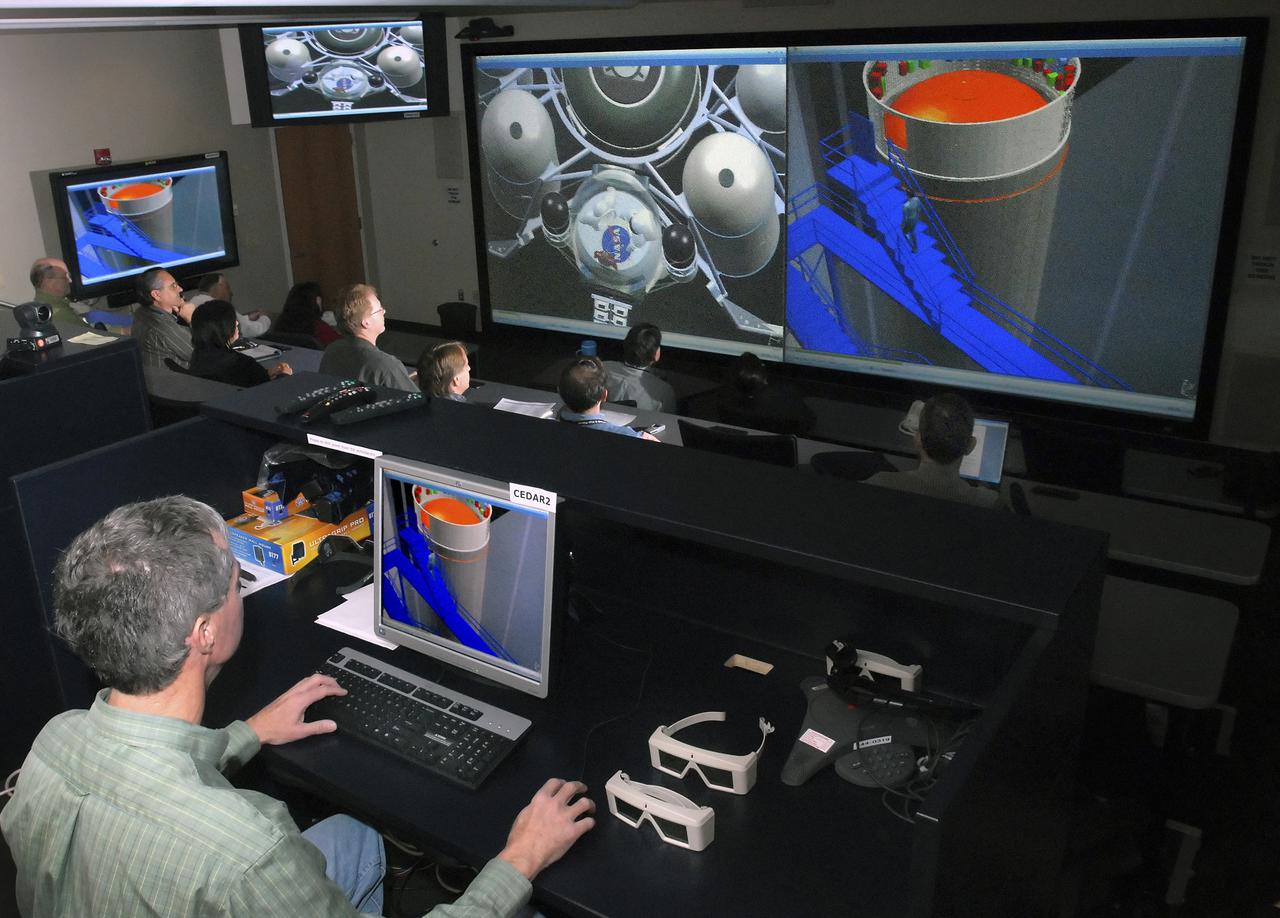

(CEDAR) Room, Computer Aided Design Room in Building 4600, Room 1106 in use.

ISS015-E-07649 (11 May 2007) --- Saskatchewan River Delta, Manitoba, Canada is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crewmember on the International Space Station. This image highlights a portion of the Saskatchewan River delta extending into Cedar Lake in the Province of Manitoba. The Saskatchewan River watershed extends from the Rocky Mountains of Alberta through the plains of Saskatchewan and Manitoba. The construction of the Grand Rapids Dam to the southeast (not shown) in the 1960s flooded the Cedar Lake basin. This has resulted in the formation of numerous shallow, muddy lakes and bogs (dark green to dark grey irregular areas and at upper right) in and around the Saskatchewan River delta. The level of saturation in these bogs is such that peat (semiconsolidated plant and organic matter) deposits have formed; over long periods of time and under the right geological conditions, such deposits can become coal. The velocity of Saskatchewan River water slows significantly as it enters Cedar Lake; as the flow velocity drops, entrained sediment comprised of silt, clay, sand, and gravel is deposited at the river mouth. These deposits, called alluvium by geologists, account for much of the light tan to grey materials bordering the active channels visible in the image (Saskatchewan River, Summerberry River). According to scientists, fossil-bearing amber -- originating from Late Cretaceous (approximately 65-99 million years ago) coal deposits over a thousand kilometers to the west of Cedar Lake -- is also found in the deltaic sediments. As the deposits accumulate, old channels are abandoned and new channels are formed, as the river seeks more favorable flow paths into the lake, this process (known as avulsion) builds out the river delta over time. A typical "birds foot" delta form is currently being constructed at the mouth of the Saskatchewan River (lower left). The birds foot structure is approximately 13 kilometers wide. The Mississippi River's active delta, while having the same general form, is much larger by comparison -- it is approximately 50 kilometers wide.
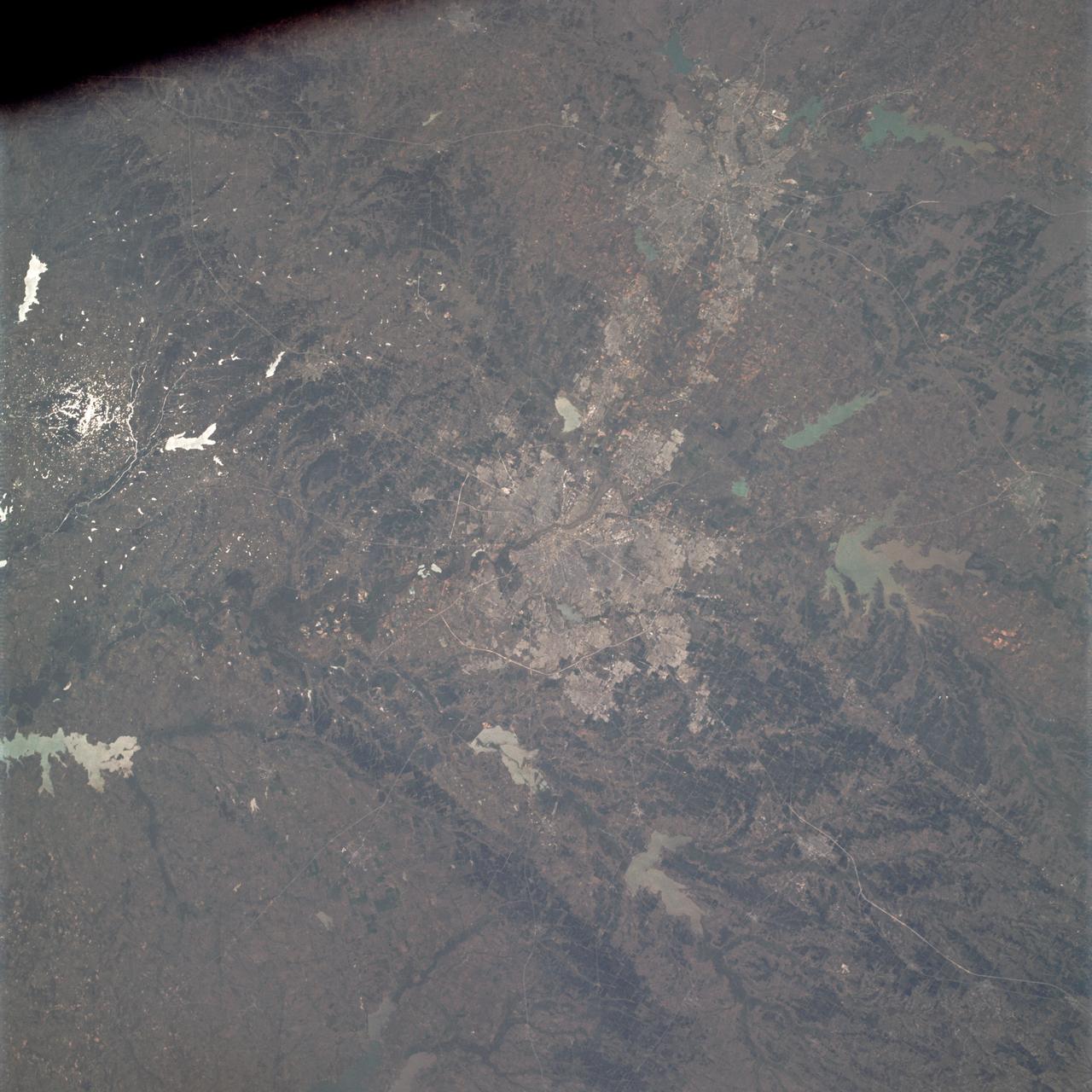

AS09-21-3299 (3-13 March 1969) --- Dallas-Fort Worth area as photographed from the Apollo 9 spacecraft during its Earth-orbital mission. The superhighways leading out of two cities are clearly visible. The largest body of water north of Dallas is the Garza-Little Elm Reservoir. Cedar Creek Reservoir is located to the southeast of Dallas. The City of Denton is near left center edge of picture at junction of two highways leading from Fort Worth and Dallas.
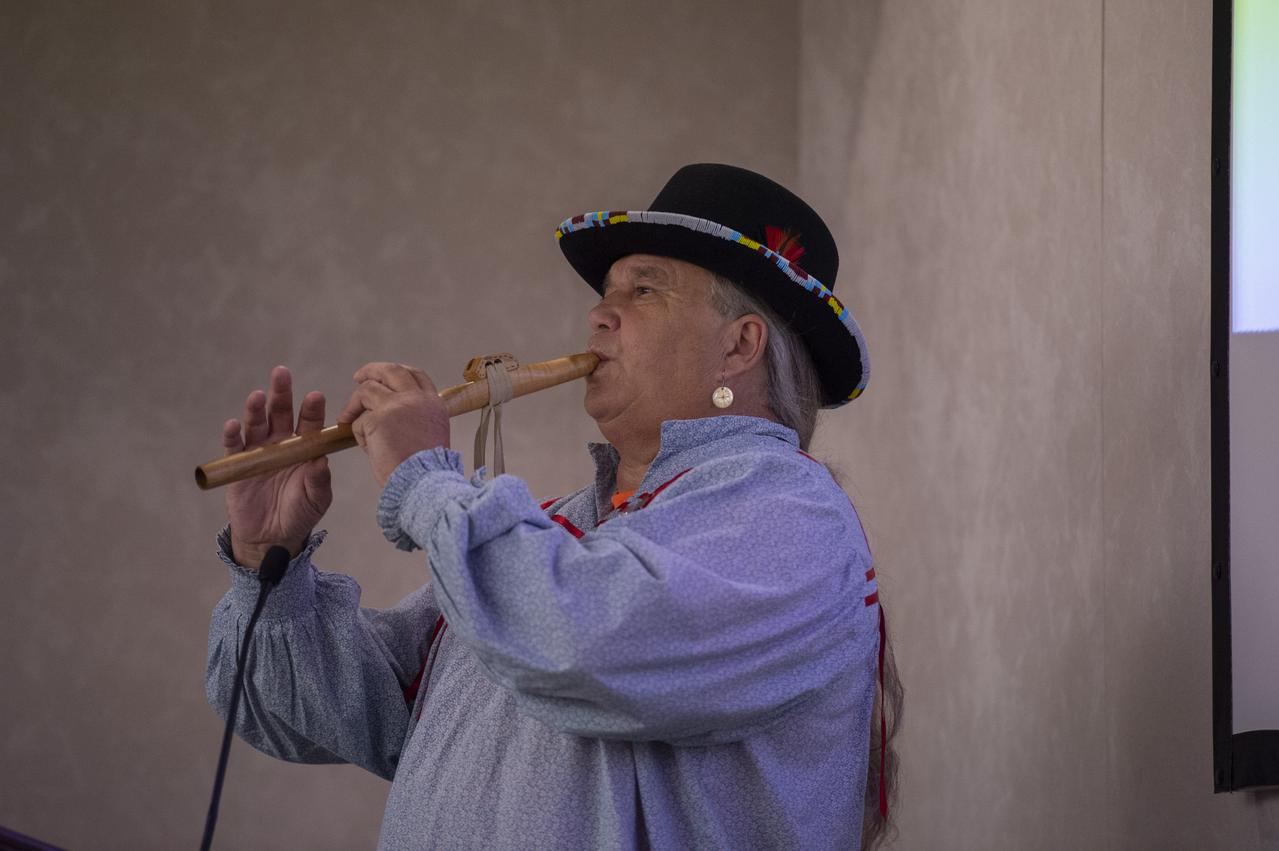

JIMMY YELLOWHORSE, FROM DECATUR, ALABAMA, PLAYS A HAND-CARVED FLUTE DURING THE NATIVE AMERICAN HERITAGE MONTH PROGRAM NOV. 13 AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER. YELLOWHORSE CRAFTED THE FLUTE HIMSELF FROM CEDAR, WALNUT AND MAHOGANY, USING TRADITIONAL CHEROKEE TECHNIQUES. THE ANNUAL OBSERVANCE, COORDINATED BY MARSHALL'S OFFICE OF DIVERSITY AND EQUAL OPPORTUNITY, HONORS THE CULTURE AND CONTRIBUTIONS OF NATIVE AMERICANS THROUGH STORYTELLING AND ETHNIC FOOD SAMPLINGS.
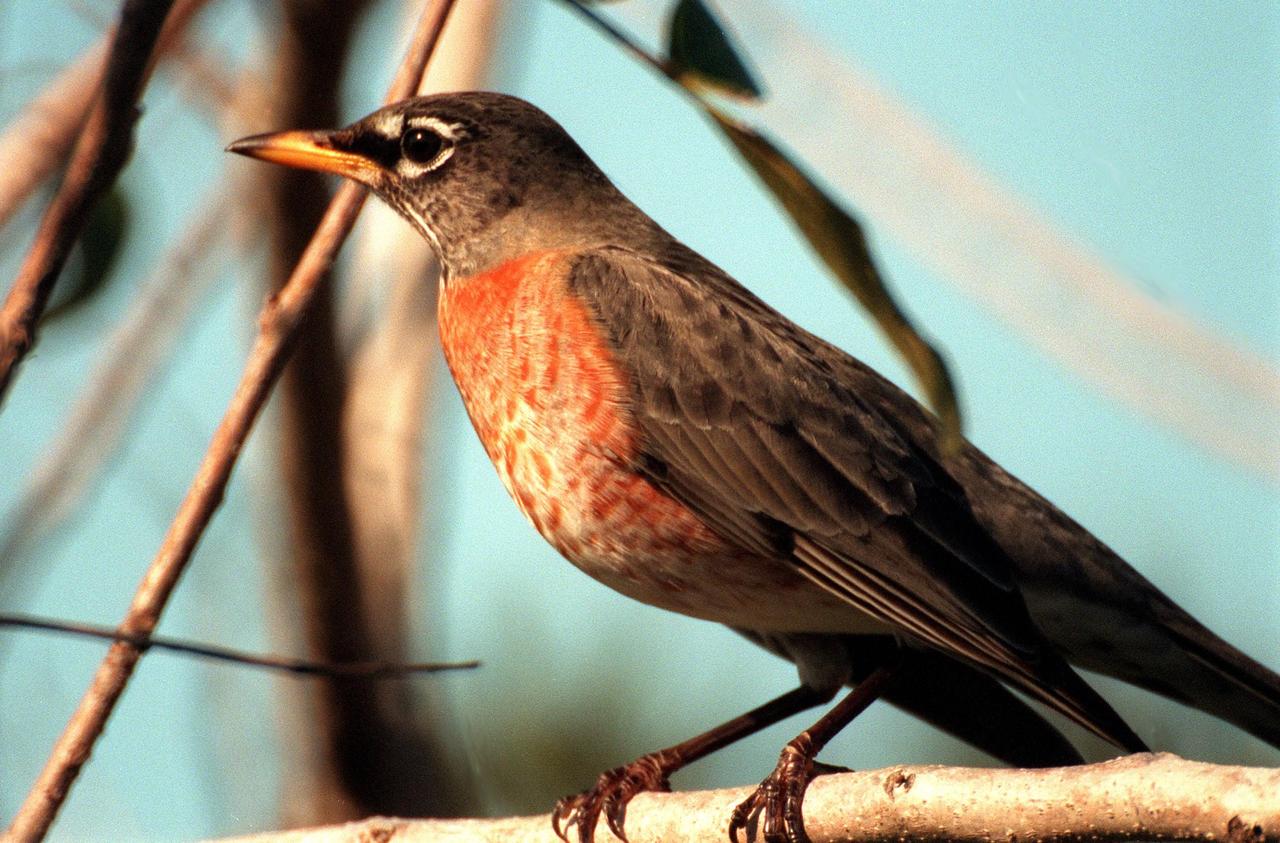

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A robin perches on a branch in the Merritt Island National <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/captions/subjects/wildlife.htm">Wildlife </a>Refuge, which shares a boundary with the space center. Robins range throughout North America, from Alaska to Florida. Although considered a harbinger of spring, they do winter in northern states, frequenting cedar bogs and swamps. They also winter in Florida, where they often can be seen in flocks of hundreds near KSC and the wildlife refuge, which comprises 92,000 acres, ranging from hardwood hammocks and pine flatwoods to fresh-water impoundments, salt-water estuaries and brackish marshes. The diverse landscape provides habitat for more than 310 species of birds, 25 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles, including such endangered species as Southern bald eagles, wood storks, Florida scrub jays, Atlantic loggerhead and leatherback turtles, osprey, and nearly 5,000 alligators
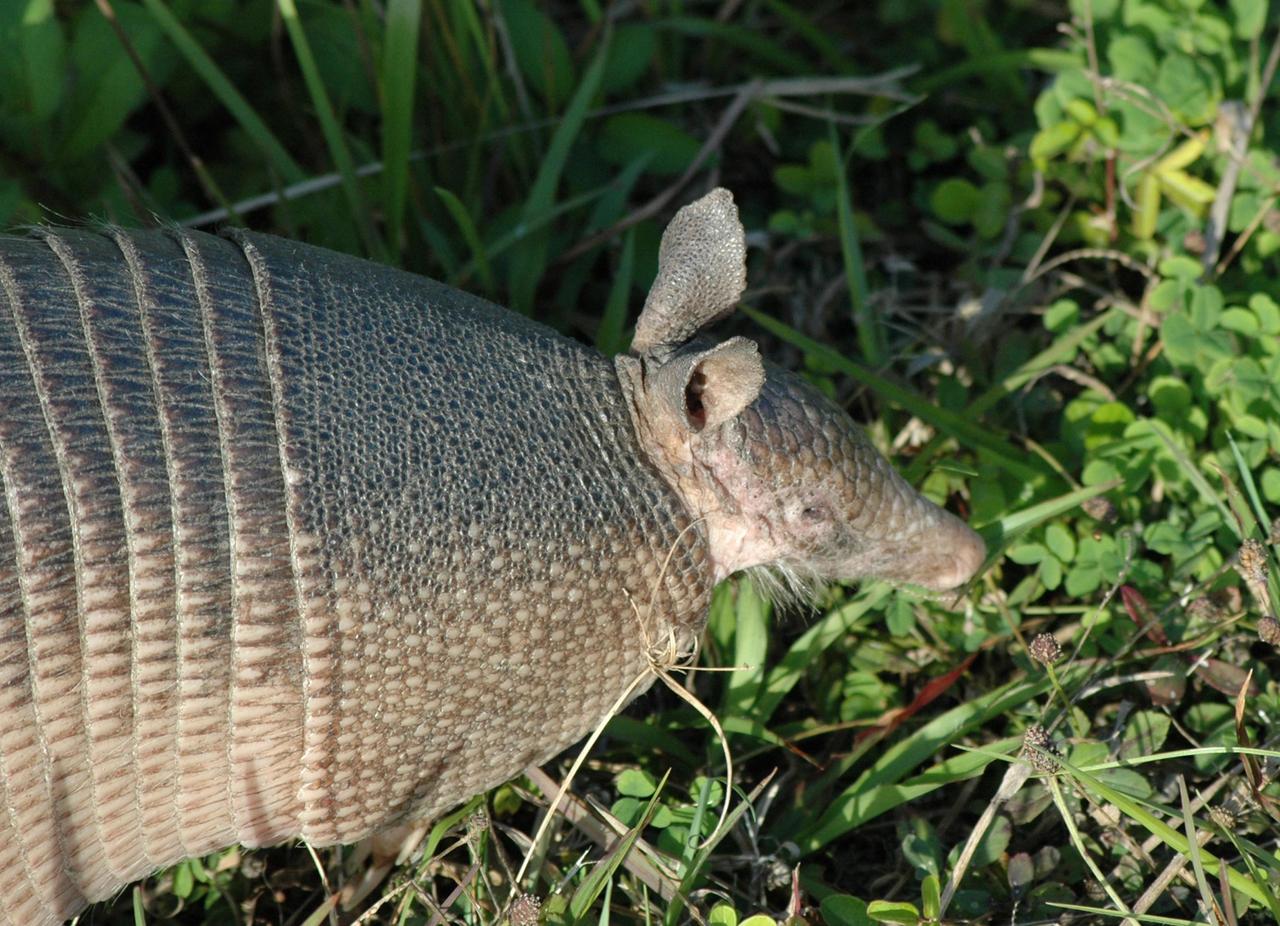

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Seen at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, this nine-banded armadillo may be looking for food. Introduced to Florida in the early 1900's, this species is found statewide in areas with dense ground cover and sandy soil. Nine bands of plates cover the body from shoulder to hip and 12 bands cover the long tail. It has a small, tapered head and snout and a long tongue. Its ears are long and hairless. It has sparse white hairs on its belly. Its diet is composed of insects, especially beetles, and other invertebrates plus some plant foods such as cedars and beautyberries. It is primarily nocturnal, sedentary, solitary and a burrower. It digs a series of dens. The multiple entrances are usually protected by stumps, palmettos, or trees. Many other animals also use armadillo dens. KSC shares a boundary with the Merritt Island Wildlife Nature Refuge. The refuge is a habitat for more than 310 species of birds, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles. In addition, the Refuge supports 19 endangered or threatened wildlife species on Federal or State lists, more than any other single refuge in the U.S. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
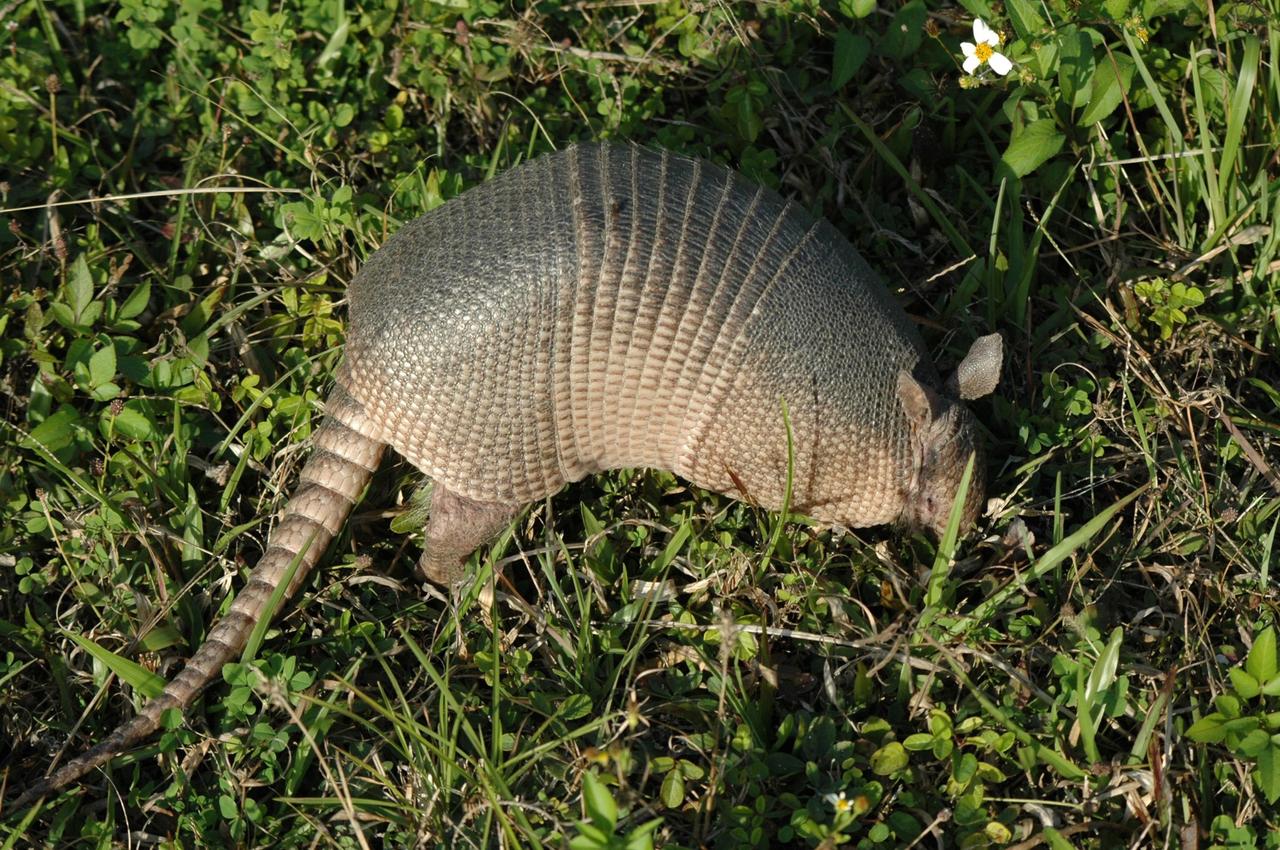

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Seen at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, this nine-banded armadillo may be looking for food. Introduced to Florida in the early 1900's, this species is found statewide in areas with dense ground cover and sandy soil. Nine bands of plates cover the body from shoulder to hip and 12 bands cover the long tail. It has a small, tapered head and snout and a long tongue. Its ears are long and hairless. It has sparse white hairs on its belly. Its diet is composed of insects, especially beetles, and other invertebrates plus some plant foods such as cedars and beautyberries. It is primarily nocturnal, sedentary, solitary and a burrower. It digs a series of dens. The multiple entrances are usually protected by stumps, palmettos, or trees. Many other animals also use armadillo dens. KSC shares a boundary with the Merritt Island Wildlife Nature Refuge. The refuge is a habitat for more than 310 species of birds, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles. In addition, the Refuge supports 19 endangered or threatened wildlife species on Federal or State lists, more than any other single refuge in the U.S. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
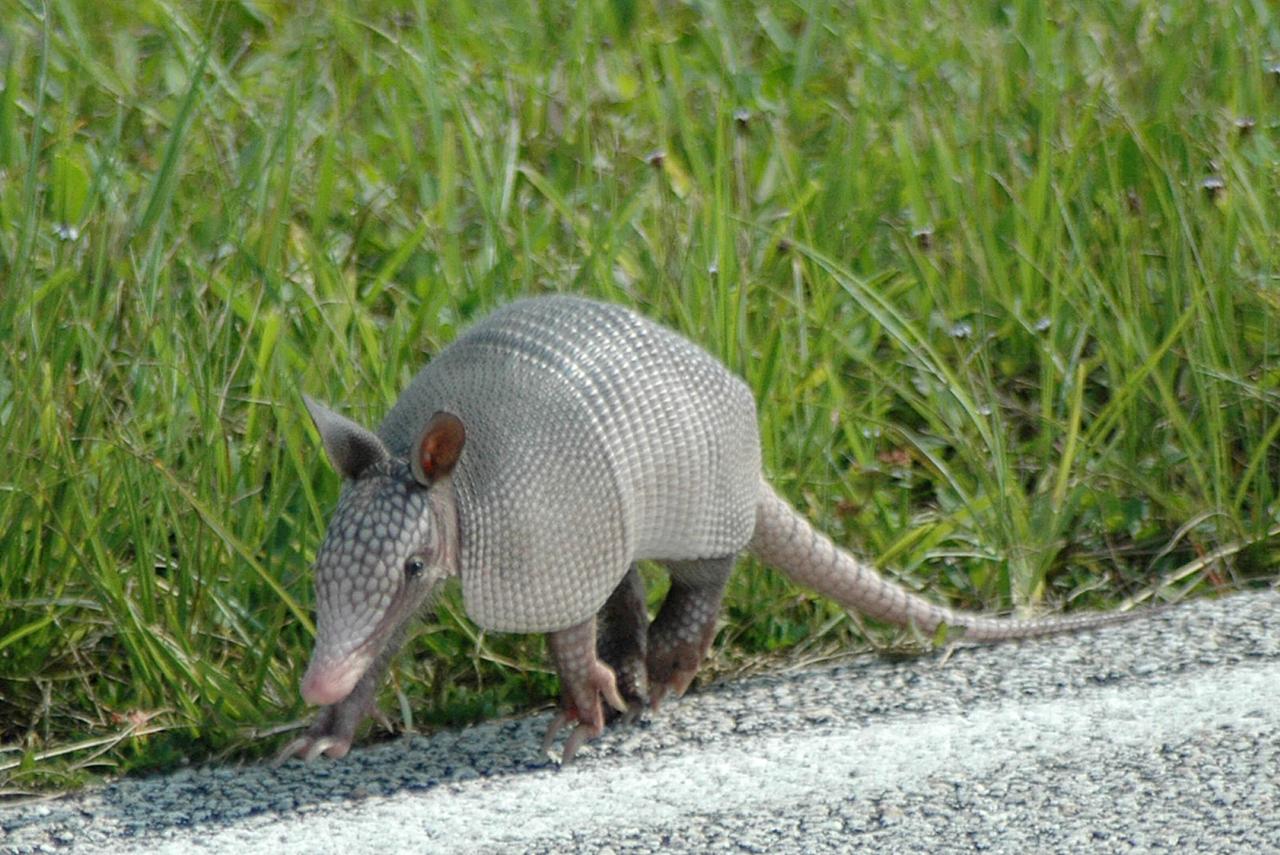

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A baby nine-banded armadillo makes its way along the roadside near Launch Pad 39A where Space Shuttle Endeavour waits for launch on mission STS-118. Introduced to Florida in the early 1900s, this species is found statewide in areas with dense ground cover and sandy soil. Nine bands of plates cover the body from shoulder to hip and 12 bands cover the long tail. It has a small, tapered head and snout and a long tongue. Its ears are long and hairless. and it has sparse white hairs on its belly. Its diet is composed of insects, especially beetles, and other invertebrates plus some plant foods such as cedars and beautyberries. It is primarily nocturnal, sedentary, solitary and a burrower. It digs a series of dens with multiple entrances usually protected by stumps, palmettos or trees. KSC shares a boundary with the Merritt Island Wildlife Nature Refuge. The refuge is a habitat for more than 310 species of birds, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
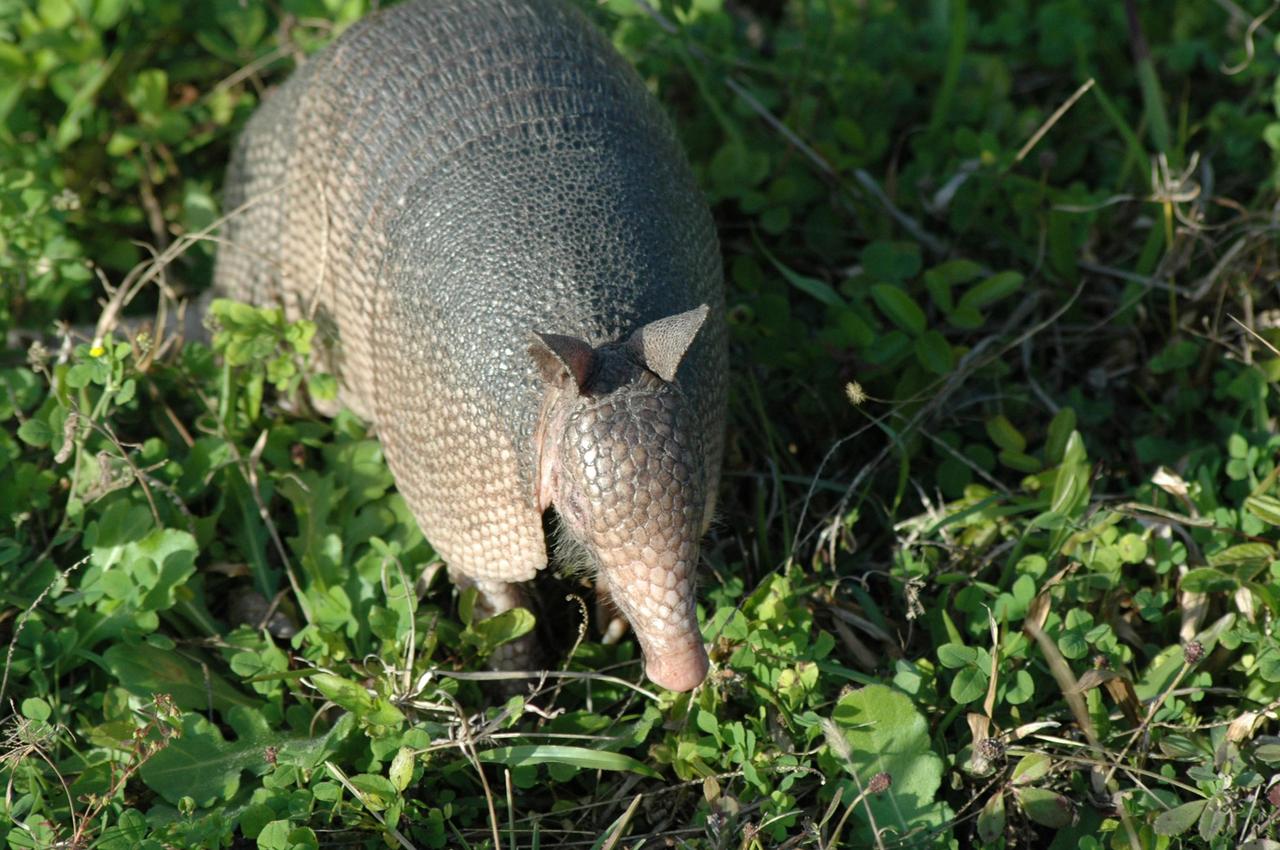

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Seen at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, this nine-banded armadillo may be looking for food. Introduced to Florida in the early 1900's, this species is found statewide in areas with dense ground cover and sandy soil. Nine bands of plates cover the body from shoulder to hip and 12 bands cover the long tail. It has a small, tapered head and snout and a long tongue. Its ears are long and hairless. It has sparse white hairs on its belly. Its diet is composed of insects, especially beetles, and other invertebrates plus some plant foods such as cedars and beautyberries. It is primarily nocturnal, sedentary, solitary and a burrower. It digs a series of dens. The multiple entrances are usually protected by stumps, palmettos, or trees. Many other animals also use armadillo dens. KSC shares a boundary with the Merritt Island Wildlife Nature Refuge. The refuge is a habitat for more than 310 species of birds, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles. In addition, the Refuge supports 19 endangered or threatened wildlife species on Federal or State lists, more than any other single refuge in the U.S. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
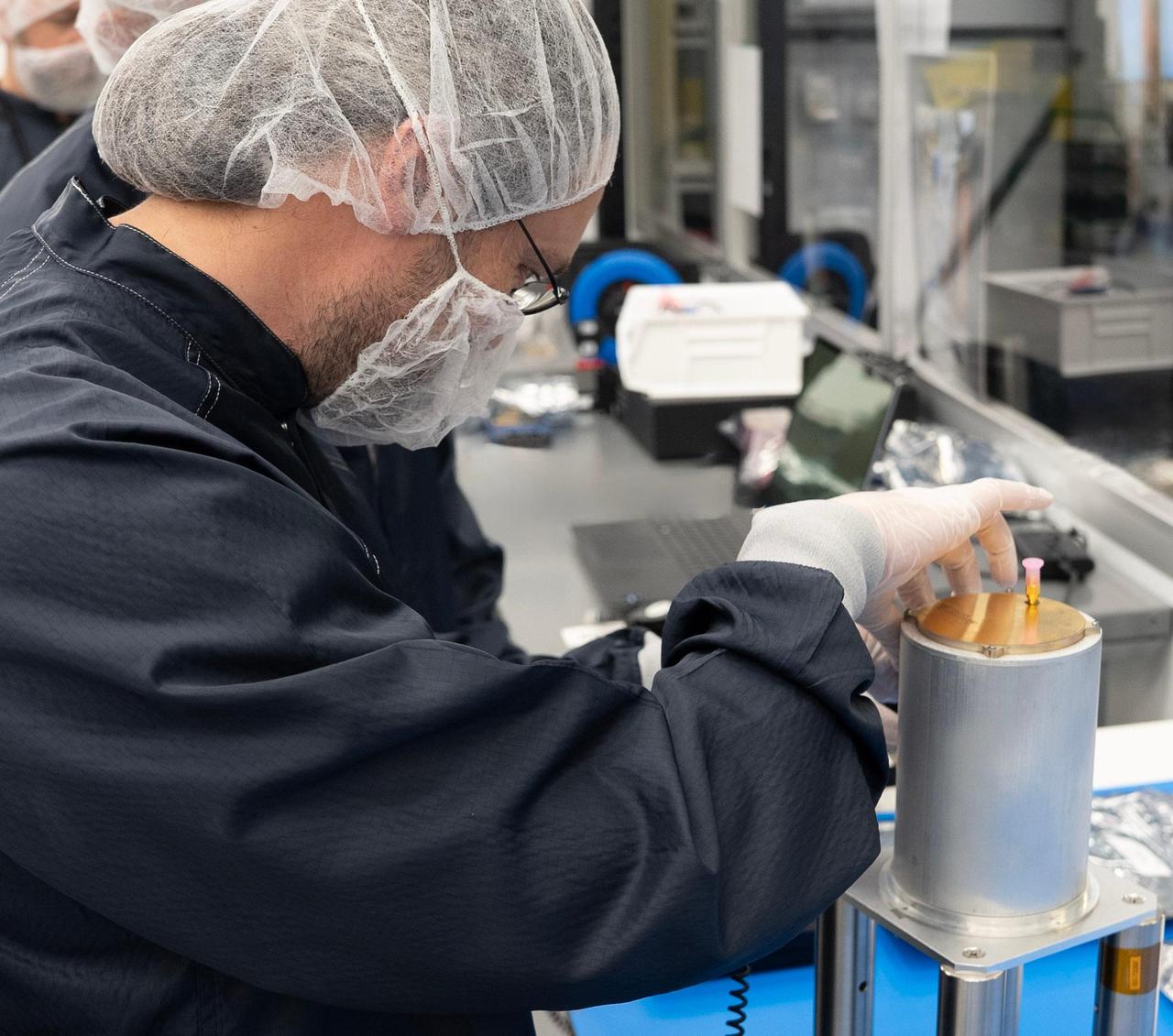

Engineer Emmanuel Decrossas of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California makes an adjustment to an antenna's connector, part of a NASA telecommunications payload called User Terminal, at Firefly Aerospace's facility in Cedar Park, Texas, in August 2025. Figure A (https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/figures/PIA26596_figA.jpg) shows members of the team from JPL and NASA (dark blue) and Firefly (white) with the User Terminal antenna, radio, and other components on the bench behind them. Managed by JPL, the User Terminal will test a new, low-cost lunar communications system that future missions to the Moon's far side could use to transfer data to and from Earth via lunar relay satellite. The User Terminal payload will be installed atop Firefly's Blue Ghost Mission 2 lunar lander, which is slated to launch to the Moon's far side in 2026 under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. NASA's Apollo missions brought large and powerful telecommunications systems to the lunar near-side surface to communicate directly with Earth. But spacecraft on the far side will not have that option because only the near side of the Moon is visible to Earth. Sending messages between the Moon and Earth via a relay orbiter enables communication with the lunar far side and improves it at the Moon's poles. The User Terminal will for the first time test such a setup for NASA by using a compact, lightweight software defined radio, antenna, and related hardware to communicate with a satellite that Blue Ghost Mission 2 is delivering to lunar orbit: ESA's (the European Space Agency's) Lunar Pathfinder. The User Terminal radio and antenna installed on the Blue Ghost lander will be used to commission Lunar Pathfinder, sending test data back and forth. After the lander ceases operations as planned at the end of a single lunar day (about 14 Earth days), a separate User Terminal radio and antenna installed on LuSEE-Night – another payload on the lander – will send LuSEE-Night's data to Lunar Pathfinder, which will relay the information to a commercial network of ground stations on Earth. LuSEE-Night is a radio telescope that expected to operate for at least 1½ years; it is a joint effort by NASA, the U.S. Department of Energy, and University of California, Berkeley's Space Sciences Laboratory. Additionally, User Terminal will be able to communicate with another satellite that's being delivered to lunar orbit by Blue Ghost Mission 2: Firefly's own Elytra Dark orbital vehicle. The hardware on the lander is only part of the User Terminal project, which was also designed to implement a new S-band two-way protocol, or standard, for short-range space communications between entities on the lunar surface (such as rovers and landers) and lunar orbiters, enabling reliable data transfer between them. The standard is a new version of a space communications protocol called Proximity-1 that was initially developed more than two decades ago for use at Mars by an international standard body called the Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems (CCSDS), of which NASA is a member agency. The User Terminal team made recommendations to CCSDS on the development of the new lunar S-band standard, which was specified in 2024. The new standard will enable lunar orbiters and surface spacecraft from various entities – NASA and other civil space agencies as well as industry and academia – to communicate with each other, a concept known as interoperability. At Mars, NASA rovers communicate with various Red Planet orbiters using the Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) radio band version of the Proximity-1 standard. On the Moon's far side, use of UHF is reserved for radio astronomy science; so a new lunar standard was needed using a different frequency range, S-band, as were more efficient modulation and coding schemes to better fit the available frequency spectrum specified by the new standard. User Terminal is funded by NASA's Exploration Science Strategy and Integration Office, part of the agency's Science Mission Directorate, which manages the CLPS initiative. JPL manages the project and supported development of the new S-band radio standard and the payload in coordination with Vulcan Wireless in Carlsbad, California, which built the radio. Caltech in Pasadena manages JPL for NASA. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26596
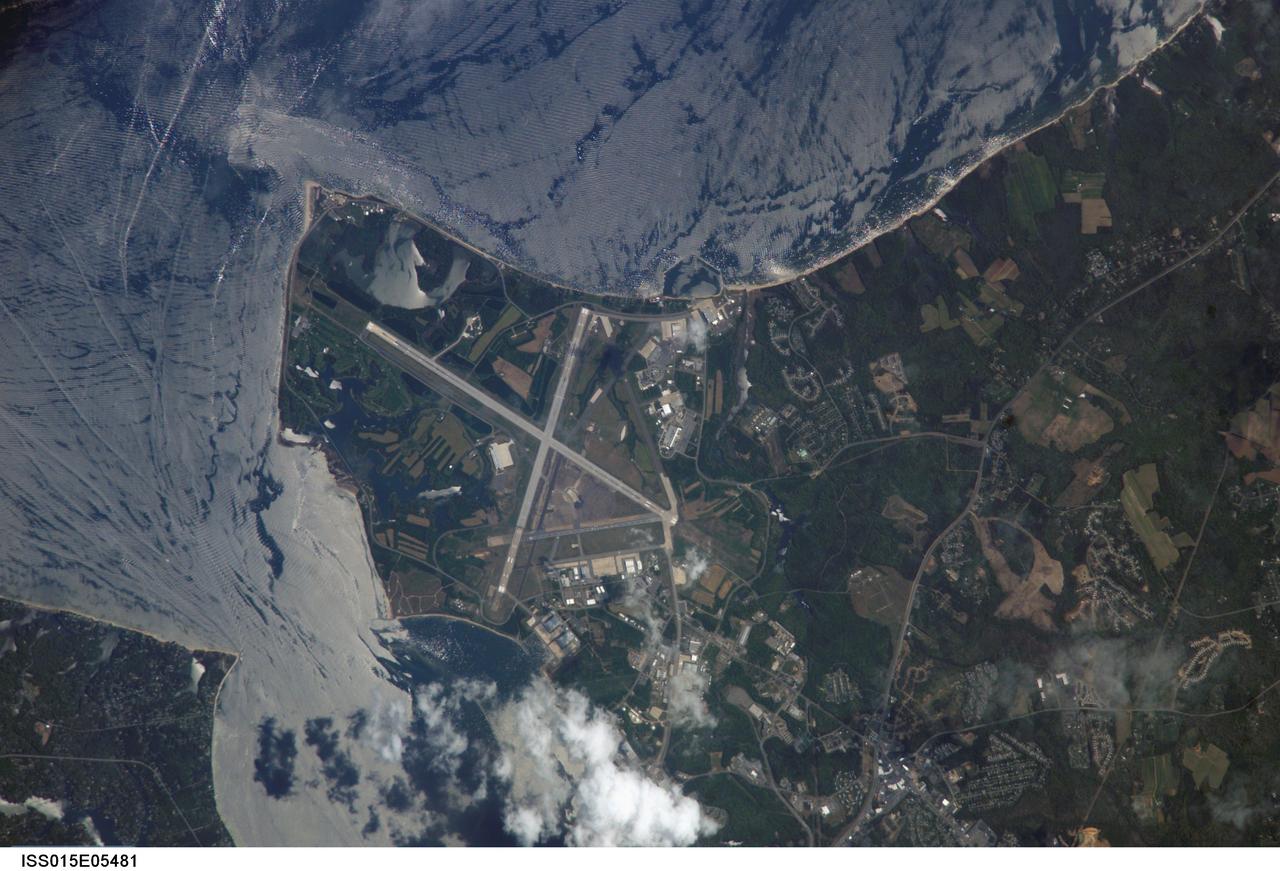

ISS015-E-05481 (28 April 2007) --- Patuxent River Naval Air Station, Maryland is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crewmember on the International Space Station. The Patuxent River Naval Air Station - or NAS Patuxent River -- is located on a small peninsula, bordered by the Patuxent River to the north-northeast and Chesapeake Bay to the east and southeast. The air station was commissioned in 1943, replacing farmlands that had occupied the peninsula less than a year earlier. The primary purpose of "Pax River" (as the site is known by the US Navy) was to consolidate geographically-dispersed air testing facilities that existed in the US prior to World War II into a central location. The NAS Patuxent River is now the primary center for naval air technology research, development, testing, and support, as well as being the location of the Navy Test Pilot School. The NAS Patuxent River is used frequently as a geographic reference point and training target by station crews. This view illustrates why --the distinctive pattern of the airfield runways and the station's location in Chesapeake Bay make it easy to spot from orbit, and provides sharp land cover boundaries for camera focusing practice. This particular image also captures surface water current patterns around the peninsula. Wind and wave-roughened water surfaces appear silver-gray due to increased reflectance of light back towards the camera (sunglint), whereas dark blue water patches indicate water smoothed by the presence of oils and surfactants. A zone of mixing from converging shoreline currents extends northeast into the bay from Cedar Point.
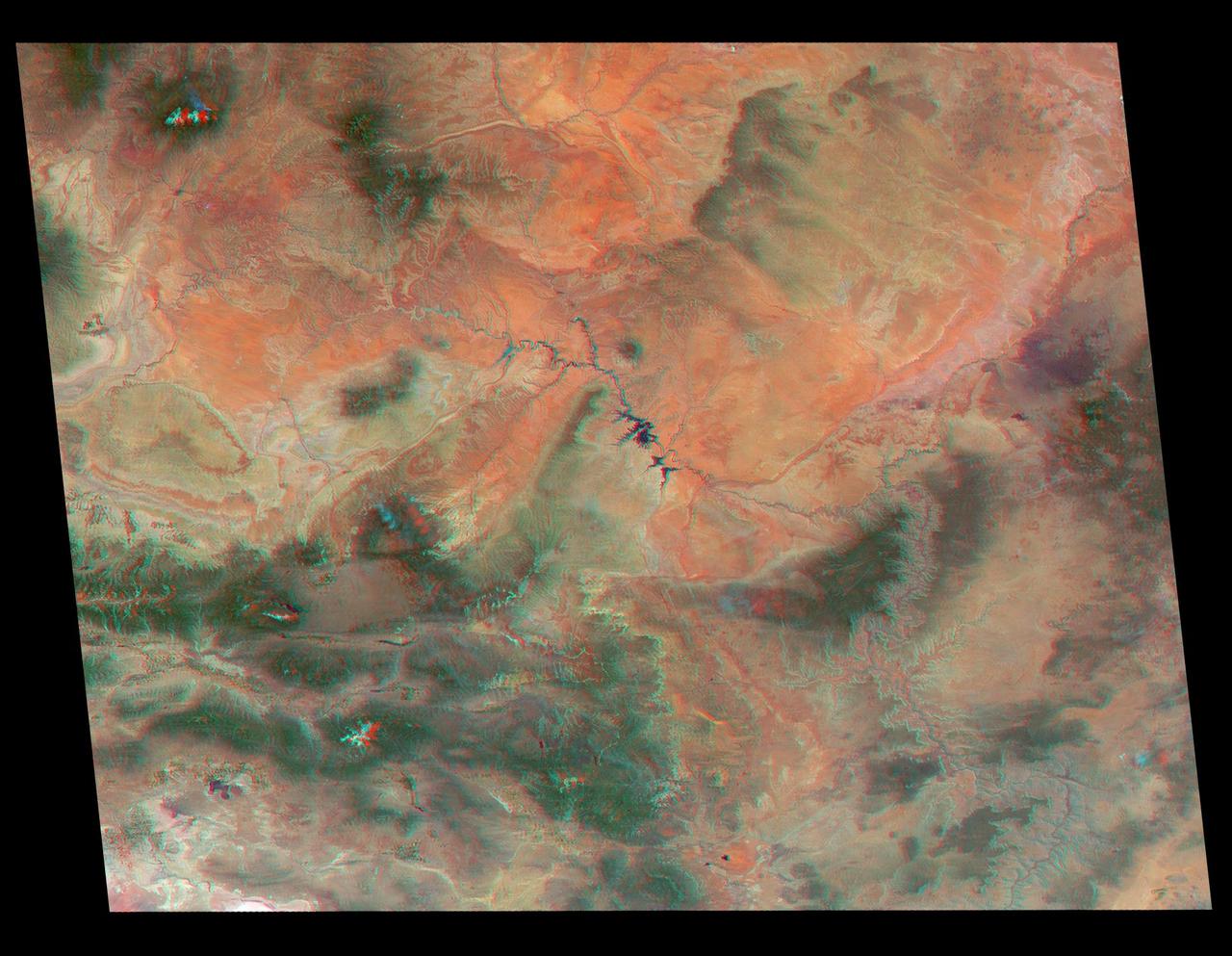
Just in time for the U.S. National Park Service's Centennial celebration on Aug. 25, NASA's Multiangle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite is releasing four new anaglyphs that showcase 33 of our nation's national parks, monuments, historical sites and recreation areas in glorious 3D. Shown in the annotated image are Walnut Canyon National Monument, Sunset Crater Volcano National Monument, Wupatki National Monument, Grand Canyon National Park, Pipe Spring National Monument, Zion National Park, Cedar Breaks National Monument, Bryce Canyon National Park, Capitol Reef National Park, Navajo National Monument, Glen Canyon National Recreation Area, Natural Bridges National Monument, Canyonlands National Park, and Arches National Park. MISR views Earth with nine cameras pointed at different angles, giving it the unique capability to produce anaglyphs, stereoscopic images that allow the viewer to experience the landscape in three dimensions. The anaglyphs were made by combining data from MISR's vertical-viewing and 46-degree forward-pointing camera. You will need red-blue glasses in order to experience the 3D effect; ensure you place the red lens over your left eye. The images have been rotated so that north is to the left in order to enable 3D viewing because the Terra satellite flies from north to south. All of the images are 235 miles (378 kilometers) from west to east. These data were acquired June 18, 2016, Orbit 87774. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20889
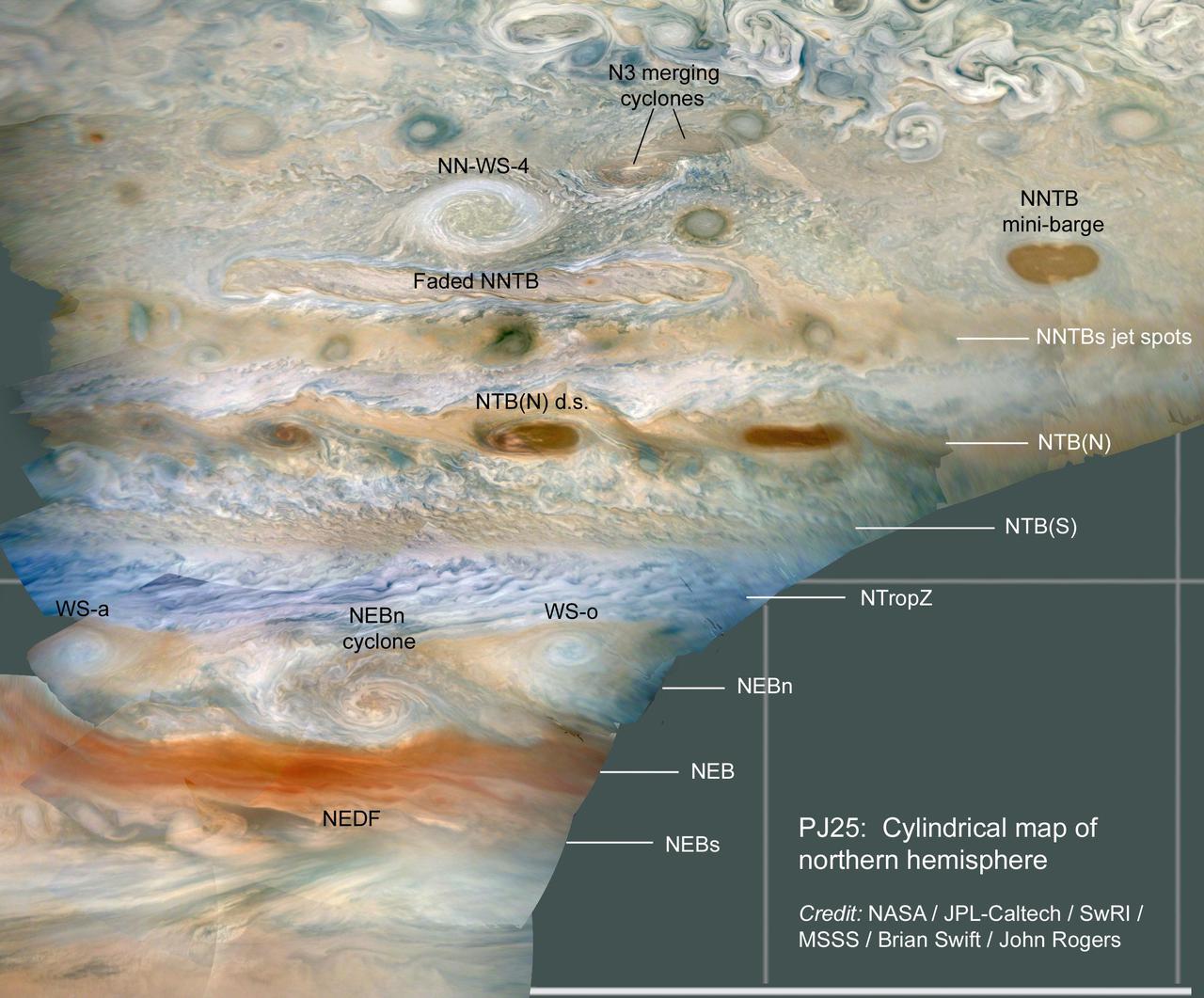
JunoCam imaged numerous storms in Jupiter's atmosphere on Juno's 25th close pass, in the region just north of Jupiter's equator. Amateurs and professional observers track these storms routinely to study the dynamics of Jupiter's atmosphere. Near the top of the image, two cyclones can be seen merging in the N3 jet stream. The next storm down is NN-WS-4 (the North North White Spot 4), rotating in an anticyclonic (clockwise rotation) direction. For scale this storm is about 4,000 miles (6,500 kilometers) across, roughly the distance between Cedar Rapids, Iowa to Honolulu, Hawaii. The elongated brown storms are familiar cyclonic (counterclockwise rotation) features, called "mini-barges." WS-a and WS-o are White Spots "a" and "o," anticyclonic storms that have persisted for over a year, separated by the North Equatorial Belt (NEB) north (NEBn) cyclone. The NEDF is the dark formation on the south edge of the NEB. Latitudinal belts and zones are labeled on the right with the conventions used by the amateur astronomy community and professional observers: NNTBs - North North Temperate Belt south; NTB(N) - North Temperate Belt (North); NTB(S) - North Temperate Belt (South); NTropZ - North Tropical Zone; NEBn - North Equatorial Belt north; NEB - North Equatorial Belt; NEBs - North Equatorial Belt south. The original JunoCam images used to produce these views were taken from altitudes between about 2,900 and 6,300 miles (4,600 and 10,200 kilometers) above Jupiter's cloud tops. Citizen scientist Brian Swift processed the images to produce a cylindrical map and enhance the color and contrast. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24236
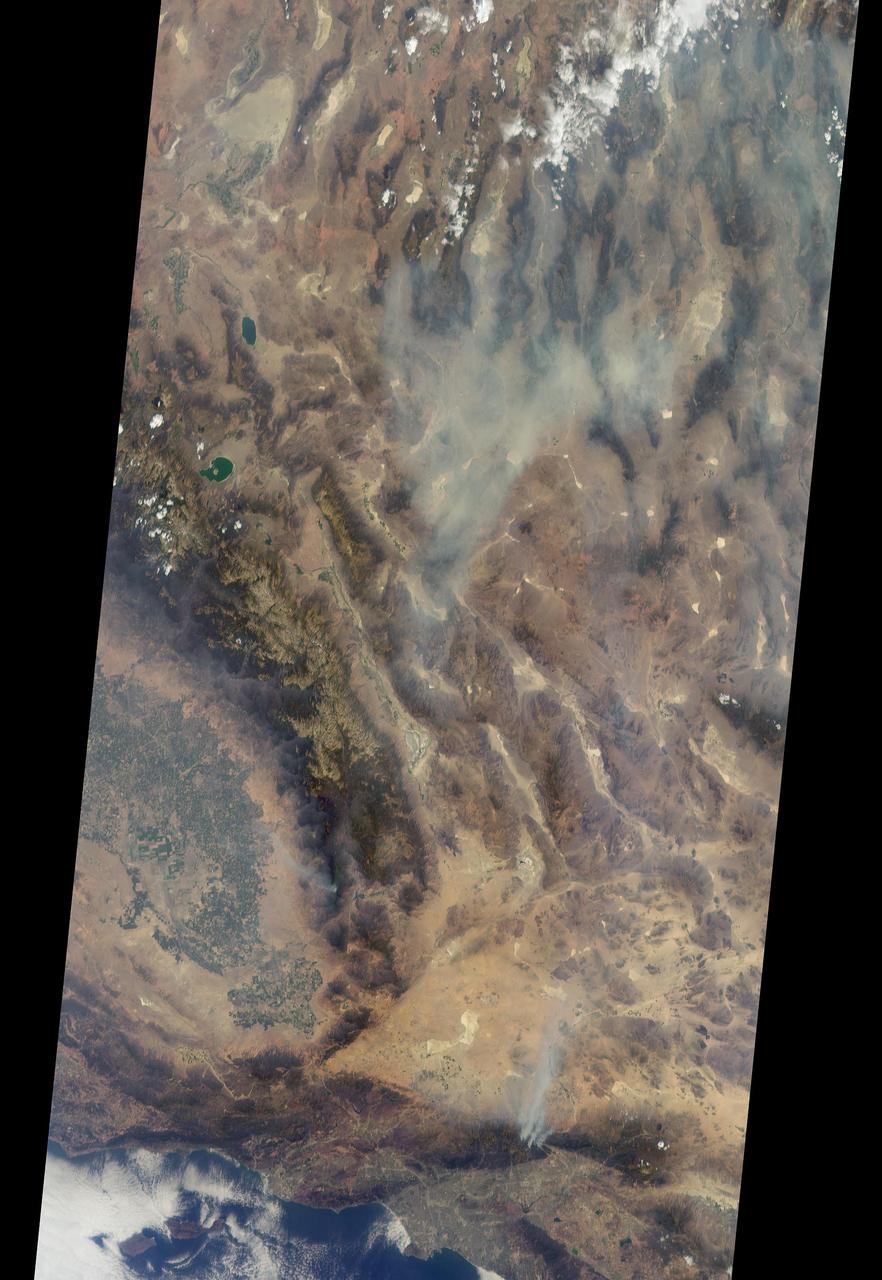

On Aug. 16, 2016, at around 10:30 a.m., a brush fire ignited in the Cajon Pass east of Los Angeles, just to the west of Interstate 15. Within a matter of hours, extreme temperatures, high winds and low humidity allowed the fire to spread rapidly, burning through brush left tinder-dry by years of drought. Firefighters quickly responded, ordering the evacuation of about 83,000 people in and around the Cajon Pass, Wrightwood, Lytle Creek, Oak Hills and surrounding areas. An as-yet uncounted number of homes and structures have burned, and Interstate 15 remains closed to downed power lines and barrier damage. By Aug. 17, the fire had expanded to more than 30,000 acres and remains zero percent contained as some 1,300 firefighters continue to battle to save homes and evacuate residents. The Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite passed over the region on Aug. 17 around 11:50 a.m. PDT and captured this natural-color image from MISR's 70-degree forward-viewing camera, which covers an areas about 257 miles (414 kilometers) wide. The oblique view angle makes the smoke more apparent than it would be in a more conventional vertical view. The Los Angeles metropolitan area is the large gray area on the coast in the center of the image. Three plumes from the Blue Cut Fire are clearly visible in the mountains to the north. This oblique view also shows an enormous cloud of smoke spreading northeastward over a significant portion of eastern California and Nevada. This smoke probably originated from the fire as it consumed almost 20,000 acres on the evening of the 16th and traveled north overnight. Also visible from this oblique view is considerable haziness filling California's Central Valley, to the northwest of the Blue Cut Fire. This haziness is most likely due to smoke from several other fires burning in California, including the Soberanes Fire near Monterey, the Clayton Fire that has destroyed 175 structures north of San Francisco, the Chimney Fire and the Cedar Fire, which is visible in the image in the southern Sierra Nevada. The total number of acres burned in California this year has tripled in just the past week. The 3D stereo anaglyph is made by combining data from MISR's 60-degree and 70-degree forward-viewing cameras. You will need red-blue glasses to view the 3D effect (ensure the red lens is over your left eye). In order to enable stereo viewing, the image has been rotated so north is to the left. These data were acquired during Terra orbit 88648. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20888
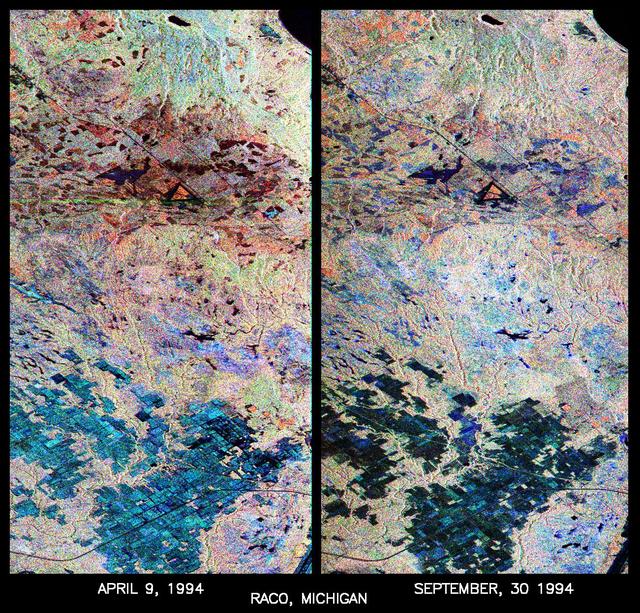
These are two false-color composites of Raco, Michigan, located at the eastern end of Michigan upper peninsula, west of Sault Ste. Marie and south of Whitefish Bay on Lake Superior. The two images (centered at 46.39 degrees north latitude, 84.88 degrees west longitude) show significant seasonal changes in the mid-latitude region of mixed deciduous and coniferous forests. The images were acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the shuttle Endeavour on the sixth orbit of each mission. In these images, red is L-band (23 cm) with horizontal/vertical polarization; green is C-band (6 cm) with horizontal/vertical polarization; blue is C-band with horizontal/horizontal polarization. The region shown is largely forested and includes a large portion of Hiawatha National Forest, as well as an agricultural region near the bottom of each image. In early April, the area was snow-covered with up to 50 centimeters (19.5 inches) of snow in forest clearings and agricultural fields. Buds had not yet broken on deciduous trees, but the trees were not frozen and sap was generally flowing. Lake Superior, in the upper right, and the small inland lakes were frozen and snow-covered on April 9, 1994. By the end of September, deciduous trees were just beginning to change color after a relatively wet period. Leaf loss was estimated at about 30 percent, depending on the species, and the soil was moist to wet after a heavy rainfall on September 28, 1994. Most agricultural fields were covered with grasses of up to 60 centimeters (23 inches) in height. In the two images the colors are related to the types of land cover (i.e. vegetation type) and the brightness is related to the amount of plant material and its relative moisture content. Significant seasonal changes between early spring and early fall are illustrated by this pair of images. For the agricultural region near the bottom of the images, the change from snow-cover to moist soil with short vegetation cover is shown by the color change from blue to green and blue. The green color corresponds to significant increases in vegetation cover and field-to-field differences in blue are the result of differences in surface roughness and soil moisture. In the forested areas, many of the conifer forests appear similar in both images (red pine forests appear red in both images). However, there is more blue and green in the September 30, 1994 image as a consequence of greater foliage and more moisture in the forest crowns. Lowland conifer forests (spruce and northern white cedars) appear as bright green in both images. Deciduous forests produce very strong radar returns at these frequencies and polarization combinations, resulting in a nearly white appearance on the images (the specific color mix is related to the local species mix). In the September 30, 1994 image, the areas of deciduous forest appear darker than in the April image because of the weaker radar signal from the foliage in the crown layer. The clear-cut areas (shown in April by the irregularly shaped dark areas in the center) change dramatically in appearance due to loss of snow cover and increases in soil moisture and vegetation cover by the end of September. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01730