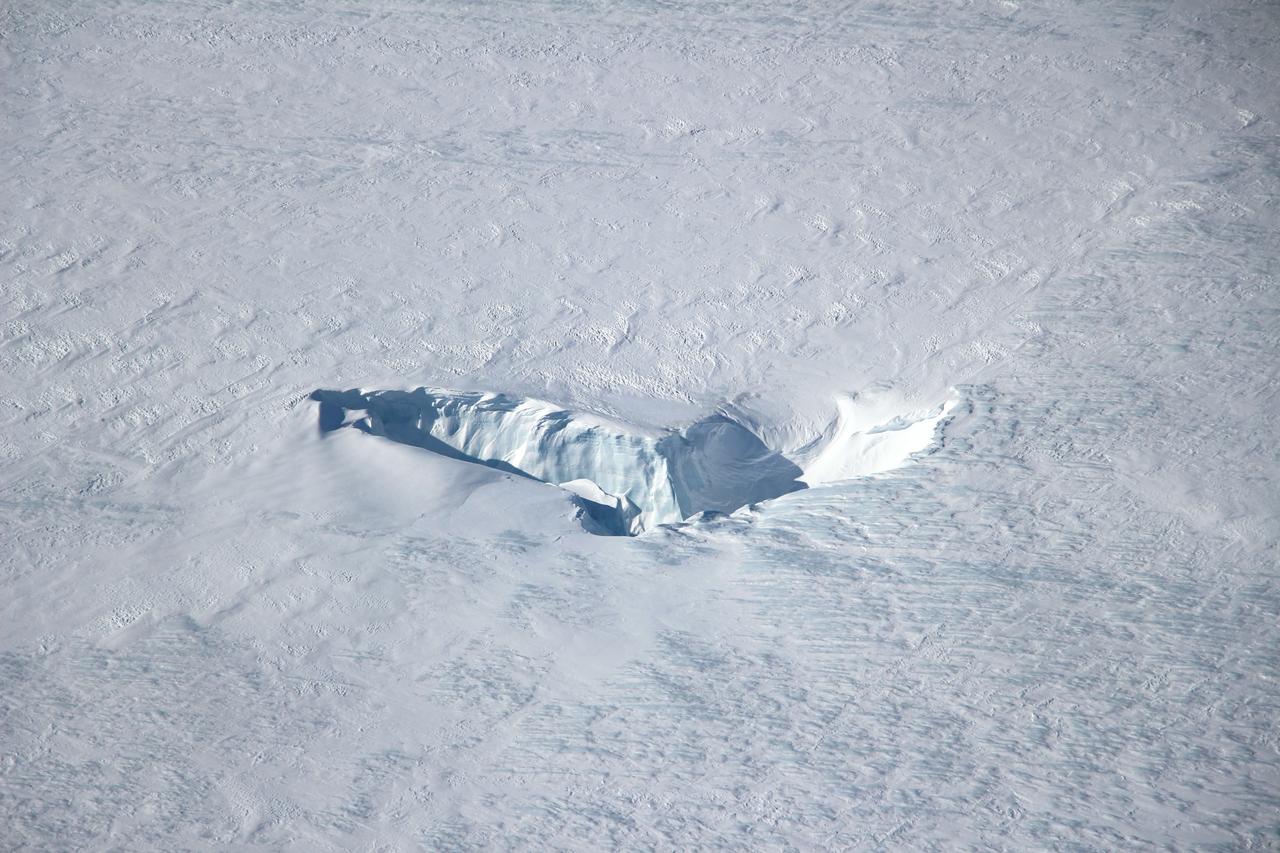

Scientists and crew with NASA’s Operation IceBridge, which makes annual aerial surveys of polar ice, are wrapping up their seventh campaign over the Arctic. In spring 2015, the team began using a different research aircraft—an adapted C-130 Hercules. They also added four new high-priority targets in the rapidly changing region of northeast Greenland. Many of the flights, however, were routine. And that’s exactly the point; making measurements over the same path each year provides continuity between NASA’s Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite (ICESat) missions—the first of which ended in 2009 and the second of which is scheduled for launch in 2017. Repeat measurements show how a landscape changes over time. One area that has been surveyed repeatedly is northern Greenland’s Ryder Glacier. This photograph, taken during the IceBridge flight on May 6, 2015, shows a large moulin—dozens of meters across—atop this glacier. Moulins are holes in the ice sheet that drain melt water from the ice sheet’s surface to the bottom or out to the sea. Scientists are working to figure out what happens to melt water once it enters a moulin. Read more: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=85858&eocn=home&eoci=iotd_title" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=85858&eocn...</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
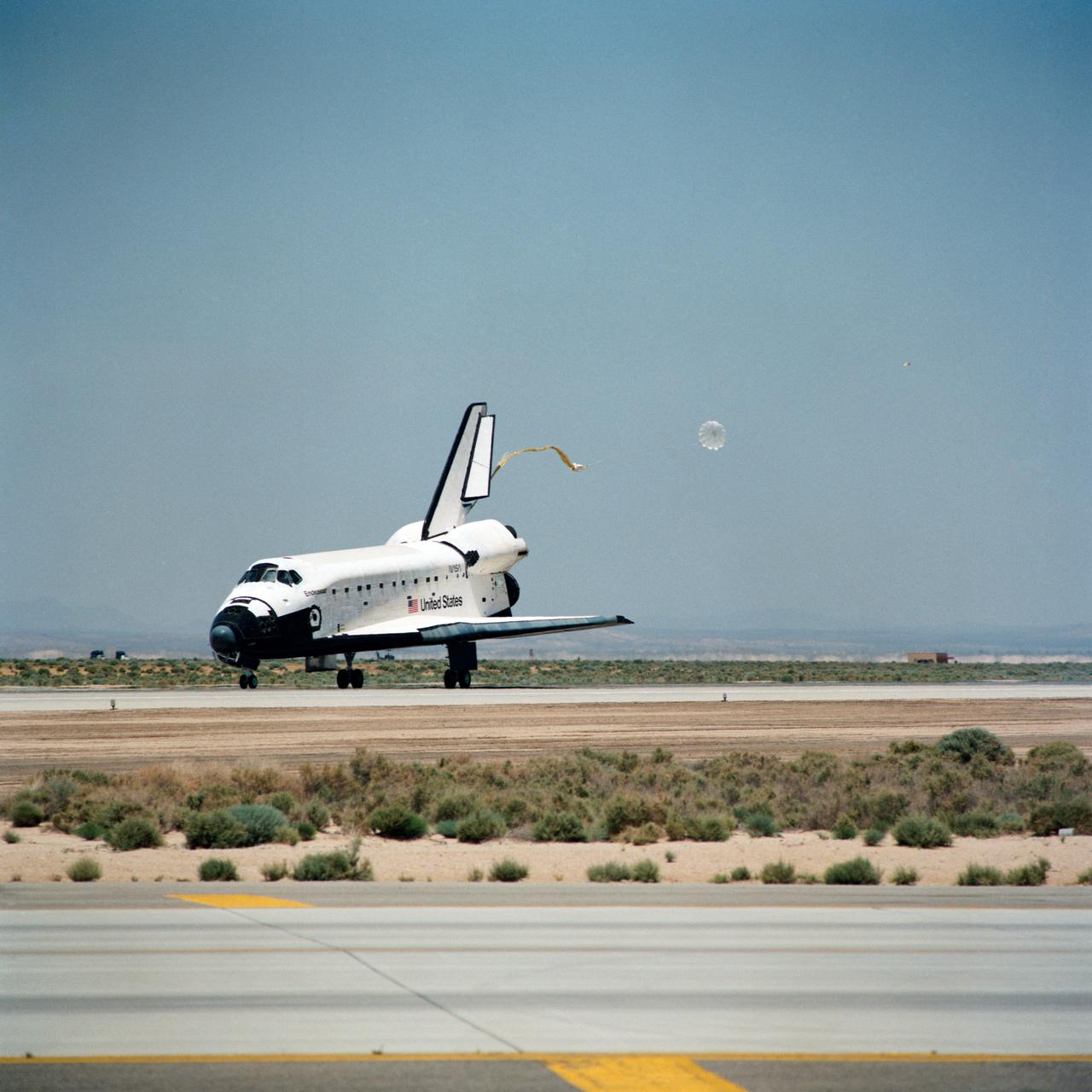

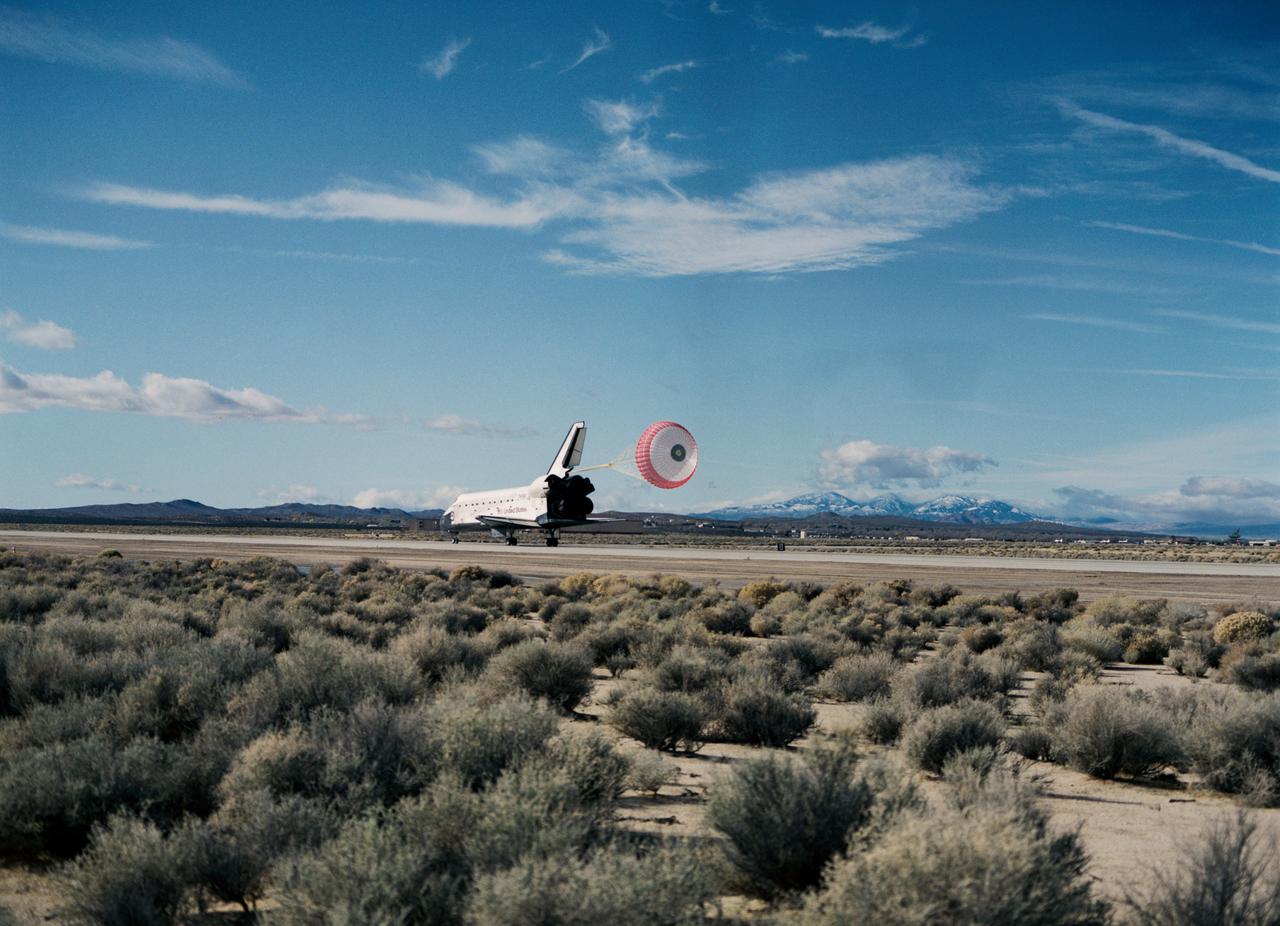
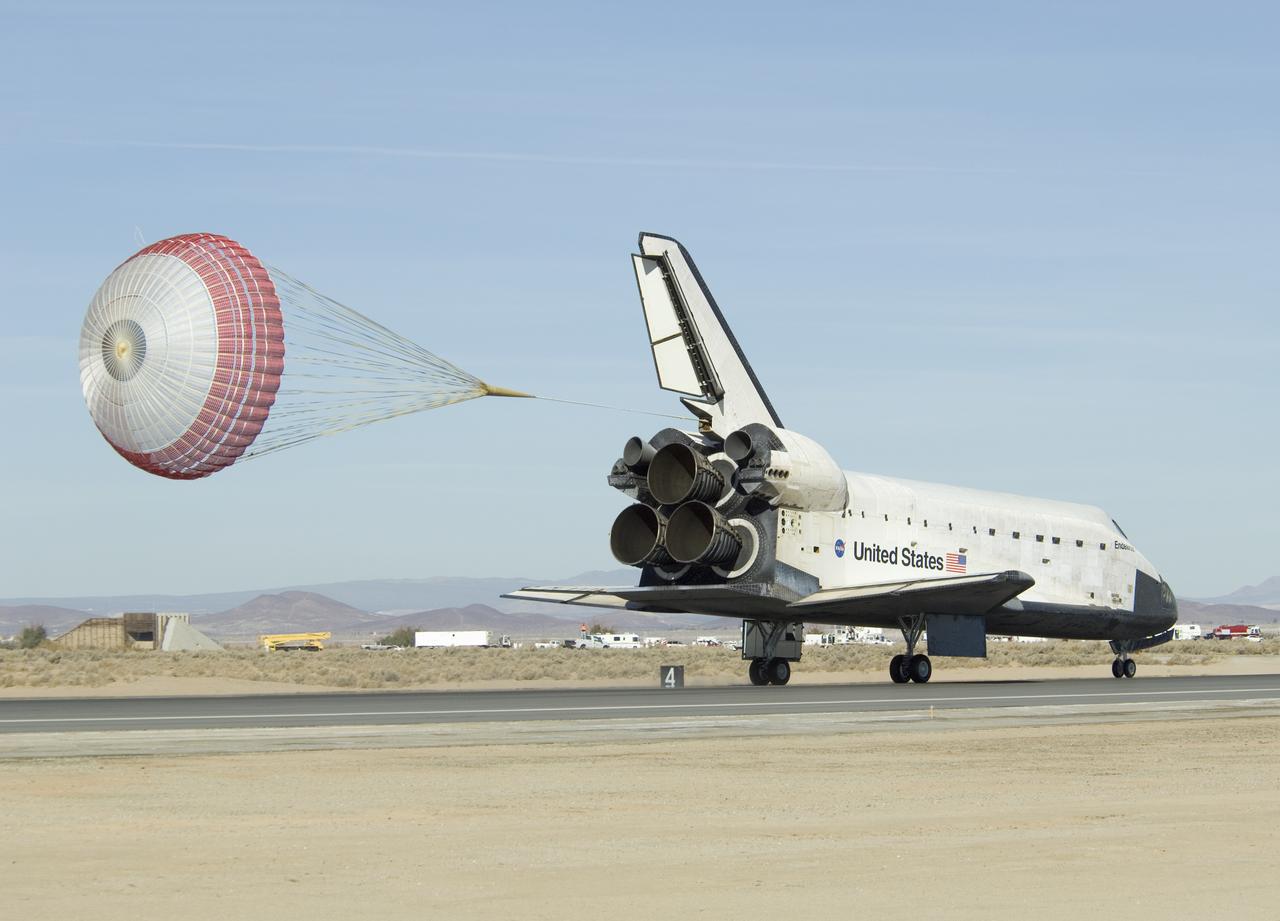
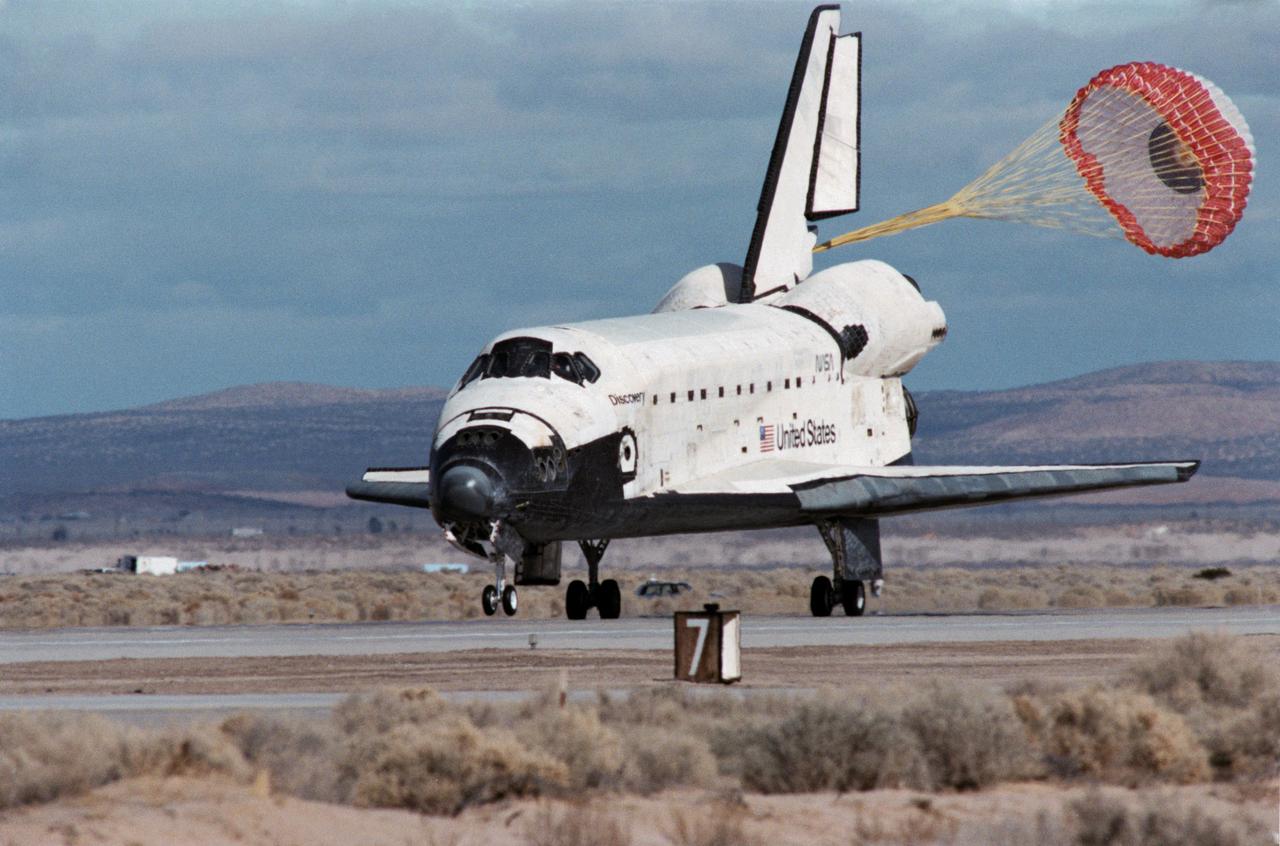
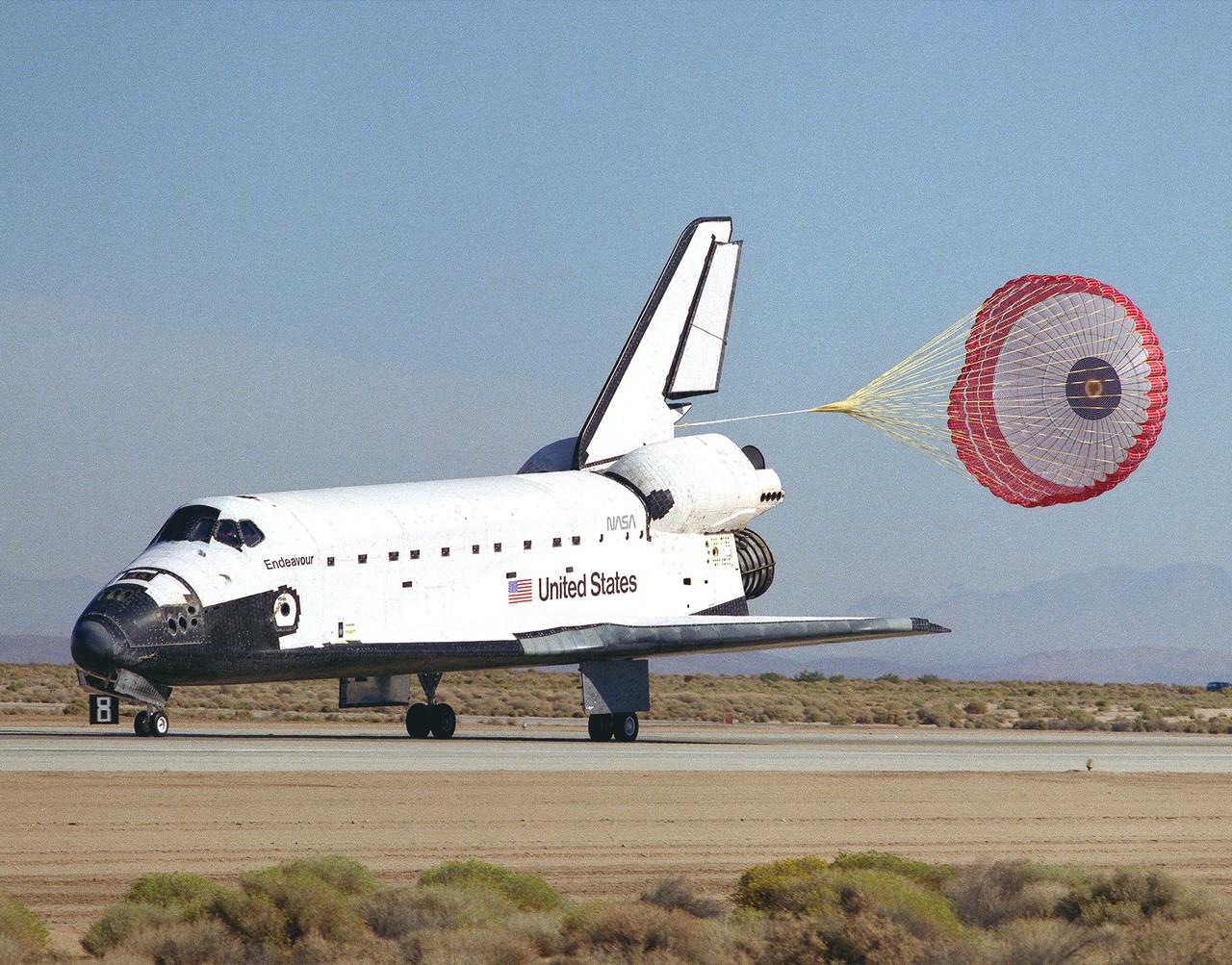
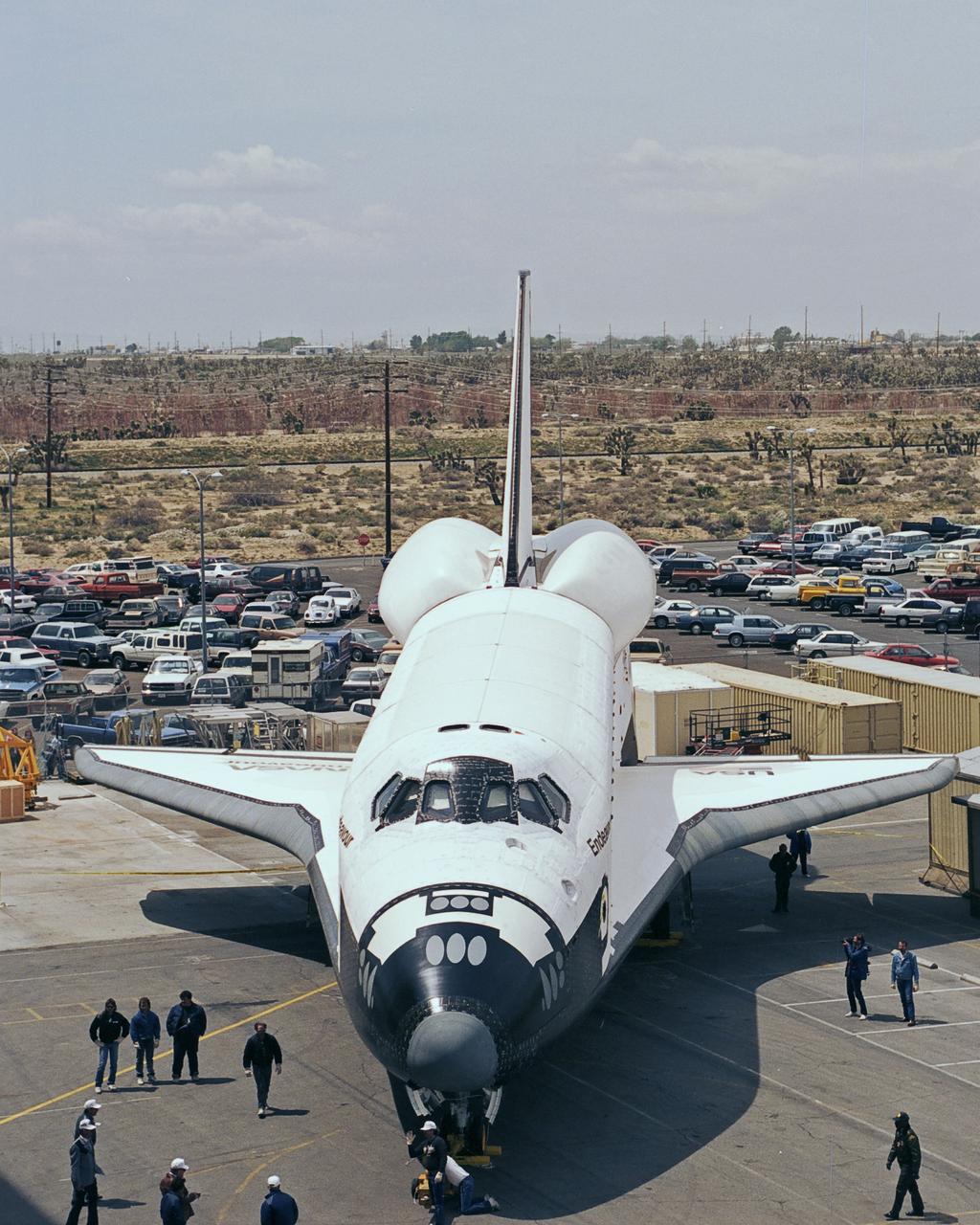
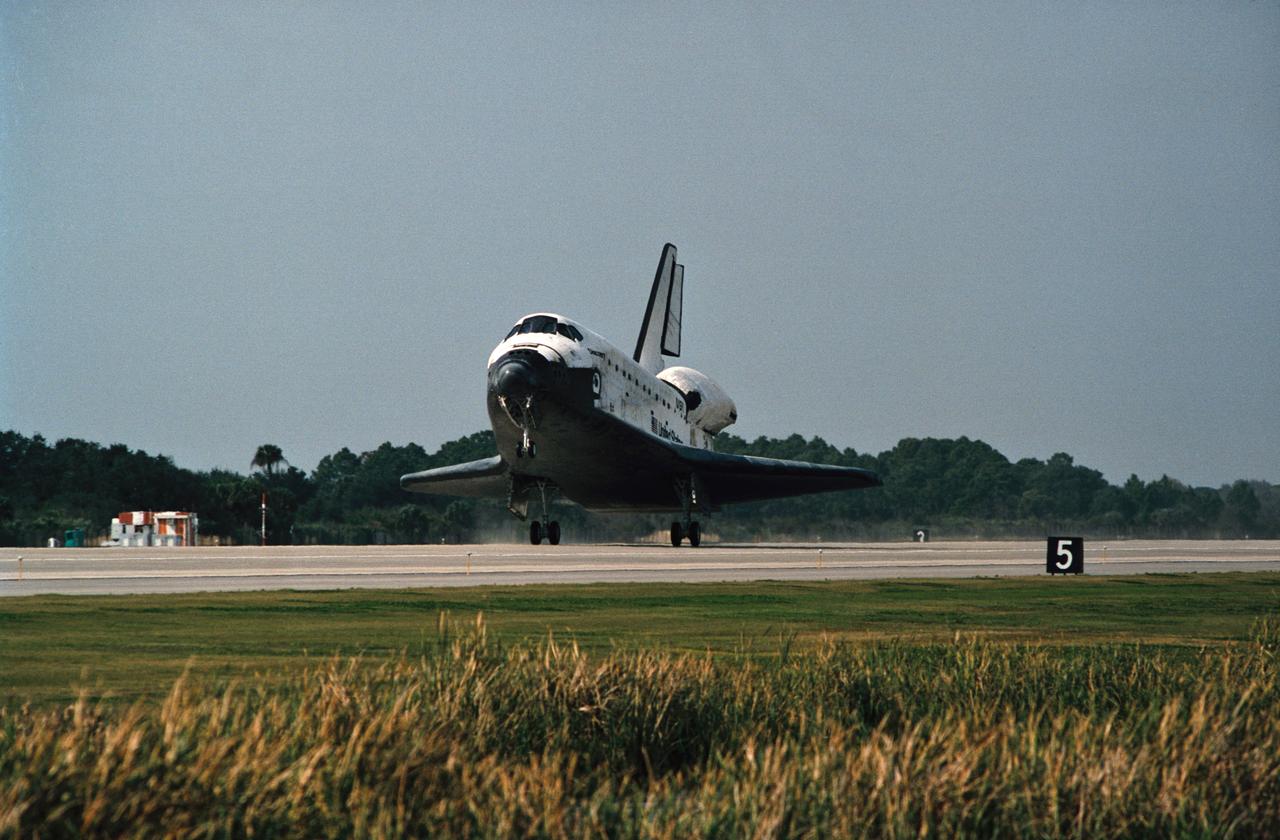
STS049-S-268 (16 May 1992) --- A three-quarter forward view of the Space Shuttle Endeavour making its first landing, following a successful nine-day mission in Earth orbit. The drogue chute precedes the main chute in NASA's first exercise of its detailed test objective (DTO-521) on the drag chute system. Main gear touchdown occurred at 1:57:38 p.m. (PDT), May 16, 1992.
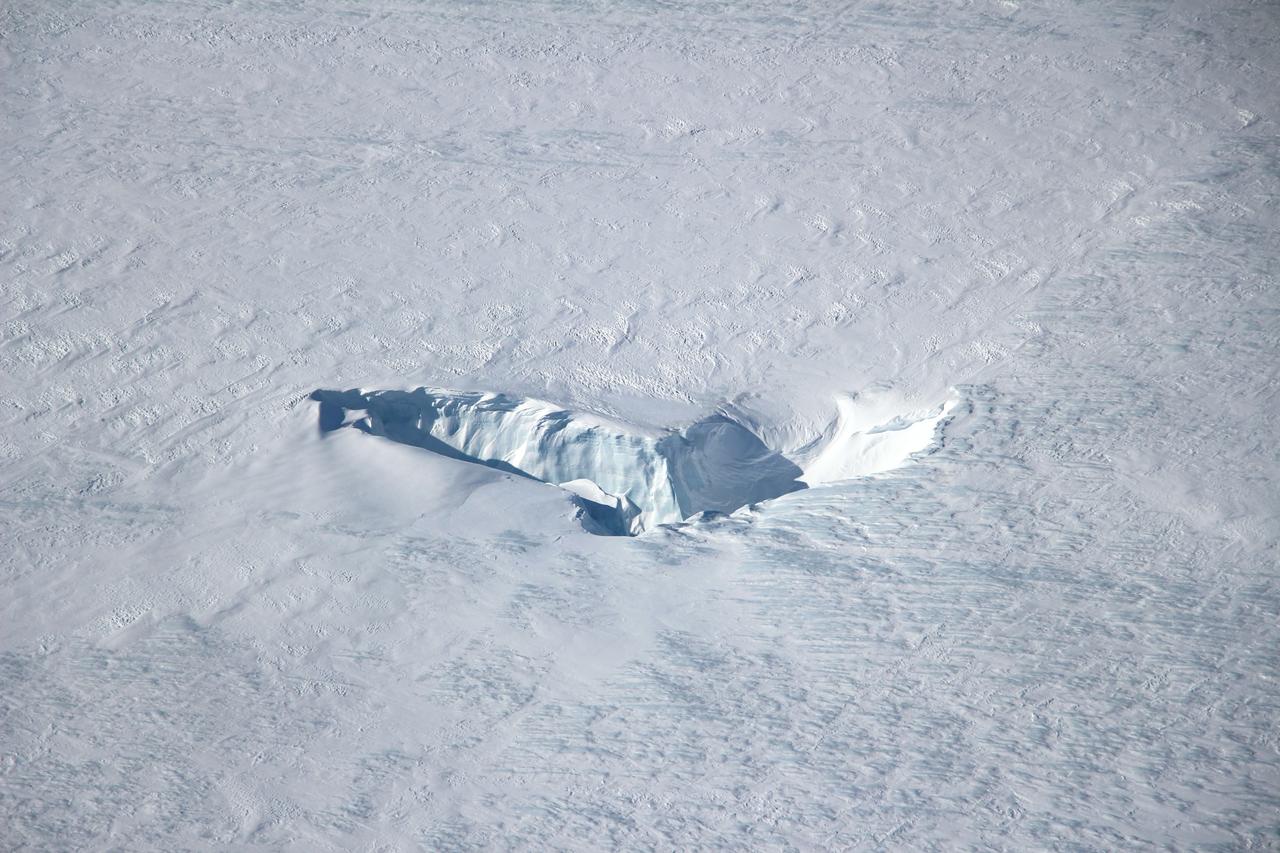

Scientists and crew with NASA’s Operation IceBridge, which makes annual aerial surveys of polar ice, are wrapping up their seventh campaign over the Arctic. In spring 2015, the team began using a different research aircraft—an adapted C-130 Hercules. They also added four new high-priority targets in the rapidly changing region of northeast Greenland. Many of the flights, however, were routine. And that’s exactly the point; making measurements over the same path each year provides continuity between NASA’s Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite (ICESat) missions—the first of which ended in 2009 and the second of which is scheduled for launch in 2017. Repeat measurements show how a landscape changes over time. One area that has been surveyed repeatedly is northern Greenland’s Ryder Glacier. This photograph, taken during the IceBridge flight on May 6, 2015, shows a large moulin—dozens of meters across—atop this glacier. Moulins are holes in the ice sheet that drain melt water from the ice sheet’s surface to the bottom or out to the sea. Scientists are working to figure out what happens to melt water once it enters a moulin.
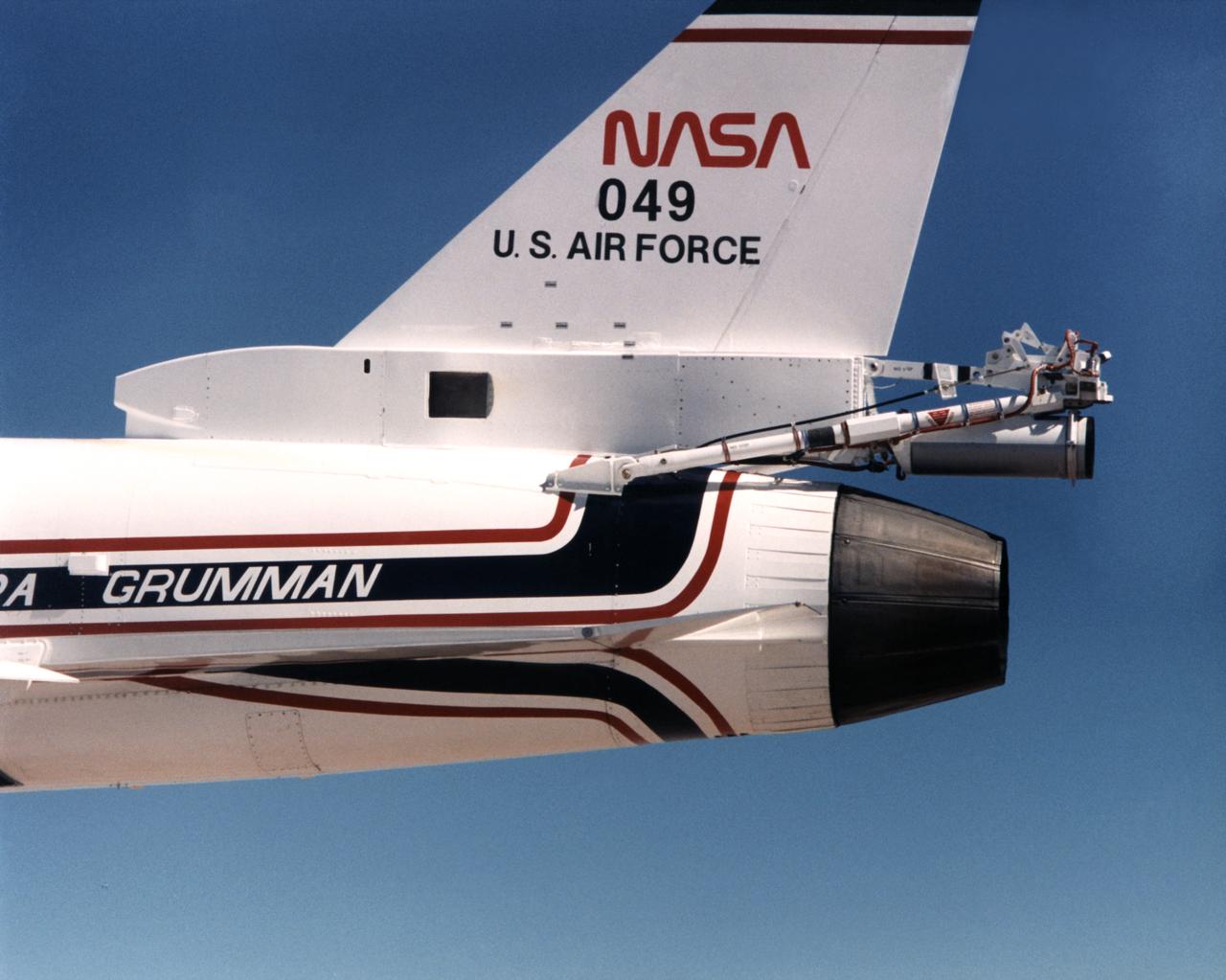

Because the number two X-29 at NASA's Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later the Dryden Flight Research Center) flew at higher angles of attack than the number one aircraft, it required a spin chute system for safety. The system deployed a parachute for recovery of the aircraft if it inadvertently entered an uncontrolled spin. Most of the components of the spin chute system were located on a truss at the aft end of the aircraft. In addition, there were several cockpit modifications to facilitate use of the chute. The parachute was made of nylon and was of the conical ribbon type.

STS049-S-301 (16 May 1992) --- A three-quarter aft view of the Space Shuttle Endeavour making its first landing, following a successful nine-day mission in Earth orbit. Fully deployed here is the main chute in NASA's first exercise of its detailed test objective (DTO-521) on the drag chute system. Main gear touchdown occurred at 1:57:38 p.m. (PDT), May 16, 1992.
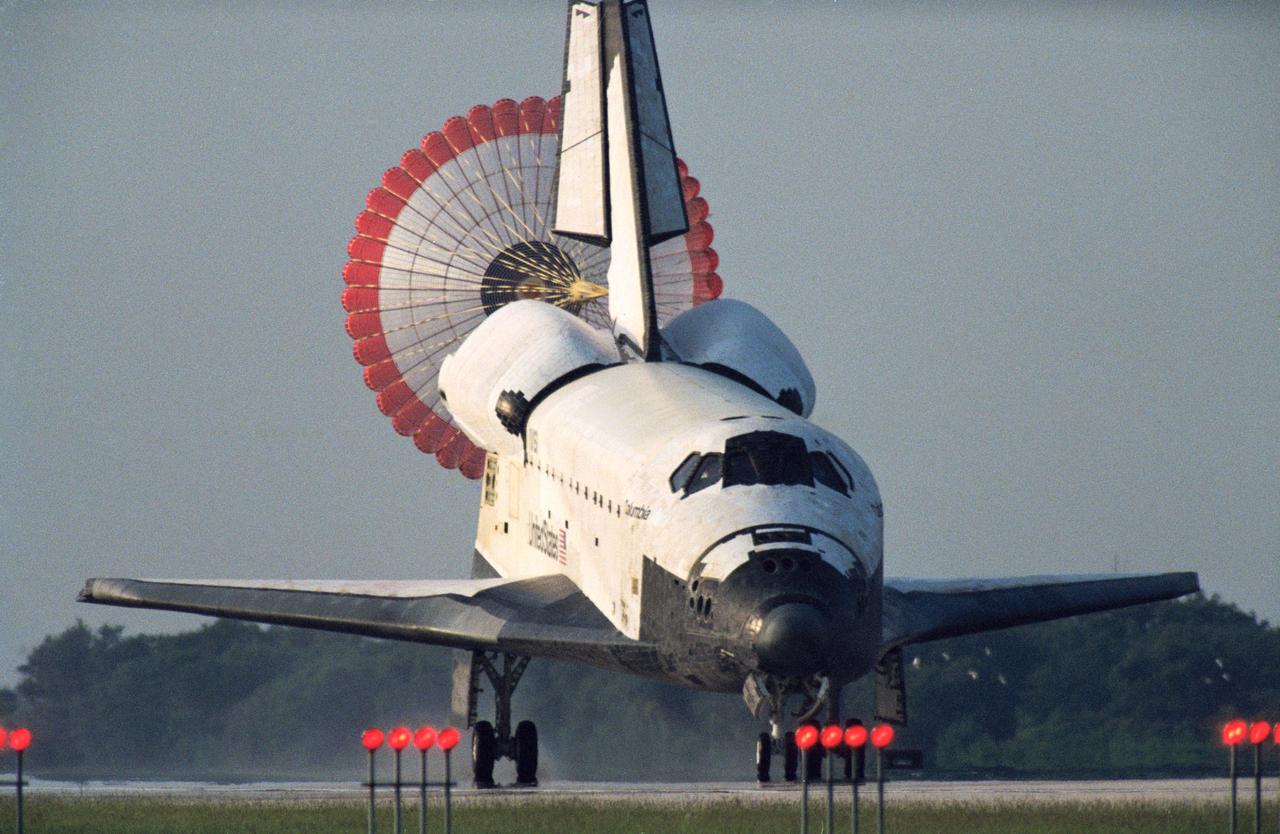

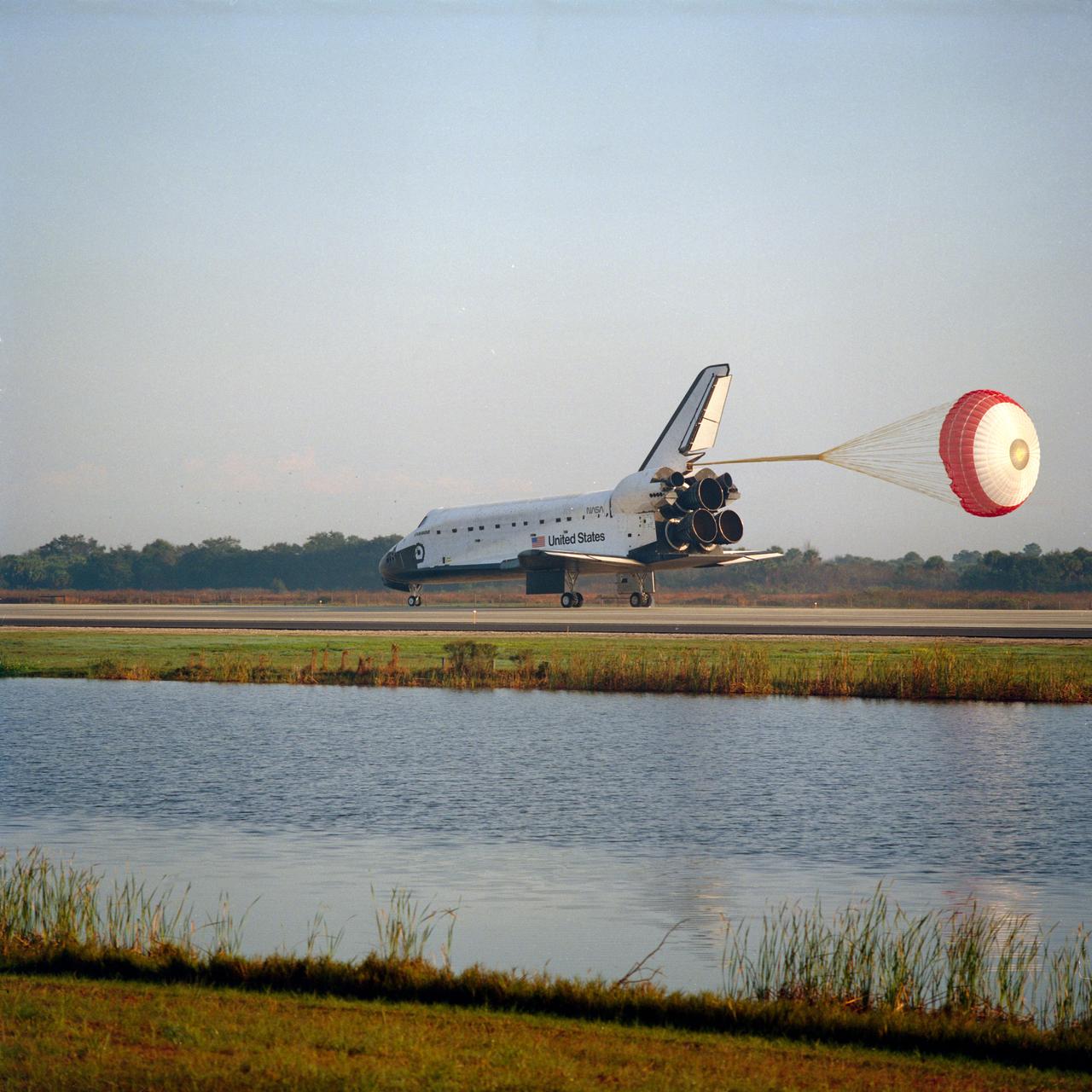
STS050-S-105 (9 July 1992) --- The main drag chute on the Space Shuttle Columbia is fully deployed soon after the Space Shuttle touches down at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) landing facility. Landing occurred at 7:42 a.m. (EDT). Seven crew members, including five astronauts and two scientists from the private sector spent 14 days in space supporting the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1). This marks the first time for usage of the parachute system for a KSC landing and the second occurrence in the program.

S69-20364 (13 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 spacecraft, with astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart aboard, approaches touchdown in the Atlantic recovery area to conclude a successful 10-day Earth-orbital space mission. Splashdown occurred at 12:00:53 p.m. (EST), March 13, 1969, only 4.5 nautical miles from the prime recovery ship, USS Guadalcanal.
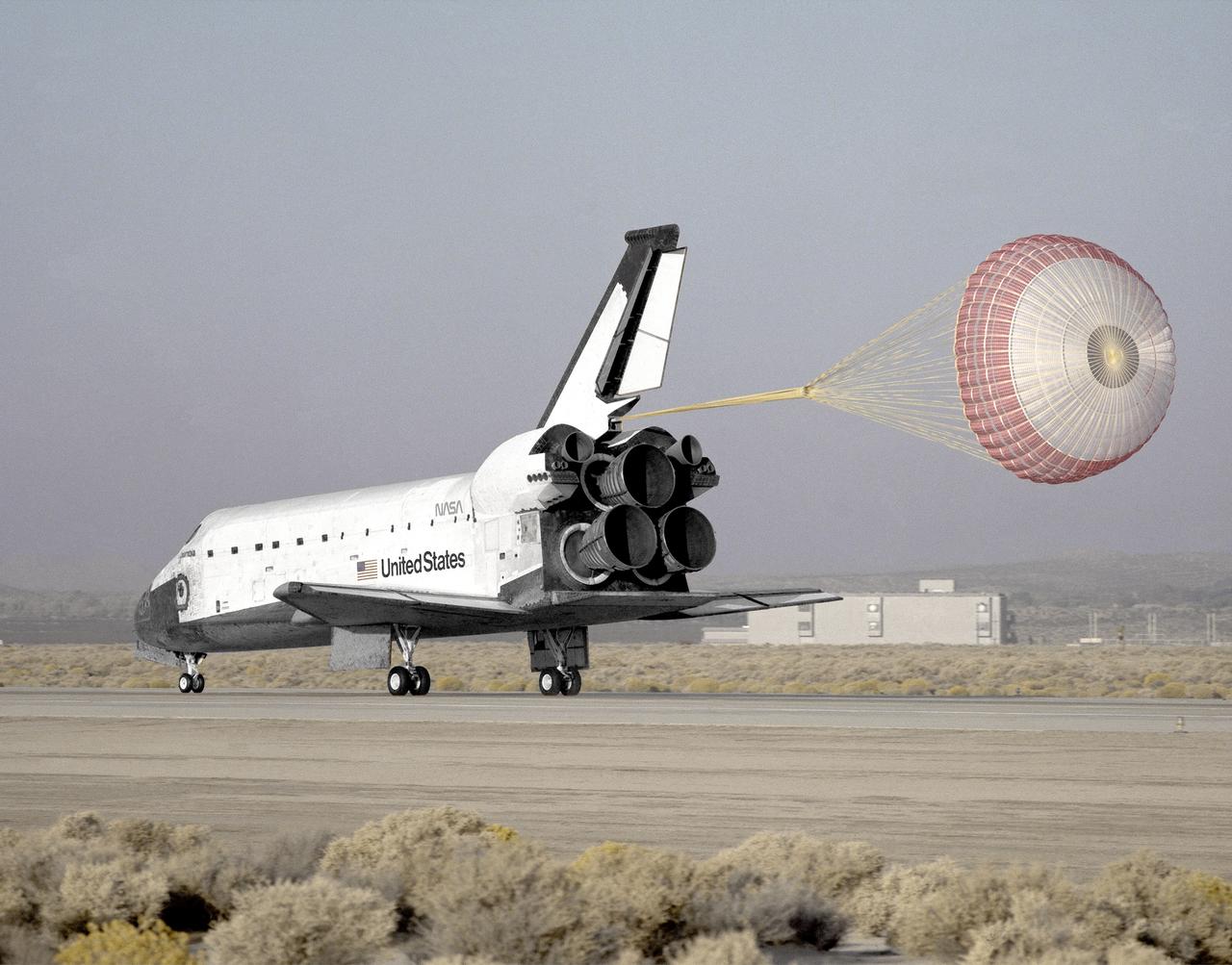

A drag chute slows the space shuttle Columbia as it rolls to a perfect landing concluding NASA's longest mission at that time, STS-58, at the Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California, with a 8:06 a.m. (PST) touchdown 1 November 1993 on Edward's concrete runway 22. The planned 14 day mission, which began with a launch from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 7:53 a.m. (PDT), October 18, was the second spacelab flight dedicated to life sciences research. Seven Columbia crewmembers performed a series of experiments to gain more knowledge on how the human body adapts to the weightless environment of space. Crewmembers on this flight included: John Blaha, commander; Rick Searfoss, pilot; payload commander Rhea Seddon; mission specialists Bill MacArthur, David Wolf, and Shannon Lucid; and payload specialist Martin Fettman.
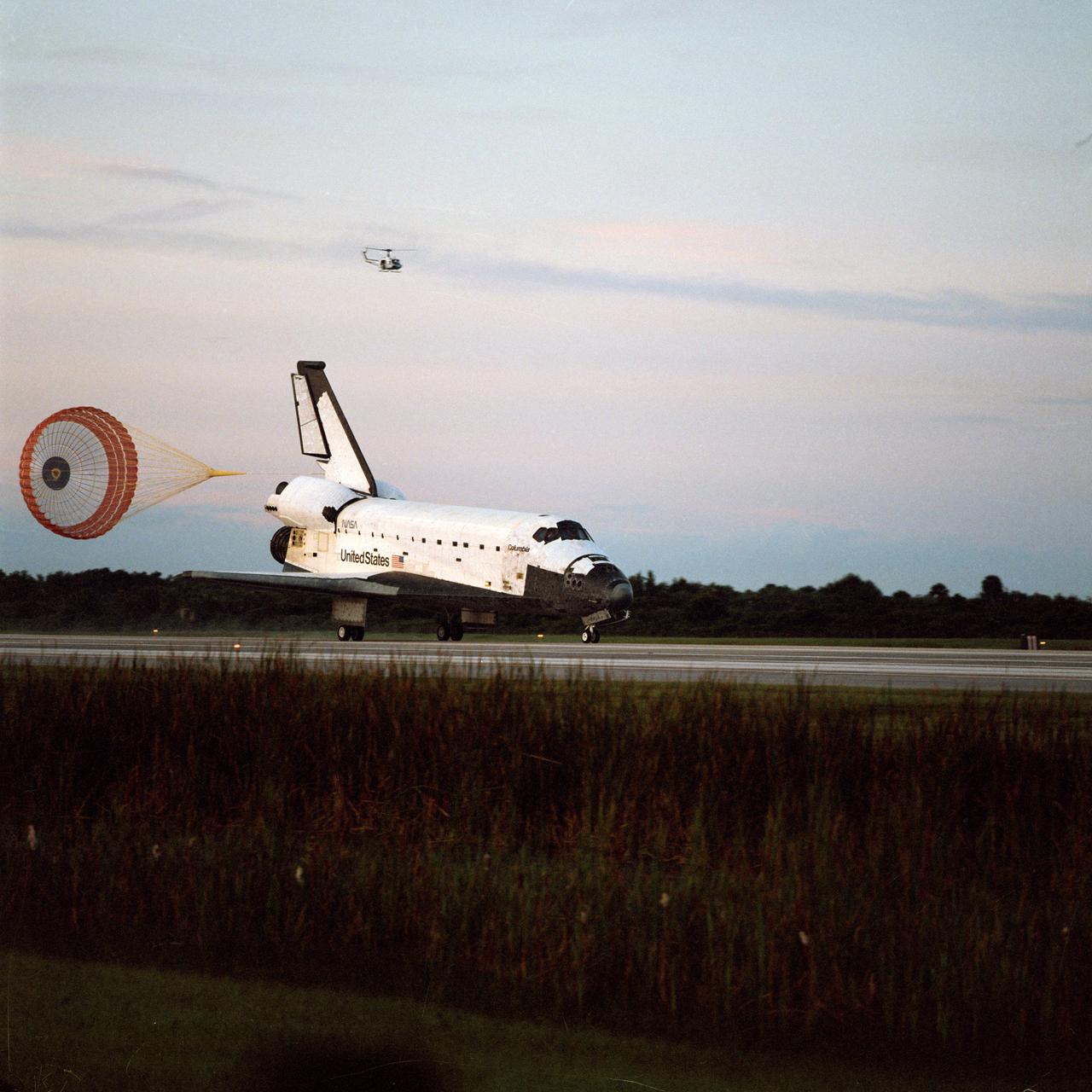

The Space Shuttle Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, its drag chute fully deployed, completes a record duration mission as it lands on Runway 33 at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF). A helicopter flying overhead observes as OV-102's nose landing gear (NLG) and main landing gear (MLG) roll along the runway. Landing occurred at 6:38 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). STS-65 mission duration was 14 days 17 hours and 56 minutes. Onboard were six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist who conducted experiments in support of the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) during the mission.
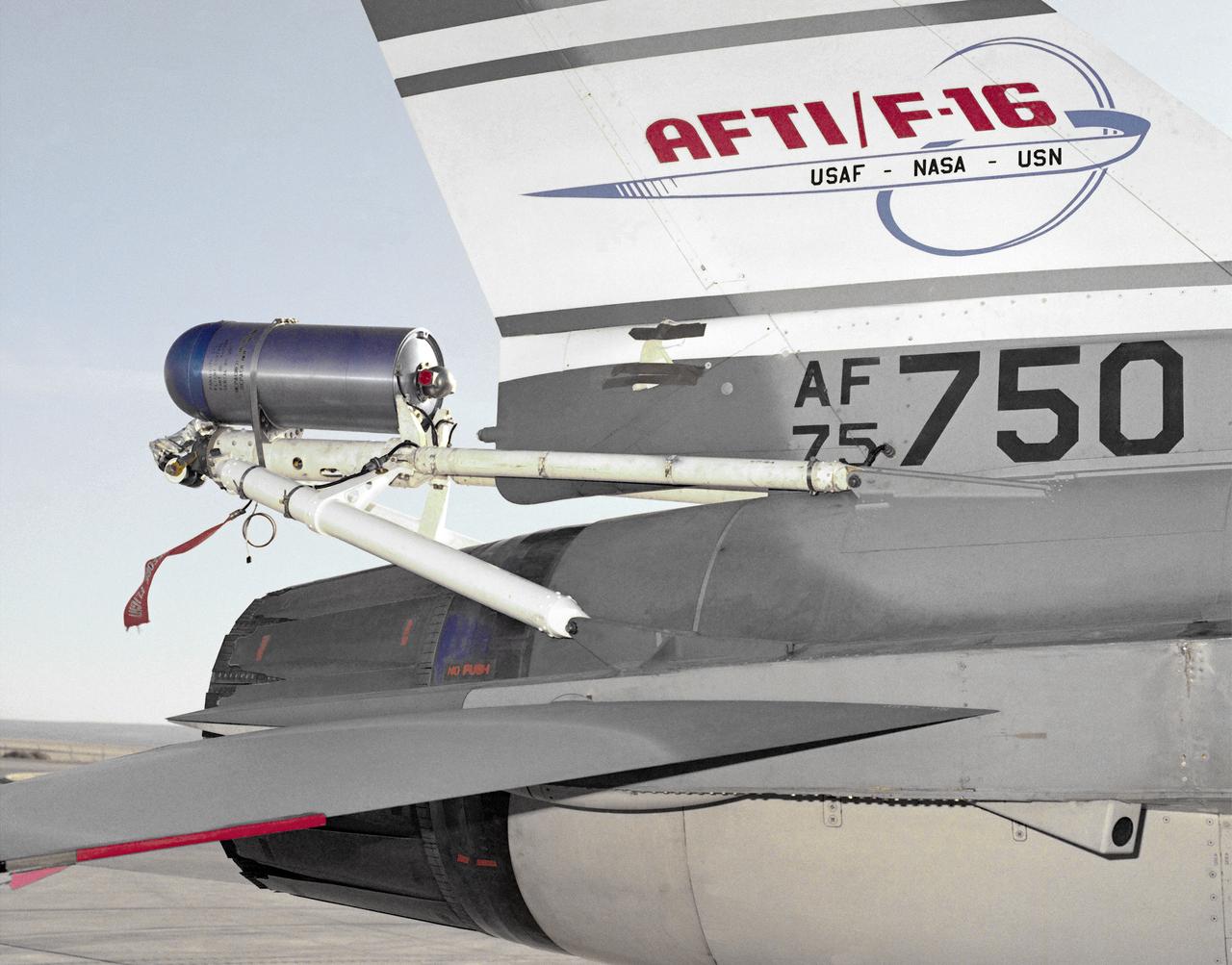

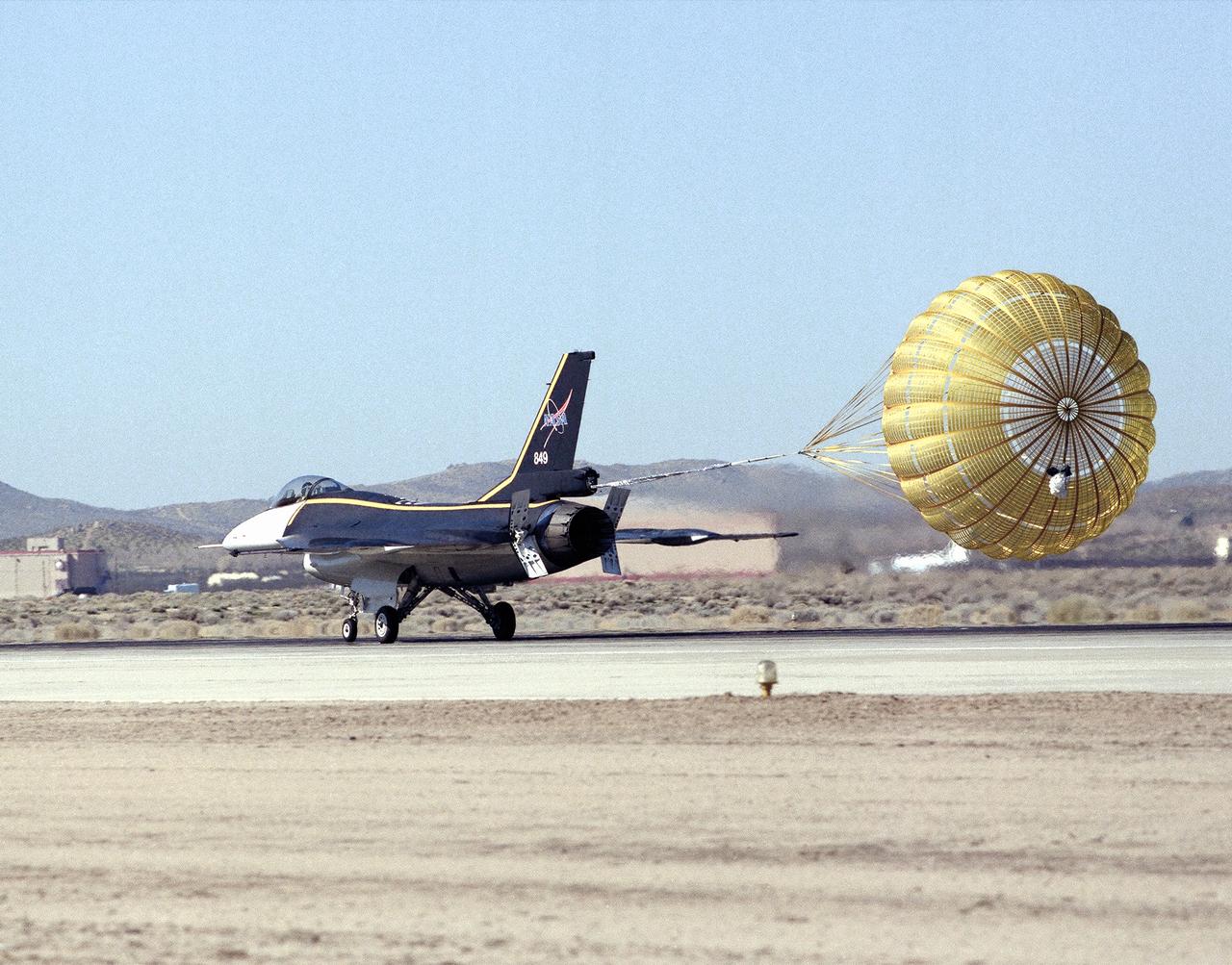
A close-up photo of the spin chute mounted on the rear fuselage of the AFTI F-16, a safety device designed to prevent the loss of aircraft in spin conditions. Under some circumstances, pilots cannot recover from spins using normal controls. It these instances, the spin chute is deployed, thus "breaking" the spin and enabling the pilot to recover. The spin chute is held in a metal cylinder attached to the AFTI F-16 by four tubes, a structure strong enough to withstand the shock of the spin chute opening. Unlike the air probe in the last photo, spin chutes are not standard equipment on research or prototype aircraft but are commonly attached expressly for actual spin tests.
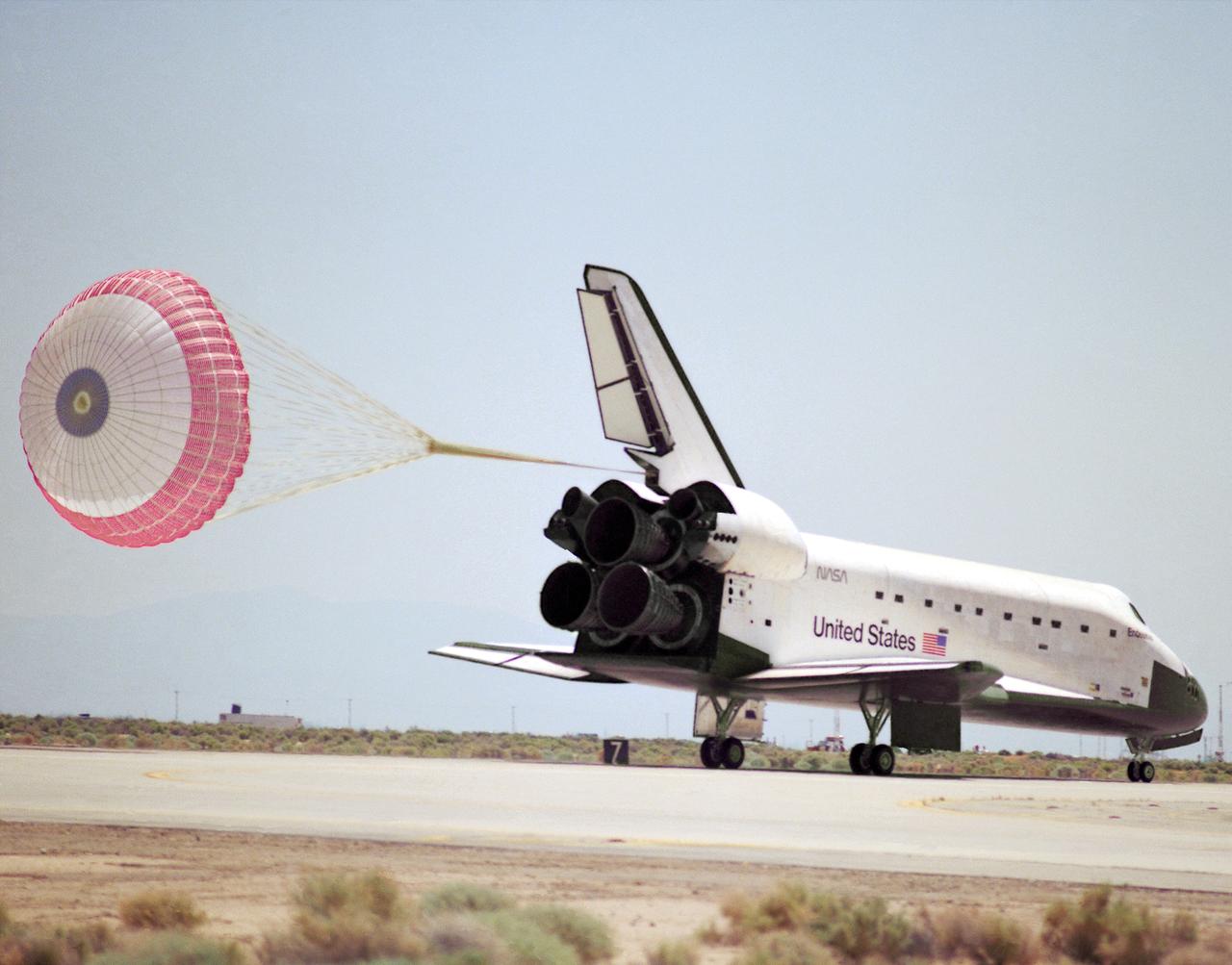

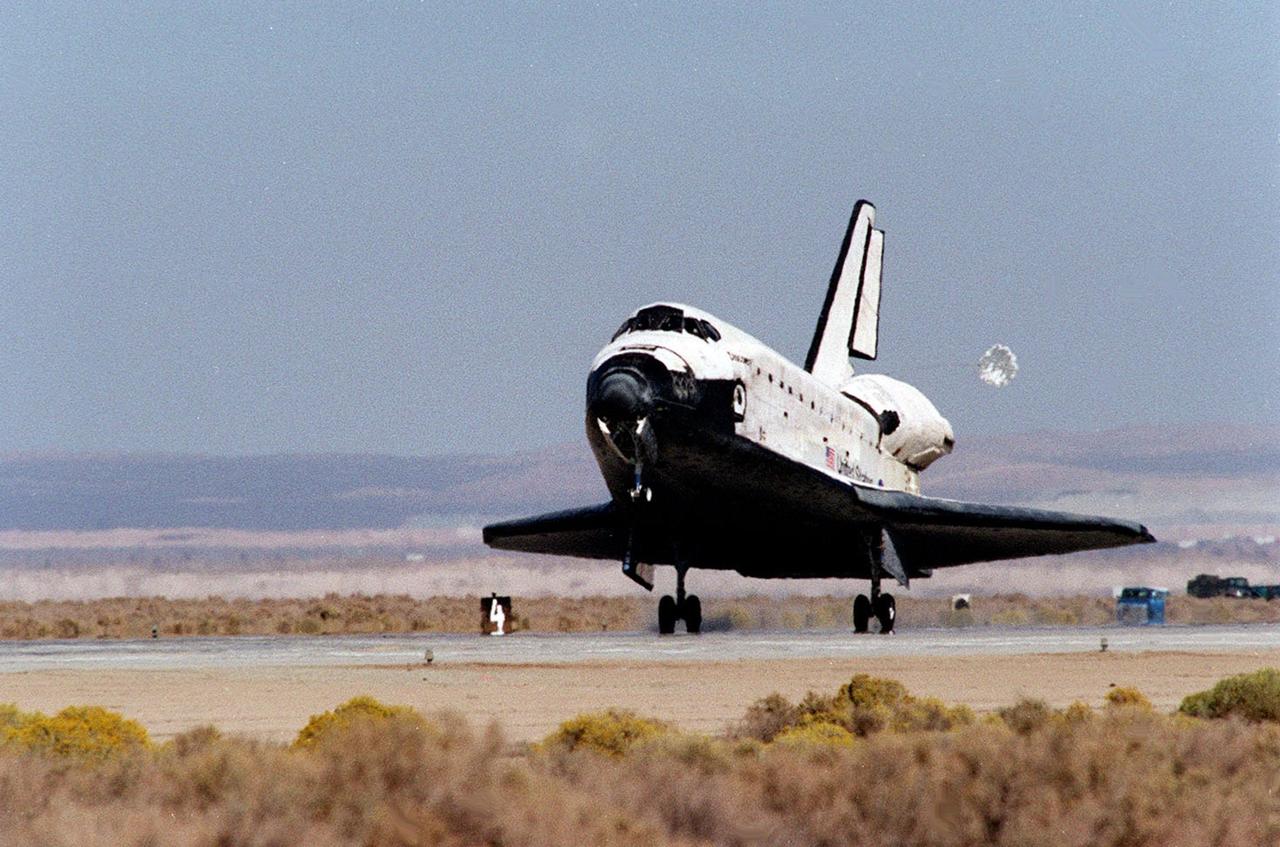
The Space Shuttle Endeavour concludes mission STS-49 at NASA's Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later redesignated Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California, with a 1:57 p.m. (PDT) landing May 16 on Edward's concrete runway 22. The planned 7-day mission, which began with a launch from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 4:41 p.m. (PFT), 7 May, was extended two days to allow extra time to rescue the Intelsat VI satellite and complete Space Station assembly techniques originally planned. After a perfect rendezvous in orbit and numerous attempts to grab the satellite, space walking astronauts Pierre Thuot, Rick Hieb and Tom Akers successfully rescued it by hand on the third space walk with the support of mission specialists Kathy Thornton and Bruce Melnick. The three astronauts, on a record space walk, took hold of the satellite and directed it to the shuttle where a booster motor was attached to launch it to its proper orbit. Commander Dan Brandenstein and Pilot Kevin Chilton brought Endeavours's record setting maiden voyage to a perfect landing at Edwards with the first deployment of a drag chute on a shuttle mission.

The space shuttle Atlantis lands with its drag chute deployed on runway 22 at Edwards, California, to complete the STS-66 mission dedicated to the third flight of the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science-3 (ATLAS-3), part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth program. The astronauts also deployed and retrieved a free-flying satellite designed to study the middle and lower thermospheres and perform a series of experiments covering life sciences research and microgravity processing. The landing was at 7:34 a.m. (PST) 14 November 1994, after being waved off from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida, due to adverse weather.

The Space Shuttle Atlantis' drag chute deploys as it rolls out on Runway 22 at Edwards AFB at the conclusion of its 13-day STS-117 mission to the ISS.
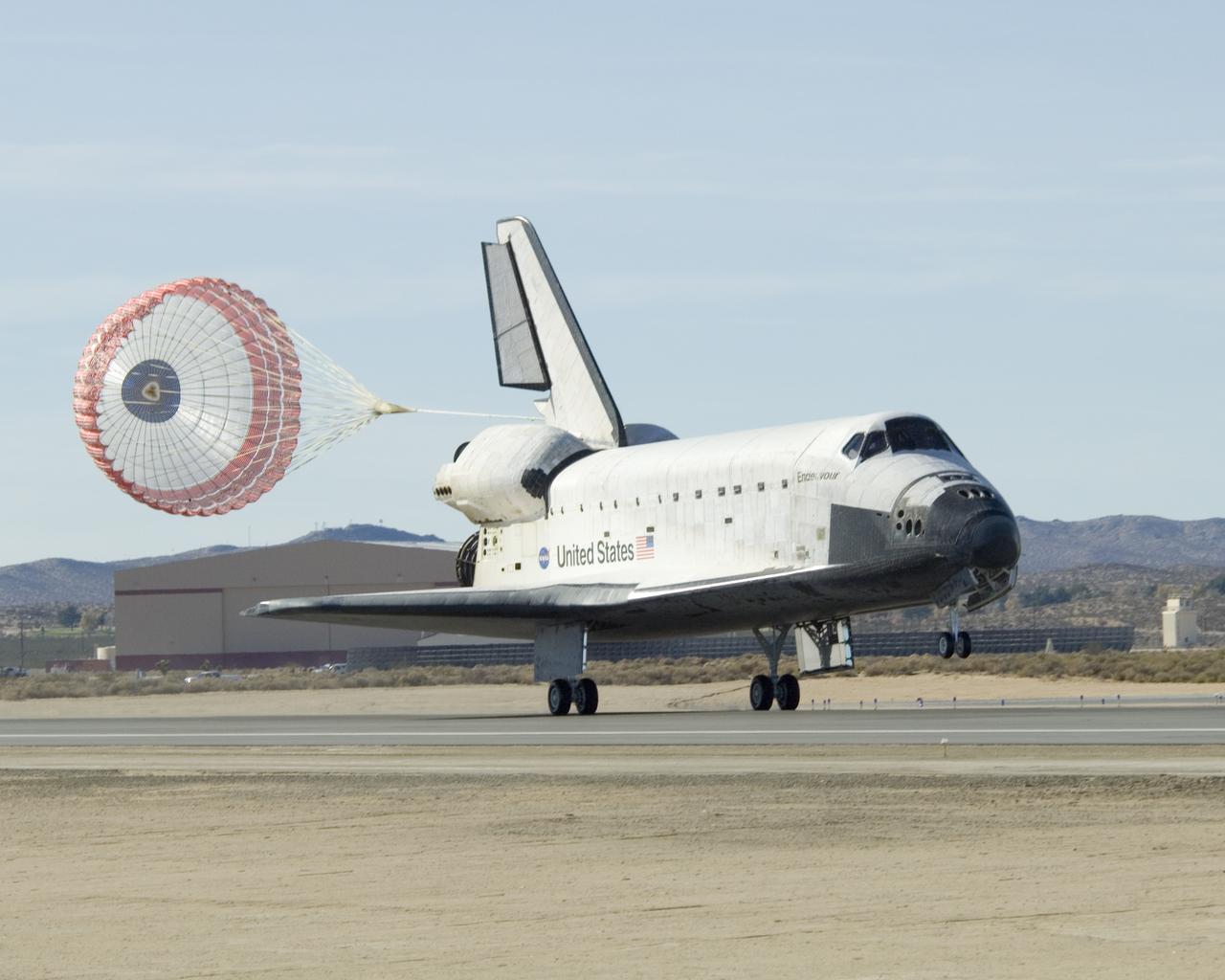

Space Shuttle Endeavour's drag chute deploys as it rolls down Runway 04-L at Edwards AFB moments after landing on Nov. 30, 2008.

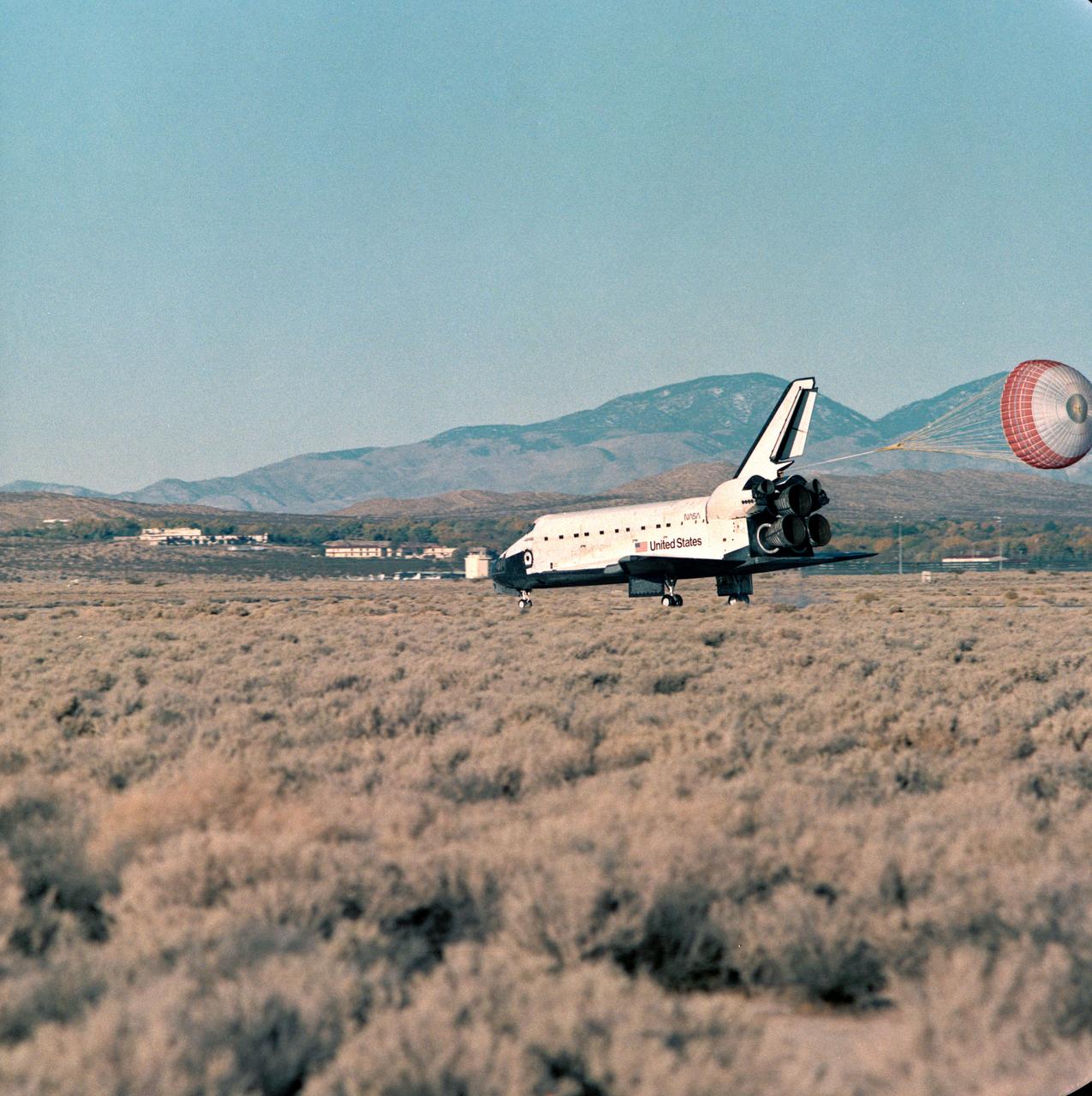
STS060-S-035 (11 Feb 1994) --- The drag chute for Space Shuttle Discovery is deployed on the Shuttle Landing Facility, marking an end to the eight-day STS-60 mission. Landing occurred at 2:19:22 p.m. (EST). Onboard were astronauts Charles F. Bolden Jr., Kenneth S. Reightler Jr., Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, N. Jan Davis and Ronald M. Sega along with Russian cosmonaut Sergei K. Krikalev.
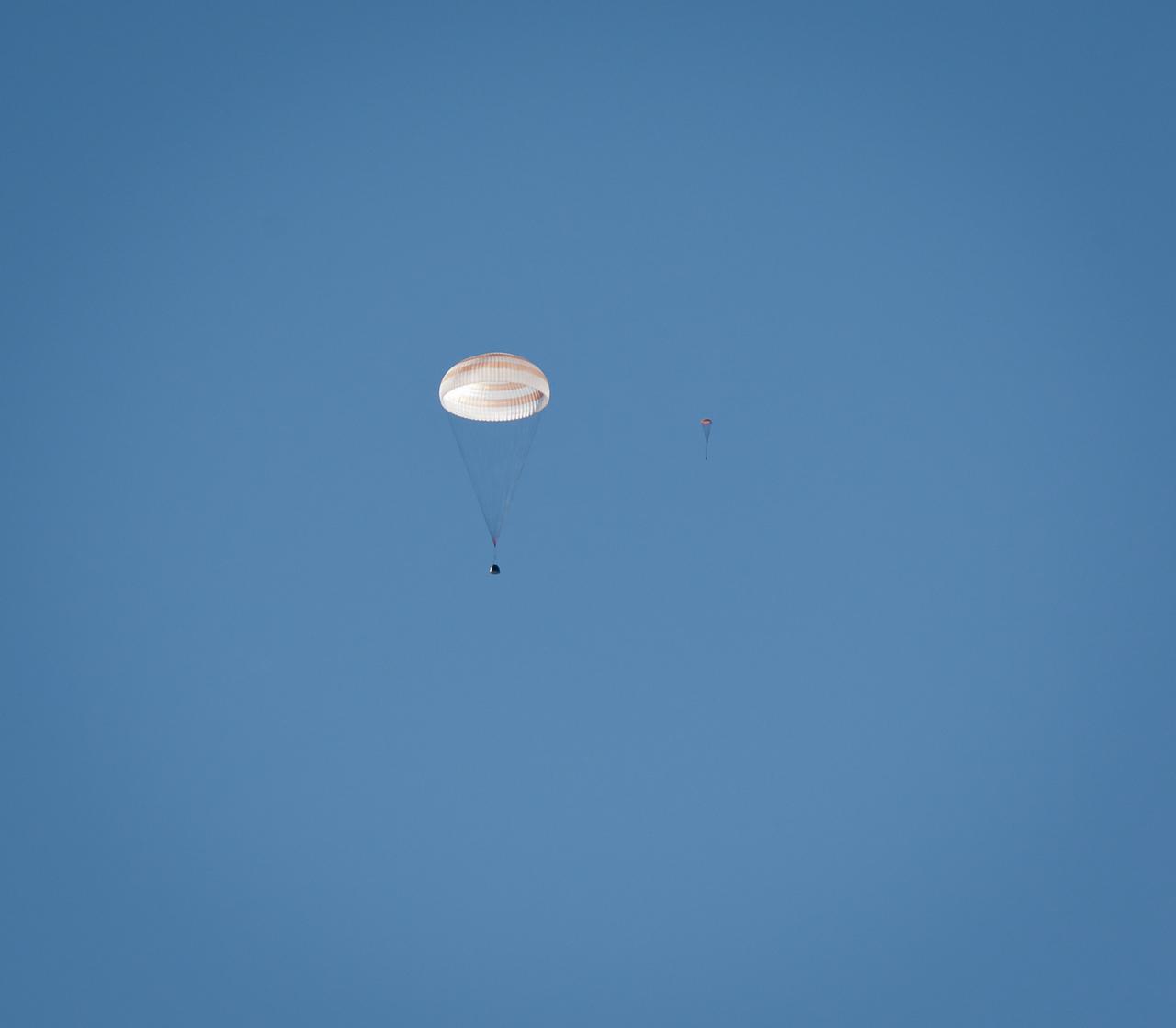

The Soyuz TMA-21 spacecraft and the drogue chute are seen during the landing with Expedition 28 Commander Andrey Borisenko, and Flight Engineers Ron Garan, and Alexander Samokutyaev in a remote area outside of the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan, on Friday, Sept. 16, 2011. NASA Astronaut Garan, Russian Cosmonauts Borisenko and Samokutyaev are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 27 and 28 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

STS-53 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is slowed by a red, white, and blue drag chute during its landing on concrete runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base (EAFB), California. Main landing gear (MLG) touchdown occurred at 12:43:17 pm (Pacific Standard Time (PST)). This aft view of OV-103 shows the drag chute deployed from its compartment at the base of the vertical tail, the speedbrake/rudder flaps open, and the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs). Both MLG and nose landing gear (NLG) ride along the runway surface. Desert scrub brush appears in the foreground and mountains are seen in the background.
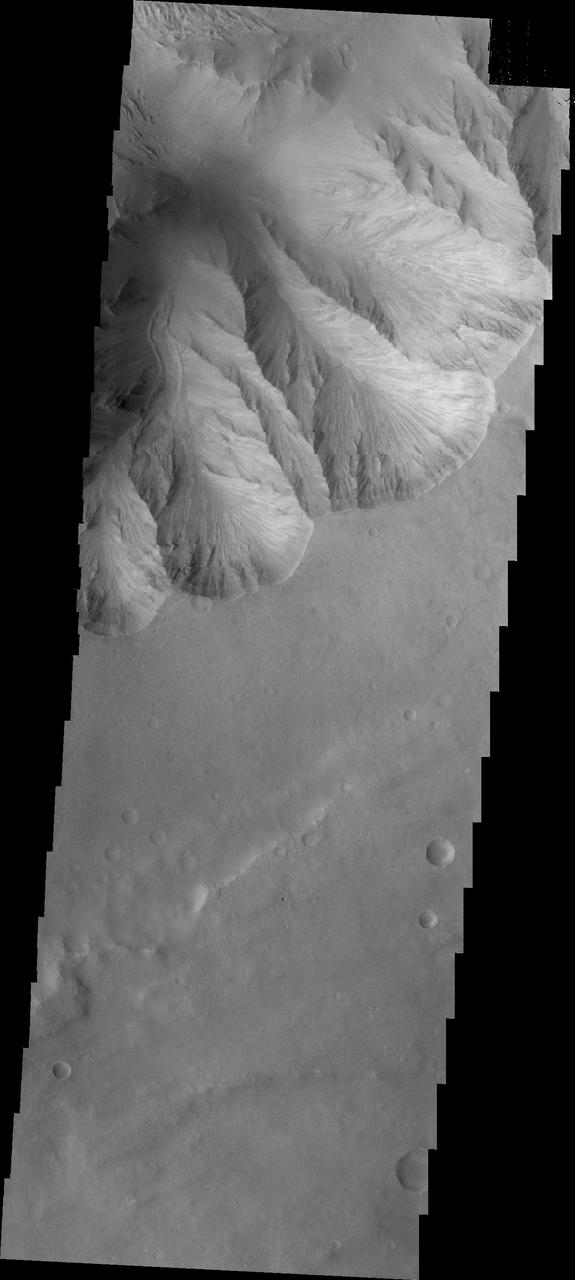

This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows a small landslide chute and deposit. This feature is located on the easternmost end of Candor Chasma.

NASA's single-seat F-16XL makes a drag chute landing on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base in California's Mojave Desert. The aircraft was most recently used in the Cranked-Arrow Wing Aerodynamics Project (CAWAP) to test boundary layer pressures and distribution. Previously it had been used in a program to investigate the characteristics of sonic booms for NASA's High Speed Research Program. Data from the program will be used in the development of a high speed civilian transport. During the series of sonic boom research flights, the F-16XL was used to probe the shock waves being generated by a NASA SR-71 and record their shape and intensity.
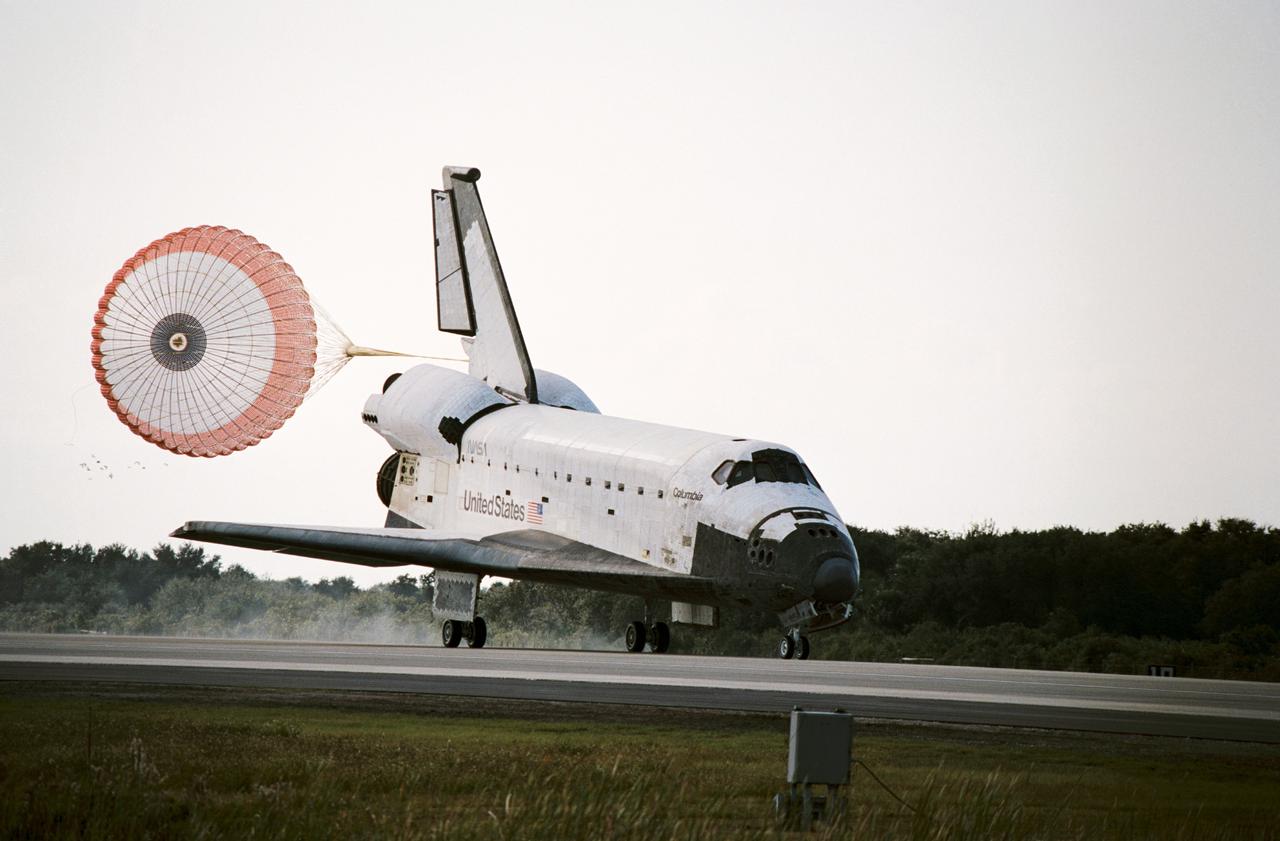

STS052-S-099 (1 Nov. 1992) --- This three-quarter front view shows the Space Shuttle Columbia just after deployment of the drag chute during landing at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility. Onboard were a crew of five NASA astronauts and a Canadian payload specialist. Landing occurred at 9:05:53 a.m. (EST), November 1, 1992. Crewmembers are astronauts James D. Wetherbee, Michael A. Baker, Tamara E. Jernigan, Charles L. (Lacy) Veach and William M. Shepherd along with payload specialist Steven G. MacLean. The photo was taken with a 35mm camera.
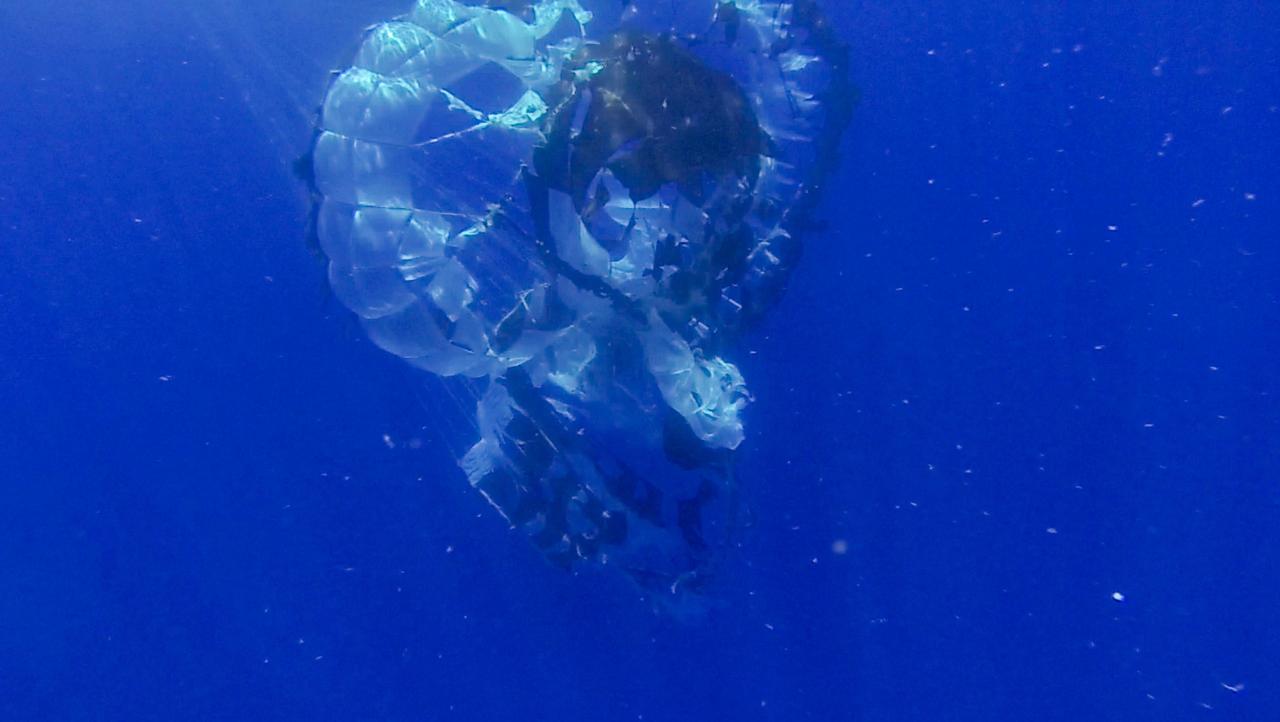

Tears are visible in the parachute from NASA Supersonic Disk Sail Parachute, which did not deploy as expected. The photo was obtained by Navy divers during recovery of the LDSD test vehicle and parachute.

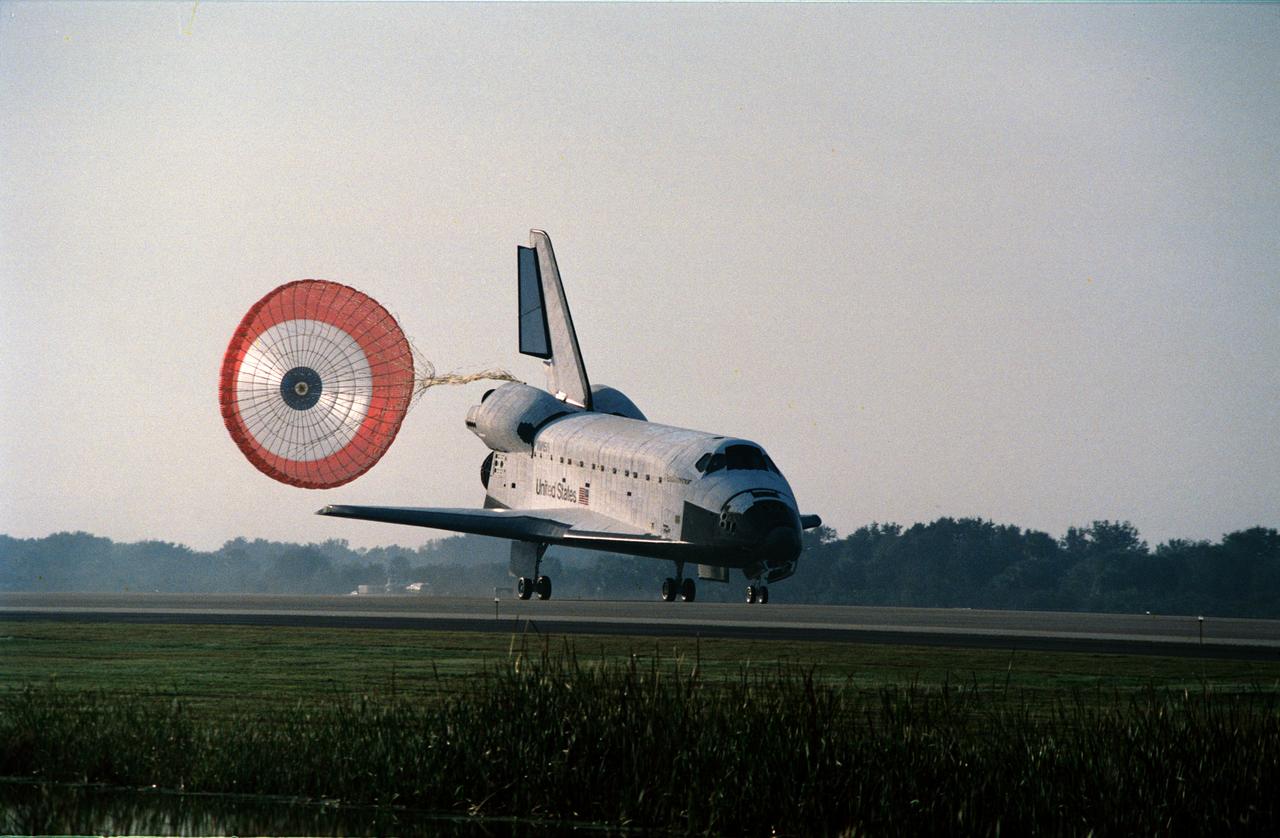
STS054-S-100 (19 Jan 1993) --- The drag chute is fully deployed as the Space Shuttle Endeavour rolls toward wheelstop at KSC's Shuttle landing facility. Landing occurred at 8:38 a.m. (EST), Jan. 19, 1993. Onboard for the six-day mission were astronauts John H. Casper, mission commander, Donald R. McMonagle, pilot, Gregory J. Harbaugh, Mario Runco Jr. and Susan J. Helms, mission specialists.

STS054-S-101 (19 Jan 1993) --- The drag chute is just about to be released as the Space Shuttle Endeavour rolls toward wheelstop at KSC's Shuttle landing facility. Landing occurred at 8:38 a.m. (EST), Jan. 19, 1993. Onboard for the six-day mission were astronauts John H. Casper, mission commander, Donald R. McMonagle, pilot, Gregory J. Harbaugh, Mario Runco Jr. and Susan J. Helms, mission specialists.

Space Shuttle Endeavour's drag chute streams behind as it rolls down on Runway 04-L at Edwards AFB to conclude mission STS-126 on Nov. 30, 2008.

The Space Shuttle Endeavour's drag chute deploys to slow the orbiter as it rolls out on Runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base at the conclusion of its 14-day STS-111 mission to the International Space Station.

The Space Shuttle Endeavour's drag chute deploys to slow the orbiter as it rolls out on Runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base at the conclusion of its 14-day STS-111 mission to the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers prepare a parachute for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
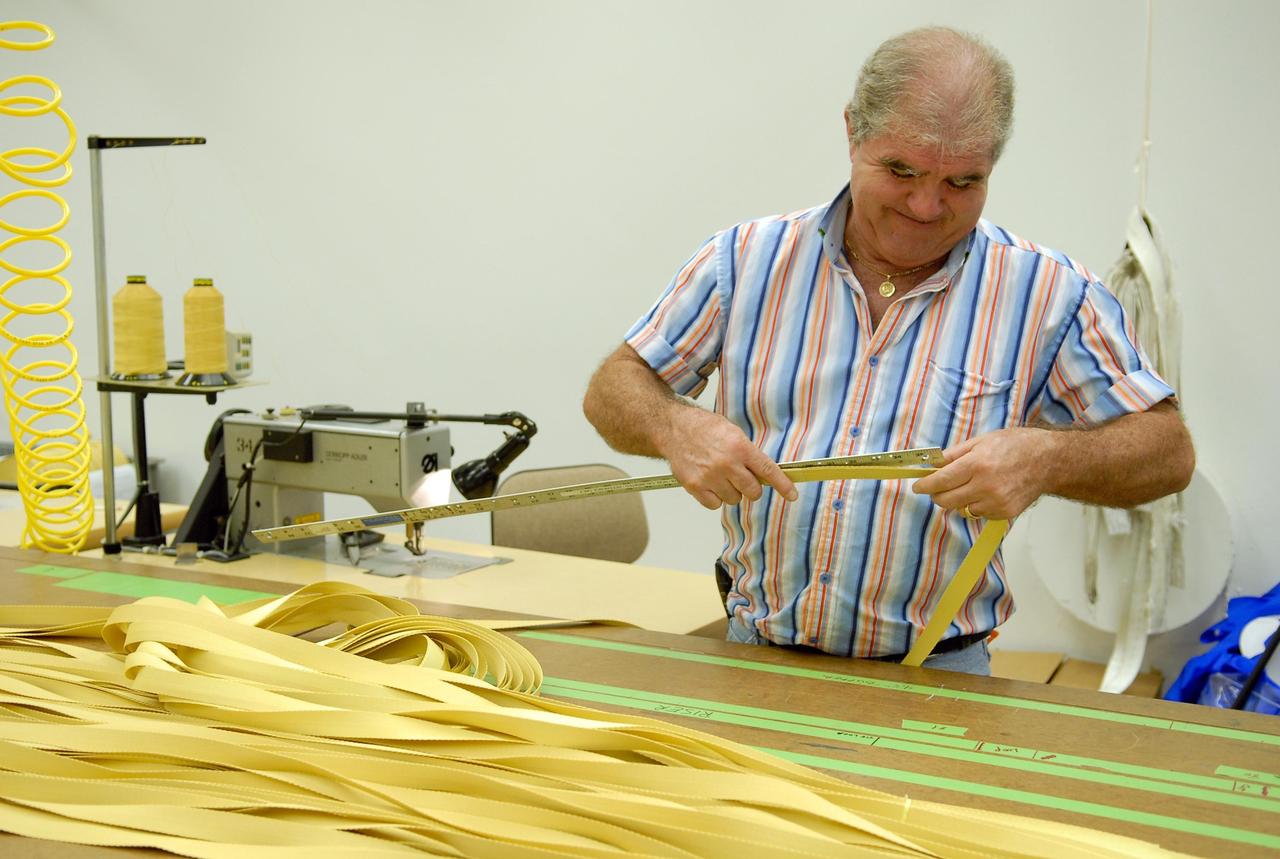

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker measures straps for parachutes being prepared for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
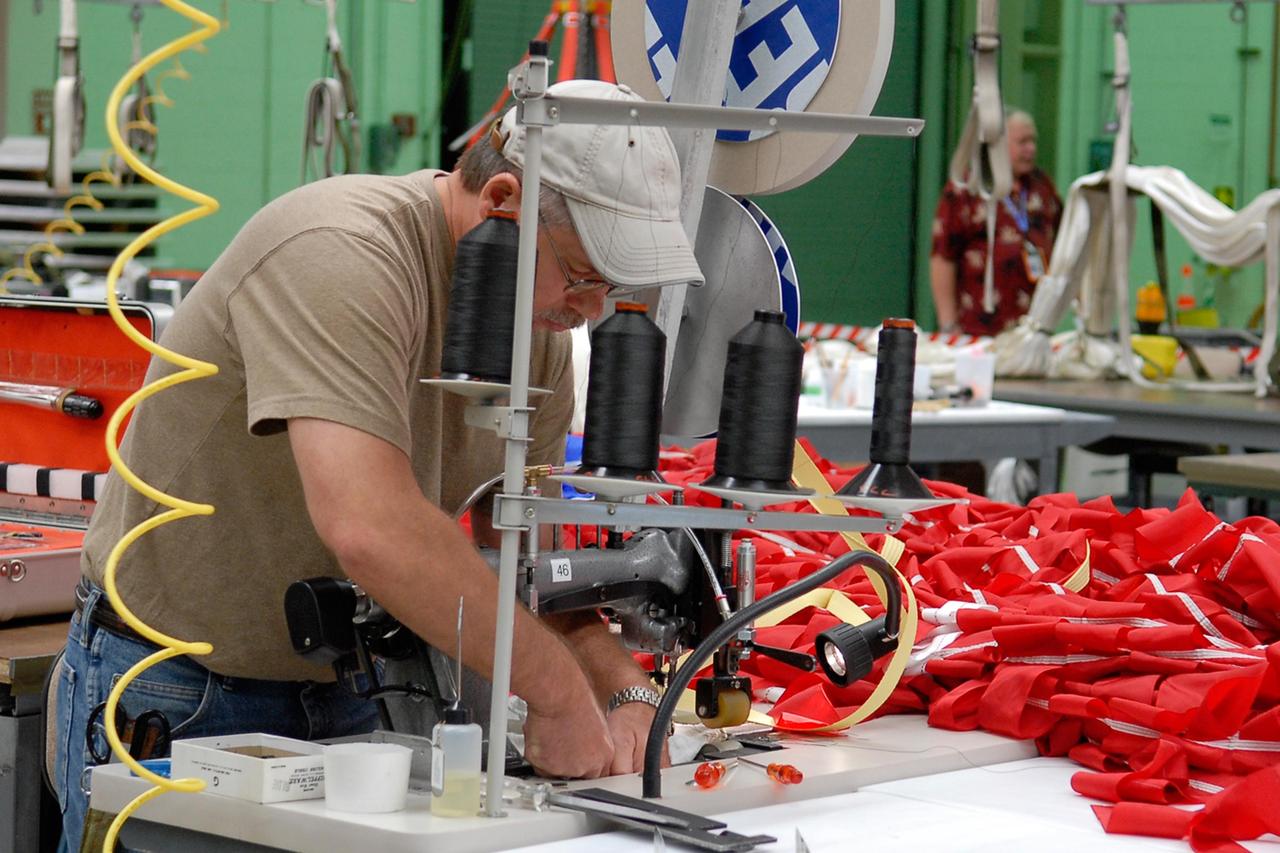

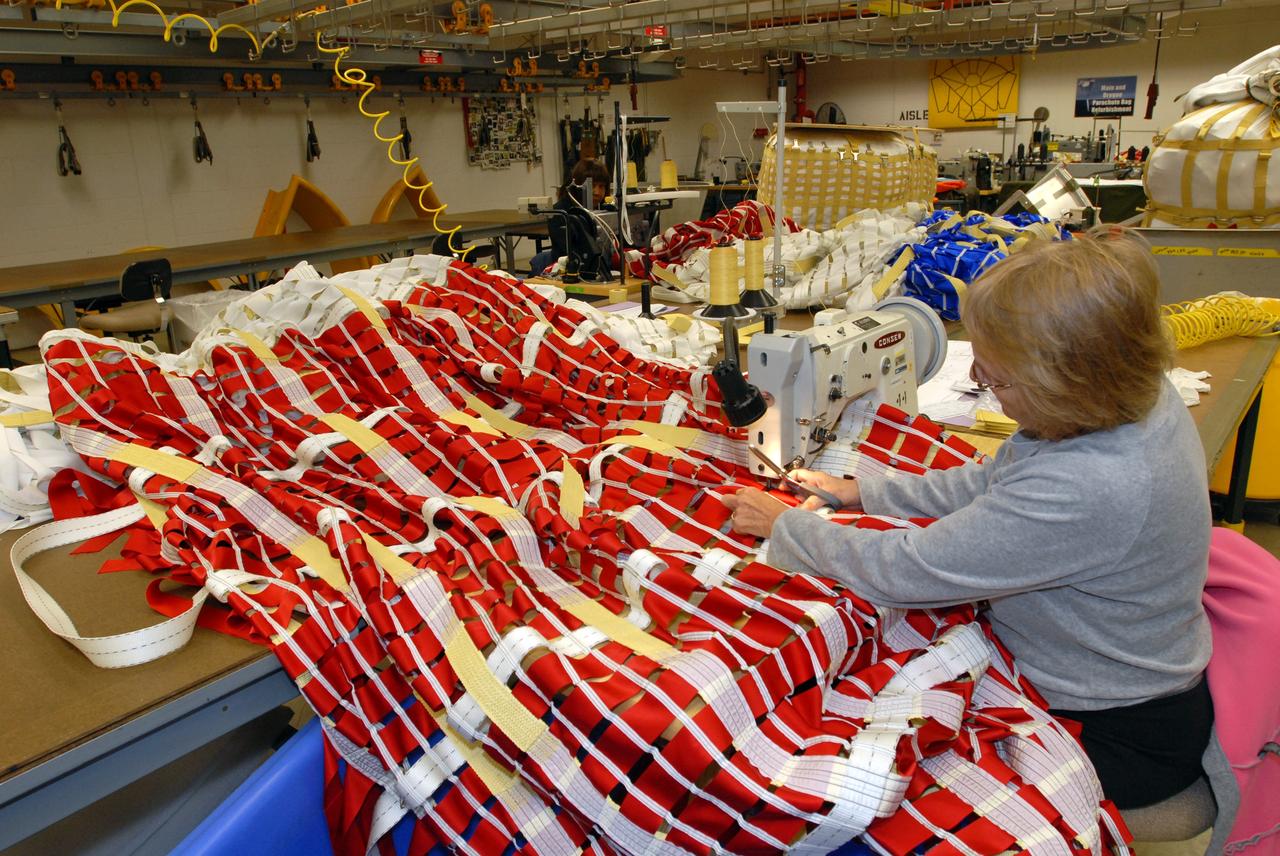
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker sews a parachute being prepared for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
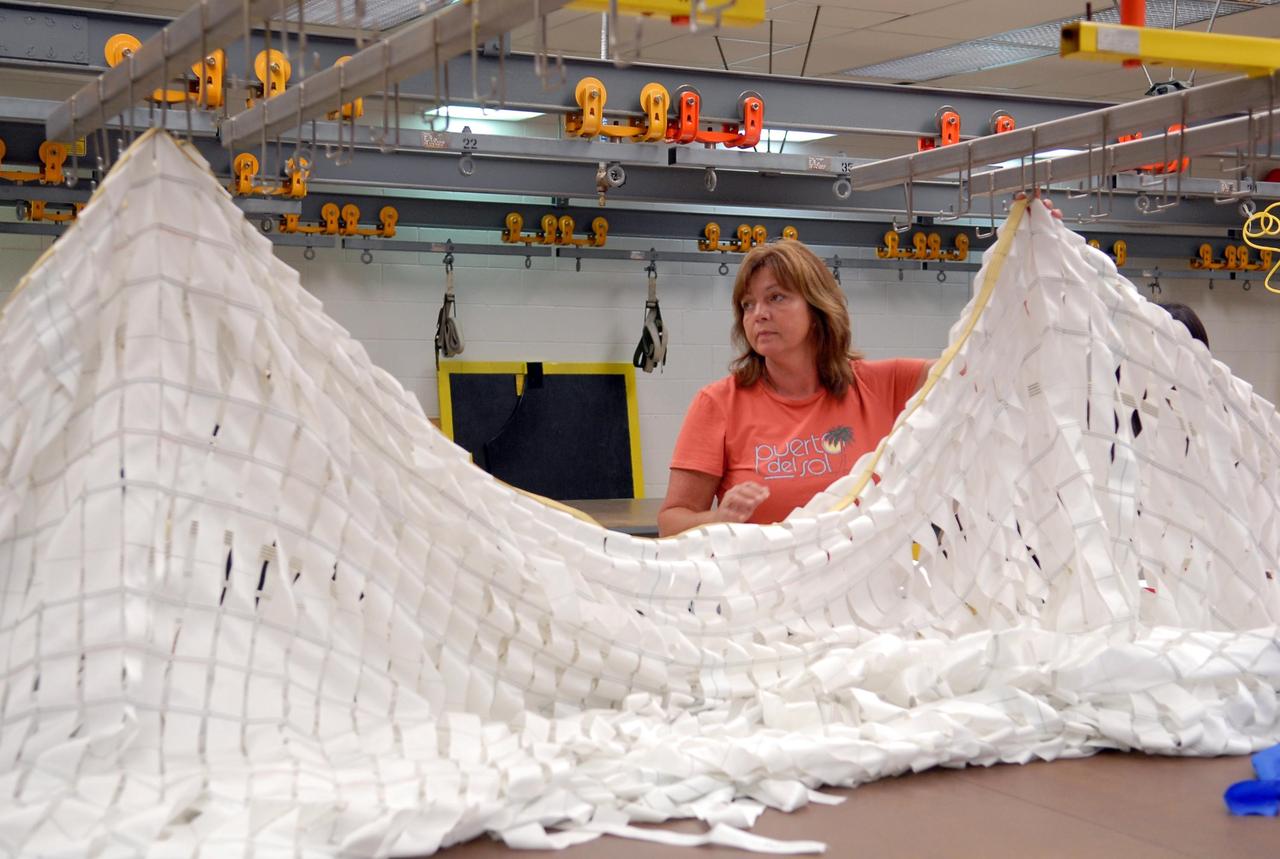

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker prepares a parachute for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
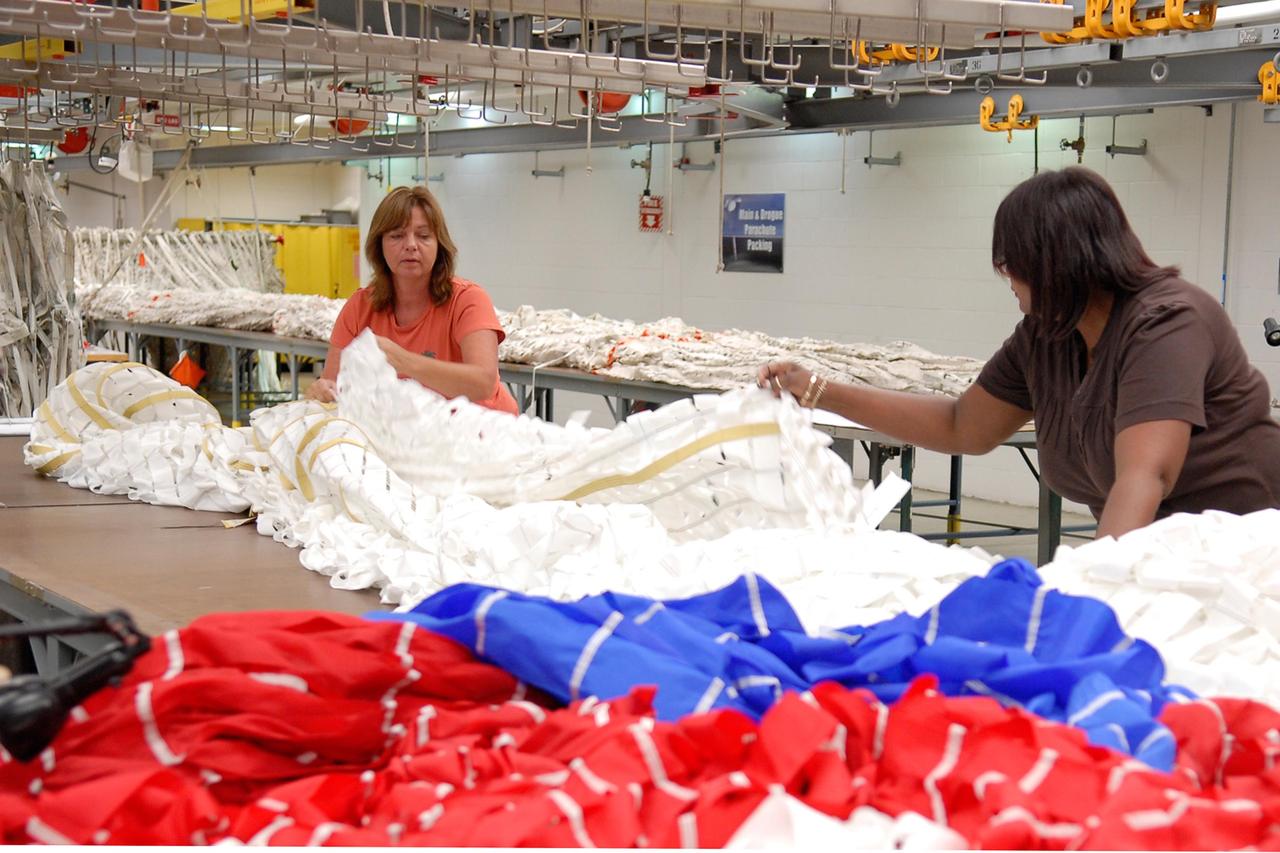

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers prepare a parachute for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
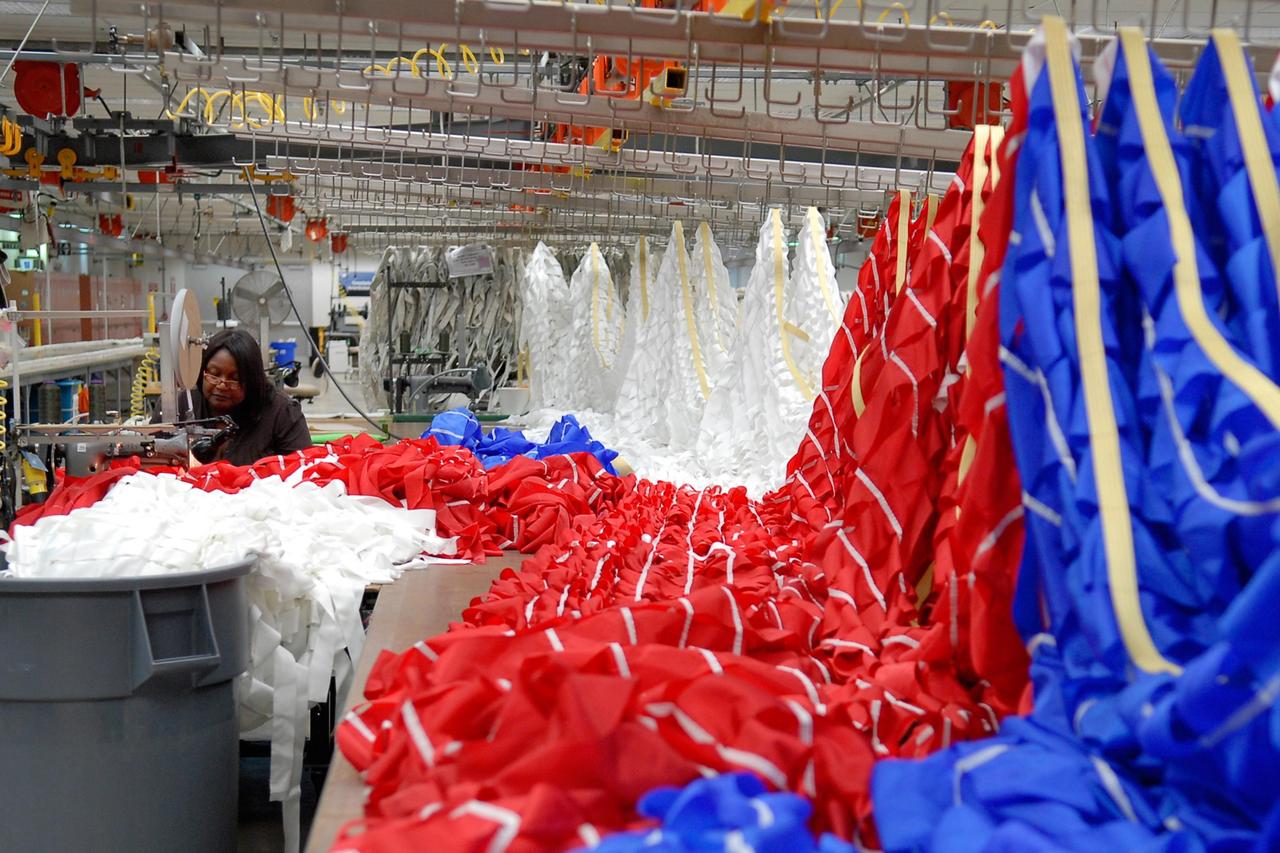

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker sews a parachute being prepared for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker prepares a parachute for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
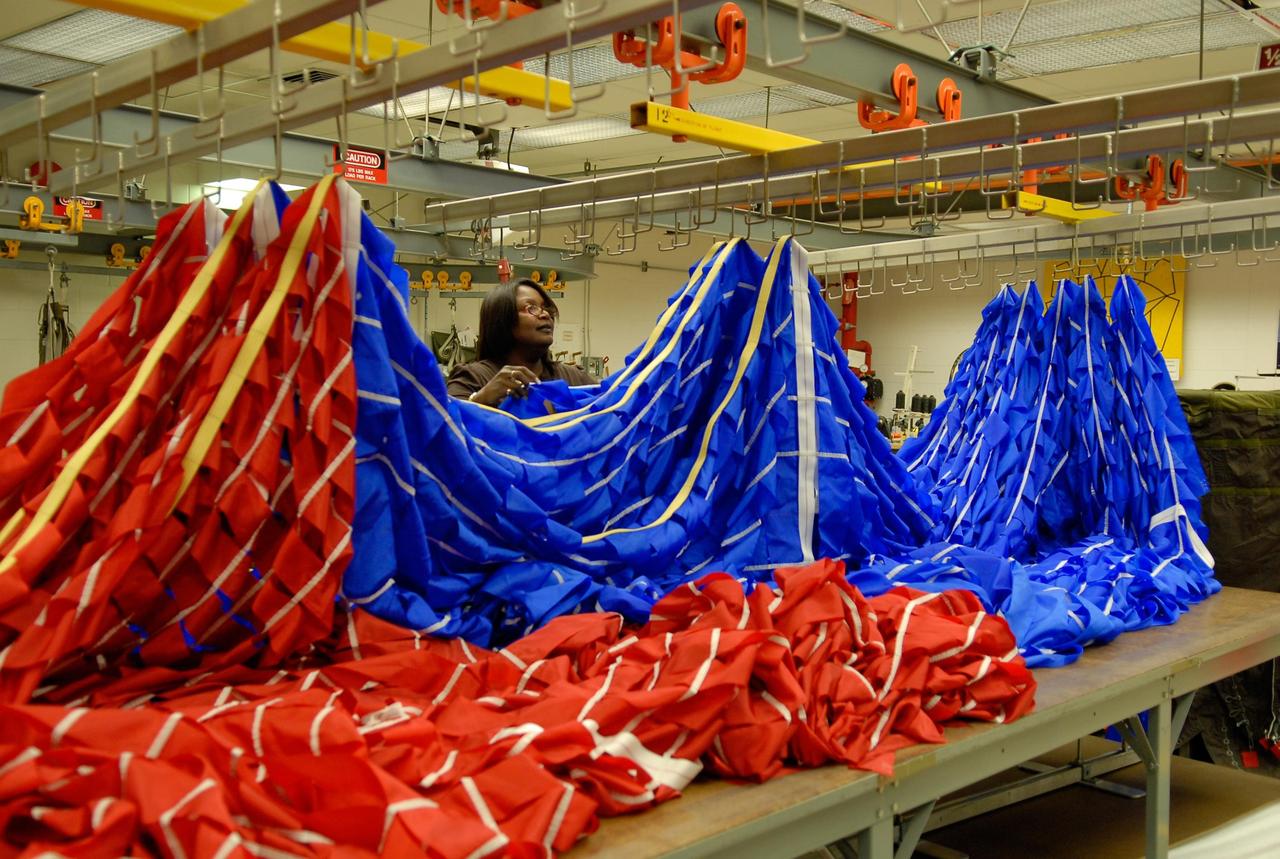

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker hangs portions of a parachute in preparation for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
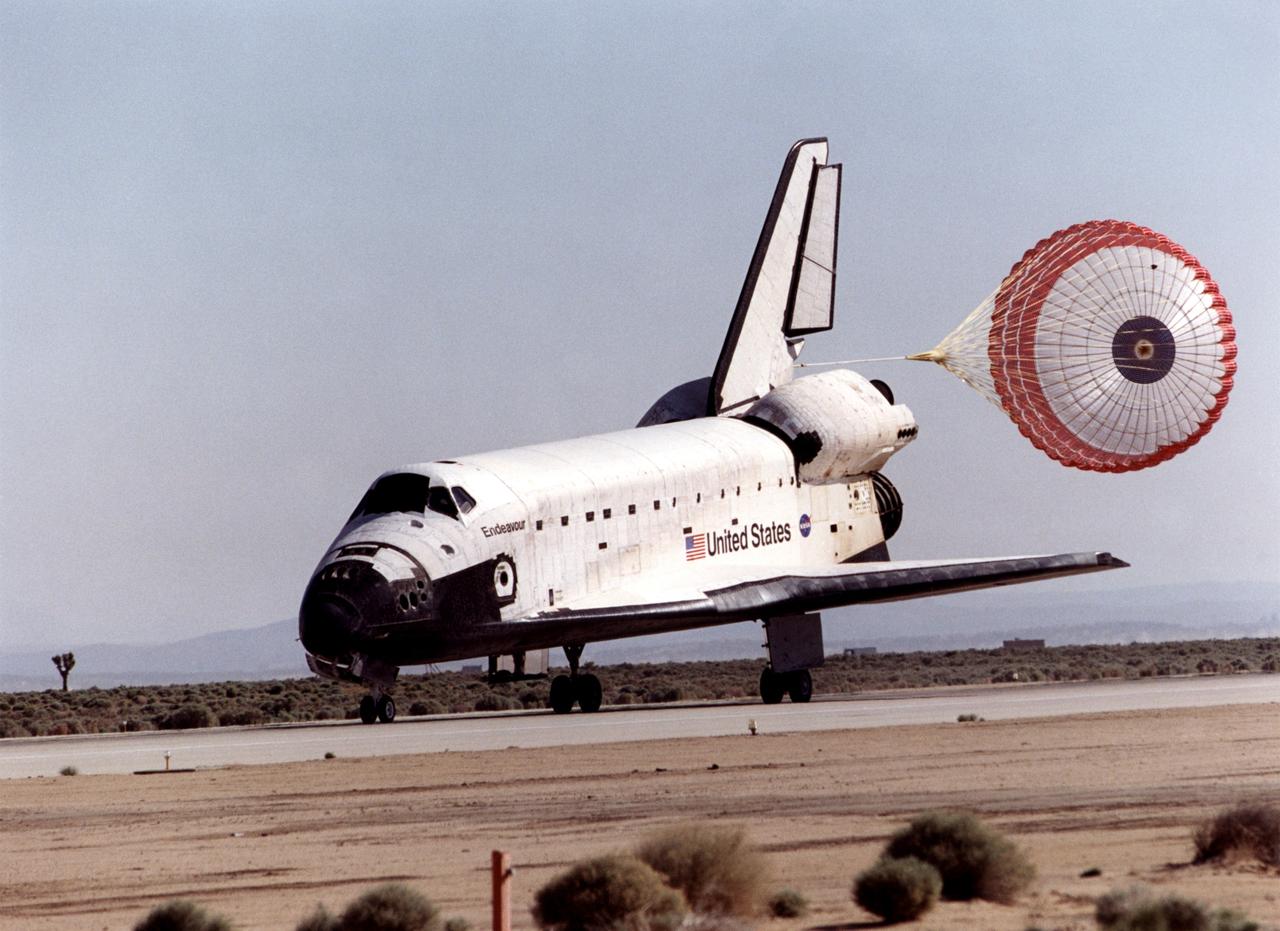

STS100-S-020 (1 May 2001) --- The drag chute on the space shuttle Endeavour helps to slow the vehicle down as it eases to the completion of the STS-100 mission on a desert runway at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Touchdown occurred at 9:11 a.m. (PDT), May 1, 2001. Onboard the shuttle were six NASA astronauts and a cosmonaut representing Rosaviakosmos. Photo credit: NASA
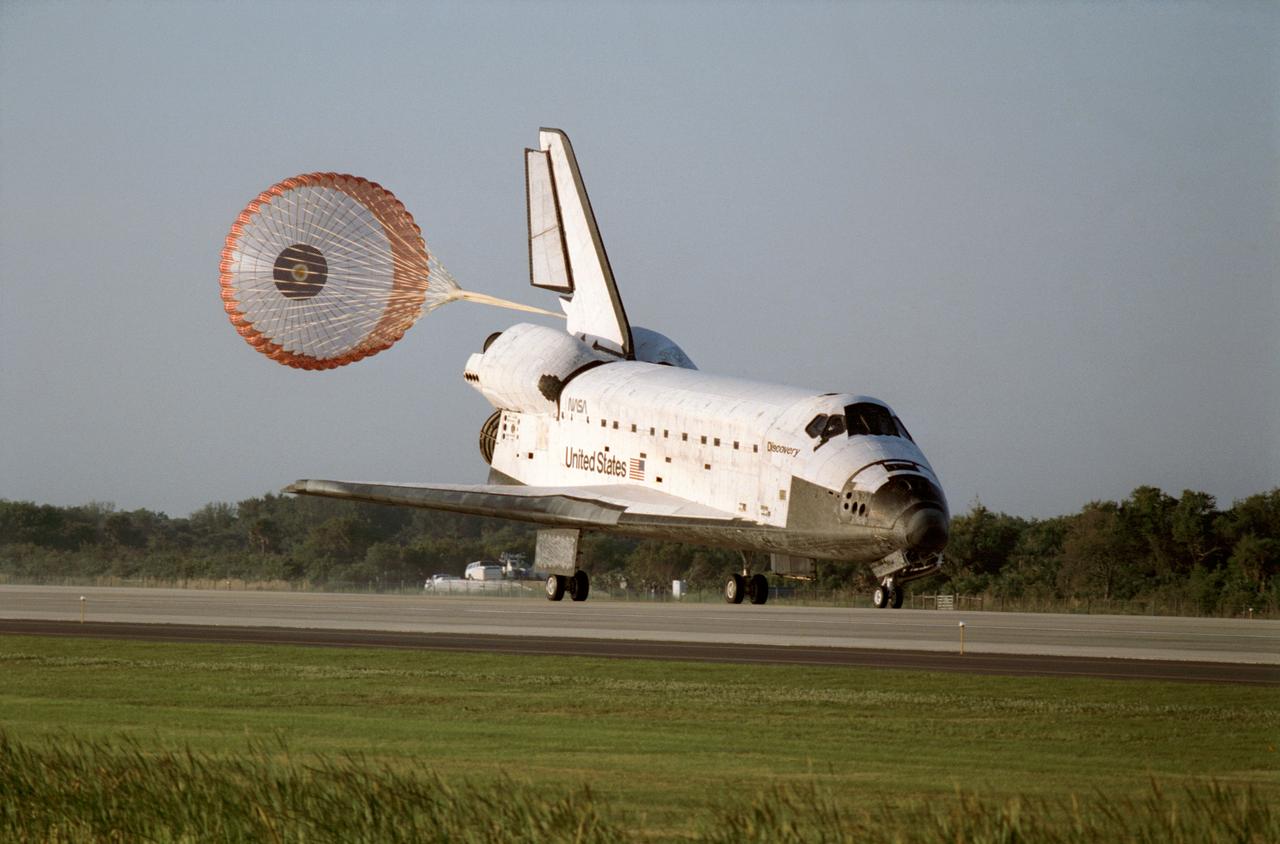

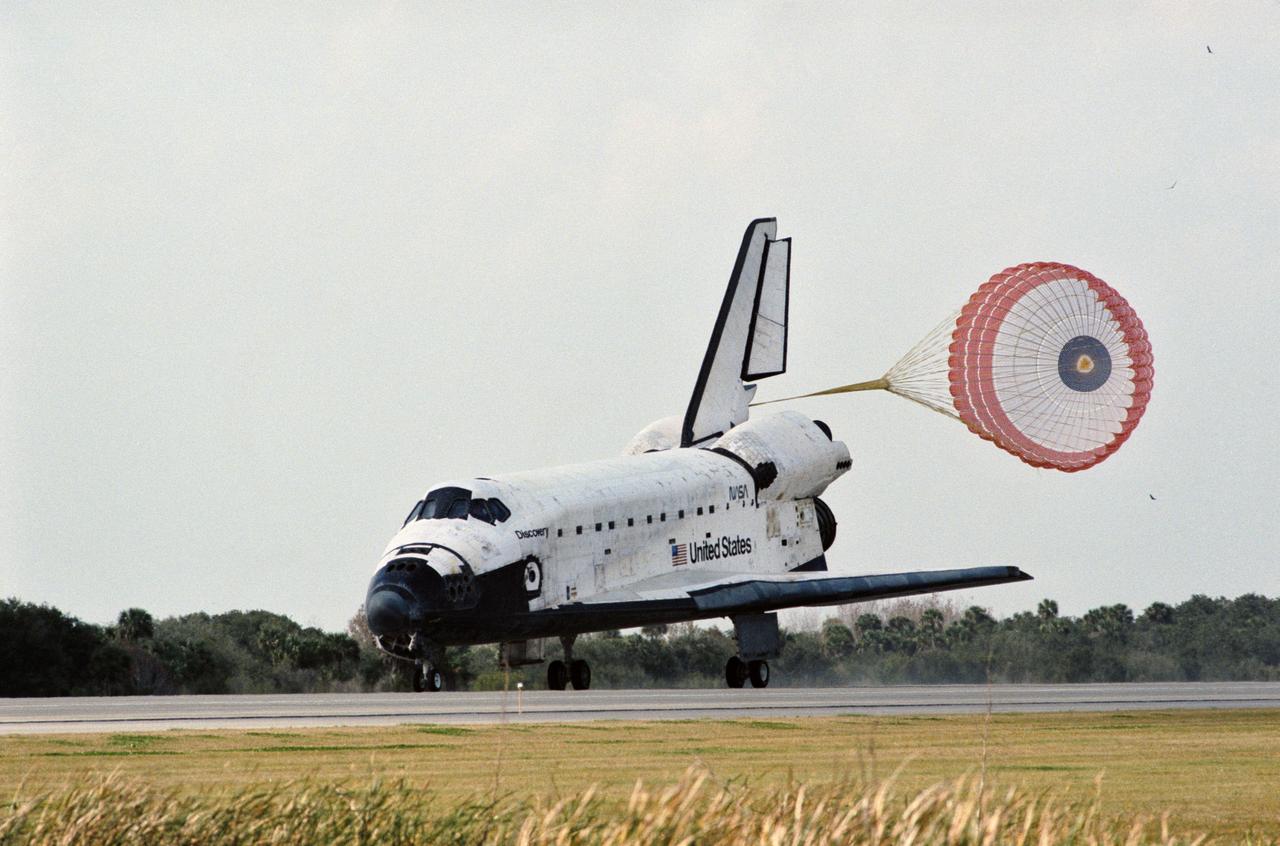
STS056-S-098 (17 April 1993) --- The drag chute is deployed following landing of the Space Shuttle Discovery on the Shuttle landing facility at the Kennedy Space Center to complete the STS-56\Atlas 2 mission. Touchdown occurred at 7:37 a.m. (EDT). Onboard the spacecraft were astronauts Kenneth D. Cameron, commander; Stephen S. Oswald, pilot; and C. Michael Foale, Ellen Ochoa and Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission specialists.

STS055-S-089 (6 May 1993) --- The main drag chute on the Space Shuttle Columbia is almost fully deployed in this three-quarter aft view of the vehicle's runway landing at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Landing occurred at 7:30 a.m. (PDT), May 6, 1993. Onboard the spacecraft were astronauts Steven R. Nagel, Terence T. (Tom) Henricks, Jerry L. Ross, Bernard Harris Jr. and Charles J. Precourt, along with German payload specialists Hans Schlegel and Ulrich Walter.

STS066-S-039 (14 November 1994) --- The drag chute is fully deployed as the Space Shuttle Atlantis heads toward a stop at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California, ending a successful 10 day, 22 hour and 34 minute space mission. Landing occurred at 7:34 a.m. (PST), November 14, 1994. Onboard were astronauts Donald R. McMonagle, commander; Curtis L. Brown, Jr., pilot; Ellen S. Ochoa, payload commander; Scott E. Parazynski and Joseph R. Tanner, both mission specialists, along with European Space Agency (ESA) mission specialist Jean-Francois Clervoy. The crew supported the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3) mission.
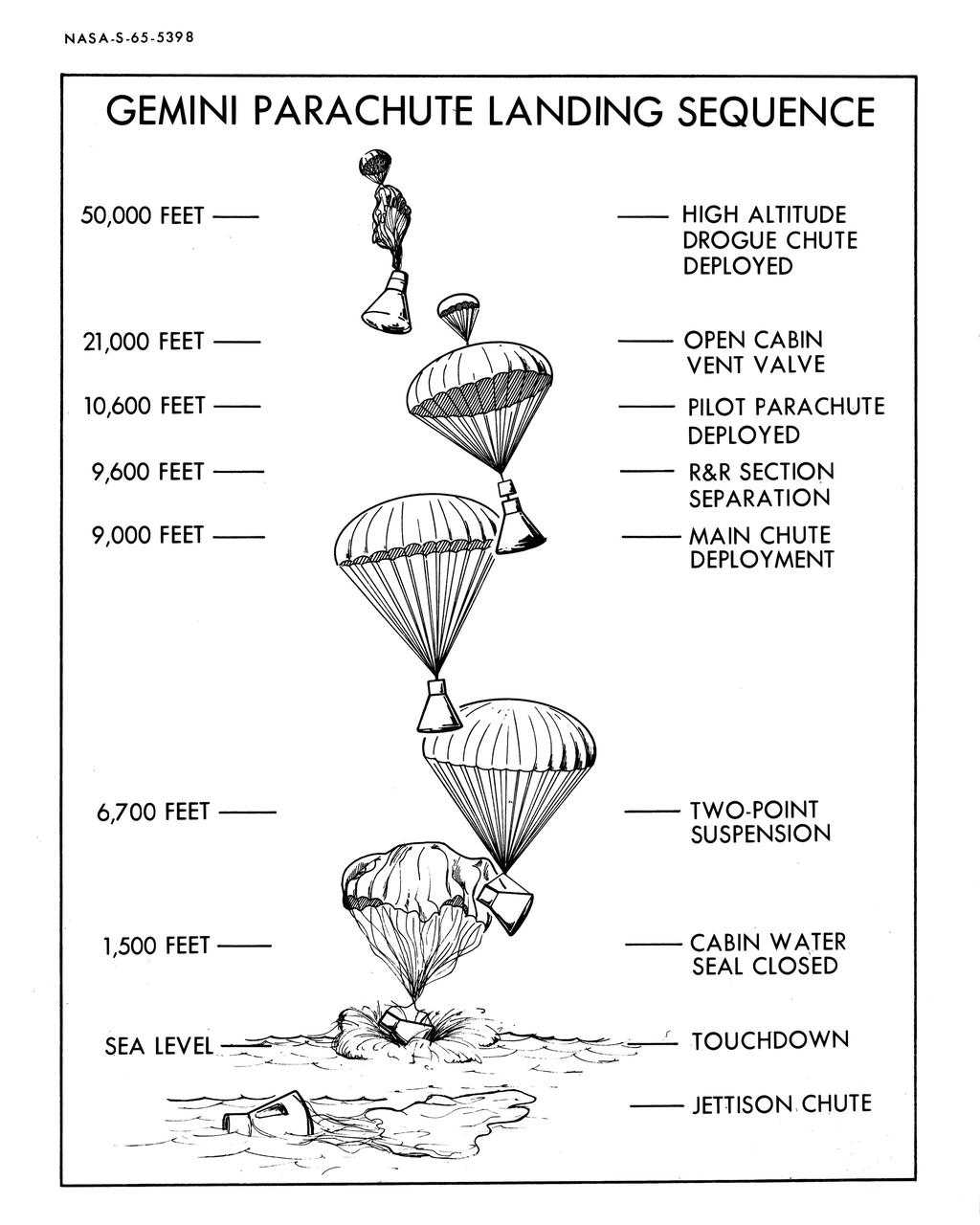
S65-05398 (1965) --- Artist concept of Gemini parachute landing sequence from high altitude drogue chute deployed to jettison of chute.

STS053-S-085 (9 Dec. 1992) --- The drag chute on the space shuttle Discovery is partially deployed during landing on Runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base. The landing ended an eight-day space mission for the STS-53 crew. Main gear touchdown occurred at 12:43:17 p.m. (PST) on Dec. 9, 1992. Onboard were astronauts David M. Walker, Robert D. Cabana, Guion S. Bluford Jr., James S. Voss and Michael R.U. (Rich) Clifford.
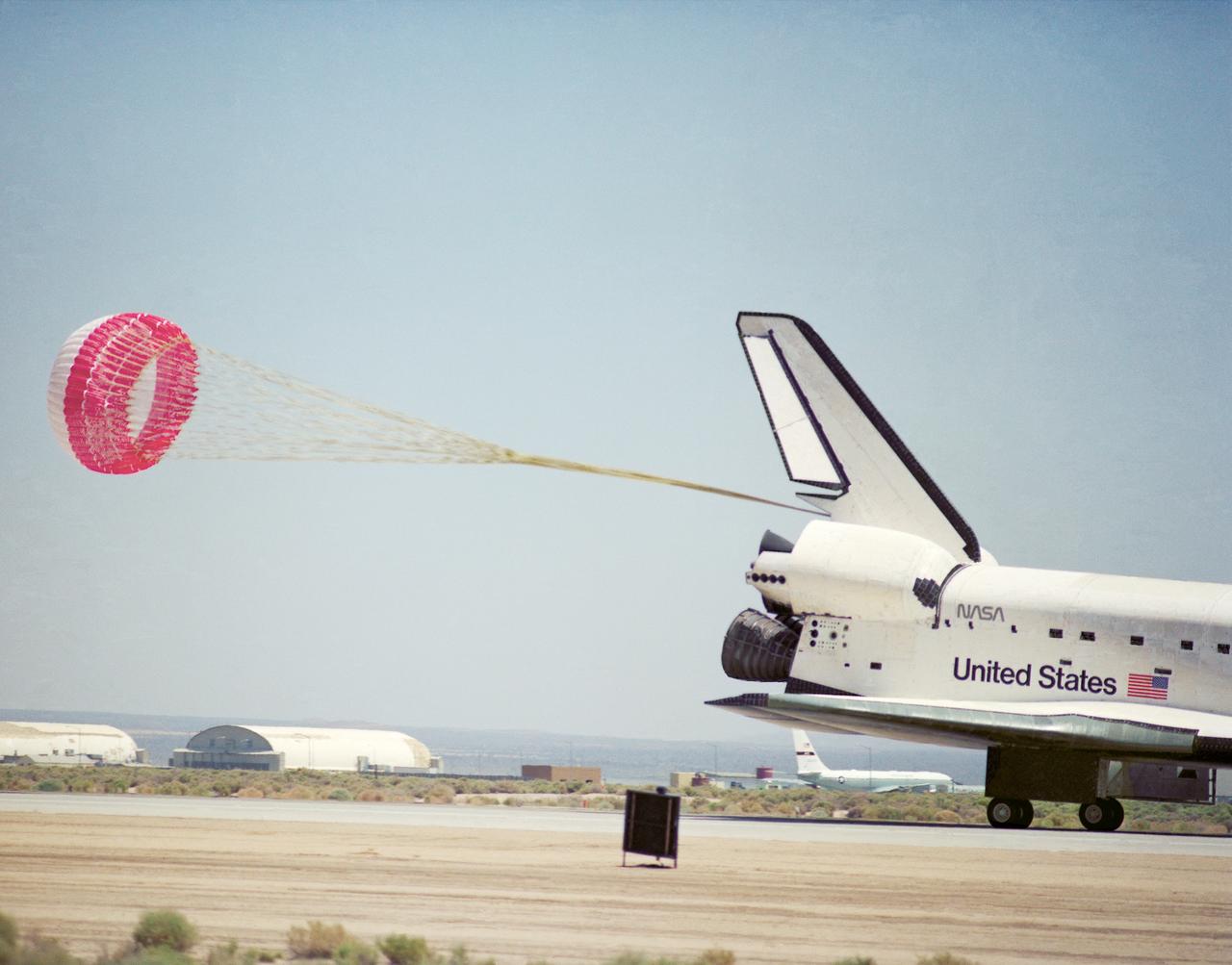

The Space Shuttle Endeavour concludes mission STS-49 at NASA's Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later redesignated Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California, with a 1:57 p.m. (PDT) landing 16 May on Edward's concrete runway 22. The planned 7-day mission, which began with a launch from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 4:41 p.m. (PFT), 7 May, was extended two days to allow extra time to rescue the Intelsat VI satellite and complete Space Station assembly techniques originally planned. After a perfect rendezvous in orbit and numerous attempts to grab the satellite, space walking astronauts Pierre Thuot, Rick Hieb and Tom Akers successfully rescued it by hand on the third space walk with the support of mission specialists Kathy Thornton and Bruce Melnick. The three astronauts, on a record space walk, took hold of the satellite and directed it to the shuttle where a booster motor was attached to launch it to its proper orbit. Commander Dan Brandenstein and Pilot Kevin Chilton brought Endeavours's record setting maiden voyage to a perfect landing at Edwards AFB with the first deployment of a drag chute on a shuttle mission.
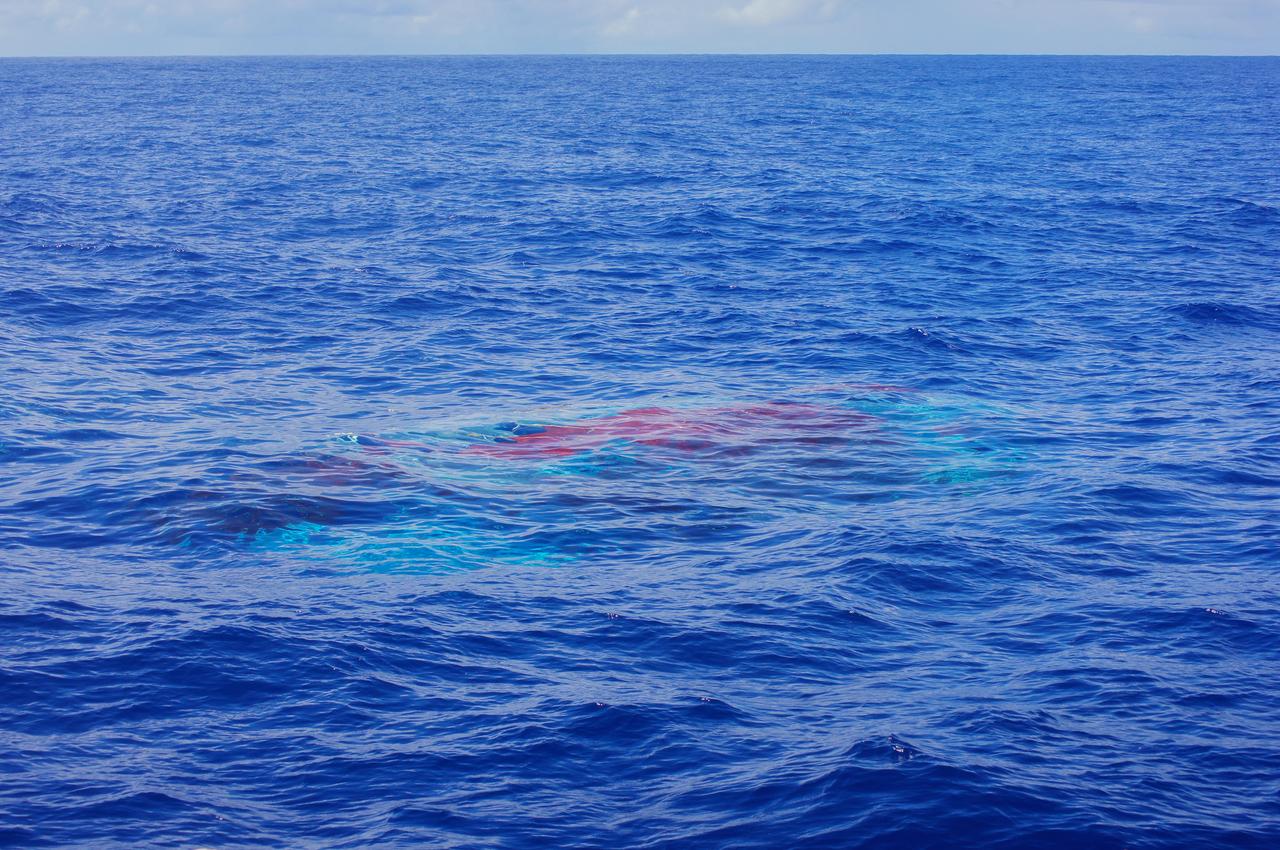

NASA Supersonic Disk Sail Parachute, one of the new technologies being developed as part of NASA Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator LDSD project, floats just below the surface of the Pacific Ocean on June 28, 2014.
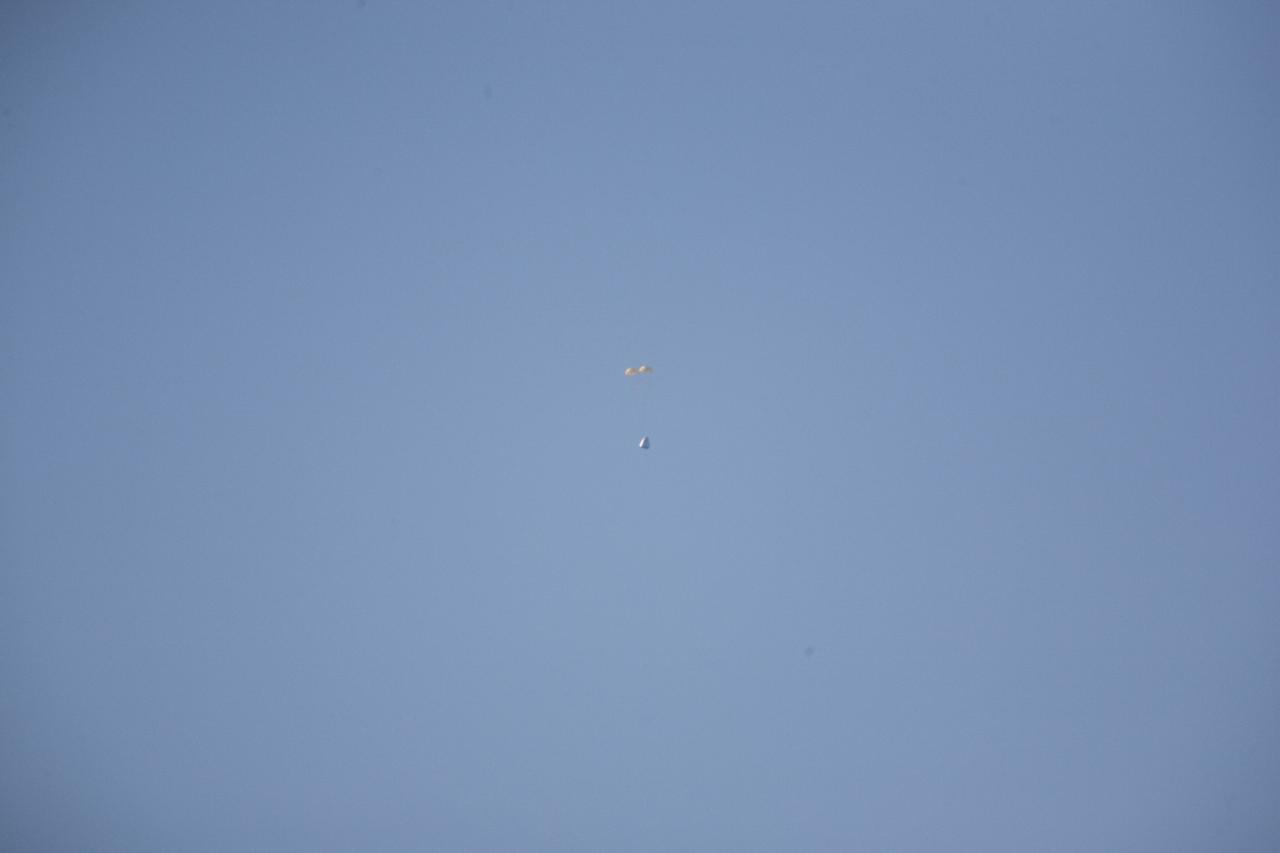

MORRO BAY, Calif. – Drogue chutes open above Dragon test article during a test to evaluate the spacecraft's parachute deployment system. The drogue chutes stabilized the vehicle, in preparation for main chute deployment as part of a milestone under SpaceX's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
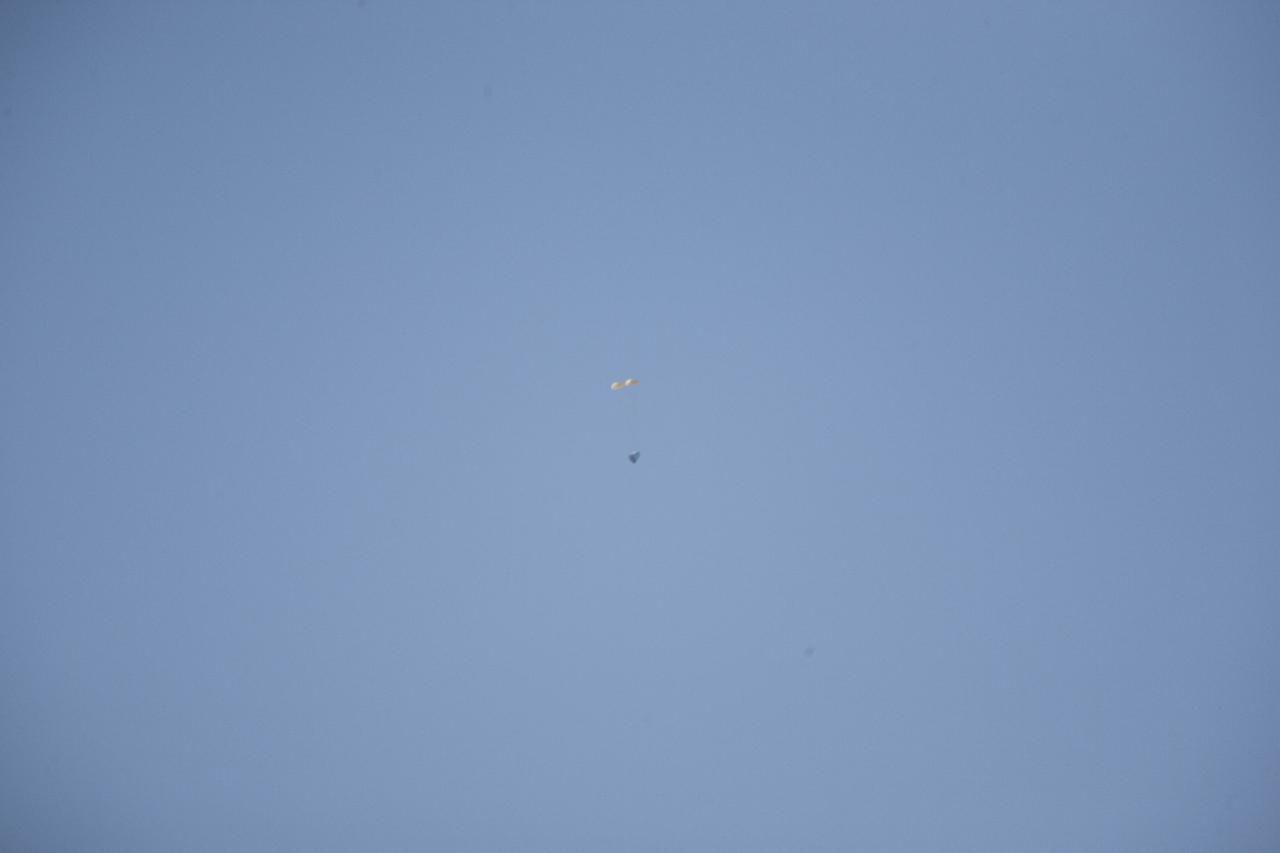

MORRO BAY, Calif. – Drogue chutes open above Dragon test article during a test to evaluate the spacecraft's parachute deployment system. The drogue chutes stabilized the vehicle, in preparation for main chute deployment as part of a milestone under SpaceX's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
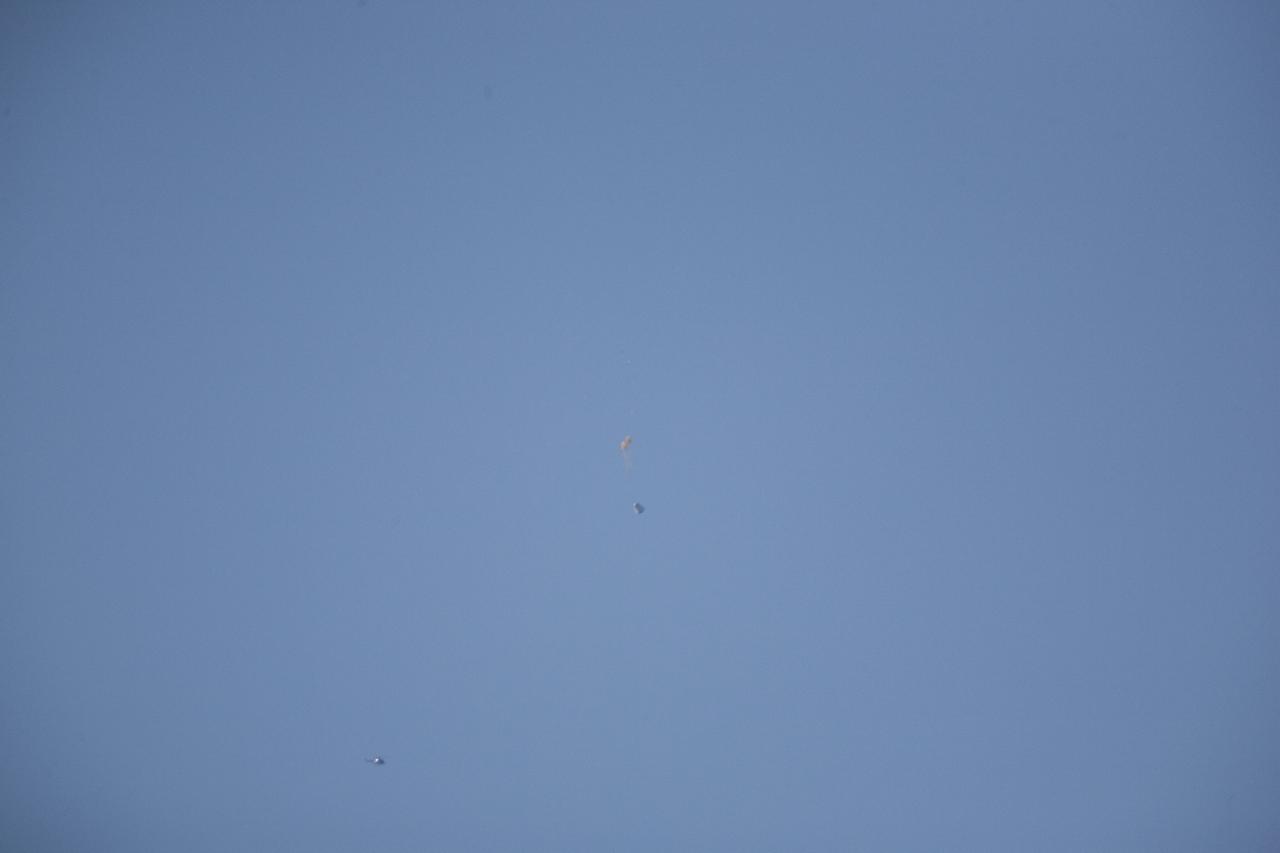

MORRO BAY, Calif. – Drogue chutes open above Dragon test article during a test to evaluate the spacecraft's parachute deployment system. The drogue chutes stabilized the vehicle, in preparation for main chute deployment as part of a milestone under SpaceX's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
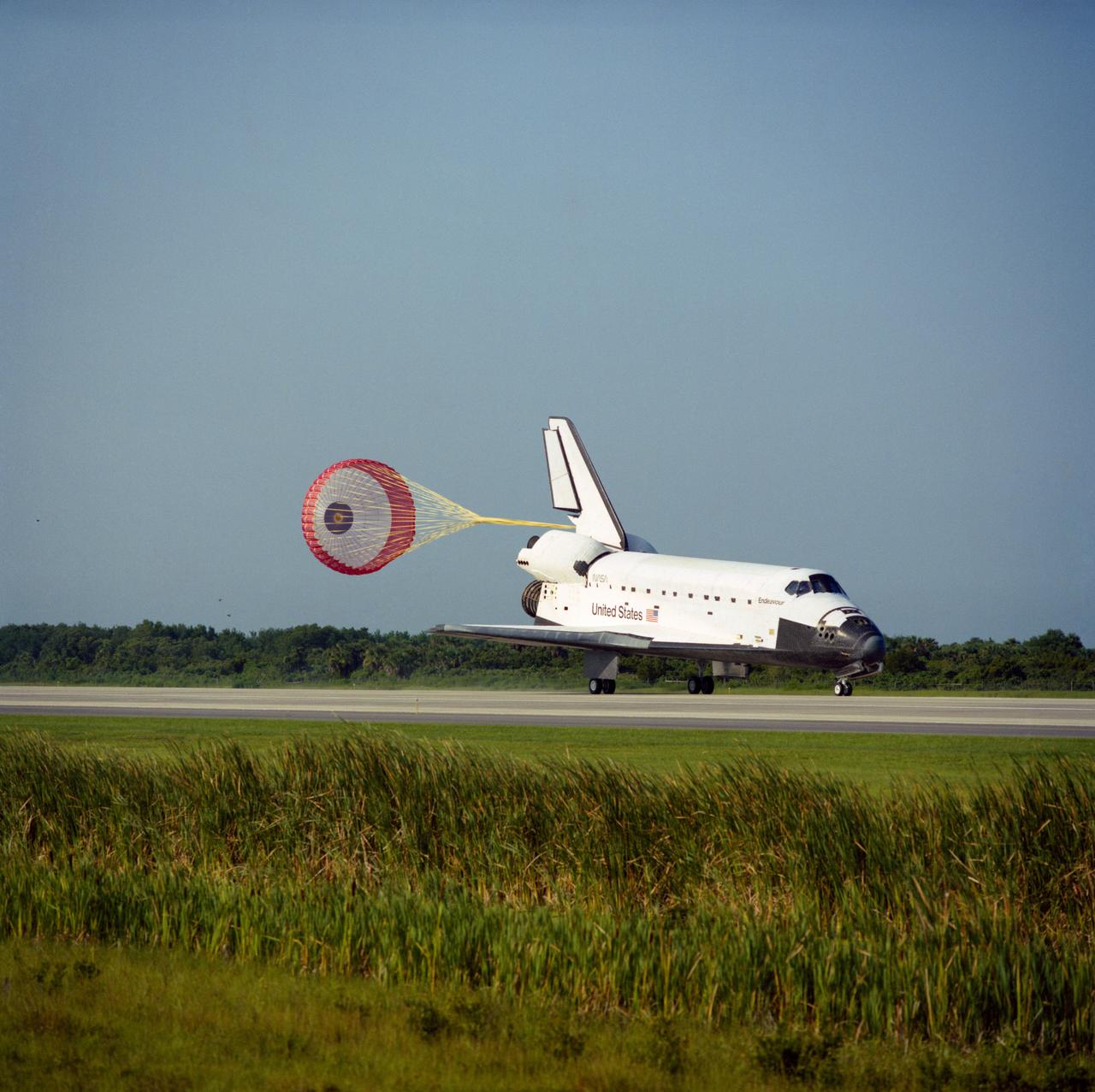

STS057-S-082 (1 July 1993) --- The drag chute on the Space Shuttle Endeavour is fully deployed in this scene on Runway 33 (KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility) as the spacecraft successfully completes a ten-day mission in Earth orbit. Official mission duration was nine days, twenty-three hours, forty-four minutes and fifty-five seconds. Main gear touchdown occurred at 8:52:16 (EDT), July 1, 1993. Onboard Endeavour for the landing were six NASA astronauts and the European Retrievable Carrier (EURECA) spacecraft. Crewmembers were astronauts Ronald J. Grabe, Brian Duffy, G. David Low, Nancy J. Sherlock, Peter J. K. (Jeff) Wisoff and Janice E. Voss.
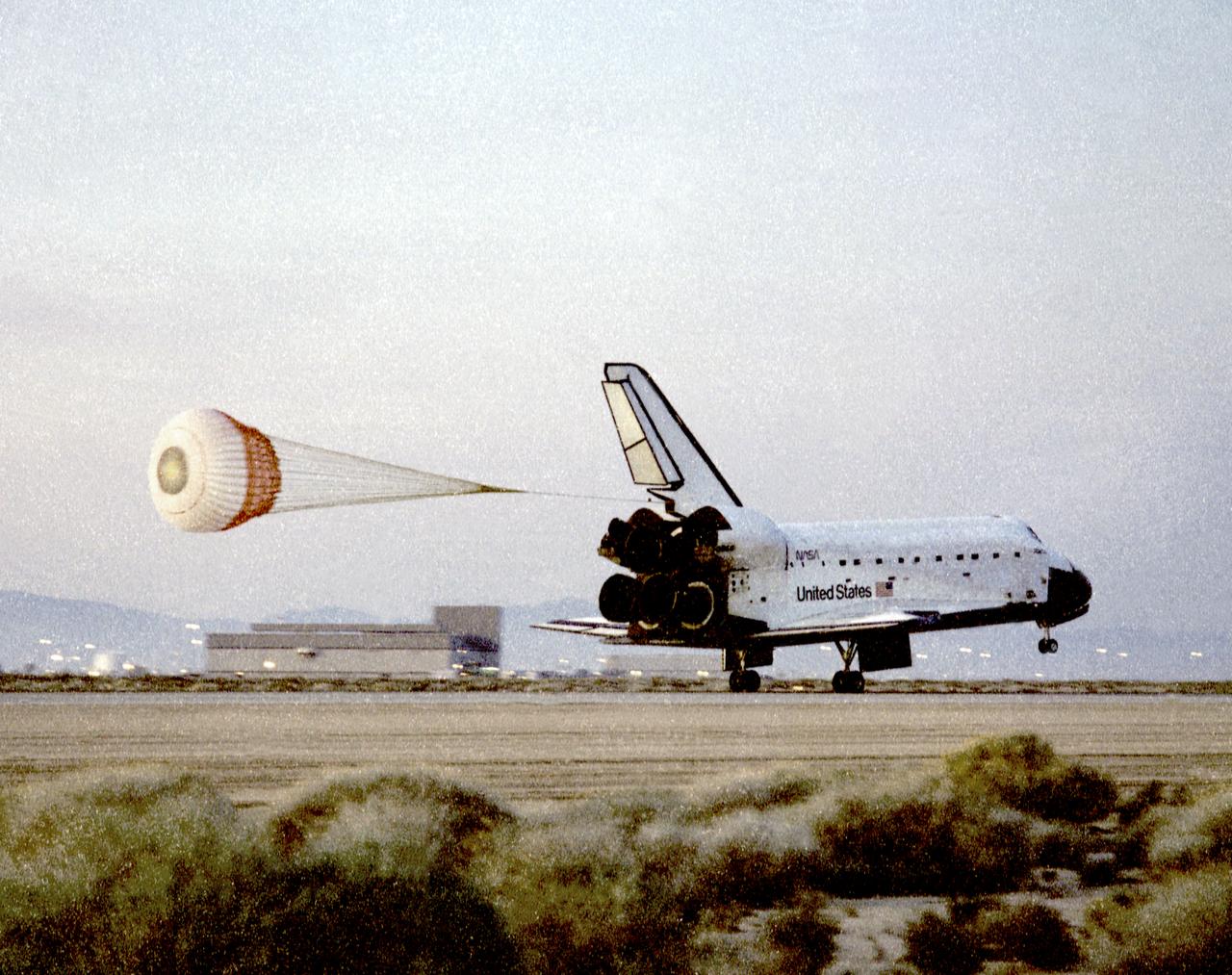

The space shuttle Atlantis touches down on the runway at Edwards, California, at approximately 5:29 a.m. Pacific Standard Time after completing the highly successful STS-76 mission to deliver Astronaut Shannon Lucid to the Russian Space Station Mir. She was the first American woman to serve as a Mir station researcher. Atlantis was originally scheduled to land at Kennedy Space Center, Florida, but bad weather there both 30 and 31 March necessitated a landing at the backup site at Edwards. This photo shows the drag chute deployed to help the shuttle roll to a stop. Mission commander for STS-76 was Kevin P. Chilton, and Richard A. Searfoss was the pilot. Ronald M. Sega was payload commander and mission specialist-1. Mission specialists were Richard Clifford, Linda Godwin and Shannon Lucid. The mission also featured a spacewalk while Atlantis was docked to Mir and experiments aboard the SPACEHAB module.
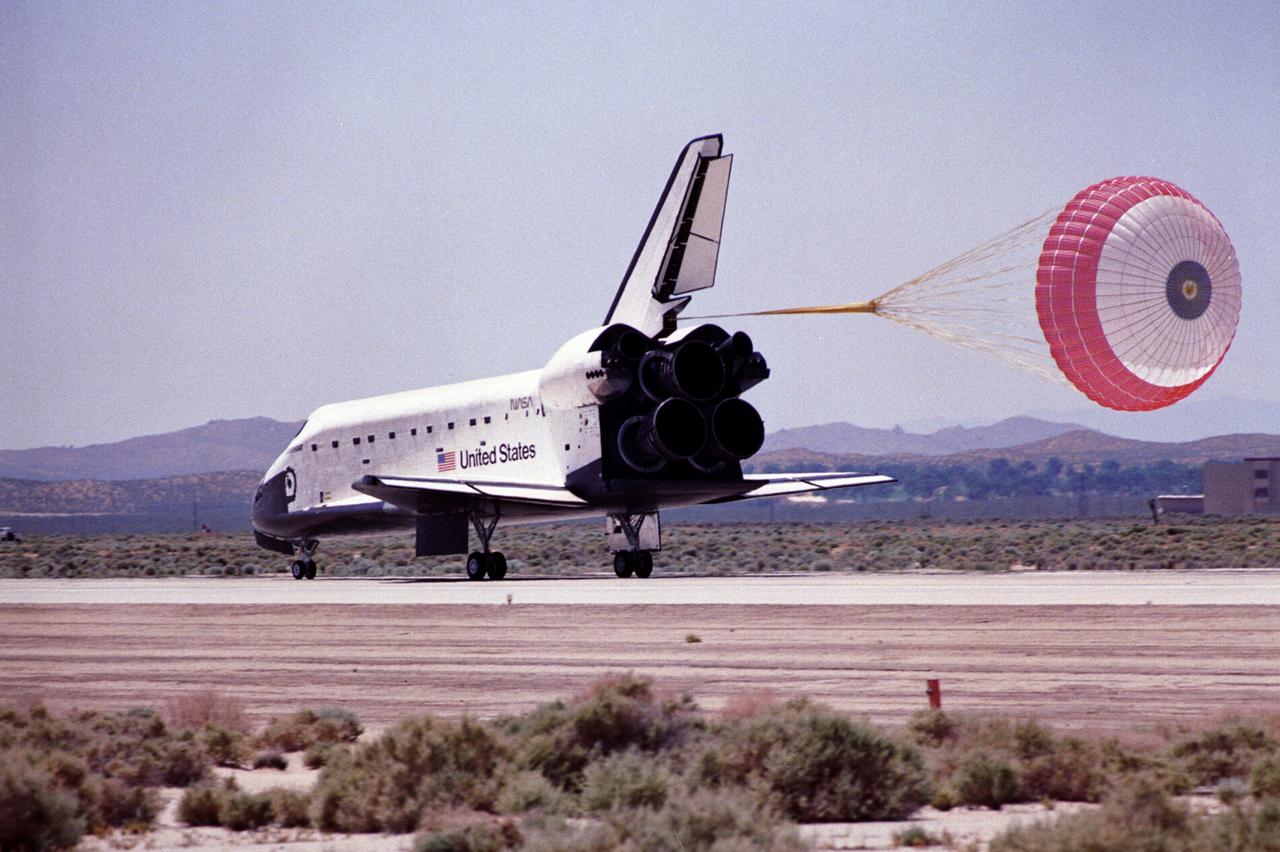

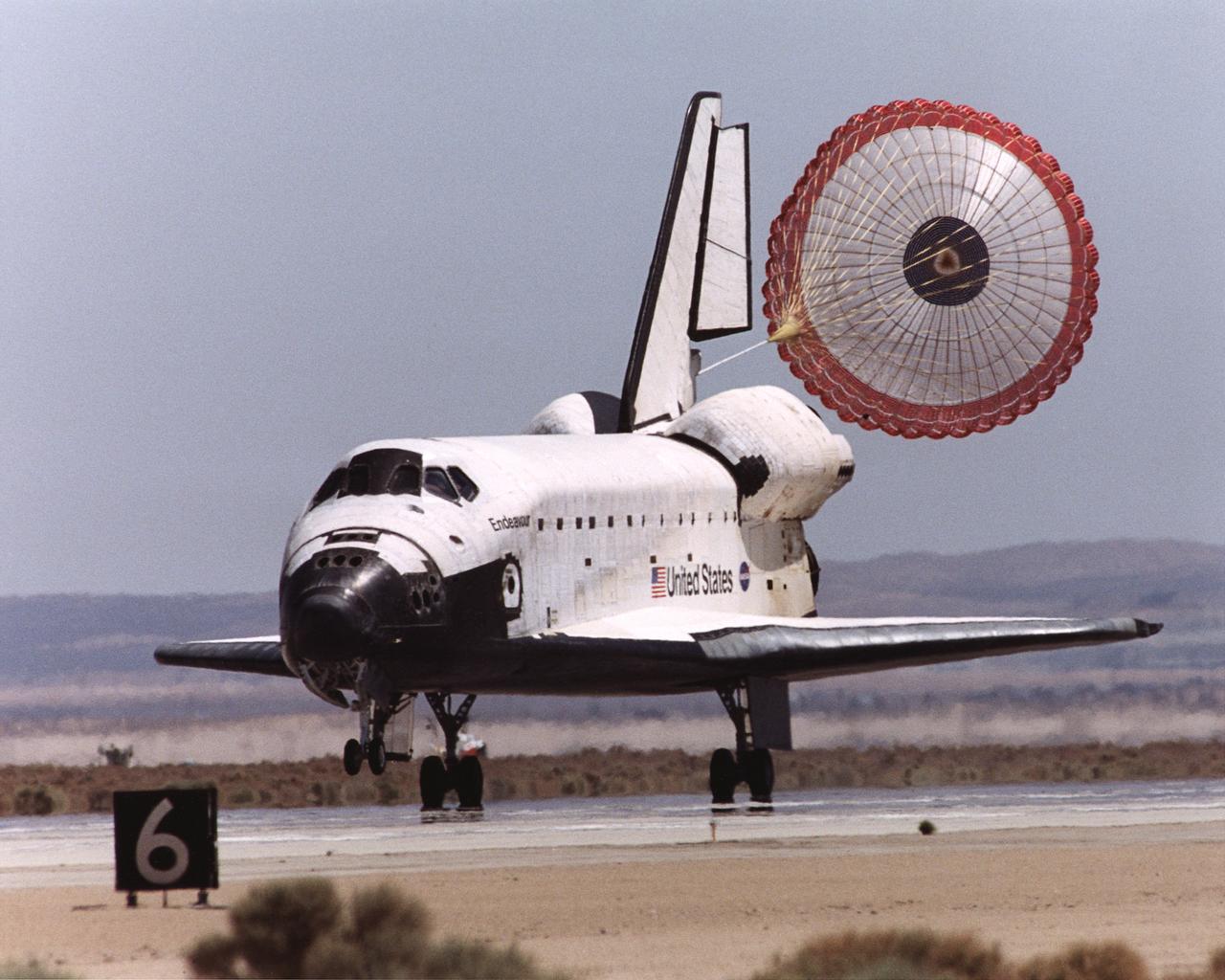
STS-49 Orbiter Endeavour landed at Edwards Air Force Base on May 16, 1992 The drogue chute precedes the main chute in NASA’s first exercise of its detailed test objective on the drag chute system. STS-49 ended its successful nine day mission dedicated to the retrieval, repair, and redeployment of the the INTELSAT VI (F-3) satellite. The communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization had been stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. The mission marked the first time 3 astronauts worked simultaneously outside the space craft.

This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows wind-caused changes in the parachute of NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft as the chute lay on the Martian ground during months after its use in safe landing of the Curiosity rover.
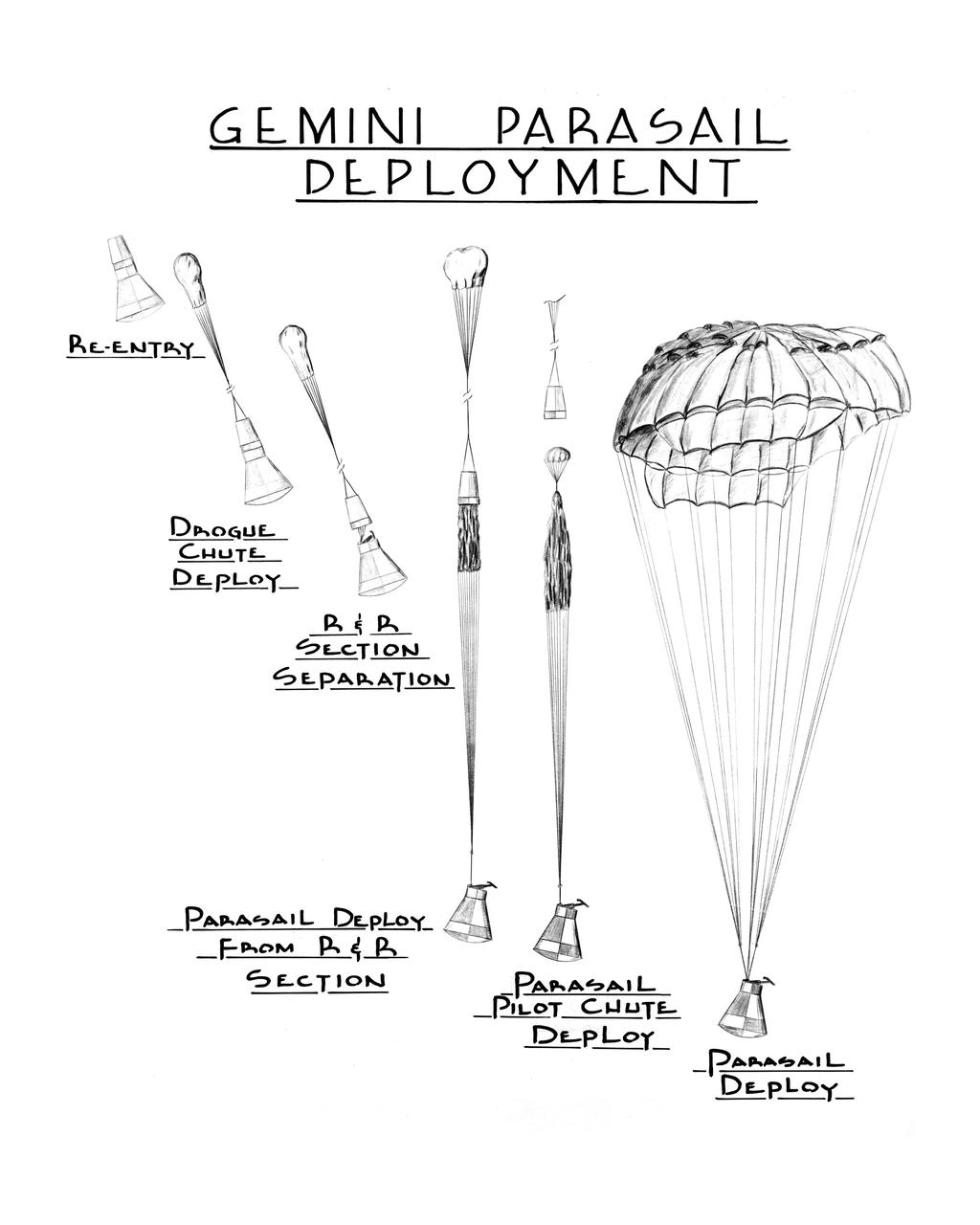
S63-12019 (1963) --- Artist concept for Gemini parasail deployment showing re-entry, drogue chute deployment, and stages of parasail deployment.
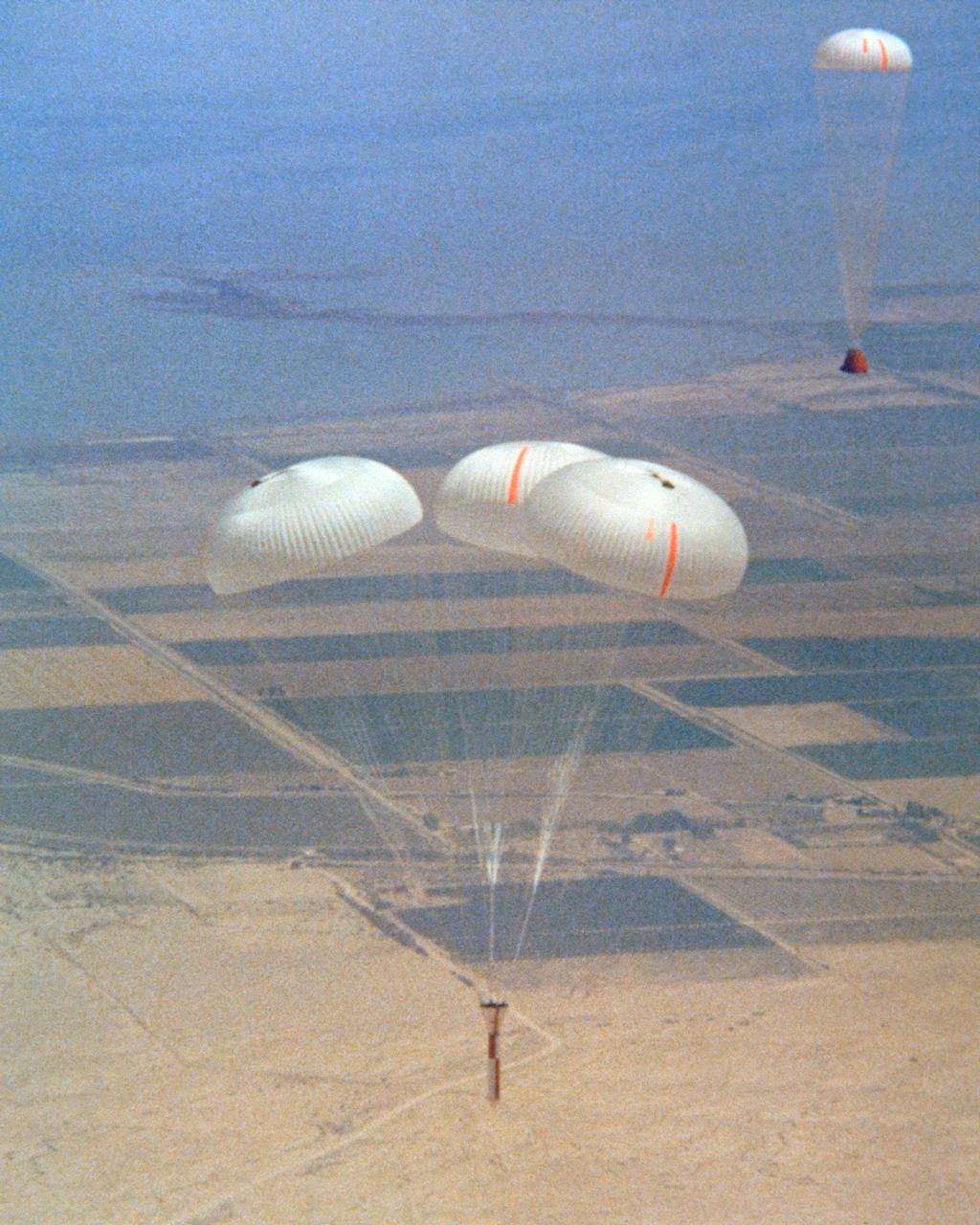

Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster Drop Test Vehicle (SRB-DTV) with chutes open after release from NB-52B
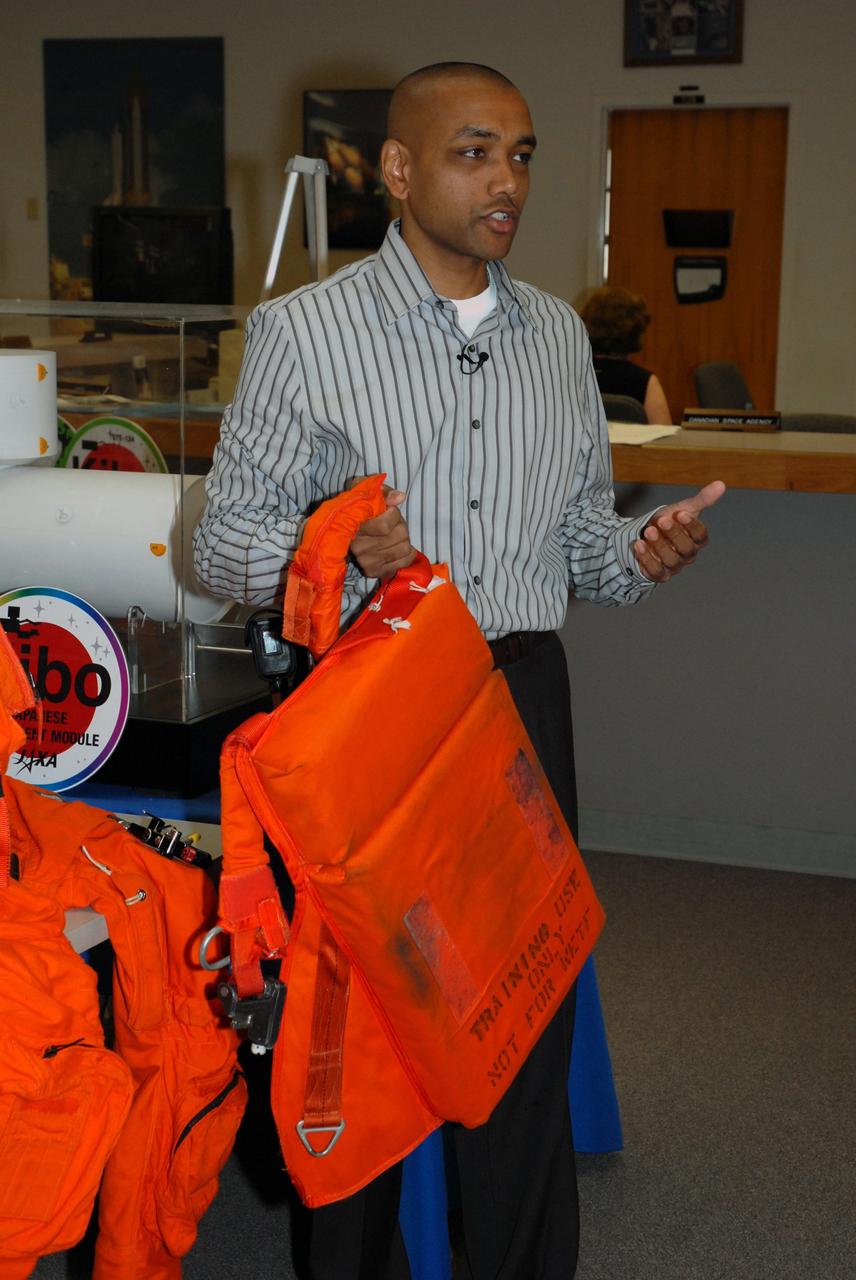

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the NASA News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Shuttle Crew Escape System Manager KC Chhipwadia describes for the media the components of the parachute worn by shuttle crews during launch and landing. On top is a pilot and drag chute. In the middle is the main chute. At bottom is a survival life raft. The elements of the suit and parachute provide safety elements in the event of an emergency. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
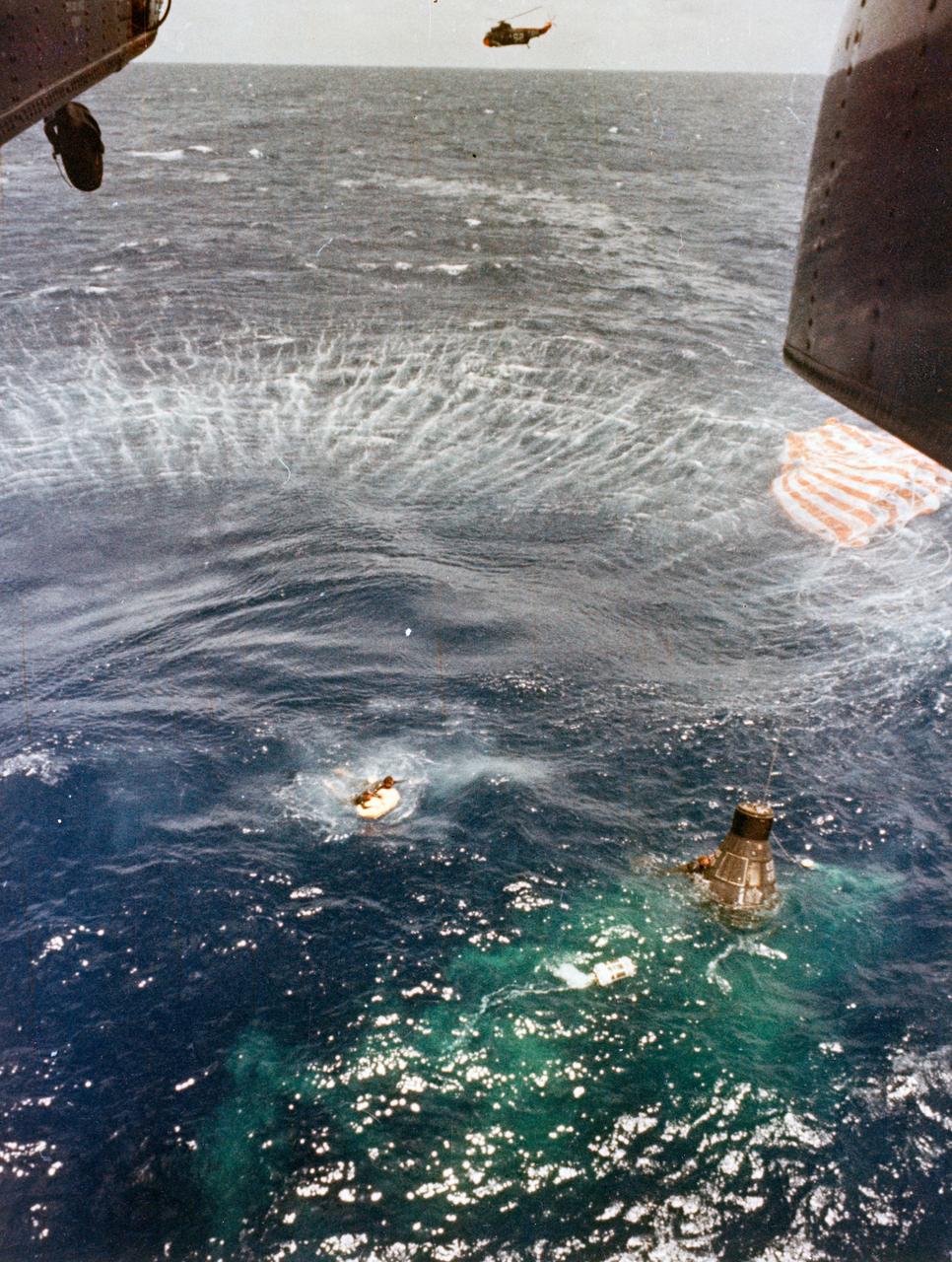

S63-07730 (16 May 1963) --- A U.S. Navy frogman, deployed from the hovering helicopter, swims next to the spacecraft and makes contact with astronaut L. Gordon Cooper Jr. inside, as his fellow team members bring up the floatation gear to be attached to the spacecraft. The main chute floats at top left, and the ejected reserve chute floats at the lower right of the spacecraft in the green dye area. Photo credit: NASA
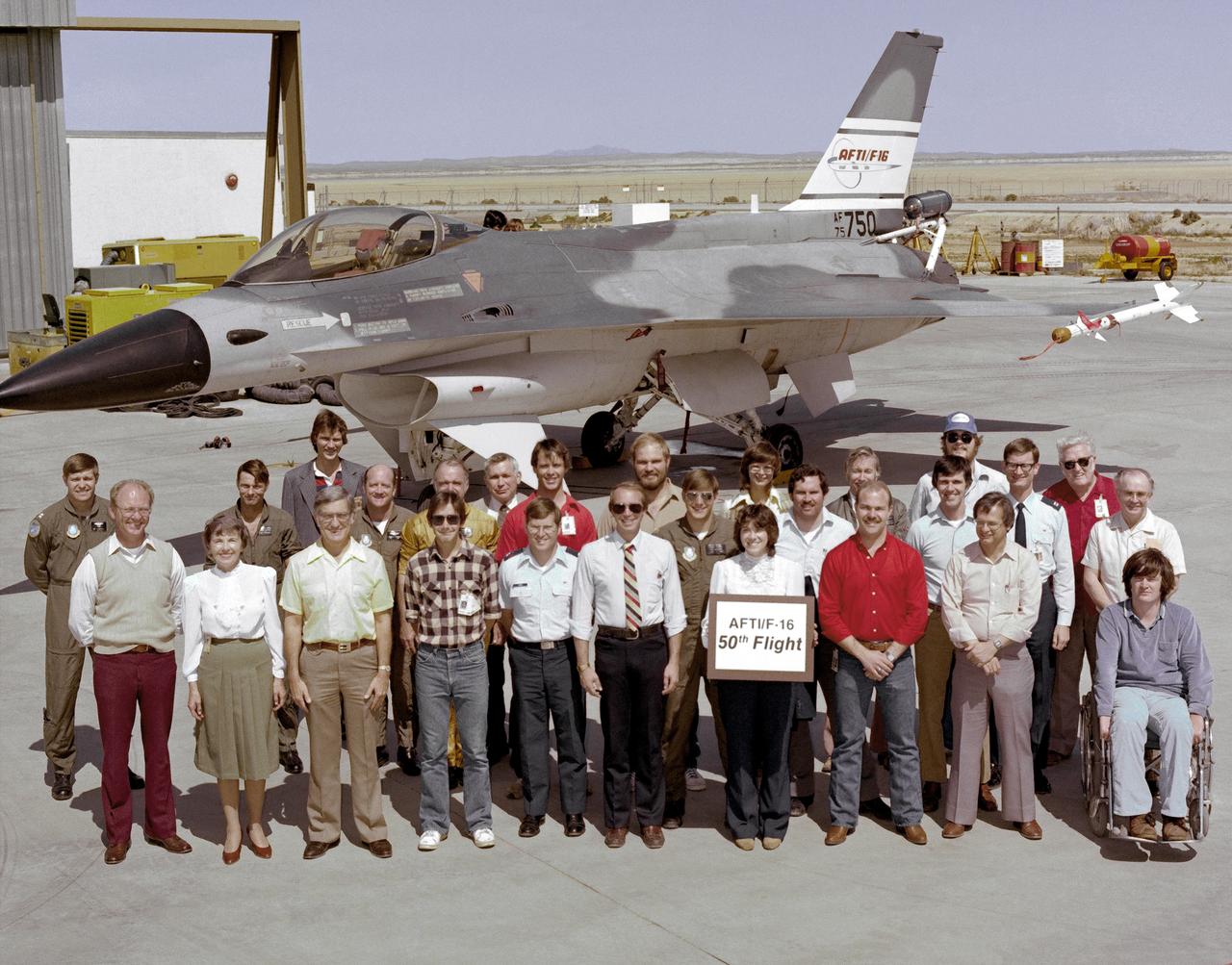

An early (1983) photograph of the AFTI F-16 team, commemorating the aircraft's 50th flight. It shows the initial configuration and paint finish of the AFTI F-16, as well as the forward mounted canards and the spin chute.

A drag chute slows the shuttle Endeavour after landing on runway 22 at Edwards, California, to complete the highly successful STS-68 mission dedicated to radar imaging of the earth's surface as part of NASA's Mission To Planet Earth program. The landing was at 10:02 a.m. (PDT) 11 October 1994, after waiving off from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida, earlier that morning due to adverse weather at Kennedy. The Endeavour crew was originally scheduled to land at Kennedy the morning of 10 October, but mission planners decided early in the flight to extend the mission by one day. Mission commander was Michael A. Baker and the pilot was Terrence W. Wilcutt. The four mission specialists were Thomas D. Jones, payload; Steven L. Smith; Daniel W. Bursch; and Peter J.K. Wisoff.

With its drag chute deployed, orbiter Discovery and its seven-member crew roll toward a stop at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., after an 11-day mission to the International Space Station. The orbiter’s main landing gear touched down on EAFB runway 22 at 5 p.m. With the aid of its drag chute, Discovery came to a complete stop at 5:01 p.m. At the conclusion of mission STS-92, Discovery and crew had traveled about 5.3 million statute miles. Following vehicle safing and preliminary offloading efforts, workers will begin preparations for Discovery’s transcontinental ferry flight back to KSC on the back of NASA’s modified Boeing 747
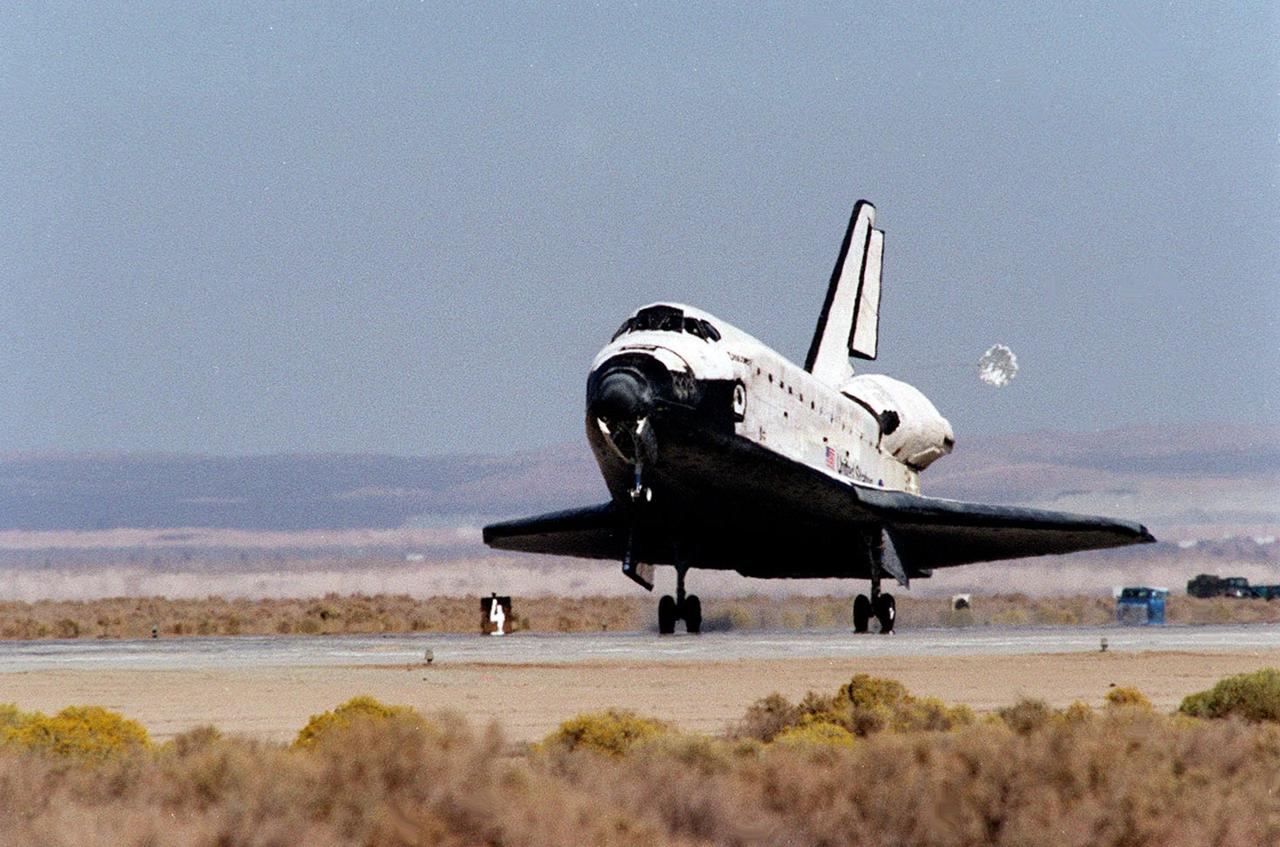

With its drag chute deployed, orbiter Discovery and its seven-member crew roll toward a stop at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., after an 11-day mission to the International Space Station. The orbiter’s main landing gear touched down on EAFB runway 22 at 5 p.m. With the aid of its drag chute, Discovery came to a complete stop at 5:01 p.m. At the conclusion of mission STS-92, Discovery and crew had traveled about 5.3 million statute miles. Following vehicle safing and preliminary offloading efforts, workers will begin preparations for Discovery’s transcontinental ferry flight back to KSC on the back of NASA’s modified Boeing 747
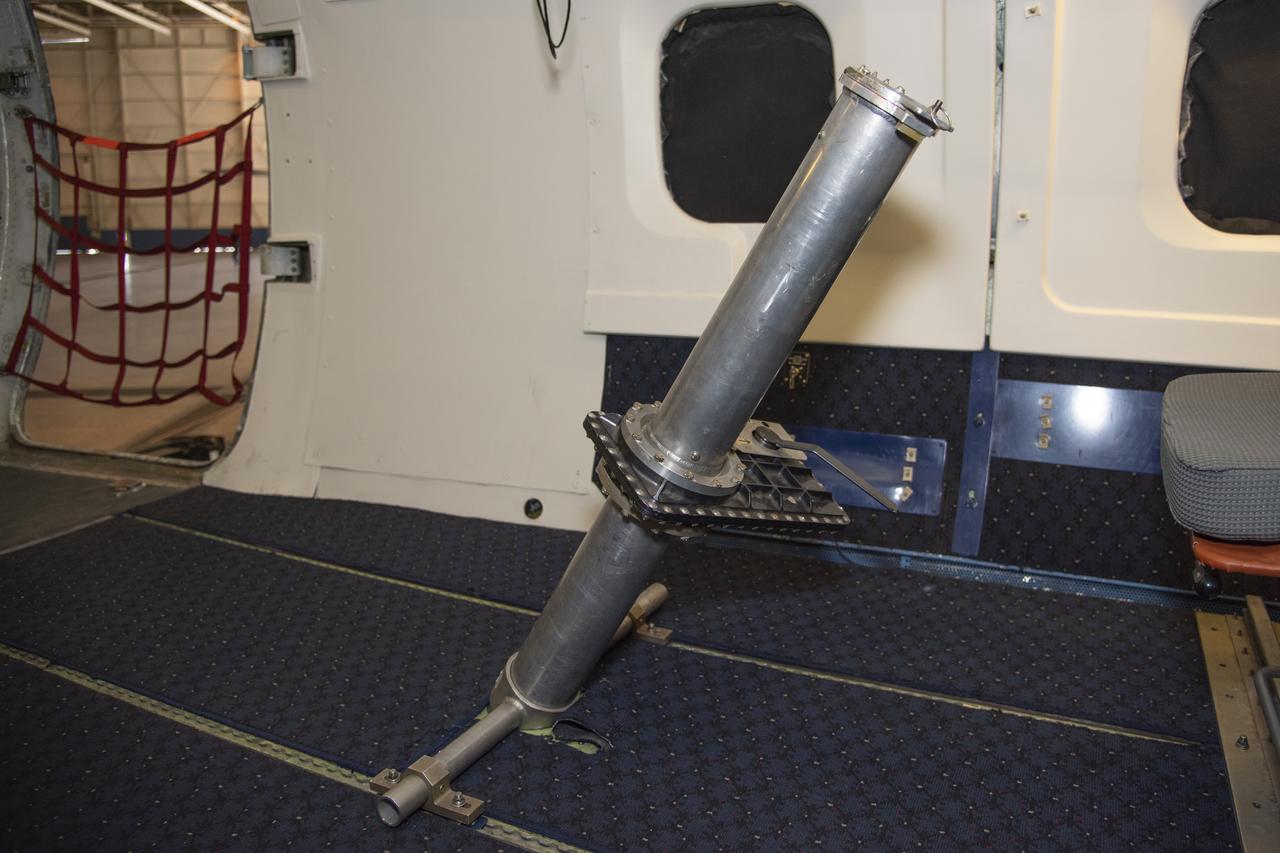

To verify the lidar data they're collecting on the DC-8 airborne science laboratory, Aeolus mission scientists will use dropsondes, which are devices they'll drop from this tube in the aircraft to collect wind and water vapor data.
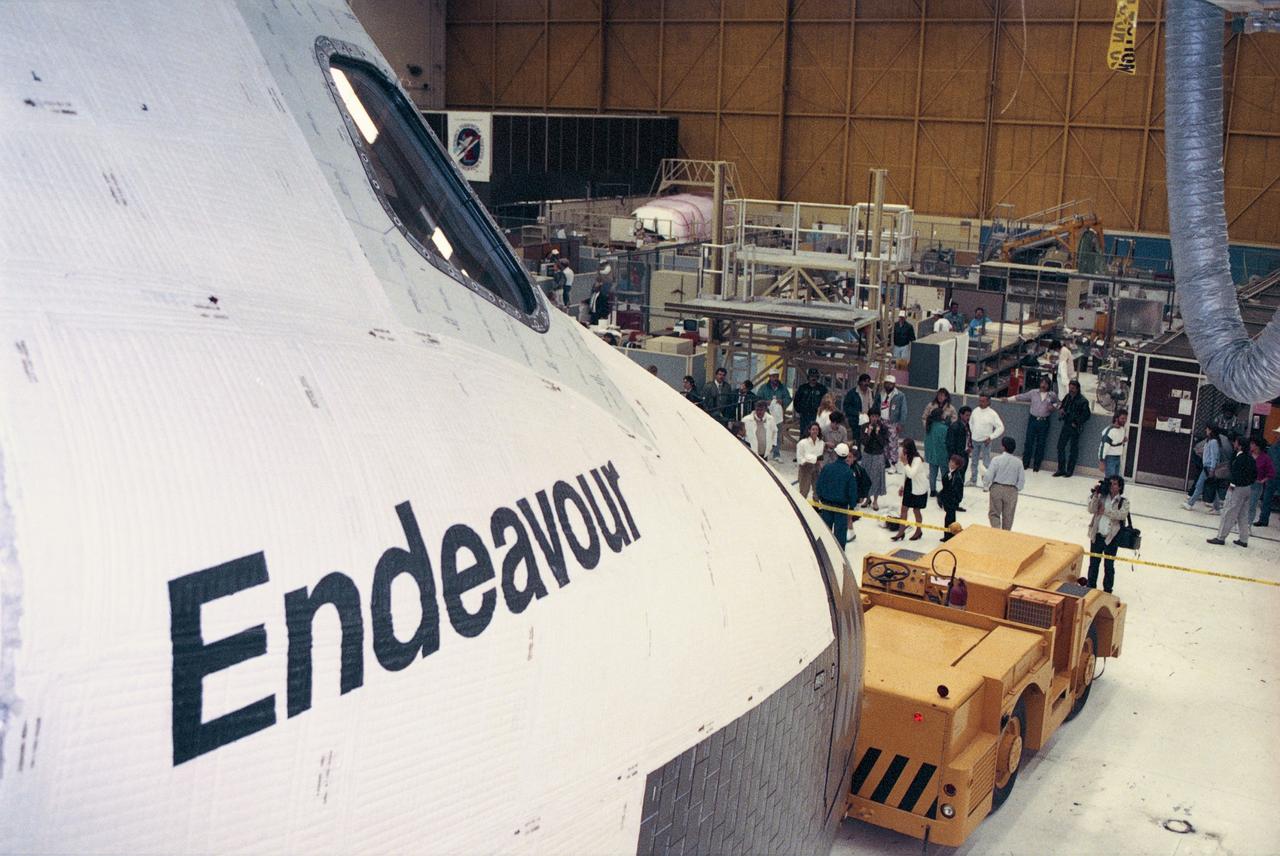

The newest space shuttle orbiter, Endeavour is ready to roll out of the hangar at Palmdale, Calif. OV-105 features many design enhancements, including a drag chute for safer landings and equipment to allow the orbiter to remain in space for up to 28 days. Photo credit: NASA
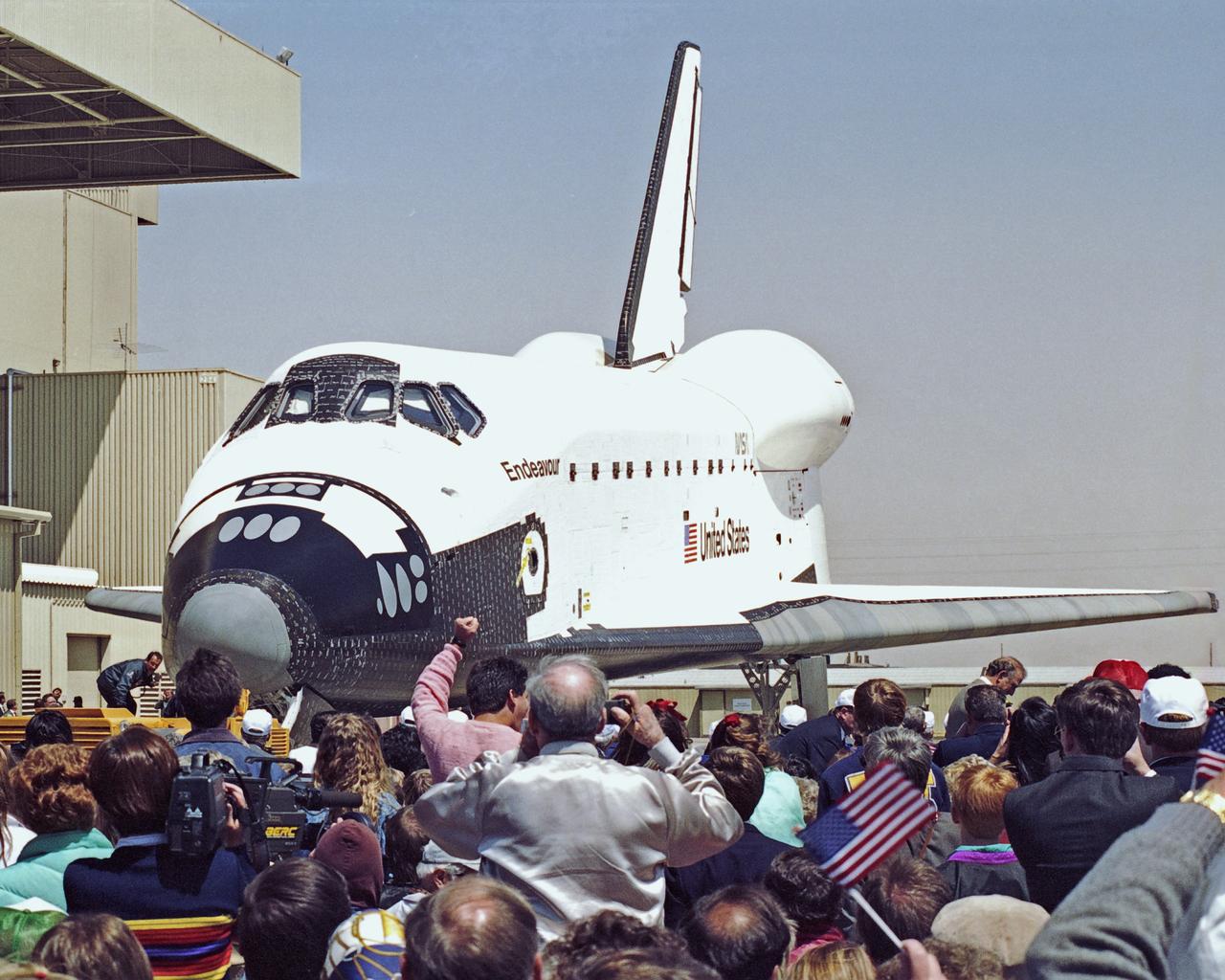

The newest space shuttle orbiter, Endeavour is ready to roll out of the hangar at Palmdale, Calif. OV-105 features many design enhancements, including a drag chute for safer landings and equipment to allow the orbiter to remain in space for up to 28 days. Photo credit: NASA
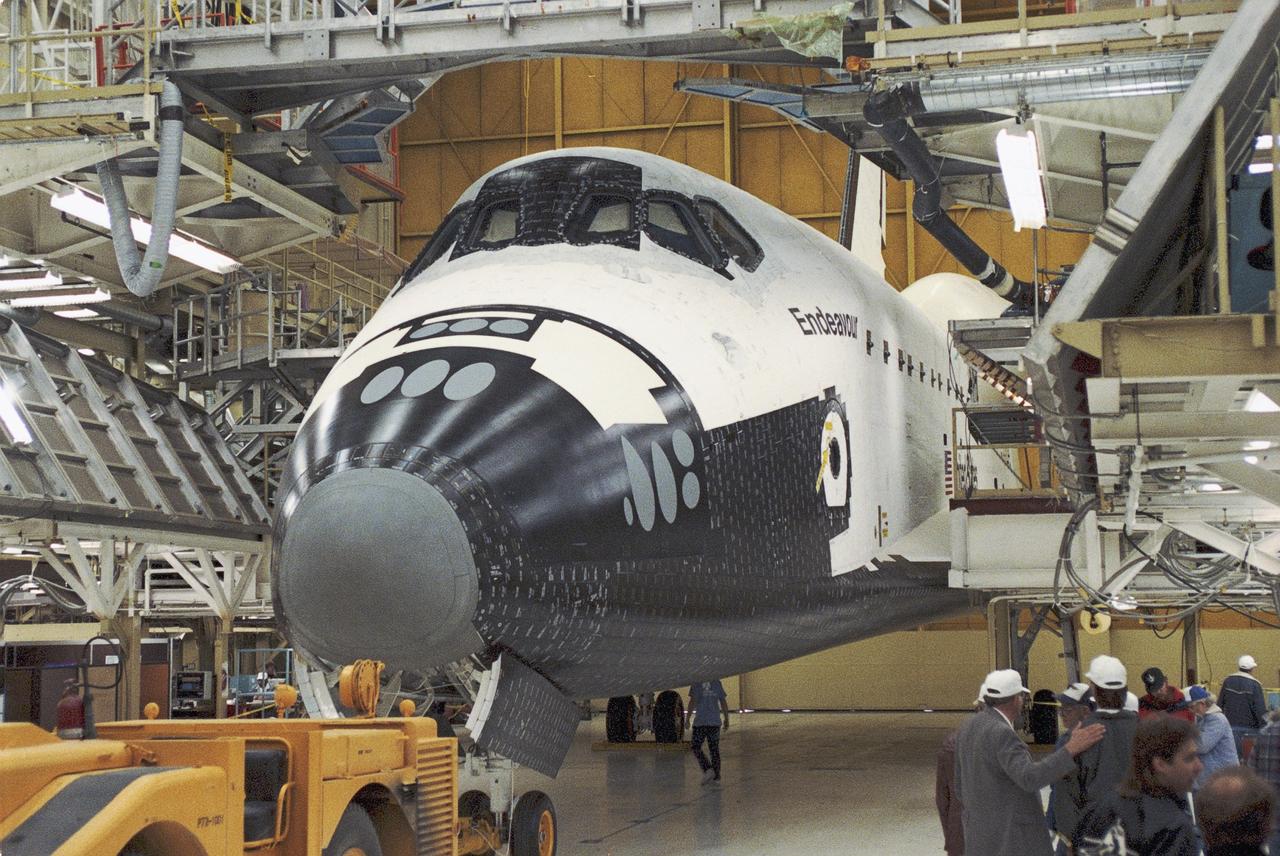

The newest space shuttle orbiter, Endeavour, is ready to roll out of the hangar at Palmdale, Calif. OV-105 features many design enhancements, including a drag chute for safer landings and equipment to allow the orbiter to remain in space for up to 28 days. Photo credit: NASA
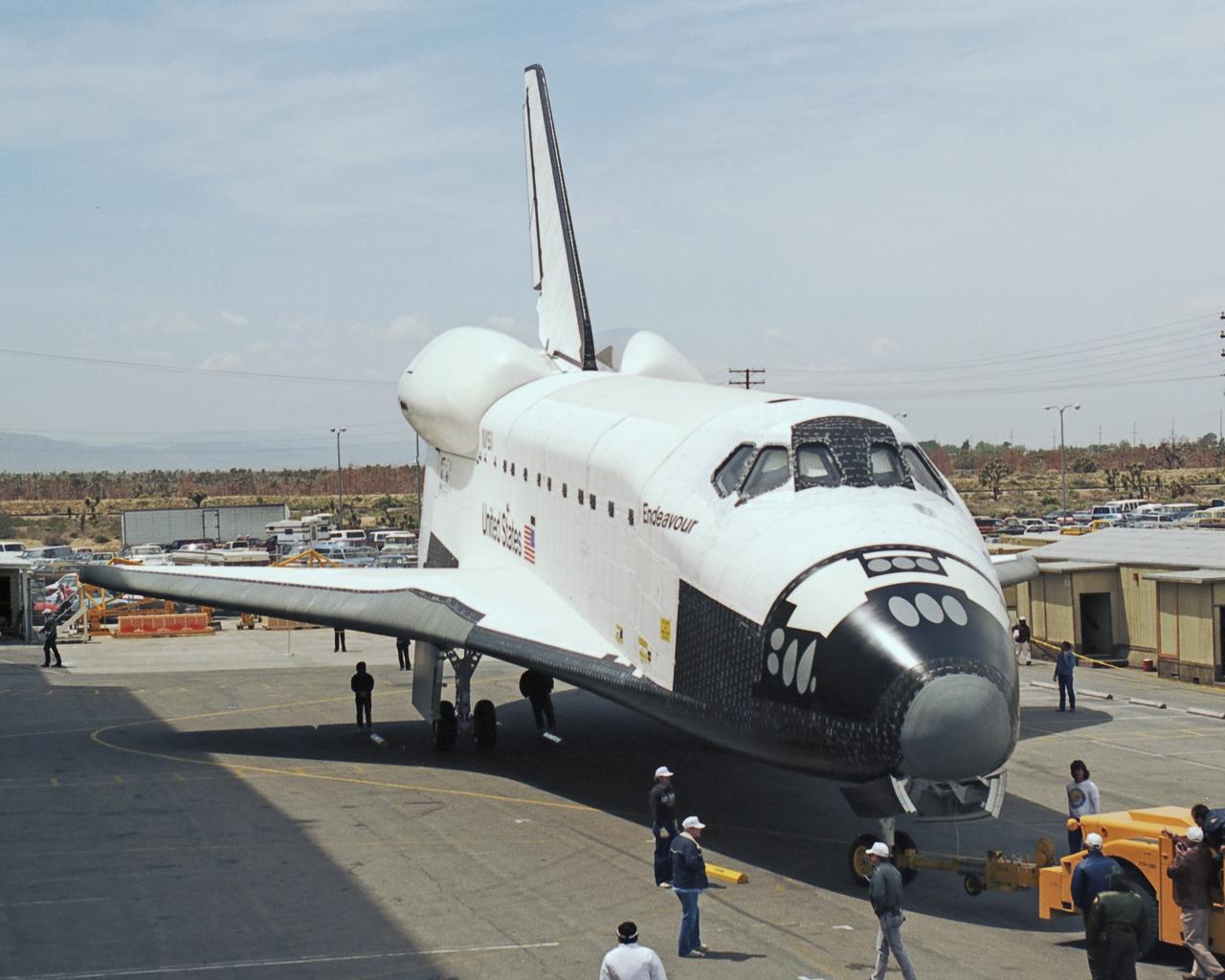

The newest space shuttle orbiter, Endeavour is ready to roll out of the hangar at Palmdale, Calif. OV-105 features many design enhancements, including a drag chute for safer landings and equipment to allow the orbiter to remain in space for up to 28 days.Photo credit: NASA
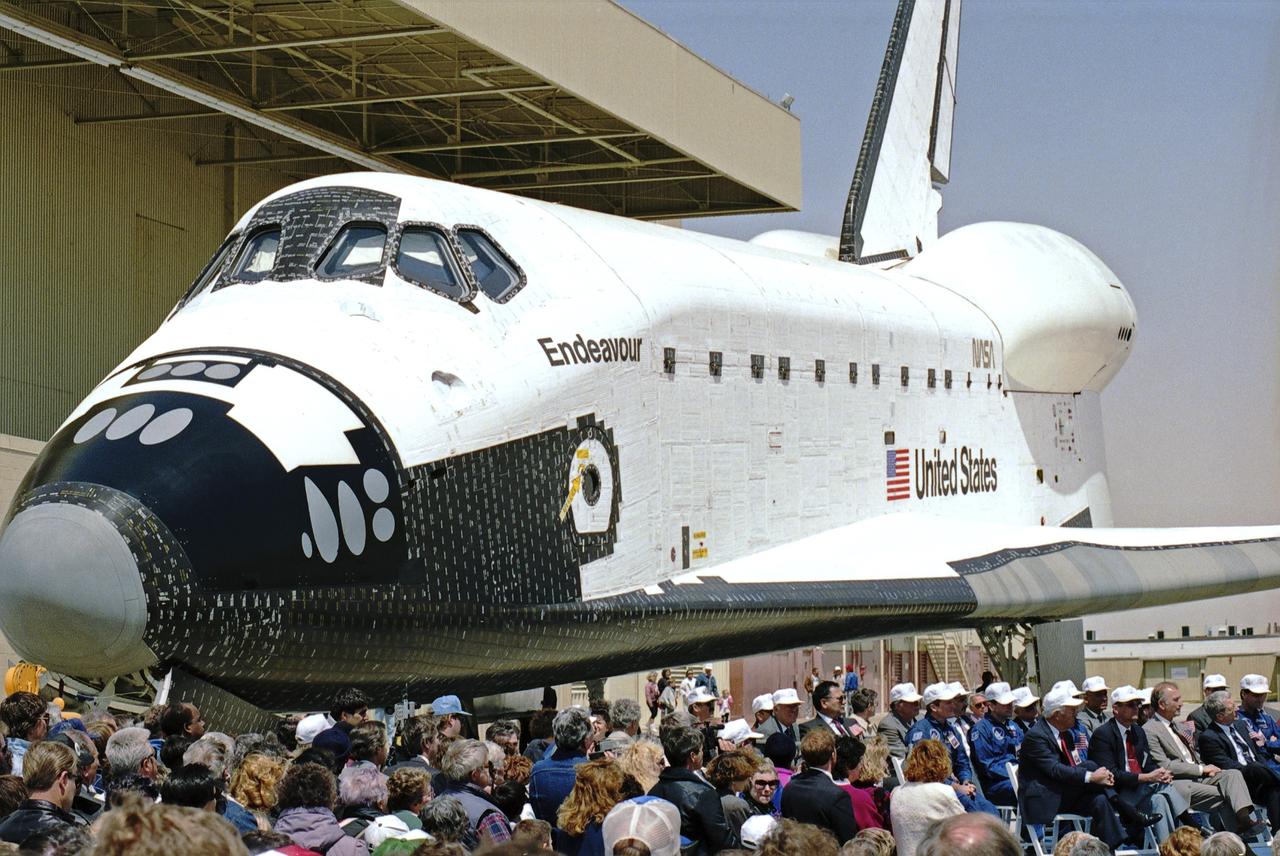

The newest space shuttle orbiter, Endeavour, rolls out of the hangar at Palmdale, Calif. OV-105 features many design enhancements, including a drag chute for safer landings and equipment to allow the orbiter to remain in space for up to 28 days. Photo credit: NASA
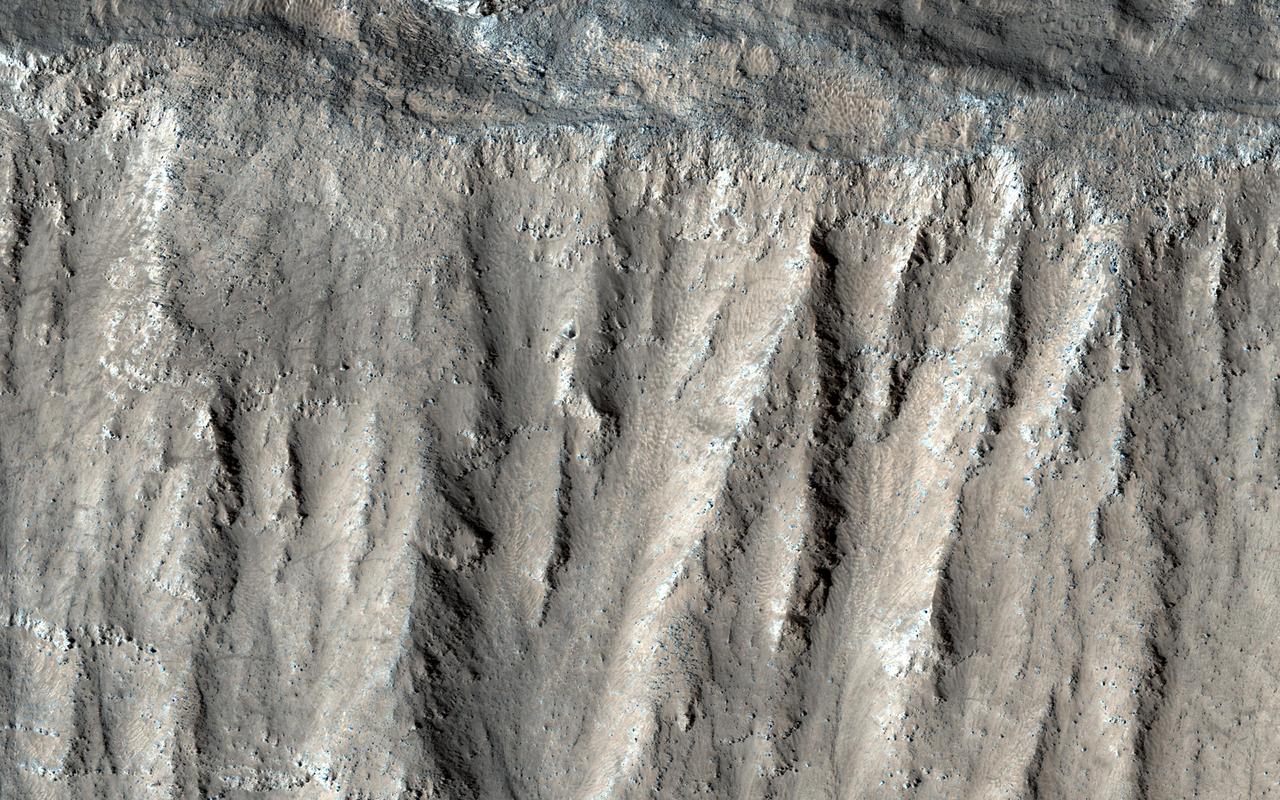

This image shows part of the steep wall of the caldera (a large volcanic crater) at the top of Ascraeus Mons, one of Mars' giant volcanoes. We can see chutes carved into the soft dust that has built up on the slope, with some similarities to gully landforms elsewhere on the planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22804

The newest space shuttle orbiter, Endeavour is ready to roll out of the hangar at Palmdale, Calif. OV-105 features many design enhancements, including drag chute for safer landings and equipment to allow the orbiter to remain in space for up to 28 days. Photo credit: NASA
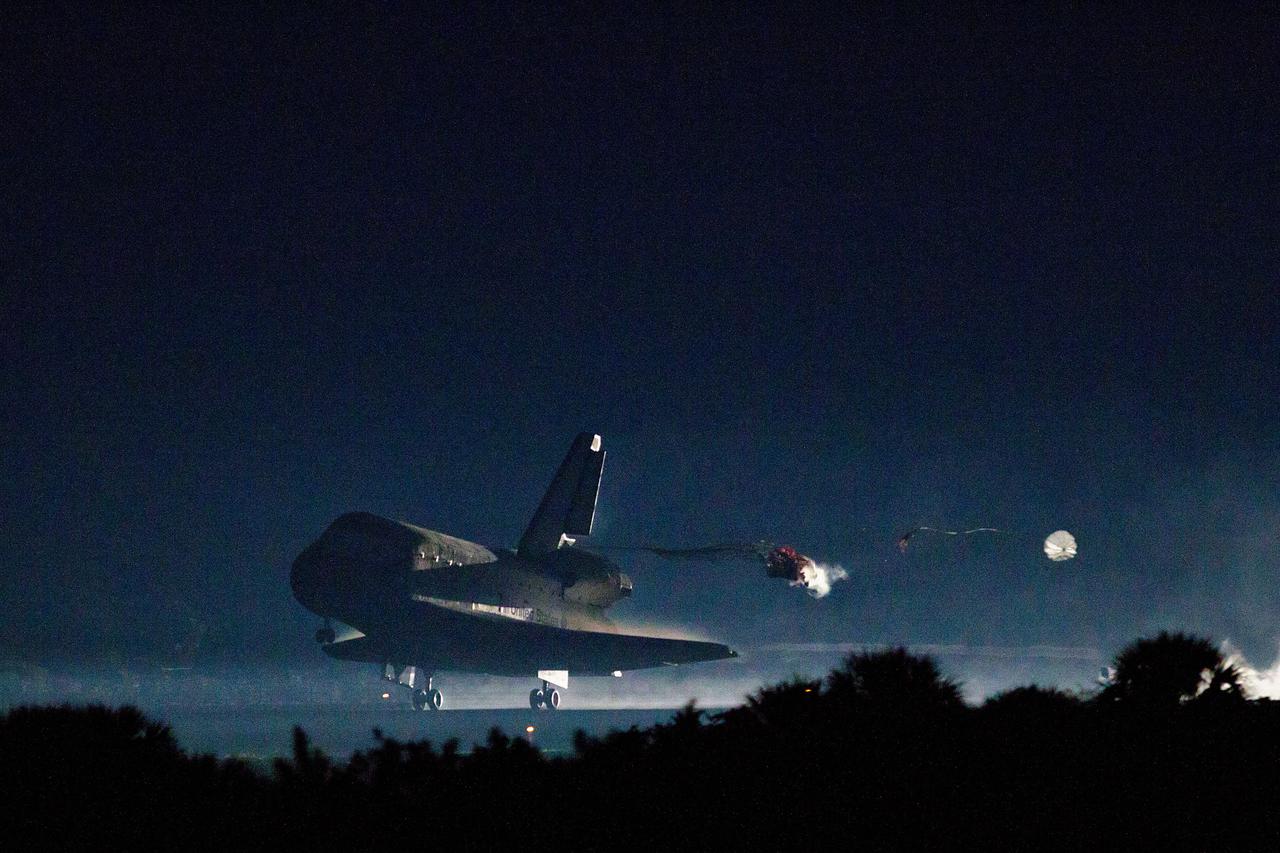

JSC2011-E-067687 (21 July 2011) --- The drag chute is deployed as the space shuttle Atlantis lands on July 21 at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The landing completed STS-135, the final mission of the NASA Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA Photo/Houston Chronicle, Smiley N. Pool
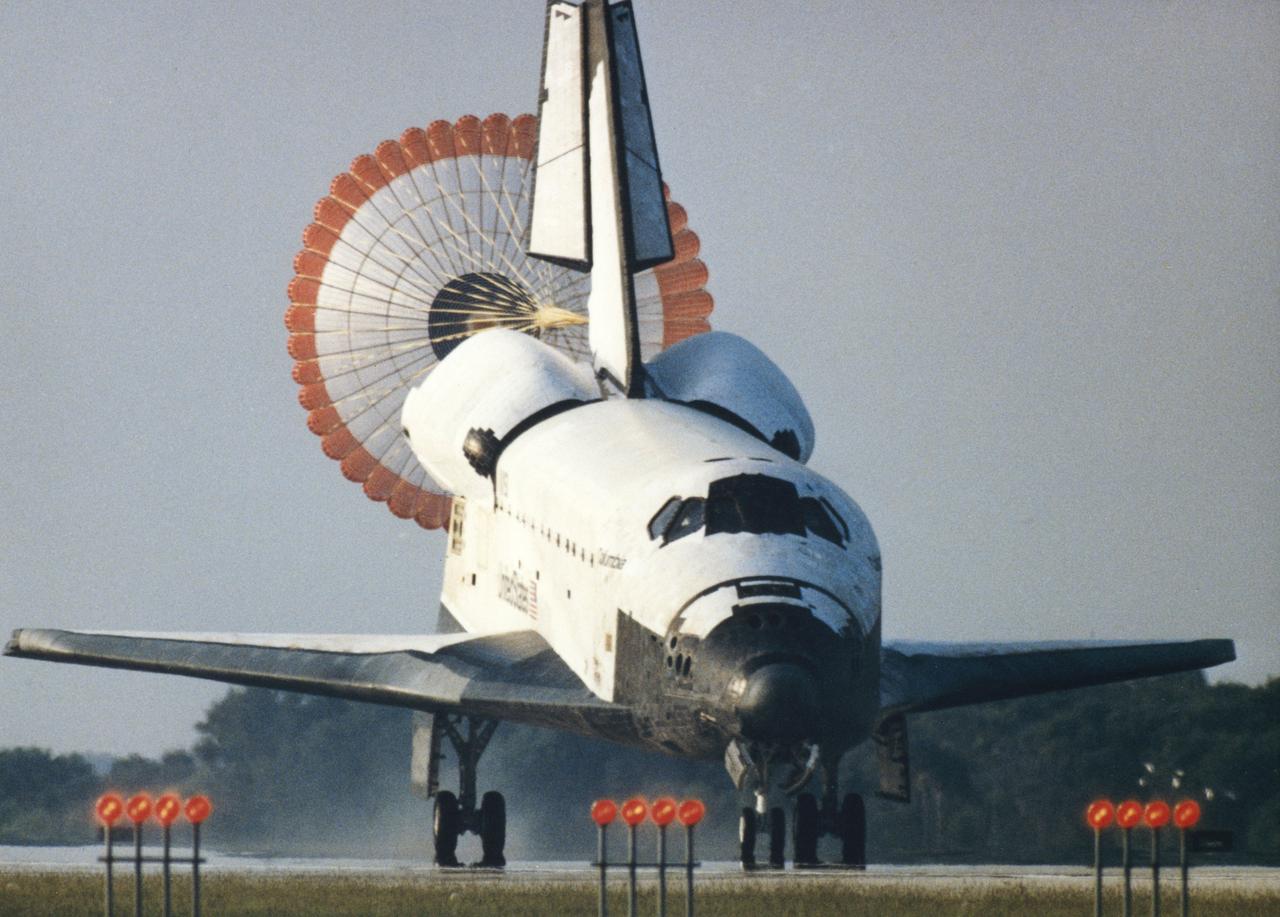

As the orbiter Columbia (STS-50) rolled down Runway 33 of Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility, its distinctively colored drag chute deployed to slow down the spaceship. This landing marked OV-102's first end-of-mission landing at KSC and the tenth in the program, and the second shuttle landing with the drag chute. Edwards Air Force Base, CA, was the designated prime for the landing of Mission STS-50, but poor weather necessitated the switch to KSC after a one-day extension of the historic flight. STS-50 was the longest in Shuttle program historyo date, lasting 13 days, 19 hours, 30 minutes and 4 seconds. A crew of seven and the USML-1 were aboard.
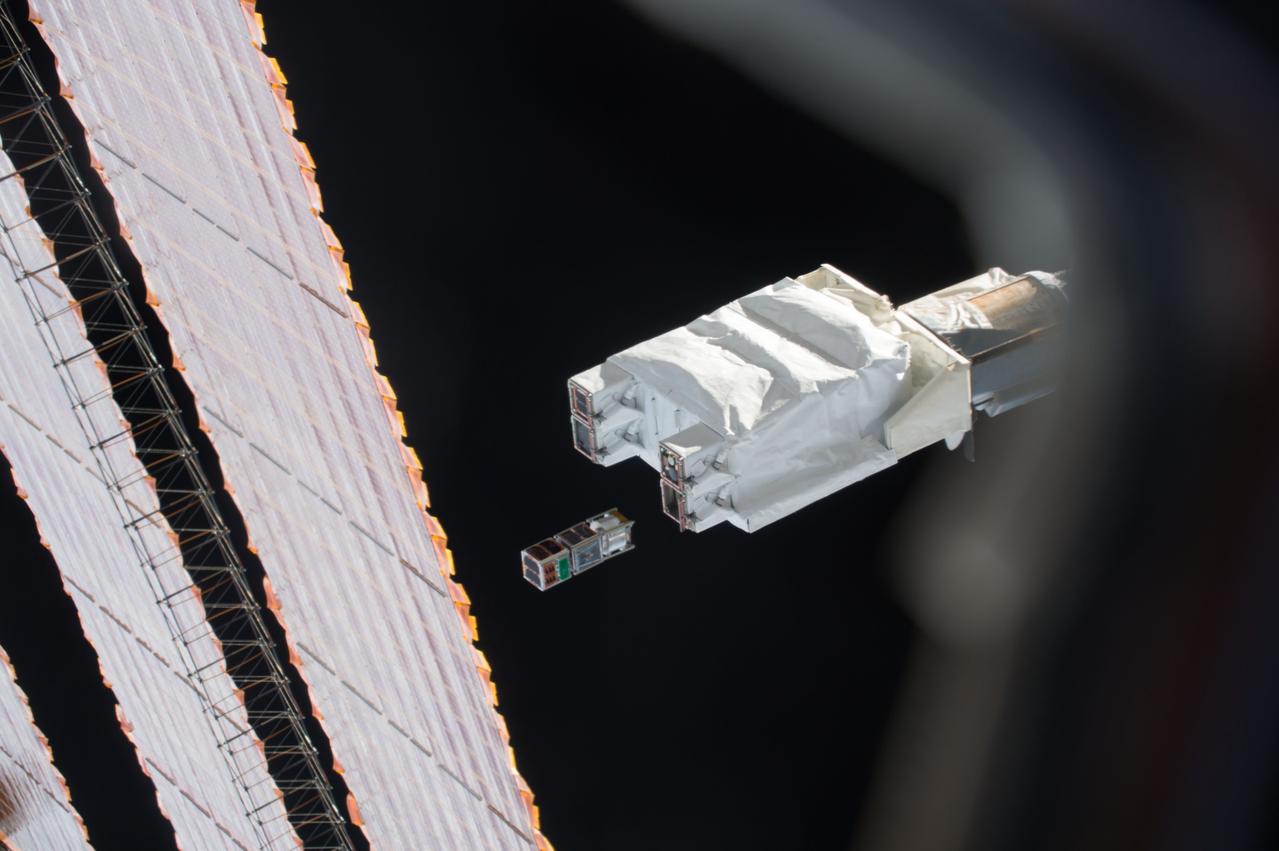
iss050e031198 (1/17/2017) --- Photo documentation of the Japanese-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer-6 (J-SSOD-6) deployment of the ITF-2, Waseda-SAT3 and Freedom CubeSats. The Imagine The Future-2 (ITF-2) CubeSat mission supports amateur radio networking by testing a micro engineered 1/20 wavelength small antenna. The WASEDA SAT-3 is a CubeSat developed by Waseda University aiming to test an ultra-light drag chute for accelerated deorbit. An LCD projector shows images on the chute with imagery sent back to Earth via an onboard camera. FREEDOM is a 1 Unit (1U) CubeSat developed by the Nakashimada Engineering Works and the Tohoku University to demonstrate a deployable deorbit device “DOM” for application in future missions for space debris mitigation.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers repair the parachutes recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission. Typically, each main canopy requires hundreds of repairs after each use. The smaller chutes and the parachute deployment bags they are packed in also require repairs. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be carefully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
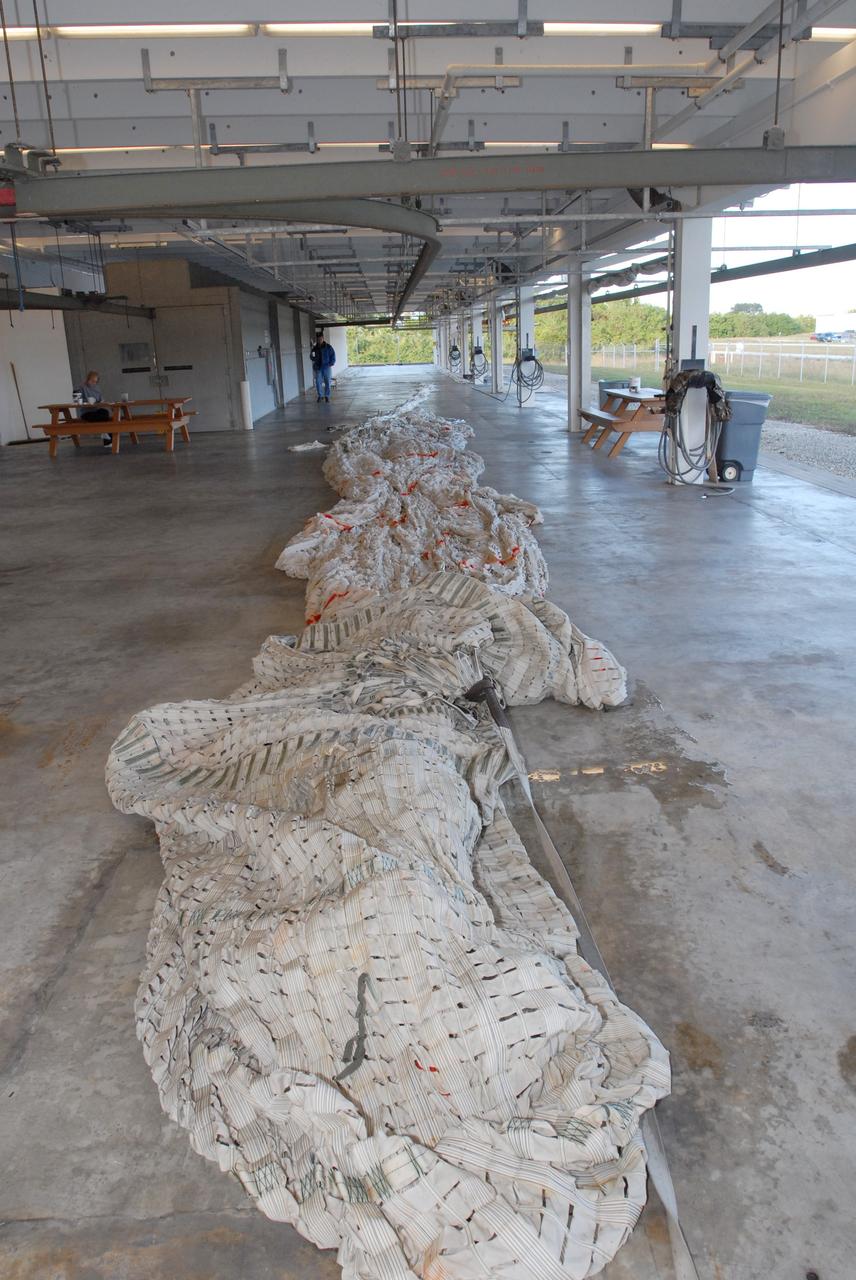

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Parachutes recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission are stretched out at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to detangle them. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. After the chutes are returned to the facility following launch, a hanging monorail system is used to transport each parachute into a 30,000-gallon washer and then into a huge dryer heated with 140-de¬gree air at 13,000 cubic feet per minute. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be care¬fully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
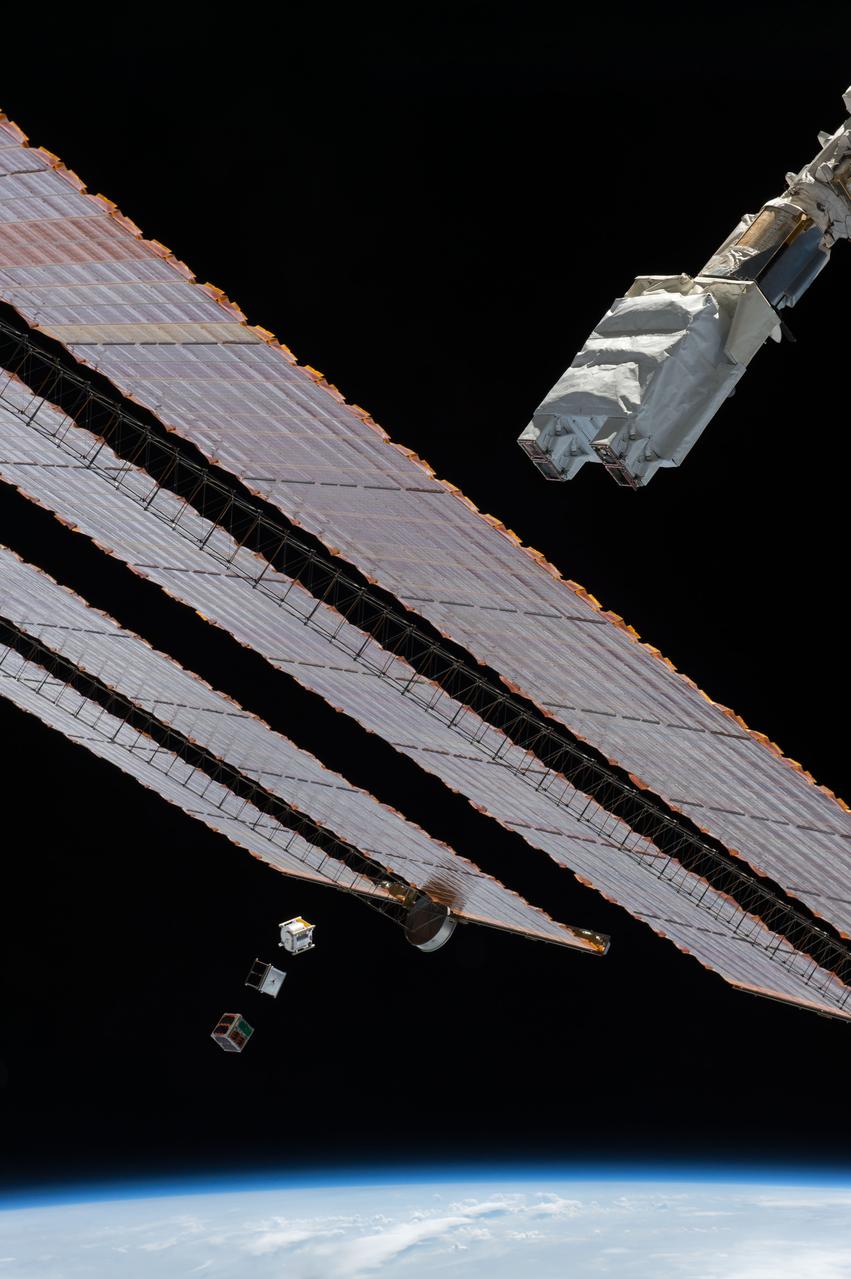

iss050e032565 (1/17/2017) --- Photo documentation of the Japanese-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer-6 (J-SSOD-6) deployment of the ITF-2, Waseda-SAT3 and Freedom CubeSats. The Imagine The Future-2 (ITF-2) CubeSat mission supports amateur radio networking by testing a micro engineered 1/20 wavelength small antenna. The WASEDA SAT-3 is a CubeSat developed by Waseda University aiming to test an ultra-light drag chute for accelerated deorbit. An LCD projector shows images on the chute with imagery sent back to Earth via an onboard camera. FREEDOM is a 1 Unit (1U) CubeSat developed by the Nakashimada Engineering Works and the Tohoku University to demonstrate a deployable deorbit device “DOM” for application in future missions for space debris mitigation.

STS074-S-022 (20 Nov 1995) --- The drag chute of the Space Shuttle Atlantis is deployed as the space vehicle touches down on Runway 33 of Kennedy Space Center?s (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility, completing its STS-74 mission. The main gear touched down at 12:01:27 p.m. (EST), November 20, 1995.
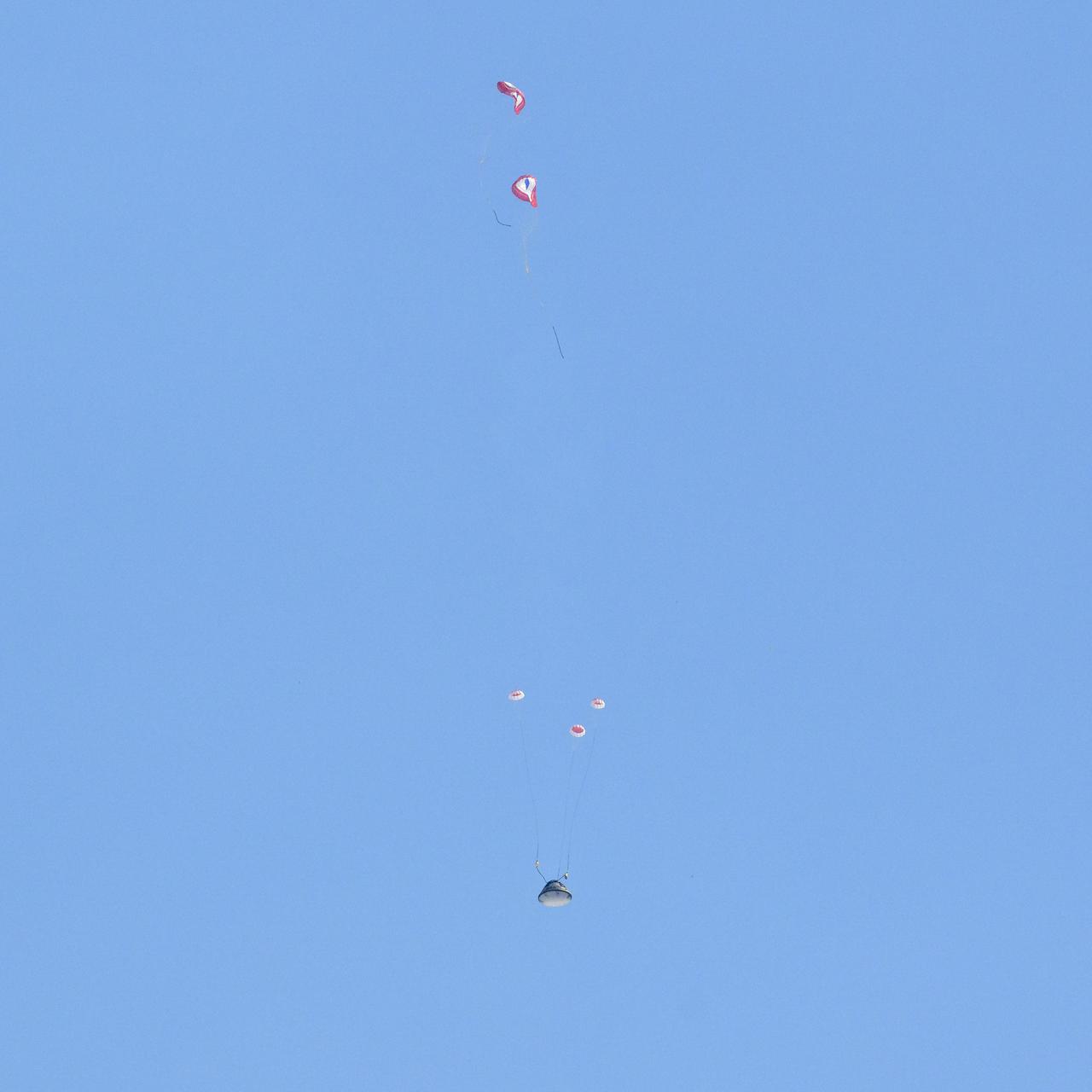

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft transitions to main chutes from drogue parachutes as it lands at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
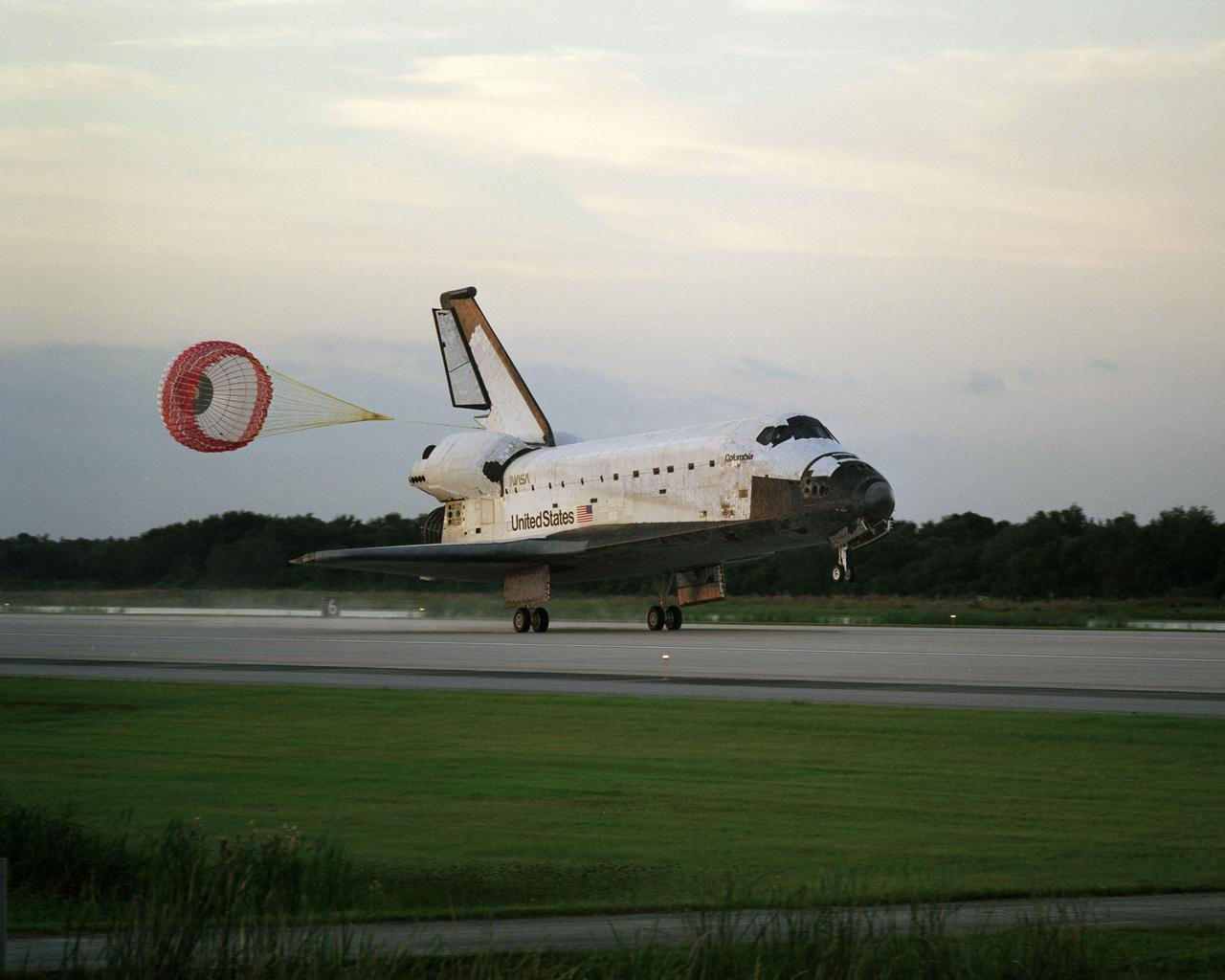

STS073-S-048 (5 November 1995) --- The drag chute on the Space Shuttle Columbia is deployed, marking the completion of its 18th Earth-orbital mission. Landing on the runway of the Shuttle Landing Facility occurred at 6:48 a.m. (EST), November 5, 1995. Onboard were five NASA astronauts and two guest researchers who had spent almost 16 full days in space in support of the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.
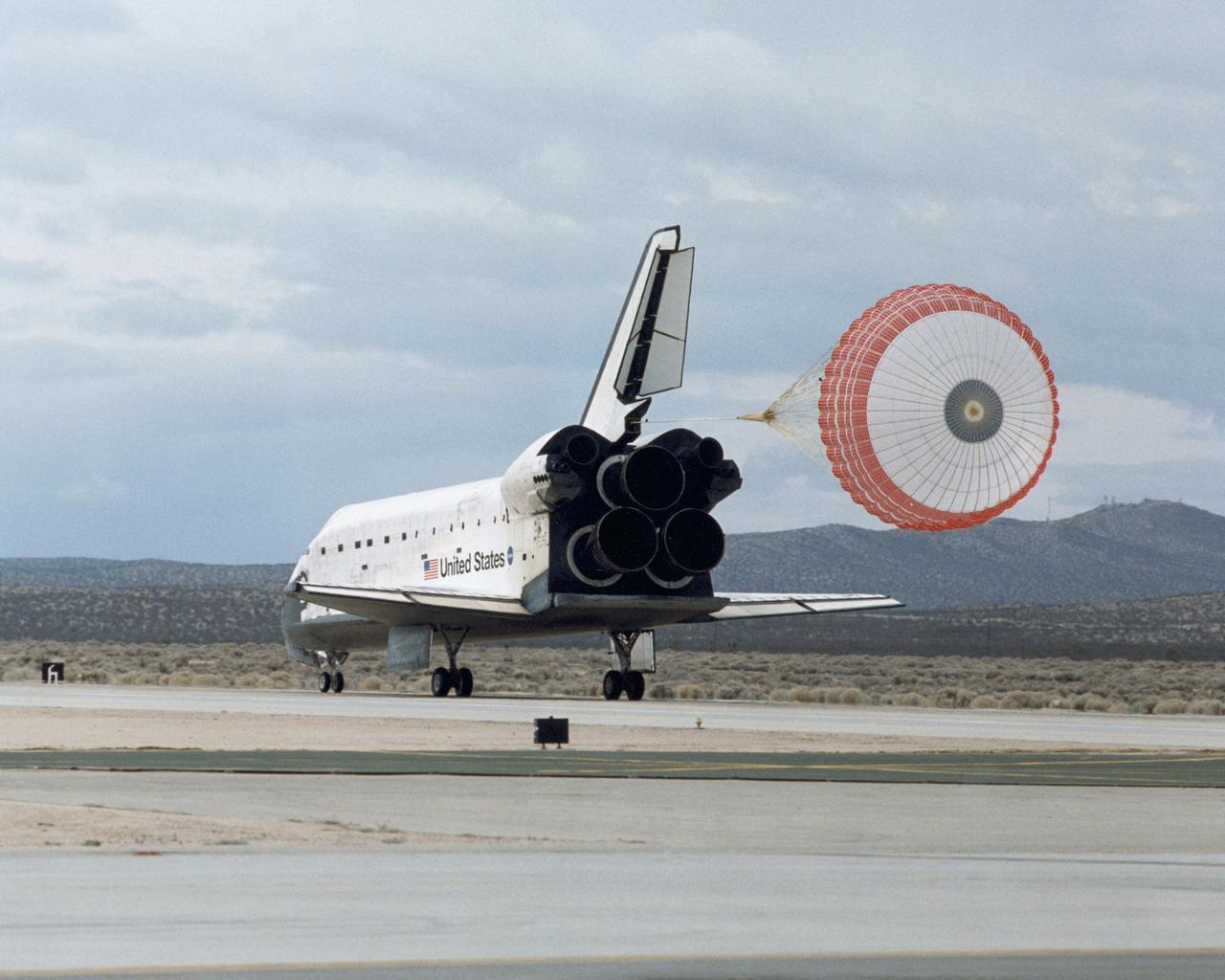

STS098-S-017 (20 Feb. 2001) --- A drag chute slows down the space shuttle Atlantis following its touchdown to mark mission completion at Edwards Air Force Base in the Mojave Desert of California. Onboard were astronauts Kenneth Cockrell, Mark Polansky, Robert Curbeam, Thomas Jones and Marsha Ivins. Atlantis touched down on Edward?s concrete runway at 2:33 p.m. (CST), Feb. 20, for a mission elapsed time of 12 days, 21 hours and 20 minutes. Photo credit: NASA
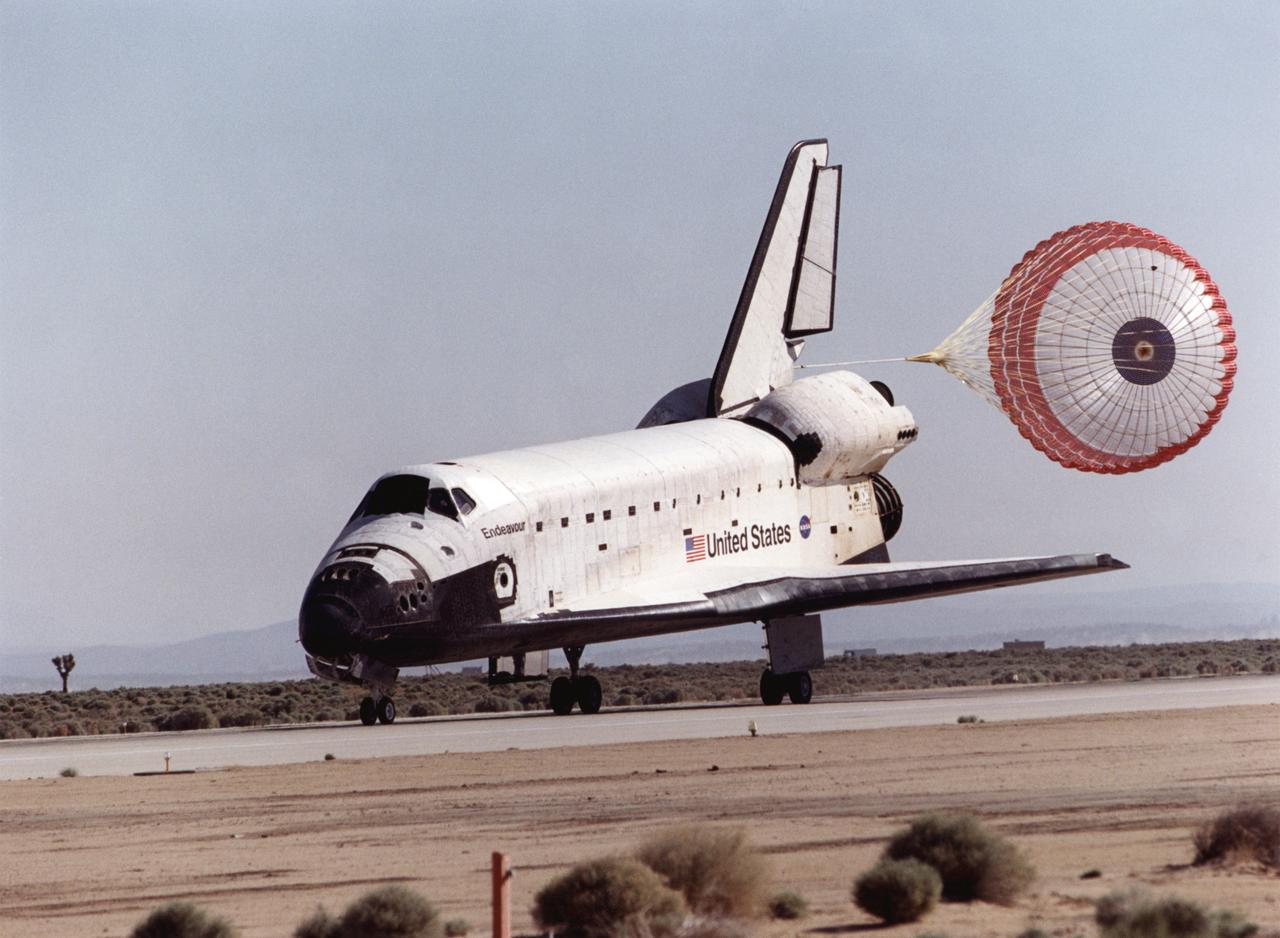

A lone desert Joshua tree greeted the arrival of Space Shuttle Endeavour at Edwards Air Force Base, California, May 1, 2001. A large drag chute helped slow Endeavour on the runway. After mounting the shuttle on a converted 747 airliner at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Endeavour will be carried back to the Kennedy Space Center for its next mission. Weather in Florida necessitated landing in California.
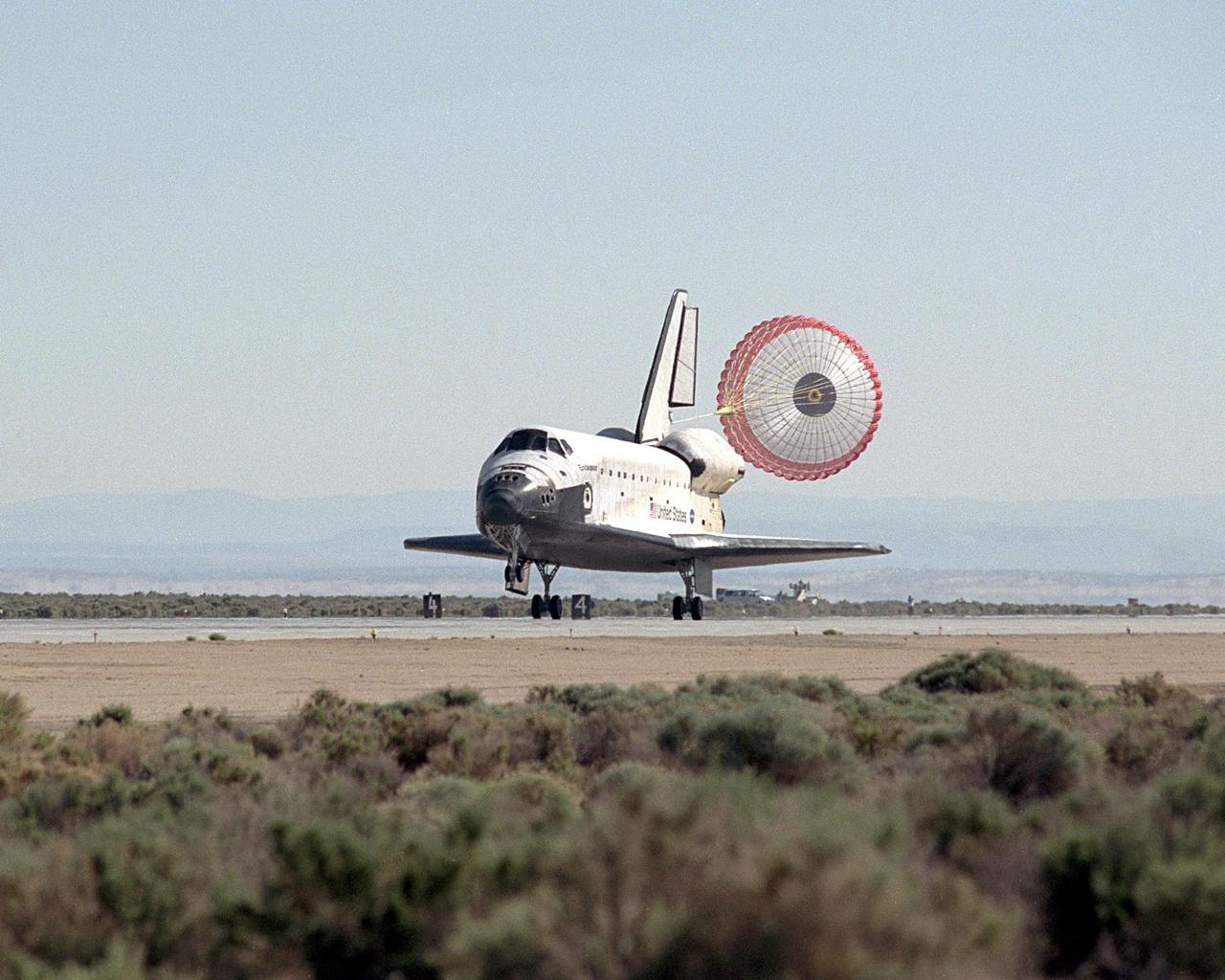

NASA/EDWARDS AFB, CALIF. -- With its drag chute deployed, Endeavour lands on runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., at 12:10:42 p.m. EDT after a mission of 11 days, 12 hours, 54 minutes to the International Space Station on mission STS-100. The orbiter and its crew of seven logged about 4.9 million statute miles in 186 orbits. Due to unfavorable weather conditions, landing at KSC was waved off. The landing marked the third consecutive landing at EAFB.
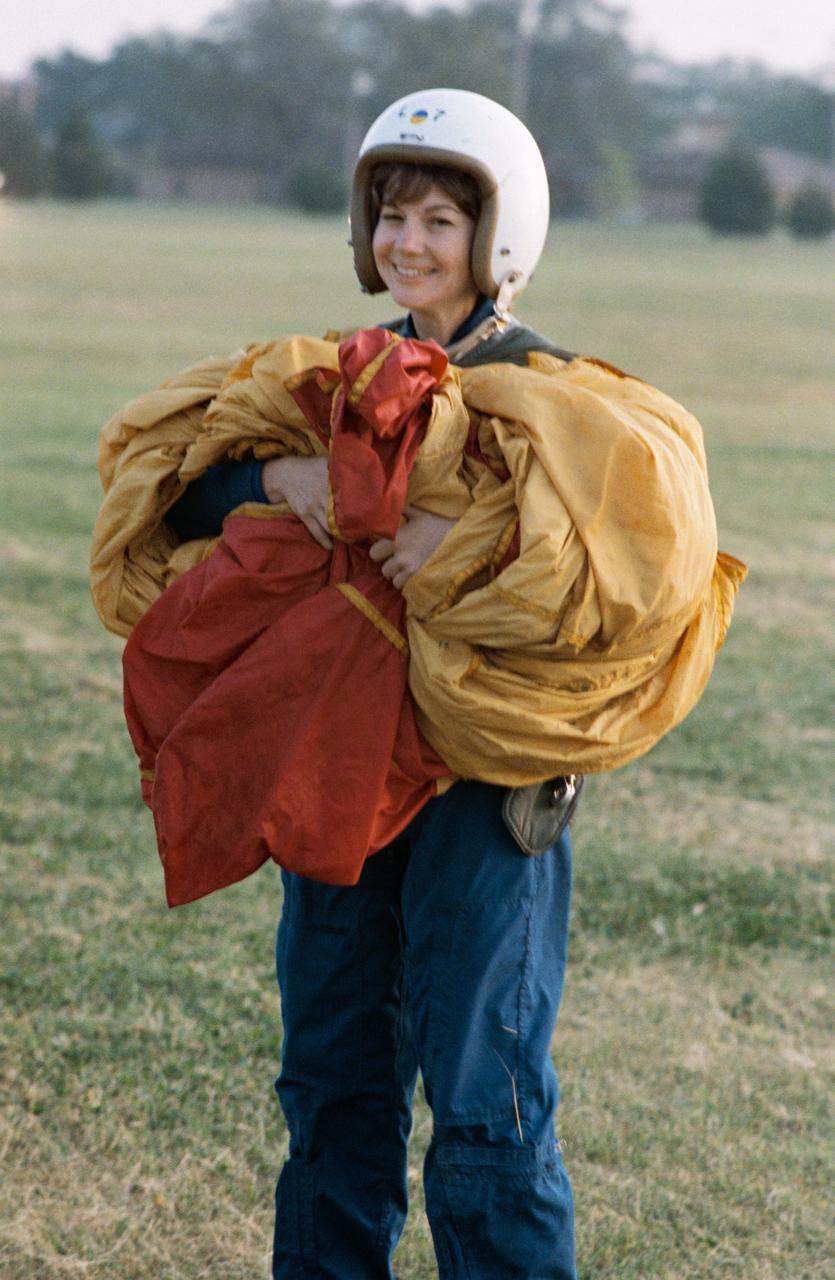

S93-38725 (12-14 Sept. 1992) --- Catherine G. Coleman, a member of the 1992 class of astronaut candidates at the Johnson Space Center (JSC), gathers up a parachute. The chute had just been used in one of many exercises experienced by the trainees at a three-day parachute/survival course hosted by Vance Air Force Base near Enid, Oklahoma. EDITOR?S NOTE: Coleman was later named as mission specialist for the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission, scheduled to fly as STS-73 in 1995.
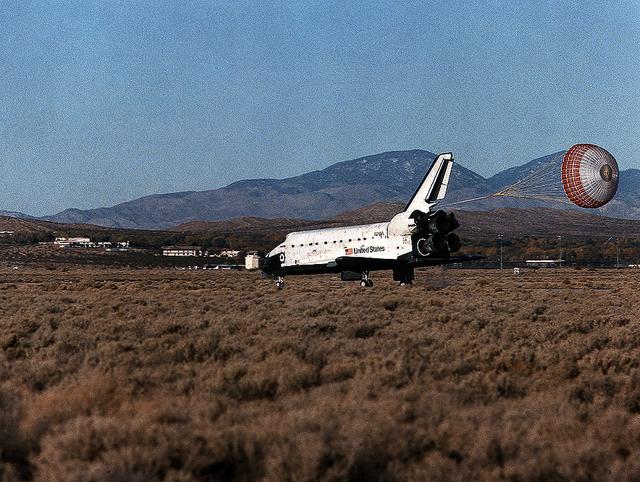

The drag-chute is fully deployed as the Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-66) heads toward a stop at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California, ending a successful mission. The crew supported the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3), conducting approximately 80 experiments. The Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometer and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite (CRISTA-SPAS), which was developed by German engineers, was successfully deployed and retrieved during this space mission.

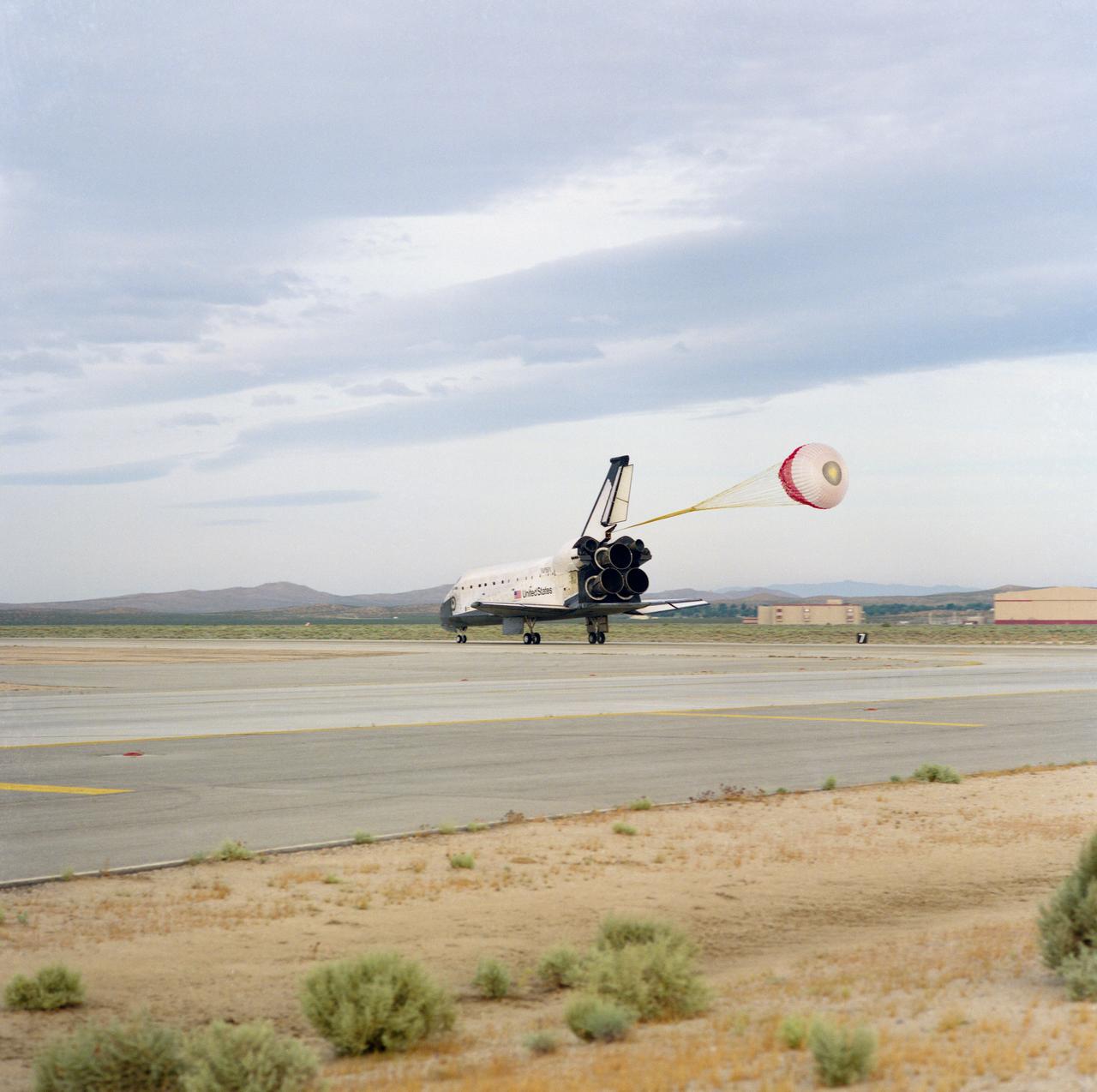
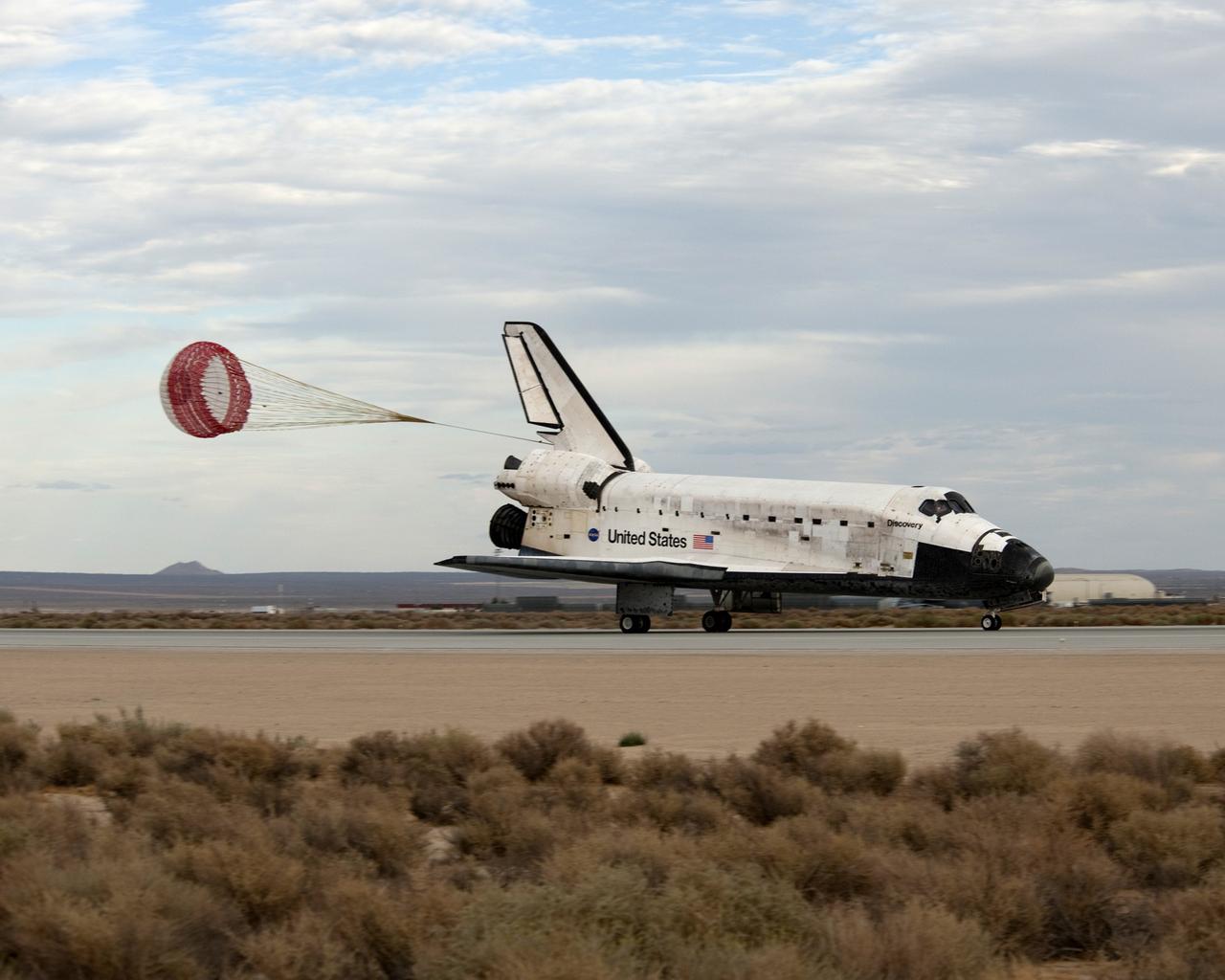
The drag chute for Space Shuttle Discovery is deployed on the Shuttle Landing Facility, marking the end to the eight-day STS-60 mission. Landing occurred at 2:19:22 p.m. (035); The main landing gear on the Space Shuttle Discovery touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility (036); The main landing gear on the Space Shuttle Discovery is about to touch down on the Shuttle Landing Facility. Note the Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA) monitoring the landing phase of the mission (037).

The drag chute for Space Shuttle Discovery is deployed on the Shuttle Landing Facility, marking the end to the eight-day STS-60 mission. Landing occurred at 2:19:22 p.m. (035); The main landing gear on the Space Shuttle Discovery touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility (036); The main landing gear on the Space Shuttle Discovery is about to touch down on the Shuttle Landing Facility. Note the Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA) monitoring the landing phase of the mission (037).

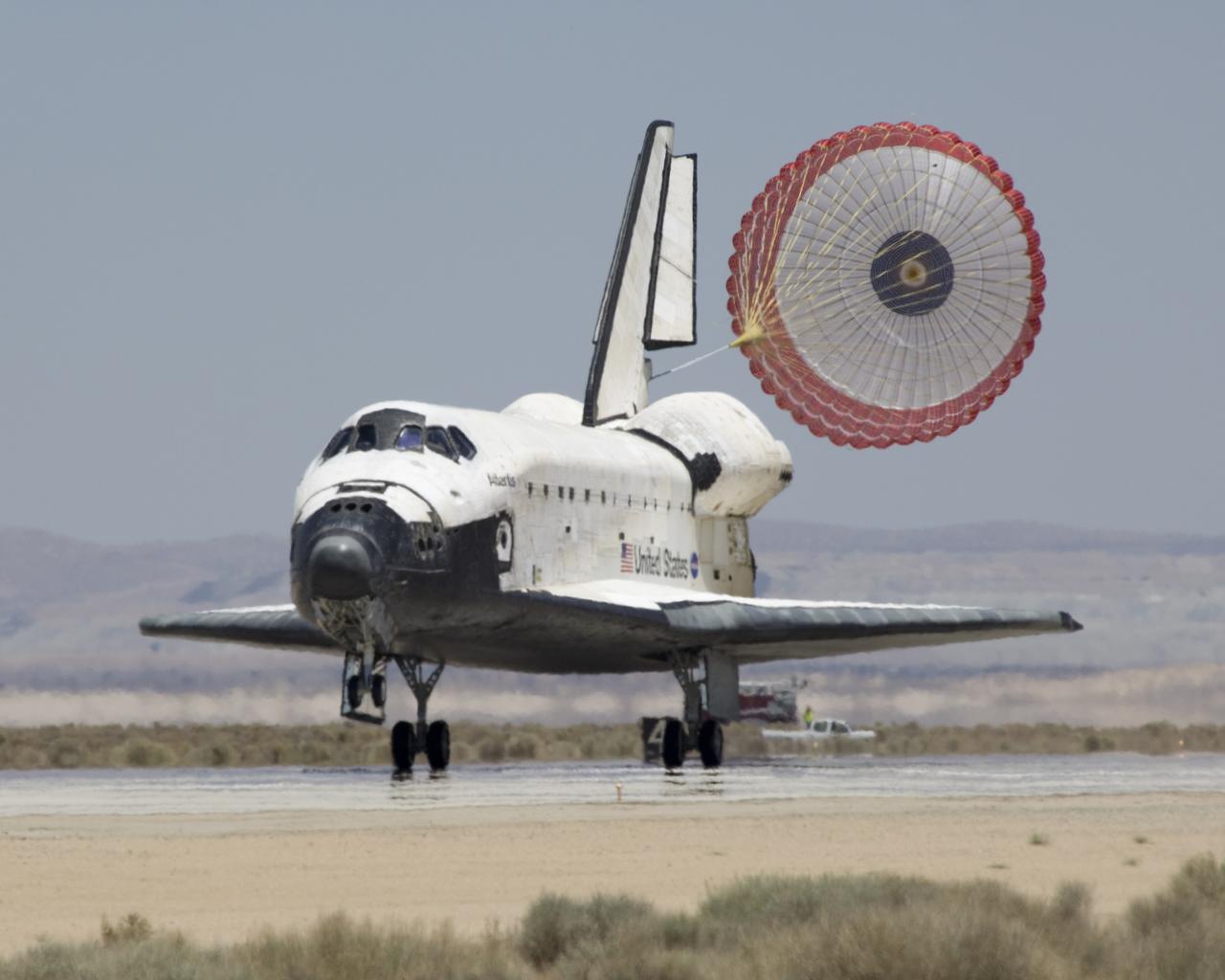
EDWARDS AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- (ED09-0253-04) Trailing its drag chute, Space Shuttle Discovery slows to a stop after landing at Edwards Air Force Base to conclude its almost 14-day, 5.7-million-mile journey to the International Space Station on mission STS-128 (NASA photo / Tony Landis)
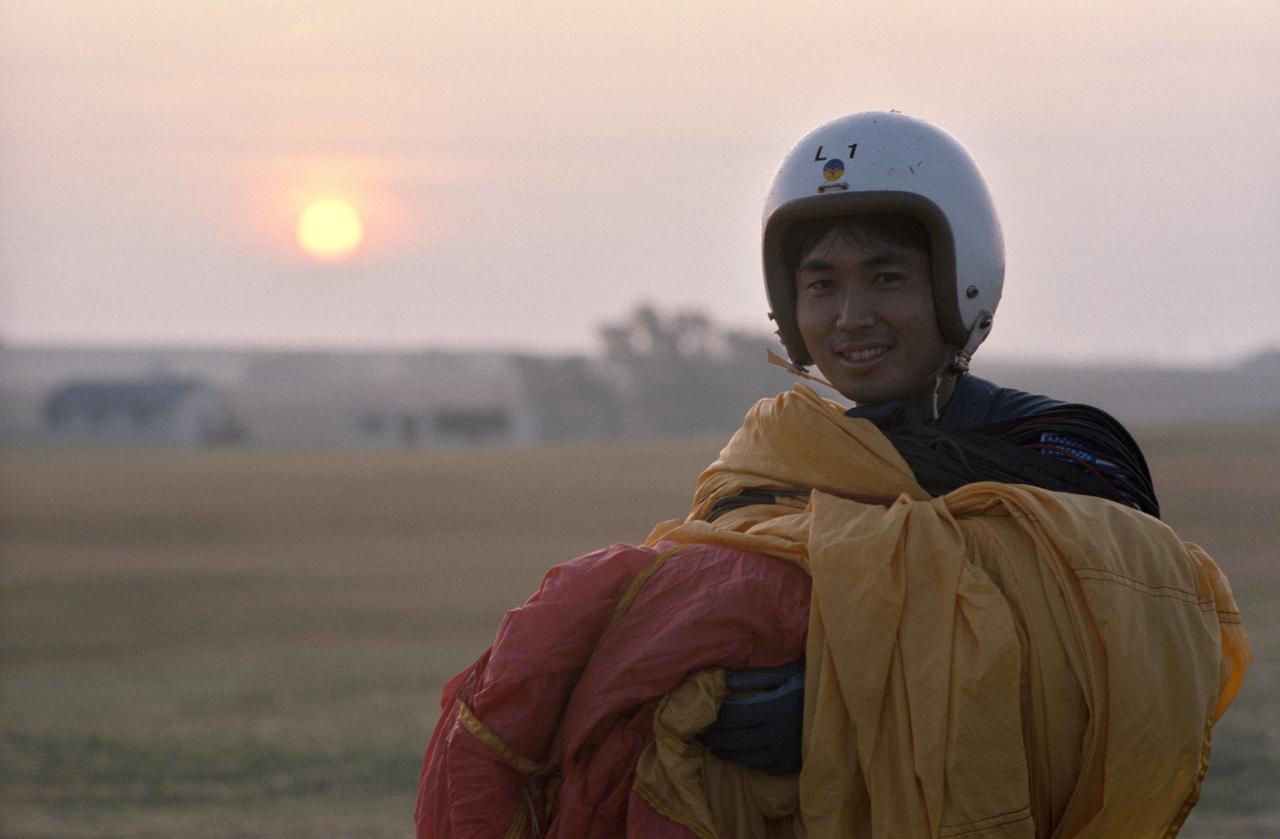

S95-00359 (12-14 September 1992) --- Astronaut candidate Koichi Wakata gathers his parachute following a simulated chute drop at Vance Air Force Base. Wakata is one of seven international mission specialist candidates who joined 19 United States astronaut candidates for the three-day parachute/survival training school at the Oklahoma Base. EDITORS NOTE: Since this photograph was taken, Wakata has been named as mission specialist for the STS-72 mission.

STS066-S-040 (14 November 1994) --- The main landing gear is on the ground and the nose gear is about to touch down as the Space Shuttle Atlantis heads toward a stop at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California, ending a successful 10 day, 22 hour and 34 minute space mission. Landing occurred at 7:34 a.m. (PST), November 14, 1994. Onboard were astronauts Donald R. McMonagle, commander; Curtis L. Brown, Jr., pilot; Ellen S. Ochoa, payload commander; Scott E. Parazynski and Joseph R. Tanner, both mission specialists, along with European Space Agency (ESA) mission specialist Jean-Francois Clervoy. The crew supported the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3) mission.
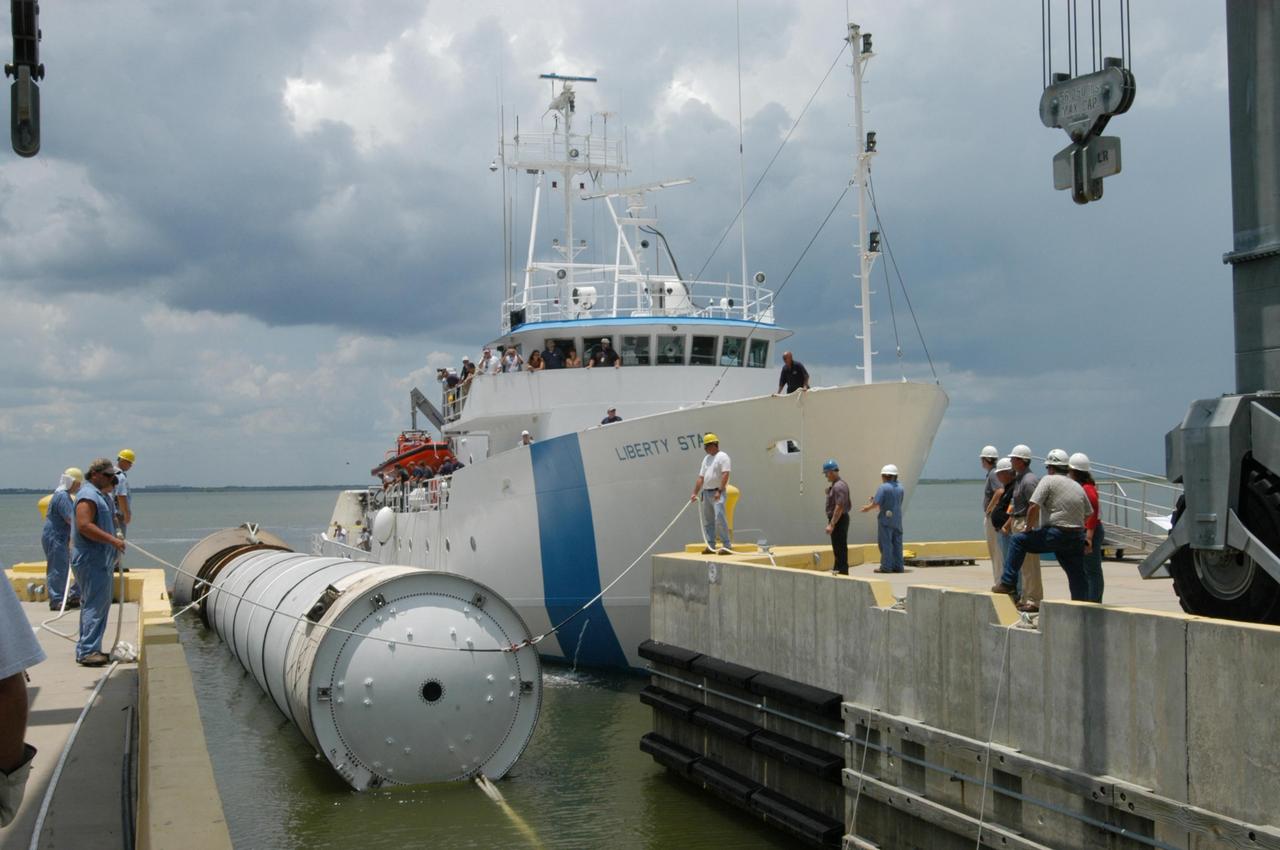

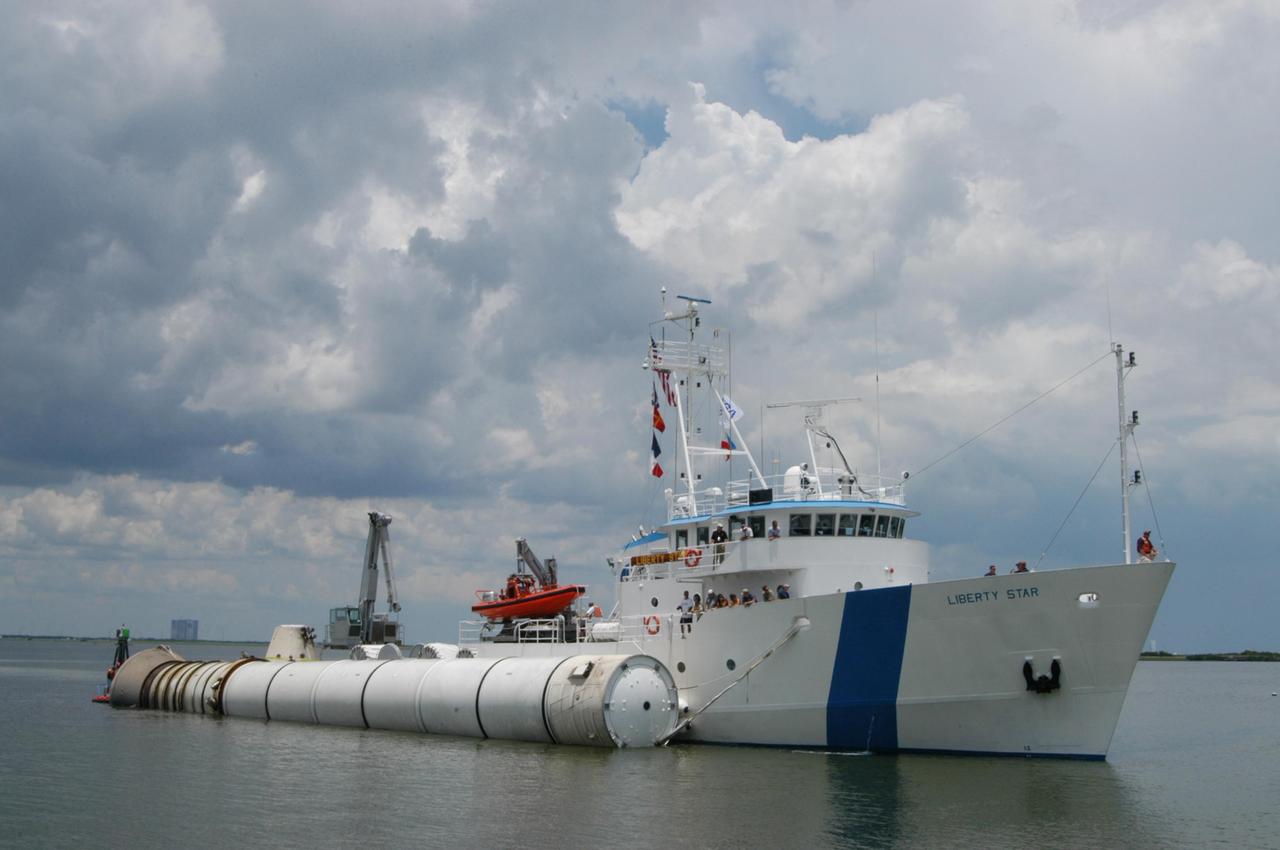
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the dock at Hangar AF, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers move the spent solid rocket booster away from the SRB Retrieval Ship Liberty Star to an area beneath the straddle crane that will lift it out of the water. The booster is from Space Shuttle Discovery, which launched on July 4. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about 6 by 9 nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and ,after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
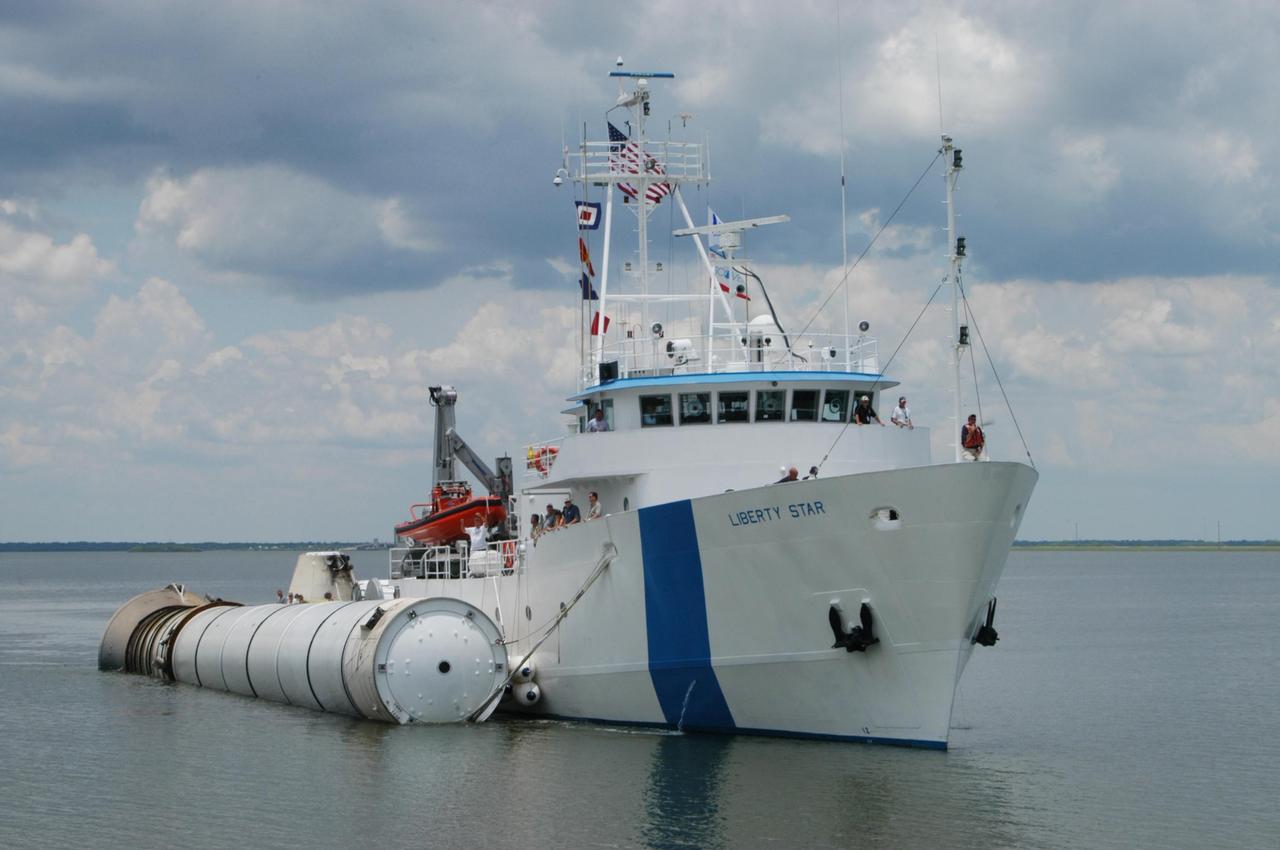

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The SRB Retrieval Ship Liberty Star closes in on the dock at Hangar AF, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, with a spent solid rocket booster alongside. The booster is from Space Shuttle Discovery, which launched on July 4. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about 6 by 9 nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and ,after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
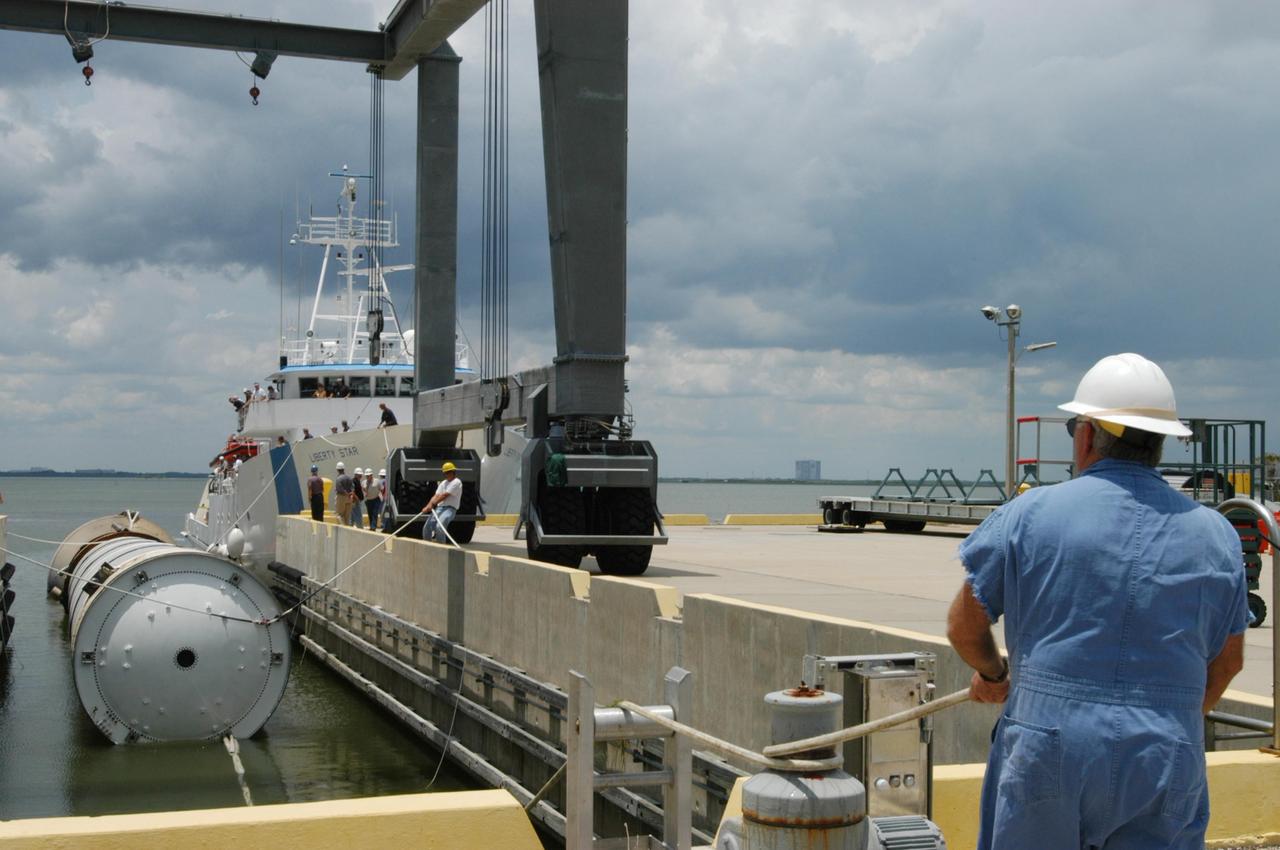

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the dock at Hangar AF, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers move the spent solid rocket booster underneath the straddle crane that will lift it out of the water. The booster is from Space Shuttle Discovery, which launched on July 4. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about 6 by 9 nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and ,after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
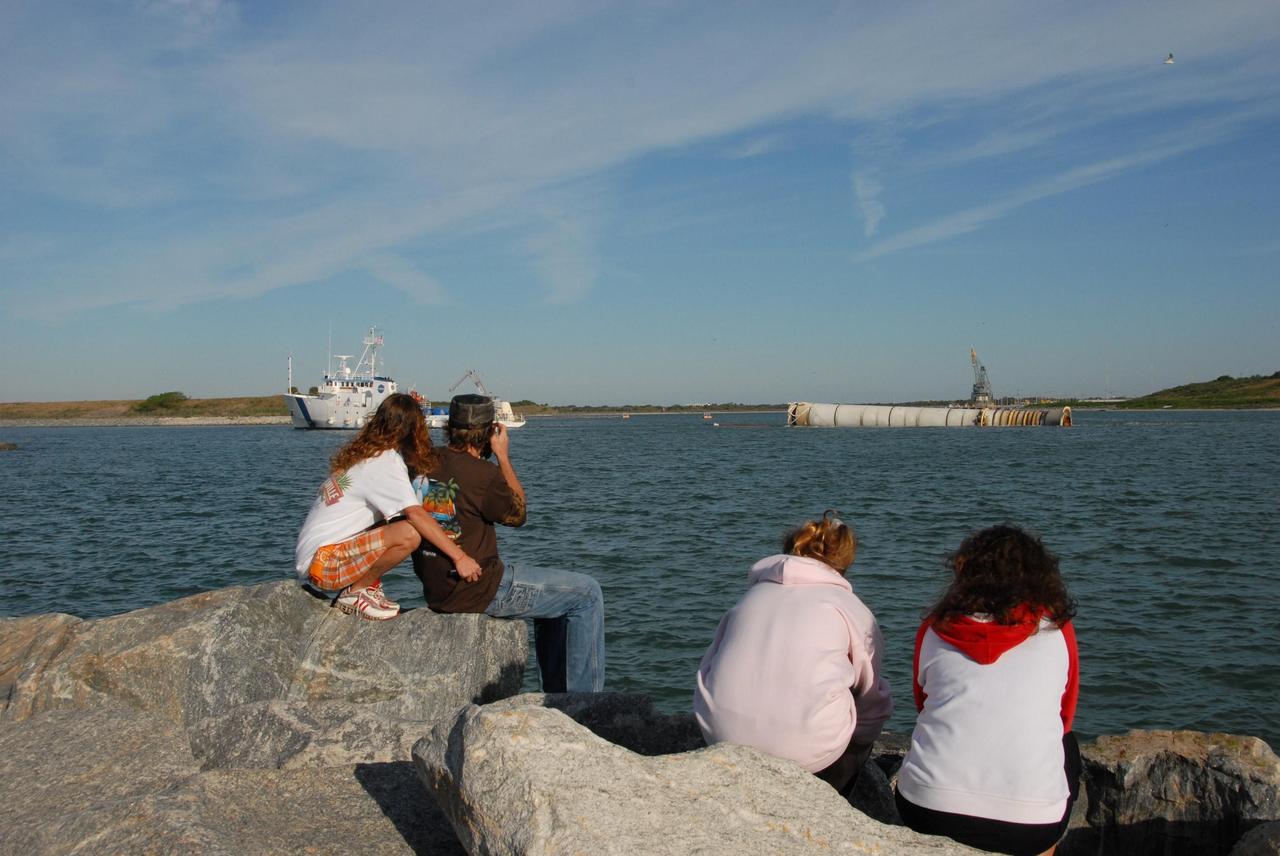

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Spectators watch as the solid rocket booster retrieval ship Freedom Star tows one of the boosters, retrieved after the launch of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-122 mission, toward Port Canaveral. The space shuttle's solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about 6 by 9 nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship's tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and, after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
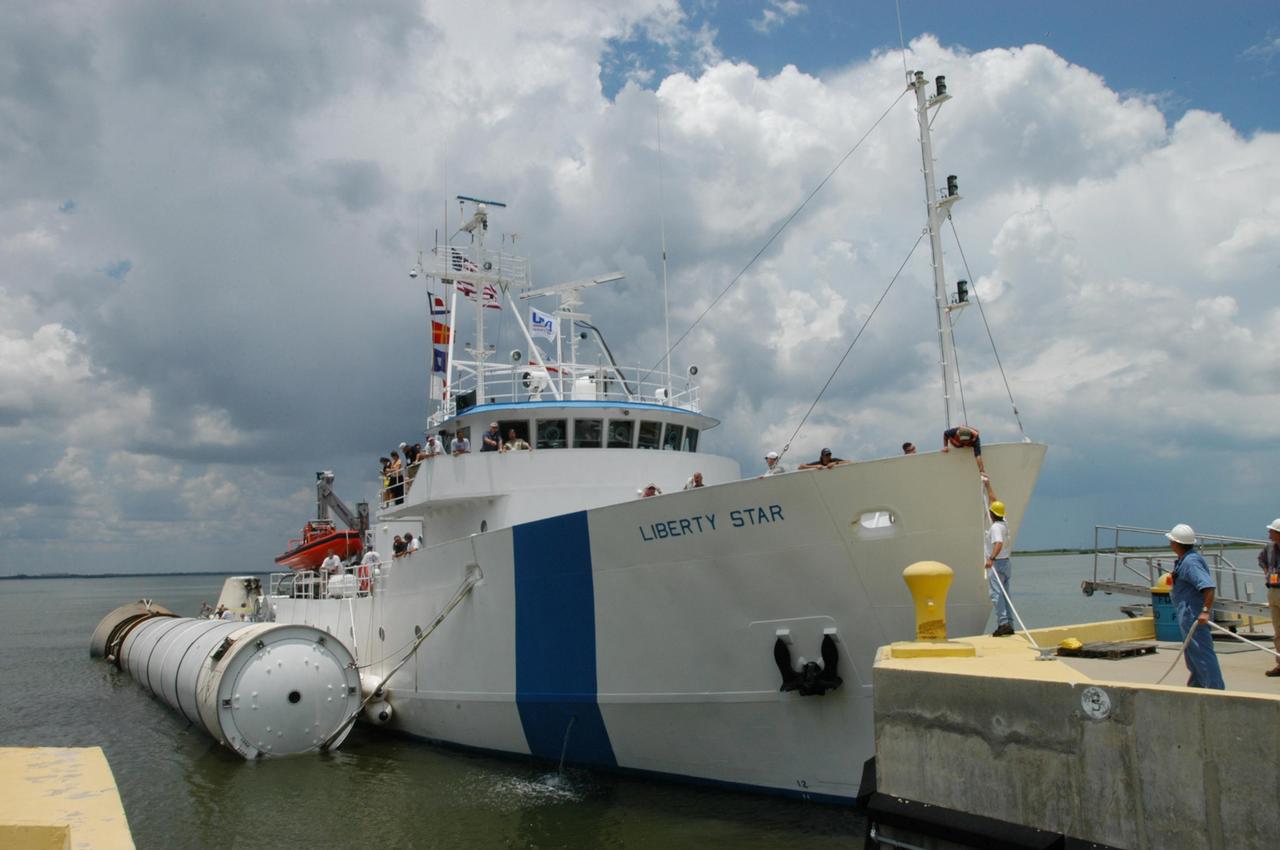

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The SRB Retrieval Ship Liberty Star arrives at the dock at Hangar AF, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, with a spent solid rocket booster alongside. The booster is from Space Shuttle Discovery, which launched on July 4. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about 6 by 9 nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and ,after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
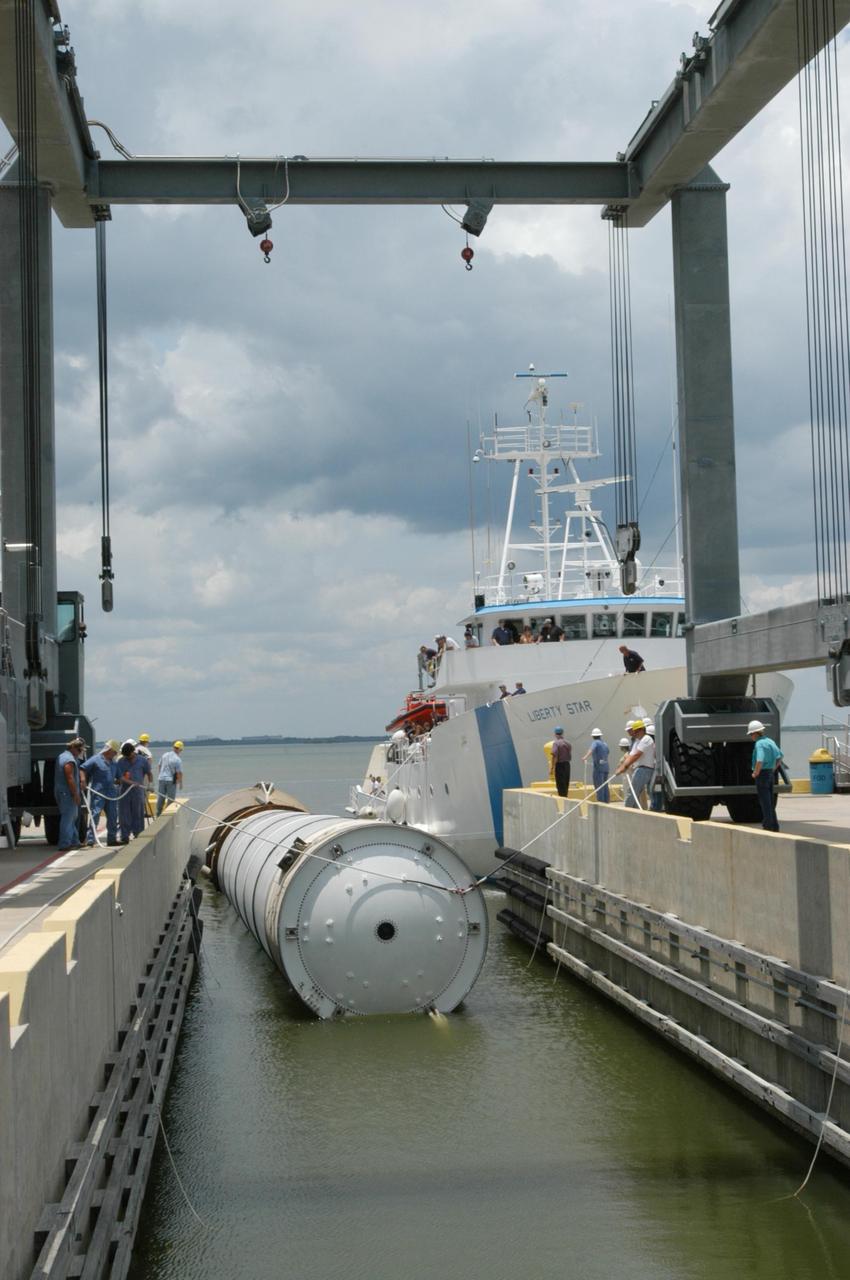

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the dock at Hangar AF, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers move the spent solid rocket booster away from the SRB Retrieval Ship Liberty Star to an area beneath the straddle crane that will lift it out of the water. The booster is from Space Shuttle Discovery, which launched on July 4. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about 6 by 9 nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and ,after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
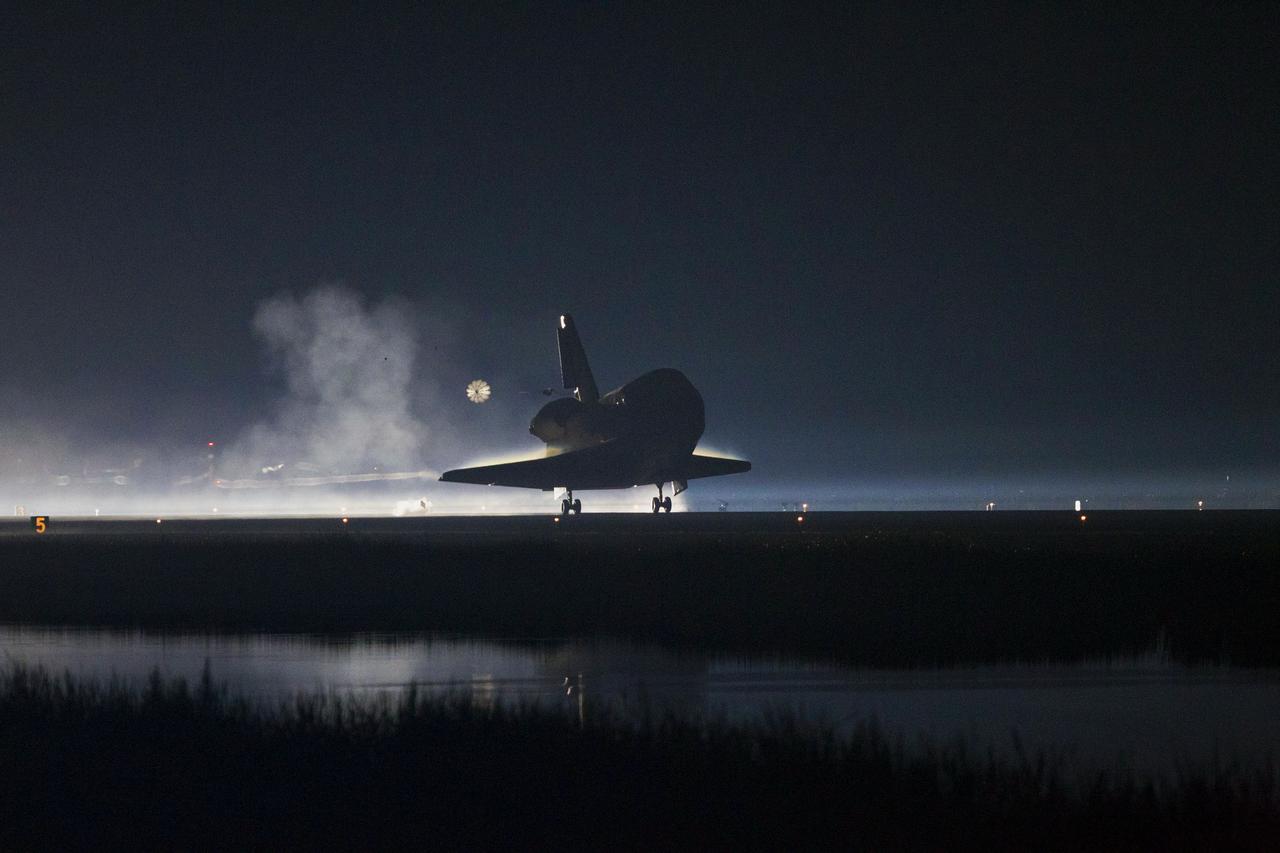

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Atlantis' pilot chute deploys, a preamble to the appearance of the shuttle's drag chute, as it lands on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Securing the space shuttle fleet's place in history, Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. Main gear touchdown was at 5:57:00 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 5:57:20 a.m., and wheelstop at 5:57:54 a.m. On board are STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim. On the 37th shuttle mission to the International Space Station, STS-135 delivered the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module filled with more than 9,400 pounds of spare parts, equipment and supplies that will sustain station operations for the next year. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. STS-135 also was the final mission of the Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kenny Allen

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the dock at Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the straddle crane lowers a spent solid rocket booster onto a transporter. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The booster is from space shuttle Endeavour, which launched Nov. 14 on the STS-126 mission. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about six by nine nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and, after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
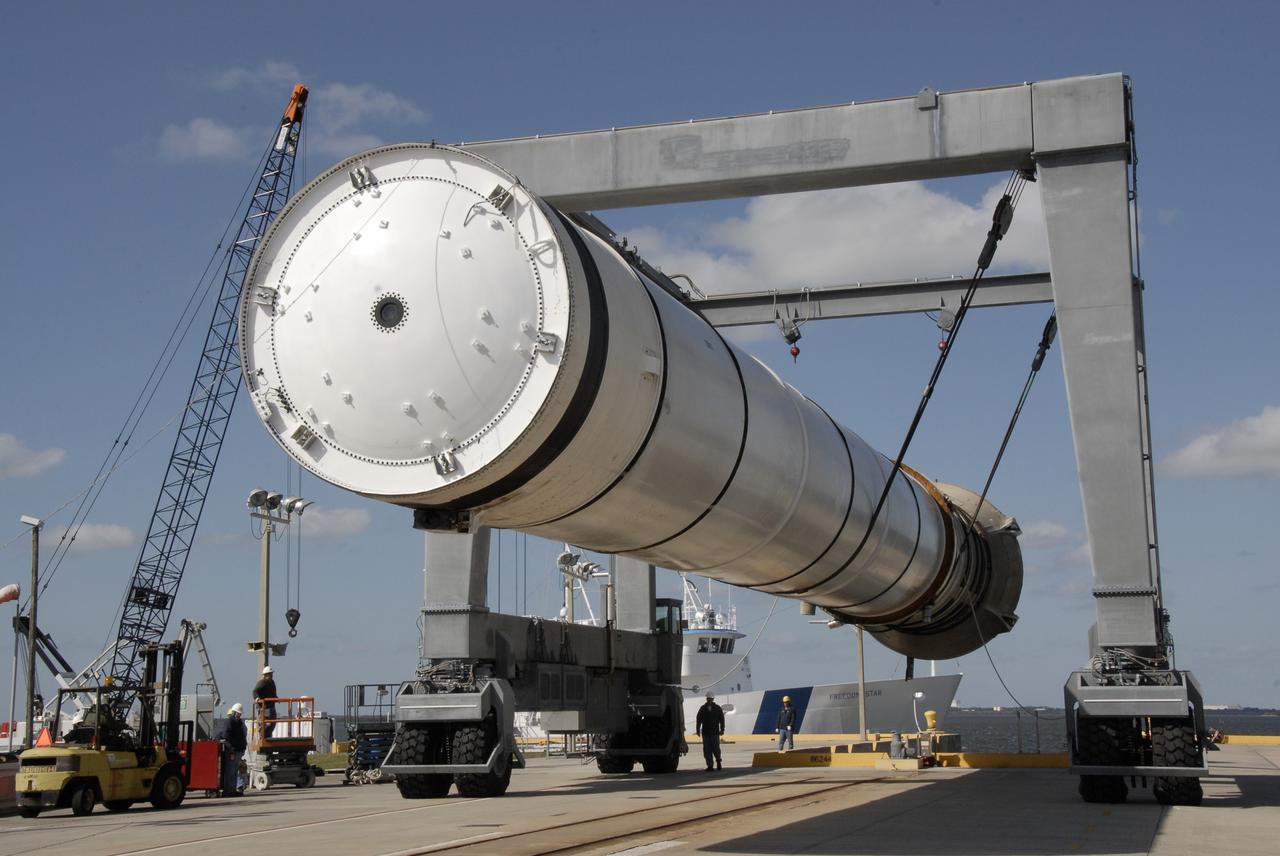

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the dock at Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the straddle crane lifts a spent solid rocket booster to allow saltwater contamination to be rinsed off. The booster is from space shuttle Endeavour, which launched Nov. 14 on the STS-126 mission. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The spent rocket was recovered by NASA's Solid Rocket Booster Retrieval Ship Freedom Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about six by nine nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and, after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
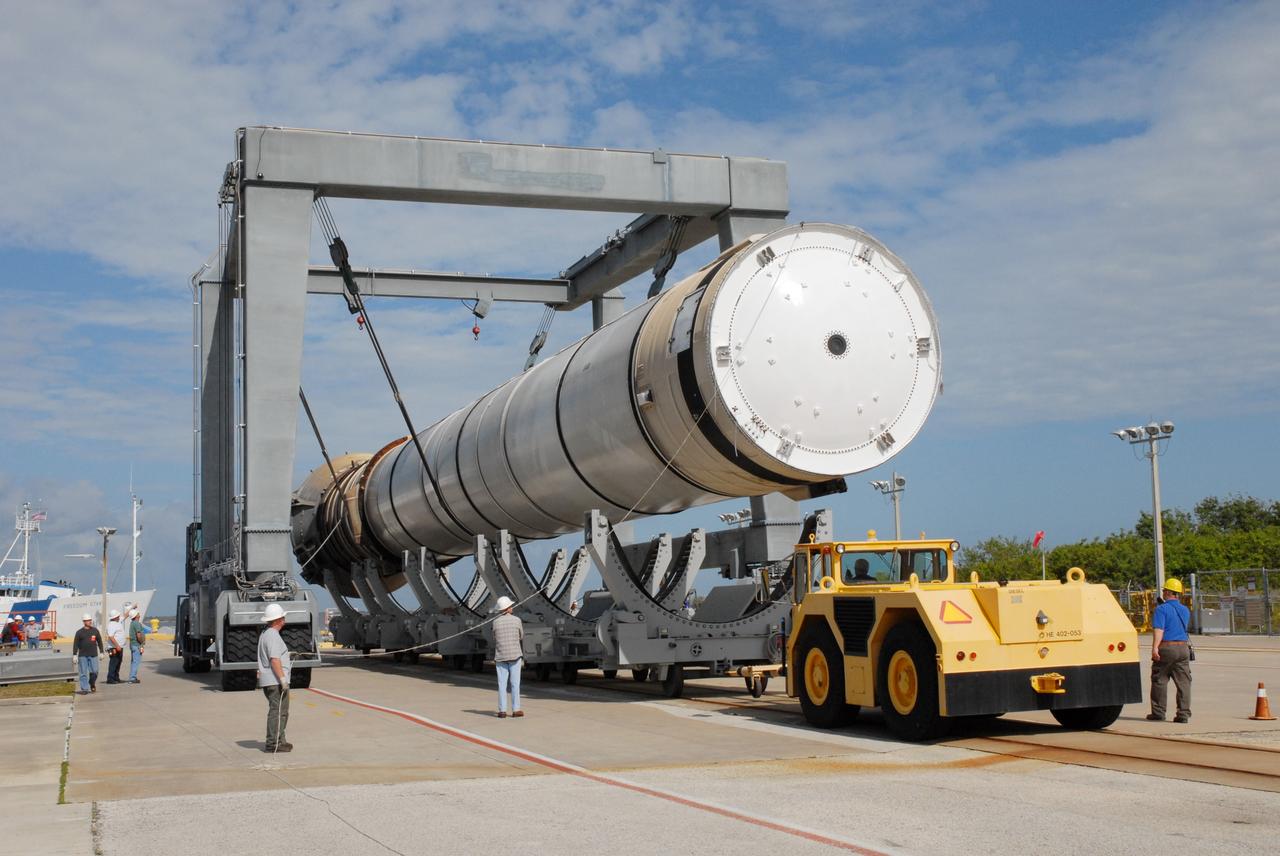

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the dock at Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the straddle crane lowers a solid rocket booster onto a transporter. The booster was used during space shuttle Discovery's launch from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida March 15 on mission STS-119. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea after a launch. The spent rockets were recovered by NASA's Solid Rocket Booster Retrieval Ships Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about six by nine nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and, after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The SRB Retrieval Ship Liberty Star closes in on the dock at Hangar AF, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, with a spent solid rocket booster alongside. The booster is from Space Shuttle Discovery, which launched on July 4. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about 6 by 9 nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and ,after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
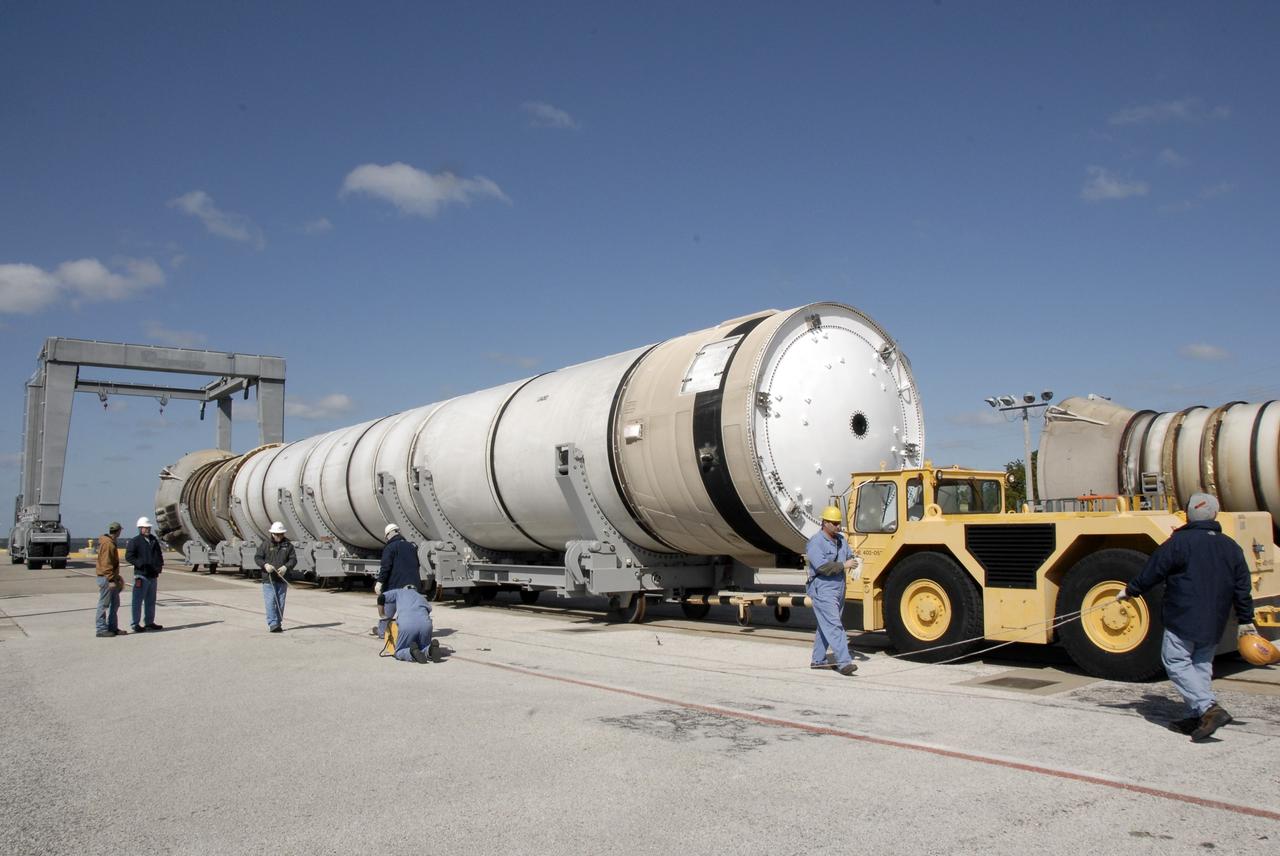

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the dock at Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, two spent solid rocket boosters begin moving to the hangar for the safing process. They will be driven through the washing bay for a cleaning and rinsing. The boosters are from space shuttle Endeavour, which launched Nov. 14 on the STS-126 mission. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about six by nine nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and, after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
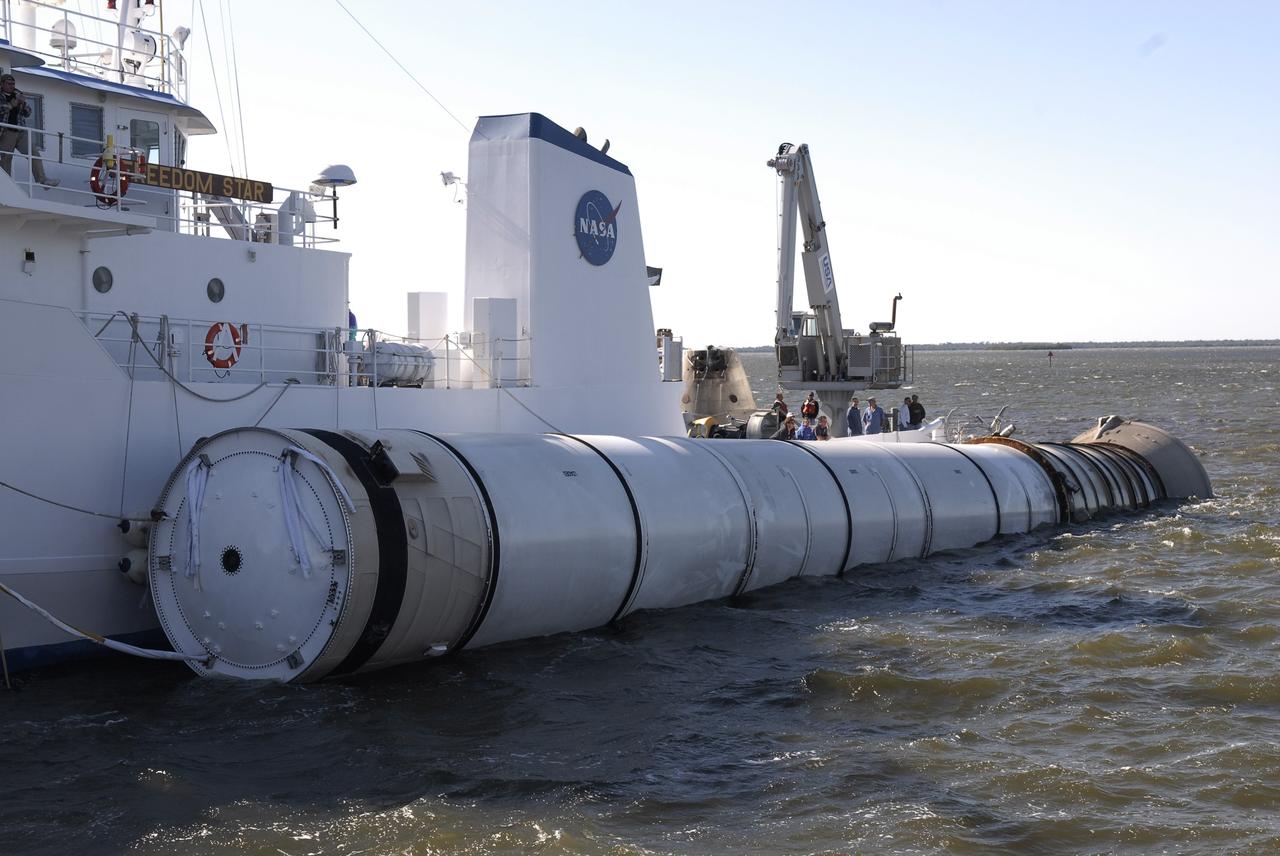

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's Solid Rocket Booster Retrieval Ship Freedom Star tows along its side one of the spent booster rockets from the space shuttle Endeavour launch Nov. 14 on the STS-126 mission. The ship is returning the spent rocket to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about six by nine nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and, after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
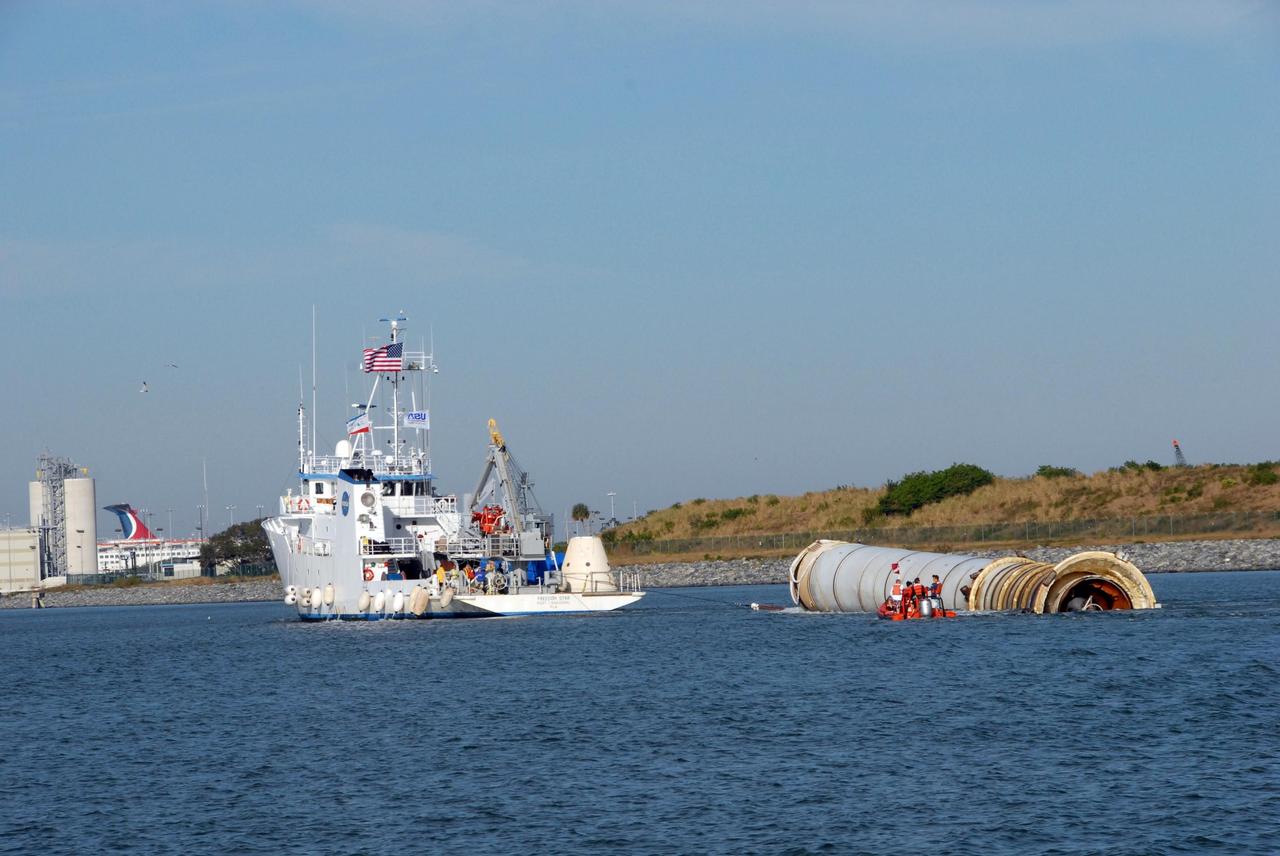

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The solid rocket booster retrieval ship Freedom Star tows toward Port Canaveral one of the boosters, retrieved after the launch of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-122 mission, toward Port Canaveral. The space shuttle's solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about 6 by 9 nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship's tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and, after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
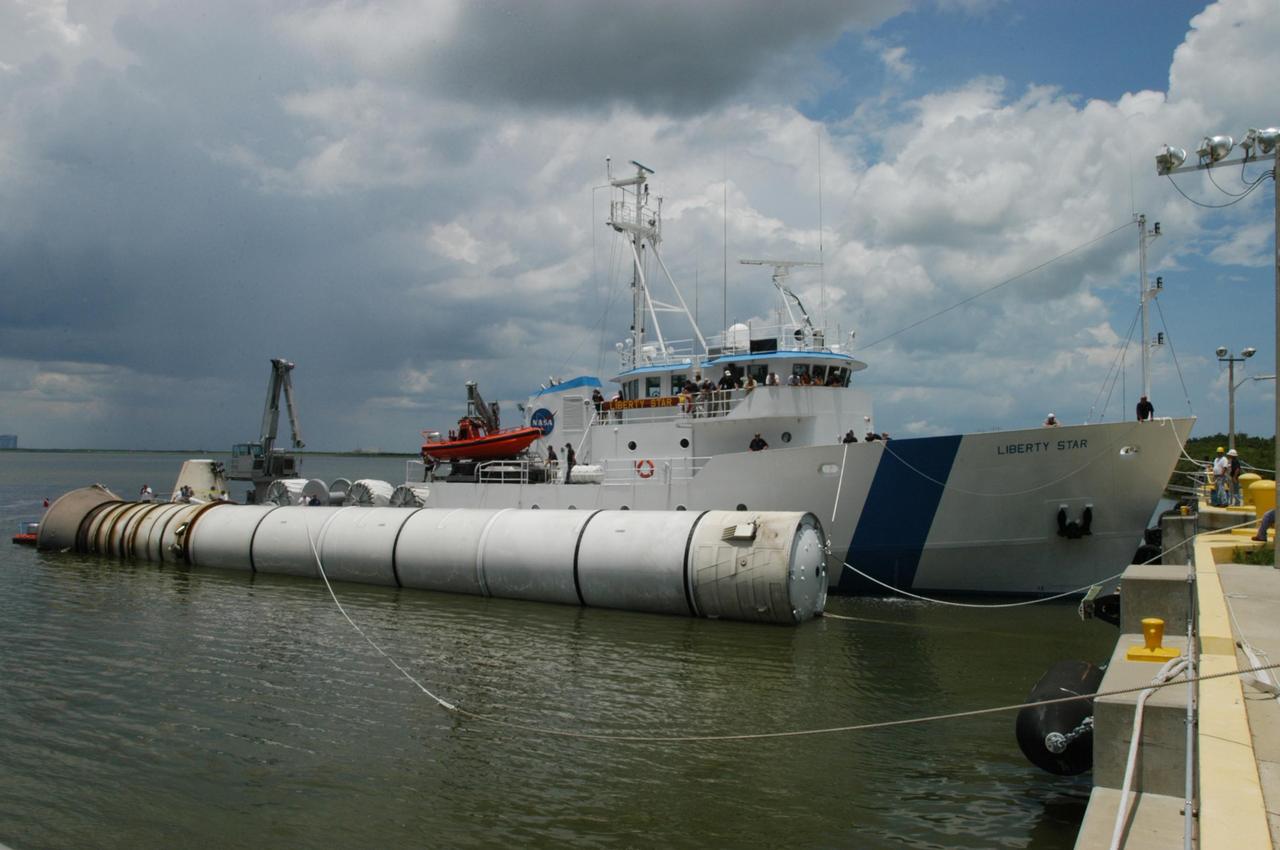

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the dock at Hangar AF, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the SRB Retrieval Ship Liberty Star gets ready to transfer the spent solid rocket booster to a straddle crane that will lift it out of the water. The booster is from Space Shuttle Discovery, which launched on July 4. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about 6 by 9 nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and ,after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
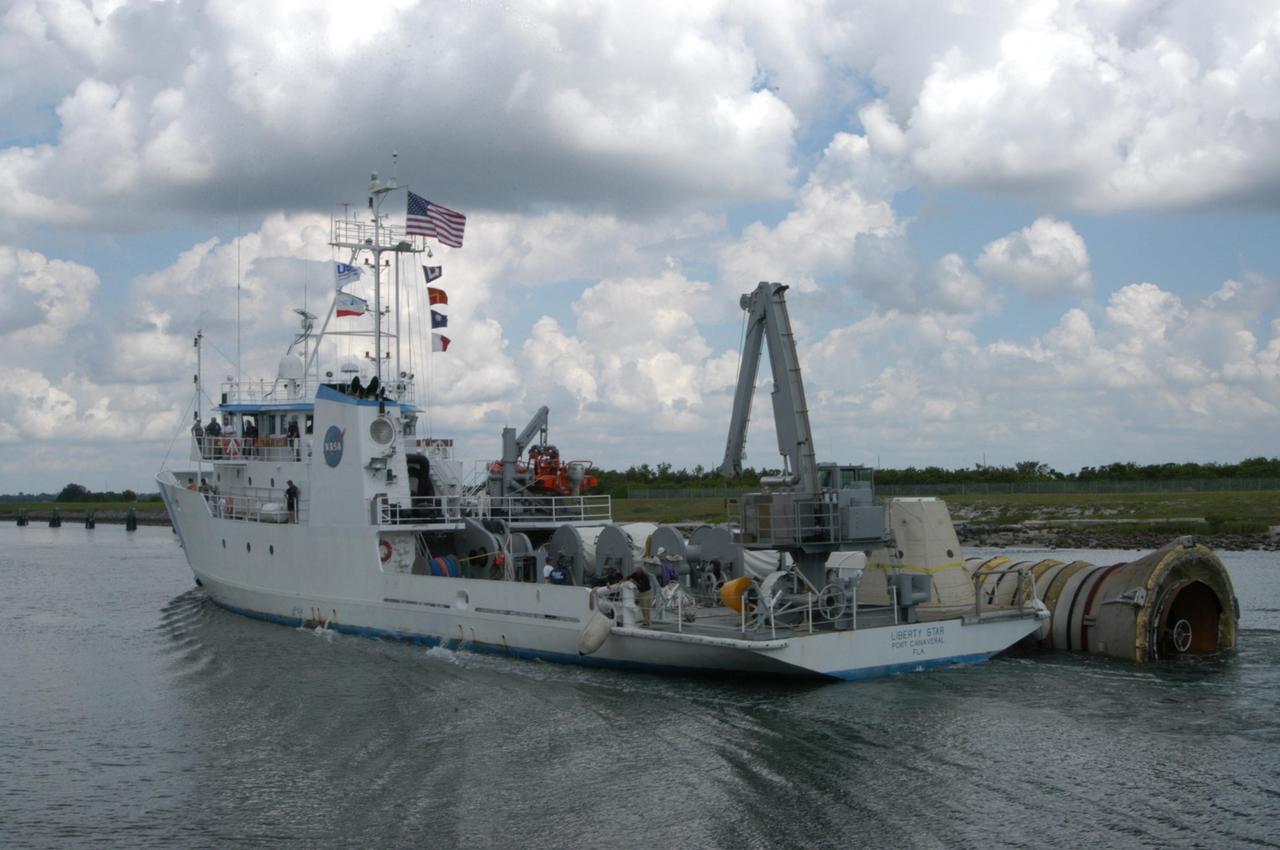

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The SRB Retrieval Ship Liberty Star heads up the Banana River to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station with a spent solid rocket booster alongside. The booster is from Space Shuttle Discovery, which launched on July 4. The space shuttle’s solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered at sea. The boosters impact the Atlantic Ocean approximately seven minutes after liftoff. The splashdown area is a square of about 6 by 9 nautical miles located about 140 nautical miles downrange from the launch pad. The retrieval ships are stationed approximately 8 to 10 nautical miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. As soon as the boosters enter the water, the ships accelerate to a speed of 15 knots and quickly close on the boosters. The pilot chutes and main parachutes are the first items to be brought on board. With the chutes and frustum recovered, attention turns to the boosters. The ship’s tow line is connected and the booster is returned to the Port and ,after transfer to a position alongside the ship, to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the expended boosters are disassembled, refurbished and reloaded with solid propellant for reuse. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton