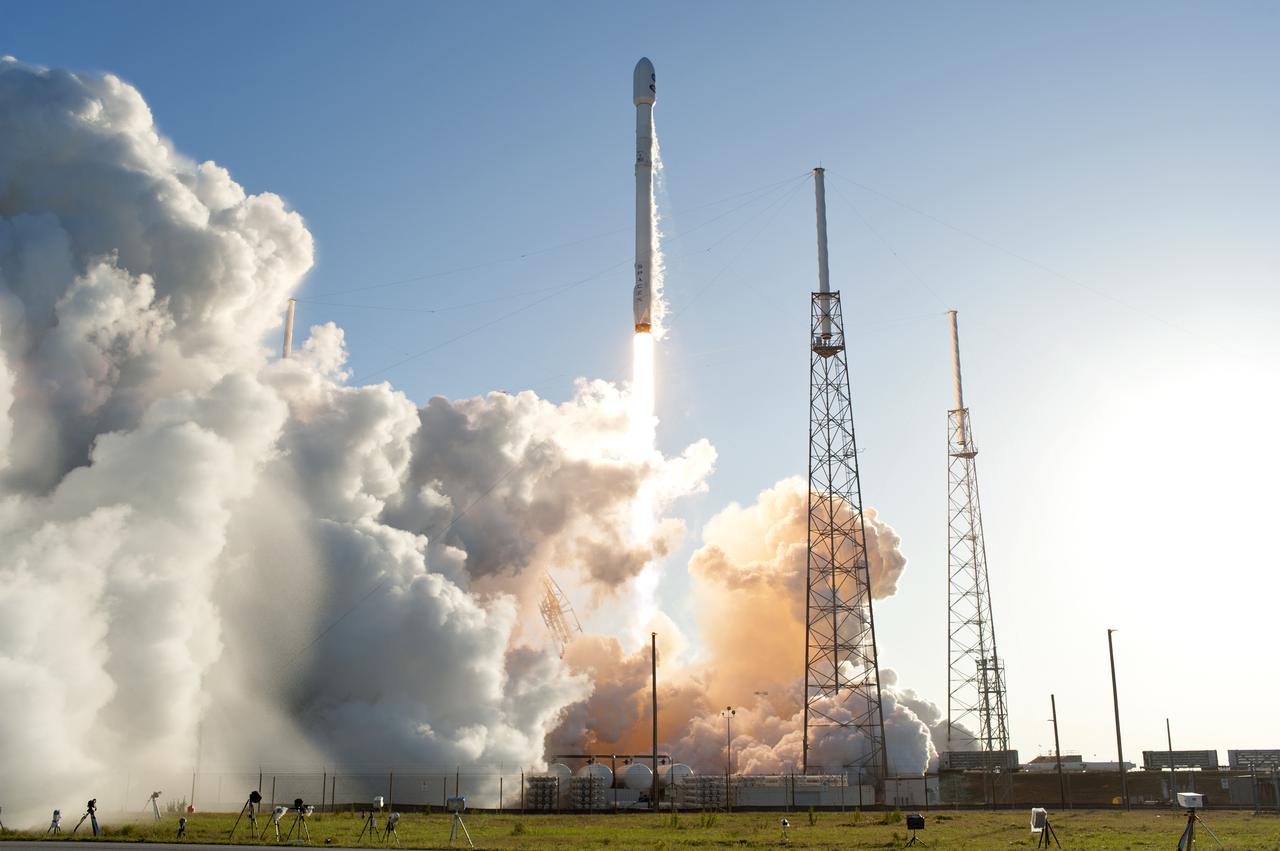

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
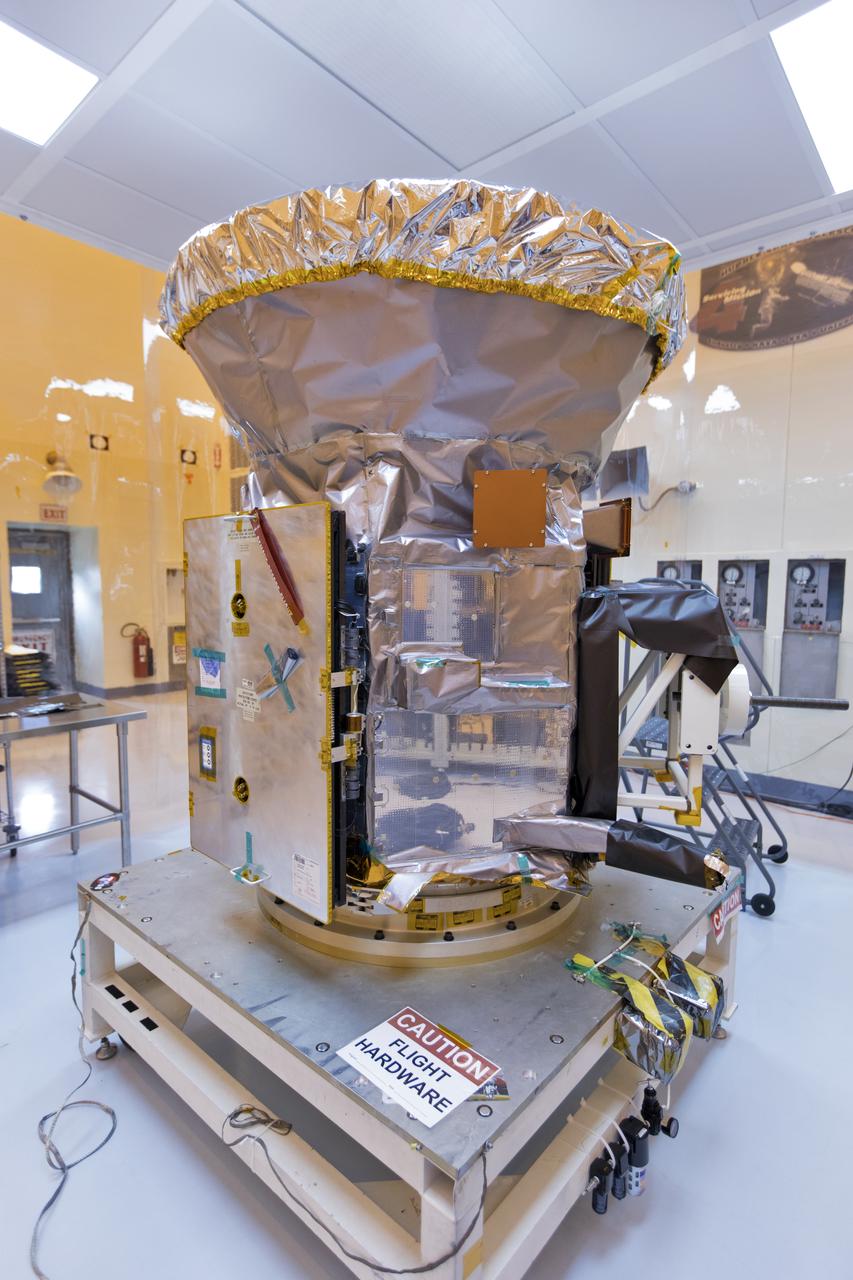

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, or TESS, has been uncreated from its shipping container for inspections and preflight processing. The satellite is NASA's next step in the search for planets outside of the solar system also known as "exoplanets." TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, and the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management. SpaceX of Hawthorne, California, is the provider of the Falcon 9 launch service. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket no earlier than April 16, 2018 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
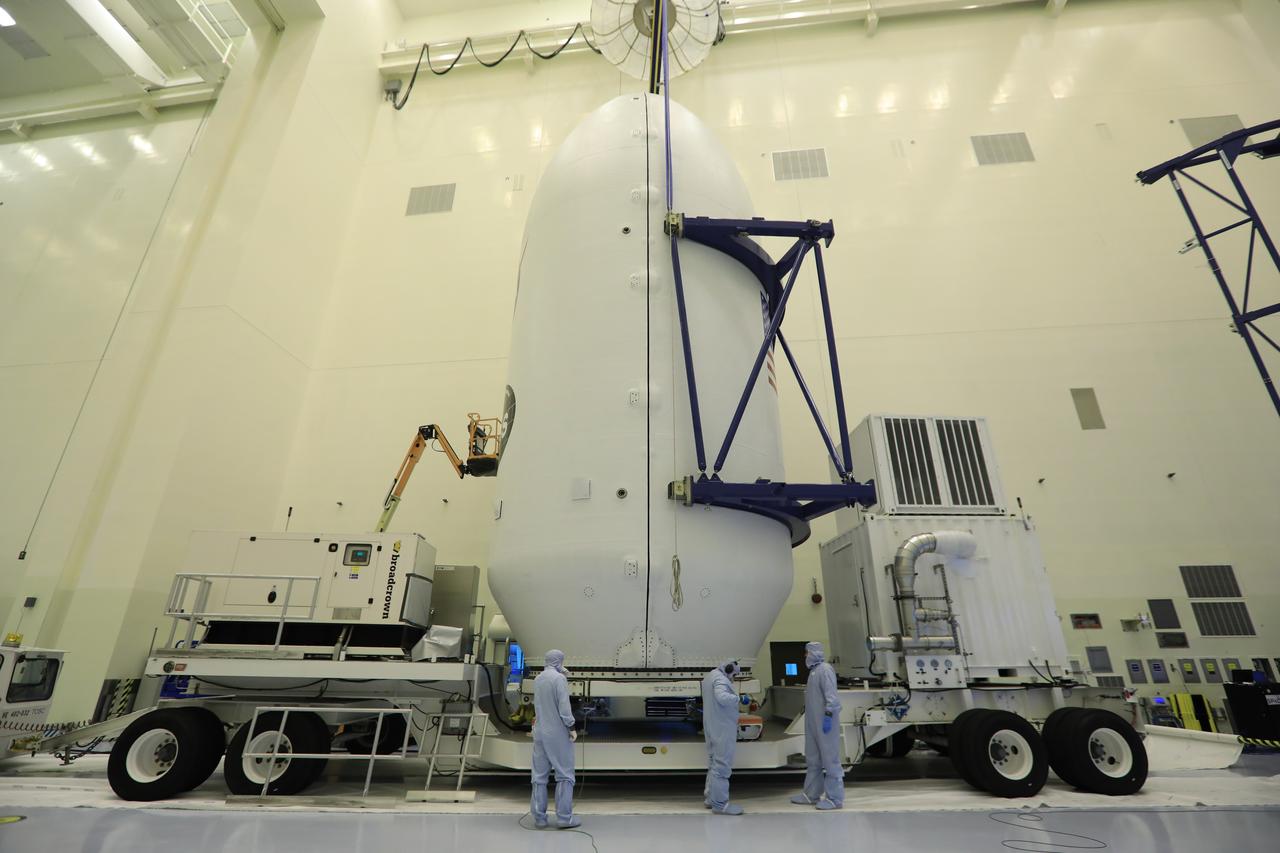

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the SpaceX payload fairing containing the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is secured onto a transporter. The fairing will be moved to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is scheduled to launch on the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
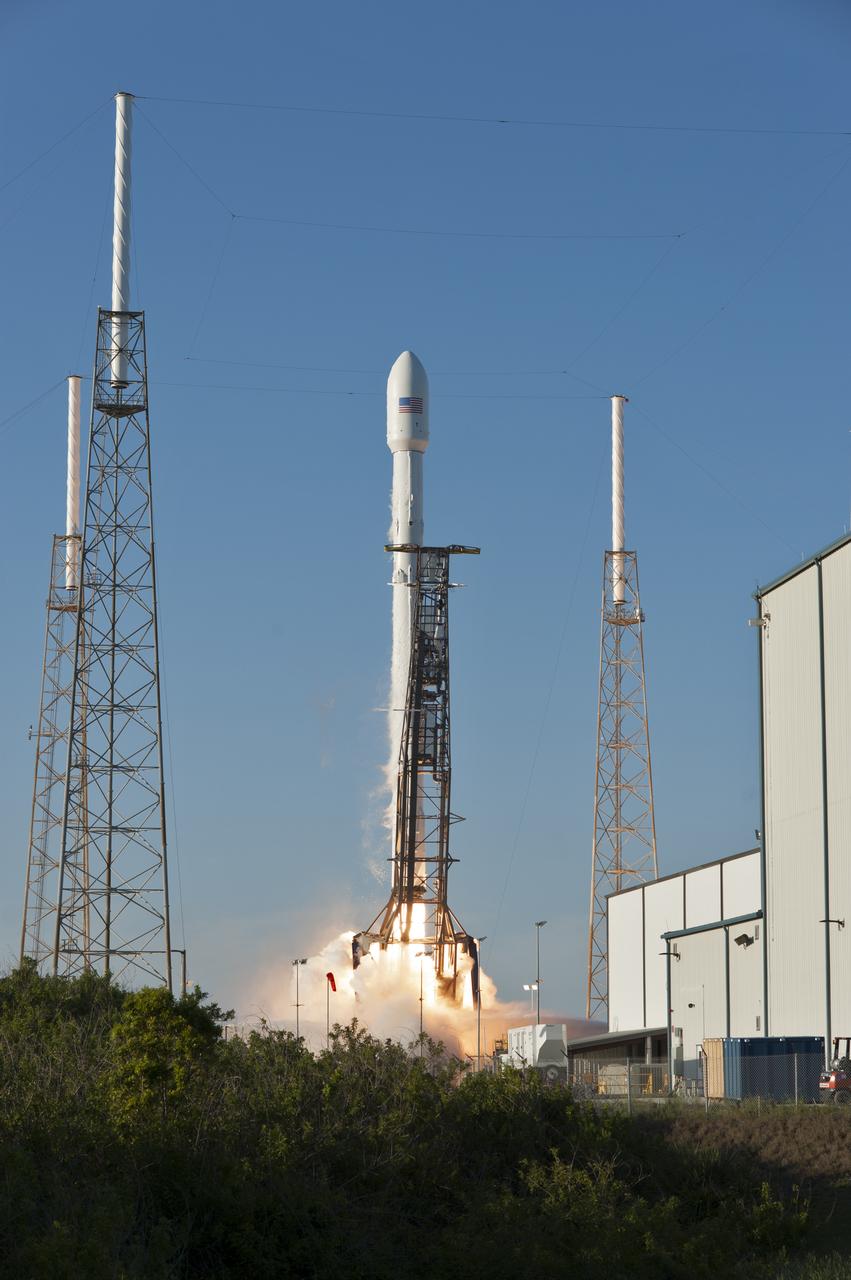

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.