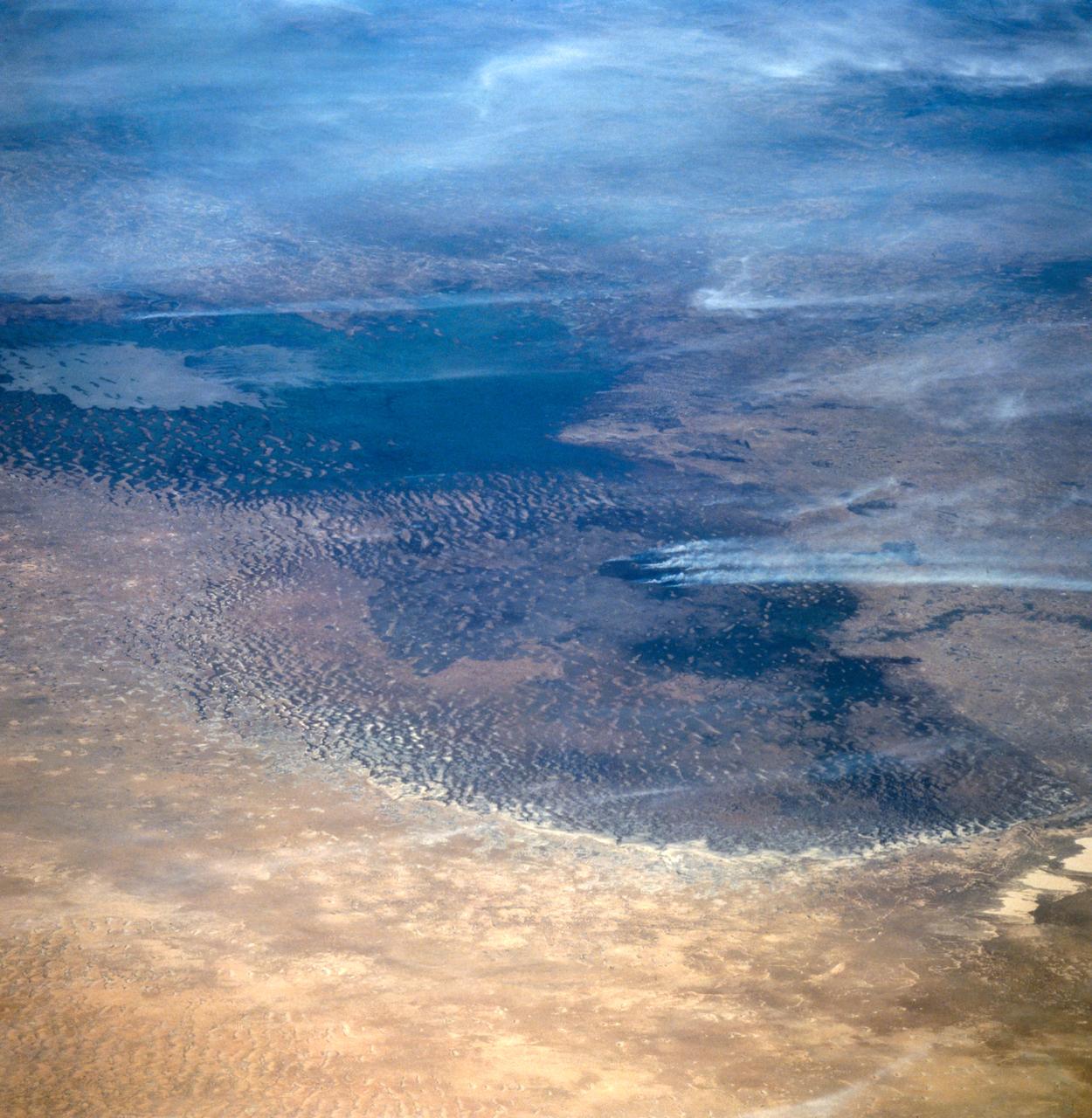

This oblique view of Lake Chad was taken by the STS-66 crew in November 1994. This lake lies mainly in the Republic of Chad and partly in Nigeria, Cameroon and Niger. The size of Lake Chad varies seasonally and is actually divided into north and south basins; neither of which is generally more than 25 feet (7.6 meters) deep. In this photograph, all the water appears to be located in the southern basin with the northern and eastern edges of both basins covered with sand dunes which have invaded the area where the water once stood. The prevailing wind direction can be seen from the agriculture burning in both basins to be from the east.
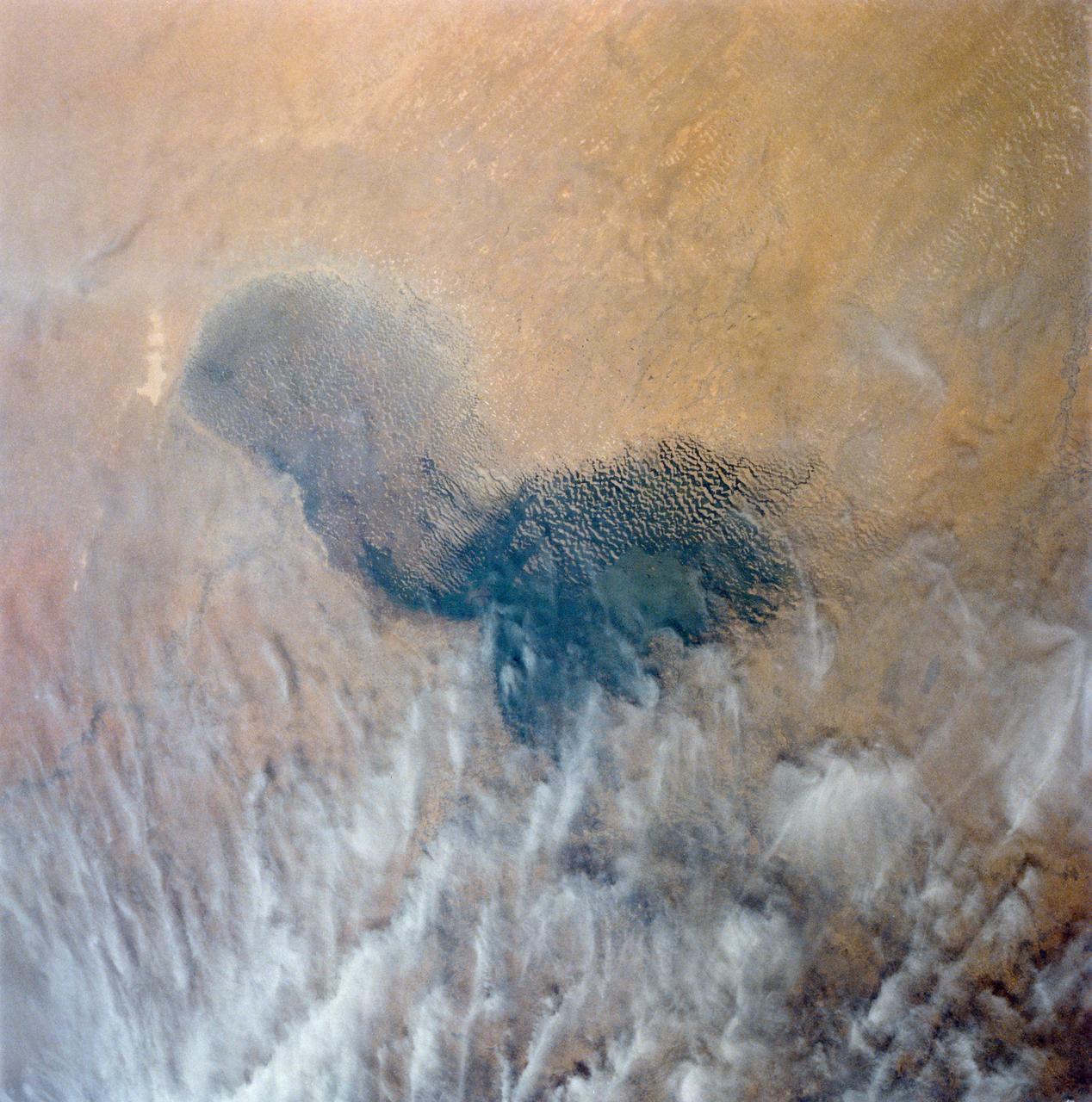

Africa's Lake Chad where the borders of Chad, Niger, Nigeria and Cameroon merge (13.0N, 14.0E) has been undergoing change for the past 25 to 30 years when it was first noticed that the lake is drying up. Since then, astronauts have been photographing it on a regular basis to record the diminishing lake bed. This lake was once the aproximate size of Lake Erie but is now only about half that size and is still receeding.
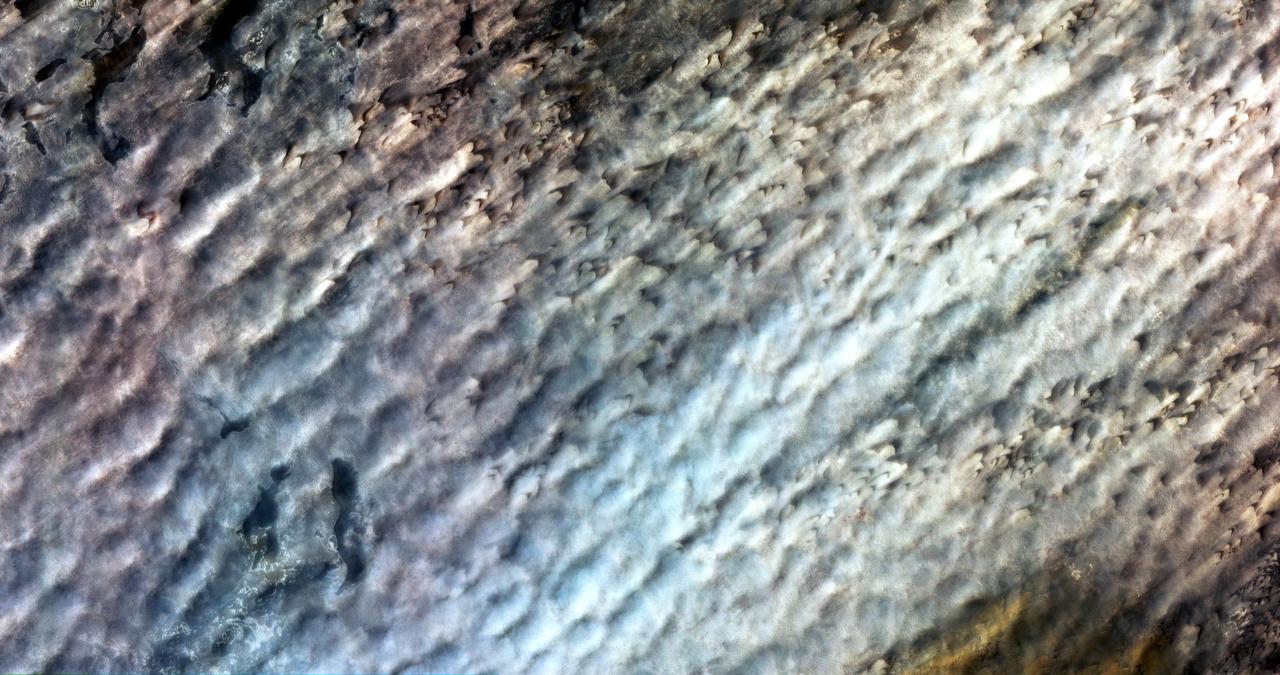

NASA Terra spacecraft monitored the migration of sand dunes in the Bodele depression of northern Chad from at various times from one month to 6.5 years

CHAD HASTINGS ATTACHES END FITTING TO BURST TEST ARTICLE

Lake Fitri is located in the center of Chad. It is fed by seasonal rainfall, so its area can triple in wet years. In extreme drought years, the lake may dry out completely. Wadi Batha empties into the lake from the east, and has created a large delta. Inundated linear sand dunes are found in the western and southwestern part of the image. The image was acquired May 19, 2017, covers an area of 48.9 by 48.9 km, and is located at 12.7 degrees north, 17.5 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24018
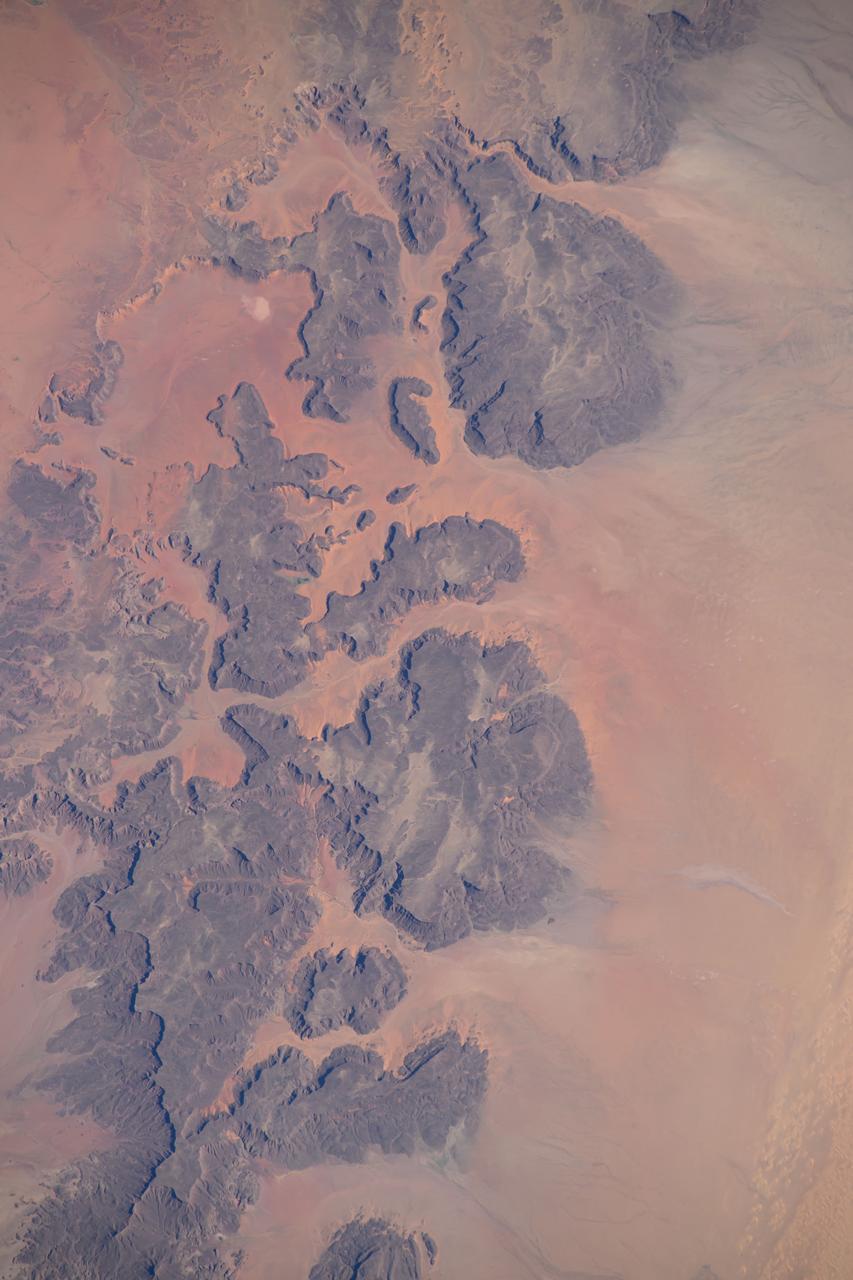

iss072e404551 (Dec. 26, 2024) --- A portion of the Ennedi Massif in Northern Chad, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Sahara, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above the African nation.
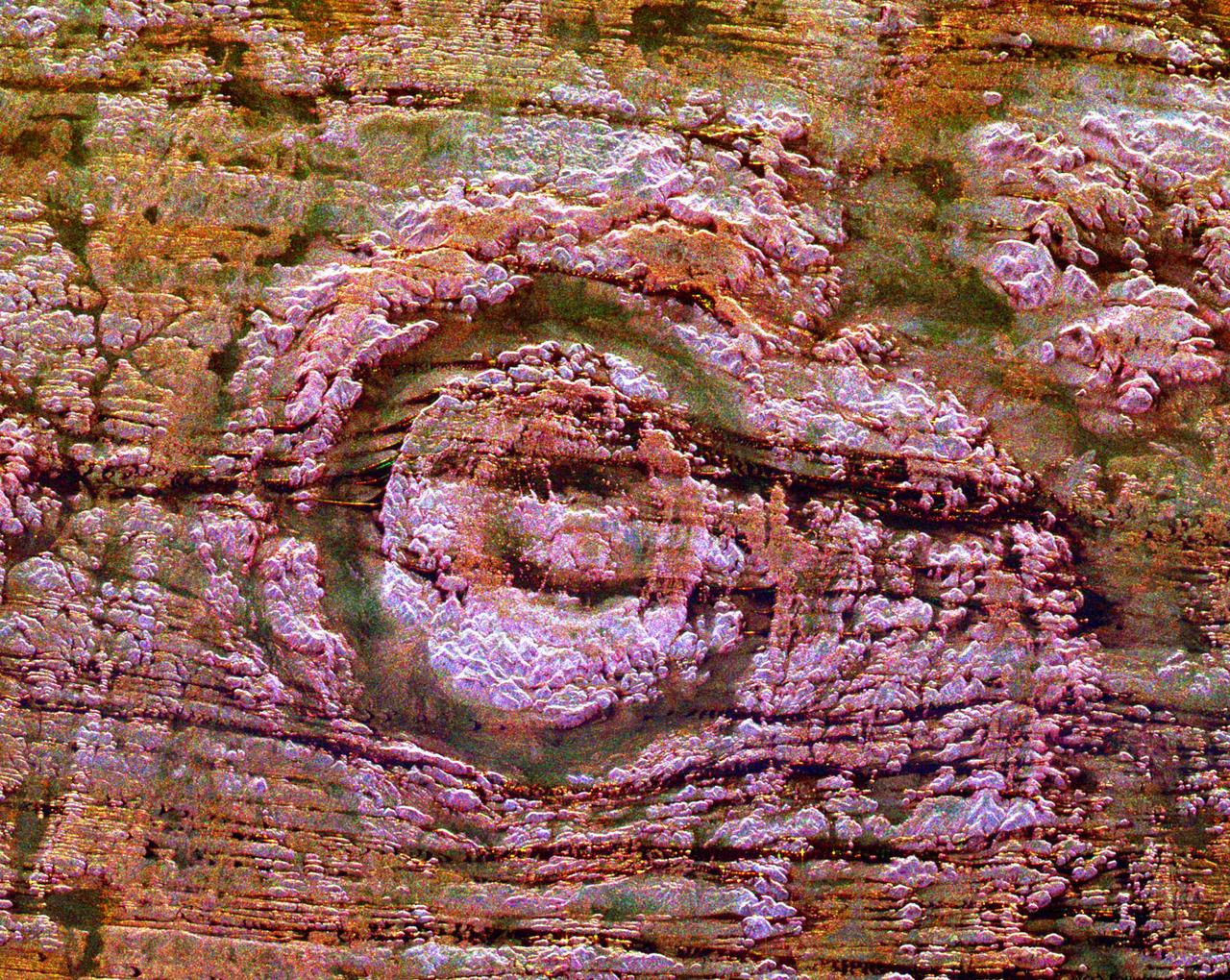

The impact of an asteroid or comet several hundred million years ago left scars in the landscape that are still visible in this spaceborne radar image of an area in the Sahara Desert of northern Chad.

MATERIALS ENGINEER CHAD HASTINGS AND ENGINEERING TECHNICIAN PHILLIP THOMPSON LAYING UP RUBBER INSULATION ON BURST TEST ARTICLE

MATERIALS ENGINEER CHAD HASTINGS AND ENGINEERING TECHNICIAN PHILLIP THOMPSON LAYING UP RUBBER INSULATION ON BURST TEST ARTICLE

iss072e404539 (Dec. 26, 2024) --- A portion of the Ennedi Massif in Northern Chad, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Sahara, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above the African nation.

Crew Earth Observations (CEO) taken during Expedition 12. Earth views over Chad, Bahr Azoum.

Commercial Crew Program (CCP) SpaceX Merlin Engine Gas Generator (GG) Baffle Assessment, Mr. Brian Richardson (background), and Mr. Chad Eberhart (foreground)

NASA Director for Human Space Flight Programs, Russia, Chad Rowe, left, with the support of NASA Interpreter Evgeny Sokol, delivers his report during a meeting to discuss the readiness for the landing of Expedition 57 crew members Serena Auñón-Chancellor of NASA, Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency), and Sergey Prokopyev of Roscosmos, Tuesday, Dec. 18, 2018. Auñón-Chancellor, Gerst, and Prokopyev are returning after 197 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 56 and 57 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Director for Human Space Flight Programs, Russia, Chad Rowe departs an AN-26 aircraft at the Zhezkazgan Airport in Kazakhstan to be in place for the Soyuz MS-08 spacecraft landing with Expedition 56 Commander Drew Feustel and Flight Engineer Ricky Arnold of NASA, along with Flight Engineer and Soyuz Commander Oleg Artemyev of Roscosmos on Thursday, Oct. 4, 2018. Feustel, Arnold, and Artemyev are returning after 197 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 55 and 56 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Director for Human Space Flight Programs, Russia, Chad Rowe, left talks during a meeting with NASA, Roscosmos and Russian Search and Recovery Forces where the readiness for the landing of Expedition 54 crew members Joe Acaba and Mark Vande Hei of NASA and cosmonaut Alexander Misurkin was discussed, Sunday, Feb. 25, 2018. Acaba, Vande Hei, and Misurkin are returning after 168 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 53 and 54 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
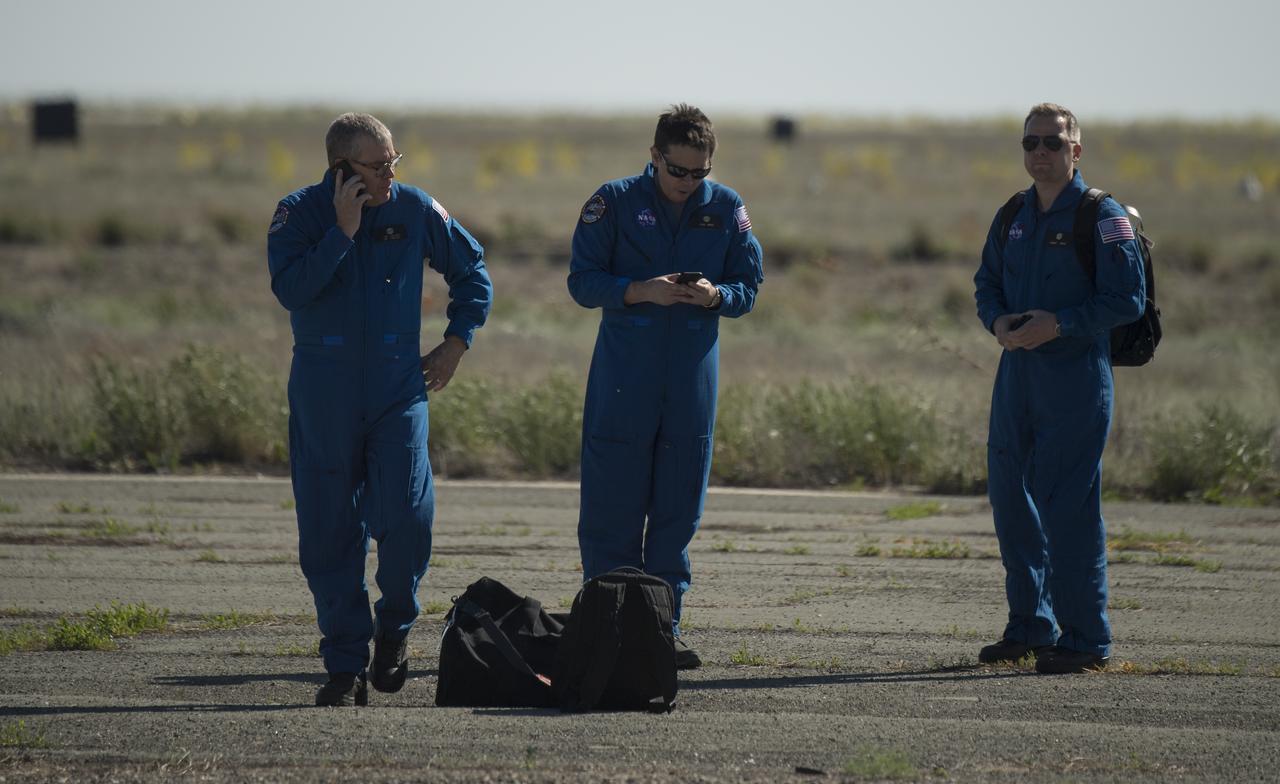

NASA Deputy International Space Station Program Manager Dan Hartman, left, NASA Director for Human Space Flight Programs, Russia, Chad Rowe, and NASA Interpreter Evgeny Sokol, right, wait at the Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan Airport to support the Soyuz landing of Expedition 55 crew members Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, Scott Tingle of NASA, Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Sunday, June 3, 2018. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai are returning after 168 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 54 and 55 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
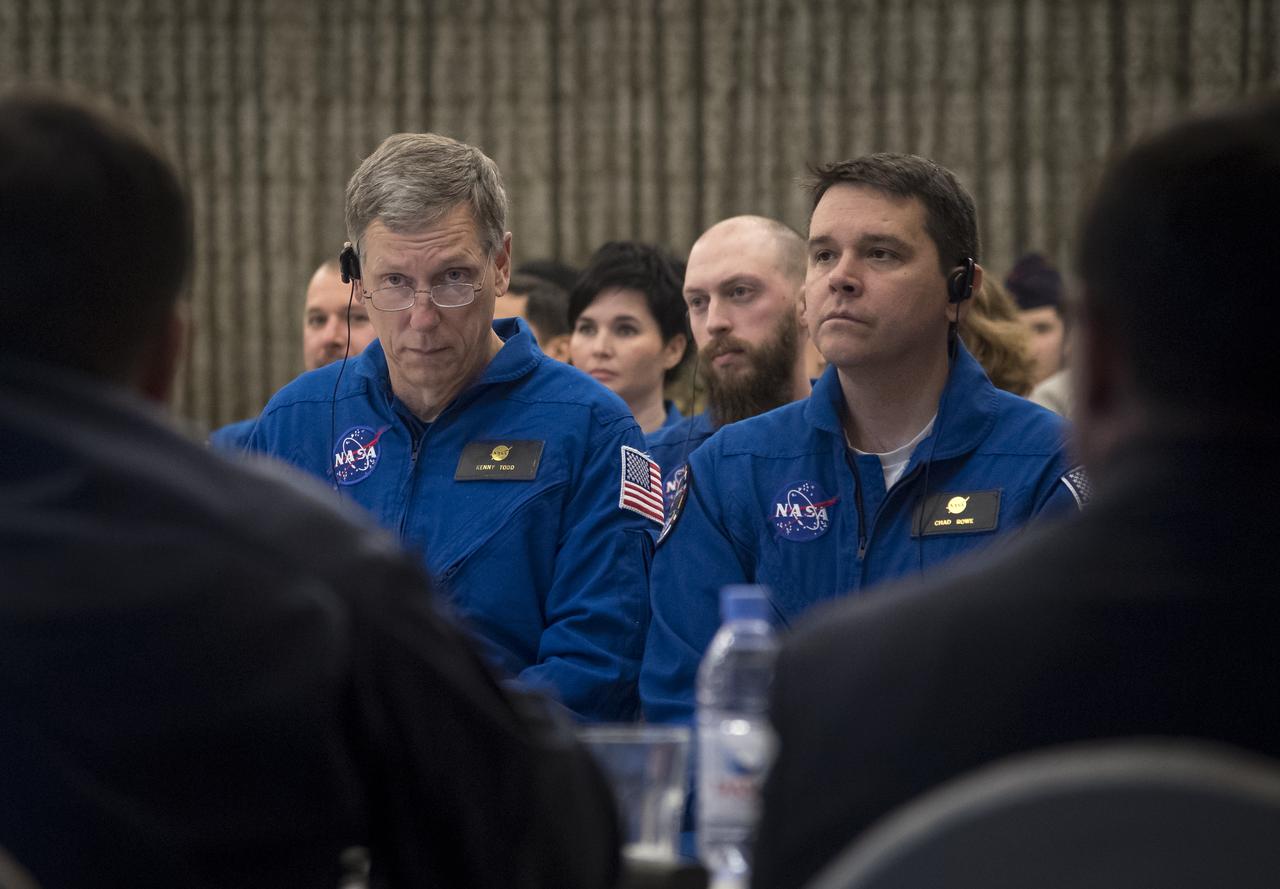

NASA International Space Station Operations Integration Manager Kenny Todd, left, and NASA Director for Human Space Flight Programs, Russia, Chad Rowe, along with Roscosmos and Russian Search and Recovery Forces, meet to discuss the readiness for the landing of Expedition 54 crew members Joe Acaba and Mark Vande Hei of NASA and cosmonaut Alexander Misurkin Sunday, Feb. 25, 2018. Acaba, Vande Hei, and Misurkin are returning after 168 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 53 and 54 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
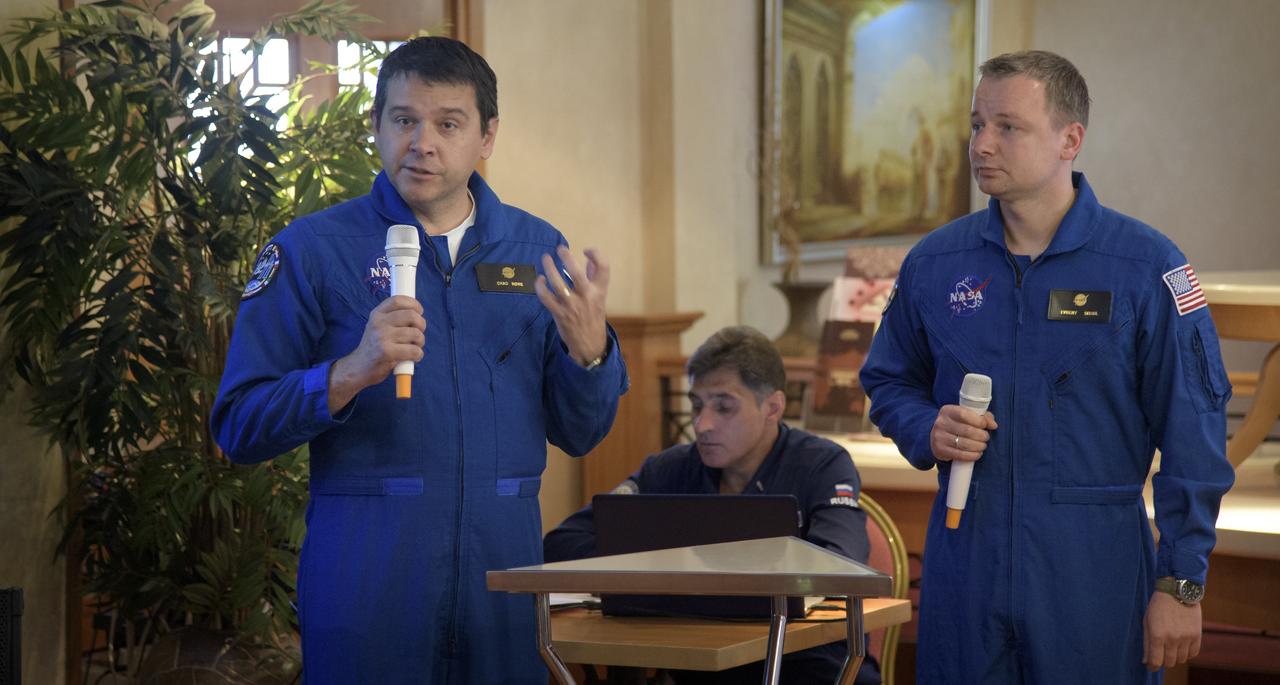

NASA Director for Human Space Flight Programs, Russia, Chad Rowe, left, with the support of NASA Interpreter Evgeny Sokol, gives a report during a meeting of NASA, Roscosmos and Russian Search and Recovery Forces to review the readiness for the landing of Expedition 56 crew members Drew Feustel and Ricky Arnold of NASA, along with Oleg Artemyev of Roscosmos Tuesday, Oct. 2, 2018, at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Karaganda, Kazakhstan. Feustel, Arnold, and Artemyev are returning after 197 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 55 and 56 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
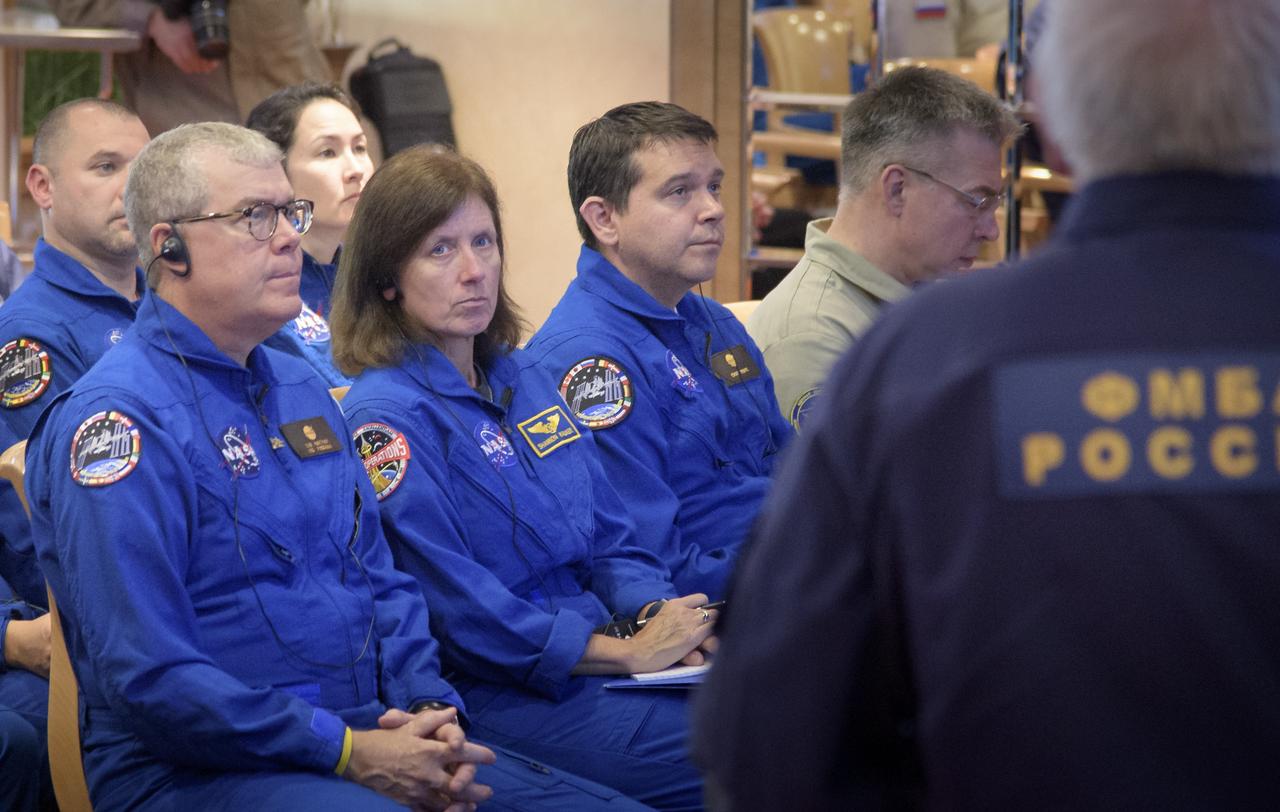

NASA Deputy International Space Station Program Manager Dan Hartman, left, NASA astronaut and Astronaut Office Representative Shannon Walker, center, and NASA Director for Human Space Flight Programs, Russia, Chad Rowe attend a NASA, Roscosmos, and Russian Search and Recovery Forces meeting to discuss the readiness for the landing of the Expedition 56 crew, Tuesday, Oct. 2, 2018. Expedition 56 crew members Drew Feustel and Ricky Arnold of NASA, along with Oleg Artemyev of Roscosmos are returning after 197 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 55 and 56 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
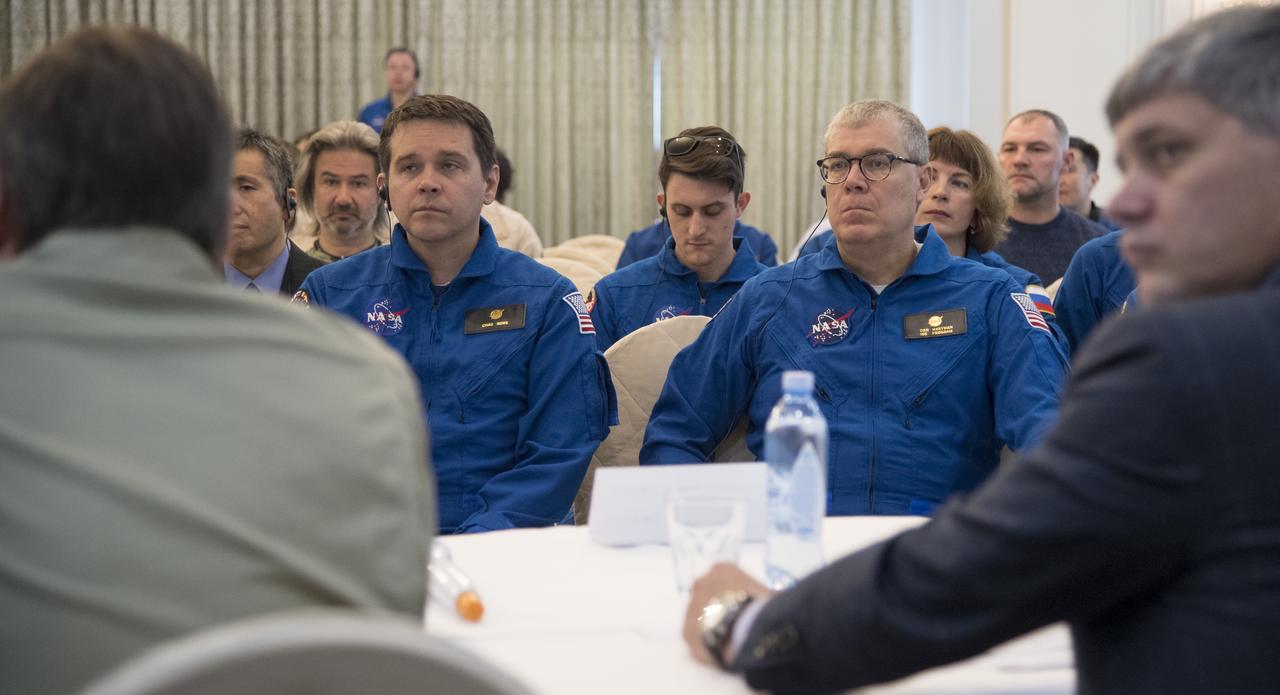

NASA Director for Human Space Flight Programs, Russia, Chad Rowe, left, and NASA Deputy International Space Station Program Manager Dan Hartman, right, are seen along with other NASA, Roscosmos, and JAXA team members during a meeting to discuss the readiness for the landing of Expedition 55 crew members Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, Scott Tingle of NASA, Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Saturday, June 2, 2018. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai are returning after 168 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 54 and 55 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
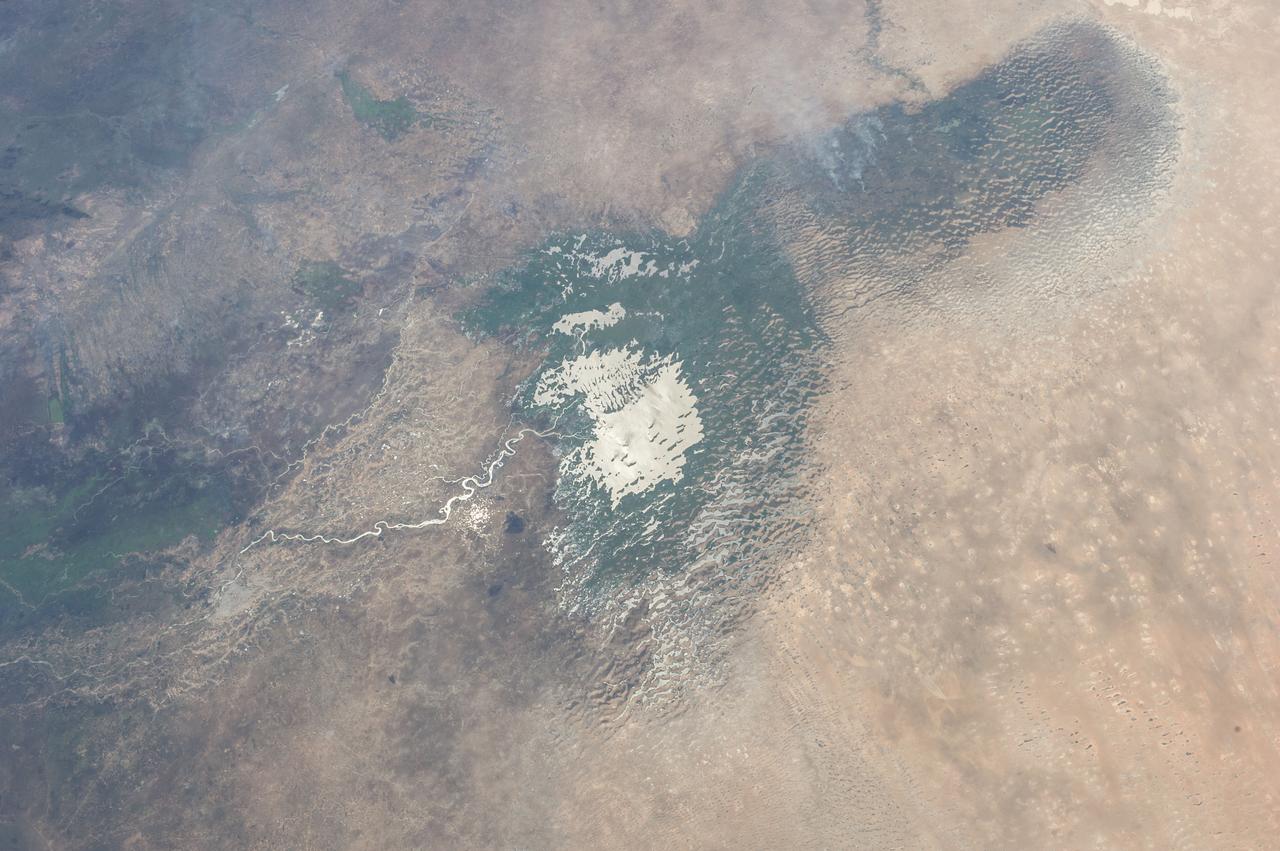

Earth observation taken during a day pass by the Expedition 37 crew. Per Twitter message: Sun glint on shallow Lake Chad in Chad & Nigeria.
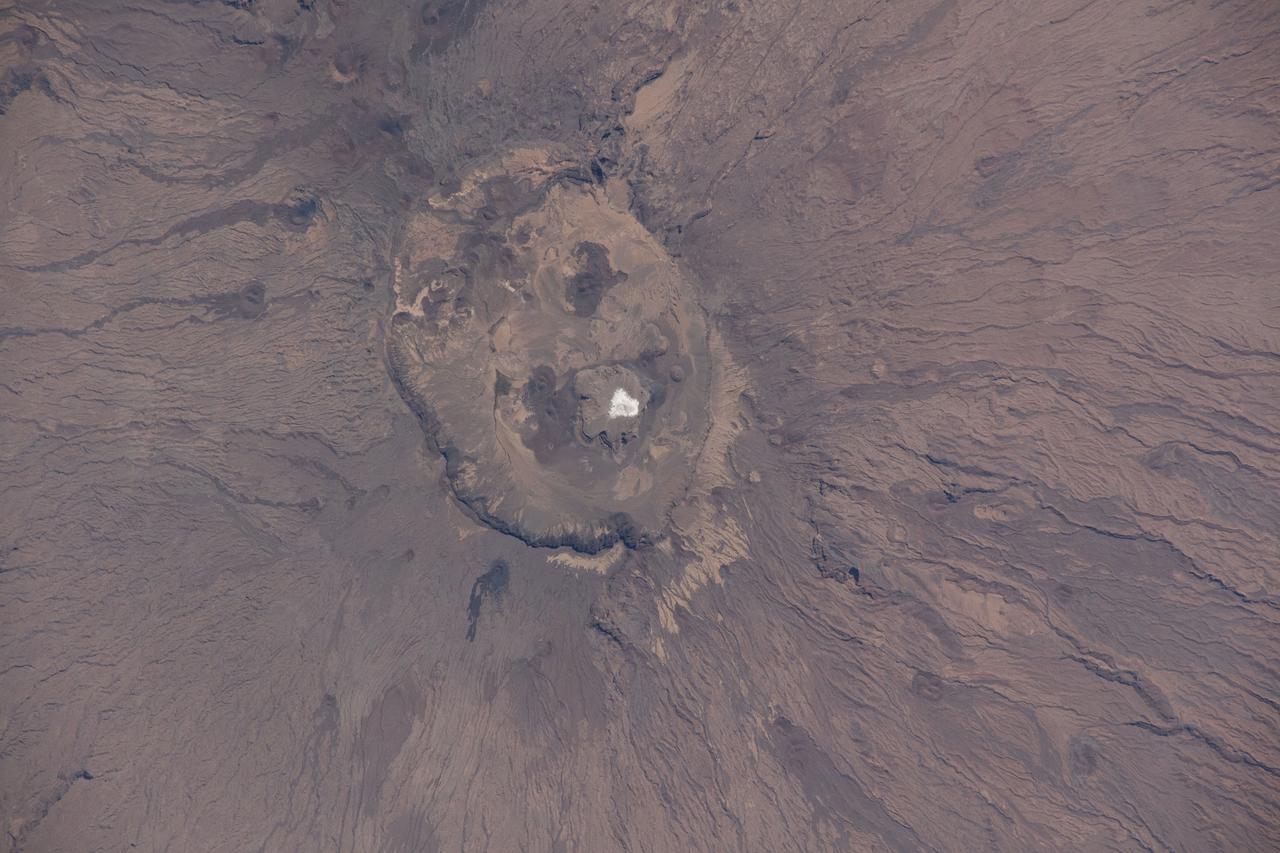

iss064e000448 (Oct. 25, 2020) --- Emi Koussi, a high pyroclastic shield volcano in northern Chad, is also the highest mountain in the Sahara. The International Space Station was orbiting above the Tibesti Mountains in Chad when this photograph was taken.

The impact of an asteroid or comet several hundred million years ago left scars in the landscape that are still visible in this spaceborne radar image of an area in the Sahara Desert of northern Chad.
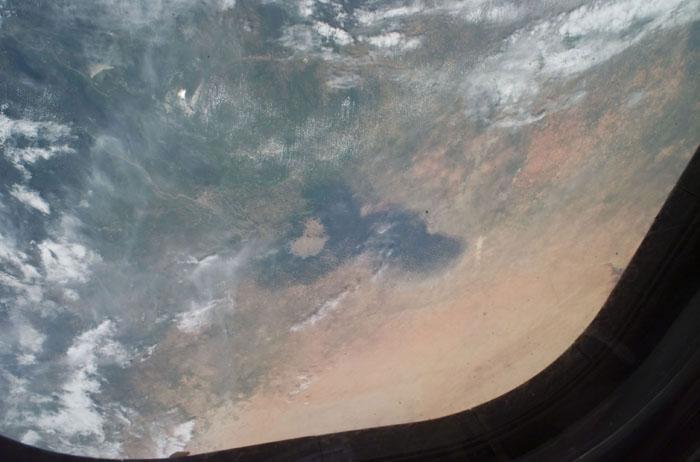

STS105-E-5434 (21 August 2001) --- Lake Chad and parts of Chad, Niger and Cameroon in Africa are pictured in this digital still camera's image recorded by the STS-105 crew members toward the end of their mission. The scene was captured though one of the overhead windows on the aft flight deck of the Space Shuttle Discovery.
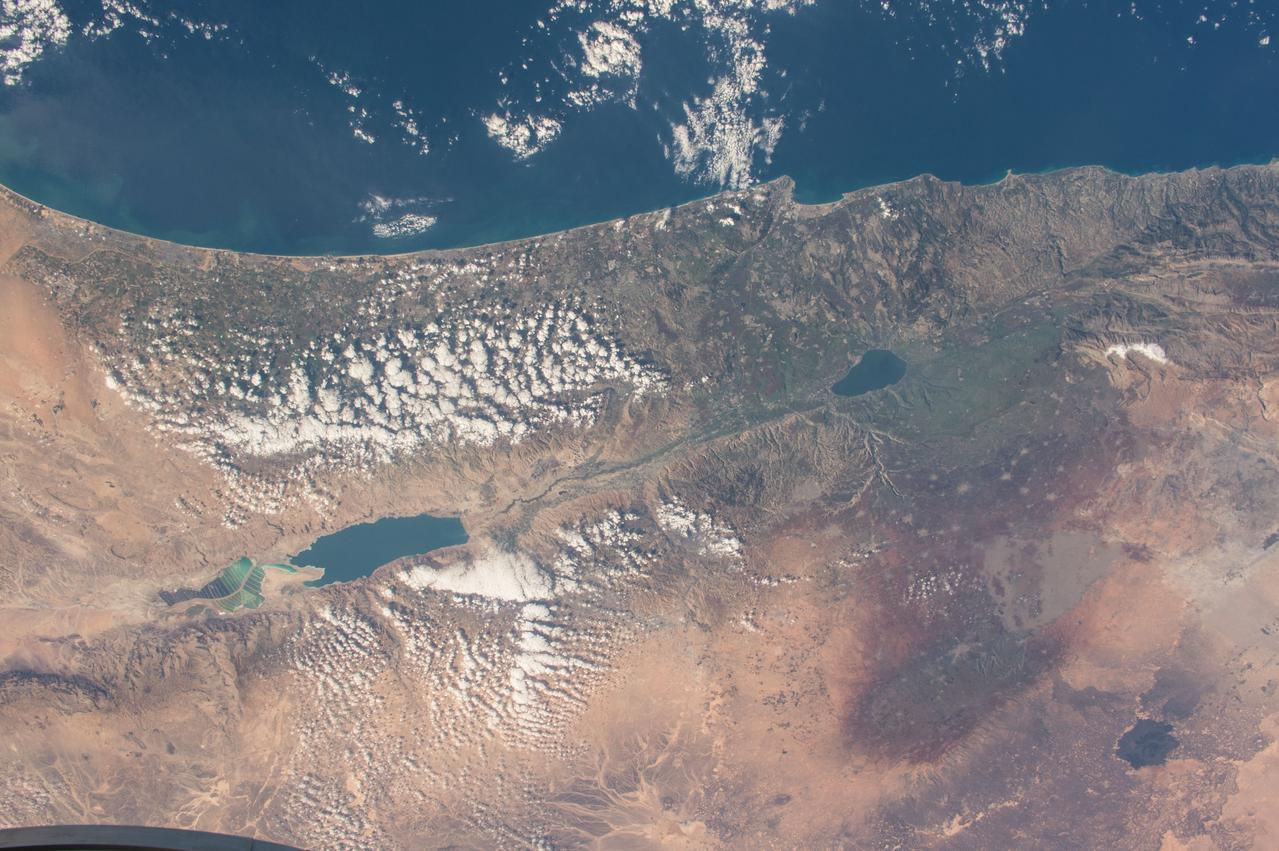

GMT358_21_53_Terry Virts_CEO chad sand dunes israel eastern turkey zoom_129
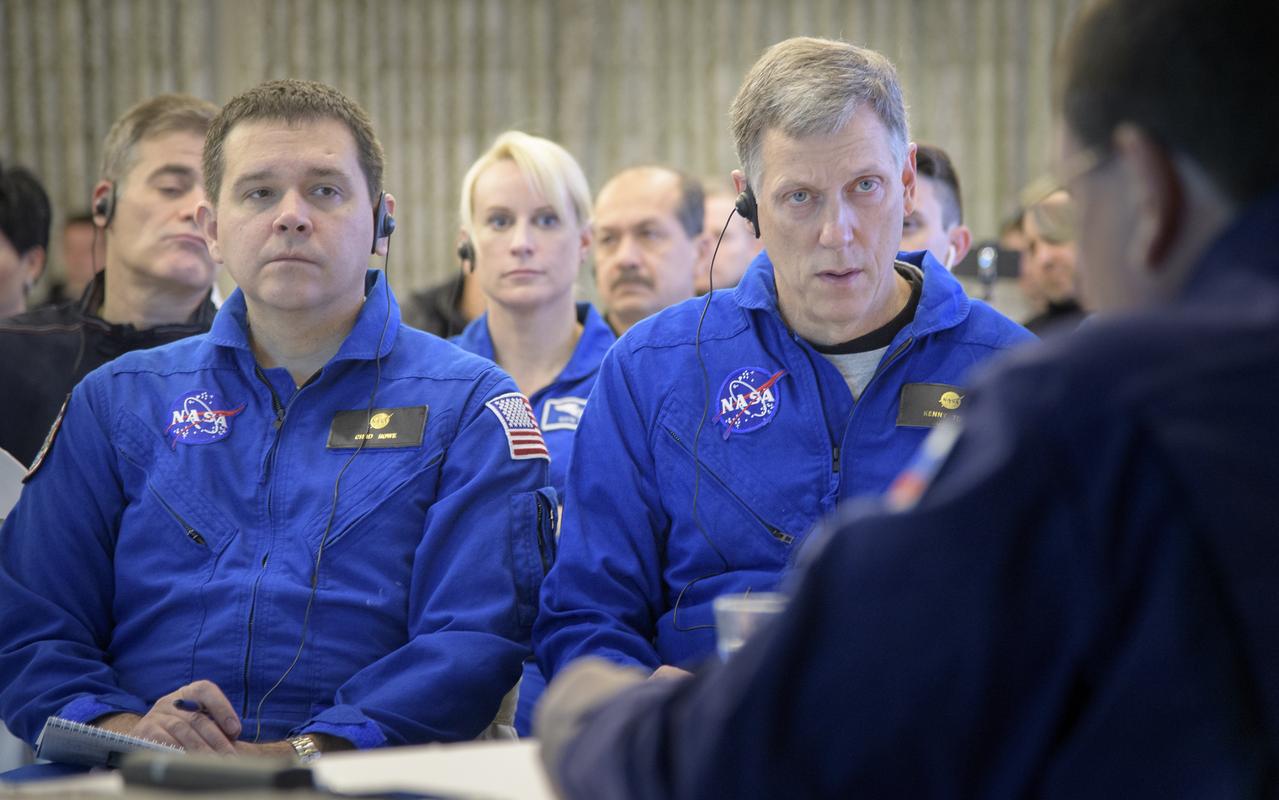

NASA Director for Human Space Flight Programs, Russia, Chad Rowe, left, NASA astronaut and Astronaut Office Representative Kate Rubins, center, and NASA International Space Station Operations Integration Manager Kenny Todd listen as NASA, ESA, Roscosmos, and Russian Search and Recovery Forces meet at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Karaganda, Kazakhstan to discuss the readiness for the landing of Expedition 57 crew members Serena Auñón-Chancellor of NASA, Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency), and Sergey Prokopyev of Roscosmos, Tuesday, Dec. 18, 2018. Auñón-Chancellor, Gerst, and Prokopyev are returning after 197 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 56 and 57 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
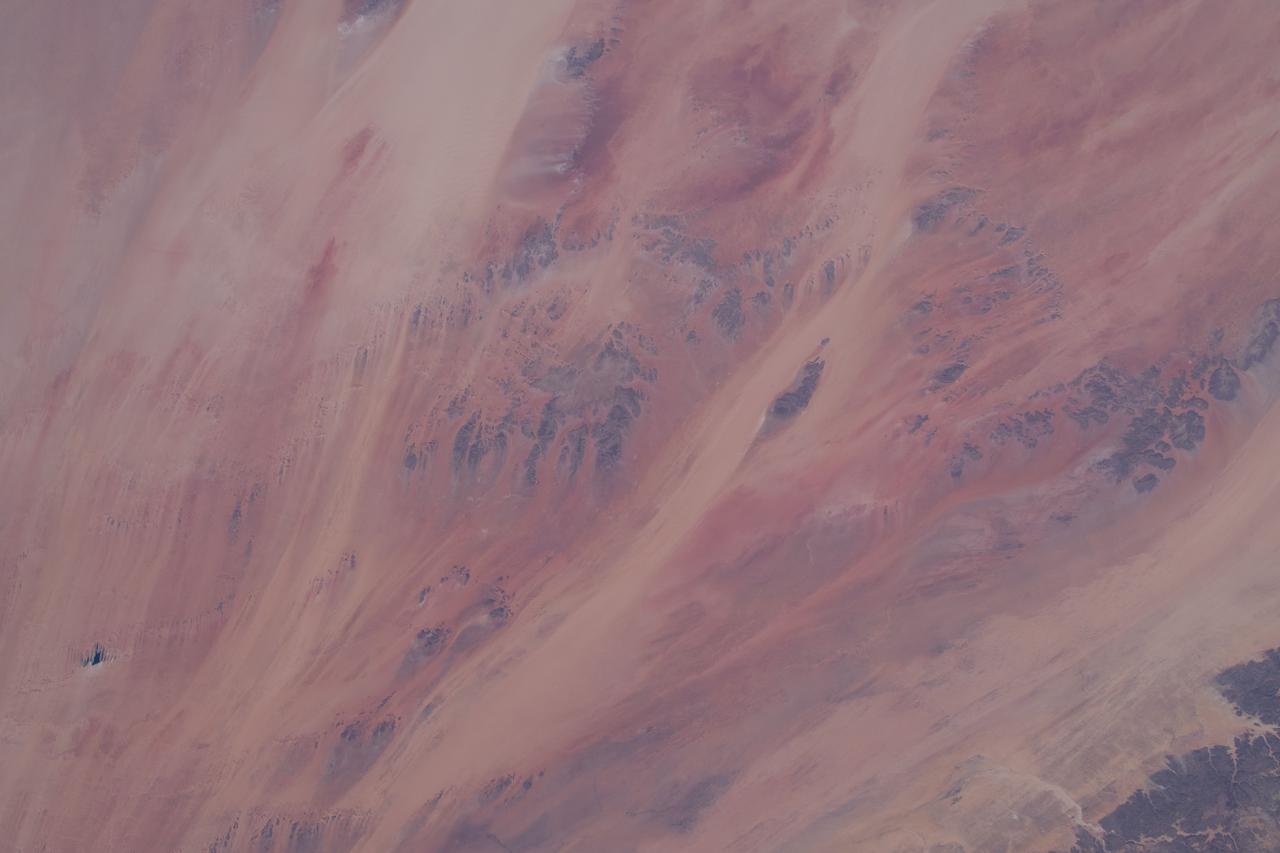

iss064e000451 (Oct. 25, 2020) --- A portion of the Sahara Desert is pictured in Chad as the International Space Station orbited above the sparsely-populated African nation.
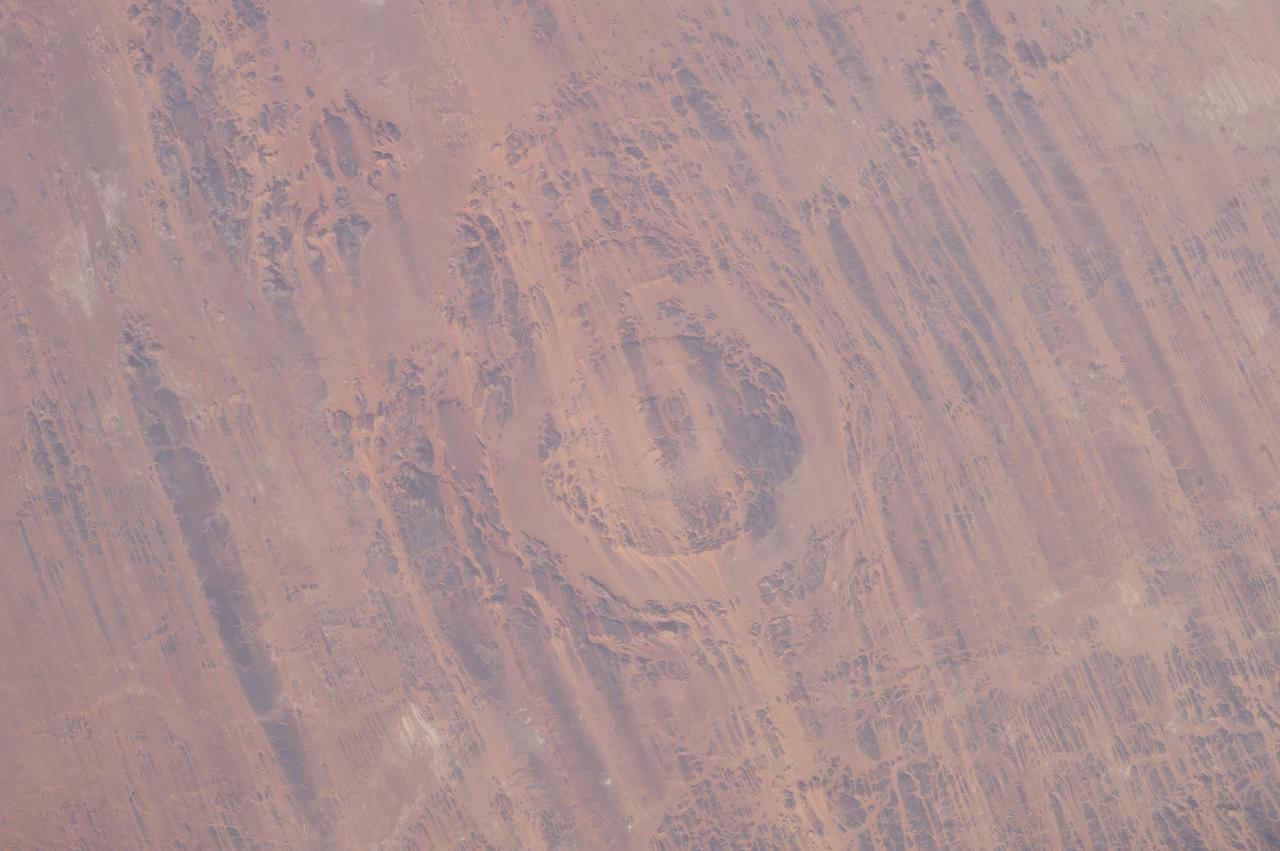

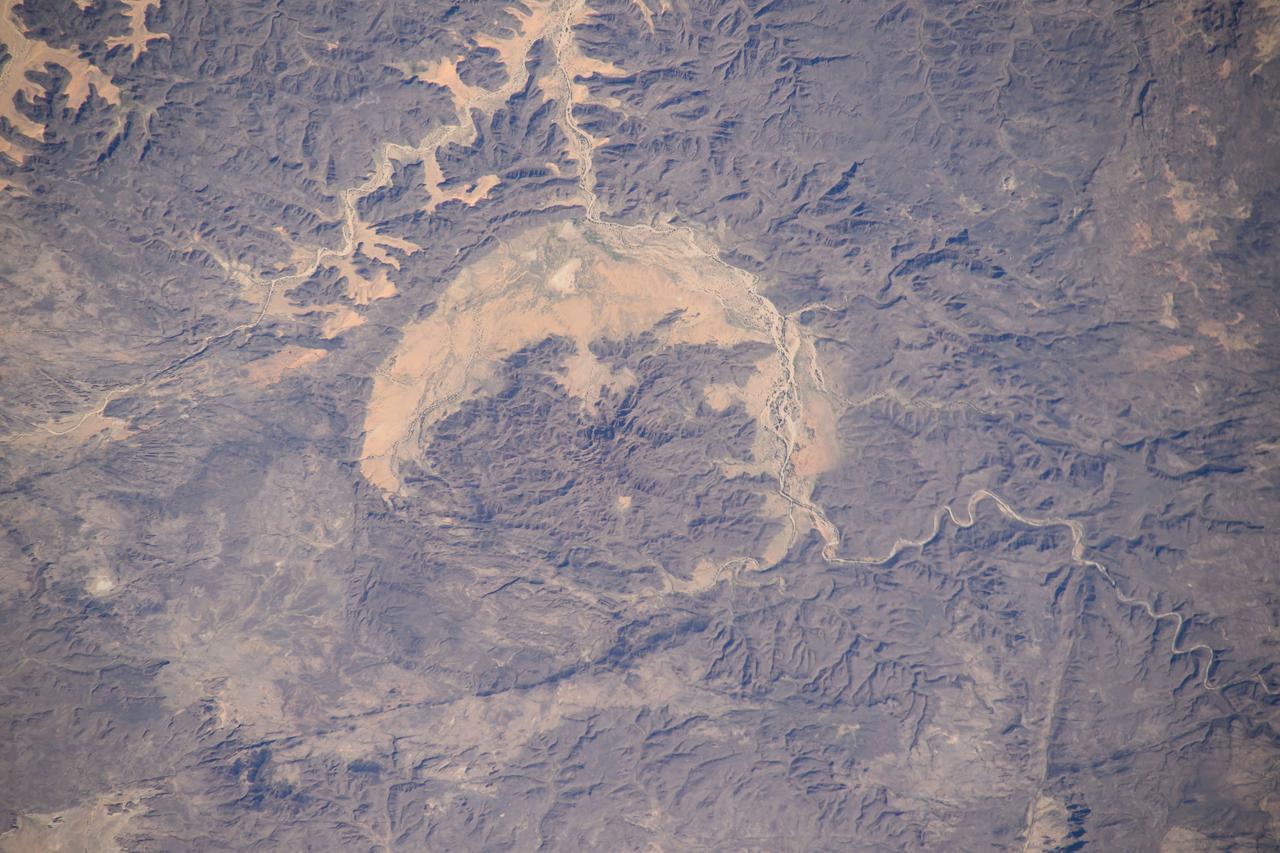
Earth observation taken by the Expedition 39 crew aboard the ISS. Image was released by astronaut on Twitter and downlinked in folder: Aorounga Impact Crater, Chad.
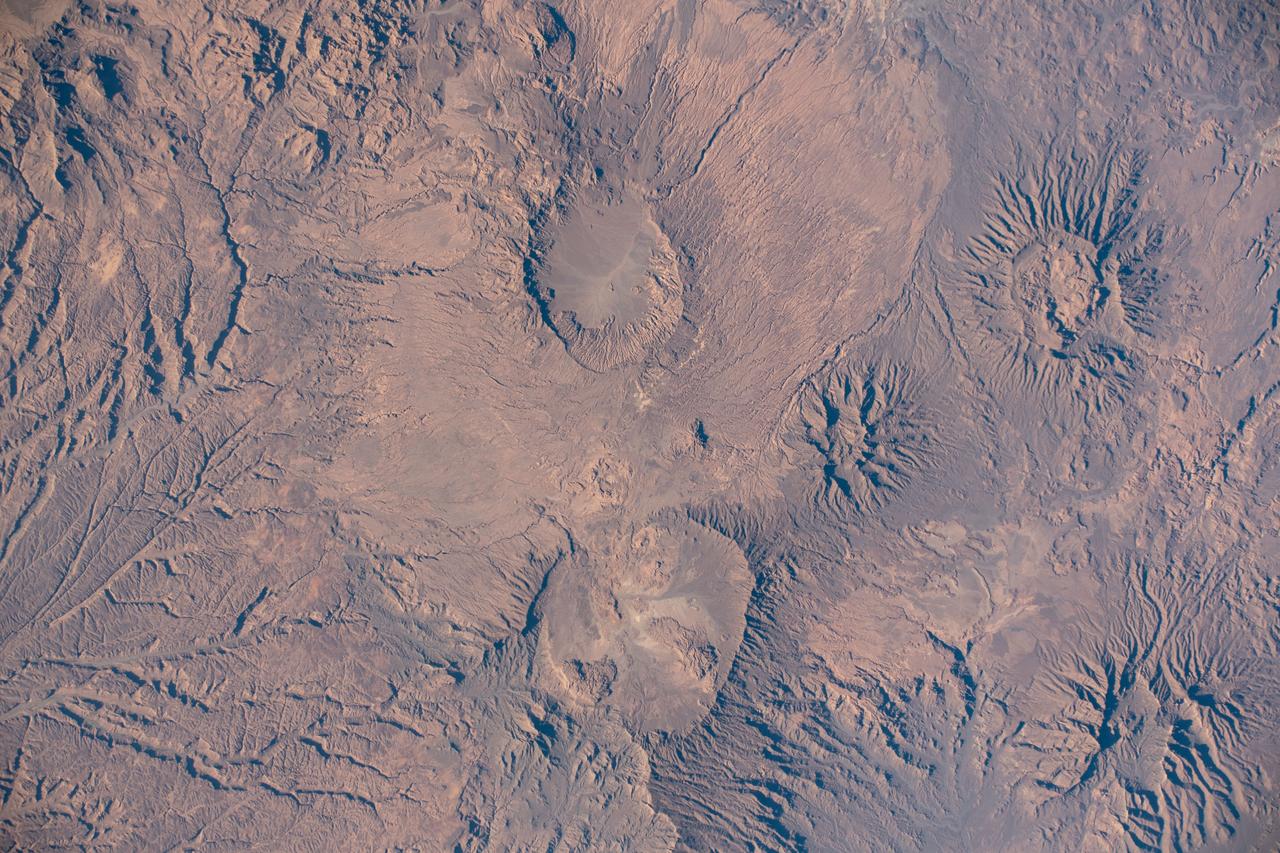

iss061e093293 (Dec. 20, 2019) --- The Tibesti Mountains in the African nation of Chad are pictured as the International Space Station orbited 259 miles above the central Sahara.
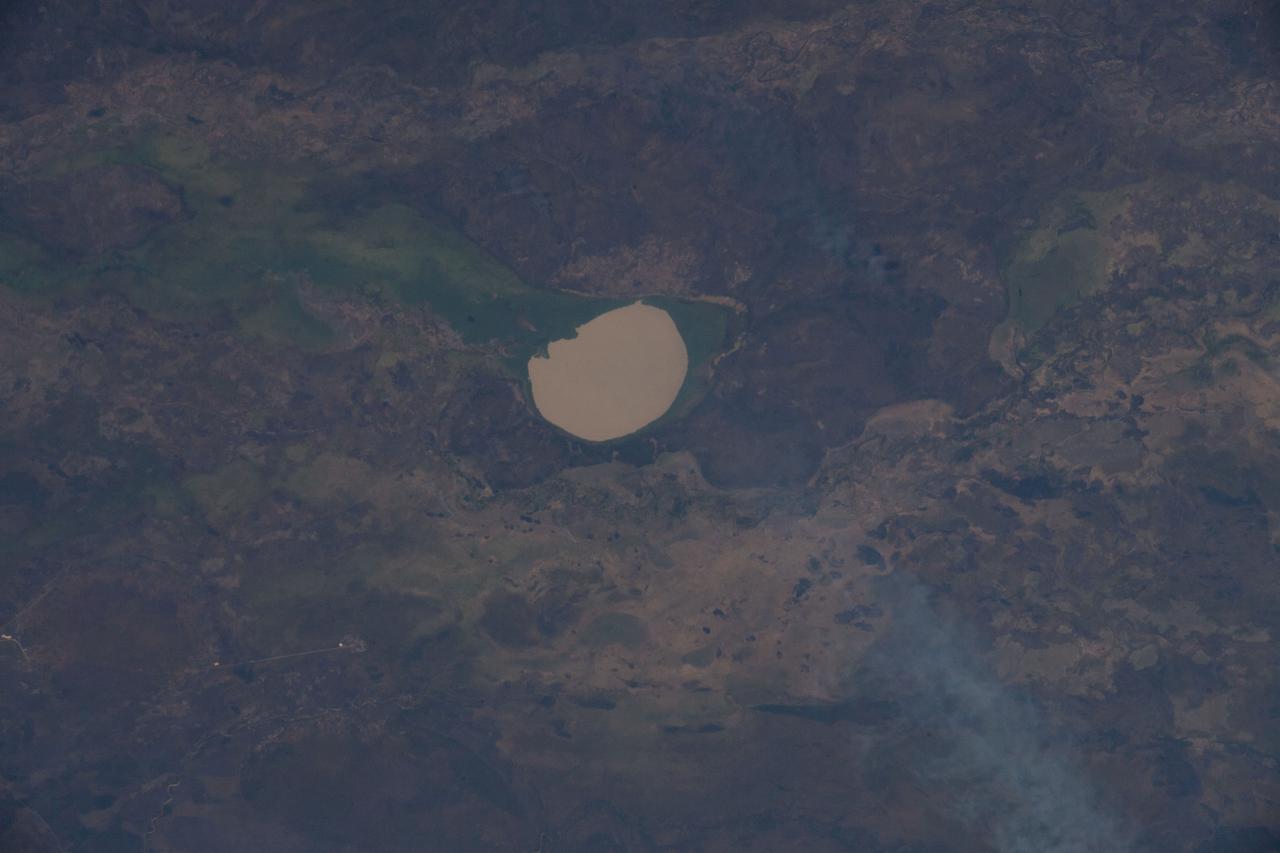

iss066e091581 (Nov. 30, 2021) --- Iro Lake in southeastern Chad is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 262 miles above the African nation.
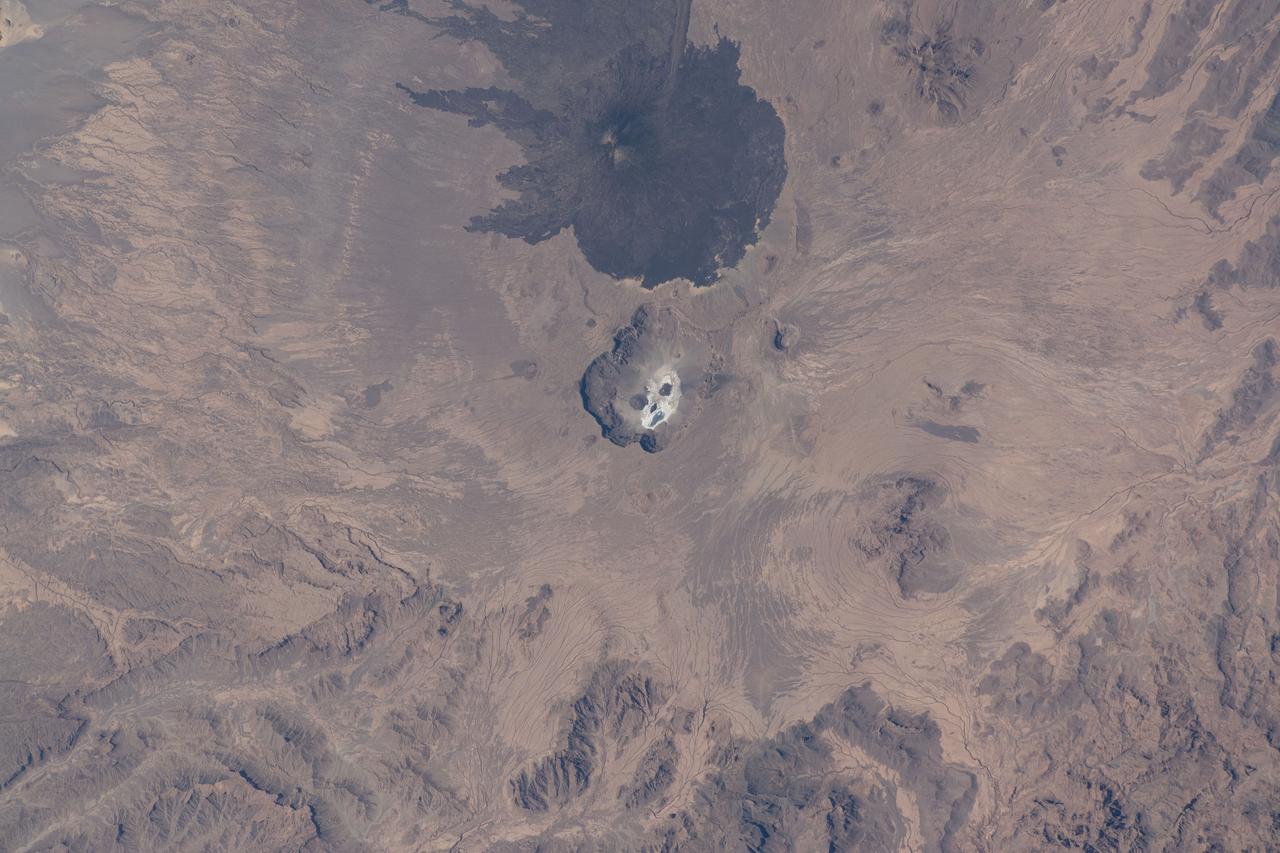

iss064e000441 (Oct. 25, 2020) --- The International Space Station was orbiting above the African nation of Chad at the time this photograph was taken of the potentially active stratovolcano Toussidé (center top) in the Tibesti Mountains
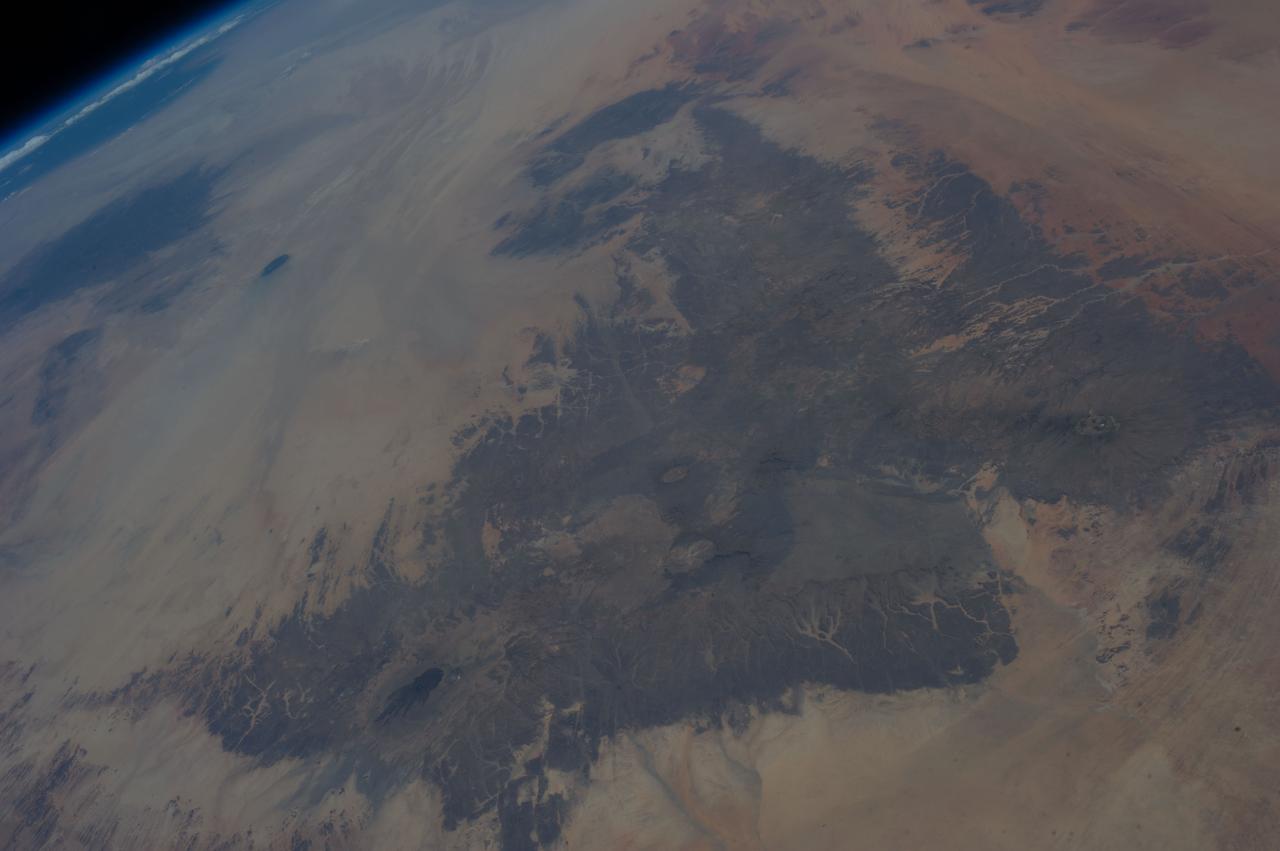

Earth Observation taken during a day pass by the Expedition 37 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Per Twitter message: Northern Chad, looking north across Libya.
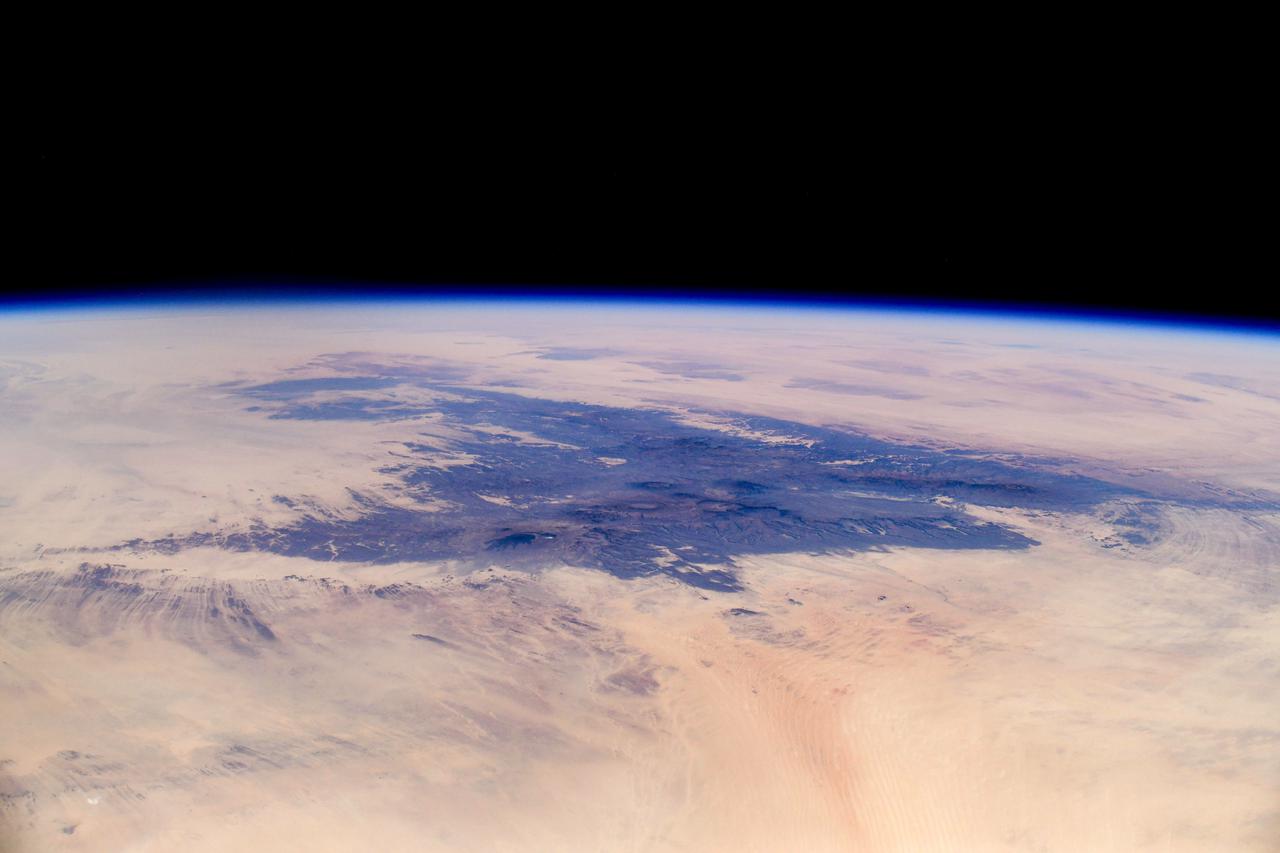

iss064e040726 (March 5, 2021) --- This picture from the International Space Station orbiting 261 miles above Africa looks northeast across Niger to the Tibesti Mountains of Chad. Credit: Roscosmos
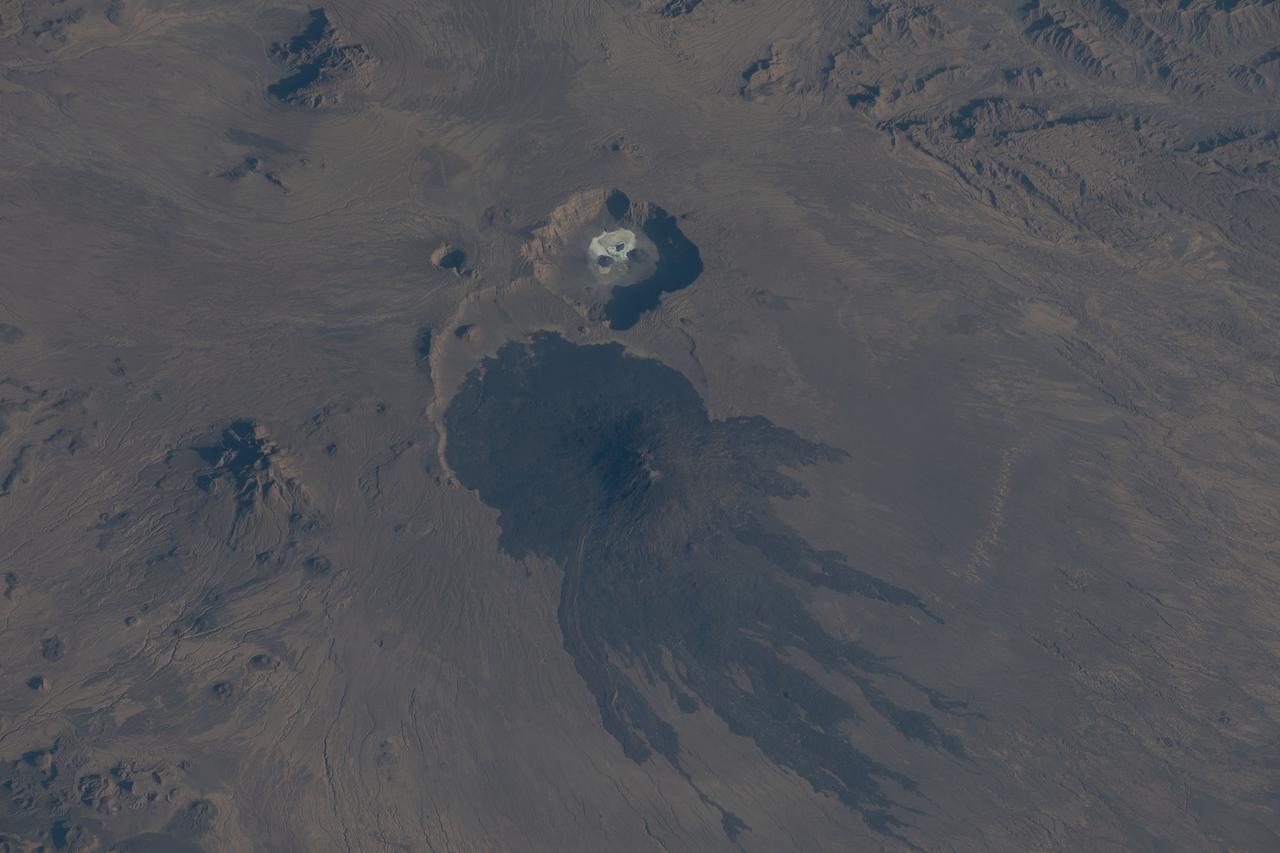

iss068e053501 (Feb. 12, 2023) --- The potentially active stratovolcano Toussidé and the Trou au Natron depression in the Tibesti Mountains are pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above the African nation of Chad.
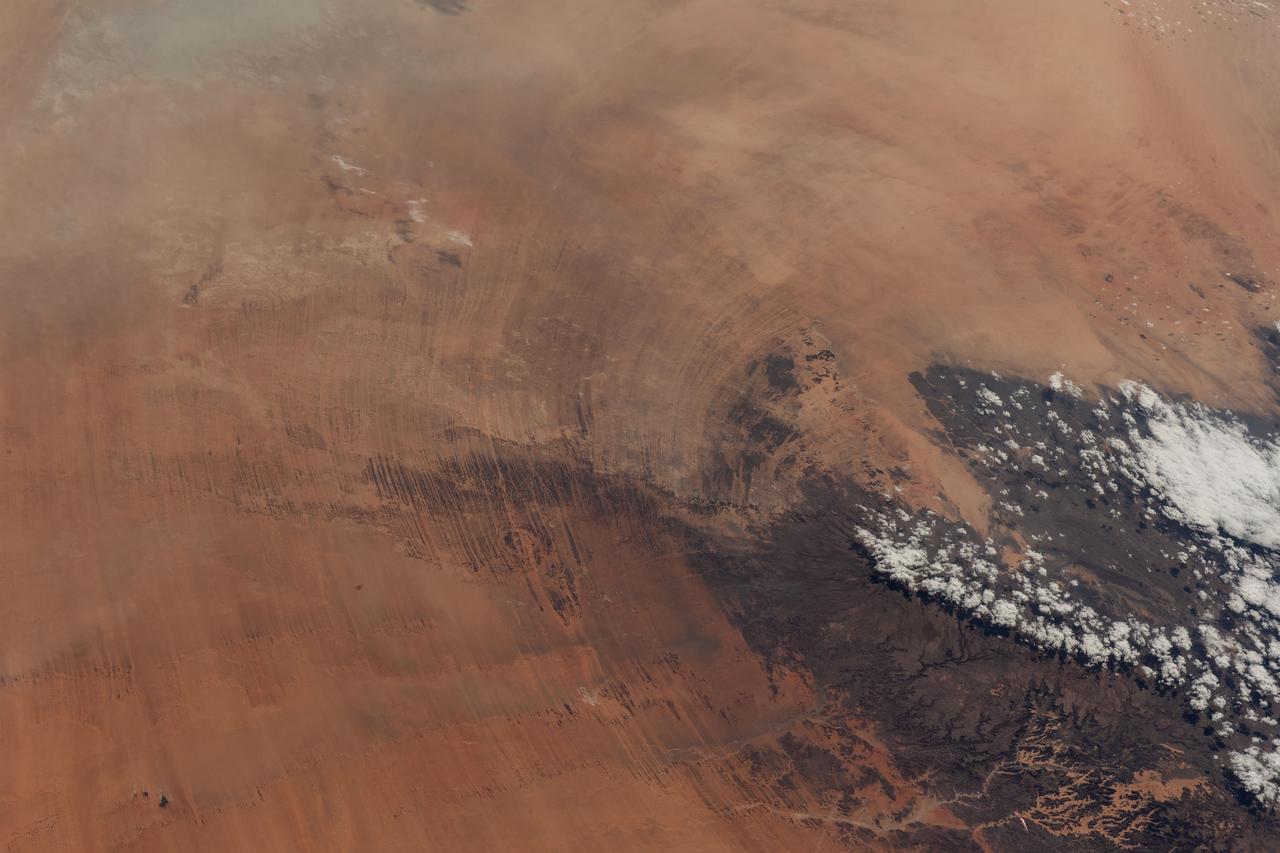

iss067e270532 (Aug. 18, 2022) --- A portion of the Tibesti Mountains (lower right), in the Saharan region of the nation of Chad, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 257 miles above the African continent.
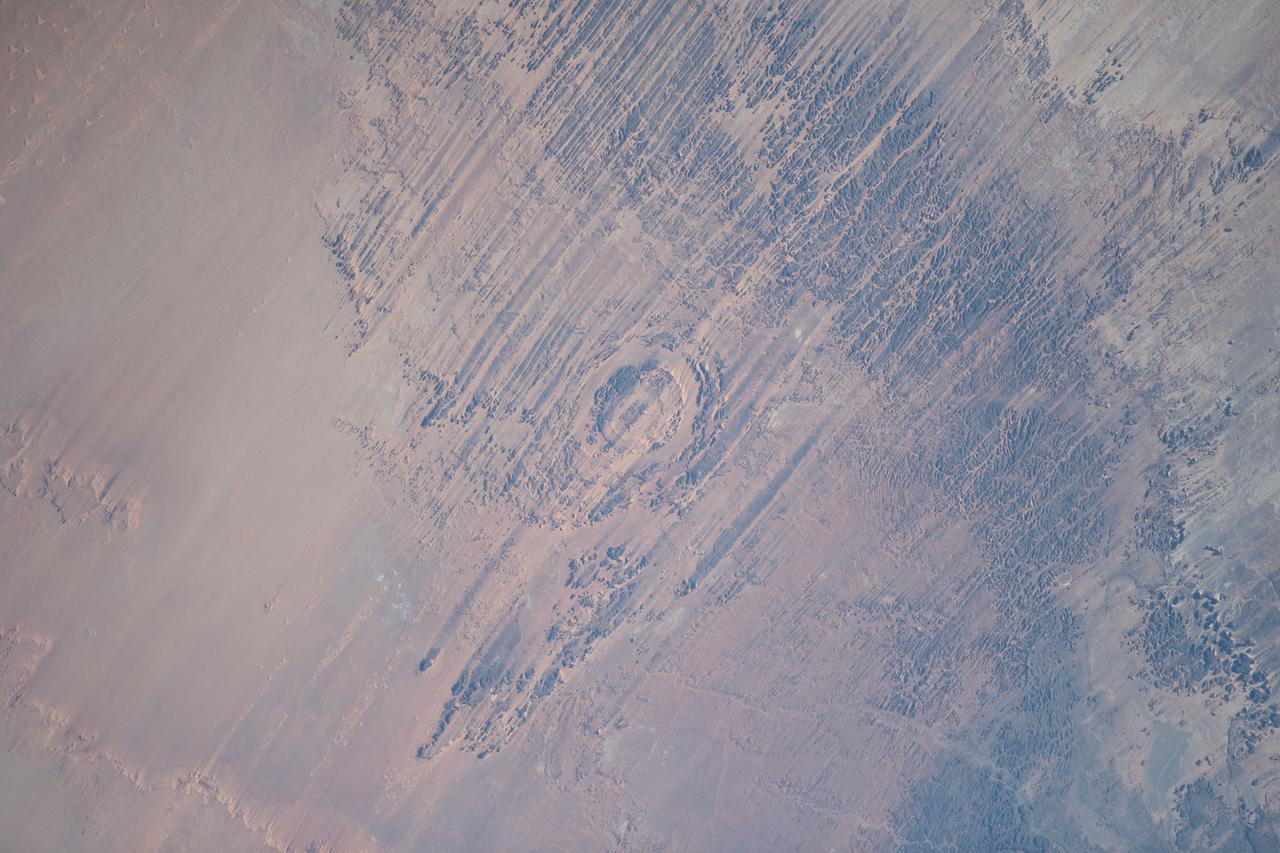

iss069e089635 (Sept. 18, 2023) --- The eroded Aorounga meteorite impact crater, also known as the "Eye of the Desert," in the African nation of Chad is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 258 miles above.
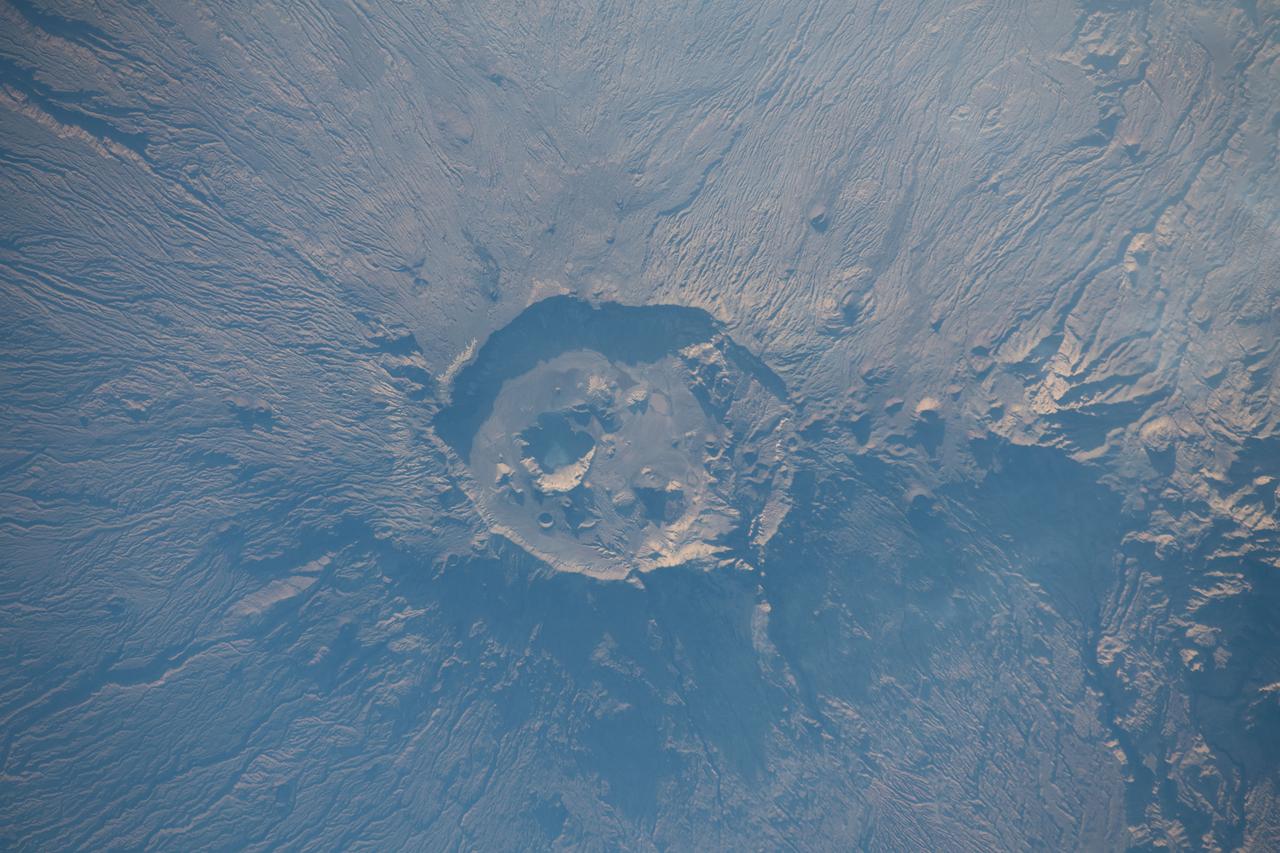

iss068e029498 (Dec. 13, 2022) --- Emi Koussi, a volcano and the highest peak in the Tibesti Mountains of Chad, was photographed from the International Space Station as it orbited 257 miles above Africa.
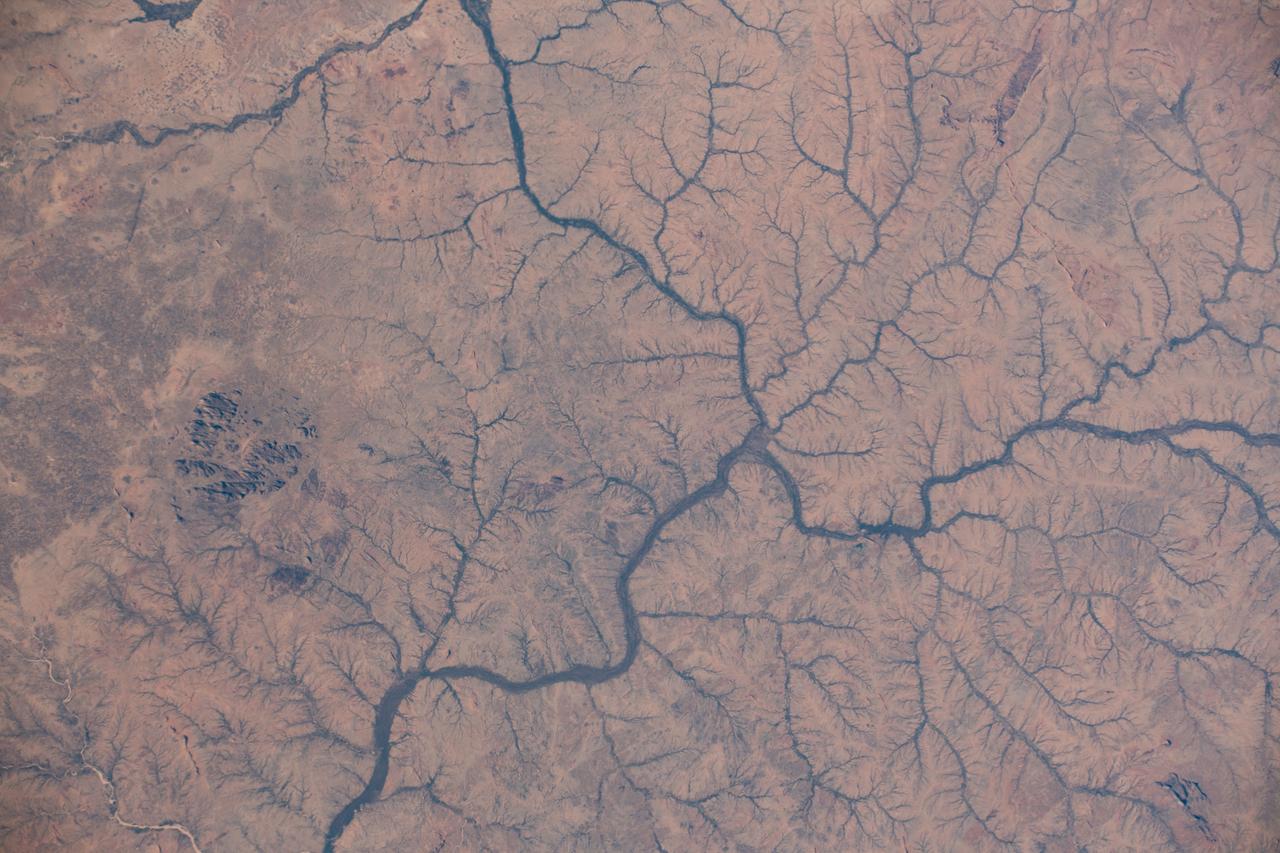

iss061e093391 (Dec. 20, 2019) --- The Kabkabiya District in western Sudan near the border of Chad is pictured as the International Space Station orbited 260 miles above the African continent.
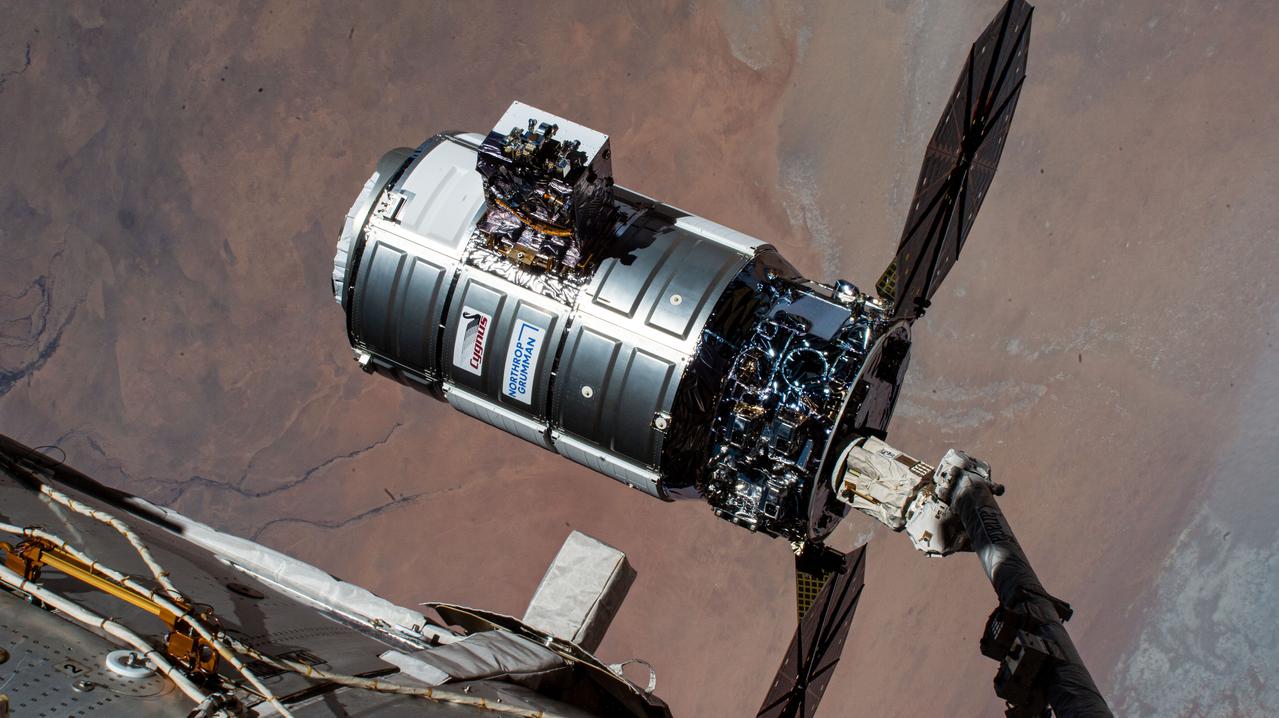

iss070e044171 (Dec. 22, 2023) --- Northrop Grumman's Cygnus space freighter is pictured in the grip of the Canadarm2 robotic arm moments before its release. The orbital complex was soaring 258 miles above the African nation of Chad at the time of this photograph.
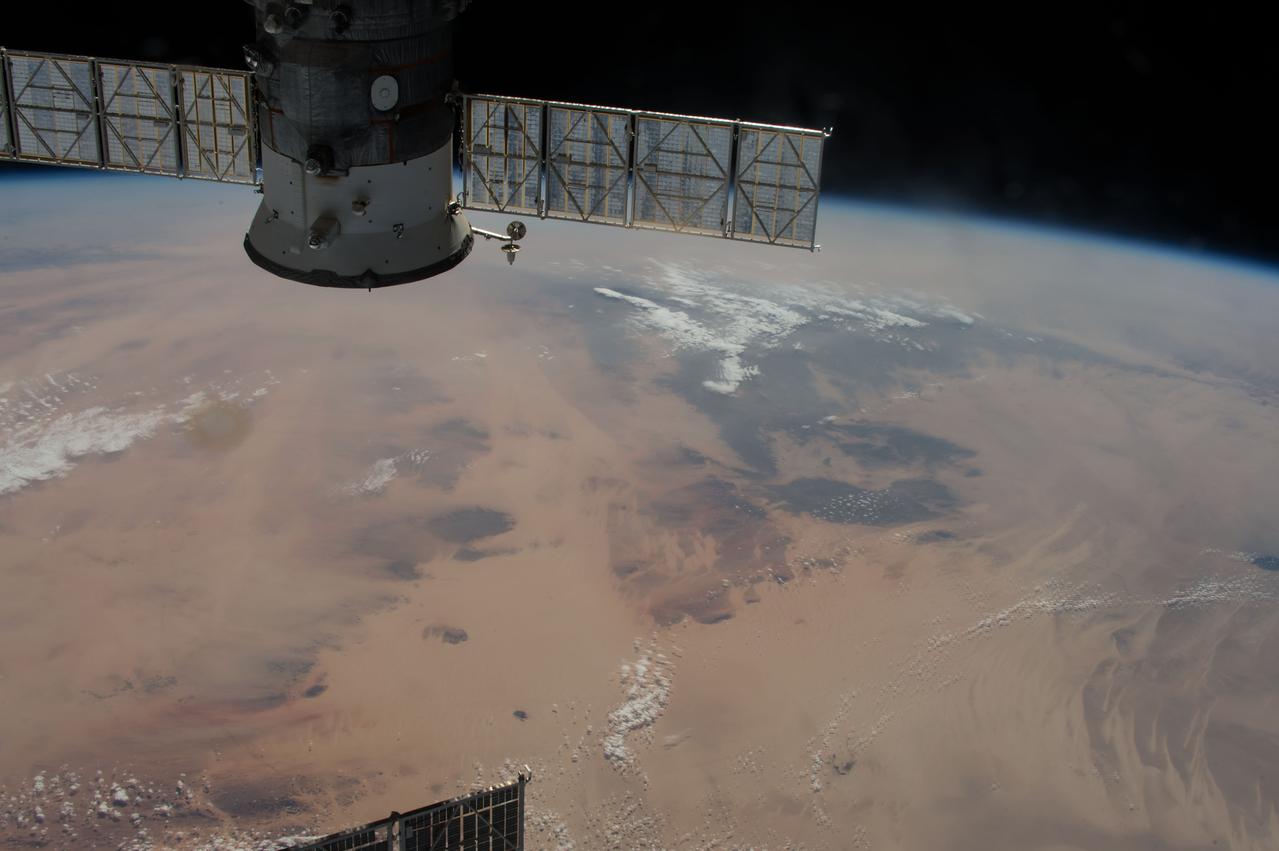

ISS042E275153 (02/15/2015) --- Expedition 42 Flight Engineer Terry Virts on the International Space Station tweeted his followers this earth observation image on Feb. 15, 2015. He commented that it was "Extensive #Africa desert of #Libya and #Chad".
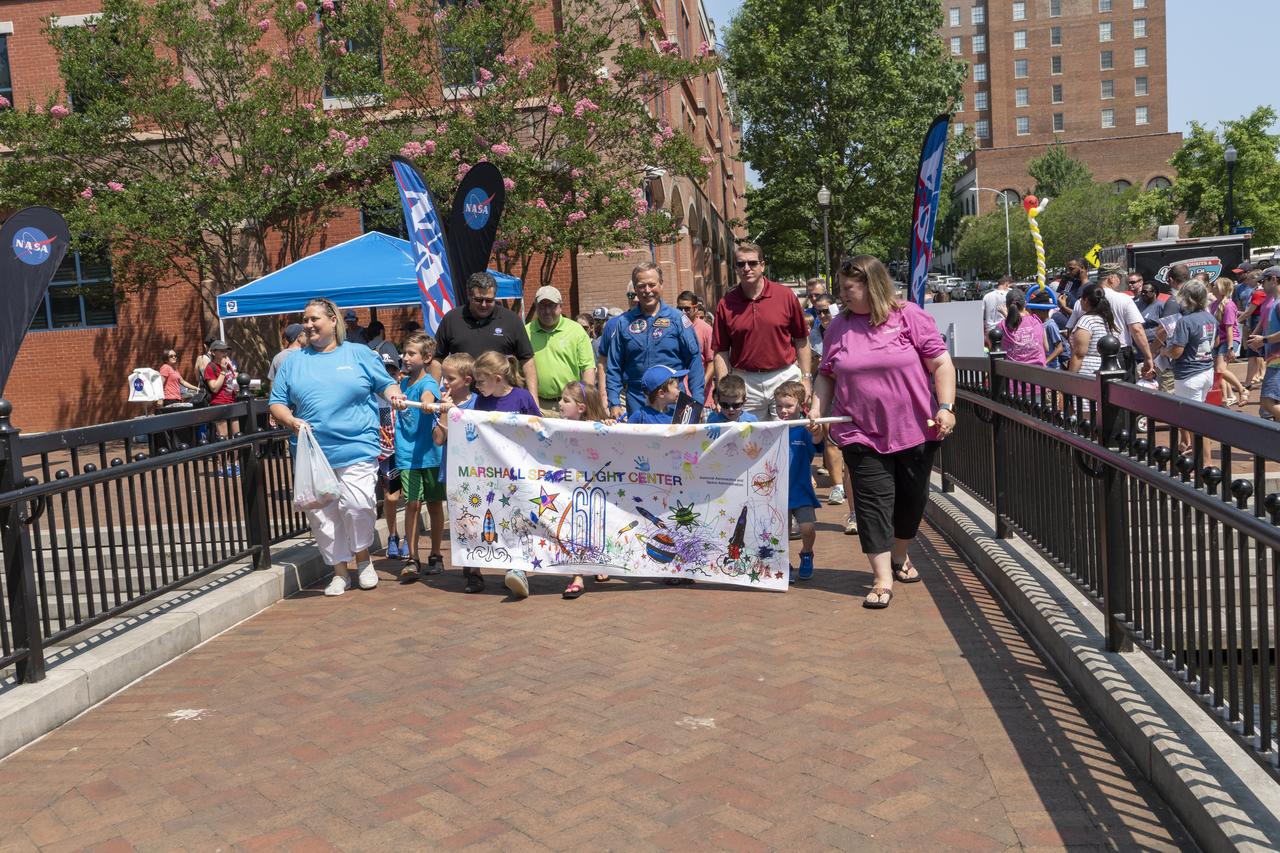

NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center showcased it's various projects for the public in Huntsville, Alabama's Big Spring Park. Exhibits were displayed by all of the various directorates of the Center with employee volunteers explaining all aspects of their projects. Adding to the festivities was the attendance of retired NASA astronaut Robert "Hoot" Gibson. The children’s parade at NASA Day in the Park is led by center director Todd May, Chad Emerson, and Retired astronaut Robert “Hoot†Gibson.
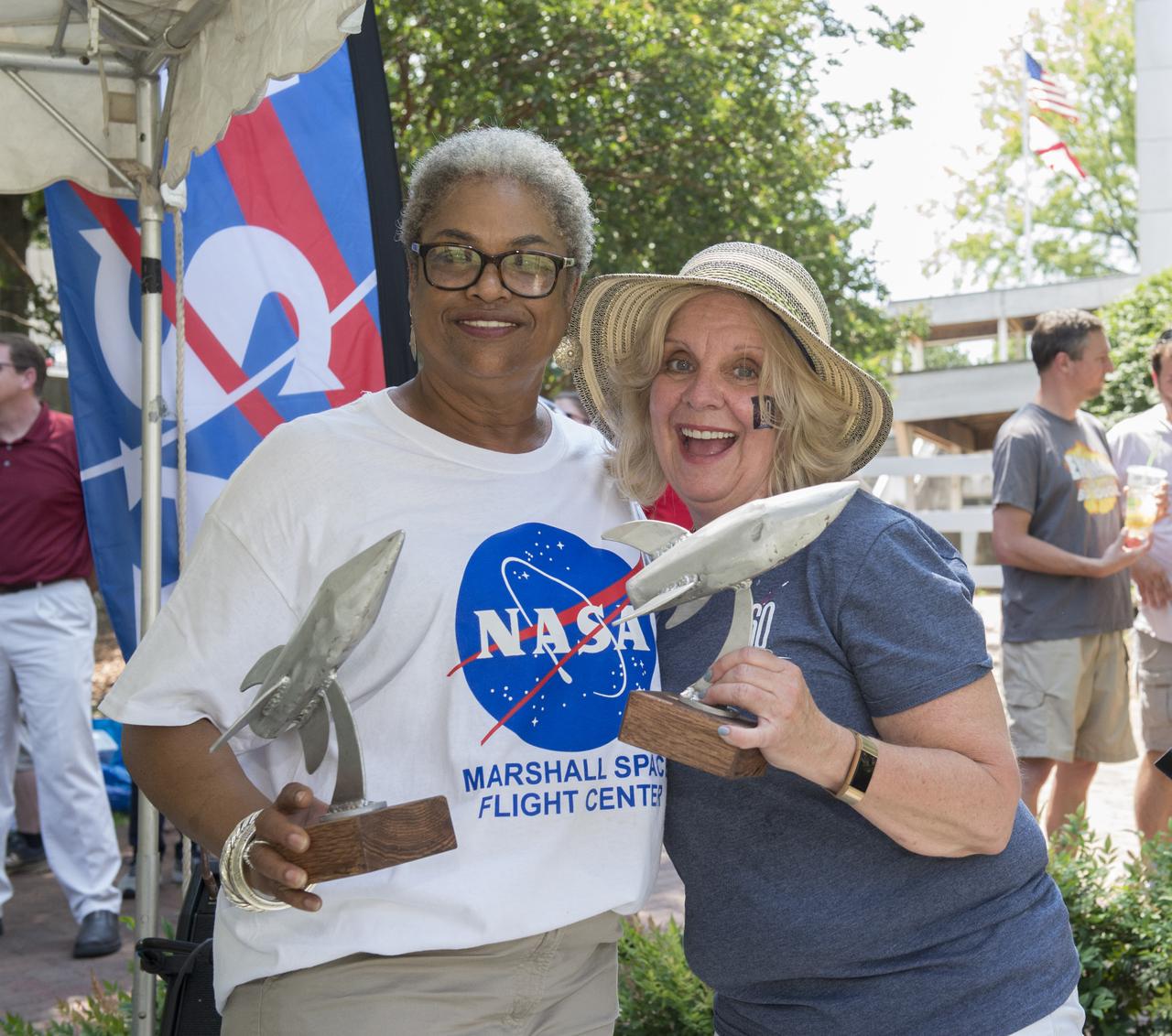

NASA in the Park on June 16 in Huntsville featured more than 60 exhibits and demonstrations by NASA experts, as well as performances by Marshall musicians, educational opportunities, games and hands-on activities for all ages. Marshall employees Ola Metcalfe (L), and Sherrie Stroud proudly display trophies awarded to them by Downtown Inc. President, Chad Emerson, in appreciation of their efforts in the five year partnership with NASA in the Park.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility, a granite plaque marks the spot where space shuttle Atlantis' nose gear came to a stop at the conclusion of STS-135, the final flight of the Space Shuttle Program. Permanent reminders indicate where on the runway the orbiters Discovery, Endeavour and Atlantis stopped rolling as each finished its last mission in 2011. In addition to the granite markers, which are installed alongside the runway, there are etchings in the grooved concrete along the runway's centerline to mark each wheelstop. The etchings and markers were created and installed by local artist Chad Stout of C Spray Glass Blasting in Cocoa, Fla. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the conference room of Operations Support Building II at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, social media participants listen to a briefing on future agency programs by, Kimberly Robinson, Space Launch System engineer, left, and Chad Brown of Ground System Development and Operations. The social media participants gathered at the Florida spaceport for the launch of the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft. Their visit included tours of key facilities and participating in presentations by key NASA leaders who updated the space agency's current efforts. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossman

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the conference room of Operations Support Building II at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, social media participants listen to a briefing on future agency programs by, Kimberly Robinson, Space Launch System engineer, left, and Chad Brown of Ground System Development and Operations. The social media participants gathered at the Florida spaceport for the launch of the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft. Their visit included tours of key facilities and participating in presentations by key NASA leaders who updated the space agency's current efforts. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossman
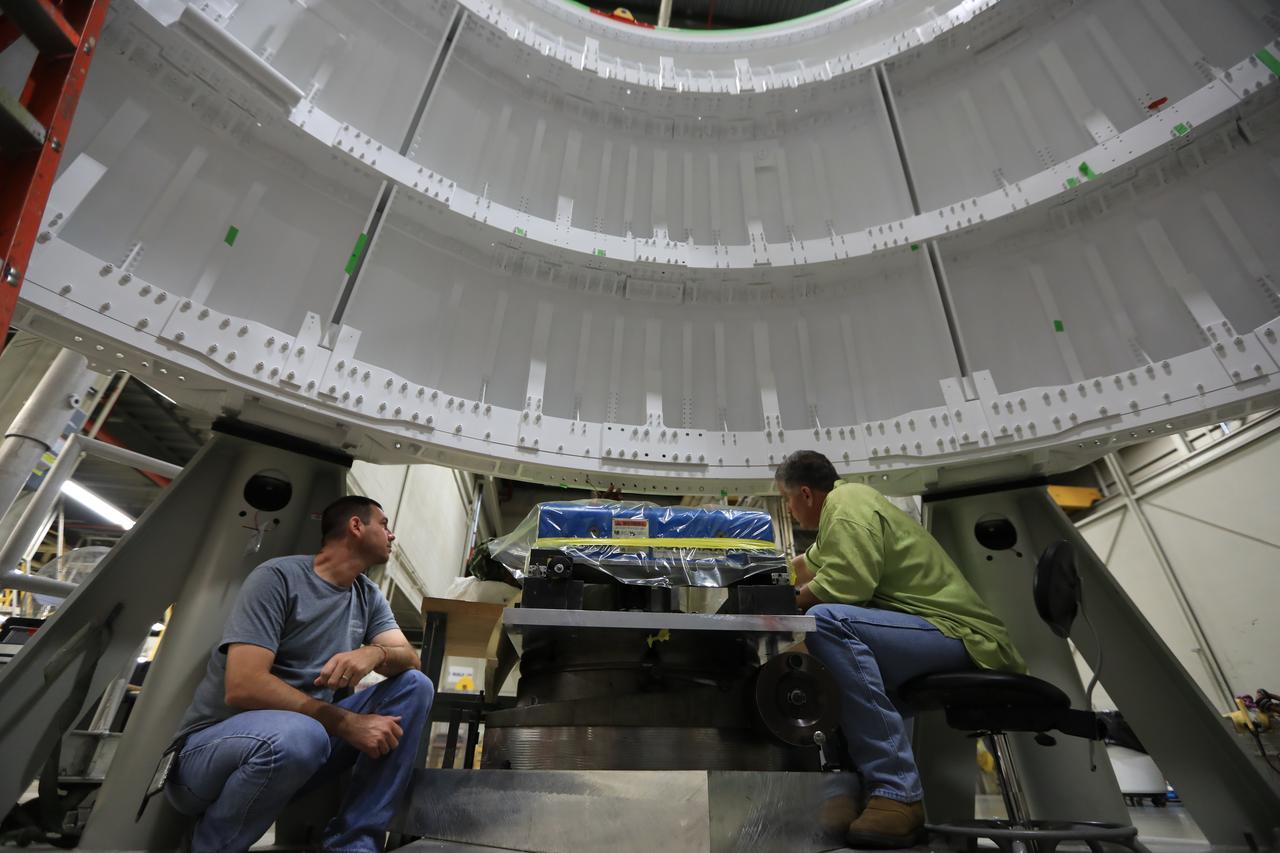

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the left hand aft skirt for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is ready for the assembly process. From left, are Chad Goetz, quality technician with Orbital ATK, and Robbie Blaue, quality assurance specialist with the Defense Contract Management Agency. The aft skirt was refurbished and painted in support facilities at the Hangar AF facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The space shuttle-era aft skirt will be used on the left hand booster of the SLS for Exploration Mission 1 (EM-1). NASA is preparing for EM-1, deep space missions, and the Journey to Mars.
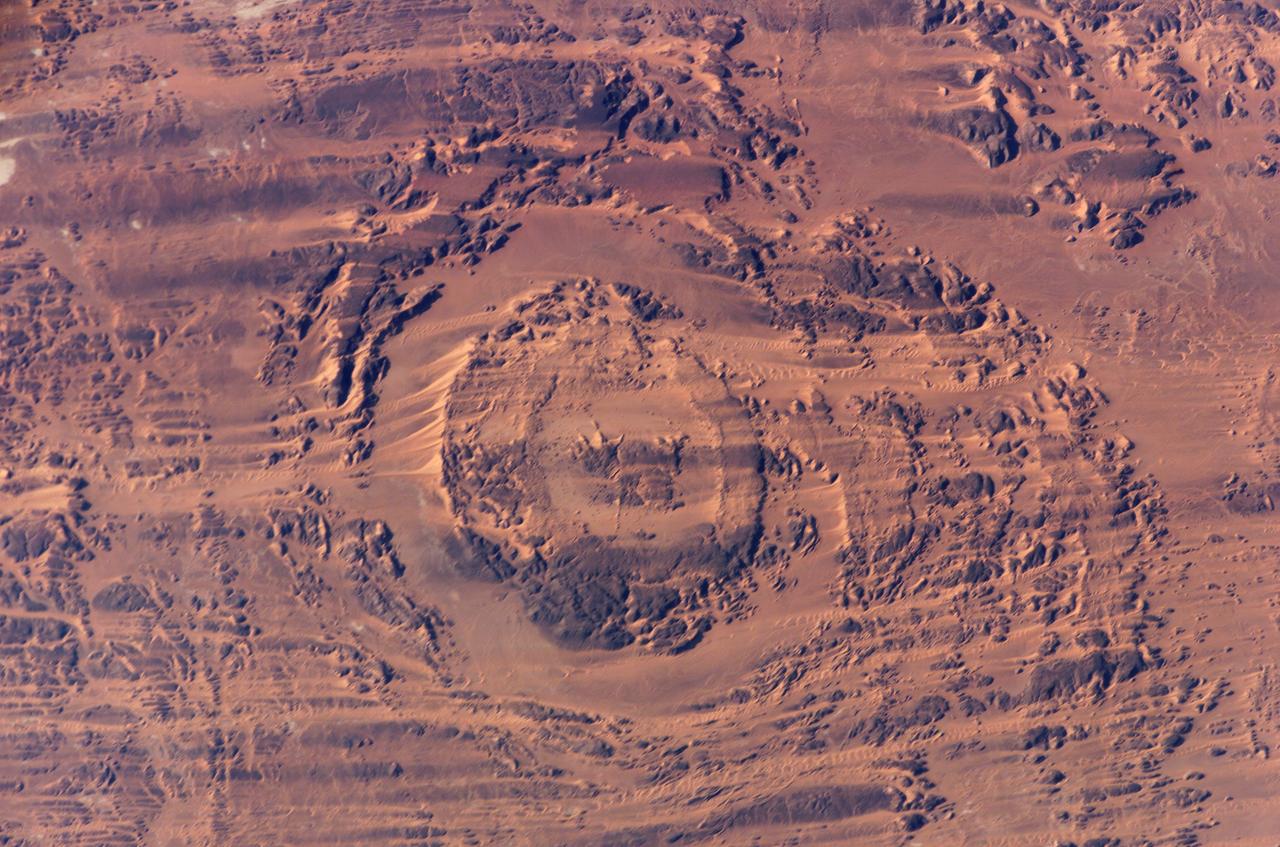

ISS012-E-09639 (29 Nov. 2005) --- The impact of an asteroid or comet several hundred million years ago, according to scientists, left scars in the landscape that are still visible in this International Space Station/Expedition 12 picture of an area in the Sahara Desert of northern Chad. The concentric ring structure is the Aorounga impact crater, with a diameter of about 17 kilometers (10.5 miles). The original crater was buried by sediments, which were then partially eroded to reveal the current ring-like appearance. Scientists note a number of valleys cut by thousands of years of wind erosion. The area shown is centered at approximately 19.1 degrees north latitude and 19.3 degrees east longitude.
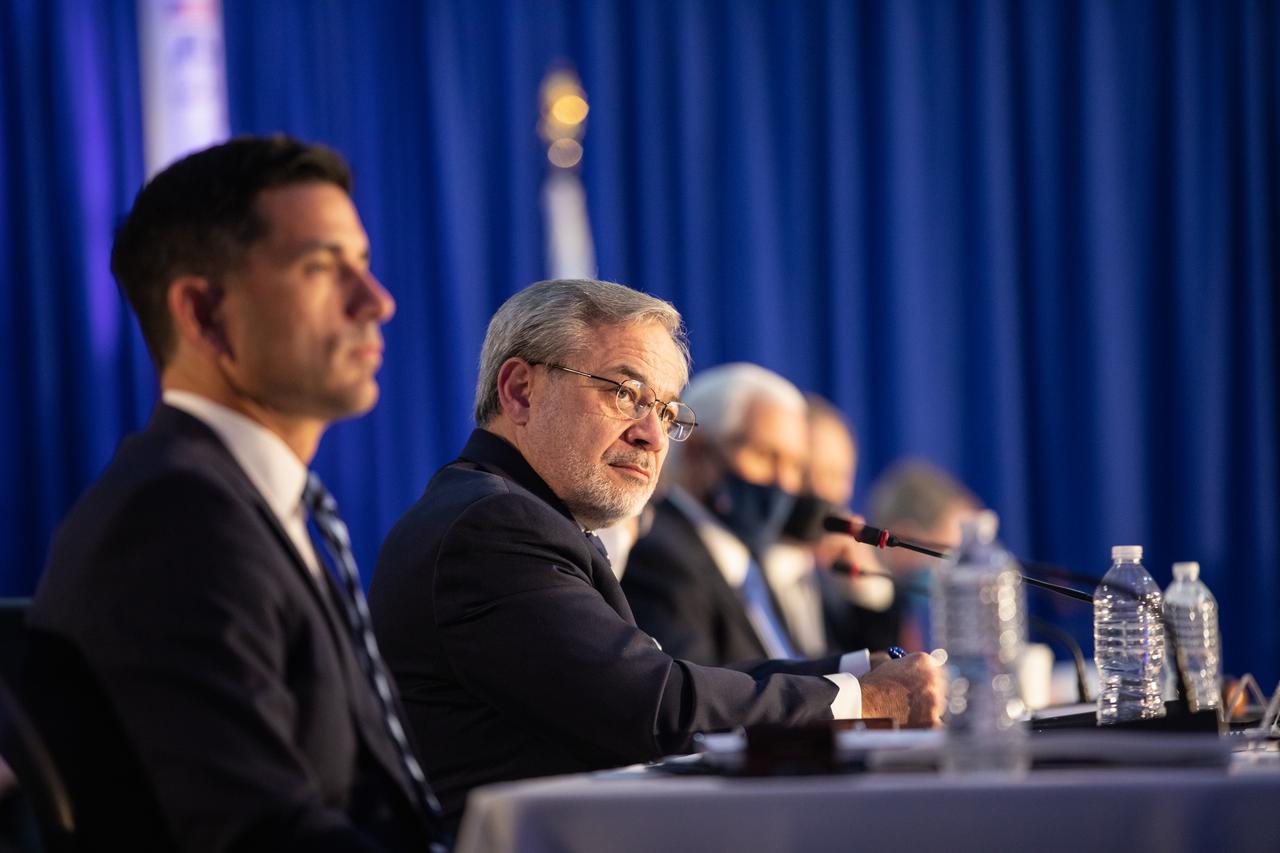

From left, Chad Wolf, acting secretary of Homeland Security, and Dan Brouillette, Secretary of Energy, attend a meeting of the National Space Council inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on Dec. 9, 2020. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and to review the nation's long-range goals for space activities. Vice President Mike Pence chaired the meeting, at which he announced the initial team of 18 astronauts eligible for early Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility, a granite plaque marks the spot where space shuttle Endeavour's nose gear came to a stop at the conclusion of STS-134, the final flight of the Space Shuttle Program. Permanent reminders indicate where on the runway the orbiters Discovery, Endeavour and Atlantis stopped rolling as each finished its last mission in 2011. In addition to the granite markers, which are installed alongside the runway, there are etchings in the grooved concrete along the runway's centerline to mark each wheelstop. The etchings and markers were created and installed by local artist Chad Stout of C Spray Glass Blasting in Cocoa, Fla. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility, a granite plaque marks the spot where space shuttle Discovery's nose gear came to a stop at the conclusion of STS-133, the final flight of the Space Shuttle Program. Permanent reminders indicate where on the runway the orbiters Discovery, Endeavour and Atlantis stopped rolling as each finished its last mission in 2011. In addition to the granite markers, which are installed alongside the runway, there are etchings in the grooved concrete along the runway's centerline to mark each wheelstop. The etchings and markers were created and installed by local artist Chad Stout of C Spray Glass Blasting in Cocoa, Fla. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
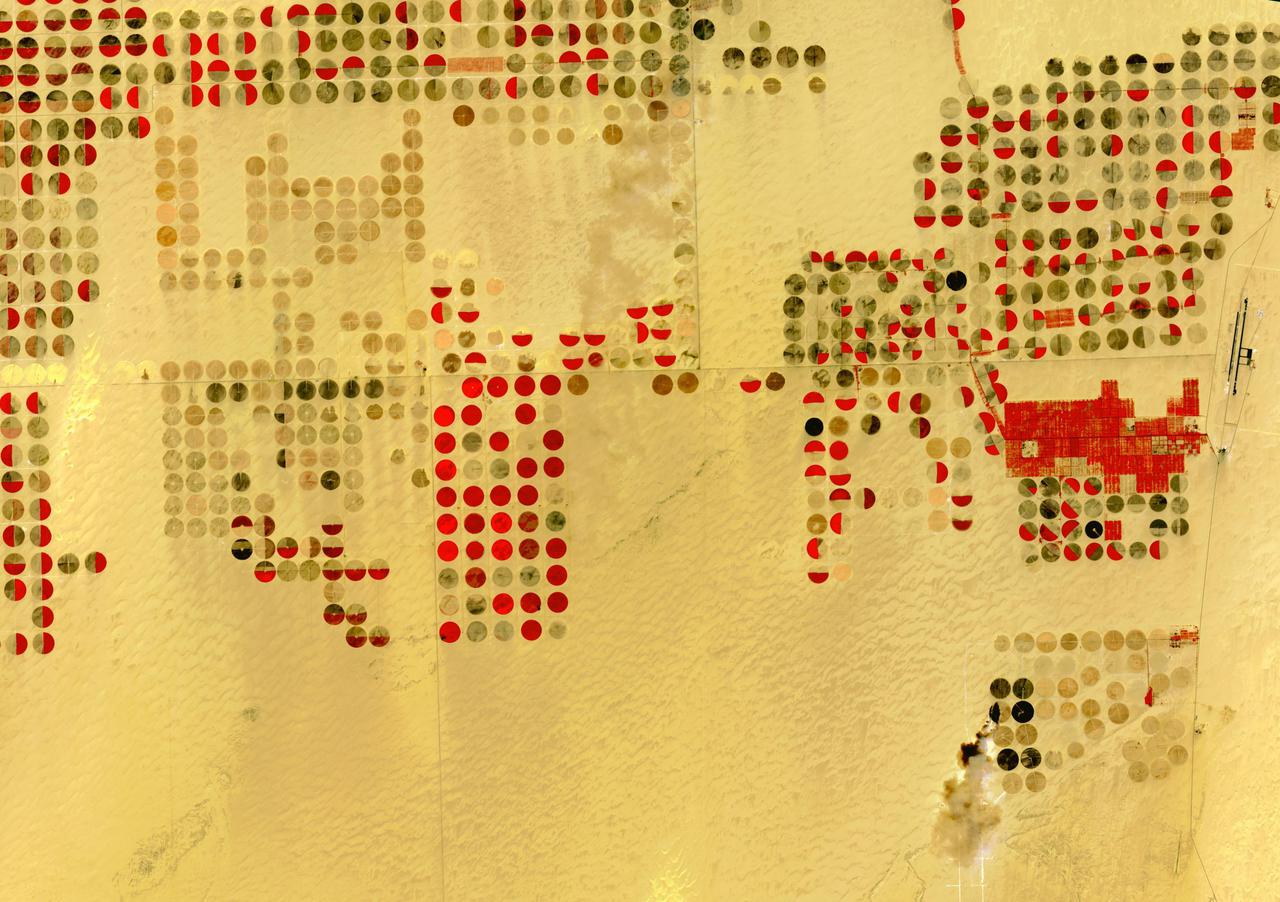
The Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System is the world's largest fossil water aquifer system. It covers an estimated area of 2.6 million square kilometers, including parts of Sudan, Chad, Libya, and most of Egypt. In the southwestern part of Egypt, the East Oweinat development project uses central pivot irrigation to mine the fossil water for extensive agricultural development. Crops include wheat and potatoes; they are transported via the airport on the eastern side. The image was acquired October 12, 2015, covers an area of 33.3 by 47.2 km, and is located near 22.6 degrees north, 28.5 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24616
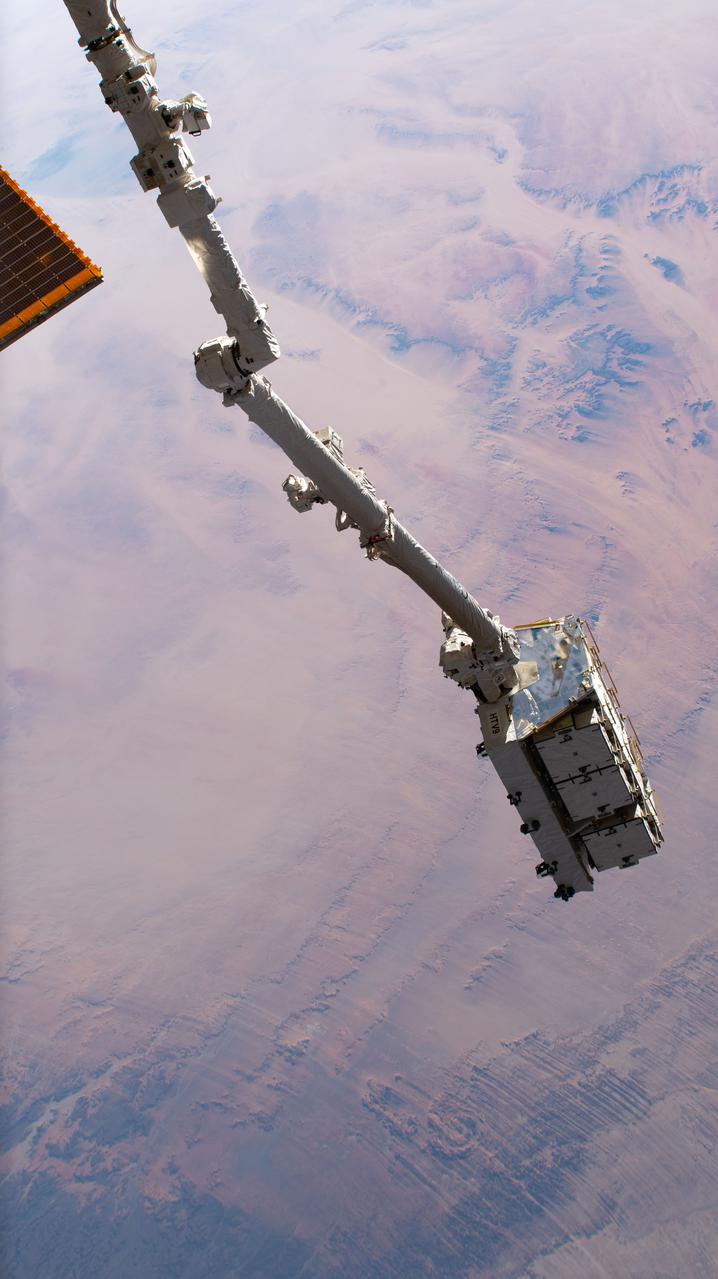

iss064e041189 (March 11, 2021) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm, with an external pallet packed with old nickel-hydrogen batteries in its grip, is pictured as the International Space Station orbited 260 miles above the Sahara in the African nation of Chad. Mission controllers in Houston later commanded the Canadarm2 to release the external pallet into space where it will orbit Earth between two to four years before burning up harmlessly in the atmosphere. The batteries were removed during previous spacewalks and replaced with newer lithium-ion batteries to continue powering the station's systems.
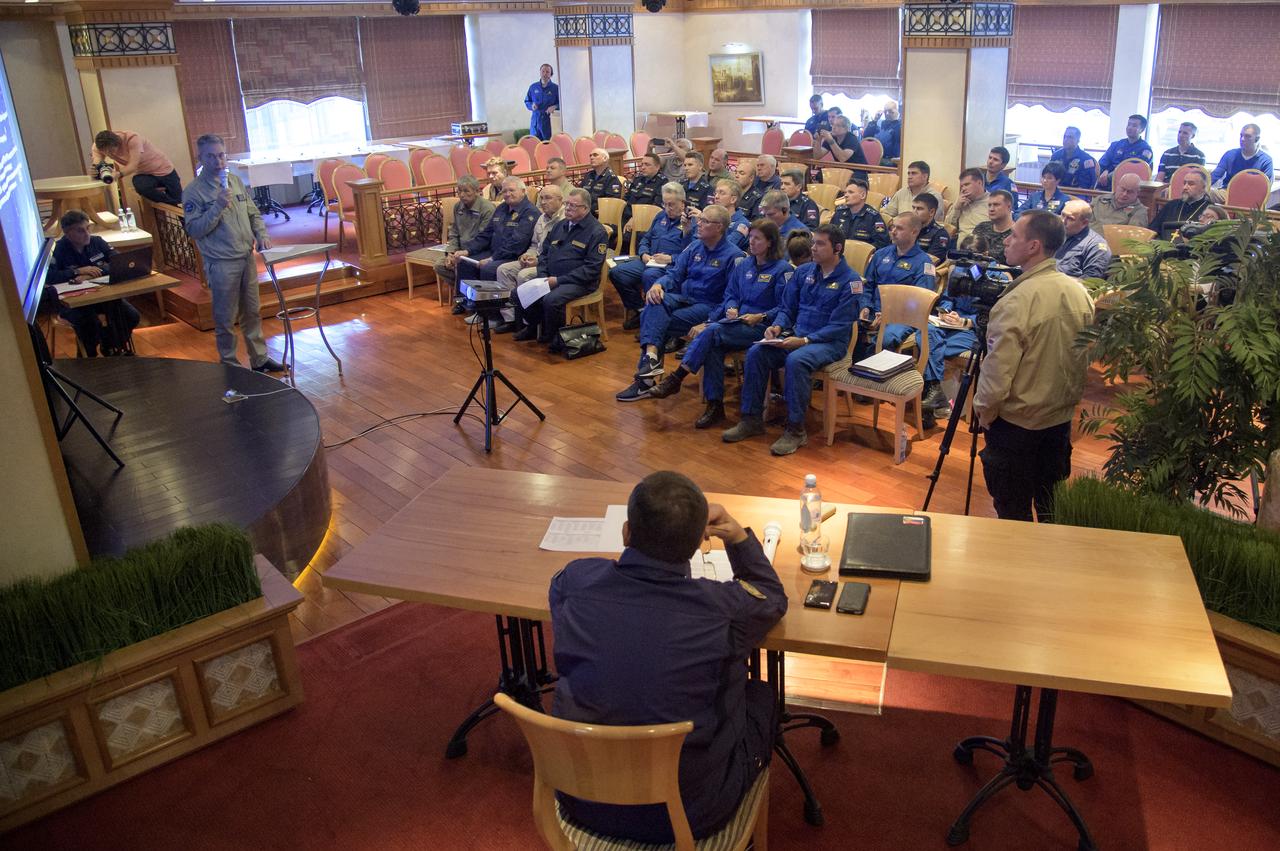

NASA and Roscosmos team members, along with Russian Search and Recovery Forces, meet at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Karaganda, Kazakhstan to discuss the readiness for the landing of Expedition 56 Commander Drew Feustel and Flight Engineer Ricky Arnold of NASA, along with Flight Engineer and Soyuz Commander Oleg Artemyev of Roscosmos Tuesday, Oct. 2, 2018. Feustel, Arnold, and Artemyev are returning after 197 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 55 and 56 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
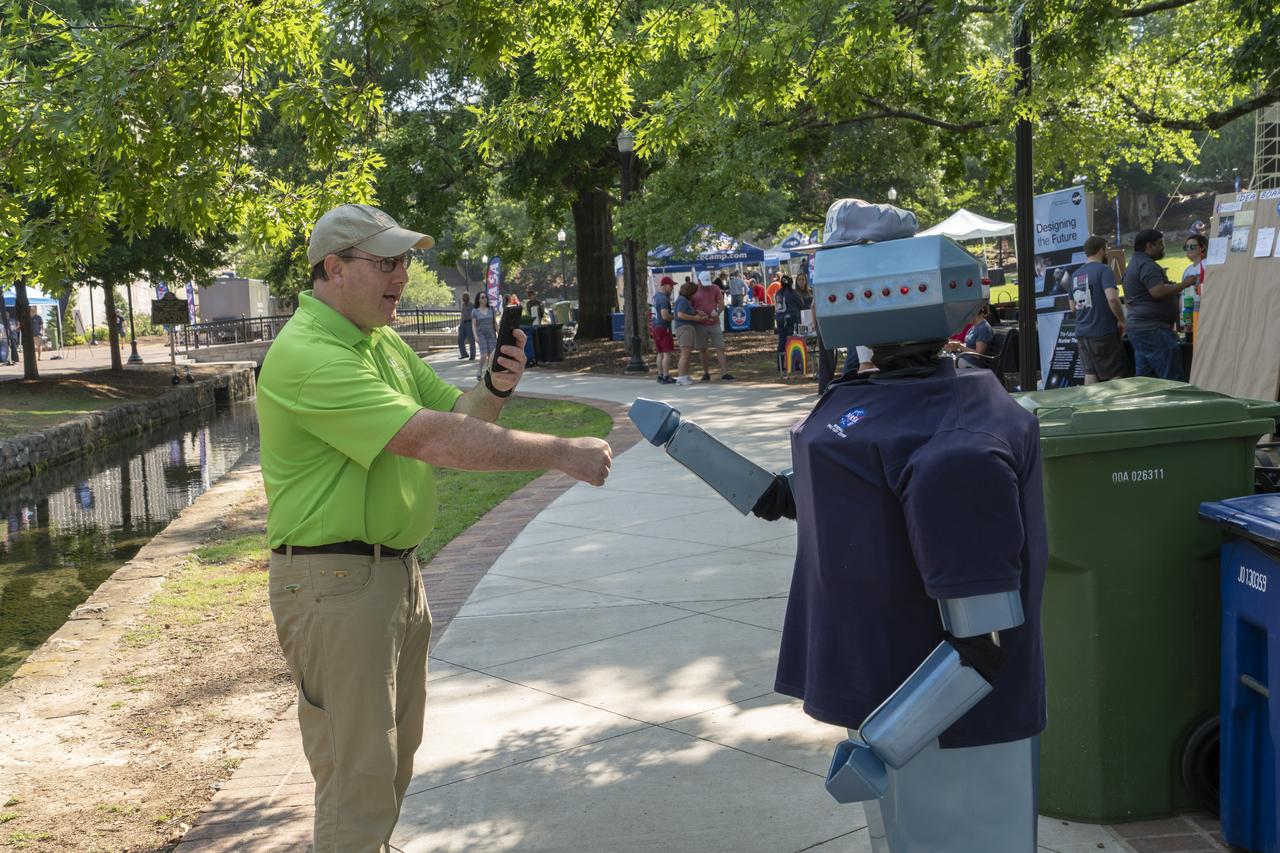

NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center showcased it's various projects for the public in Huntsville, Alabama's Big Spring Park. Exhibits were displayed by all of the various directorates of the Center with employee volunteers explaining all aspects of their projects. Adding to the festivities was the attendance of retired NASA astronaut Robert "Hoot" Gibson.Chad Emerson, President of Downtown Huntsville, Inc., fist bumps with Oscar the Robot.

Evening With The Stars - 2019
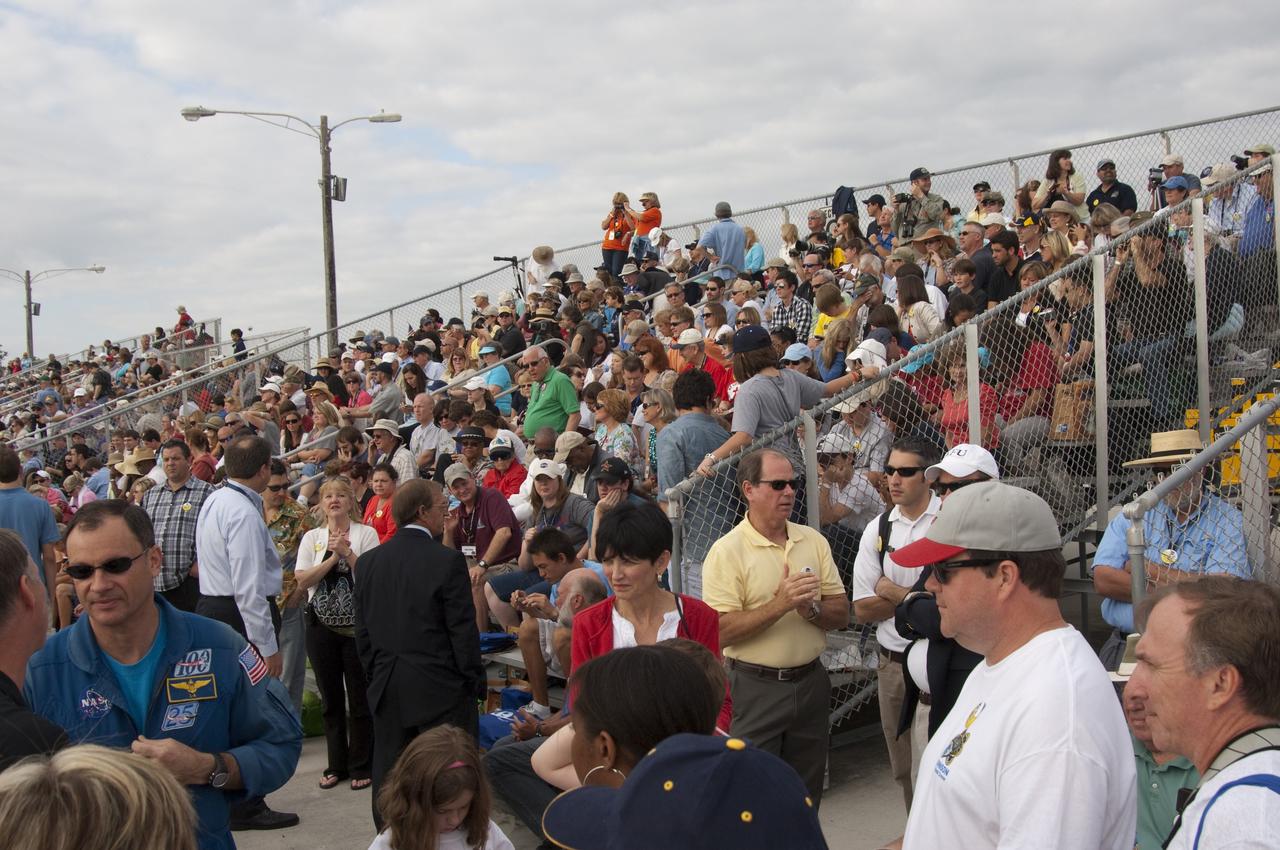

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida await the liftoff of space shuttle Endeavour. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
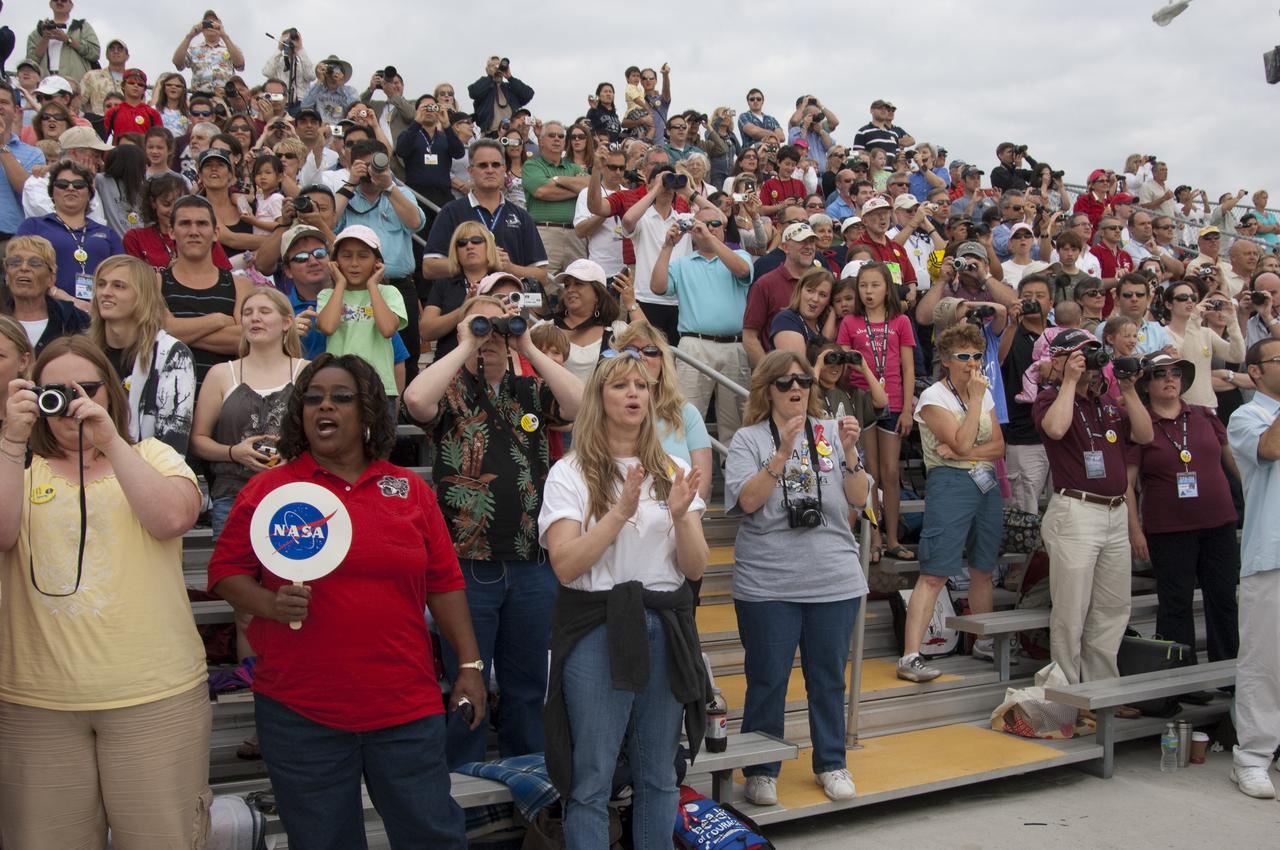

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as space shuttle Endeavour soars skyward. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
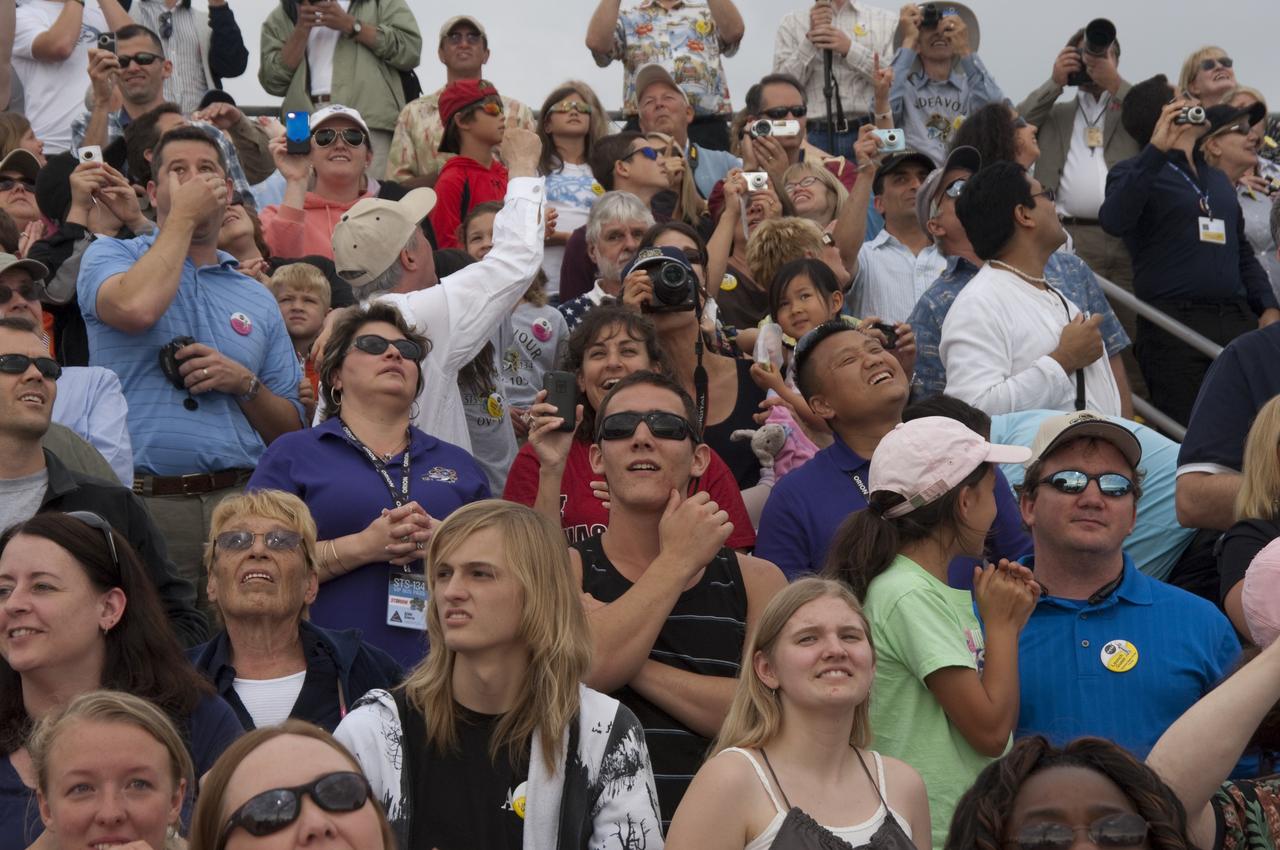

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as space shuttle Endeavour soars skyward. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
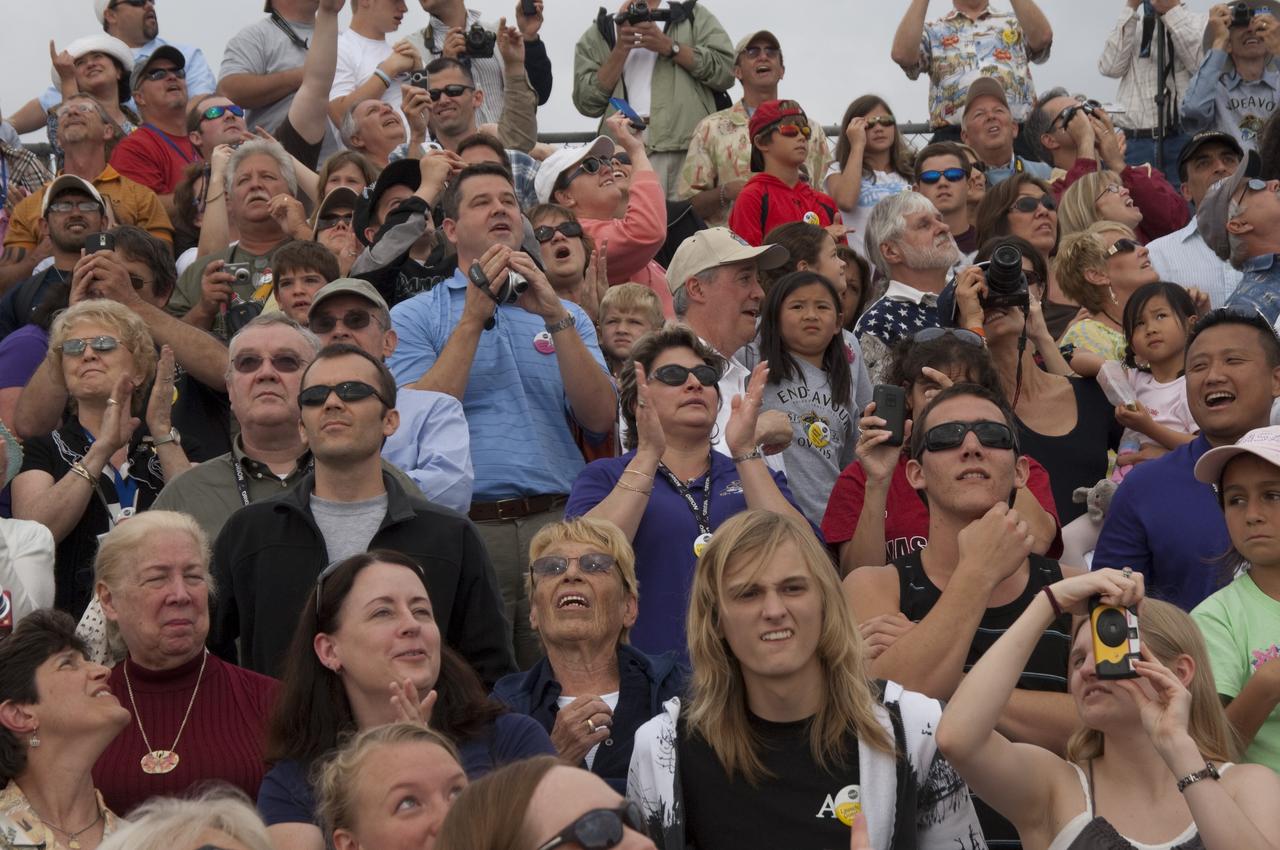

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as space shuttle Endeavour soars skyward. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
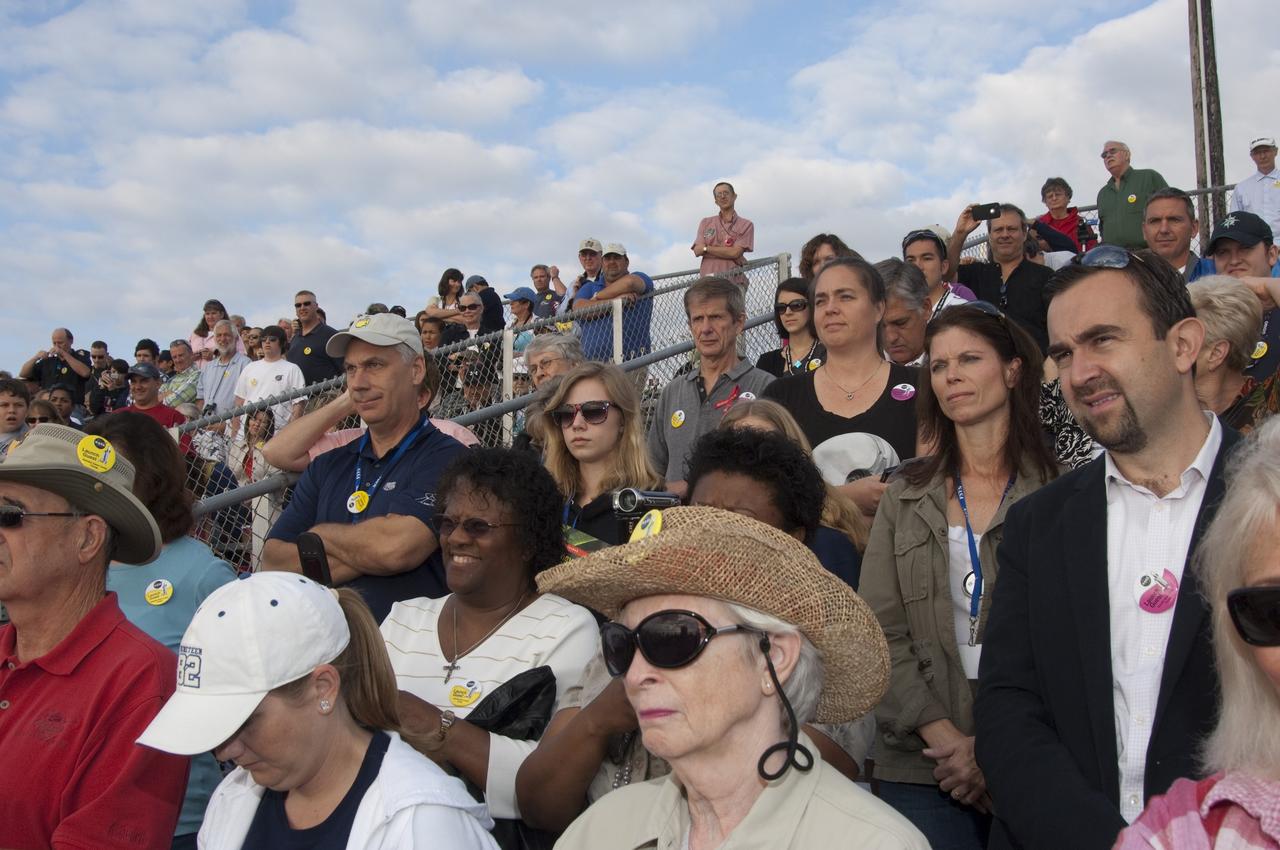

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida await the liftoff of space shuttle Endeavour. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
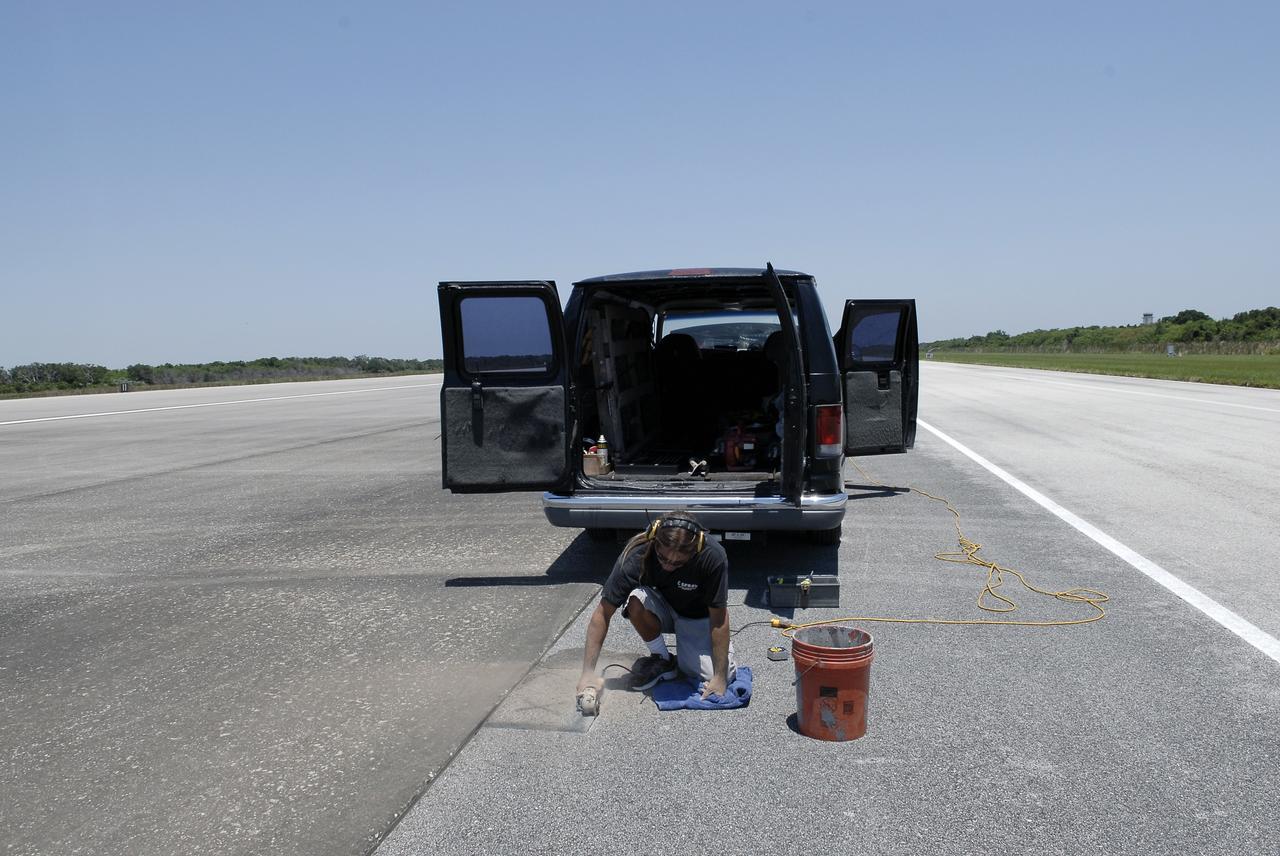

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility SLF at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Chad Stout with C Spray Glass Blasting in Cocoa, Fla., prepares to install a special plaque to mark the nose gear wheel stop of space shuttle Atlantis. Stout is cutting the 15,000 by 1,000-foot-long concrete runway to accommodate the black granite plaque, which is 16 by 28 inches. It is the third plaque permanently mounted to commemorate the final landing of each of the three orbiters. Atlantis completed the STS-135 mission by landing at the SLF on July 21, 2011, at 5:57 a.m. Atlantis flew 33 missions, completed 4,848 orbits of the Earth, traveled nearly 126 million miles and spent 307 days in space. Atlantis carried 207 astronauts to space. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
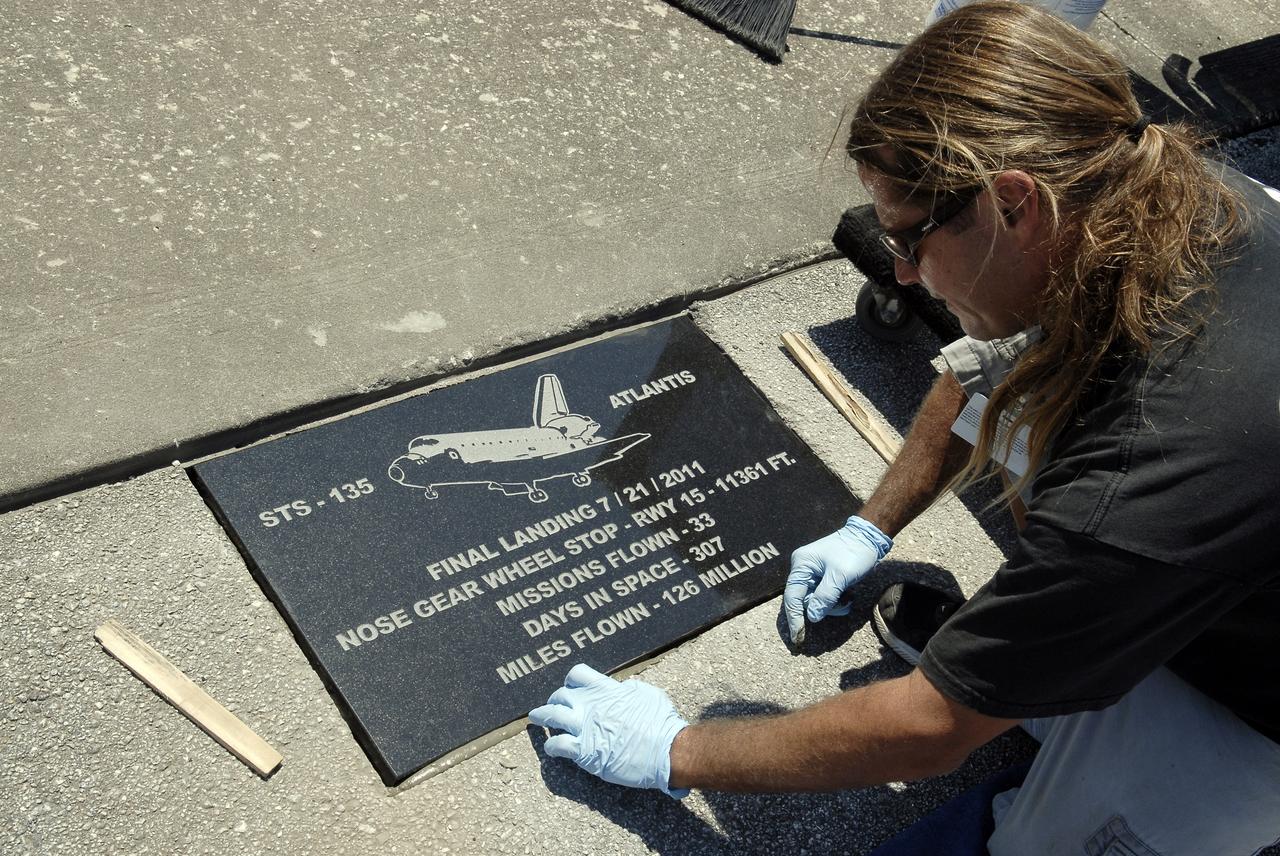

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility SLF at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Chad Stout with C Spray Glass Blasting in Cocoa, Fla., installs a special plaque to mark the nose gear wheel stop of space shuttle Atlantis. The plaque, which is 16 by 28 inches, is the third black granite plaque permanently mounted to commemorate the final landing of each of the three orbiters. Atlantis completed the STS-135 mission by landing at the SLF on July 21, 2011, at 5:57 a.m. Atlantis flew 33 missions, completed 4,848 orbits of the Earth, traveled nearly 126 million miles and spent 307 days in space. Atlantis carried 207 astronauts to space. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
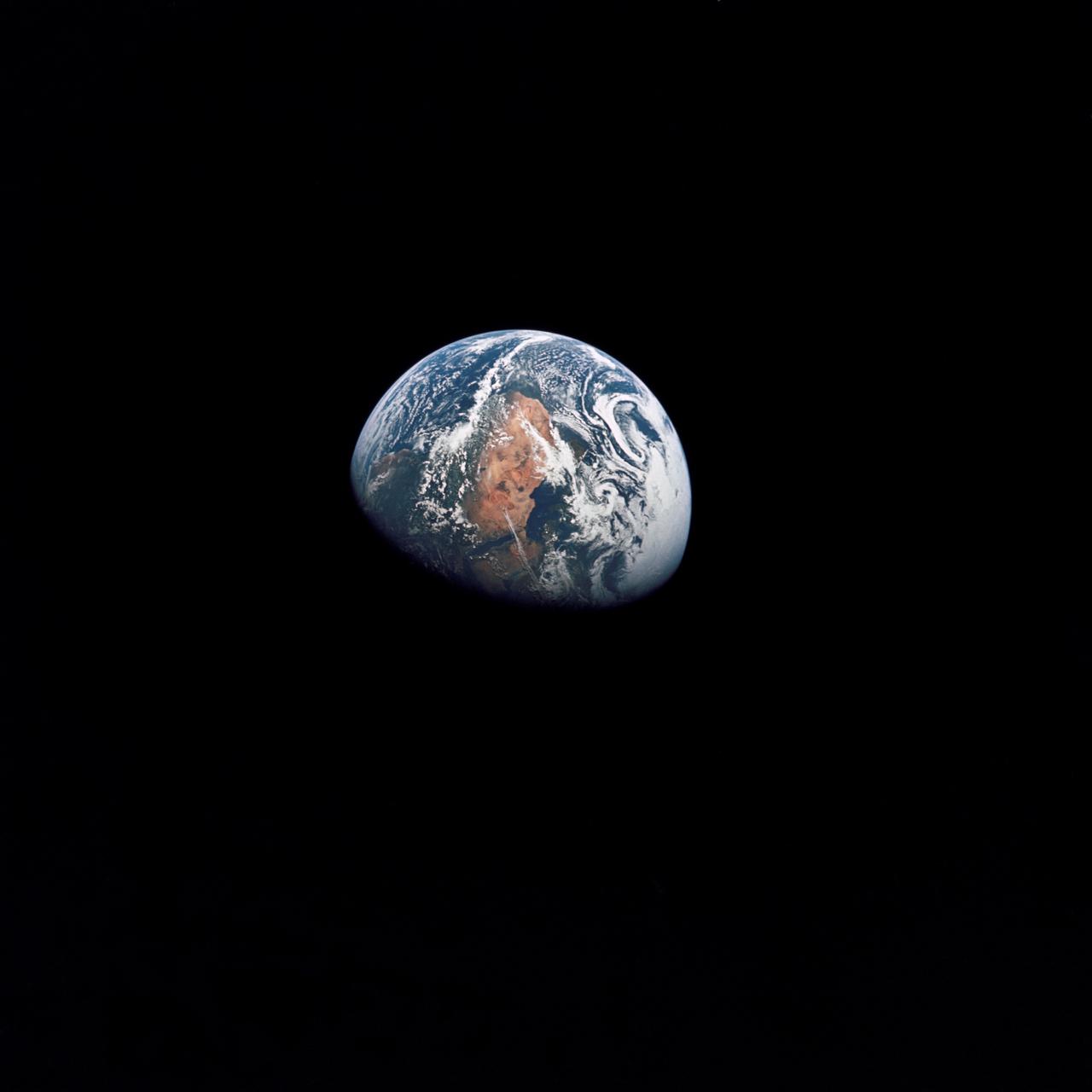

AS10-34-5026 (18-26 May 1969) --- An Apollo 10 photograph of Earth taken from 100,000 miles away. Visible are many areas of Europe and Africa. Among the features and countries identifiable are Portugal, Spain, Italy, the Mediterranean Sea, Greece, Turkey, Bulgaria, the Black Sea, Libya, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, the Sinai Peninsula, the Nile Delta, Lake Chad, and South Africa. The crew members for Apollo 10 are astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene E. Cernan, lunar module pilot. Astronaut Young remained in lunar orbit, in the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Charlie Brown", while astronauts Stafford and Cernan descended to within nine miles of the lunar surface, in the Lunar Module (LM) "Snoopy".
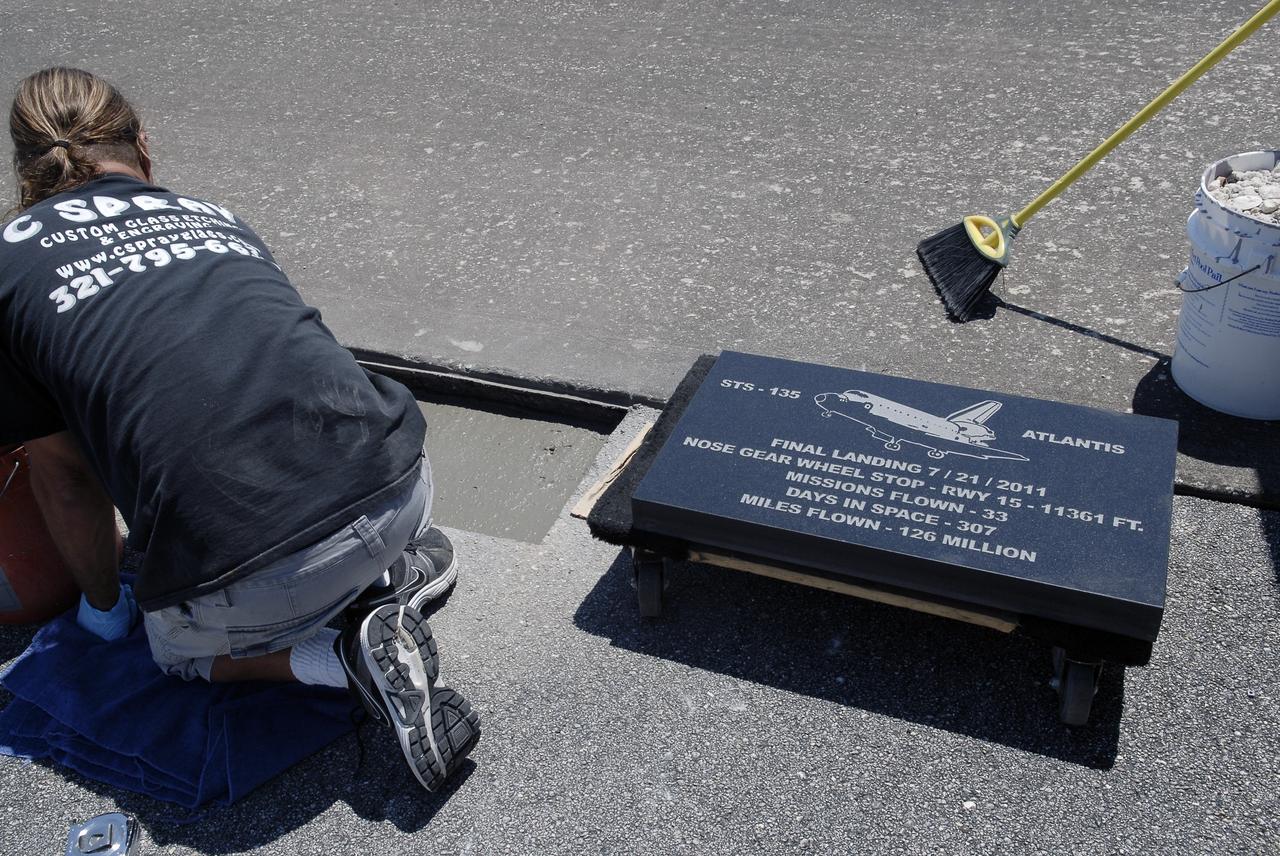

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility SLF at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Chad Stout with C Spray Glass Blasting in Cocoa, Fla., prepares to install a special plaque to mark the nose gear wheel stop of space shuttle Atlantis. The black granite plaque, which is 16 by 28 inches, is the third plaque permanently mounted to commemorate the final landing of each of the three orbiters. Atlantis completed the STS-135 mission by landing at the SLF on July 21, 2011, at 5:57 a.m. Atlantis flew 33 missions, completed 4,848 orbits of the Earth, traveled nearly 126 million miles and spent 307 days in space. Atlantis carried 207 astronauts to space. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

ISS026-E-017074 (11 Jan. 2011) --- Emi Koussi volcano in Chad is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 26 crew member on the International Space Station. The large Emi Koussi volcano is located in northern Chad at the southeastern end of the Tibesti Range. The dark volcanic rocks of the volcano provide a sharp contrast to the underlying tan and light brown sandstones exposed to the west, south, and east. Emi Koussi is a shield volcano formed from relatively low viscosity lavas—flowing more like motor oil as opposed to toothpaste—and explosively-erupted ignimbrites that produce a characteristic low and broad structure that covers a wide area (approximately 60 x 80 kilometers). This photograph highlights the entire volcanic structure; at 3,415 meters above sea level, Emi Koussi is the highest summit of the Sahara region. The summit area contains three calderas formed by powerful eruptions. Two older, and overlapping, calderas form a depression approximately 12 x 15 kilometers in area bounded by a distinct rim (center). According to scientists, the youngest and smallest caldera, Era Kohor, formed as a result of eruptive activity that occurred within the past 2 million years. Young volcanic features including lava flows and scoria cones are also thought to be less than 2 million years old. There are no historical records of eruptive activity at Emi Koussi, but there is an active thermal area on the southern flank of the volcano.
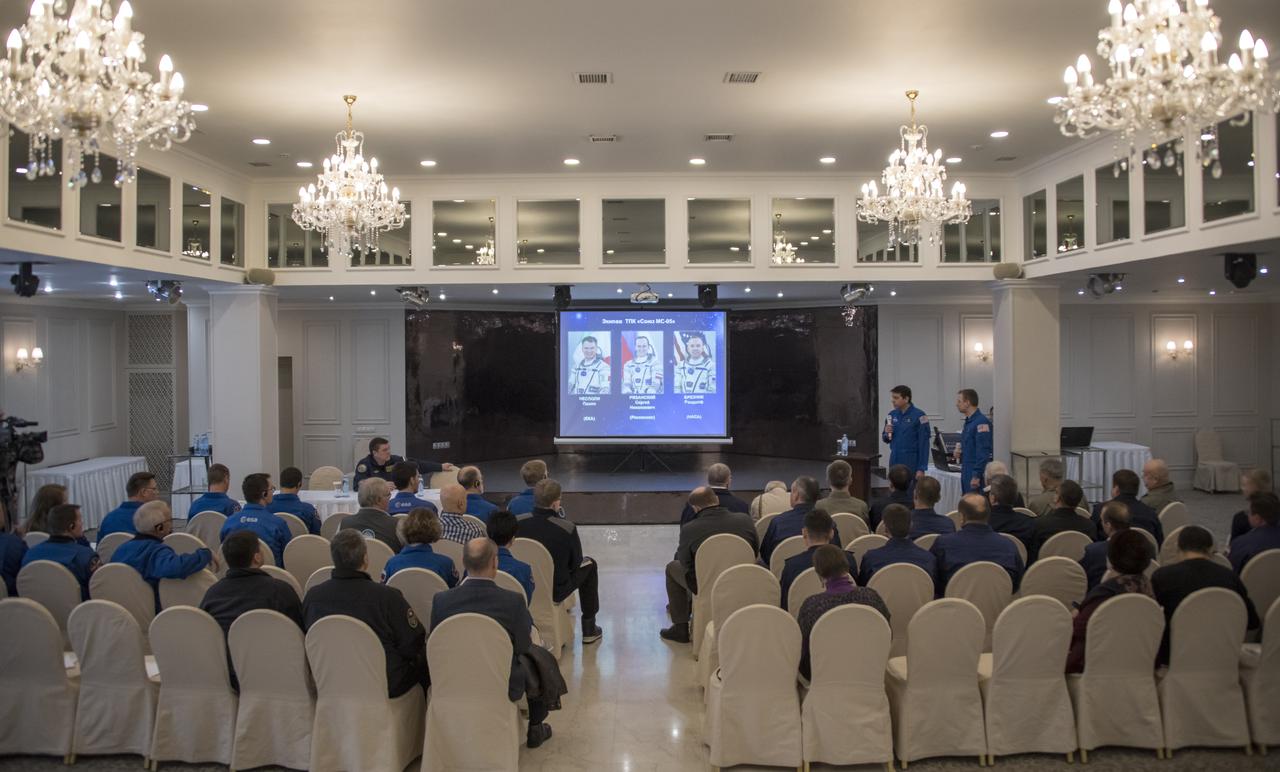

NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), Roscosmos, along with Russian Search and Recovery Forces, meet to discuss the readiness for the landing of Expedition 53 Commander Randy Bresnik of NASA and Flight Engineers Paolo Nespoli of ESA (European Space Agency) and Sergey Ryazanskiy of the Russian space agency Roscosmos Tuesday, Dec. 12, 2017. Bresnik, Nespoli and Ryazanskiy are returning after 139 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 52 and 53 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Inside the Launch Control Center’s Firing Room 1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Artemis I launch team rehearse the procedures for fueling the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with super cold propellants, or cryogenics, on Aug. 18, 2020. During the cryogenic simulation, potential problem scenarios were introduced to test the tools, processes, and procedures necessary for fueling the rocket. Artemis I will be the first integrated test flight of SLS and the Orion spacecraft – the system that will ultimately land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
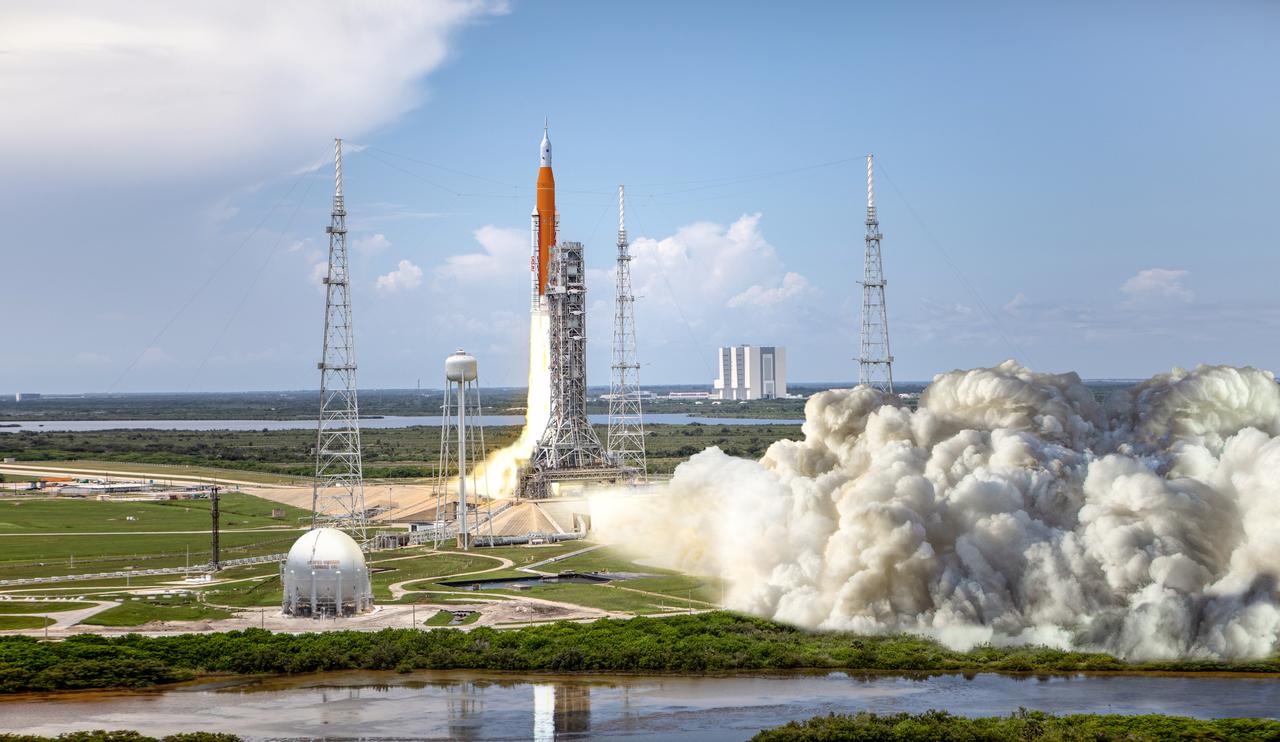

The following artist rendering shows NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft lifting off from Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Pad 39B for the Artemis I mission -- an uncrewed test flight that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA will launch the first woman and next man to the lunar surface, using the Moon as a testing ground before venturing on to Mars.
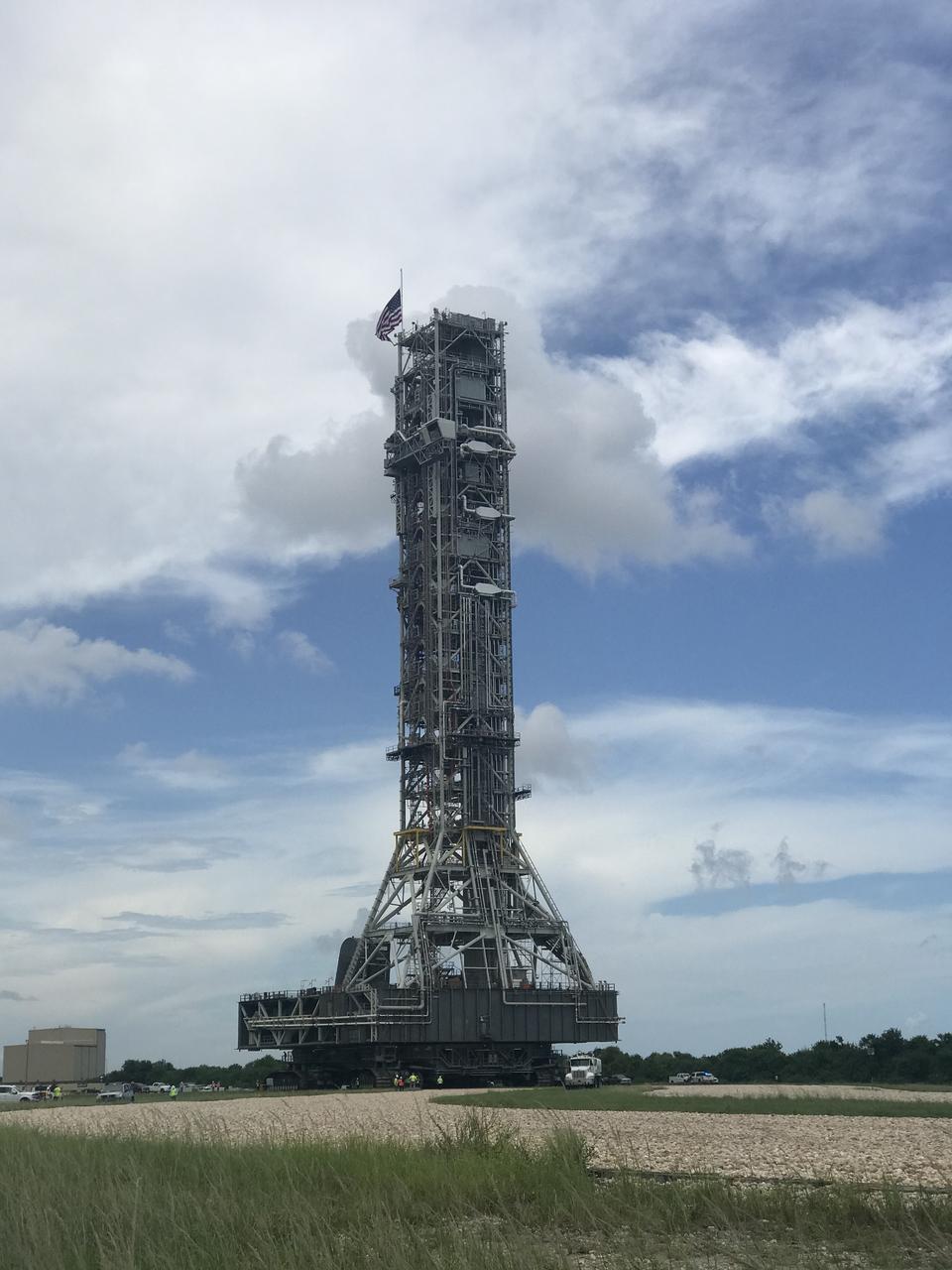

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 begins its trek to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 30, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check on the surface of the pad, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

Inside the Launch Control Center’s Firing Room 1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Artemis I launch team rehearse the procedures for fueling the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with super cold propellants, or cryogenics, on Aug. 18, 2020. During the cryogenic simulation, potential problem scenarios were introduced to test the tools, processes, and procedures necessary for fueling the rocket. Artemis I will be the first integrated test flight of SLS and the Orion spacecraft – the system that will ultimately land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

Inside the Launch Control Center’s Firing Room 1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Artemis I launch team rehearse the procedures for fueling the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with super cold propellants, or cryogenics, on Aug. 18, 2020. During the cryogenic simulation, potential problem scenarios were introduced to test the tools, processes, and procedures necessary for fueling the rocket. Artemis I will be the first integrated test flight of SLS and the Orion spacecraft – the system that will ultimately land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

Inside the Launch Control Center’s Firing Room 1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Artemis I launch team rehearse the procedures for fueling the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with super cold propellants, or cryogenics, on Aug. 18, 2020. During the cryogenic simulation, potential problem scenarios were introduced to test the tools, processes, and procedures necessary for fueling the rocket. Artemis I will be the first integrated test flight of SLS and the Orion spacecraft – the system that will ultimately land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

Inside the Launch Control Center’s Firing Room 1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Artemis I launch team rehearse the procedures for fueling the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with super cold propellants, or cryogenics, on Aug. 18, 2020. During the cryogenic simulation, potential problem scenarios were introduced to test the tools, processes, and procedures necessary for fueling the rocket. Artemis I will be the first integrated test flight of SLS and the Orion spacecraft – the system that will ultimately land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

Artemis I Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson stands at her console inside the Launch Control Center’s Firing Room 1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a simulation rehearsing propellant loading on Aug. 18, 2020. The simulation involved members of the launch team practicing the procedures for loading the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with cryogenics, or super cold propellants. During the exercise, potential problem scenarios were introduced to test the tools, processes, and procedures necessary for fueling the rocket. Artemis I will be the first integrated test flight of SLS and the Orion spacecraft – the system that will ultimately land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

Artemis I Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson stands at her console inside the Launch Control Center’s Firing Room 1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a simulation rehearsing propellant loading on Aug. 18, 2020. The simulation involved members of the launch team practicing the procedures for loading the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with cryogenics, or super cold propellants. During the exercise, potential problem scenarios were introduced to test the tools, processes, and procedures necessary for fueling the rocket. Artemis I will be the first integrated test flight of SLS and the Orion spacecraft – the system that will ultimately land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
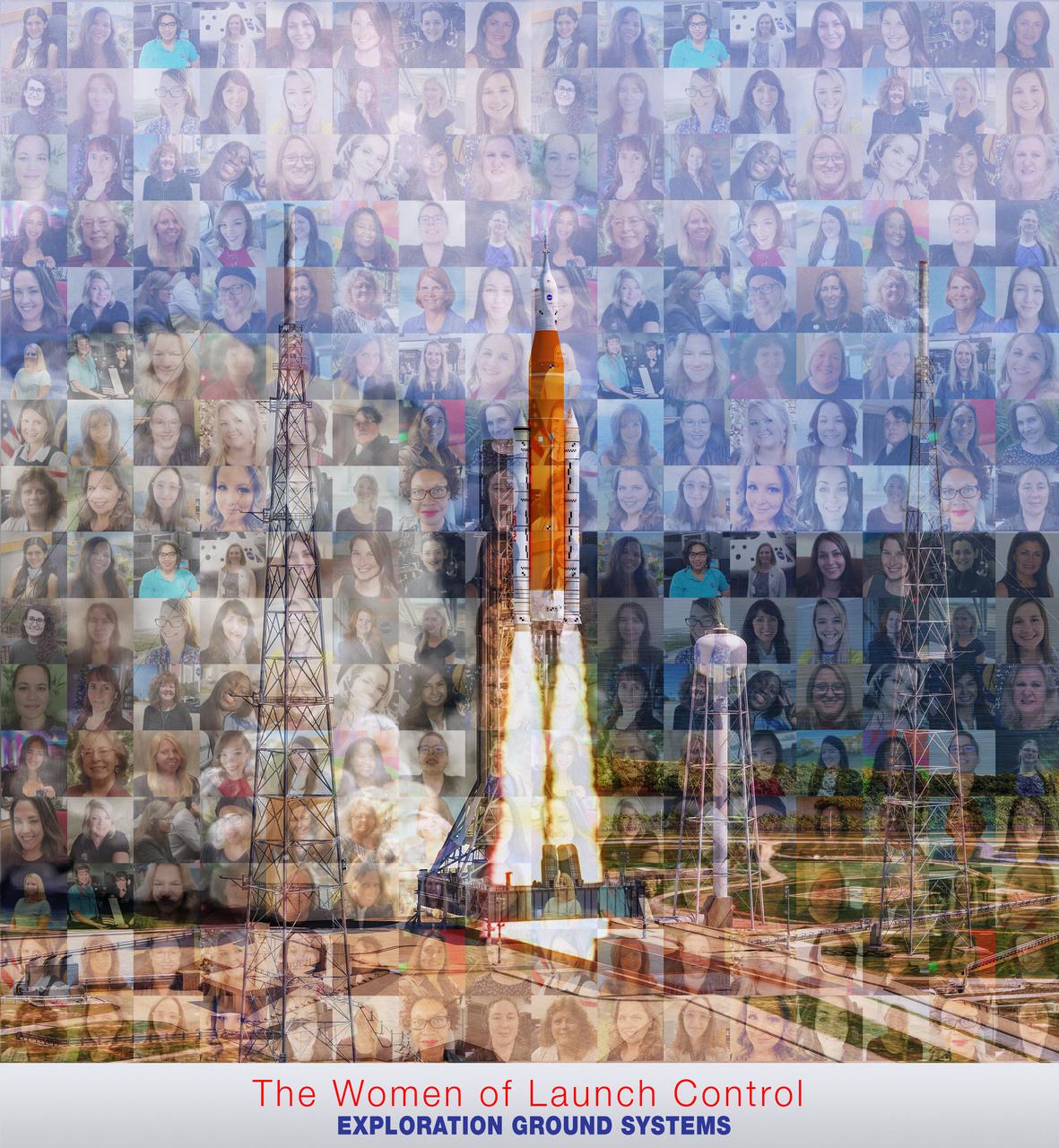

NASA has come a long way since the Apollo program when there was only one woman — JoAnn Morgan — working in Firing Room 1 of Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Control Center. Now, about 30% of the staff responsible for launching and monitoring the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for the Artemis program are women. Under the Artemis program, NASA will launch the first woman and next man to the lunar surface, using the Moon as a testing ground before venturing on to Mars.
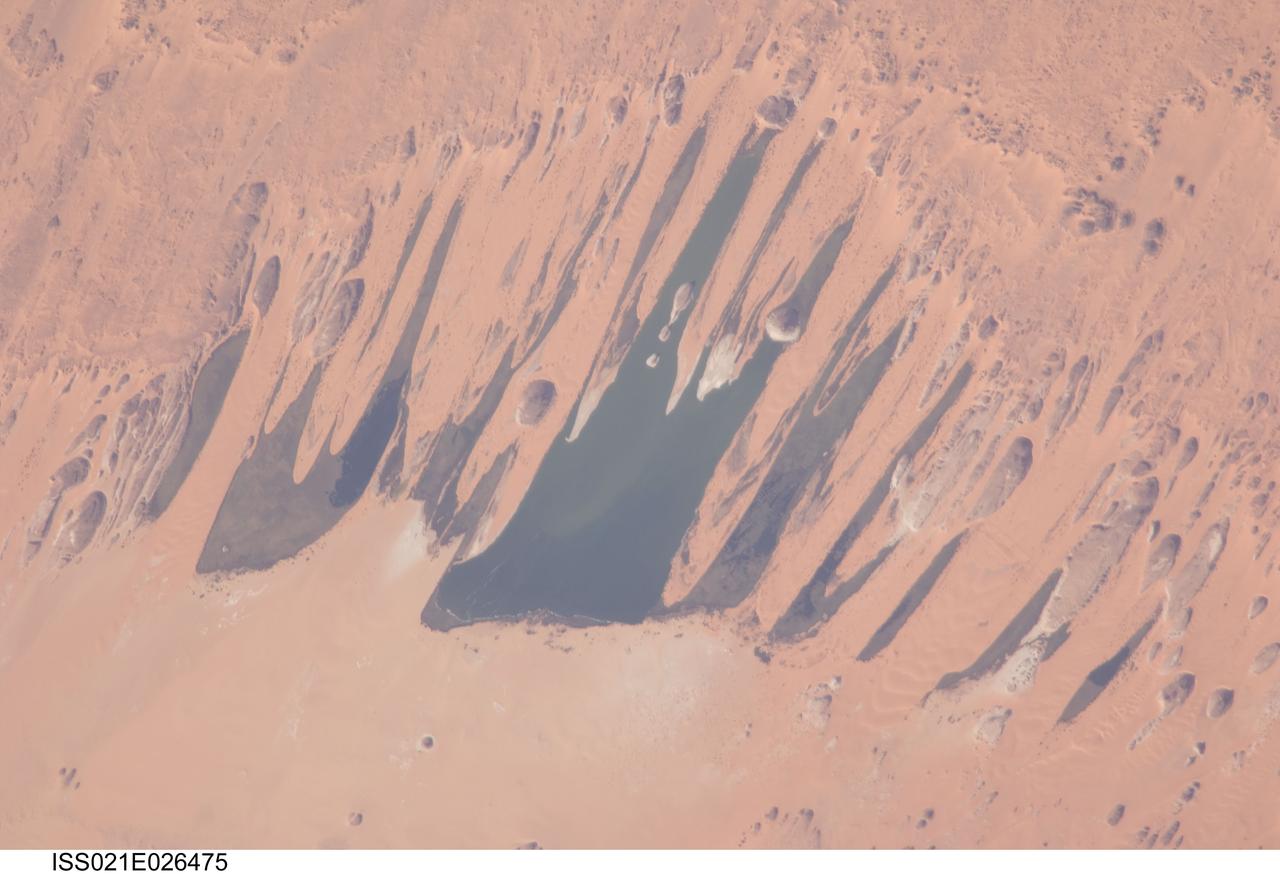

ISS021-E-026475 (14 Nov. 2009) --- Ounianga Lakes in the Sahara Desert, in the nation of Chad are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 21 crew member on the International Space Station. This view features one of the largest of a series of ten, mostly fresh water lakes in the Ounianga basin in the heart of the Sahara Desert of northeastern Chad. According to scientists, the lakes are the remnant of a single large lake, probably tens of kilometers long that once occupied this remote area approximately 14,800 to 5,500 years ago. As the climate dried out during the subsequent millennia, the lake was reduced in size and large wind-driven sand dunes invaded the original depression dividing it into several smaller basins. The area shown in this image measures approximately 11 x 9 kilometers, with the dark water surfaces of the lake segregated almost completely by orange linear sand dunes that stream into the depression from the northeast. The almost year-round northeast winds and cloudless skies make for very high evaporation (an evaporation rate of greater than six meters per year has been measured in one of the nearby lakes). Despite this, only one of the ten lakes is saline. According to scientists, the reason for the apparent paradox of fresh water lakes in the heart of the desert lies in the fact that fresh water from a very large aquifer reaches the surface in the Ounianga depression in the form of the lakes. The aquifer is large enough to keep supplying the small lakes with water despite the high evaporation rate. Mats of floating reeds also reduce the evaporation in places. The lakes form a hydrological system that is unique in the Sahara Desert. Scientists believe the aquifer was charged with fresh water, and the large original lake evolved, during the so-called African Humid Period (approximately 14,800 to 5,500 years ago) when the West African summer monsoon was stronger than it is today. Associated southerly winds brought Atlantic moisture well north of modern limits, producing sufficient rainfall in the central Sahara to foster an almost complete savanna vegetation cover. Pollen data from lake sediments of the original 50-meters-deep Ounianga Lake suggests to scientists that a mild tropical climate with a wooded grassland savanna existed in the region. This vegetation association is now only encountered 300 kilometers further south. Ferns grew in the stream floodplains which must have been occasionally flooded. Even shrubs that now occur only on the very high, cool summits (greater than 2,900 meters, greater than 9,500 feet) of the Tibesti Mts. have been found in the Ounianga lake sediments.
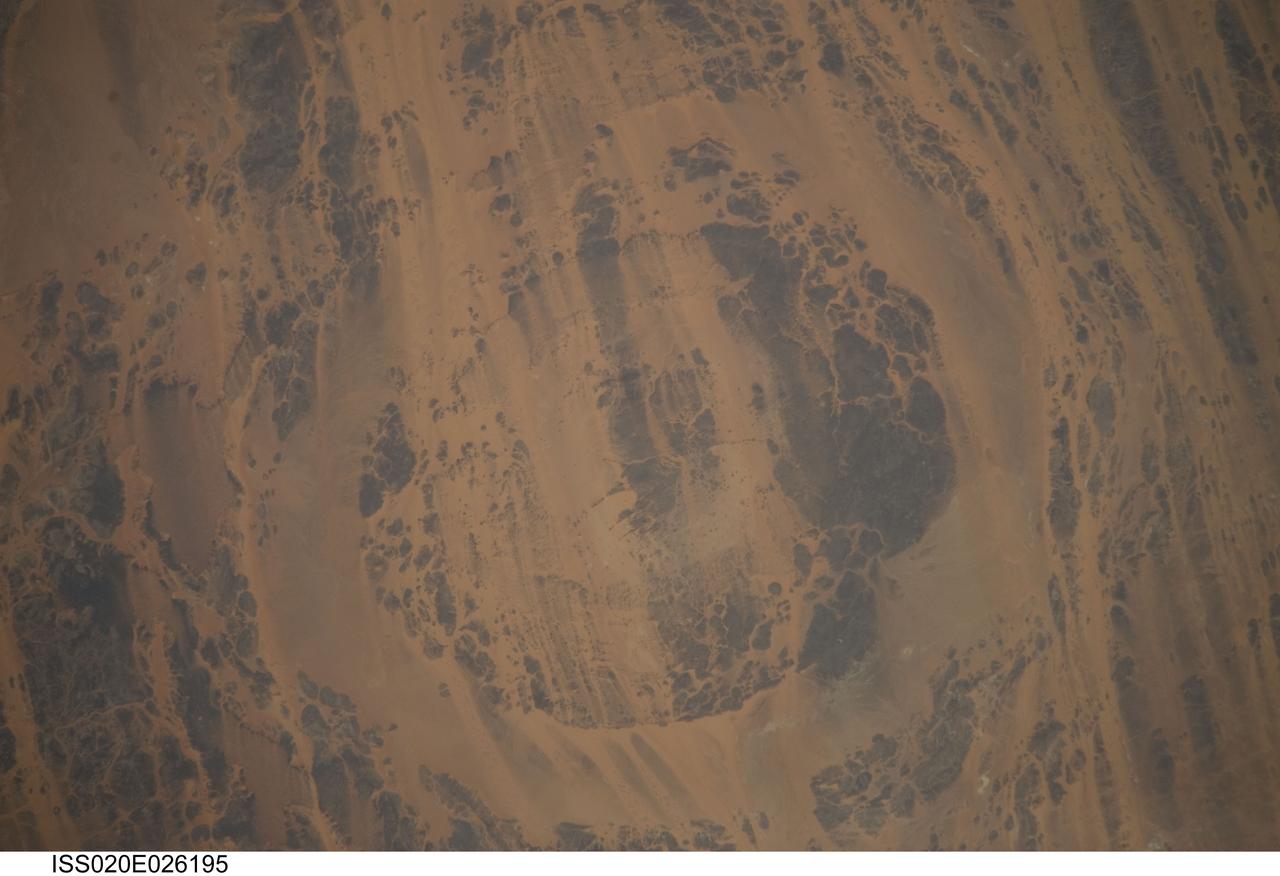

ISS020-E-026195 (25 July 2009) --- Aorounga Impact Crater is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 20 crew member on the International Space Station. Aorounga Impact Crater is located in the Sahara Desert of north-central Chad and is one of the best preserved impact structures in the world. According to scientists, the crater is thought to be middle or upper Devonian to lower Mississippian (approximately 345 ? 370 million years old) based on the age of the sedimentary rocks deformed by the impact. Spaceborne Imaging Radar (SIR) data collected in 1994 suggests that Aorounga is one of a set of three craters formed by the same impact event. The other two suggested impact structures are buried by sand deposits. The concentric ring structure of the Aorounga crater ? renamed Aorounga South in the multiple-crater interpretation of SIR data ? is clearly visible in this detailed photograph. The central highland, or peak, of the crater is surrounded by a small sand-filled trough; this in turn is surrounded by a larger circular trough. Linear rock ridges alternating with light orange sand deposits cross the image from upper left to lower right; these are called yardangs by geomorphologists. Yardangs form by wind erosion of exposed rock layers in a unidirectional wind field. The wind blows from the northeast at Aorounga, and sand dunes formed between the yardangs are actively migrating to the southwest.
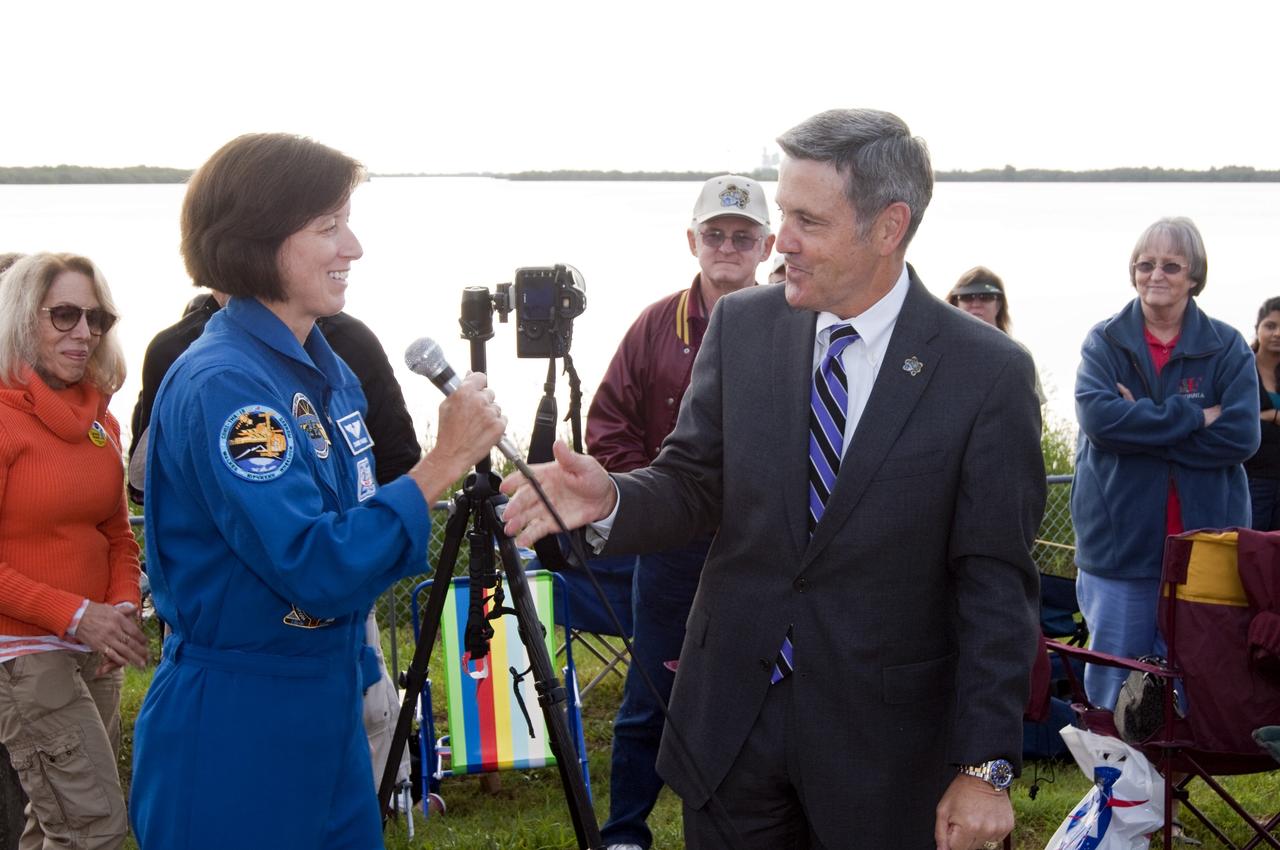

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA astronaut Shannon Walker, left and Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana talk to a crowd of spectators gathered at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to watch the launch of space shuttle Endeavour. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
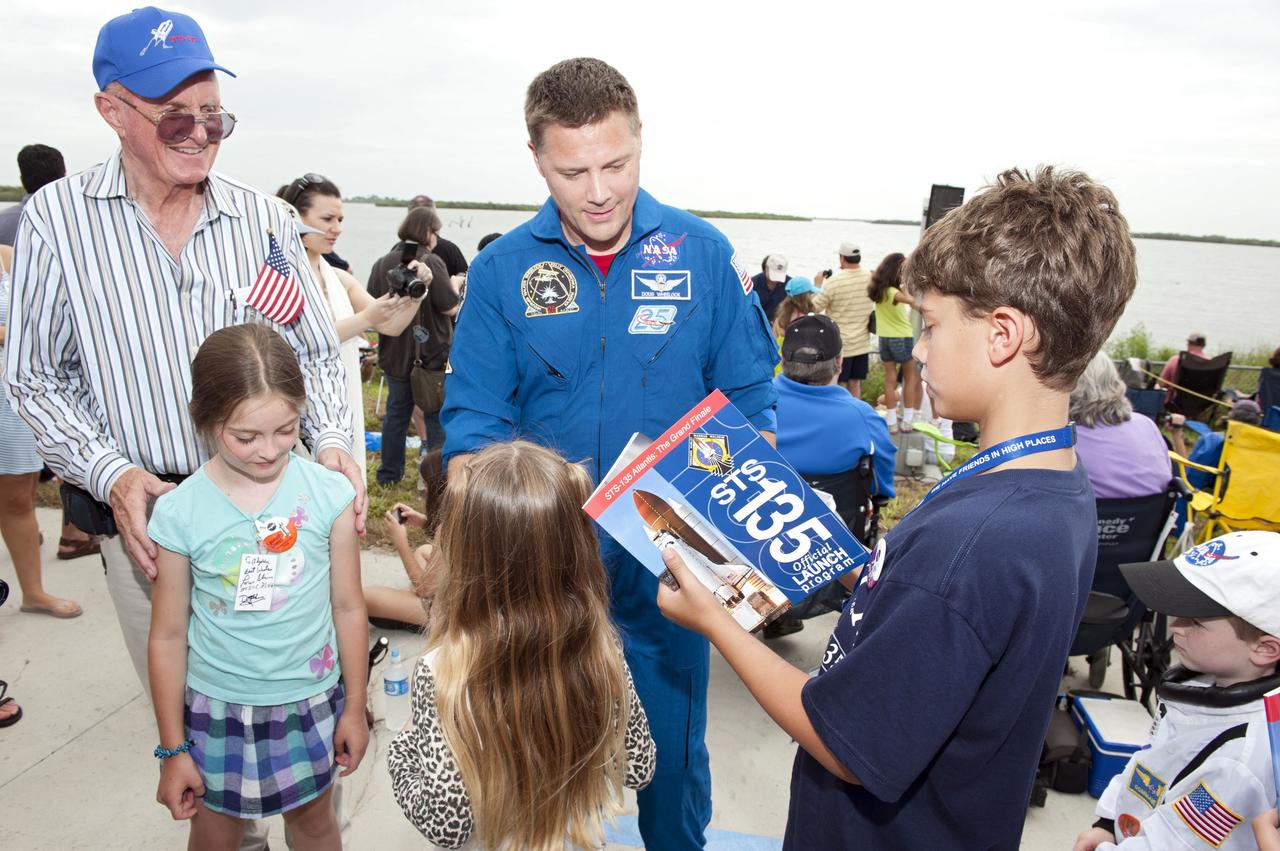

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, youngsters delight in meeting NASA astronaut Doug Wheelock before the launch of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson (second from right) meets with members of the “red crew” after the launch of Artemis I at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 16, 2022. Members of the red crew include Jacobs/TOSC ERC employees Billy Cairns, cryogenic engineering technician (left); Chad Garrett (second from left), safety engineer; and Trent Annis (right), cryogenic engineering technician. The team of technicians are part of the personnel specially trained to conduct operations at the launch pad during cryogenic loading operations at the launch pad. Prior to the launch of Artemis I, the red crew entered the zero deck, or base, of the mobile launcher and tightened several bolts to troubleshoot a valve used to replenish the core stage with liquid hydrogen which showed a leak with readings above limits. NASA has historically sent teams to the pad to conduct inspections during active launch operations as needed. Artemis I launch successfully at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, from Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.
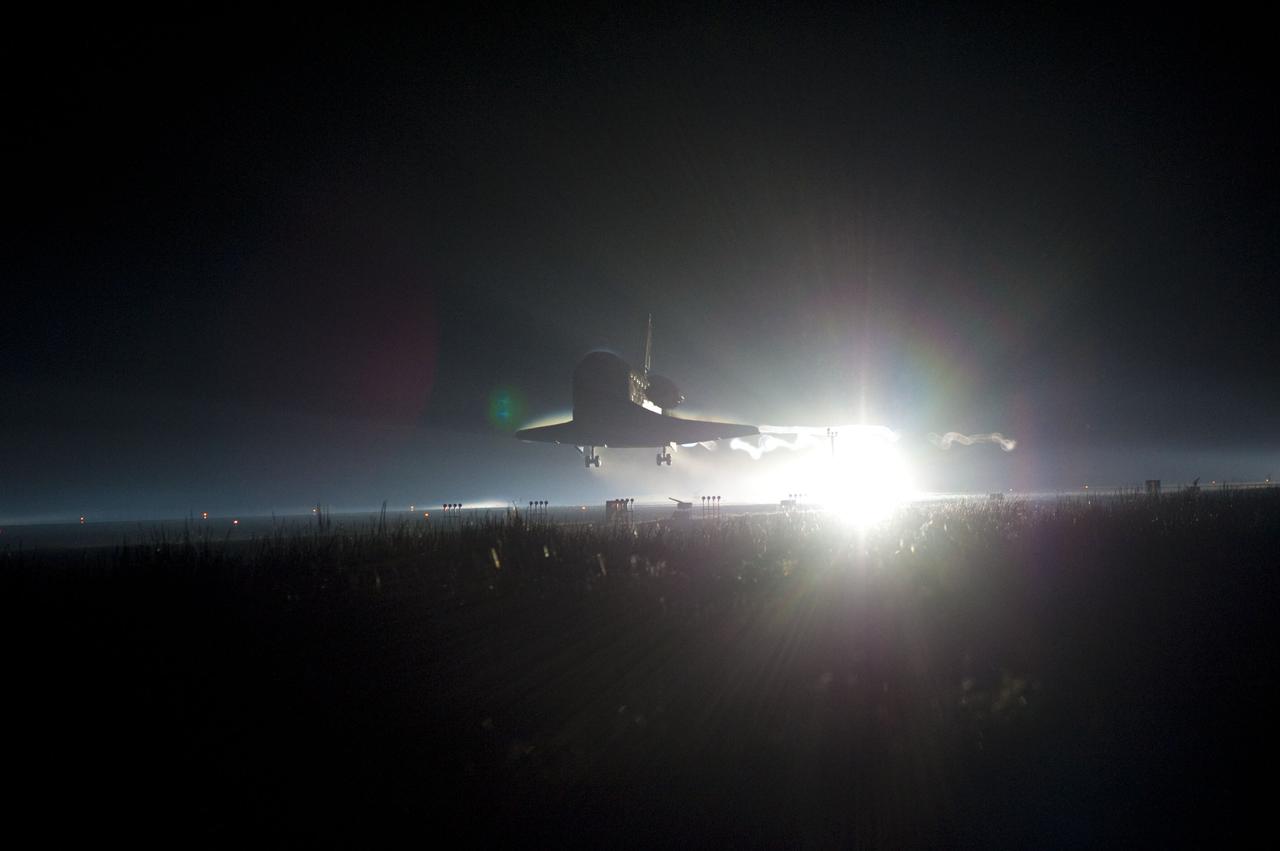

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Backlit by the xenon lights on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility, space shuttle Atlantis nears touchdown for the final time at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Securing the space shuttle fleet's place in history, Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. Main gear touchdown was at 5:57:00 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 5:57:20 a.m., and wheelstop at 5:57:54 a.m. On board are STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim. On the 37th shuttle mission to the International Space Station, STS-135 delivered the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module filled with more than 9,400 pounds of spare parts, equipment and supplies that will sustain station operations for the next year. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. STS-135 also was the final mission of the Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
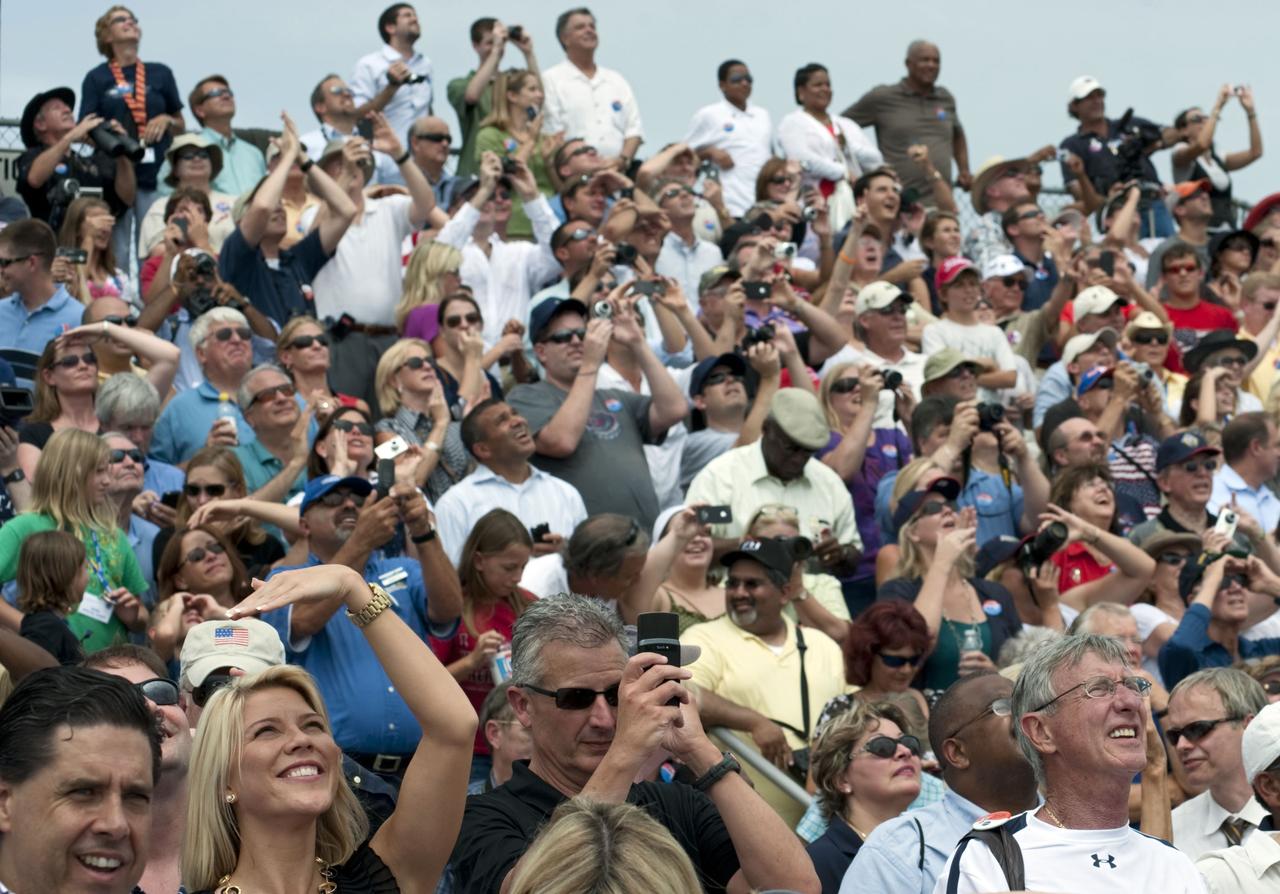

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spectators smile with delight as they watch space shuttle Atlantis soar into space on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana speaks to media and spectators before the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen also are Stennis Space Center Director Patrick Scheuermann (left), Marshall Space Flight Center Director Robert Lightfoot and Johnson Space Center Director Mike Coats. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
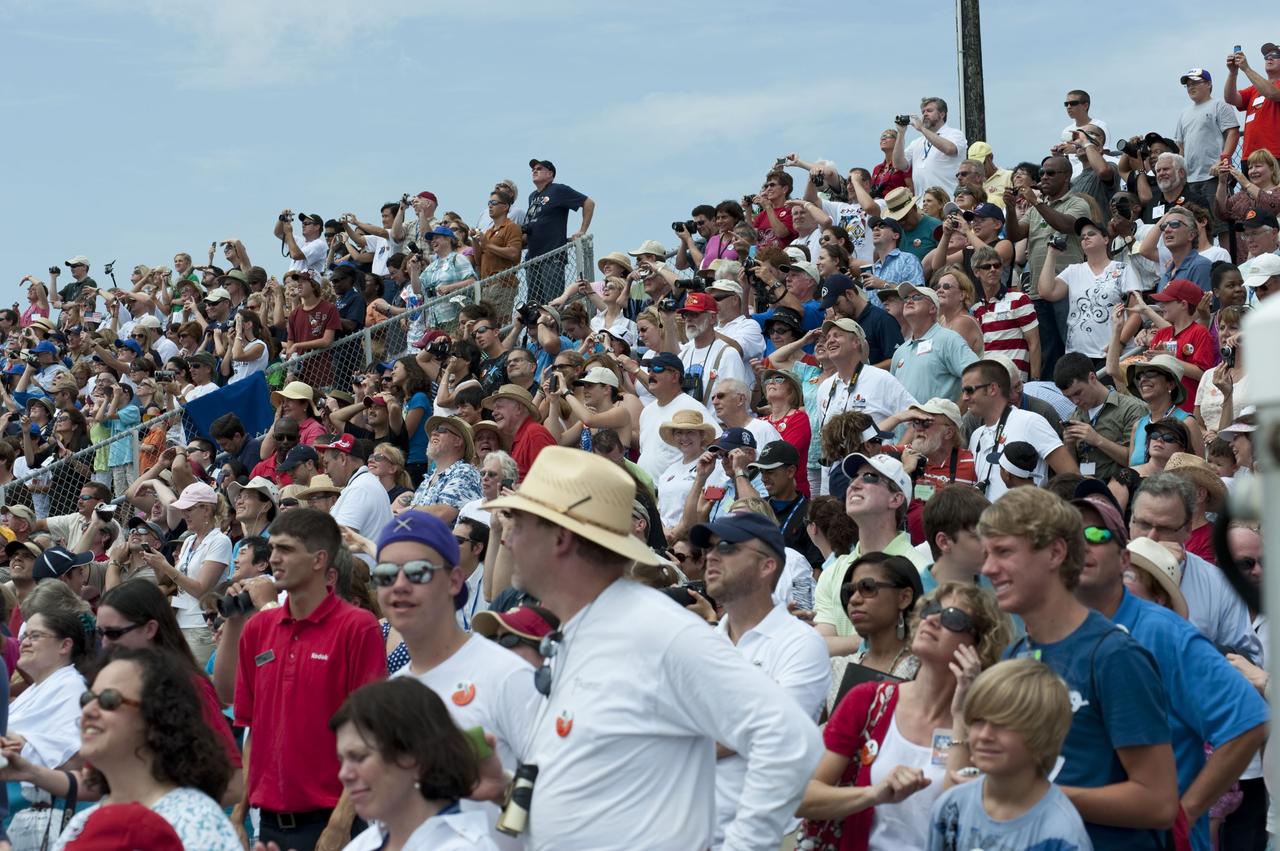

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spectators smile with delight as they watch space shuttle Atlantis soar into space on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
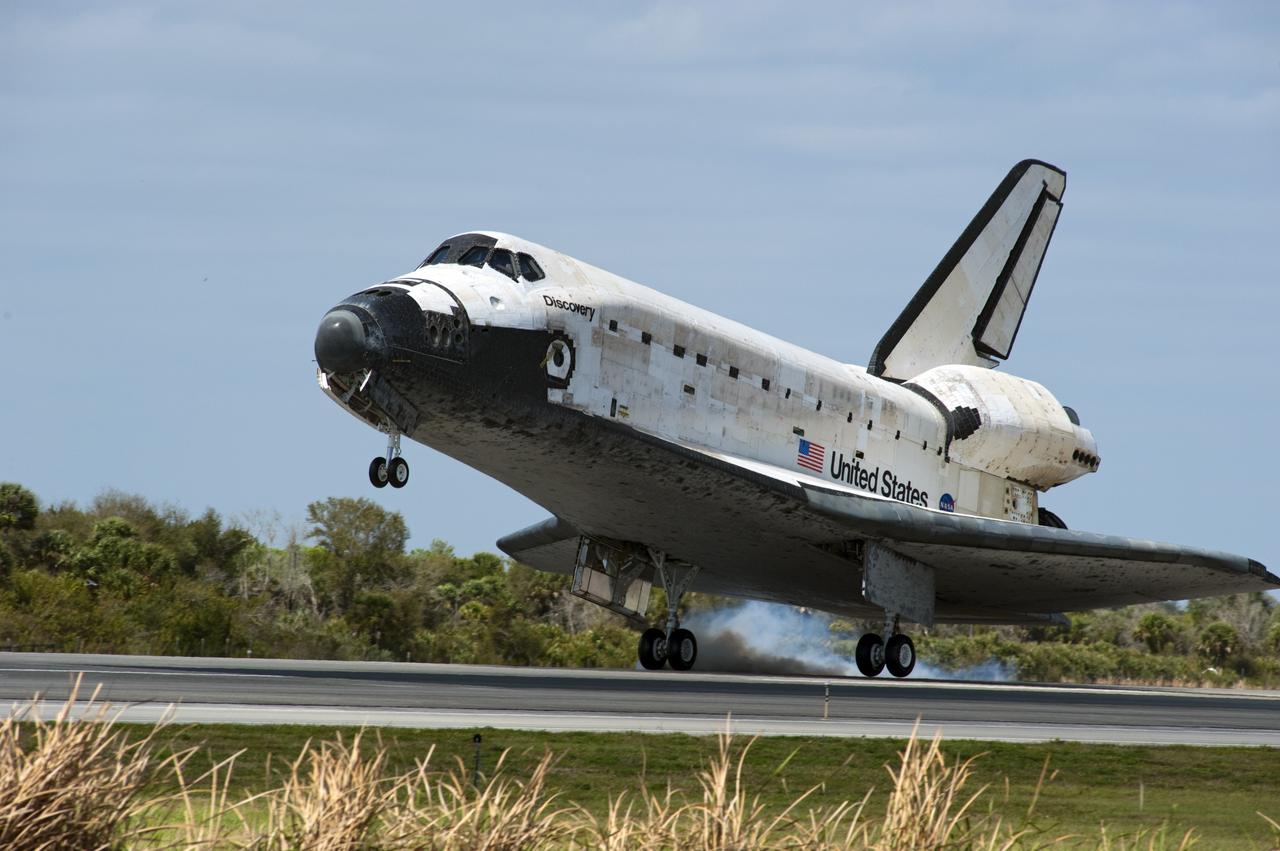

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Discovery touches down on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landing was at 11:57 a.m. EST, completing the 13-day STS-133 mission to the International Space Station. Main gear touchdown was at 11:57:17 a.m., followed by nose gear touchdown at 11:57:28, and wheelstop at 11:58:14 a.m. On board are Commander Steve Lindsey, Pilot Eric Boe, and Mission Specialists Nicole Stott, Michael Barratt, Alvin Drew and Steve Bowen. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
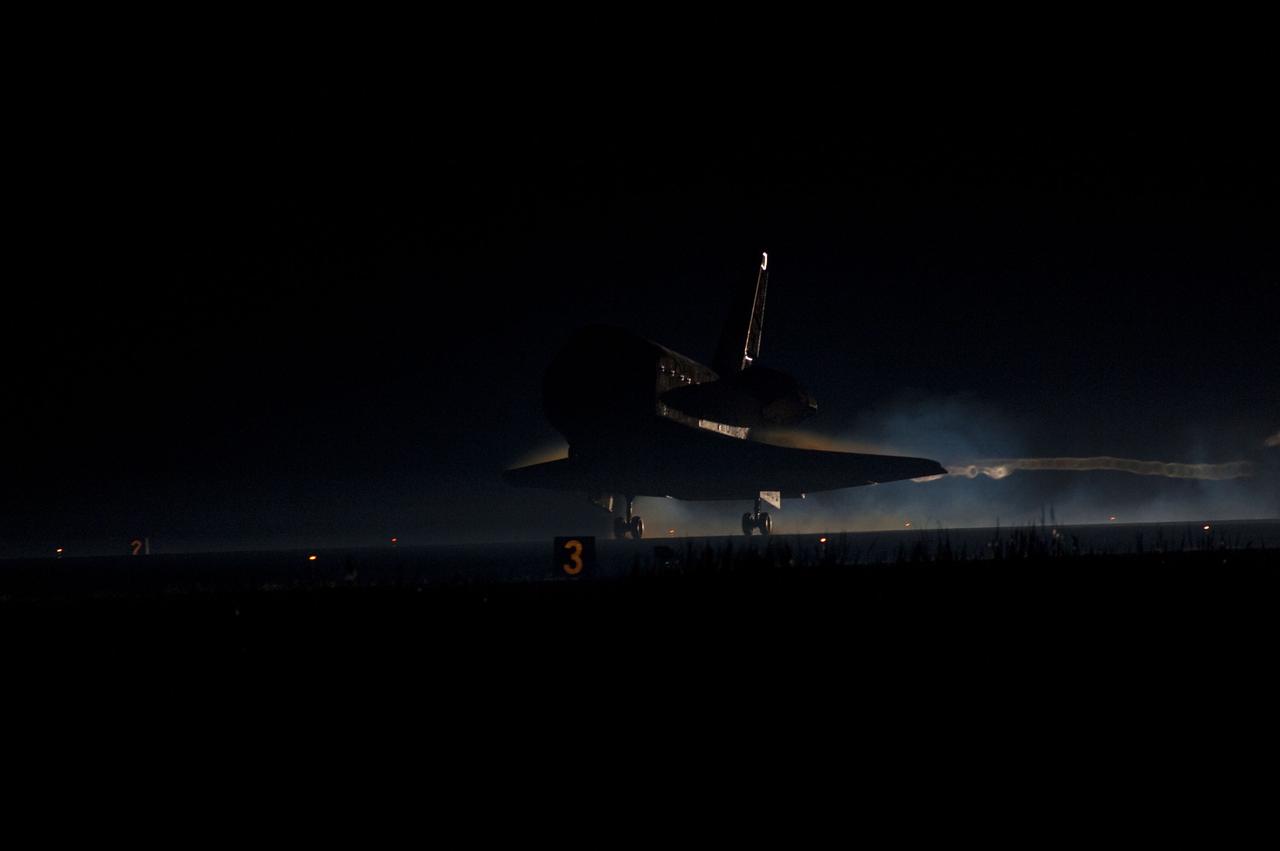

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Atlantis seems almost a mirage as in lands on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Securing the space shuttle fleet's place in history, Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. Main gear touchdown was at 5:57:00 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 5:57:20 a.m., and wheelstop at 5:57:54 a.m. On board are STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim. On the 37th shuttle mission to the International Space Station, STS-135 delivered the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module filled with more than 9,400 pounds of spare parts, equipment and supplies that will sustain station operations for the next year. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. STS-135 also was the final mission of the Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Marshall Space Flight Center Director Robert Lightfoot speaks to media and spectators before the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Also seen here are Stennis Space Center Director Patrick Scheuermann (left) and Johnson Space Center Director Mike Coats. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
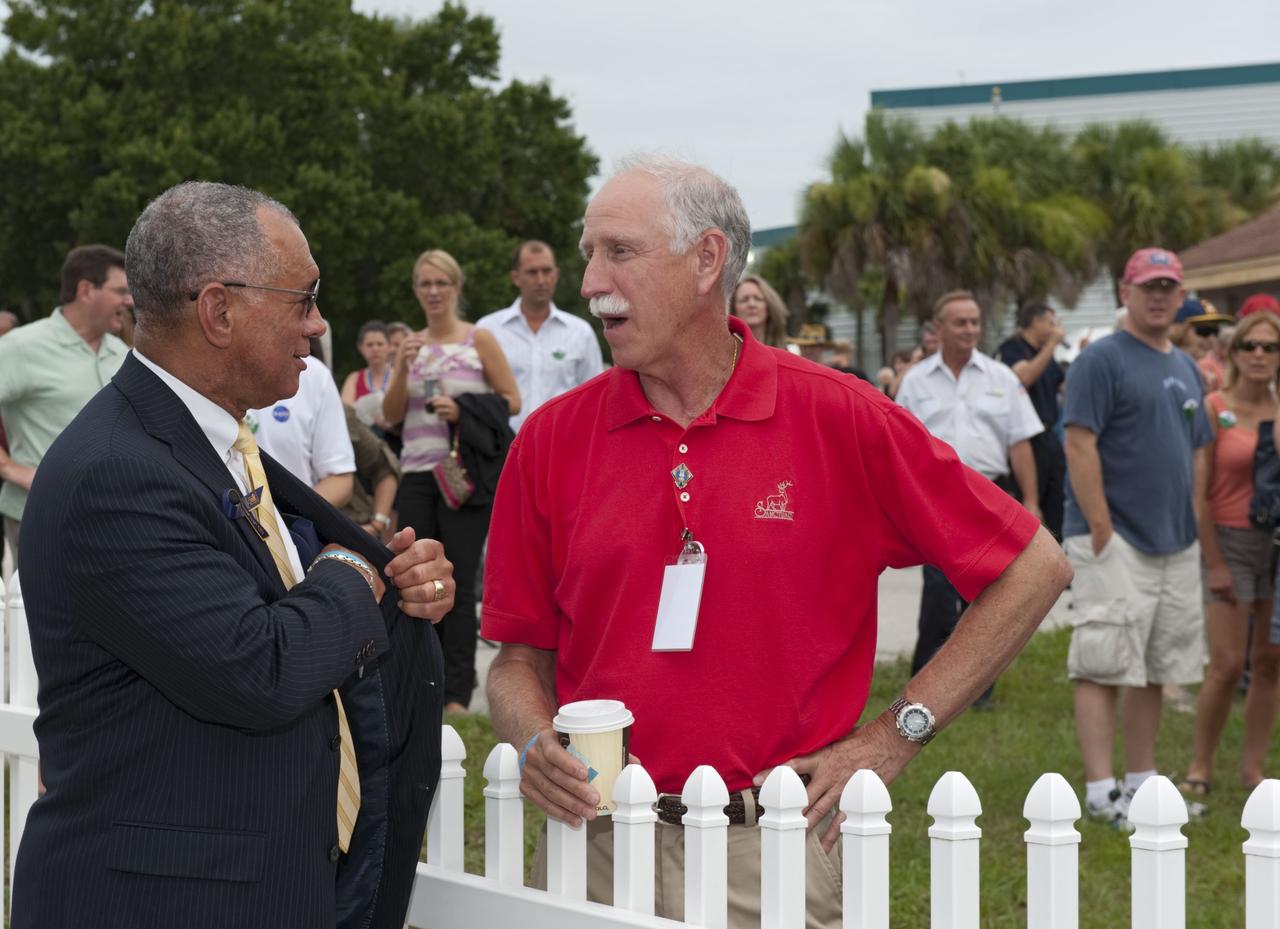

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden speaks with former NASA astronaut Richard "Dick" Covey before the upcoming launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, youngsters delight in meeting NASA astronaut Doug Wheelock before the launch of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spectators watch the countdown clock as liftoff of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission to the International Space Station ticks down to the last few seconds. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
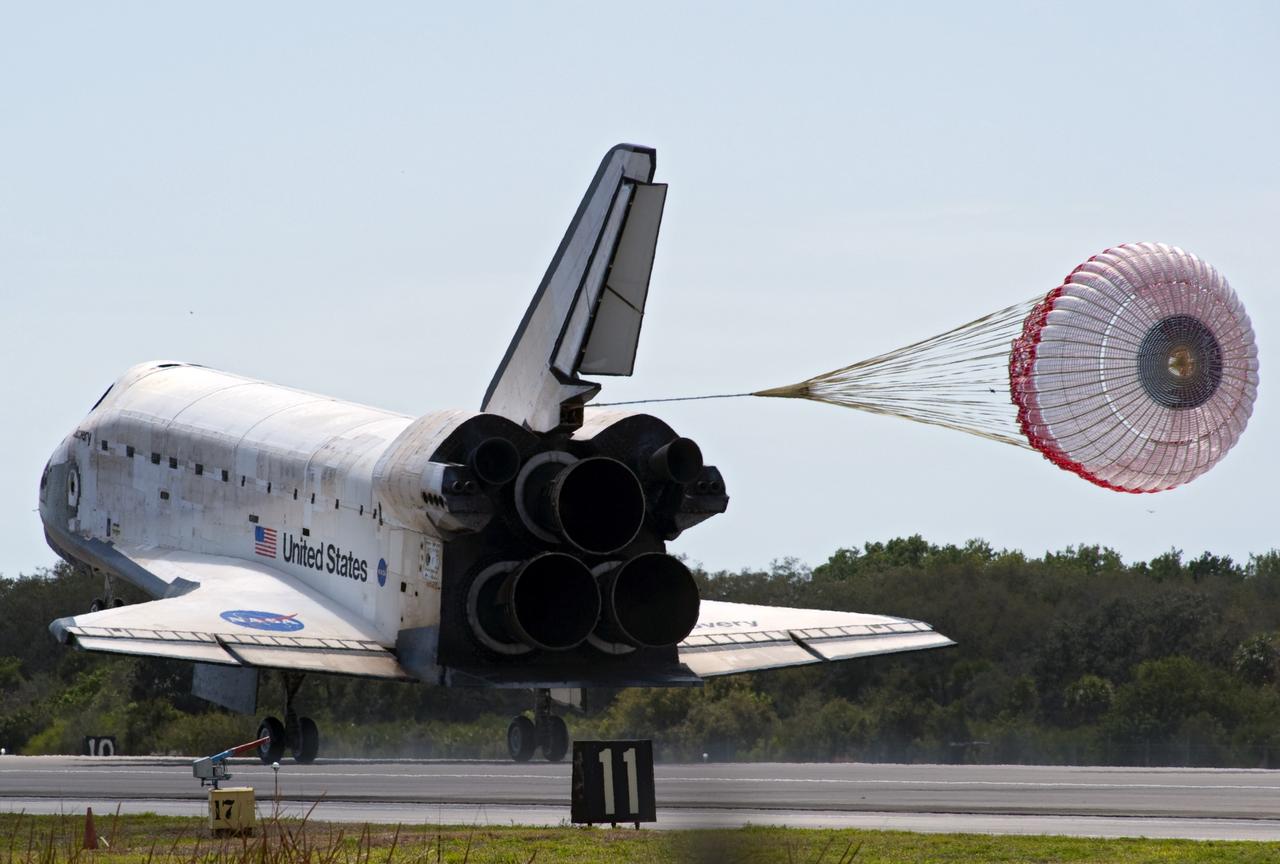

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- With its drag chute unfurled, space shuttle Discovery rolls down on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landing was at 11:57 a.m. EST, completing the 13-day STS-133 mission to the International Space Station. Main gear touchdown was at 11:57:17 a.m., followed by nose gear touchdown at 11:57:28, and wheelstop at 11:58:14 a.m. On board are Commander Steve Lindsey, Pilot Eric Boe, and Mission Specialists Nicole Stott, Michael Barratt, Alvin Drew and Steve Bowen. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Joe Dowdy, special operations manager at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, talks to a crowd of spectators gathered at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to watch the launch of space shuttle Endeavour. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
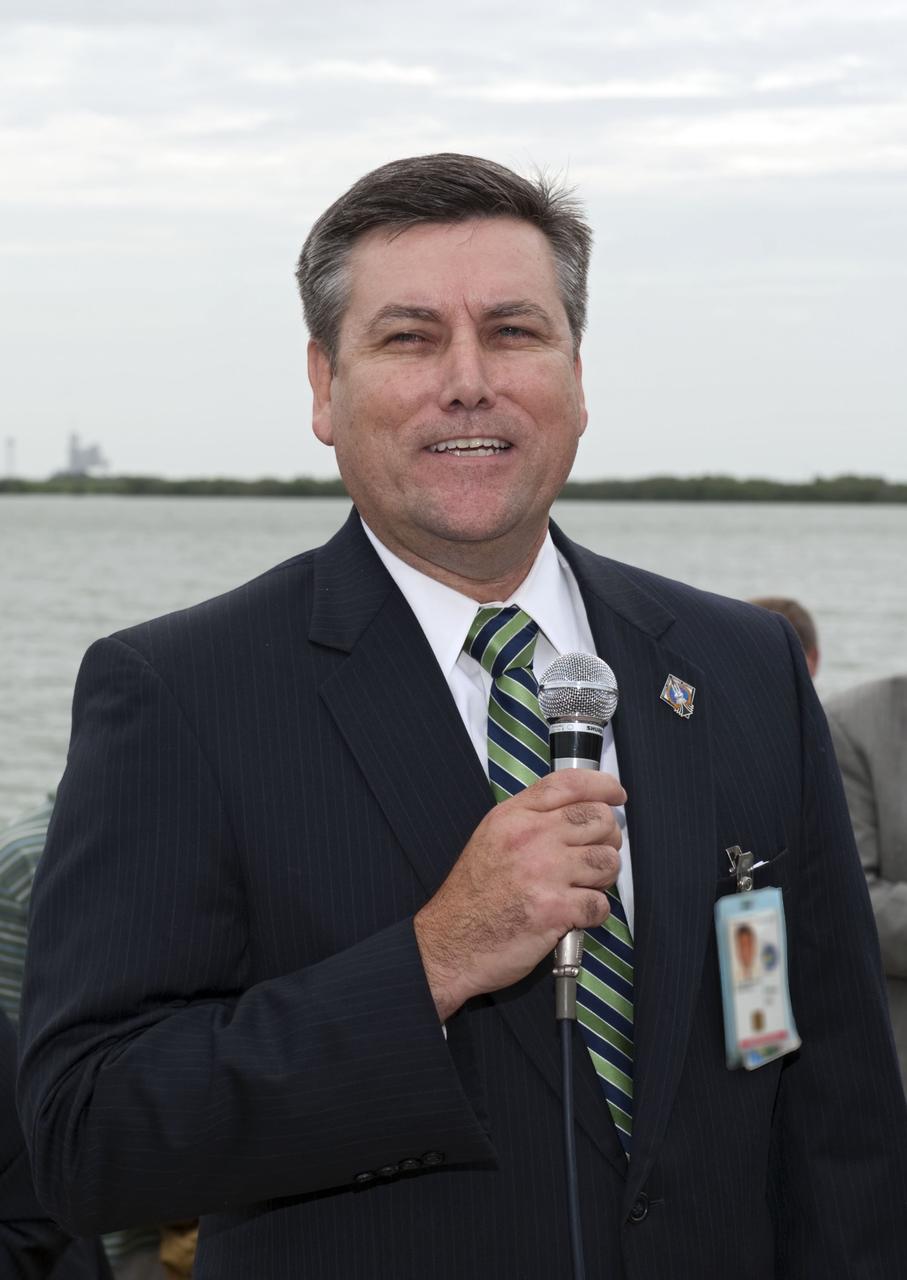

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Stennis Space Center Director Patrick Scheuermann speaks to media and spectators before the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
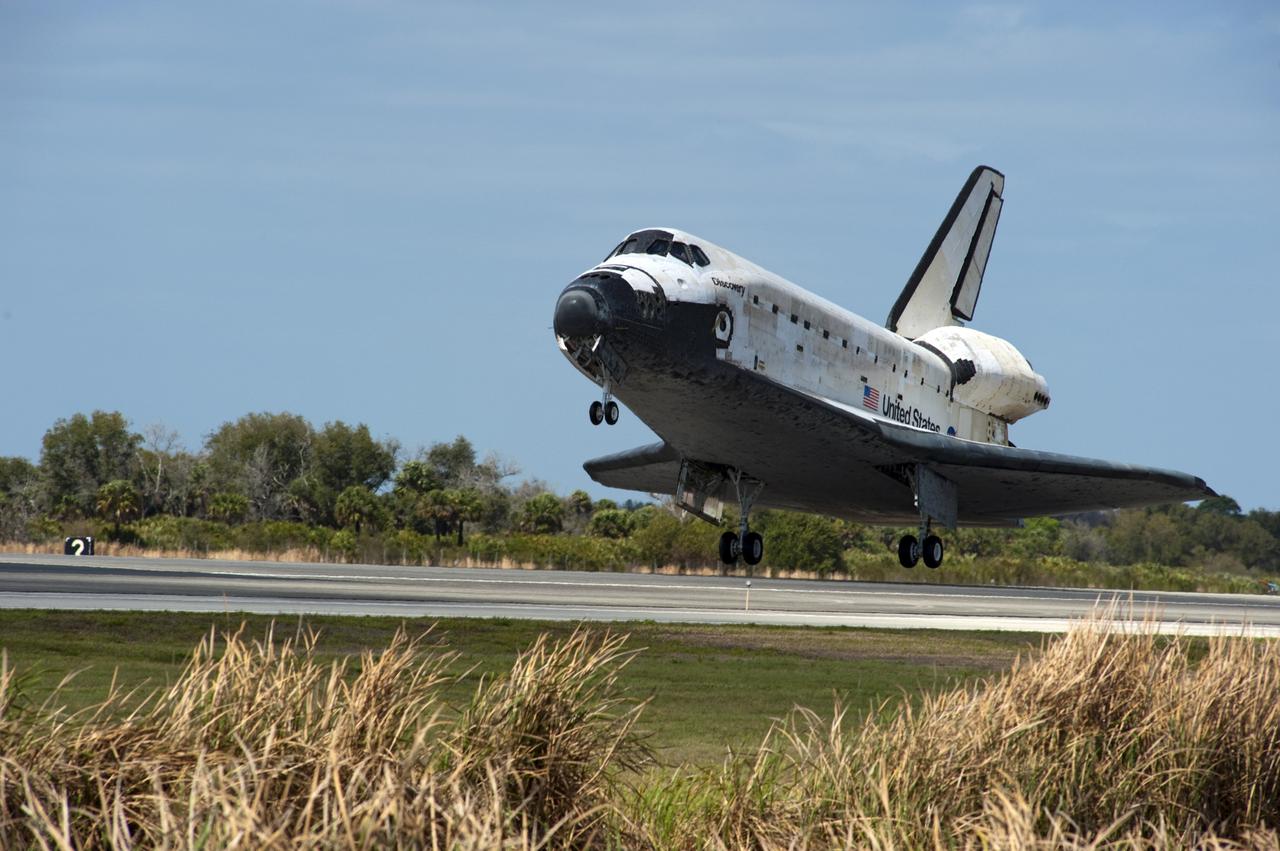

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery glides above Runway 15 before touching down at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landing was at 11:57 a.m. EST, completing the 13-day STS-133 mission to the International Space Station. Main gear touchdown was at 11:57:17 a.m., followed by nose gear touchdown at 11:57:28, and wheelstop at 11:58:14 a.m. On board are Commander Steve Lindsey, Pilot Eric Boe, and Mission Specialists Nicole Stott, Michael Barratt, Alvin Drew and Steve Bowen. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
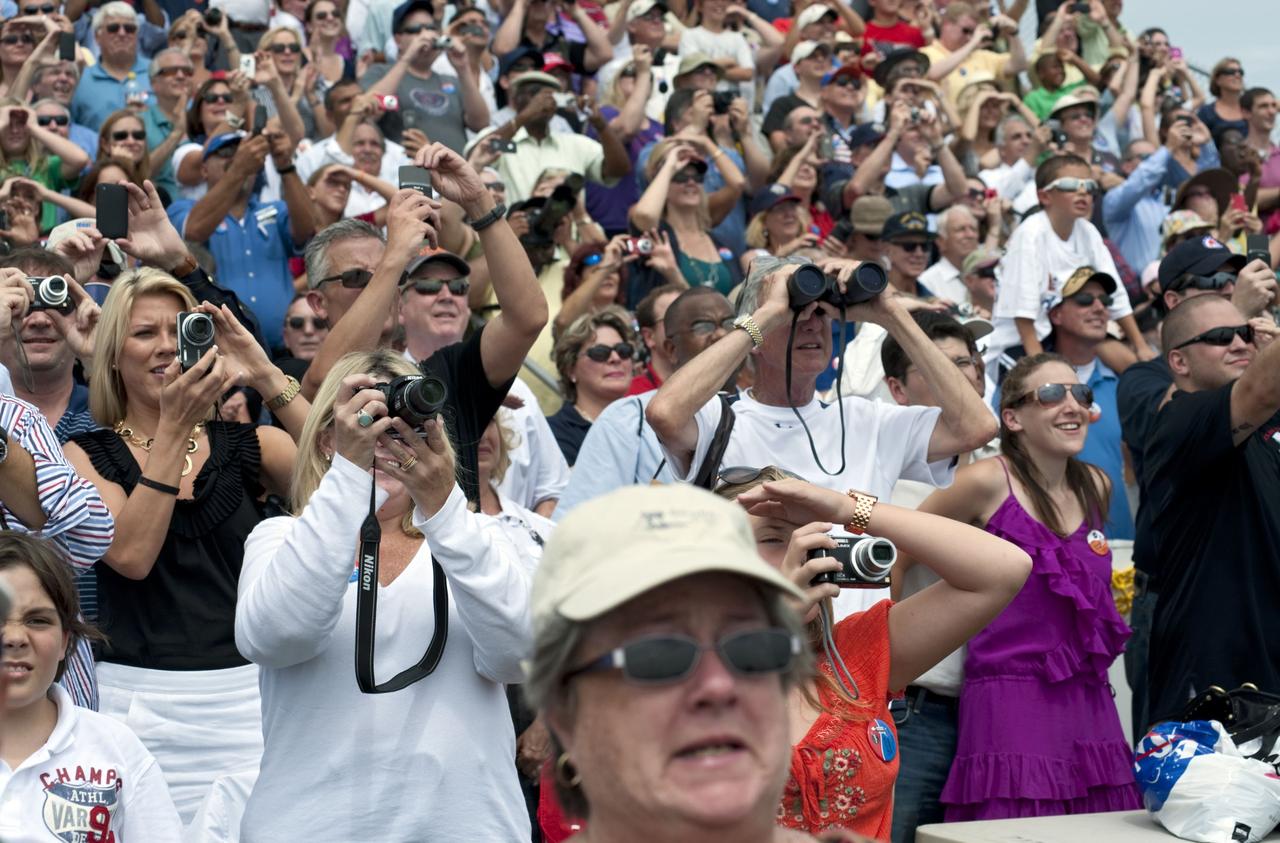

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spectators have their cameras trained on Launch Pad 39A as space shuttle Atlantis lifts off to begin its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
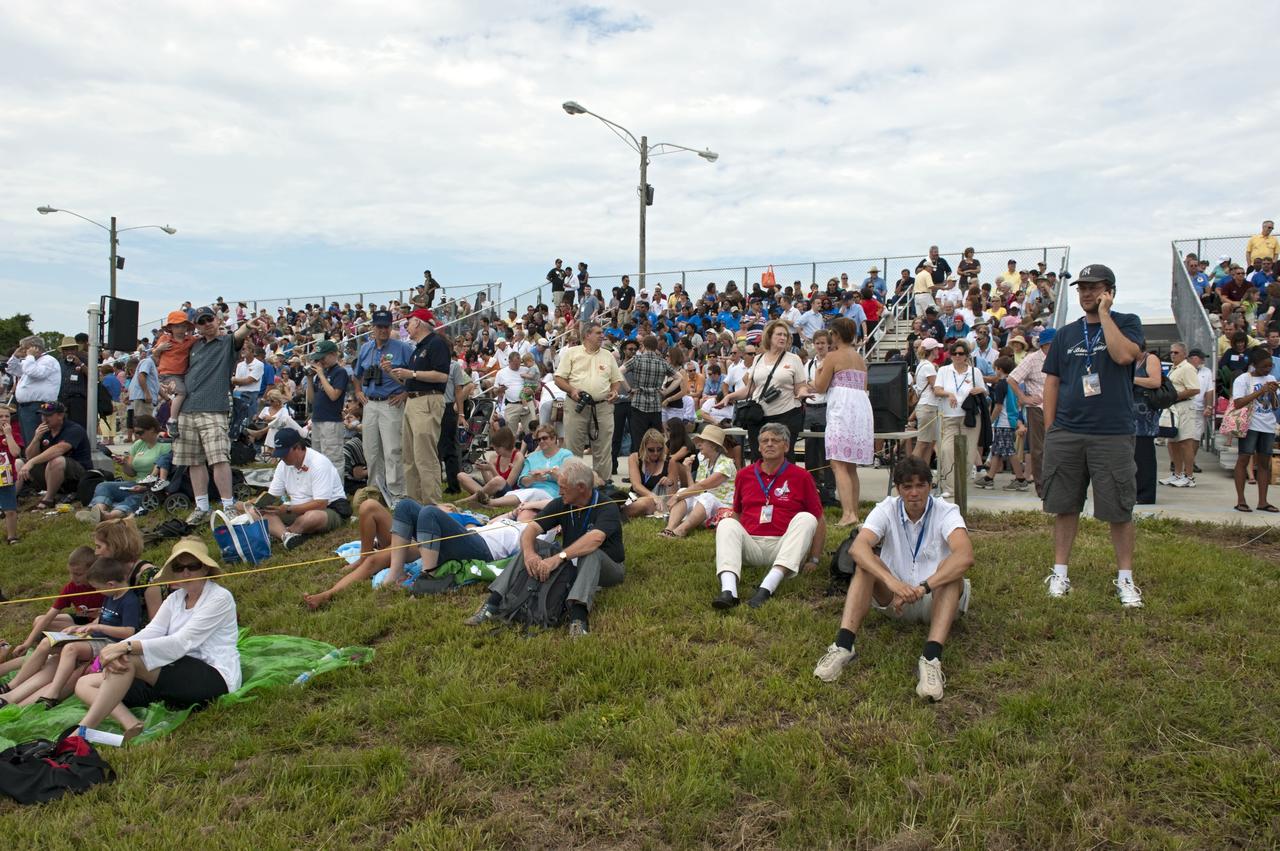

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spectators relax before the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
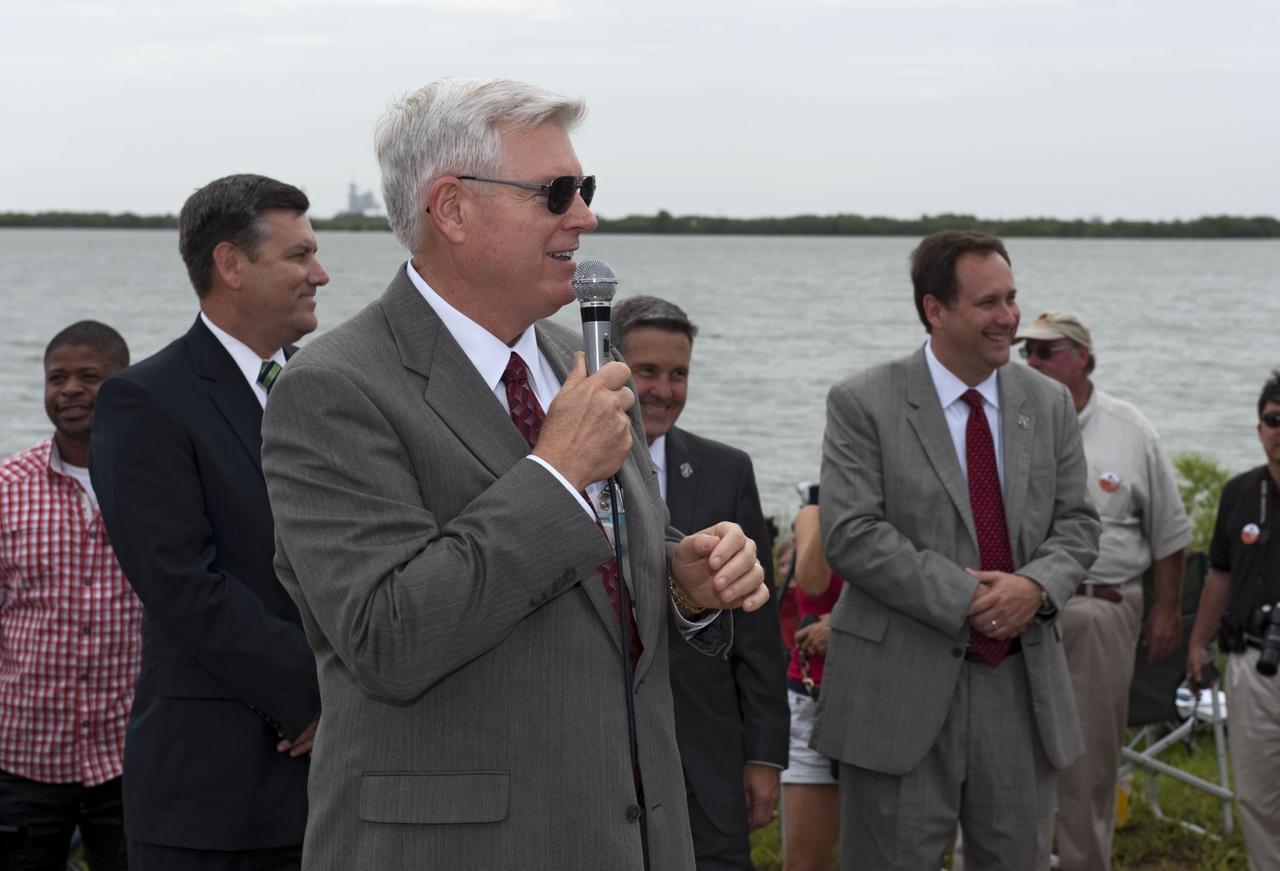

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Johnson Space Center Director Mike Coats speaks to media and spectators before the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen also Stennis Space Center Director Patrick Scheuermann (left), Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana and Marshall Space Flight Center Director Robert Lightfoot. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spectators relax before the upcoming launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
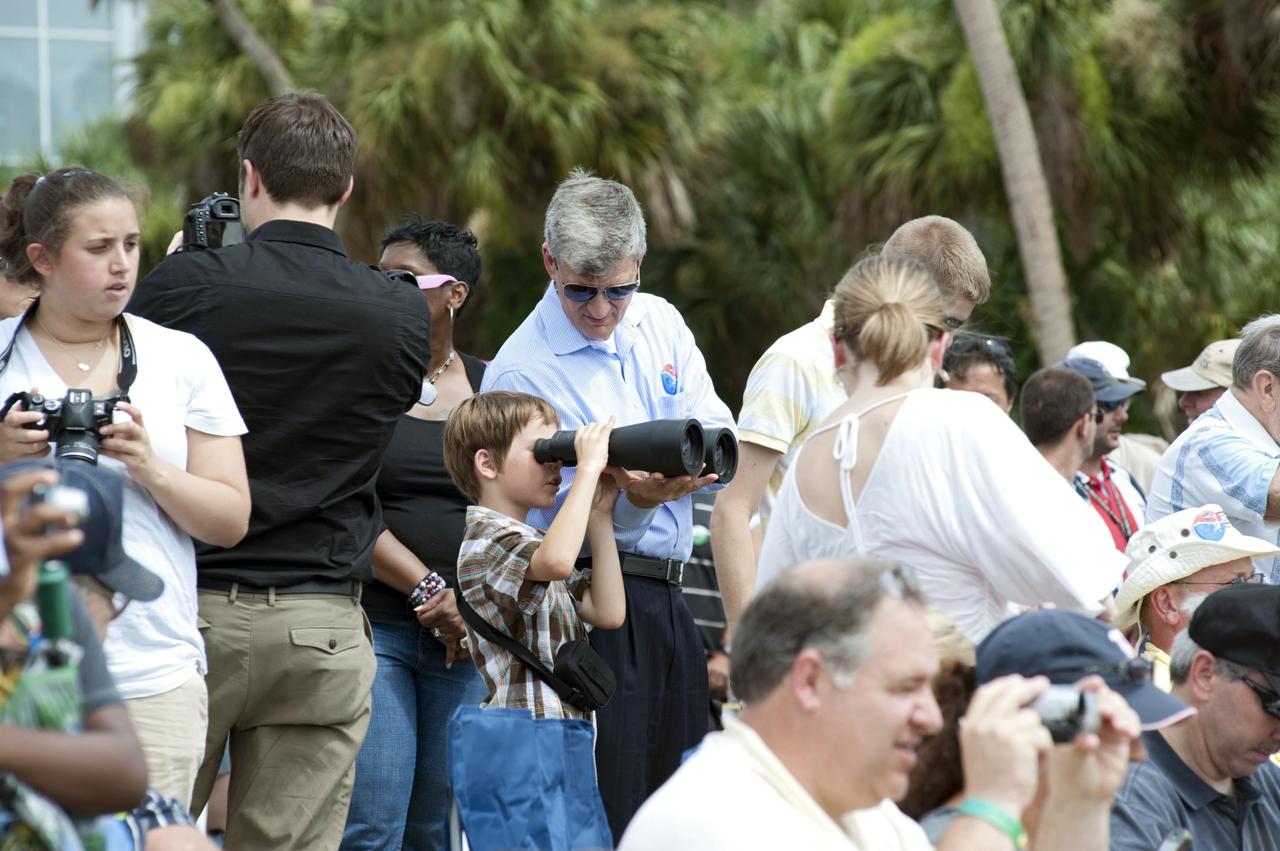

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spectators relax before the launch of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer